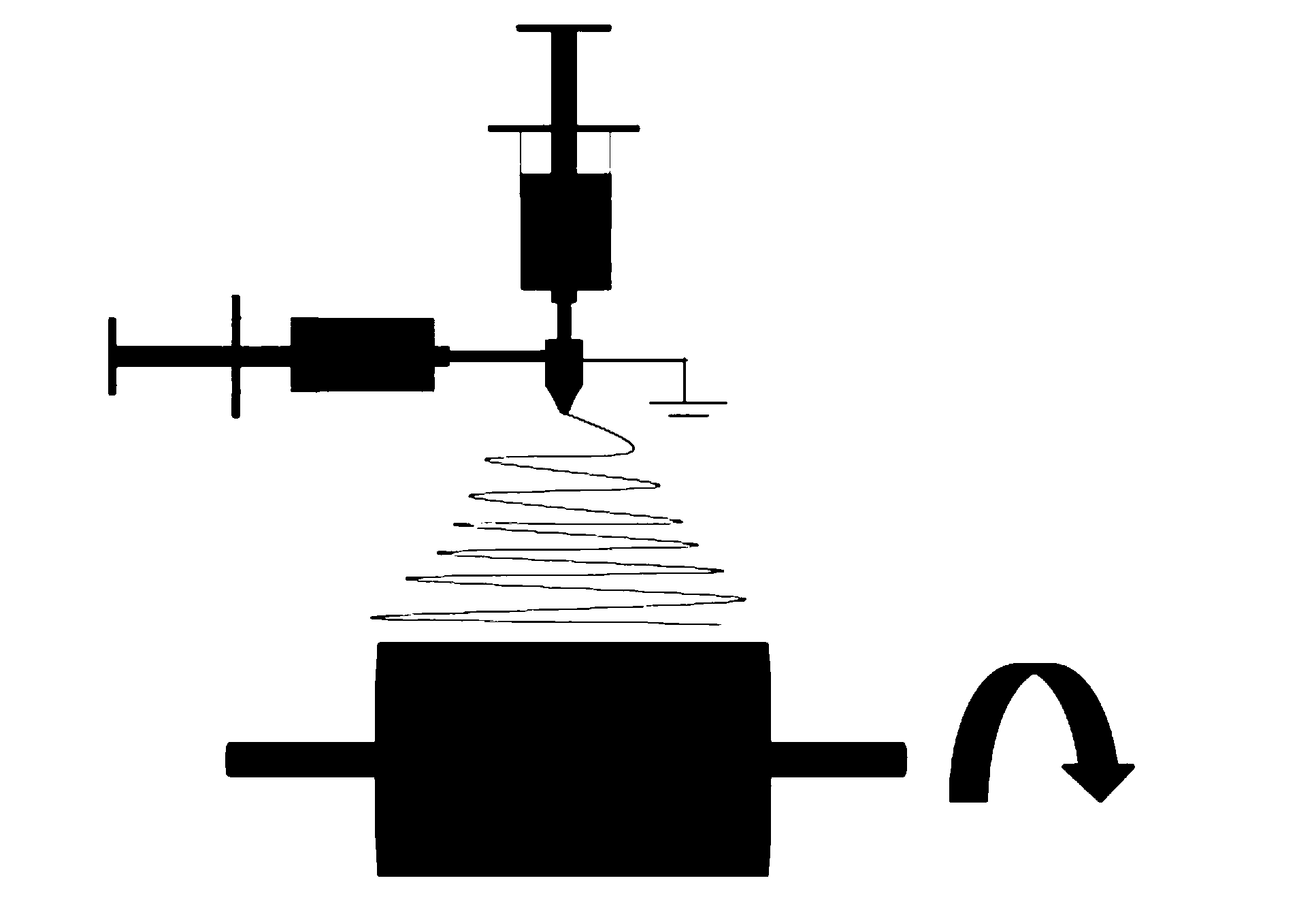
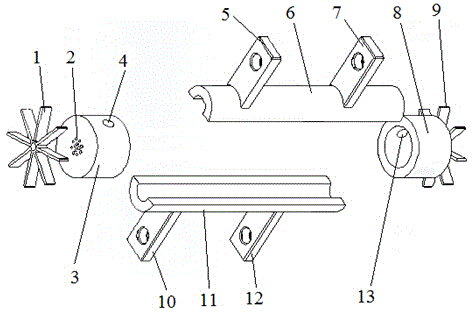
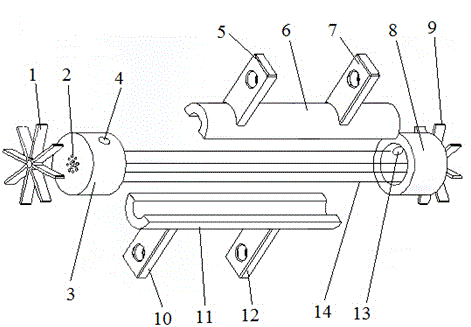
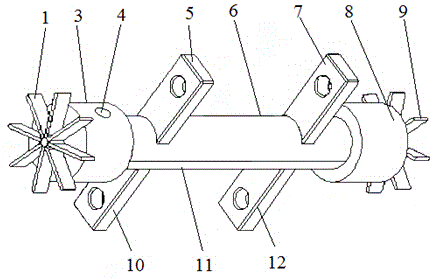
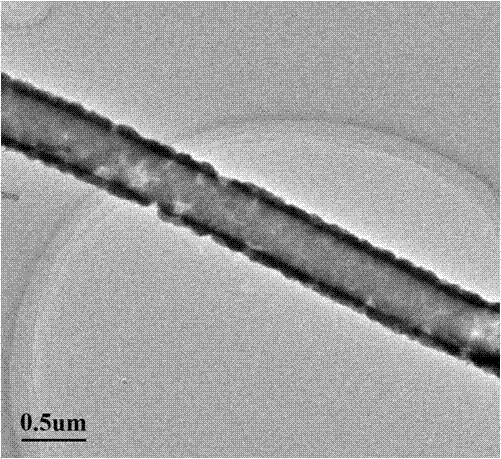
Patents
Literature
235 results about "Nerve repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) differentiate into neuron-like phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, engrafted into normal or denervated rat striatum. The BMSC did not remain localized to the site of the graft, but migrated throughout the brain and integrated into specific brain regions in various architectonic patterns. The most orderly integration of BMSC was in the laminar distribution of cerebellar Purkinje cells, where the BMSC-derived cells took on the Purkinje phenotype. The BMSC exhibited site-dependent differentiation and expressed several neuronal markers including neuron-specific nuclear protein, tyrosine hydroxylase and calbindin. BMSC can be used to target specific brain nuclei in strategies of neural repair and gene therapy.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
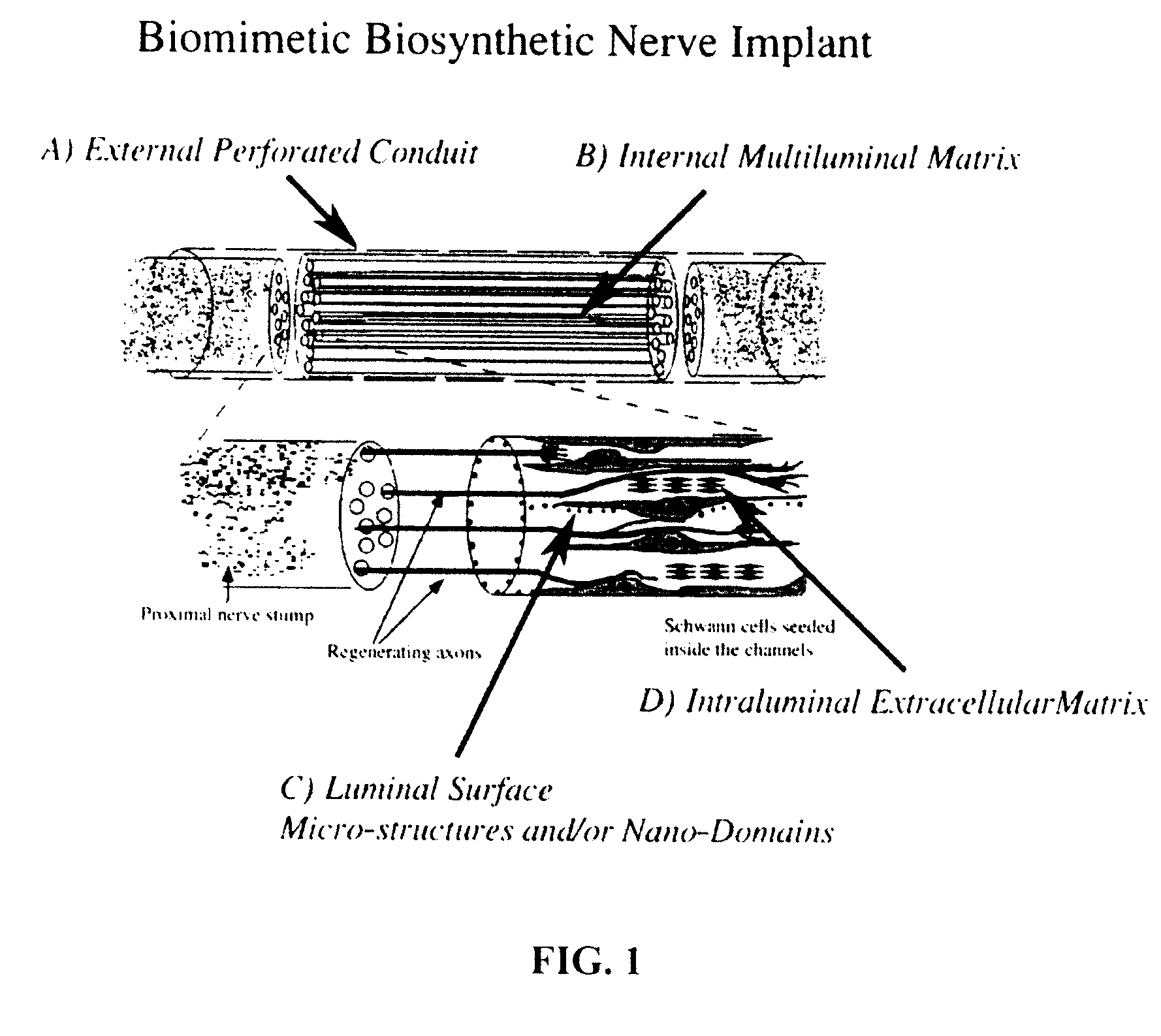
A Biomimetic Synthetic Nerve Implant
InactiveUS20070100358A2Enhanced and directed nerve regenerationPromotes and directs nerve regenerationElectrotherapyTissue regenerationAnatomical structuresSpinal cord
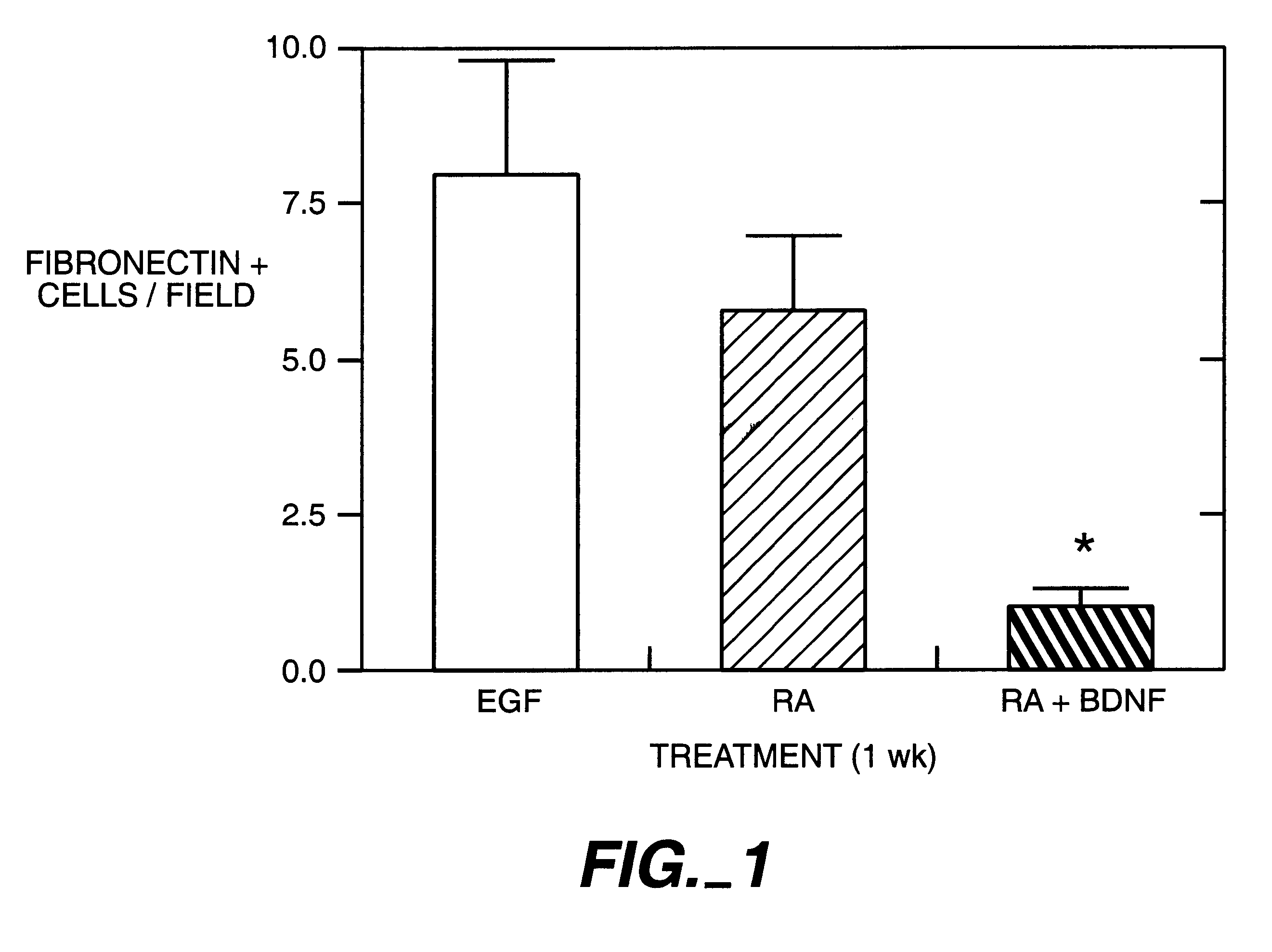
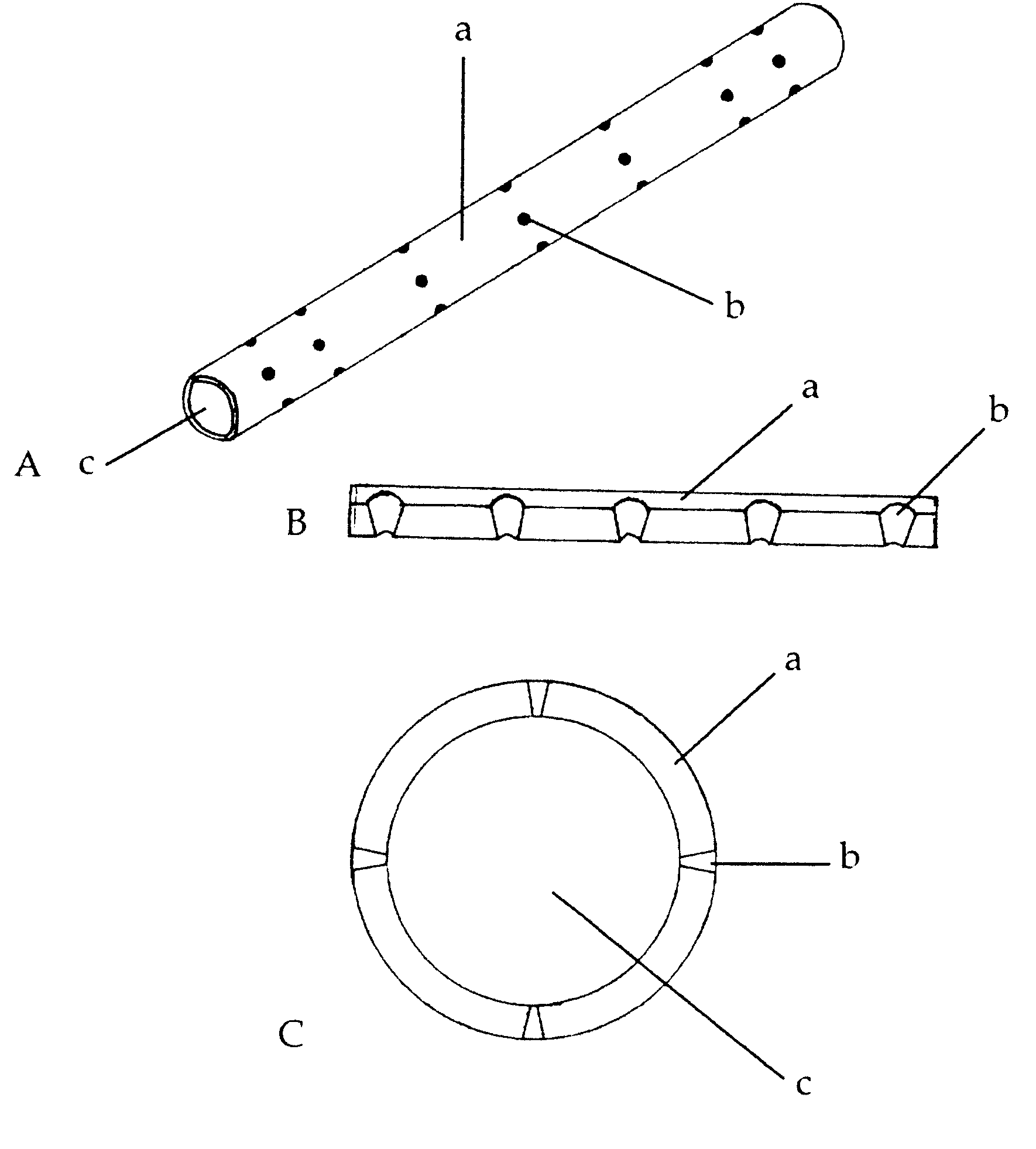
