Patents
Literature
1718 results about "Conduction type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
General Information. Conduction type thermostats are a type of thermostat that sense temperature through thermal conduction, meaning they are mounted on a surface that will output heat and they will react. We offer three classes of conduction type thermostats; adjustable, fixed & sealed, and fixed w/out sealing.
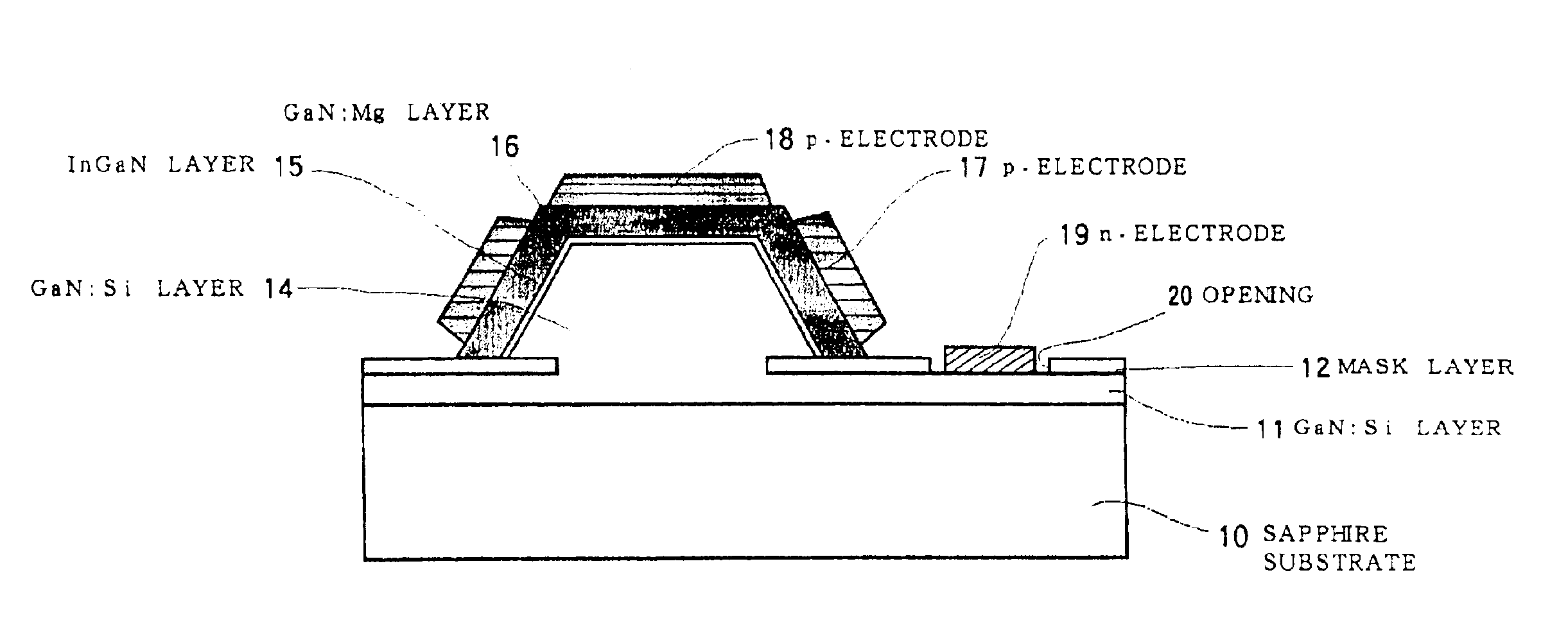
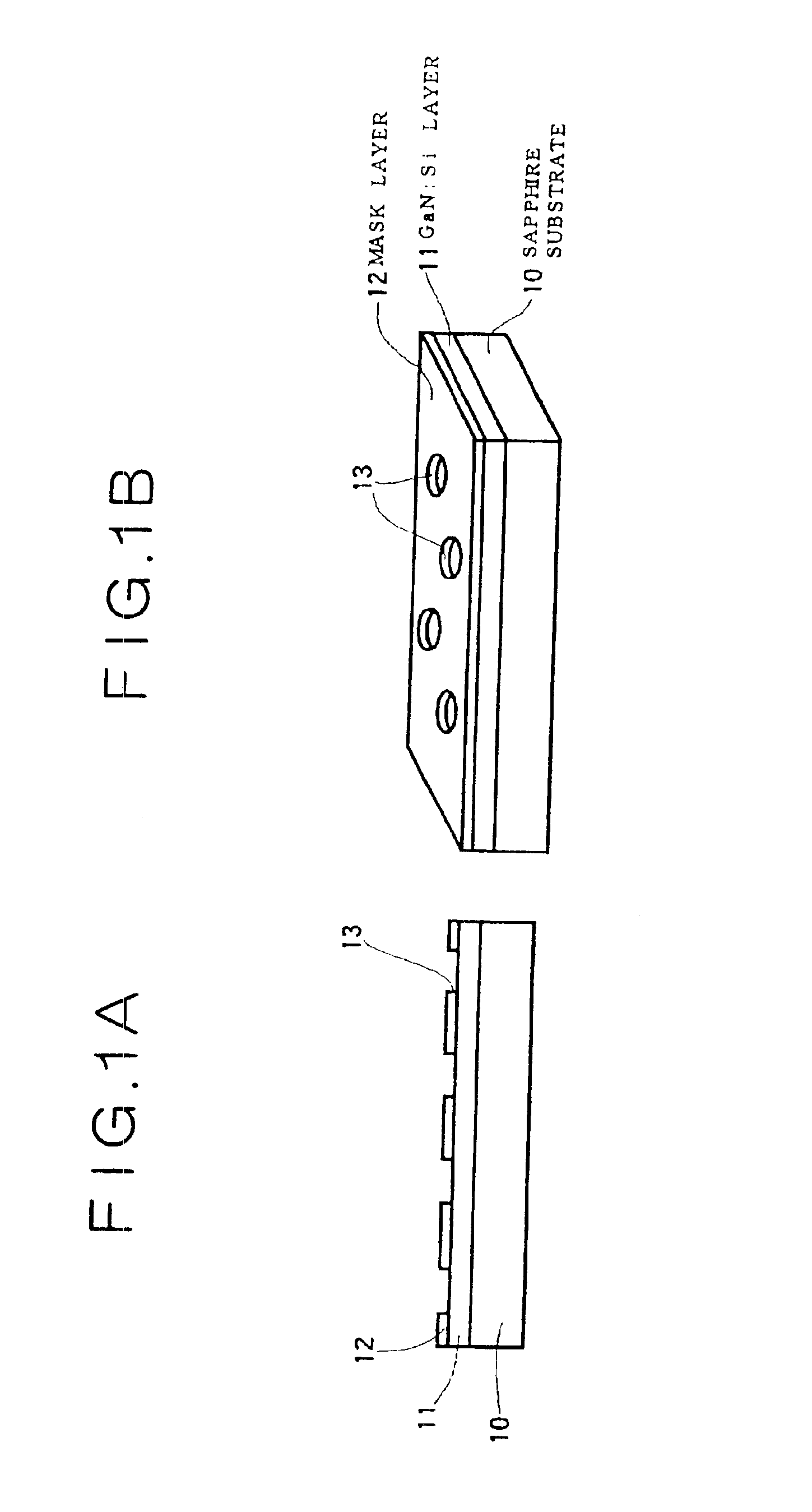
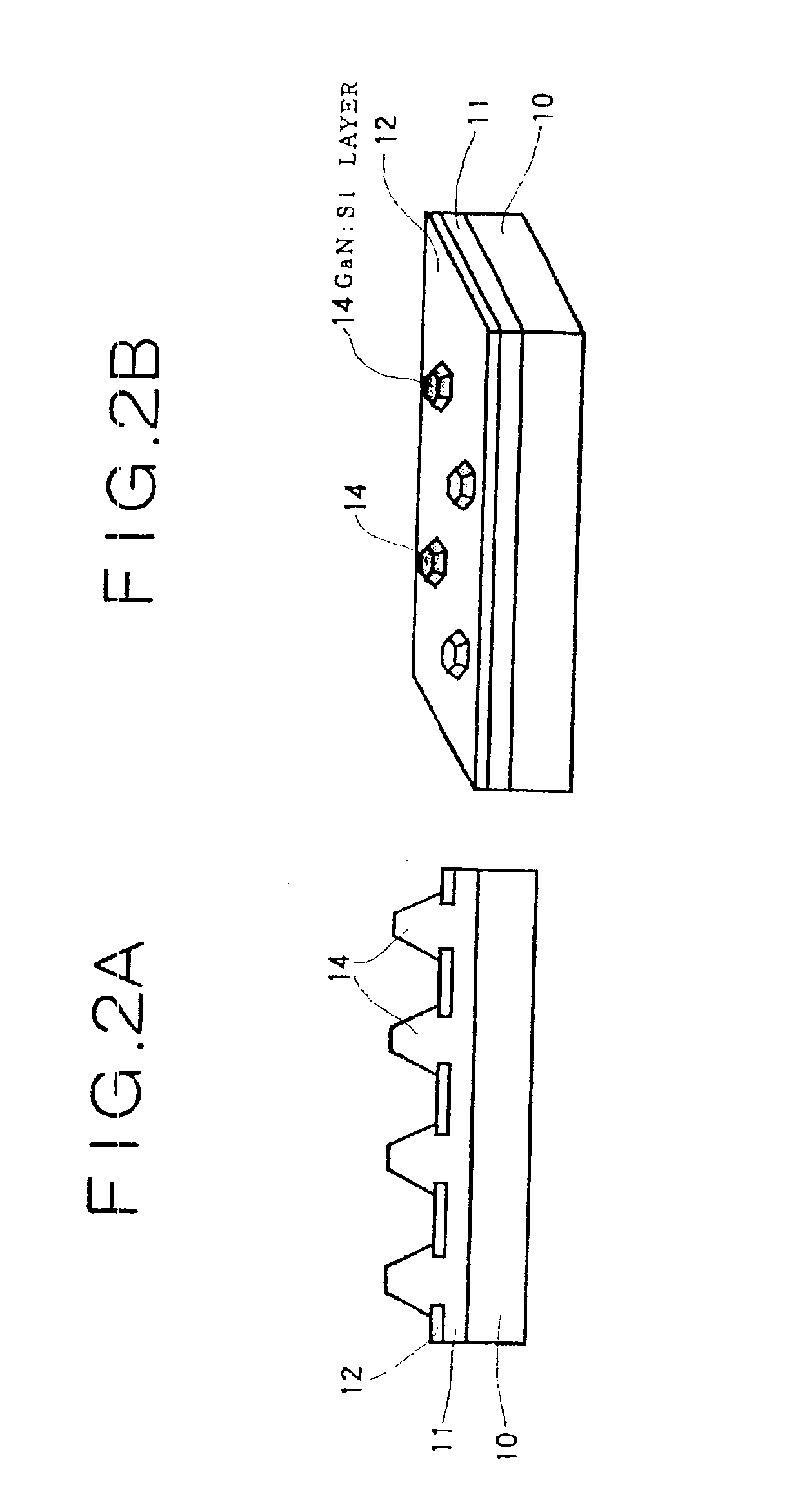
Semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS7087932B2Well formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal planeCrystallinity
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Silicon-on-insulator chip with multiple crystal orientations
A silicon-on-insulator chip includes an insulator layer, typically formed over a substrate. A first silicon island with a surface of a first crystal orientation overlies the insulator layer and a second silicon island with a surface of a second crystal orientation also overlies the insulator layer. In one embodiment, the silicon-on-insulator chip also includes a first transistor of a first conduction type formed on the first silicon island, and a second transistor of a second conduction type formed on the second silicon island. For example, the first crystal orientation can be (110) while the first transistor is a p-channel transistor, and the second crystal orientation can be (100) while the second transistor is an n-channel transistor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
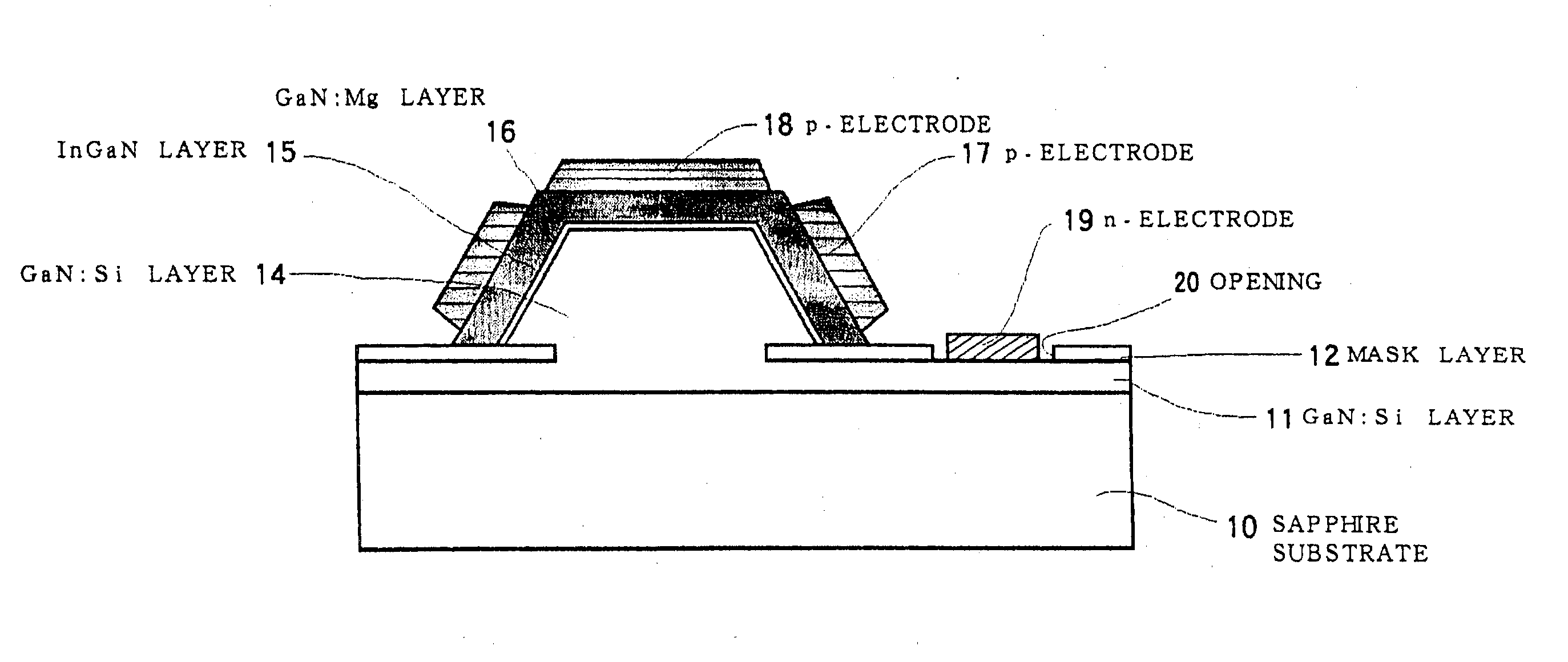
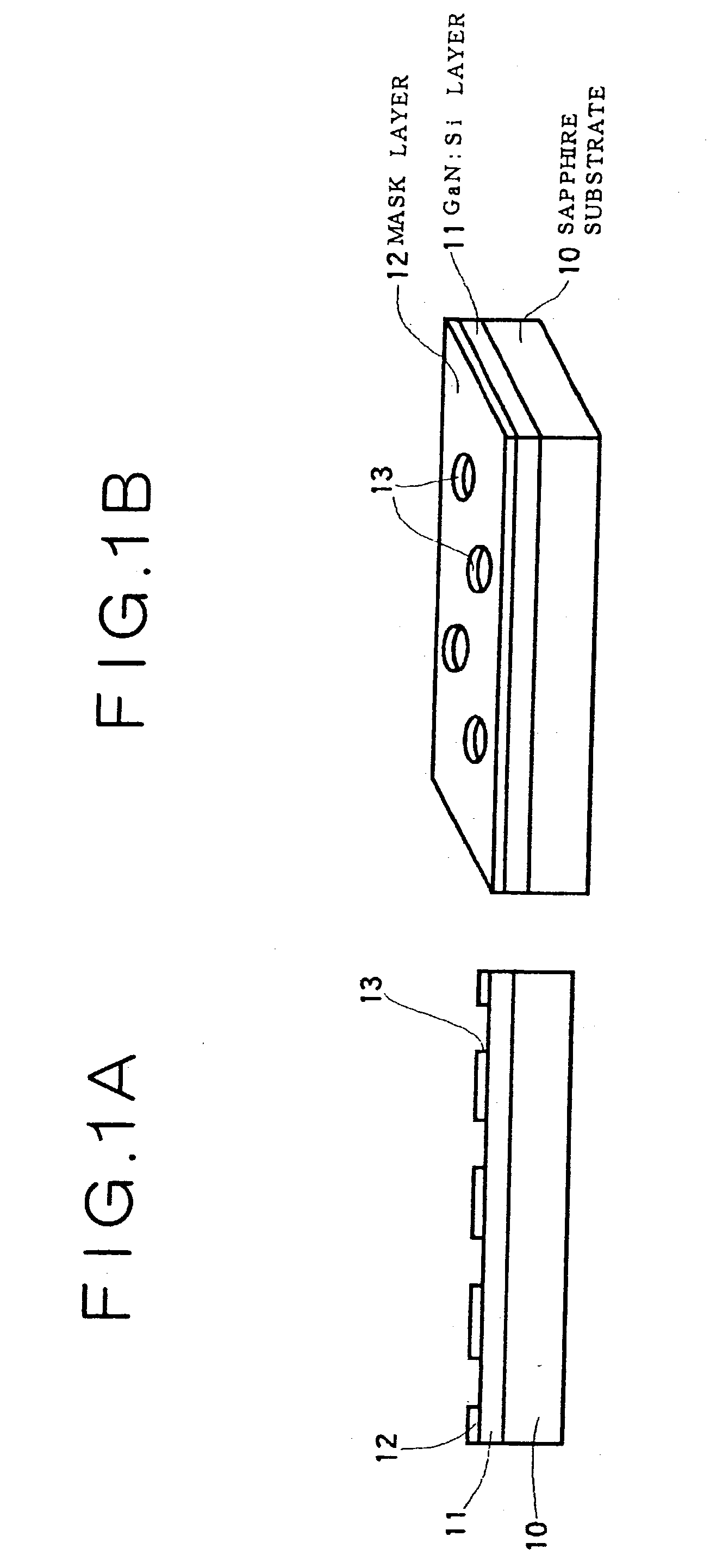
Light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing same, integrated light-emitting diode and method for manufacturing same, method for growing a nitride-based iii-v group compound semiconductor, substrate for growing a nitride-based iii-v group compound semiconductor, light source cell unit, light-emitting diode backlight, light-emitting diode illuminating device, light-emitting diode display and electronic instrument, electronic device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20070085093A1Low luminous efficiencyLight extraction efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A method for manufacturing a light-emitting diode, which includes the steps of: providing a substrate having a plurality of protruded portions on one main surface thereof wherein the protruded portion is made of a material different in type from that of the substrate and growing a first nitride-based III-V Group compound semiconductor layer on each recess portion of the substrate through a state of making a triangle in section wherein a bottom surface of the recess portion becomes a base of the triangle; laterally growing a second nitride-based III-V Group compound semiconductor layer on the substrate from the first nitride-based III-V Group compound semiconductor layer; and successively growing, on the second nitride-based III-V Group compound semiconductor layer, a third nitride-based III-V Group compound semiconductor layer of a first conduction type, an active layer, and a fourth nitride-based III-V compound semiconductor layer of a second conduction type.
Owner:SONY CORP
Insulated gate semiconductor device
InactiveUS6342709B1Improve reliabilityImprove adaptabilitySemiconductor devicesHigh voltageElectric field
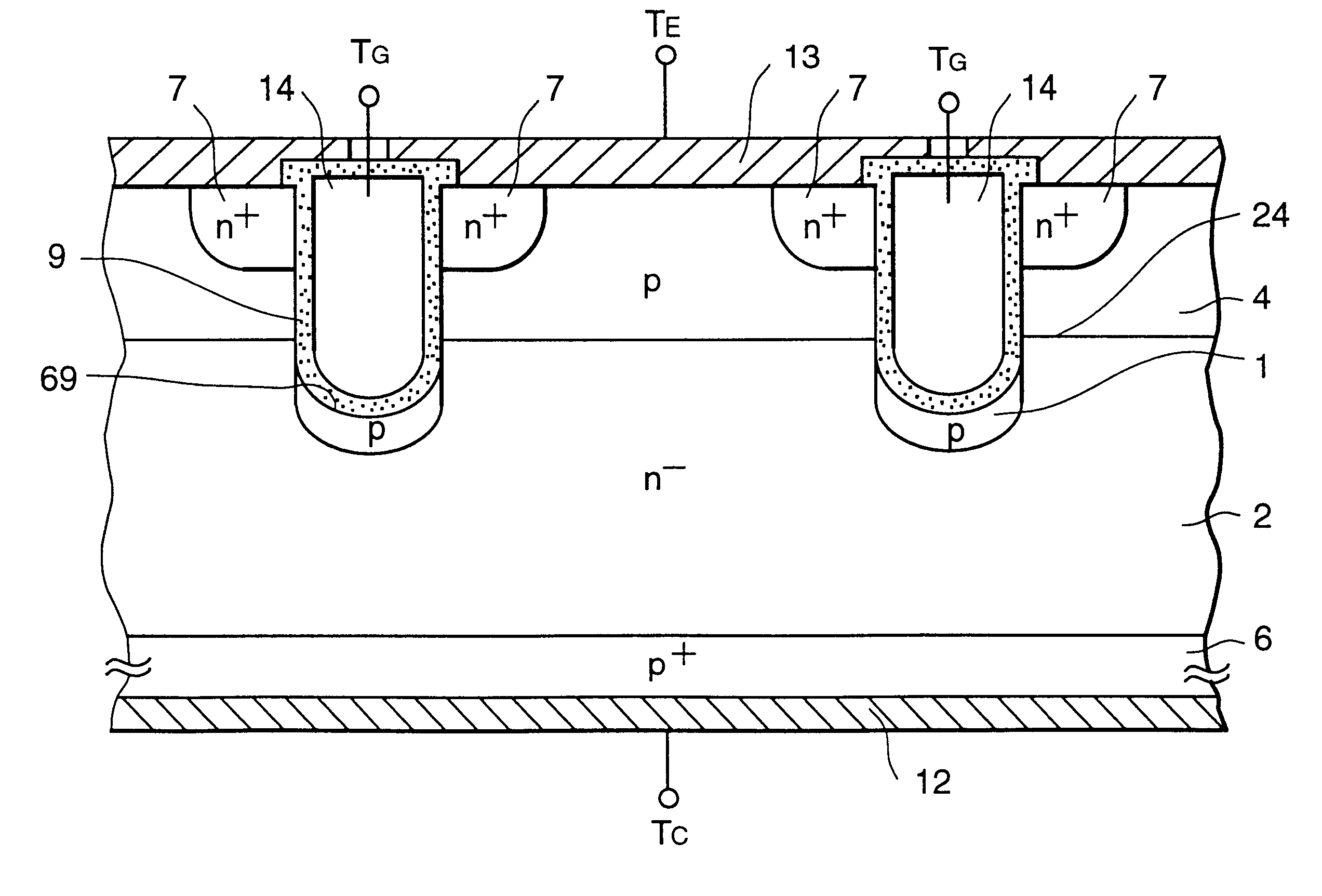
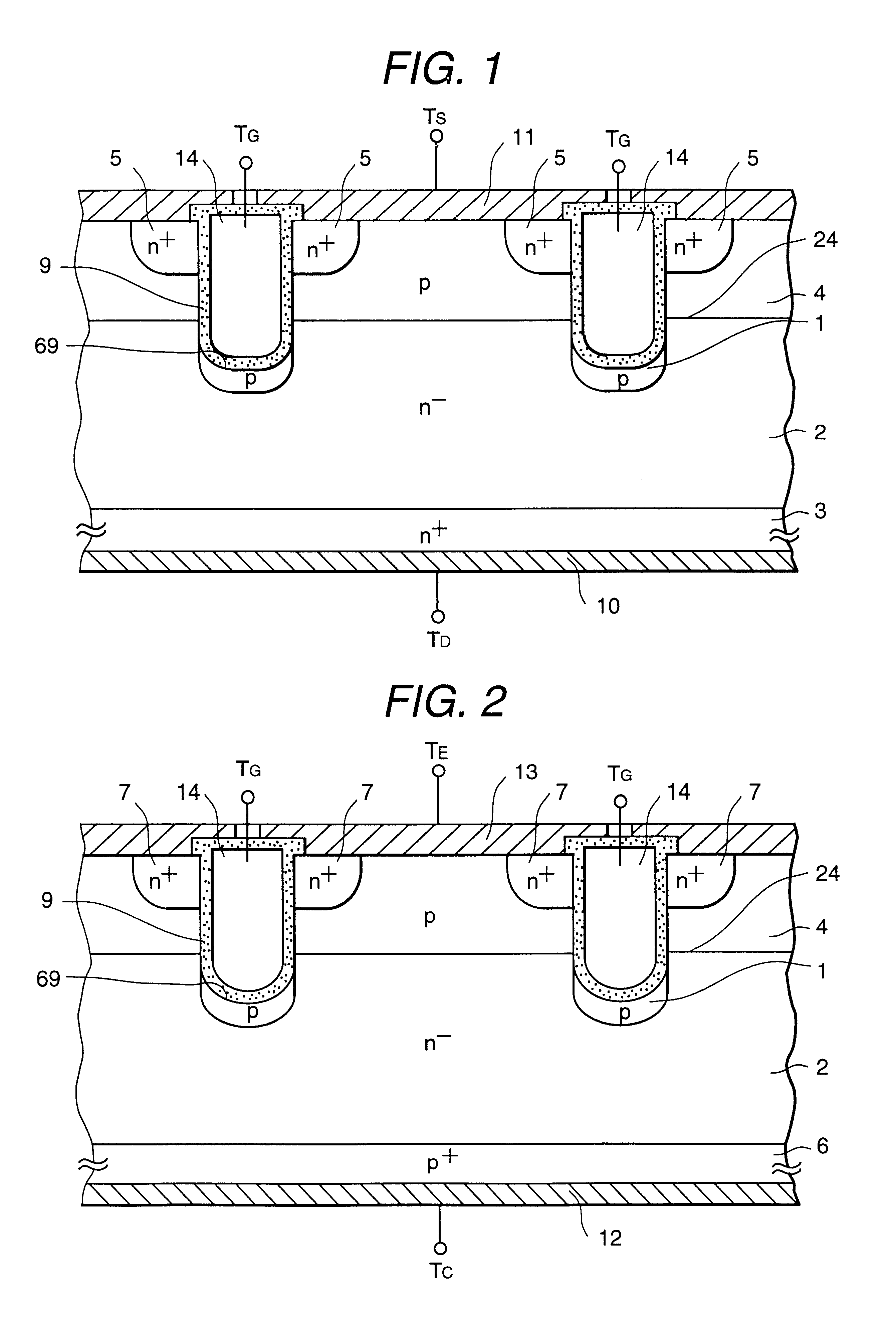
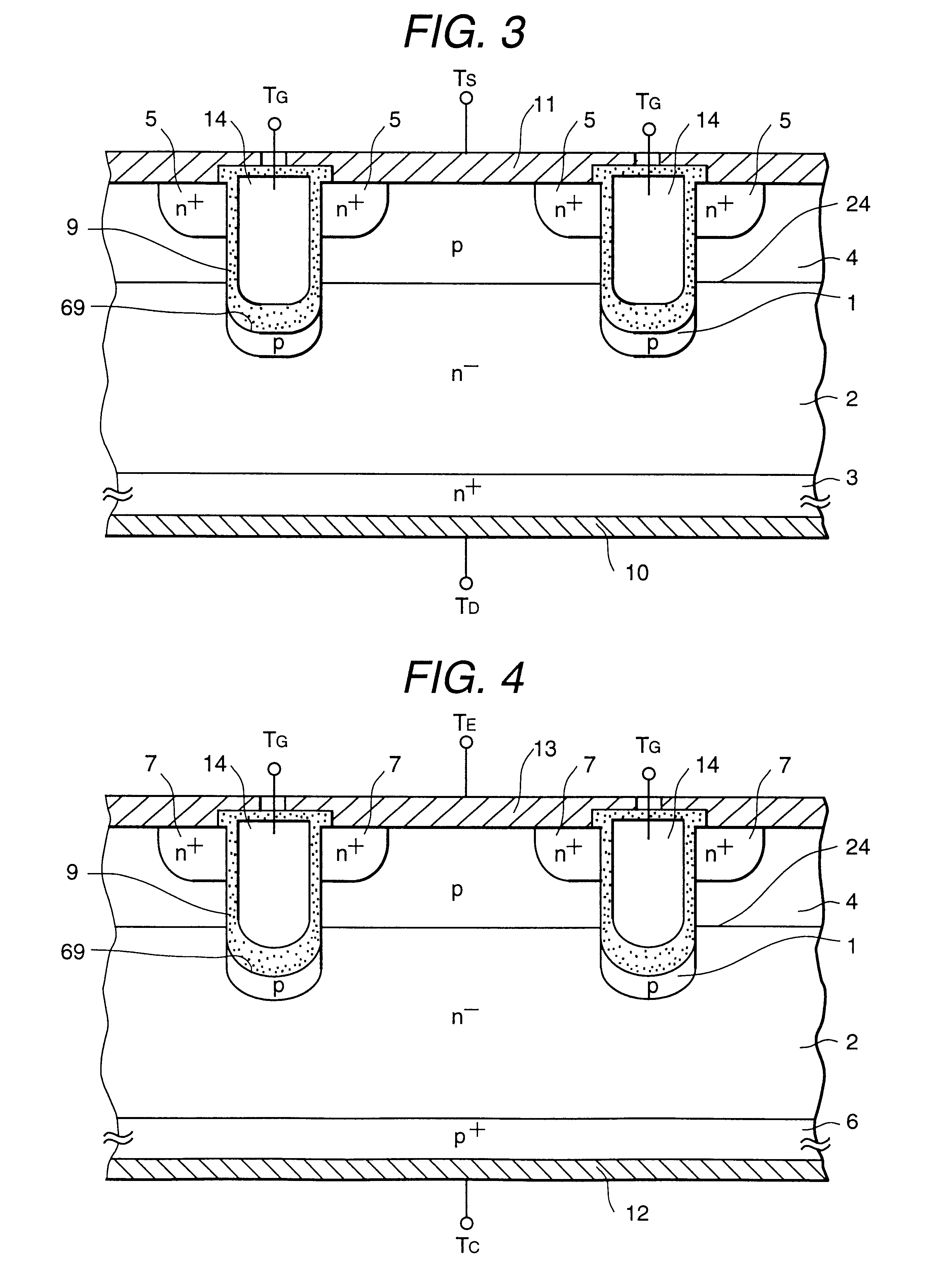
