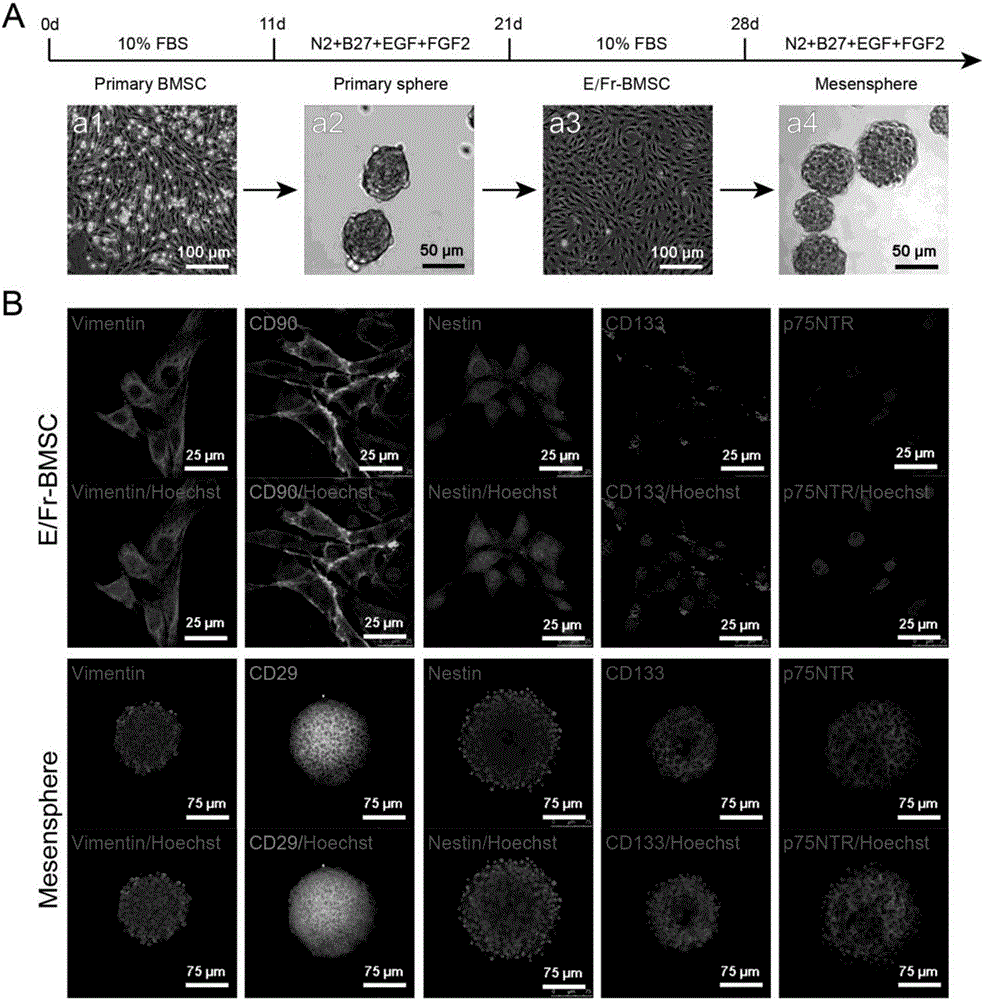
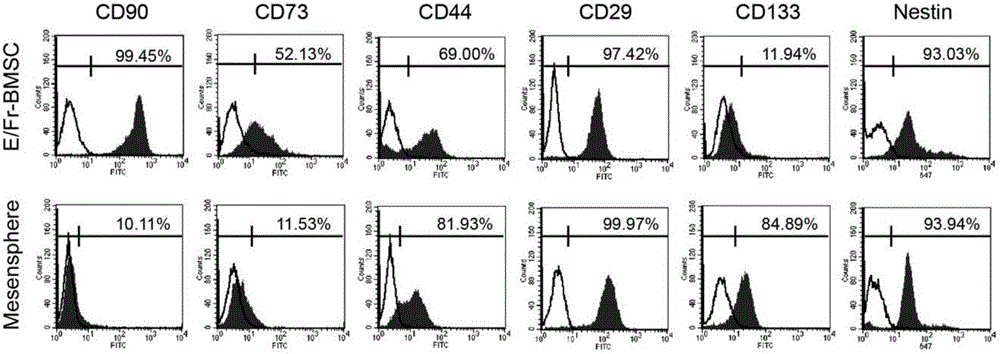
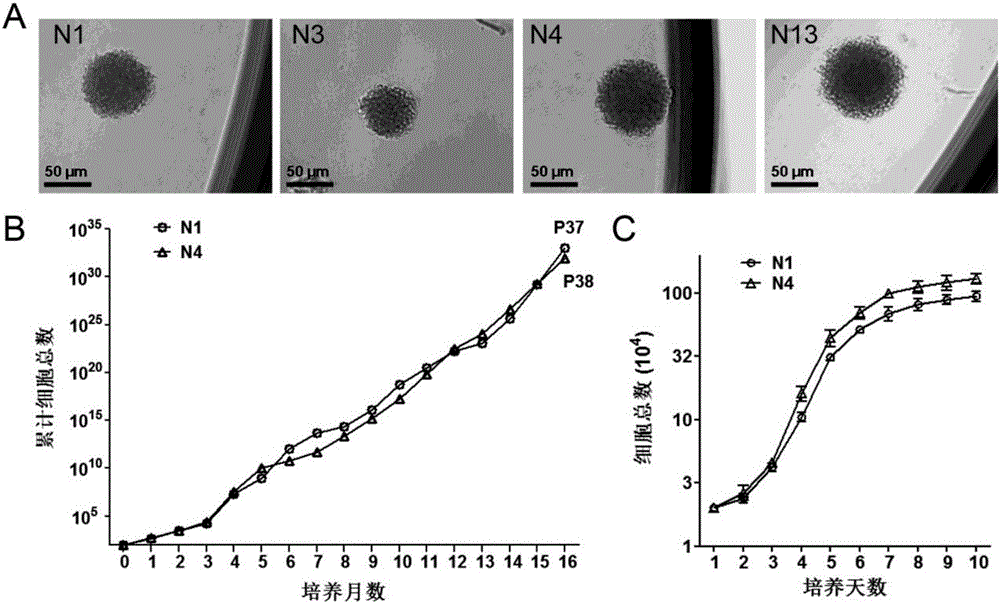
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Neural crest" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to chordates of the group Cristozoa that arise from the embryonic ectoderm cell layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia.
Cell therapy for chronic stroke
A method of treating stroke in a patient who has undergone a stroke comprising administering at least 2 million suitable neuronal cells to at least one brain area involved in the stroke. The method comprises the step of using a twist drill or a burr to form a hole in the skull through which the cells could be administered. Exemplary cells are hNT neuronal cells, HCN-1 cells, fetal pig cells, neural crest cells, neural stem cells, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed herein is a pharmaceutical composition of 95% pure hNT neuronal cells, which composition further includes a vial containing PBS and human neuronal cells. This vial is provided in a container with liquid nitrogen, whereby the composition is frozen and maintained at -170° C. before use. Also disclosed are methods of improving speech, cognitive, sensory, and motor function in a person who has experienced brain damage which interferes with function by administering a sterile composition of a sufficient number of neuronal cells or neural stem cells to the damaged area. Also disclosed is a method of replacing central nervous cells lost to neurodegenerative disease, trauma, ischemia or poisoning.
Owner:LAYTON BIOSCI +1
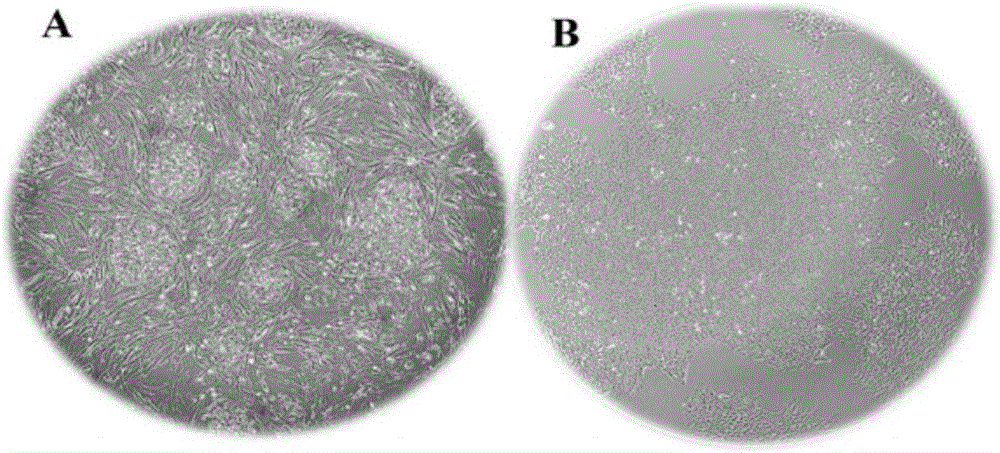
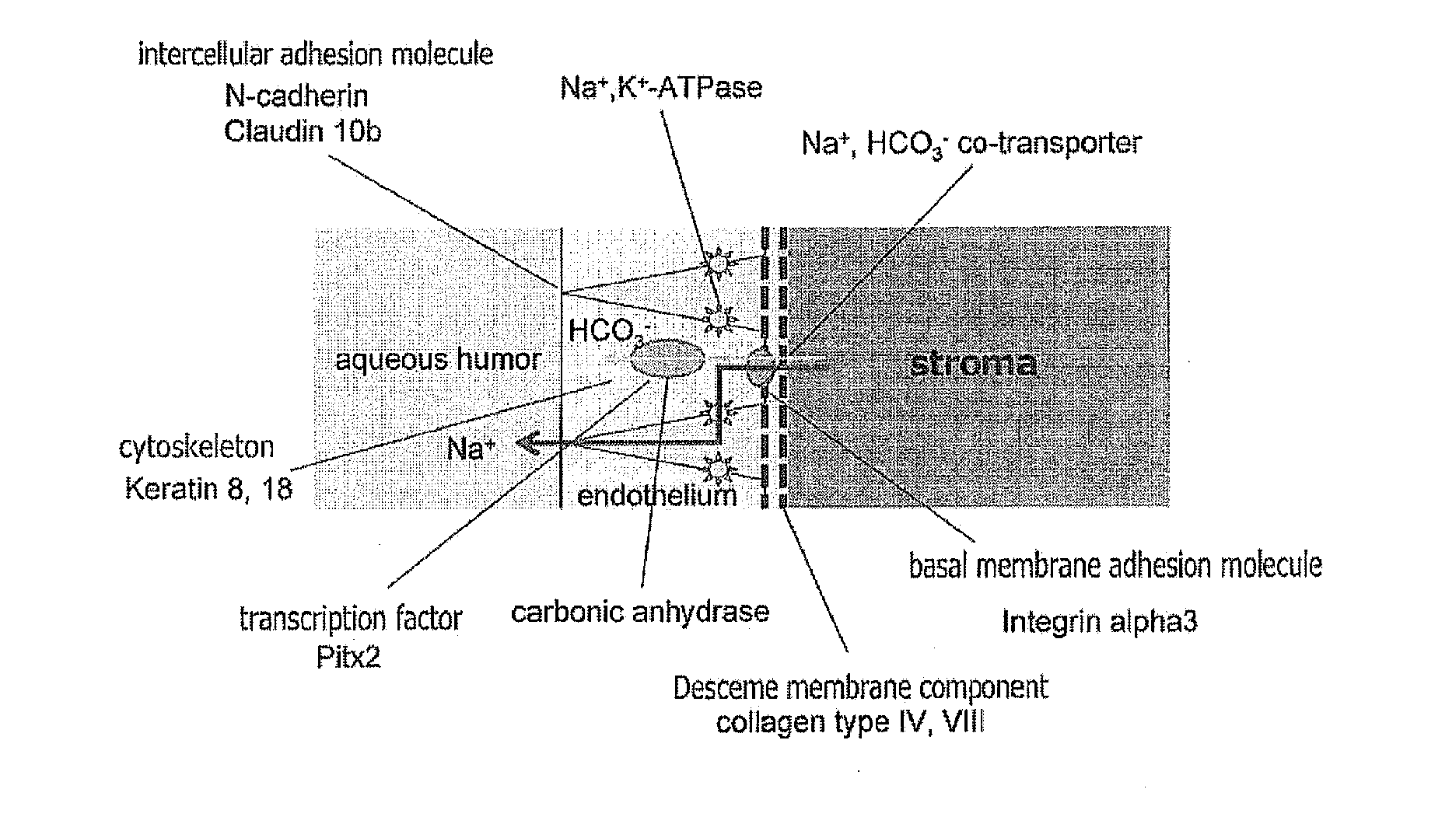
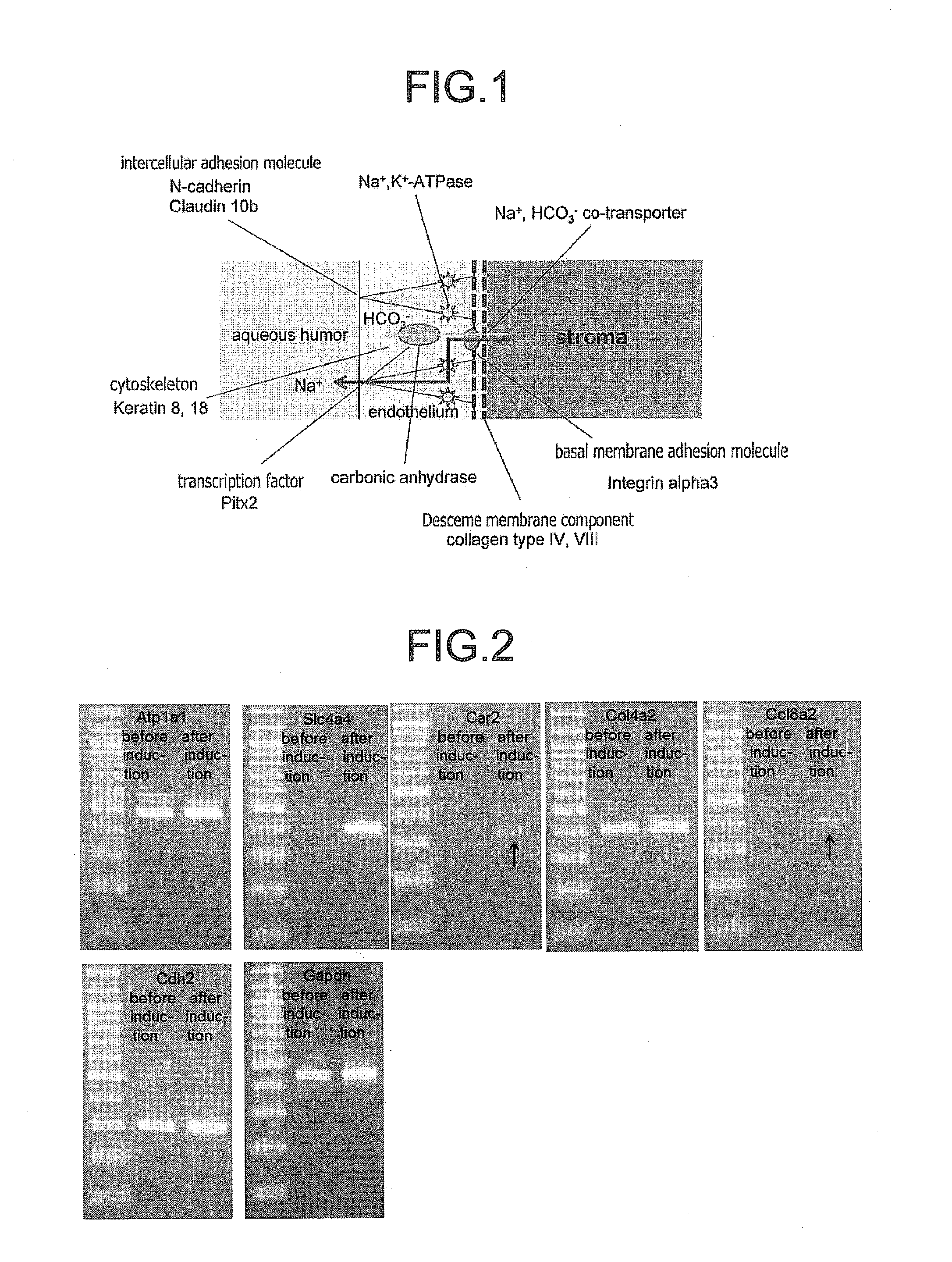
Inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells
The invention discloses an inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells. The method comprises the steps of: cultivating the human embryonic stem cells on a mouse embryonic fibroblast feed layer; sorting human embryonic stem cell clone groups in good state; grafting the groups on a human corneal stromal fibroblast layer processed by mitomycin C and cultivating for 7 days, wherein the human embryonic stem cells are differentiated to rosettes; separating and transferring the rosettes from the human corneal stromal fibroblast layer to a culture bottle; cultivating continuously for 7 days by using a neural crest stem cell culture medium; sorting the neural crest stem cells by a flow cytometry; adding the neural crest stem cells into the culture bottle; placing in a 5% CO2 incubator for incubating and cultivating at 37 DEG C by using a human corneal endothelial cell culture medium; changing the liquid every other day; and cultivating for