Patents
Literature
2684 results about "System identification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
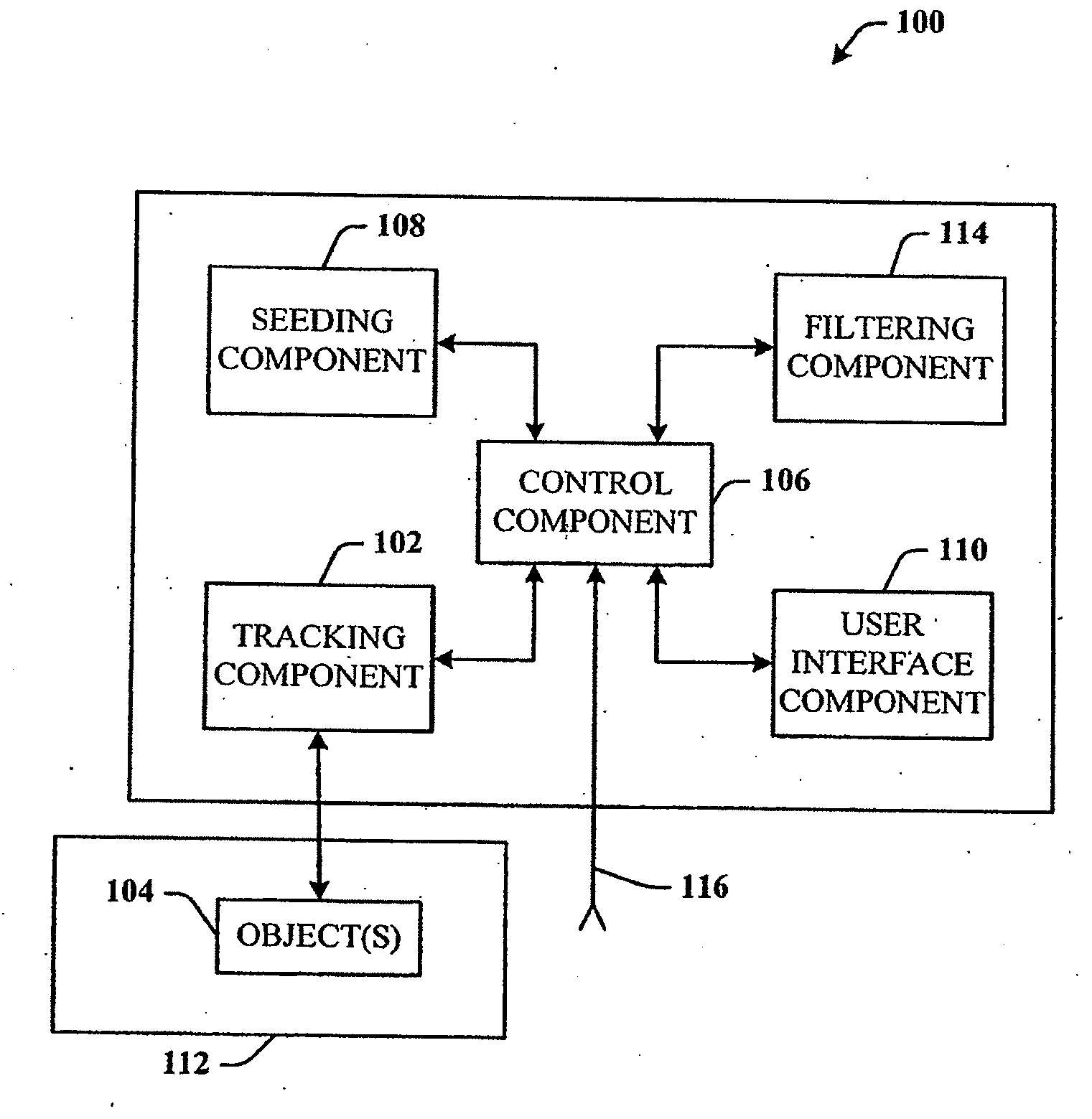
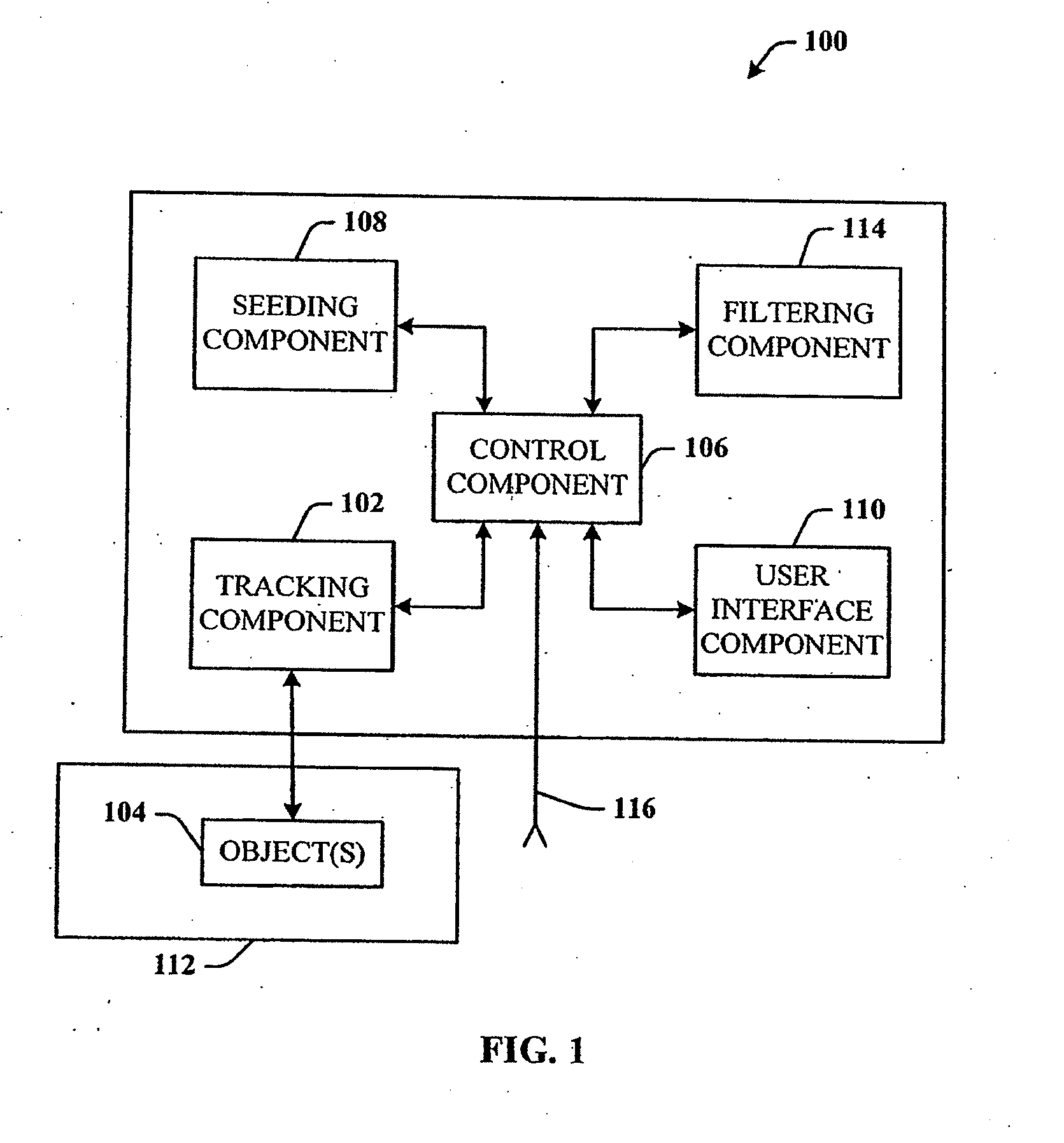
The field of system identification uses statistical methods to build mathematical models of dynamical systems from measured data. System identification also includes the optimal design of experiments for efficiently generating informative data for fitting such models as well as model reduction.
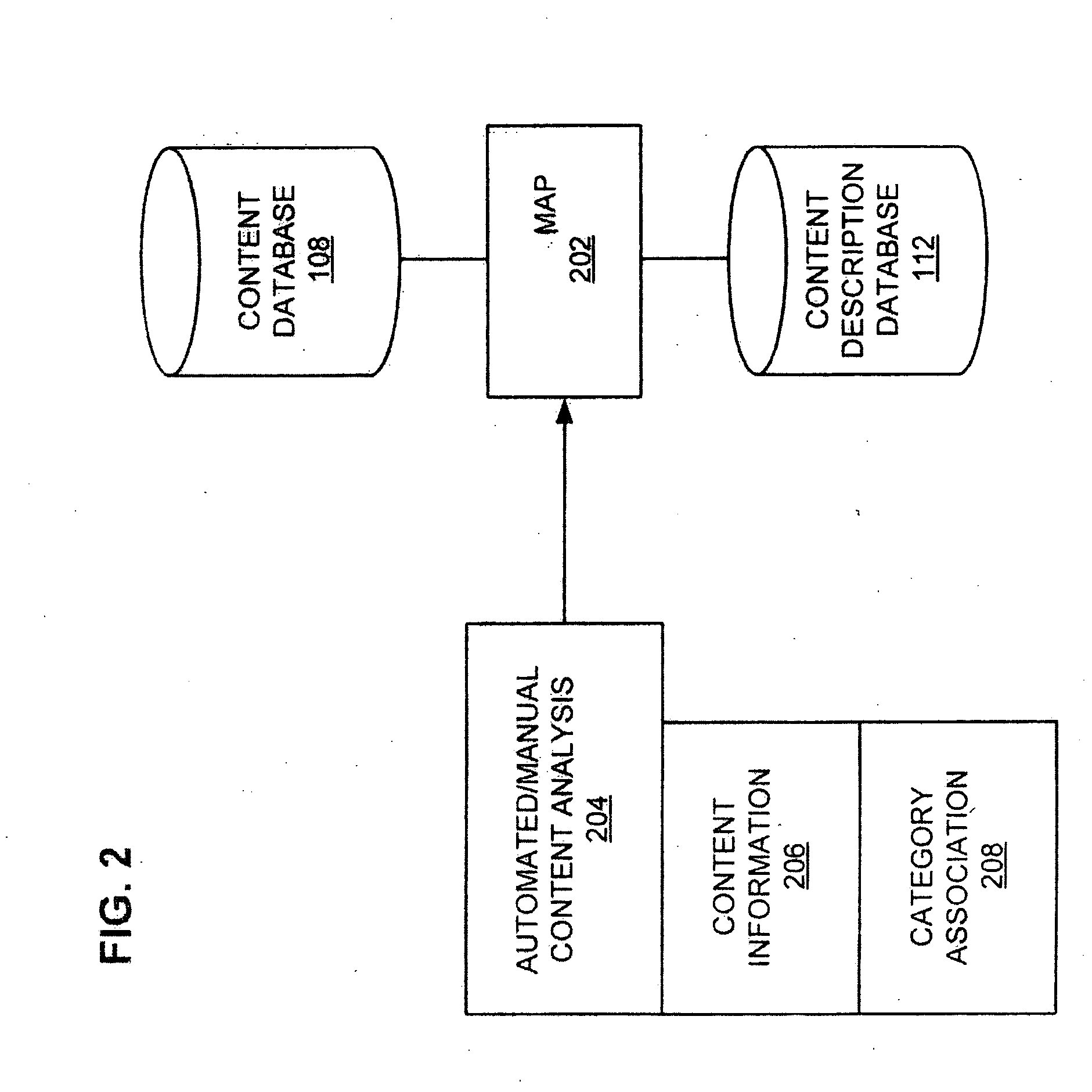
Information retrieval based on historical data
ActiveUS20050071741A1Handy search resultsWeb data indexingCommercePaper documentDocument preparation
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems and methods for performing a search based on a media content snapshot image
ActiveUS20110282906A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsMetadata video data retrievalUser inputData mining
Systems and methods are provided for performing a search based on a snapshot image captured from media content presented to a user. The snapshot image contains features of the media content that the user wishes to target for the search. A search system recognizes features of the snapshot image and creates a search query based on the snapshot image. The search query is used to identify features of the snapshot image, and search results related to the identified features are presented to the user. Supplemental data or user input received with the snapshot image may be used in analyzing and identifying features of the snapshot image.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
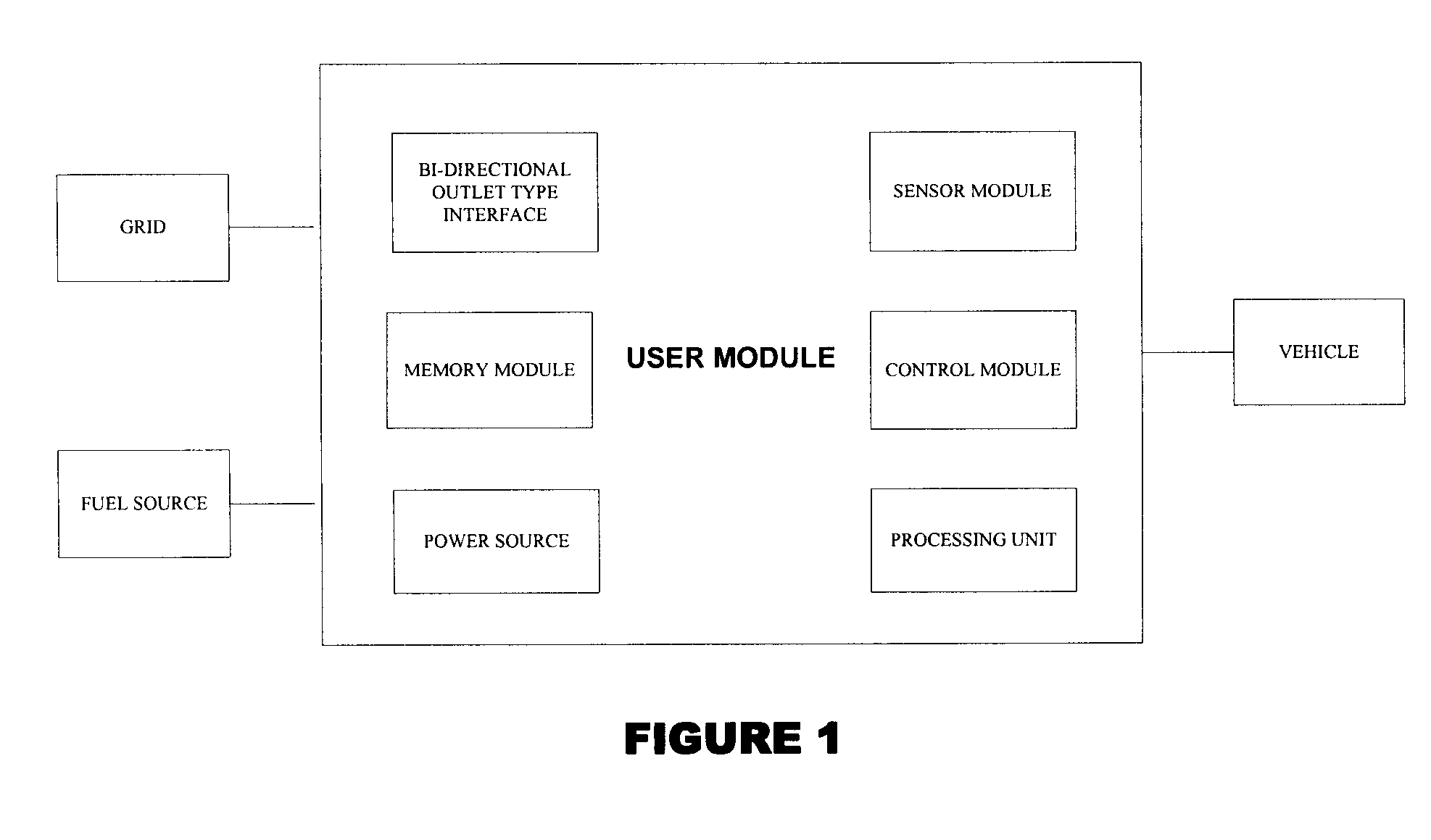
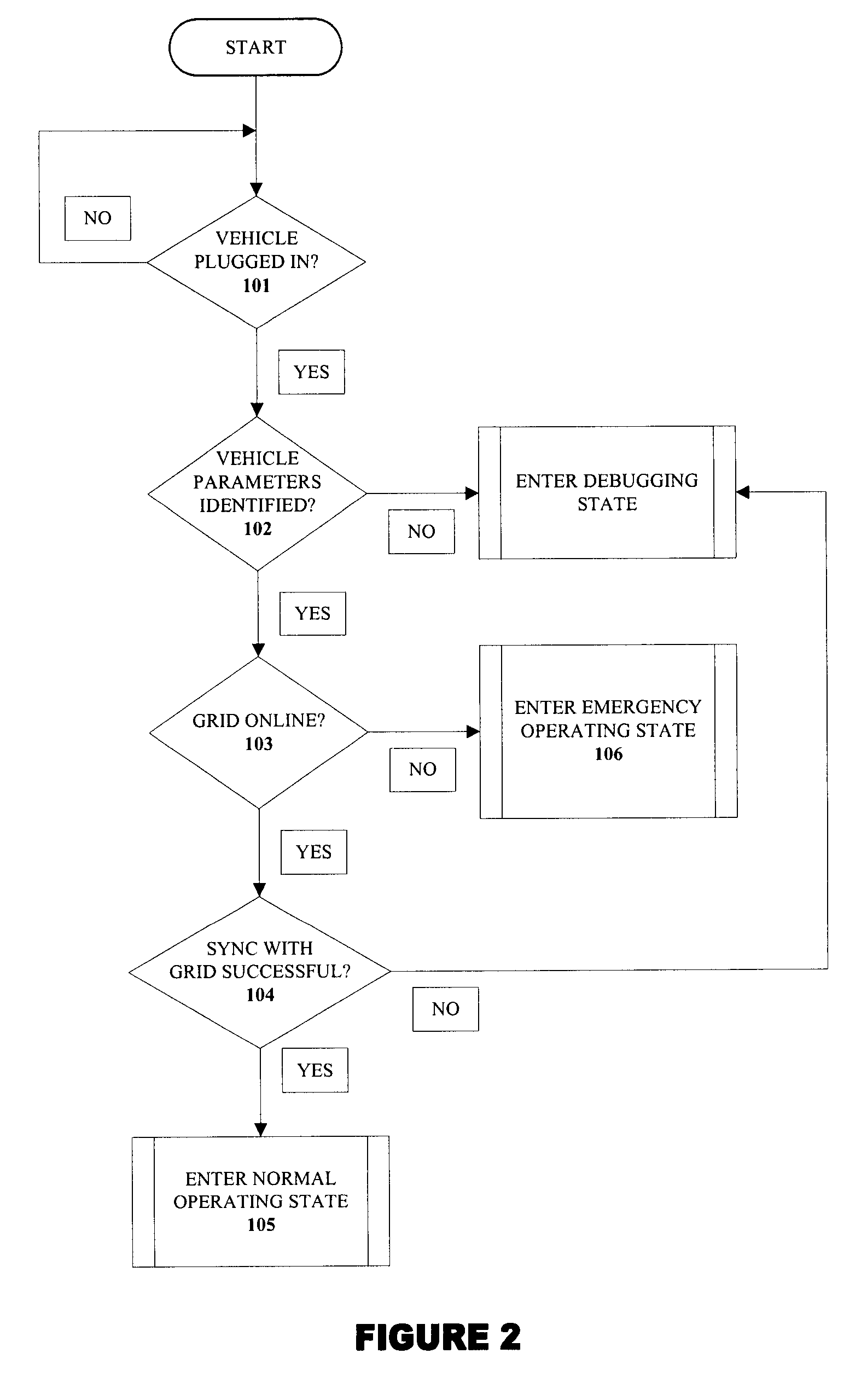
Vehicle charger safety system and method
InactiveUS20110074346A1Safety concern can be addressedFix security issuesMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsForeign objectSystem identification
Wireless vehicle charger safety systems and methods use a detection subsystem, a notification subsystem and a management subsystem. The detection subsystem identifies a safety condition. The notification subsystem provides an indication of the safety condition. The management subsystem addresses the safety condition. In particular, undesirable thermal conditions caused by foreign objects between a source resonator and a vehicle resonator are addressed by sensing high temperatures, providing a warning and powering down a vehicle charger, as appropriate for the environment in which the charger is deployed.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Method and system for locating a portable medical device
InactiveUS6937150B2Located reliablyOvercome problemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsHeart defibrillatorsWireless dataSystem identification
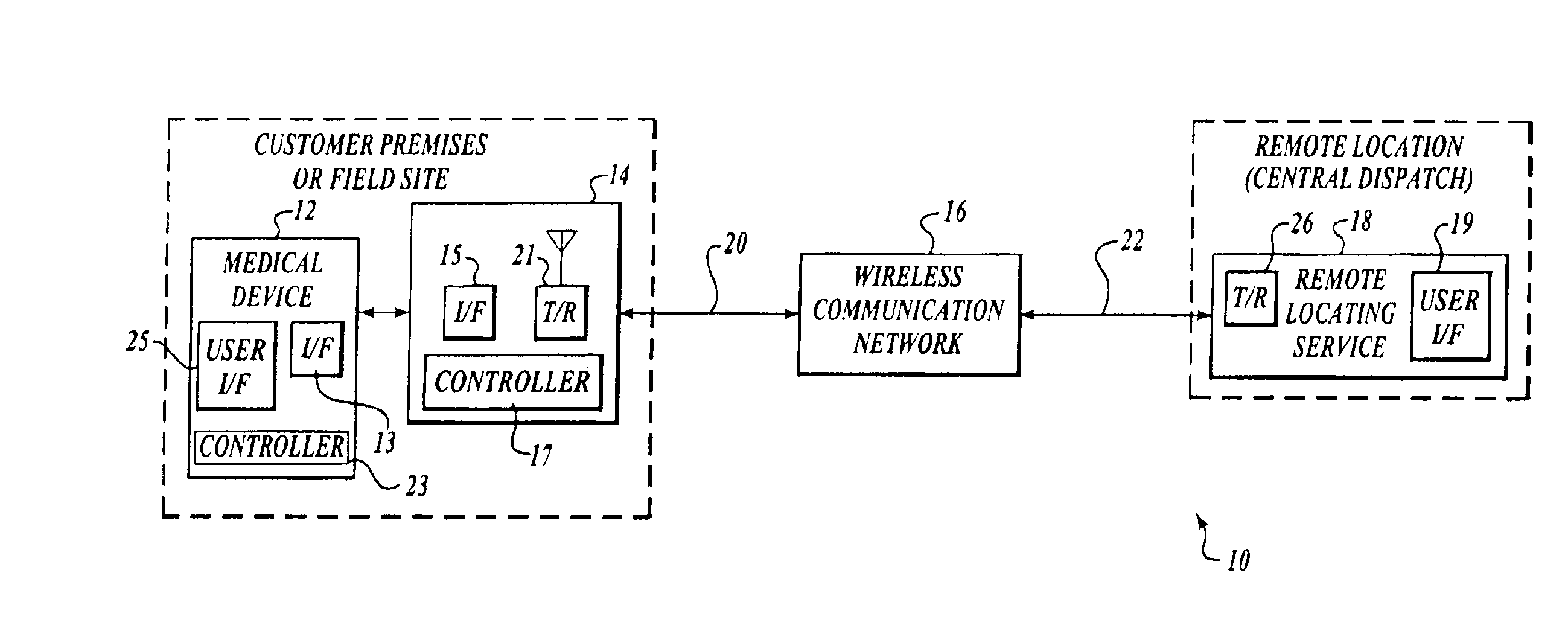
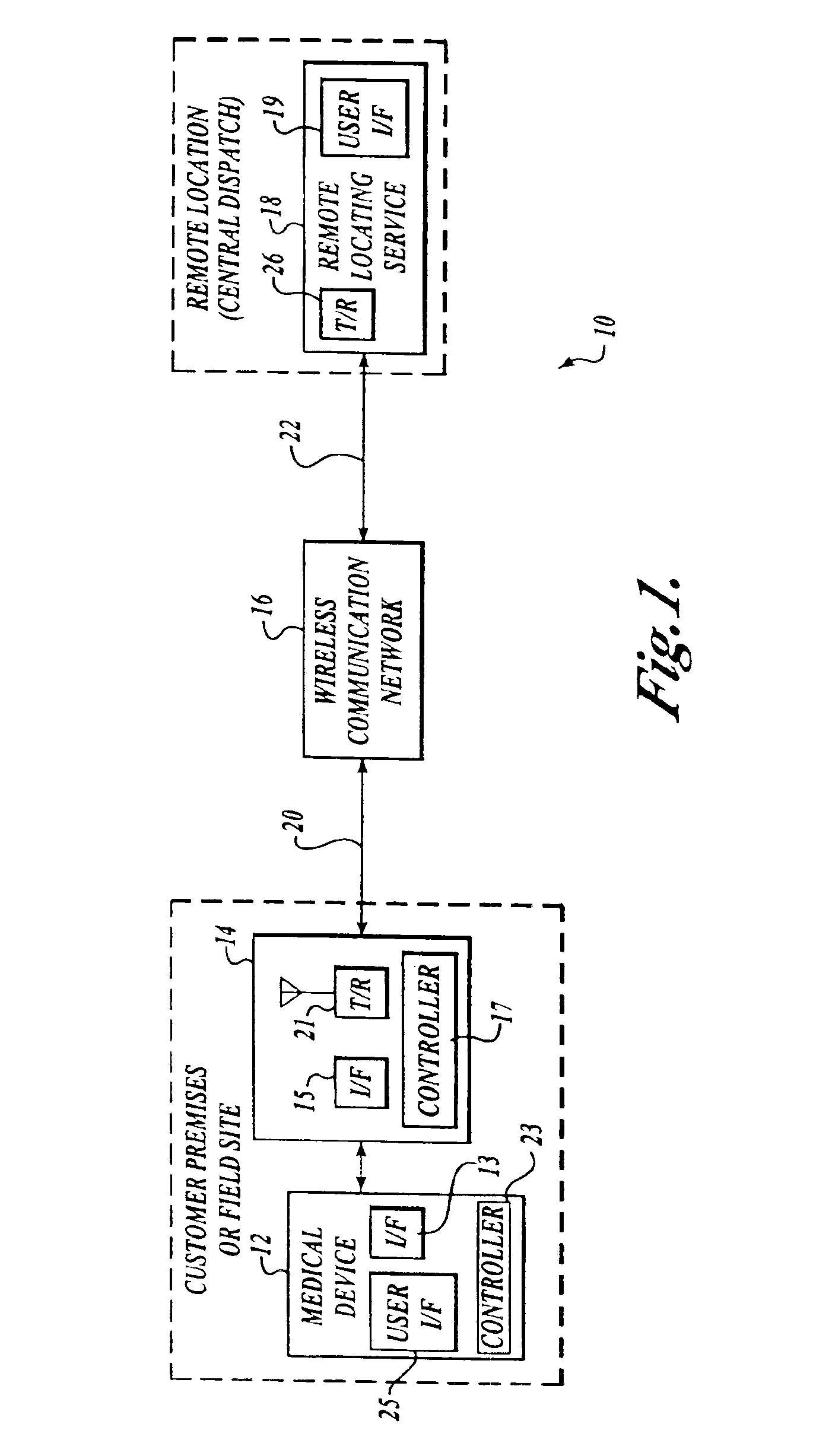
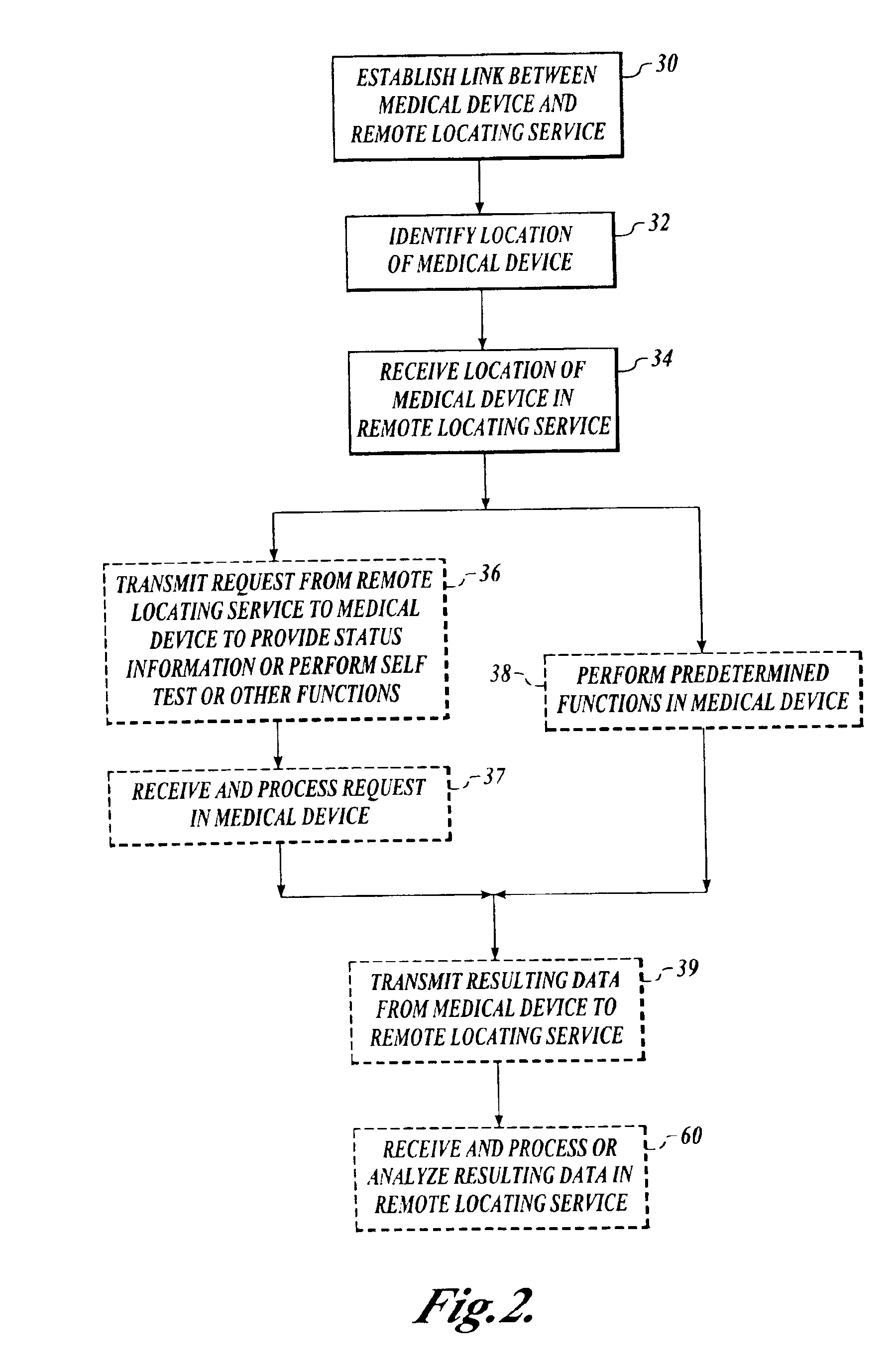
The invention provides a wireless automatic location identification (ALI) capable system (10), including a medical device (12) having a wireless data communicator (14), a wireless communication network (16), and a remote locating service (18) for remotely locating and monitoring one or more medical devices over the wireless communication network. When the medical device is linked to the remote locating service over the communication network, the ALI-capable system identifies the location of the medical device and relays the location information to the remote locating service. The system permits reliable determination of the location of the medical device wherever the medical device is situated. The medical device may further be configured to transmit signals indicative of its status, condition, or self-test results, to the remote locating service. This feature allows the remote locating service to centrally monitor the status or condition of a plurality of medical devices.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
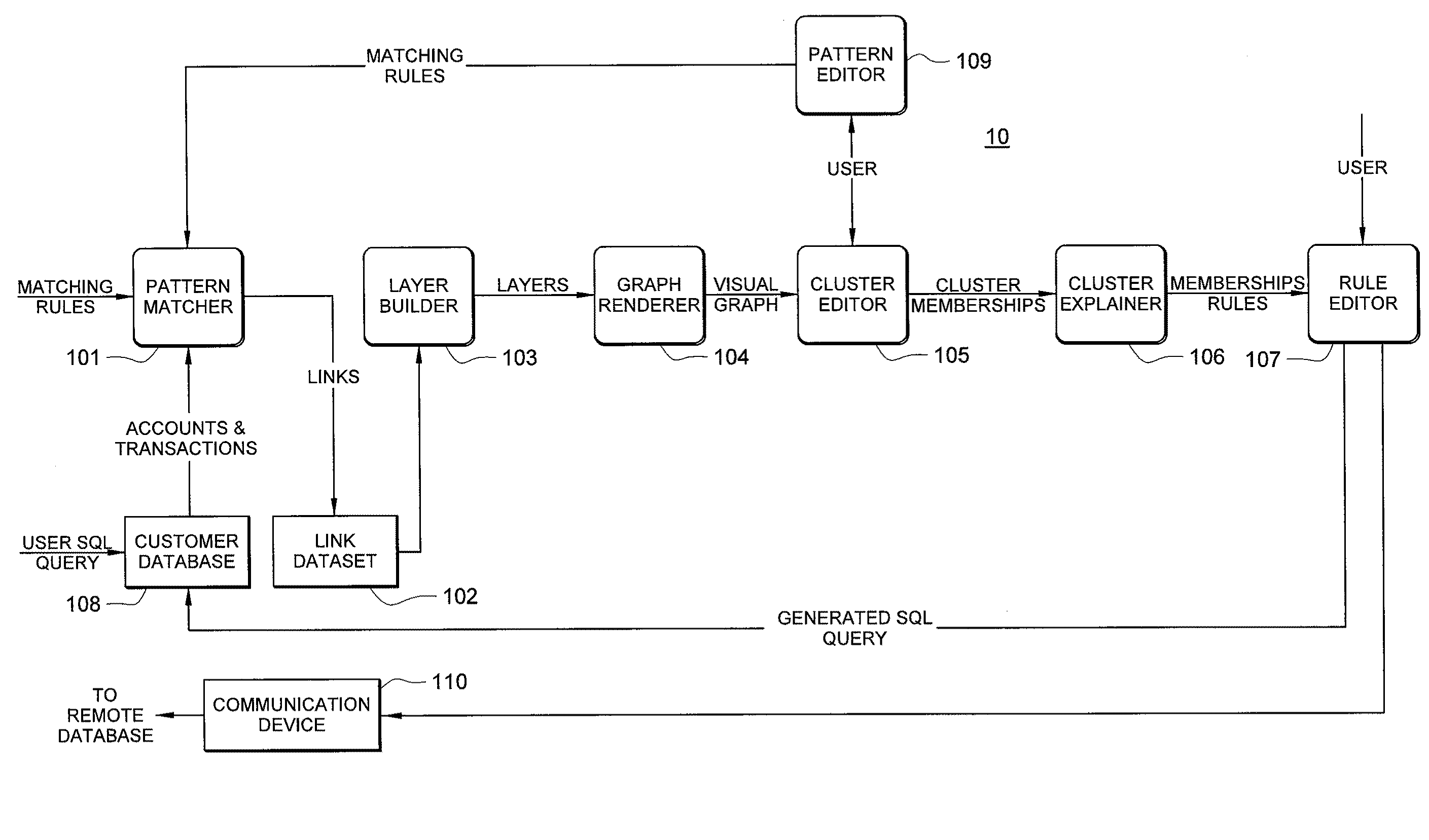
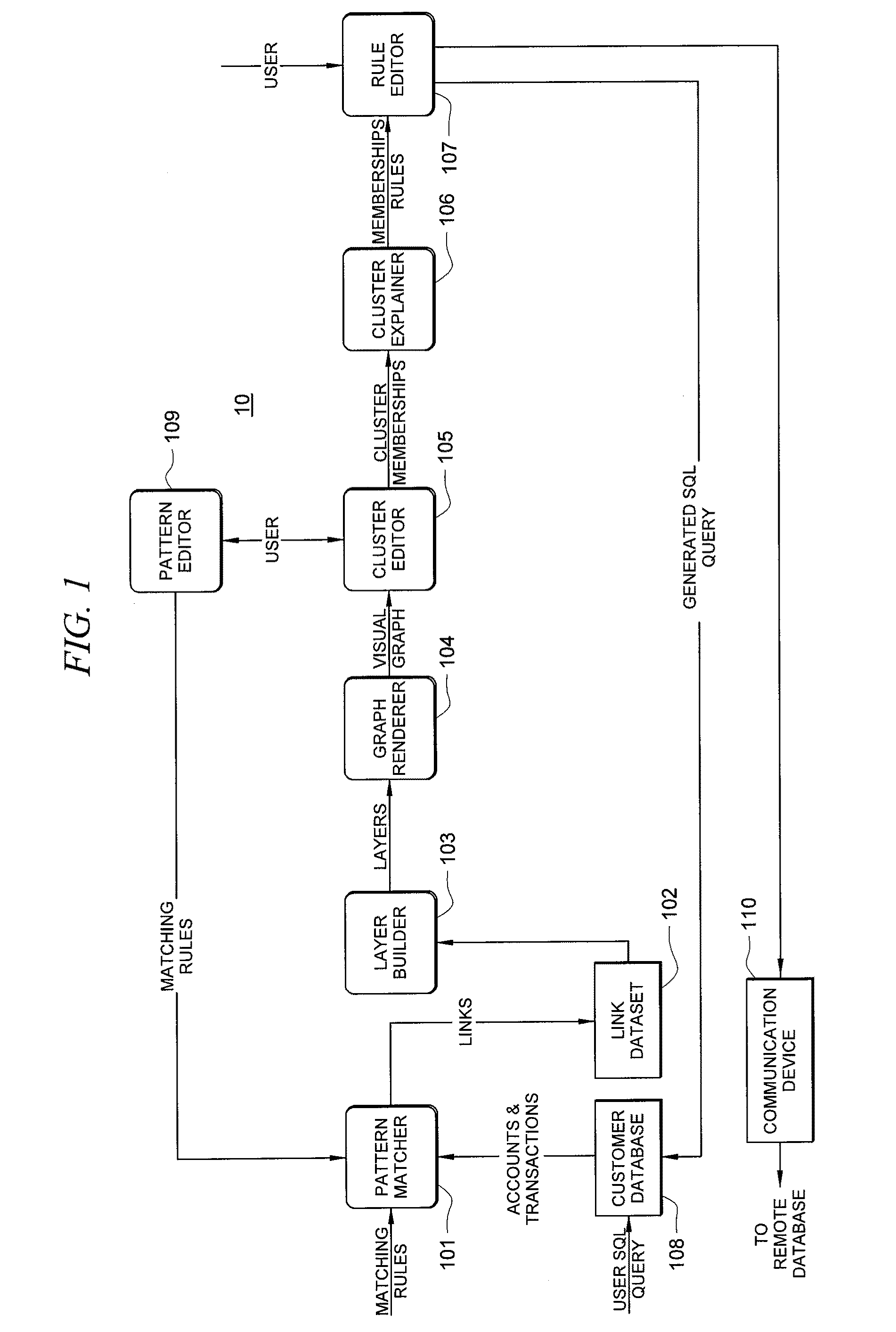
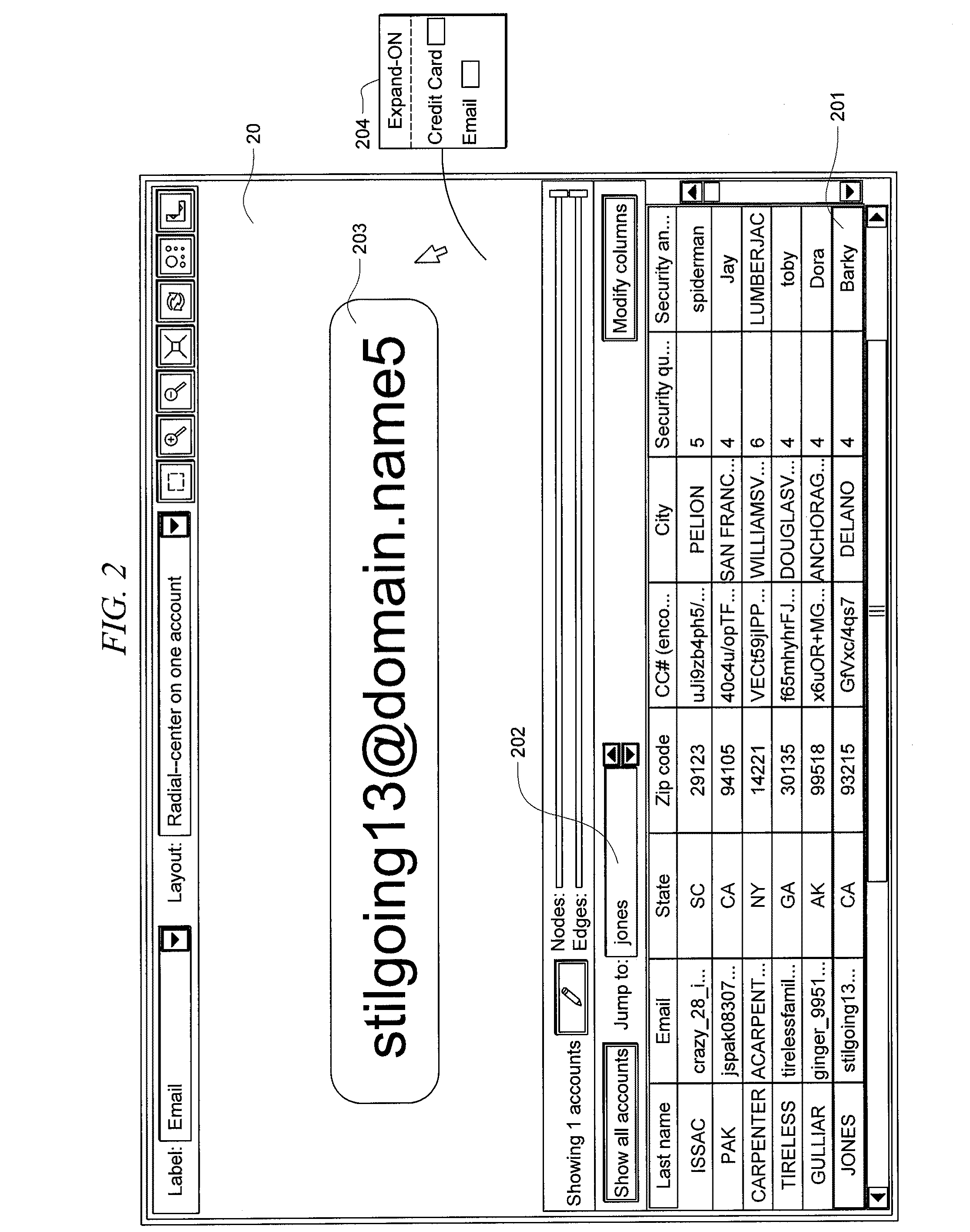
Systems and methods for fraud detection via interactive link analysis