In a semiconductor device having a trench type insulated gate structure, in the case where a drift layer 2 of an n- conduction type has a high carrier density, when a high voltage is applied between a drain and a source in such a manner that a channel is not formed, the electric field strength of an insulator layer 9 below the trench type insulated gate is increased, thus causing breakdown. The withstand voltage of the semiconductor device is limited by the breakdown of the insulator layer 9, and it is difficult to realize high withstand voltage.In the characteristic of the present invention, a field relaxation semiconductor region 1 of a conduction type opposite to the conduction type of the drift layer 2 is formed within the drift layer 2 below the insulator layer 9 in the trench of the trench type insulated gate semiconductor device. Also, the thickness of a bottom portion of the insulator layer 9 provided in the trench of the trench type insulated gate semiconductor device is made significantly greater than the thickness of a lateral portion thereof.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
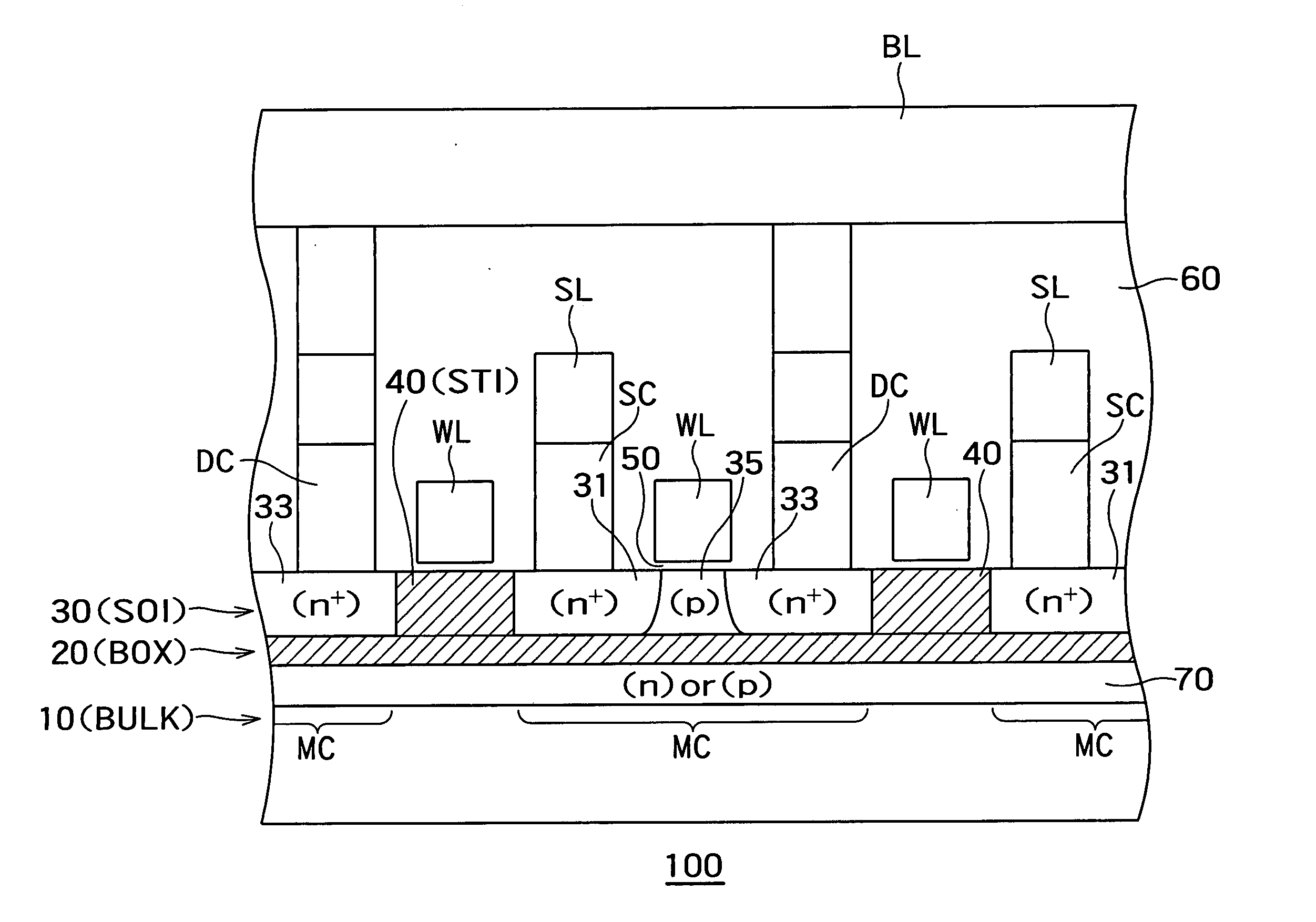
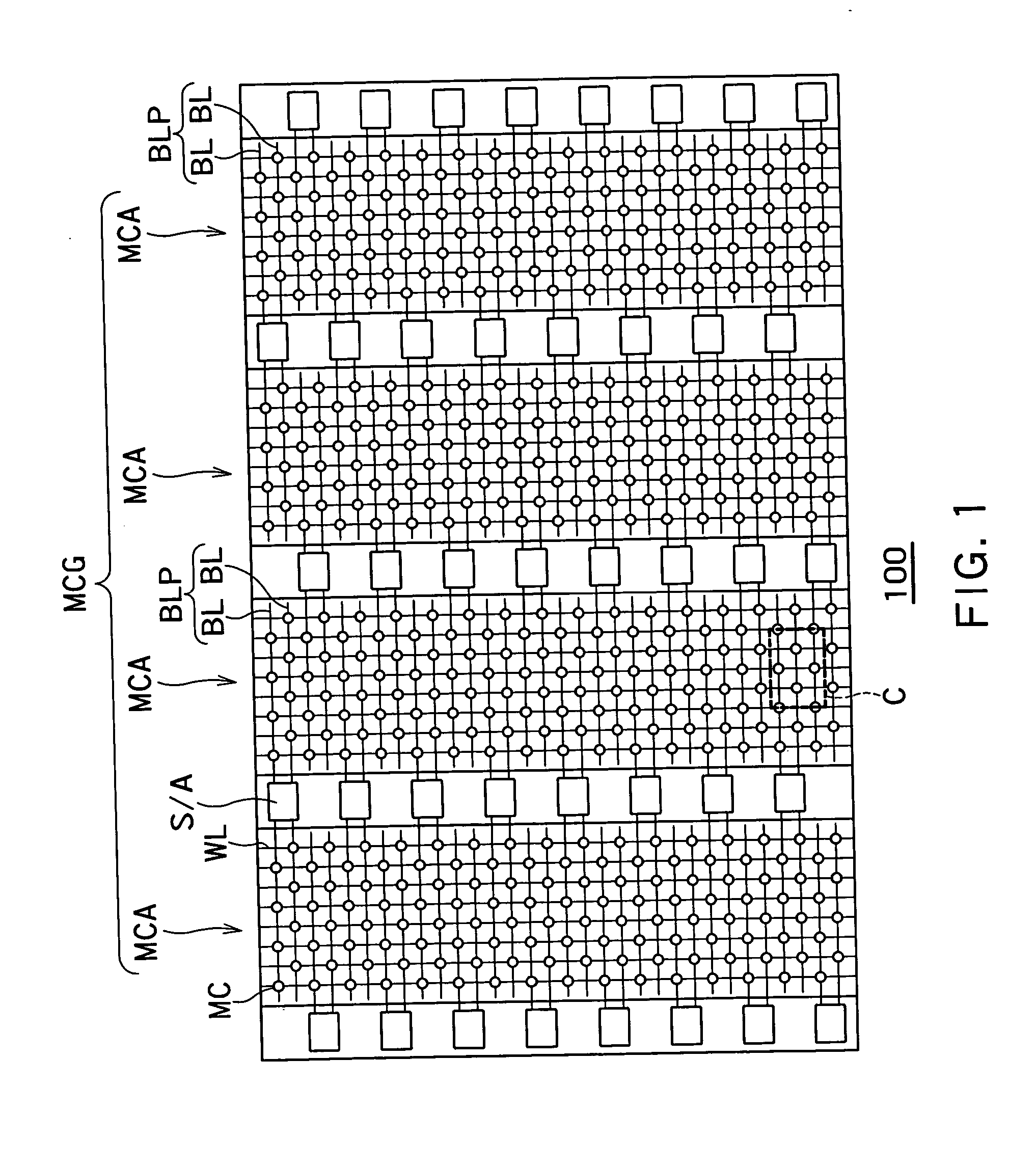
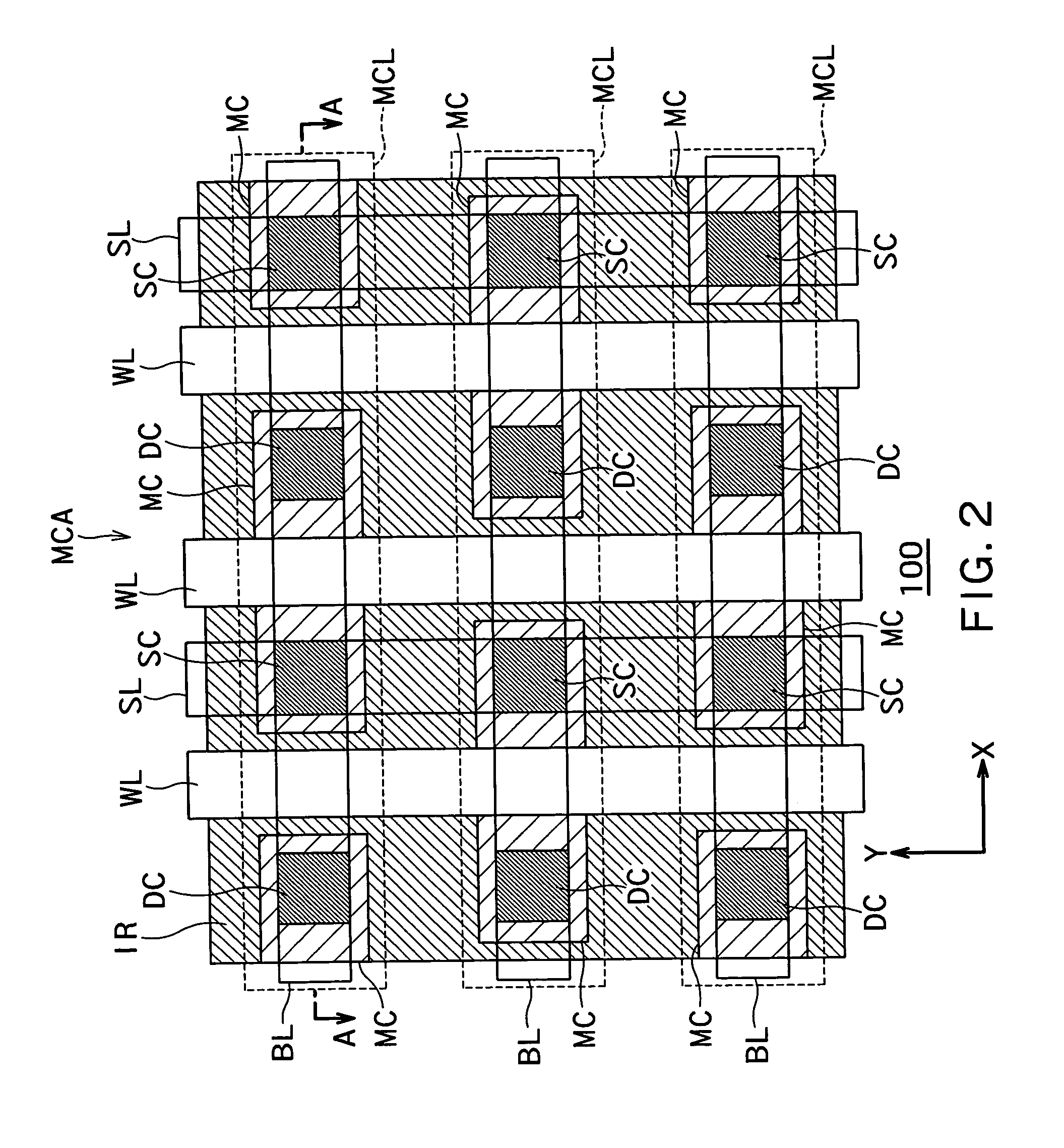
Semiconductor storage device
A semiconductor storage device comprises a semiconductor substrate; an insulating layer formed on the semiconductor substrate; a first semiconductor layer formed on the insulating layer and insulated from the semiconductor substrate; memory cells each having a source region of a first conduction type and a drain region of the first conduction type both formed in the first semiconductor layer, and having a body of a second conduction type formed in the first semiconductor layer between the source region and the drain region, said memory cells being capable of storing data by accumulating or releasing electric charge in or from their respective body regions; memory cell lines each including a plurality of said memory cells aligned in the channel lengthwise direction; and a memory cell array including a plurality of said memory cell lines aligned in a channel widthwise direction of the memory cells, wherein said memory cells on a common memory cell line are aligned to uniformly orient the directions from their source regions to the drain regions whereas directions of said memory cells from their source regions to the drain regions on said memory cell line are opposite from those of memory cells on neighboring said memory cell lines.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
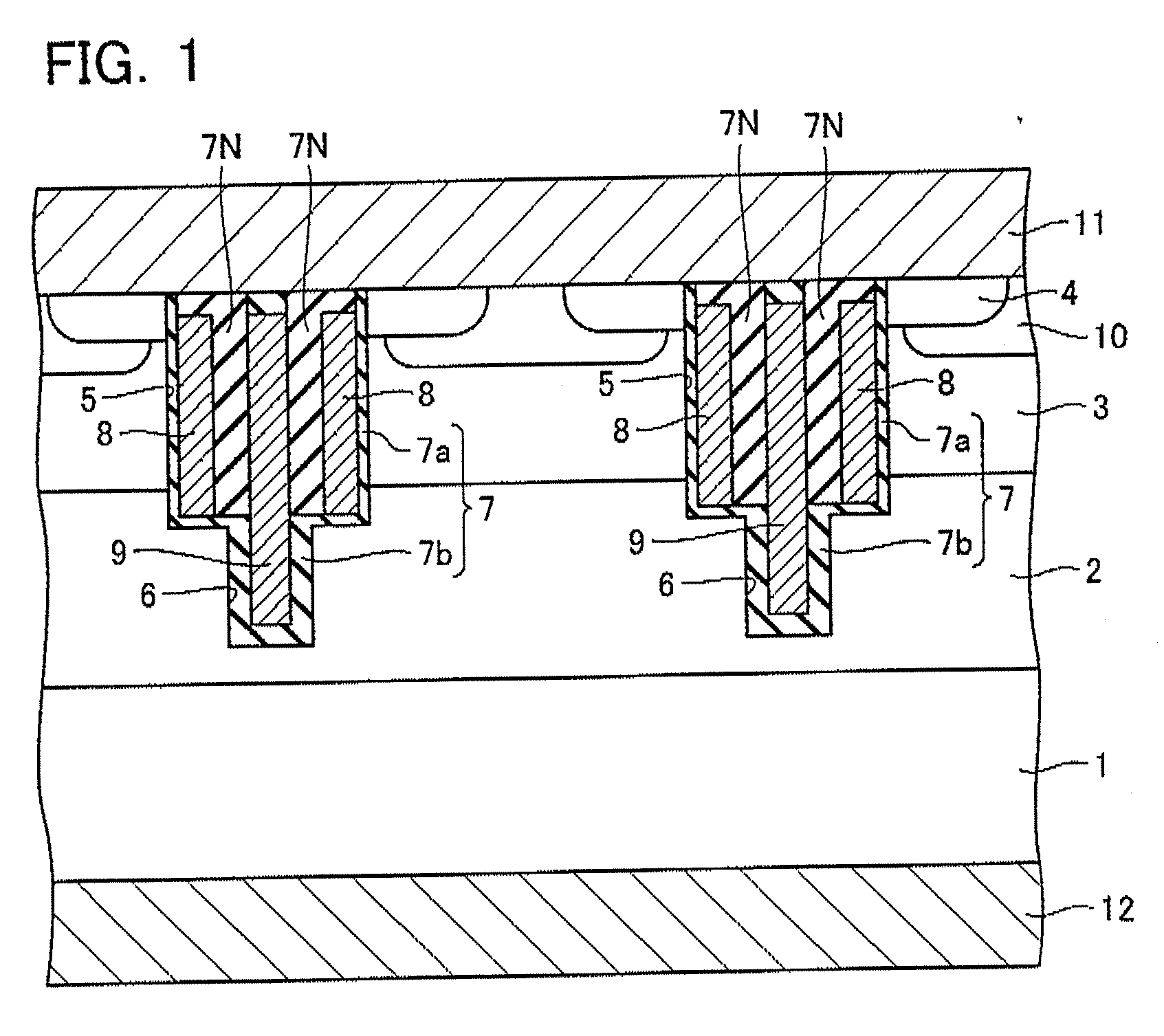
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20070138547A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device comprises a semiconductor region of the first conduction type. A first main electrode is connected to the semiconductor region. A base region of the second conduction type is formed on the semiconductor region. A diffused region of the first conduction type is formed on the base region. A second main electrode is connected to the diffused region and the base region. A first trench is formed extending from a surface of the diffused region to the semiconductor region. A second trench is formed from the first trench deeper than the first trench. A gate electrode is formed on a side of the first trench via a first insulator film. A protruded electrode is formed in the second trench via a second insulator film as protruded lower than the gate electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060197152A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor packageOptoelectronics
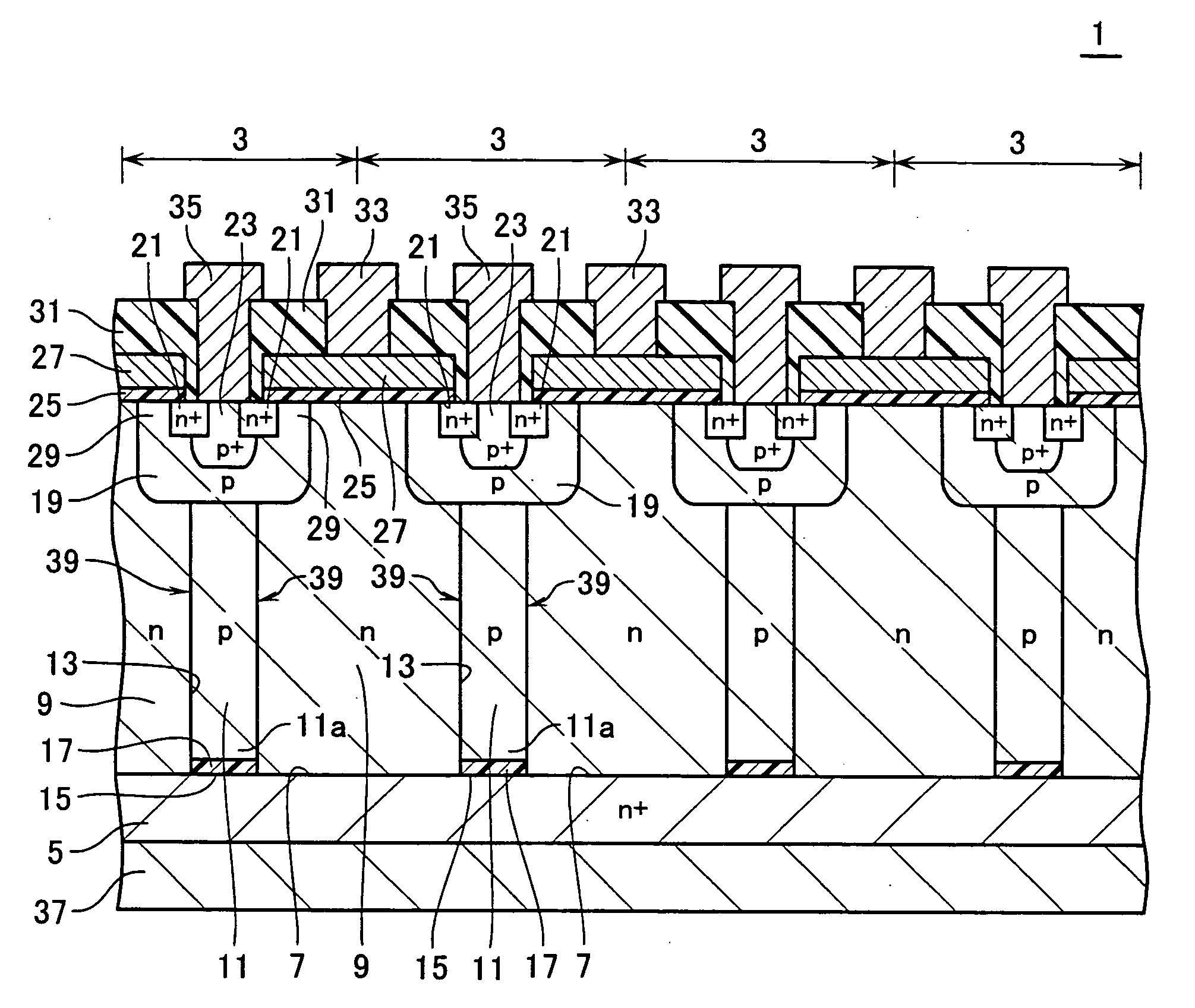
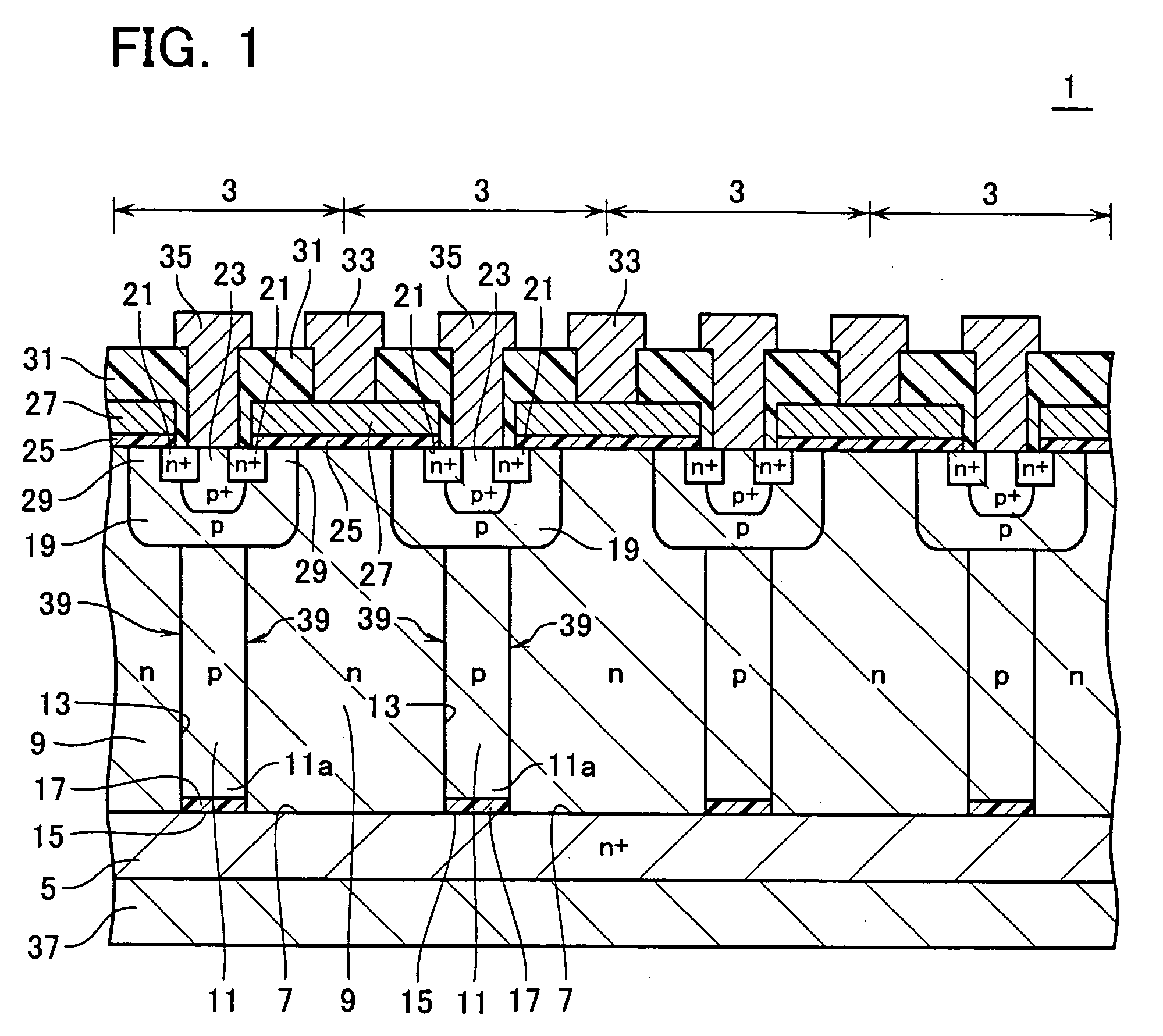
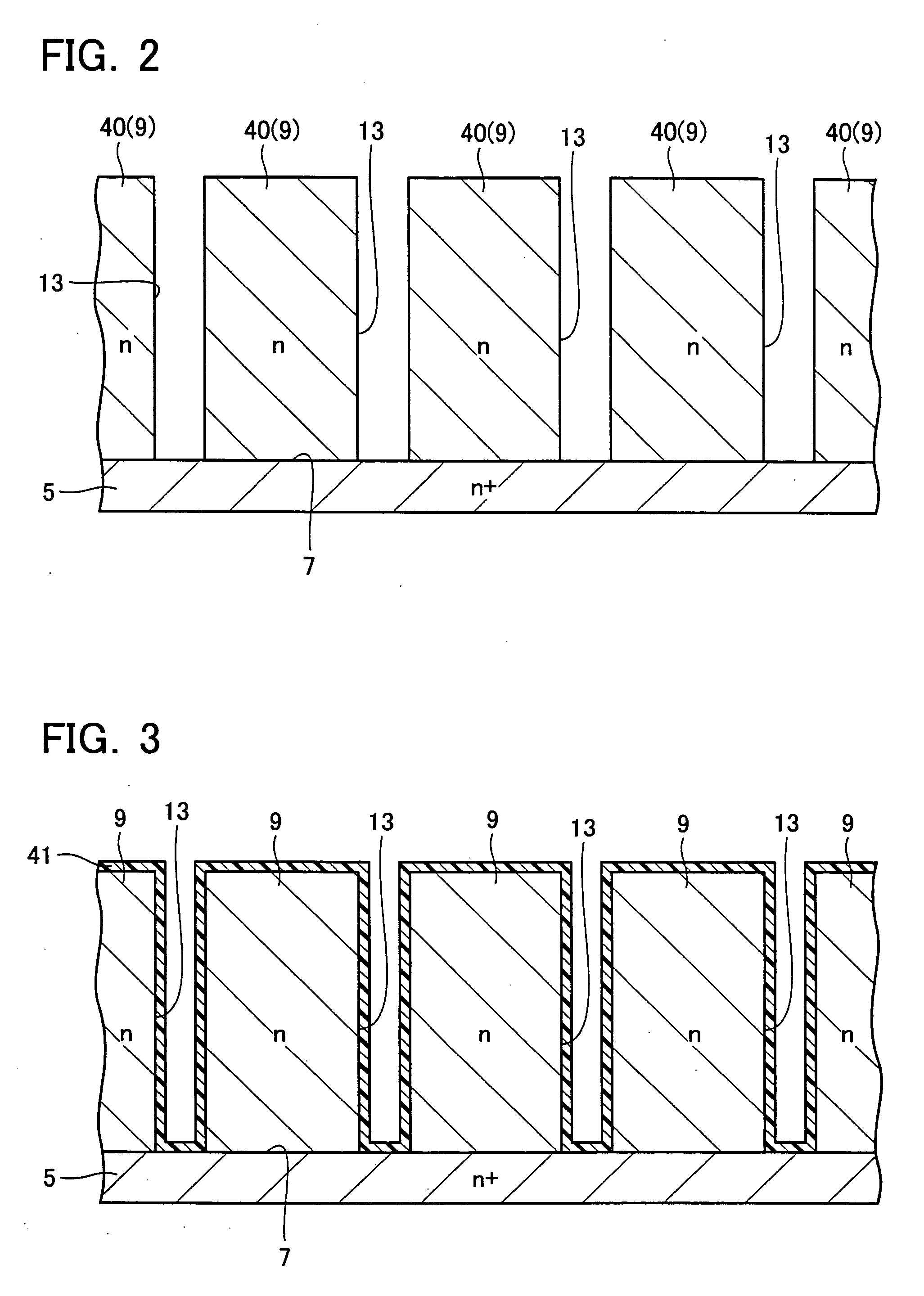
A single crystal semiconductor layer of a first conduction type is disposed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of trenches are provided in the semiconductor layer to form a plurality of first semiconductor regions of the first conduction type at intervals in a direction parallel to the surface. An epitaxial layer is buried in the plurality of trenches to form a plurality of second semiconductor regions of a second conduction type. The plurality of second semiconductor regions each includes an outer portion with a high impurity concentration formed against an inner wall of the trench, and an inner portion with a low impurity concentration formed inner than the outer portion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetoresistive memory cell using floating body effect, memory device having the same, and method of operating the memory device