about 10 days to obtain the corneal endothelial cells. The multiplication capacity of the corneal endothelial cells are similar to that of human corneal endothelial cells and the corneal endothelial cells can be transferred to 1-2 generations in vitro maximally. The corneal endothelial cells can be used as seed cells for cornea construction and transplant in tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for producing corneal endothelial cell
ActiveUS9347042B2Efficient productionSenses disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
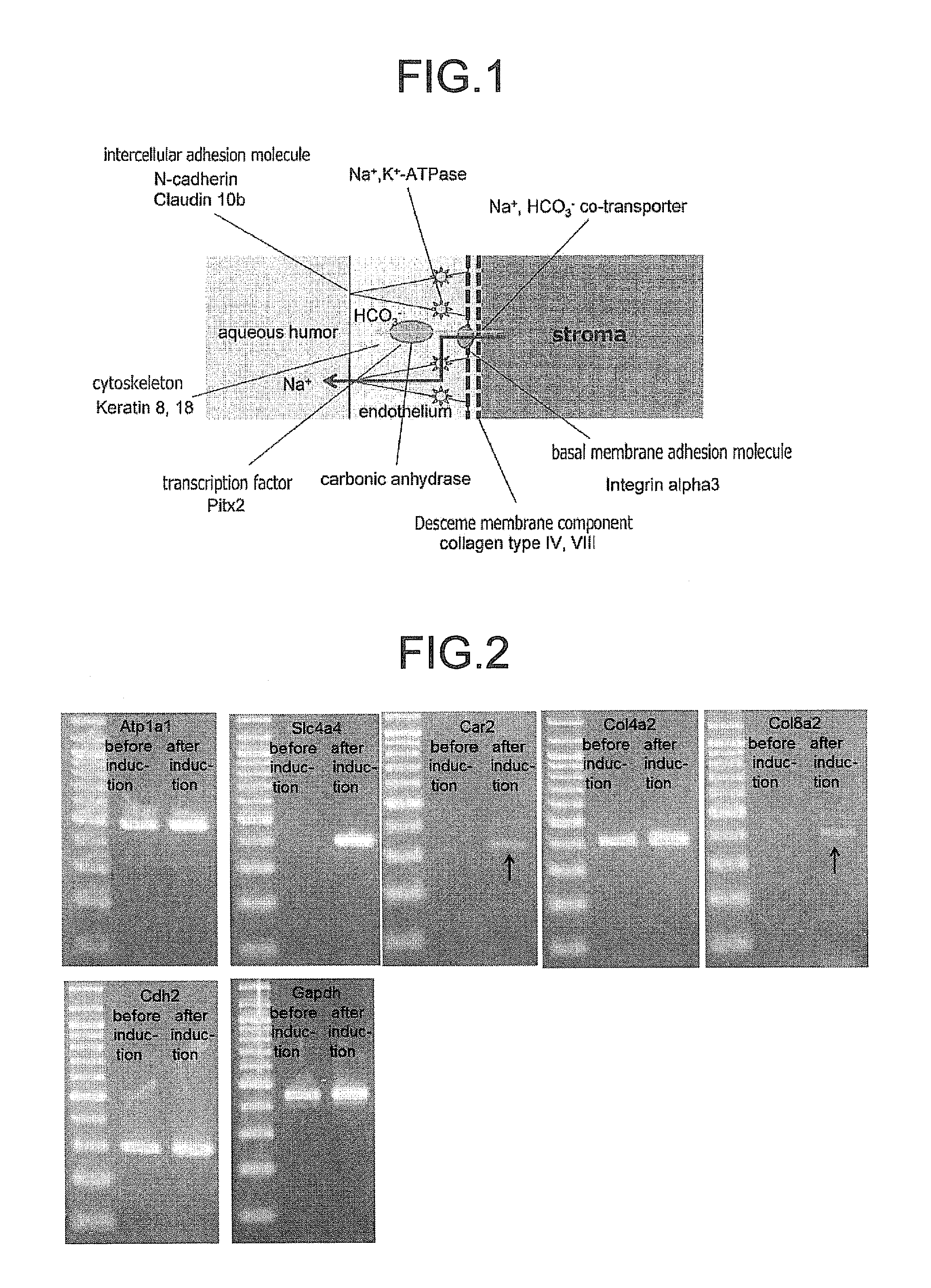
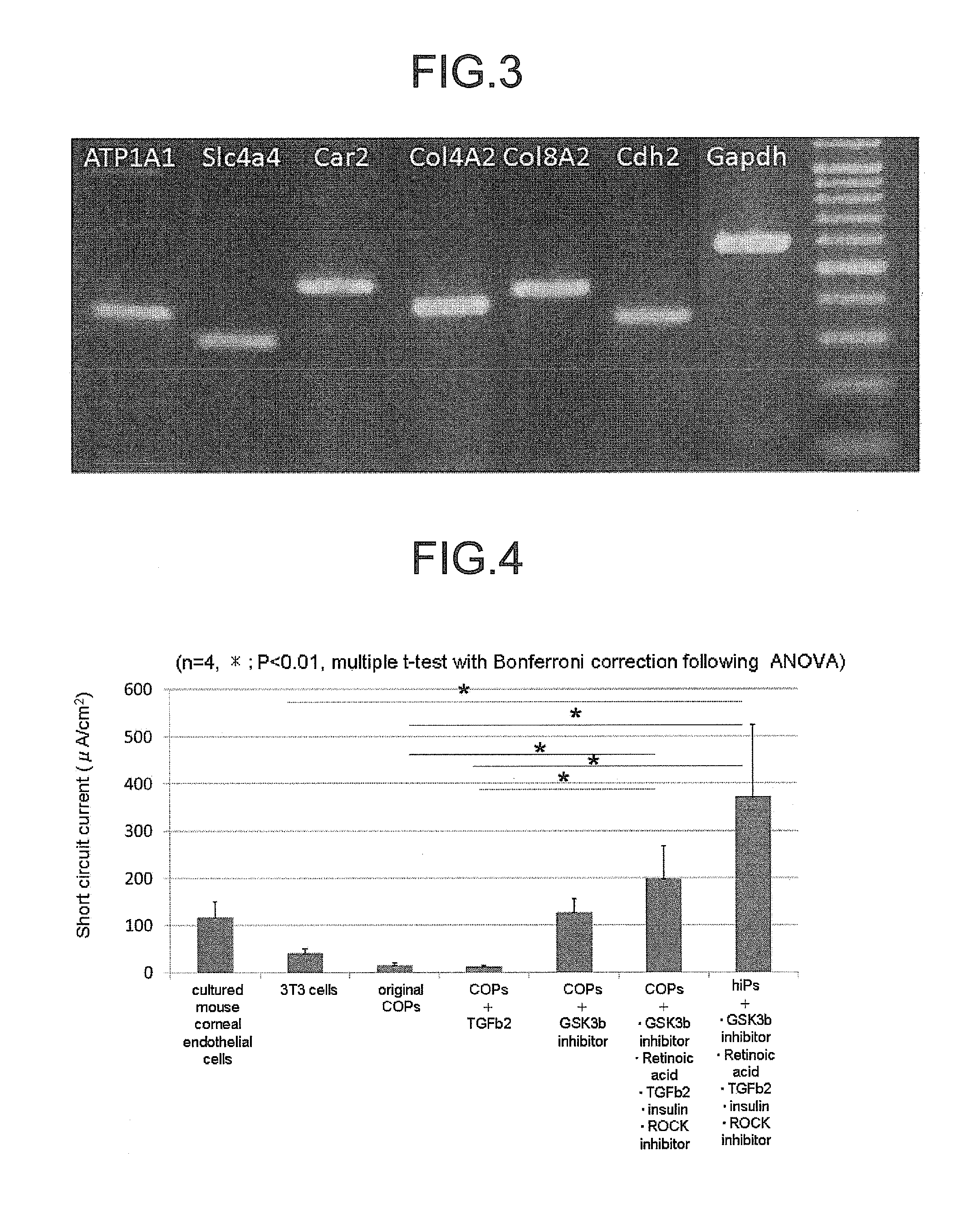
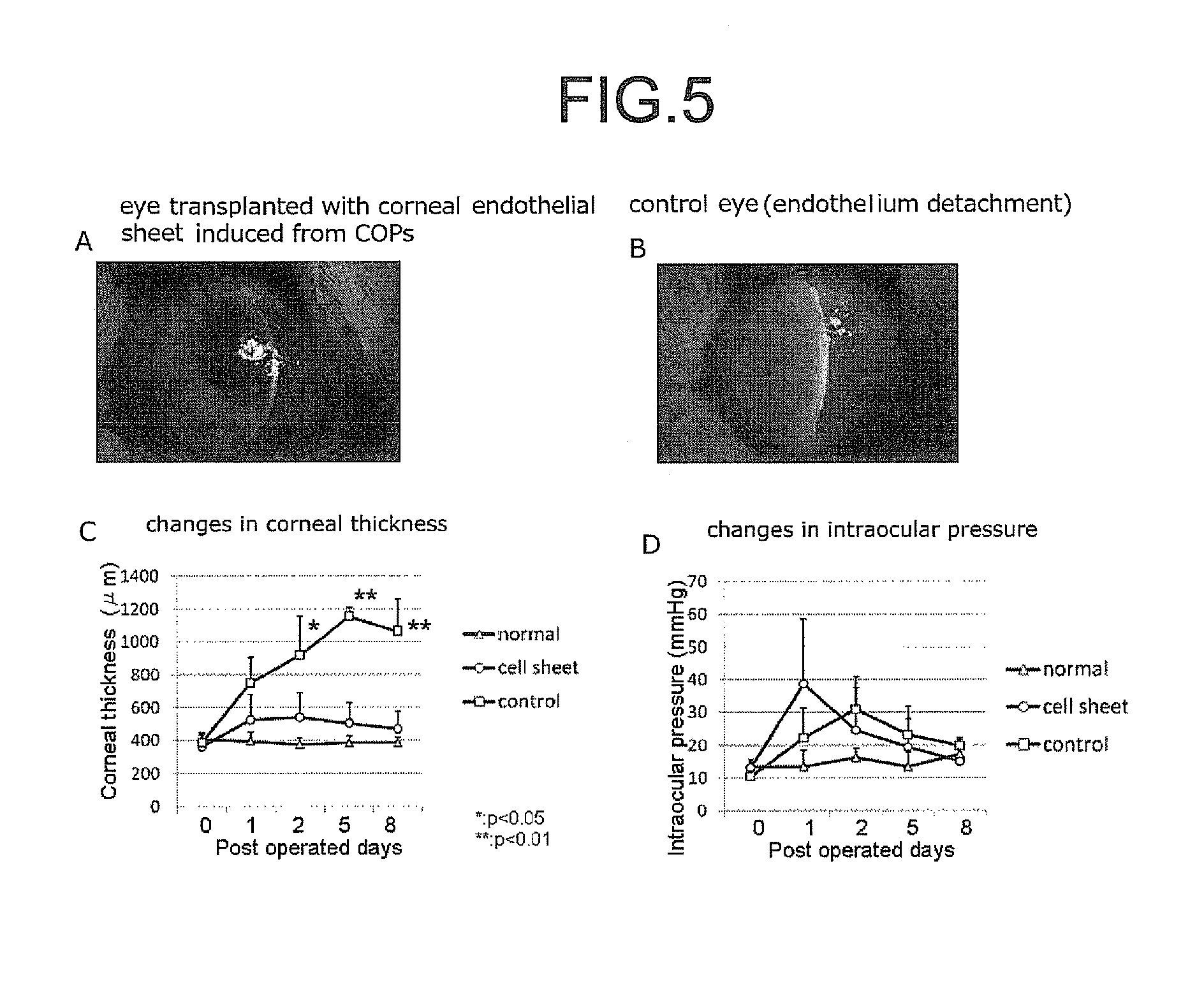
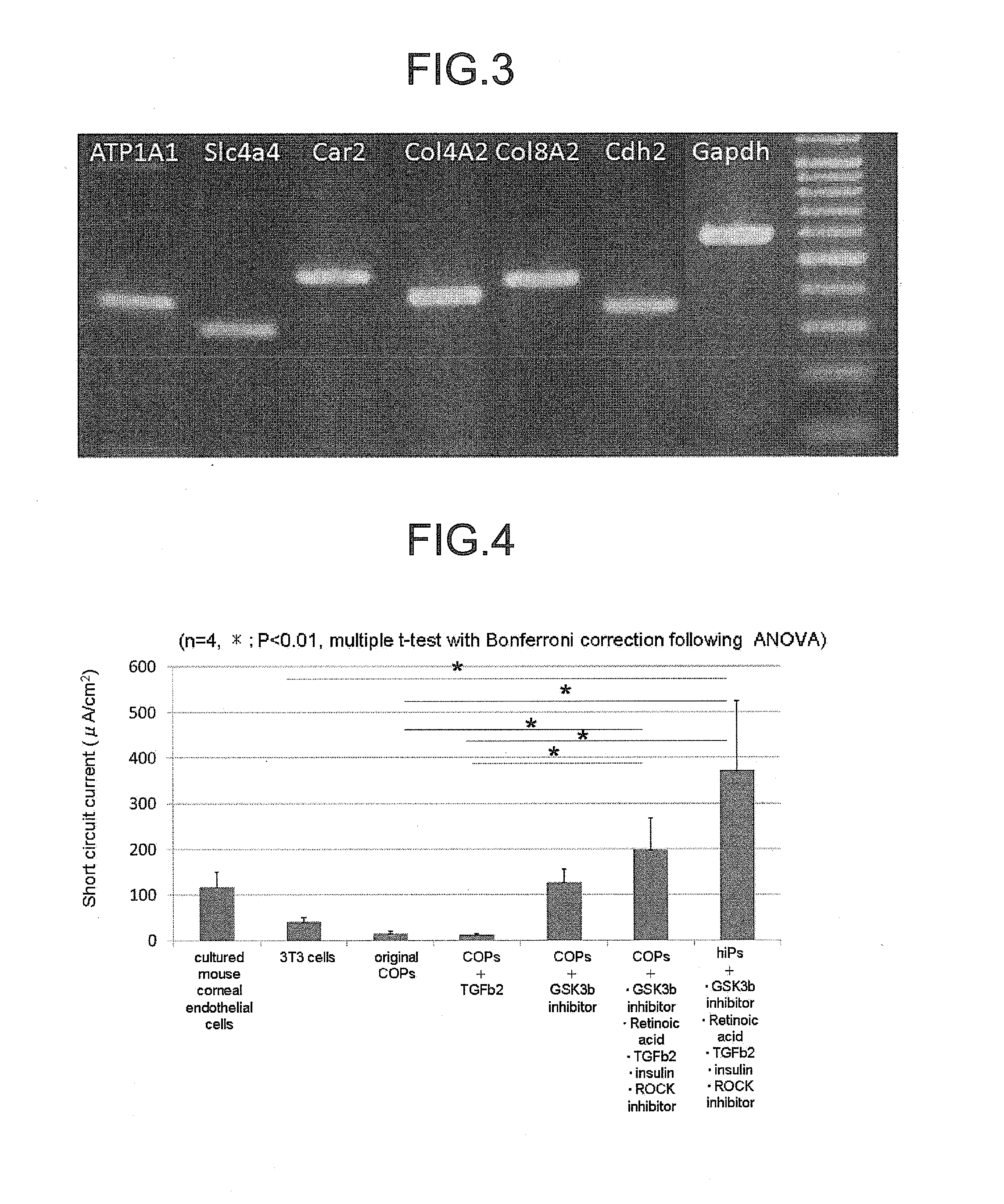
The invention provides a method of efficiently producing corneal endothelial cells, particularly from corneal stroma or iPS cell-derived neural crest stem cells, a method of producing corneal endothelial cells stably in a large amount by inducing more efficient differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells, and a medicament containing corneal endothelial cells. The method of inducing differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells includes a step of culturing the stem cells in a differentiation induction medium containing a GSK3 inhibitor (preferably a GSK3β inhibitor) and retinoic acid, with the differentiation induction medium preferably further containing one or more of TGFb2, insulin, a ROCK inhibitor, and the like.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
A directional differentiation induction method of human embryonic stem cells to obtain corneal endothelial cells
ActiveCN106167790AConsistent proliferative abilityCulture processNervous system cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
A directional differentiation induction method of human embryonic stem cells to obtain corneal endothelial cells is provided. The method includes inducing the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate into human neural crest stem cells, inducing the human neural crest stem cells to differentiate into the human corneal endothelial cells, and other steps. The method adopts a primary human corneal stroma cell culture supernatant fluid, a human corneal endothelial cell culture supernatant fluid and a human lens cell culture supernatant fluid as a conditioned medium. Through adding retinoic acid and a plurality of recombinant proteins into the medium, and combining three-dimensional and two-dimensional culture methods, a corneal endothelial cell development process is simulated to induce the human embryonic stem cells to directionally differentiate into the human corneal endothelial cells, the corneal endothelial cells morphological structures of which are similar to those of normal human corneal endothelial cells can be obtained, and in-vitro subculture results show that proliferation of the obtained human corneal endothelial cells is consistent with proliferation of the normal human corneal endothelial cells.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for producing corneal endothelial cell
