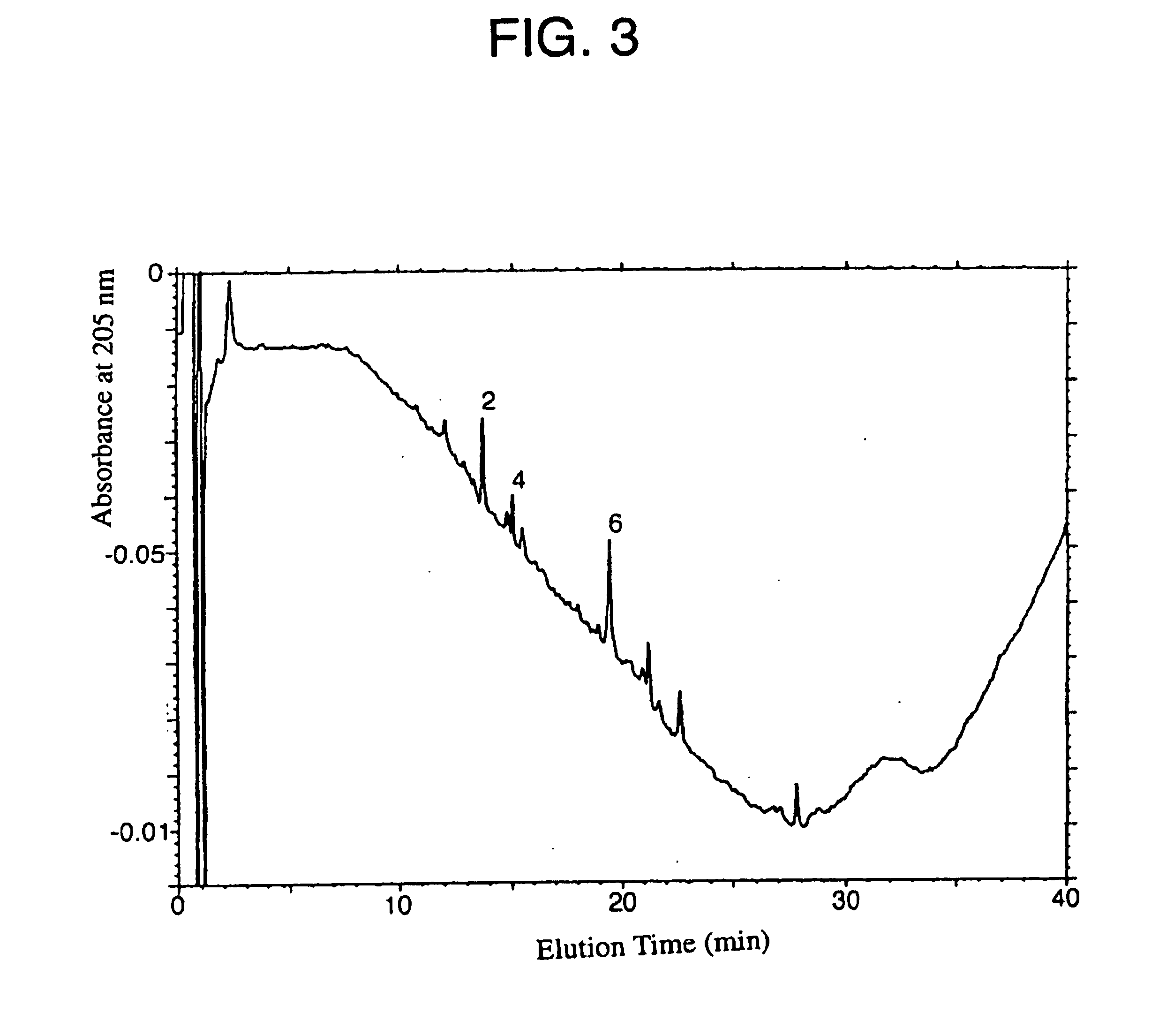
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Neuronal Growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
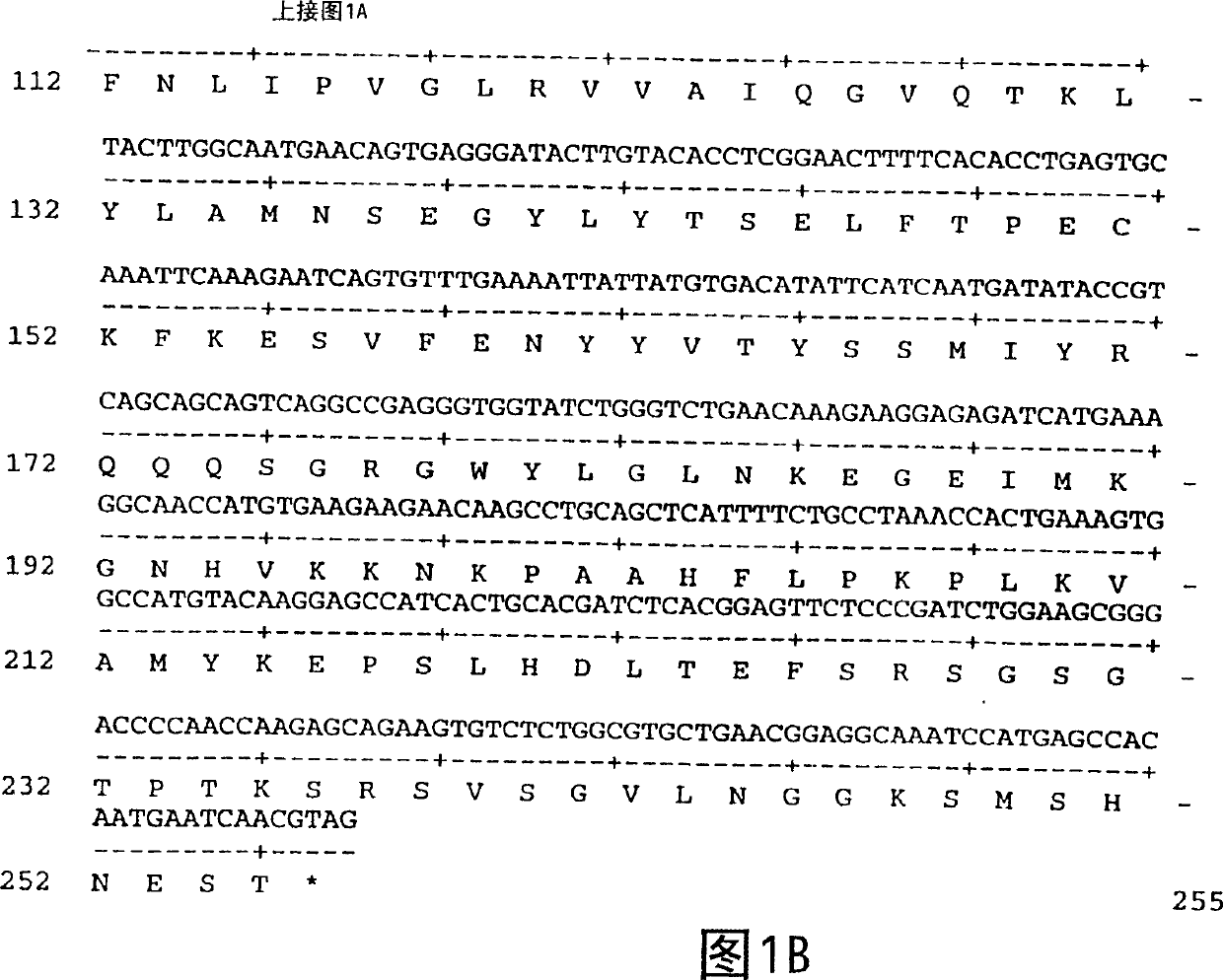
Neurons grow via a growth cone, an area at the leading edge of the developing neuron, that guides the direction of the axon development. The growth cone looks like a large round area teeming with activity at the end of a long straight growing axon.
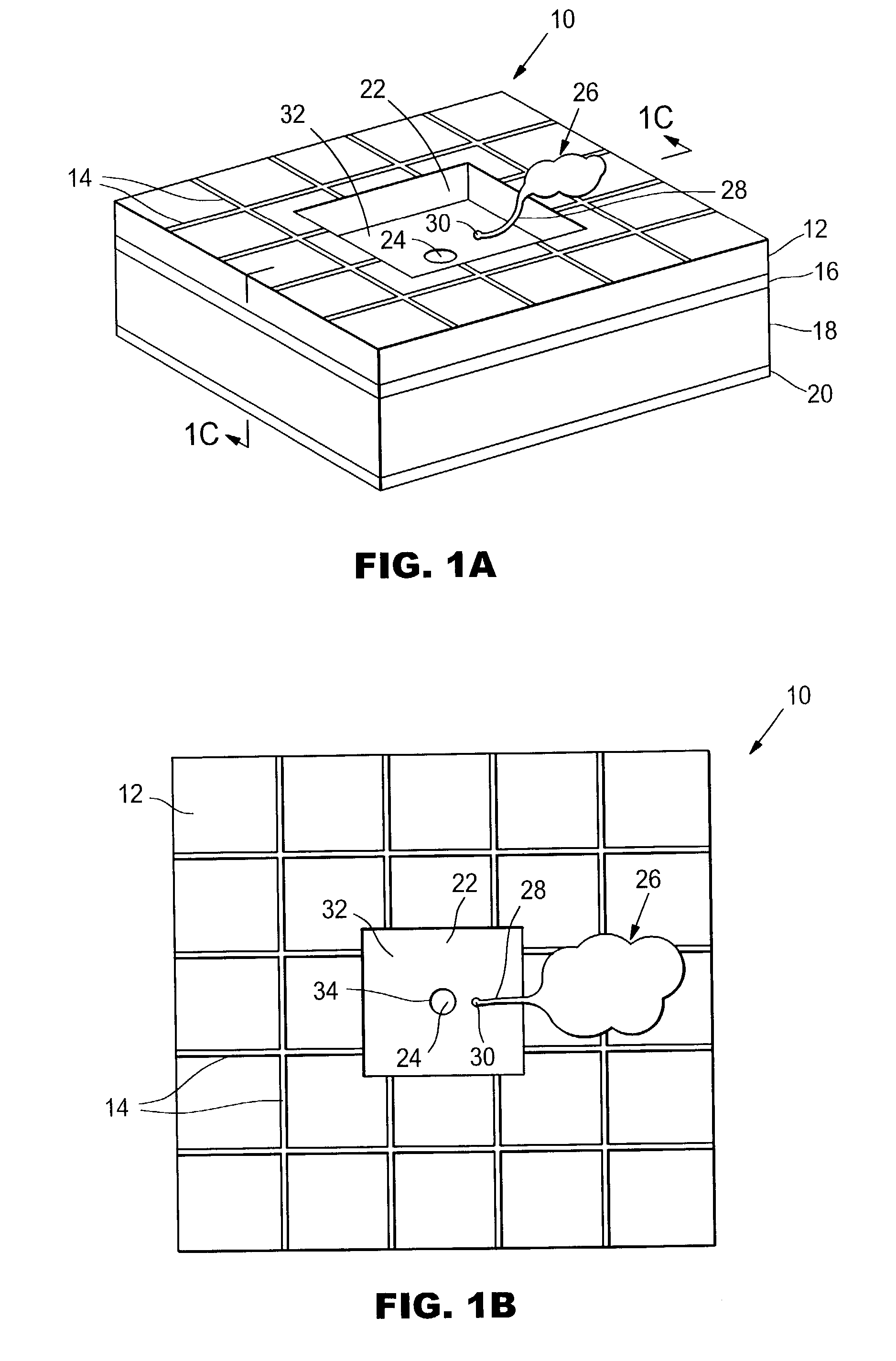
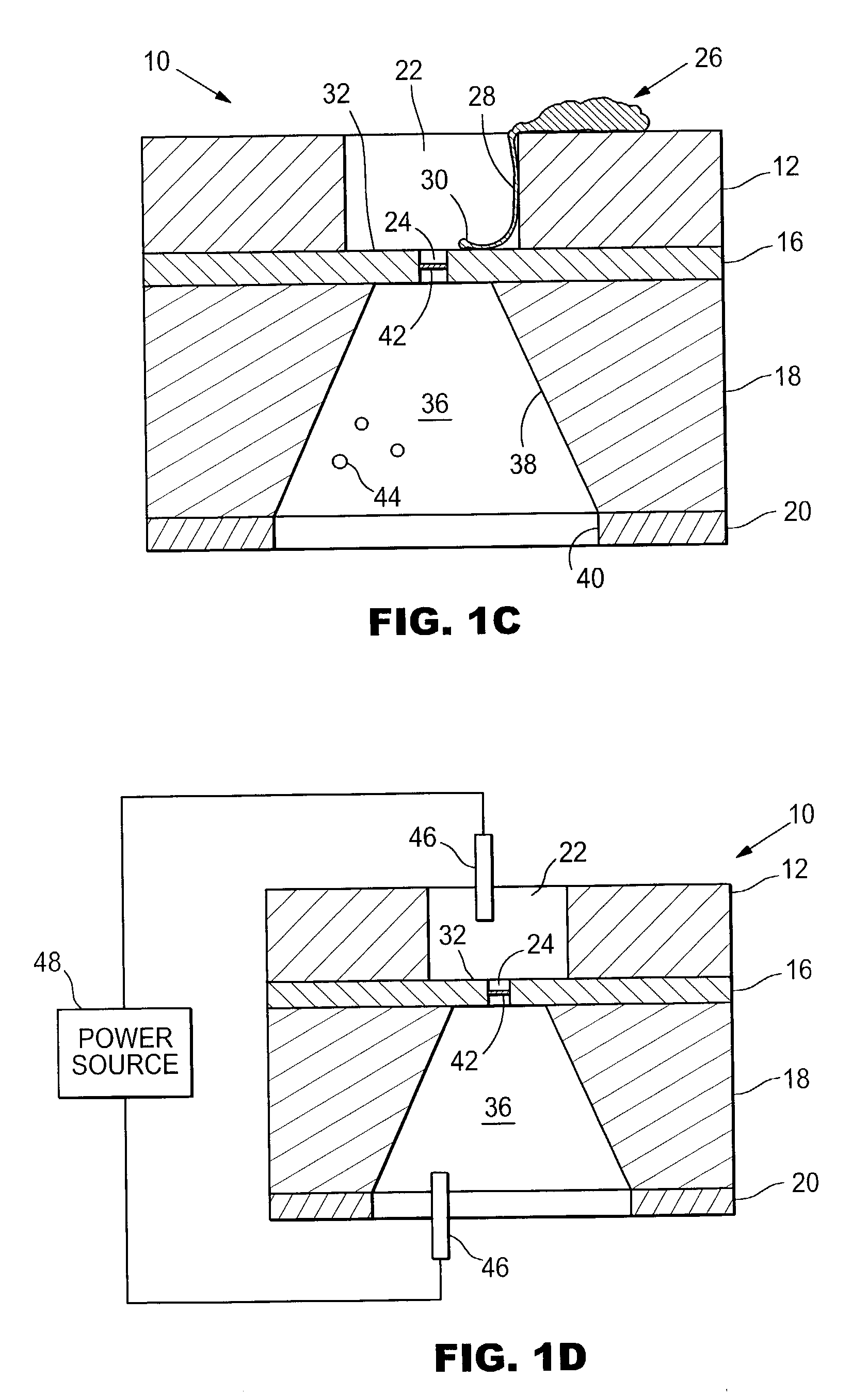
Methods for promoting nerve regeneration and neuronal growth and elongation
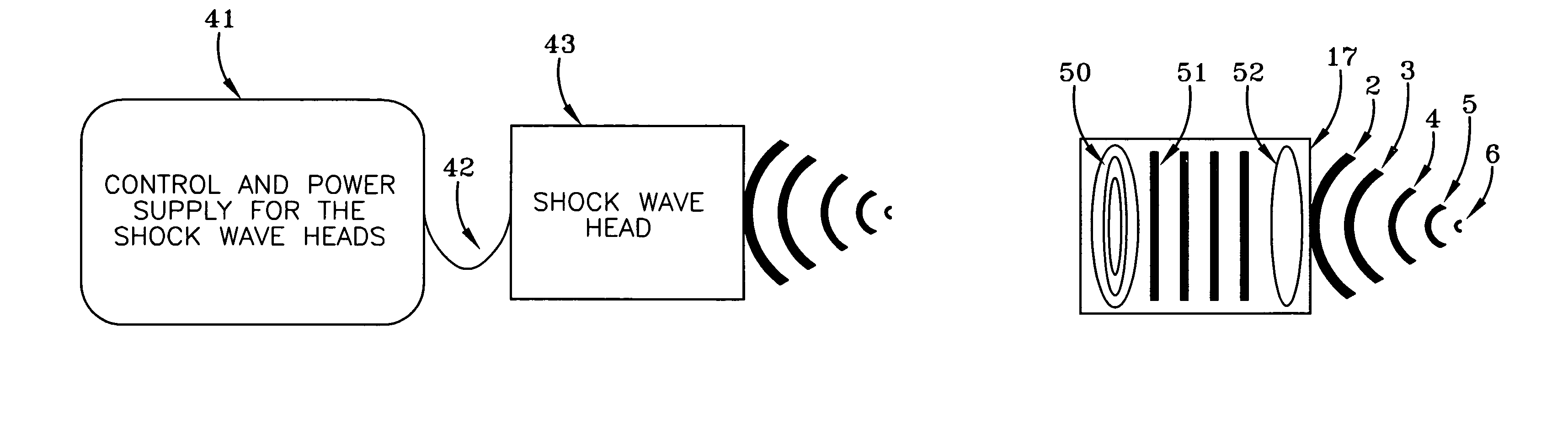
ActiveUS20070239080A1Increase amplitudeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesNervous systemRisk stroke
A method of enhancing the regeneration of injured nerves has the step of administering an effective exposure of pressure pulses or acoustic shock waves in a pulse or wave pattern to the zone of injury of the nerve during the regeneration process. The inventive method may include enhancing the stimulation of neuronal cell growth or regeneration by administering an effective exposure of pressure pulses or acoustic shock waves in a pulse or wave pattern to stimulate neuronal cell growth or regeneration, wherein the administering of the treatment is applied to a patient who has a pathological condition where neuronal repair can be facilitated including peripheral nerve damage caused by injury or disease such as diabetes, brain damage associated with stroke, and for the treatment of neurological disorders related to neurodegeneration, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral, sclerosis multiple sclerosis and disseminated sclerosis. The treatment is ideally suited for neural regeneration after a degenerative condition due to any neurological infections or any other pathological condition.
Owner:SOFTWAVE TISSUE REGENERATION TECH LLC
Artificial synapse chip interface for electronic prosthetic retina
InactiveUS7001608B2Efficient deliveryRecovery functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoElectron
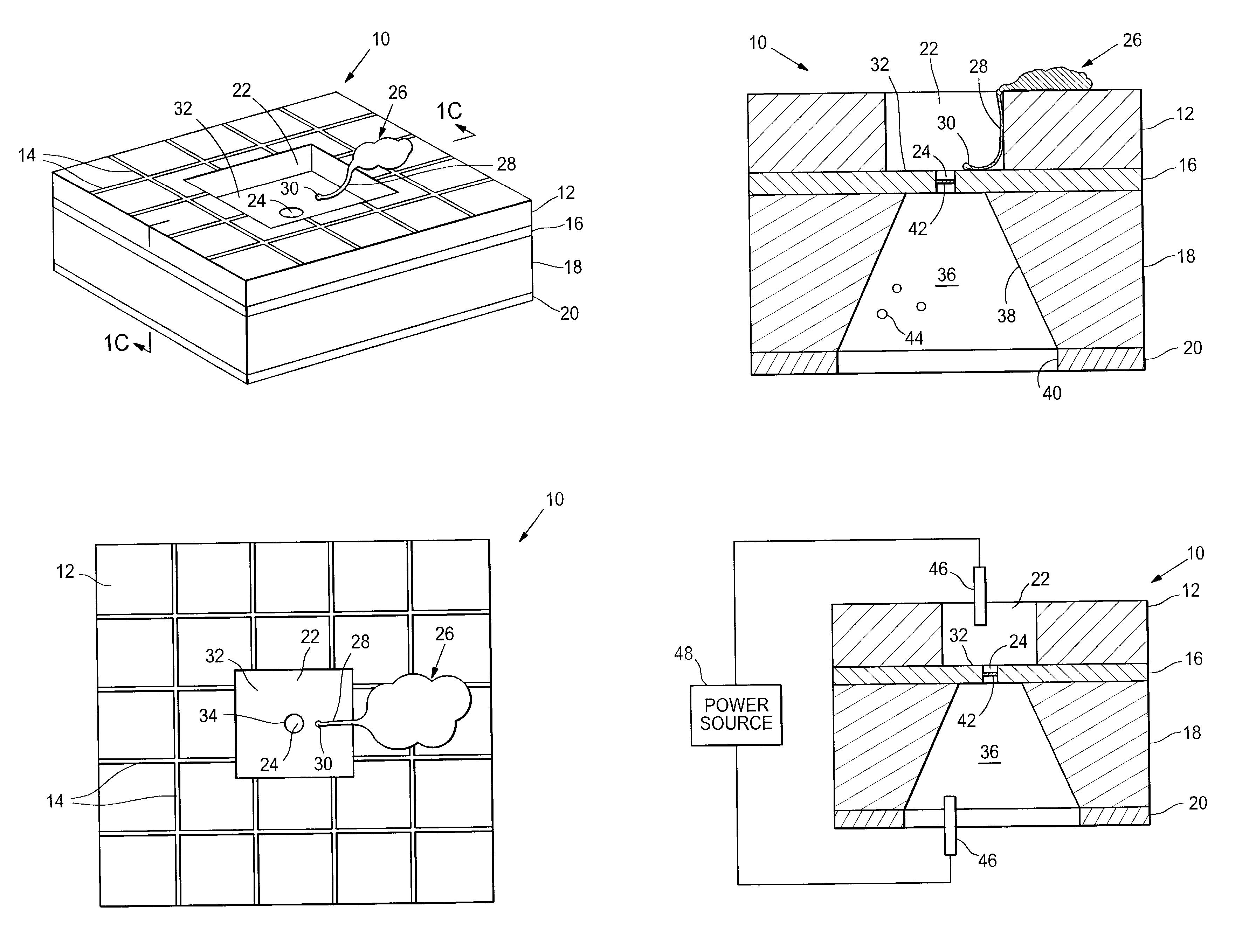
The invention provides microfabricated devices and methods for directing the growth of a cell process to form an artificial synapse. The devices are called artificial synapse chips. The artificial synapse comprises a nanofabricated aperture (about 50–100 nm in size) that connects the cell process to a chemical or electrical means of neuronal excitation. Such an aperture width mimics the length scales of a natural synapse and thus emphasizes the localized spatial relationship between a neuron and a stimulation source. The invention further provides devices and methods for regenerating a nerve fiber into an electrode. The invention thus provides a regeneration electrode that uses a novel neural interface for stimulation and that uses novel surface methods for directing neuronal growth making possible in vivo connection of the devices to neural circuitry in a retina and other anatomical locations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Neuronal growth factor galectin-1
InactiveUS6890531B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNerve degenerationADAMTS Proteins
This invention relates to a remedy for neuropathy, such as nerve injury, nerve degeneration, and hypofunction upon nerve grafting, which contains as the active ingredient galectin-1 having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or its derivative; a protein having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or one having a homology of 90% or more at the amino acid level with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and carrying a disulfide bond(s) at least between Cys at the 16-position (Cys 16) and Cys at the 88-position (Cys 88) among cystein residues at the 2-position (Cys 2), 16-position (Cys 16), 42-position (Cys 42), 60-position (Cys 60), 88-position (Cys 88) and 130-position (Cys 130); and a process for producing the galectin-1 or its derivative protein by using an affinity column having an antibody to the above protein.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Diamond neural devices and associated methods
InactiveUS20110282421A1Internal electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMaterials science
The present disclosure provides devices for neuronal growth and associate methods. In one aspect, for example, a neuronal growth device is provided including a layer of nanodiamond particles having an exposed neuronal growth surface, a doped diamond layer contacting the layer of nanodiamond particles opposite the neuronal growth surface, and a semiconductor layer coupled to the doped diamond layer opposite the layer of nanodiamond particles. In one aspect, the nanodiamond particles are substantially immobilized by the doped diamond layer.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Methods for promoting nerve regeneration and neuronal growth and elongation
ActiveUS7544171B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesNervous systemRisk stroke
A method of enhancing the regeneration of injured nerves has the step of administering an effective exposure of pressure pulses or acoustic shock waves in a pulse or wave pattern to the zone of injury of the nerve during the regeneration process. The inventive method may include enhancing the stimulation of neuronal cell growth or regeneration by administering an effective exposure of pressure pulses or acoustic shock waves in a pulse or wave pattern to stimulate neuronal cell growth or regeneration, wherein the administering of the treatment is applied to a patient who has a pathological condition where neuronal repair can be facilitated including peripheral nerve damage caused by injury or disease such as diabetes, brain damage associated with stroke, and for the treatment of neurological disorders related to neurodegeneration, including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral, sclerosis multiple sclerosis and disseminated sclerosis. The treatment is ideally suited for neural regeneration after a degenerative condition due to any neurological infections or any other pathological condition.
