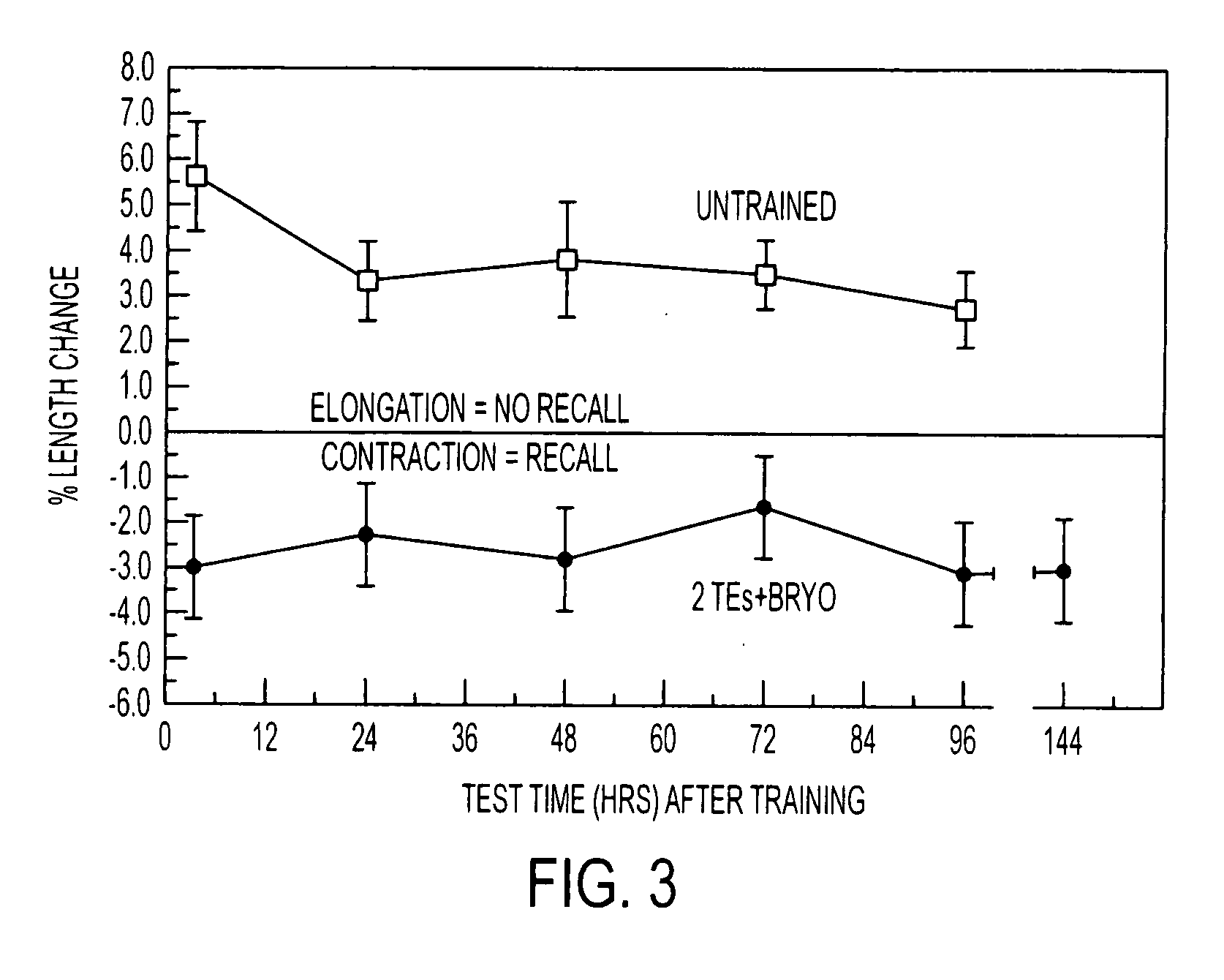
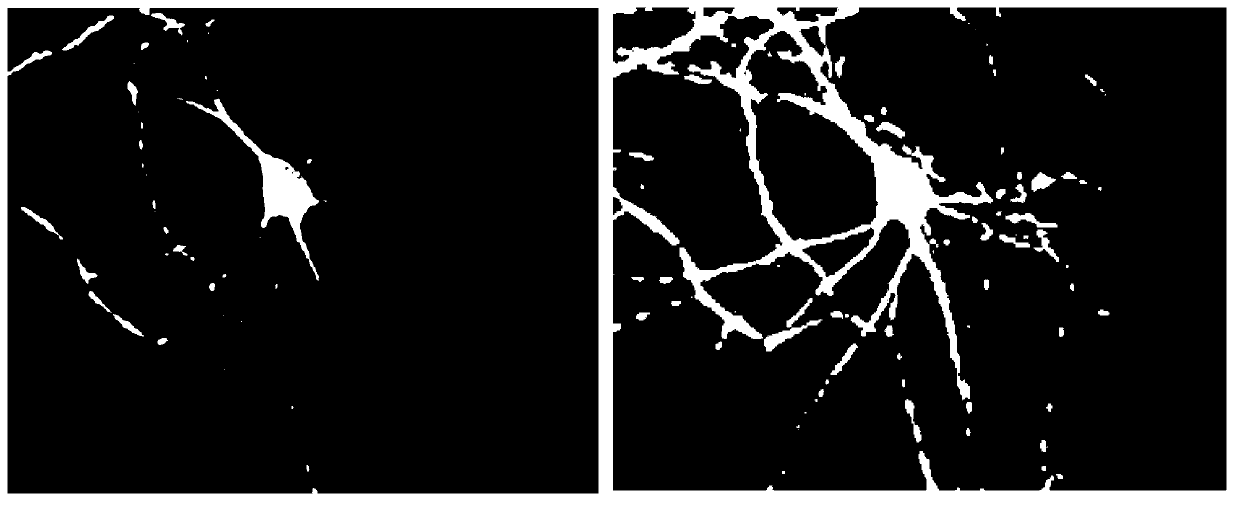
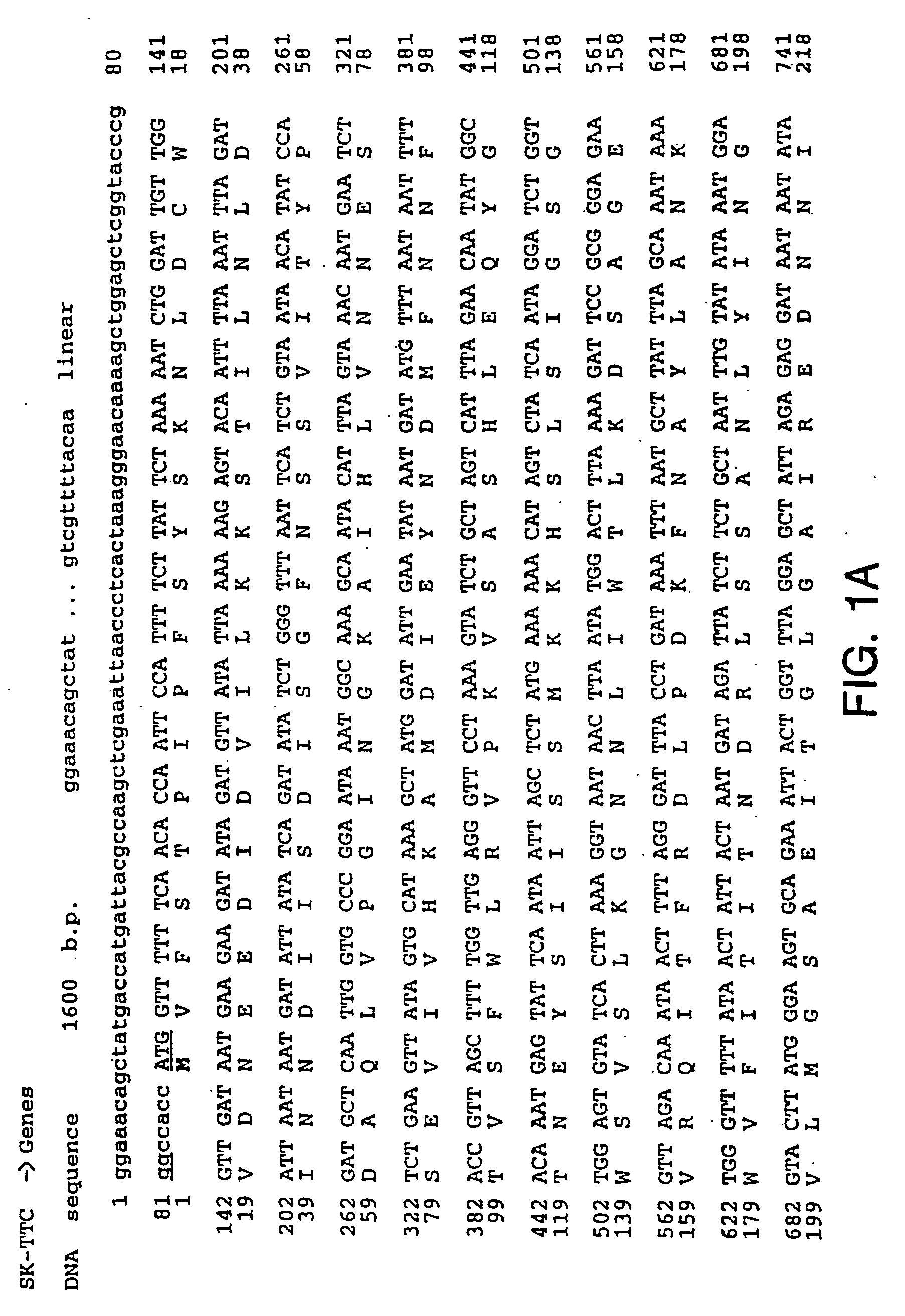
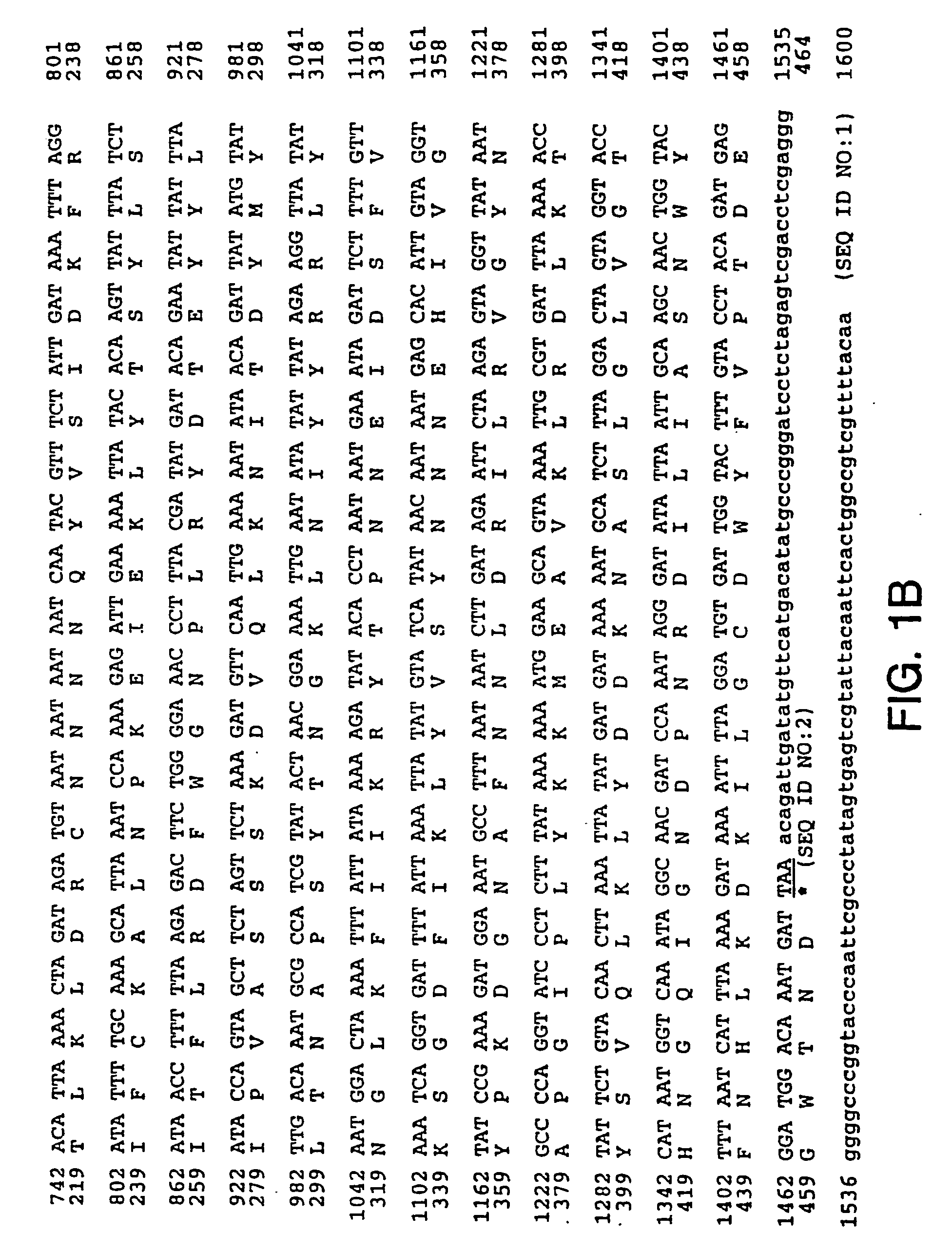
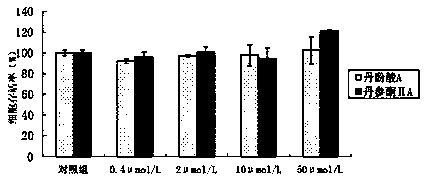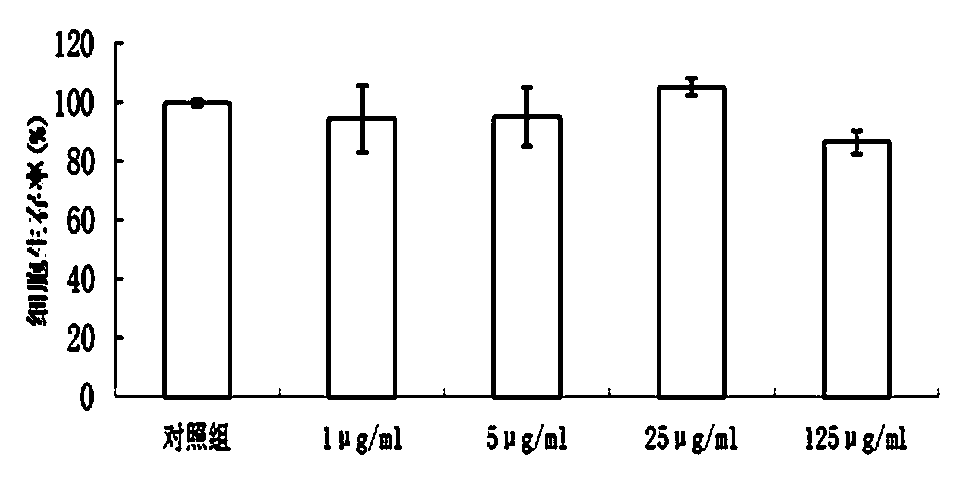Patents
Literature
45 results about "Dendritic spine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
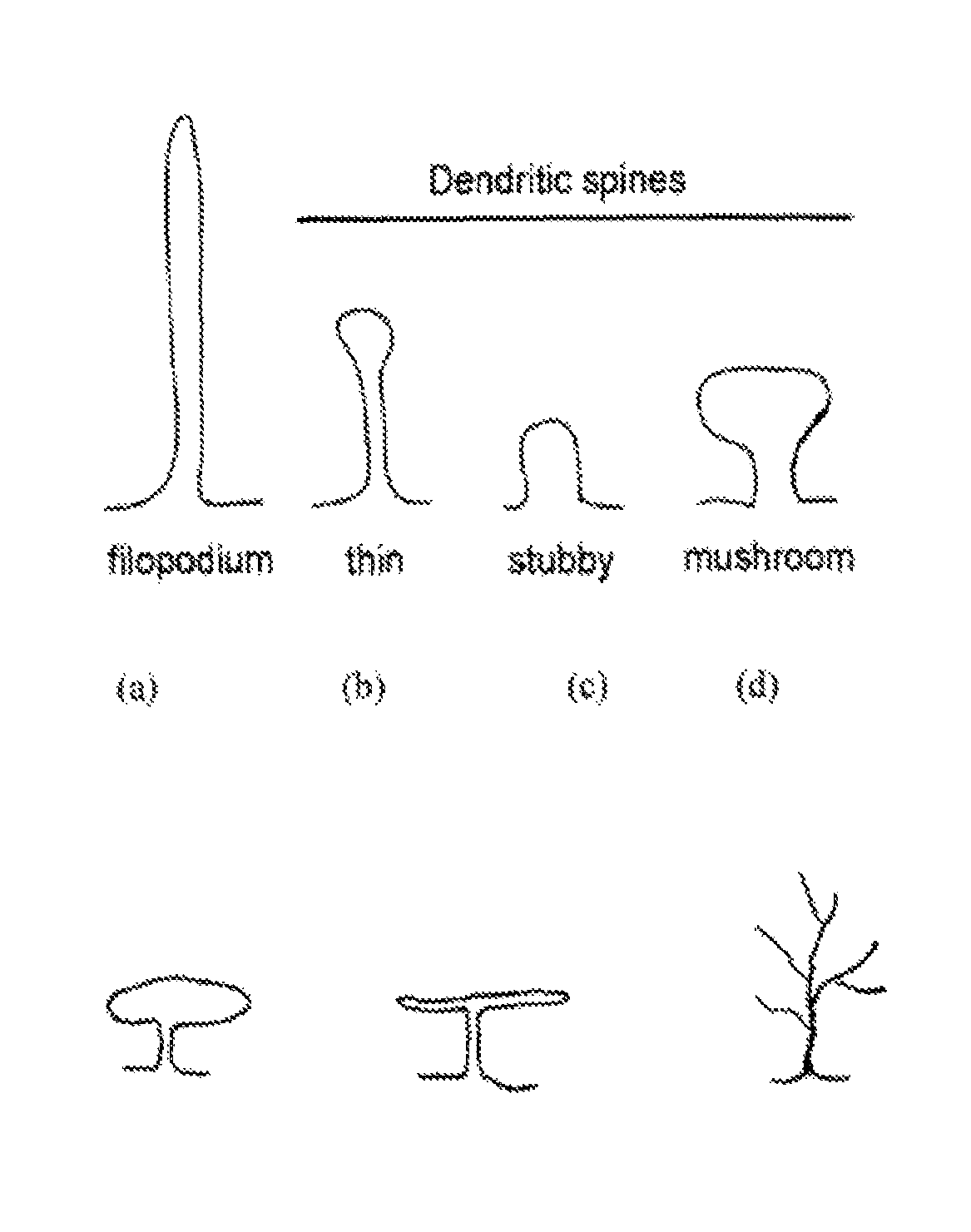
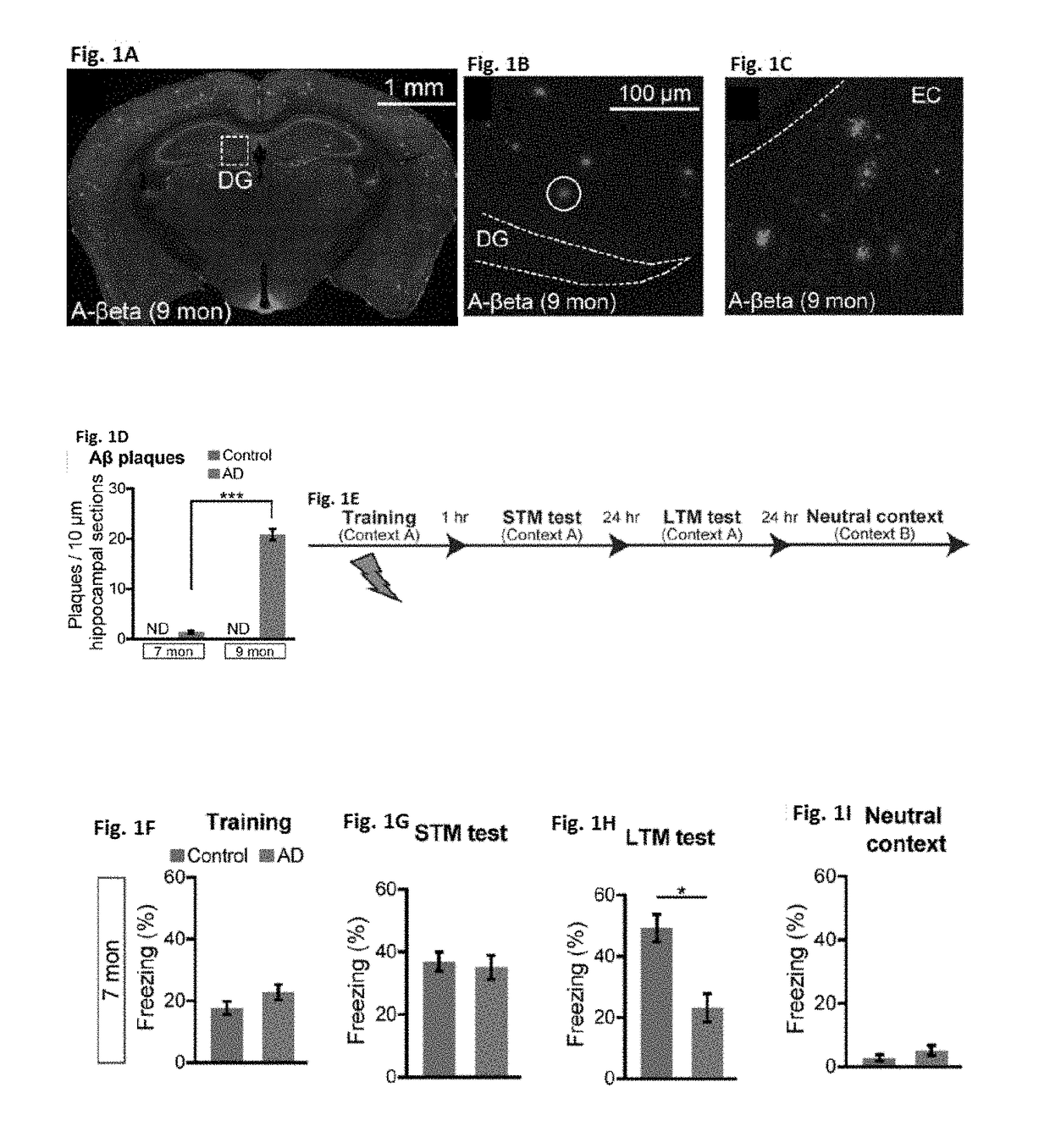
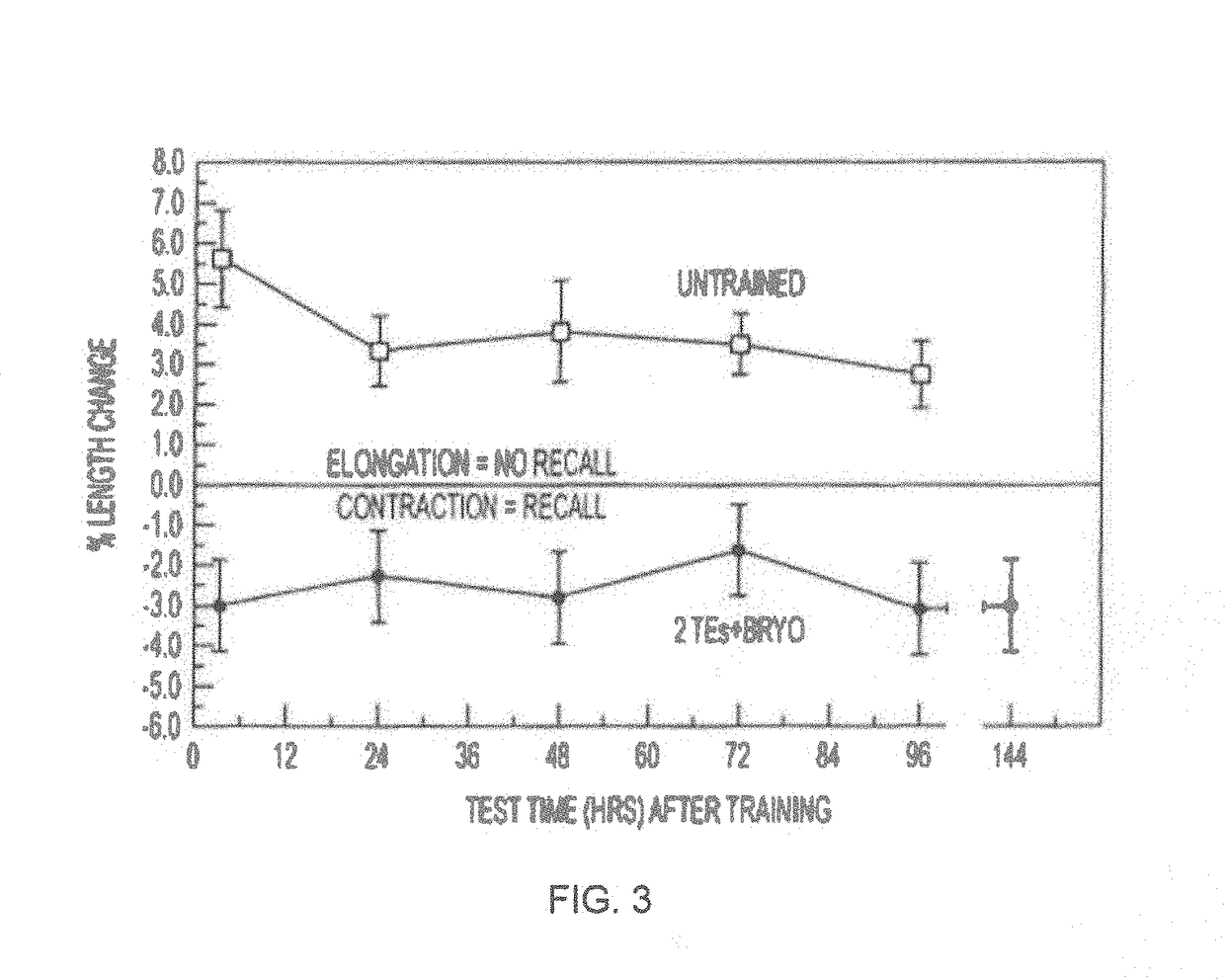
A dendritic spine (or spine) is a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single axon at the synapse. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body. Most spines have a bulbous head (the spine head), and a thin neck that connects the head of the spine to the shaft of the dendrite. The dendrites of a single neuron can contain hundreds to thousands of spines. In addition to spines providing an anatomical substrate for memory storage and synaptic transmission, they may also serve to increase the number of possible contacts between neurons.
