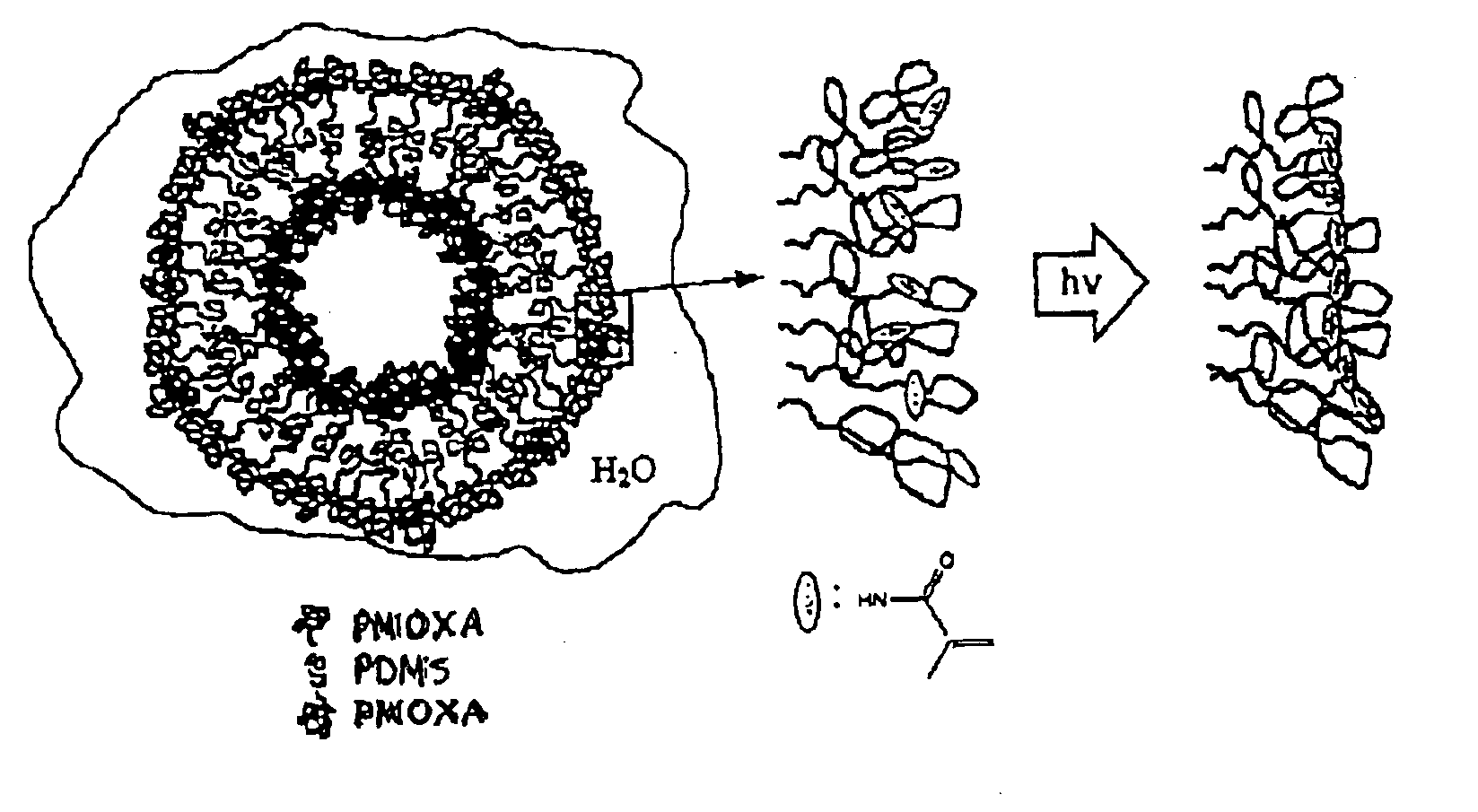
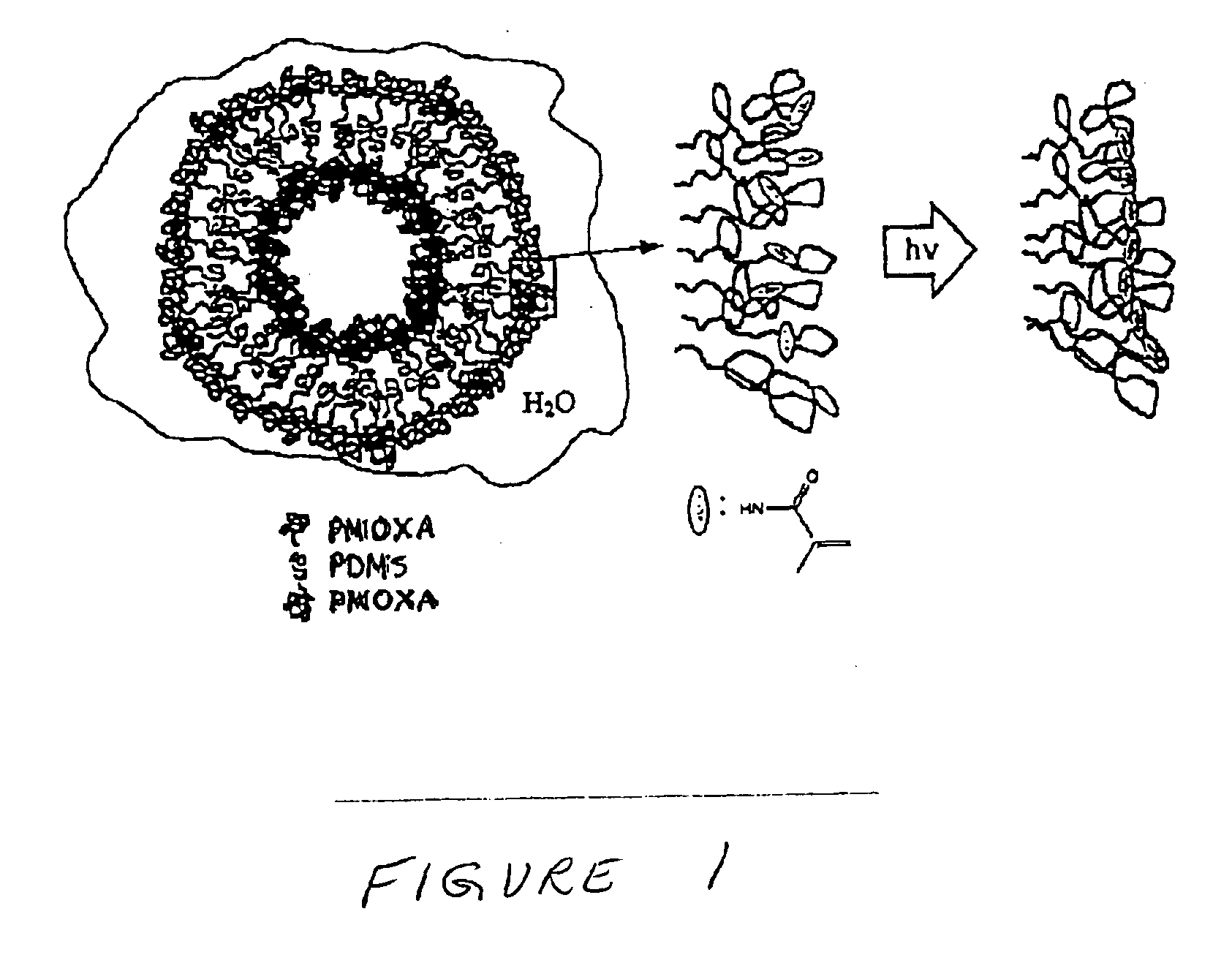
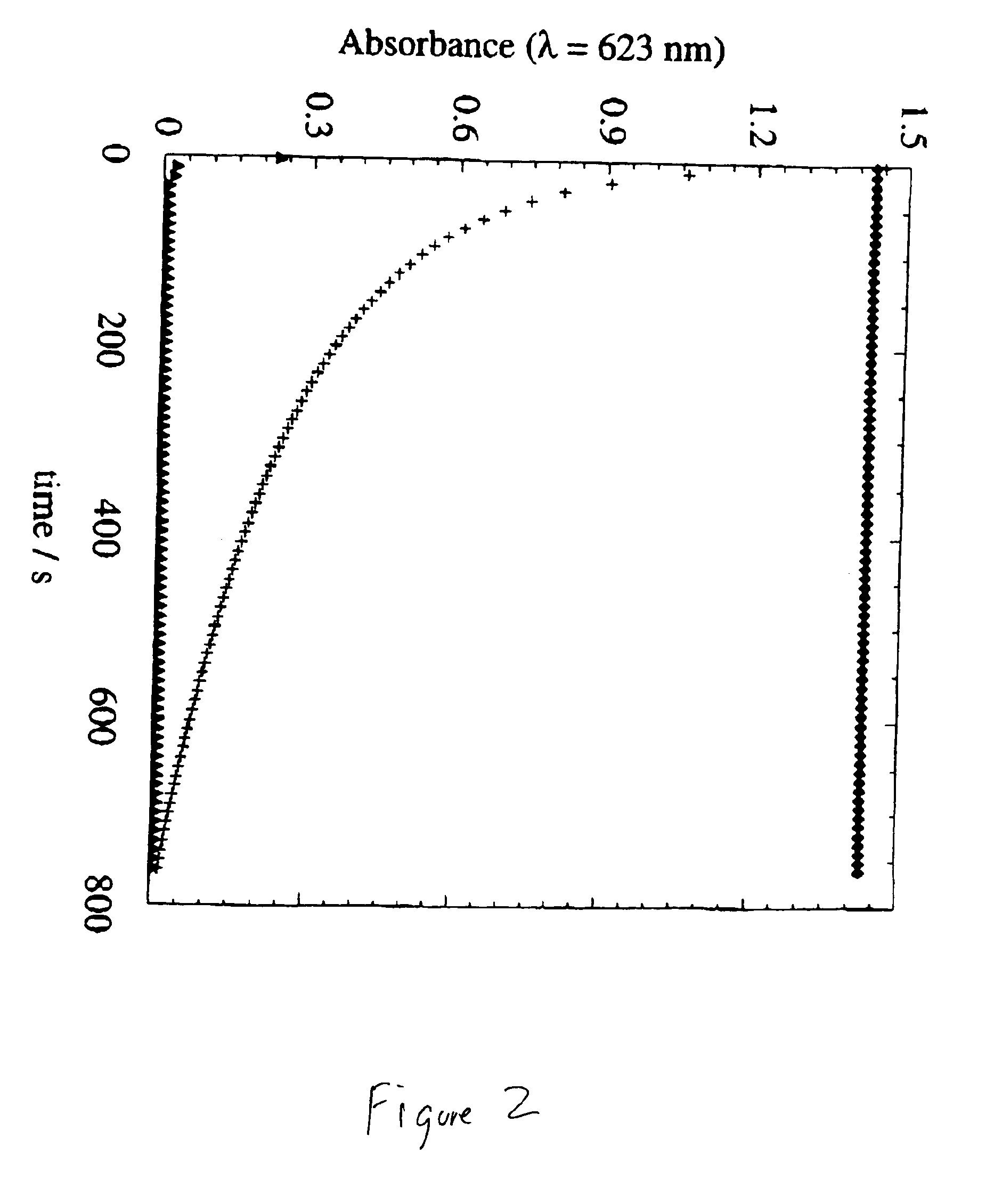
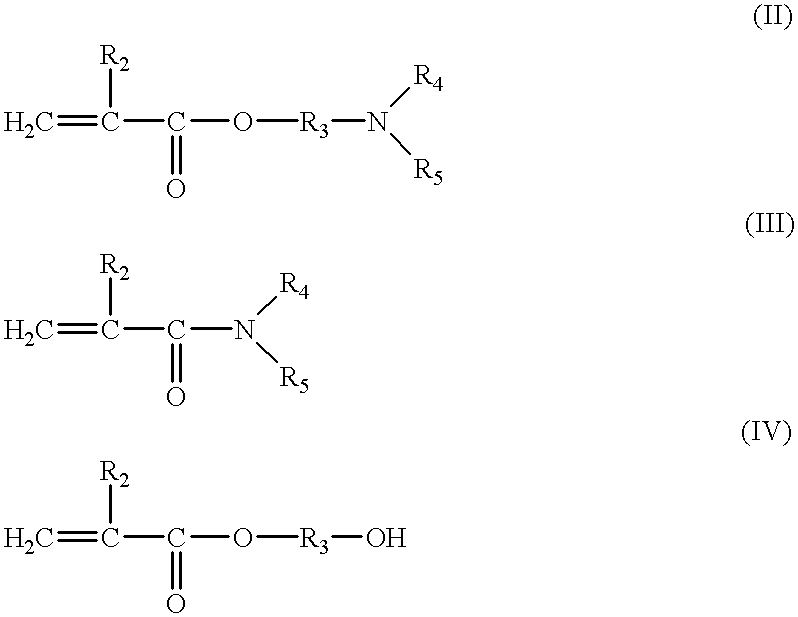
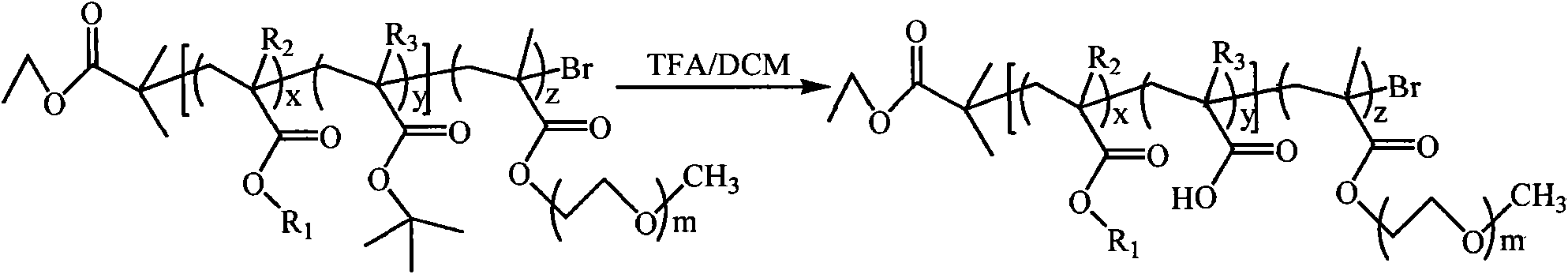
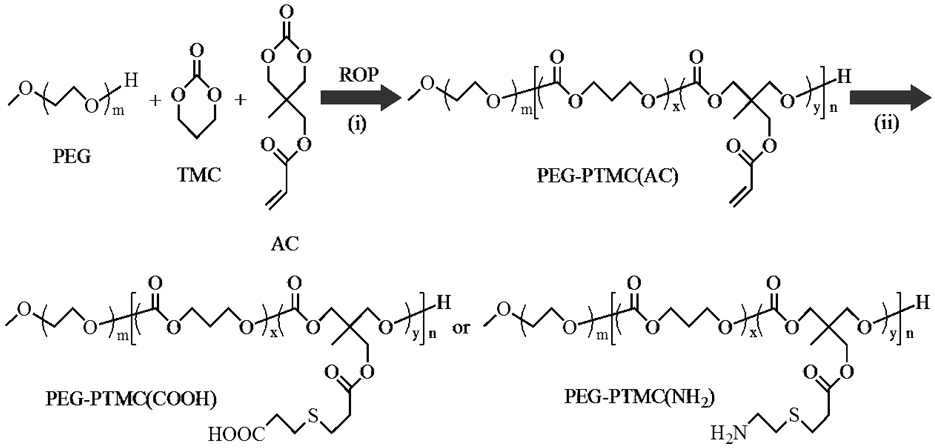
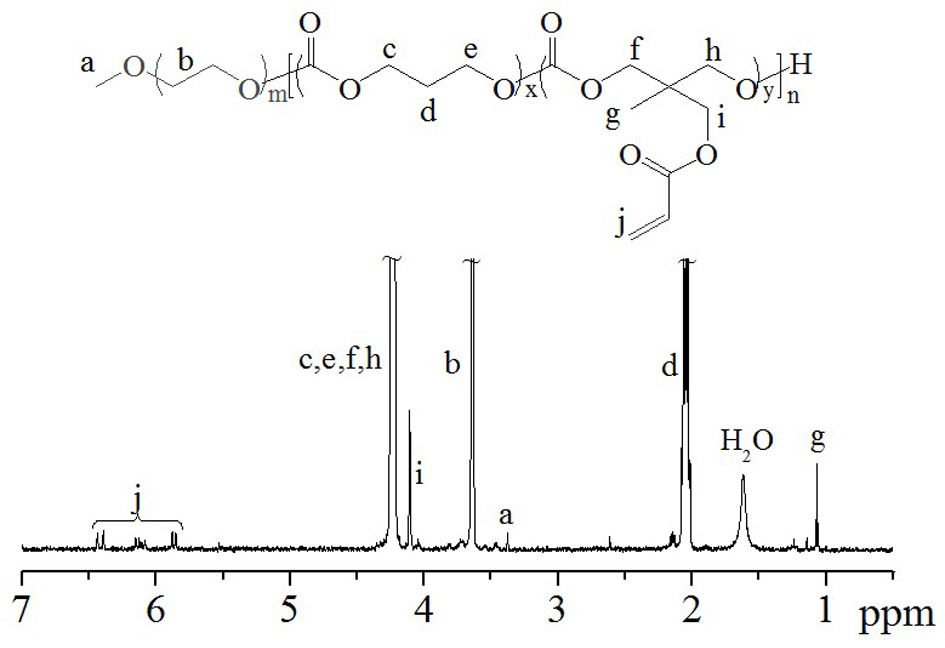
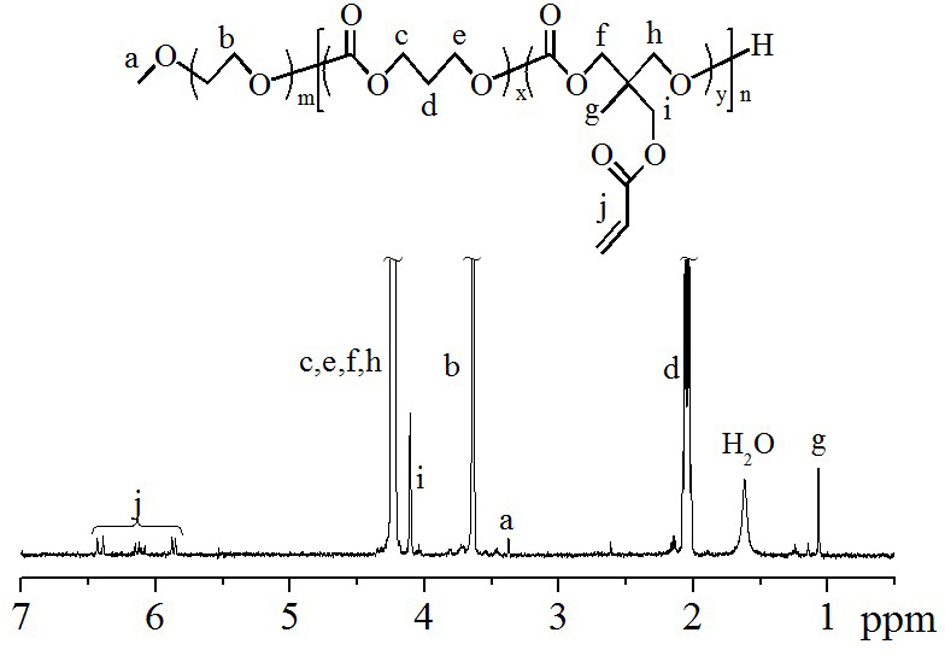
Patents
Literature
362 results about "Amphiphilic copolymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
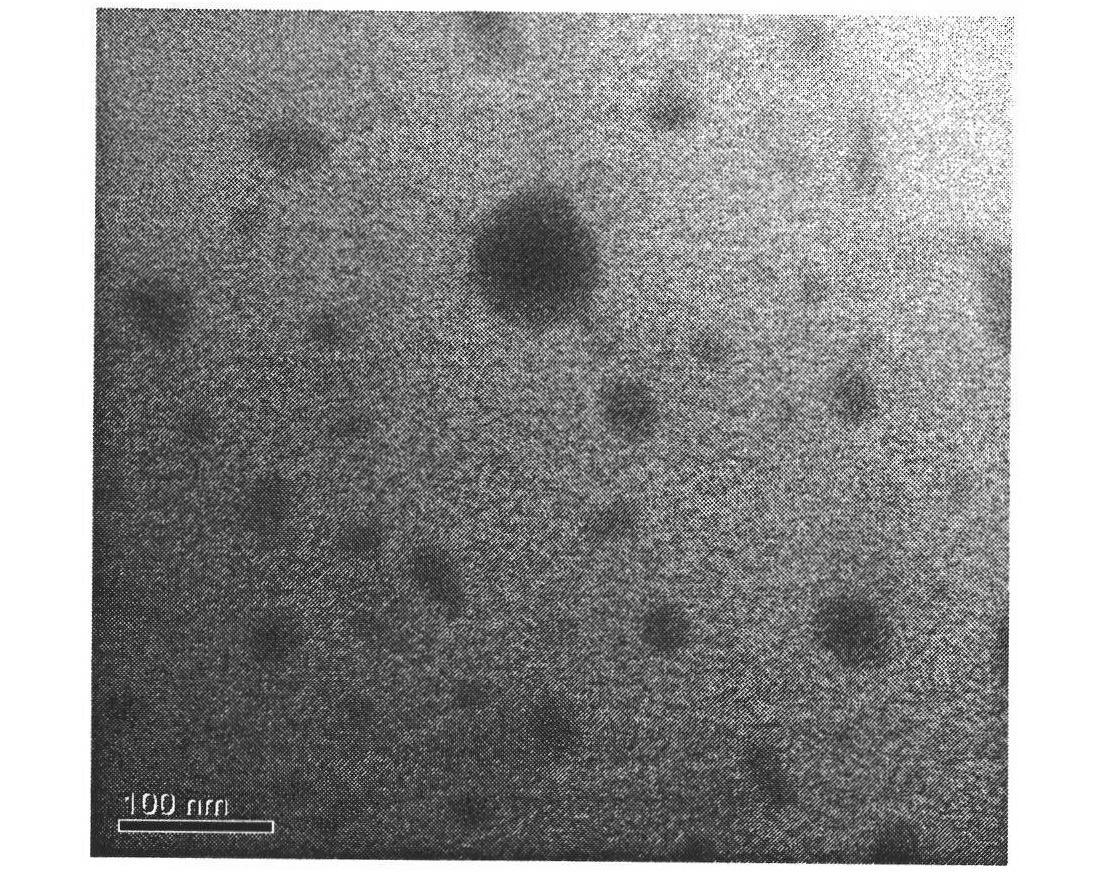
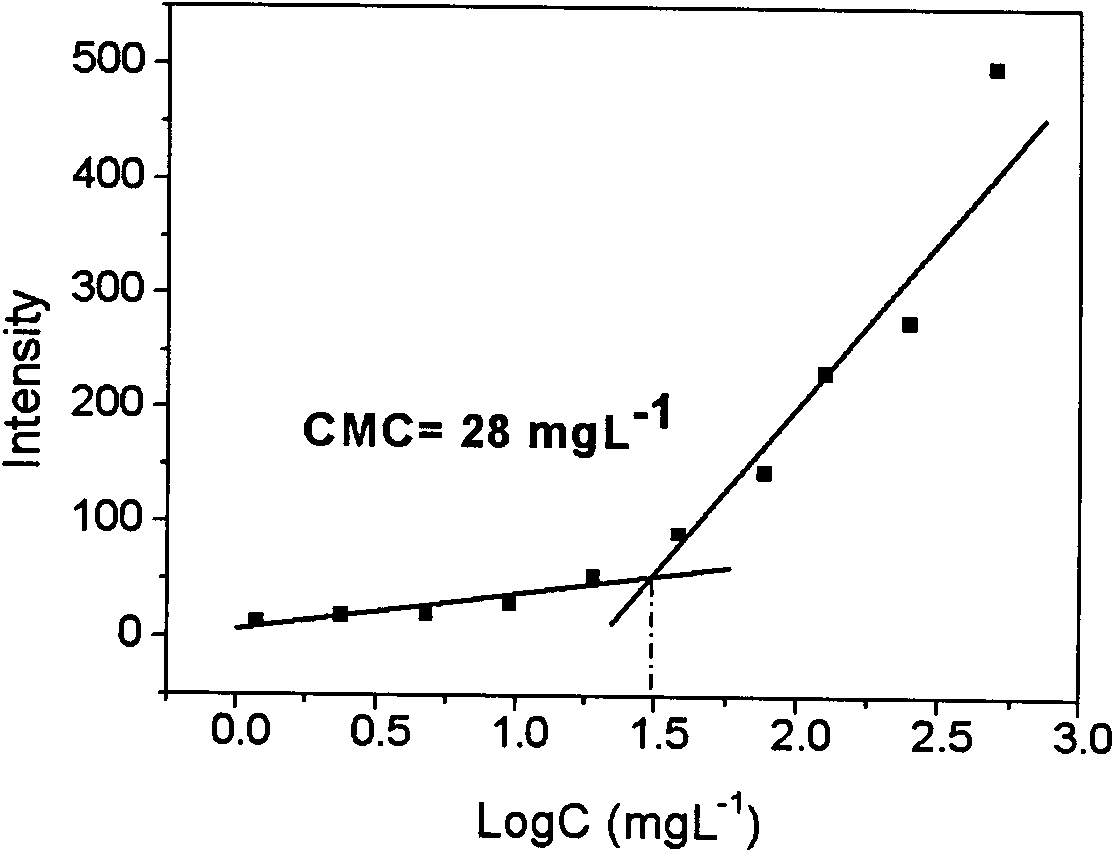
Amphiphilic polymers. Amphiphilic polymers are composed of hydrophilic ("water-loving") and hydrophobic ("water-hating") parts. They are important throughout industry in many applications (e.g. as emulsifiers).
Sutures and surgical staples for anastamoses, wound closures, and surgical closures
InactiveUS8016881B2Improve featuresControlled release rateSuture equipmentsStentsSurgical stapleMicroparticle
The invention relates to sutures and surgical staples useful in anastomoses. Various aspects of the invention include wound closure devices that use amphiphilic copolymer or parylene coatings to control the release rate of an agent, such as a drug or a biological material, polymerizing a solution containing monomers and the agent to form a coating, using multiple cycles of swelling a polymer with a solvent-agent solution to increase loading, microparticles carrying the agent, biodegradable surgical articles with amphiphilic copolymer coatings, and sutures or surgical staples the deliver a drug selected from the group consisting of triazolopyrimidine, paclitaxol, sirolimus, derivatives thereof, and analogs thereof to a wound site.
Owner:MIRUS LLC
Sutures and surgical staples for anastamoses, wound closures, and surgical closures
ActiveUS20050038472A1Good storage stabilityRemove moistureSuture equipmentsPowder deliverySurgical stapleMicroparticle
The invention relates to sutures and surgical staples useful in anastomoses. Various aspects of the invention include wound closure devices that use amphiphilic copolymer or parylene coatings to control the release rate of an agent, such as a drug or a biological material, polymerizing a solution containing monomers and the agent to form a coating, using multiple cycles of swelling a polymer with a solvent-agent solution to increase loading, microparticles carrying the agent, biodegradable surgical articles with amphiphilic copolymer coatings, and sutures or surgical staples the deliver a drug selected from the group consisting of triazolopyrimidine, paclitaxol, sirolimus, derivatives thereof, and analogs thereof to a wound site.
Owner:MIRUS LLC
Amphiphilic polymeric vesicles
InactiveUS6916488B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryNanocapsulesCell Membrane Proteins
