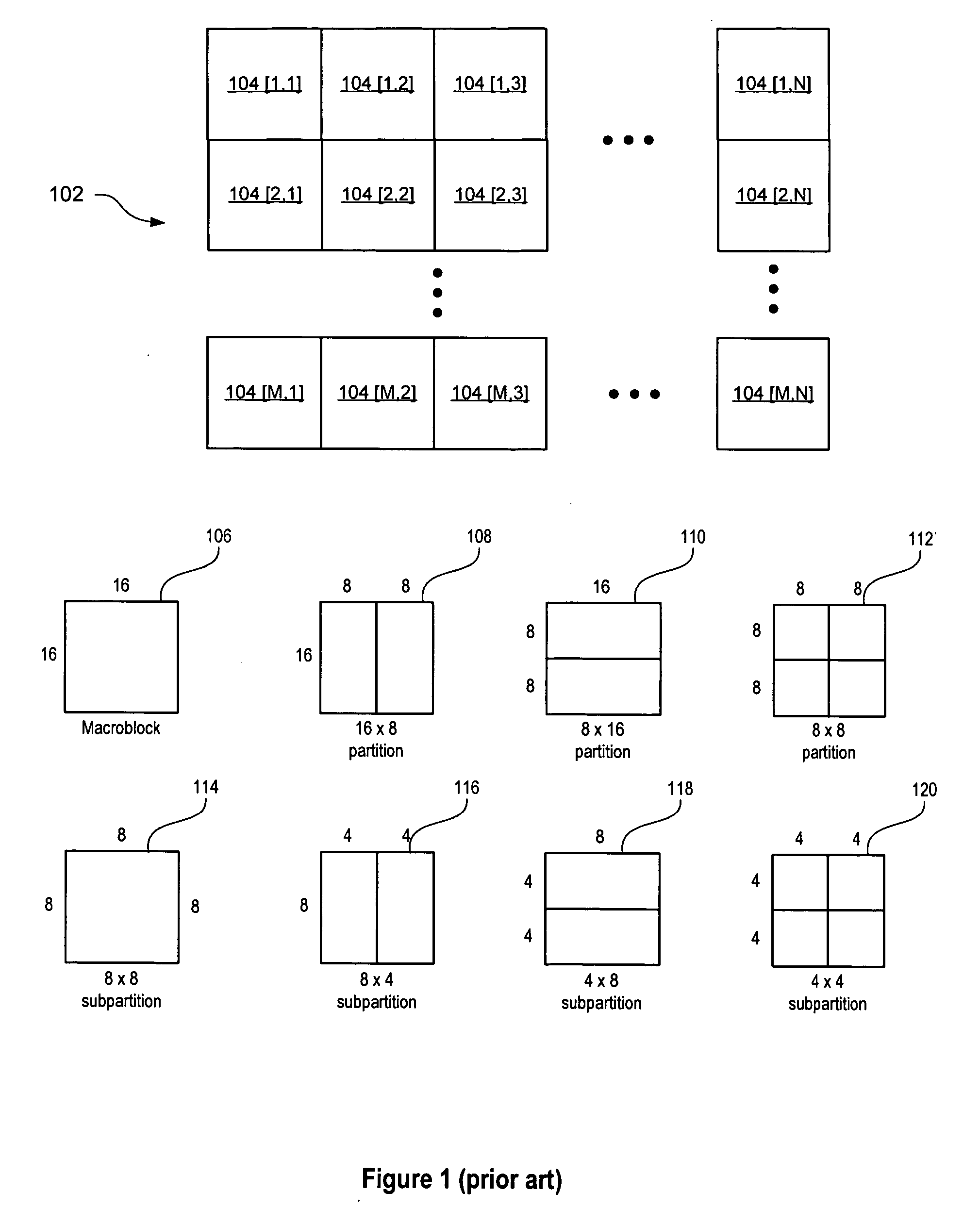
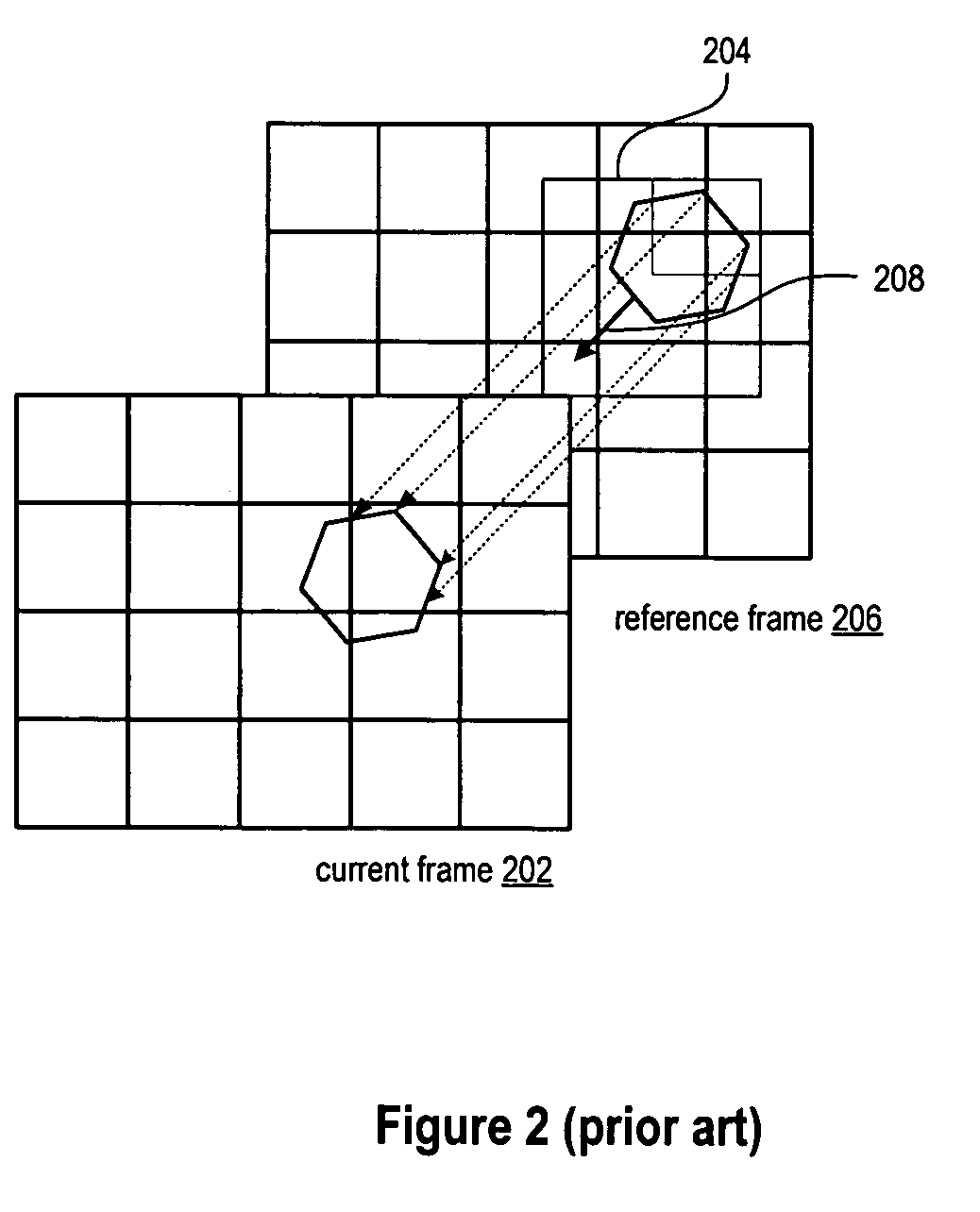
Patents
Literature
346 results about "Error reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Error reduction. Error reduction encompasses intentional strategies to manage complacency, complexity and the source of errors. It begins with leadership. Leaders must acknowledge their role and seek out and implement techniques to reduce the potential for, and impact of human errors.
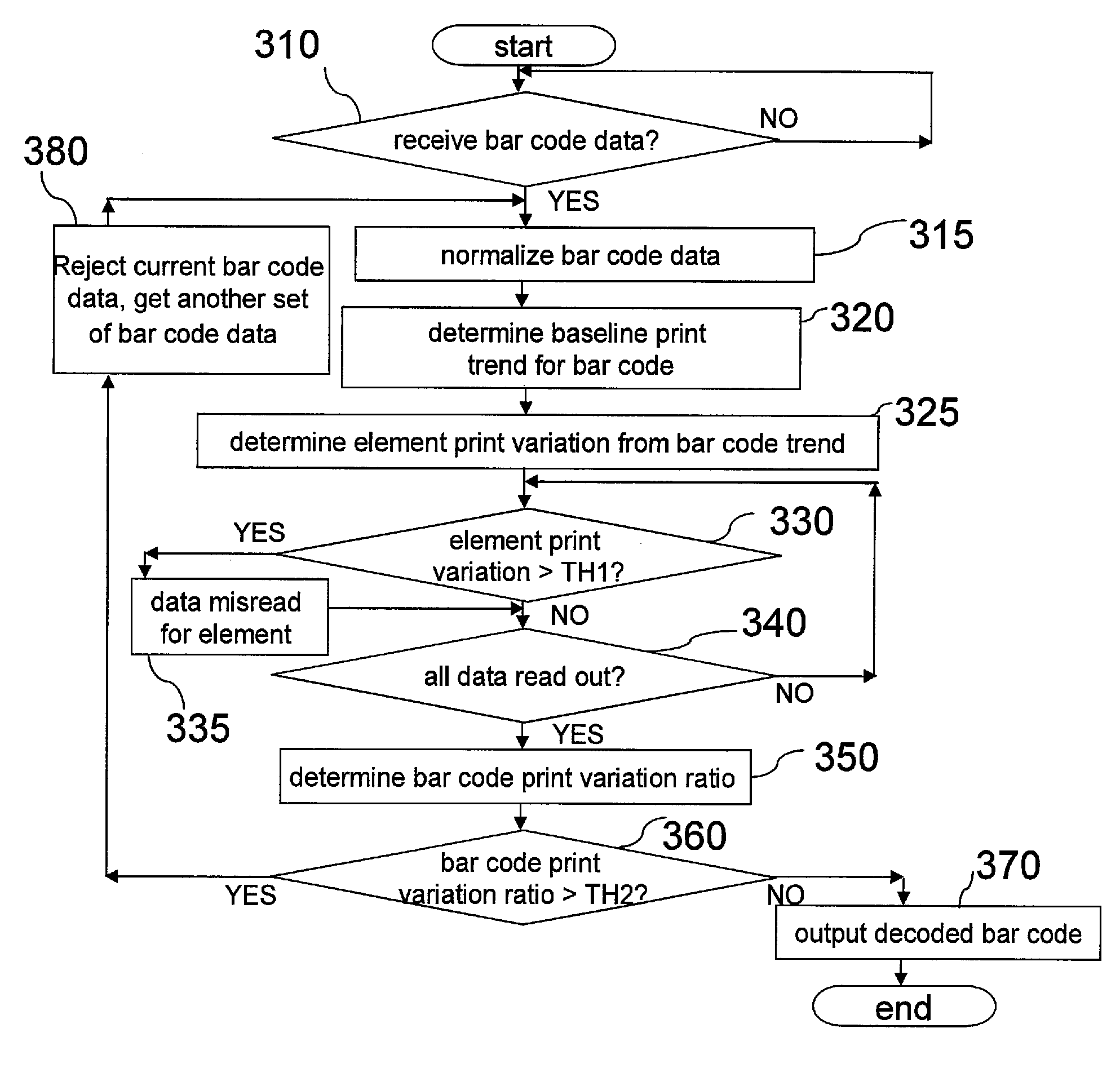
Bar code reader terminal and methods for operating the same having misread detection apparatus
ActiveUS8668149B2Increase read data rateRecord information storageCharacter and pattern recognitionError reductionBarcode
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
Computer-Implemented Method, System, and Apparatus for Electronic Patient Care
A medical error reduction system may include a medical error reduction software for use in creating and revising at least one drug library. The software configured to provide one of a plurality of sets of privileges to each of a plurality of sets of users. Each of the plurality of sets of privileges arranged to allocate a degree of software functionality to one of the plurality of sets of users. The degree of software functionality configured to define the ability of a user to alter the at least one drug library. The medical error reduction system may include at least one server. The medical error reduction system may include at least one editor computer each of the at least one editor computer comprising a processor in communication with a display. The at least one editor computer and at least one server may be configured to communicate via a network in a client-server based model. Each of the at least one drug library may be for use in at least one medical device.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
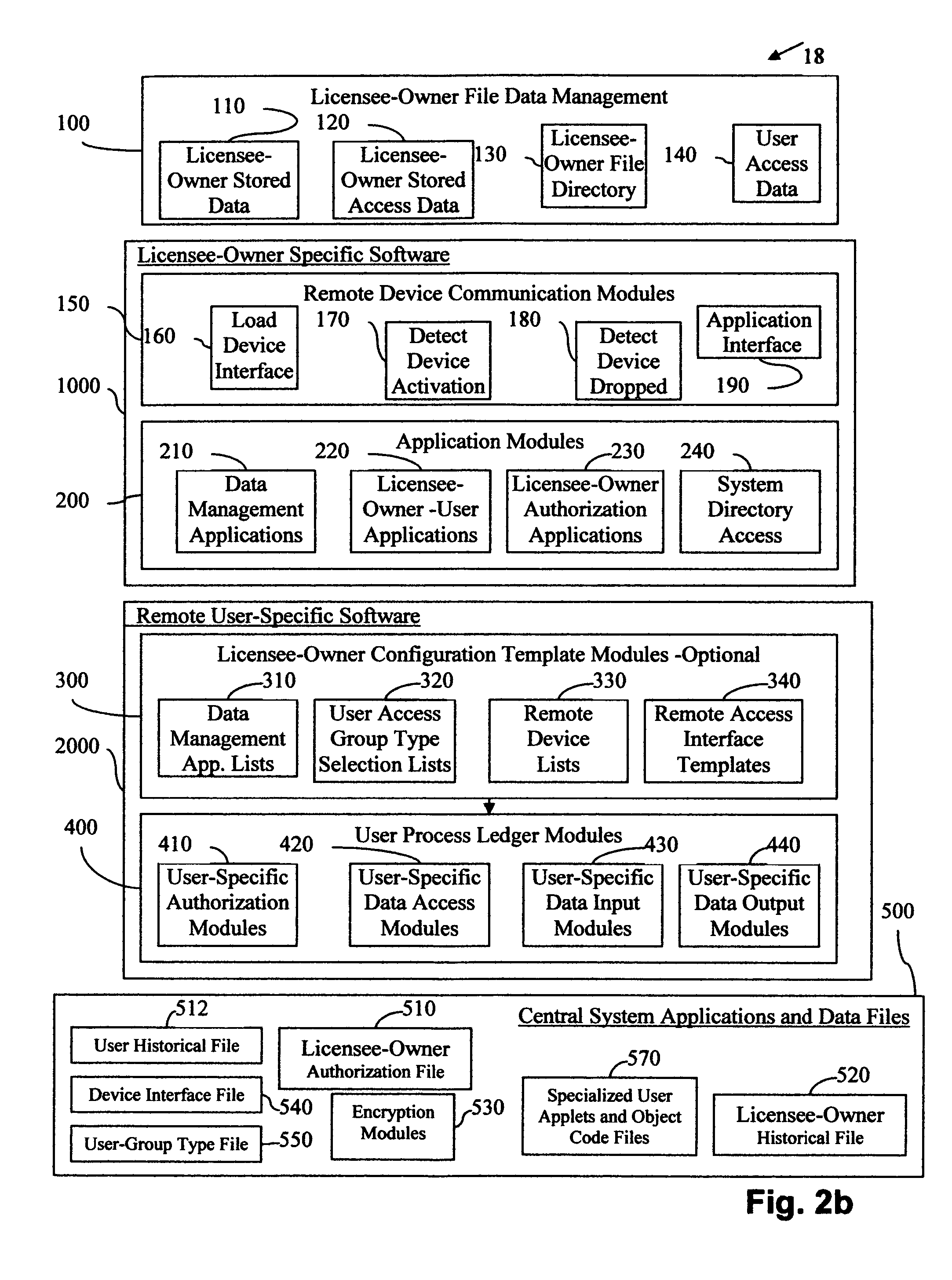
Central work-product management system for coordinated collaboration with remote users
InactiveUS7761591B2Easy accessFinanceMultiple digital computer combinationsService product managementMulti protocol
Client-specified methods, systems and computer program product with multi-protocol access for data input requests designed around a client's business application. It does this by interfacing IVR / telephony programming of multiple communication device protocols to separate data source input protocol programming, including remoting programming. Data input is by selected IVR / telephony responses designed around the needs of the individual client through selection process within a variety of configuration templates. The templates are designed to interface with the business applications through programming procedures for data entry specific to each application's protocol. The advantage, templates reduce user / client's interface with the business applications resulting in minimal time and knowledge of each applications data requirements, and limits each user's access to the system to specific data input. System response for data output is limited to the requested input for error reduction.
Owner:GRAHAM JEAN A
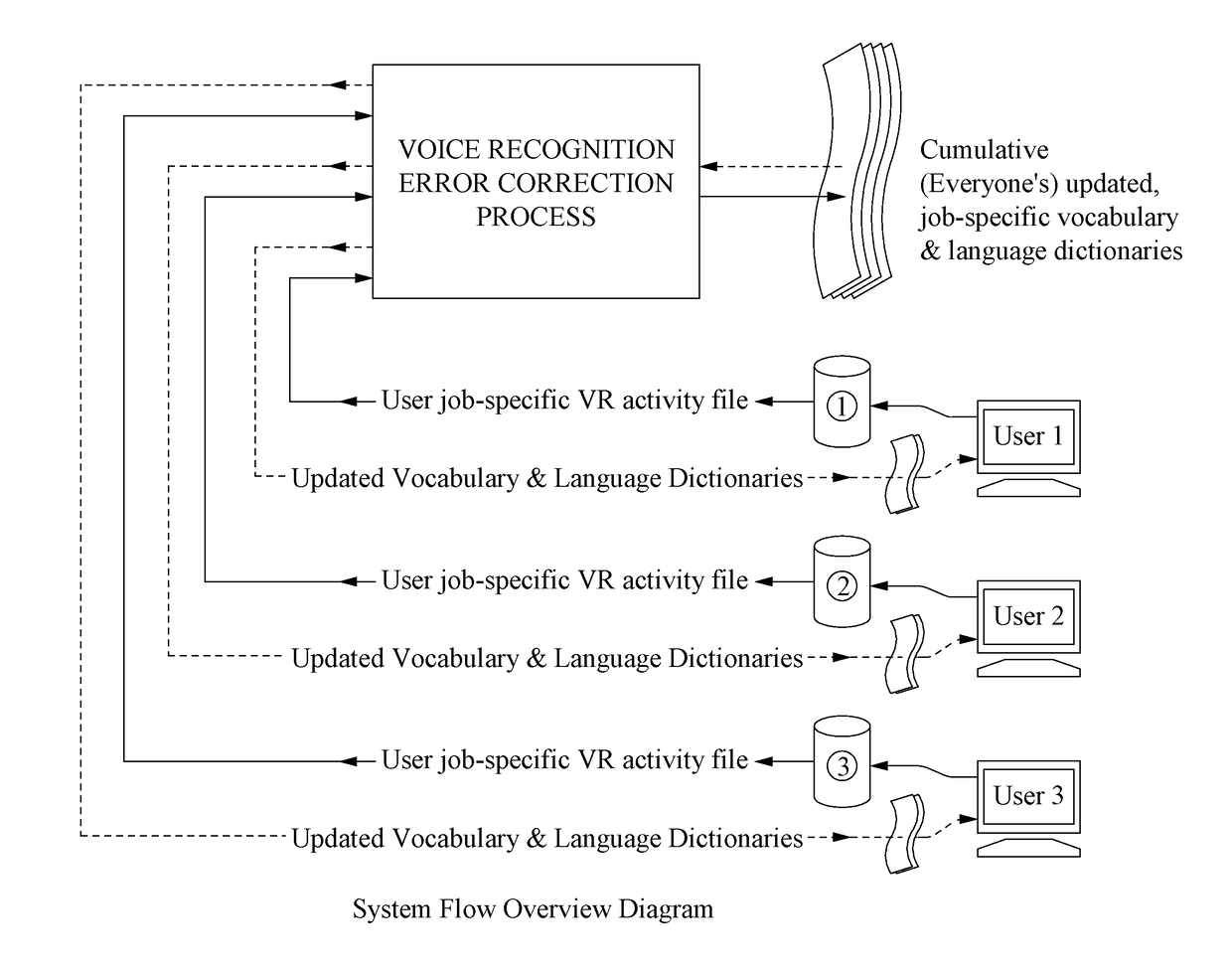
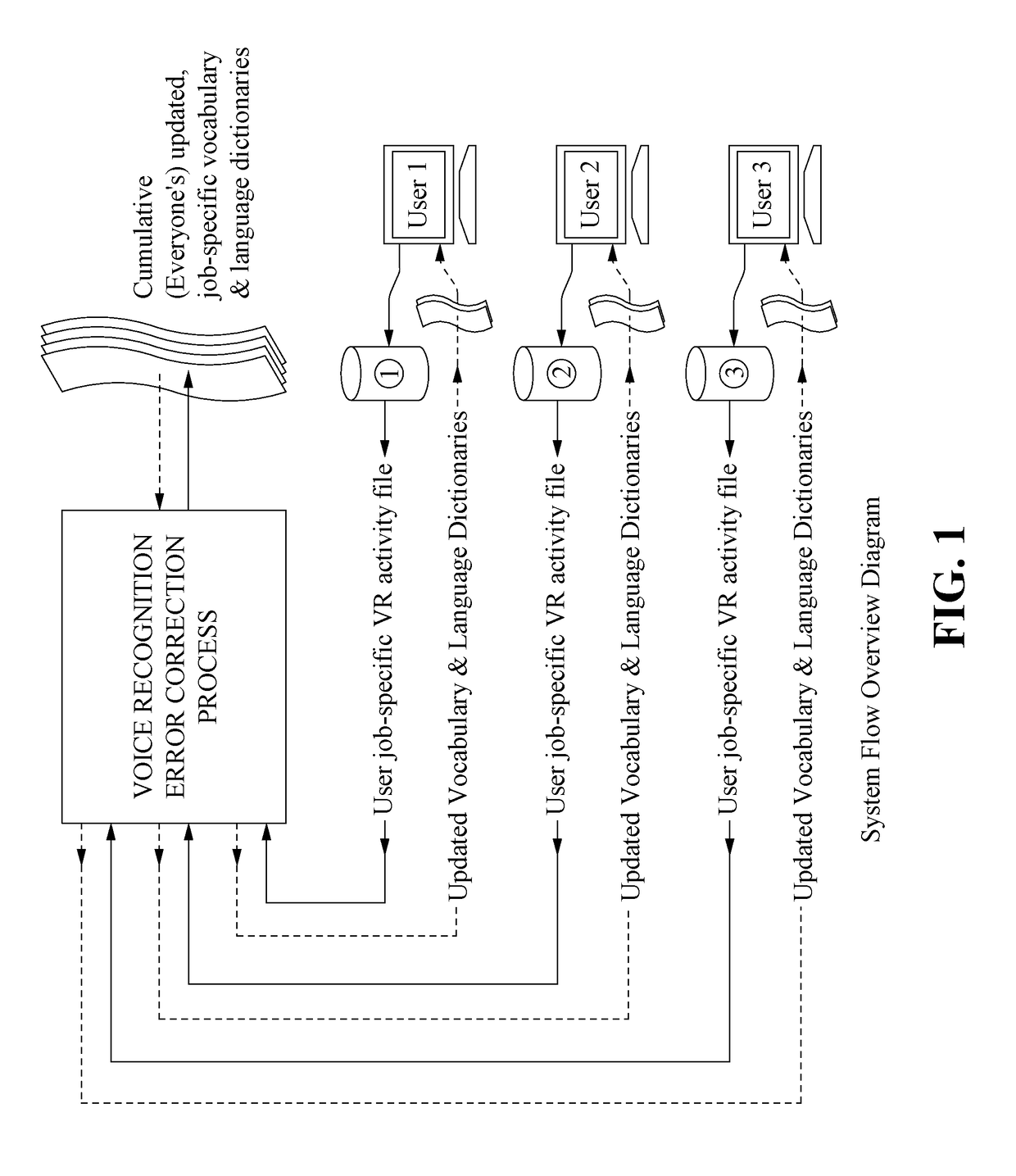
Method for Substantial Ongoing Cumulative Voice Recognition Error Reduction
ActiveUS20170133007A1Reduce probabilityNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionError reductionSpeech identification
In an embodiment, speech is recorded and converted to digital text based on a shared vocabulary dictionary. During the session, voice recognition errors, that is, speech that could not be automatically identified (if any exists), are identified by the system and associated with digital text. When text for the voice recognition error is identified (e.g., by an editor), the shared vocabulary dictionary is updated (so that that particular voice recognition error will not occur again), thereby improving the performance of the system for all users that use the shared vocabulary dictionary. The identification of voice recognitions errors and the updated of the vocabulary dictionary are performed on an ongoing basis, so that the performance of the system for all users continually improves.
Owner:COMM INNOVATION TECH LLC
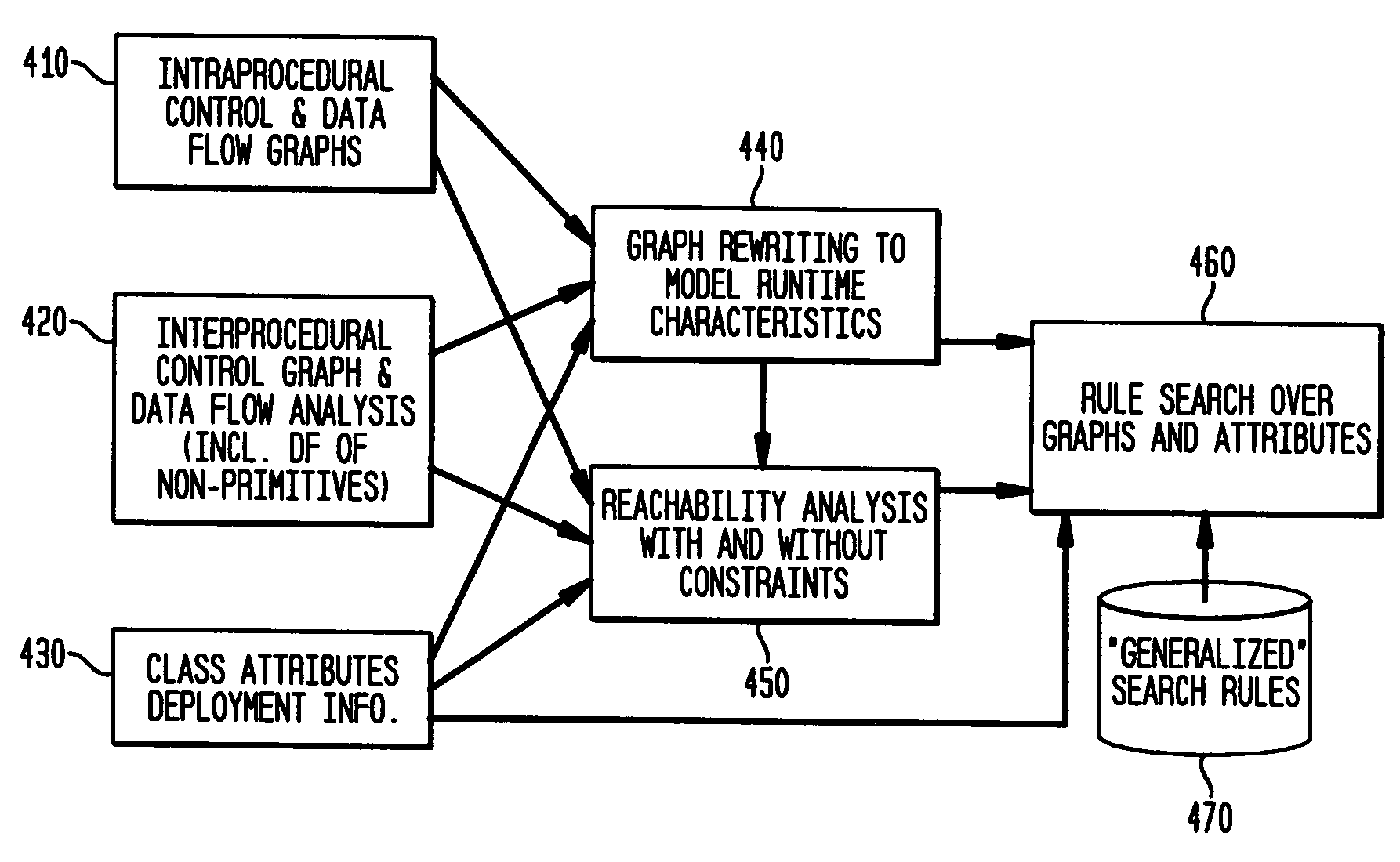
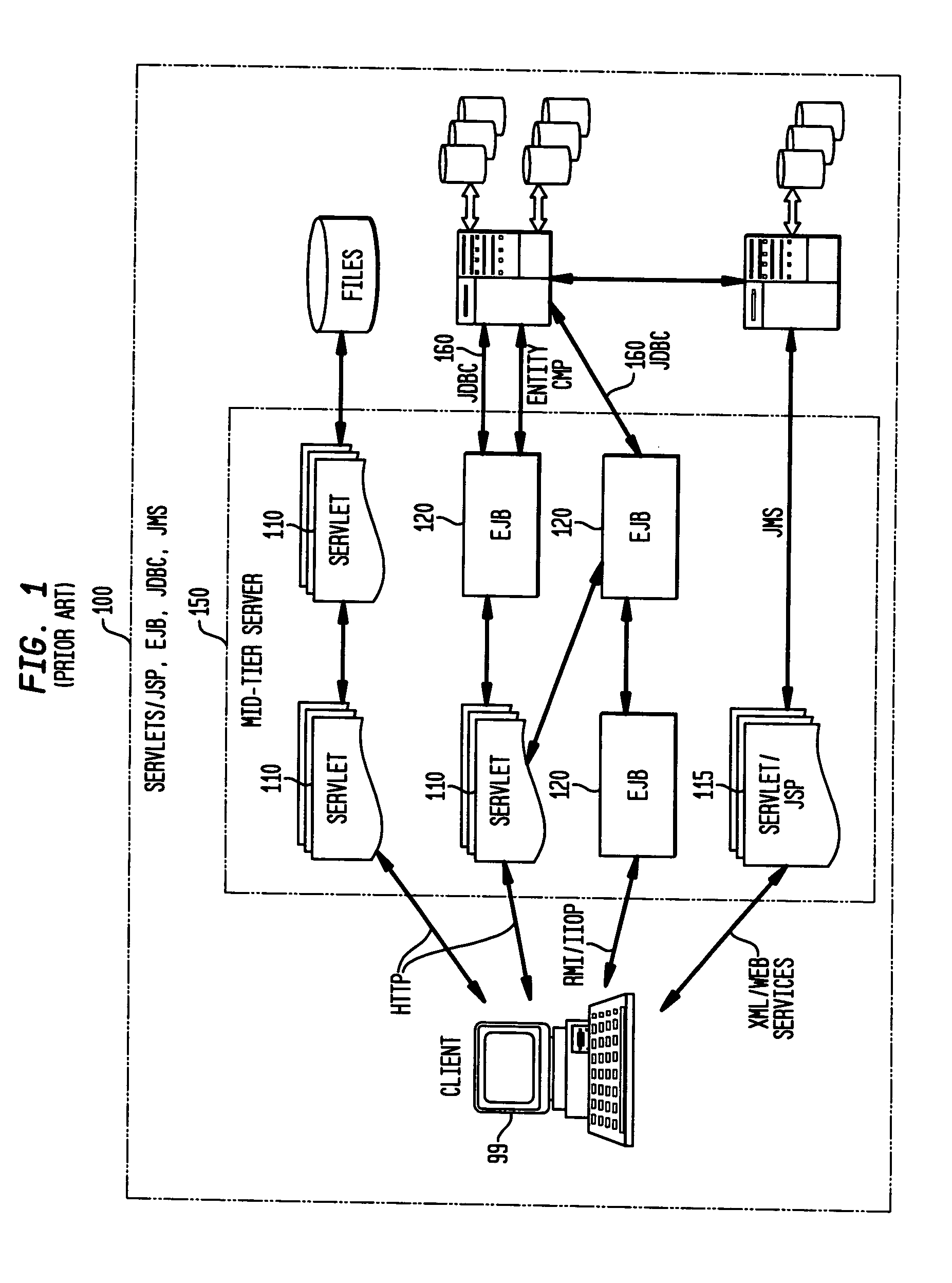
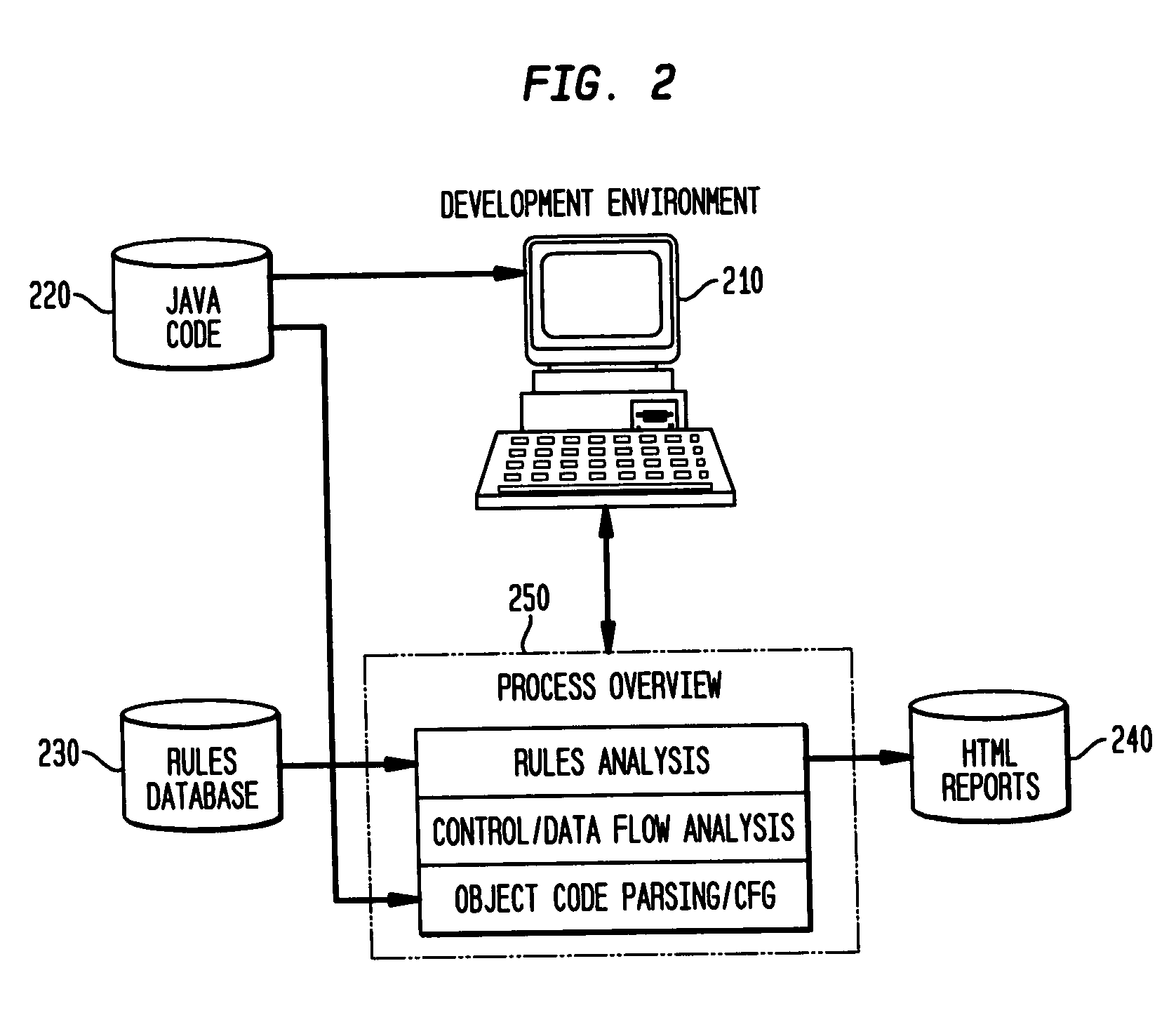
Static analysis based error reduction for software applications
InactiveUS20050015752A1Easy to liftSimple technologyError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsError reductionMaintainability
A system and method for providing “static analysis” of programs to aid in improving runtime performance, stability, security and privacy characteristics of deployed application code. The method includes performing a set of analyses that sifts through the program code and identifies programming security and / or privacy model coding errors. In particular the invention focuses on identifying coding errors that cause loss of correctness, performance degradation, security, privacy and maintainability vulnerabilities. A deep analysis of the program is performed using detailed control and data flow analyses. These deeper analyses provide a much better perspective of the overall application behavior. This deep analysis is in contrast to shallow analyses in current industry tools, which inspect or model a single or a few classes at a time.
