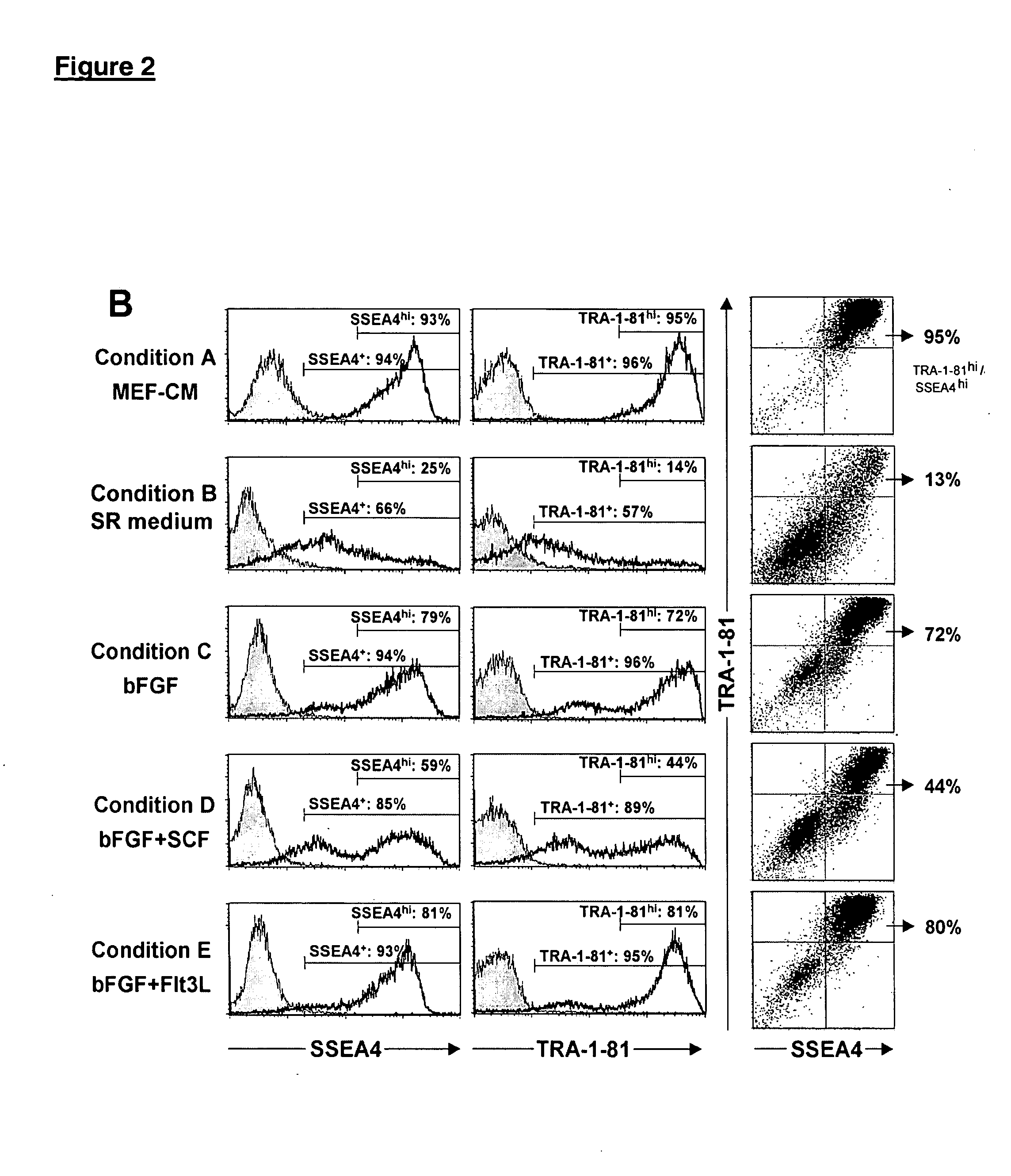
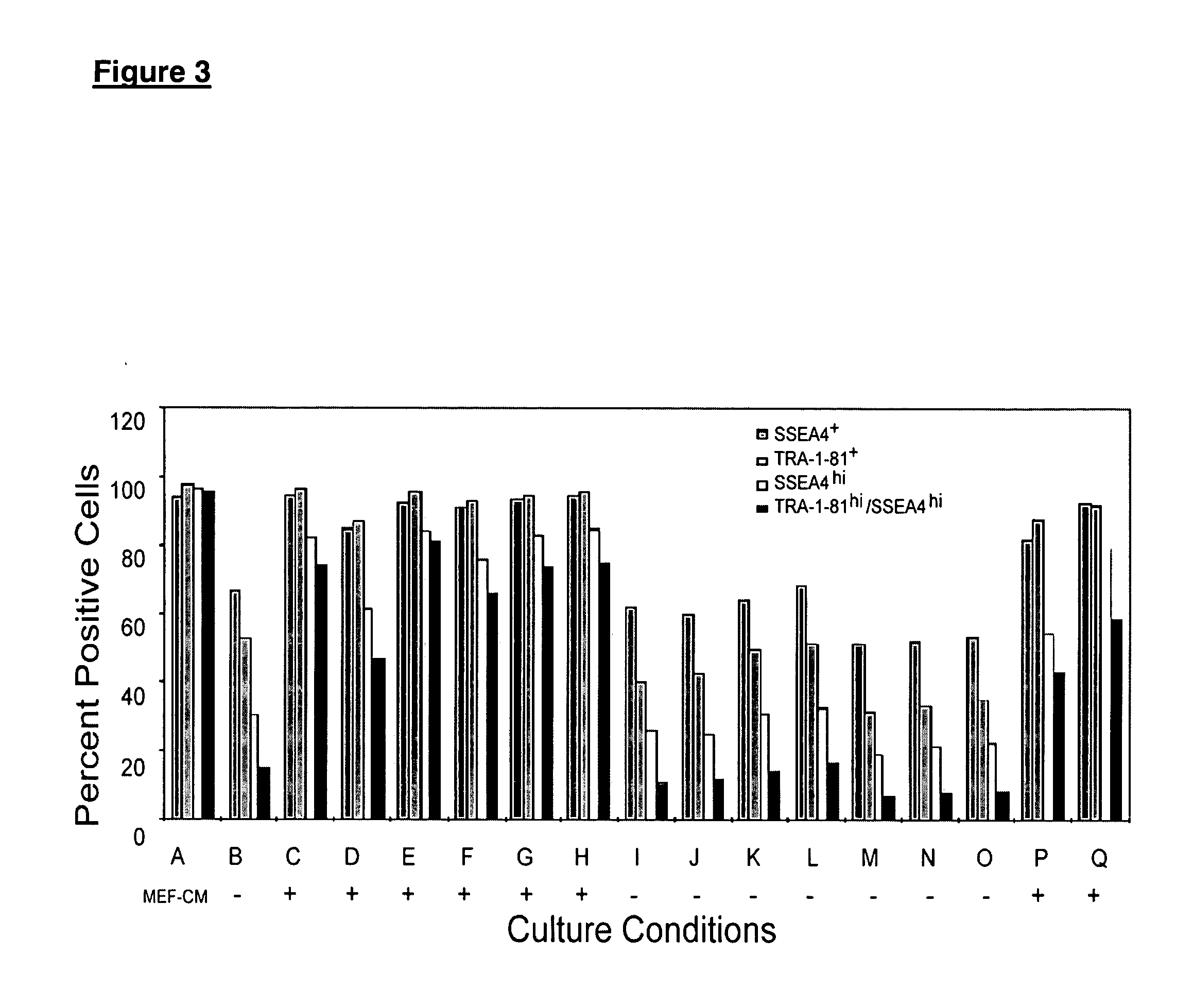
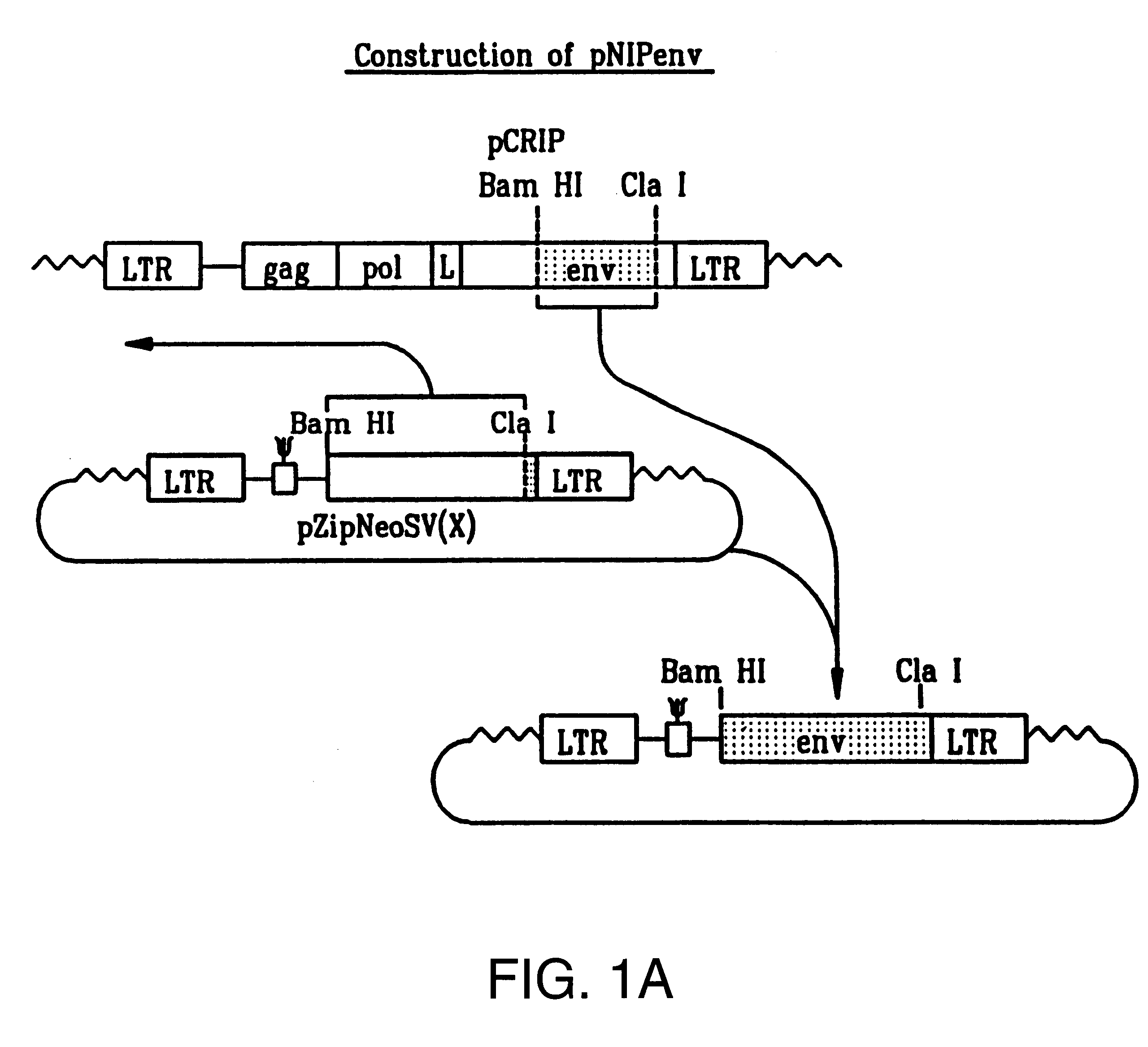
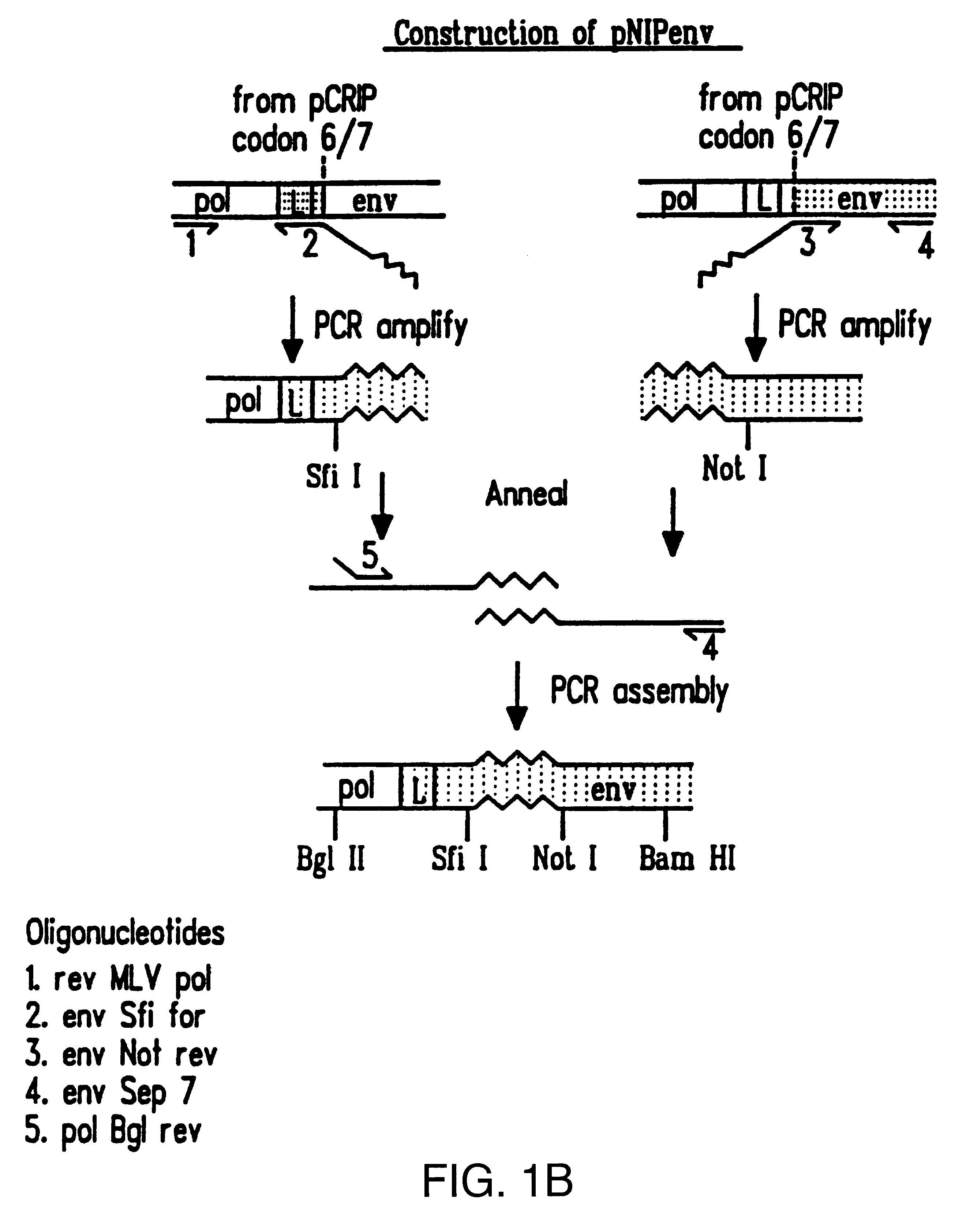
Patents
Literature
106 results about "Mouse Fibroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
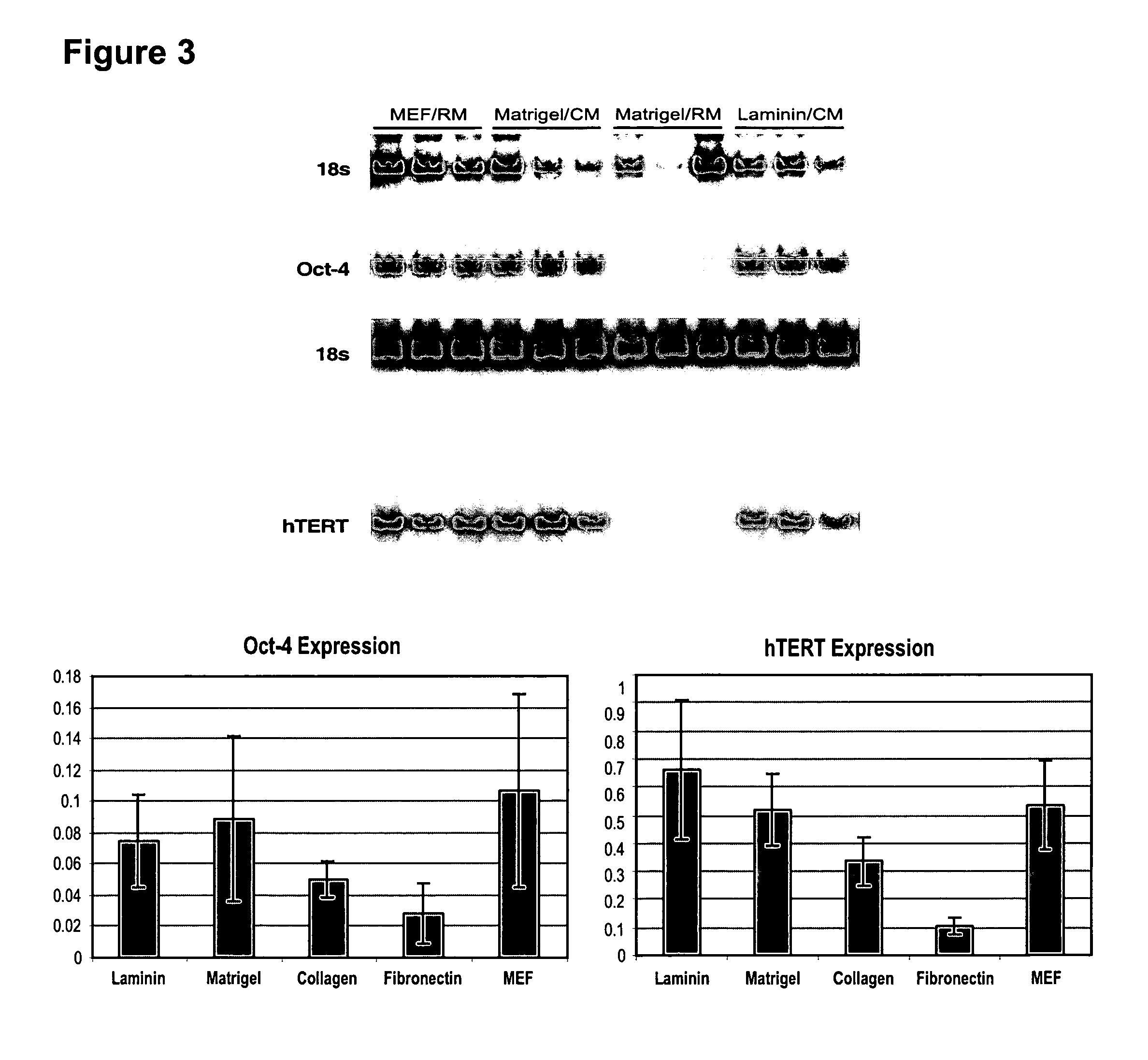
Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) are a type of fibroblast prepared from mouse embryo. MEFs show a spindle shape when cultured in vitro, a typical feature of fibroblasts. The MEF is a limited cell line.