Vesicles made from amphiphilic copolymers are disclosed. The amphiphilic copolymers can be ABA copolymers, where one of A and B is hydrophilic and the other is hydrophobic. AB copolymers can also be used. The copolymers may be crosslinked to form nanocapsules. Crosslinking can be accomplished using a variety of methods, including end to end polymerization of copolymers having terminal unsaturated groups. Molecules, such as membrane proteins, can be incorporated into the wall of the vesicles or nanocapsules.
Owner:BIOCURE
Biological implants of semipermeable amphiphilic membranes
An implantable biological device including a semipermeable membrane formed into a geometric shape capable of encapsulating biological cells and capable of immunoisolating the biological cells upon introduction into the body, the semipermeable membrane including an amphiphilic copolymer network having hydrophobic segments and hydrophilic segments, wherein the hydrophobic segments include polyolefins terminated with radicals selected from the group consisting of acryloyl groups, methacryloyl groups and mixtures thereof and wherein the hydrophilic segments include polyacrylates. Also provided is a method of encapsulating and immunoisolating cells using the semipermeable membrane and method of treating ailments using the implantable biological device.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Modified-release microparticles based on amphiphilic copolymer and on active principles(s) and pharmaceutical formulations comprising them
The present invention relates to novel microparticles formed of amphiphilic polyamino acids which transport active principle(s), AP(s), in particular protein and peptide active principle(s), and to novel modified-release pharmaceutical formulations comprising said AP microparticles. The aim of the invention is to develop novel microparticles, charged with AP, obtained by aggregation of nanoparticles of amphiphilic polyamino acids and having improved properties, in particular in the dry solid form, with regard to their ability to be dispersed and, concerning the reconstituted suspension, its stability and its ability to be easily handled and injected. The invention relates firstly to microparticles of amphiphilic polyamino acid (PO) comprising at least one AP (associated noncovalently) which spontaneously form a colloidal suspension of nanoparticles in water, at pH 7.0, under isotonic conditions; which microparticles a. are obtained by atomization of a solution or colloidal suspension of PO comprising at least one AP, b. have a size of between 0.5 and 100 microns, c. and are dispersible in colloidal suspension. The invention also relates to the process for the preparation of these microparticles, to a liquid formulation comprising a suspension of these PO / AP microparticles, to a reconstitution process and kit for this formulation and to a dry form of this formulation.