ActiveUS20090044279A1Facilitate fraud detectionFinanceDigital data processing detailsHigh probabilitySystem identification
Fraud detection is facilitated by developing account cluster membership rules and converting them to database queries via an examination of clusters of linked accounts abstracted from the customer database. The cluster membership rules are based upon certain observed data patterns associated with potentially fraudulent activity. In one embodiment, account clusters are grouped around behavior patterns exhibited by imposters. The system then identifies those clusters exhibiting a high probability of fraud and builds cluster membership rules for identifying subsequent accounts that match those rules. The rules are designed to define the parameters of the identified clusters. When the rules are deployed in a transaction blocking system, when a rule pertaining to an identified fraudulent cluster is triggered, the transaction blocking system blocks the transaction with respect to new users who enter the website.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
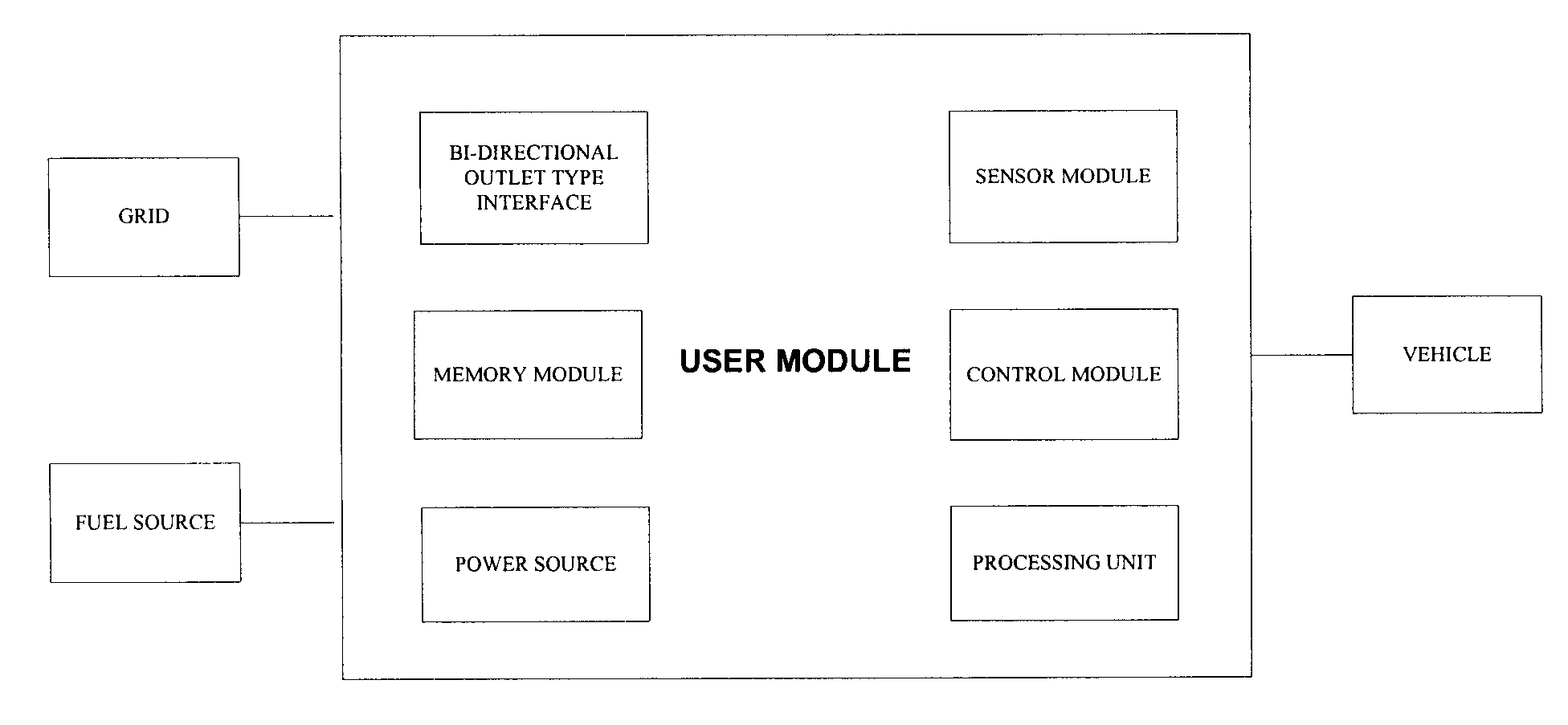
System and method for transferring electrical power between grid and vehicle
InactiveUS20090030712A1Low loading amountIncrease available powerBatteries circuit arrangementsRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric power transmissionElectrical battery
The present invention discloses a system for transferring electrical power between a grid and at least one vehicle. The vehicle can be Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) or Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV). The type of vehicle will be recognized and controlled by the system to support demand response and supply side energy management. Vehicle recognition can be carried out by load signature analysis, power factor measurement or RFID techniques. In an embodiment of the invention, the grid is a Smart Grid. The present invention also discloses a method for facilitating electrical power transfer between the grid and the vehicle.
Owner:ITRON NETWORKED SOLUTIONS INC
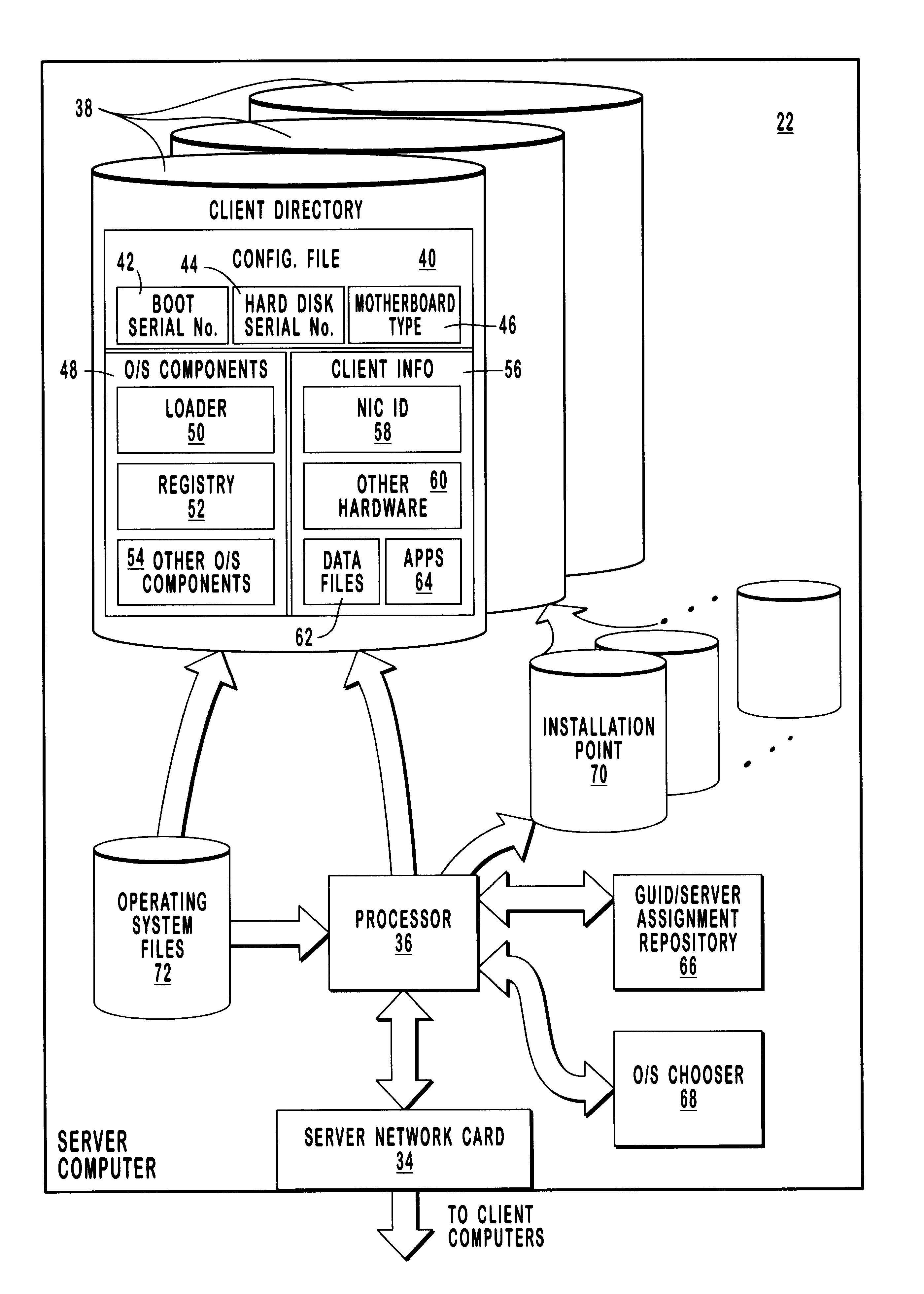
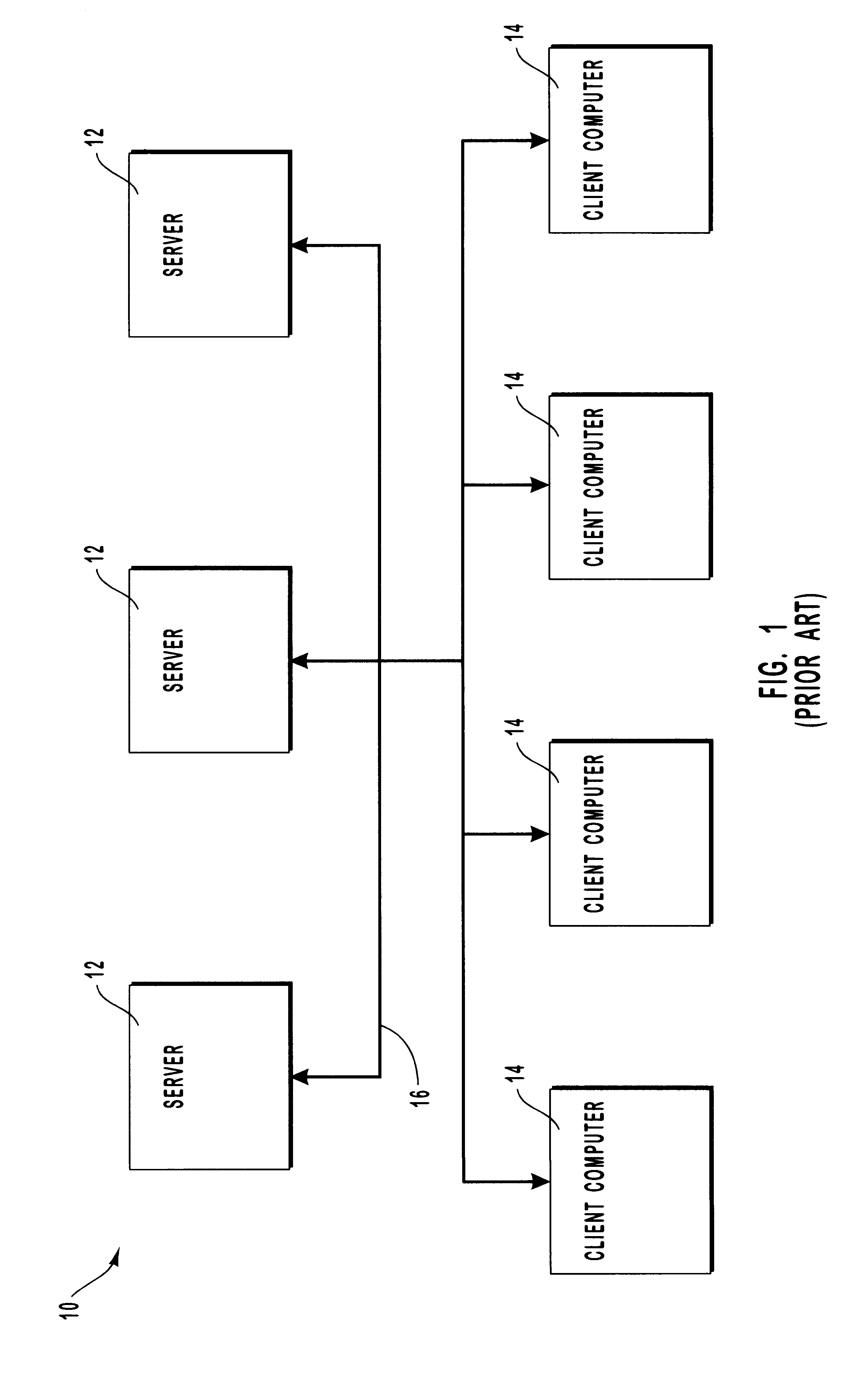
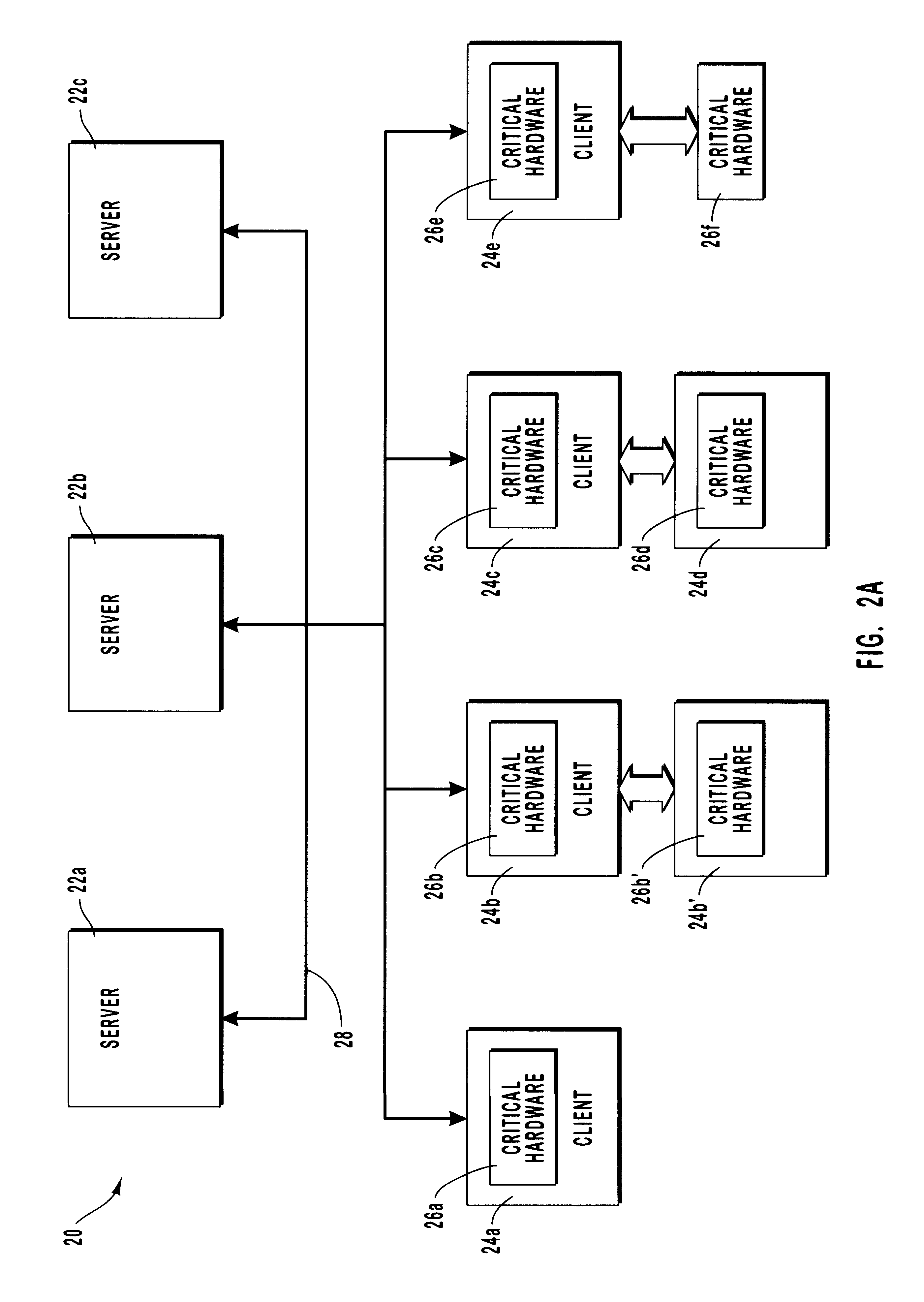
Correcting for changed client machine hardware when using a server-based operating system
InactiveUS6209089B1Reduces administrative effortReduce attentionDigital computer detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionComputer hardwareOperational system
Methods and systems for adjusting an operating system configuration according to changes in hardware components of a client computer. The adjusted operating system can boot on the client computer regardless of changes in the hardware configuration of the client computer since it was last connected to a network server. Before the operating system boots, a preliminary connection is established between the client computer and the server. During the preliminary connection, the system identifies hardware components that are new and that must be supported by the operating system for bootup to occur. In particular, the server sends information relating to the previous client hardware configuration to the client computer. The client computer compares its current hardware configuration to the previous hardware configuration information, thereby identifying its new hardware components. Information identifying the new hardware components is sent to the server. The server locates operating system components or device drivers that support the new hardware components and stores them in a specified repository at the server. The operating system, which is now reconfigured to support the current client hardware components, is downloaded to the client computer and boots thereon.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
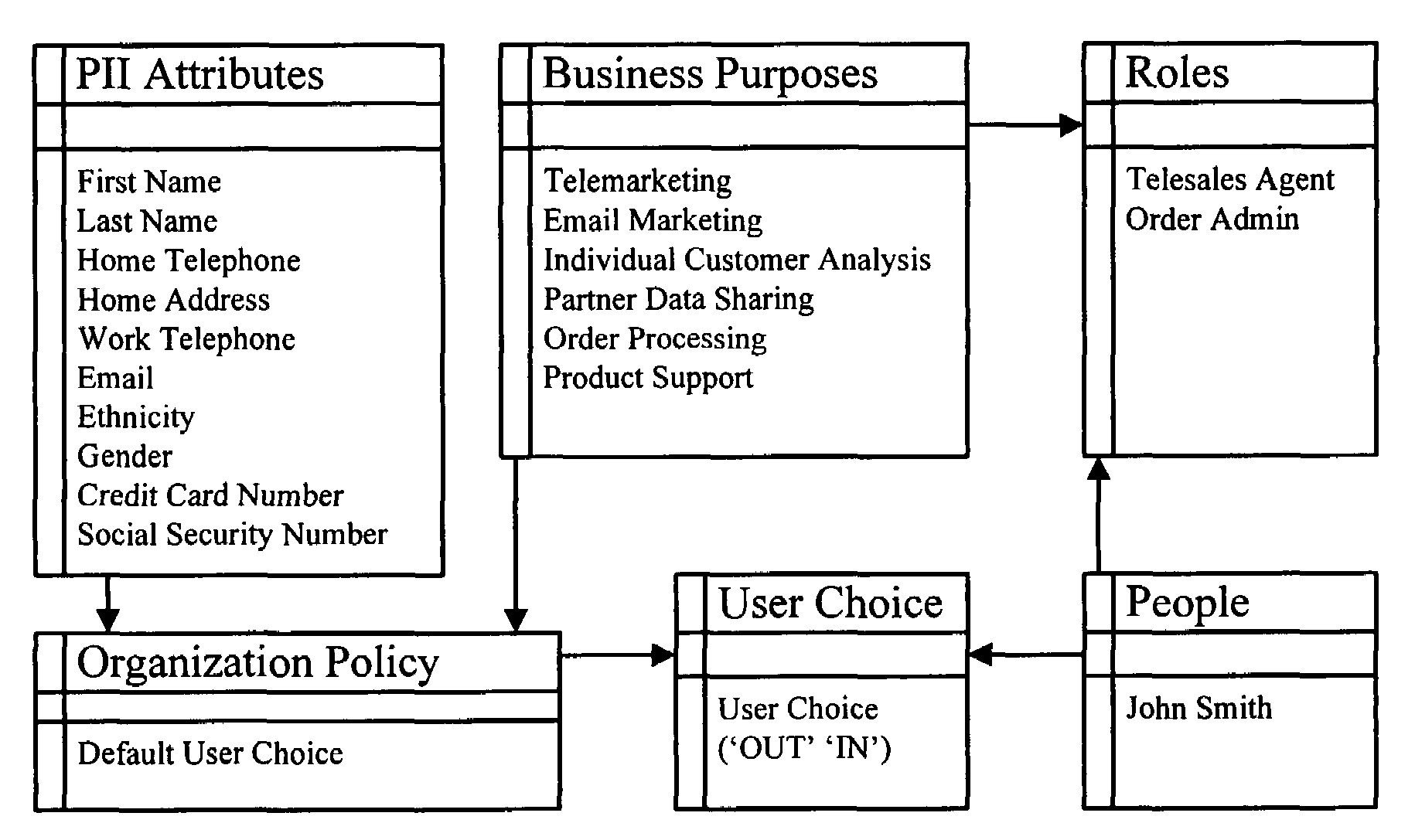
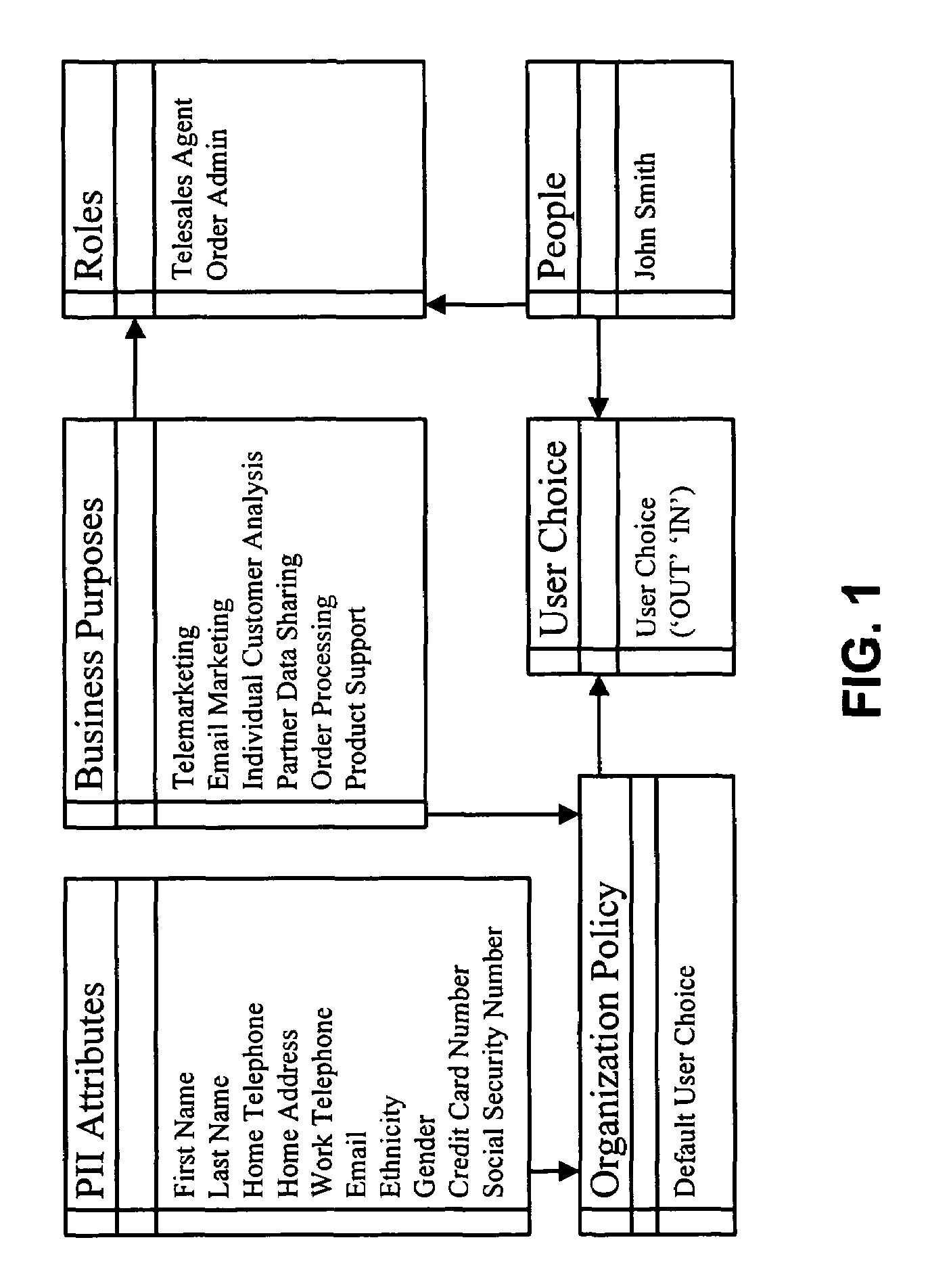
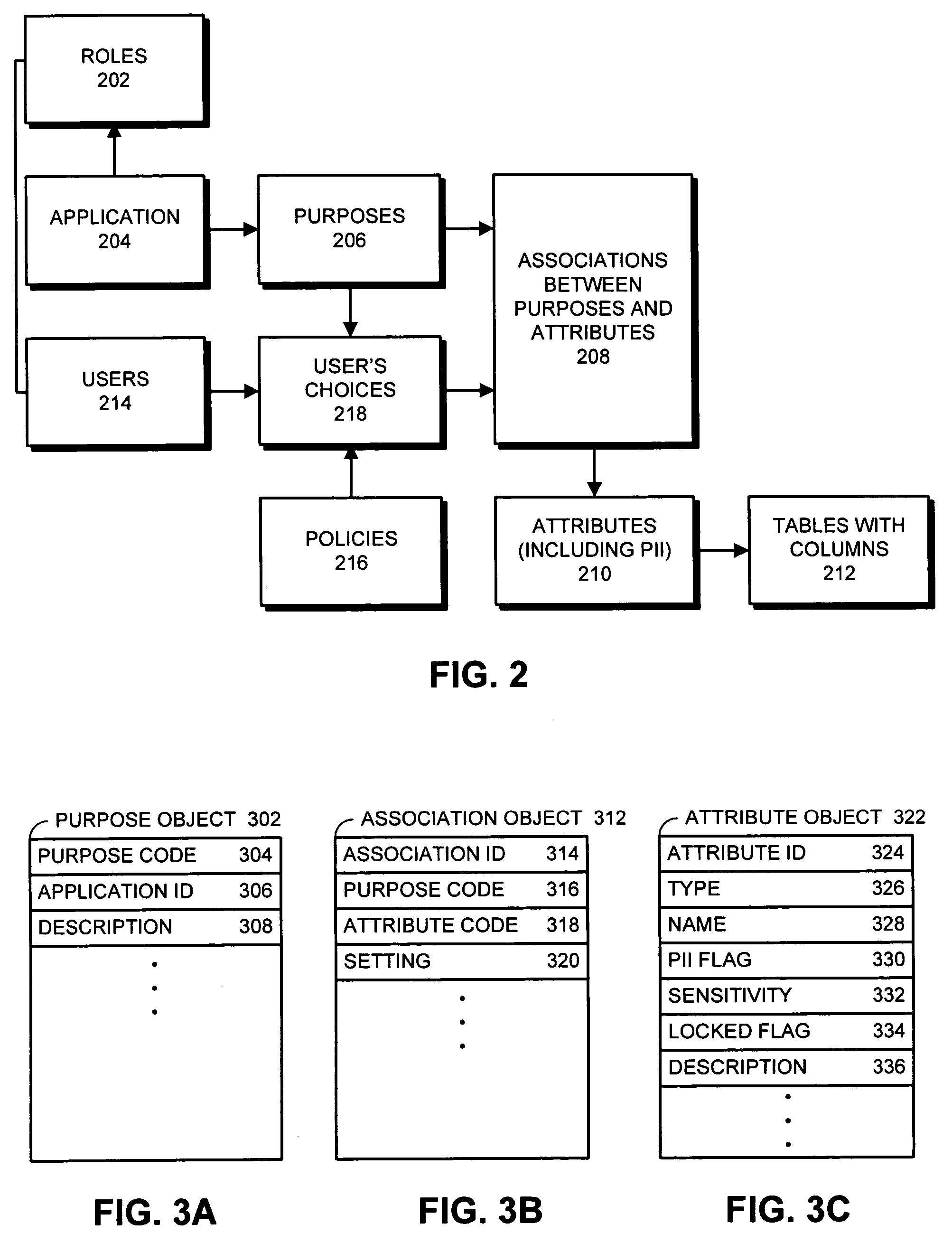
Method and apparatus for controlling access to personally identifiable information
ActiveUS7716242B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInternet privacyApplication software
