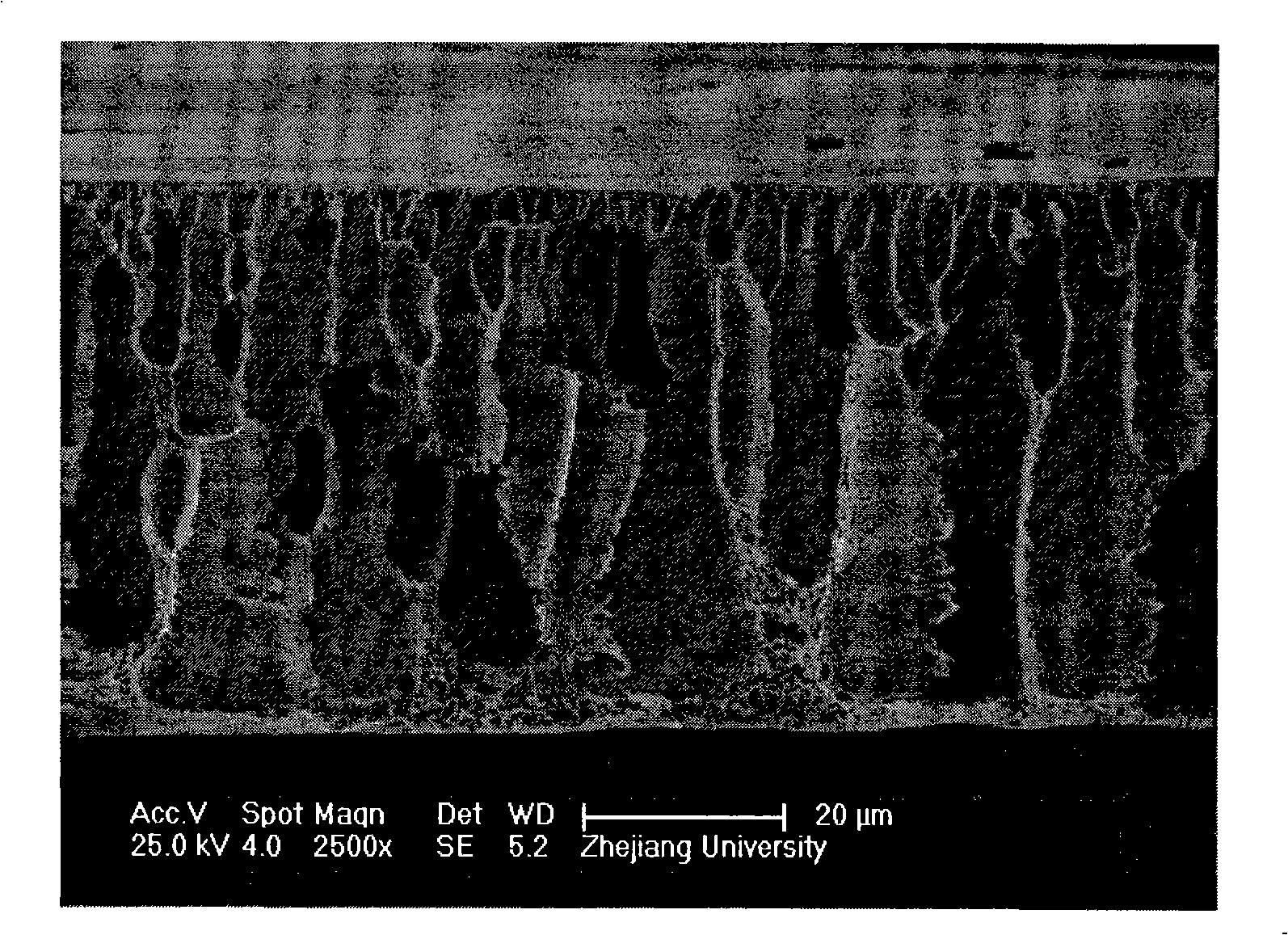
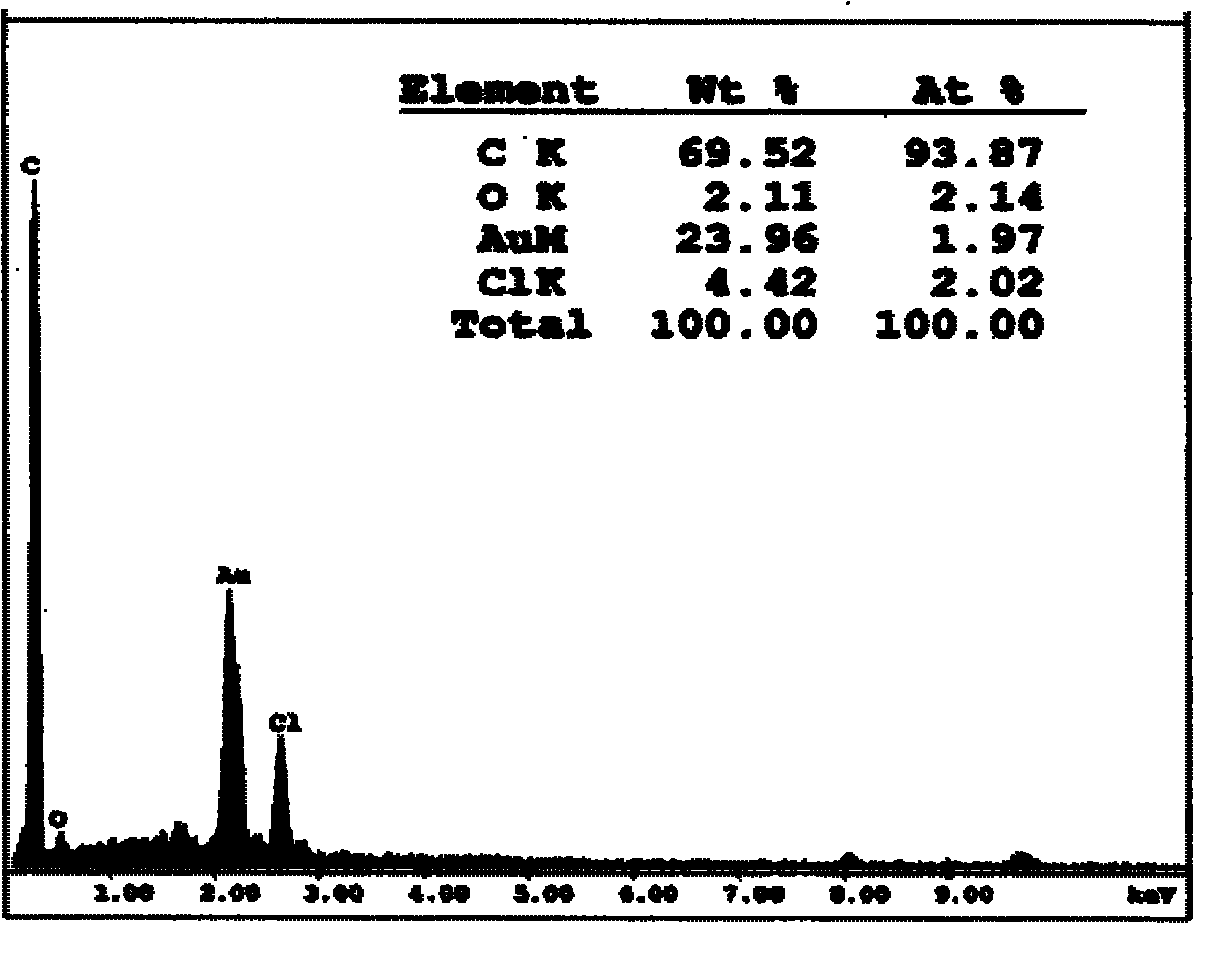
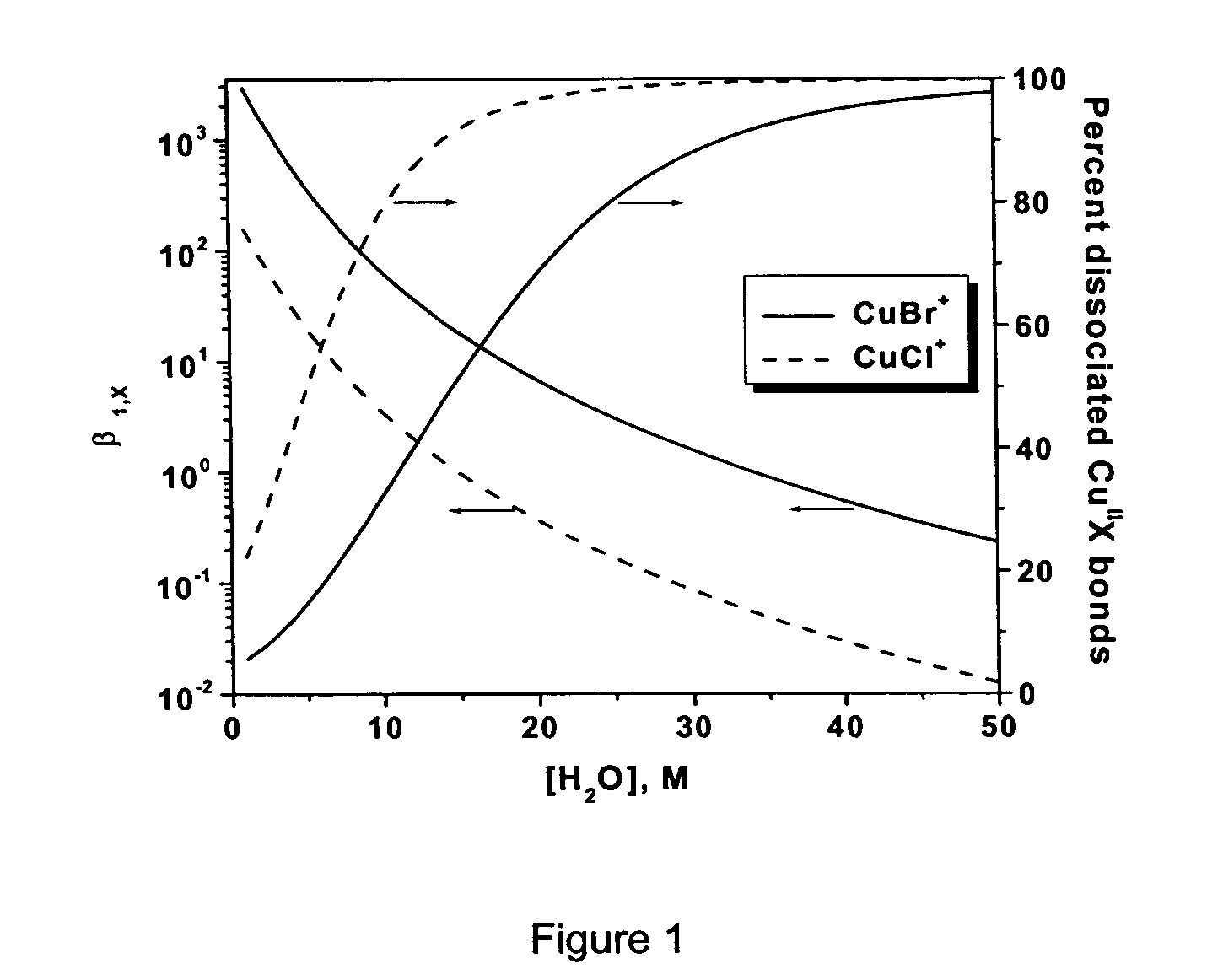
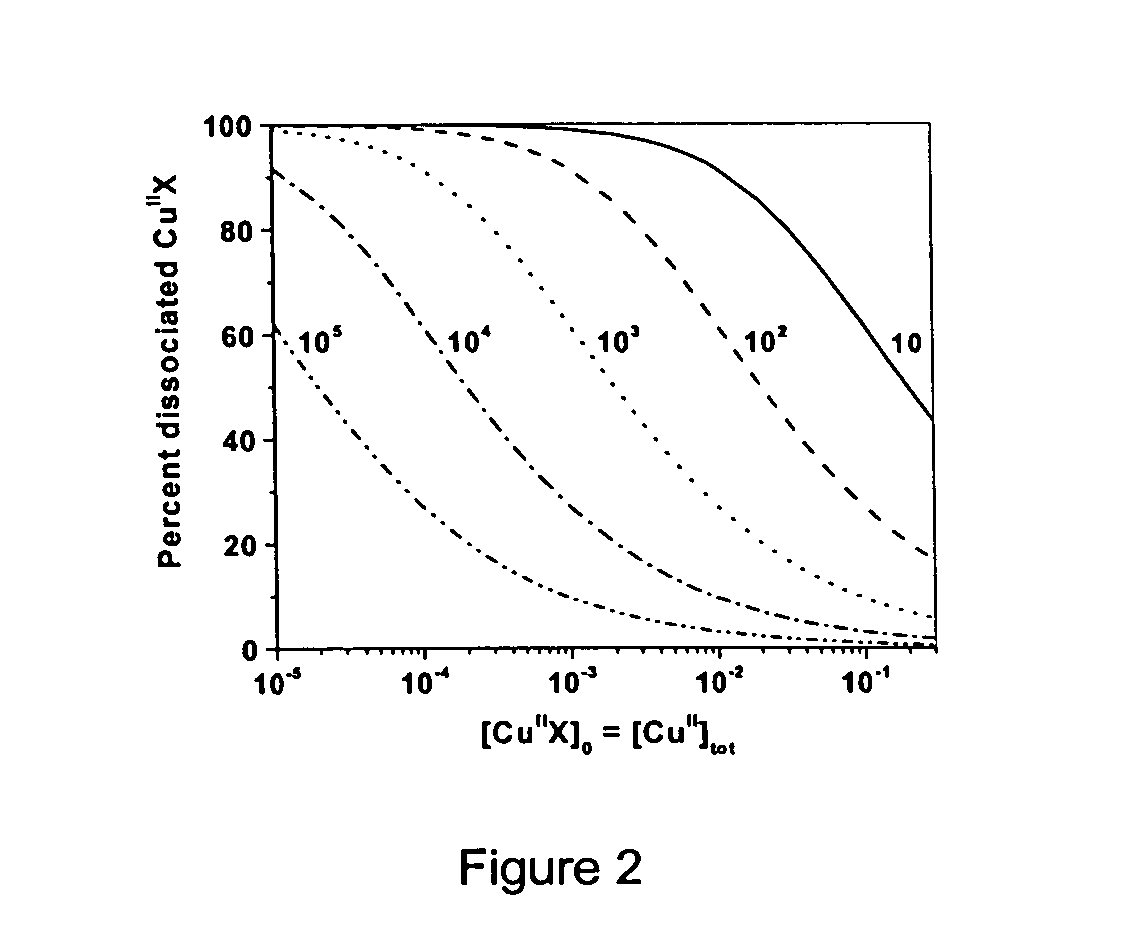
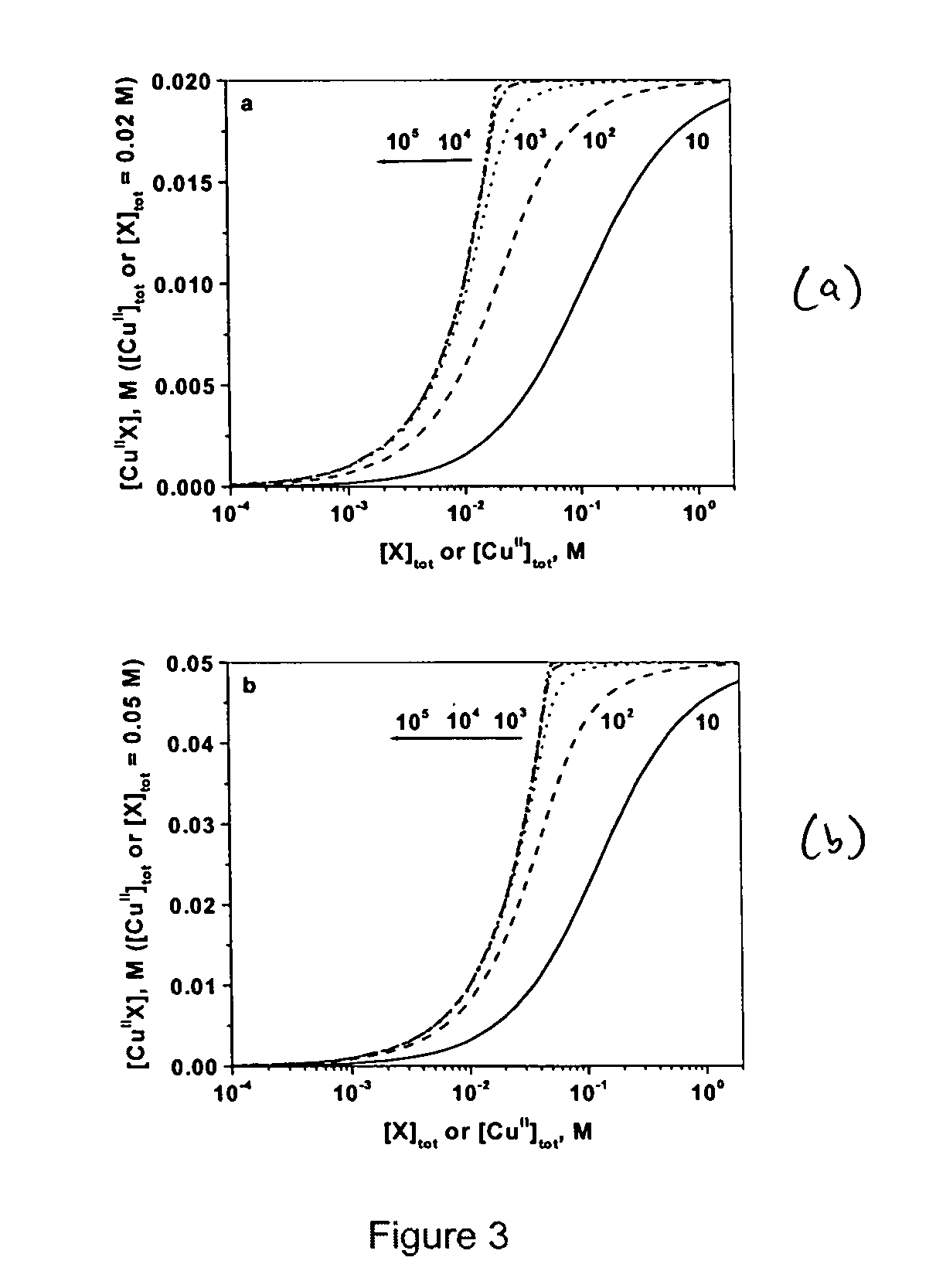
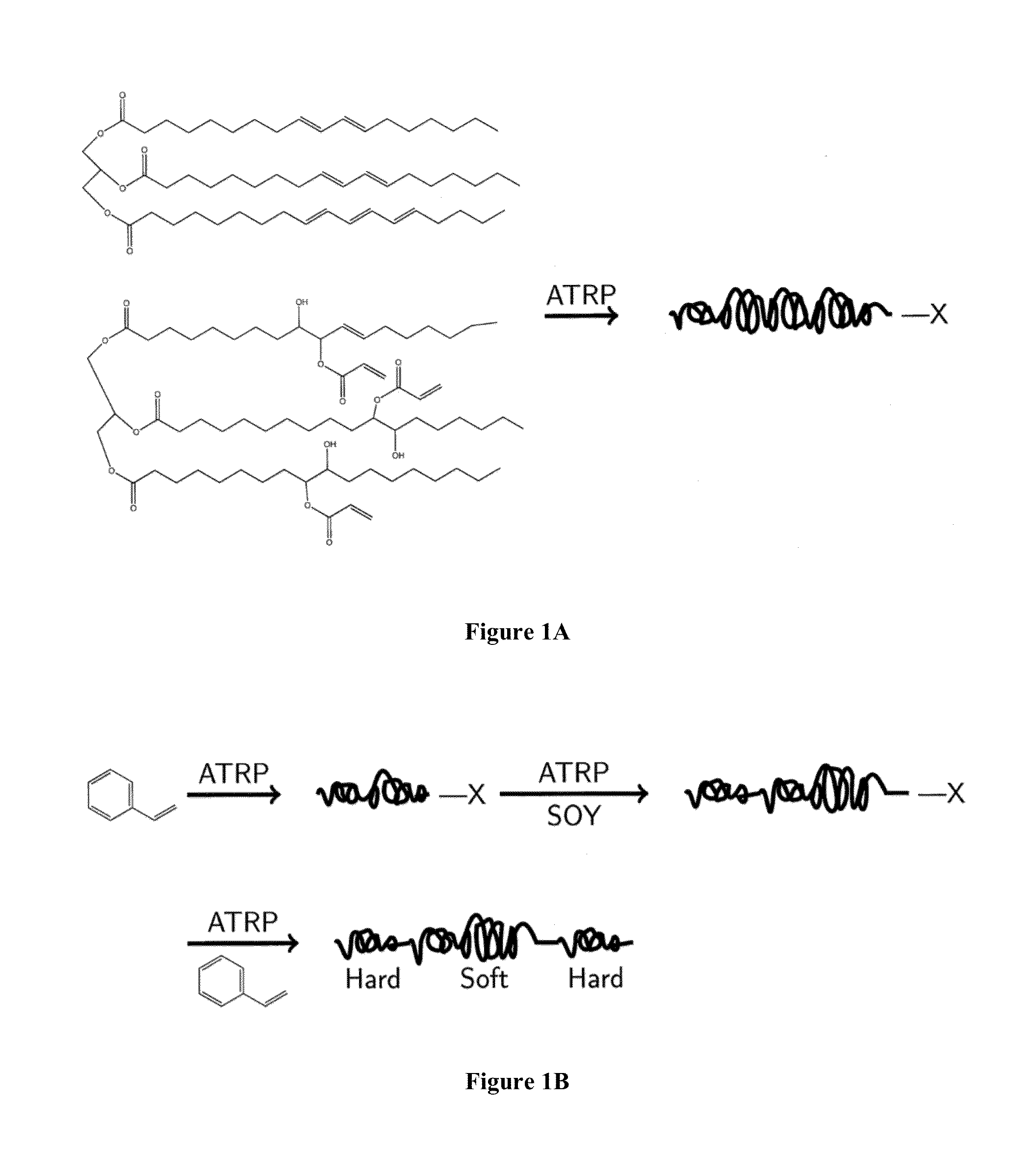
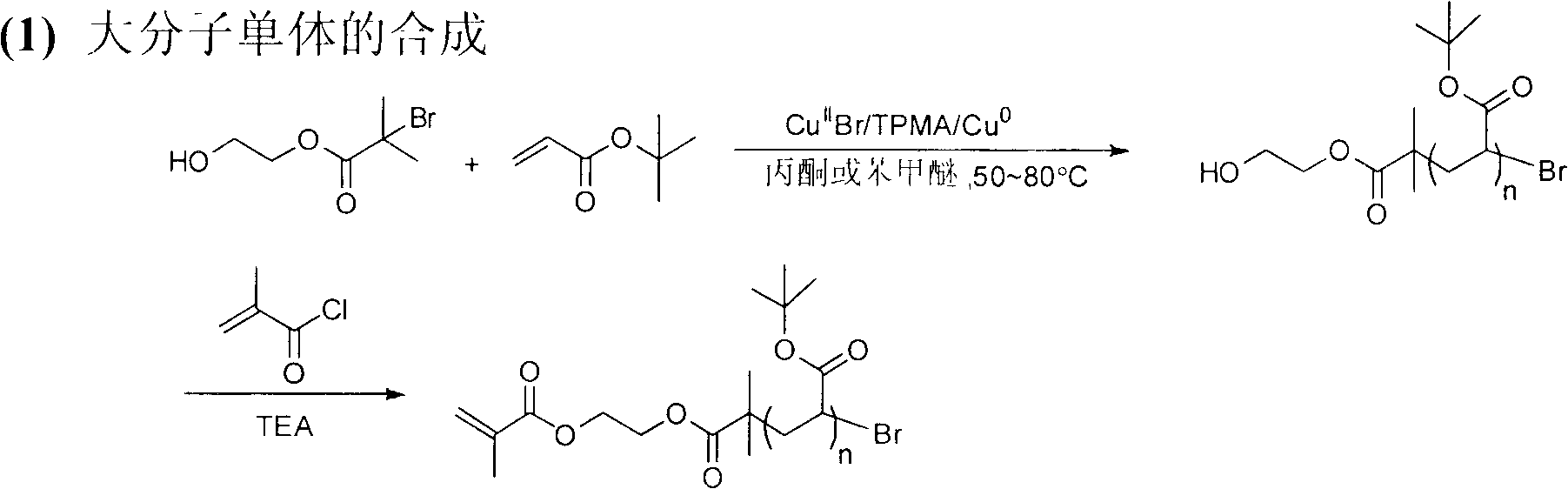
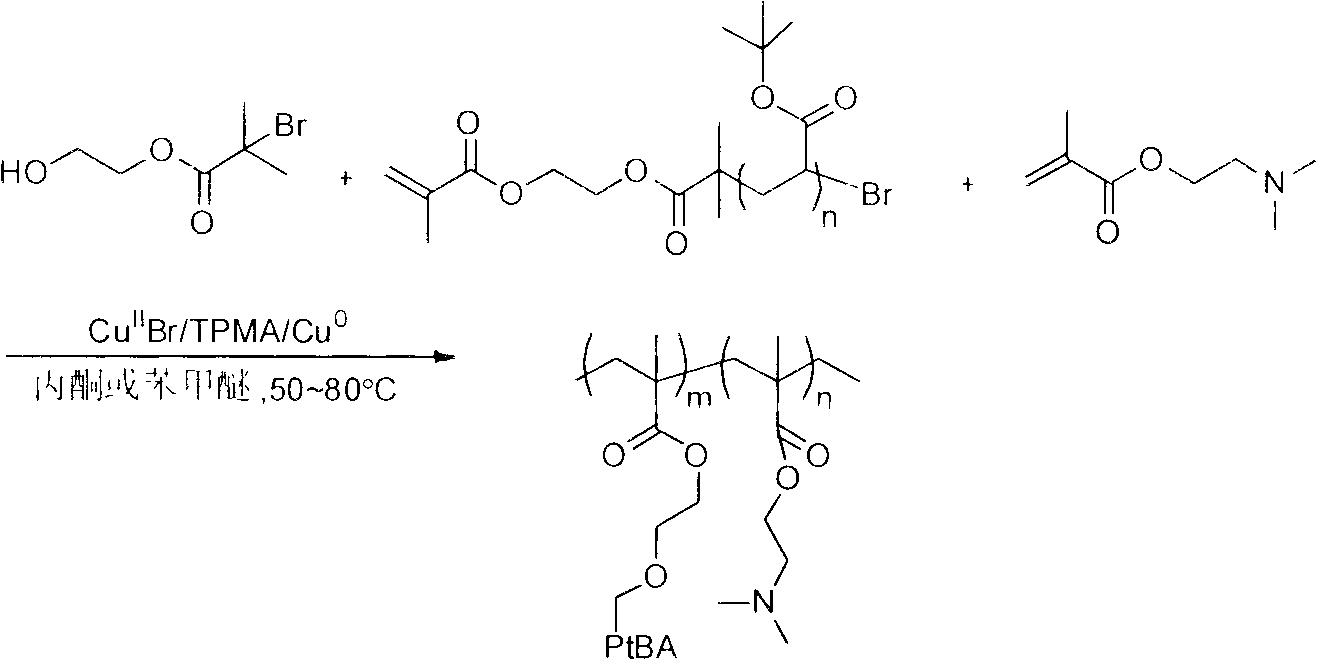
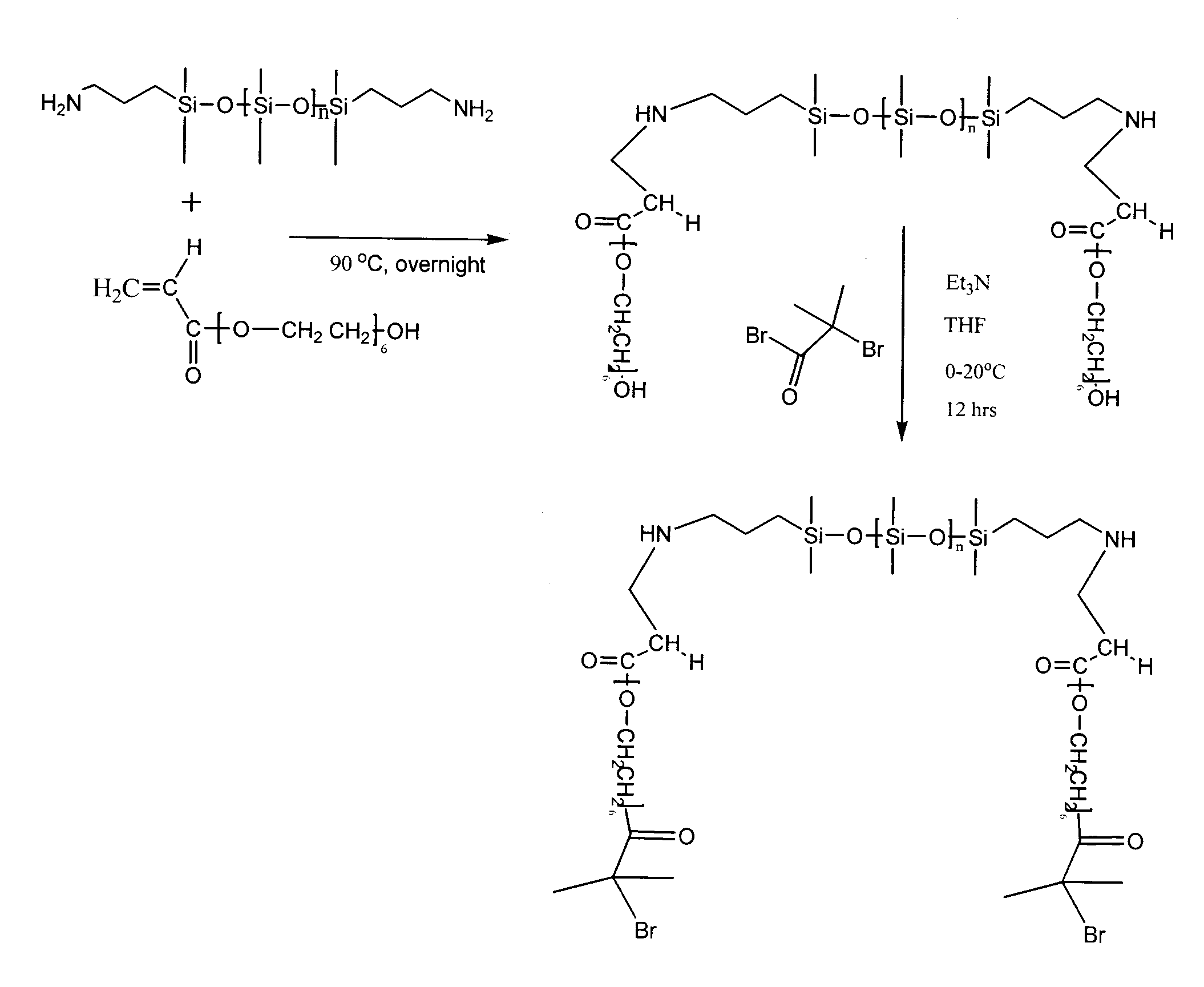
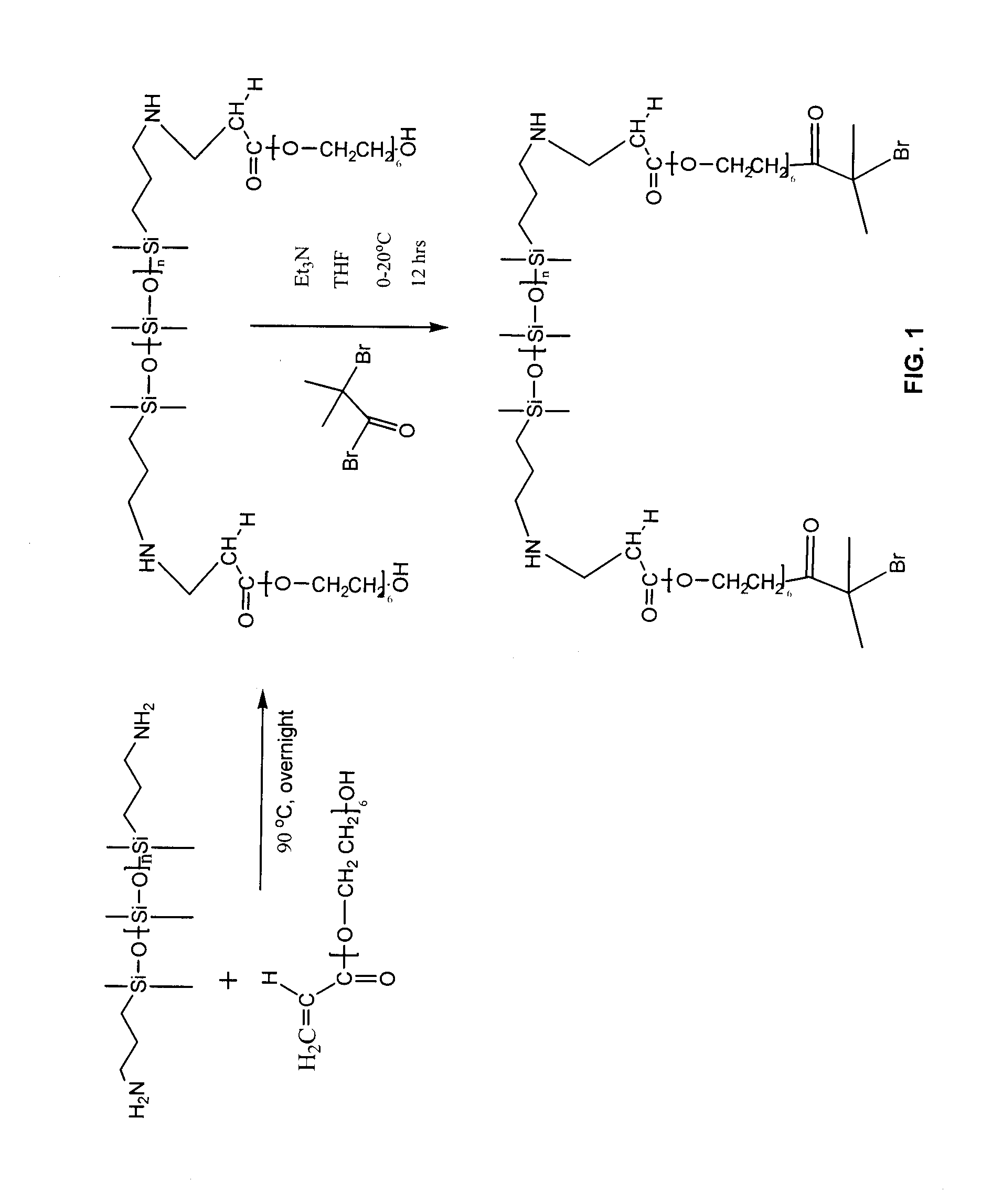
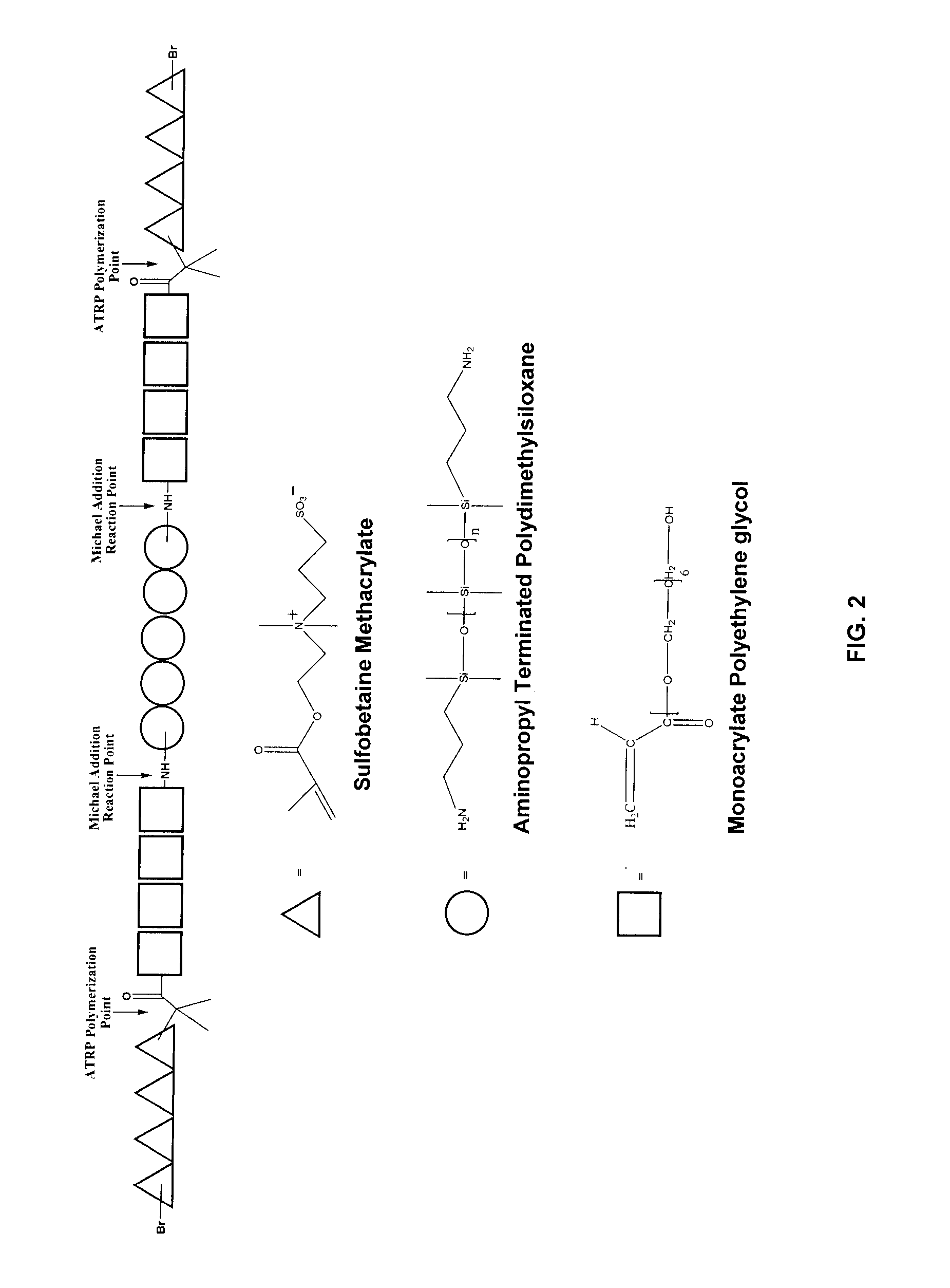
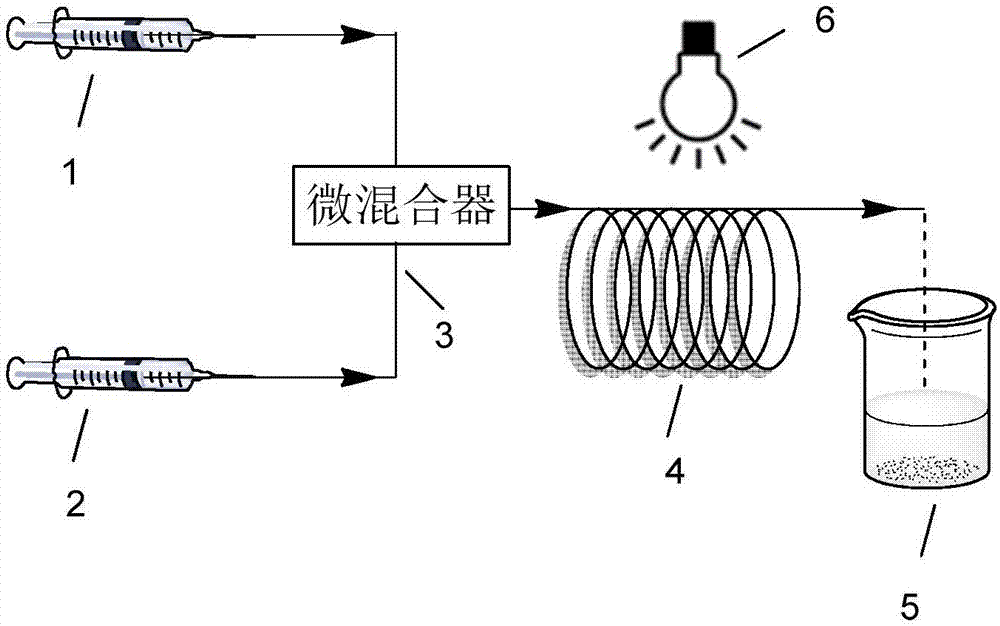
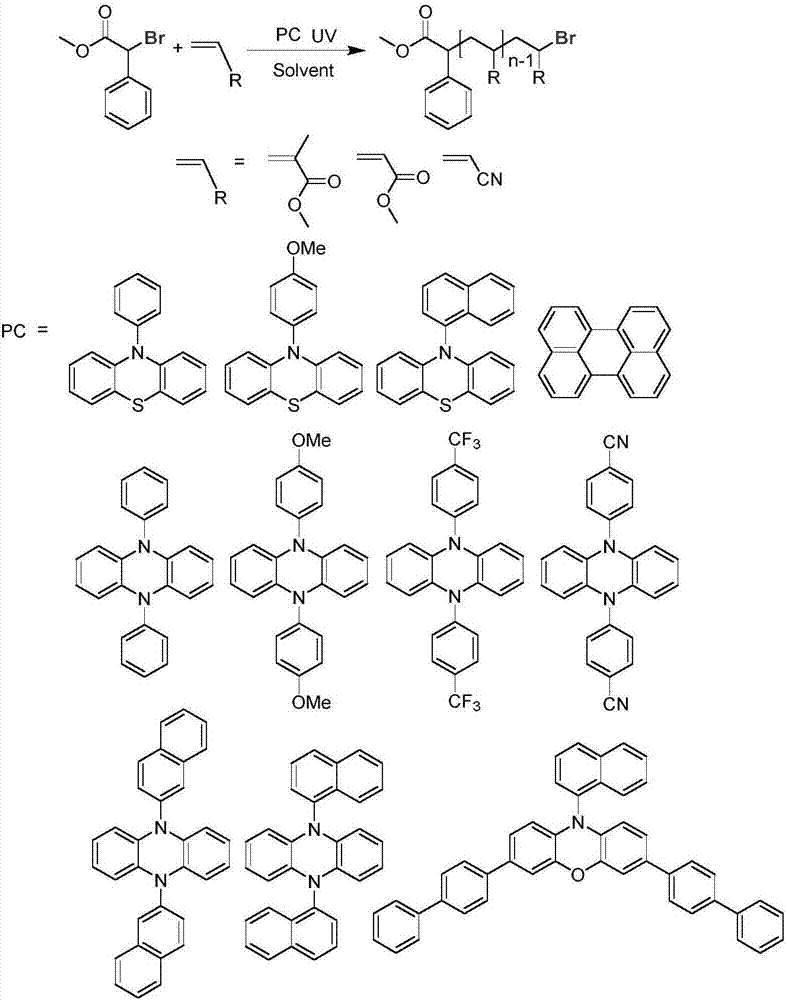
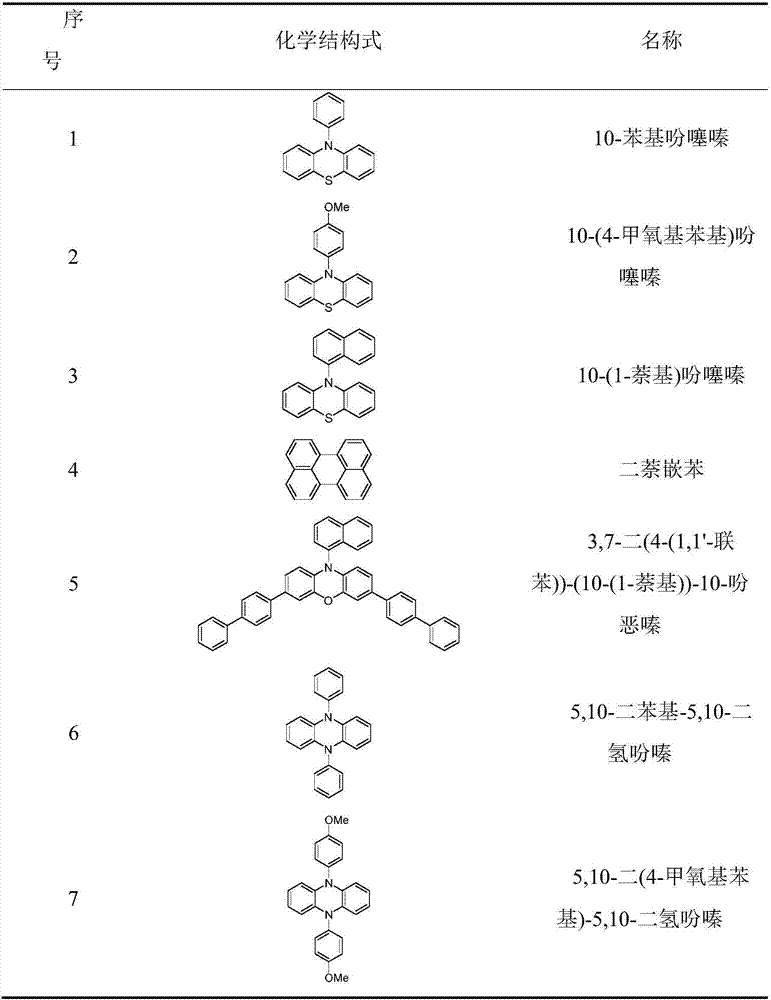
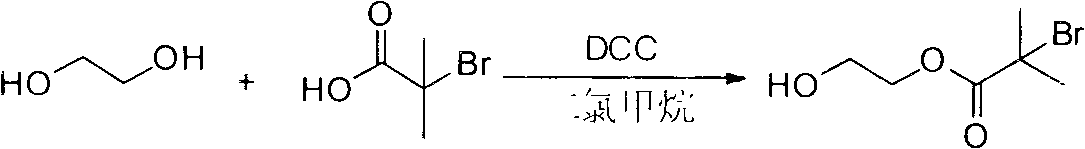Patents
Literature
1213 results about "Atom-transfer radical-polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
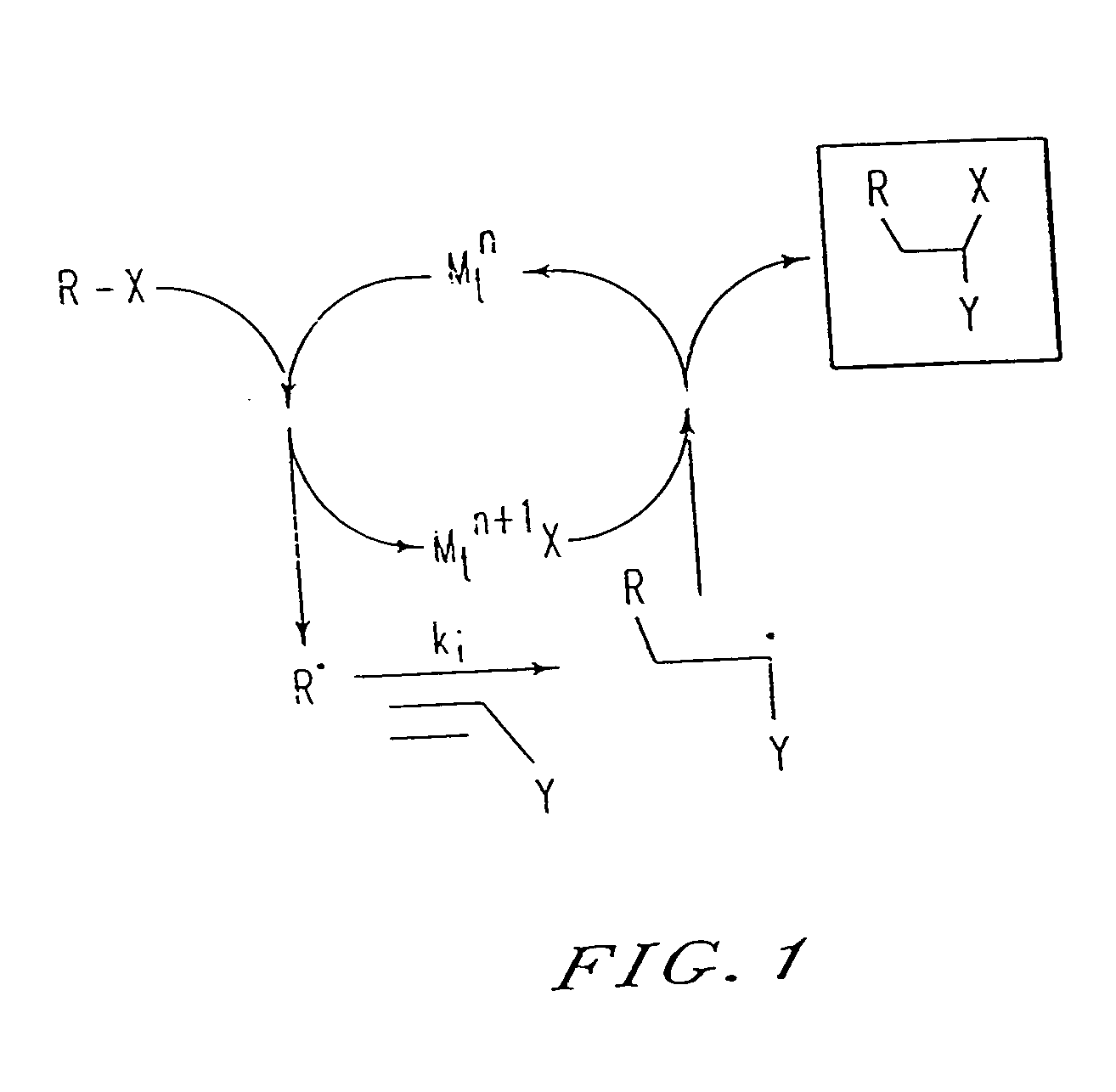
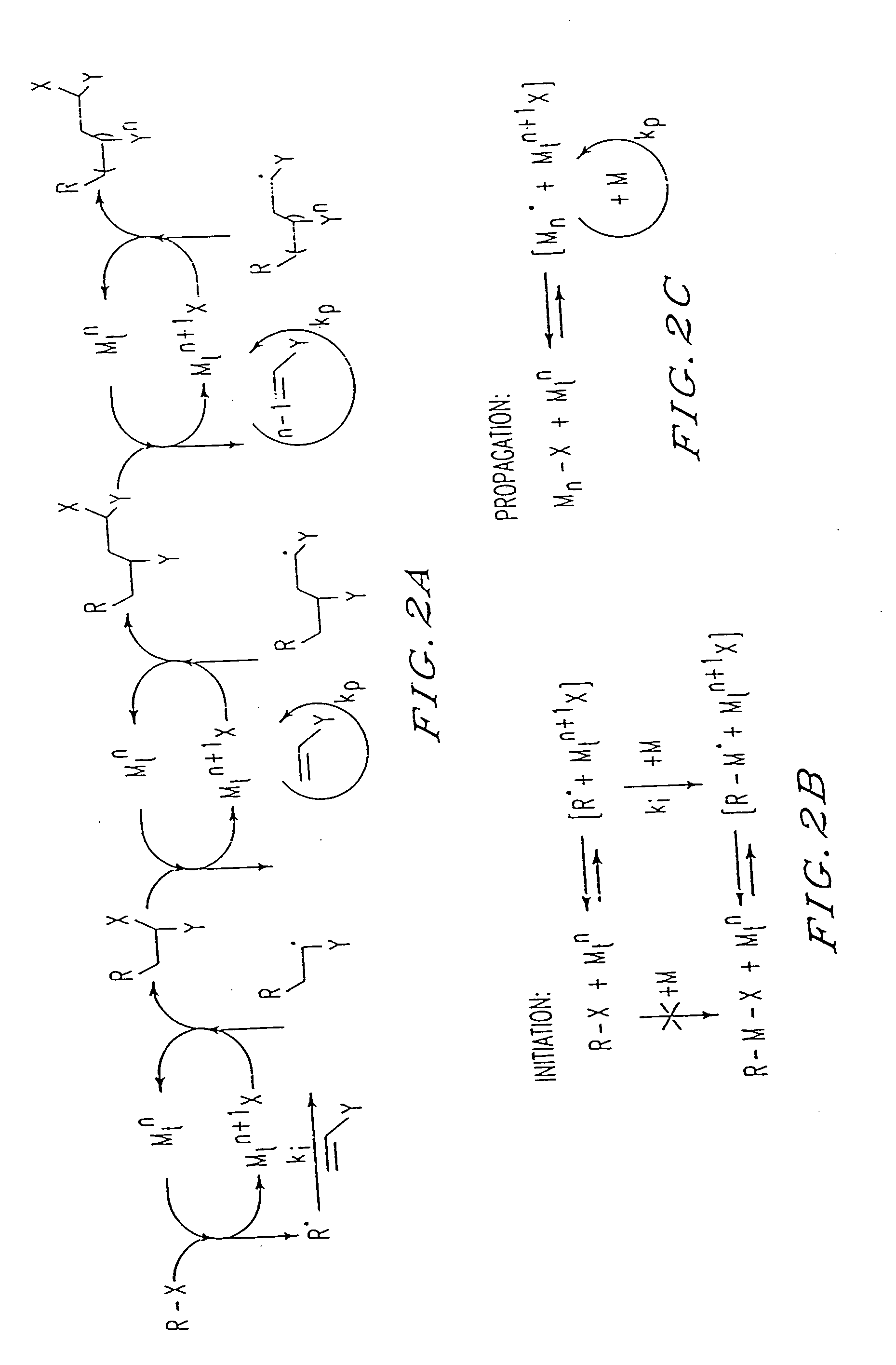
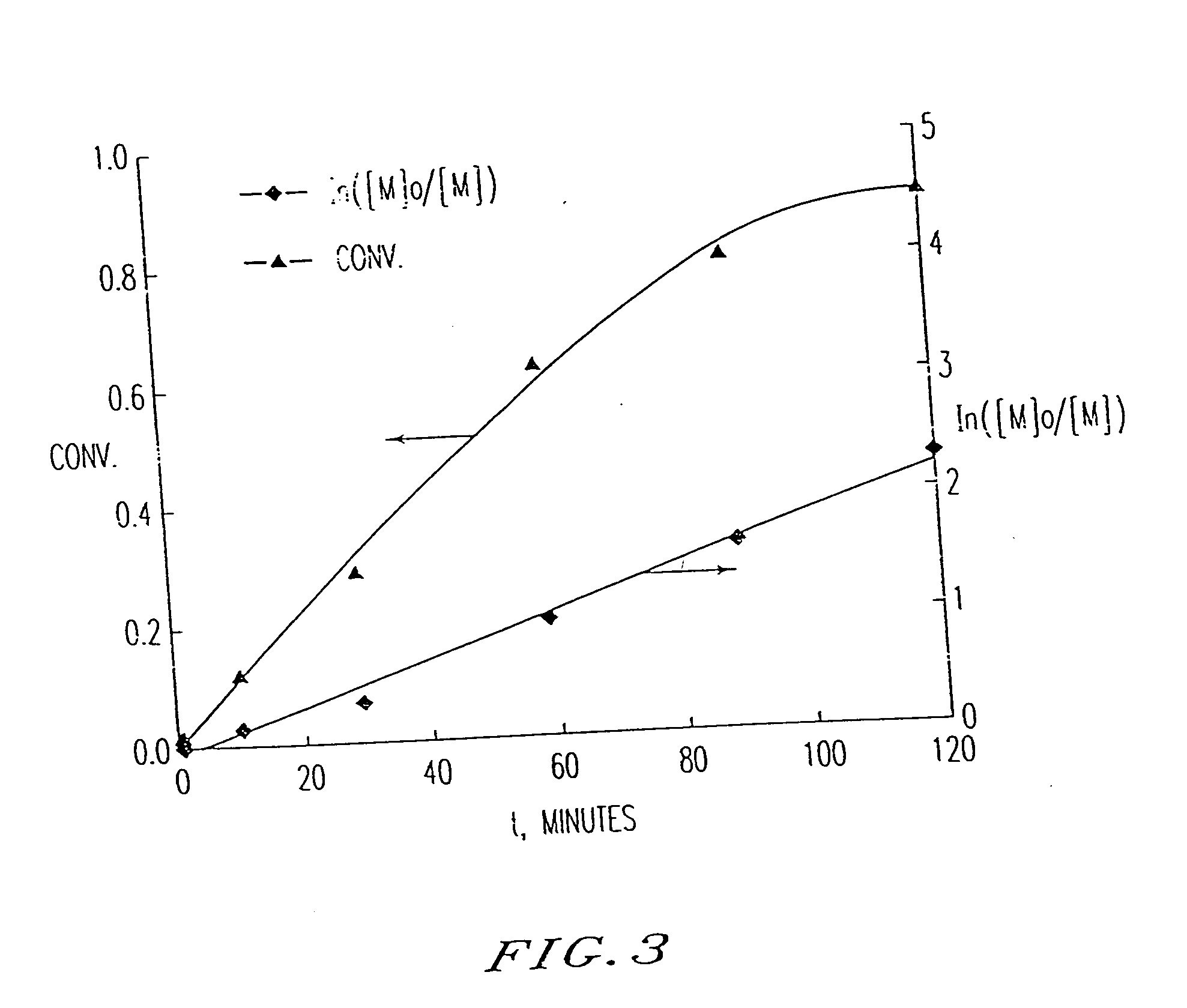
Atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is an example of a reversible-deactivation radical polymerization. Like its counterpart, ATRA, or atom transfer radical addition, ATRP is a means of forming a carbon-carbon bond with a transition metal catalyst. The polymerization from this method is called atom transfer radical addition polymerization (ATRAP). As the name implies, the atom transfer step is crucial in the reaction responsible for uniform polymer chain growth. ATRP (or transition metal-mediated living radical polymerization) was independently discovered by Mitsuo Sawamoto and by Jin-Shan Wang in 1995.
Preparation of novel homo- and copolymers using atom transfer radical polymerization
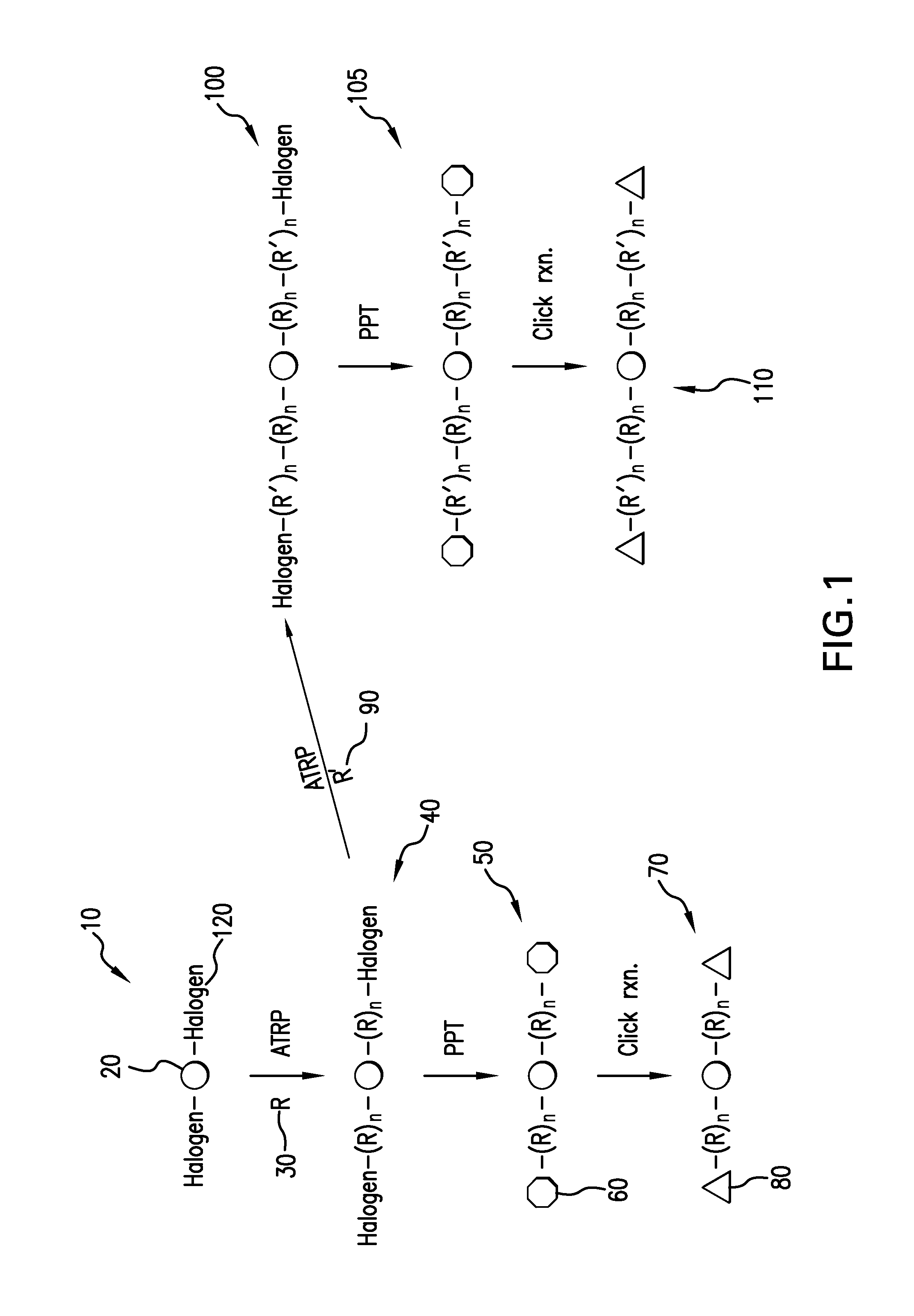
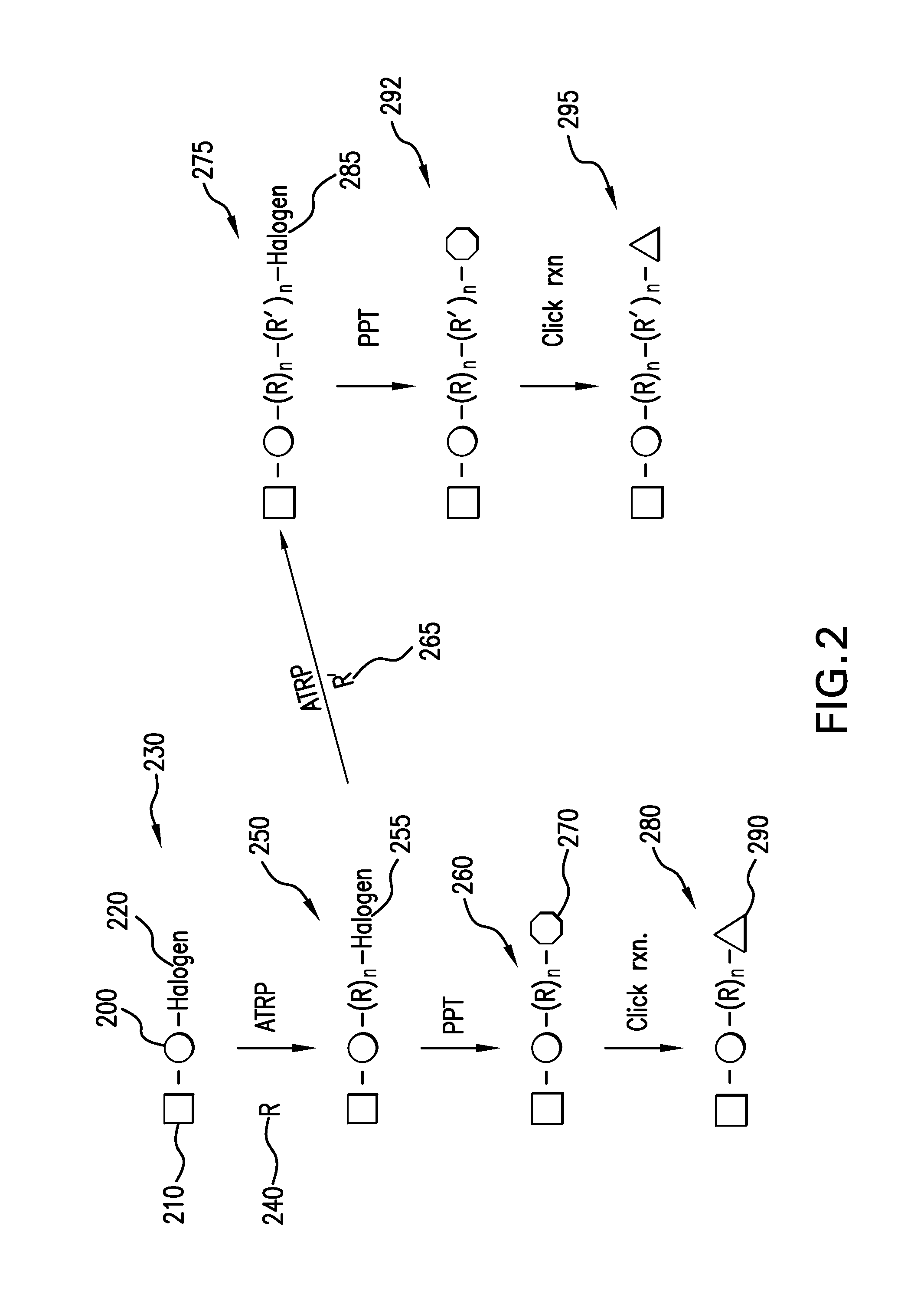
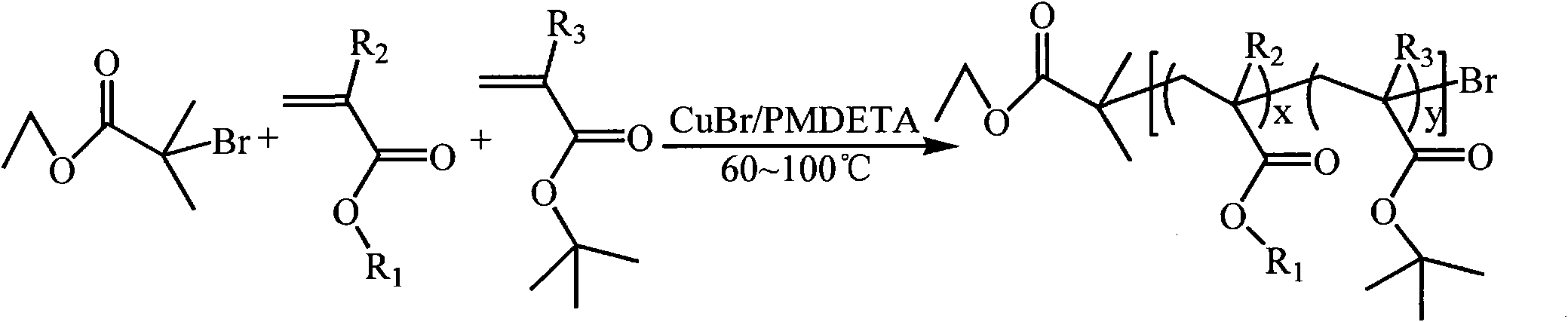
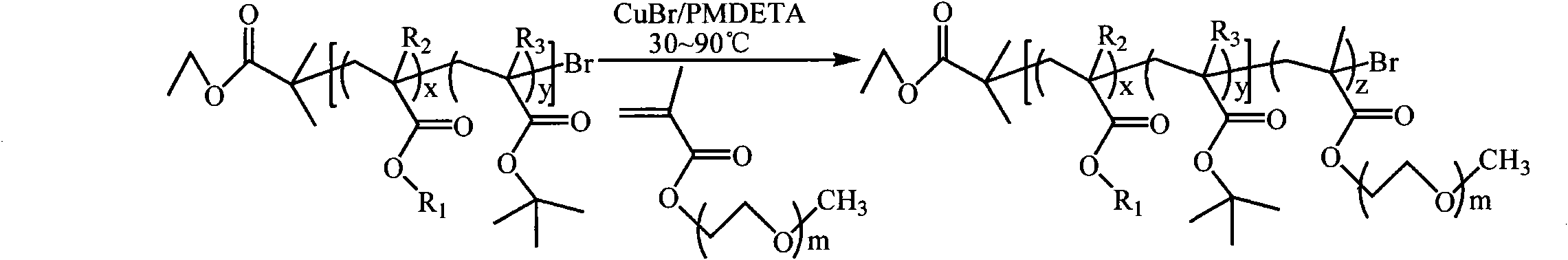
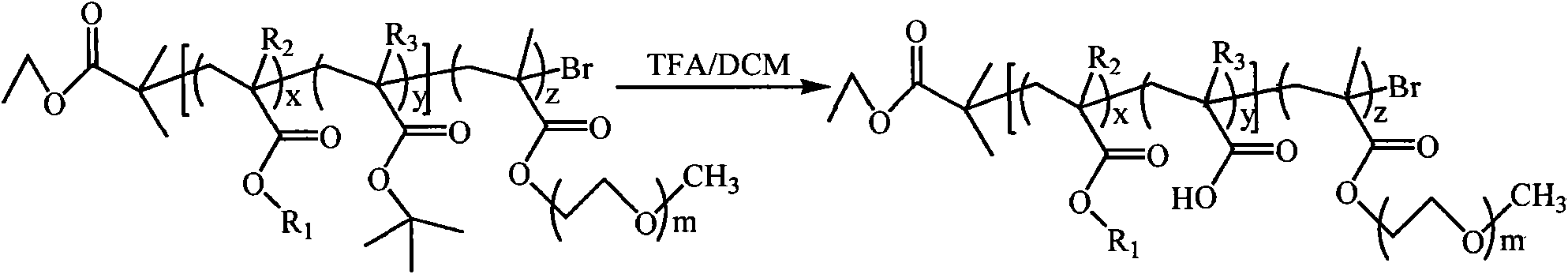
The present invention is directed to a process of atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of novel homopolymer or a block or graft copolymer, optionally containing at least one polar group, with well defined molecular architecture and narrow polydipersity index, in the presence of an initiating system comprising (i) an initiator having a radically transferrable atom or group, (ii) a transition metal compound, and (iii) a ligand, the present invention is also directed to the synthesis of a macromolecule having at least two halogen groups which can be used as a macroinitiator component (i) to subsequently form a block or graft copolymer by an atom or group transfer radical polymerization process; the present invention is also directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a branched or hyperbranched polymer; in addition, the present invention is directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a macroinitiator which can subsequently be used to produce a block or graft copolymer.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Electrophoretic particles and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20090009852A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsElectrophoresisAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