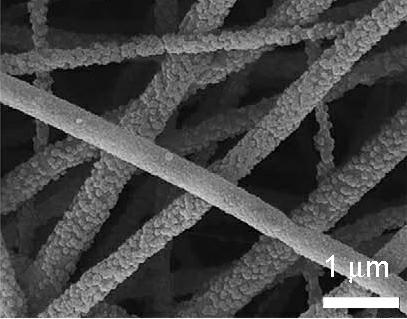
A biomimetic biosynthetic nerve implant (BNI) that uses a hydrogel-based, transparent, multi-channel matrix as a 3-D substrate for nerve repair is disclosed. Novel scaffold-casting devices were designed for reproducible fabrication of grafts containing several micro-conduits, and further tested in vivo using a sciatic nerve animal model and repair of the adult hemitransected spinal cord. At 16 weeks post-injury of the sciatic nerve, empty tubes formed a single nerve cable. In sharp contrast, animals that received the multi-luminal BNI showed multiple nerve cables within the available microchannels, better resembling the multi-fascicular anatomy and ultra structure of the normal nerve. In the injured spinal cord, the BNI loaded with genetically engineered Schwann cells were able to demonstrate survival of the grafted cells inside the BNI, and robust axonal regeneration through the implant up to 45 days after repair.
Owner:TEXAS SCOTTISH RITE HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN
Nerve repair unit and method of producing it
A nerve repair unit comprising a resorbable polymeric support and an alginate matrix containing human Schwann cells is enclosed. A method of producing the nerve repair unit is also described. The Schwann cells are preferably cells cultured from a nerve biopsy sample from the patient who is going to receive the nerve repair unit as an implant.
