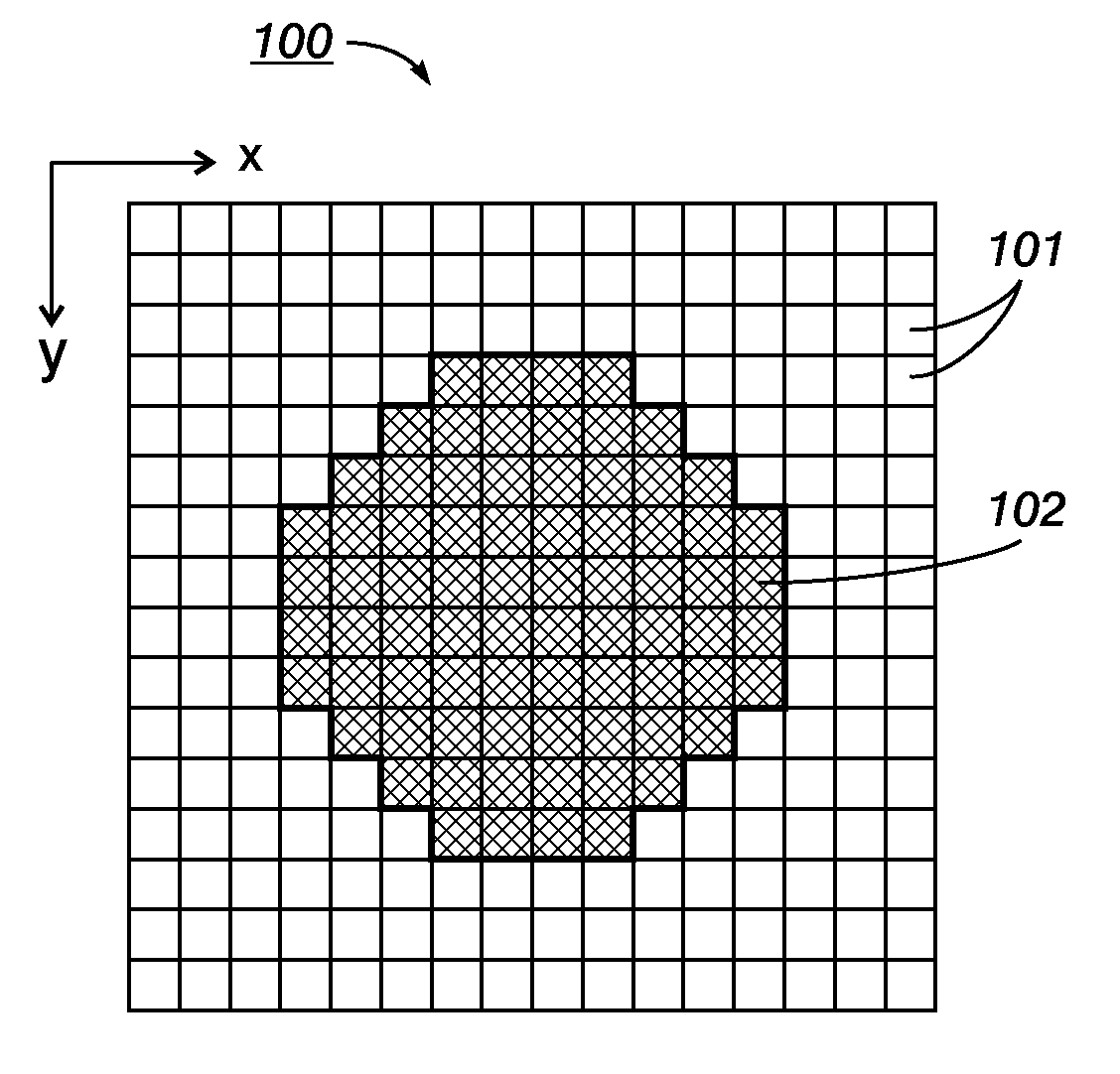
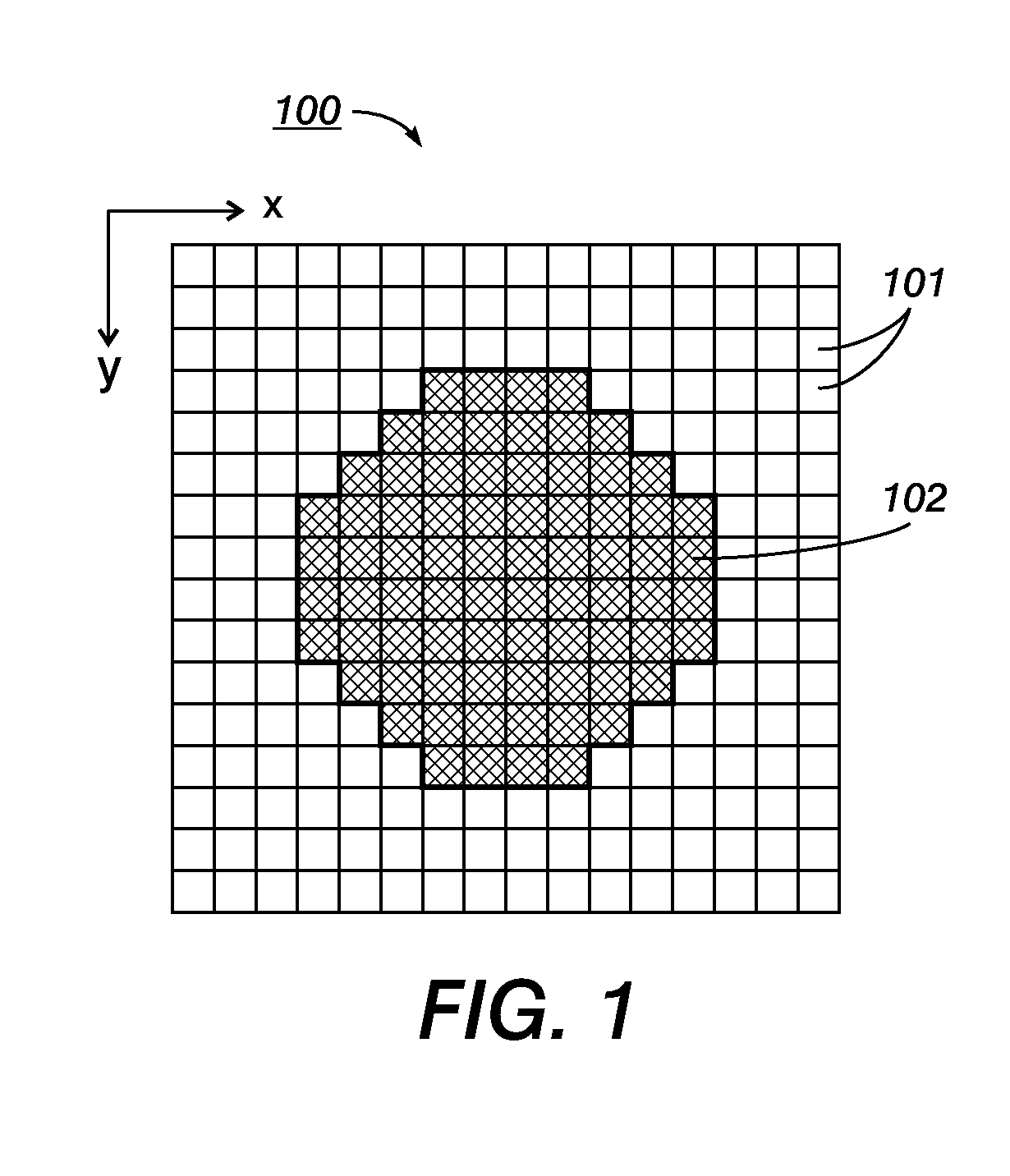
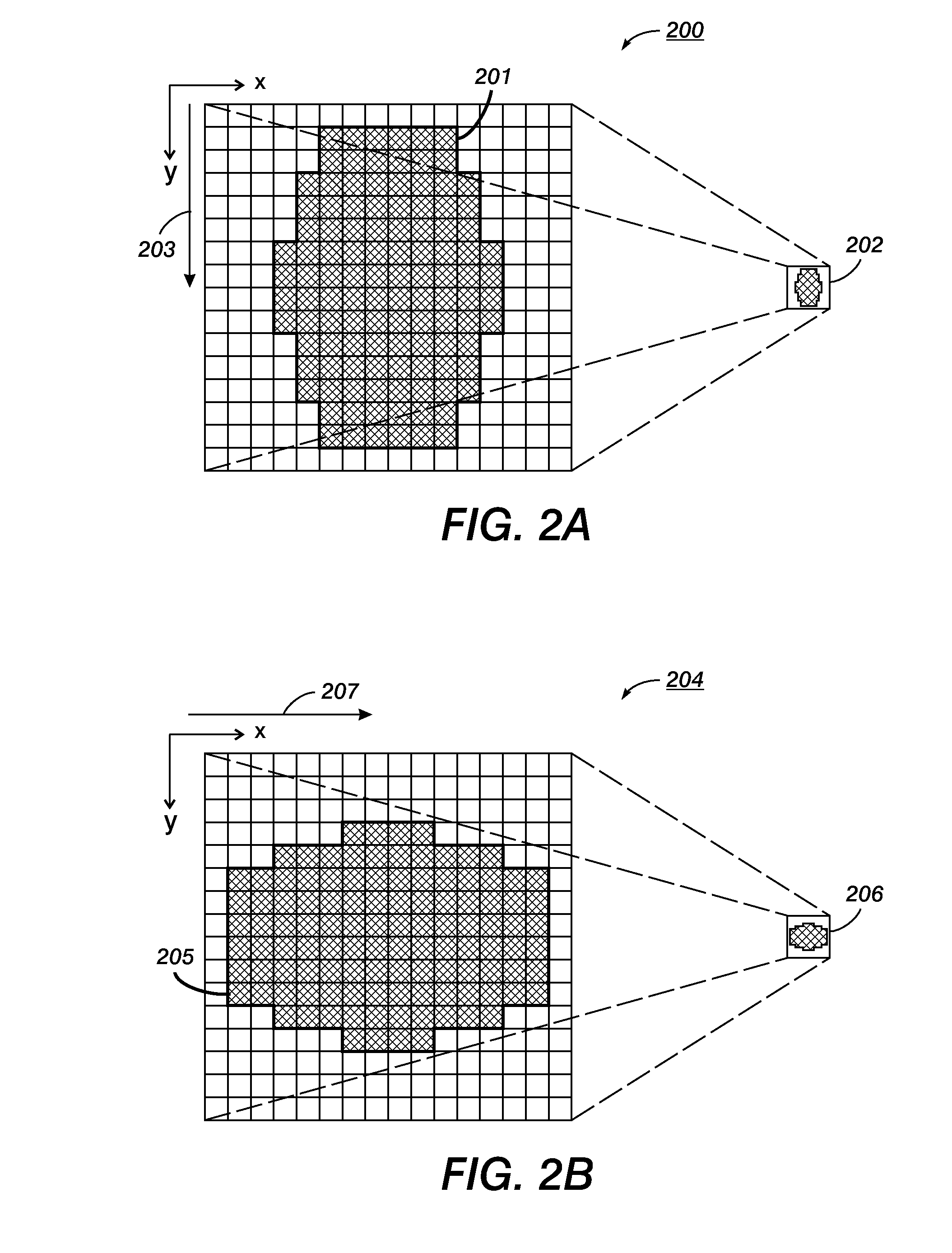
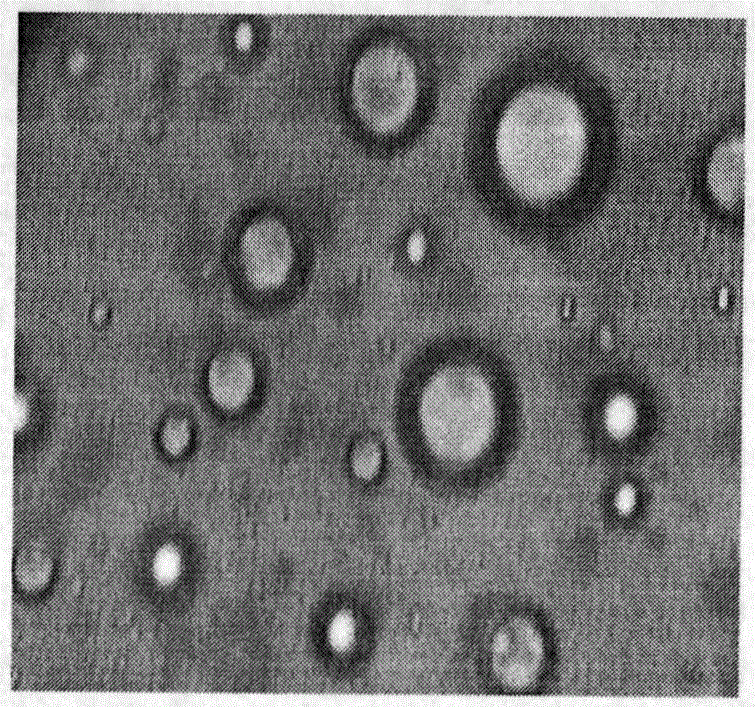
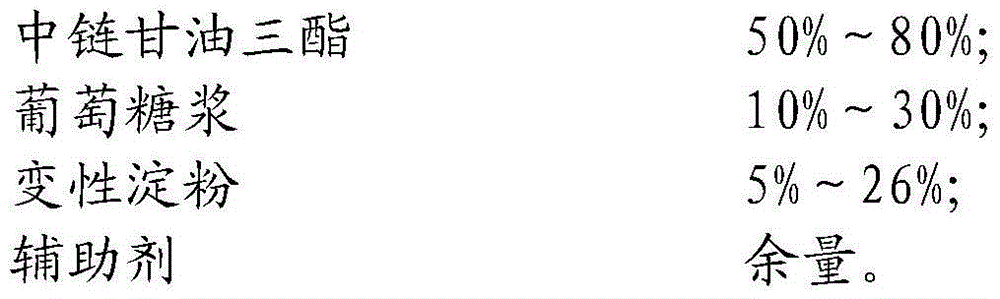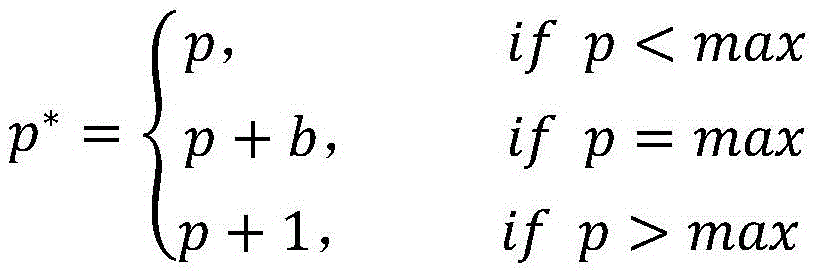Patents
Literature
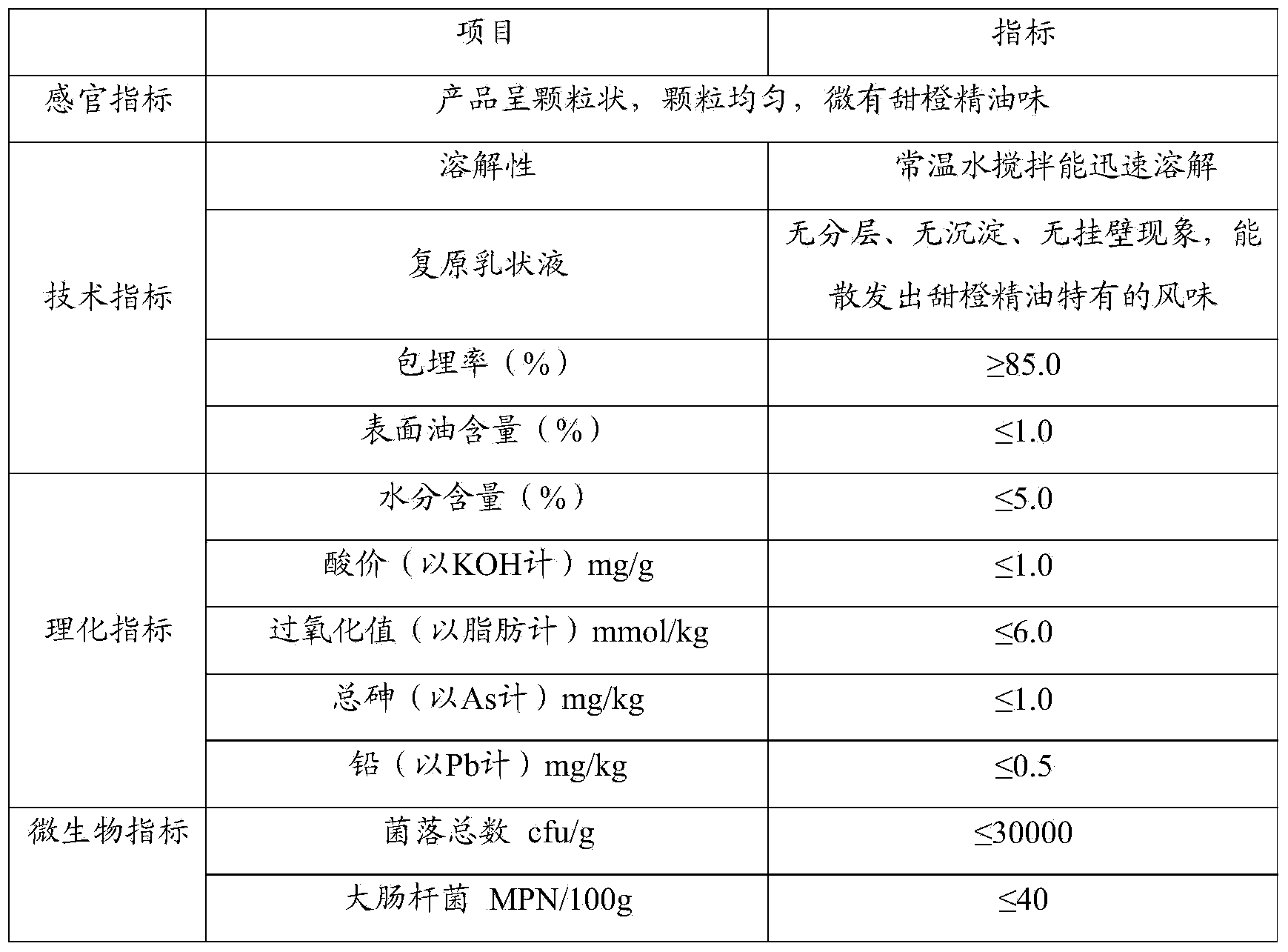
399 results about "Embedding rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
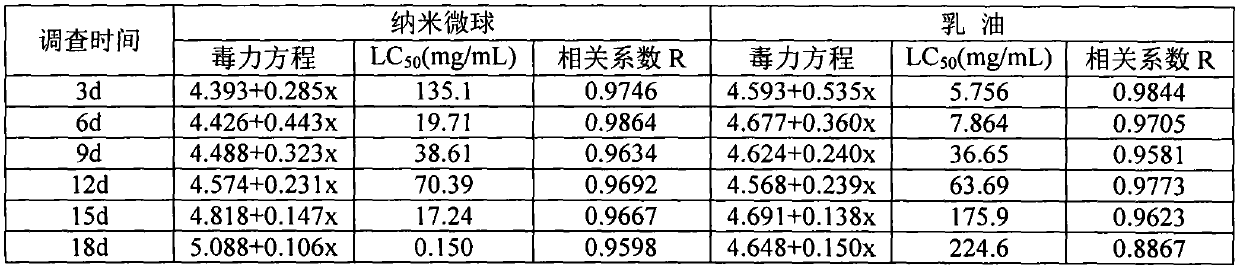
Method for preparing mono-disperse microemulsion, liposome and microsphere based on microfluidic technology
InactiveCN102068409ABest size rangeHigh activityImmobilised enzymesGranular deliveryDispersion stabilityOil phase
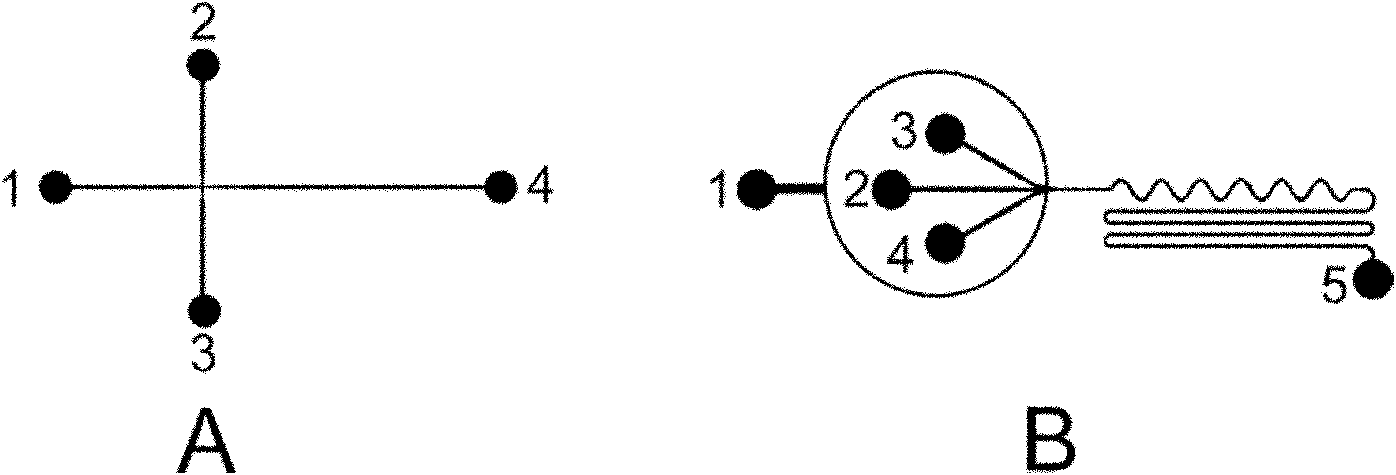
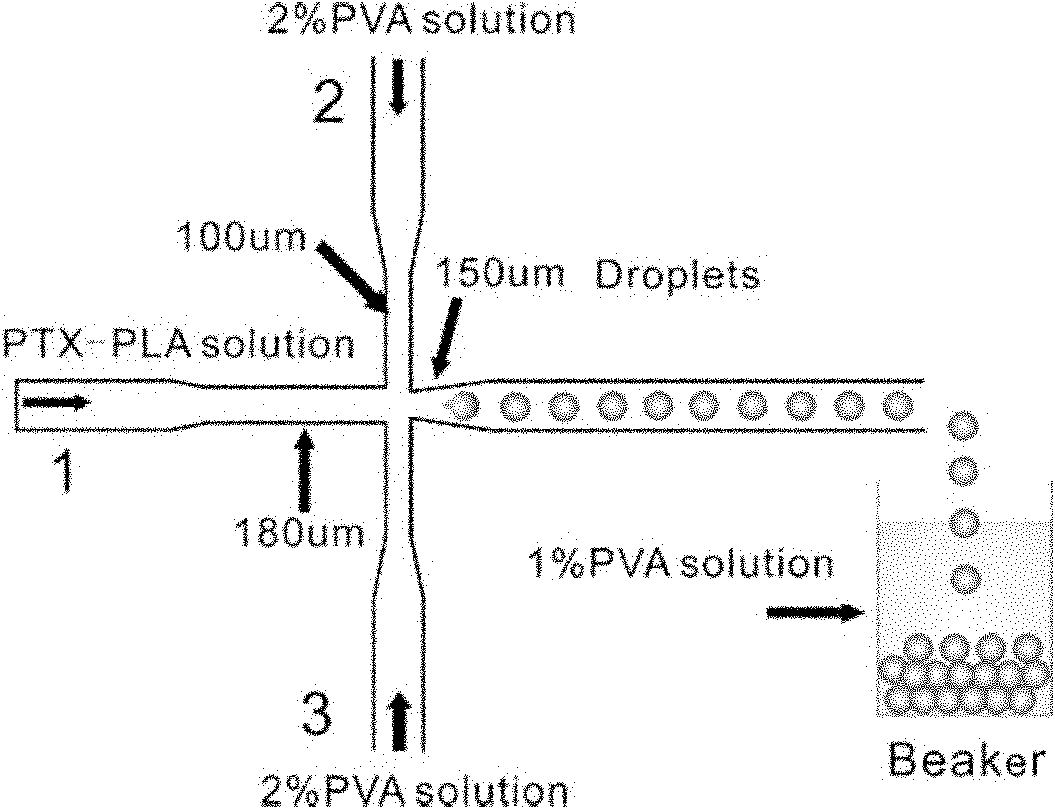
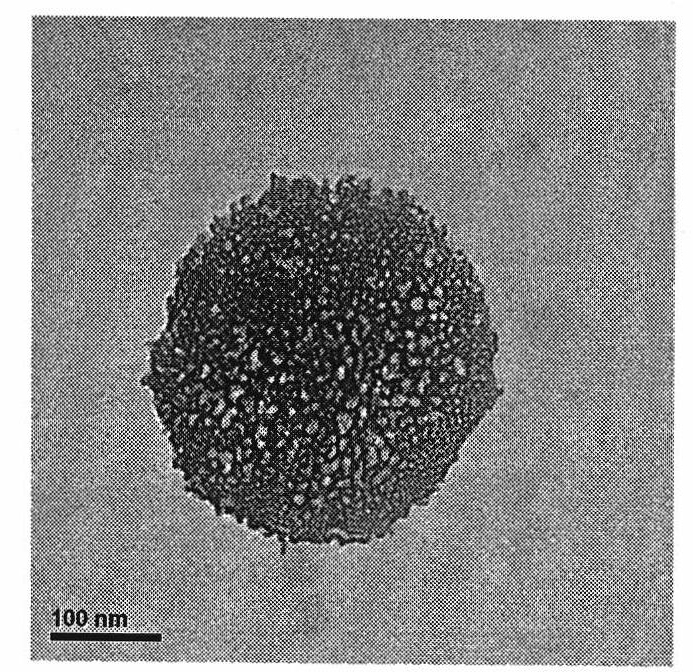
The invention discloses a method for preparing mono-disperse microemulsion, liposome and microspheres based on a microfluidic technology. The method comprises the following steps: taking aqueous solution (or oily solution) of a hydrophilic medicine (or a lipid-soluble medicine) as a disperse phase; taking an oil phase (or an aqueous phase) as a continuous phase; and respectively conveying the disperse phase and the continuous phase into corresponding micro-channels of a microfluidic chip device, shearing the phases into mono-disperse liquid drops of the encapsulated medicine, then curing the liquid drops by a certain curing method, and finally obtaining the medicine-carrying liposome, microspheres or the biodegradable microspheres with uniform size and dispersion stability. Under an optimum condition, the diameter distribution coefficients of the microemulsion and the