Polymer-coated pigment particles produced using atom transfer radical polymerization provide electrophoretic media having improved bistability without requiring addition to the electrophoretic fluid of additives which increase switching time.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
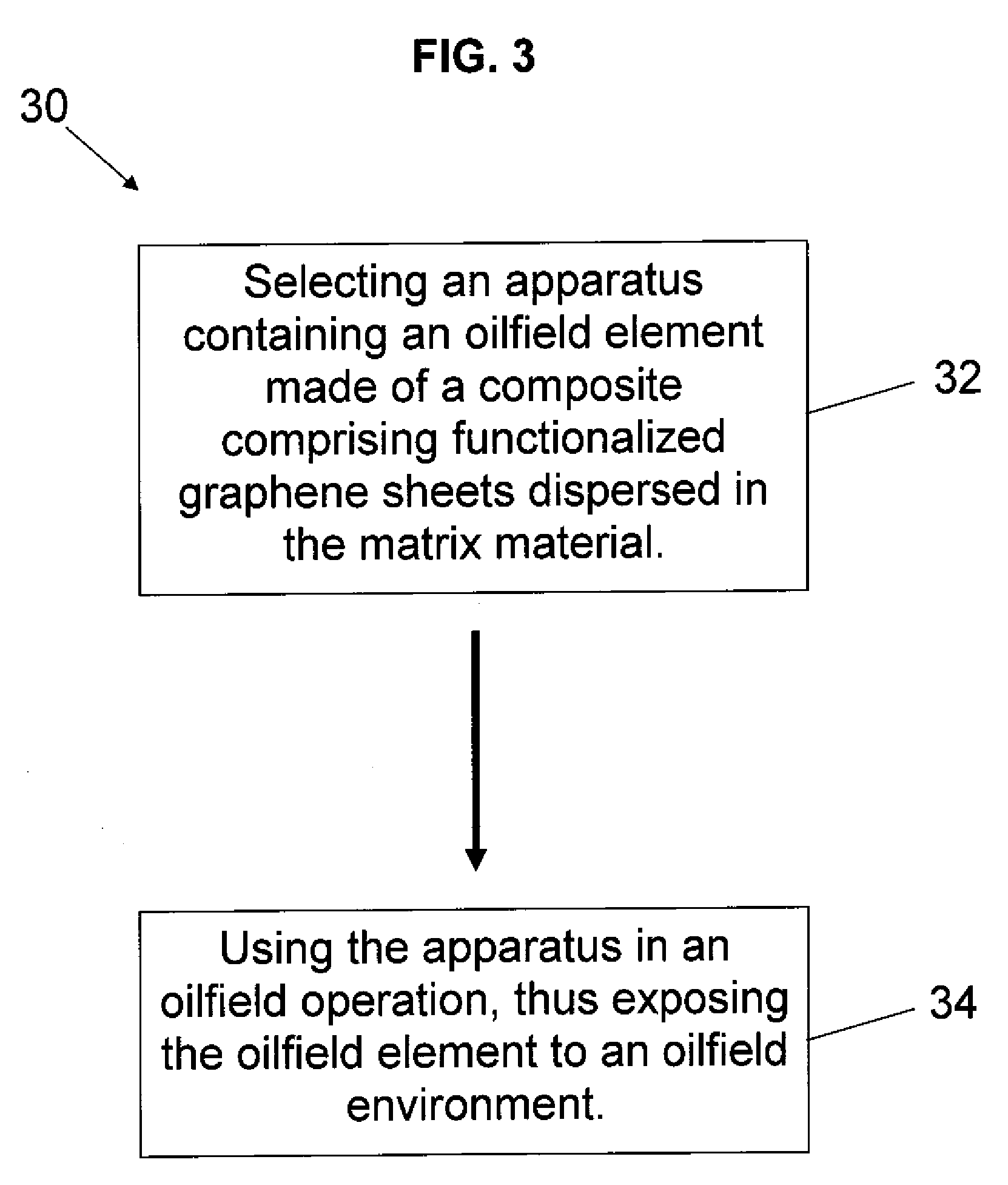
Oilfield nanocomposites
ActiveUS20090036605A1Individual molecule manipulationSealing/packingAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationEngineering
An oilfield apparatus includes an oilfield element made of a composite that includes a matrix material; and a plurality of functionalized graphene sheets dispersed in the matrix material. A method of oilfield operation includes selecting an oilfield apparatus having an oilfield element, wherein at least a portion of the oilfield element is made of a composite comprising a plurality of functionalized graphene sheets dispersed in a matrix material; and using the oilfield apparatus in an oilfield operation, thereby exposing the oilfield element to an oilfield environment. A method for modifying a functionalized graphene sheet includes obtaining the functionalized graphene sheet; and subjecting the functionalized graphene sheet to atom transfer radical polymerization to attach polymers on surfaces of the functionalized graphene sheet. The polymers attached to the surfaces of the functional graphene sheet may comprise co-polymers or magnetic particles.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Block copolymer membranes and associated methods for making the same
A separation matrix comprises a porous surface layer; and a bulk porous support, wherein both the porous surface layer and the bulk porous support comprising a block copolymer. The block copolymer comprises A-B or A-B-A repeating units, wherein A and B at each occurrence are two different blocks of oligomer, or polymer. A structural unit of block A is derived from one or more atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP)-active monomer or oligomer and a structural unit of block B is derived from a thermoplastic ATRP-active macro initiator. A poly dispersity index of the block copolymer is at least about 2.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Atom or group transfer radical polymerization
A polymerization process comprising initiating a first polymerization of monomers using an initiator functionalized with an ATRP initiating site, wherein the first polymerization is selected from the group of cationic polymerization, anionic polymerization, conventional free radical polymerization, metathesis, ring opening polymerization, cationic ring opening polymerization, and coordination polymerization to form a macroinitiator comprising an ATRP initiating site and further initiating an ATRP polymerization of radically polymerizable monomers using the macroinitiator comprising an ATRP initiating site. Novel block copolymers may be formed by the disclosed method.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Graft copolymers and related methods of preparation