Owner:IBM CORP
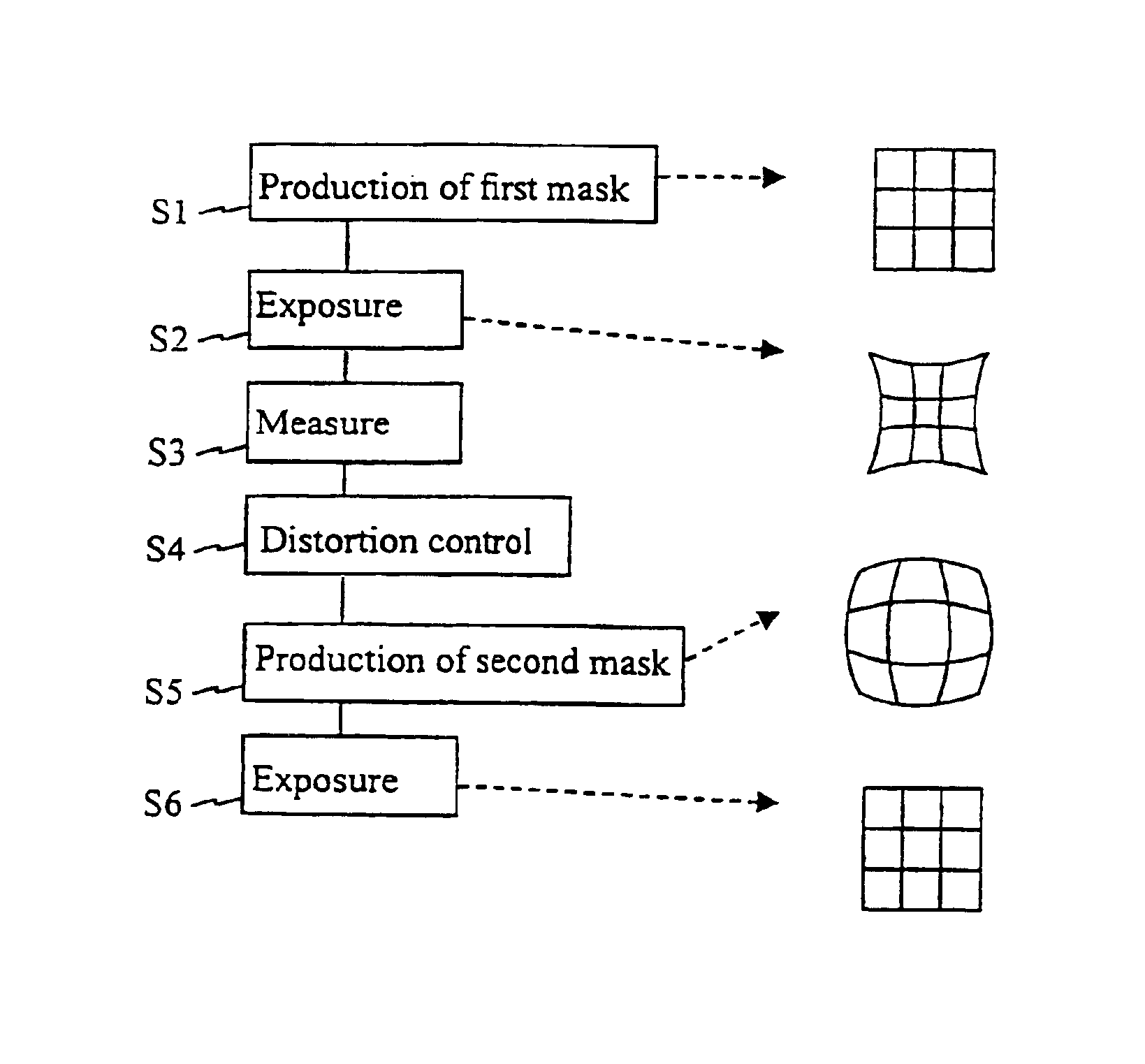
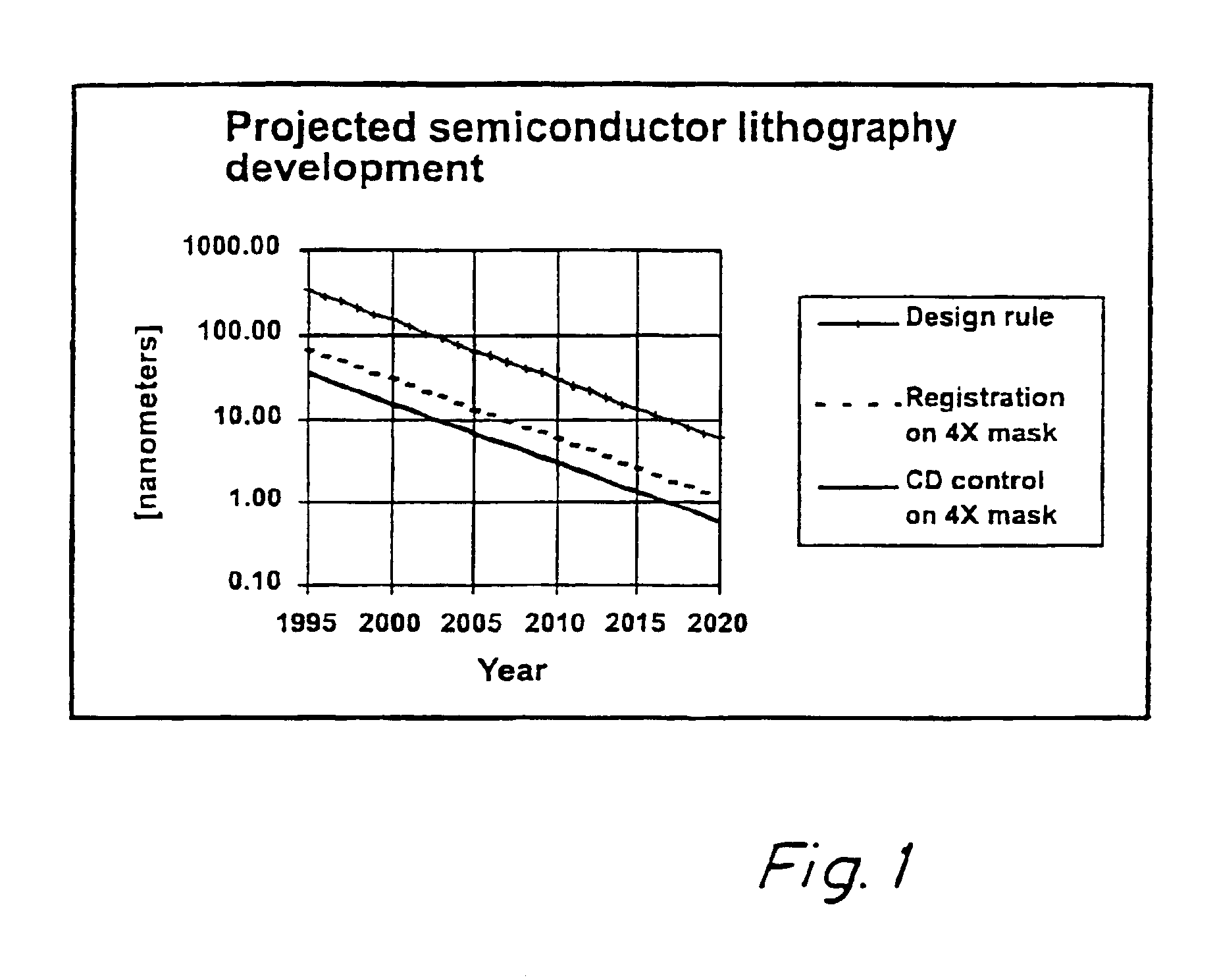
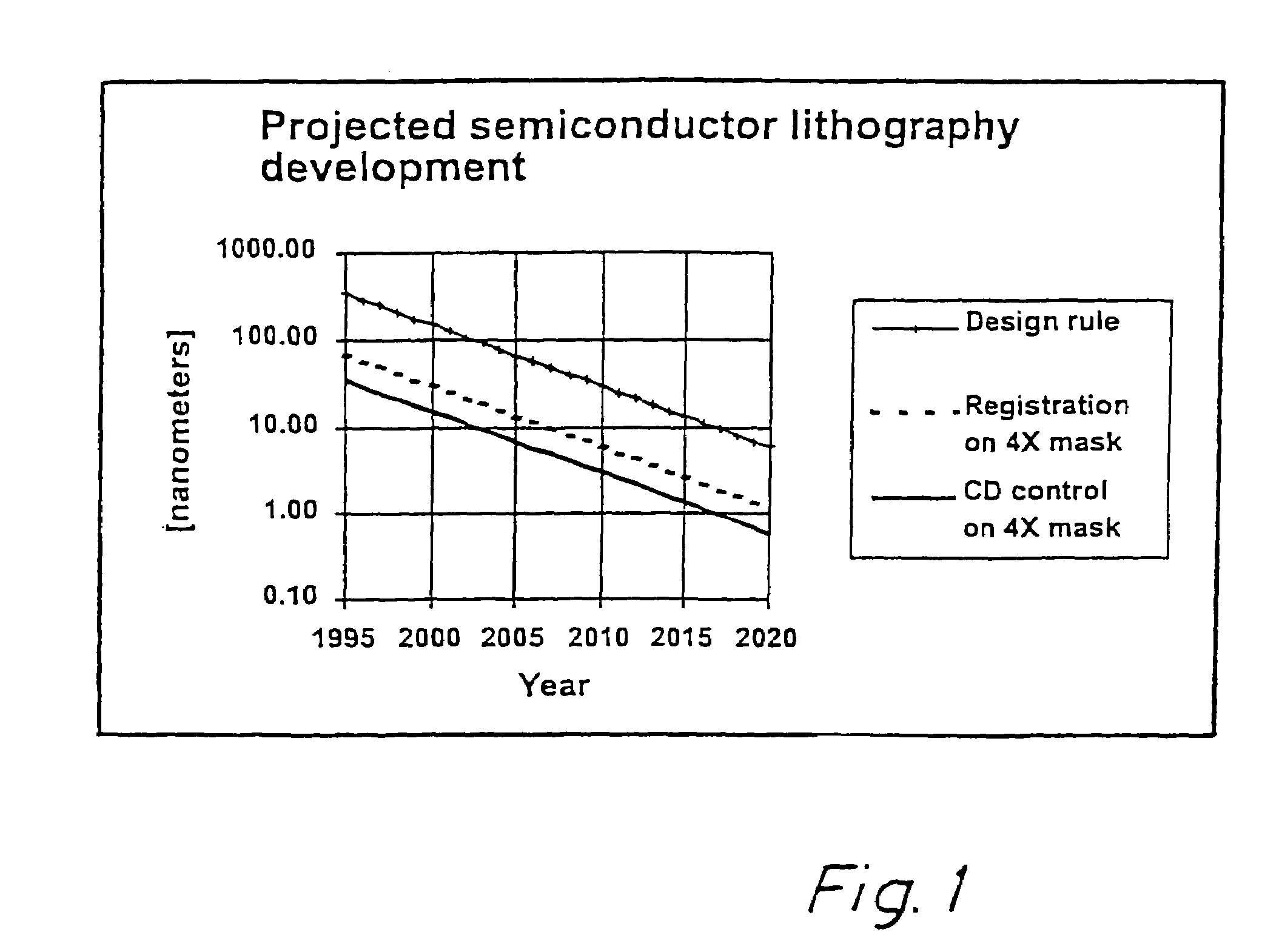
Method for error reduction in lithography
InactiveUS6883158B1High precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusError reductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for predicting and correcting geometrical errors in lithography using masks, such as large-area photomasks or reticles, and exposure stations, such as wafer steppers or projection aligners, printing the pattern of said masks on a workpiece, such as a display panel or a semi-conductor wafer. The method according to the invention comprises the steps of collecting information about a mask substrate, a mask writer, an exposure stati n, and / or about behavior of a processing step that will occur after the writing of the mask. Further the method comprises predicting from the combined information distorsions occuring in the pattern, when it is subsequently printed on the workpiece; calculating from said prediction a correction to diminish said predicted distorsion, and exposing said pattern onto said mask substrate while applying said correction for said distorsions.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Systems and methods for improving the performance of a quantum processor by reducing errors
ActiveUS20150032994A1Improve performanceImprove usabilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsError reductionIntrinsics
Techniques for improving the performance of a quantum processor are described. Some techniques employ improving the processor topology through design and fabrication, reducing intrinsic / control errors, reducing thermally-assisted errors and methods of encoding problems in the quantum processor for error correction.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
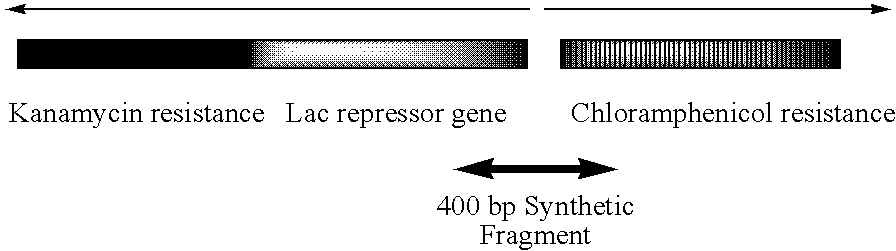
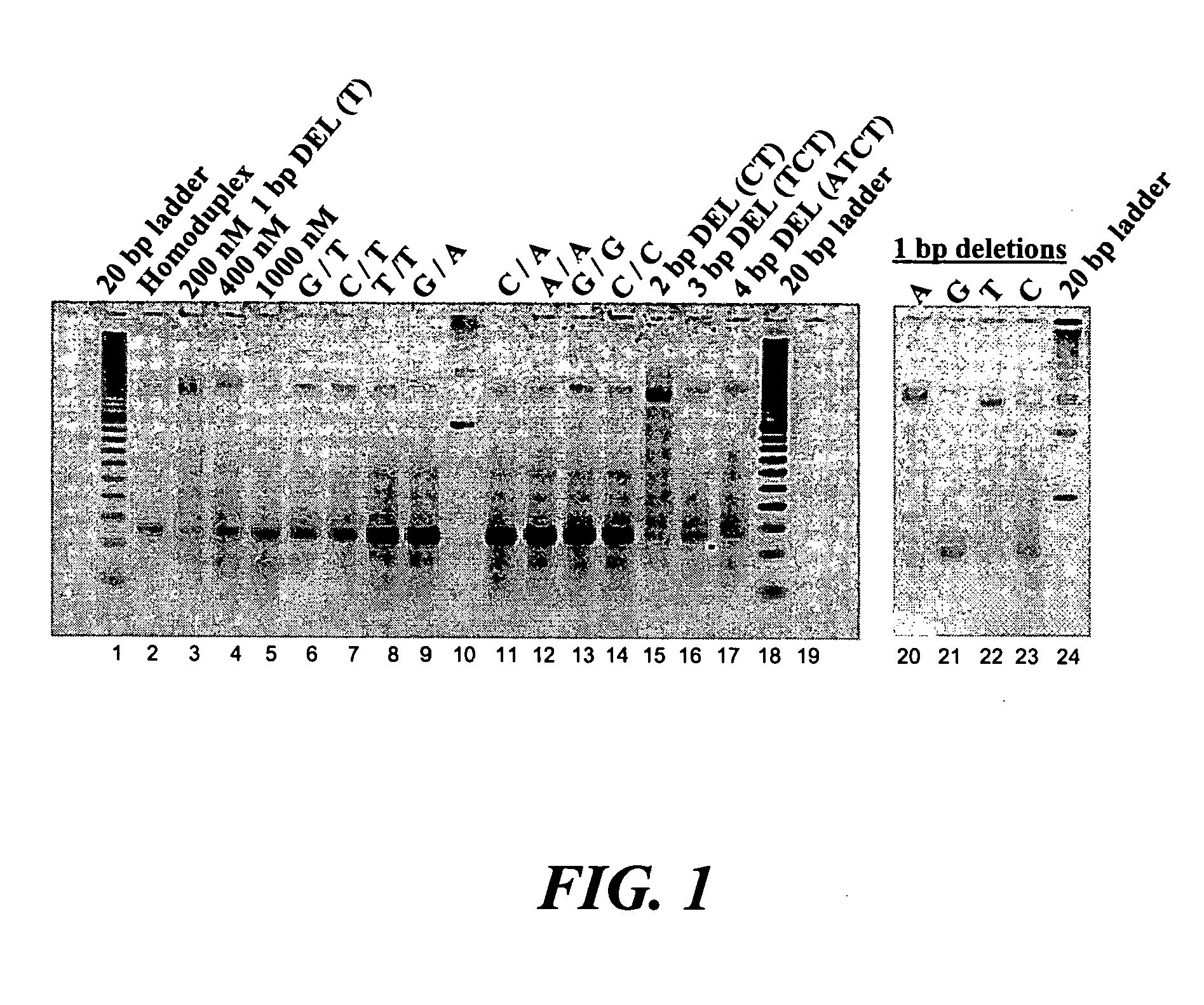
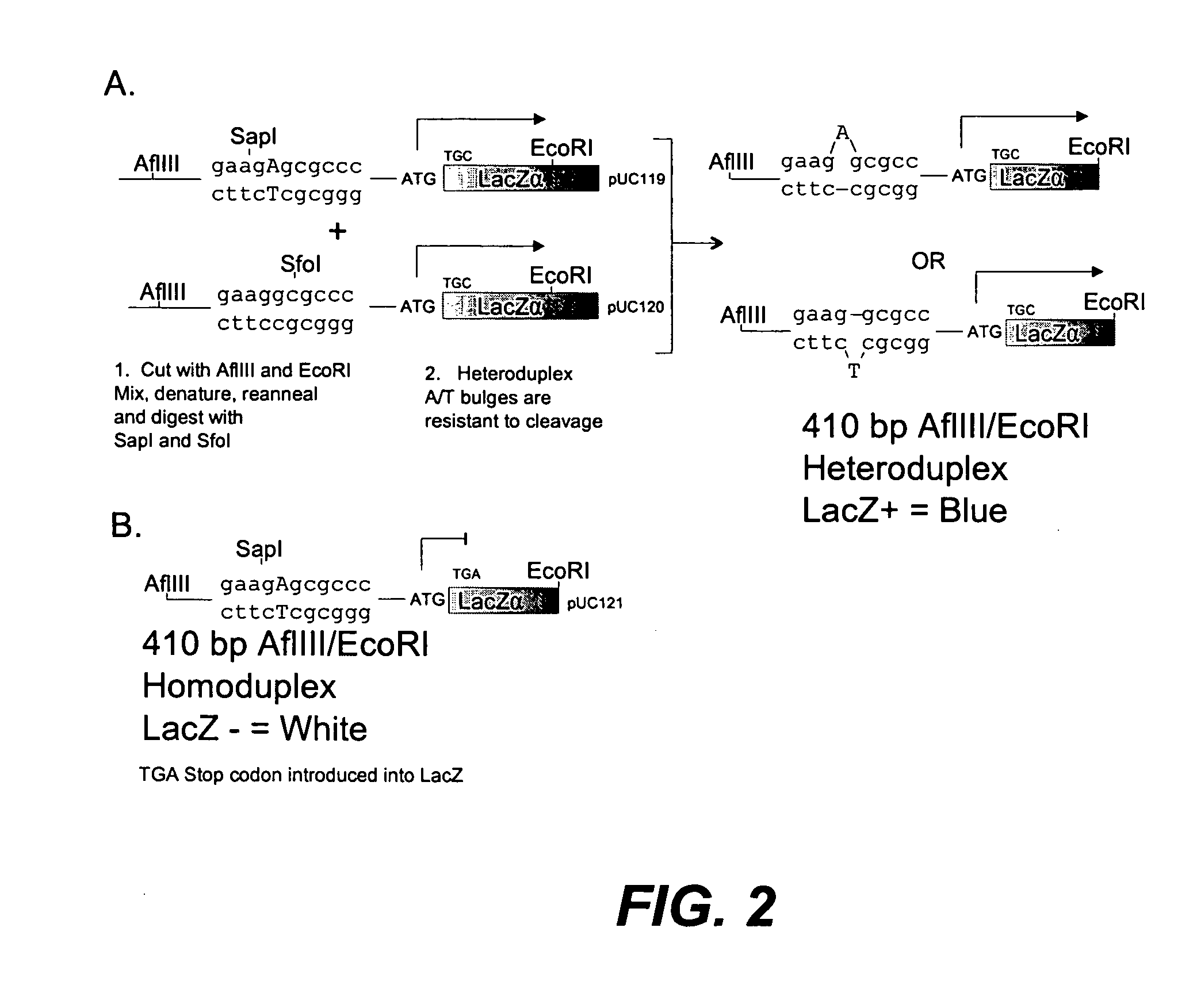
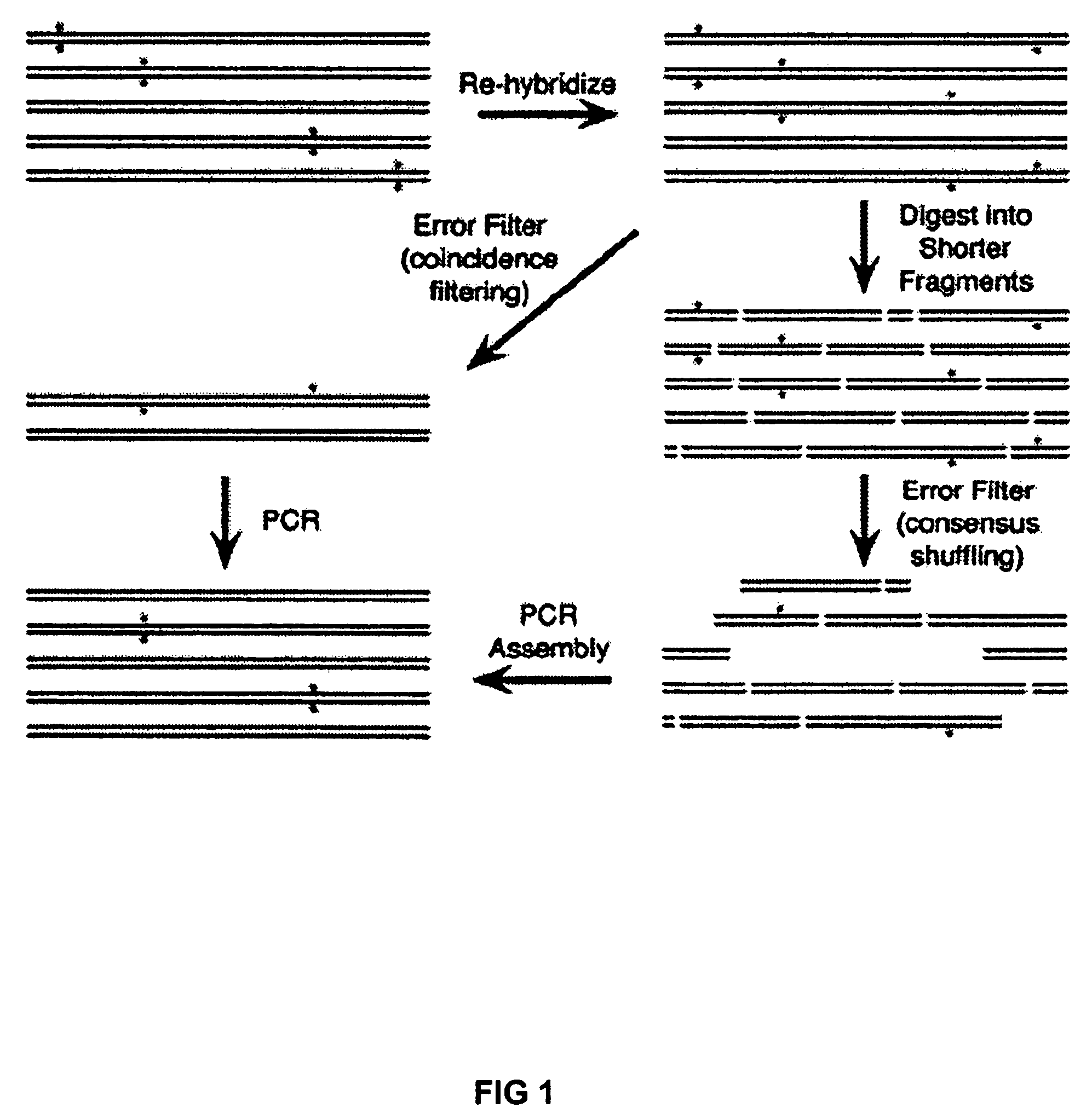
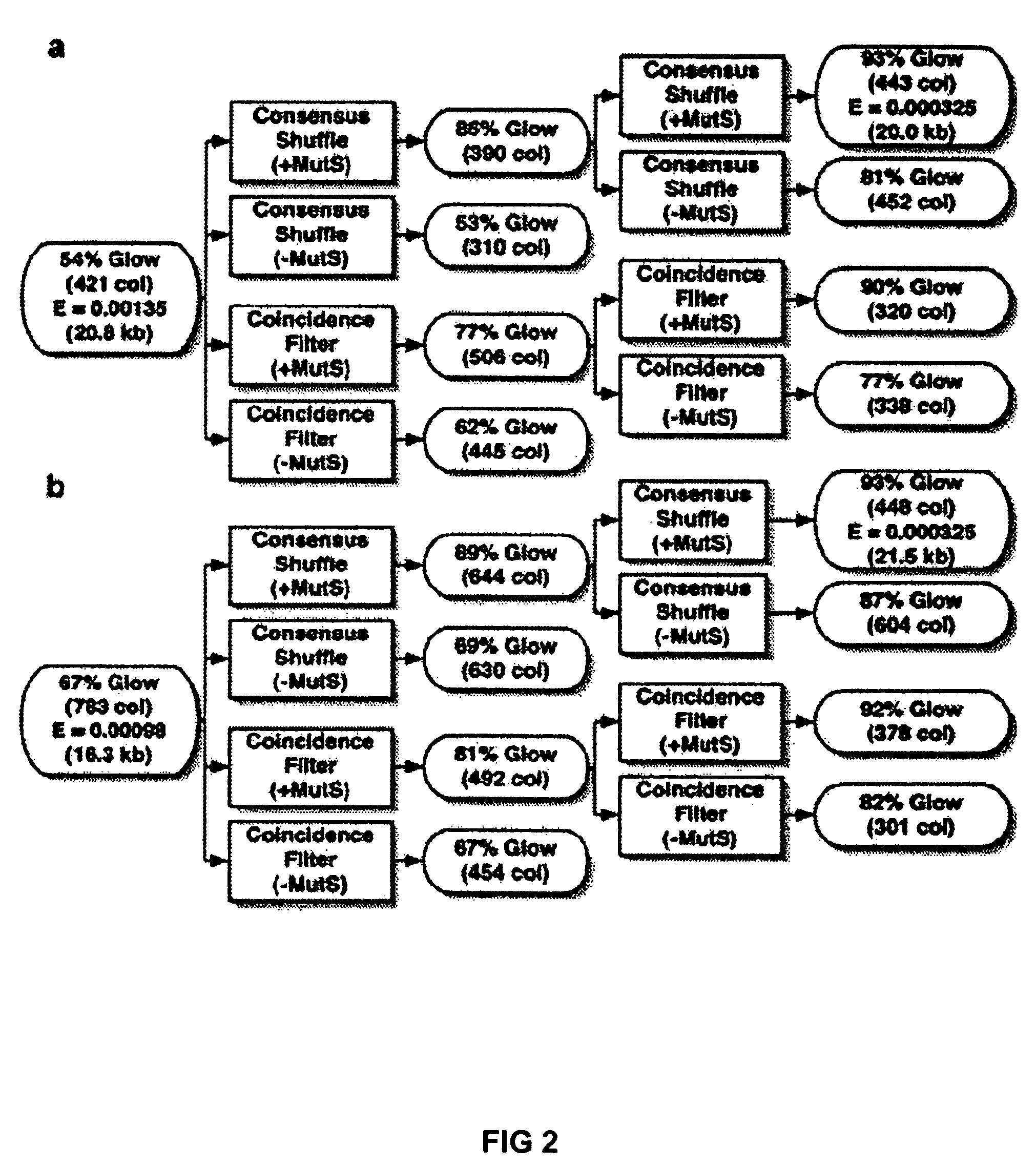
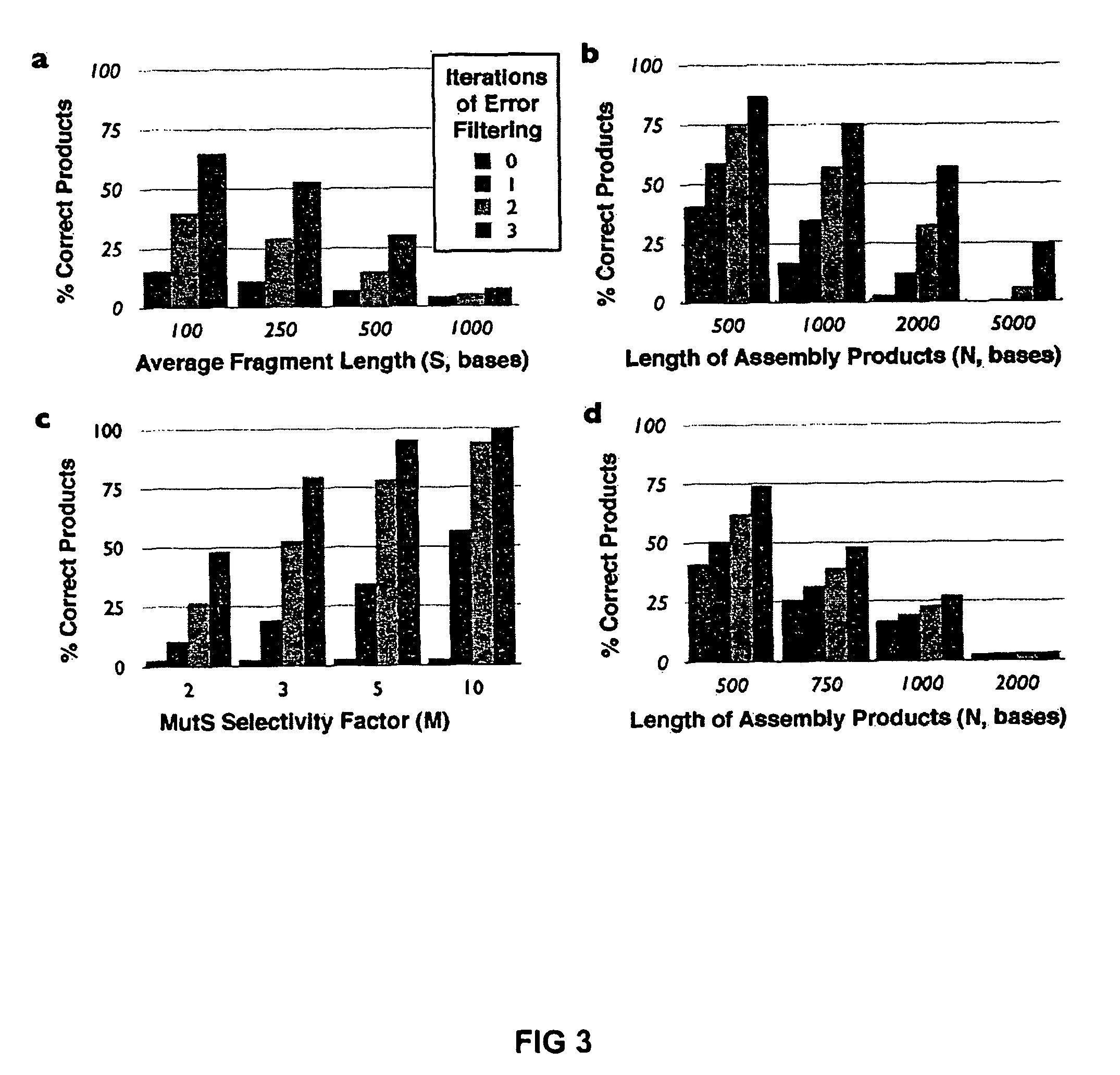
Error reduction in automated gene synthesis
In embodiments of the present invention, methods are provided for removing double-stranded oligonucleotide (e.g., DNA) molecules containing one or more sequence errors, generated during nucleic acid synthesis, from a population of correct oligonucleotide duplexes. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotides are generated enzymatically. Heteroduplex (containing mismatched bases) oligonucleotides may be created by denaturing and reannealing the population of duplexes. The reannealed oligonucleotide duplexes are contacted with a mismatch recognition protein that interacts with (e.g., binds and / or cleaves) the duplexes containing a base pair mismatch. The oligonucleotide heteroduplexes that have interacted with such a protein are separated, simultaneously with contacting or sequentially in a separate step, from homoduplexes. These methods are also used in another embodiment to remove heteroduplex oligonucleotides (e.g., DNA) that are formed directly from chemical nucleic acid synthesis. In other embodiments of the present invention, kits and compositions useful for the methods are provided.
