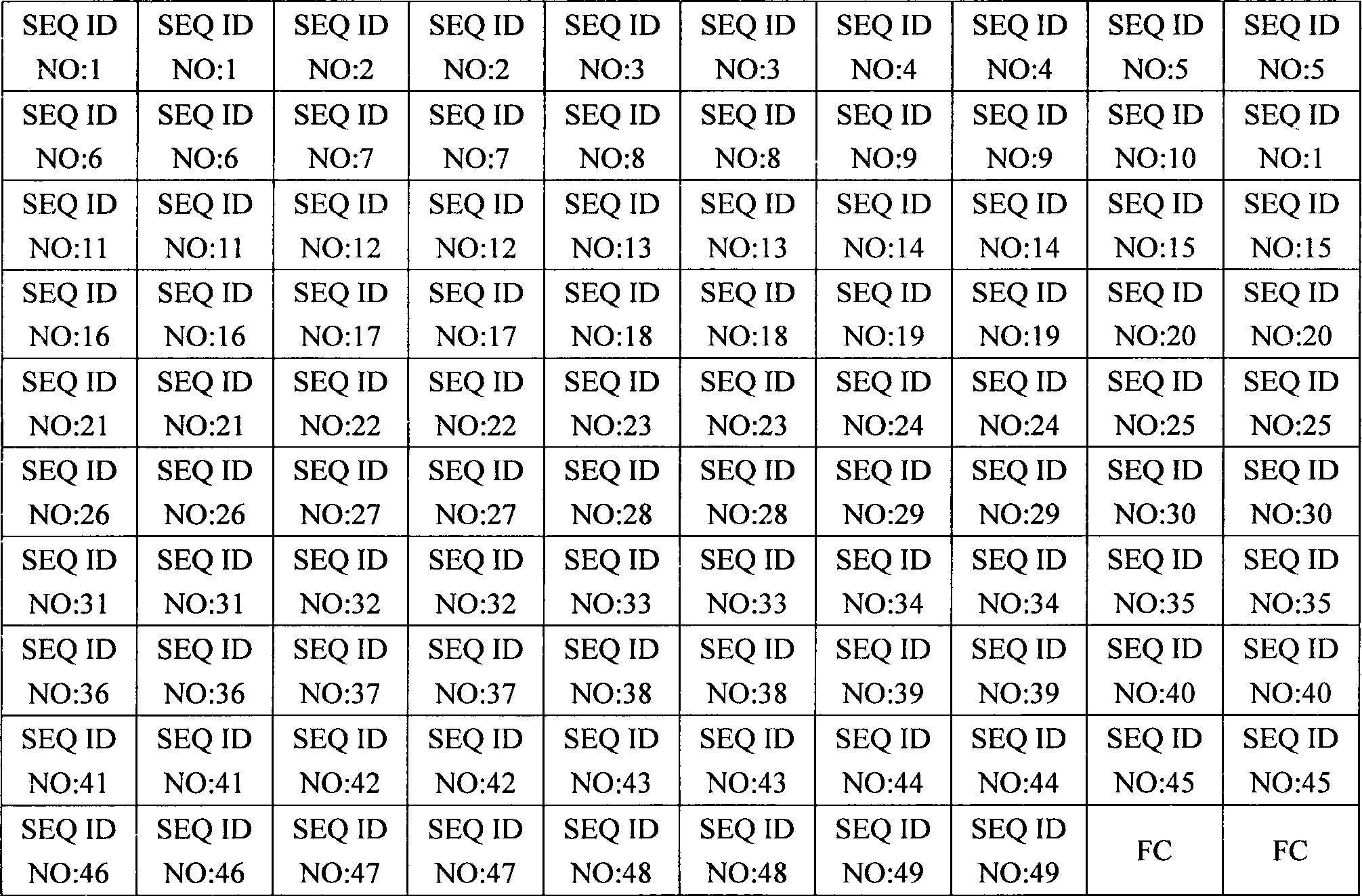Patents
Literature
37 results about "DNA Microarray Chip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An orderly array of DNA samples affixed to a support. Using robots thousands of samples can be arrayed on a single chip. The chip is used in various types of hybridization experiments.
Virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC)
InactiveCN102025482ASolve the first sharing problemHuge key spaceGenetic modelsSecuring communicationPlaintextDNA Microarray Chip
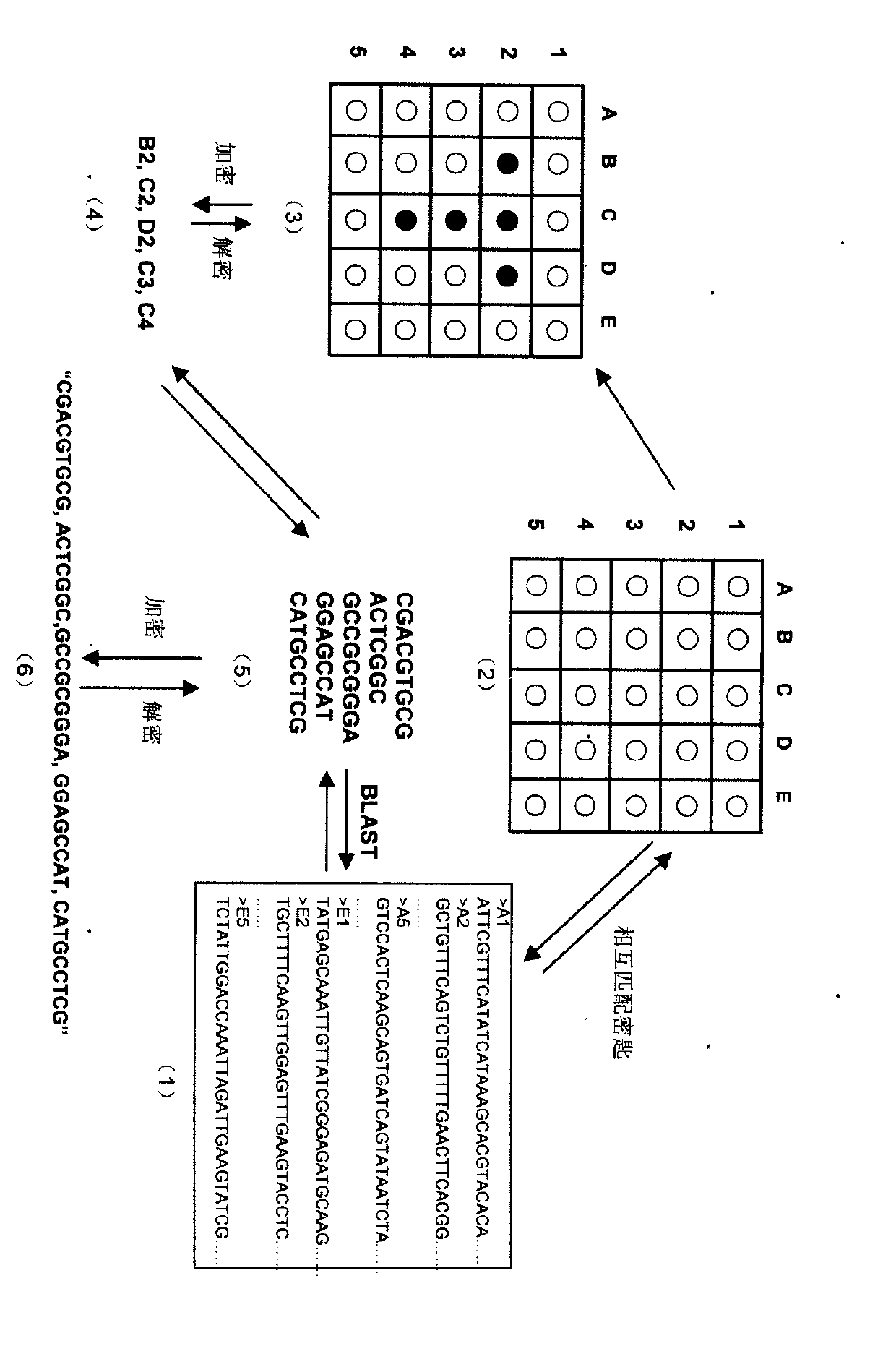
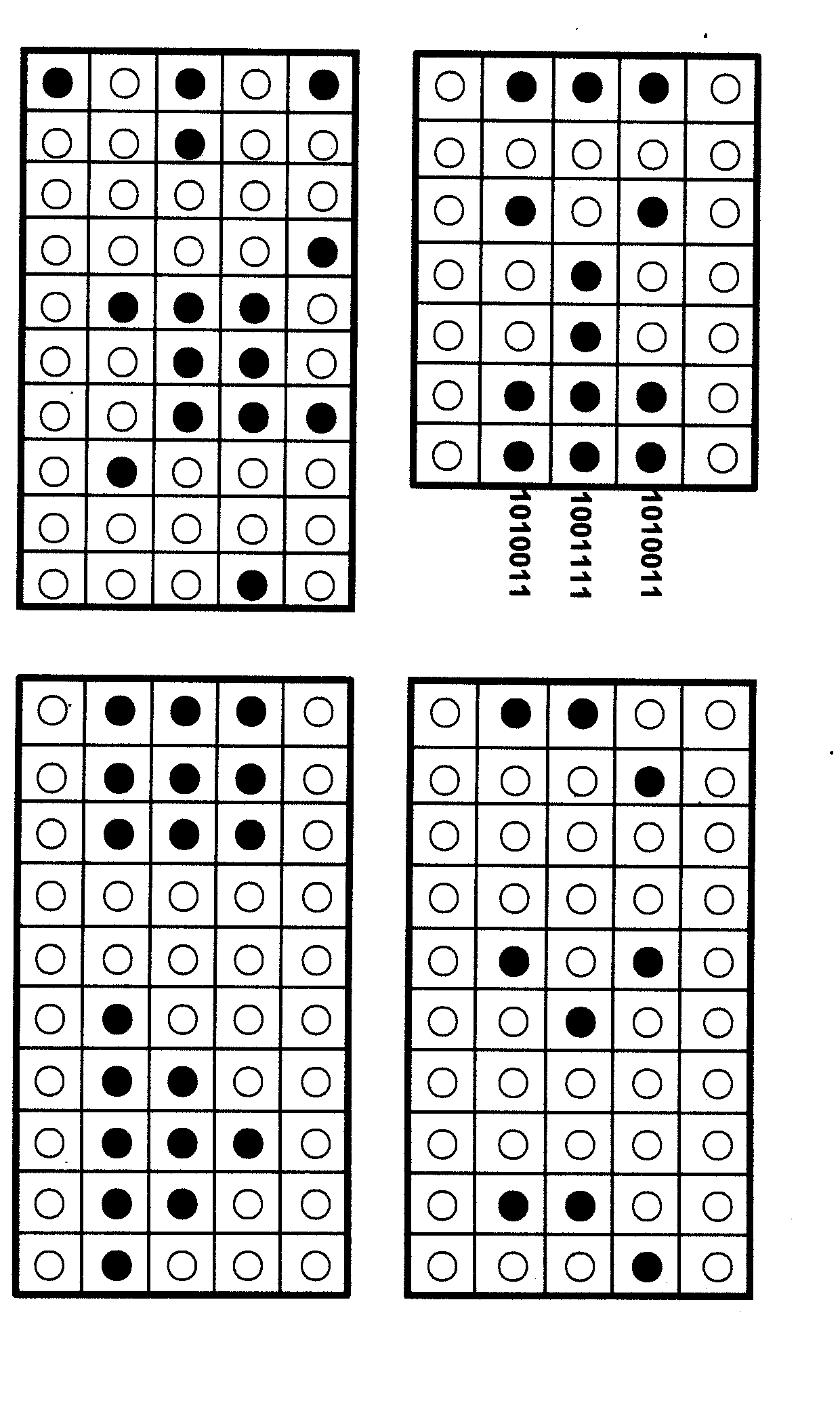
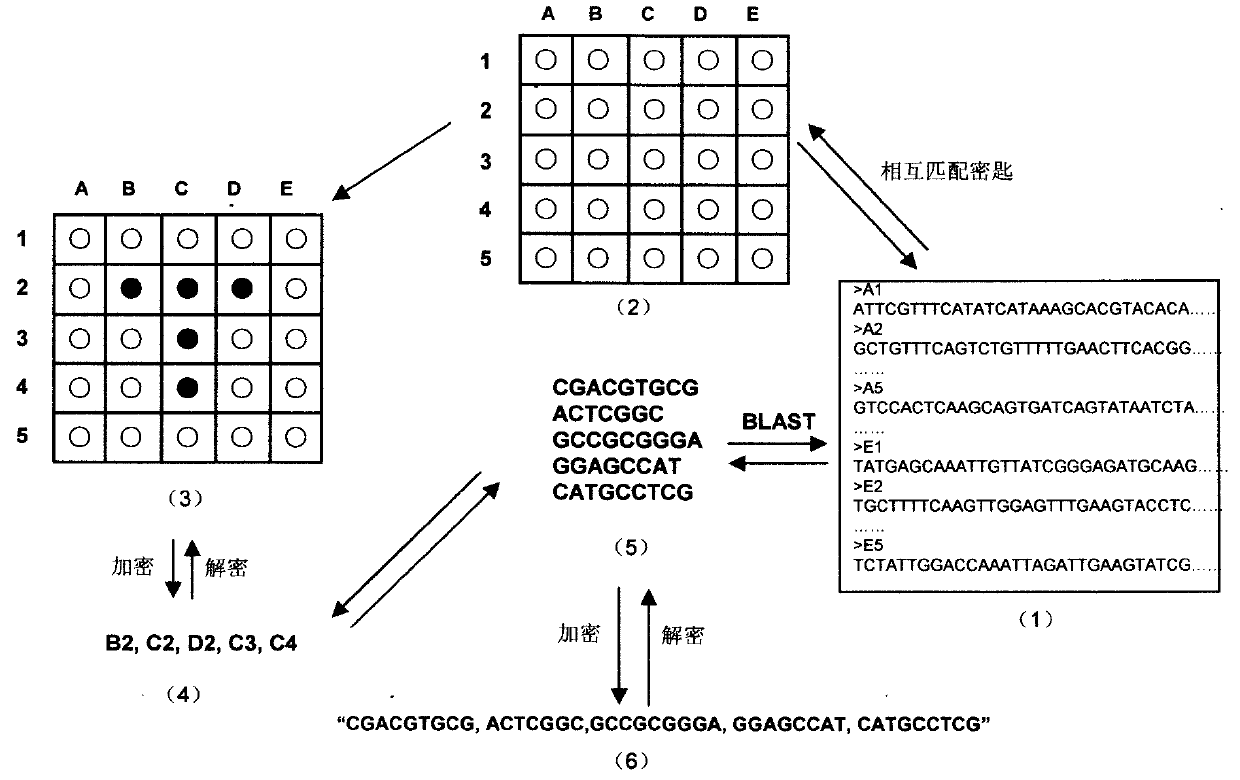
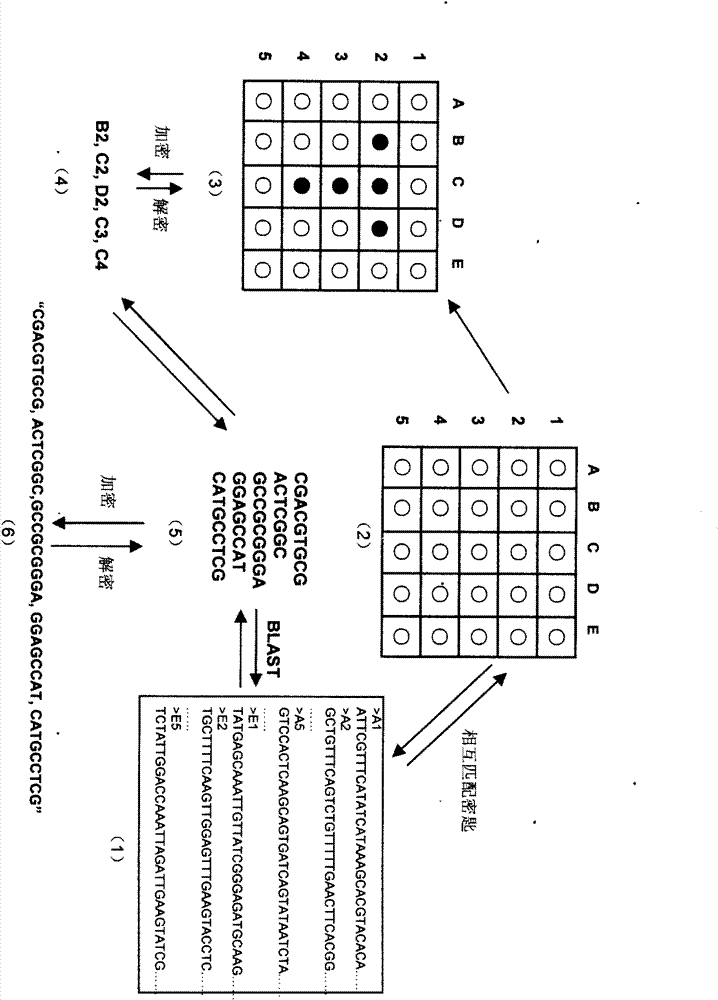
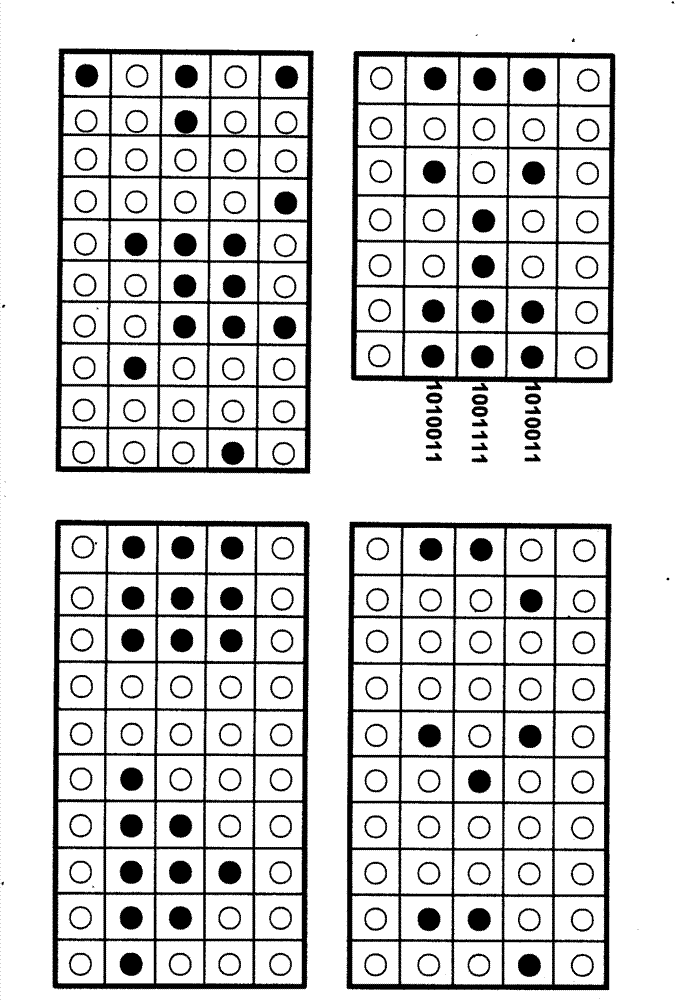
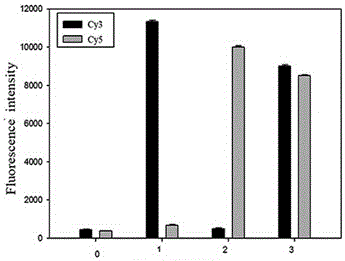
The invention relates to information security technology, in particular to a virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC). The cryptosystem is provided with two matched keys, of which one is a virtual genome database (VGDB) consisting of random deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences and the other one is a position table that virtual genes of the VGDB are randomly distributed in a two-dimensional microarray, namely a virtual DNA microarray chip (VDMC). Any plaintext information can be freely written on the VDMC, namely points for forming the plaintext information are selected from the VDMC microarray. The selected points correspond to the virtual genes in the VGDB; small segments of DNA sequences are randomly selected from the virtual genes; and the uniqueness of the small segments of DNA sequences in the VGDB is determined by using a common tool of the bioinformatics, namely a basic local alignment search tool (BLAST), or other character string search algorithms such as a Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) algorithm and the like. A cipher text is combined by the small segments of DNA sequences. The small segments of DNA sequences need only to perform BLAST on the VGDB during decryption, namely the points for forming the plaintext information can be discovered, and the plaintext information can be restored according to the VDMC. Any non-VGDB sequence can be randomly inserted into the cipher