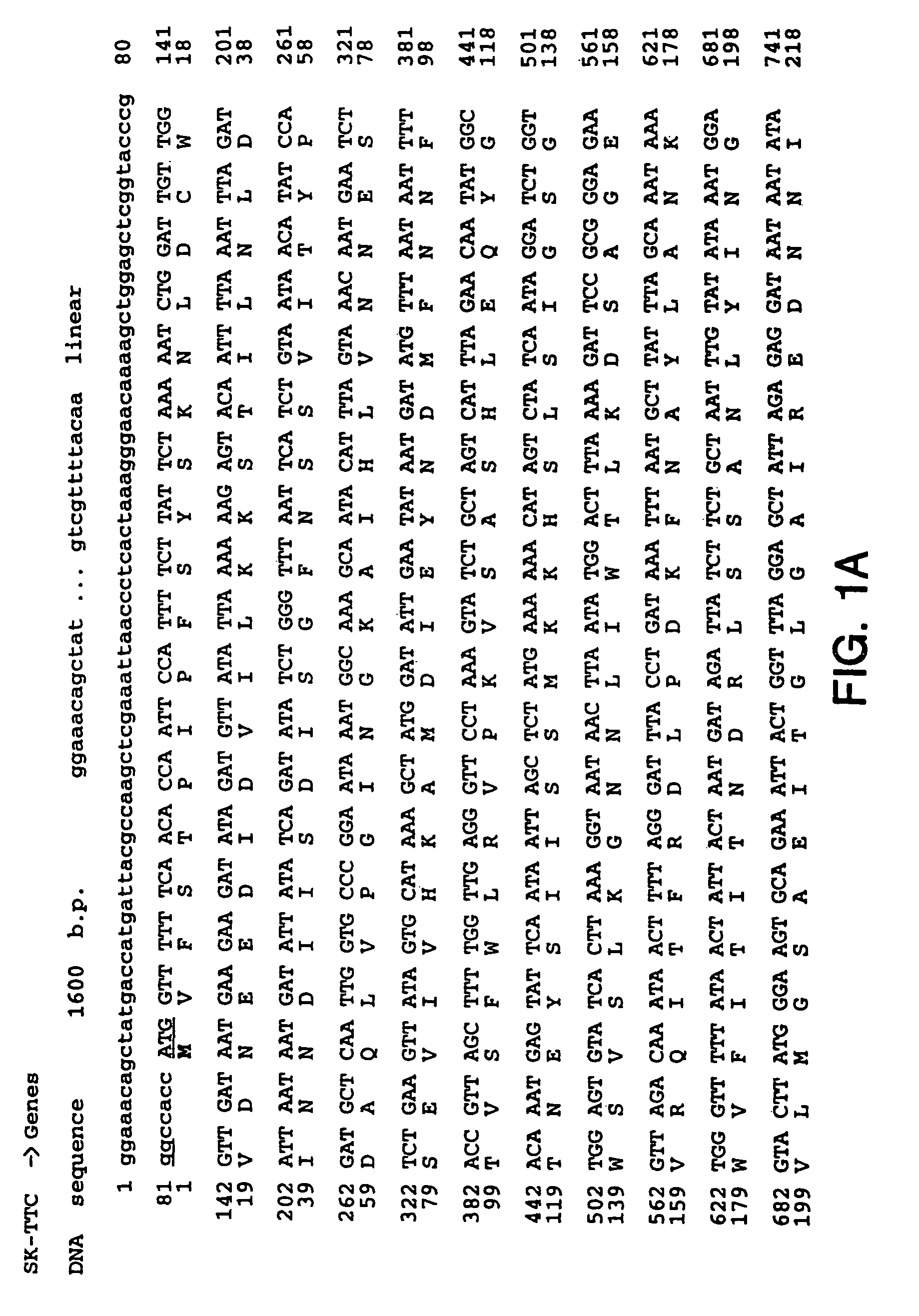
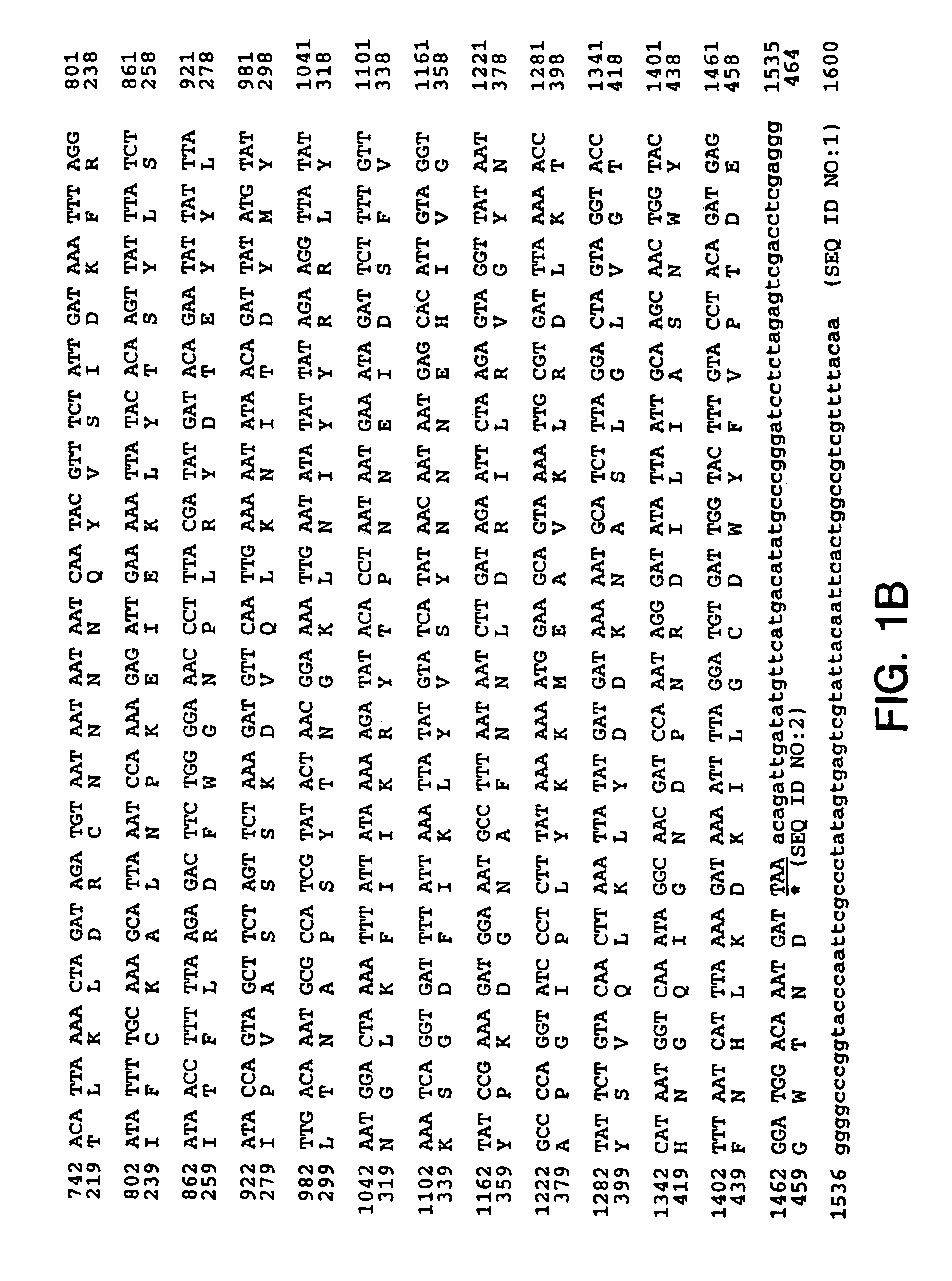
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS7923015B2Easy to transportEasy to operateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCell biologyTetanus Toxins
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
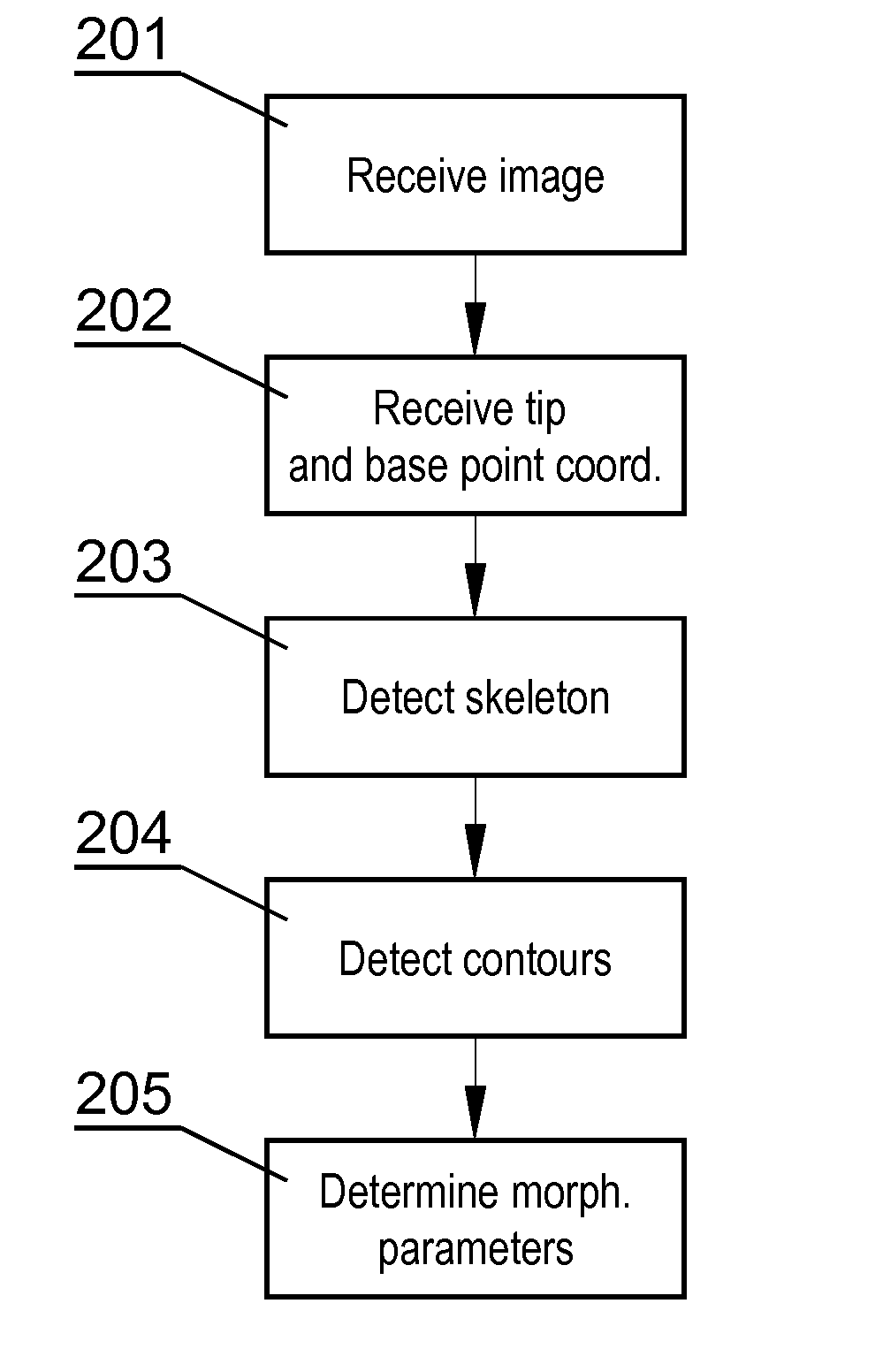
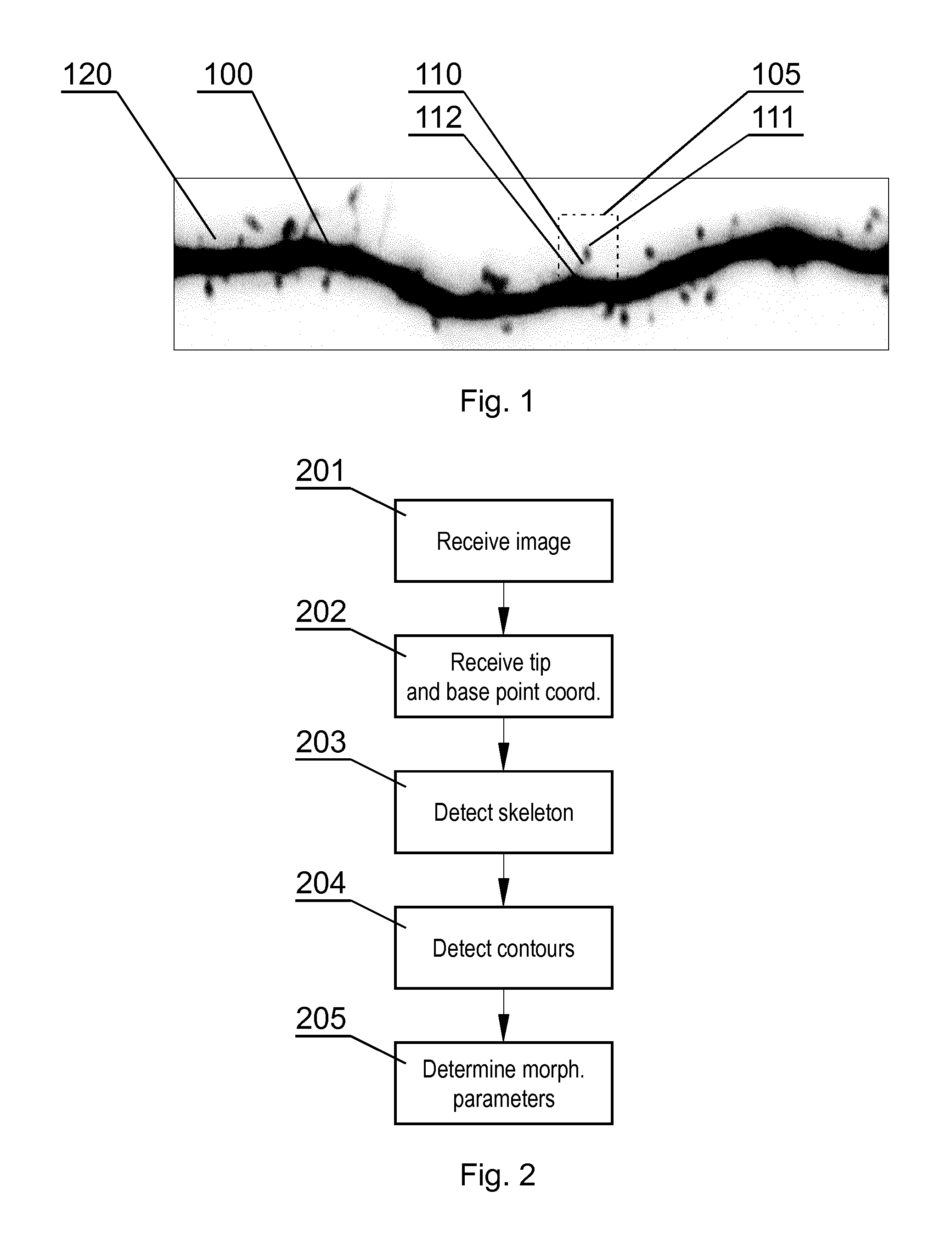
Method and a system for processing an image comprising dendritic spines
InactiveUS20140169647A1Image analysisDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionComputer visionBrightness perception
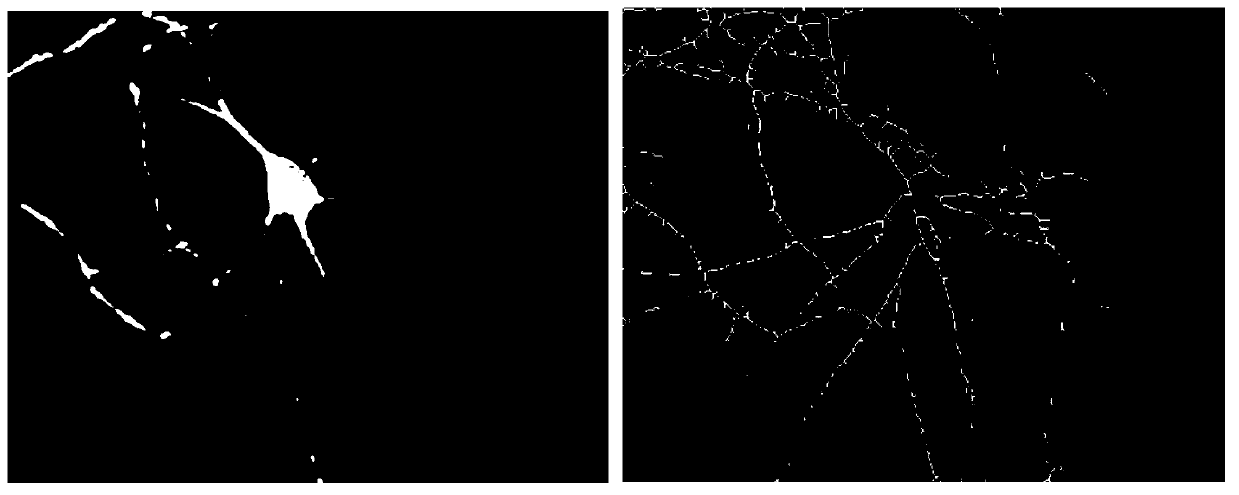
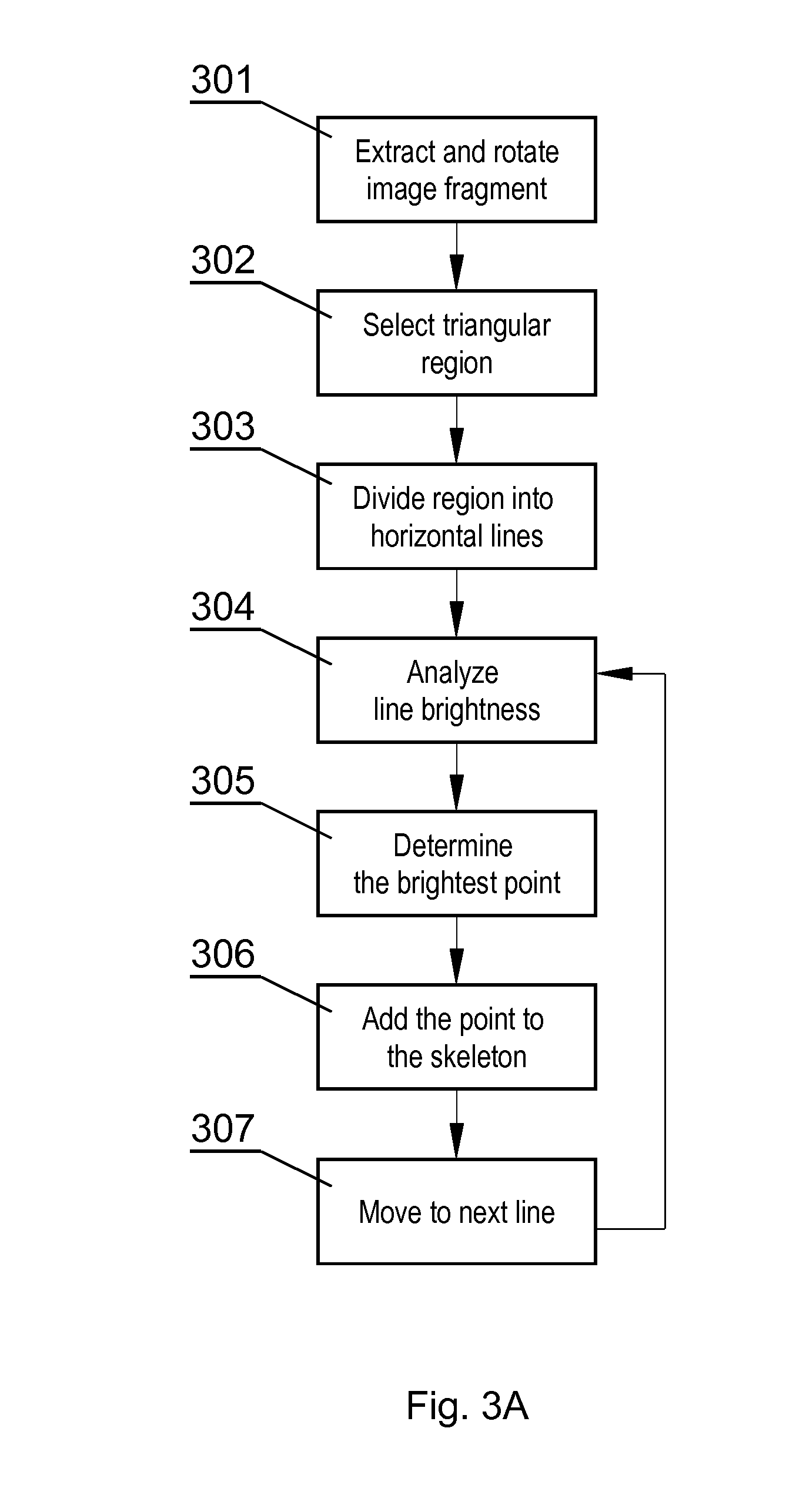
A computer-implemented method for processing an image comprising dendritic spines, the method comprising the steps of obtaining the image comprising at least one dendritic spine (110), obtaining the coordinates of the tip point (311) and the base point (312), detecting the skeleton (317) of the dendritic spine (110) by analyzing the brightness of consecutive image portions (316) arranged perpendicularly to an axis extending through the tip point (311) and the base point (312) and for each image portion (316) selecting the brightest point distanced not more than a predefined threshold (s) from the brightest point (314) of the previous image portion (316), detecting the contour (319) of the dendritic spine (310) by analyzing the brightness of consecutive image portions (318) arranged perpendicularly to the skeleton (317) and selecting the contour points (320) as points at which the plot brightness of the image portion transits the point having the brightness lower than the brightness (B) of the skeleton point multiplied by a brightness factor (η) at a furthest distance from the skeleton (317).