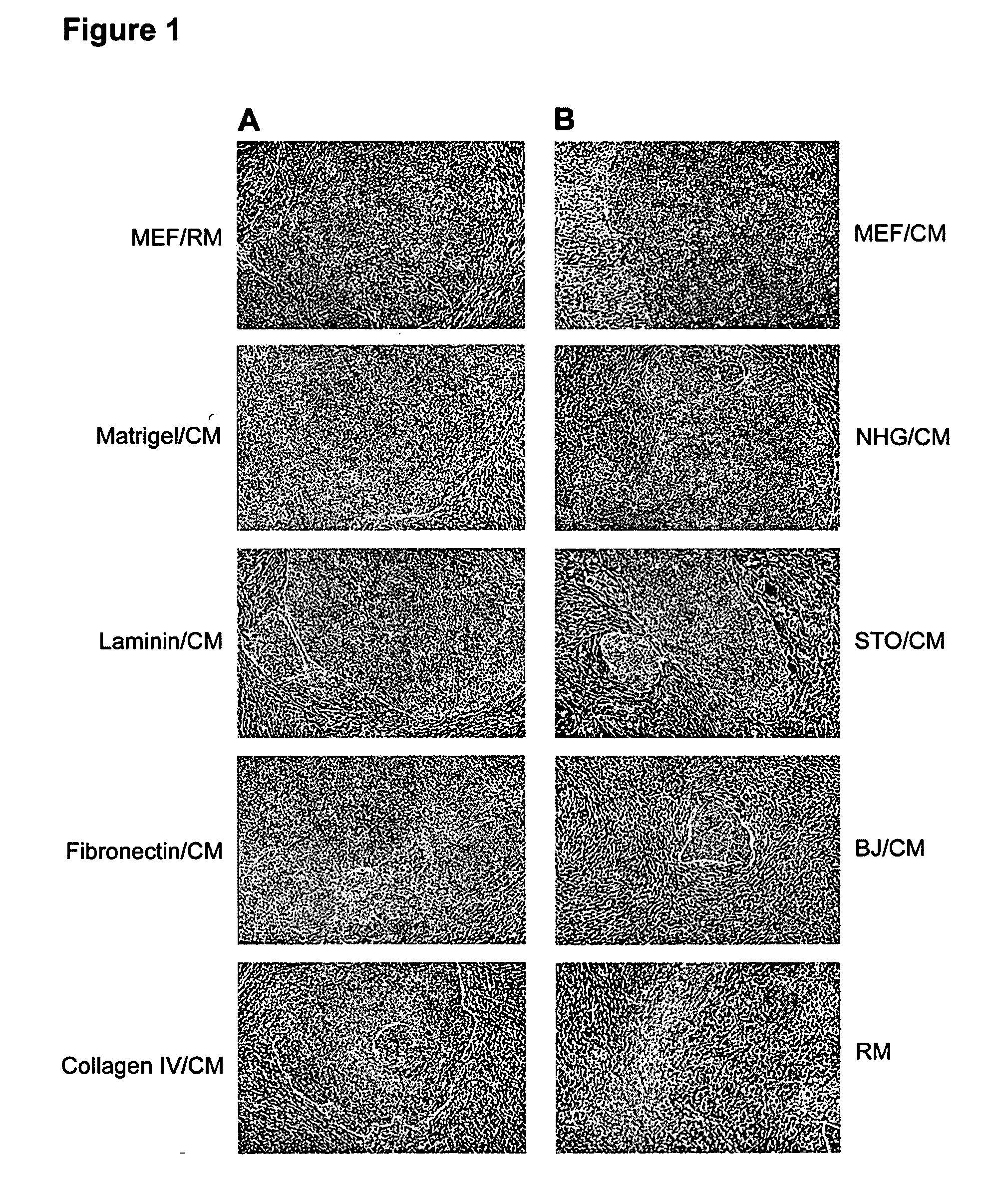
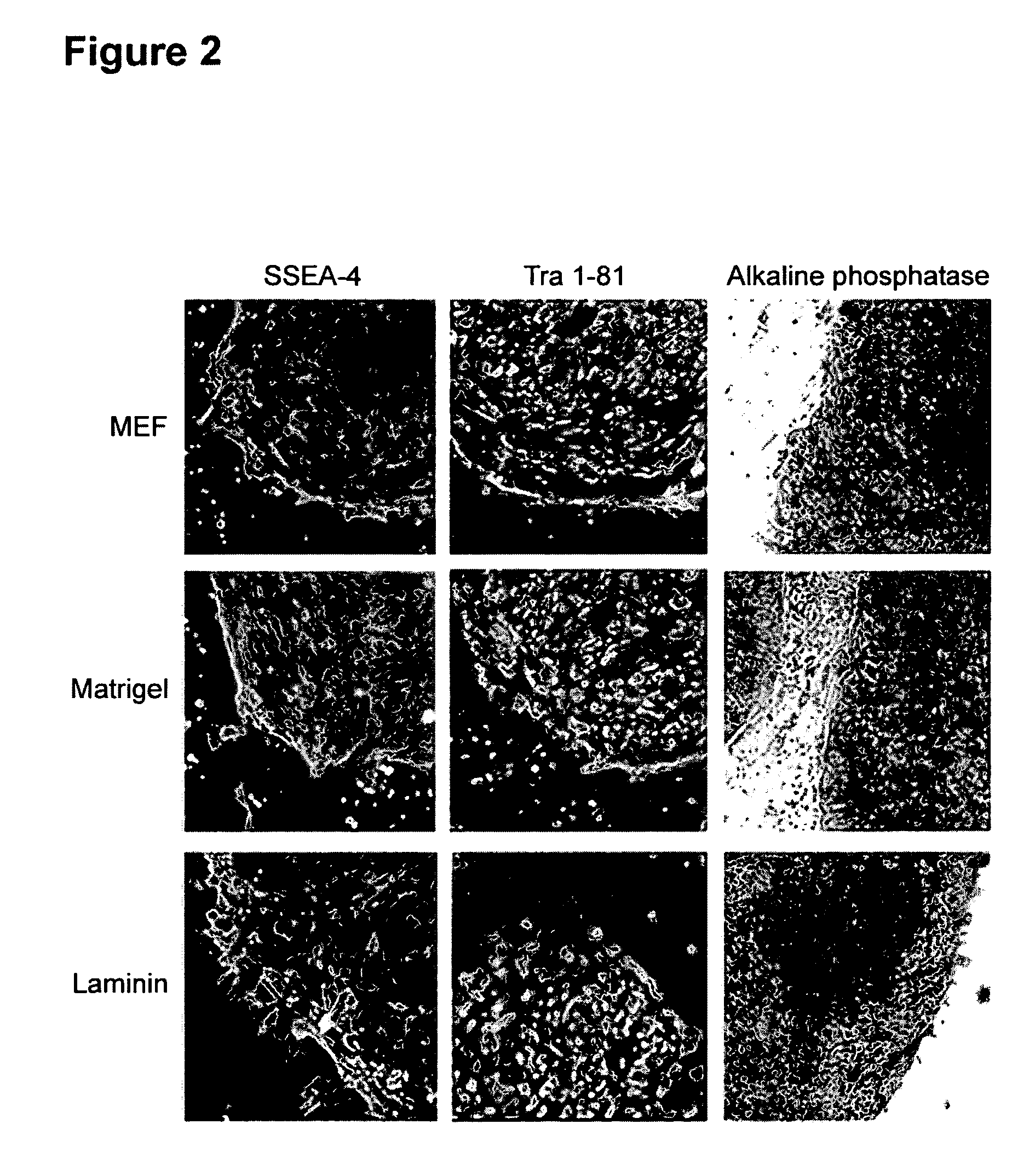
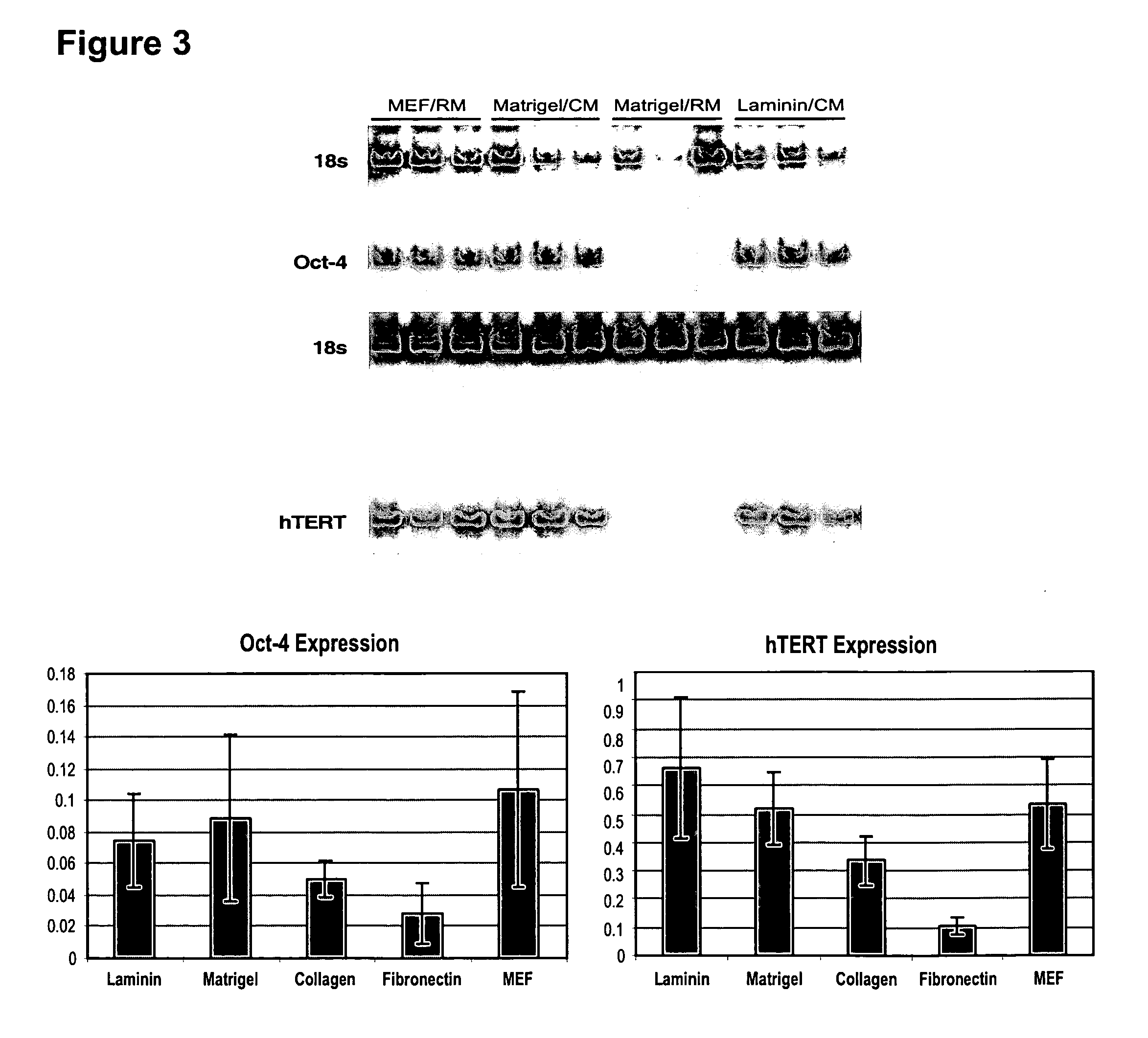
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
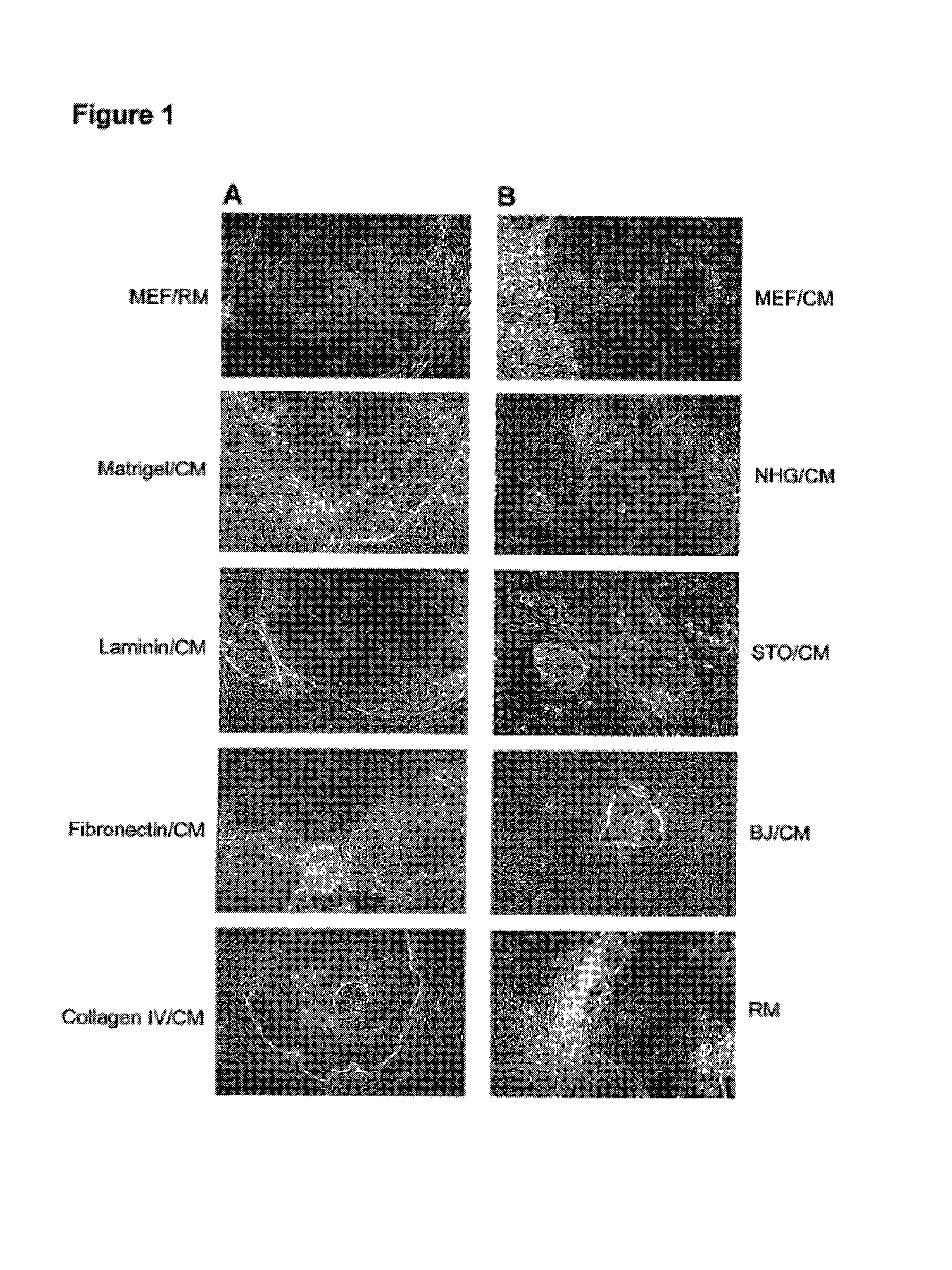
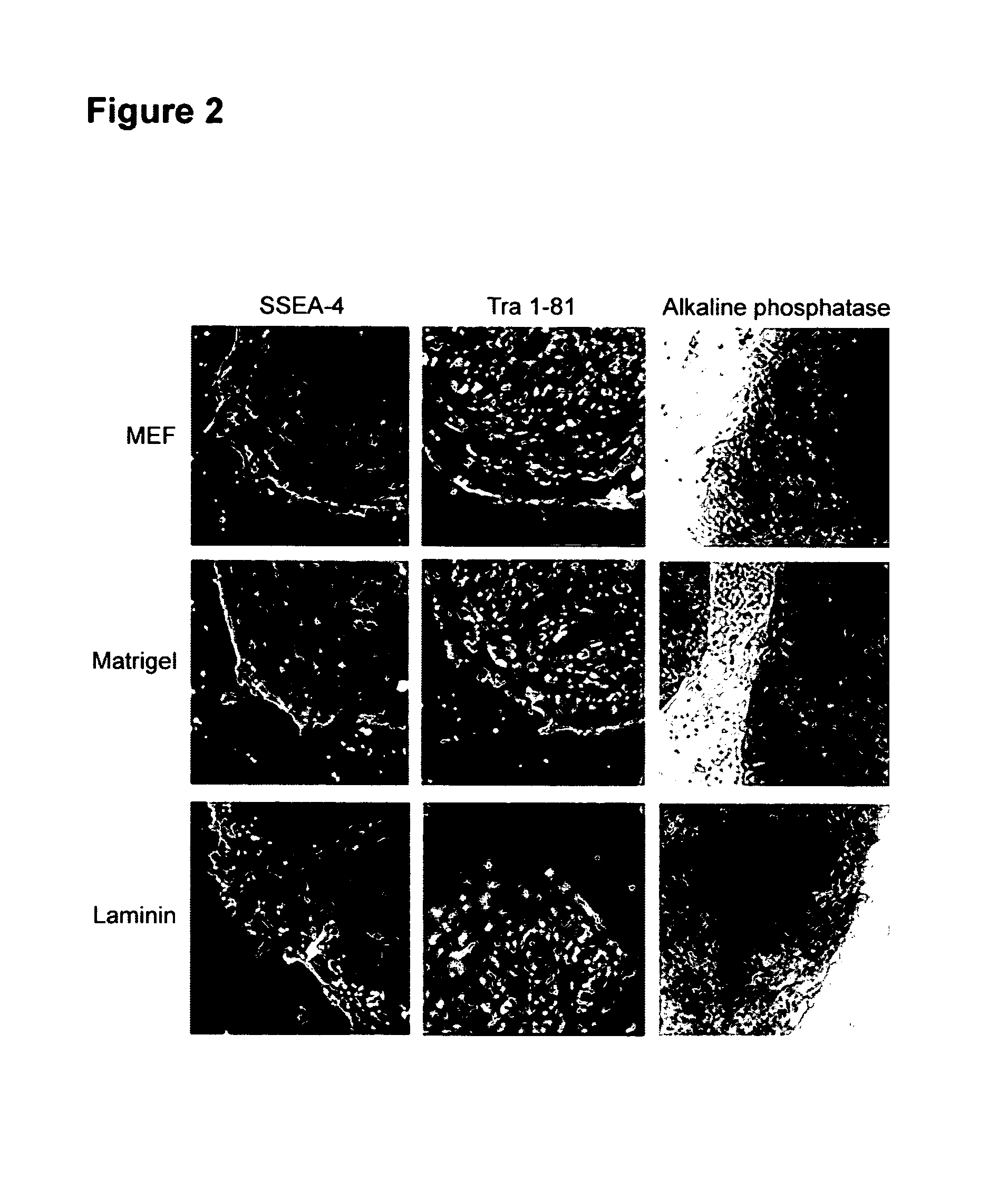
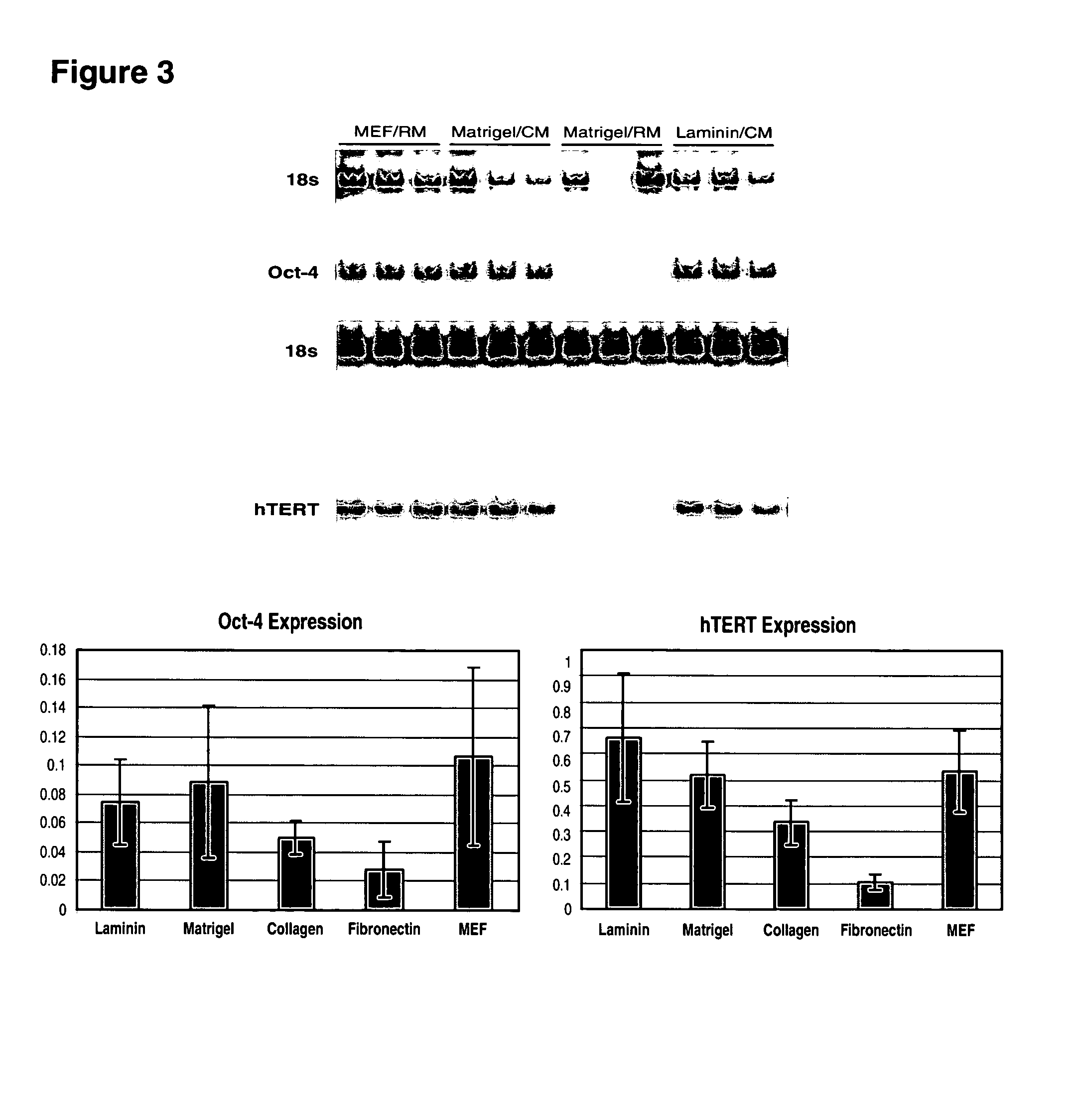
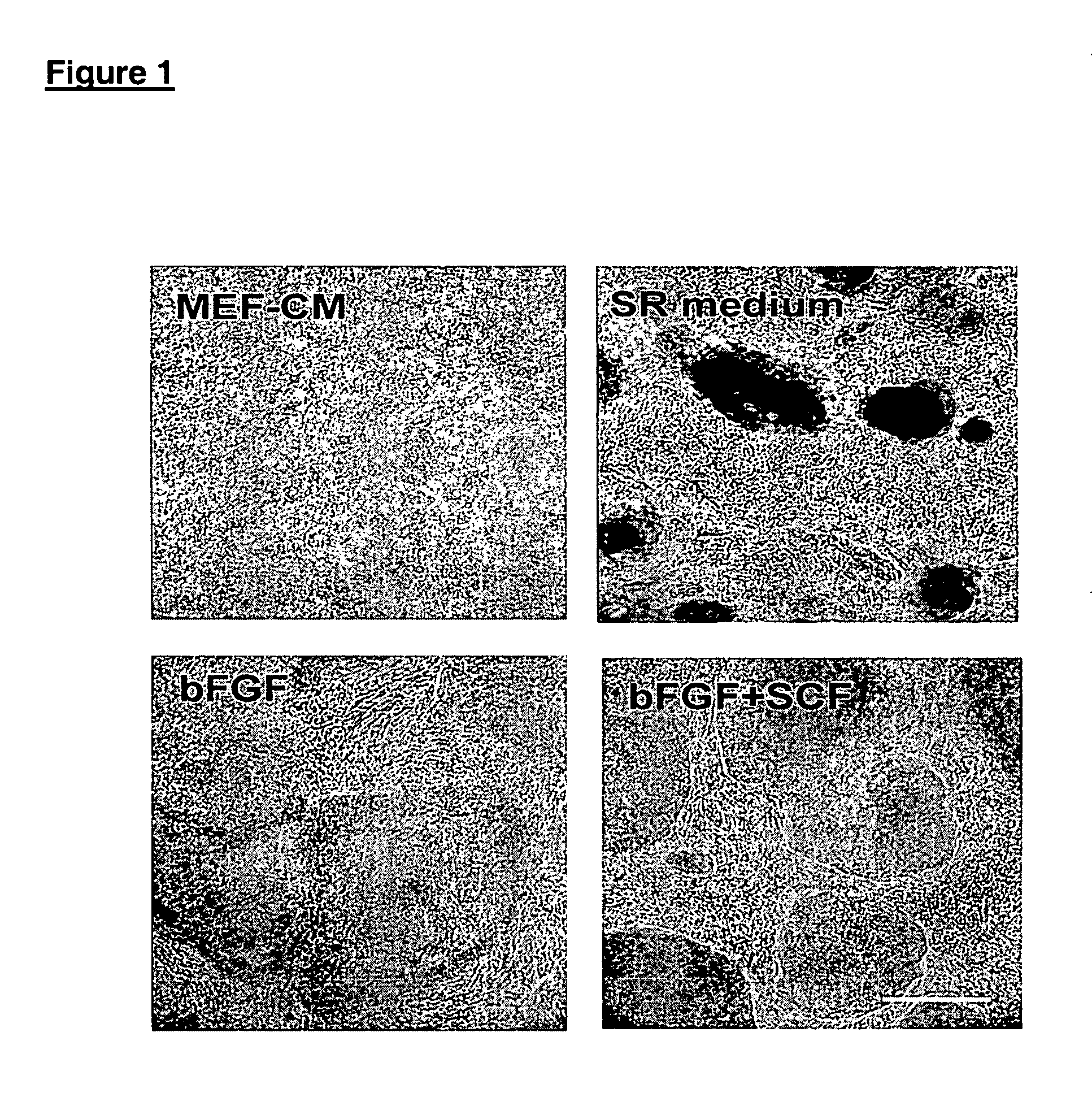
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050037492A1Rapid productionCost-effectiveDrug screeningNervous system cellsGerm layerLipid formation
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by defined components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. The medium contains an isotonic buffer, a blend of essential nutrients such as protein and lipids, and an effective growth factor or combination of factors that promote proliferation while inhibiting differentiation. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium on an extracellular matrix according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Recombinant viruses displaying a nonviral polypeptide on their external surface
InactiveUS6297004B1Genetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersGene deliveryAntibody fragments
We have made retrovirus particles displaying a functional antibody fragment. We fused the gene encoding an antibody fragment directed against a hapten with that encoding the viral envelope protein (Pr80env) of the ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus. The fusion gene was co-expressed in ecotropic retroviral packaging cells with a retroviral plasmid carrying the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (neo), and retroviral particles with specific hapten biding activities were recovered. Furthermore the hapten-binding particles were able to transfer the neo gene and the antibody-envelope fusion gene to mouse fibroblasts. In principle, the display of antibody fragments on the surface of recombinant retroviral particles could be used to target virus to cells for gene delivery, or to retain the virus in target tissues, or for the construction of libraries of viral display packages.
Owner:BIOFOCUS DICOVERY
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7455983B2Cost-effectiveRapid productionMicroorganismsDrug screeningGerm layerLipid formation
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by defined components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. The medium contains an isotonic buffer, a blend of essential nutrients such as protein and lipids, and an effective growth factor or combination of factors that promote proliferation while inhibiting differentiation. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium on an extracellular matrix according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
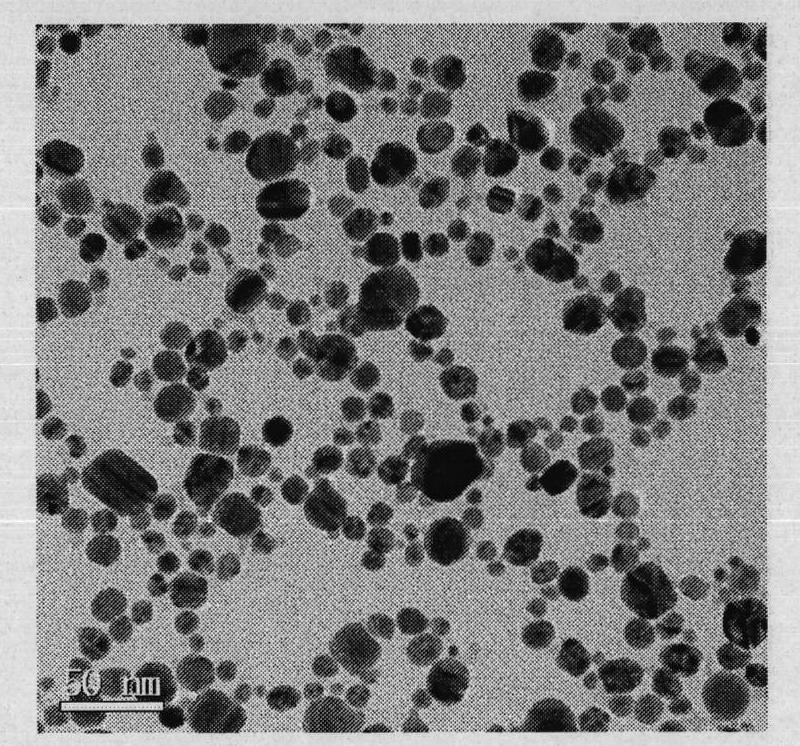
Method for preparing nanosilver/nano silicon dioxide-containing antibacterial biological dressing
InactiveCN101912634AGood biocompatibilityGood hemostasis and antibacterialAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberBiological dressing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanosilver / nano silicon dioxide-containing antibacterial biological dressing, and relates to the field of antibacterial biological dressings. The nanosilver / nano silicon dioxide-containing antibacterial biological dressing is prepared by adding mixed solution of chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol and silver-carried silicon dioxide powder during the acetalation of the polyvinyl alcohol. The nanosilver / nano silicon dioxide-containing antibacterial biological dressing of the invention can accelerate the wound healing, slowly release the silver nanoparticles and continuously act on reproductive bacteria, has the characteristic of durable and high-efficiency sterilization and does not produce medicament resistance; and through the researches on the toxicity of the material to mouse fibroblast cells, the product does not produce obvious toxicity to the cells but promotes the growth of the cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells
The invention discloses an inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells. The method comprises the steps of: cultivating the human embryonic stem cells on a mouse embryonic fibroblast feed layer; sorting human embryonic stem cell clone groups in good state; grafting the groups on a human corneal stromal fibroblast layer processed by mitomycin C and cultivating for 7 days, wherein the human embryonic stem cells are differentiated to rosettes; separating and transferring the rosettes from the human corneal stromal fibroblast layer to a culture bottle; cultivating continuously for 7 days by using a neural crest stem cell culture medium; sorting the neural crest stem cells by a flow cytometry; adding the neural crest stem cells into the culture bottle; placing in a 5% CO2 incubator for incubating and cultivating at 37 DEG C by using a human corneal endothelial cell culture medium; changing the liquid every other day; and cultivating for about 10 days to obtain the corneal endothelial cells. The multiplication capacity of the corneal endothelial cells are similar to that of human corneal endothelial cells and the corneal endothelial cells can be transferred to 1-2 generations in vitro maximally. The corneal endothelial cells can be used as seed cells for cornea construction and transplant in tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