text and does not have any influence on the encryption. Thus, the VGC is an excellent information hiding system. In addition, the VGC key can be updated automatically so as to realize an indecipherable one-time-pad system. The cryptosystem is used for real-time quick secret information communication, digital signature and identity authentication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of high flux screening, capturing and separating target molecule from complex composition matter such as traditional Chinese medicine and chemical mixture
InactiveCN1590560AImprove bindingIncrease transcriptionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipDisease
A process for high-flux screening, capturing and separation of target moleculae from complex substance (Chinese medicine or chemical mixer) includes preparing a ds DNA microarray chip to make its probe have a binding sites of dsDNA bindin, measuring the affinity of the sites, creating the standard affinity parameter system, mixing the microarray chip with said complex substance, reacting, detecting the affinity variation, screening the varied targets, linking them to the surface of chromatographic column, filling the complex substance in it, capturing the effective moleculae by probes, eluting and collecting the effective moleculae.
Owner:王进科 +2
Preparation method of DNA microarray chip based on gel fixed nucleic acid
InactiveCN1733935AMultiple fixed capacityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipGel based
The invention discloses a process for preparing DNA micro array chips based on gel fixed nucleic acid, which comprises mixing acrylamide modified nucleic acid, acrylamide monomer, ammonium peroxodisulfate, glycerin and water into pre-polymer, wherein the concentration of the nucleic acid is between 0.001-100uM, the monomer weight concentration of acrylamide is between 1-30%, the weight concentration of the ammonium peroxodisulfate is between 0.01-5%, the weight concentration of glycerin is between 10-50%, then applying the sample of the prepolymer onto a solid substrate, loading the sample applying substrate into an airtight case containing tetramethylethylenediamine, so as to make the tetramethylethylenediamine volatilize.