Owner:MIKAEL WIBERG
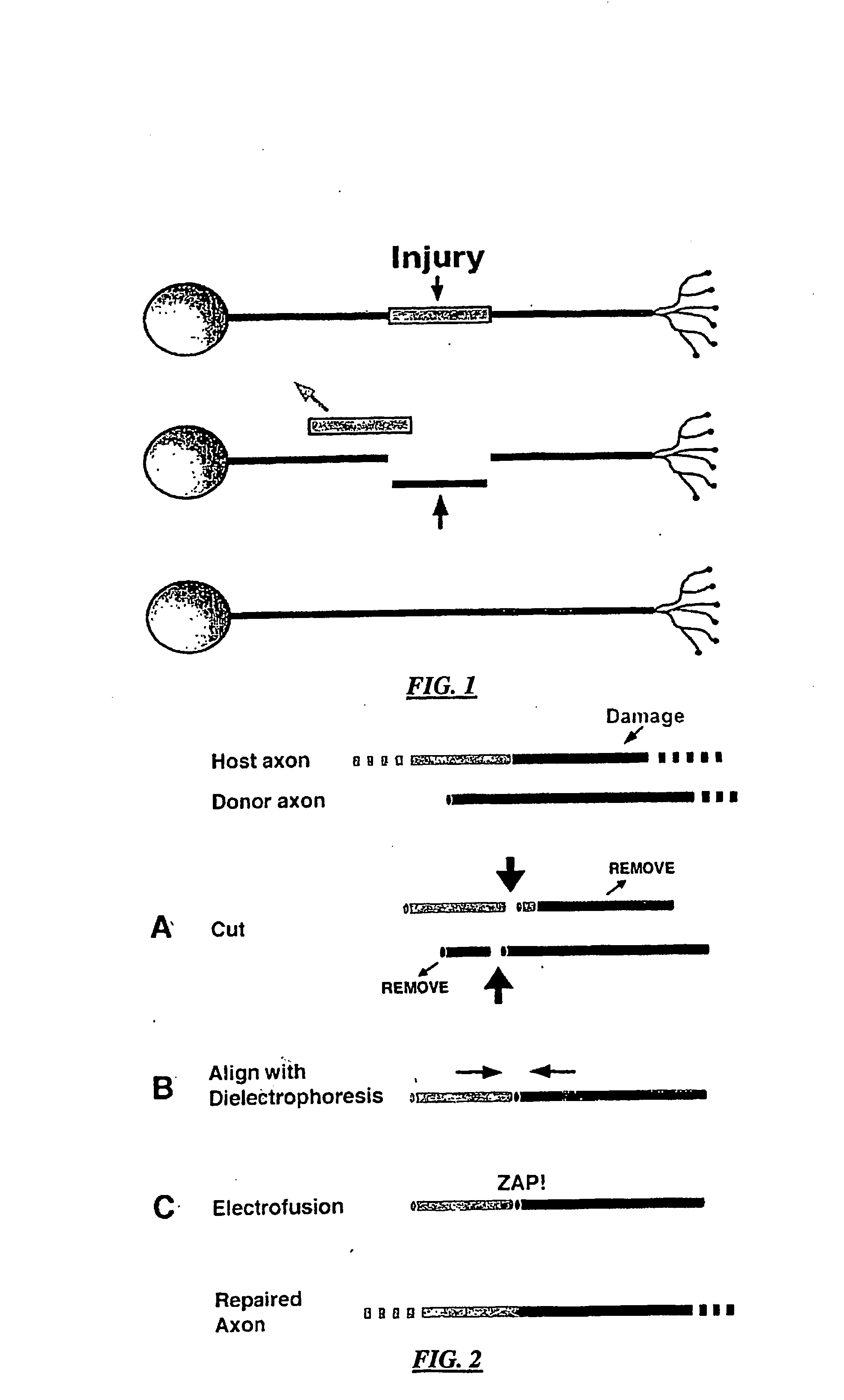
Method and system for nerve repair, nanoknife, mems platform and uses thereof
Method and systems for nerve repair and for microfabrication. In specific embodiments, nerve repair is accomplished by repairing axons. In further embodiments, a modular, 3D system having very small dimentions is described. In further embodiments, a method ans system for performing surgery on axons is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nerve conduit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102688076AAddress barriers to developmentModerate intensitySurgeryCatheterCatheterNerve repair
The invention discloses a nerve conduit and a preparation method thereof. The nerve conduit consists of an inner layer, an outer layer and at least one minitype cavity for storing a bioactive factor solution, wherein the inner layer is of a hydrophilic cell scaffold layer, and the outer layer is of a hydrophobic nerve conduit scaffold layer. The nerve conduit can further comprise a transition layer between the inner layer and the outer layer. The preparation method of the nerve conduit comprises the steps of preparing the inner layer by adopting an electrostatic spinning method, then adding the material for preparing the cavity, then preparing the outer layer, and taking out or dissolving the material for preparing the cavity, thus obtaining the nerve conduit. The nerve conduit has the minitype cavity, so that bioactive factors can be loaded by a manner of injection, soaking and the like as required before operation, thus not only leading the production quality to be easily controlled, but also being capable of greatly improving the survival rate of the bioactive factors, more efficiently promoting the regeneration of nerves, and enhancing the restoration effect of nerves.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Artificial silk fibroin nano-fiber nerve repair conduit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101579246APlay a role in guiding nerve regenerationPrevent collapseSurgeryCatheterFiberMedicine
The invention discloses a nerve repair conduit and a preparation method thereof. The nerve repair conduit consists of an inner layer conduit and an outer layer fiber wall, wherein the inner layer conduit consists of silk fibroin fibers arranged in the extending direction of the conduit, the outer layer fiber wall consists of the silk fibroin fibers encircling the conduit vertically and arranged axially, and the diameters of the silk fibroin fibers are between 50 and 3,000 nanometers; and the method for preparing the nerve repair conduit comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a regenerative silk fibroin film; (2) dissolving a pure regenerative silk fibroin film and preparing the silk fibroin fibers by using electrostatic spinning; and (3) collecting the silk fibroin fibers by using a roller device to obtain the nerve repair conduit. The nerve repair conduit is made from high-purity silk fibroin and is biodegradable, and the inner layer is made from parallel fibers arranged in the extending direction of the conduit and can conduct nerve cell migration; and the outer layer fibers are arranged by encircling the conduit axially and can support the conduit to prevent collapse.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Muscle-derived cells (MDCs) for promoting and enhancing nerve repair and regeneration
ActiveUS20050238625A1Promote and enhance treatmentPromote and enhance and repairBiocideNervous disorderMuscle tissueNervous system
The present invention describes methods involving the use of muscle derived cells (MDCs), preferably obtained from skeletal muscle, to support the innervation and repair of damaged tissues and organs, particularly associated with nerve damage or neuropathy. The invention relates to MDCs for use in methods for promoting or enhancing innervation of nerve cells, particularly in the peripheral nervous system, and their ability to contribute to the development of neuronal tissue when MDCs are introduced at or near a tissue or organ site in need of repair due to injury, damage, disease, or dysfunction. Such methods are useful for the treatment of central and peripheral nervous system disorders and to alleviate, abate, or eliminate the symptoms of neurologic or neurodegenerative diseases in animals, particularly mammals, including humans. The methods are also useful for treating both nerve and muscle tissue following injury, damage, or dysfunction to these tissue types.
Owner:UNIV OF PITTSBURGH THE
Preparation method for conduction and sustained release type nervous tissue engineering scaffold
ActiveCN104225685AGood cell compatibilityExtended highFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsConductive polymerDefect repair
The invention relates to a preparation method for a conduction and sustained release type nervous tissue engineering scaffold. The method comprises the following steps: silk fibroin Silk and lactic acid-caprolactone copolymer are dissolved in a solvent, dissolved and stirred to obtain a solution, then polyaniline and camphorsulfonic acid are added and stirred and mixed uniformly to obtain a cortex electrospinning solution, and NGF (nerve growth factors) are dissolved in ultrapure water completely to obtain a core electrospinning solution; and the cortex electrospinning solution and the core electrospinning solution are accommodated in an injector respectively for coaxial electrospinning, and then fumigation treatment and vacuum drying are performed to obtain the conduction type nervous tissue engineering scaffold. According to the prepared nanofiber scaffold, the nerve repair speed is increased from ways including external electrical stimulation (conductive polymer), biochemistry (NGFs), a topological structure required by nerve regeneration (orientation guide) and the like. The method is simple to operate, good in repeatability and high in economic benefit, and provides novel experimental thought for nerve defect repair in clinical application.
Owner:诺一迈尔(山东)医学科技有限公司
Multi-channel nerve repair conduit with tissue induced function and mold
ActiveCN104399131ATo achieve a sustained release effectNot easy to collapseCatheterSalidrosideTissue fluid
The invention discloses a multi-channel nerve repair conduit with a tissue induced function and a mold; chitosan-coated salidroside microspheres and composite type salidroside slow-release microspheres are prepared, the drug cumulative release amount is calculated, the composite type salidroside slow-release microspheres with different contents are mixed with I-type collagen, and salidroside slow-release microspheres / I-type collagen is obtained; a multi-aperture cylindrical nerve conduit core layer is prepared by using the mold, a nano fiber nerve conduit shell layer is prepared by a high-pressure electrostatic spinning technology, the core layer and the shell layer are nested, and thus the multi-channel nerve repair conduit with the tissue induced function is prepared. The shell layer of the conduit has a good role in exchanging with a tissue fluid, and has a function of guiding nerve growth; the core layer has the functions of guiding nerve fiber orientation growth, promoting stem cells to directionally differentiate to schwann cells and accelerating the nerve fiber growth and function recovery, effectively repairs peripheral nerve defects, has good degradation and biocompatibility, and meets the requirements of a tissue engineering scaffold material.
Owner:甘肃伯骊江3D打印科技有限公司
High-artificial tissue engineering nerve repair material NGCS and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high simulation tissue engineering nerve repairing material NGCS and a preparing method thereof which is characterized in that the NGCS material comprises one, two or three raw materials of type I collagen, chitosan and gelatin. The NGCS material is made of the following raw materials by weight portions: 1-10 portions of type I collagen, 1 portion of chitosan and 1 portion of gelatin. The NGCS can be applied to both the basic research of the nerve injury repairing and the bridge repairing of clinical human spinal and peripheral nerve injuries or defects. The NGCS material is beneficial for the growth of nerve regenerated fiber and can be applied to the repairing of spinal and peripheral nerve injuries.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGPULAN MEDICAL DEVICE
Multi-aperture nerve repairing tube and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102688110AGood tissue compatibilityImprove plasticityTubular organ implantsCylindromaSpinal nerve
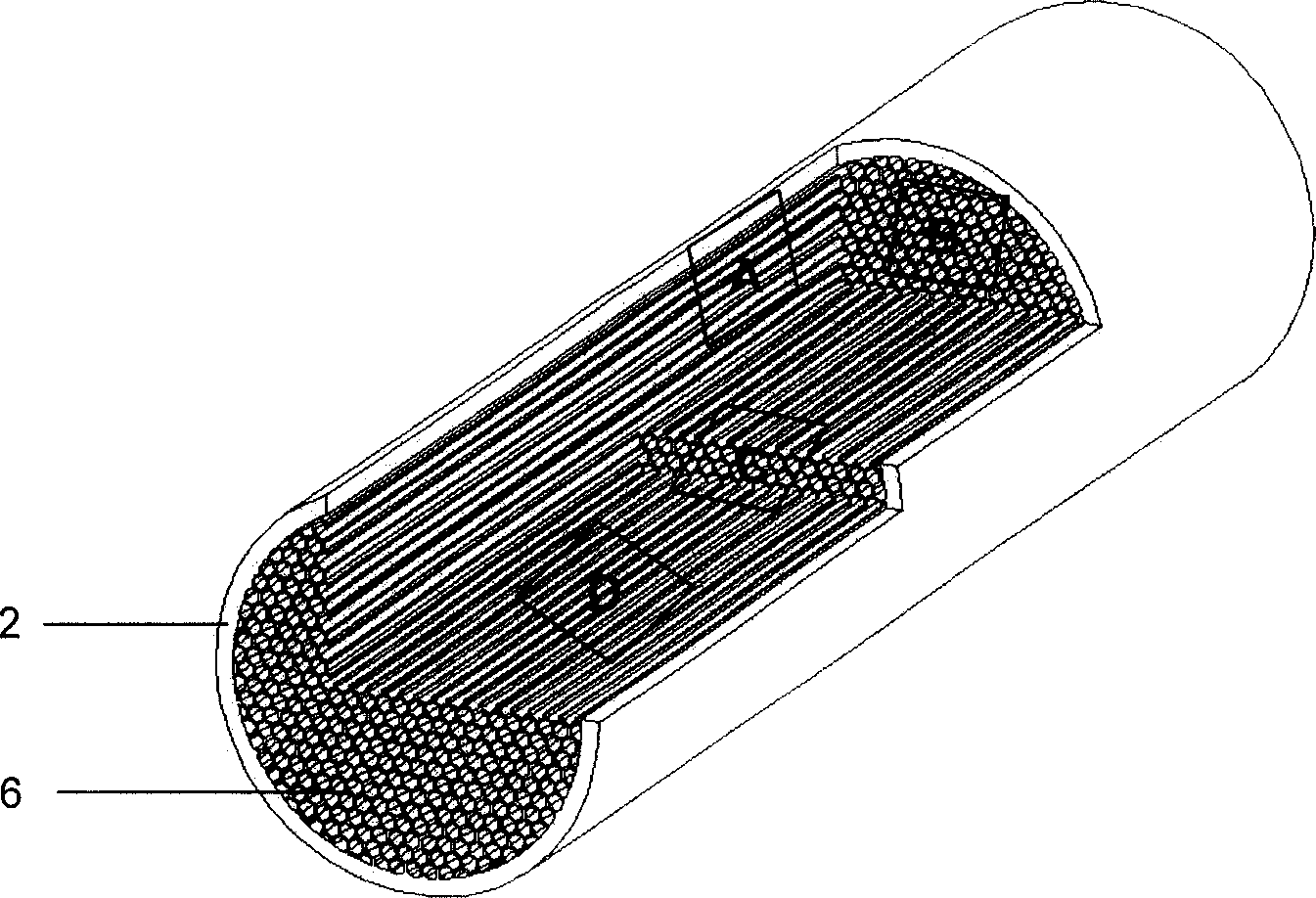
The invention relates to a multi-aperture nerve repairing tube and a preparation method and application thereof. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube is a cylinder with a length-diameter ratio of 0.1-1, and multiple microtube channels are axially distributed in parallel inside; and the ratio of the diameter of each microtube channel to the diameter of the cylinder is 0.04-0.2. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention has good histocompatibility, proper and controllable degradation absorbability, low antigenicity and good plasticity and mechanical properties. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention can effectively promote the repair of the injured spinal nerve, and also can be used as a cell transplantation carrier to carry different nerve growth factors and stem cells for repairing the spinal nerve injury. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube provided by the invention is favorable for the intrusion, differentiation and growth of the nerve cell; and the tubular biomaterial is connected with the far and near broken ends of the nerve, and can induce the axon of the regenerated nerve to grow from the near end to the far end along the tube cavity and stimulate the growth of the neuron of the organism. The multi-aperture nerve repairing tube can be used for promoting the repair of spinal nerves.
