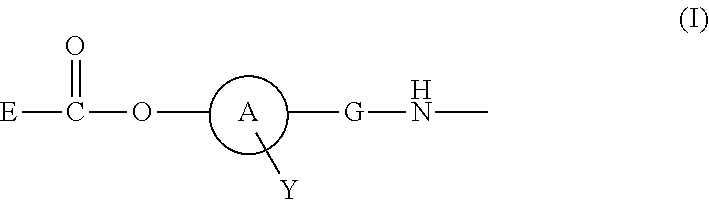Patents
Literature
314 results about "Drug release rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus for heating to a desired temperature for improved administration of pharmaceutically active compounds
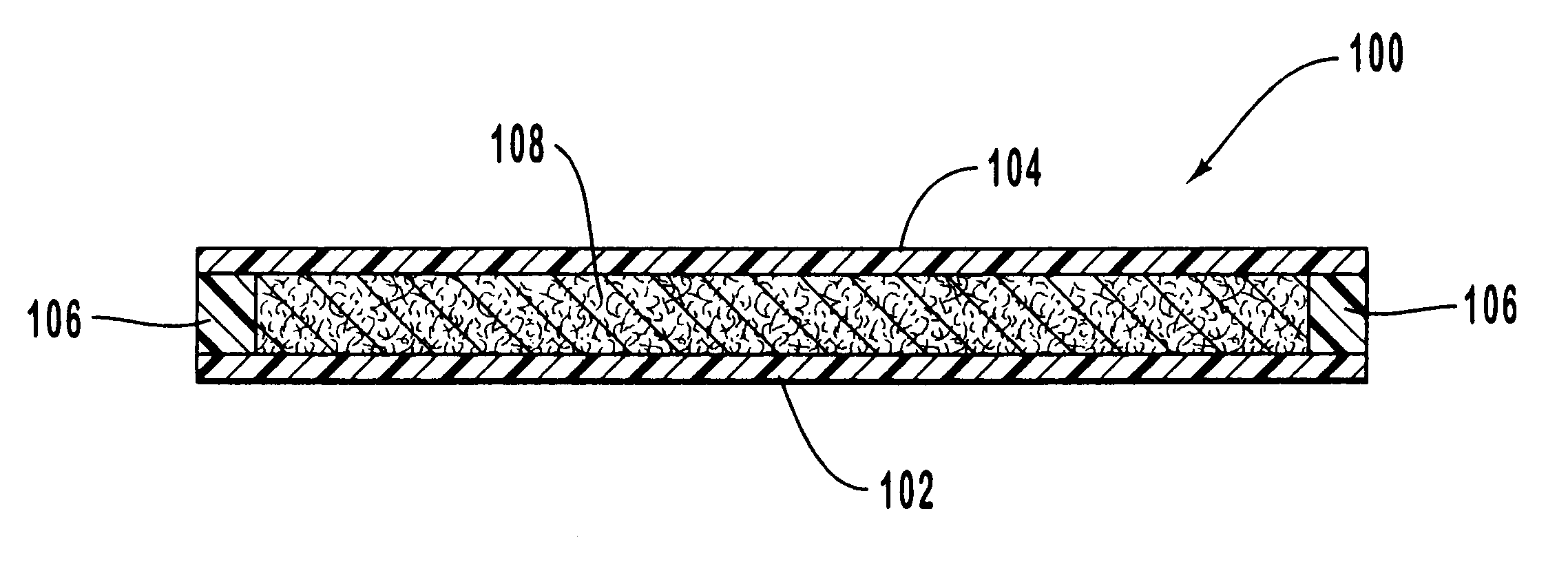
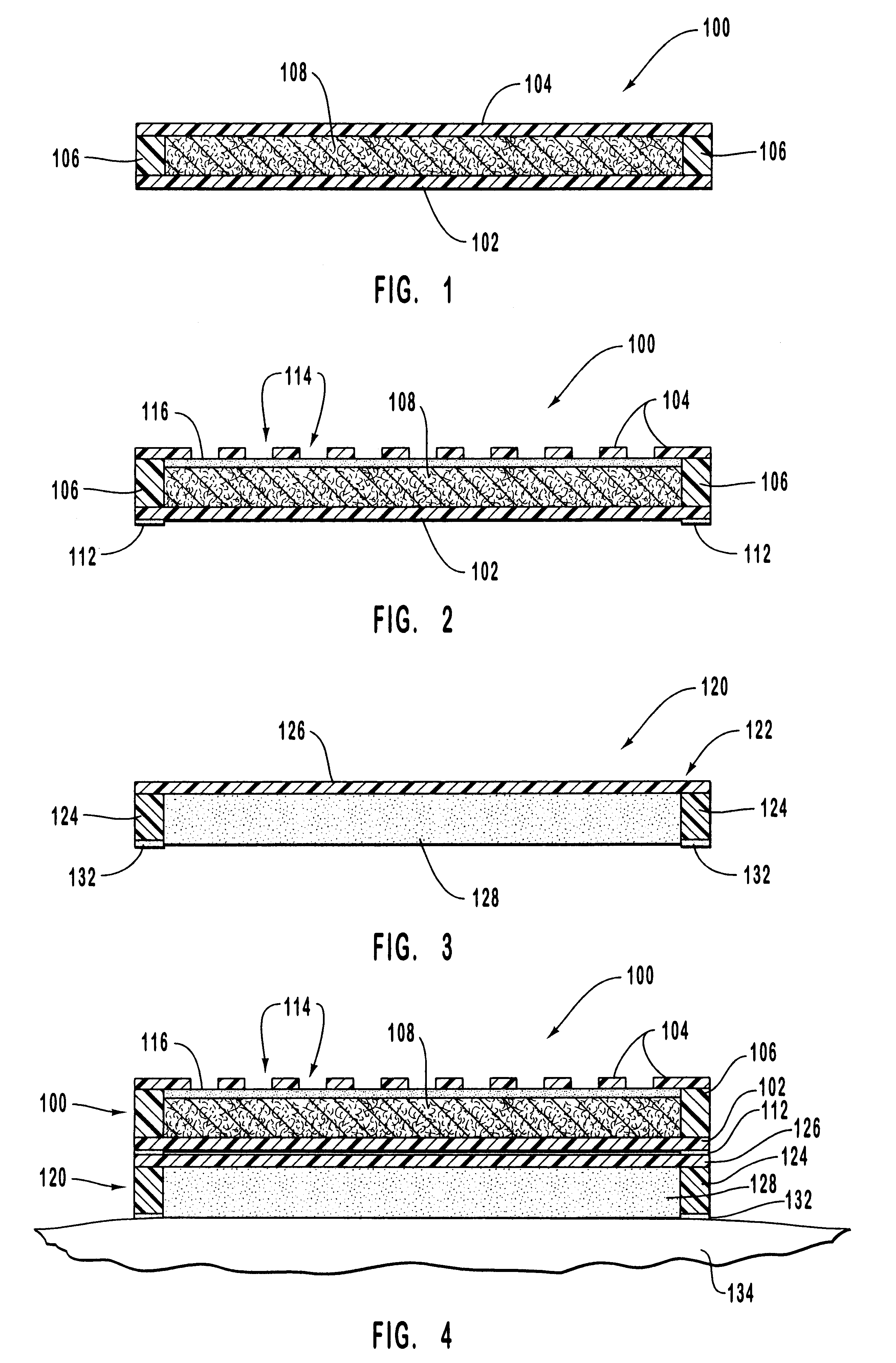
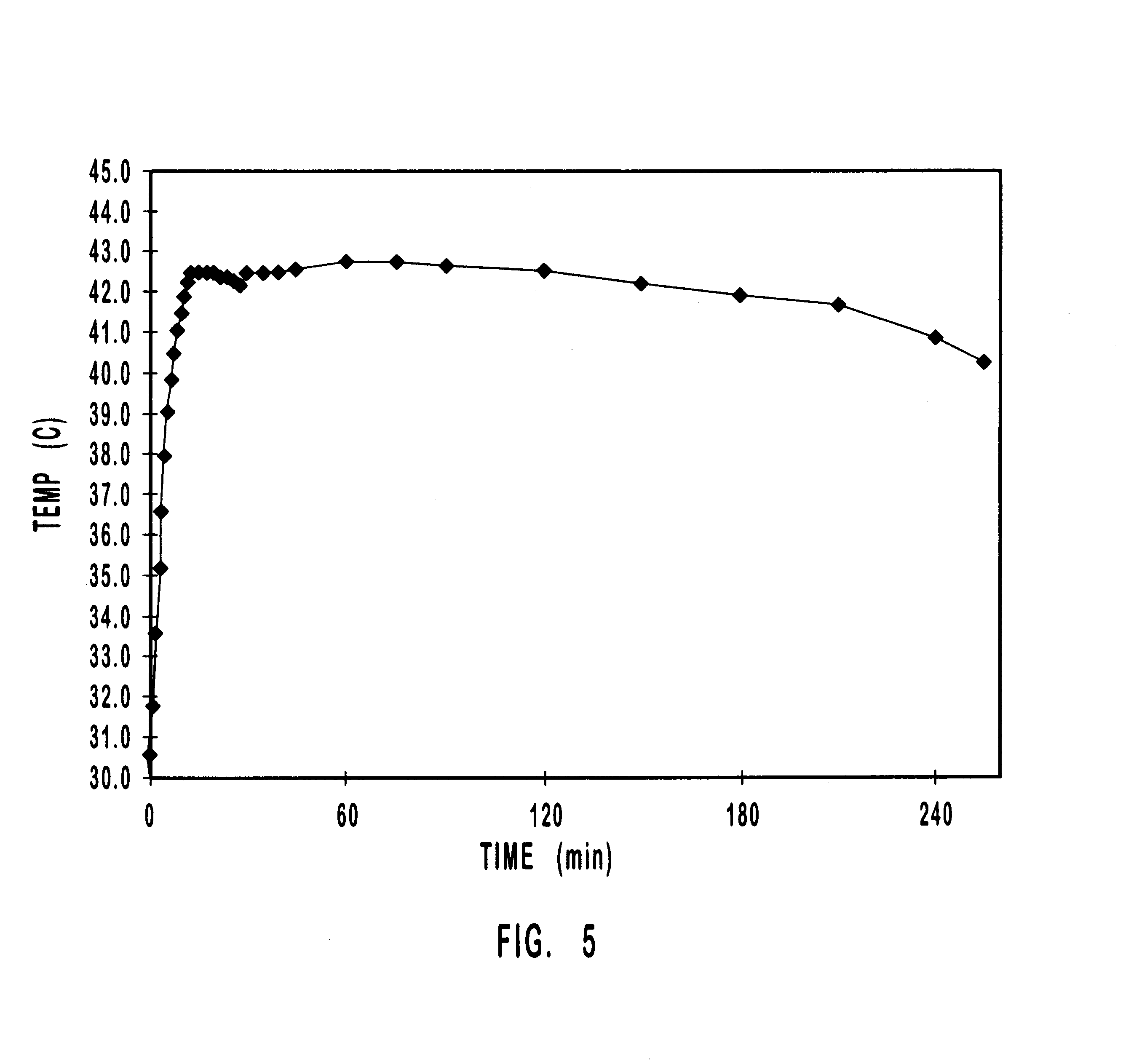
Methods and apparatus for improving administration of drugs through the use of heat and other physical means. The present invention relates to the use of heat and other physical means in conjunction with specially designed dermal drug delivery systems, conventional commercial dermal drug delivery systems, or drugs delivered into a sub-skin depot site via injection and other methods to alter, mainly increase, the drug release rate from the dermal drug delivery systems or the depot sites to accommodate certain clinical needs.