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that controls access to personally identifiable information (PII) in a database system. During operation, the system receives a request from an application to perform a function which involves accessing information in the database system. In response to the request, the system identifies a purpose that the application has in making request to perform the function. Next, the system uses the purpose to identify a set of attributes in the database system, which are associated with the purpose. The system then determines if any of the identified attributes contain PII. If so, the system enforces access controls while accessing the identified attributes containing PII.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
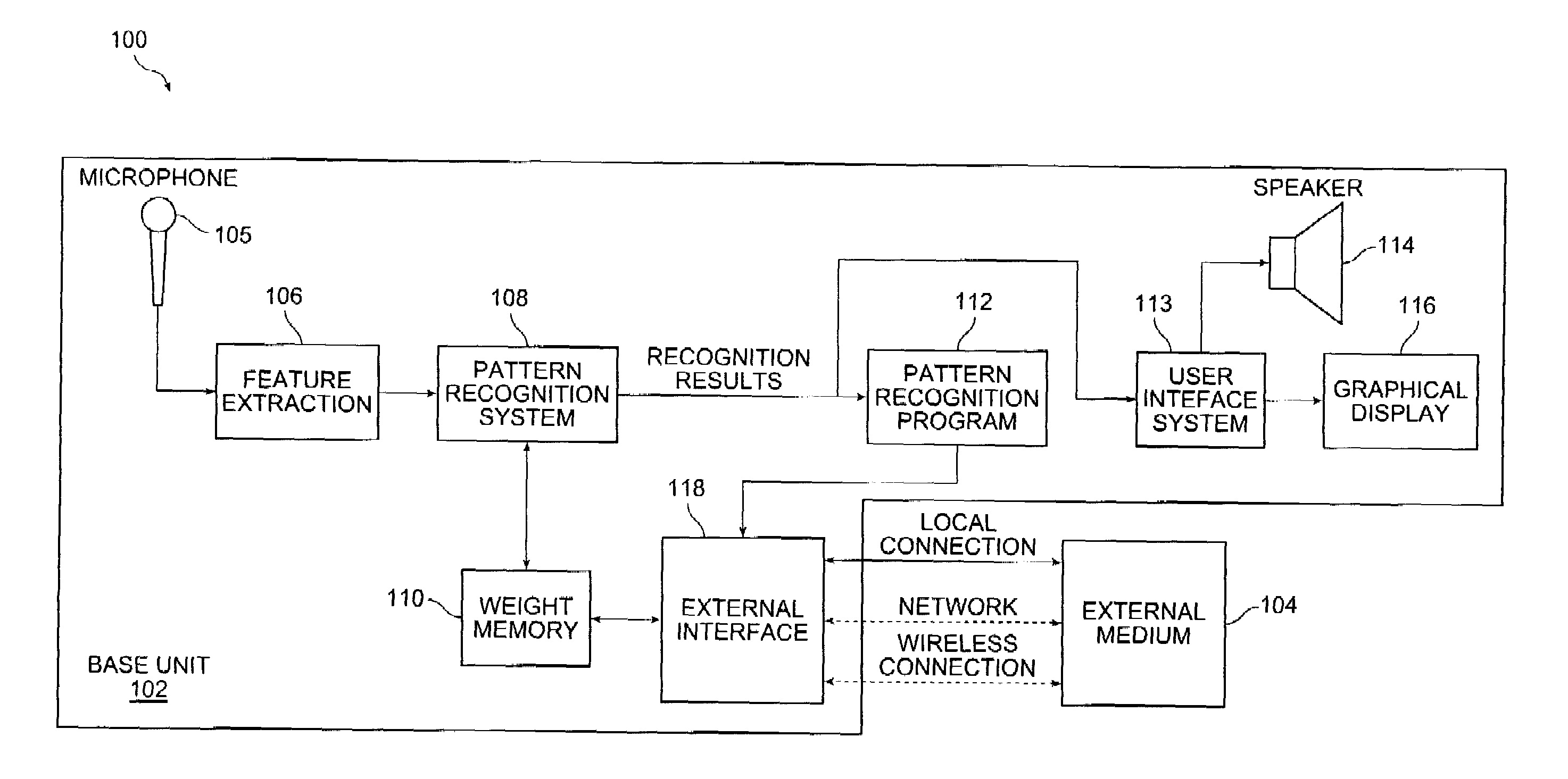
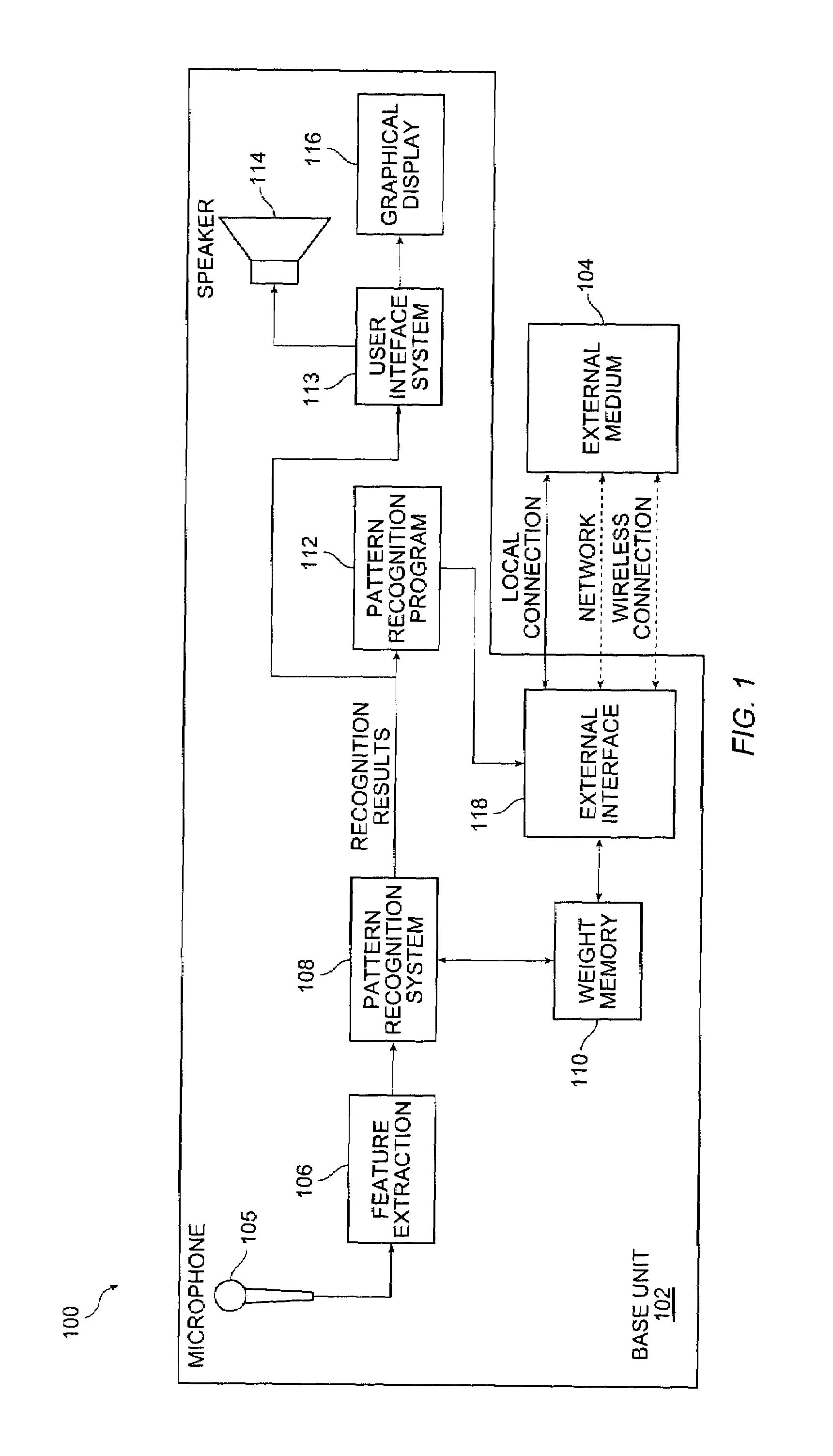
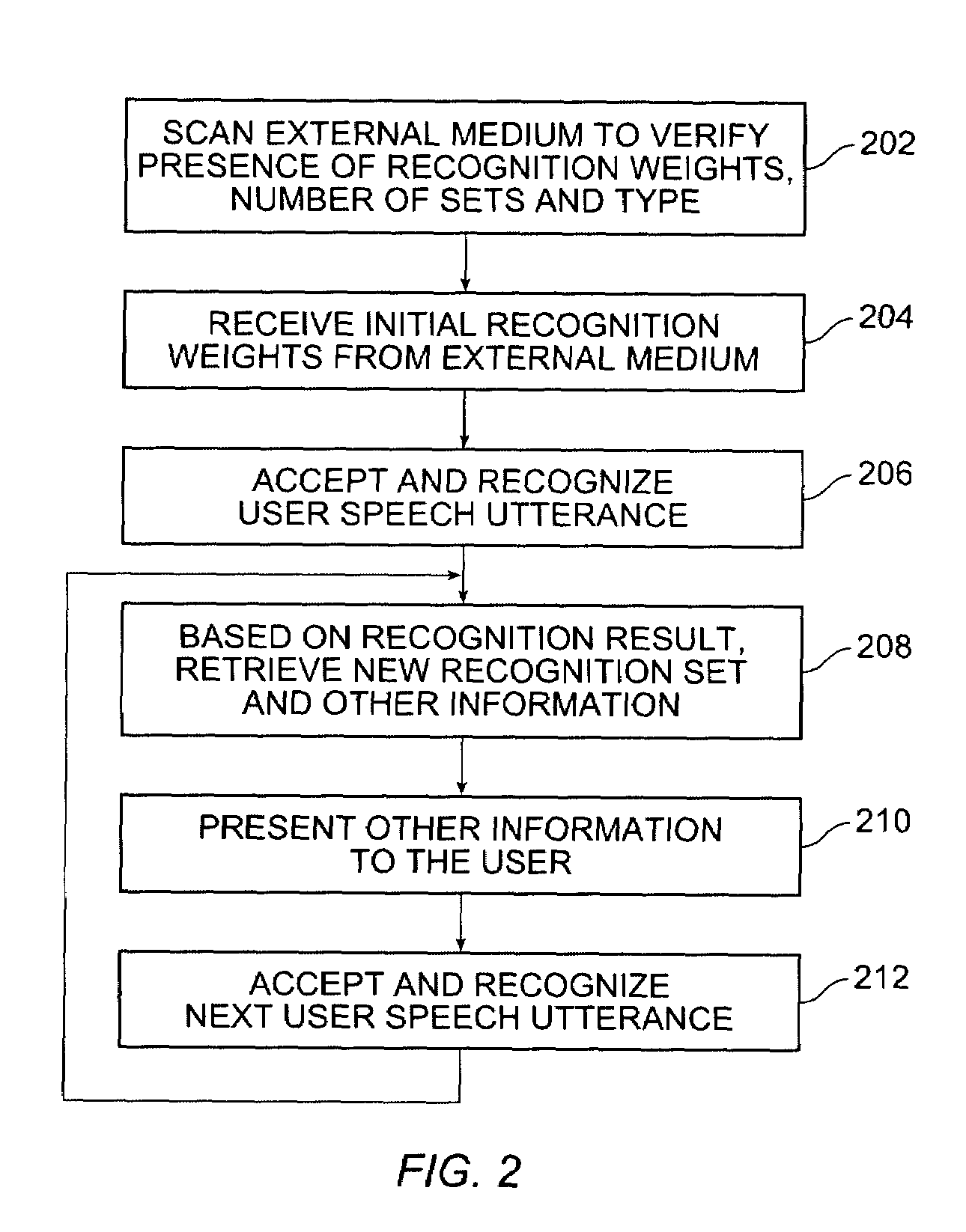
Speech recognition programming information retrieved from a remote source to a speech recognition system for performing a speech recognition method
InactiveUS6999927B2Time-pieces with integrated devicesSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSystem identification
Embodiments of the present invention include a speech recognition method. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving from an external system first recognition information to recognize a first plurality of words in a first system, programming the first system with the first recognition information to recognize the first plurality of words, generating first recognition results in response to receiving at least one of the first plurality of words in the first system, receiving from the external system second recognition information to recognize a second plurality of words, wherein the second recognition information is selected based on the first recognition results, and programming the first system with the second recognition information to recognize a second plurality of words.
Owner:SENSORY
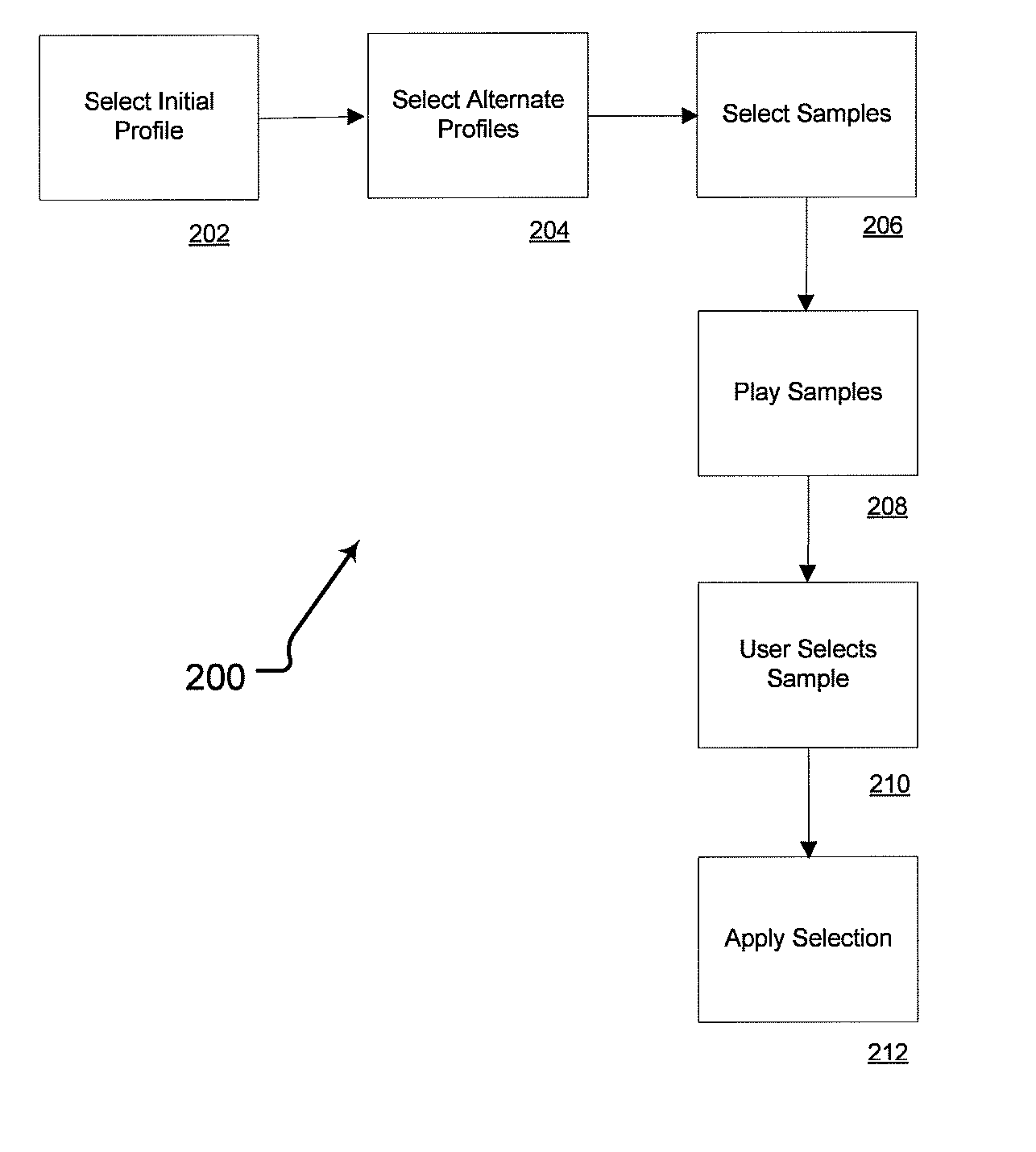
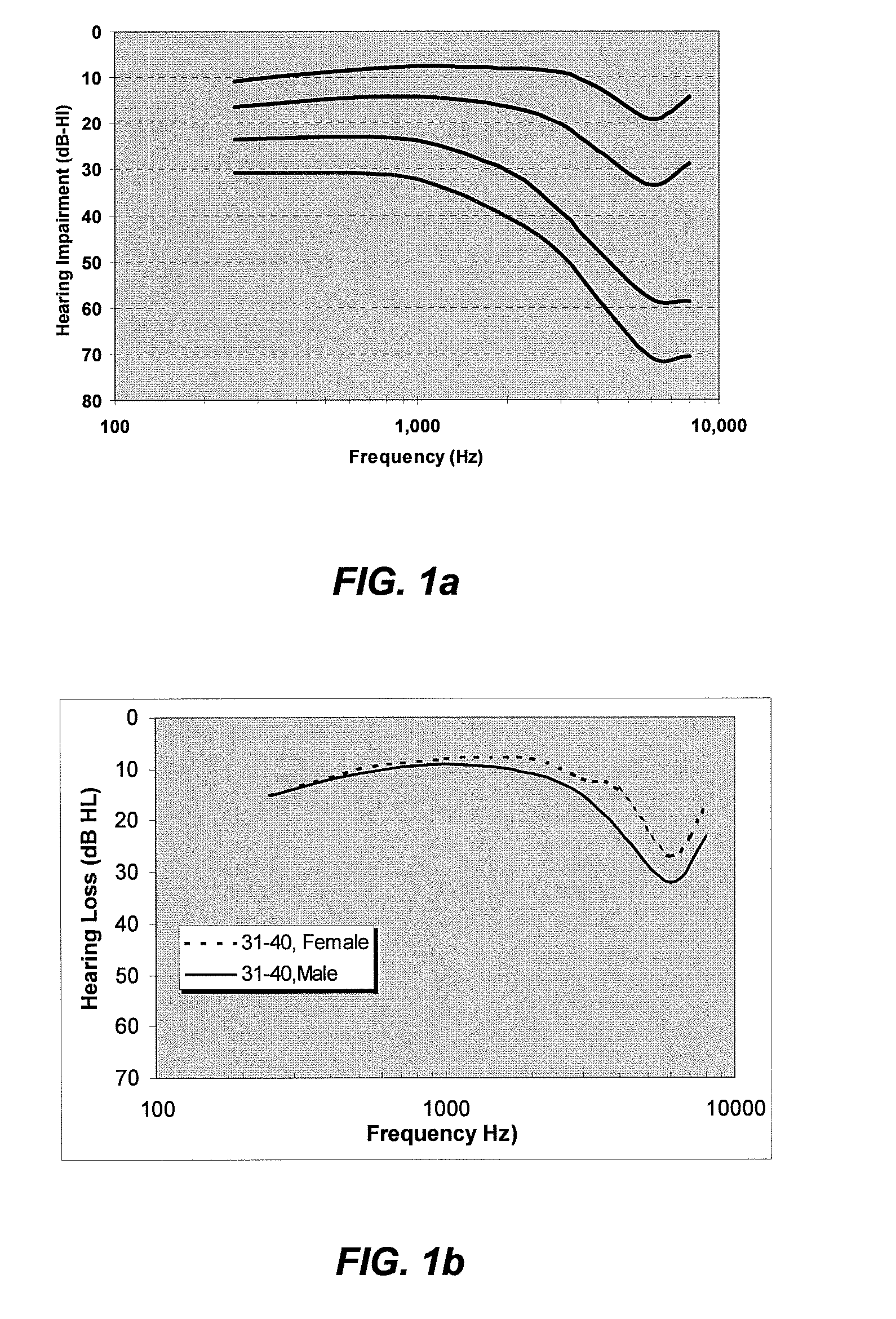
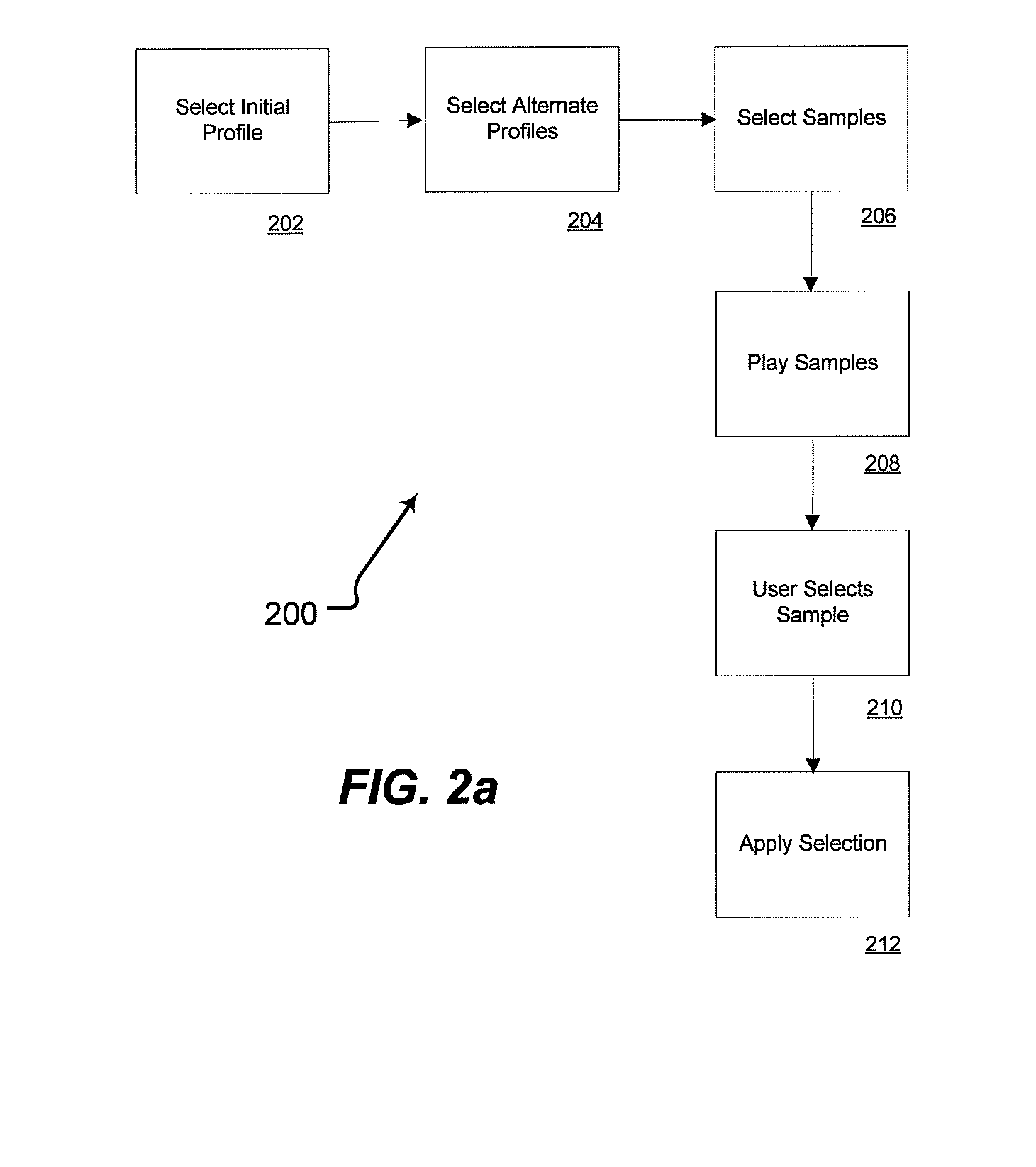
Personalized sound system hearing profile selection process
ActiveUS20080165980A1High sensitivityReduce sensitivityStereophonic circuit arrangementsDigital/coded signal combination controlPersonalizationUser input
A method of generating a personalized sound system hearing profile for a user. The method begins by selecting an initial profile, based on selected factors of user input. In an embodiment, the initial profile is selected based on demographic factors. Then the system identifies one or more alternate profiles, each having a selected relationship with the initial profile. The relationship between alternate profiles and the initial profile can be based on gain as a function of frequency, one alternate profile having a higher sensitivity at given frequencies and the other a lower sensitivity. The next step links at least one audio sample with the initial and alternate profiles and then plays the selected samples for the user. The system then receives identification of the preferred sample from the user; and selects a final profile based on the user's preference. An embodiment offers multiple sound samples in different modes, resulting in the selection of multiple final profiles for the different modes. Finally, the system may apply the final profile to the sound system.
Owner:HIMPP
Data extraction for feed generation
ActiveUS20060167860A1Quick assemblyDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsTemplate matchingUnstructured data
A system (and a method) automatically generates a feed from structured or unstructured data. The system identifies a resource having two or more data elements. The resource is matched with a pre-defined template. The pre-defined template is structured for a feed and includes a plurality of fields. The system extracts data elements from the two or more data elements of the resources. Each extracted data element corresponds to a field or the plurality of fields in the pre-defined template. Each extracted data element is then merged into the corresponding field or the plurality of fields in the pre-defined template to generate the feed.