InactiveUS20070244262A1Reduce side effectsEasy to controlSide chainAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
Graft copolymers as can comprise a wide range of graft side chains, available using atom transfer radical polymerization techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Atom transfer radical polymerization
Exposing to visible light atom transfer radical polymerizations of vinyl monomers that use transition metal compounds often results in faster polymerizations and / or the need for less transition metal compound. Disclosed is a process for the polymerization of vinyl monomers by atom transfer radical polymerization using a first compound containing a transition metal and a second compound capable of radically transferring an atom or group to said first compound, wherein the improvement comprises, irradiating with visible light with an intensity of at least about 5 mW / cm2 a liquid in which said polymerization is taking place. The polymers made are useful for molding resins and coatings.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101798372AHigh mechanical strengthImprove stress resistanceMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationMicrosphereAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention discloses a polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof. The microsphere comprises a core and surface graft; wherein the core is monodispersed polystyrene-divinyl benzene microsphere with crosslinking degree of 60-90% and grain diameter of 2-20 microns, and the surface graft is polyglycidyl methacrylate or derivate thereof. Friedel-Crafts acylation is utilized, alpha-halogenacyllhalide is taken as acylation agent, initiator molecule is bonded on the surface of the microsphere; conventional atom transfer radical polymerization method is utilized to initiate monomers glycidyl methacrylate to condense; then different nucleopilic reagent is utilized for opening ring, and amino, hydroxyl, hydrazine, carboxyl and sulfydryl groups are introduced onto the surface of the microsphere. The polymer microsphere can be used as separation material for different chromatographs for high efficiency ion exchange, chelation and high efficiency affiliation, also can be used as carrier for fixing enzyme and catalyst and is an excellent functional microsphere.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +2
Block poly-carboxylic acid concrete high-efficiency water reducing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103482897AControl structureControl its molecular weight distributionStructural regularityPolymer science