Owner:NUVO RES
Stent coatings with engineered drug release rate
Coatings and methods of forming coatings for implantable medical devices, such as stents, are described. The coatings are used for the sustained release of a therapeutic agent or drug.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Electrospun Skin Capable Of Controlling Drug Release Rates And Method
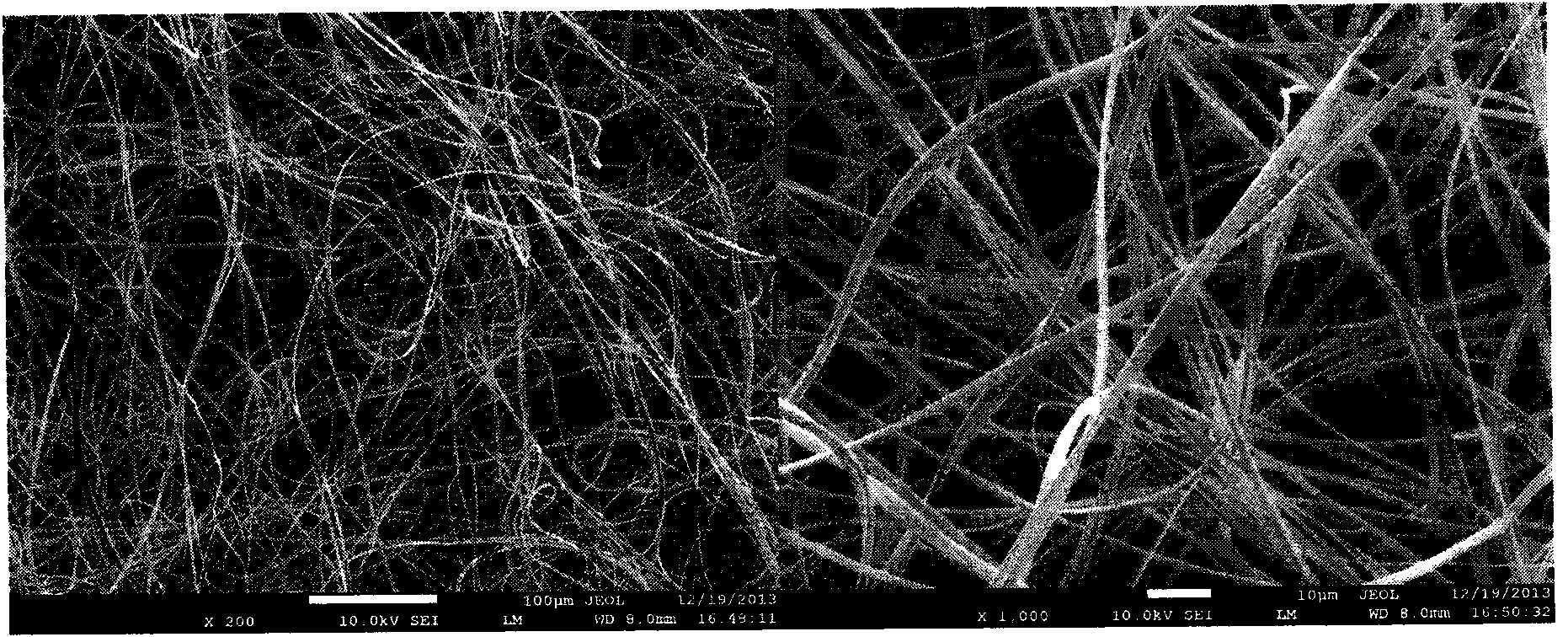
InactiveUS20070087027A1High tensile strengthChange in permeabilityStentsSynthetic resin layered productsFiberDrug release rate
A versatile covering process enabled through the identification and manipulation of a plurality of variables present in the electrospinning method of the present invention. By manipulating and controlling various identified variables, it is possible to use electrospinning to predictably produce thin materials having desirable characteristics. The fibers created by the electrospinning process have diameters averaging less than 100 micrometers. Proper manipulation of the identified variables ensures that these fibers are still wet upon contacting a target surface, thereby adhering with each other to form a cloth-like material and, if desired, adhering to the target surface to form a covering thereon. The extremely small size of these fibers, and the resulting interstices therebetween, provides an effective vehicle for drug and radiation delivery, and forms an effective membrane for use in fuel cells.
Owner:GREENHALGH SKOTT E +1
Durable Biocompatible Controlled Drug Release Polymeric Coatings for Medical Devices
Disclosed herein are biocompatible durable controlled drug releasing polymeric coatings for medical devices. The drug release rates of the polymers are controlled by adjusting monomer ratios and glass transition temperatures Tgs. The polymers are durable; they do not delaminate from the coated medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Stents with ceramic drug reservoir layer and methods of making and using the same
A method of making a drug eluting stent comprises forming a porous stent body surface layer by ion implantation, applying a layer of ceramic particles on the porous layer and compressing the layer of ceramic particles. The layer of ceramic particles can be compressed to successively higher densities. Drugs can be loaded into the layer of ceramic materials at a relatively low density before the layer of ceramic materials is compressed to a higher density to achieve a desired low drug release rate.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Apparatus and method for delivery of mitomycin through an eluting biocompatible implantable medical device
InactiveUS7396538B2Increase the diameterPrevent proliferationStentsOrganic active ingredientsQuinoneDrug release rate
The present invention is an apparatus and a method for delivery of mitomycin through an eluting biocompatible implantable medical device. A biocompatible drug release matrix comprises a biocompatible drug release matrix and a drug incorporated into the biocompatible drug release matrix. The drug has antibiotic and anti-proliferative properties and is an analogue related to the quinone-containing alkylating agents of a mitomycin family. The drug is initially released from the biocompatible drug release matrix at a faster rate followed by a release at a slower rate. The drug release rate maintains tissue level concentrations of the drug for at least two weeks after implantation of the medical device. The present invention provides a coating for a vascular prosthesis that elutes the drug at a controlled rate to inhibit proliferation of smooth muscle cells causing restenosis.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR DEVICES INC
Method for preparing medicine sustained-releasing bracket
ActiveCN101185779ANo oxidative decompositionThickness is easy to controlStentsSurgeryDrug release rateSustained release drug
A preparation method of a drug sustained-release stent includes a preparation stent, a drug sustained-release stent constituted by drug coating on the stent, and the drug coating of the stent is composed of the following steps sequentially: (1) the preparation of a sustained-release drug coating layer; (2) the coating of the sustained-release drug coating layer; (3) drying. The dosages of the drug components on the sustained-release drug stent of the invention are in line with the designed dosages, and the drug can be released according to the stipulated dosages in the stipulated time of the design requirements completely in vitro tests. The invention has good biocompatibility, low cost of spraying process, high yield, controllable thickness of the coating layer, and slow and stable drug release rate.
Owner:上海赢生医疗科技有限公司
Stent coatings with engineered drug release rate
Coatings and methods of forming coatings for implantable medical devices, such as stents, are described. The coatings are used for the sustained release of a therapeutic agent or drug.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Modification of polymer stents with radiation
InactiveUS7794776B1Reduces and prevents exposureStentsRadiation applicationsDrug release rateMedicine
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
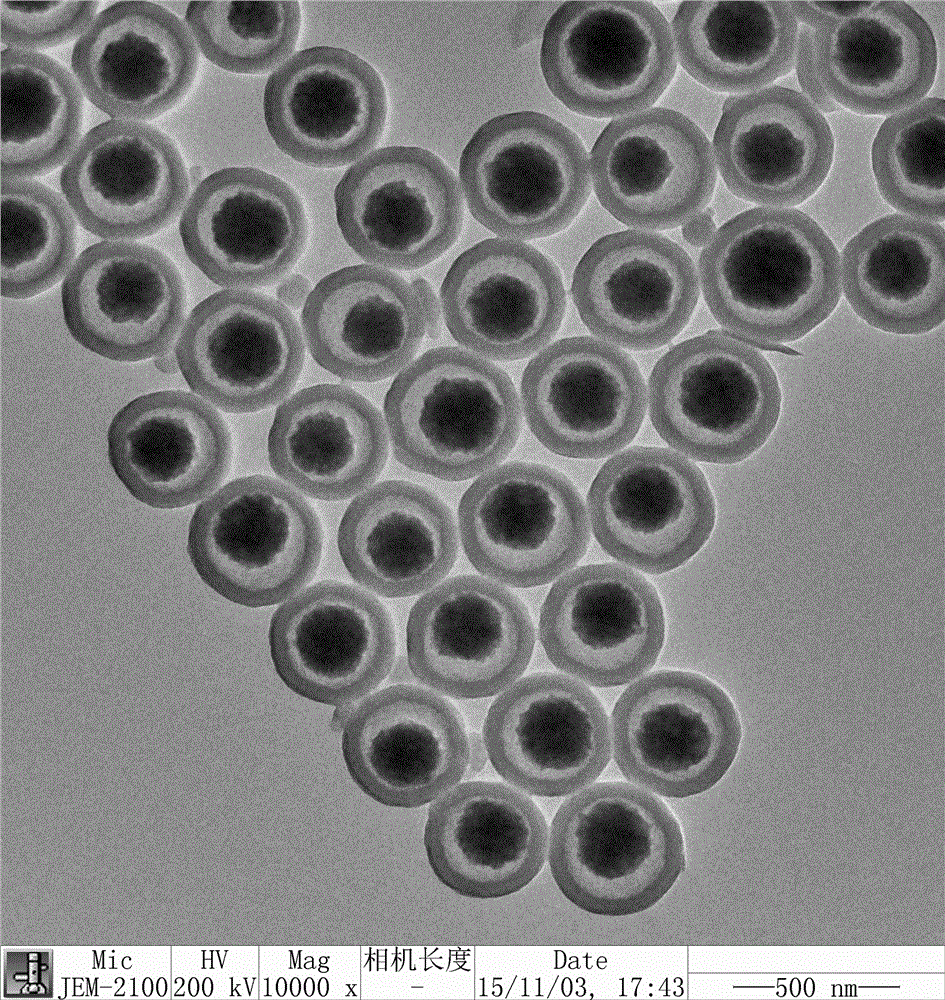
Multi-layer drug sustain-release nano fiber membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103599090AEasy to shapeFlat surfaceAntibacterial agentsKetone active ingredientsFiberDrug release rate
The invention discloses a multi-layer drug sustain-release nano fiber membrane and a preparation method thereof. The inner layer and outer layer of the multi-layer membrane are both composed of a polymer A nano fiber with a good biological compatibility, and the middle layer is a drug-carrying nano fiber which is prepared by blending curcumin (CM) and a polymer B with a good biological compatibility. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the polymer A into a solvent, subjecting the polymer A to an electrostatic spinning process so as to prepare the inner layer, then subjecting a mixed solution of the polymer B and CM to an electrostatic spinning process, continuously depositing the mixed solution on the inner layer so as to obtain the middle layer, finally subjecting the polymer A to an electrostatic spinning process for a second time, and continuously depositing the polymer A on the middle layer so as to obtain the outer layer. The membrane preparation method is simple, can effectively relieve the burst release phenomenon in the early release stage, and can control the drug release by changing the thickness of the polymer A. Taking polymer A-polylactic acid (PLA), and polymer B-cellulose acetate (CA) as an example, the in vitro drug release test results have shown that the drug release rate of the multi-layer drug-carrying membrane is both less than that of a single layer drug loaded membrane no matter after 1 hour or after 240 hours.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Coated stent and method of making the same
A coated implantable medical device and a method of coating an implantable medical device is disclosed, the method includes applying a composition onto the device and drying the composition at elevated temperature in an environment having increased relative humidity. A pre-screening method for a manufacturing lot of coated stents to determine the number of drug coating layers for a desired drug release rate is disclosed. The method including coating and testing small groups of stents, and applying the results of the tests to determine the number of drug coating layers to apply to the manufacturing lot of stents.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method to enhance drug release from a drug-releasing material
A method of enhancing the drug release rate from a composite material. The composite material includes a synthetic, bioabsorbable polymer matrix and a drug particle phase dispersed therein. The release rate of the drug from the polymer matrix is enhanced by orienting the composite material. The drug release rate of the oriented composite material is greater than the drug release rate from an otherwise comparable non-oriented composite material.