Owner:BLUE HERON BIOTECH
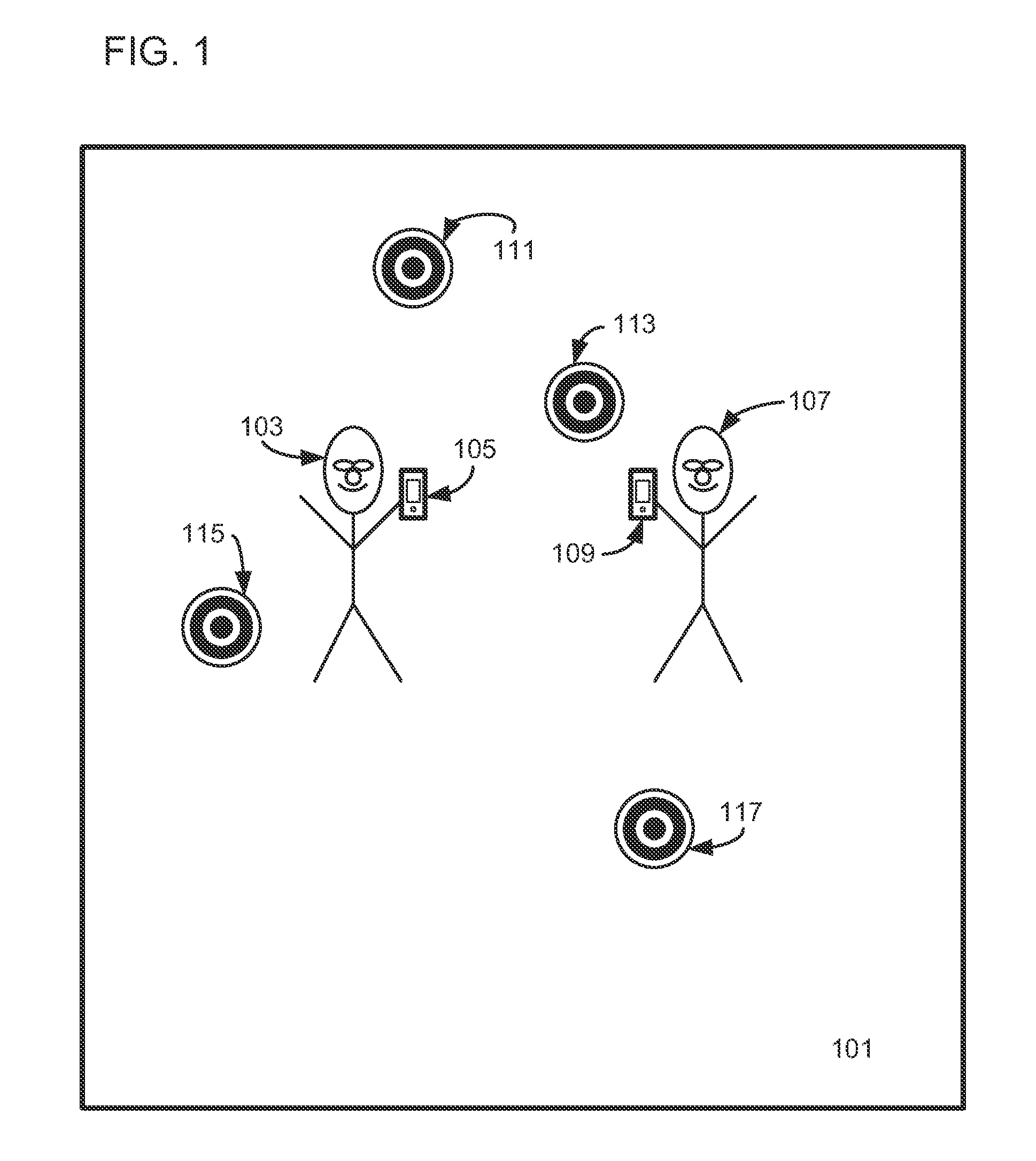
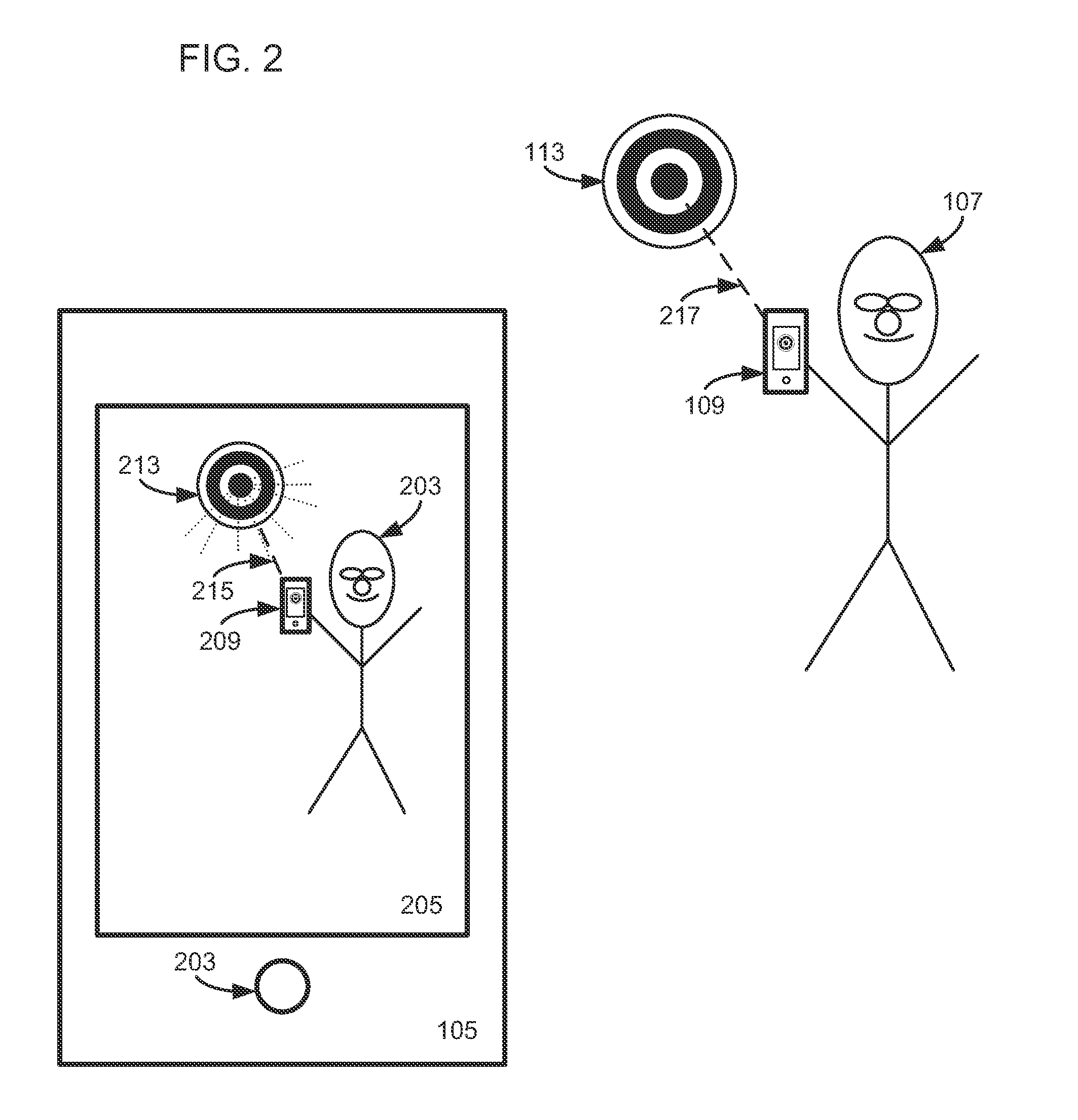
Sensor Error Reduction in Mobile Device Based Interactive Multiplayer Augmented Reality Gaming Through Use of One or More Game Conventions
Interactive multiplayer augmented reality game play is enhanced in a mobile device used in such game play by establishing a virtual world coordinate system based on one or more game conventions and by reducing device sensor error before, during or after game play using one or more such game conventions.
Owner:CIVIC RESOURCE GRP INT INC
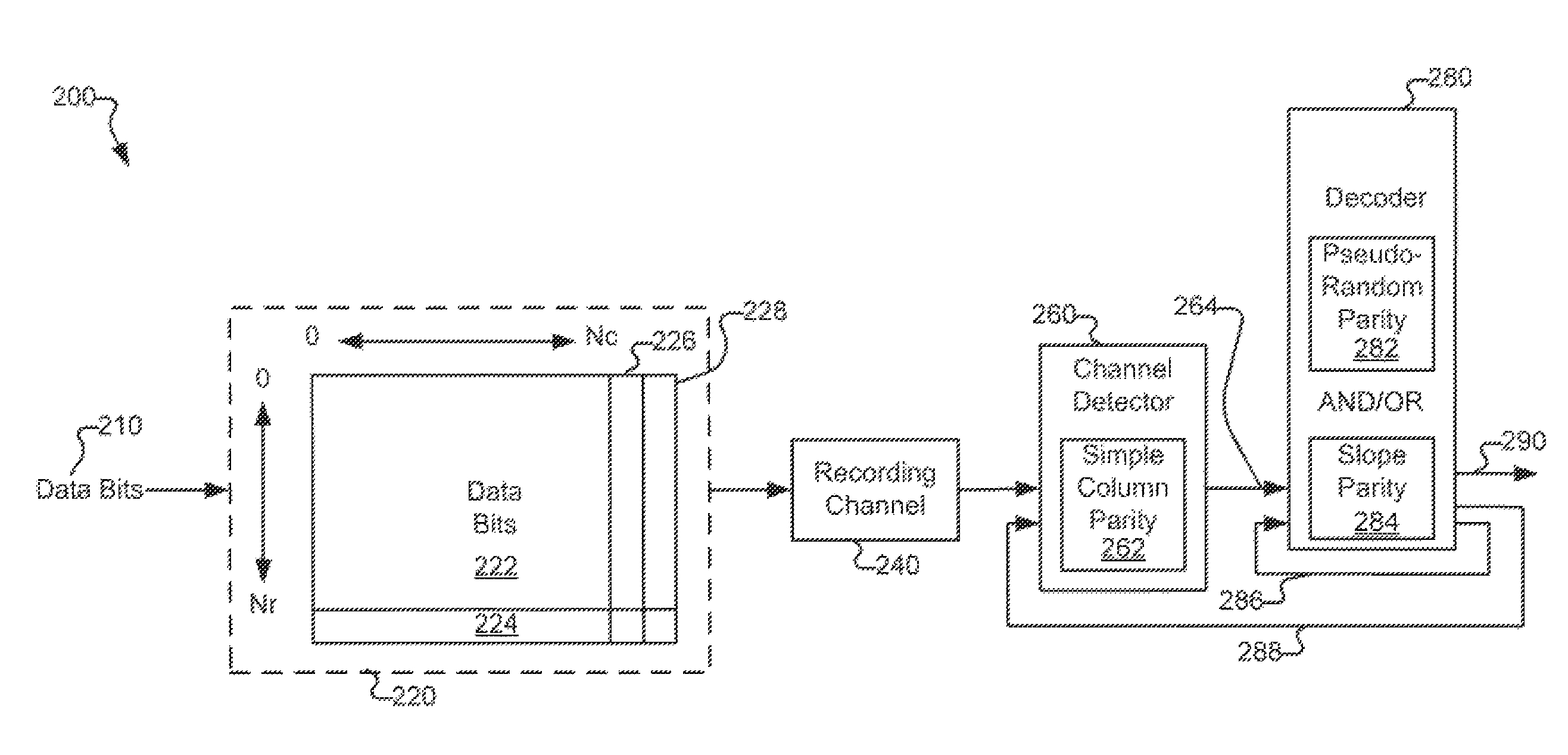
Systems and methods for code based error reduction
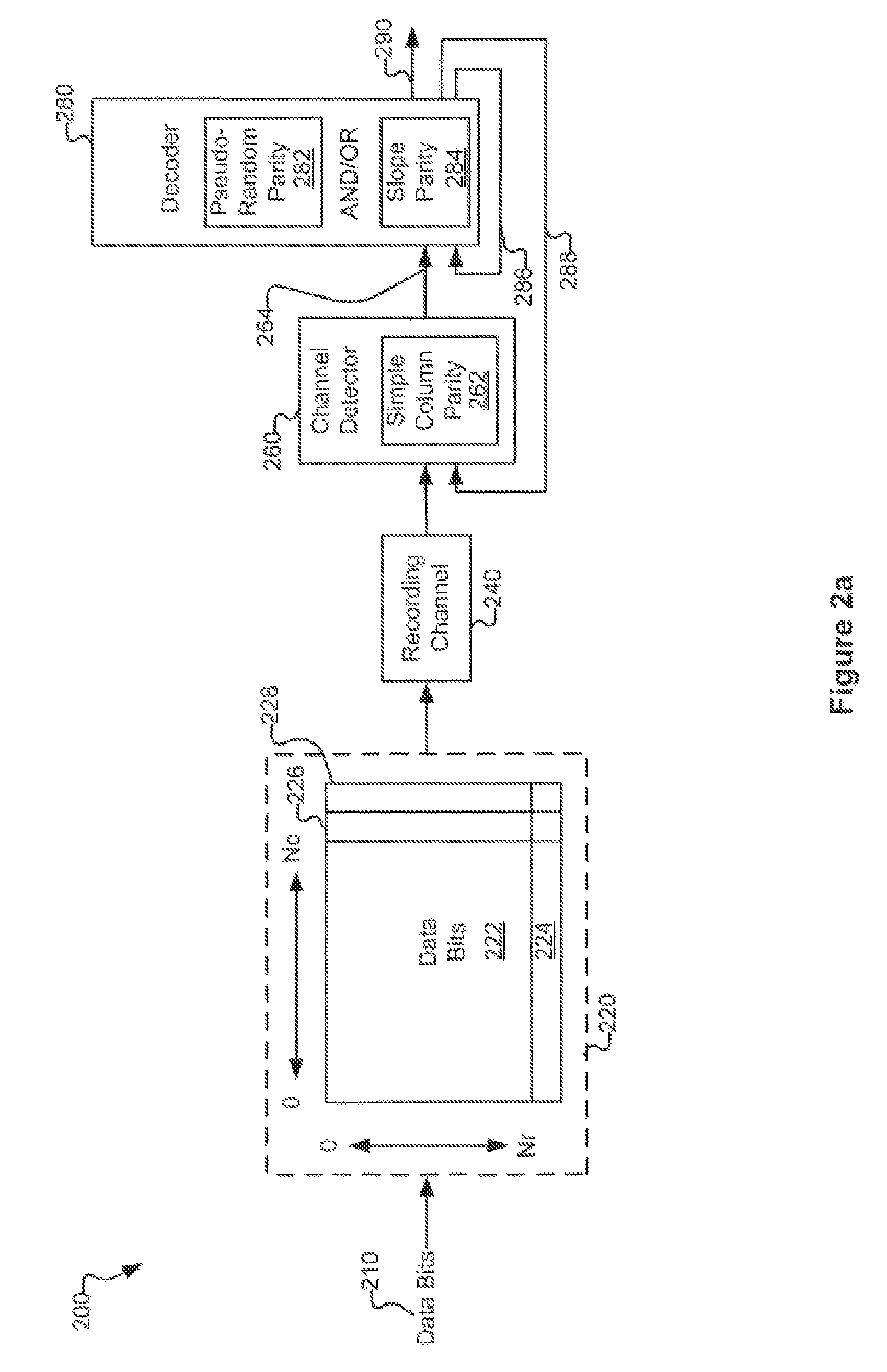
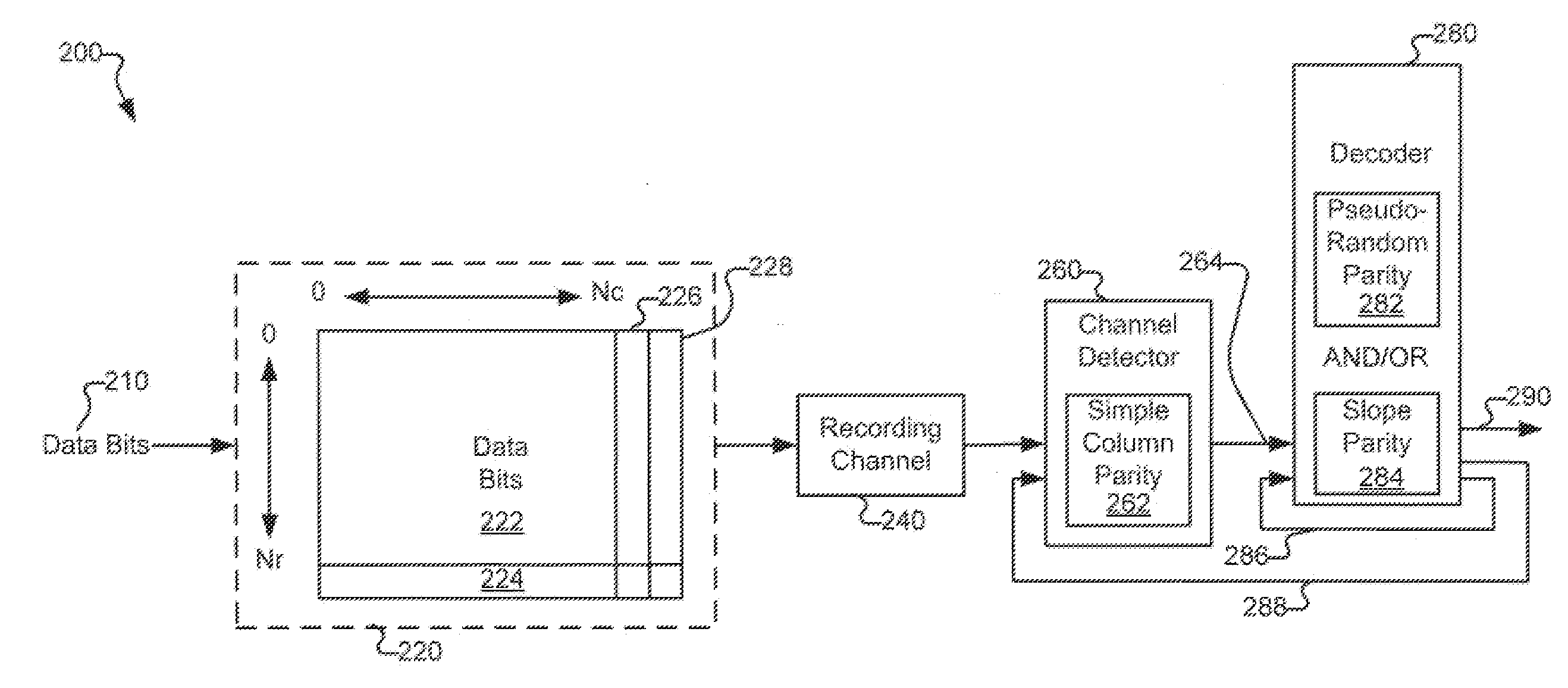
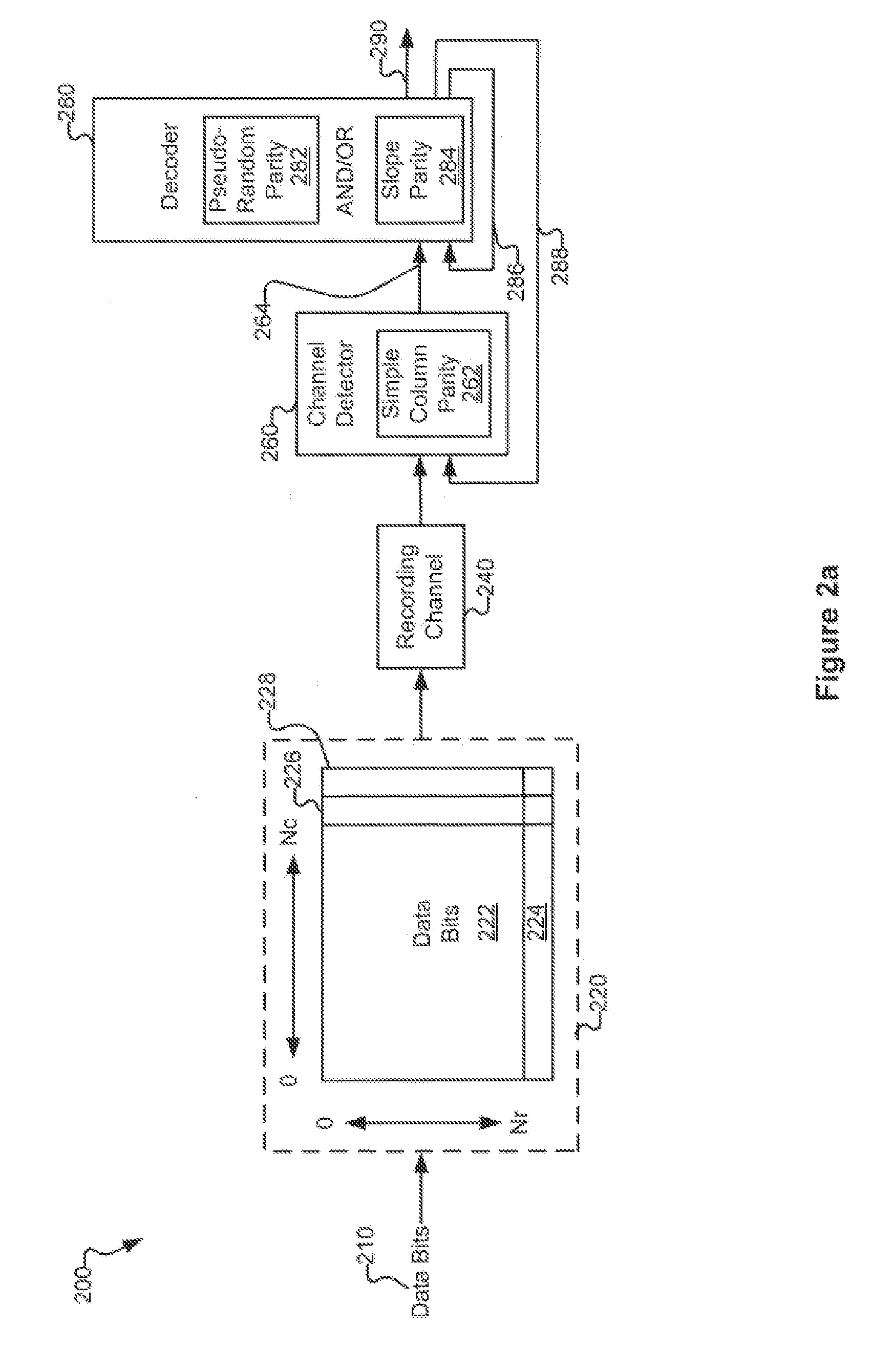
Various systems and methods for code based error reduction. For example, in one digital information system including a channel detector and a decoder, the channel detector receives an encoded data set and is operable to perform a column parity check. The channel detector provides an output representing the encoded data set. The decoder receives the output from the channel detector and is operable to perform two checks. The two checks may be one of: two pseudo-random parity checks, a pseudo-random parity check and a slope parity check, and two slope parity checks. In addition, the decoder provides another output representing the encoded data set.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and Methods for Code Based Error Reduction
Various systems and methods for code based error reduction are disclosed herein. For example, a digital information system including a channel detector and a decoder is disclosed. In the system, the channel detector receives an encoded data set and is operable to perform a column parity check. The channel detector provides an output representing the encoded data set. The decoder receives the output from the channel detector and is operable to perform two checks. The two checks may be one of: two pseudo-random parity checks, a pseudo-random parity check and a slope parity check, and two slope parity checks. In addition, the decoder provides another output representing the encoded data set.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
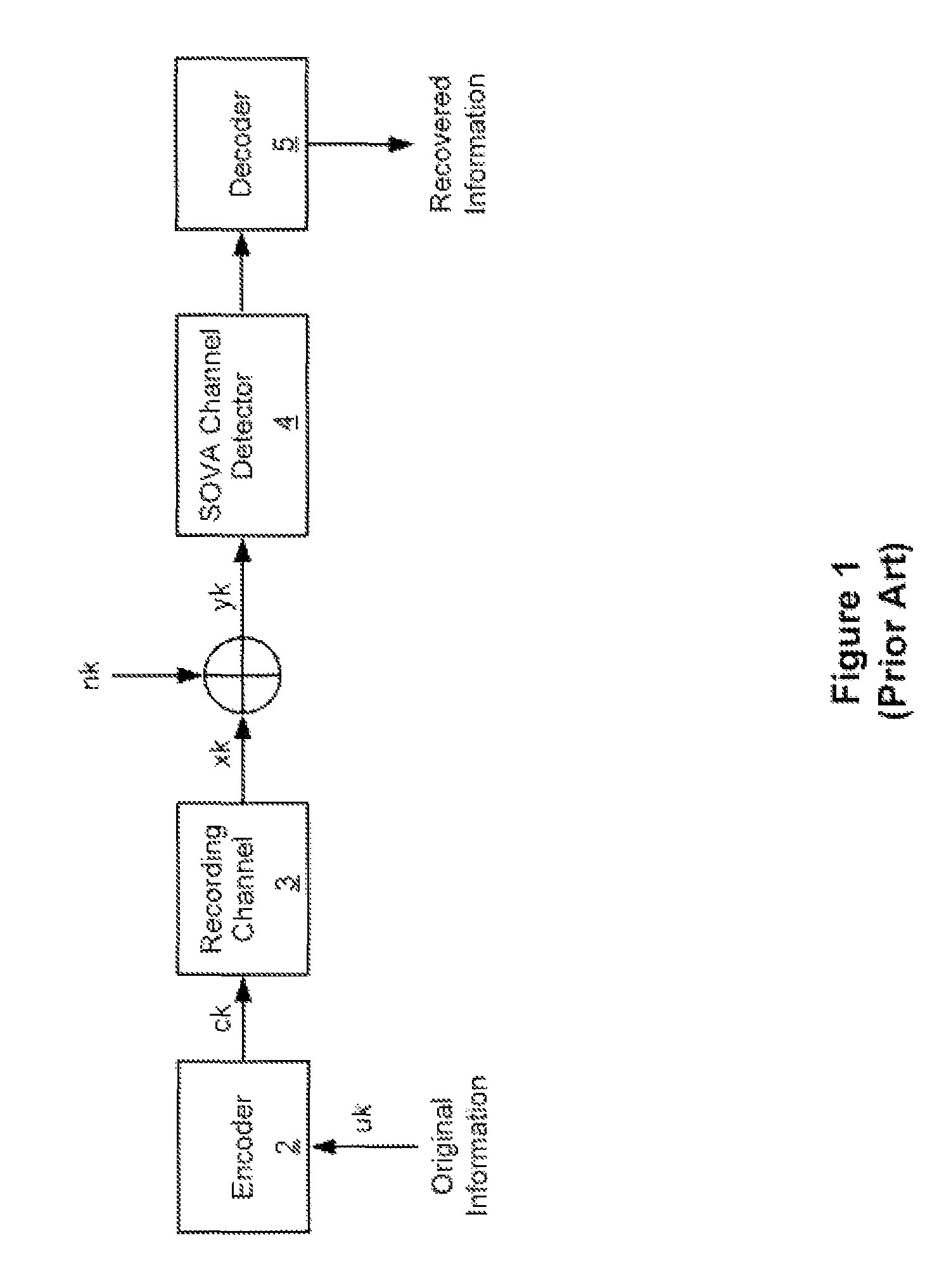
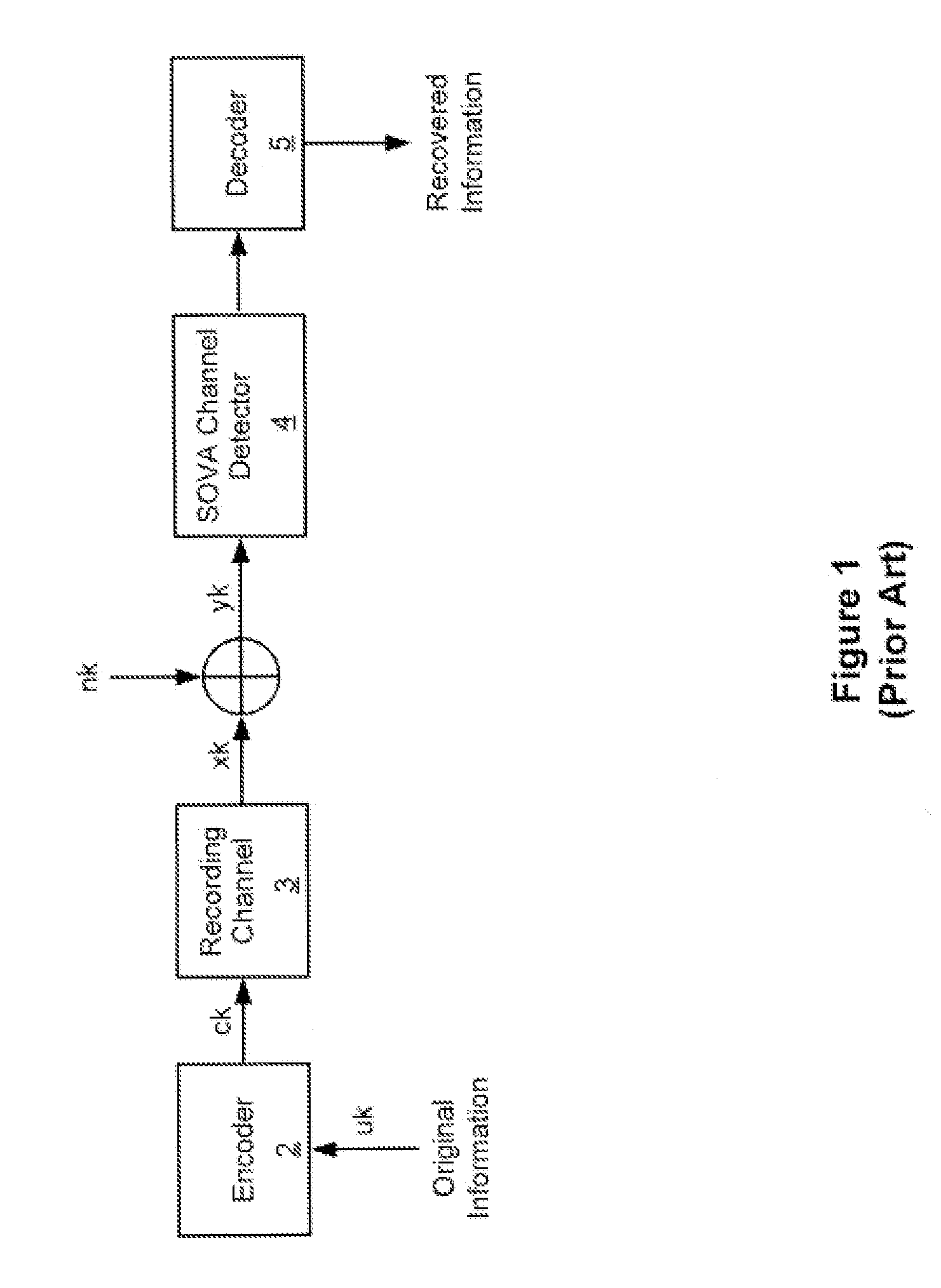
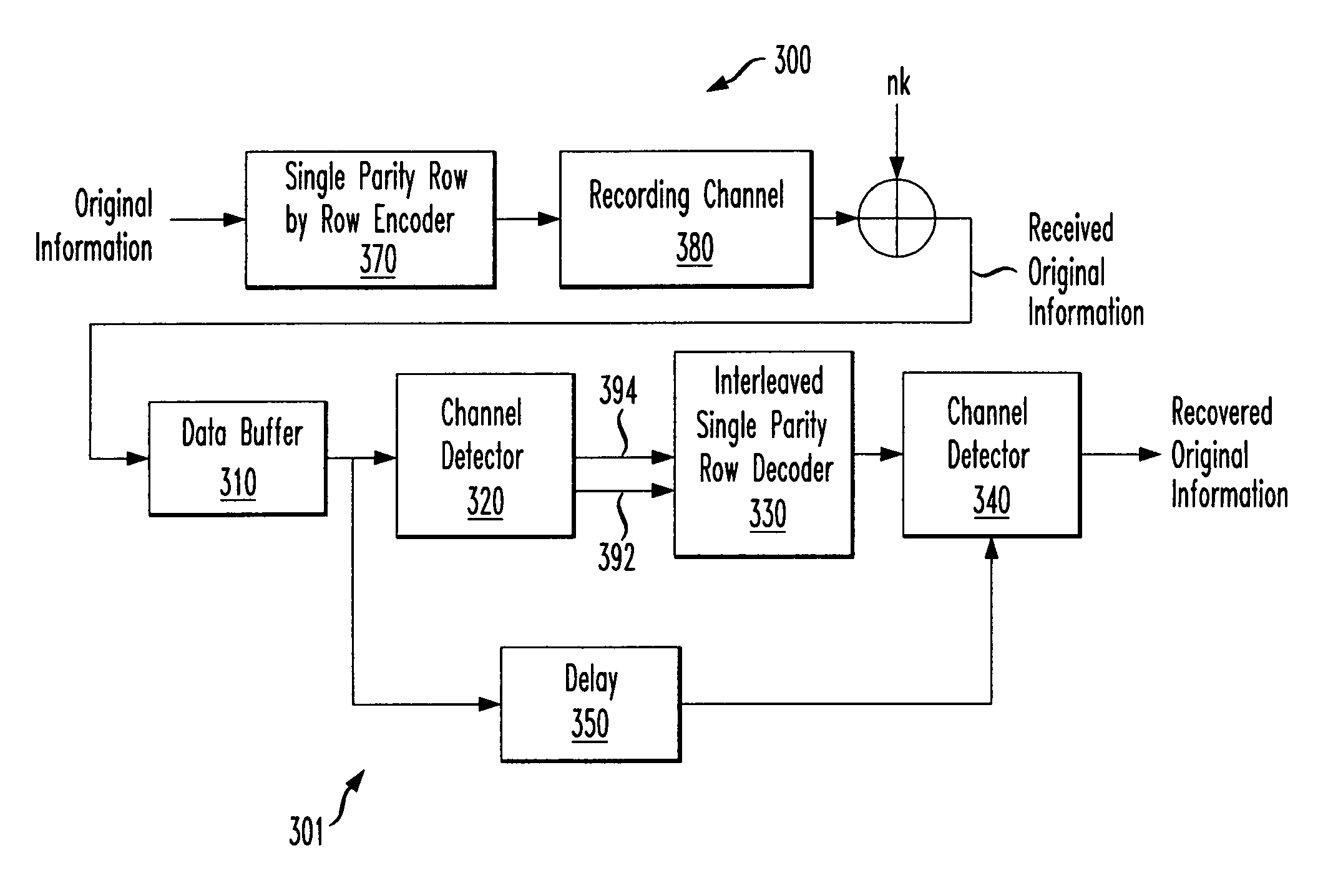
Systems and methods for error reduction associated with information transfer
Various systems and methods for error reduction in a digital information system are disclosed herein. As one example, a digital storage system is provided that includes a soft output Viterbi algorithm channel detector operable to receive an encoded data set, and to provide a hard and a soft output representing the encoded data set. The hard and the soft output from the soft output Viterbi algorithm channel detector are provided to a single parity row decoder that provides another hard output that is an error reduced representation of the encoded data set. The encoded data set is additionally provided from the buffer to another channel detector via a delay element. The hard output from the single parity row decoder and the time shifted encoded data set are provided to coincident with each other to another channel detector.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
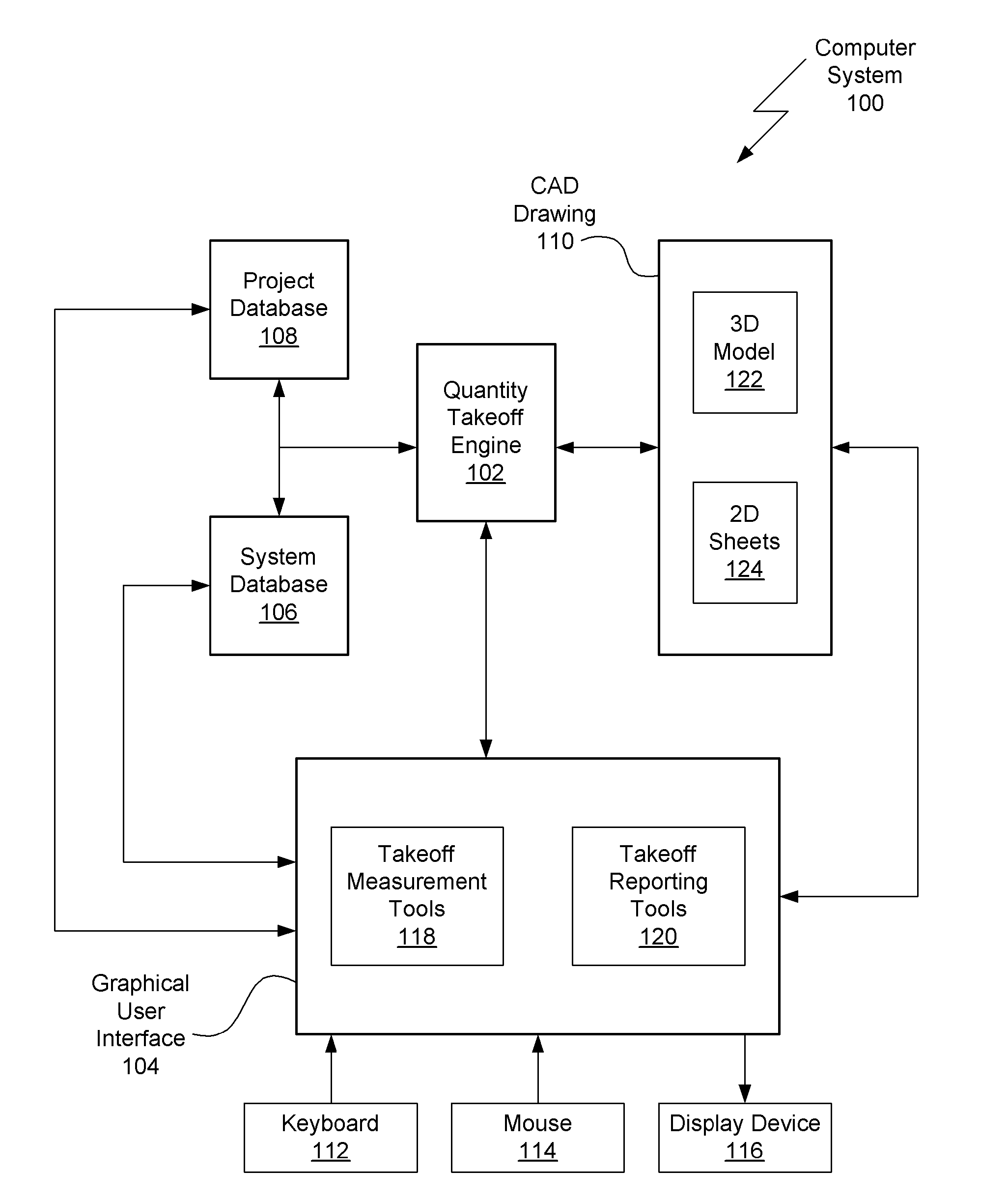