The invention provides a block poly-carboxylic acid concrete high-efficiency water reducing agent with an ordered structure and a preparation method thereof. The block poly-carboxylic acid is prepared by using atom transfer radical polymerization, the structural regularity and the molecular weight distribution of the poly-carboxylic acid are controlled effectively, and the water reducing agent is used in a cement dispersing process. By adoption of the block poly-carboxylic acid concrete high-efficiency water reducing agent and the preparation method thereof, the problems of uncontrollable molecular weight of the poly-carboxylic acid, wider molecular weight distribution, un-designable molecular structure and the like are solved.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS +1
Stabilization of transition metal complexes for catalysis in diverse environments
This present invention is directed towards the identification or design, preparation, and use of suitable transition metal complexes for use as catalysts. The transition metal complexes may comprise heterodonor ligands. The present invention is also directed toward a method of determining the suitability of a transition metal complex for use in a catalytic reaction, such as, but not limited to, atom transfer radical polymerization (“ATRP”), atom transfer radical addition (“ATRA”), atom transfer radical cyclization (“ATRC”), and other catalytic redox reactions. The method assists in the approximate determination of the fundamental properties of the transition metal complex in a reaction media, such as, but not limited to, solubility, redox potential, stability towards acidic, basic, or ionic species, conditional radically transferable atom phylicity, and propensity toward disproportionation and therefore, the suitability of the complex to be used as a catalyst in the reaction media. The method provides a basis for prediction and evaluation of the properties of a transition metal complex for a particular selective catalytic reaction in a broad range of reaction environments. An understanding of the principles of the disclosed method allows a transition metal complex to be tuned to specific reaction medium by selecting a transition metal complex and ligand combination having the desired qualities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Thermoplastic elastomers via atom transfer radical polymerization of plant oil
