Method for isolating, culturing and differentiating neural crest stem cells from DRG (dorsal root ganglion)
A technology of dorsal root ganglion and neural crest, applied in the field of stem cell biology, can solve the problems of large cell loss and incomplete enteric nervous system, and achieve the effect of strong proliferation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1, Isolation and purification of neural crest stem cells derived from dorsal root ganglion
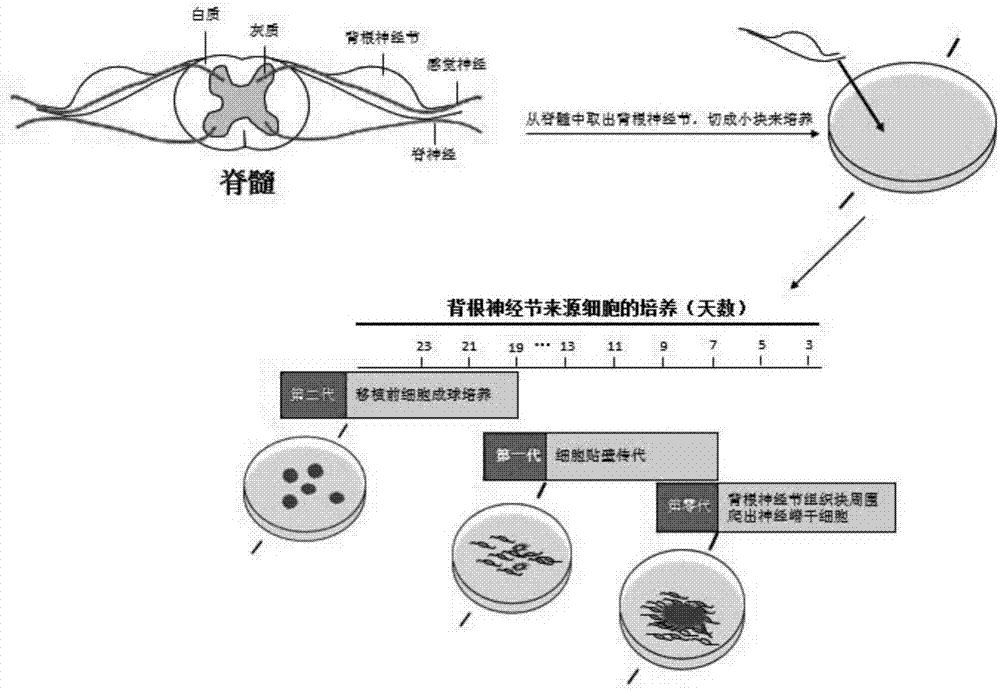
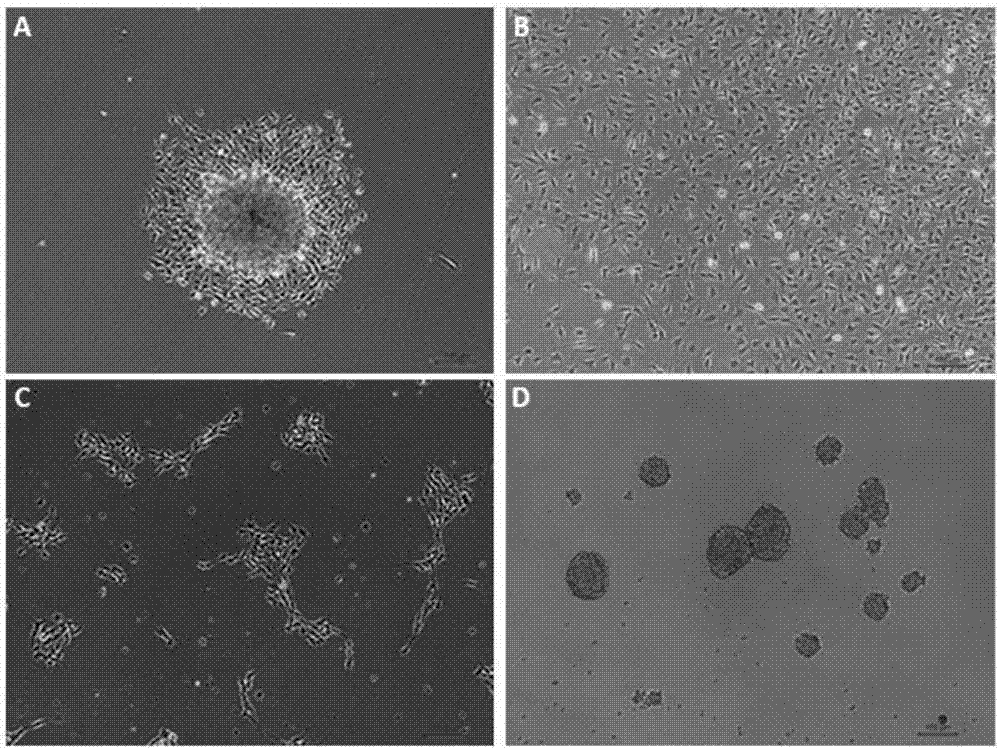
[0031] Take out the C57 mice about 6 days after birth, soak them in alcohol for 15 minutes, incise the back under the ultra-clean table, take out the neural tube, and take out the dorsal root ganglion at the edge of the neural tube under a microscope, cut it into pieces of about 2 mm, After rinsing with PBS, centrifuge at 800rmp for 5 minutes to collect the tissue pieces, resuspend the tissue pieces in the primary medium, and transfer them to poly-ornithine-coated plates, such as figure 1 shown in the flow chart. The primary medium is: DMEM / F12 medium, 1% N2, 2% B27, 20ng / ml bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor), 20ng / ml EGF (endothelial growth factor), 100IU / L penicillin / streptomycin. Placed in a 37-degree constant temperature incubator containing 5% CO2 for cultivation. After two days in culture, cells crawled out around the tissue block, as figure 2 ‐As shown i...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2, identification of neural crest stem cells derived from dorsal root ganglia.