Owner:南京普东兴生物科技有限公司
DNA micro-array chip, detection method thereof and uses in CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and MDR1 gene polymorphism detection
InactiveCN101481736AEasy to makeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipMdr1 gene
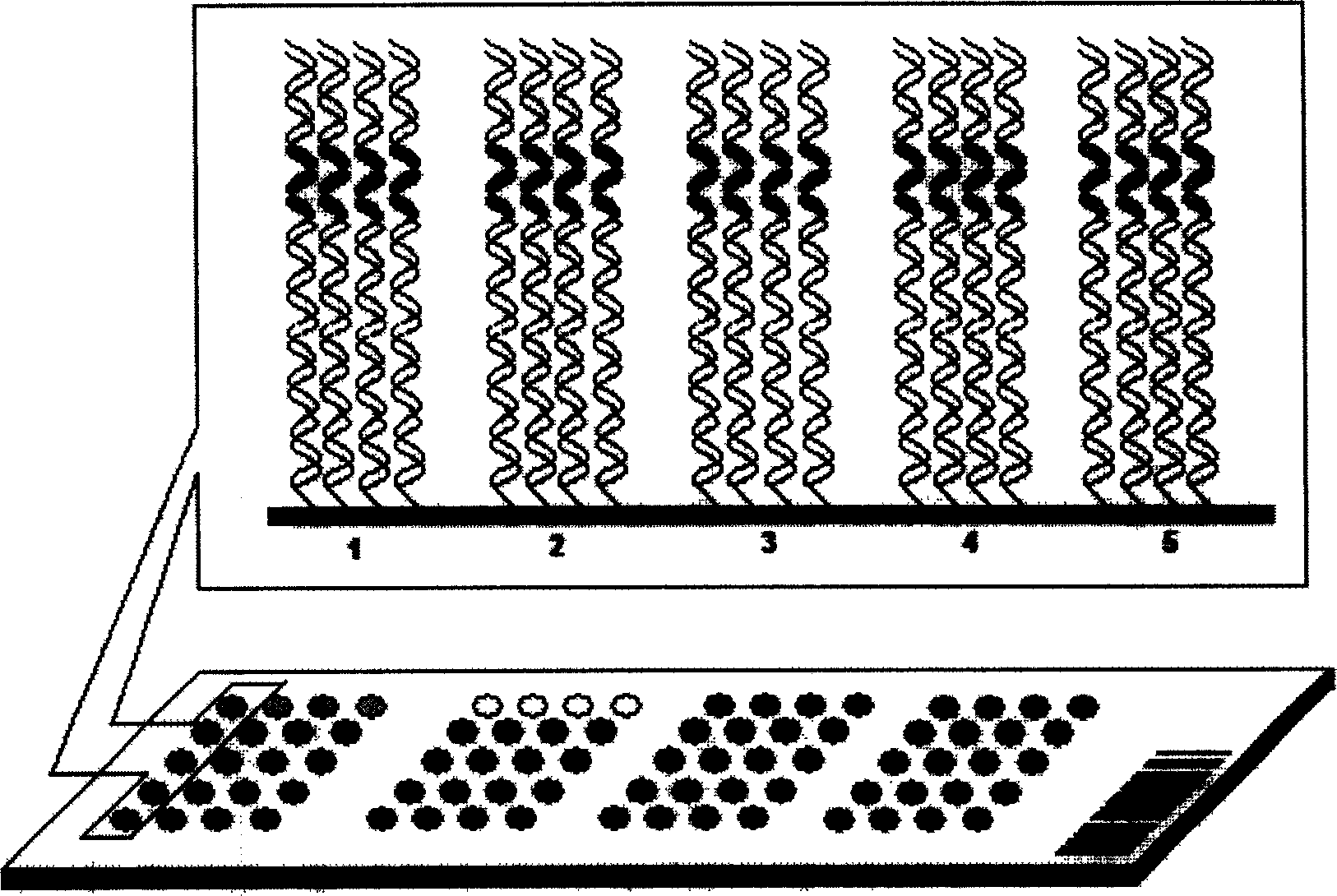
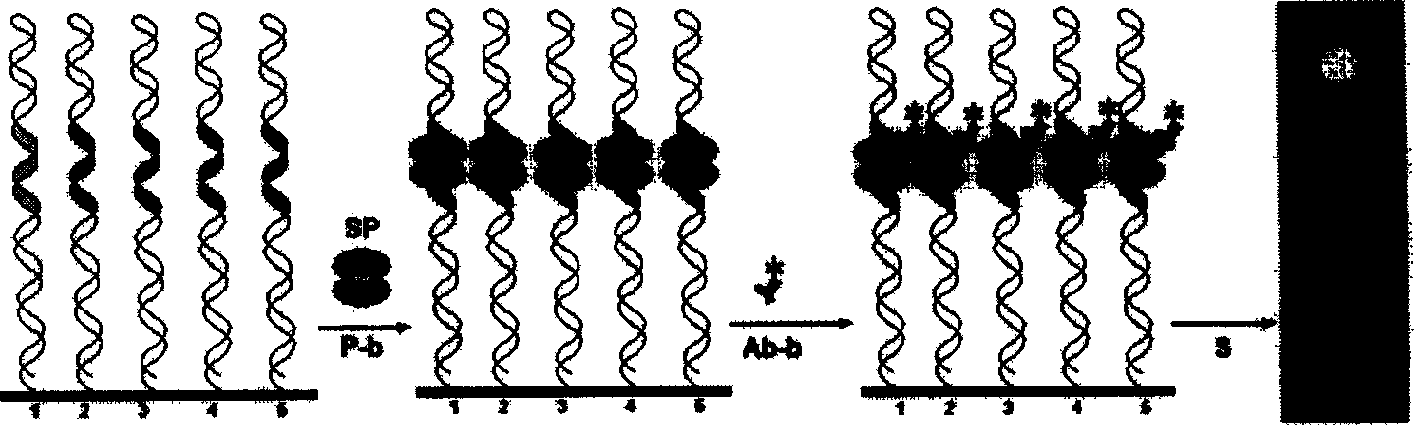
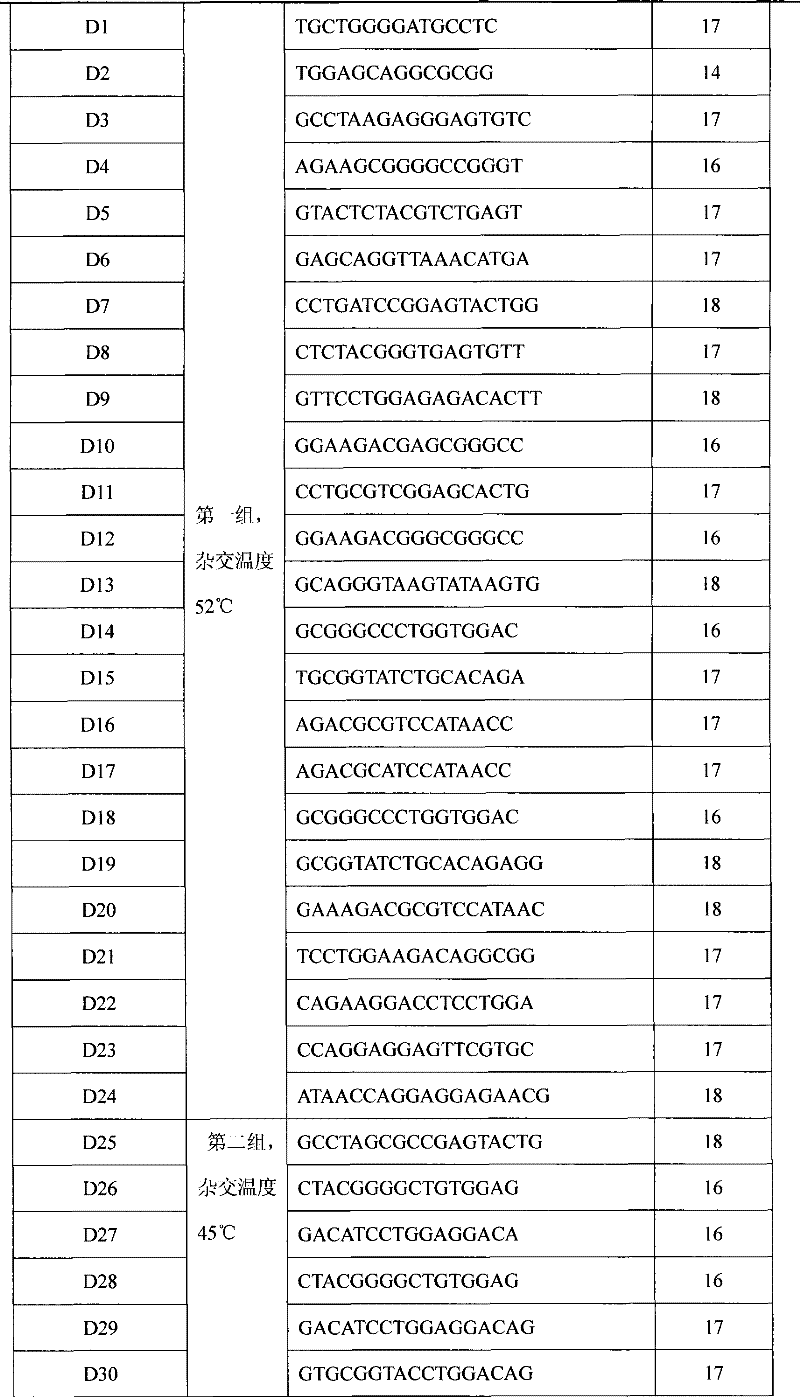
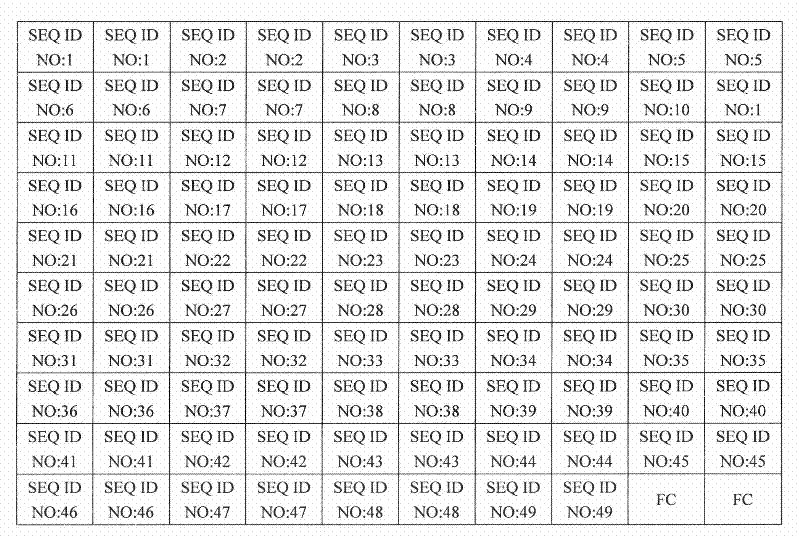
The invention discloses a DNA micro-array chip and a detection method thereof and the application on detecting the polymorphism of CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and MDR1 genes. The chip comprises a solid phase carrier and a probe. The nucleotide sequence of the probe is shown as SEQ ID No: 1-SEQ ID No: 49. The probe is firstly arranged on the solid phase carrier. And then the target nucleotide sequence of a sample to be detected is marked and prepared. After that, the target nucleotide sequence is hybridized with the probe on the chip. Finally, the hybridization result is detected to obtain the information of the CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and MDR1 genes in the sample to be detected. The chip of the invention can be used for the detection of a plurality of genes of a plurality of samples simultaneously once only and has the advantages of simple operation and high result accuracy. Large amount of genetic information of patients can be obtained through detection once. The DNA micro-array chip and the detection method thereof can be used for instructing the formulation of reasonable drug schemes and realizing the personalized medical treatment.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
HCV genotyping DNA microarray chip
InactiveCN101660002AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA Microarray ChipHCV Genotyping