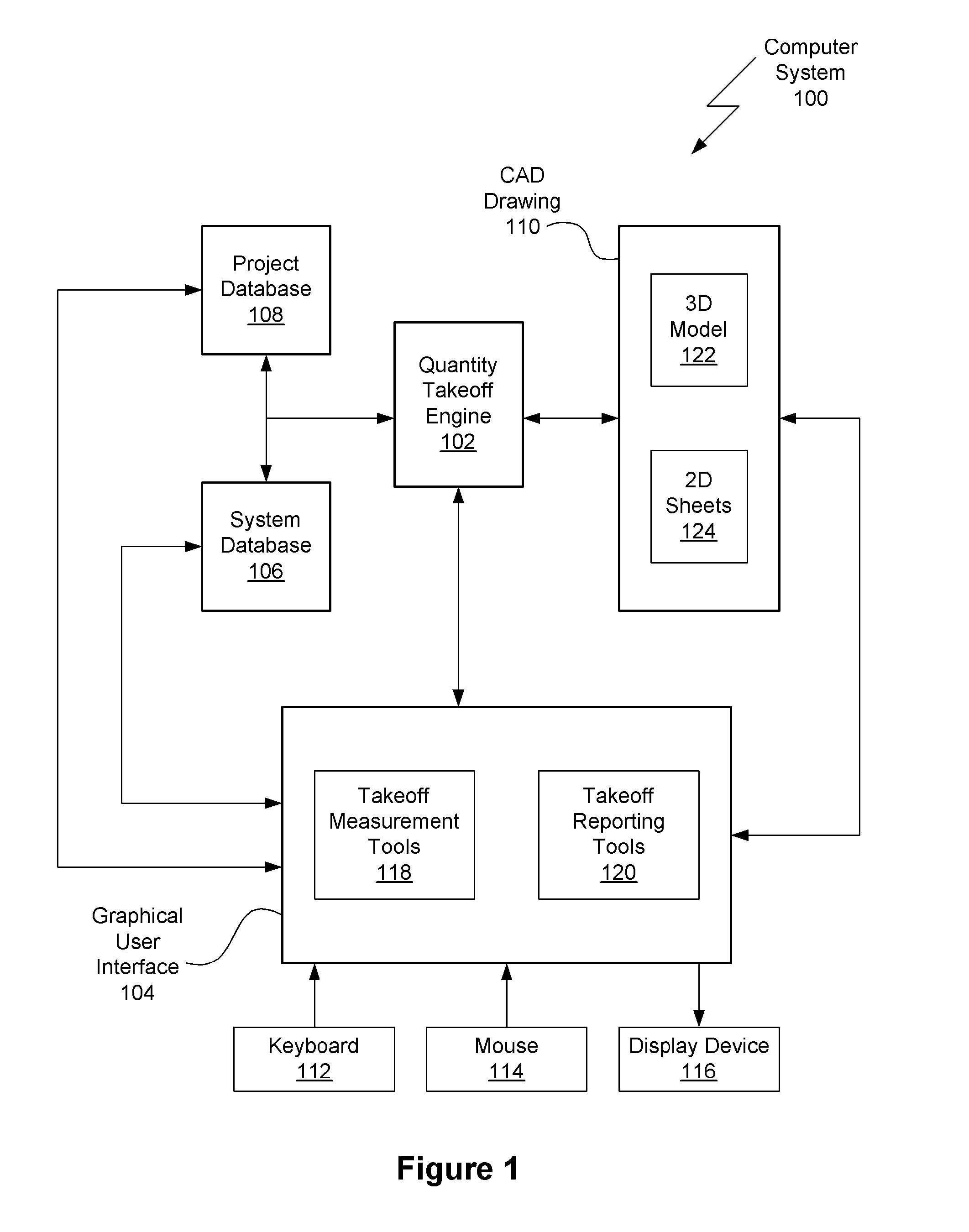
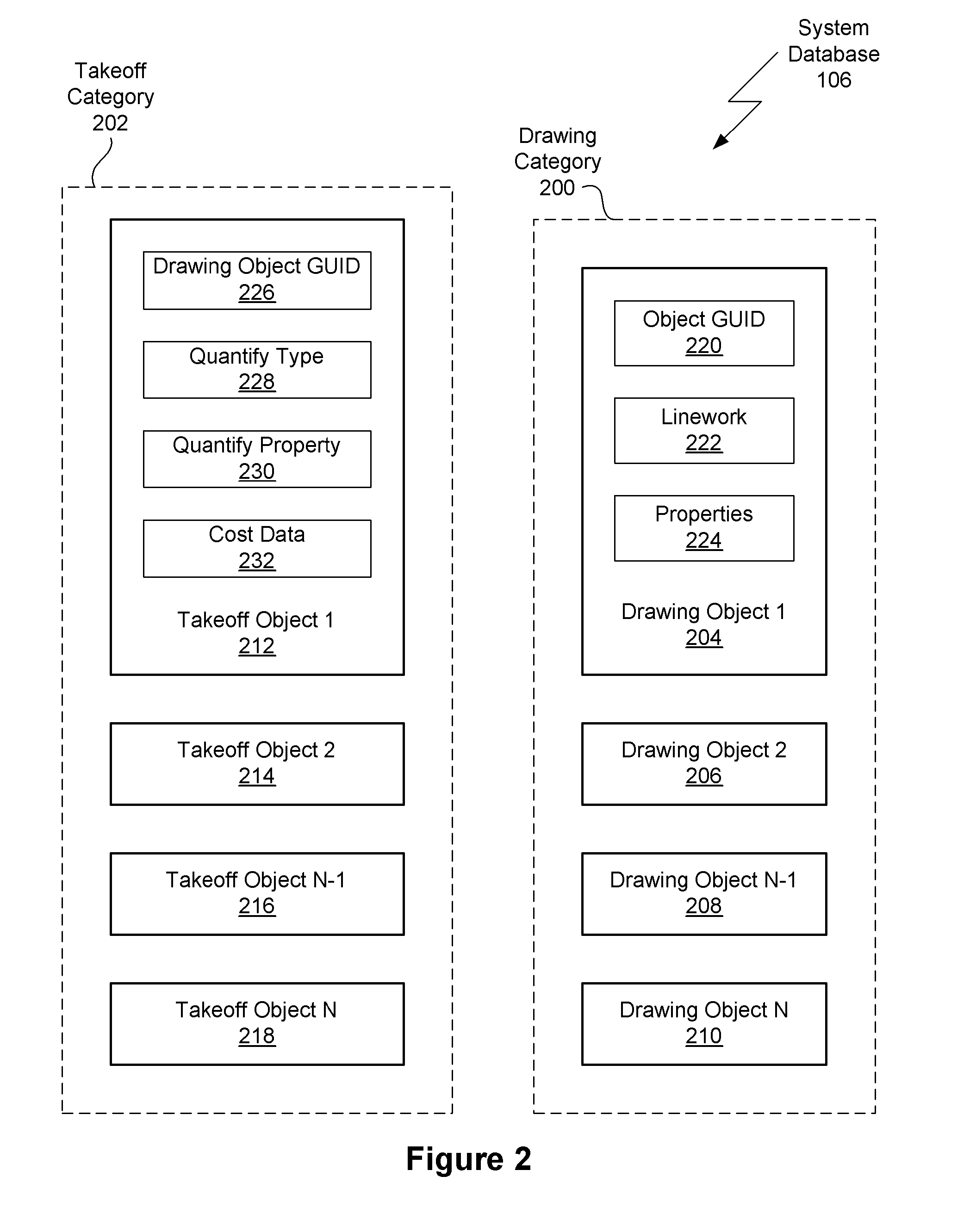
Method for semi-automatic quantity takeoff from computer aided design drawings
ActiveUS20090070071A1Improve consistencyImprove abilitiesGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignError reduction
Embodiments of the present invention include methods for semi-automatic quantity takeoff from computer aided design (CAD) drawings. For each drawing object a corresponding takeoff object is created. A takeoff object may include the dimension of geometry (e.g., numerical, lineal, area) to quantify, the object parameter to be quantified for all instances of the object, and the takeoff calculations to be performed. After a takeoff object is defined, the corresponding instances are automatically identified and quantified. The cost of each instance is then calculated and added to the project cost. Using automated methods, instead of manual techniques, reduces errors and increases the accuracy of the generated cost estimate. Advantageously, the takeoff objects may be saved in the system database and reused for different projects, thereby ensuring consistency between projects. Furthermore, reusing takeoff information, both between instances of an object and between projects, reduces the time required to perform cost estimates.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
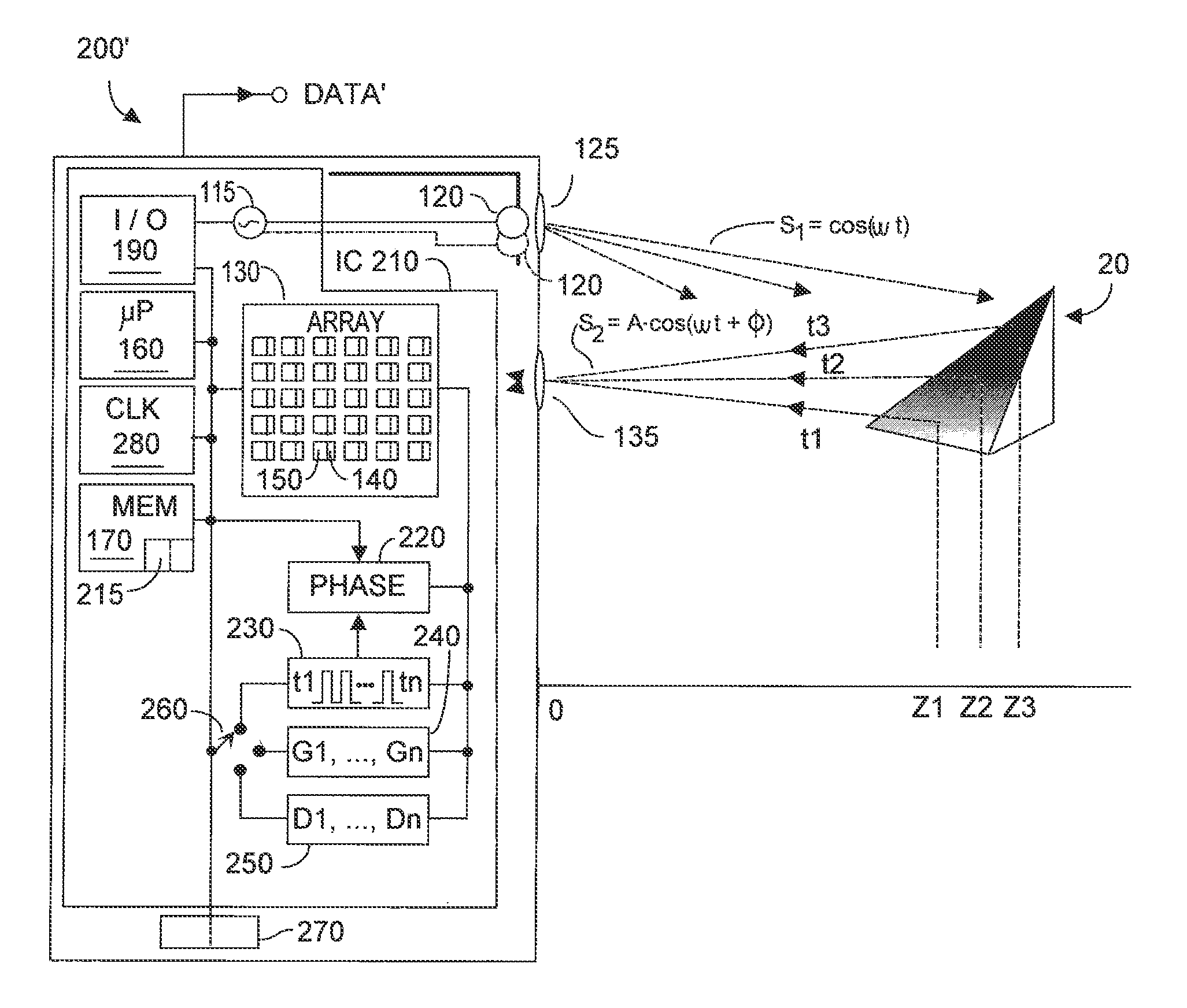
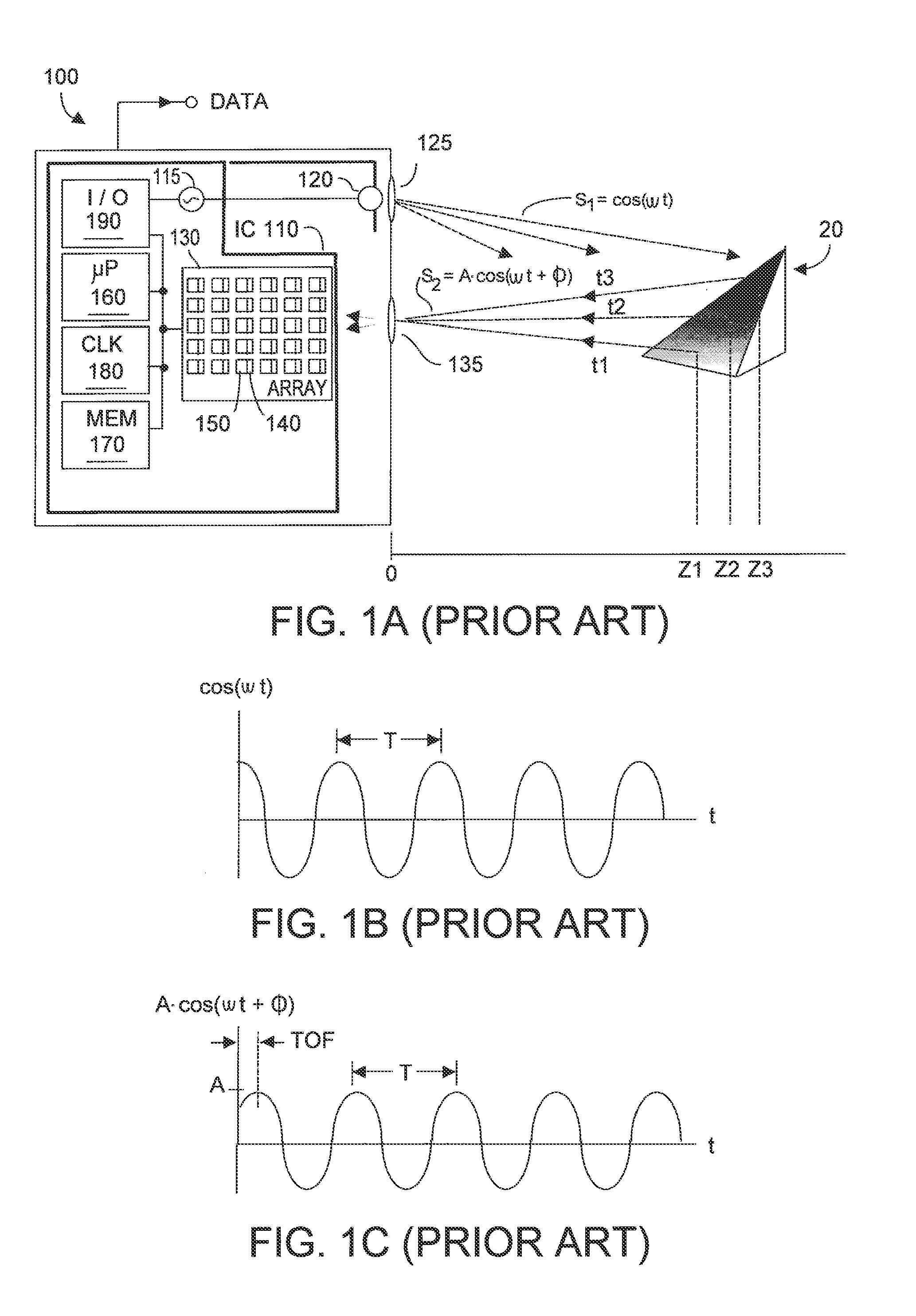
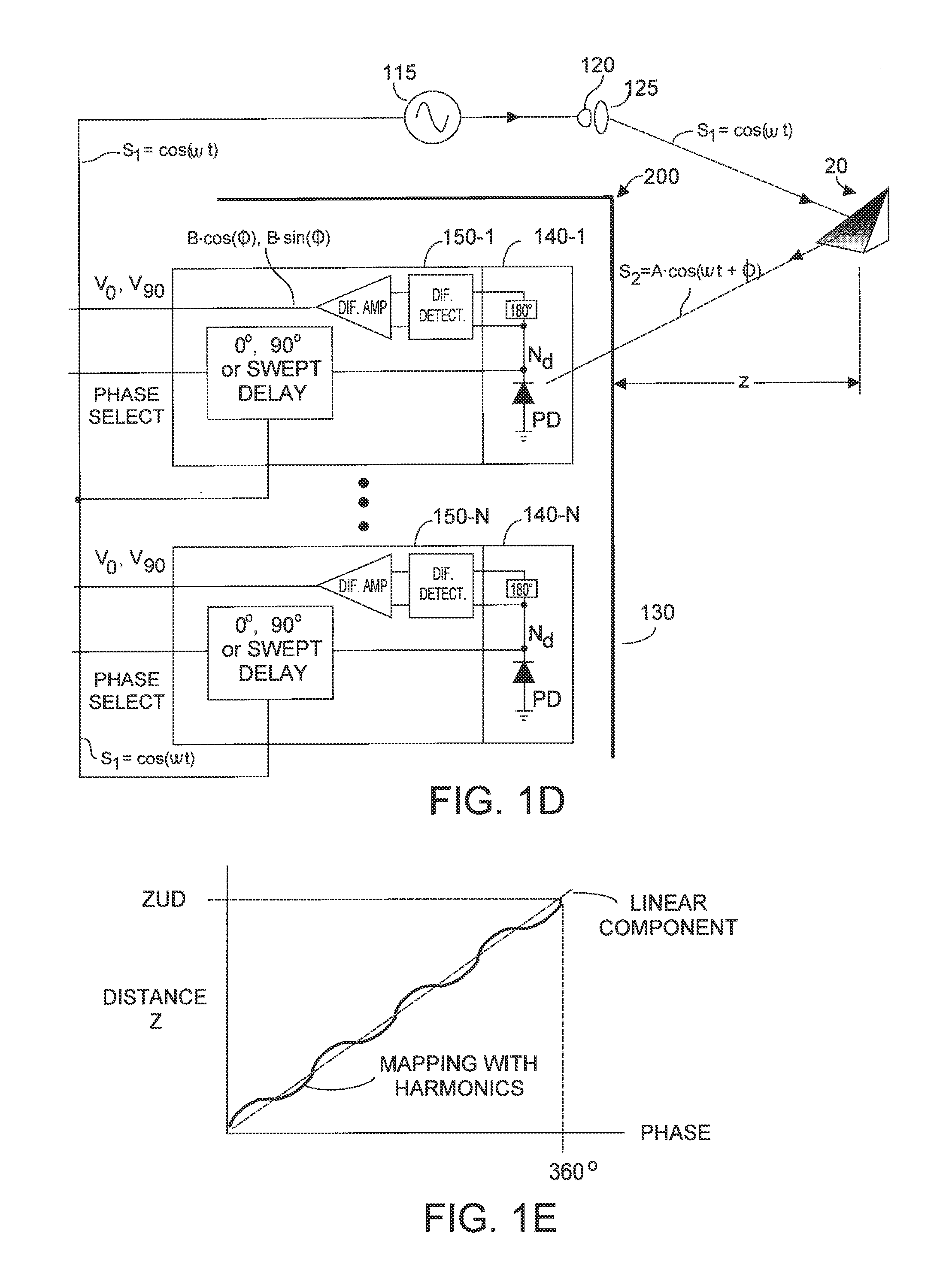
Method and system for multi-phase dynamic calibration of three-dimensional (3D) sensors in a time-of-flight system
ActiveUS20120013887A1Reduces bias errorMaximize modulation contrastOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationAudio power amplifierFall time
A phase-based TOF system preferably generates an optical waveform with fast rise and fall times, to enhance modulation contrast, notwithstanding there will be many high order harmonics. The system is preferably operated with an odd number of phases, to reduce system bias error due to the higher order harmonics, while maintaining good modulation contrast, without unduly increasing system memory requirements. Preferably the system can dynamically calibrate (and compensate for) higher order harmonics in the TOF generated optical energy waveform, over time and temperature. Within the optical energy transmission channel, or within the optical energy detection channel, detection amplifier gain may be modified, and / or detector signal integration time may be varied, and / or digital values may be employed to implement calibration and error reduction The resultant TOF system can operate with improved phase-vs-distance characteristics, with reduced calibration requirements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
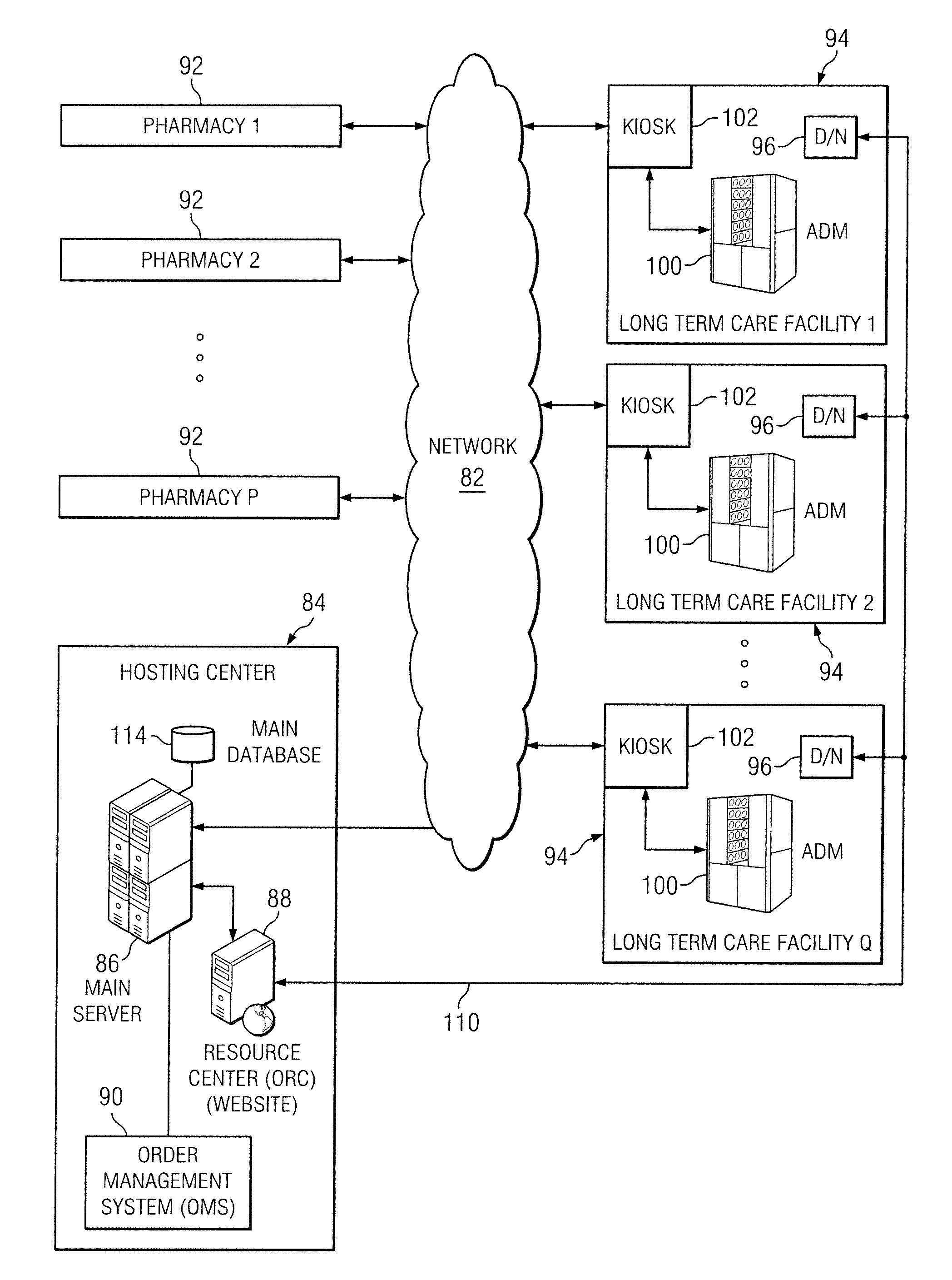
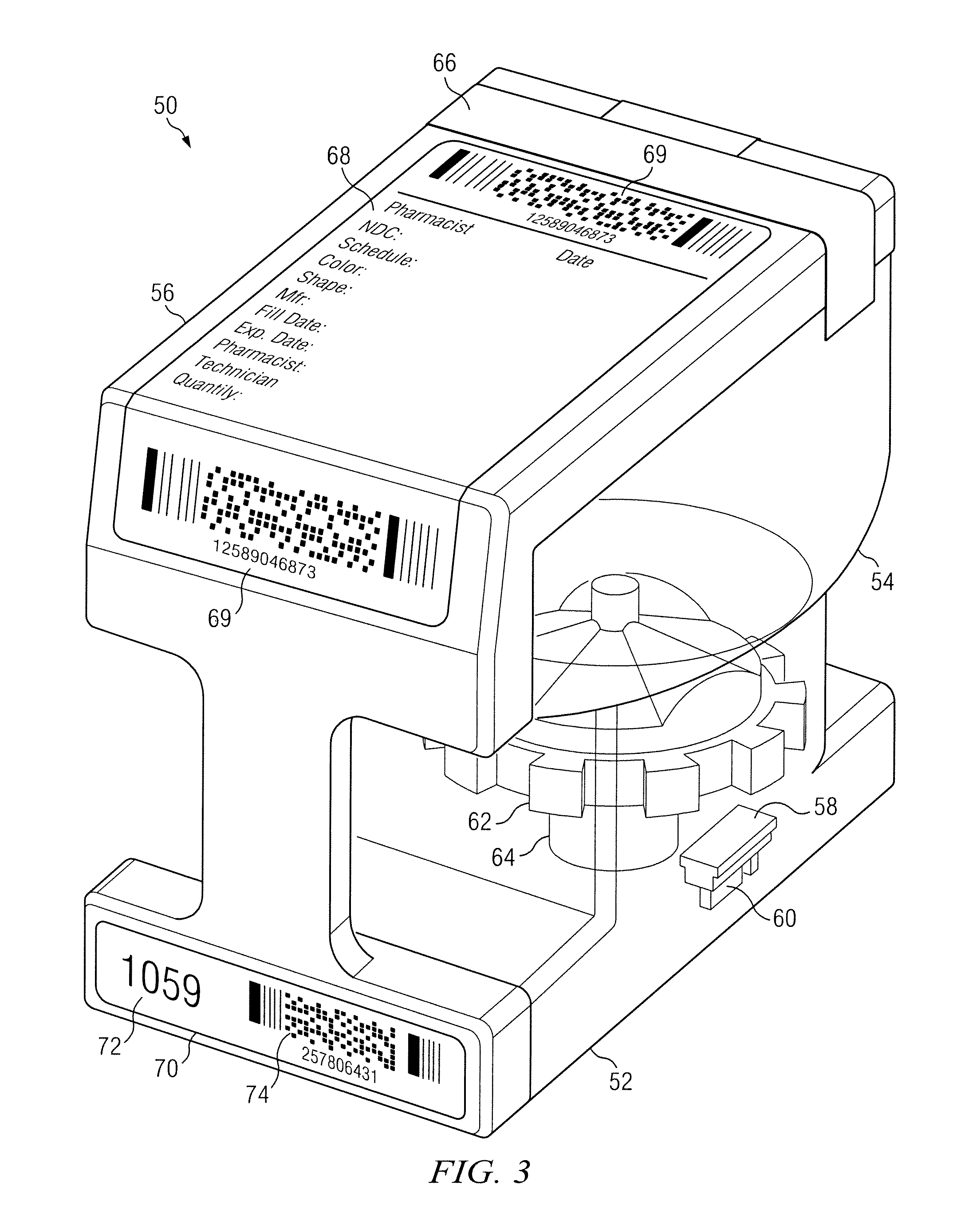
On Site Prescription Management System and Methods for Health Care Facilities
ActiveUS20110251850A1Reduce delaysData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMemory chipPharmacy
A system and method for control of prescription drug packaging and dispensing machines located in an in-patient health care facility including centralized control and enhanced communication between system components. Delay and errors in processing item data in the prescription dispensing system are reduced by using concise ID data incorporated into each canister memory chip and storing canister contents data elsewhere. Canisters are configured in a pharmacy using interchangeable parts. Data being processed is synchronized by a combination of user tokens (who), data identifiers (what), and unique Ids for the entities in the system (where). The foregoing combination enables substantial efficiency improvements and error reduction.