Owner:SIMPLEFEED
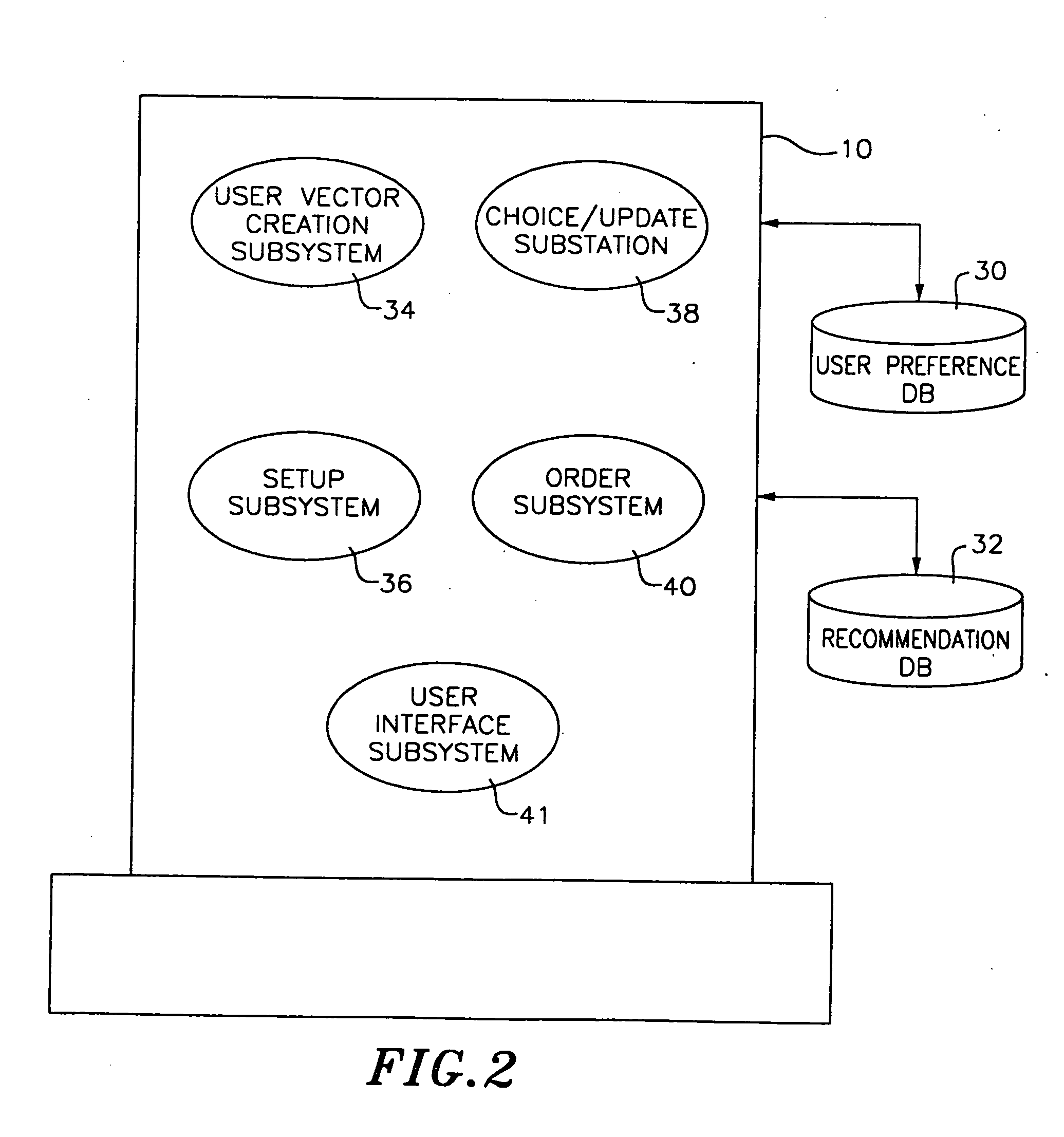
Method and apparatus for automated selection, organization, and recommendation of items based on user preference topography
InactiveUS20060020614A1Stay interestedMore interestingDigital data processing detailsResourcesArtificial intelligenceSystem identification
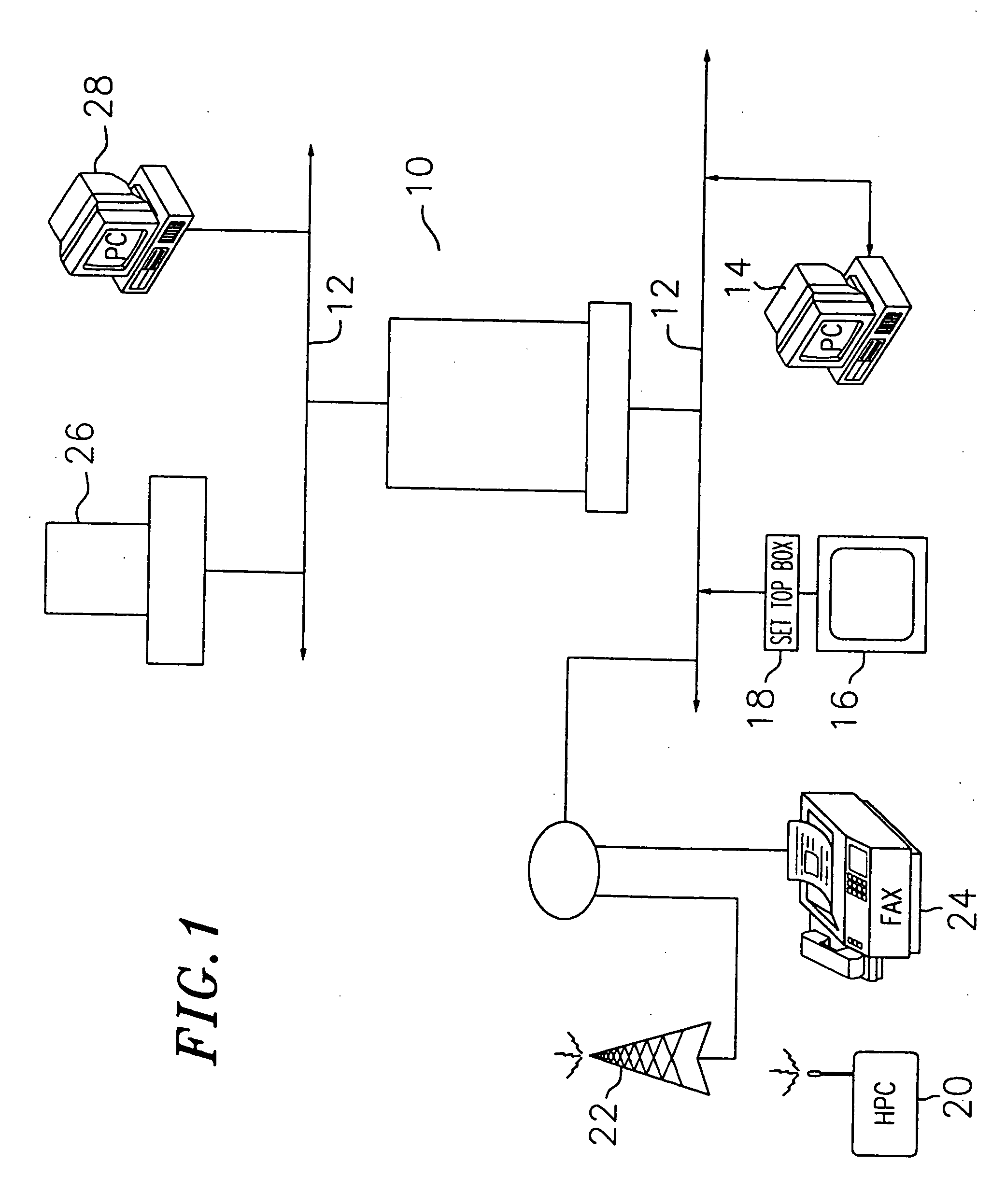
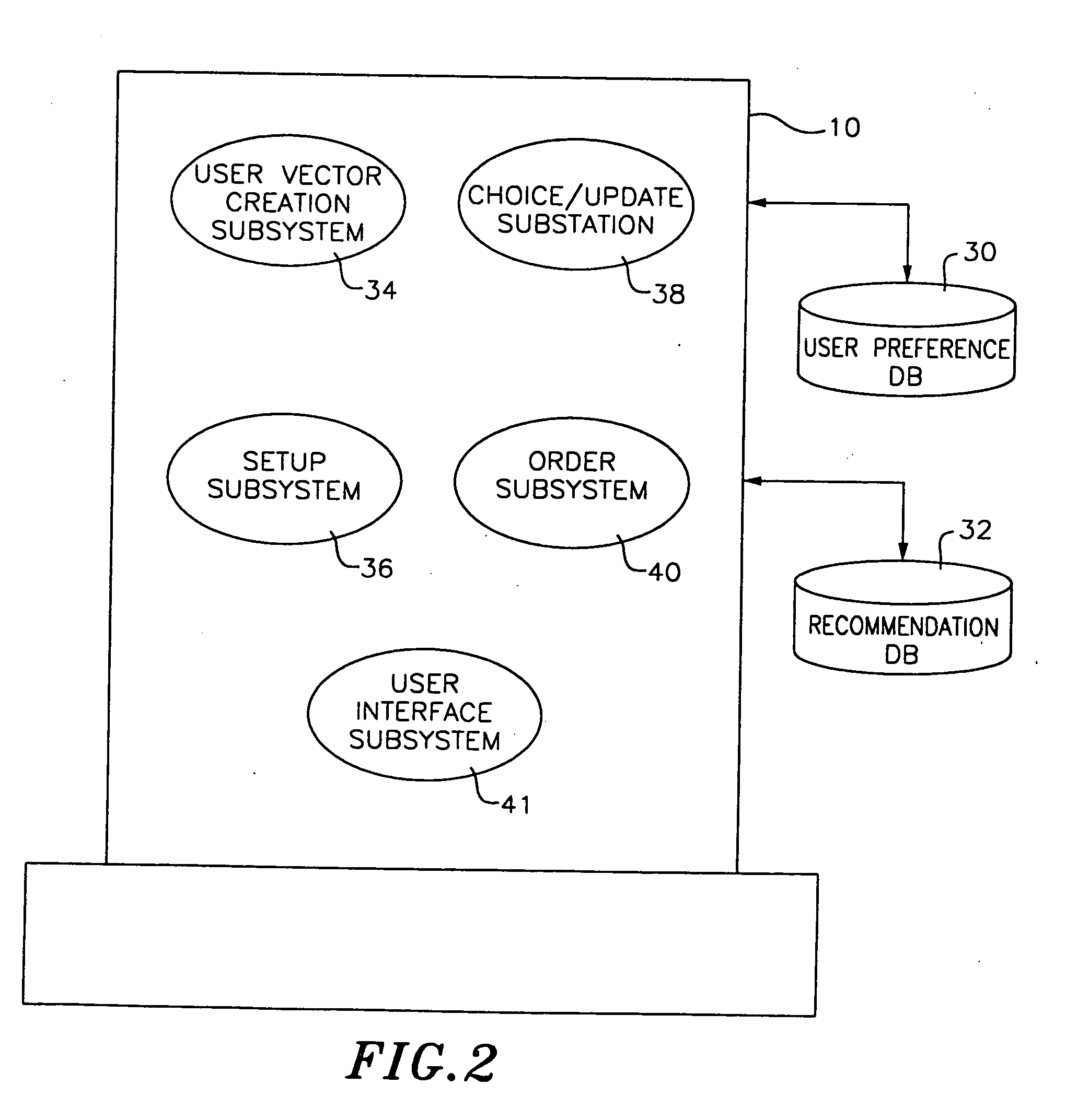
A computer system representing user preferences in an N-dimensional preference topography and making recommendations based on such topography. The preference topography depicts user ratings of products in a recommendation database. Each product is represented by a product vector associated with N objectively measurable characteristics. The user rating of a product, therefore, represents the user's preference for the particular combination of the N objectively measurable characteristics making up the product. In making a recommendation of products to the user, the system assigns a rating to each product in the recommendation database based on the preference topography. The system then selects a plurality of maximally unique choices from the rated products for recommendation to the user. These maximally unique choices are calculated to be as diverse from one another as possible but still to the user's liking. In another embodiment of the invention, the system identifies portions of the N-dimensional rating space for which the user has indicated a positive association (a positive preference cluster) or a negative association (a negative preference cluster). In making a recommendation of a potential product, the system determines the similarities of products that fall in the positive preference cluster with the potential product. The system also takes into account the products that fall in the nearest negative cluster and determines the similarities with such products and the potential product. In one particular aspect of the invention, the system presents a virtual character for making the usage of the system more user-friendly and interesting. The virtual character is programmed to interact with the user for obtaining user ratings of products and thus determining where the user preferences lie.
Owner:MUSICIP CORP
Reprogrammable circuit board with alignment-insensitive support for multiple component contact types
InactiveUS20080143379A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWave amplification devicesSignal conditioningContact type
The present invention is directed to a system that programmably interconnects integrated circuit chips and other components at near-intra-chip density. The system's contact structure allows it to adapt to components with a wide variety of contact spacings and interconnection requirements, the use of releasable attachment means allows component placement to be modified as needed, the system identifies the contacts and the components to facilitate specifying the inter-component connections, and the system provides signal conditioning and retiming to minimize issues with signal integrity and signal skew.
Owner:NORMAN RICHARD
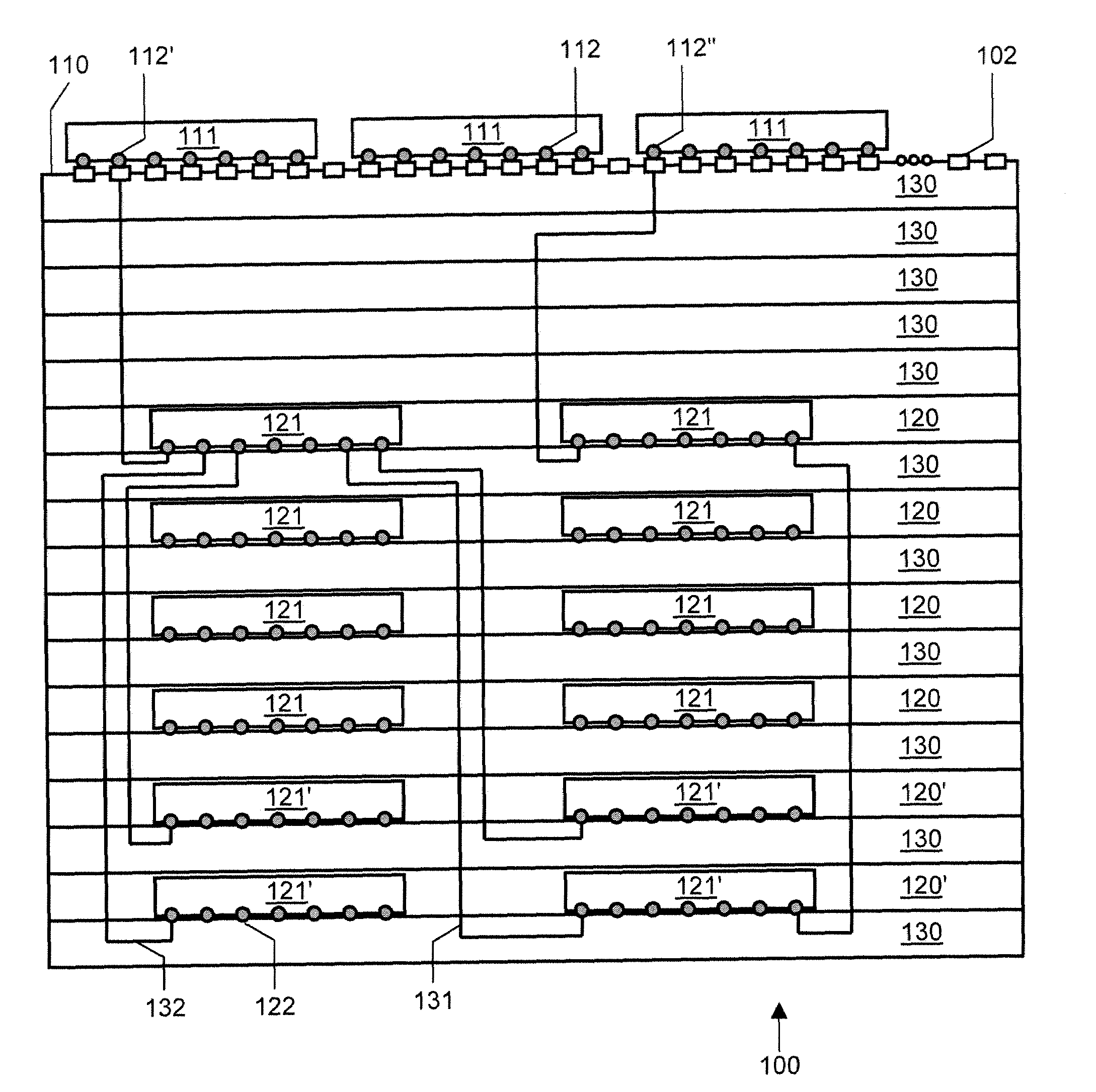
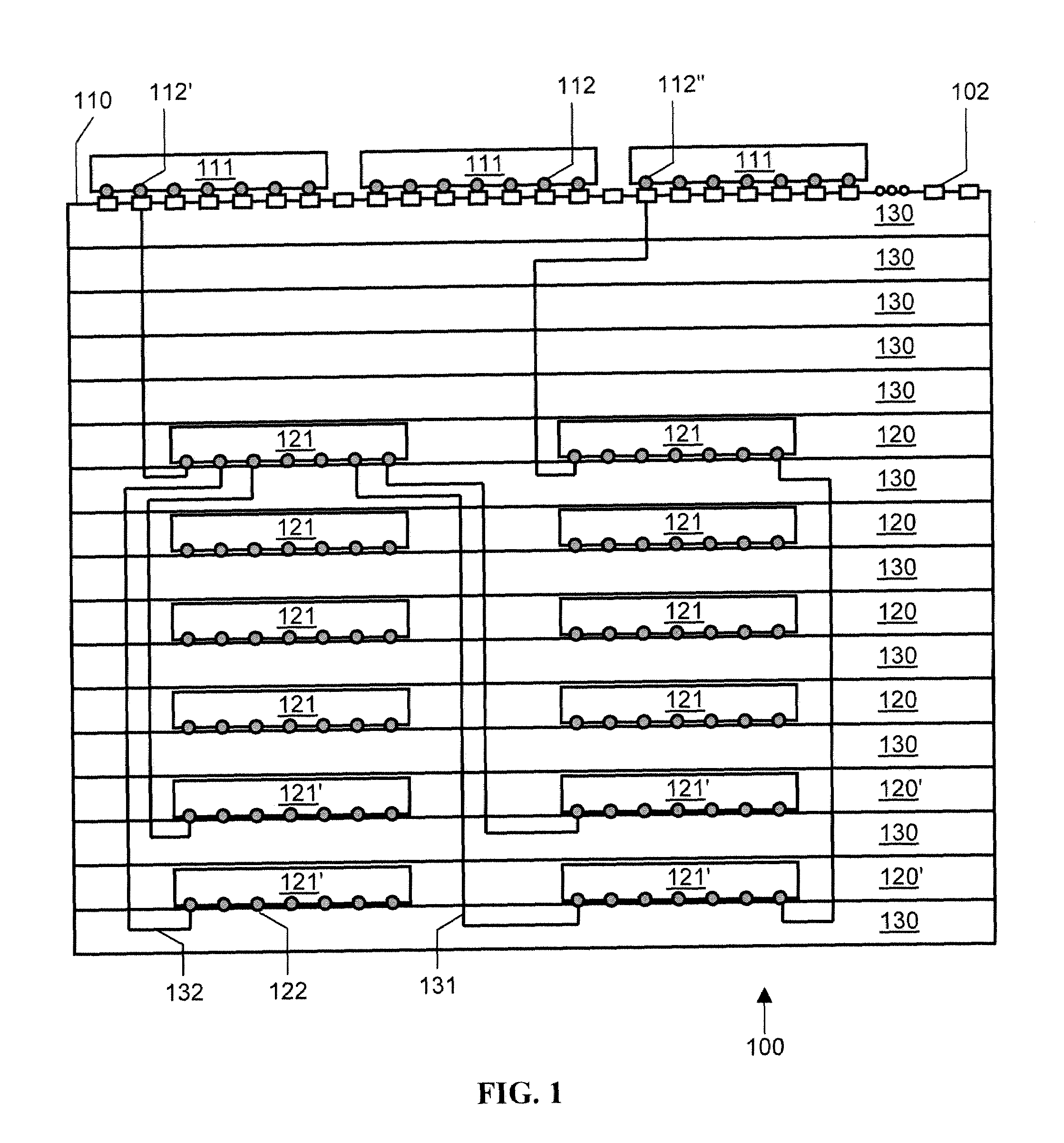
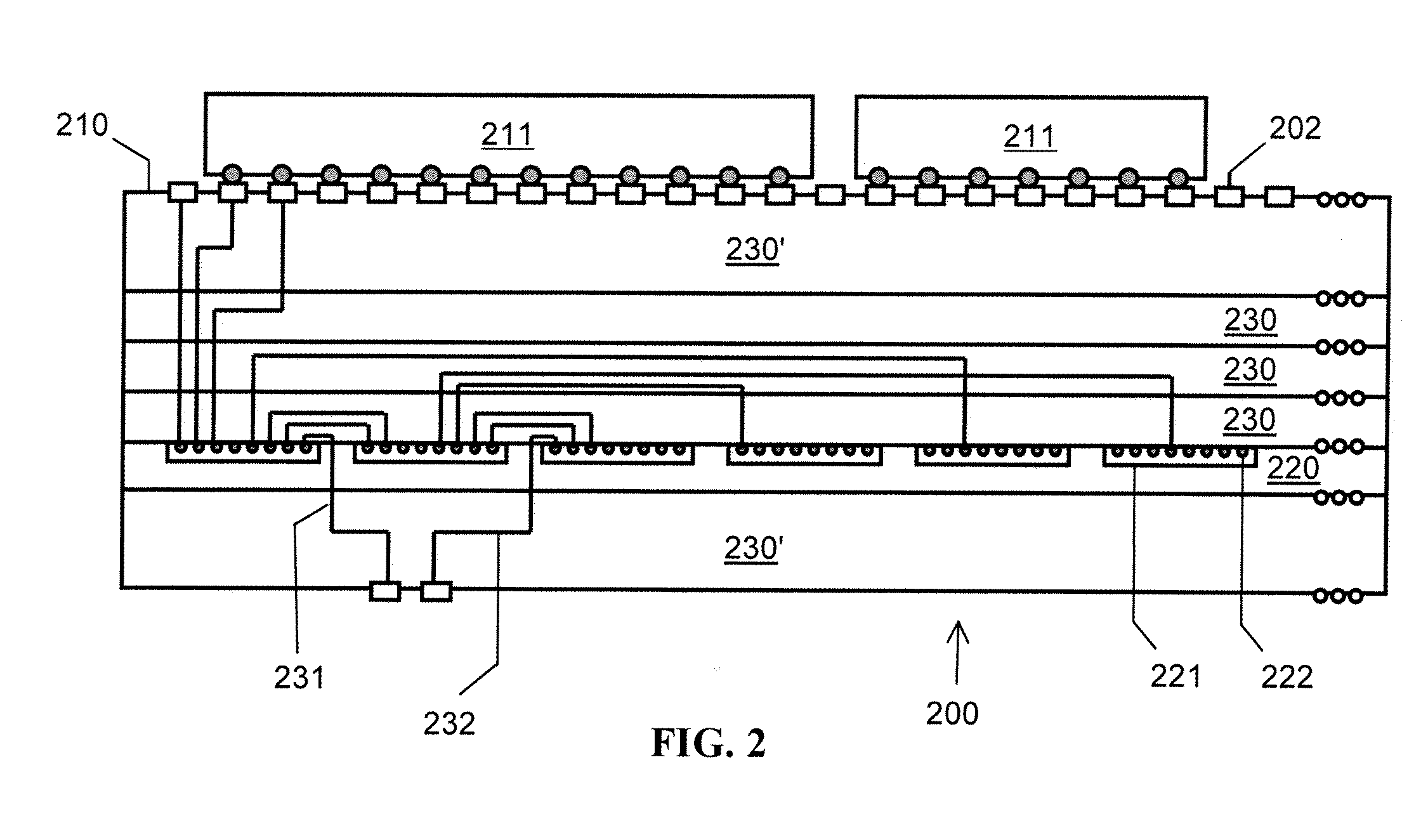
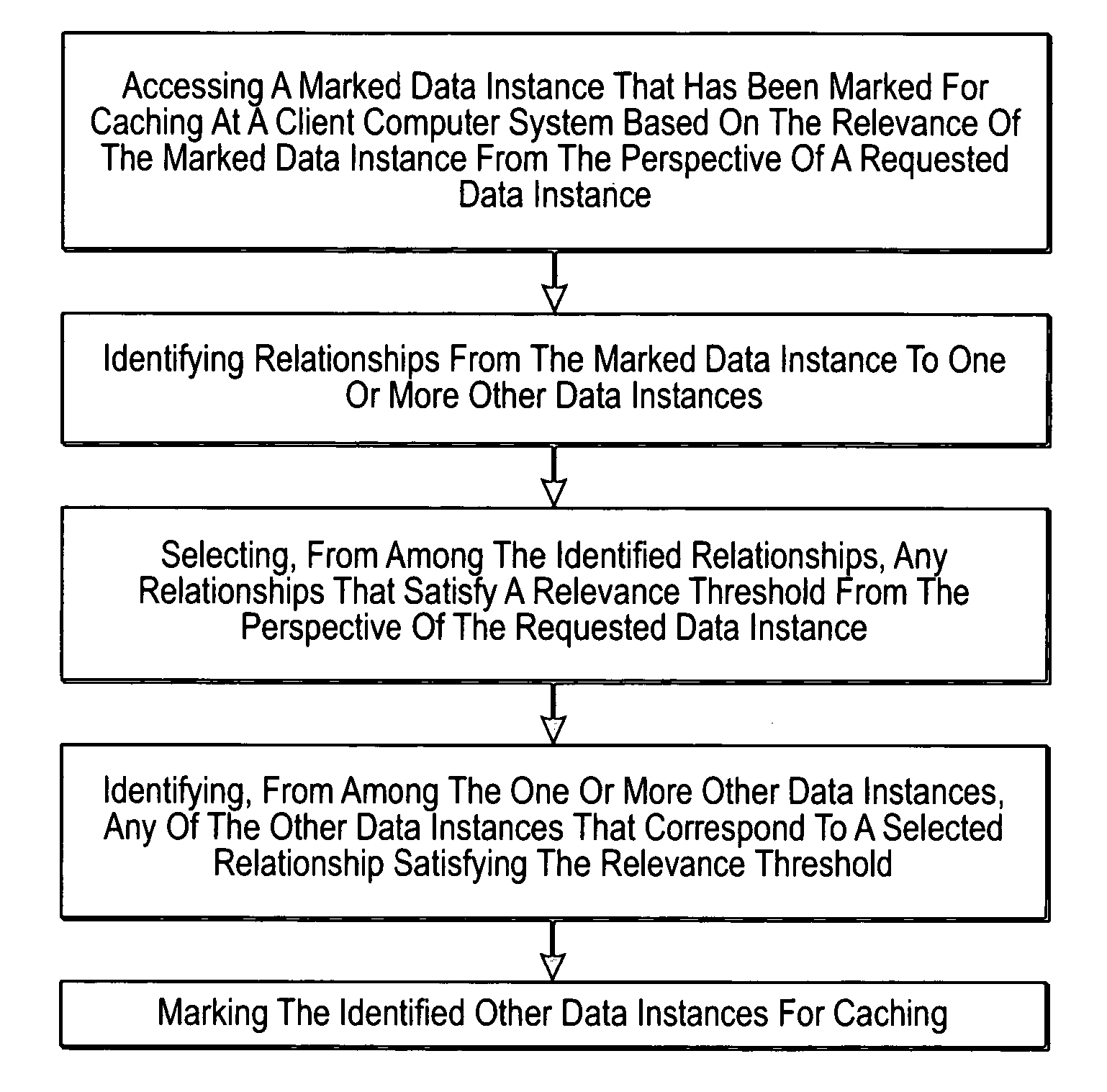
Identifying relevant data to cache
InactiveUS20070005892A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsRelevant informationClient-side
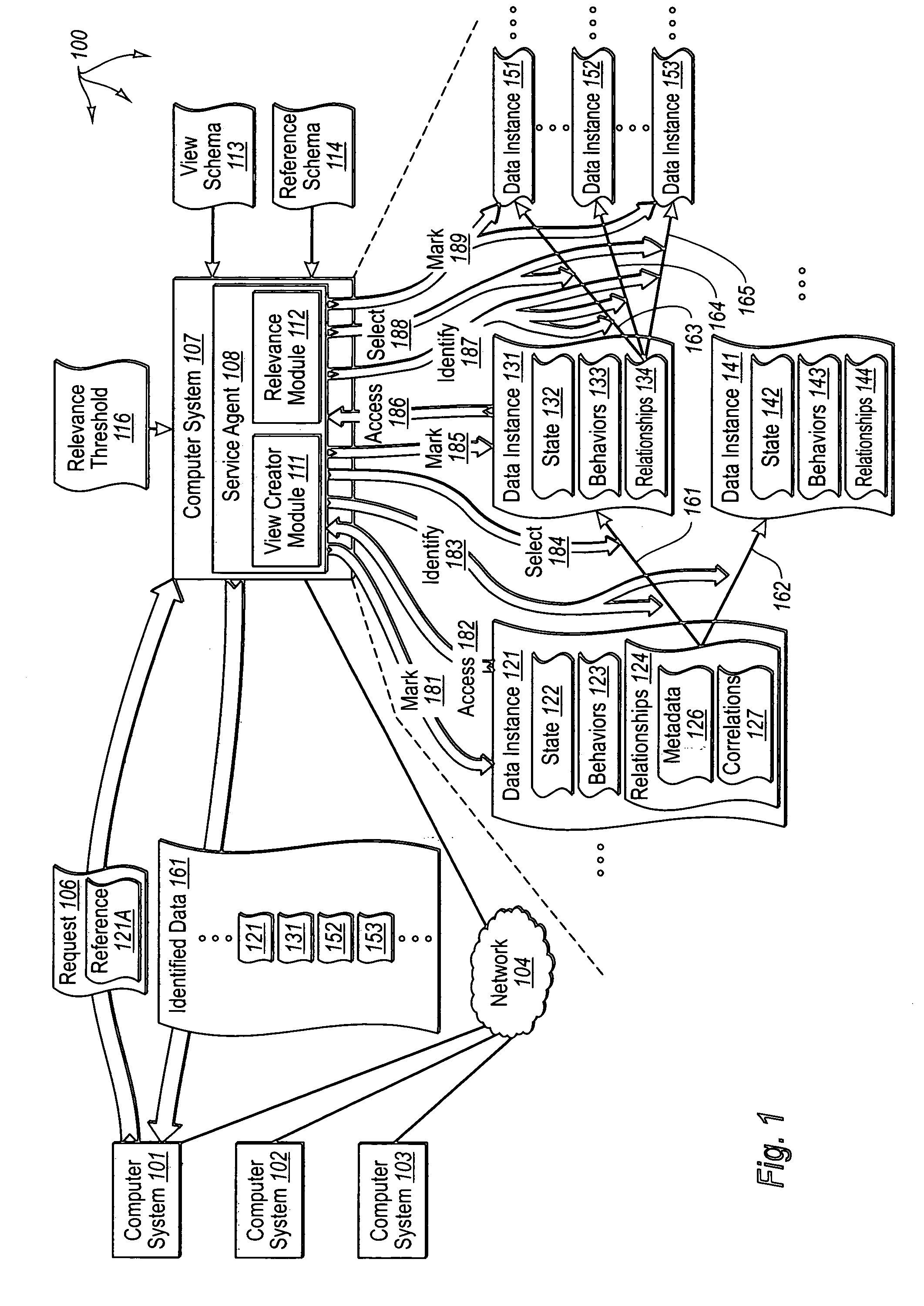
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for identifying relevant information to cache. A computer system accesses a marked data entity that has been marked for caching at a client computer system. The marked data entry is marked for caching based on the relevance of the marked data entity from the perspective of a requested data entity. The computer system identifies relationships from the marked data entity to one or more other data entities. The computer system selects, from among the identified relationships, any relationships that satisfy a relevance threshold from the perspective of the requested data entity. The computer system identifies, from among the one or more other data entities, any of the other data entities that correspond to a selected relationship satisfying the relevance threshold. The computer system marks the identified other data entities for caching.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Controller for Non-Volatile Memories and Methods of Operating the Memory Controller
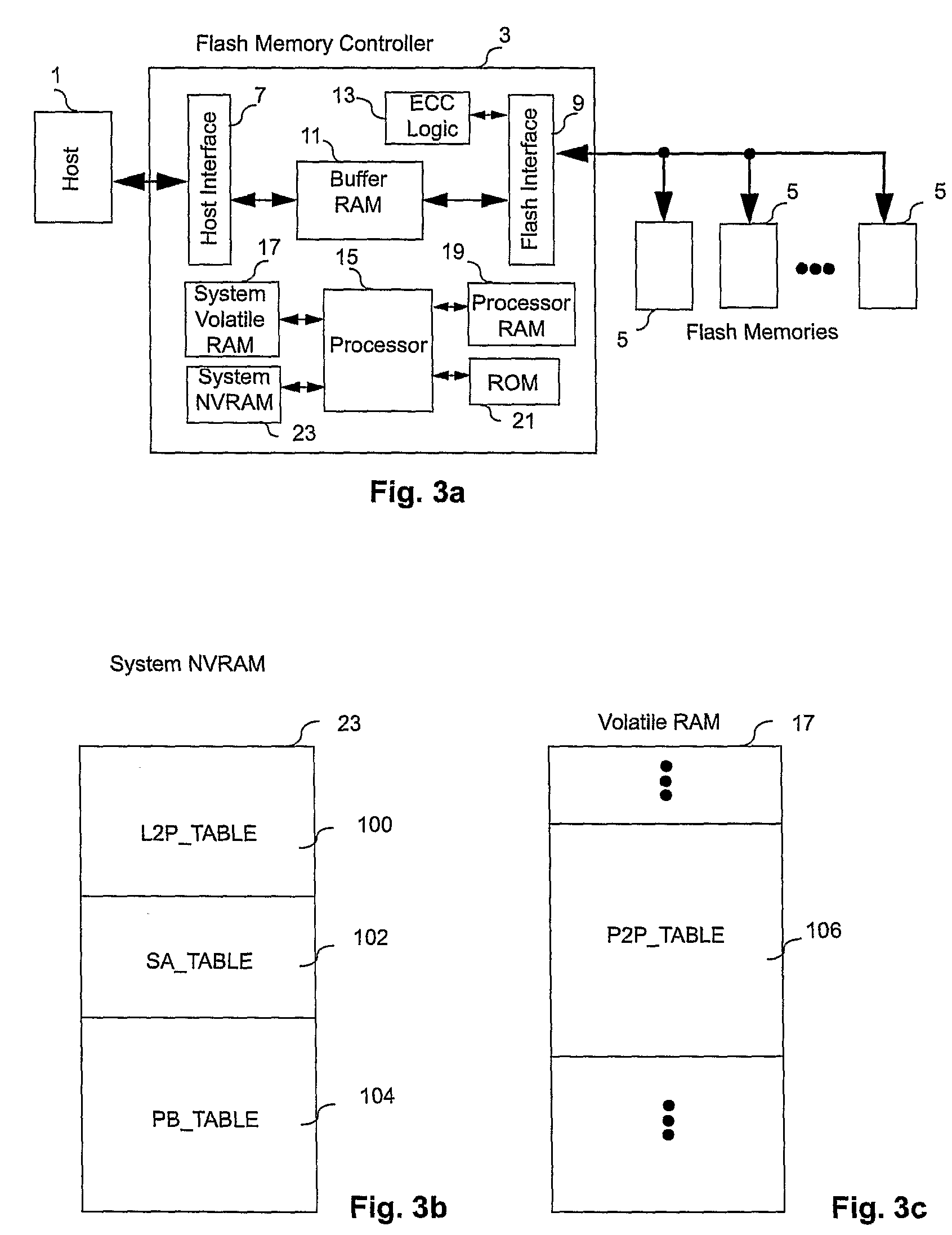
ActiveUS20080270680A1Improve system performanceReduce stepsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesMemory controllerByte
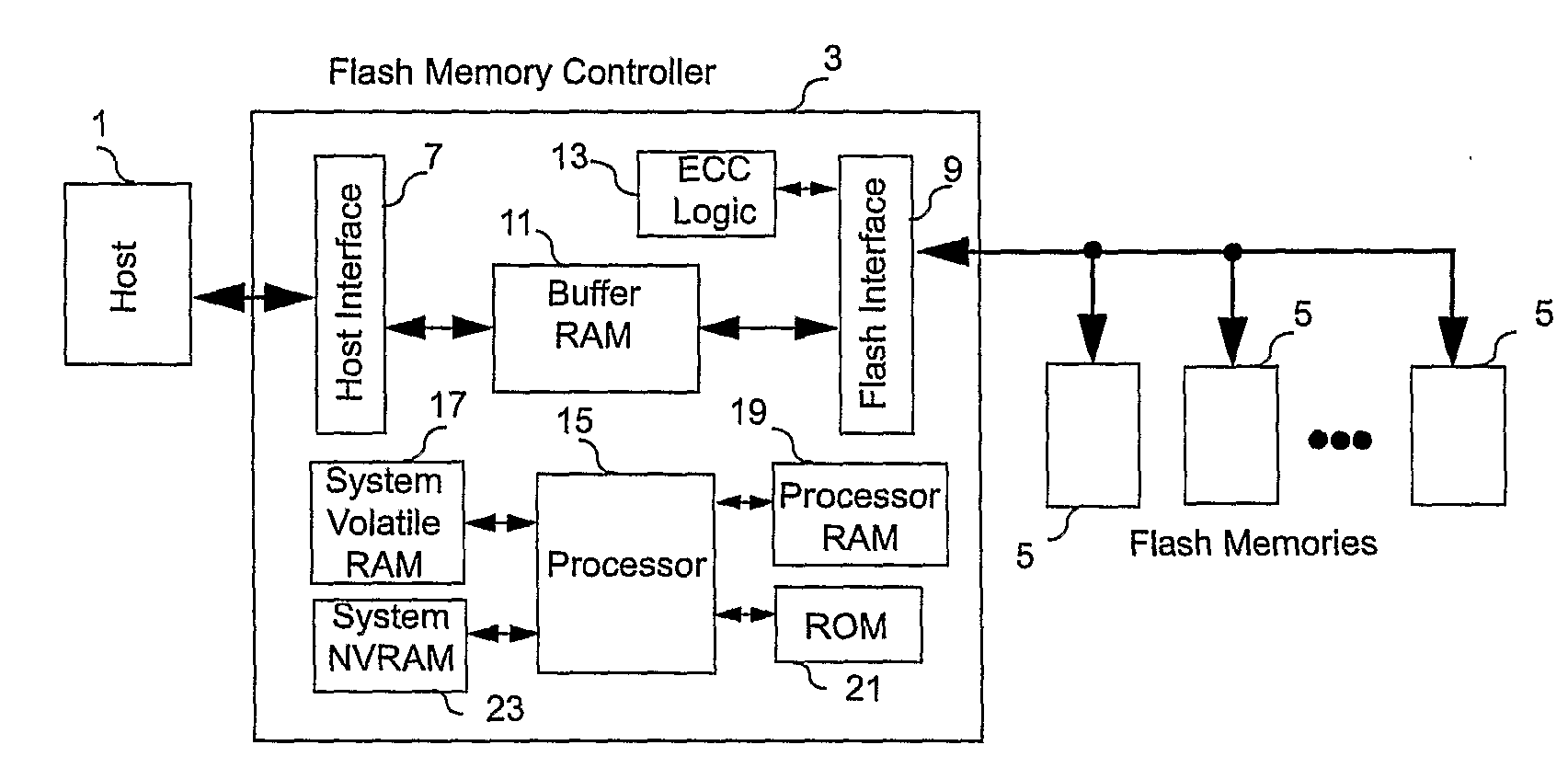
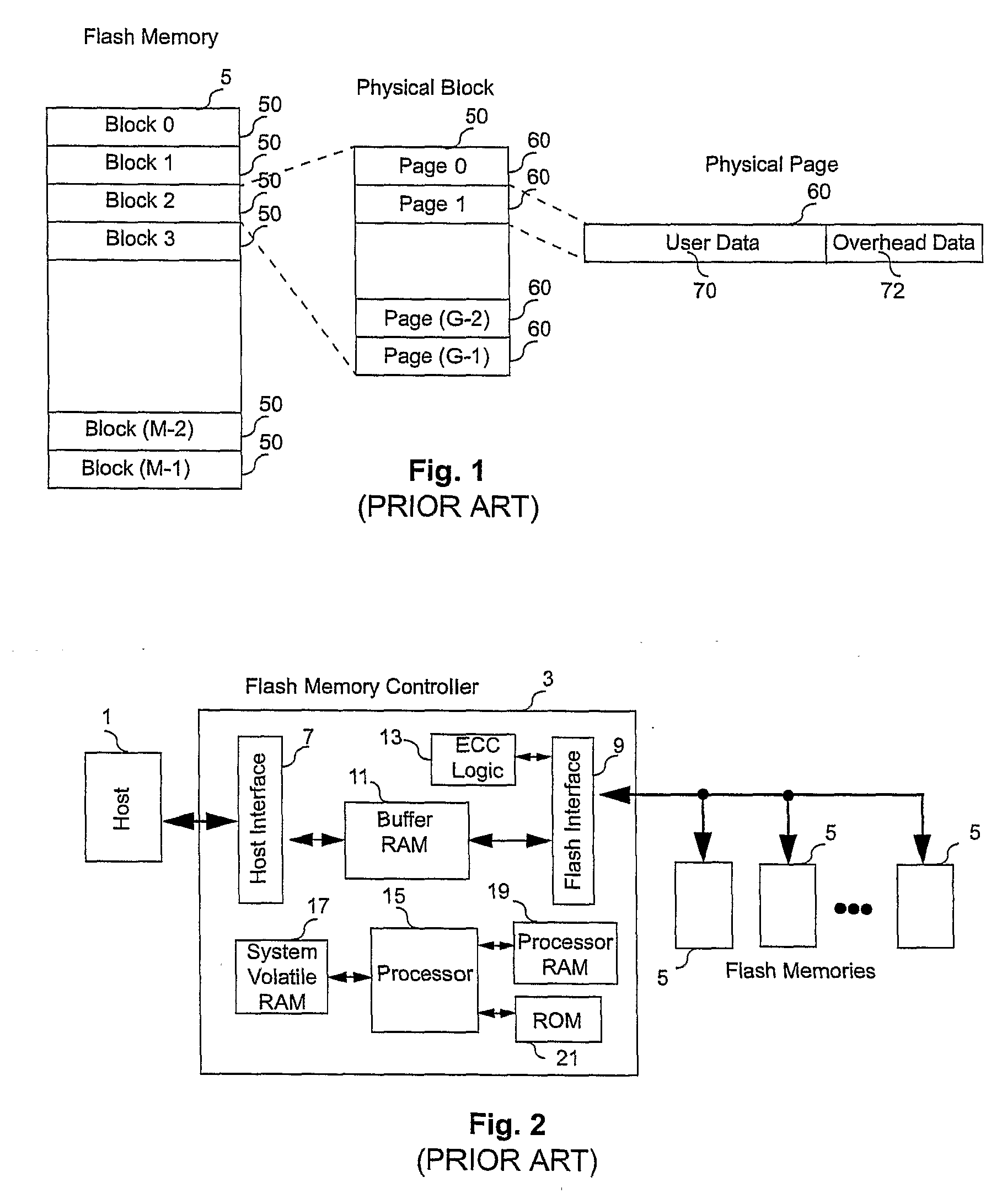
A non-volatile memory system (3) is proposed consisting of a first non-volatile flash memory (5) having a plurality of blocks, each block having a plurality of pages, each block being erasable and each page being programmable, and a second non-volatile random access memory (23) having a plurality of randomly accessible bytes. The second non-volatile memory (23) stores data for mapping logical blocks to physical blocks and status information of logical blocks. Each logical block has an associated physical page pointer stored in the second non-volatile memory (23) that identifies the next free physical page of the mapped physical block to be written. The page pointer is incremented after every page write to the physical block, allowing all physical pages to be fully utilized for page writes. Furthermore, a method of writing and reading data is disclosed whereby the most recently written physical page associated with a logical address is identifiable by the memory system without programming flags into superseded pages, or recording time stamp values in any physical page or block of the first non-volatile memory (5). Furthermore, a method is provided for a logical block to be mapped to two physical blocks instead of one to provide additional space for page writes, resulting in reduction in page copy operations, thereby increasing the performance of the system.