ActiveUS20100157664A1Drive capability can be improvedImprove rendering capabilitiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffusionFloating body effect
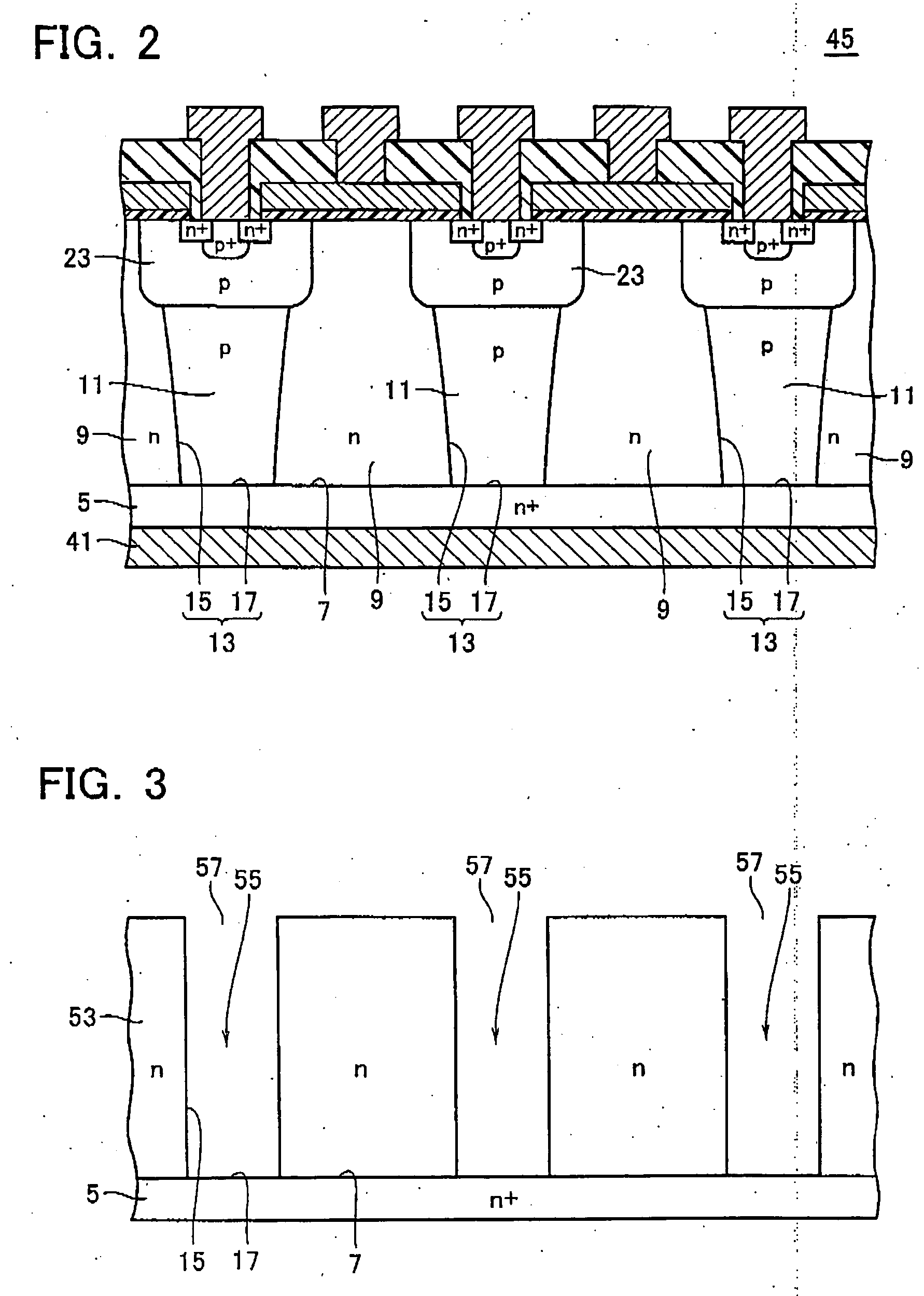
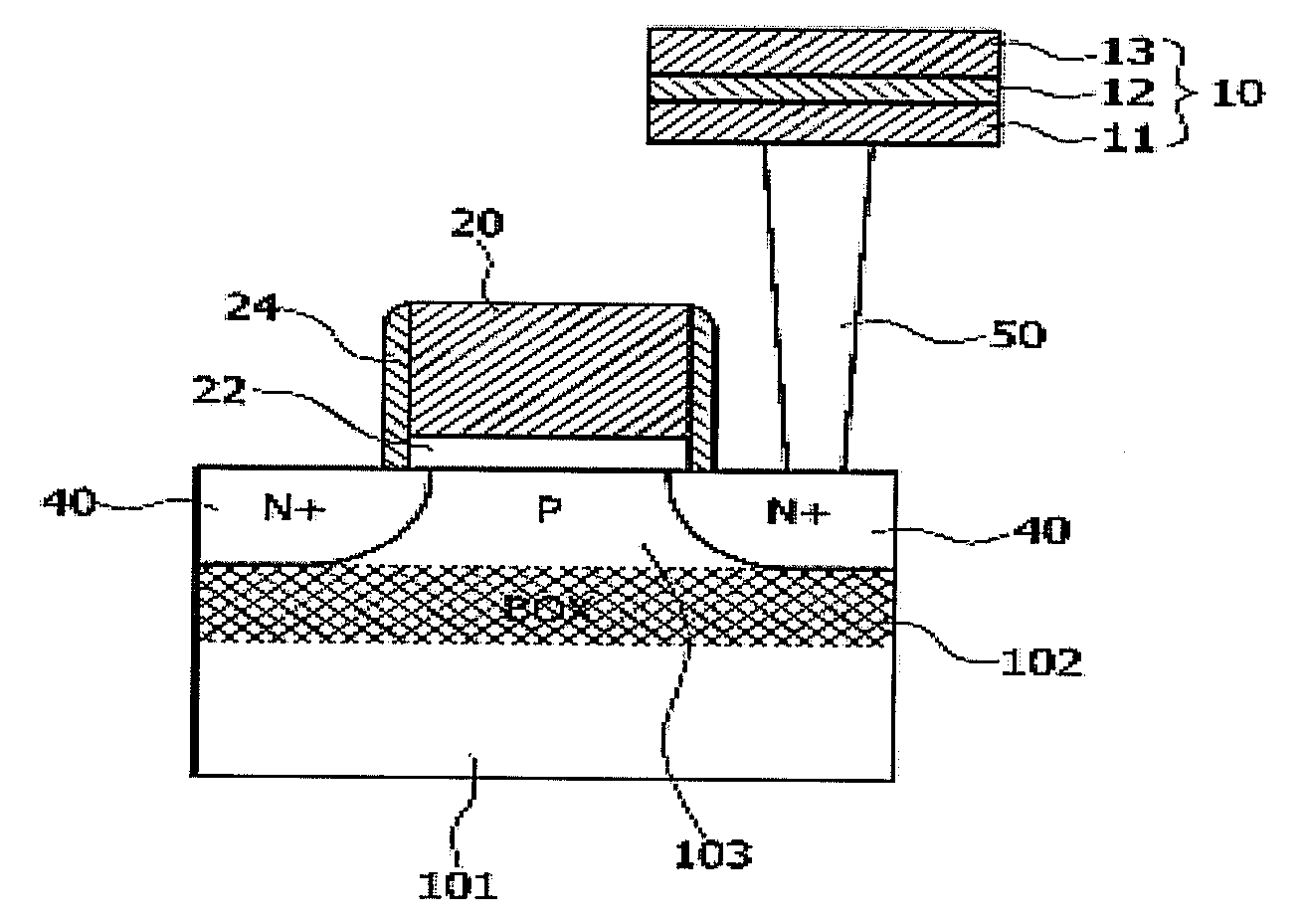
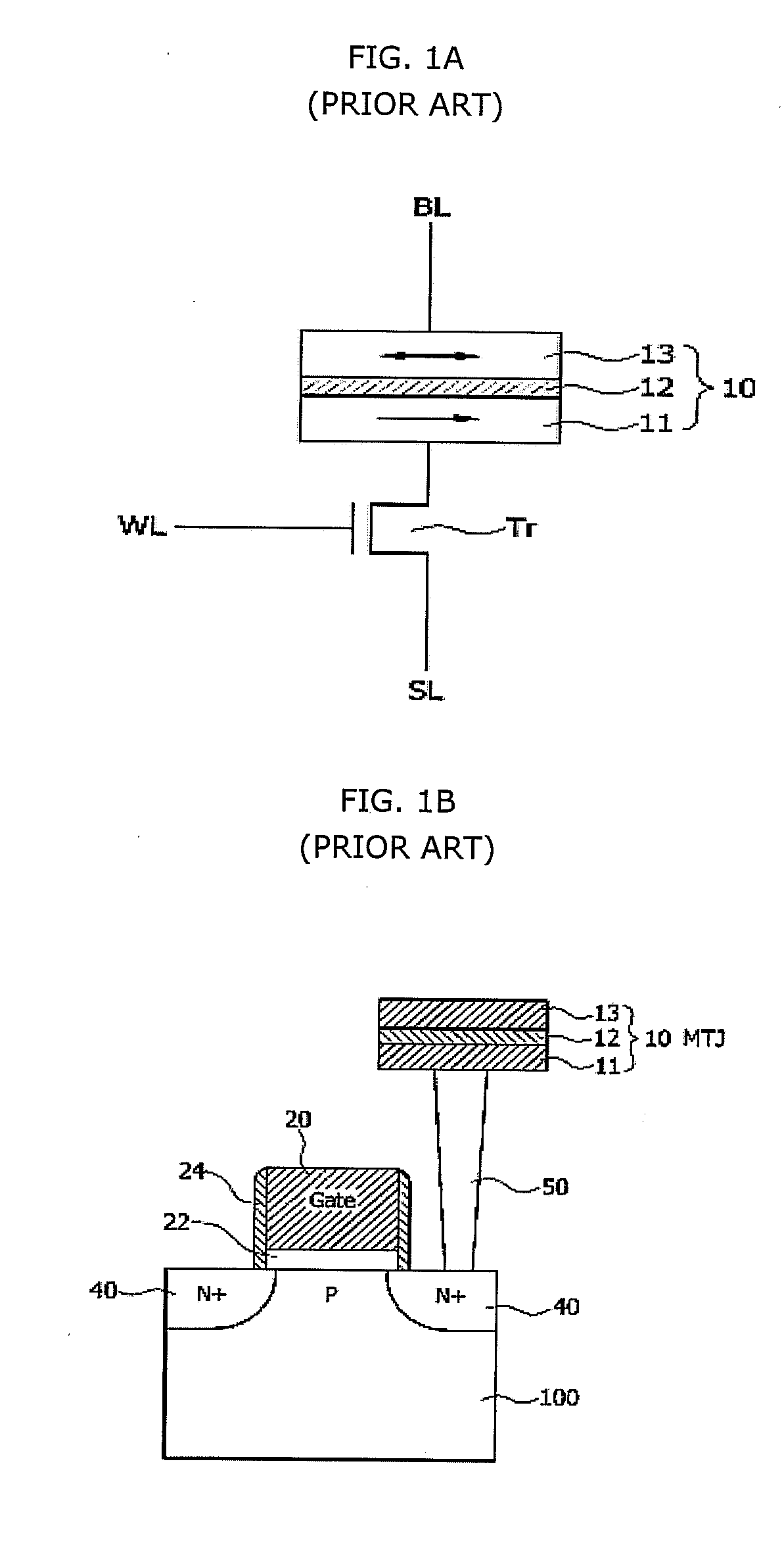
A magnetoresistive memory cell includes an MTJ device and a select transistor. The select transistor includes a first conduction-type semiconductor layer, a gate electrode formed by disposing a gate insulating layer on top of the semiconductor layer, and first and second diffusion regions formed in the semiconductor layer to be spaced apart from each other and to have a second conduction type. A part of the semiconductor layer between the first and second diffusion regions is formed as an electrically floating body region. By using a high-performance select transistor with a floating body effect, high integration of a magnetoresistive memory device may be achieved.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060006458A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSingle crystal
A semiconductor device comprises a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of first semiconductor regions are formed in a single crystal semiconductor layer of a first conduction type disposed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate as defined by a plurality of trenches provided in the single crystal semiconductor layer. A plurality of insulating regions are respectively formed on bottoms in the trenches. A plurality of second semiconductor regions are formed of a single crystal semiconductor layer of a second conduction type buried in the trenches in the presence of the insulating regions formed therein. The first semiconductor regions and second semiconductor regions are arranged alternately in a direction parallel to the surface of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
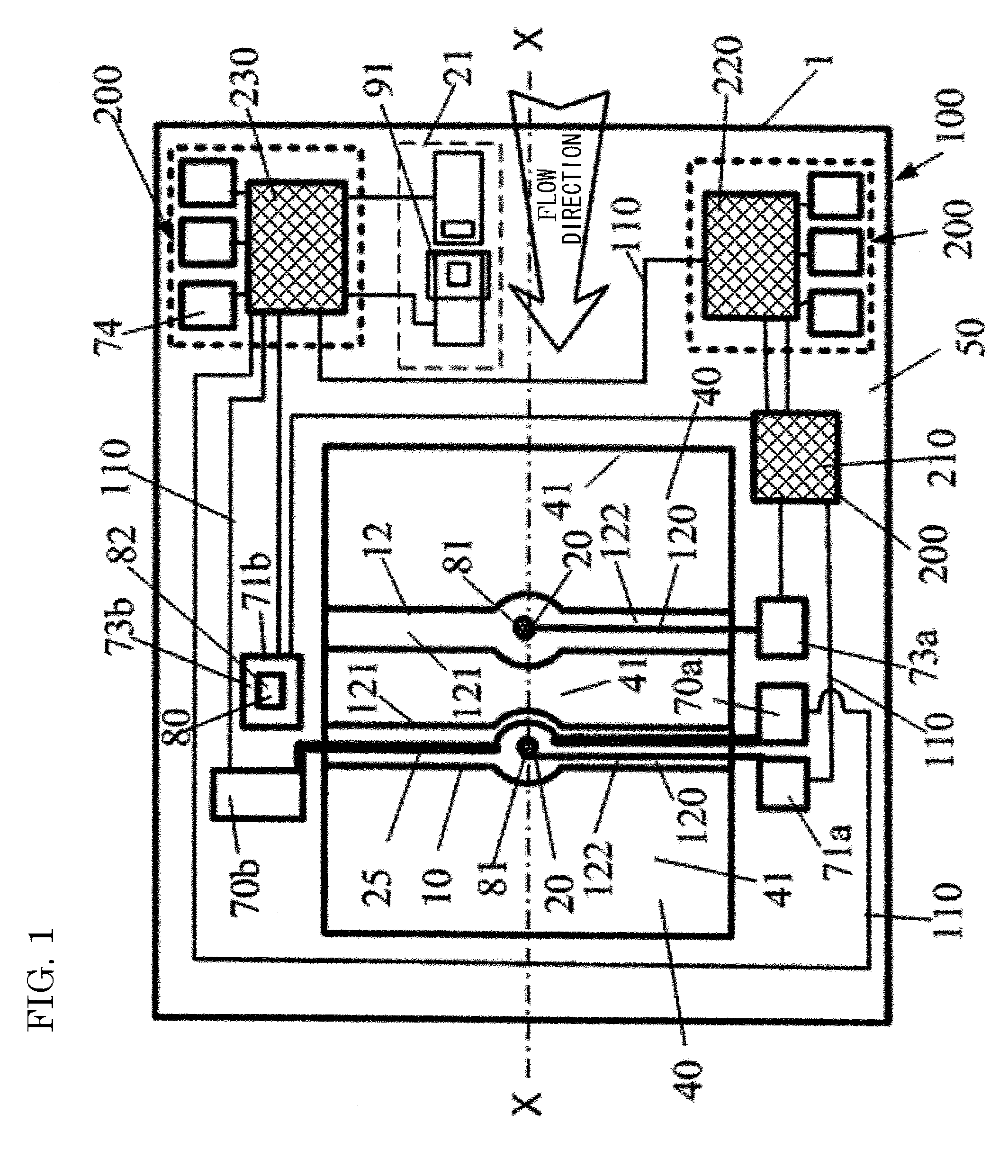
Heat conduction-type sensor for calibrating effects of temperature and type of fluid, and thermal flow sensor and thermal barometric sensor using this sensor
InactiveUS8667839B2Eliminate the effects ofWell formedVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsThermometer testing/calibrationThin film thermocouplesGas pressure transducer
A heat conduction-type sensor corrects (calibrate) effects of a temperature of a measurement target fluid and a type of the fluid on a measurement value in measurement of a flow velocity, a mass flow, or an atmospheric pressure. Also provided is a thermal flow sensor and a thermal barometric sensor with this correcting function, high sensitivity, simple configuration, and low cost. At least two thin films that are thermally separated from a substrate through the same cavity are provided, one thin film comprises a heater and a temperature sensor, and the other thin film comprises at least one temperature sensor, the temperature sensors being thin-film thermocouples. The thin film is arranged in proximity so that it is heated only through the measurement target fluid by heating of the heater. A calibration circuit calculates and compares quantities concerning heat transfer coefficients of a standard fluid and the unknown measurement target fluid.
Owner:GAKUIN TOHOKU
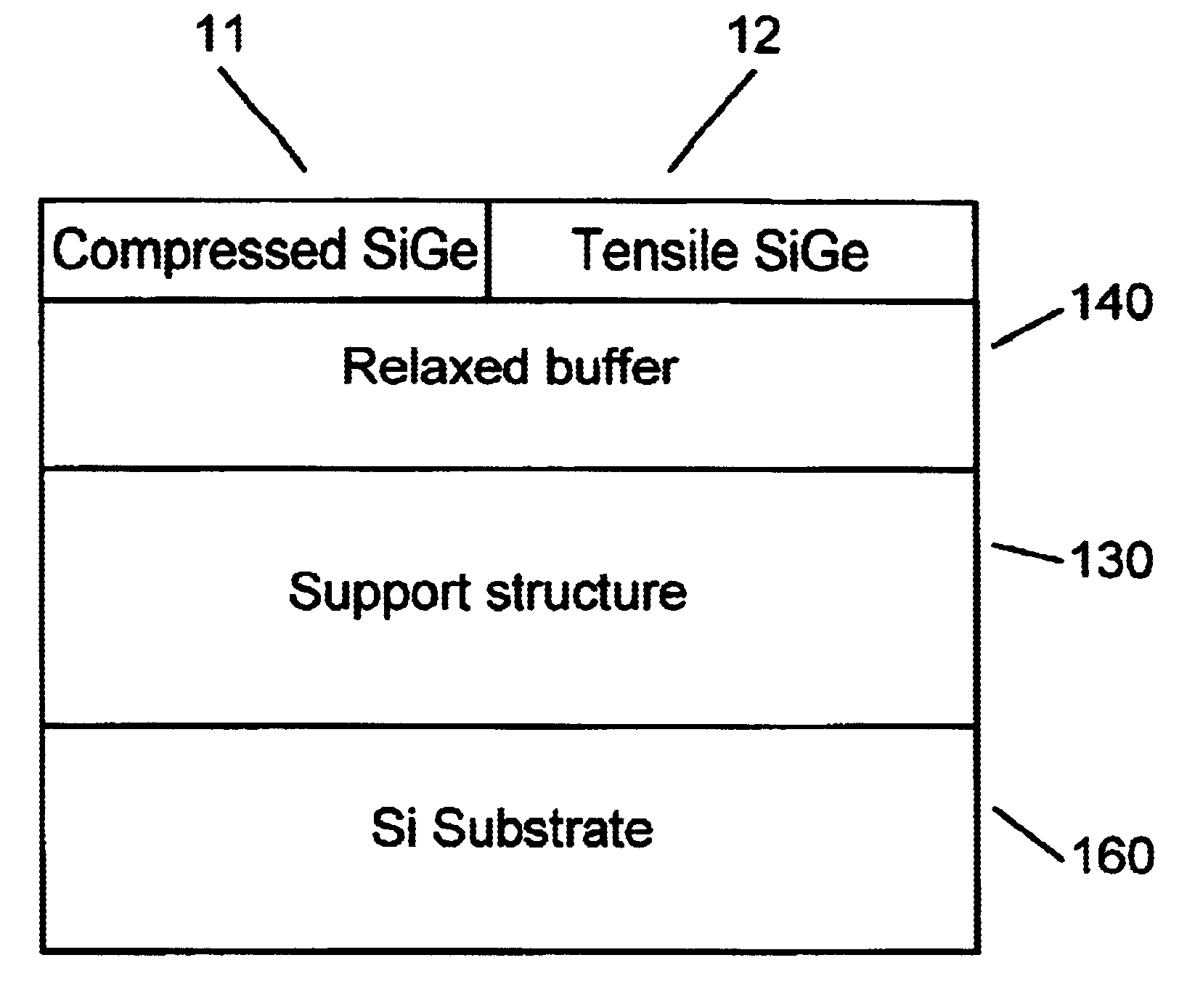
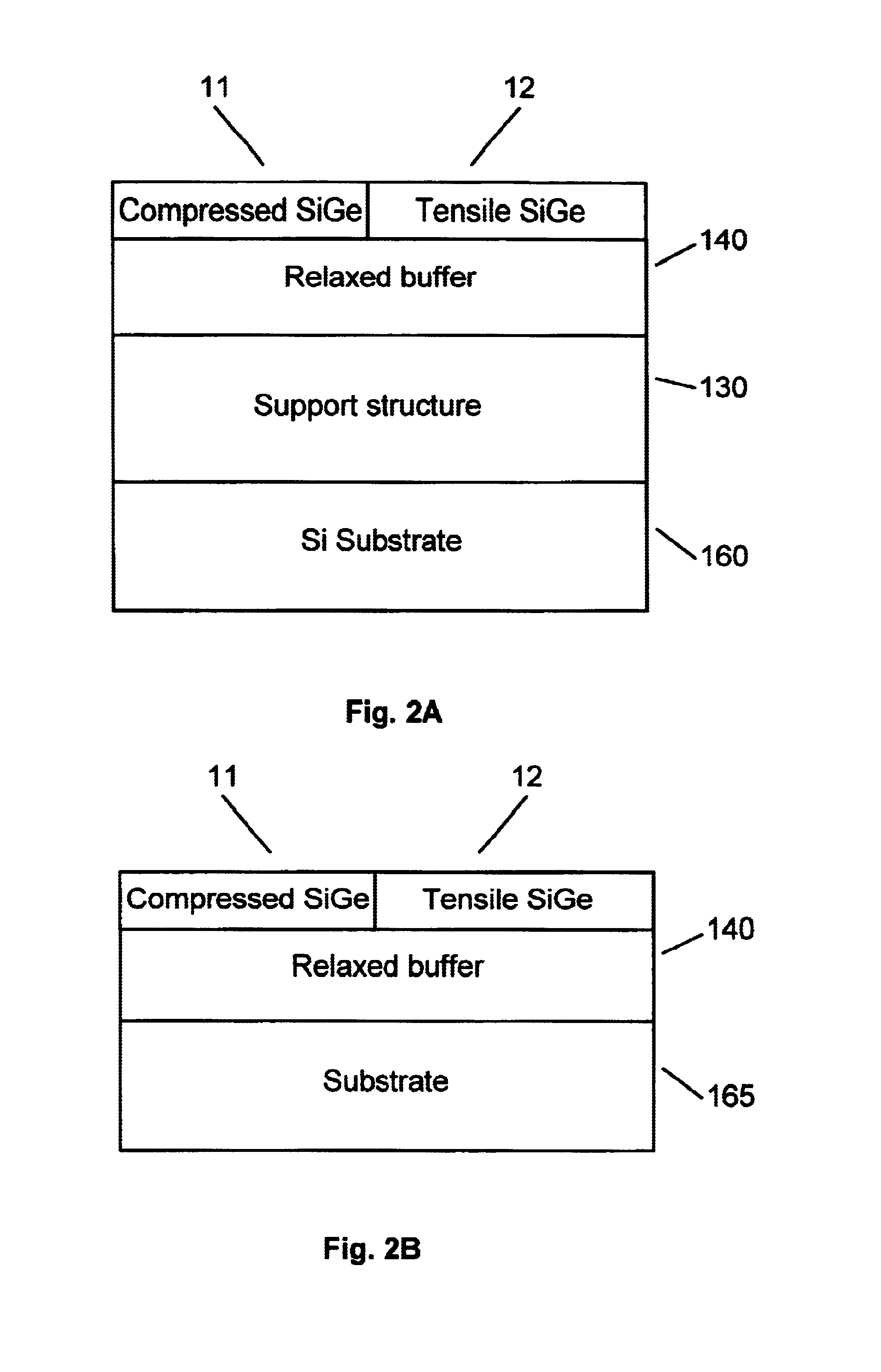
Dual strain-state SiGe layers for microelectronics
InactiveUS6963078B2Promote growthEasy to compressTransistorSolid-state devicesCrystallizationChemistry
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and memory circuit
InactiveUS20060081930A1Guaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageMemory circuits
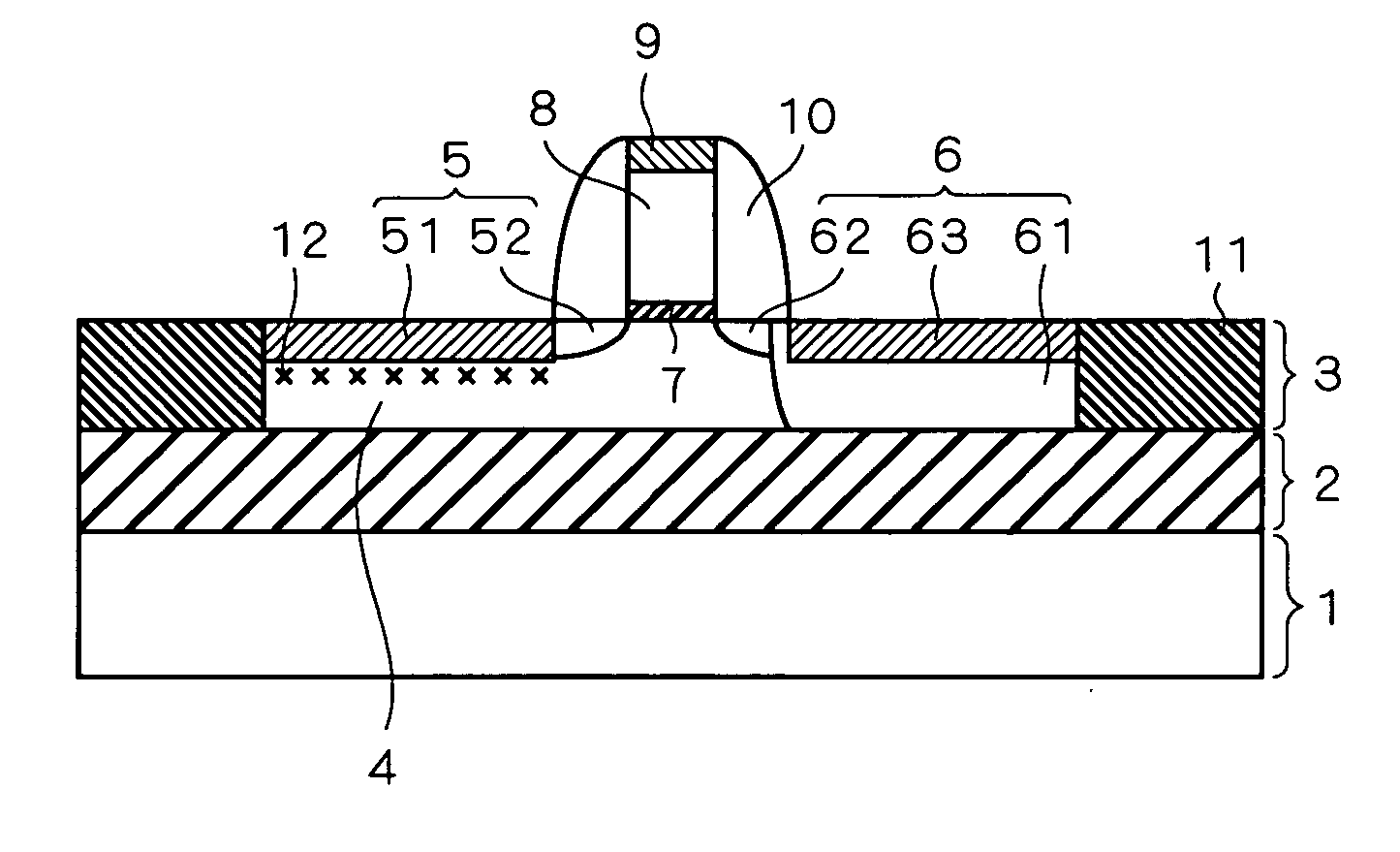
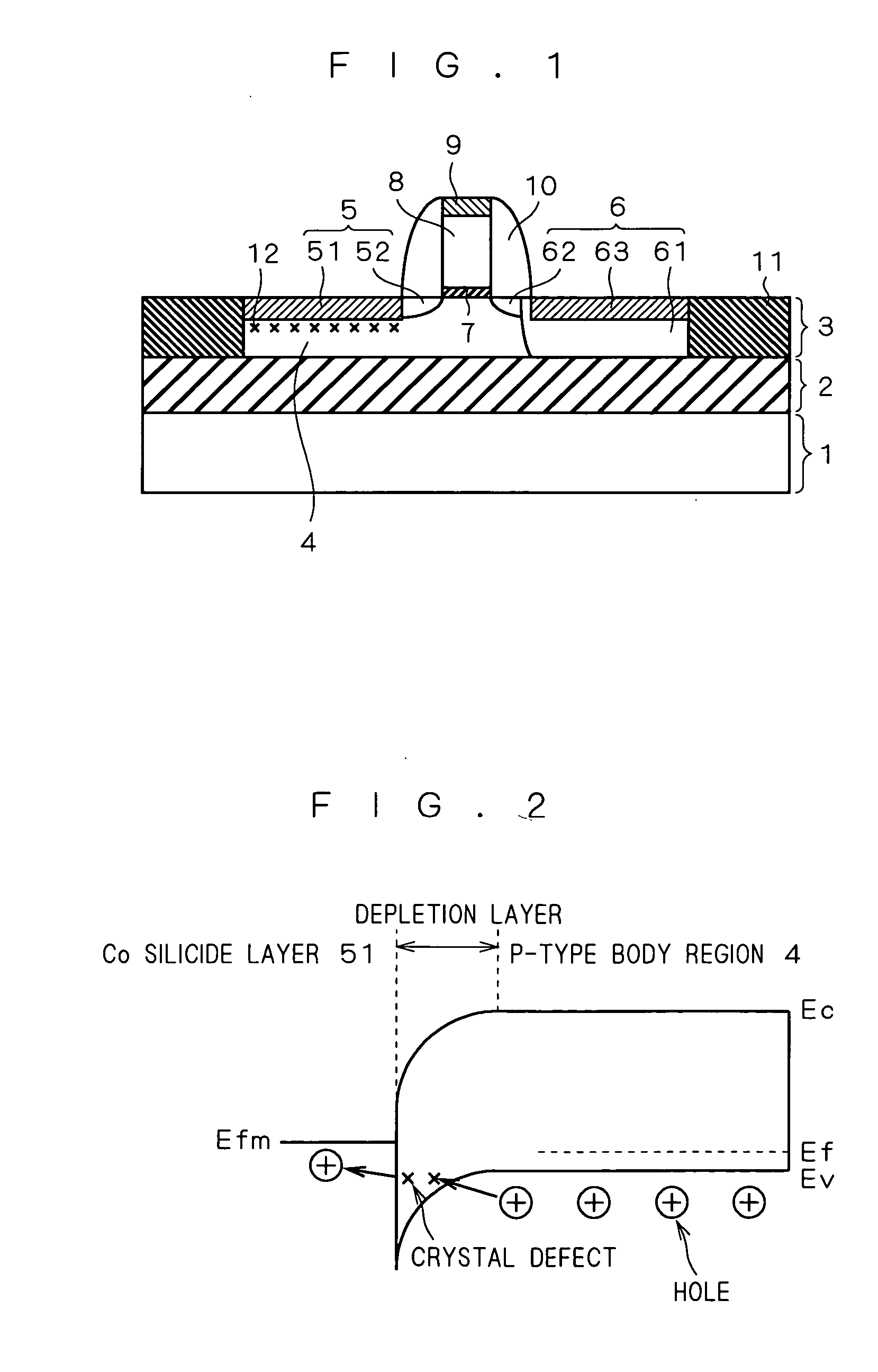
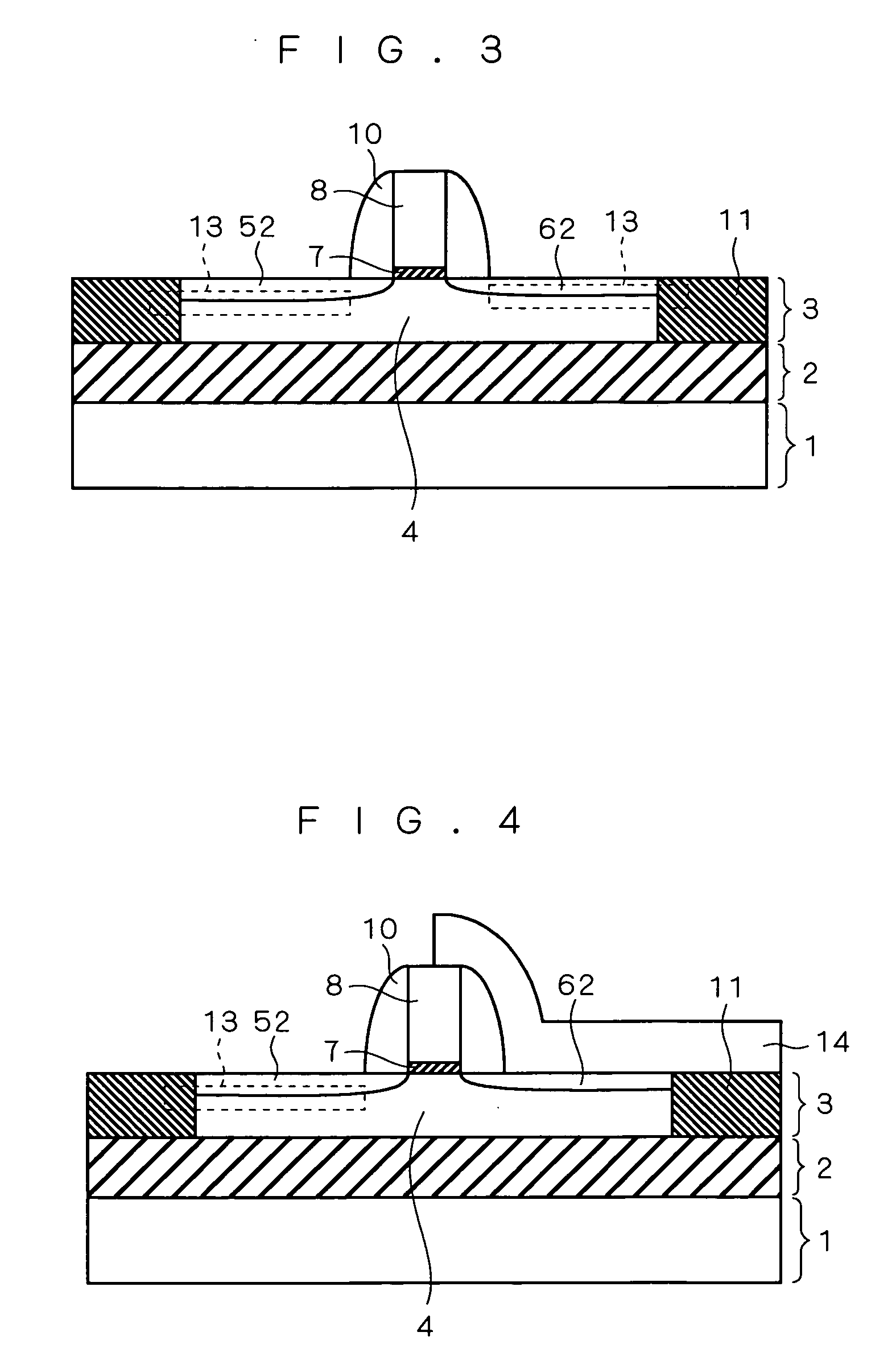