Owner:PROVIDER MEDS LP +1
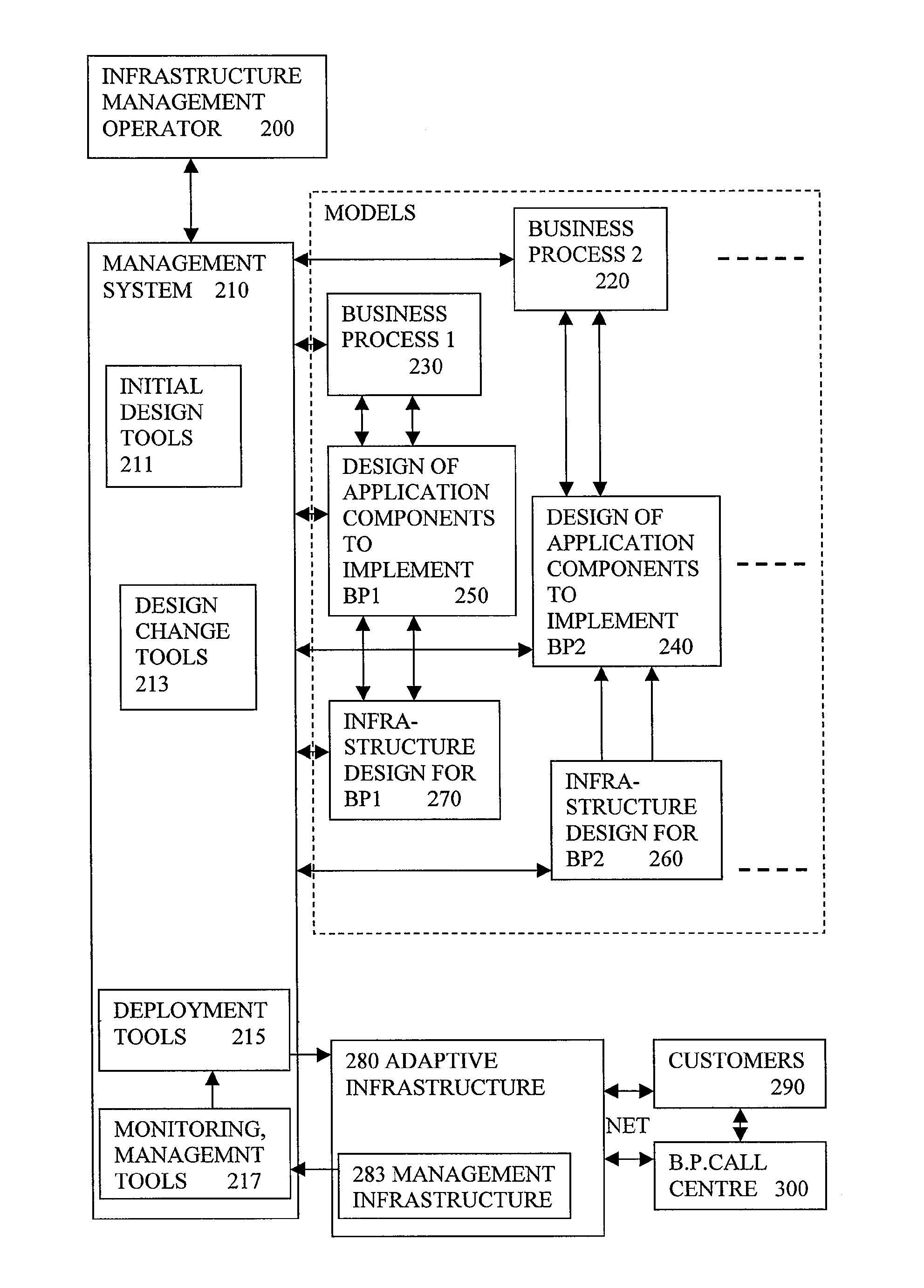
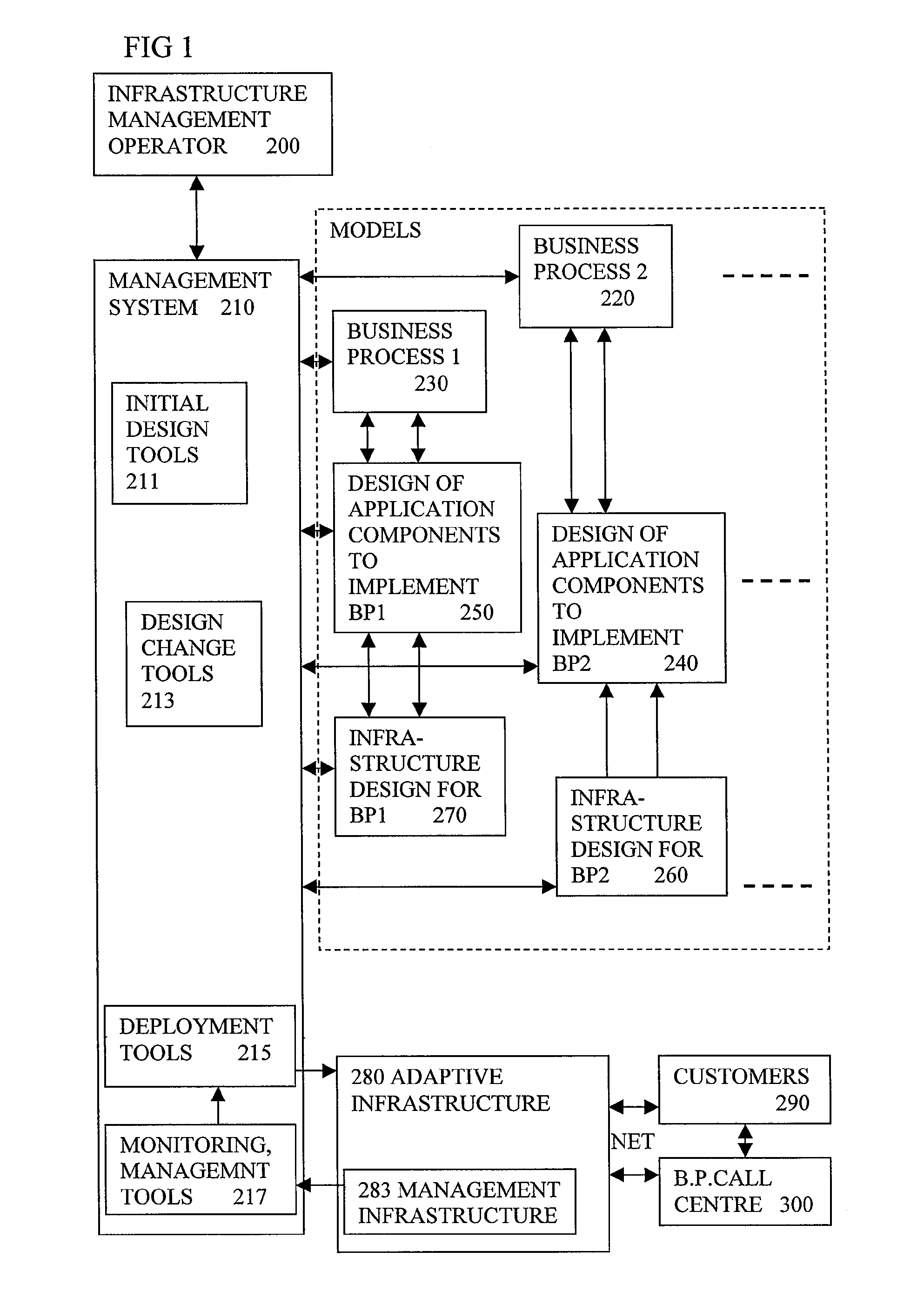
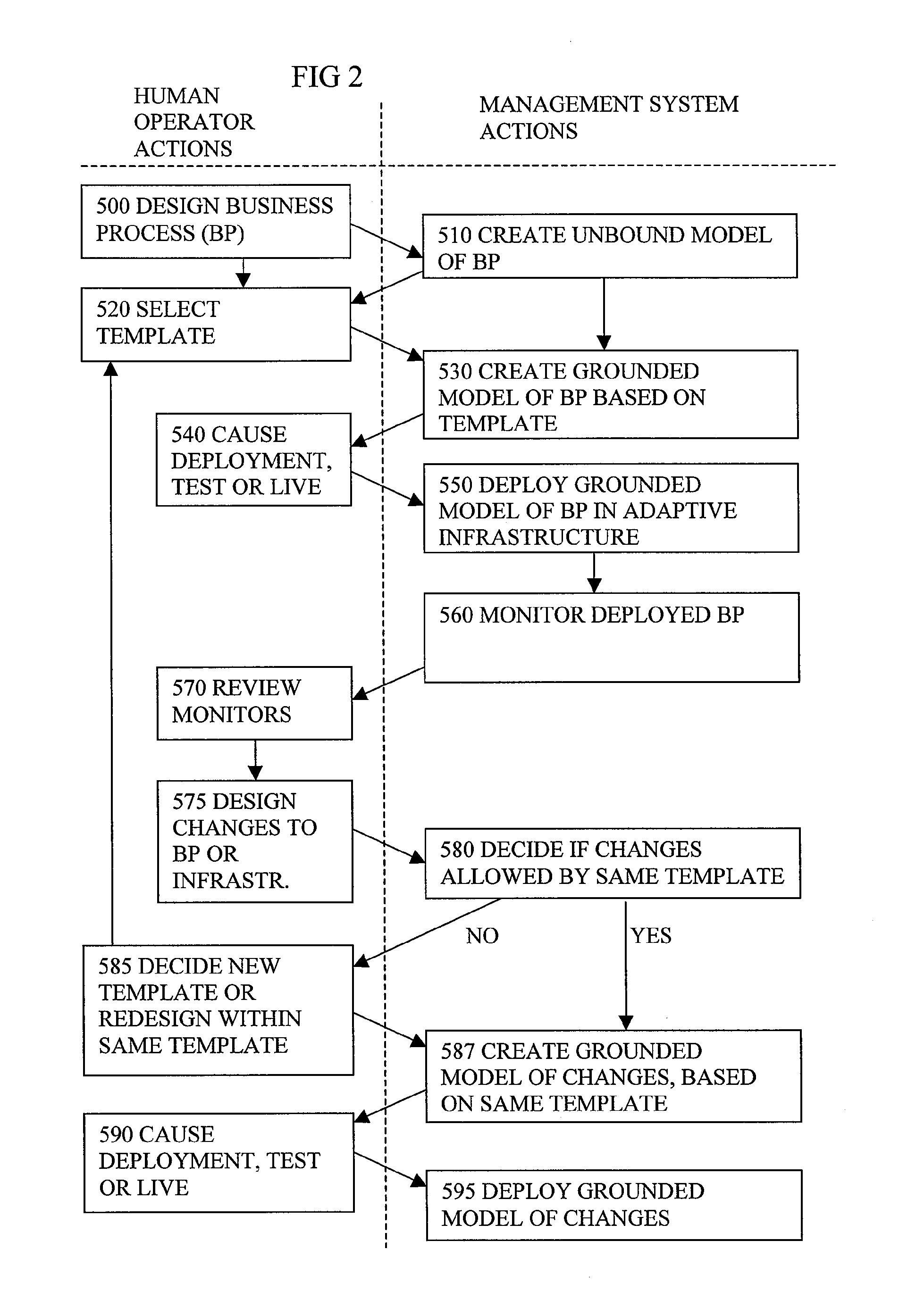
Automated Model Generation For Computer Based Business Process
A system for generating a model representing an existing computer based business process involves analysing existing source content (910) which has annotations (920) added, to provide information for the modelling. Static analysis of the annotations can provide some of the information. Other information can be discovered at run time if the annotations alter the run time behaviour to generate monitoring events showing the behaviour. The annotations need not be restricted to codes or symbols or structures of the language of the source content, and can use concepts closer to those in the model being generated. Using annotations rather than manual modelling can reduce errors and lead to better predictions of performance from the model, and result in better reconfiguration of the software or the computing infrastructure to make more efficient usage of shared resources.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
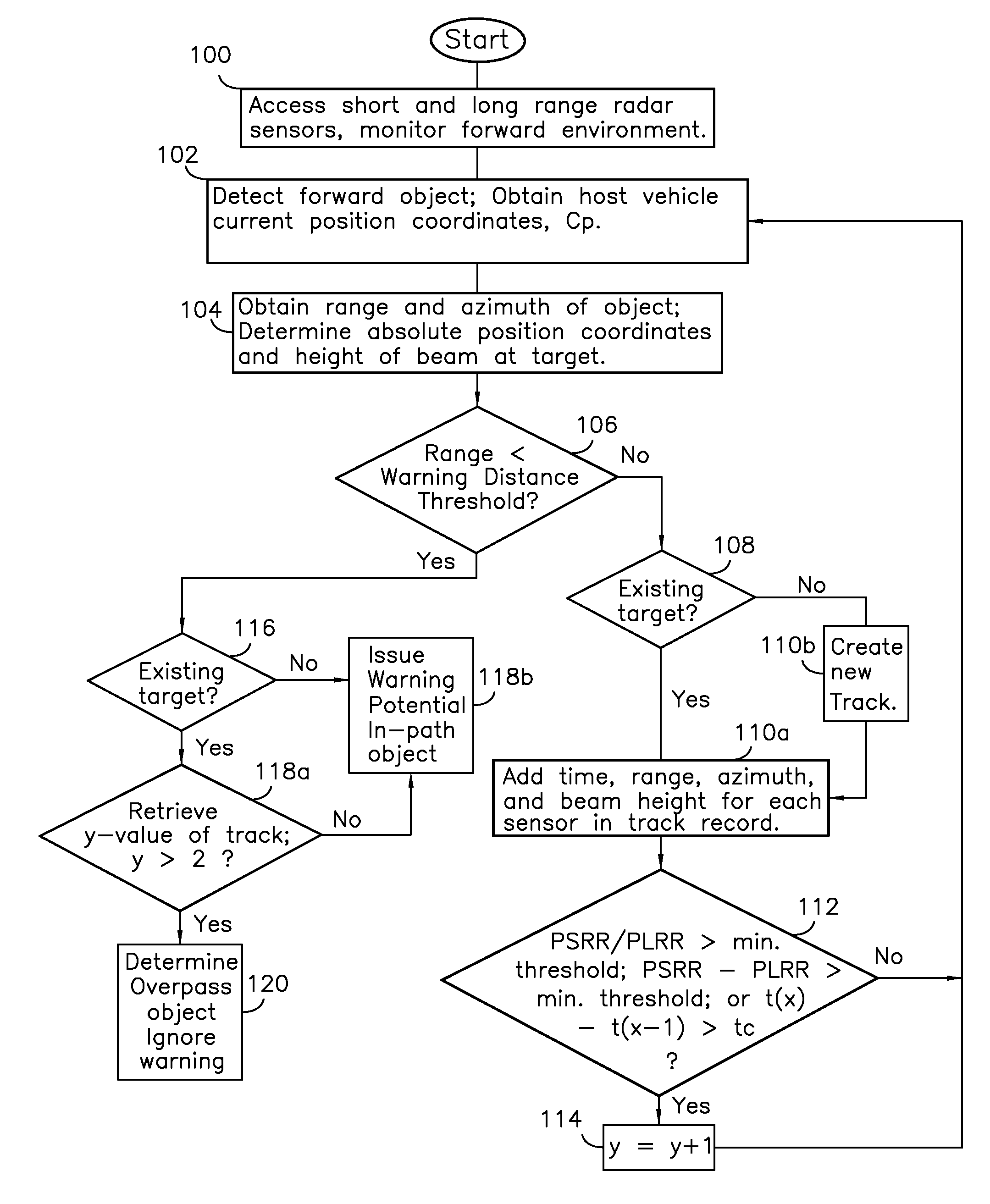
Method of estimating target elevation utilizing radar data fusion
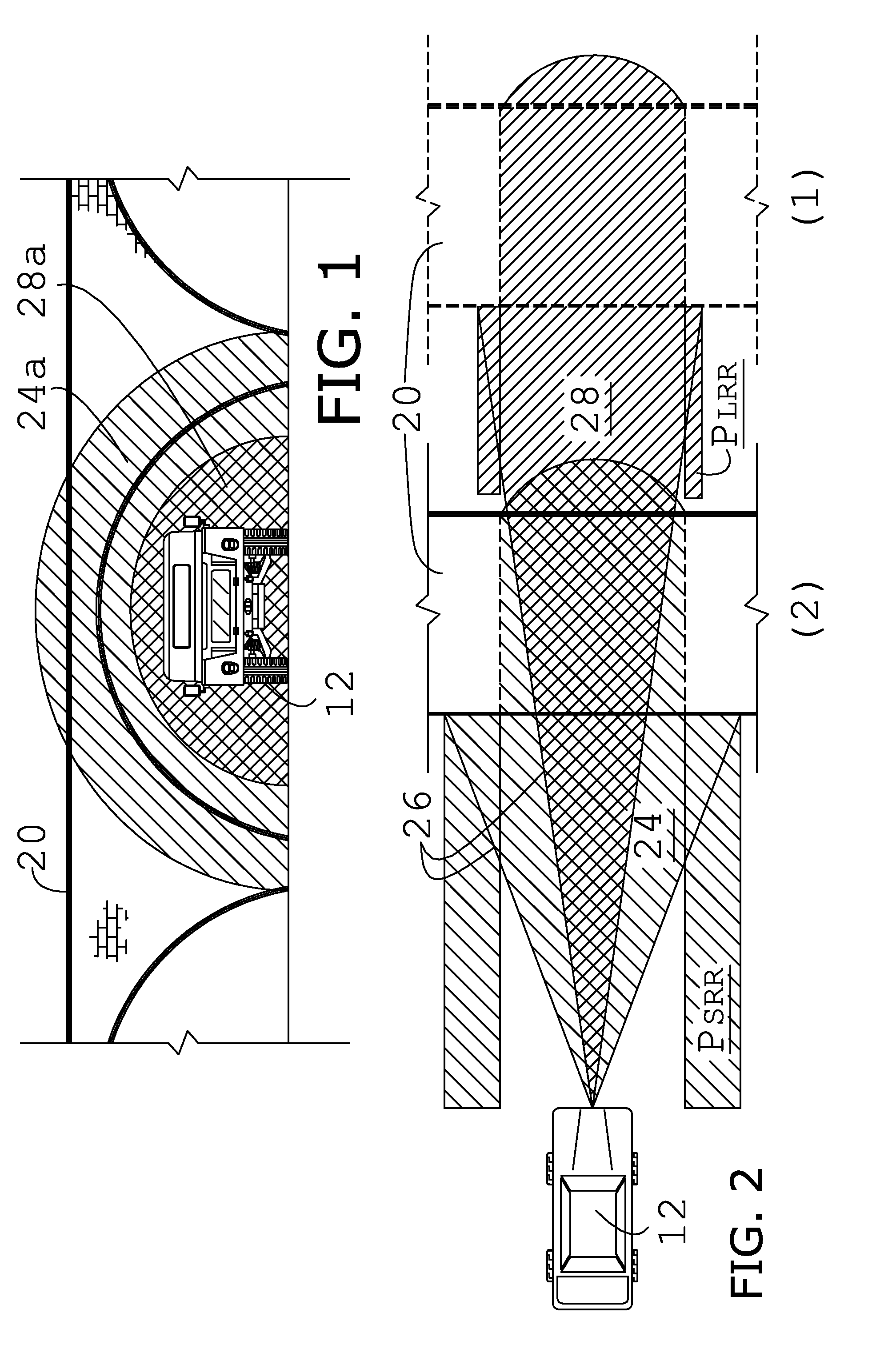
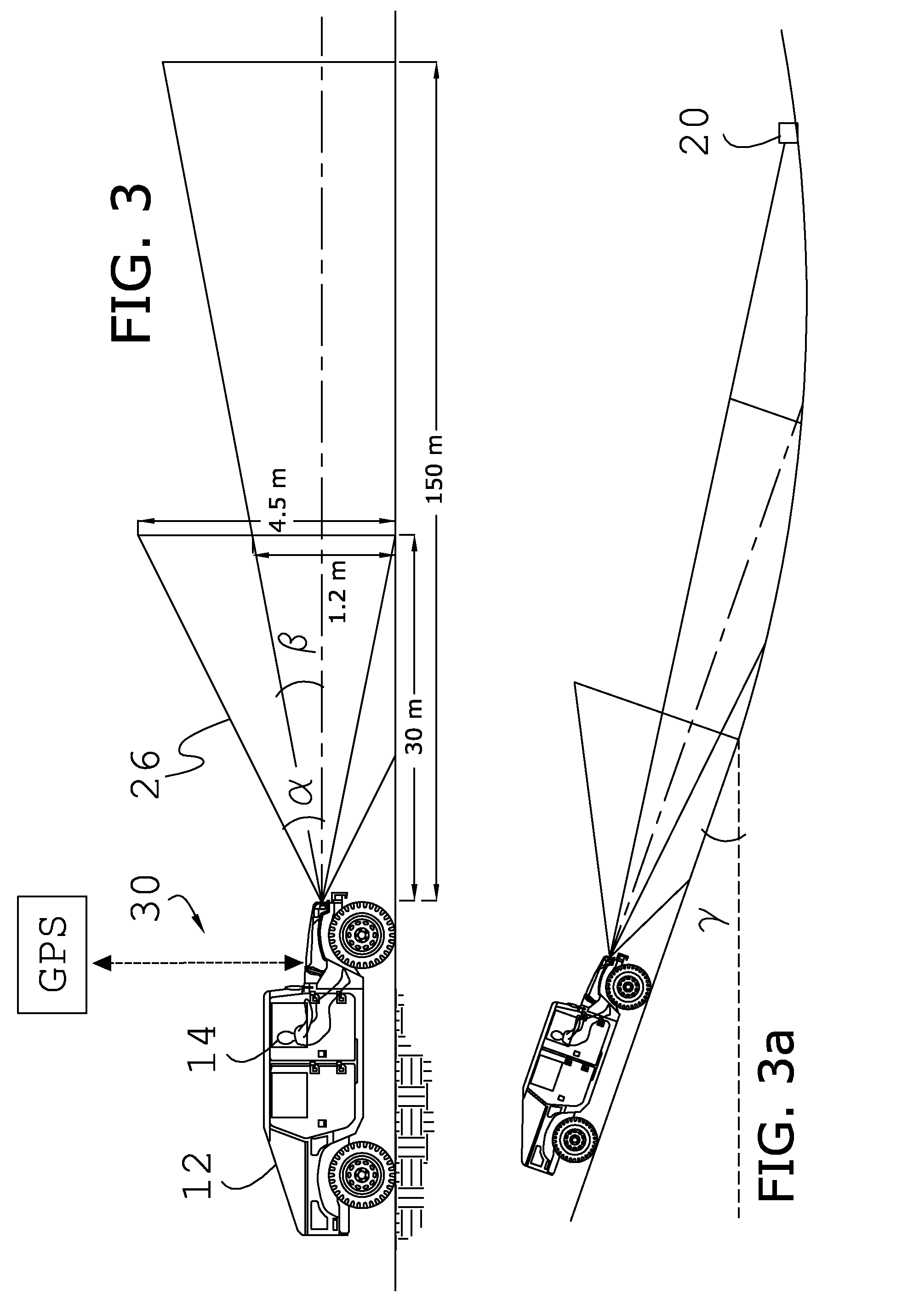
ActiveUS7592945B2Reduce in quantityEfficient and reliable and accurate determinationIncline measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam angleError reduction
A collision avoidance system for reducing false alerts by estimating the elevation of a target, includes short and long range single-dimensional scanning radar sensors having differing ranges and beam angles of inclination, and a digital fusion processor, and preferably includes a locator device, an inclinometer, and a memory storage device cooperatively configured to further perform trend analysis, and target tracking.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Endurance enhancement coding of compressible data in flash memories
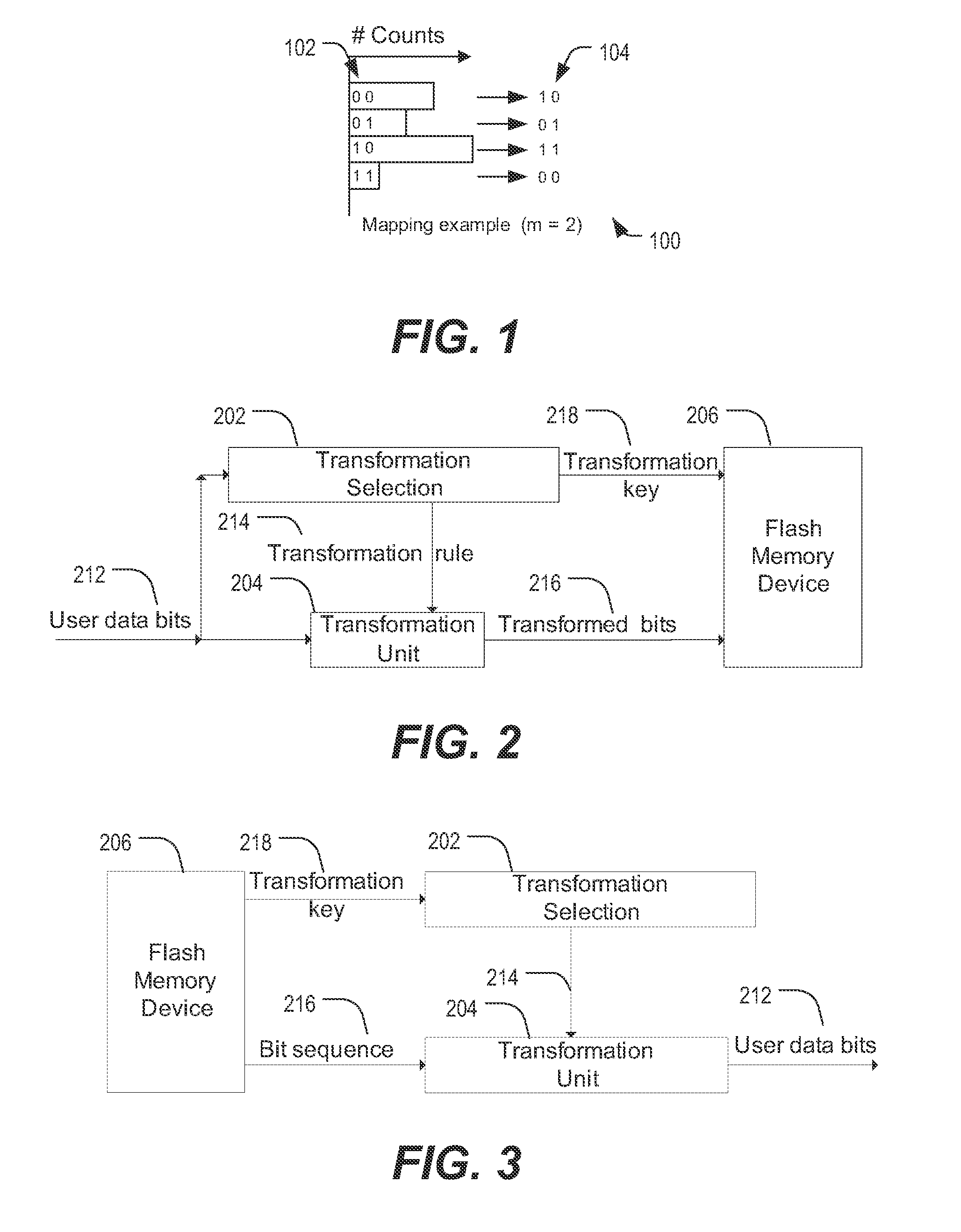
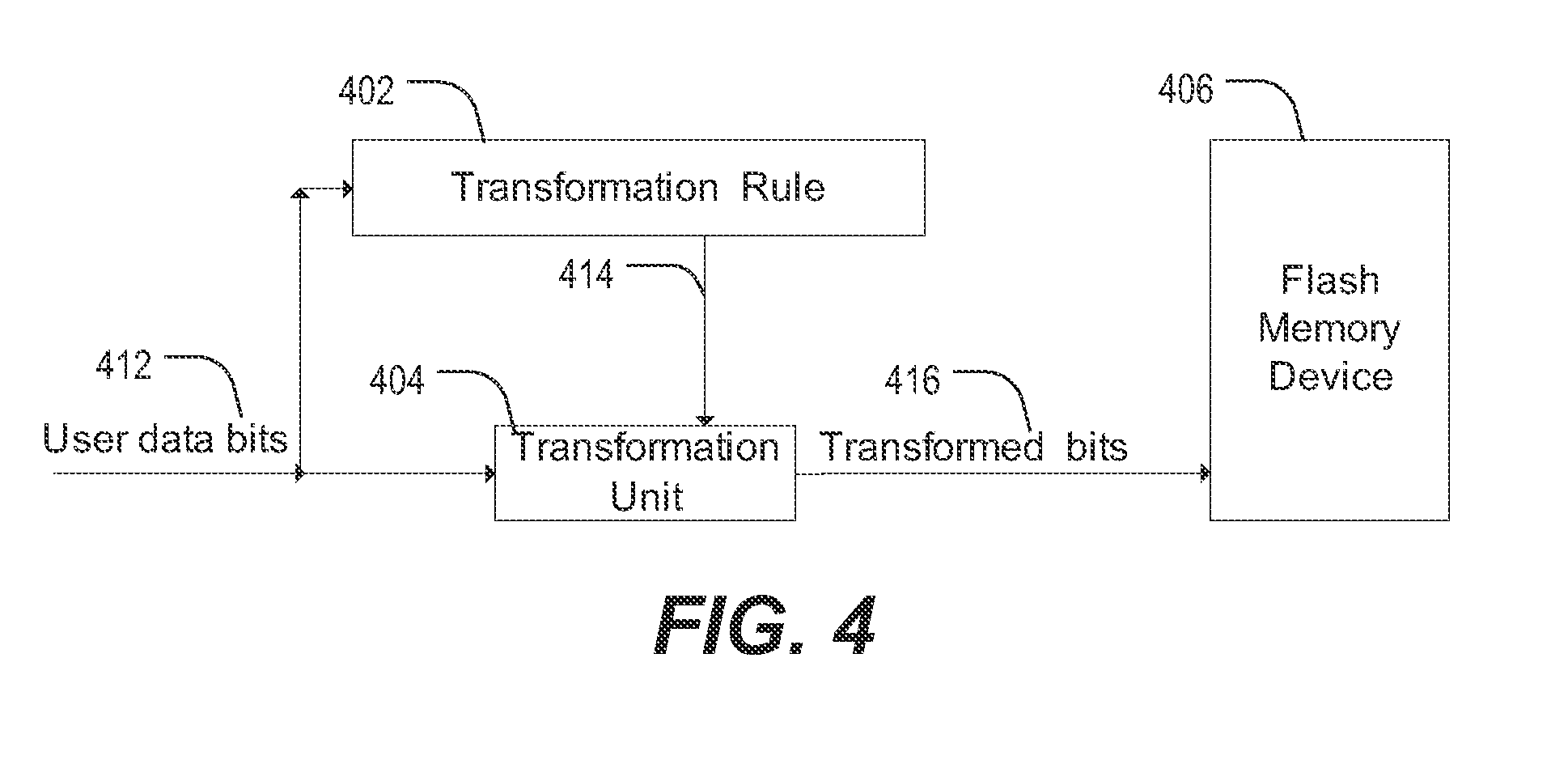
ActiveUS20130103891A1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationError reductionOriginal data
Methods described in the present disclosure may be based on a direct transformation of original data to “shaped” data. The disclosed methods may be performed “on-the-fly” and the disclosed methods may utilize an inherent redundancy in compressible data in order to achieve endurance enhancement and error reduction. In a particular example, a method comprises generating a first portion of output data by applying a mapping of input bit sequences to output bit sequences to a first portion of input data, updating the mapping of the input bit sequences to the output bit sequences based on the first portion of the input data to generate an updated mapping, reading a second portion of the input data, and generating a second portion of the output data by applying the updated mapping of the input bit sequences to the output bit sequences to the second portion of the input data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multi-detection of heartbeat to reduce error probability
