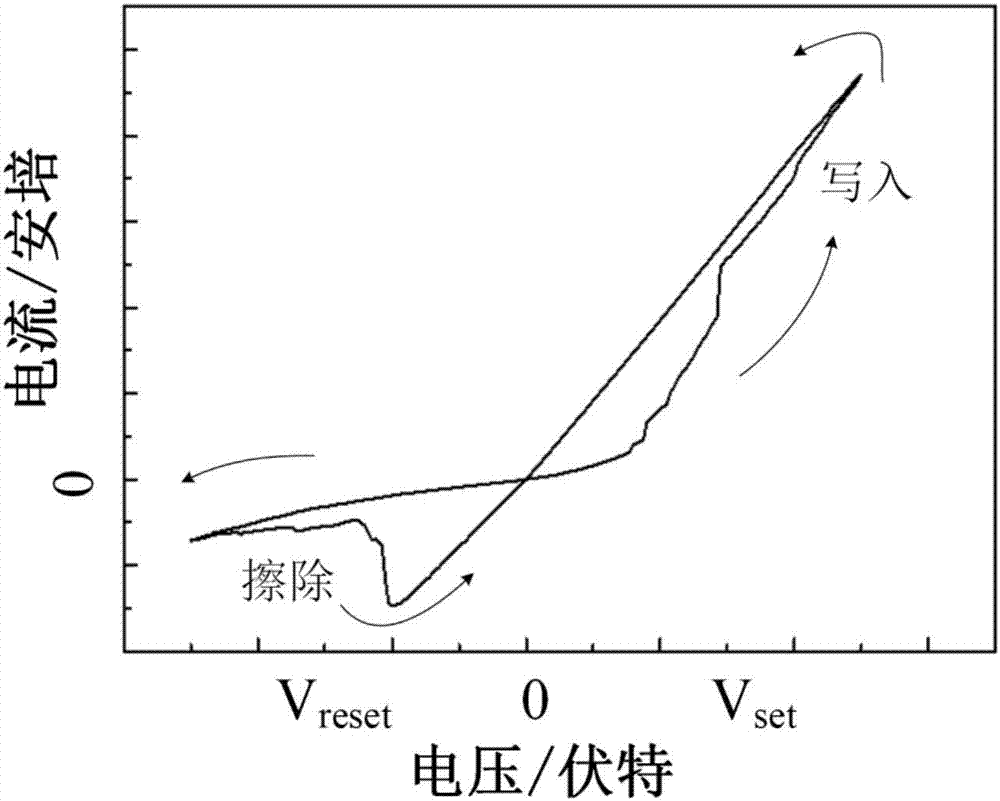
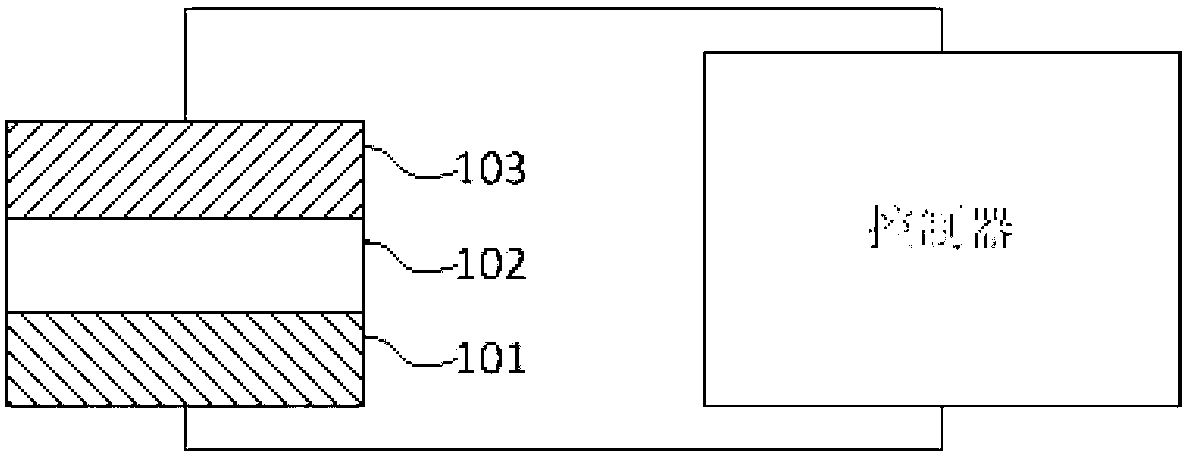
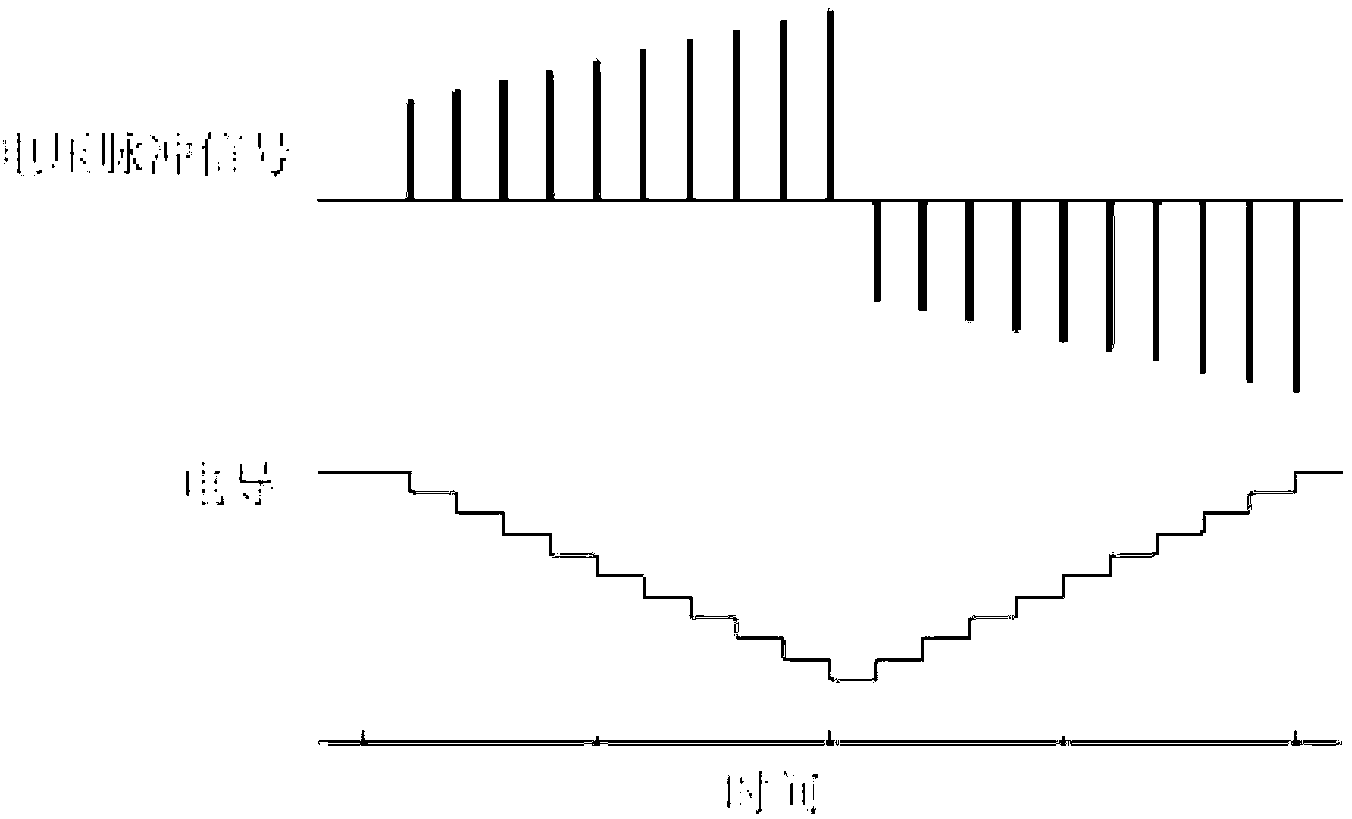
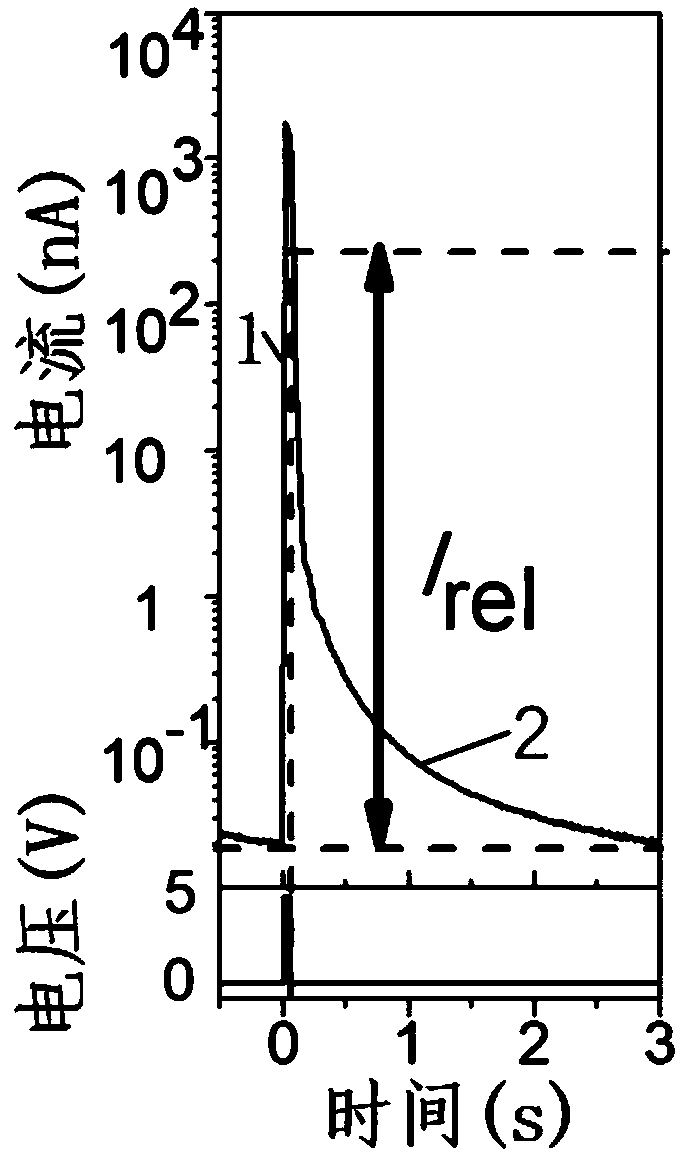
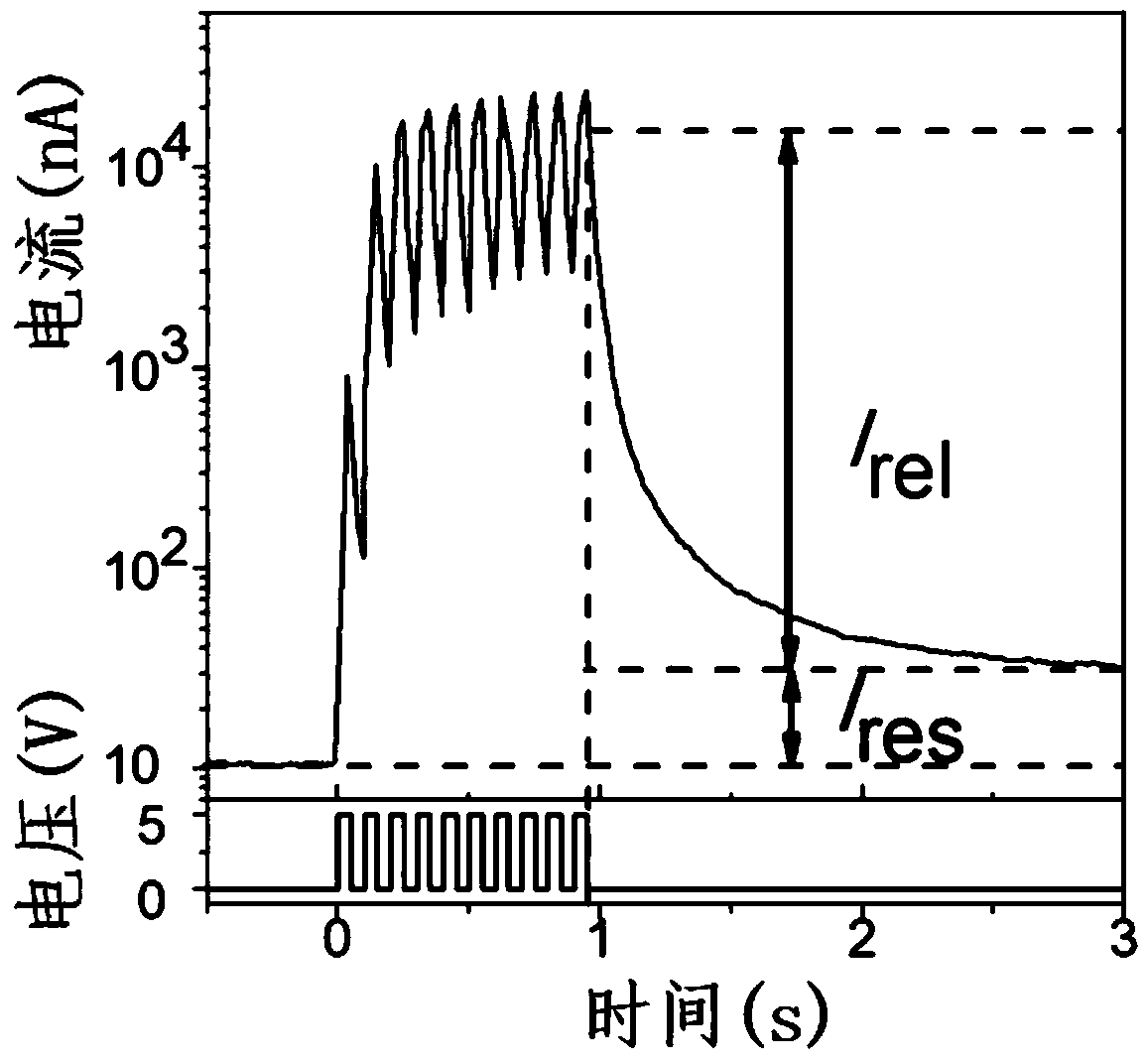
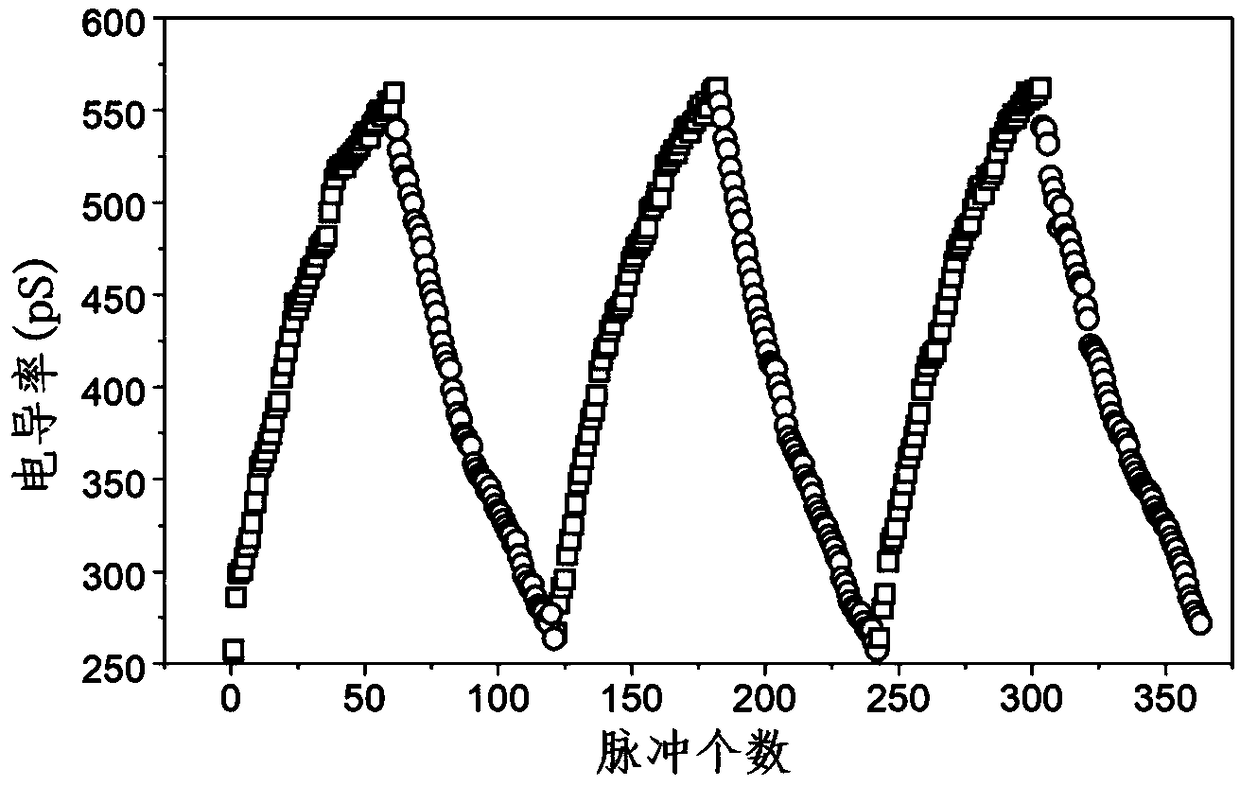
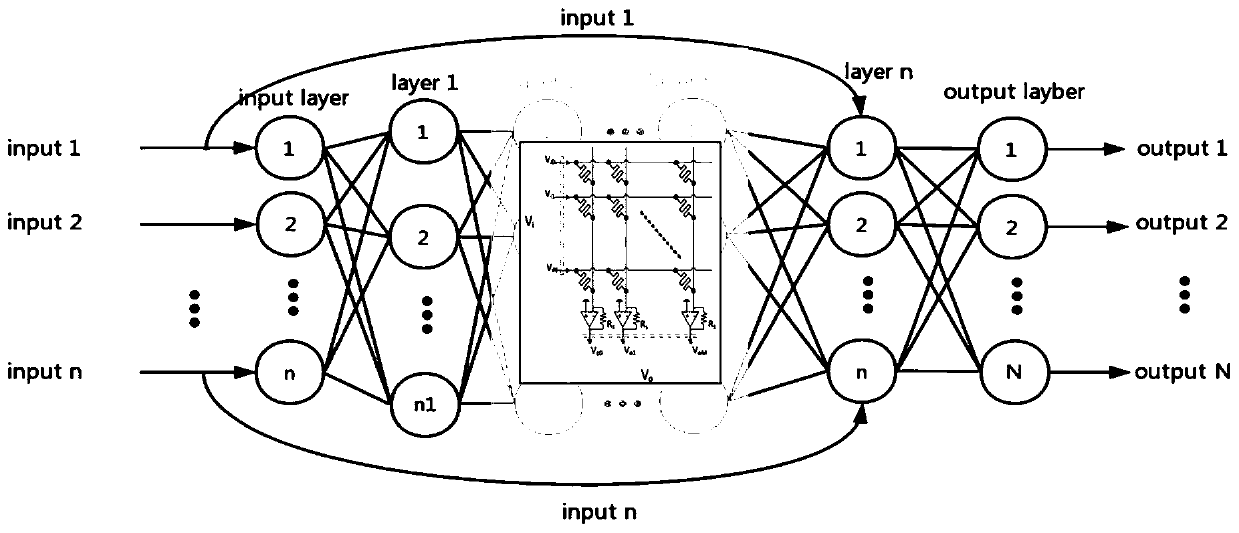
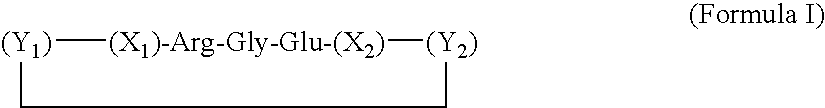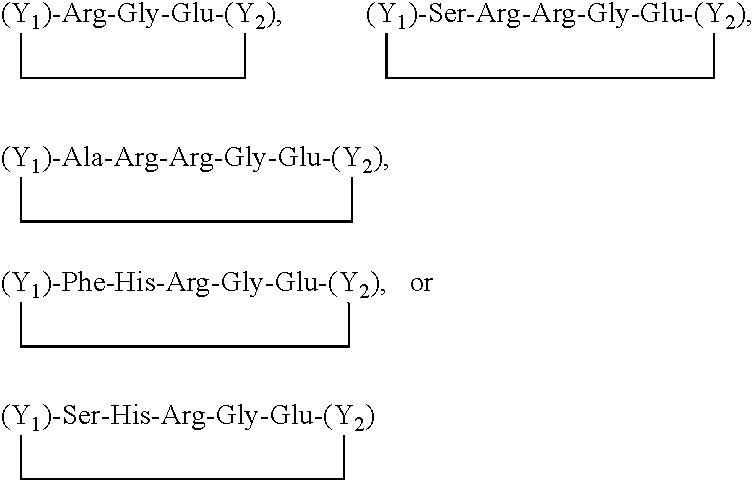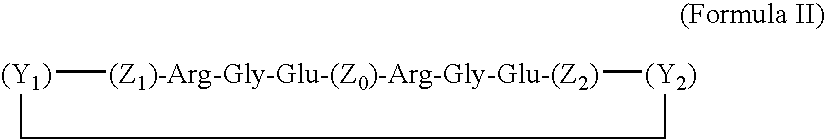Patents
Literature
95 results about "Synaptic plasticity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
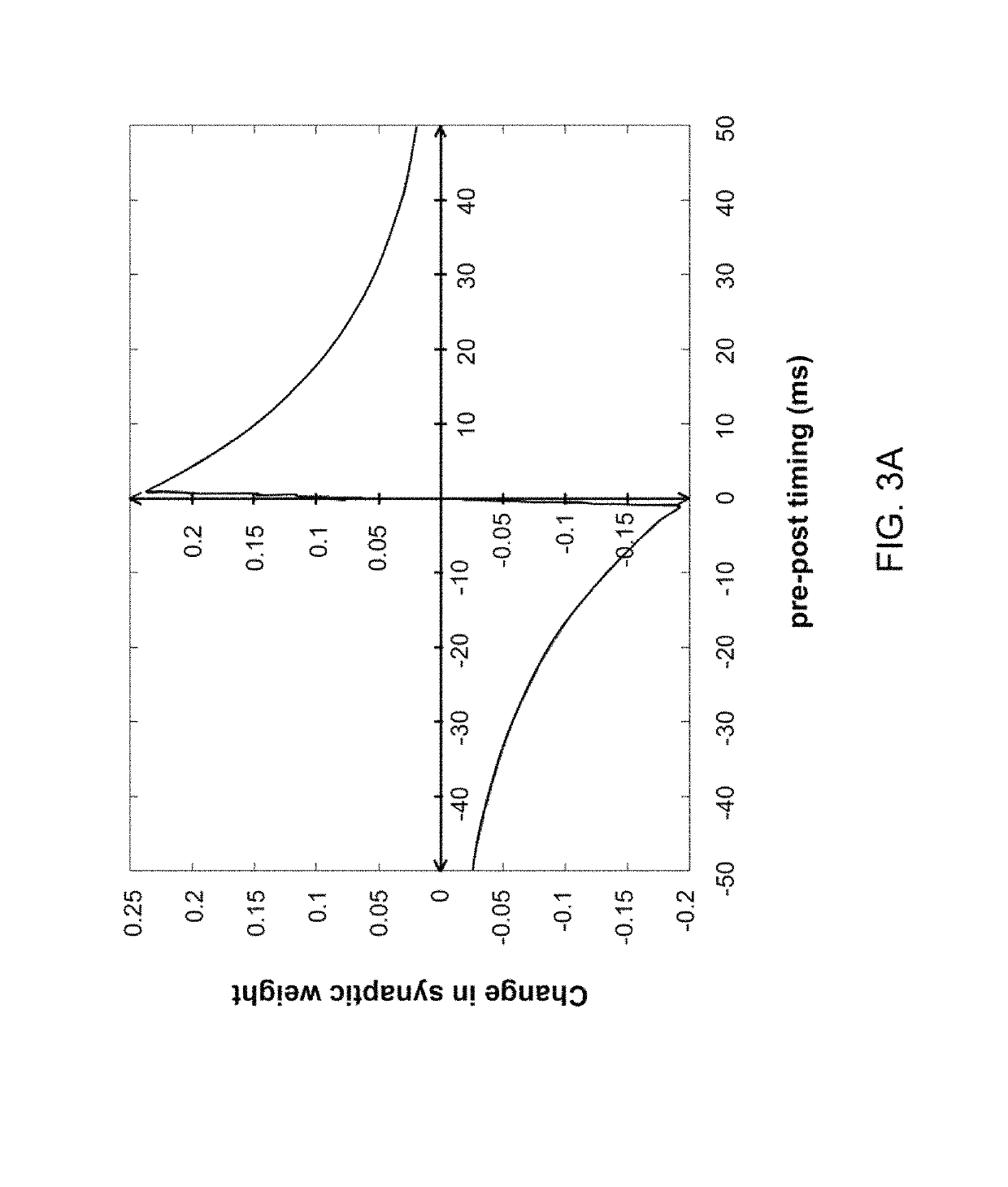
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (see Hebbian theory).