System for expanding and differentiating human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153445A1Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
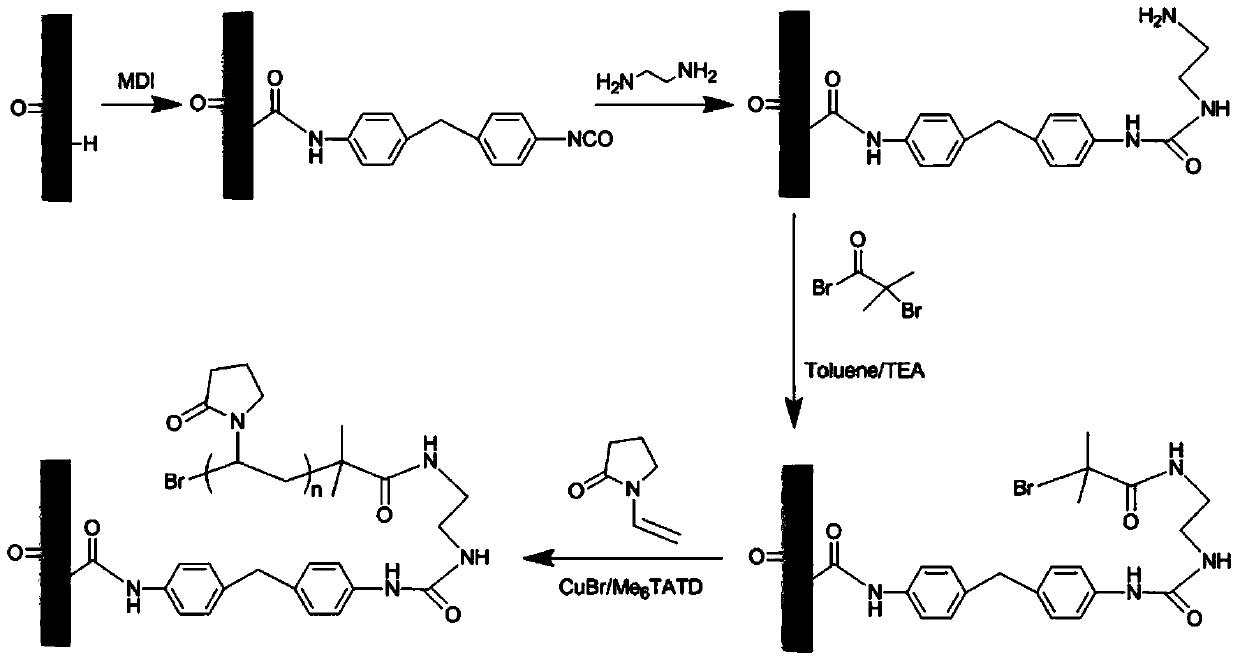
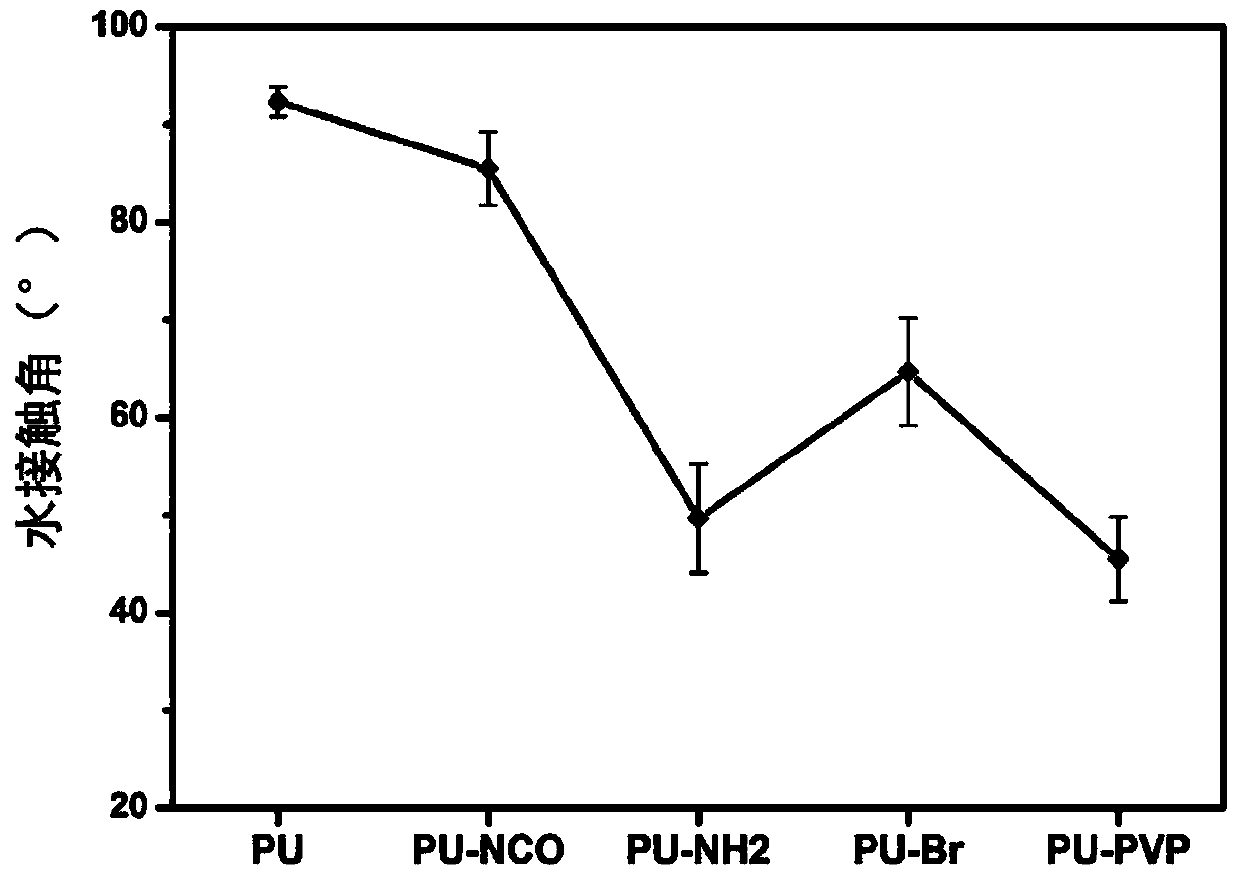
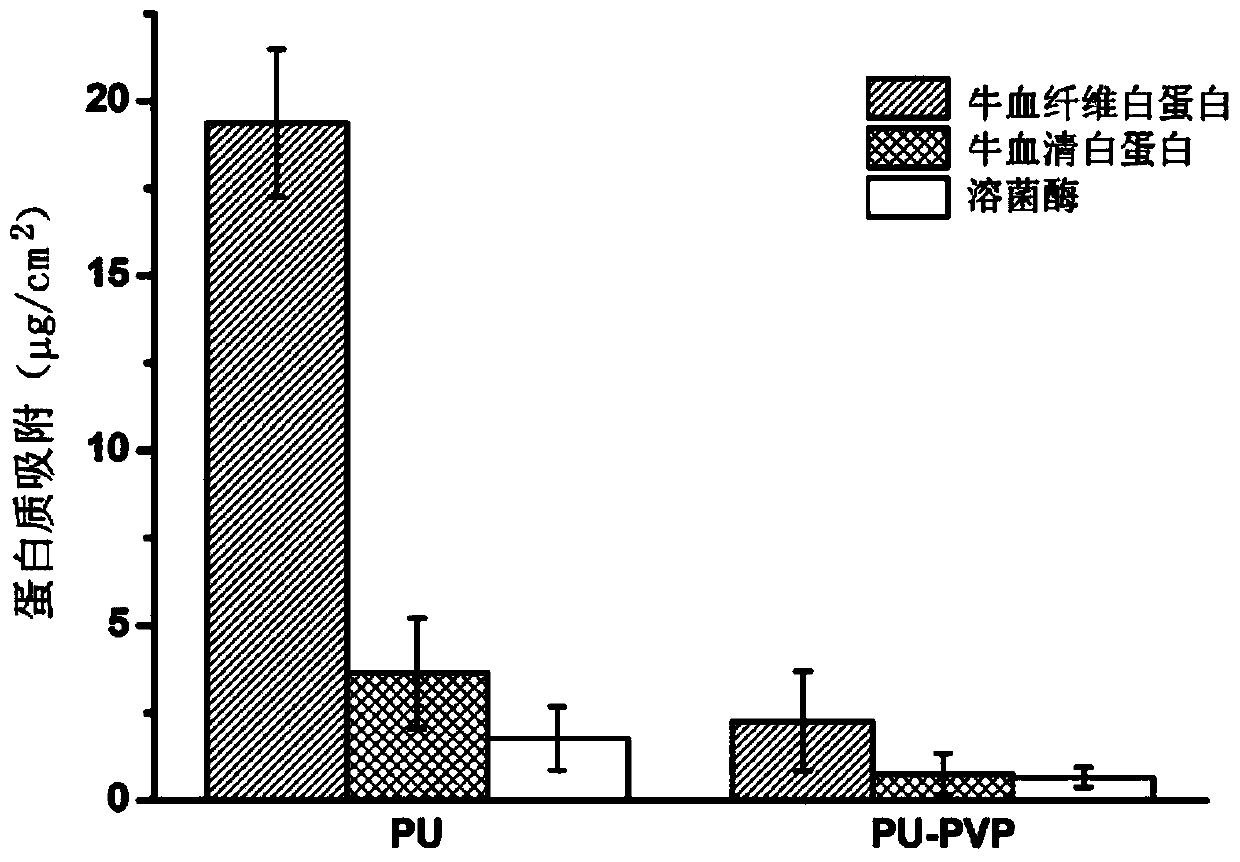
Polyurethane material with protein adsorption resistance and cell adhesion resistance and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104262668AImprove hydrophilicityAnti-protein non-specific adsorption functionCatheterFiberCell adhesion
The invention relates to a polyurethane material with protein adsorption resistance and cell adhesion resistance and a preparing method thereof. The material comprises a substrate and a modification layer. The substrate is made of polyurethane. The modification layer is obtained by polymerizing a vinyl pyrrolidone monomer on the surface of the substrate by utilization of an atom transfer radical polymerization technology. The material is prepared by steps of: subjecting the polyurethane to isocyanic acid esterification, performing amination, fixing a bromine initiator, and initiating graft polymerization of the vinyl pyrrolidone on the surface of the material. The surface of the polyurethane material prepared by the method has good hydrophilicity, good resistance to bovine serum fibrinogen adsorption, bovine serum albumin adsorption and lysozyme adsorption, and a function of resisting cell adhesion of mouse fibroblast cells (L-929), so that the polyurethane material is suitable for preparing biomedical catheter materials with complex shape structures.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Using fibroblast growth factor to establish a line of embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153444A1Rapid productionSimple systemHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
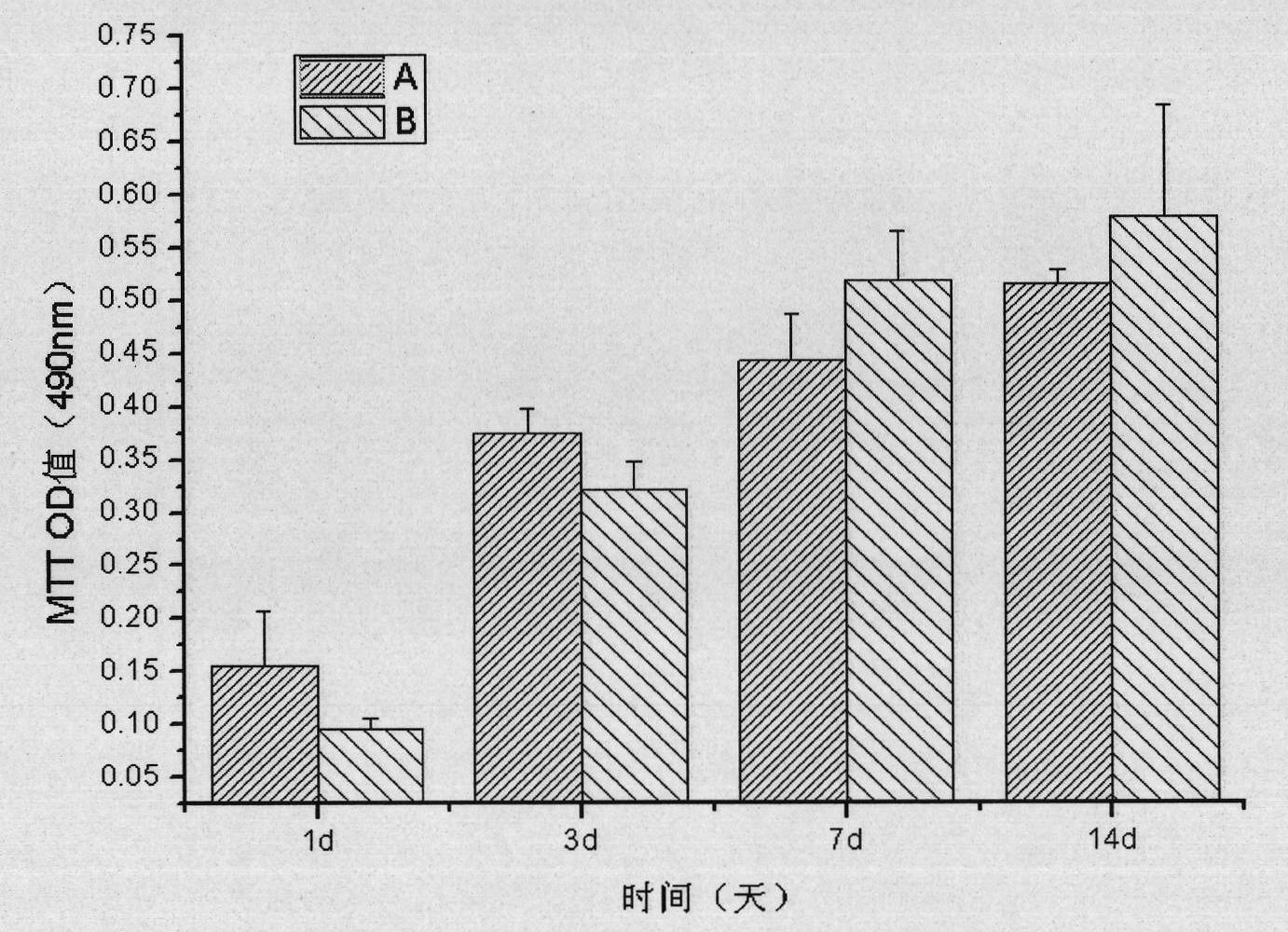
Preparation method of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol sponge dressing containing nano-silver
InactiveCN101927029AGood biocompatibilityGood hemostasis and antibacterialAbsorbent padsBandagesPolyvinyl alcohol spongeFiber
The invention discloses a preparation method of a chitosan / polyvinyl alcohol sponge dressing containing nano-silver. The invention relates to an antibacterial dressing for therapy of trauma, and the chitosan / polyvinyl alcohol sponge dressing containing the nano-silver is prepared by adding nano-silver / polyvinyl alcohol solution and polyvinyl alcohol / chitosan blend solution. The obtained dressing has good biocompatibility and hemostatic and antibacterial effects, and can promote the wound healing; the product can accelerate the wound healing, release nano-silver particles in a sustained manner, be acted on regenerated bacteria constantly, have the lasting and high-efficient sterilization characteristics and avoid the drug resistance during the wound treatment process; the research on the toxic effect of the material to mouse fibroblasts shows that the product has no obvious toxicity to the cells and has the effect of promoting the growth of the cells; and preparation method has simple process equipment and low price of experimental raw materials and is conductive to industrialization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
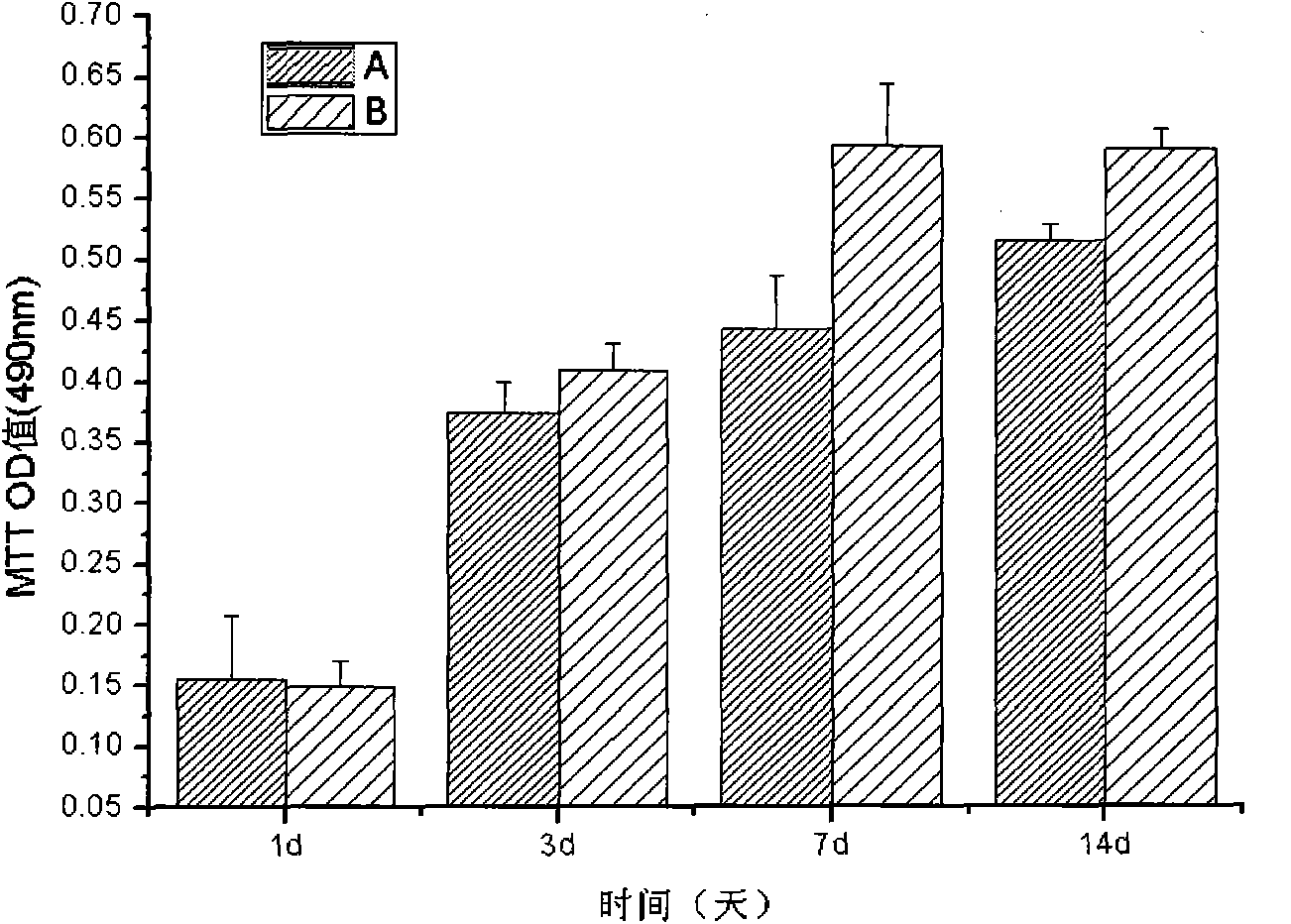
Preparation method of chitosan/ acetalized poval medical dressing
The invention discloses a preparation method of chitosan / acetalized poval medical dressing, and in particular relates to a preparation technology of poval sponge. A dressing with bioactivity can be prepared by adding a poval / chitosan mixed solution in poval acetalation reaction. The chitosan / acetalized poval medical dressing has biocompatibility,the effects of inflammation, blood stopping, wound surface healing promotion, good breathability, water absorbability and tensile strength; in addition, proved by the search on toxic effect on mouse fibroblast cells, the chitosan / acetalized poval medical dressing has no obvious toxicity to the mouse fibroblast cells, but has the effect of promoting the growth of the mouse fibroblast cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for culturing induced pluripotent stem cells by using human mesenchymal stem cells as trophoblast
InactiveCN102161980ANo pollution in the processReduce pollutionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousForeskin
The invention provides a method for culturing human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by using human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as a trophoblast. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining the human iPSCs from child foreskin fibroblasts by using third to fifth generation human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells obtained through subculture and culture after thawing from low-temperature freezing, performing amplification culture, and inoculating into trophoblast cells to obtain the human iPSCs. In the method, the human iPSCs are cultured by using the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as the trophoblast cells instead of mouse embryonic fibroblasts in the conventional method, so that the pollution of heterologous cells in a culture system is reduced, that the culture system can make the human iPSCs amplified in vitro is proved, biological characteristics and multipotency of the human iPSCs are maintained for a long time, and the possibility of clinical application of the human iPSCs is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nanostructured material formulated with bone cement for effective antibiotic delivery
ActiveUS20120308633A1Preventing postoperative osteomyelitisEnhanced and controlled elutionAntibacterial agentsBiocideFiberCytotoxicity
This invention uses mesoporous silica nanoparticles and other nanostructured materials to formulate polyacrylate-based bone cement for achieving an enhanced and controlled elution of active ingredients such as antibiotics. This invention overcomes the limitation of low antibiotic release from commercial polyacrylate-based bone cements using for example, PMMA. In certain aspects, the formulation enables a sustained release of antibiotics from the bone cement over a period of 80 days and achieves 70% of total drug release, whereas the commercial antibiotic bone cement (e.g., SmartSet GHV) only releases about 5% of the antibiotics on the first day and subsequently an almost negligible amount. In addition, the mechanical properties of our formulated bone cements are well retained. The inventive bone cement exhibits good antibacterial properties and has very low cytotoxicity to mouse fibroblast cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
New Periplaneta Americana polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair, and applications thereof
ActiveCN106977586APromote proliferationPromote migrationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectTissue repair
The present invention relates to the field of traditional Chinese medicines, natural medicines and daily chemicals, particularly to a new Periplaneta Americana polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair, and applications thereof, wherein the new polypeptide capable of promoting tissue repair is named Periplapeptide B, has a structure represented by a formula I, can promote the proliferation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts and the migration of human immortalized epidermal cells at a low concentration, has advantages of low toxic-side effect and good application prospect, and can be used for preparing drugs for treatment of trauma, scald and ulcer, or cosmetics for improving skin beauty, and daily chemicals. The formula I is H-Ala-Ala-Pro-Pro-Ser-Asn-Leu-Lys-Glu-Val-Pro-Ile-Ile-Ala-Tyr-OH.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Sulfonic quantum dot/silk fibroin composite nanofiber membrane and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110453378AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentElectro-spinningFiberFreeze-drying
The invention provides a sulfonic quantum dot / silk fibroin composite nanofiber membrane and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps that degumming treatment is performed on natural silk, and silk fibroin is obtained; then, fibroin is dissolved in a lithium bromide water solution, and a silk fibroin sponge is obtained through dialysis, centrifugal and freeze drying; the silk fibroin sponge is dissolved into formic acid to be mixed to be uniform, then, a sulfonate graphene quantum dot water solution is ultrasonically and uniformly dispersed into a silk fibroin-formic acid solution, and a composite nanofiber membrane is prepared through electrostatic spinning equipment; mouse fibroblasts are used for performing cell viability evaluation on the composite nanometer member, and it shows that the composite nanometer membrane has the excellent biocompatibility. The prepared composite fiber membrane has the good biocompatibility and degradability, has the potential for promoting proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow storm stem cells, and has the good biologic medical material application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
In-vitro separating and culturing method for germline stem cell
ActiveCN102250830AStrong shadingEasy to useArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsGerm layerMatrigel
The invention discloses an in-vitro separating and culturing method for a germline stem cell. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a cell from germinal epithelium of an ovary of a female mammal, differentiating and separating a non-adherent germline stem cell from other adherent cultured cells by adopting gelatin with the concentration 0.2 percent and a Matrigel differential adherence combination cloning method; and culturing the germline stem cell obtained by separating on an MEF (Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast) feeder layer. The separated germline stem cell has ES (Embryonic Stem) characteristic and the potential of differentiating into a muscle cell, an adipose cell and oocyte-like cell and various cells with three internal germinal layers.