Owner:INST BIOLOGII DOSWIADCZALNEJ IM M NENCKIEGO PAN
Methods of stimulating cellular growth, synaptic remodelling and consolidation of long-term memory
InactiveUS20080058396A1Stimulates dendritic growthPromote formationBiocideNervous disorderProtein kinase activationLTM - Long-term memory
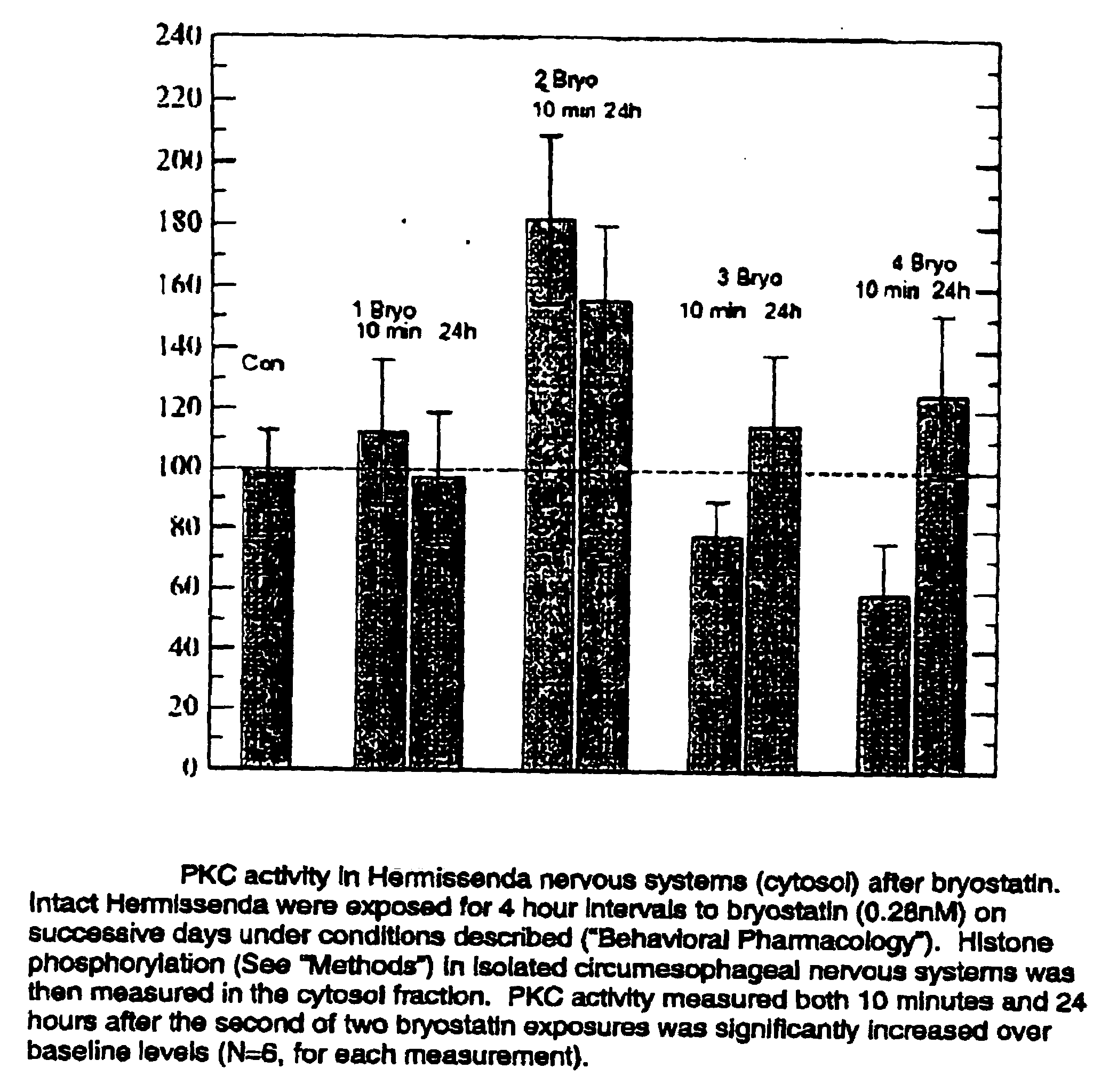
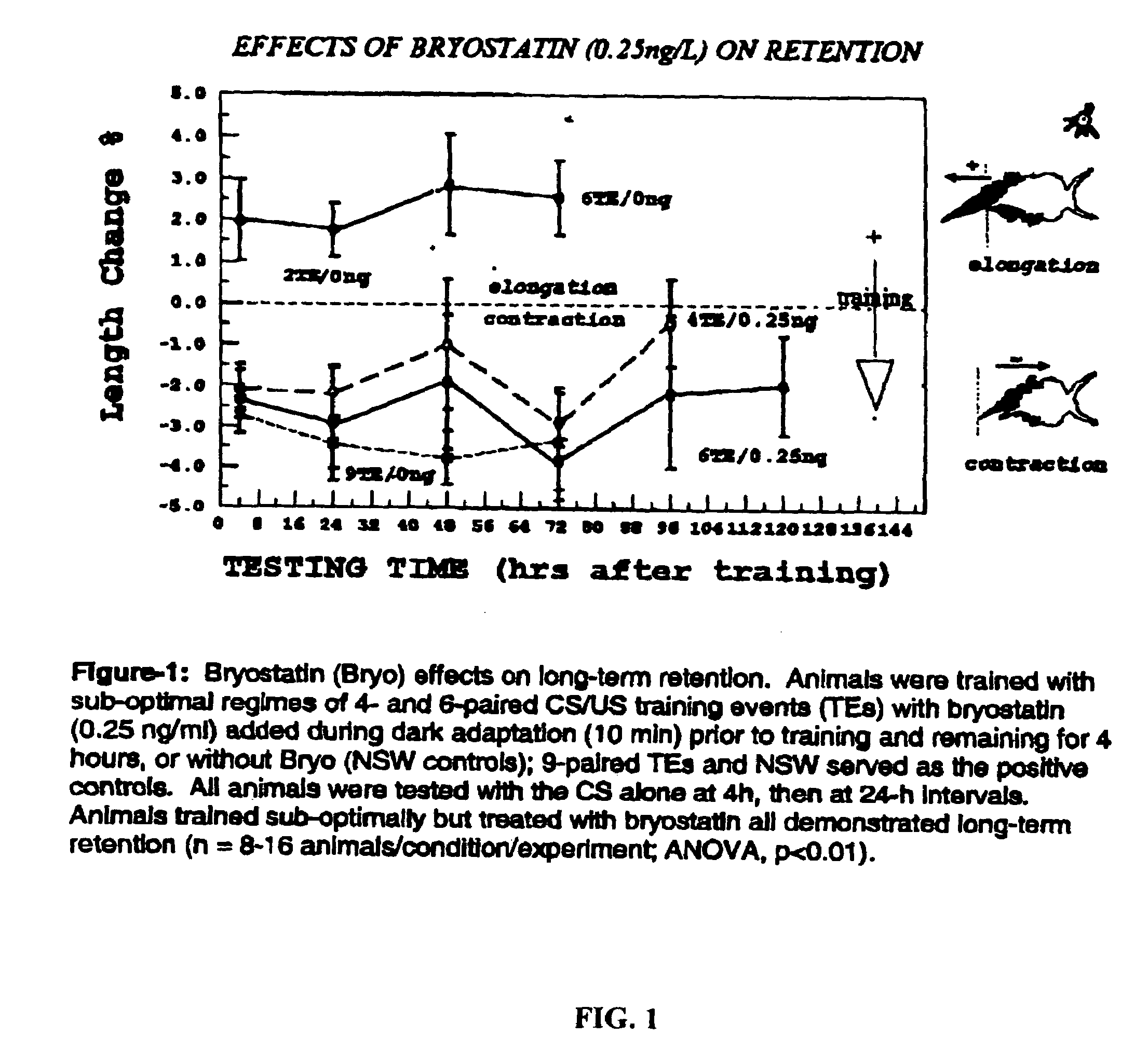
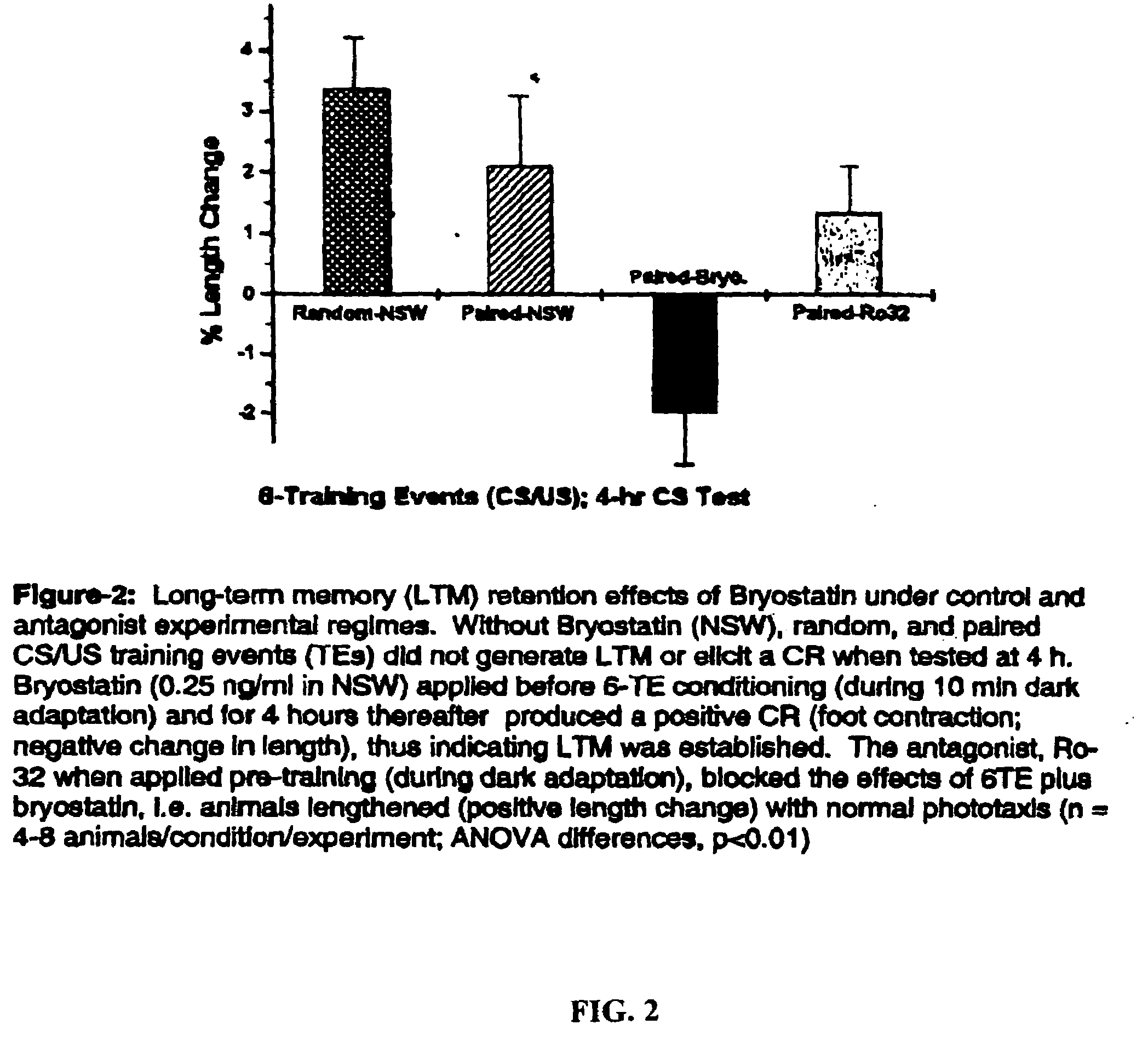
The present invention provides methods of slowing or reversing the loss of memory and learning comprising the steps of contacting an effective amount of a PKC activator with a protein kinase C (PKC) in a subject identified with memory loss slowing or reversing memory loss. The present invention provides methods of stimulating cellular growth, neuronal growth, dendritic growth, dendritic spine formation, dendritic spine density, and the translocation of ELAV to proximal dendrites, and synaptic remodeling. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to stimulate the synthesis of proteins sufficient to consolidate long-term memory. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to downregulate PKC.
Owner:ALKON DANIEL L
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS20050060761A1Easy to transportEasy to operateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologic markerFragment C tetanus toxin
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
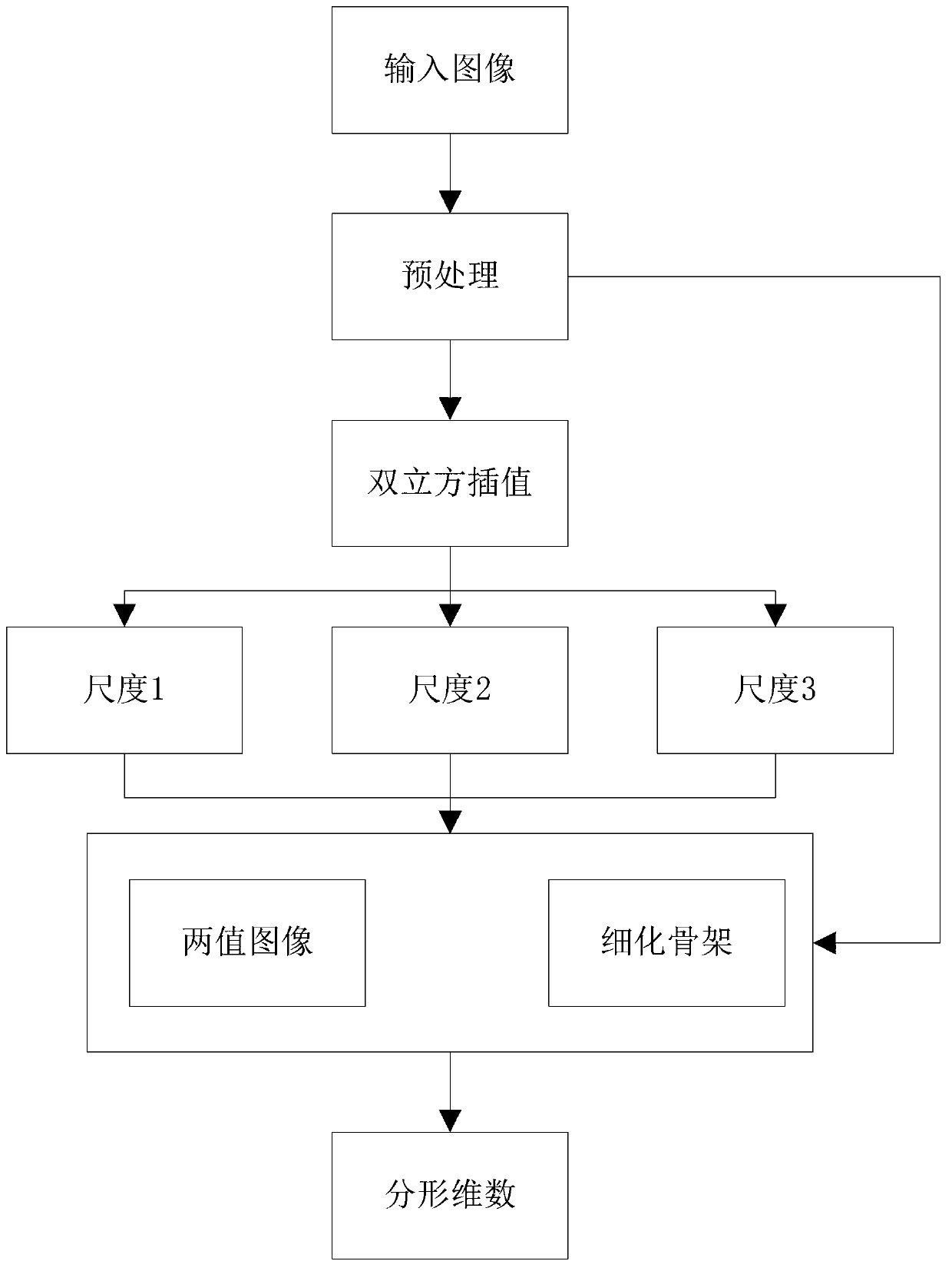
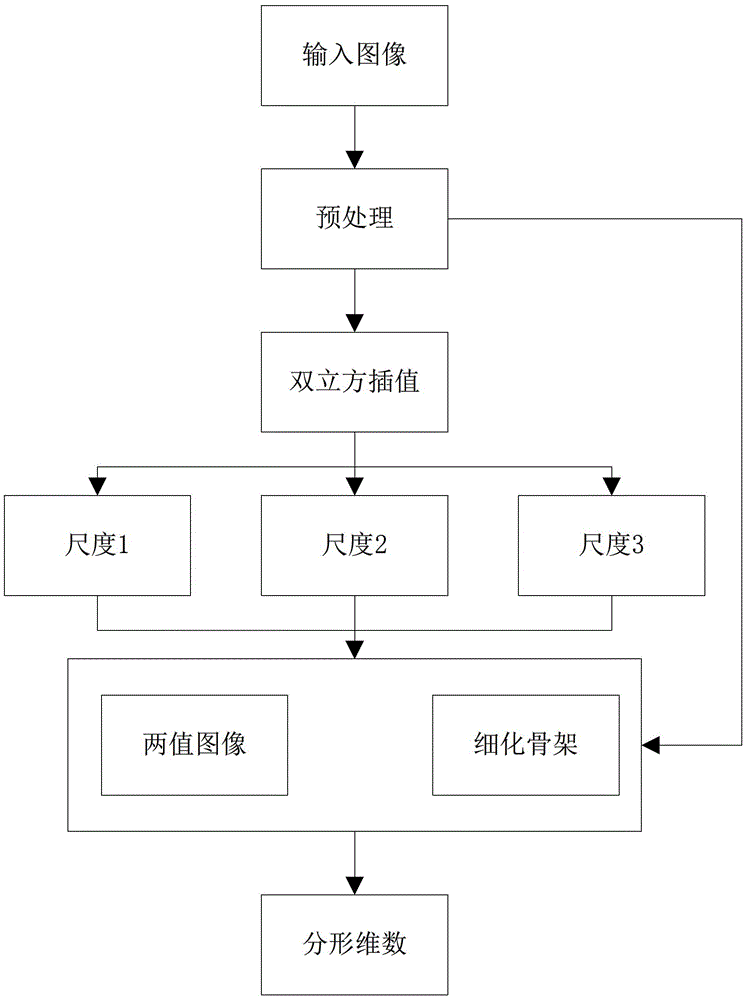
Nerve dendritic spine image classification method based on multiresolution fractal features
ActiveCN103150573AImprove classification accuracyClassification results are stableCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionClassification methods
The invention discloses a nerve dendritic spine image classification method based on multiresolution fractal features. The method includes the following steps of (1) extracting features of nerve dendritic spine images to obtain the multiresolution fractal features of the nerve dendritic spine images; and (2) classifying the nerve dendritic spine images based on the multiresolution fractal features of the nerve dendritic spine images in the method of linear discriminant analysis (LDA). According to the method, classification precision is high and classification results are stable.