microspheres can be less than 5%, and the diameter is 10-500microns. By utilizing the method, the problems such as uneven size, low embedding rate, poor dispersibility, poor targeting property, low bioavailability, low bioactivity of enzyme and cells, immune suppression and the like of the medicine-carrying microemulsion, the liposome and the microspheres prepared by the traditional ultrasonic method, agitation emulsification method and film hydration-dispersion method are solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of essential oil microcapsule
ActiveCN103861537AWell mixedOvercome volatilityEssential-oils/perfumesMicroballoon preparationSolubilityEmbedding rate
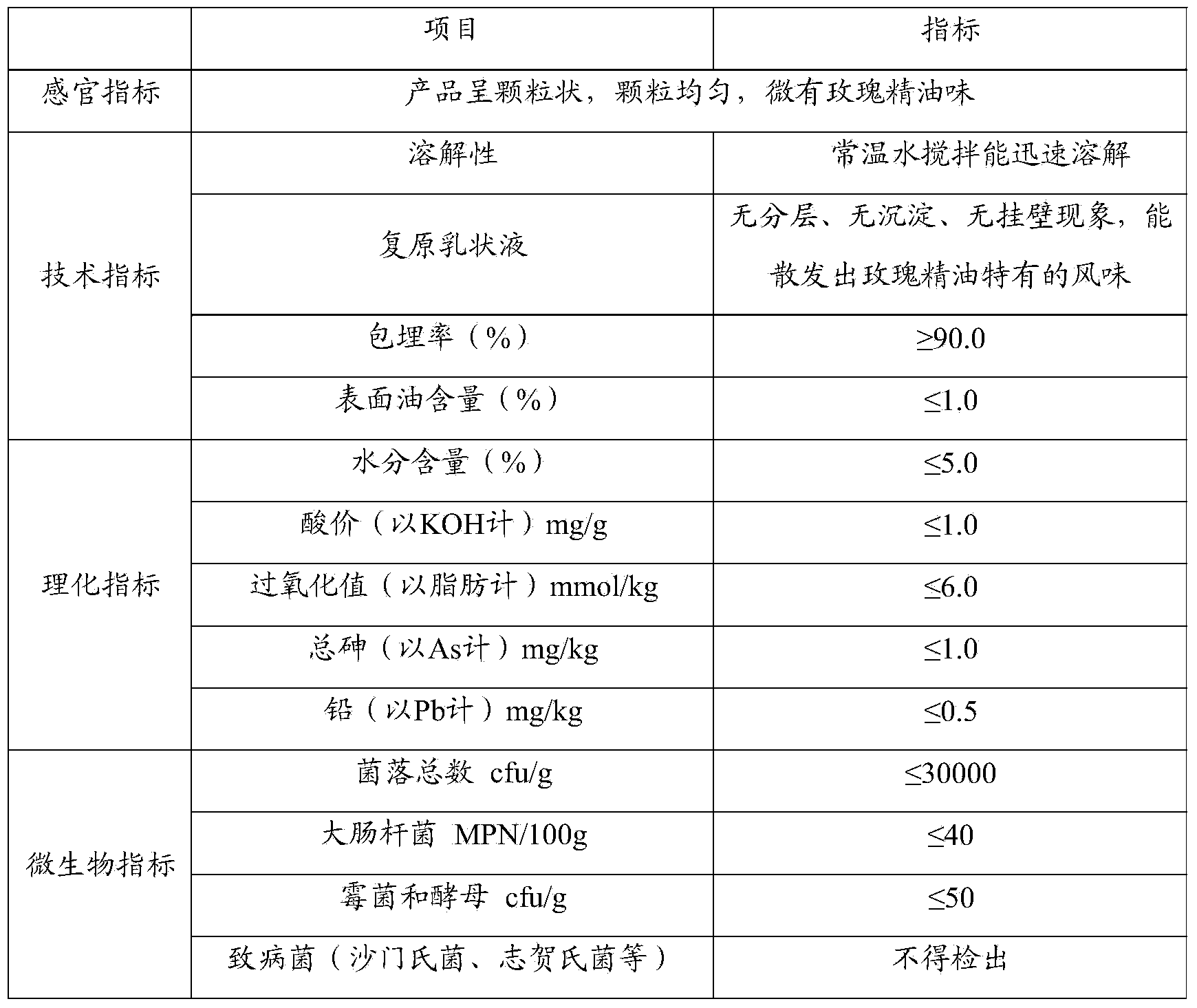
The invention discloses a preparation method of an essential oil microcapsule. The preparation method of the essential oil microcapsule comprises the following steps: preparing a wall material water phase, preparing a core material oil phase, mixing the two phases, emulsifying and homogenizing, carrying out spray drying through a fluidized bed and screening materials. Through the method, the defects of volatilization and loss of the essential oil which are easily caused due to high spraying temperature in a conventional spray drying method can be avoided; a whole preparation process can be carried out at low temperature, thus retaining components of the essential oil maximally; the prepared essential oil microcapsule is high in embedding rate, low in water content, good in solubility and durable in fragrance retention, so that the application of the essential oil is improved and expanded; meanwhile, a novel technical manner guidance is provided for preparation and development of other microcapsule products prepared from thermosensitive core materials. The essential oil microcapsule prepared by the preparation method can be widely applied in the fields such as food, tobacco and household chemicals.
Owner:AGRI PRODS PROCESSING RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
High-content medium chain triglyceride powdered oil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104054849AImprove organizational structureGood appearanceEdible oils/fatsSolubilityOil and grease
The invention relates to high-content medium chain triglyceride powdered oil which is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 50%-80% of medium chain triglyceride, 10%-30% of grape syrup, 5%-26% of modified starch and the balance of auxiliary agents. The high-content medium chain triglyceride powdered oil disclosed by the invention is obtained by carrying out mirco-encapsulated embedding on medium chain triglyceride and achieving an oil powdered effect by adopting advanced process technologies, namely high-pressure homogenized emulsification, spray drying and the like, through formula design and process optimization, achieves the oil content as high as 80% and the oil embedding rate more than 98%, and has the advantages of good solubility and stability and convenience for transportation and storage. The product can be applied to multiple foods and health-care foods and is used for enhancing the nutrition value of the foods, improving the tissue structures, appearance quality and palatability of the foods and prolonging the quality guarantee period of a product.