The invention relates to a DNA microarray chip, in particular to a hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotyping DNA microarray chip. A solid-phase carrier substrate is used, and an oligonucleotide probe is designed in view of different genotypes of HCV so as to prepare the DNA microarray chip; and when matched with a PCR primer and other components, the DNA microarray chip can quickly and accurately classify the types of the hepatitis C virus in a blood sample.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
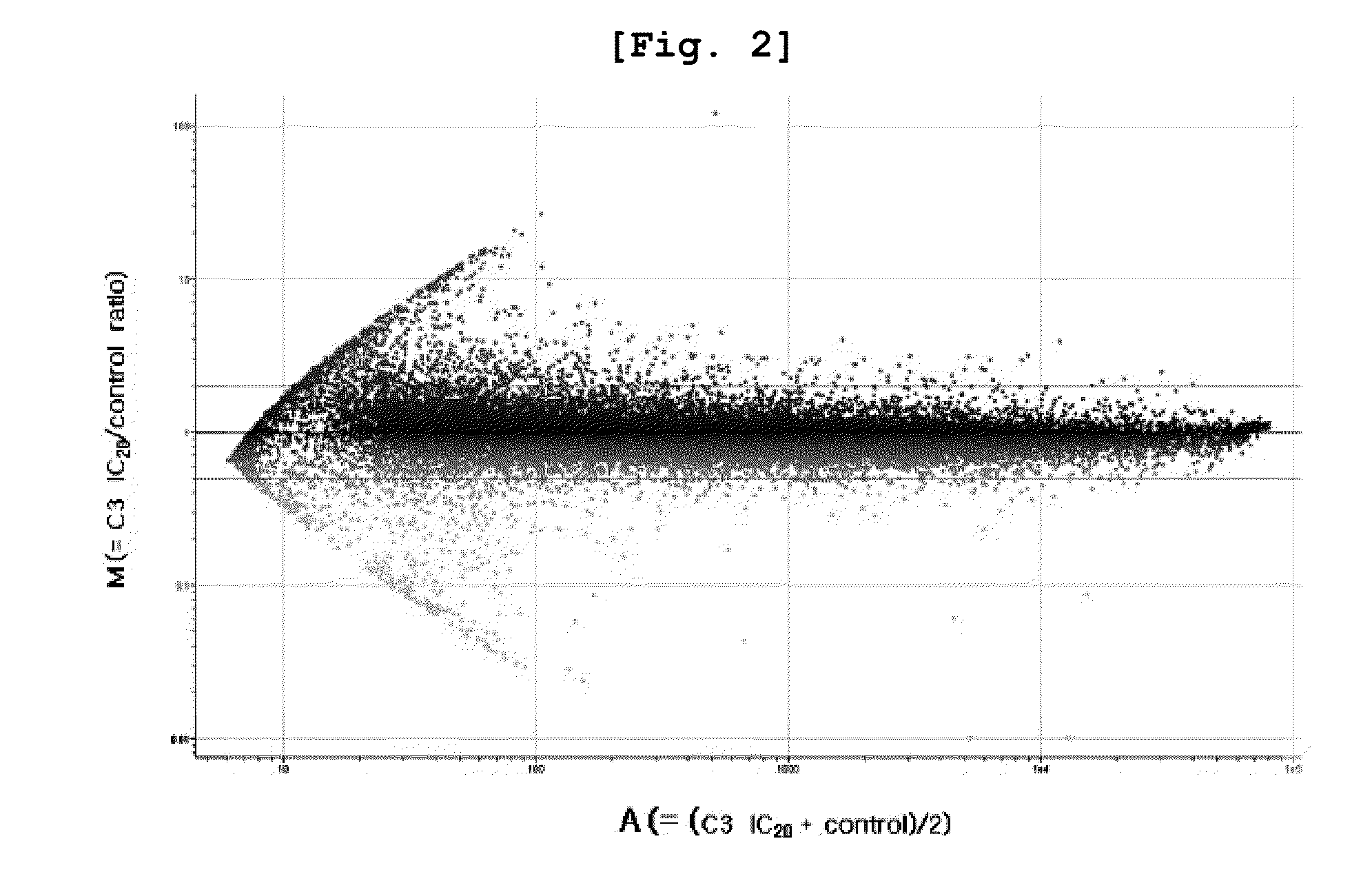
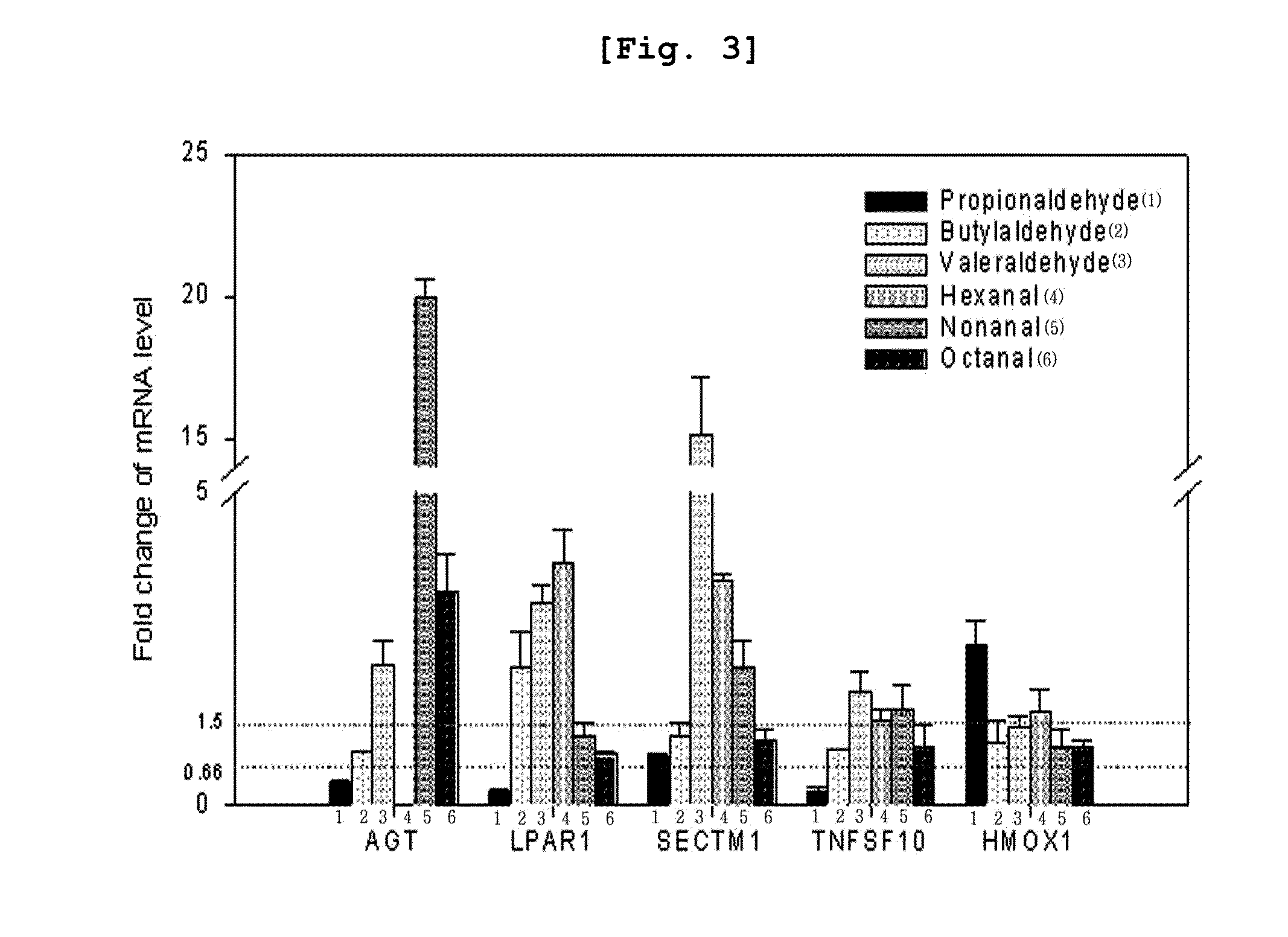
Specific biomarker for identification of exposure to lower aliphatic saturated aldehydes and the method of identification using the same
InactiveUS20130324428A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA Microarray ChipBiologic marker
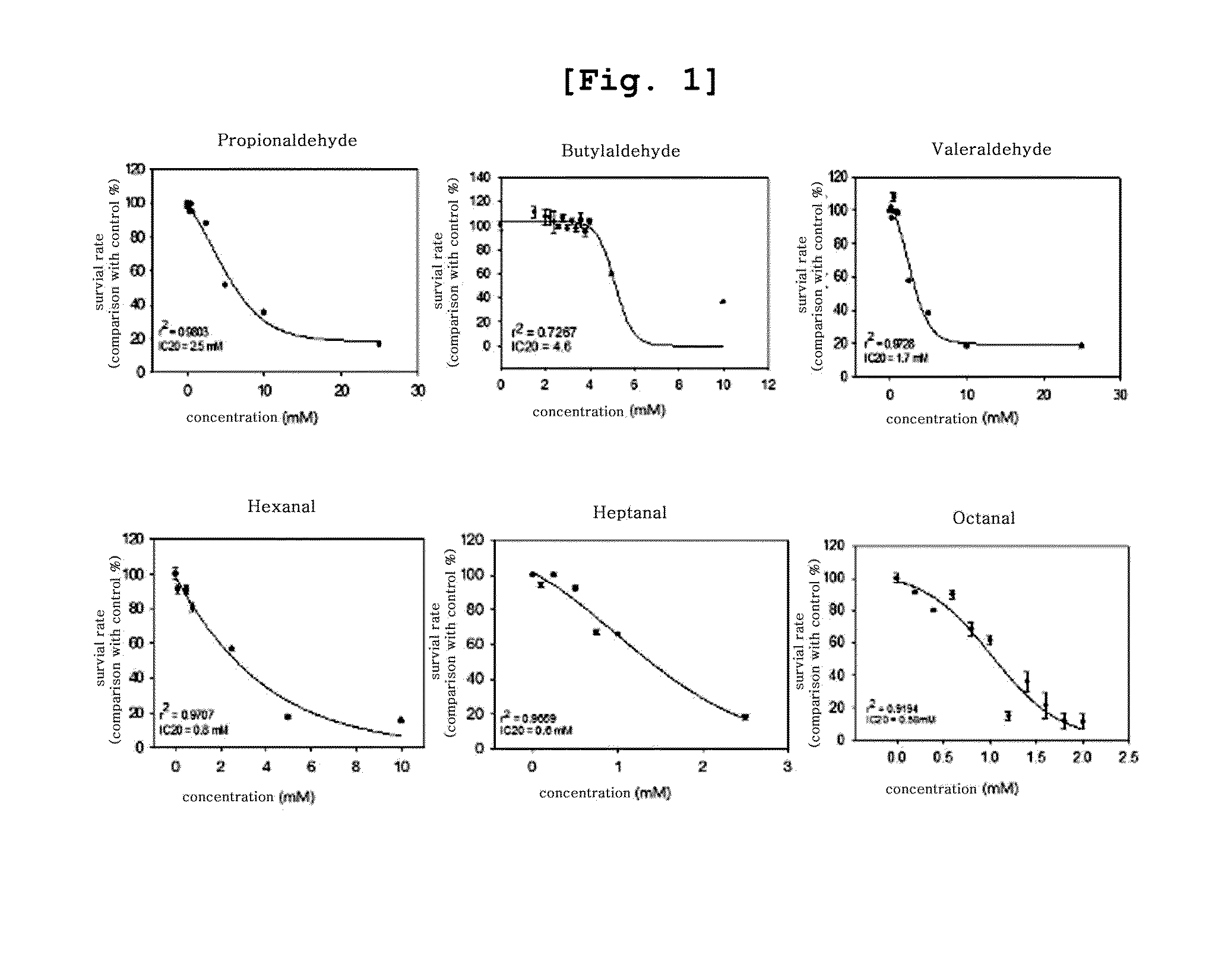
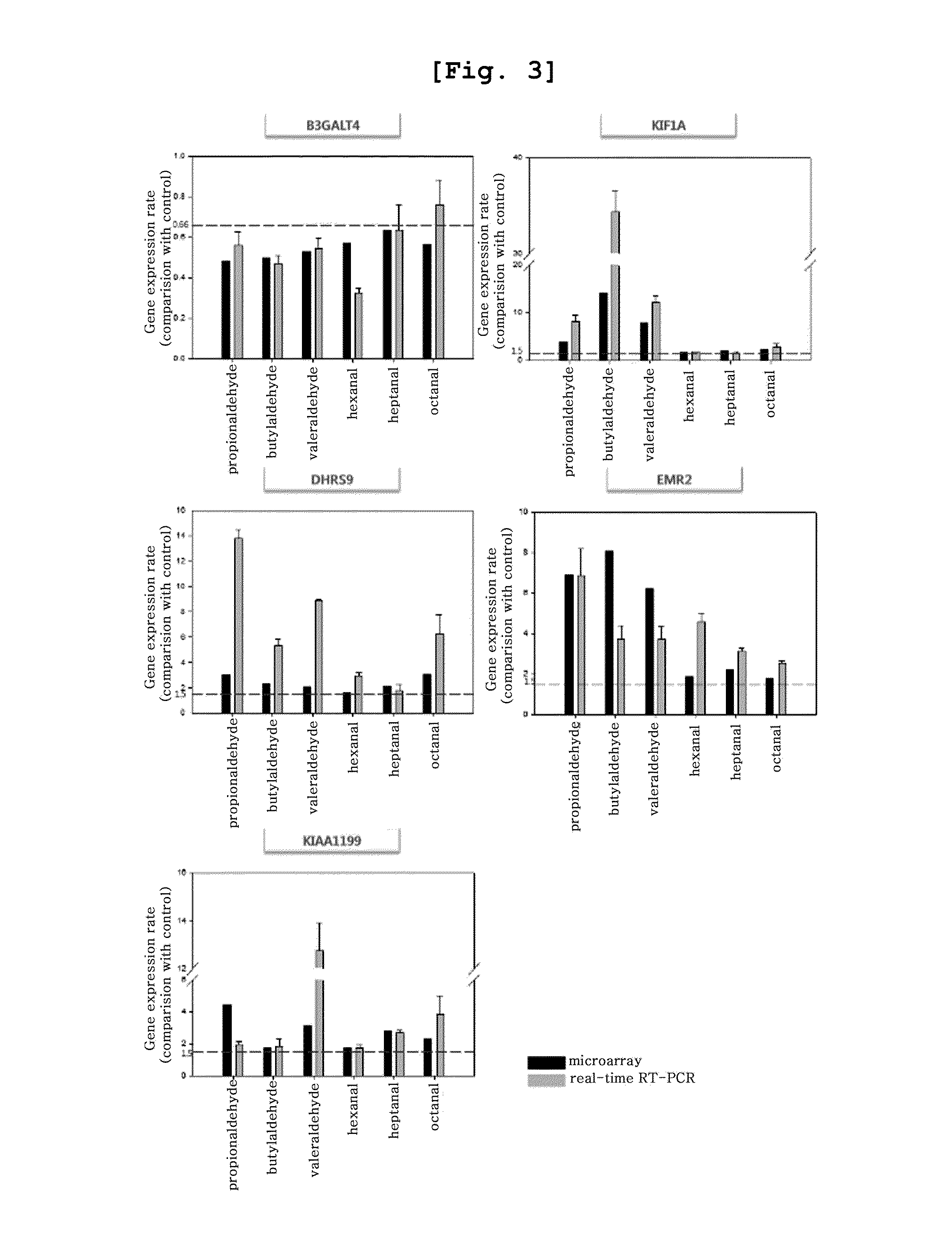
The present invention relates to a biomarker for the identification of specific exposure to lower aliphatic saturated aldehydes which are volatile organic compounds exposed in the environment, and a method for the identification of specific exposure to lower aliphatic saturated aldehydes using the same, precisely a biomarker which is up- or down-regulated specifically by lower aliphatic saturated aldehyde exposure and a method for the identification of specific exposure to lower aliphatic saturated aldehydes using the biomarker. The biomarker of the present invention is the reacted genes selected by using DNA microarray chip, which can be effectively used for the monitoring and evaluation of lower aliphatic saturated aldehyde contamination in the environment samples and at the same time as a tool for the investigation of the toxic mechanism induced specifically by lower aliphatic saturated aldehydes.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
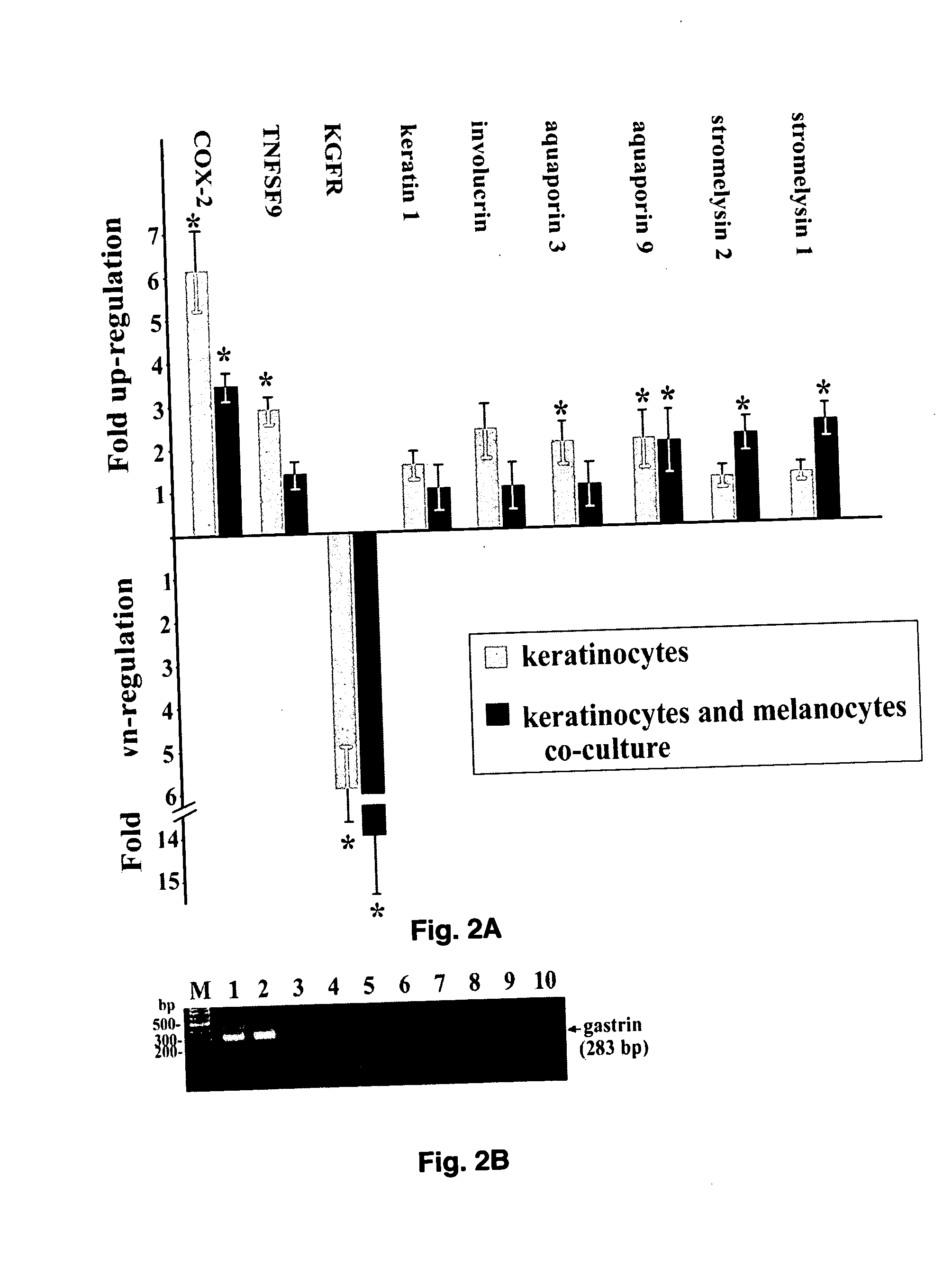
Microarray for evaluation of stress-related genes in skin
InactiveUS20070059711A1Improve the level ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA Microarray ChipCuticle