Owner:SOFTWAVE TISSUE REGENERATION TECH LLC
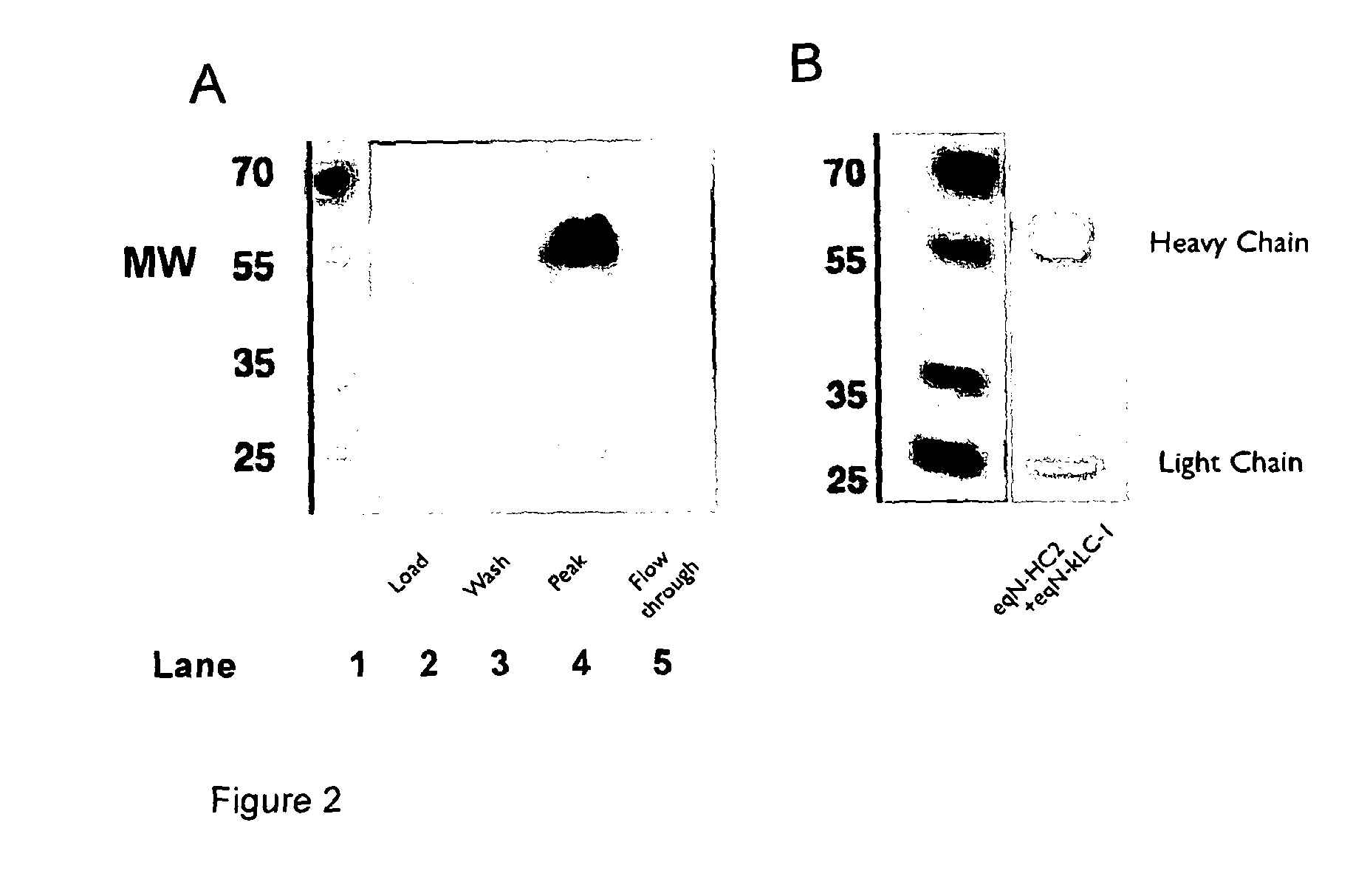
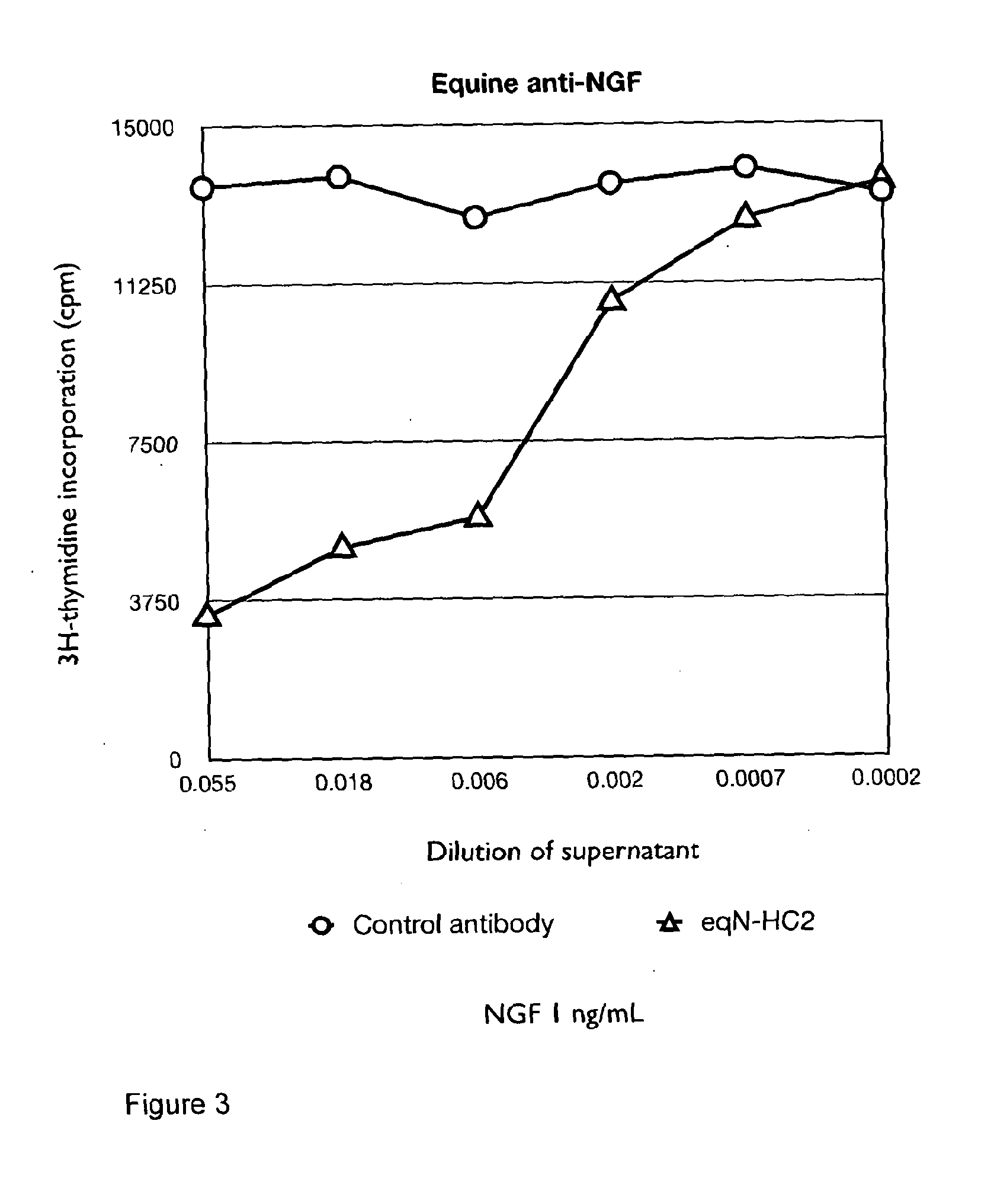
Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
InactiveUS20140170136A1Prevents upregulationSensation of pain be reducedNervous disorderSugar derivativesArthritisNGF Receptor
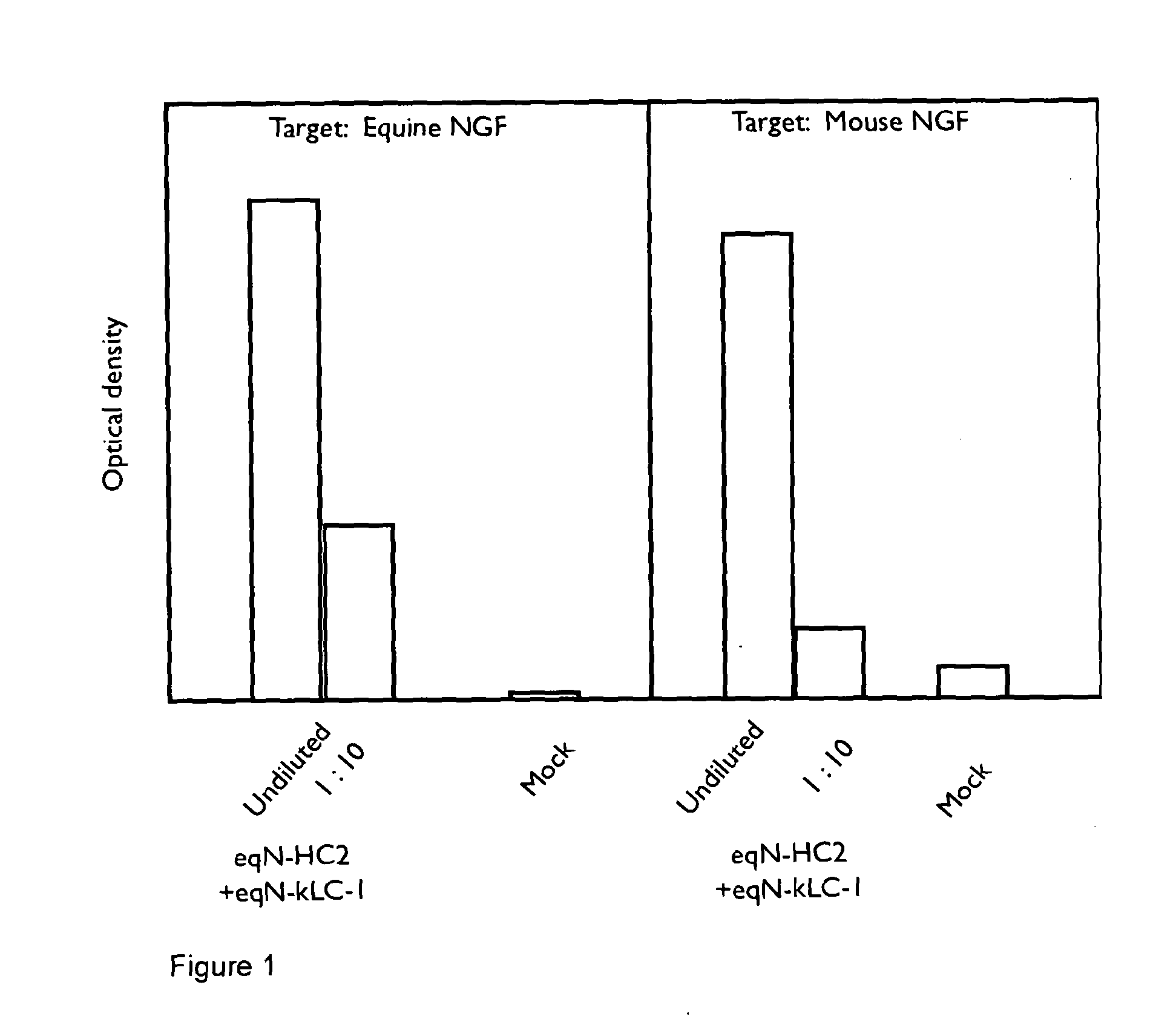
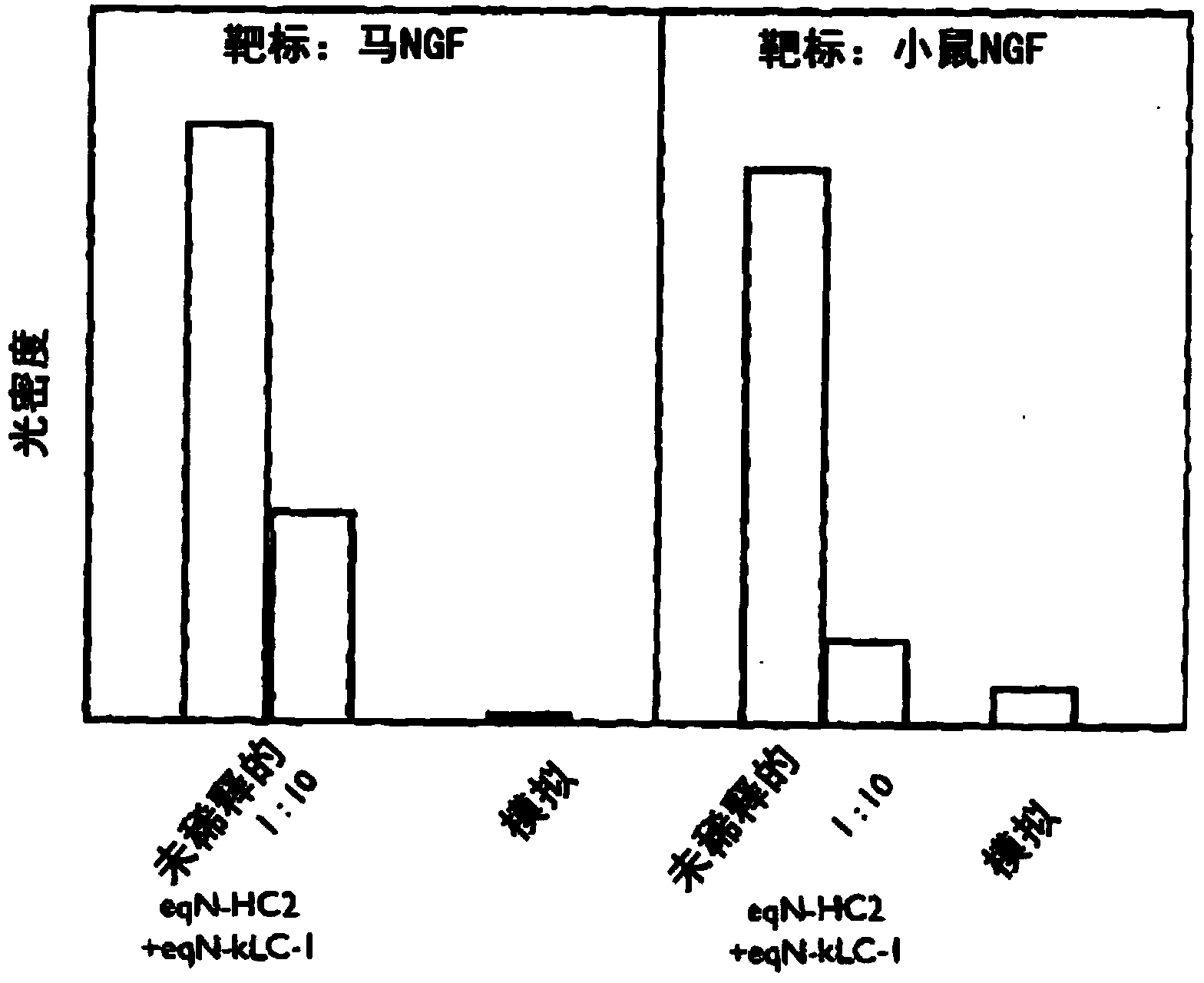
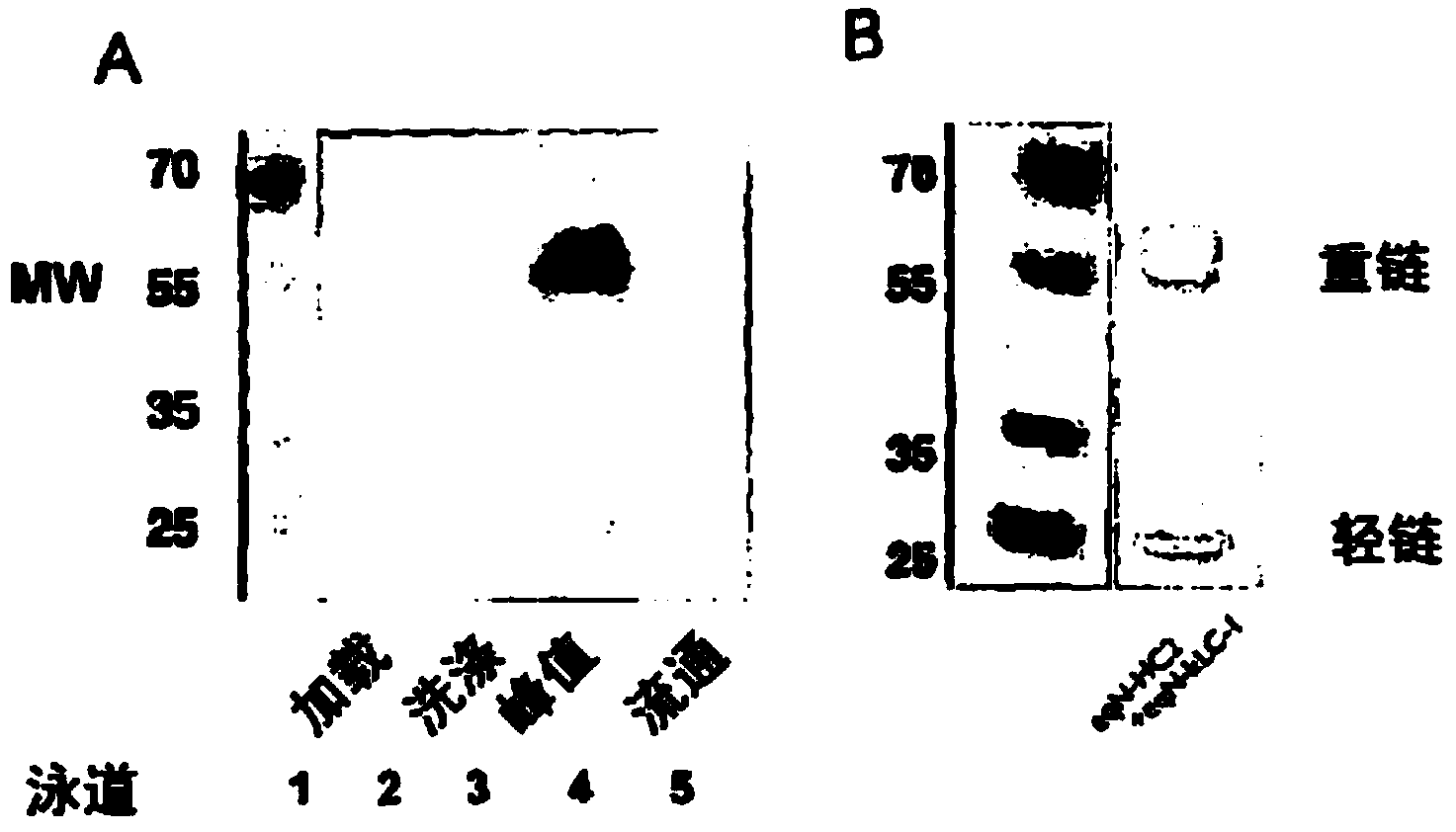
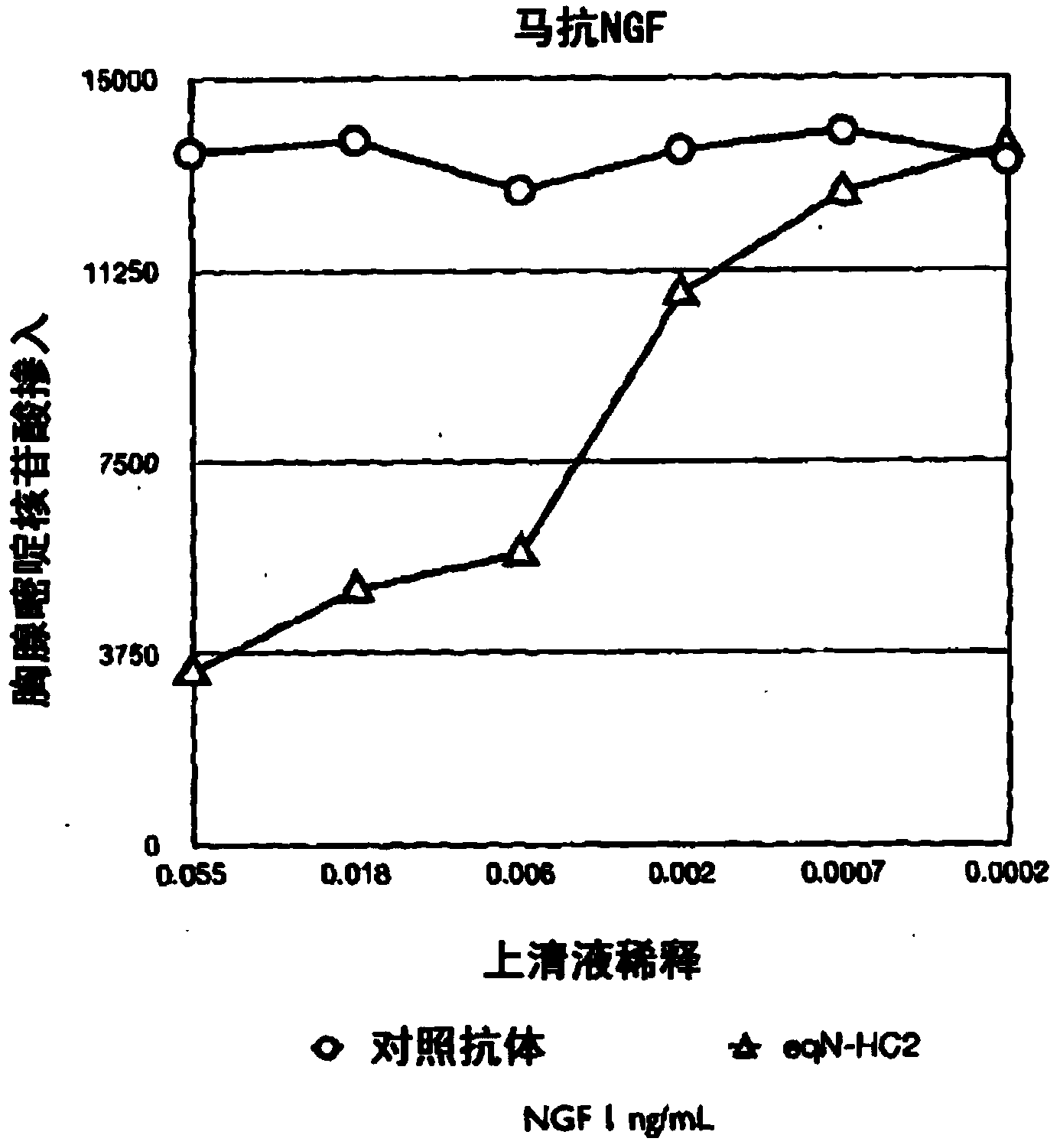
A method of preparing an antibody suitable for use in an equine is provided. Also provided are equinised antibodies which specifically bind to equine neuronal growth factor (NGF) and neutralise the ability of equine NGF to bind to the p75 or TrkA equine NGF receptor. The invention extends to nucleic acids encoding same and to methods of treating pain and arthritis in an equine using said antibodies and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:NEXVET AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Promoters of neural regeneration
InactiveUS6268352B1Promote nerve growthImprove the level ofBiocideNervous disorderProtein kinase ABiophysics
The invention provides methods and compositions for promoting neural cell growth and / or regeneration. The general methods involve contacting with an activator of a cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase a neural cell subject to growth repulsion mediated