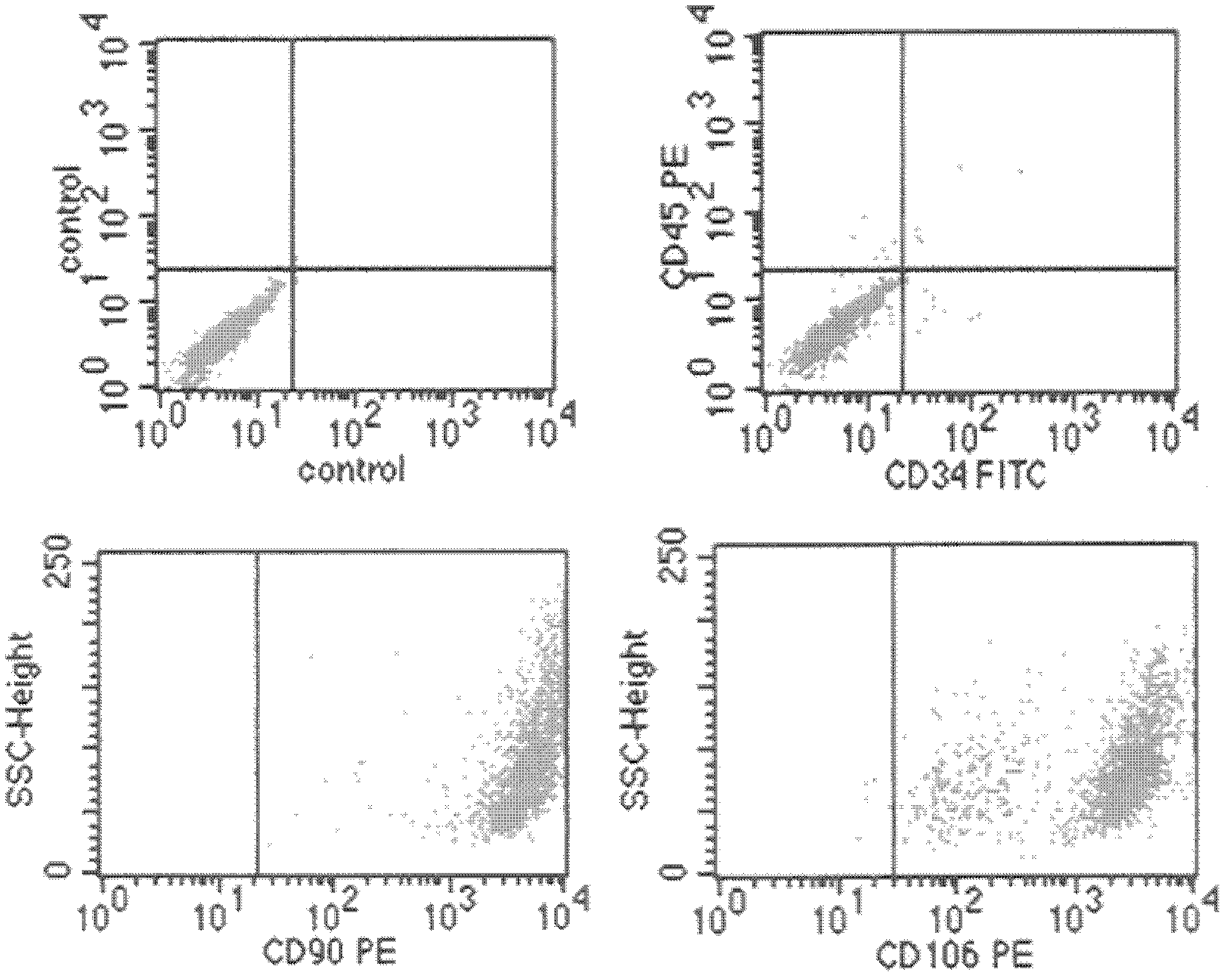
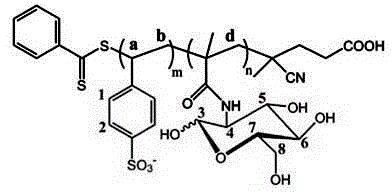
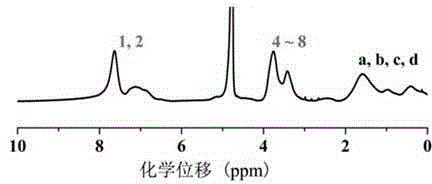
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Neural differentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
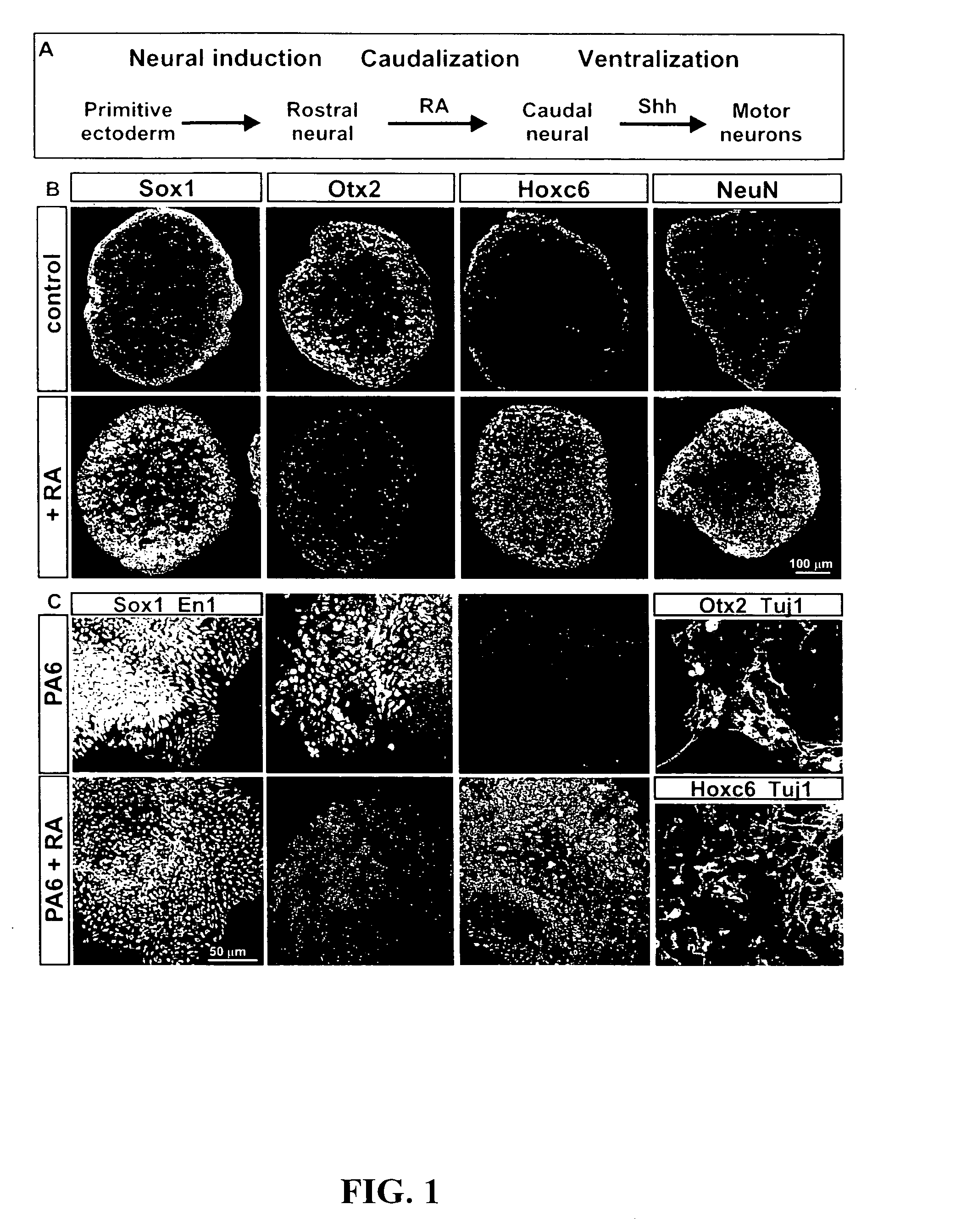
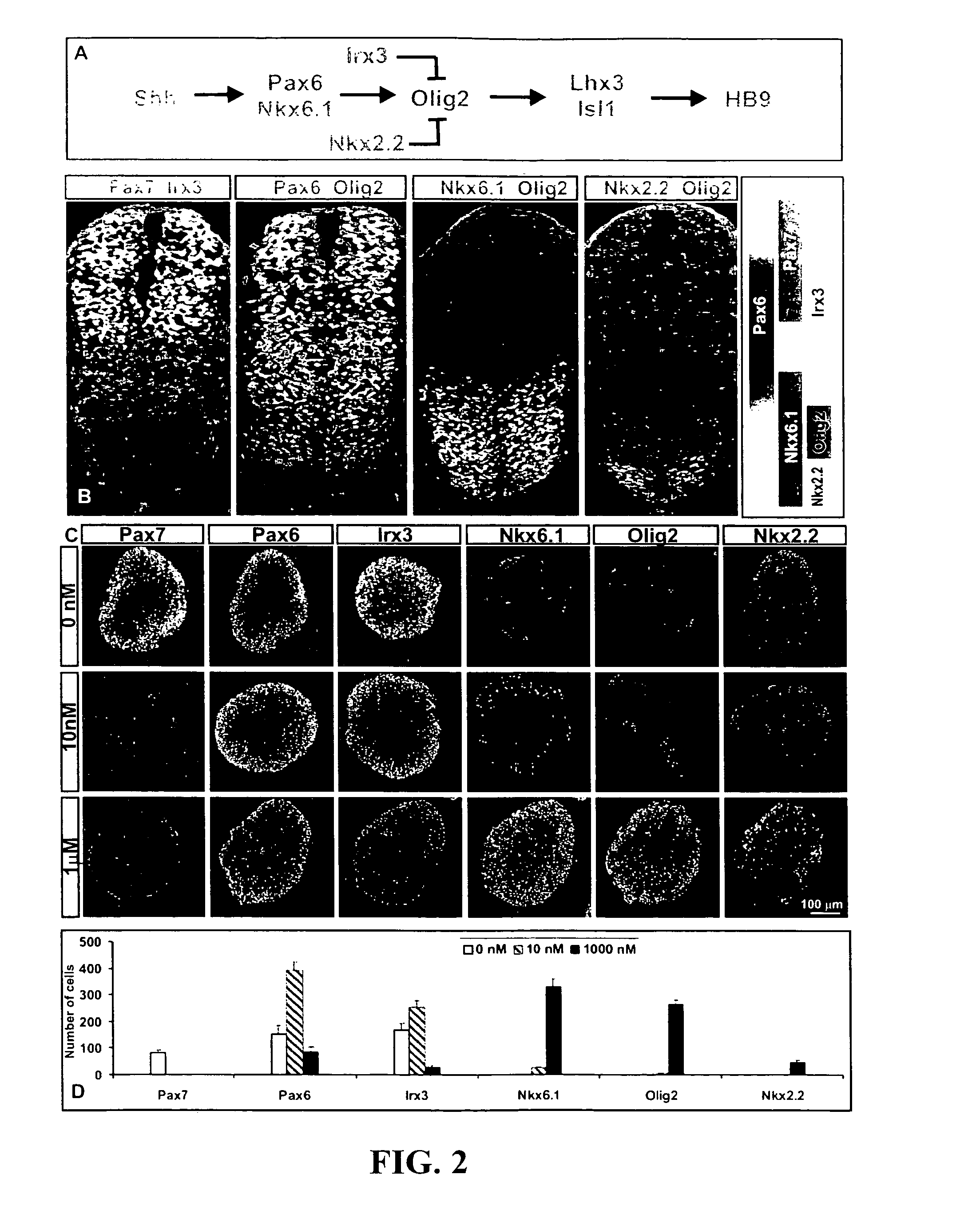
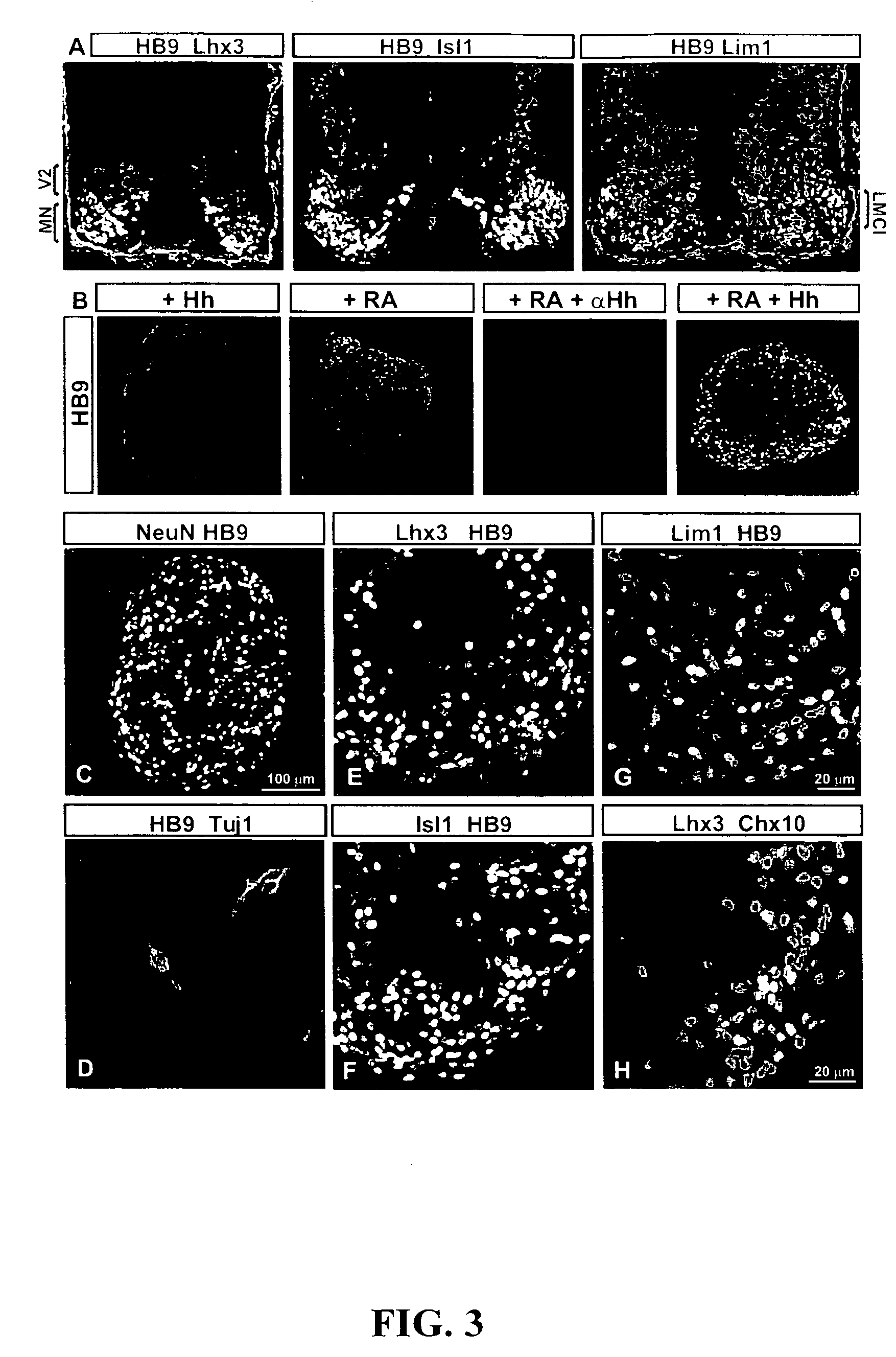
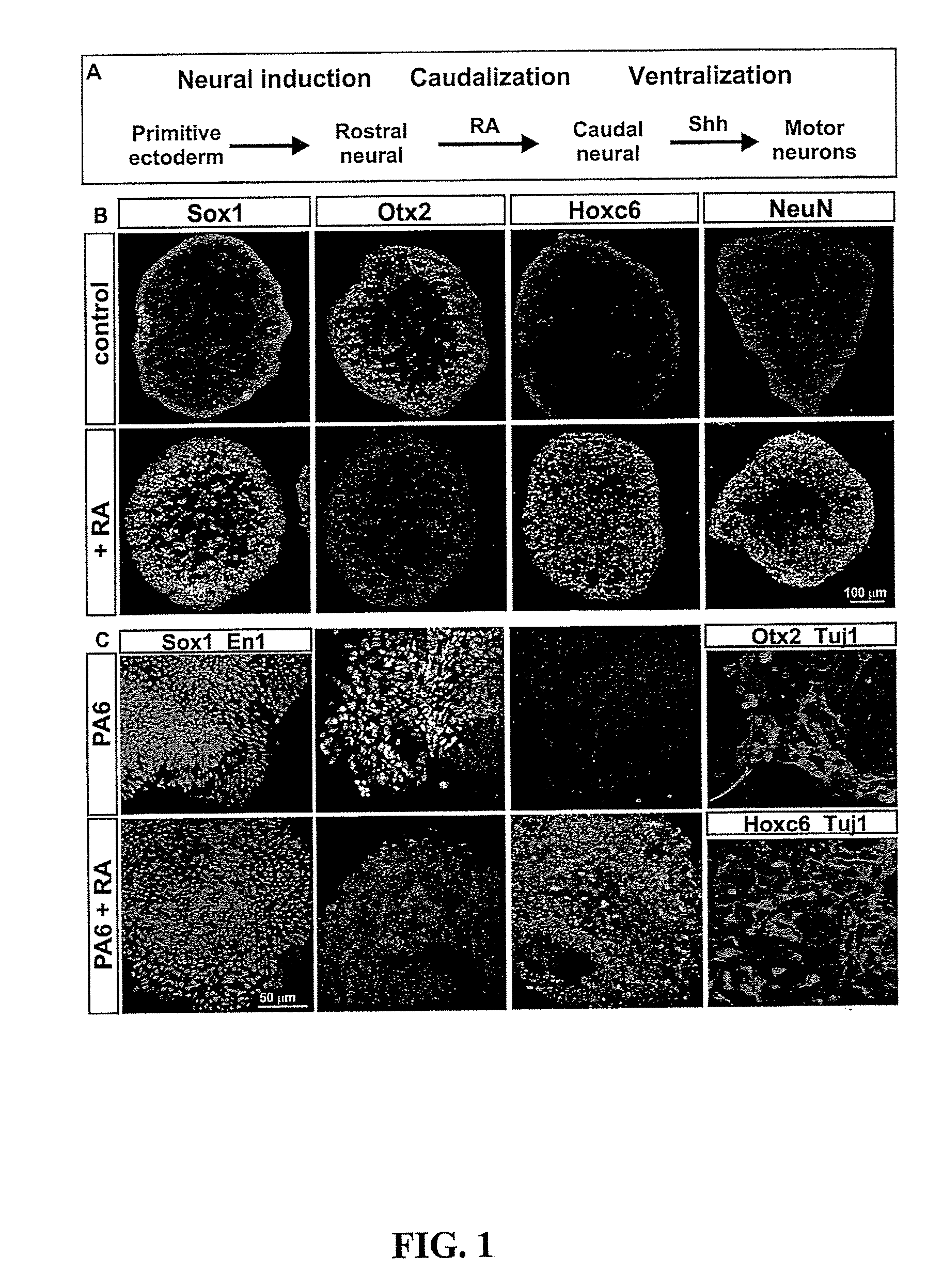
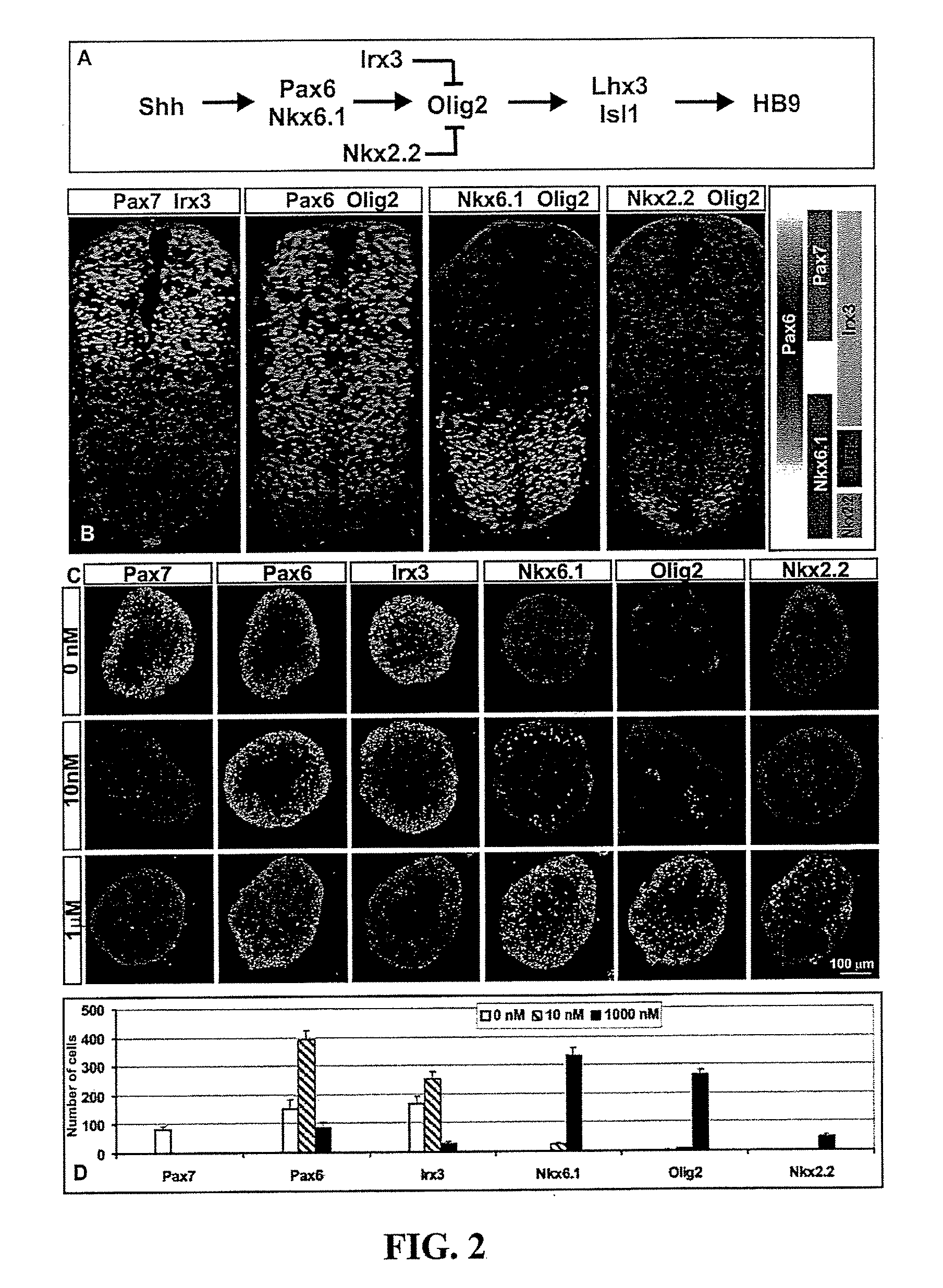
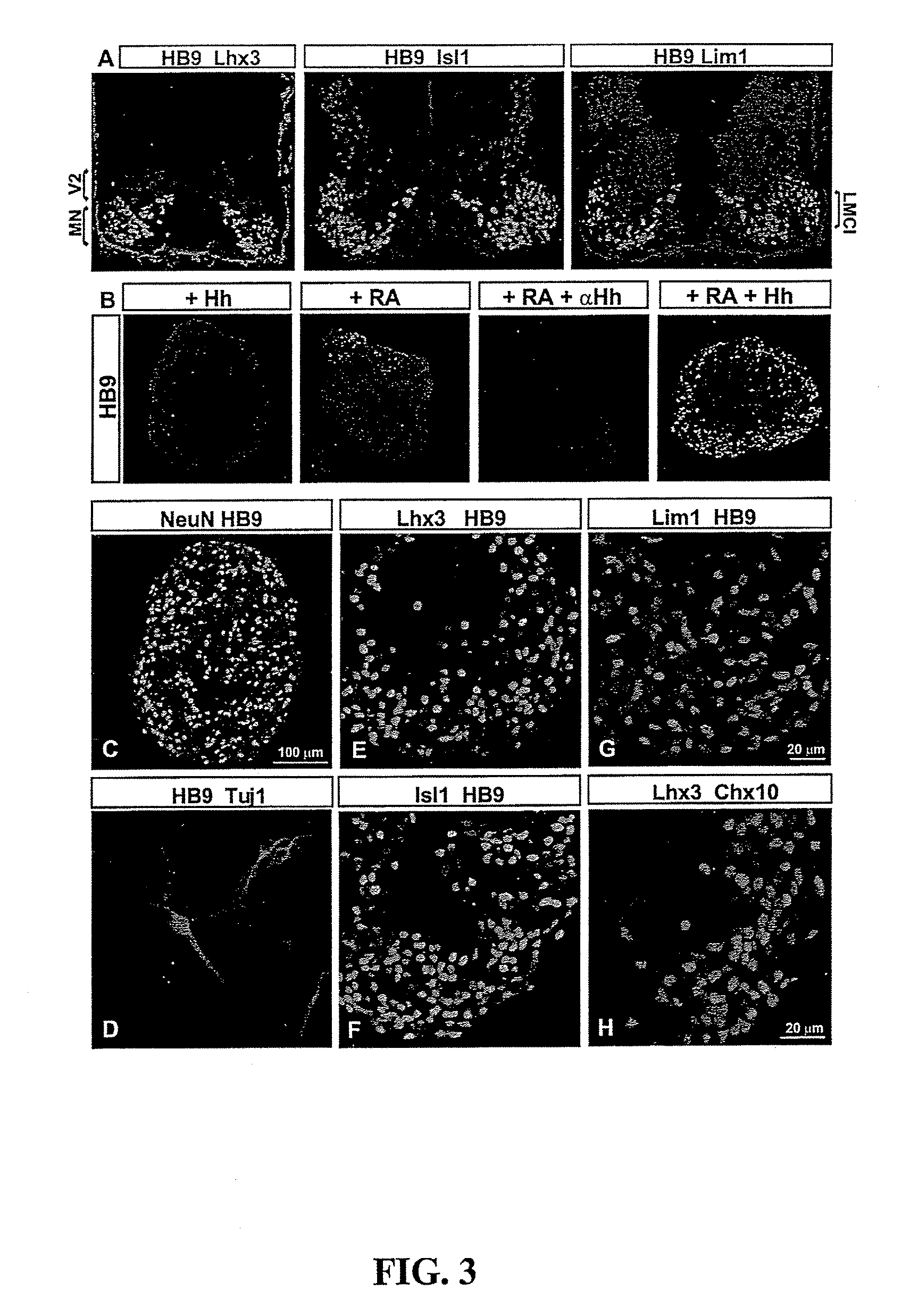
Differentiation is the process by which an embryonic precursor cell develops into a specialized mature cell. The first step in the differentiation of the nervous system is the formation of a flat strip of cells called the neural plate. This structure is formed from rapidly dividing ectoderm cells.
