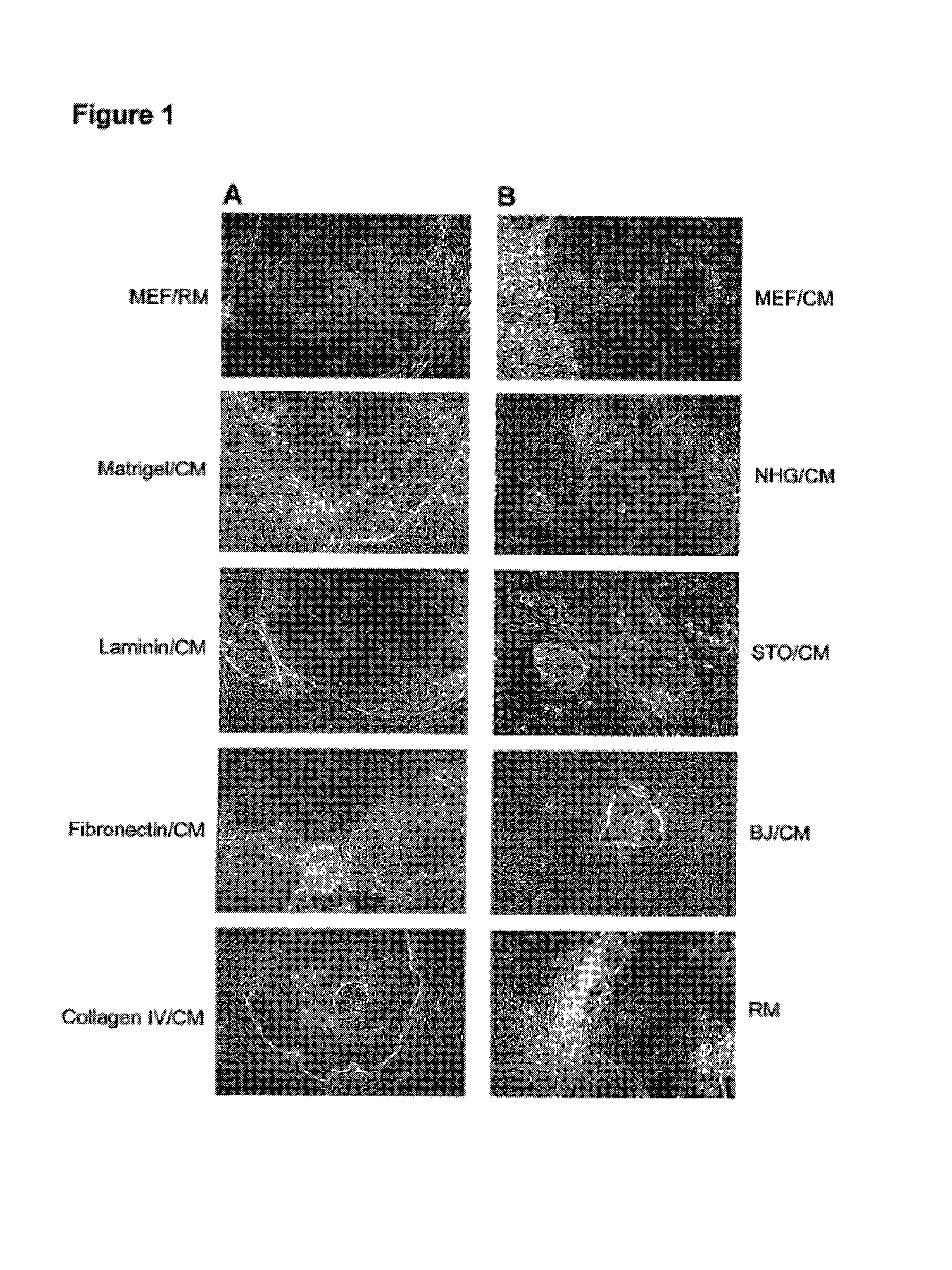
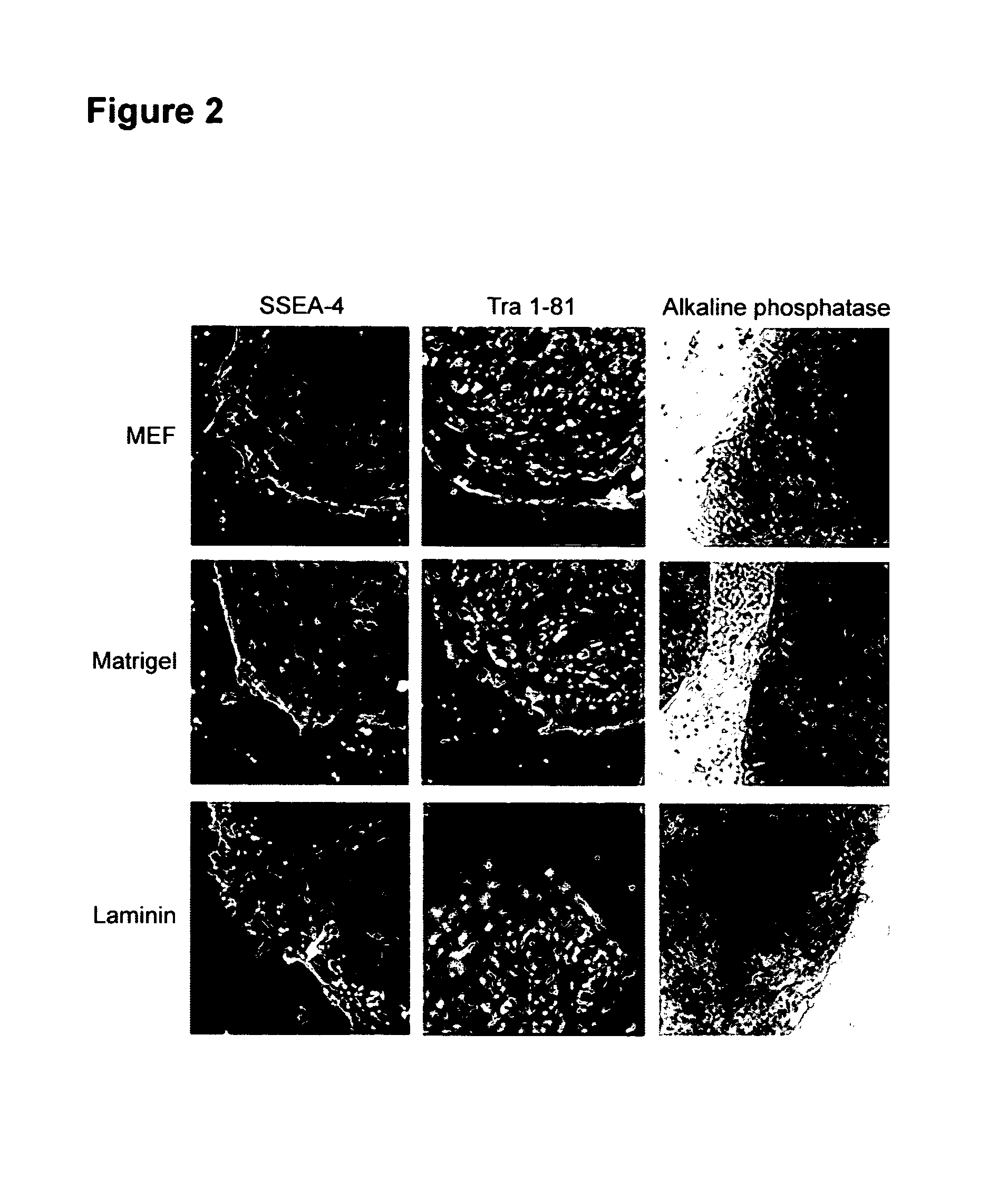
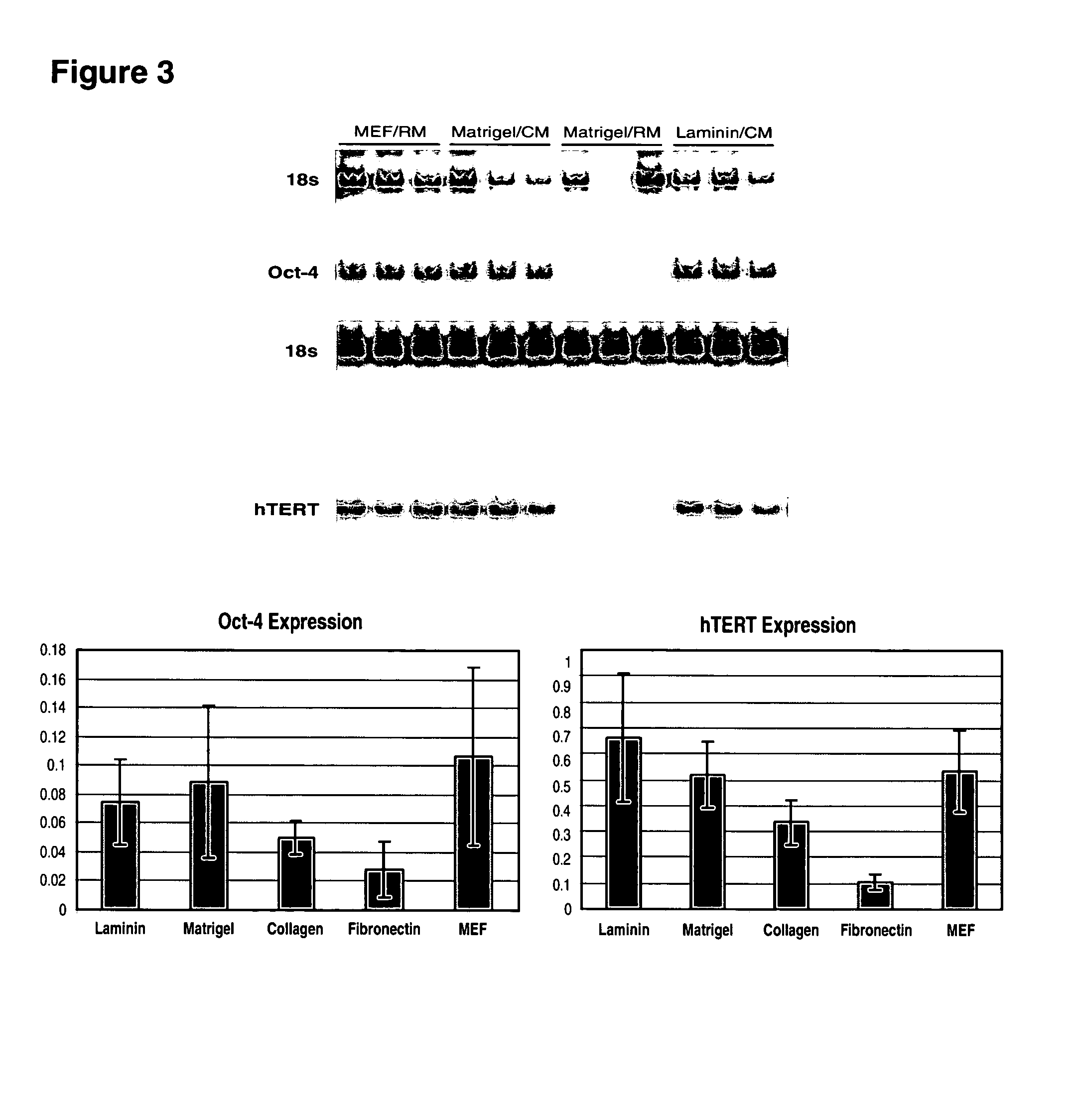
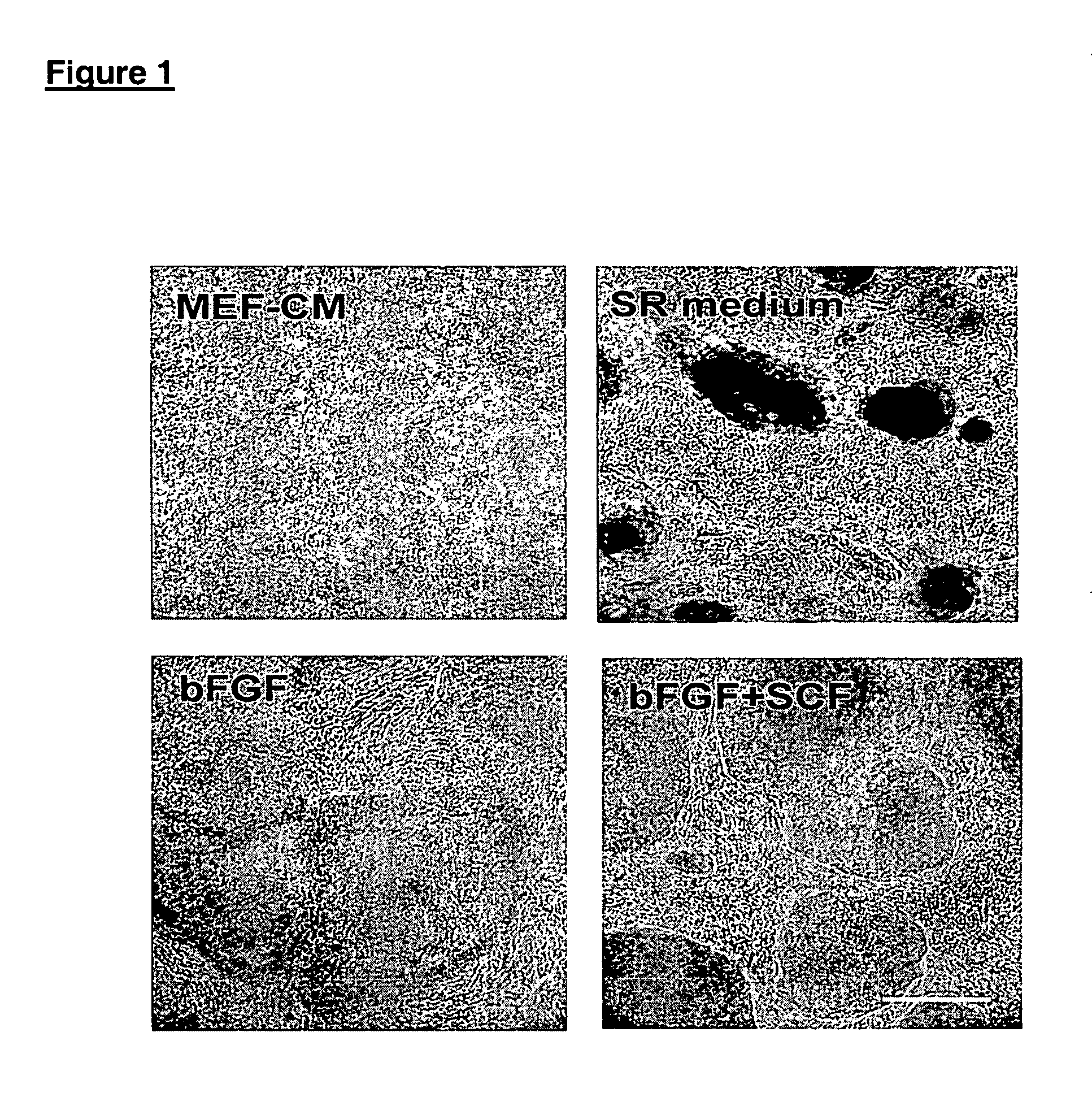
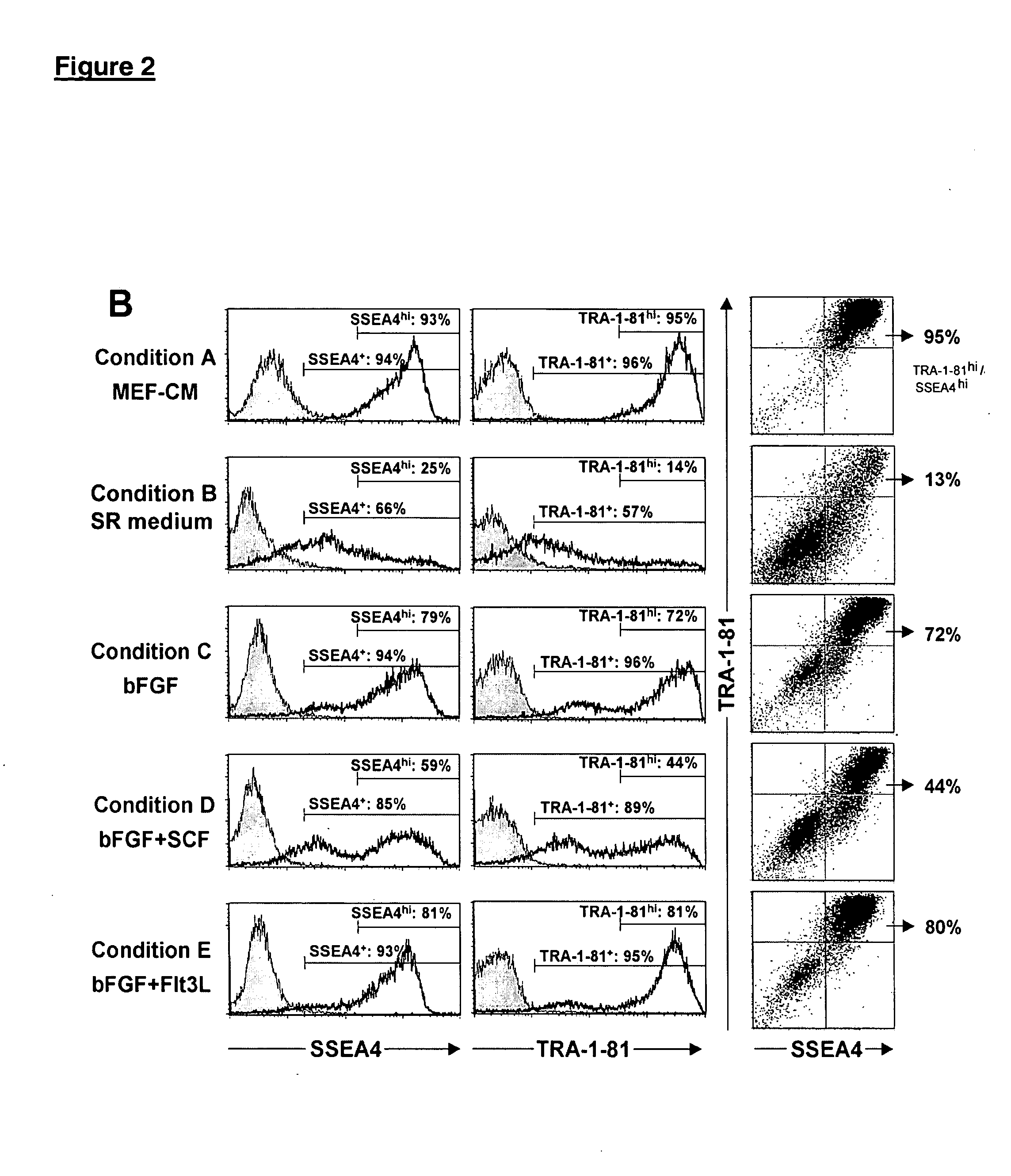
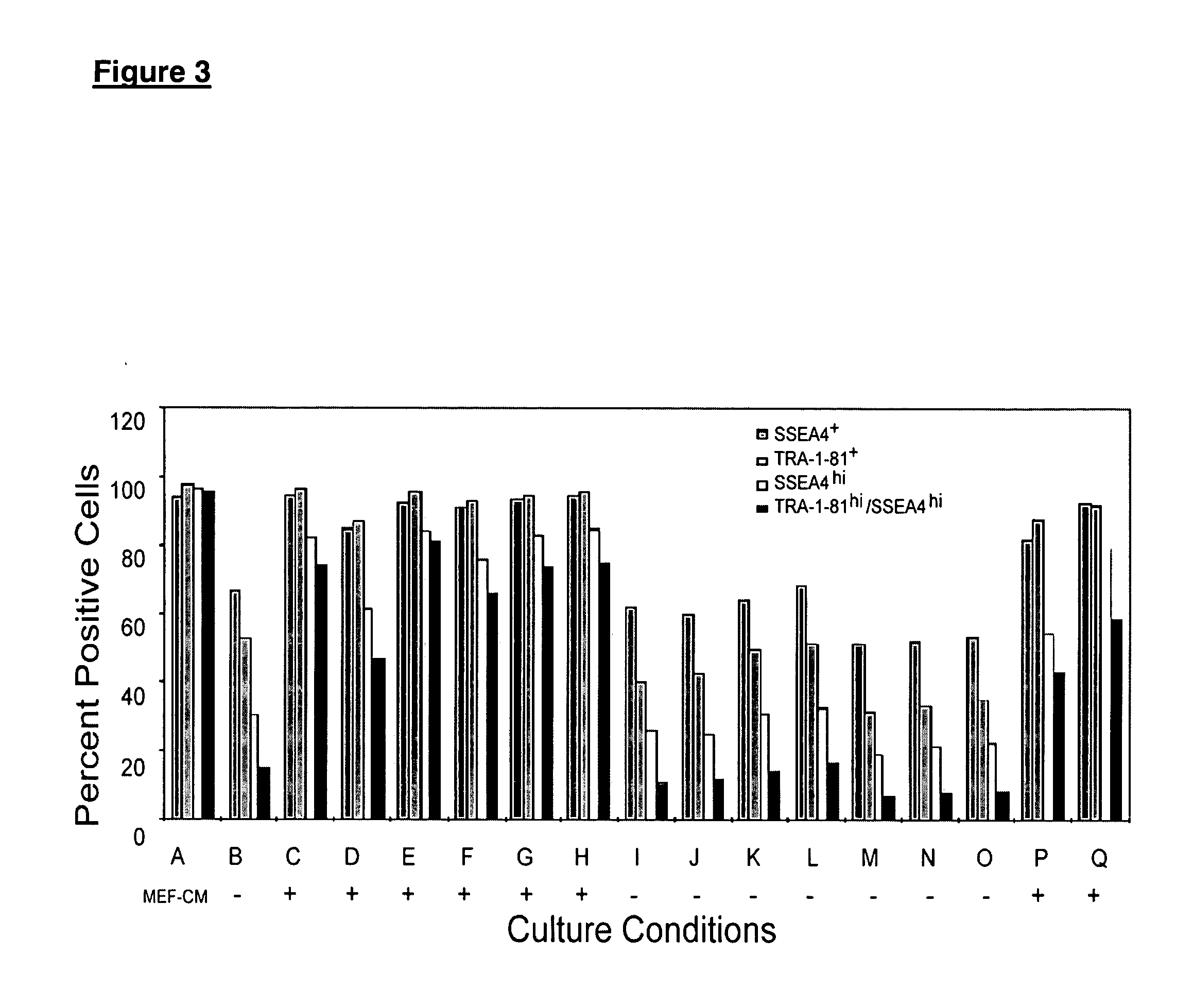
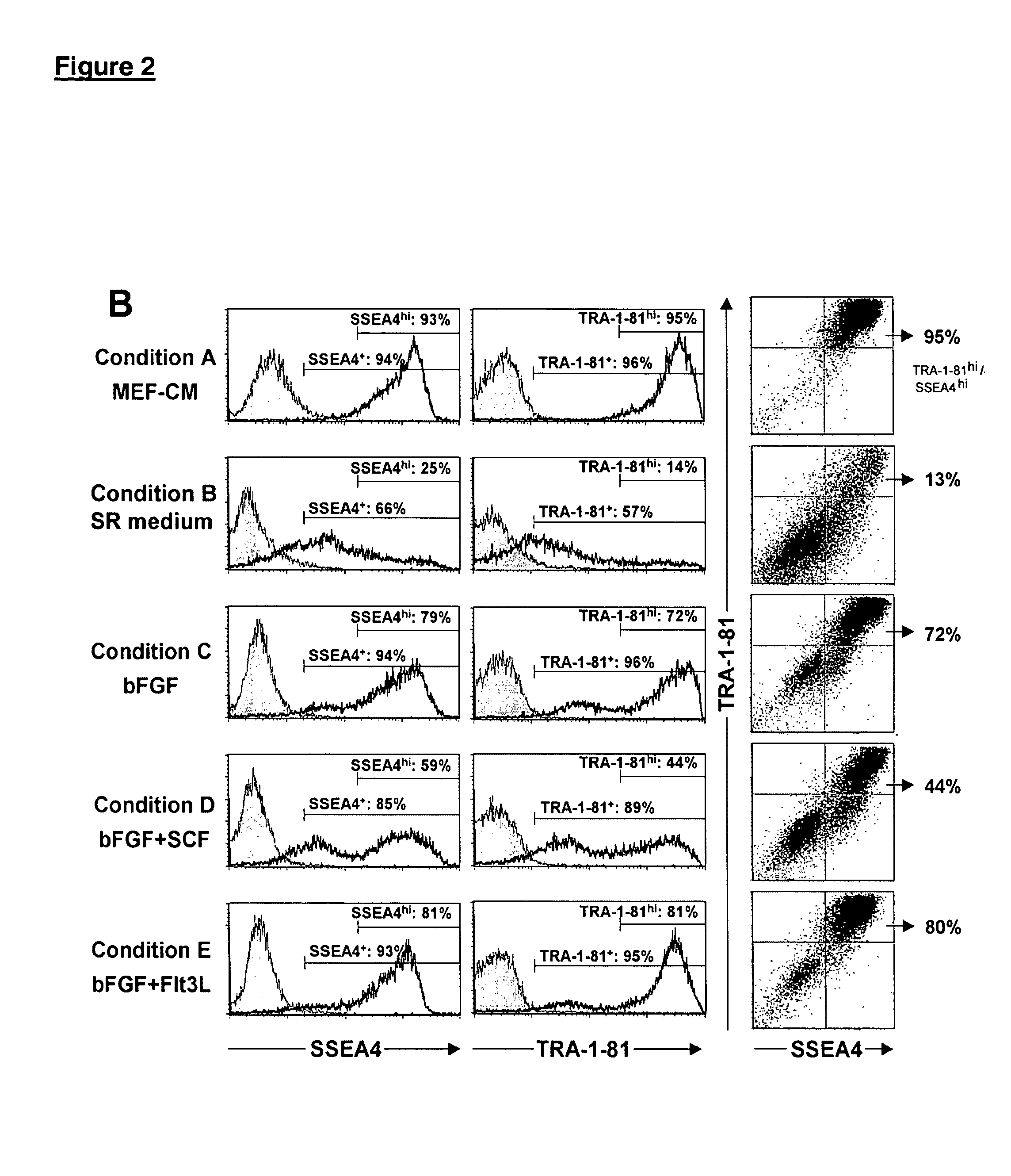
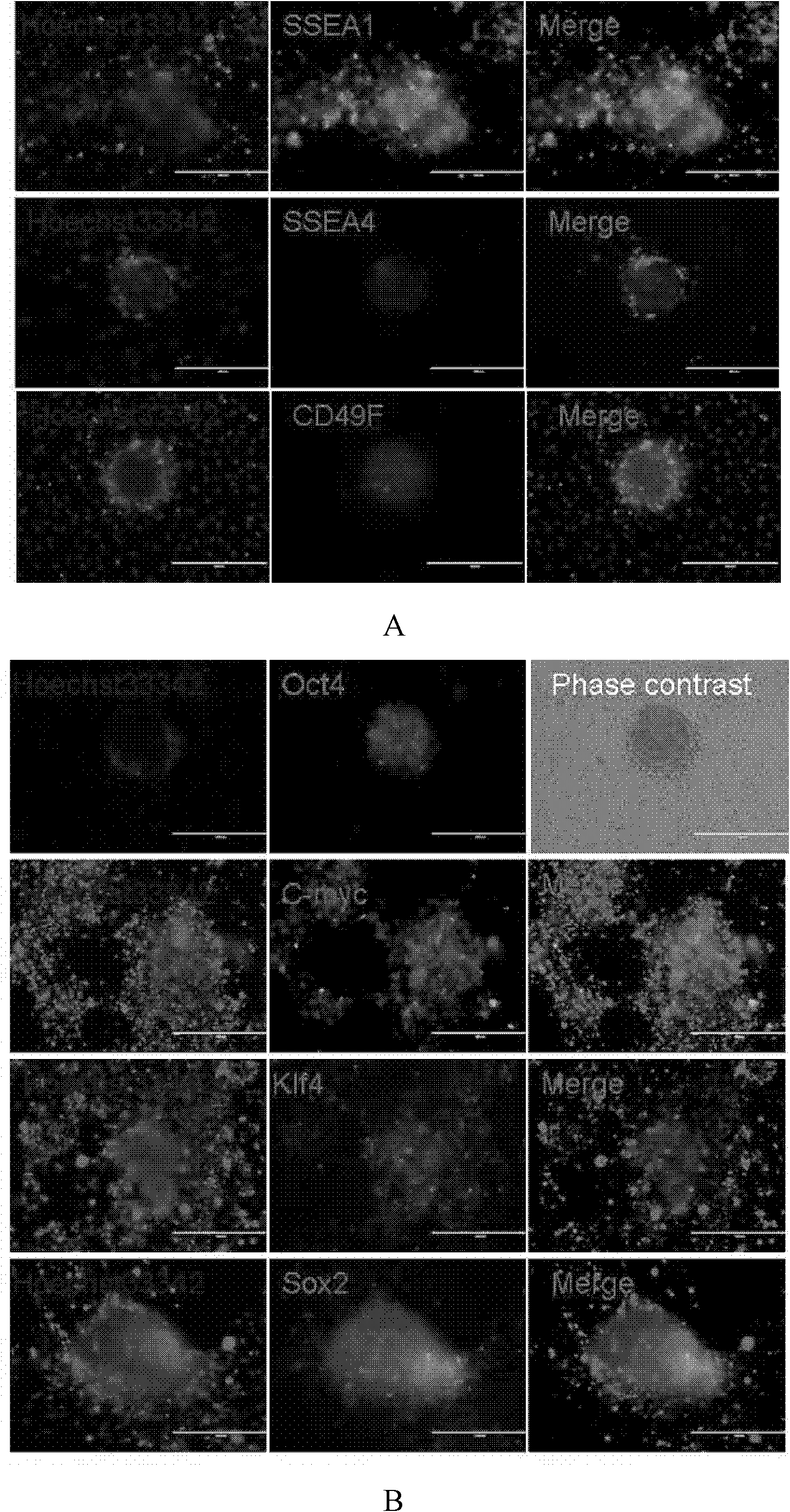
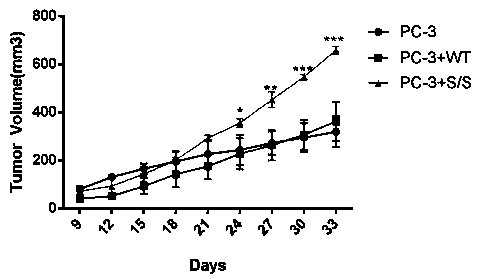