by a neural cell growth repulsion factor. The activator may comprise a direct or an indirect activator of the protein kinase; the repulsion factor typically comprises one or more natural, endogenous proteins mediating localized repulsion or inhibition of neural cell growth; and the target cells are generally vertebrate neurons, typically injured mammalian neurons. The subject compositions include mixtures comprising a neural cell, an activator of a cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and a neural cell growth repulsion factor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for Treating Neurological Disorders
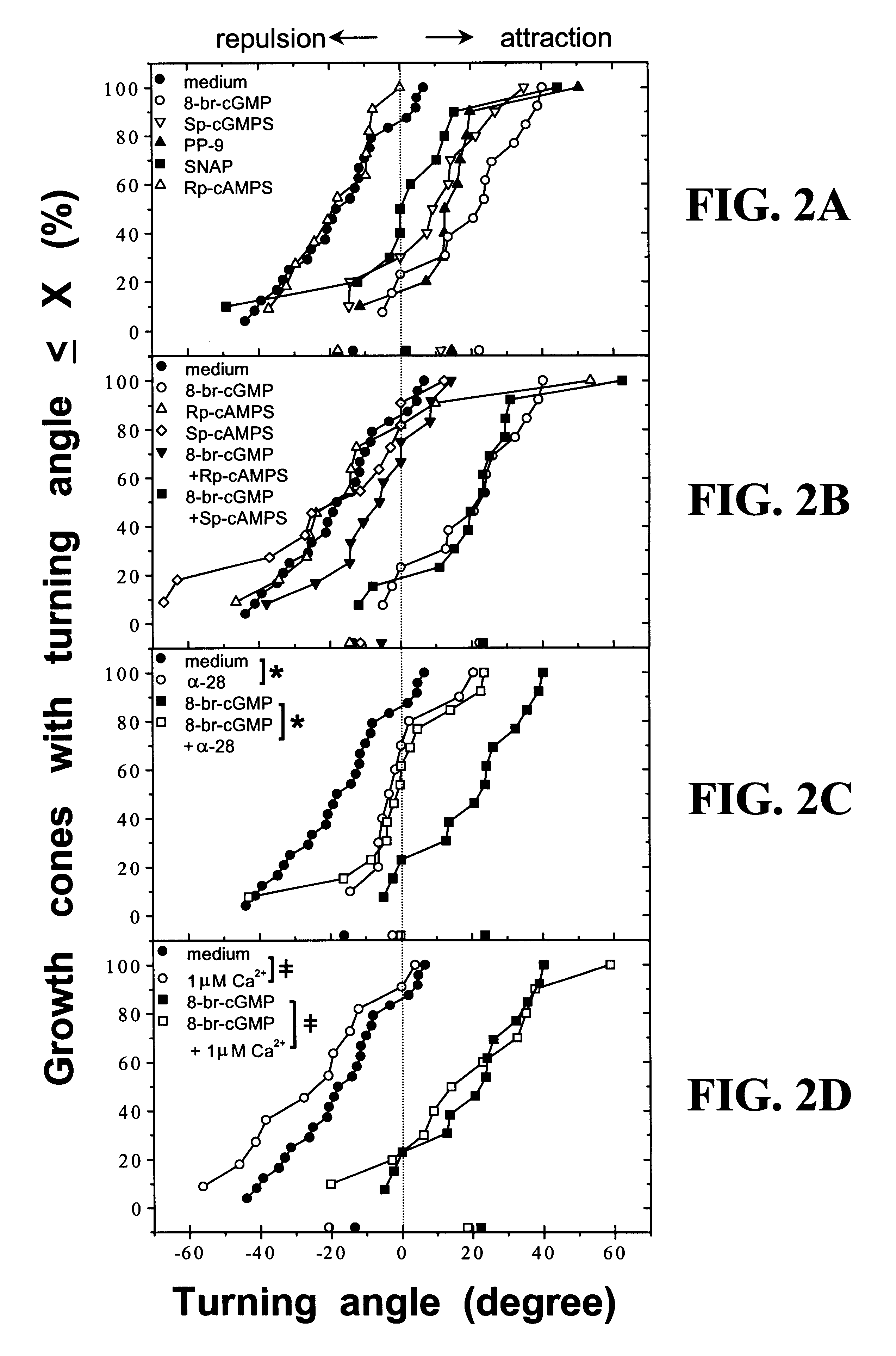
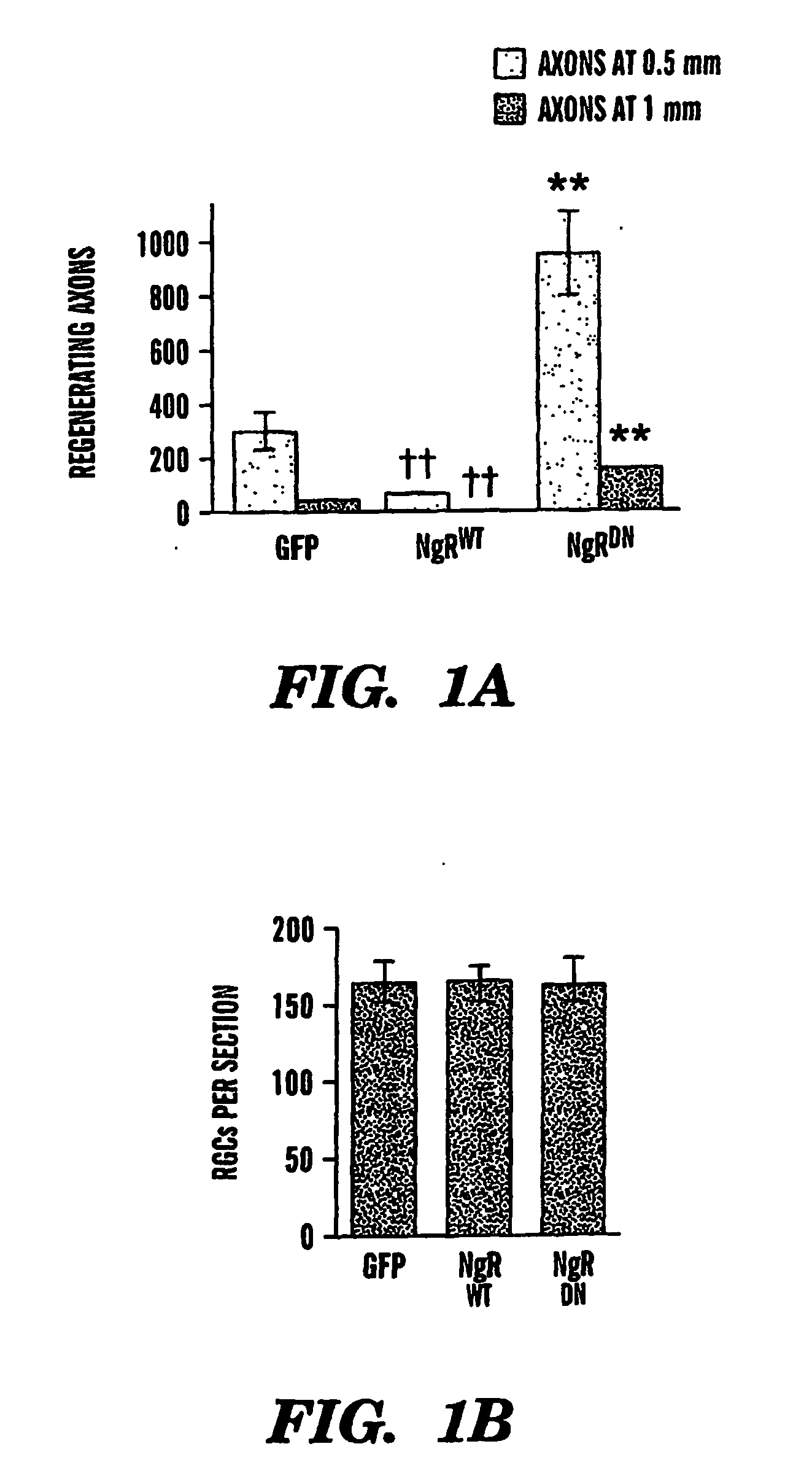
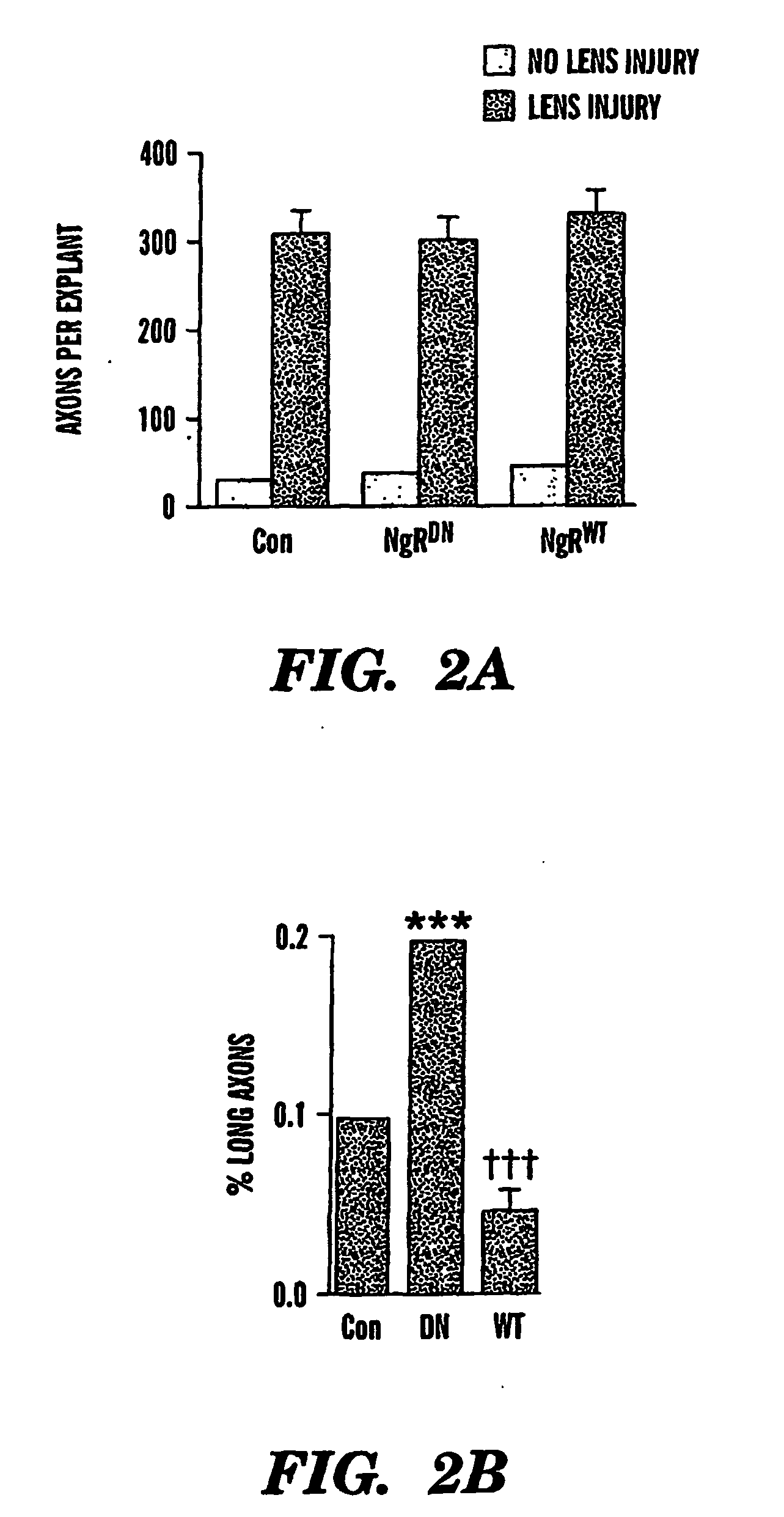
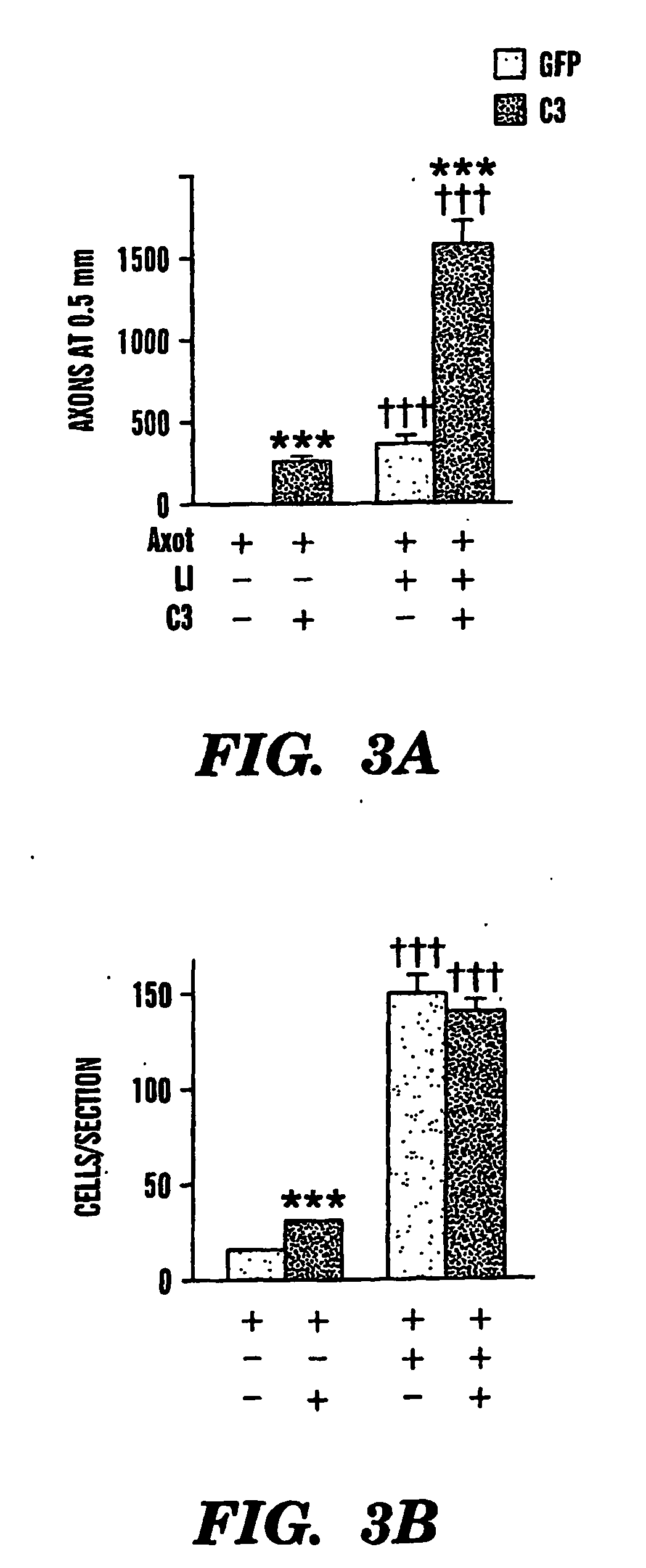
The present invention is based on the discovery that suppressing the activity of the Nogo receptor (NgR) alone does not result in extensive axon regeneration unless the intrinsic growth program of neurons is also activated Accordingly, the present invention is directed to methods of stimulating axon regeneration using a combination therapy wherein agents that inhibit NgR activity or downstream pathways activated by inhibitory signals are combined with agents that activate the growth pathway of neurons (e.g. polypeptide growth factors, activators of macrophages, purine nucleosides, or hexoses).