Owner:FLAMEL TECHNOLOGIES
Method for modifying polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane by amphiphilic co-polymer
InactiveCN101264428AImprove hydrophilicityReduce energy consumptionSemi-permeable membranesUltrafiltrationDumbbell shaped
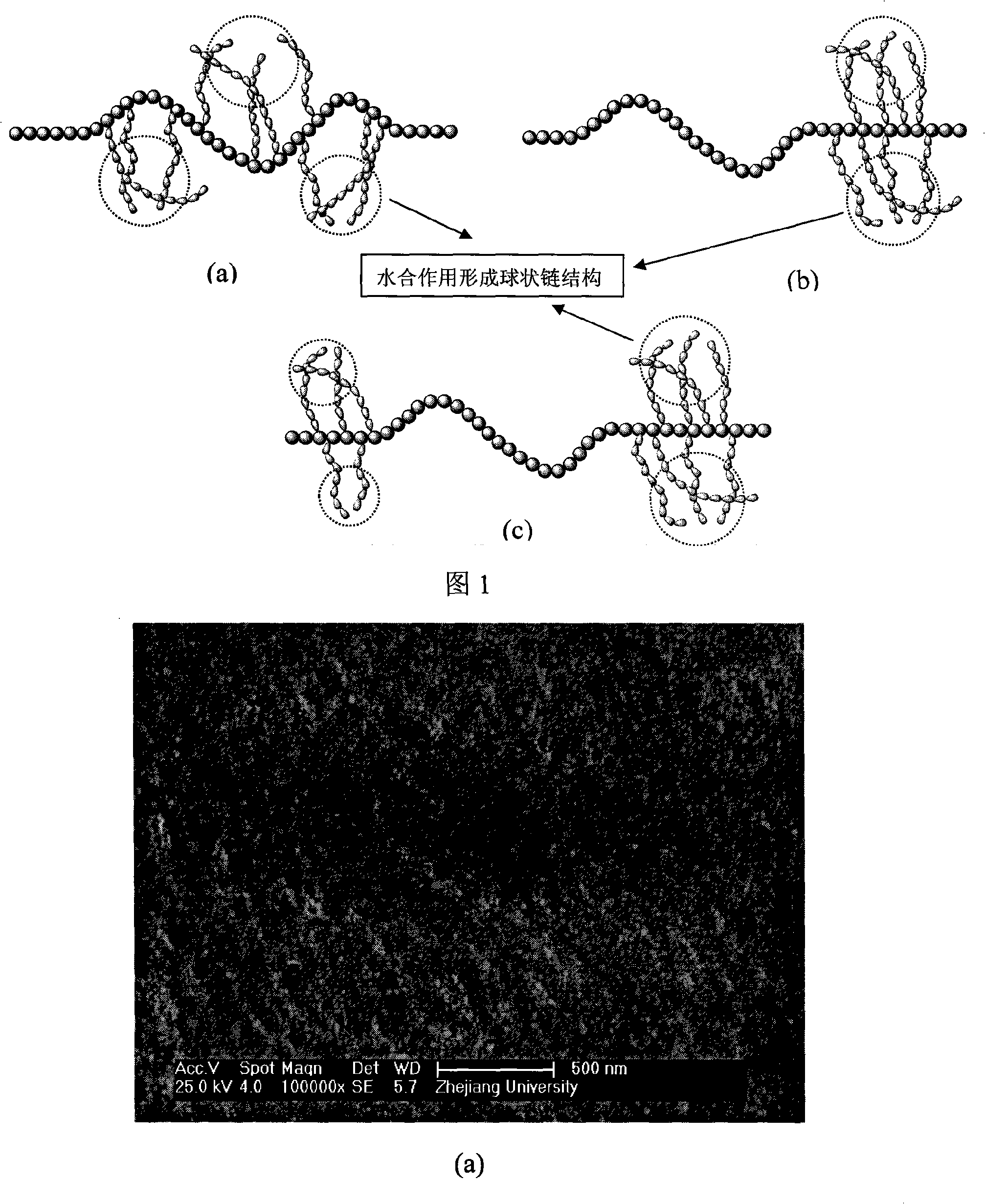
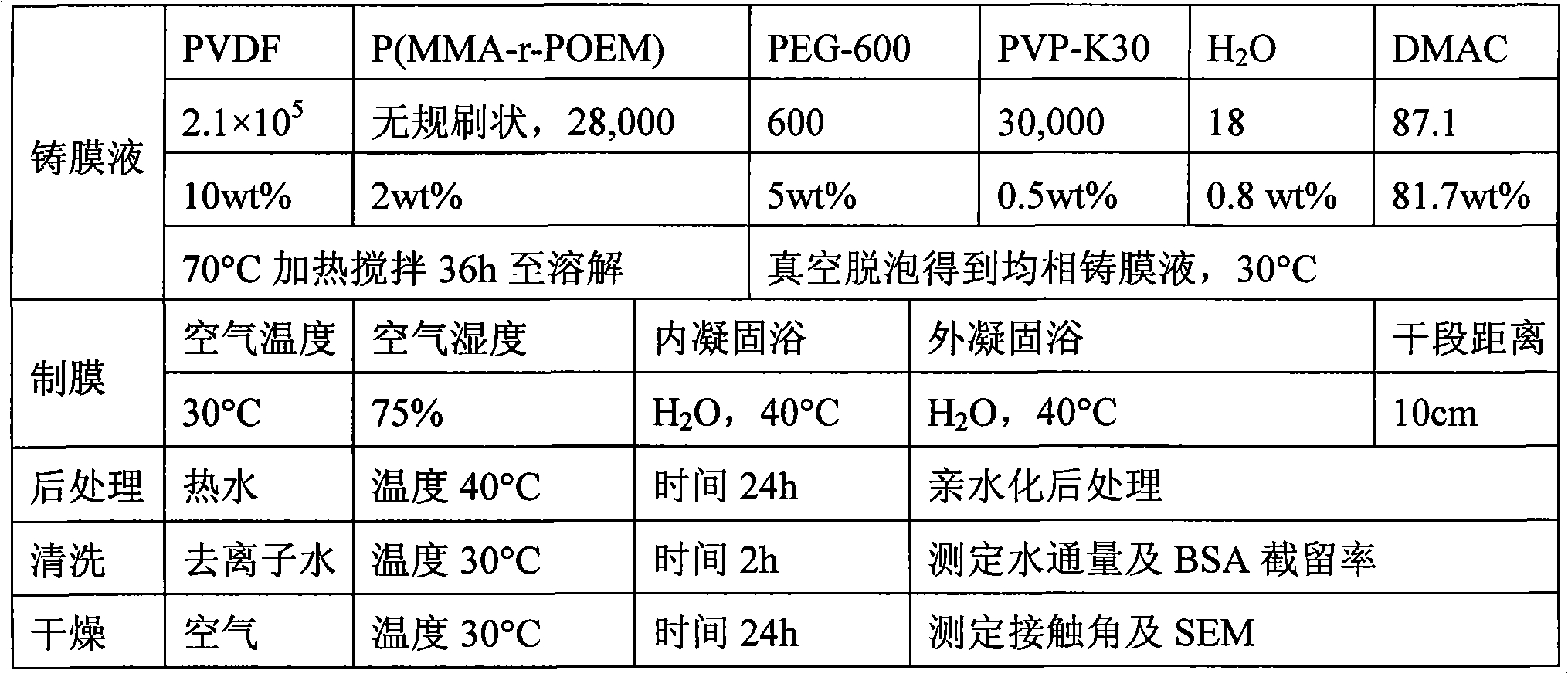
The invention discloses a method of producing the hyperfiltration membrane of amphiphilic copolymer modified polyvinylidene fluoride, comprising the following steps: 1) mixing polyvinylidene fluoride, poly (methyl methacrylate - monomethyl ether polyoxyethylene methyl methacrylate), additives, non-solvent and solvent to form the casting film solution; 2) making the casting film solution into the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane by using the film forming machine and then soaking in the coagulation bath; 3) conducting the posttreatment of hydrophilicity; 4)obtaining the hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane after cleaning and drying. The method is characterized in that the brush shape, chain ball shape or dumbbell shape amphiphilic copolymer are mixed with the polyvinylidene fluoride to produce the polyvinylidene fluoride hyperfiltration membrane with hydrophilicity, anti-pollution, large flux and high retention rate by adopting the solution phase conversion method. The method has the advantages that the obtained membrane is provided with dozens to hundreds nanometer of particular densified hydrogel surface layers, the contact angle of the membrane surface can be reduced below 60 degrees and can be lowered to 0 degree within tens of seconds, the water flux can reach 1000L / m<2> / h (0.1Mpa) or above, the retention rate of BSA can reach 90% or more and the recovery rate of water cleaning flux can reach 90% or higher.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Biodegradable triblock copolymers, synthesis methods therefore, and hydrogels and biomaterials made there from
InactiveUS20080057128A1Interesting propertyVivo degradation ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
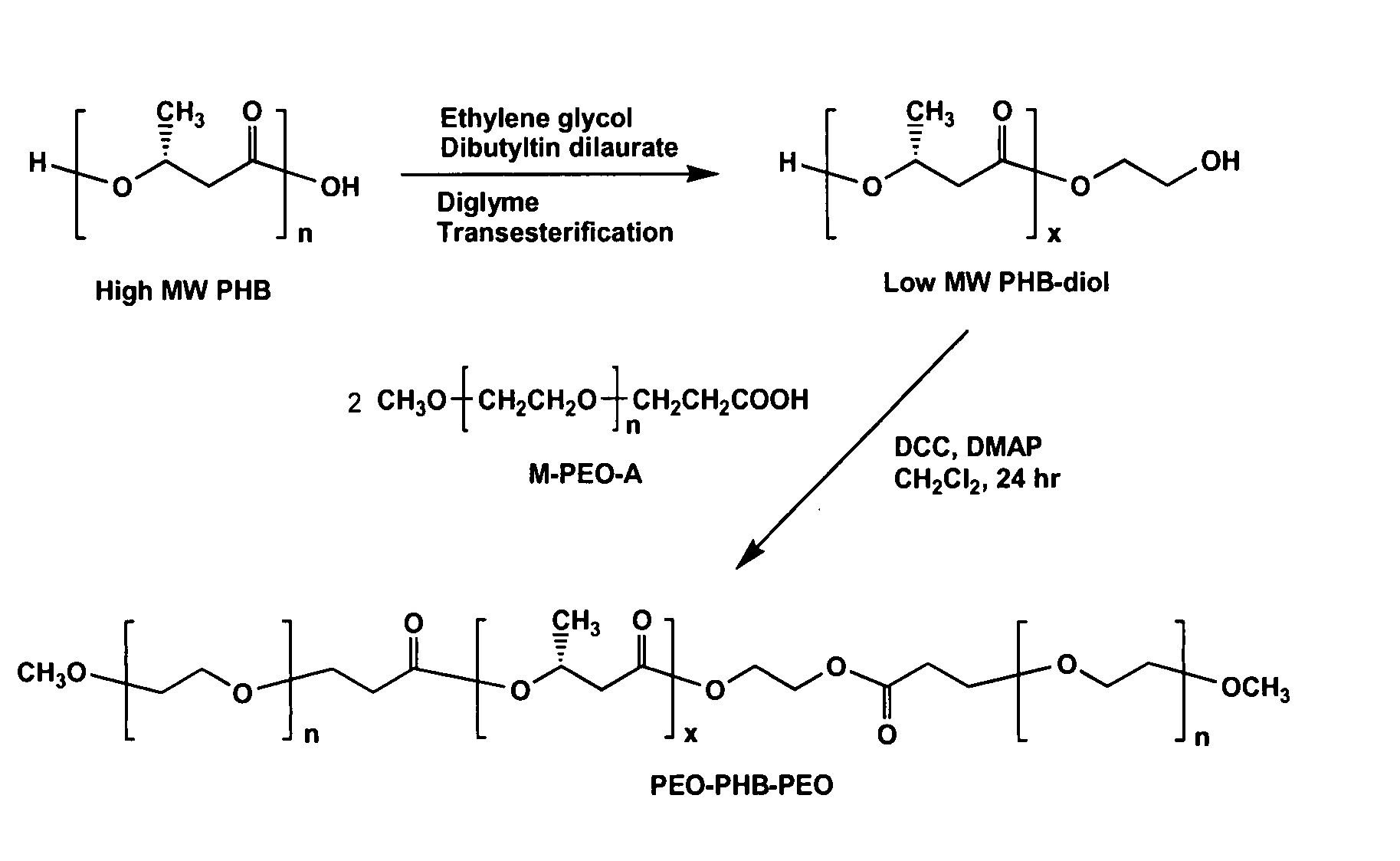
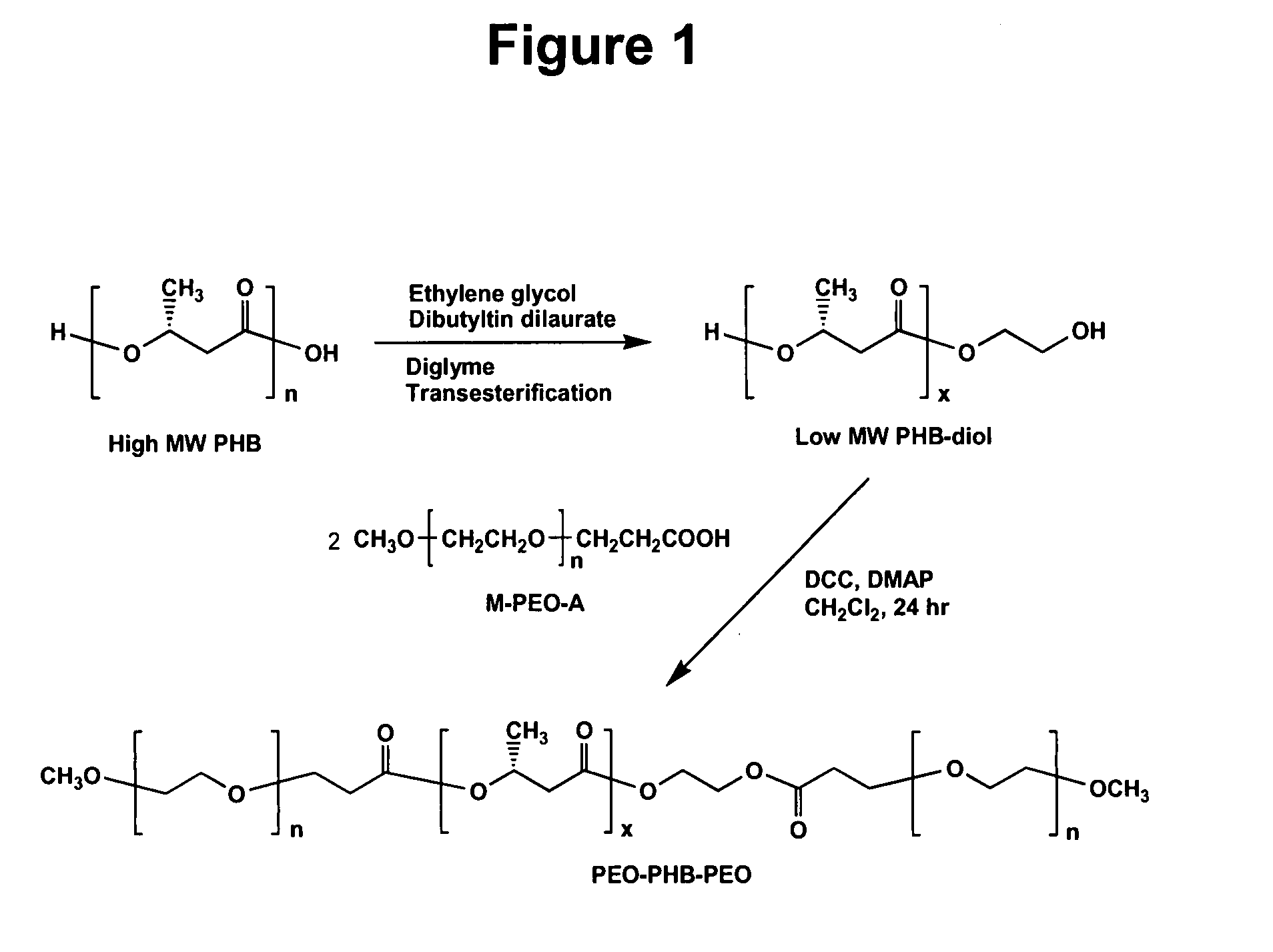
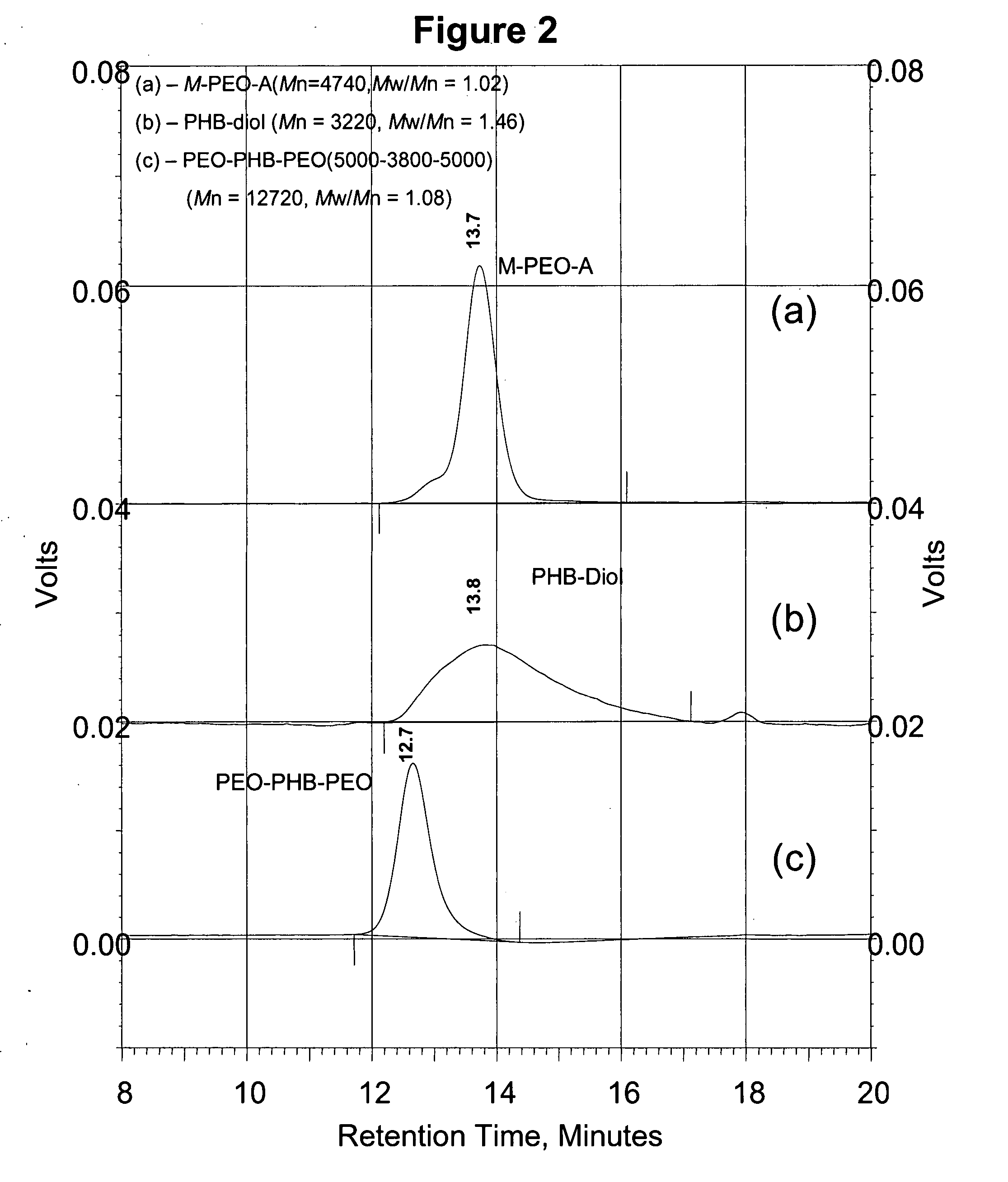
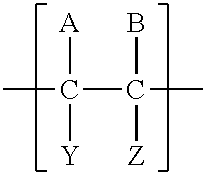
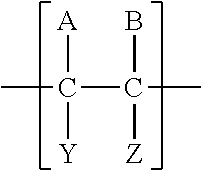
A drug delivery system that includes micelles formed from an amphiphilic copolymer that includes an A polymer block comprising a poly(alkylene oxide) and a B polymer block comprising a poly(hydroxyalkanoate), and a therapeutically effective amount of at least one therapeutic agent intimately contained within the micelles. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, the A polymer block is poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the B polymer block is poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB), and the copolymer is the triblock ABA copolymer PEO-PHB-PEO. A method of synthesizing the amphiphilic triblock copolymer is also provided.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Polycarbonate block copolymers
The disclosure pertains to amphiphilic block copolymers comprising an aliphatic polycarbonate chain coupled to a hydrophilic polymer. Such amphiphilic polymers may have the formula A-L-B, where A- is a polycarbonate or polyethercarbonate chain having from about 3 to about 500 repeating units, L is a linker moiety and —B is a hydrophilic oligomer having from about 4 to about 200 repeating units. Provided copolymers are useful as surfactants capable of emulsifying aqueous solutions and supercritical carbon dioxide. Provided copolymers also have utility as additives for use in enhanced oil recovery methods.
Owner:SAUDI ARAMCO TECH CO
Preparation method of polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite microporous film with strong interface binding power
InactiveCN101357303AHigh mechanical strengthIncrease backwash pressureSemi-permeable membranesFiberInterfacial bonding