ActiveUS20140315305A1Efficient productionProduce efficientlySenses disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
The invention provides a method of efficiently producing corneal endothelial cells, particularly from corneal stroma or iPS cell-derived neural crest stem cells, a method of producing corneal endothelial cells stably in a large amount by inducing more efficient differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells, and a medicament containing corneal endothelial cells. The method of inducing differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells includes a step of culturing the stem cells in a differentiation induction medium containing a GSK3 inhibitor (preferably a GSK3β inhibitor) and retinoic acid, with the differentiation induction medium preferably further containing one or more of TGFb2, insulin, a ROCK inhibitor, and the like.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Derivation of neural crest stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20170260501A1Nervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDiseaseRho-associated protein kinase
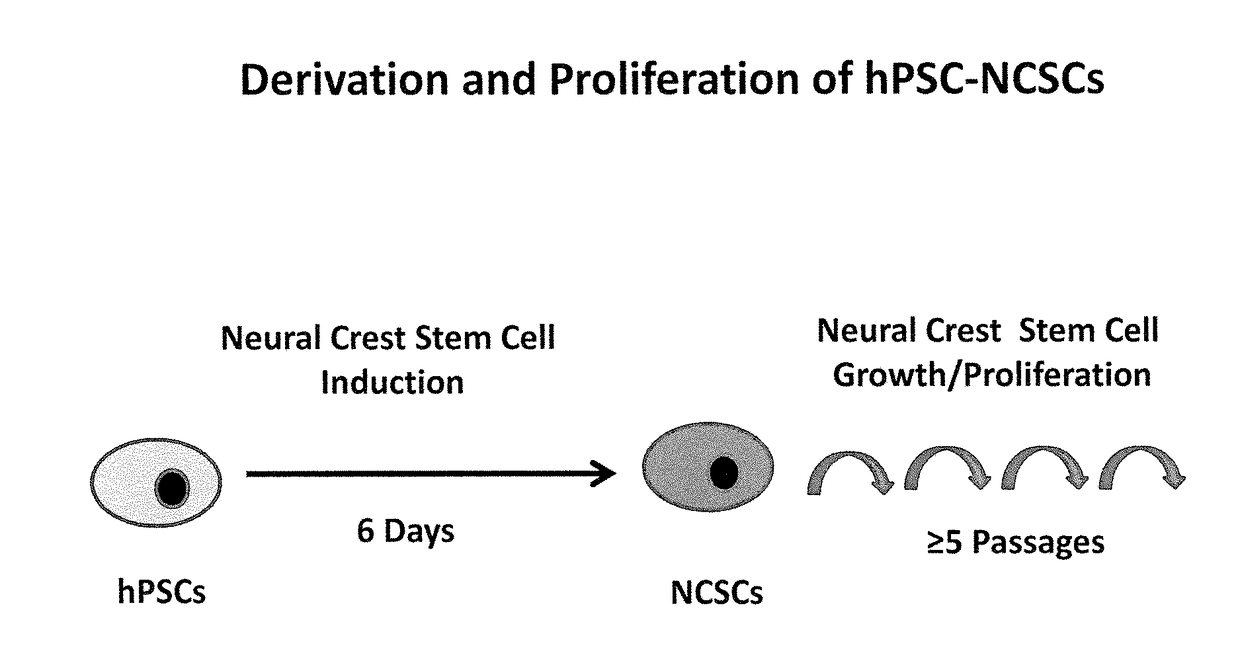
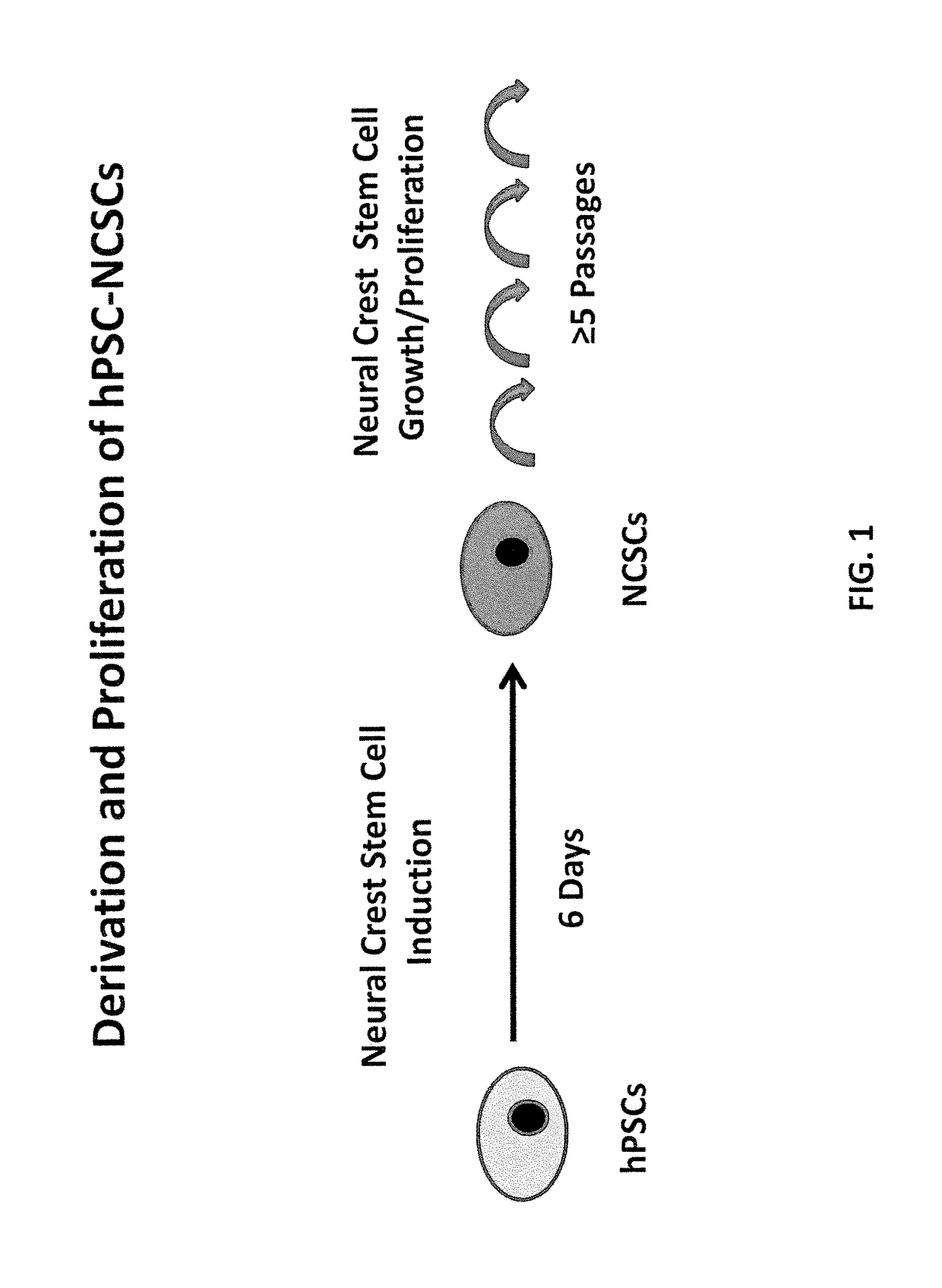
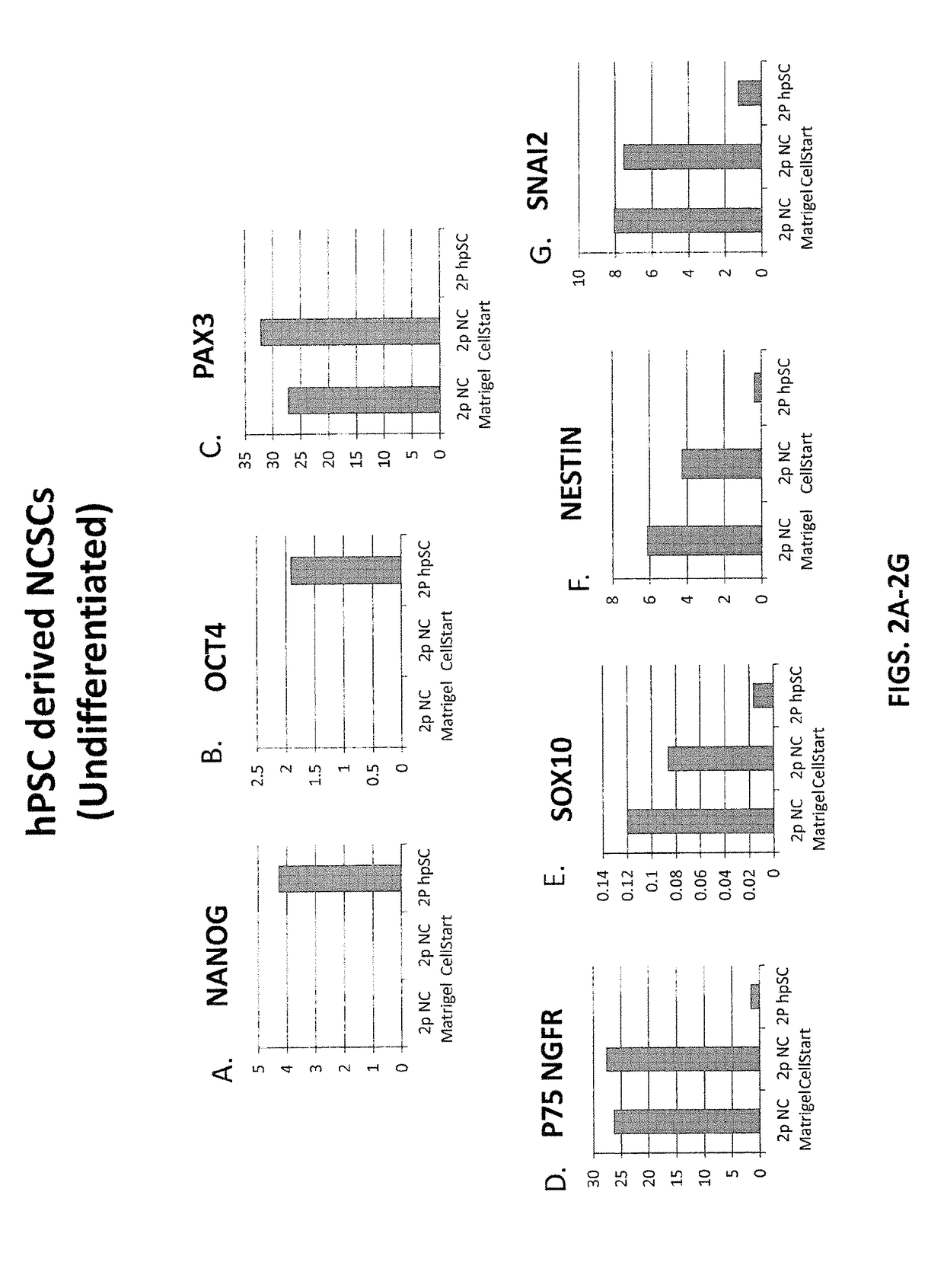
The present invention is based in part the discovery of methods for the generation of neural crest stem cells (NCSCs) from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). Specifically, the present invention discloses methods for the use of a combination of rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitors, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitors, activing receptor like kinase (ALK) receptor inhibitors and bone morphogenic protein (BMP) receptor inhibitors to derive NCSCs from hPSCs. The present invention also discloses methods to treat neurocristopathic diseases and disorders using NCSCs derived from hPSCs.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Induced differentiation method for differentiating human induced pluripotent stem cells into leydig cells and application thereof
InactiveCN105255826AIncrease serum testosterone levelsPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processPluripotential stem cellLeydig cell