Owner:上海英莱腾医药研究有限公司
Flaxseed oil microcapsule and production method thereof
ActiveCN102934703AFit for consumptionImprove stabilityFood shapingEdible oils/fatsSodium CaseinateOil phase
The invention discloses a flaxseed oil microcapsule and a production method thereof. The core material of the flaxseed oil microcapsule is flaxseed oil, and the wall material is made of modified starch, maltodextrin and sodium caseinate. The production method comprises steps of adding the modified starch, the maltodextrin and the sodium caseinate to hot water with high-speed stirring until the the modified starch, the maltodextrin and the sodium caseinate are dissolved completely and forming a water phase; weighing and taking the flaxseed oil, adding vitamin E, rosemary and tea polyphenol step by step, stirring the mixture until the mixture is dissolved completely and forming an oil phase; conducting high-speed cutting for the obtained water phase by using a cutting machine, adding the obtained oil phase slowly and obtaining an emulsion; homogenizing the emulsion by using a high-pressure homogenizer; sterilizing the emulsion which is homogenized by using an ultra high-temperature sterilizing machine; and spraying and drying the sterilized and obtaining the flaxseed oil microcapsule. The embedding rate of the flaxseed oil microcapsule is more than 90%, the capacity of the flaxseed oil can reach 45%, the process is simple, the taste is special, the scent is obvious and the shelf life is long.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD +3
Method for encoding and decoding data in a color barcode pattern
ActiveUS20100282851A1Large capacitySuccessfully recoveredCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesPattern recognitionPresent method
What is disclosed is a system and method for encoding and decoding data in a color barcode pattern using dot orientation and color separability. The spectral (wavelength) characteristics of the CMY colorants, commonly used in digital printing, and those of RGB sensors are exploited to achieve high capacity data embedding rates in color barcodes. The present method embeds independent data in two different printer colorant channels using dot orientation modulation. In the print end, dots of two colorants occupy the same spatial region. At the detector end, by using the complementary sensor channels to estimate the colorant channels, data is recovered in each colorant channel. The method approximately doubles the capacity of encoding methods based upon a single colorant channel and enables embedding rates which match or exceed that of other hardcopy barcodes known in the arts. The method is robust against inter-separation misregistration with a small symbol error rate.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Vitamin powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102716087AHigh mechanical strengthGood dispersionPowder deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsEmbedding rateAntioxidant
The invention mainly discloses vitamin powder and a preparation method of the vitamin powder. The vitamin comprises the following components in mass percentage: 5-60% of fat soluble vitamin, 30-70% of wall material, 5-30% of assistant wall material, 0.5-2% of emulsifier, 0.1-2% of antioxidant and 0.1-3% of cross linking agent. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the vitamin powder. By using a microencapsulation technique, the fat soluble vitamin oil (e.g. vitamin A, vitamin D3, vitamin E and vitamin K) is embedded to a micro-capsule, the wall material used in the embeeding process is starch sodium octenylsuccinate, the vitamin oil is embeeded in the wall and then the micro-capsule is subjected to cross linkage, mist spraying and drying are carried out to form the vitamin powder, and the embedding rate of the vitamin is more than 95.3%. According to the invention, the process is simple, the cost is low, the obtained vitamin powder is not soluble in water, high in oil loading amount and good in flowability, and can be used in the fields such as foods, daily-used industrial chemicals and medicines.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGTONG TECH
Compound microcapsule wall material and application thereof in essence microcapsules for cigarettes
InactiveCN103396886AImprove solubilityGood emulsifying effectEssential-oils/perfumesSucroseSodium Caseinate
The invention provides a compound microcapsule wall material and an application thereof in essence microcapsules for cigarettes. The compound microcapsule wall material is mixed by the following components in percentage by weight: 30.0-50.0% of starch octenylsuccinate, 15.0-30.0% of maltodextrin, 10.0-30.0% of sodium carboxymethyl starch, 10.0-30.0% of soy isolate protein, 1.0-5.0% of Arabic gum, 1.0-5.0% of sodium caseinate, 1.0-5.0% of saccharose, 0.1-0.5% of sodium alginate, 0.1-0.5% of xanthan gum and 0.1-0.5% of pullulan. The compound microcapsule wall material provided by the invention is good in solubleness, good in emulsibility, good in film-forming property, low in solution viscosity, and economical and practical benefits. Higher embedding rate can be obtained by using the wall material to prepare the essence microcapsules for cigarettes, and the product is good in sensory performance, smooth and uniform in particle, compact in capsule wall, lower in moisture content, good in dispersibility and stronger in practicality.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +1
Preparation process of peony seed oil micro-capsule powder
ActiveCN104206561AGood instant solubilityImprove stabilityFood shapingEdible oils/fatsSodium CaseinateWarm water
The invention discloses a preparation process of peony seed oil micro-capsule powder. The preparation process is characterized by sequentially comprising the following steps: (1) dissolving a wall material and an emulsifying agent by using warm water; (2) adding peony seed oil into the dissolved wall material and emulsifying agent, and uniformly mixing and stirring to obtain a mixed solution; (3) homogenizing the mixed solution obtained in the step (2) under high pressure to obtain a solution in a good emulsification state; and (4) spray-drying the solution obtained in the step (3) to obtain the peony seed oil micro-capsule powder, wherein the wall material is one or a mixture of more of sodium caseinate, starch sodium octenylsuccinate, gelatin, arabic gum and malt syrup, and the emulsifying agent is one or a mixture of more of mono-and diglycerides of fatty acids, sodium stearyl lactate and diacetyl monostearin tartrate. The peony seed oil micro-capsule powder prepared by virtue of the process is high in peony seed oil embedding rate and high in grease content; the process flow is simple and efficient, and facilitates large-scale production and application.
Owner:BEIJING ALCHEMIST TECH
Linseed oil microcapsule powder and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN104544092AImprove liquidityGood rehydration stabilityFood shapingEdible oils/fatsEmbedding rateAlpha-Linolenic acid
The invention relates to linseed oil microcapsule powder and a preparation process thereof. The microcapsule powder is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 38-45 parts of linseed oil, 0.002-0.02 part of an antioxidant, 48-54 parts of a filling agent, 6-8 parts of an emulsifier, 0-0.1 part of a stabilizer and 65-80 parts of water. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing an aqueous phase, preparing an oil phase, performing pre-emulsification, homogenizing and granulating. According to the final product obtained in the technical scheme of the invention, the surface is spherical under an environment scanning electron microscope, the particle size ranges from 35 microns to 100 microns, and the obtained product is a quick-dissolving product and is high in liquidity, high in re-watering stability, high in microcapsule oil embedding rate, good in embedding performance, good in taste and high in absorption rate; and moreover, the preparation process is simple, large-scale production is conveniently realized, contact between the linseed oil and air is effectively isolated by virtue of the microcapsule embedding technology, the biological activity of alpha-linolenic acid in the linseed oil is protected, waste residues and wastewater are not produced in the production process, and the product is green and environment-friendly.