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite microporous membrane which has strong interfacial bonding force. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) neutral or amphiphilic substances which have good bonding force with braided fiber tubes and the polyvinylidene fluoride are prepared into dilute solution; 2) the dilute solution of the neutral or amphiphilic substances is coated once on the braided fiber tubes; 3) casting membrane liquid is used for secondary coating on the coated braided fiber tubes, and the polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite membrane is obtained by a solution phase transition method; 4) post-hydrophilization treatment is carried out; 5) the polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite membrane is cleaned and dried to obtain the hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite microporous membrane. The preparation method takes the braided fiber tubes as supporting tubes, uses an amphiphilic copolymer and the polyvinylidene fluoride to be blended, and prepares the polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite microporous membrane which has strong interfacial bonding force, hydrophilicity, pollution resistance, large flux, high interception rate and high mechanical strength by the solution phase transition method.
Owner:TONGXIANG JIANMIN FILTER MATERIALS
Compositions comprising superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymers and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS8258250B2Less irritatingOvercome disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsPolymer chemistryCopolymer
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymers and processes for making the same
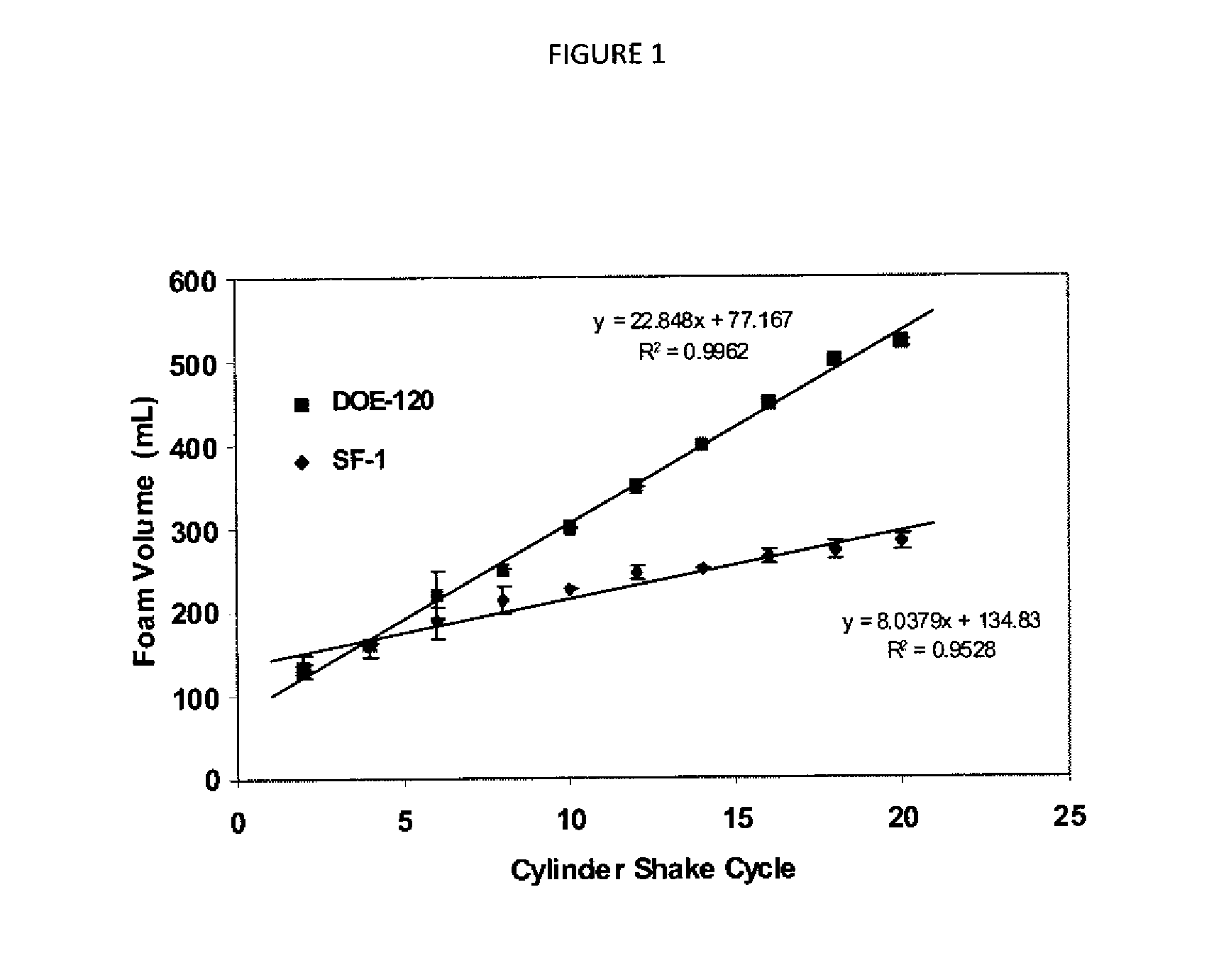
A superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymer and process for making the superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymer includes a low molecular weight polysaccharide modified with a hydrophobic reagent, such as substituted succinic anhydride. The superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymer system generates stable foam for use in applications, such as healthcare formulations, with low irritation of the eyes and skin.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Compositions comprising superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymers and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20110082105A1Less irritatingOvercome disadvantagesBiocideCosmetic preparationsCopolymerPolymer chemistry
Provided are compositions comprising a superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymer and a carrier and composition comprising a superhydrophilic amphiphilic copolymer, a micellar thickener and a carrier.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Particulate Constructs For Release of Active Agents
InactiveUS20080299205A1Increase load capacityLow toxicityCosmetic preparationsBiocideParticulatesActive agent
Particulate constructs stabilized by amphiphilic copolymers and comprising at least one active coupled to a hydrophobic moiety provide sustained release of the active in both in vitro and in vivo environments.
Owner:CELATOR PHARMA INC +1
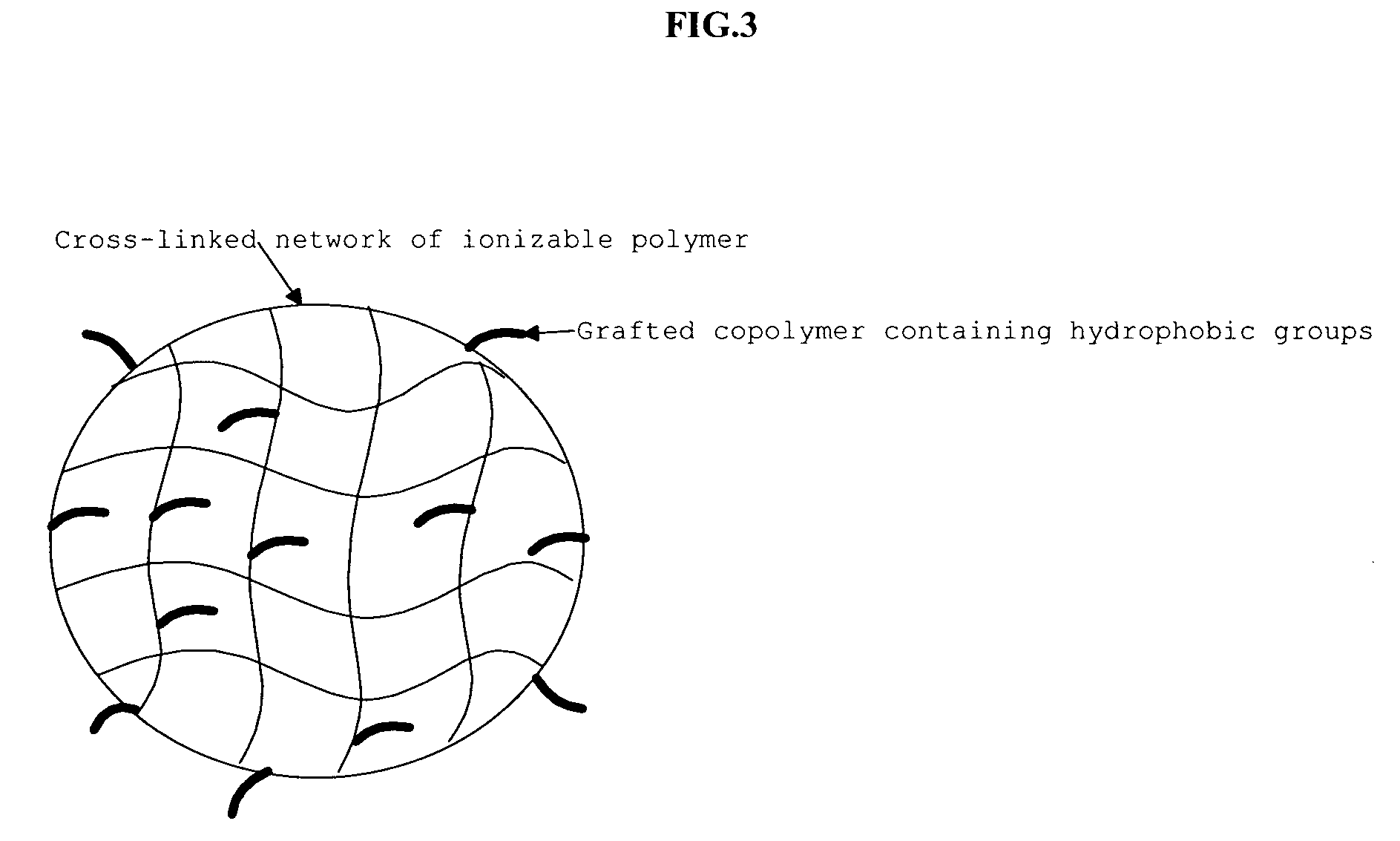
Responsive microgel and methods related thereto
A responsive microgel is provided which responds volumetrically and reversibly to a change in one or more aqueous conditions selected from the group consisting of (temperature, pH, and ionic conditions) comprised of an ionizable network of covalently cross-linked homopolymeric ionizable monomers wherein the ionizable network is covalently attached to an amphiphilic copolymer to form a plurality of ‘dangling chains’ and wherein the ‘dangling chains’ of amphiphilic copolymer form immobile micelle-like aggregates in aqueous solution. A responsive microgel is further provided that comprises at least one therapeutic entity and delivers a substantially linear and sustained release of the therapeutic entity under physiological conditions.