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
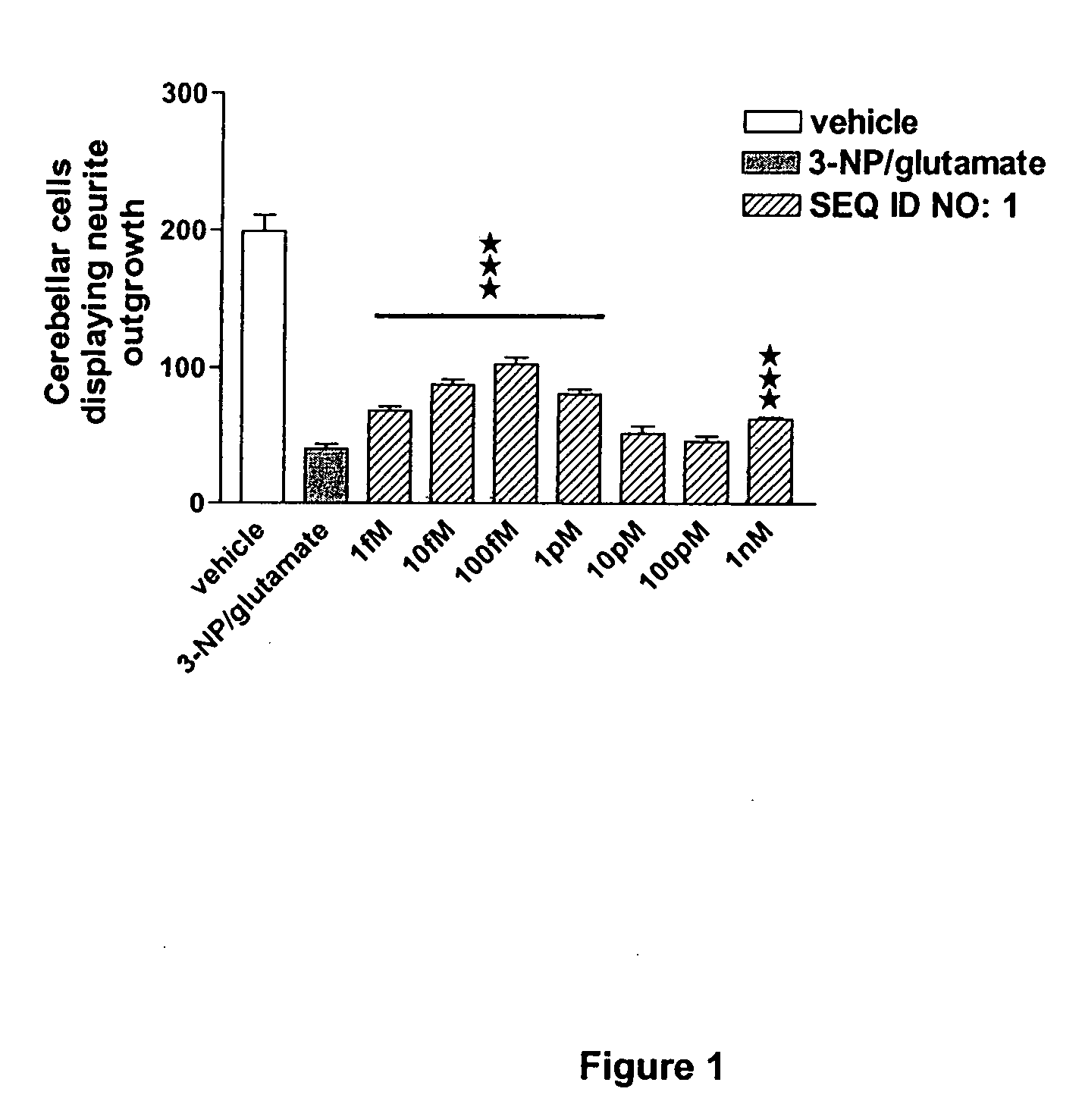
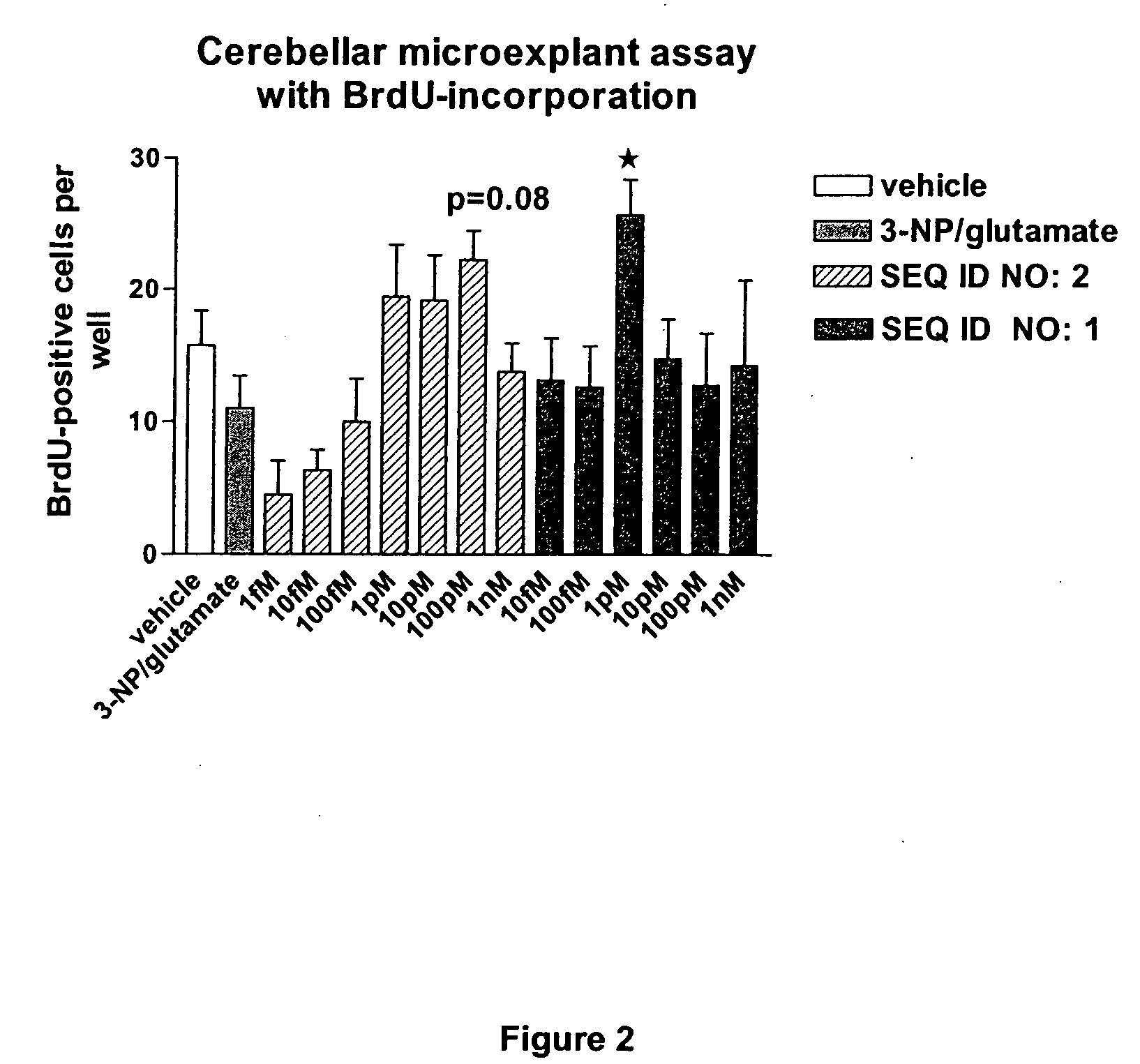
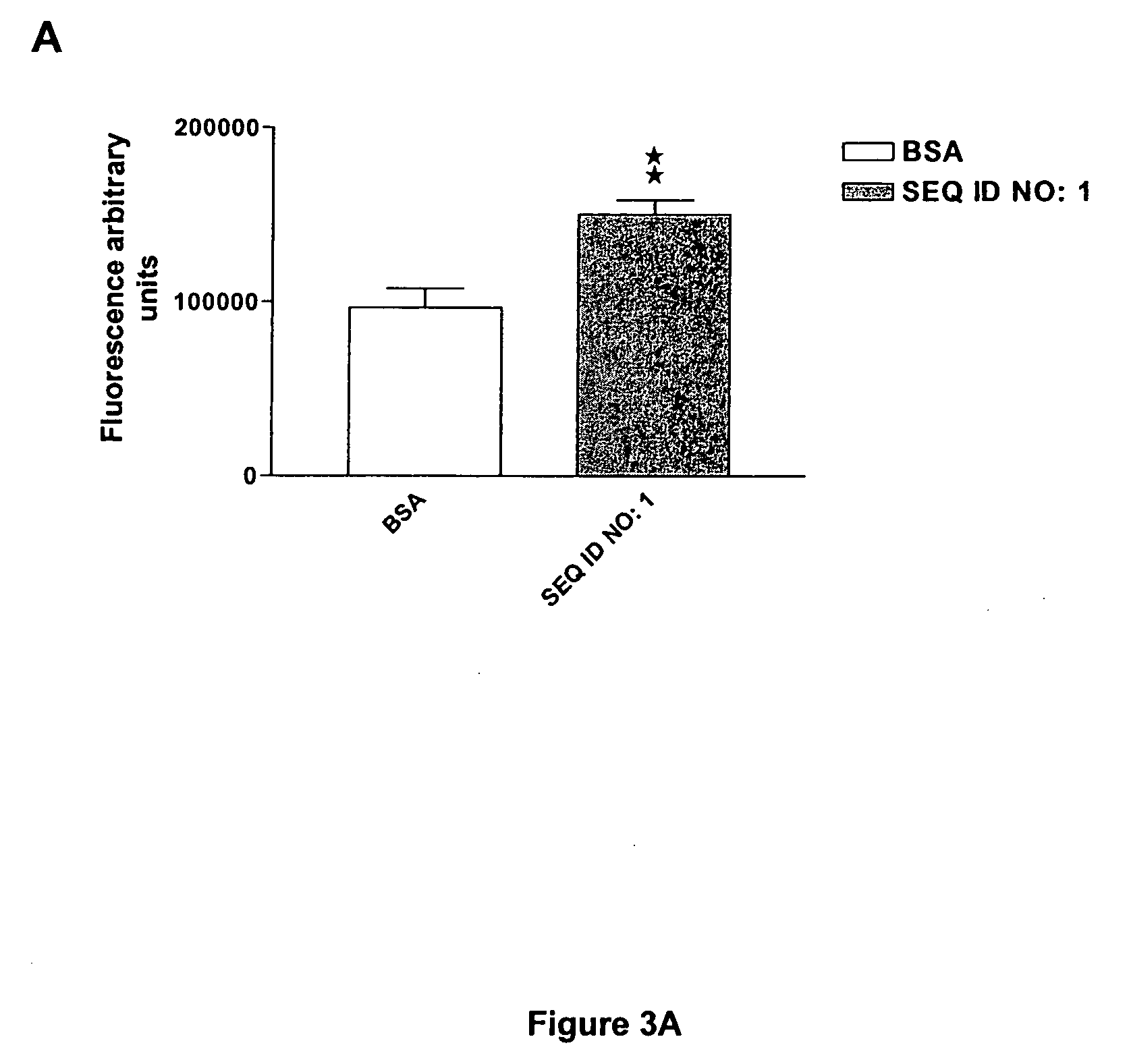
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
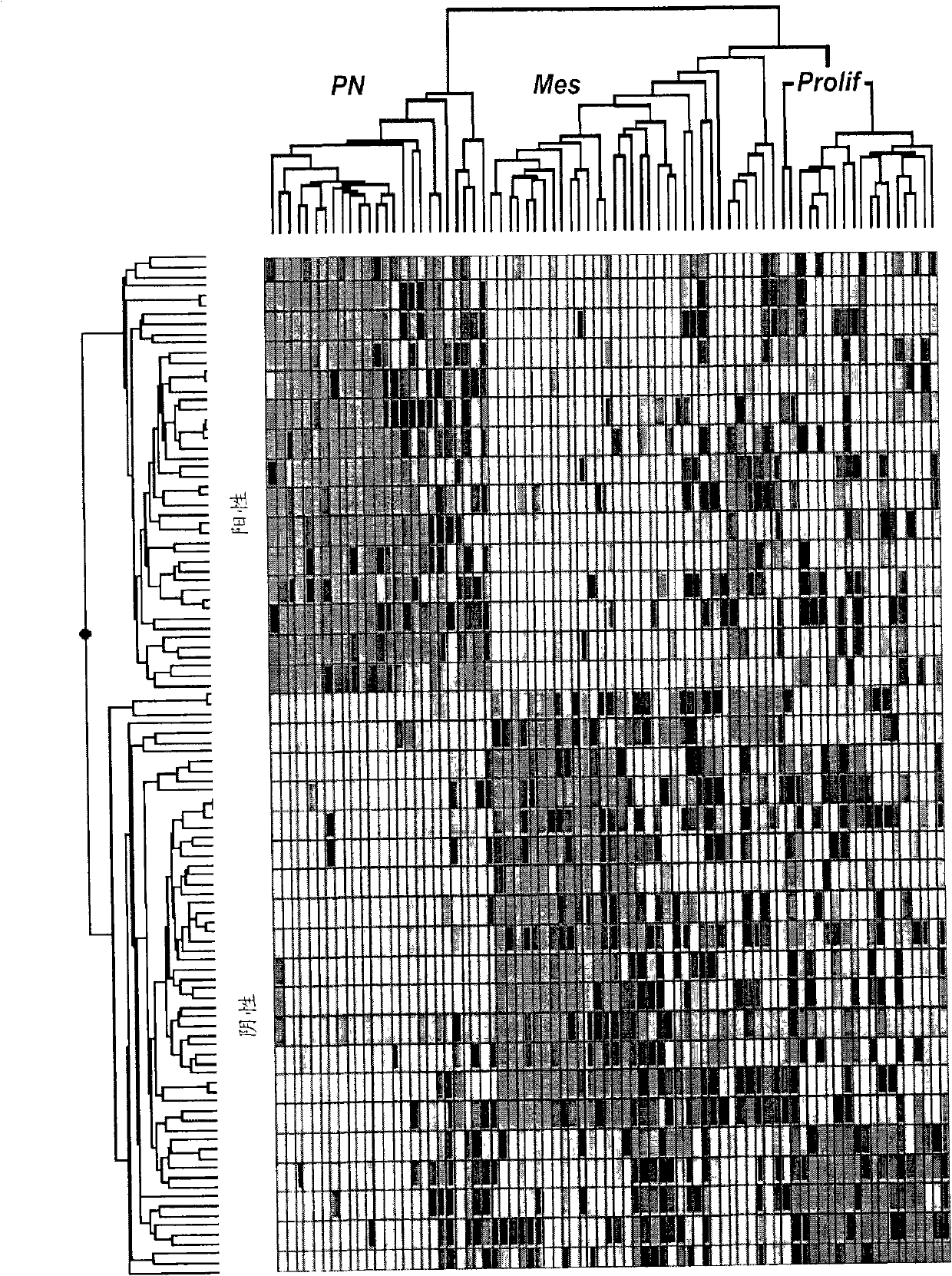
Method for Diagnosing, Prognosing and Treating Glioma
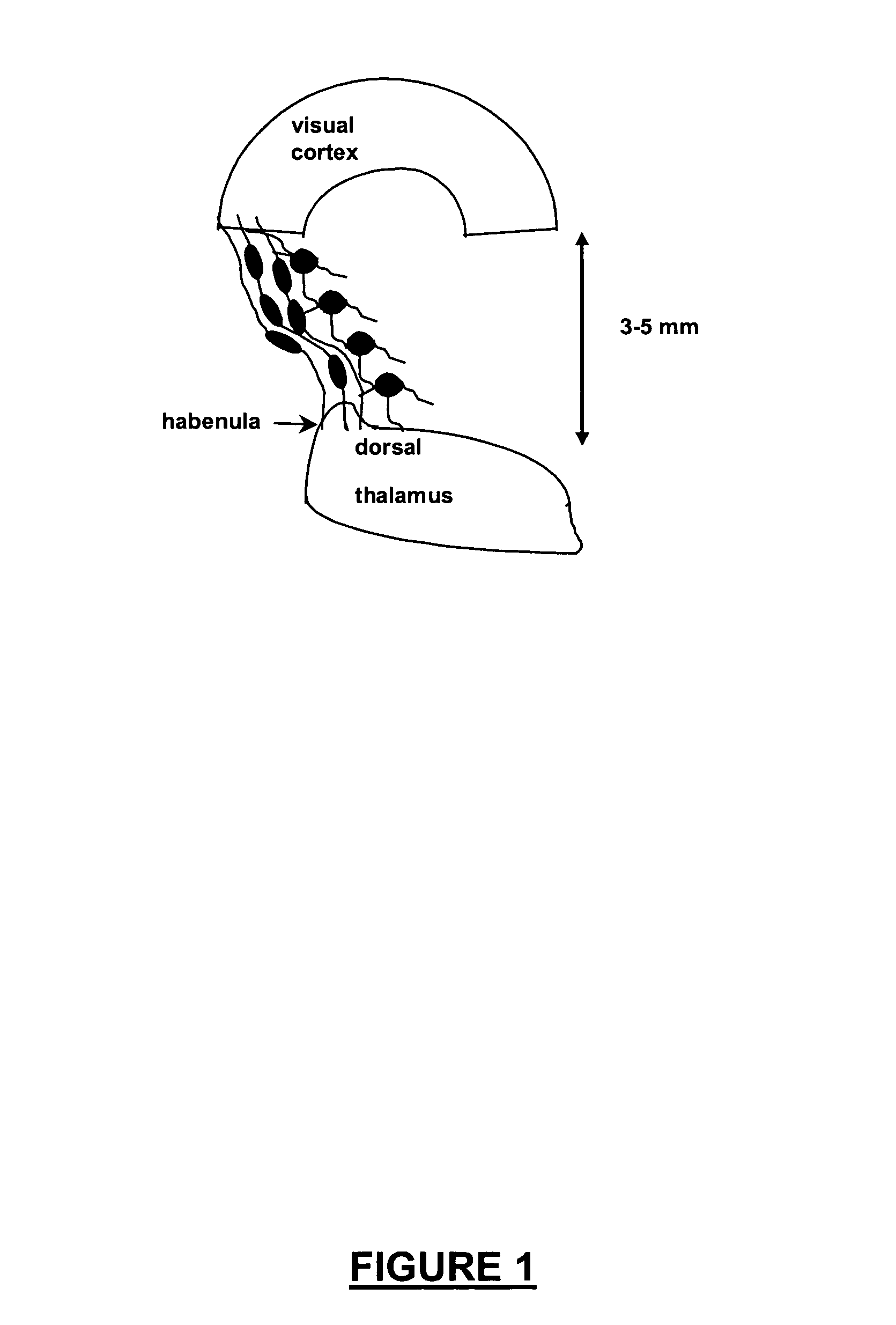
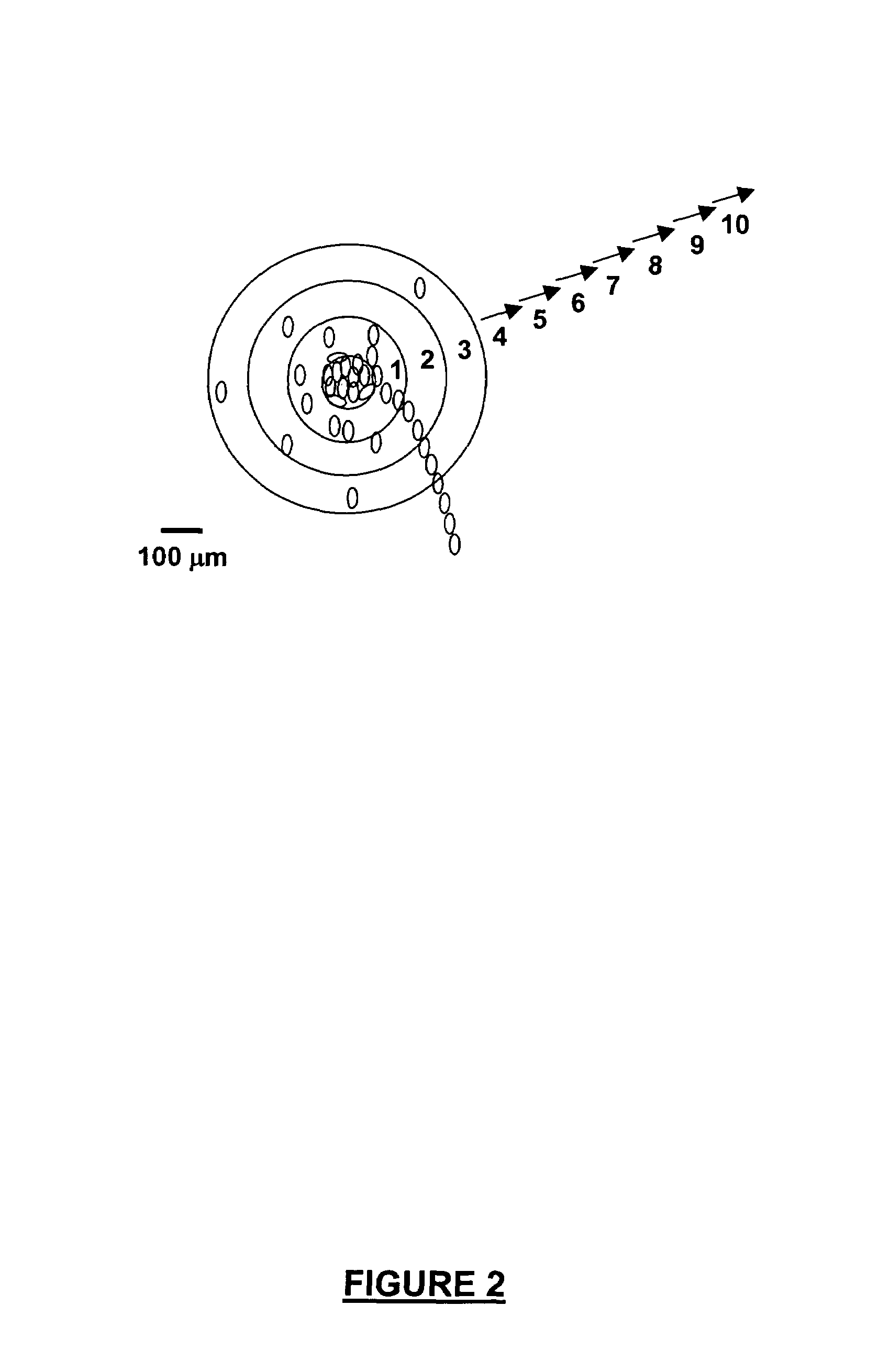
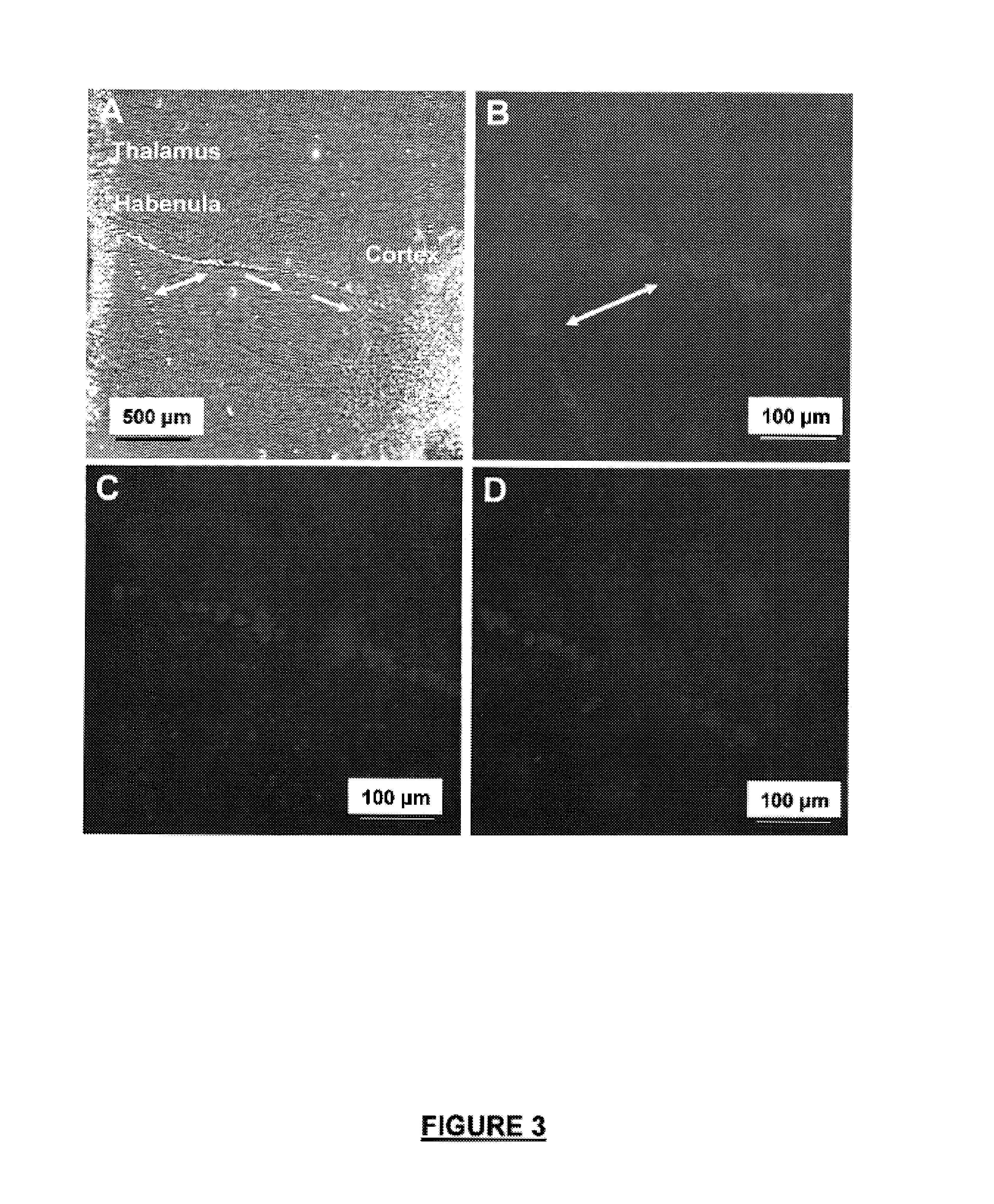
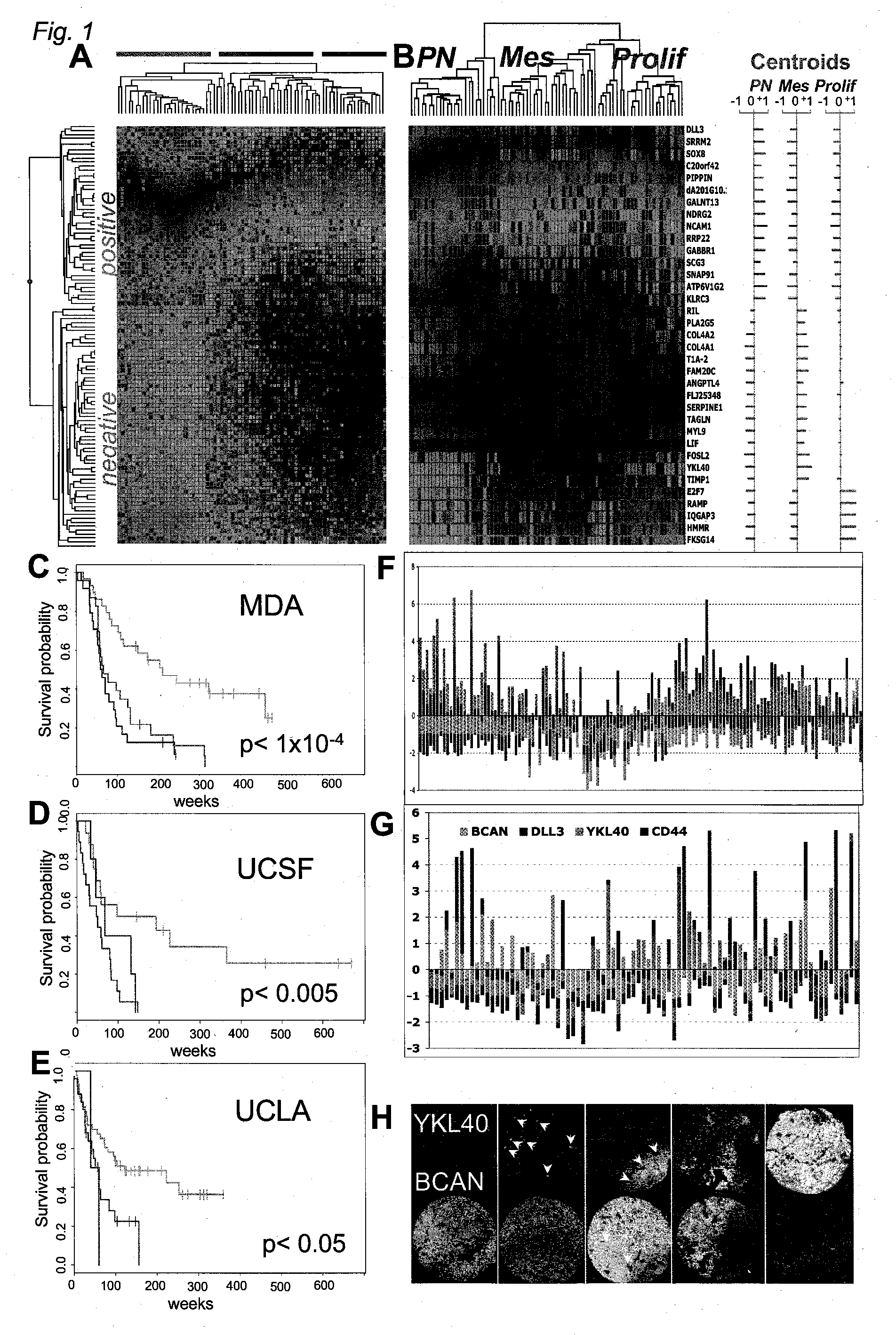
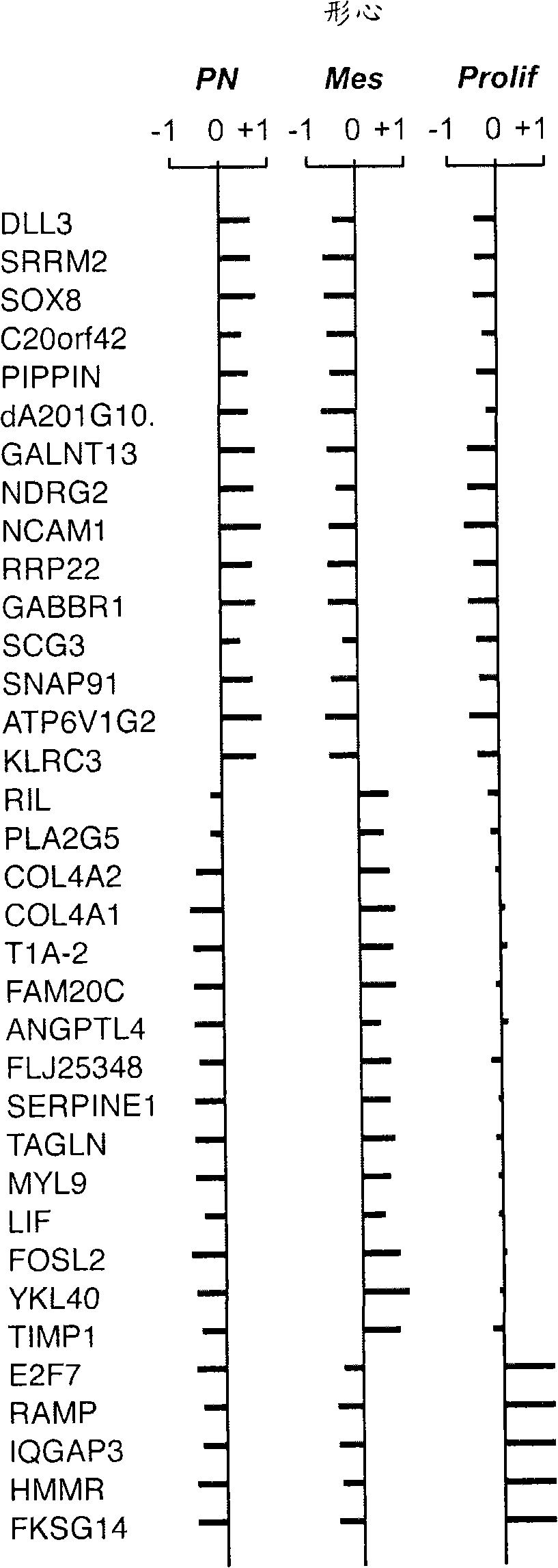
InactiveUS20070141066A1Long median patient survivalShort overall survivalHeavy metal active ingredientsCompound screeningAbnormal tissue growthAnti mitotic
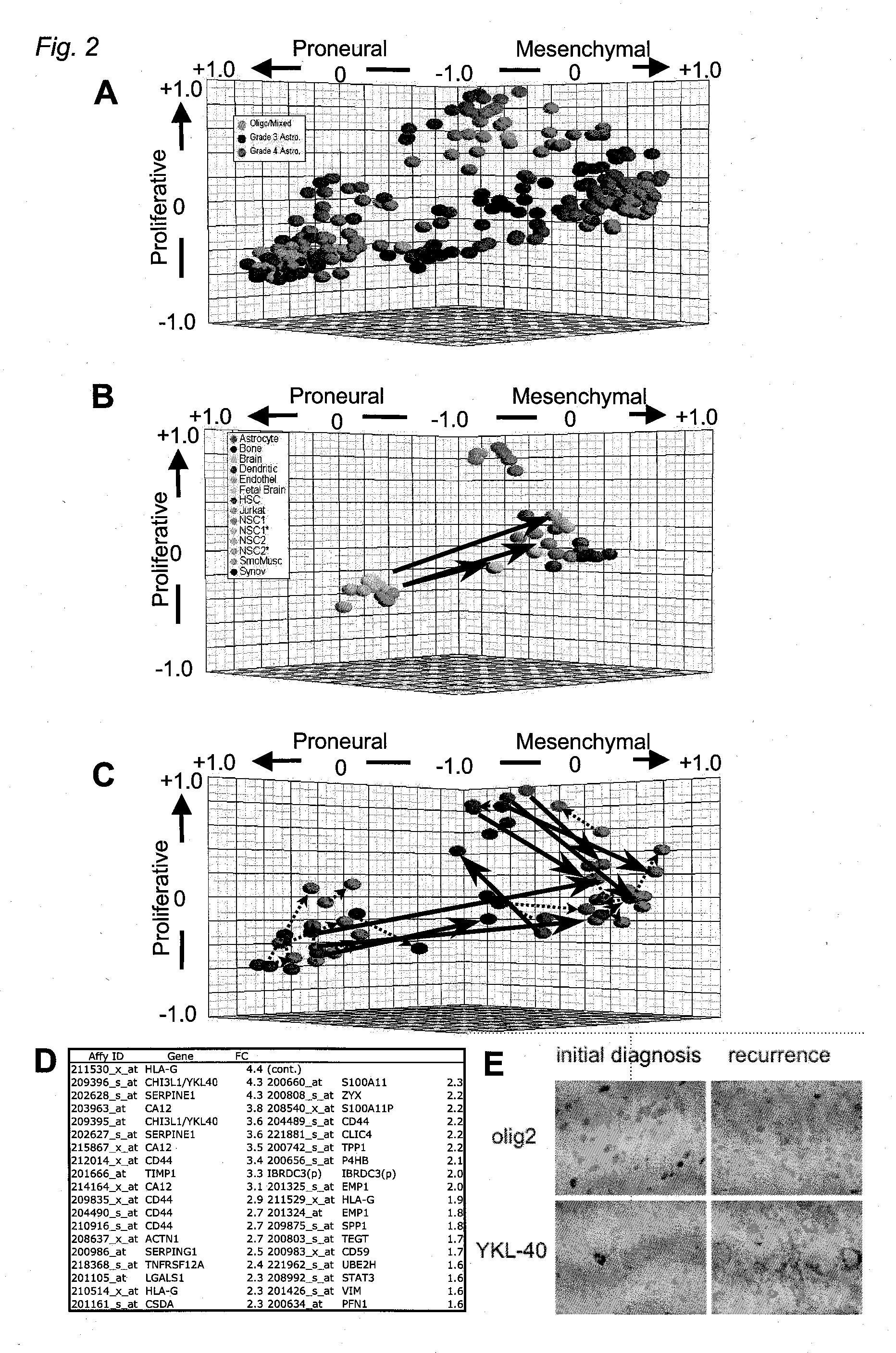
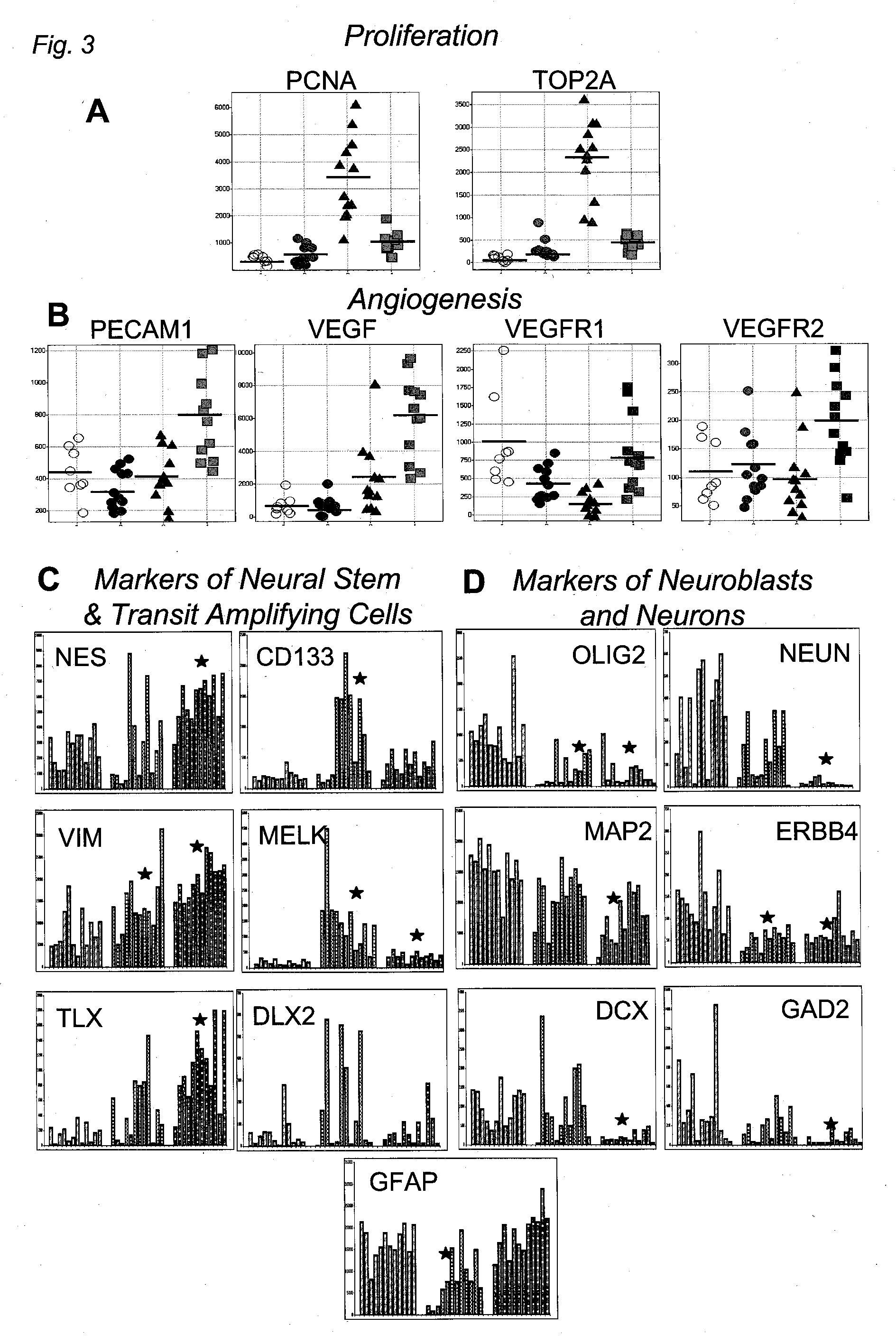
The invention provides generally a method of monitoring, diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma. Specifically, the invention provides for three (3) prognostic subclasses of glioma, which are differentially associated with activation of the akt and notch signaling pathways. Tumor displaying neural or proneural PN lineage markers (including notch pathway elements) show longer median patient survival, while the two remaining tumor markers Prolif and Mes are associated with shortened survival. Tumors classified in this manner may also be treated with the appropriate PN- Prolif- or Mes-therapeutic corresponding to the subclassification in combination with anti-mitotic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, Akt antagonists, and neural differentiation agents. Alternatively, the invention also provides for method of prognosing and diagnosing glioma with a two-gene model based on the expression levels of PTEN and DLL3.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
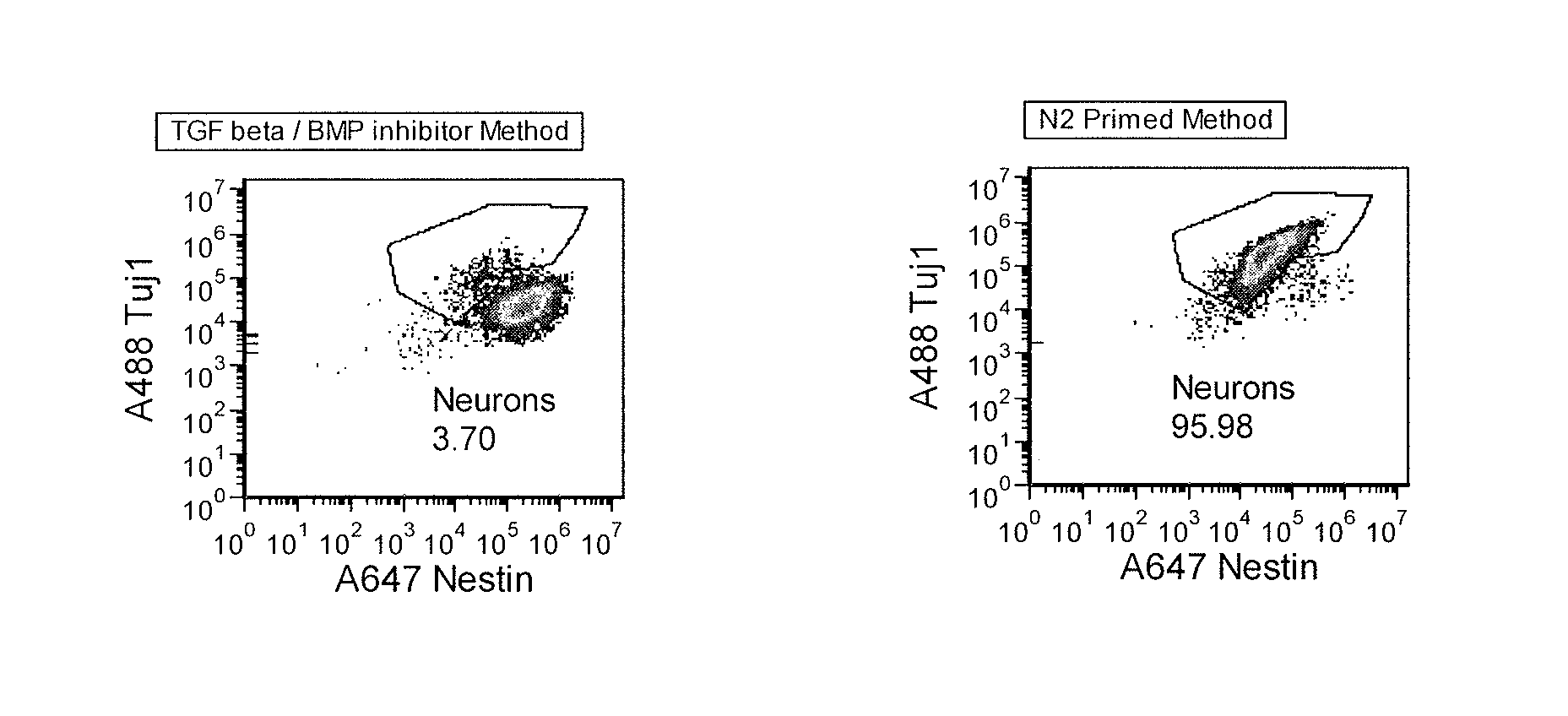
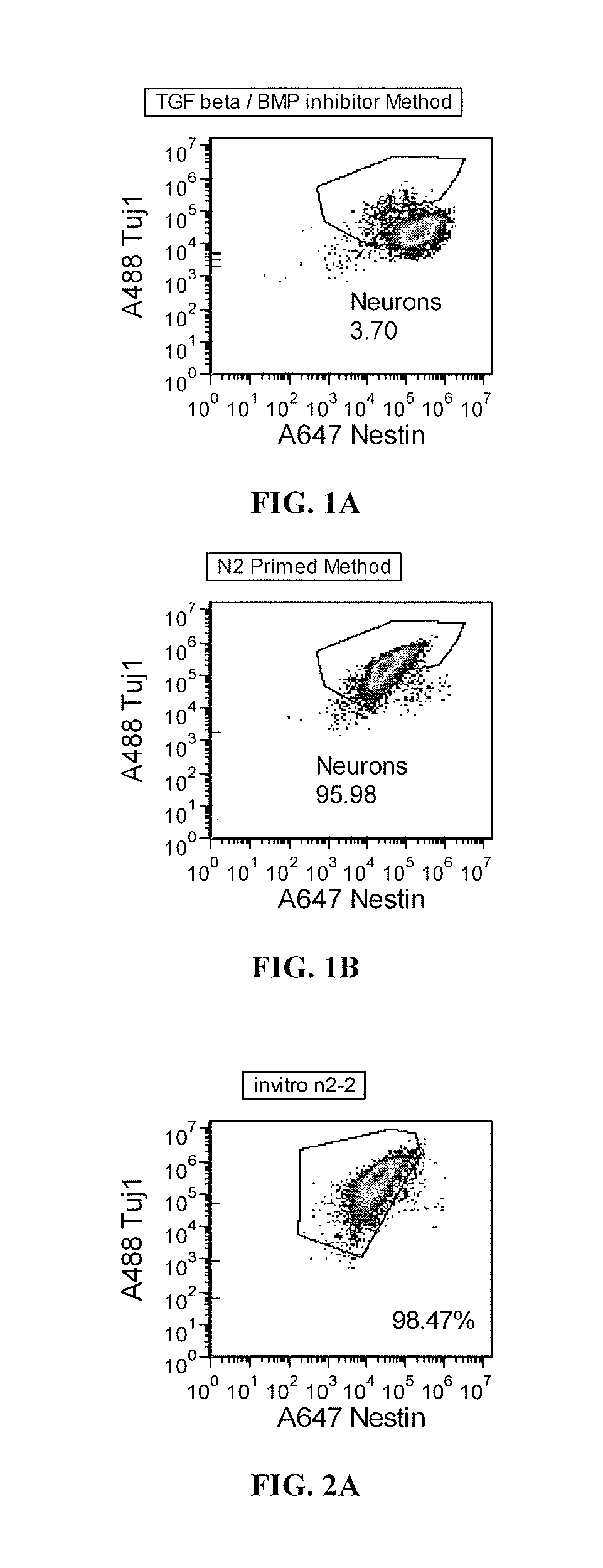
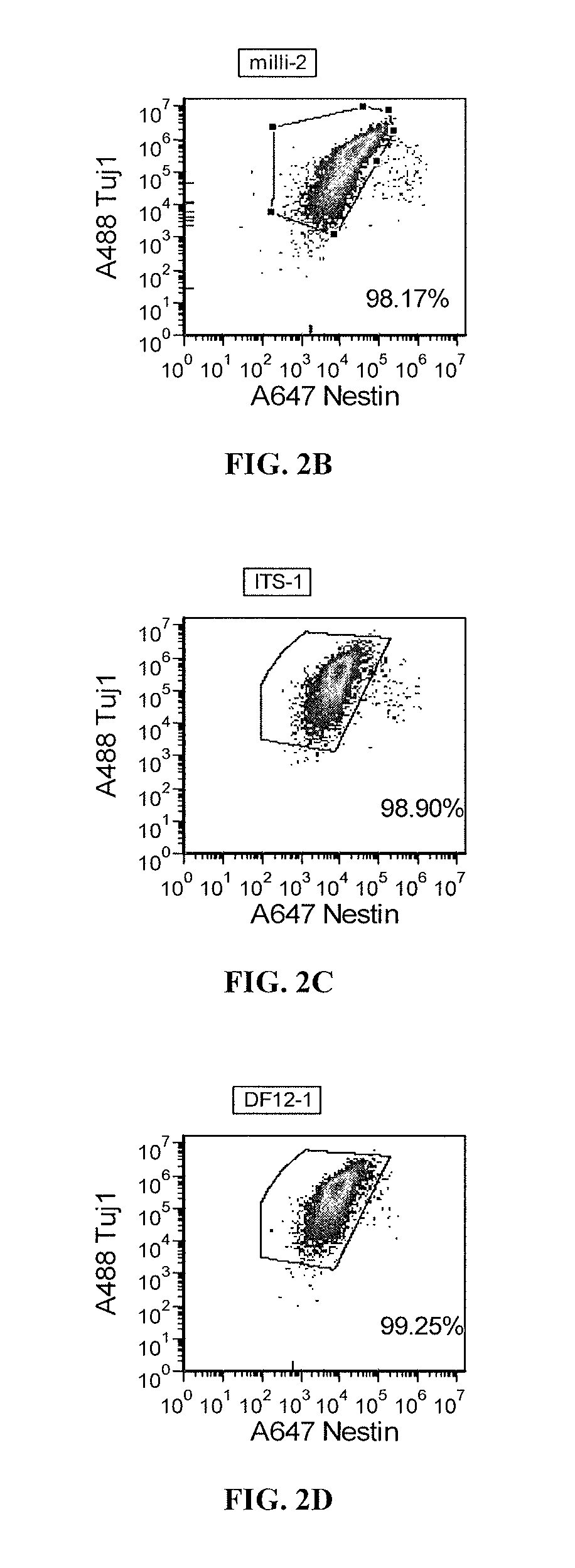
Method and Medium for Neural Differentiation of Pluripotent Cells
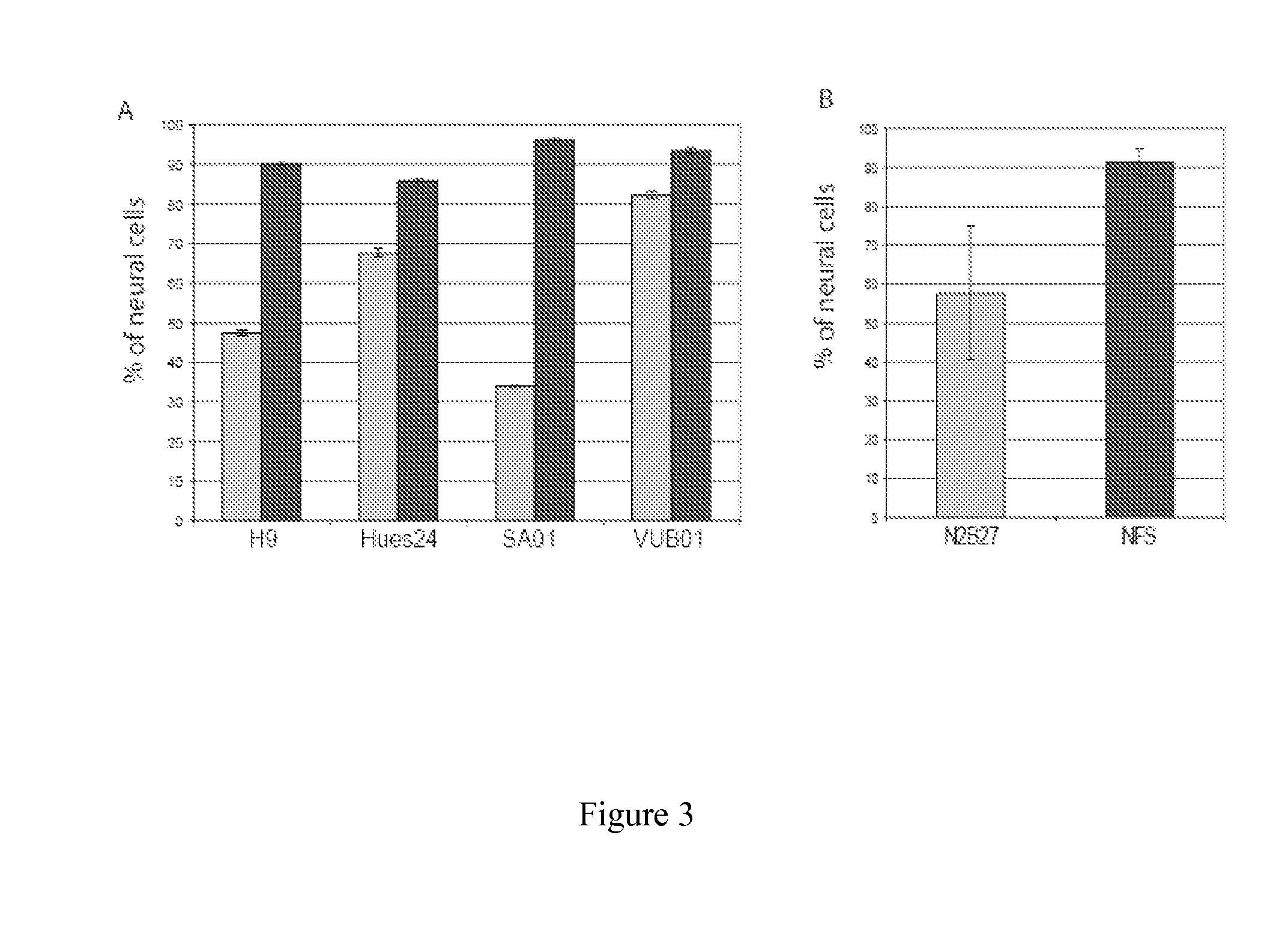
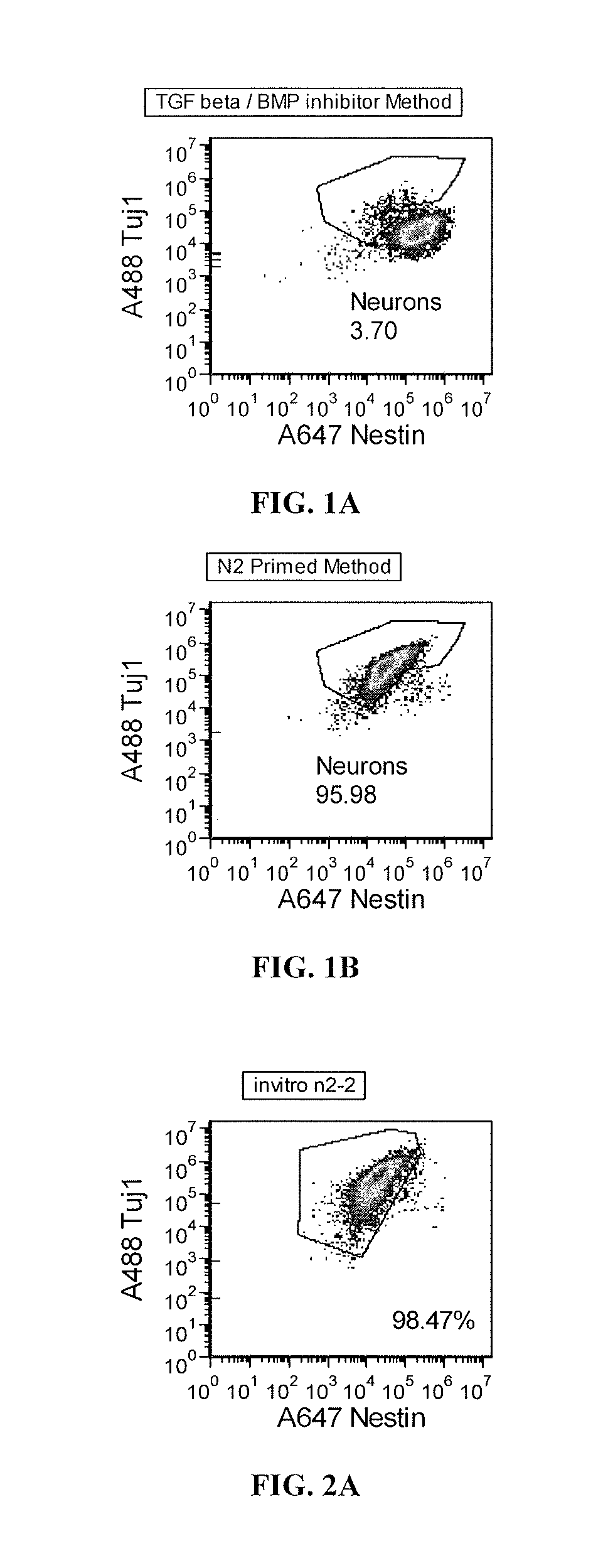
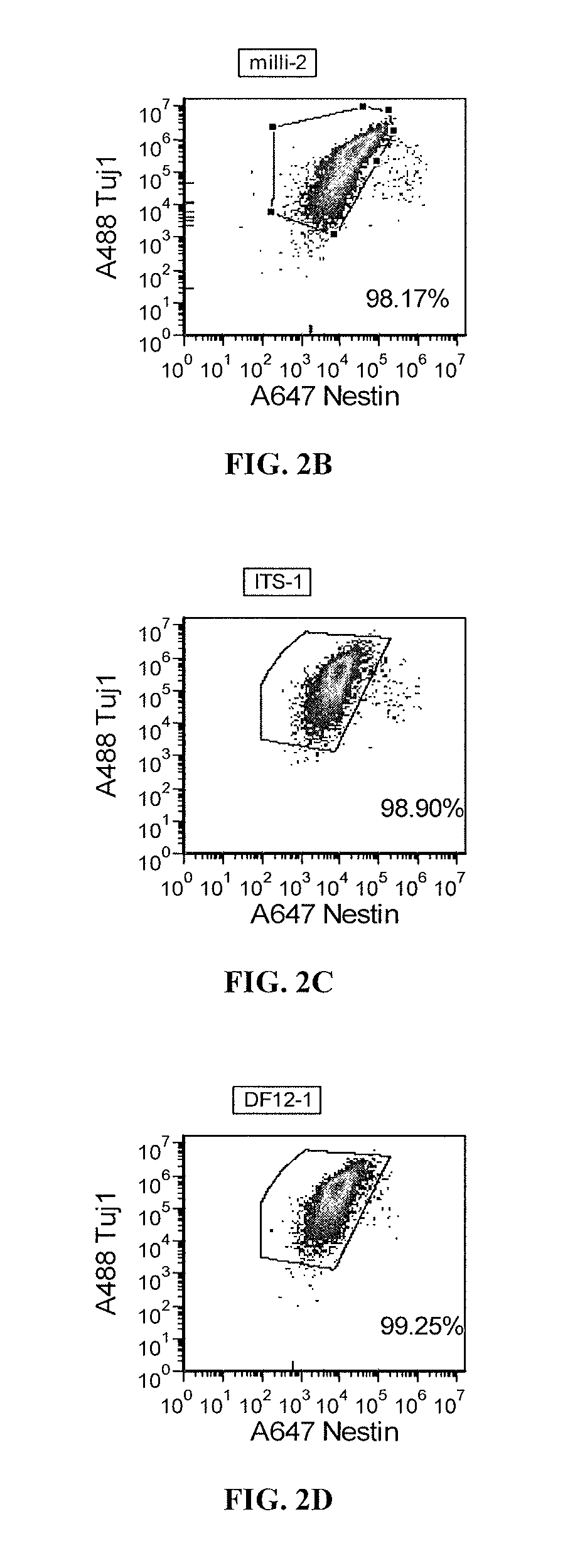
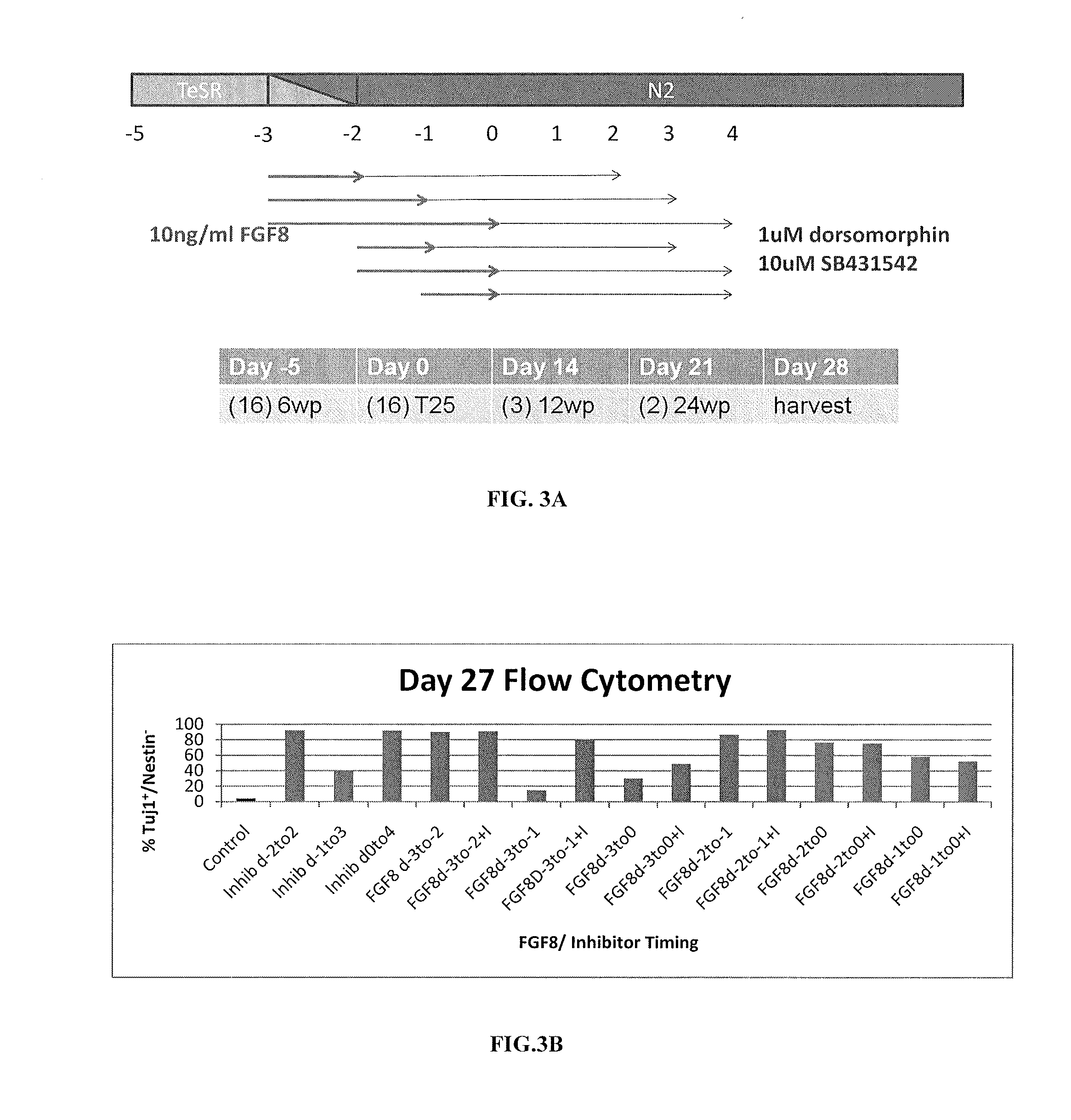
The invention relates to a culture medium comprising an inhibitor of the BMP signaling pathway; and an inhibitor of the TGF / activin / nodal signaling pathway and to a method for obtaining a population of neural precursors using said culture medium.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Implanting neural progenitor cells derived for human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7011828B2Eliminate inhibitory influenceSolve the shortageBiocideNervous disorderNeural cellIn vivo
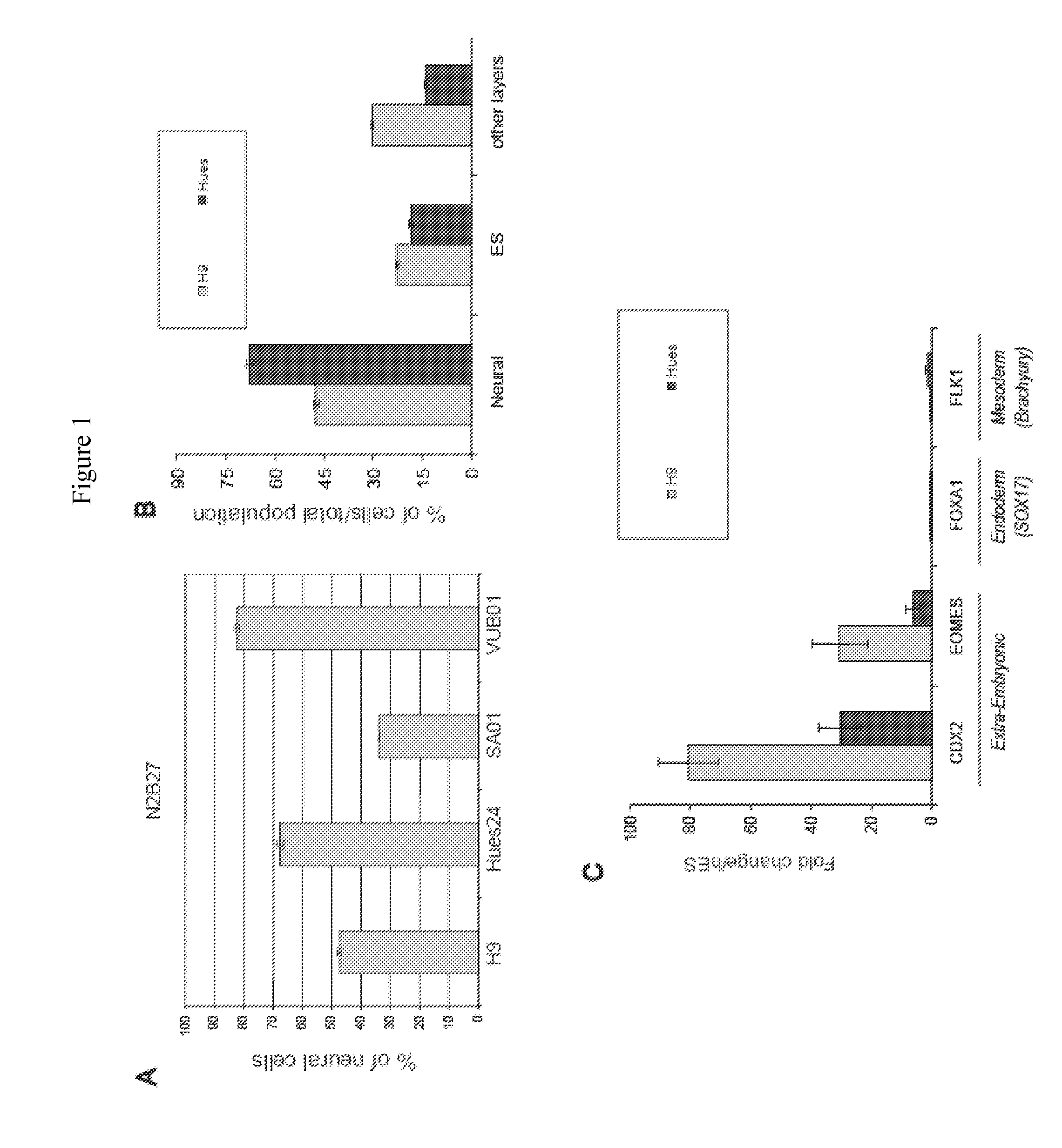
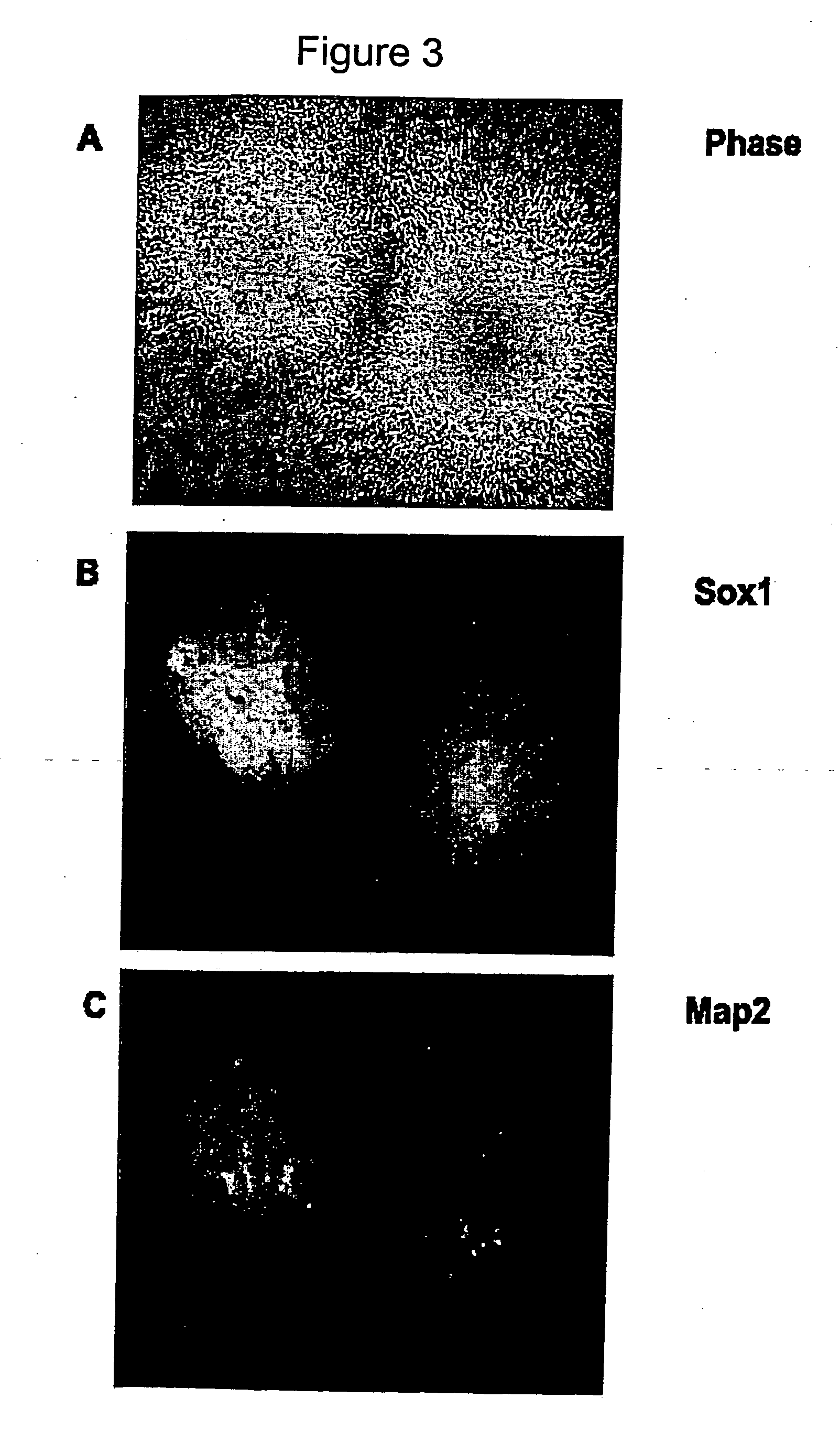