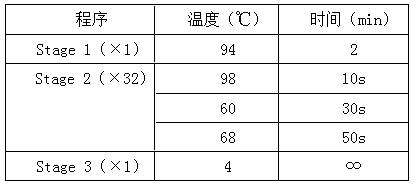
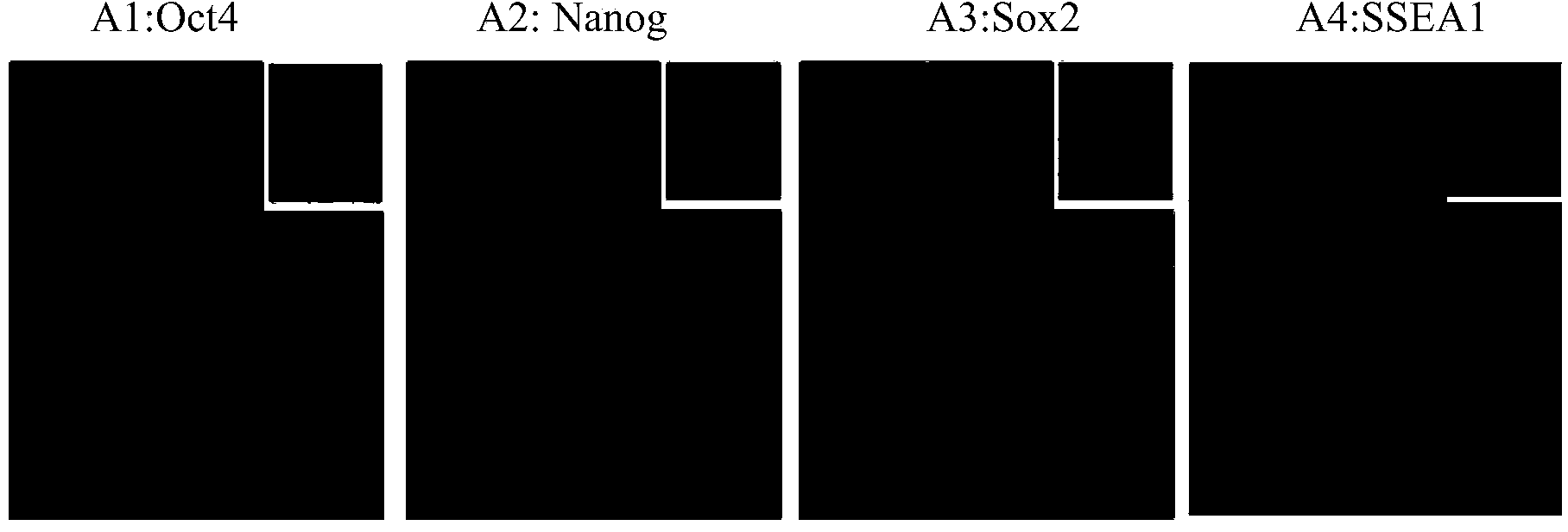
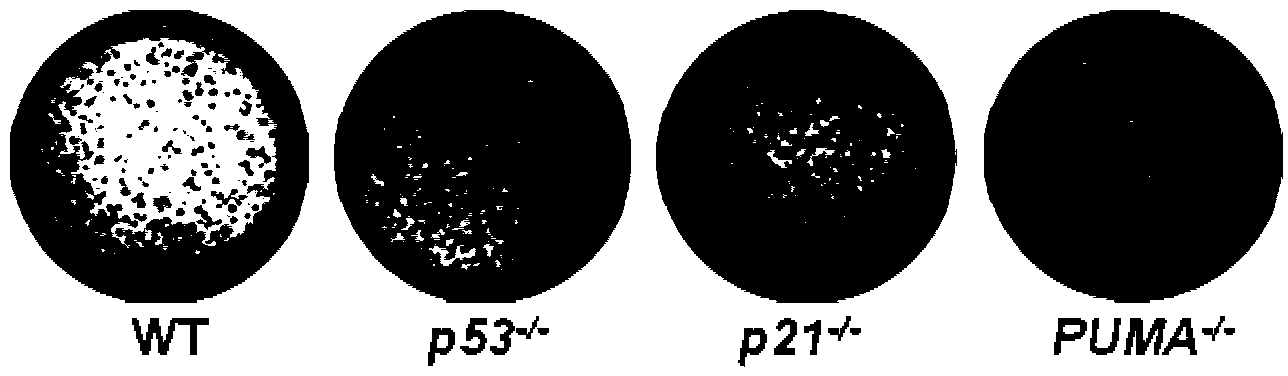Patents
Literature
65 results about "Mouse embryonic fibroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
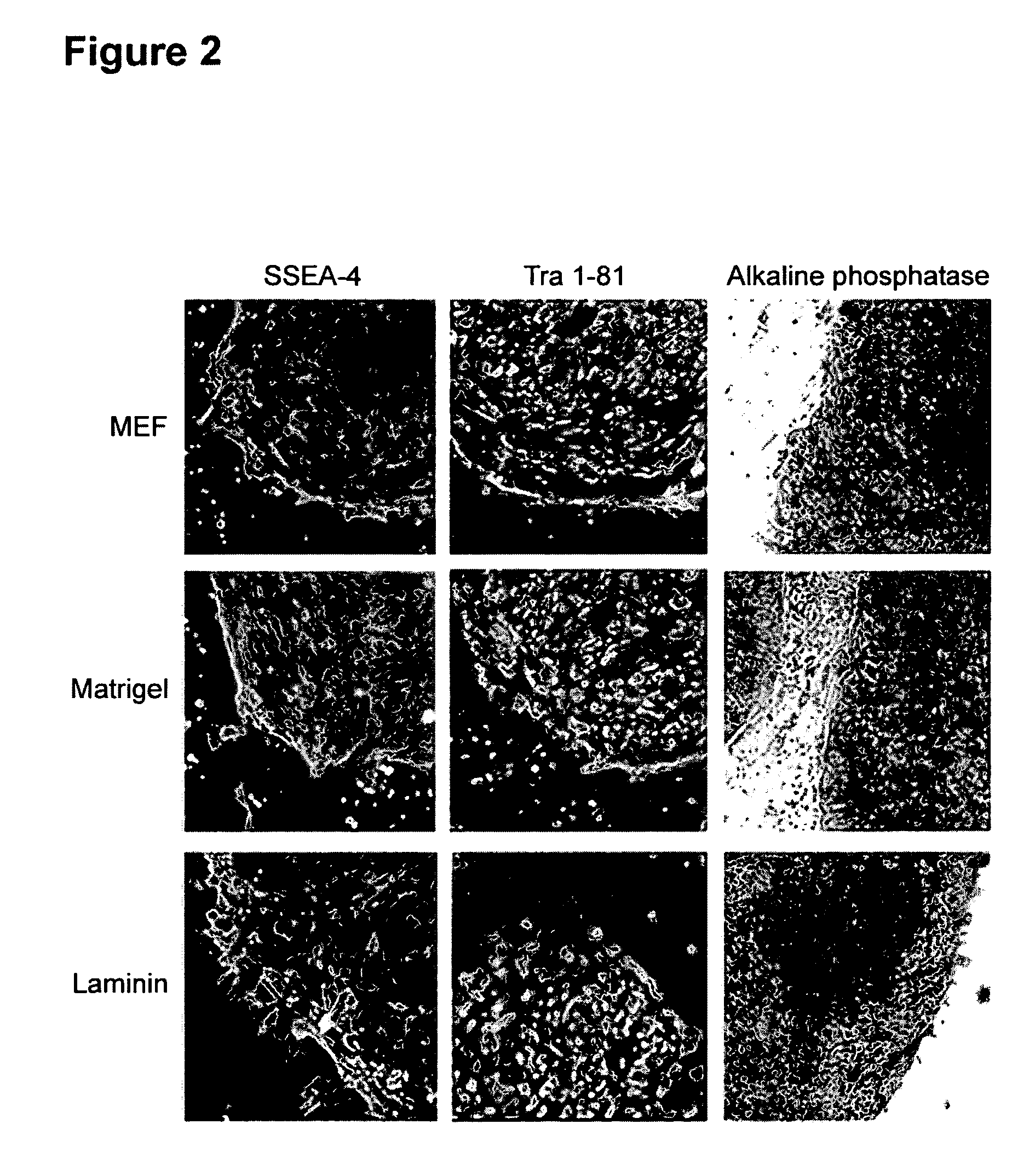
Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) are a type of fibroblast prepared from mouse embryo. MEFs show a spindle shape when cultured in vitro, a typical feature of fibroblasts. The MEF is a limited cell line. After several transmission, MEFs will senescence and finally die off. Nevertheless, researchers can use several strategies, like virus infection or repeated transmission to immortalize MEF cells, which can let MEFs grown indefinitely in spite of some changes in characters.