Owner:CHANG CHEE KENG
Method and apparatus for detecting incorrectly translated text in a document
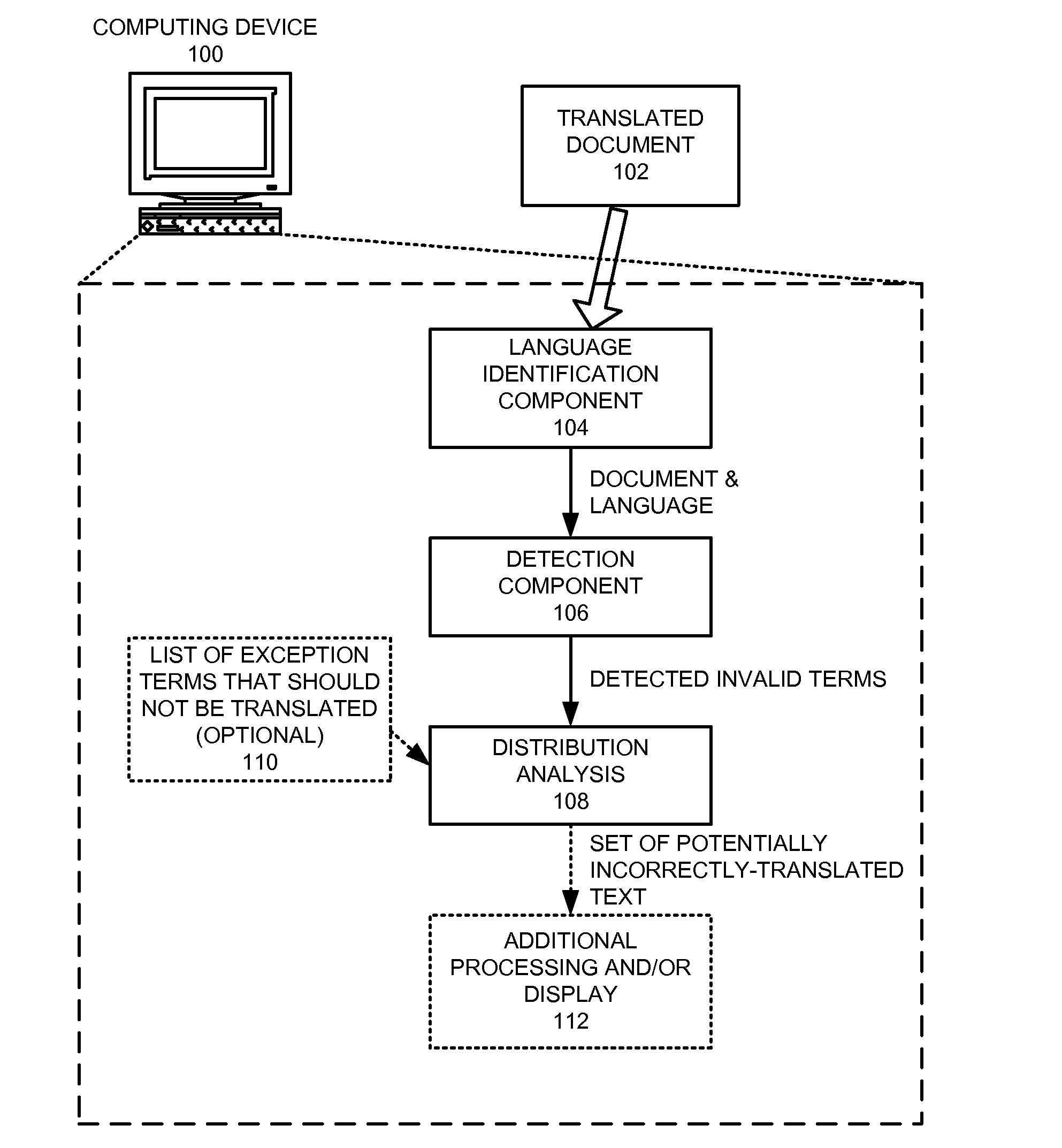
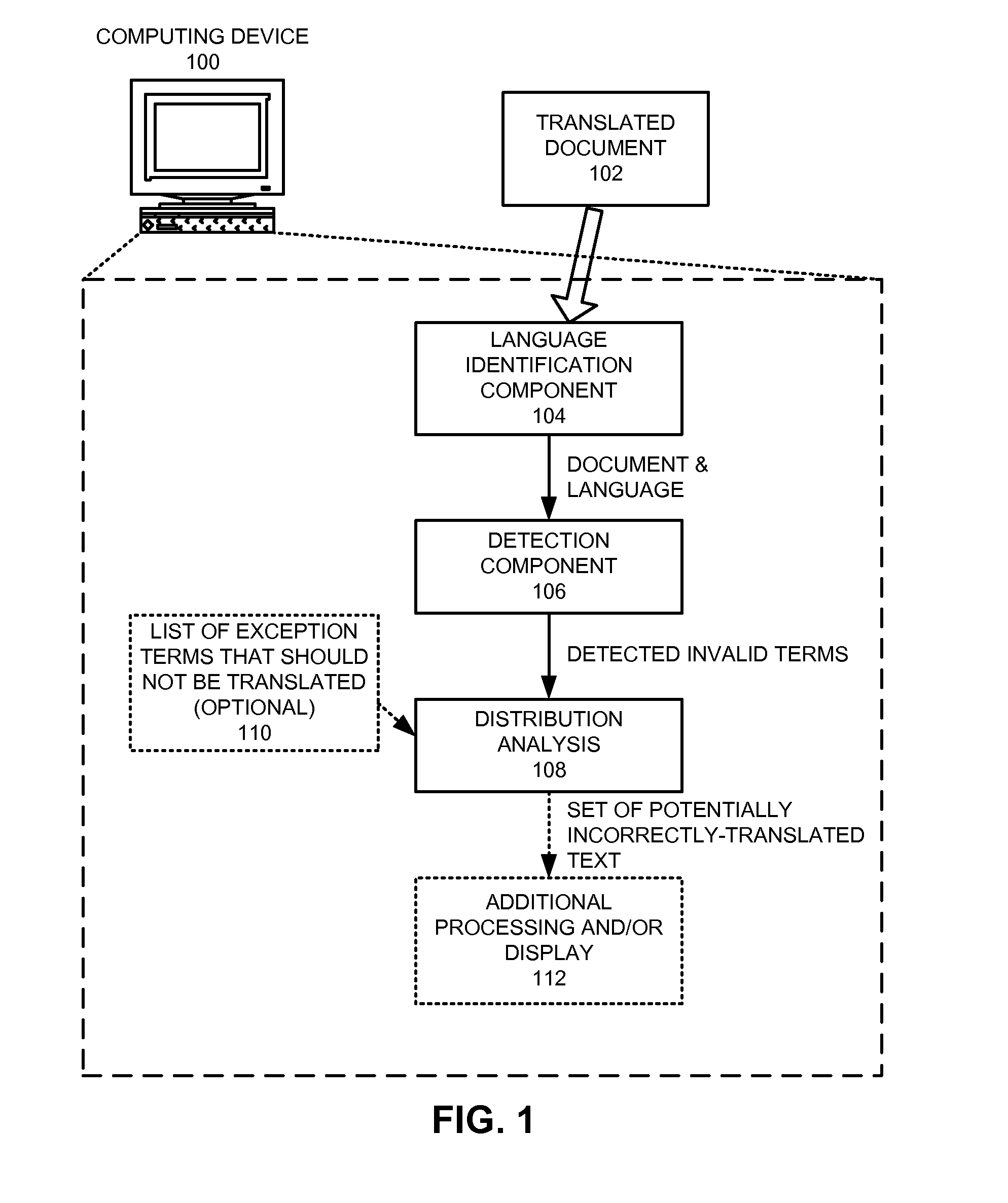
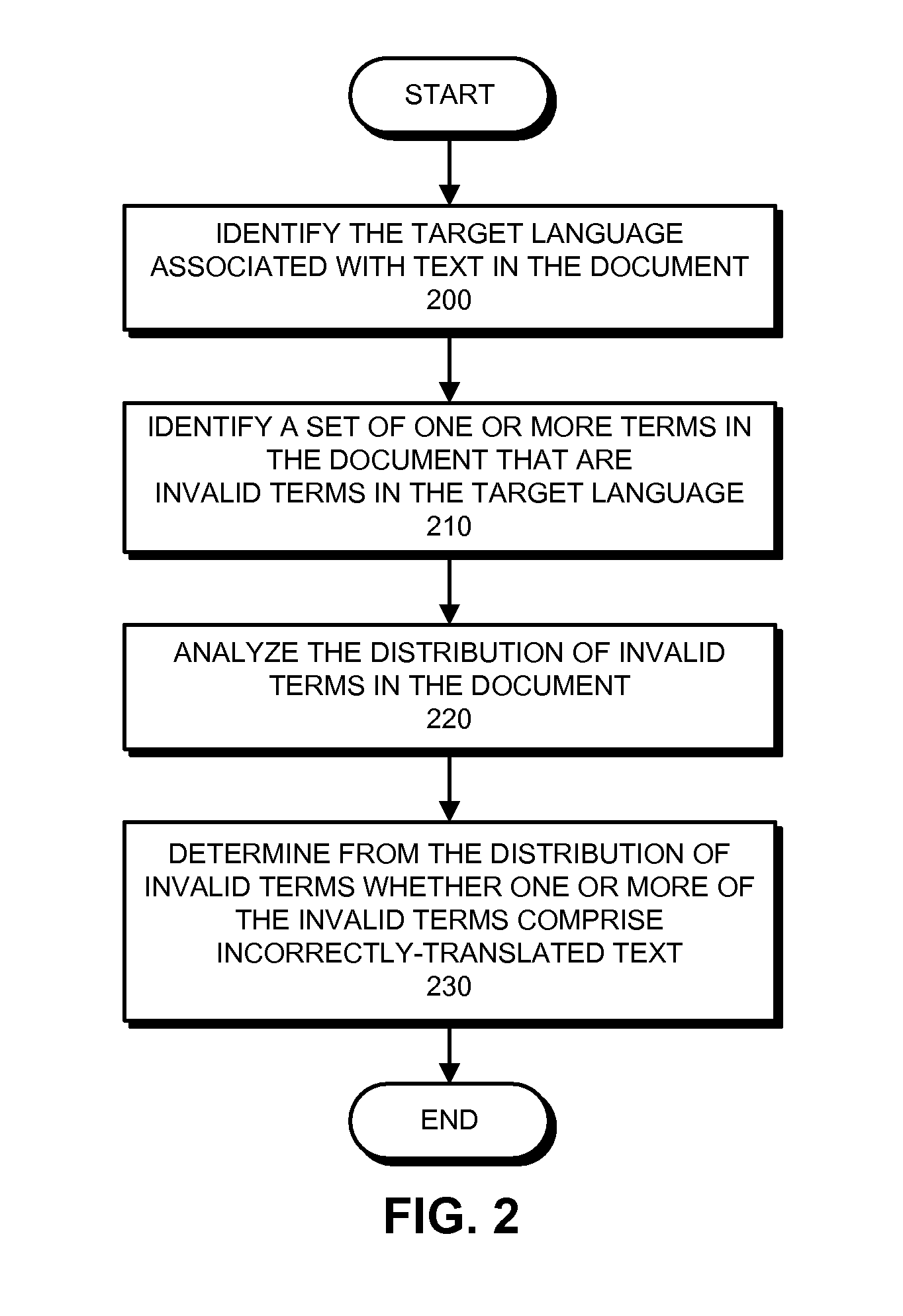
InactiveUS8296124B1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language processingSystems analysis
A system that detects incorrectly translated text in a document. During operation, the system determines a target language for the document. The system then identifies one or more terms in the document that are invalid terms for the language. Next, the system analyzes correlations between these invalid terms, and, based on these correlations, determines whether one or more of the invalid terms comprise incorrectly translated text.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
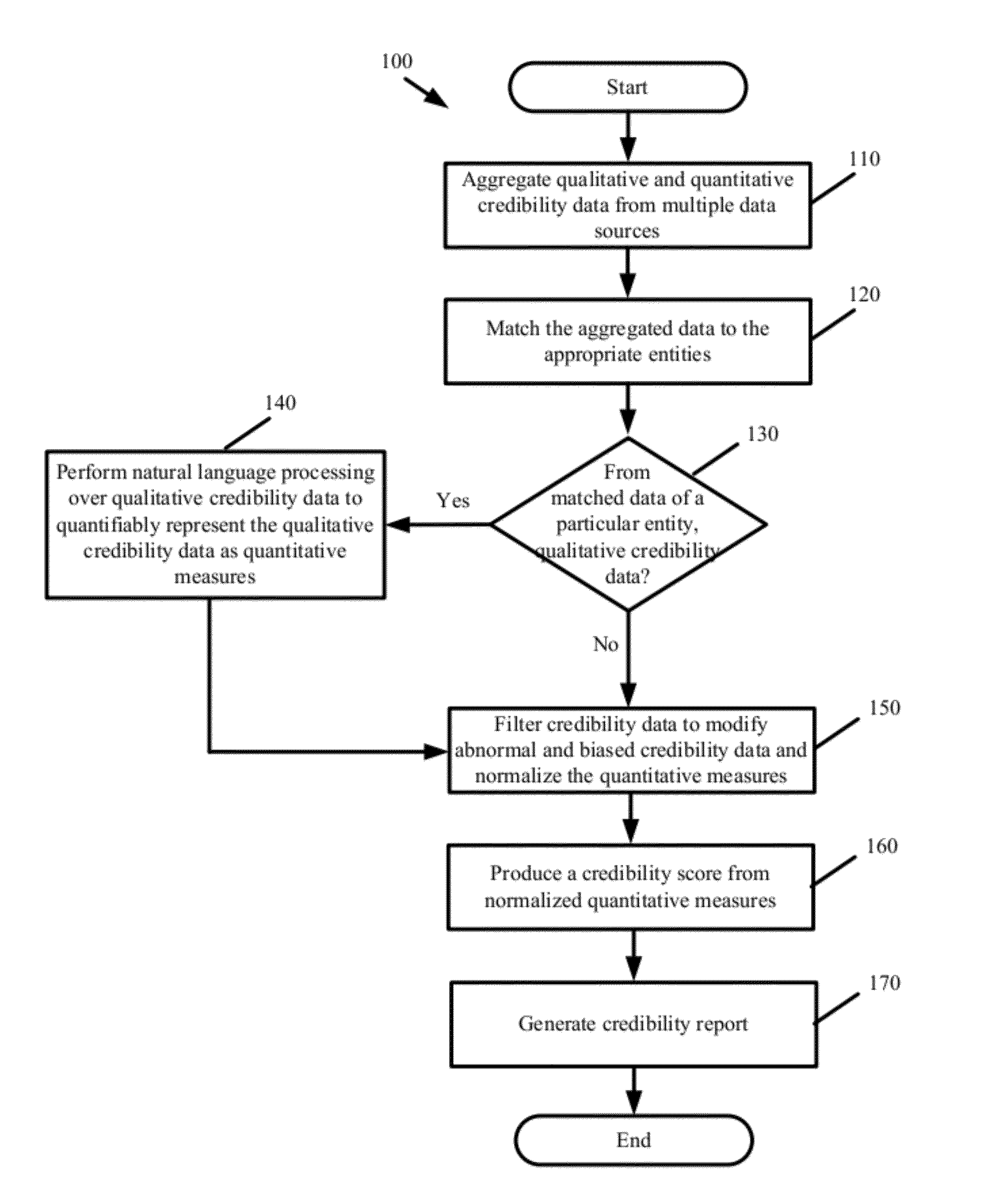
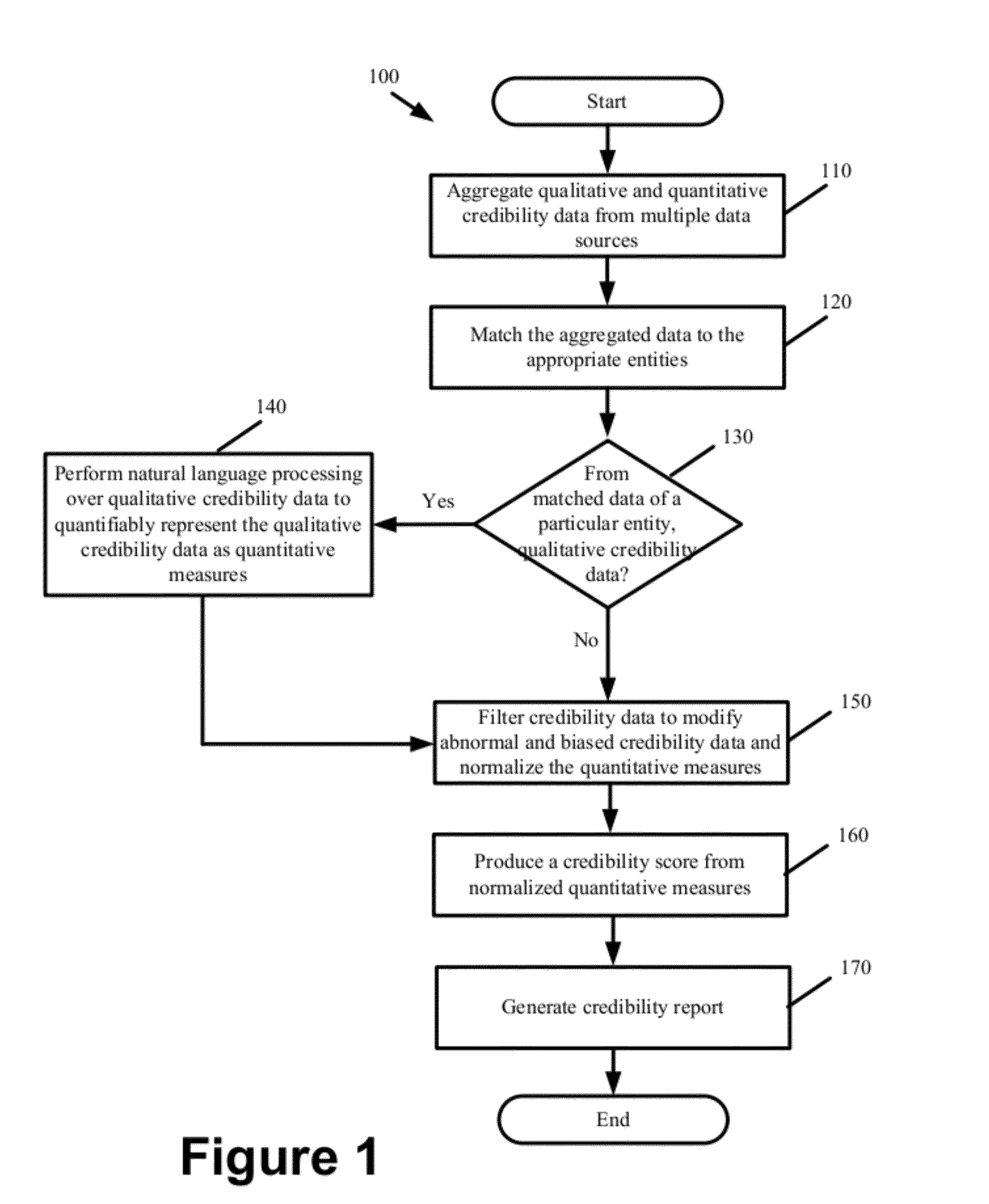
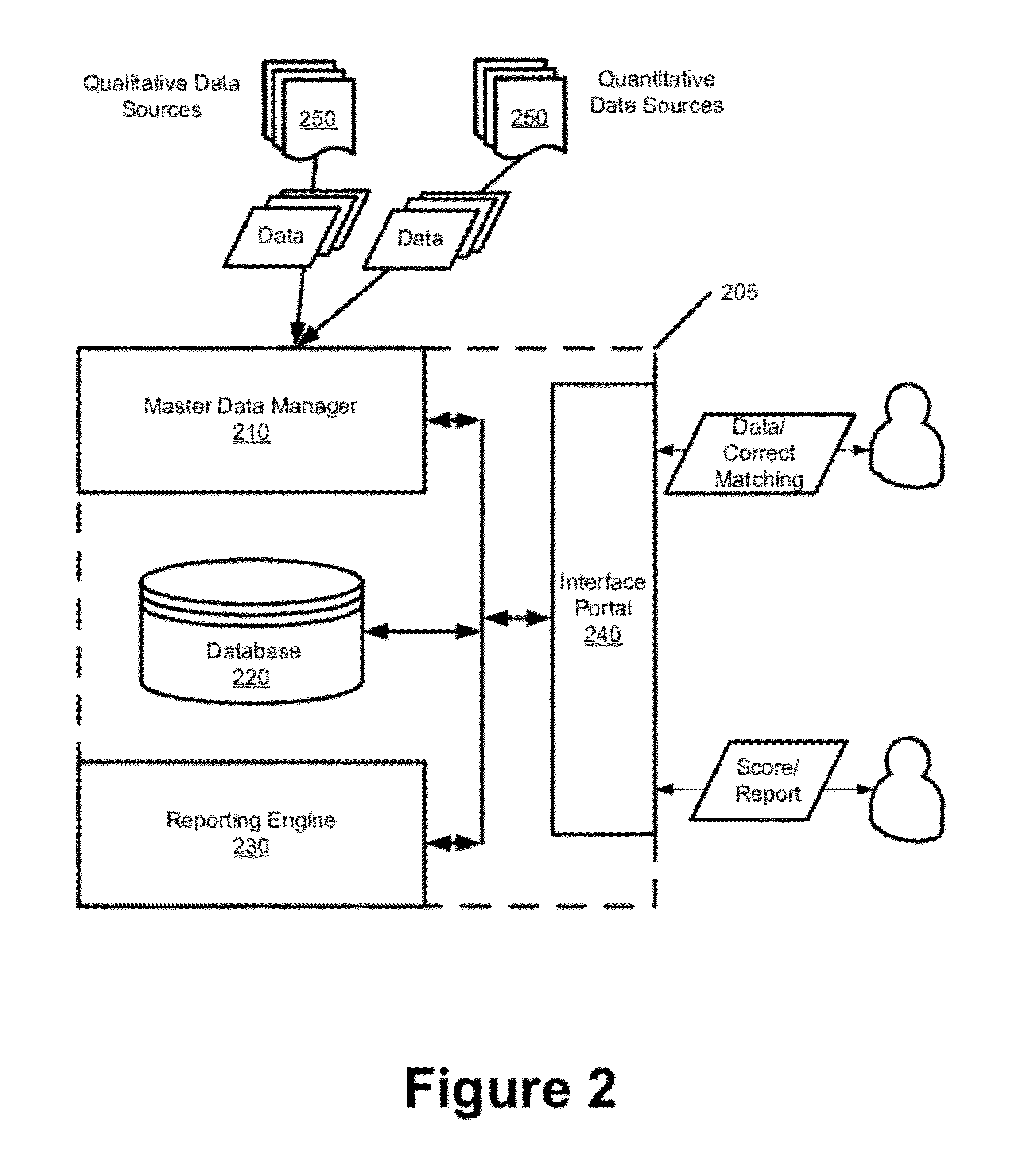
Indices for Credibility Trending, Monitoring, and Lead Generation
ActiveUS20120278767A1Credibility of may fallIncrease credibilityFinanceInput/output processes for data processingBusiness enterpriseBusiness practice
Some embodiments provide a credibility system that computes credibility scores to quantify the credibility of different businesses and to coalesce the generated credibility scores into various indices. The indices comparatively present the credibility of a particular business relative to other businesses along one or more dimensions. Based on the indices, the system identifies trends in the credibility of a particular business. The system derives preliminary credibility for a new business for which credibility data has not yet been obtained based on credibility that has been previously established for other businesses in an index associated with the new business. The system provides automated services for monitoring credibility of a business and for generating alerts to notify the business that its credibility has reached various thresholds. The system identifies business practices that improve upon or adversely affect the credibility of a particular business.