The present invention provides a novel DNA microarray chip that can be used for simultaneous testing of transcriptional responses to cutaneous stressors in the context of neuro-endocrine-immune functions of the skin. The transcriptional responses to ultraviolet radiation in epidermal keratinocytes were tested using such microarray chip containing more than 700 neuro-endocrine-immune related genes. The gene expression pattern was non-random and time dependent; it included increased expression of genes involved in water and salt balance, prostaglandin synthesis, keratinocyte differentiation as well as genes coding for stress effectors, cytokines and metalloproteinases. In contrast, expression was decreased for genes coding for growth factors and their receptors, and for elements of extracellular matrix. This stochastic pattern suggests that transcriptional responses are coordinated and aimed at preservation of epidermal barrier function, prevention of early carcinogenic events and remodeling of extracellular matrix.
Owner:SLOMINSKI ANDRZEJ +1
Construction method of virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC)
InactiveCN102025482BHuge key spaceSolve the first sharing problemGenetic modelsSecuring communicationPlaintextDNA Microarray Chip
The invention relates to information security technology, in particular to a virtual genome-based cryptosystem (VGC). The cryptosystem is provided with two matched keys, of which one is a virtual genome database (VGDB) consisting of random deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences and the other one is a position table that virtual genes of the VGDB are randomly distributed in a two-dimensional microarray, namely a virtual DNA microarray chip (VDMC). Any plaintext information can be freely written on the VDMC, namely points for forming the plaintext information are selected from the VDMC microarray. The selected points correspond to the virtual genes in the VGDB; small segments of DNA sequences are randomly selected from the virtual genes; and the uniqueness of the small segments of DNA sequences in the VGDB is determined by using a