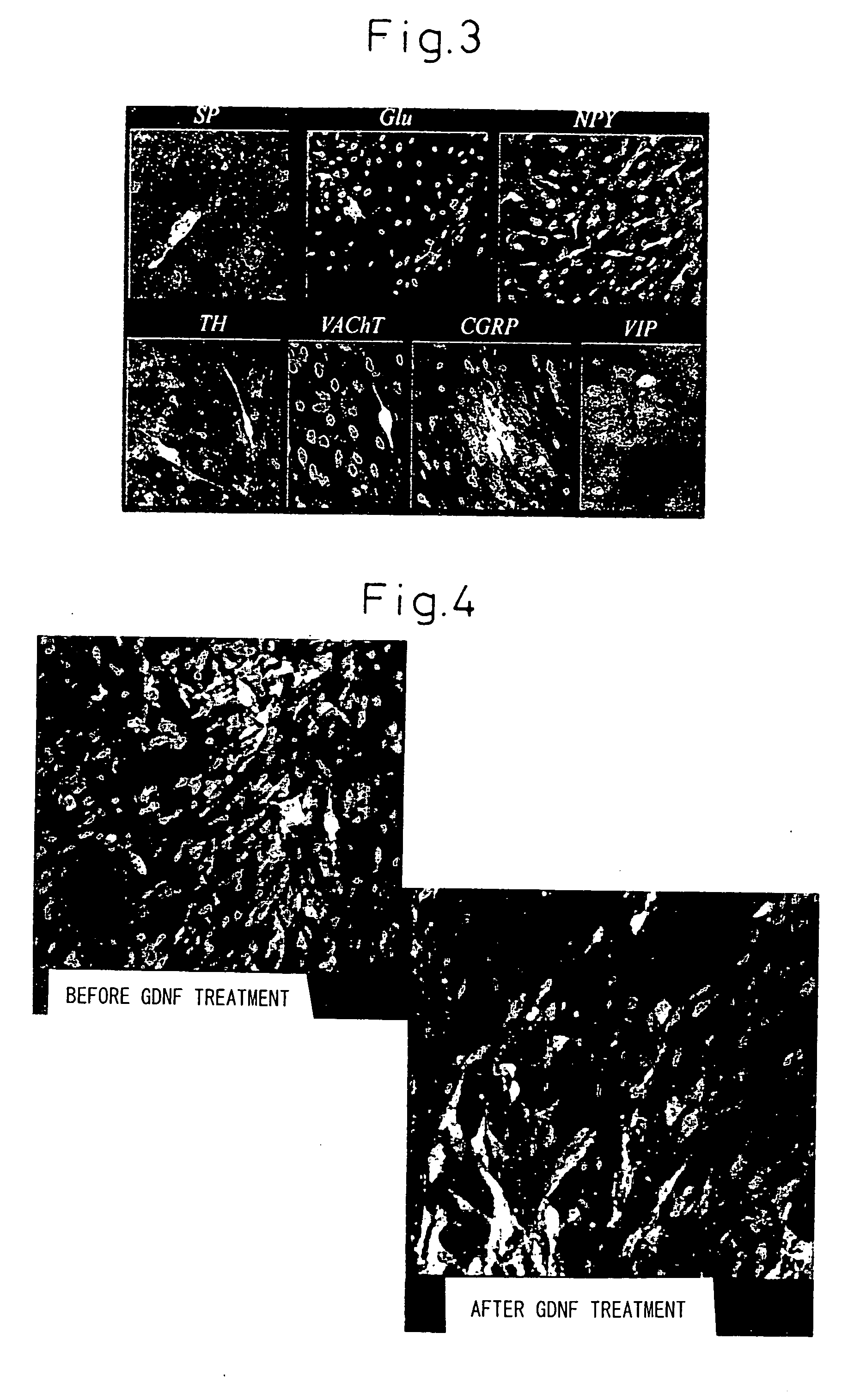
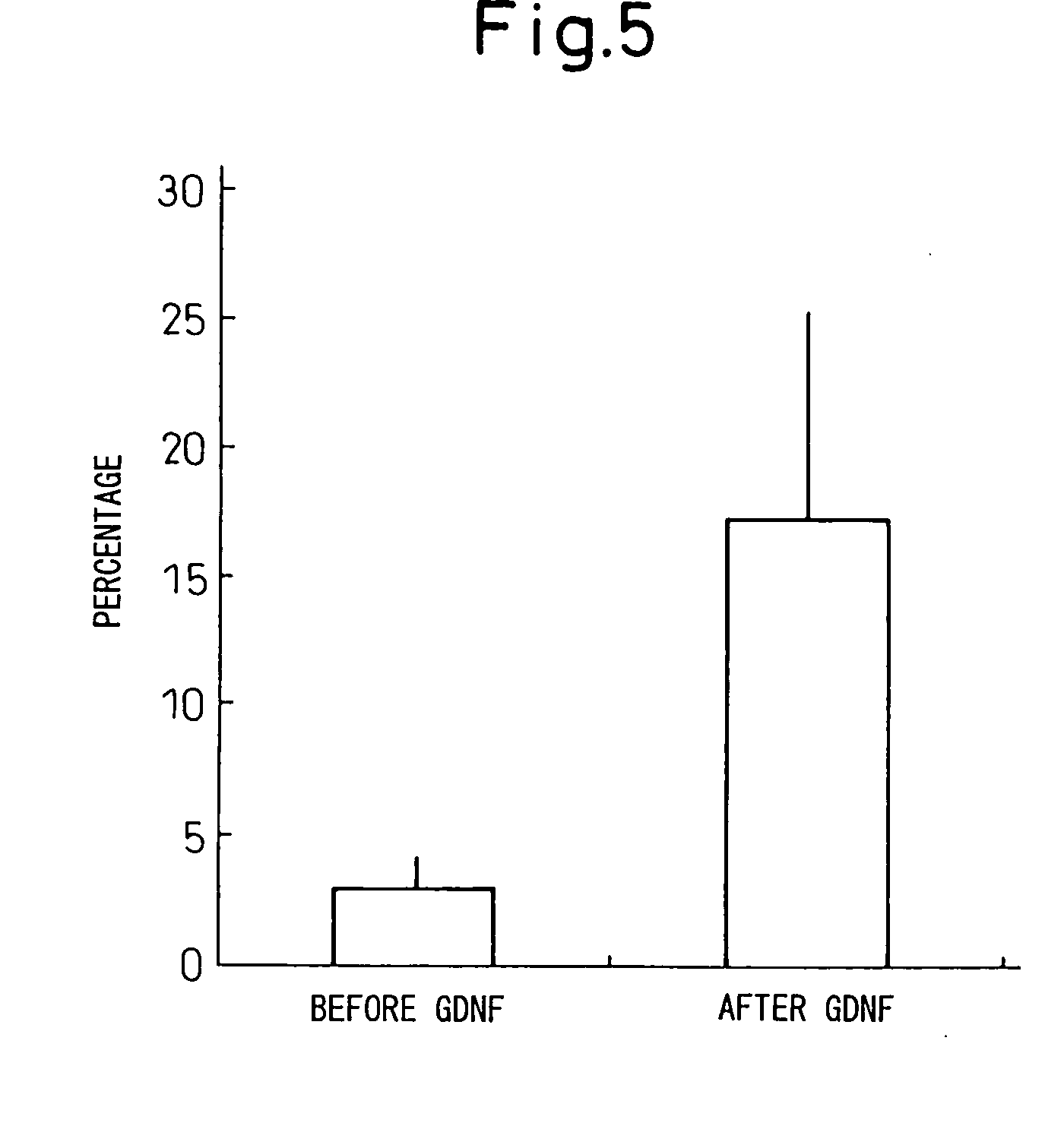
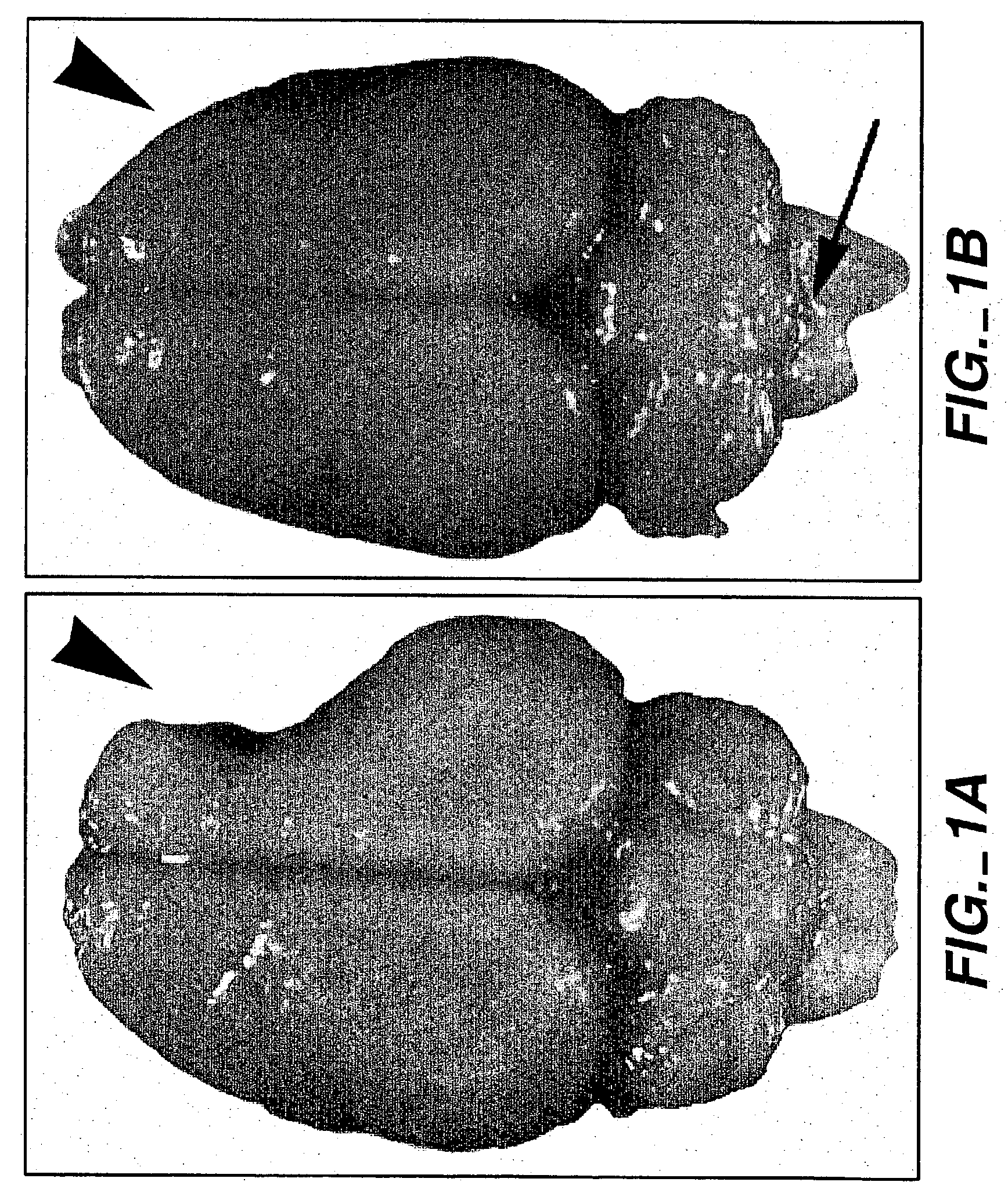
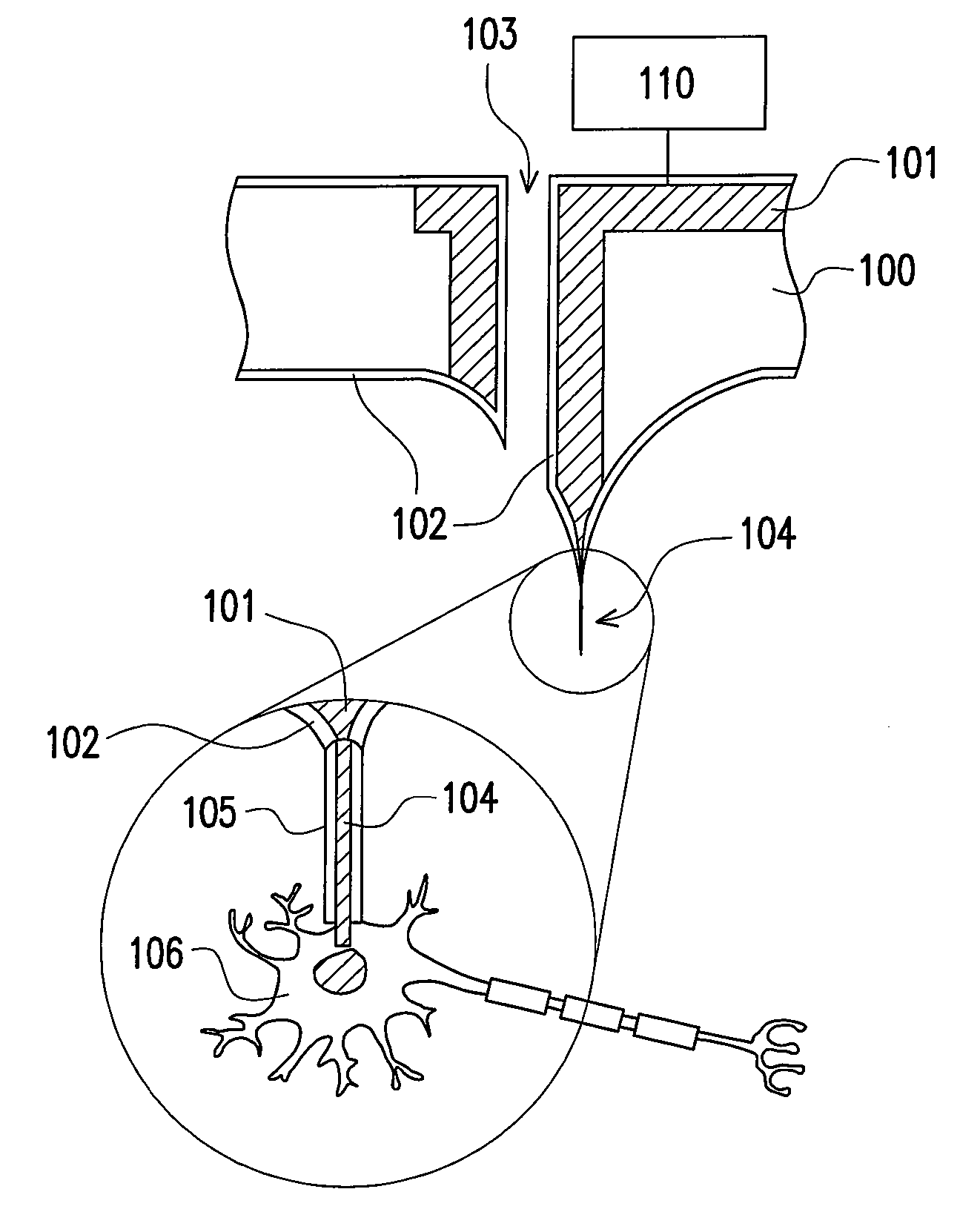
Patents
Literature
420 results about "Neural cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A neural cell, also known as a neuron, is the basic biochemical cell located within the nervous system. Neural cells come in a variety of different forms; however, the most common delineation between types stems from their function.
Human cord blood as a source of neural tissue for repair of the brain and spinal cord
InactiveUS20020028510A1Easy to distinguishImprove neurological dysfunctionNervous disorderCell differentiationDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The present invention relates to the use of umbilical cord blood cells from a donor or patient to provide neural cells which may be used in transplantation. The isolated cells according to the present invention may be used to effect autologous and allogeneic transplantation and repair of neural tissue, in particular, tissue of the brain and spinal cord and to treat neurodegenerative diseases of the brain and spinal cord.
Owner:SANERON CCEL THERAPEUTICS +1
Methods for using tetanus toxin for beneficial purposes in animals (mammals)
Methods of using tetanus toxin to modulate or control neural functions or nonneural cellular activities at selected sites in animals, particularly in mammals, and more particularly in humans, are provided. Pharmaceutical formulations to modulate neural functions or non-neural cellular activities of an animal at selected sites in animals, particularly in mammals, and more particularly in humans are also provided. Uses of tetanus toxin in preparation of medicaments for methods of treating clinical disorders or symptoms of animals, particularly mammals and more particularly humans are also provided.