The present invention provides a semiconductor device capable of suppressing a body floating effect, and a manufacturing method thereof. A semiconductor device having an SOI structure includes a silicon substrate, a buried insulating layer formed on the silicon substrate, and a semiconductor layer formed on the buried insulating layer. The semiconductor layer has a body region of a first conduction type, a source region of a second conduction type and a drain region of the second conduction type, and a gate electrode is formed on the body region between the source region and the drain region via a gate oxide film. The source region includes an extension layer of the second conduction type, and a silicide layer which makes contact with the extension layer at its side face, and a crystal defect region is formed on a region of a depletion layer generated in a boundary portion between the silicide layer and the body region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Light-emitting diode, method for making light-emitting diode, integrated light-emitting diode and method for making integrated light-emitting diode, method for growing a nitride-based iii-v group compound semiconductor, light source cell unit, light-emitting diode backlight, and light-emitting diode display and electronic device
InactiveUS20060258027A1Light emission efficiency is reducedImprove light emission efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
A method for making a light-emitting diode, which including the steps of: providing a substrate having at least one recessed portion on one main surface and growing a first nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer through a state of making a triangle in section having a bottom surface of the recessed portion as a base thereby burying the recessed portion; laterally growing a second nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer from the first nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer over the substrate; and successively growing a third nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer of a first conduction type, an active layer and a fourth nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer of a second conduction type on the second nitride-based III-V group compound semiconductor layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
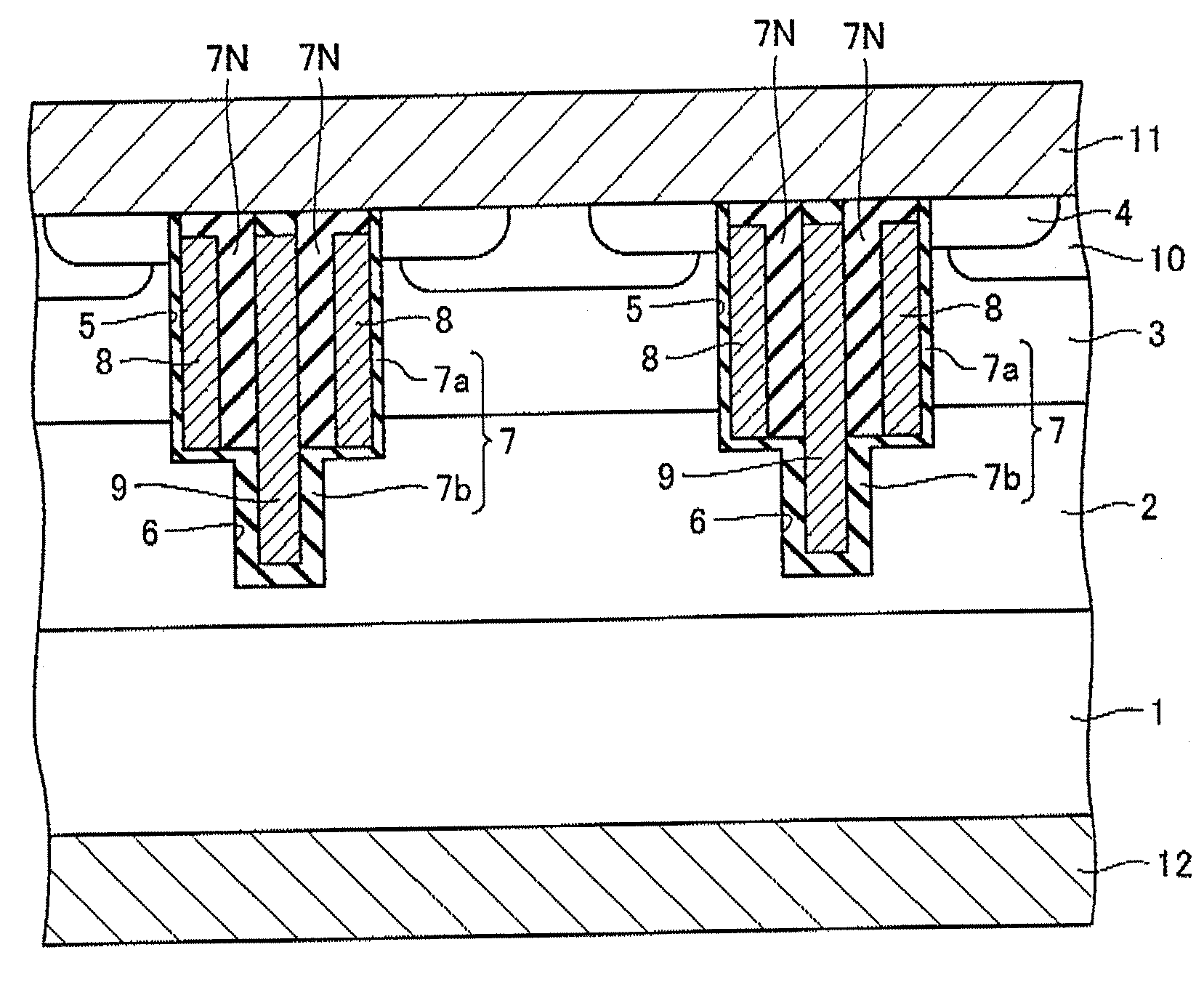
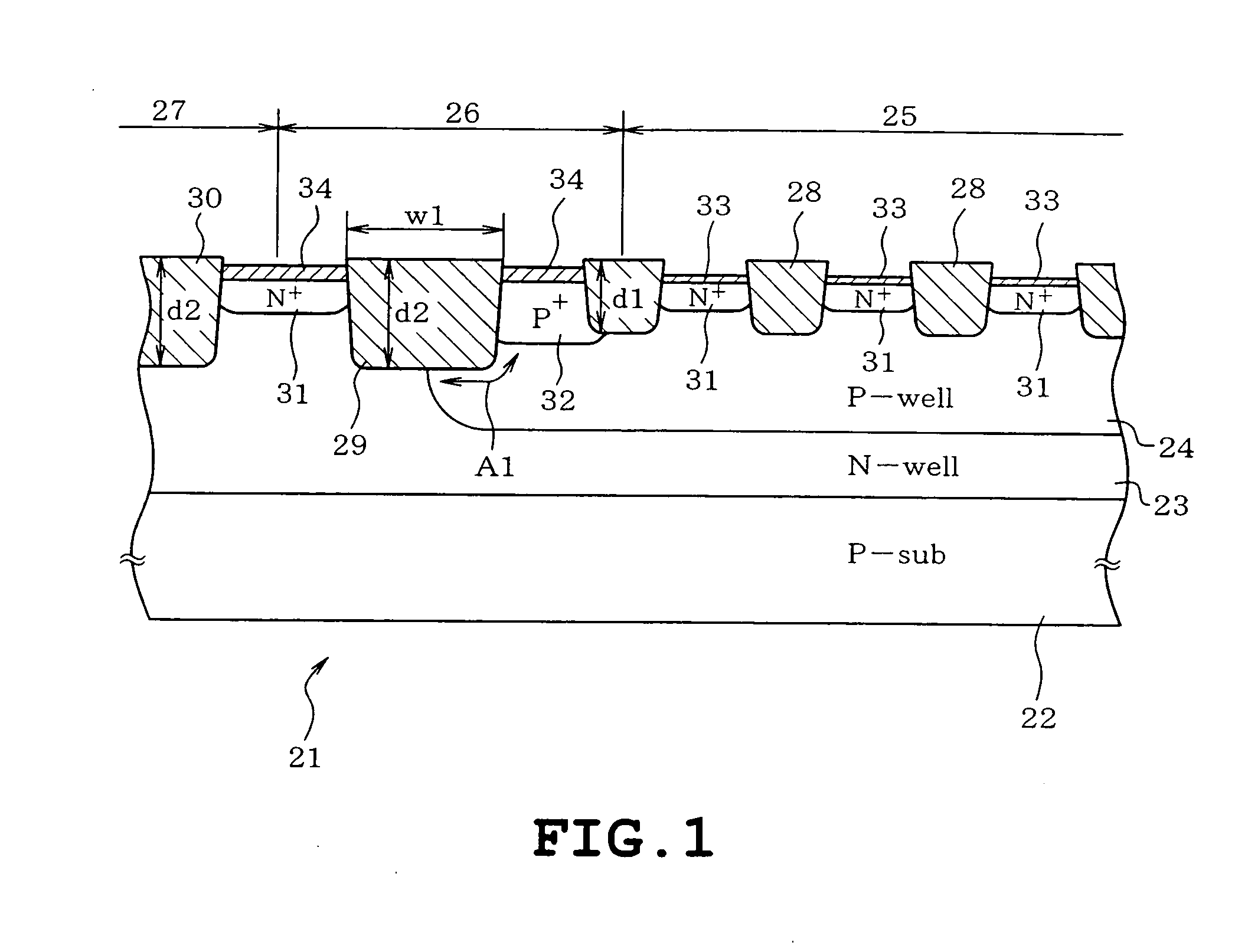
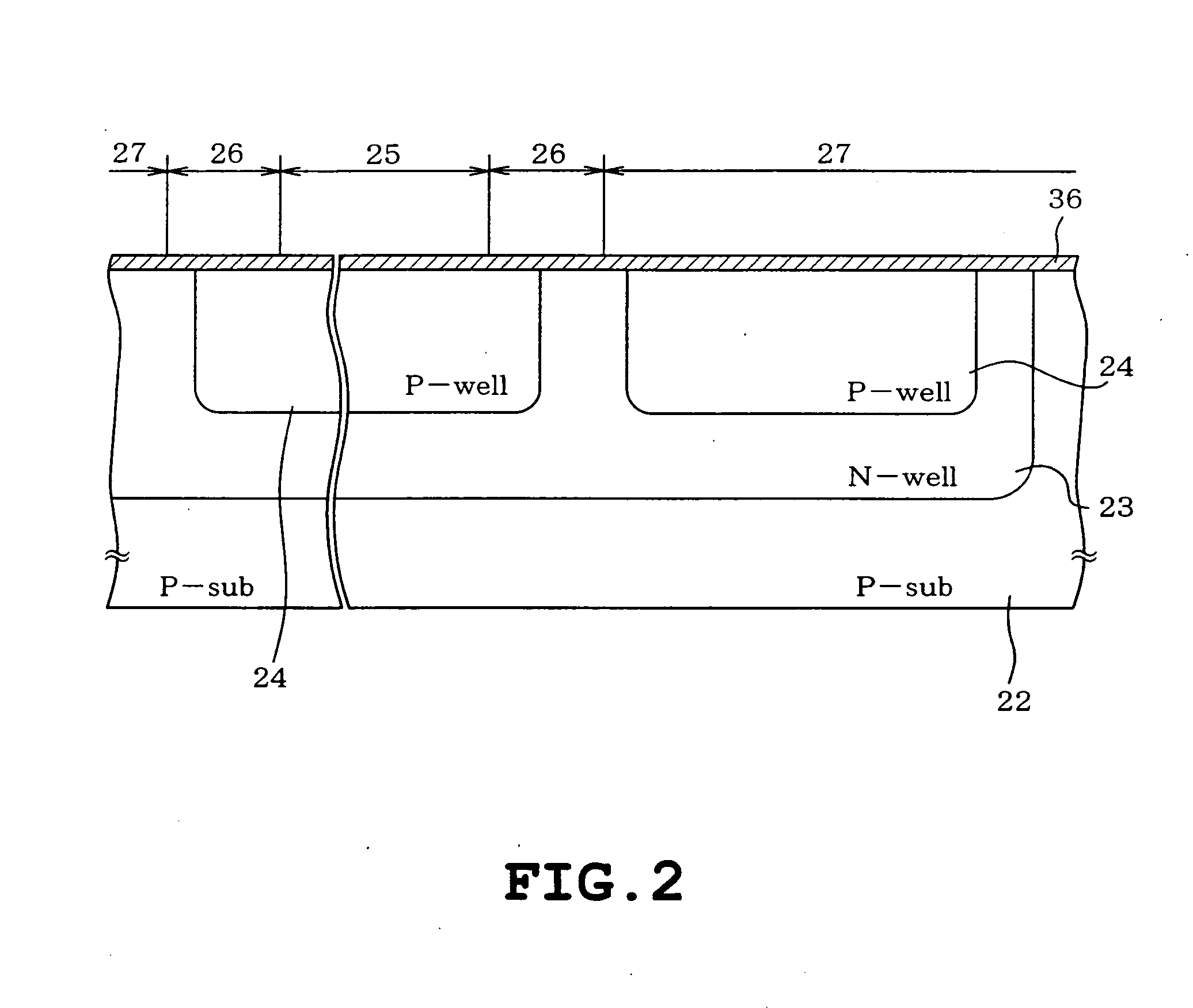
InactiveUS20050127473A1Increase in the chip area and occurrence of dishing or the like can be preventedTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityP–n junction
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate of a first conduction type, a first well of a second conduction type formed on the semiconductor substrate, a plurality of second wells of the first conduction type provided in the first well for forming memory cells and a peripheral circuit respectively, each second well having a first depth, a first trench isolating region formed so as to isolate an element within the second well for the memory cells and having a first depth, a guard-ring diffusion region of the first conduction type provided in the vicinity of a peripheral edge of each second well for the memory cells and doped with a high density impurity so as to encompass a forming region of the memory cells, a second trench isolating region formed so that a p-n junction of each second well terminates on a bottom thereof in the vicinity of an outside of the guard-ring diffusion region, the second trench isolating region having a second depth larger than the first depth of each second well, and a third trench isolating region isolating an element formed in each second well for the peripheral circuit, the third trench isolating region having the second depth.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor light-emitting device and semiconductor light-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS20030107047A1Easily feasibleReduce lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyCrystal plane
