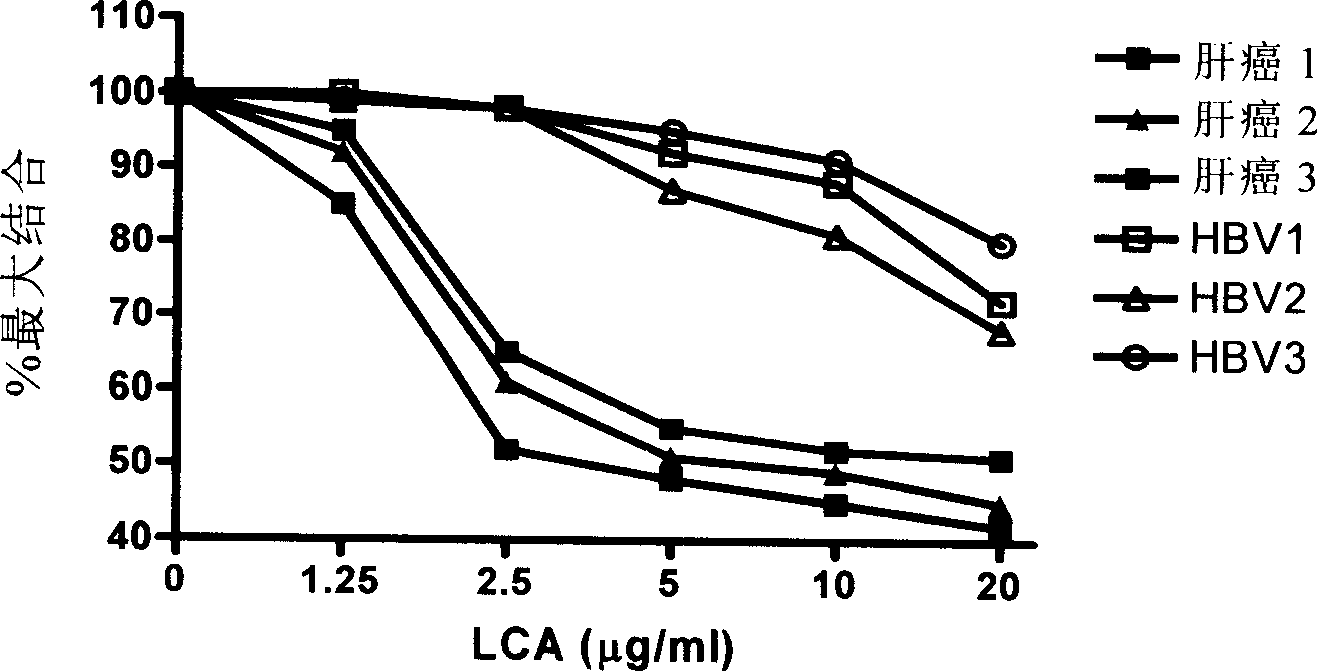
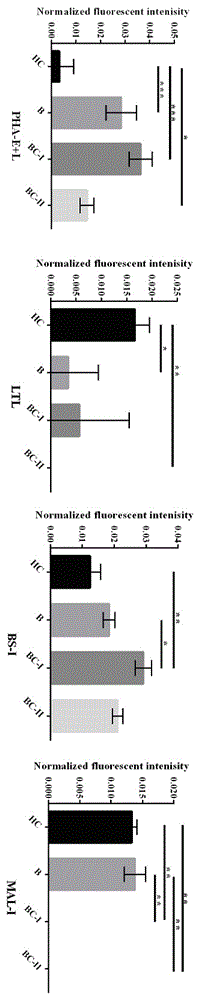
Patents
Literature
274 results about "Agglutinin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An agglutinin is a substance in the blood that causes particles to coagulate and aggregate; that is, to change from fluid-like state to a thickened-mass (solid) state. Agglutinins can be antibodies that cause antigens to aggregate by binding to the antigen-binding sites of antibodies. Agglutinins can also be any substance other than antibodies, such as sugar-binding protein lectins.
Neuronal growth factor galectin-1
InactiveUS6890531B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNerve degenerationADAMTS Proteins
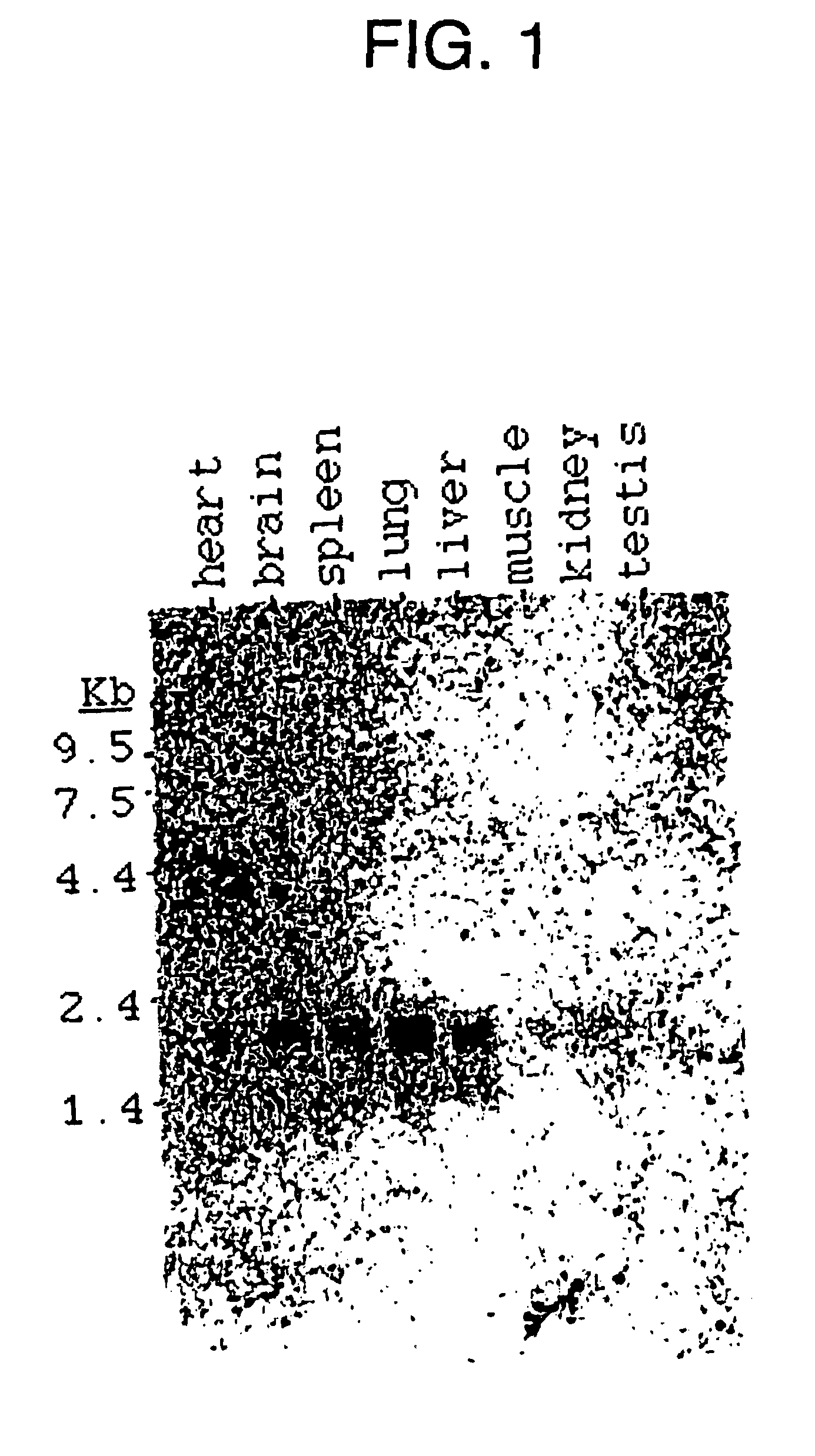
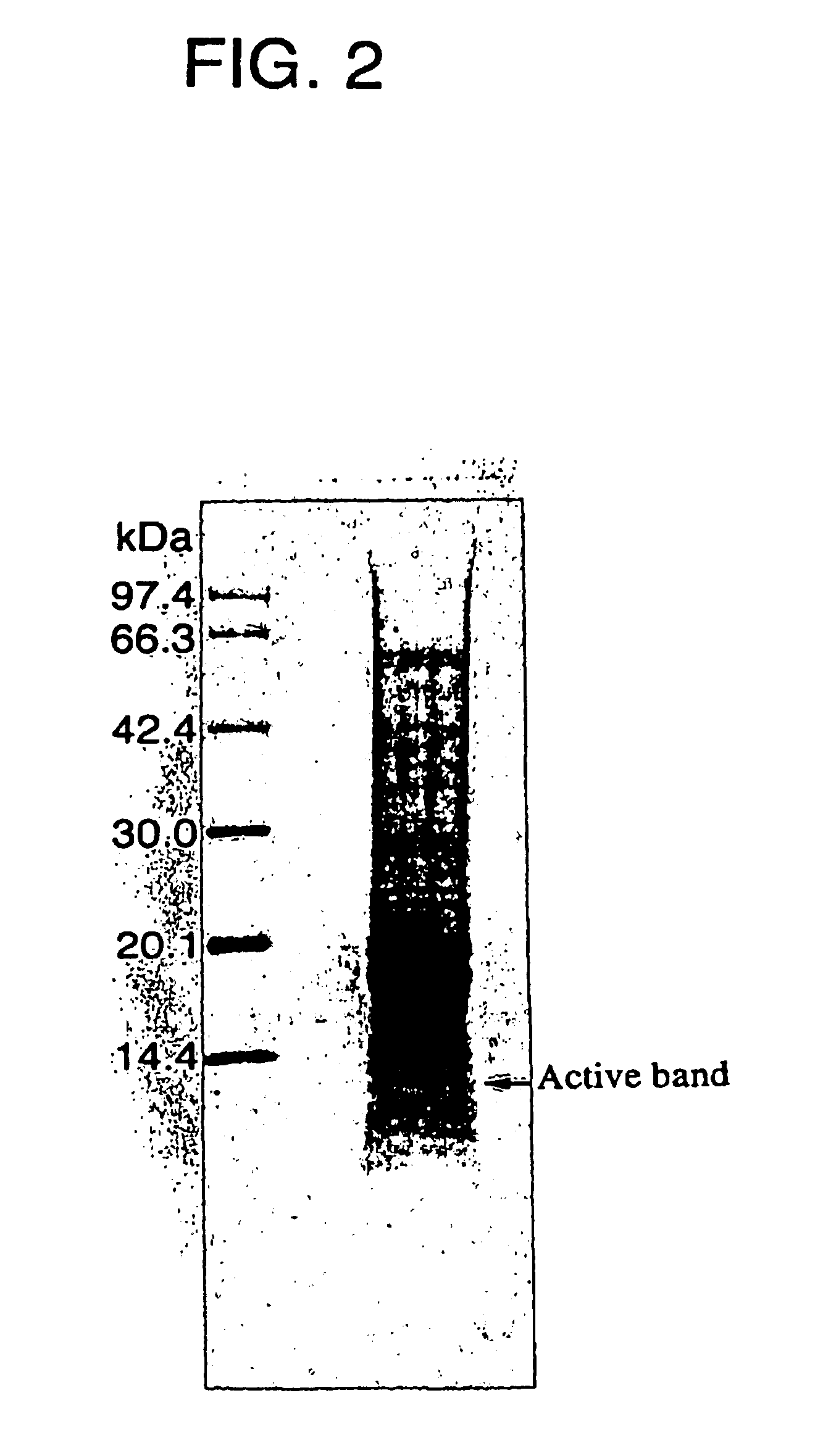
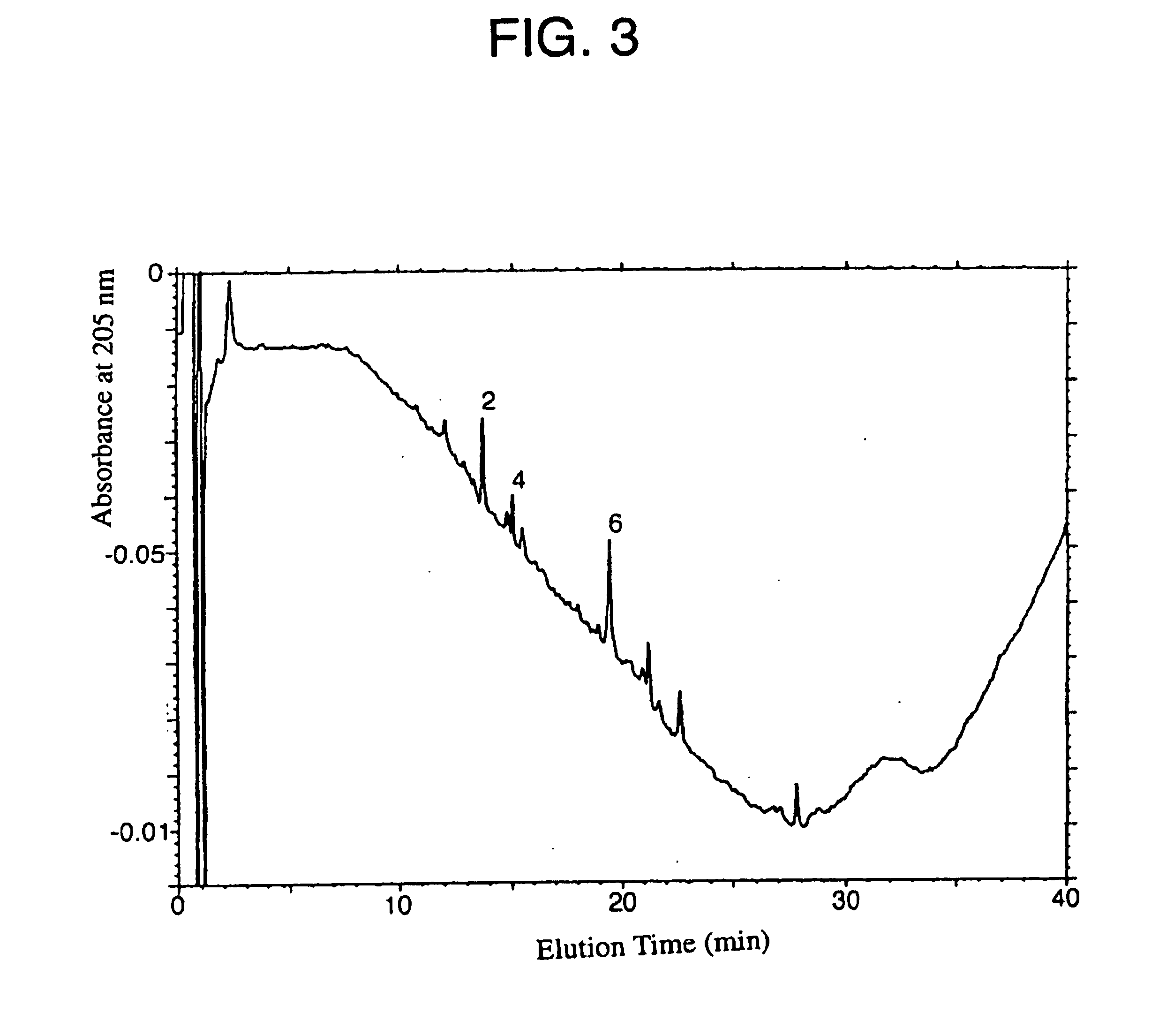
This invention relates to a remedy for neuropathy, such as nerve injury, nerve degeneration, and hypofunction upon nerve grafting, which contains as the active ingredient galectin-1 having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or its derivative; a protein having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or one having a homology of 90% or more at the amino acid level with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and carrying a disulfide bond(s) at least between Cys at the 16-position (Cys 16) and Cys at the 88-position (Cys 88) among cystein residues at the 2-position (Cys 2), 16-position (Cys 16), 42-position (Cys 42), 60-position (Cys 60), 88-position (Cys 88) and 130-position (Cys 130); and a process for producing the galectin-1 or its derivative protein by using an affinity column having an antibody to the above protein.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Method for detecting alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in saliva, serum and urine
The invention provides a method for detecting alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in saliva, serum and urine so as to detect expression information of alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in a rapid, convenient and accurate manner. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing agglutinin chips corresponding to detection of saliva, serum and urine samples respectively; 2) pretreating stock solutions of saliva, serum and urine samples, removing impurities and purifying proteins, labeling by using a fluorescent reagent and removing redundant fluorescence by using G-25 columns to obtain corresponding samples to be detected; and 3) respectively loading three samples to be detected onto corresponding agglutinin chips to obtain respective glycoprotein sugar chain spectrum in each sample to be detected, and obtain information of the alternative biological markers according to reaction results of any sample to be detected. By the method, the sensibility during detection is high and detection results are accurate; moreover, the method has the advantages of safety, no damage, convenience for sample collection, simplicity in storage and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method for analyzing glucoprotein
ActiveCN101308141ASimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingOrganismTime of flight
Disclosed is a method for analyzing glycoprotein, which comprises steps of firstly preparing a spotting buffer solution, spotting a chip, closing, cleaning and then drying, finally obtaining an agglutinin chip. A biological specimen is directly added on the agglutinin chip for undergoing steps of incubation, cleaning for removing hybridprotein, forming a crystal and dissociating the crystal, a time-of-flight mass spectrometer is used for detecting the flying time of charged ions in a vacuum electric field so as to obtain the glycoprotein graphical spectrum information, visually display the glycoprotein information such as molecular weight and abundance in the detected biological specimen, and identify the glycoprotein differential expression. Comparing the glycoprotein graphical spectrum information of the detected biological specimen with the sample graphical spectrum information can obtain the glycoprotein information of the differential expression. The method solves the technical problems of low detection flux, complicated detection steps and long cycle in the background technique. The method has advantages of convenient operation, high sensitivity and good repeatability, and is applied to the fast analysis and application in clinic medicine.