The present invention relates to a block copolymer comprising at least one PA block and at least one PB block. The PA block represents a polymer block comprising one or more units of monomer A, and the PB block represents a polymer block comprising one or more units of monomer B. Monomer A is a vinyl, acrylic, diolefin, nitrile, dinitrile, or acrylonitrile monomer. Monomer B is a radically polymerizable plant oil monomer containing one or more triglycerides. The present invention also relates to a method of preparing a thermoplastic block copolymer by radical polymerizing a radically polymerizable monomer with a radically polymerizable plant oil monomer containing one or more triglycerides, in the presence of an initiator and a transition-metal catalyst system to form the thermoplastic block copolymer. The polymerized plant oil-based block copolymers are useful in a variety of applications, such as asphalt modifiers, rubber compositions, adhesives, tires, in the automobile industry, footwear, packaging, etc.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Aqueous anticorrosive modified graphene coating material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105838183AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove water resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsPolymer modifiedWater dispersible
The invention relates to an aqueous anticorrosive modified graphene coating material, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: oxidizing natural graphite in an oxidant, modifying the surface of the obtained graphite oxide with an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) initiator with different structures, adding a monomer, a high-valence catalyst, a ligand and a reducing agent to make the monomer undergo atom transfer radical polymerization (AGET ATRP) on the surface of graphene for electron transfer to generate an activator, and reducing graphene oxide (GO) by the reducing agent to obtain a water-dispersible polymer modified graphene material. The polymer modified graphene material can be used to prepare aqueous coatings, can be used to protect the surfaces of metal materials, can effectively isolate a corrosion medium from a substrate, and has excellent water, corrosion and weather resistance, and the preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency, easy industrial production and wide application values.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HUAKE POLYMERS
Actinically-crosslinkable siloxane-containing copolymers
The invention provide a class of actinically-crosslinkable silicone-containing prepolymers obtained by functionalizing an intermediary copolymer to have two or more thiol or ethylenically-unsaturated groups covalently attached thereto, wherein the intermediary copolymer is an atom-transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) product of a reactive mixture comprising a polysiloxane ATRP macroinitiator and at least one hydrophilic vinylic monomer. The present invention is also related to silicone hydrogel contact lenses made from a prepolymer of the invention and methods for making the contact lenses in a cost-effective way and with high consistency and high fidelity to the original lens design.