Compositions and methods for enhancing cognitive function and synaptic plasticity
InactiveUS20060089335A1Improve cognitive functionEnhance synaptic plasticityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorAction potential firing
The present invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. According to the method, Ca++ influx into excitatory neurons (nerve cells) is decreased by treatment with a number of different agents including divalent cations (e.g., Mg++), GABAB agonists, GABAA agonists, calcium channel blockers, and / or compounds that decrease action potential firing such as sodium channel blockers. Decreasing Ca++ influx results in increased synaptic plasticity and enhanced cognitive function. In particular, decreasing Ca++ influx associated with uncorrelated neural activity results in long-lasting increases in synaptic plasticity and cognitive function. This is achieved by administration of agents that cause a voltage-dependent block of NMDA receptors (e.g., divalent cations such as Mg++) or by administration of GABAB agonists such as baclofen. The invention further provides screening methods useful in identifying compounds that enhance synaptic plasticity and cognitive function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
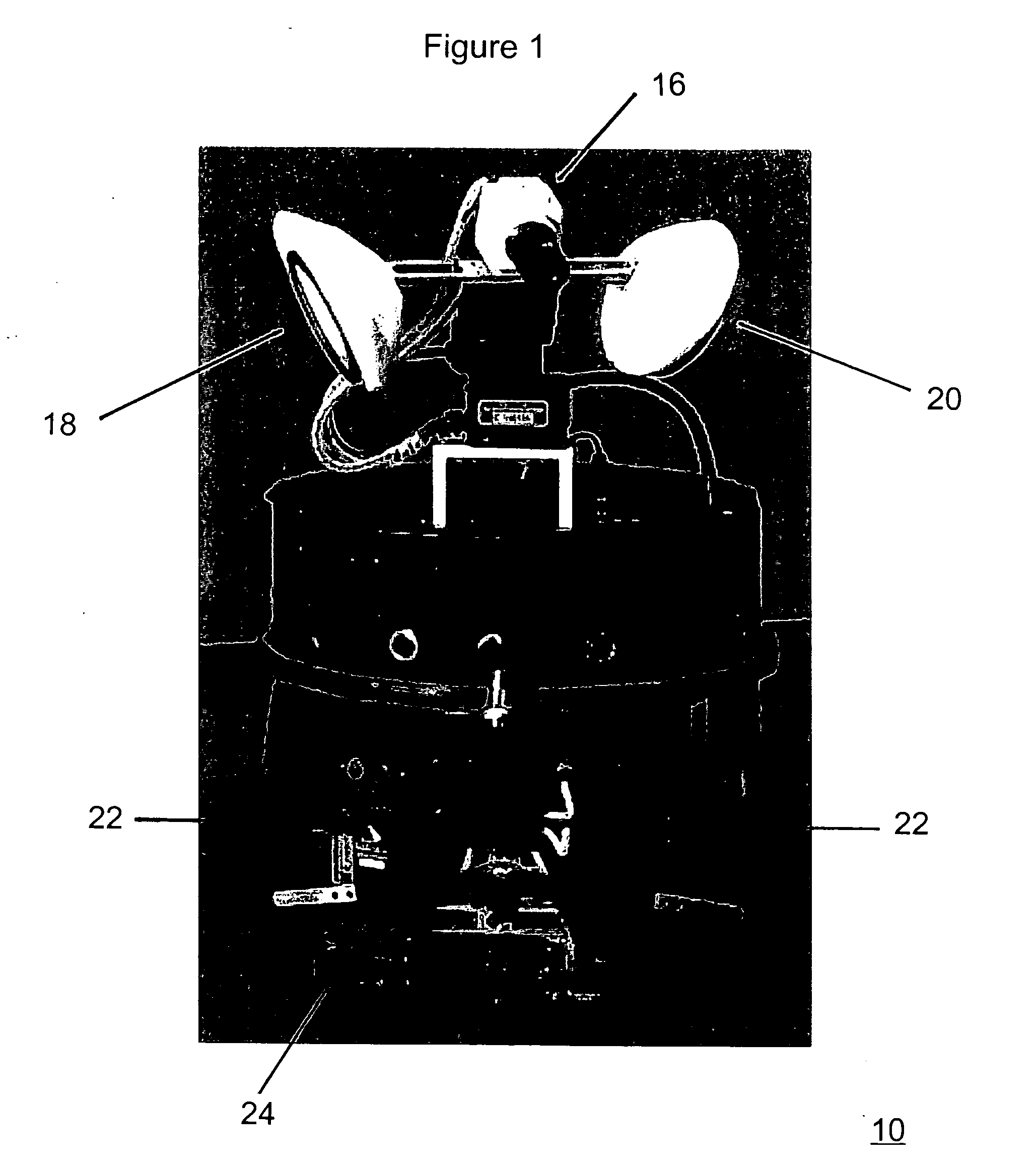
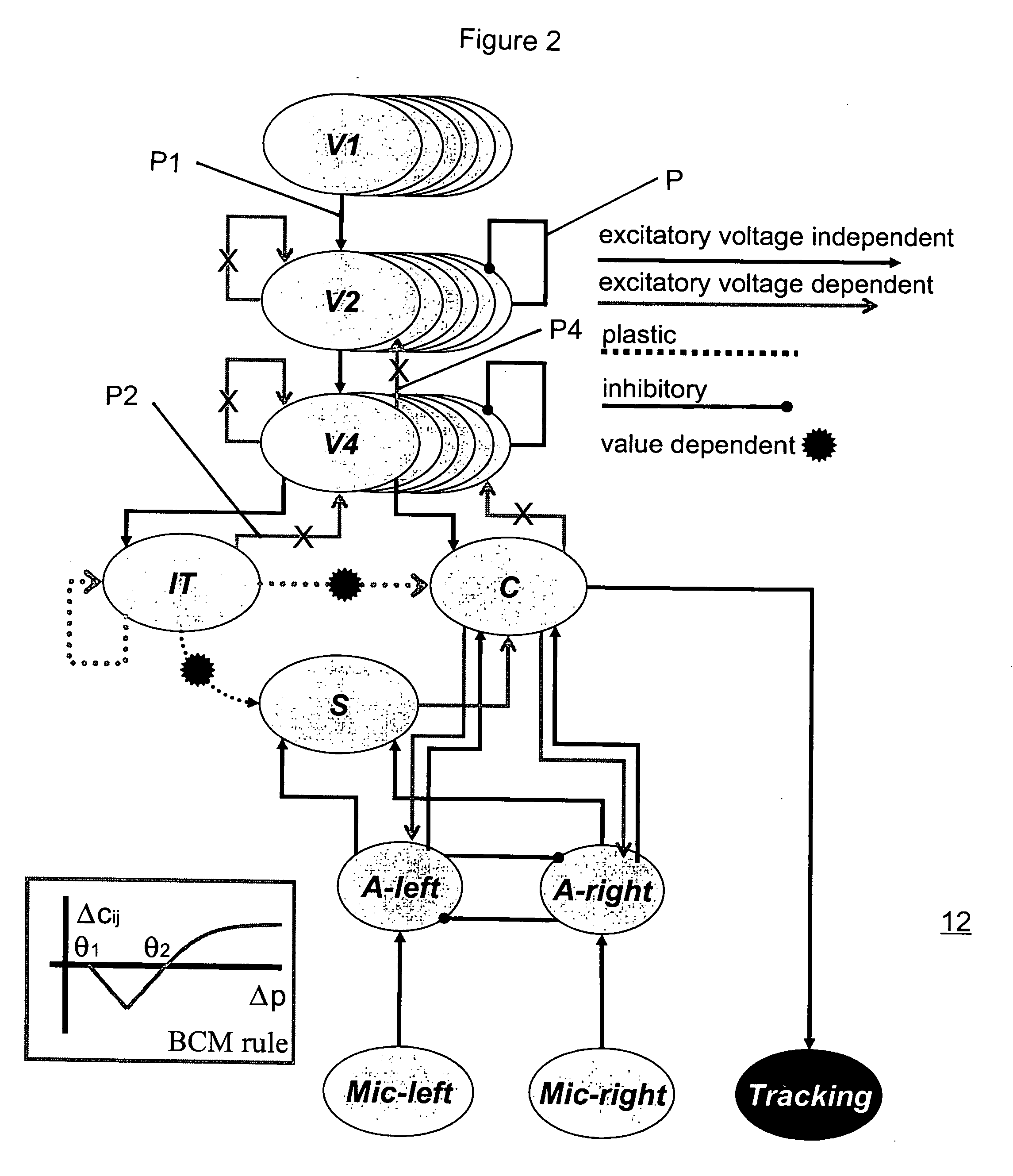
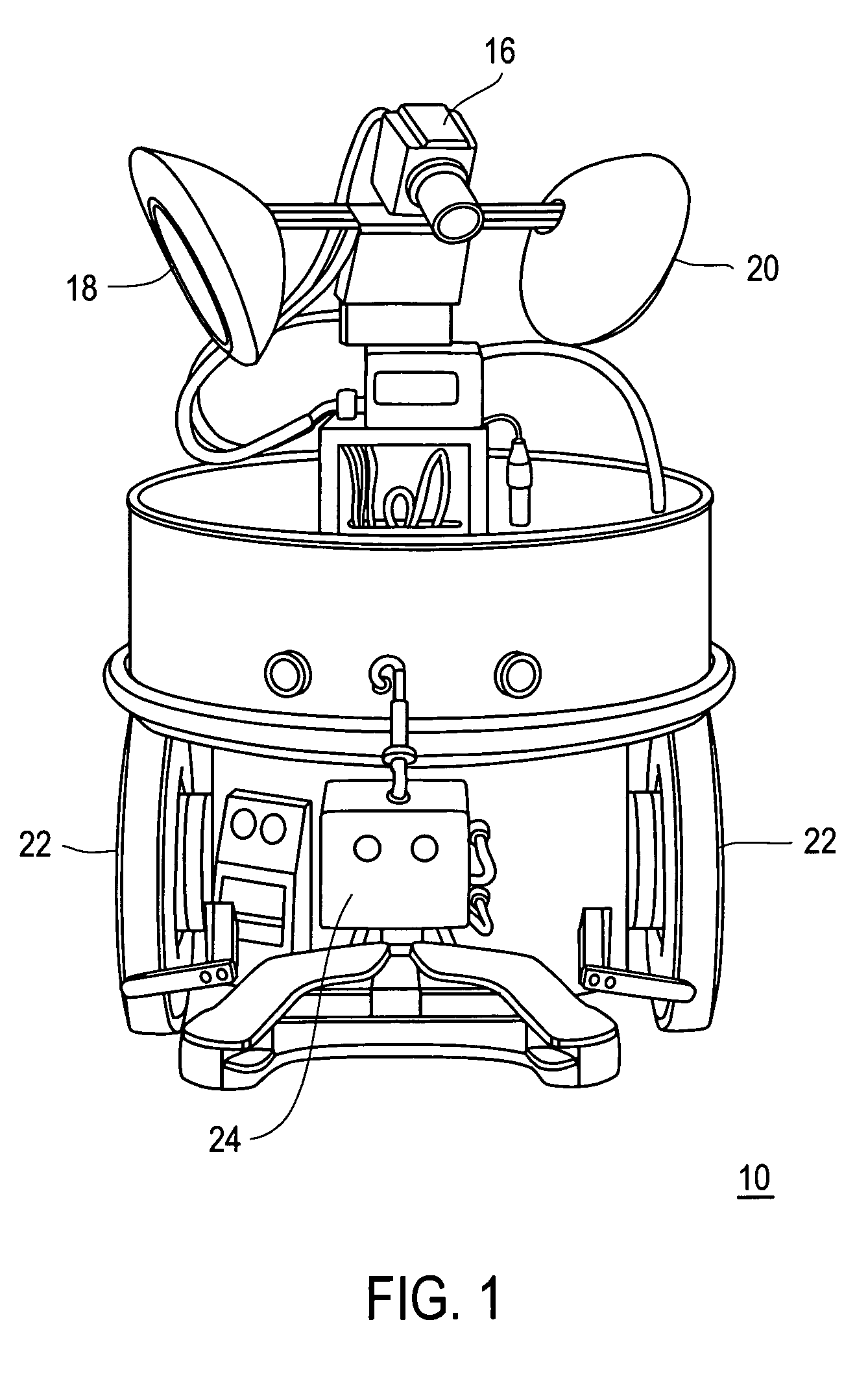
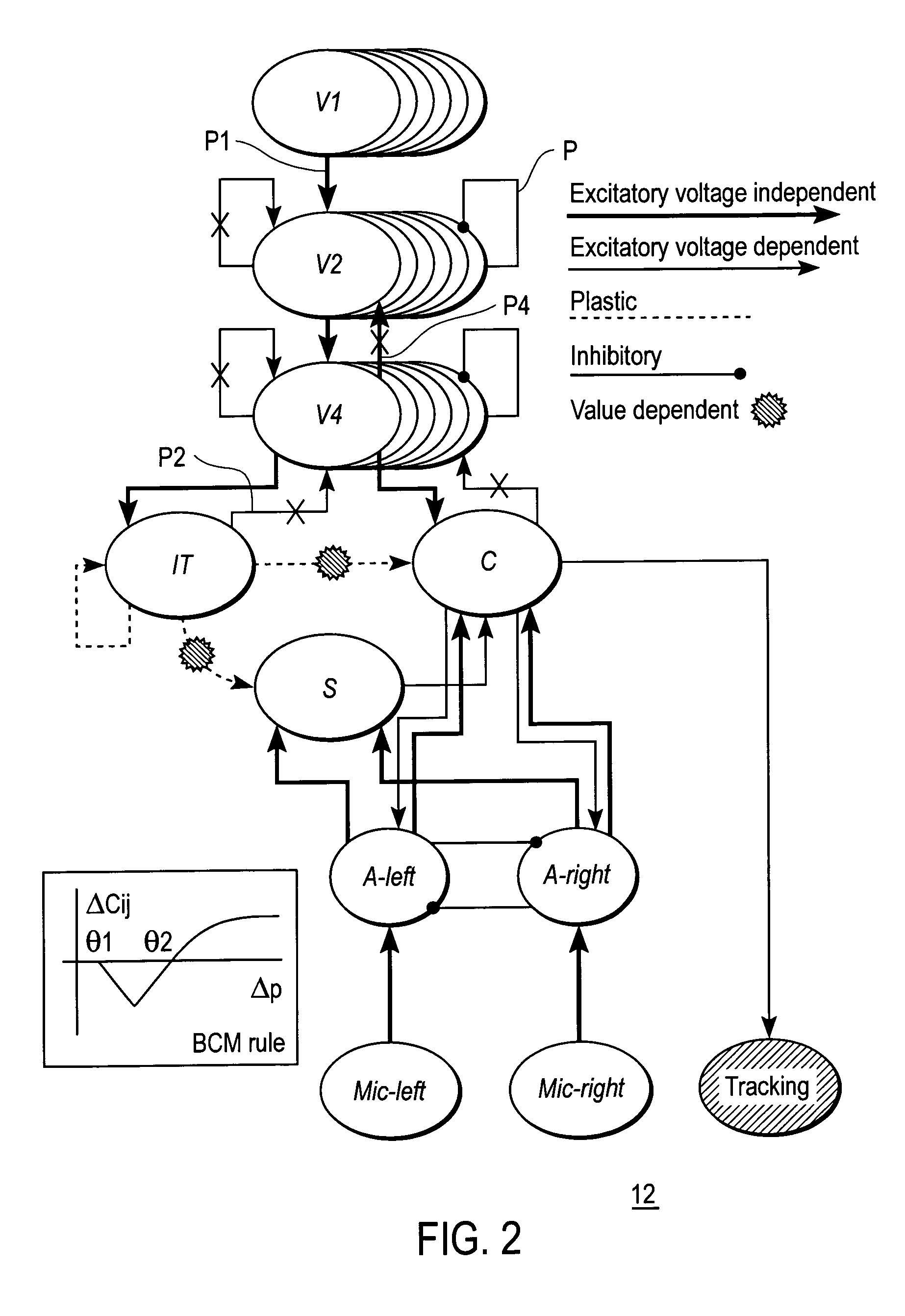
Mobile brain-based device for use in a real world environment
InactiveUS20050261803A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionNervous systemVisual Objects
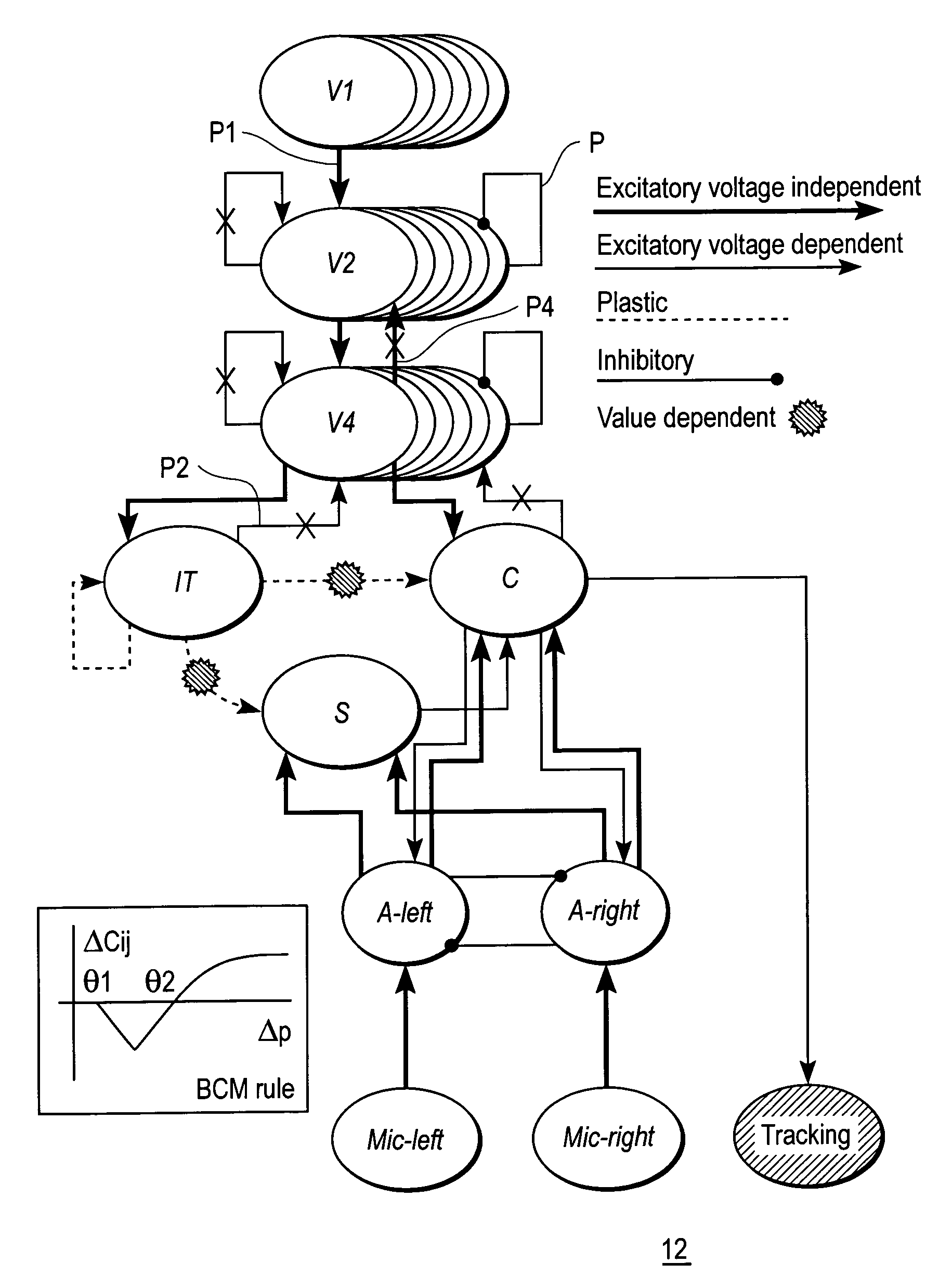
A mobile brain-based device BBD includes a mobile base equipped with sensors and effectors (Neurally Organized Mobile Adaptive Device or NOMAD), which is guided by a simulated nervous system that is an analogue of cortical and sub-cortical areas of the brain required for visual processing, decision-making, reward, and motor responses. These simulated cortical and sub-cortical areas are reentrantly connected and each area contains neuronal units representing both the mean activity level and the relative timing of the activity of groups of neurons. The brain-based device BBD learns to discriminate among multiple objects with shared visual features, and associated “target” objects with innately preferred auditory cues. Globally distributed neuronal circuits that correspond to distinct objects in the visual field of NOMAD 10 are activated. These circuits, which are constrained by a reentrant neuroanatomy and modulated by behavior and synaptic plasticity, result in successful discrimination of objects. The brain-based device BBD is moveable, in a rich real-world environment involving continual changes in the size and location of visual stimuli due to self-generated or autonomous, movement, and shows that reentrant connectivity and dynamic synchronization provide an effective mechanism for binding the features of visual objects so as to reorganize object features such as color, shape and motion while distinguishing distinct objects in the environment.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
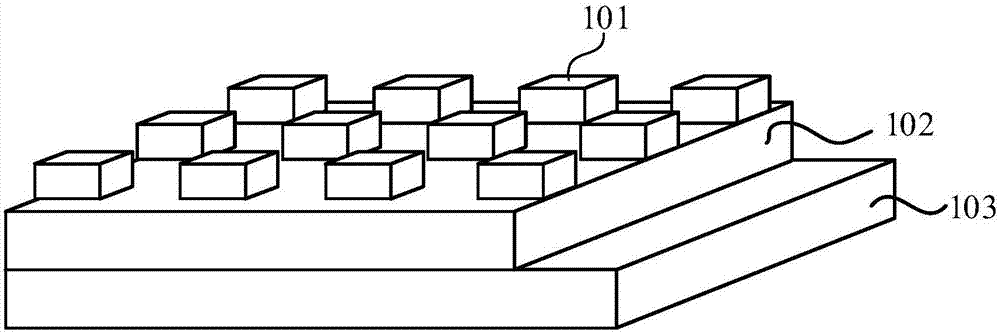
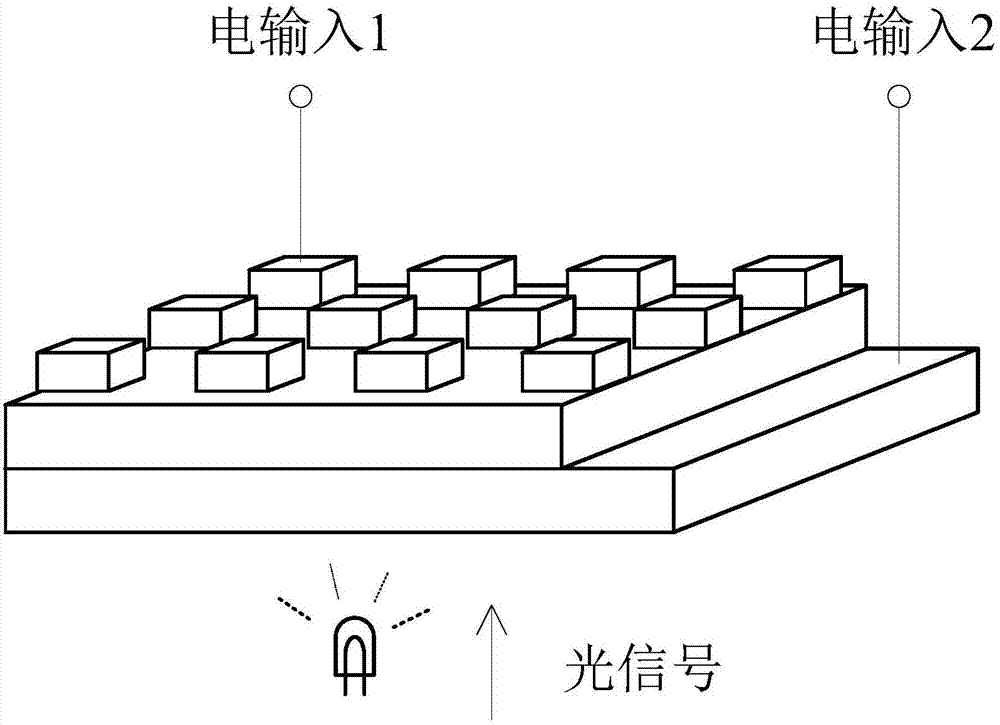
Artificial synaptic device based on photoelectric coupling memristor and modulation method of artificial synapse device
The invention discloses an artificial synaptic device based on a photoelectric coupling memristor and a modulation method of the artificial synaptic device. The artificial synaptic device comprises an upper electrode, a lower electrode and a functional material layer, wherein the functional material layer is arranged between the upper electrode and the lower electrode, the upper electrode, the functional material layer and the lower electrode jointly form a sandwich structure, the functional material layer is made of a material having a photoelectric effect, the lower electrode is a transparent conductive electrode, an electrical signal is input through the upper electrode and the lower electrode, and an optical signal is input through the transparent conductive electrode. In the artificial synaptic device provided by the invention, light is introduced as a control signal of the other end except the electrical signal, two control ends of the artificial synapse device are expanded to three ends, the artificial synaptic device can generate resistance change under an external optical excitation signal by the additionally-arranged end, the artificial synaptic device can be configured to be in a plurality of resistance states correspondingly by selection and control of intensity, frequency and optical pulse time of the optical excitation signal, and various synaptic plasticity functions are correspondingly achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Unit, device and method for simulating biological neuronal synapsis
ActiveCN103078055AHighly integratedReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusNeural architecturesSynaptic weightDevice form
The invention discloses a unit, a device and a method for simulating biological neuronal synapsis on the basis of chalcogenide compounds. The unit comprises a first electrode layer, a function material layer and a second electrode layer, wherein the first electrode layer receives first pulse signals, and the second electrode layer receives second pulse signals. A device can change electric conductance simulation synapsis weight changes according to input signals. When the difference value between the frequency of the first pulse signals and the frequency of the second pulse signals is plus or minus, the electric conductance is changed , and the simulation of the pulse frequency dependent synaptic plasticity function of the biological neuronal synapsis is realized. When the signal difference peak value between the first pulse signals and the second pulse signals is plus or minus, the electric conductance is changed, and the simulation of the pulse time dependent synaptic plasticity function of the biological neuronal synapsis is realized. The unit, the device and the method have the advantages that the basic function of the biological neuronal synapsis can be realized on single inorganic devices, the basic device forming the artificial neural network can be provided, and the effects of integration degree improvement and power consumption reduction can be obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synaptic transistor based on two-dimensional semiconductor material and preparation method of synaptic transistor
InactiveCN109473549AIncrease surface areaImprove linearitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
The invention discloses a synaptic transistor based on a two-dimensional semiconductor material and a preparation method of the synaptic transistor. The synaptic transistor comprises an insulating substrate, and a channel, a source electrode, a drain electrode and a gate electrode which are arranged on the substrate, wherein the channel is a two-dimensional semiconductor material; the source electrode and the drain electrode are arranged at the two ends of the channel respectively and form an ohmic contact with the channel material; the gate electrode and an electrical interconnection system formed by the channel, the source electrode and the drain electrode are kept in electronic insulation; an organic electrolyte covers a channel region and most of the gate electrode and comprises an organic carrier capable of being electrically insulated and ions capable of being migrated, and effective ion control of the gate to the channel material is formed. According to the synaptic transistor based on the two-dimensional semiconductor material and the preparation method of the synaptic transistor, an ion attachment-intercalation mechanism is utilized, and the characteristics of large surface area and adjustable resistance value of the two-dimensional material are combined, so that the device shows long-term and short-term synaptic plasticity, and the two characteristics can change witheach other along with the change of a gate signal. Meanwhile, the device has good linearity and ultralow operational power consumption, and the implementation and large-scale integration application of a high-precision neuromorphic device are facilitated.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
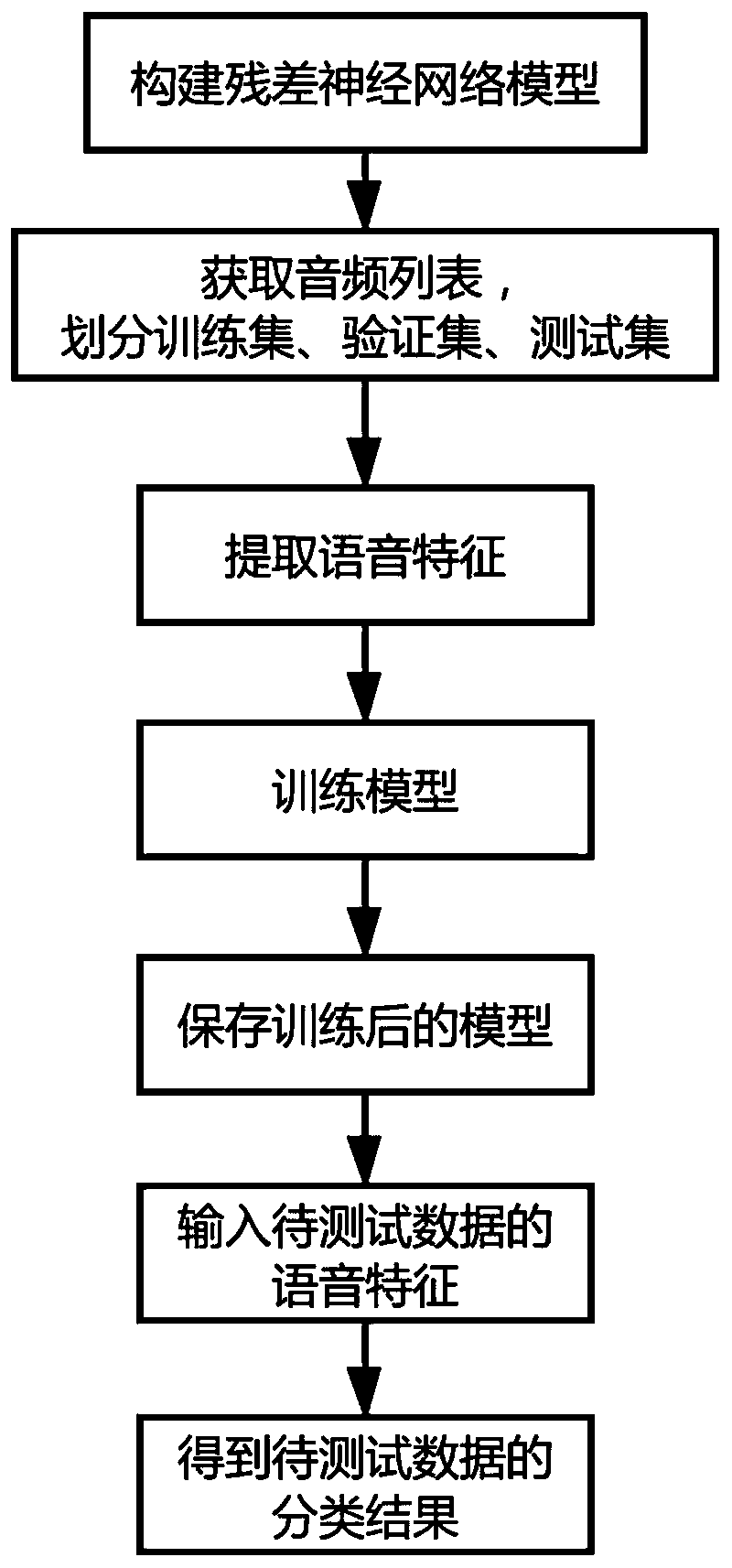
Memristor network-based residual neural network model and application method thereof
ActiveCN110991633AIncreased complexityGood at extractingSpeech recognitionPhysical realisationMassively parallelResidual neural network