Owner:王维义
Euphausia superba oil microcapsule capable of enhancing blood lipid reducing effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104799278AChange embedding effectMeet embedding requirementsLipidic food ingredientsFood shapingEmbedding rateChemistry
The invention relates to a euphausia superba oil microcapsule capable of enhancing a blood lipid reducing effect and a preparation method thereof. The euphausia superba oil microcapsule prepared through the preparation method provided by the invention is high in embedding rate; after euphausia superba oil is embedded to be prepared into the microcapsule, the euphausia superba oil takes the shape of solid powder, so that the euphausia superba oil is convenient to store, process and use. An excellent raw material is provided for food and health food, and euphausia superba oil application product forms are broadened.
Owner:武汉天天好生物制品有限公司
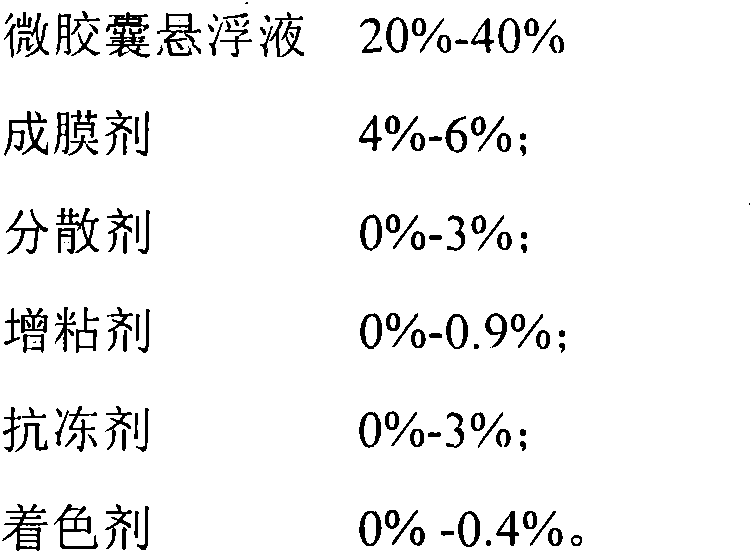
Micro-capsulated suspended microbial seed coating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104430307AReduce adverse effectsGuaranteed effective bacteria contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSurvivabilityPseudomonas
The invention relates to a micro-capsulated suspended microbial seed coating agent and a preparation method thereof. The micro-capsulated suspended microbial seed coating agent comprises a functional bacteria microcapsule and auxiliaries, wherein the functional bacteria microcapsule is prepared from wall materials such as sodium alginate and gelatin by virtue of an endogenous emulsion process, the grain size of the microcapsule is 20-60 mu m, the content of functional bacteria is not lower than 10<9>cfu / g, and the embedding rate is over 80%. Functional microbes are selected from two or more of pseudomonas, bacillus subtilis, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, enterobacter cloacae, raoultella planticola and bacillus atrophaeus. The auxiliaries comprise one or more of a film-forming agent, a dispersant, a tackifier, an anti-freezing agent and a coloring agent. The prepared functional bacteria microcapsule is uniformly mixed with the auxiliaries to obtain a finished product. The product has the advantages of good film-forming performances, thallus persistence, high survivability, good slow-controlled release, strong application stability, environment friendliness, convenience in use, and the like, can be used for promoting seed germination and seedling growth of cottons, soya beans, wheat and potatoes, and the like, controlling the diseases at the seedling stage, improving stress resistance, and the like.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY +1
Medicine carrying fibroin microsphere and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101244277AGood denaturation effectHigh drug loadingOrganic non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryEmbedding rateOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a drug-loaded microsphere and the preparation method, belonging to the technical field of biomedicine, which comprises following steps: adopting water / oil / water multiple emulsion technology and self-assembly technology of protein to fully mix the water soluble medicine and regenerated silk fibroin solution; adding the mixture in oil phase with emulsifier with certain amount during stirring for emulsification; adding organic solvent and stirring, thereby the silk fibroin is denaturalized and Beta structured to form milky crystalline silk fibroin fine particle, and the medicine is embedded; removing supernatant liquid through centrifugal effect; adding organic solvent; further crystallizing the silk fibroin and embedding the medicine; removing solvent and residual oil phase through centrifugal effect and collecting the microsphere. The average particle size of the silk fibroin drug-loaded microsphere is between 5.84 to 86.27Mum, the embedding rate is 42 to 99%, the drug loading dosage is 2.5 to 8.5%. The drug-loaded microsphere has the advantages of applicability to requirements for different purposes and wide application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing perilla oil powder through microencapsulation
InactiveCN103054030AGood emulsifying effectGood film formingFood shapingFood preparationDispersitySolubility
The invention discloses a method for preparing perilla oil powder through microencapsulation, and provides a method for preparing perilla oil powder with simple technology and good water solubility. The method comprises the following steps of: heating to gelatinize starch octenylsuccinate at 90-100 DEG C, and cooling to room temperature; preparing the gelatinized starch octenylsuccinate into an aqueous solution of starch octenylsuccinate with mass concentration of 30-40%; adding perilla oil into the aqueous solution of starch octenylsuccinate, and stirring for emulsification at high temperature to obtain an emulsion; and homogenizing the emulsion, and spray-drying to obtain perilla oil powder. The preparation method disclosed by the invention adopts starch octenylsuccinate as a wall material, does not need addition of an emulsifier and realizes high embedding rate; the operation technology is simple; and the perilla oil powder has good water solubility, good dispersity and good stability. Moreover, the starch octenylsuccinate has low price, the product cost can be lowered, and the product popularization is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Vitamin E microcapsule preparation method
InactiveCN101444495AReduce lossesPlay the packageOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsFood additiveWater content
A vitamin E microcapsule preparation method belongs to the technical field of preparation of controlled-release microcapsule for food additives and bioactive substances. The vitamin E microcapsule preparation method can improve the stability of vitamin E and amplify the application range. The method comprises the following steps: selecting chitosan and maltodextrin as wall material, selecting soybean lecithin (P powder) and Tween-80 as the composite emulsifying agent; and synthesizing vitamin E microcapsule by spray drying. The vitamin E microcapsule has embedding rate up to 92.45%, retention rate up to 91.73%, and water content lower than 3%, and has wide application prospect in the fields of bread or snack products, beverages, biscuits, health products and nutrient fortified food, etc. The method has the advantage of low cost and simple process, can meet the environmental protection and practical requirement.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
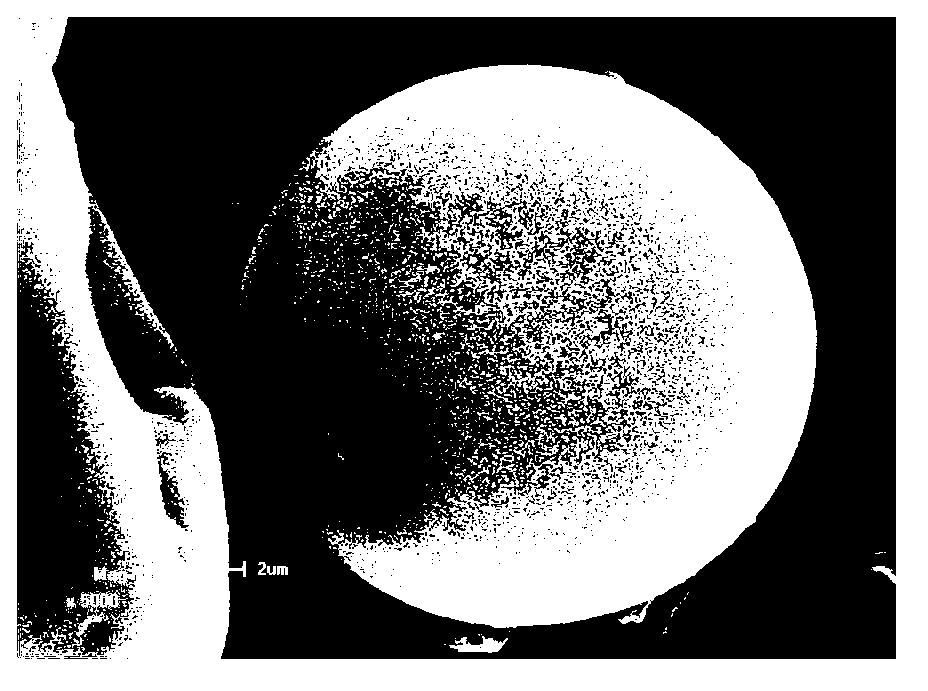
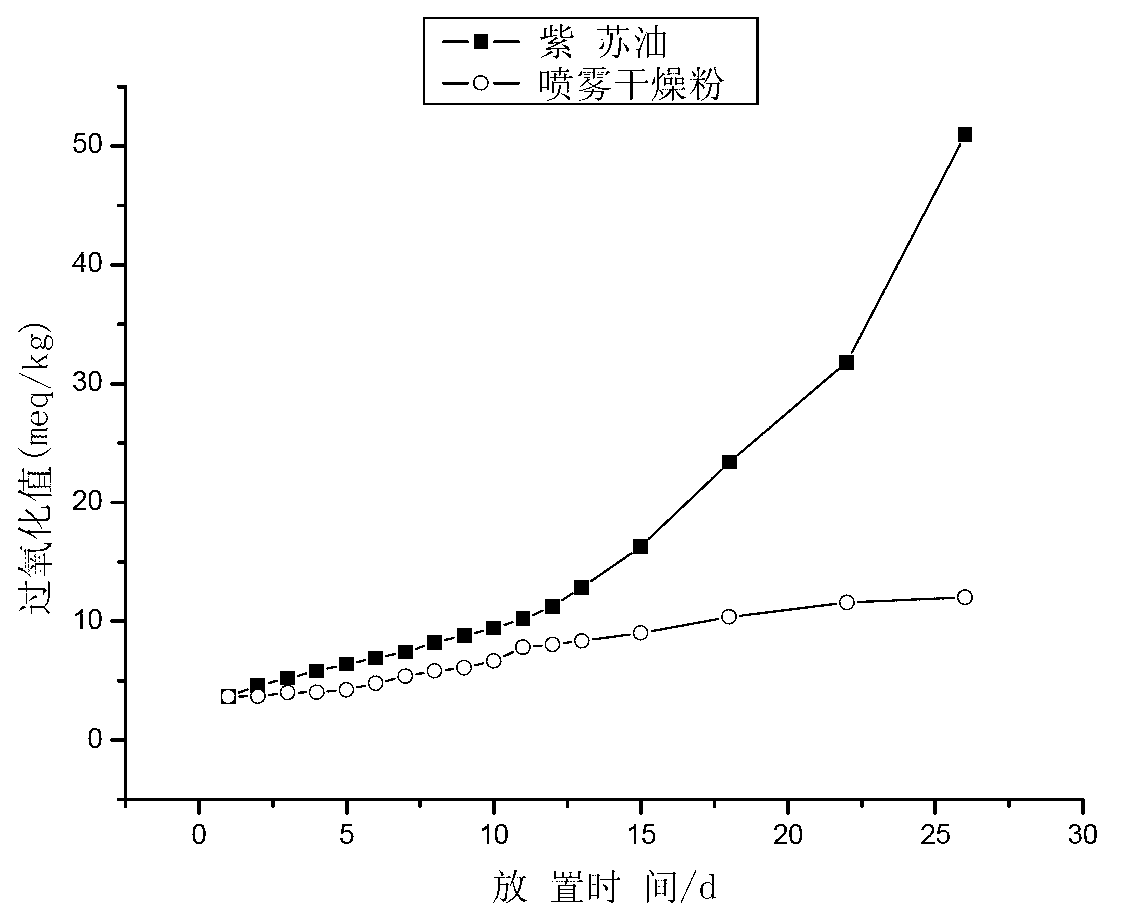
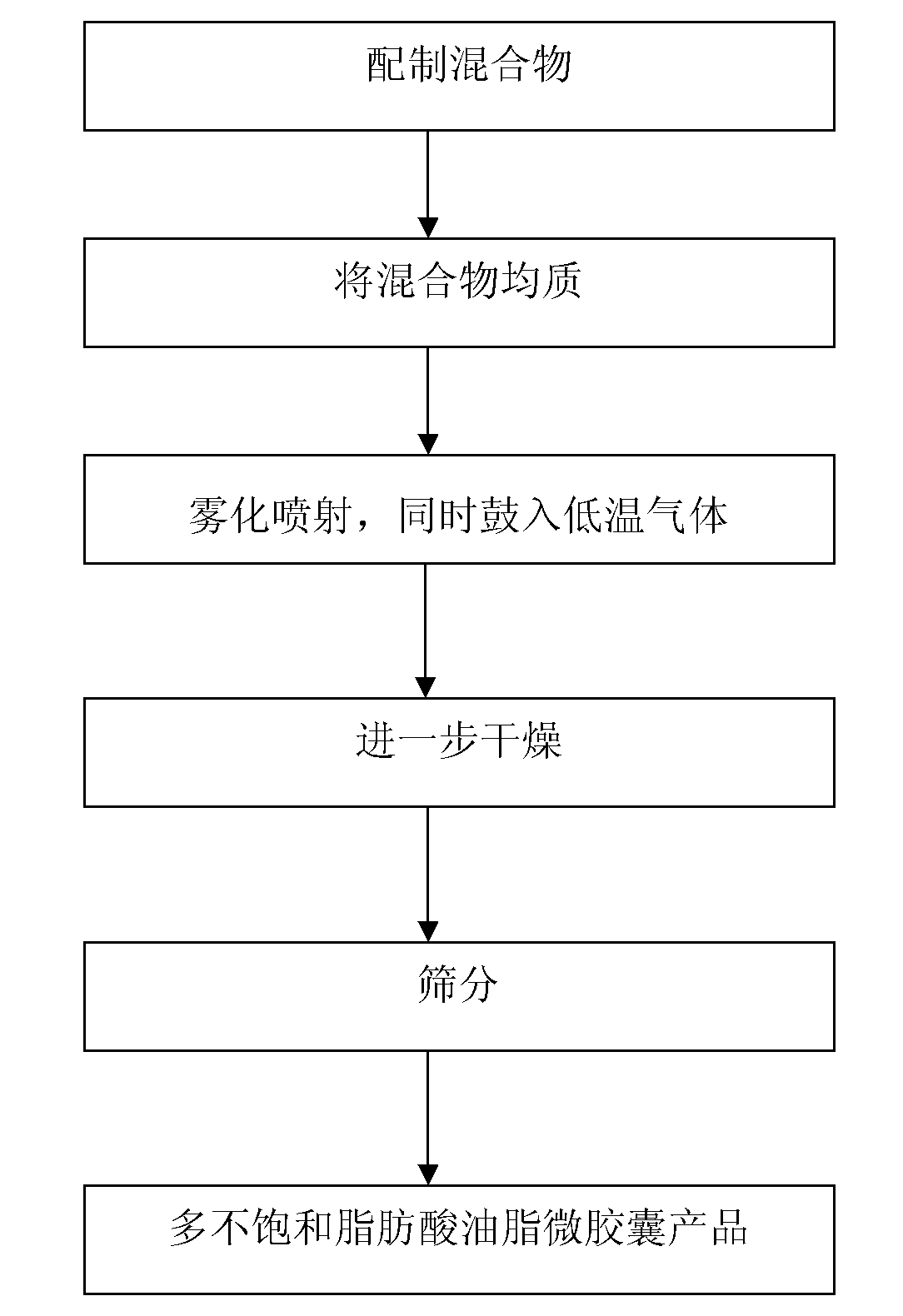
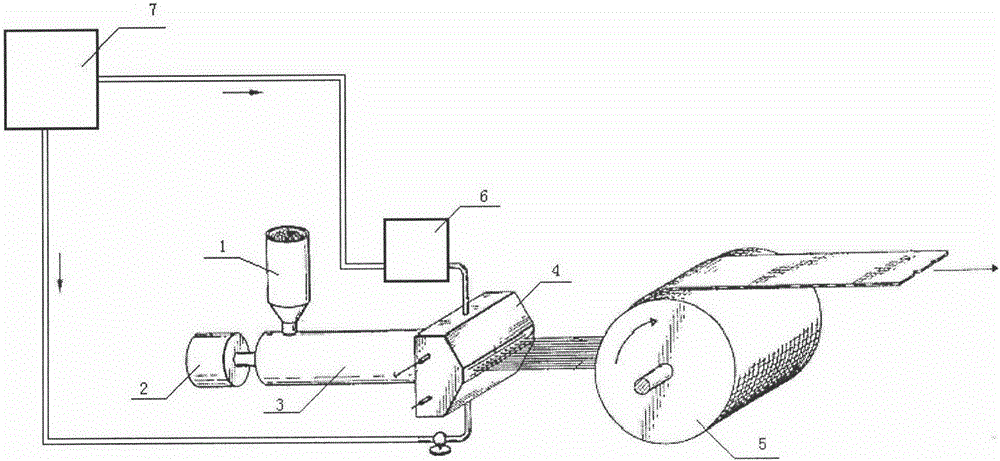
Spray freeze-drying preparation technology for polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule
The invention relates to a spray freeze-drying preparation technology for a polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule, which comprises the following technological steps: mixing oil containing polyunsaturated fatty acid with emulsifier and water to obtain mixture; homogenizing the mixture to obtain emulsion; atomizing the emulsion into liquid drops which are sprayed into a spray drying device with temperature of negative 60 DEG C to negative 10 DEG C, wherein powder embedding materials are contained at the bottom part of the spray drying device, and blasting low-temperature gas to fully mix the materials in the spray drying device and to keep the temperature in the spray drying device to be the set temperature; and further drying and screening to obtain polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule products. The invention has the advantages that the drying temperature of the preparation technology is low, the speed is fast and the nutritional ingredients are not apt to be damaged; the technology is simple and convenient and the automatic mass production can be realized; and the oil embedding rate of the obtained independent polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule particles is high, the embedding performance is good, the product shelf life is long and the stability is good.