A semiconductor light-emitting element having a structure that does not complicate a fabrication process, can be formed in high precision and does not invite any degradation of crystallinity is provided. A light-emitting element is formed, which includes a selective crystal growth layer formed by selectively growing a compound semiconductor of a Wurtzite type, and a clad layer of a first conduction type, an active layer and a clad layer of a second conduction type, which are formed on the selective crystal growth layer wherein the active layer is formed so that the active layer extends in parallel to different crystal planes, the active layer is larger in size than a diffusion length of a constituent atom of a mixed crystal, or the active layer has a difference in at least one of a composition and a thickness thereof, thereby forming the active layer having a plurality of light-emitting wavelength region whose emission wavelengths differ from one another. The element is so arranged that an electric current or currents are chargeable into the plurality of light-emitting wavelength regions. Because of the structure based on the selective growth, it is realized that the band gap energy varies within the same active layer, thereby forming an element or device in high precision without complicating a fabrication process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
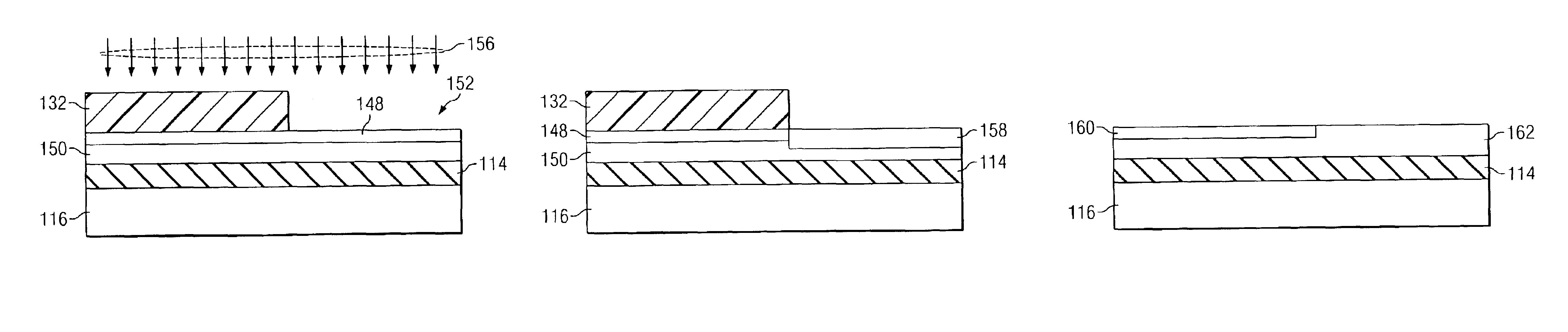
Method of manufacturing semiconductor article
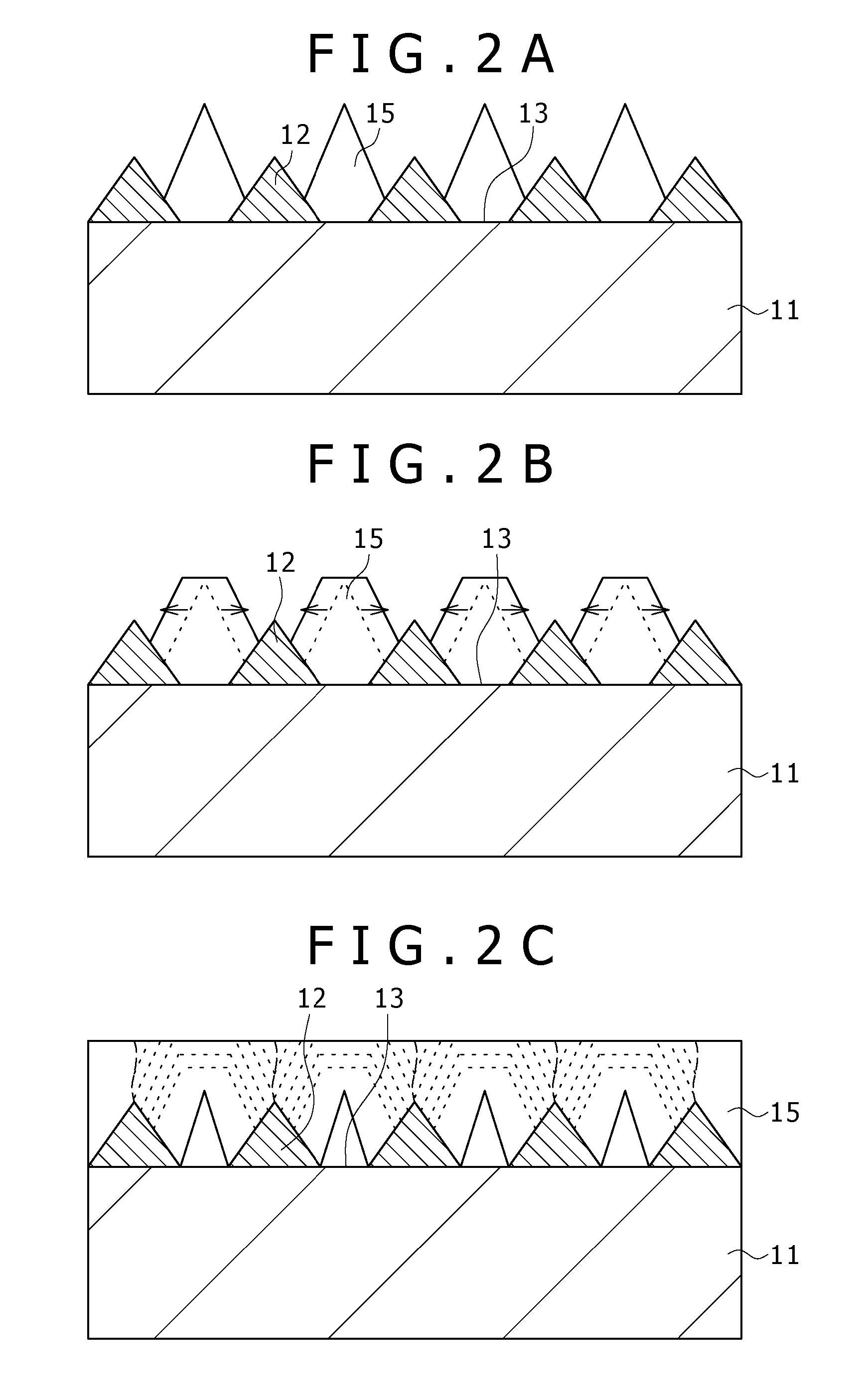
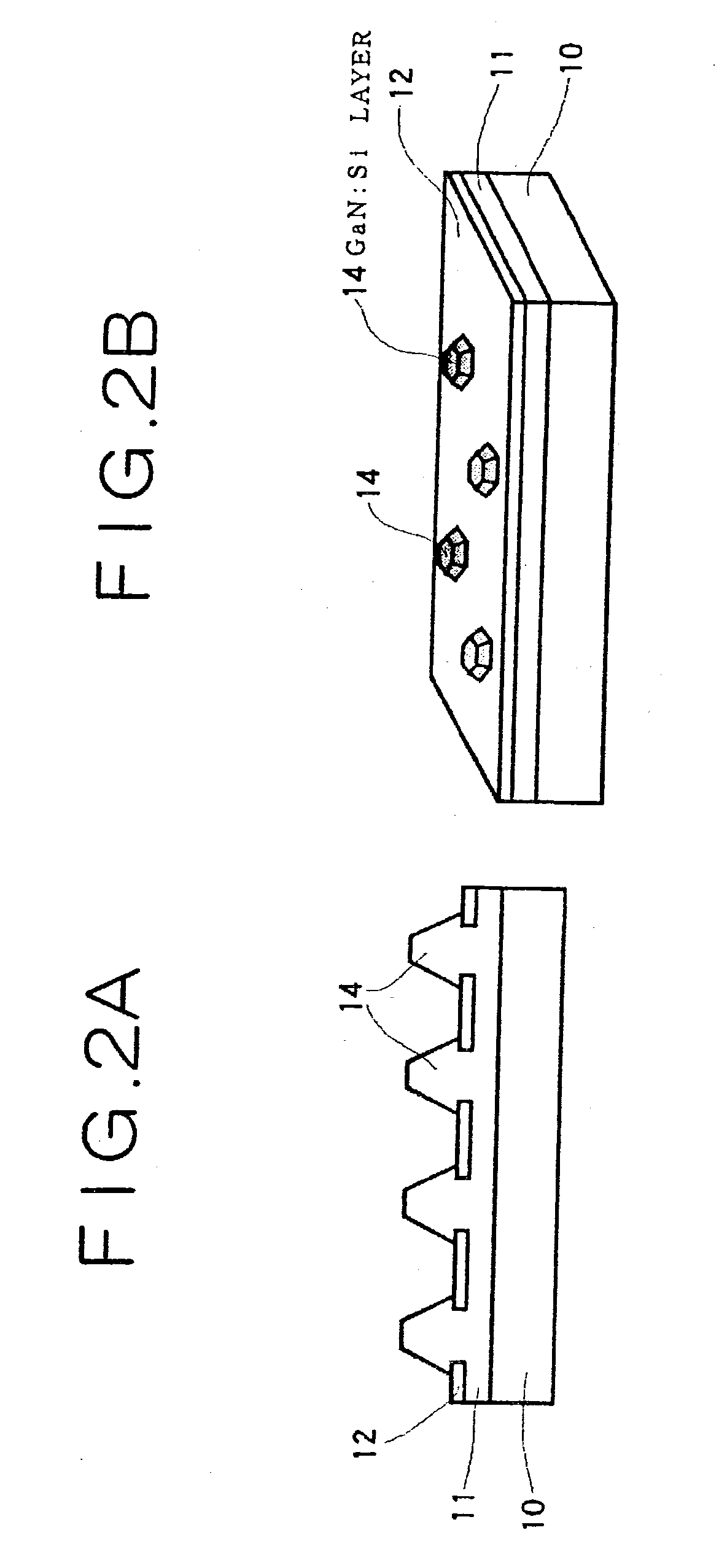
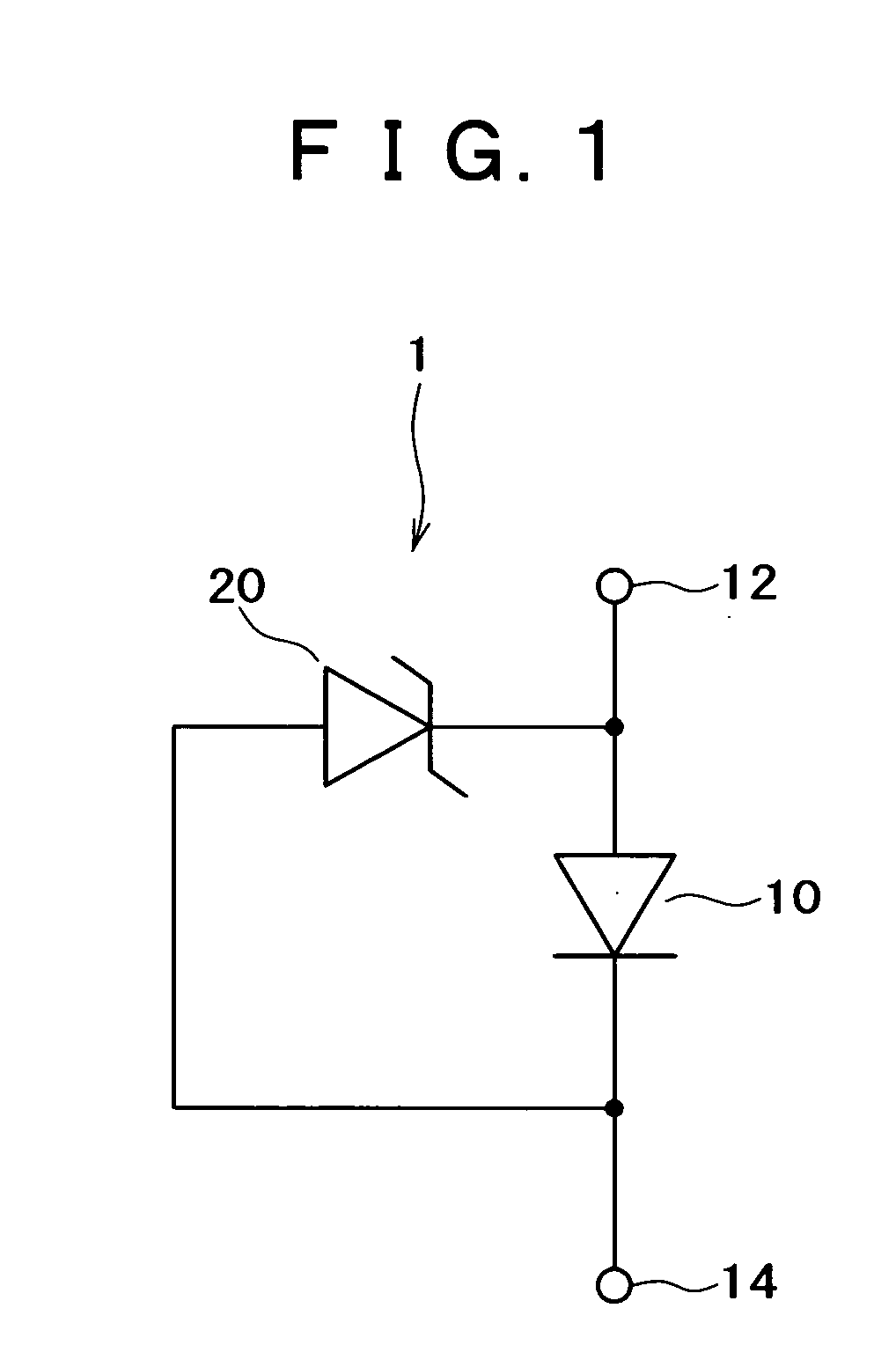
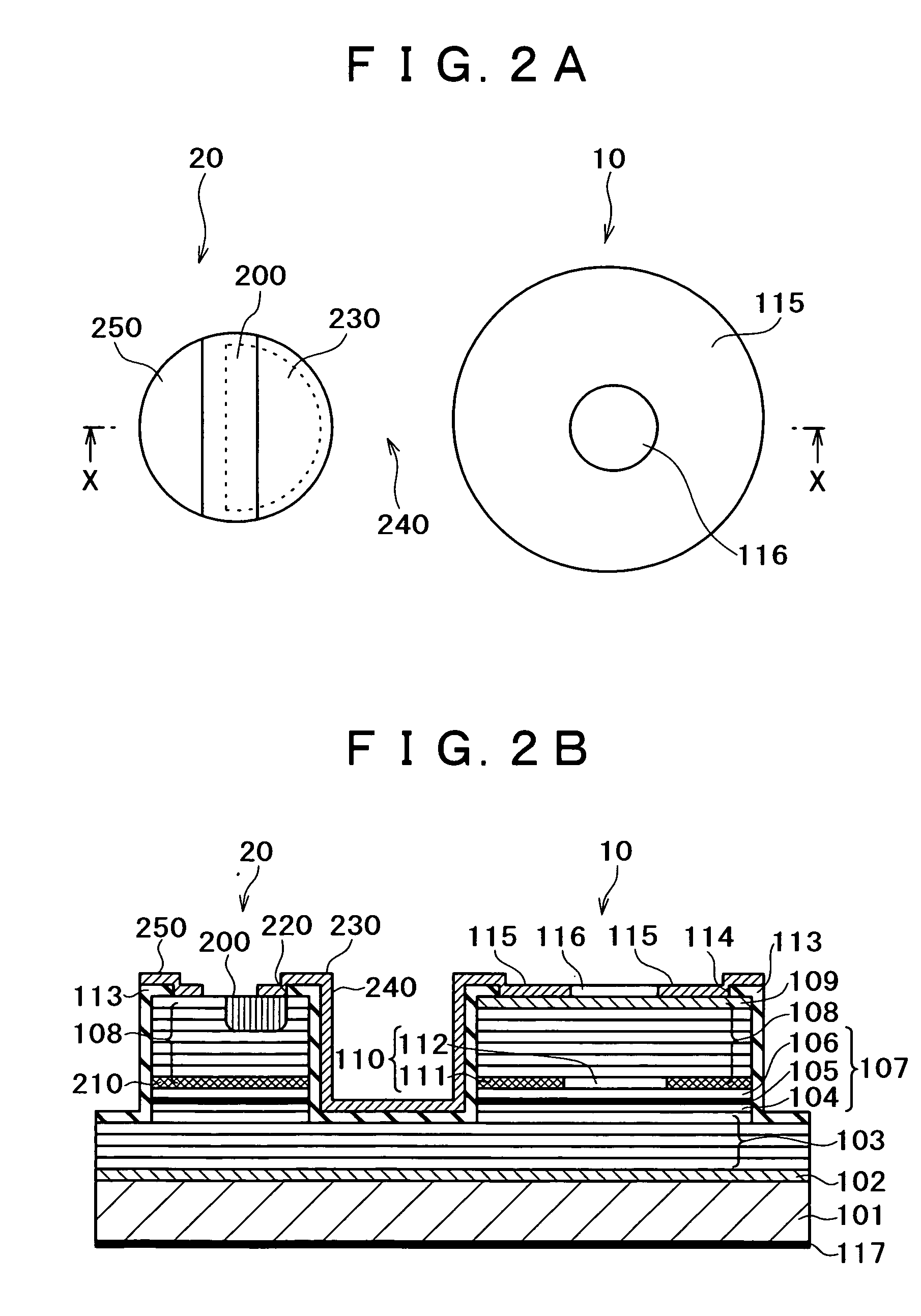
InactiveUS6100165AExpensive to replaceLess costlySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorous siliconConduction type
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor article comprises steps of forming a diffusion region at least on the surface of one of the sides of a silicon substrate by diffusing an element capable of controlling the conduction type, forming a porous silicon layer in a region including the diffusion region, preparing a first substrate by forming a nonporous semiconductor layer on the porous silicon layer, bonding the first substrate and a second substrate together to produce a multilayer structure with the nonporous semiconductor layer located inside, splitting the multilayer structure along the porous silicon layer but not along the diffusion region and removing the porous silicon layer remaining on the split second substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090032849A1Increase currentReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes a cylindrical main pillar that is formed on a substrate and of which a central axis is perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, source and drain diffused layers that are formed in a concentric shape centered on the central axis at upper and lower portions of the main pillar and made from a first-conduction-type material, a body layer that is formed at an intermediate portion of the main pillar sandwiched between the source and drain diffused layers and made from the first-conduction-type material, and a front gate electrode that is formed on a lateral face of the main pillar while placing a gate insulating film therebetween. Moreover, a back gate electrode made from a second-conduction-type material is formed in a pillar shape penetrating from an upper portion to a lower portion on an inner side of the main pillar.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
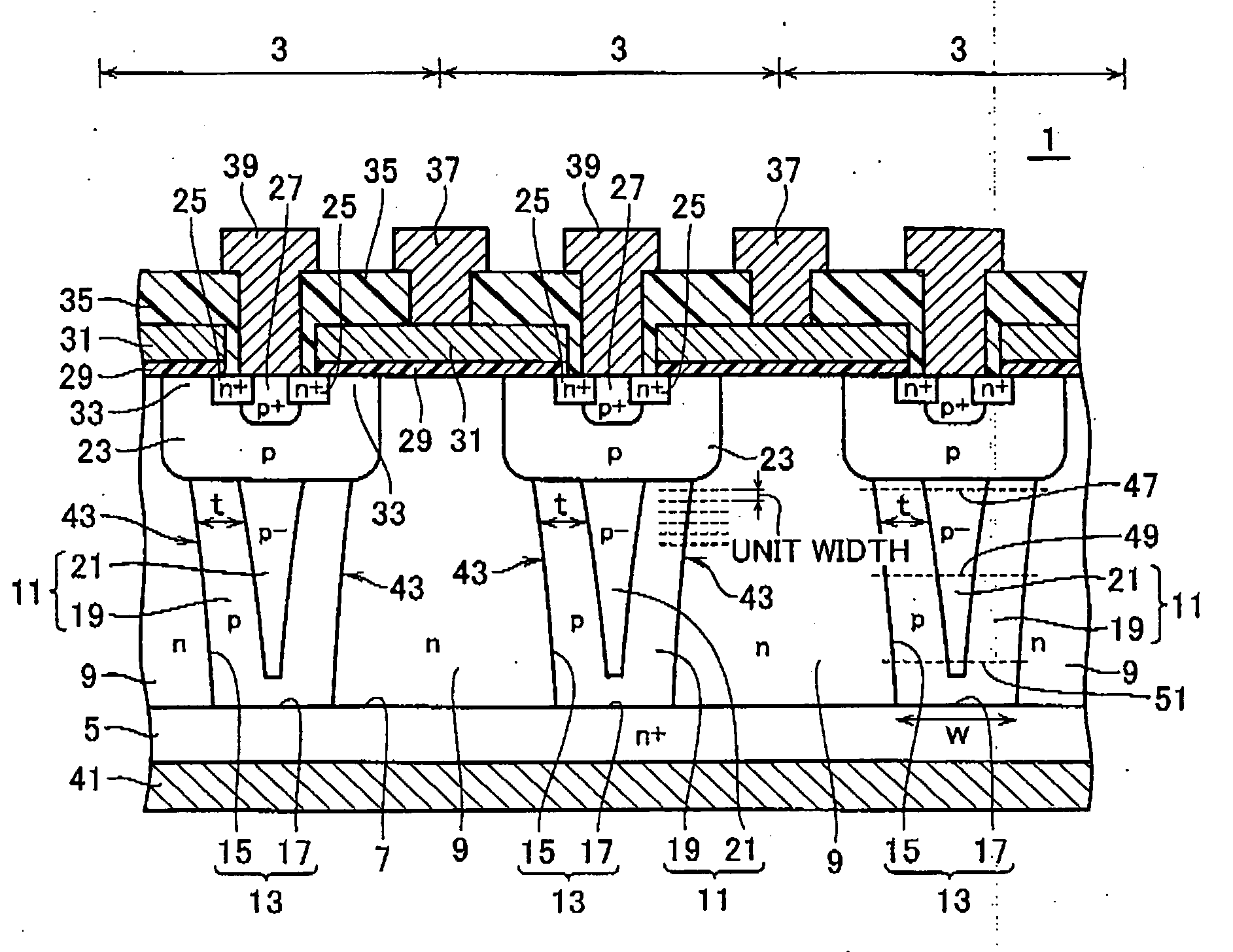
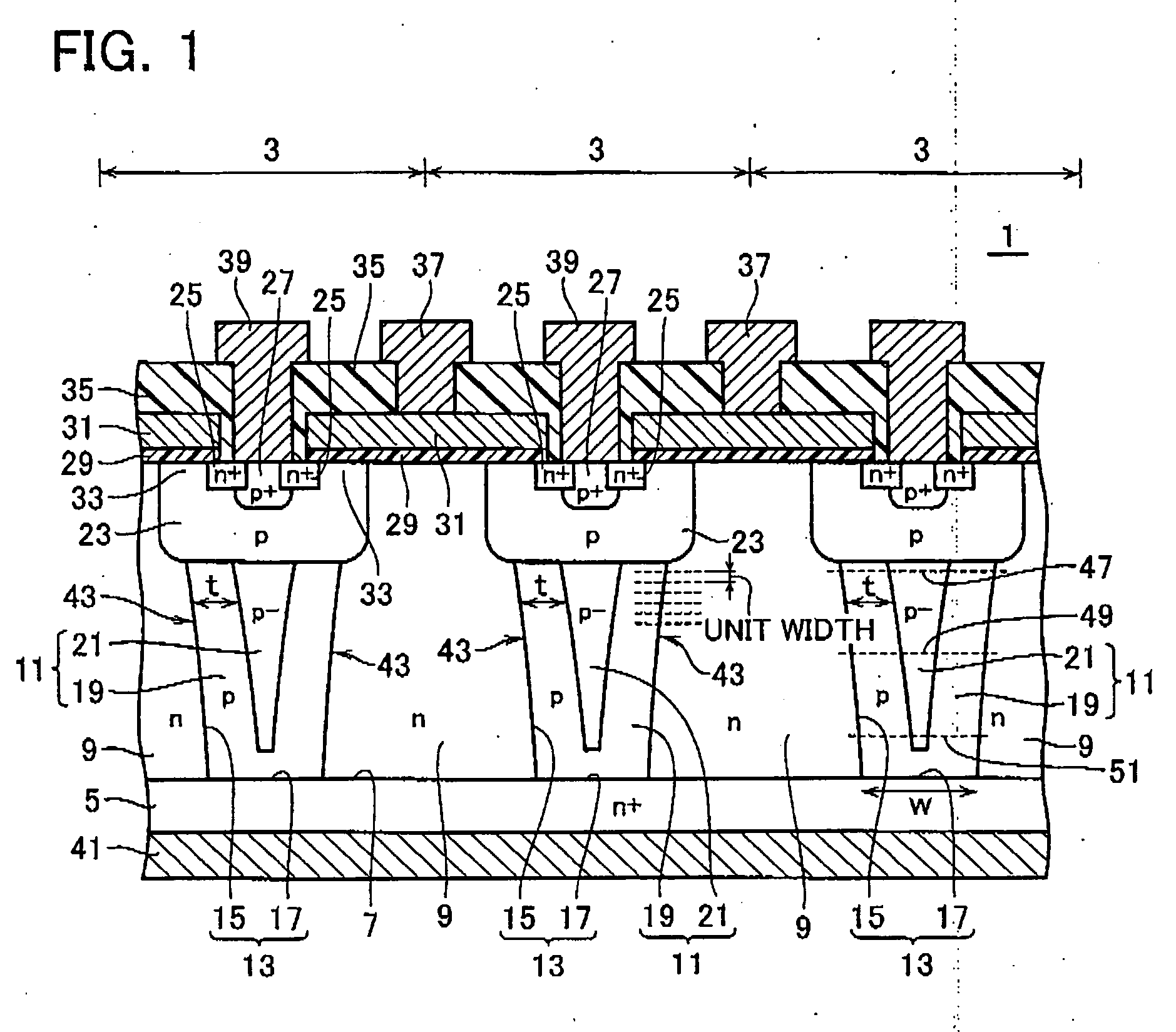
Semiconductor device
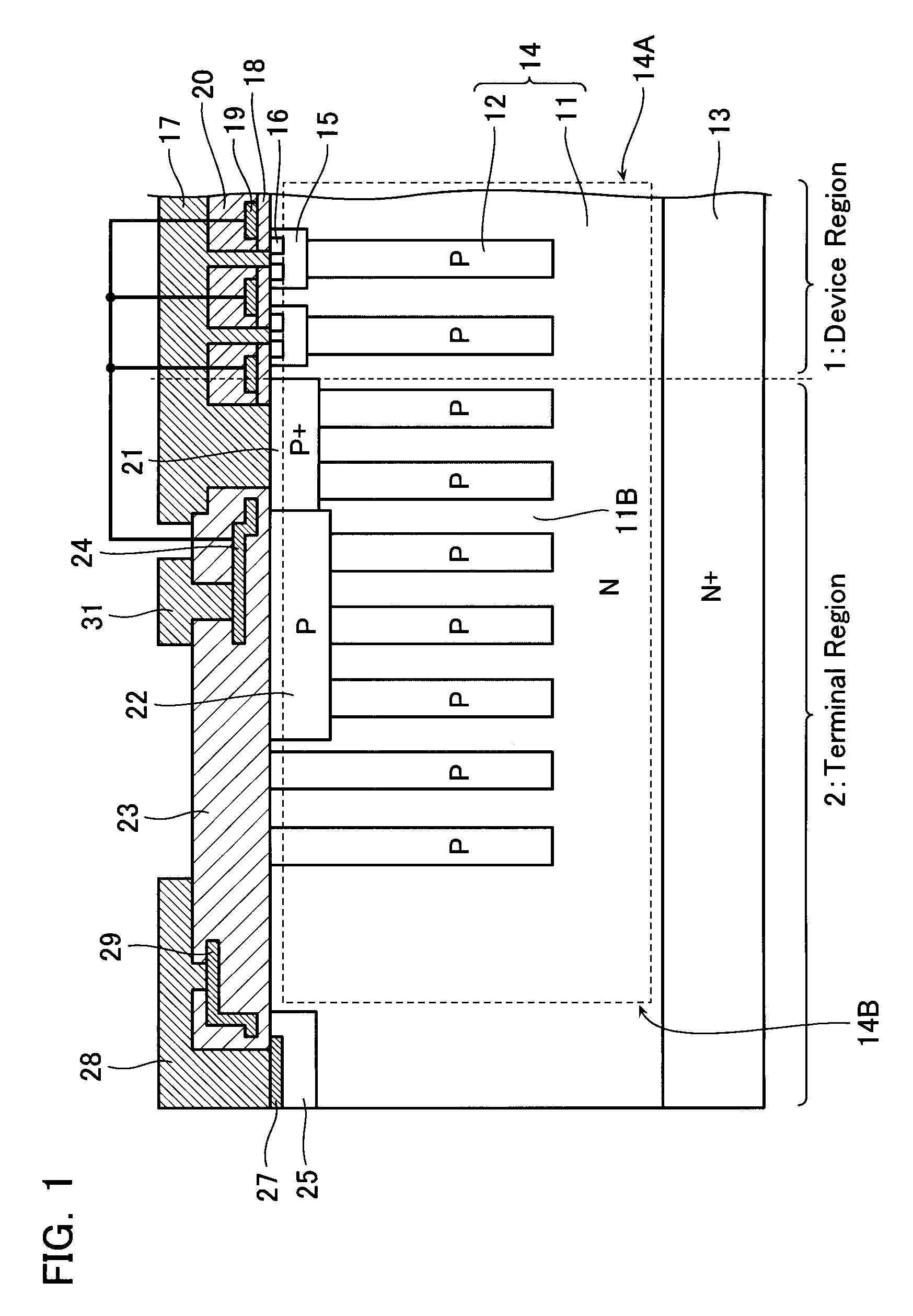
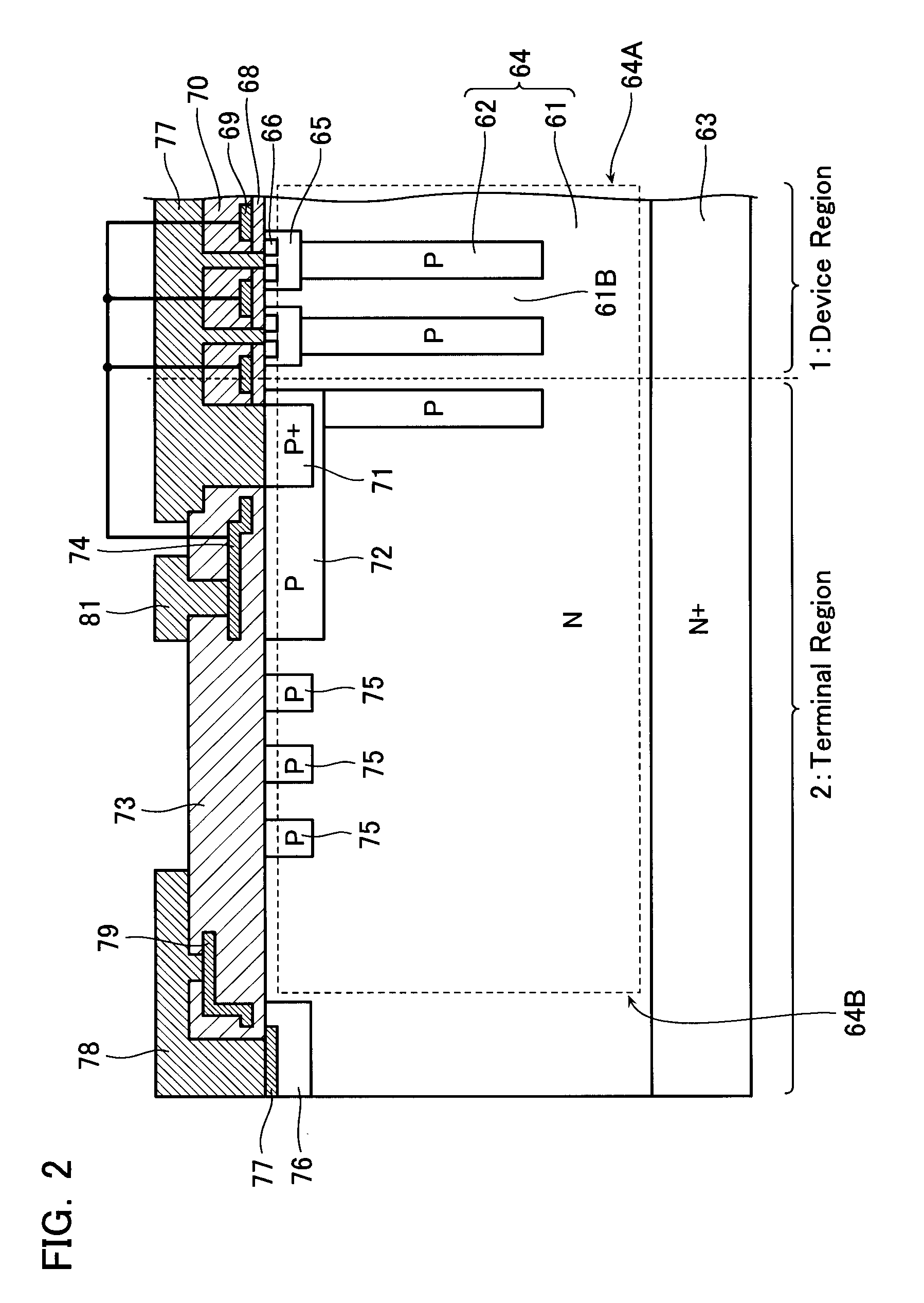
InactiveUS20080315297A1Increase resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorCharge carrier
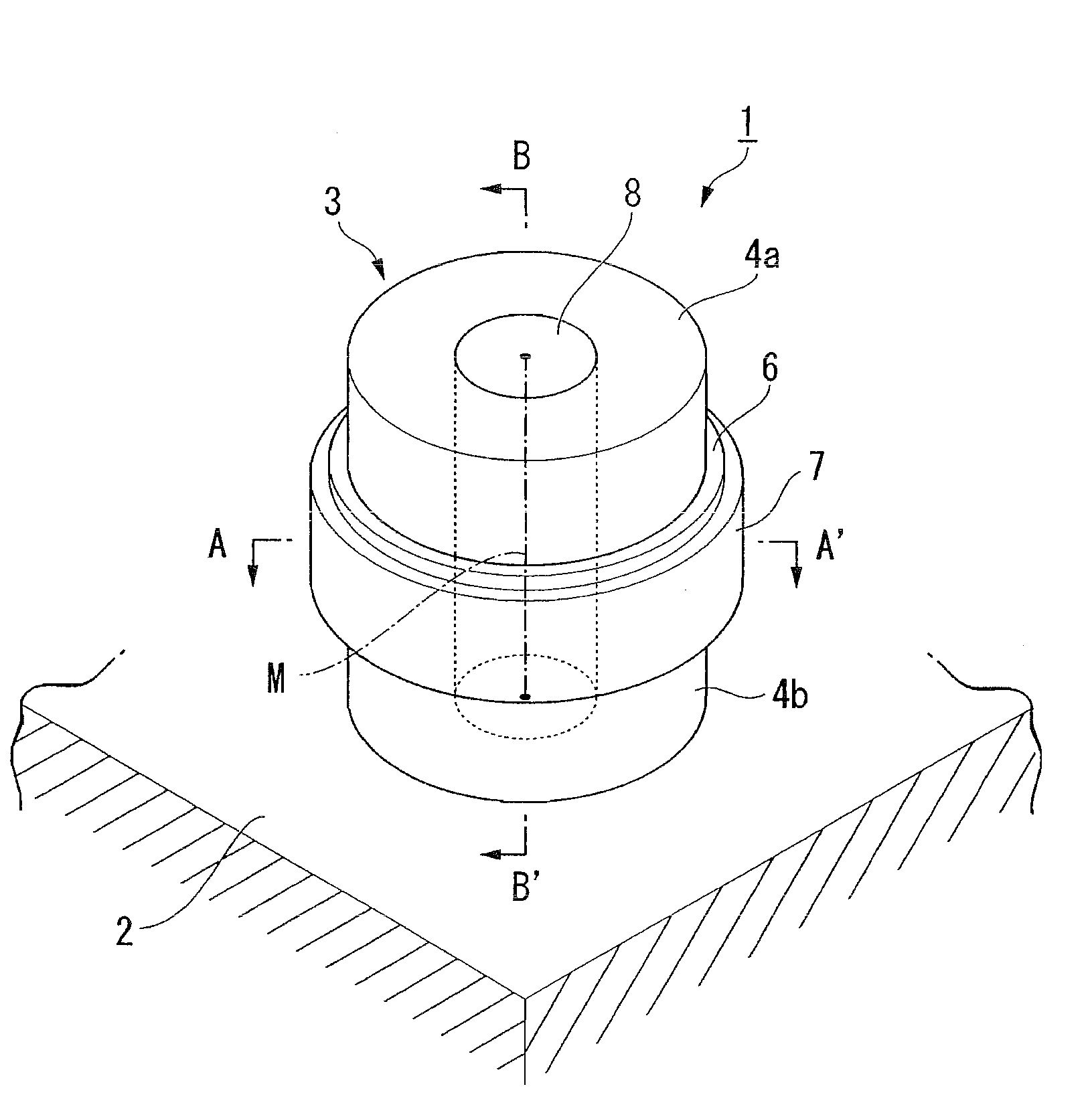
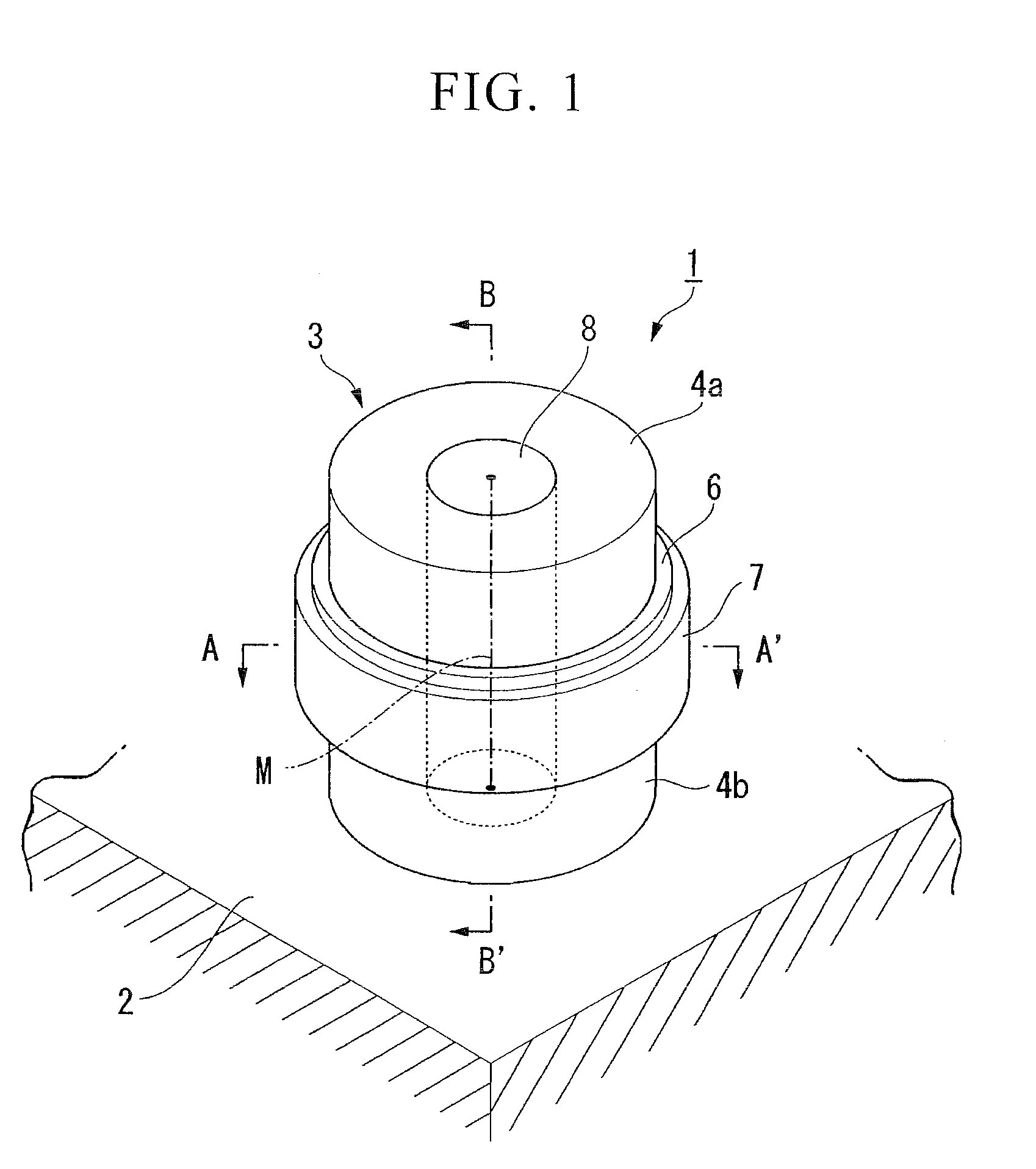
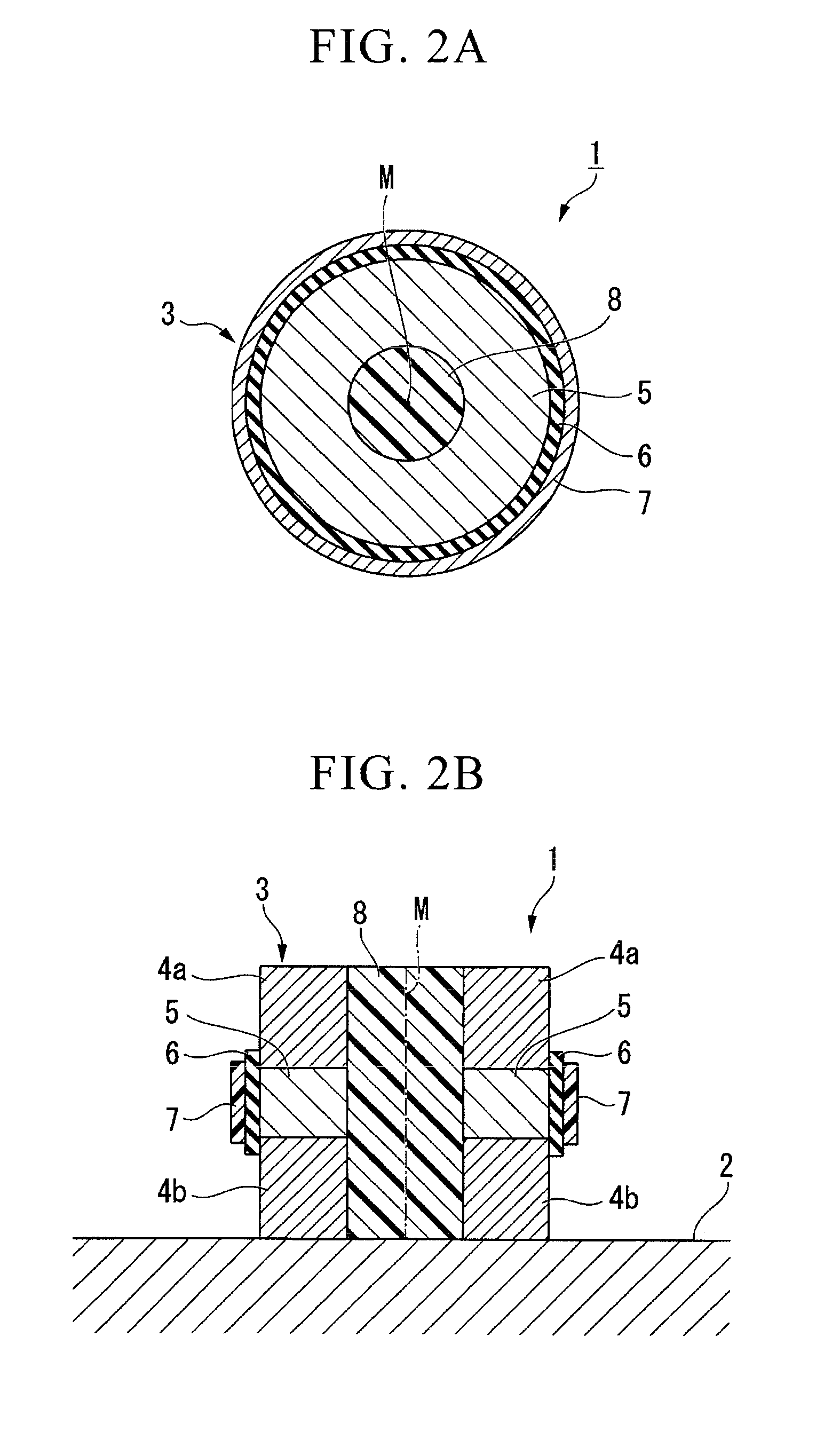
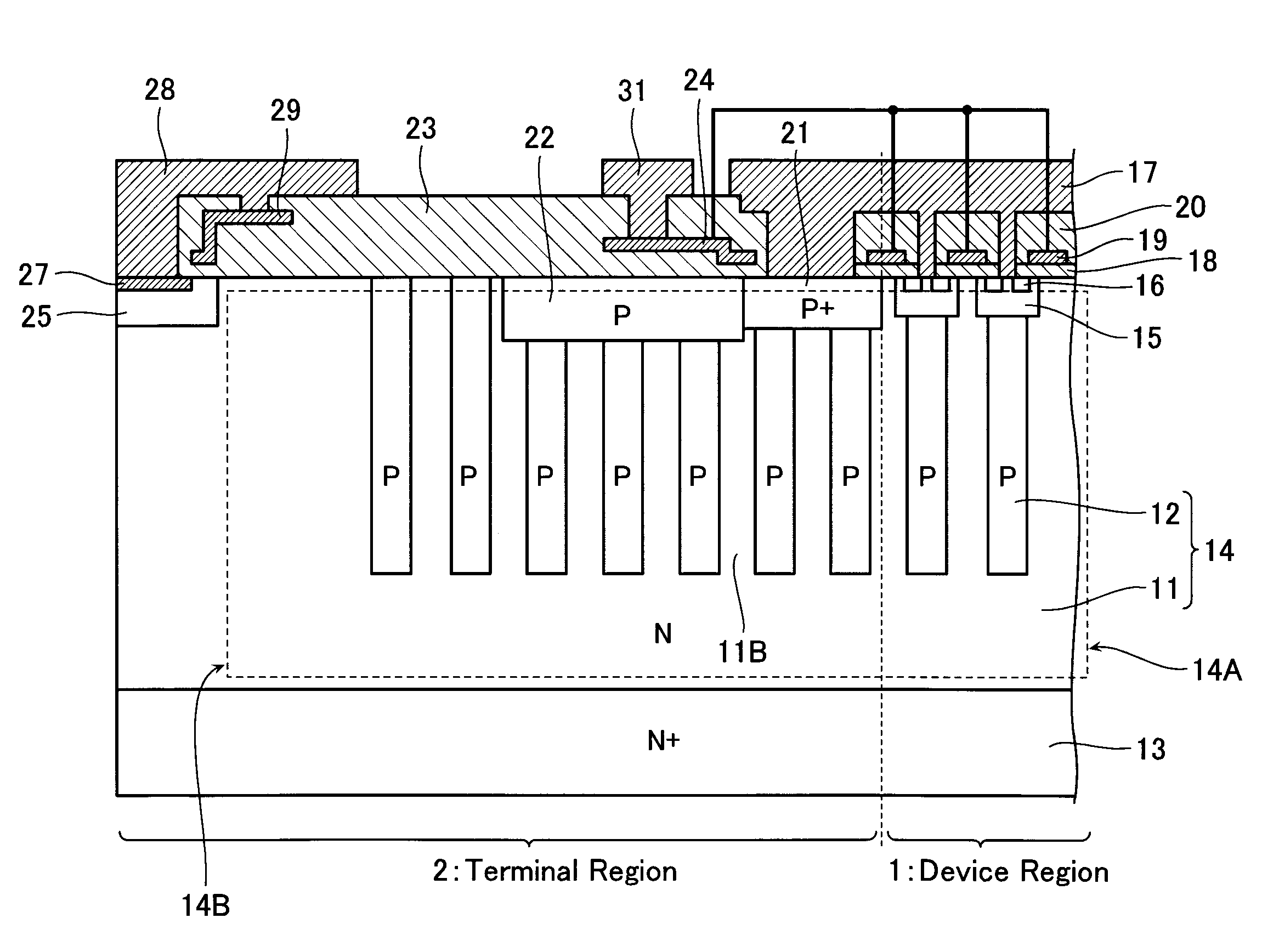
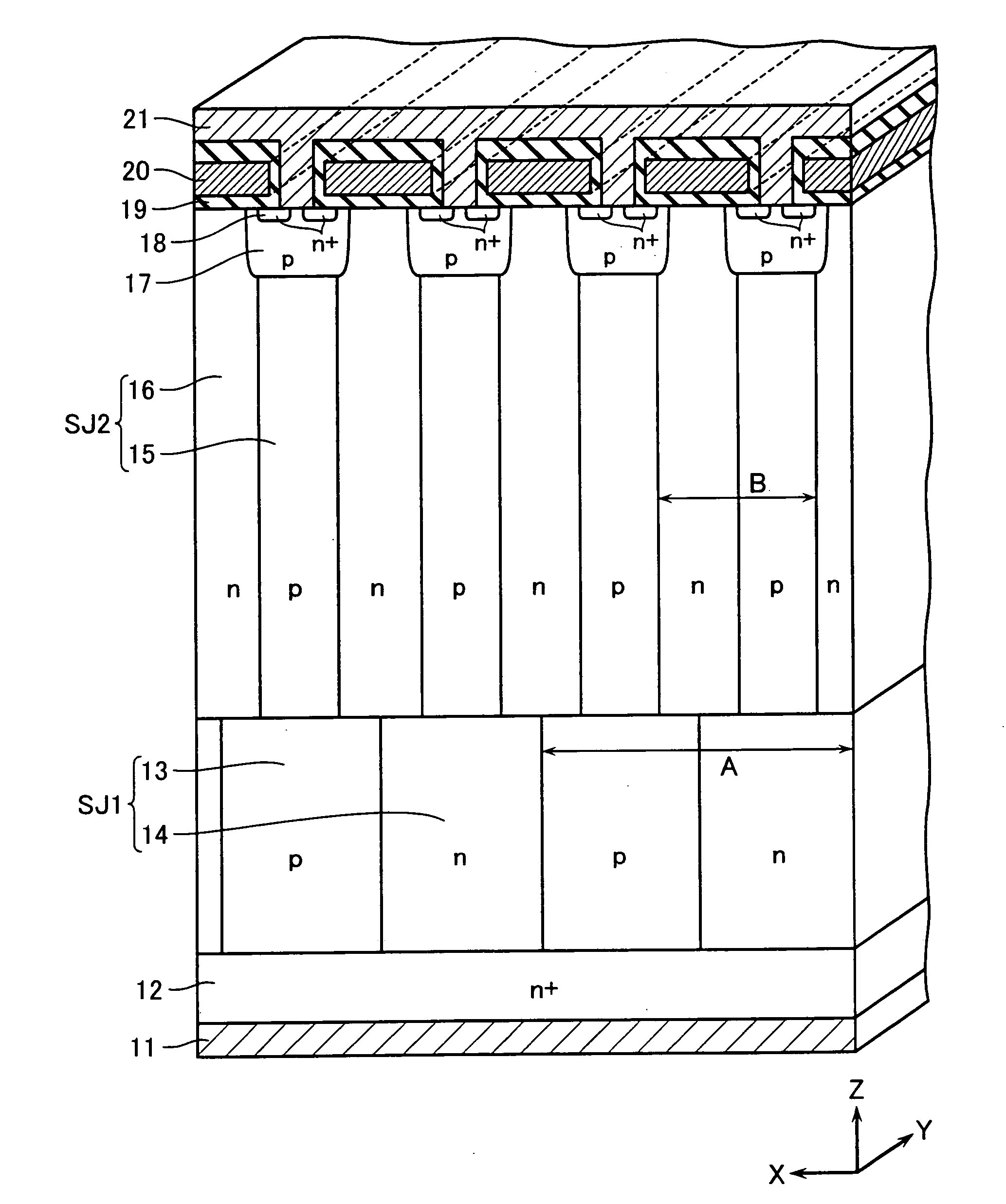
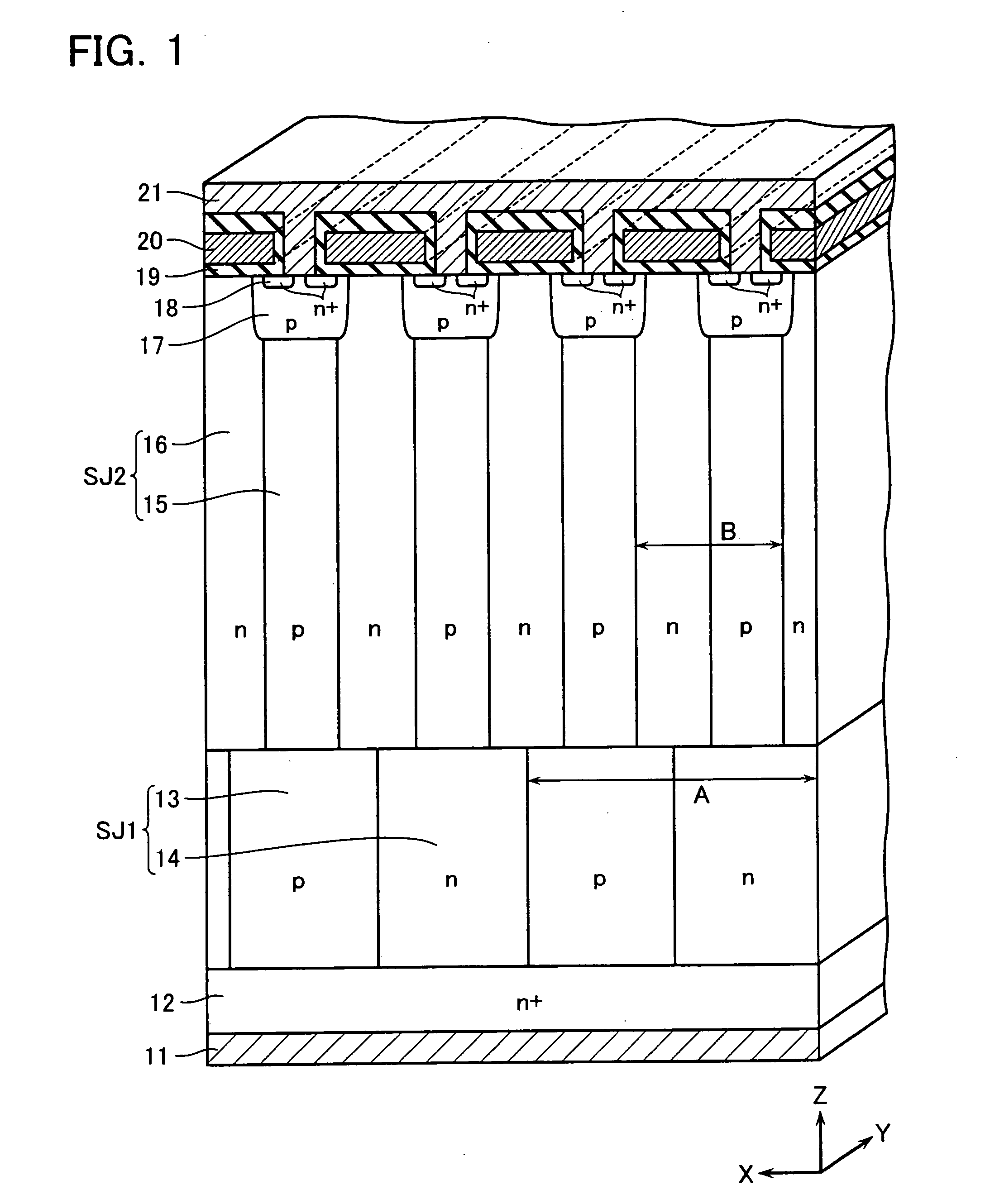