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
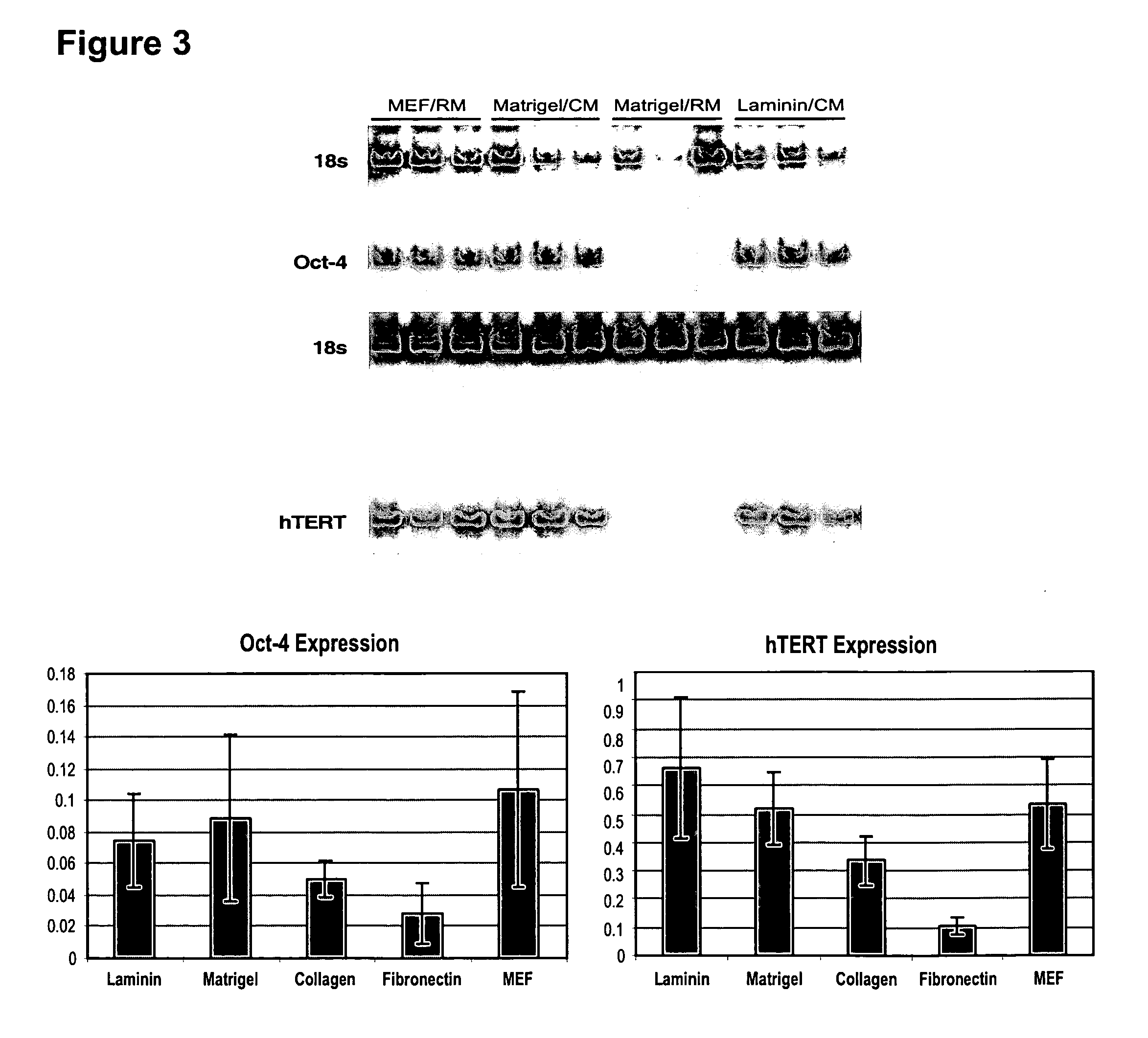
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050037492A1Rapid productionCost-effectiveDrug screeningNervous system cellsGerm layerLipid formation
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by defined components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. The medium contains an isotonic buffer, a blend of essential nutrients such as protein and lipids, and an effective growth factor or combination of factors that promote proliferation while inhibiting differentiation. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium on an extracellular matrix according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7455983B2Cost-effectiveRapid productionMicroorganismsDrug screeningGerm layerLipid formation
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by defined components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. The medium contains an isotonic buffer, a blend of essential nutrients such as protein and lipids, and an effective growth factor or combination of factors that promote proliferation while inhibiting differentiation. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium on an extracellular matrix according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells
The invention discloses an inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells. The method comprises the steps of: cultivating the human embryonic stem cells on a mouse embryonic fibroblast feed layer; sorting human embryonic stem cell clone groups in good state; grafting the groups on a human corneal stromal fibroblast layer processed by mitomycin C and cultivating for 7 days, wherein the human embryonic stem cells are differentiated to rosettes; separating and transferring the rosettes from the human corneal stromal fibroblast layer to a culture bottle; cultivating continuously for 7 days by using a neural crest stem cell culture medium; sorting the neural crest stem cells by a flow cytometry; adding the neural crest stem cells into the culture bottle; placing in a 5% CO2 incubator for incubating and cultivating at 37 DEG C by using a human corneal endothelial cell culture medium; changing the liquid every other day; and cultivating for about 10 days to obtain the corneal endothelial cells. The multiplication capacity of the corneal endothelial cells are similar to that of human corneal endothelial cells and the corneal endothelial cells can be transferred to 1-2 generations in vitro maximally. The corneal endothelial cells can be used as seed cells for cornea construction and transplant in tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
System for expanding and differentiating human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153445A1Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Using fibroblast growth factor to establish a line of embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153444A1Rapid productionSimple systemHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Method for culturing induced pluripotent stem cells by using human mesenchymal stem cells as trophoblast
InactiveCN102161980ANo pollution in the processReduce pollutionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousForeskin
The invention provides a method for culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by using human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as a trophoblast. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining the human iPSCs from child foreskin fibroblasts by using third to fifth generation human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells obtained through subculture and culture after thawing from low-temperature freezing, performing amplification culture, and inoculating into trophoblast cells to obtain the human iPSCs. In the method, the human iPSCs are cultured by using the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as the trophoblast cells instead of mouse embryonic fibroblasts in the conventional method, so that the pollution of heterologous cells in a culture system is reduced, that the culture system can make the human iPSCs amplified in vitro is proved, biological characteristics and multipotency of the human iPSCs are maintained for a long time, and the possibility of clinical application of the human iPSCs is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
New Periplaneta Americana polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair, and applications thereof
ActiveCN106977586APromote proliferationPromote migrationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectTissue repair
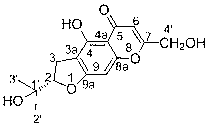
The present invention relates to the field of traditional Chinese medicines, natural medicines and daily chemicals, particularly to a new Periplaneta Americana polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair, and applications thereof, wherein the new polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair is named Periplapeptide B, has a structure represented by a formula I, can promote the proliferation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts and the migration of human immortalized epidermal cells at a low concentration, has advantages of low toxic-side effect and good application prospect, and can be used for preparing drugs for treatment of trauma, scald and ulcer, or cosmetics for improving skin beauty, and daily chemicals. The formula I is H-Ala-Ala-Pro-Pro-Ser-Asn-Leu-Lys-Glu-Val-Pro-Ile-Ile-Ala-Tyr-OH.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
In-vitro separating and culturing method for germline stem cell
ActiveCN102250830AStrong shadingEasy to useArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsGerm layerMatrigel
The invention discloses an in-vitro separating and culturing method for a germline stem cell. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a cell from germinal epithelium of an ovary of a female mammal, differentiating and separating a non-adherent germline stem cell from other adherent cultured cells by adopting gelatin with the concentration 0.2 percent and a Matrigel differential adherence combination cloning method; and culturing the germline stem cell obtained by separating on an MEF (Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast) feeder layer. The separated germline stem cell has ES (Embryonic Stem) characteristic and the potential of differentiating into a muscle cell, an adipose cell and oocyte-like cell and various cells with three internal germinal layers.
Owner:陕西九州细胞基因工程有限公司
Method for preparing amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane
ActiveCN102166374AAvoid breakingConvenient for clinical operationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsEpitheliumFeeder Layer
The invention relates to a method for preparing an amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a sterile amniotic membrane with epithelium removed, placing the epithelial surface of the amniotic membrane downwards on an end face of a sleeve made of a poly propylene material, and covering an embedded culture transwell on the amniotic membrane of the sleeve to obtain an amniotic-membrane-embedded culture mold; placing the culture mold in holes in a 6-hole plate on which a mouse embryonic fibroblast cell feeder layer is spread; and finally, preparing a corneal limbus stem cell suspension by using a digestion method, inoculating the suspension on the epithelial surface of the amniotic membrane, inoculating 2.0-3.0*10<5> corneal limbus stem cells for each culture mold, and culturing the corneal limbus stem cells for 10 days to obtain the amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane. Compared with the traditional amniotic membrane spreading method and the latex ring amniotic membrane fixing method, the amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane prepared with the method has flat amniotic membrane culturing surface and uniform corneal limbus stem cell stratified layer and especially has the advantage of convenience for clinic application and difficulty in rapture of the amniotic membrane.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
Method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells to differentiate toward nerve cells
InactiveCN101892191ALow toxicityEasy to observe shape changesEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) to differentiate toward nerve cells. Primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (PMEF) are used as a feeder layer. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating the mESCs to the feeder layer, inoculating the mESCs to mixed solution of stem cells and mESCs culture liquid, and culturing nerve stem cell culture solution; and gradually changing the culture into the culture of nerve cell culture solution by completely using serum-free added alkali fibroblast growth factors, wherein the optimal serum concentration of the mixed solution for primary inoculation is 12.5 percent, the optimal inoculation density of primary mESCs inoculation is 1.0*108<-1>, and the time of completely changing the serum-free culture solution is the 5th day. By induction of the method, the mouse stem cells can be differentiated into the nerve cells in vitro. The method has the advantages of short experimental period, simple and convenient experimental process and stable and efficiency inducing results, can quickly finish a cell culture period, and is favorable for subsequent experiments.