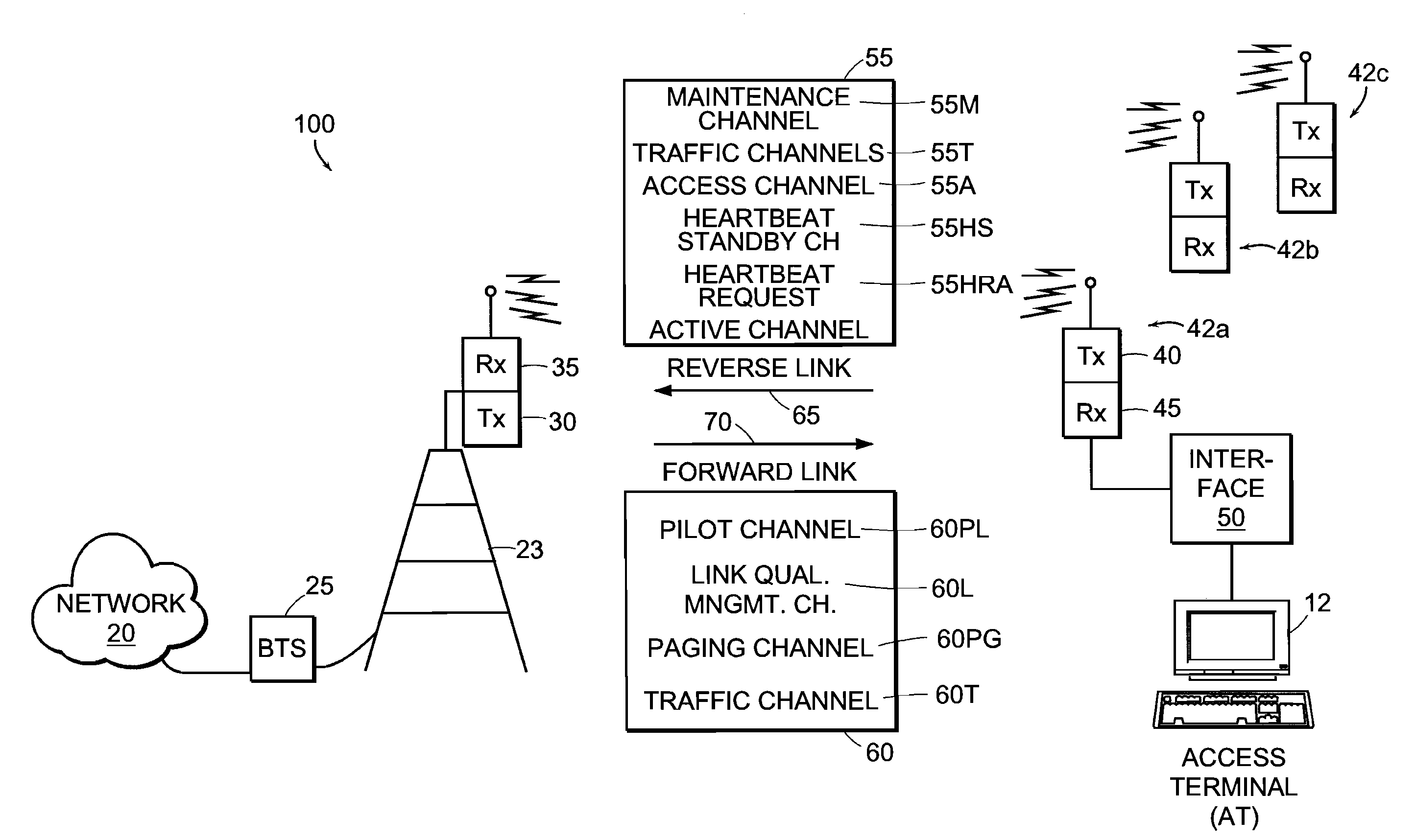
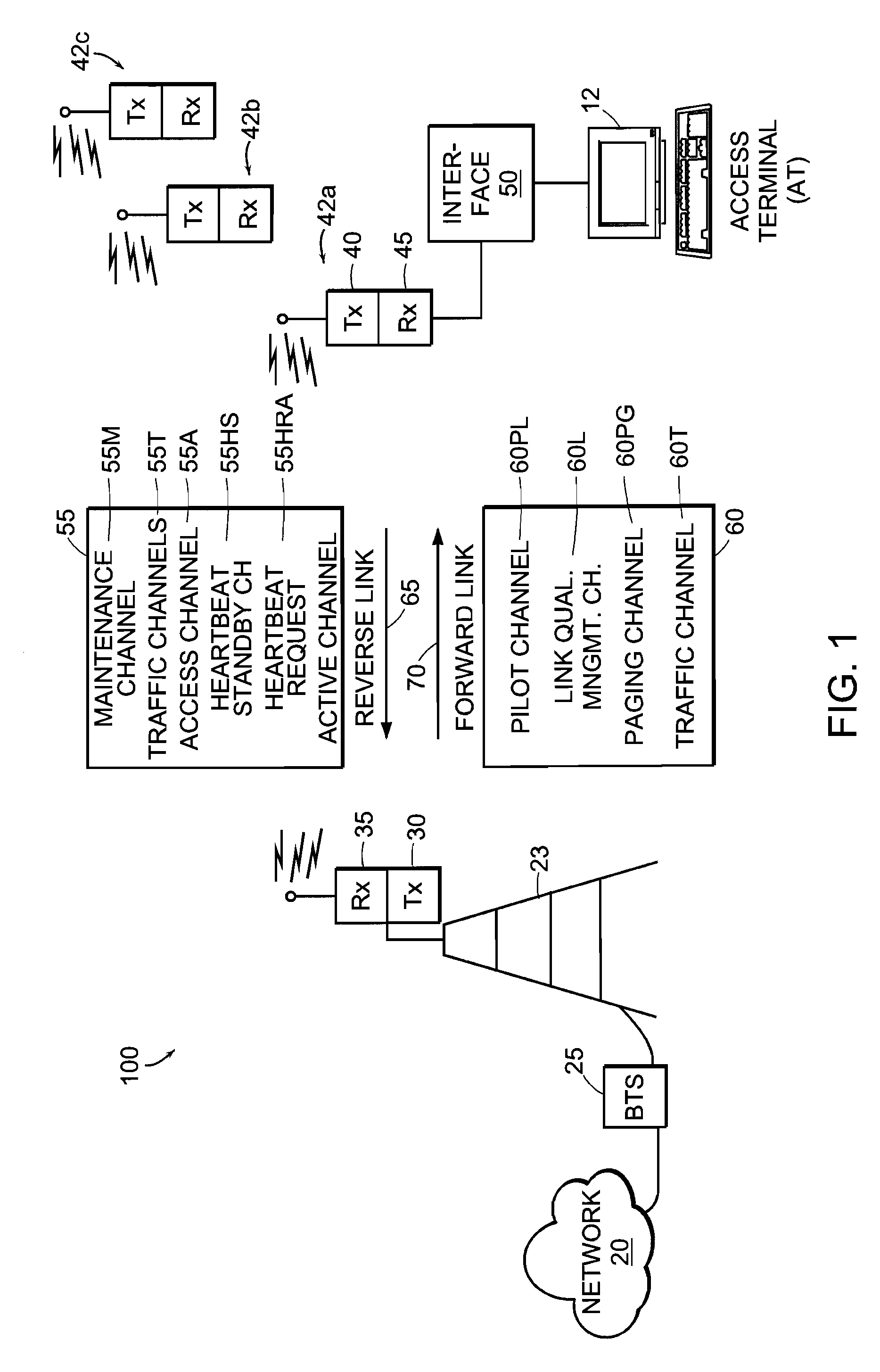
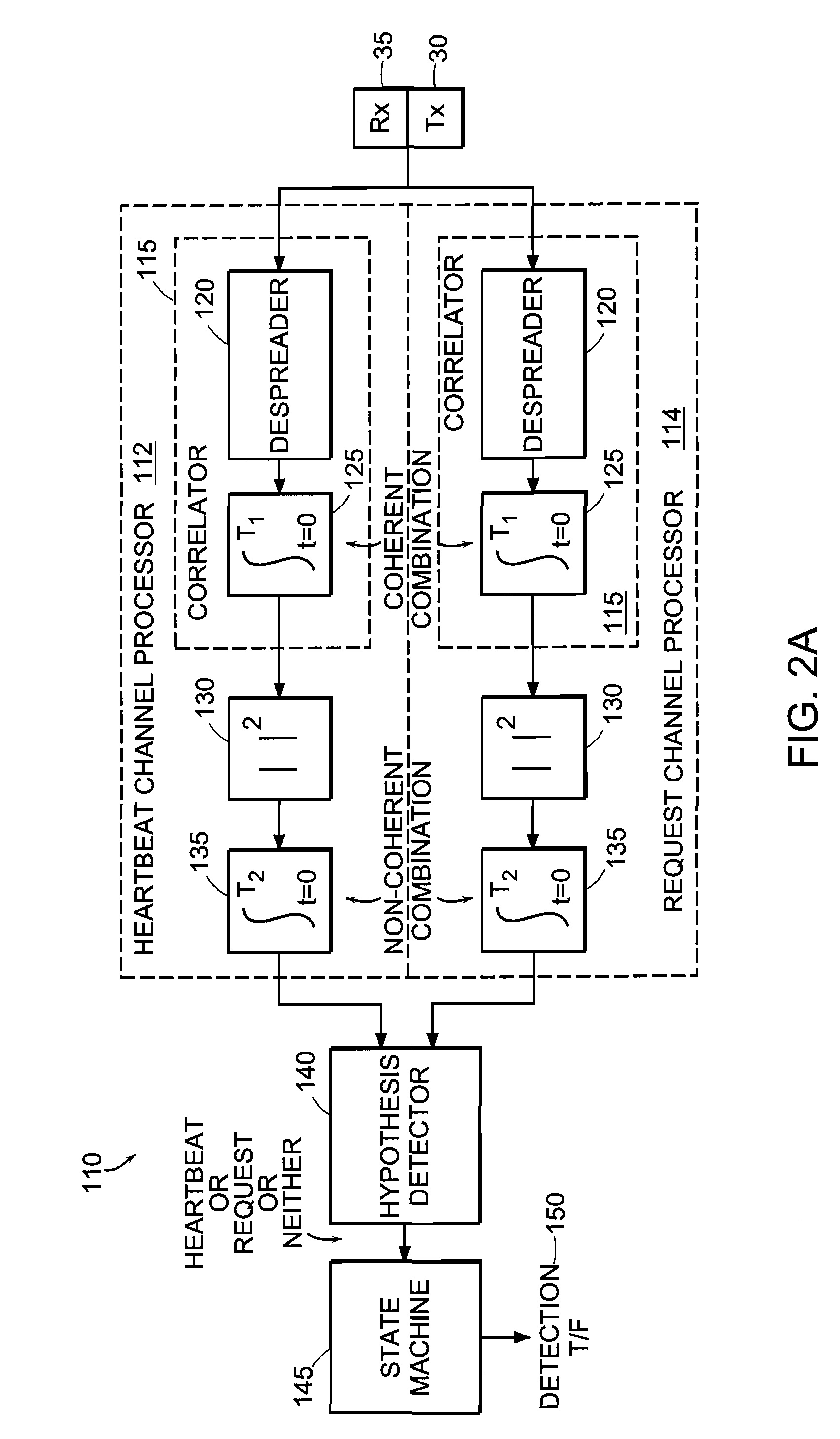
InactiveUS7394791B2Improve performanceReduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel dividing arrangementsSupporting systemCommunications system
A communications system improves performance of detecting a signal having an indication of a request to change communications states by making at least two positive identifications of the request in a given time frame. The system may further improve performance by applying a difference in power levels for a non-request state (i.e., steady state or ‘control hold’ state) versus a request state (i.e., ‘request to change’ state). In one particular application, a base station determines a request to change communications states with a reasonably high probability of detection and a reasonably low probability of false detection. The system has a reduced number of erroneous communications states, such as erroneous traffic channel allocations. The detection technique is compatible with 1xEV-DV systems and I-CDMA systems, but general enough to support systems employing various other communications protocols used in wired and wireless communications systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
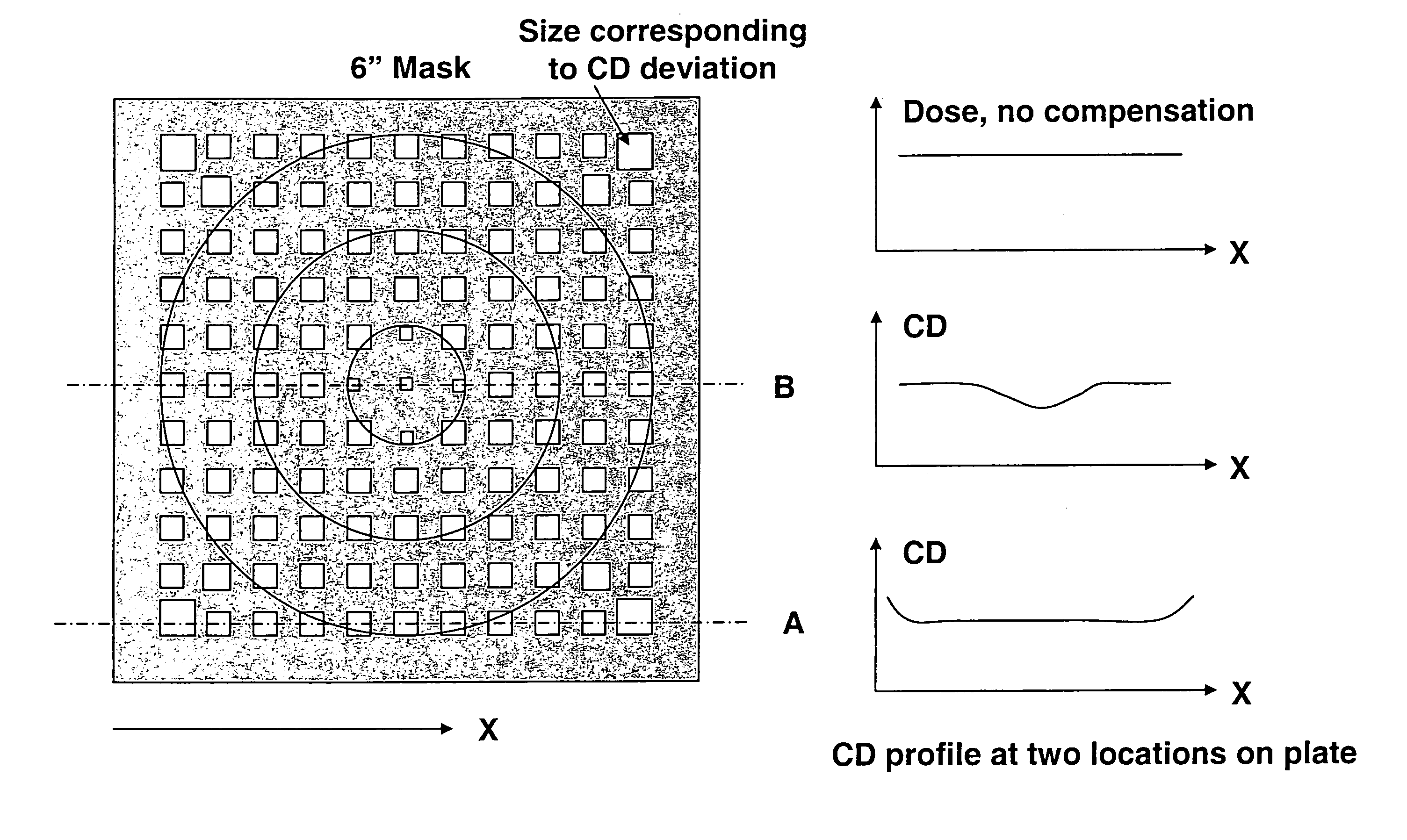
Method for error reduction in lithography
InactiveUS7444616B2High precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusError reductionEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a system for predicting and / or measuring and correcting geometrical errors in lithography using masks, such as large-area photomasks or reticles, and exposure stations, such as wafer steppers or projection aligners, printing the pattern of said masks on a workpiece, such as a display panel or a semiconductor wafer. A method to compensate for process variations when printing a pattern on a workpiece, including determining a two-dimensional CD profile in said pattern printed on said workpiece, generating a two-dimensional compensation file to equalize fluctuations in said two-dimensional CD-profile, and patterning a workpiece with said two-dimensional compensation file.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
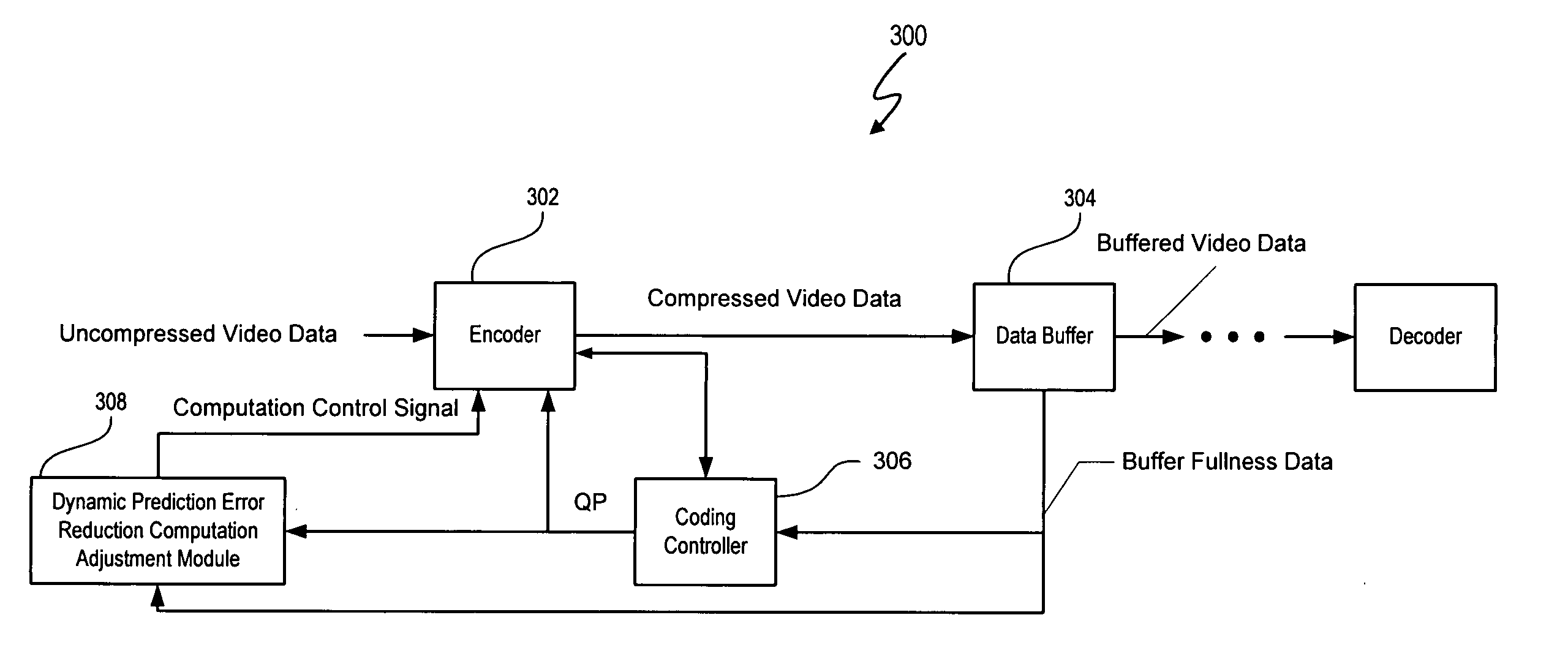
Resource efficient video processing via prediction error computational adjustments
ActiveUS20070104272A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionError reductionData set
A video processing system dynamically adjusts video processing prediction error reduction computations in accordance with the amount of motion represented in a set of image data and / or available memory resources to store compressed video data. In at least one embodiment, video processing system adjusts utilization of prediction error computational resources based on the size of a prediction error between a first set of image data, such as current set of image data being processed, and a reference set of image data relative to an amount of motion in a current set of image data. Additionally, in at least one embodiment, the video processing adjusts utilization of prediction error computation resources based upon a fullness level of a data buffer relative to the amount of motion in the current set of image data.