Owner:DUN & BRADSTREET EMERGING BUSINESSES
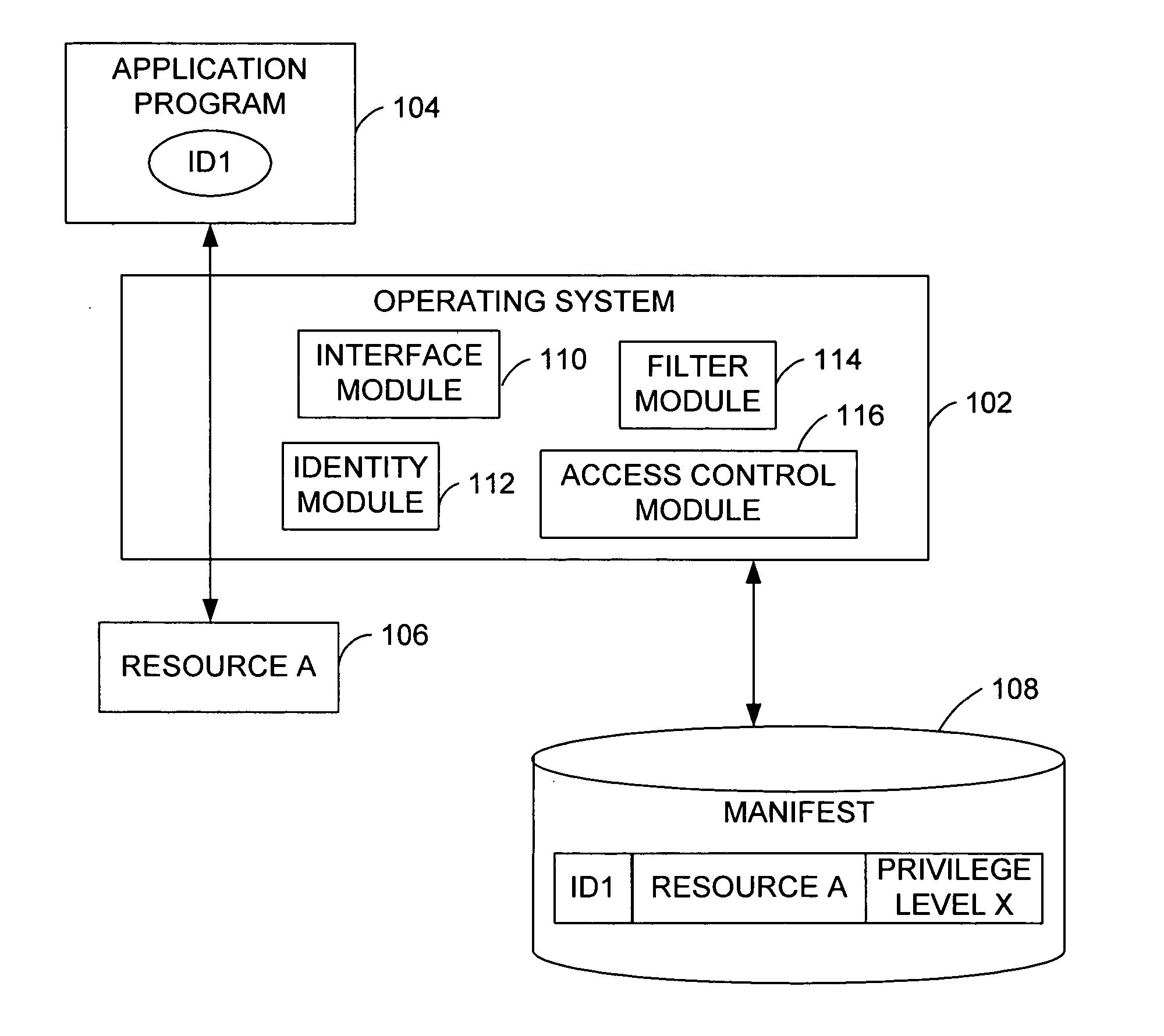
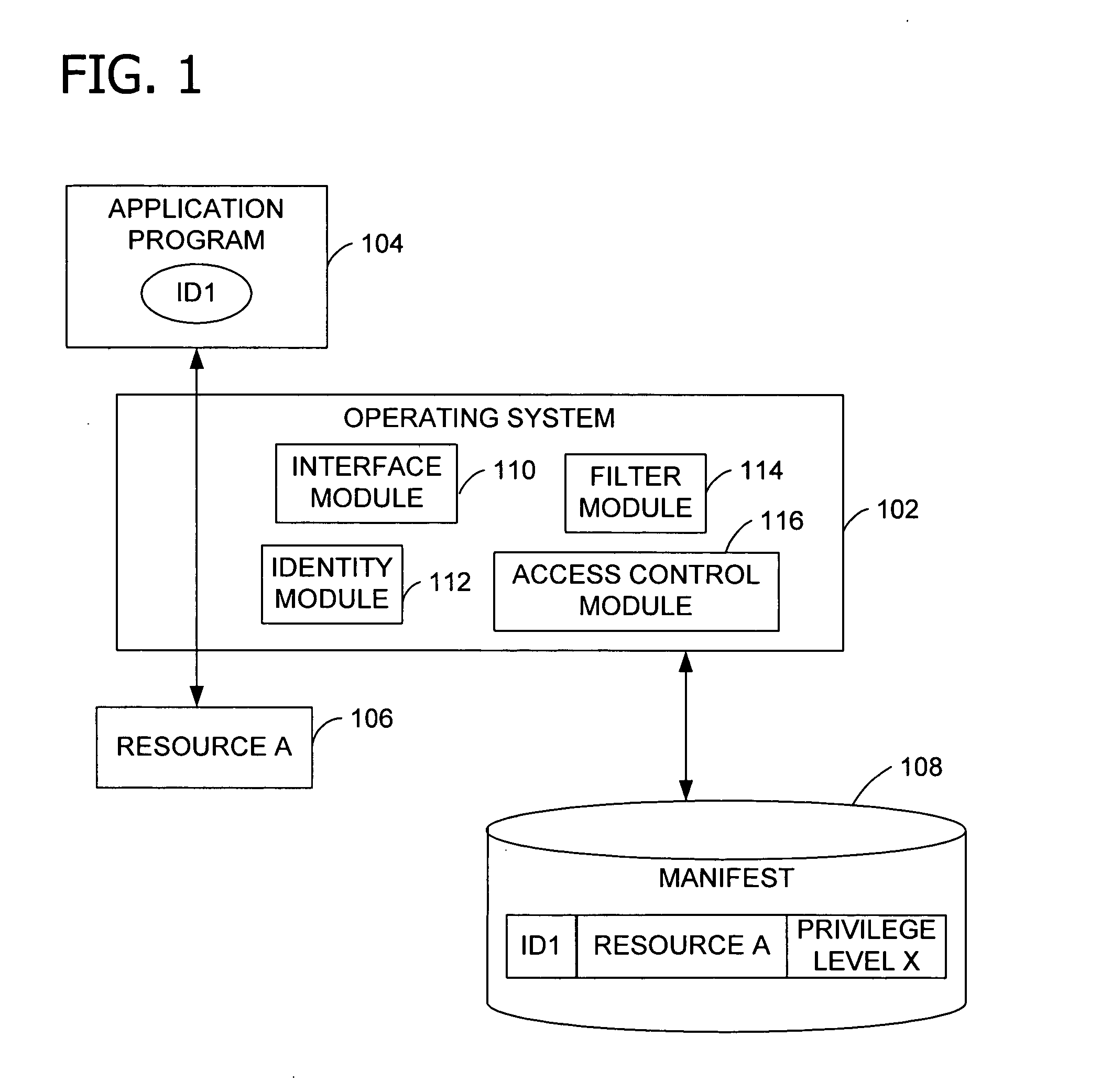
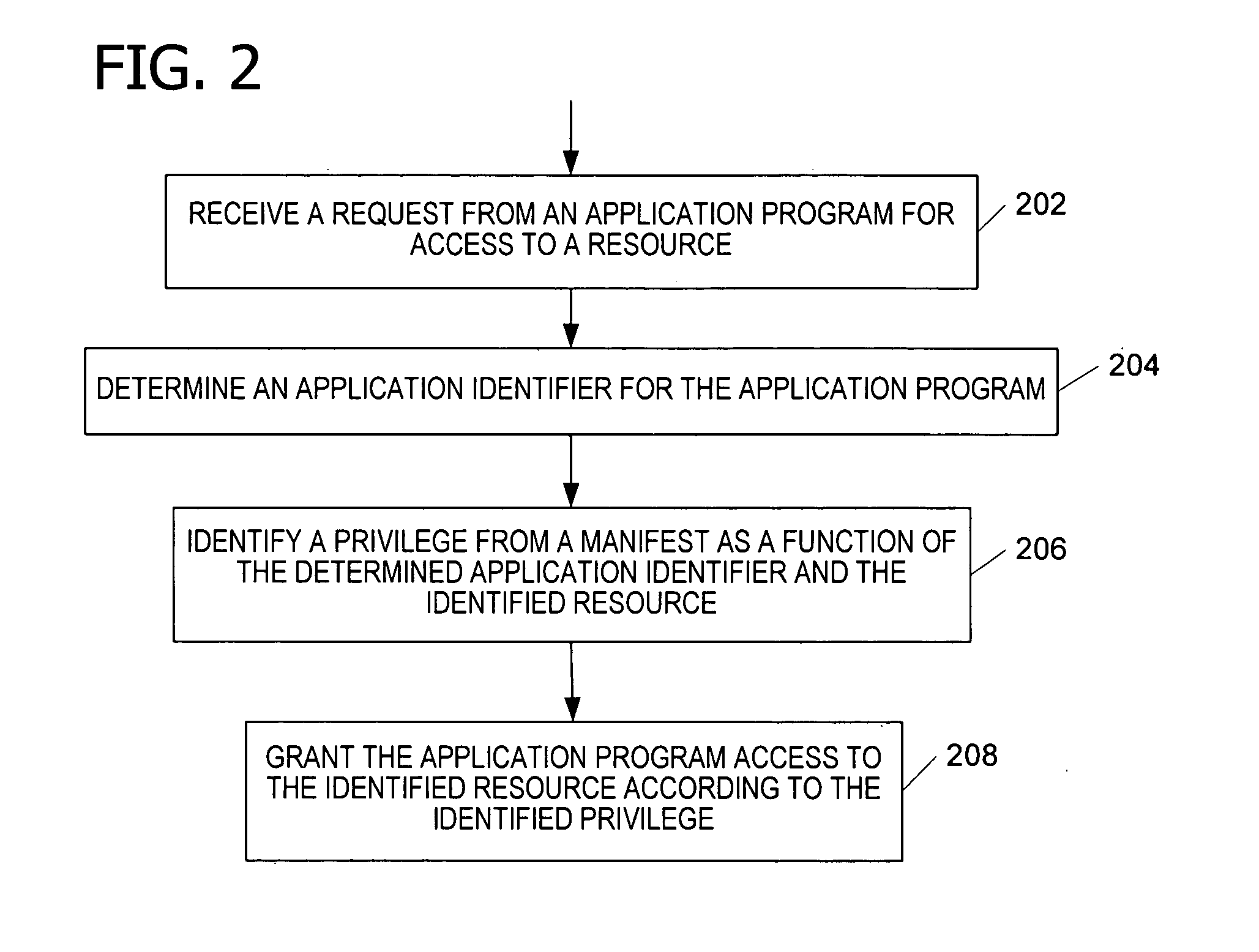
Operating system resource protection
PendingUS20050091658A1Resource allocationDigital data processing detailsResource protectionOperational system
Granting an application program access to a resource as a function of a privilege associated with the application program. An embodiment of the invention employs a persistent, individual identity associated with the components of an application program or a group of application programs to allow an operating system to identify and differentiate between different application programs or groups of application programs installed on a computing system. The identity associated with each component of an application program enables the identification and removal or uninstallation of the application program. The identity also enables isolation of resources of the application program and protection of operating system resources.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
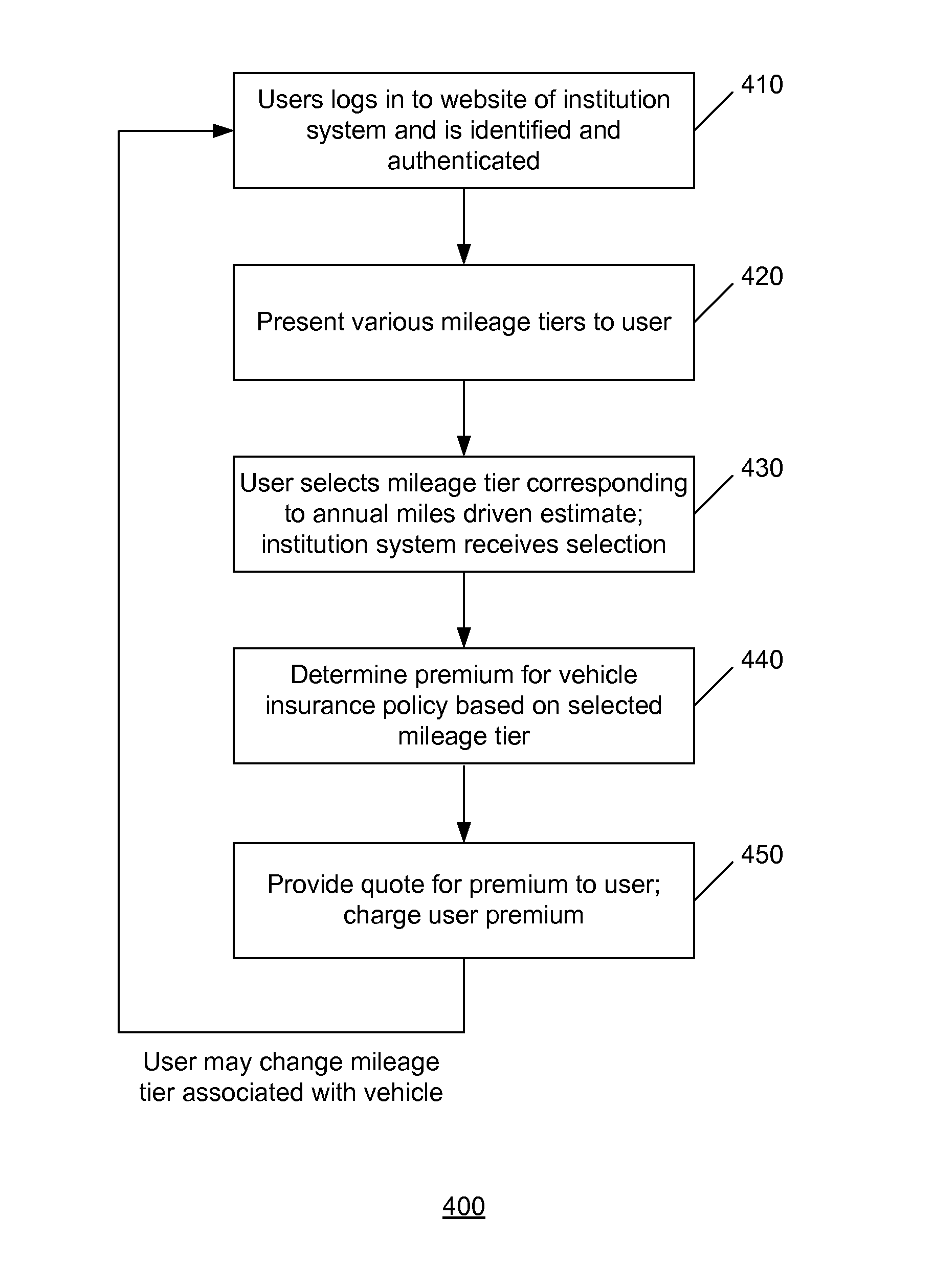
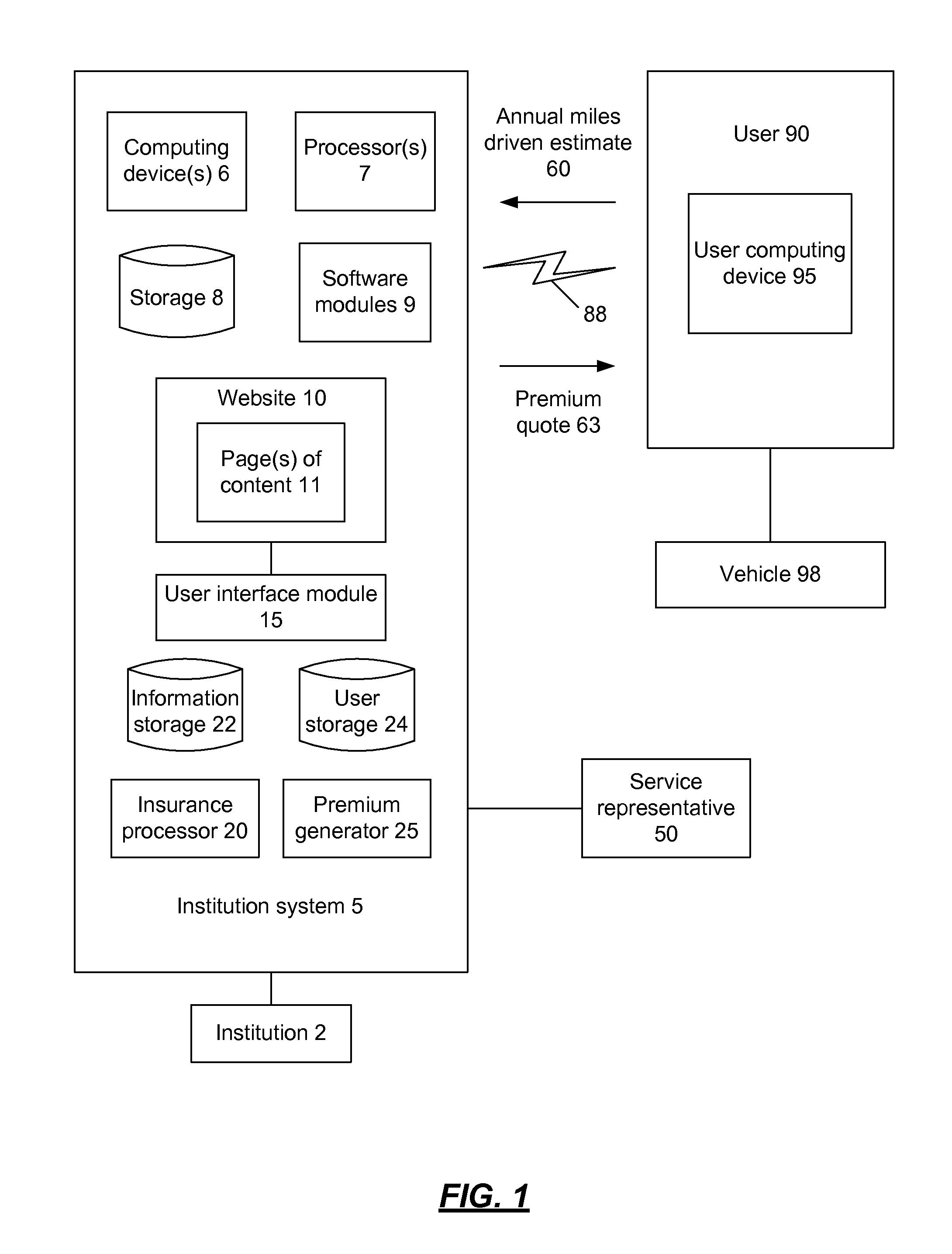
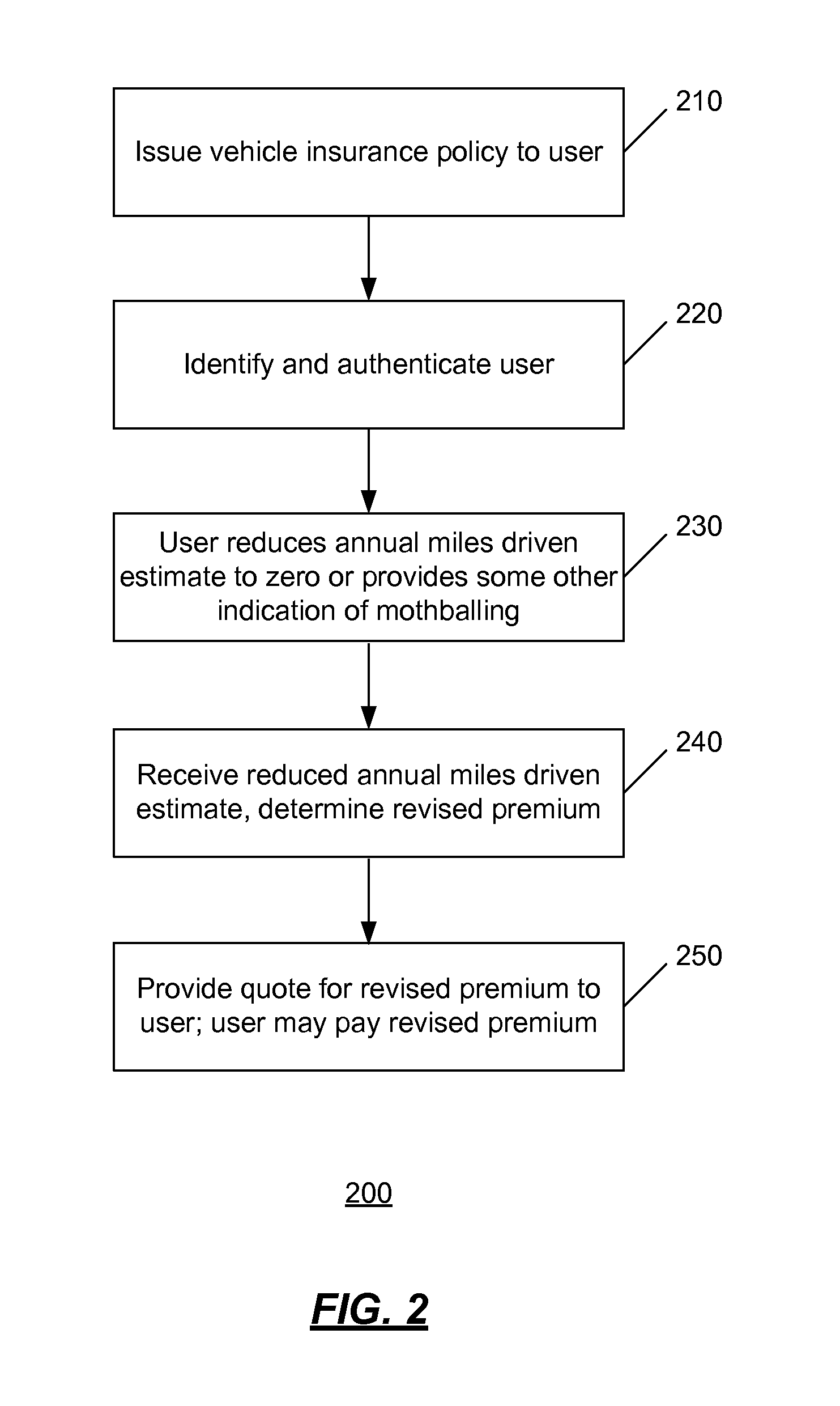
Systems and methods for self-service vehicle risk adjustment
A user may be identified and authenticated to an institution system and may adjust the annual miles driven estimate for their vehicle. The annual miles driven estimate is used in the determination of the premium for the vehicle insurance for the vehicle. The premium for the vehicle insurance may be revised based on the adjustment by the user to the annual miles driven estimate. In an implementation, the user may reduce the annual miles driven estimate to zero to indicate that they are not driving the vehicle. The user may keep some elements of the vehicle insurance coverage and the vehicle insurance policy may remain active although the annual miles driven estimate is zero.
Owner:USAA
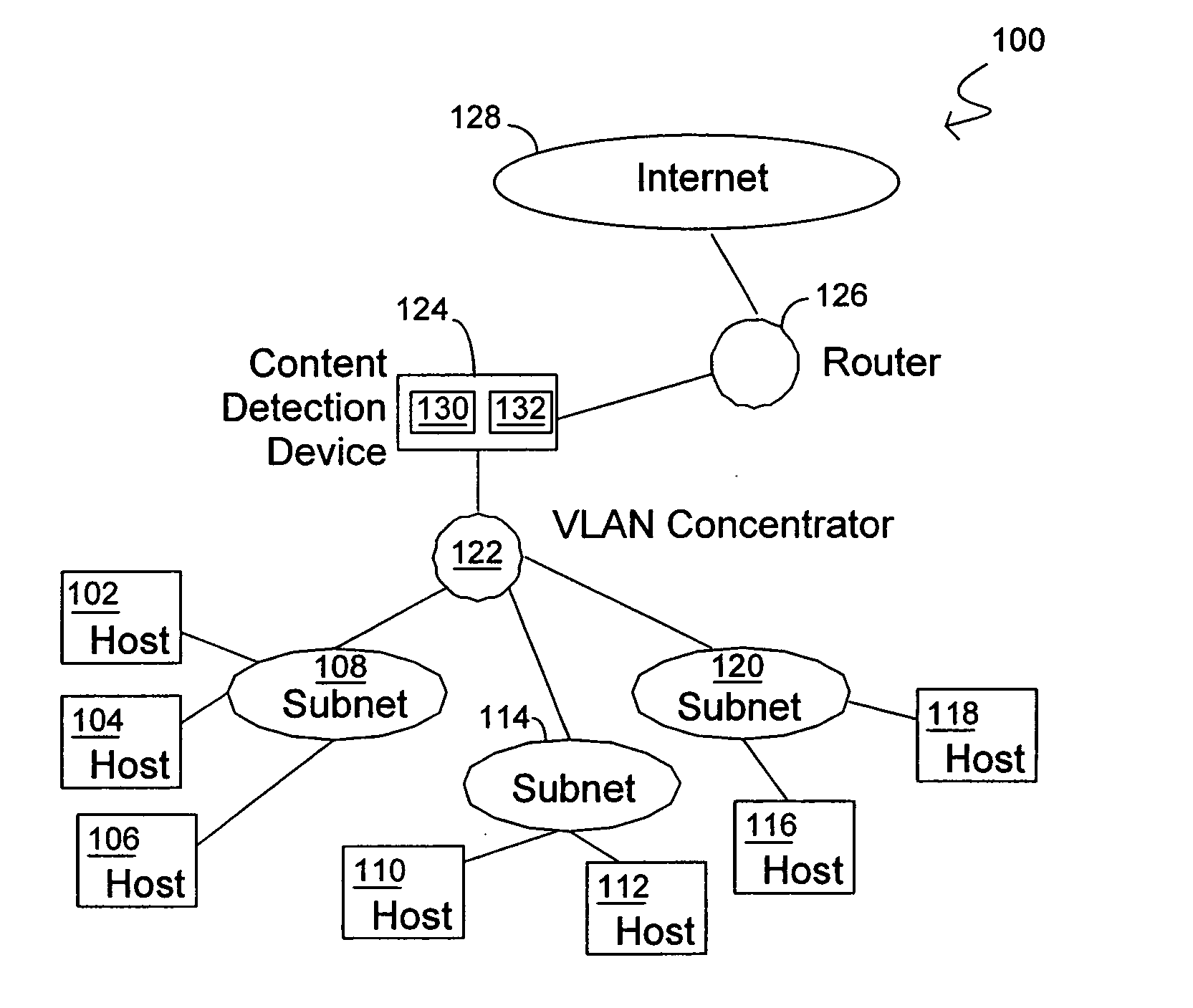
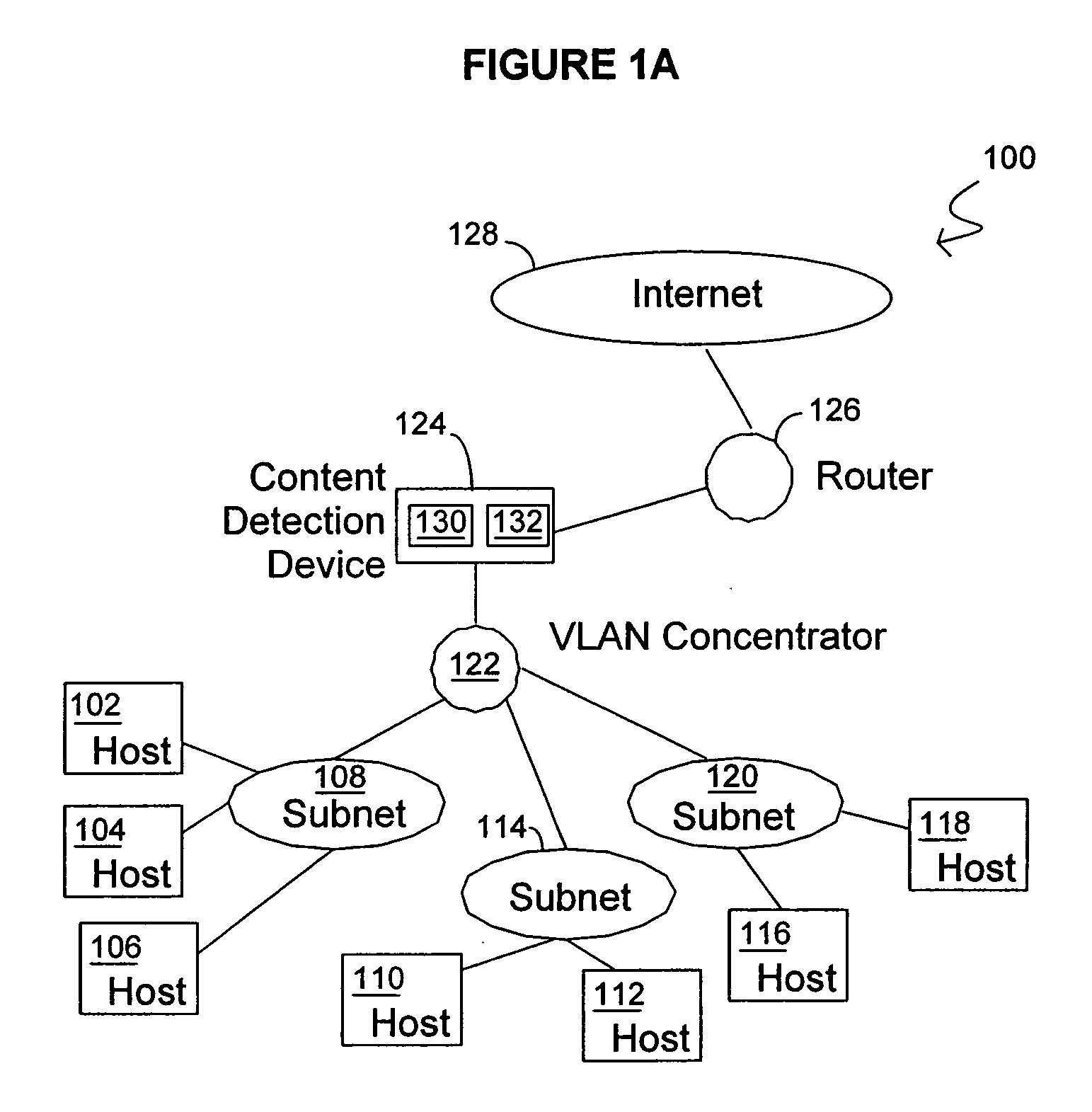
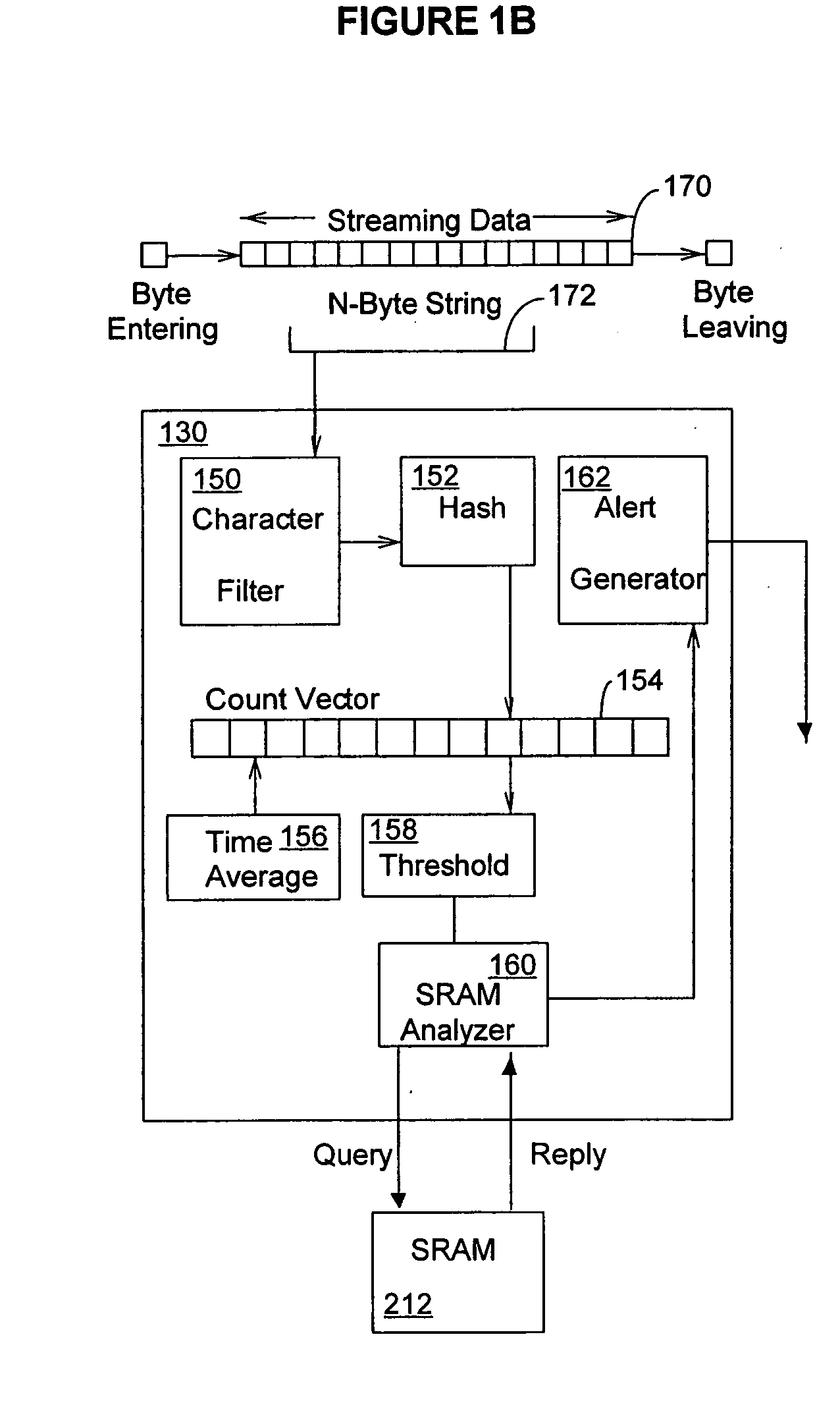
Methods and systems for content detection in a reconfigurable hardware
InactiveUS20060053295A1Improve throughputMaintain throughputMemory loss protectionPublic key for secure communicationDuplicate contentHash function
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention identify a repeating content in a data stream. A hash function is computed for at least one portion of a plurality of portions of the data stream. The at least one portion of the data stream has benign characters removed therefrom to prevent the identification of a benign string as the repeating content. At least one counter of a plurality of counters is incremented responsive to the computed hash function result. Each counter corresponds to a respective computed hash function result. The repeating content is identified when the at least one of the plurality of counters exceeds a count value. It is verified that the identified repeating content is not a benign string.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method to dynamically determine a user's language for a network
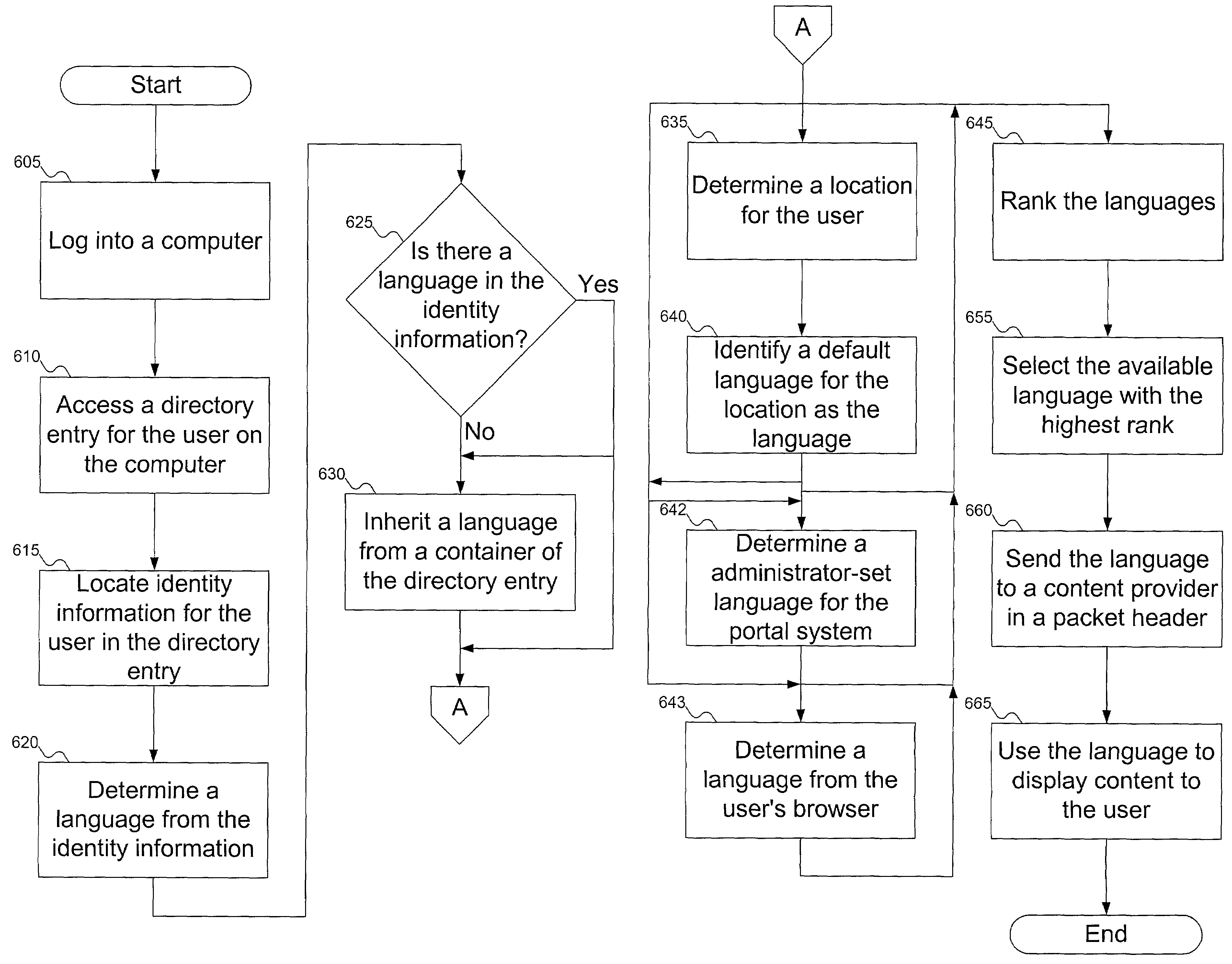
InactiveUS7412374B1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsSystem identificationWorld Wide Web
A portal system identifies a language in which content can be displayed to the user. Possible languages can be determined from one or more of identity information for the user, a container for the user's directory entry, and the user's location. The determined languages can be ranked, and the highest-ranked available language can be selected for content display to the user.