Owner:中国医科大学
Method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells by adopting transcription factors
InactiveCN101705247ANormal growth characteristicsGood pluripotencyGenetic engineeringFermentationFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by adopting transcription factors, concretely comprising the following steps: 1) isolation and culture of bovine dermal fibroblasts; 2) cloning of bovine transcription factor genes maintaining pluripotency and construction of retroviral vectors of the transcription factor genes; 3) retrovirus packaging and preparation; and 4) infection of bovine dermal fibroblasts by retrovirus and acquisition of bovine inducted pluripotent stem cells. The invention first adopts the acellular human amniotic membranes as support to replace the mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to maintain in vitro proliferation of the bovine iPSCs and keep the bovine iPSCs in undifferentiated pluripotent states for long time. The method which adopts gene inducing to generate the PSCs not only solves the technical problem that the PSCs of the animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs and other livestock are difficult to obtain but also avoids the problem of heterogeneous animal cell pollution caused by the feeder layer which applies the MEFs as the stem cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
In-vitro separation and preparation method of male germline stem cells of goat
InactiveCN102154195AHas the characteristics of ES cellsStrong shadingArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsSeminiferous tubuleCells heart
The invention discloses an in-vitro separation and preparation method of male germline stem cells of a goat. Spermatogonium can be obtained from male convoluted tubules of the goat. The separation and preparation method of germline stem cells of a male goat comprises the following steps: carrying out differential adhesion by using 0.2% gelatin and Matrigel through combining a cloning method; and distinguishing and separating non-adhesion male germline stem cells of the goat with other adhesion culture cells, wherein the culture of separated male germline stem cells of the goat is MEF (mouse embryonic fibroblast) feeder culture or feeder-free culture. The separated male germline stem cells of the goat have embryonic stem (ES) cell features and proficiency of differentiating to be nerve cells, cardiocytes and sperm-like cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Medical applications of four buxus alkaloids compounds
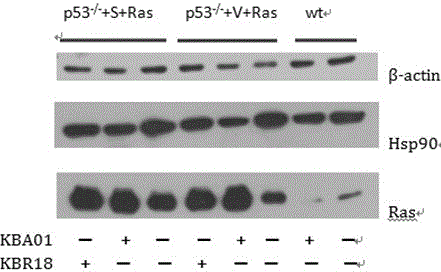
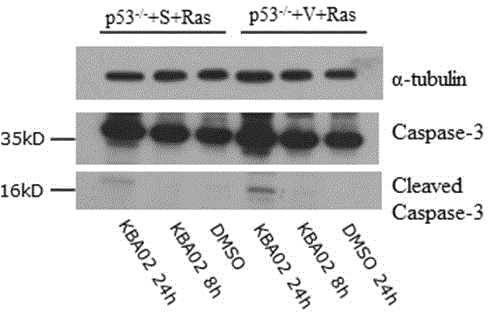
The invention discloses medical applications of four buxus alkaloids compounds in the preparation of antitumor medicines. Experiment results show that the four compounds KBA01, KBA02, KBA03 and KBR18, under the condition of concentration without toxicity to wild normal mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, can selectively kill mouse tumor cells with tumor specific mutant genes p53 and Ras; accordingly, the compounds are very strong in killing activity to human colon cancer cell strains with p53 mutants, but not strong in killing activity to human wild colon cancer cell strains with p53 mutants; and as shown in a GFP (Green Fluorescence Protein) reporter vector screening system of a gene promoter, the compounds KBA02 and KBA03 can activate a promoter of a cancer suppressor gene p16. The characteristics indicate that the compounds from the four buxus plant origins have application potentials for preparing personalized treatment medicines aiming at the tumor mutant genes p53 and Ras as well as the cancer suppressor gene p16.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Periplaneta americana tissue repair factor PA1 and application thereof
ActiveCN111484549AImprove repair effectPromote proliferationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue repairFibroblast
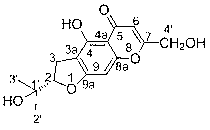