Owner:陕西九州细胞基因工程有限公司
Method for inducing mouse fibroblasts into cartilage by adopting small-molecule composition
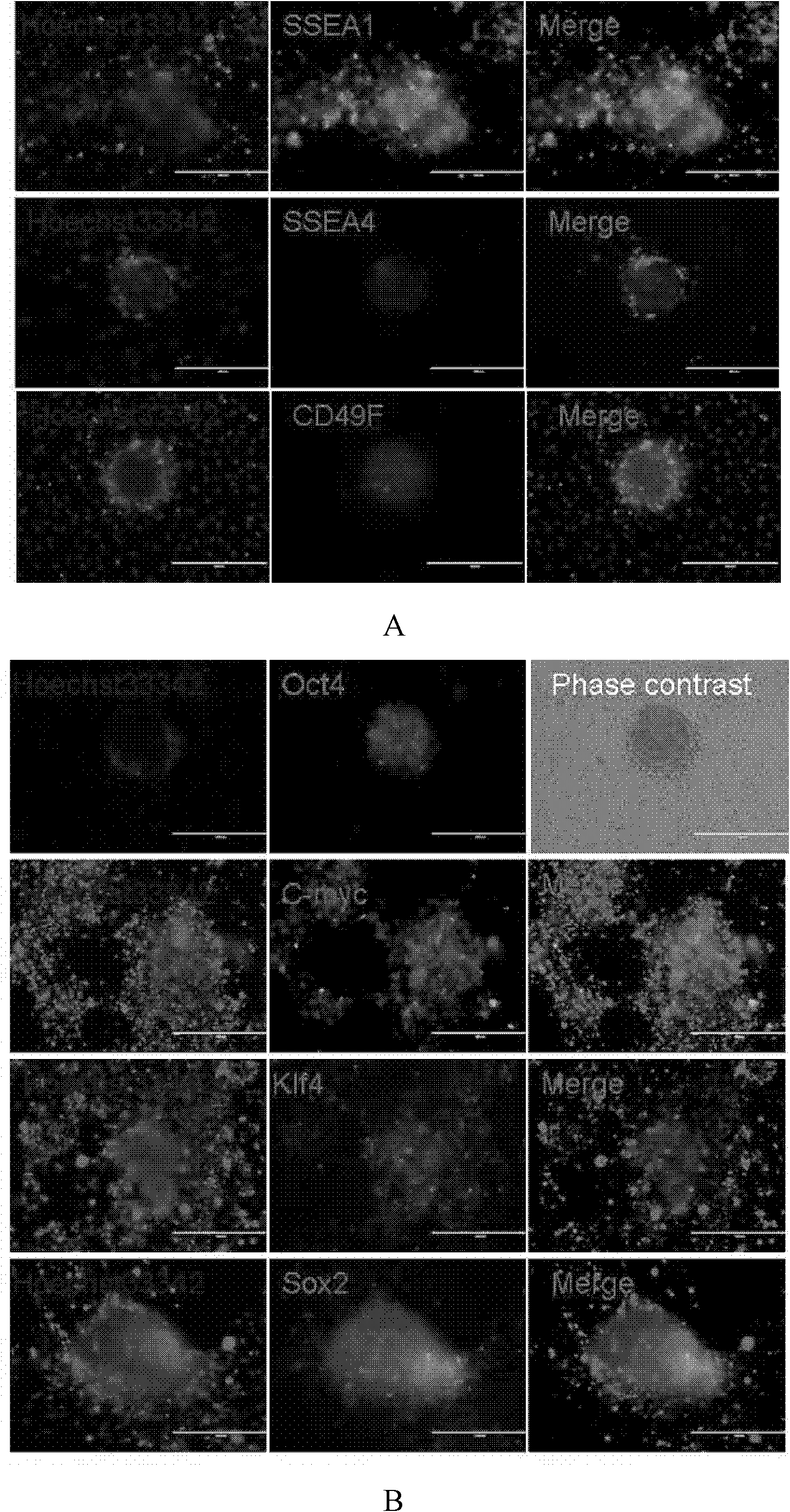
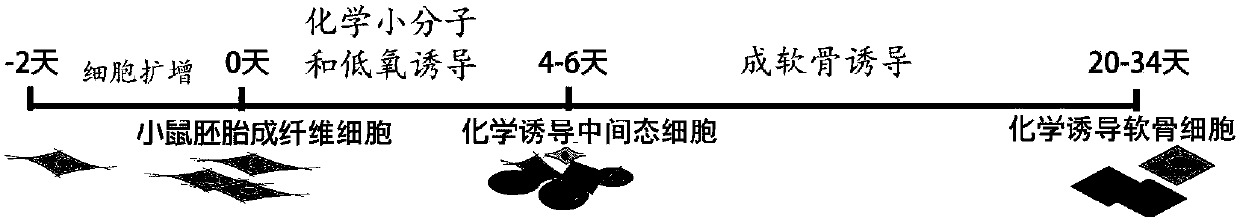
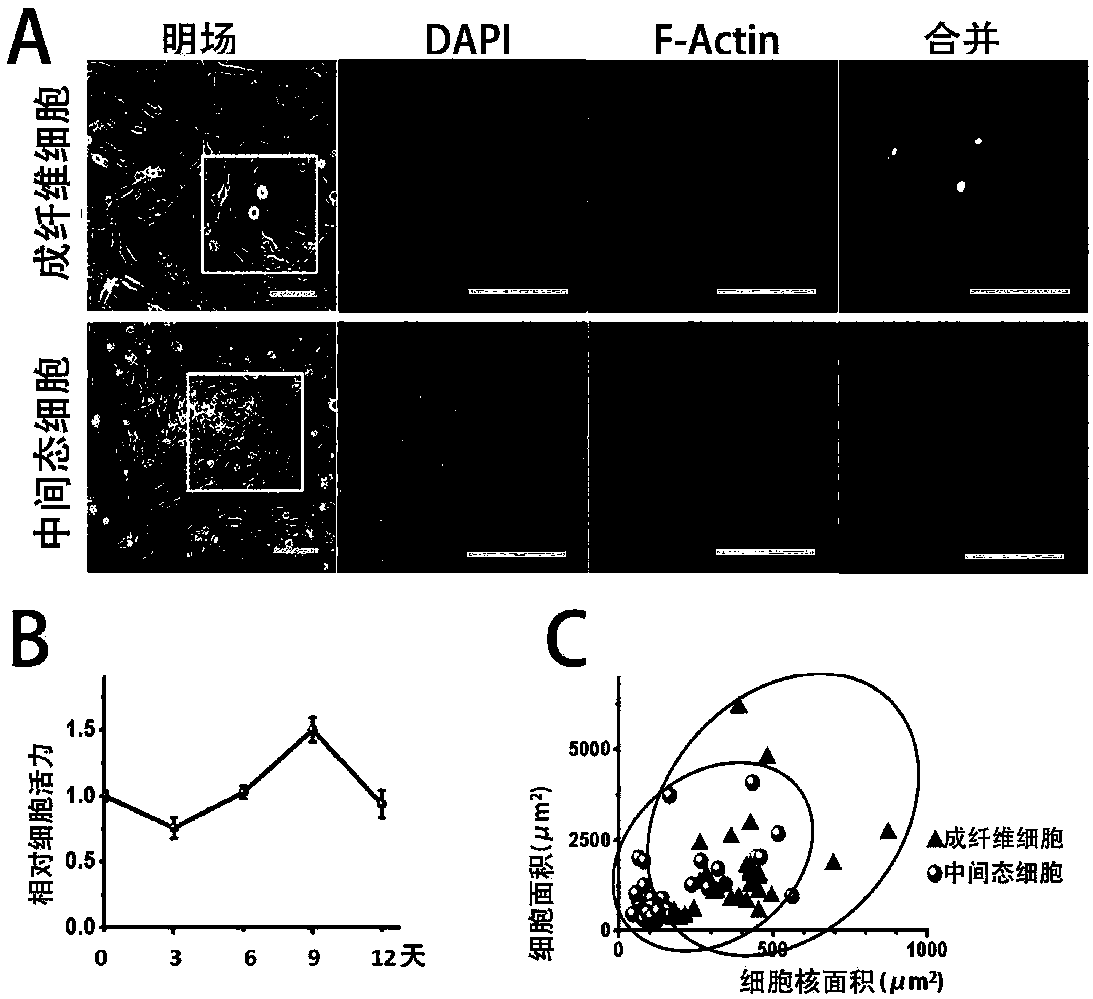
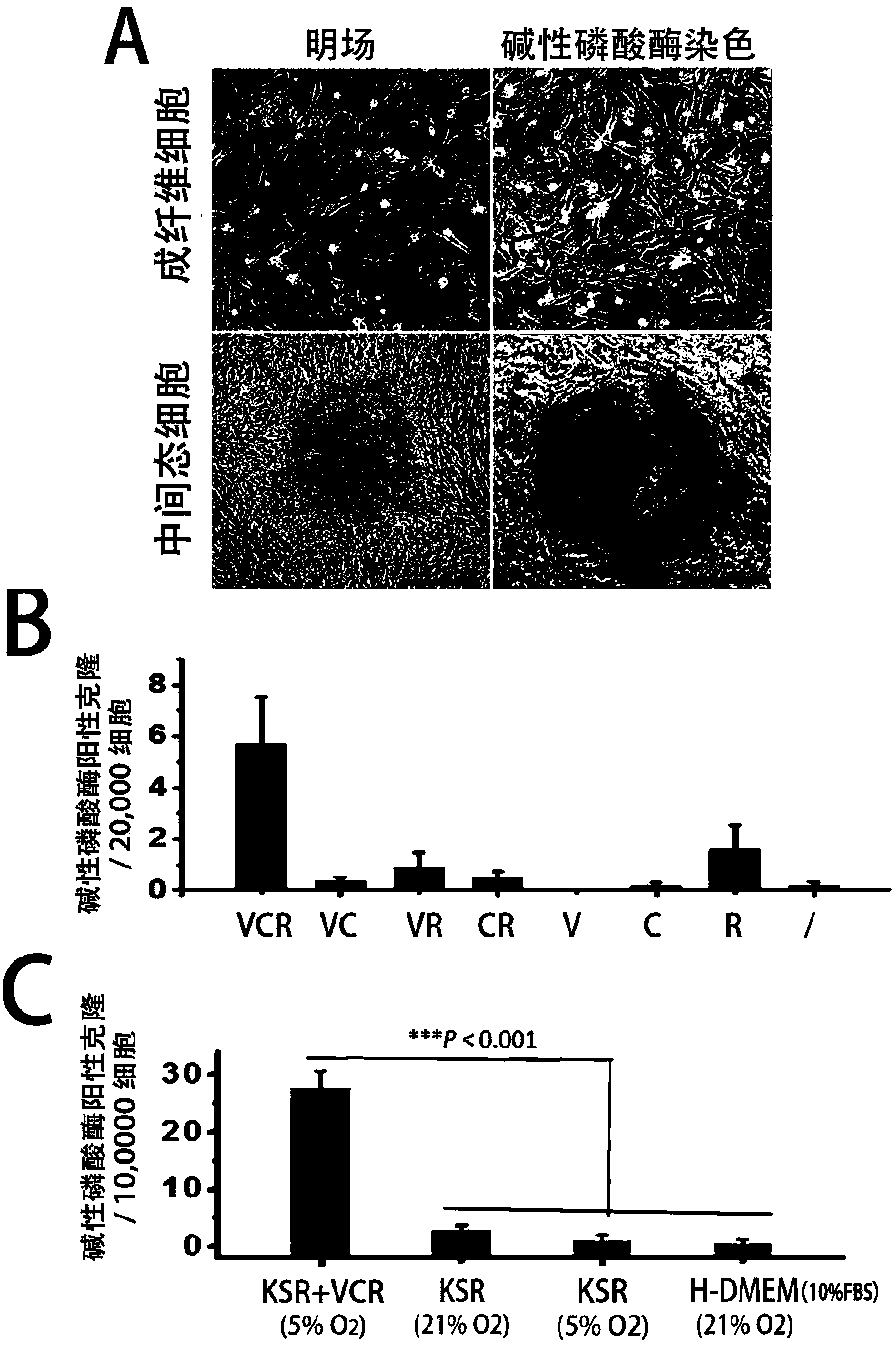
ActiveCN107674859AAvoid missingImprove induction efficiencyCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCartilage cellsTransdifferentiation
The invention discloses a method for inducing mouse fibroblasts into cartilage by adopting a small-molecule composition. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out adherent culture on mouse embryo fibroblasts, removing a culture medium, slowly adding a chemical induction culture medium containing the small-molecule composition, carrying out culturing in the environment having the temperature of 37 DEG C and containing 3-8% of oxygen, 3-8 % of carbon dioxide and the balance of nitrogen, wherein the chemical induction culture medium containing the small-molecule composition is replaced every 2-3 days; carrying out continuous culturing for 4-12 days, thus obtaining intermediate state cells, wherein the small-molecule composition comprises an HDAC inhibitor, a GSK-3 inhibitor and aTGF-beta signal channel inhibitor; and transferring the intermediate state cells to a cartilage inducing medium, carrying out culturing in the environment having the temperature of 37 DEG C and containing 15-25% of oxygen, 3-8 % of carbon dioxide and the balance of nitrogen, wherein the cartilage inducing medium is replaced by the fresh cartilage inducing medium once every 3-4 days, and carryingout culturing for 14-28 days, thus obtaining a cartilage cell cluster. With the method provided by the invention, the problem that in the traditional methods, the fibroblasts can be induced to form cartilage cells through transdifferentiation only after an exogenous gene is introduced is solved, and the method provided by the invention is expected to be used for further solving the problem that seed cells of cartilage cells are in shortage or in-situ focus fibrosis exists.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane
ActiveCN102166374AAvoid breakingConvenient for clinical operationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsEpitheliumFeeder Layer
The invention relates to a method for preparing an amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a sterile amniotic membrane with epithelium removed, placing the epithelial surface of the amniotic membrane downwards on an end face of a sleeve made of a poly propylene material, and covering an embedded culture transwell on the amniotic membrane of the sleeve to obtain an amniotic-membrane-embedded culture mold; placing the culture mold in holes in a 6-hole plate on which a mouse embryonic fibroblast cell feeder layer is spread; and finally, preparing a corneal limbus stem cell suspension by using a digestion method, inoculating the suspension on the epithelial surface of the amniotic membrane, inoculating 2.0-3.0*10<5> corneal limbus stem cells for each culture mold, and culturing the corneal limbus stem cells for 10 days to obtain the amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane. Compared with the traditional amniotic membrane spreading method and the latex ring amniotic membrane fixing method, the amniotic compound corneal limbus stem cell membrane prepared with the method has flat amniotic membrane culturing surface and uniform corneal limbus stem cell stratified layer and especially has the advantage of convenience for clinic application and difficulty in rapture of the amniotic membrane.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
Mouse fibroblast and application thereof
ActiveCN108504625AStrong value-added vitalityStatus freshEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsMitomycin CIndividualized treatment
The invention discloses a mouse fibroblast and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of cell biology. The cell is named mouse fibroblast MFC / HL-041 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:C201714. The mouse fibroblast treated by mitomycin C or irradiated by radioactive rays is used for separation and subculture of normal primary epithelial cells and primary tumor cells. Obtained humanpulmonary normal primary epithelial cells and lung cancer primary epithelial cells are fresh and live in state, tight in arrangement, clear in cell boundary, high in stereoscopic impression and polygonal when examined under a microscope. The mouse fibroblast can be used for physiological study of human or animal normal cells, a virus infection model of in-vitro normal cells, drug sensitivity tests of the in-vitro normal cells for different drugs, drug screening for individualized treatment of cancer patients as well as research and development of new anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:深圳涌泰生物科技有限公司
Method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells to differentiate toward nerve cells
InactiveCN101892191ALow toxicityEasy to observe shape changesEmbryonic cellsGerm cellsFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) to differentiate toward nerve cells. Primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (PMEF) are used as a feeder layer. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating the mESCs to the feeder layer, inoculating the mESCs to mixed solution of stem cells and mESCs culture liquid, and culturing nerve stem cell culture solution; and gradually changing the culture into the culture of nerve cell culture solution by completely using serum-free added alkali fibroblast growth factors, wherein the optimal serum concentration of the mixed solution for primary inoculation is 12.5 percent, the optimal inoculation density of primary mESCs inoculation is 1.0*108<-1>, and the time of completely changing the serum-free culture solution is the 5th day. By induction of the method, the mouse stem cells can be differentiated into the nerve cells in vitro. The method has the advantages of short experimental period, simple and convenient experimental process and stable and efficiency inducing results, can quickly finish a cell culture period, and is favorable for subsequent experiments.