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Prominin-1 peptide fragments and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110190210A1Improve angiogenesisPromote migrationNervous disorderSkeletal disorderMedicineVasodilation
Described herein are peptide compositions of a prominin-1, which have regenerative activity. As such the peptides are useful when regeneration is needed, for example, to enhance angiogenesis, increase VEGF binding to endothelial cells, promote vasodilation, enhance cell migration, enhance cell proliferation, stimulate neuronal growth, prevent neurodegeneration, and / or promote neuroregeneration.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
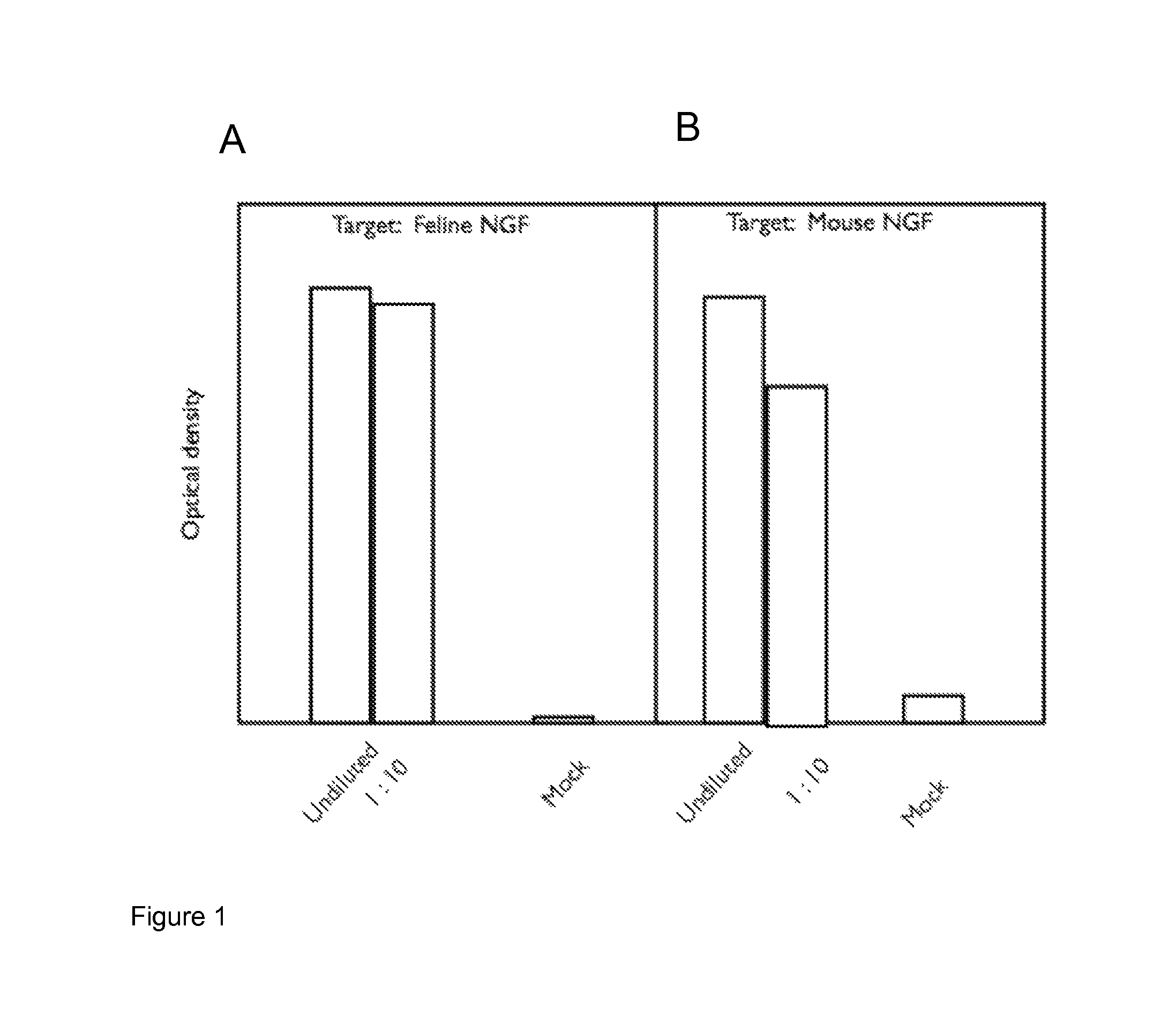
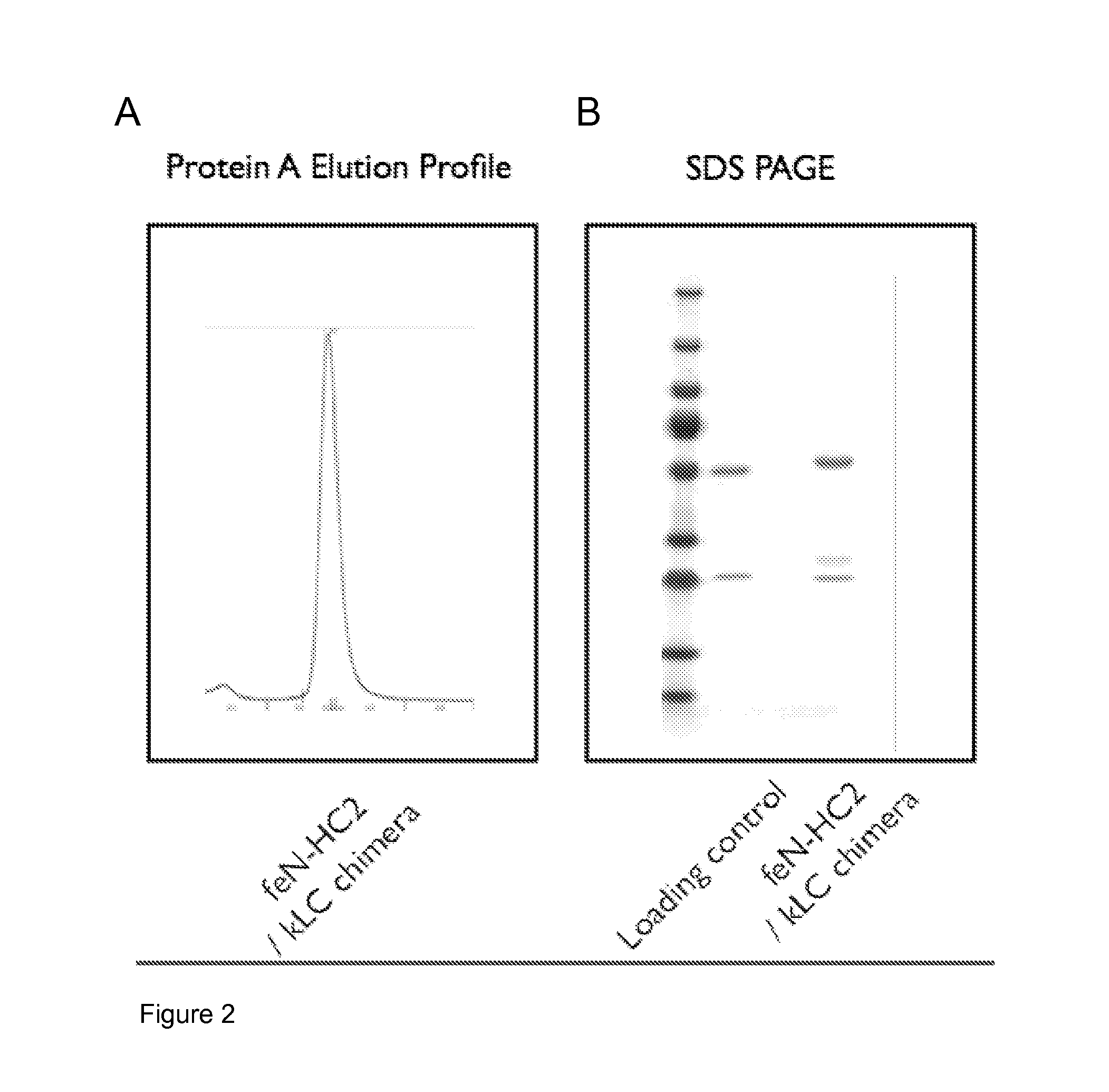
ActiveUS20140147439A1Enhance and complement therapeutic effectPrevents upregulationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsArthritisNGF Receptor
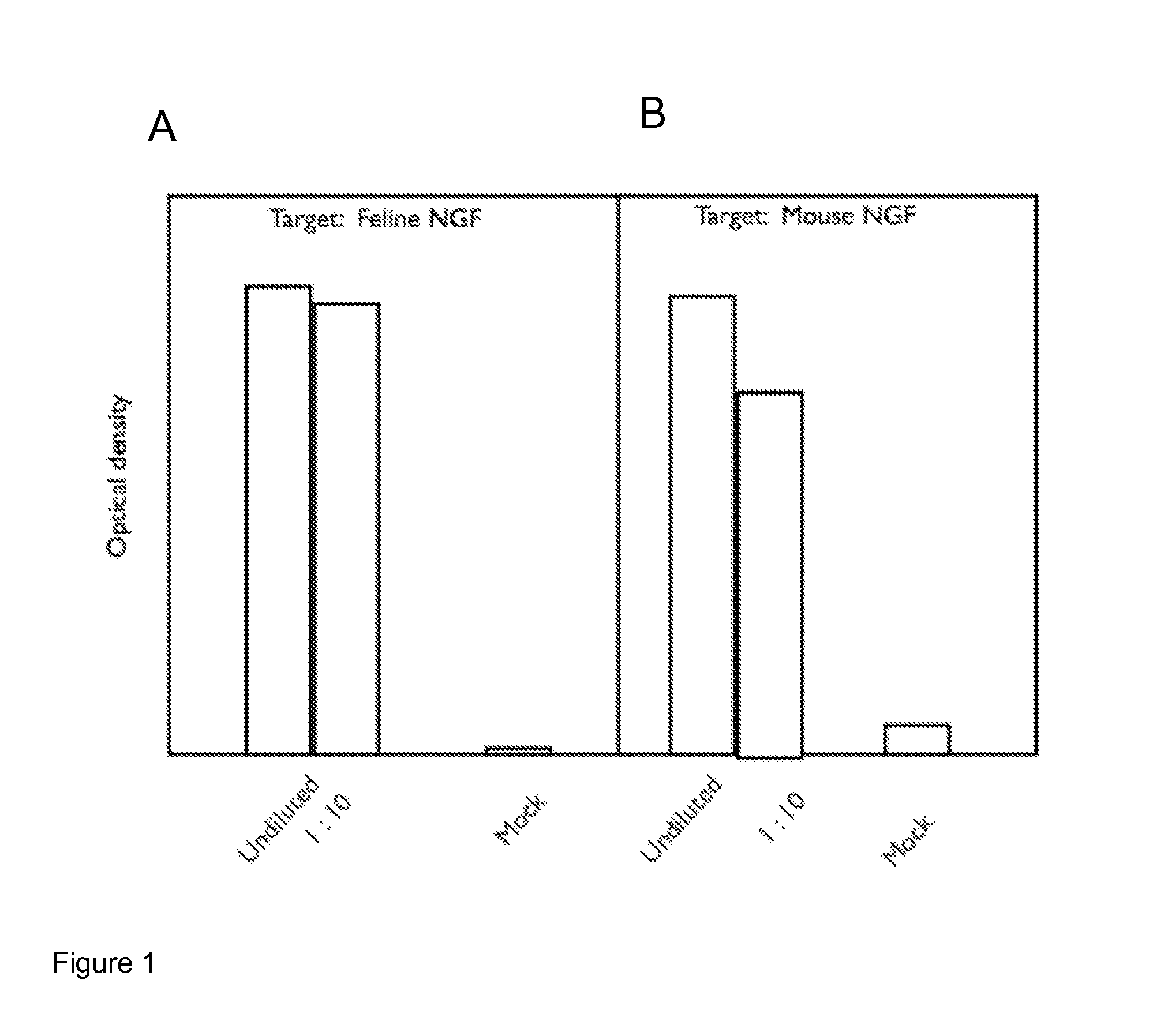
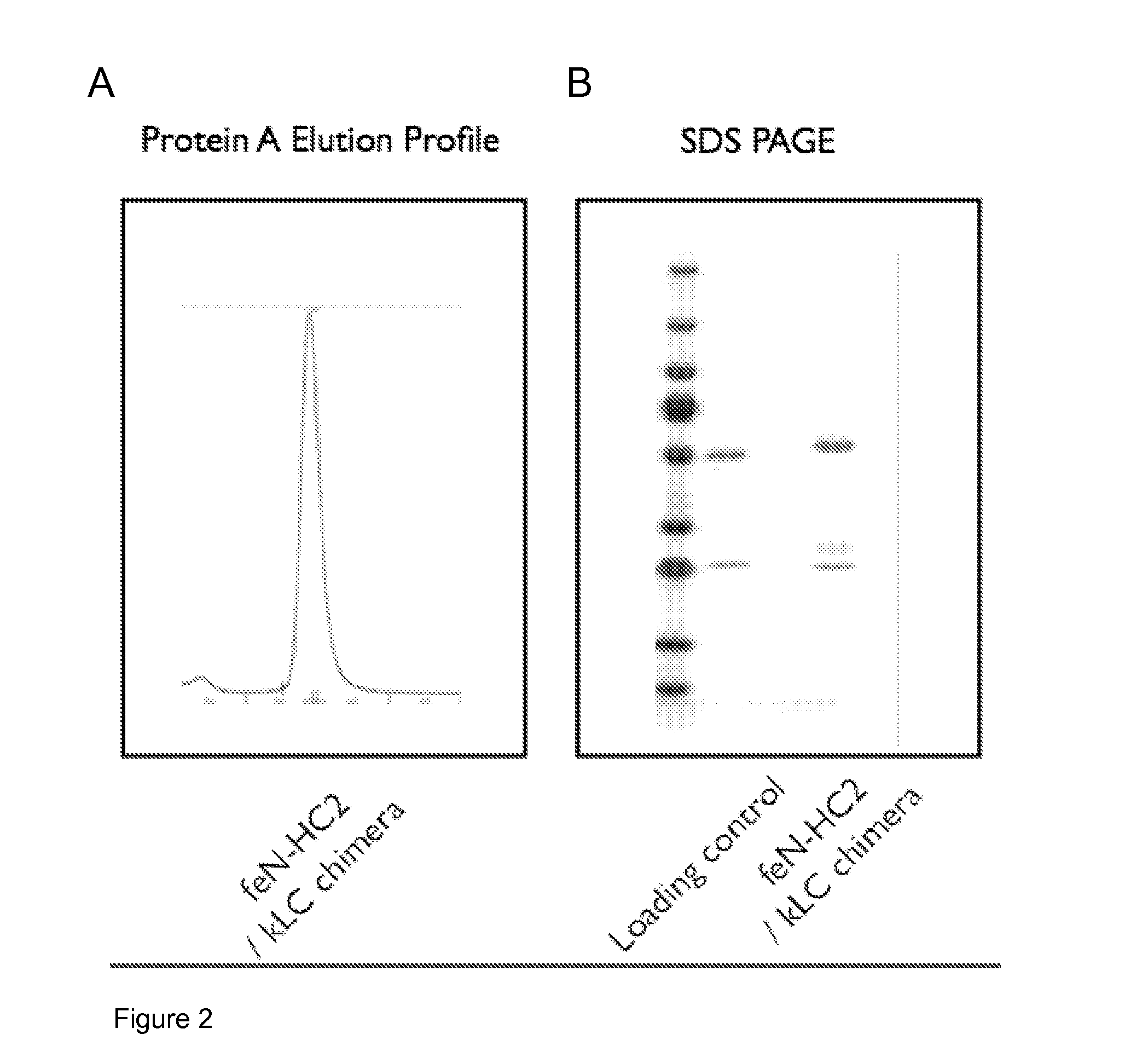
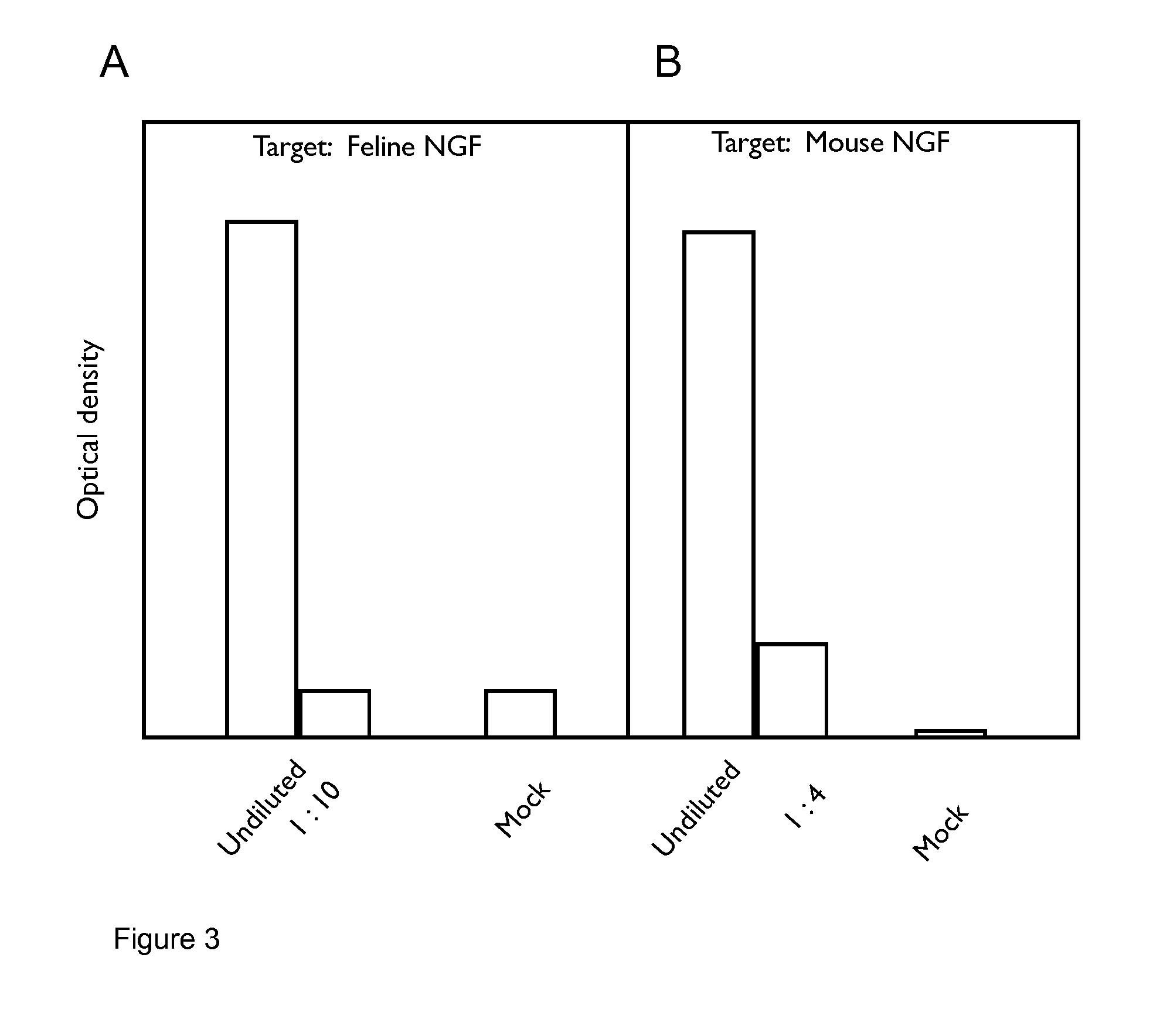
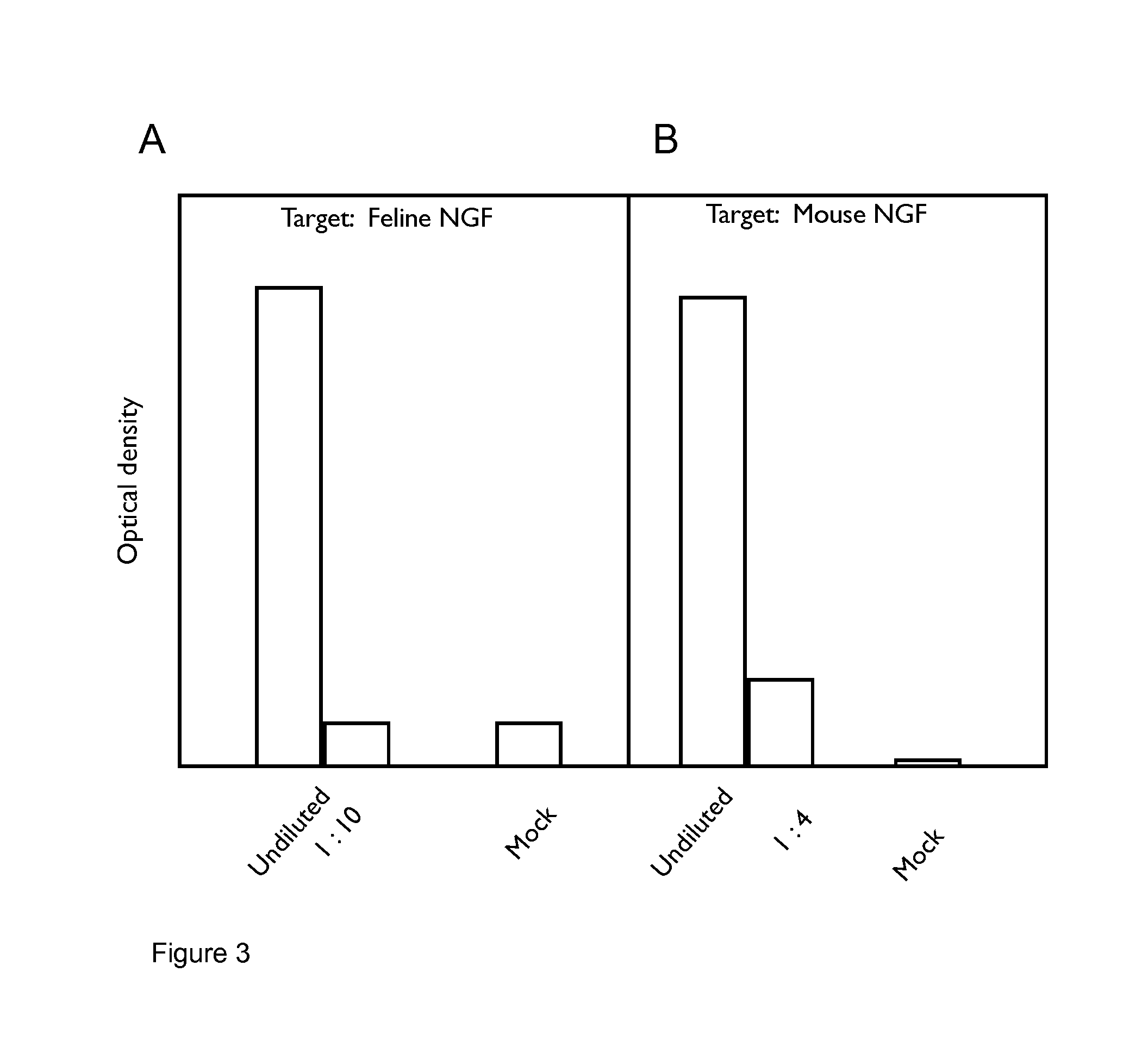
A method of preparing an antibody suitable for use in a feline is provided. Also provided are chimeric and felinised antibodies which specifically bind to feline neuronal growth factor (NGF) and neutralise the ability of feline NGF to bind to the p75 or TrkA feline NGF receptor. The invention extends to nucleic acids encoding same and to methods of treating pain and arthritis in a feline using said antibodies and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Methods and compositions for nerve regeneration