Owner:ALCON INC
Diblock copolymer containing full-fluorine cyclobutyl aryl aether block and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492520AThe synthesis method is simpleMixingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylateAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention provides a bi-block polymer containing perfluorocyclobutyl aryl ether-based polymer, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The preparation method comprises two reaction steps: firstly, a macroinitiator formed through atom transfer radical polymerization is prepared; and then the macroinitiator is used for initiating an acrylic ester monomer and a metacrylic acid ester monomer, which contain perfluorocyclobutyl aryl ether structures, to carry out the atom transfer radical polymerization, thus obtaining the diblock polymer containing the perfluorocyclobutyl aryl ether-based polymer. The obtained diblock polymer can be used for preparing an aggregate with microscopic shape and can be potentially applied to such fields as a pollution-resistant reagent, a surfactant, an emulsifier, a drug carrier, photoconductive materials, photonic crystals, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
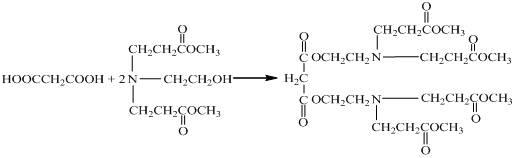
Hyperbranched polymer, hyperbranched type water reducing agent of polycarboxylic acid series and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102002134AGood dispersionAvoid reunionAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationPolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a hyperbranched polymer and a preparation method thereof, wherein the preparation method comprises the steps of taking methyl acrylate, ethanolamine, 2-bromoethanol and propandioic acid as raw materials to synthesize a hyperbranched poly (amine-ester) nuclear molecule comprising a bromine terminal group; taking cuprous bromide and 2,2-bipyridyl as a catalyst and a coordinating agent; respectively grafting acrylic acid and single methyl oxygen radical sealed allyl polyethylene glycol into the hyperbranched poly (amine-ester) comprising bromine terminal group by means of an atom transfer radical polymerization method so as to obtain a hyperbranched polymer. The invention further provides a hyperbranched type water reducing agent of polycarboxylic acid series mainly comprising the hyperbranched polymer and the application thereof, wherein the water reducing agent improves the faults of existing water reducing agent of which the adding quantity is large and the cement adaptability is bad and the like,. and has the advantages that the adding quantity is low, the water reducing efficiency is high, the loss of slump is less, the compatibility to the cement is good, the frozen resistance is strong and the like, the properties of the product are stable, and the water reducing agent has no tendency of layering and precipitating and has no toxicity and pollution after storing for a long time.
Owner:江苏超力建材科技有限公司
Method for preparing branched high vinyl polybutadiene rubber using molybdenum series catalysis
The invention relates to a method for preparing branched high ethenyl butadiene rubber with molybdenum catalyst, recombining macromolecular monomer prepared through polymerization of molybdenum catalyst butadiene atom free radical or butadiene anion initiated by organic lithium, naphthalene sodium, with coordinate polymerization of butadiene or original position polymerization, to prepare said product with controllable construction. The method is characterized by simple process, special construction of polymer, proper molecular weight and molecular distribution, more than 80% of ethenyl content, controllable property, length, distribution and degree of branching of branch chain in a certain range, good processing behavior and physical mechanics property and low production cost.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polysiloxane block copolymers in topical cosmetic and personal care compositions
A process for making a polysiloxane block copolymer which is built up from units of the formula [A] [B], in which A is a polymeric block built up from radically polymerisable monomer, and B is a polysiloxane block, the process comprising the steps of forming a polysiloxane macroinitiator by grafting a radical initiator onto a polysiloxane via a nucleophilic displacement reaction between groups on the polysiloxane and radical initiator respectively, and reacting the polysiloxane macroinitiator so obtained with radically polymerisable monomers in an atom transfer radical polymerisation reaction to form a polysiloxane block copolymer. Also provided are cosmetic and personal care compositions, such as hair styling compositions, containing the polysiloxane block copolymers.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Soakage reversibly variable temperature-responsive copolymer film preparation method
InactiveCN1569933AEasy to prepareWide applicabilityPolymer scienceAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
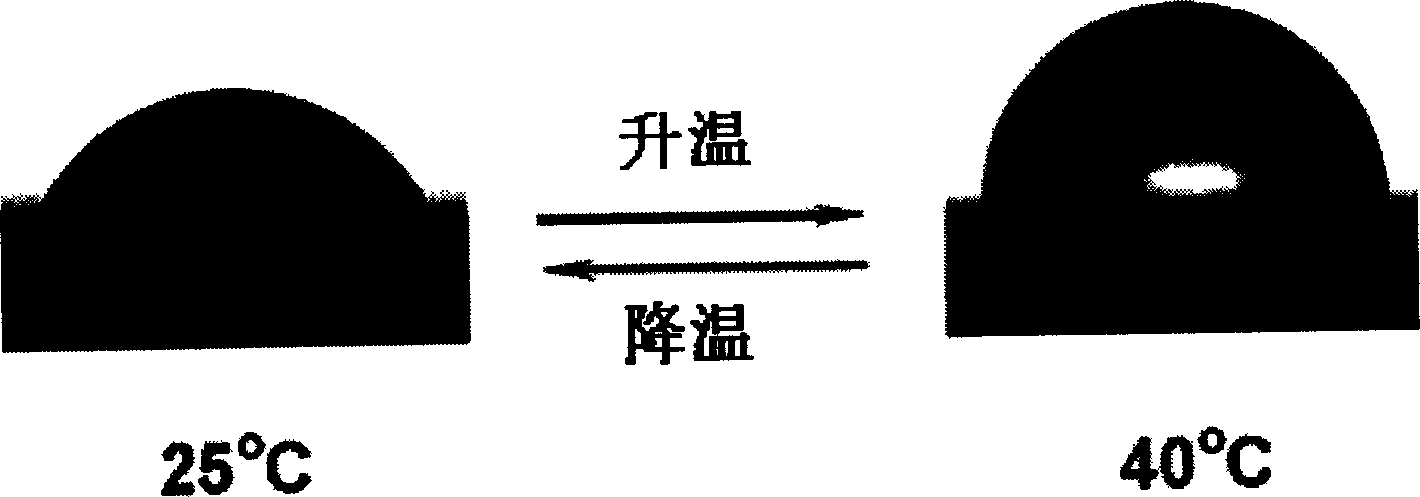
The invention relates to a process for preparing temperature-responsive polymeric thin films which consists of, carrying out free radical polymerization reaction through surface triggering atom transition on smooth surfaces or rough surfaces with micrometer or nano structure, thus making the material surface have reversible soakage.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing hydrophilic polyvinyl chloride alloy ultrafiltration membrane
InactiveCN101293183ASimple processImprove hydrophilicitySemi-permeable membranesUltrafiltrationAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
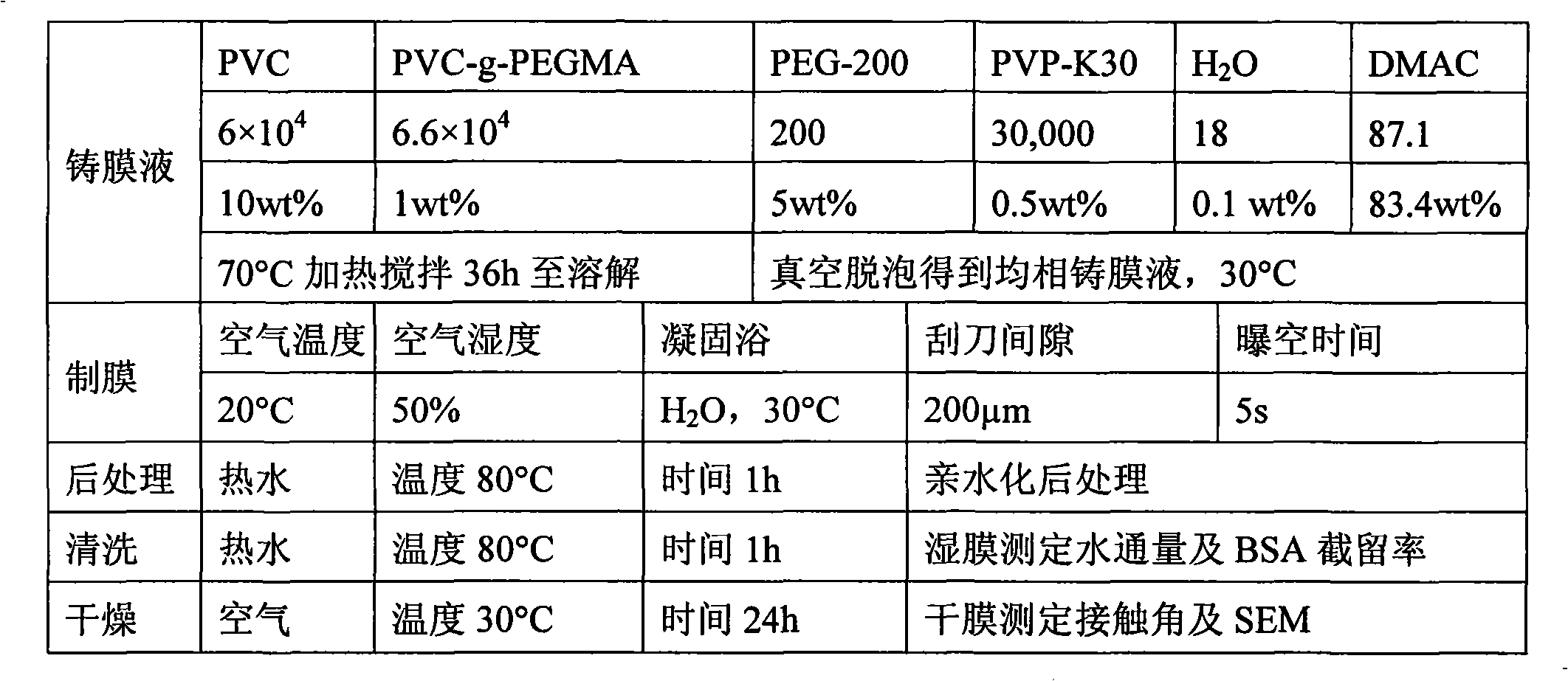
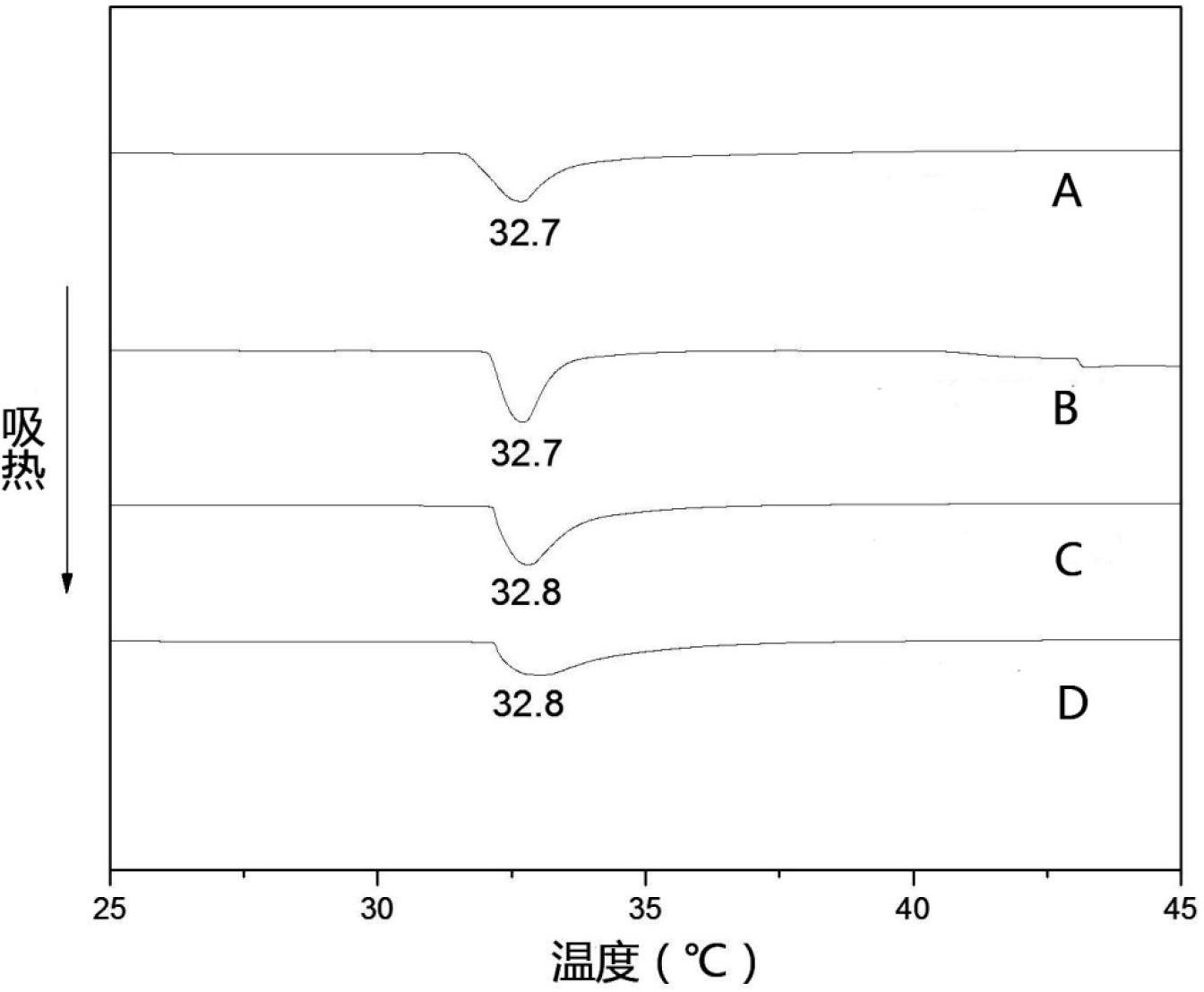
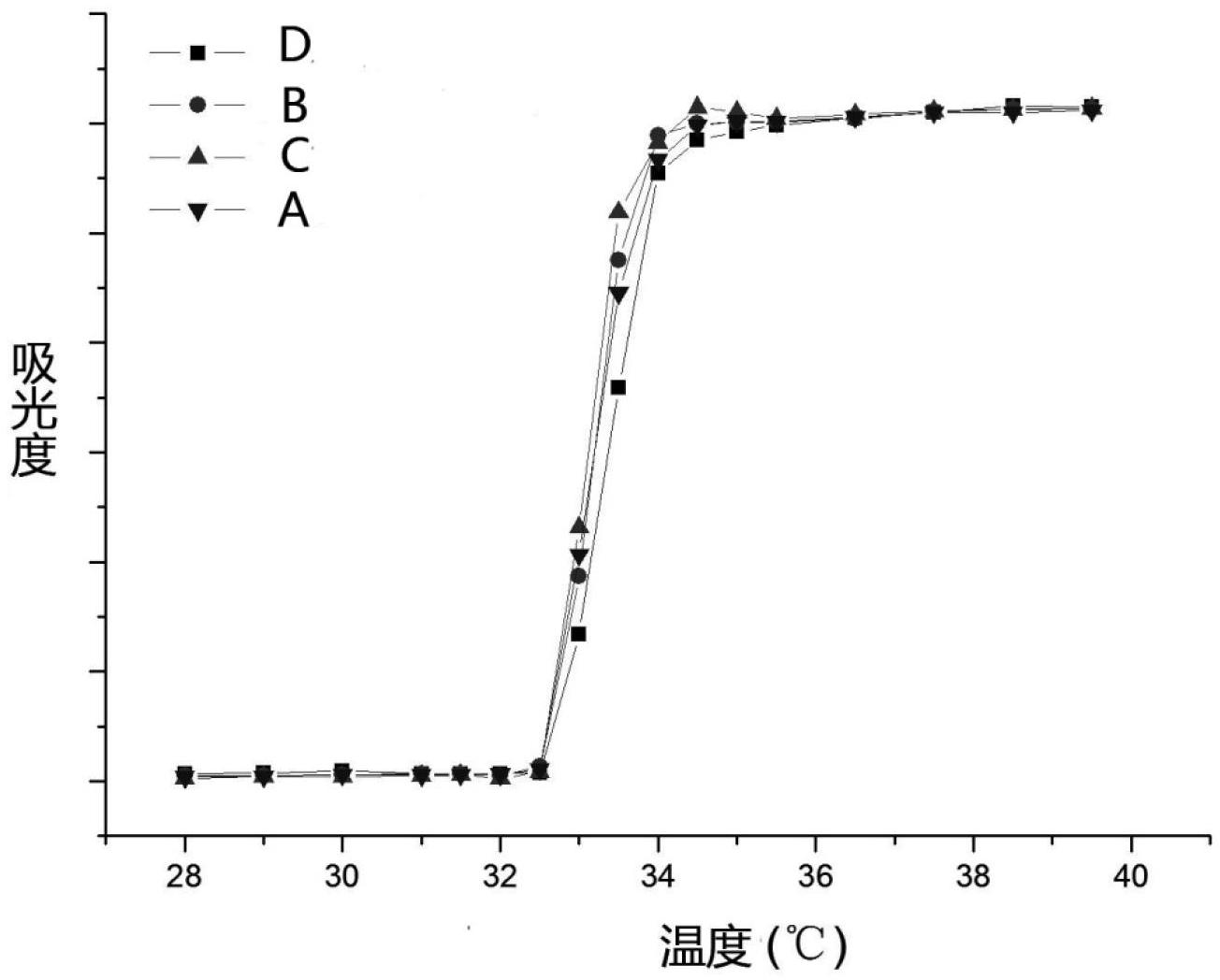
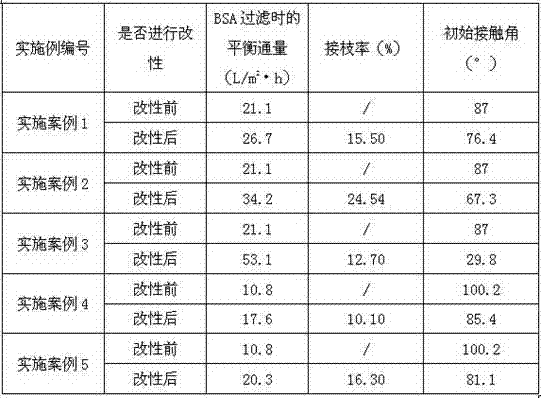
The present invention discloses a preparation method of hydrophilic PVC alloy ultrafiltration membrane. PVC amphiphilic graft copolymer is synthesized through an atom-transfer-free radical polymerization method, which is taken as a hydrophilic modifier and is blended with PVC to prepare the PVC alloy ultrafiltration membrane with controllable structure, hydrophilicity, pollution resistance, large flux and high rejection rate by a solution transformation method. The hydrophilic chain of the amphiphilic graft copolymer can self-assemble and transfer to the membrane surface for microphase separation in the process of solution phase inversion, thus forming a relatively thin hydrophilic surface layer (dozens to hundreds of nanometers). The membrane preparation and hydrophilic modification are carried out simultaneously and the hydrophilic modification of membrane and the interior of the membrane hole can be achieved. The surface contact angle of the ultrafiltration membrane is less than 60 degrees and can be reduced to 0 degree within dozens of seconds; the water flux reaches above 500L / m<2> h(0.1Mpa); the BSA rejection rate reaches above 90 percent; the recovery rate of water cleaning flux is above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Macromonomers for preparation of degradable polymers and model networks