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
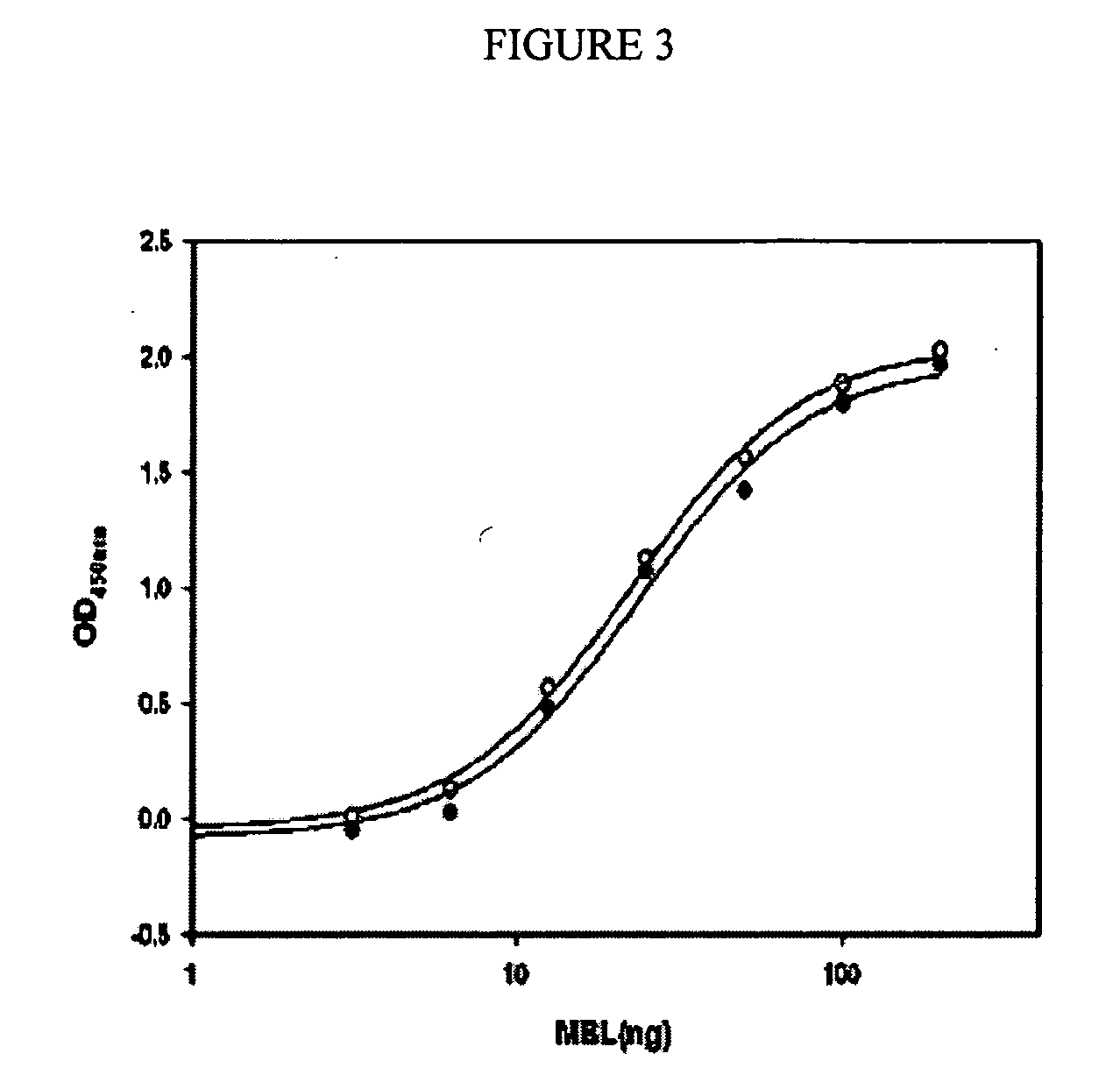
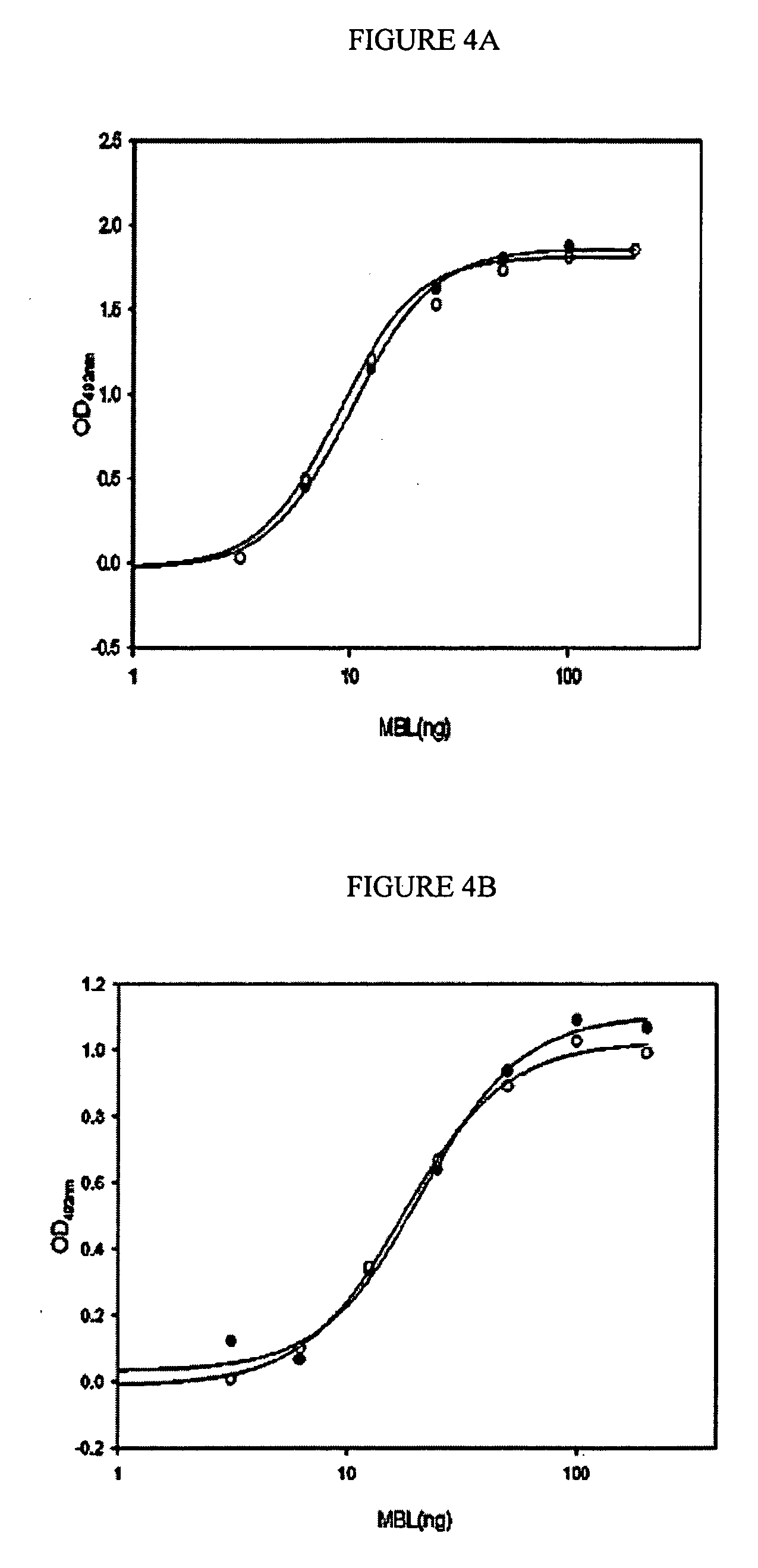
Antibody pairs and kits for immunochemical determination of mannan-binding lectin
InactiveUS7211396B2Increased to exacerbationIncreased susceptibilityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEnzymologyDiseaseAutoimmune disease
Various antibodies with different binding characteristics for MBL A or MBL B bound to mannan or MBL A or MBL B bound to an antibody against MBL are provided. Also provided are methods for selecting antibodies against MBL with different binding characteristics and methods and kits for using these antibodies to measure MBL capable of binding to mannan or oligomerized MBL and abnormal, poorly oligomerized MBL in a sample. The methods and kits are useful in diagnosing increased susceptibility to and exacerbation of infections and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ANTIBODYSHOP
Agglutinant competitive process liver cancer a-fetoglobulin heteroplasmon AFP-L3 quantitative test reagent kit
The present invention provides a monoclonal antibody, It is obtained by utilizing screened hybridoma with monoclonal antibody which can be combined with AFP heteroplasmon glycochain and can be competed with dolichos agglutinin site and cloning it. Said invention also provides kit containing said monoclonal antibody, its preparation method and its application. Said kit can be used as index for early diagnosis of liver cancer.
Owner:BEIJING WEILONG ARRAY BIOLOGICAL TECH
Agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein, reagent kit and application of reagent kit
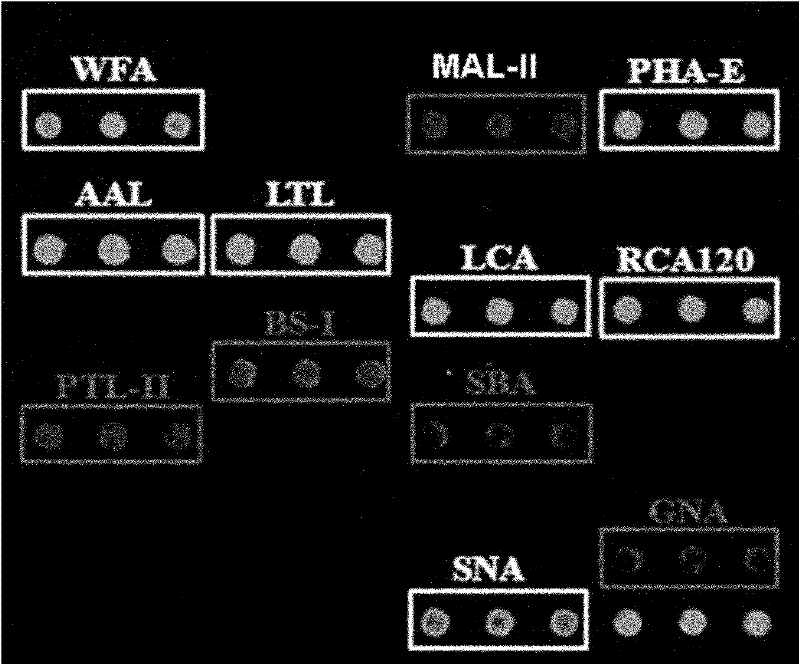
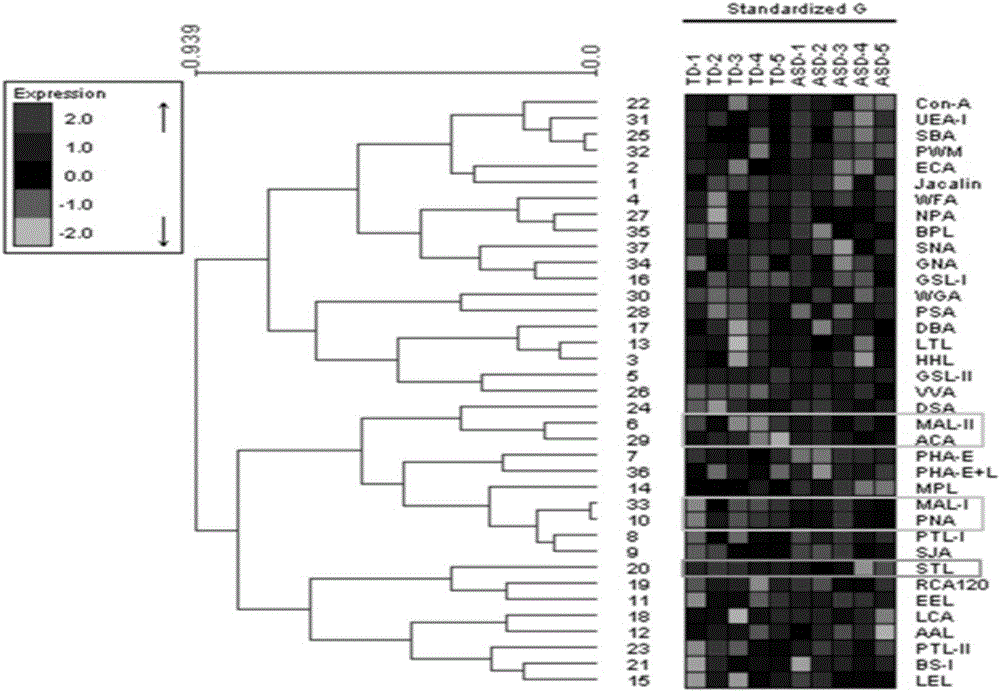
The relates to an agglutinin chip used for identifying cancer, in particular to an agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein, a reagent kit and application of the reagent kit, and aims at providing an agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer in a non-destructive mode through the change of carbohydrate chains in saliva, a reagent kit and application of the reagent kit. The agglutinin chip for identifying breast cancer based on sialoprotein comprises an agglutinin testing probe set. The agglutinin testing probe set at least comprises a combination of PHA-E+L, LTL, BS-I, MAL-I, LCA, BPL, PTL-II, NPA and GSL-I, or at least comprises a combination of LTL, BS-I, MAL-I, LCA, BPL, NPA and GSL-I. By means of the agglutinin chip, differentially-expressed glycoprotein carbohydrate chain structures in a patient saliva sample can be rapidly detected, whether a corresponding person suffers from a breast tumor or not is detected, and whether the breast tumor is breast cancer or not is determined; besides, saliva is adopted as an object to be detected and is easy and convenient to collect, and health risks existing when a serum sample is collected for detection in the prior art are avoided.
Owner:深圳格道糖生物技术有限公司
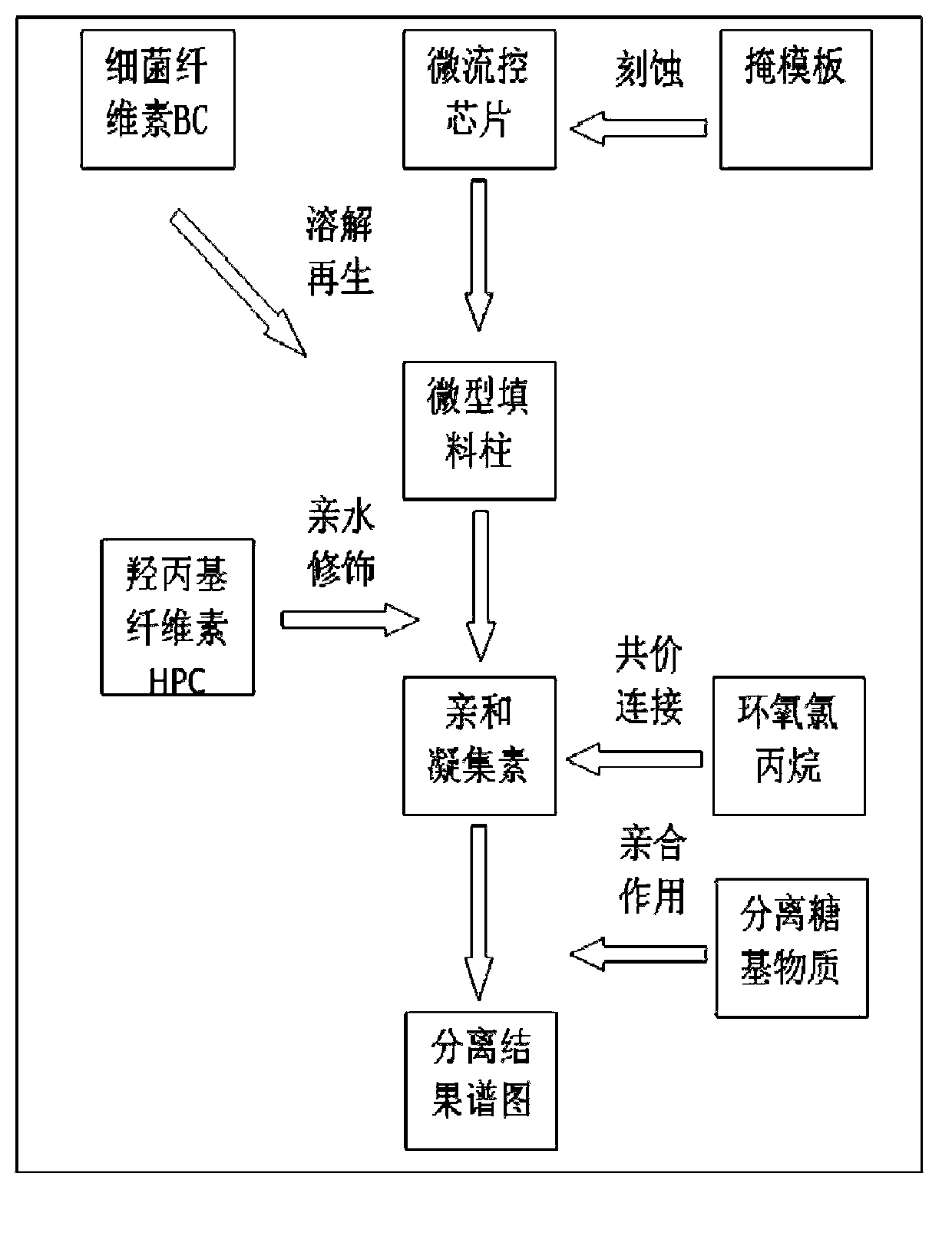
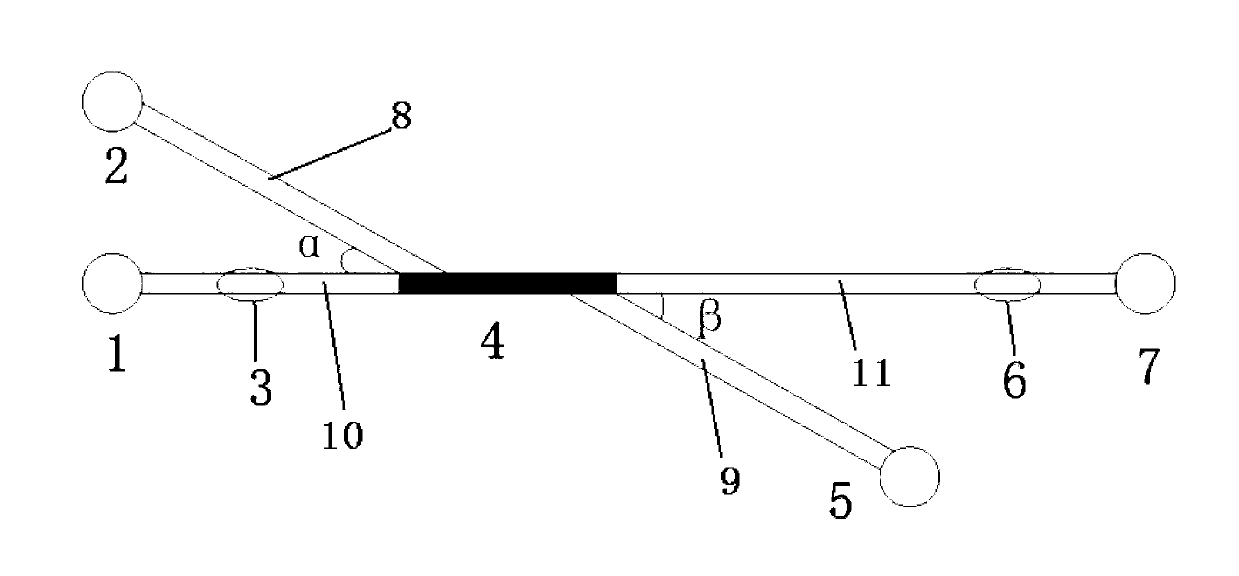
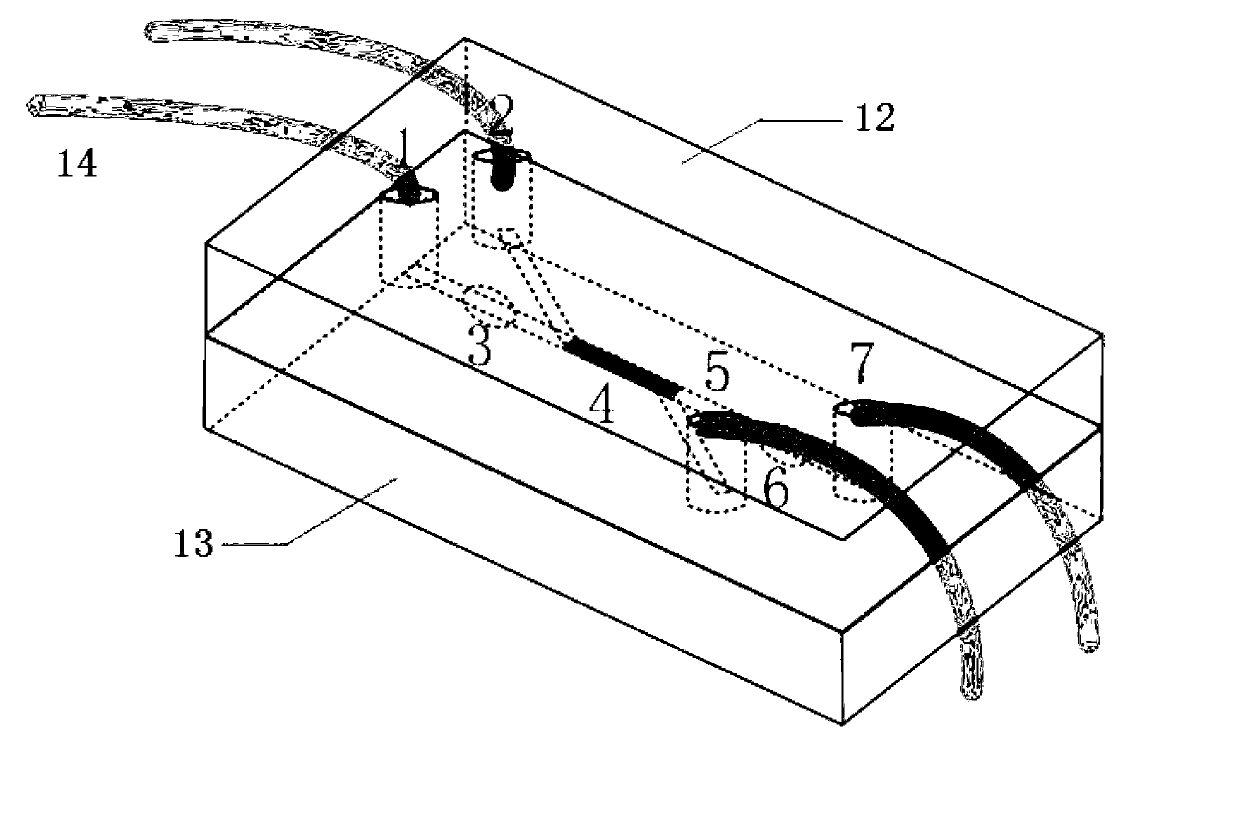
Micro-fluidic agglutinin chip for glycosyl separation, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103344464AIncrease contact areaGood reproducibilityPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresTemperature controlAgglutinin
The invention relates to a micro-fluidic agglutinin chip, specifically to a method for preparing and modificating a micro-fluidic chip. The micro-fluidic chip is designed and prepared through a micro electro mechanical technology. Dissolved bacterial cellulose is regenerated in a micro channel to be as a filling material of chip channel columns, and agglutinin is fixed on the filling material surface which is subjected to hydrophilic modification; and according to specific affinity effect of agglutinin to glycosyl, substances containing specific glycosyl on the surface, such as glycoprotein and lipopolysaccharide and the like, are separated. The chip consists of a glass base material, channel graph is etched on the base material by an ultraviolet etching technology, and high-temperature bonding is performed by program temperature control. The chip is provided with an inlet and an outlet of a separation sampling, an inlet and an outlet of the filling material, a bacterial cellulose filled column, a sample micro channel and on-line monitoring points. By taking regenerated bacterial cellulose as the chip filling material, the micro-fluidic agglutinin chip has the main advantages of being excellent in effects of bacterial cellulose, simple in fixing step of agglutinin, convenient to perform spectrum monitor, and substantial in glycosyl separation effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological chip for detecting specific glycoprotein, antibody or antigen by surface plasmon resonance technology
ActiveCN101968440AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsBiological testingAntigenBiochip
The invention relates to the field of biological chips, in particular to a protein chip for detecting a specific glycoprotein, antibody or antigen by surface plasmon resonance technology and a surface plasmon resonance principle-based detection method. The chip is provided with a metal film on a substrate; a connection layer is fixed on the surface of the metal film; agglutinin or other antigen or antibody is fixed on the connection layer; and the connection layer is prepared by activating a self-assembled monomolecular layer consisting of long-chain mercaptoethanol of which one end is provided with an active group and the other end reacts with the metal film through mercapto. The chip diagnoses diseases by the specific binding of the agglutinin and the specific glycoprotein and the binding of the specific antigen and antibody and provides a new way for disease diagnosis. The method is simple and practical, has low cost, simplifies operation steps, shortens detection time and is a novel method suitable for popularization.