InactiveUS20080299135A1Reduced strengthGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMammalTherapeutic Technique
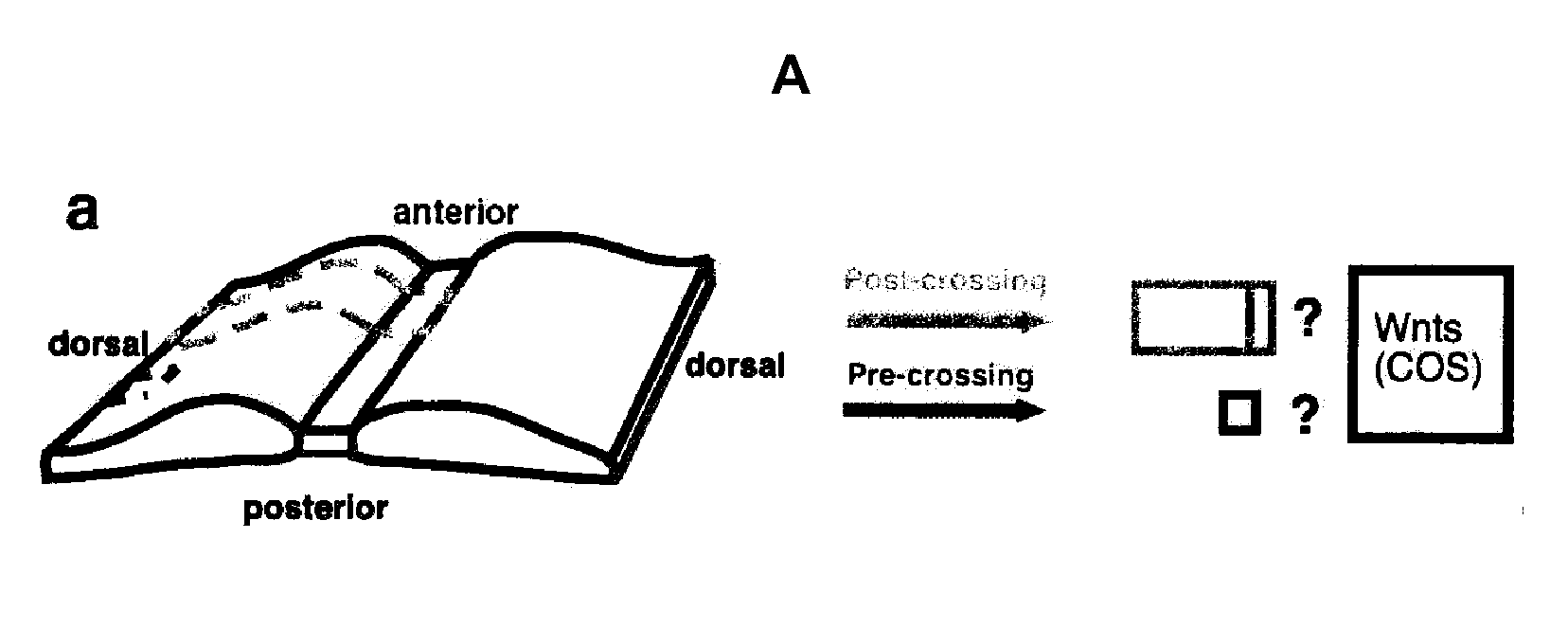
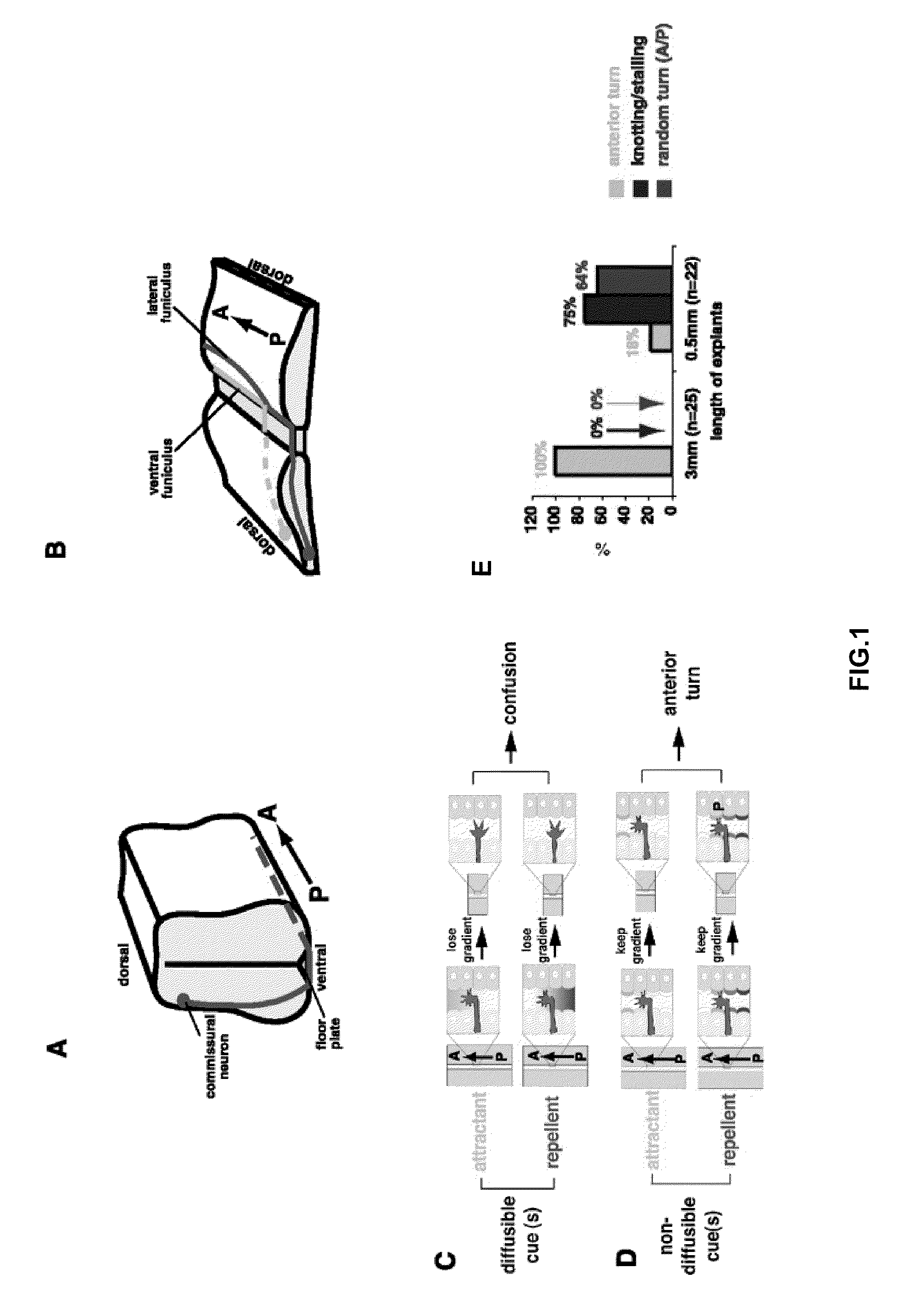
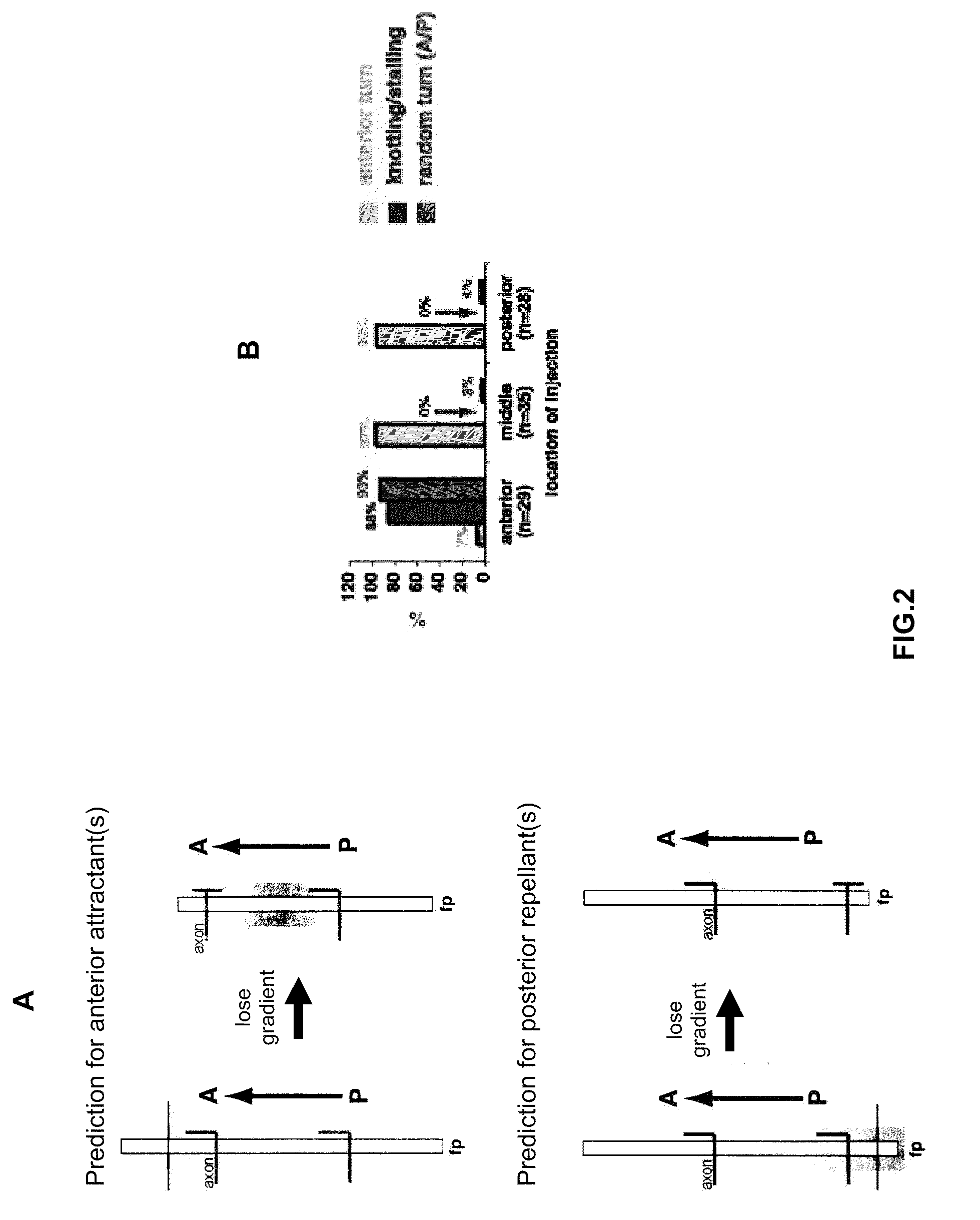
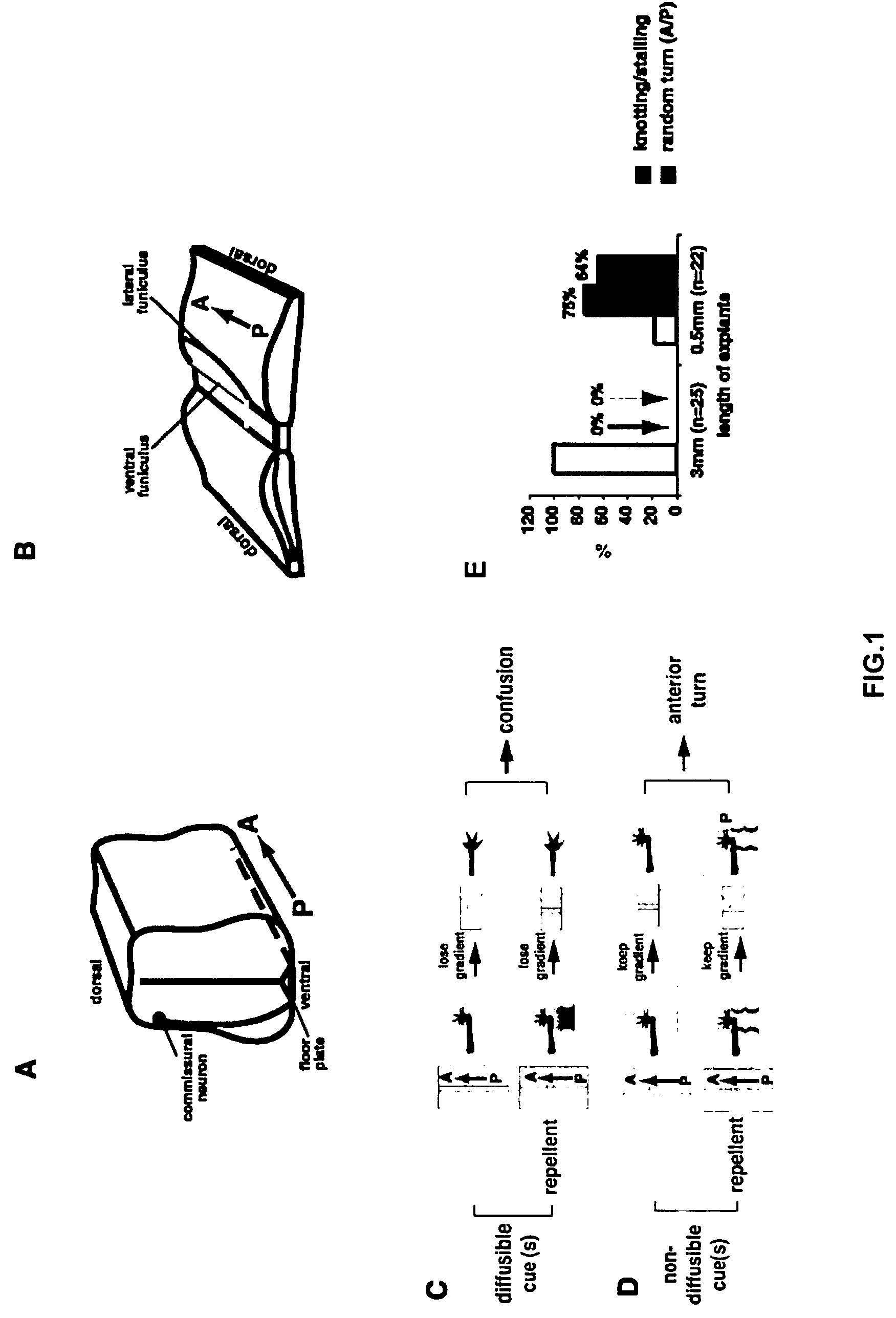
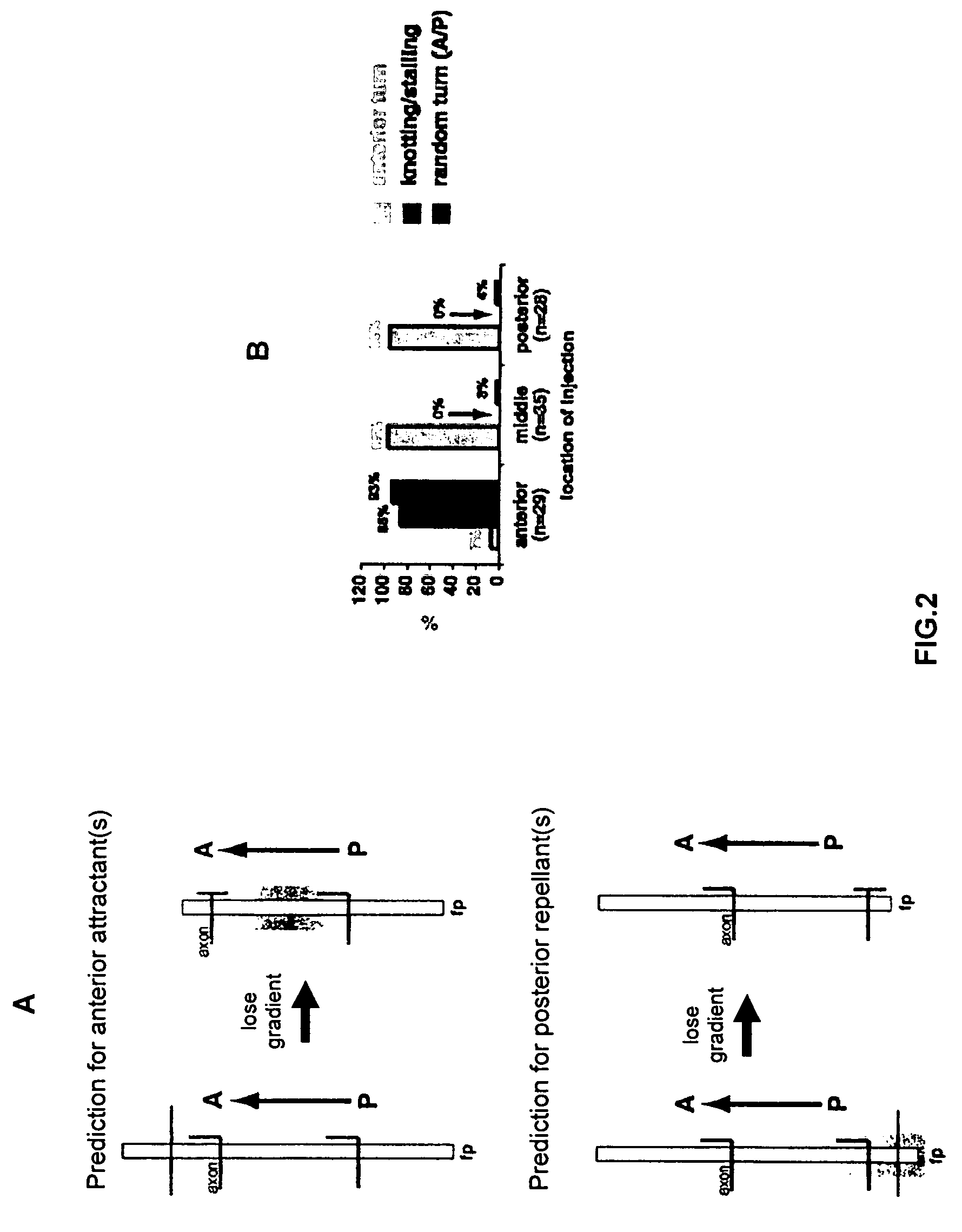
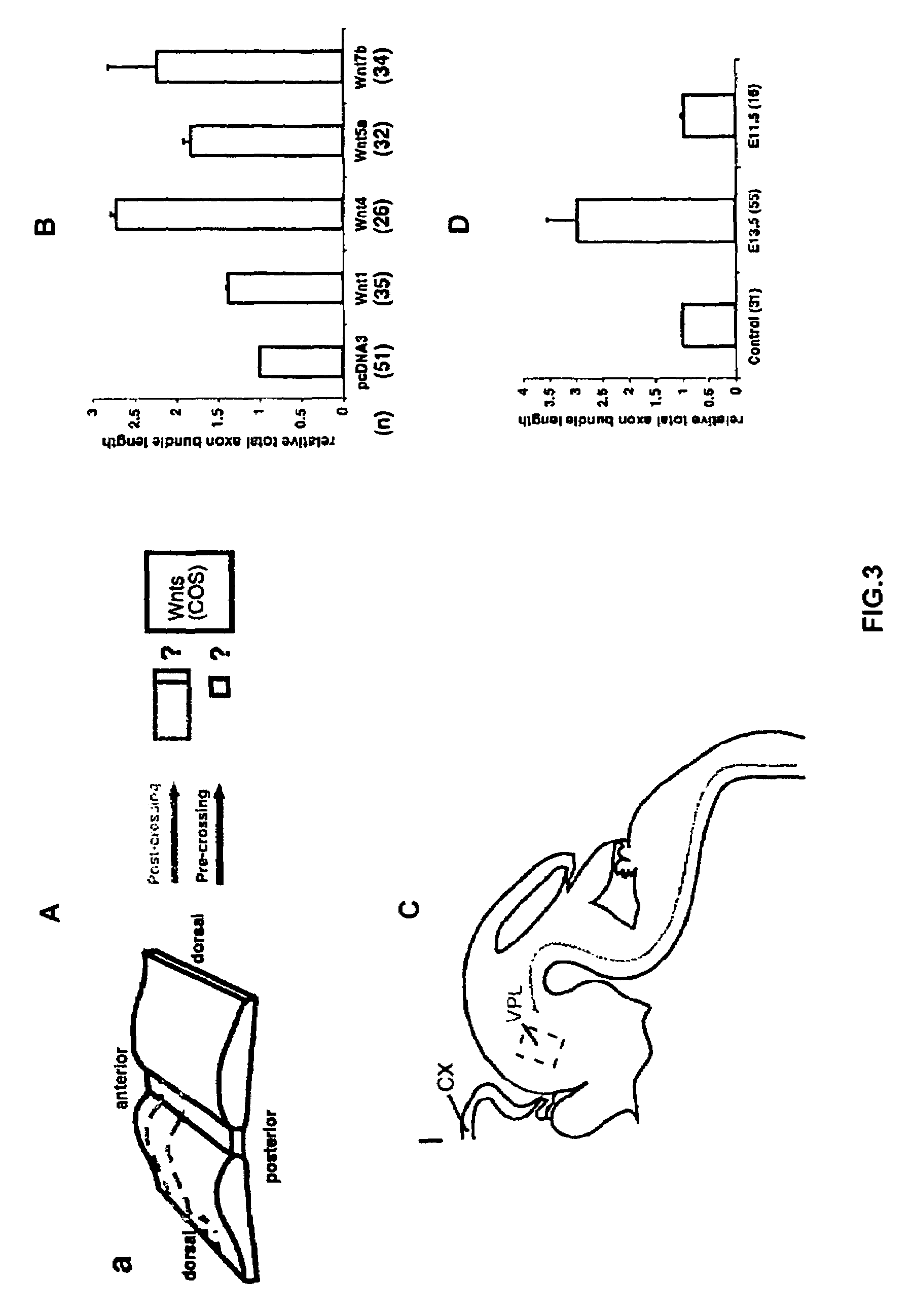
Methods and compositions for modulating growth of a neuron with a Wnt, a Wnt-like substance, and / or a chemical compound affecting a Wnt signaling pathway are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for identifying a substance that modulates growth of a neuron by obtaining a candidate substance and contacting the candidate substance with the neuron are disclosed and methods for modulating growth of a neuron in a subject using a Wnt, a Wnt-like substance, and / or a chemical compound affecting a Wnt signaling pathway. The Wnt, Wnt-like substance, and / or chemical compounds affecting a Wnt signaling pathway can be delivered to the subject using gene therapy techniques. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions for modulating growth of a neuron in a mammal that include a Wnt or a Wnt-like substance. Methods and compositions for inhibiting growth of a neuron are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Rotamase enzyme activity inhibitors
InactiveUS7056935B2Improve survivalPotent in augmenting neurite outgrowthBiocideOrganic chemistryNeuronal degenerationNeuron
This invention relates to methods of using neurotrophic compounds having an affinity for FKBP-type immunophilins to stimulate or promote neuronal growth or regeneration and to prevent neuronal degeneration.