Owner:BIORETEC
Gastric retentive oral dosage form with restricted drug release in the lower gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS20110301129A1Minimizes variabilityIncreasing and decreasing drug loadingAntibacterial agentsBiocideDrug release rateErosion rate
Owner:DEPOMED SYST INC
Polymer Conjugate Of Folic Acid Or Folic Acid Derivative
ActiveUS20110294980A1Practical chemical stabilityExcellent in vivo drug release efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug release rateSide chain
Disclosed is a polymer conjugate of folic acid or a folic acid derivative, wherein an amide bond is not used. The compound has chemical stability and adequate drug release rate in the living organism. Specifically disclosed is a polymer conjugate of folic acid or a folic acid derivative, wherein a substituent represented by formula (I) is bonded to a carboxy group of a block copolymer which is composed of a polyethylene glycol and a polymer having a carboxy group in a side chain, or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof.[In the formula, A represents a monocyclic or fused aromatic group; G represents an optionally substituted (C1-C6) alkylene group; Y represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent; and E represents a residue of folic acid or a folic acid derivative.]
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Method for preparing shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier
InactiveCN102397236AEnhanced inhibitory effectFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHigh concentrationDrug release rate
The invention relates to a method for preparing a shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier. The drug carrier is a disulfide bond bridging amphiphilic copolymer, and the disulfide bond can be rapidly cracked under reduction environment in cells to realize the intelligent drug release function through the shell shedding, so the amphiphilic copolymer can rapidly self-assemble into micelle nanoparticles and loading drugs in water. Compared with drug carriers prepared with the prior art, the shell-sheddable polymer micelle drug carrier allows the drug release rate under high concentration glutathione environment to be 3-5 times faster than the drug release rate under glutathione-free environment, can be used to control the release of drugs in tumor cells, and has obvious inhibition on the tumor cells, and the drug carrying micelle particles can stably clad anticancer drugs, so a novel high efficiency drug carrier system is provided for the tumor treatment.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Halloysite nano composite gel microspheres and preparation method thereof
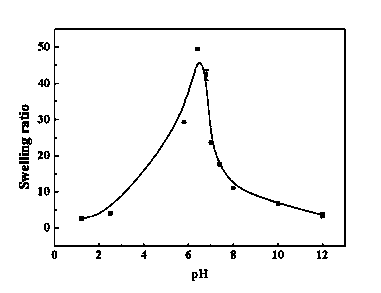
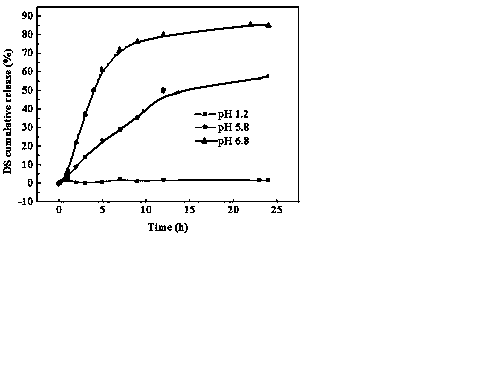
ActiveCN103520113AGood pH responsivenessSlow down swellingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrug release rateMicrosphere