Owner:SUPRATEK PHARMA
Hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite membrane and preparation method
The invention discloses a hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber composite membrane and a preparation method. The aperture of the membrane is 0.01 to 0.1 micron; the porosity of the membrane is 60 to 80 percent; a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film is coated on the outer surface of a hollow woven fiber pipe; the thickness of the coating is 0.1 to 0.4 millimeter; the outer diameter of the membrane is 1.5 to 2.5 millimeters; and the PVDF film comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 80 to 95 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride, and 5 to 20 percent of amphiphilic copolymer, namely polyoxyethylene / polyoxypropylene / polyoxyethylene (PEO-PPO-PEO). The preparation method sequentially comprises the following steps of: preparing film casting solution, coating the hollow woven fiber pipe, forming a coagulating bath, cleaning, drying and the like. The hollow fiber composite membrane prepared by the method is stable and long-lasting in structure; the hydrophily of the membrane can be obviously improved; and the production cost is reduced and mass production is easy to realize by the method.
Owner:王剑鸣
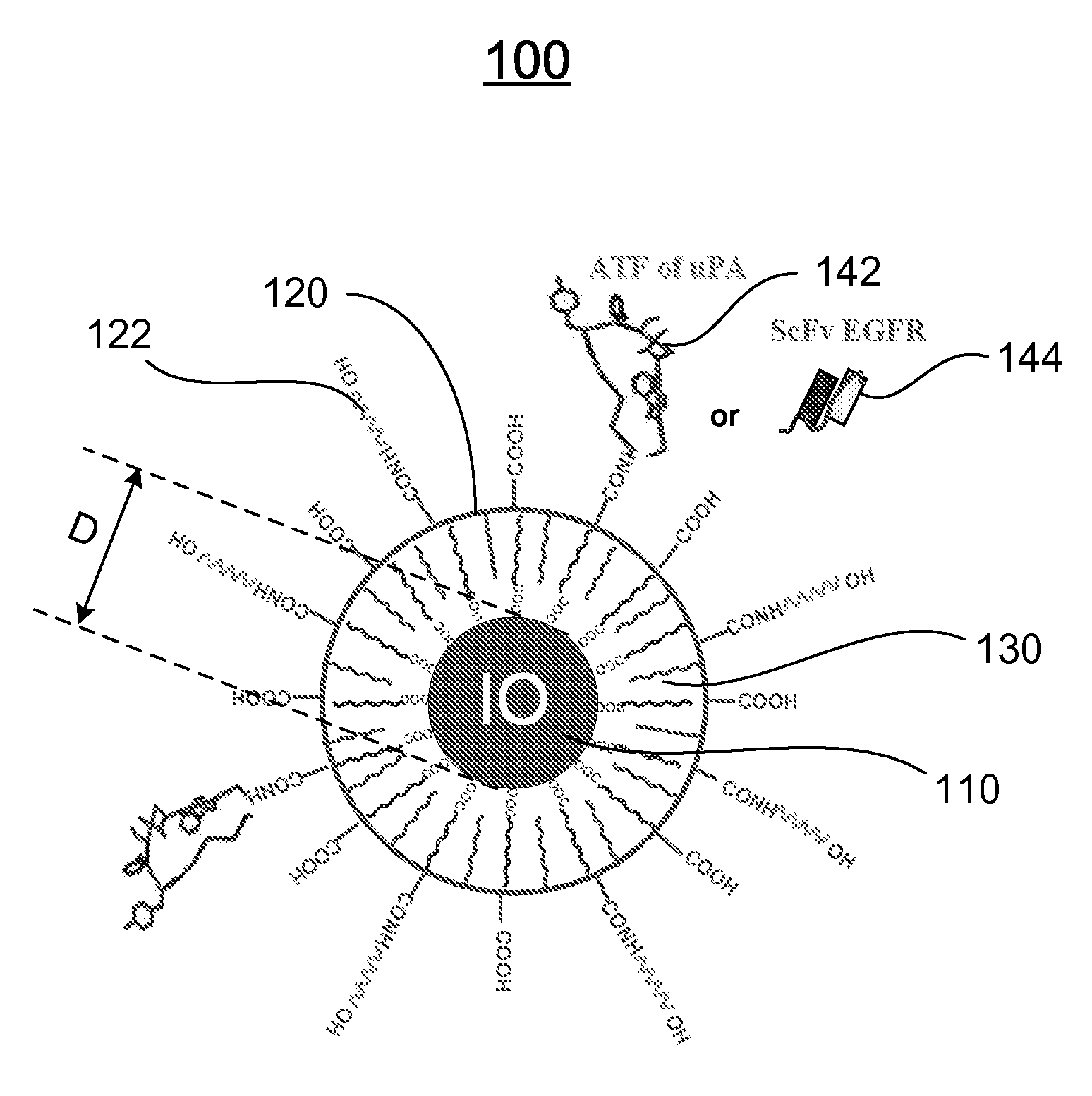
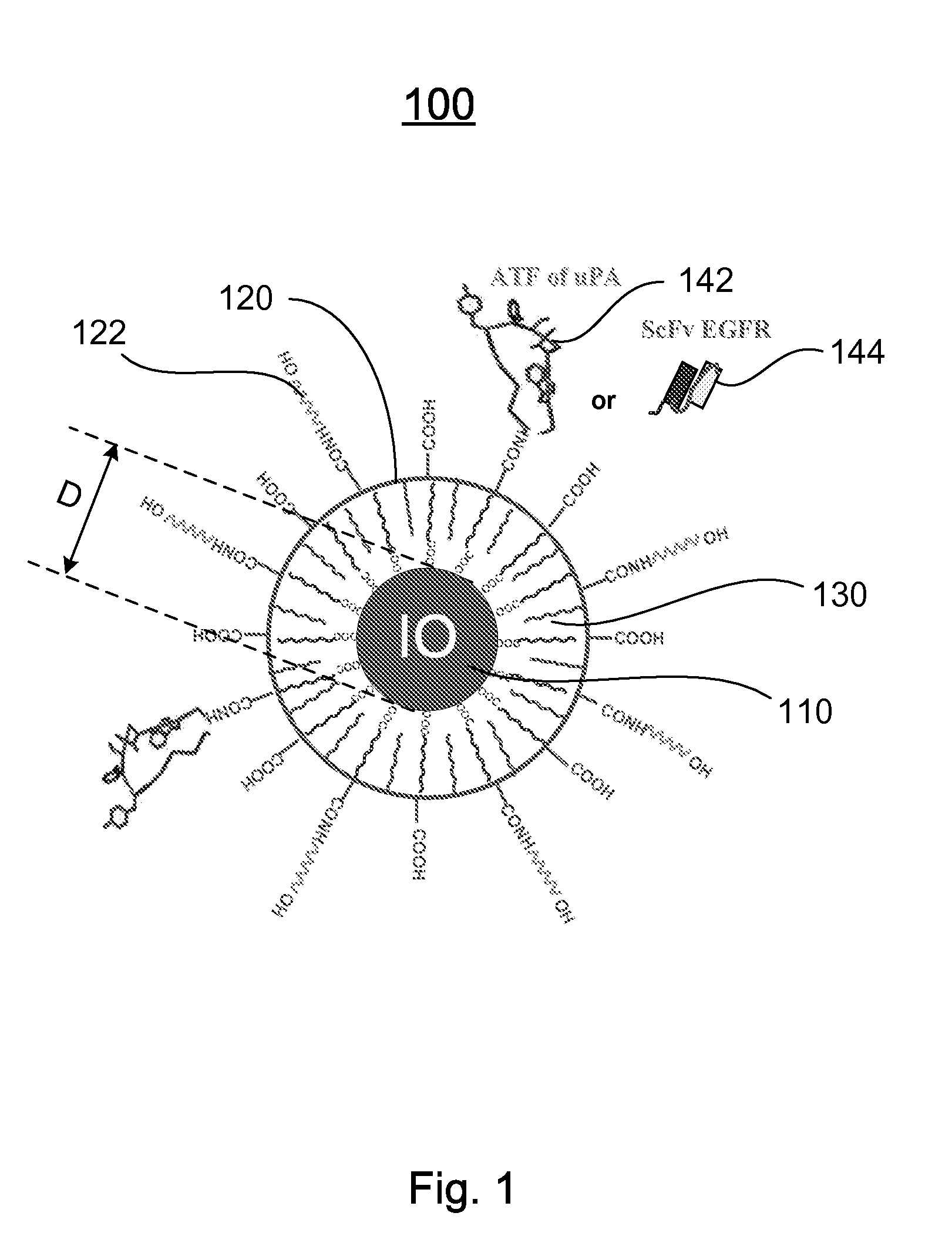
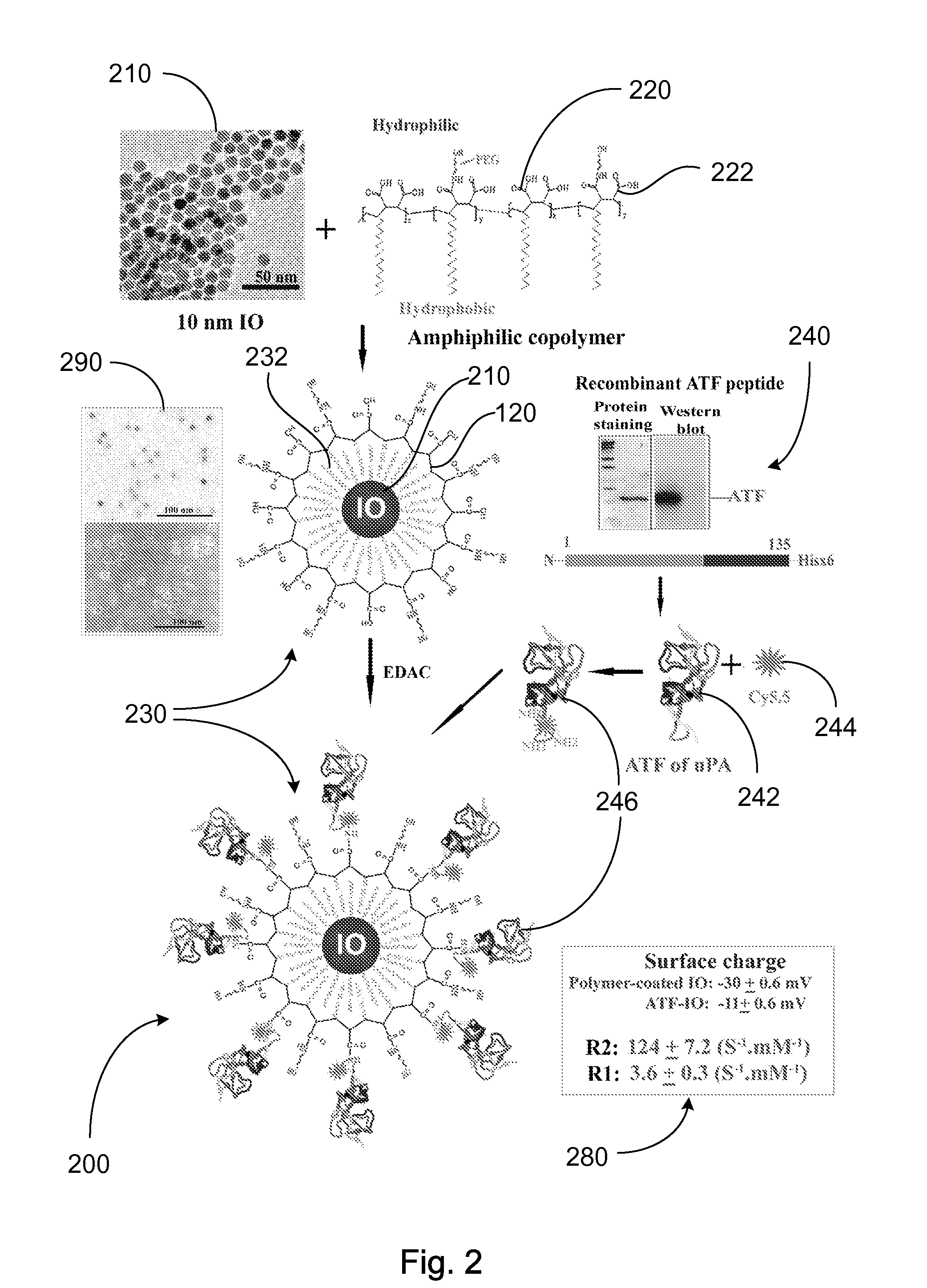
Nanostructures, methods of synthesizing thereof, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20090196831A1Powder deliveryImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCrystallographySynthesis methods
A nanostructure and methods of synthesizing same. In one embodiment, the nanostructure includes a magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle, a hydrophobic protection structure including at least an amphiphilic copolymer, wherein the hydrophobic protection structure encapsulates the magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle, and at least one amino-terminal fragment (ATF) peptide or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody conjugated to the amphiphilic copolymer.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Amphiphilic block copolymers and their use
ActiveUS7847025B2Preventing secondary cataractSilicon organic compoundsBiocidePosterior capsule opacificationIntraocular lens
The present invention relates to amphiphilic block copolymers comprising at least one block of hydrophilic units and at least one block of hydrophobic units, wherein at least one hydrophobic block contains siloxane units. The present invention may be particularly useful as a tissue adhesive or as a coating for an intraocular lens (IOL). As an IOL coating, copolymers according to the invention may be used, for example, to promote tissue adhesion for the prevention of posterior capsule opacification.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Liquid membrane suitable for water extraction
ActiveUS20120152841A1Easy to produceEasy to eliminateGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentDesalinationSalt water
A liquid membrane matrix is disclosed in the form of an aquaporin containing bulk liquid membrane matrix (BLM), wherein said liquid membrane matrix is formed from a solution of an amphiphilic copolymer detergent wherein transmembrane proteins have been functionally incorporated and wherein said matrix further contains a stabilising oil phase. The uses of the membrane matrix include water extraction from liquid aqueous media by forward osmosis, e.g. for desalination of salt water.