Owner:XIAN JIAOTONG LIVERPOOL UNIV
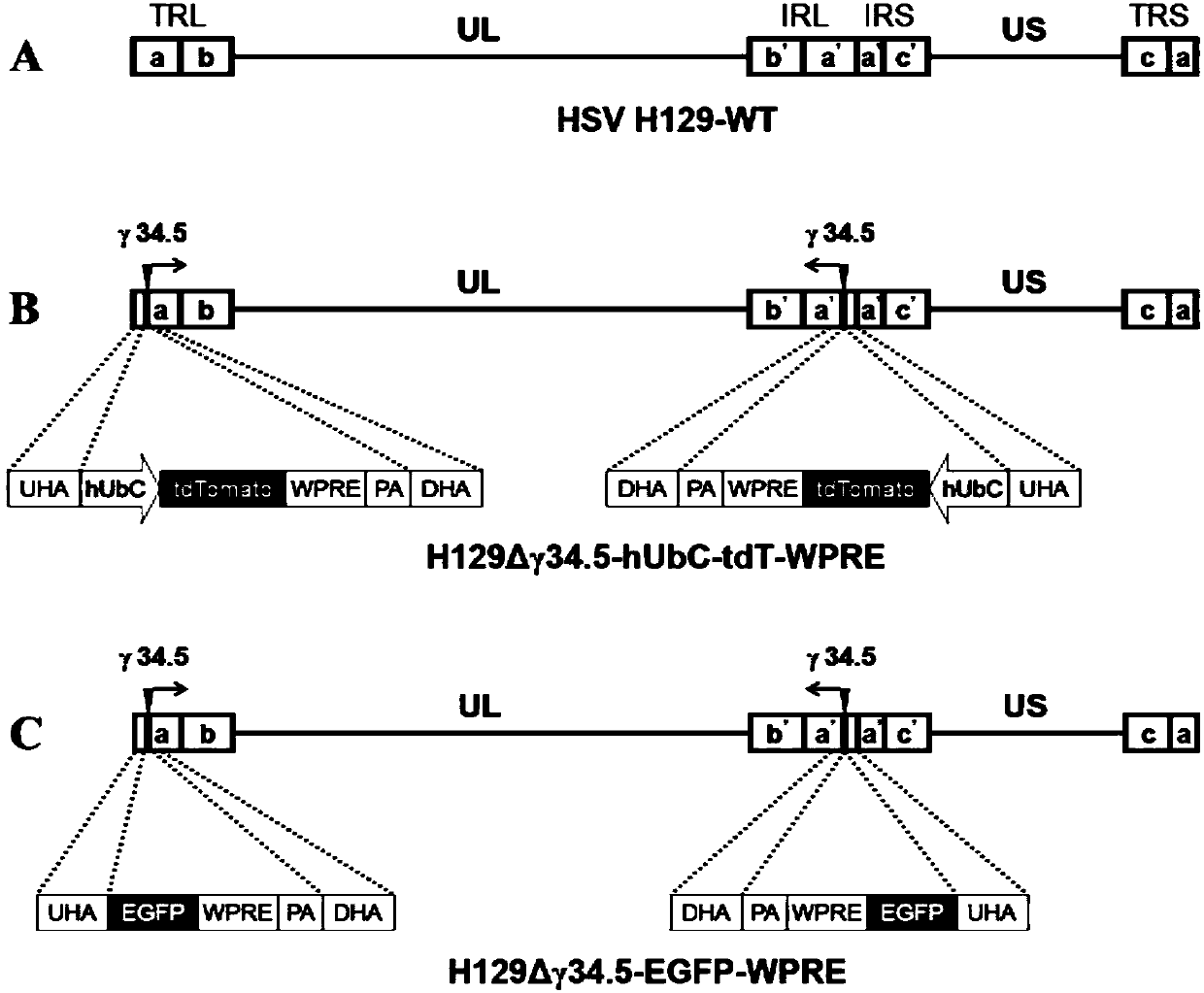
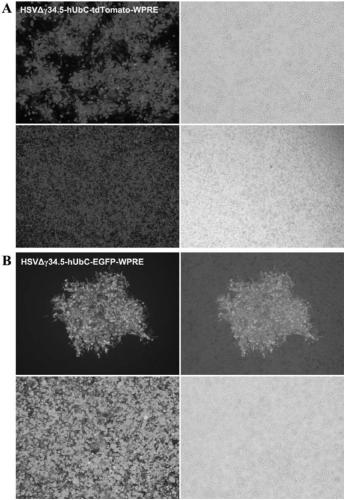
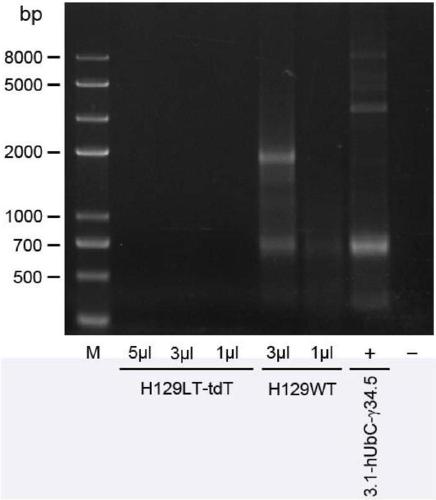
Low-toxic herpes simplex virus system and construction method and application thereof
PendingCN110117577AEasy genetic manipulationEasy to insertVirus peptidesFermentationDiseaseFine structure
The invention discloses a recombinant low-toxic herpes simplex virus system derived from a herpes simplex virustype I H129 clinical toxic strain and a construction method and application thereof. A recombinant virus constructed by a target vector is a remarkably attenuated H129 recombinant virus, the abundance of exogenous gene expression is very high, the characteristics of low toxicity and long-term high expression are shown in in vitro test or animal in vivo test, center infected animals cannot cause diseases, many neurons in brain regions are highlighted, and neuron cell bodies, axonal / dendritic fiber, dendritic spines and other fine structures are marked clearly. The low-toxic herpes simplex virus is suitable for serving as a target gene long-term and high-expression gene transductionvector and achieving long-term structure tracing of a neural circuit, and due to low toxicity, the low-toxic herpes simplex virus is also suitable for functional neural circuit analysis; in addition,the low-toxic HSV has wide application value in the aspects of nervous system targeted gene therapy, virus replication and pathogenesis analysis, animal infection model establishment, antiviral drugscreening, oncolytic therapy and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
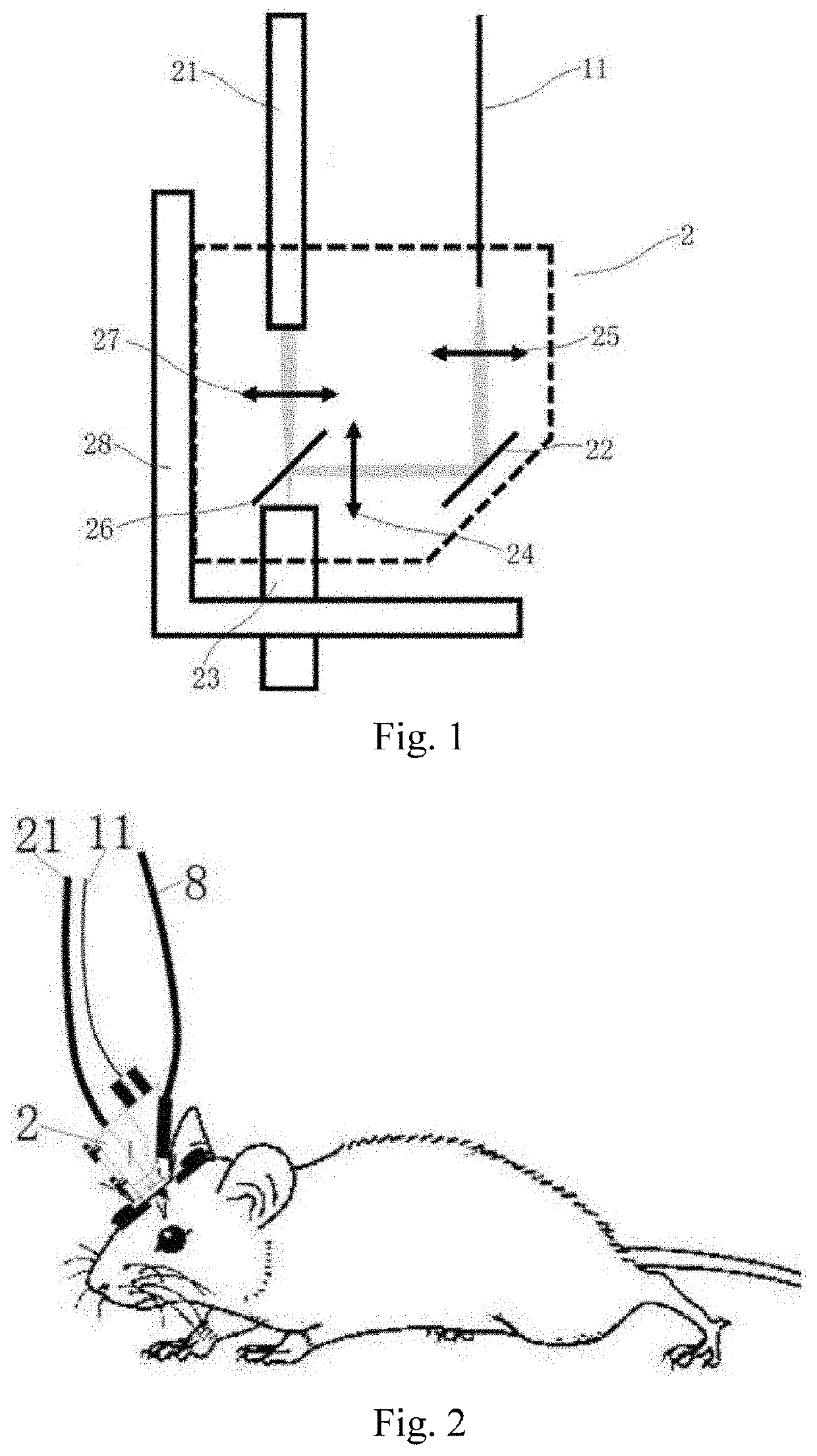
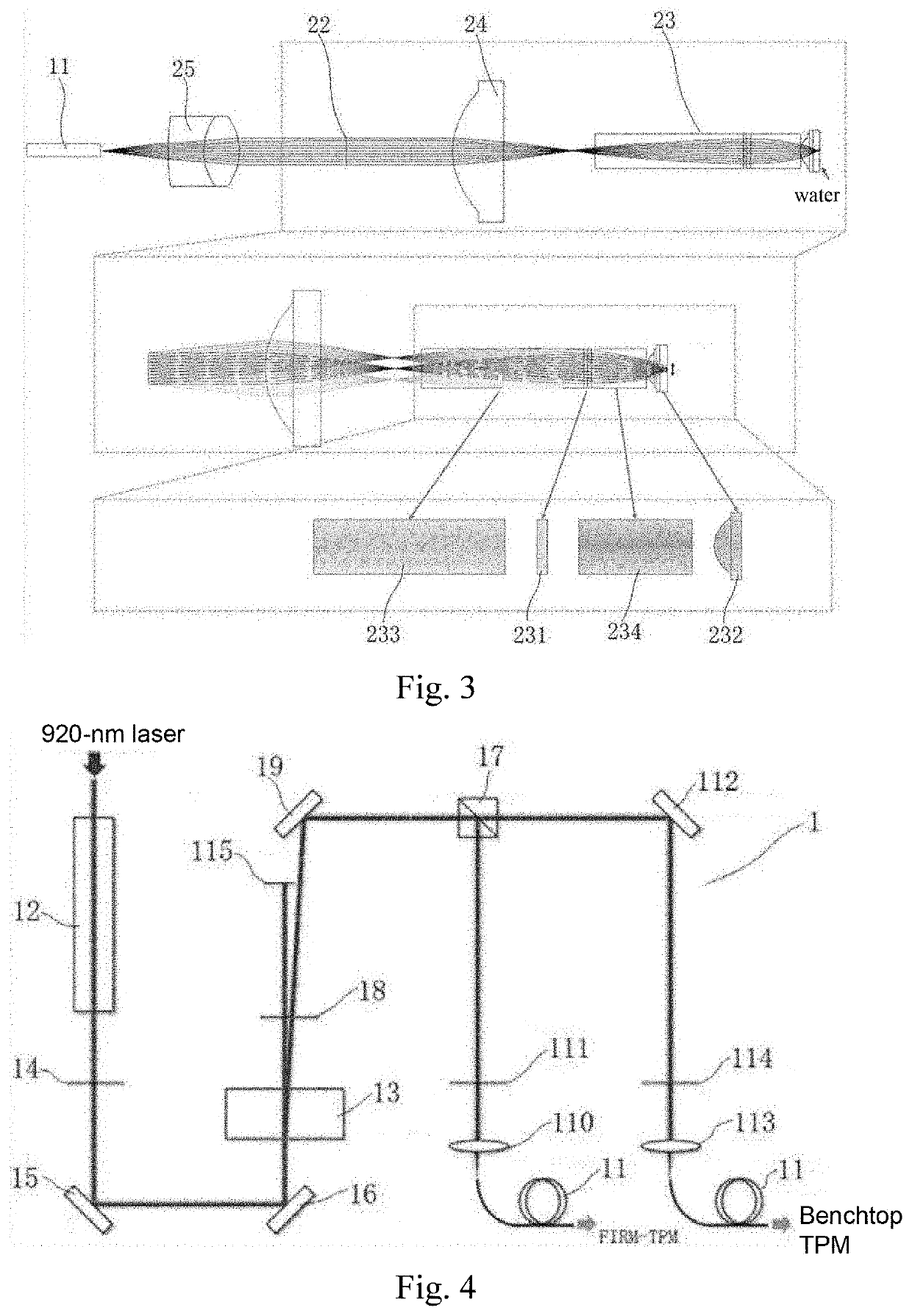
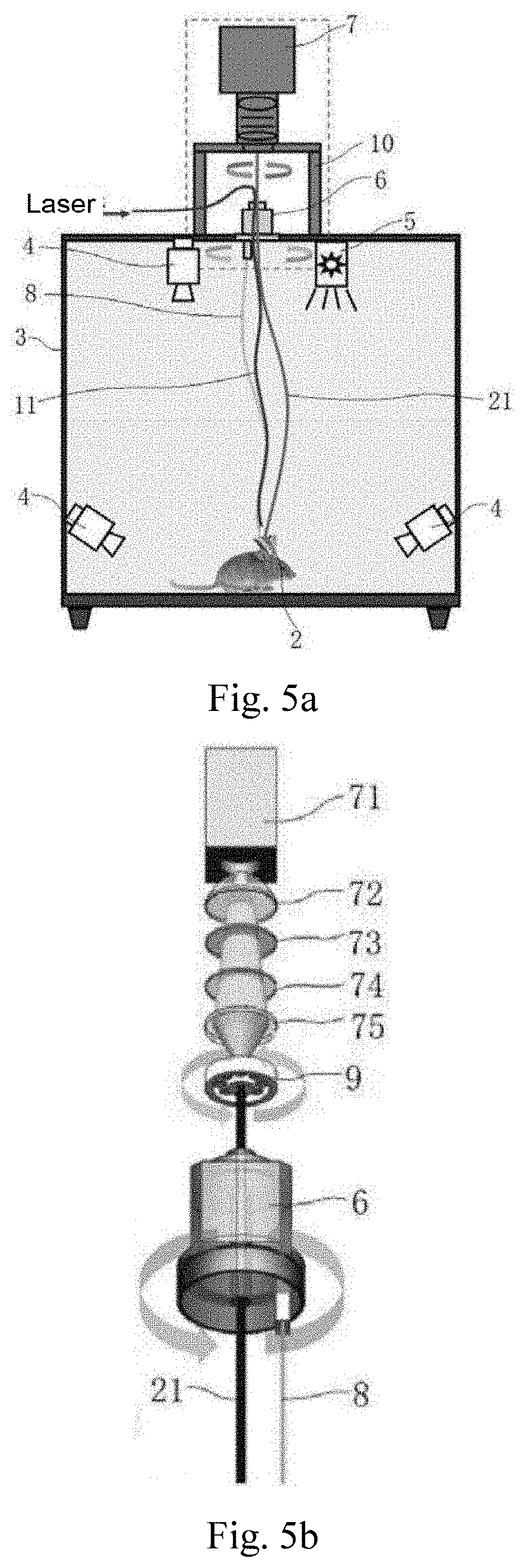
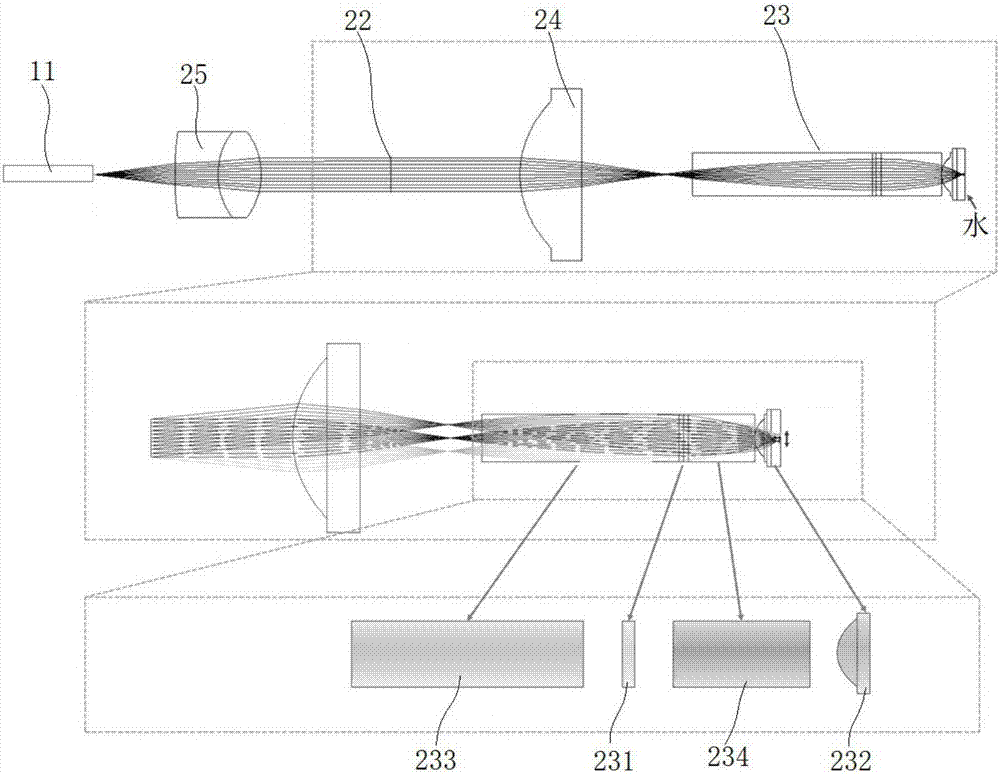
Femtosecond pulse laser modulator and miniature two-photon microscopic imaging device
InactiveUS20190380585A1Efficient excitationHigh in applicationLaser detailsDianostics using fluorescence emissionDendritic spineFiber
The present invention provides a femtosecond pulse laser modulator and a miniature two-photon microscopic imaging device. The femtosecond pulse laser modulator includes a negative dispersion light path and a positive dispersion light path, wherein the negative dispersion light path includes a laser input fiber, which is configured to transmit laser compensated for through prechirp; the positive dispersion light path is located between a femtosecond pulse laser and the negative dispersion light path, and is configured to compensate for, through prechirp, negative dispersion of the laser produced in the laser input fiber. The femtosecond laser modulator provided in the present invention provides distortion-free transmission for the femtosecond pulse laser with a center wavelength in 920 nm, and effectively excites commonly used biological indicators. The miniature two-photon microscopic imaging device including this femtosecond laser modulator has high speeds in test and application, with high resolution, and is capable of solving the problem of imaging single dendritic spines in a freely behaving animal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Femtosecond pulse laser modulator and fast high resolution miniature two-photon microscope having same
ActiveCN107069391AHigh speedHigh resolutionLaser detailsDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFemtosecond pulsed laserLaser beams
The invention discloses a femtosecond pulse laser modulator and a fast high resolution miniature two-photon microscope having the same. The femtosecond pulse laser modulator comprises a negative dispersion optical path and a positive dispersion optical path, wherein the negative dispersion optical path comprises a laser input optical fiber for transmitting a pulse-widened prechirp compensated laser beam to a scanning imaging portion; and the positive dispersion optical path is located between a femtosecond pulse laser device and the negative dispersion optical path and is used for compensating the negative dispersion caused by the laser input optical fiber in a laser transmission process. The femtosecond pulse laser modulator is capable of providing a favorable condition for the fast high resolution miniature two-photon microscope to stably observe the dendrites and the dendritic spine of unrestrained animals in a natural physiological environment.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
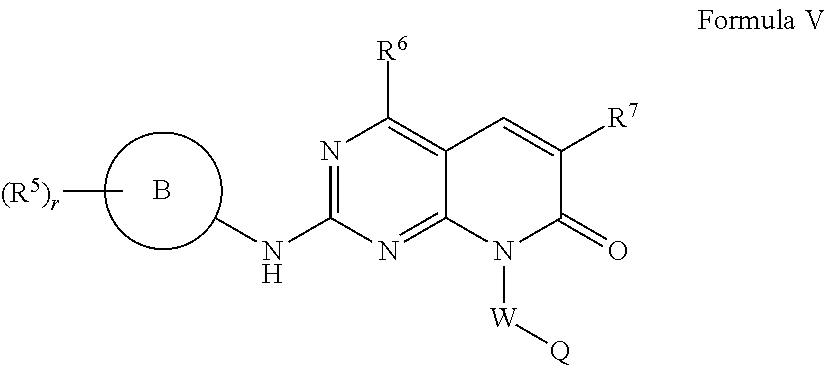
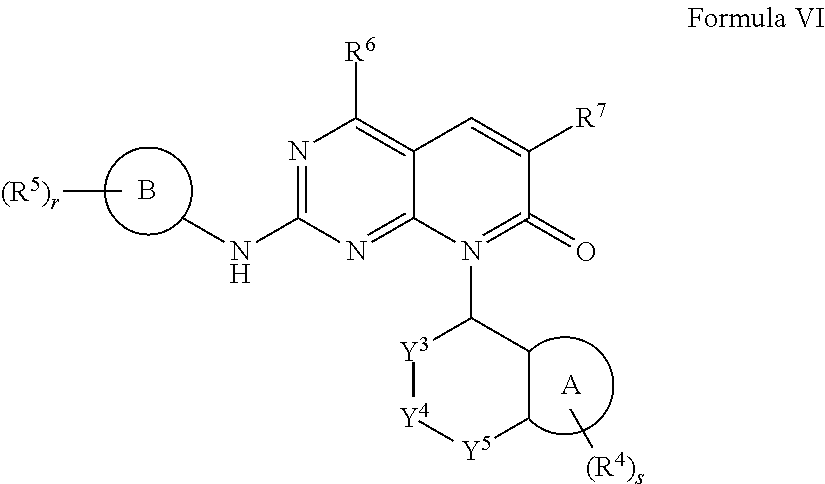
Compounds for treating neuropsychiatric conditions
InactiveUS8674095B2Improves one or more of MATRICS cognition scoresBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
Provided herein are pyrido[2,3-D]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one compounds and compositions useful as PAK inhibitors. Also provided herein are methods of utilizing these compounds for the treatment of neuropsychiatric conditions. The compounds modulate dendritic spine morphology and / or synaptic function.