The invention discloses halloysite nano composite gel microspheres and a preparation method thereof. The microspheres comprise the following components in percentage by mass: 50-90% of halloysite and 10-50% of a chitosan derivative. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing the halloysite and the chitosan derivative into a suspension and a gel solution respectively; then adding the halloysite suspension into the chitosan derivative gel solution; and finally, after 2-4 hours of reaction at room temperature, preparing the nano composite drug-loaded gel microspheres through an ion-gel method. According to the halloysite nano composite gel microspheres and the preparation method thereof disclosed by the invention, the swelling rate and drug release rate of the microspheres can be reduced, and the halloysite nano composite gel microspheres have pH sensitivity and can be used as intestinal drug slow-release carriers.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
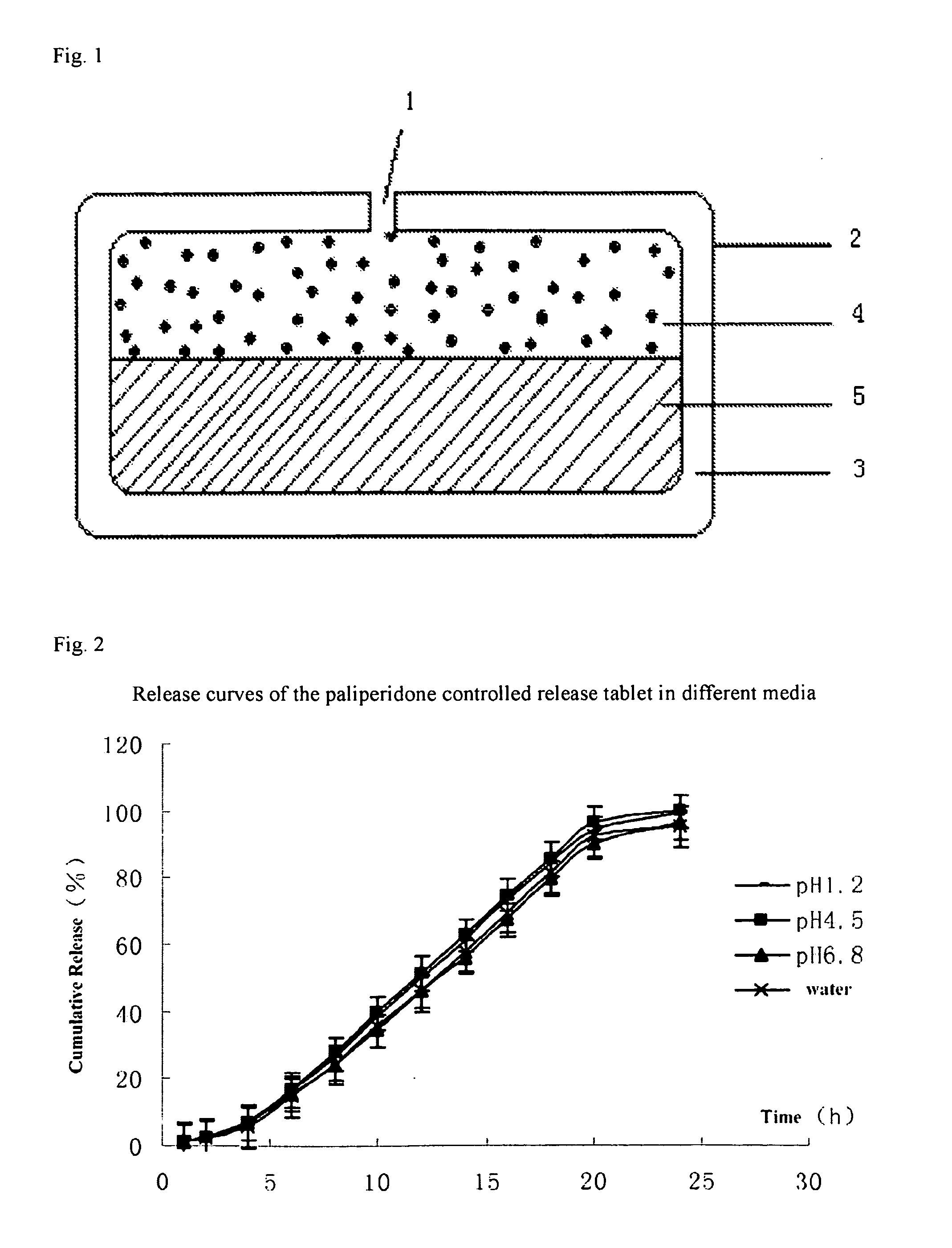
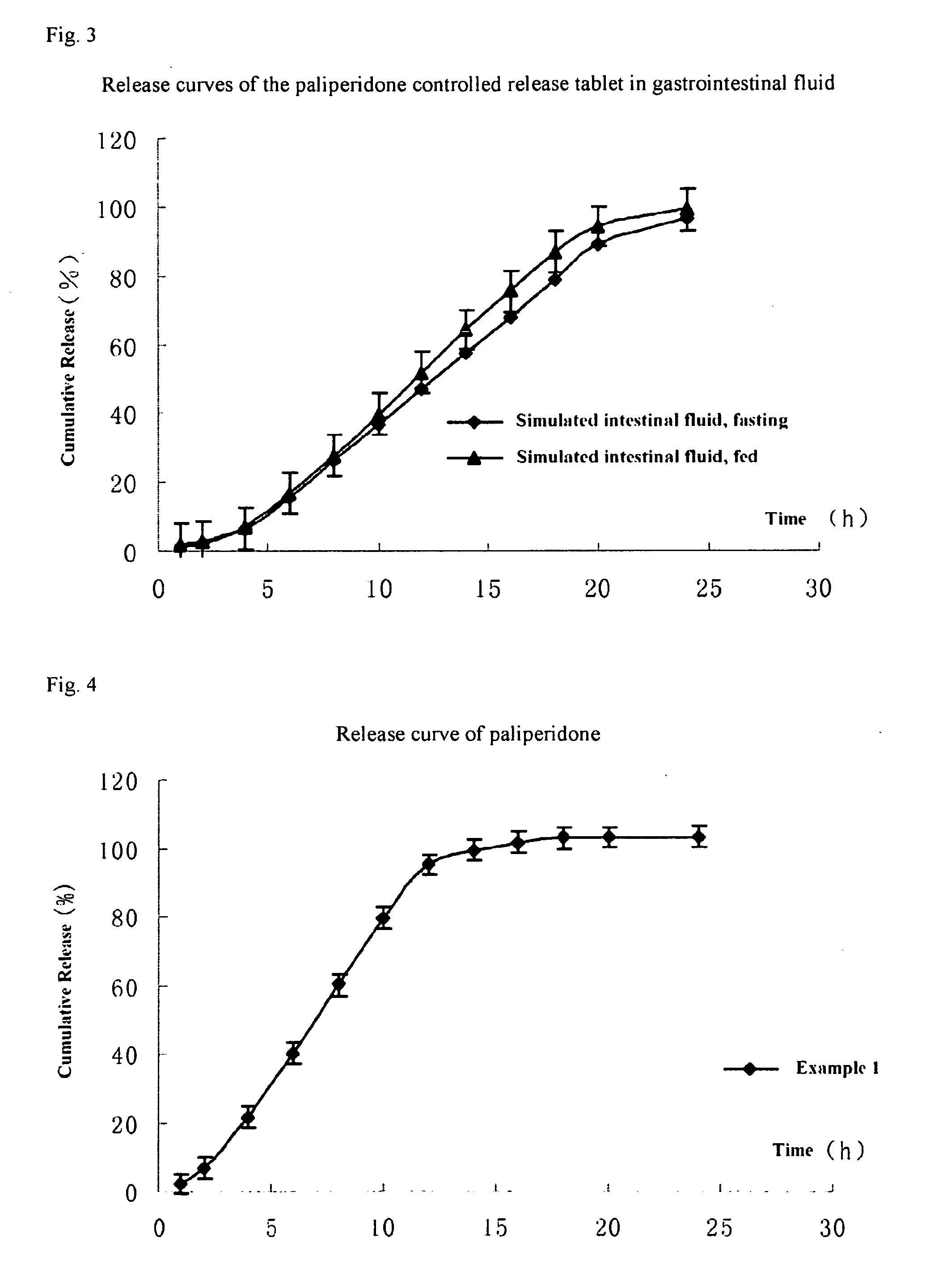
Paliperidone double-layered osmotic pump controlled release tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20120301547A1Increase release rateRapid onsetOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDrug release rateHydrophilic polymers
A paliperidone double-layered osmotic pump controlled release tablet and the preparation method thereof are disclosed. The double-layered osmotic pump controlled release tablet comprises a rigid membrane, a push layer, a drug layer, an isolation layer and an aesthetic coating, wherein the rigid membrane contains a semi-permeable polymer, a porogen and / or a plasticizer and has one or more drug release orifices on one end, the push layer comprises an expanding material, an osmotic agent, a binder, a colorant and a lubricant, the drug layer contains a pharmaceutically active ingredient, a hydrophilic polymer, an osmotic agent, a colorant, a lubricant and an antistatic agent, the isolation layer is located between the inner surface of the rigid membrane and the push layer, and contains a hydrophilic polymer. The paliperidone double-layered osmotic pump controlled release tablet shows an increasing drug release rate at early stage and keeps a constant drug release rate at later stage.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for preparing tiny mesoporous silica drug sustained-release material
InactiveCN104030296AFast release rateSilicaPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAspirinDrug release rate
The invention provides a method for preparing a tiny mesoporous silica drug sustained-release material and a tiny mesoporous hollow tubular silicon dioxide material obtained through the method. The drug loading capacity, calculated through a TG method, of the tiny mesoporous hollow tubular silicon dioxide material for aspirin model drugs is 15%, the sustained-release stage is the time of six hours of the initial stage of an experiment, and the drug releasing rate is high; after six hours, the stage of release balancing is achieved, and the amount of balanced release is 73.6%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method and application of Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere
InactiveCN105832699AGuarantee a high degree of decentralizationGood monodispersityOrganic active ingredientsMaterial nanotechnologyDrug release rateYolk