The present invention relates to undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells, methods of cultivation and propagation and production of differentiated cells. In particular it relates to the production of human ES cells capable of yielding somatic differentiated cells in vitro, as well as committed progenitor cells such as neural progenitor cells capable of giving rise to mature somatic cells including neural cells and / or glial cells and uses thereof.This invention provides methods that generate in vitro and in vivo models of controlled differentiation of ES cells towards the neural lineage. The model, and cells that are generated along the pathway of neural differentiation may be used for: the study of the cellular and molecular biology of human neural development, discovery of genes, growth factors, and differentiation factors that play a role in neural differentiation and regeneration, drug discovery and the development of screening assays for teratogenic, toxic and neuroprotective effects.
Owner:ES CELL INT +1
Priming of pluripotent stem cells for neural differentiation
ActiveUS20120276063A1Improve efficiencyMass productionBiocideSenses disorderPluripotential stem cellNeurulation
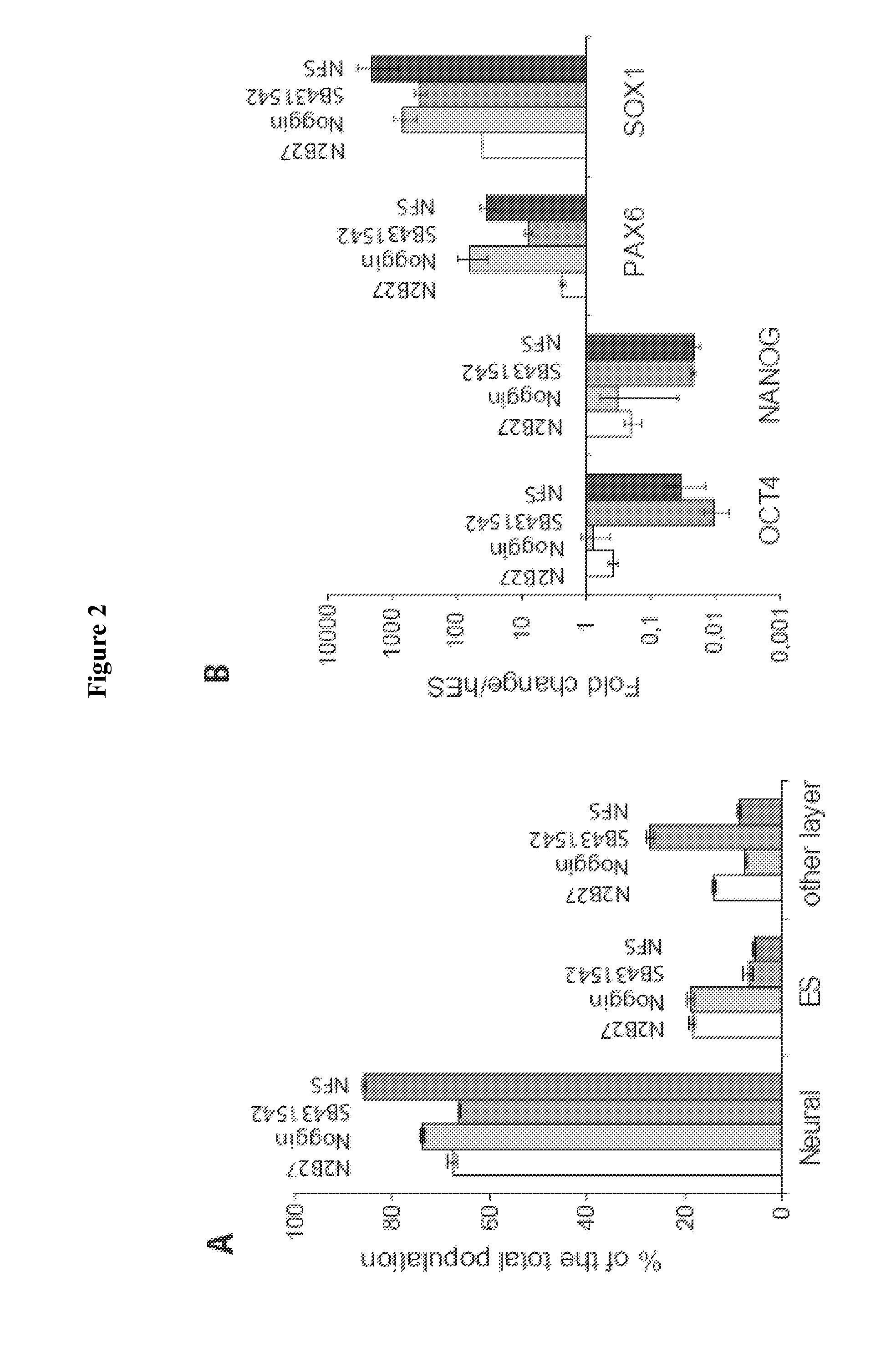
Methods and composition for differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including priming stem cells for neural differentiation in a culture medium essentially free of growth factors such as FGF and TGFβ. As an advantage, the neural cells may be provided with improved consistency and purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Neural progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20060078543A1Eliminate inhibitory influenceSolve the shortageBiocideNervous disorderNeural cellIn vivo
The present invention relates to undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells, methods of cultivation and propagation and production of differentiated cells. In particular it relates to the production of human ES cells capable of yielding somatic differentiated cells in vitro, as well as committed progenitor cells such as neural progenitor cells capable of giving rise to mature somatic cells including neural cells and / or glial cells and uses thereof. This invention provides methods that generate in vitro and in vivo models of controlled differentiation of ES cells towards the neural lineage. The model, and cells that are generated along the pathway of neural differentiation may be used for: the study of the cellular and molecular biology of human neural development, discovery of genes, growth factors, and differentiation factors that play a role in neural differentiation and regeneration, drug discovery and the development of screening assays for teratogenic, toxic and neuroprotective effects.
Owner:REUBINOFF BENJAMIN +2
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
ActiveUS20050131212A1High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
Systems and methods for screening for modulators of neural differentiation