Owner:CABIO BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
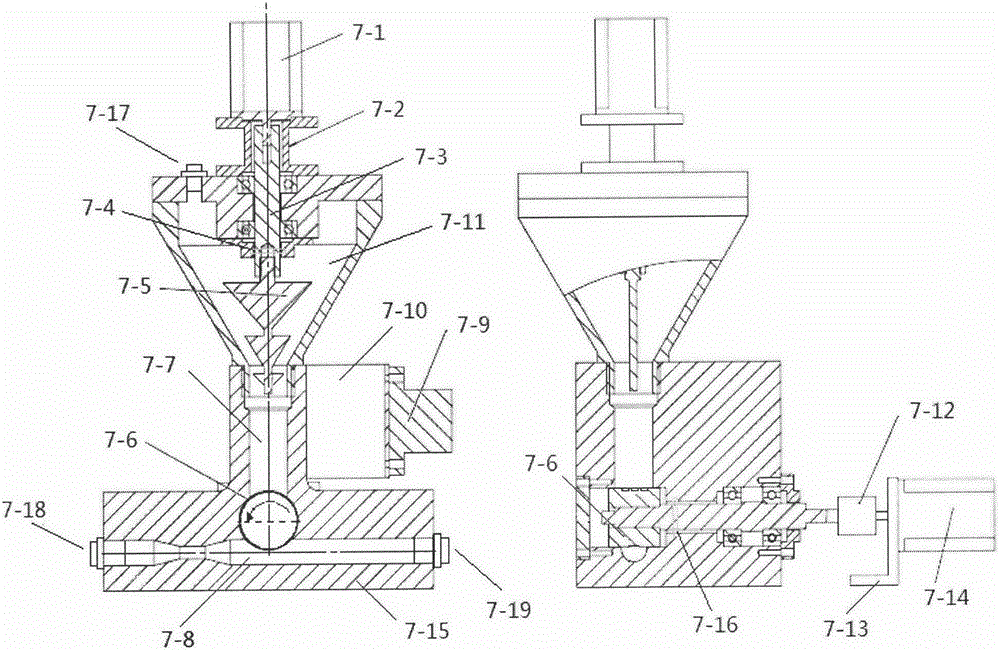
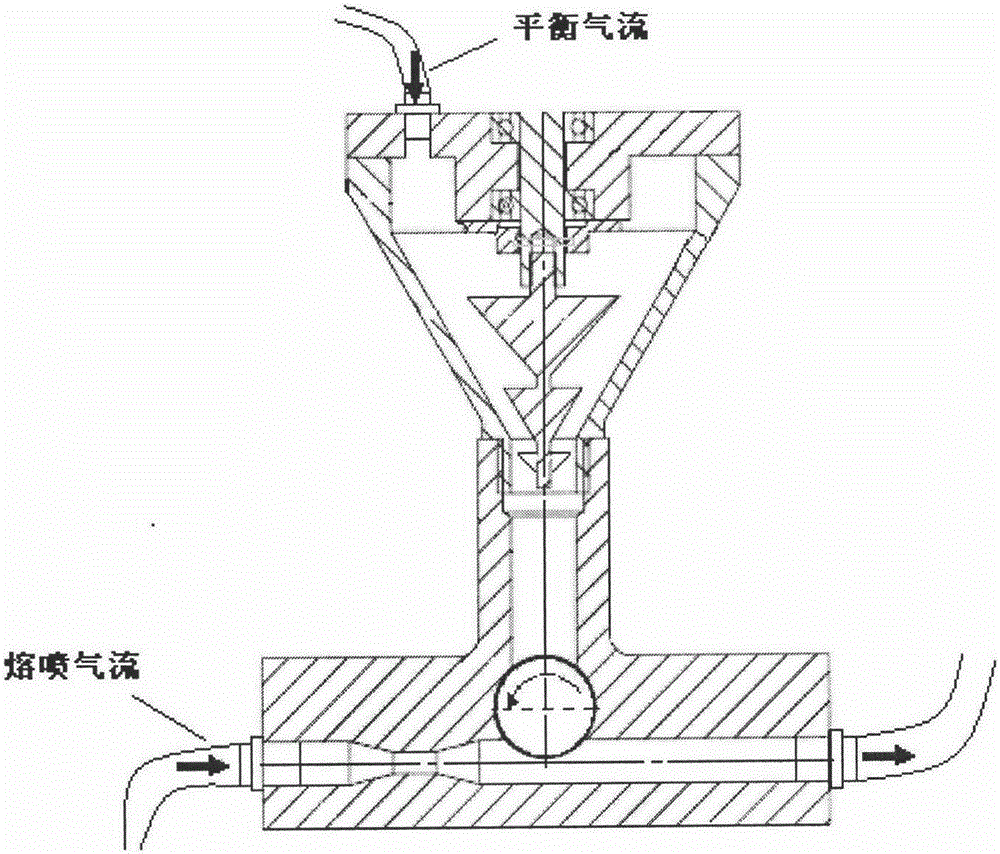
Melt-blown nonwoven fabric production system capable of increasing particle embedding rate
InactiveCN106592106AHigh embedding rateImprove bonding fastnessSpinning head liquid feederNon-woven fabricsActivated carbonEmbedding rate
The invention discloses a melt-blown nonwoven fabric production system capable of increasing a particle embedding rate. The system comprises a feeding hopper, a system motor, a screw extruder, a die head, a reception roller, a hot air source, and a feeding device. The feeding device includes a stirring motor, a connecting flange, a rigid coupler, a sealing ring I, a stirring rod, a powder wheel, a powder falling cavity, a hot air channel, an air vibrator, channel steel, a storage chamber, a flexible coupler, a motor support, a drive motor, a T stand, a sealing ring II, a nozzle, an airflow inlet, and an airflow outlet. The characteristics and beneficial effects of the melt-blown nonwoven fabric production system are that activated carbon nanoparticles can be guided to melt-blow airflows, high-temperature and high-pressure airflows mixed with the activated carbon nanoparticles draw melt-blown fibers, the nanoparticles mixed in the hot airflows act on the melt-blown fibers at a certain speed and are adhered to the surfaces of the melt-blown fibers, and thus the binding strength between the activated carbon nanoparticles and melt-blown fabrics can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Anti-adhesion fiber membrane with hemostasis and antibiosis functions and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102397580AIncrease embedding volumeHigh embedding rateAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberSurgical operation
The invention discloses an anti-adhesion fiber membrane with hemostasis and antibiosis functions and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving medicinal molecules into an organic or inorganic solvent to prepare a medicinal molecular solution; dissolving different high molecular materials into medicinal solutions of a hemostasis agent and an antibiosis agent respectively to prepare a high molecular solution; and performing electrostatic spinning on a mixed solution of organic high molecules and the hemostasis agent and a mixed solution of high molecules and the antibiosis agent to obtain a compound fiber material. In the invention, nanofiber is produced by using an electrostatic spinning technology; an organic high molecular solution and the medicinal molecules are mixed for electrostatic spinning to obtain the compound fiber material; by adjusting the high molecular material, the embedding amount and embedding rate of medicaments are increased, a fiber material which can keep the medicinal bioactivity and is used for controlling the release of different medicaments at different stages is prepared, and dual effects of preventing postoperative adhesion and postoperative infection can be achieved; and moreover, the entire preparation process is simple, has low cost, and has wide application prospect in the field of surgical operation.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Method for producing coconut-taste coconut oil powdered grease
The invention belongs to the field of functional food and relates to a method for producing coconut-taste coconut oil powdered grease. The coconut-taste coconut oil powdered grease is produced by using edible coconut oil as a core material and using microporous starch, maltodextrin and Arabic gum as wall materials and performing spray drying. A suitable composite emulsifying agent is adopted according to the characteristics of the core material and the wall materials, so embedding rate is high, water solubility is high and cost is low. The coconut-taste coconut oil powdered grease does not comprise essence preservative, has aromatic coconut taste, and can be conveniently added into food requiring coconut taste, such as bread, ice cream, fast food, solid beverage, soup, cakes, candies and the like.
Owner:海南省粮油科学研究所
Pyraclostrobin nanoparticle and preparation method of pyraclostrobin nanoparticle
The invention discloses a pyraclostrobin nanoparticle and a preparation method of the pyraclostrobin nanoparticle. The pyraclostrobin nanoparticle is prepared by adopting an ultrasonic emulsification-volatilization method; a solid spherical nanoparticle is prepared by taking polyester as a carrier and taking arabic gum as a dispersing agent; and the drug loading capacity of the prepared nanoparticle is 5.0-30%, the embedding rate is 65-90%, and the volume immediate diameter is about 0.6 micron. The pyraclostrobin nanoparticle disclosed by the invention has quick release and slow release functions, and the lasting period is lower than that of a conventional particle and is higher than that of missible oil. The nanoparticle prepared by the method is secondarily processed into a conventional dosage form, and can be applied to foliar spraying to prevent and treat various diseases of crops.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Probiotics microcapsule wall material and probiotics microcapsule preparation method
InactiveCN108323571AGuaranteed survivalImprove embedding yieldMilk preparationFood ingredient functionsFiberWater baths
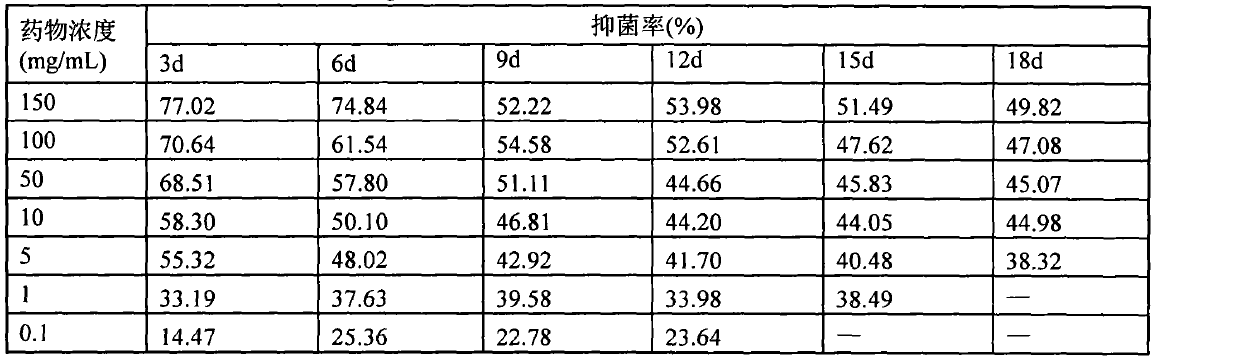
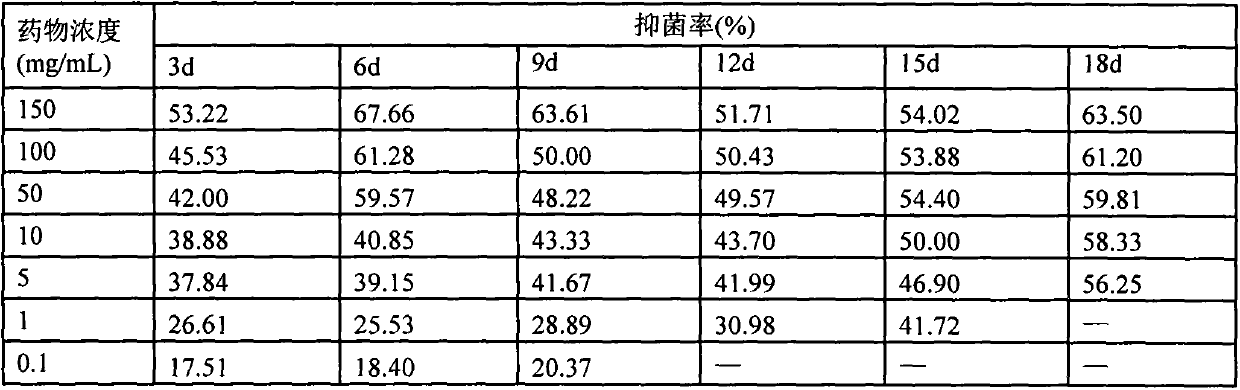
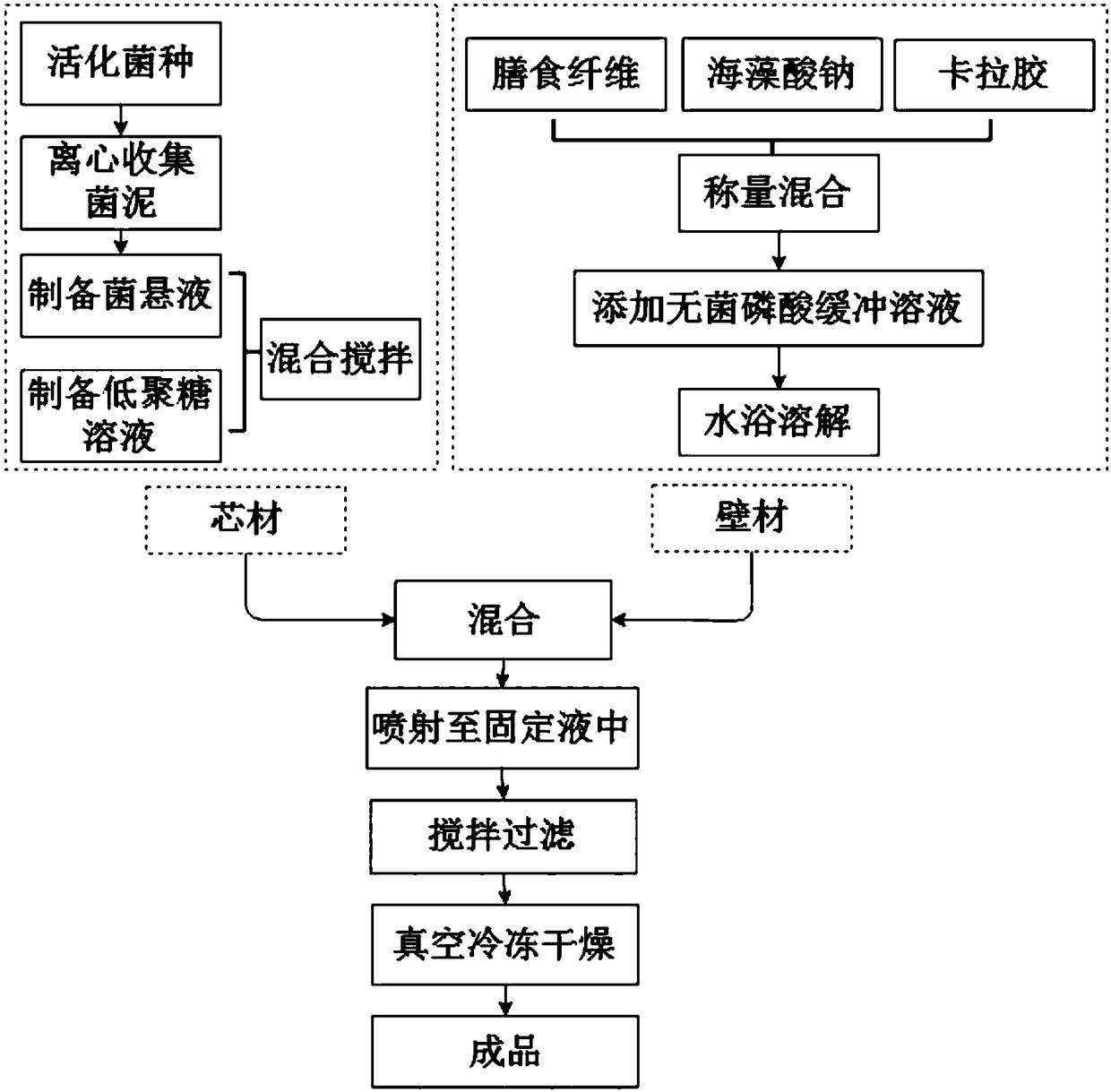
The invention discloses a probiotics microcapsule wall material preparation method. The probiotics microcapsule wall material preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing sodium alginate,carrageenan and meal fiber, performing ultraviolet lamp irradiation for 15-30 min, mixing a mixture with an aseptic phosphoric acid buffer solution with a pH value being with 6.8-7.4, performing water-bath dissolving at the temperature of 70-85 DEG C to prepare a wall material solution with mass concentration being 8.5-10.5%, wherein in the wall material solution, the mass concentration of the meal fiber is 1-5%, the mass concentration of sodium alginate is 2-4%, and the mass concentration of carrageenan is 4.5-6.5%. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the probiotics microcapsule, the volume ratio of an oligosaccharide solution (the mass concentration is 3-5%) to a probiotics suspension (greater than 5*107 CFU / mL) is 1:2-2:1. The probiotics microcapsule has the advantages of high embedding rate, high live bacteria number, high stress resistance, simple operation, economic performance, easy operation, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Embedding system based on eutectic solvent and using eutectic solvent as solvent
ActiveCN108186575ALow priceEasy to manufactureOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsControlled releasePolyol