Owner:AFRAXIS HLDG
Methods and compositions for treating alzheimer's disease and other memory-associated disorders and conditions
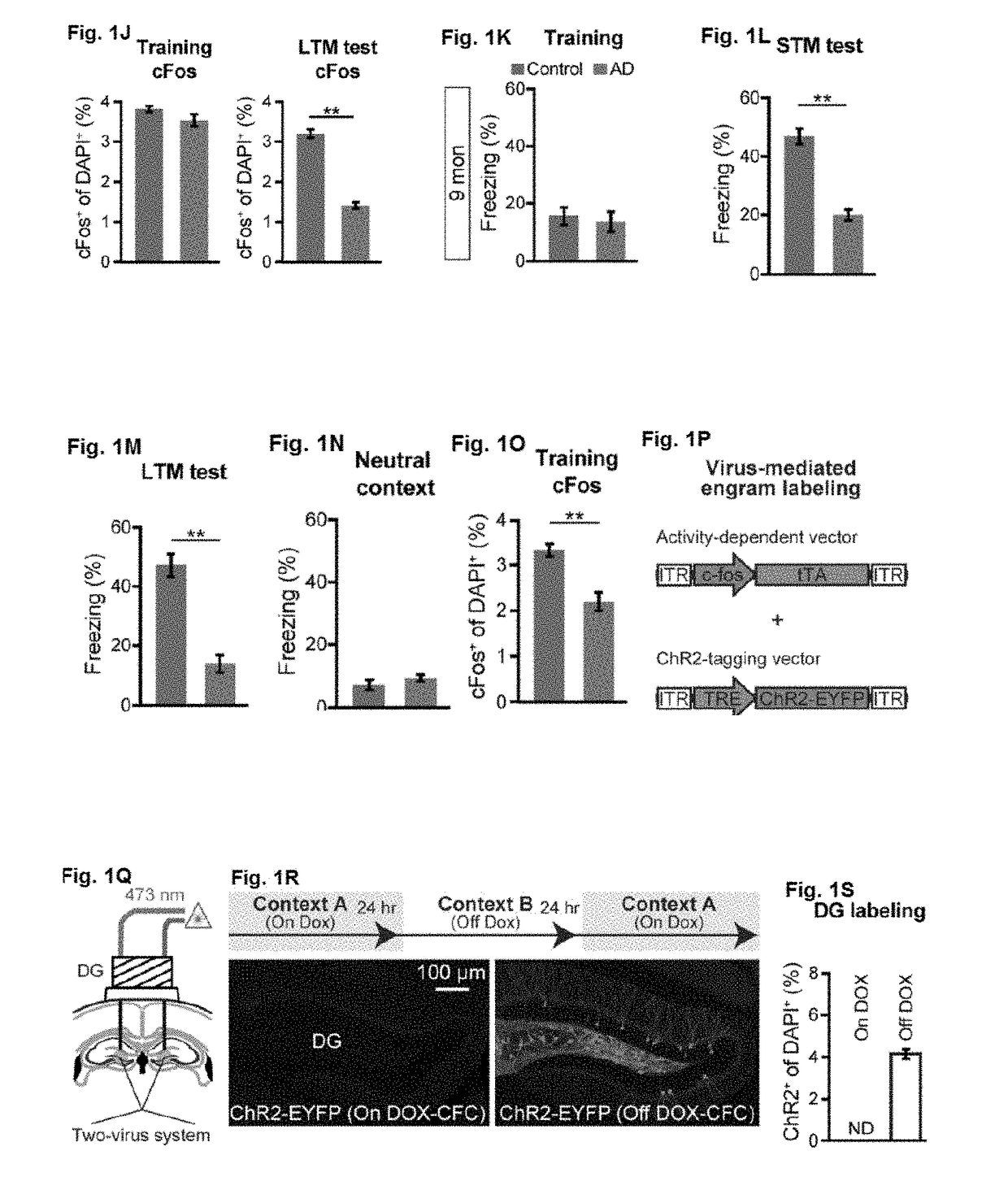
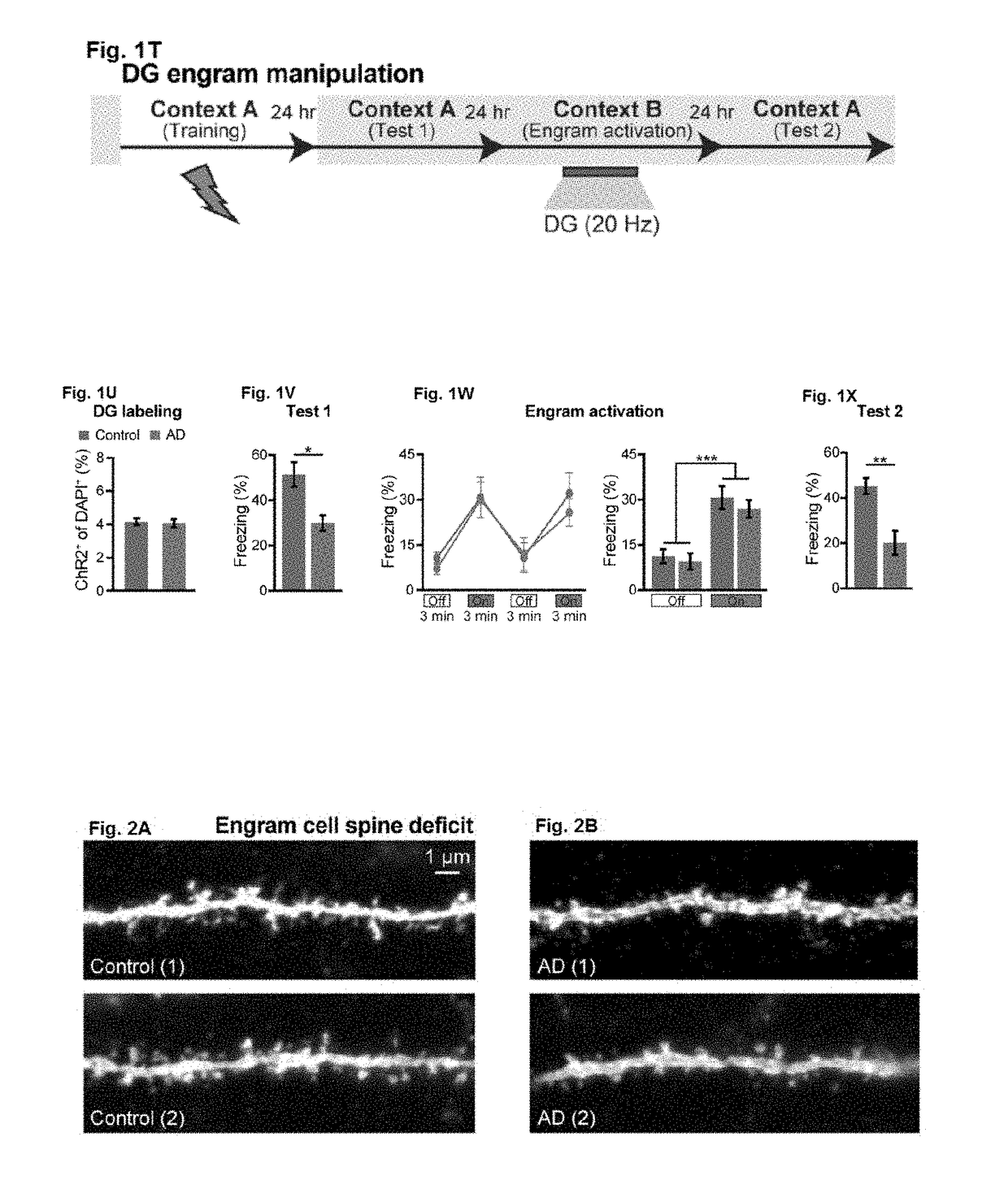
InactiveUS20180078609A1Increasing dendritic spine densityLower Level RequirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsLight therapyDiseaseOptogenetics
The invention, in part, relates to the use of optogenetic methods to increase dendritic spine density on DG memory engram cells in treatment methods for memory-impairment-associated diseases and conditions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
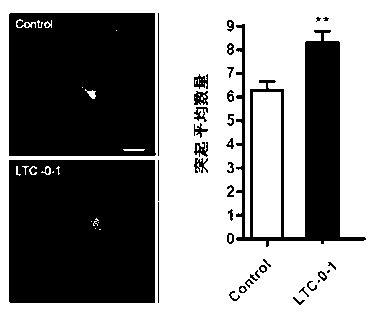
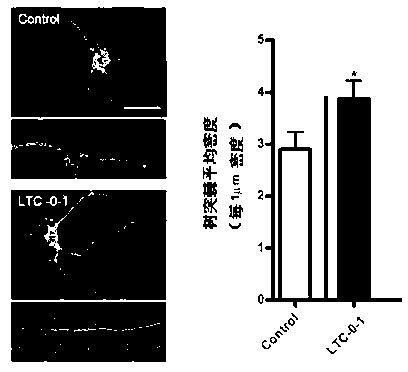
Wintergreen pure polysaccharide LTC-0-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN102838685AImprove memory dysfunctionFacilitate or improve learning and memoryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNutritionSynaptic membrane
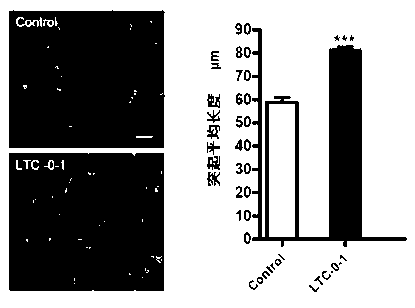
The invention provides a wintergreen pure polysaccharide LTC-0-1 and an application thereof, which belong to the field of medicines and healthcare foods. The invention discloses an extracting method of the wintergreen pure polysaccharide LTC-0-1, a composition of the LTC-0-1 and a molecular weight of the LTC-0-1; it is proved by experiments that the LTC-0-1 can be used for increasing average lengths of hippocampal neurons of a GFP green fluorescent protein transgenic mouse, increasing the number of the neurons, obviously increasing dendritic spine densities of neuron dendrons in a unit length, increasing neuronal post-synaptic membrane protein expression and promoting the neurons to be more mature; the LTC-0-1 can be also used for inducing neuron-like differentiation of PC12 cells, promoting enation of the cells, enhancing activity of cell acetylcholinesterase AchE and increasing expression index of cell growth related protein GAP-43 and obtains neurotrophic activity; and the LTC-0-1 shows a growth promoting effect, a differentiation effect, a maturing effect and a damaged nerve cell function recovery effect on nerve cells and has broad prospects in development and application in the technical field of medicines and healthcare foods.
Owner:THE KEY LAB OF CHEM FOR NATURAL PROD OF GUIZHOU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS20070092449A1Easy to transportEasy to operateDisease diagnosisIn-vivo testing preparationsBiologic markerFragment C tetanus toxin
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Methods of stimulating cellular growth, synaptic remodeling and consolidation of long-term memory
InactiveUS20080025961A1Strengthen associationIncreased activationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderProtein translocationBiology
The present invention provides methods of slowing or reversing the loss of memory and learning comprising the steps of contacting an effective amount of a PKC activator with a protein kinase C (PKC) in a subject identified with memory loss slowing or reversing memory loss. The present invention provides methods of stimulating cellular growth, neuronal growth, dendritic growth, dendritic spine formation, dendritic spine density, and the translocation of ELAV to proximal dendrites, and synaptic remodeling. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to stimulate the synthesis of proteins sufficient to consolidate long-term memory. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to downregulate PKC.
Owner:BLANCHETTE ROCKEFELLER NEUROSCI INST
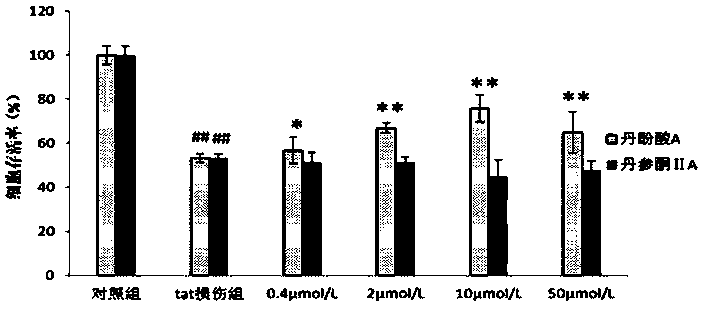
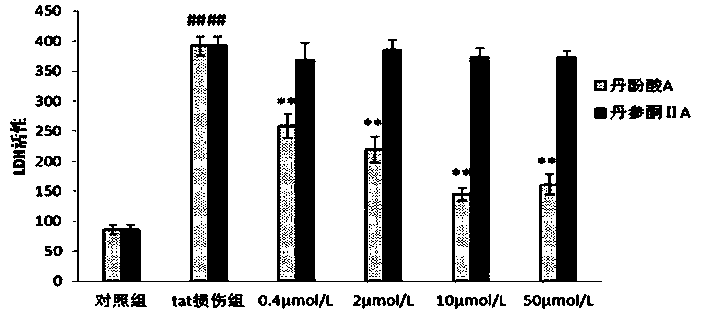
Application of danshinolic acid A in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating AIDS encephalopathy
InactiveCN103860537AGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAIDS EncephalopathyPharmacy
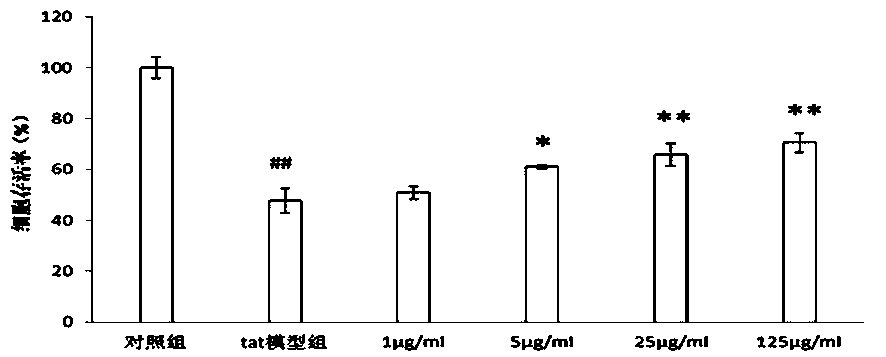
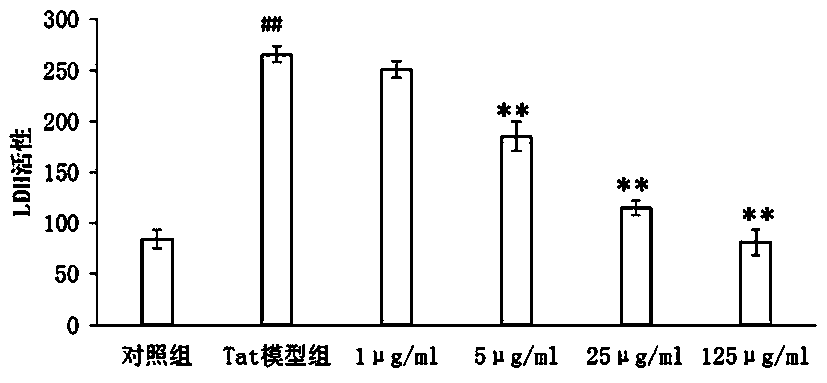
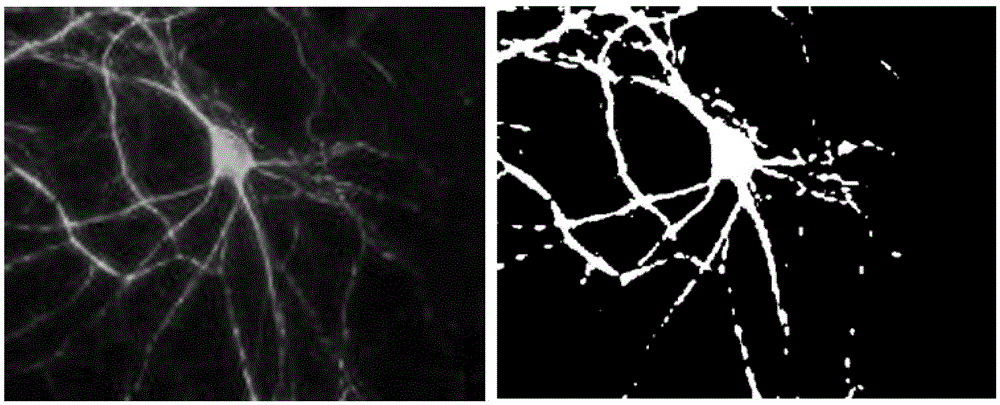
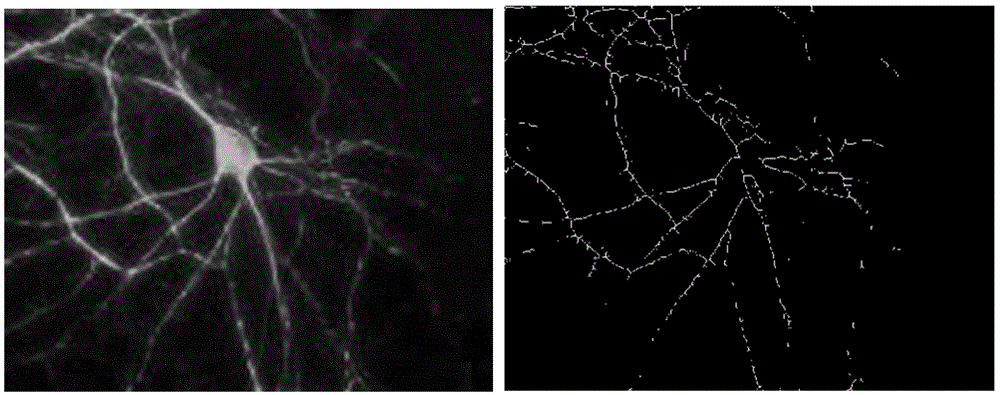
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy, and particularly relates to an application of danshinolic acid A in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating AIDS encephalopathy as well as nerve damages caused by an HIV-1Tat protein. According to the invention, an HIV-1Tat protein damage type nerve cell line PC 12 and nerve cells on mouse brain slices are protected by using danshinolic acid A with different concentrations, and the effect of reducing the death of the nerve cells caused by the Tat protein of the danshinolic acid A is respectively detected by an MTT experiment, LDH detection and a Tunnel experiment; and dendritic spines are labeled by scattering Dil gold particles, and the effect of reducing Tat protein damage synaptic connectivity of the danshinolic acid A is detected. Through statistical analysis of experimental results, the danshinolic acid A is found to have a good protection effect against damages of the nerve cells caused by the Tat protein and can be used for preparing the medicines for preventing and treating the nerve damages caused by the Tat protein as well as the AIDS encephalopathy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
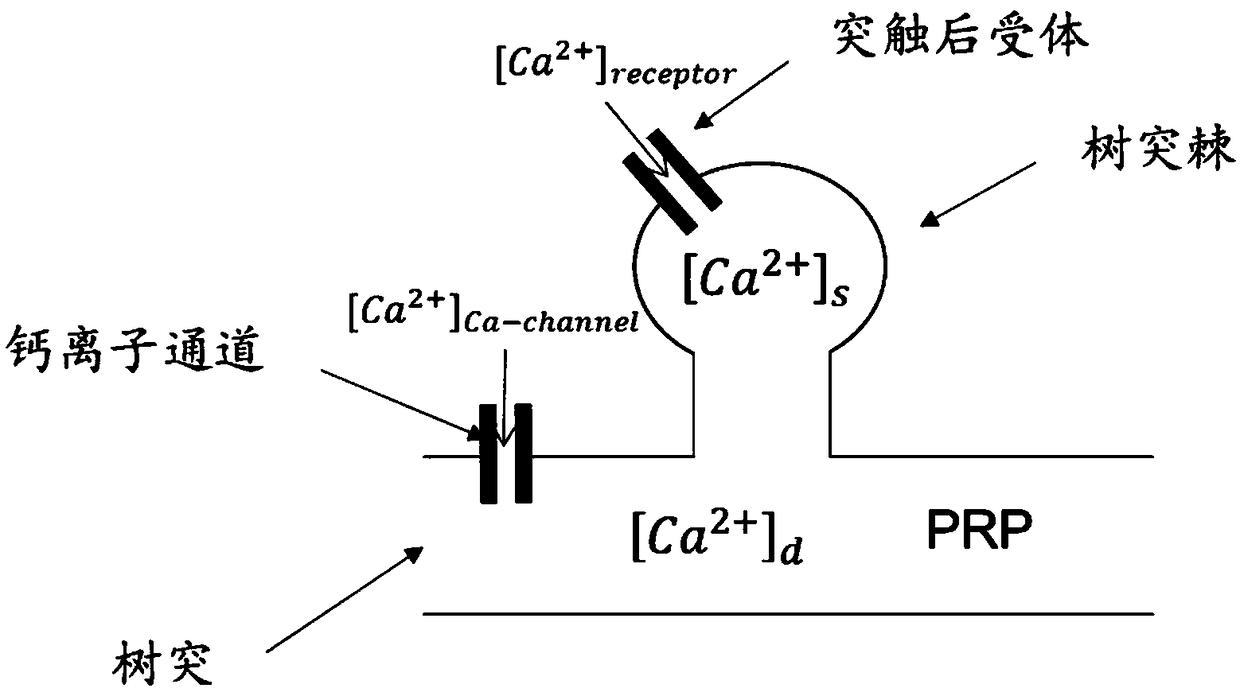
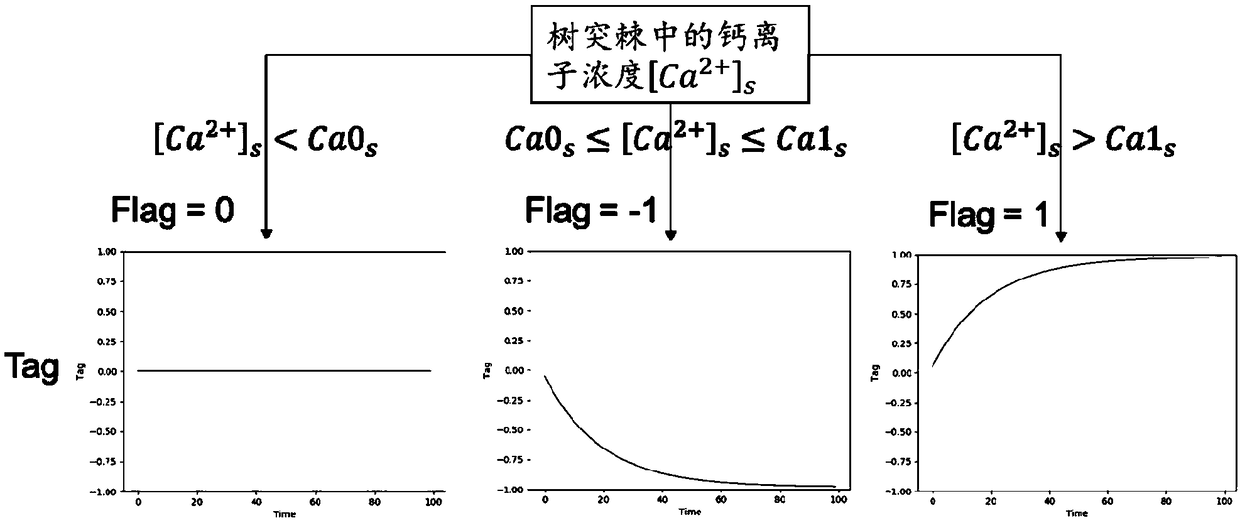
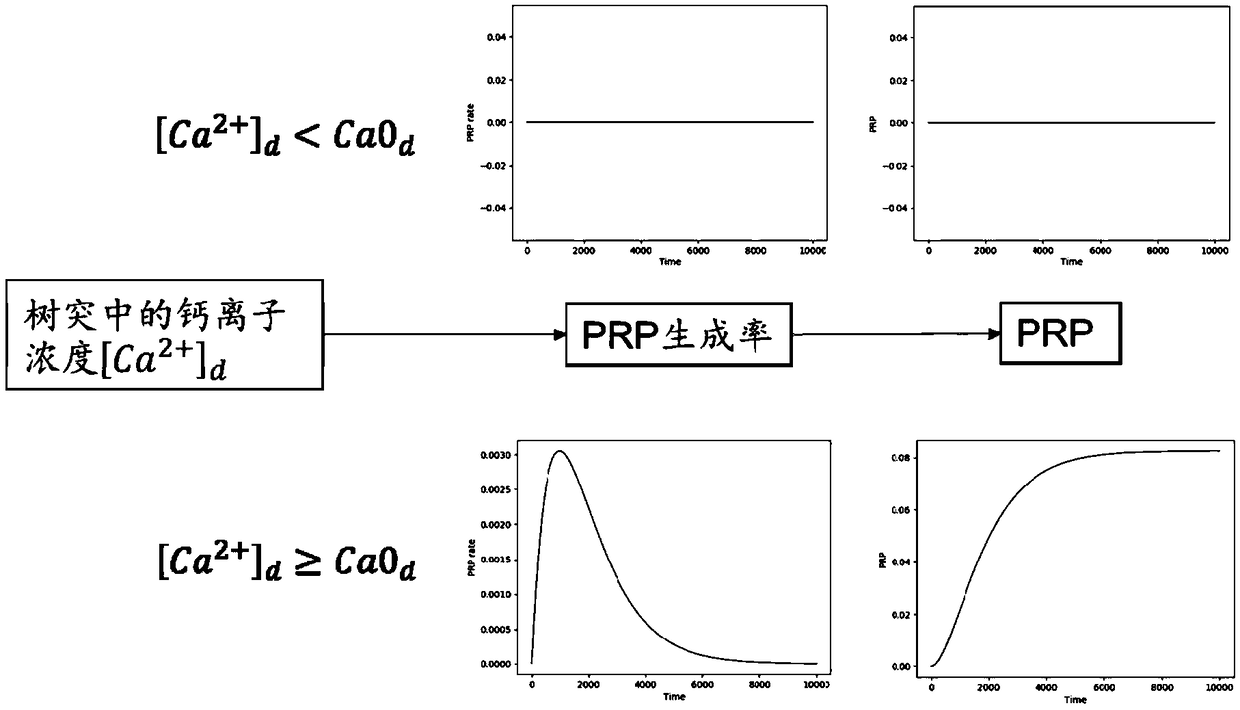
Calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration
The invention relates to a calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration, which relates to the field of brain simulation, in particular to the calculation problem ofneural synaptic plasticity of impulse neural network in brain simulation. The first is the calculation of calcium ion concentration. According to the membrane potential values of presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic neurons at the initial time t0 and the initial connecting weight w0 of synapses, the calcium ion concentrations in dendrites and spines at the next time t1 are calculated respectivelyfor the synapses that need to be calculated. Secondly, according to the calcium ion concentration in dendritic spine, the direction of weight change was obtained by comparing with the calcium ion concentration threshold Ca0s and Ca1s. According to the synaptic state tag Tag and the plasticity related protein PRP concentration, the change of synaptic weight was calculated, and the new weight at time t1 was obtained. the above procedure is repeated to calculate the strength of synaptic connections within the simulation time. The method of the invention is applied to constructing a brain-like neural network, completing the simulation of the learning and memory process required by the brain-like intelligence, realizing the universal strong artificial intelligence, and is applied to intelligentmedia, medical treatment and the like.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Method for detecting form of neuron dendritic spine in brain slice
PendingCN113466014ASimplify the Scattering ProcessAvoid high background distractionsPreparing sample for investigationStainingCranial nerves
The invention belongs to the field of brain neuron research, and particularly relates to a method for detecting the form of a neuron dendritic spine in a brain slice. In order to solve the technical problems that the existing method for dyeing dendritic spines in the brain is complex in steps, long in process and high in cost, and highly toxic reagents and special instruments harmful to a human body need to be used, the invention provides a rapid detection method for neuron dendritic spines in a brain slice. According to the invention, the low-concentration dye and the high-strength vortex are adopted, so that the DIL working solution forms extremely small particles, and high background interference caused by DIL solid dye residues is avoided by controlling the contact time of the DIL working solution and the brain slice and an appropriate observation time window, so that a single neuron cell is clearly distinguished. According to the method, the original DIL scattering method process is greatly simplified, special instruments are not needed, the operation steps are simple, the dyeing effect is stable, and the method is suitable for laboratory popularization.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
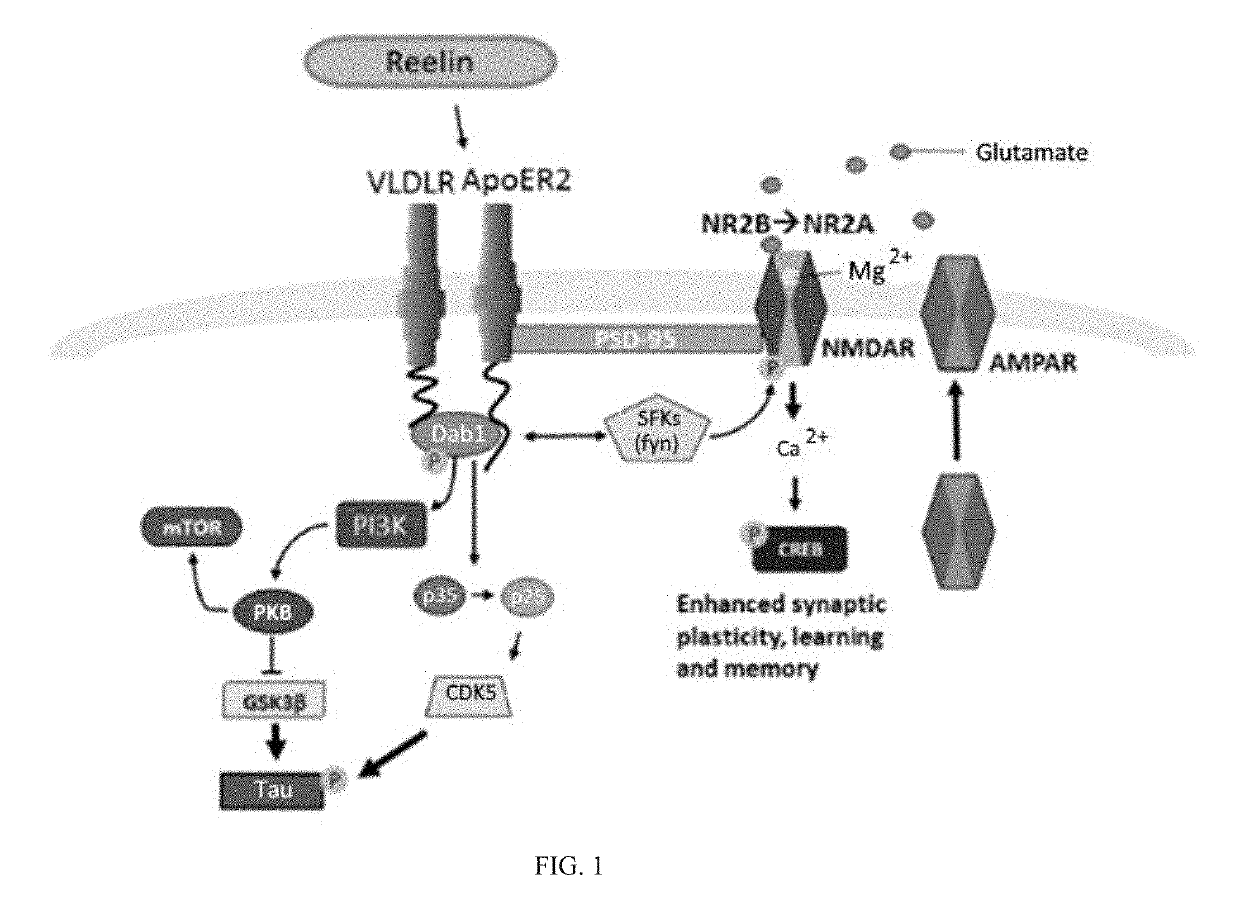
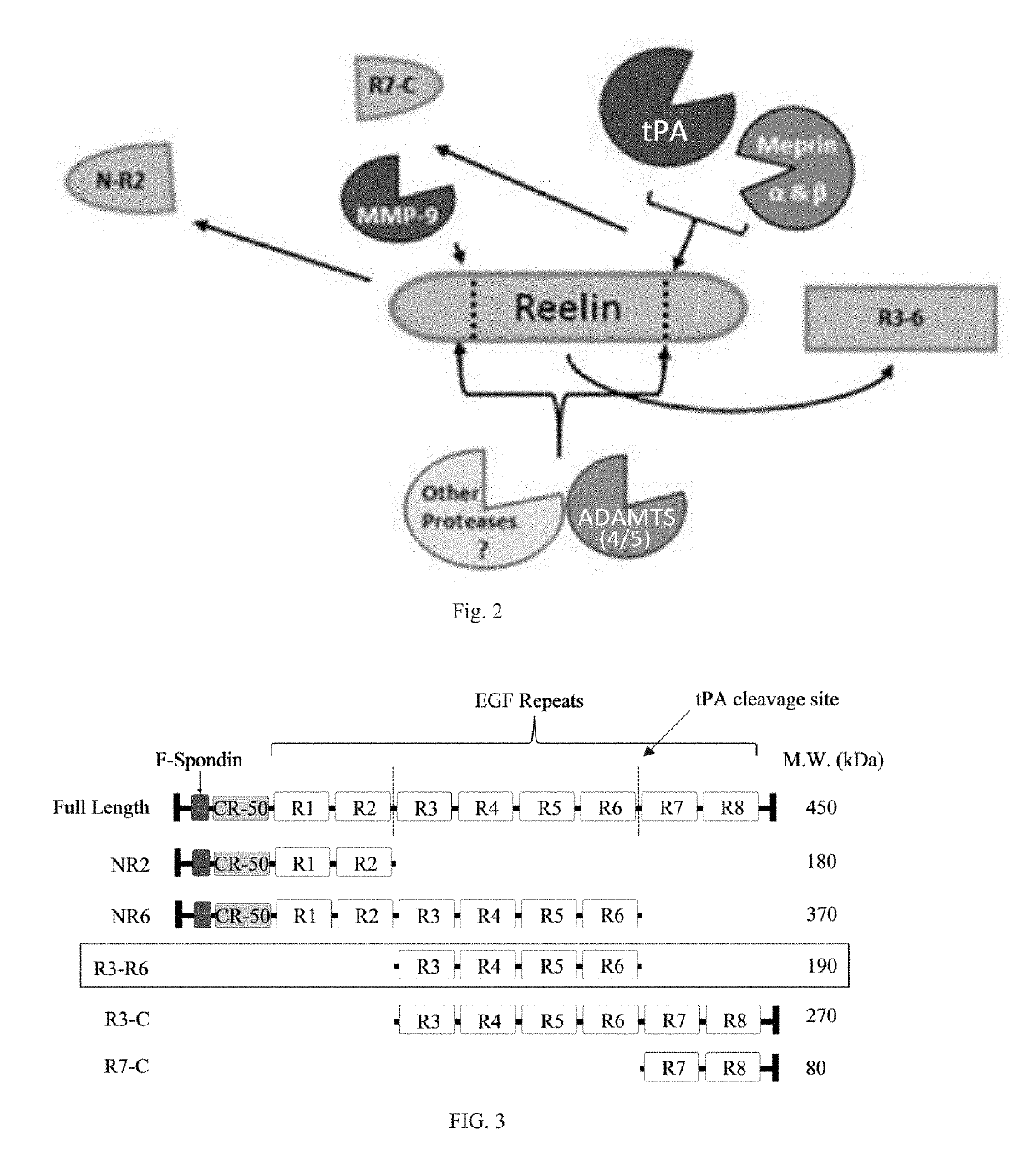
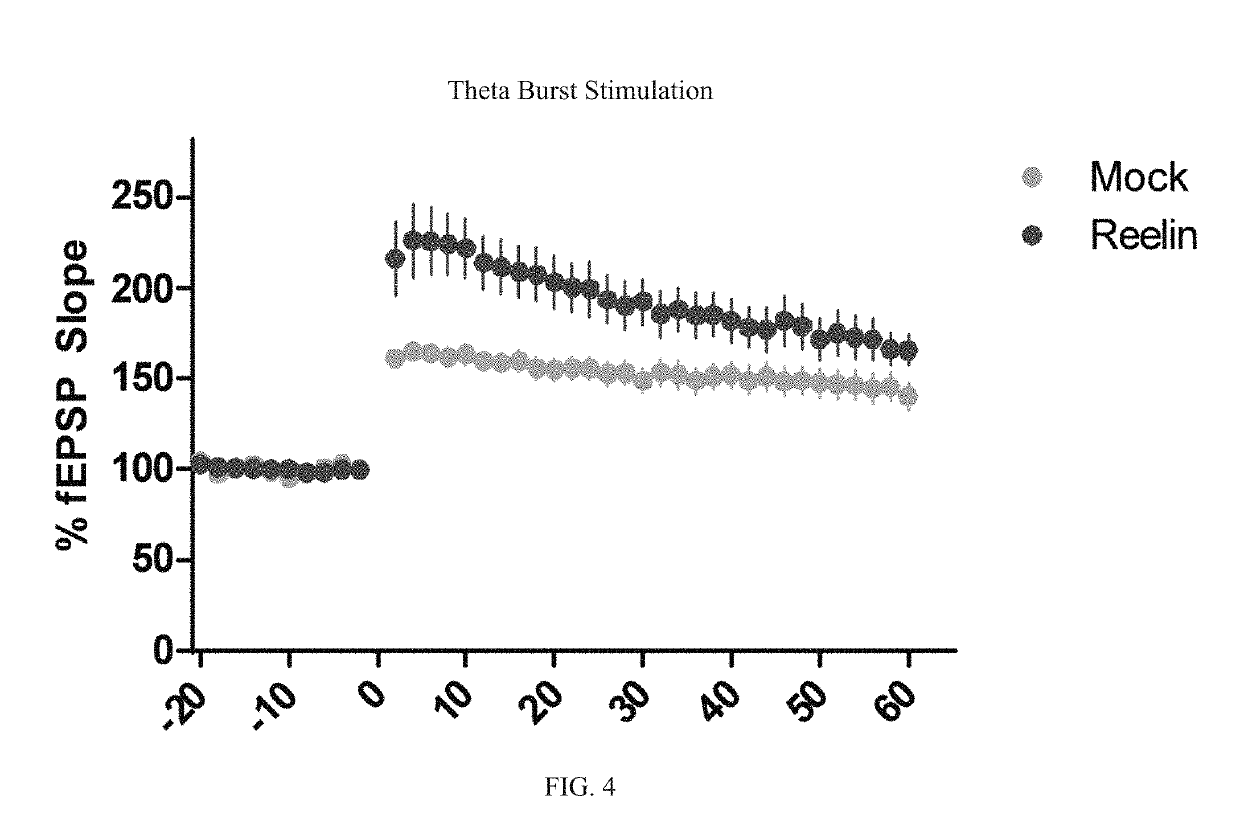
Reelin compositions for treatment of neurological disorders
PendingUS20190169246A1Improve plasticityImprove cognitive functionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFragile X chromosomeReelin
Changes in Reelin levels as well as Reelin signaling alter cognitive function. This can be accomplished by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a repeat fragment of Reelin, or a construct formed from fragment repeats of Reelin to a patient or subject. Changes to Reelin levels can be used to treat various neurodegenerative diseases, neuronal insults, or stroke, such as fragile X syndrome, William's syndrome, Rett syndrome, Down's syndrome, Angelman syndrome, autism, ischemia, hypoxia, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. Reelin can also be used to alter dendritic spine density, diminished long-term potentiation, and diminished synaptic plasticity and associative learning deficits. Constructs formed from repeat region 3 of full length Reelin and repeat region 5 of full length Reelin, or repeat region 3 of full length Reelin and repeat region 6 of full length Reelin have been found particularly useful.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Application of GCS inhibitor in preparation of medicine for treating cocaine addiction
ActiveCN113893346AInhibitory behavioral effectReduce contentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDepressantDendrite
The invention discloses application of a GCS inhibitor in preparation of a medicine for treating cocaine addiction, and belongs to the field of drug rehabilitation medicines. Experiments prove that the GCS inhibitor can specifically reduce the content of glucosylceramide sphingolipid in the nucleus-isolated brain region, reduce the dendritic branch number and the dendritic spine density, and effectively inhibit the behavioral effects (behavioral sensitization, reward effect and autonomous administration behavioral effect) of cocaine on mice. The GCS inhibitor is used for preparing the medicine for treating cocaine addiction, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Methods of stimulating cellular growth, synaptic remodeling and consolidation of long-term memory
Owner:BLANCHETTE ROCKEFELLER NEUROSCI INST
Preparation method of adeno-associated virus with epigenetic modification function and application thereof
InactiveCN110863012AImprove efficiencySignificant epigenetic modificationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousAdenoassociated virus
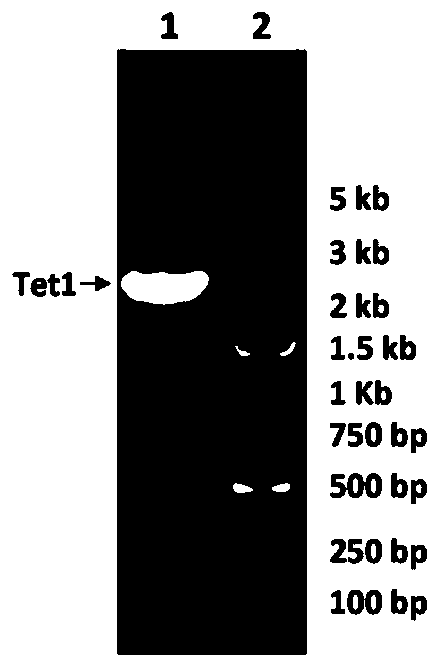
The invention relates to an application of a recombinant single-stranded DNA virus vector with a heterologous nucleic acid sequence in preparation of a medicine for treating stress cognitive impairment, which comprises a pharmaceutical composition comprising the virus vector, a method for preparing the virus vector, and an application of the virus vector in research on an epigenetic regulation mechanism and treatment on cognitive disorder caused by stress. Wherein the recombinant single-stranded DNA virus vector is an adeno-associated virus vector, and the heterologous nucleic acid encodes therapeutic protein; wherein the therapeutic protein is TET1 (1418 to 2136aa). The adeno-associated virus with the epigenetic modification function is artificially prepared, expression of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF can be induced through epigenetic modification after the adeno-associated virus infects an organism, neuron survival and neurogenesis are maintained, dendritic spine maturation is promoted, and therefore the effect of resisting and treating stress cognitive injuries is achieved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Method and system for automatically detecting single neuron dendritic spine in fluorescence image
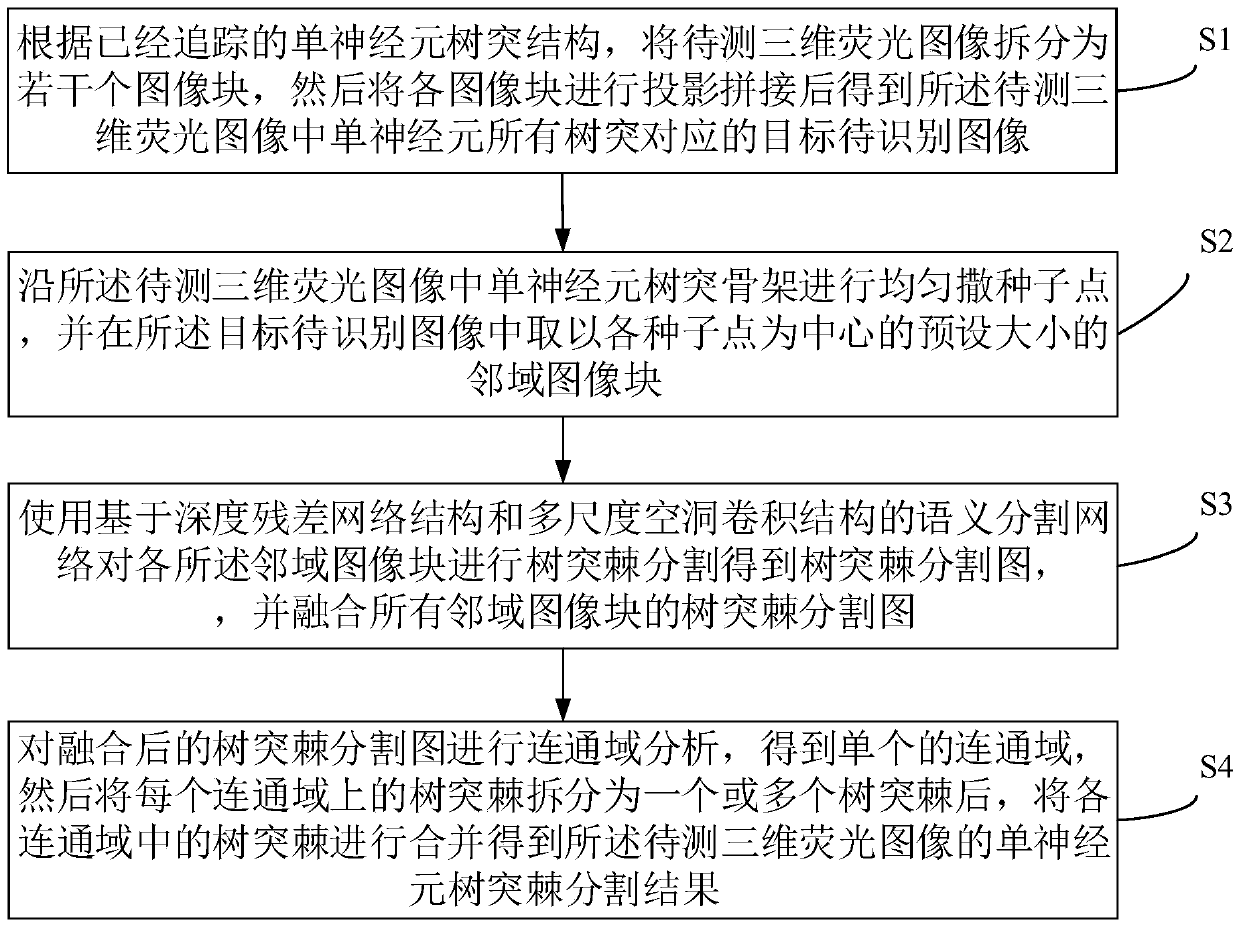