Owner:上海睿昂基因科技股份有限公司 +1
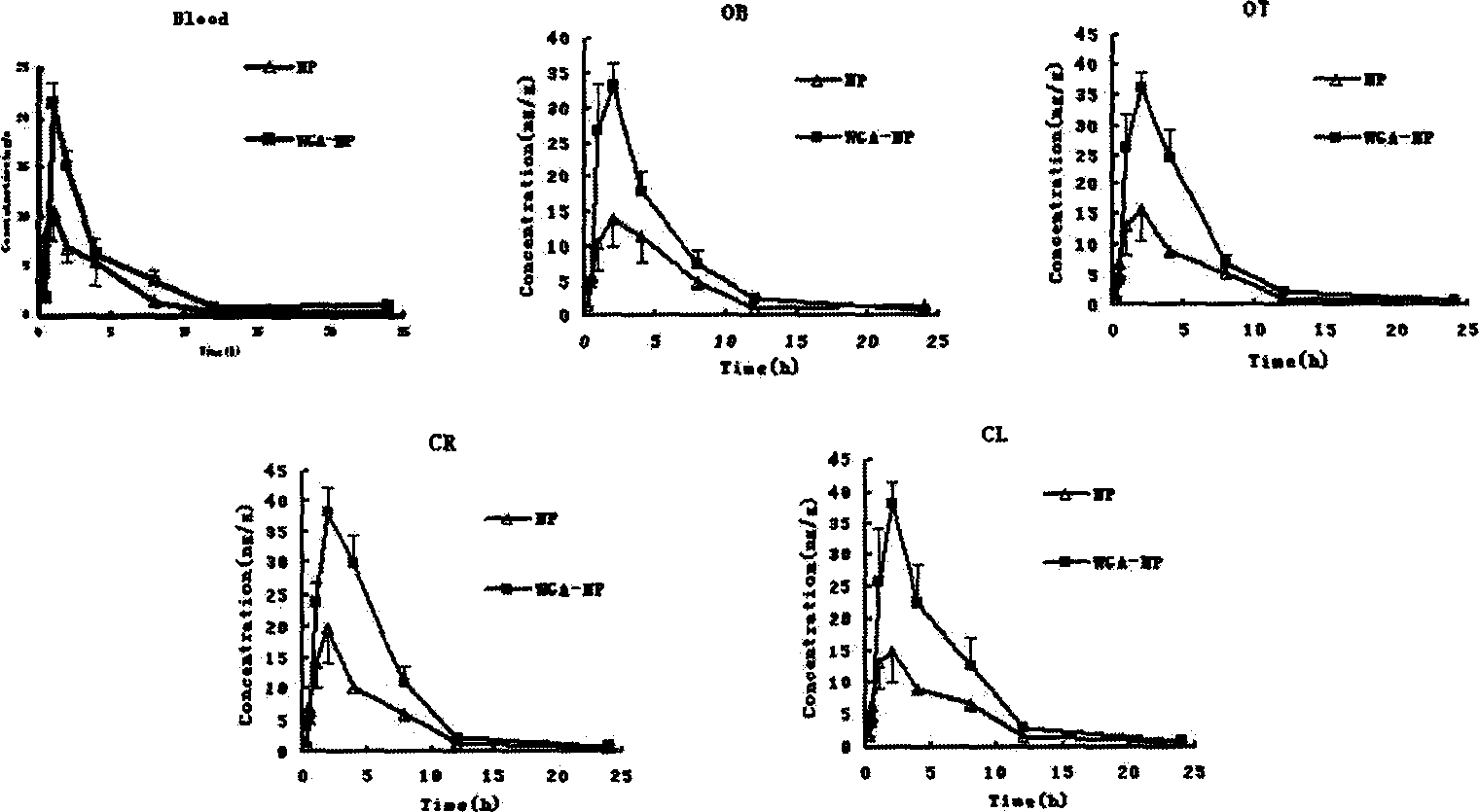
Agglutinin-modified drug delivery system from nose to brain
InactiveCN1839799ASmall toxicityImprove central preventionPowder deliveryNervous disorderNasal cavitySide effect
This invention belongs to chemistry pharmaceutical field and relates to a medication transfer system, especially relates to an agglutinin masked medication-load transfer mechanism transferring from nose to brain. This invention comprises medication carrier nanograin, vesicle or lipid body surface finish agglutinin. By using the transfer system, resort time of medication-load system on nasal mucosa can be prolonged, dielectric mucosa absorb the medication-load system and selectively deliver small molecular chemistry medication, diagnosis medication, polypeptide proteins and gene medication into brain. This invention can deliver more medication into brain and relatively decrease medication in outer tissue, so it can depress toxic action at every pore while toning up prevention, cure and diagnosis effect of backbone diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
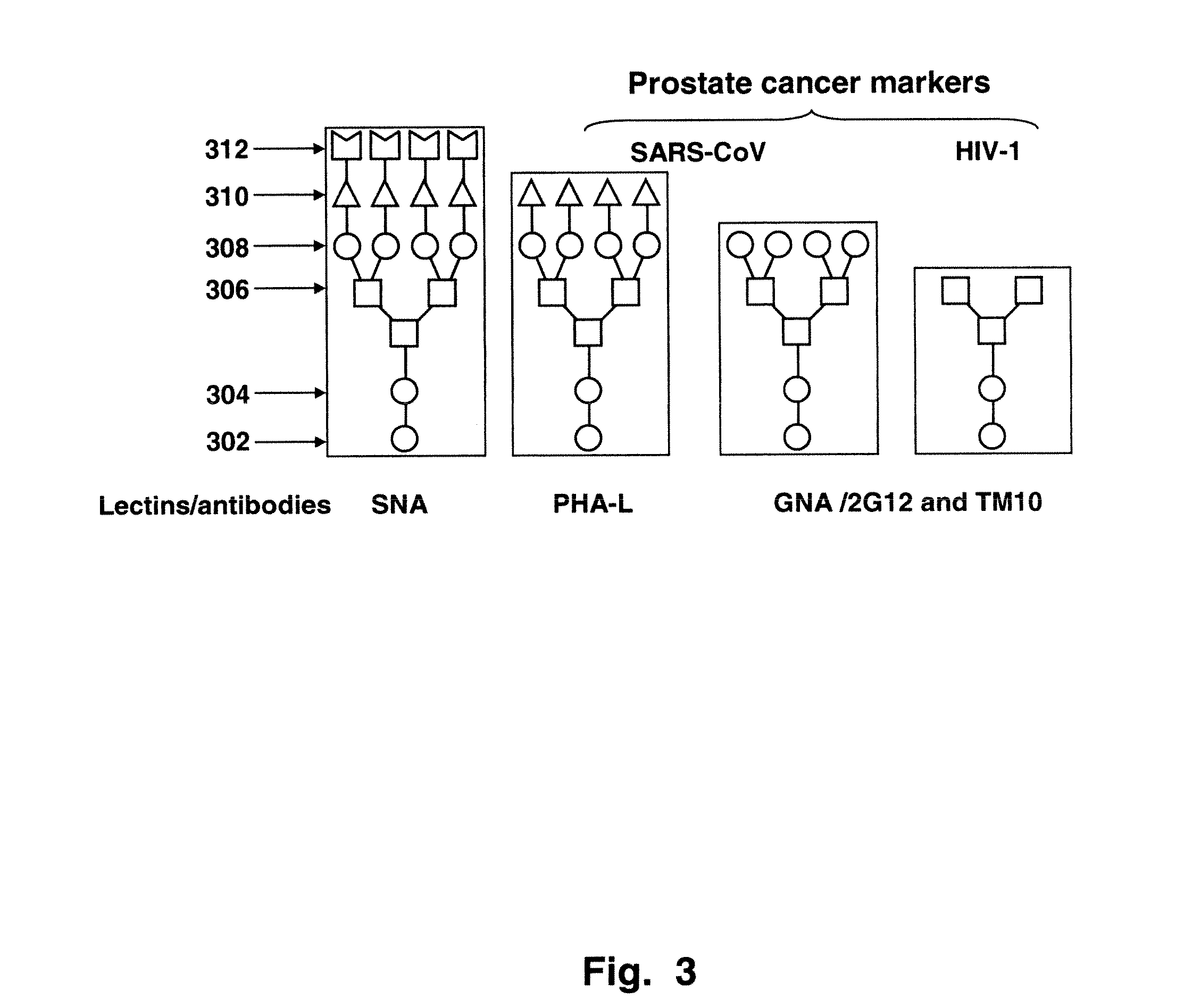
Prostate Cancer Glycan Markers and Autoantibody Signatures
ActiveUS20090258792A1High degreeSaccharide librariesLibrary screeningProstate cancer cellGriffonia simplicifolia
Disclosed are methods for probing the immunogenic sugar moieties of prostate cancer cells. The methods detect a number of glyco-epitopes that are highly and differentially expressed among prostate cancers of various Gleason grades. The glyco-epitopes exist on the surfaces of prostate cells. The methods also comprise the detection of autoantibodies in prostate cancer subjects. The antibodies bound to a glyco-motif of N-glycans that is normally “cryptic.” This target is highly expressed in prostate cancers. Lectins and antibodies that detect these glyco-epitopes that expressed in prostate cancer tissues include Euonymus europaeus lectin (EEL); Psophocarpus Tetragonolobus Lectin-I (PTL-I); Griffonia Simplicifolia Lectin-I-A4 (GSL-I-A4); Griffonia Simplicifolia Lectin-I-B4 (GSL-I-B4); Sambucus nigra I agglutinin (SNA-I; Phaseolus vulgaris-L (PHA-L; Galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA); Narcissus pseudonarcissus agglutinin (NPA); Artocarpus integrifolia agglutinin (Jacalin); and mAb TM10 (IgM).
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Agglutinin protein of astragalus root and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1687115AGood antifungal activityEnhanced inhibitory effectAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsIon exchangeAgglutination
The present invention provides an agglutinant protein obtained by separating plant astragalus root and purifying its extract and its preparation method. In the concrete, said invention uses the astragalus root as raw material, and utilizes ammonium sulfate with different saturations to make fractional precipitation and multistep ion exchange column chromatography so as to obtain astragalus agglutinant protein which can be used for blood agglutination and has the obvious antifungal action.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
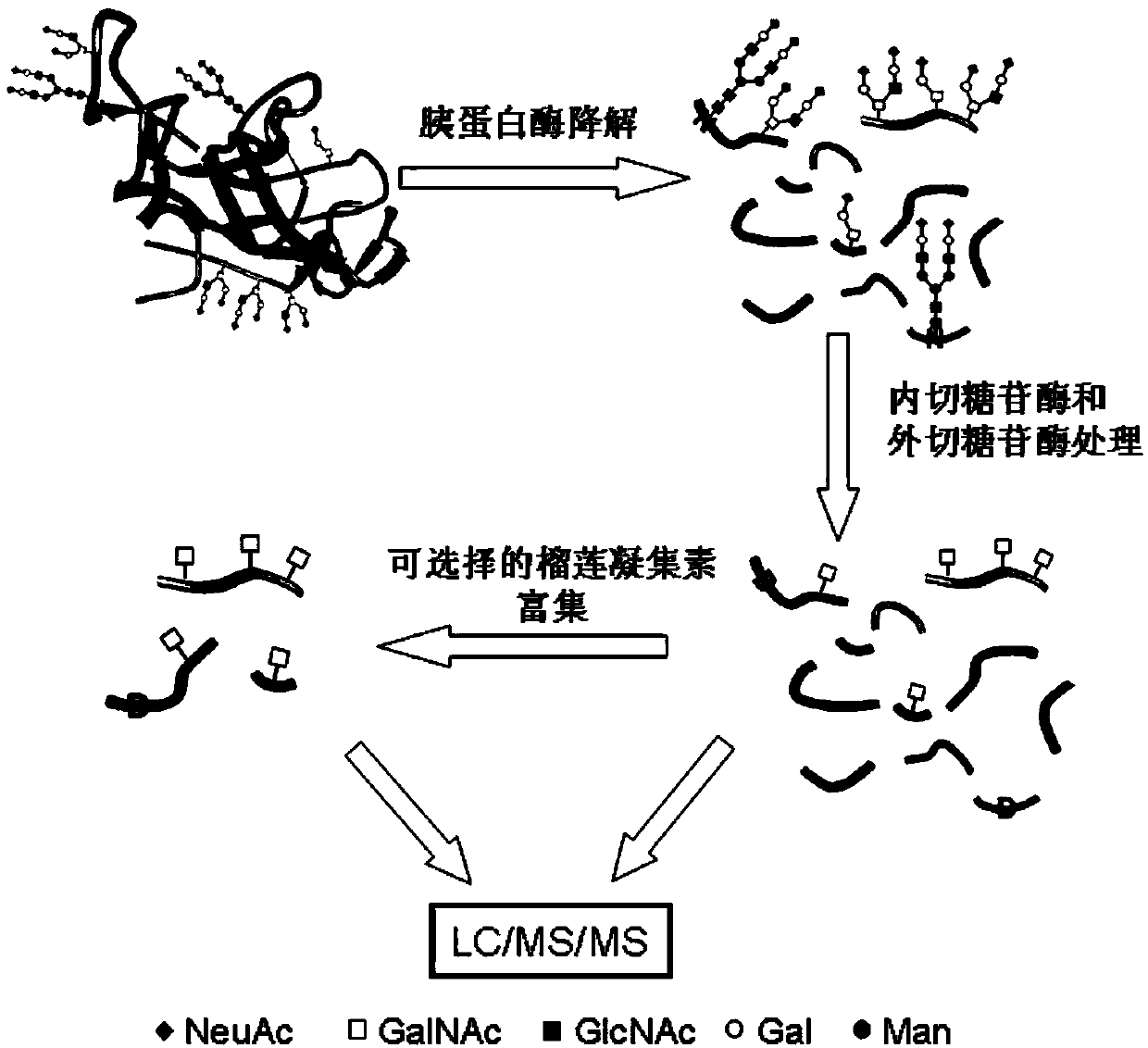
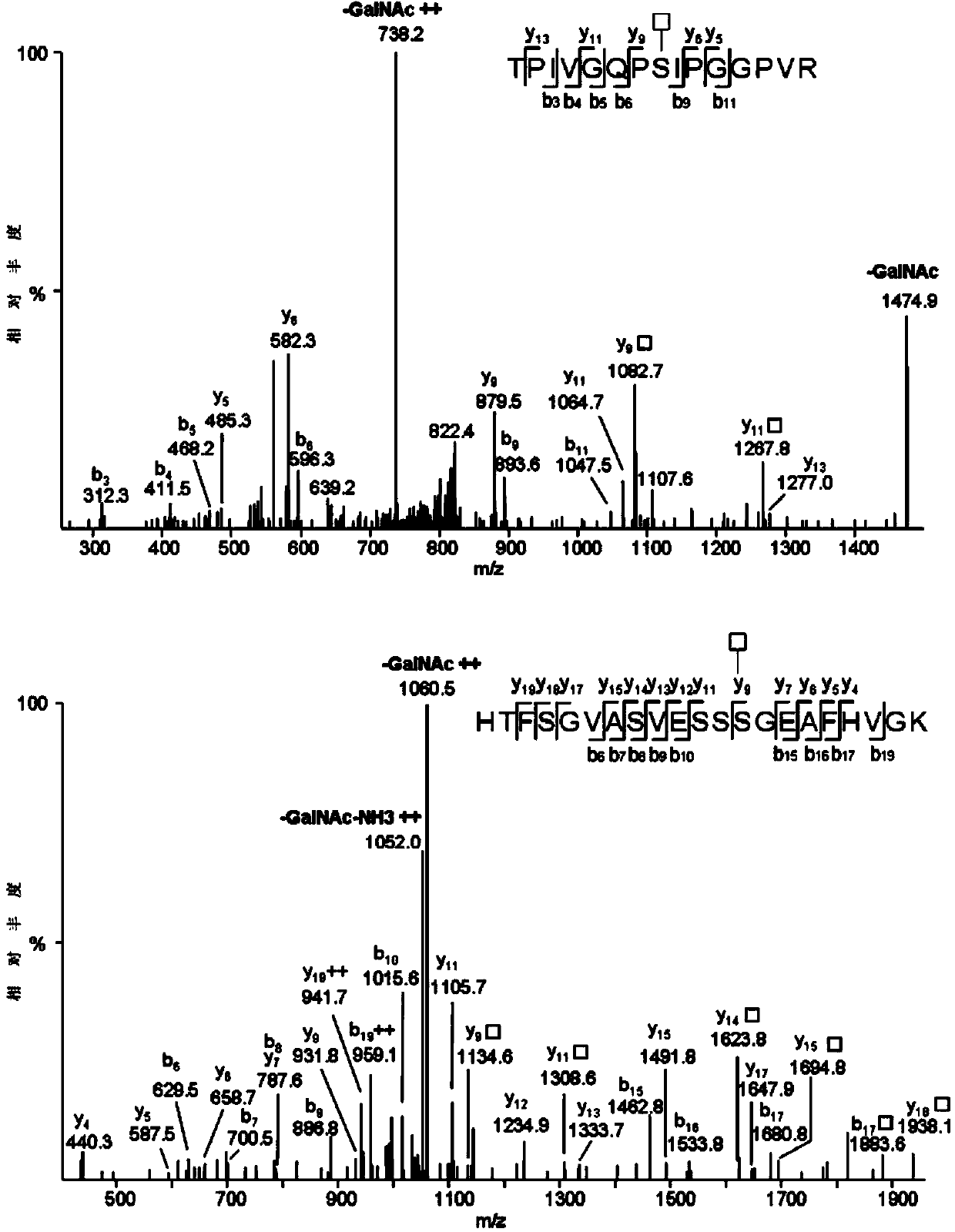
Method for analyzing protein O-glycosylation sites
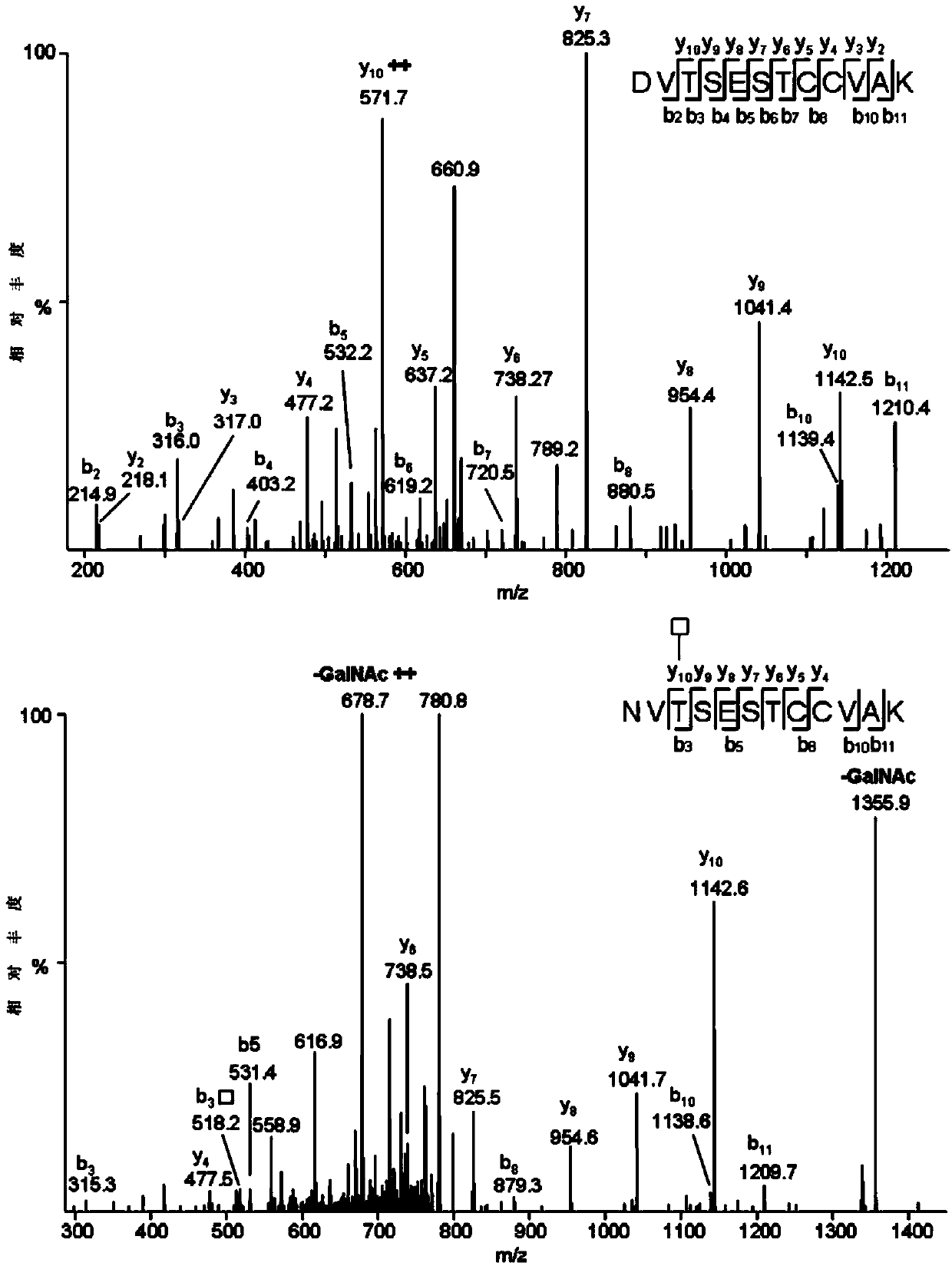
The invention relates to a method for analyzing protein O-glycosylation sites. The method comprises the following steps: (1), sequentially carrying out endonuclease digestion, endoglycosidase and exoglycosidase digestion on a proteome sample or a single protein sample to prepare a peptide and non-glycopeptide protein sample or single protein sample with a GalNAc label; (2) loading the sample on a durian agglutinin chromatographic column and separating to prepare a proteomic sample; (3) separating the single protein sample or the proteomic sample through with a C18 reversed-phase chromatographic column, and then detecting by a high-definition mass spectrometer in a cation mode to obtain a high-definition mass spectrogram; (4) processing the obtained mass spectrometric data and obtaining protein glycosylation site information though the searched result. The site information can be more rapidly, more accurately and more comprehensively obtained through establishing the method for detecting the O-glycosylation sites of glycoproteins in the single protein sample and the proteomic sample.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