The invention provides an embedding system based on a eutectic solvent and using the eutectic solvent as a solvent. The embedding system comprises an embedding material, a carrier and the eutectic solvent, and the eutectic solvent is formed by a hydrogen bond donor and a hydrogen bond acceptor through hydrogen bond association; the hydrogen bond acceptor includes quaternary ammonium salt, and thehydrogen bond donor includes one or more of urea, polyol, monosaccharide and carboxylic acid. The embedding system uses the eutectic solvent to serve as the solvent, and the eutectic solvent can increase the embedding rate of medicine, is low in toxicity and degradable, can reduce the side effects of the medicine in a controlled release and medicine delivery process and can improve the permeability and controllable release performance of cell membranes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Water-soluble sea buckthron oil microcapsules with high oil carrying capacity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106343577AEasy to prepareEasy to operateFood shapingFood ingredient functionsWater dispersibleOperability
The invention provides water-soluble sea buckthron oil microcapsules with high oil carrying capacity and a preparation method thereof. The microcapsules mainly take starch sodium octenylsuccinate as a wall material. A specific process comprises the following steps: dissolving the wall material by using a suitable amount of water and performing pasteurizing; then, cooling to 50 to 60 DEG C and performing high-speed shearing; adding pretreated sea buckthron oil to prepare a macro emulsion with the soluble solid content of 40 percent or higher; performing spray-drying after high-pressure homogenizing to obtain the sea buckthron oil microcapsule powder. The oil carrying capacity of the microcapsules reaches 48 percent, and the embedding rate of the microcapsules exceeds 97 percent. The product prepared by the preparation does not use an emulsifying agent, is high in water dispersibility, simple in process flow, high in operability, high in repeatability and suitable for industrialized continuous production, and has the shelf life of 18 months.
Owner:BEIJING POWDERY FOOD
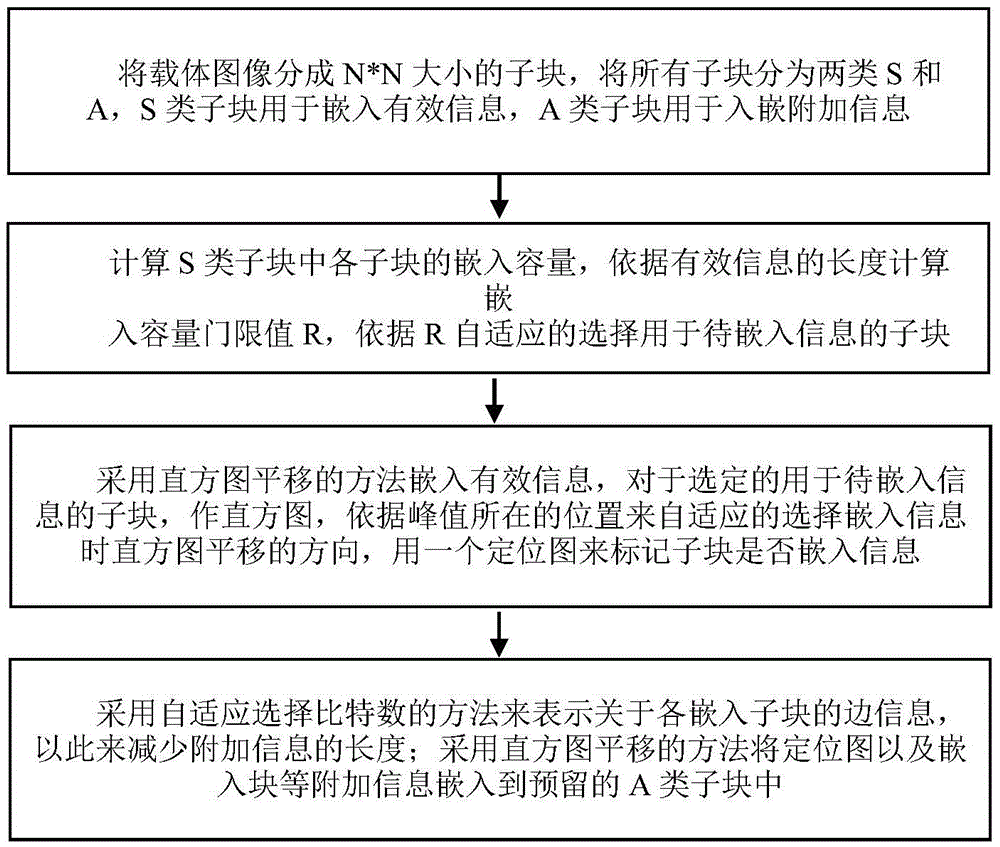
Reversible information hiding method based on blocked self-adaptive histogram translation
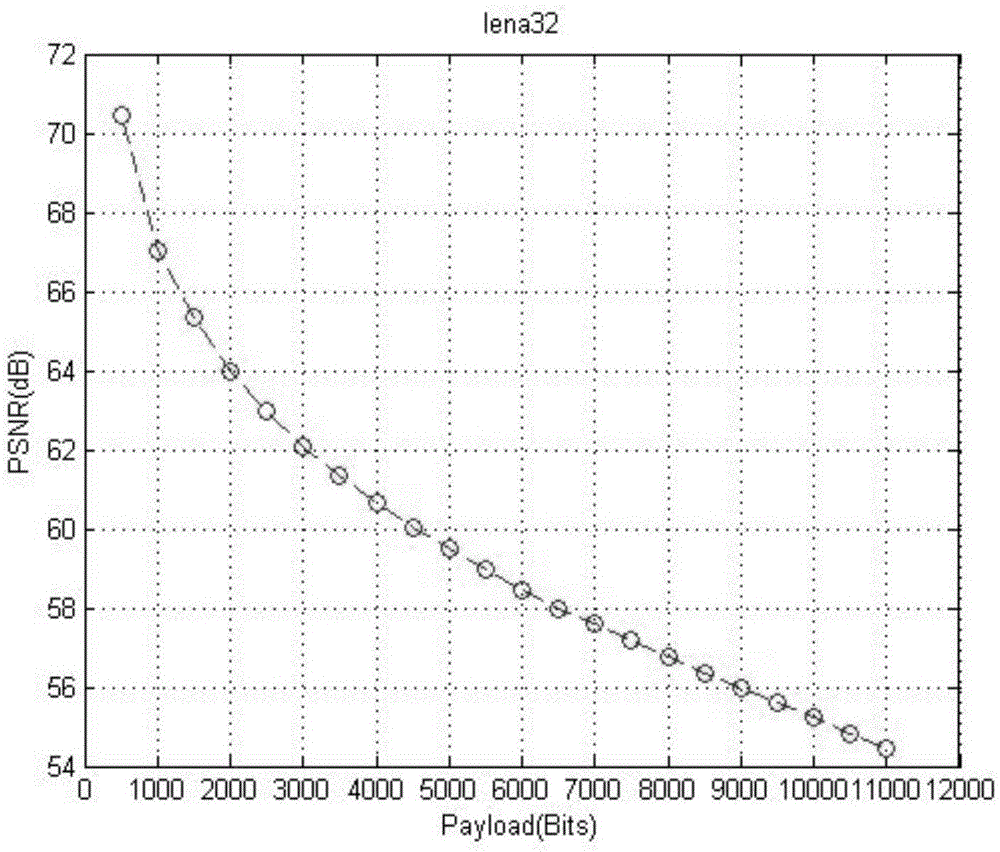
InactiveCN105488773ALossless extractionImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityPeak value
The invention relates to the field of multimedia information security, in particular relates to a reversible information hiding method based on blocked self-adaptive histogram translation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) blocking a carrier image, and computing a peak value of each sub-block histogram; (2) self-adaptively selecting a sub-block for embedding information according to embedding capacity of each sub-block; (3) adopting a method for self-adaptively selecting histogram translation direction while embedding the information. The invention is a novel histogram translation method which is capable of effectively embedding the information and losslessly extracting the embedded information and recovering an original image; through the adoption of the blocked method, the embedded information is safer and the integral embedding rate is improved, the self-adaptive selected histogram translation direction can effectively improve the peak signal to noise ratio of the image to further improve the image quality, thereby providing help for the medical treatment, military and the like applications. Through the adoption of the method, the higher the precision of the image is, the better the reversible information hiding effect is.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Microcapsule production technology
InactiveCN104324675APrevent volatilizationInhibitory activityCapsule deliveryMicroballoon preparationCarrageenanEmbedding rate
The invention discloses a microcapsule production technology including five steps of preparation of a wall material solution, emulsification mixing of a core material and a wall material, ultrasonic embedding, homogeneous dispersion and micro capsule spray drying. The preparation technology has the advantages of simple operation, selection of the reasonable wall materials such as octenyl succinic starch ester, seaweed gum, carrageenan and the like, easily obtained raw materials, wide scope of application, safe and reliable use, capability of well preventing the volatilization, oxidation or inactivation of instable raw materials, and effectively preventing the release of the core material, by selection of a suitable emulsifier and stirring speed, the micro capsule embedding rate is improved; microcapsule is prepared by spray drying method, and the microcapsule production technology is high in production capacity, simple in technology, and suitable for continuous industrial and automatic production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHUNBAO CAPSULES
Biodegradable microorganism sustained-release agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106957840AGood slow releaseHigh embedding rateWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesNitrogen removalMicroorganism
The invention relates to a biodegradable microorganism sustained-release agent. The biodegradable microorganism sustained-release agent is prepared from microorganism bacterium powder, a carbon-source sustained-release body and a hydrogel bacterium agent carrier, wherein the microorganism bacterium powder and the carbon-source sustained-release body are suspended in the hydrogel bacterium agent carrier; the mass ratio of the carbon-source sustained-release body to the hydrogel bacterium agent carrier is 1 to (1 to 10000); the invention further relates to a preparation method and application of the microorganism sustained-release agent. The microorganism sustained-release agent provided by the invention has a remarkable sustained-release effect, the embedding rate of the microorganism bacterium powder is high and the sustained-release effect of the microorganism bacterium powder is remarkable; furthermore, the preparation method is simple and secondary pollution is effectively avoided; controllable release of a carbon source can be realized; the biodegradable microorganism sustained-release agent is applied to sewage management and waste of the carbon source, caused by flowing of a water body, can be effectively avoided through sustained-release of the carbon source, so that the utilization efficiency of microorganisms on the carbon source is improved and the nitrogen removal efficiency is improved; the ammonia-nitrogen reducing rate can reach 80 percent or more and the reducing rate of total nitrogen can reach 20 percent; a relatively good quality effect is realized.