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
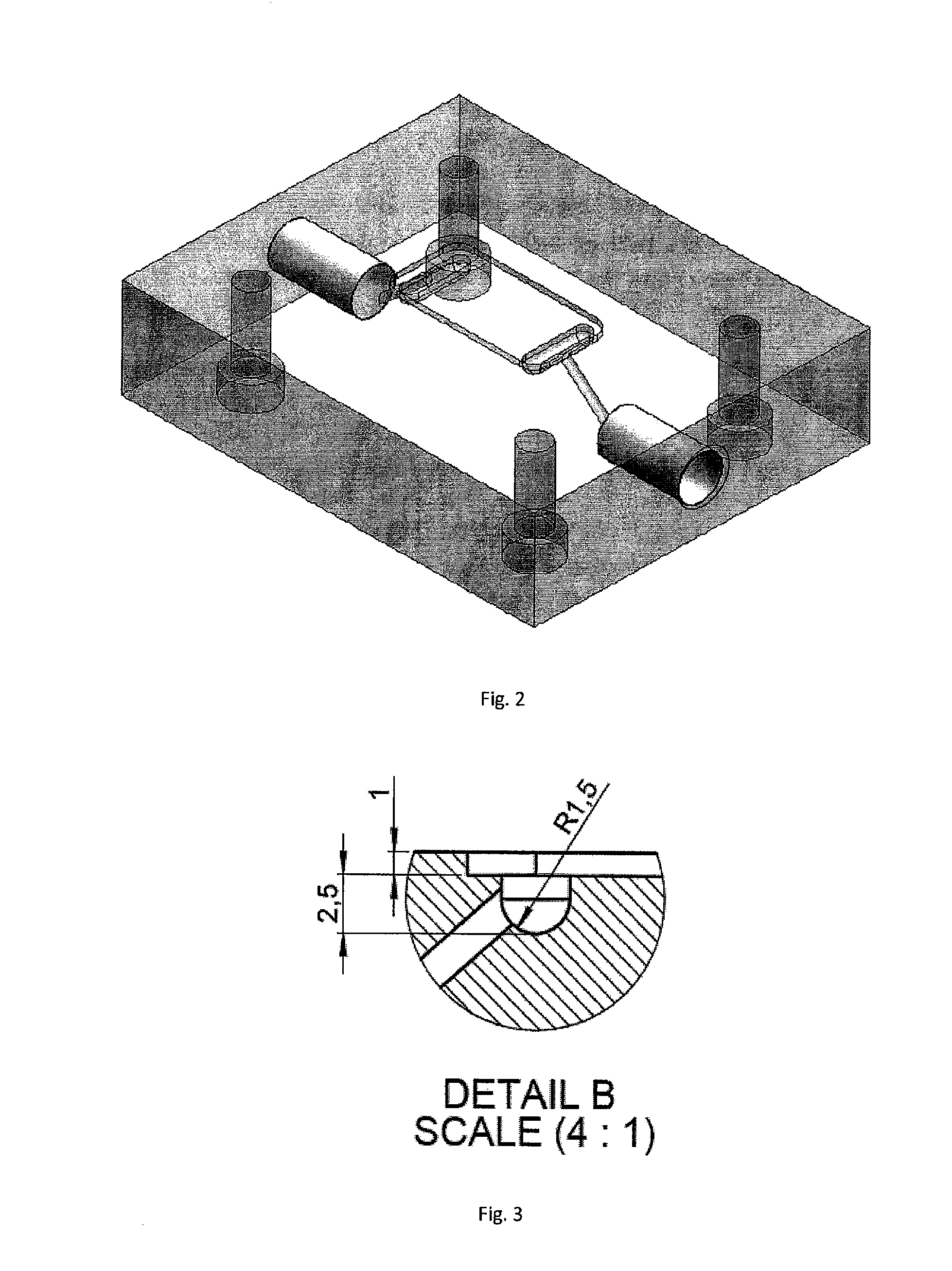
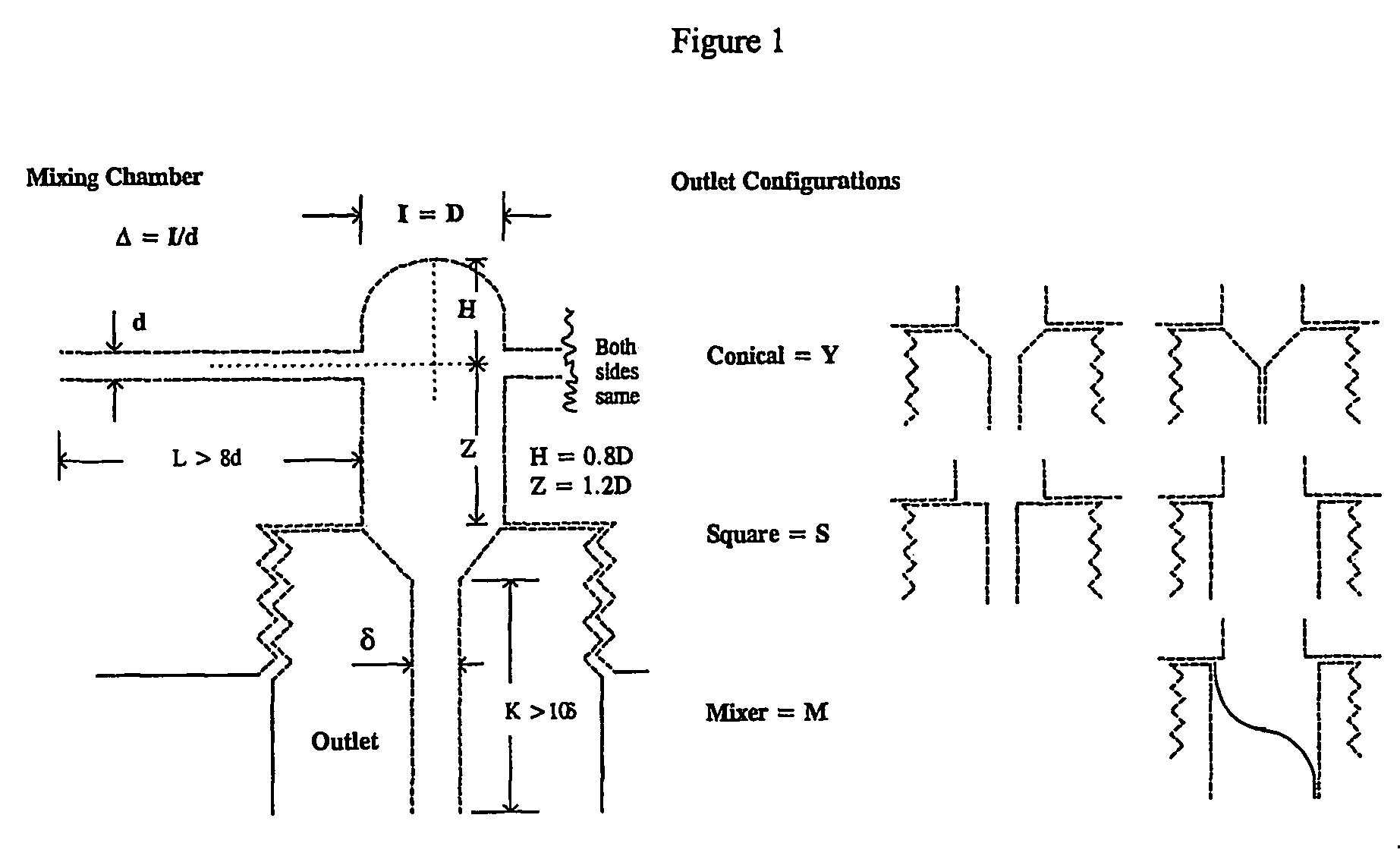
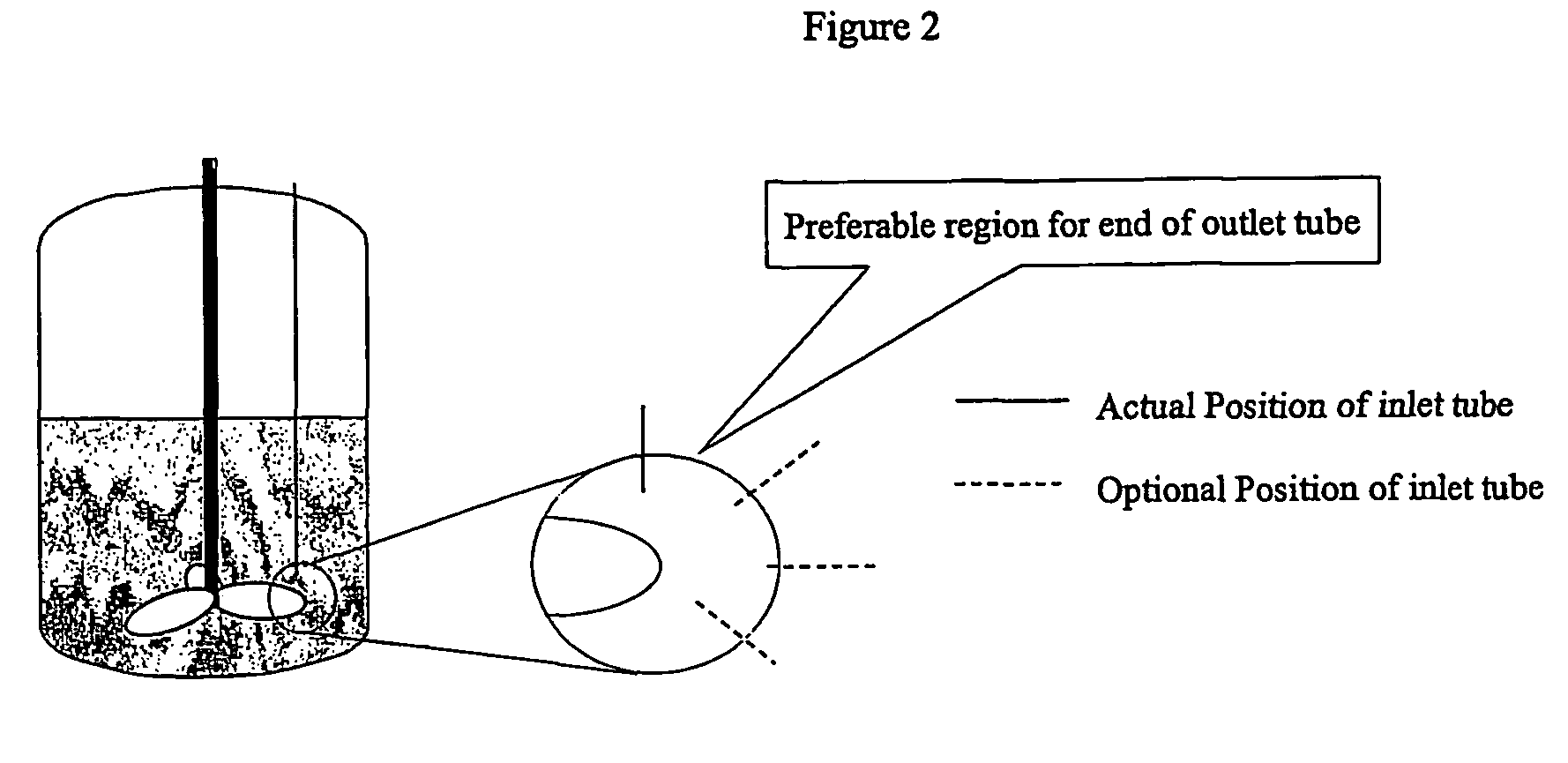
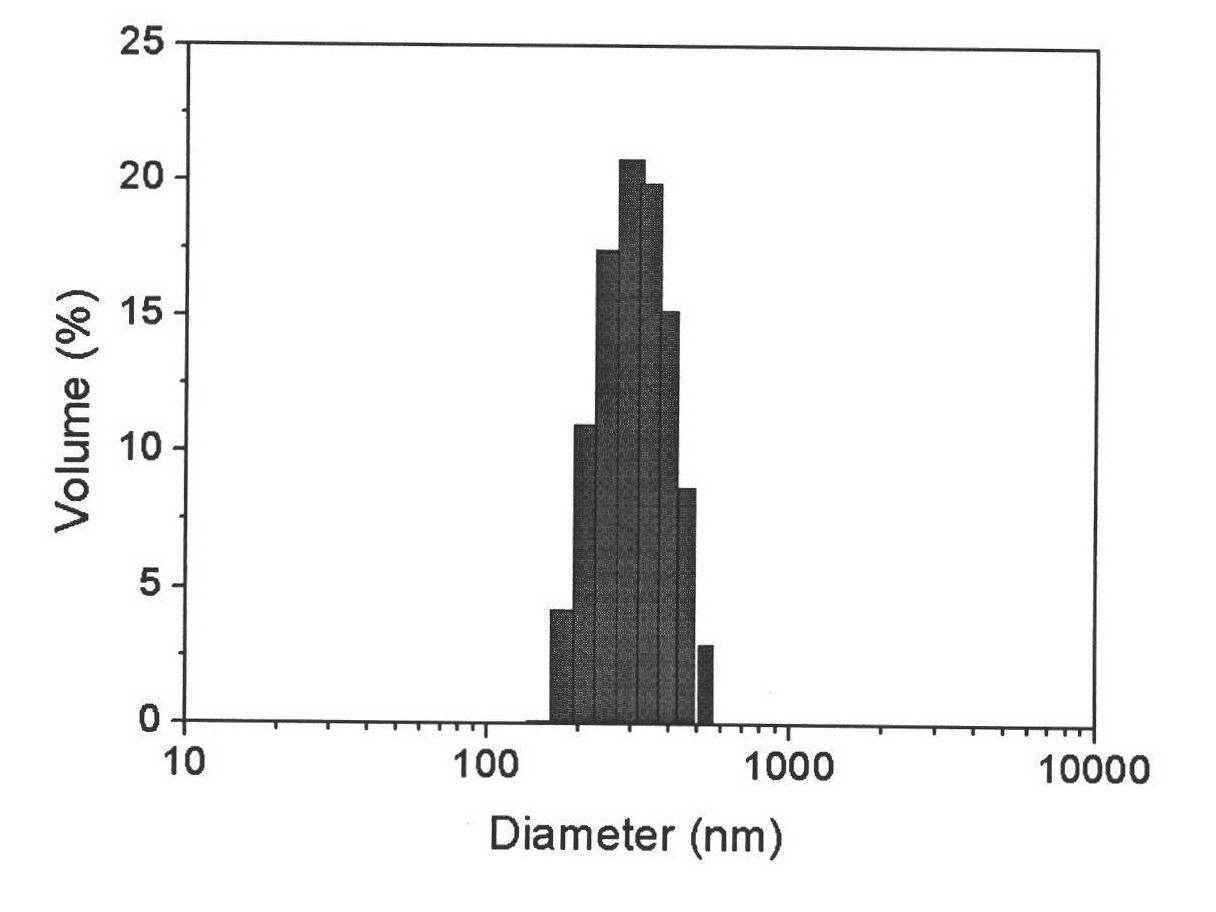
Process and apparatuses for preparing nanoparticle compositions with amphiphilic copolymers and their use
ActiveUS8137699B2Enhance resultant propertyHigh yieldBiocideTransportation and packagingProduction rateSolubility
This invention discloses a process for making nanopanticles of amphiphilic copolymers by flash precipitation. Nanoparticles may be of amphiphilic copolymer alone or may contain an additive target molecule, preferably an organic active. The inclusion of additive target molecules in amphiphilic copolymer nanoparticles can alter their water solubility characteristics, fluid dynamics, and / or stability. Changing an additive target molecule's solubility and stability in an nanoparticle can make a water insoluble compound suitable for pharmaceutical administration as well as specifically target the molecule to a specific area of a patient's body. The process affords the production of nanoparticles at high absolute active content, at high yield, high productivity, and high processing rates while using unusually low amounts of amphiphilic copolymers. Furthermore, the resulting particles exhibit sufficient stability for post processing as desired. The invention also discloses two apparatuses for the production of nanoparticles of amphiphilic copolymers by flash precipitation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Responsive microgel and methods related thereto
A responsive microgel is provided which responds volumetrically and reversibly to a change in one or more aqueous conditions selected from the group consisting of (temperature, pH, and ionic conditions) comprised of an ionizable network of covalently cross-linked homopolymeric ionizable monomers wherein the ionizable network is covalently attached to an amphiphilic copolymer to form a plurality of ‘dangling chains’ and wherein the ‘dangling chains’ of amphiphilic copolymer form immobile micelle-like aggregates in aqueous solution. A responsive microgel is further provided that comprises at least one therapeutic entity and delivers a substantially linear and sustained release of the therapeutic entity under physiological conditions.