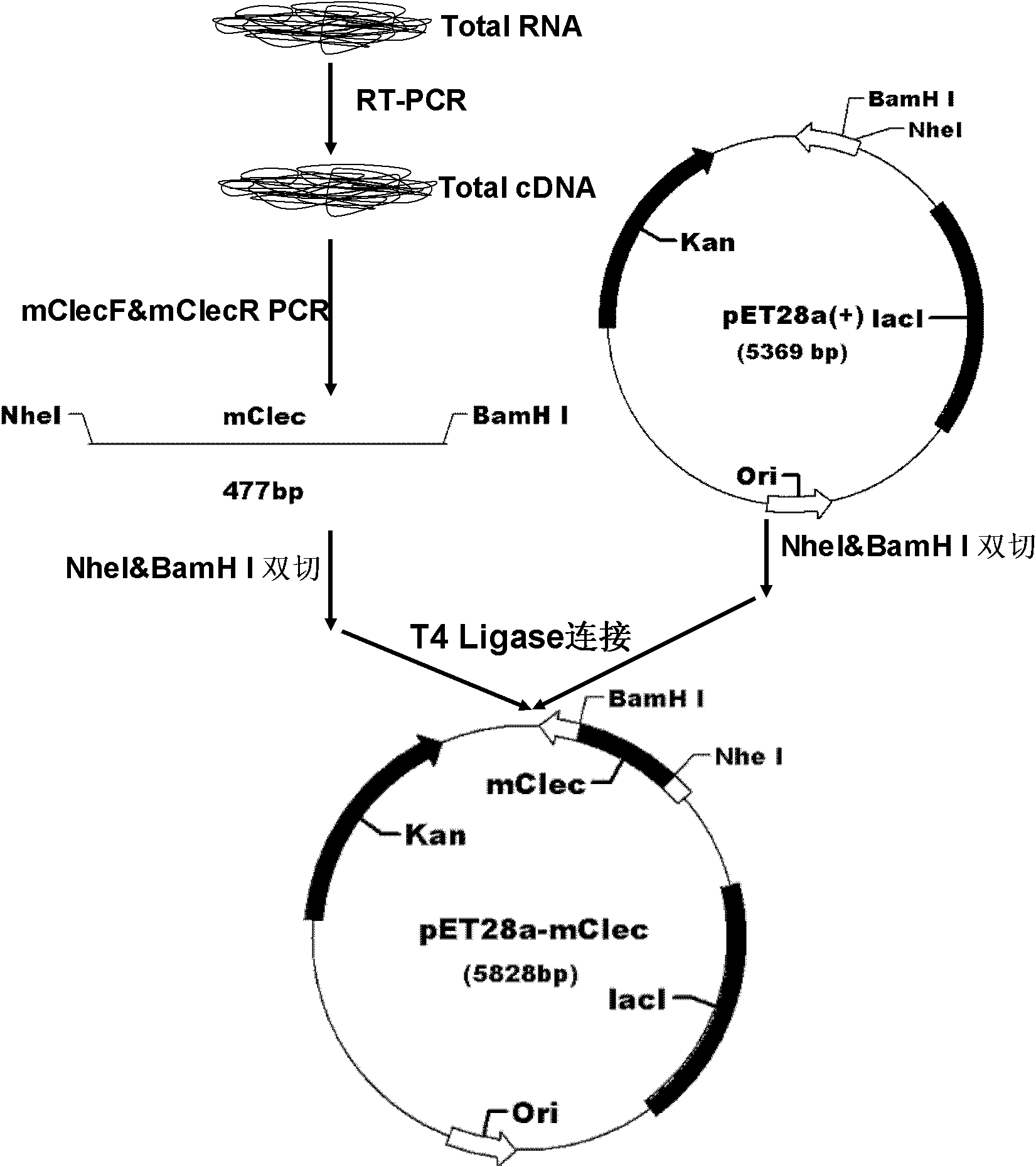
C-type agglutinin gene of procambarus clarkia as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102321628AHas agglutinating effectPromote phagocytosisAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsEscherichia coliTotal rna
The invention discloses a C-type agglutinin gene of procambarus clarkia as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The method comprises the following steps: A. extracting total RNA (ribose nucleic acid); B. synthetizing a first chain cDNA; C. acquiring partial nucleotide sequences; D. acquiring the nucleotide sequences at 3'-RACE: 3' end; E. acquiring the nucleotide sequences at 5'-RACE: 5' end; F. acquiring the complete nucleotide sequences of the gene; and G. coding an amino acid sequence of protein by the C-type agglutinin gene. From the cloning in procambarus clarkia to theC-type agglutinin gene, the gene is cloned to a PET-28a carrier, recombinant protein mClec is expressed in colon bacillus BL21 (DE3), and the purified mClec expresses agglutination effect to multiplebacteria and rabbit red blood cells; and the protein mClec or recombinant agglutinin obtained from cloning prokaryotic expression vector on the agglutinin gene can be used for producing shrimp and fish antivirus and antibacterial medicaments.
Owner:HUBEI TAIYANGHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting cell glycosylation level
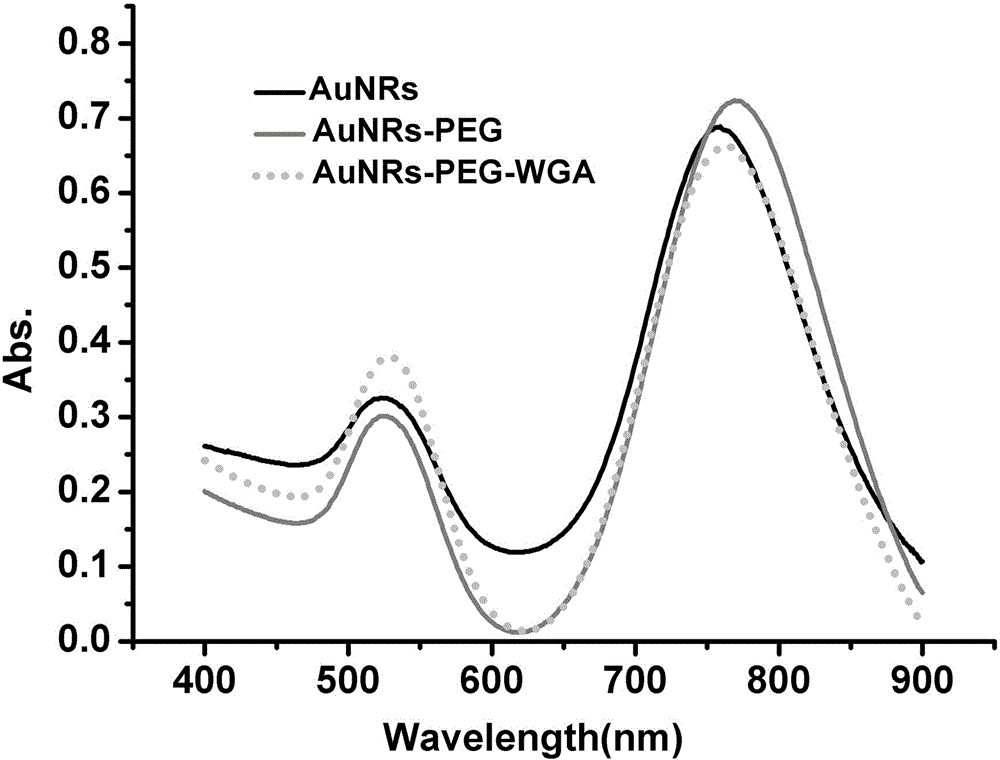
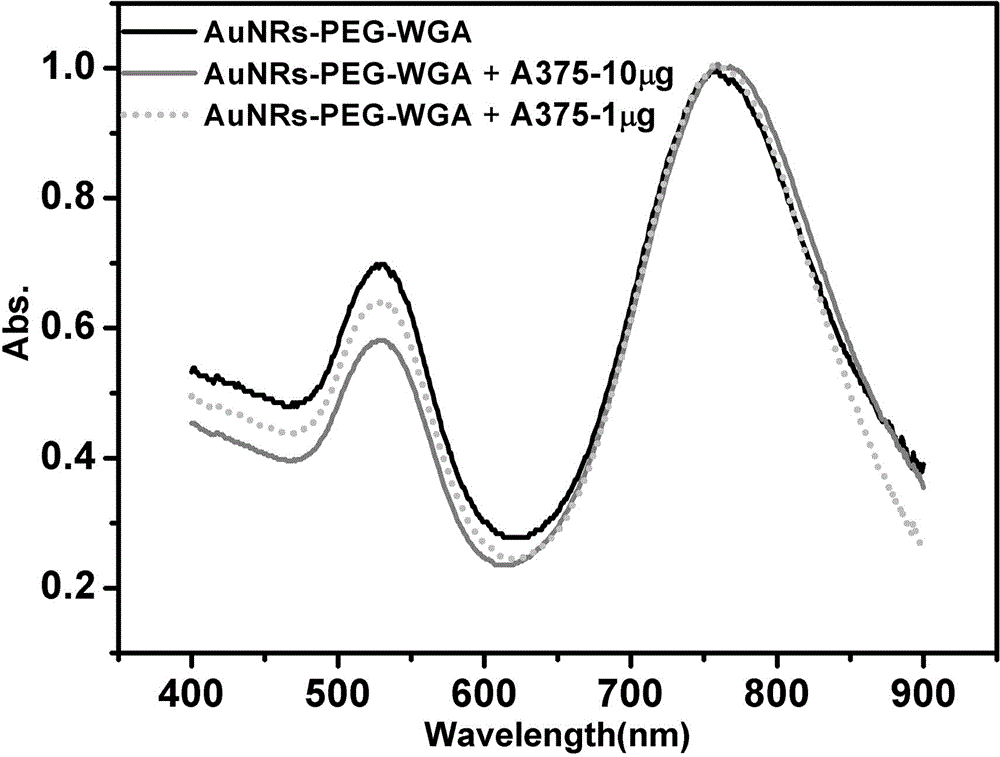
The invention provides a method for detecting cell glycosylation level by utilizing gold nano rods. The method comprises the following steps: dripping chloroauric acid into a CTAB solution, and then adding a sodium borohydride solution to prepare a seed solution; adding silver nitrate, chloroauric acid and vitamin C into the CTAB solution to prepare a growth solution; dripping the seed solution into the growth solution, and centrifuging after reaction to obtain gold nano rods; adding COOH-PEG-SH and sulfydryl malic acid into the gold nano rods for reaction to realize bio-functionalization activation of the gold nano rods so as to prepare an activated gold nano rod solution; connecting WGA agglutinin to the activated gold nano rods to obtain the activated gold nano rods provided with the WDA agglutinin and used for detecting the glycosylation level; and detecting corresponding glycosylated proteins in a cell lysis buffer by observing changes of an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Reagent plate for rapidly detecting hepatocarcinoma, making method thereof and applications
InactiveCN101424690AFor long-term storageApplicable to on-site inspectionMaterial analysisReagent stripAgglutinin-B
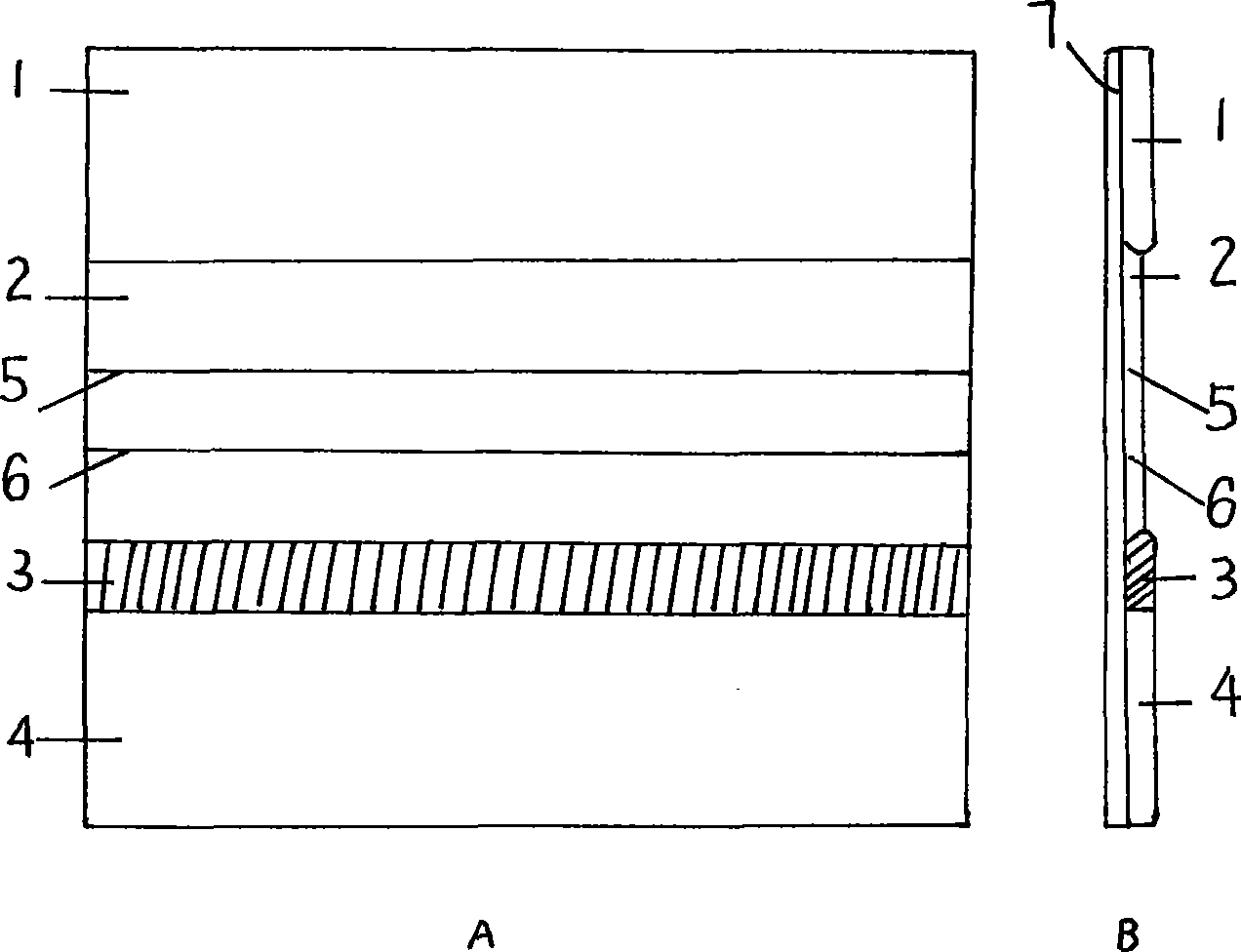
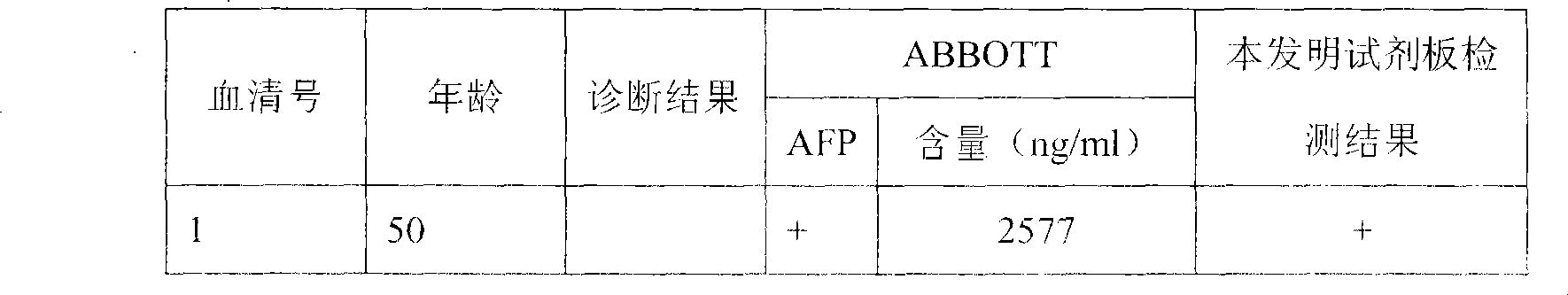
The invention discloses an agent plate for testing hepatocarcinoma and a preparation method and the application thereof. The agent plate is composed of a rigid plate and an agent strip attached to the rigid plate, and the agent strip is formed by sequentially and closely splicing absorbent filter paper, a pyroxylin membrane, a glass fibre membrane and a sample adsorption glass fibre membrane from top to bottom, wherein a gold-labeled anti-mouse AFP monoclonal antibody is absorbed by the glass fibre membrane; an agglutinin coated detection line is arranged at one end of the pyroxylin membrane, which is adjacent to the glass fibre membrane, and a goat anti mouse IgG coated contrast line is arranged at the other end which is adjacent to the absorbent filter paper; and the lower end of the sample adsorption glass fibre membrane is provided with a row of loading holes. The agent plate for testing hepatocarcinoma has the advantages that a fluorescence microscope, an Elisa tester and other expensive instruments are not needed, and the agent plate is much more suitable for field test; the agent plate is safer since radioactive isotopes, TMB and other harmful substances or chemical substances are not needed in testing processes; test results can be preserved for a long time; and the operation of the agent plate is easy and fast, and the agent plate can be operated by a single person.