The invention provides a memristor network-based residual neural network model and an application method thereof. A memristor network constructed based on a memristor can perform large-scale parallelprocessing, and meanwhile, has huge memory space. The resistance state of the memristor can be flexibly changed by adjusting applied voltage at the two ends of the memristor, and therefore, synaptic plasticity is achieved. The memristor-based memristor network has the advantages of low power consumption, high speed, modularization and the like, and can be built into various neural networks according to the requirements of developers. The memristor network built by the memristor is used as the hardware support of a residual error neural network; on the basis of the memristor network, a residualneural network model is constructed; the functions of training, testing and the like of the residual neural network model are further achieved; and the resistance value of the memristor is controlledby applying voltages to the two sides of the memristor, and therefore, various needed arithmetic operations in the residual neural network model are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
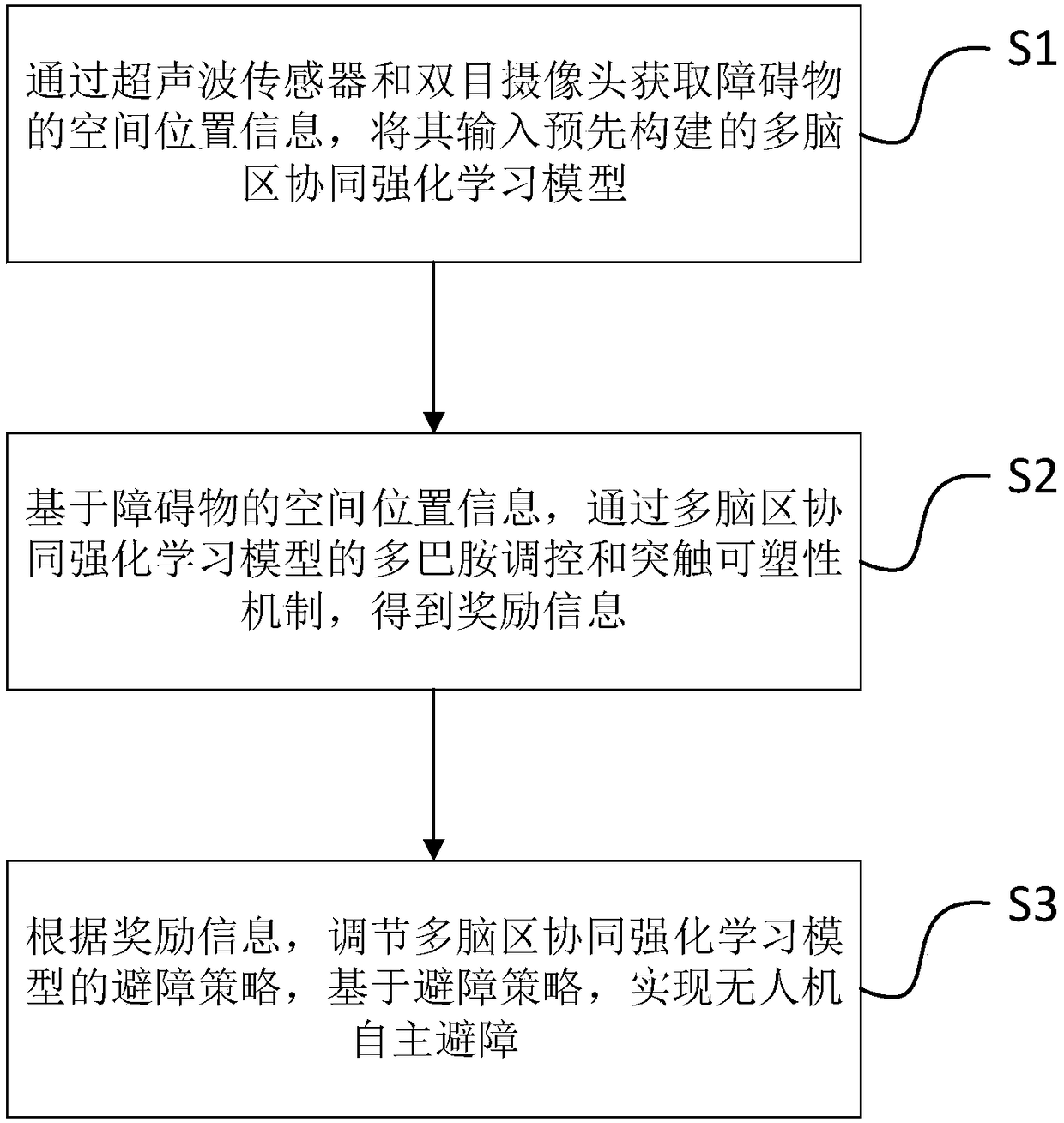
Multi-brain area cooperative autonomous decision making method based on multi-modal fusion
ActiveCN108197698ARealize autonomous obstacle avoidanceReduce uncertaintyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFault toleranceSimulation
The invention belongs to the cognitive nerve technology field and especially relates to a multi-brain area cooperative autonomous decision making method based on multi-modal fusion. Problems that thecost of an existing unmanned aerial vehicle obstacle avoidance technology is high; the technology is not flexible; and an existing reinforcement learning method requires a control object to have a high fault tolerance capability are solved. The multi-brain area cooperative autonomous decision making method based on multi-modal fusion comprises the following steps of acquiring the space position information of an obstacle and inputting into a multi-brain area cooperative reinforcement learning model which is constructed in advance; and according to the reward information fed back by an environment, through dopamine regulation and control and a synaptic plasticity mechanism, updating the multi-brain area cooperative reinforcement learning model, and realizing unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous obstacle avoidance. In the invention, the dangerous degree of the obstacle in a scene can be accurately assessed, a brain autonomous learning process is simulated, the unmanned aerial vehicle can rapidly and accurately learn an obstacle avoidance strategy, autonomous obstacle avoidance is realized and a task is completed.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel uses for 4-phenylbutyrate (4PBA) and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts
InactiveUS20110027251A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderPhosphorylationReticulum cell
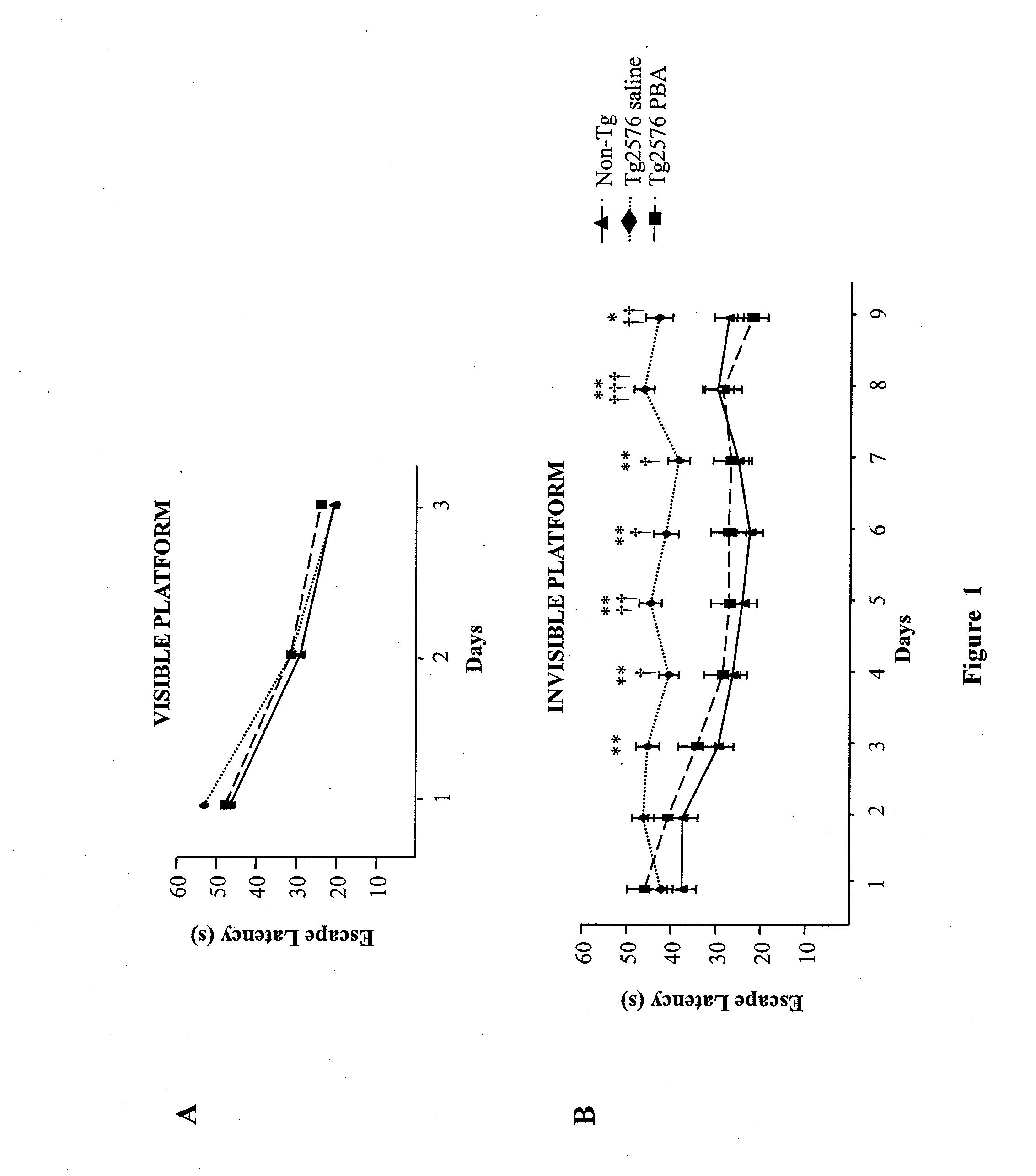
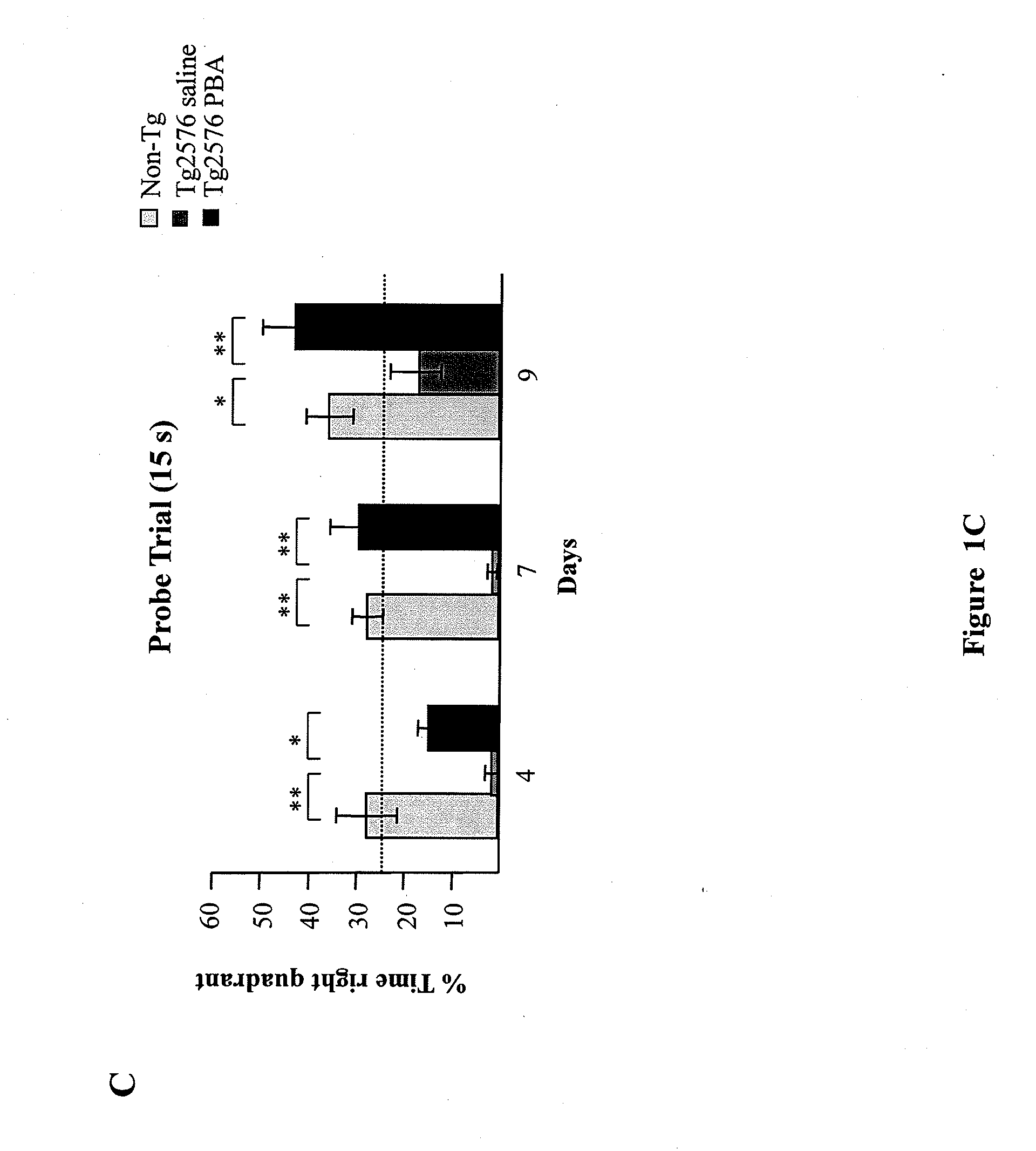
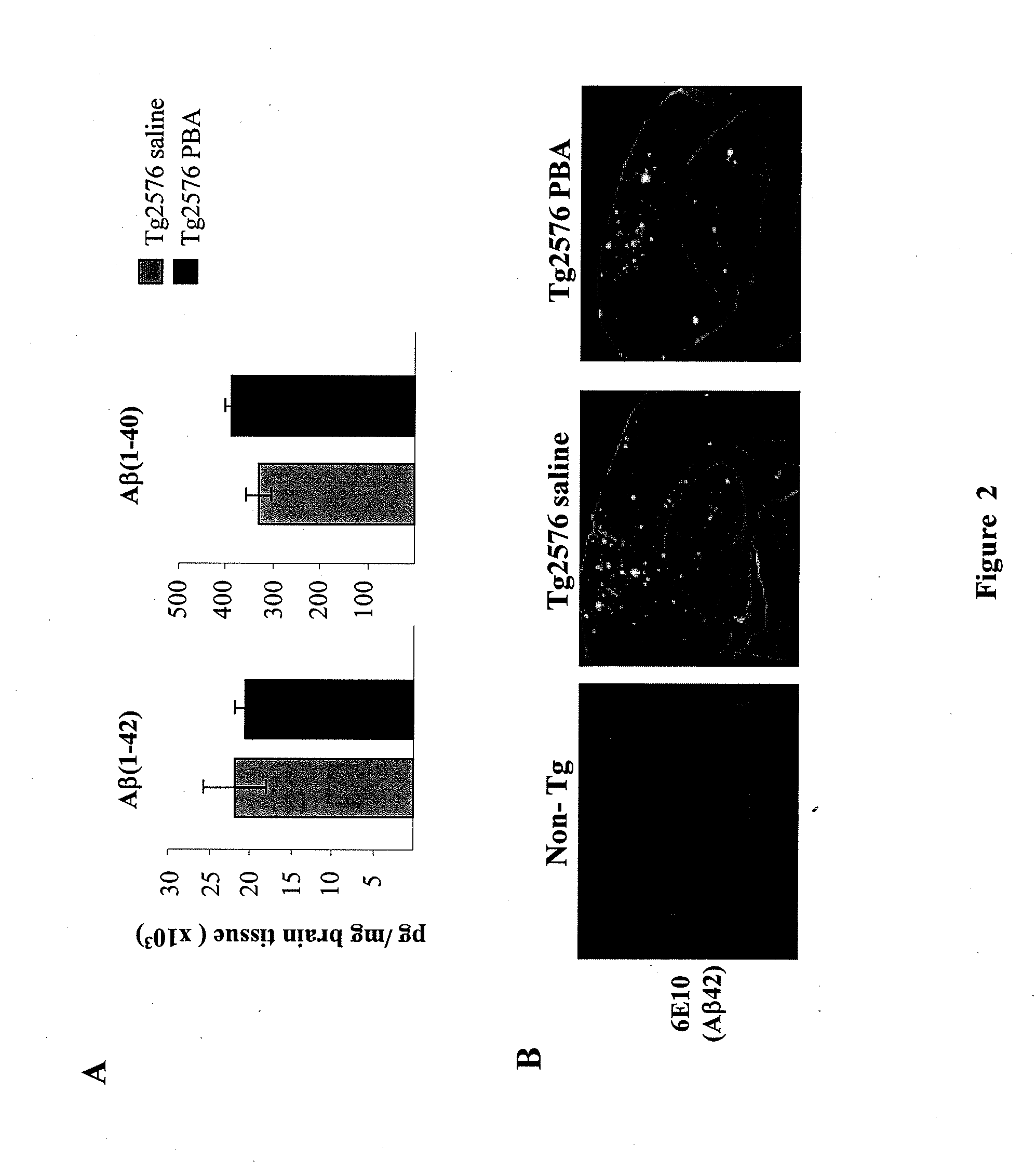
Novel uses for 4-phenylbutyrate (4PBA) and its pharmaceutically acceptable saltsThe use of 4PBA in the manufacture of a medicament useful to treat cognitive disorders in dementias coursing with tauopathies is described.The treatment with 4PBA improves cognitive deficit in a classic murine experimental model of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) (Tg 2576) that is accompanied by decreasing levels of a marker characteristic to AD pathologies, such as phosphorylated Tau, and increasing levels in the synthesis of some synaptic plasticity marker proteins such as GluR1 and PSD95. As mediating mechanism for the therapeutic effect we propose a decreasing stress in the endoplasmic reticulum as manifested by increasing levels of the GRP78 protein. On the other hand its inhibiting effect on histone deacetylation and its involvement in chromatin remodeling facilitates protein synthesis processes, which improves synaptic plasticity.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
Mobile brain-based device for use in a real world environment
InactiveUS7519452B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionVision processingNervous system
A mobile brain-based device BBD includes a mobile base equipped with sensors and effectors (Neurally Organized Mobile Adaptive Device or NOMAD), which is guided by a simulated nervous system that is an analogue of cortical and sub-cortical areas of the brain required for visual processing, decision-making, reward, and motor responses. These simulated cortical and sub-cortical areas are reentrantly connected and each area contains neuronal units representing both the mean activity level and the relative timing of the activity of groups of neurons. The brain-based device BBD learns to discriminate among multiple objects with shared visual features, and associated “target” objects with innately preferred auditory cues. Globally distributed neuronal circuits that correspond to distinct objects in the visual field of NOMAD 10 are activated. These circuits, which are constrained by a reentrant neuroanatomy and modulated by behavior and synaptic plasticity, result in successful discrimination of objects. The brain-based device BBD is moveable, in a rich real-world environment involving continual changes in the size and location of visual stimuli due to self-generated or autonomous, movement, and shows that reentrant connectivity and dynamic synchronization provide an effective mechanism for binding the features of visual objects so as to reorganize object features such as color, shape and motion while distinguishing distinct objects in the environment.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
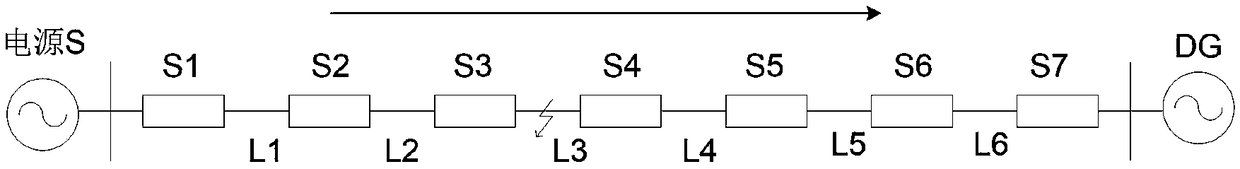
Fault location method of distributed generation including power distribution network of synaptic plasticity based SNP system
ActiveCN109507527AAccurate fault locationImprove fault location speedFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemElectricityReasoning algorithm
The invention relates to a fault location method of a distributed generation including power distribution network of a synaptic plasticity based SNP system. The fault location method comprises the following steps of (1), selecting a power cut interval; (2), establishing a fault location model of the distributed generation including power distribution network of the synaptic plasticity based SNP system; (3), determining a fault section; according to fault information and a forward synaptic matrix which are read by the system, carrying out operation on the established fault location model; (4),verifying fault location accuracy; according to a fault location result obtained by a reasoning algorithm and the value of a sequential pulse train in a bidirectional functional neuron O, verifying the accuracy of the fault location result by combining an actual current matrix C and the reasoning algorithm; and (5), completing the fault location and the verification of the fault location accuracythrough a fault judgment standard and a fault current information verification standard. The fault location method of the distributed generation including power distribution network of the synaptic plasticity based SNP system, which is provided by the invention, has high accuracy and high reliability, and can be widely applied to the fault location of the distributed generation including power distribution network.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI & RES INST OF STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
Compounds that modulate neuronal growth and their uses
InactiveUS20050164920A1Enhancing Trk mediated activityEnhances Trk mediated activityNervous disorderDepsipeptidesCyclic peptideNervous system
Cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics are provided that bind to and / or modulate activities associated with Trk receptors, including processes associated with the growth and repair of the central nervous system (e.g., neuronal growth and survival, axonal growth, neurite outgrowth and synaptic plasticity). Cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics are also provided that block or reduce the effect of other factors that inhibit growth and / or repair of the central nervous system. Pharmaceutical compositions and other formulations comprising these compounds are provided. In addition, the invention provides methods for using the cyclic peptides and peptidomimetics to modulate Trk mediated activities, including processes such as neuronal growth, survival and recover, axonal growth, neurite outgrowth, and synaptic plasticity. Further, the invention provides methods for promoting central nervous system (CNS) neuron growth by administering a p75 receptor binding agent.