common tool of the bioinformatics, namely a basic local alignment search tool (BLAST), or other character string search algorithms such as a Knuth-Morris-Pratt (KMP) algorithm and the like. A cipher text is combined by the small segments of DNA sequences. The small segments of DNA sequences need only to perform BLAST on the VGDB during decryption, namely the points for forming the plaintext information can be discovered, and the plaintext information can be restored according to the VDMC. Any non-VGDB sequence can be randomly inserted into the cipher text and does not have any influence on the encryption. Thus, the VGC is an excellent information hiding system. In addition, the VGC key can be updated automatically so as to realize an indecipherable one-time-pad system. The cryptosystem is used for real-time quick secret information communication, digital signature and identity authentication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
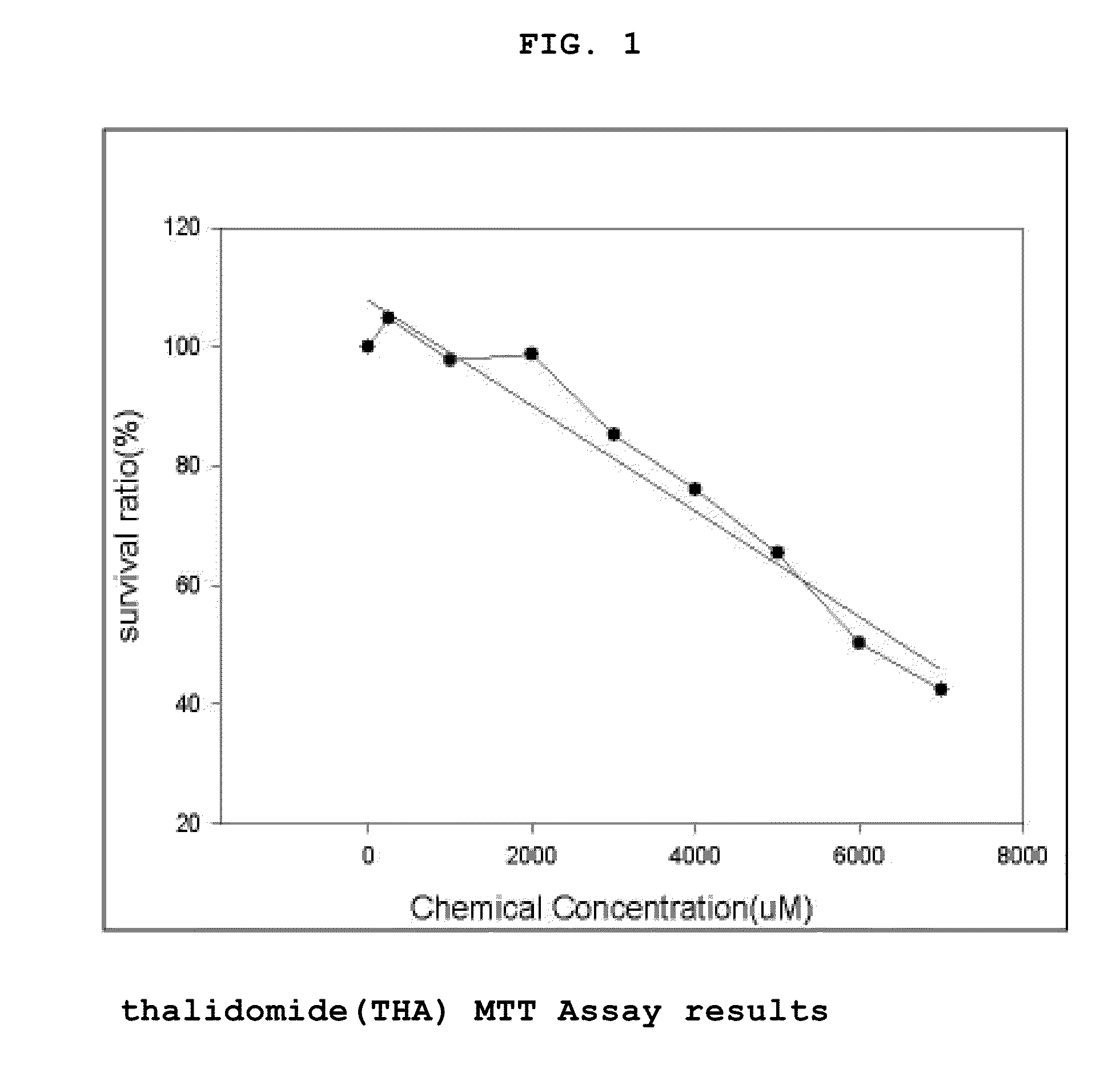
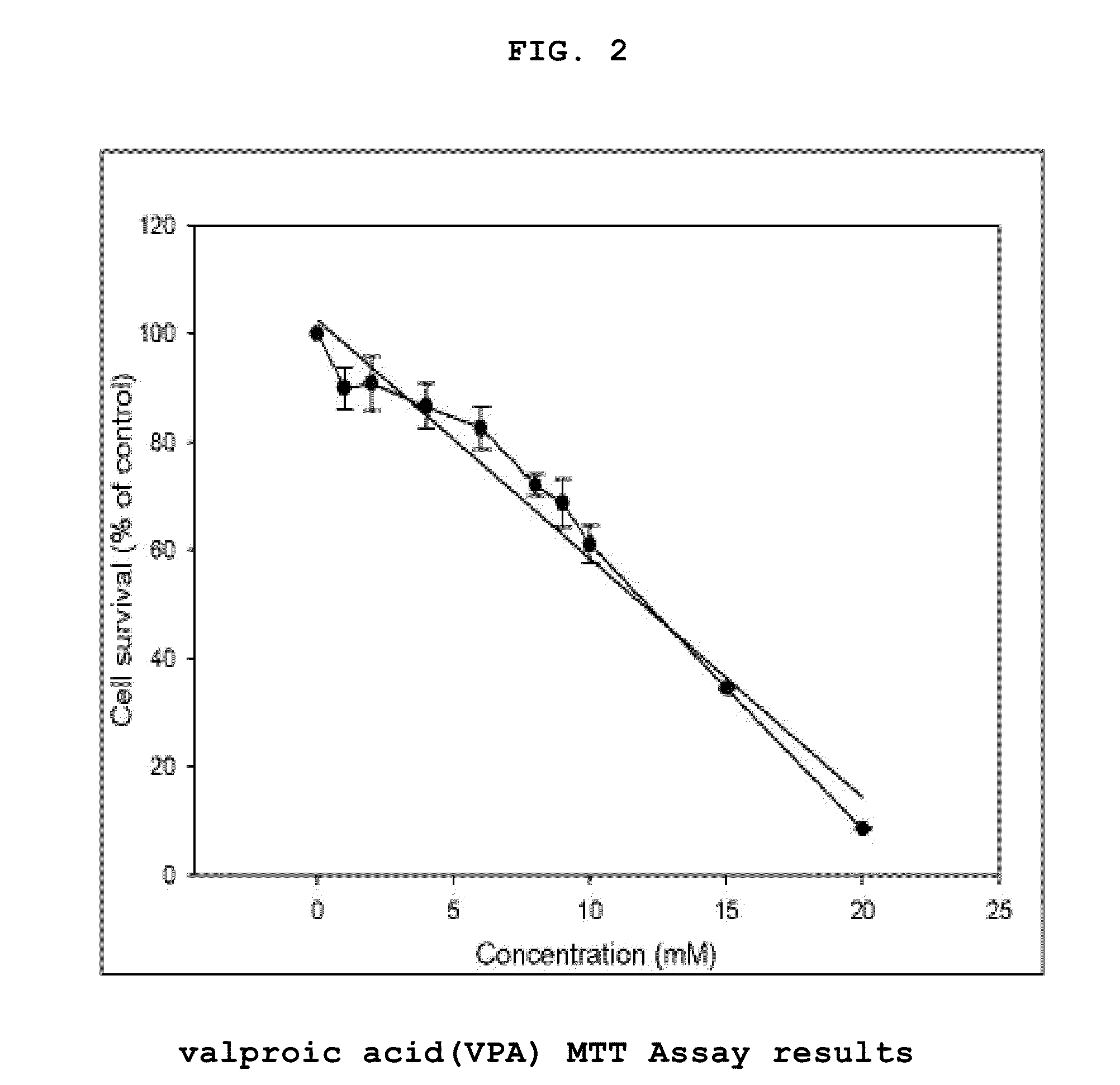
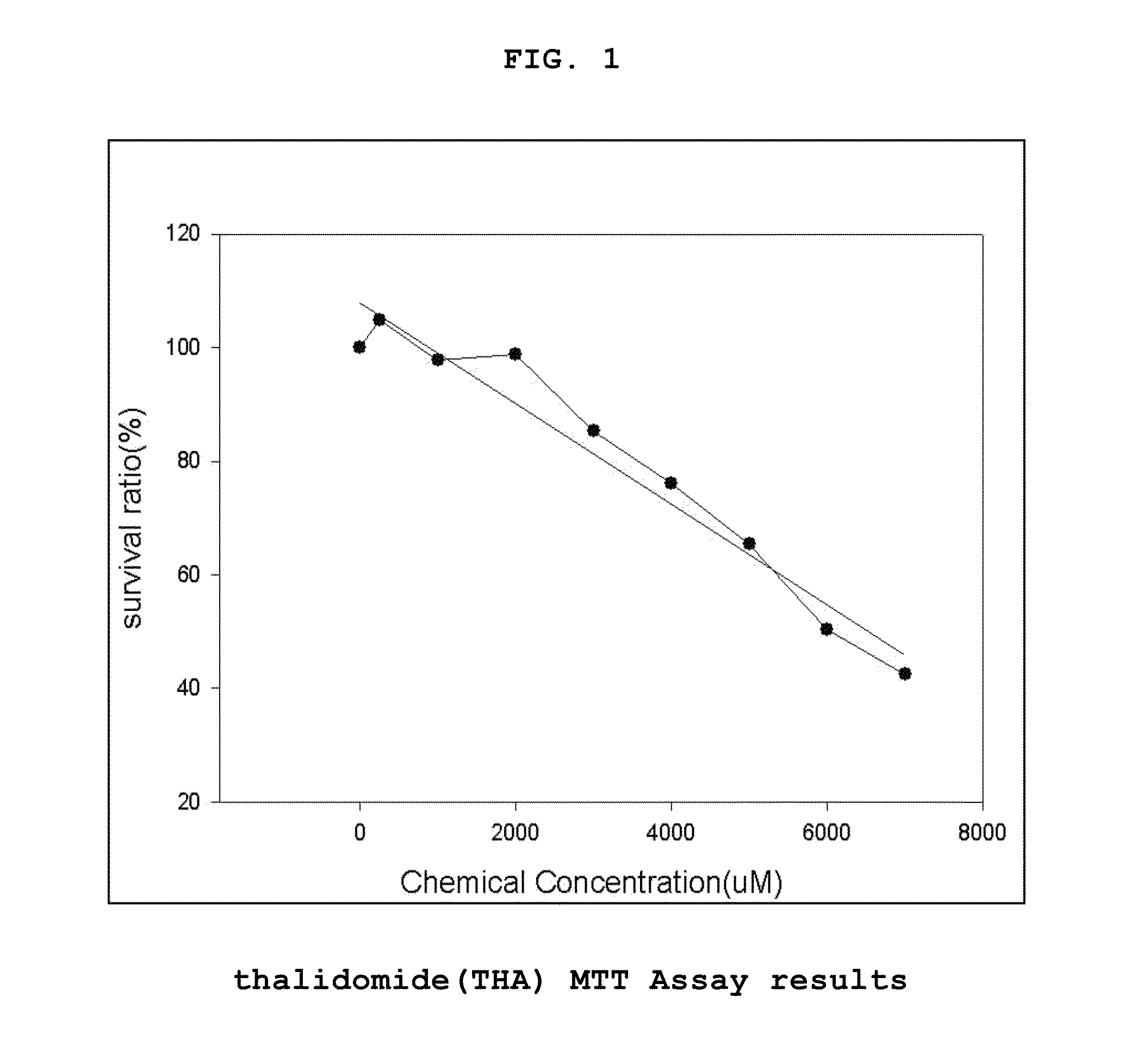
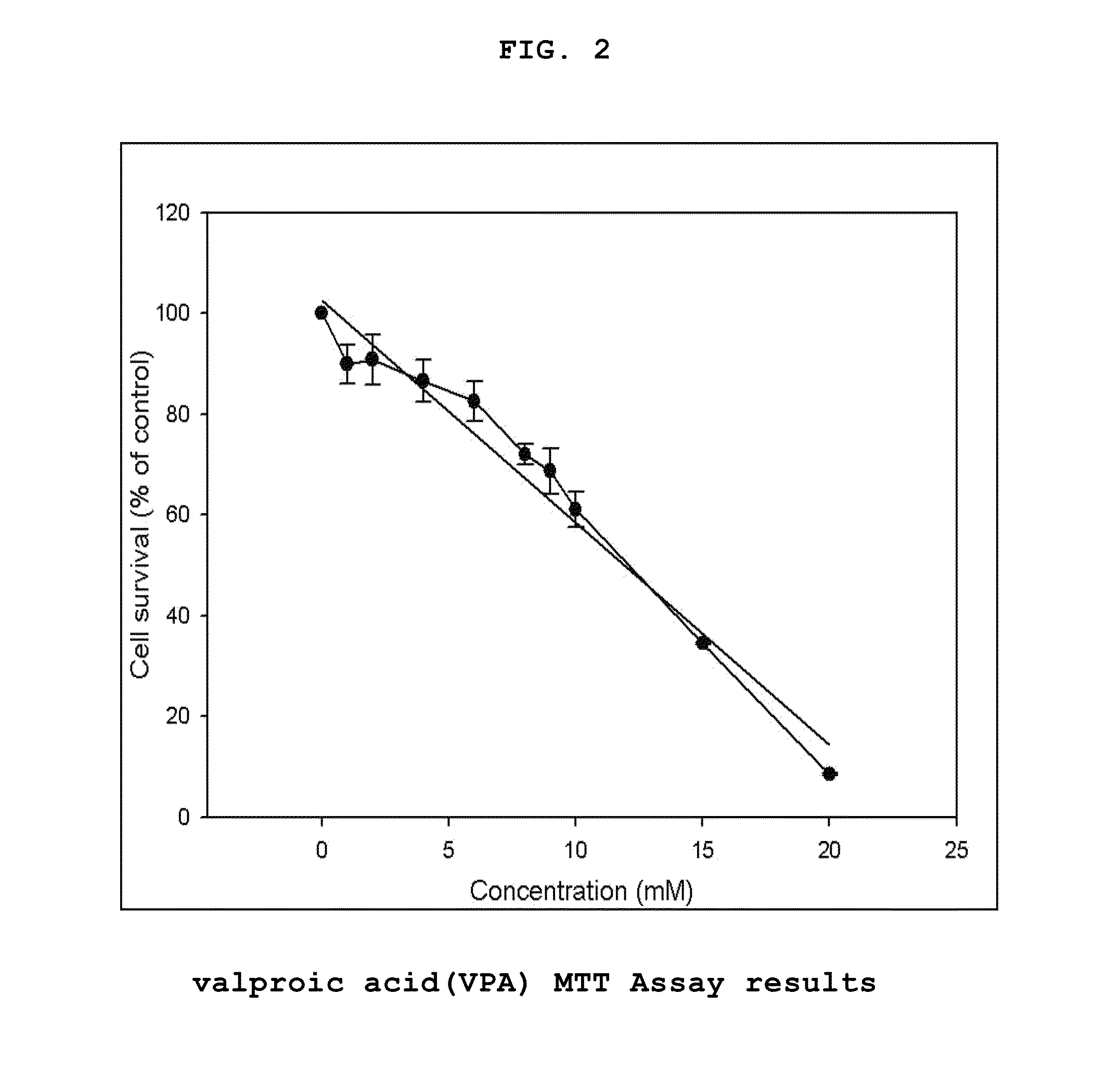
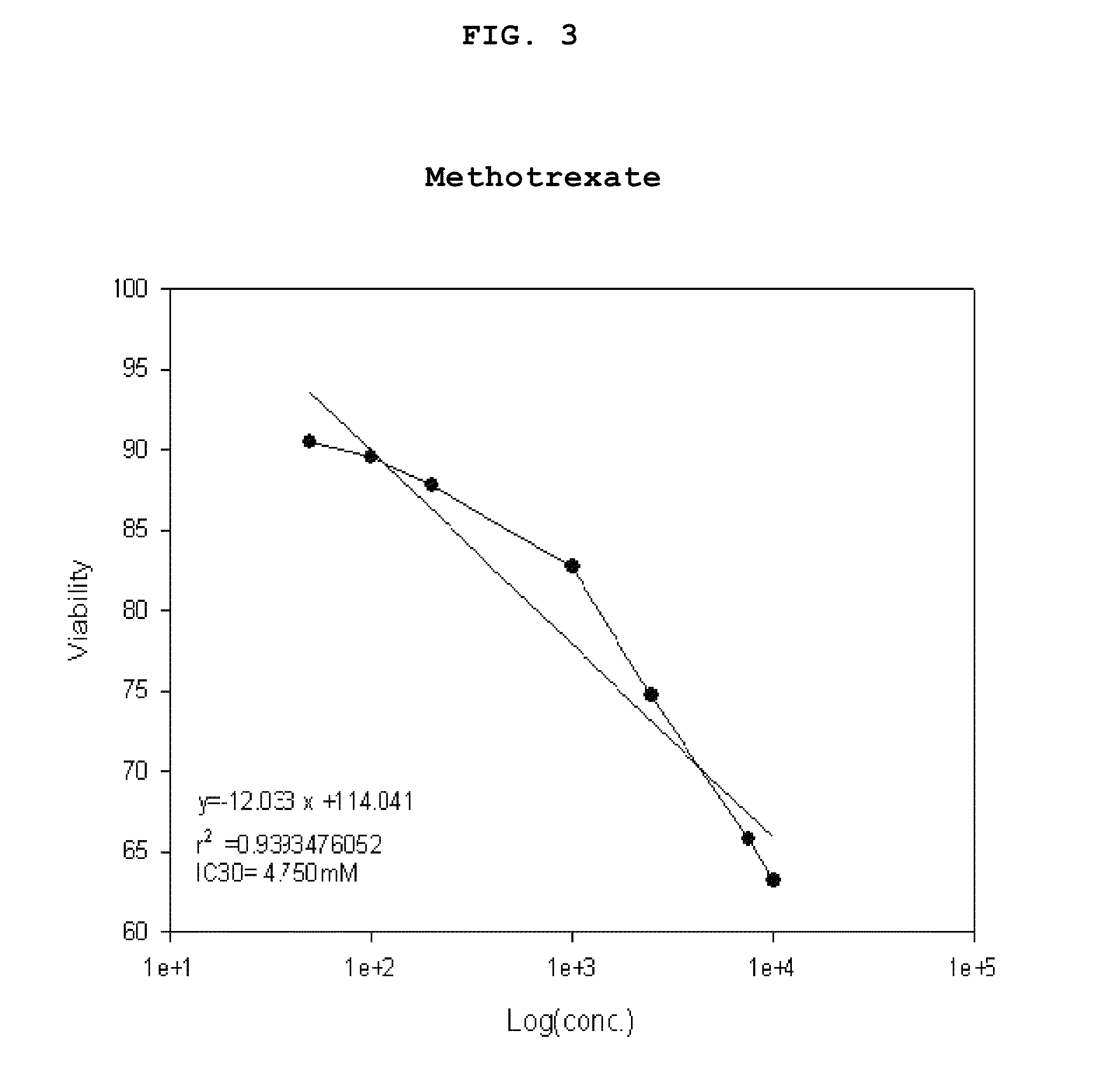
Genes Based on Thalidomide, Valproic Acid and Methotrexate Treatment for Screening of Drug Inducing Teratogenicity and Screening Method Using Thereof
ActiveUS20100256000A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA Microarray ChipValproic Acid
The present invention relates to a screening method using the genes related to teratogenicity, more precisely the genes up- or down-regulated by a drug inducing teratogenicity such as thalidomide, valproic acid, and methotrexate and a method for screening of thalidomide, valproic acid and methotrexate using the genes. The genes of the present invention is based on reactive genes selected by DNA microarray chip, so that it is very effective in risk assessment and monitoring drugs or chemicals having high risk of teratogenicity and at the same time it can be used as a tool to examine mechanism of teratogenicity.