Owner:TIANXINFU (BEIJING) MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
Nerve tissue engineering electric conduction nano-fiber tubular stent and preparation method thereof
The present invention relates to a nerve tissue engineering electric conduction nano-fiber tubular stent and a preparation method thereof. The nerve tissue engineering electric conduction nano-fiber tubular stent comprises an electric conduction nano-fiber tube and an electric conduction hydrogel filling material, wherein the electric conduction nano-fiber tube is formed by compounding an inner layer and an outer layer, the inner layer is an electric conduction nano-fiber film arranged in a parallel manner and oriented along the axial direction of the catheter, the outer layer is a non-electric conduction non-woven arrangement nano-fiber film, and the filling material is formed by compounding a natural macromolecular hydrogel and growth factor-loading electric conduction nano-tubes. According to the present invention, the catheter stent material can provide the multifunctional bionic microenvironment for nerve tissue engineering, has good biocompatibility, and can provide nutrients for nerve repair, wherein the two-dimensionally oriented fiber morphology can promote the differentiation and growth of nerve cells, and with the adding of the electric conduction material, the differentiation degree of nerve cells can be further improved, the cell proliferation can be promoted, and the conditions required by nerve regeneration can be well met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
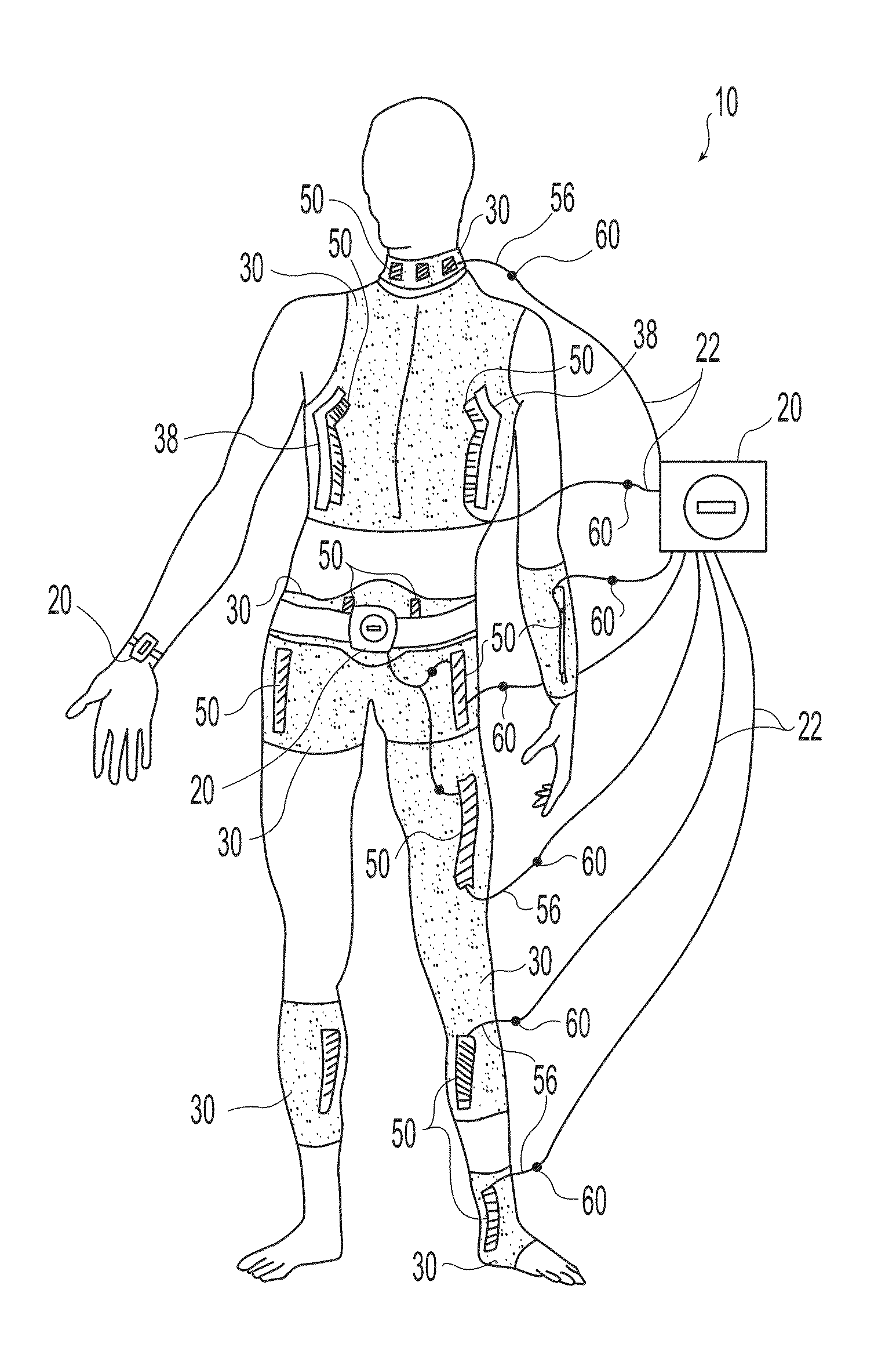
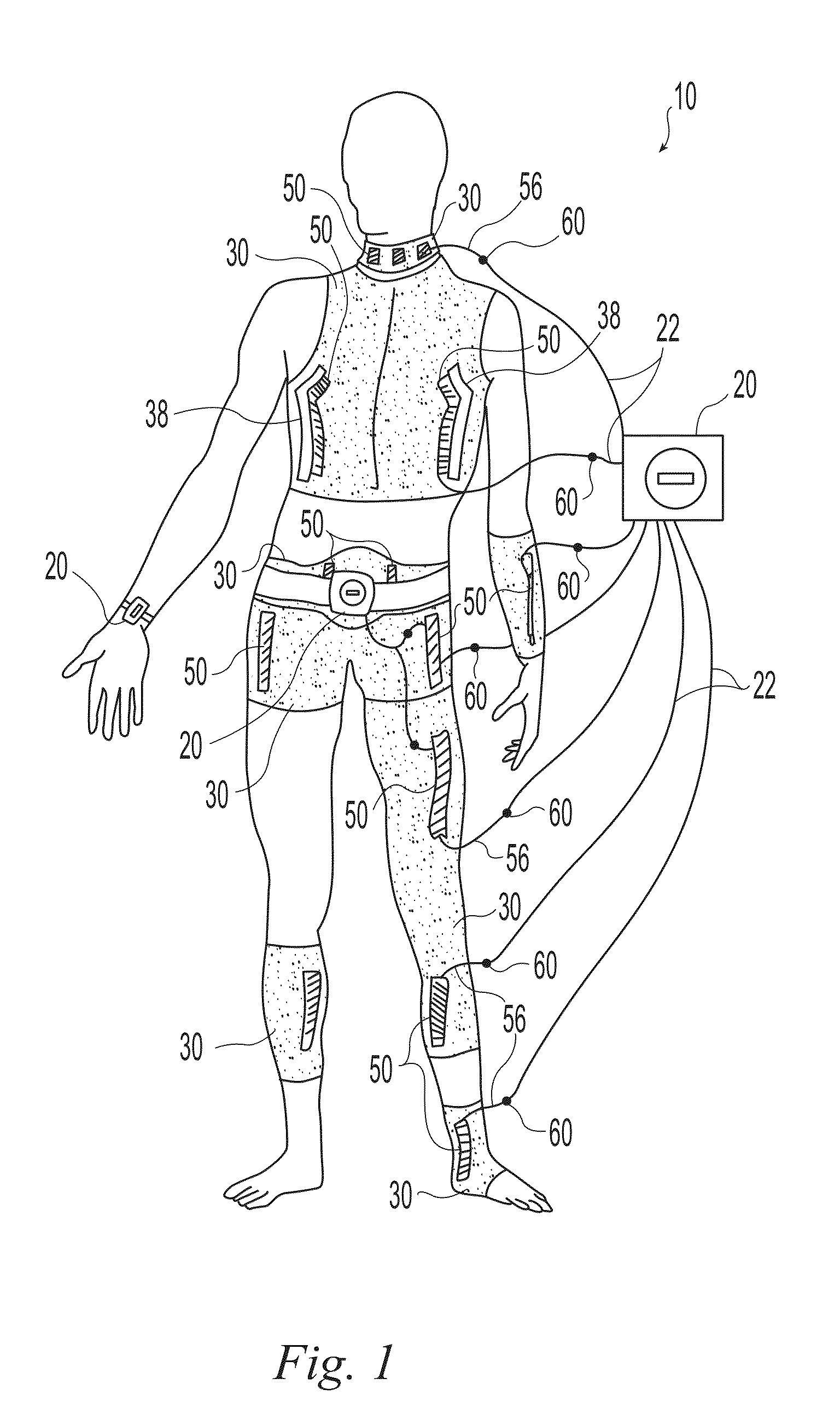
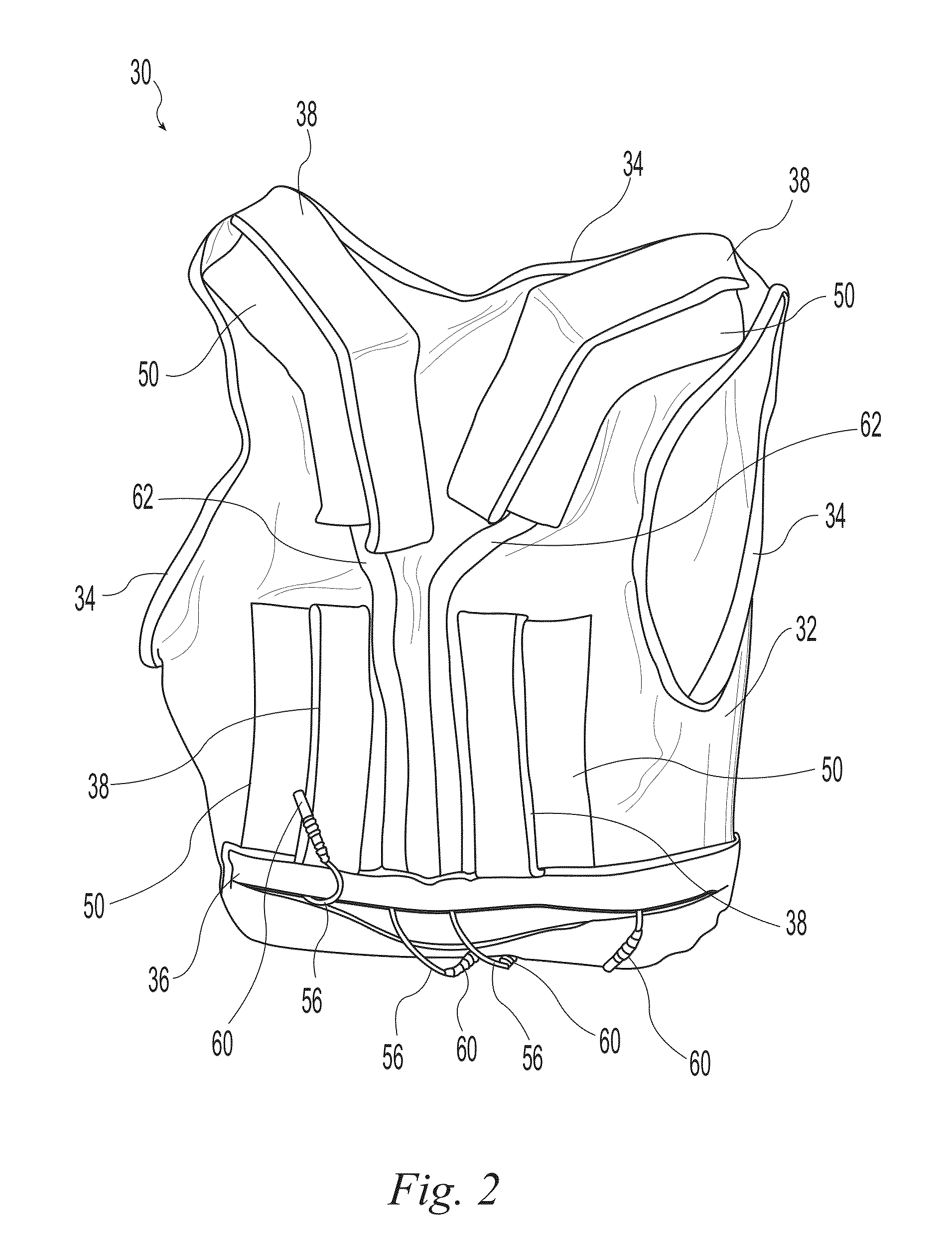
Neuromuscular stimulation system
A wearable neuromuscular stimulation and neuroprosthetic system and device for treating spinal cord injury, stroke, and other neurological conditions; and for the management of chronic pain. This invention provides a system for transcutaneous neuromuscular stimulation and typically comprises a wearable item that further includes a flexible, non-conductive material; at least one flexible, generally flat electrode attachable to or embedded within the wearable item; and a programmable electrical stimulation device connectable to the electrode(s). Each electrode typically includes a silver-impregnated or silver-treated material.
Owner:MUCCIO PHILIP E
Method and system for nanoknife and MEMS platform
Method and systems for nerve repair and for microfabrication. In specific embodiments, nerve repair is accomplished by repairing axons. In further embodiments, a modular, 3D system having very small dimentions is described. In further embodiments, a method ans system for performing surgery on axons is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
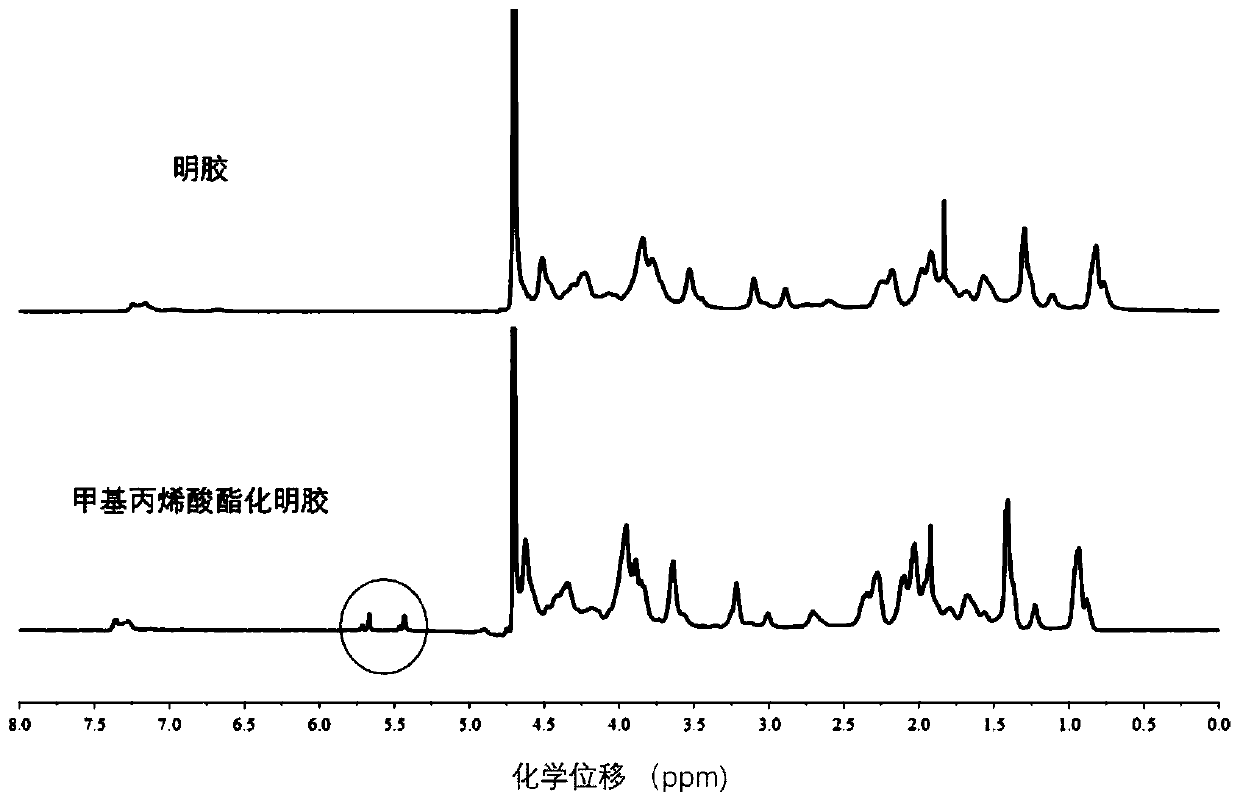
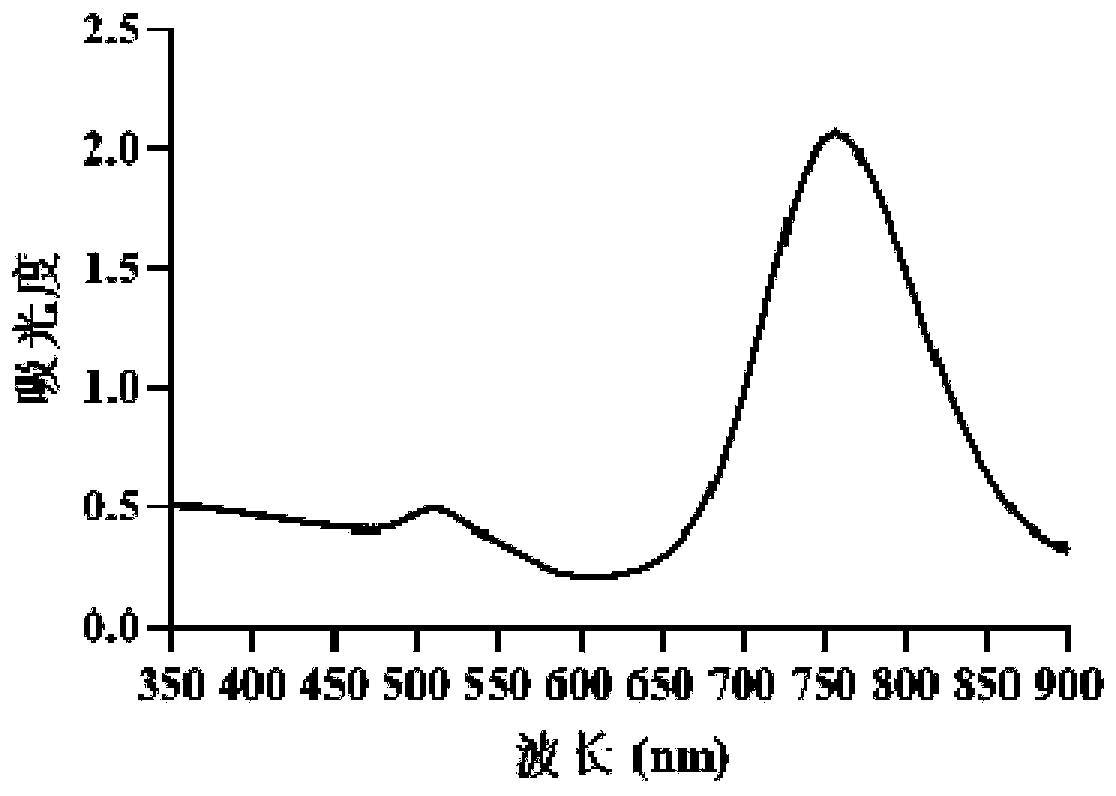
Piezoelectric composite dressing for promoting peripheral nerve repair and wound healing and loading exosome of traditional Chinese medicine and preparation method
ActiveCN110464867AReduce manufacturing costImprove conductivityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsInjury mouthNerve repair