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
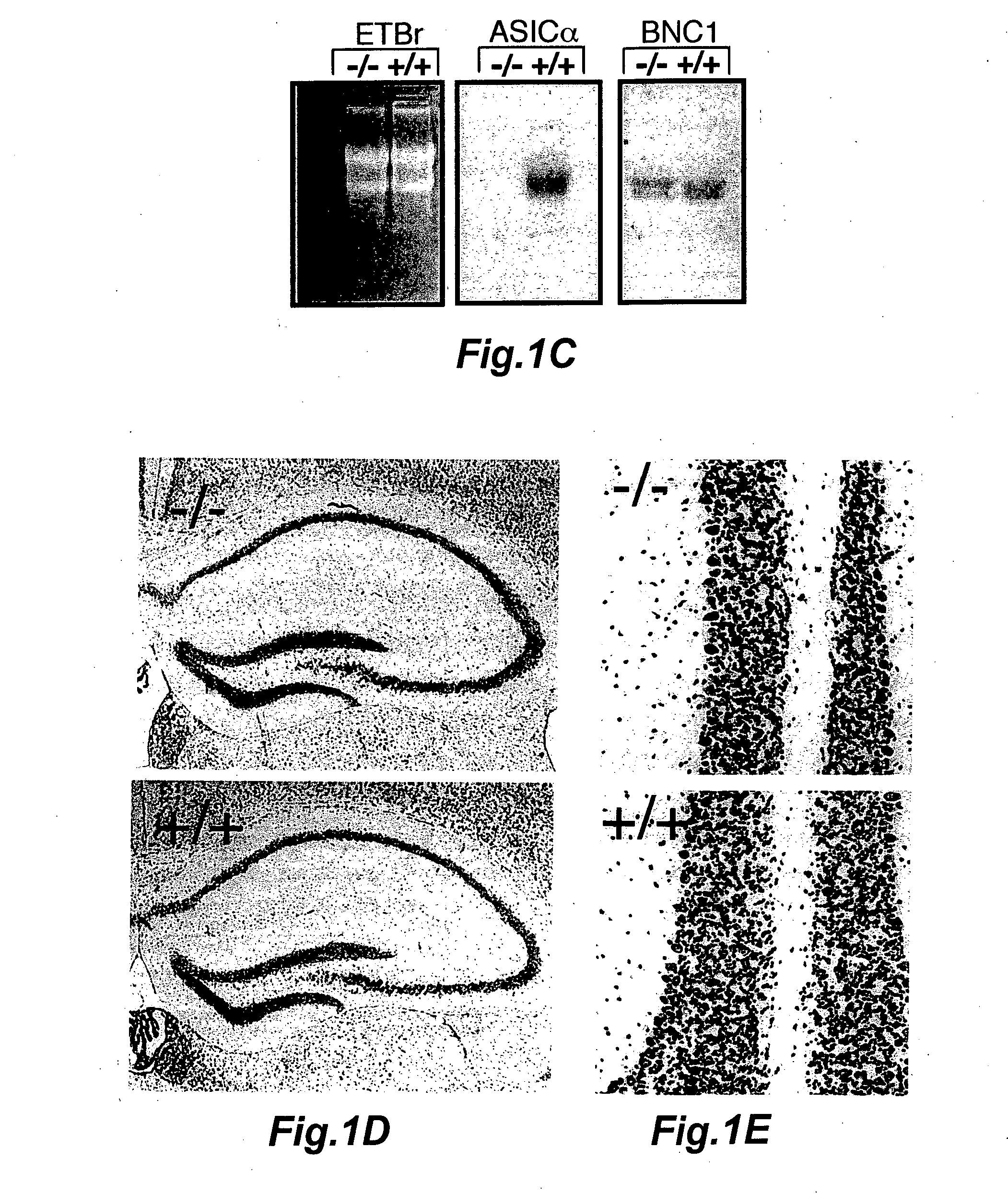
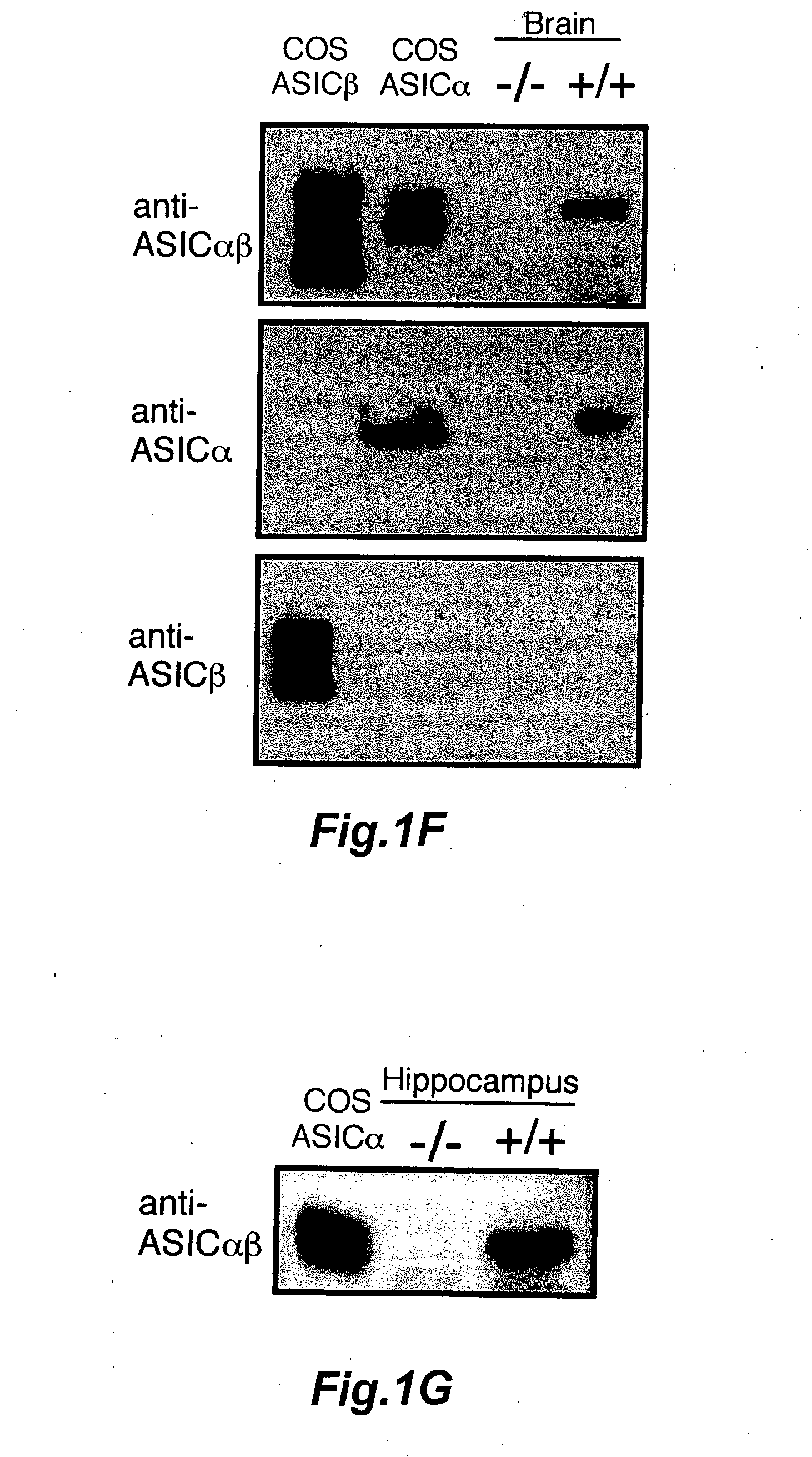
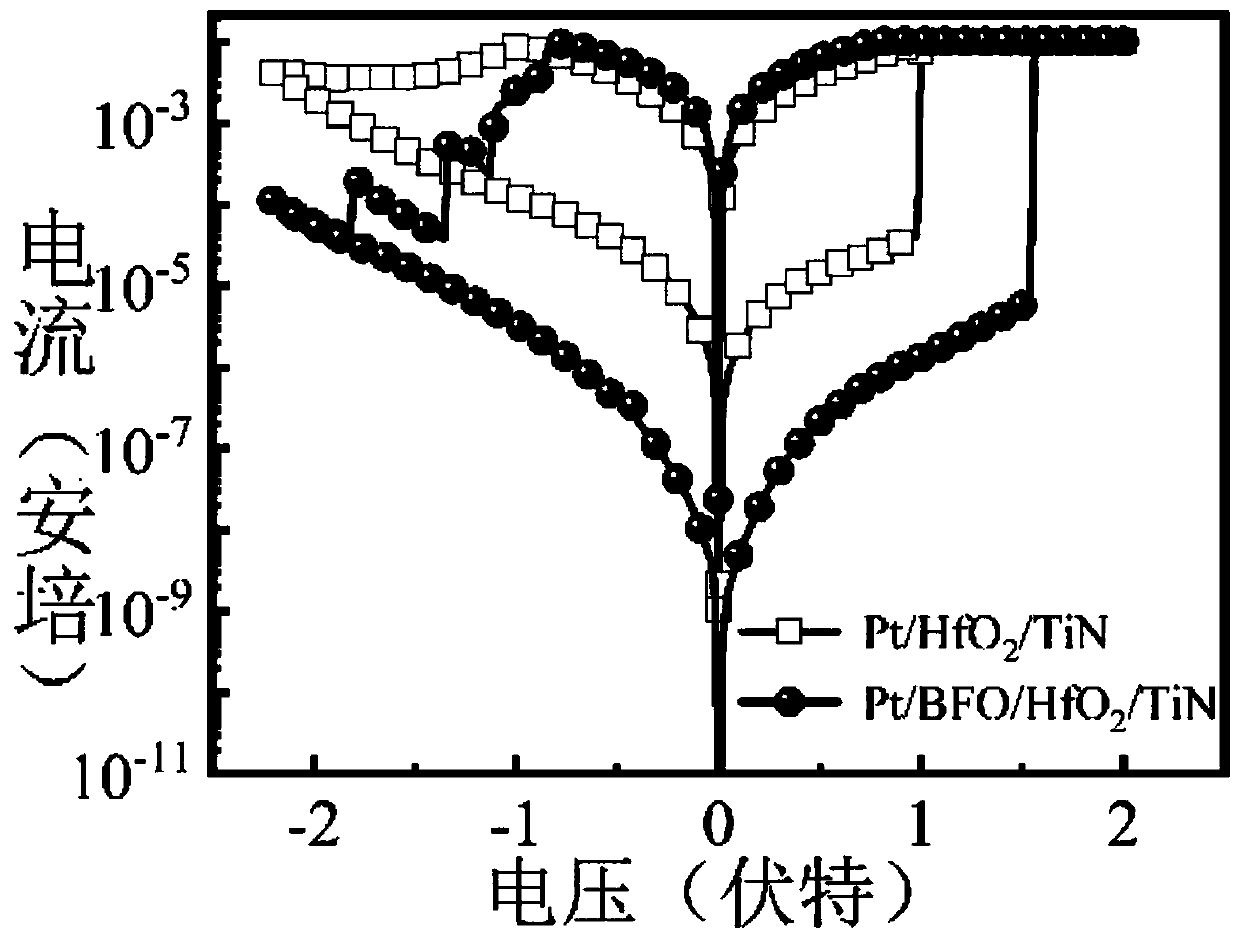
Novel compositions and methods for modulating the acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC)
InactiveUS20070087964A1Avoid damaging effectsEnhance learning and memoryBiocideNervous disorderCognitive diseasesSynaptic plasticity
Novel compositions for modulating acid-sensing ion channels (ASIC) function comprising ASICα, ASICβ, and BNC1 and derivatives thereof; methods for modulating ASIC function and methods for treating cognitive disorders and for memory enhancement using the novel compositions of the invention; and a method for increasing synaptic plasticity are described.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
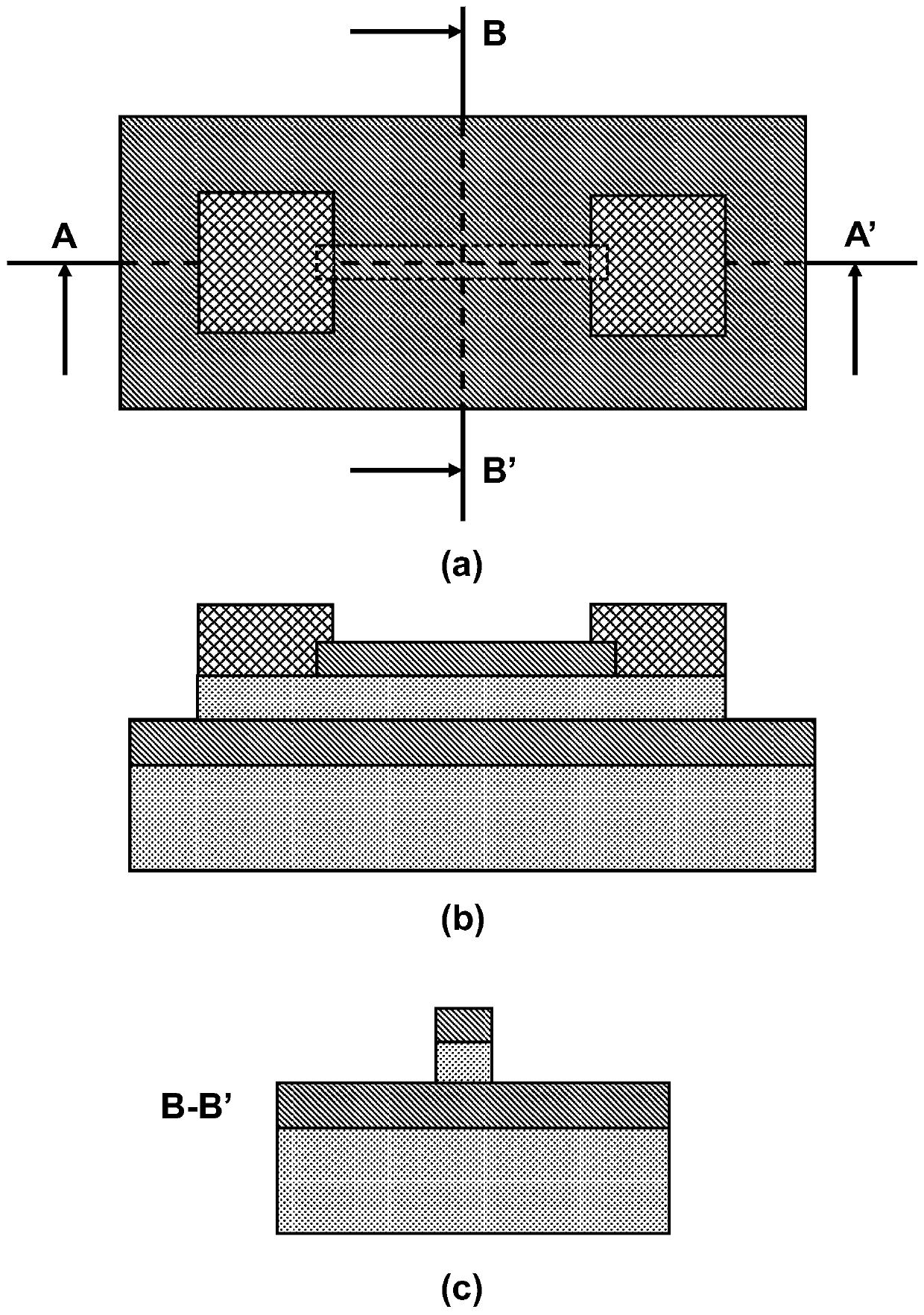
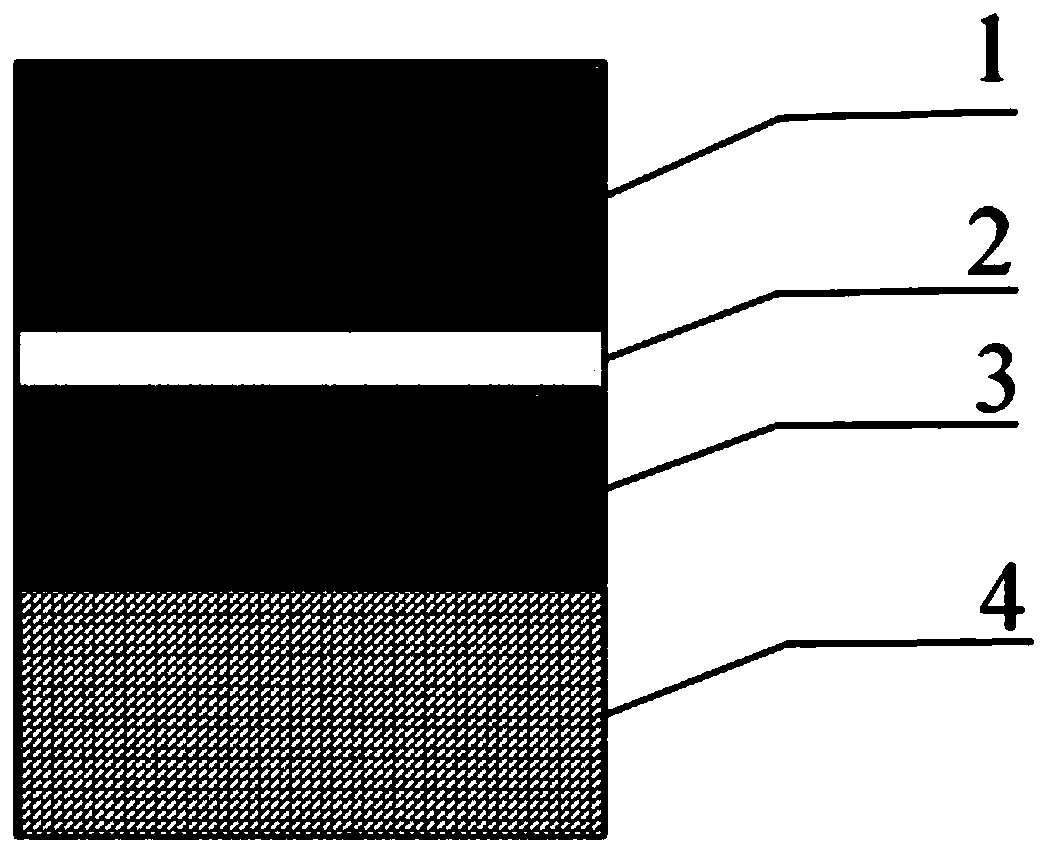
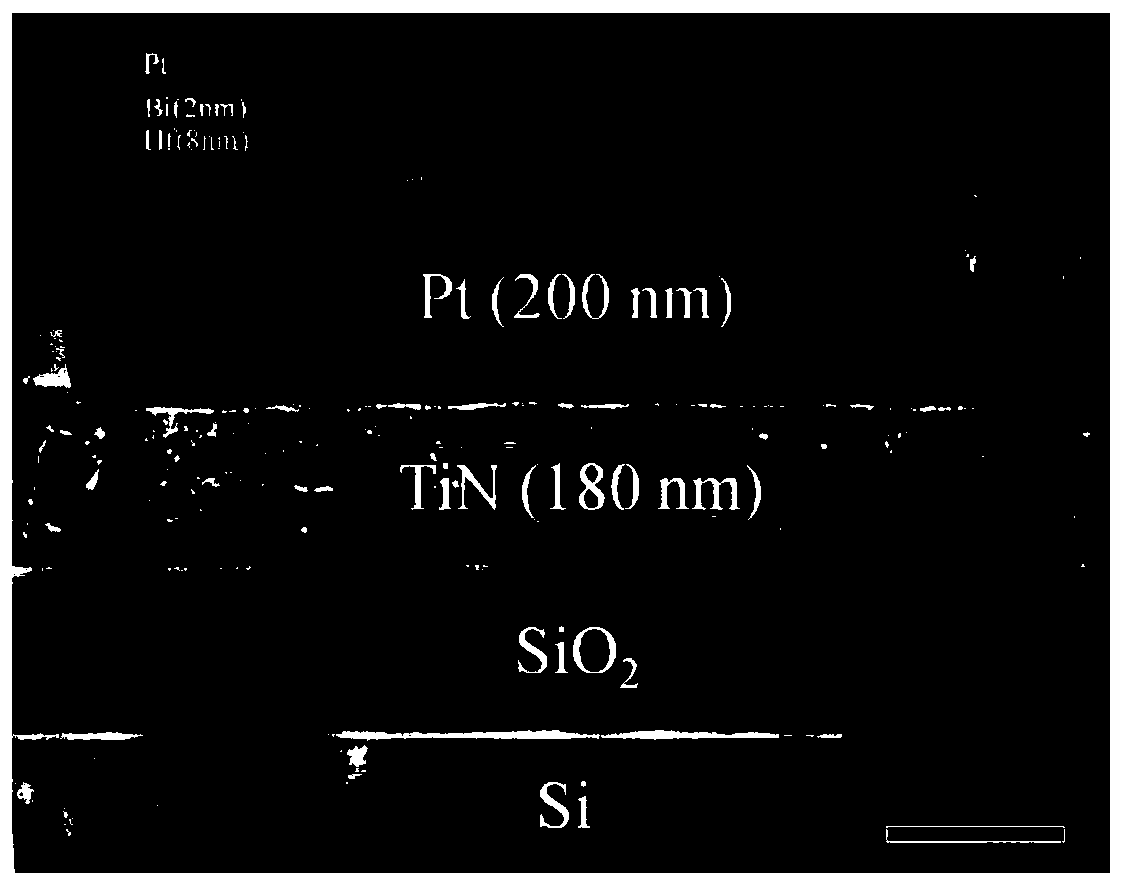
Low-voltage multifunctional charge trapping synaptic transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111564499AEnhanced interfacial electric fieldConducive to tunnelingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNanowireNeural network hardware
The invention discloses a low-voltage multifunctional charge trapping type synaptic transistor and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of synaptic devices oriented to neural networkhardware application. According to the invention, a silicon nitride and hafnium oxide double-capture-layer structure is adopted to simultaneously realize short-long-time synaptic plasticity on a single device, so that the functions of the synaptic device are enriched; a three-gate nanowire structure is beneficial to enhancing an interface electric field, so that the FN tunneling width at the interface is reduced, the tunneling probability at the interface is enhanced, and the operation voltage and the device power consumption are reduced; and the device has complete CMOS material and processcompatibility, and due to the excellent device characteristics, the device has potential to be applied to a future large-scale neural network computing system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Application of salidroside in preparation of medicine for treating stroke
The invention relates to the field of medicines, and in particular relates to application of salidroside in preparation of a medicine for treating stroke. The salidroside shows good treatment effect in animal-related model experiments, can effectively increase the score on reduction of nerve function deficit, and also can reduce the volume of cerebral infarction, as well as prolong the stroke therapeutic time window to 48 hours; the salidroside can regulate gene related to nerve synaptic plasticity is proved for the first time.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
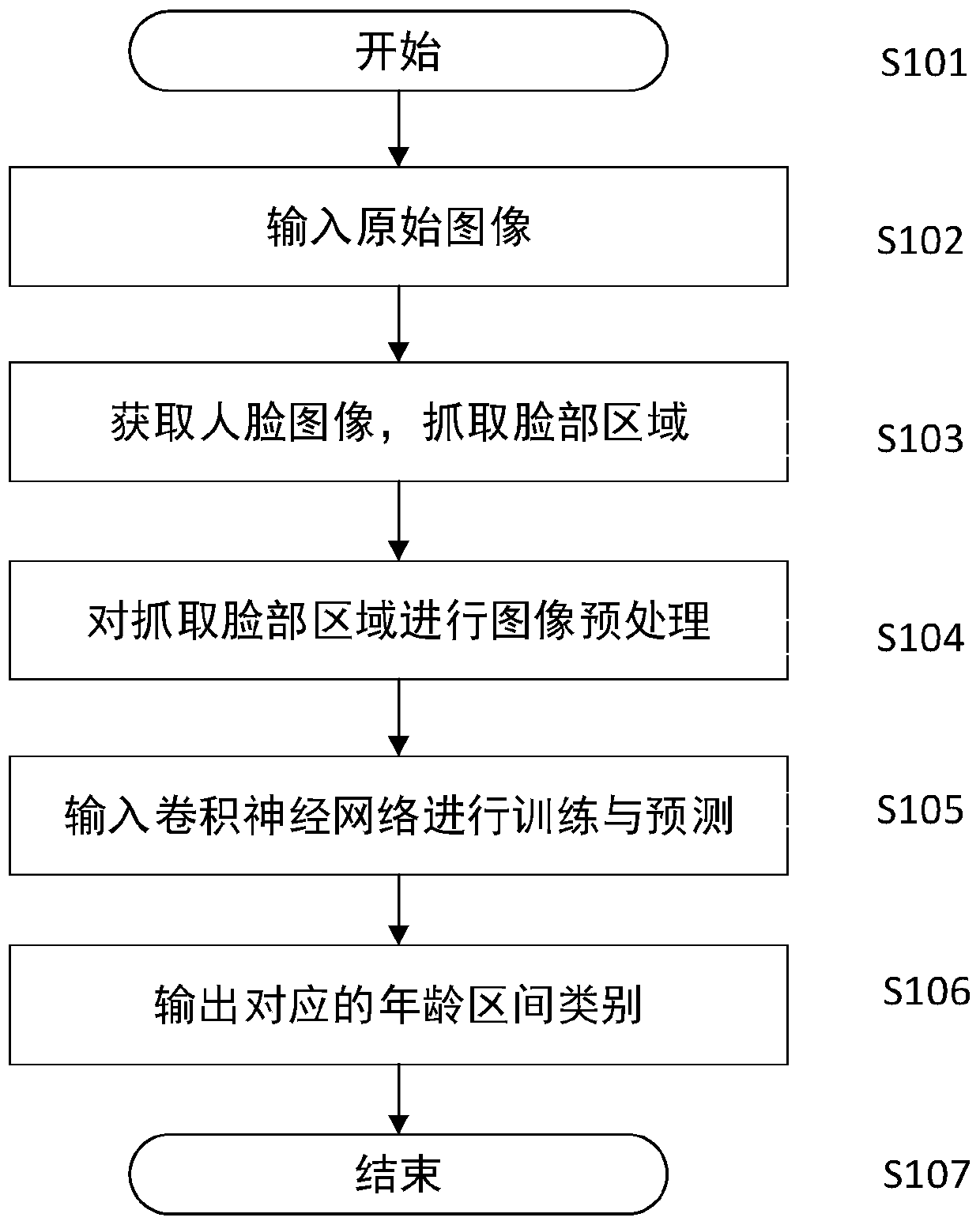
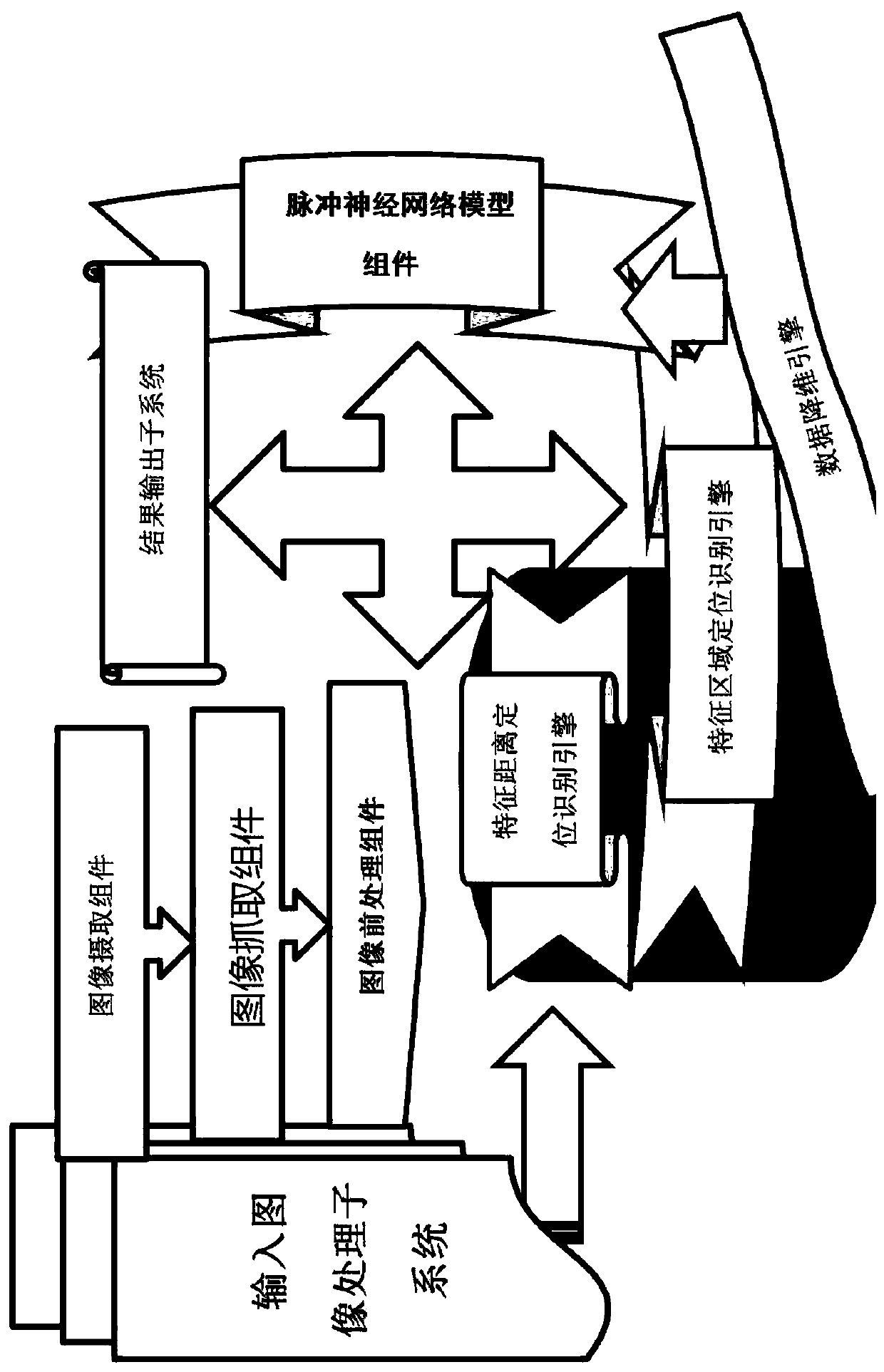
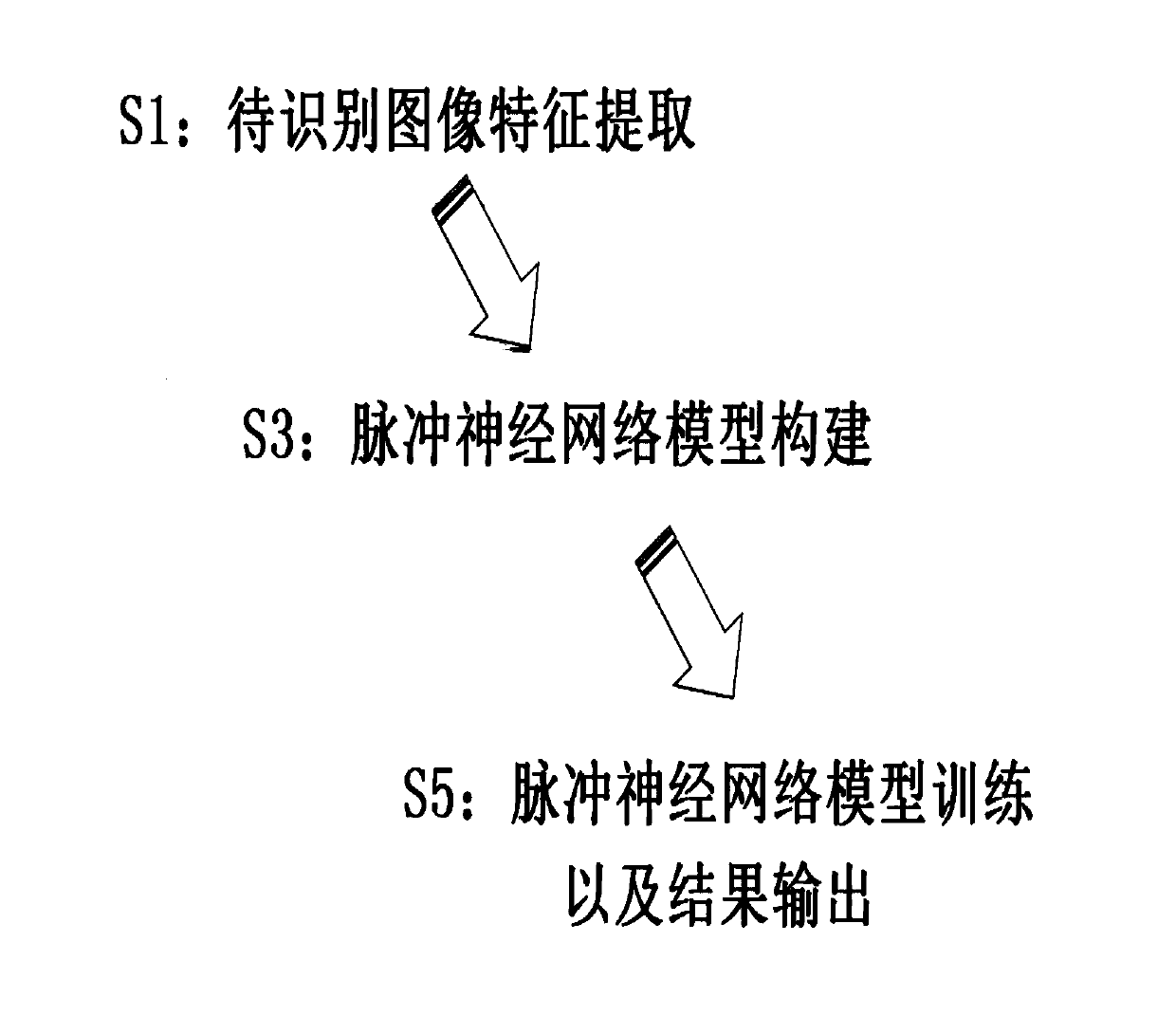
Facial age recognition system and method based on spiking neural network
ActiveCN110705428ASolving problems that only work with static datasetsGood effectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSpiking neural networkProgram calculation
The invention provides a facial age recognition system and method based on a spiking neural network, and a system for performing facial age recognition based on an unsupervised facial feature vector,a computer program and a computer readable storage medium, which are used for executing the method, and can achieve a good effect on a dynamic data set. Compared with a traditional method, according to the technical scheme of the invention, a spiking neural network model is built by using spiking neurons, an STDP rule (a synaptic plasticity rule related to pulse time) is used for training a pulseneural network, and meanwhile, a lateral suppression method is used for obtaining an unsupervised self-organizing mapping neural network, so that the method can continuously adapt to the change of actual data. Therefore, the problem that the prior art is only suitable for static data sets is solved.
Owner:北京智能工场科技有限公司
Memristor with double resistance change layer and preparation method
PendingCN110676375AIncreased durabilityEasy to prepareElectrical apparatusSolid state electrolyteElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a memristor with double resistance change layer and a preparation method. The memristor with double resistance change layer comprises a bottom electrode, a first resistance change layer, a second resistance change layer and a top electrode which are stacked in sequence, wherein the first resistance change layer is prepared from one or more of multi-element perovskite oxide,binary metal oxide, chalcogenide solid electrolyte or nitride; and the second resistance change layer is prepared from a ferroelectric material. The memristor has the beneficial effects that (1) the preparation method is simple and easy to operate; (2) the memristor has the advantages of large resistance change window, good device durability, long retention time and the like after being inserted into the resistance change layer prepared from the ferroelectric material, and obtains a multi-stage storage function; (3) the resistance can be continuously regulated and controlled when voltage stimulation is applied, and a biological synapse bionic function is achieved; and (4) time sequence dependence synaptic plasticity learning rules in the biological synapses can be simulated, and an autonomous learning function is achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Novel compositions and methods for modulation of the acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC) for the treatment of anxiety and drug addiction