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing Fe2O3 nanoparticles by using a solvothermal method; under the condition that no surfactant is added and TEOS is used as a silicon source, preparing a Fe3O4@SiO2 composite microsphere with controllable morphology under mild conditions by using a combination of a template method and a hydrothermal method; corroding the Fe3O4@SiO2 composite microsphere with hydrochloric acid with a certain concentration so as to obtain a Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere; and carrying out reduction so as to prepare the Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere with superparamagnetism. The prepared Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere has a specific surface area of 173 m<2> / g and drug loading capacity of 139 mg / g; and with doxorubicin hydrochloride as a drug model, the Fe3O4@SiO2 yolk-eggshell-structured hollow composite microsphere has a drug release rate of as high as 68.4% within 72 h in a PBS buffer solution with a pH value of 7.4, so the composite microsphere presents good slow drug release performance.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical composition for external use
ActiveUS20120264742A1Good skin permeabilityImprove skinBiocideNervous disorderDrug release rateSkin permeability
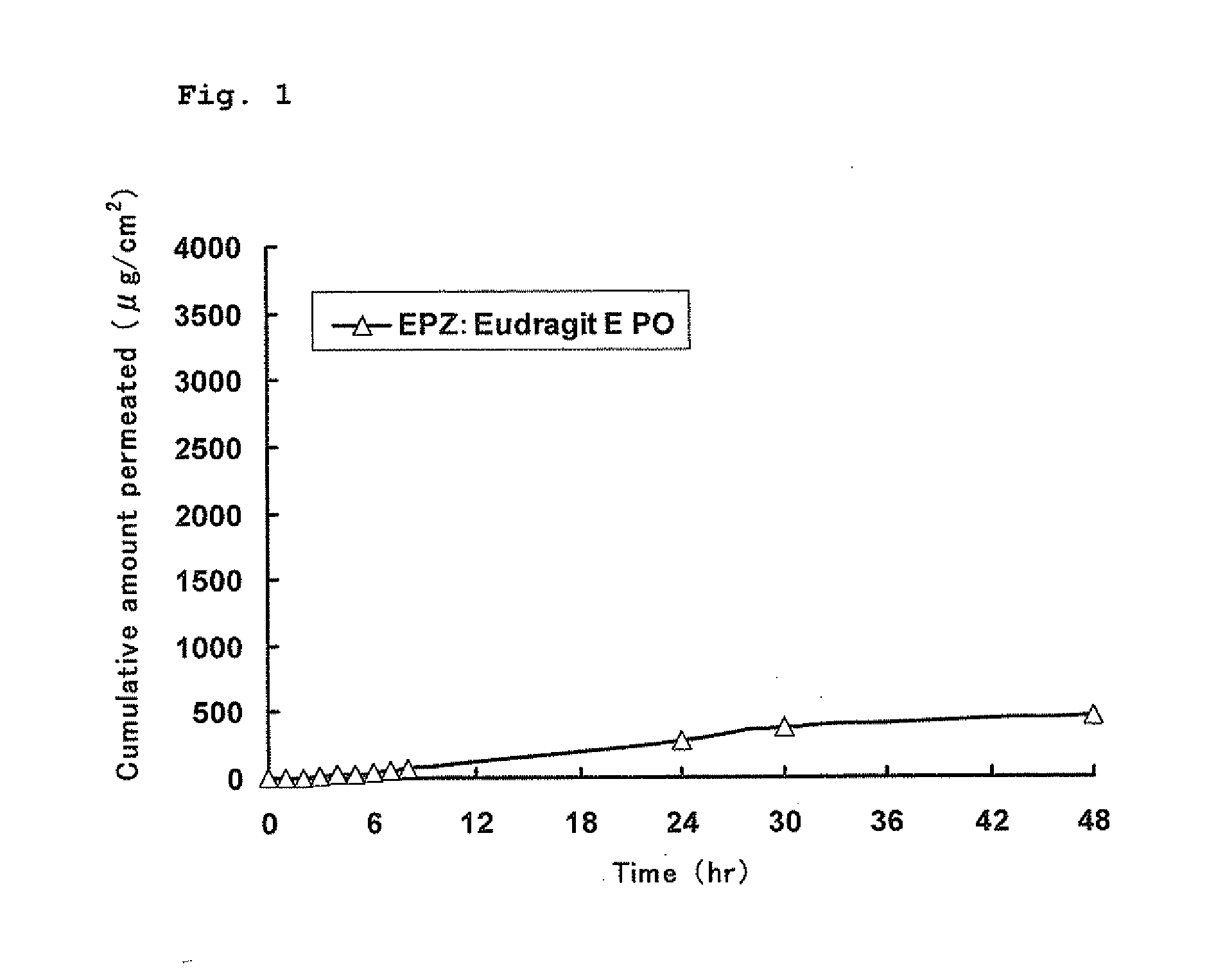
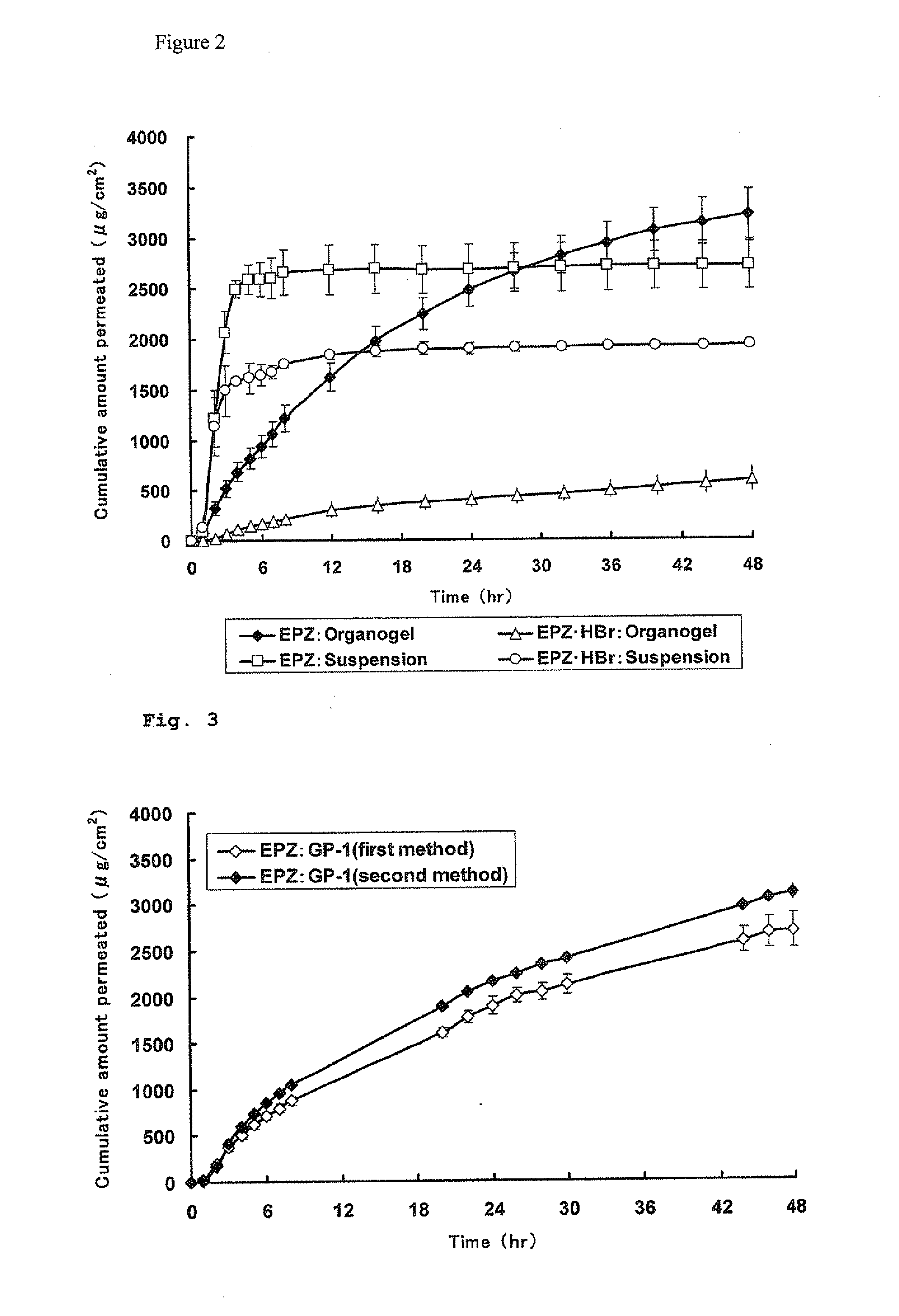
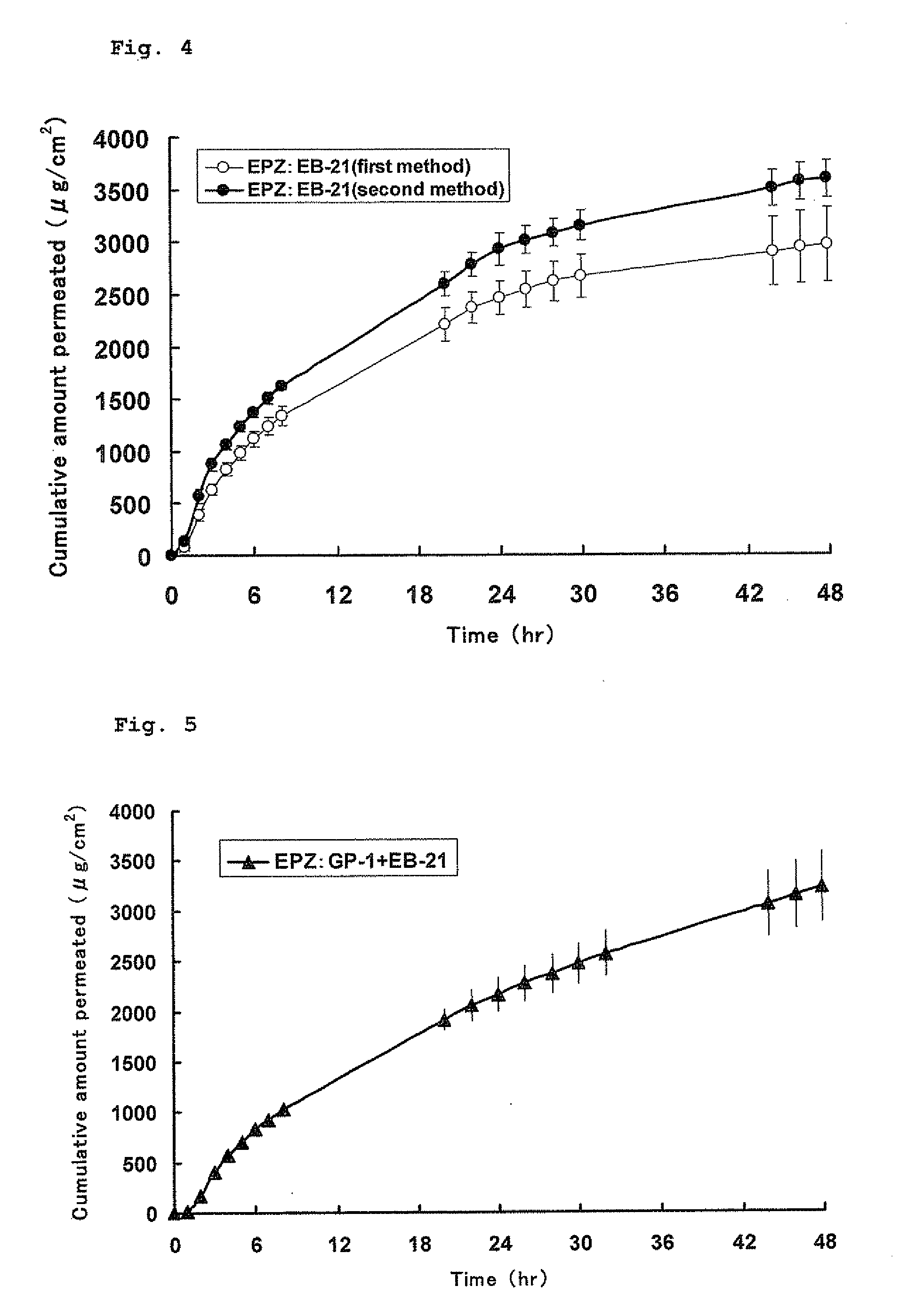
A pharmaceutical composition for external use which is an organogel containing a fatty acid ester and a glycerolglycerin fatty acid ester, in particular, a novel transdermally absorbable pharmaceutical composition for external use which has a drug such as non-narcotic analgesics as an active ingredient made in organogel form containing a drug such as non-narcotic analgesics as an active ingredient, a fatty acid ester and a glycerolglycerin fatty acid ester, and a method for producing the composition. The pharmaceutical composition significantly improves skin permeability of drugs such as non-narcotic analgesics and allows a sufficient amount of drug to permeate the skin sustainably. Moreover, since the pharmaceutical composition is in organogel form, it can be easily applied to a preparation in practice. In addition, the pharmaceutical composition can provide efficient use and the like of drugs due to a high drug release rate and therefore is highly useful.
Owner:NIHON UNIVERSITY +1
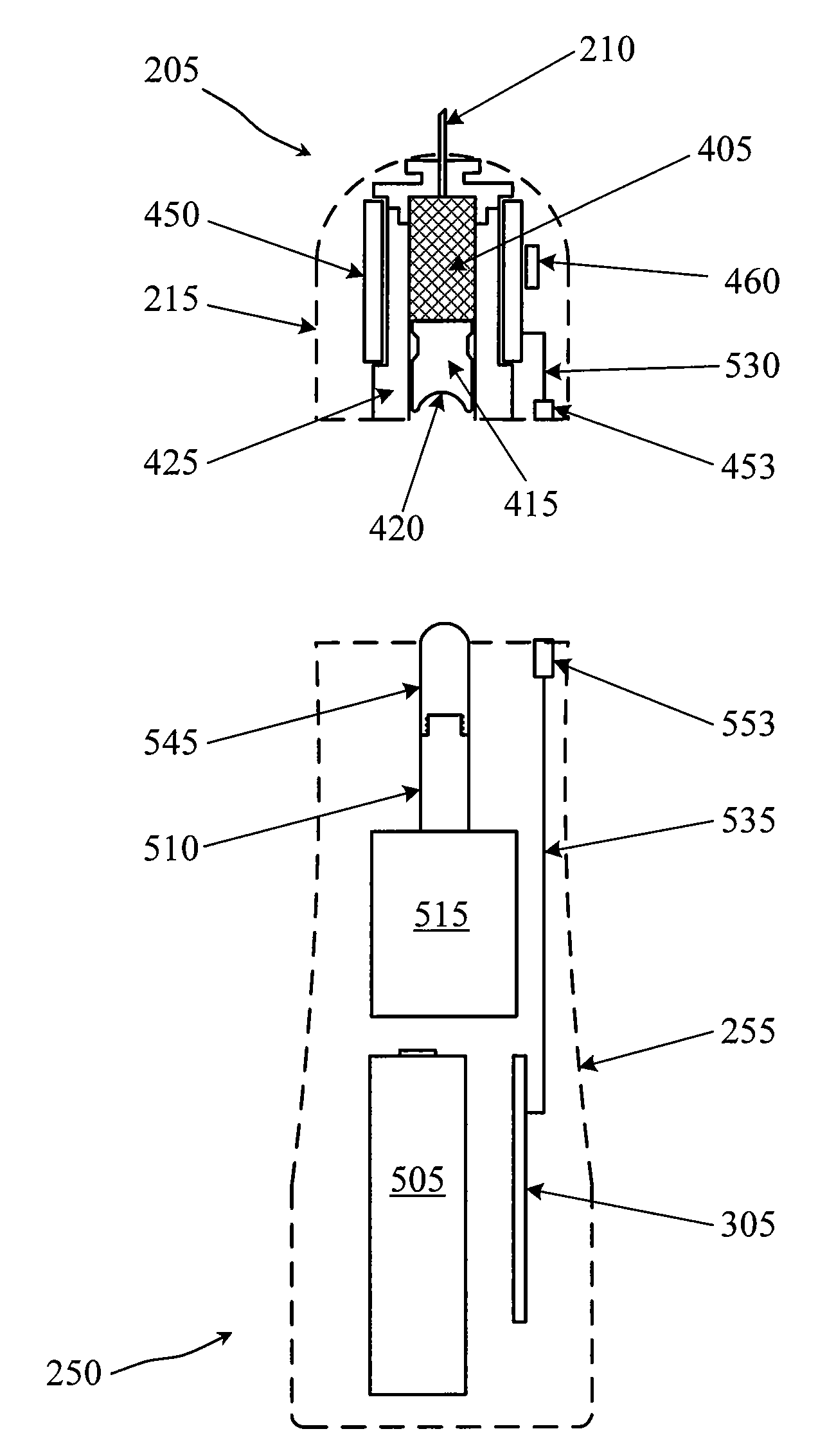
Method of controlling a drug release rate
InactiveUS7666462B2Eliminate needEasy doseSurgeryVacuum evaporation coatingDrug release rateMedicine
A method of controlling the drug release rate of a drug coated endovascular stent by depositing a drug material layer on the stent and then modifying the drug material using gas cluster ion beam irradiation to create a carbon matrix with interstices containing the original drug. The rate at which the drug elutes through the interstices can be controlled by processing parameters. Multiple layers may be employed to create time varying release rates.