The invention provides an external directional induced differentiation method for differentiating human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells into leydig cells (LCs) through neural crest stem cells (NCSCs). By the utilization of an animal model, it is verified that the LCs from the iPS cells have the capacity of regenerating aged or damaged LCs, and a new testosterone-supplying scheme is provided for a patient with hypogonadism and particularly an LOH patient.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Postnatal neural crest stem cells
ActiveUS20040110288A1Reduced neuronal subtype potentialAffects determinationCulture processNervous system cellsNeural crestIn vivo
The present invention relates to compositions and methods employing postnatal (e.g., adult) neural crest stem cells. The stem cells are multipotent and differentiate when transplanted in vivo. Transplantation methods are provided for therapeutic, diagnostic, and research applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of isolating epidermal neural crest stem cells
InactiveUS20060281177A1Improve scalabilityDissecting the hair folliclesNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsNeural crestHair follicle
The present invention describes novel methods for isolating a substantially pure cell population of non-embryonic epidermal neural crest stem cells from the bulge-region of mammalian hair follicles. Also disclosed is the substantially pure cell population of follicular bulge-derived neural crest stem cells for medical research and therapeutic use.
Owner:MAYA SIEBER BLUM
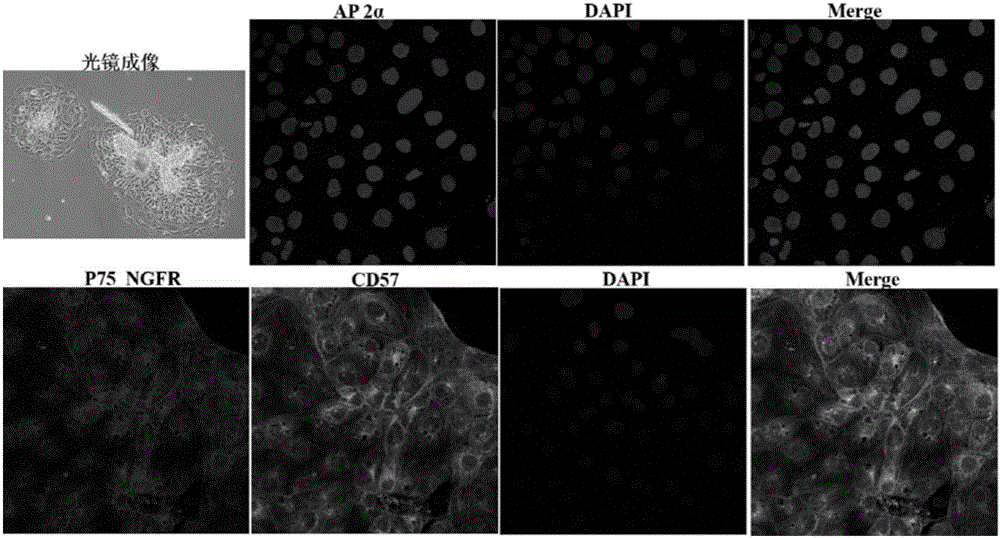
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to multipotent neural crest cells
ActiveUS20160237405A1Increase profitEffectively lead to differentiationNervous system cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsSmooth muscleInduced pluripotent stem cell
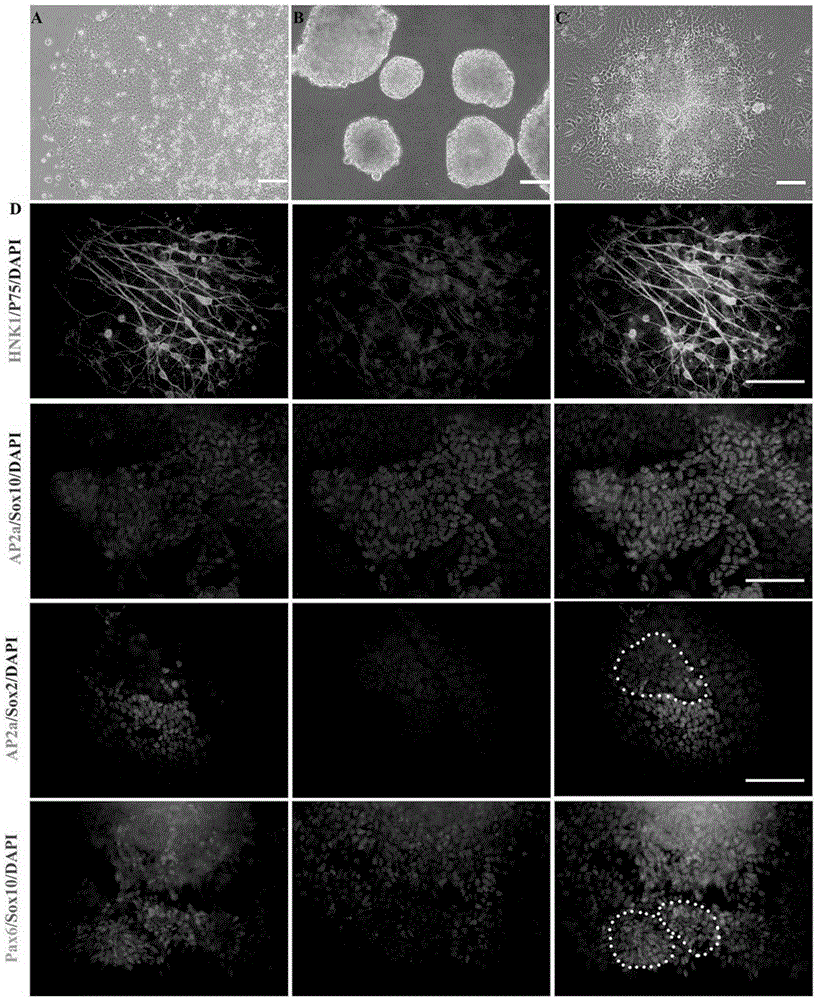
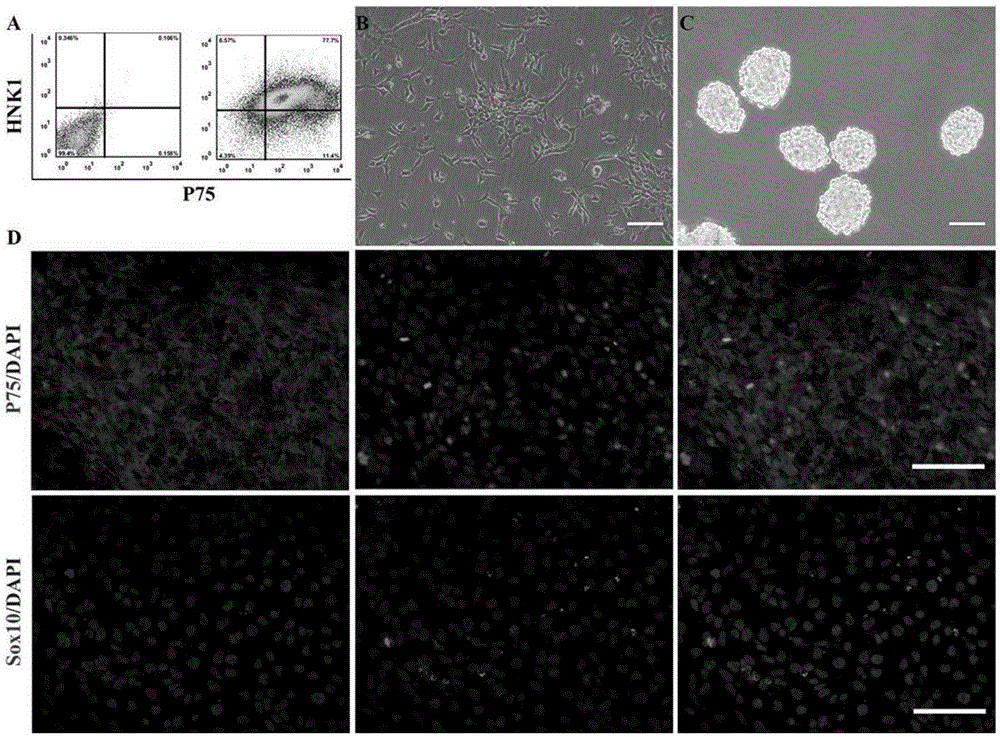
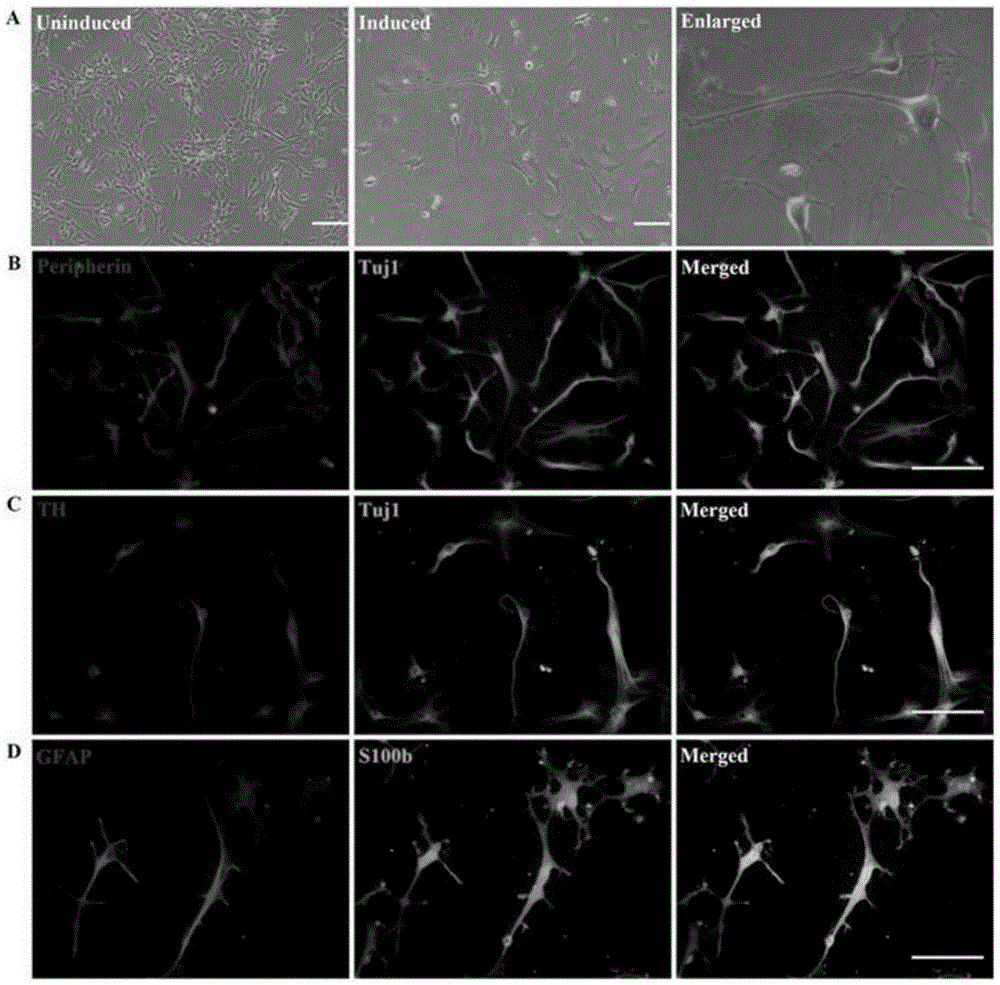
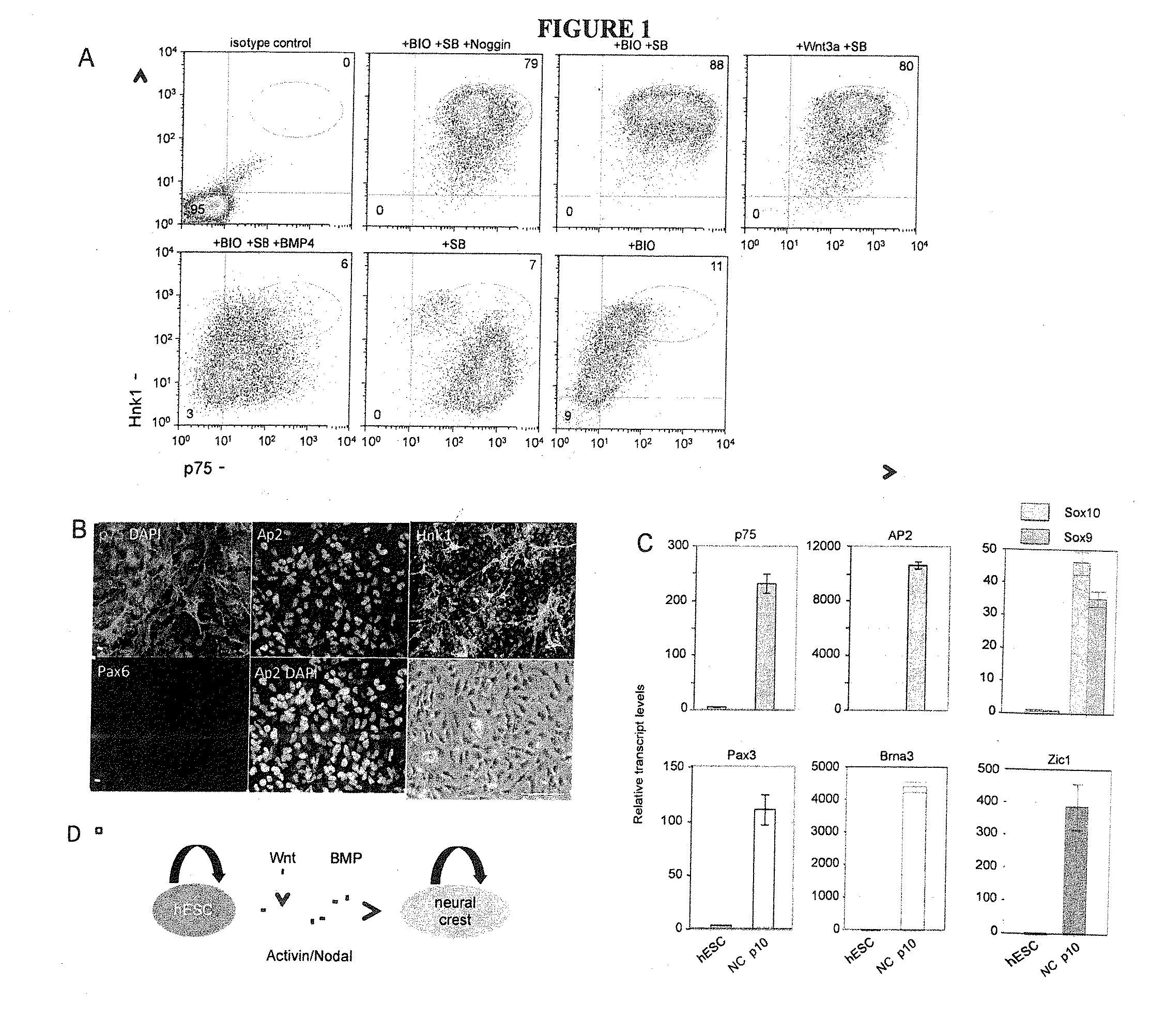
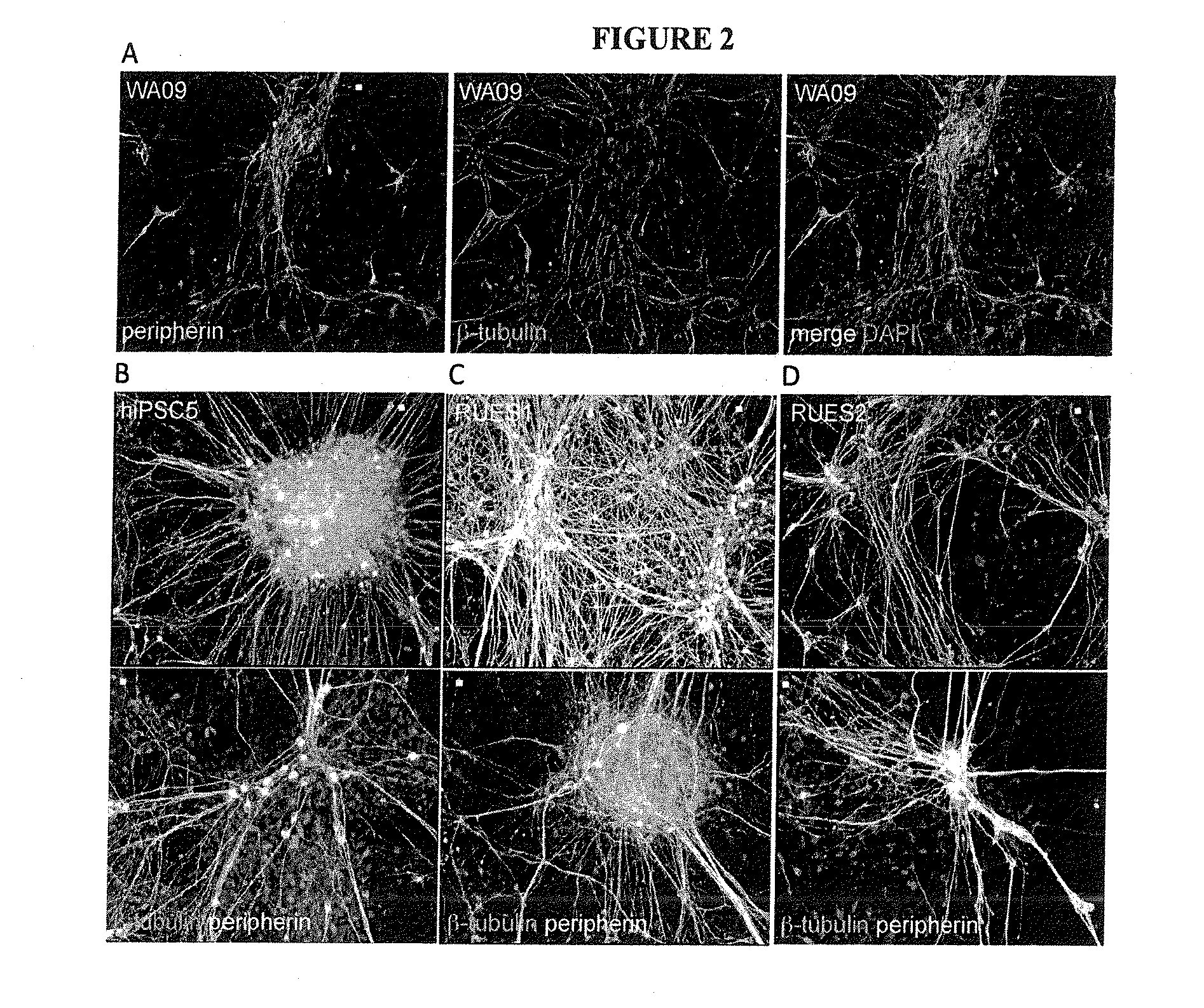
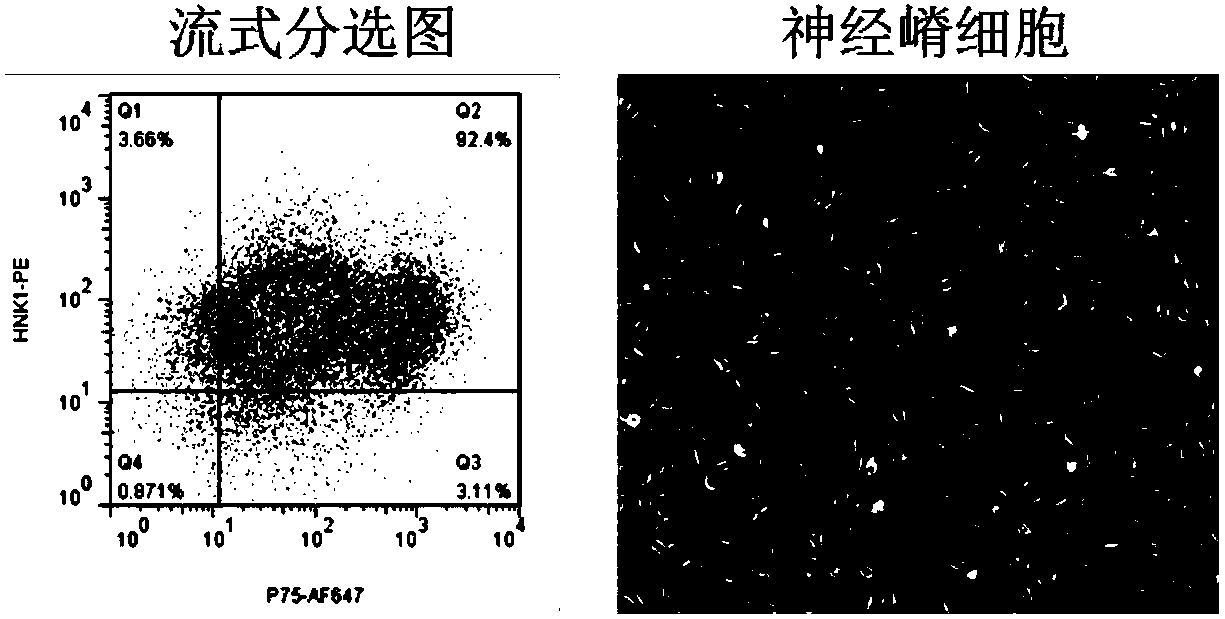
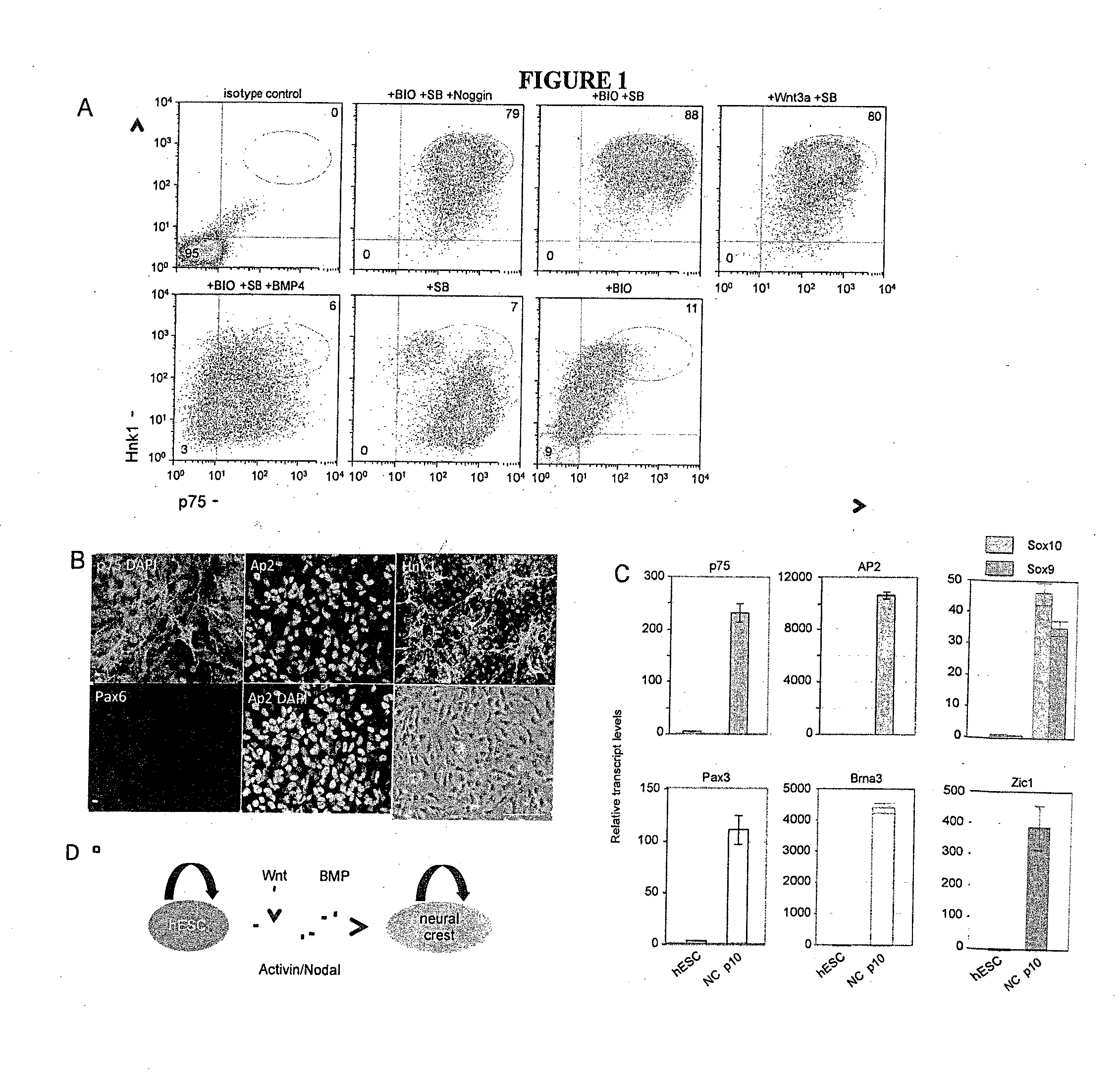
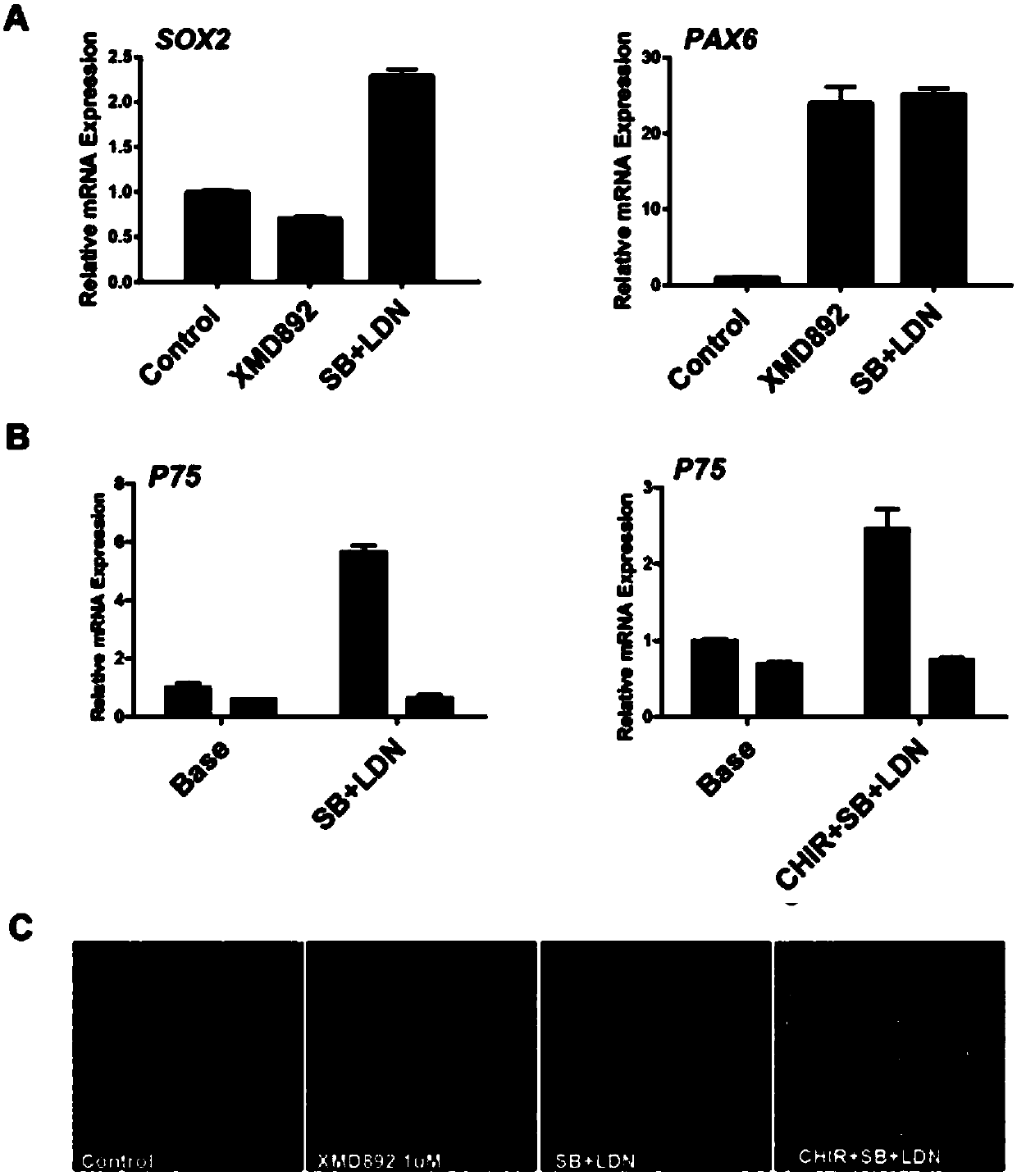
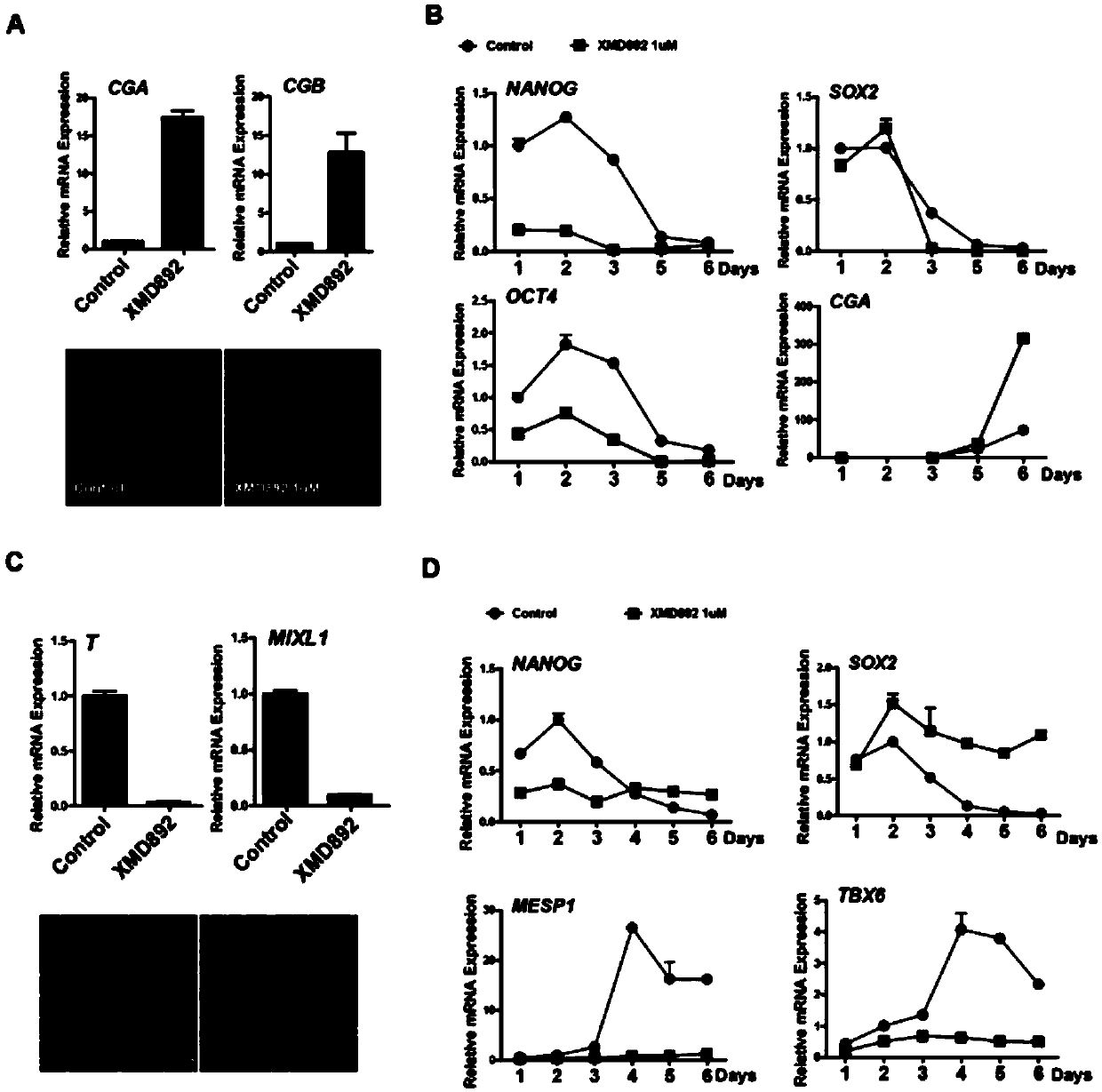
The present invention relates to the differentiation of human pluripotent cells, including human pluripotent stems cells to produce a self-renewing multipotent neural crest cell population in a single step method without the requirement of isolation of intermediate cells and without appreciable contamination (in certain preferred instances, virtually none) with Pax6+ neural progenitor cells in the population of p75+Hnk1+Ap2+ multipotent neural crest-like cells. The multipotent neural crest cell population obtained can be clonally amplified and maintained for >25 passages (>100 days) while retaining the capacity to differentiate into peripheral neurons, smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal precursor cells.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Neural crest spectrum mesenchymal cell derived from pluripotent stem cells and induced differentiation method thereof