The present invention provides in vitro systems for use in identifying modulators of neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these systems. The present invention further provides methods for identifying a modulator of neural differentiation, a modulator of a Wnt signalling pathway, a modulator of Wnt-dependent neural differentiation, a modulator of a BMP signalling pathway, a modulator of BMP-dependent neural differentiation, a modulator of a Hh signalling pathway, and a modulator of Hh-dependent neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method used for high efficiency collecting of neural stem cells in vitro
InactiveCN107828826AEasy accessEfficiently obtainedHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAFluorescenceIn vivo
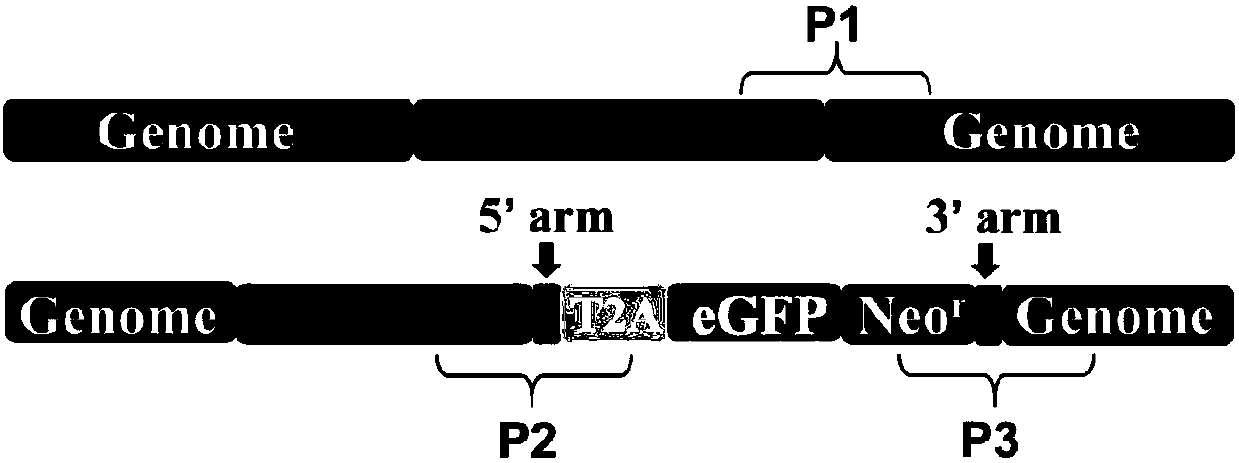
The invention belongs to the technical field of cytobiology, and more specifically relates to a method used for high efficiency collecting of neural stem cells in vitro. The method comprises followingsteps: A, an embryonic stem cell line containing Pax6-GFP reporting system is constructed through CRISPR / Cas9 system; B, the Pax6-GFP ES reporting system is used for guiding neural differentiation invitro and in vivo; C, the Pax6-GFP reporting system is used for enriching and purifying neural stem cells. According to the method, the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing tool is adopted to construct the cellline containing the Pax6-GFP reporting system, and realize rapid high efficiency collecting of neural stem cells in vitro through the cell line.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Systems and methods for screening for modulators of neural differentiation
InactiveUS20070224650A1Biological material analysisNervous system cellsRetinoidSystem identification
The present invention provides in vitro systems for use in identifying modulators of neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these systems. The present invention further provides methods for identifying a modulator of neural differentiation, a modulator of an FGF signalling pathway, a modulator of FGF-dependent neural differentiation, a modulator of a retinoid signalling pathway, and a modulator of retinoid-dependent neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems and methods for screening for modulators of neural differentiation
The present invention provides in vitro systems for use in identifying modulators of neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these systems. The present invention further provides methods for identifying a modulator of neural differentiation, a modulator of a Wnt signalling pathway, a modulator of Wnt-dependent neural differentiation, a modulator of a BMP signalling pathway, a modulator of BMP-dependent neural differentiation, a modulator of a Hh signalling pathway, and a modulator of Hh-dependent neural differentiation. Also provided are modulators identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma