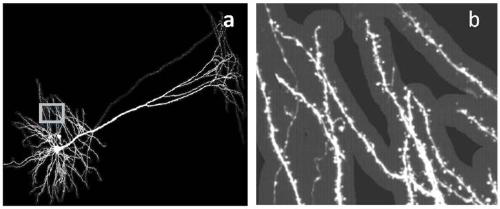
ActiveCN111091530AHigh precisionStructural inefficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork structureComputer vision
The invention discloses an automatic detection method and system for a single neuron dendritic spine in a fluorescence image. The method comprises the steps: splitting a to-be-detected three-dimensional fluorescence image into a plurality of image blocks, carrying out the projection splicing of the image blocks, and obtaining a target to-be-recognized image corresponding to all dendrites of a single neuron; uniformly scattering seed points along the single neuron dendritic skeleton, and taking neighborhood image blocks taking the seed points as centers from the target to-be-identified image; performing dendrite spine segmentation on each neighborhood image block by using a semantic segmentation network based on a deep residual network structure and a multi-scale cavity convolution structure to obtain a dendrite spine segmentation image, and fusing the dendrite spine segmentation images; and carrying out connected domain analysis on the fused dendritic spine segmentation map to obtain asingle connected domain, splitting the dendritic spine on each connected domain into one or more dendritic spines, and combining the dendritic spines in each connected domain to obtain a single neuron dendritic spine segmentation result. According to the invention, the accuracy of identifying the dendritic spine is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Increase of protein synthesis ameliorates synaptopathy-related neurological disorders
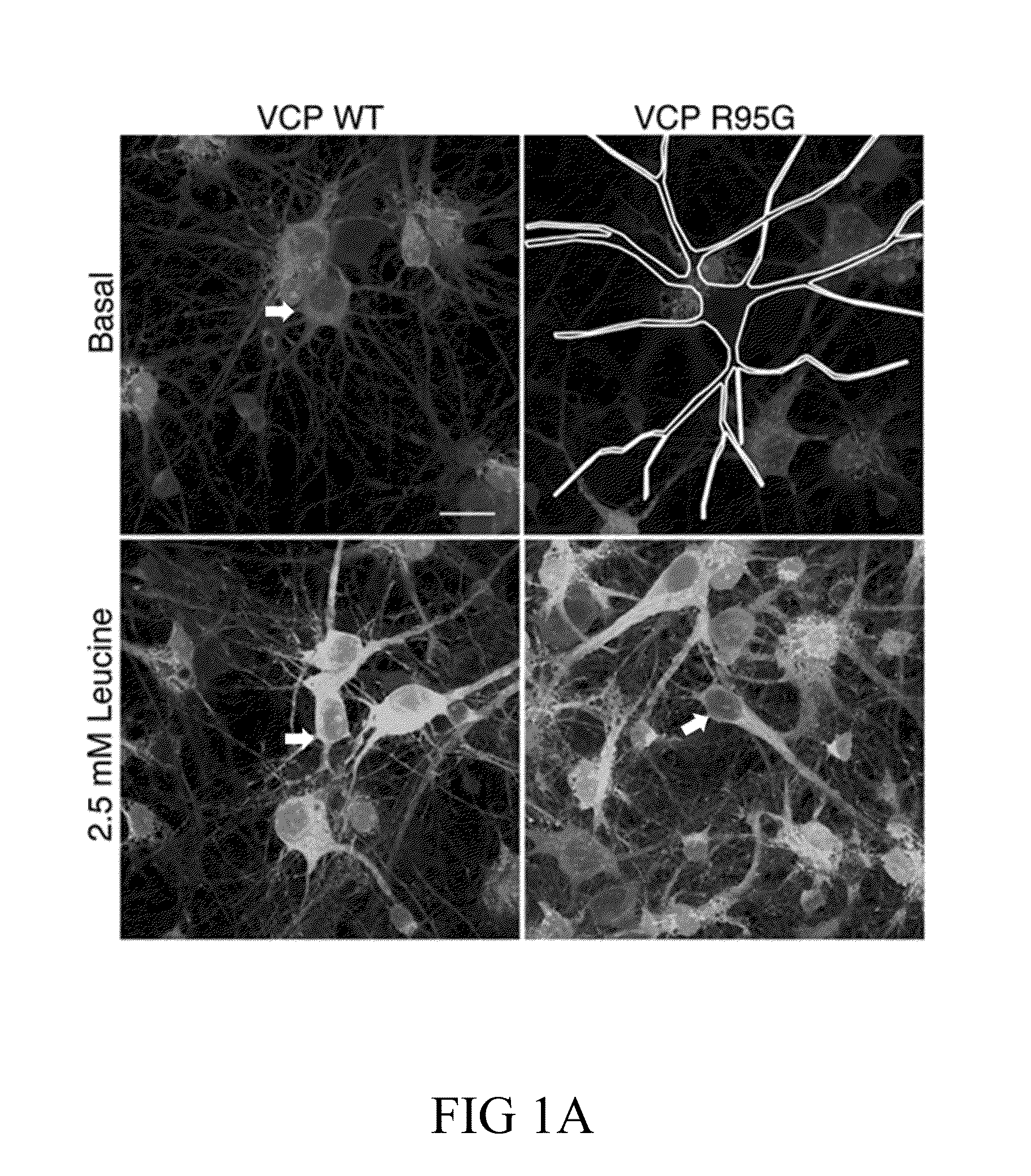
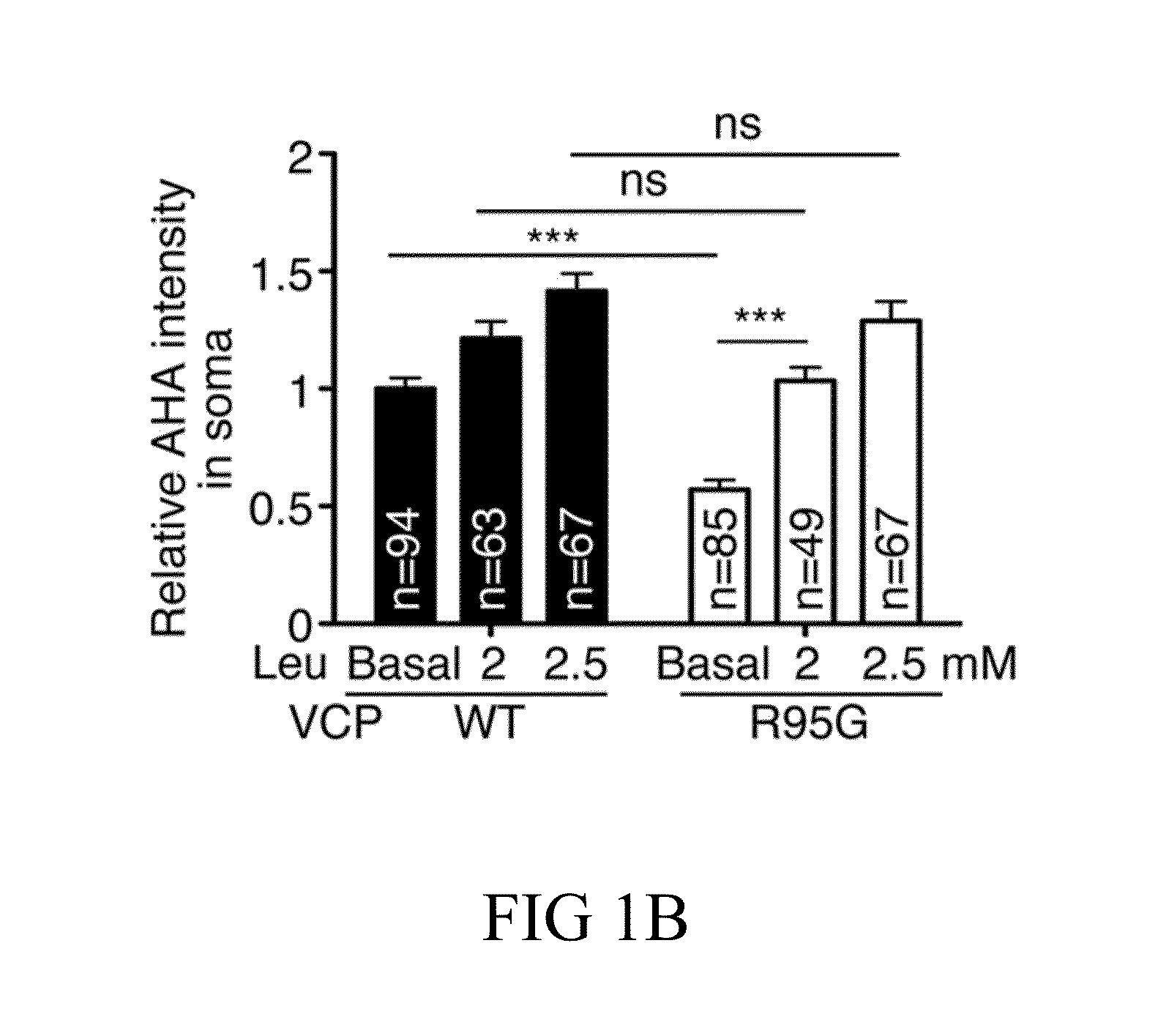
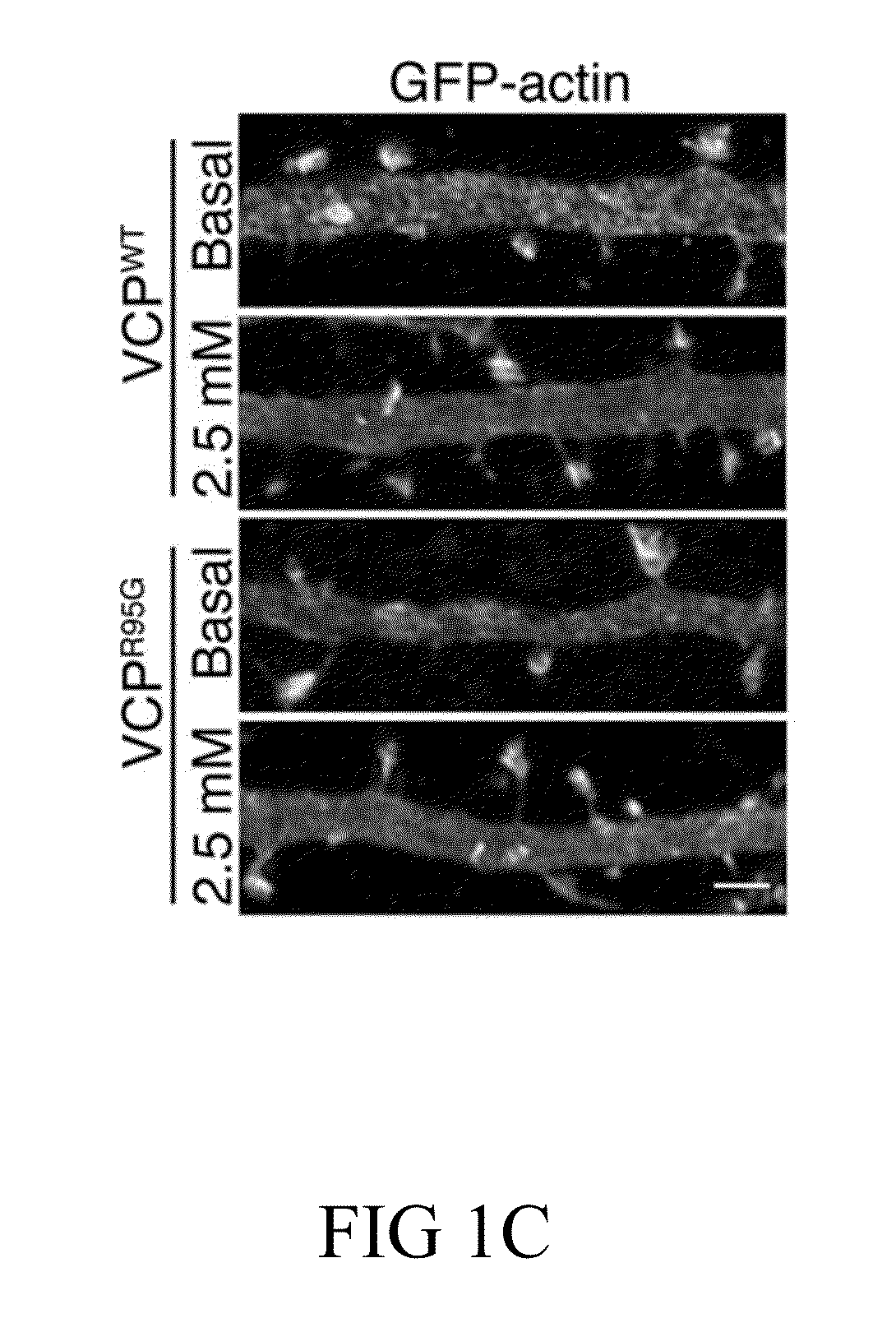
ActiveUS20160120831A1Decreased AHA intensityReduce in quantityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
Disclosed herein is a method for increasing the dendritic spine formation or dendritic spine density in a subject, whom is affected by a dendritic spine defect caused by the impairment in neurofibromin (NF1 protein), valosin-containing protein (VCP), atlastin-1 (ATL1), or superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1). Accordingly, also disclosed herein is a method for treating a subject having or suspected of having a synaptopathy caused by the impairment in NF1, VCP, ATL1, or SOD1.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Biguanide substance and application thereof
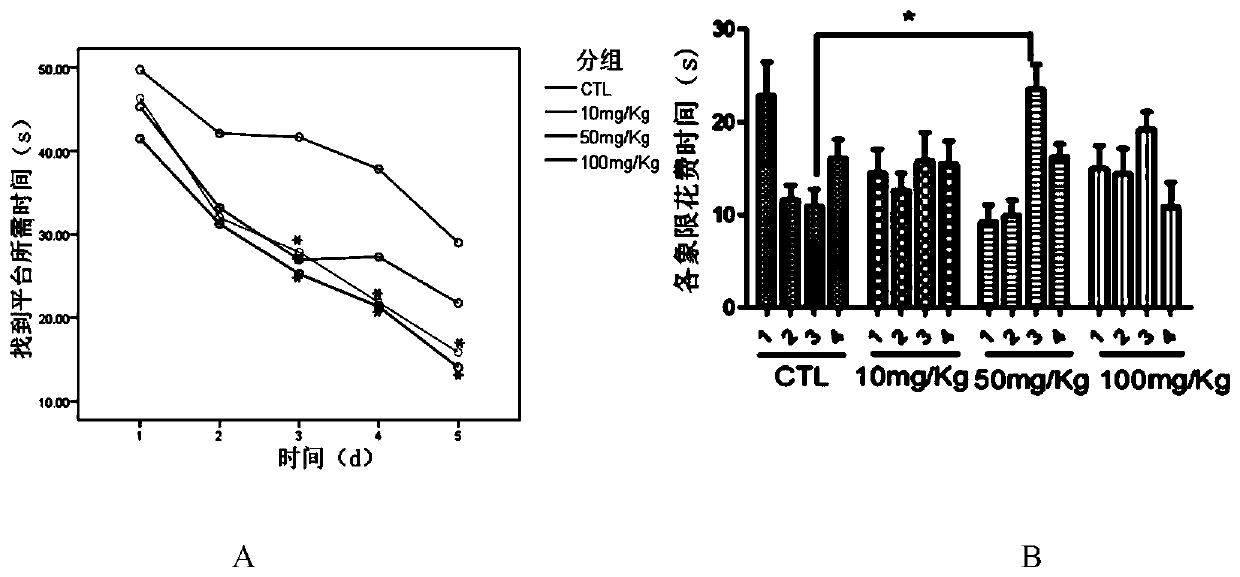
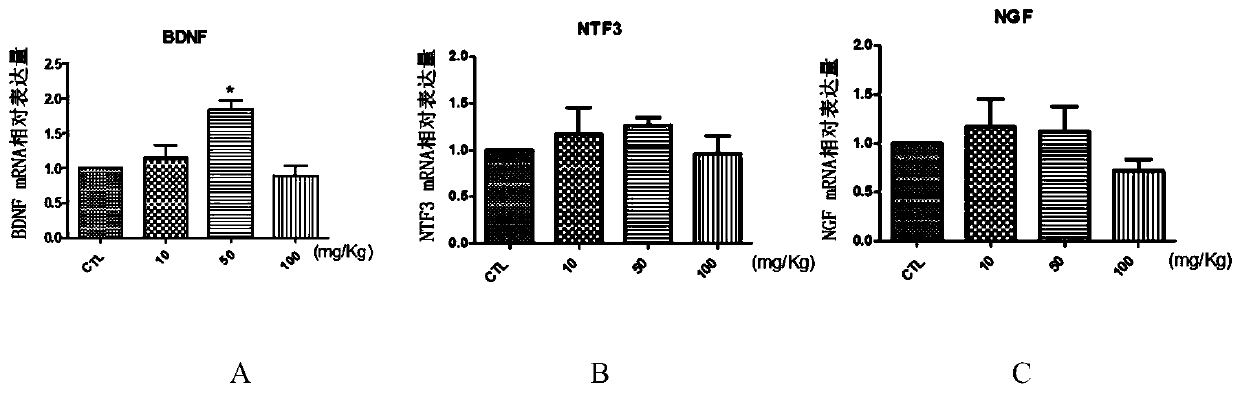
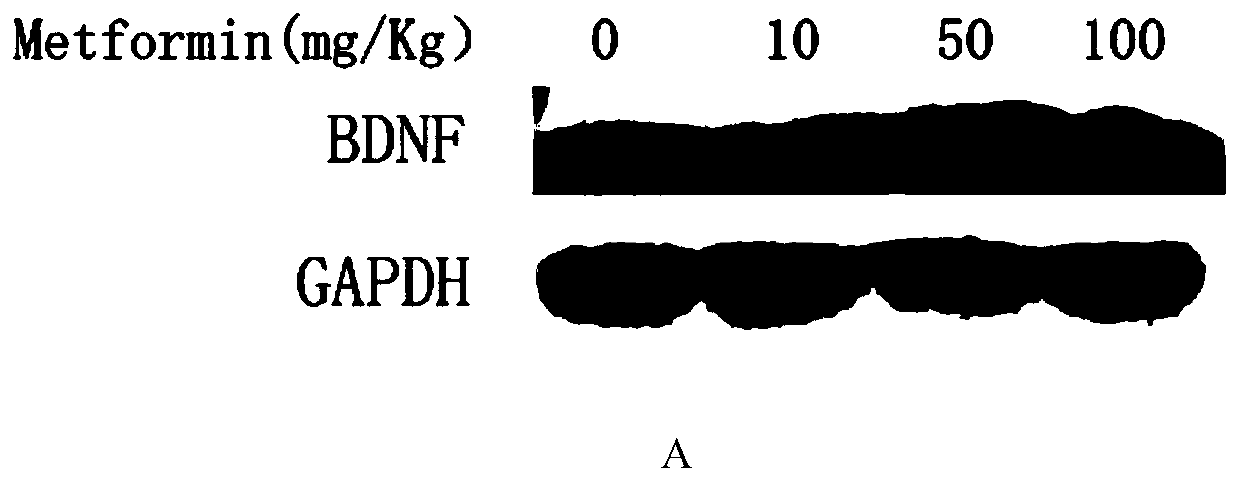
InactiveCN110063950AImprove activity efficiencyStrengthens and improves cognitive functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMetformin HydrochlorideNeuron
The invention discloses a biguanide substance and application thereof. The biguanide substance, especially metformin hydrochloride can promote the learning and memory ability of adolescents and can promote the learning and memory ability of adolescent mice through an AMPK / PKA-CREB signaling pathway, dentate gyrus newborn neurons are added, the complexity of hippocampal neuron axons is improved, and the number of dendritic spines is increased; a mechanism LTP closely related to learning and memory is adjusted by activating AMPK in the brains of the mice, the PKA signaling pathway is activated,the learning and memory ability of the adolescents is improved, and an experimental basis is provided for research of new nootropic drugs.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Application of salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules in preparing medicine for preventing and treating AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) encephalopathy
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy, and in particular relates to an application of salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules in preparing medicine for preventing and treating nerve injury caused by AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) encephalopathy and HIV-1Tat (human immunodeficiency virus-1Tat) proteins. According to the application an HIV-1 Tat protein injured neural cell line PC12 and a neural cell on a mouse brain slice are protected with the salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules in different concentrations, and the effect of the salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules in reducing neural cell death due to Tat protein is respectively detected by an MTT (thiazolyl blue) experiment, LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) detection and a Tunel experiment; and the effect of the salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules in reducing Tat protein injury neural cell synaptic connection function is detected by using Dil golden granule diOlistic labeling dendritic spine. Statistic analysis on experiment results discover that the salvia miltiorrhiza formula granules have a good protecting effect to neural cell injury caused by Tat protein, and can be used for preparing a medicine for preventing and treating AIDS encephalopathy and Tat protein.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Image classification method of neural dendritic spines based on multi-resolution fractal features
ActiveCN103150573BImprove classification accuracyClassification results are stableCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionClassification methods
Owner:XIAN JIAOTONG LIVERPOOL UNIV
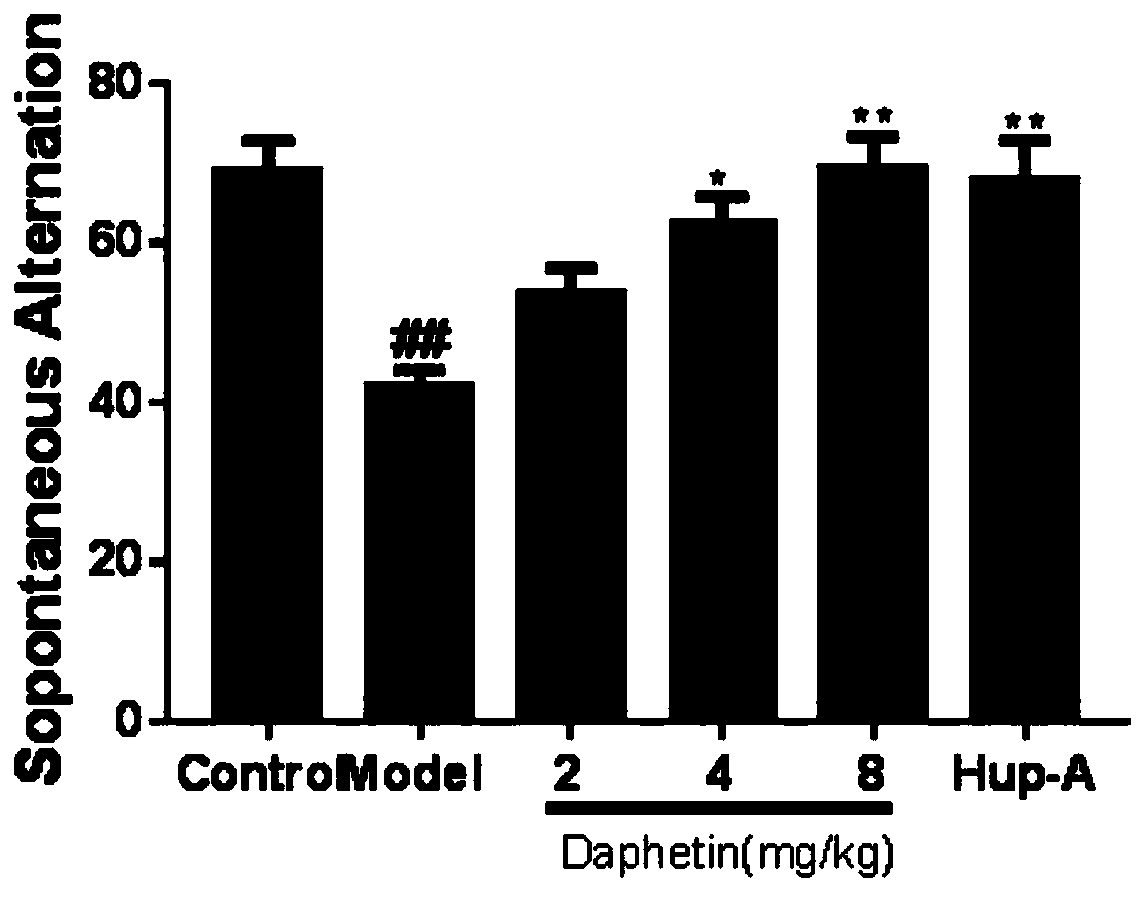
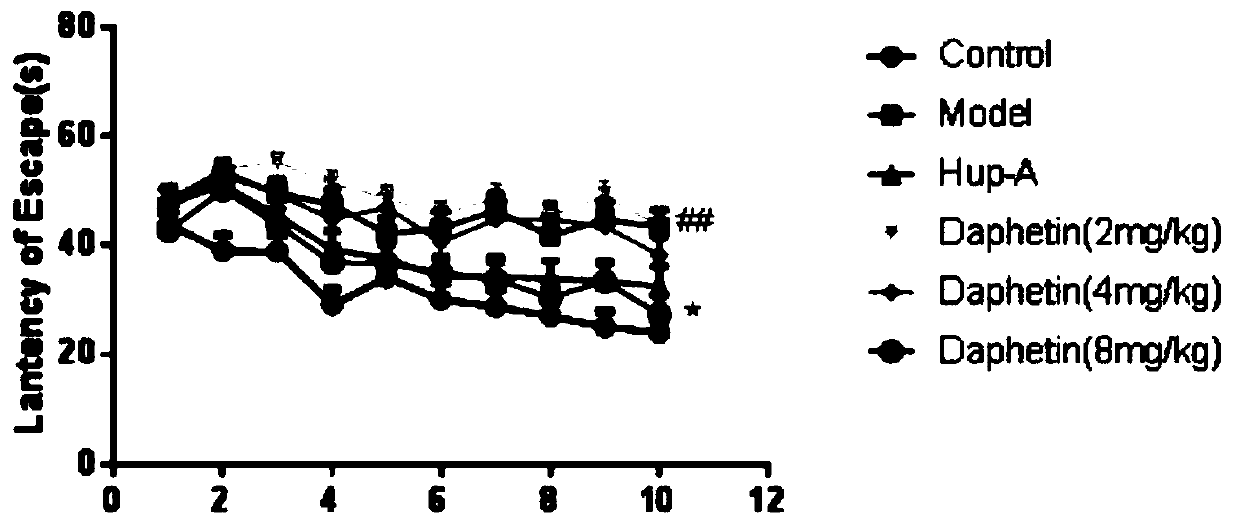
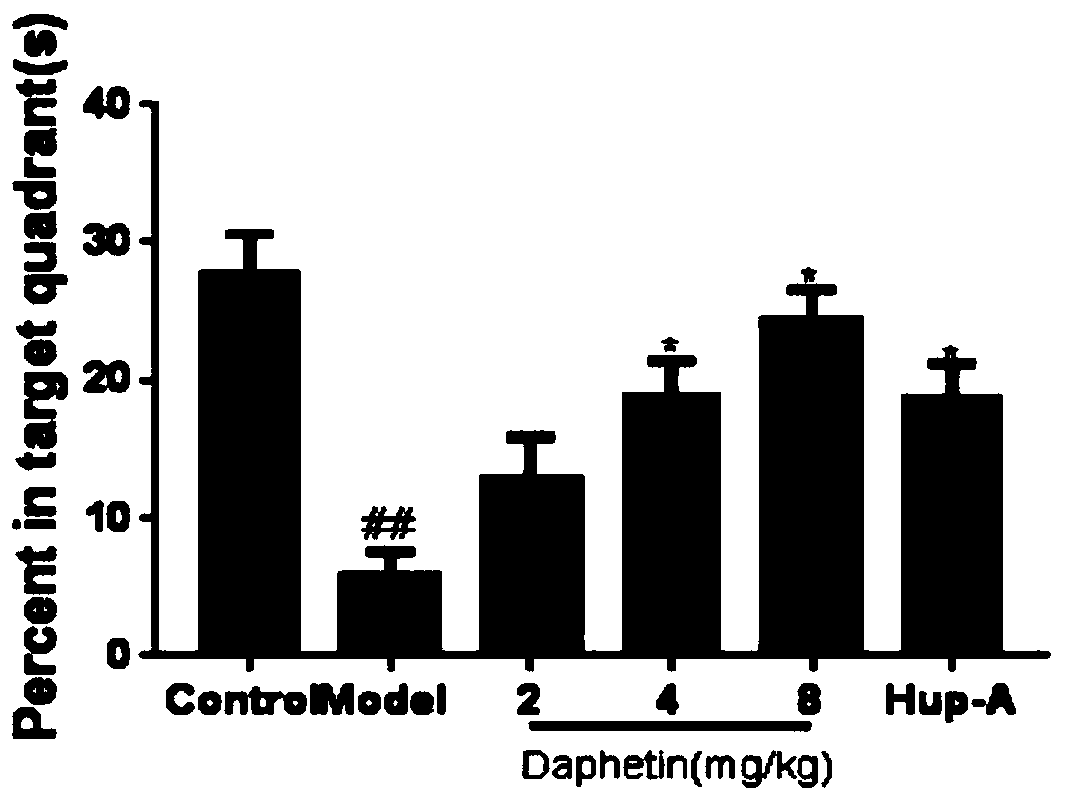
New application of daphnetin in preparation of drugs for preventing and treating neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveCN109939107AImprove cognitive impairmentFacilitated releaseNervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorCell Aggregations