InactiveCN107858328AEnhanced CytologyIncreased therapeutic functionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCell phenotypeCulture fluid
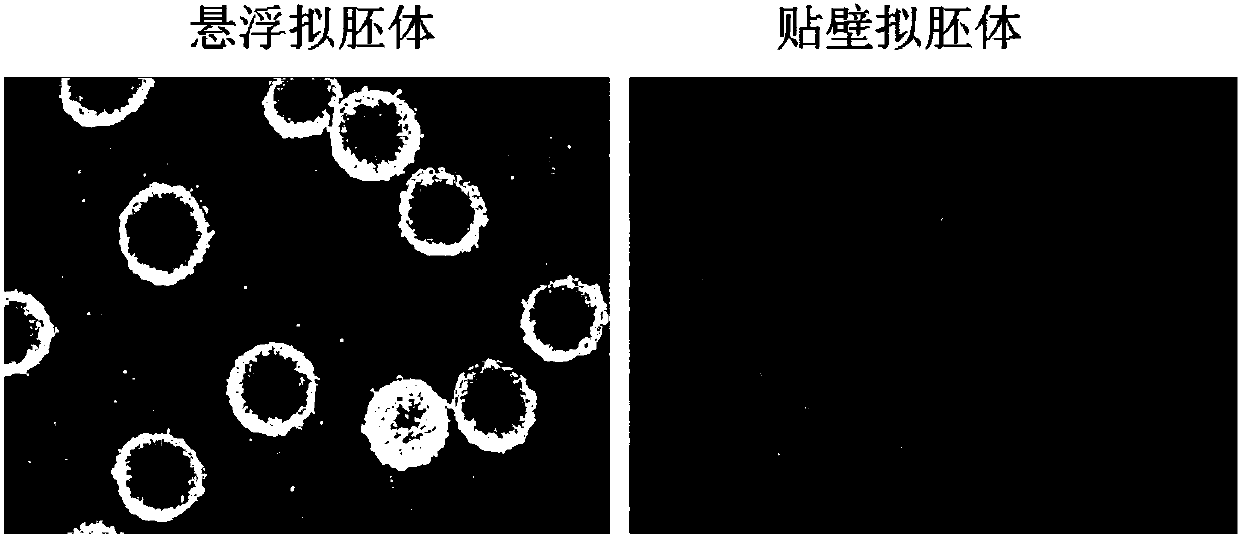
The invention discloses a neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell derived from pluripotent stem cells and an induced differentiation method thereof. The induced differentiation method of the neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell comprises the following steps: dissociating the pluripotent stem cells to obtain cell aggregates, carrying out suspension culture to form embryoid bodies, replacing a culture solution with a neural crest cell culture solution, carrying out suspension culture of the embryoid bodies, collecting the embryoid bodies and replacing the culture solution every day; enabling the embryoid bodies to grow for a certain time by adhering to the wall after culturing for a certain time; digesting and collecting cells; culturing the collected cells by enabling the cells to adhere to the wall, replacing the culture solution with a mesenchymal stem cell culture solution, carrying out passage culture, then detecting the mesenchymal cell phenotype to obtain the neural crest spectrum mesenchymal cell. Through the method, the defects of heterogeneity and hybridity between adult-derived mesenchymal stem cells and other mesenchymal stem cells derived from the pluripotentstem cells of non-finite induction pathways can be solved; the prepared neural crest spectrum mesenchymal stem cell has higher immunoregulation and osteogenic differentiation capabilities; the standardized induced differentiation process is capable of ensuring that cell populations prepared between different batches have good consistency.
Owner:广州赛隽生物科技有限公司
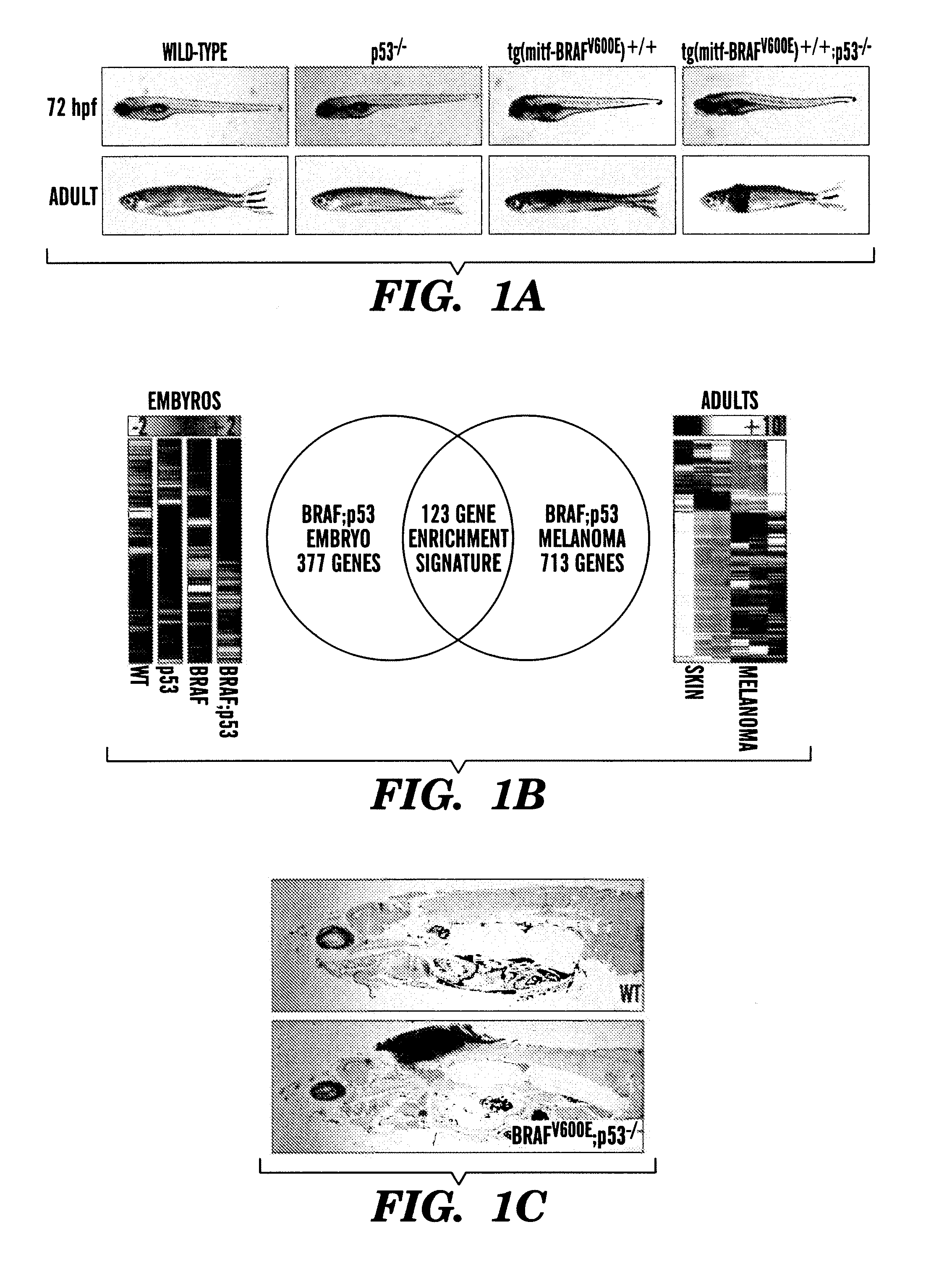
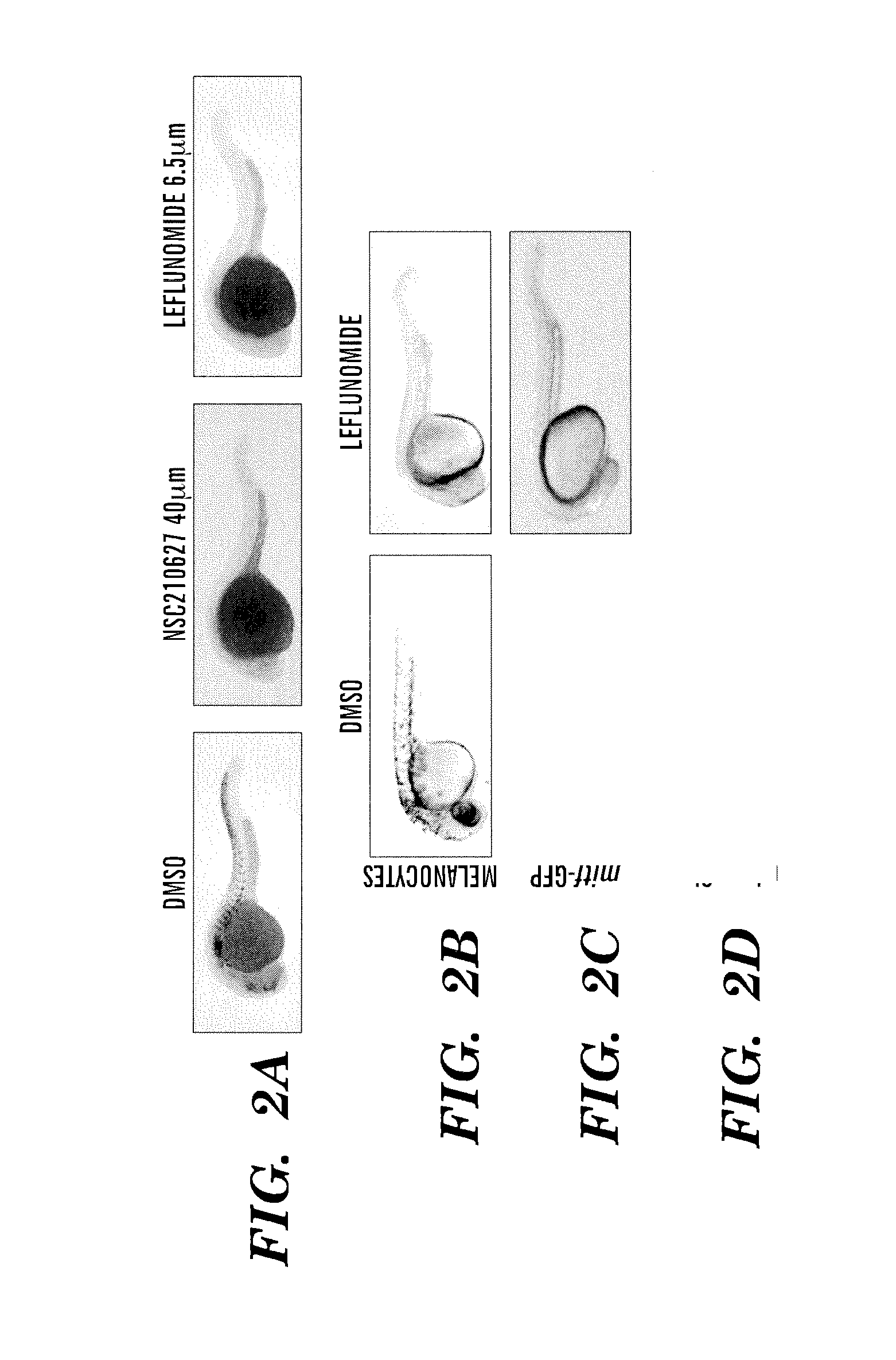
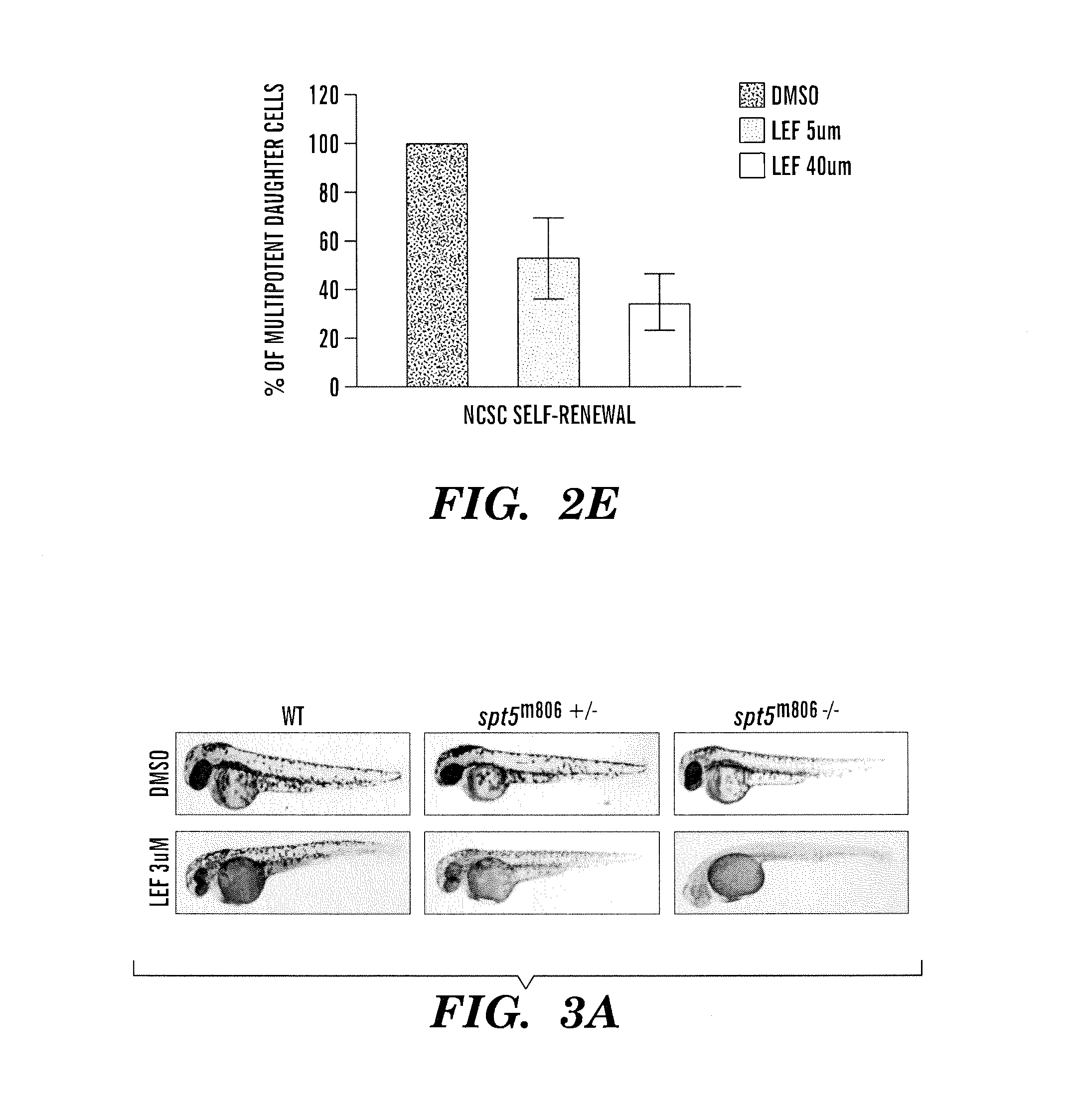
Methods for treatment of melanoma
InactiveUS20140031383A1Utility in treatmentUseful in treatmentBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorNeural crest
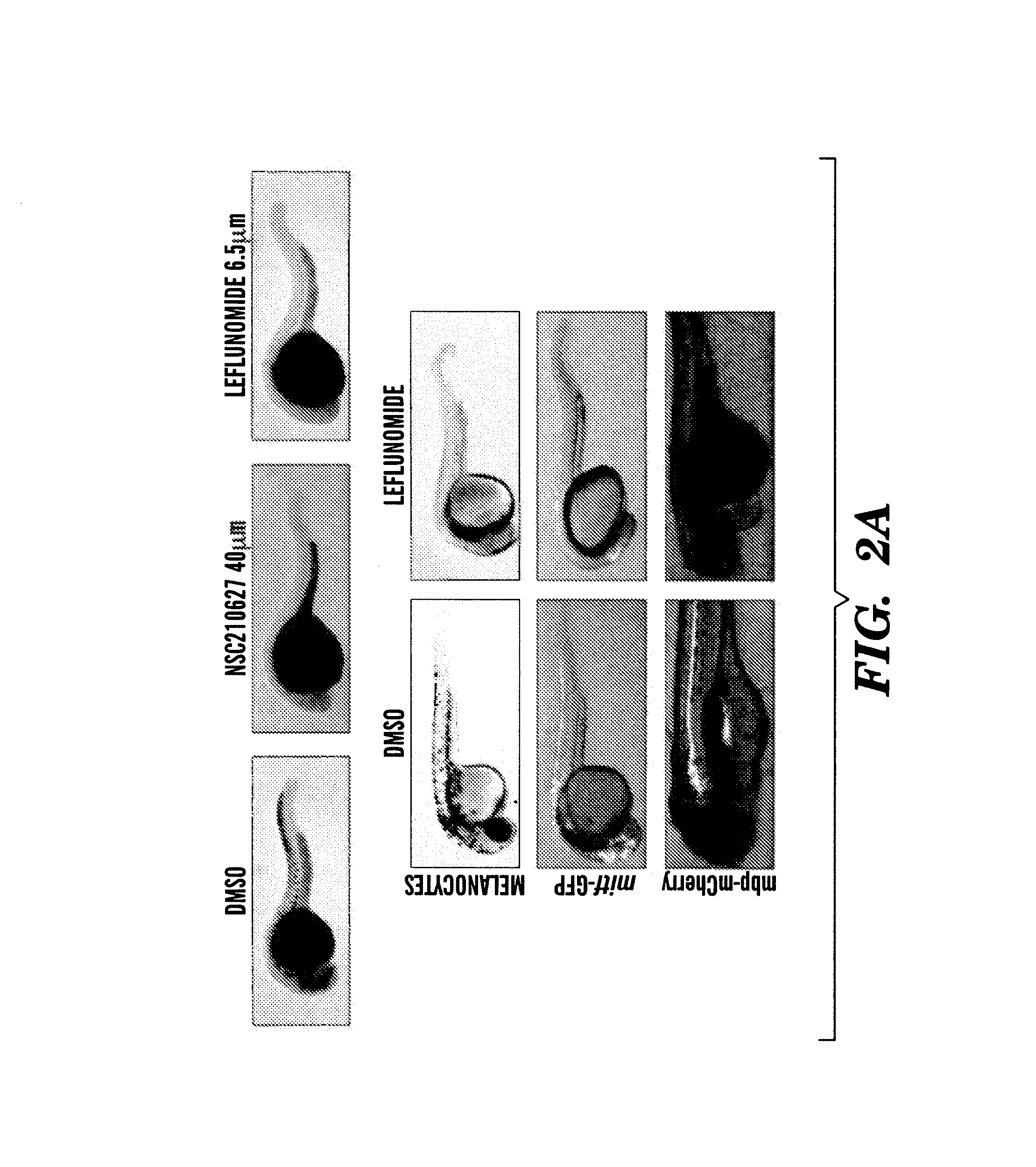
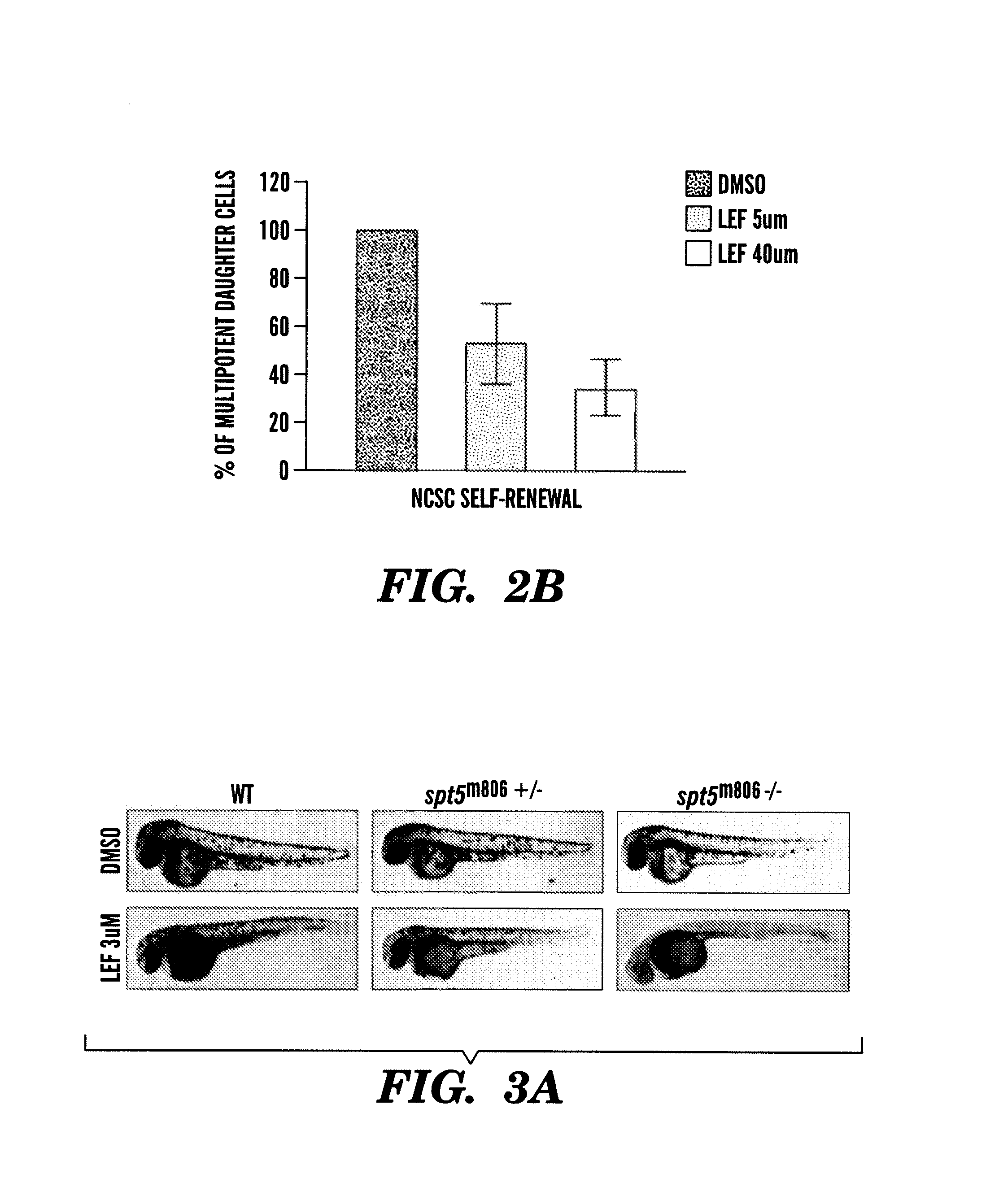
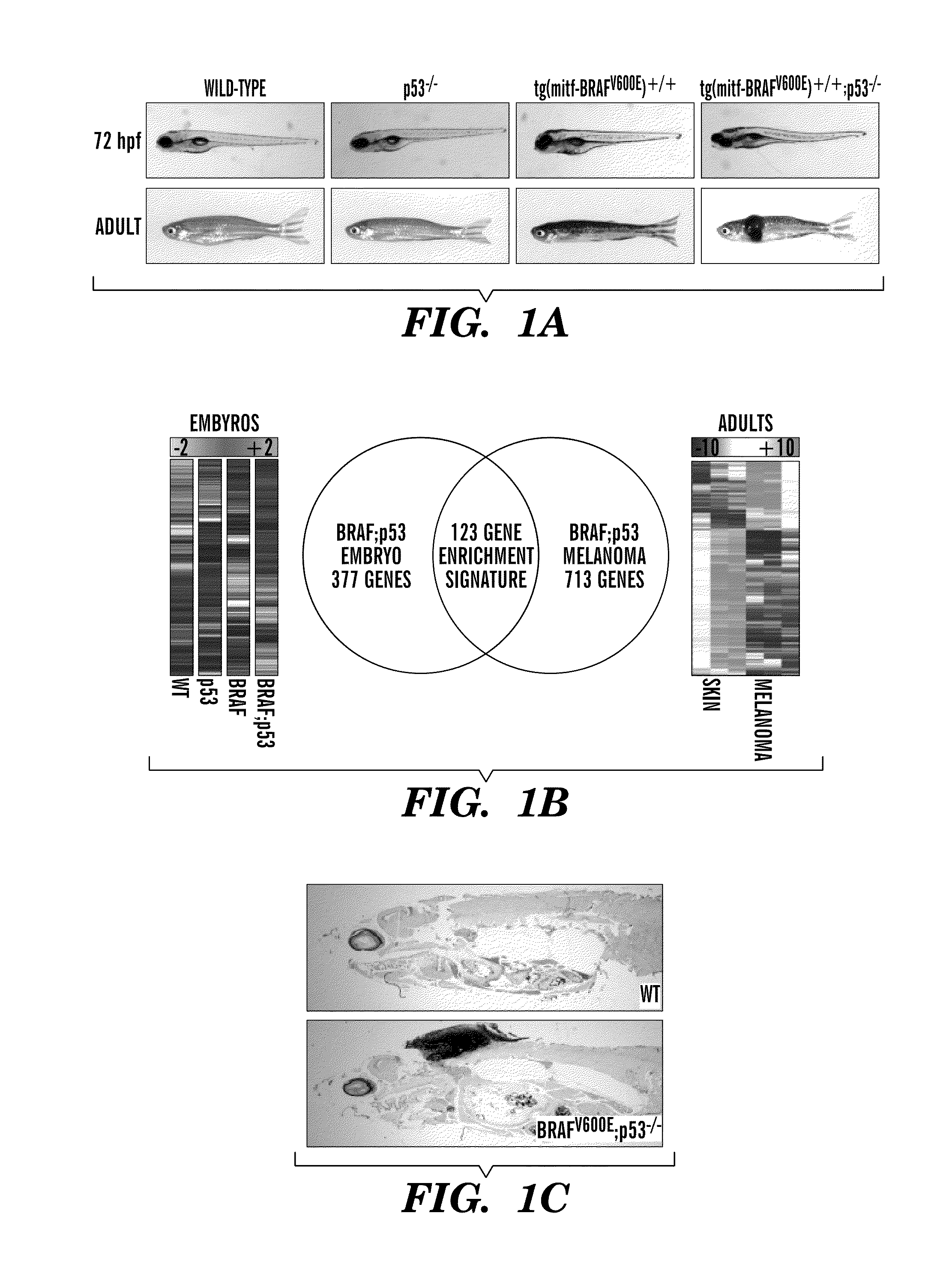
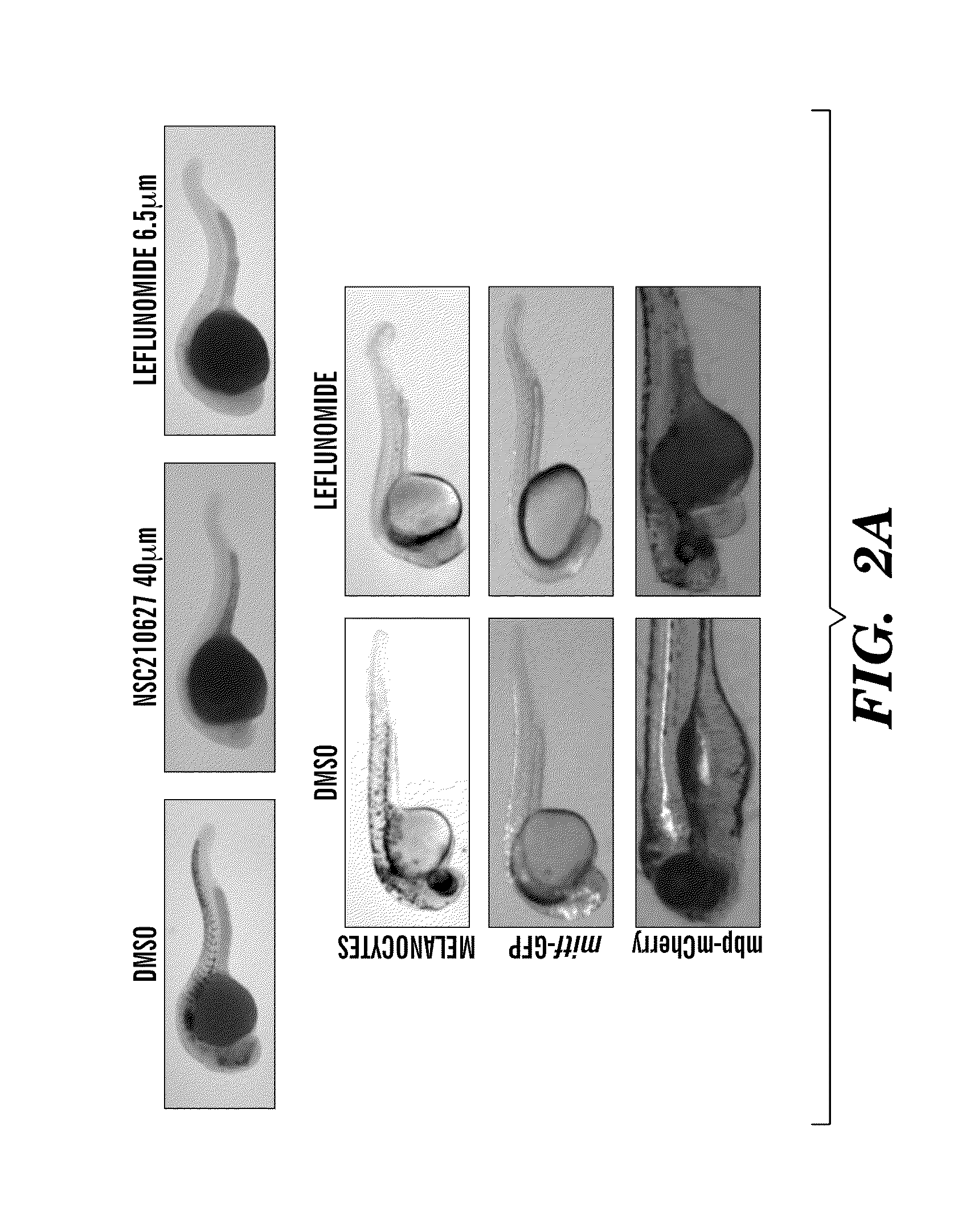
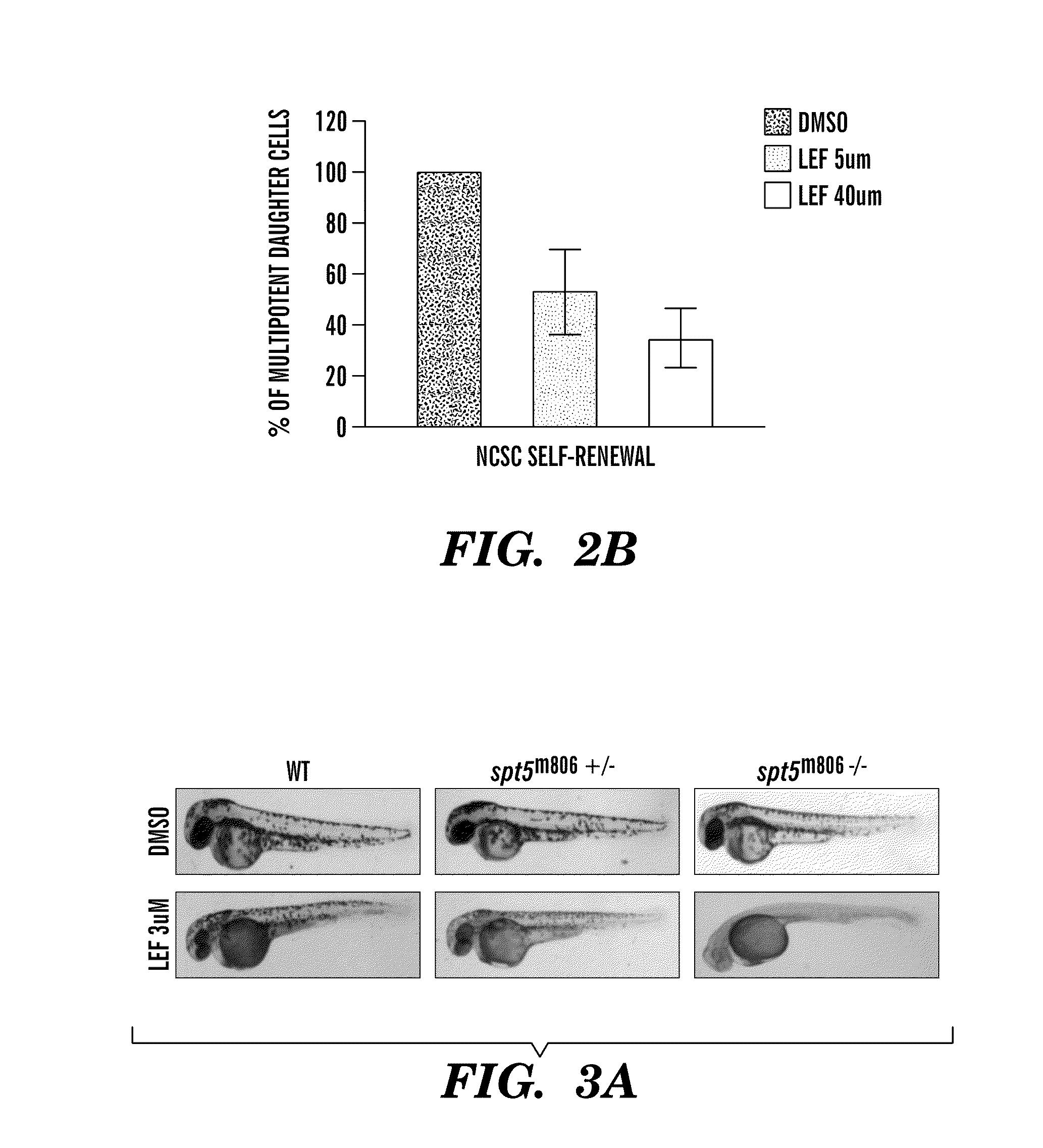
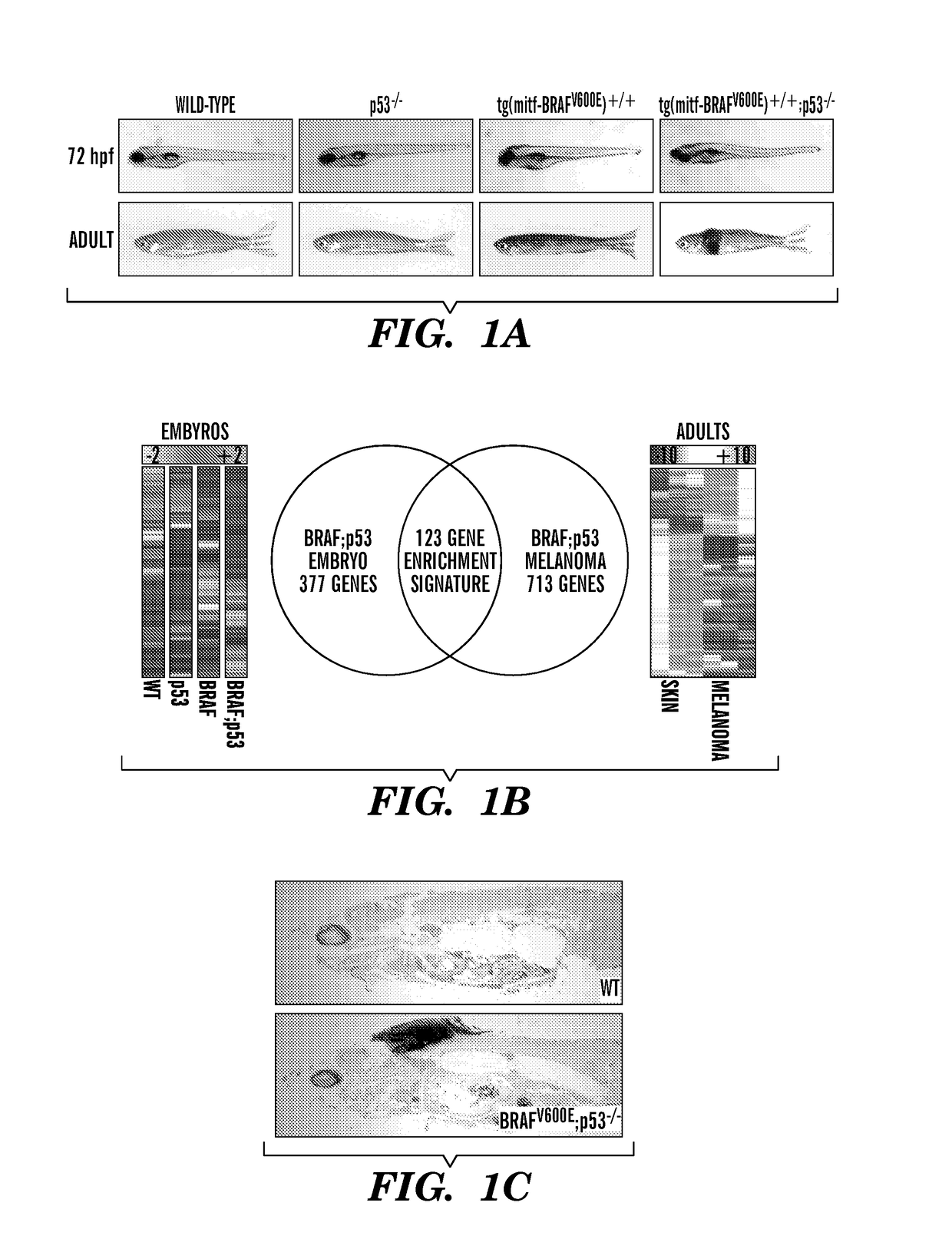
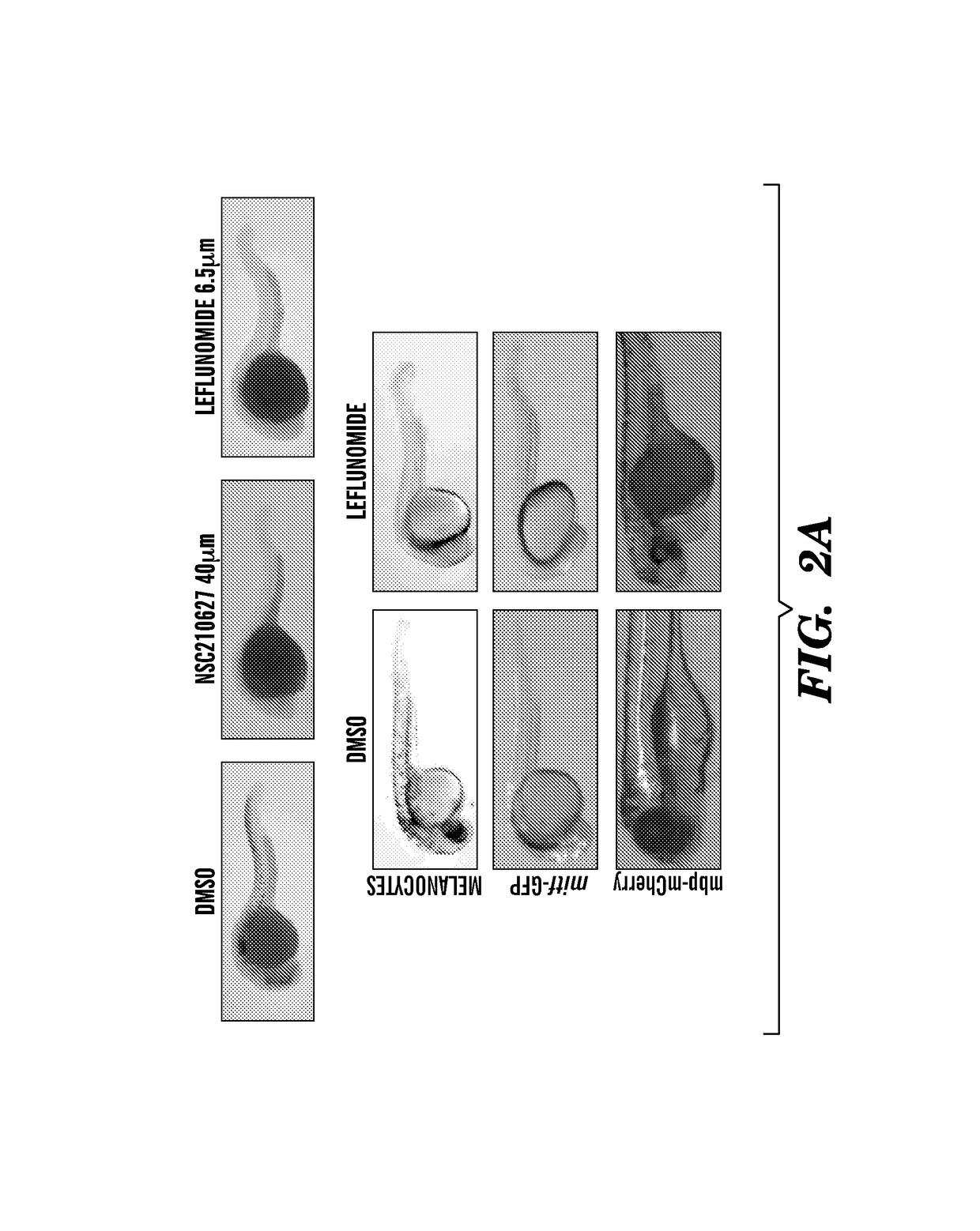
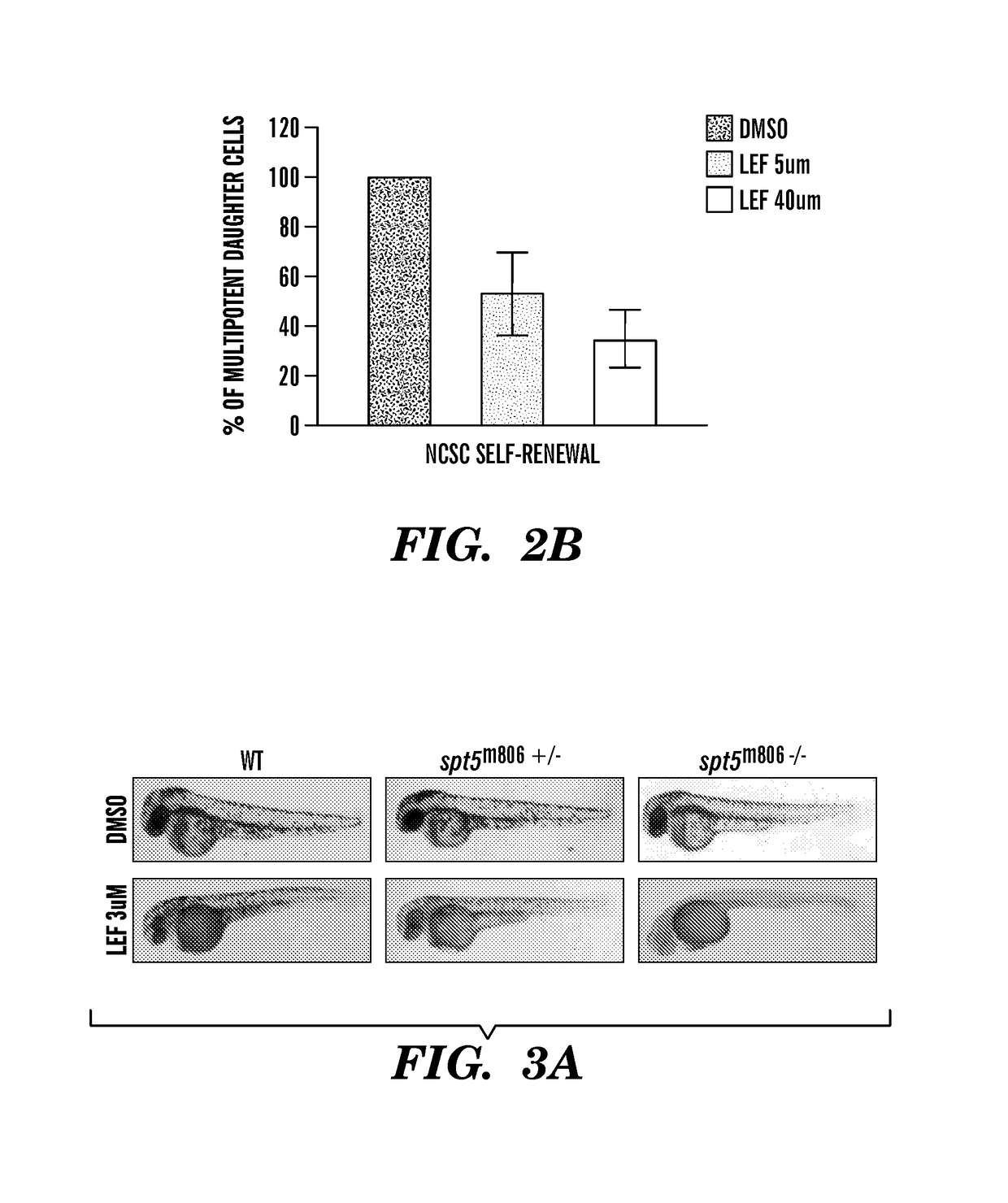