The invention provides generally a method of monitoring, diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma. Specifically, the invention provides for three (3) prognostic subclasses of glioma, which are differentially associated with activation of the akt and notch signaling pathways. Tumor displaying neural or proneural PN lineage markers (including notch pathway elements) show longer median patient survival, while the two remaining tumor markers Prolif and Mes are associated with shortened survival. Tumors classified in this manner may also be treated with the appropriate PN- Prolif- or Mes- therapeutic corresponding to the subclassification in combination with anti-mitotic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, Akt antagonists, and neural differentiation agents. Alternatively, the invention also provides for method of prognosing and diagnosing glioma with a two- gene model based on the expression levels of PTEN and DLL3.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
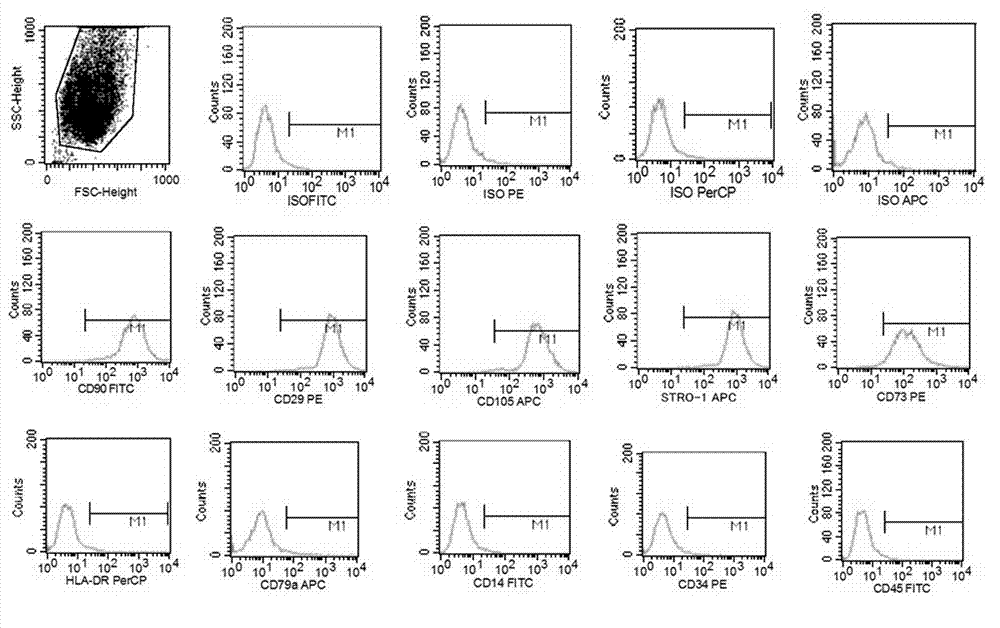
Method for inducing dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into nerve cells
The invention provides a method for inducing dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated into nerve cells. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells by virtue of an enzyme digestion method, inoculating the dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells to a culture dish coated with polylysine and laminin, adding an optimized culture medium, and performing culture amplification under a low-oxygen condition; then performing double-layer coating on the collected dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells by using an acellular amniotic membrane substrate, and performing induced differentiation by using a nerve cell induction solution; and finally, maintaining long-term culture of the nerve cells by using a nerve cell maintenance solution. According to the method provided by the invention, the optimized culture medium and the low-oxygen condition are used for culture, so that the number of the dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells is increased; the double-layer acellular amniotic membrane substrate is used for simulating a neurolemma structure to achieve an effect of guiding the growth of the nerve cells, and meanwhile, the nerve cell induction solution is used for inducing the dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells to be differentiated towards nerves, so that the differentiation rate is improved; and the nerve cell maintenance solution is used for maintaining the activity of the nerve cells for a long term, so that a clinician can flexibly control the treatment time conveniently.