Owner:GPI NIL HLDG INC +1
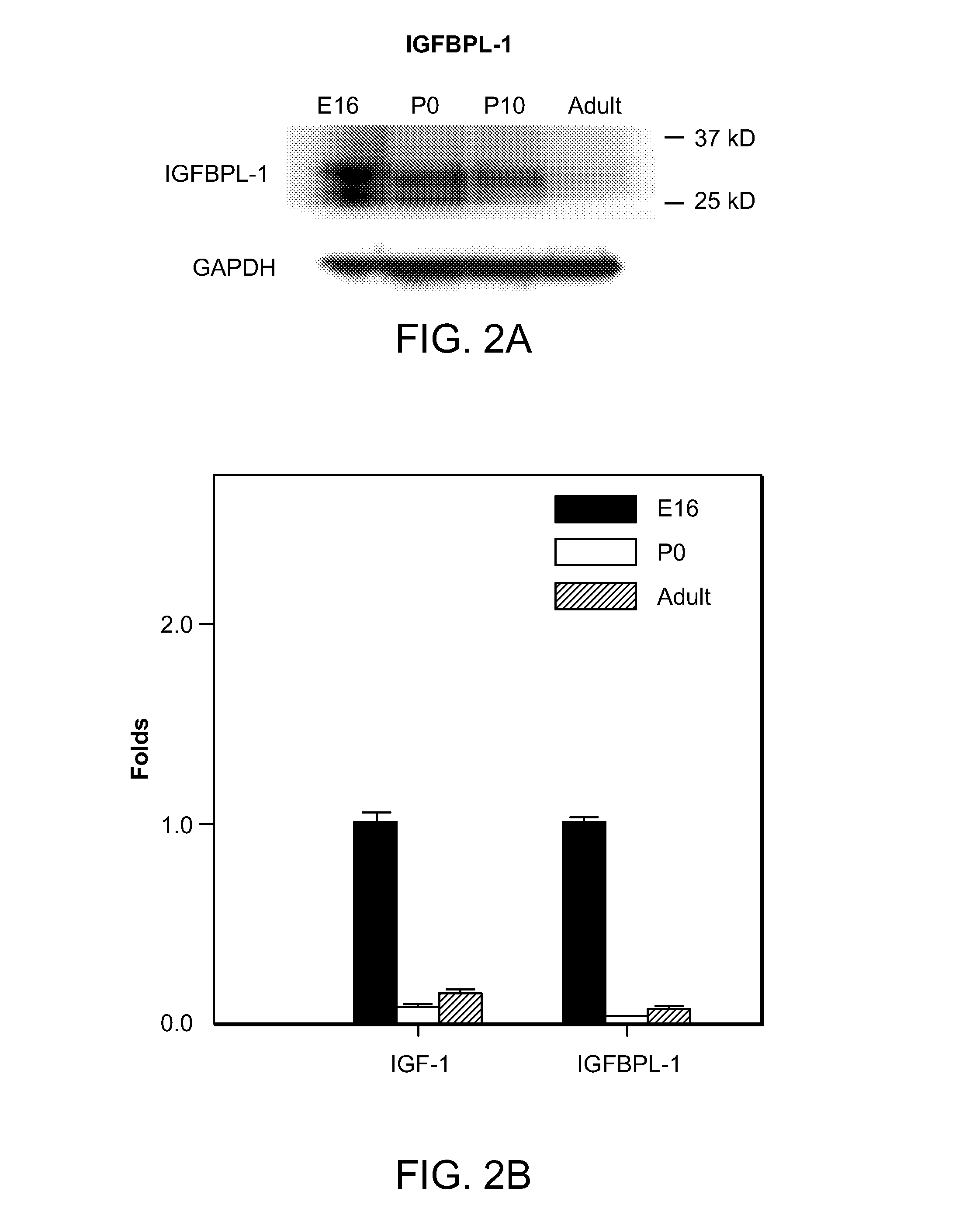
Compositions for Controlling Neuronal Outgrowth
ActiveUS20140128322A1Reduction in severity and frequencyFacilitate improvement and remediationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineNeuron
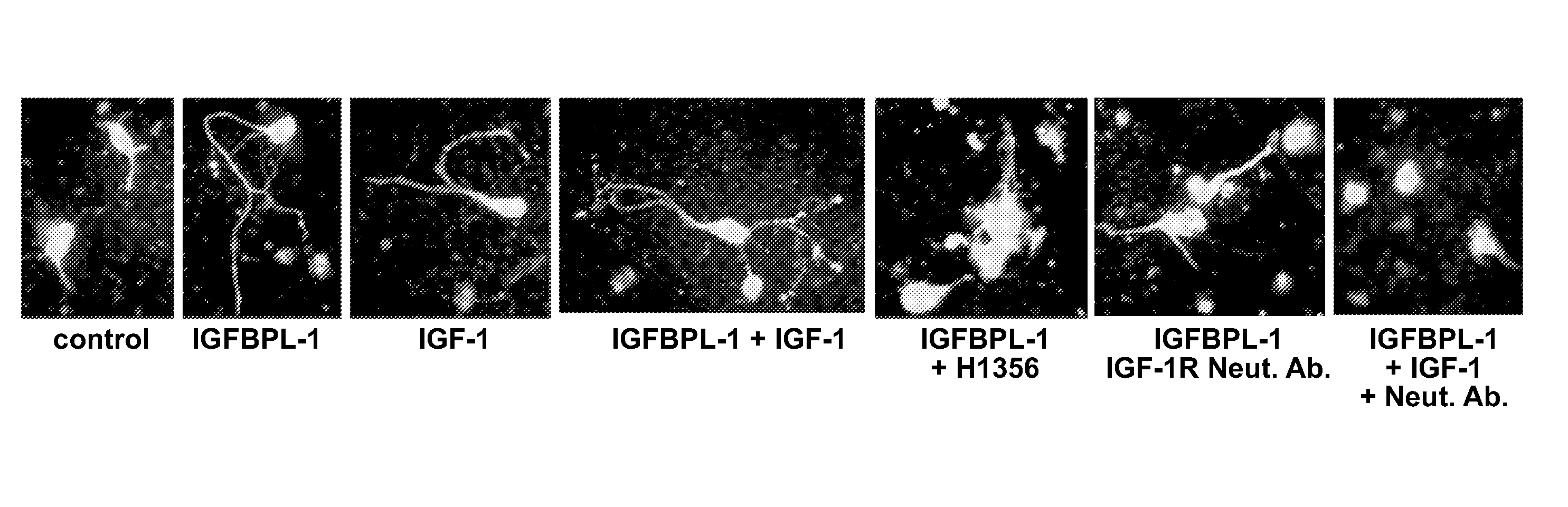
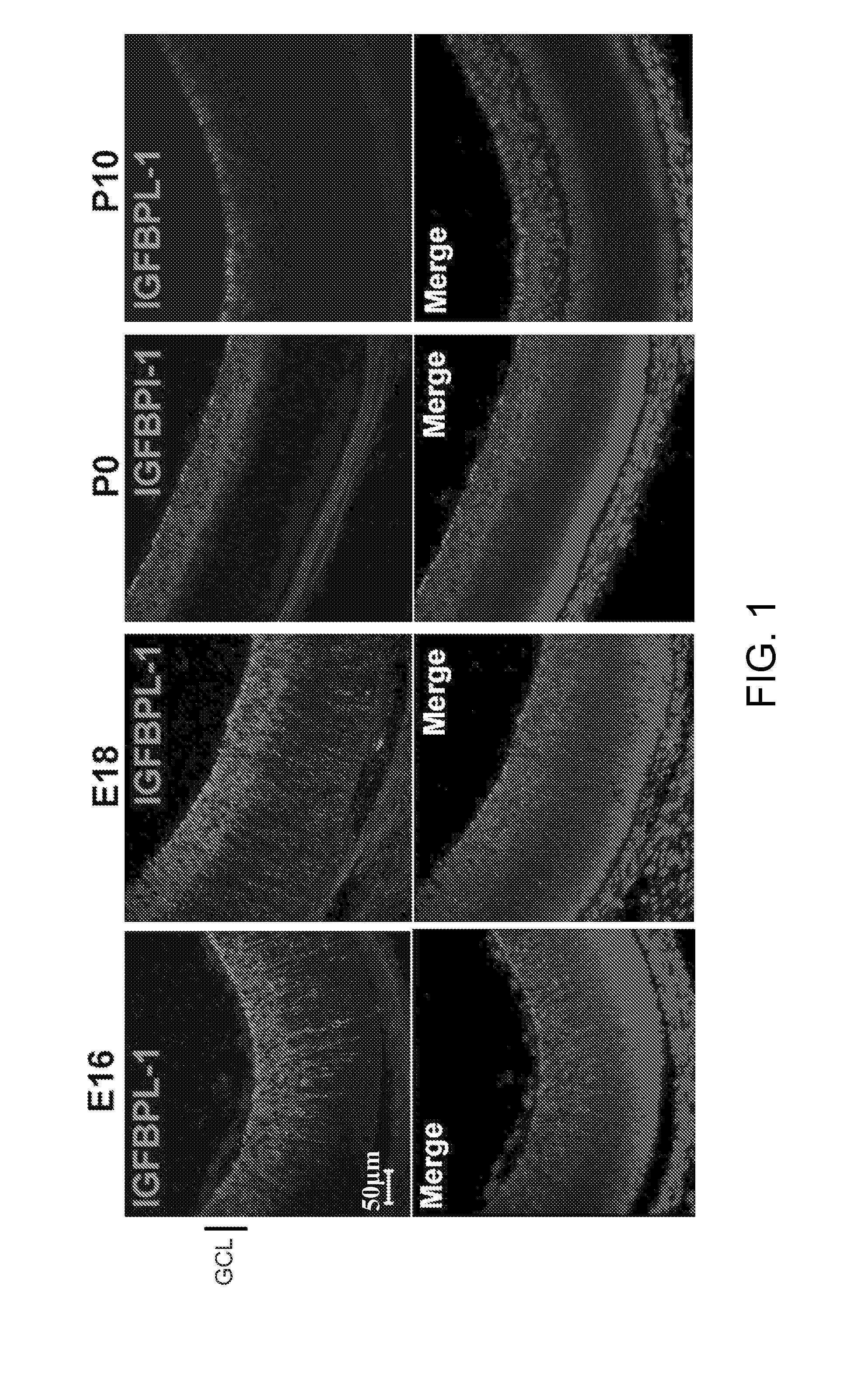
Disclosed is a method of promoting neuronal growth by administering IGFBPL-1, or an agent that increases or stabilizes IGFBPL-1 activity to a subject in need thereof, e.g., a subject in need of treating optic nerve degeneration.
Owner:THE SCHEPENS EYE RES INST
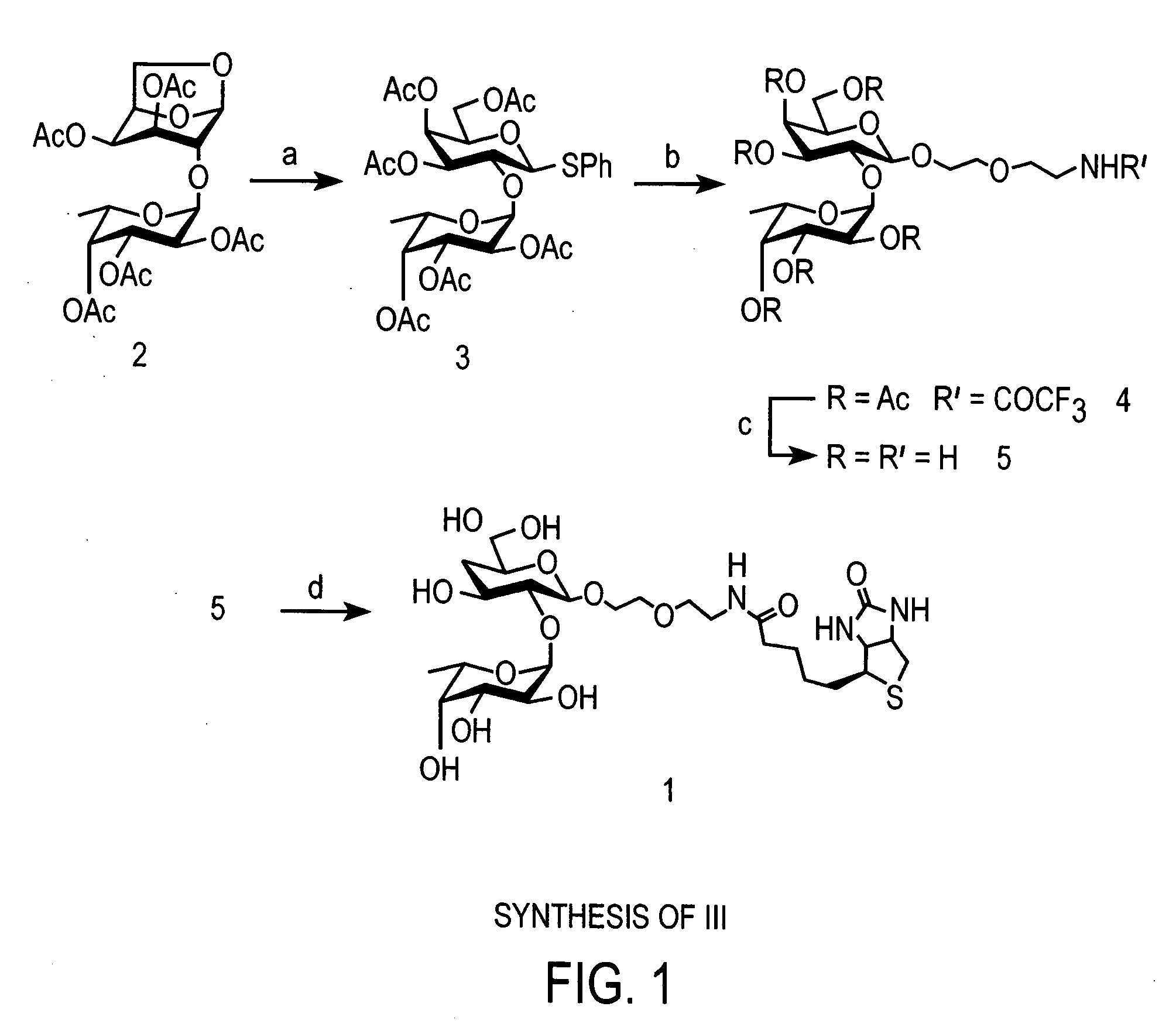
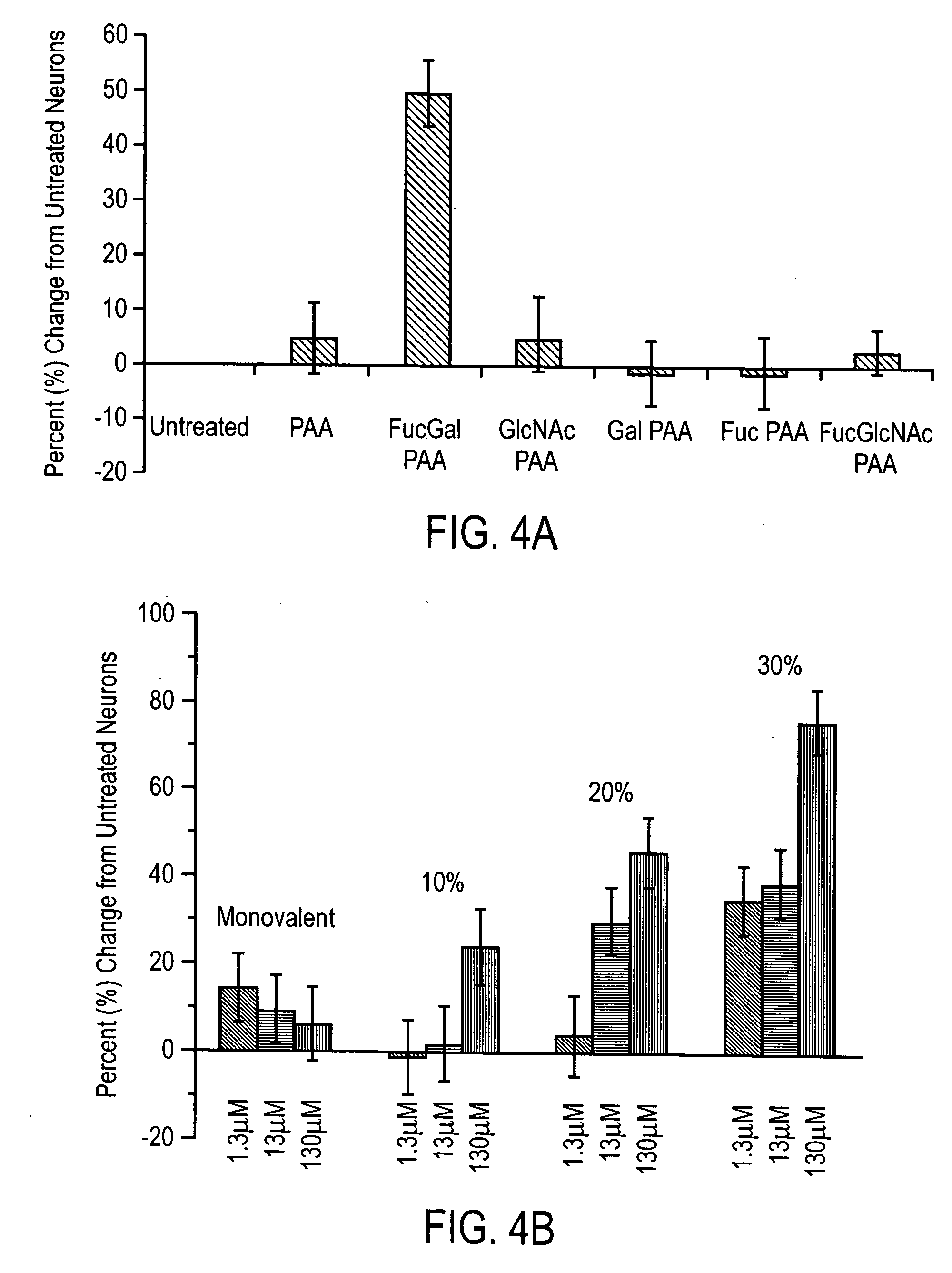
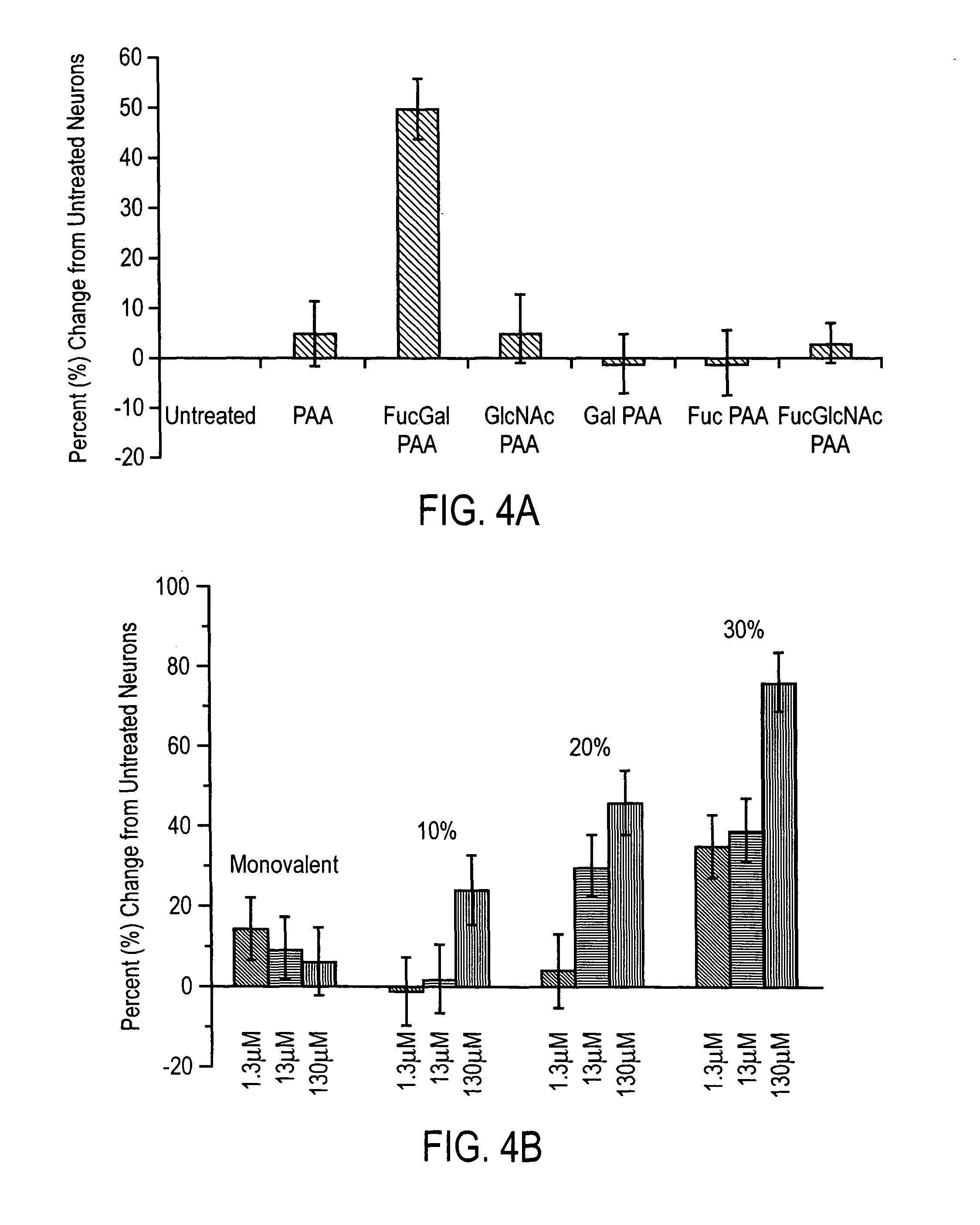
Carbohydrate modifiers of neuronal growth
InactiveUS20060177413A1Good effectForming failureBiocideOrganic active ingredientsProgenitorInjury brain
Fucose galactose carbohydrates have been shown to induce neuronal outgrowth. The invention includes methods of inducing neuronal outgrowth using carbohydrates, assemblies, and polymers bearing fucose-galactose moieties, as well as associated proteins. Cell growth can be stimulated in cells in culture or in cells within an animal or patient. Growth stimulation has application to understanding and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases including, for example, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis and conditions such as stroke, brain injury and spinal cord injury. Such compounds, polymers, and assemblies also can be used to increase neural stem or progenitor cells in culture or in an animal, and to enervate engineered tissue.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Nutrient Medium for Maintaining Neural Cells in Injured Nervous System
InactiveUS20080160006A1Improve neural cell viabilitySupporting survivalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNervous systemLiquid medium
Owner:BREWER GREGORY J
Methods of stimulating cellular growth, synaptic remodelling and consolidation of long-term memory
InactiveUS20080058396A1Stimulates dendritic growthPromote formationBiocideNervous disorderProtein kinase activationLTM - Long-term memory
The present invention provides methods of slowing or reversing the loss of memory and learning comprising the steps of contacting an effective amount of a PKC activator with a protein kinase C (PKC) in a subject identified with memory loss slowing or reversing memory loss. The present invention provides methods of stimulating cellular growth, neuronal growth, dendritic growth, dendritic spine formation, dendritic spine density, and the translocation of ELAV to proximal dendrites, and synaptic remodeling. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to stimulate the synthesis of proteins sufficient to consolidate long-term memory. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to downregulate PKC.