The present invention is directed to methods for treatment of melanoma using an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) and to combination therapies that involve administering to a subject an inhibitor of oncogenic BRAF (e.g. BRAF(V600E)), as well as an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). Assays for identifying compounds useful for the treatment of melanoma are also provided. The methods herein are directed to screening for compounds or agents that inhibit neural crest progenitor formation in a zebra fish model of melanoma.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
PHOX2B polymorphisms as hirschsprung's disease diagnostic markers and methods based thereon
ActiveUS20030224424A1Increased riskAccurately and non-invasively screenSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenes mutationDisease
The invention relates generally to polymorphisms or mutations of the PHOX2B gene. More particularly, the invention relates to polymorphisms or mutations of the PHOX2B gene that are responsible for the disease Hirschsprung's disease (HSCR), which is a neural crest-associated developmental disorder. Specifically, the invention relates to the detection of a single base-pair polymorphism in the PHOX2B gene that is associated with HSCR. The invention also relates to methods and kits for screening for carriers of mutations of the PHOX2B gene and the diagnosis of increased risk of HSCR. The invention further relates to diagnosing predisposition or susceptibility to increased risk of developing HSCR by screening for the presence of a polymorphism associated with HSCR. The invention also relates to compositions for screening for the polymorphism and treatment choices for patients having the polymorphism of the present invention. The invention further relates to providing polymorphisms in the PHOX2B gene for forensic use and in paternity test. The invention also relates to screening assays and therapeutic and prophylactic methods.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Composition of mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20160129043A1Reduce wrinklesSuppress peripheral blood lymphocyte proliferationCell dissociation methodsBiocideNeurulationGerm layer
This invention relates in general to a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy. This invention further relates to the isolation and applications of gingiva derived mesenchymal stem cells. More particularly, this invention relates to the isolation and applications of the neural crest derived gingiva mesenchymal stem cells and / or mesoderm derived gingiva mesenchymal stem cells. This invention also relates to a composition comprising a neural crest derived gingiva mesenchymal stem cell and / or a mesoderm derived gingiva mesenchymal stem cell. This composition may be used for wound healing and / or in the treatment of inflammatory and / or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to multipotent neural crest cells