Owner:NXP USA INC
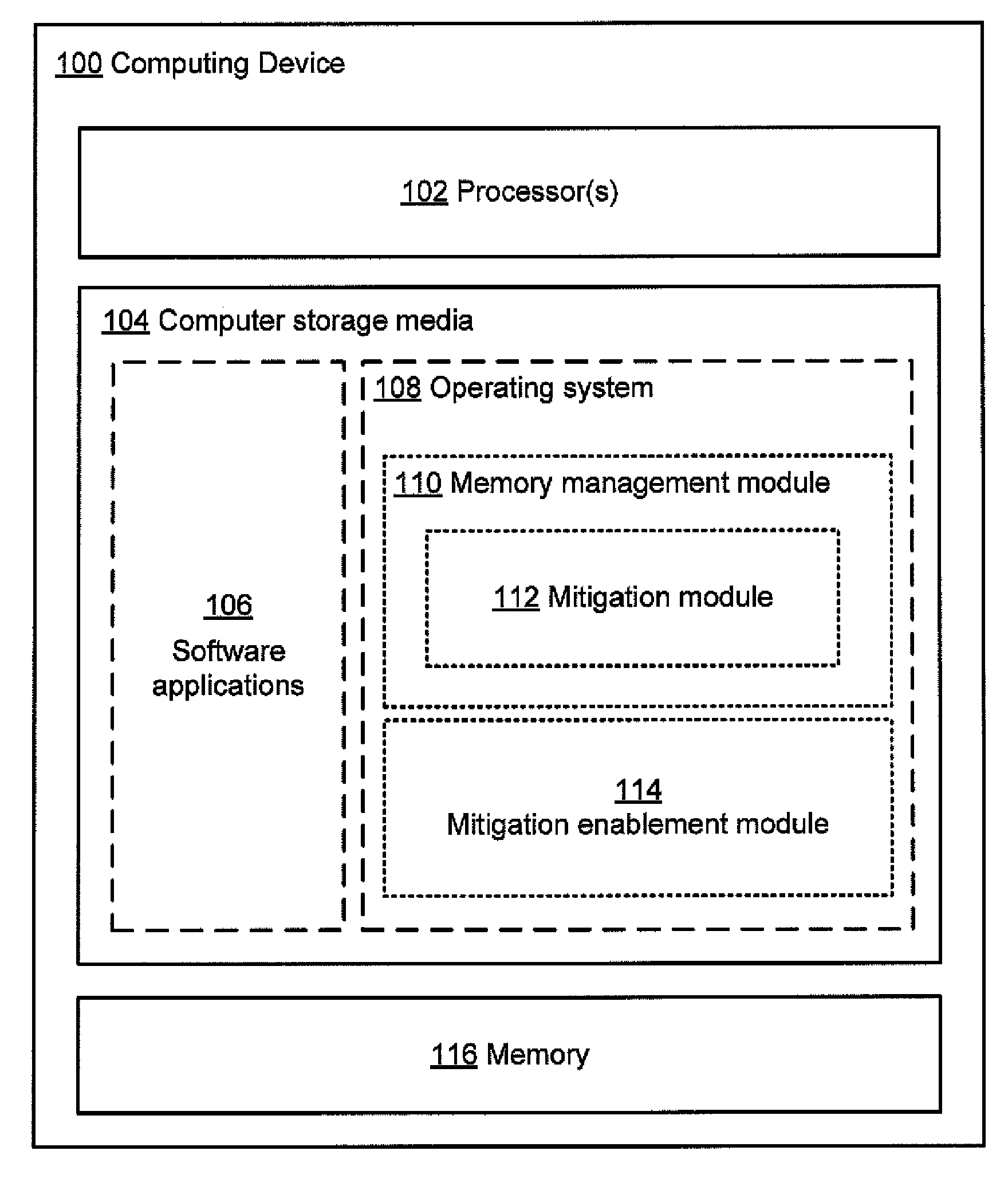
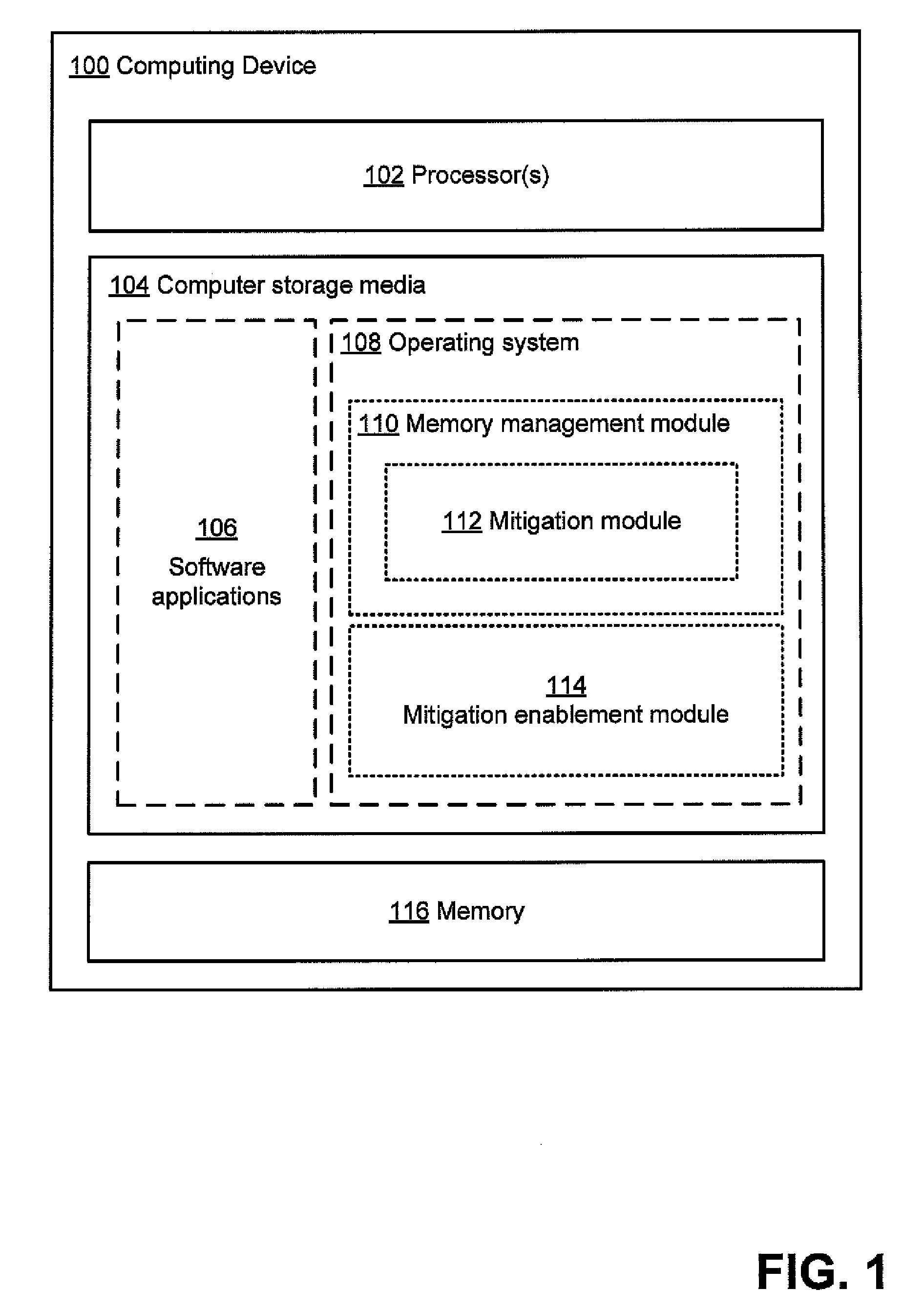
Evaluating effectiveness of memory management techniques selectively using mitigations to reduce errors
InactiveUS20100083048A1Improve user experienceReduce errorsSoftware testing/debuggingNon-redundant fault processingError reductionError prevention
A mitigation enablement module for a computer that improves application reliability. When performing memory management operations, the mitigation enablement module and associated memory manager selectively use mitigations that are intended to prevent an application bug from cause an application error. The memory manager may selectively apply mitigations for each of one or more applications based on the likelihood that such mitigations are successful at preventing bugs from causing application errors. The likelihood is determined from historical information on whether the mitigations, when applied, prevented bugs from causing memory operations that could cause application errors. This historical information can be gathered on a single computer over multiple invocations of the application or may be aggregated from multiple computers, each invoking the application. The determined likelihood may then be used to determine whether or for how long to apply the mitigation actions for memory operations requested by the application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of reducing false alarms during auto-arm
A method for reducing false alarms for a security system when the security system is programmed to automatically arm the security system. The method reduces false alarms by preventing the security system to auto-arm the system in away mode based upon certain detected events within the premises. The method comprise the steps of determining if a current time equals or is within a predetermined detection period, judging whether at least one of a plurality of motion sensors have detected an event within a protected area during the predetermined detection period, determining if a premises exit signal has been generated within a predetermined period from said detected movement, generating an automatic arm adjustment signal based upon said detected event and the premises edit signal; and executing a modification to the programmed automatic arm based upon the automatic arm adjustment signal. The method will also notify the owner that the auto-arm mode failed.
Owner:ADEMCO INC
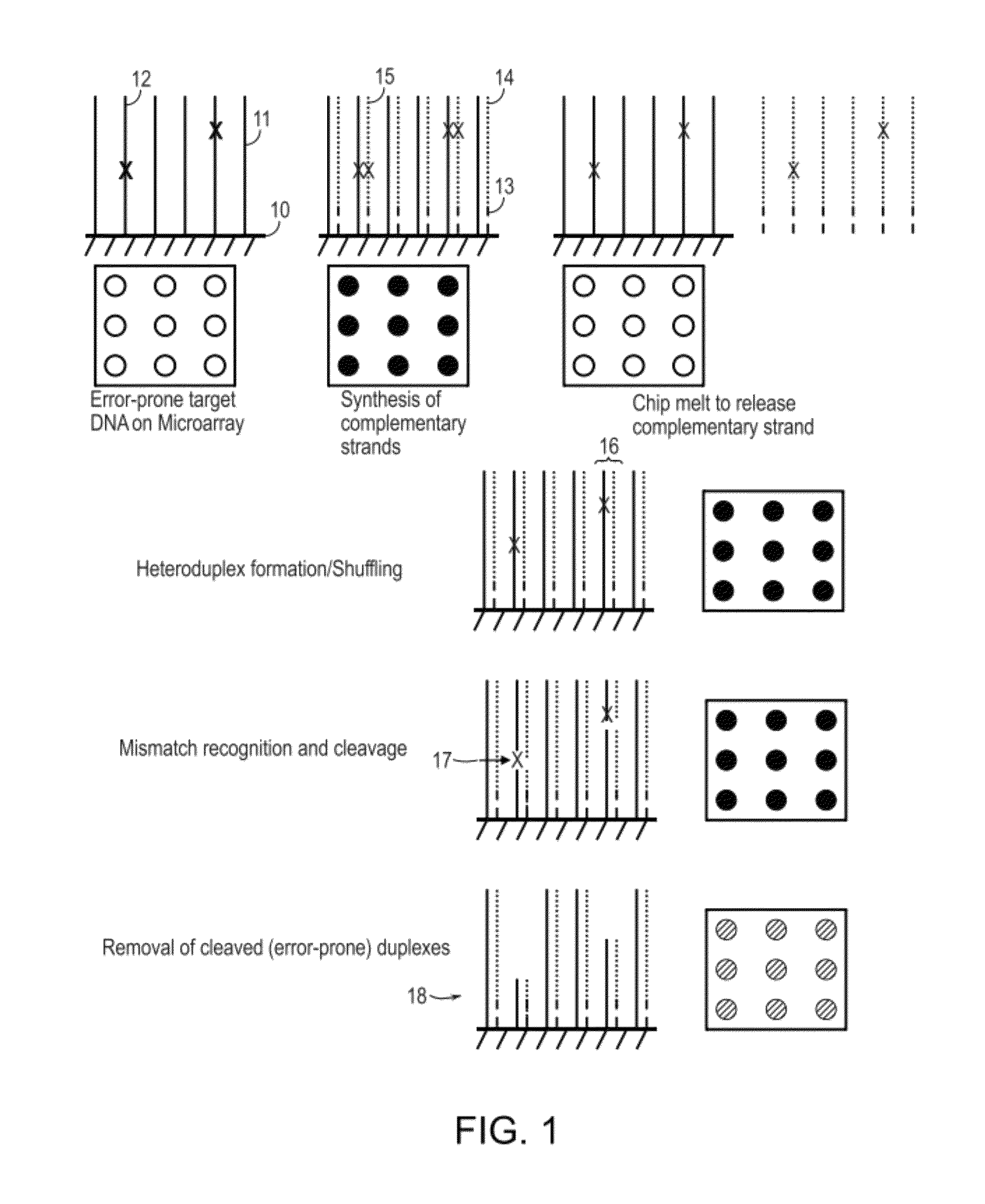
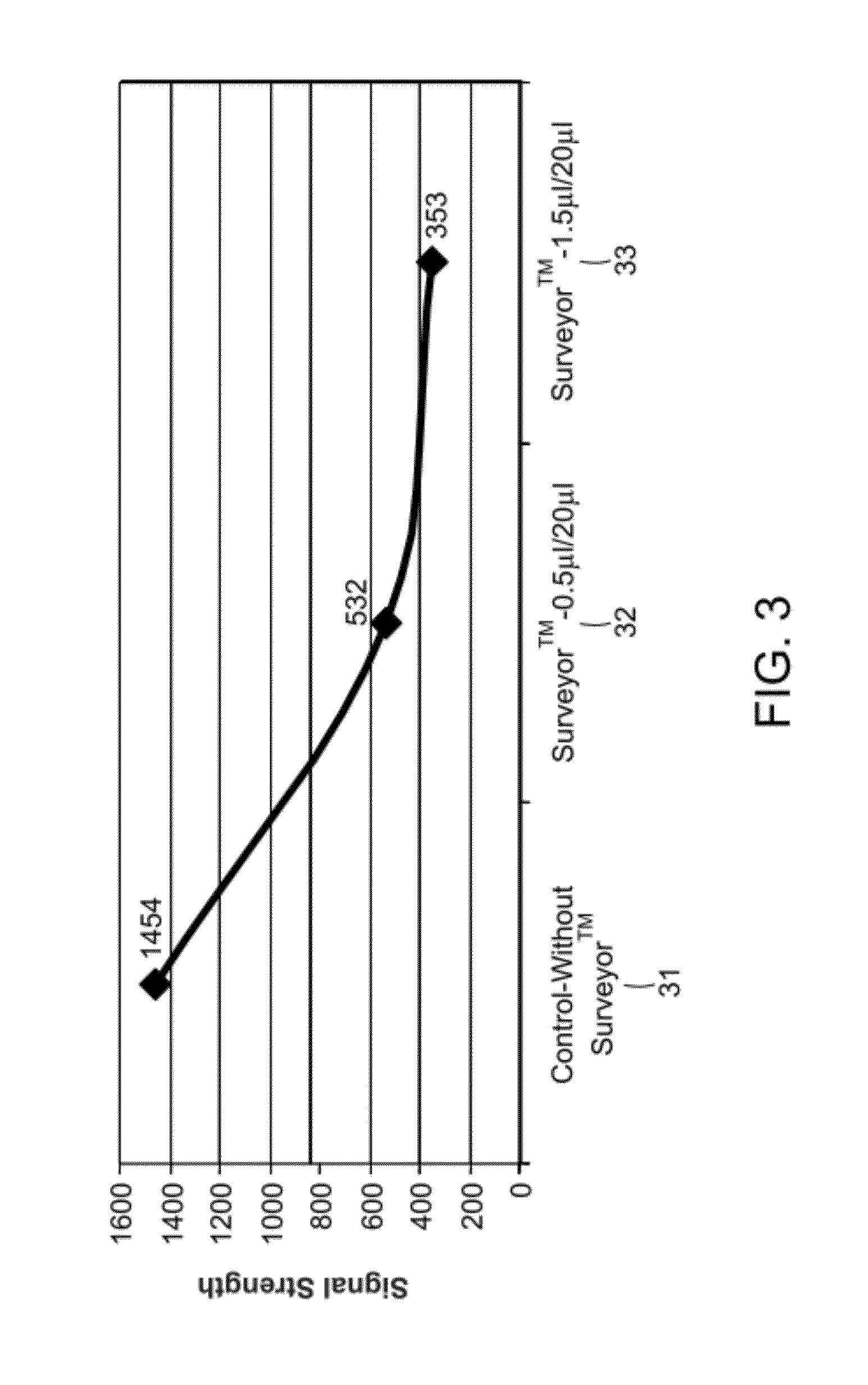
Methods and apparatuses for chip-based DNA error reduction
ActiveUS9422600B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeterologousHeteroduplex
Methods and apparatus relate to reduction of sequence errors generated during synthesis of nucleic acids on a microarray chip. The error reduction can include synthesis of complementary stands (to template strands), using a short universal primer complementary to the template strands and polymerase. Heteroduplex can be formed be melting and re-annealing complementary stands and template strands. The heteroduplexes containing a mismatch can be recognized and cleaved by a mismatch endonuclease. The mismatch-containing cleaved heteroduplexes can be removed from the microarray chip using a global buffer exchange. The error free synthetic nucleic acids generated therefrom can be used for a variety of applications, including synthesis of biofuels and value-added pharmaceutical products.
Owner:GEN9
Method of estimating target elevation utilizing radar data fusion
ActiveUS20090002222A1Reduce in quantityEfficient and reliable and accurate determinationIncline measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam angleError reduction
A collision avoidance system for reducing false alerts by estimating the elevation of a target, includes short and long range single-dimensional scanning radar sensors having differing ranges and beam angles of inclination, and a digital fusion processor, and preferably includes a locator device, an inclinometer, and a memory storage device cooperatively configured to further perform trend analysis, and target tracking.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
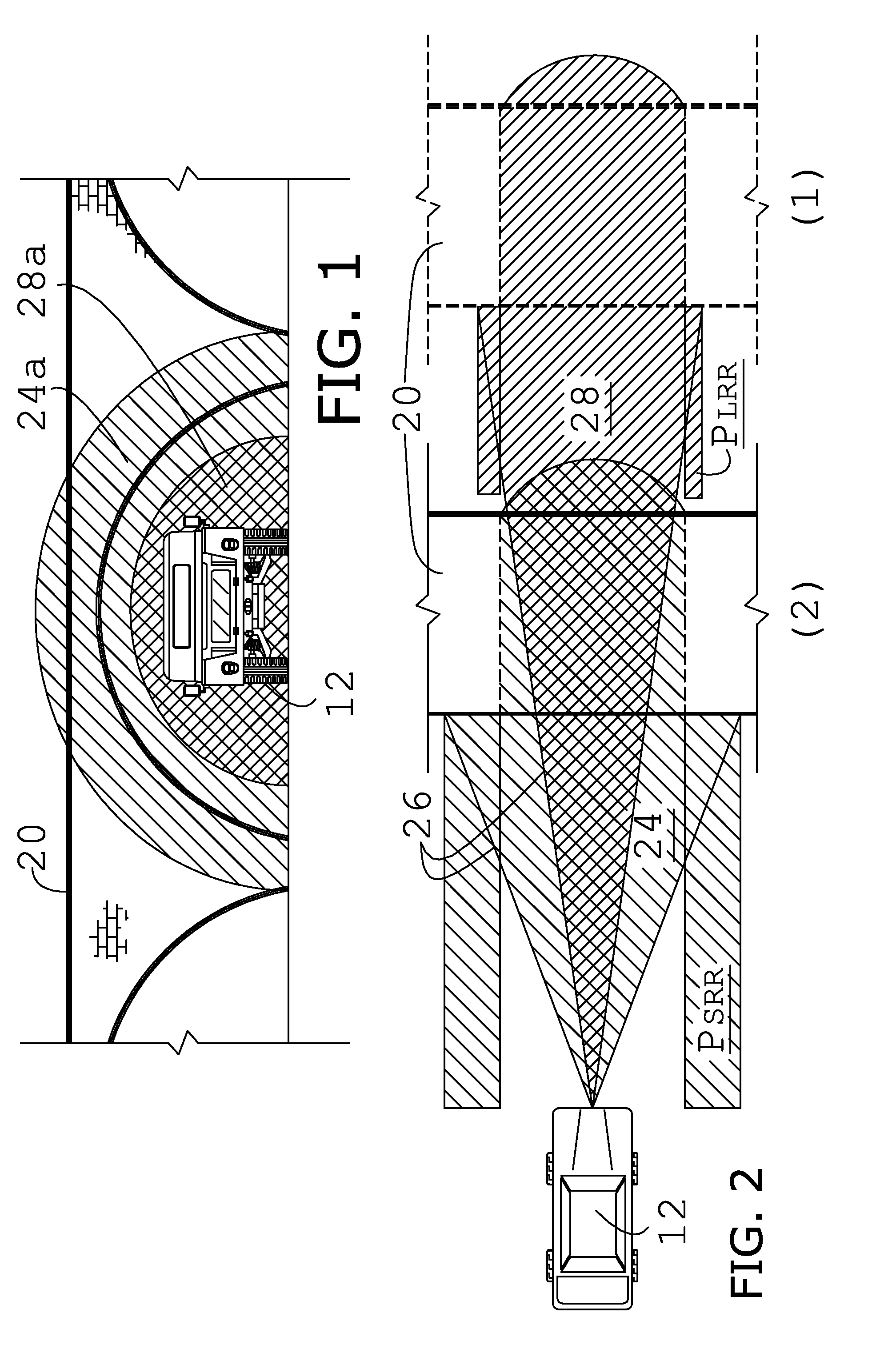
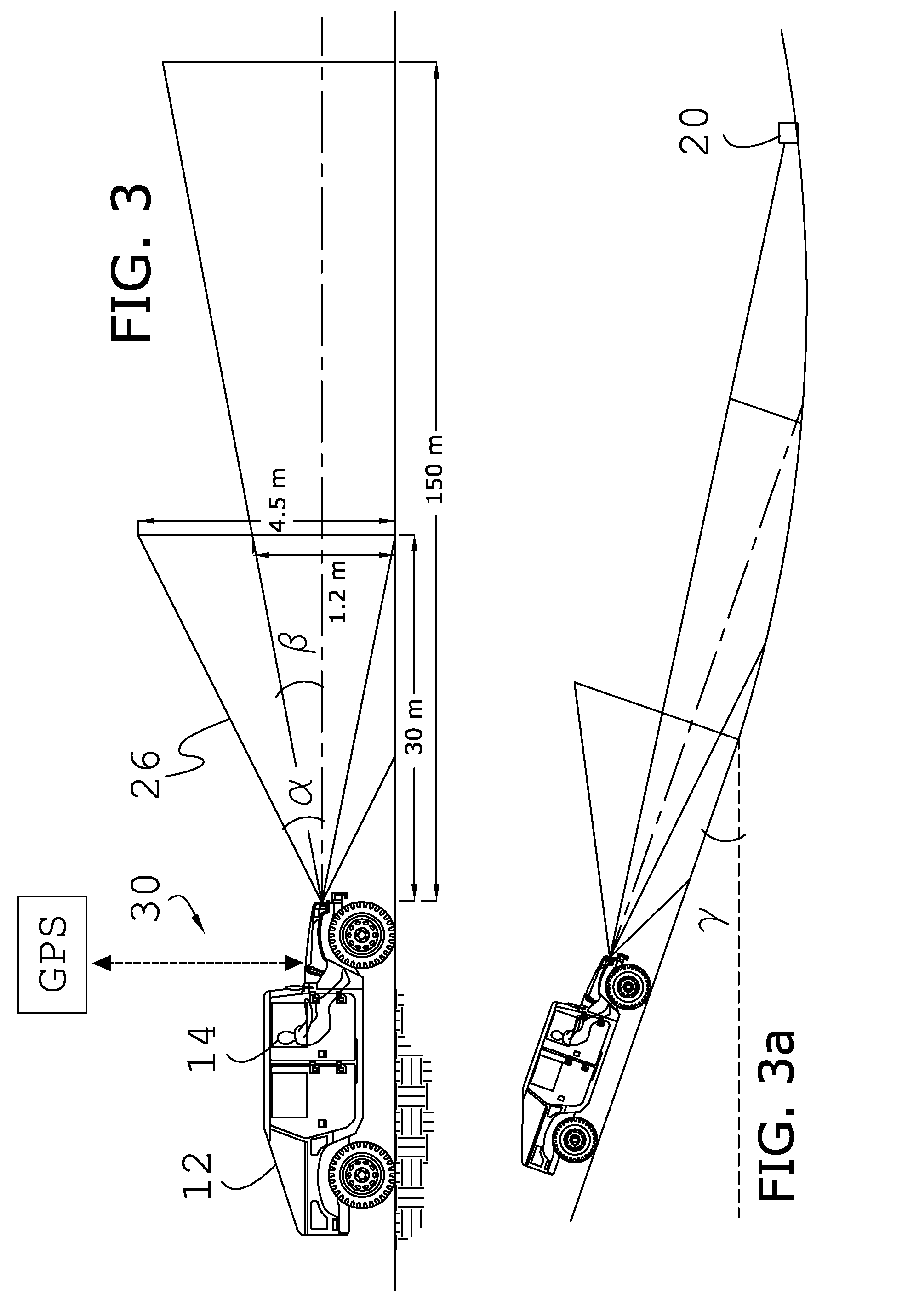
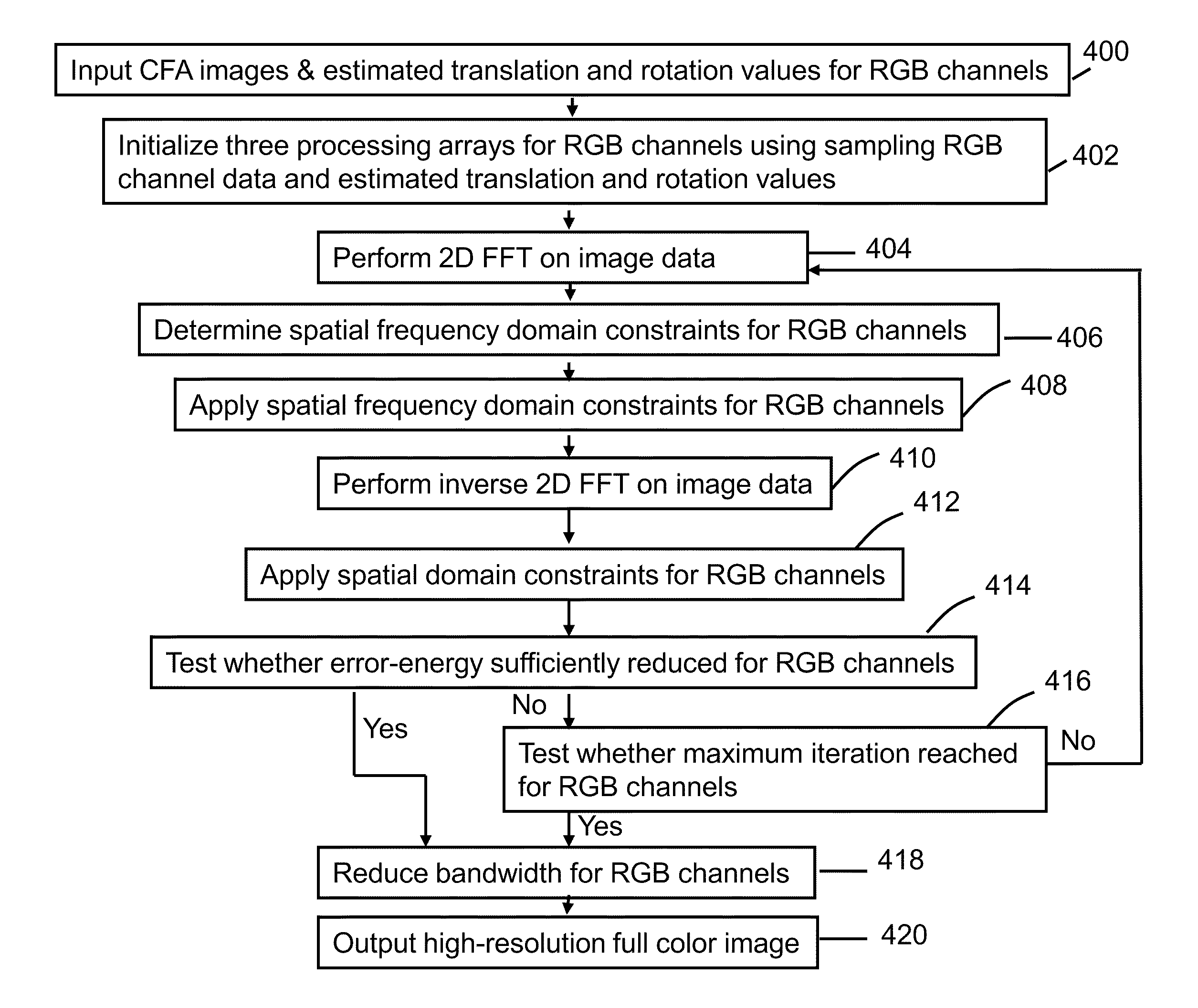
System and method for super-resolution imaging from a sequence of color filter array (CFA) low-resolution images
InactiveUS8577184B2Improve picture qualityGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageColor filter array