Owner:中国医科大学
Method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells by adopting transcription factors
InactiveCN101705247ANormal growth characteristicsGood pluripotencyGenetic engineeringFermentationFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by adopting transcription factors, concretely comprising the following steps: 1) isolation and culture of bovine dermal fibroblasts; 2) cloning of bovine transcription factor genes maintaining pluripotency and construction of retroviral vectors of the transcription factor genes; 3) retrovirus packaging and preparation; and 4) infection of bovine dermal fibroblasts by retrovirus and acquisition of bovine inducted pluripotent stem cells. The invention first adopts the acellular human amniotic membranes as support to replace the mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to maintain in vitro proliferation of the bovine iPSCs and keep the bovine iPSCs in undifferentiated pluripotent states for long time. The method which adopts gene inducing to generate the PSCs not only solves the technical problem that the PSCs of the animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs and other livestock are difficult to obtain but also avoids the problem of heterogeneous animal cell pollution caused by the feeder layer which applies the MEFs as the stem cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
In-vitro separation and preparation method of male germline stem cells of goat
InactiveCN102154195AHas the characteristics of ES cellsStrong shadingArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsSeminiferous tubuleCells heart
The invention discloses an in-vitro separation and preparation method of male germline stem cells of a goat. Spermatogonium can be obtained from male convoluted tubules of the goat. The separation and preparation method of germline stem cells of a male goat comprises the following steps: carrying out differential adhesion by using 0.2% gelatin and Matrigel through combining a cloning method; and distinguishing and separating non-adhesion male germline stem cells of the goat with other adhesion culture cells, wherein the culture of separated male germline stem cells of the goat is MEF (mouse embryonic fibroblast) feeder culture or feeder-free culture. The separated male germline stem cells of the goat have embryonic stem (ES) cell features and proficiency of differentiating to be nerve cells, cardiocytes and sperm-like cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Capsid protein of adeno-associated virus (AAV), vector of AAV as well as construction method and application of vector of AAV
ActiveCN110950934AReduce dosageSimple production processGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesViral vectorImmunity response
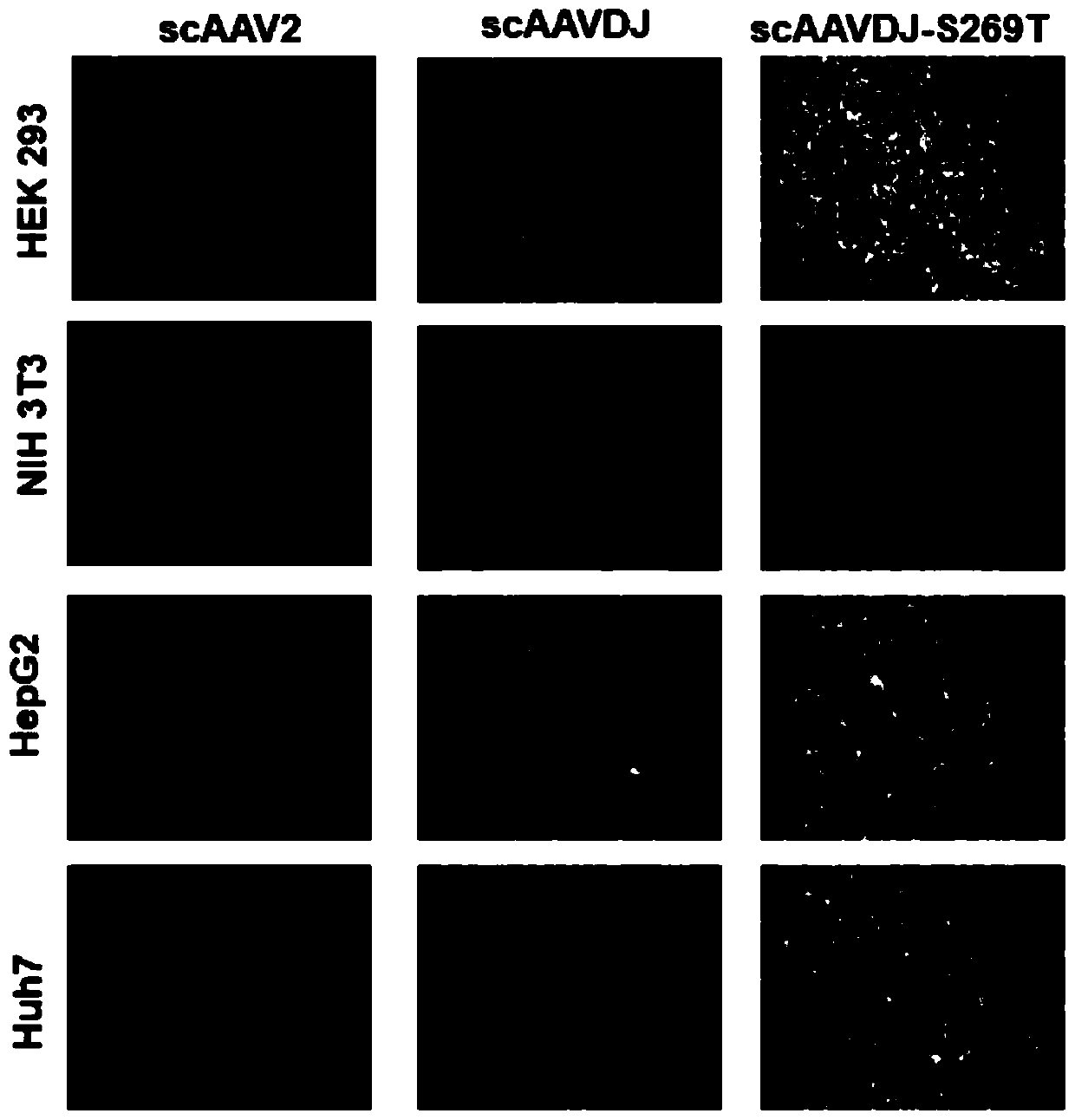
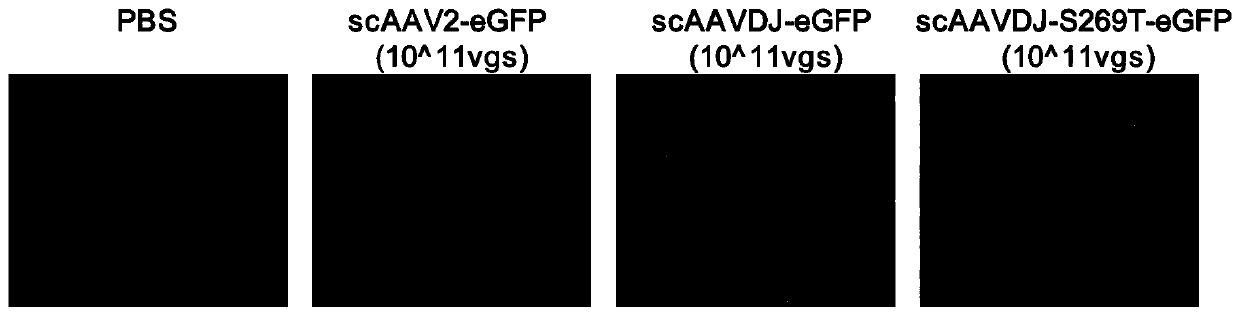
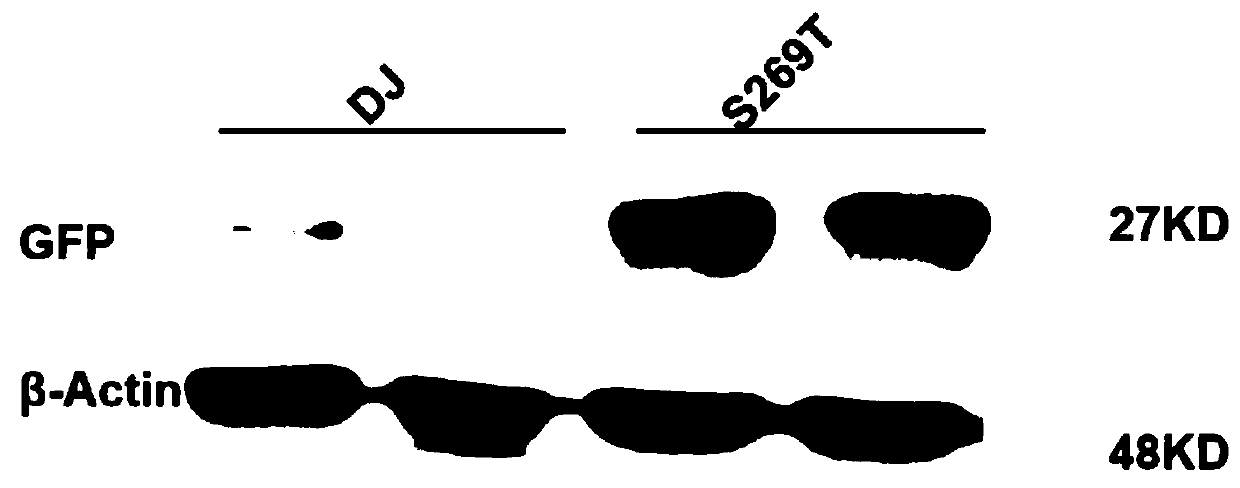
The invention discloses a capsid protein of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) which has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses an isolated nucleic acid molecule whichencodes the capsid protein of the AAV. The invention further discloses a vector of the AAV which encodes the capsid protein of the AAV. The invention still further discloses a construction method andapplication of the vector of the AAV. According to the capsid protein of the AAV, modification is performed on the capsid protein of the AAV-DJ , so that the AAV-DJ has significantly improved transduction efficiency in cell lines, including HEK293, various liver cancer cells, mouse fibroblasts and the like, and mouse livers compared with wild-type AAV, so that immune response in subjects caused by high-dose injection of virus vectors is avoided; and moreover, production process of the AAV is optimized so as to reduce production cost. Thus, clinical progress of AAV gene therapy products is promoted
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
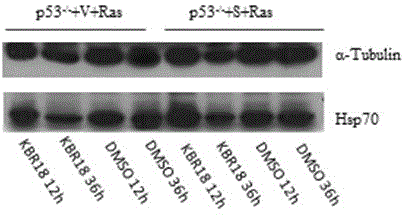
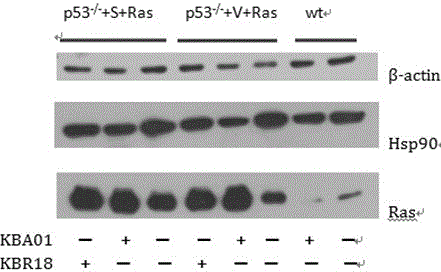
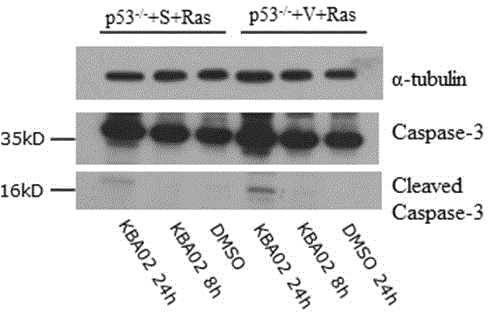
Medical applications of four buxus alkaloids compounds