InactiveUS20130280804A1Increase profitEffectively lead to differentiationNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsSmooth muscleInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention relates to the differentiation of human pluripotent cells, including human pluripotent stems cells to produce a self-renewing multipotent neural crest cell population in a single step method without the requirement of isolation of intermediate cells and without appreciable contamination (in certain preferred instances, virtually none) with Pax6+ neural progenitor cells in the population of p75+ Hnk1+ Ap2+ multipotent neural crest-like cells. The multipotent neural crest cell population obtained can be clonally amplified and maintained for >25 passages (>100 days) while retaining the capacity to differentiate into peripheral neurons, smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal precursor cells.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
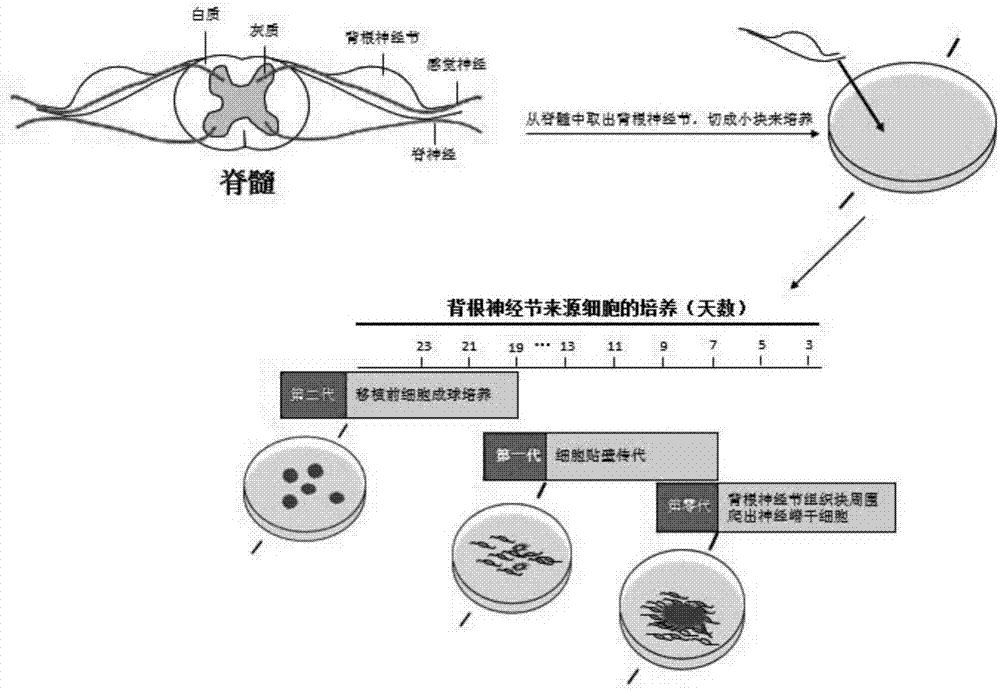
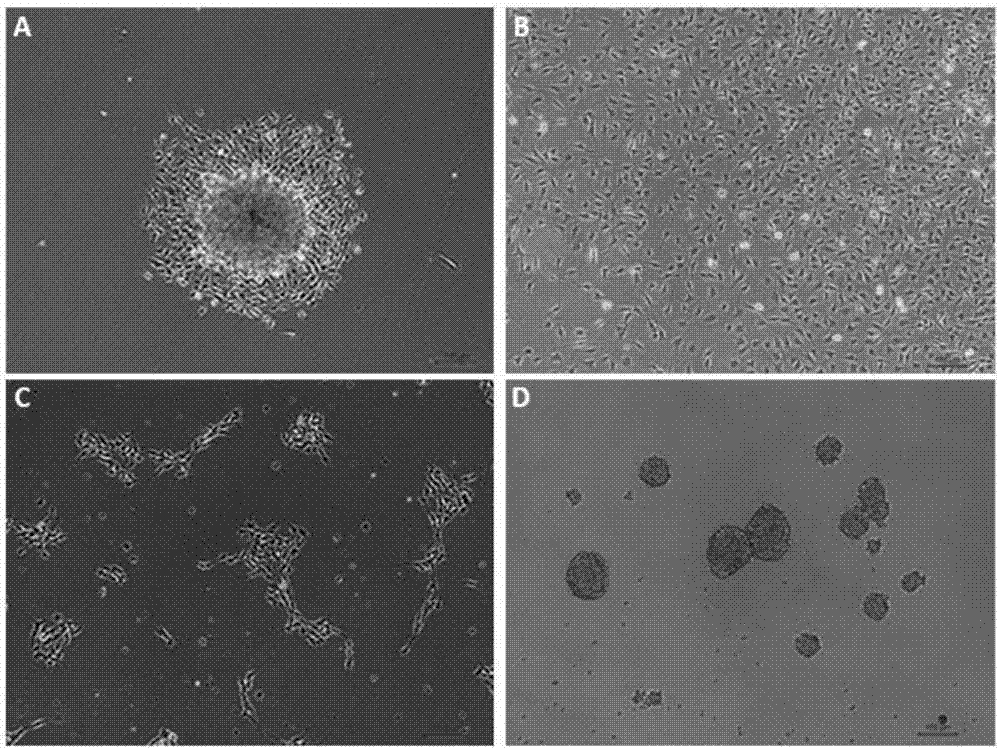
Method for isolating, culturing and differentiating neural crest stem cells from DRG (dorsal root ganglion)
ActiveCN107475200AHigh purityImprove proliferative abilityCulture processNervous system cellsNeural crestNeural stem cell
The invention provides a novel method for isolating, culturing and differentiating neural crest stem cells from DRG (dorsal root ganglion). The method comprises steps as follows: (1) primary isolation of the neural crest stem cells from DRG; (2) purification and culture amplification of the neural crest stem cells from DRG; (3) induced differentiation of the neural crest stem cells from DRG. The obtained neural crest stem cells have higher multiplication capacity and still have multiplication capacity after being continuously cultured for generations in vitro.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cell-based treatment and drug discovery in hirschsprung's disease enabled by pluripotent stem cell-derived human enteric neural crest lineages
PendingUS20180291339A1Nervous disorderGenetically modified cellsPluripotential stem cellHirschsprung's disease
The presently disclosed subject matter provides for in vitro methods of inducing differentiation of stem cells into enteric neural crest lineage cells, and enteric neural crest lineage cells by such methods. The presently disclosed subject matter also provides for uses of such enteric neural crest lineage cells for preventing and / or treating enteric nervous system disorders (e.g, Hirschsprung's disease), and for screening compounds suitable for preventing and / or treating enteric nervous system disorders (e.g., Hirschsprung's disease).