Owner:EAN HIGHTECH CO LTD
Preparation and use of micro-array chip for HLA-B27 genotyping
ActiveCN101353693AReliability advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman leucocyte antigenDNA Microarray Chip
The invention relates to a gene detection kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the preparation and the usage of a micro-array chip used for HLA-B27 genotyping. A DNA micro-array chip technology is adopted, and the kit can carry out partign to human leucocyte antigen B27, with high pass, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
HBV YMDD mutation, precore region mutation/BCP region mutation and genotyping integrated-detection DNA microarray chip
InactiveCN101660000AImprove throughputImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipHbv genotype
The invention relates to a DNA microarray chip, in particular to an HBV YMDD mutation, precore region mutation / BCP region mutation and genotyping integrated-detection DNA microarray genetic chip. A solid-phase carrier substrate is used, and an oligonucleotide probe is designed in view of the HBV YMDD mutation, the precore region / BCP region mutation sites and the HBV genotype so as to prepare the DNA microarray chip. The DNA microarray chip can simultaneously detect three indexes at one time and can simultaneously detect a plurality of samples. The DNA microarray chip can be widely used to individual medicine taking guidance in the clinical process of treating HBV infections.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
Detection of DNA binding protein with exonuclease protective DNA probe and hybrid DNA microarray chip
InactiveCN1746318AEfficient analysisFacilitate scientific researchMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipProtein insertion
The invention is to detect the DNA conjugated protein using the hybrid DNA micro-array slug of exonuclease to protect DNA probe. The process is: (a) preparing the combined protein with DNA probe, the vector PCR, Tag-DNA; (b) combining the combined protein with DNA probe and the DNA conjugated protein; (c) treating with the exonuclease; (d) PCR amplifying and marking; detecting the hybrid product of PCR and the Tag-DNA. The method can detect many kinds of the DNA conjugated protein simultaneously but not modifying and marking the protein.
Owner:王进科 +1
HLA-DQB1 gene typing DNA micro-array chip reagent kit
The invention relates to a gene detecting kit that is used in clinical detection, in particular to a DNA microarray chip detecting kit, which can realize subtype detection of human leukocyte antigen DQB1(HLA-DQB1) gene in high flux, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Preparation and use of micro-array chip for HLA-DR4 genotyping
ActiveCN101353691AReliability advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipGenotyping
The invention relates to a genetic testing kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the preparation of a microarray chip and a method thereof for HLA-DR4 genotyping. By adopting a DNA microarray chip technology, the kit can carry out the genotyping to HLA DR4 gene, with high pass, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
Gene mutation detection kit for GS (Gilbert syndrome)
The invention relates to a gene mutation detection kit for the GS (Gilbert syndrome) and belongs to the technical field of biology. The kit comprises DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) micro-array chips formed by fixing an acrylamide modified PCR (polymerase chain reaction) product and other components on a propylene group modified slide as well as 6 nucleotide probe parts. The kit adopts a DNA micro-array technology, is simple and convenient to operate, low in price and capable of being applied to screening and clinical auxiliary diagnosis of diseases related to the GS caused by gene mutation.
Owner:吴旭平
HPV high risk and low risk subtype typing DNA micro-array chip
ActiveCN101487042AImprove throughputImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipLower risk
The invention relates to DNA microarray chips, in particular to DNA microarray chips under human papilloma virus (HPV) high-risk and low-risk subtype classification. A solid-phase carrier substrate is adopted and matched with oligonucleotide probes of each HPV subtype so as to prepare the DNA microarray chips, which can simultaneously detect the HPV high-risk and low-risk subtypes of multiple samples at one time in high sensitivity and high specificity, and can be widely applied into qualitative and subtype detection of HPV infection.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD +1
Sequencing primers, kit and detection method for detecting CYP2C19 gene polymorphism
InactiveCN103866023AFlexible throughputEasy to combine freelyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA Microarray ChipA-DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of gene polymorphism detection, and in particular relates to sequencing primers, a kit and a detection method for detecting CYP2C19 gene polymorphism, which aim at overcoming the defects that a DNA microarray chip method for detecting CYP2C19 gene polymorphism is long in consumed time, relatively high in cost and inflexible in use in the prior art. The sequencing primers provided by the invention comprise a CYP2C19*2 sequencing primer of which the 3'-end base sequence comprises -ccactatcattgattatttc-3', and further comprises a CYP2C19*3 sequencing primer of which the 3'-end base sequence comprises -ttgtaagcaccccct-3'. The kit provided by the invention is short in detection time, low in detection cost and flexible in use, and the detection method is easy in operation.
Owner:康熙雄 +7
Reagent kit for parting detection of HLA-DRB1 gene
ActiveCN101314790AHigh detection throughputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA Microarray ChipAntigen
The invention relates to a gene detecting kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the kit which adopts a DNA micro-array chip and a dual-temperature hybridization probe to execute the detection and typing on human leukocyte antigen gene in a high-throughput, high-efficiency and high-specificity manner and the usage thereof.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
Genes based on thalidomide, valproic acid and methotrexate treatment for screening of drug inducing teratogenicity and screening method using thereof
ActiveUS8445207B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA Microarray ChipTeratogenic risk
The present invention relates to a screening method using the genes related to teratogenicity, more precisely the genes up- or down-regulated by a drug inducing teratogenicity such as thalidomide, valproic acid, and methotrexate and a method for screening of thalidomide, valproic acid and methotrexate using the genes. The genes of the present invention is based on reactive genes selected by DNA microarray chip, so that it is very effective in risk assessment and monitoring drugs or chemicals having high risk of teratogenicity and at the same time it can be used as a tool to examine mechanism of teratogenicity.
Owner:EAN HIGHTECH CO LTD
Integrated detection DNA microarray chip for HBV, HCV and HIV-1 in blood
ActiveCN101660003AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA Microarray ChipWhole blood product
The invention relates to a DNA microarray chip, in particular to an integrated high-flux detection DNA microarray chip for hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1). A solid-phase carrier substrate is used, and an oligonucleotide probe is designed in view of genes of HBV, HCV and HIV-1 so as to prepare the DNA microarray chip; and when matched witha PCR primer and other components, the DNA microarray chip can simultaneously detect the three viruses in a plurality of samples with high sensitivity and high specificity. The DNA microarray chip ismainly used for screening the virus nucleic acid in blood and blood products.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BDS BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Micro-array chip based on double layer nano-structure substrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107486270AReduce consumptionSimple methodNanostructure manufactureLaboratory glasswaresDNA Microarray ChipAgglutinin-B
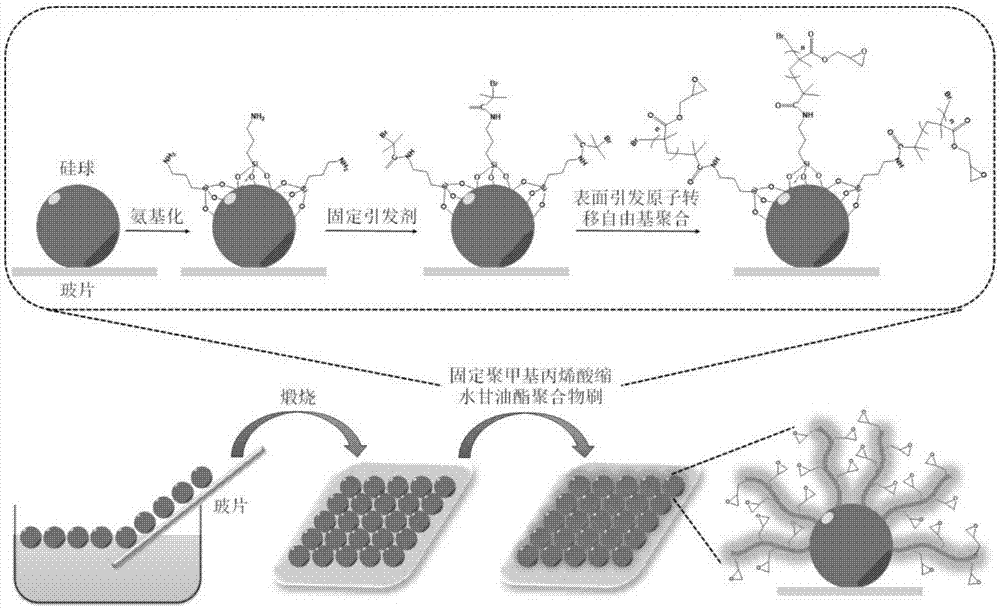
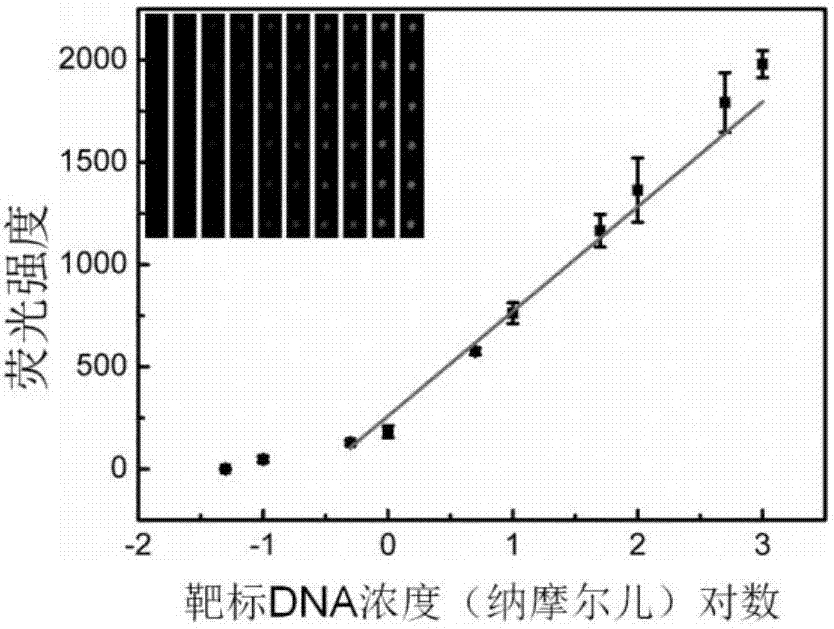
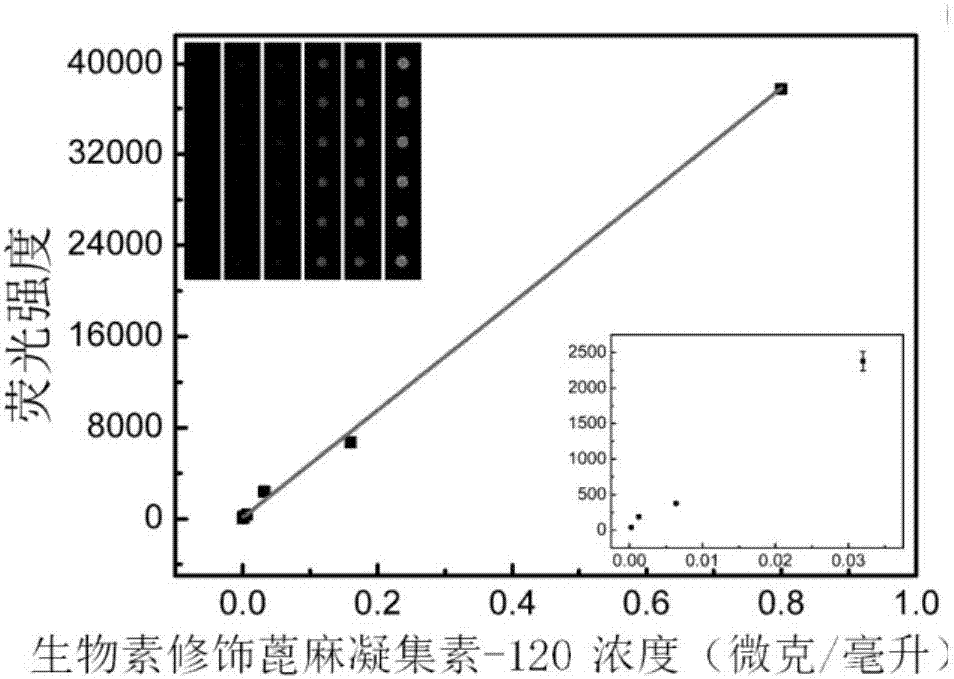
The invention provides a micro-array chip based on a sphere-brush double layer nano-structure substrate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the micro-array chip has versatility, and has the advantages of convenient process and less equipment requirement, and is suitable for large batch production; the micro-array chip can realize the analysis detection of interacting between nucleotide and nucleotide, sugar and protein, and protein and protein, and has the advantages of simpleness, less sample consumption and high sensitivity. The experiment result shows that the sugar micro-array chip prepared by the method has the detection limit on biotin-modified castor-oil plant agglutinin-120 and biotin-modified concanavalin agglutinin being 1 ng / mL, and the DNA micro-array chip has the detection limit on target DNA being 0.1 nmol / L; the glycoprotein micro-array chip has the detection limit on the biotin-modified castor-oil plant agglutinin-120 being 0.3 ng / ml, and the antibody micro-array chip has the detection limit on the CY5-modified rabbit-anti-human antibody being 10 pg / mL.