The invention discloses medical applications of four buxus alkaloids compounds in the preparation of antitumor medicines. Experiment results show that the four compounds KBA01, KBA02, KBA03 and KBR18, under the condition of concentration without toxicity to wild normal mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, can selectively kill mouse tumor cells with tumor specific mutant genes p53 and Ras; accordingly, the compounds are very strong in killing activity to human colon cancer cell strains with p53 mutants, but not strong in killing activity to human wild colon cancer cell strains with p53 mutants; and as shown in a GFP (Green Fluorescence Protein) reporter vector screening system of a gene promoter, the compounds KBA02 and KBA03 can activate a promoter of a cancer suppressor gene p16. The characteristics indicate that the compounds from the four buxus plant origins have application potentials for preparing personalized treatment medicines aiming at the tumor mutant genes p53 and Ras as well as the cancer suppressor gene p16.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
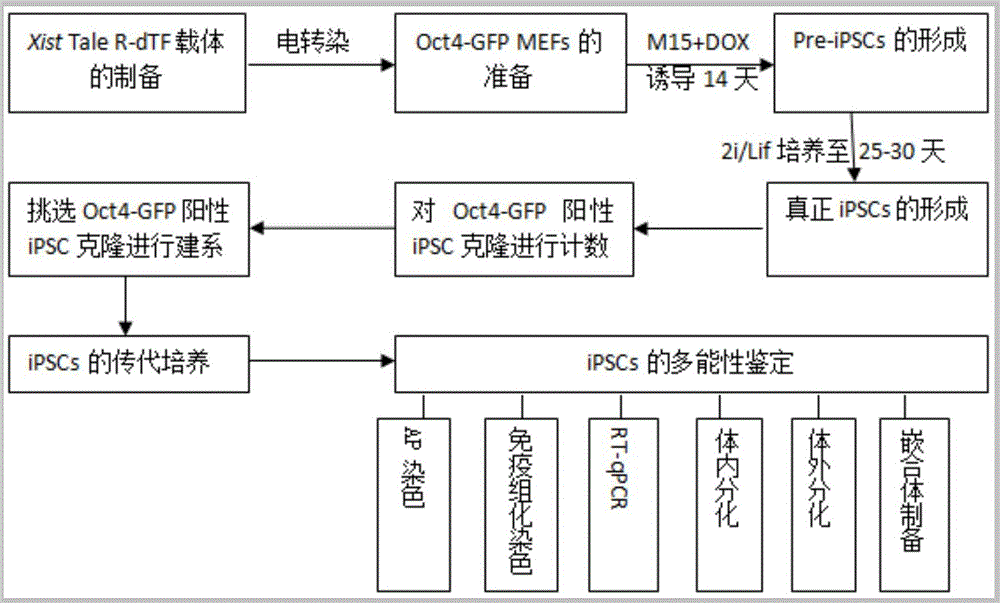
Method for preparing induced pluripotent stem cells by using Xist Tale inhibitory transcription factor
ActiveCN106754729AImprove induction efficiencyConvenient for clinical operationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsMurine fibroblastHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
The present invention discloses a method for preparing induced pluripotent stem cells by using a Xist Tale inhibitory transcription factor. Synergism of the transcriptional activator-like effectors (Tale)-based inhibitory transcription factor combined to a first intron region of Xist, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc enhances the efficiency of induction of mouse fibroblasts to the induced pluripotent stem cells. Obtained iPSCs have typical pluripotent stem cell characteristics including involvement in the development of chimeric mice. The method actively promotes the clinical application and researches of the iPSCs, and provides new technical and theoretical bases for studying how to obtain and improve the iPSCs in people, pigs, cattle and other mammals.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA SAIKEXING LIVESTOCK BREEDING & SEED IND BIOTECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells by adopting transcription factors
InactiveCN101705248ANormal growth characteristicsGood pluripotencyGenetic engineeringFermentationFeeder LayerEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for transfecting bovine somatic cells into inducted pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by adopting transcription factors, concretely comprising the following steps: 1) isolation and culture of bovine dermal fibroblasts; 2) cloning of bovine transcription factors maintaining pluripotent genes and construction of retroviral vectors of the transcription factors; 3) retrovirus packaging and preparation; and 4) infection of bovine dermal fibroblasts by retrovirus and acquisition of bovine inducted pluripotent stem cells. The invention first adopts the acellular human amniotic membranes as support to replace the mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) to maintain in vitro proliferation of the bovine iPSCs and keep the bovine iPSCs in undifferentiated pluripotent states for long time. The method which adopts gene inducing to generate the PSCs not only solves the technical problem that the PSCs of the animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs and other livestock are difficult to obtain but also avoids the problem of heterogeneous animal cell pollution caused by the feeder layer which applies the MEFs as the stem cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
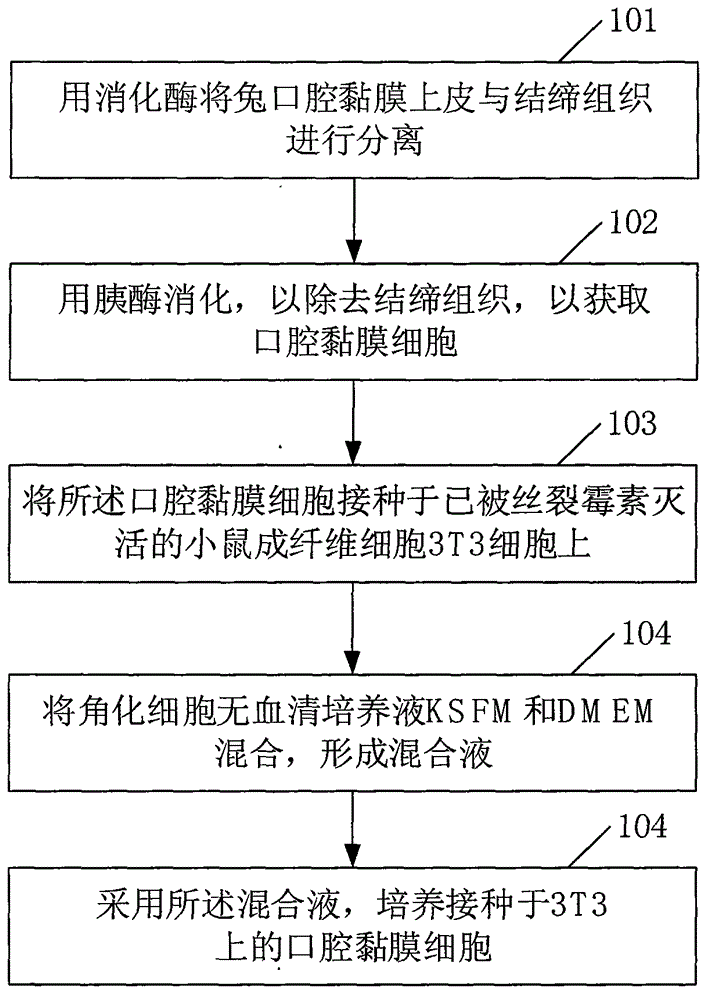
Method for culturing oral mucosa cells
InactiveCN104862269AHigh separation purityImprove proliferative abilityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsUrethral stentsDigestive enzyme