Owner:BEIJING WANTAI BIOLOGICAL PHARMACY ENTERPRISE
Multivalent immunogenic composition
ActiveCN103394082AImprove securitySave the number of seedsBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininTetanus toxoids
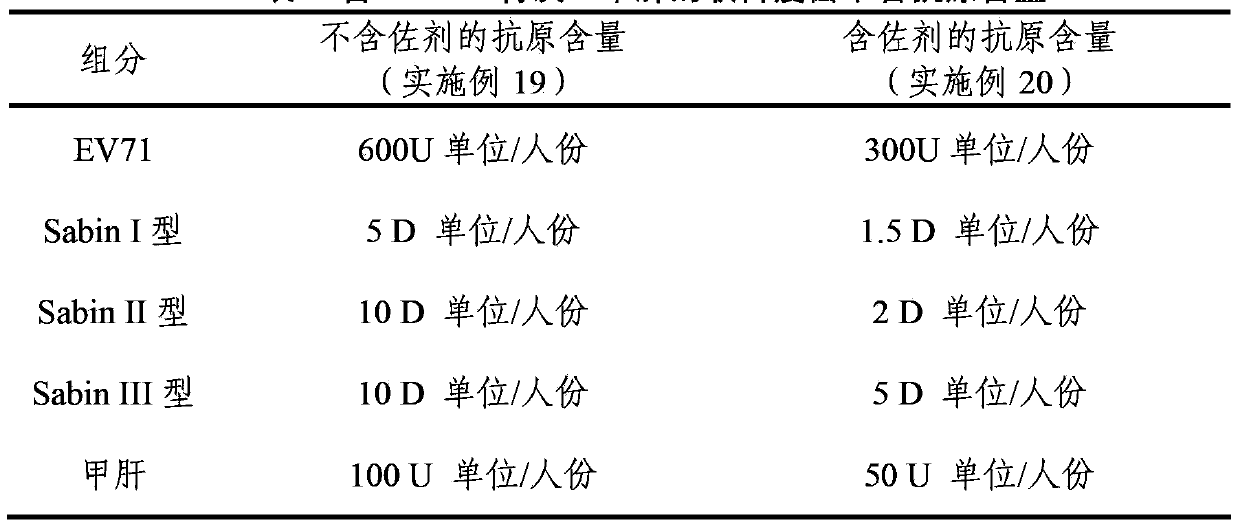
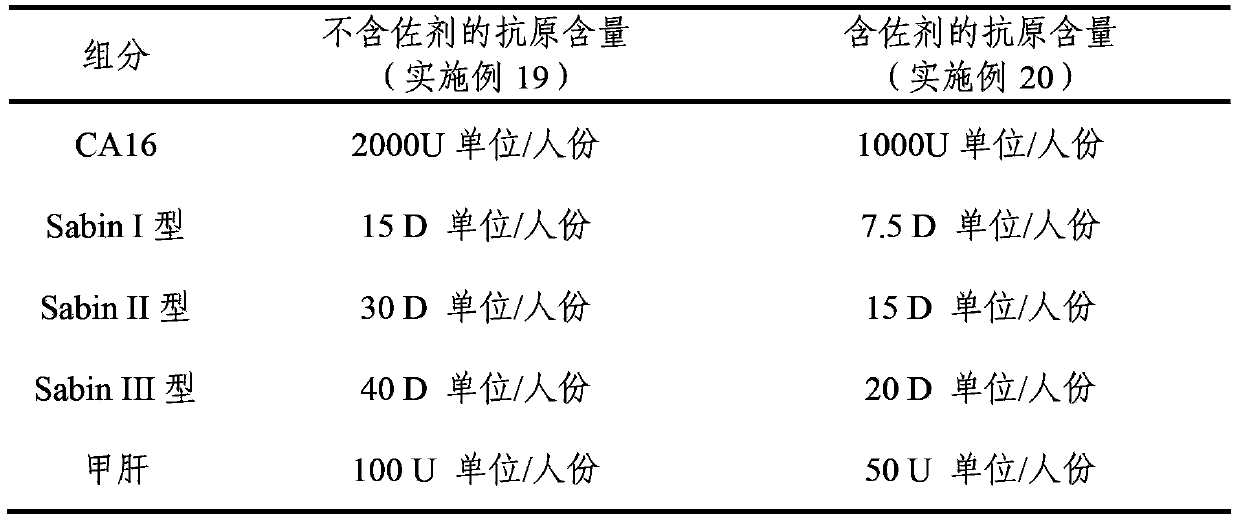
The invention provides a multivalent immunogenic composition, which includes an inactivated hepatitis A antigen and an inactivated poliovirus. The composition also can further include over one or two of a purified pertussis antigen, diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, filamentous hemagglutinin, Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide, Neisseria meningitidis capsular polysaccharide, a hepatitis B virus antigen, enterovirus 71 and a coxsackievirus A16 antigen, and a physiologically acceptable carrier. The composition involved in the invention is employed to immunize the inoculated population in the form of a bivalent vaccine or more combined vaccines. Without reducing the immune effects of each immunizing antigen, the inoculation number of times can be reduced at the same time, and the time and human resources can also be saved.
Owner:SINOVAC BIOTECH
Kit for detecting protein glycosylation subtype and detection method thereof
InactiveCN104502611AWide applicabilityAchieve semi-quantitative detectionBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexPolystyrene
The invention discloses a kit for detecting protein glycosylation subtype and a detection method thereof. The detection kit comprises agglutinin, confining liquid, a biotin labeled antibody, horse radish peroxidase labeled streptavidin, a 3',3',5',5'-tetramethyl benzidine substrate developing solution, a stop solution and a cleaning buffer solution. The detection method comprises the following steps: fixing the agglutinin onto a polystyrene solid phase carrier to be used for recognizing and binding glycoprotein in the sample based on specific recognition of agglutinin and an oligosaccharide chain, recognizing the glycoprotein needing to be detected by virtue of specific binding of the protein and the antibody thereof, and realizing semi-quantitative analysis of the glycoprotein. According to the detection kit and the detection method disclosed by the invention, semi-quantitative detection of single protein glycosylation subtype can be realized, and the kit is easy and convenient to operate and low in cost.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
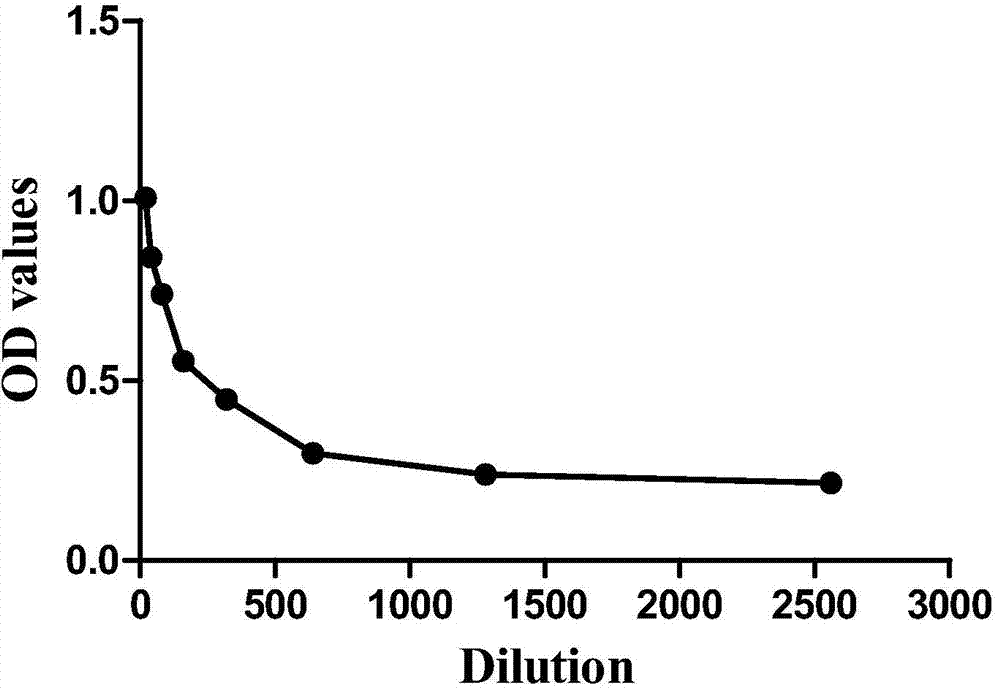
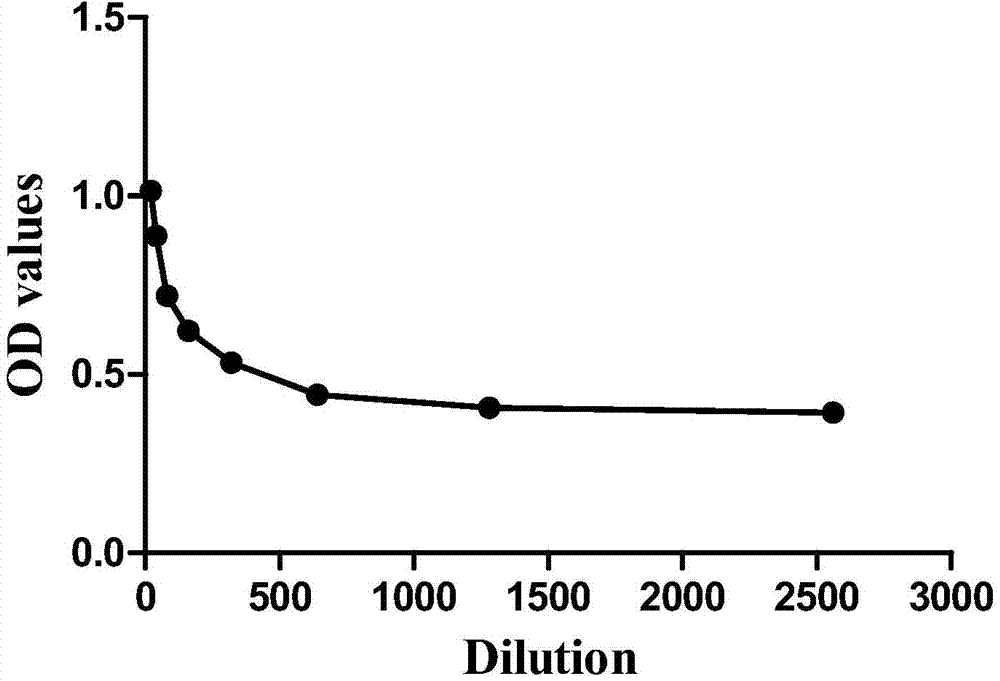
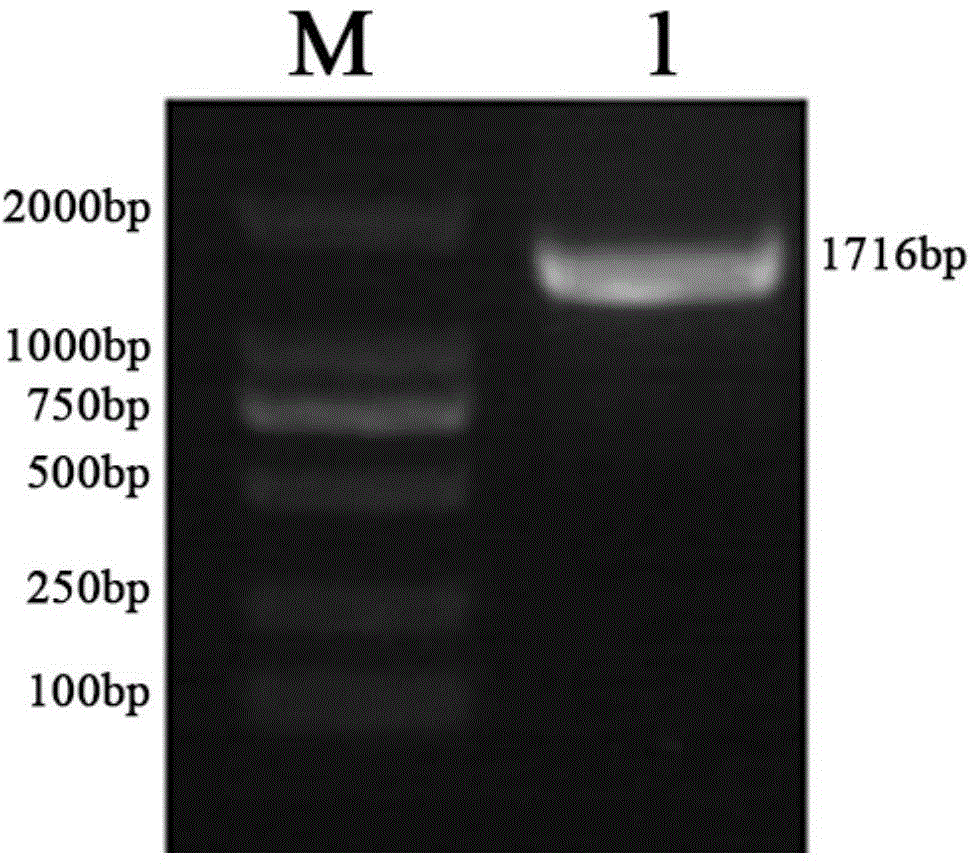
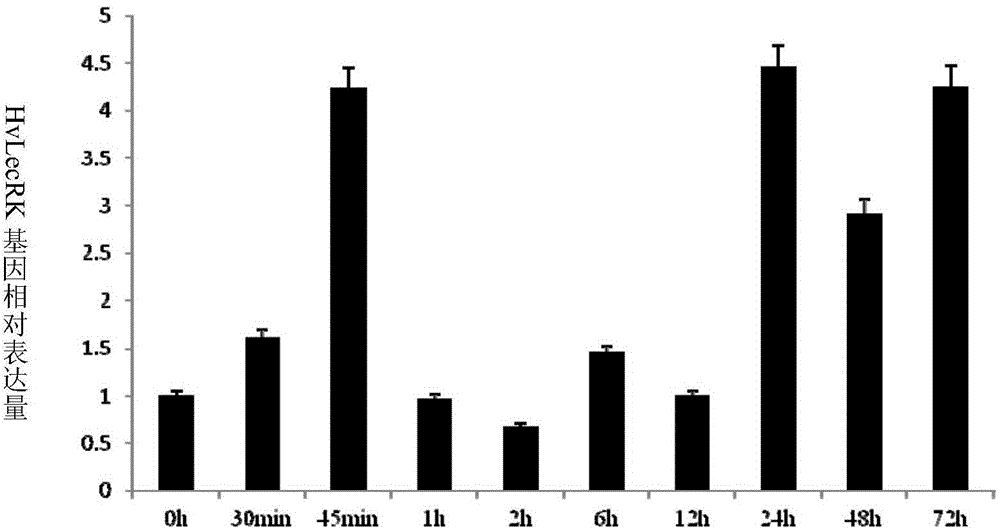
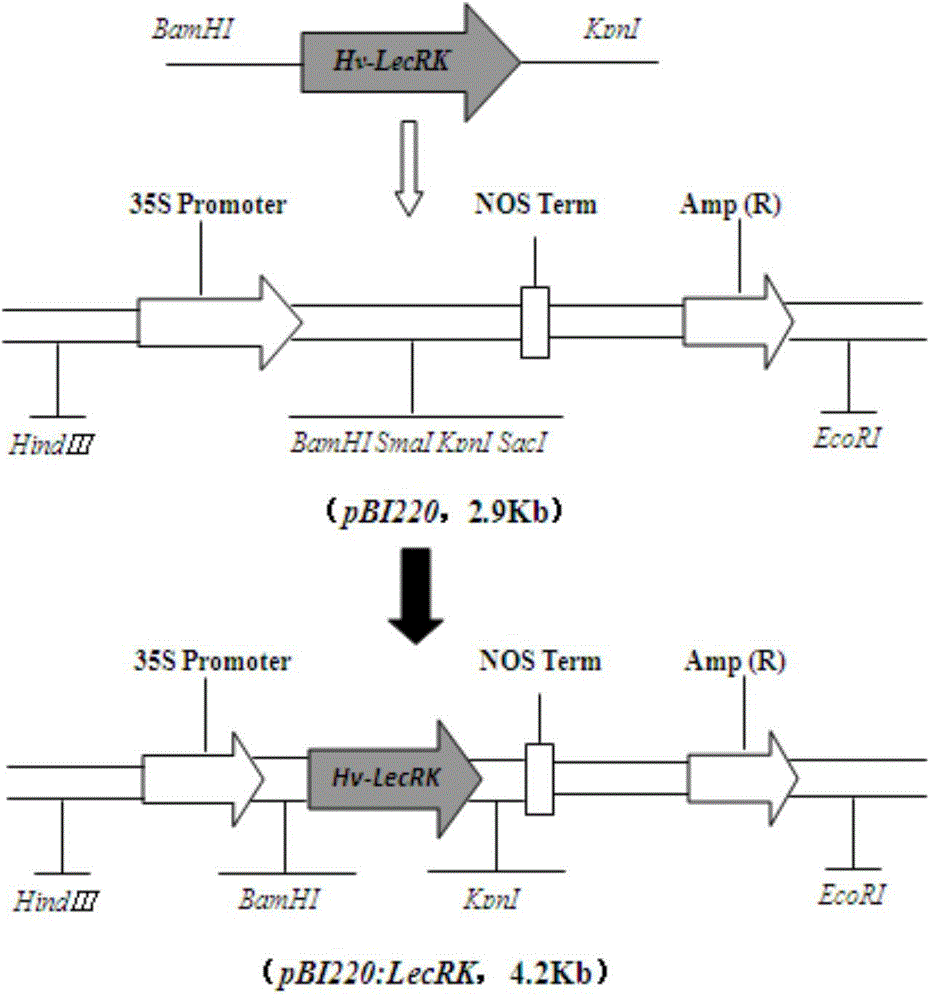
Haynaldia villosa agglutinin receptor-like kinase gene and expression vector and application
ActiveCN105821055AIncrease resistanceImprove powdery mildew resistanceTransferasesFermentationTriticeaeGene conversion
The invention discloses a tufting wheat lectin receptor kinase gene, its expression carrier and application, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The cDNA sequence of Hv-LecRK is SEQ ID NO.1 and the encoded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2. The gene comes from diploid W. villosa (Haynaldia villosa, L., 2n=2x=14, genome VV), and can interact with powdery mildew resistance-related gene Hv-CMPG, and is resistant to powdery mildew in diploid W. villosa Enhanced expression induced by powdery mildew. The gene was transformed into the susceptible wheat variety Yangmai 158 by transient expression, and the results showed that the overexpression of Hv-LecRK gene could reduce the haustoria index of Yangmai 158. Therefore, Hv-LecRK is expected to be used in genetic engineering breeding, and introducing it into wheat varieties susceptible to powdery mildew is expected to improve the powdery mildew resistance of wheat.
Owner:王秀娥 +2
Modified fresh-keeping agent for aquatic products
InactiveCN104041572AReasonable formulaEasy to useMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsSodium sorbatePolyphenol
A disclosed modified fresh-keeping agent for aquatic products is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of water, 30-40 parts of chitosan oligosaccharide, 5-8 parts of citric acid, 15-25 parts of mussel agglutinin, 8-12 parts of sodium chloride, 15-30 parts of tea polyphenol, 7-10 parts of glacial acetic acid lysozyme, 15-20 parts of ethanol, 8-18 parts of glycine, 4-11 parts of chitosan, 10-15 parts of sodium sorbate, 6-9 parts of lactic acid and 6-9 parts of potassium sorbate. The provided modified fresh-keeping agent for aquatic products is reasonable in formula, good in usage effect, low in cost, capable of prolonging fresh-keeping period of aquatic products and guaranteeing food safety.