Owner:上海格荣生物科技有限公司
Specific biomarker for identificaton of exposure to propionaldehyde and the method of identification using the same
InactiveUS20130281311A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA Microarray ChipBiomarker identification
The present invention relates to a biomarker for the identification of specific exposure to propionaldehyde which is one of volatile organic compounds exposed in the environment, and a method for the identification of specific exposure to propionaldehyde using the same, precisely a biomarker which is up-regulated or down-regulated specifically by propionaldehyde and a method for the identification of specific exposure to propionaldehyde using the biomarker. The biomarker of the present invention is the reacted genes selected by using DNA microarray chip, which can be effectively used for the monitoring and evaluation of propionaldehyde contamination in the environment samples and at the same time as a tool for the investigation of the toxic mechanism induced specifically by propionaldehyde.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
A gilbert syndrome gene mutation detection kit
ActiveCN104805199BMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologyDNA Microarray Chip
Owner:吴旭平
Integrated detection DNA microarray chip for HBV, HCV and HIV-1 in blood
ActiveCN101660003BImprove throughputImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA Microarray ChipWhole blood product
The invention relates to a DNA microarray chip, in particular to an integrated high-flux detection DNA microarray chip for hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1). A solid-phase carrier substrate is used, and an oligonucleotide probe is designed in view of genes of HBV, HCV and HIV-1 so as to prepare the DNA microarray chip; and when matched witha PCR primer and other components, the DNA microarray chip can simultaneously detect the three viruses in a plurality of samples with high sensitivity and high specificity. The DNA microarray chip ismainly used for screening the virus nucleic acid in blood and blood products.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BDS BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Reagent kit for parting detection of HLA-DRB1 gene
ActiveCN101314790BHigh detection throughputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAntigenDNA Microarray Chip
The invention relates to a gene detecting kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the kit which adopts a DNA micro-array chip and a dual-temperature hybridization probe to execute the detection and typing on human leukocyte antigen gene in a high-throughput, high-efficiency and high-specificity manner and the usage thereof.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
A dna microarray chip and its detection method and its application in the detection of cyp3a4, cyp3a5 and mdr1 gene polymorphisms
InactiveCN101481736BEasy to makeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipMdr1 gene
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for detecting Type 2 diabetes related mononucleotide polymorphism by using DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) microarray chip
ActiveCN104388555AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipNucleotide
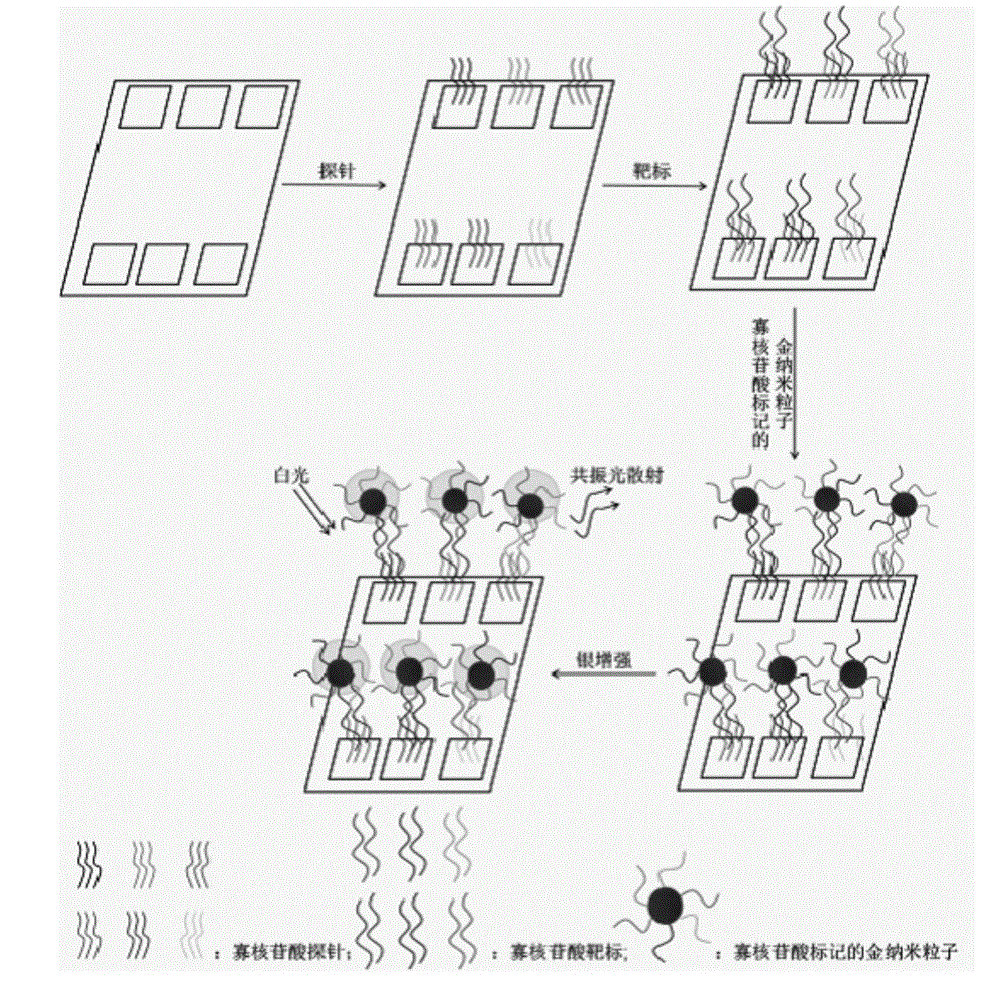
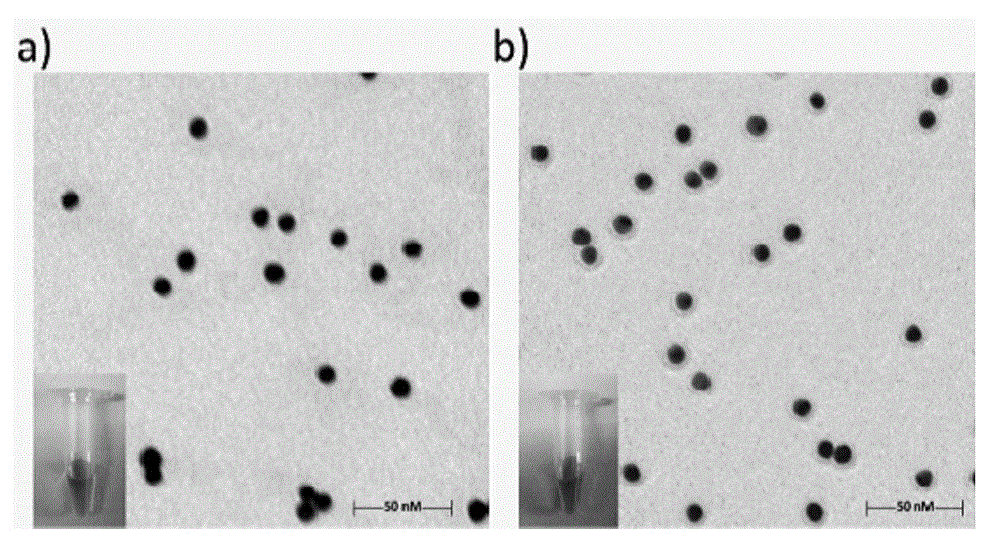
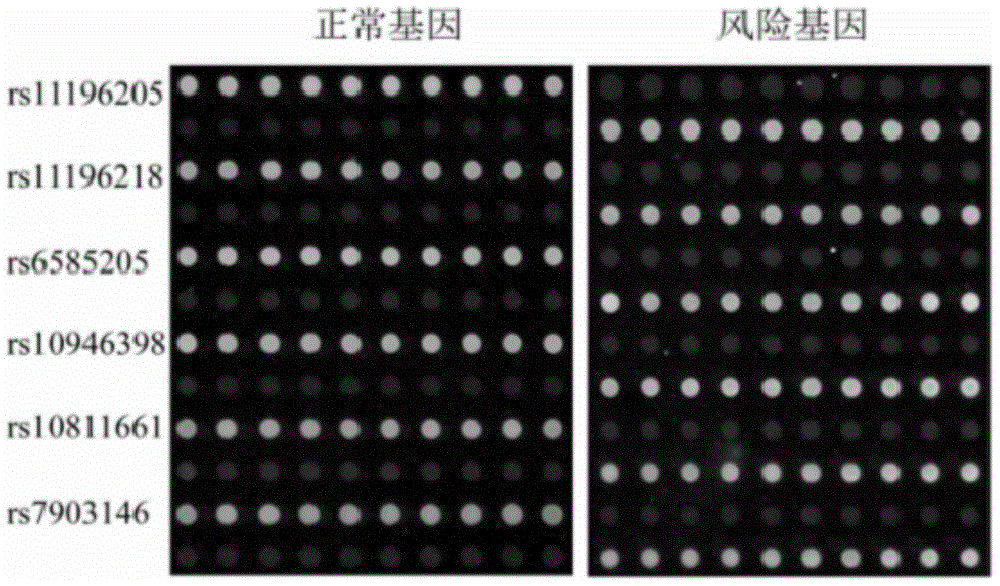
The invention relates to a method for detecting Type 2 diabetes related mononucleotide polymorphism by using a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) microarray chip, belonging to the technical field of DNA microarray chips. By using 6-oligonucleotide-modified gold nanoparticles as the markers in combination with 6 oligonucleotide probes for Type 2 diabetes detection, a microarray chip inspection method capable of simultaneously detecting 6 Type 2 diabetes related mutant sites is developed, thereby implementing the detection on DNA samples of simulated Type 2 diabetes and actual samples of Type 2 diabetes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
HLA-B27 genotyping detection kit
The invention relates to a gene detection kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the preparation and the usage of a micro-array chip used for HLA-B27 genotyping. A DNA micro-array chip technology is adopted, and the kit can carry out partign to human leucocyte antigen B27, with high pass, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Preparation and use of micro-array chip for HLA-A genotyping
ActiveCN101353694BHigh detection throughputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipGenotyping
The invention relates to a gene test kit used for clinical detection, in particular to the preparation and the usage of a micro-array chip used for HLA-A genotyping. A DNA micro-array chip technology and a dual temperature hybridization method are adopted, and the kit can carry out parting to the HLA-A gene, with high pass, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
HLA-C gene typing DNA micro-array chip reagent kit
ActiveCN101487043BReliability advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringDNA Microarray ChipHuman leukocyte antigen C
The invention relates to a gene detecting kit that is used in clinical detection, in particular to a DNA microarray chip kit, which can realize subtype detection of human leukocyte antigen C(HLA-C) gene in high flux, high efficiency and high specificity.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com