InactiveUS20090259016A1Suitable for preparationReduce polydispersityOrganic chemistryAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationClick chemistry
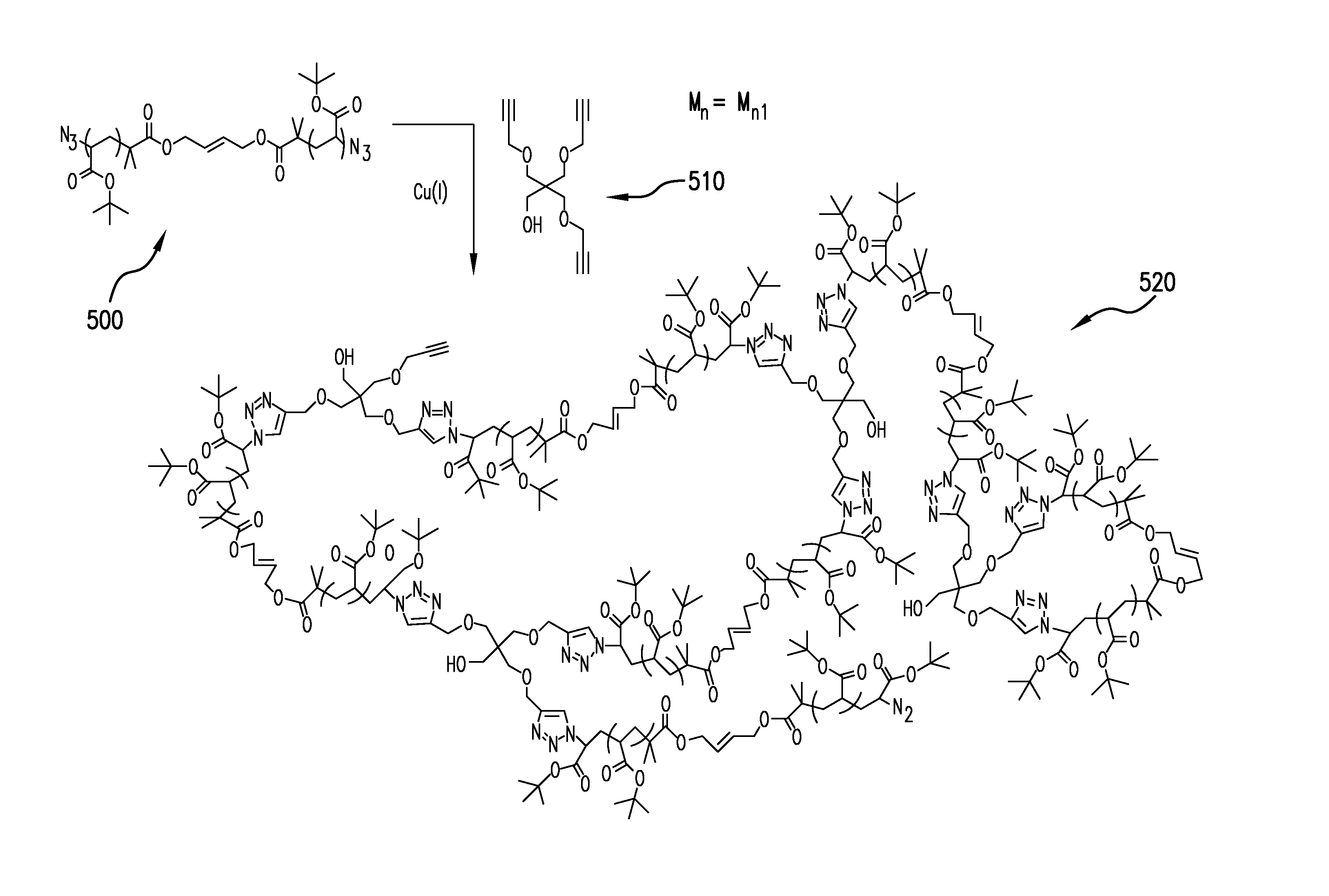
The present invention relates to methods for preparing degradable model networks from any monomer functionality with any degradation methodology. It is based on the use of Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerization and CLICK chemistry to form the desired product.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Noel (co) polymers and a novel polymerization process based on atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization
InactiveUS20050090632A1Increase in the rate of side reactionsReduce rateCoatingsGraft polymer adhesivesElastomerMeth-
A new polymerization process (atom transfer radical polymerization, or ATRP) based on a redox reaction between a transition metal (e.g., Cu(I) / Cu(II), provides “living” or controlled radical polymerization of styrene, (meth)acrylates, and other radically polymerizable monomers. Using various simple organic halides as model halogen atom transfer precursors (initiators) and transition metal complexes as a model halogen atom transfer promoters (catalysts), a “living” radical polymerization affords (co)polymers having the predetermined number average molecular weight by Δ[M] / [I]0 (up to Mn>105) and a surprisingly narrow molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn), as low as 1.15. The participation of free radical intermediates in ATRP is supported by end-group analysis and stereochemistry of the polymerization. In addition, polymers with various topologies (e.g., block, random, star, end-functional and in-chain functional copolymers [for example, of styrene and methyl (meth)acrylate]) have been synthesized using the present process. The polymeric products encompassed by the present invention can be widely used as plastics, elastomers, adhesives, emulsifiers, thermoplastic elastomers, etc.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Pigment dispersions containing dispersants having pendent hydrophobic polymeric segments prepared by controlled radical polymerization
A pigment dispersion comprising pigment, an aqueous carrier selected from water and a mixture of water and at least one organic solvent, and a pigment dispersant is described. The pigment dispersant is prepared by polymerizing (i) at least one prepolymer having a radically polymerizable group, and (ii) at least one second monomer. The prepolymer is prepared by controlled radical polymerization, e.g., atom transfer radical polymerization, of at least one radically polymerizable first monomer. The second monomer forms a polymeric backbone segment of the pigment dispersant, and the prepolymer forms polymeric segments that are pendent to the backbone. The backbone segment of the pigment dispersant is hydrophilic, while at least a portion of each pendent polymeric segment is hydrophobic.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Fluorocoating resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102040900ALower surface energyReduce surface propertiesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEpoxy resin coatingsPolymer scienceAcrylic resin
The invention discloses fluorocoating resin, belongs to the field of chemical materials, and relates to coating resin prepared by mixing fluorinated acrylate block copolymer synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization and other resin. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing fluorinated block copolymer with narrow molecular weight distribution and controllable molecular weight, wherein the mass ratio of the fluorinated block to the non-fluorinated block is 1:9-1:1, and the total molecular weight is 2,000-100,000; and mixing the fluorinated block copolymer and other resin, wherein the fluorinated block copolymer accounts for 0.5 to 100 percent of the total mass of the resin, and the other resin is acrylic resin and polyurethane. The prepared block polymer has controllable molecular weight and clear structure. The fluorocoating resin has a mall amount of fluorine-containing monomer, and has excellent comprehensive performance such as surface performance, ageing-resistant performance and the like.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102675565AStrong fluorescenceImprove performanceSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrowaveModified carbon
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and a preparation method thereof. An N-isopropylacrylamide polymer is grafted to the surface of carbon quantum dots obtained by microwave treatment by adopting an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATPR) method. The preparation method is simple, convenient and mild in conditions. Modified carbon nano particles have fluorescence property and temperature sensitivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Surface modification method for polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) film
InactiveCN102558595AImprove the effect of graftingImprove controllabilityAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a surface modification method for a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film or a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) film. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) performing vacuum low temperature plasma treatment on the PVDF film or the PVC film at the power of 5 to 100W and the reaction vacuum degree of 2 to 100Pa for 1 to 20 minutes; and (2) mixing a solution which is formed by mixing methanol and deionized water and serves as a solvent, cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide serving as a catalyst, 2,2'-bipyridyl or a derivative thereof serving as a ligand, and sulphobetaine methyl methacrylate or allyl polyethylene glycol serving as a grafting monomer, controlling reaction temperature to 20-100 DEG C, and performing atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) reaction for 1 to 24 hours to obtain a product, wherein the molar ratio of the catalyst to the ligand is 1:(0.5-4), and the molar ratio of the film to the monomer is (100-0.1):1. The methodhas the advantages that: the hydrophilicity and anti-pollution capacity of the film can be improved, environment friendliness is achieved, and operation steps are simple.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Amphiphilic polymer pigment wetting dispersant for water-based coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102040711AEffective dispersionPrecise control of compositionCoatingsWater basedPolymer science