Owner:RPX CORP
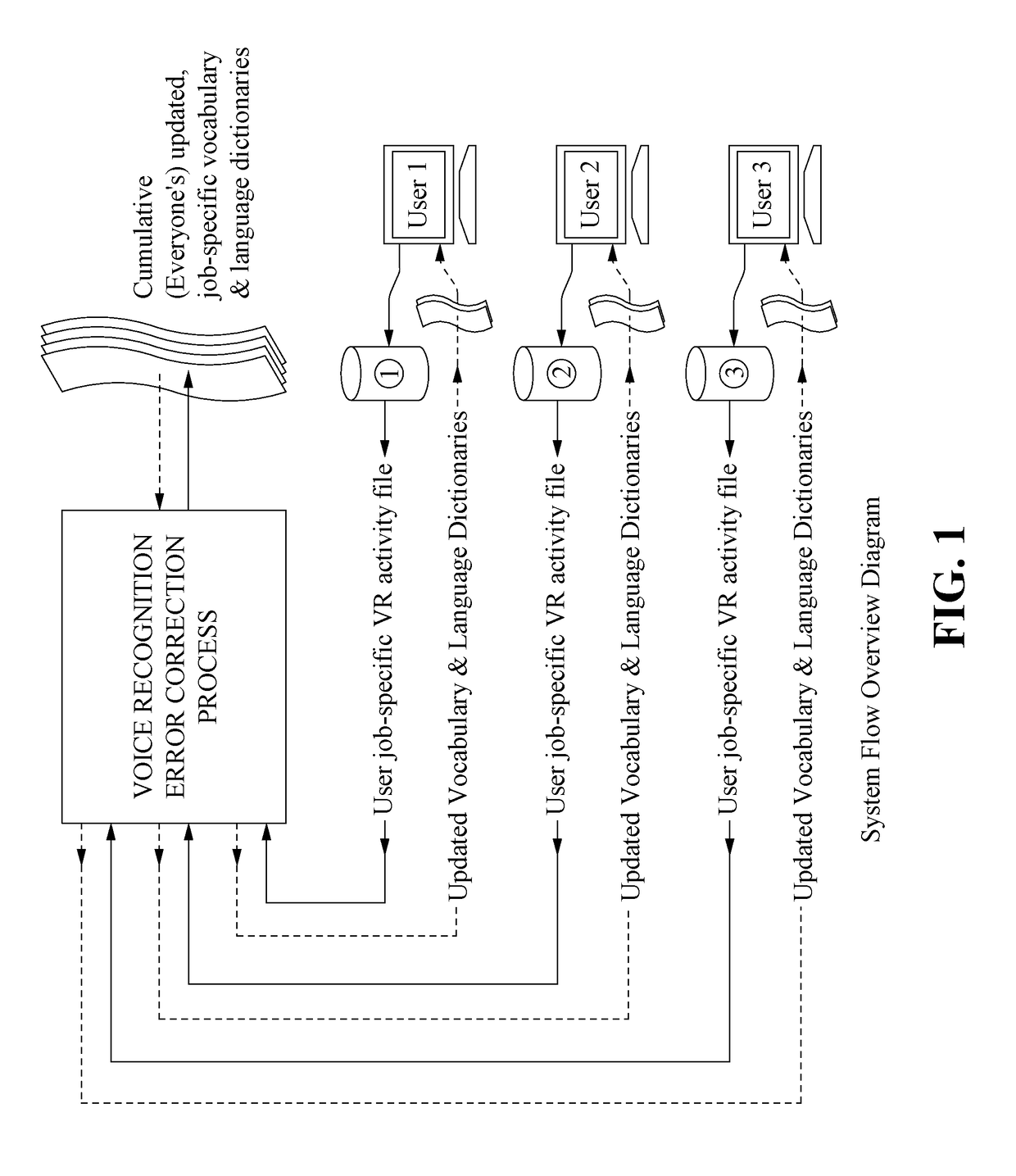
Method for Substantial Ongoing Cumulative Voice Recognition Error Reduction
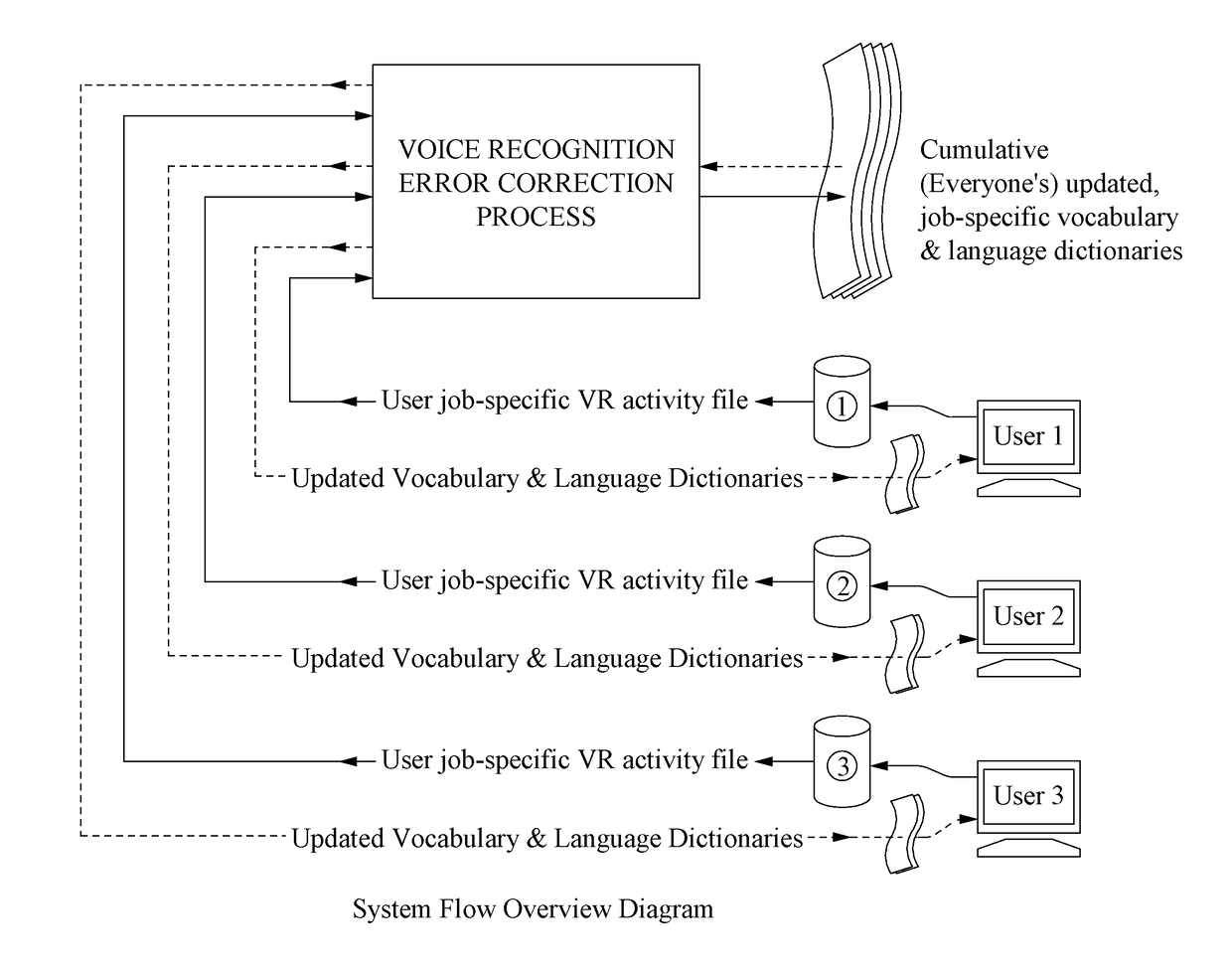
ActiveUS20170133007A1Reduce probabilityNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionError reductionSpeech identification
In an embodiment, speech is recorded and converted to digital text based on a shared vocabulary dictionary. During the session, voice recognition errors, that is, speech that could not be automatically identified (if any exists), are identified by the system and associated with digital text. When text for the voice recognition error is identified (e.g., by an editor), the shared vocabulary dictionary is updated (so that that particular voice recognition error will not occur again), thereby improving the performance of the system for all users that use the shared vocabulary dictionary. The identification of voice recognitions errors and the updated of the vocabulary dictionary are performed on an ongoing basis, so that the performance of the system for all users continually improves.
Owner:COMM INNOVATION TECH LLC
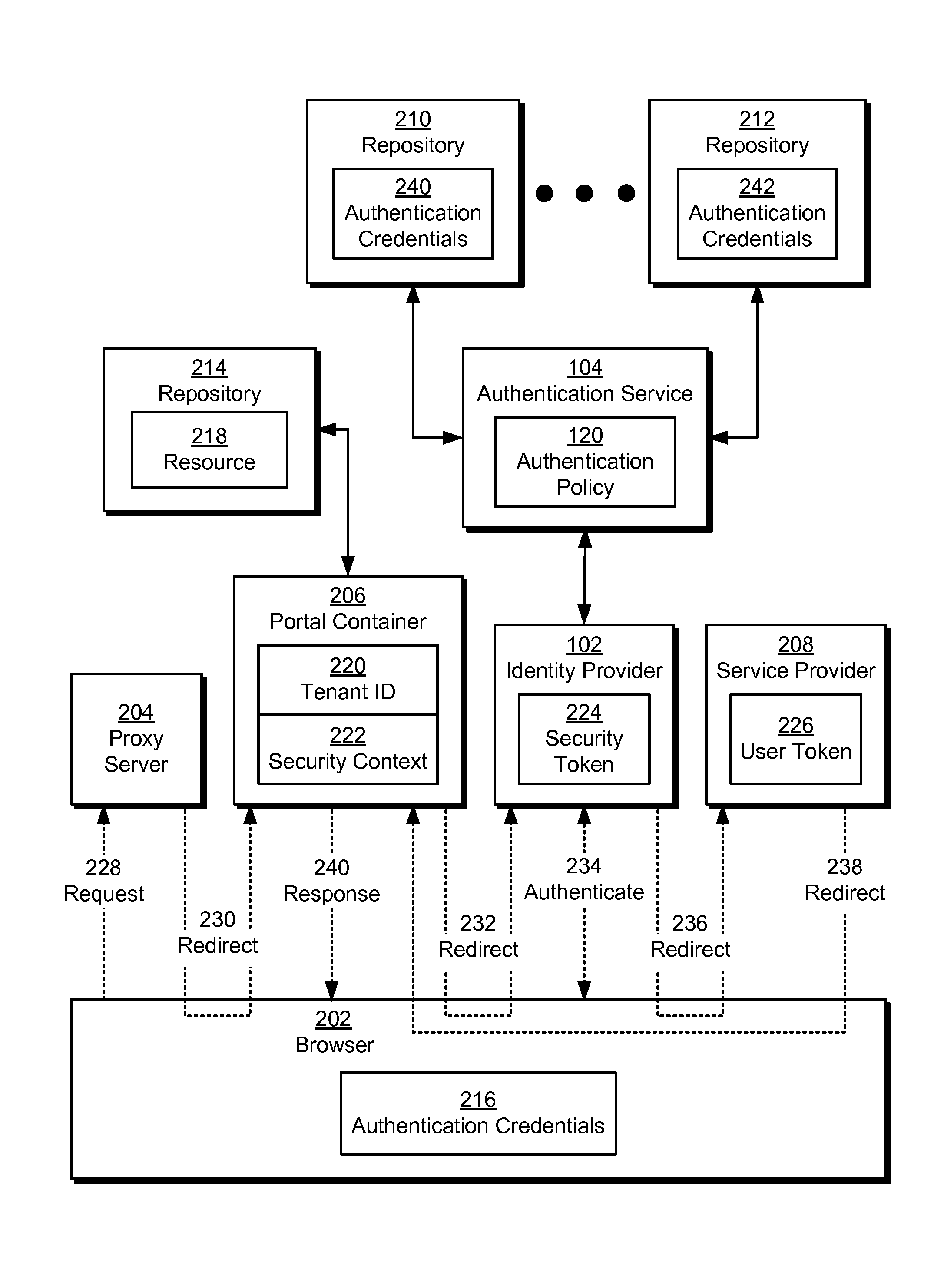
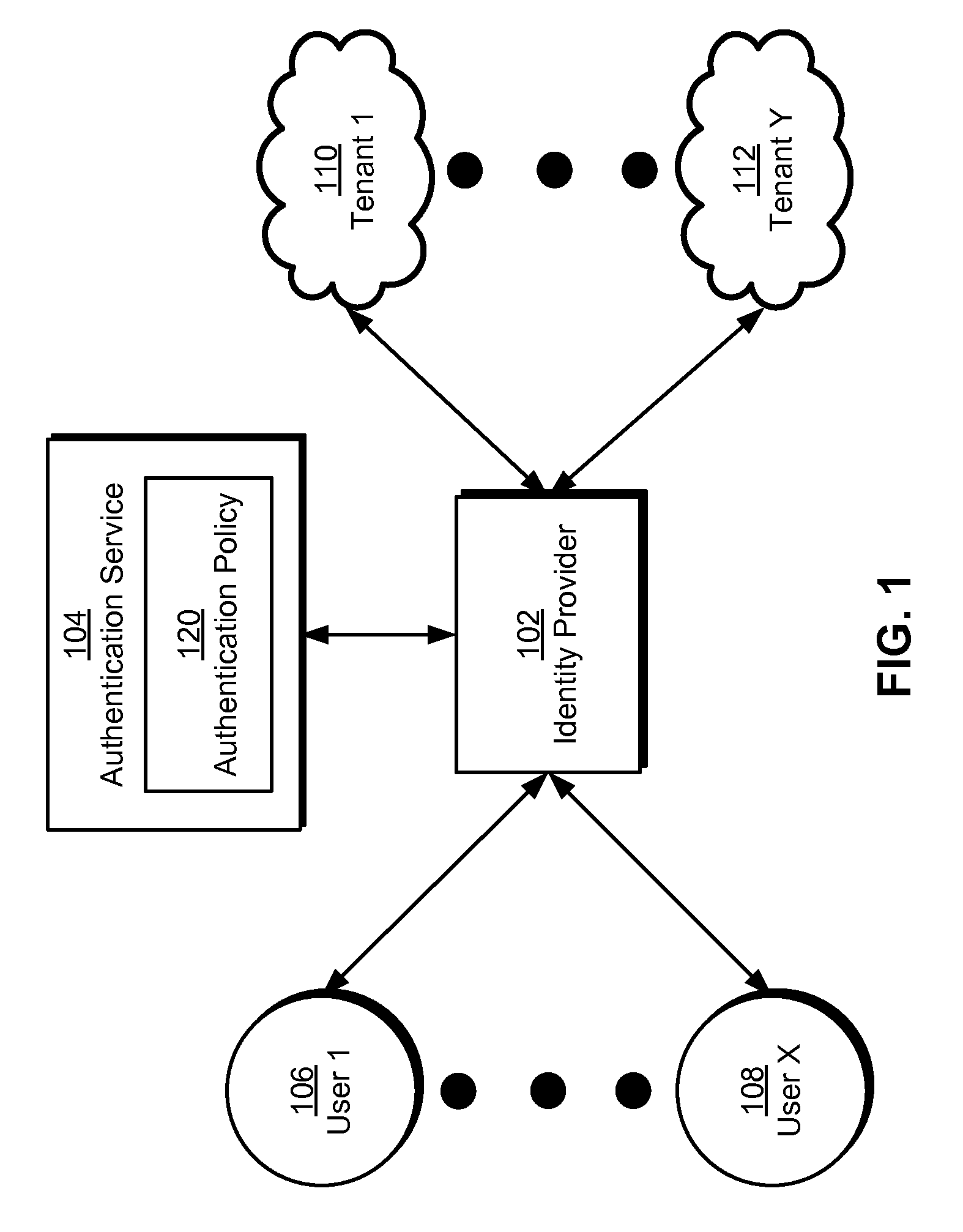
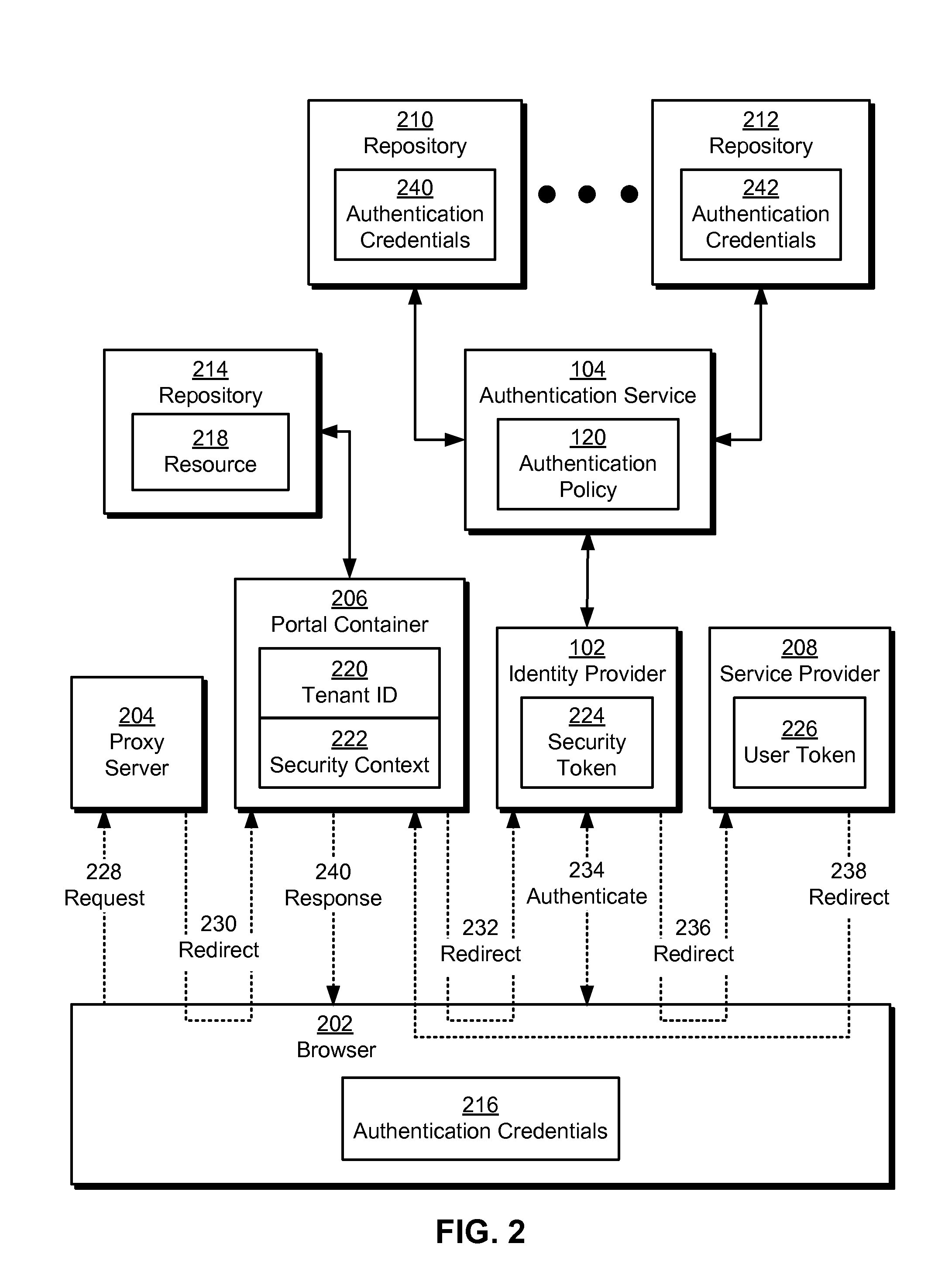
Single sign-on in multi-tenant environments
ActiveUS20140090037A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet privacySystem usage
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that authenticates a user. During operation, the system identifies a first tenant associated with a first request for a first resource from the user and obtains an authentication policy for the first tenant. Next, the system uses an authentication mechanism associated with the authentication policy to authenticate the user. Upon authenticating the user, the system provides a first security token for enabling access to the first resource by the user.
Owner:INTUIT INC
System and method for executing a game process
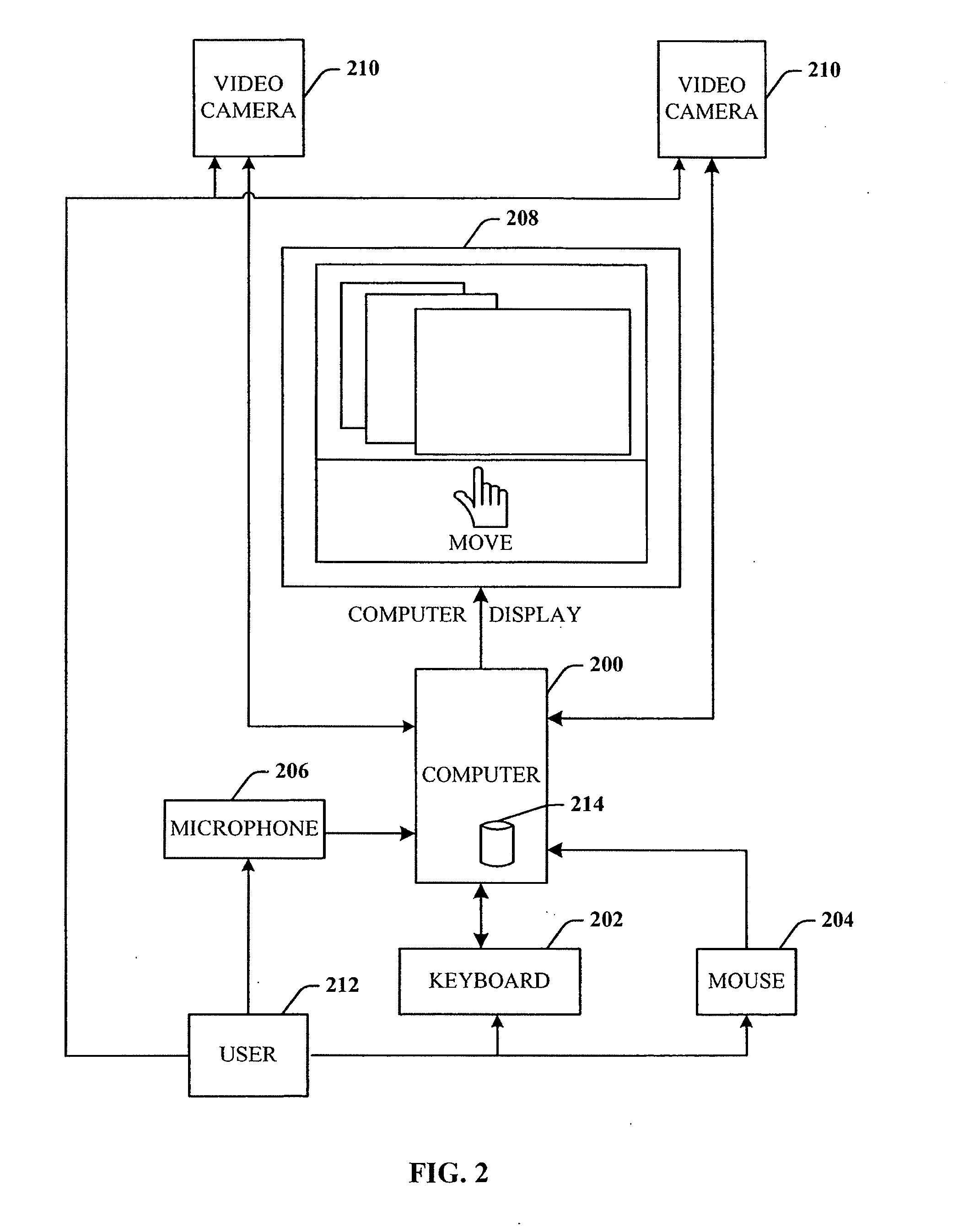
InactiveUS20100151946A1Facilitate control of computerEasy to adaptInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisSystem identificationConnected device
A 3-D imaging system for recognition and interpretation of gestures to control a computer. The system includes a 3-D imaging system that performs gesture recognition and interpretation based on a previous mapping of a plurality of hand poses and orientations to user commands for a given user. When the user is identified to the system, the imaging system images gestures presented by the user, performs a lookup for the user command associated with the captured image(s), and executes the user command(s) to effect control of the computer, programs, and connected devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Network optimisation systems
InactiveUS20100110932A1Easy to troubleshootEnhances capacity managementData switching by path configurationOperational systemNetwork management
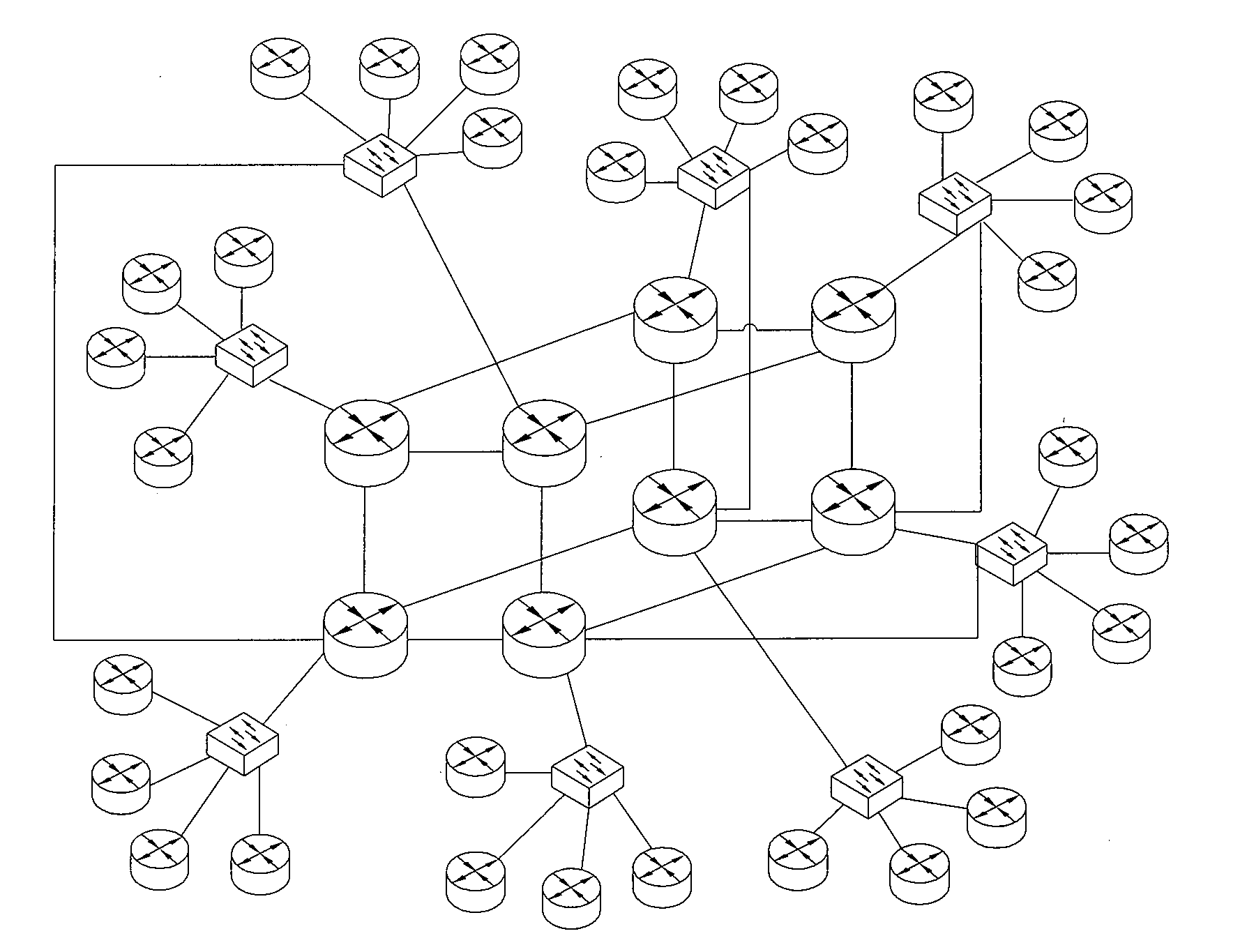
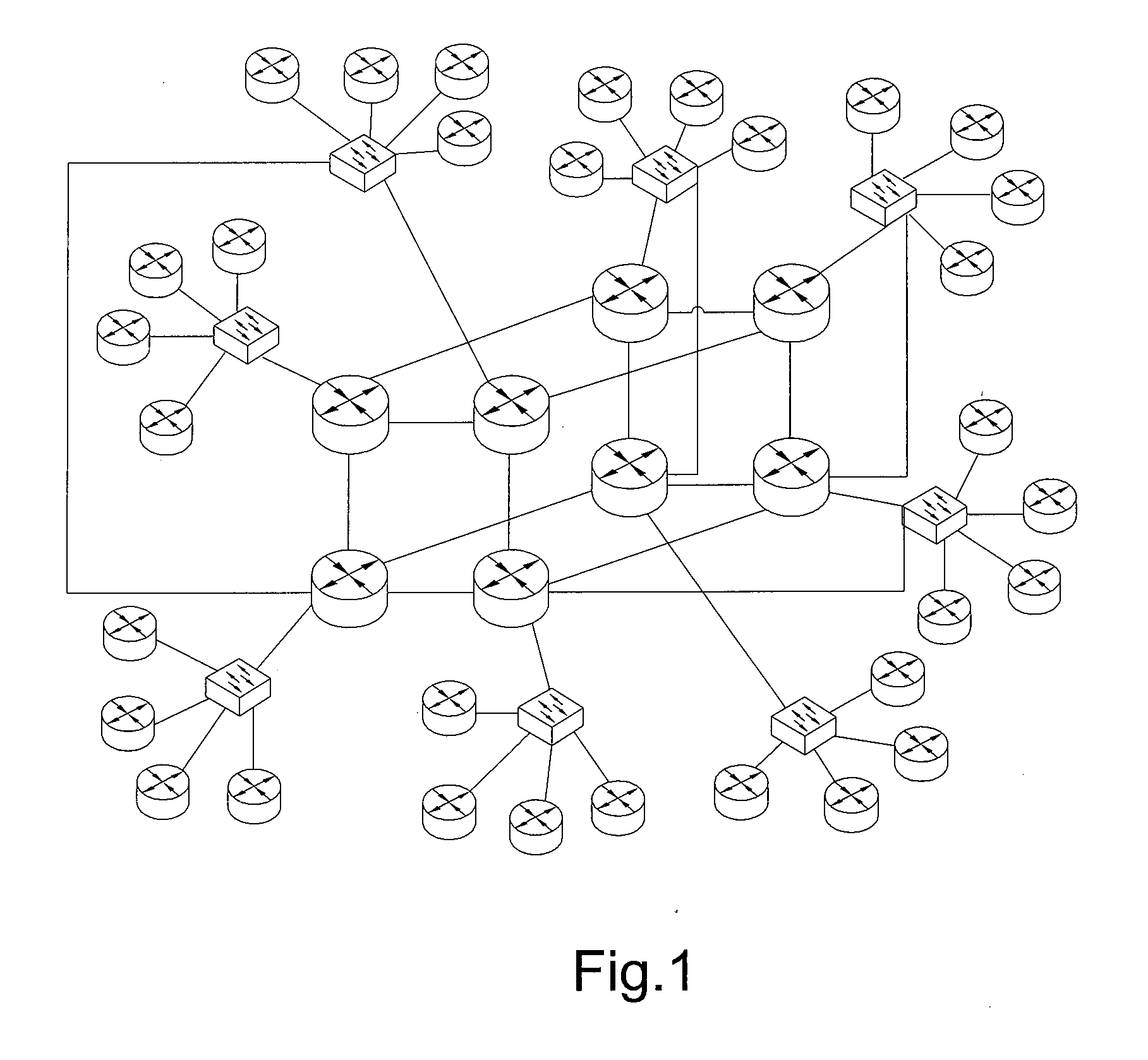
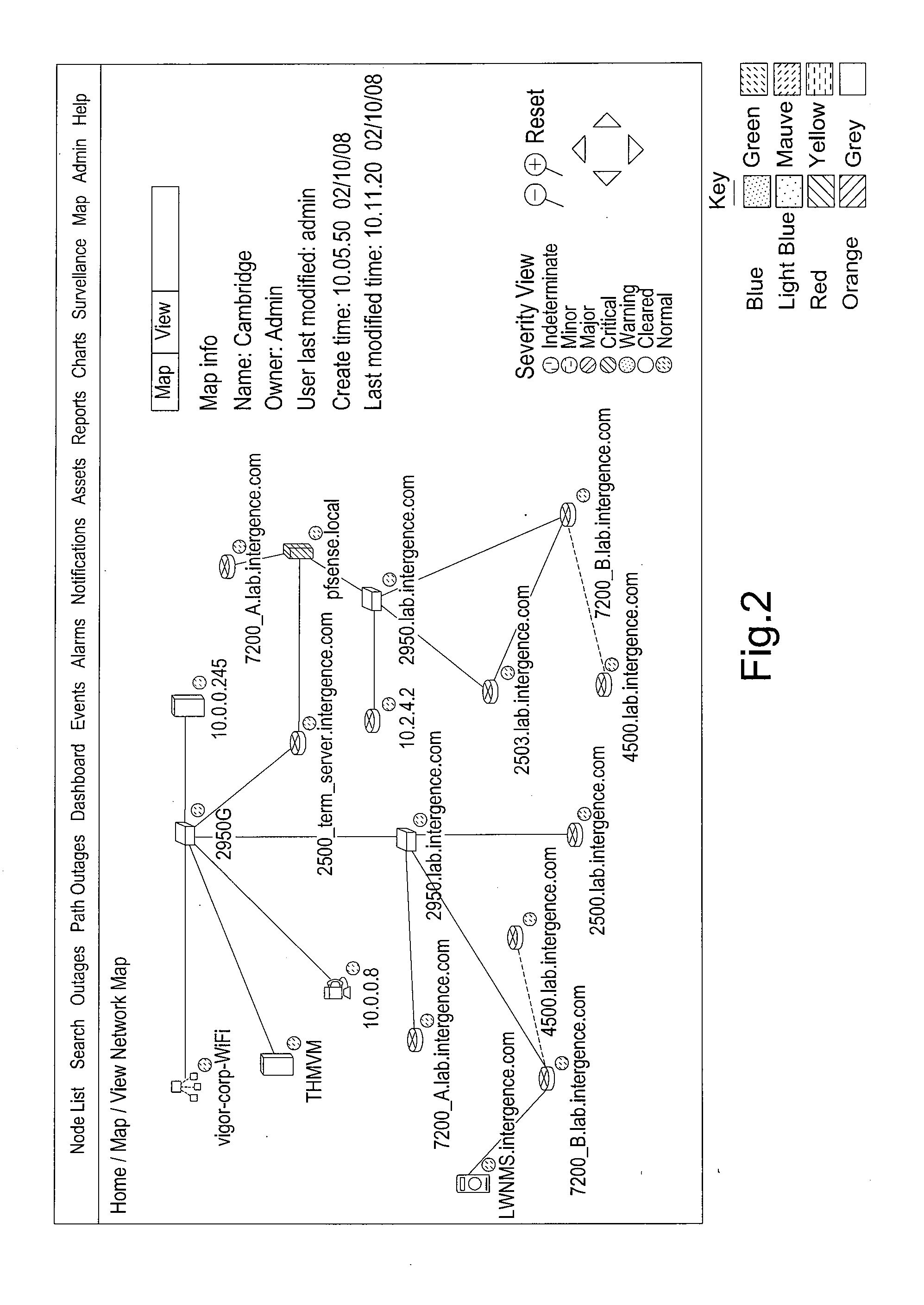
We describe a 3D computer network optimisation tool using network management data including one or more of: network device data including hardware identification data, interface data characterising one or more interfaces of a said network device, firmware identification data for a said network device, operating system identification data for a said network device; information flow data relating to information flow within the network including network device information flow load data and link bandwidth data / statistical information flow data; as well as environmental data for a network device such as temperature or power consumption data and / or physical network device location data. The tool also uses captured network data and sniffer data from communication links; and connectivity of the network devices. A three-dimensional (3D) visualisation module constructs a 3D representation of said network including 3D representations of said network devices in conjunction with a representation of said connectivity in three dimensions.