The invention provides a piezoelectric composite dressing for promoting peripheral nerve repair and wound healing and loading exosome of traditional Chinese medicine and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps that gelatin and methacrylic anhydride react to prepare methacrylate gelatin; the exosome of the Chinese medicine is prepared through differential centrifugation;a conductive pregel system is prepared through the recombination of gold nanorods, the exosome and the methacrylate gelatin; and the conductive pregel and a polyvinylidene fluoride ethylene piezoelectric thin film arerecombined, and the piezoelectric composite dressing is prepared. The dressing prepared by the preparation method is a novel dressing for piezoelectric stimulation composite medicine action, polyvinylidene fluoride ethylene produces electricity potential to stimulate a wound area through the conductive gel, wound healing and nerve regeneration are promoted with the exosomeof the traditional Chinese medicine, and the problems in the current wound repair and nerve repair process can be effectively solved. Therefore, the composite dressing has a wide application value inthe treatment of trauma and nerve repair.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for in-situ polymerizing and preparing polypyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun composite membrane
The invention relates to a method for in-situ polymerizing and preparing a polypyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun composite membrane. The method includes the steps: (1) preparing pyrrole solution, (2) preparing benzene sulfonate solution, (3) preparing ferric chloride solution, (4) preparing mixed solution of pyrrole and benzene sulfonate, and (5) in-situ polymerizing a pyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun membrane to obtain the polypyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun composite membrane. The polypyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun composite membrane is a new biological material with a great application value, and especially the polypyrrole-coated polylactic acid electrospun composite membrane can be applied to bionic nerve tissue engineering materials and nerve repair materials.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Nerve repairing film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104740685APromote regenerationAvoid stickingProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixNerves regeneration
The invention discloses a nerve repairing film and a preparation method thereof. The method mainly comprises the steps of treating raw materials, decellularizing, dissolving matrix, drying to form a film, neutralizing and washing and the like. According to the nerve repairing film prepared by the method, active ingredients of the extracellular matrix are maintained, the peripheral nerve suture is directly coated, so that an excellent microenvironment is provided to nerve regeneration, nerves are prevented from adhering to peripheral tissues, and nerve regeneration is promoted.