The invention relates to the field of medicines and daily chemicals, in particular to a periplaneta americana new polypeptide for promoting tissue repair and application of the periplaneta americana new polypeptide, the structure of the periplaneta americana new polypeptide is shown as a formula I, and the periplaneta americana new polypeptide is named as a tissue repair factor PA1. The new polypeptide can promote proliferation of mouse embryo fibroblasts and migration of human immortalized epidermal cells even at a low concentration, has low toxic and side effects and has a good application prospect, so that the polypeptide can be used for preparing medicines for treating wounds, scalds and ulcers or cosmetics and daily chemical products for improving skin beauty.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells by adopting transcription factors
InactiveCN101705248ANormal growth characteristicsGood pluripotencyGenetic engineeringFermentationFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by adopting transcription factors, concretely comprising the following steps: 1) isolation and culture of bovine dermal fibroblasts; 2) cloning of bovine transcription factors maintaining pluripotent genes and construction of retroviral vectors of the transcription factors; 3) retrovirus packaging and preparation; and 4) infection of bovine dermal fibroblasts by retrovirus and acquisition of bovine inducted pluripotent stem cells. The invention first adopts the acellular human amniotic membranes as support to replace the mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to maintain in vitro proliferation of the bovine iPSCs and keep the bovine iPSCs in undifferentiated pluripotent states for long time. The method which adopts gene inducing to generate the PSCs not only solves the technical problem that the PSCs of the animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs and other livestock are difficult to obtain but also avoids the problem of heterogeneous animal cell pollution caused by the feeder layer which applies the MEFs as the stem cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
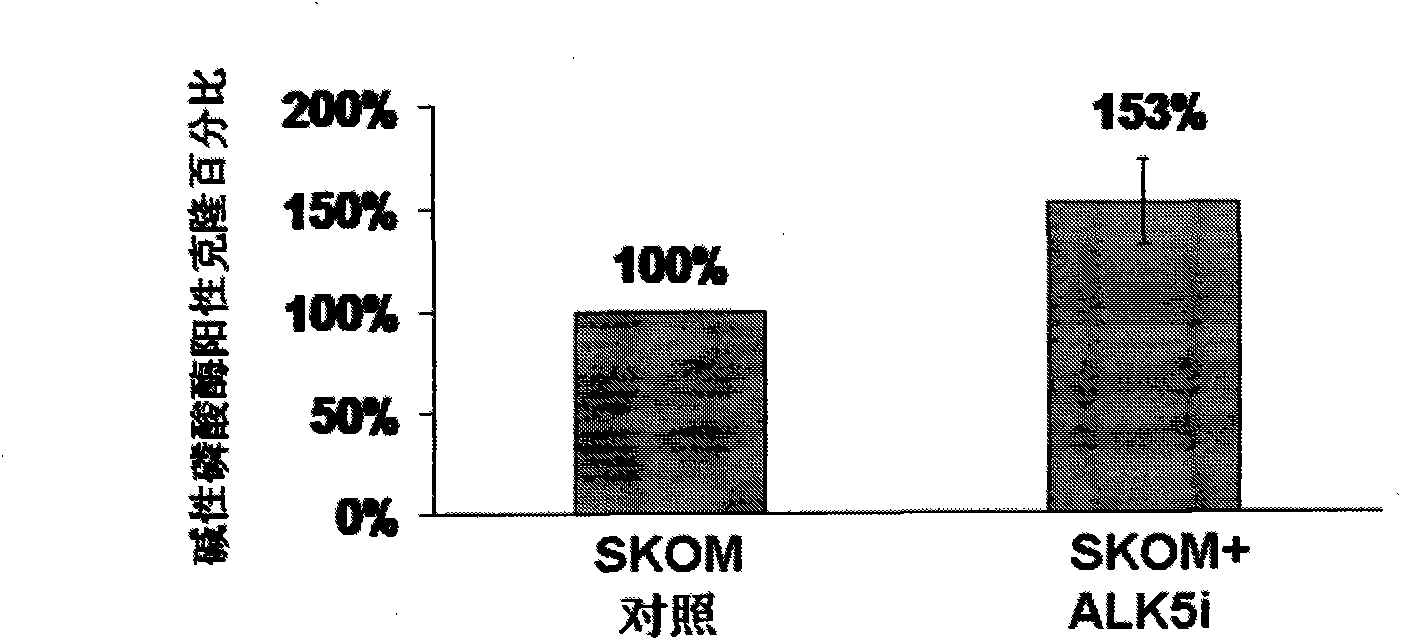
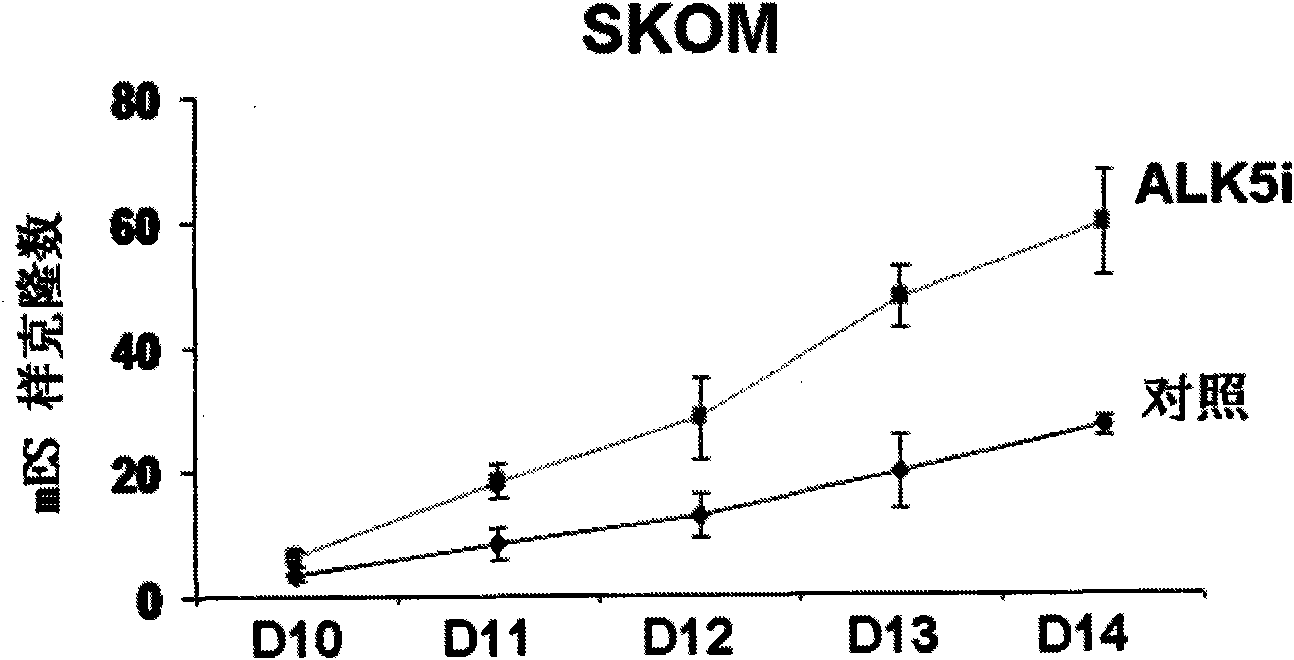
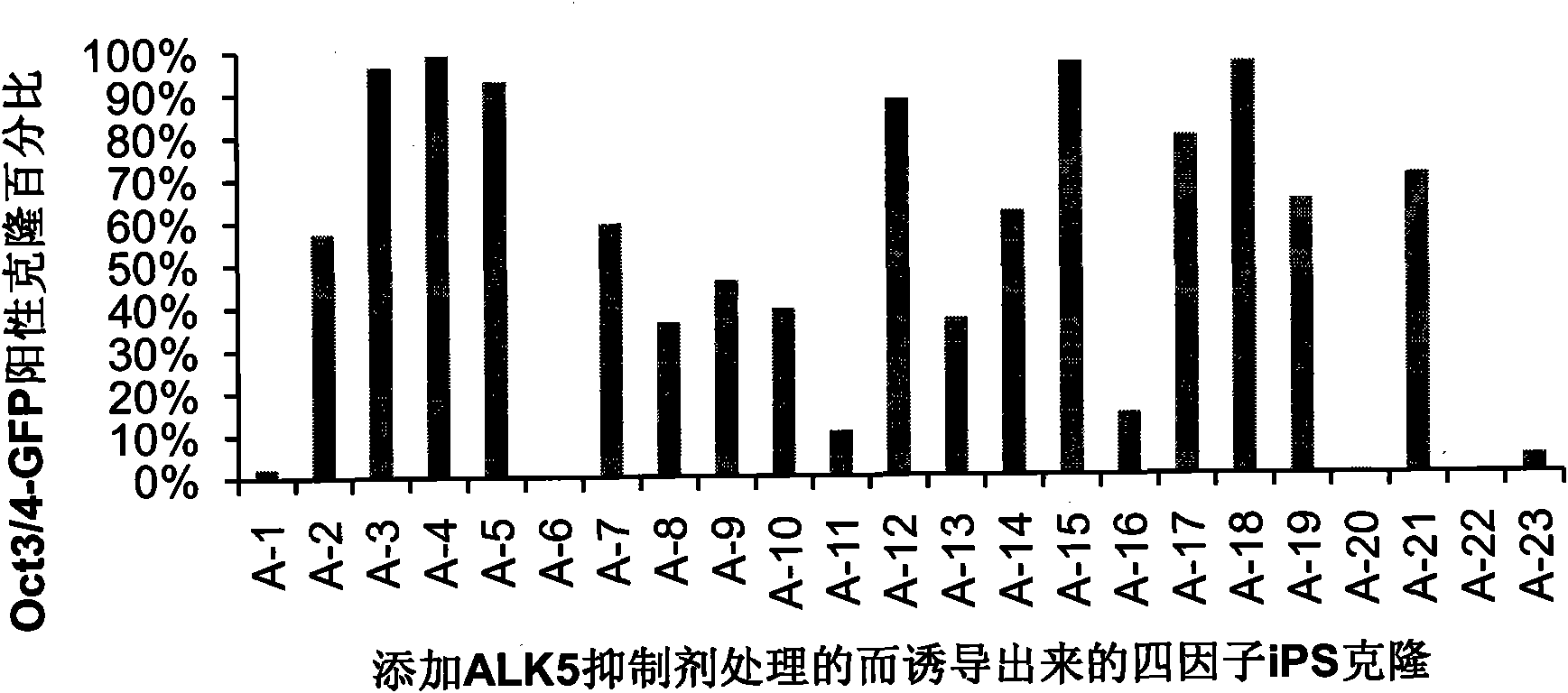
Application of I type transforming growth factor receptor inhibitor in producing induced multi-potent stem cells and method thereof
The invention discloses application of an I type transforming growth factor receptor (ALK5) inhibitor in producing induced multi-potent stem cells (iPS) and a method thereof. The invention applies a culture medium containing the I type transforming growth factor receptor inhibitor to the producing induced multi-potent stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: inducing cDNA of multi-potent stem cell factors to mouse embryonic fibroblasts; culturing the mouse embryonic fibroblasts treated in the step (1) by using the culture medium added with the ALK5 inhibitor; and identifying clone of induced multi-potent stem cells. The I type transforming growth factor receptor (ALK5) inhibitor of the invention can efficiently produce induced multi-potent stem cells (iPS); and the method forefficiently inducing iPS cells has significance for promoting the medical application of the iPS, establishing a disease model, transplanting treatment, and developing safe iPS technology.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
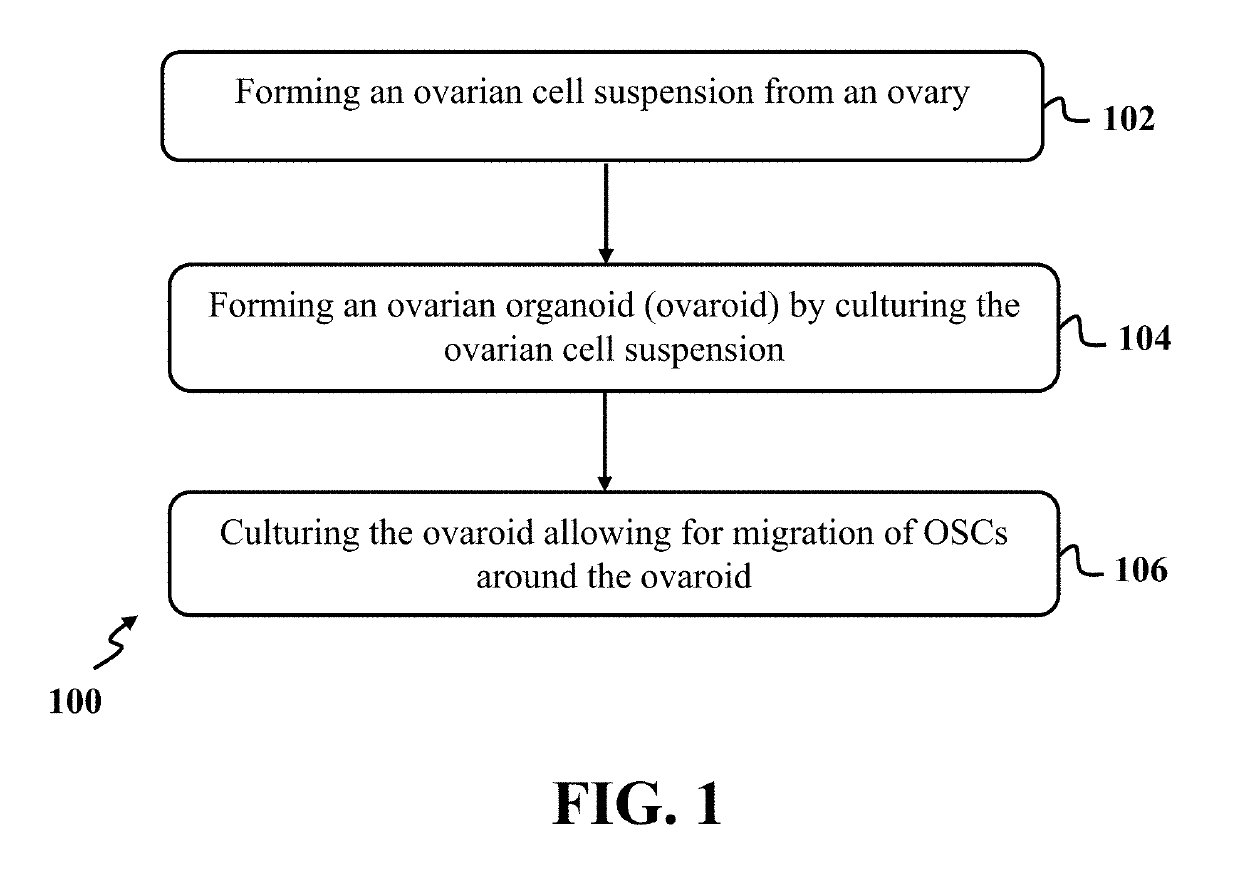
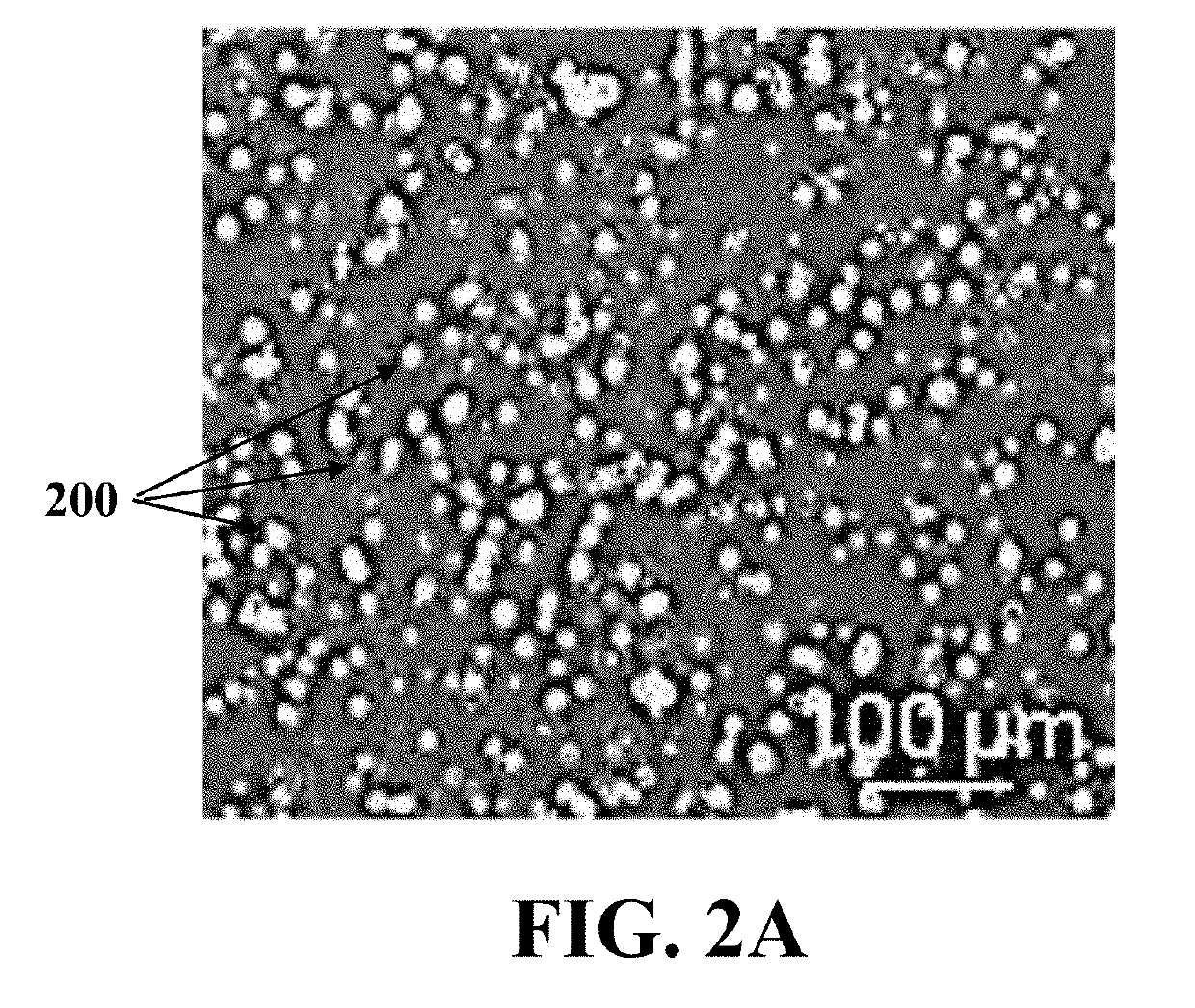
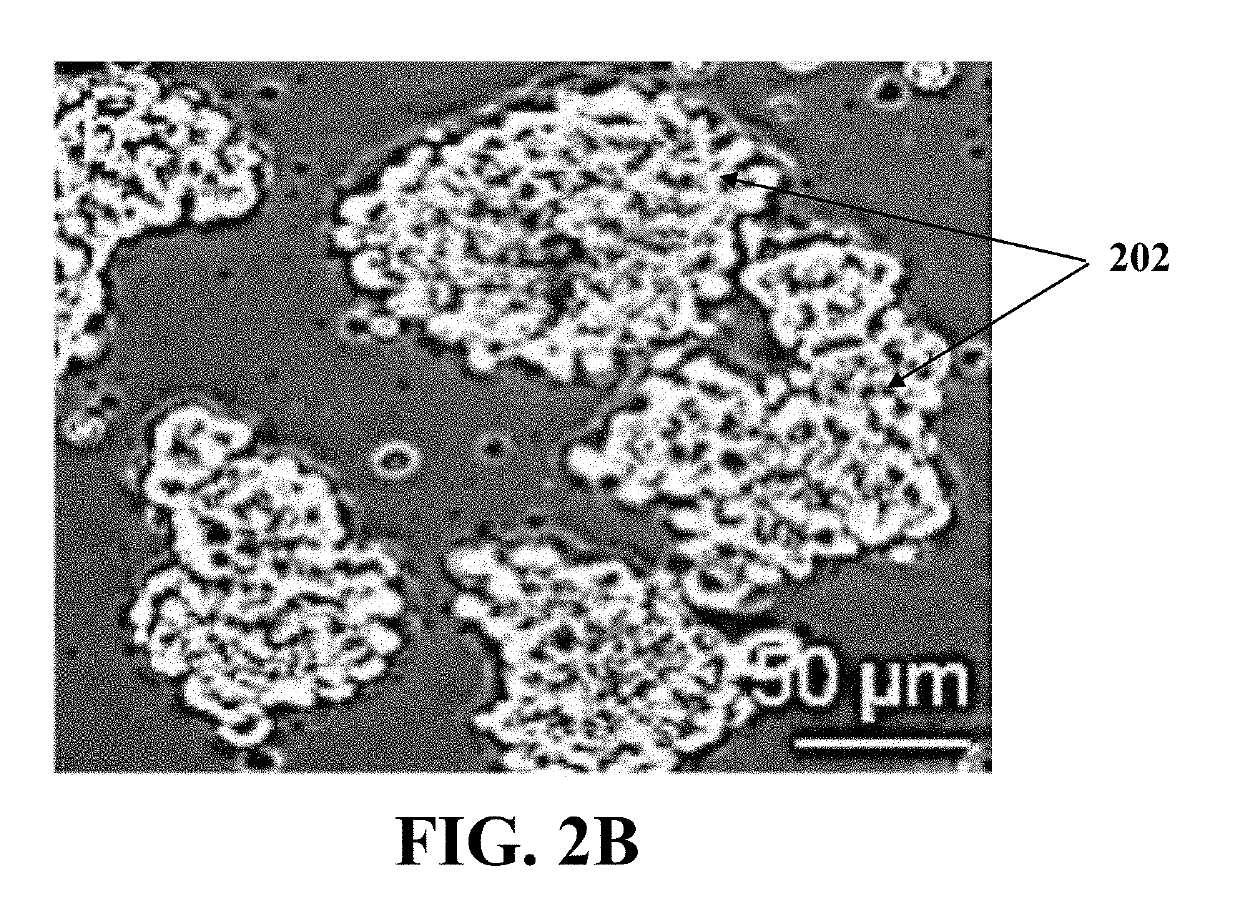
Isolation of oogonial stem cells
InactiveUS20190177689A1Cell culture supports/coatingCell culture active agentsPhysiologyOogonial Stem Cells
A method for isolating oogonial stem cells (OSCs) including forming an ovarian cell suspension from an ovary, forming ovaroids by culturing the ovarian cell suspension in a three-dimensional culture, and migrating the OSCs around the ovaroids by culturing the ovaroids on a mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF)-coated plate.