A method and system for improving picture quality of color images by combing the content of a plurality of frames of the same subject; comprising: at least one processor; the at least one processor comprising a memory for storing a plurality of frames of a subject; the at least one processor operating to combine the content of plurality of frames of the subject into a combined color image by performing: a process in which at least two multicolored frames are converted to monochromatic predetermined color frames; a gross shift process in which the gross shift translation of one monochromatic predetermined color frame is determined relative to a reference monochromatic predetermined color frame; a subpixel shift process utilizing a correlation method to determine the translational and / or rotational differences of one monochromatic predetermined color frame to the reference monochromatic predetermined color frame to estimate sub-pixel shifts and / or rotations between the frames; and an error reduction process to determine whether the resolution of the resulting combined color image is of sufficient resolution; the error reduction process comprising applying at least one spatial frequency domain constraint and at least one spatial domain constraint to the combined color image to produce at least one high-resolution full color image.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
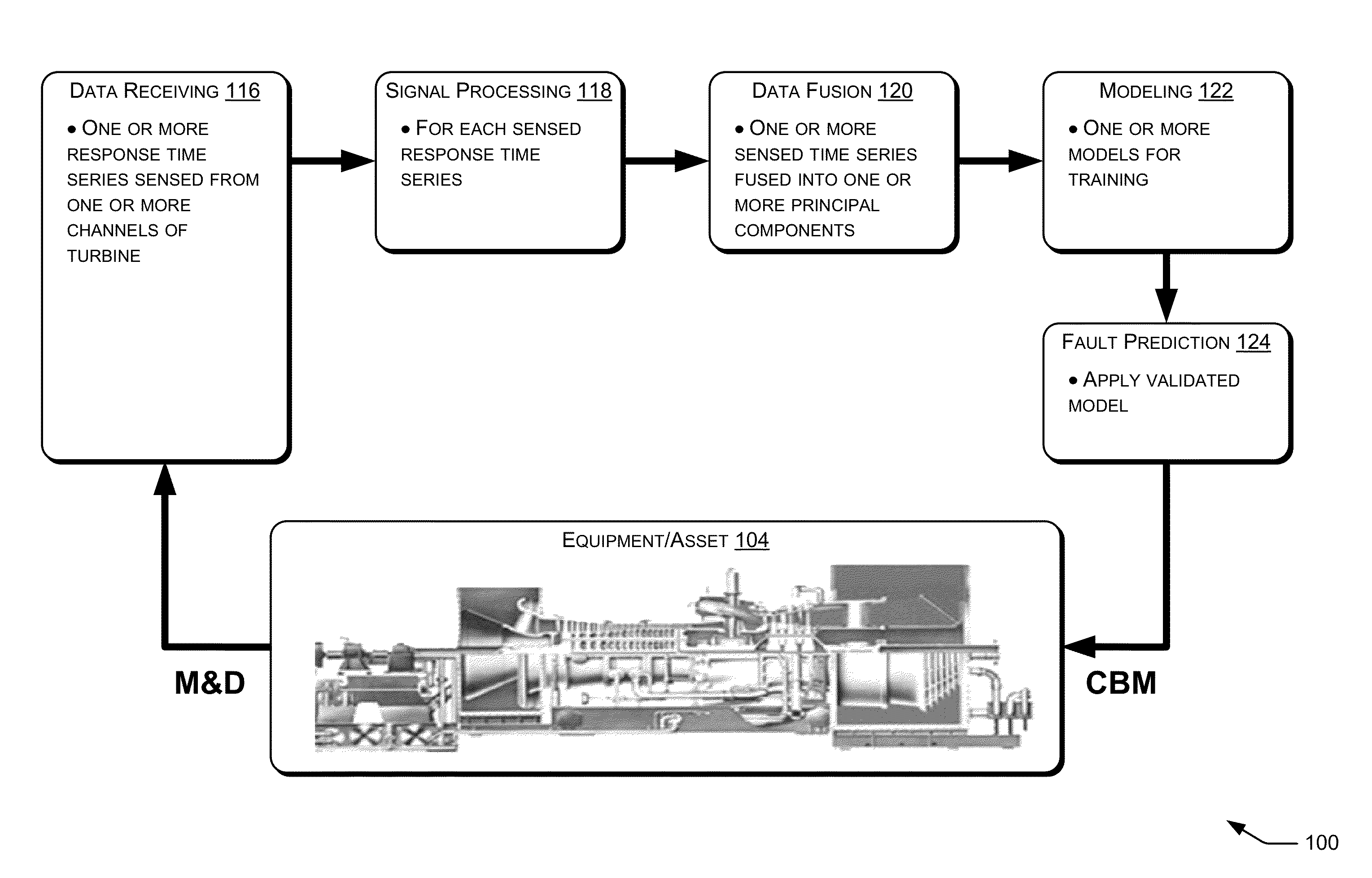
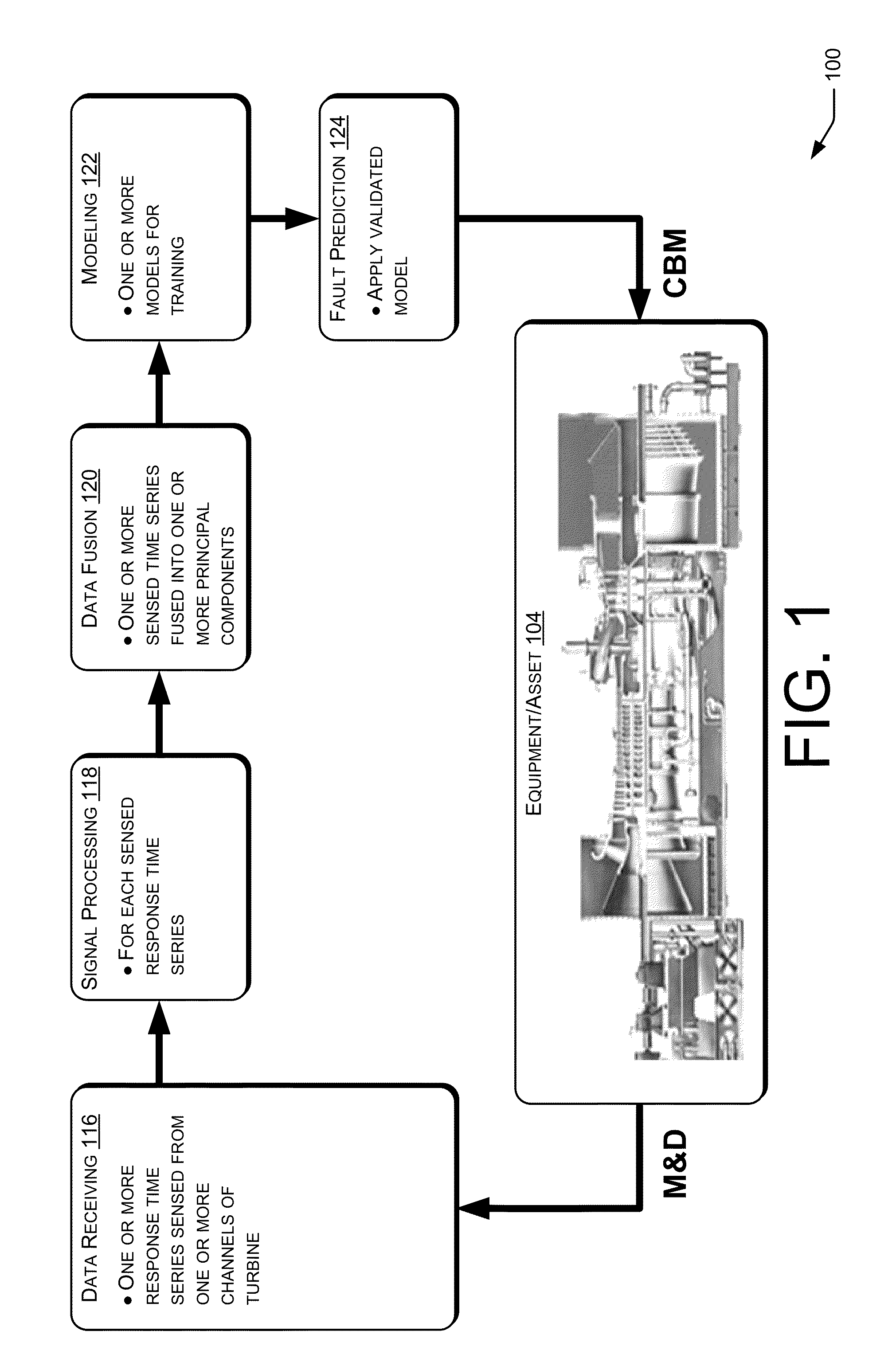
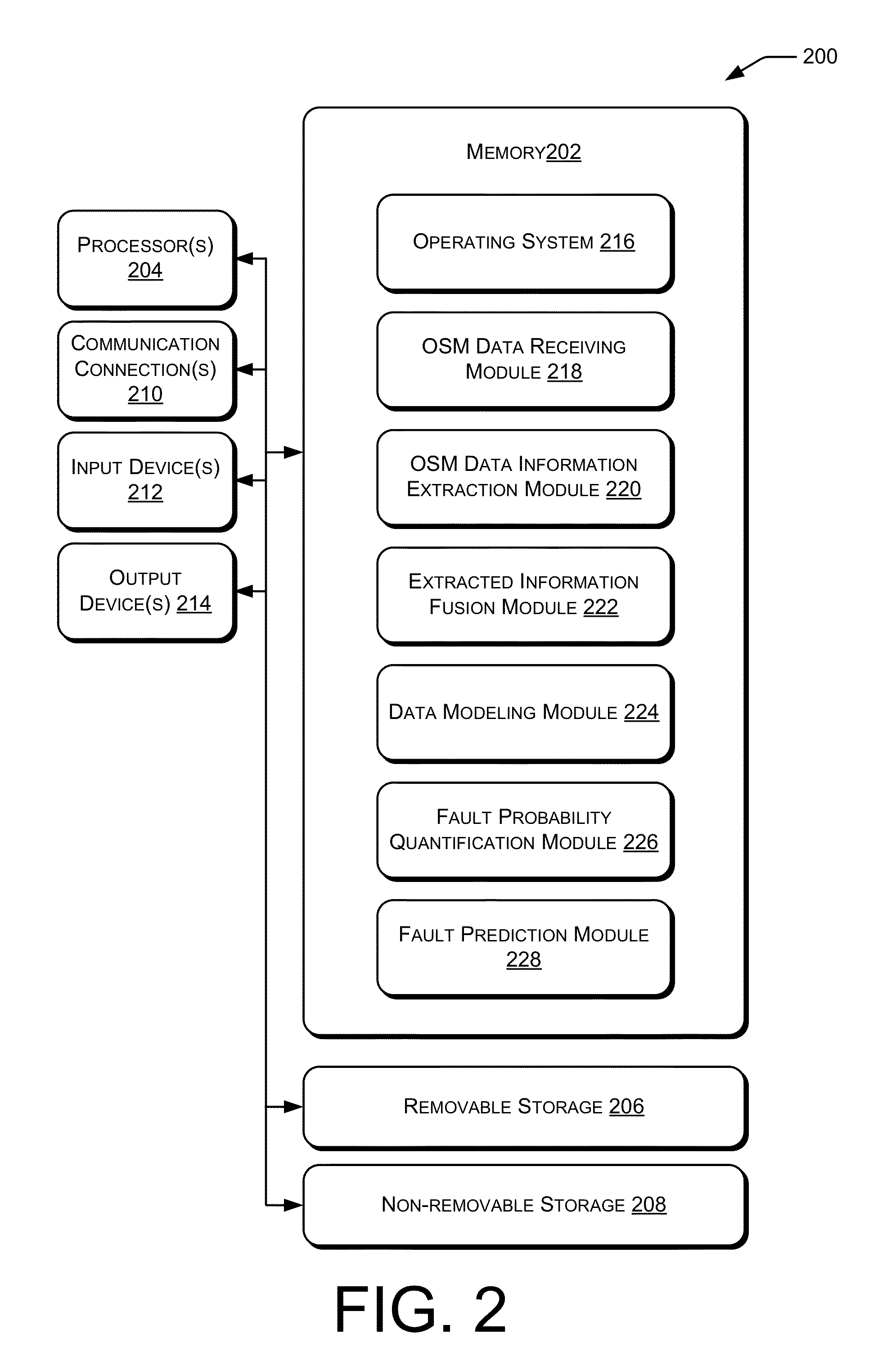
Fault Prediction of Monitored Assets
ActiveUS20130204808A1Digital computer detailsReliability/availability analysisError reductionMonitor equipment
Systems and methods for fault prediction are described to reduce equipment failure by effectively monitoring equipment, removing anomalous data, and reducing false alarms. Such systems and methods can be used to receive monitoring data, extract information from the data, and combine extracted information for establishing prediction models. Additionally, fault probabilities may be quantified and faults may be predicted based on the probabilities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
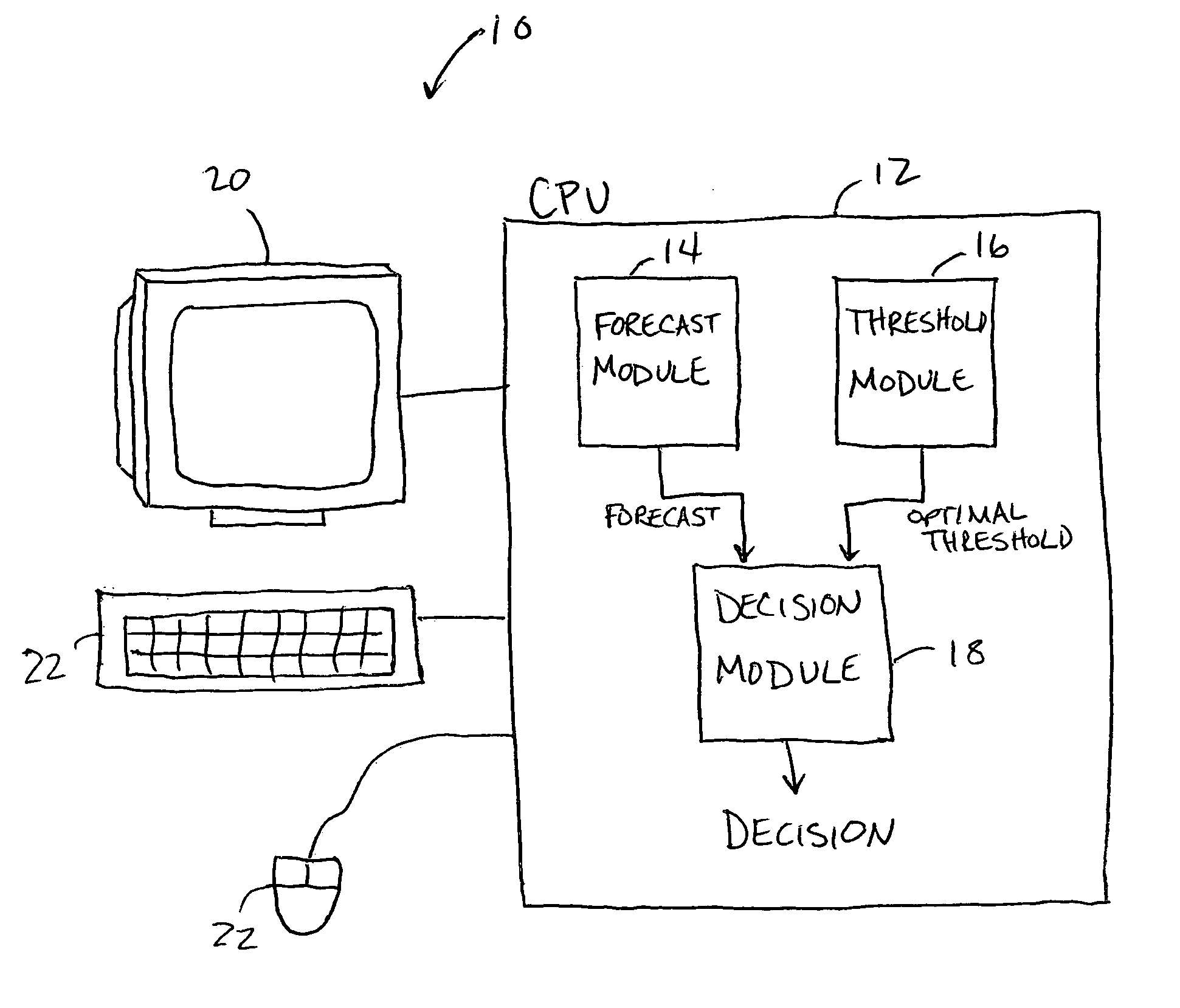
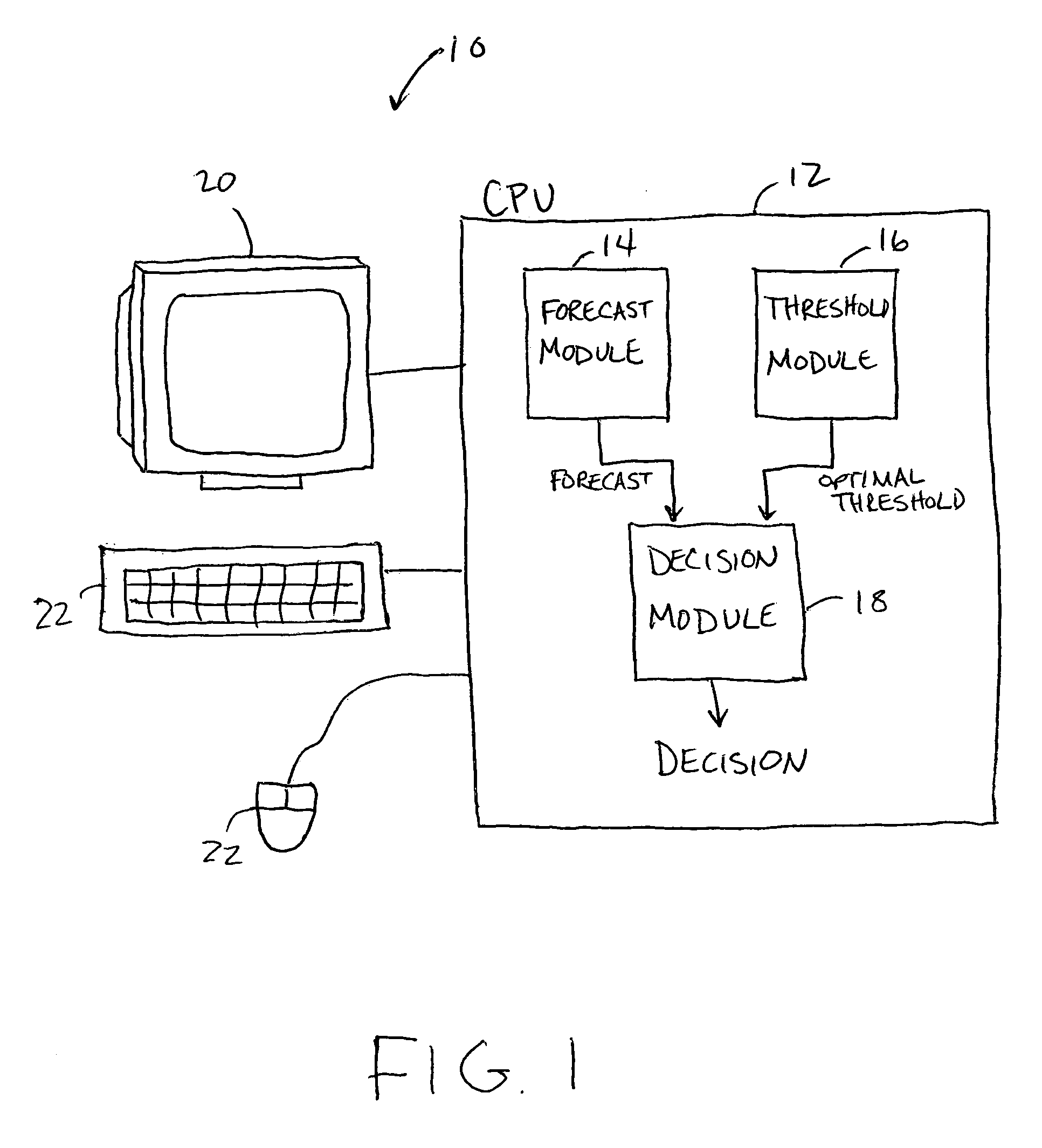
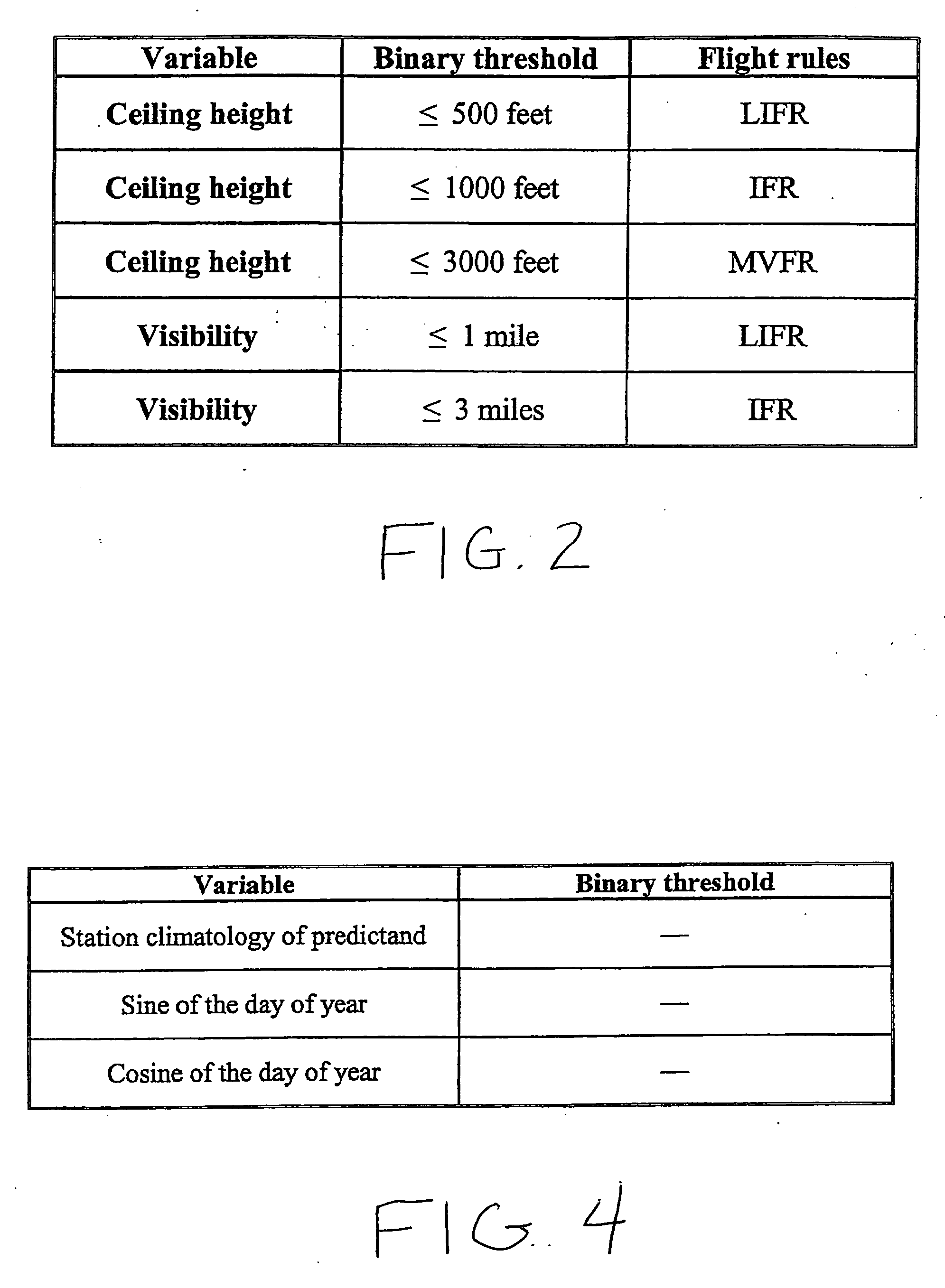
Forecast decision system and method
InactiveUS20060085164A1Increase valueGreat forecast valueAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficVisibilityDecision system
A system and method for making a decision of whether to carry additional fuel on an aircraft for a particular flight based on a forecast, such as for low visibility and ceiling. Preferably, observations-based probabilistic forecasts are utilized. The forecast probability of the weather at the planned aerodrome being below a prescribed minimum level is calculated using statistical regression analysis of past data. An optimal probability is estimated using cost parameters on an individual flight bases. If this forecast probability is greater than the optimal probability for a particular flight, then extra fuel is carried by that flight. This is in contrast to current practice whereby the same categorical forecast is applied to all flights. The combination of improved short-term forecasts and identification of optimal forecast probabilities minimizes the financial impact of errors and weather forecasts on airline operations thereby providing a superior financial outcome.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA THE BOARD THE
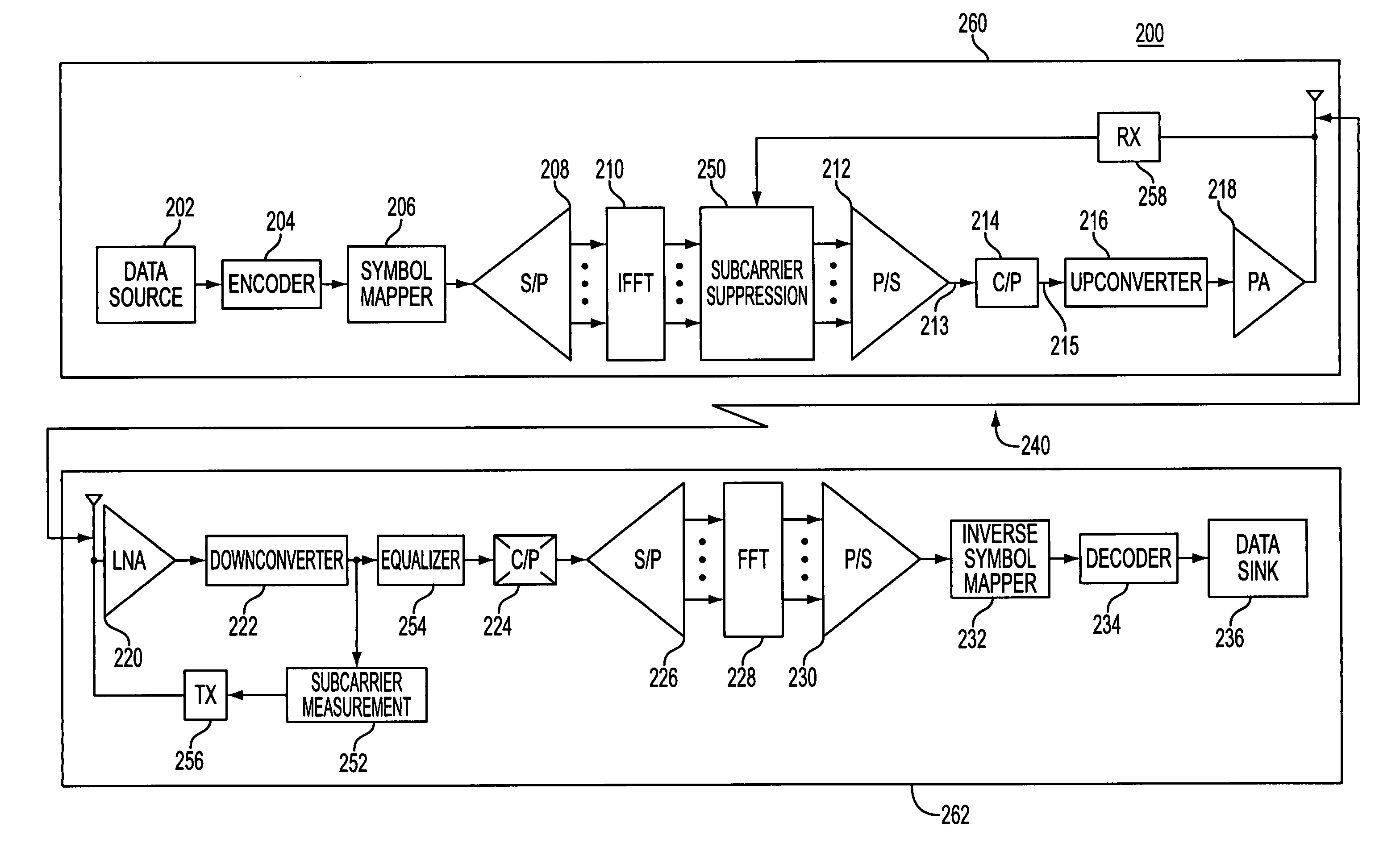
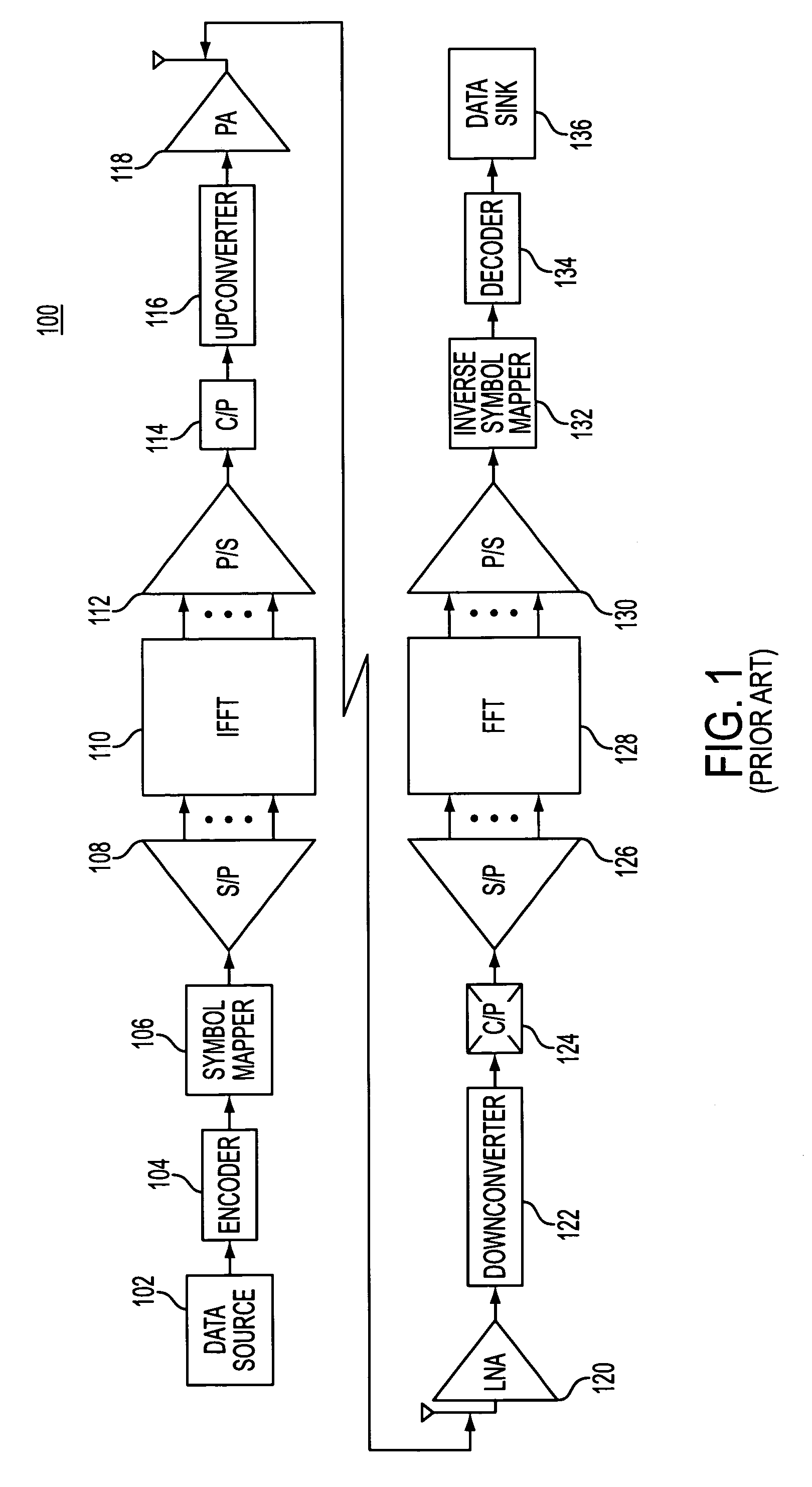
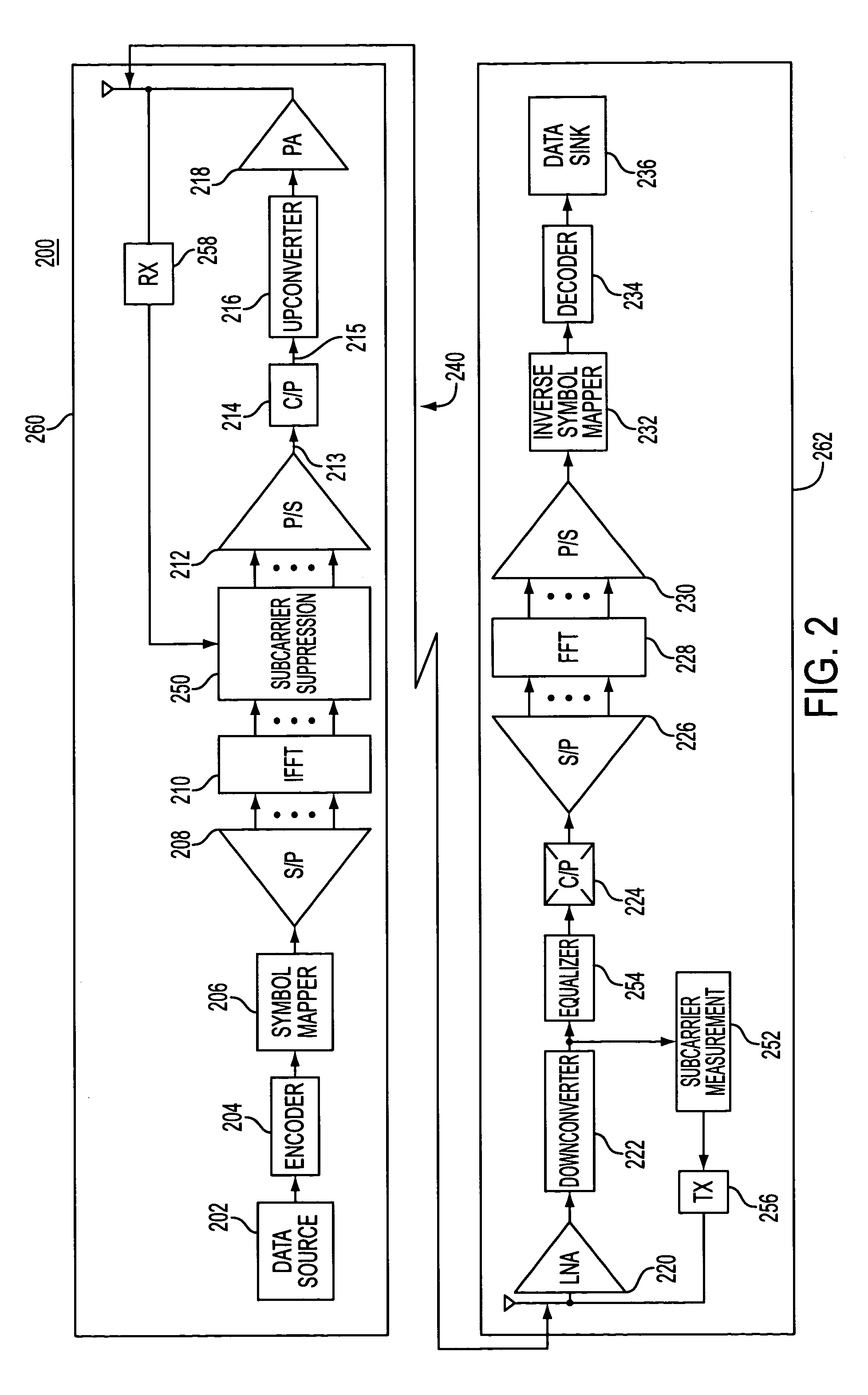
Method and apparatus for error reduction in an orthogonal modulation system
InactiveUS7054375B2Reduce errorsReduce signal distortionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionSignal qualityError reduction
A method and apparatus reduces error in a communication system that includes multiple orthogonal subcarriers by suppressing a subcarrier in a transmitting communication device and by equalizing a received signal in a receiving communication device. Subcarrier suppression is based on a determination of a signal quality metric with respect to each subcarrier or is based on a determination of excessive signal power overdriving an amplifier of the receiving communication device. Equalization of the received signal is based on an equalization function that reduces a multipath delay introduced to the transmitted signal when the multipath delay exceeds a tolerable multipath delay.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method of error reduction in nucleic acid populations
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The complement of each segment is also made in the microarray. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will hybridize to form duplexes. The duplexes are then separated using a DNA binding agent which binds to improperly formed DNA helixes to remove errors from the set of DNA molecules. The segments can then be hybridized to each other to assemble the larger target DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com