This invention provides novel compositions and methods for modulating acid-sensing ion channels (ASIC) function comprising ASIC and derivatives thereof; methods for modulating ASIC function and methods for treating anxiety or anxiety disorders and drug addiction using the novel compositions of the invention; and a method for increasing synaptic plasticity are described.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Fast memory coding method and device based on multi-synaptic plasticity spiking neural network
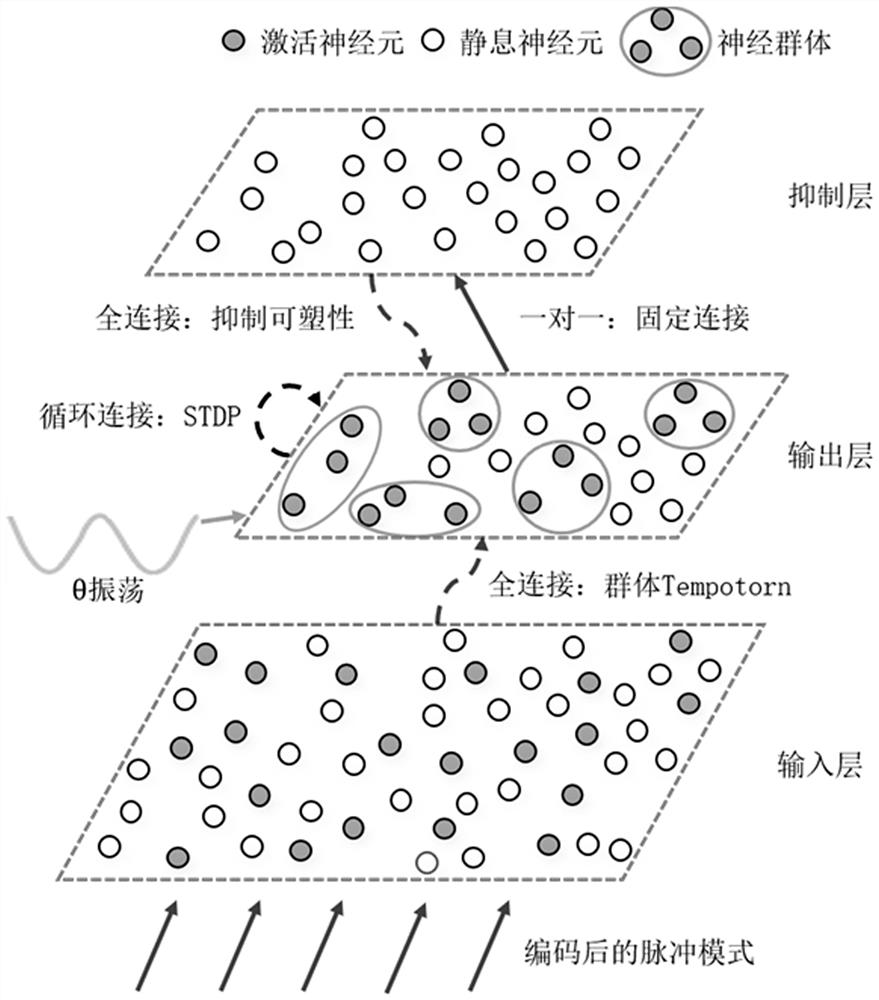
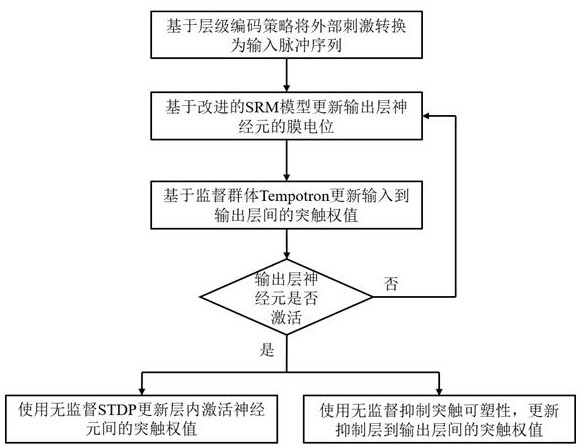
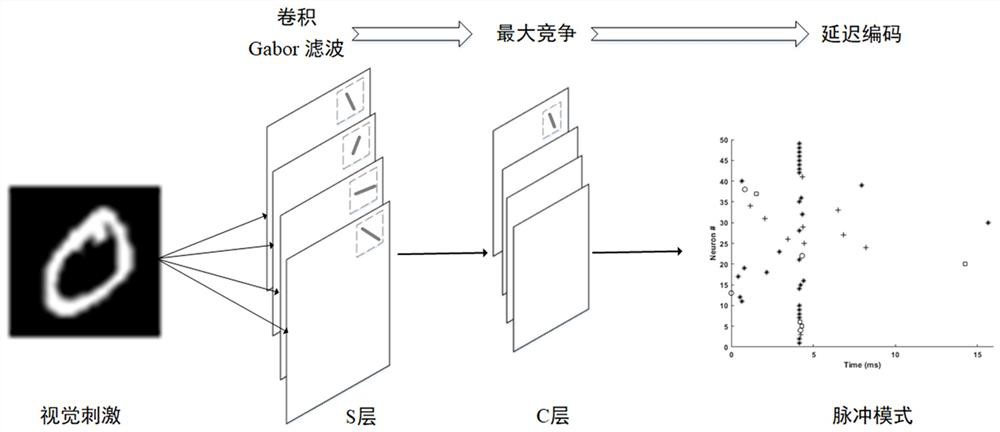
PendingCN114118383AImprove encoding speedImprove stabilityNeural architecturesPhysical realisationSynaptic weightPulse sequence
The invention provides a fast memory coding method based on a multi-synaptic plasticity pulse neural network. The fast memory coding method comprises the steps of 1, converting external stimulation into an input pulse sequence based on a hierarchical coding strategy; 2, after the pulse neural network receives an input pulse, updating a membrane potential of neurons of an output layer based on an improved SRM model; 3, updating a synaptic weight input to an output layer by using a supervisory group Tempotron, and activating neuron memory input of the output layer; step 4, after the neurons of the output layer are activated, using the unsupervised STDP to update synaptic weights among the activated neurons in the layer, and forming an enhanced cyclic sub-network storage memory; and step 5, while executing the step 4, using unsupervised inhibition synaptic plasticity, updating a synaptic weight between an inhibition layer and an output layer, and inhibiting separation of distribution time of neural populations with different inputs of feedback guarantee memories. The invention further provides a fast memory coding device based on the multi-synaptic plastic spiking neural network. According to the invention, the coding speed and stability of memory are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
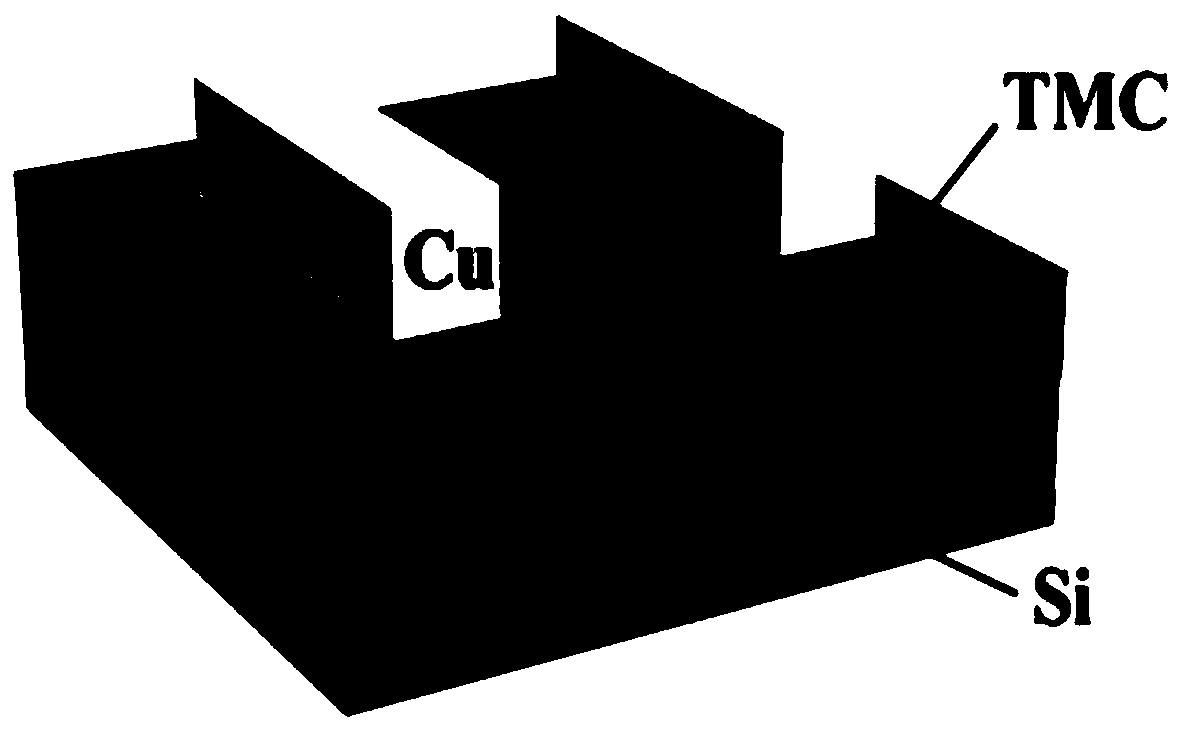
Memristive device based on transition metal carbide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109962162AGood electrical conductivityGood stabilityElectrical apparatusTransition metal carbidesCarbide
The invention provides a memristive device based on transition metal carbide. The memristive device comprises a top electrode, a resistive layer and a bottom electrode which are arranged in order fromtop to bottom, wherein the resistive layer and the bottom electrode match a substrate in shape and size; the resistive layer includes a dielectric layer and a transition metal carbide film disposed over the dielectric layer; the top electrode is sputtered on the top of the transition metal carbide film through the opening of a mask plate; and the top and the bottom of the bottom electrode are incontact with the dielectric layer and the substrate. The memristive device has good conductivity and stability, can simulate the change of synaptic weighting, realizes a function of simulating the synaptic plasticity, and has a broad application prospect. In addition, the preparation method of the invention is simple, efficient, and low in cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for adjusting synaptic plasticity of metal oxide synaptic transistor
ActiveCN111048582AImprove stabilityLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBottom gateActive layer
The invention relates to a method for adjusting the synaptic plasticity of a metal oxide synaptic transistor. The metal oxide synapse transistor is of a bottom gate top contact structure and comprisesa substrate, an insulating layer, an active layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top; after the insulating layer of the metal oxide synaptictransistor is prepared, laser irradiation treatment is conducted; and the synaptic response characteristic of the metal oxide synaptic transistor is adjusted by adjusting laser irradiation parameters.The method is beneficial for quickly and conveniently adjusting the synaptic plasticity of the synaptic transistor at low temperature.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
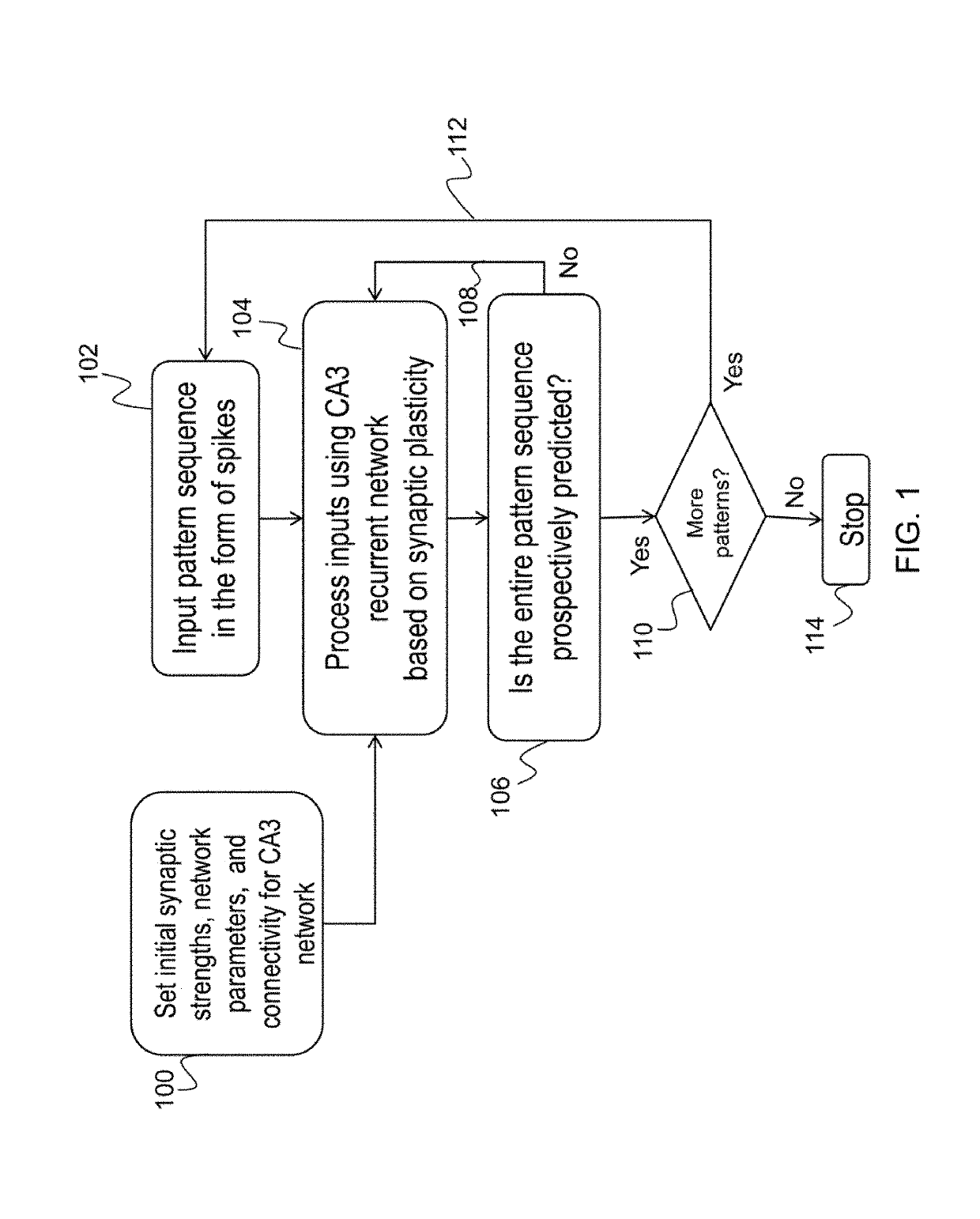
Method and apparatus for learning, prediction, and recall of spatiotemporal patterns
Described is a system for learning, prediction, and recall of spatiotemporal patterns. An input spatiotemporal sequence is learned using a recurrent spiking neural network by first processing the input spatiotemporal sequence using the recurrent spiking neural network. The recurrent spiking neural network comprises neurons having excitatory synaptic connections and inhibitory synaptic connections. Balanced inhibitory connectivity exists between neurons having excitatory synaptic connections. The recurrent spiking neural network uses distinct forms of synaptic plasticity for excitatory synaptic connections and inhibitory synaptic connections, such that excitatory synaptic connections strengthen and inhibitory synaptic connections weaken. In another aspect, the system is able to recall the learned spatiotemporal sequence and predict a future spatiotemporal sequence through activation of the recurrent spiking neural network.