There is provided a semiconductor device having a drift layer with a pillar structure including first semiconductor layer portions of the first conduction type and second semiconductor layer portions of the second conduction type formed in pillars alternately and periodically on a semiconductor substrate. A device region includes a plurality of arrayed transistors composed of the first semiconductor layer portions and the second semiconductor layer portions. A terminal region is formed at the periphery of the device region without the transistors formed therein. The drift layer in the terminal region has a carrier lifetime lower than ⅕ the carrier lifetime in the drift layer in the device region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
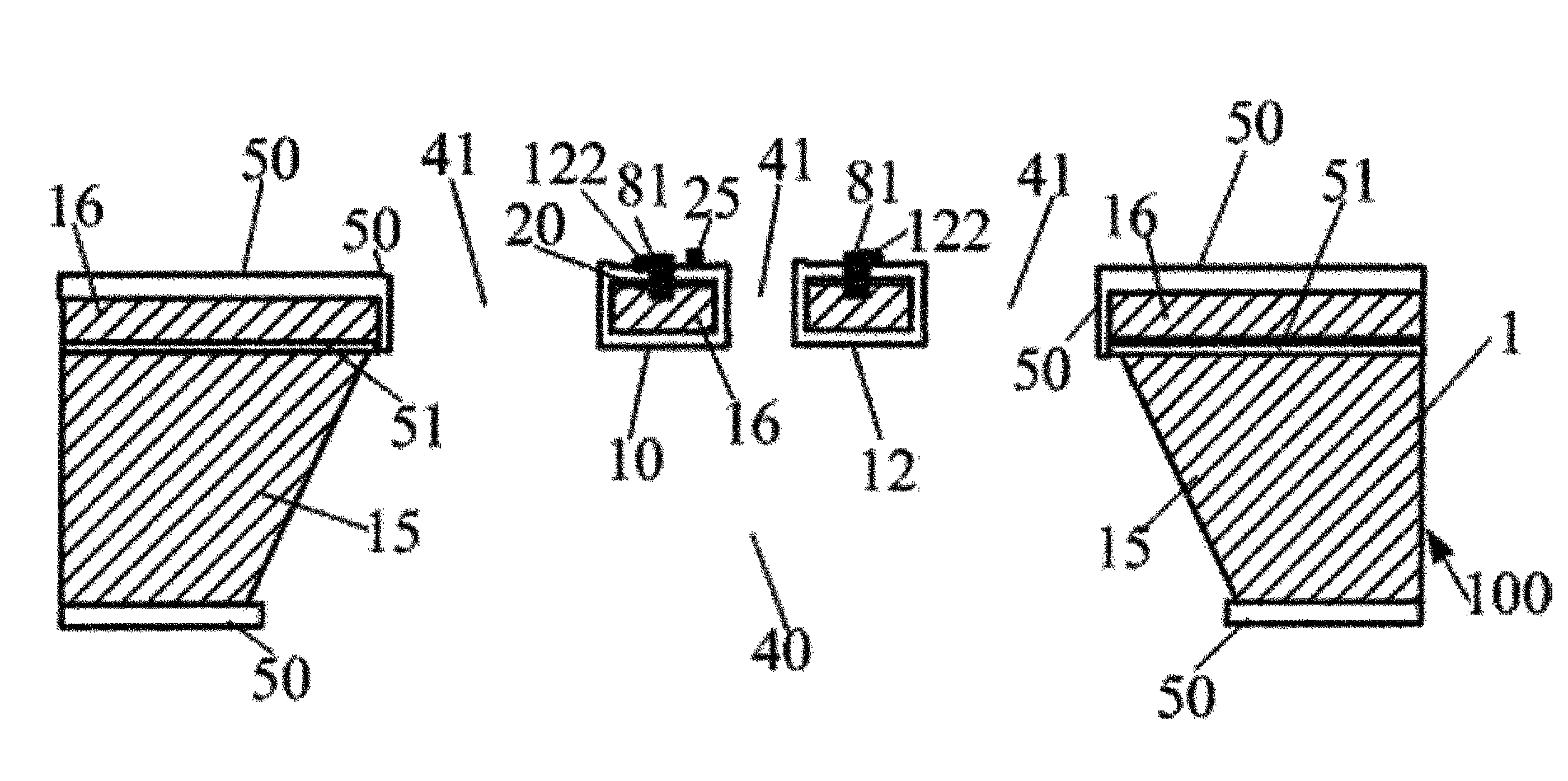
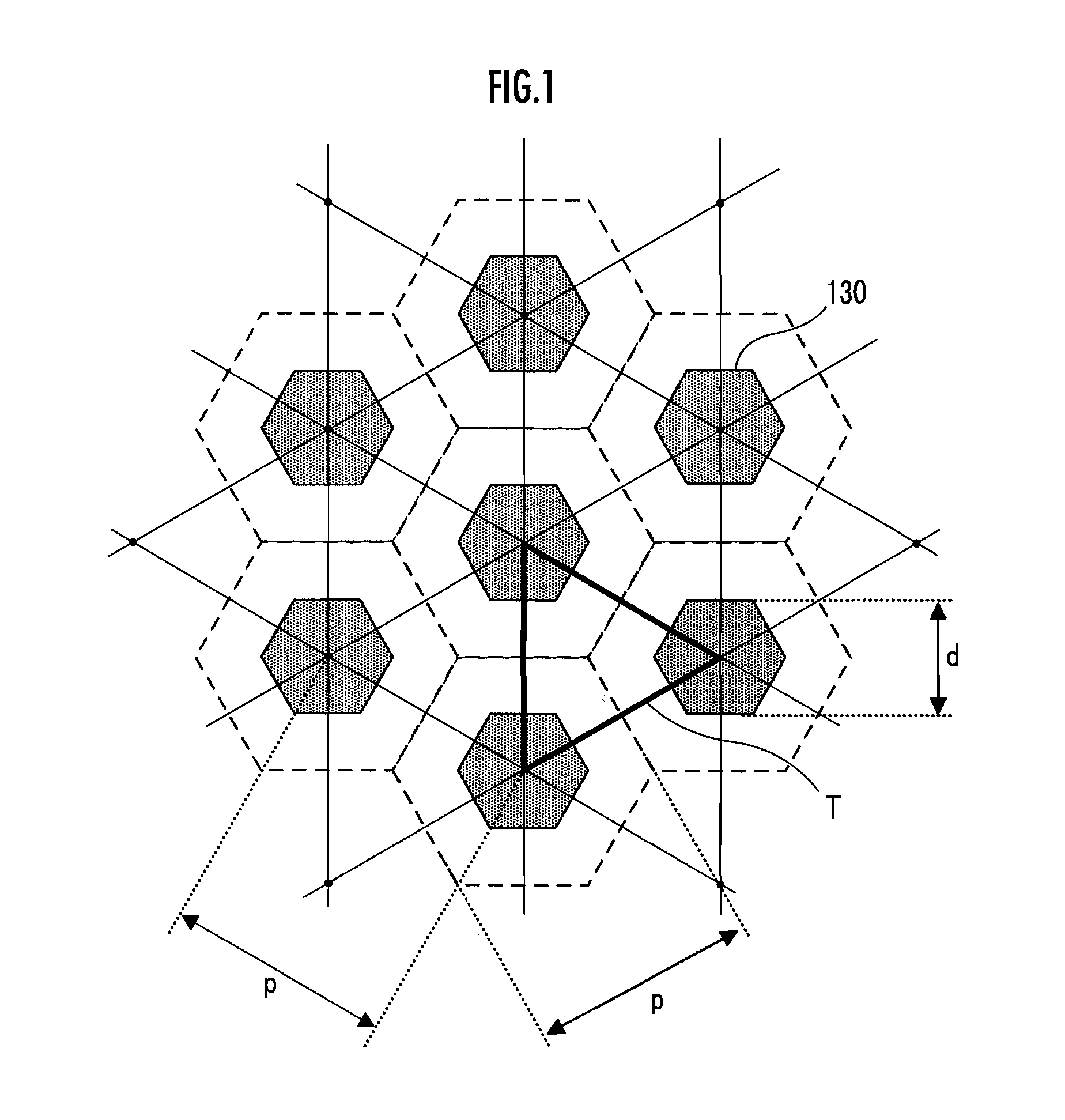
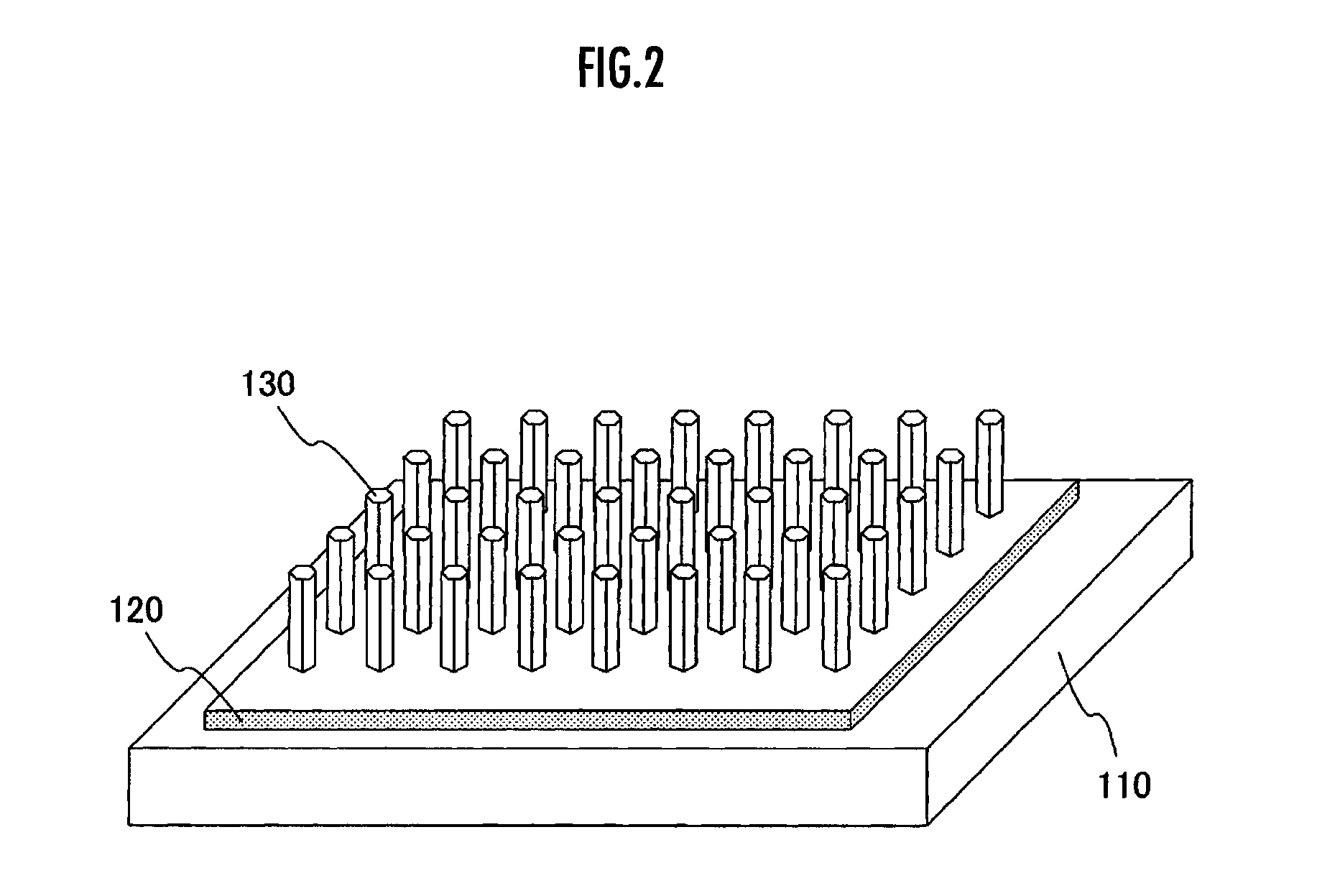
Solar Cell Element, Color Sensor and Method of Manufacturing Light Emitting Element and Light Receiving Element
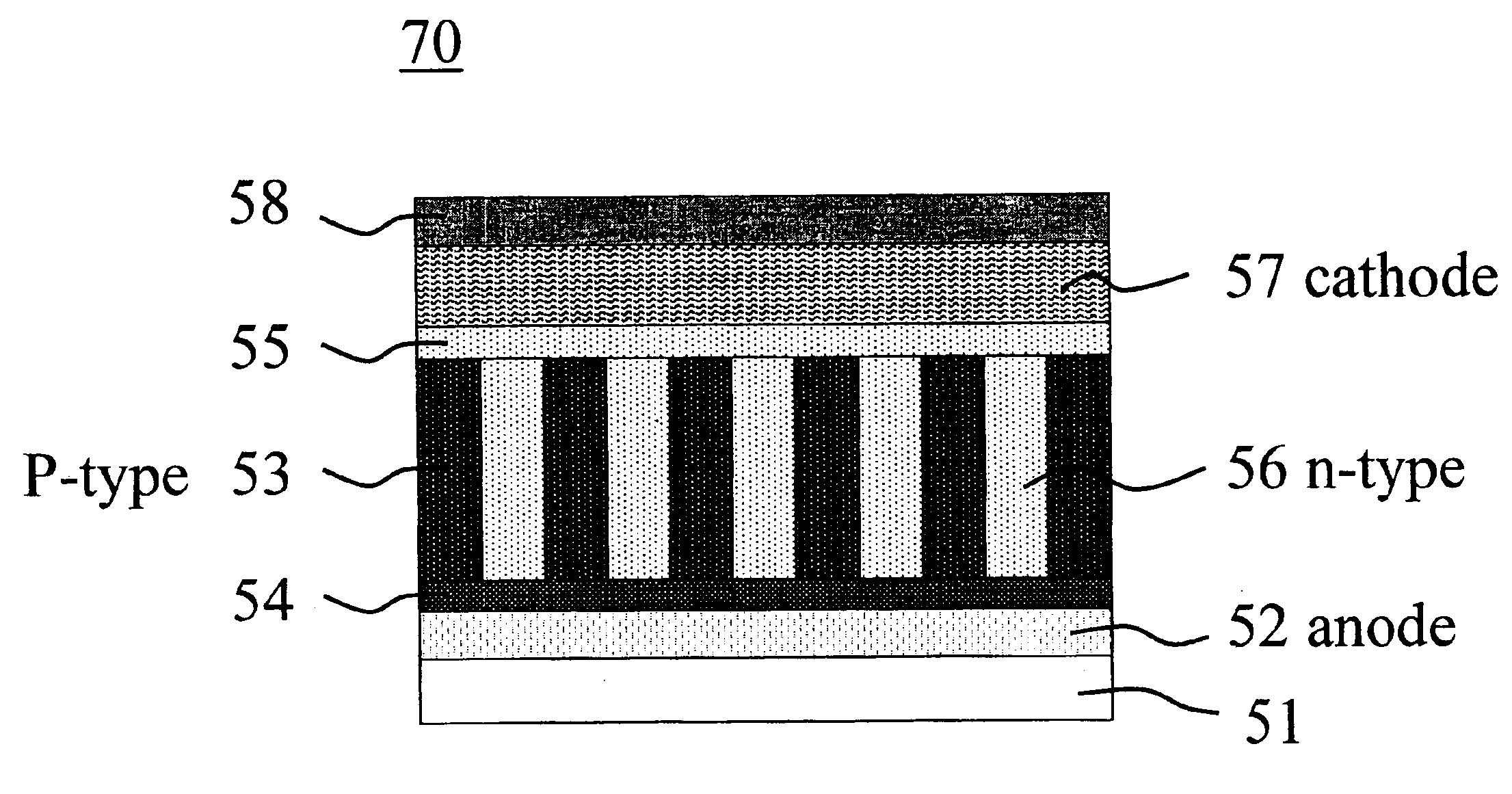
A solar cell element having improved power generation efficiency is provided. A solar cell element 100 has a substrate 110, a mask pattern 120, semiconductor nanorods 130, a first electrode 150 and a second electrode 160. The semiconductor nanorods 130 are disposed in triangular lattice form as viewed in plan on the substrate 110. The ratio p / d of the center-to-center distance p between each adjacent pair of the semiconductor nanorods 130 and the minimum diameter d of the semiconductor nanorods 130 is within the range from 1 to 7. Each semiconductor nanorod 130 has a central nanorod 131 formed of a semiconductor of a first conduction type, a first cover layer 132 formed of an intrinsic semiconductor and covering the central nanorod 131, and a second cover layer 138 formed of a semiconductor of a second conduction type and covering the first cover layer 132.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
A semiconductor integrated circuit device comprises a semiconductor substrate; an insulating layer formed on the semiconductor substrate; a semiconductor layer insulated from the semiconductor substrate by the insulating layer; source regions of a first conduction type and drain regions of the first conduction type both formed in the semiconductor layer; body regions of a second conduction type formed in the semiconductor layer between the source regions and the drain regions to store data by accumulating or releasing an electric charge; word lines formed on the body regions in electrical isolation from the body regions to extend in a first direction; bit lines connected to the drain regions and extending in a direction different from the first direction; and buried wirings formed in the insulating layer in electrical isolation from the semiconductor substrate and the semiconductor layer, said buried wirings extending in parallel with the bit lines.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor integrated device
InactiveUS20060046408A1Prevent reversalSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi substrateEngineering
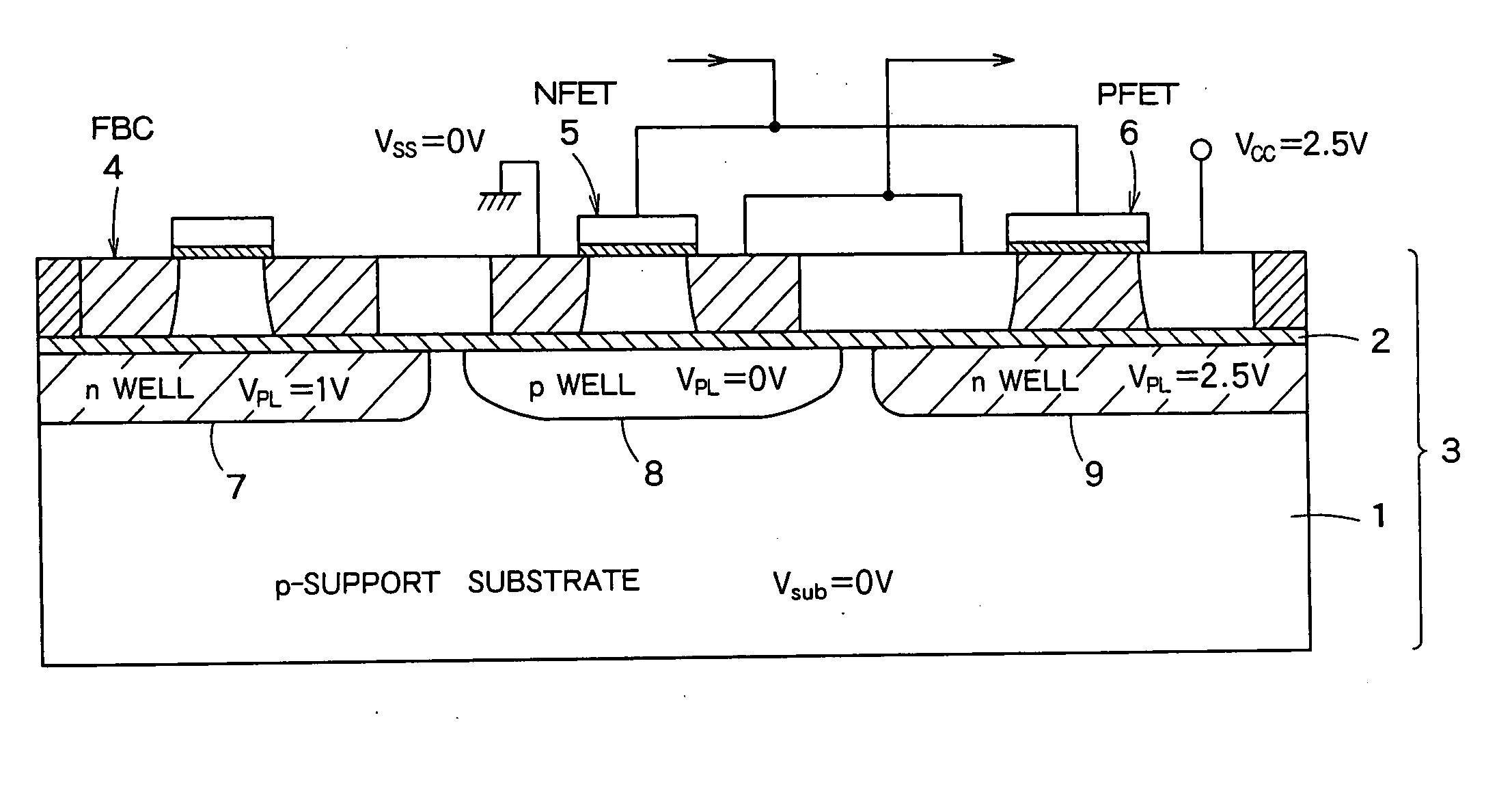
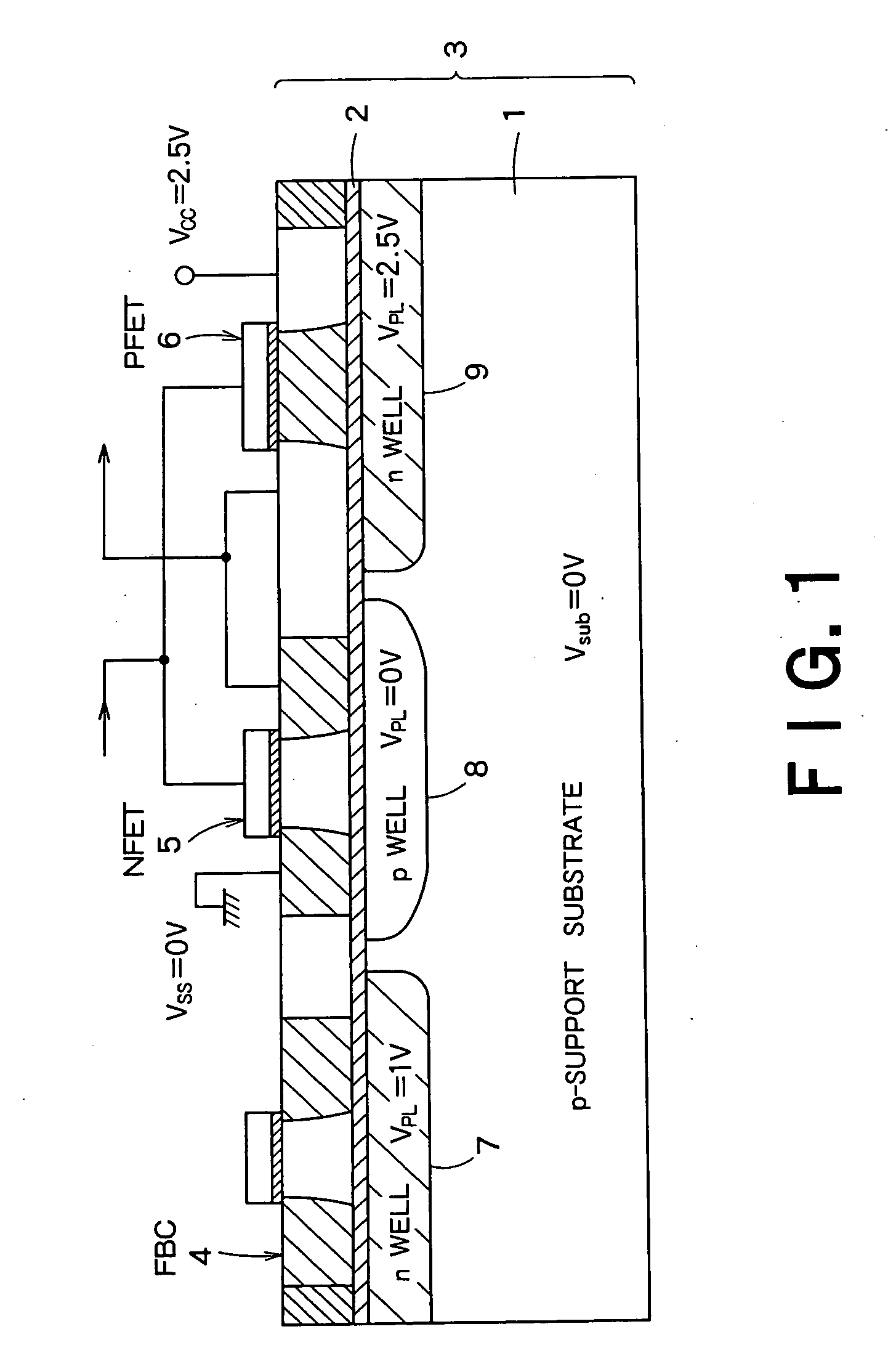
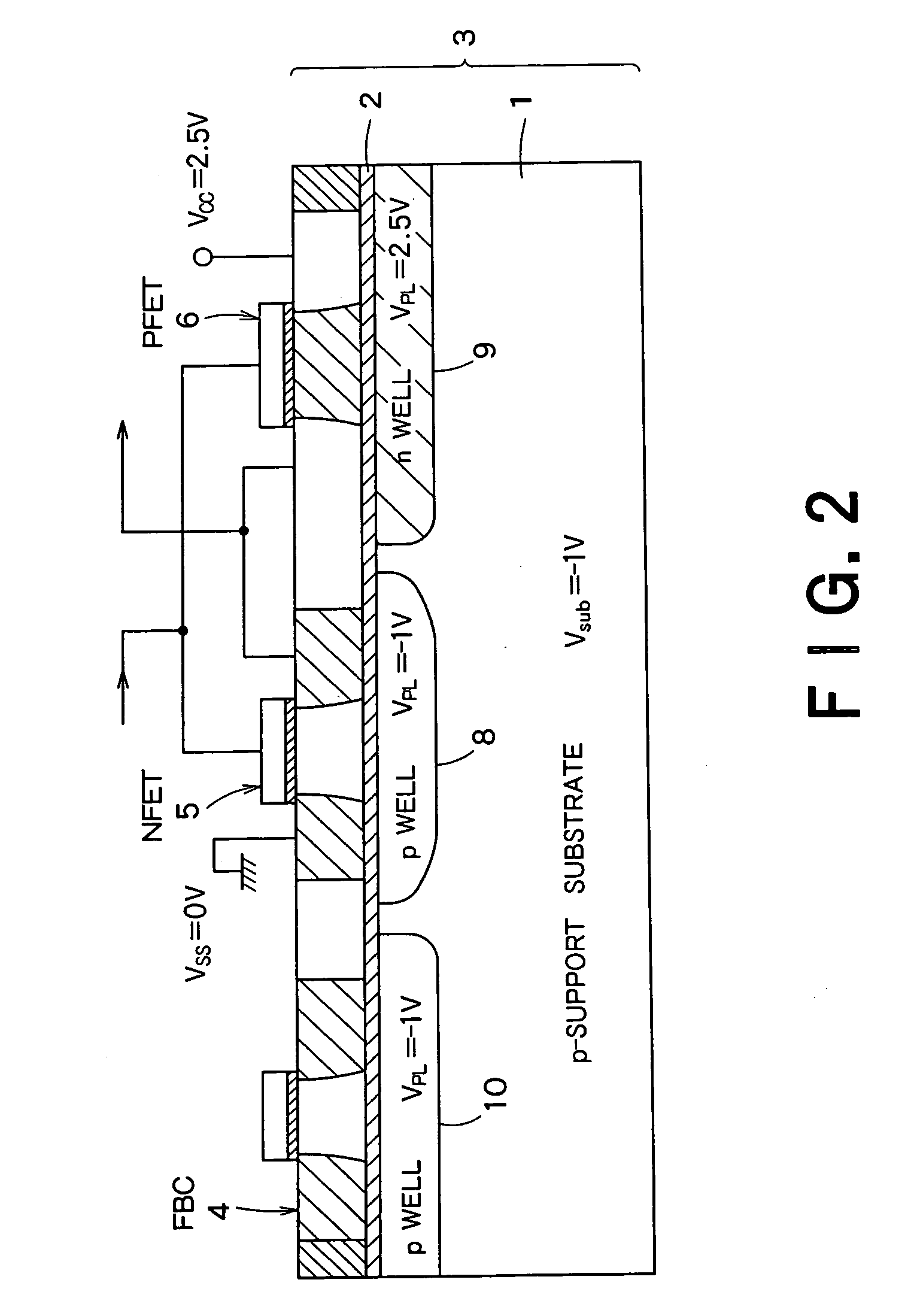
A semiconductor integrated apparatus, comprising: an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate which has a support substrate and an embedded insulation film; an NMOSFET, a PMOSFET and an FBC (Floating Body Cell) formed on the SOI substrate separately from each other; a p type of first well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the NMOSFET; an n type of second well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the PMOSFET; and a conduction type of third well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
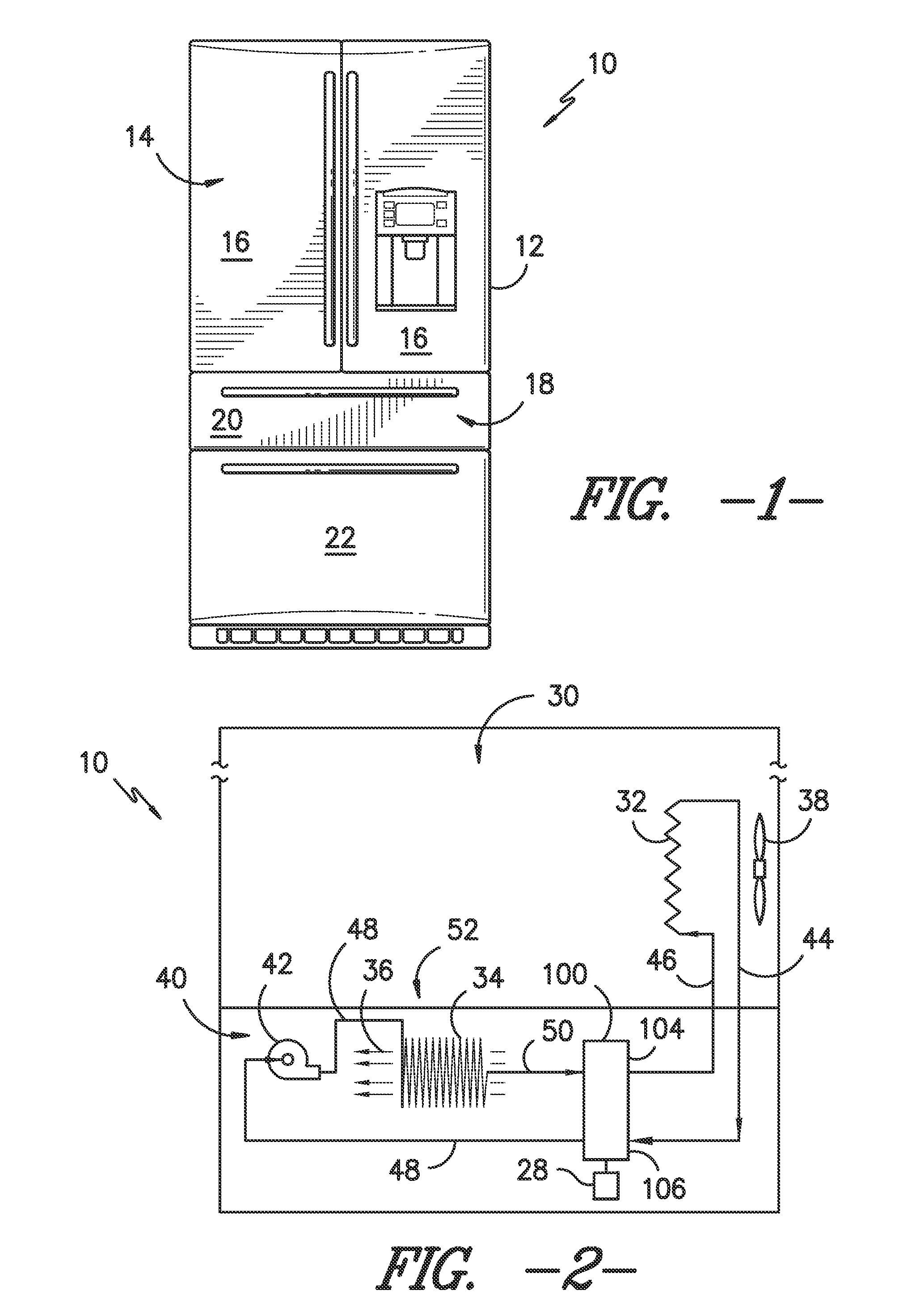
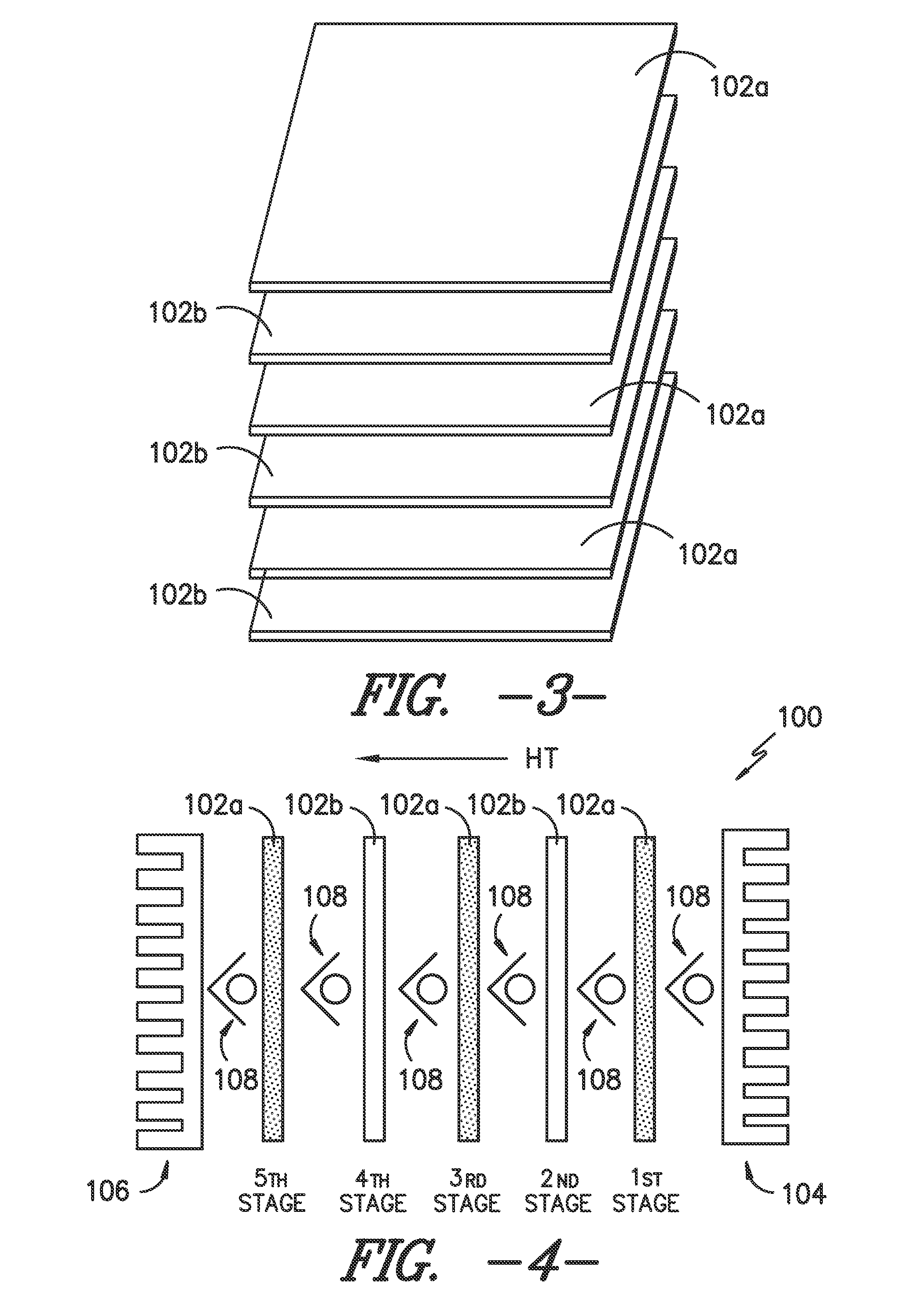
Conduction based magneto caloric heat pump
ActiveUS20140290273A1Machines using electric/magnetic effectsSustainable buildingsEngineeringRefrigeration
A heat pump is provided that uses multiple stages of MCMs to cause heat transfer between a heat receiving end and a heat transmitting end. Thermal blocks are placed along the direction of heat transfer at locations in the heat pump that preclude the transfer of heat in a direction from the heat transmitting end towards the heat receiving end. The heat pump can be, for example, part of a refrigeration loop or can be connected directly with the object for which heating or cooling is desired. An appliance incorporating such a heat pump is also provided.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