Owner:ALKON DANIEL L
Compound for promoting the growth of neural cells
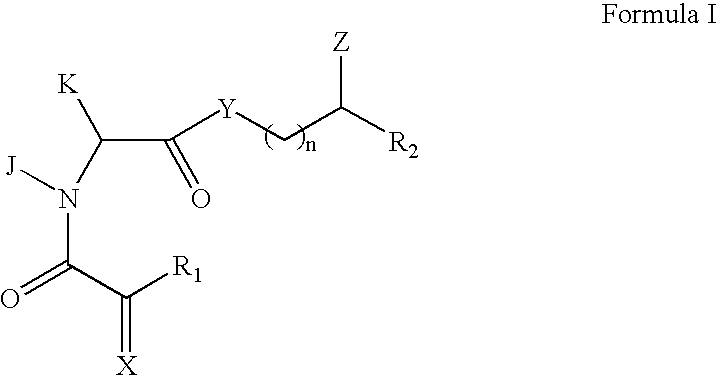
ActiveUS7585892B2Small molecular sizeImprove survival rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNeural cellNeuron
Disclosed is a compound capable of promoting the growth and development of neurons, the proliferation of neural stem cells and inducing the neural stem cells to differentiate into neurons, which is represented by a general formula as (I).The compound of the present invention can increase the survival rate of neural cells even at a low cellular density in a culture medium. The compound of the present invention can also promote the growth of neurons, which is revealed by the increase in the thickness, length and number of branches in the neurites (neural fibers). In addition, the compound of the present invention can be used to promote the development of neural stem cells and induce them to differentiate into neurons.
Owner:NATURE WISE BIOTECH & MEDICALS CORP
Method for promoting induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be nerve cells
ActiveCN105331583ASpeed up induction of differentiationGood growthNervous system cellsNeurulationSpinal cord
The invention discloses a method for promoting induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be nerve cells, which comprises steps: induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are blown and absorbed to disperse to be single cell suspension after being digested, and are separately planted in culture holes, and rock (ROCK) inhibitors are added into each culture hole; a supernate is adsorbed to discard in the first day after the iPS cells are separately planted, is added into a neural induction complete culture medium, and rapamycin needs to be added into the neural induction complete culture medium to promote autophagy; the neural induction complete culture medium is changed to add low concentration rapamycin to promote autophagy neural cells to differentiate the neural induction complete culture medium after two days, and can be induced to differentiate to be neural cells after being cultured for 12-15 days. The method for promoting the induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be the nerve cells can speed up neurons to induce and differentiate, and improves neuron growth states ofspinocerebellum ataxic three-type iPS.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for modulation of the effects of aging on the primate brain
InactiveUS7157435B2Minimizing surgical invasionImprove neurological functionBiocideVirusesNeurulationNervous system
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compounds that modulate neuronal growth and their uses
InactiveUS20050164920A1Enhancing Trk mediated activityEnhances Trk mediated activityNervous disorderDepsipeptidesCyclic peptideNervous system
Cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics are provided that bind to and / or modulate activities associated with Trk receptors, including processes associated with the growth and repair of the central nervous system (e.g., neuronal growth and survival, axonal growth, neurite outgrowth and synaptic plasticity). Cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics are also provided that block or reduce the effect of other factors that inhibit growth and / or repair of the central nervous system. Pharmaceutical compositions and other formulations comprising these compounds are provided. In addition, the invention provides methods for using the cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics to modulate Trk mediated activities, including processes such as neuronal growth, survival and recover, axonal growth, neurite outgrowth, and synaptic plasticity. Further, the invention provides methods for promoting central nervous system (CNS) neuron growth by administering a p75 receptor binding agent.
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
ActiveUS20150017154A1Prevents upregulationSensation of pain be reducedBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsArthritisBiology
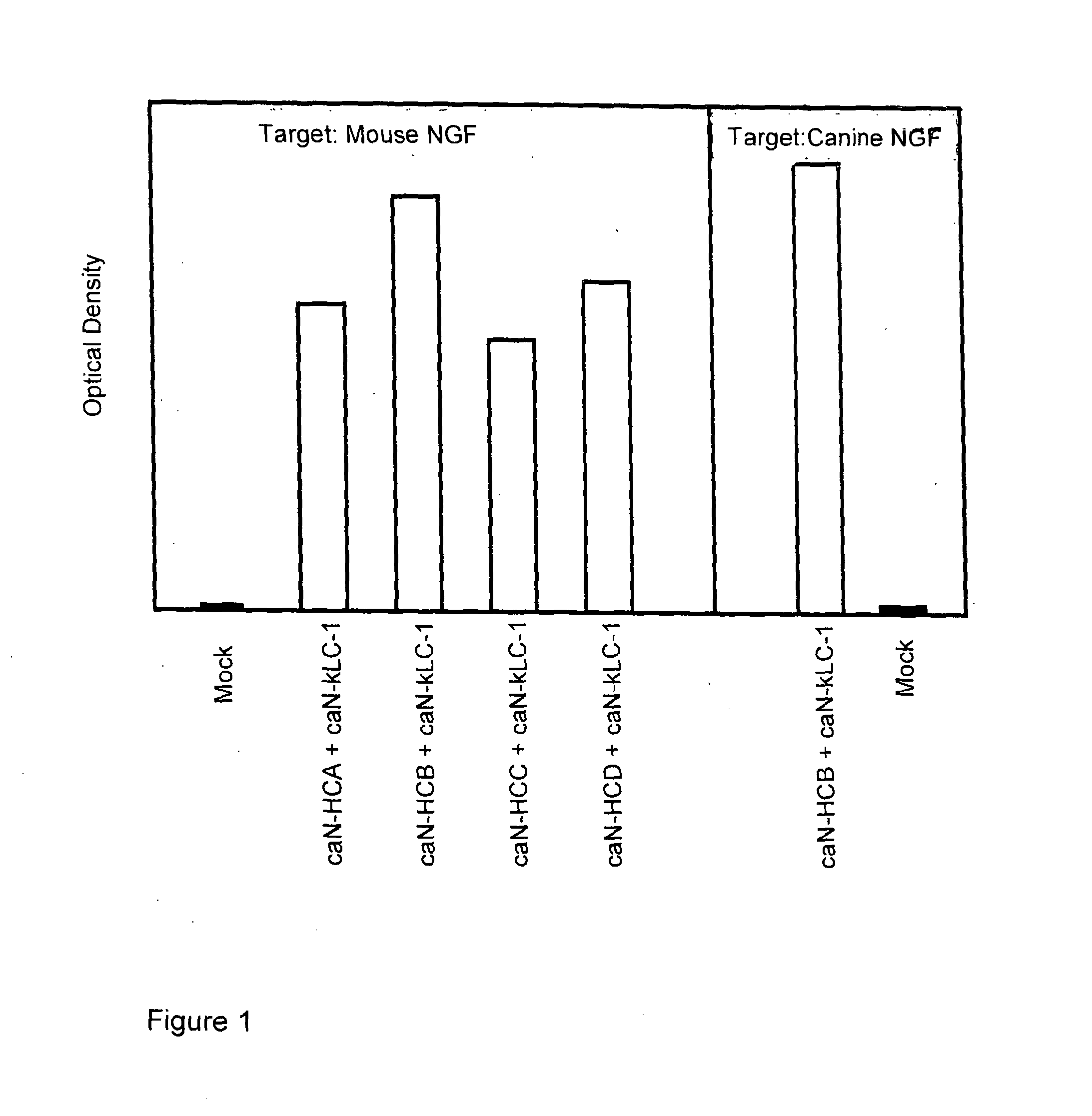
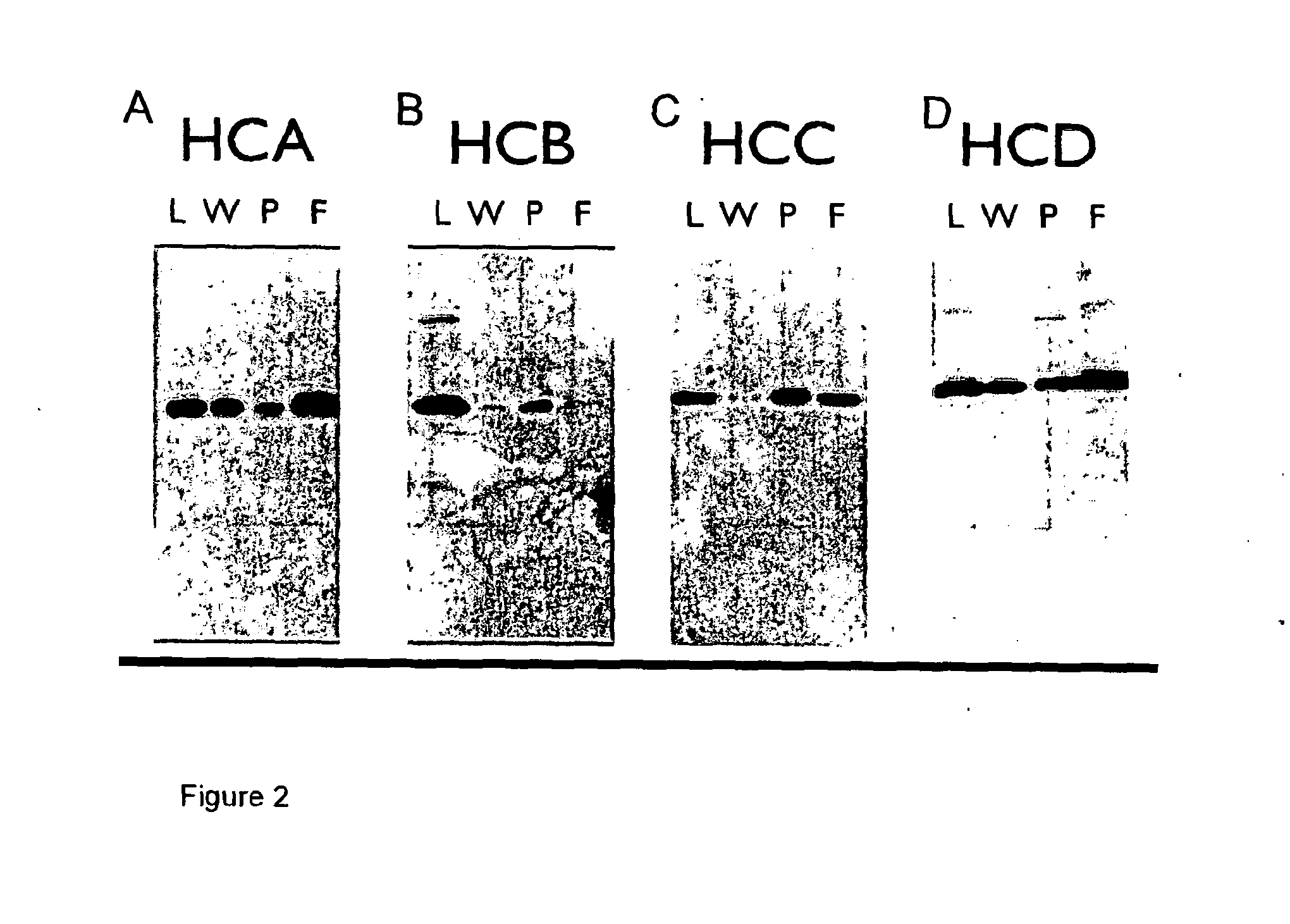
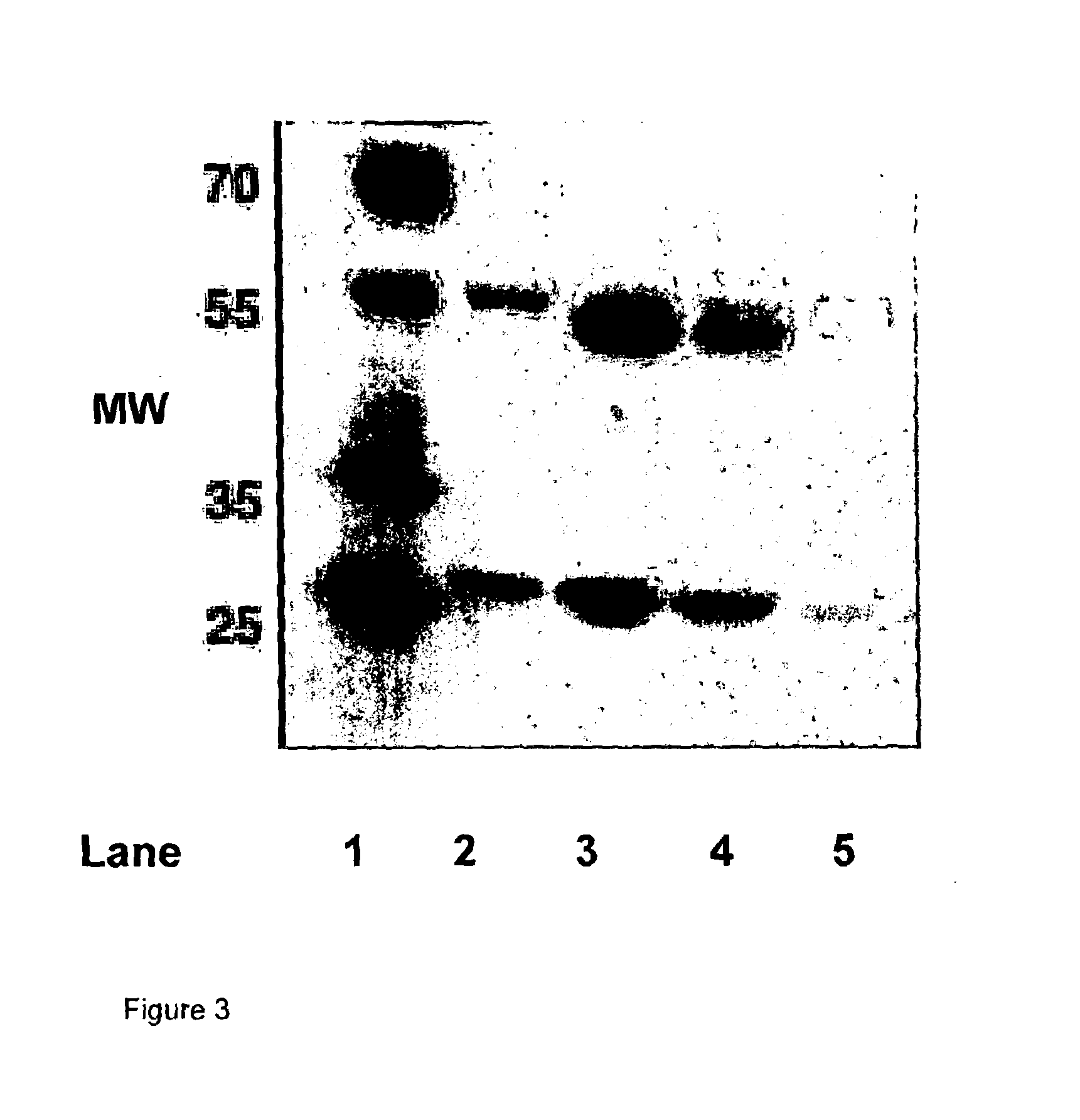
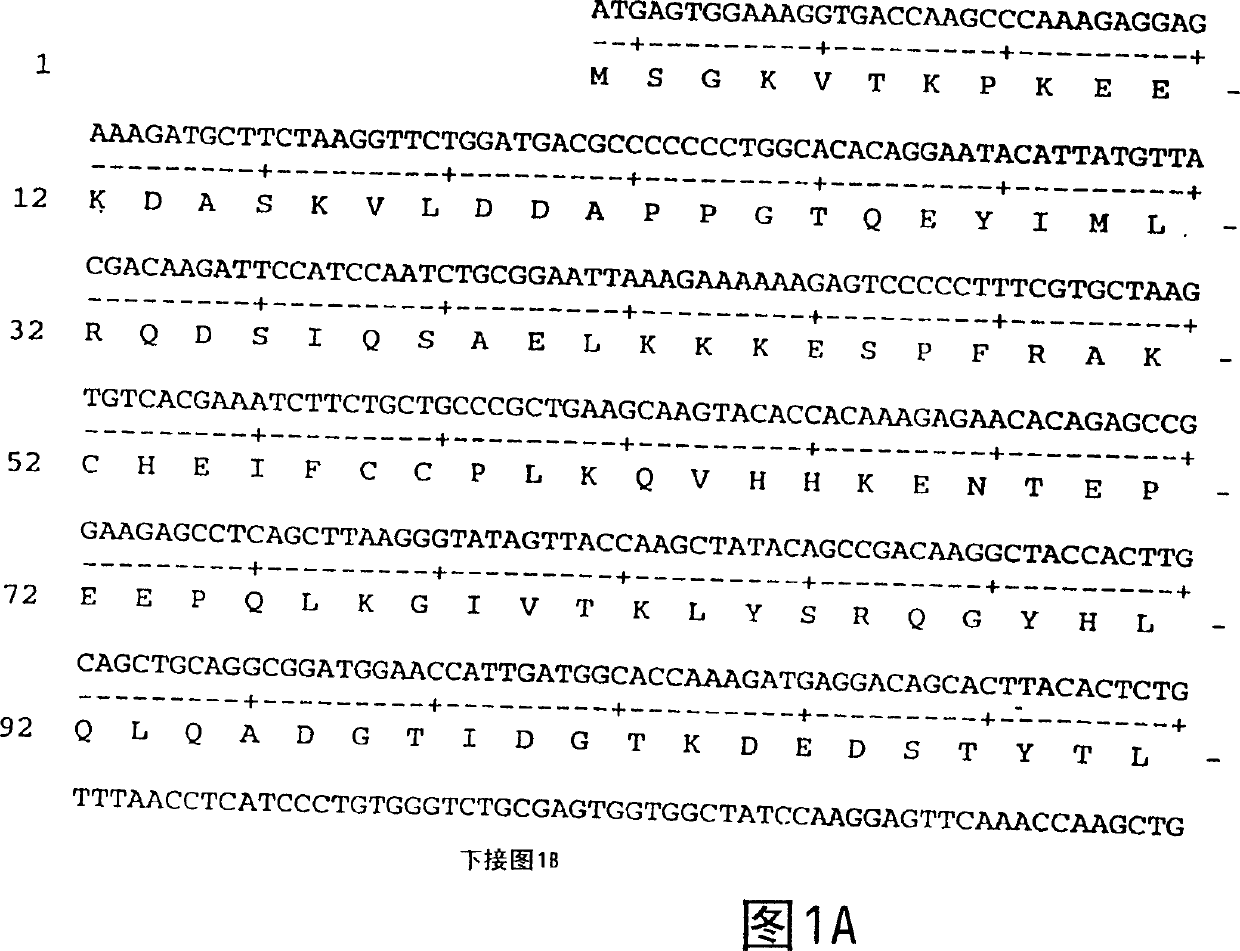
A method of preparing an antibody suitable for use in a canine is provided. Also provided are caninised antibodies which specifically bind to canine neuronal growth factor (NGF) and neutralise the ability of canine NGF to bind to the p75 or TrkA canine NGF receptor. The invention extends to nucleic acids encoding same and to methods of treating pain and arthritis in a canine using said antibodies and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Prominin-1 peptide fragments and uses thereof
ActiveUS8618055B2Improve angiogenesisPromote migrationNervous disorderMetabolism disorderAngiogenesis growth factorArterial Vasodilation
Described herein are peptide compositions of a prominin-1, which have regenerative activity. As such the peptides are useful when regeneration is needed, for example, to enhance angiogenesis, increase VEGF binding to endothelial cells, promote vasodilation, enhance cell migration, enhance cell proliferation, stimulate neuronal growth, prevent neurodegeneration, and / or promote neuroregeneration.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Desmocyte growth factor 11 antibody, antagonist and agonist