Owner:QINGDAO BOHONG MARINE BIOTECH
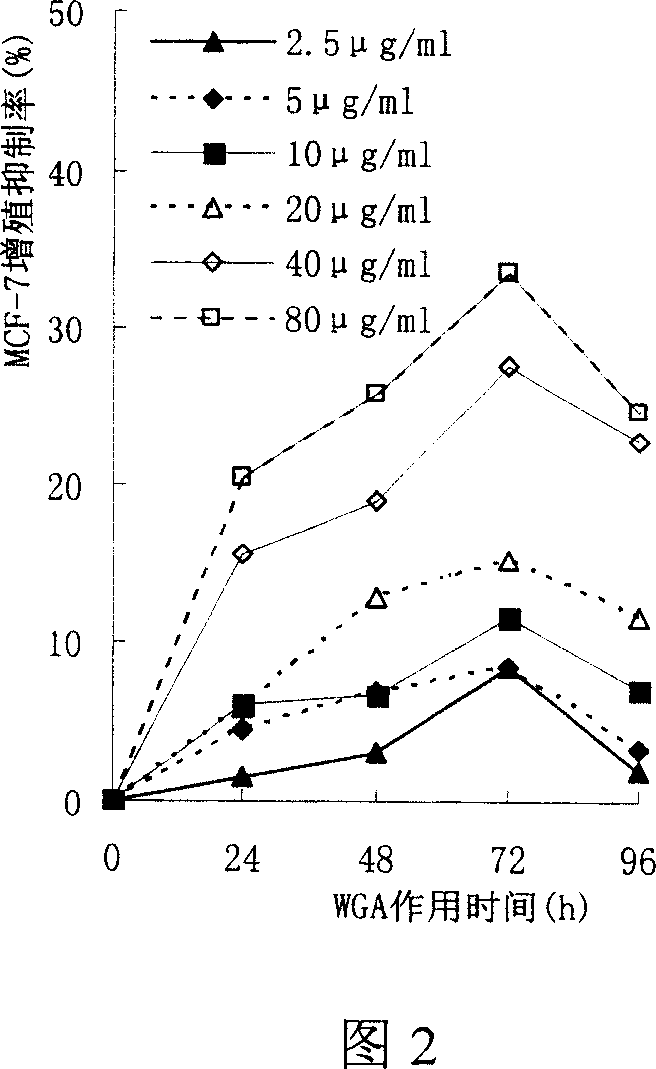
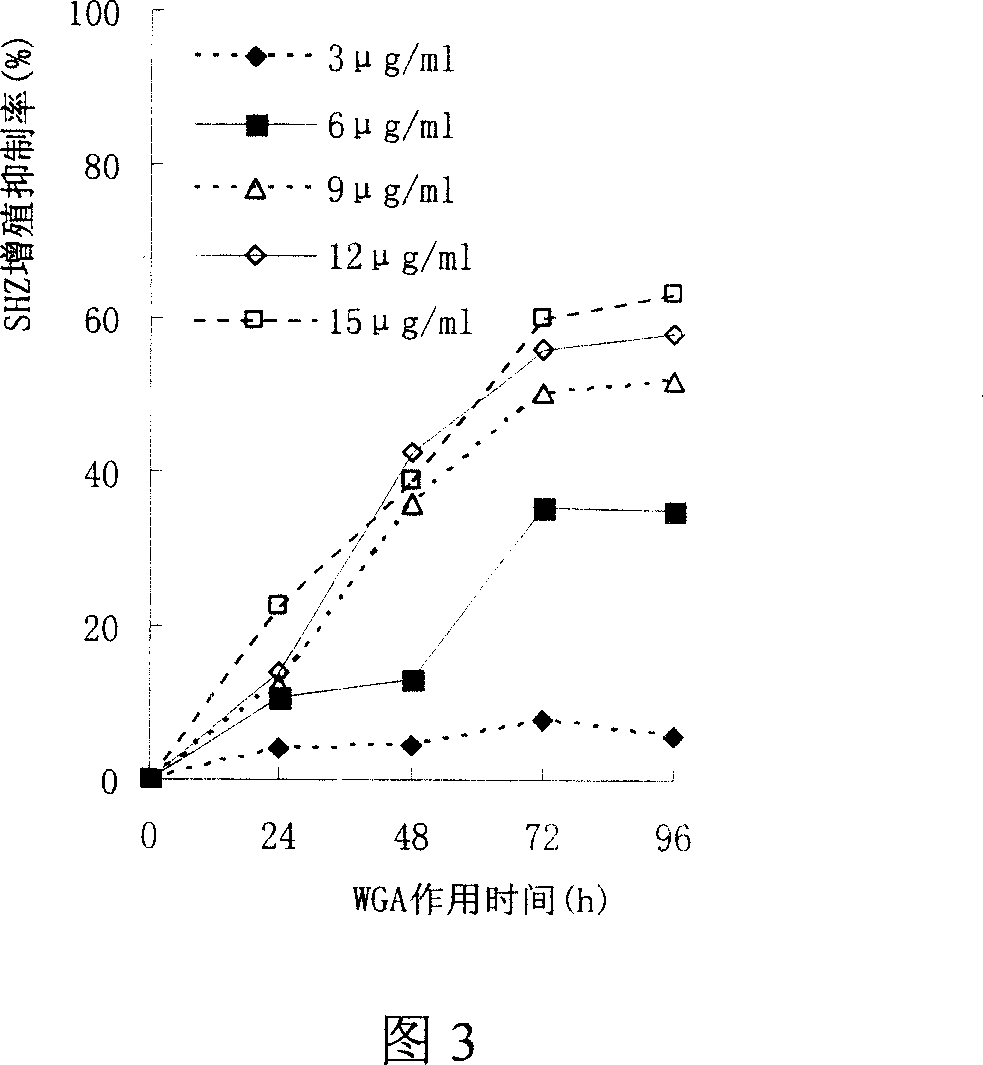
Preparation method of wheat germ agglutinin and its application in inhibiting mammary gland cancer activity
InactiveCN1948337AImprove the utilization value of deep processingHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingRed blood cell
This invention relates to the preparation of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and its application in restraining breast cancer's activity. It belongs to a field of wheat by-product material's deep processing technology. The wheat germ was comminuted, degreased,deep comminuted, super sound intensified acid extracted, salting out, heat treated, ultrafiltrated and affinity chromatographed, then the composition which have red cell agglutinating activity was desalted and freeze dried, and at last WGA is gained. Cell culture determines that the WGA has depressant effect on rat breast cancer cell strain SHZ and trypsin dependent form human breast cancer cell strain MCF-7. This invention's technology design is scientific and reasonable, manipulate is convenient and procedure is not polluted. The invention provides groundwork for exploiting drug of restraining cancer, and can enhance the utilization value of wheat germ deep processing and related industry's economic returns.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
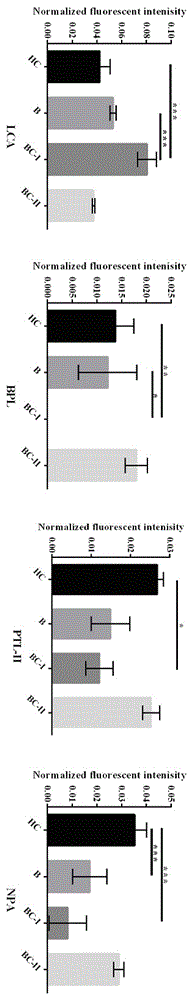
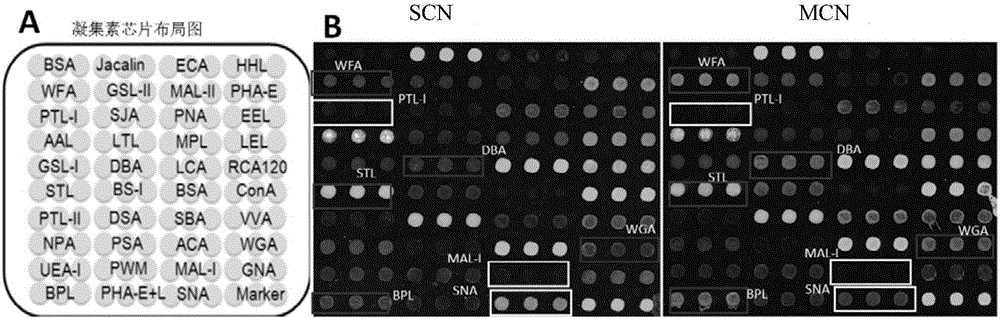
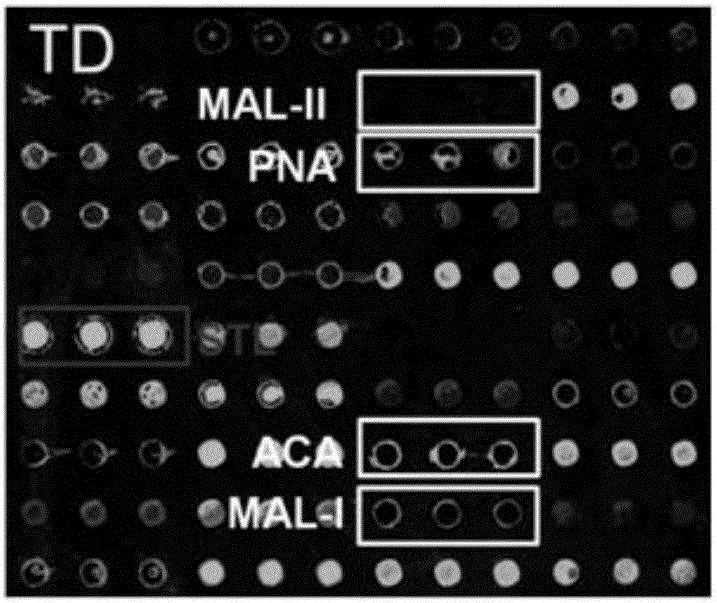
Application of lectin group recognized carbohydrate chain in distinguishing mucinous cystic neoplasm from serous cystic neoplasm
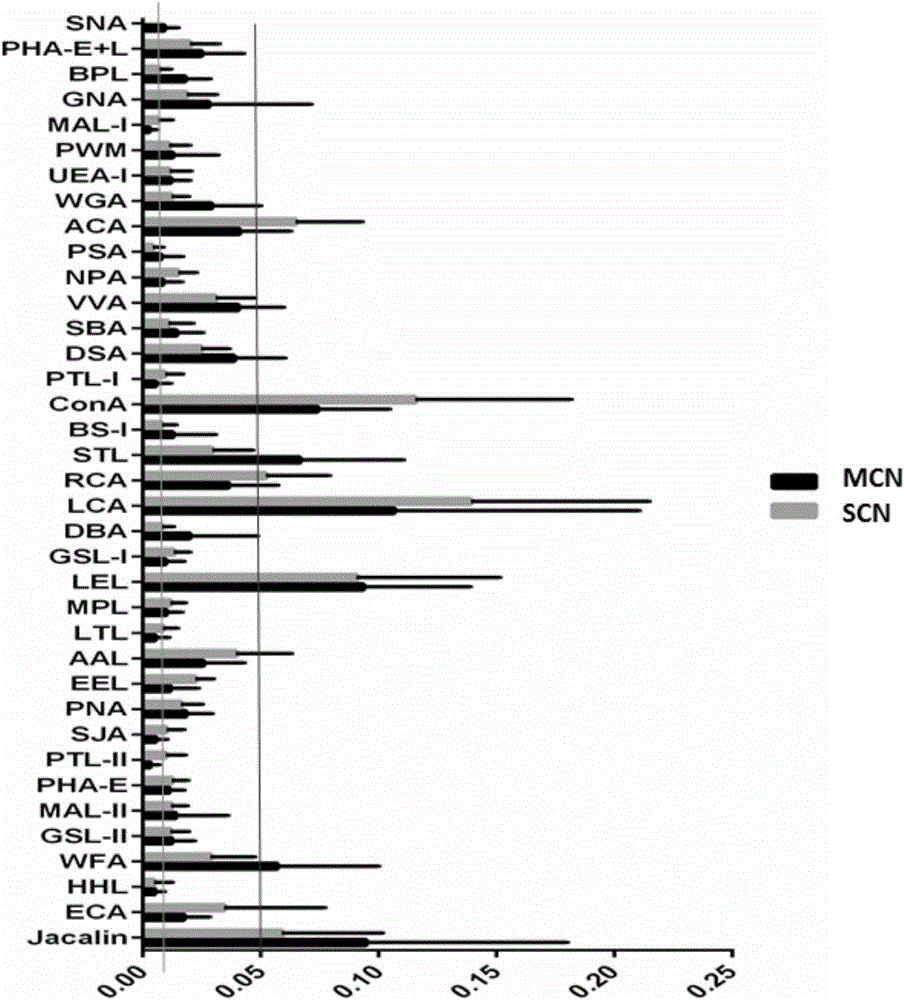
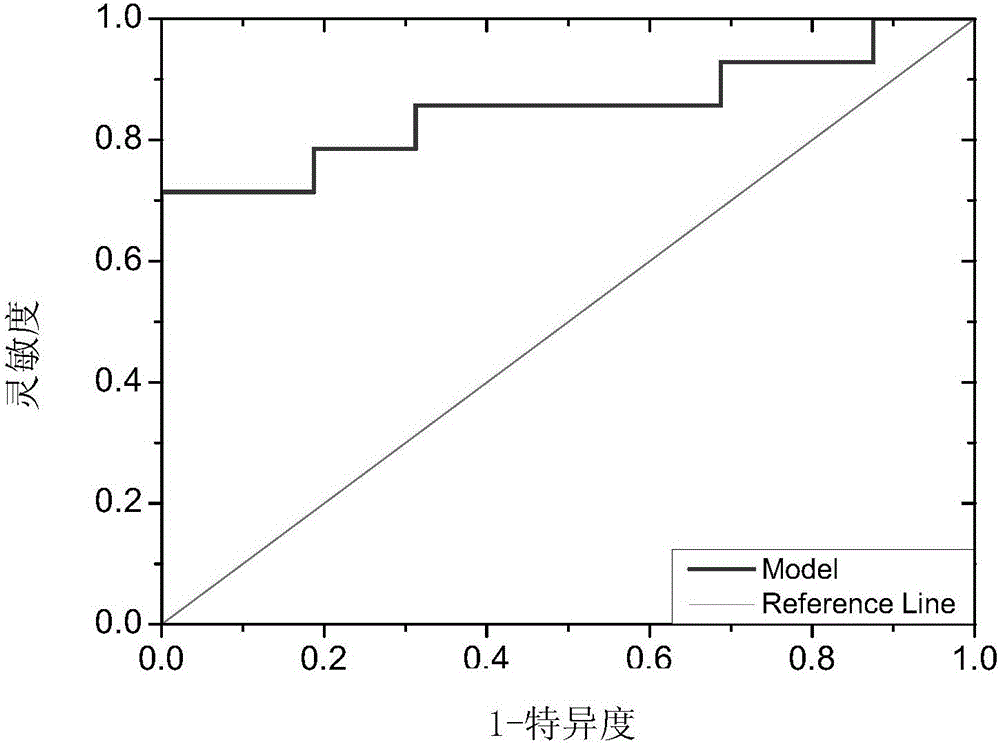
The invention discloses application of lectin group recognized carbohydrate chains in distinguishing mucinous cystic neoplasm from serous cystic neoplasm. The lectin group recognized carbohydrate chains disclosed by the invention are glycosylated protein carbohydrate chains recognized by lectin groups consisting of WGA (trticum vulgaris agglutinin), BPL (bauhinia purpurea lectin), STL (solanum tuberosum (potato) lectin), DBA (dolchos biflorus agglutinin), PTL-I (psophocarpus tetragonolobus lectin I) and MAL-I (maackia amurensis lectin I). The carbohydrate chains are different in capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from mucinous cystic neoplasm and serous cystic neoplasm, the contents of the carbohydrate chains recognized by STL, WGA, BPL and DBA in the capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from MCN (mucinous cystic neoplasm) are remarkably higher than those in the capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from SCN (serous cystic neoplasm), the contents of the carbohydrate chains recognized by PTL-I and MAL-I in the capsula pancreatic fluid of the patients suffering from MCN are remarkably lower than those in the capsula pancreatic fluid of the patients suffering from SCN, the sensitivity of the combination of WGA and BPL in distinguishing the patients suffering from SCN from the patients suffering from MCN is 0.714, and the specificity is 1. The results show that the lectin group can be used for distinguishing the patients from SCN from the patients suffering from MCN.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for marking and detecting glucide biochip
InactiveCN101493455AThe synthesis method is simpleImprove stabilityScattering properties measurementsBiological testingBiochipLinear range
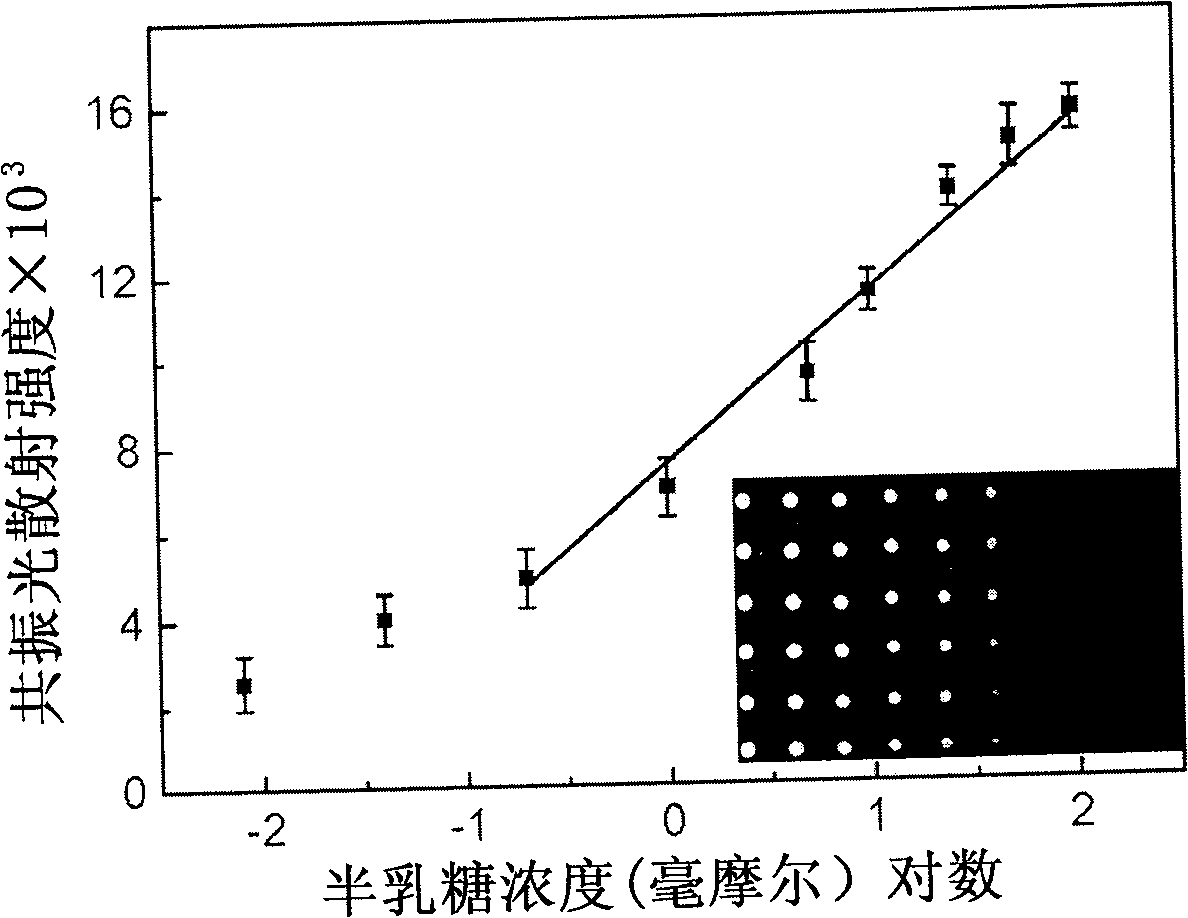
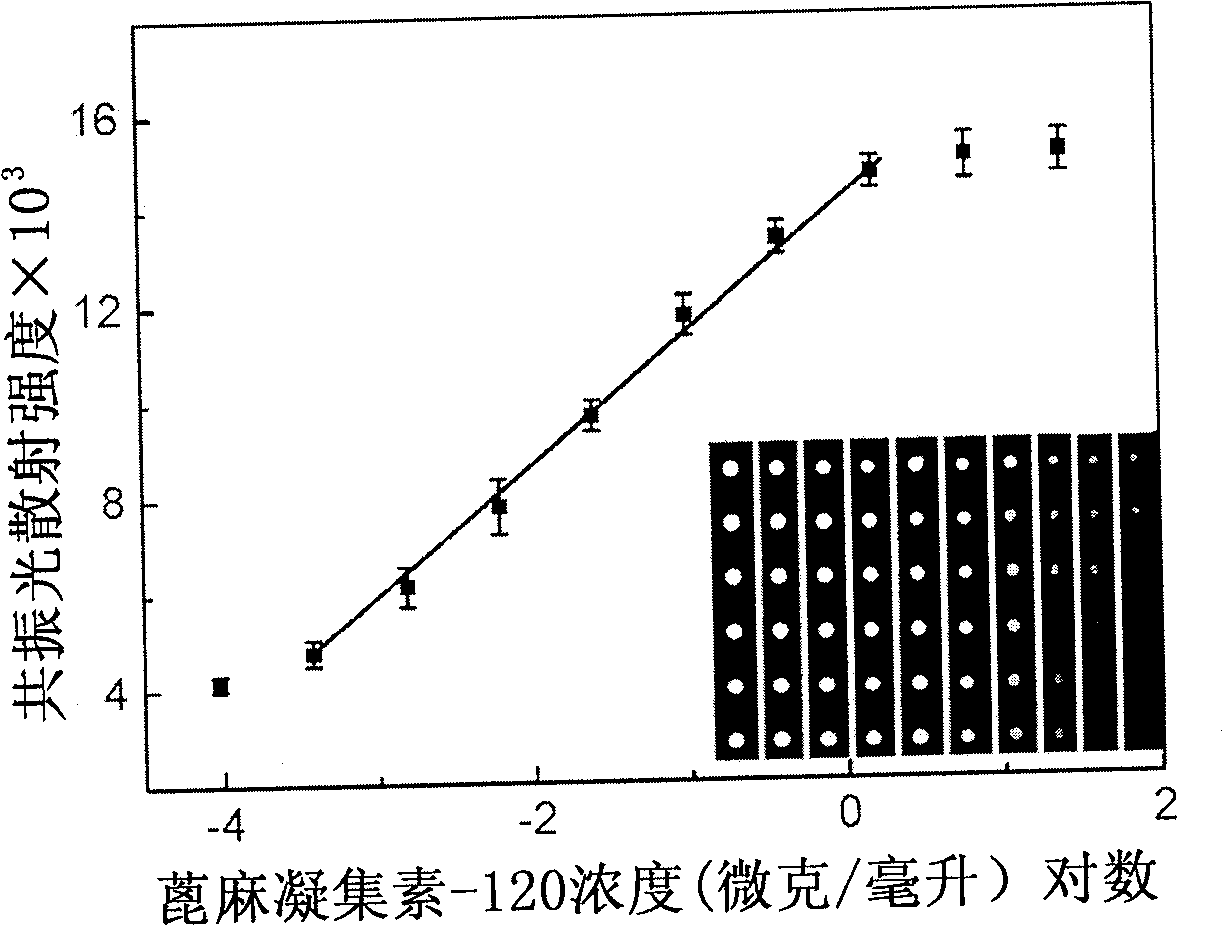
The invention provides a saccharide biochip marking and detecting method. The method takes the polypeptide-modified gold nanoparticles as the marker of a saccharide biochip, takes resonance light scattering spectroscopy as the detecting means of the saccharide biochip, and marks the reaction process by the reaction of avidin and biotin. The method is versatile and characterized by high sensitivity being up to 32ng / mL, good selectivity and less sample consumption amount. The detection limit of monosaccharides obtained by the method is 8 mu M; the detection limit of agglutinin is 100pg / mL; the linear range of the monosaccharides and the agglutinin is 3 order of magnitudes; the detection limit of obtained glycoprotein is 32ng / ml; the detection limit of agglutinin is 25.6pg / mL; and the linear range of the glycoprotein and the agglutinin is 3 order of magnitudes. The method can realize the research among the monosaccharides, the glycoprotein detection, the saccharide and corresponding agglutinin.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