Owner:EXOGENESIS CORP
Preparation and applications of novel alkyl cage silsesquioxane nanometer hybrid
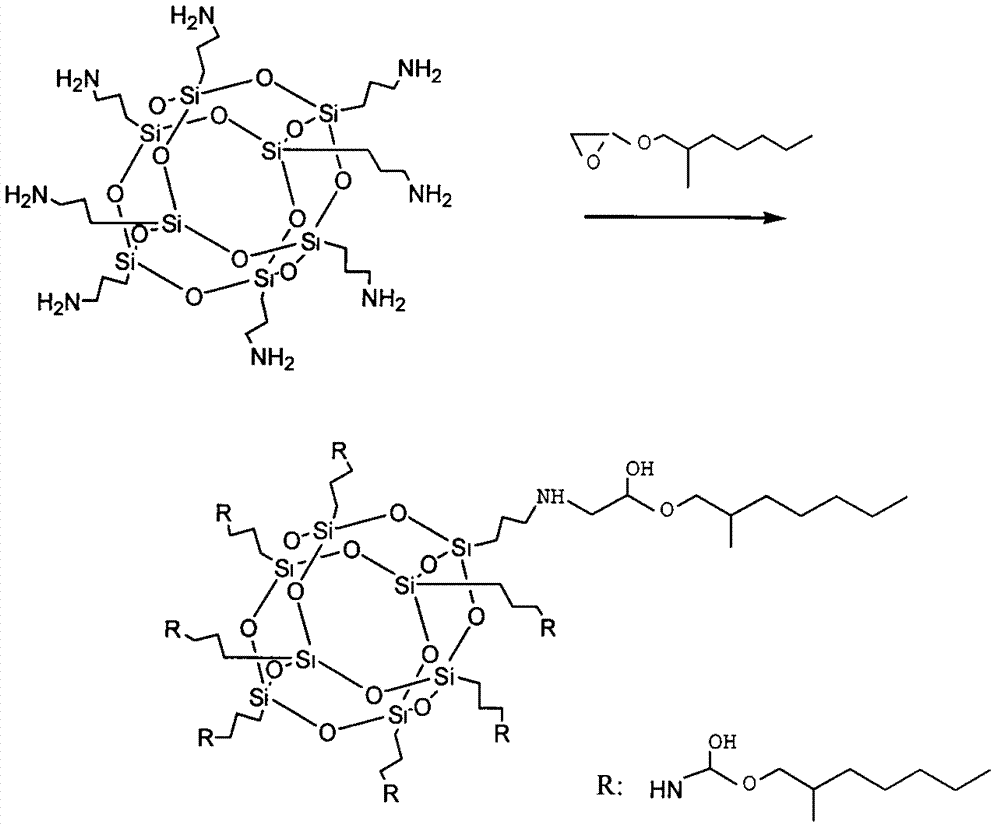
InactiveCN103087088AImprove hydrophobicityGood for load rateSilicon organic compoundsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrug release rateAlkyl transfer
The invention relates to a novel alkylation cage silsesquioxane nanometer hybrid prepared in an alkaline solution, wherein a diameter of hybrid molecules is 1-2 nm, a center of the molecule has a cubic cage type structure, eight vertexes are connected with a product prepared through carrying out ring opening addition on propylamino and 2-ethylhexyl glycidyl ether, and the hybrid has strong hydrophobicity. According to the present invention, the hybrid is dispersed in a 1.5 w% sodium alginate aqueous solution through an emulsification and high speed stirring method, and the obtained solution is added to a 3% calcium chloride aqueous solution in a dropwise manner to prepare a nanometer hybrid modified sodium alginate hydrogel, wherein the obtained modified hydrogel has characteristics of enhanced mechanical strength and enhanced stability compared to the pure sodium alginate hydrogel, and hydrophobic drug embedding rate is increased and drug release rate is slowed when the obtained modified hydrogel is used as a drug carrier.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Tetrodotoxin quick-release pellet preparation and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN106063780AHigh rate of drug useGood content uniformityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDrug release rateOral medication
The invention discloses a tetrodotoxin quick-release pellet preparation and its preparation method and use and relates to the field of a medicinal preparation technology and use. The tetrodotoxin quick-release pellet preparation is suitable for oral administration and utilizes a blank pellet core as a carrier and a tetrodotoxin aqueous solution containing a cosolvent and a binder as a drug feeding solution. A weight ratio of the tetrodotoxin to the pellet core is 0.0025%-0.3% and an oral dosage of the tetrodotoxin is less than or equal to 300 micrograms. The tetrodotoxin quick-release pellet preparation has the advantages of high superimpose rate, good content uniformity, fast drug release rate and fast pain easing. The tetrodotoxin quick-release pellet preparation has the characteristics of good clinical use compliance and high safety. The blank pellet core fluidized bed-based drug superimpose method is suitable for preparation of a very low specification tetrodotoxin oral preparation.
Owner:XIAMEN ZHAOYANG BIOLOGICAL ENG
Huperzine A mono-layer osmotic pump controlled release tablets
InactiveCN101485640AStable release rateConstant plasma concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderWeight gainDrug release rate
The invention discloses a huperzine A single-layer osmotic pump controlled-release tablet. The controlled-release tablet comprises a tablet core containing huperzine A and pharmaceutic adjuvants in effective dosage, and a semipermeable coating membrane coating the tablet core, wherein the coating membrane is provided with a drug release hole. The controlled-release tablet is characterized in that: the tablet core contains the following components in percentage by weight: 0.01 to 1.0 percent of huperzine A, 1.0 to 10 percent of retarder and 1.0 to 40 percent of permeation enhancer; and the weight ratio of polyethylene glycol 6,000 contained in the coating liquid to cellulose acetate is (0.05-0.25):1, and the weight gain of the coating membrane against the weight of the tablet core is between 5 and 25 percent. The controlled-release tablet has the advantages that the drug release rate is stable, the blood consentration of patients is relatively constant after the patients take the controlled-release tablet, and the drug taking frequency of the patients is reduced, so that the controlled-release tablet is a novel drug formulation which is safer, more effective, stable, controllable and convenient for application in clinically treating senile dementia.