Owner:SANDERS
Biological Cell Acoustic Enhancement and Stimulation
InactiveUS20080045882A1Improve efficiencyAccelerate patient recoverySonopheresisUltrasound therapyBiological cellAcoustic energy
A method for enhancing the uptake of a therapeutic biological agent by treated cells. A low-power, unfocused field of acoustic energy is directed at the treated cells after the delivery of the therapeutic agent to the treated cells. A related method for stimulating either neural cells or cells in a cell culture. A portable sized device provides the field, and may include either an array of emitters or a scanable emitter.
Owner:FINSTERWALD P MICHAEL
Differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
Method for differentiating mesenchymal stem cells into neural cells
A method for differentiating mesenchymal stem cells of bone marrow into neural cells comprises culturing the mesenchymal stem cells in a medium containing epidermal growth factor(EGF), basic fibroblast growth factor(bFGF) and hepatocyte growth factor(HGF), and the neural cells produced thereby can be employed for the treatment of a neural disease.
Owner:PHARMICELL +1
Method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
Cell therapy for chronic stroke
A method of treating stroke in a patient who has undergone a stroke comprising administering at least 2 million suitable neuronal cells to at least one brain area involved in the stroke. The method comprises the step of using a twist drill or a burr to form a hole in the skull through which the cells could be administered. Exemplary cells are hNT neuronal cells, HCN-1 cells, fetal pig cells, neural crest cells, neural stem cells, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed herein is a pharmaceutical composition of 95% pure hNT neuronal cells, which composition further includes a vial containing PBS and human neuronal cells. This vial is provided in a container with liquid nitrogen, whereby the composition is frozen and maintained at -170° C. before use. Also disclosed are methods of improving speech, cognitive, sensory, and motor function in a person who has experienced brain damage which interferes with function by administering a sterile composition of a sufficient number of neuronal cells or neural stem cells to the damaged area. Also disclosed is a method of replacing central nervous cells lost to neurodegenerative disease, trauma, ischemia or poisoning.
Owner:LAYTON BIOSCI +1
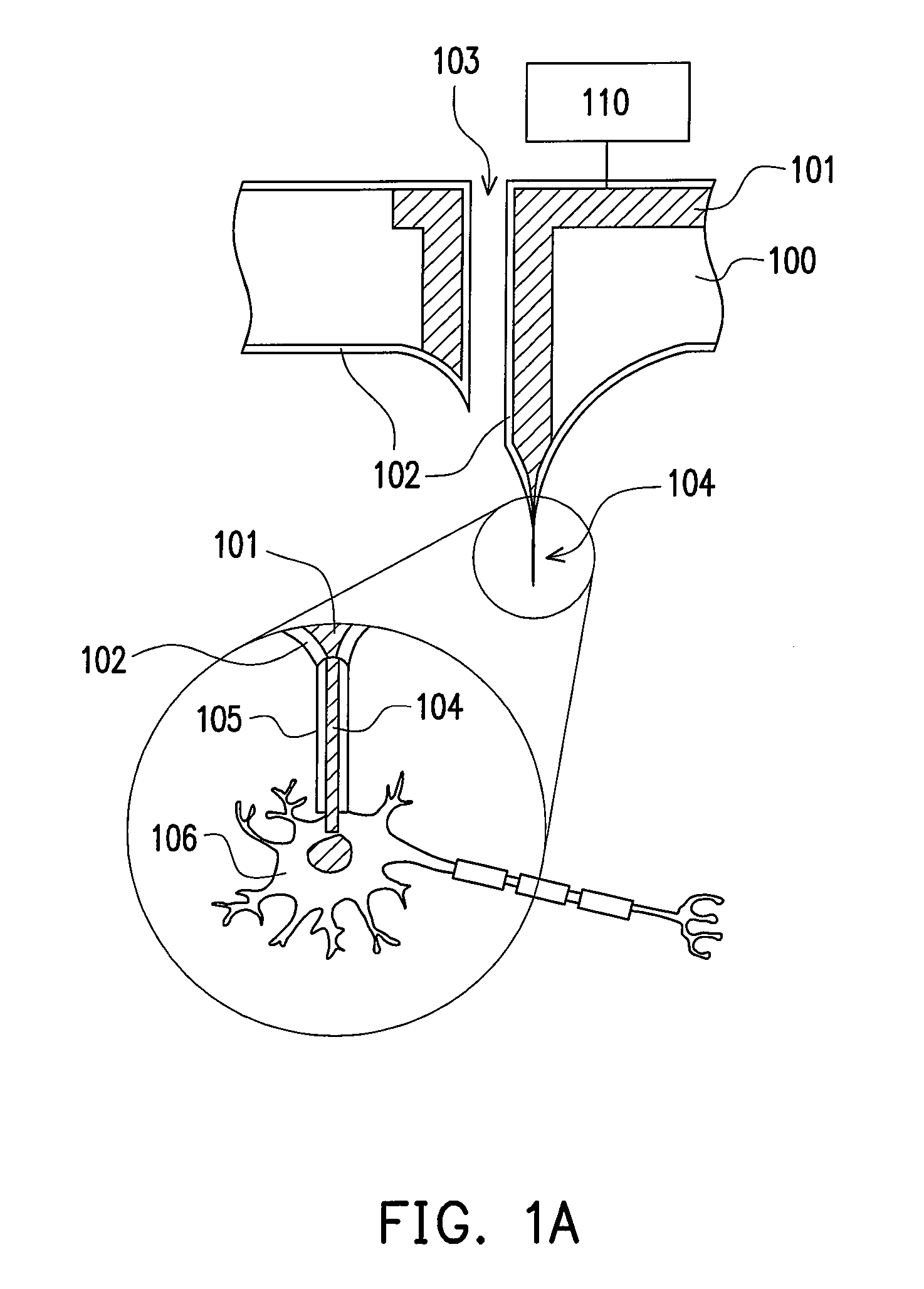
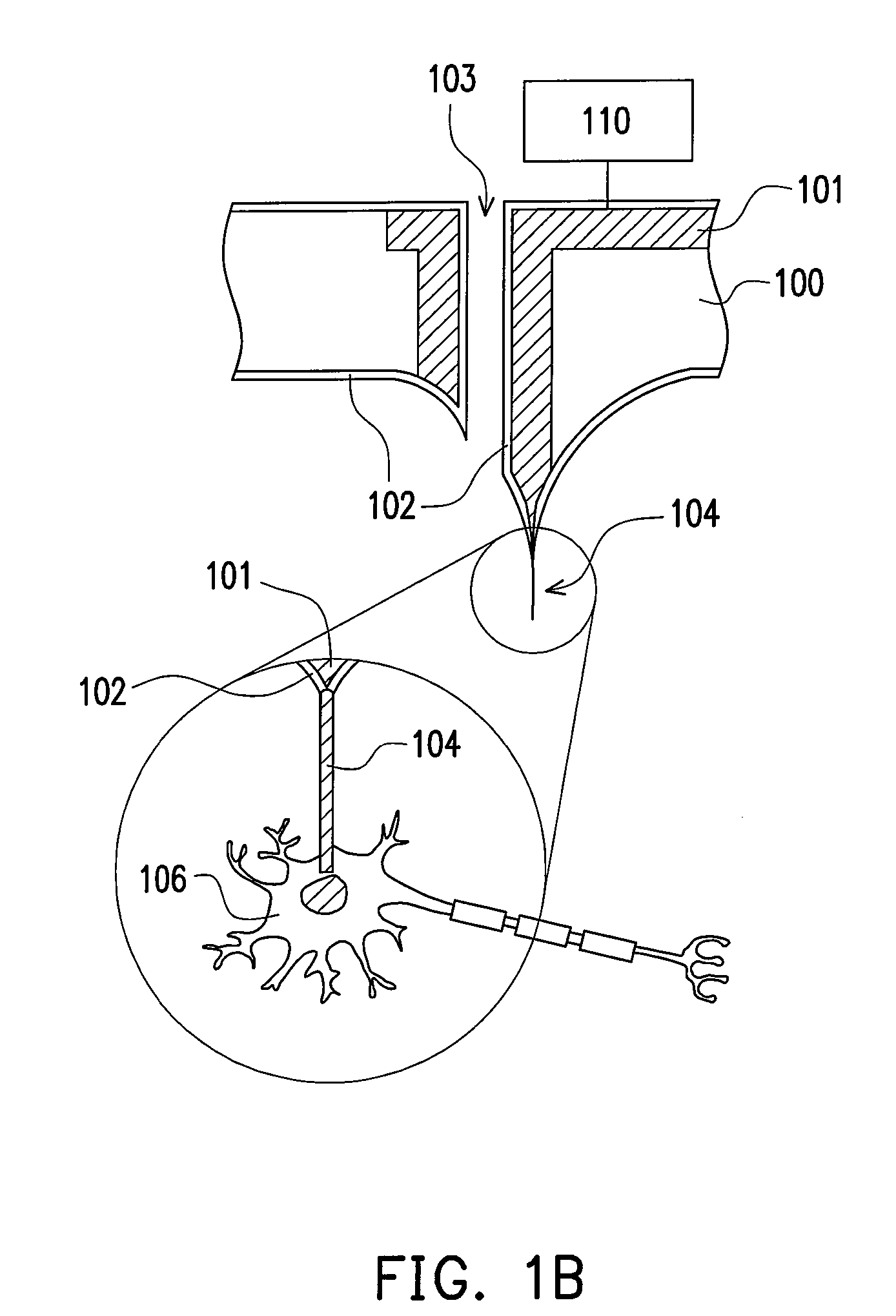
Multifunctional nano-probe interface structure for neural prostheses and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080140195A1Accurately and regionally stimulateEasy to combineSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNeural cellIsolation layer
A novel multifunctional nano-probe interface is proposed for applications in neural stimulation and detecting. The nano-probe interface structure consists of a carbon nanotube coated with a thin isolation layer, a micro-electrode substrate array, and a controller IC for neural cell recording and stimulation. The micro-electrode substrate array contains wires connecting the carbon nanotube with the controller IC, as well as microfluidic channels for supplying neural tissues with essential nutrition and medicine. The carbon nanotube is disposed on the micro-electrode substrate array made by silicon, coated with a thin isolation layer around thereof, and employed as a nano-probe for neural recording and stimulation.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Biomarkers of aging for detection and treatment of disorders
InactiveUS20130040844A1Modulate activityVirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNeural cell
Provided are methods of diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of aging using biomarkers that have been discovered to be linked to biological aging process. Methods for increasing neural cell regeneration and cognitive function are also provided. The methods are, at least in part, based on a discovery that altered expression patterns of certain biological markers are associated with biological aging processes. These markers comprise at least Eotaxin / CCL11, 2-microglobulin, MCP-1 and Hap-toglobulin, increased expression of which has been shown to be associated with increase in biological aging process.
Owner:DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS VA +1
Derivation of terminally differentiated dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20060211109A1Simple methodIncrease percentageNervous disorderCulture processNervous systemNeural cell
The present disclosure is directed to improved methods for efficiently producing neuroprogenitor cells and differentiated neural cells such as dopaminergic neurons and serotonergic neurons from pluripotent stem cells, for example human embryonic stem cells. Using the disclosed methods, cell populations containing a high proportion of cells positive for tyrosine hydroxylase, a specific marker for dopaminergic neurons, have been isolated. The neuroprogenitor cells and terminally differentiated cells of the present disclosure can be generated in large quantities, and therefore may serve as an excellent source for cell replacement therapy in neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Complete medium with low serum concentration for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells and method for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells using same
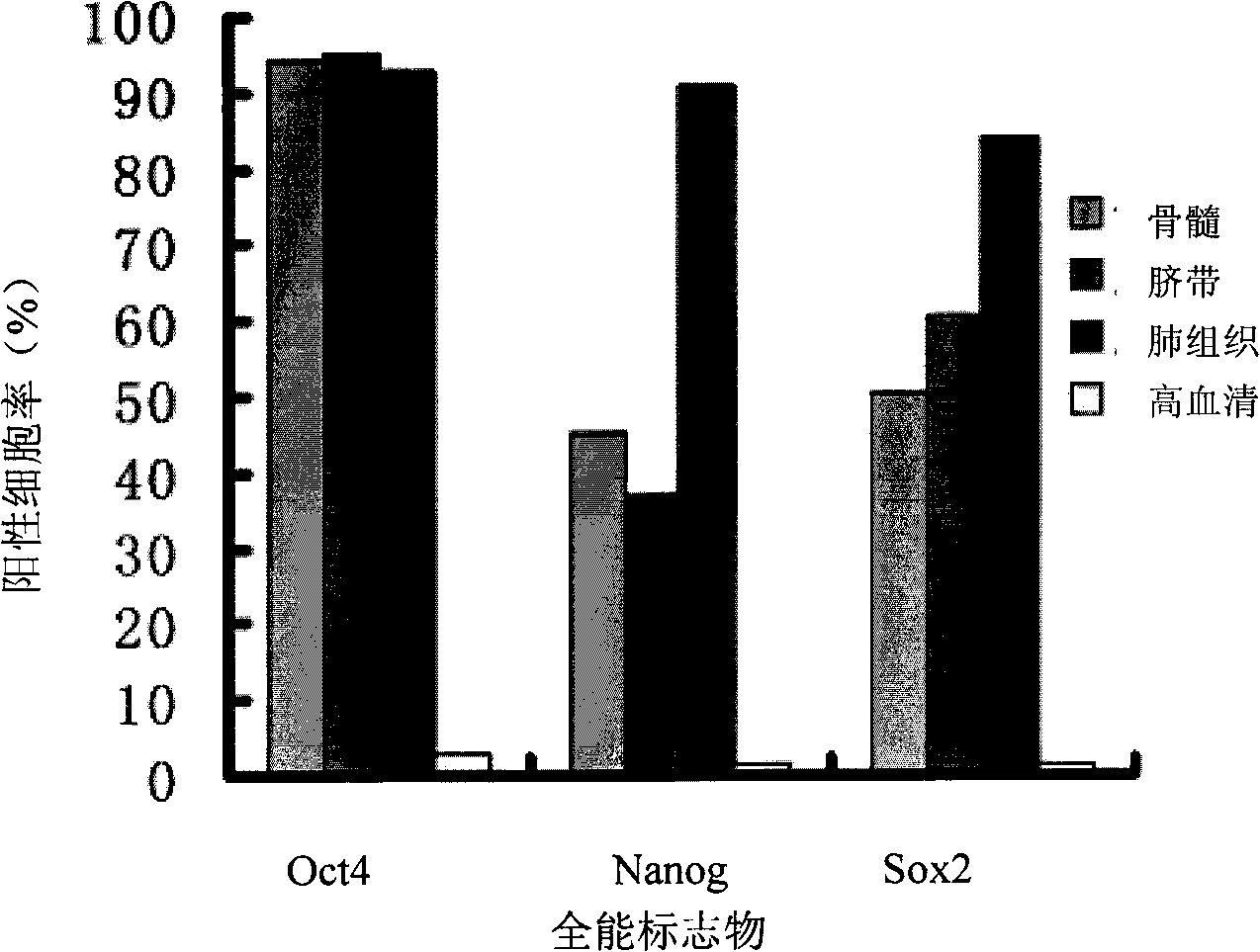
The invention discloses a complete medium with low serum concentration for cultivating mesenchymal stem cells and a method for cultivating the mesenchymal stem cells using same. The complete medium comprises a cell basic medium, fetal calf serum with final concentration of 1-100 mul / ml, an epidermal growth factor with final concentration of 1-100 ng / ml, and a basic fibroblast growth factor with final concentration of 1-100 ng / ml. The complete medium with low serum concentration successfully reaches equal or even better function of promoting cell proliferation than a culture reagent with high serum concentration. The cultured cells have the typical biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells, and can also express an omnipotent mark of the embryonic stem cell and high express the idiosyncratic mark of the neuron under the condition of in vitro inducement. And the difference between the cell batches is little, the cost is low and the security is good. Compared with the prior cultivating method, the method has advantages of simple operation, low probability of pollution and high success ratio of cultivating cells.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Implanting neural progenitor cells derived for human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7011828B2Eliminate inhibitory influenceSolve the shortageBiocideNervous disorderNeural cellIn vivo
The present invention relates to undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells, methods of cultivation and propagation and production of differentiated cells. In particular it relates to the production of human ES cells capable of yielding somatic differentiated cells in vitro, as well as committed progenitor cells such as neural progenitor cells capable of giving rise to mature somatic cells including neural cells and / or glial cells and uses thereof.This invention provides methods that generate in vitro and in vivo models of controlled differentiation of ES cells towards the neural lineage. The model, and cells that are generated along the pathway of neural differentiation may be used for: the study of the cellular and molecular biology of human neural development, discovery of genes, growth factors, and differentiation factors that play a role in neural differentiation and regeneration, drug discovery and the development of screening assays for teratogenic, toxic and neuroprotective effects.