Owner:SUPRATEK PHARMA
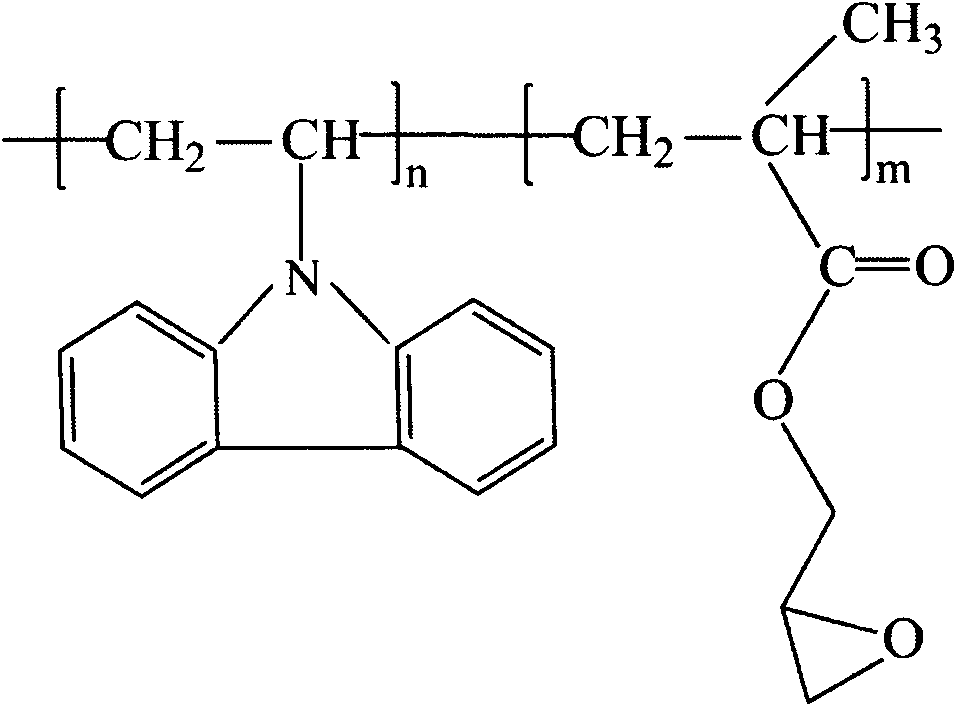
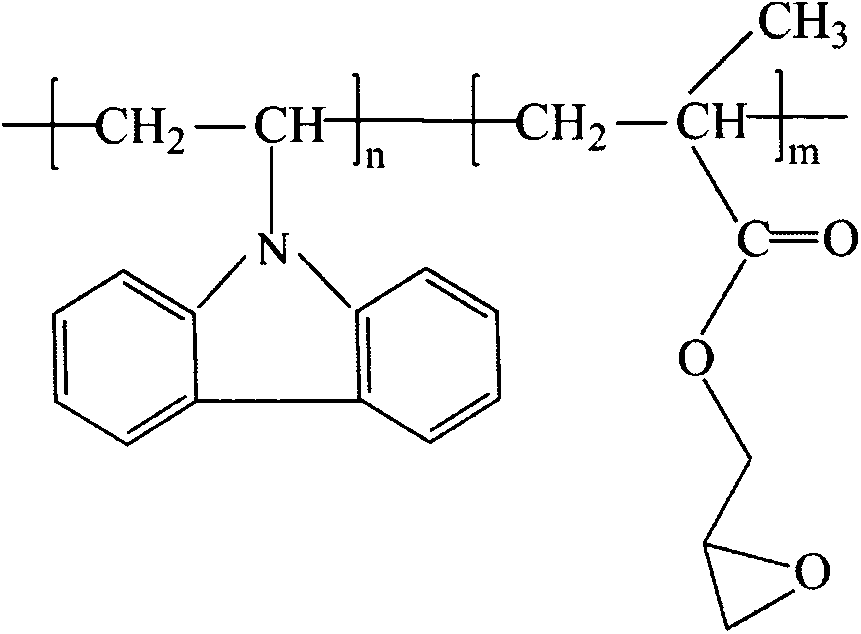
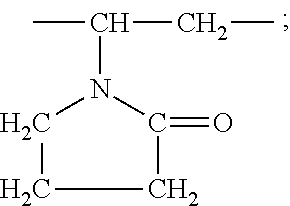
Amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness, preparation method thereof and use thereof
InactiveCN101891870APrecise molecular weight controlPrecise Control of DispersionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMethacrylateFunctional monomer
The invention discloses an amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness and a preparation method thereof. Particularly, the invention discloses an amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness comprised of a block, which is formed by the copolymerization of a hydrophobic group and a pH response group, and a hydrophilic brush-shaped block. In the invention, a copolymer of a hydrophobic monomer and a pH response functional monomer is obtained by atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), then the copolymer is used as a macromolecular initiator to perform the ATRP polymerization of monomethoxypoly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate (PEGMA) which is a hydrophilic macromolecular monomer, and finally, a selective hydrolysis reaction is performed to prepare the amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of simple process and high yield. The synthesized amphiphilic copolymer brush with pH responsiveness has a novel structure and an adjustable functional group proportion, and is suitable to be used in the transmission of entrapped insoluble medicaments.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel method for amphiphilic copolymer modified PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) hollow fiber ultra-filtration membranes
InactiveCN103007787AStrong anti-pollutionImprove throughputSemi-permeable membranesFiltration membraneFoaming agent
The invention relates to a novel method for amphiphilic copolymer modified PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) hollow fiber ultra-filtration membranes, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of PVDF membranes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) PVDF, amphiphilic copolymer, pore-foaming agent, nonsolvent and solvent are fully mixed, and are dissolved to obtain membrane casting liquid; (2) the membrane casting liquid is fed in a hollow fiber membrane spinning machine for extruding, is condensed and formed in a coagulating bath, and is wound and collected to obtain the PVDF hollow fiber membranes; (3) the PVDF hollow fiber membranes are dipped in hot water; and (4) finished products are obtained after cleaning and drying. The amphiphilic copolymer modified PVDF hollow fiber ultra-filtration membranes, prepared by the method, have the characteristics of permanent hydrophilcity, excellent pollution resistance, high throughput and high reject rate.
Owner:SHAOXING REEYEE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Vesicles consisting of amphiphilic polymer and application of vesicles
InactiveCN102657873AEasy to packEfficient packagingGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBackbone chainDouble bond
The invention discloses vesicles consisting of amphiphilic polymer and application of the vesicles. A main chain of the amphiphilic polymer consists of a hydrophilic chain segment and a biodegradable hydrophobic chain segment, wherein the molecular weight of the hydrophilic chain segment is 4 to 6kDa; the molecular weight of the hydrophobic chain segment is 3 to 5 times that of the hydrophilic chain segment; the hydrophobic chain segment is formed by performing random copolymerization on a monomer A and a monomer B in a molar ratio of (5-20):1; the monomer A is trimethylene carbonate or cyclic carbonate; the monomer B is acrylate-based carbonate or vinyl sulfone-based carbonate; the hydrophobic chain segment is grafted with a short branched chain; the grafting position is a double bond of the monomer B; a monomer forming the short branched chain is 3-mercaptopropionic acid, cysteamine hydrochloride or cysteine; and the grafting rate is 0.3 to 1. The vesicles are directly prepared from the amphiphilic polymer in an aqueous solution and used as a carrier and a release system of a protein medicine, the encapsulating efficiency and bioavailability of the protein medicine can be improved, and the stability of the encapsulated protein is enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104226124AEasy to prepareLow costSemi-permeable membranesPolyvinylidene difluoridePolyvinylidene fluoride
The invention relates to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. The membrane casting liquid comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 10-25% of polyvinylidene fluoride resin, 1-4% of diatomite, 1-5% of amphiphilic copolymer, 4-12% of organic pore-forming agent, 0.2-3% of inorganic pore-forming agent, 0.1-3% of surfactant and the balance of solvent. According to the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane, the diatomite and the amphiphilic copolymer are added; by virtue of the diatomite, the mechanical strength and pure water flux of the membrane are improved; the amphiphilic copolymer and polyvinylidene fluoride have good compatibility; the combination force is strong; the copolymer is unlikely to run off and the continuous hydrophily of the membrane is guaranteed. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly stirring the membrane casting liquid, standing and defoaming; (2) enabling the membrane casting liquid to vertically flow in the air by virtue of a spinning spinneret, so that the membrane casting liquid enters the coagulating bath and is cured and formed; (3) soaking the spun and formed polyvinylidene fluoride membrane in pure water and a glycerol water solution in sequence and drying so as to obtain the polyvinylidene fluoride membrane.
Owner:安徽指南针科创园发展有限公司
Organosol including amphipathic copolymeric binder having crystalline material, and use of the organosol to make dry tones for electrographic applications
InactiveUS7005225B2Reduce polydispersityExceptional uniformityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternCrystalline materialsCopolymer
The present invention relates to amphipathic copolymeric binder particles that incorporate polymerizable crystallizable compounds chemically incorporated into a dispersible (D) portion and / or solvatable (S) portion of the copolymer. The invention also pertains to dry particulate electrophotographic toners incorporating an amphipathic copolymer comprising one or more polymerizable crystallizable compounds. Methods of making these dry electrophotographic toner particles, and methods of electrophotographically forming an image on a substrate using these toners, are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
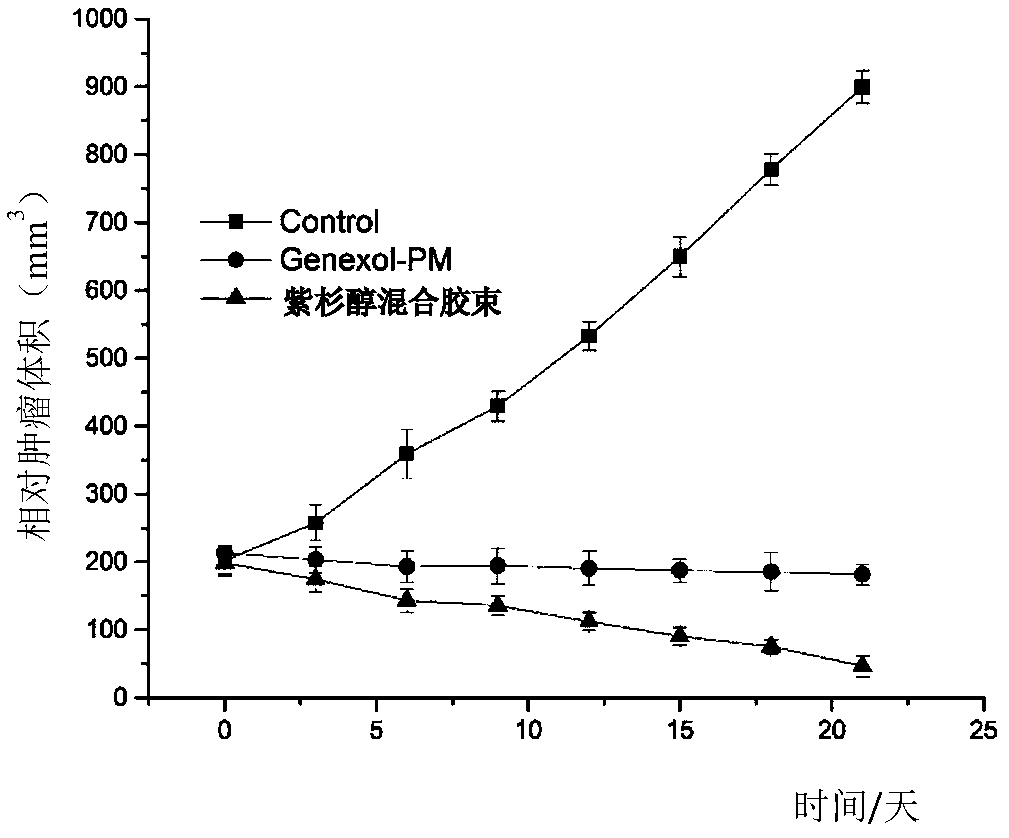
Blank mixed micelle, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108420793AImprove uniformityReliable uniformityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsMixed micelleCurative effect
The invention discloses blank mixed micelle, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The blank mixed micelle comprises an amphiphilic copolymer and ginsenoside represented by formula I, ishigh in efficiency, is safe, is stable, is high in targeting performance, is excellent in homogeneity, is stable in quality, is convention in preparation technology, can be used for coating one or a plurality of active substances in drugs or cosmetics and health care substances, and is capable of forming mixed micelle containing loaded active substances. Compared with conventional nanometer micelle, the blank mixed micelle possesses following advantages: the mixed micelle loaded with active substances is excellent in drug forming performance, multiple drug resistance, stability, homogeneity, and safety performance, and is small in particle size; and the curative effect of loaded active drugs on drug resistant cells is better.