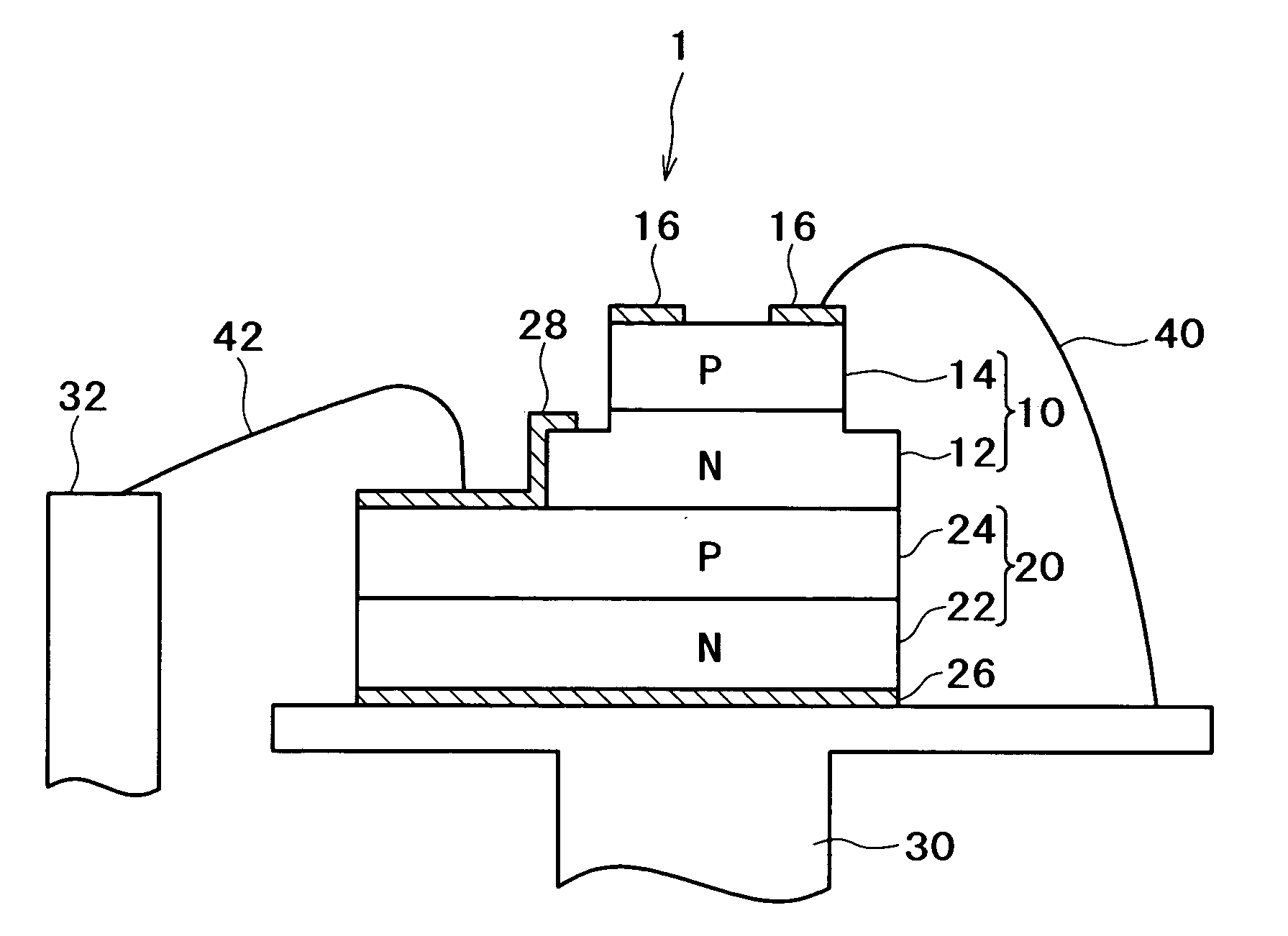
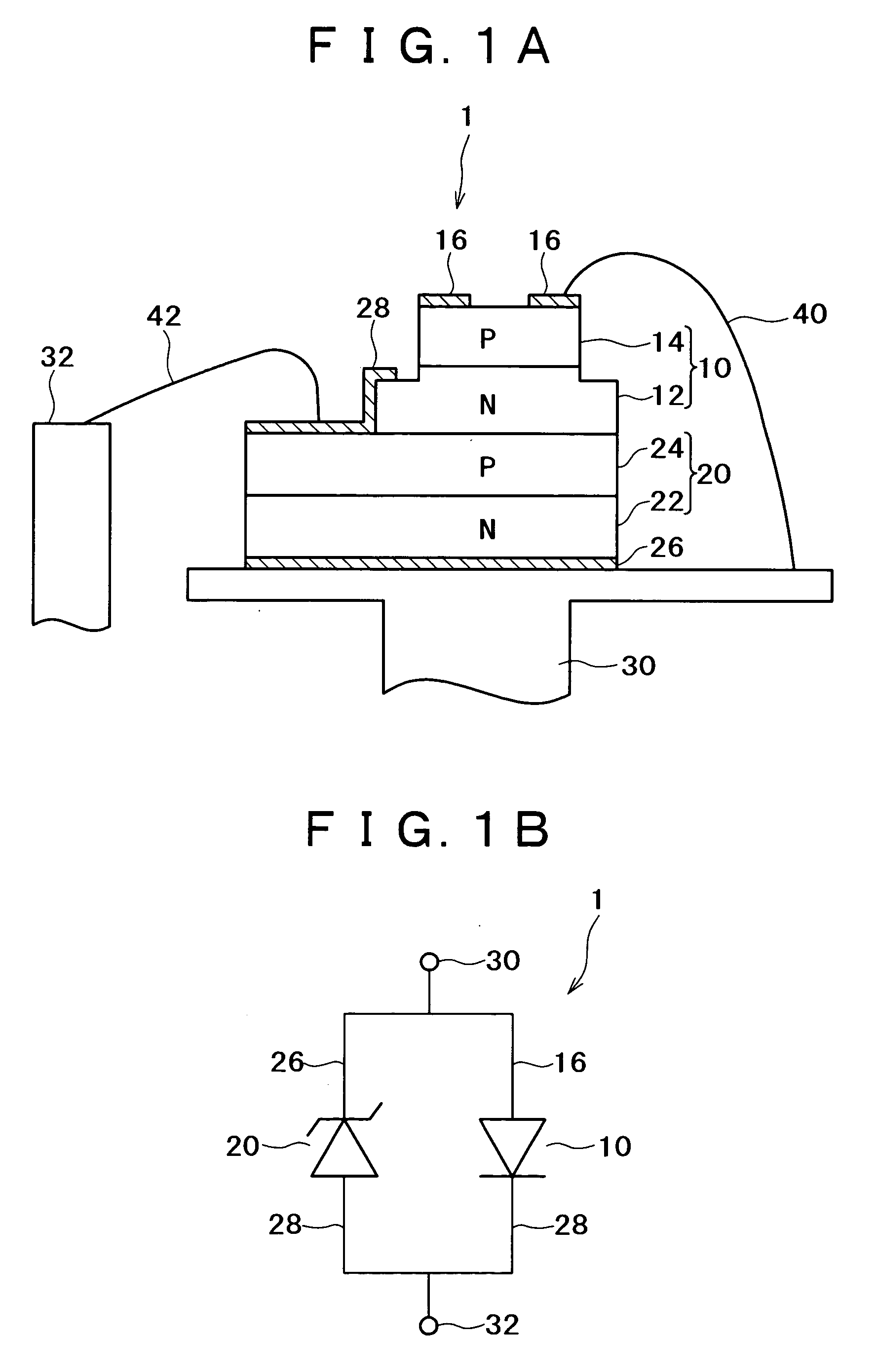
Semiconductor laser apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050271107A1Improve resistance to static voltage break downImprove reliabilityLaser detailsSolid-state devicesZener diodePhysics
A semiconductor laser apparatus has a Zener diode containing a first semiconductor region of a first conduction type and a second semiconductor region of a second conduction type joined with the first semiconductor region, and a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser diode stacked above the Zener diode and containing at least a first mirror layer of a first conduction type, a second mirror layer of a second conduction type and an active region sandwiched between the first and second mirror layers. The first semiconductor region and the second mirror layer are electrically connected and the second semiconductor region and the first mirror layer are electrically connected.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Semiconductor photodetector and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20060273421A1Avoid failureImprove reliabilitySemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorPhotodetector
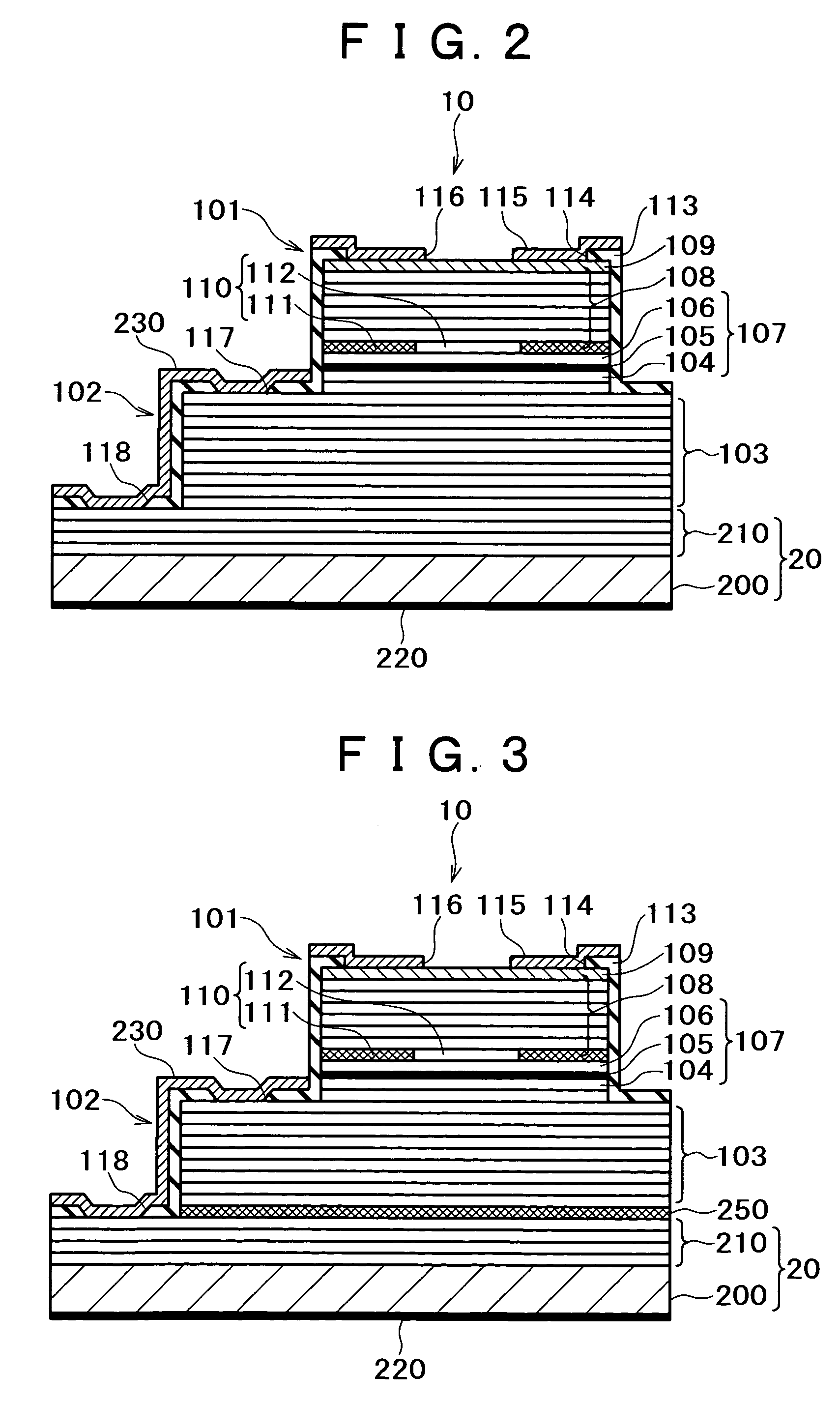
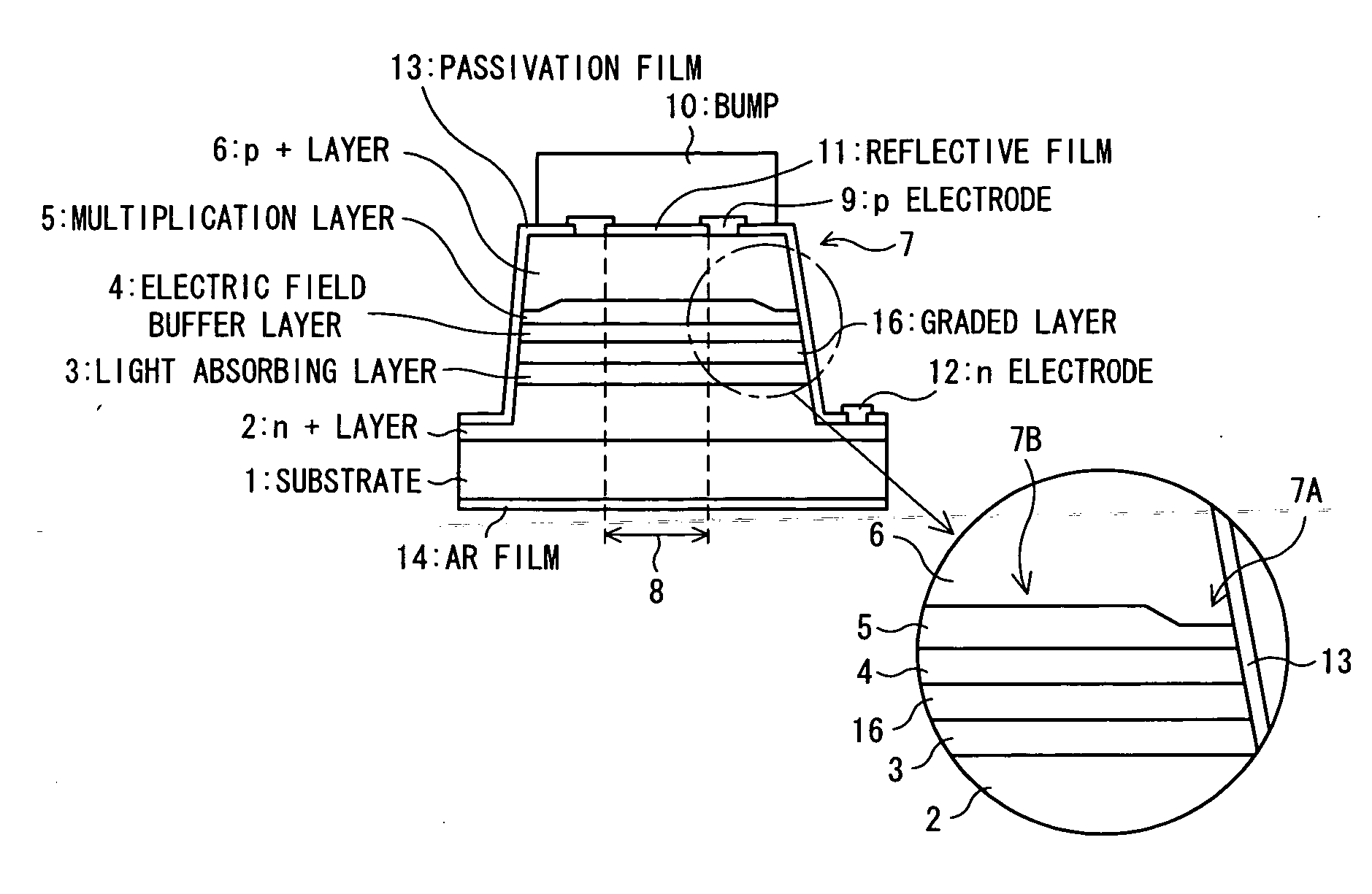
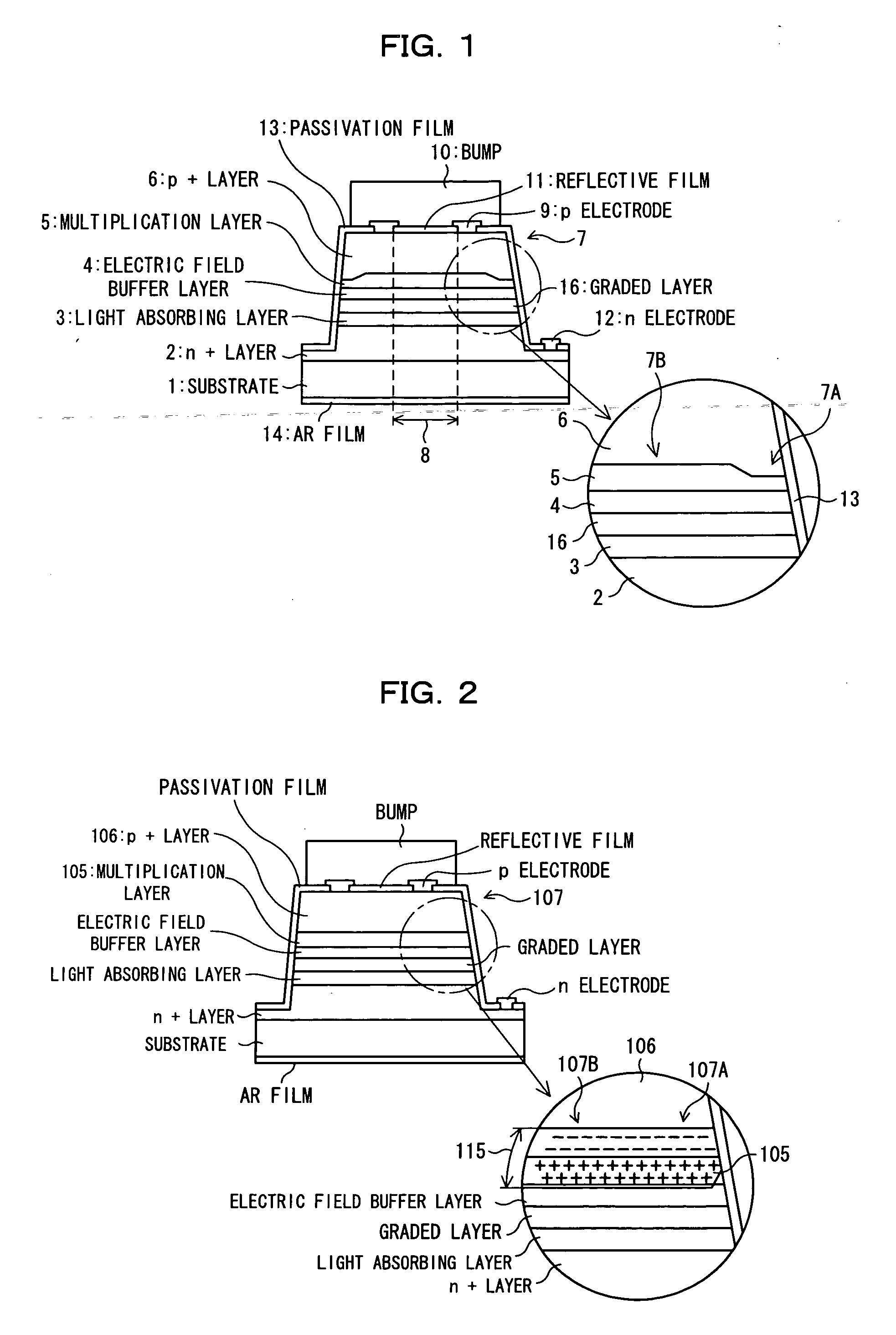
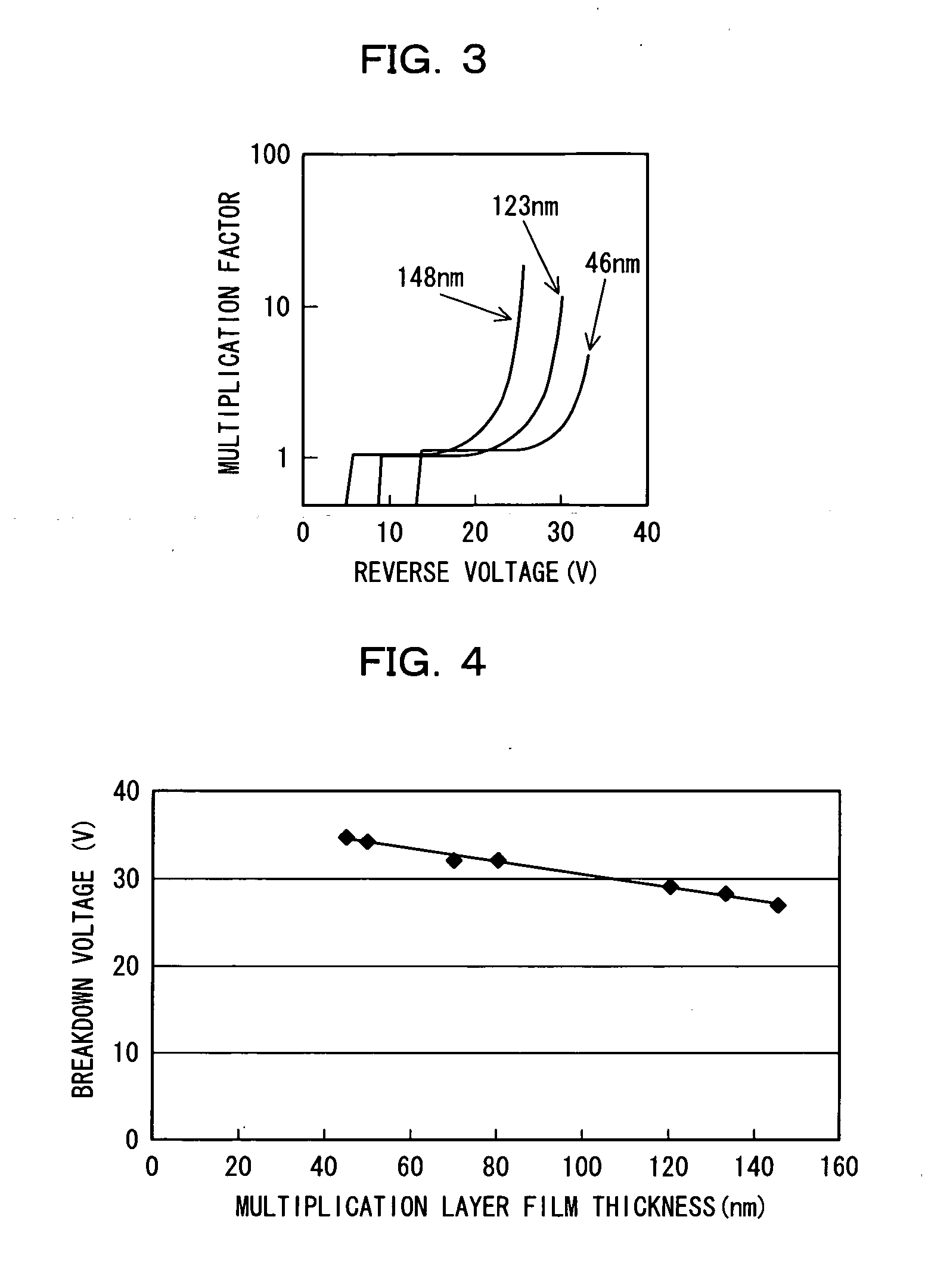
In order to improve reliability by preventing an edge breakdown in a semiconductor photodetector having a mesa structure such as a mesa APD, the semiconductor photodetector comprises a mesa structure formed on a first semiconductor layer of the first conduction type formed on a semiconductor substrate, the mesa structure including a light absorbing layer for absorbing light, an electric field buffer layer for dropping an electric field intensity, an avalanche multiplication layer for causing avalanche multiplication to occur, and a second semiconductor layer of the second conduction type, wherein the thickness of the avalanche multiplication layer at the portion in the vicinity of the side face of the mesa structure is made thinner than the thickness at the central portion of the mesa structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC DEVICE INNOVATIONS
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
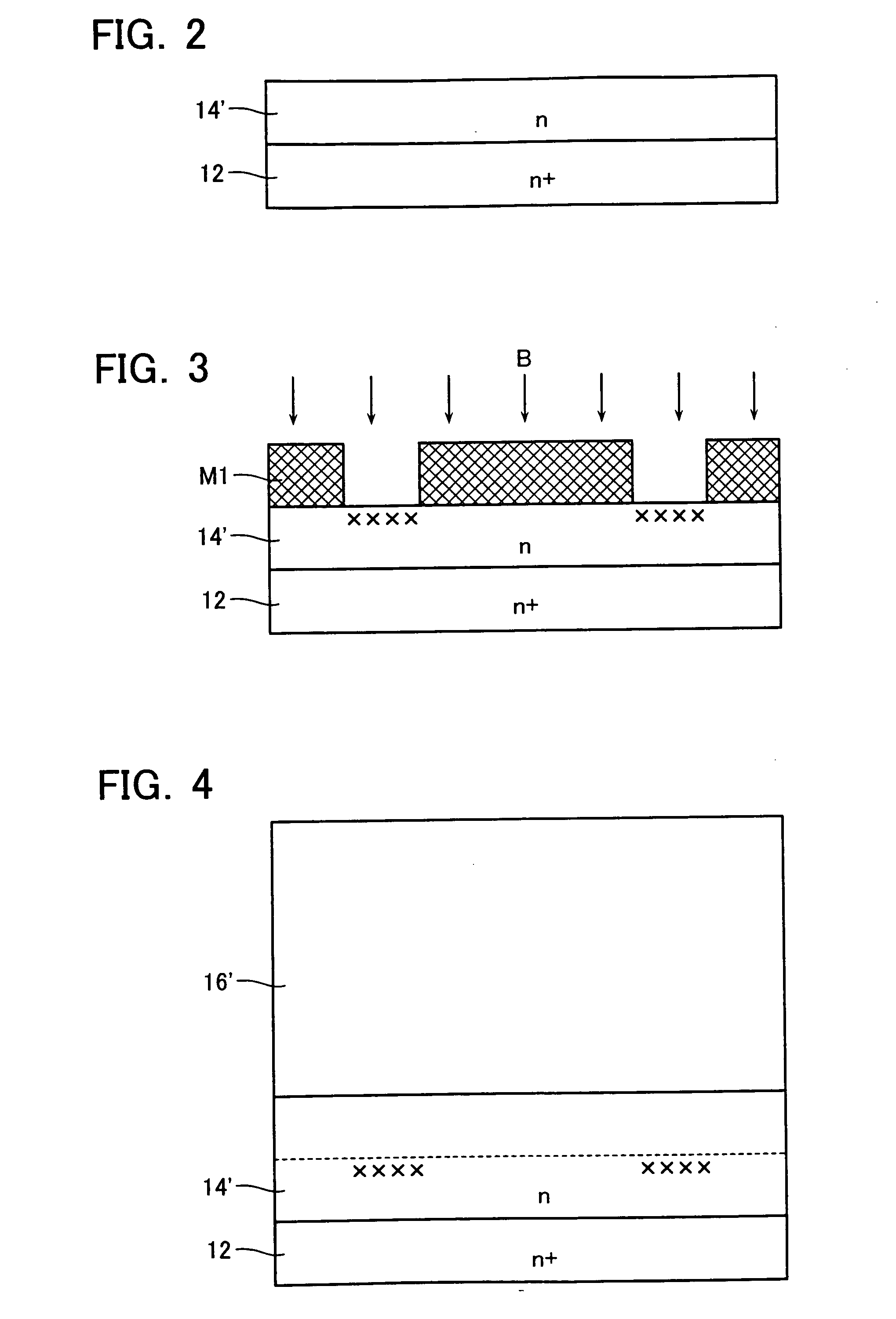
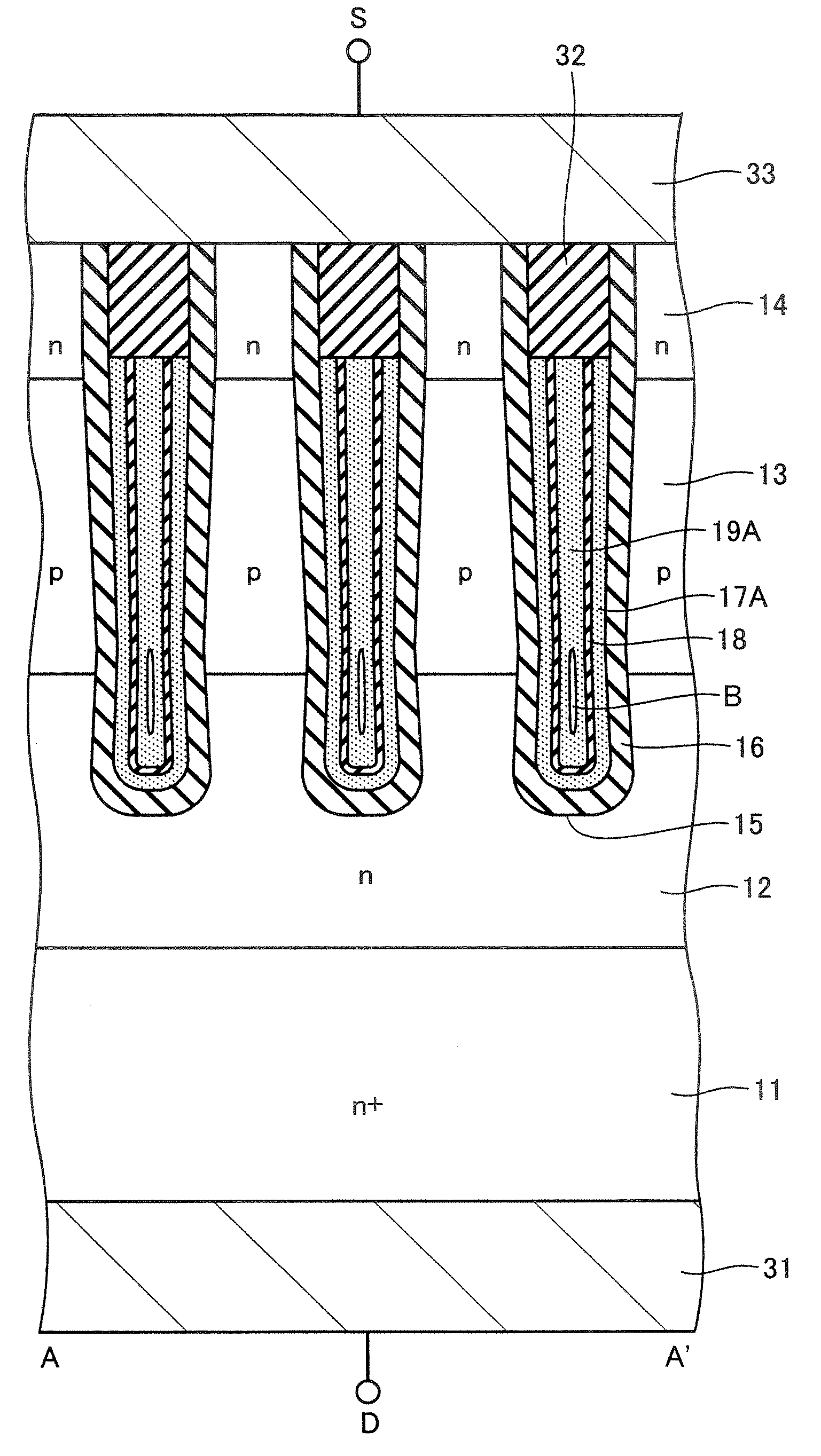
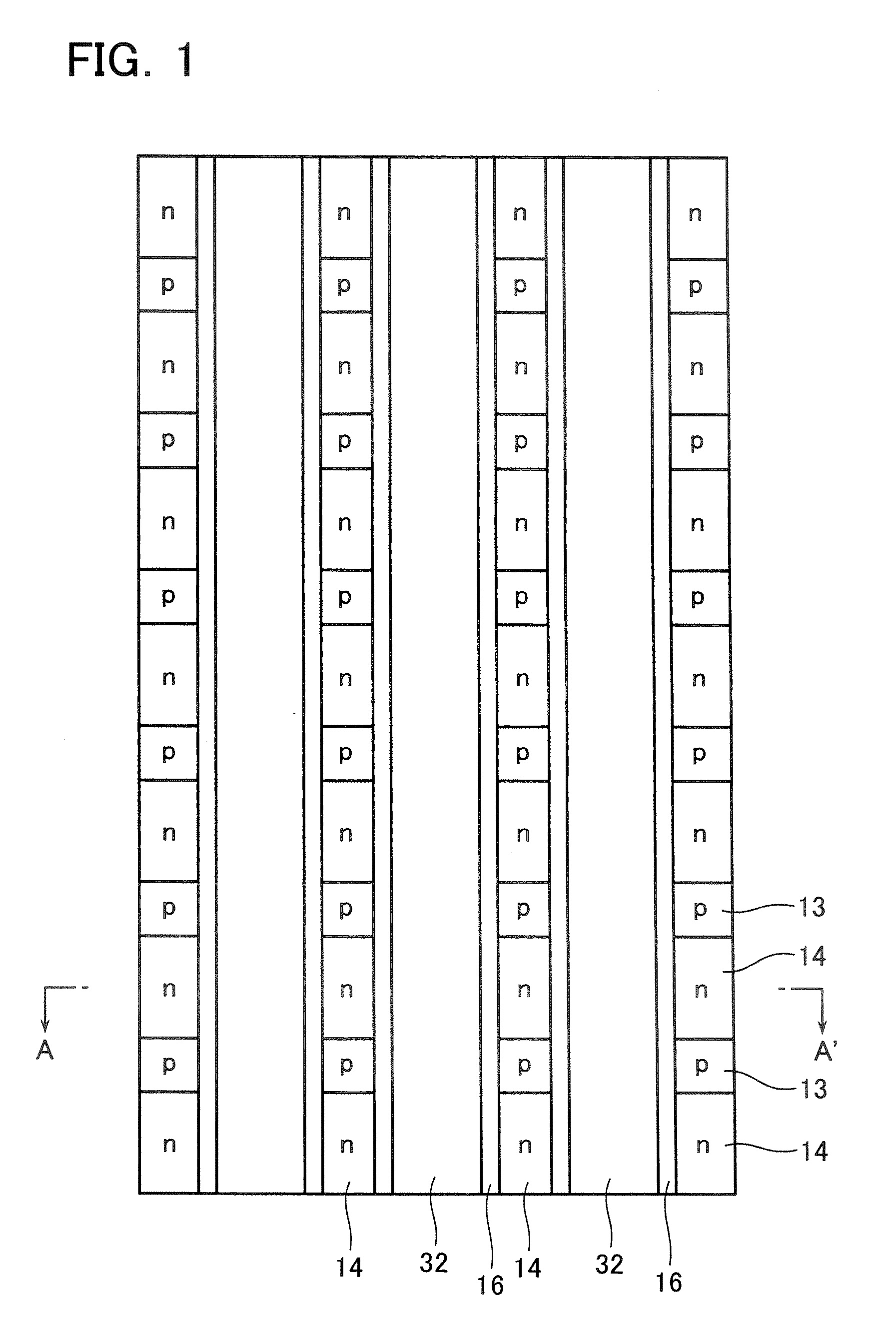
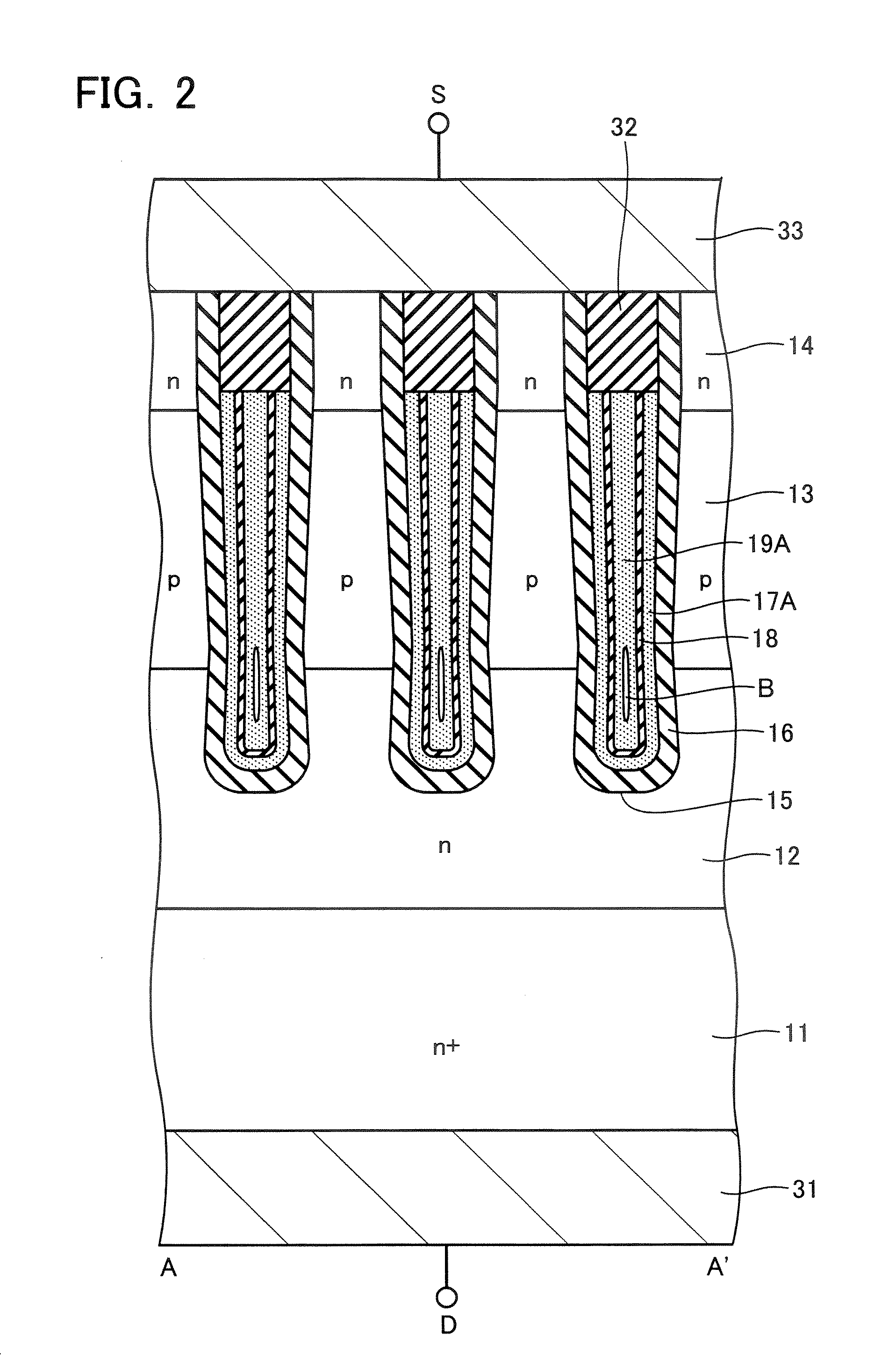
First semiconductor pillar layers of a first conduction type and second semiconductor pillar layers of a second conduction type are arranged on a first semiconductor layer of the first conduction type laterally, periodically and alternately at a first period to forma first pillar layer. Third semiconductor pillar layers of the first conduction type and fourth semiconductor pillar layers of the second conduction type are arranged on the first pillar layer laterally, periodically and alternately at a second period smaller than the first period to form a second pillar layer. A semiconductor base layer of the second conduction type is formed on a surface of the fourth semiconductor pillar layer. A semiconductor diffused layer of the first conduction type is formed on a surface of the semiconductor base layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Organic semiconductor devices and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS6891191B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsConductive polymer
Owner:XIAO STEVEN SHUYONG
Silicon-on-insulator chip with multiple crystal orientations
InactiveUS7368334B2Improve performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal orientationP channel