Owner:ES CELL INT +1
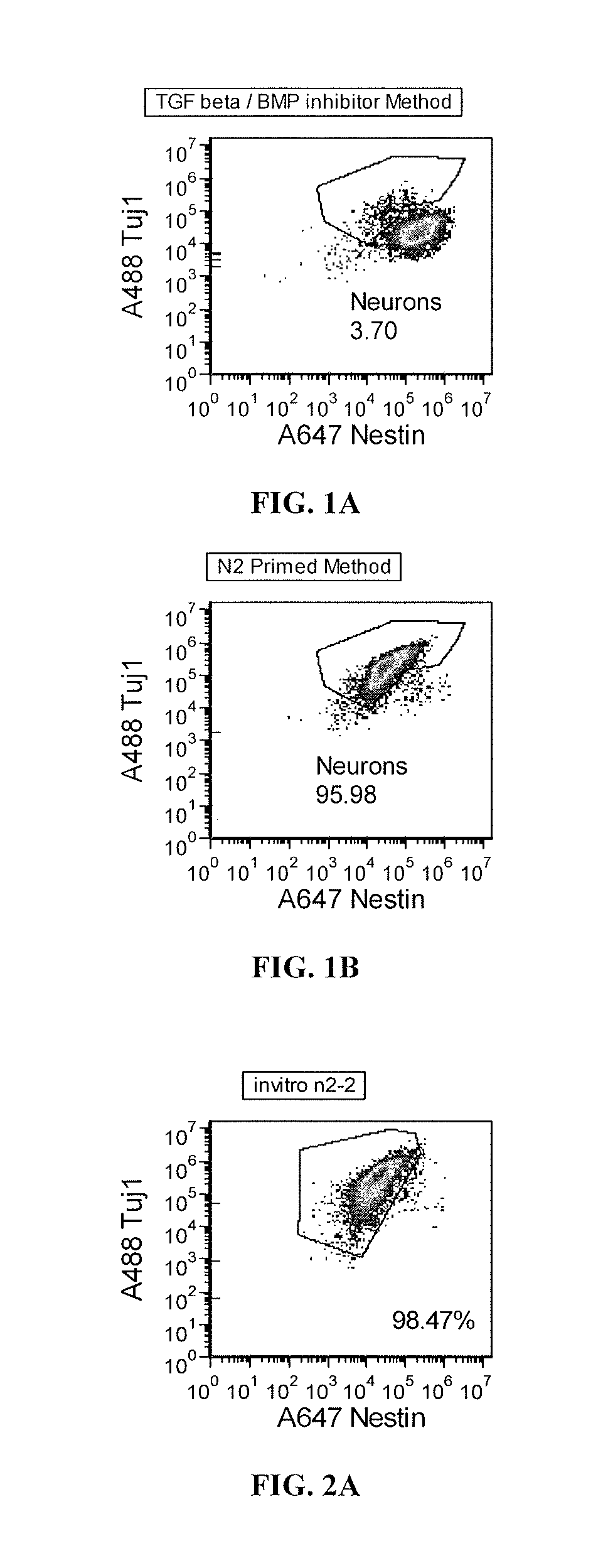
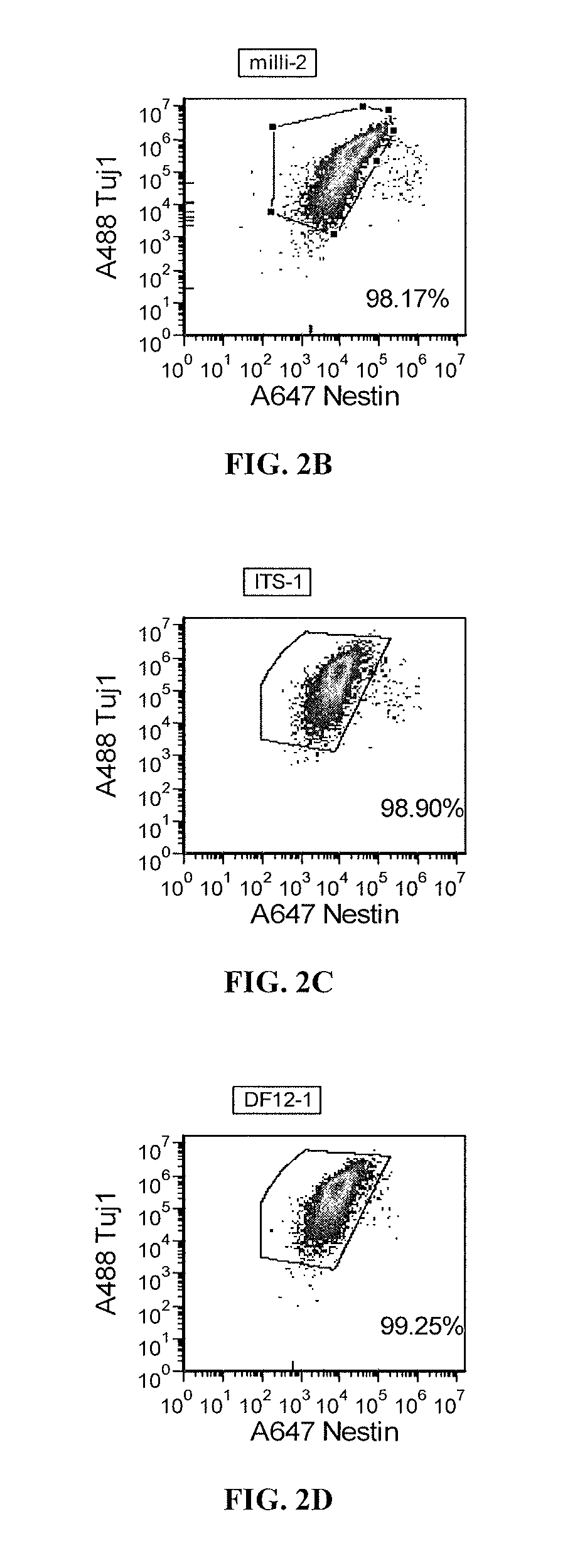
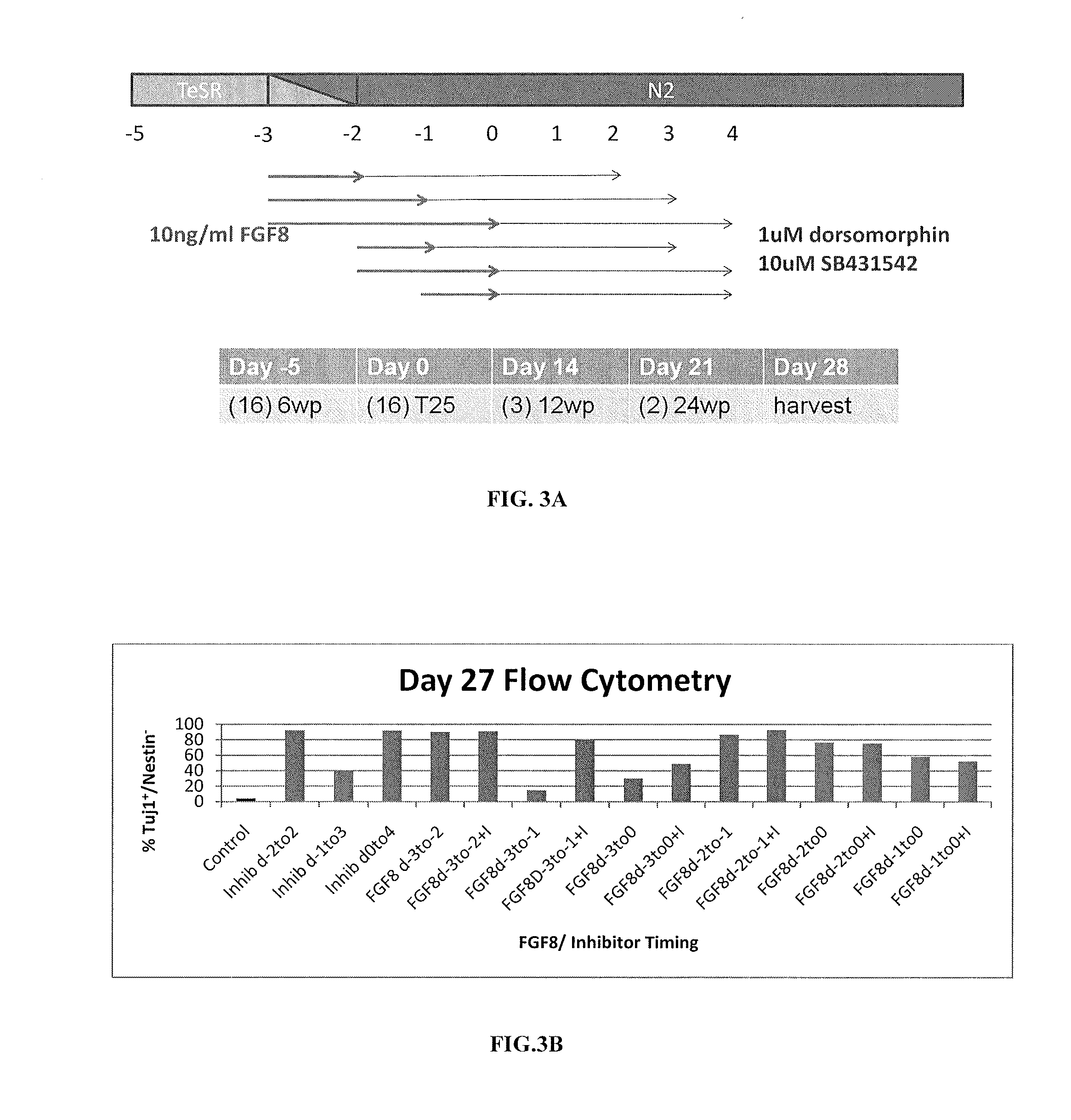
Priming of pluripotent stem cells for neural differentiation
ActiveUS20120276063A1Improve efficiencyMass productionBiocideSenses disorderPluripotential stem cellNeurulation
Methods and composition for differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including priming stem cells for neural differentiation in a culture medium essentially free of growth factors such as FGF and TGFβ. As an advantage, the neural cells may be provided with improved consistency and purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Neural progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20060078543A1Eliminate inhibitory influenceSolve the shortageBiocideNervous disorderNeural cellIn vivo
The present invention relates to undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells, methods of cultivation and propagation and production of differentiated cells. In particular it relates to the production of human ES cells capable of yielding somatic differentiated cells in vitro, as well as committed progenitor cells such as neural progenitor cells capable of giving rise to mature somatic cells including neural cells and / or glial cells and uses thereof. This invention provides methods that generate in vitro and in vivo models of controlled differentiation of ES cells towards the neural lineage. The model, and cells that are generated along the pathway of neural differentiation may be used for: the study of the cellular and molecular biology of human neural development, discovery of genes, growth factors, and differentiation factors that play a role in neural differentiation and regeneration, drug discovery and the development of screening assays for teratogenic, toxic and neuroprotective effects.