Owner:HRL LAB
Glial-like cell neuromorphic device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109585650AReduce power consumptionHigh degree of bionicElectrical apparatusEtchingSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a glial-like cell neuromorphic device and a preparation method thereof. The device includes an insulating substrate and a bottom electrode, a resistive layer, a dielectric layer and a top electrode located on the substrate. The bottom electrode is located on the insulating substrate, the dielectric layer is located on the bottom electrode, a hole structure is subjected to graphic etching in the dielectric layer, and the bottom portion of the hole is exposed out of the bottom electrode; the resistive layer covers the bottom portion and the side wall of the hole and coatsthe dielectric layer around the hole; the top electrode is located on the resistive layer; the resistive layer and the dielectric layer are semiconductor materials, the ionic mobility or the ionic concentration in the resistive layer is different from that of the dielectric layer, and the thickness of the dielectric layer is larger than that of the resistive layer. The voltage is applied to the top electrode and the bottom electrode to change the electric field intensity distribution in the dielectric layer and the resistive layer and generate interaction of ions of the dielectric layer and the resistive layer so as to influence the formation and fusing kinetics of conductive fine wires in the resistive layer and effectively simulate the influence of synaptic surroundings on synaptic plasticity.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
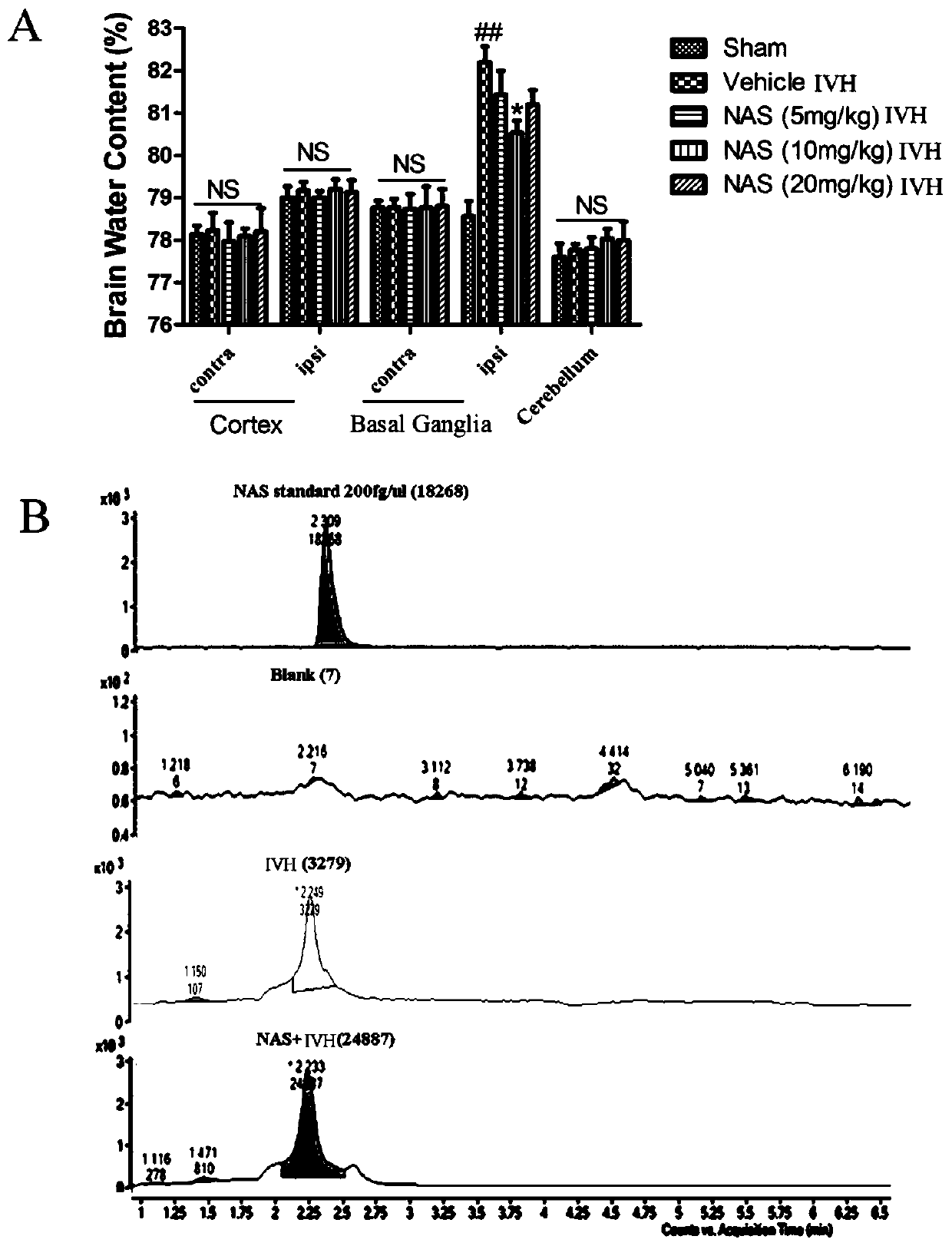
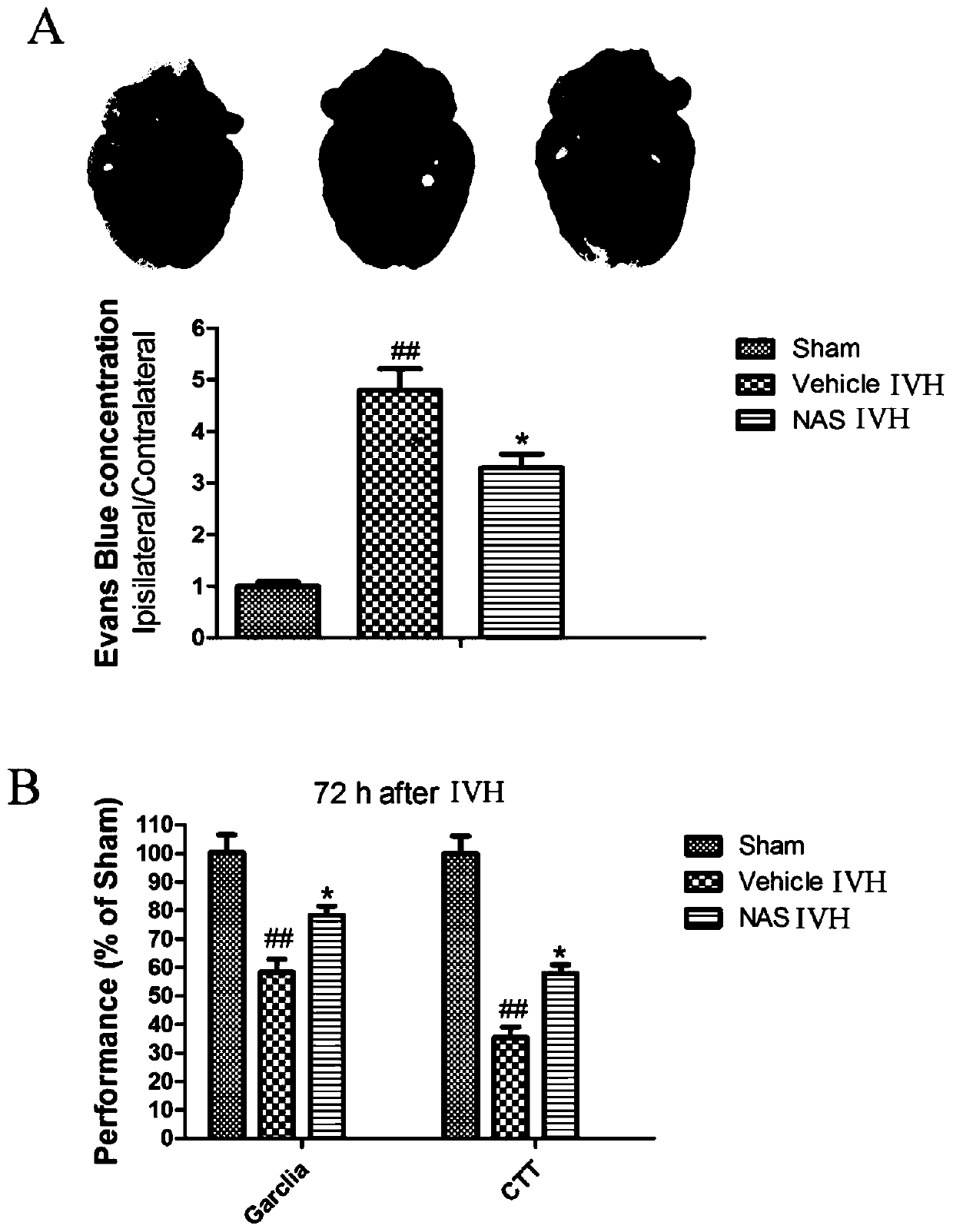
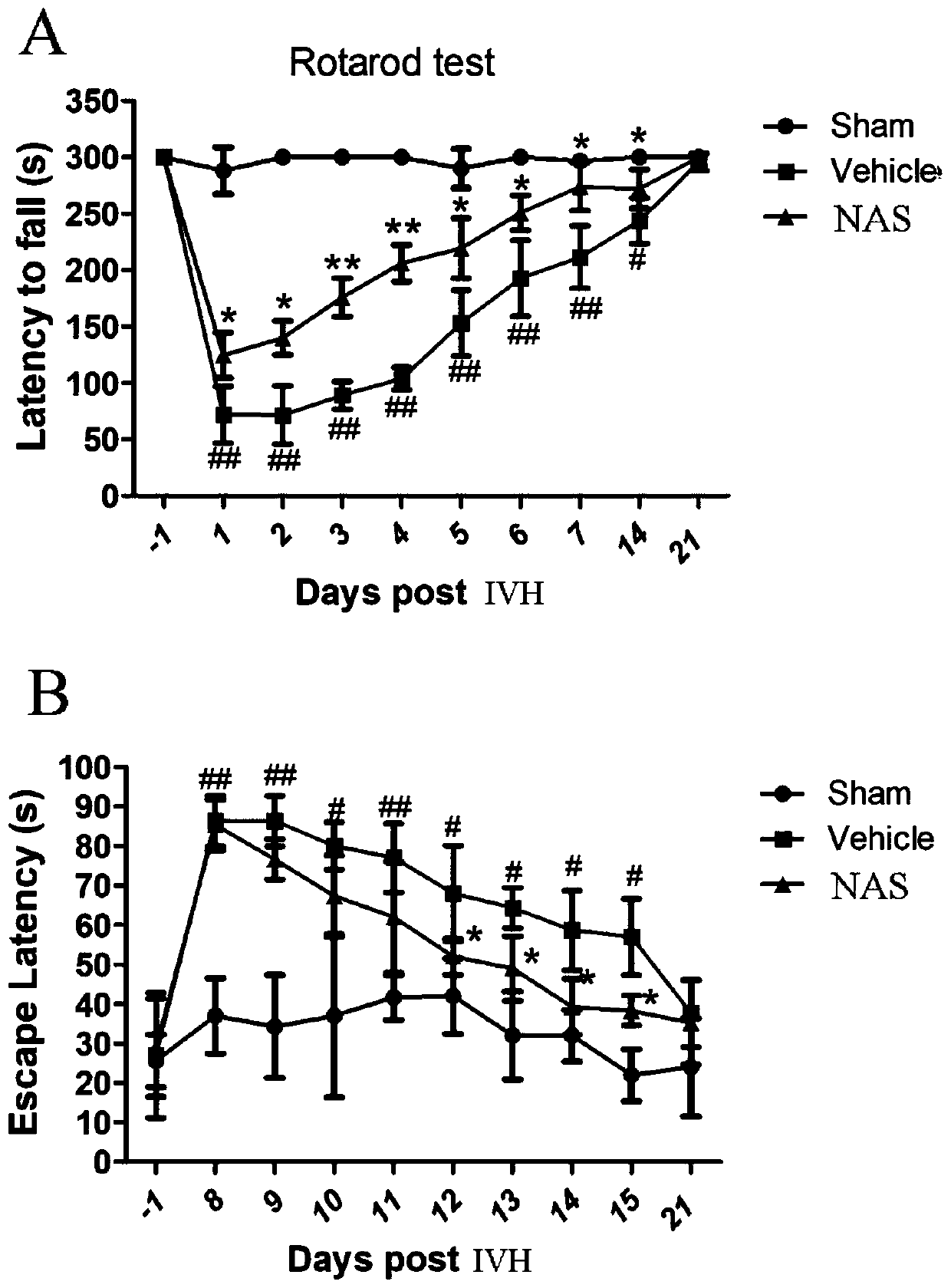
Application of N-acetylserotonin in preparation of drug for treating intraventricular hemorrhage
InactiveCN111374973AReduce oxidative stressImproves oxidative stressOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSerotoninCerebral ventricular
The invention discloses application of N-acetylserotonin in preparation of a drug for treating intraventricular hemorrhage and belongs to the technical field of biomedicines. The invention discloses and proves that the N-acetylserotonin can relieve cerebral edema and blood brain barrier destruction caused by the intraventricular hemorrhage; it is discovered that the N-acetylserotonin has an improvement effect on sports and learning memory disorder induced by the intraventricular hemorrhage; it is disclosed that a protection effect of the N-acetylserotonin is related to relief of oxidative stress, inhibition of ferroptosis and improvement on synaptic plasticity; and in addition, in a primary cortex neuron haemorrhage cell model, it is proven that the NAS can obviously inhibit neuron death induced by Hemin and relieve axon injury. According to the application, a scientific basis is provided for utilizing the N-acetylserotonin to treat the intraventricular hemorrhage as a novel drug.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
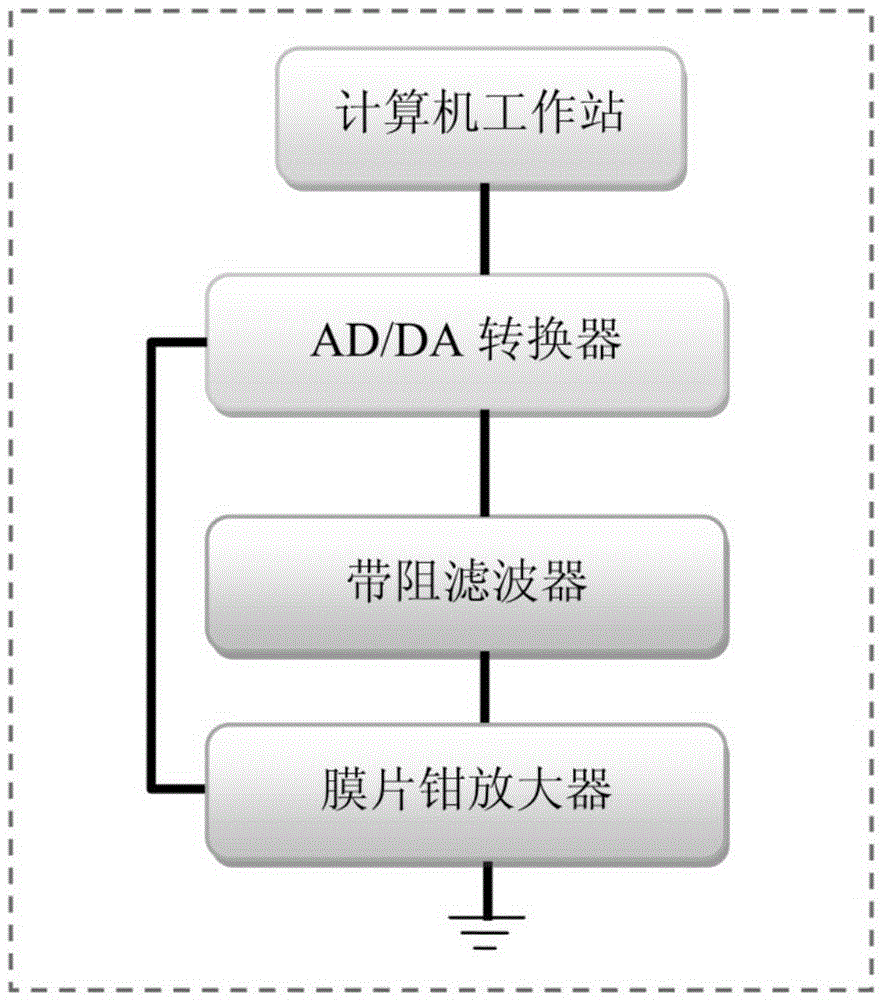
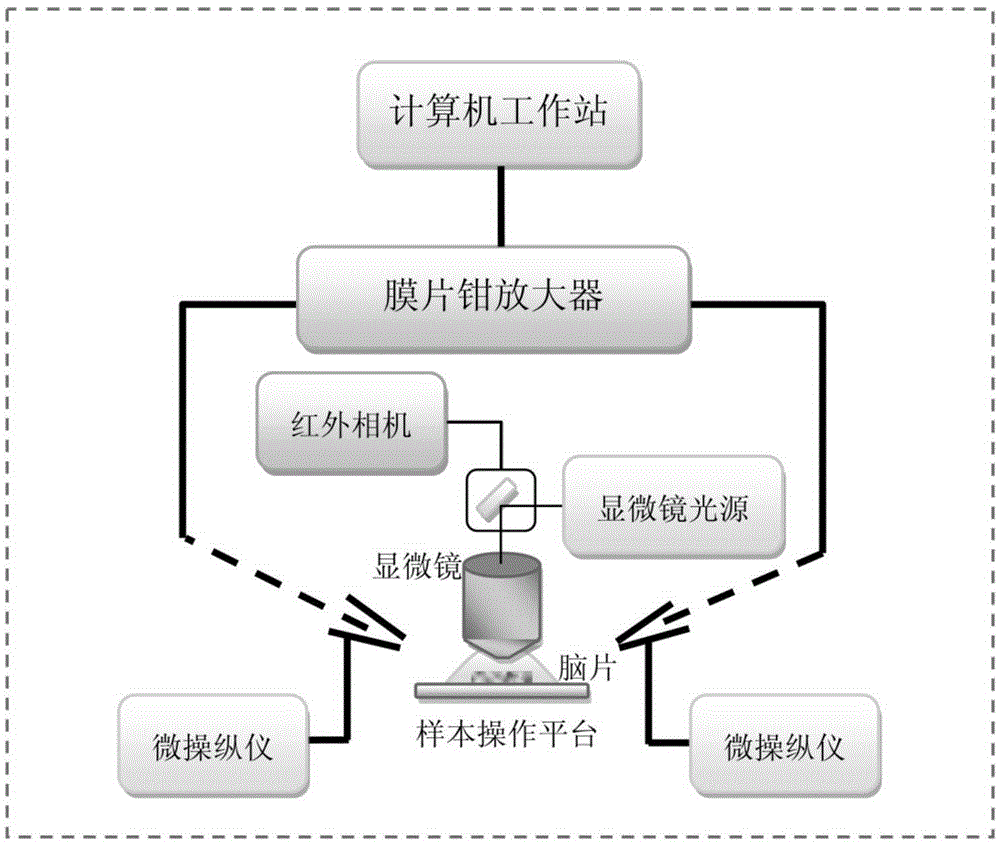
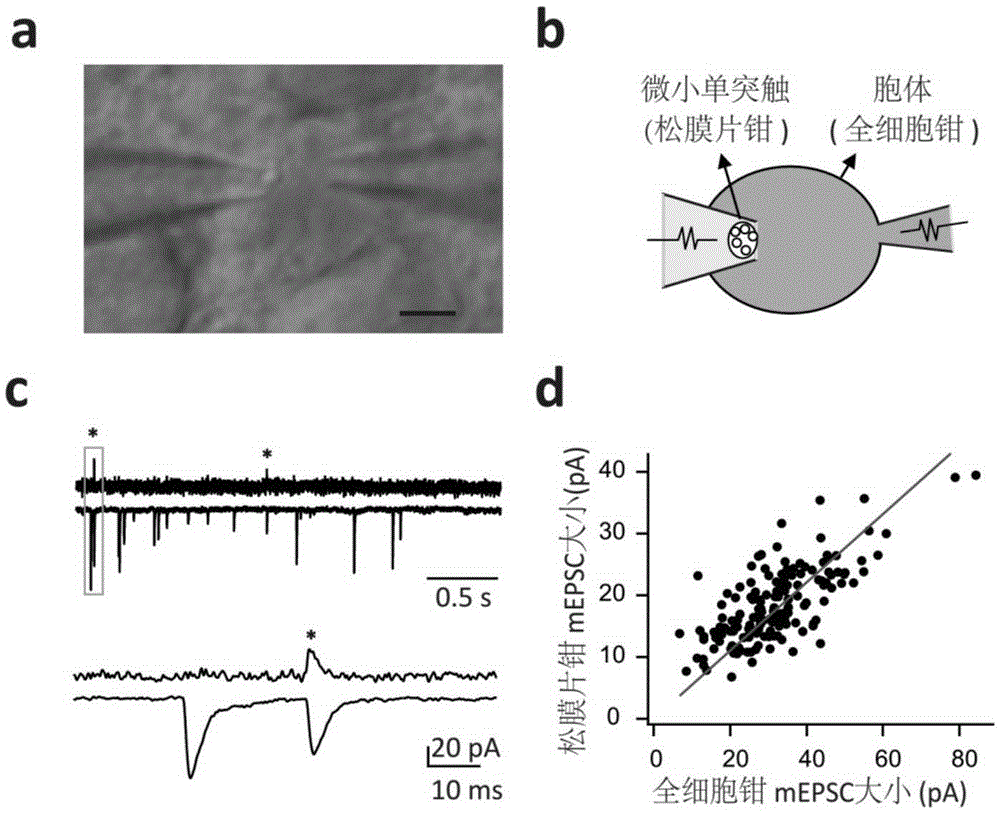
Electrical activity recording method for tiny single synaptic neurons
The invention discloses an electrical activity recording method for tiny single synaptic neurons and belongs to the field of neurobiology research. Based on the conventional patch clamp technique, electrical signals input through all tiny presynaptic neurons can only be recorded through postsynaptic neurons, while electrical signals input by each tiny presynaptic neuron cannot be recognized. In this way, the invention provides the above method. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the loose-patch clamp technique and the whole-cell patch clamp technique are integrated, and the electrical activity of each tiny single synapsis can be recorded simply on a brain slice in the physiological state. Therefore, based on the method, the dynamic characteristics of the vesicle spontaneous release and the vesicle induced release of the single synapsis can be detected. The method provides a direct, quantitative, real-time and high-time-resolution detection method for the dynamic characteristics of the vesicle release of the single synapsis and the synaptic plasticity.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