Owner:中国医科大学 +1
Priming of pluripotent stem cells for neural differentiation
ActiveUS9487752B2Improve efficiencyMass productionBiocideSenses disorderNeurulationPluripotential stem cell
Methods and composition for differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including priming stem cells for neural differentiation in a culture medium essentially free of growth factors such as FGF and TGFβ. As an advantage, the neural cells may be provided with improved consistency and purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
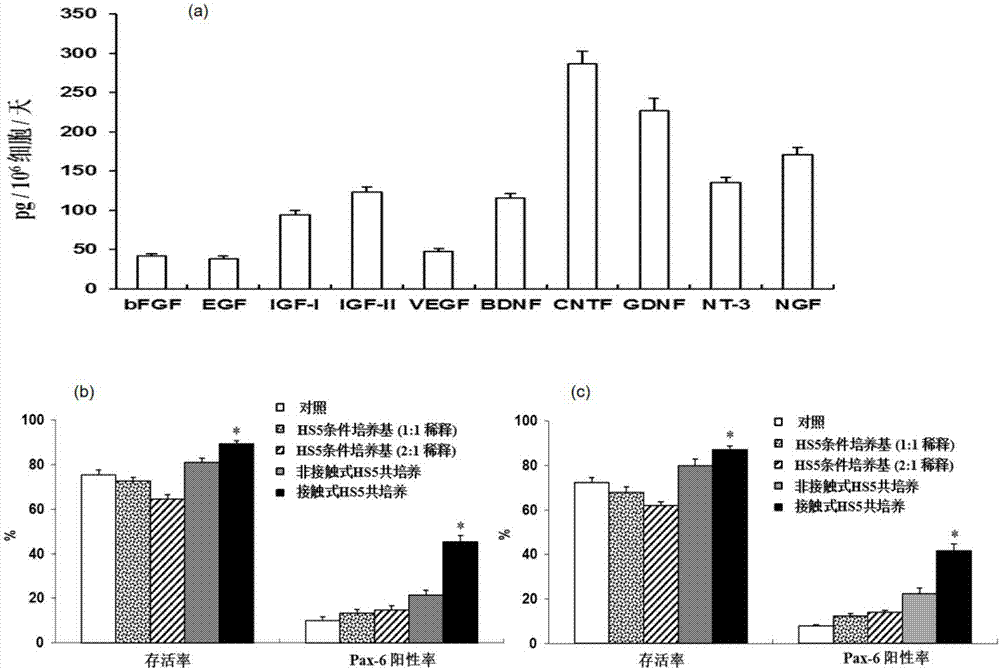
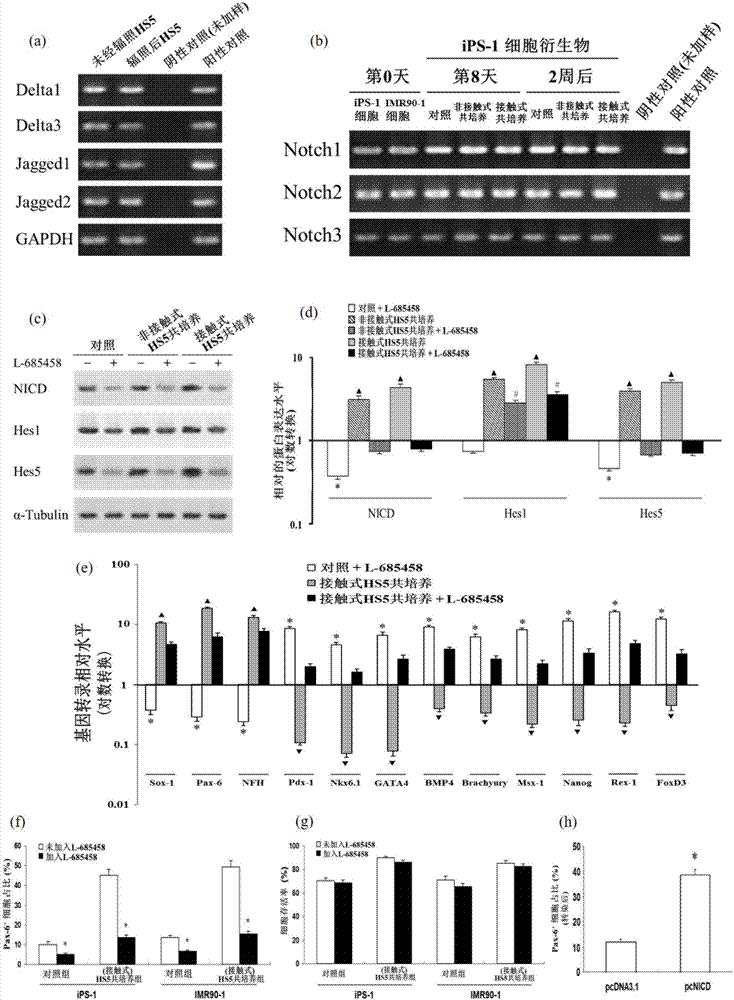
Neural cell system obtained by enabling human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) to differentiate by means of directional induction, and induction method and application of neural cell system
ActiveCN107326013ASuppress generationEffective treatmentGenetically modified cellsMutant preparationBone Marrow Stromal CellInjury brain
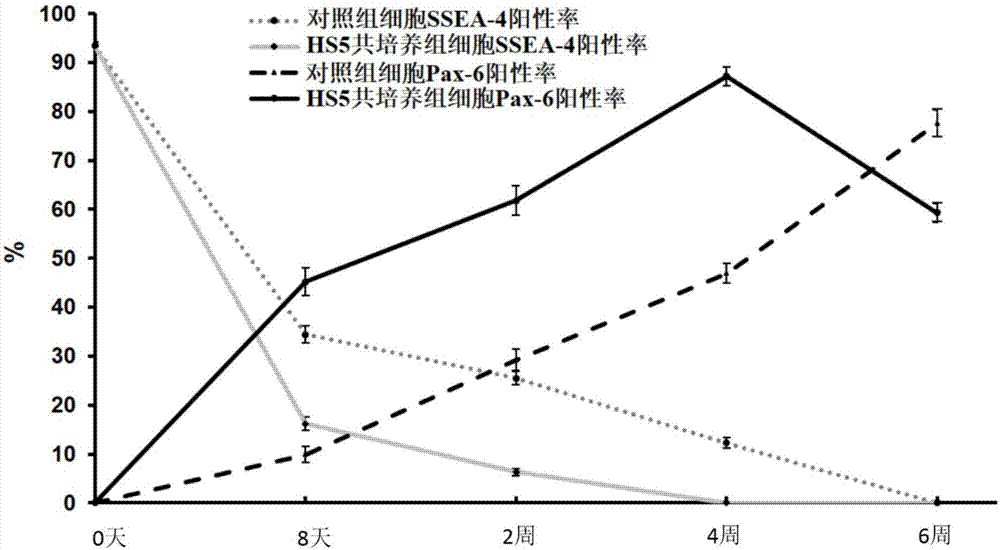
The invention discloses a neural cell system obtained by enabling human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) to differentiate by means of directional induction, and an induction method and application of the neural cell system. The method comprises the step of culturing the hiPSC by stages so as to induce the neuronal differentiation of the hiPSC, wherein the stages comprises a. carrying out co-culture on the hiPSC and bone marrow stromal cells (HS5) in an induced medium; b. continuously culturing the hiPSC by using an HS5 conditioned medium; c. using a basic medium for culturing neuronal cells to continuously culture the hiPSC. The method provided by the invention can induce the hiPSC to directionally differentiate into nervous system cells and inhibit the generation of non-nervous system cells at the same time, thus obtaining a mature and broad-spectrum neural cell group. The neural cell group is not only proved to be mature neurons having electrical impulse discharge by means of in vitro validation, but is also confirmed to have a function of effectively treating nervous system diseases (such as brain stroke and brain injury) in experiments of mice in vivo.
Owner:杨涛
Method for inducing neural differentiation
InactiveUS20050287665A1Safe and effective in changeFix bugsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factorBone Marrow Stem Cell
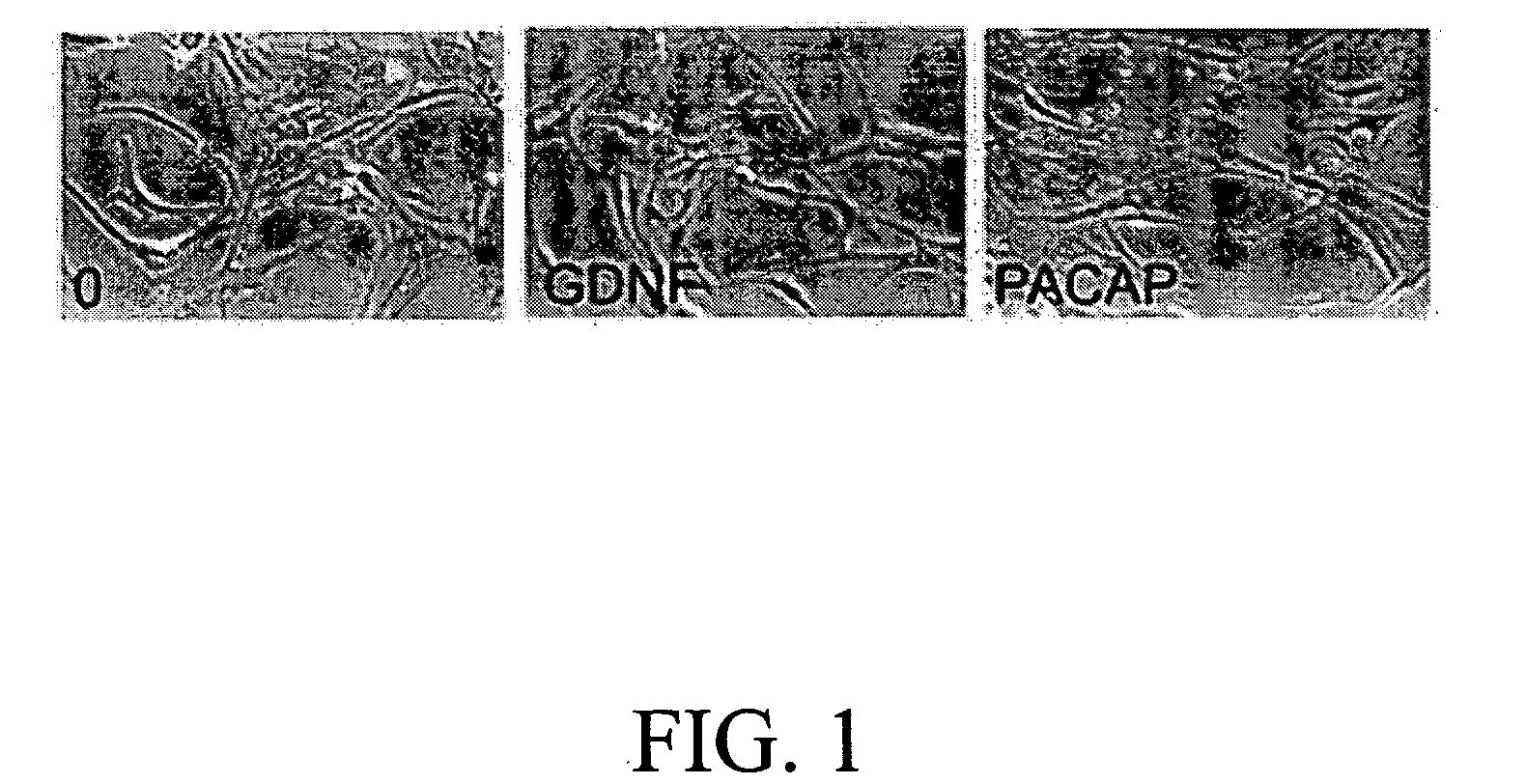
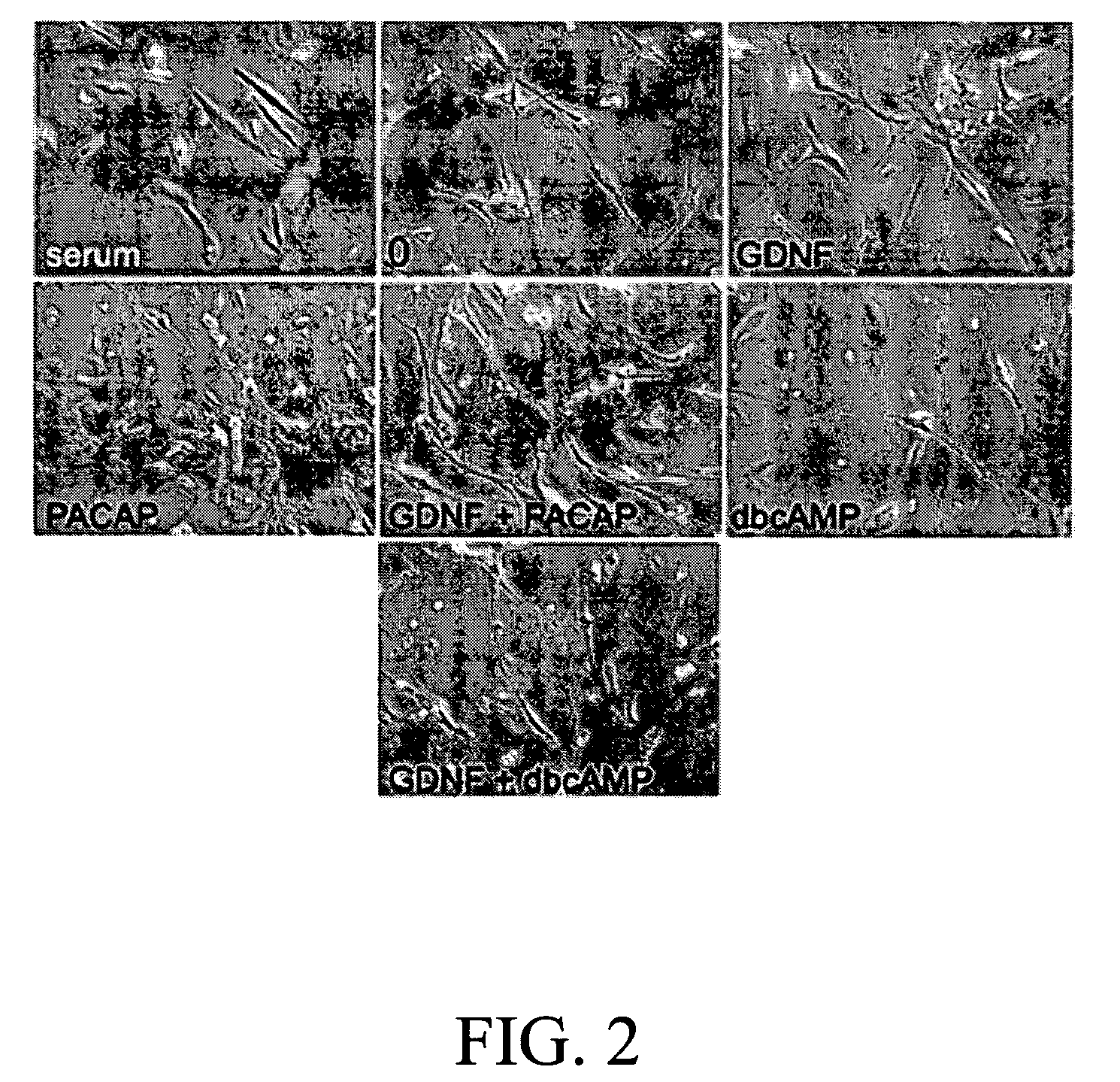
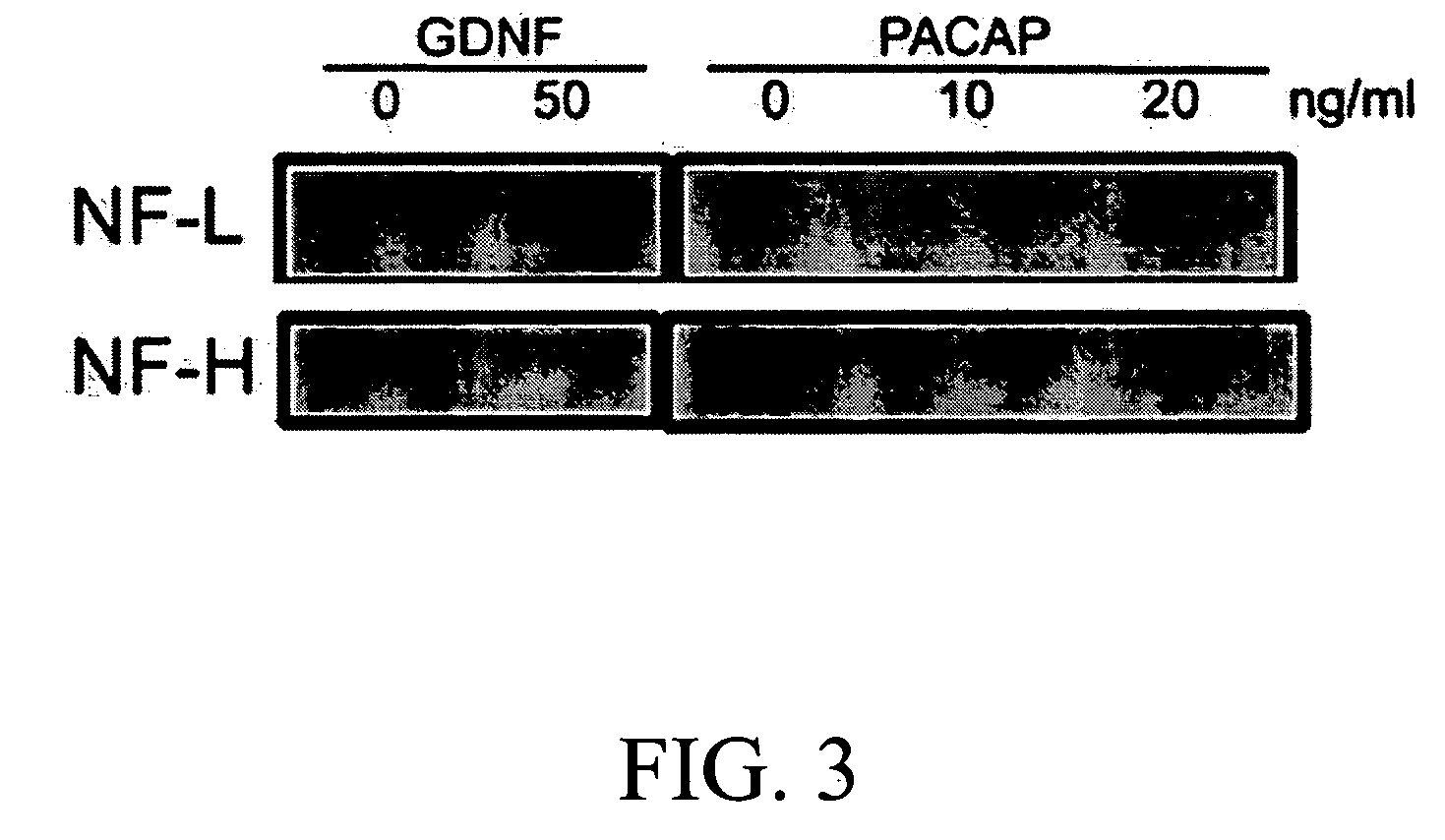
The present invention provides a method for inducing neural differentiation comprising treating a bone marrow stem cell with a neurotrophic factor and / or dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP), wherein the neurotrophic factor comprises glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) or pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP).