Owner:REUBINOFF BENJAMIN +2
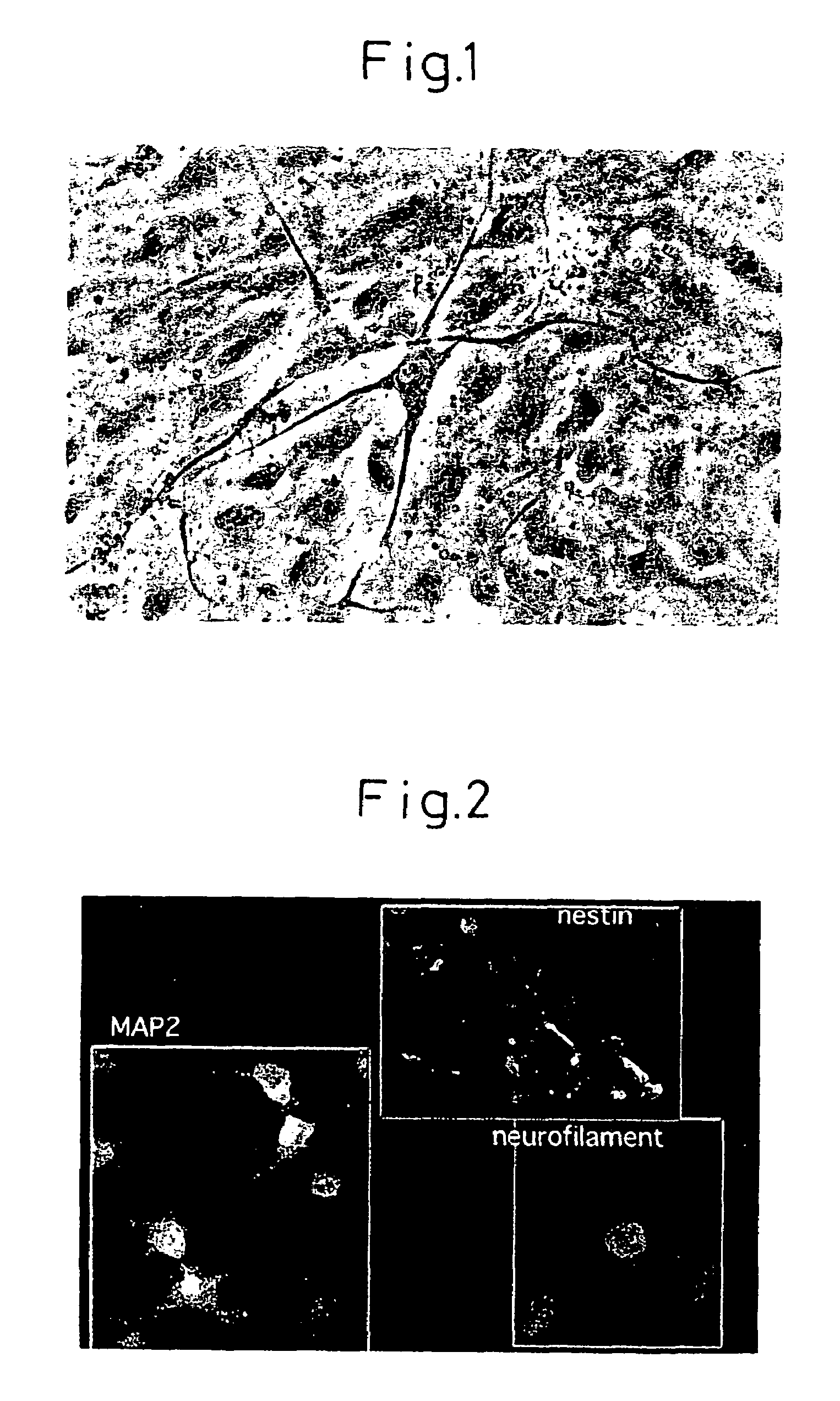
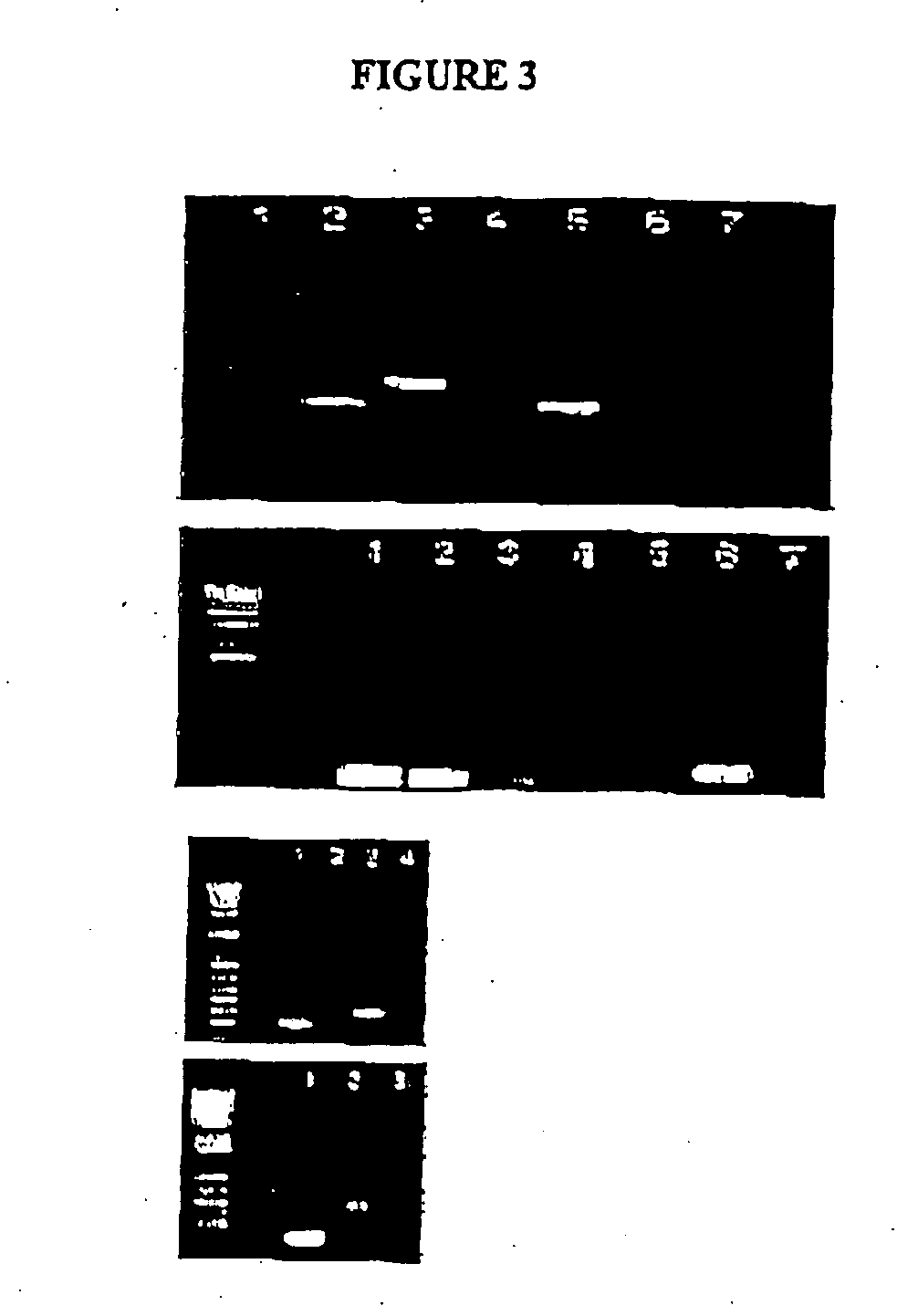
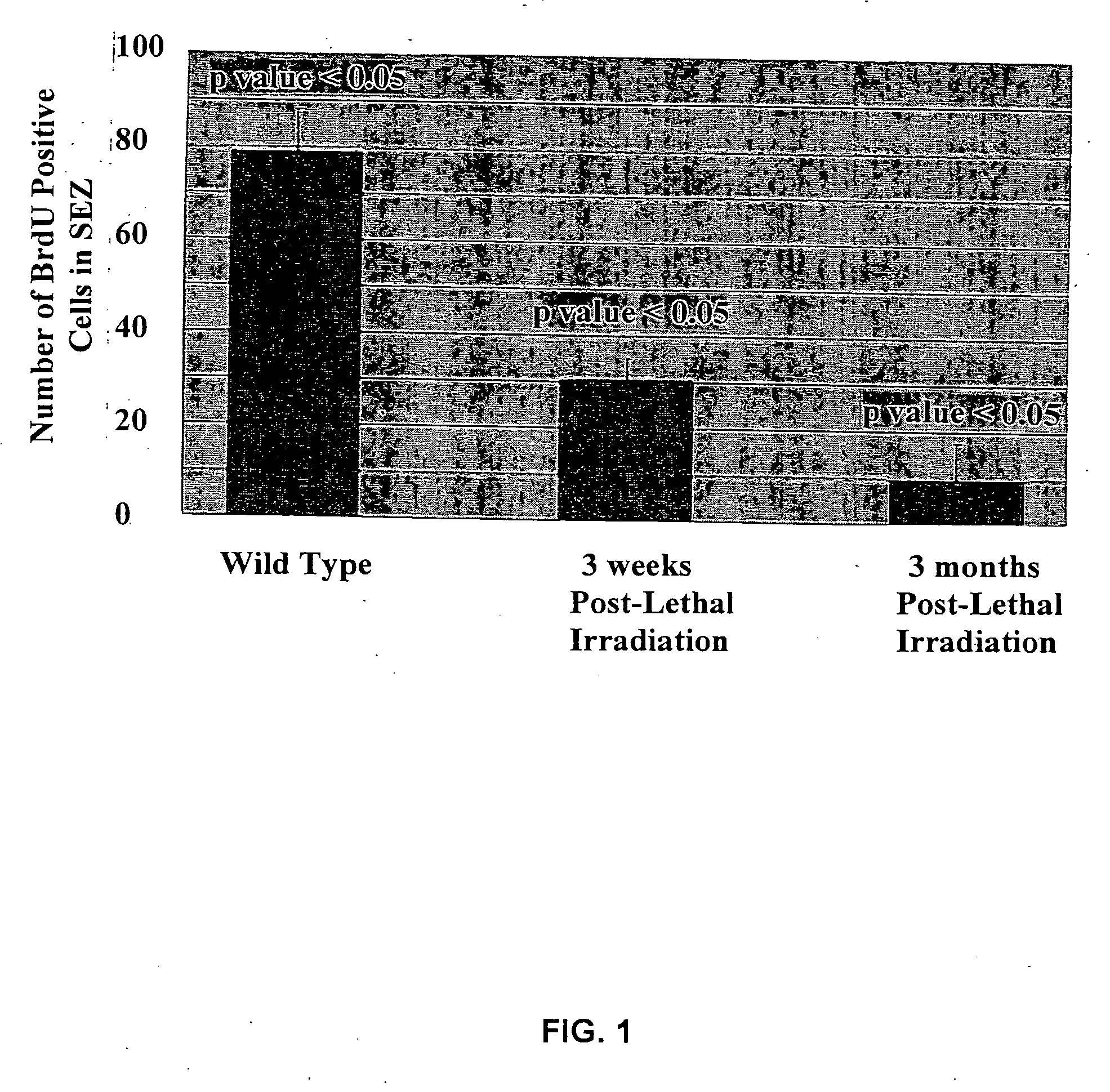
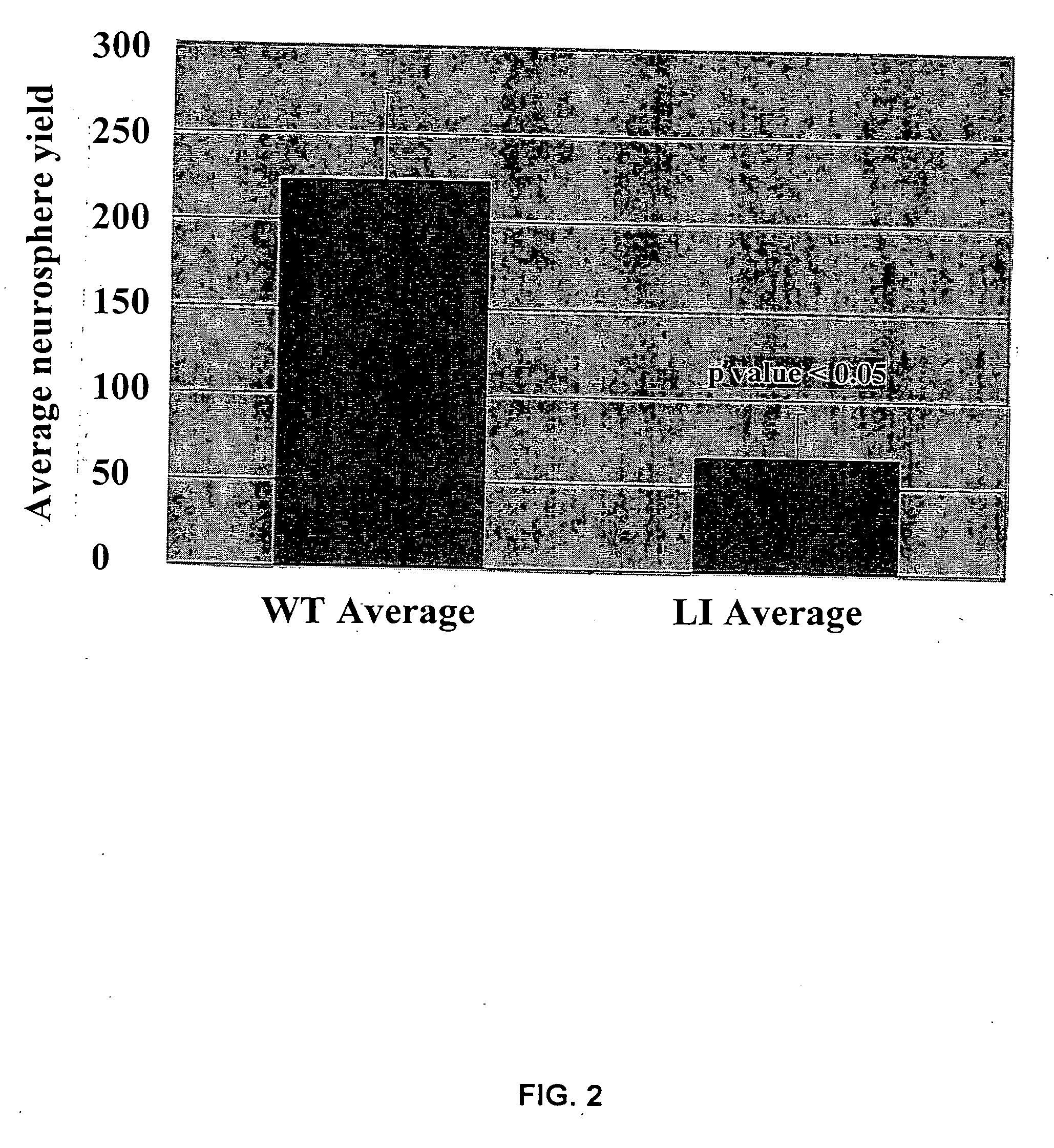
Neural cell assay
InactiveUS20050031538A1Increase neurogenesisNeurogenesis is increasedCompounds screening/testingBiological testingNeurogenesisNeural cell
Methods and assay systems for analyzing effects of chemical and cellular agents on brain cell neurogenesis in vivo, comprising administering an agent to a test animal and determining responses of cells of brain marrow tissues, including irradiated brain marrow tissue depleted of neurogenic stems cells, and cells in brain marrow-derived neurospheres cultured in vitro.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
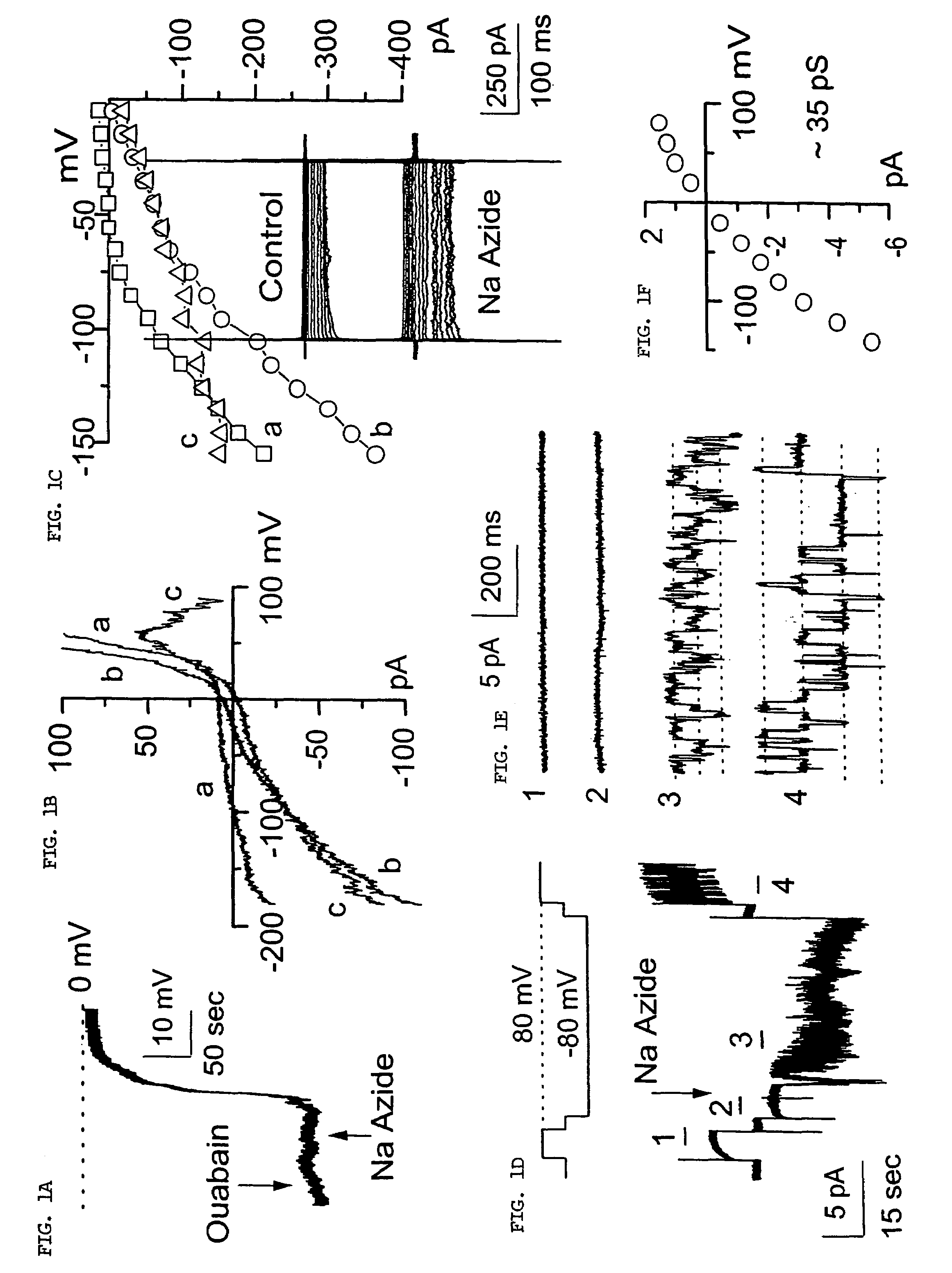
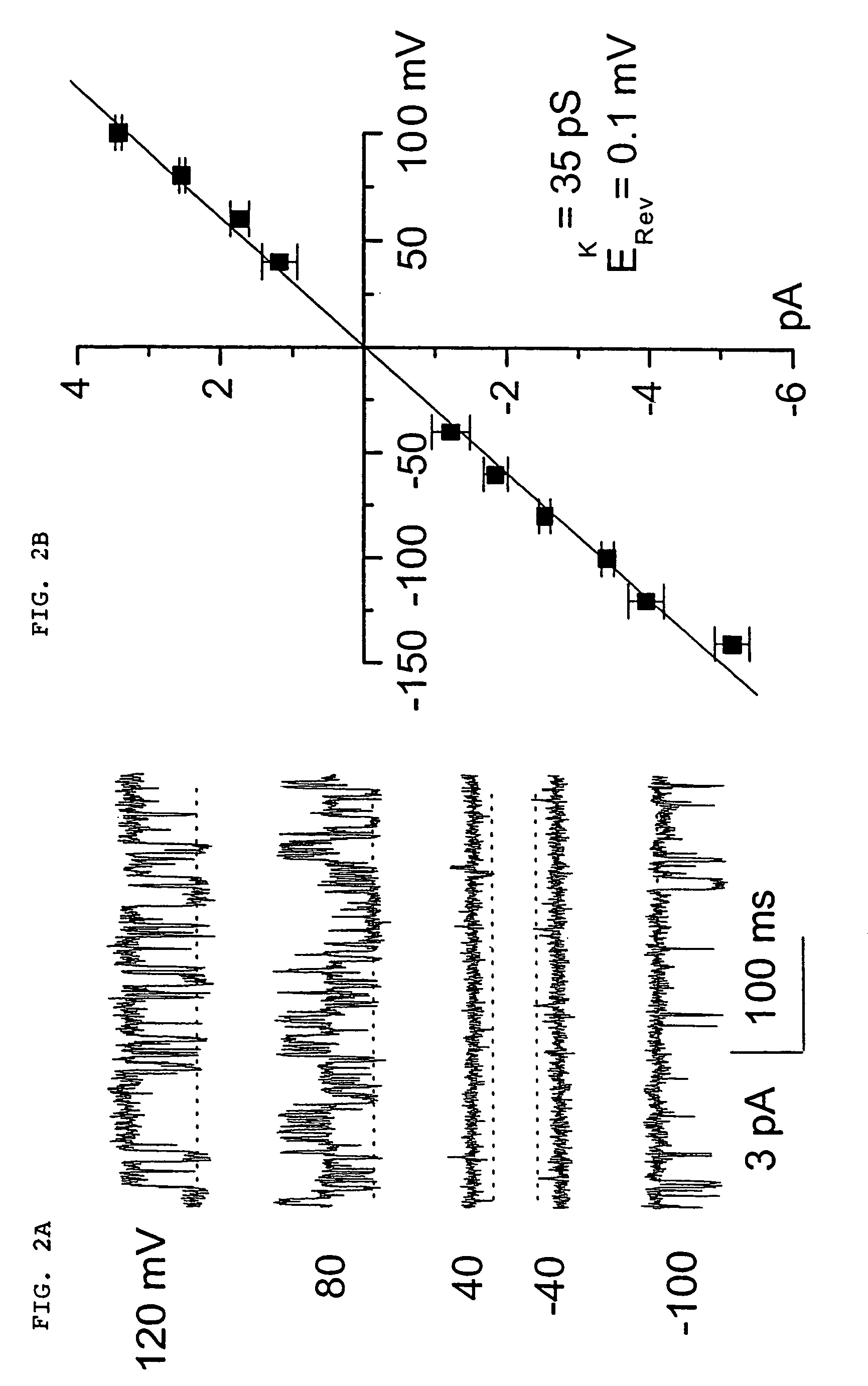
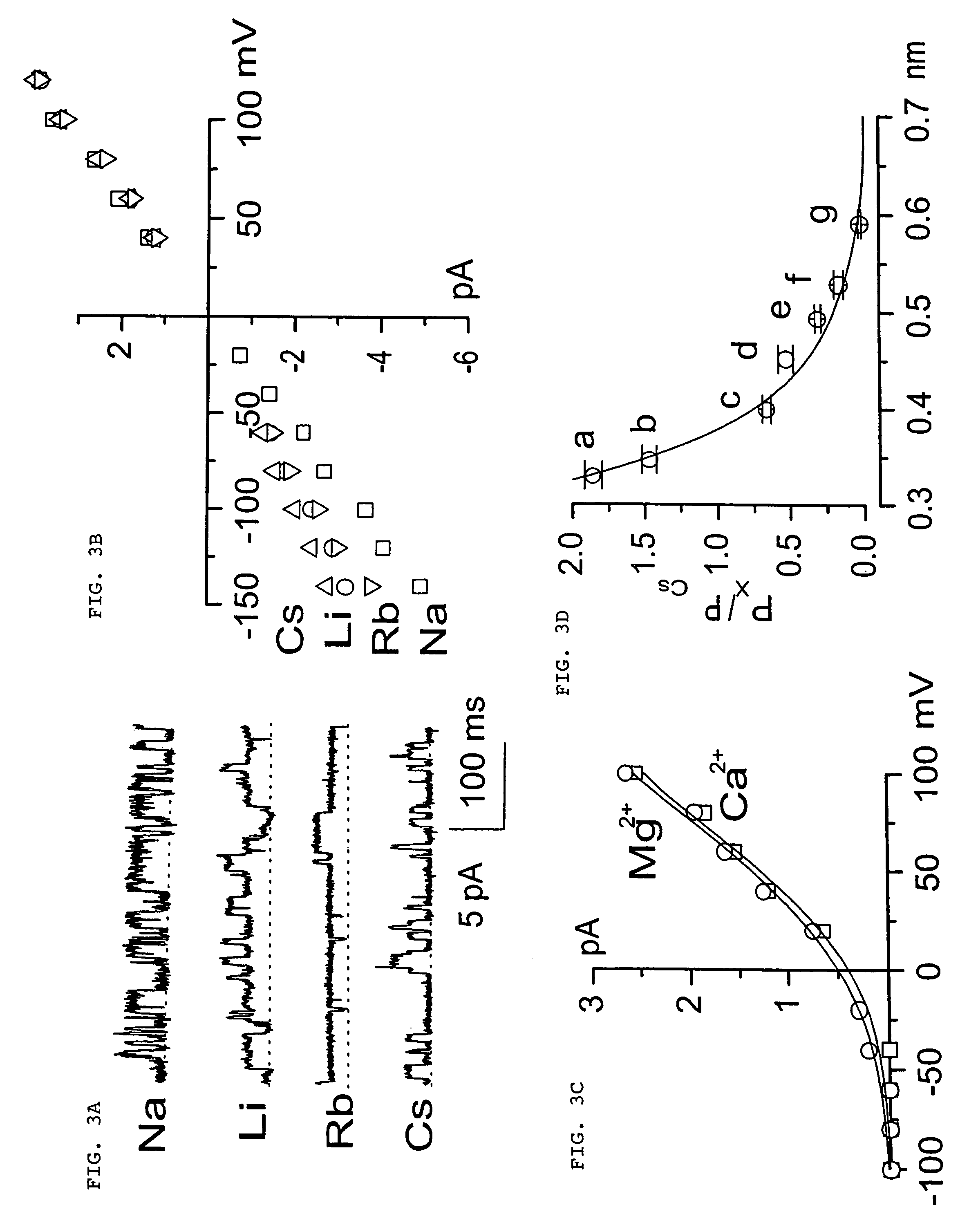
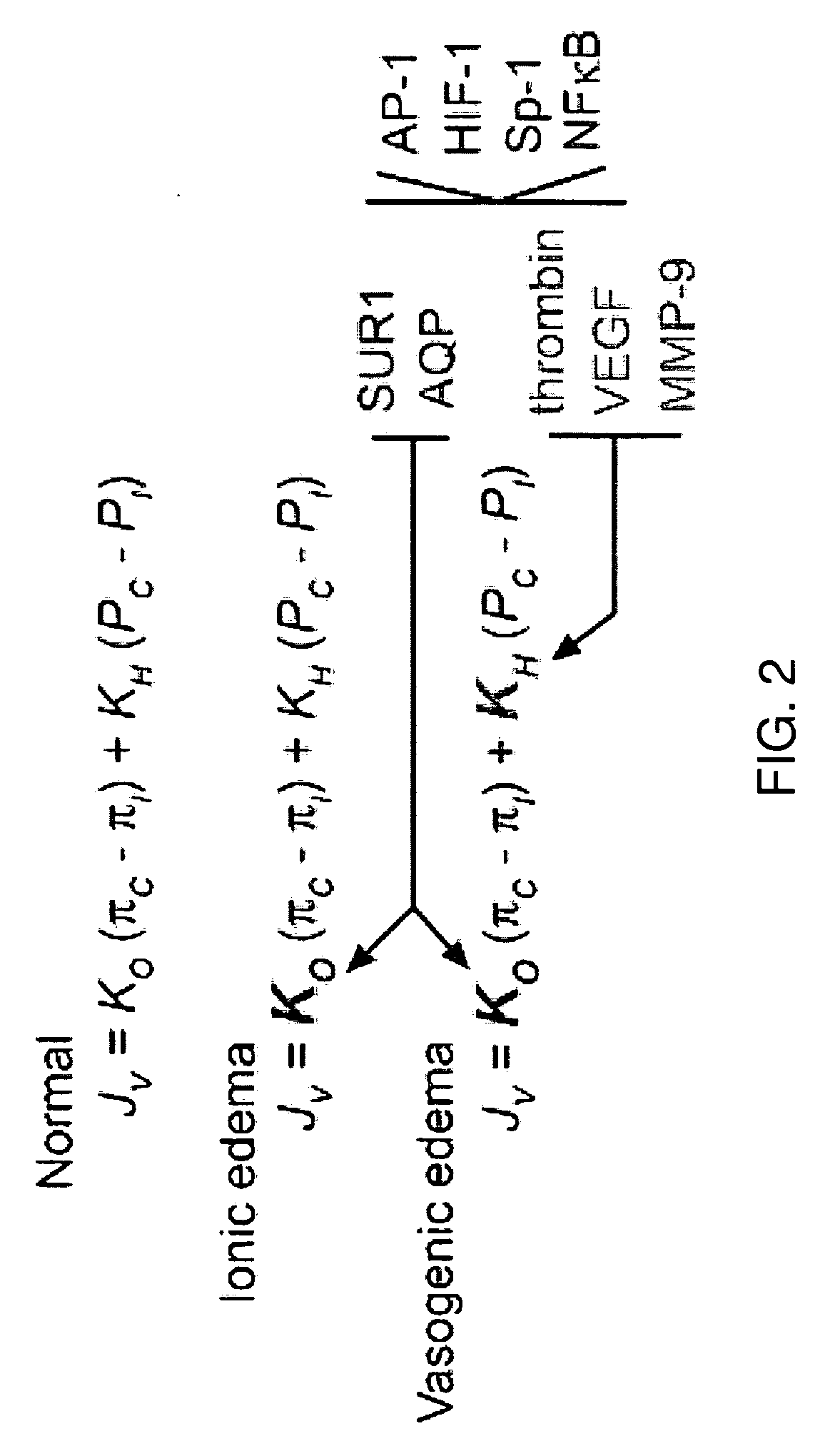
Methods for treating neural cell swelling
A composition comprising a novel Ca2+-activated, [ATP]i-sensitive nonspecific cation (NCCa-ATP) channel is described. The channel is found in mammalian neural cells and exhibits a different sensitivity to block by various adenine nucleotides, and is activated by submicromolar [Ca]i. The NCCa-ATP channel is activated under conditions of ATP depletion, which causes severe cell depolarization, followed by cell swelling. The NCCa-ATP channel is regulated by a sulfonylurea receptor and is inhibited by sulfonylurea compounds glibenclamide and tolbutamide. Methods employing compositions comprising the NCCa-ATP channel to screen for compounds that block the channel and the use of such antagonists as therapeutics in preventing brain swelling and damage are described. In addition, methods employing compositions comprising the Kir2.3 channel to screen for compounds that open the channel and the use of such antagonists as therapeutics in preventing brain swelling and damage are described.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Antagonists of a non-selective cation channel in neural cells