Owner:ROYAN INST
Cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method
ActiveCN103114075BPromote growthGood effectMicroorganism based processesEmbryonic cellsStem cell lineSomatic cell
The invention provides a cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method which comprises the following steps: inoculating hemiblastula of which zona pellucida is removed through pronase treatment into a feed layer in mouse embryonic fibroblast subjected to mitomycin treatment and Wnt-3A mouse subcutaneous connective tissue cells, adding 2i small-molecule inhibitor culture solution to perform continuous cell culture of cells, and establishing a cattle trophoderm stem cell system. The method can be used for obtaining and culturing cattle trophoderm stem cells under in-vitro conditions for a long time. The cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method can be applied to large animal transgenosis and somatic cell cloning and can be further used for cattle embryo implantation and placenta differentiation.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method
ActiveCN103114075APromote growthGood effectMicroorganism based processesEmbryonic cellsStem cell lineSomatic cell
The invention provides a cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method which comprises the following steps: inoculating hemiblastula of which zona pellucida is removed through pronase treatment into a feed layer in mouse embryonic fibroblast subjected to mitomycin treatment and Wnt-3A mouse subcutaneous connective tissue cells, adding 2i small-molecule inhibitor culture solution to perform continuous cell culture of cells, and establishing a cattle trophoderm stem cell system. The method can be used for obtaining and culturing cattle trophoderm stem cells under in-vitro conditions for a long time. The cattle trophoderm stem cell system establishment method can be applied to large animal transgenosis and somatic cell cloning and can be further used for cattle embryo implantation and placenta differentiation.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Application of anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) drug amprenavir in preparation of antitumor drug
InactiveCN103536605AShorten the development cycleReduce R&D investmentOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsL929 cellFibroblastic Tumor
The invention discloses application of anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) drug amprenavir in preparation of an antitumor drug. The anti-HIV drug amprenavir identified by food and drug administration (FDA) is taken as a material; the killing effect of the amprenavir on a tumor cell is detected by adopting a microwave theory and techniques (MTT) method. An experiment proves that the amprenavir has a significant inhibiting effect on multiplication of a plurality of tumor cells, such as a breast cancer michigan cancer foundation (MCF-7) cell, a non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell, a mouse embryonic fibroblast glioblastoma multiforme L929 cell, a colon cancer HT29 cell, a brain glioma U87 cell and the like, so as to clarify new use of an old drug. Therefore, foundation is provided for development of a novel anti-tumor drug.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
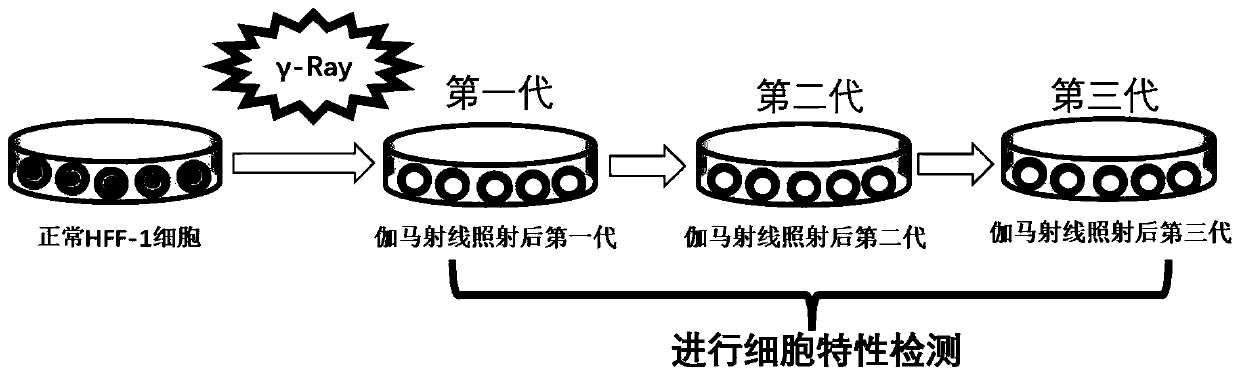
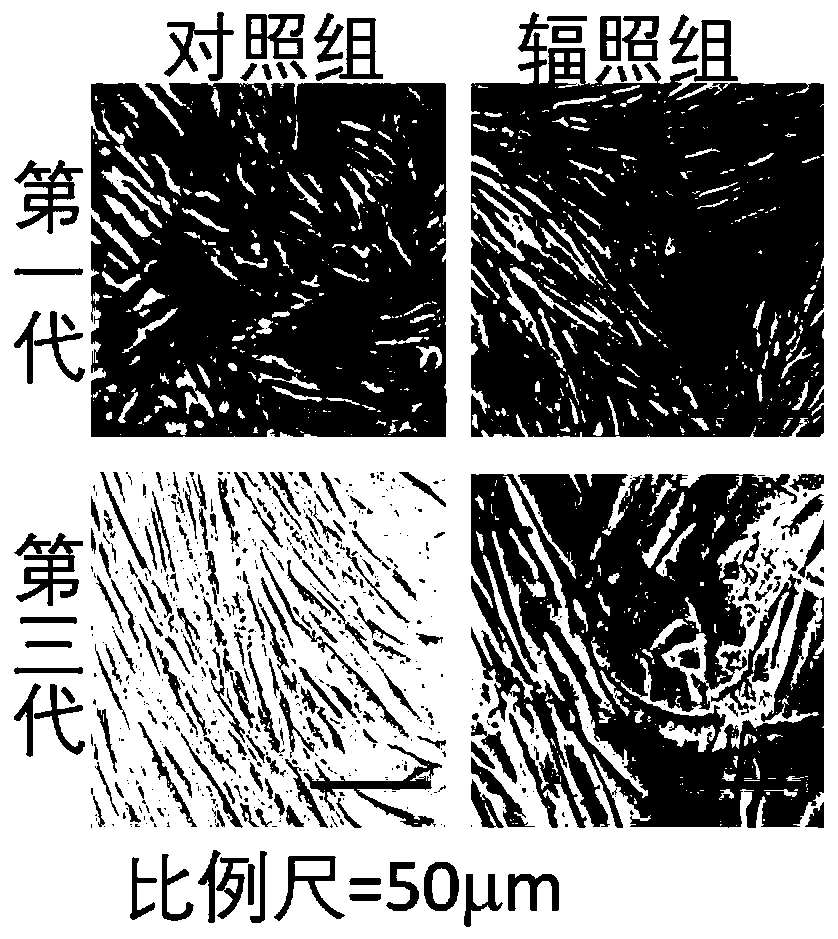
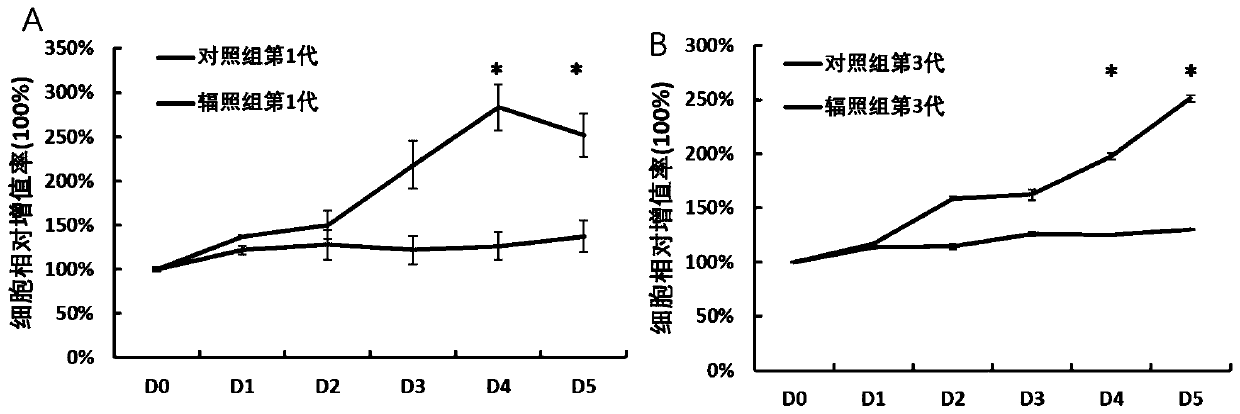
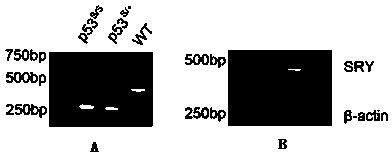
Cell strain subjected to long-term passage after gamma ray irradiation of human skin fibroblasts and construction method of cell strain
InactiveCN110669726AHigh scientific researchIncrease production capacityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsApoptosisBiomedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedicine, in particular to a cell strain subjected to long-term passage after gamma ray irradiation of human skin fibroblasts (HFF-1) and a construction method of the cell strain. According to the invention, human skin fibroblasts (HFF-1) are used as induction objects, after the induction objects are subjected to a specific dose (10Gy) of gamma rays for irradiation and mouse embryo fibroblasts irradiation, the cell proliferation is slowed down, apoptosis is increased, the migration capacity is weakened, and the change of the characteristics ofthe cells is not changed along with the increase of cell passage number and can be inherited to the next generation along with the passage of the cells. The cell model is closer to clinical practiceof long-term non-healing of wounds after skin squamous cell carcinoma radiotherapy in practical application, and has important application prospects in the aspects of research of pathological mechanisms of non-healing of wounds after radiotherapy, research and development of new drugs and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Application of p53 gene mutation in cancer-associated fibroblasts
PendingCN108486248AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTumor-Associated FibroblastsTumor therapy
The invention discloses application of p53 gene mutation in cancer-associated fibroblasts, and particularly relates to application of p53 gene mutation in the cancer-associated fibroblasts in screening and preparation of cancer therapy medicines. An experimental result shows that the growth of cancer can be promoted by mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) carrying p53N236S mutation, thus it is suggested that p53 mutation activates the cancer-associated fibroblast characteristic of the MEF, and the favorable microenvironment is provided for multiplication, migration and the like of the cancer. Thenew function of p53 mutation in the cancer-associated fibroblasts is disclosed for the first time, through the discovery, the new idea and research direction are provided for p53 mutation in cancer research, a new action target is provided for cancer therapy, and a new strategy is also provided for cancer therapy.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for inhibiting PUMA function and improving iPS (induced Pluripotent Stem) cell construction effect
ActiveCN103571794AHigh reprogramming efficiencyProtection stabilityGenetic engineeringFermentationEscherichia coliFiber
The invention provides a method for inhibiting PUMA function and improving iPS (induced Pluripotent Stem) cell construction effect. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing fibroblast MEF (Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast) of a PUMA- / - (PUMA gene knocked out) mice or PUMA- / + mice, and performing passage and frozen storage; (2) converting plasmid PMX-Oct 4, PMX-Sox2, PMX-c-Myc and PMX-KLF4 through DH5 alpha escherichia coli strain, and respectively highly and slightly extracting plasma; (3) packing retrovirus, tittering and performing frozen storage; (4) knocking out reprogramming of embryo fibroblasts MEF of the mice or PUMA- / + mice through PUMA gene; and (5) knocking down the programming of human fibroblast of the PUMPA function. The method has the beneficial effects that the PUMA function is inhibited and the iPS cell construction effect is improved during programming somatic cell; the stability of iPS cell genome can be protected at the same time.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Medicinal application of chromone compound
InactiveCN103156838AEliminate lethal effectsLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsWild typeChromone
The invention discloses new application of a chromone compound KY12 in preparation of a targeted anti-tumor medicament. Experimental results show that the compound KY12 can selectively kill tumor cells with tumor specific mutant genes p53 and Ras under the concentration which is nontoxic for wild normal mouse embryo fibroblasts, namely the compound has application potential for preparing the personalized treatment medicament for the tumor specific mutant genes p53 and Ras.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Cyclometalated platinum complex and preparation method thereof
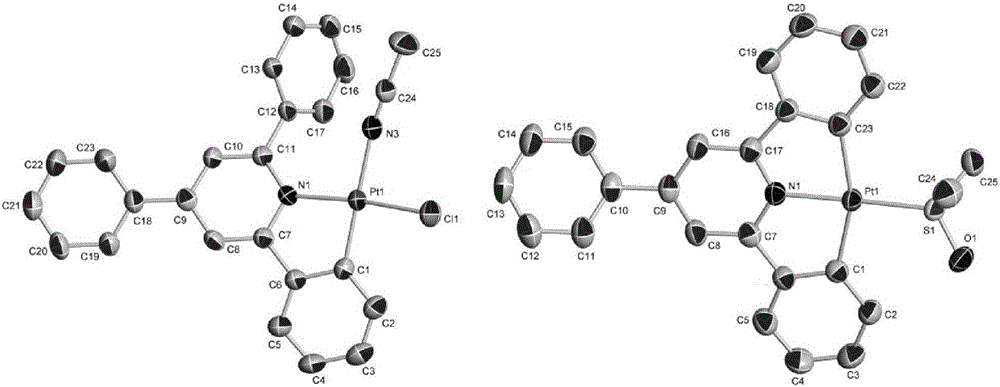
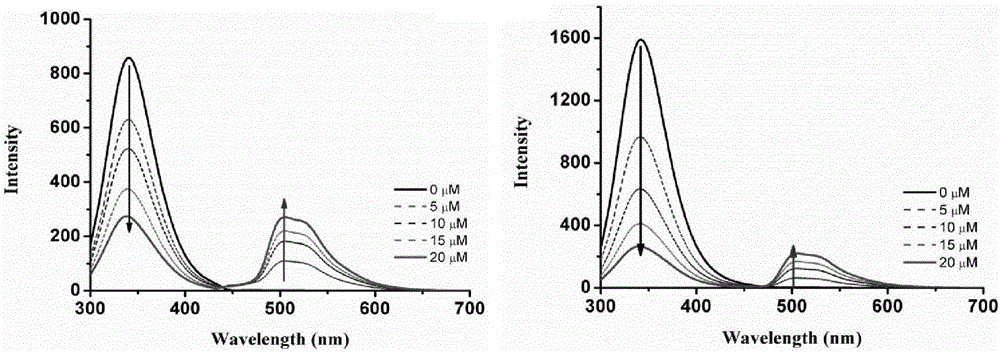
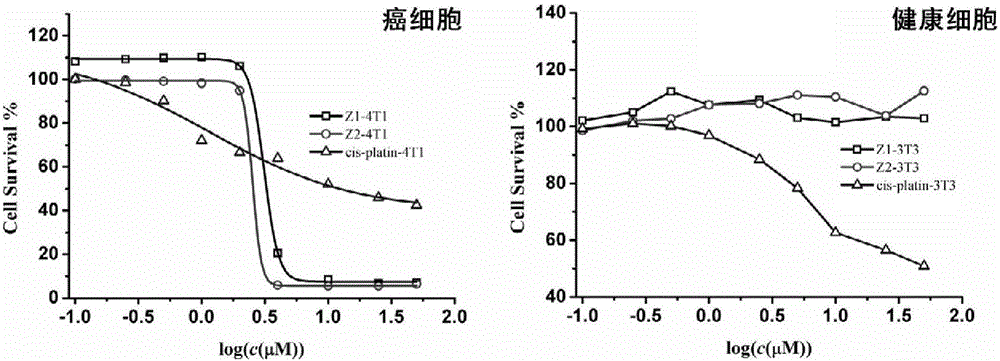
ActiveCN106008609AGood killing effectLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPlatinum organic compoundsCancer cellFluorescence
The invention discloses a cyclometalated platinum complex and a preparation method thereof, wherein the cyclometalated platinum complex has the structural formula defined in the specification. With cheap and easily available benzaldehyde, acetophenone and the like as raw materials, an organic ligand is simply and efficiently synthesized and then is subjected to a reaction with potassium chloroplatinite, and the target product-cyclometalated platinum complex is obtained. Property studies indicate that the cyclometalated platinum complex can generate fluorescence enhancement response on proteins and can be applied in developing and imaging of living cells. Cell toxicity tests indicate that the cyclometalated platinum complex has relatively strong killing efficiency on cancer cells-mouse breast cancer cells (4T1), has quite small toxicity on healthy cells-mouse embryonic fibroblasts (3T3). Therefore, the cyclometalated platinum complex has wide application prospect in the field of anticancer drug research.