Owner:山东隽秀生物科技股份有限公司
Multi-channel nerve rehabilitating tube, its preparation process and dedicated mold
InactiveCN1729949AEasy to operateImprove performanceCatheterTubular organ implantsThermal insulationEngineering
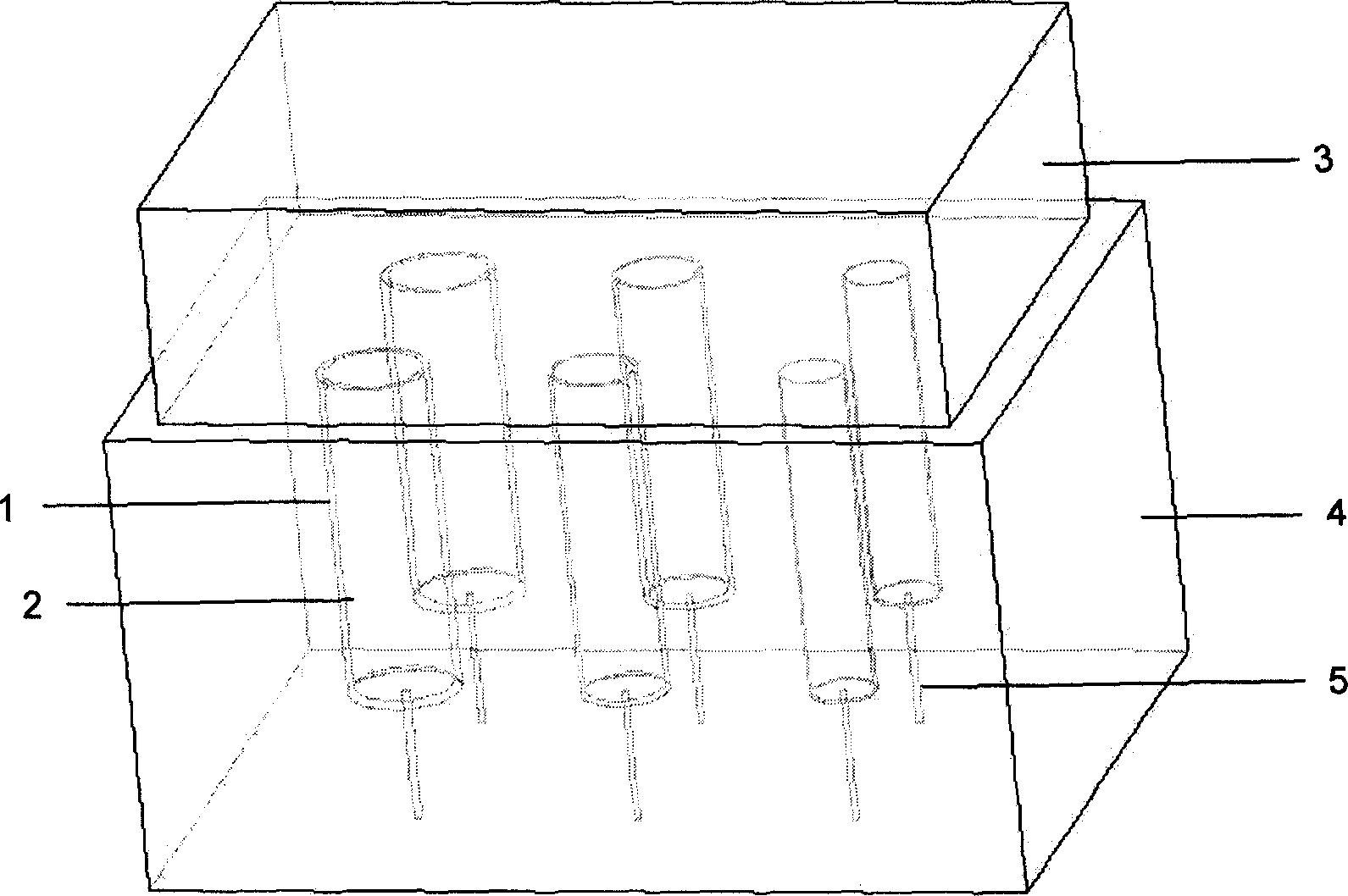
The invention relates to a multi-path nerve-restoring duct, its manufacturing method and special mould. Wherein, the duct is comprised by a chitose round duct and an internal base material with axial multi-path; the mould is formed by a Styrofoam thermal insulation chassis and a stainless steel cover plate while a plurality of cylindrical holes in different inner diameters are regularly arranged on the thermal insulation chassis and a fine needle hole is arranged on the bottom of holes through to the base of chassis. And the manufacturing method of multi-path nerve restoring duct comprises inserting the chitose round ducts in different diameters into the holes of relative diameter of the mould chassis; filling different filling base material into the chitose round ducts according to the demand; using the pre-cooling stainless steel cover plate to quickly cover the chitose round ducts to be stored in low-temperature refrigerator for more than 12 hours; freezing, drying, deacidifying, and poaching with distilled water to the neutral ones; then to be dried in room temperature to attain the multi-path nerve restoring duct. Said manufacturing process is simple with stable result which applies batch production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Double-nerve-factor connected polypyrrole-polylactic acid parallel conductive porous composite filament membrane and preparing thereof
InactiveCN106075571ALarge amount of connectionsUnique inducing propertiesFilament/thread formingTissue regenerationFiberIn situ polymerization
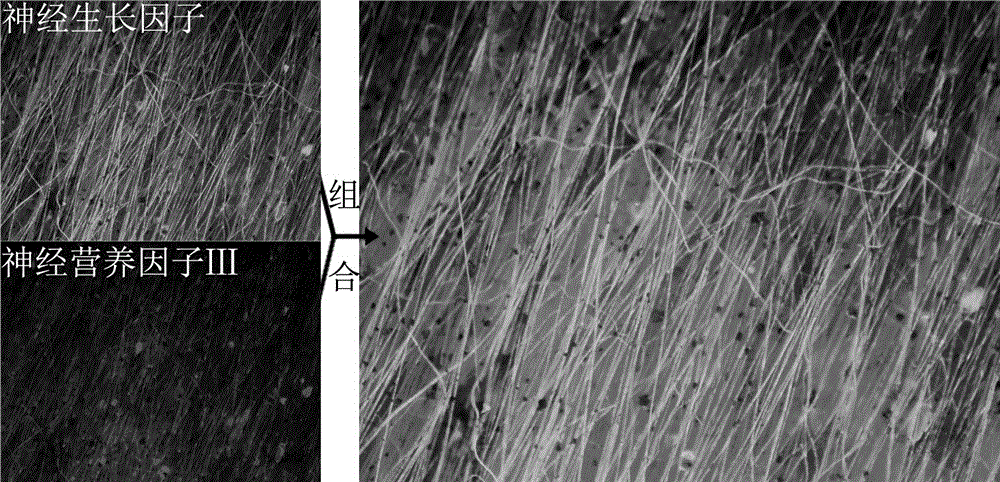
The invention relates to a two-nerve-factor NGF and NT-3 connected polypyrrole-polylactic acid parallel conductive porous composite filament membrane and a preparing method thereof. Firstly, a parallel porous polylactic acid filament membrane with the diameter ranging from 50 nm to 2000 nm is put into a mixed aqueous solution containing sodium alkyl sulfonate, polyglutamic acid, FeCl3 and pyrrole, then a sufficient reaction is carried out for 2-24 h with an in-situ polymerization method, the surface of the parallel filament membrane is evenly coated with polypyrrole nano-particles, washing and drying are carried out, and then conductive polypyrrole wrapped polylactic acid fiber filament membrane with the diameter ranging from 60 nm to 2500 nm is obtained; then, protein of the two nerve factors, namely, NGF and NT-3, is connected to the parallel conductive porous composite filament membrane in sequence with the carbodiimide technology, and the conducive composite filament membrane which can release nerve factors and promote nerve axon elongation and peripheral nerve repair under electrical field stimulation is obtained. The two-nerve-factor NGF and NT-3 connected polypyrrole-polylactic acid parallel conductive porous composite filament membrane and the preparing method thereof have the advantages that implementation is easy, the nerve factor connection efficiency is high, the material conductivity is high, and the nerve repair time is short.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods and devices for connecting nerves
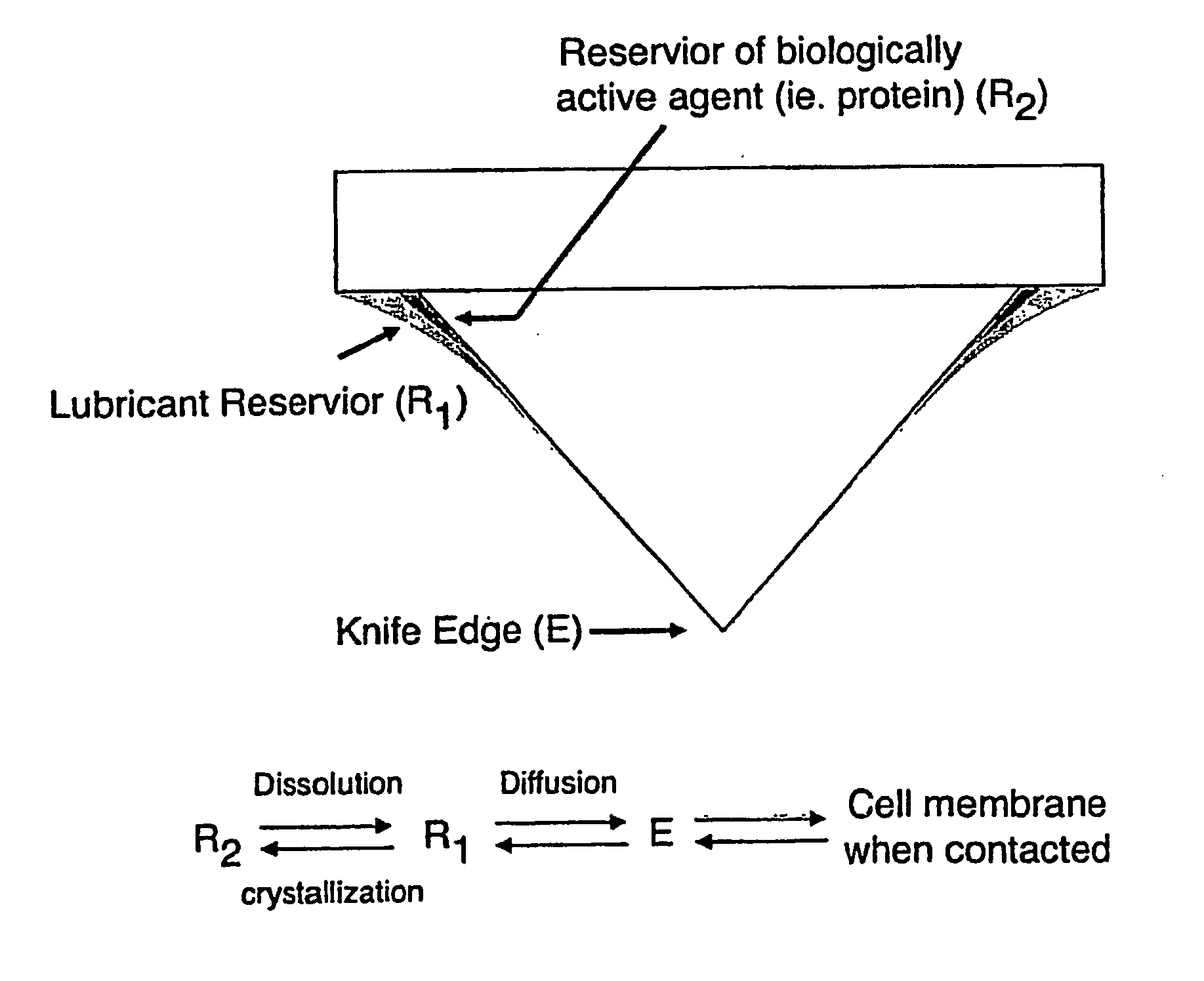
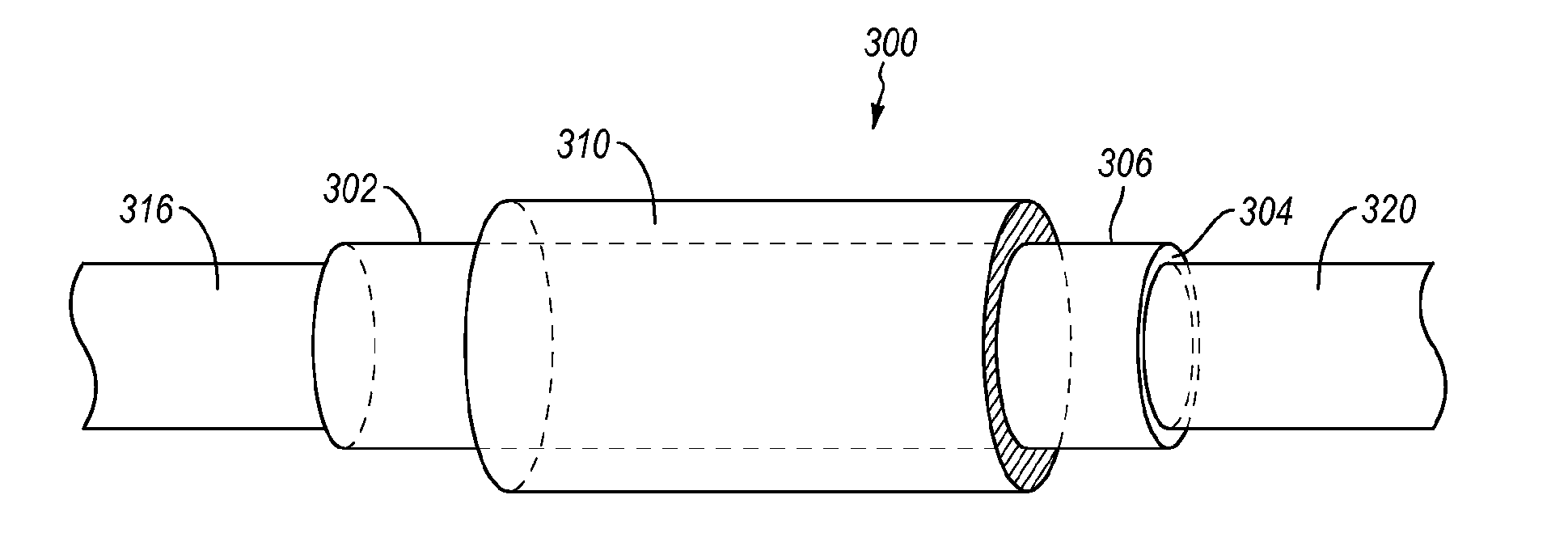
ActiveUS20140336681A1Increase ratingsDegree of improvementTissue regenerationProsthesisDrug reservoirSemipermeable membrane