A human fibroblast growth factor-polypeptide 11, the DNA (RNA) for coding it, the process for preparing said polypeptide by recombination, the method for using said polypeptide in medical purpose, the antagon of said polypeptide and its medical application, and the diagnosing method by detecting the mutation in coding sequence and the change in polypeptide concentration are disclosed.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Methods and compositions for treating neuronal damage or degeneration
InactiveUS20110020359A1Promotes and improves locomotor functionPromote growthNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuronal damageMedicine
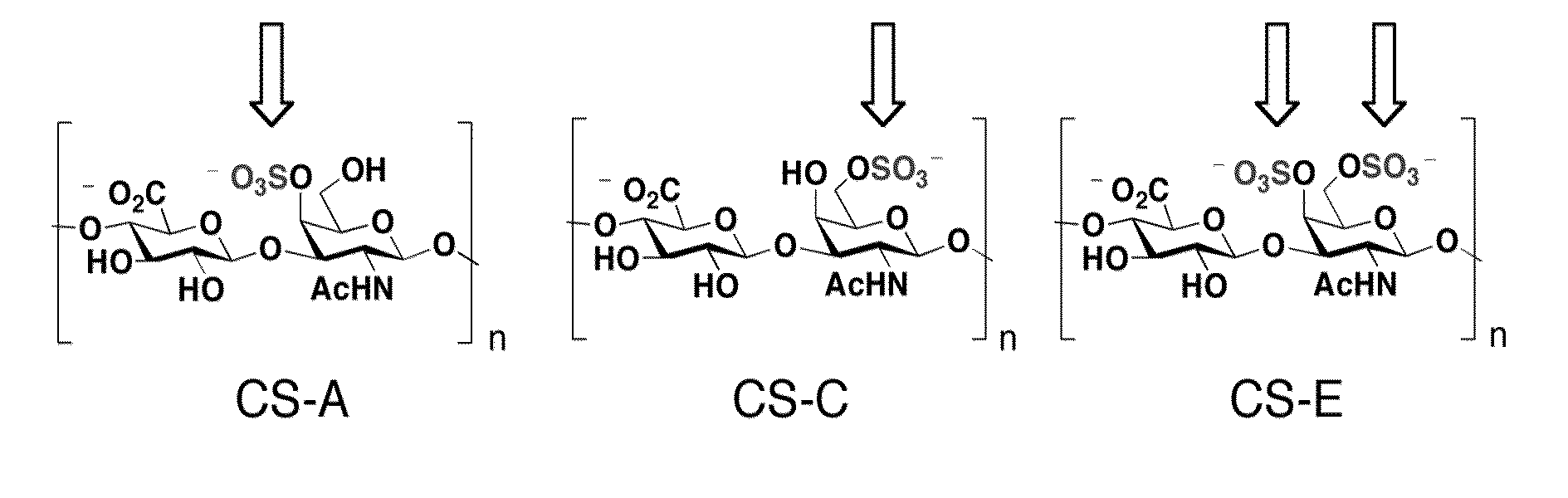
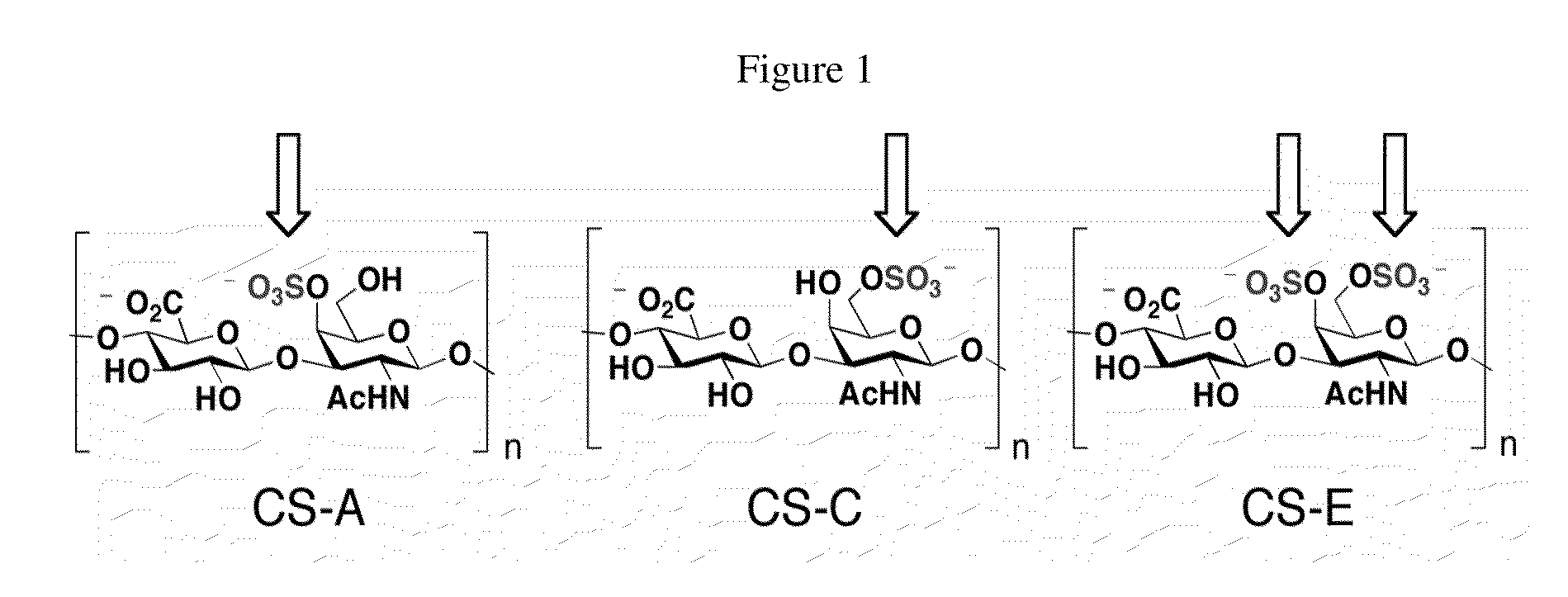
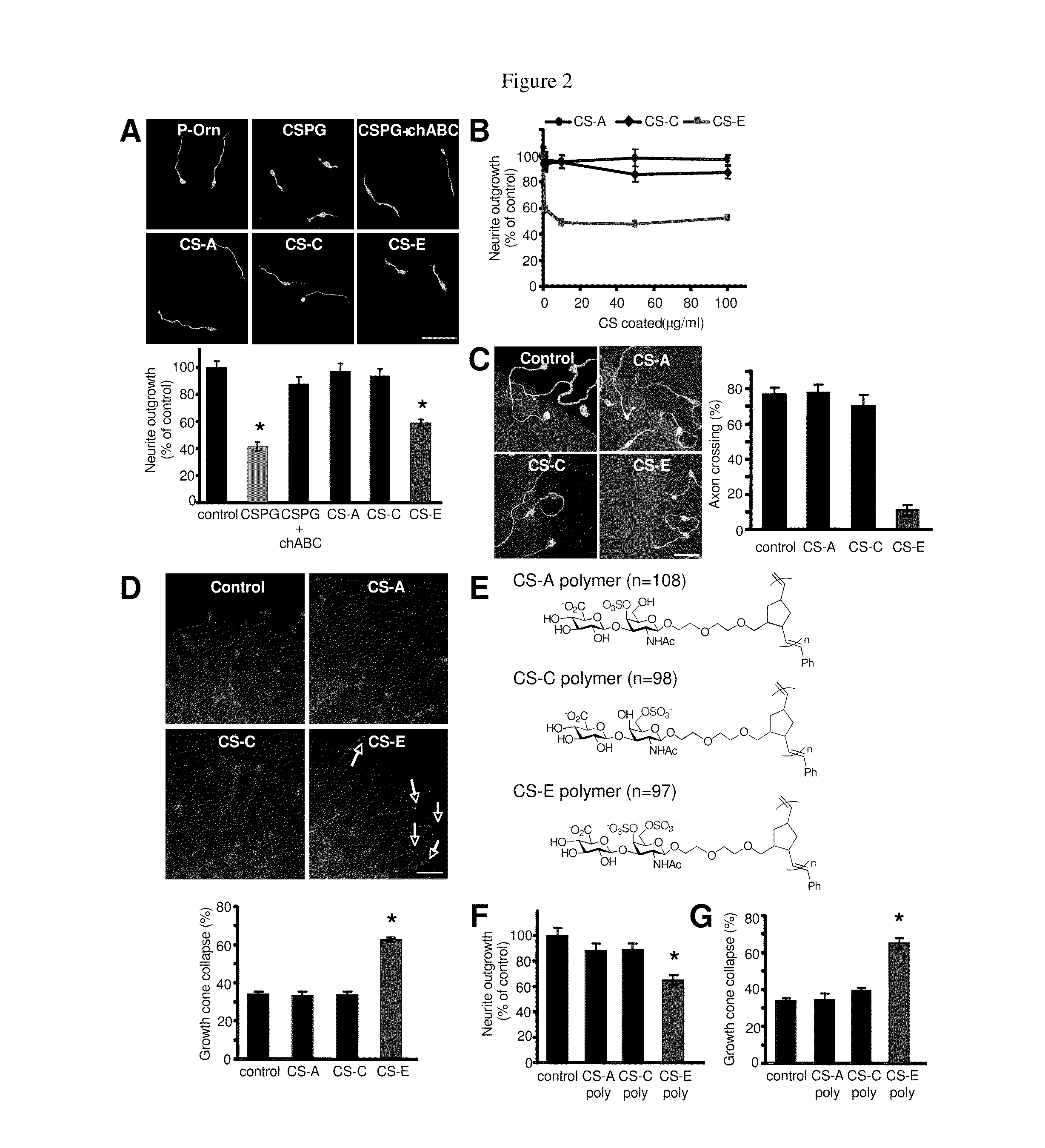
This invention provides methods and compositions for reducing chondroitin-sulfate-proteoglycan-mediated inhibition of neuronal growth. The methods and compositions provided herein are particularly useful for treatment of neuronal damage or degeneration.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for nerve regeneration
InactiveUS7374760B2Reduced strengthGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChemical compoundMammal
Methods and compositions for modulating growth of a neuron with a Wnt, a Wnt-like substance, and / or a chemical compound affecting a Wnt signaling pathway are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for identifying a substance that modulates growth of a neuron by obtaining a candidate substance and contacting the candidate substance with the neuron are disclosed and methods for modulating growth of a neuron in a subject using a Wnt, a Wnt-like substance, and / or a chemical compound affecting a Wnt signaling pathway. The Wnt, Wnt-like substance, and / or chemical compounds affecting a Wnt signaling pathway can be delivered to the subject using gene therapy techniques. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions for modulating growth of a neuron in a mammal that include a Wnt or a Wnt-like substance. Methods and compositions for inhibiting growth of a neuron are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
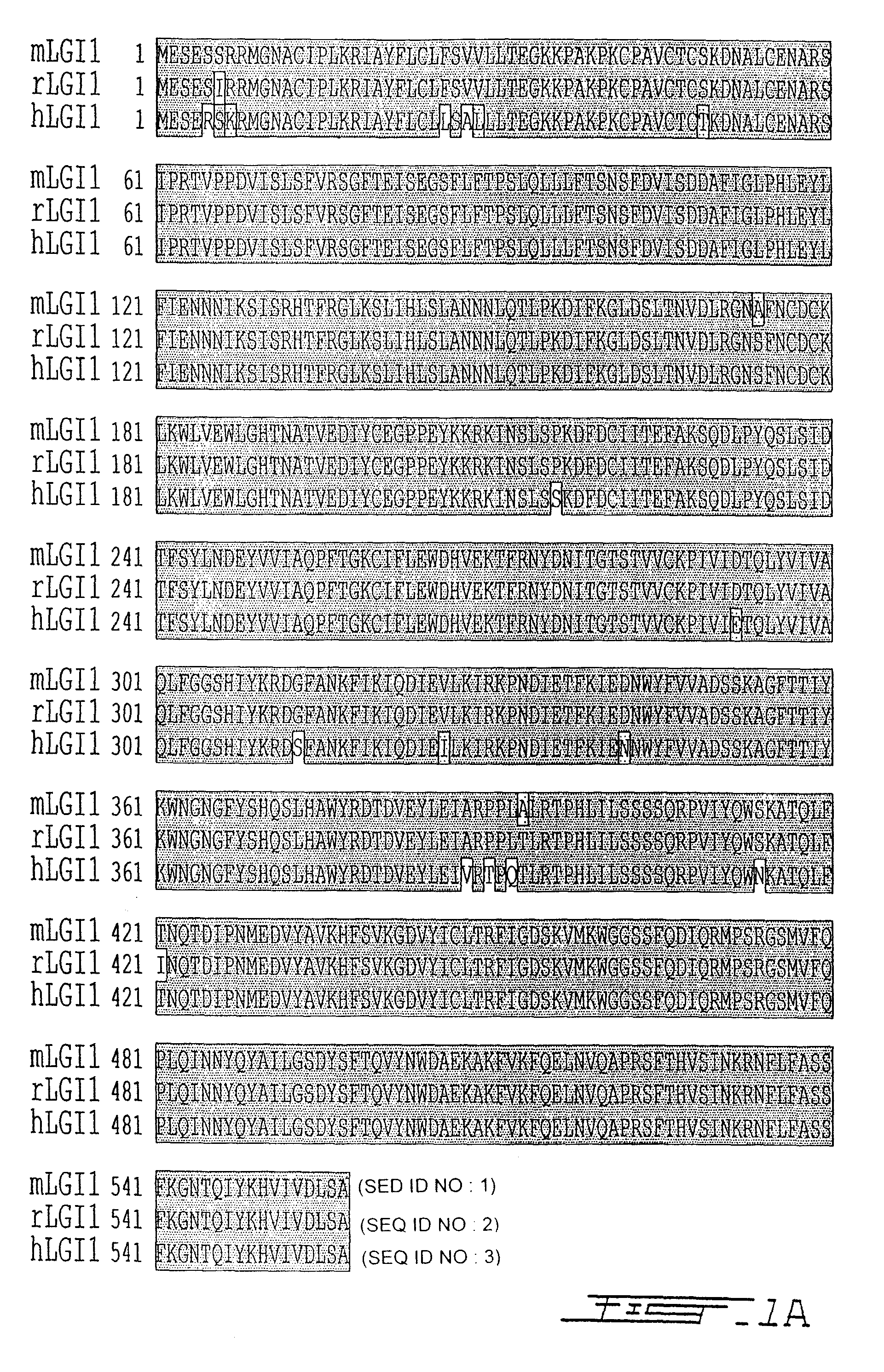
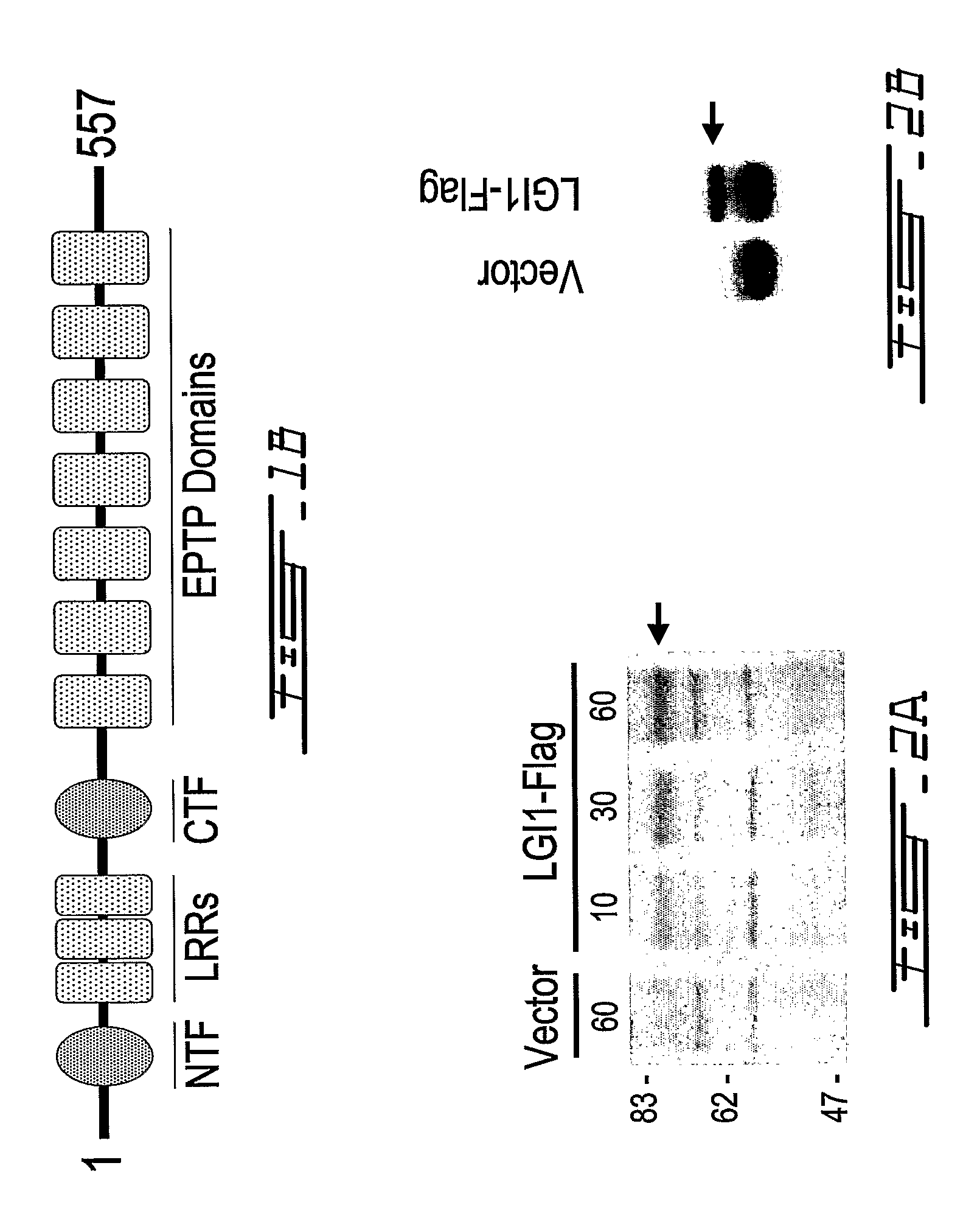
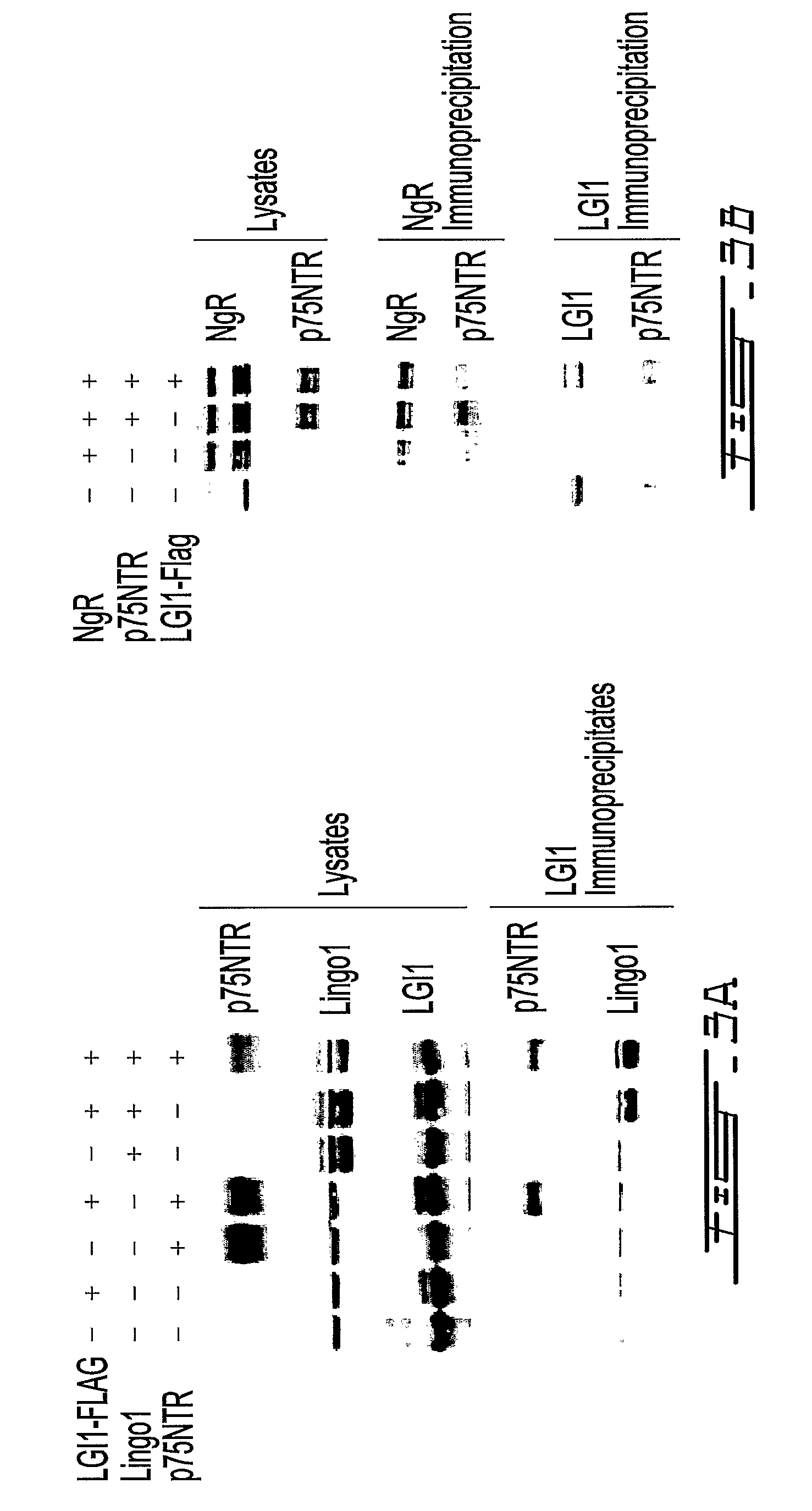
LGI, LINGO and p75NTR family members: novel modulators of neuronal growth
InactiveUS8309517B2Improve abilitiesInhibit growthCompound screeningNervous disorderNeurophysinsNervous system
The present invention relates to a novel method to promote regeneration or repair of the central or peripheral nervous system following injury The present invention concerns the use of a leucine-rich, glioma-inactivated protein (LGIn), or an analog or derivative thereof, to promote the regeneration or remyelination of neurons after injury to the central nervous system LGIns are endogenous proteins secreted by central neurons that promote regeneration of neurons after injury to the central nervous system The present invention includes an assay to measure the interaction of LGIn with LINGOn and p75NTRn as well as to identify factors that enhance or disrupt these interactions The invention further includes cell lines capable of expressing LGIn, LINGOn and p75NTRn molecules, as well as the proteins purified from these cells.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
ActiveUS9328164B2Prevents upregulationReduce removalNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNGF ReceptorNeuronal Growth
A method of preparing an antibody suitable for use in a feline is provided. Also provided are chimeric and felinized antibodies which specifically bind to feline neuronal growth factor (NGF) and neutralize the ability of feline NGF to bind to the p75 or TrkA feline NGF receptor. The invention extends to nucleic acids encoding same and to methods of treating pain and arthritis in a feline using said antibodies and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Neuronal regeneration
InactiveUS20150190377A1Enhances neurite outgrowthAvoid Cutting InjuriesBiocideAnimal repellantsNeuronNeuronal Growth
There are provided, inter alia, methods and compositions useful for neuronal regeneration, including methods for increasing expression of a regeneration-associated marker gene, and methods for increasing neuronal growth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Anti-nerve growth factor antibodies and methods of preparing and using the same
A method of preparing an antibody suitable for use in an equine is provided. Also provided are equinised antibodies which specifically bind to equine neuronal growth factor (NGF) and neutralise the ability of equine NGF to bind to the p75 or TrkA equine NGF receptor. The invention extends to nucleic acids encoding same and to methods of treating pain and arthritis in an equine using said antibodies and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:NEXVET AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Methods of inducing neuronal growth by a Fucose-α(1-2) galactose (fuc-α(1-2) gal) moiety and a lectin
Fucose galactose carbohydrates have been shown to induce neuronal outgrowth. The invention includes methods of inducing neuronal outgrowth using carbohydrates, assemblies, and polymers bearing fucose-galactose moieties, as well as associated proteins. Cell growth can be stimulated in cells in culture or in cells within an animal or patient. Growth stimulation has application to understanding and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases including, for example, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis and conditions such as stroke, brain injury and spinal cord injury. Such compounds, polymers, and assemblies also can be used to increase neural stem or progenitor cells in culture or in an animal, and to enervate engineered tissue.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com