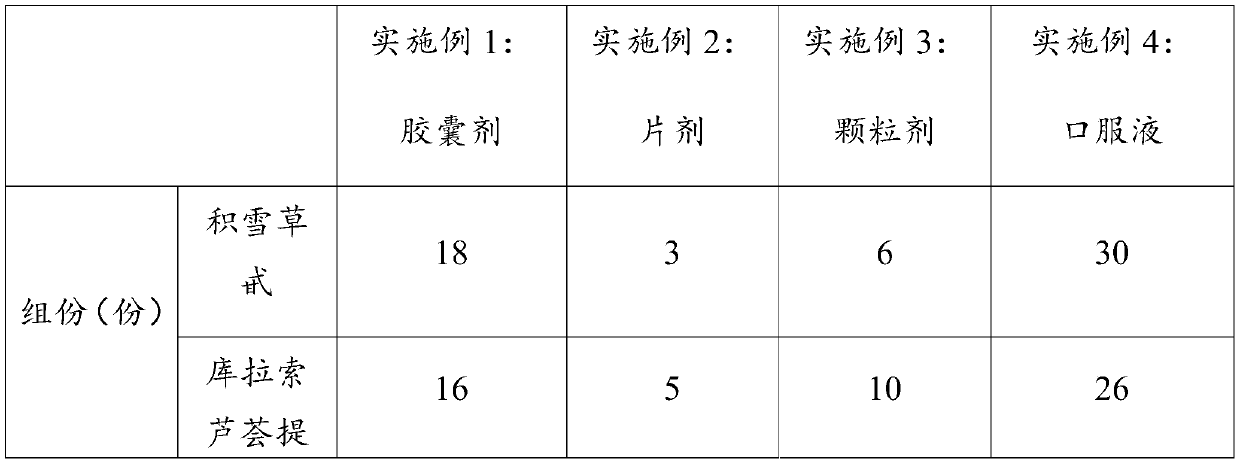
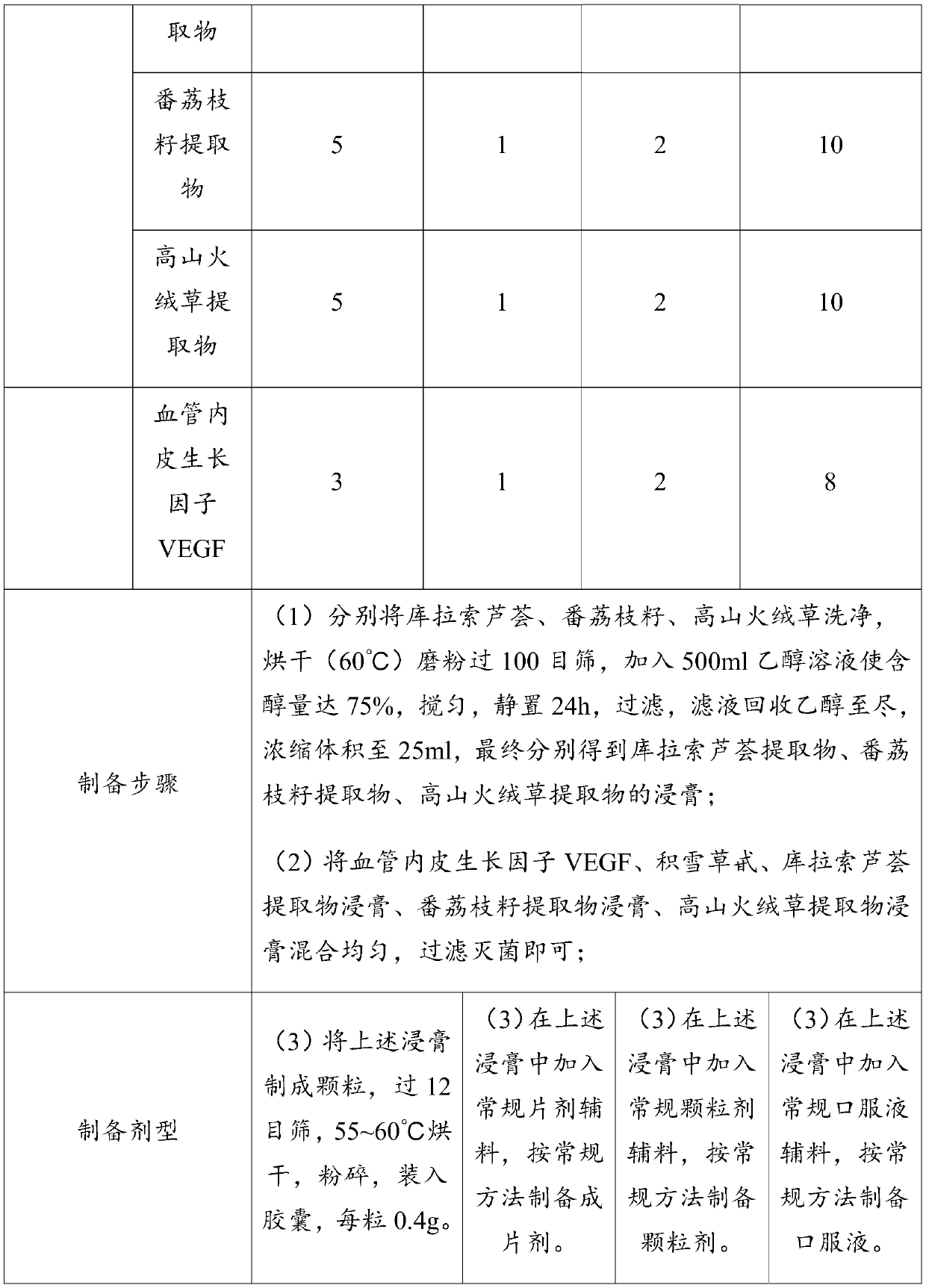
Pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing nerve damage
ActiveCN110075274AEasy to passFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMuscle strengthLeontopodium alpinum extract
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating or preventing nerve damage. The pharmaceutical composition comprises the following components: asiaticoside, an Aloe vera extract, a sweetsop seed extract, a leontopodium alpinum extract, and a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The pharmaceutical composition of the invention is useful for inducing neurite outgrowth, for promoting stem cell function, and / or for promoting functional recovery and enhancing synapse formation and synaptic plasticity in damaged and / or injured neurons in acute and chronic injury, and can significantly alleviate impaired sciatic nerve function, increase nerve conduction velocity, increase axon count, and repair axons. Clinical studies show that the pharmaceutical composition of the inventioncan improve muscle strength, accelerate repair of damaged nerve tissue, and improve nerve tissue transmission and metabolic disorders in patients with peripheral nerve injury.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV +1
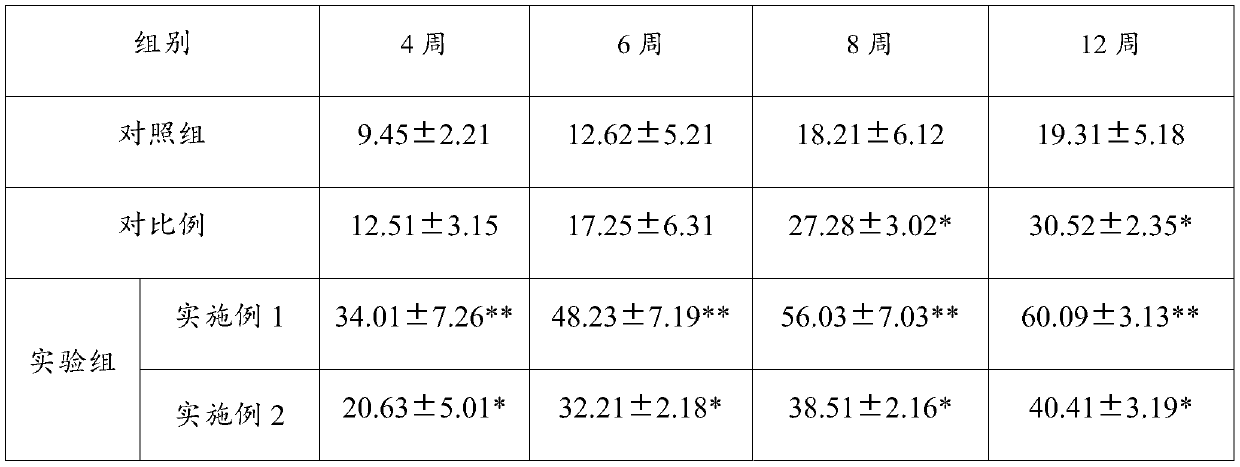
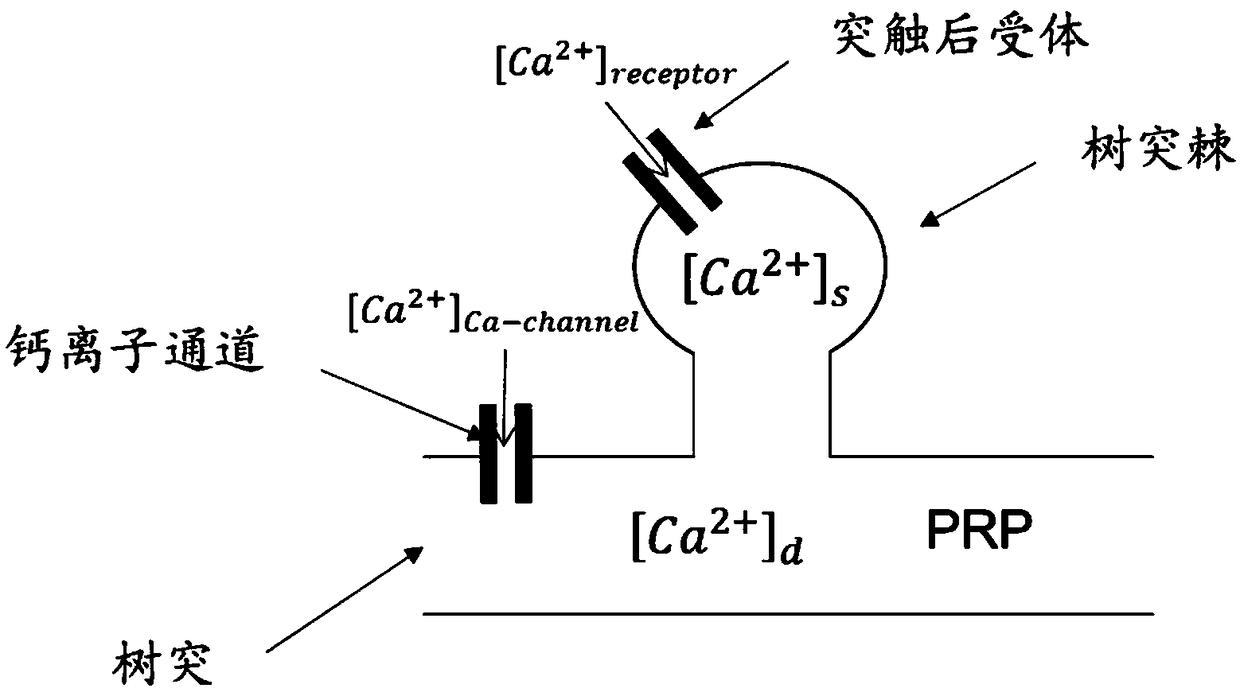
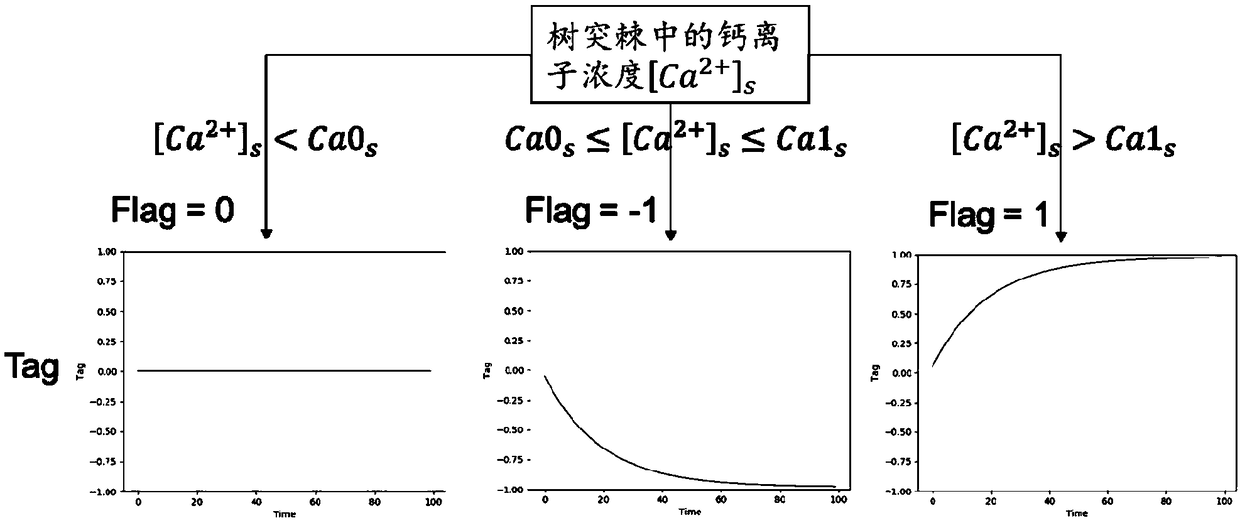
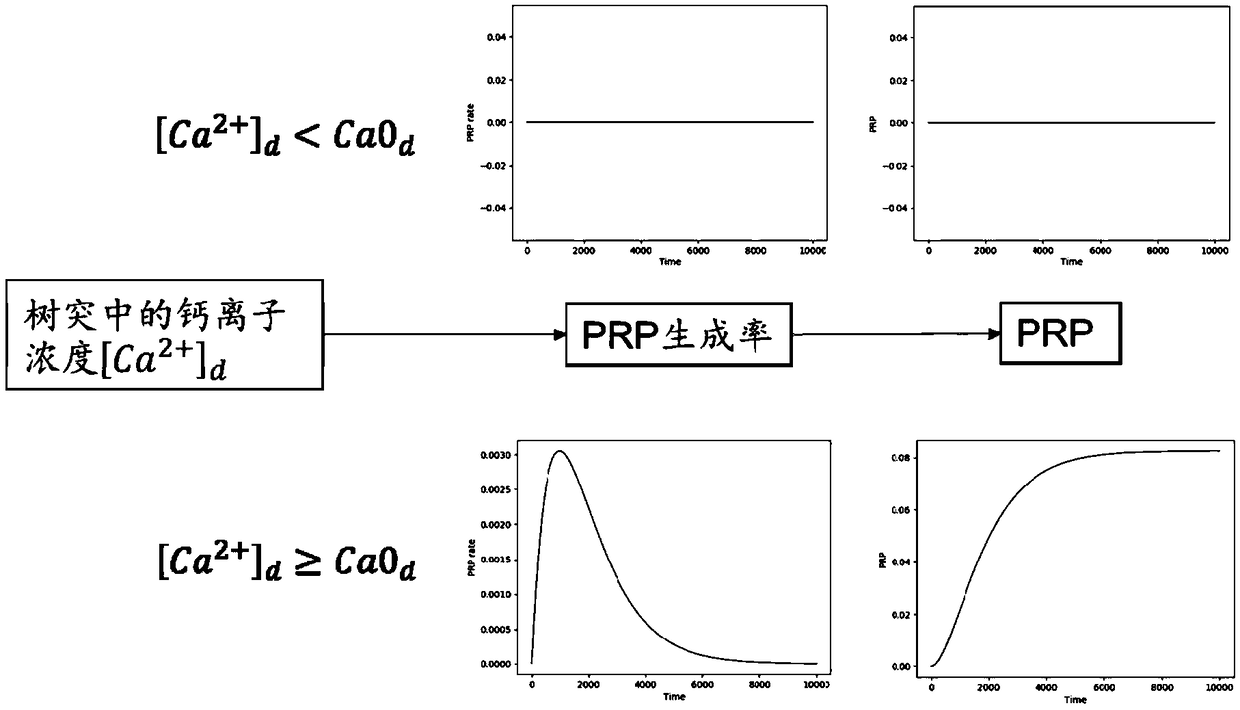
Calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration
The invention relates to a calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration, which relates to the field of brain simulation, in particular to the calculation problem ofneural synaptic plasticity of impulse neural network in brain simulation. The first is the calculation of calcium ion concentration. According to the membrane potential values of presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic neurons at the initial time t0 and the initial connecting weight w0 of synapses, the calcium ion concentrations in dendrites and spines at the next time t1 are calculated respectivelyfor the synapses that need to be calculated. Secondly, according to the calcium ion concentration in dendritic spine, the direction of weight change was obtained by comparing with the calcium ion concentration threshold Ca0s and Ca1s. According to the synaptic state tag Tag and the plasticity related protein PRP concentration, the change of synaptic weight was calculated, and the new weight at time t1 was obtained. the above procedure is repeated to calculate the strength of synaptic connections within the simulation time. The method of the invention is applied to constructing a brain-like neural network, completing the simulation of the learning and memory process required by the brain-like intelligence, realizing the universal strong artificial intelligence, and is applied to intelligentmedia, medical treatment and the like.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Neurotrophic peptides
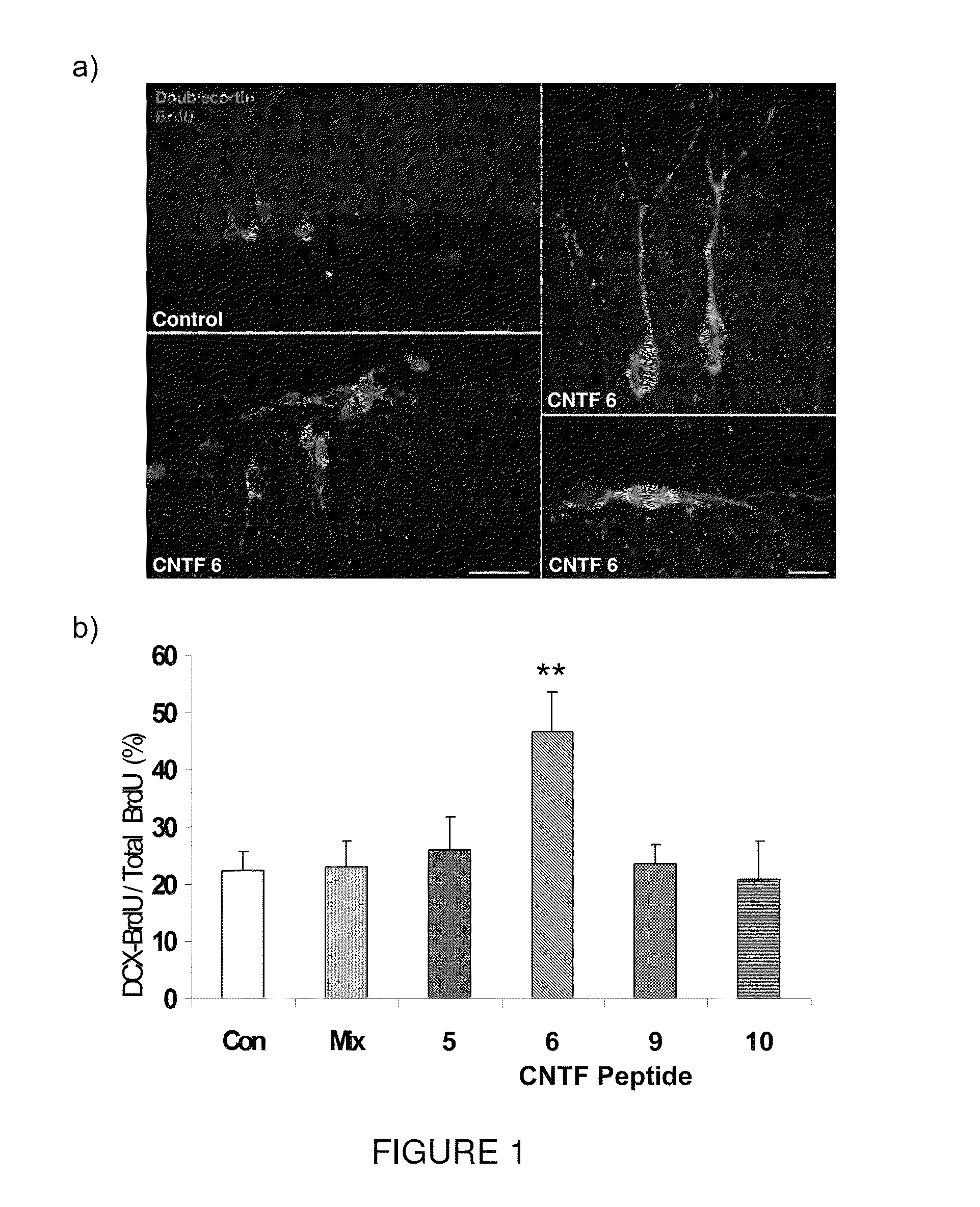
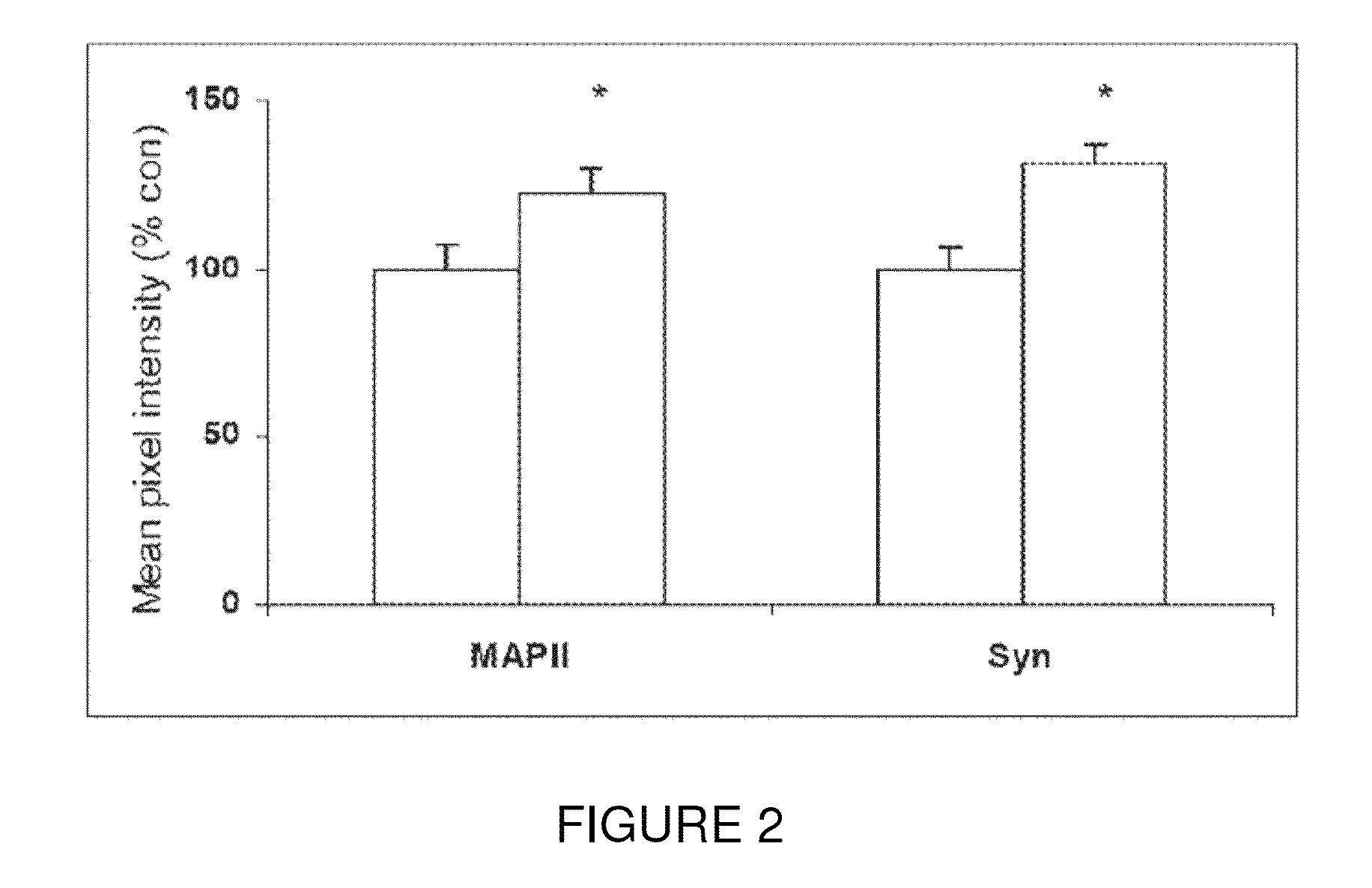
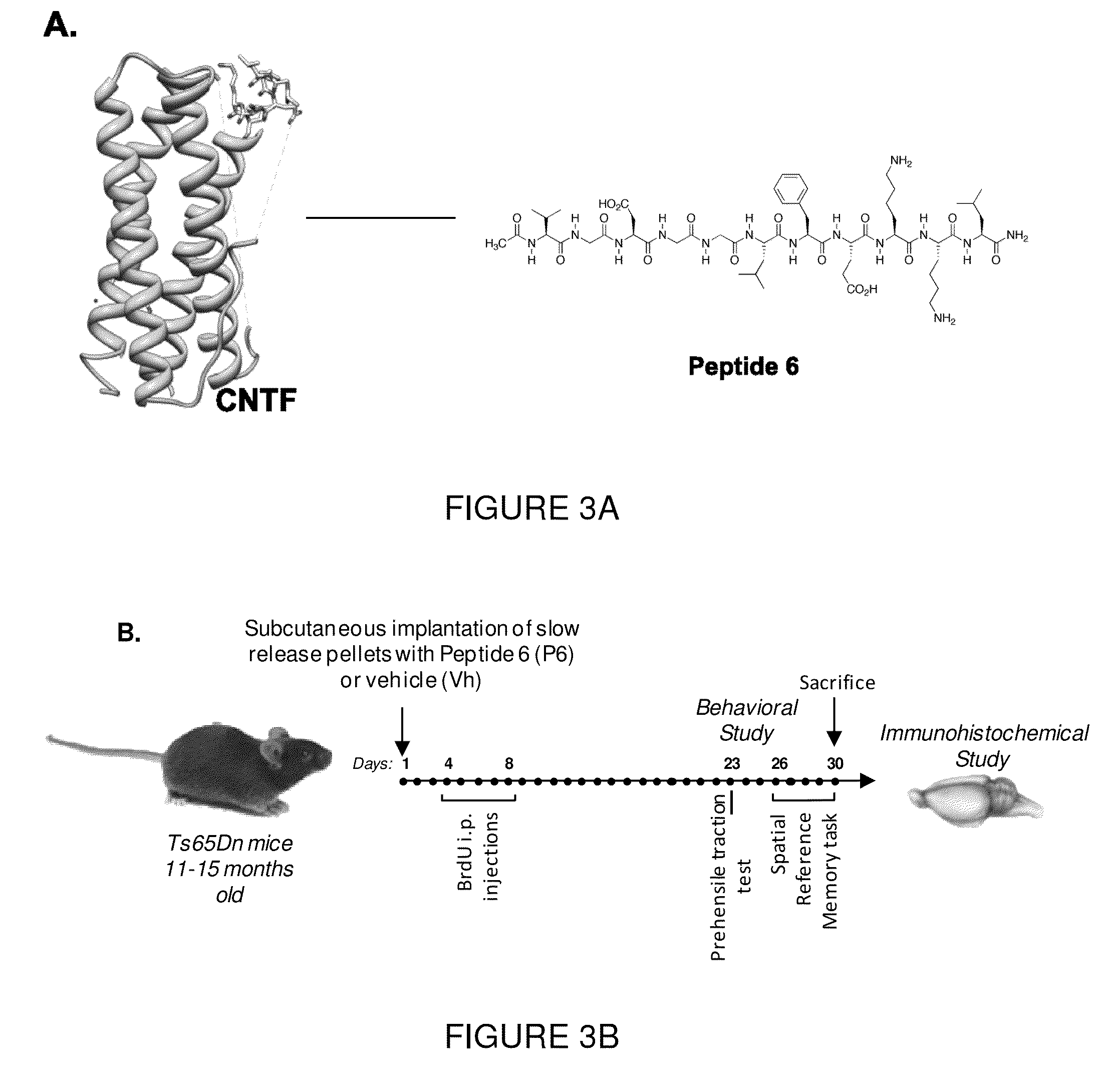
The present invention relates to a neurotrophic peptide having an amino acid sequence of VGDGGLFEKKL (SEQ ID NO:1) and alternatively comprising an adamantyl group at the C- and / or N-terminal end. The neurotrophic peptide can rescue cognition, correct impairments in neural cell proliferation and synaptic plasticity, and thus address the cognitive defects associated with Down syndrome.