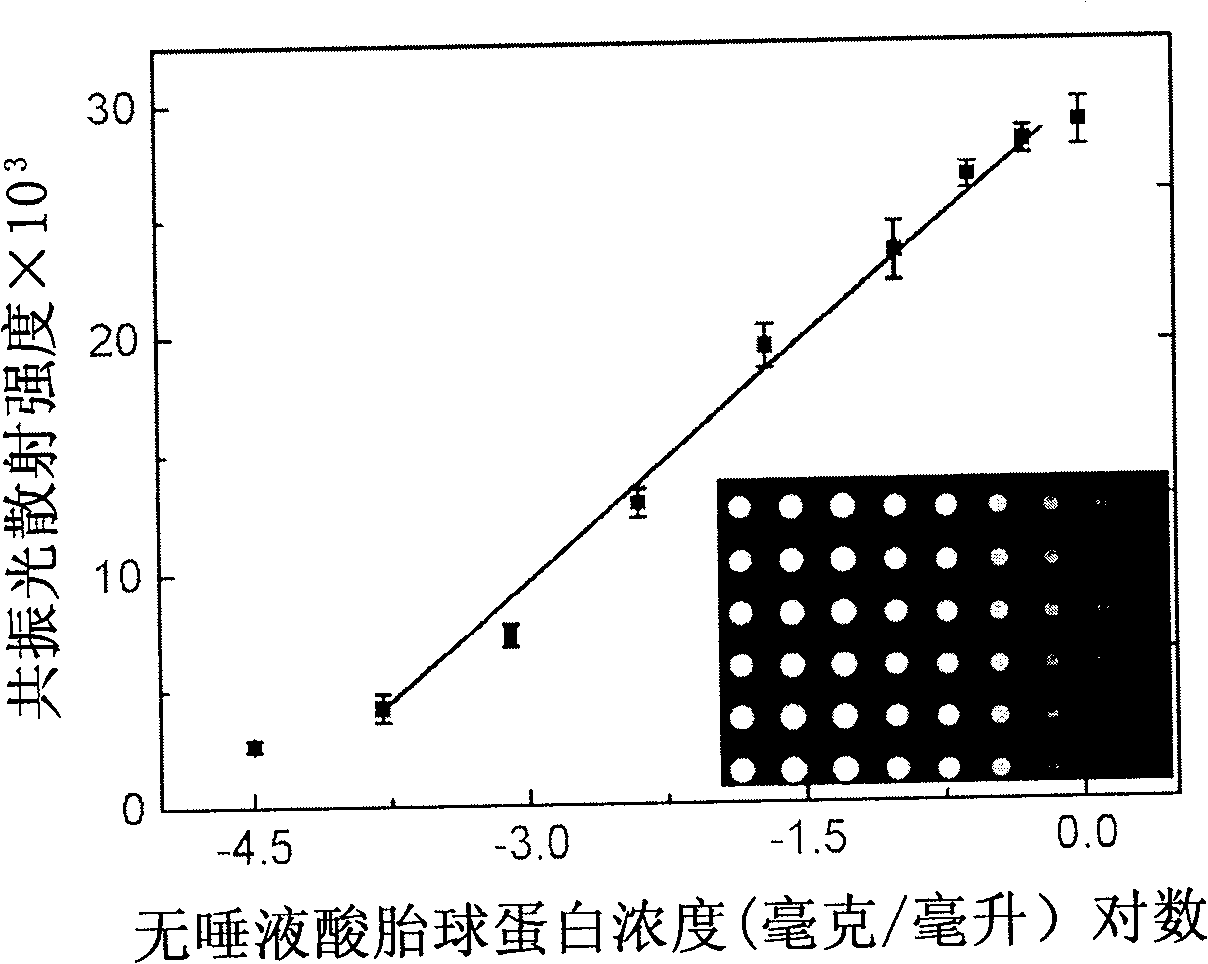
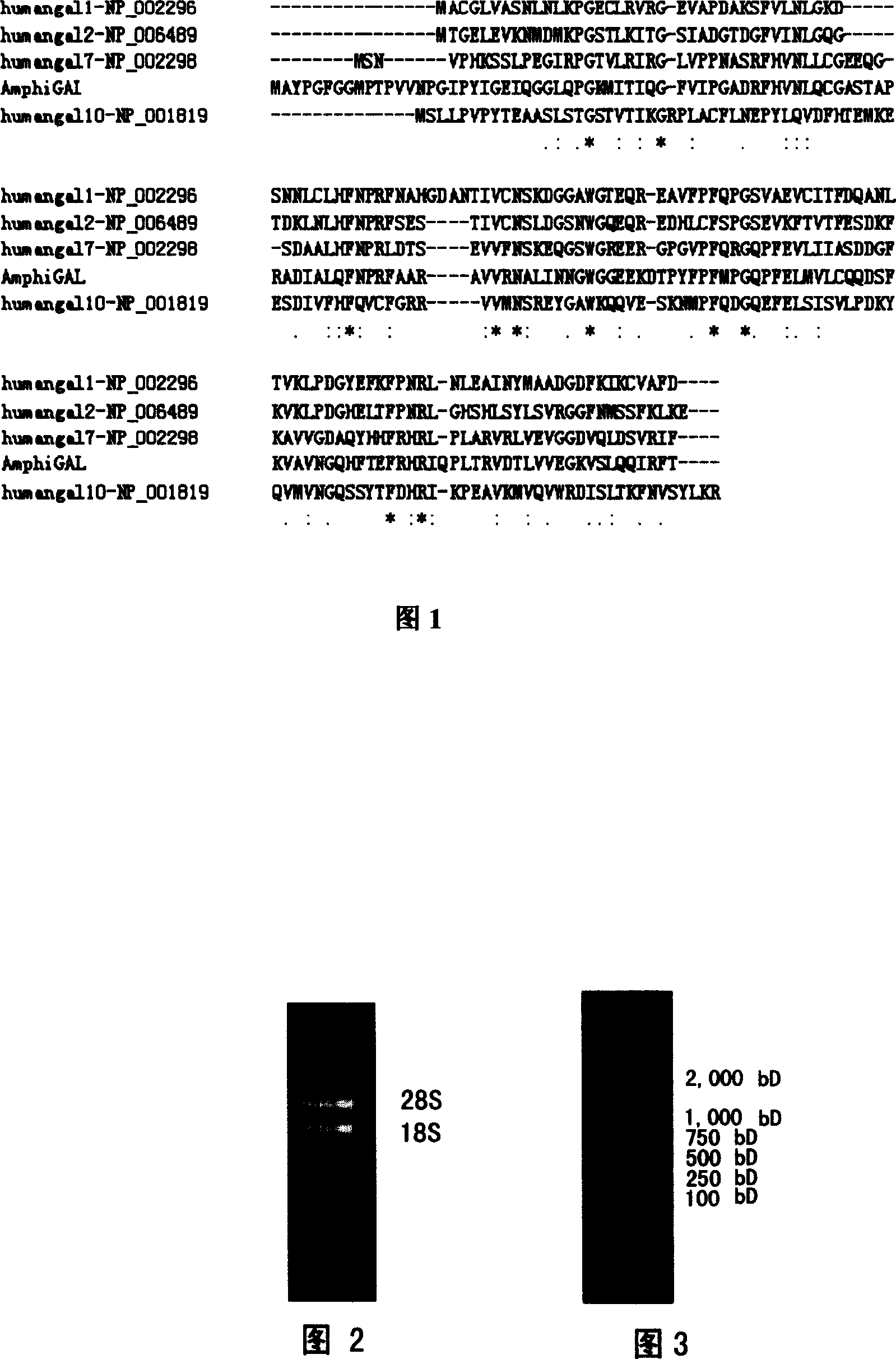
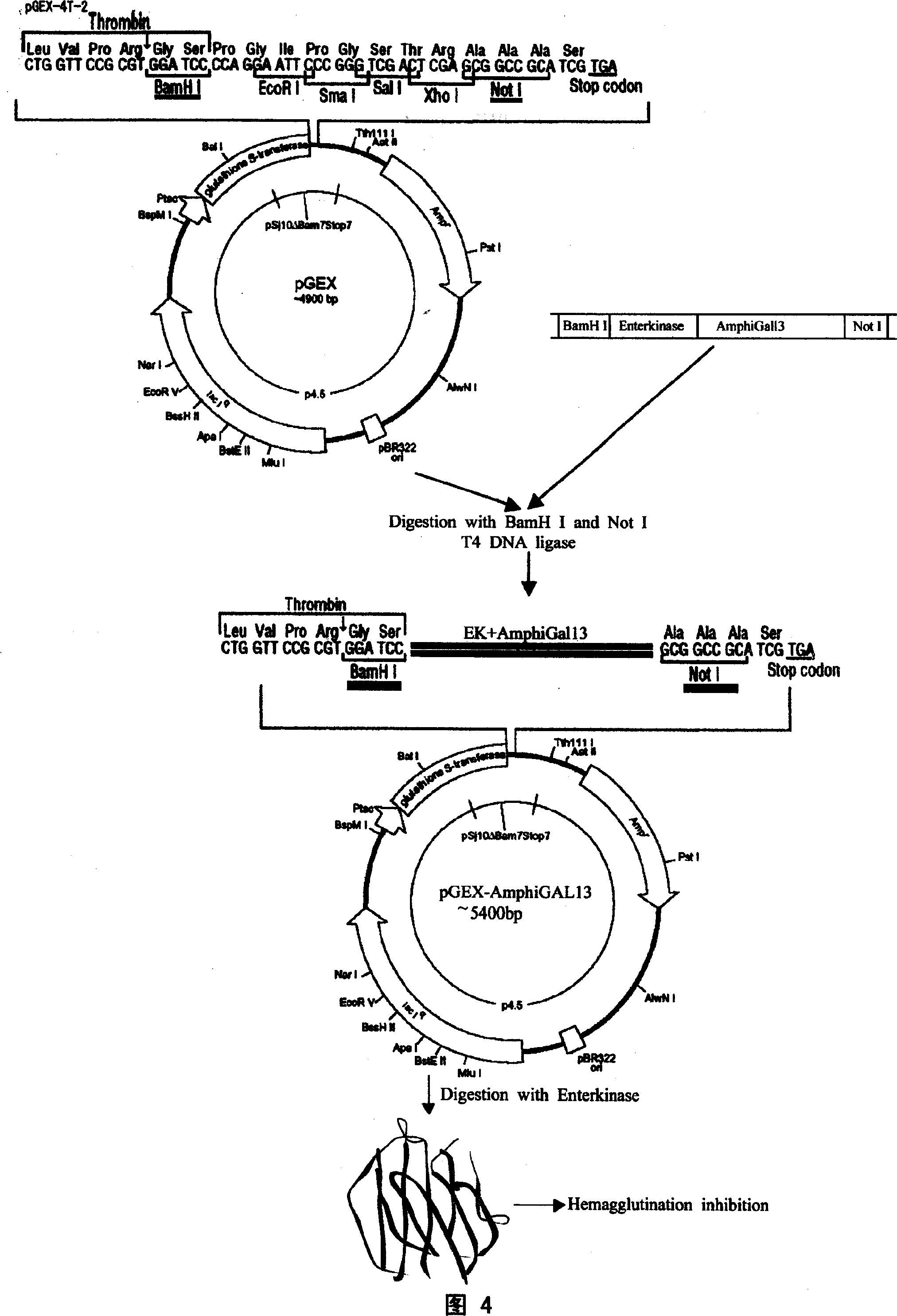
Amphioxus galactose lectin AmphiGAL13-gene and its use
Chinese amphioxus galactose agglutinin AmphiGAL13 gene and its production are disclosed. The process is carried out by constructing cDNA library, large-scaled sequencing, and separating out AmphiGAL13 gene from digestive tube of Chinese amphioxus. It expresses recombinant amphioxus GST-PGAL13 protein by GST fusion and obtains agglutinin by EK enzyme digestion. It can be used to develop and research for natural small molecule biological granular preparation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nose and throat anti-influenza solution and method of use
InactiveUS20080274163A1Reduce the possibilityEasy to implementSnap fastenersBiocideDiseaseNasal cavity
A nose and throat anti-influenza solution is described that decreases the likelihood influenza infection and its spread. The solution's components are readily available and have been used to treat humans for other ailments previously, leading to an easily implemented, scalable, safe, and cost-effective solution. The core components of the solution include: specially denatured alcohol (SDA); Triton x-100; sodium saccharin; 1,8 cineole (eucalyptol); thymol; methyl salicylate; menthol; sorbitol and / or glycerin; sodium benzoate; poloxamer 407; polysorbate 80; and distilled water. Optionally, the solution also includes one or more of the following: citric acid; sambucus nigra agglutinin; a lectin that binds 2,3 sialic acid; nonoxynol-9; sialyllactose; a protease; a protease inhibitor; and / or chloroquine. The solution is applied to the nasal cavity via a pre-moistened cotton swab or a pre-moistened facial tissue and the solution is applied to the back of the throat via a spray, gum, or gargle solution. Further a nebulizer, atomizer, or inhaler can be used to apply the solution to the back of the throat, to the pharynx, and / or to the respiratory tract.
Owner:SCHWARTZ STEVE W
Method for simultaneously analyzing influenza A virus subtype and virulence thereof by utilizing agglutinin chip
InactiveCN102192848AHigh sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceVirulent characteristicsAgglutinin
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously analyzing influenza A virus subtype and virulence thereof by utilizing an agglutinin chip, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing the agglutinin chip and preparing a biological sample; and then, loading the biological sample to the agglutinin chip to detect the glycoprotein chain in the influenza A virus, thereby rapidly judging the subtype of the influenza A virus and the pathogenicity density of the influenza A virus. The method provided by the invention can be used for solving the technical problem that the conventional method for detecting influenza virus cannot be used for rapidly and simultaneously detecting the influenza A virus subtype and the virulence thereof; and the method provided by the invention has the advantages of rapidness, simplicity, convenience, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Spray-dried collectin compositions and process for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070154406A1Excellent characteristicsImprove propertiesAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryCollectinFungal microorganisms
The present invention relates to a spray-dried composition comprising as an active ingredient at least one member protein of the collectin family or its functional equivalent for treating and preventing microbial infectious diseases. The present invention also relates to a method for producing the same composition. The composition produced by the method of the present invention is effective in suppressing infections caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Since the composition is developed in a form suitable for inhalation, it can directly provide the active ingredient to the sites of infection from these microbes, and thus treat and prevent respiratory infections and external wounds.