InactiveUS20100092469A1Reduce mortalityReduces stroke sizeBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention is directed to a combination of therapeutic compounds and treatment methods and kits using the combination. In particular, one of the combination affects the NCca-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system. Exemplary SUR1 and / or TRPM4 antagonists that inhibit the NCca-ATP channel may be employed in the combination. The combination therapy also employs one or more of a non-selective cation channel blocker and / or an antagonist of VEFG, NOS, MMP, or thrombin. Exemplary indications for the combination therapy includes the prevention, diminution, and / or treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury, for example. In other embodiments, there are methods and compositions directed to antagonists of TRPM4, including at least for therapeutic treatment of traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, central nervous system (CNS) damage, peripheral nervous system (PNS) damage, cerebral hypoxia, or edema, for example.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Formative agent of protein complex
InactiveUS20020119946A1Keep for a long timePromote resultsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCartilage cellsCuticle
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
Biomarkers of aging for detection and treatment of disorders
InactiveUS20140255424A1Modulate activityVirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNeural cell
Provided are methods of diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of aging using biomarkers that have been discovered to be linked to biological aging process. Methods for increasing neural cell regeneration and cognitive function are also provided. The methods are, at least in part, based on a discovery that altered expression patterns of certain biological markers are associated with biological aging processes. These markers comprise at least Eotaxin / CCL11, β2-microglobulin, MCP-1 and Haptoglobulin, increased expression of which has been shown to be associated with increase in biological aging process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
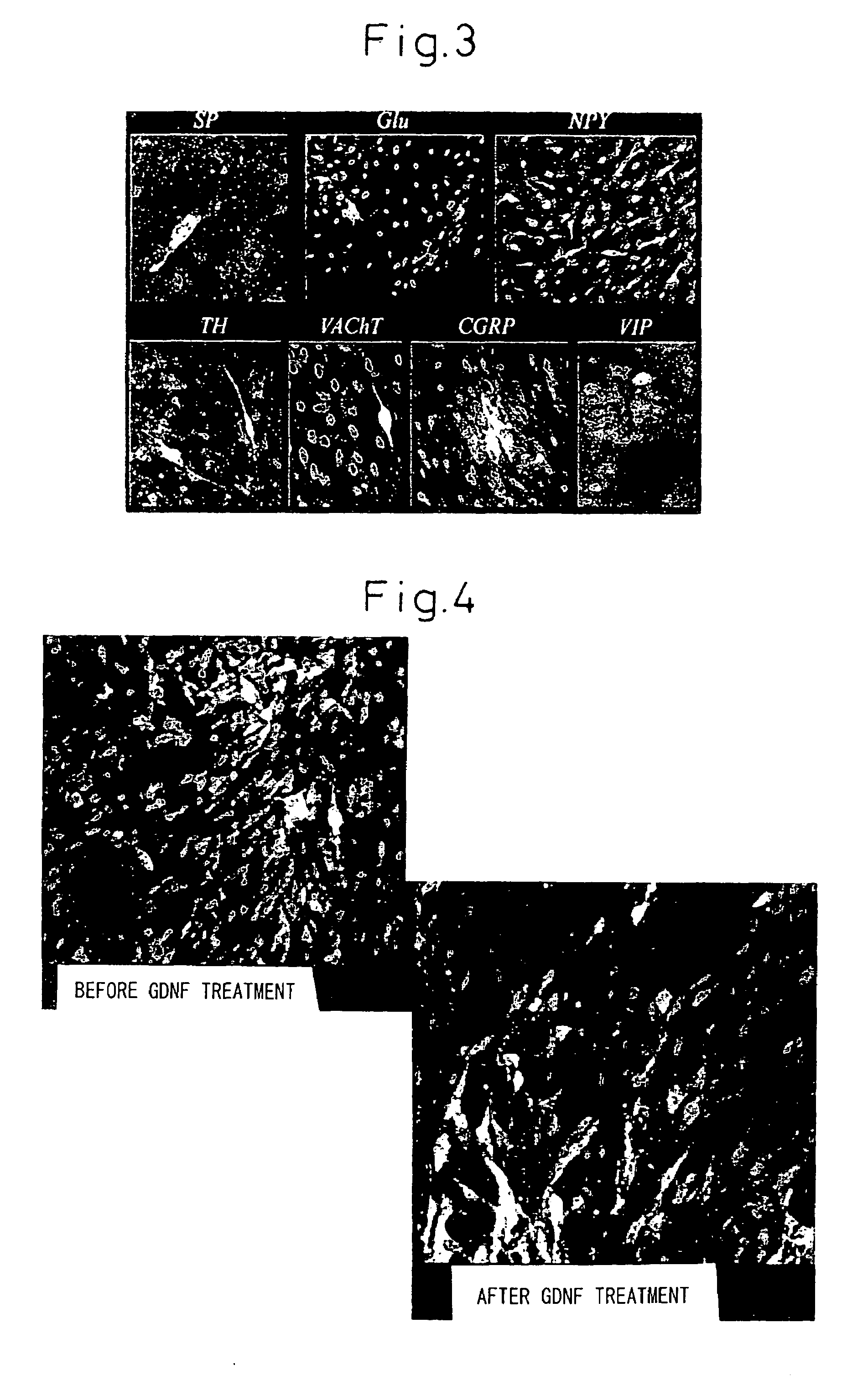
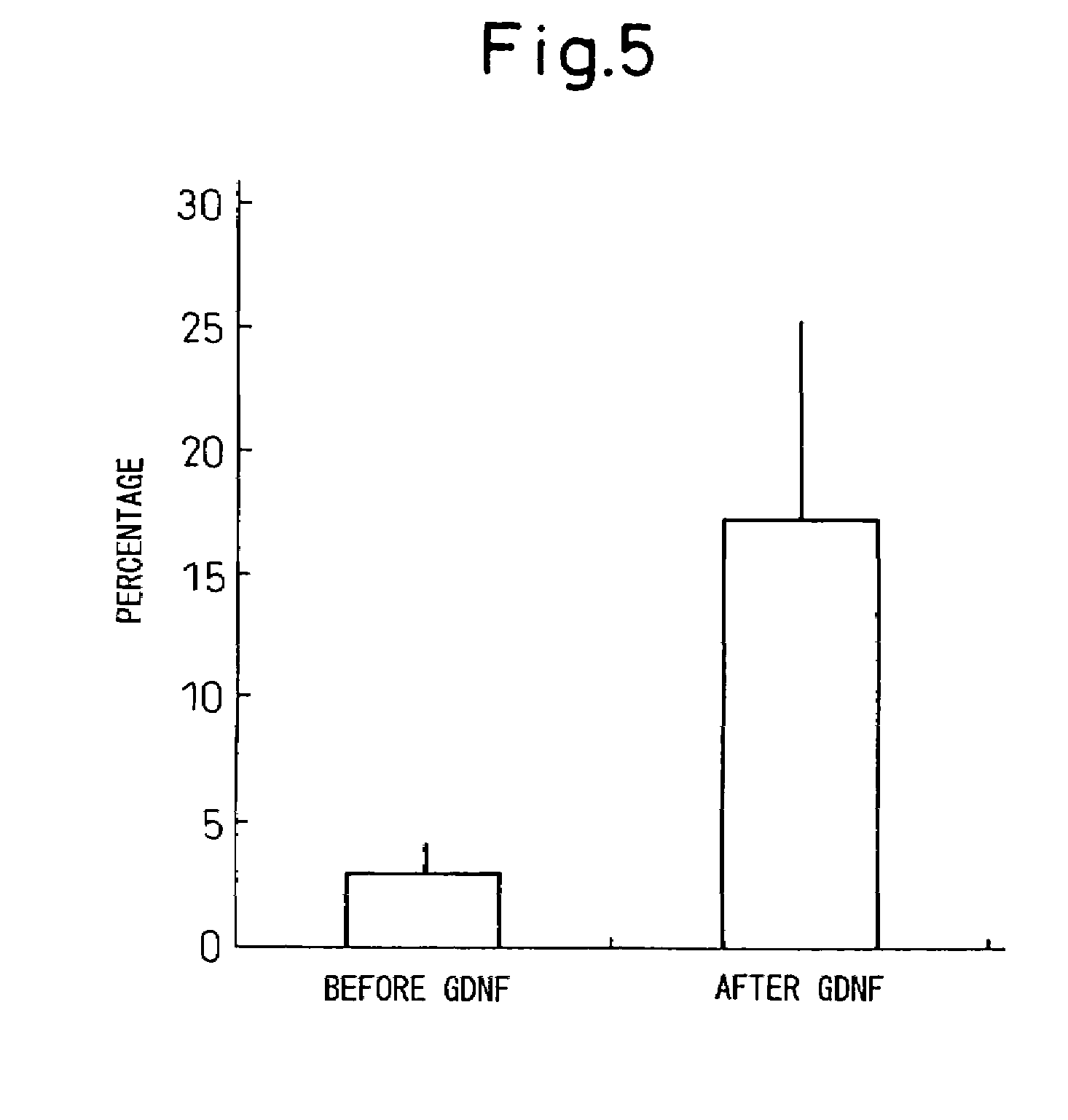
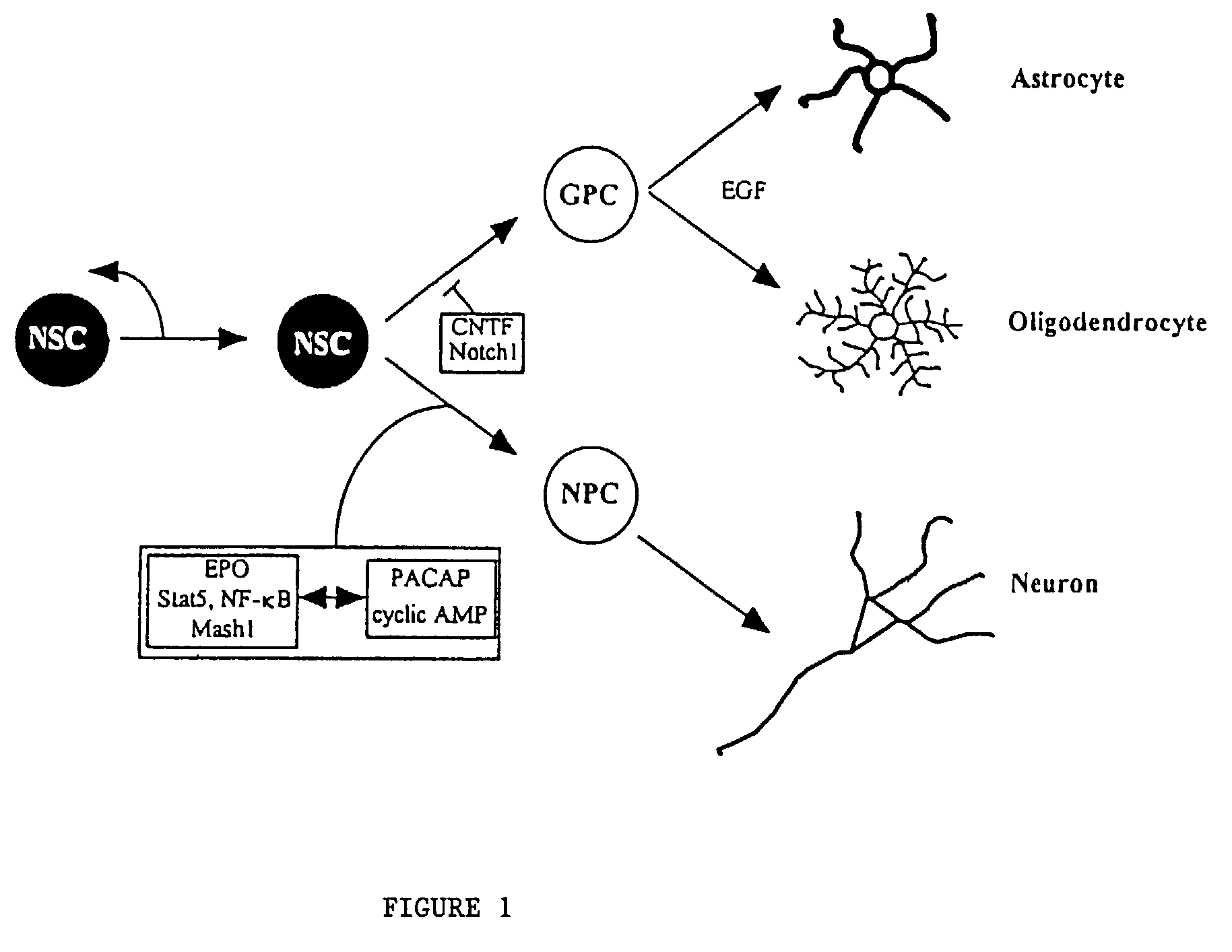
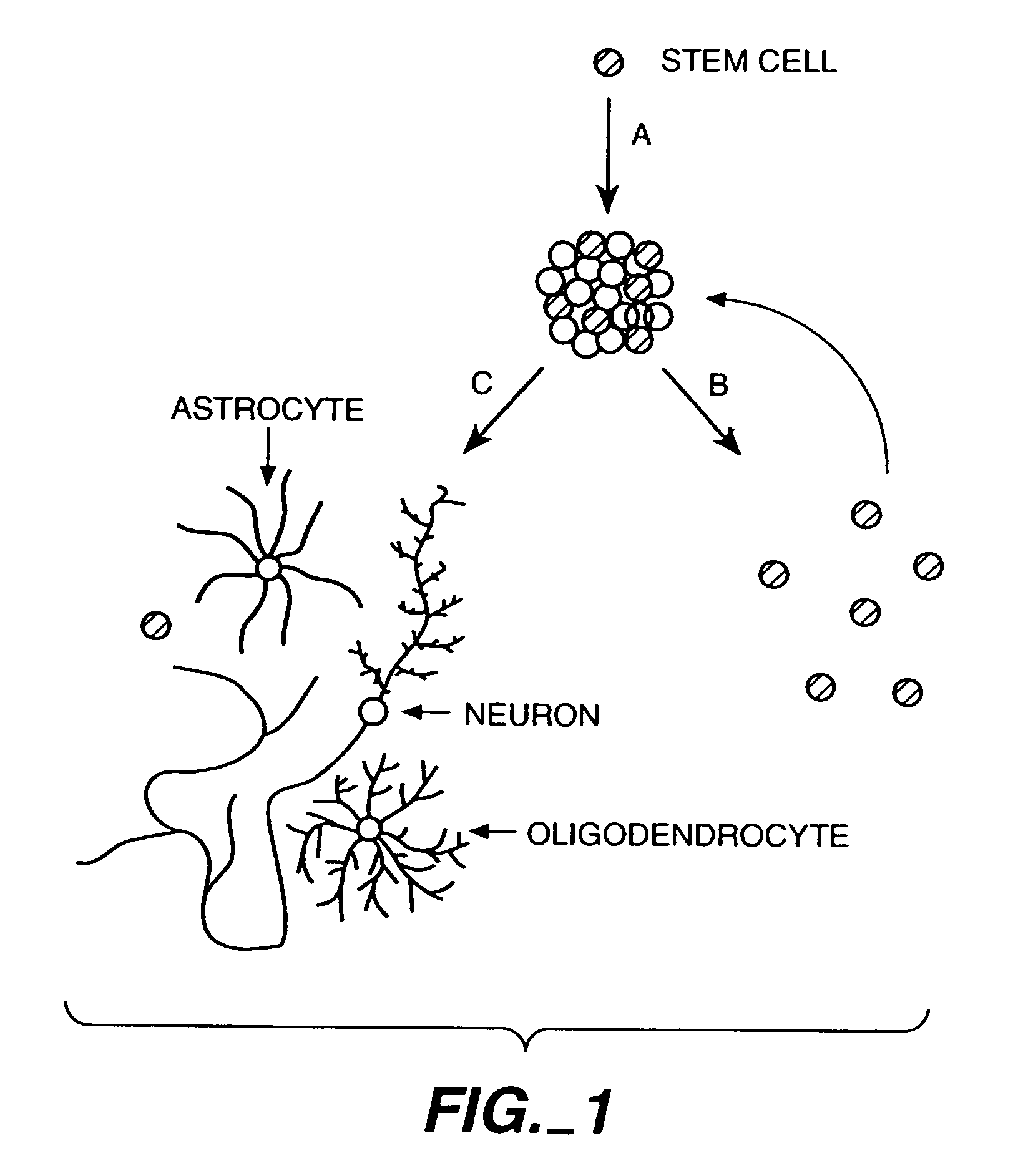
Combined regulation of neural cell production
InactiveUS7048934B2Increase the number ofIncrease productionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeurulationDisease
This invention relates to a method of selectively producing neural cells, including neurons or glial cells, in vitro or in vivo. Also provided are methods of treating or ameliorating neurodegenerative disease or medical conditions by producing neural cells. Thus, a combination of factors is used to achieve two steps: increasing the number of neural stem cells and instructing the neural stem cells to selectively become neurons or glial cells.
Owner:STEM CELL THERAPEUTICS
Chimeric protein
InactiveUS20060153827A1Avoid developmentInhibit growthHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNeural cellChimera Protein
A chimeric protein is disclosed for promoting repair and regeneration of neurons damaged by disease or physical injury wherein the chimeric protein is a combination of a first polypeptide possessing matrix modification activity and a second polypeptide possessing regenerating activity for neural cells.