Owner:RES FOUDATION FOR MENTAL HYGIENE INC
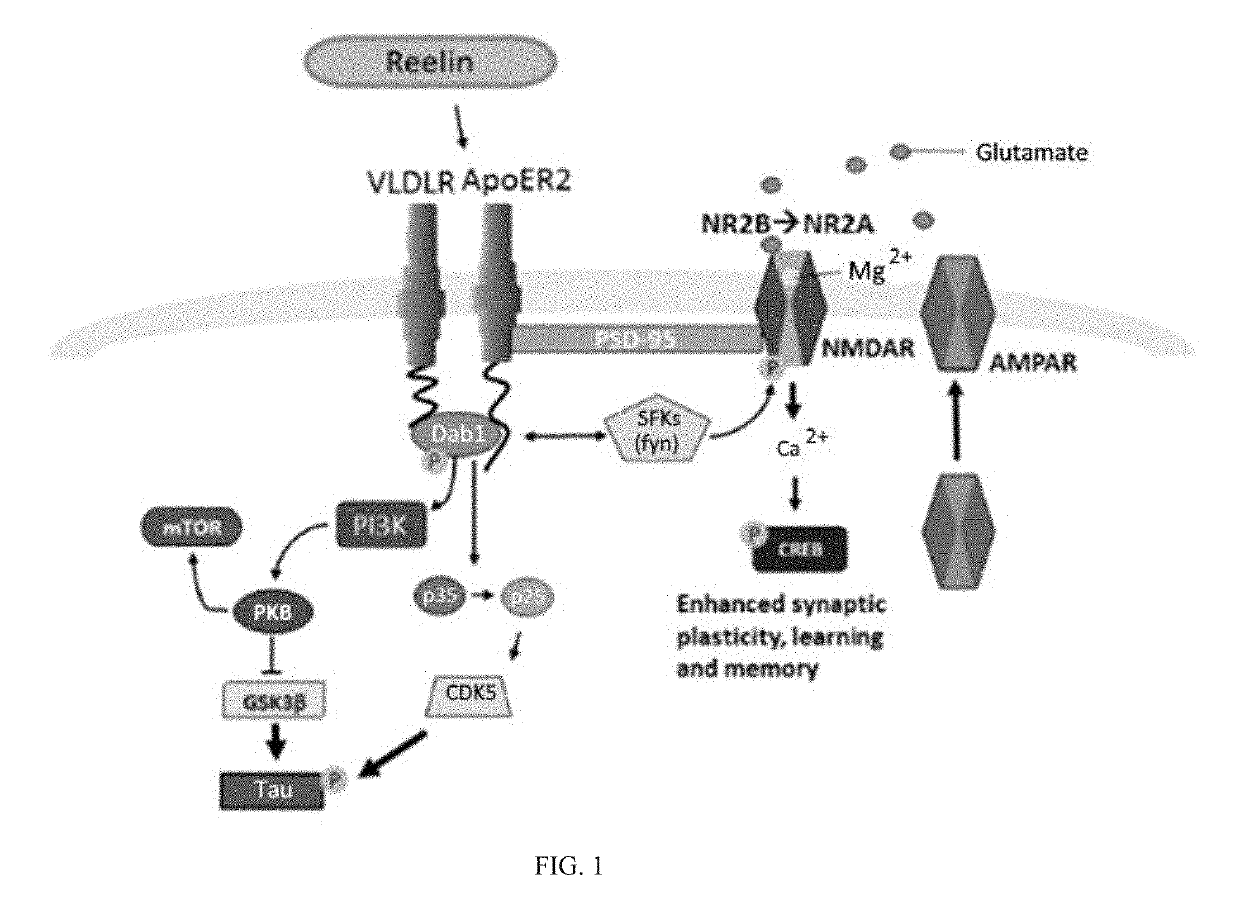
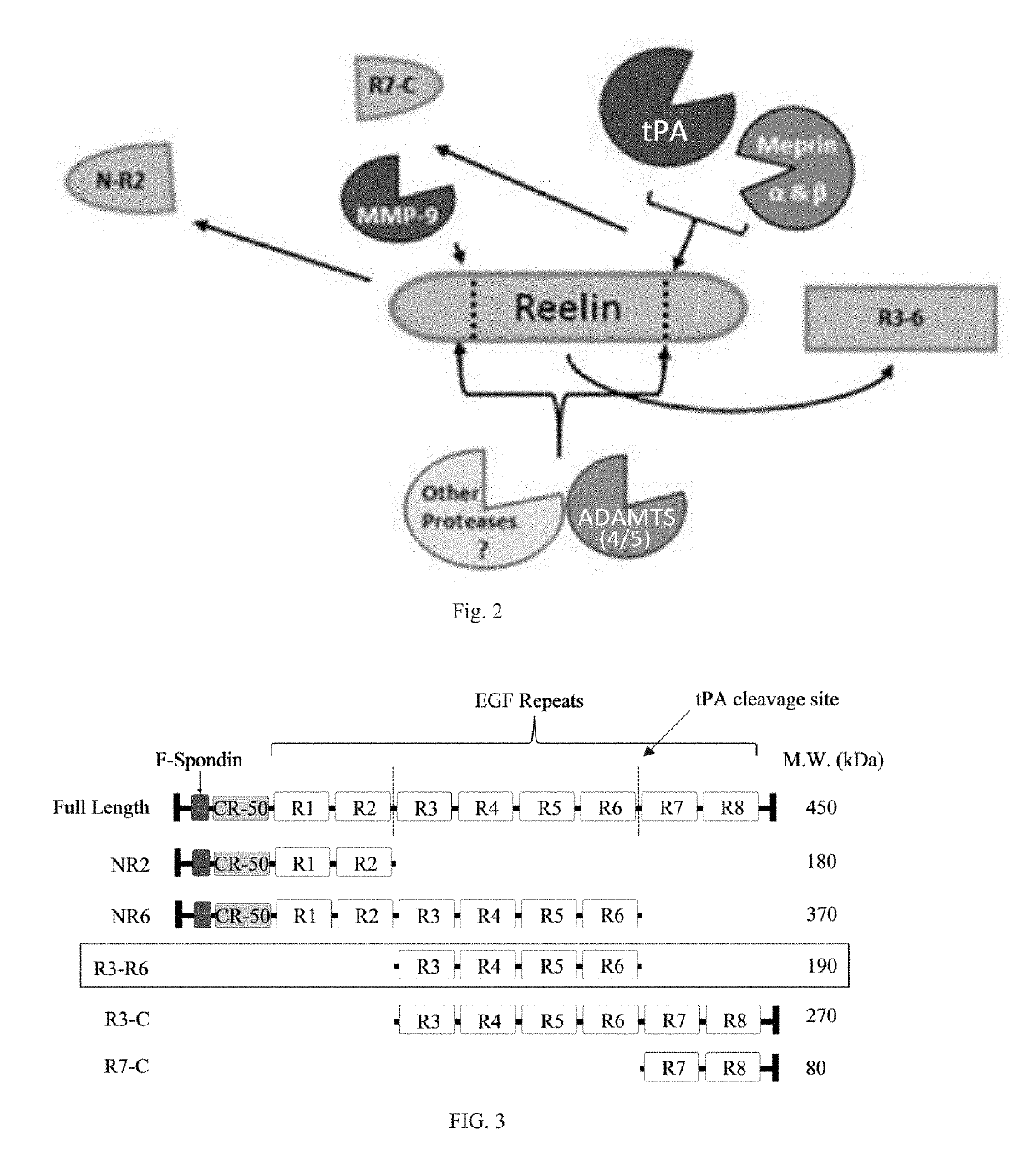
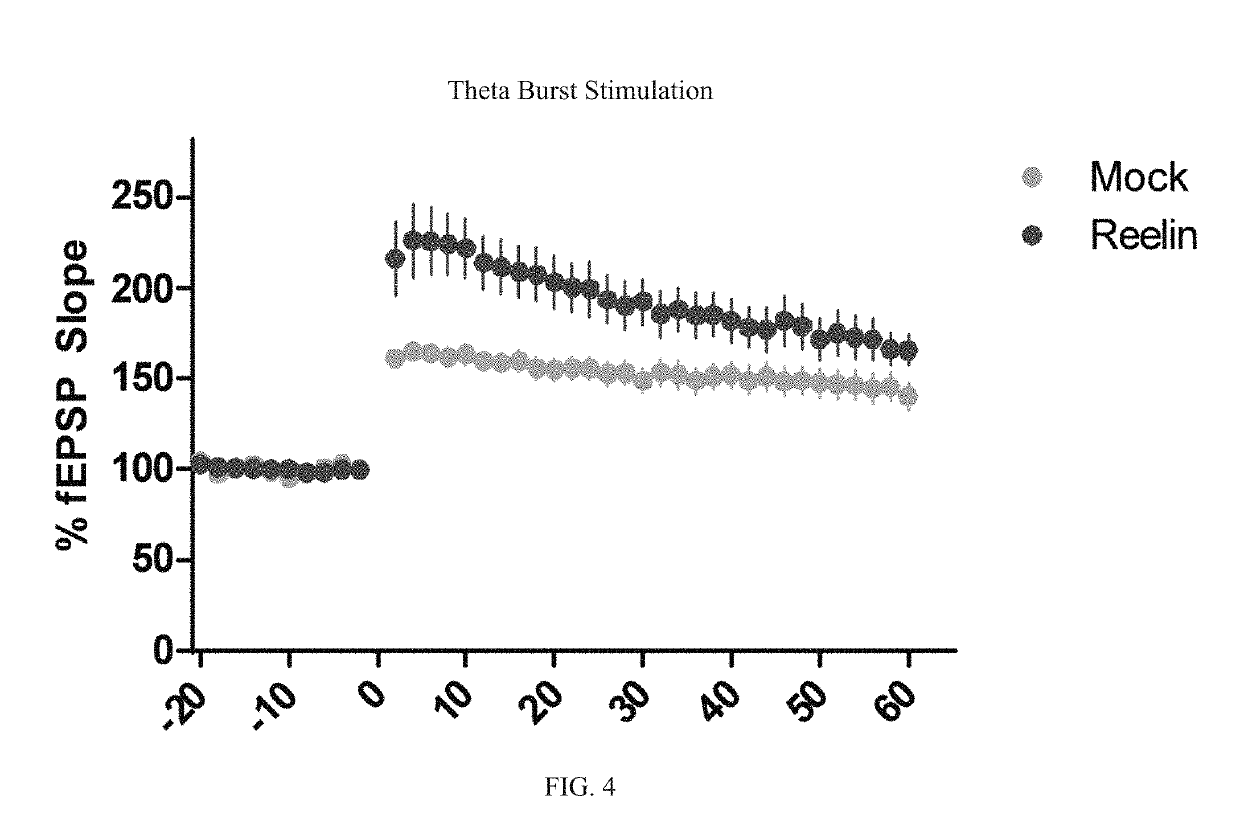
Reelin compositions for treatment of neurological disorders
PendingUS20190169246A1Improve plasticityImprove cognitive functionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFragile X chromosomeReelin
Changes in Reelin levels as well as Reelin signaling alter cognitive function. This can be accomplished by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a repeat fragment of Reelin, or a construct formed from fragment repeats of Reelin to a patient or subject. Changes to Reelin levels can be used to treat various neurodegenerative diseases, neuronal insults, or stroke, such as fragile X syndrome, William's syndrome, Rett syndrome, Down's syndrome, Angelman syndrome, autism, ischemia, hypoxia, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. Reelin can also be used to alter dendritic spine density, diminished long-term potentiation, and diminished synaptic plasticity and associative learning deficits. Constructs formed from repeat region 3 of full length Reelin and repeat region 5 of full length Reelin, or repeat region 3 of full length Reelin and repeat region 6 of full length Reelin have been found particularly useful.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
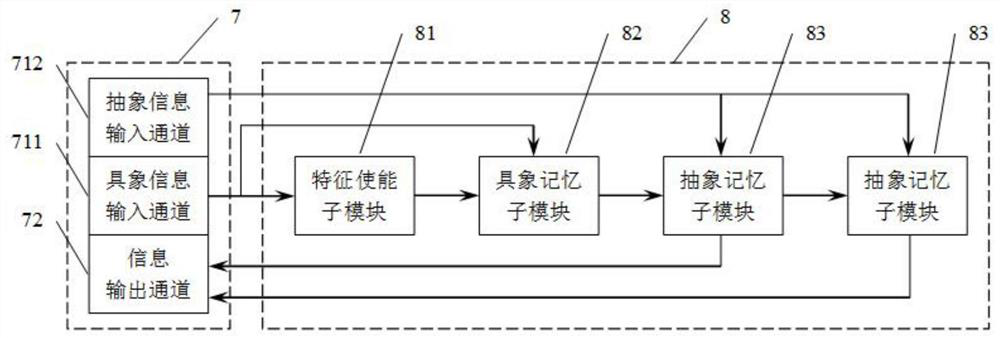
Brain-like neural network with memory and information abstraction functions
PendingCN113688981AEasy to analyzeEasy to debugNeural architecturesPhysical realisationHippocampal regionSynaptic plasticity
The invention discloses a brain-like neural network with memory and information abstraction functions, the brain-like neural network uses working principles of a hippocampus region and a plurality of peripheral brain regions of a biological brain for reference, and the brain-like neural network comprises a memory module capable of forming scene memory, so that an intelligent agent can efficiently identify an object and carry out space navigation, reasoning and autonomous decision making. Features of each object can be quickly remembered, abstraction and meta-learning can be performed, generalization ability is high, lifelong learning can be performed, a synaptic plasticity process is adopted to adjust weights, partial differential operation is avoided, calculation overhead is lower than that of traditional deep learning, and a basis is provided for design and application of a neural mimicry chip.
Owner:NEUROCEAN TECH INC
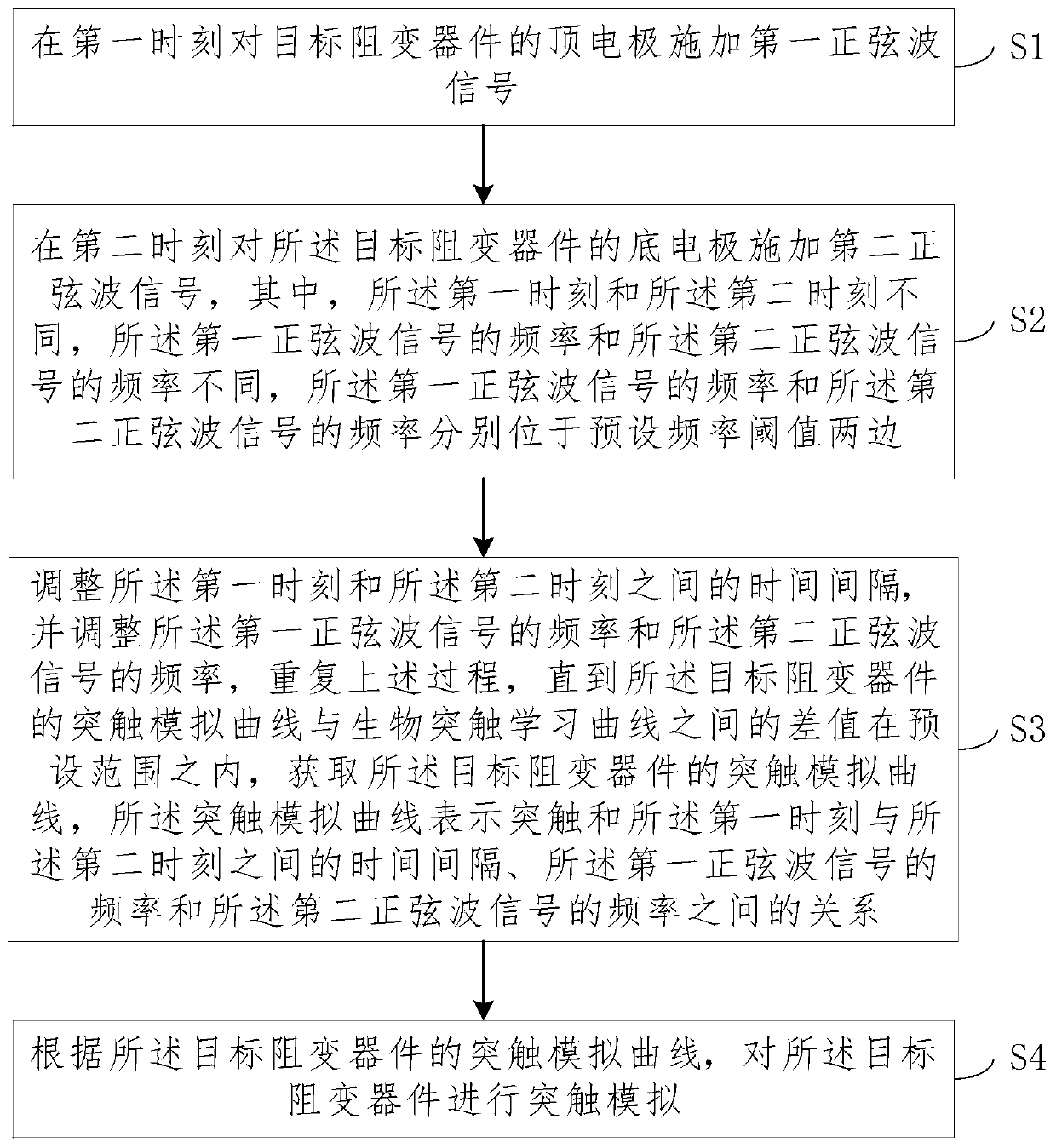
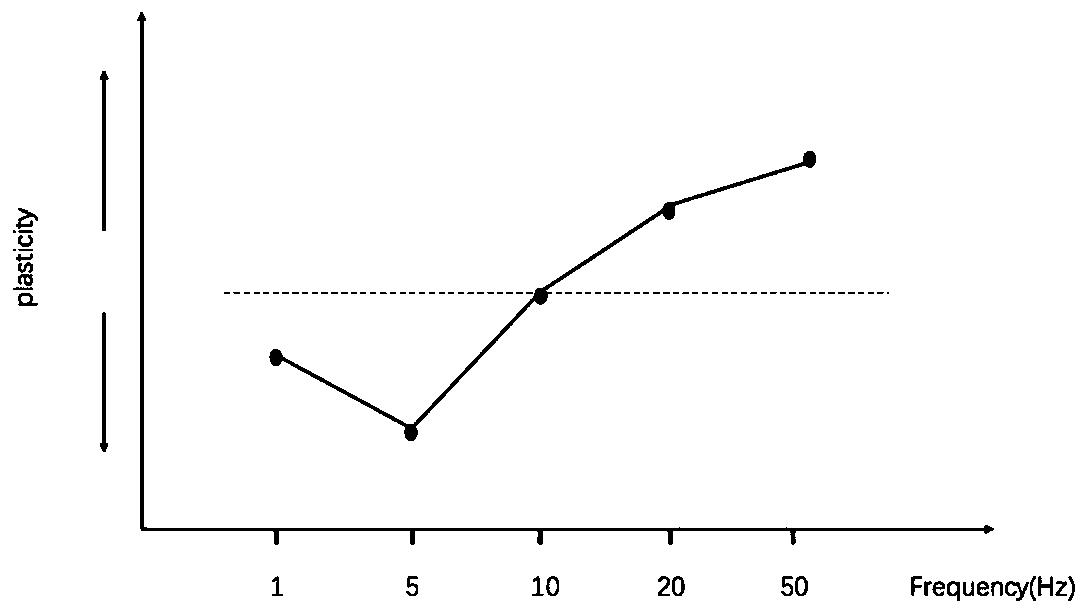
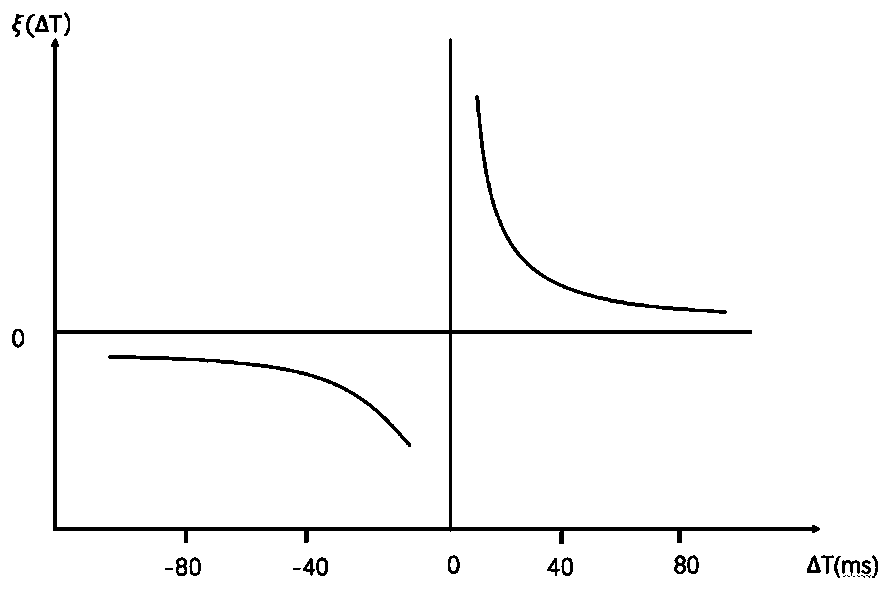
Synapse simulation method and system for resistive random access memory
The embodiment of the invention provides a synapse simulation method and system for a resistive random access memory. The method comprises the following steps: applying a first sine wave signal to a top electrode of a target resistive random access memory at a first moment; applying a second sine wave signal to the bottom electrode of the target resistive random access memory at a second moment; adjusting the time interval between the first moment and the second moment, adjusting the frequency of the first sine wave signal and the frequency of the second sine wave signal, and obtaining a synaptic simulation curve of the target resistive random access memory; and performing synapse simulation on the target resistive device according to the synapse simulation curve of the target resistive device. According to the synapse simulation method and system for the resistive random access memory, synapse plasticity of the resistive random access memory can be tested, the change relation betweenthe synapse of the resistive random access memory and the two aspects of time and frequency is obtained, and therefore when the resistive random access memory is used, the resistive random access memory can better simulate the synapse.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com