Owner:普尔药物科技开发(深圳)有限公司
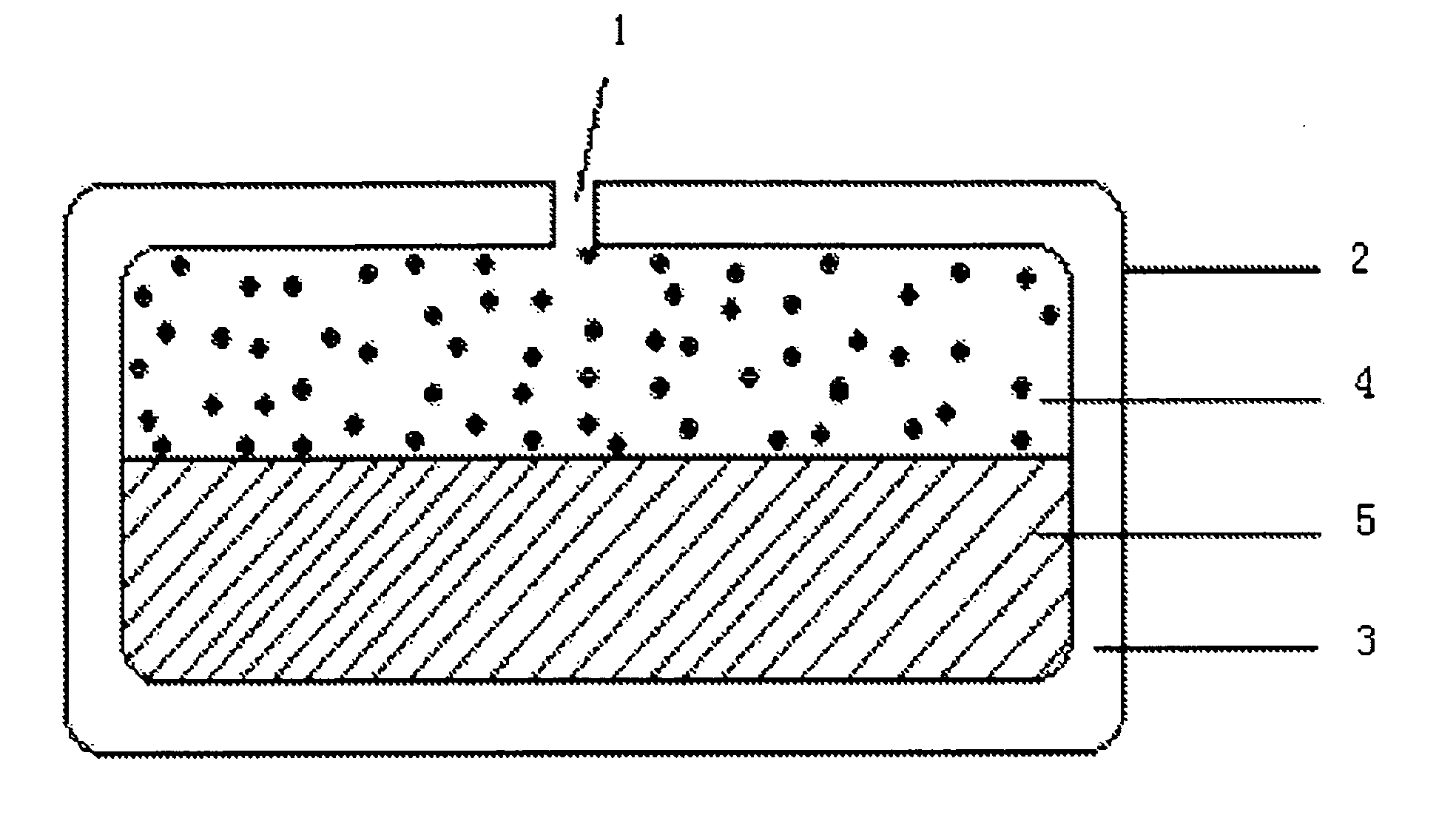
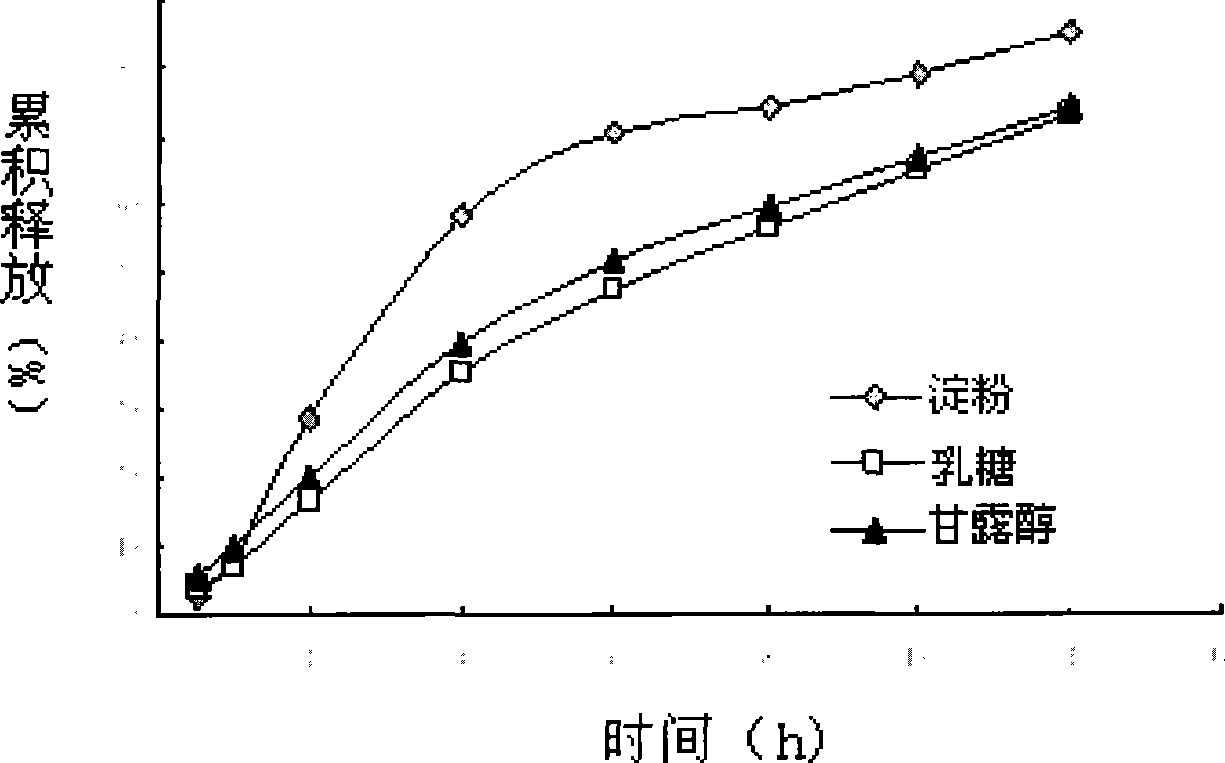
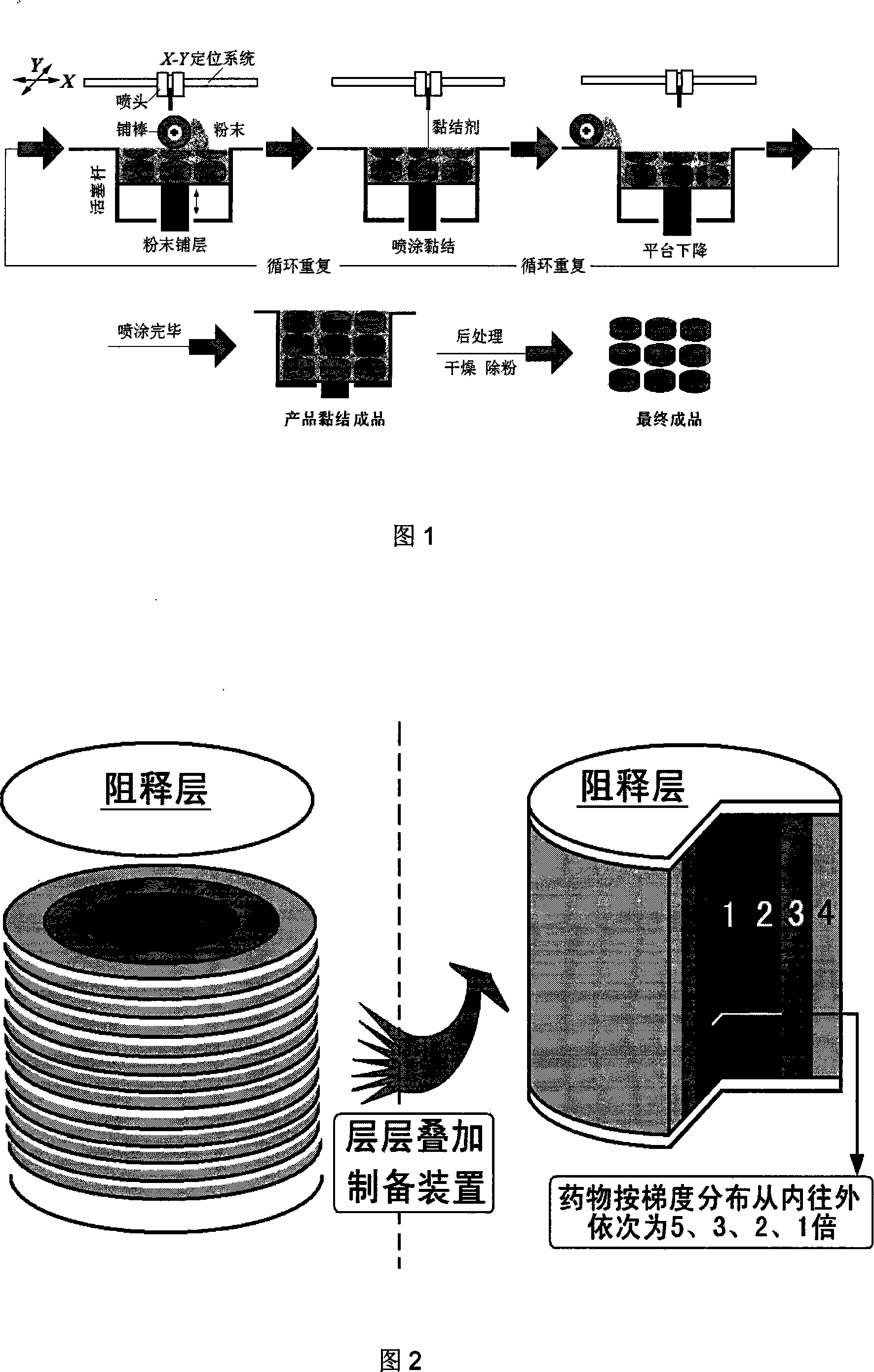
Medicine gradient zero level implantation controlled-release drug administration device and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101209240ADiffusion release distance extendedConstant release ratePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsControlled releaseDrug release rate
The invention relates to a drug gradient zero-grade implantation controlled release drug delivery device and the preparation method thereof; the drug delivery device takes the controlled release polymer as a frame, the top surface and the bottom surface are formed by bonding of the insoluble polymer, that is, the release resistant materials, and the middle drug is radially distributed according to the gradient. The axial two sides of the drug deliver system are sealed by the polymer, and then the drug is released radially and two-dimensionally; the radial drug concentration difference is obtained by the change of the times of printing and spraying the drug-carrying adhesives, the peripheral drug release area is big, the spraying times are less, and the drug concentration is low; the drug release area of the central area is small, the spraying times are more, and the drug concentration is high. The drug concentration takes the gradient distribution and the drug release rate is constant. The technique has simple preparation, high degree of automation and good reproducibility.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
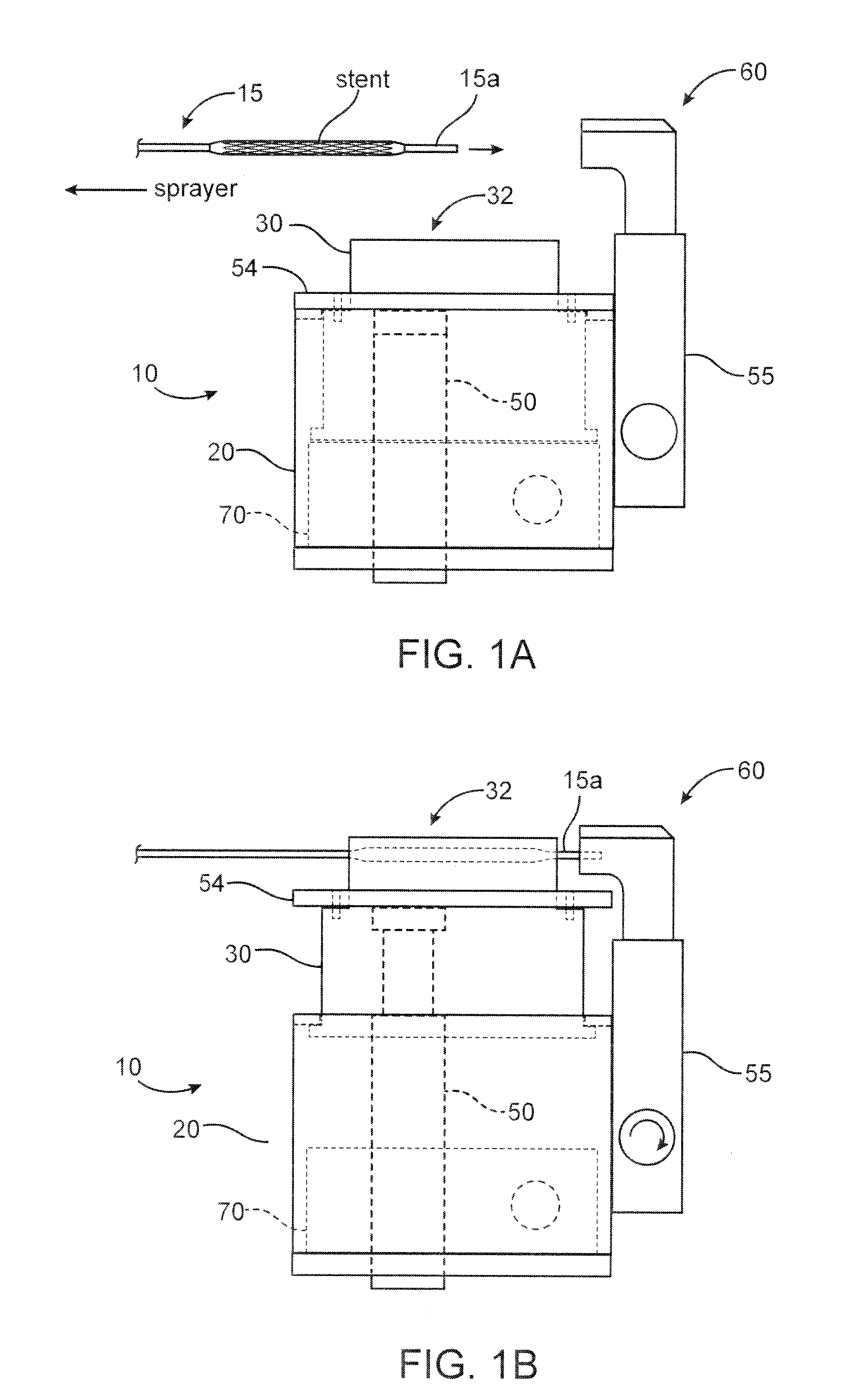
Dryers For Removing Solvent From A Drug-Eluting Coating Applied To Medical Devices
InactiveUS20130071549A1Maximizing in-process drying efficiencyMaximizing uniformityPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesDrug release rateSolvent
A coating device for coating a medical device with a drug-eluting material uses an in-process drying station between coats to improve a drug release profile. The drying station includes a dryer having a telescoping plenum which provides a drying chamber for the stent or scaffold to reside while a heated gas is passed over the stent / scaffold. The drying chamber improves efficiency in drying, predictability or drug release rate, uniformity of coating material properties lengthwise over the stent / scaffold and provides a platform that can effectively support stents that are over 40 mm in length.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
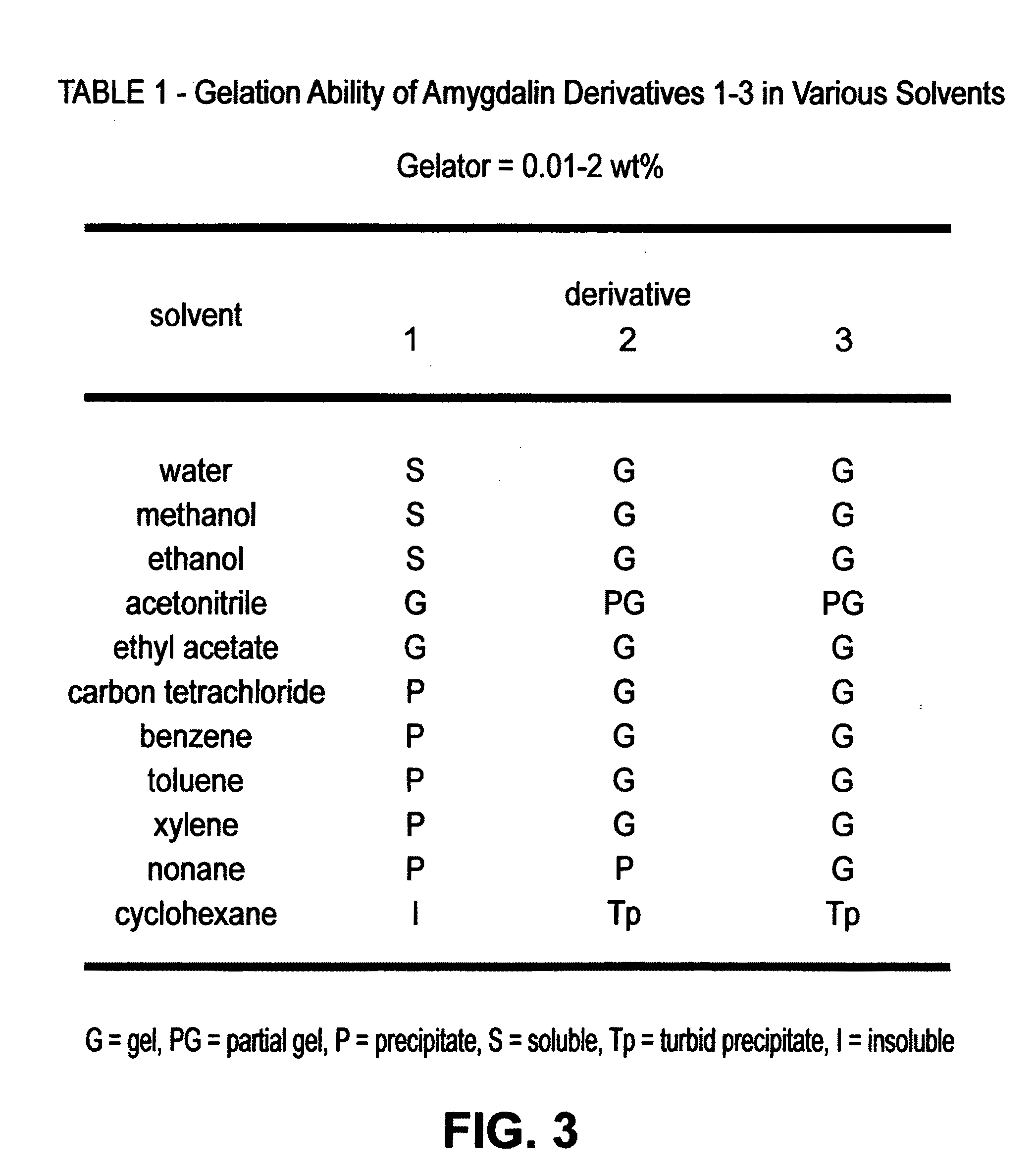
Method for preparing hydro/organo gelators from disaccharide sugars by biocatalysis and their use in enzyme-triggered drug delivery
ActiveUS20100129451A1Avoid disadvantagesHigh yieldCosmetic preparationsBiocideDrug release rateDelivery vehicle