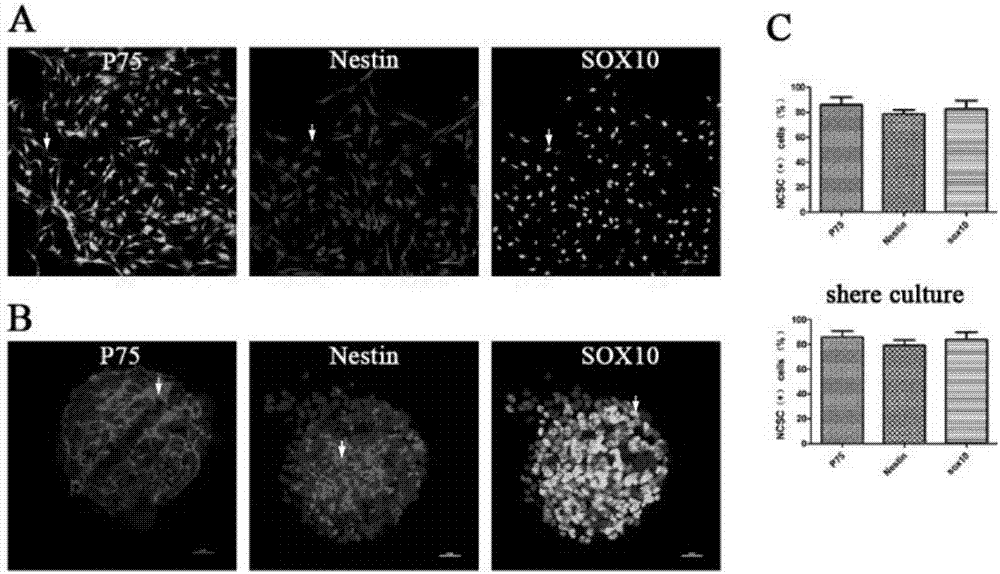
[0033] Take the cells that have been cultured for 2 passages and sphere culture, rinse twice with PBS, fix with paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, block with blocking solution (1% BSA) containing 0.3% (volume ratio) triton for 30 minutes at room temperature, and work with the primary antibody diluted 1:100 Solution (P75, Nestin, SOX10) was incubated at room temperature for 2 hours, washed three times with PBS, incubated with secondary antibody dilution (1:500) for one hour at room temperature, rinsed three times with PBS, observed and photographed under a fluorescence microscope, and counted by image J software The proportion of positive cells. Such as image 3 As shown, the neural crest stem cells derived from the dorsal root ganglion obtained by the method of the present invention have relatively high purity, and more than 90% of the neural crest stem cells derived from the dorsal r...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3, analysis of neural crest stem cell expansion ability derived from dorsal root ganglion
[0035] The neural stem cells obtained from the primary generation are subcultured and expanded in two forms, one is single-layer adherent culture, and the other is spheroid suspension culture, such as figure 2 (C-D) Both cultures shown in (C-D) can be expanded for several generations in vitro.
[0036] The cells of the first and fifth passages of adherent culture were taken, rinsed twice with PBS, fixed with 4% (mass ratio) paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, blocked with 0.3% triton blocking solution (1% BSA) at room temperature for 30 minutes, 1 :200 diluted Ki67 primary antibody working solution was incubated at room temperature for 2 hours, washed three times with PBS, incubated with secondary antibody dilution (1:500) for 1 hour at room temperature, rinsed three times with PBS, observed and photographed under a fluorescence microscope, through image J The software cou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com