A silicon-on-insulator chip includes an insulator layer, typically formed over a substrate. A first silicon island with a surface of a first crystal orientation overlies the insulator layer and a second silicon island with a surface of a second crystal orientation also overlies the insulator layer. In one embodiment, the silicon-on-insulator chip also includes a first transistor of a first conduction type formed on the first silicon island, and a second transistor of a second conduction type formed on the second silicon island. For example, the first crystal orientation can be (110) while the first transistor is a p-channel transistor, and the second crystal orientation can be (100) while the second transistor is an n-channel transistor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device comprises on a surface of a first semiconductor layer of the first conduction type a second semiconductor layer of the first conduction type. A semiconductor base layer of the second conduction type is formed on the second semiconductor layer, and a semiconductor diffusion layer of the first conduction type is formed on a surface of the semiconductor base layer. A trench is formed from the surface of the semiconductor diffusion layer to a depth reaching the second semiconductor layer. A gate electrode is formed of a conductor film buried in the trench with a gate insulator interposed therebetween. The conductor film includes a first conductor film formed along the gate electrode to have a recess and a second conductor film formed to fill the recess.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
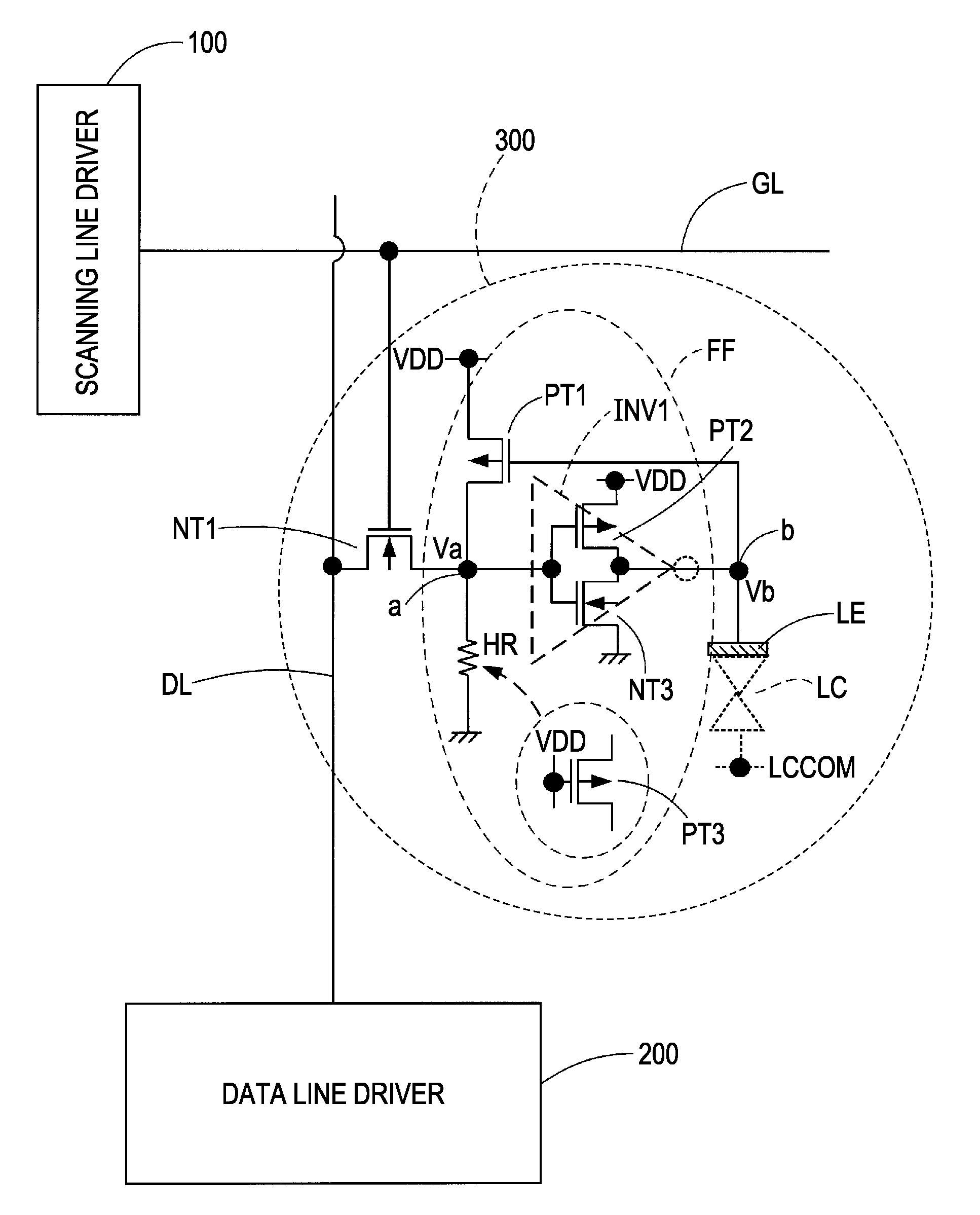
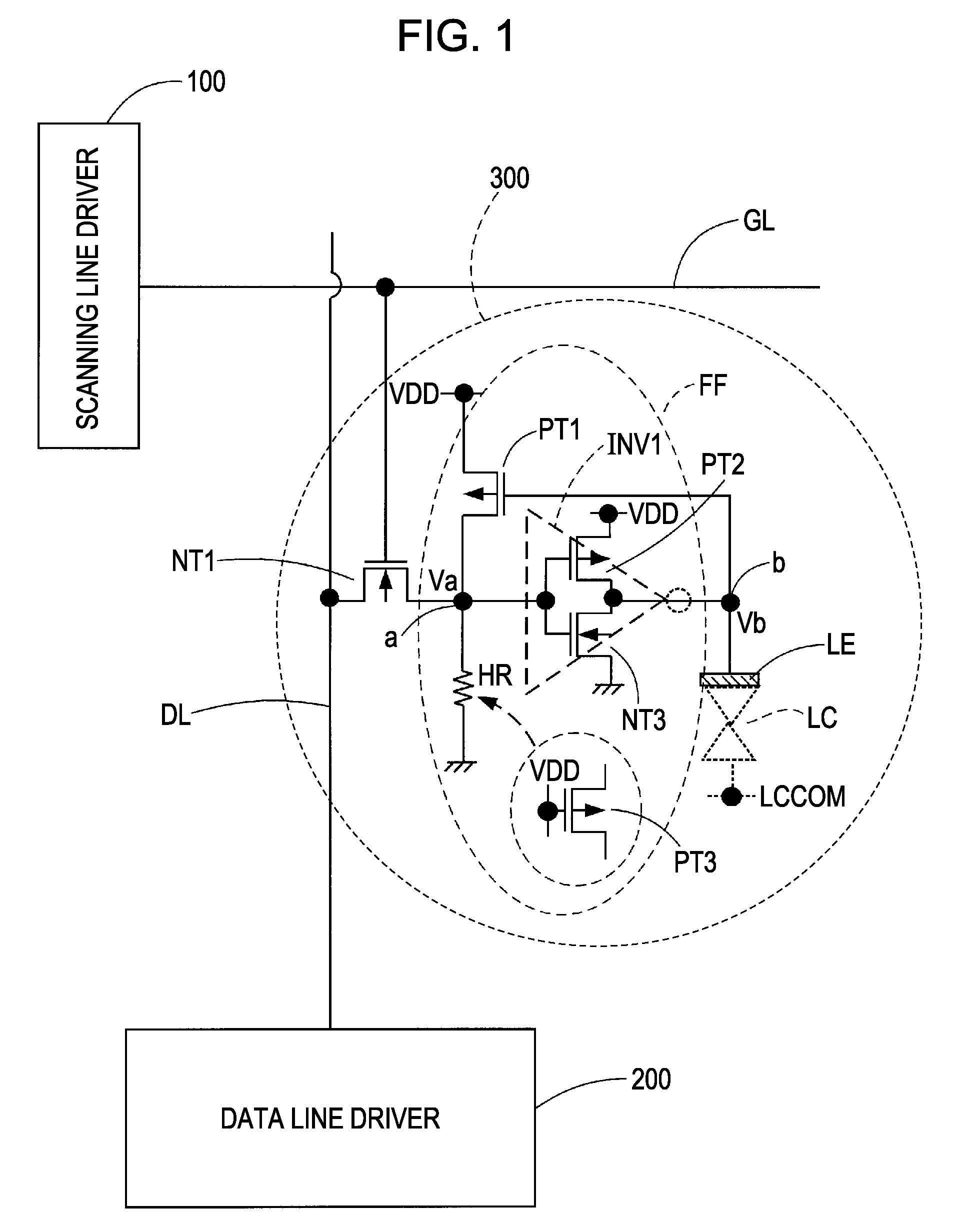
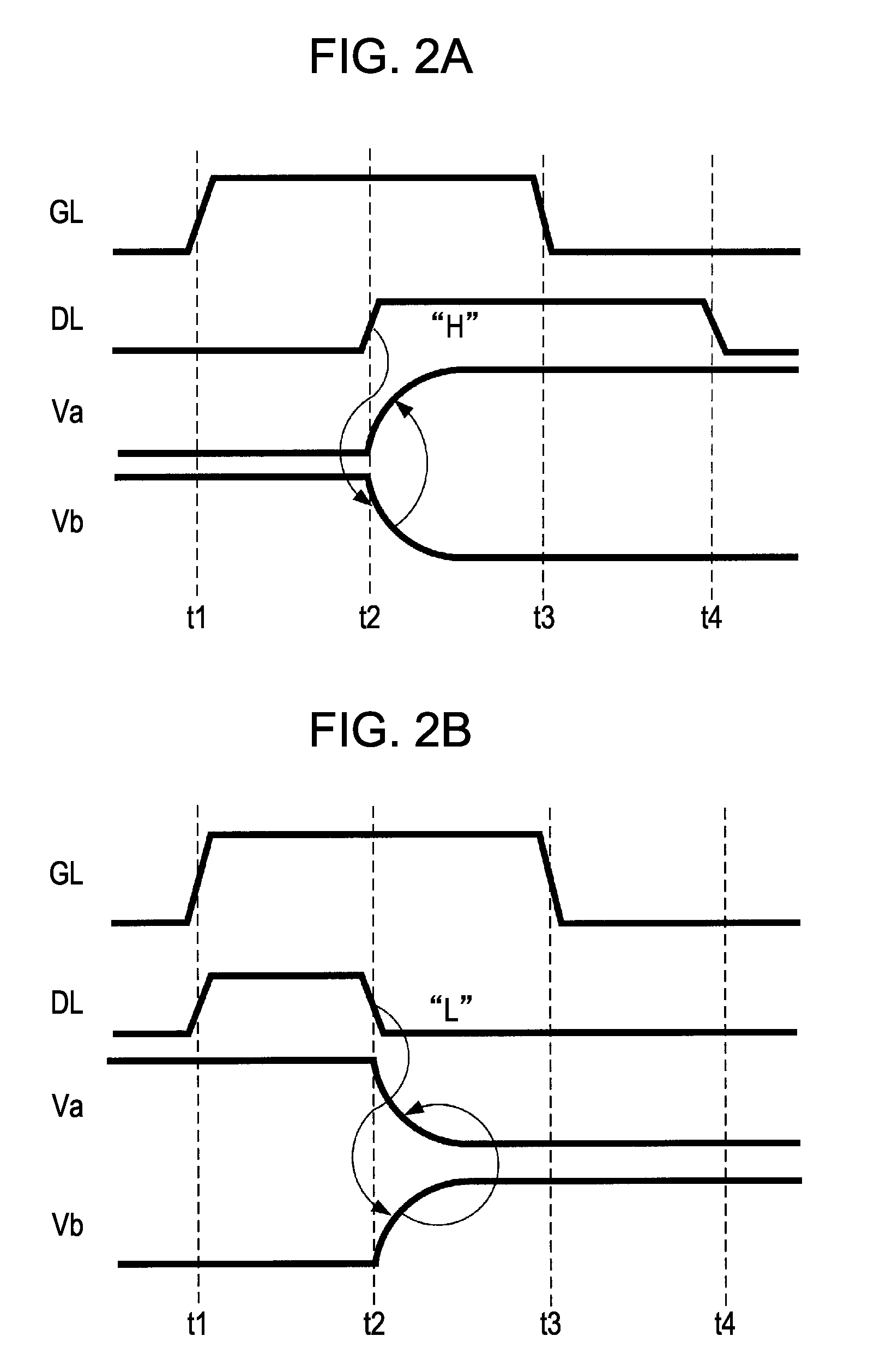
Pixel circuit having flip-flop with inverter and feedback transistor, electro-optical device having said pixel circuit, and electronic apparatus having said electro-optical device
ActiveUS7952060B2Highly reliable pixelReduce areaStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectronTransistor
A pixel circuit includes a pixel electrode, a pixel transistor of a first conduction type, and a flip-flop. The pixel transistor has a control node connected to a scanning line, a first node connected to a data line, and a second node. The flip-flop has an inverter and a feedback transistor of a second conduction type opposite to the first conduction type. The inverter has an input node connected to the second node of the pixel transistor, and an output node connected to the pixel electrode. The feedback transistor is controlled to be turned on or off in accordance with an output of the inverter for supplying a high-level power source voltage or a low-level power source voltage to a common connection point of the second node of the pixel transistor and the input node of the inverter, in the ON state.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor laser apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050238076A1Improve resistance to static voltage breakdownImprove reliabilityLaser detailsLaser active region structureZener diodePhysics
A semiconductor laser apparatus includes a substrate, a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser diode (VCSEL) including a first and second mirror layers of a first and second conduction types, respectively, an active region between the first and second mirror layers, a first and second electrode layers electrically connected with the first and second mirror layers, respectively, and at least one Zener diode including a first and second semiconductor regions of a first and second conduction types, respectively, and a third and fourth electrode layers electrically connected with the first and second semiconductor regions, respectively. The second semiconductor region is formed in a portion of the first semiconductor region and forms a PN junction with the first semiconductor region. The VCSEL and the Zener diode are formed on the substrate. The first and second electrode layers are electrically connected with the fourth and third electrode layers, respectively.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com