Owner:合肥欧申福德生物科技有限责任公司
Cimicifuga triterpenoid compound and application thereof
The invention discloses a cimicifuga triterpenoid compound and application thereof in preparation of anti-tumor drugs. Shown by targeted screening results directed at tumor-specific mutation gene products, at the concentration of being non-toxic to wild-type normal mouse embryonic fibroblast, a compound KY40 can selectively kill tumor cells with tumor-specific mutation genes; and shown by a GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) reporting vector screening system of a gene p16 promoter, the compound KY40 can act on the p16 promoter, and shown by the characteristics, the novel cimicifuga triterpenoid compound and pharmaceutical compositions taking the cimicifuga triterpenoid compound as an effective treatment amount have application potential in the preparation of individualized treatment drugs directed at tumor-specific mutation genes p53 and tumor suppressor genes p16.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for improving induction efficiency of neural stem cells and promoting differentiation of neurons
InactiveCN111518766AImprove induction efficiencyPromote differentiationCulture processNervous system cellsTrypsinizationMurine embryo
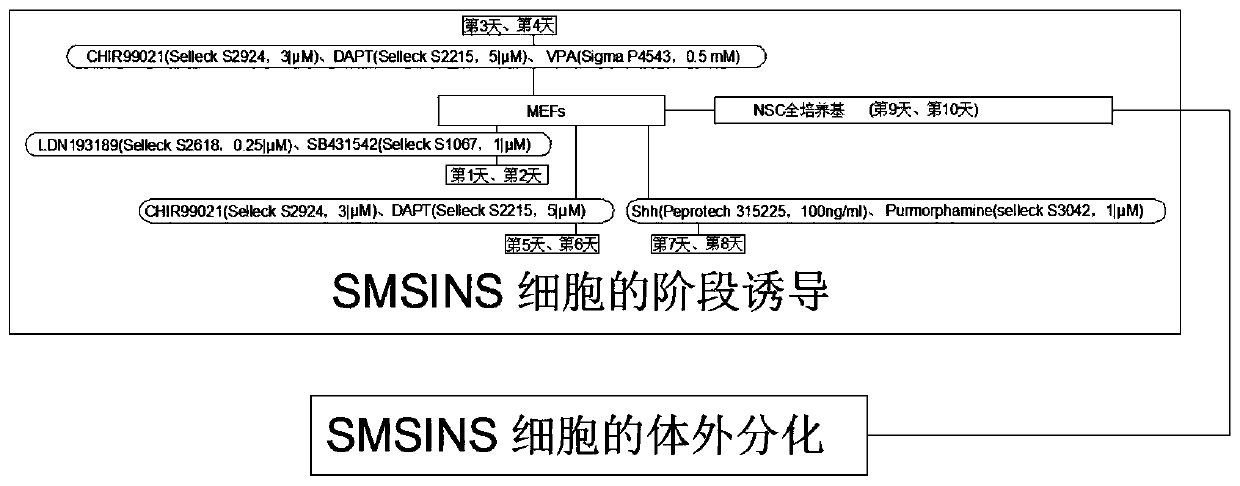
The present invention discloses a method for improving induction efficiency of neural stem cells and promoting differentiation of neurons. A programmed induction of SMSINS cells is as follows: using LDN193189 (Selleck S2618, 0.25 [mu]M) and SB431542 (Selleck S1067, 1 [mu]M) on the 1st and 2nd days to treat mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs); using CHIR99021 (Selleck S2924, 3 [mu]M) DAPT (Selleck S2215, 5 [mu]M) and VPA (Sigma P4543, 0.5 mM) on the 3rd and 4th day; using CHIR99021 (Selleck S2924, 3 [mu]M) and DAPT (Selleck S2215, 5 [mu]M) on the 5th and 6th days; adding Shh (Peprotech 315225, 100 ng / ml) and Purmorphamine (selleck S3042, 1 [mu]M) on the 7th and 8th days to improve neural differentiation; and removing all small molecule compounds on the 9th and 10th days and conducting changeto a NSC complete culture medium. At the time, SMSINS cells can be trypsinized into single cells and can be inoculated into 24-well plates without coating PDL / L in the NSC complete culture medium; and the SMSINS cells are subjected to in vitro neuronal differentiation. The method is simple and convenient to operate, can improve induction of the neural stem cells and promote the differentiation ofthe neurons, and is beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Manganese-based nano-enzyme as ferroptosis inhibitor and application of manganese-based nano-enzyme in liver injury
ActiveCN114533760AInhibition of ferroptosisHas a relieving effectInorganic active ingredientsDigestive systemFibroblastFerroptosis
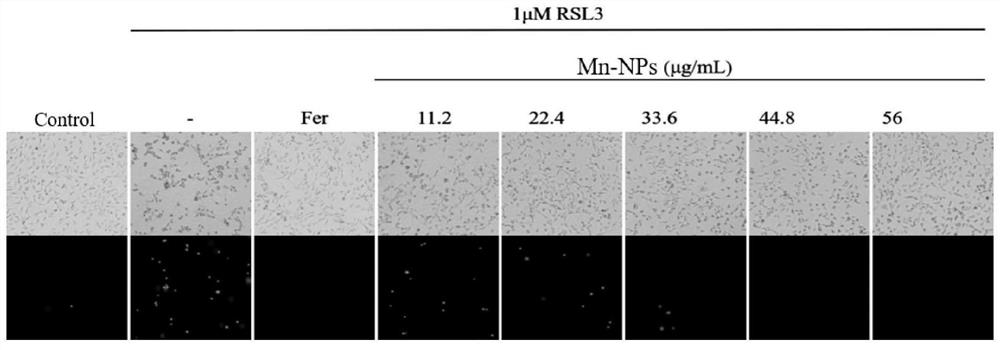
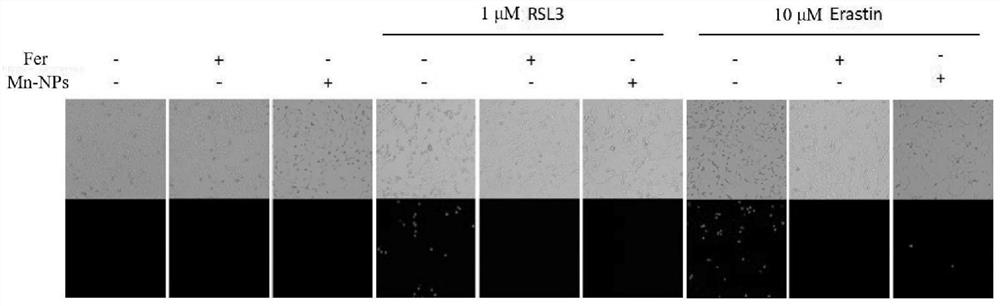
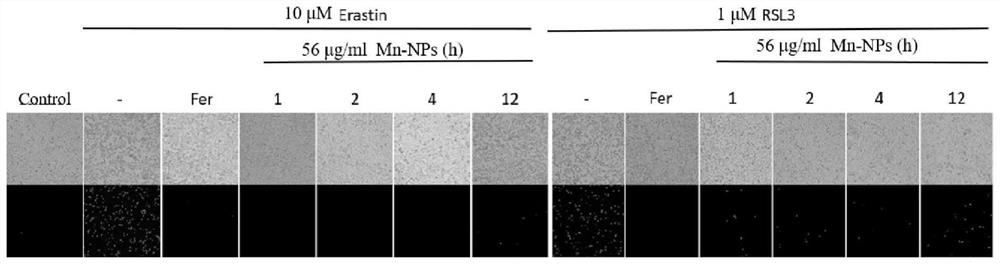
The invention relates to the technical field of medical application, and discloses a manganese-based nano-enzyme preparation (Mn-NPs) as a ferroptosis inhibitor and application of the manganese-based nano-enzyme preparation in liver injury. The manganese-based nano-enzyme preparation is applied to mouse embryo fibroblasts and living mice, and it is found that the manganese-based nano-enzyme preparation as a ferroptosis inhibitor can significantly inhibit cell ferroptosis induced by RSL3 and Erastin, has a long-term stable inhibition effect, and also has a relieving effect on acetaminophen (APAP)-induced mouse drug-induced liver injury.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for culturing human artificially induced pluripotent stem cells by using human amnion mesenchyme cells as culture layer
InactiveCN102409022ASafe and reliable trainingArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsMesenchymeCell culture media
The invention relates to a method for culturing human artificially induced pluripotent stem cells by using human amnion mesenchyme cells as a culture layer, which comprises the steps that: a human amnion mesenchyme cell culture medium is used, and exosomatic human amnion mesenchyme cells are cultured in a 15cm cell culture bottle for reaching 80 to 90 percent fusion; then, a human artificially induced pluripotent stem cell culture medium is added for use; and human artificially induced pluripotent stem cells put in the 15cm cell culture bottle are blown and beaten to be crushed into smaller stem cell masses, the stem cell masses are put into a human amnion mesenchyme cell culture bottle for culture, when human embryo stem cells grow to 4mm to 6mm, the stem cells are repeatedly blown and beaten to be crushed into smaller stem cell masses, and the stem cell masses are put into a new amnion mesenchyme cell culture bottle for continuous culture or are used for other purposes. By the method, cells with the same form as the human artificially induced pluripotent stem cells cultured on mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) are obtained, and in addition, higher safety is realized through beingcompared with the MEF culture.
Owner:李凌松 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com