Owner:HENRICH CHENG
System for inducing nerve stem cell differentiation and inducing method thereof
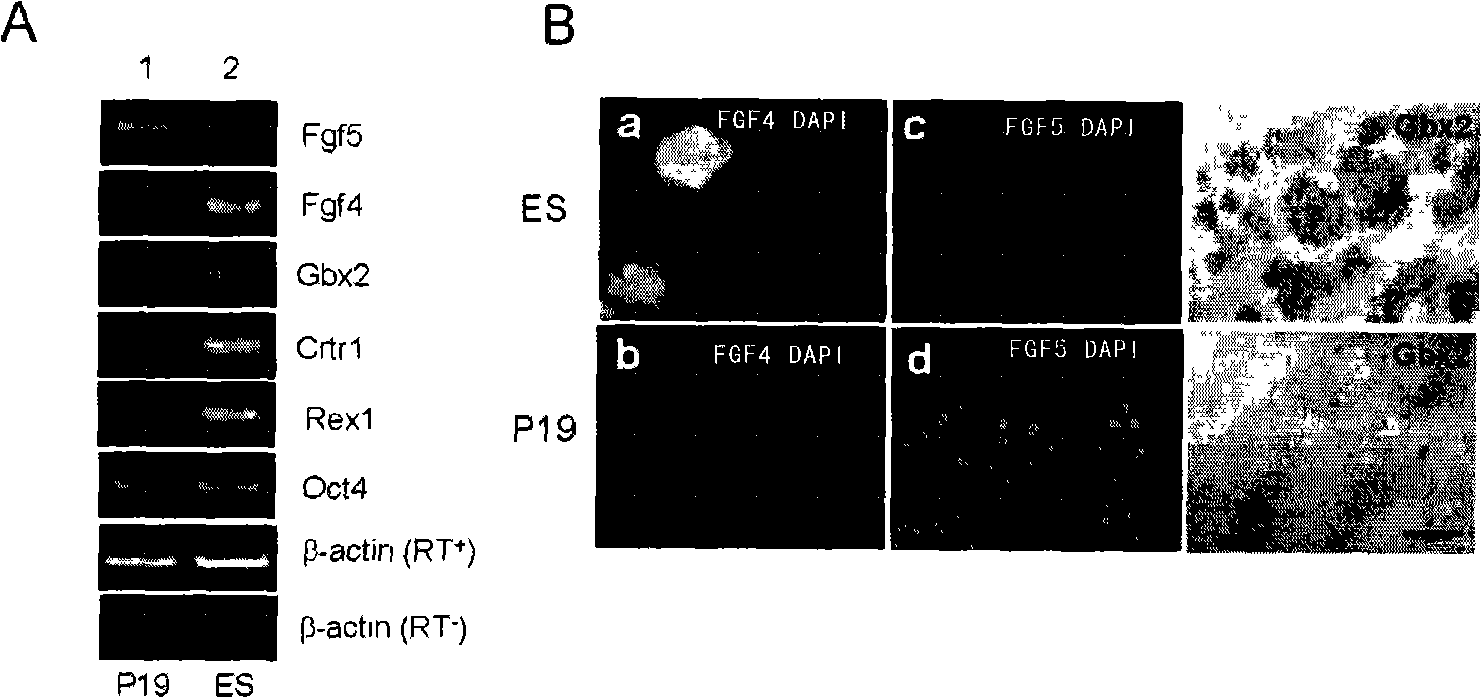
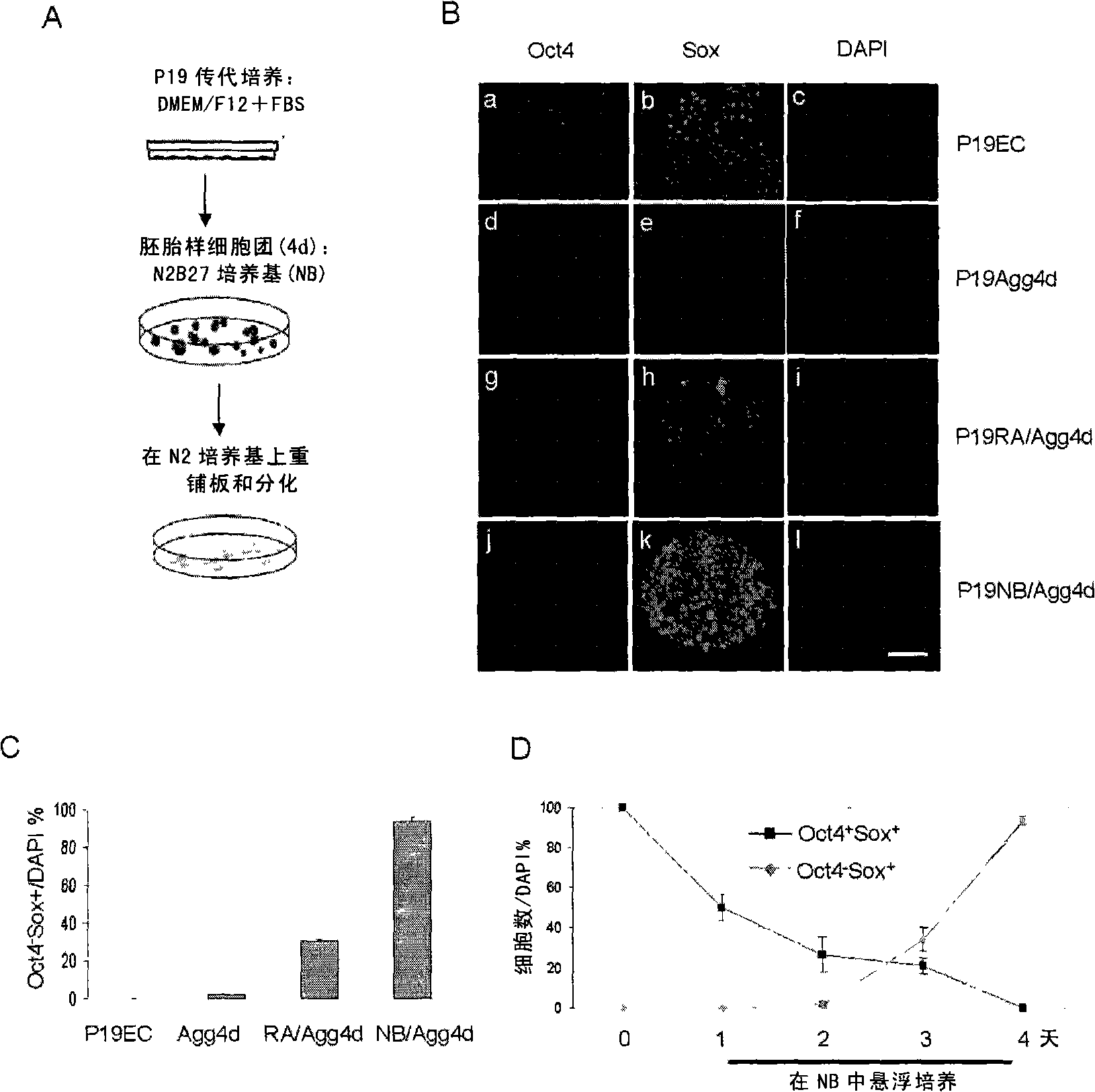
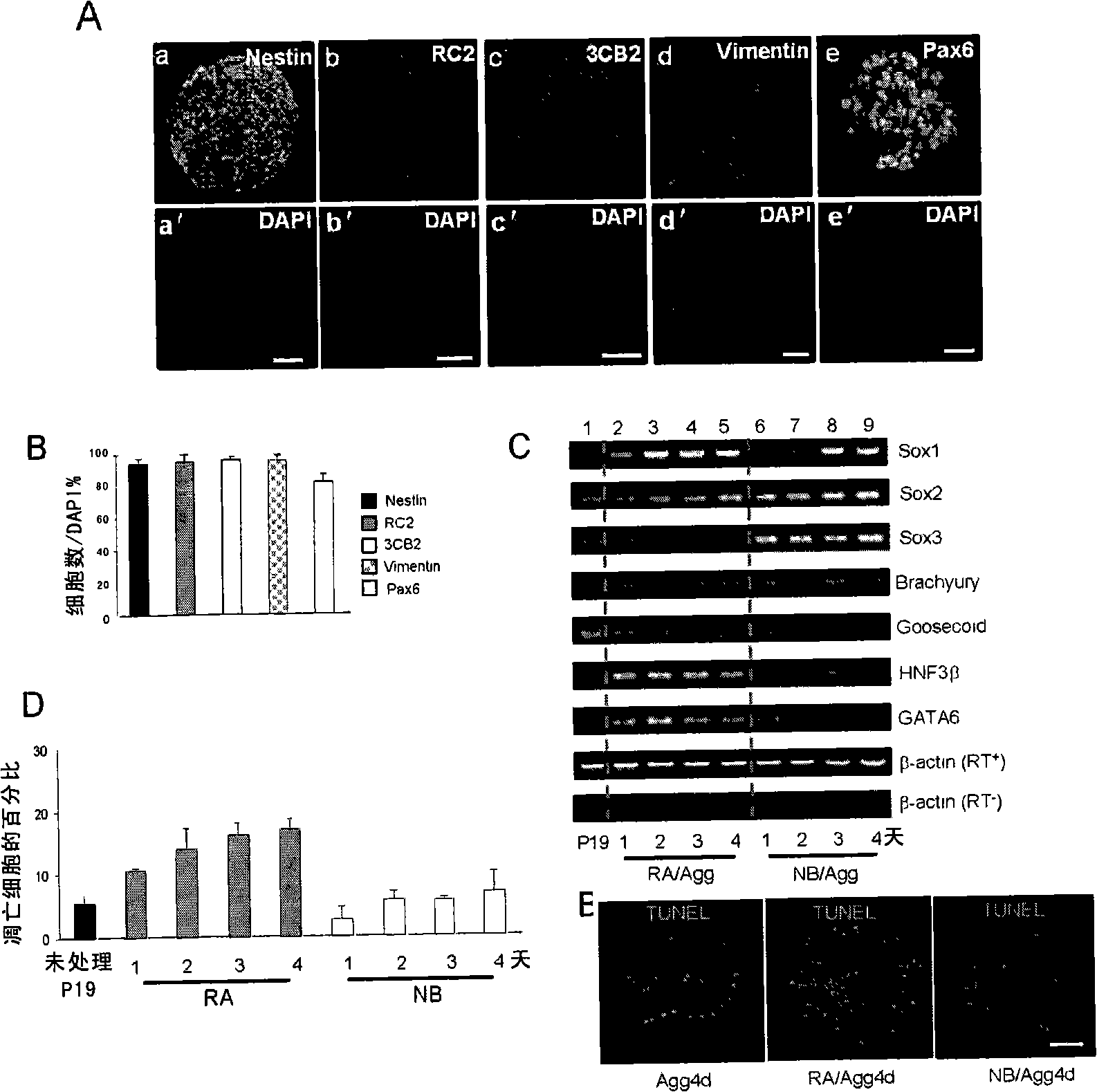
The invention discloses a method for preparing neural stem cells, which comprises a step of inductively culturing P19 cells in N2B27 culture medium to obtain a cell group containing neural stem cells above 94%. The method can culture the P19 cells in an environment without blood serum and retinoic acid, thus suppressing the interference of the blood serum with complex components and preventing the obtained neural stem cells from being transformed posteriorly by retinoic acid. Moreover, the method can directly transform pluripotent stem cells to neutral stem cells without resulting in selective cell apoptosis. The neutral stem cells obtained by the invention have anterior neutral plate characteristics and totipotency, and can well simulate the neurogenesis process in body. Accordingly, the neural stem cells can be used as the research model for analyzing neural induction and neural differentiation process from epiblast to neuroderm, thus providing an ideal path for researching development of embryo after nidation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
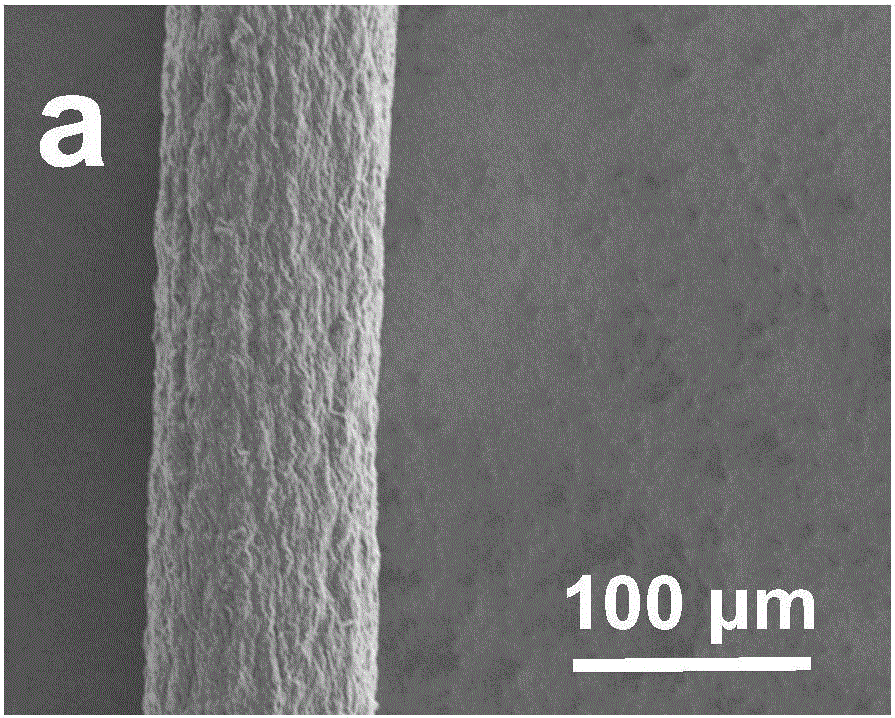
Graphene micron fibers and preparation method thereof, nerve tissue scaffold, and repair system
ActiveCN106592007AImprove conductivityGood compatibilityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberDoped graphene
The present invention provides modified and reduced graphene oxide micron fibers and a preparation method thereof, a nerve tissue scaffold and a self-driving nerve repair system. The micron fibers comprise reduced graphene oxide and an electric conduction macromolecule polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), are continuous, and have a regular surface porous nanometer structure. The modified and reduced graphene oxide micron fiber preparation method comprises: preparing a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped graphene oxide mixing solution, and preparing the modified and reduced graphene oxide micron fibers by using the solution. The nerve tissue scaffold comprises the modified and reduced graphene oxide micron fibers. The self-driving nerve repair system comprises the nerve tissue scaffold and a self-driving separate type friction nanometer power generator. According to the present invention, the micron fibers have characteristics of good shape, good surface appearance and good electrical conductivity, provide good adhesion and proliferation ability to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and promote the neural differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Method of inducing the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve by serum-free suspension culture
ActiveUS8492147B2Effectively lead to differentiationEfficient inductionNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsSerum free mediaNervous system
The present invention provides a clinically applicable method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells into forebrain neurons. More specifically, the present invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, comprising culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of the embryonic stem cells into nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neurons and sensory organ cells; a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells obtained by culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium; and cells derived from a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells, particularly nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neuron, sensory organ cells such as retinal precursor cells, and the like.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for neuroepithelial cells differentiation from pluripotent stem cells and medium using same
ActiveCN103160466AHigh purityShorten the differentiation timeNervous system cellsCell culture active agentsNeurulationInduced pluripotent stem cell
Owner:鸿雁生技有限公司
Method for inducing neural differentiation of stem cells
InactiveCN102533647AHigh differentiation efficiencyImprove survival rateNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsNeuronNerve cells
The invention relates to a method for inducing neural differentiation of stem cells. All-transretinoicacid (ATRA) serves as an inducer and a modified neuronal induction medium (MNM) serves as a culture medium used for treating the stem cells, so the neural differentiation of the stem cells can be promoted effectively, differentiation ratio and survival ratio are increased, neuron-like cells with the neuronal function are prepared, a good in-vitro model is provided for research on development of nerve cells, and powerful basis is provided for the stem cells applied to clinical treatment on nerve system diseases.
Owner:YEACELL BIOTECH INC
Novel glycosaminoglycan analogue and synthetic method thereof, and application of novel glycosaminoglycan analogue in invitro embryonic stem cell proliferation and directional neural differentiation
ActiveCN104926976AImprove biological activitySimple processNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsN dimethylformamideSolvent
The invention provides a novel glycosaminoglycan analogue and a synthetic method thereof, and an application method of the novel glycosaminoglycan analogue in invitro embryonic stem cell proliferation and directional neural differentiation. The synthetic method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a sodium p-styrenesulfonate monomer or / and a 2-methacrylamide glucopyranose monomer into a mixed solvent according to a certain proportion, wherein the mixed solvent is a mixture of water and N,N-dimethylformamide; and carrying out polymerization by applying a method of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer(RAFT) so as to respectively obtain a plurality of polymers of the sodium p-styrenesulfonate monomer or / and the 2-methacrylamide glucopyranose monomer in different proportions. According to the invention, a macromolecule substance capable of promoting an embryonic stem cell to proliferation in invitro and inducing the embryonic stem cell to realizing highly-efficient directional neural differentiation is obtained with a RAFT synthetic technology by utilizing a sulfonate-group-contained monomer and a sugar-contained monomer and controlling relative proportion of the sulfonate-group-contained monomer and the sugar-contained monomer to adjust the structure of a polymer.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for inducing differentiation of adult stem cells and nerve cells using electromagnetic field
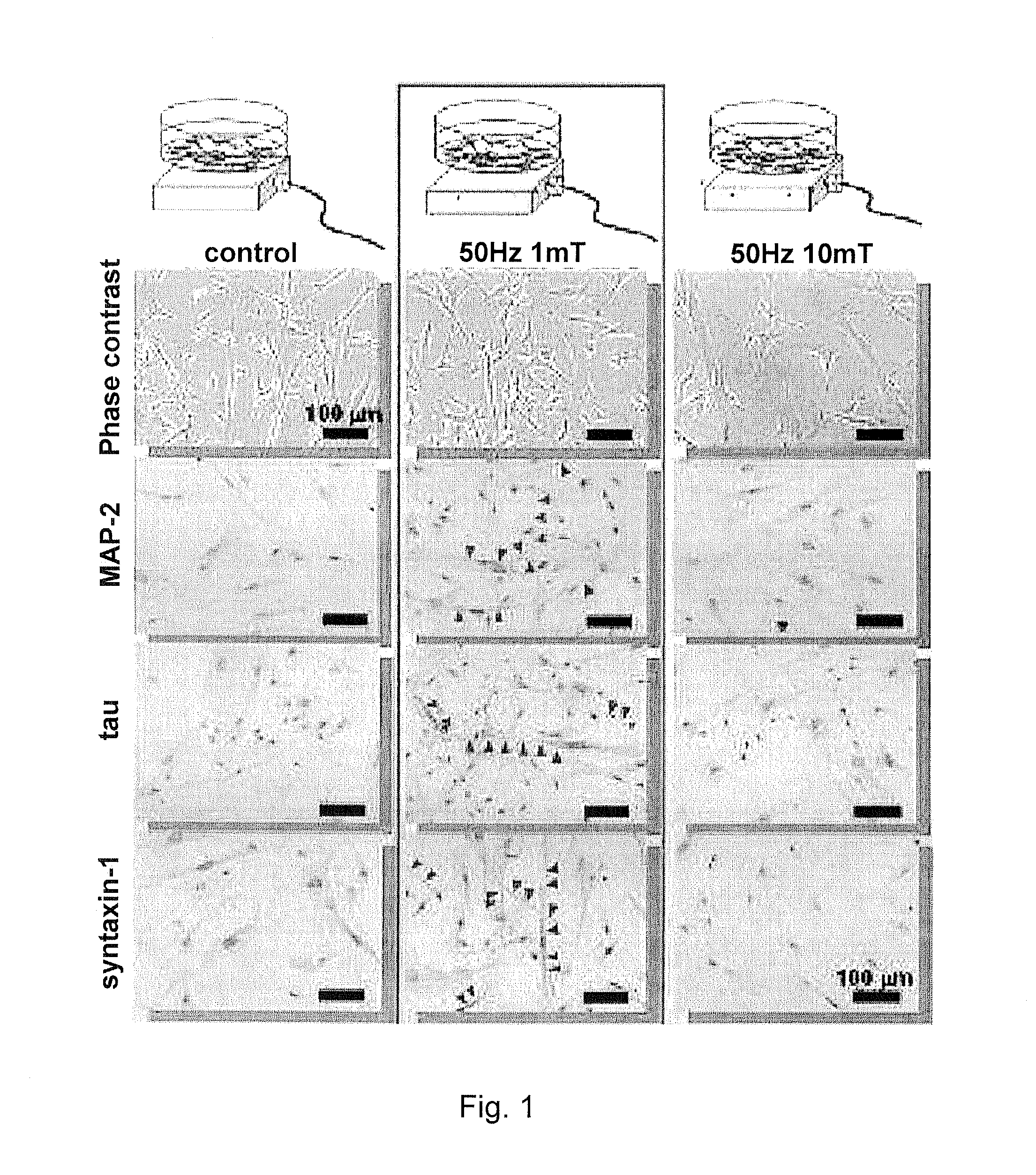
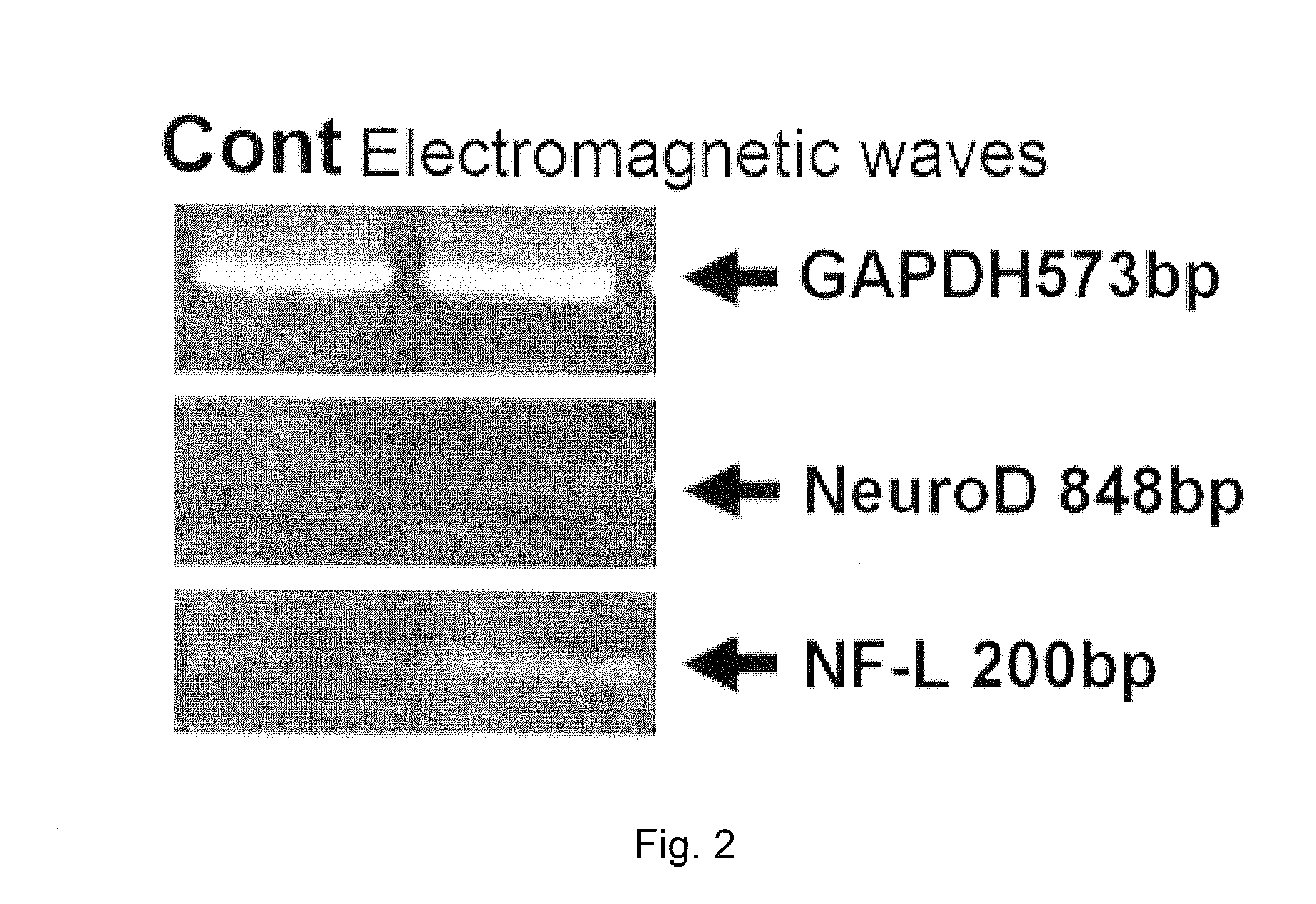
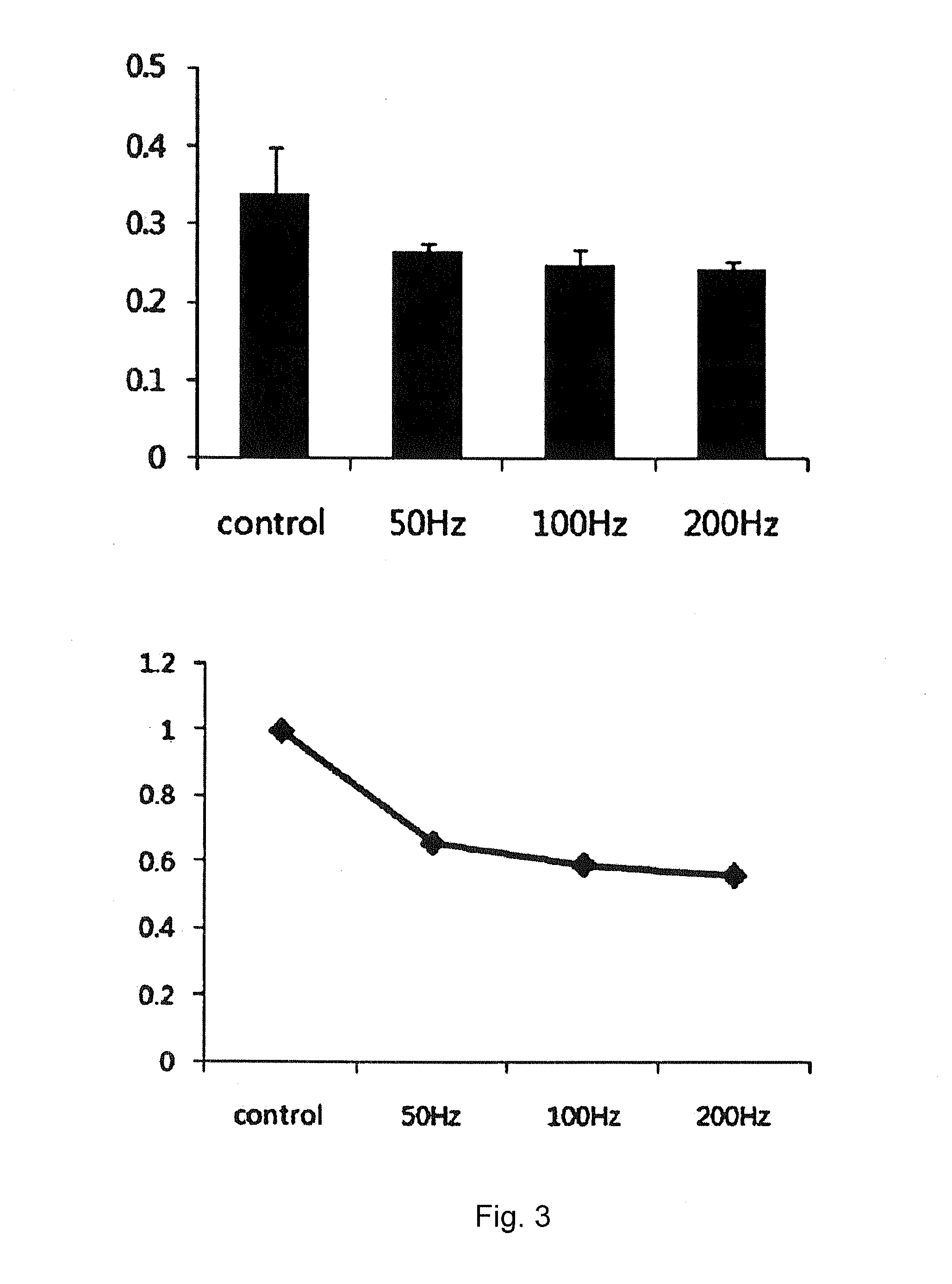
The present invention relates to a method for differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells or dental pulp stem cells. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for differentiating stem cells to neural cells by applying mesenchymal stem cells or dental pulp stem cells with a low-frequency electromagnetic field. The differentiation method according to the present invention can induce differentiation even with low-cost mediums rather than induced neural differentiation mediums which are expensive due to addition of growth factors, and the neural cells differentiated according to the present invention may be useful for treatment of neurological brain diseases.