Owner:CHA VACCINE RES INST CO LTD
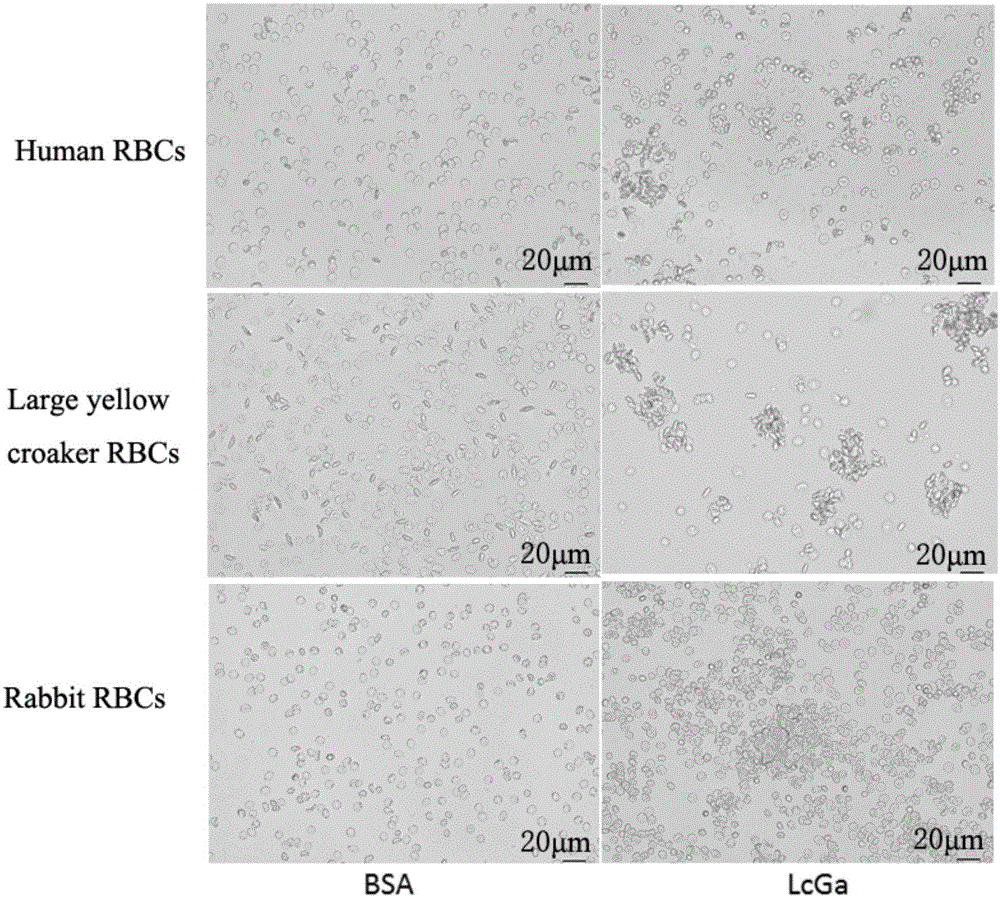
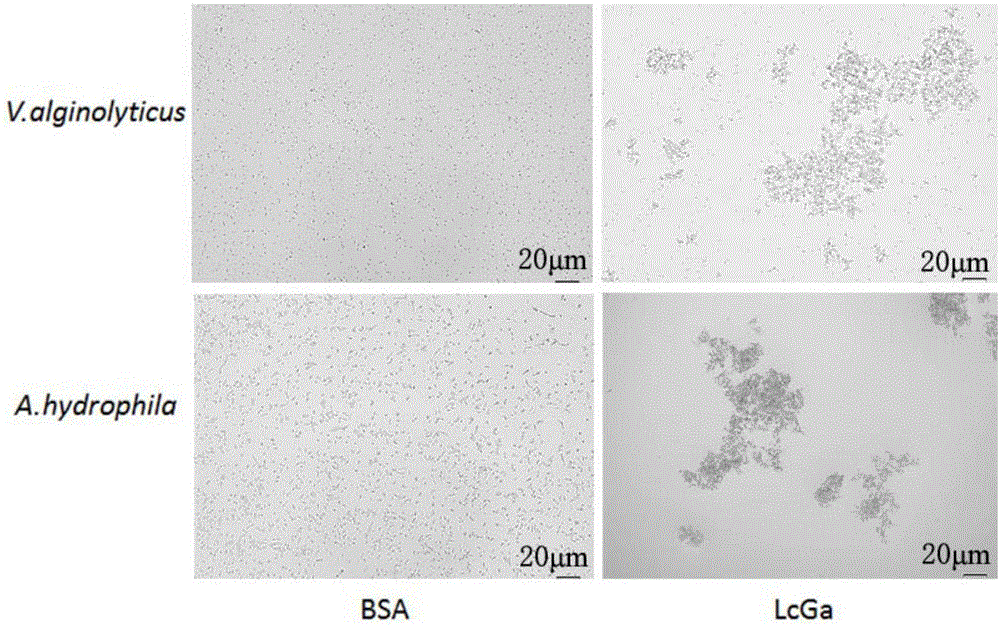
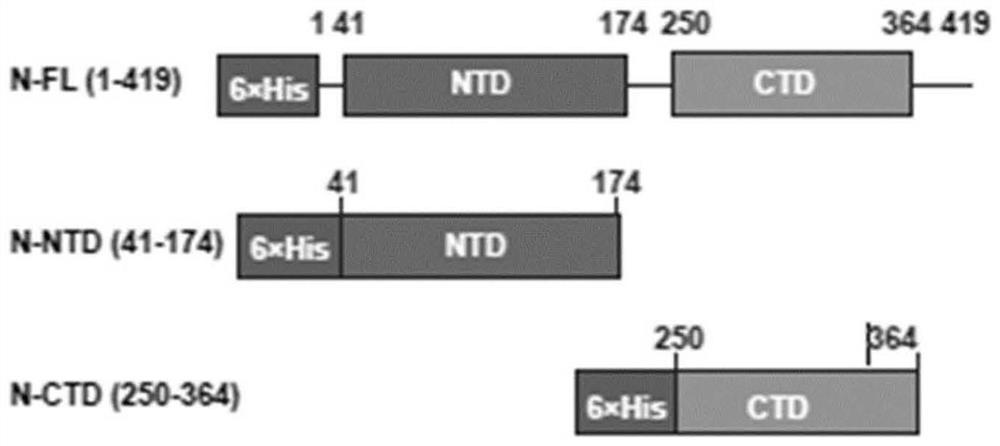
Preparation method and application of LcGa recombinant protein of galaptins of larimichthys crocea
InactiveCN105063076AMaintain natural biological activityEasy to prepareAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides a preparation method and an application of LcGa recombinant protein of galaptins of larimichthys crocea, and relates to genetic engineering. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: 1), a pGEX-6P1-LcGa recombinant expression vector is constructed; 2), an escherichia coli expression strain pGEX-6P1-LcGa-BL21 with high-copy transformants is acquired; 3), fermented cultivation and induced expression of the transformants are performed; the recombinant protein LcGa is purified. The LcGa recombinant protein of galaptins of the larimichthys crocea can be applied to mediated bacteria agglutination and mediated red blood cell agglutination, and can be applied to preparation of fish immune additives and bacterial control drugs. The prokaryotic expression recombinant protein exists in a soluble mode, and the natural bioactivity of the recombinant protein is kept; further, the preparation method is simple and easy to operate, the yield is high, the low-cost scale production becomes possible, and a new way is provided for development of the novel fish immune additives and the bacterial control drugs.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
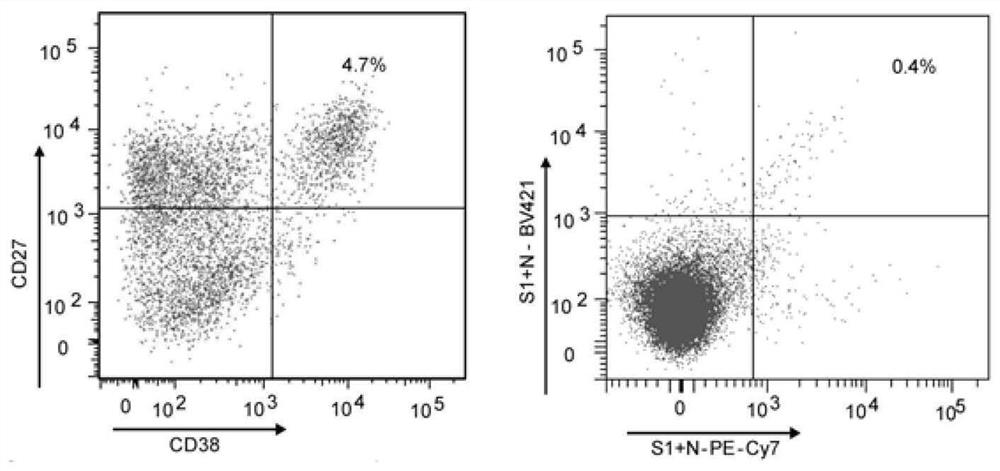
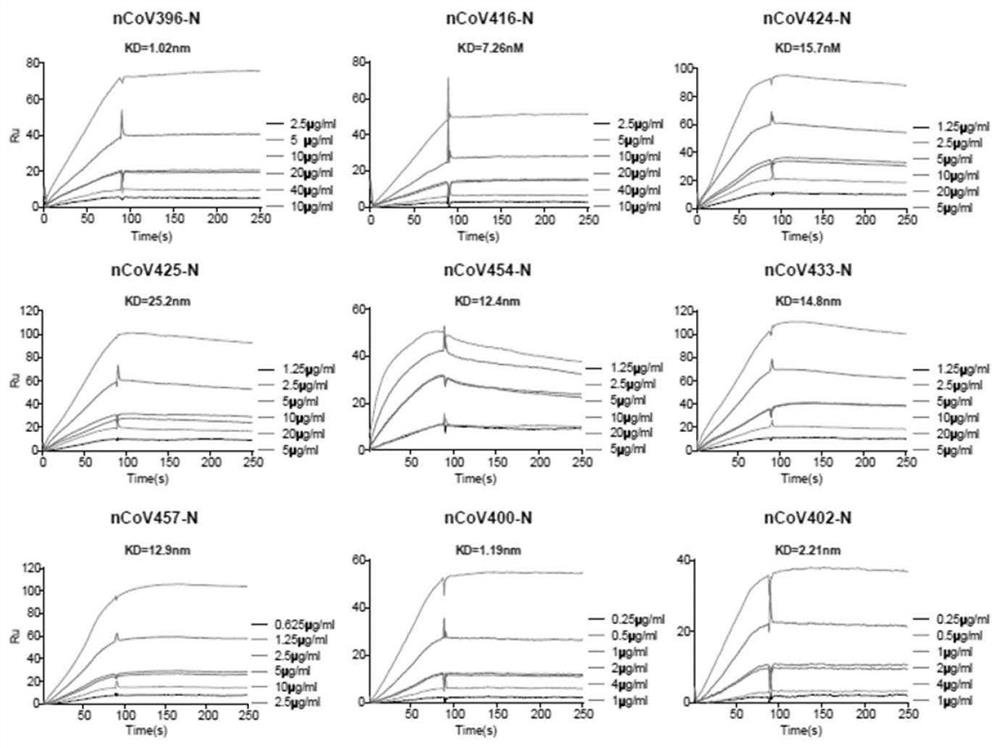
Antibody specifically binding to novel coronavirus
InactiveCN113234145ASsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesARDs - Acute respiratory distress syndromeCapsid
The complement activation is a risk factor for the morbidity and mortality of novel coronavirus-19 (COVID-19) patients, and is mediated by a highly immunopathogenic nucleocapsid protein (N) in which severe acute respiratory distress syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) binds to serine protease MASP-2 in the agglutinin pathway of complement activation. According to the invention, a dominant antibody with anti-SARS-CoV-2 virus N protein is separated and identified from a rapidly recovered COVID-19 convalescent person, and the antibody has high binding affinity. In addition, based on the cleavage activity of the complement protease MASP-2 on a specific fluorescence quenching peptide substrate, the invention further develops a virus-free complement hyper-activation analysis method.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
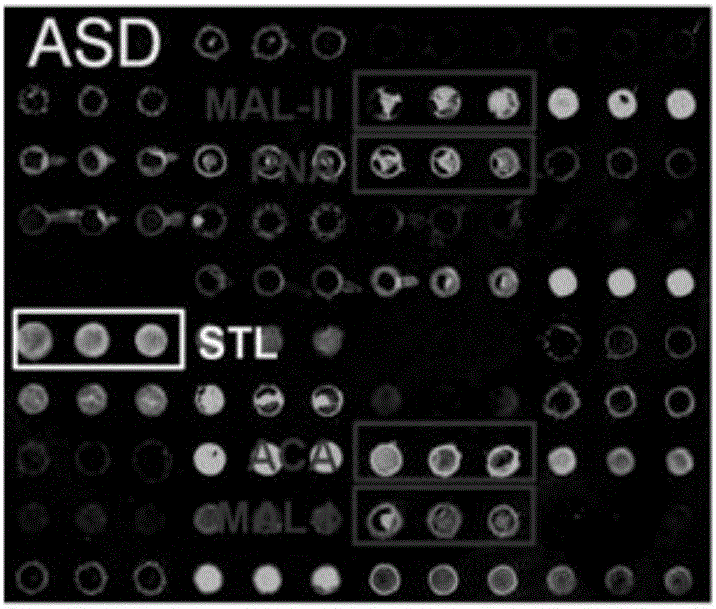
Use of autism seroglycoid marker
The invention discloses use of an autism seroglycoid marker. High-expression Apolipoprotein D (APOD) in ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorders) serum is simultaneously verified in agglutinin chip combined protein mass spectrometry forward verification and agglutinin / sugar-antibody chip reverse verification manners, and the APOD can serve as a seroglycoid marker for autism diagnosis, According to the use, vacancies in biochemical diagnosis on autism are made up.
Owner:广东辰辉生物医学技术有限公司
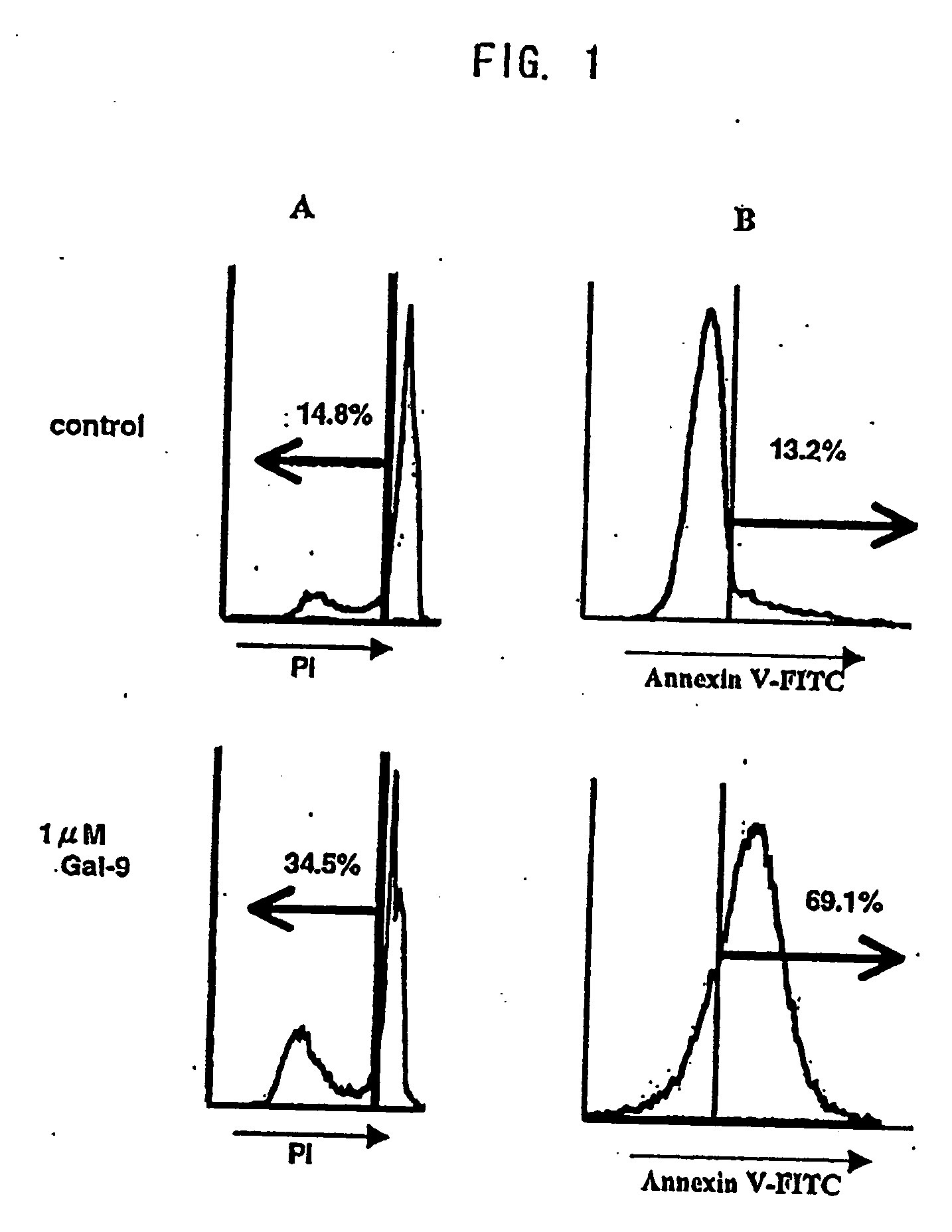
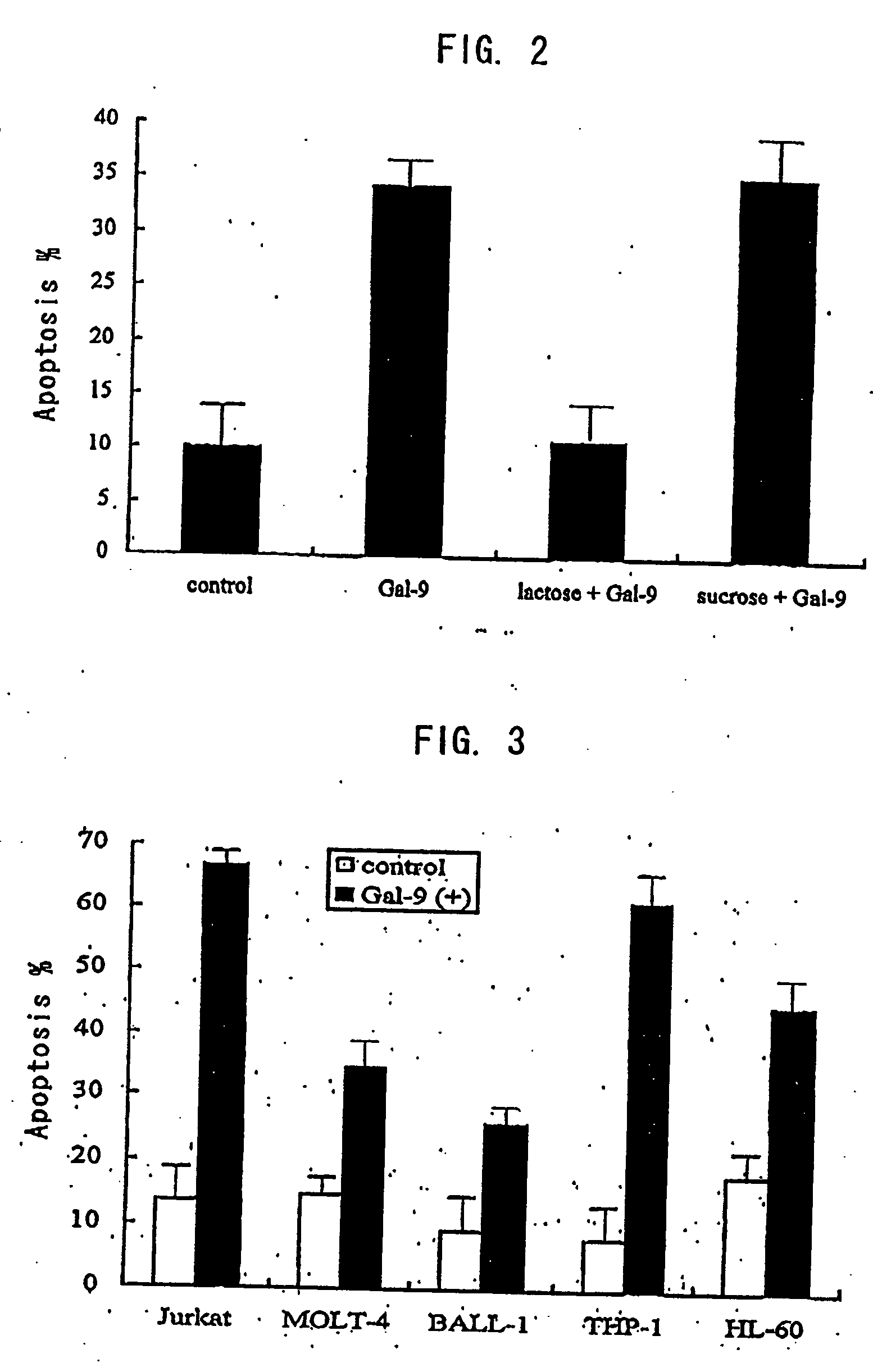
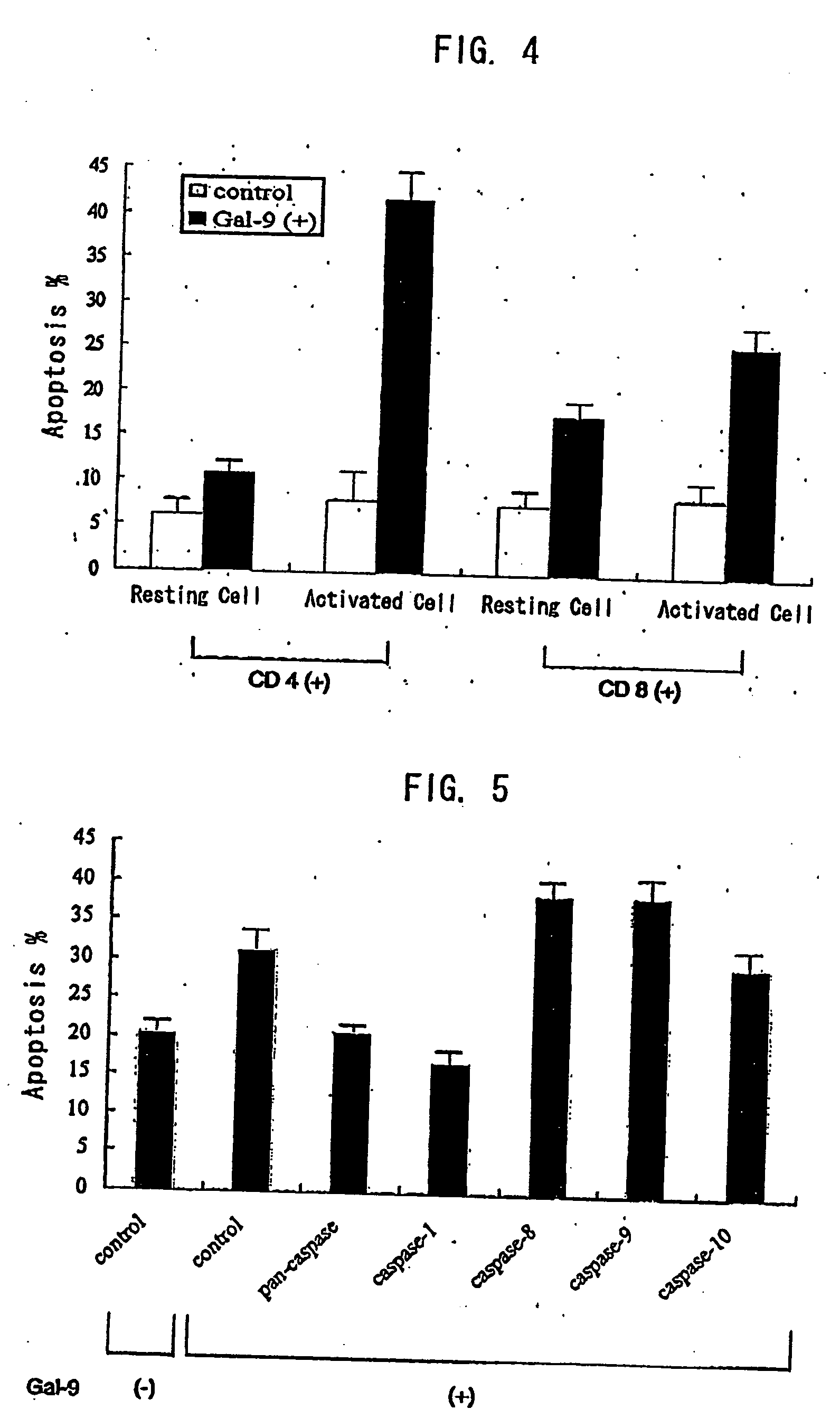
Drugs containing galectin 9
Galectin 9 exerts various functions depending on its localizations. On the other hand, galectin 9 is expected as participating in various biological functions. Thus, it has been required to clarify the detailed biological activities of galectin 9 and develop galectin 9-related techniques including development of drugs. Human galectin 9 shows a cytotoxic activity and an apoptosis-inducing activity on tumor cells but shows neither cytotoxic activity nor apoptosis-inducing activity on normal cells. Therefore, it is possible to employ galectin 9 proteins, galectin 9 agonists, galectin 9 antagonists, anti-galectin 9 binding protein antibodies, anti-galectin 9 binding sugar chain antibodies, galectin 9-producing, releasing or inducing substances, etc. as antitumor, antiallergic, immunosuppressive agents, drugs for autoimmune diseases, anti-inflammatory agents and active ingredients for adrenocortical steroid hormone alternatives.
Owner:GALPHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com