Owner:ACORDA THERAPEUTICS INC
Oligodendrocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells for remyelination and treatment of spinal cord injury
ActiveUS7285415B2Enhances late-stage differentiationEfficient productionBiocideSenses disorderNeural cellRemyelination
This invention provides populations of neural cells bearing markers of glial cells, such as oligodendrocytes and their precursors. The populations are generated by differentiating pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells under conditions that promote enrichment of cells with the desired phenotype or functional capability. Various combinations of differentiation factors and mitogens can be used to produce cell populations that are over 95% homogeneous in morphological appearance, and the expression of oligodendrocyte markers such as GalC. The cells are capable of forming myelin sheaths, and can be used therapeutically improve function of the central nervous system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
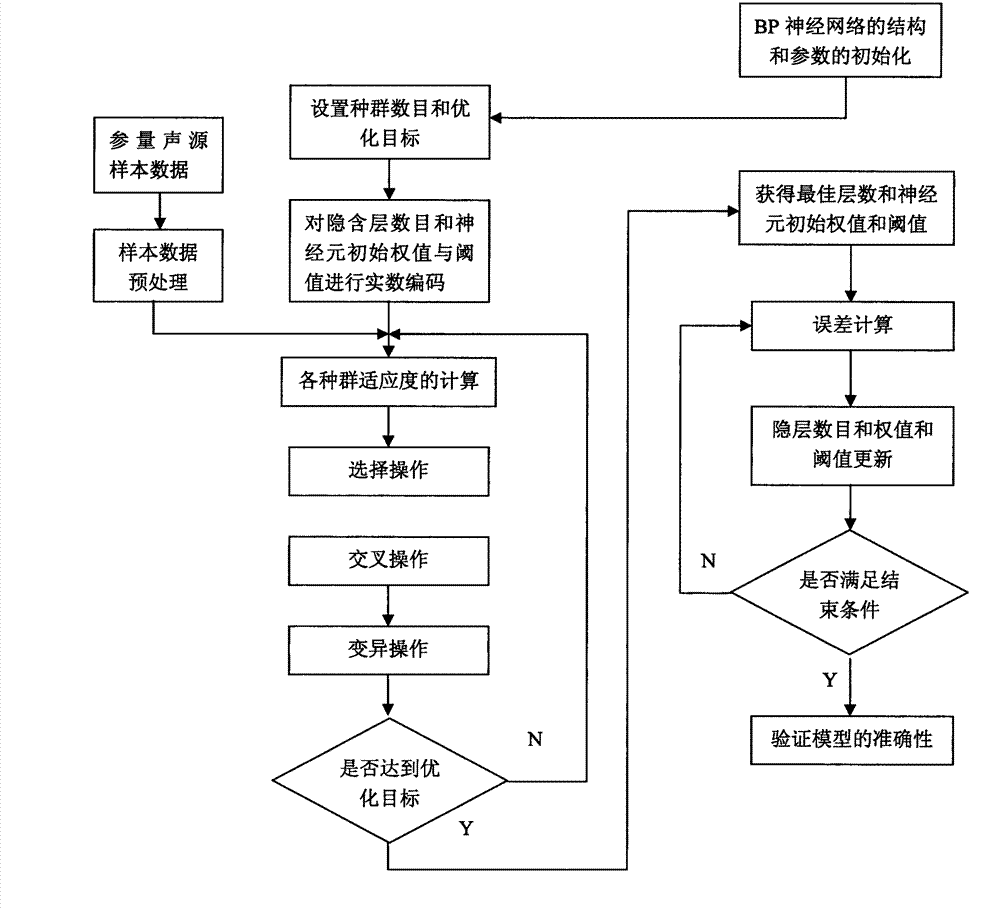
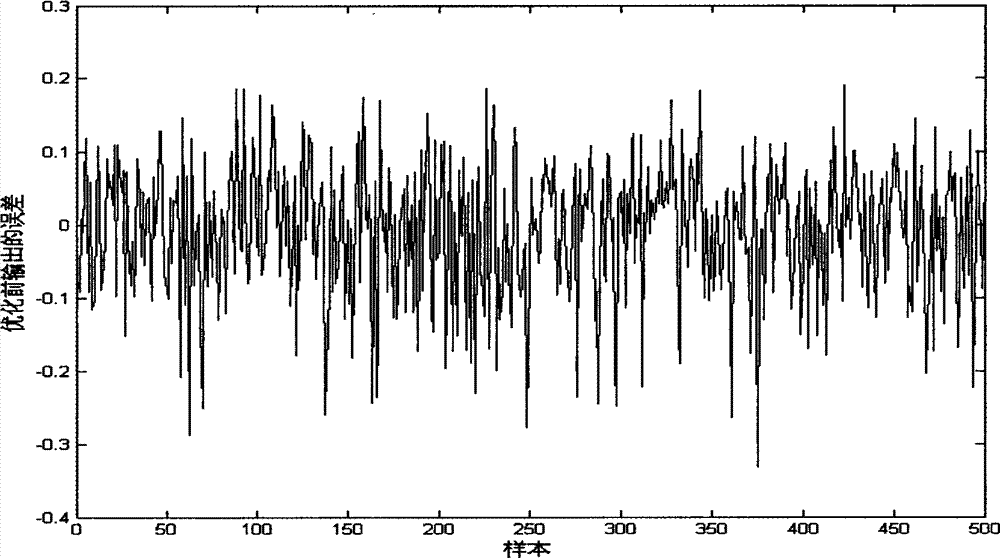
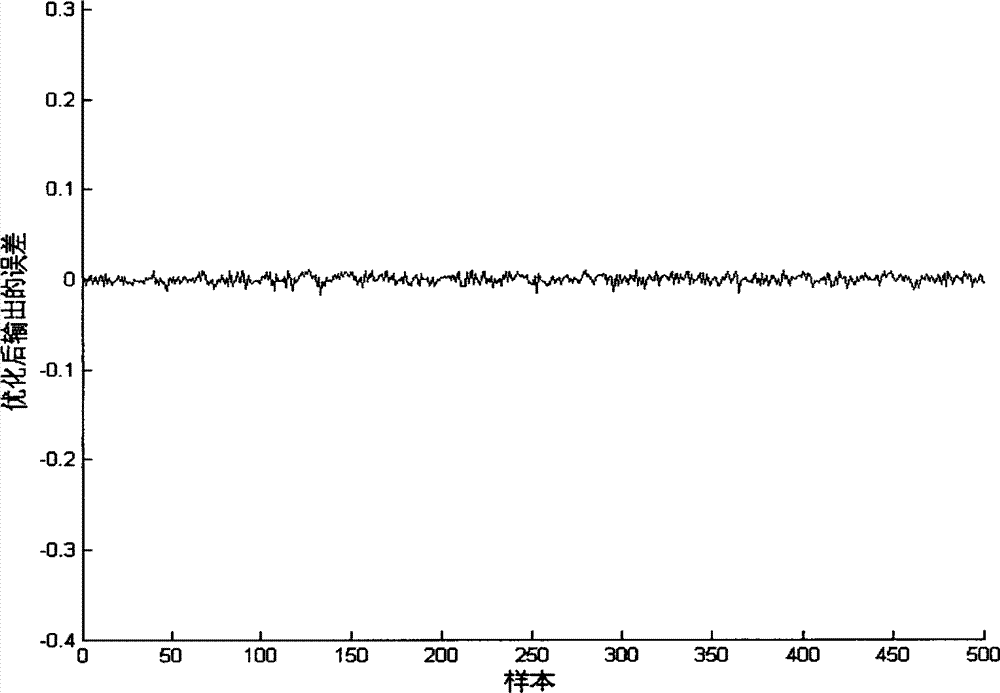
Parameter sound source modeling method based on improved BP (Back Propagation) neural network
ActiveCN103077267ASimplify the build processHigh precisionGenetic modelsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkSound sources
The invention provides a parameter sound source modeling method based on an improved BP (Back Propagation) neural network, in order to solve the problem of difficulty in modeling a parameter sound source system at present. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting sufficient training and testing sample data and preprocessing the data; establishing a neural network model; adopting a genetic algorithm for performing optimizing process on the structure and parameter of the neural network model; searching for an initial weight value and a threshold value between the number of better neural network hidden layers and neural cells; and lastly, training and testing an established parameter sound source model based on the improved BP neural network by using the sample data. The model has the advantages of reliability and higher assessing precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Compositions and methods for treating neurogenic disorders of the pelvic floor
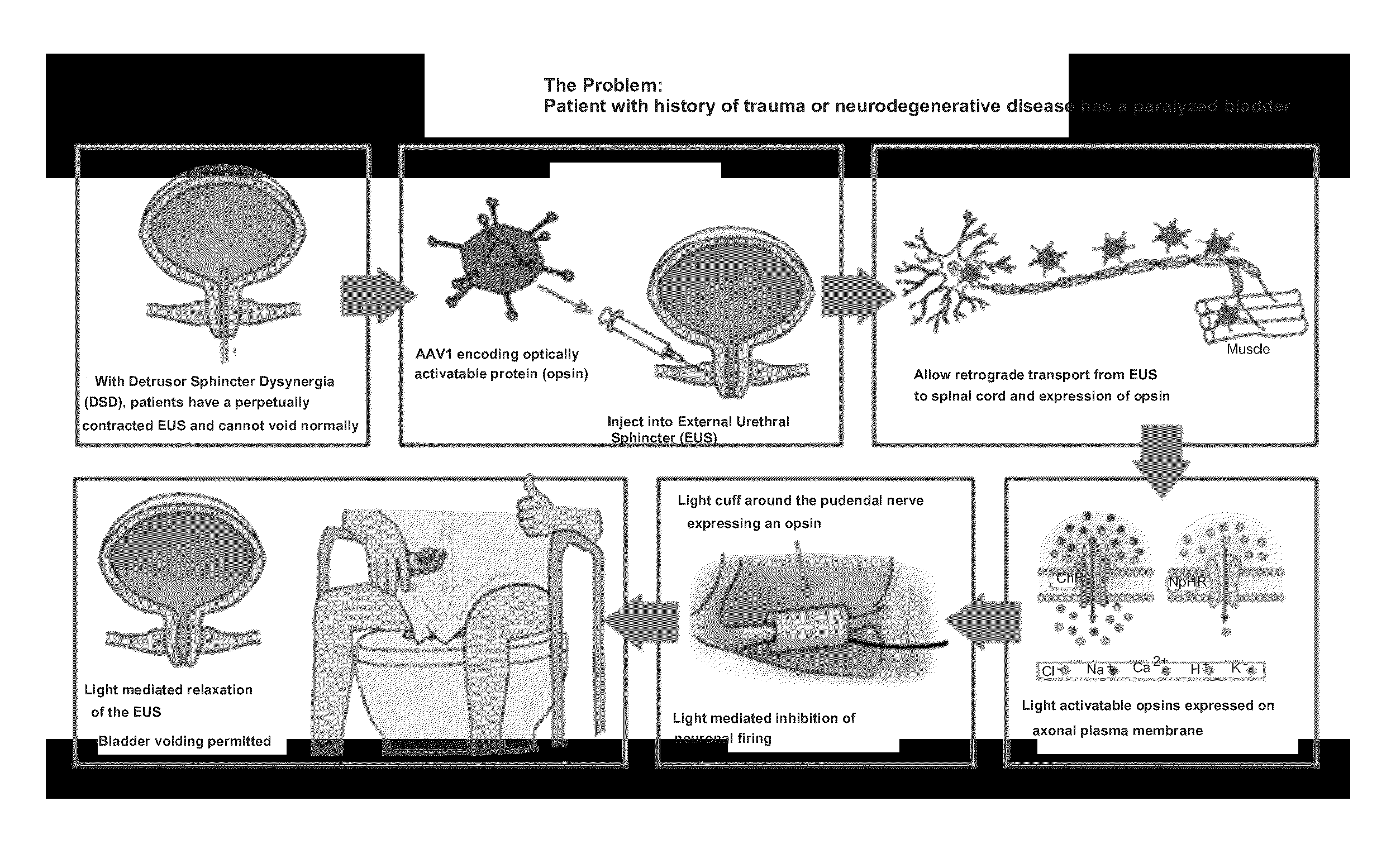
ActiveUS20160038761A1Induce depolarizationCompounds screening/testingElectrotherapyDetrusor hyperreflexiaPelvic diaphragm muscle
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of bladder dysfunction, including detrusor hyperreflexia and detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia, fecal incontinence, and / or sexual dysfunction in an individual via the use of stably expressed light-responsive opsin proteins capable of selective hyperpolarization or depolarization of the neural cells that innervate the muscles responsible for physiologic functioning of urinary bladder, external urinary sphincter, external anal sphincter, and the male and female genitalia.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS +1
Methods of proliferating undifferentiated neural cells
The invention discloses methods of proliferation and differentiation of multipotent neural stem cells. Also provided are methods of making cDNA libraries and methods of screening biological agents which affect proliferation differentiation survival phenotype or function of CNS cells.
Owner:BOCO SILICON VALLEY INC
Methods for inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS7390659B2Effective treatmentImprove regenerative abilityBiocideNervous disorderProgenitorHuman animal
The present invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of an embryonic stem cell into a differentiated neural cell. The present invention further provides a method for producing differentiated neural cells, and a population of cells comprising the differentiated neural cells. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for repopulating a spinal cord in a subject, and a method for treating nervous tissue degeneration in a subject in need of treatment. The present invention further provides neural progenitor cells, differentiated neural cells, and uses of same. Also provided is a transgenic non-human animal containing the differentiated neural cells. The present invention is further directed to a method for isolating a population of differentiated neural cells. Finally, the present invention provides a method for identifying an agent for use in treating a condition associated with neuron degeneration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Brain specific exosome based diagnostics and extracorporeal therapies
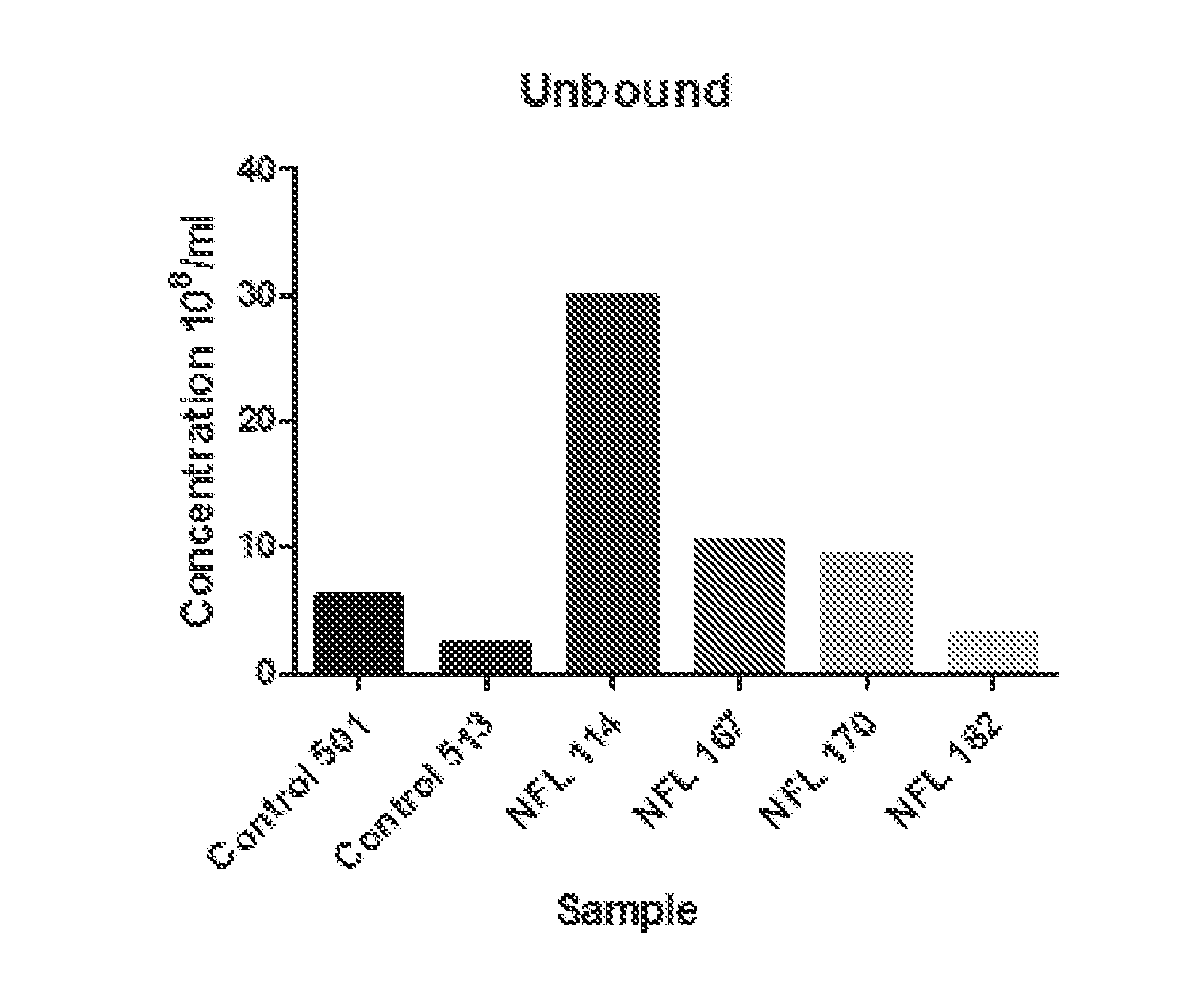
InactiveUS20170014450A1Reliable and inexpensive and portable and rapid and simple approachMinimally invasive, inexpensive, portable, and reliableCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPsa ncamPhosphorylation
Disclosed are methods, compositions, devices, and kits for the isolation of brain-specific exosomes. Specifically, methods, compositions, devices, and Unbound kits comprising an isolated brain-specific extracellular vesicle or exosome joined to a first binding agent that is specific for tau, β-amyloid, SlOO β, neuron-specific enolase, glycoprotein A2B5, CD133, NQ01, synaptophysin, neuronal nuclei, MAB 1569, polysialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM), or neurogenic differentiation 1 (NeuroD or Beta2), or glycosylated or phosphorylated forms of these molecules, are provided.