The invention discloses an amphiphilic polymer pigment wetting dispersant for a water-based coating and a preparation method thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: polymerizing macromer or polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate macromer with polymerizable double bonds with one or two hydrophobic (methyl) polyacrylate monomers in the presence of ARGET ATRP (activators regenerated by electron transfer-atom transfer radical polymerization) to obtain a comb-shaped polymer, and further introducing an anchoring functional group in the comb-shaped polymer for preparing the solid wetting dispersant; or polymerizing the macromer or the polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate macromer with the polymerizable double bonds with the (methyl) polyacrylate monomer with the anchoring functional group in the presence of ARGET ATRP to obtain the comb-shaped polymer which is the solid wetting dispersant. By using the preparation method, the cost can be greatly reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the performances of the product can be greatly improved. The obtained wetting dispersant has good dispersion effect and bright color, and the stability of a dispersion system is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Zwitterionic/amphiphilic pentablock copolymers and coatings therefrom
InactiveUS20110218290A1Antifouling/underwater paintsFilm/foil adhesivesAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationPolyurethane coating
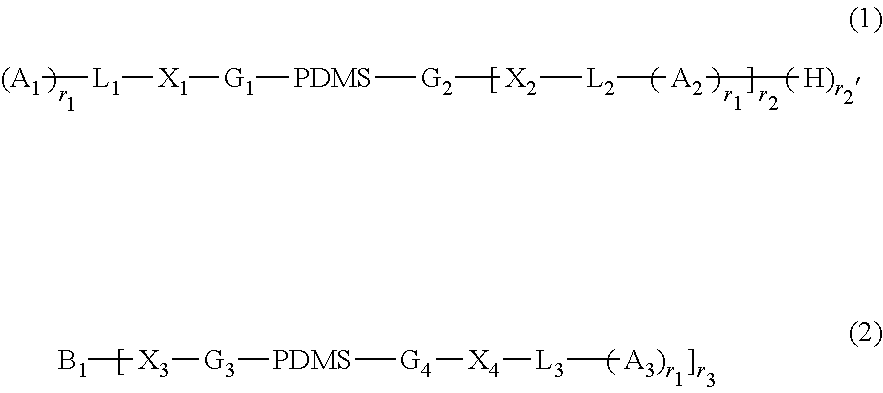
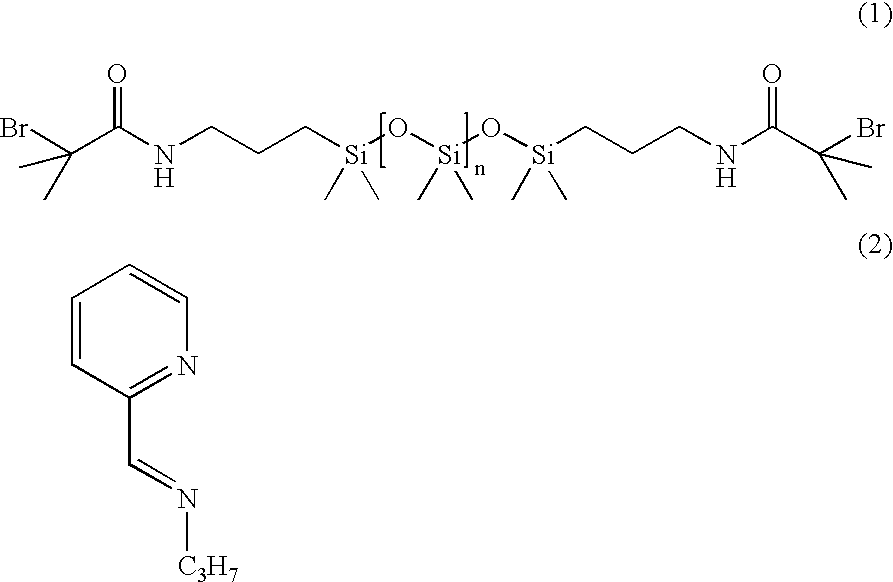
A zwitterionic / amphiphilic pentablock copolymer was prepared using atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). The pentablock copolymer is prepared for the atom transfer radical polymerization of a PDMS-PEO-Br macroinitiator and SBMA. The pentablock copolymer is incorporated into a polyurethane coating composition which is useful for antifouling and / or fouling release applications.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for preparing polymer by micro-scale photo-induced organic catalysis
ActiveCN106893015AImprove mixing efficiencyImprove mass transfer efficiencyChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMicroreactorPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polymer by micro-scale photo-induced organic catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: using alkyl halide as an initiator in a microreactor; and using an organic small molecule as a catalyst to catalyze atom-transfer radical-polymerization, so as to prepare the polymer. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has advantages of high reaction speed, controllable molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of a polymerization product, no residue, and wide application in fields of optoelectronic materials and biomedical materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness, preparation method thereof and use thereof
InactiveCN101891870APrecise molecular weight controlPrecise Control of DispersionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylateFunctional monomer
The invention discloses an amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness and a preparation method thereof. Particularly, the invention discloses an amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness comprised of a block, which is formed by the copolymerization of a hydrophobic group and a pH response group, and a hydrophilic brush-shaped block. In the invention, a copolymer of a hydrophobic monomer and a pH response functional monomer is obtained by atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), then the copolymer is used as a macromolecular initiator to perform the ATRP polymerization of monomethoxypoly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate (PEGMA) which is a hydrophilic macromolecular monomer, and finally, a selective hydrolysis reaction is performed to prepare the amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of simple process and high yield. The synthesized amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness has a novel structure and an adjustable functional group proportion, and is suitable to be used in the transmission of entrapped insoluble medicaments.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
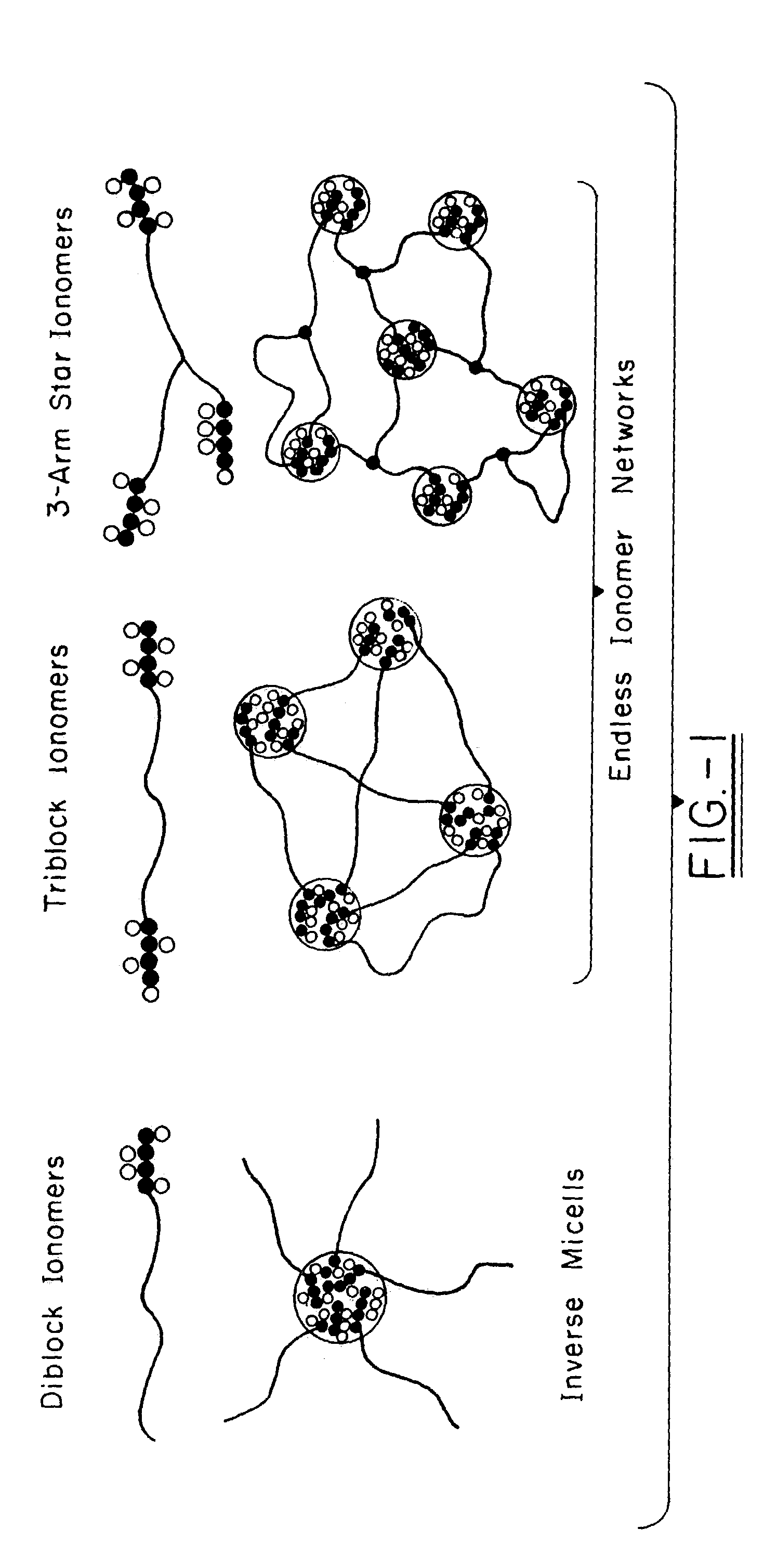
Polyisobutylene-based block anionomers and cationomers and synthesis thereof
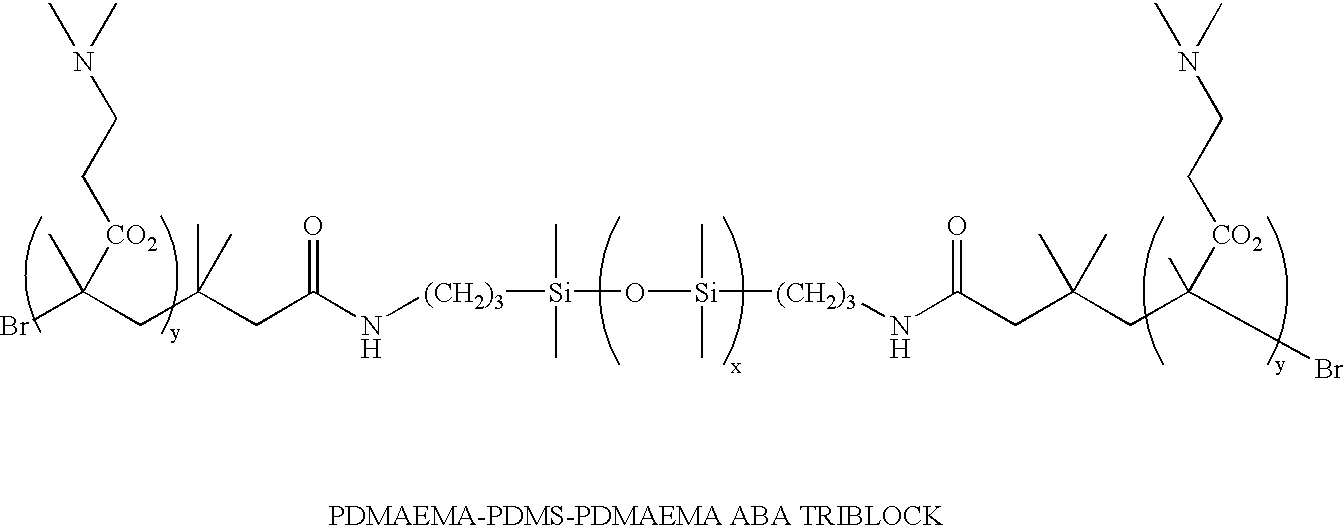
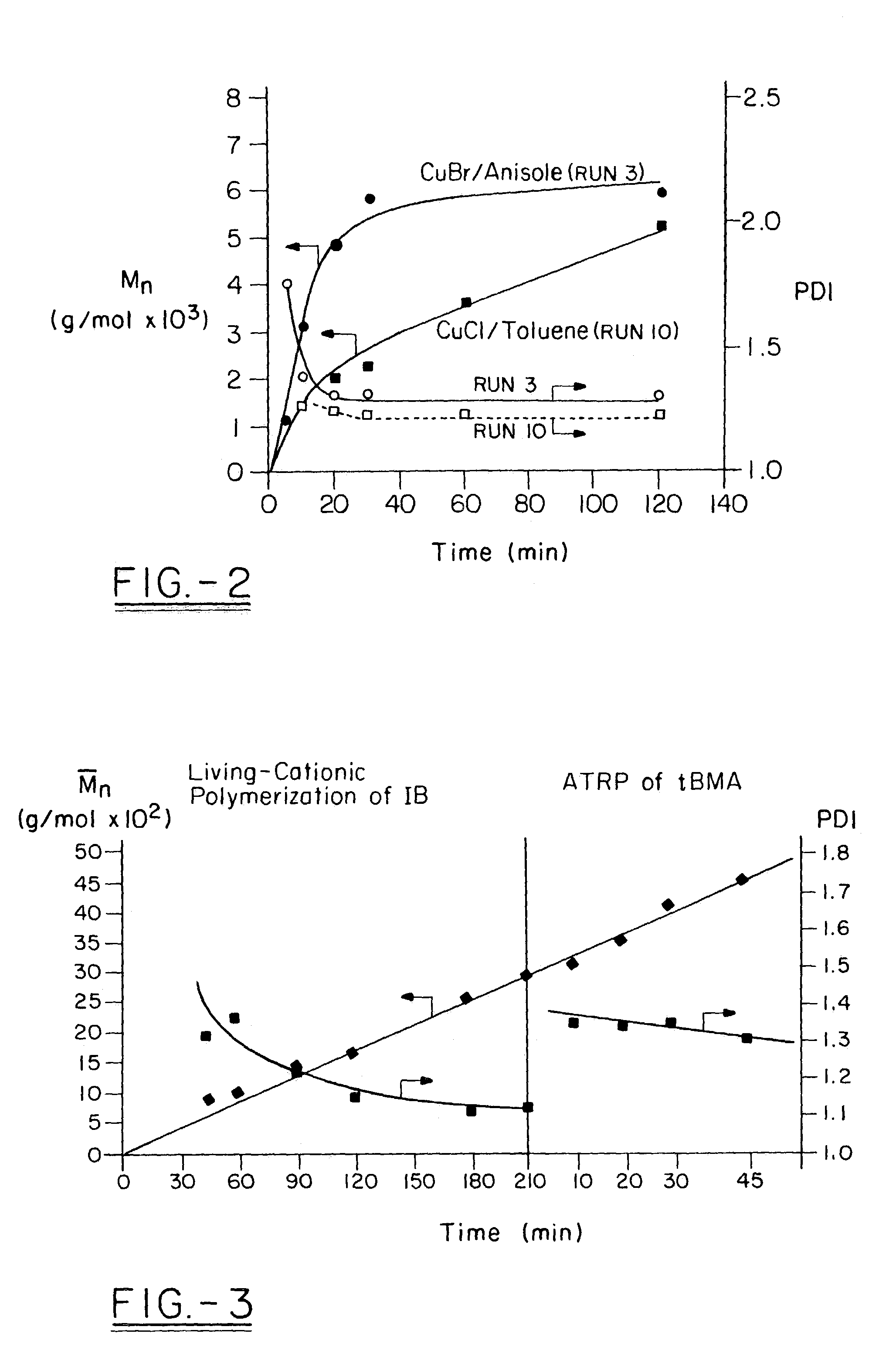
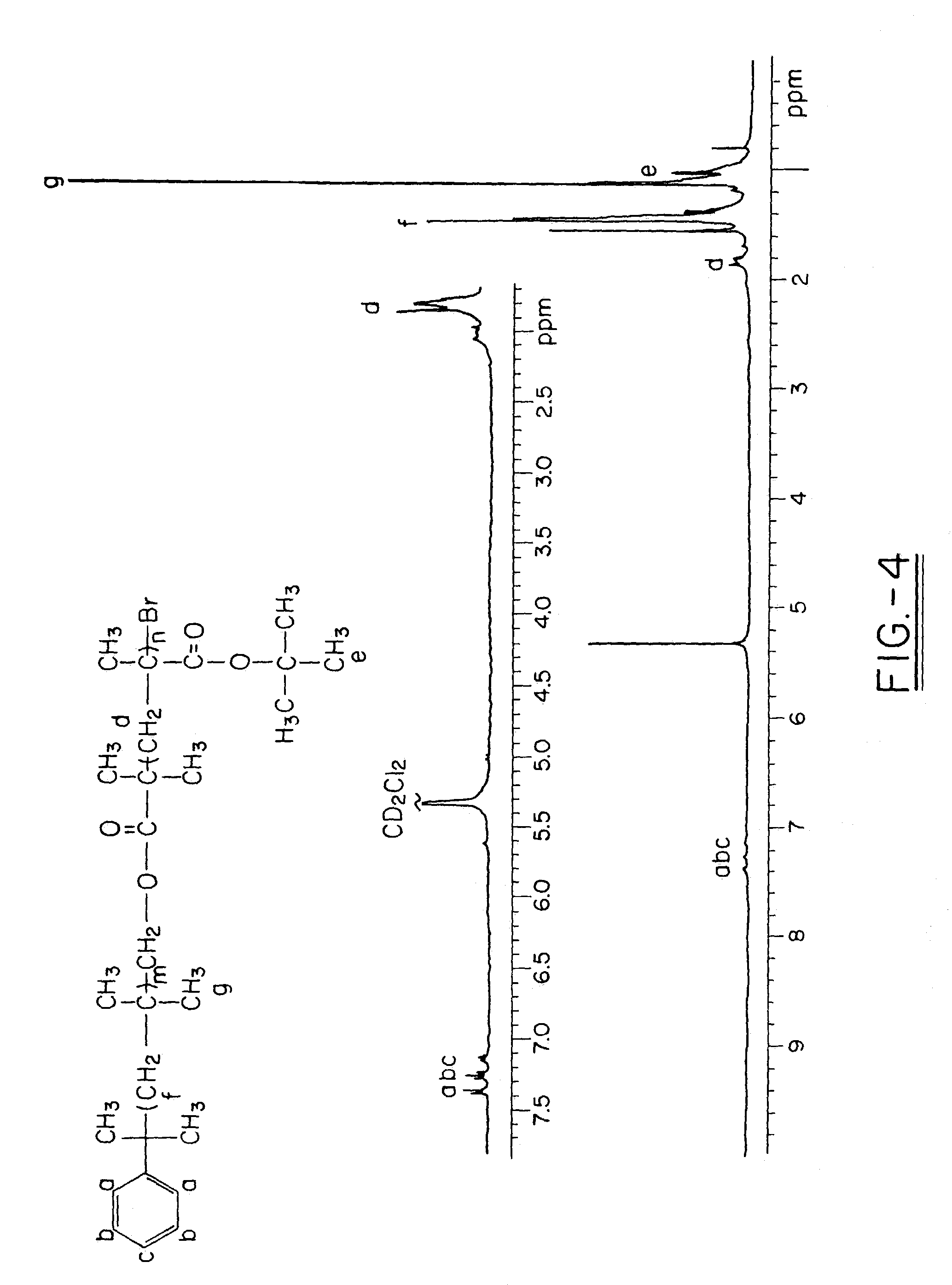
Various novel block cationomers comprising polyisobutylene (PIB) and poly(2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) segments have been synthesized and characterized. The specific targets were various molecular weight diblocks (PDMAEMA+) and triblocks (PDMAEMA+-b-PIB-b-PDMAEMA+) with the PIB blocks in the DPn=50–200−(Mn=3,000–9,000 g / mol) range connected to blocks of PDMAEMA+ cations in the DPn=5–20 range. The overall synthetic strategy for the preparation of these block cationomers comprised four steps: 1) Synthesis by living cationic polymerization of mono- and di-allyltelechelic polyisobutylenes, 2) End group transformation to obtain PIBs fitted with termini capable of mediating the atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of DMAEMA, 3) ATRP of DMAEMA and 4) Quaternization of PDMAEMA to PDMAEMA+I− by CH3I. Kinetic and model experiments provided guidance to develop convenient synthesis methods. The microarchitecture of PIB-PDMAEMA di- and triblock and the corresponding block cationomers were confirmed by 1H NMR and FTIR spectroscopy and solubility studies.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com