A nerve repair conduit configured to be secured on first and second portions of a selected nerve. The nerve repair conduit includes a polymeric body having a proximal end, a distal end, an exterior surface and an interior surface defining an interior lumen. In addition, the nerve conduit includes at least one drug reservoir to hold agent(s) that may, for example, facilitate nerve regeneration. The drugs diffuse from the drug reservoir(s) into the nerve repair conduit through an outlet (e.g., a semipermeable membrane) in proximity to the first and second portions of a selected nerve. The nerve repair conduit may be configured to deliver the agent(s) at a rate having substantially zero-order kinetics and / or at a constant rate over a selected period of time (e.g., at least 1 week).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Duct filler material in use for bridge grafting nerves, and preparation method
InactiveCN1872354APrevent pipe wall from collapsingEasy to useSurgeryProsthesisSodium hyaluronateBiomedical engineering
A filler of the guide tube used for bridging nerve is a high-purity transparent gel prepared from sodium hyaluronate and the physiologically balanced liquid through purifying by filter method. The cells or factors for promoting the repair and growth of nerve are added to the gel.
Owner:锦州医学院附属第一医院 +1
Biomedical degradable double-layer stent for nerve repair and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109876186AAdjustment diameterAdjustable thicknessFilament/thread formingProsthesisPolyesterPorosity
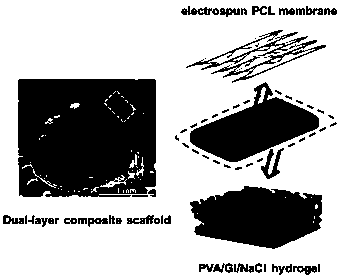
The invention relates to a biomedical degradable double-layer stent for nerve repair and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises first dissolving a polyester material in an organic solvent to obtain a polyester polymer solution; performing electrospinning to obtain an electrospinning fiber membrane; drying the electrospinning fiber membrane to obtain a fiber layer of a biodegradable double-layer stent; dissolving a polyvinyl alcohol material in deionized water, adding glycerin and sodium chloride in the heating, stirring and dissolving process, and obtaining a PVA / GI / NaCl polymer solution by ultrasonic processing; adding the PVA / GI / NaCl polymer solution into a glass die, laying the fiber layer on the surface of the solution, standing, freezing and thawing twice, to obtain hydrogel, and removing salt by washing to obtain the biomedical degradable double-layer stent for nerve repair. The biomedical degradable double-layer stent has excellent mechanical properties,controllable degradation time, small pore size and large porosity, a physiological structure of nerve fibers is mimicked, nutrient exchange and cell proliferation are facilitated, and the repair and regeneration against nerve damage are accelerated.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Three-dimensional sleeve material for nerve repair
InactiveCN107789669AGood biocompatibilityStable structureFilament/thread formingTissue regenerationHuman bodyTissue fluid
The invention discloses a tissue engineering scaffold material for nerve repair and a preparation method thereof. Gelatin protein is taken as a shell structure of a fiber by utilizing a preparation mode of coaxial high-voltage electrostatic spinning, a polycaprolactone and poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer is taken as an inner core structure, and a single fiber membrane is spun first; and then, the fiber membrane is coiled into a sleeve shape by taking a polyethylene mono-filament as an axis, so that the fiber membrane can be used as a nerve sleeve. The three-dimensional sleeve materialprepared by the method provided by the invention is implanted into a human body, has good biocompatibility with blood, tissue fluid and body fluid, has a stable structure and is not easy to collapse.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Separation and culturing method of ectomesenchyme stem cell
A process for separating and culturing the ectomesenchyme stem cells which can be used for bone tissue engineering, muscle tissue engineering, tooth tissue engineering and repairing peripheral nerve nicludes such steps as preparing culture medium, separating, culturing and purifying.