Owner:XIAMEN GINPOSOME PHARM CO LTD
Nanoparticles coated with amphiphilic block copolymers
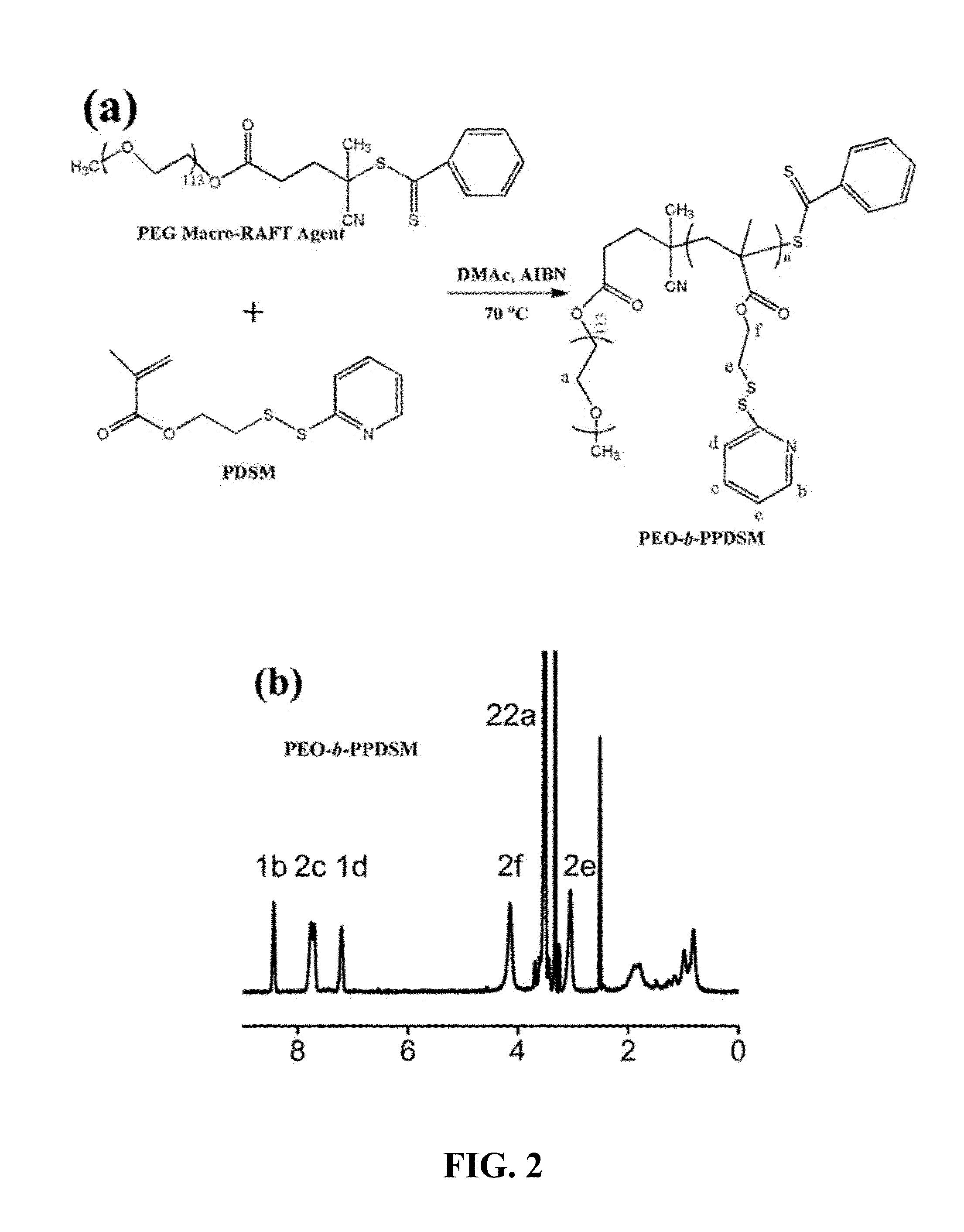
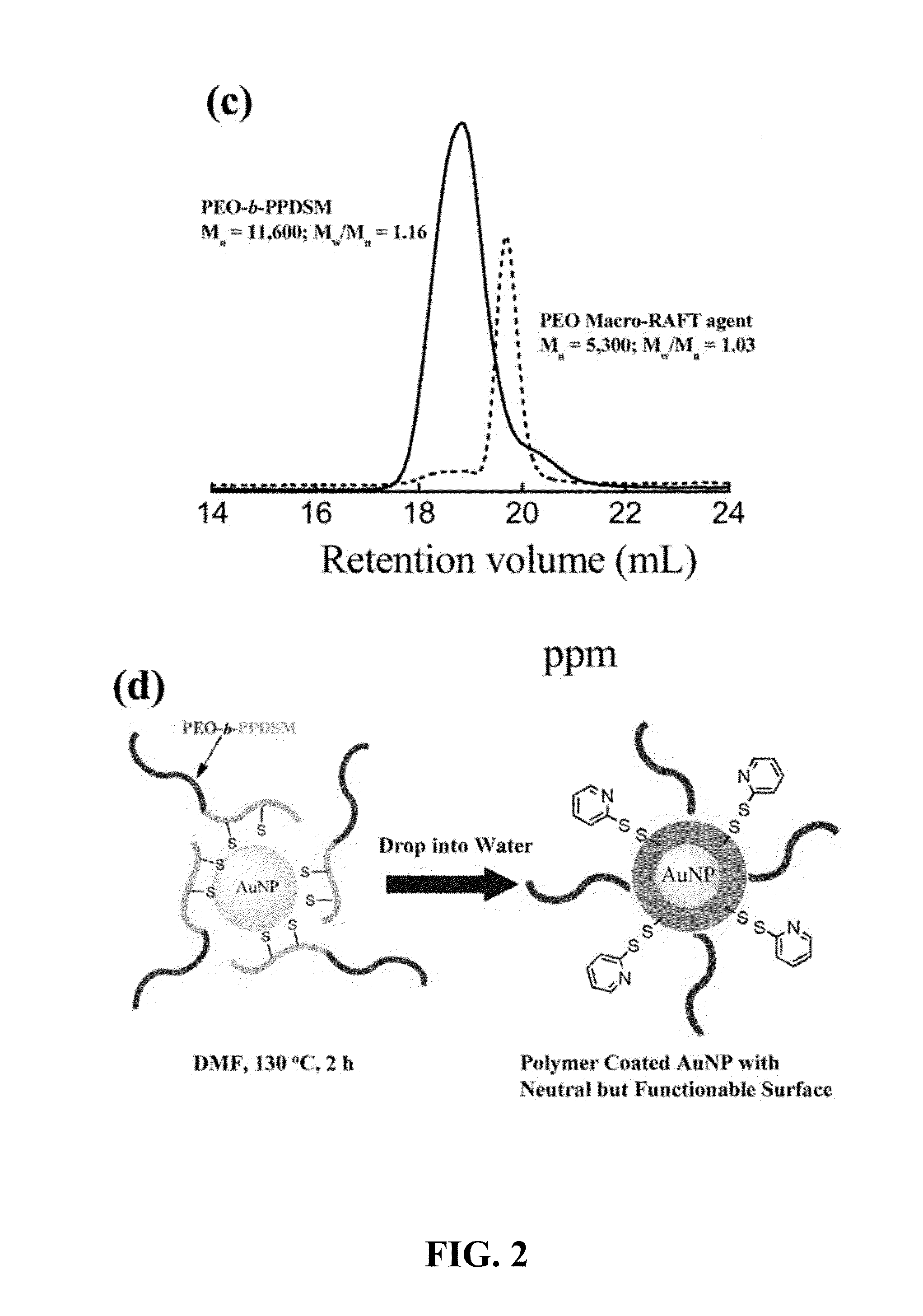
InactiveUS20130243874A1Uniform sizeImprove stabilityPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyNanoparticleMedical device
The present provides amphiphilic block copolymer coated surfaces (e.g., nanoparticles, medical devices, etc.) and methods of preparing such surfaces. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides amphiphilic block copolymer coated single dispersed nanoparticles, which are stable in buffer (e.g., PBS) and have neutral but functionable surfaces, and methods of preparing the same.
Owner:IMRA OF AMERICA +1
Method for modifying epoxy resin by using amphiphilic copolymer modified graphene
The invention discloses a method for modifying epoxy resin by using amphiphilic copolymer modified graphene. The method comprises the steps of preparing a graphene oxide from graphene serving as a raw material by adopting a Hummers oxidation method; polymerizing glycidyl methacrylate and vinylcarbazole by adopting a free radical polymerization method to obtain an amphiphilic polymer; dispersing the graphene oxide and the amphiphilic polymer into a solvent together, adding hydrazine hydrate, and reducing to obtain the amphiphilic copolymer modified graphene. The operation process is simple and convenient, and the amphiphilic copolymer modified graphene is easily synthesized in large batch. The prepared amphiphilic copolymer modified graphene has good dispersion performance in the epoxy resin, and can significantly improve the toughness of the epoxy resin. The mechanical properties of a graphene / epoxy resin composite material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention are greatly improved, wherein the tensile property is improved by over 30%, and the bending property is improved by over 50%.
Owner:沛县度创科技发展有限公司
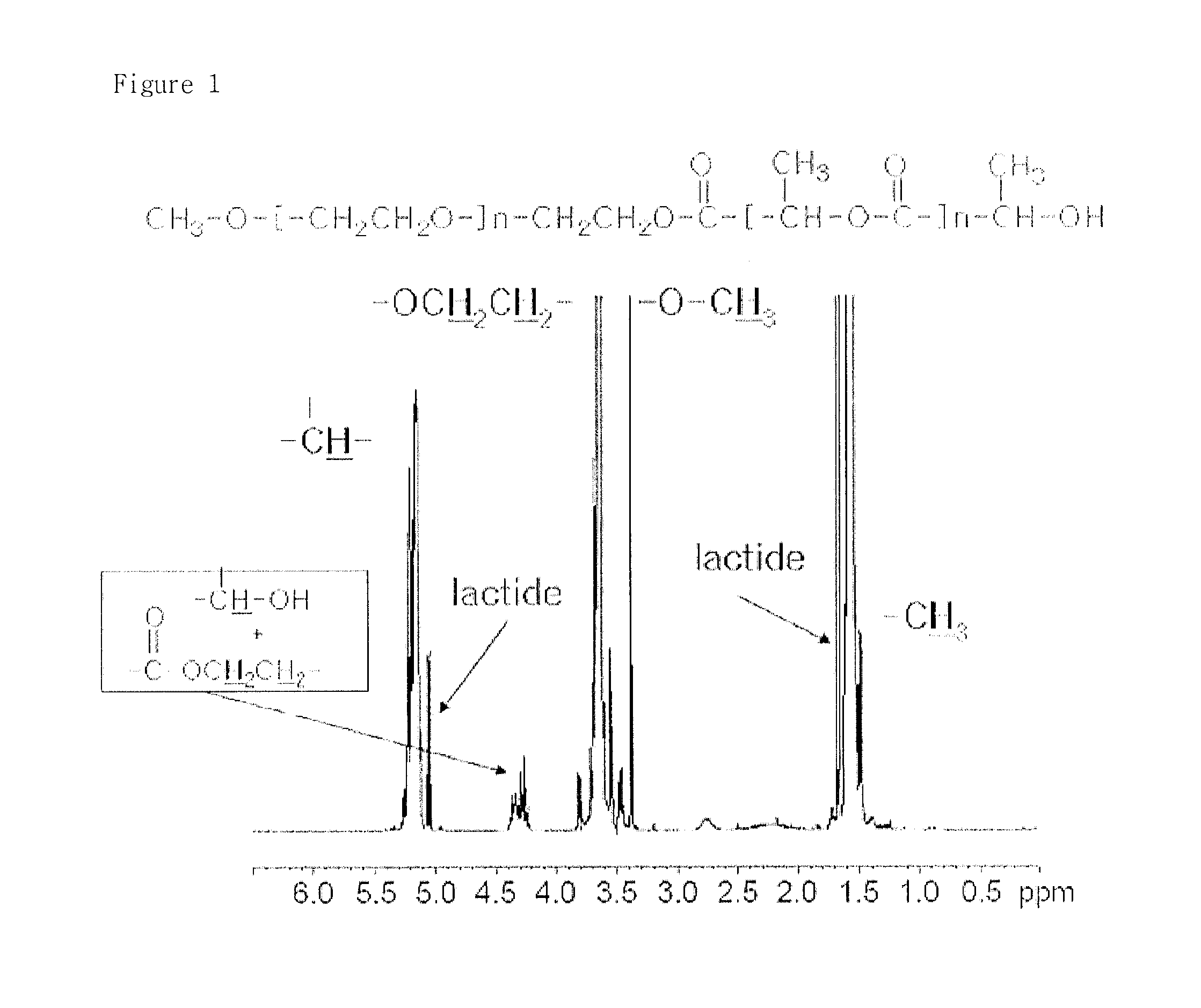
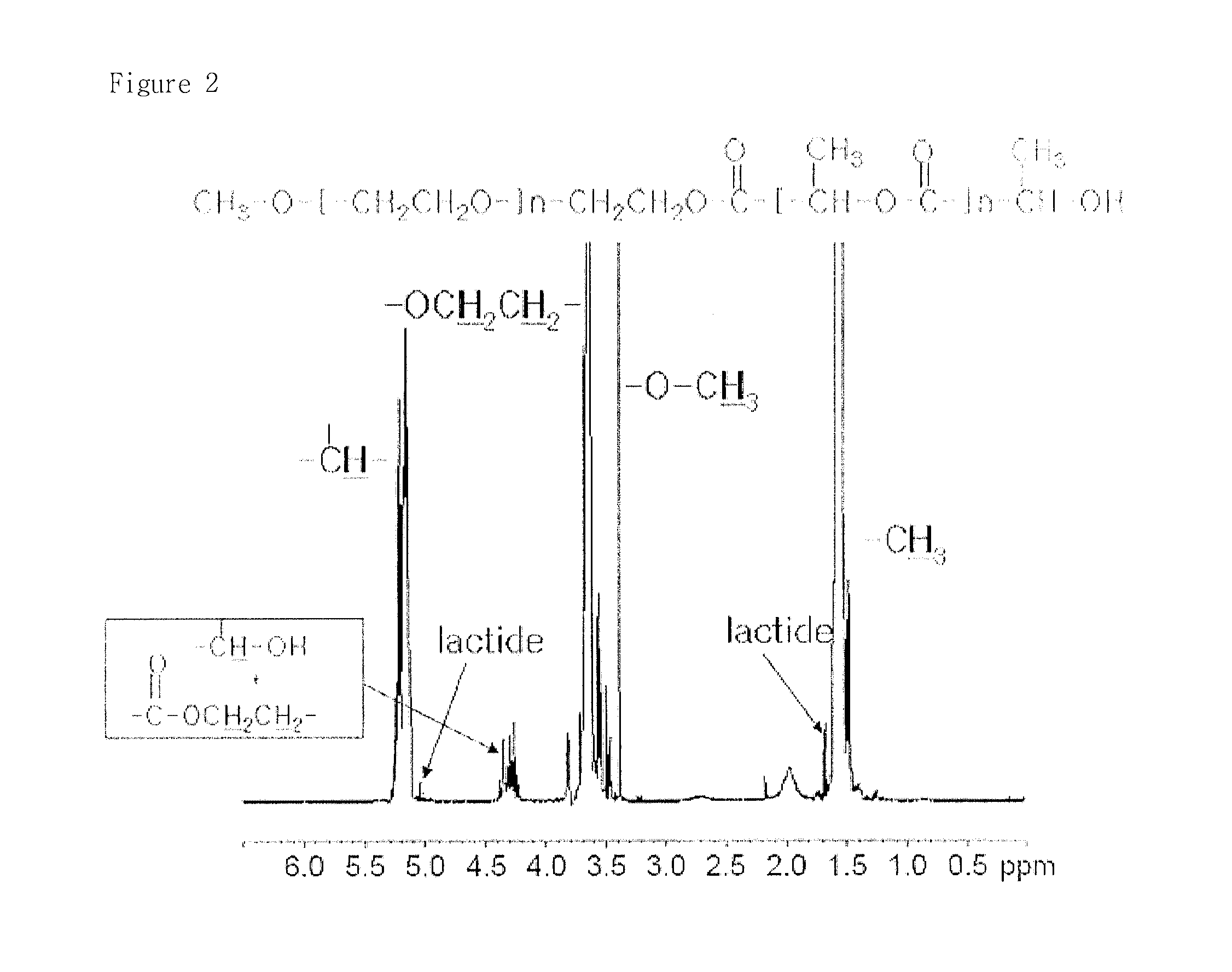
Highly pure amphiphilic copolymer comprising hydrophobic block from alpha-hydroxy acid and process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS8853351B2Applicability is hinderedHighly pure polymerOrganometallic catalysisHydrophobic polymer
Disclosed are a highly pure amphiphilic block copolymer including a hydrophobic polymer block of a poly(α-hydroxy acid), and a method for preparing the same. The method for preparing a highly pure amphiphilic block copolymer including a hydrophobic polymer block of a poly(α-hydroxy acid) includes removing α-hydroxy acid, lactone monomers thereof, oligomers thereof and an organometal catalyst in polymerizing the amphiphilic block copolymer.
Owner:SAMYANG HLDG CORP
Method for preparing shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier
InactiveCN102397236AEnhanced inhibitory effectFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationDrug release rate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier. The drug carrier is a disulfide bond bridging amphiphilic copolymer, and the disulfide bond can be rapidly cracked under reduction environment in cells to realize the intelligent drug release function through the shell shedding, so the amphiphilic copolymer can rapidly self-assemble into micelle nanoparticles and loading drugs in water. Compared with drug carriers prepared with the prior art, the shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier allows the drug release rate under high concentration glutathione environment to be 3-5 times faster than the drug release rate under glutathione-free environment, can be used to control the release of drugs in tumor cells, and has obvious inhibition on the tumor cells, and the drug carrying micelle particles can stably clad anticancer drugs, so a novel high efficiency drug carrier system is provided for the tumor treatment.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com