Owner:DONGGUK UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use
ActiveUS20100130410A1Prevent degenerationAvoid deathBiocideNervous disorderNeuronal migrationCell type
Embodiments of this invention include novel peptides that can promote survival of neurons and other cell types. Other embodiments of this invention include the methods for the use of peptides to promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation, neuronal survival and / or trophoblast proliferation, trophoblast migration and trophoblase survival. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly or indirectly via a replicable vehicle. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dosage forms for therapeutic use. Kits containing pre-determined doses of an NRP can be used to conveniently store, prepare and administer an NRP to a subject in need thereof.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
Compositions and methods for neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells
The present invention provides compositions and methods for human neural cell production. More particularly, the present invention provides cellular differentiation methods employing an essentially serum free MEDII conditioned medium for the generation of human neural cells from pluripotent and multipotent human stem cells.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Preparation method of micro-nano fiber for micro-environment responsive immune regulation and nerve regeneration promotion
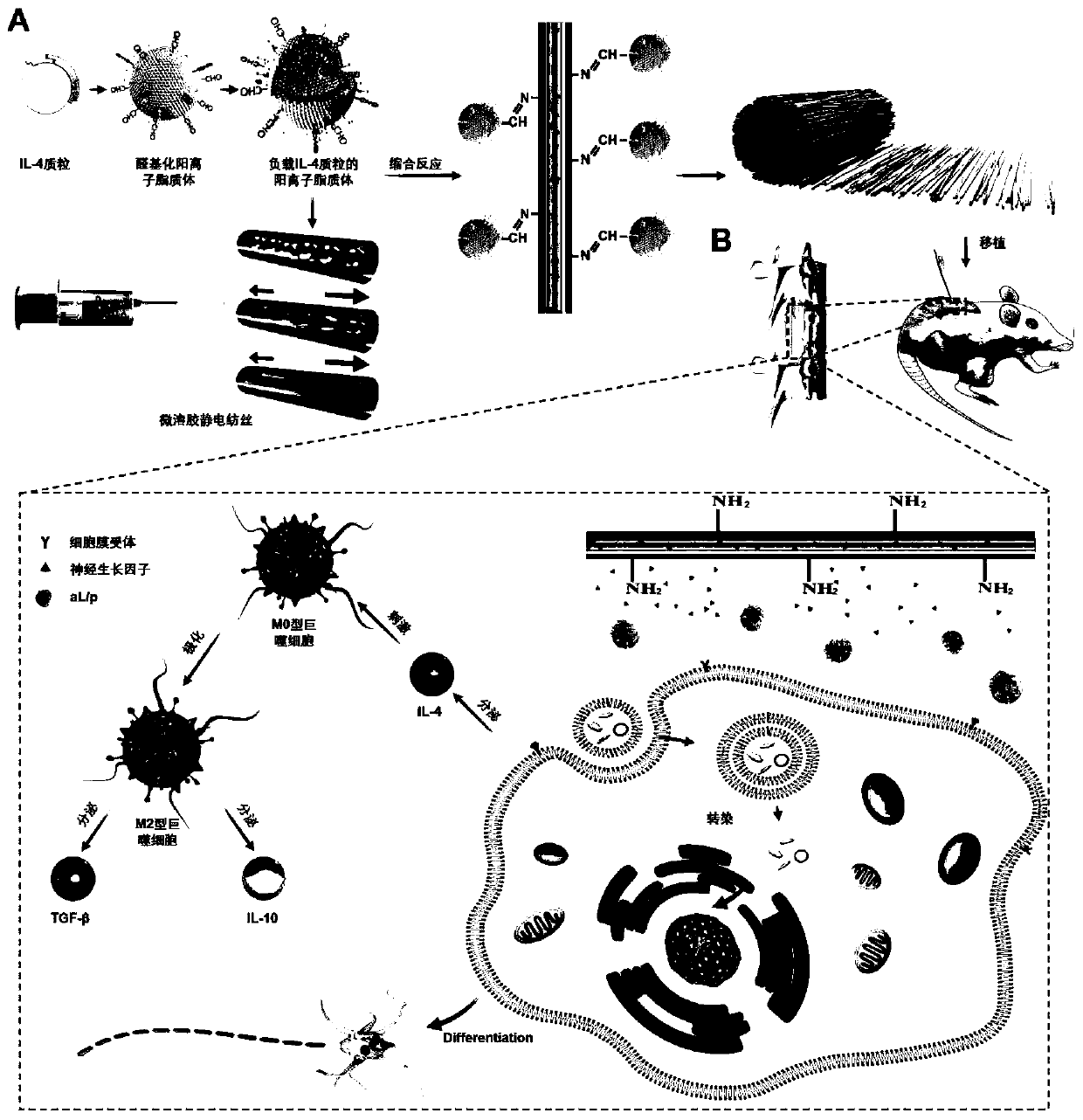
ActiveCN111494723ADownregulation of secretionReduce formationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectro-spinningBiologic scaffoldSpinal cord lesion
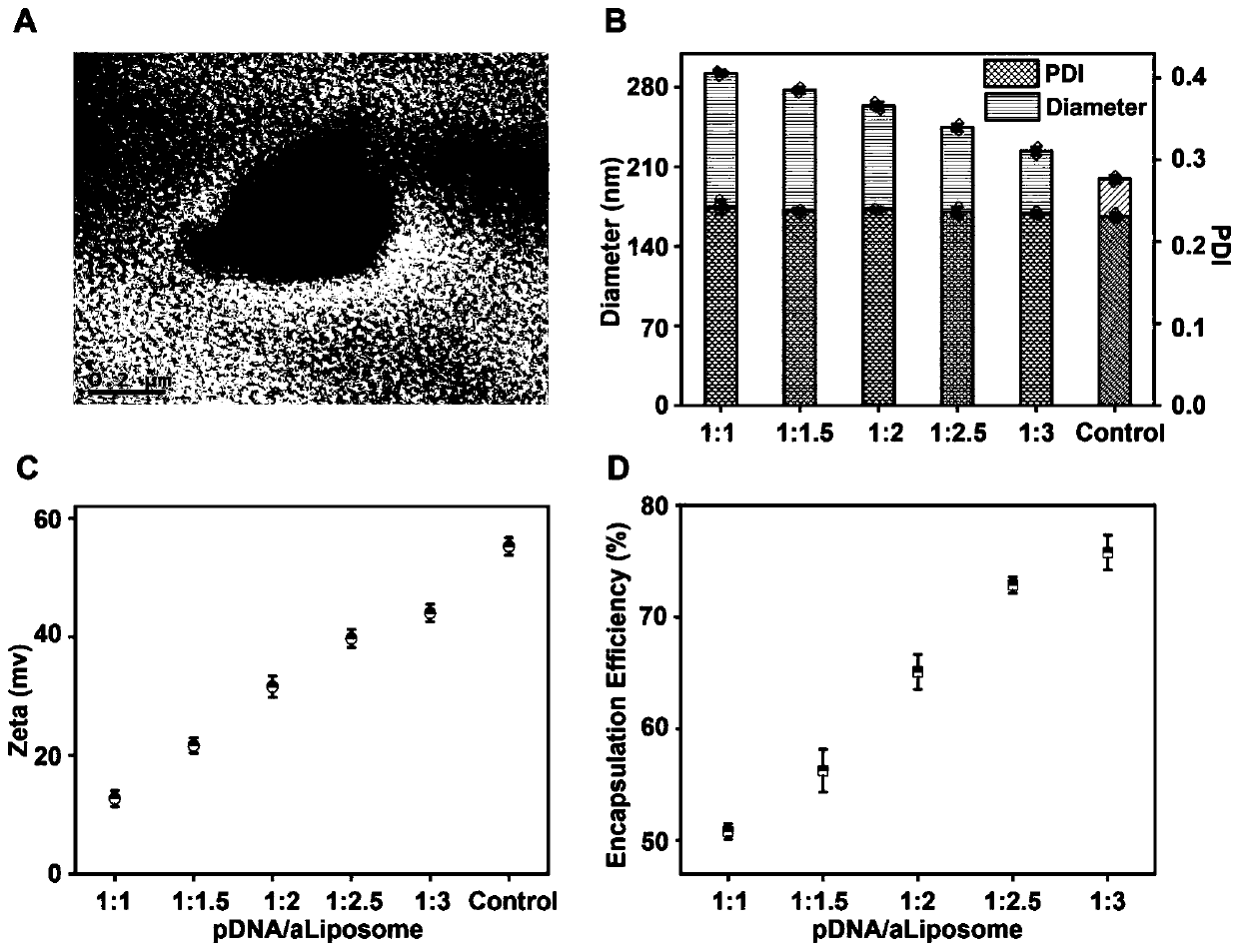
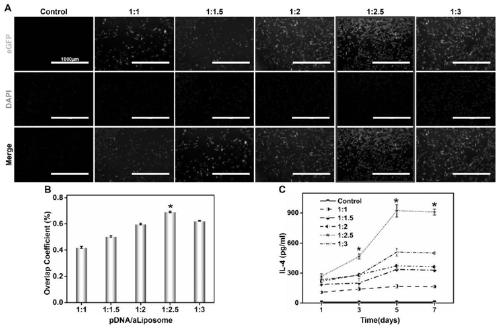
The invention discloses a preparation method of micro-nano fibers for micro-environment responsive immune regulation and nerve regeneration promotion. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing aldehyde cationic liposome; (2), performing preparation of a liposome loaded with an eGFP-IL-4 plasmid; (3), preparing a directional electrostatic spinning fiber membrane; and (4),preparing a micro-nano fiber for micro-environment responsive immune regulation and nerve regeneration promotion. The micro-nano fiber can reduce inflammatory response, lower glial fiber acidic protein secretion, reduce scar tissue formation, promote angiogenesis and continuously release NGF to promote neural differentiation capacity and function recovery of endogenous stem cells. Therefore, themicro-nano fiber is a functional biological scaffold for innovative responsive sequential immunoregulation and nerve regeneration promotion, which is used for preferentially carrying out local microenvironment immunoregulation on spinal cord injury and then providing a nerve differentiation platform for endogenous stem cells as a treatment purpose, and a biek strategy is provided for tissue engineering treatment of spinal cord injury.
Owner:海南德拉米克投资有限公司
Method for neuroepithelial cells differentiation from pluripotent stem cells and medium using same
InactiveUS20130157358A1Avoid time costHigh purityNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsAgonistNeuron
The present invention discloses a neural induction medium comprising Wnt-signal agonist, TGFβ-signal inhibitor and FGF-signal agonist for inducing neural differentiation. The neural induction medium used in a culture system is capable for inducing the neural differentiation of stem cells into neuroepithelial cells which are useful for the clinical applications. Therein, the neuroepithelial cells can further differentiate into mature neurons for the practical applications including regeneration medicine and drug discovery for neural disorders.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG HSING UNIVERSITY
Compound inducing culture medium and method for inducing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells by virtue of compound inducing culture medium
ActiveCN107058225AStable survivalShort induction timeCulture processNervous system cellsCell survivalUmbilical cord
The invention discloses a compound inducing culture medium. The compound inducing culture medium contains three differentiation culture solutions AD, DB and DC. A method for inducing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells by virtue of the compound inducing culture medium comprises the following steps: pre-inducing the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for 2 days by virtue of the differentiation culture solution DA; carrying out differentiation culture for 1 day by virtue of the differentiation culture solution DB; finally, carrying out maintenance culture for 1 day by virtue of the differentiation culture solution DC; and observing the morphological characteristics of the induced neuron-like cells, and detecting the mRNA level of induced neural differentiation relevant genes and the expression conditions of neuron migration proteins DCX and neuron specific enolase NSE which induce the neuron-like cells, wherein positive subjects of DCX expression are neural precursor cells, and positive subjects of NSE expression are the neuron-like cells. According to the method, the induction process is divided into three stages, and different culture mediums are adopted in each stage, so that the induction time is short, the induction efficiency is high, and the induced differentiated neuron-like cells can stably live and have no repellence after being transplanted.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method for promoting human pluripotent stem cells into mature neurons through directional differentiation
InactiveCN108486058AInhibition of proliferative abilityExcellent maturity rateGenetically modified cellsCulture processDiseaseNeurulation
The invention discloses a method for promoting human pluripotent stem cells into mature neurons through directional differentiation. Through a neural induction and a neural differentiation medium, thehuman pluripotent stem cells differentiate into the neurons. By means of the method, time needed for mature neuron obtained through differentiation can be obviously shortened; compared with the priorart, the method has the advantages that the human pluripotent stem cells can be induced to become the mature neurons in vitro in a short time, so that time consumption of neural differentiation is greatly reduced, and a cell model is provided for cell transplantation treatment, drug screening and pathological mechanism study of neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
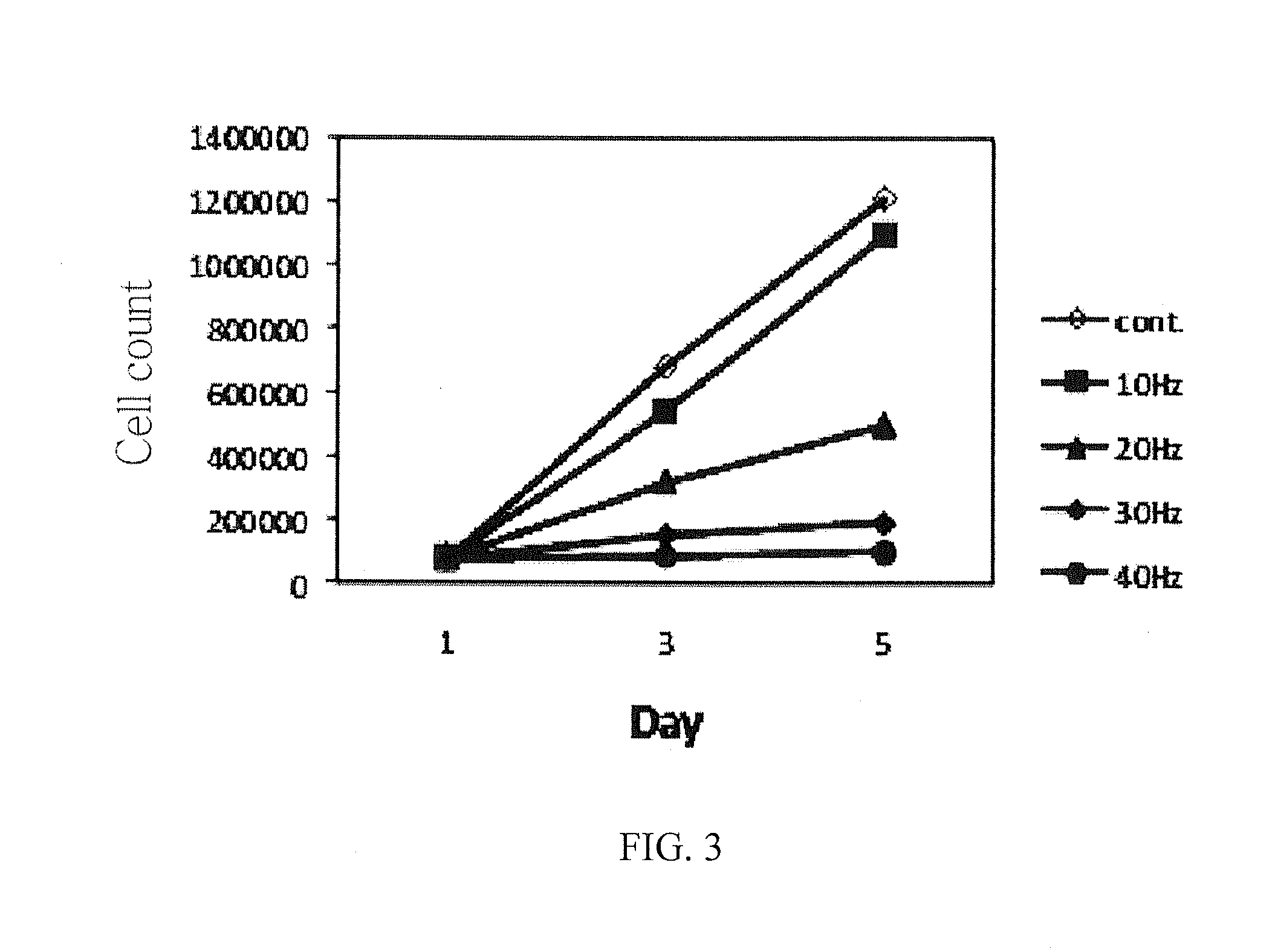
Method for inducing differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to nerve cells using sound waves
Owner:DONGGUK UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com