Owner:STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL NO 4 ARMY MEDICAL COLLEGE PLA
Nerve repairing material and preparation method thereof
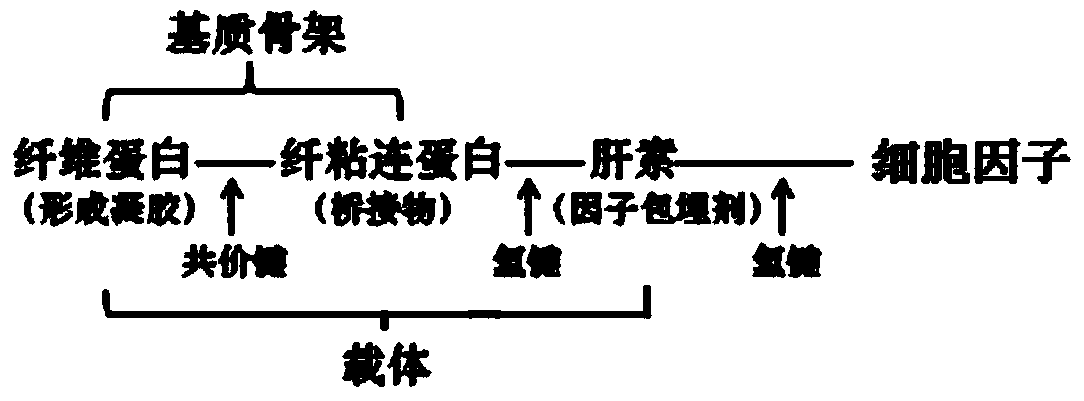
ActiveCN103933619AQuick combinationAvoid inactivationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular endotheliumNerve repair
The invention discloses a nerve repairing material and a preparation method thereof. The nerve repairing material comprises a combination of cell factors capable of promoting nerve growth, and a controlled-release carrier of the cell factors, wherein the carrier is mainly composed of fibrinogen, fibronectin, heparin, fibrin stabilizing factor, thrombin and calcium chloride, wherein the combination of the cell factors capable of promoting nerve growth is optimally at least two of nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial cell growth factor, and is embedded in the carrier. According to the nerve repairing material, the speed of releasing cell factors can be regulated according to the nerve repairing progress by utilizing 'intelligent release' of the controlled-release carrier, so that the functions of cell factors can be progressively played; furthermore, the nerve repairing can be further promoted by utilizing the synergy of the cell factors.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Materials and method for promotion of nerve regeneration
ActiveUS20050244399A1Improve abilitiesPotentiate axonal growthNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNerves regenerationNerve repair
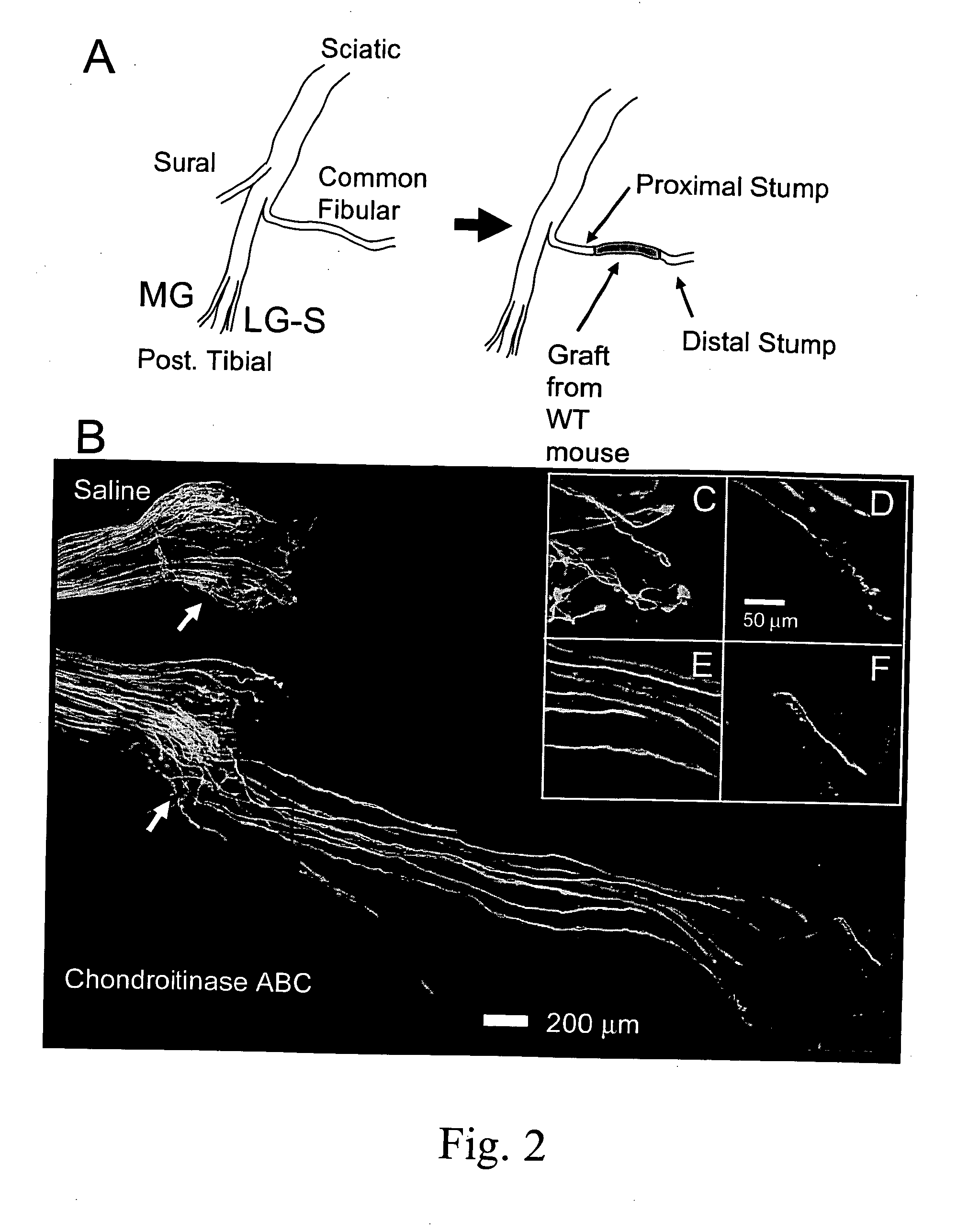
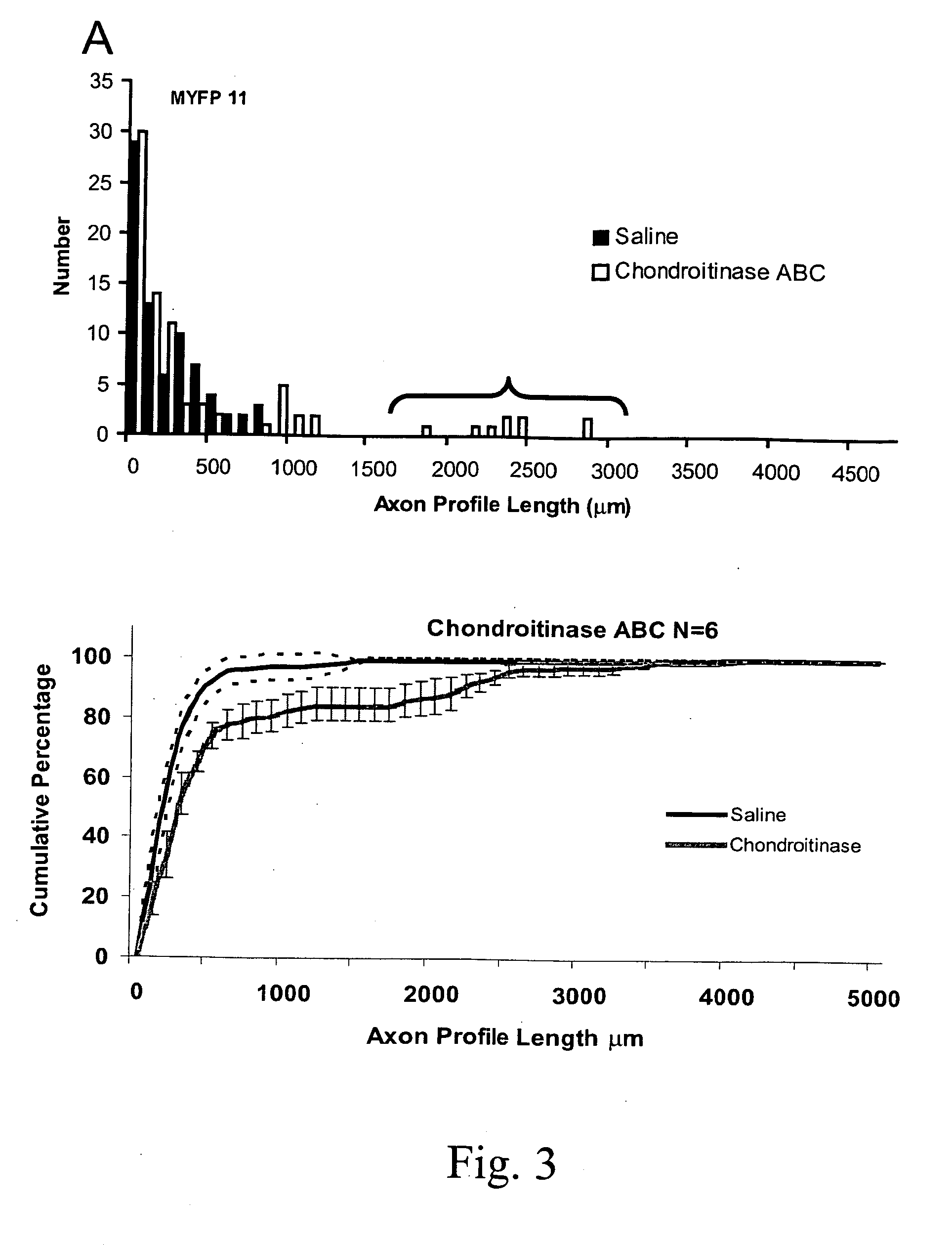
The subject invention pertains to the therapeutic use of certain GAG-degrading enzymes, and enzyme combinations, to promote nerve repair and regeneration.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Scaffold material for nerve regeneration based on silk fibroin fibers
InactiveCN107693850ASolve the problem of poor electrical conductivity, which cannot be used for nerve repairGood biocompatibilityTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberPersulfate
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological materials, and particularly relates to a scaffold material for nerve regeneration based on silk fibroin fibers. Silk fibroin is obtain aftera series of treatments are performed on silkworm cocoons, and a silk fibroin solution is obtain after the silk fibroin is dissolved with formic acid; aniline reacts in a hydrochloric acid solution ofammonium persulfate to obtain polyaniline powder which is dissolved in part of the silk fibroin solution to obtain a polyaniline silk fibroin solution; and finally, the silk fibroin solution and the polyaniline silk fibroin solution are mixed for electrostatic spinning to obtain the scaffold material. The invention solves the problem that the silk fibroin has low electric conductivity and cannot be used for nerve repair, and the prepared scaffold material not only has high biocompatibility and mechanical property, but also has a high electrophilic property, and the conduction of a nerve conduit to an electric signal is not blocked.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Device and method for a nanofiber wrap to minimize inflamation and scarring
ActiveUS20170095591A1Promote healingPrevent penetrationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectro-spinningFiberNerve repair
The present invention is directed to a device and method for a nanofiber wrap to minimize inflation and scarring of nerve tissue and maximize the nutrient transport. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a novel semi-permeable nanofiber construct prepared from biocompatible materials. The nanofiber construct is applied around a nerve repair site following end-to-end anastomosis. The nanofiber construct is porous and composed of randomly oriented nanofibers prepare using an electrospinning method. The nanofiber construct has a wall that is approximately 50-100 μm thick with pores smaller than 25 μm. The nanofiber construct prevents inflammatory cells from migrating into the nerve coaption site, while still permitting the diffusion of growth factors and essential nutrients. The nanofiber construct allows for enhanced neuroregeneration and optimal function outcomes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Electrical stimulation system for promoting in vivo nerve repair
PendingCN111408046ASimple structureWide range of materialsSpinal electrodesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanogeneratorPhysical therapy
The invention relates to the field of biomedicines and discloses an electrical stimulation system for promoting in vivo nerve repair. The electrical stimulation system comprises a nanogenerator, a wire and an electrode, wherein the nanogenerator is connected with the electrode through the wire to transmit current or voltage of the nanogenerator to the electrode; and the electrode can apply the current or voltage to an organism. The system for promoting in vivo nerve repair disclosed by the invention has the advantages that an electrical stimulation source is simple in structure, environment-friendly in materials, wide in material source, easy to be flexible and easy to miniaturize, and can be self-driven by motion and force of a body to generate electricity.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com