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Methods for treatment of melanoma
ActiveUS20150306080A1Utility in treatmentUseful in treatmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorNeural crest
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods for treatment of melanoma using an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) and to combination therapies that involve administering to a subject an inhibitor of oncogenic BRAF (e.g. BRAF(V600E)), as well as an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). Assays for identifying compounds useful for the treatment of melanoma are also provided. The methods comprise screening for compounds or agents that inhibit neural crest progenitor formation in a zebra fish model of melanoma.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Neural crest stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060263876A1Treat and prevent and reduce diseaseCulture processNervous system cellsHeterologousDamages tissue
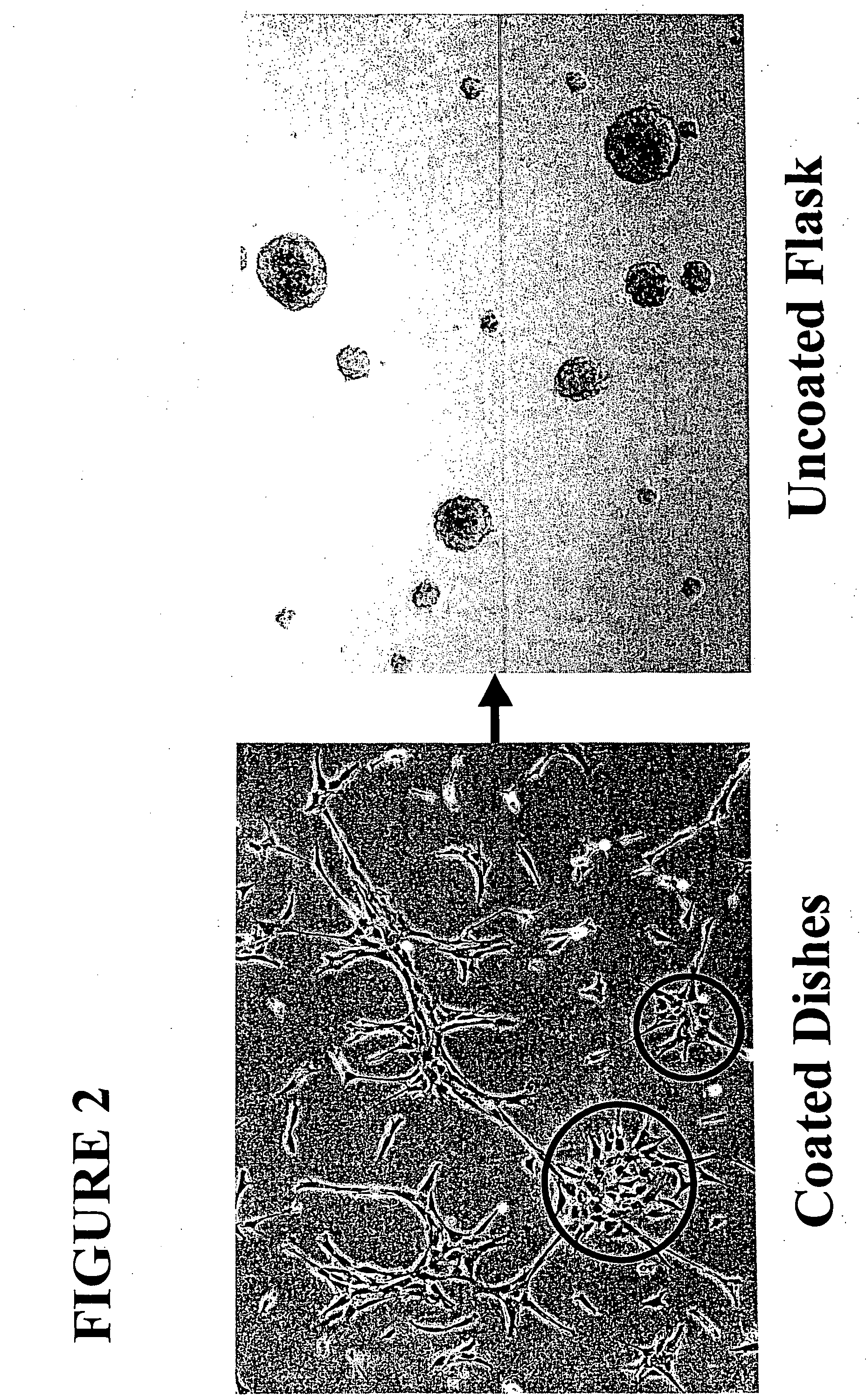
This present invention features methods and composition for the isolation and proliferation of neural crest stem cells (NCSCs) from embryonic tissues as well as from tissues from a post-natal mammal. According to this invention, NCSCs are capable of producing non-neuronal and neuronal cells under the appropriate conditions. The cells of the invention therefore provide an accessible source for autologous and heterologous transplantation into the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, as well as other damaged tissues.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
In vitro differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells, methods and reagents related thereto
InactiveUS20070065829A1Easy to identifyInhibitory activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetically modified cellsSmooth musclePhenotypic response
This invention is directed to an in vitro system for rapidly and uniformly inducing immortalized neural crest cells to differentiate to vascular smooth muscle cells. As excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells is a phenotypic response to the development of occlusive arteriosclerotic disease, the in vitro system of this invention is used to identify molecular regulators of smooth muscle cell development and differentiation. As the molecular regulators of smooth muscle cell differentiation are identified, the invention also encompasses methods to isolate the genes coding for these regulators. This invention also relates to molecules identified through the use of the invention's in vitro system, as well as to compounds that inhibit or regulate the identified molecules.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Functional myelination of neurons
Hair follicle bulge region / LLP region CD34(+) MeSCs can be isolated from mammalian skin bearing hair follicles. These cells are multipotent and retain the ability to differentiate into cells of neural crest lineage, including glia-like cells that express the glial marker Gfap, and are able to express myelin basic protein, and to remyelinate naked (unmyelinated or demyelinated) neuronal processes with a functional, dense myelin sheath. These cells of neural crest lineage can be used to produce a dense myelin sheath on neurons which lack myelin due to genetic defect, trauma, toxin, infection, or disease process. Therefore, embodiments of the invention provide methods for preparing such cells, the cells themselves and compositions containing the cells, as well as methods for using the cells.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Full-automatic segmentation system and method for microscopic image of neural crest cells
ActiveCN106296712AThe number of divisions is reasonableAccurate and clear edgesImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageGround truth
The invention relates to the microscopic image segmentation technology, and discloses a full-automatic segmentation system and method for a microscopic image of neural crest cells. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1, building a microscopic image with a mark, i.e., carrying out the marking through a manual method, and obtaining binary ground truth images; 2, segmenting the microscopic image through employing a conventional Normalized Cut segmentation method; 3, carrying out the adjustment and optimization of the parameters in the conventional Normalized Cut segmentation method at step 2 through combining with the images at step 1, and achieving the Supervised Normalized Cut segmentation method. The method employs a supervised method for image segmentation, and improves the accuracy of image segmentation.
Owner:SICHUAN MUNIULIUMA INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
ERK5 kinase and application of ERK5 inhibitor in stem cell differentiation
The invention discloses an ERK5 kinase and application of an ERK5 inhibitor in stem cell differentiation, and relates to the technology of stem cell differentiation regulation. Research shows that ERK5 plays an important role in the differentiation of stem cells and the ERK5 inhibitor can regulate the differentiation direction of stem cells; therefore, the ERK5 inhibitor has the application in thepreparation of any of the following reagents: (1) a reagent for regulating the differentiation of stem cells toward nerve cells, and the nerve cells are neural progenitor cells or neural crest cells;(2) an agent for regulating the differentiation of stem cells toward a germ layer, the germ layer is a trophoblast or mesoderm; and (3) an agent for promoting the differentiation of stem cells into cardiomyocytes. A new idea is provided for the differentiation of the stem cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
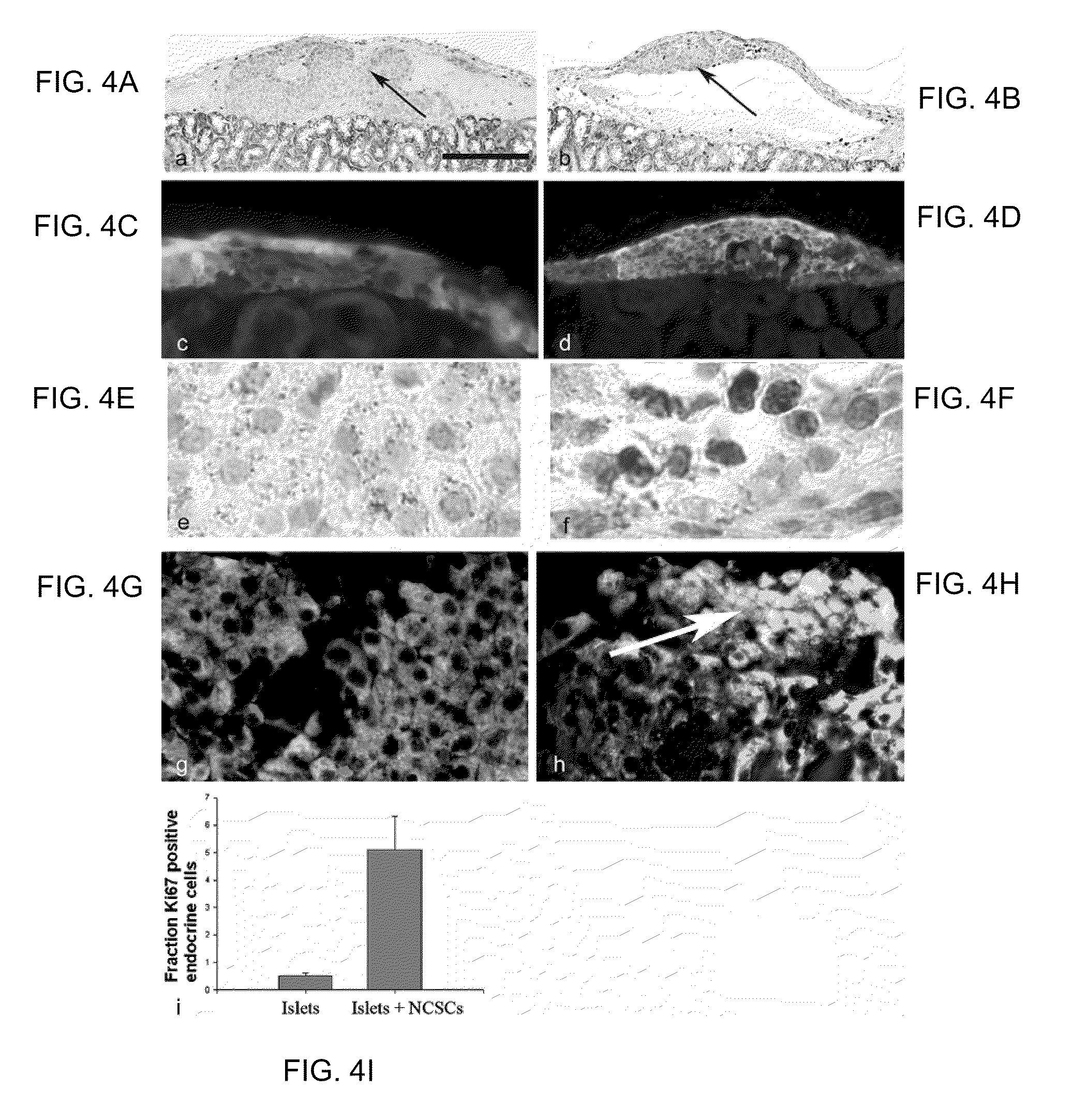
Methods and Kits for Enhancing Cell Survival, Stimulating Cell Proliferation, Treating Diabetic Patients, and/or Reinnervation
InactiveUS20110064702A1Enhance cell viabilityImprove reinnervationBiocideMetabolism disorderProgenitorNeural cell
Methods for enhancing beta cell survival and / or for stimulating beta cell proliferation, comprise co-transplanting pancreatic islets, beta cells, and / or stem cells which can generate beta cells, with (i) neural crest stem cells (NCSCs), (ii) tetracycline-regulated gene expression system (Tet-System)-containing neural stem / progenitor cells (TetStock neural stem / progenitor cells), and / or (iii) pre-differentiated stem / progenitor neural cells. Methods for reinnervation in an organ or tissue transplant patient comprise co-transplanting with the organ or tissue (i) neural crest stem cells (NCSCs), (ii) tetracycline-regulated gene expression system (Tet-System)-containing neural stem / progenitor cells (TetStock neural stem / progenitor cells), and / or (iii) pre-differentiated stem / progenitor neural cells. Kits for conducting such methods employ at least one of (i) neural crest stem cells (NCSCs), (ii) tetracycline-regulated gene expression system (Tet-System)-containing neural stem / progenitor cells (TetStock neural stem / progenitor cells), and (iii) pre-differentiated stem / progenitor neural cells.
Owner:KOZLOVA ELENA +1
Methods for treatment of melanoma
InactiveUS20150328204A1Reduce the overall heightBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorMedicine
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods for treatment of melanoma using an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) and to combination therapies that involve administering to a subject an inhibitor of oncogenic BRAF (e.g. BRAF(V600E)), as well as an inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). Assays for identifying compounds useful for the treatment of melanoma are also provided. The methods comprise screening for compounds or agents that inhibit neural crest progenitor formation in a zebra fish model of melanoma.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Schwarm progenitor cell derived from marrow neural crest cell and application of Schwarm progenitor cell to promotion of nerve regeneration
ActiveCN105925528AAvoid bad effects of differencesPromote regenerationNervous disorderCulture processNeural crestNerves regeneration
The invention relates to the technical field of tissue engineering, in particular to a Schwarm progenitor cell derived from a marrow neural crest cell and application of the Schwarm progenitor cell to promotion of nerve regeneration. The rat marrow-derived neural crest cell N1, namely, BM-NCC clone N1, is provided, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:C201647, and the rat marrow-derived neural crest cell N1 has the performance of the Schwarm progenitor cell (SCP). The invention further provides a subculture method of the BM-NCC clone N1 and a method for induced directional differentiation to the Schwarm cell (SC). The BM-NCC clone N1 is expected to be applied to nerve regeneration promotion therapy based on cells.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Method of isolating epidermal neural crest stem cells
InactiveUS8030072B2Improve scalabilityDissecting the hair folliclesNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsNeural crestHair follicle
The present invention describes novel methods for isolating a substantially pure cell population of non-embryonic epidermal neural crest stem cells from the bulge-region of mammalian hair follicles. Also disclosed is the substantially pure cell population of follicular bulge-derived neural crest stem cells for medical research and therapeutic use.
Owner:MAYA SIEBER BLUM
Neural crest stem cell preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN108753693AGuaranteed normal reproductionStable growthCulture processCell culture active agentsNeurulationImmunofluorescence
The invention specifically discloses a neural crest stem cell preparation and application thereof. The neural crest stem cell preparation provided by the invention is obtained by culturing a neural tube in vitro, wherein the neural tube is derived from a 10-day pregnant mouse embryo. The neural crest stem cell preparation disclosed by the invention and obtained by culturing the neural tube derivedfrom a 10-day pregnant mouse embryo in vitro identifies neural crest stem cells by immunofluorescence; P0 generation cells and P3 generation cells respectively express characteristics of neural crestand do not express the characteristics of neural stem, which indicates that the cultured cells successfully maintain the characteristics of mouse neural crest stem cells in vitro; and in-vitro culture experiments show that the neural crest stem cells can grow stably in a provided culture medium and normal proliferation of cells is maintained.
Owner:广州沙艾生物科技有限公司
PHOX2B polymorphisms as Hirschsprung's disease diagnostic markers and methods based thereon
The invention relates generally to polymorphisms or mutations of the PHOX2B gene. More particularly, the invention relates to polymorphisms or mutations of the PHOX2B gene that are responsible for the disease Hirschsprung's disease (HSCR), which is a neural crest-associated developmental disorder. Specifically, the invention relates to the detection of a single base-pair polymorphism in the PHOX2B gene that is associated with HSCR. The invention also relates to methods and kits for screening for carriers of mutations of the PHOX2B gene and the diagnosis of increased risk of HSCR. The invention further relates to diagnosing predisposition or susceptibility to increased risk of developing HSCR by screening for the presence of a polymorphism associated with HSCR. The invention also relates to compositions for screening for the polymorphism and treatment choices for patients having the polymorphism of the present invention. The invention further relates to providing polymorphisms in the PHOX2B gene for forensic use and in paternity test. The invention also relates to screening assays and therapeutic and prophylactic methods.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods for treatment of melanoma
ActiveUS10016402B2Reduce the overall heightHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAssayNeural crest
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com