The invention relates to the field of preparation of urethral stents and discloses a method for culturing oral mucosa cells. The method comprises the following steps: separating oral mucosal epithelium and connective tissues of a rat by using digestive enzymes, and digesting by using pancreatin so as to remove the connective tissues, thereby obtaining the oral mucosa cells; inoculating the oral mucosa cells to mouse fibroblast cells 3T3 which are inactivated by mitomycin, and mixing keratinocyte serum-free culture solution KSFM and DMEM to form the mixed solution; and culturing the oral mucosa cells inoculated to the cells 3T3 by adopting the mixed solution. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the separation purity of the oral mucosa cells is improved, and the adherence and proliferation capacities of seed cells can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
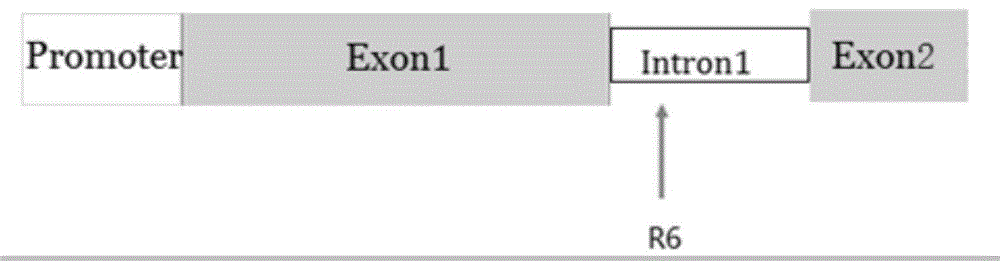
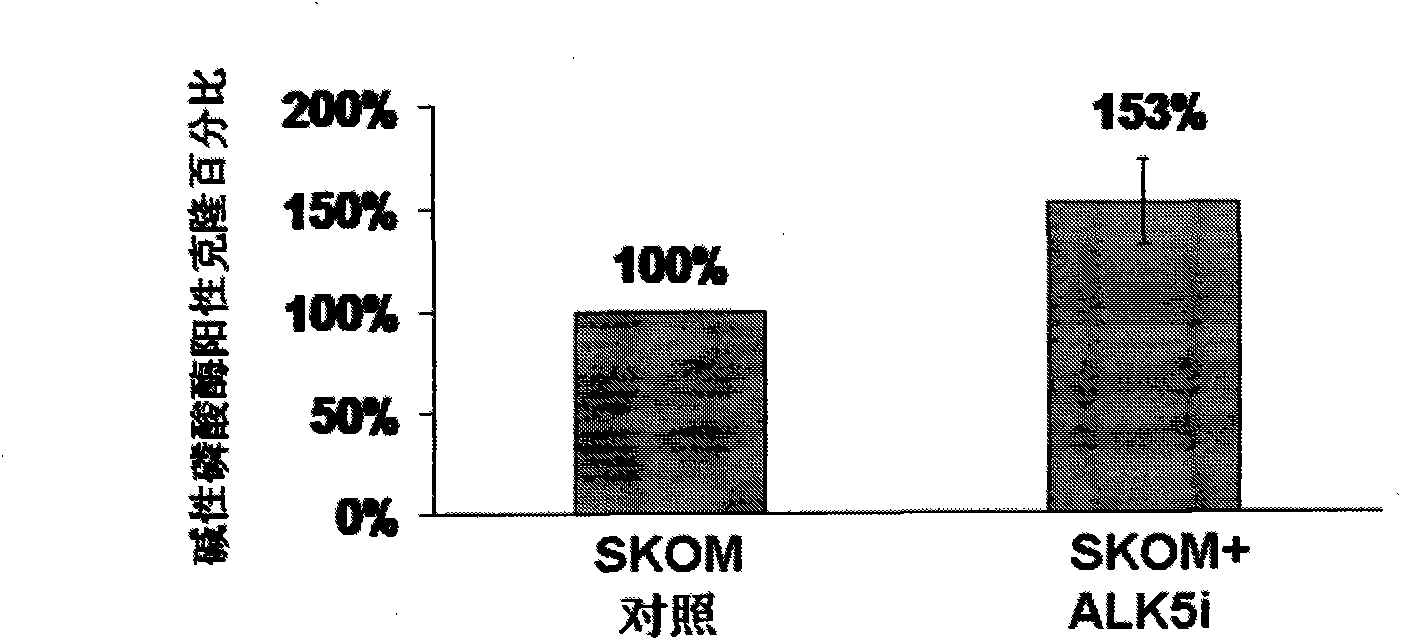
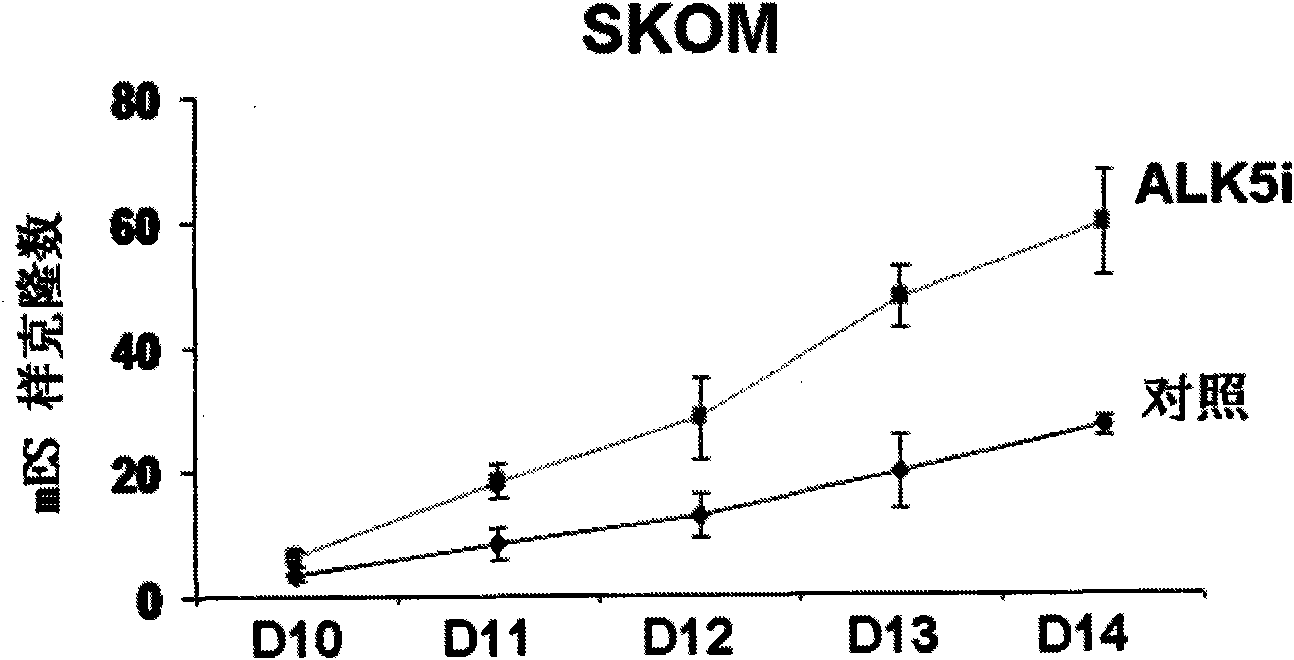
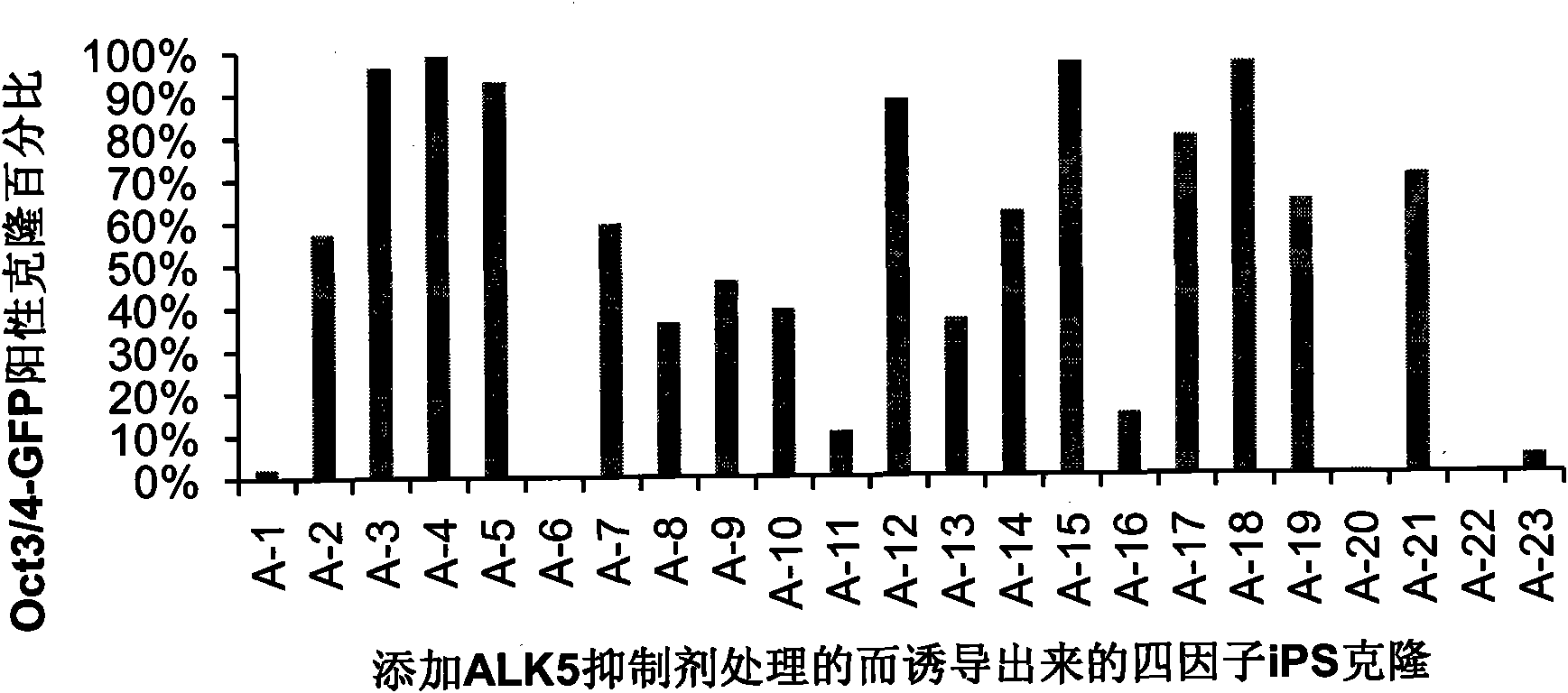
Application of I type transforming growth factor receptor inhibitor in producing induced multi-potent stem cells and method thereof
The invention discloses application of an I type transforming growth factor receptor (ALK5) inhibitor in producing induced multi-potent stem cells (iPS) and a method thereof. The invention applies a culture medium containing the I type transforming growth factor receptor inhibitor to the producing induced multi-potent stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: inducing cDNA of multi-potent stem cell factors to mouse embryonic fibroblasts; culturing the mouse embryonic fibroblasts treated in the step (1) by using the culture medium added with the ALK5 inhibitor; and identifying clone of induced multi-potent stem cells. The I type transforming growth factor receptor (ALK5) inhibitor of the invention can efficiently produce induced multi-potent stem cells (iPS); and the method forefficiently inducing iPS cells has significance for promoting the medical application of the iPS, establishing a disease model, transplanting treatment, and developing safe iPS technology.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
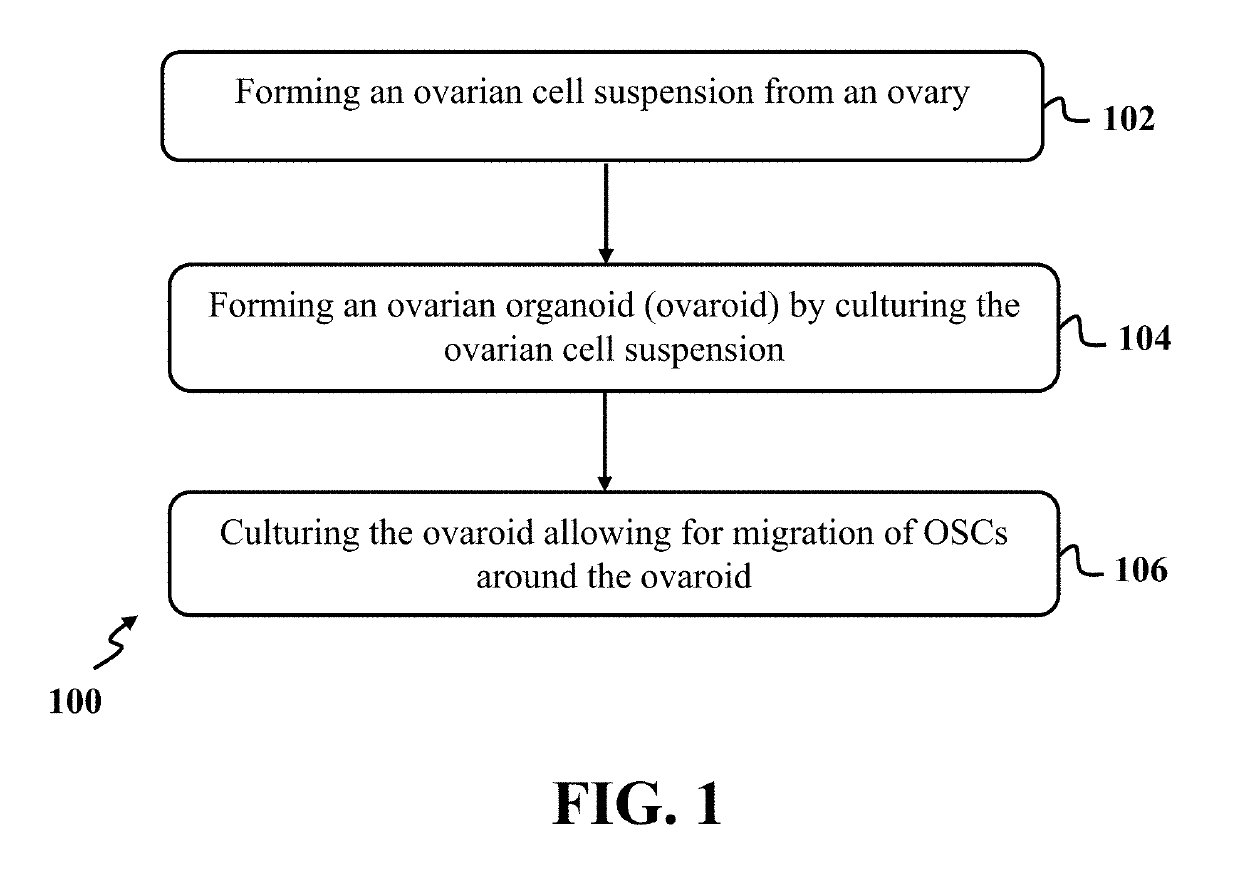
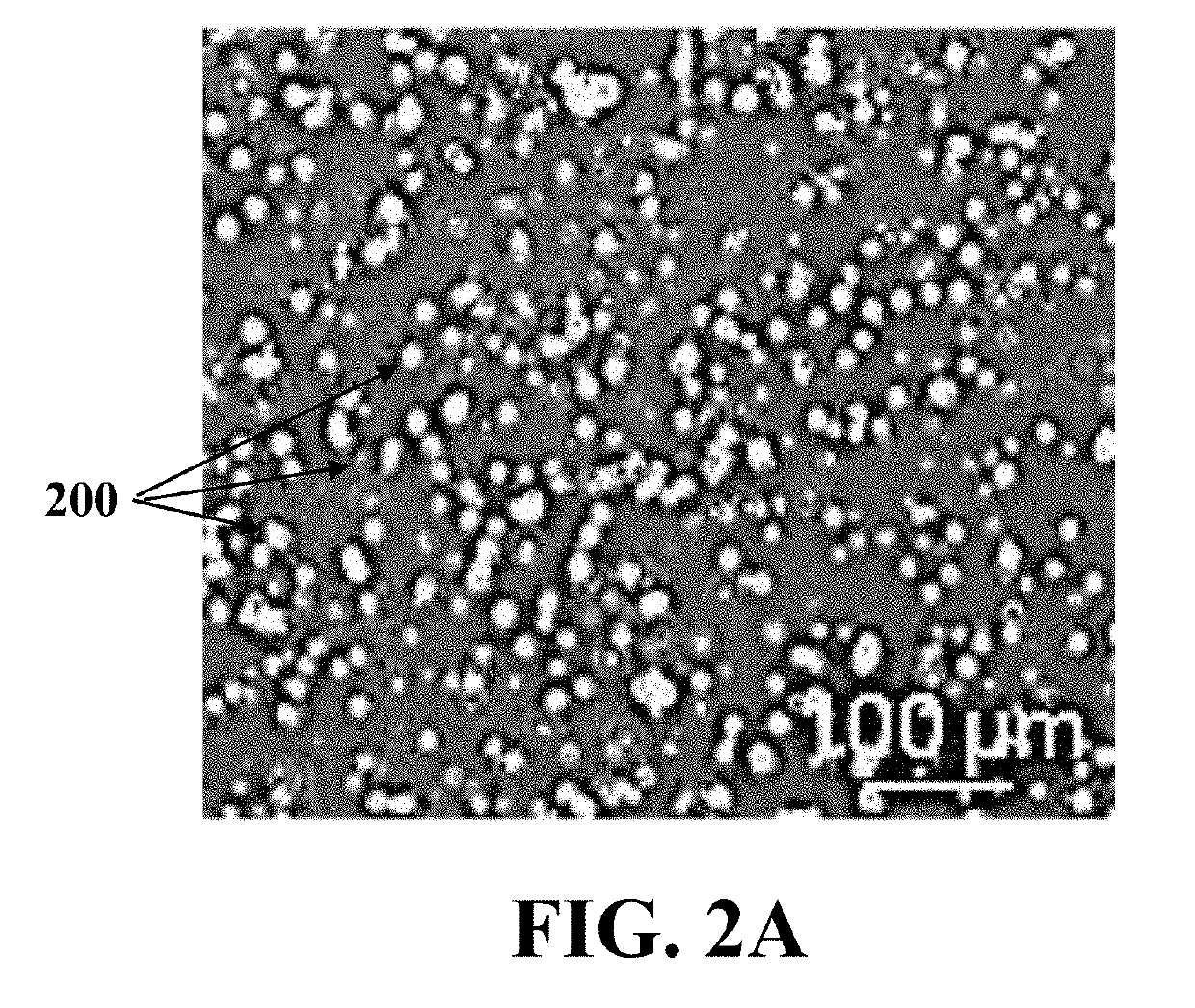
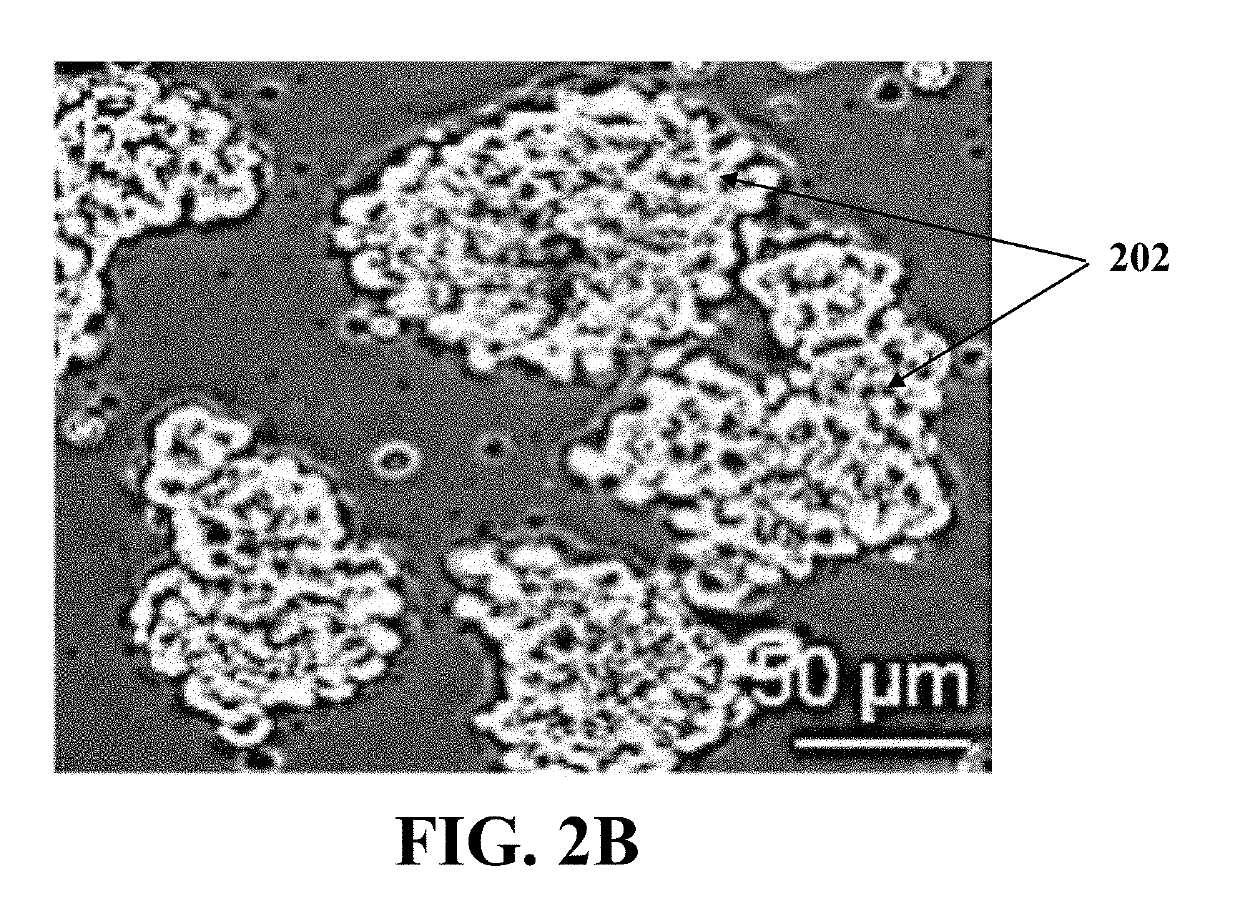
Isolation of oogonial stem cells
InactiveUS20190177689A1Cell culture supports/coatingCell culture active agentsPhysiologyOogonial Stem Cells
A method for isolating oogonial stem cells (OSCs) including forming an ovarian cell suspension from an ovary, forming ovaroids by culturing the ovarian cell suspension in a three-dimensional culture, and migrating the OSCs around the ovaroids by culturing the ovaroids on a mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF)-coated plate.
Owner:ROYAN INST
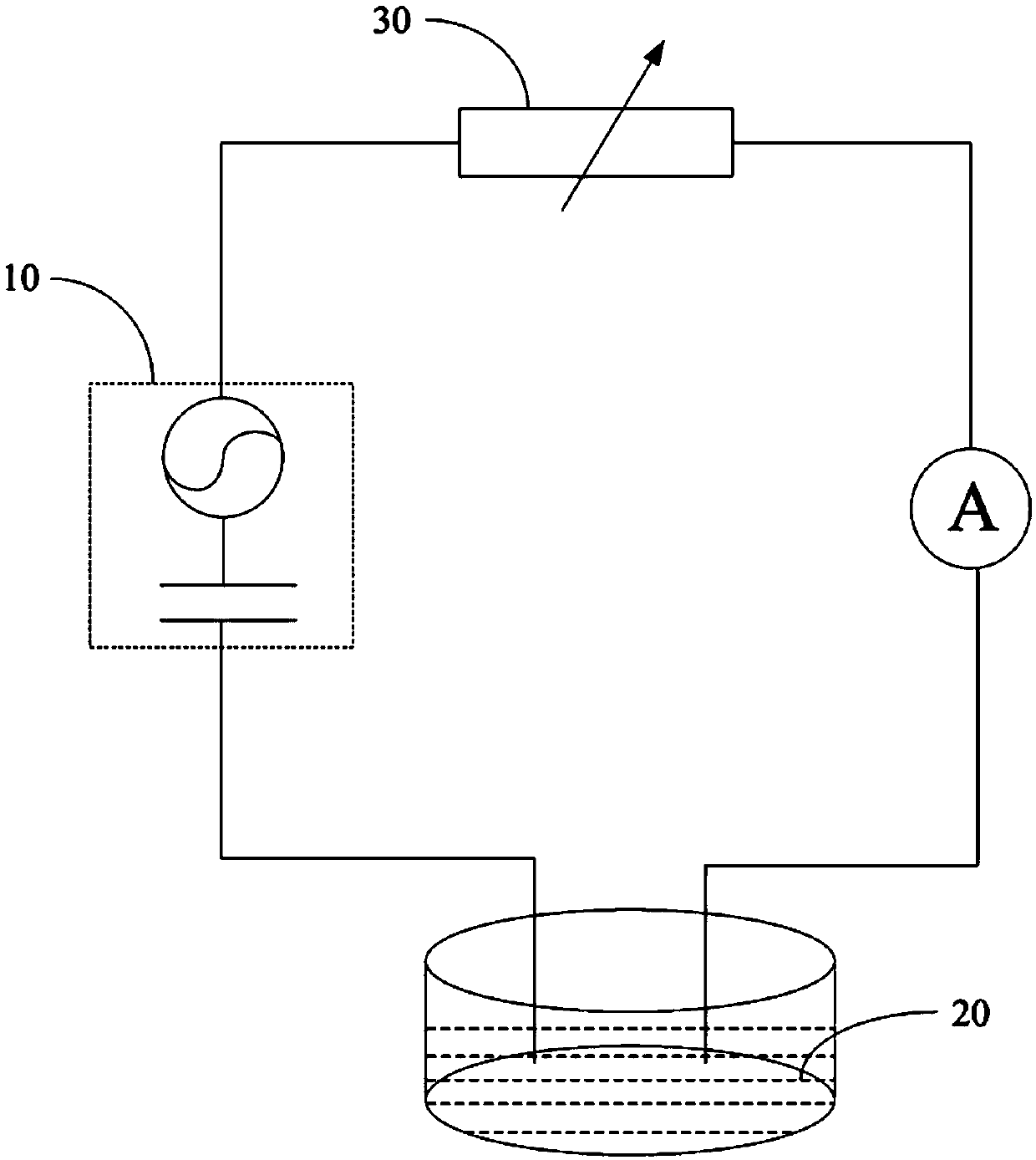
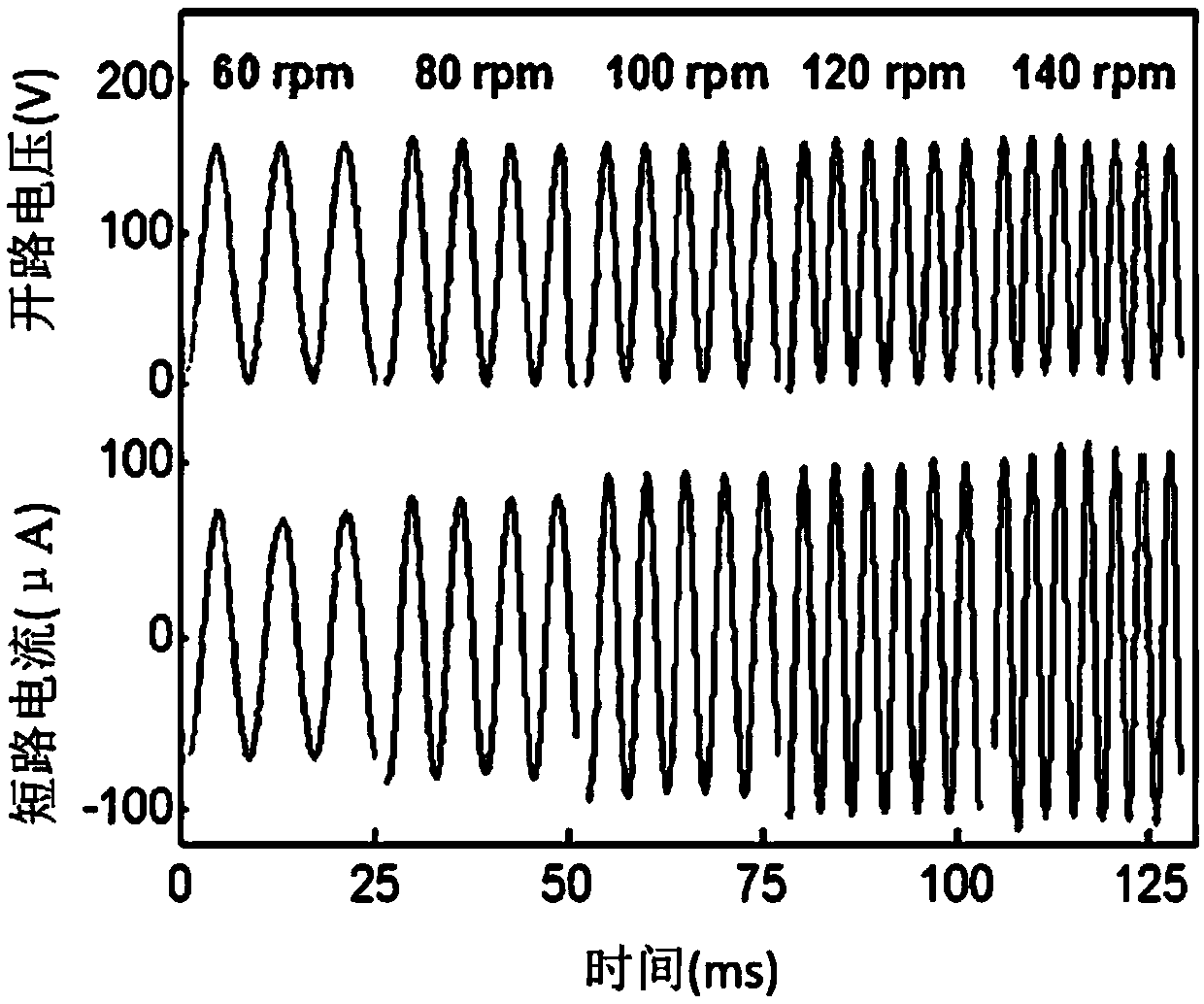
Self-driven electrical stimulation system, band-aid and cancer cell inhibition capsule
PendingCN109603004APrevent proliferationInhibit migrationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationNanogeneratorCancer cell
The present invention provides a self-driven electrical stimulation system, a band-aid, a cancer cell inhibition capsule, and a portable electrical stimulation system. The self-driven electrical stimulation system comprises: a triboelectric nano-generator is used for converting external mechanical energy into electrical energy; a cell culture medium comprises cells to be stimulated, the cell culture medium is connected by electrodes to the circuit of the triboelectric nano-generator; and a rheostat is connected to the circuit and is used for adjusting the magnitude of current in the circuit byadjusting the magnitude of resistance, thereby promoting or inhibiting proliferation and migration of the cells to be stimulated. In the scheme of the invention, under the current stimulation of 10-75 [mu]A, the output of the triboelectric nano-generator is applied to mouse fibroblast, and the triboelectric nano-generator significantly enhances the proliferation and cross-scratch migration of themouse fibroblast during the wound healing process. Moreover, the current stimulation greater than 75 [mu]A or greater than 100 [mu]A can also be applied to inhibit proliferation and migration of thecells to be stimulated.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com