A method for preparing hydro / organo gelators from disaccharide sugars by biocatalysis and their use in enzyme-triggered drug delivery. Controlled delivery of an anti-inflammatory, chemopreventive drug is achieved by an enzyme-triggered drug release mechanism via degradation of encapsulated hydrogels. The hydro- and organo-gelators are synthesized in high yields from renewable resources by using a regioselective enzyme catalysis and a known chemopreventive and anti-inflammatory drug, curcumin, is encapsulated in the gel matrix and released by enzyme triggered delivery. The release of the drug occurs at the physiological temperature and control of the drug release rate is achieved by manipulating the enzyme concentration and temperature. The by-products formed after the gel degradation clearly demonstrated the site specificity of degradation of the gelator by enzyme catalysis. The present invention has applications in developing cost effective, controlled drug delivery vehicles from renewable resources, with a potential impact on pharmaceutical research and molecular design and delivery strategies.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
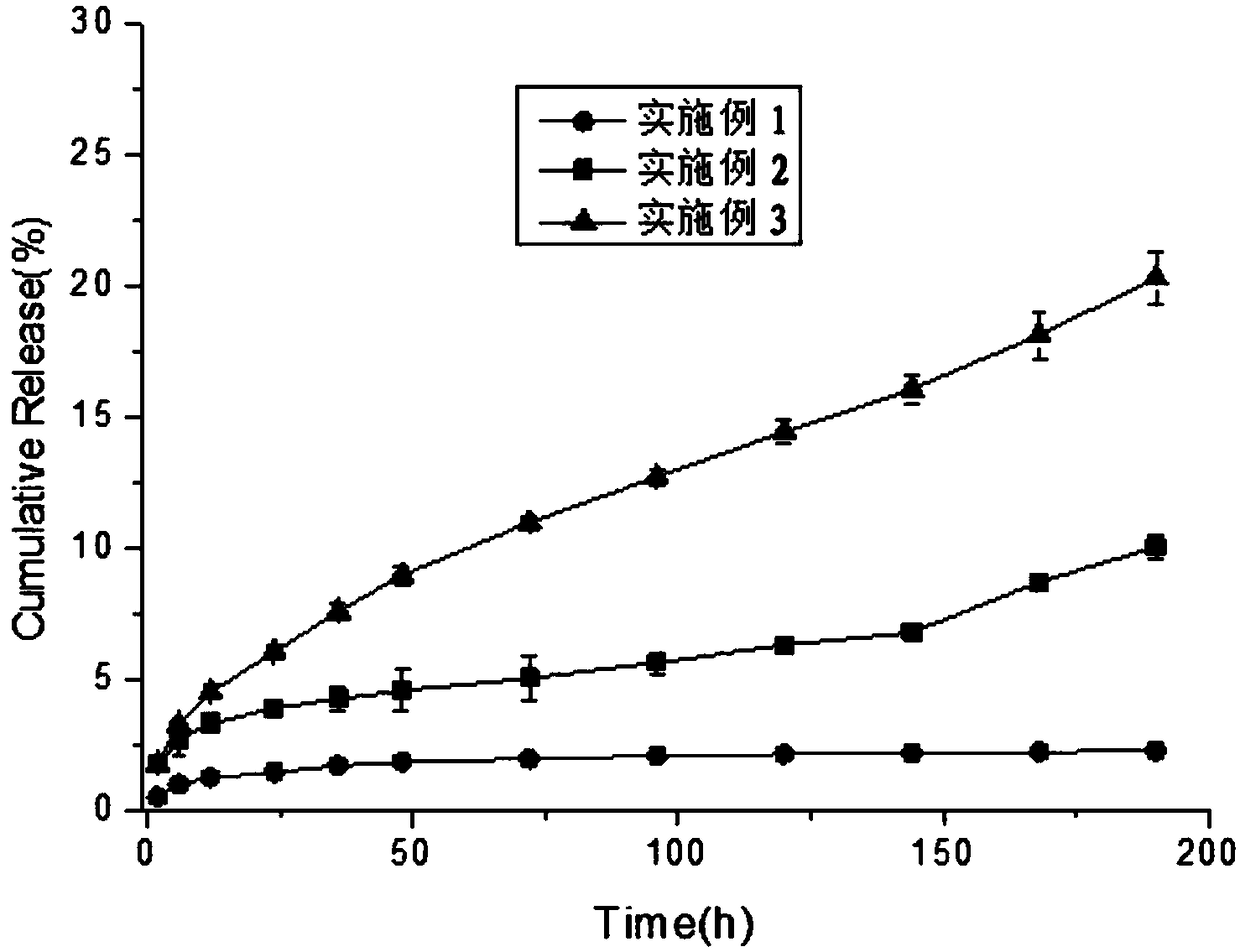
Doxorubicin hydrochloride light-controlled sustained-release liquid crystal gel preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108309927ALow viscosityImprove liquidityOrganic active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyGel preparationDrug release rate
The invention discloses a doxorubicin hydrochloride light-controlled sustained-release liquid crystal gel preparation and a preparation method thereof. The light-controlled sustained-release liquid crystal gel preparation is prepared from 15-40 wt% of phospholipid, 60-70 wt% of glyceride, 1-20 wt% of a cosolvent, 0.01-2 wt% of doxorubicin hydrochloride and 0.001-0.2 wt% of a photosensitizer. The doxorubicin hydrochloride light-controlled sustained-release liquid crystal gel preparation has the advantages of low viscosity, good fluidity, easiness in injection, rapidness in formation of the liquid crystal gel after being injected into or around a tumor or being placed in a post-operative tumor cavity, and realization of in-situ slow release of doxorubicin hydrochloride; and lights cause phase change of the liquid crystal gel and increase the drug release rate, and the preparation prolongs the drug action time, reduces the administration frequency, reduces the toxic and side effects of the drug, releases the drug as needed by adjusting the release of the drug through adjusting the illumination frequency or time according to the tumor pathological conditions of a patient, and greatly improves the bioavailability of the drug.
Owner:武汉百纳礼康生物制药有限公司
Method of Delivering A Rate And Temperature - Dependent Substance Into The Eye
A method of injecting a mixture into an eye includes: providing the mixture in a dispensing chamber with an air gap located between the mixture and an interior surface of a dispensing chamber housing, when the mixture and dispensing chamber housing are near room temperature; bringing the dispensing chamber housing and mixture to a temperature range, other than near room temperature, at which the mixture expands and is in a more liquid state; maintaining air in a needle after the mixture expands and prior to an injection; selecting a drug release rate; and injecting the mixture so as to form a shape with a surface area that results in the selected drug release rate.
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
Durable biocompatible controlled drug release polymeric coatings for medical devices
Disclosed herein are biocompatible durable controlled drug releasing polymeric coatings for medical devices. The drug release rates of the polymers are controlled by adjusting monomer ratios and glass transition temperatures Tgs. The polymers are durable; they do not delaminate from the coated medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com