Owner:EXOSOME SCI
Method for preparing stem cell preparations
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
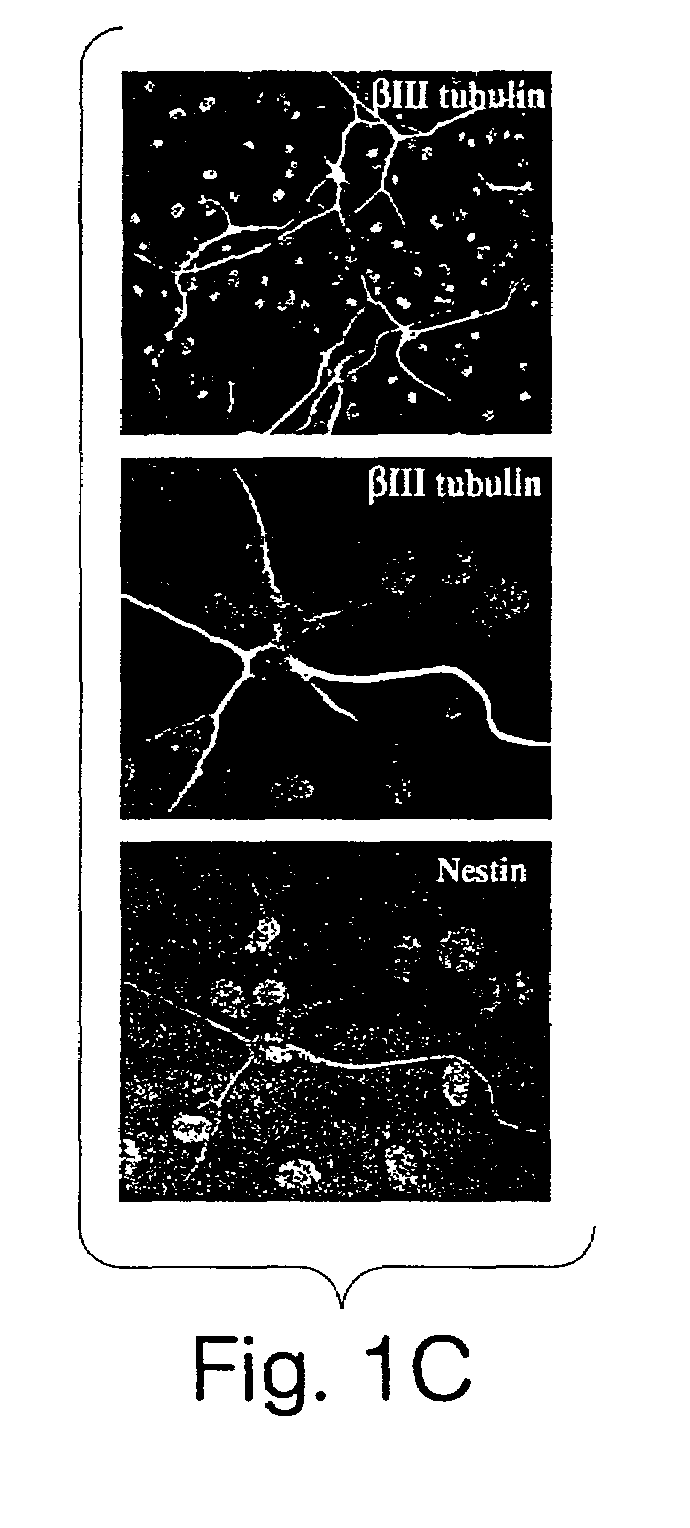
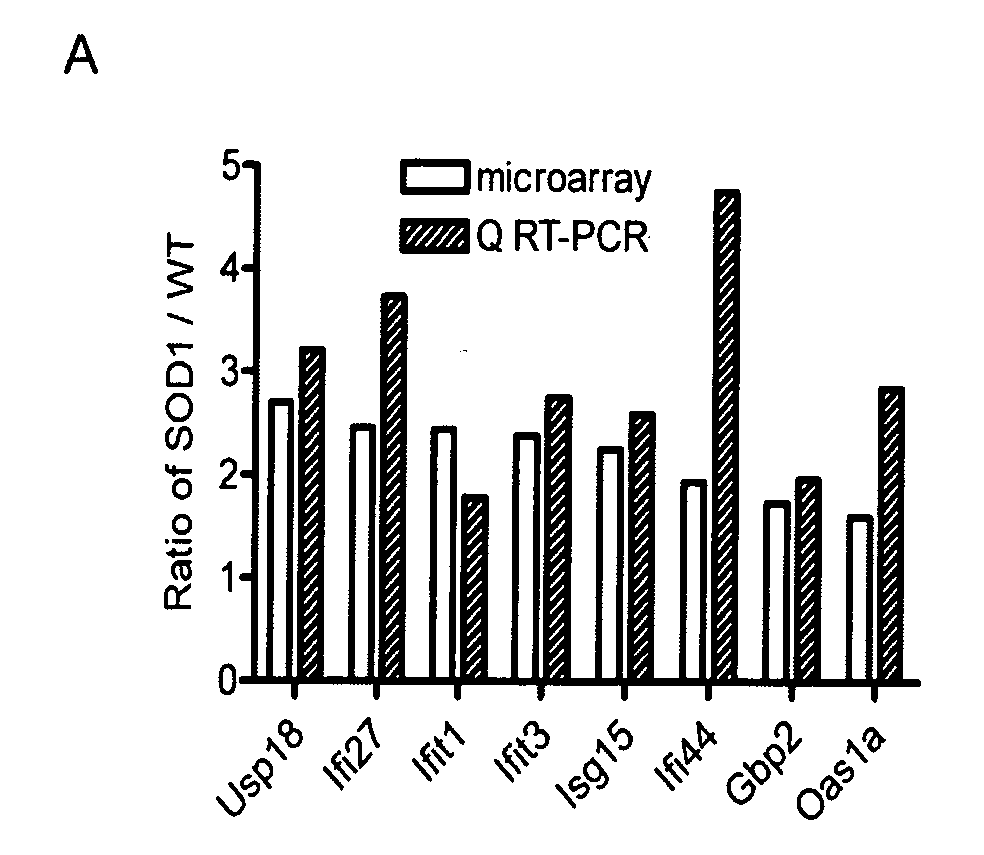
Biomarkers of neurodegenerative disease
InactiveUS20080261226A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingNeural cellAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The present invention provides biomarkers and diagnostic methods employing such biomarkers based on the discovery of genes that have a two-fold or greater difference in gene expression in the spinal cord of a pre-symptomatic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Such biomarkers and diagnostic methods are useful for early detection of neural cell injury and death in acute and degenerative disease.
Owner:WANG RENGANG +1
Methods for producing retinal tissue and retina-related cell
ActiveUS20140341864A1Improve efficiencySolve low usageBiocideNervous system cellsSerum free mediaNeural cell
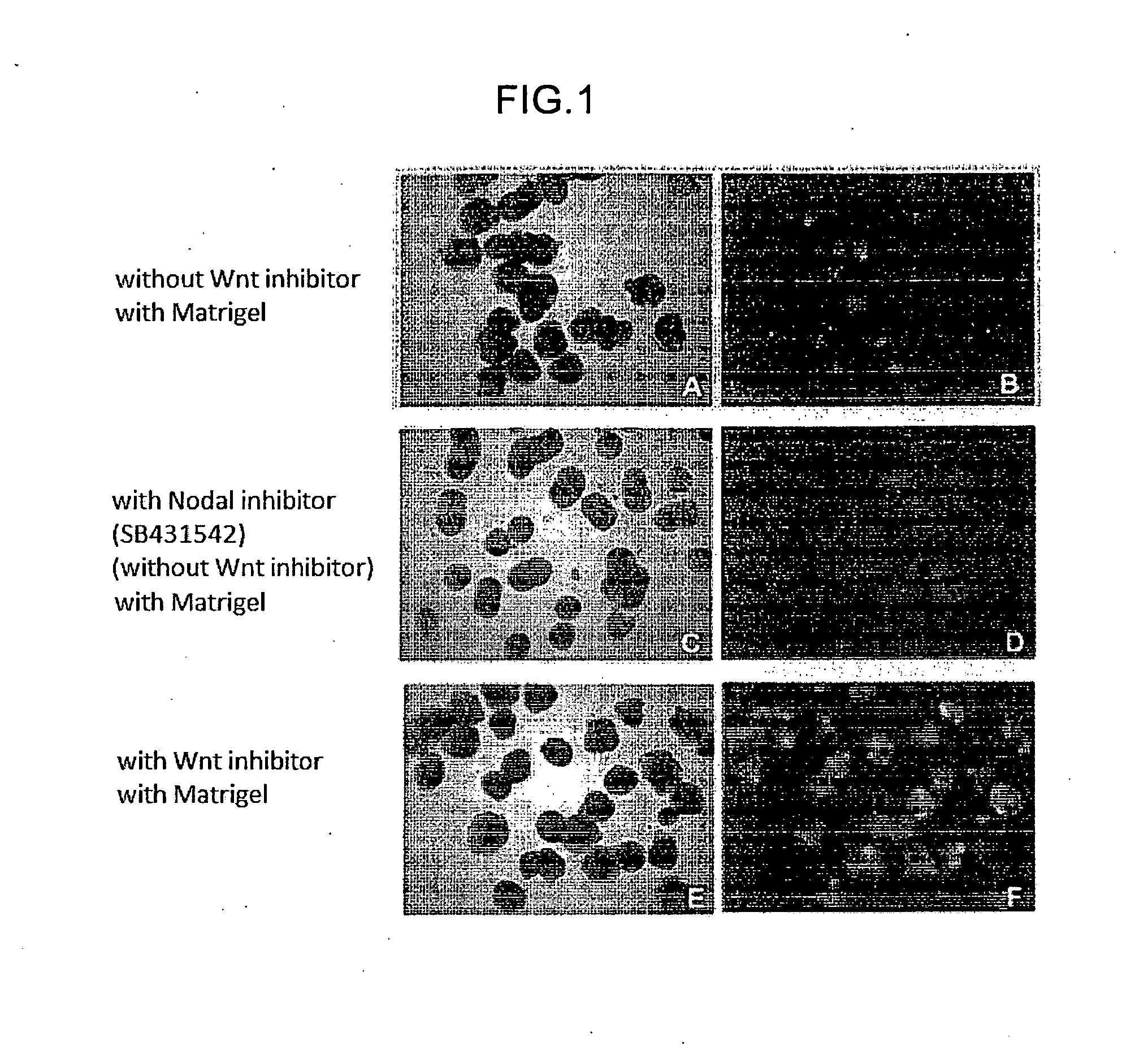
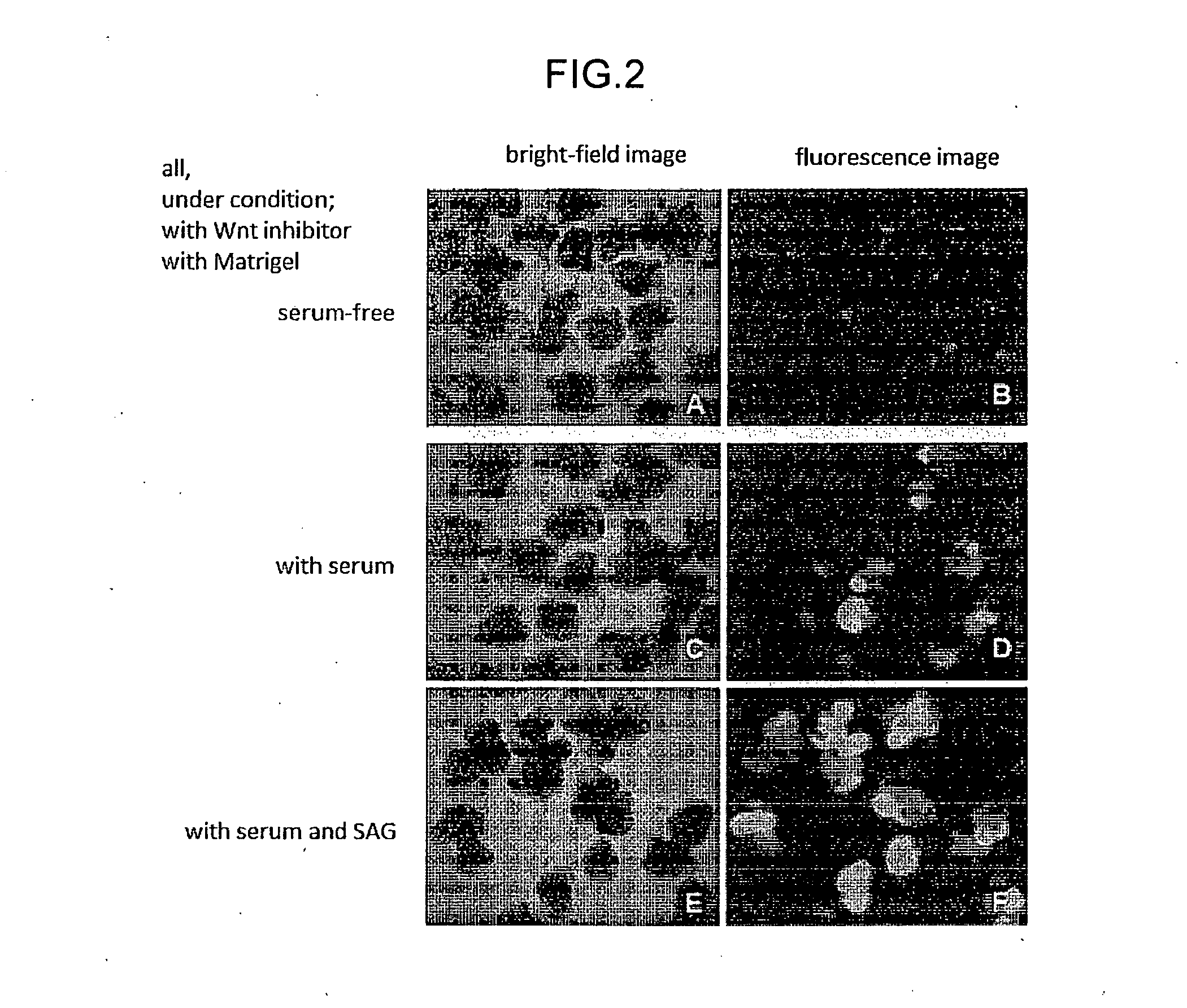
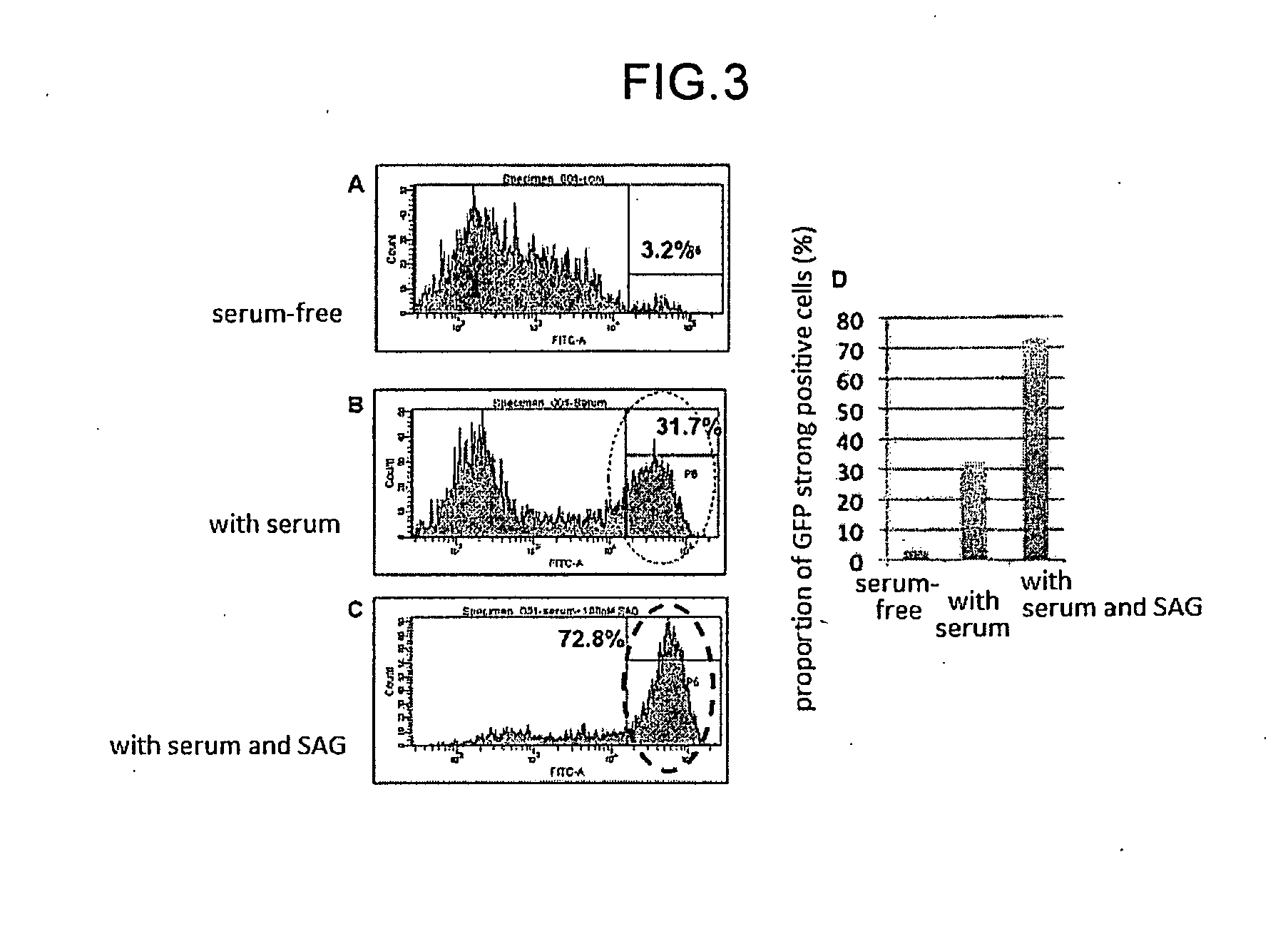
The invention provides a method for producing a retinal tissue by (1) subjecting pluripotent stem cells to floating culture in a serum-free medium containing a substance inhibiting the Wnt signal pathway to form an aggregate of pluripotent stem cells, (2) subjecting the aggregate to floating culture in a serum-free medium containing a basement membrane preparation, and then (3) subjecting the aggregate to floating culture in a serum-containing medium. The invention also provides a method for producing an optic-cup-like structure, a method for producing a retinal pigment epithelium, and a method for producing a retinal layer-specific neural cell.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com