The invention discloses a new application of daphnetin in preparation of drugs for preventing and treating neurodegenerative diseases, which comprises the application of daphnetin in preparation of the drugs for inhibiting beta amyloid protein aggregation in the brain. The preparation of daphnetin promotes synaptic basal release of brain neurons, and improves the application of synaptic plasticitydrugs. The application of daphnetin in preparation of drugs for improving brain cognitive impairment, the application of daphnetin in preparation of drugs for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease. Experiments show that the daphnetin has the effects of improving cognitive impairment of 5xFAD mice, inhibiting the enzymatic activity of BACE1, promoting the enzymatic activity of TACE and ADAM17, reducing the production of A beta; and increasing the content of NMDA receptor, increasing the number of dendritic spines, increasing the content of postsynaptic protein PSD95 and enhancing synaptic plasticity, with higher clinical application value and development prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Construction method of neural network architecture for simulating dendritic spine change
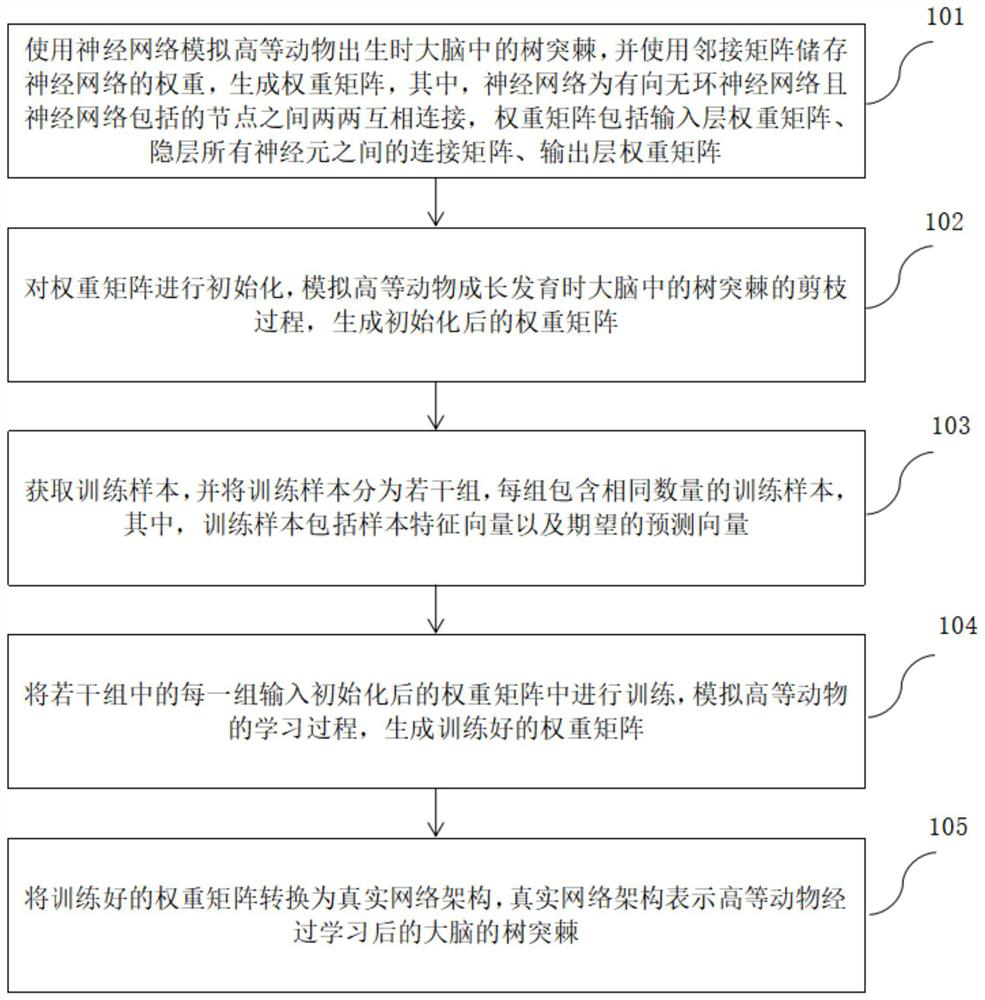
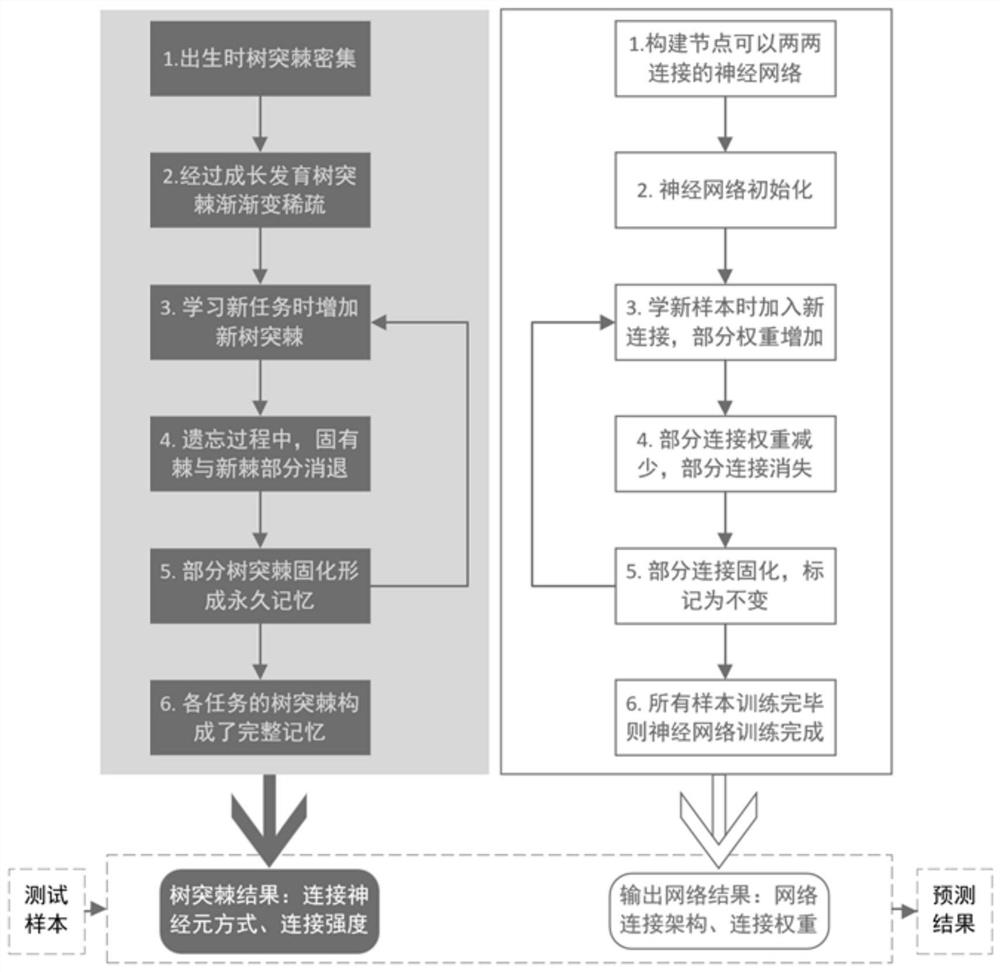
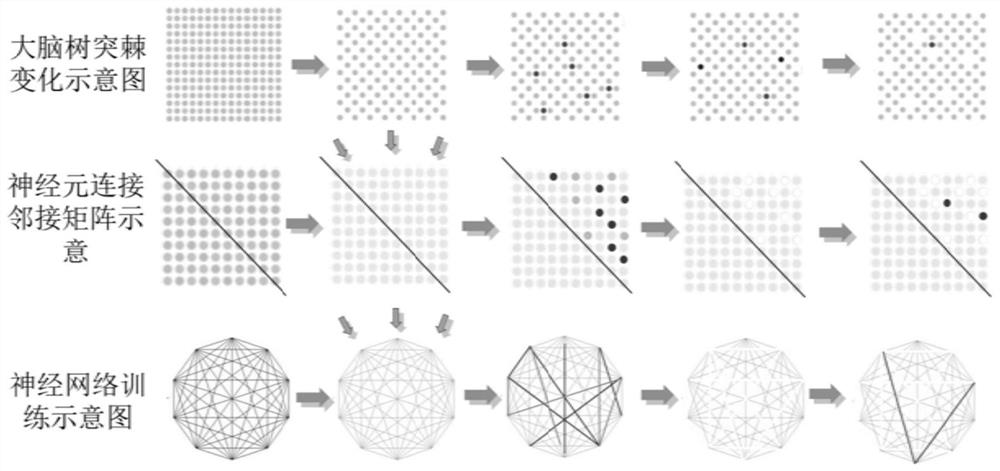
PendingCN113554081AGood training resultsAdaptableCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNetwork architectureNeural Network Simulation
The invention provides a construction method of a neural network architecture for simulating dendritic spine change, which comprises the following steps: simulating a dendritic spine in the brain of a higher animal during birth by using a neural network, storing the weight of the neural network by using an adjacent matrix, and generating a weight matrix; initializing the weight matrix, simulating the pruning process of dendritic spines in the brain during growth and development of higher animals, and genrating the initialized weight matrix; obtaining training samples, and dividing the training samples into a plurality of groups, wherein each group comprises the same number of training samples; inputting each of the plurality of groups into the initialized weight matrix for training, simulating the learning process of higher animals, and generating a trained weight matrix; and converting the trained weight matrix into a real network architecture, wherein the real network architecture represents the dendritic spines of the brain of the higher animal after learning. The method can be used for a supervised image recognition task, can train a proper neural network architecture for different problems, and has high adaptability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
TARGETING P18 FOR mTOR-RELATED DISORDERS
PendingUS20210163555A1Reduce expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderNervous systemLysosome localization
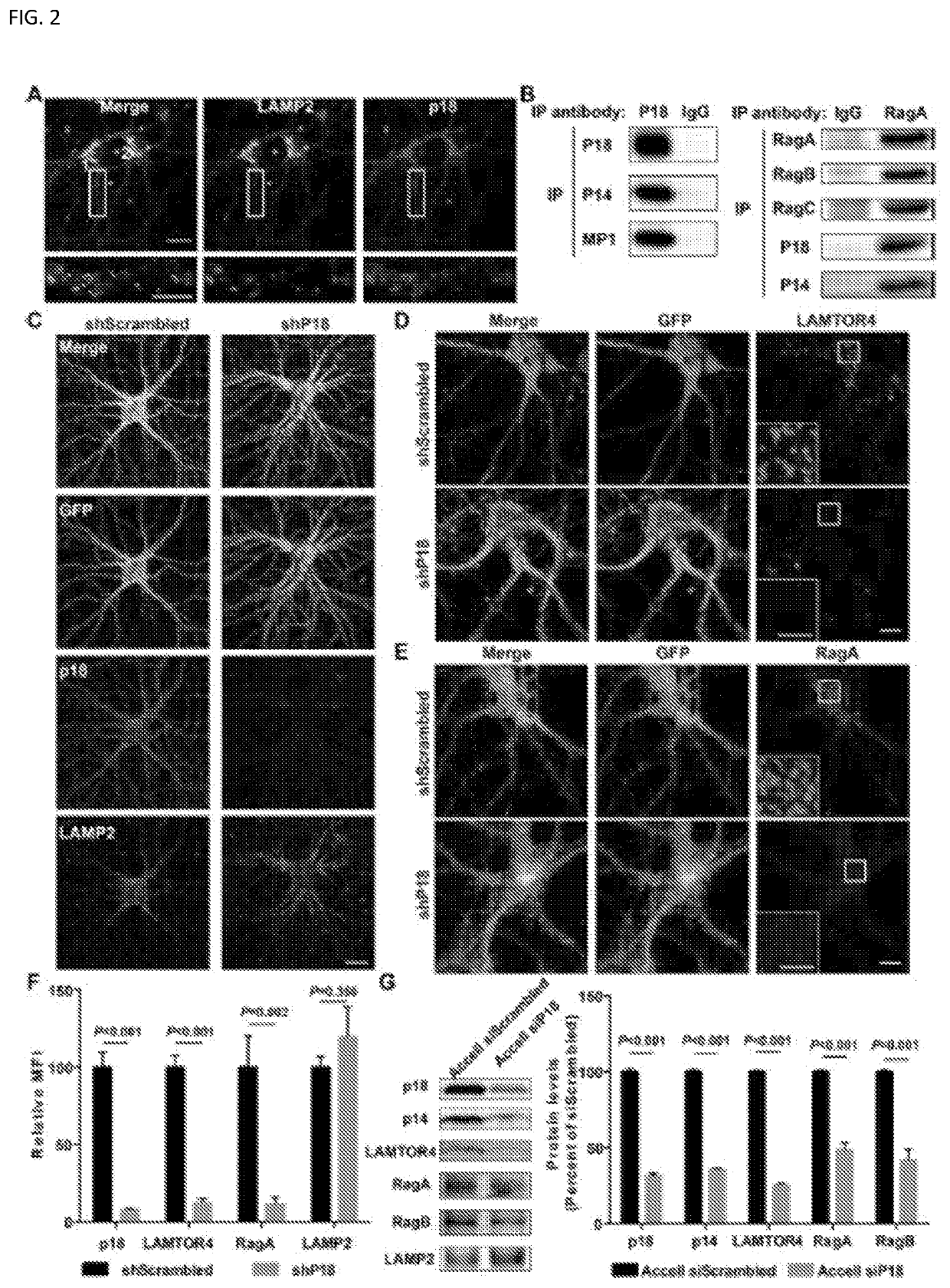
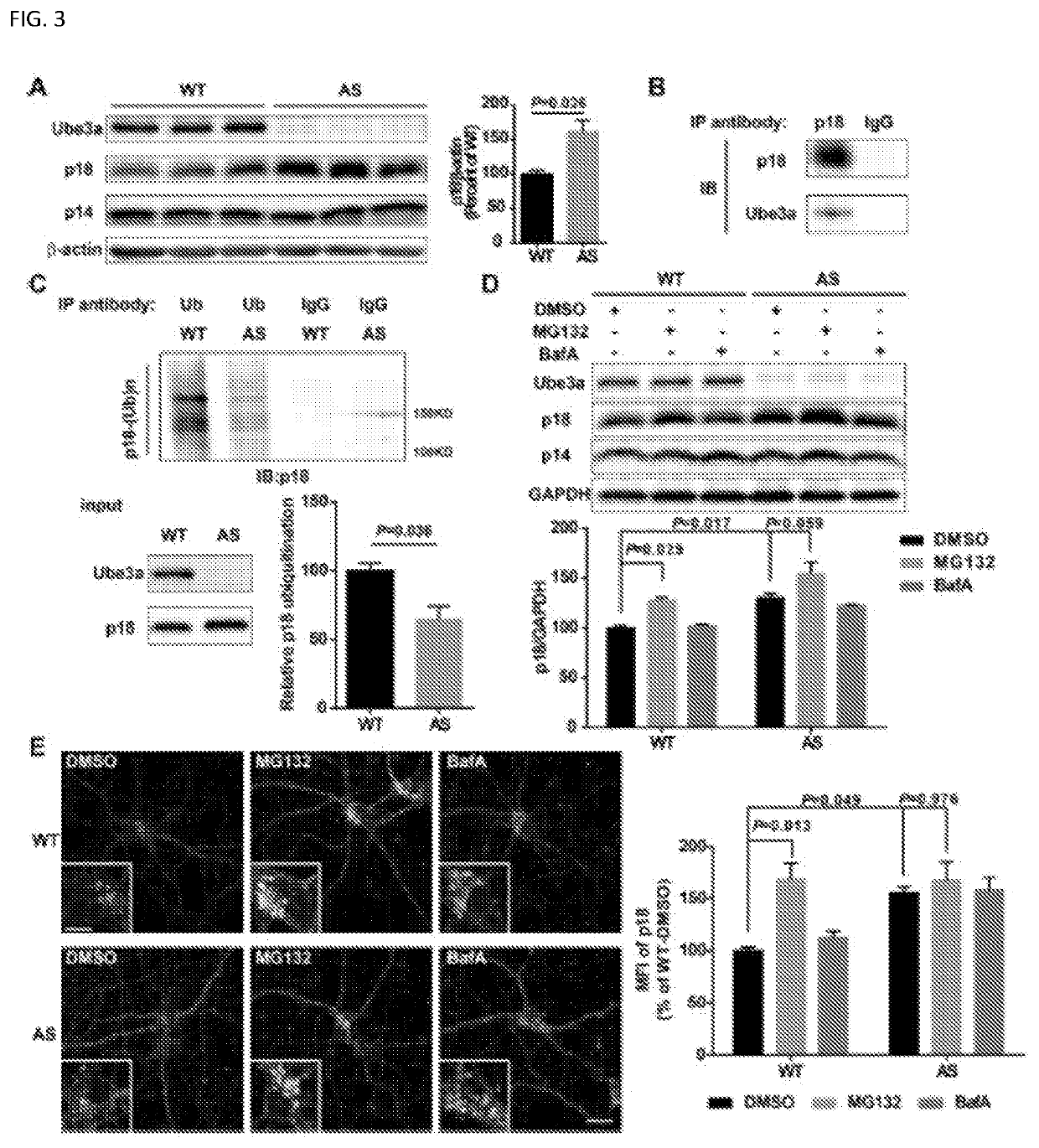
Accumulating evidence indicates that the lysosomal Ragulator complex is essential for full activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Abnormal mTORC1 activation has been implicated in several developmental neurological disorders, including Angelman syndrome (AS), which is caused by maternal deficiency of the ubiquitin E3 ligase UBE3A. Here, it is reported that Ube3a regulates mTORC1 signaling by targeting p18, a subunit of the Ragulator. Ube3a ubiquinates p18, resulting in its proteasomal degradation, and Ube3a deficiency in the hippocampus of AS mice induces increased lysosomal localization of p18 and other members of the Ragulator-Rag complex, and increased mTORC1 activity. p18 knockdown in hippocampal CA1 neurons of AS mice reduces elevated mTORC1 activity and improves dendritic spine maturation, long-term potentiation (LTP), as well as learning performance. The results described herein indicate that Ube3a-mediated regulation of p18 and subsequent mTORC1 signaling is critical for typical synaptic plasticity, dendritic spine development, and learning and memory.
Owner:WESTERN UNIV OF HEALTH SCI
Methods of stimulating cellular growth, synaptic remodeling and consolidation of long-term memory
The present invention provides methods of slowing or reversing the loss of memory and learning comprising the steps of contacting an effective amount of a PKC activator with a protein kinase C (PKC) in a subject identified with memory loss slowing or reversing memory loss. The present invention provides methods of stimulating cellular growth, neuronal growth, dendritic growth, dendritic spine formation, dendritic spine density, and the translocation of ELAV to proximal dendrites, and synaptic remodeling. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to stimulate the synthesis of proteins sufficient to consolidate long-term memory. The present invention also provides methods of contacting a protein kinase C (PKC) activator with a PKC activator in a manner sufficient to downregulate PKC.
Owner:COGNITIVE RES ENTERPRISES INC
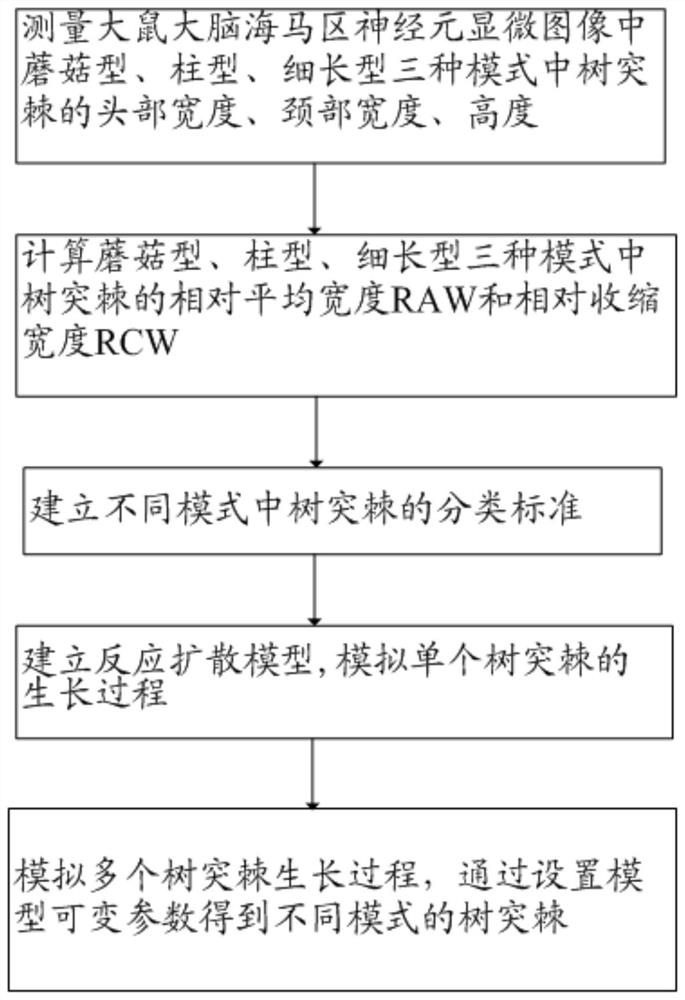
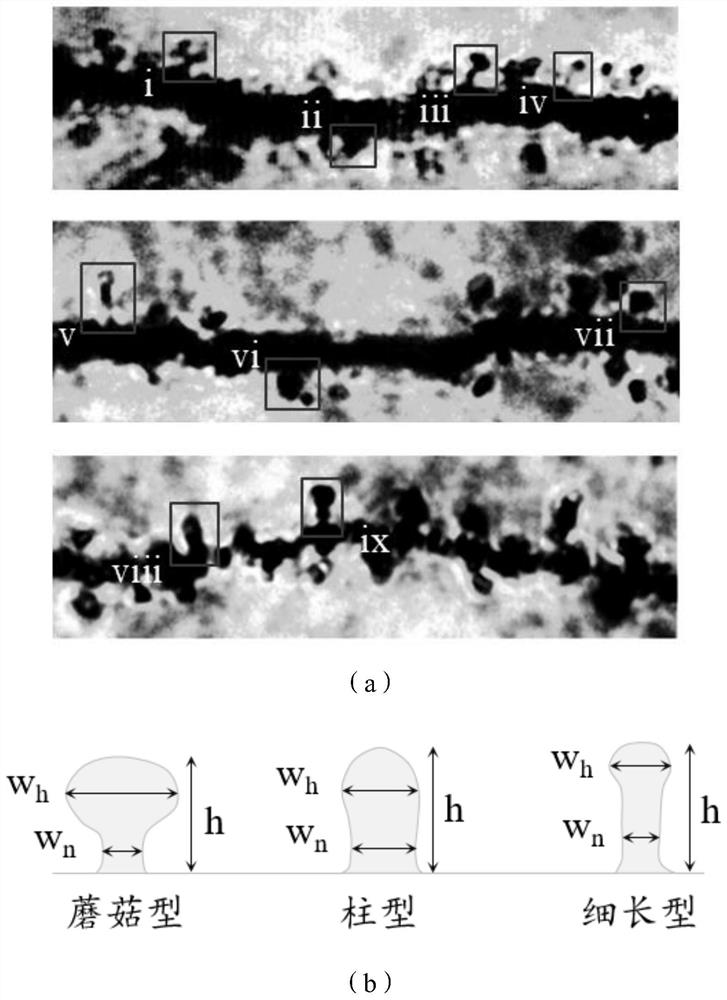
Method for establishing neuron dendritic spine development mode based on reaction diffusion model
The invention provides a method for establishing a neuron dendritic spine development mode based on a reaction diffusion model, which comprises the steps of formulating a dendritic spine shape classification standard by using the neuron dendritic spine shape of a rat brain hippocampus, simulating the growth process of a single dendritic spine under different conditions by using the reaction diffusion model, classifying simulation results by using a shape classification standard, and further simulating a process of growing dendritic spines with different densities by using the reaction diffusion model under different conditions so as to obtain neuron dendritic spines with different modes. Compared with an existing research method, a large number of animal experiments are effectively avoided; and meanwhile, the reaction diffusion model is applied to the establishment process of the neuron dendritic spine development mode for the first time, and a foundation is laid for subsequent research on the pathogenesis of diseases caused by abnormal dendritic spine modes.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com