Owner:INTERGENCE SYST
Methods and systems for generating and providing program guides and content
ActiveUS20150237389A1Television system detailsColor television detailsThird partySystem identification
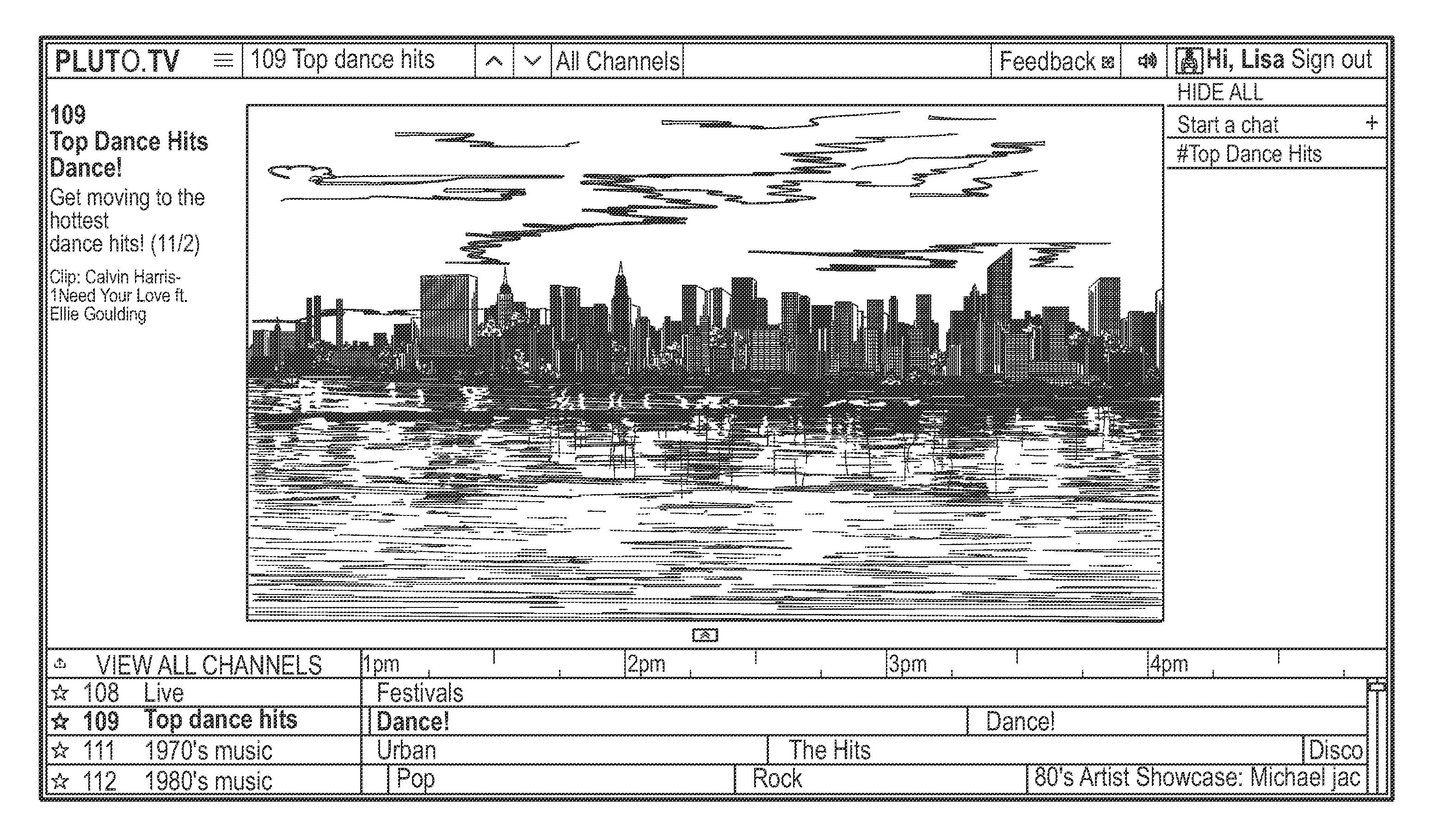
Systems and methods for identifying, assembling, and publishing content are described. A content item, such as a video, having a first time length, is identified by a system to be included in a program scheduled for a first time period. The video may be hosted on a third party system. A first span of time within the first program is allocated for the video, wherein the first span of time is longer than the first time length. The system determines, prior to or at the first time period, a time difference between a current length of the video and the first span of time. At least partly in response to determining that the video has a time length shorter than the first span of time, the system selects supplemental content based at least in part of the determined time difference to be streamed to user terminals over a data network within the first time period.
Owner:PLUTO
System to deliver internet media streams, data & telecommunications
InactiveUS20050249139A1Maximize service qualityMaximise of efficiency of spectrumSpecial service provision for substationPower managementData packSelection system
A system for delivering broadcast and communications services, wherein said services comprise provision of one or more Internet media streams; the system comprising one or more gateways which provide connections to external communications networks and nodes and internal loopbacks from which said services are obtained, each of said gateways comprising: a selection system to selectively establish communication channels with said external communication nodes networks and said loopbacks to establish an individual bidirectional channel between each node network and allow recipients to obtain the communication channel of their choice; a processing system comprising non-blocking matrix switching or routing system, buffering, packeting, and addressing systems; processing said channels containing services into digitized packaged data format and said addressing systems identifying, storing and updating the location of each recipient, and applying routing information to each packet of digitized packaged data to enable packets to be correctly routed through the system.
Owner:NESBIT PETER
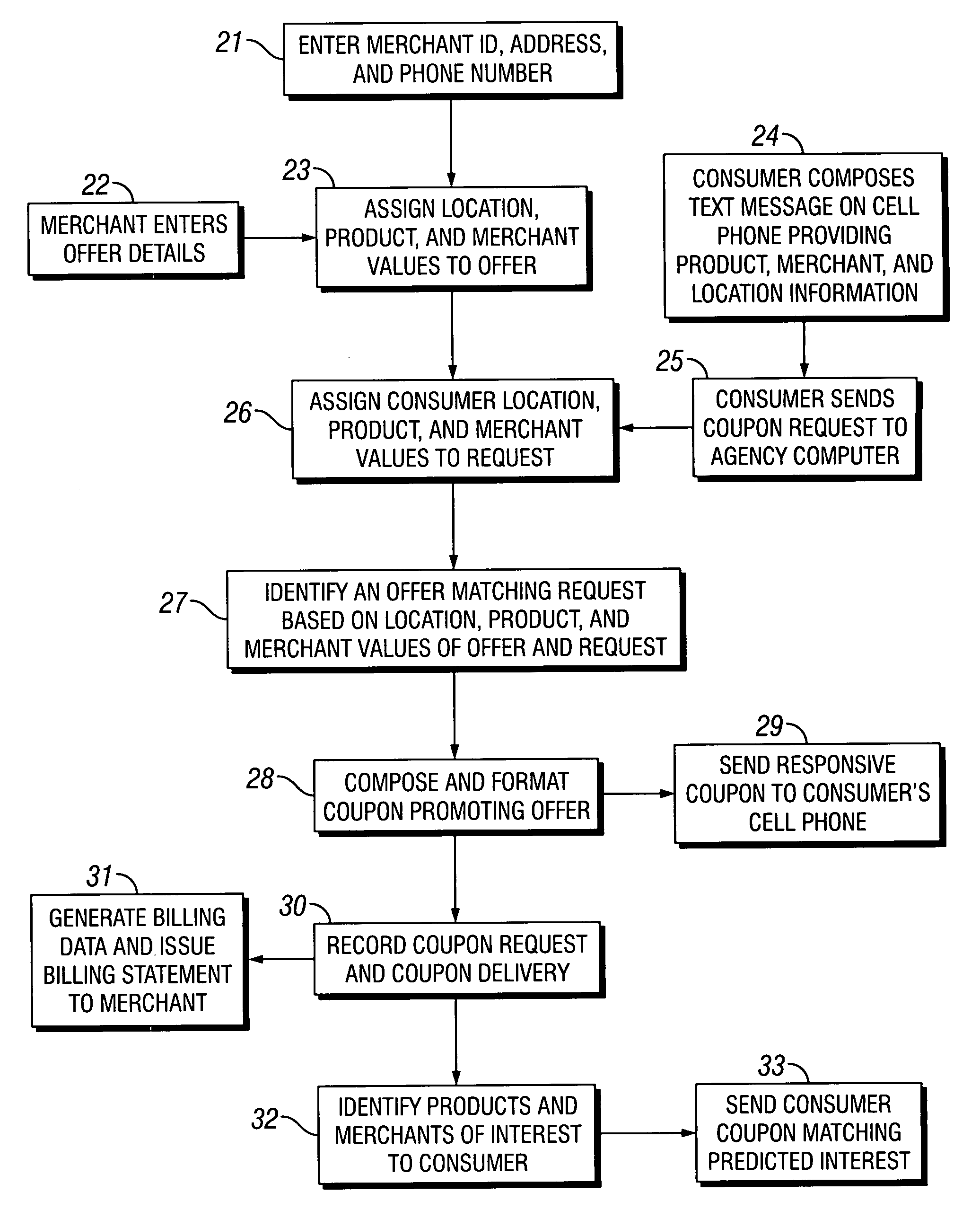
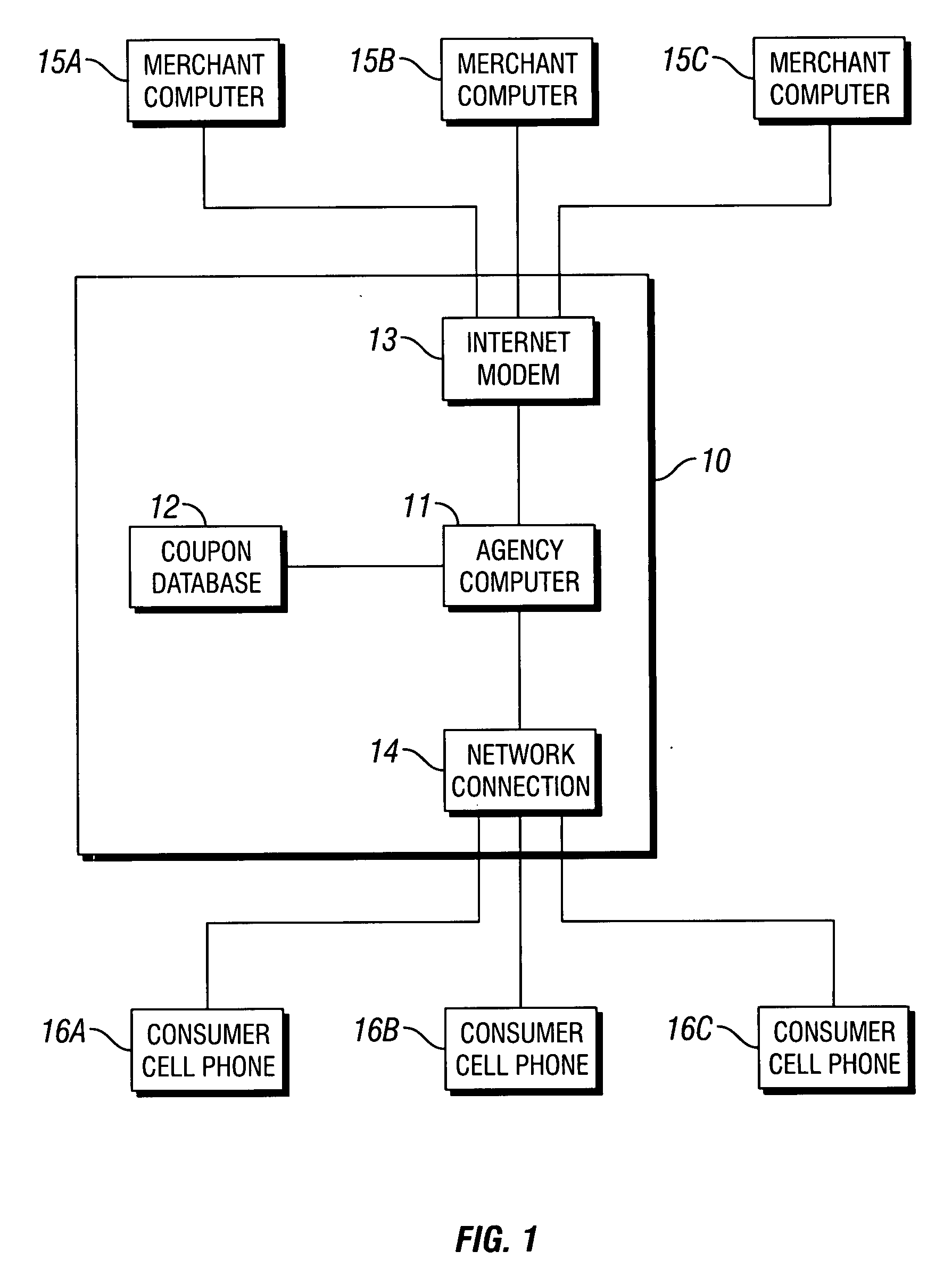
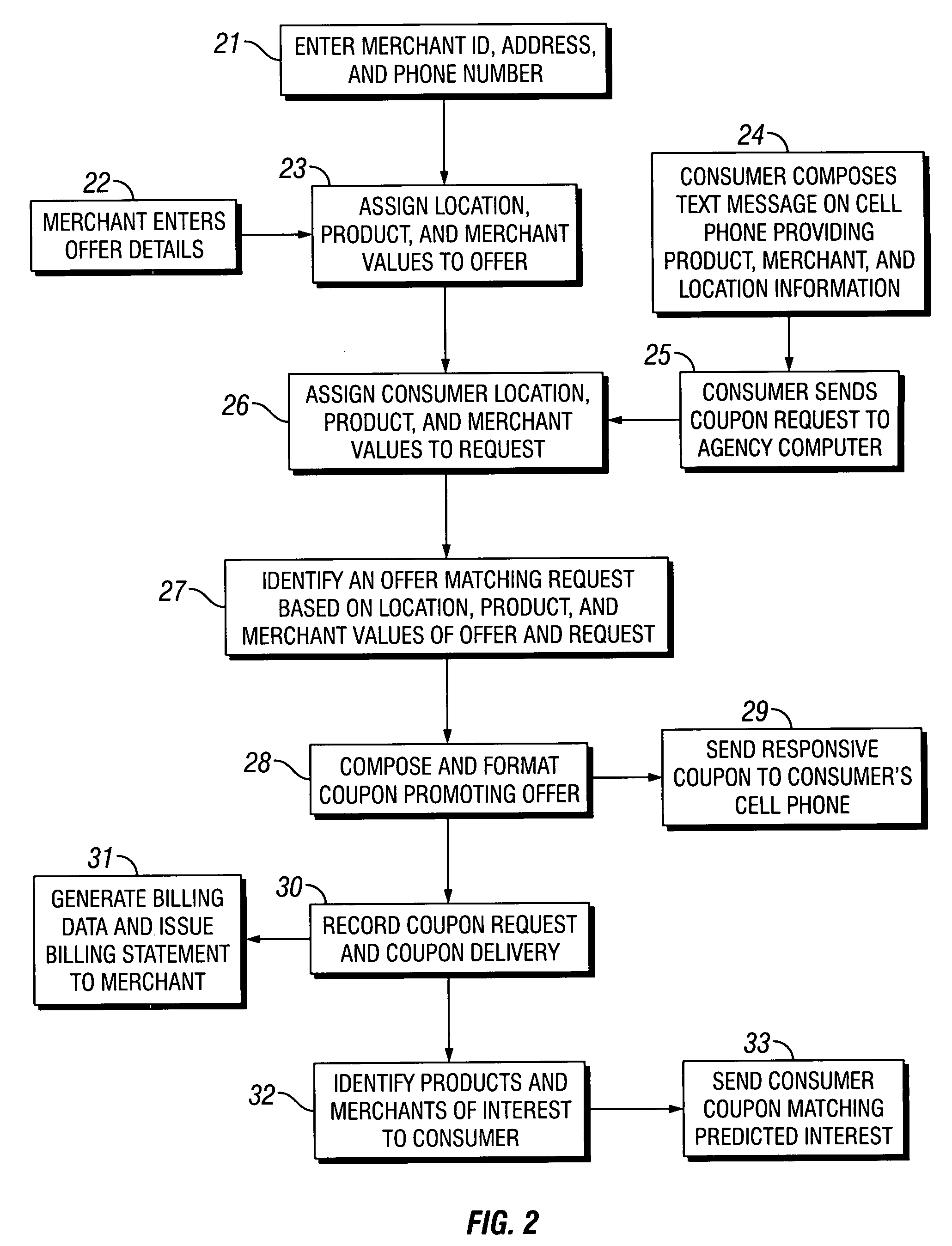
Coupons and systems for generating coupons on demand
InactiveUS20080027810A1High redemption ratePromote effectiveMarketingSystem identificationInformation agents
Coupons which are displayed as a text message on a mobile telecommunication device and include a code uniquely identifying the coupon are provided for. Systems for generating coupons on demand are also provided for. The system comprises an agency computer having access to a coupon database. The coupon database comprises information on offers and a location value assigned to each offer. The agency computer is connectable to a mobile communications network or other network for transmitting electronic mail. It receives requests for coupons from consumers that are transmitted via the network. Preferably, the requests originate from cells phones or other mobile telecommunication devices and are transmitted to the agency computer via a mobile communications network. The request is a text message that includes information identifying the consumer's location. The agency computer system identifies a coupon in the coupon database that is responsive to the coupon request based on the consumer's location and the offer location value. It then sends the identified coupon to the consumer via the network.
Owner:WHAMMOBILE
Method and apparatus for automated selection, organization, and recommendation of items based on user preference topography
InactiveUS20060026048A1More interestingReduce usageResourcesMarketingArtificial intelligenceSystem identification
A computer system representing user preferences in an N-dimensional preference topography and making recommendations based on such topography. The preference topography depicts user ratings of products in a recommendation database. Each product is represented by a product vector associated with N objectively measurable characteristics. The user rating of a product, therefore, represents the user's preference for the particular combination of the N objectively measurable characteristics making up the product. In making a recommendation of products to the user, the system assigns a rating to each product in the recommendation database based on the preference topography. The system then selects a plurality of maximally unique choices from the rated products for recommendation to the user. These maximally unique choices are calculated to be as diverse from one another as possible but still to the user's liking. In another embodiment of the invention, the system identifies portions of the N-dimensional rating space for which the user has indicated a positive association (a positive preference cluster) or a negative association (a negative preference cluster). In making a recommendation of a potential product, the system determines the similarities of products that fall in the positive preference cluster with the potential product. The system also takes into account the products that fall in the nearest negative cluster and determines the similarities with such products and the potential product. In one particular aspect of the invention, the system presents a virtual character for making the usage of the system more user-friendly and interesting. The virtual character is programmed to interact with the user for obtaining user ratings of products and thus determining where the user preferences lie.
Owner:MUSICIP CORP
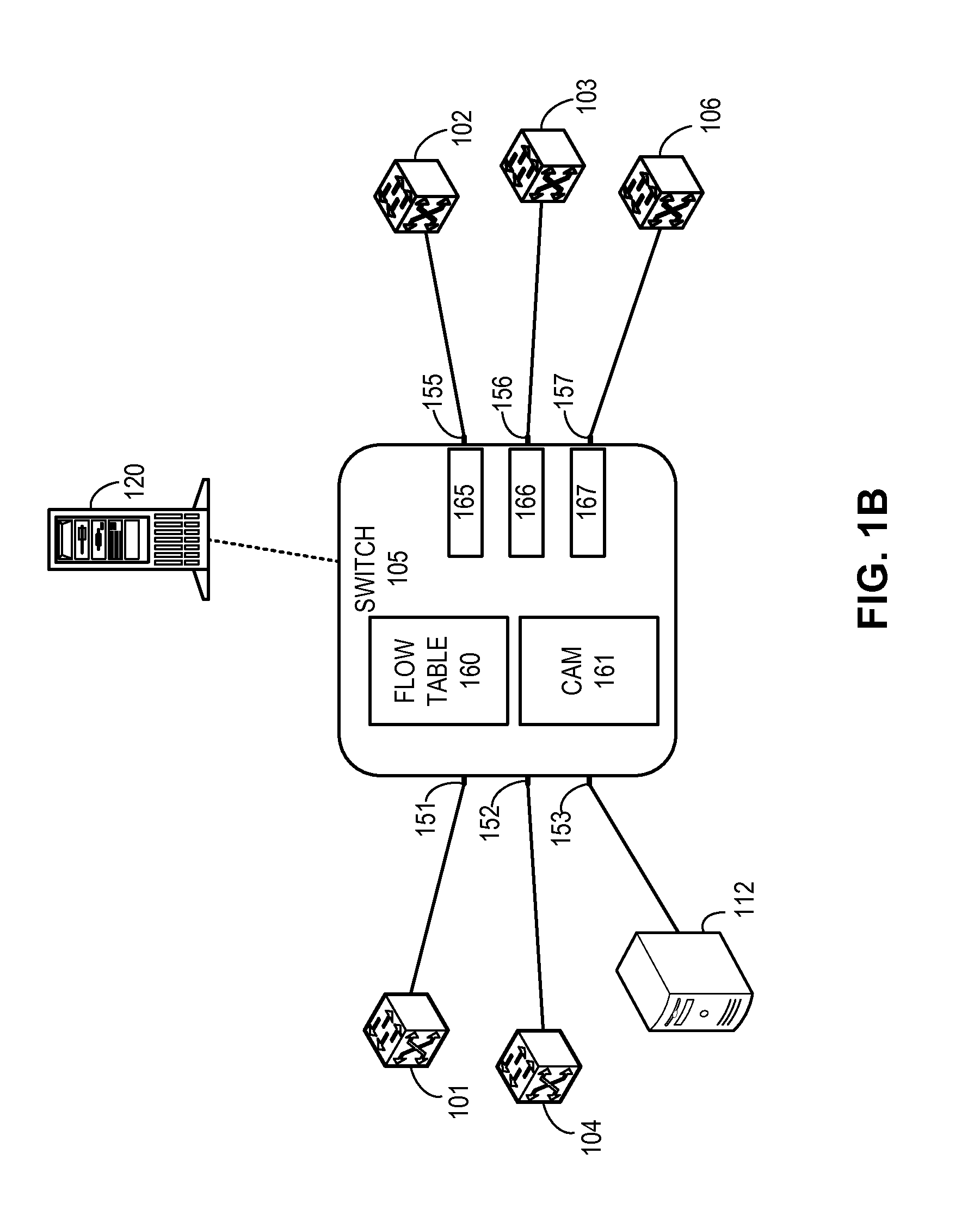
System and method for flow management in software-defined networks
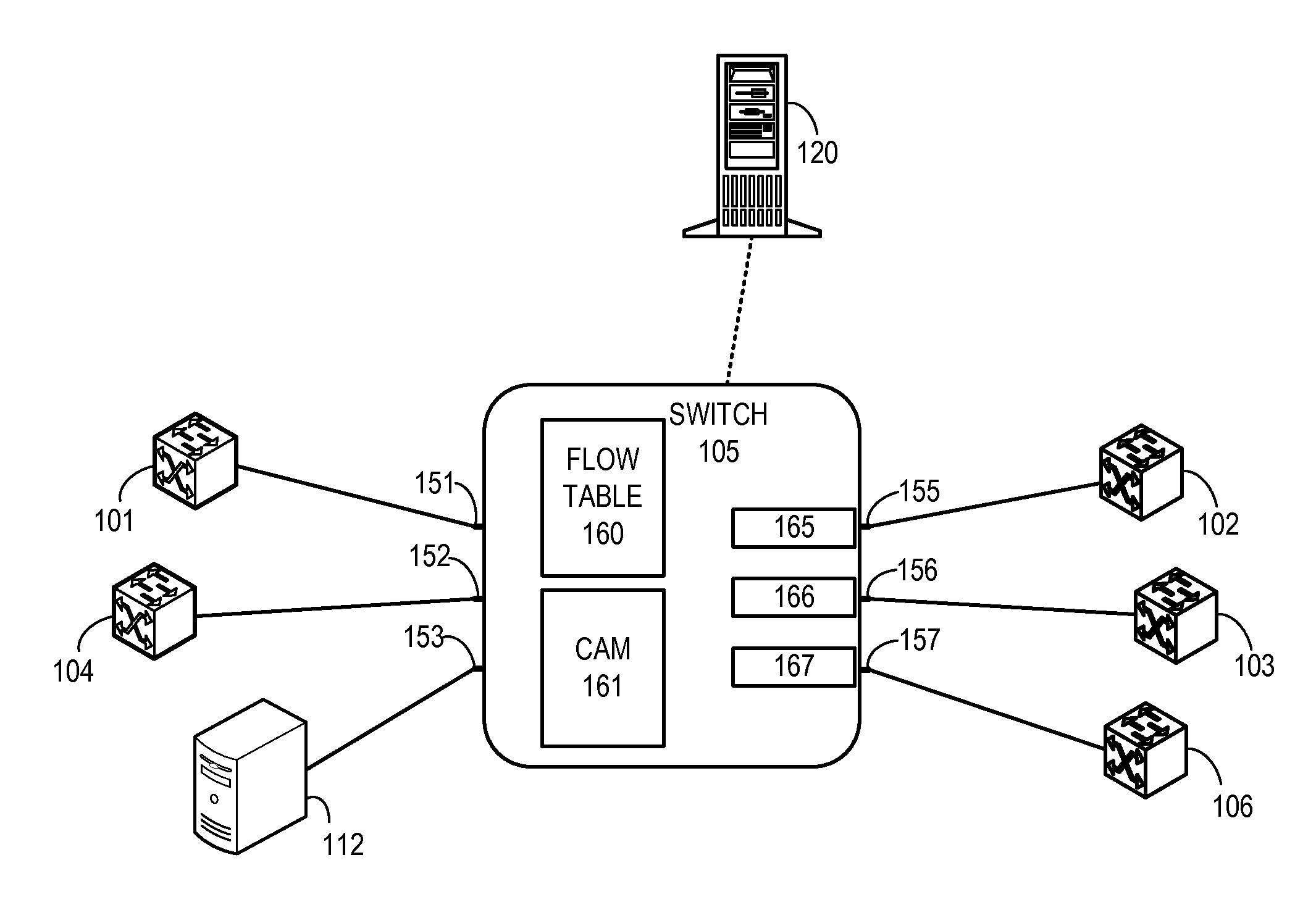
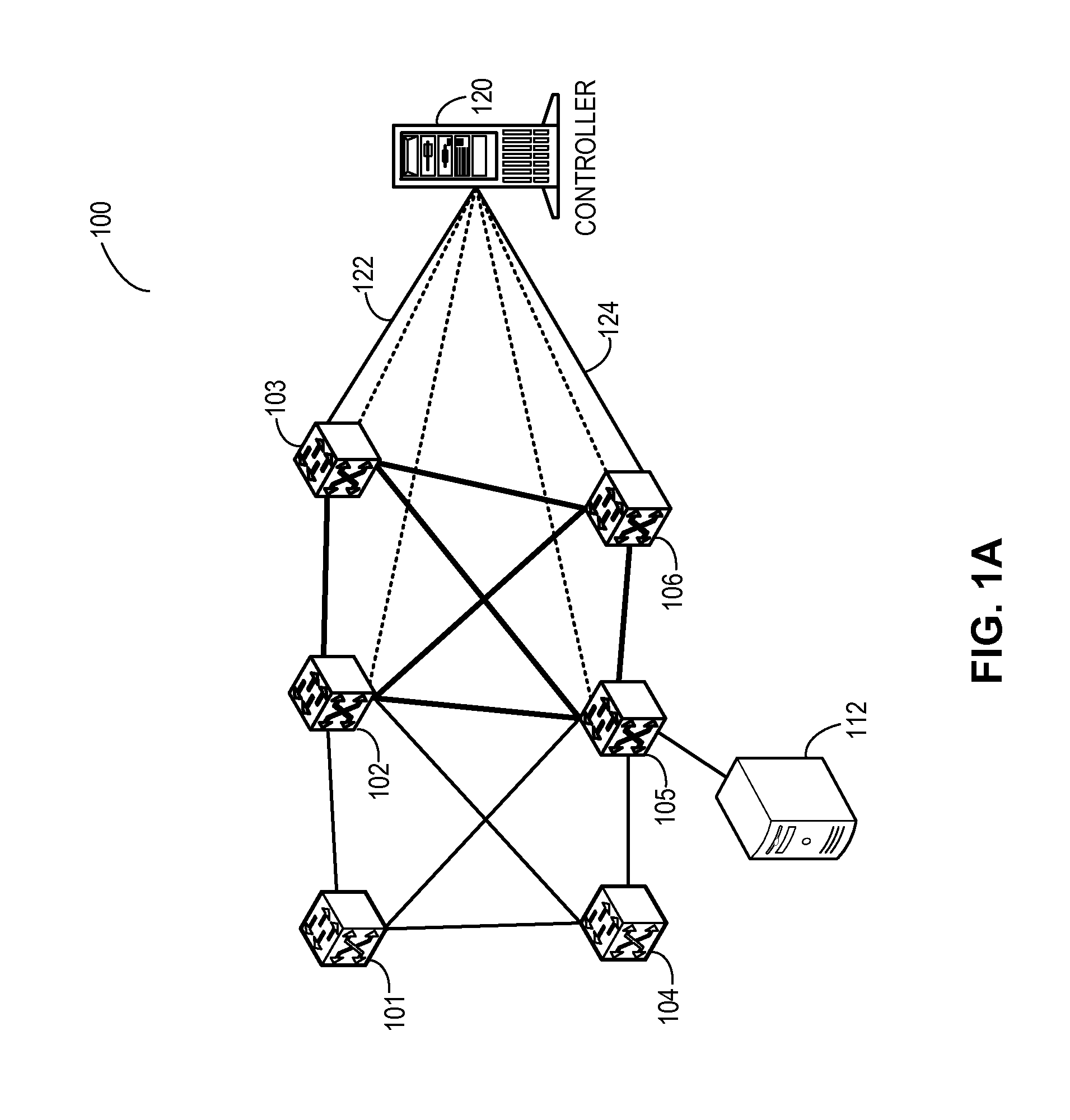
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating flow definition management in a switch. During operation, the system identifies a generic flow definition which specifies a flow that is not specific to any input port of a switch. The system further stores in a flow lookup data structure one or more port-specific flow rules based on the generic flow definition, wherein each port-specific flow rule corresponds to a respective port capable of processing data flows.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com