Owner:浙江天韵生态环境工程有限公司 +1
Preparation method and application of daily chemical microencapsulated probiotic
ActiveCN103160489AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove acid resistanceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLactobacillus rhamnosusFreeze-drying
The invention provides a method for preparing daily chemical microencapsulated probiotic. The method comprises the steps that: first, three probiotics which are lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus rhamnosus are fermented and centrifuged; such that wet cells are obtained; emulsifying, pre-freezing and freeze-drying are carried out; First embedding is carried out upon the obtained probiotic powder by using a crosslinked product of gelatin and TG enzyme; and second embedding is carried out by using a mixture of soluble starch, maltose and maltodextrin. With the method, the prepared microencapsulated probiotic has an embedding rate reaching 87%. The microencapsulated probiotic can be used in daily chemicals used for inhibiting acnes, relieving allergy symptoms, and lightening spots.
Owner:BIOGROWING CO LTD
Preparation technology for polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule
The invention relates to a preparation technology for polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsules, which comprises the following technological steps: mixing oil containing polyunsaturated fatty acid with emulsifier and water to obtain mixture; homogenizing the mixture to obtain emulsion; atomizing the emulsion into liquid drops which are sprayed into a preheated fluidized drying device, wherein the temperature in the fluidized drying device is 30-90 DEG C and powder embedding materials are contained at the bottom part of the fluidized drying device, and blasting air for drying to keep the temperature in the fluidized drying device to be 30-90 DEG C; and further drying and screening to obtain polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule products. The invention has the advantages that the temperature of the preparation technology is low and the nutritional ingredients are not apt to be damaged; the technology is simple and the automatic mass production is facilitated; and the oil embedding rate of the obtained independent polyunsaturated fatty acid oil microcapsule particles is high, the embedding performance is good, the product shelf life is long and the stability is good.
Owner:CABIO BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Abscisic acid-embedded chitosan nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102090395ANo adhesionRelease stabilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcetic acidChitosan nanoparticles
The invention discloses abscisic acid-embedded chitosan nanoparticles and a preparation method thereof. The abscisic acid-embedded chitosan nanoparticles are nanoparticles formed by wrapping aqueous solution of abscisic acid by an embedding material which is formed by dilute solution of acetic acid of chitosan and a crosslinking agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding the chitosan into the dilute solution of acetic acid to be dissolved, and then adding solution of sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to obtain dilute solution of acetic acid of the chitosan; preparing abscisic acid into aqueous solution; preparing the crosslinking agent into aqueous solution; adding the solution of dilute acetic acid of the chitosan into the aqueous solution of abscisic acid, and then adding the aqueous solution of crosslinking agent drop by drop; and fully mixing uniformly to obtain the abscisic acid-embedded chitosan nanoparticles. The method is simple and easy, and has high embedding rate; the obtained embedding nanoparticles have no adhesion, good glomeration and round surface; after the embedding, the abscisic acid can be protected from external interference, and the stability of the abscisic acid can be improved; the abscisic acid is steadily and slowly released, which prolongs action time and strengthens induced resistance effect; and the chitosan serving as a wall material has disease-resistant and induced resistance effects.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI INST
Image forming apparatus
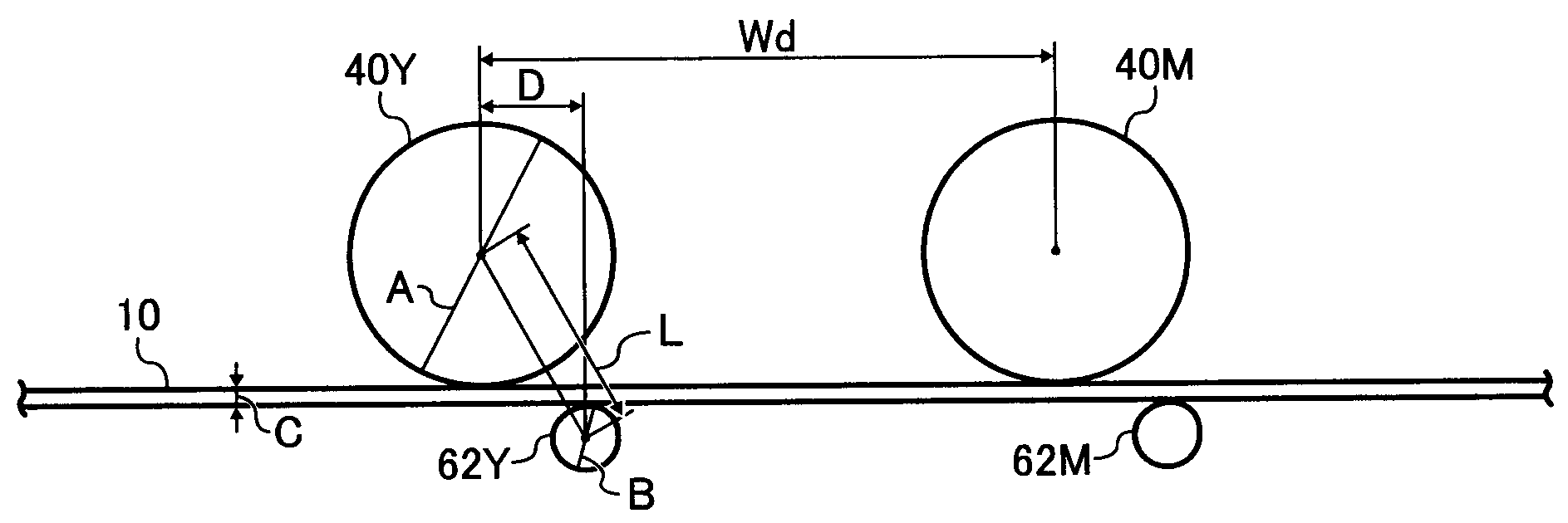
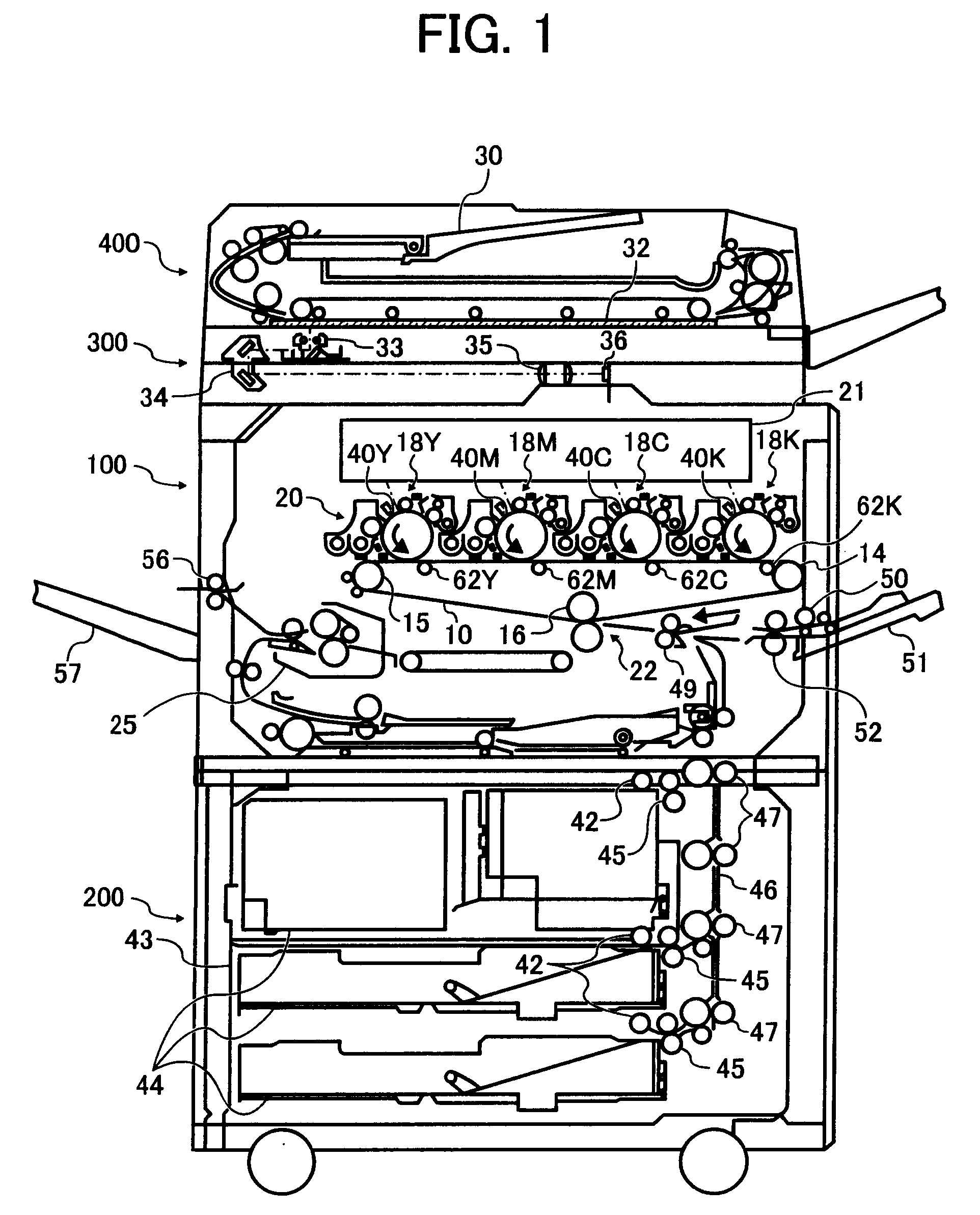
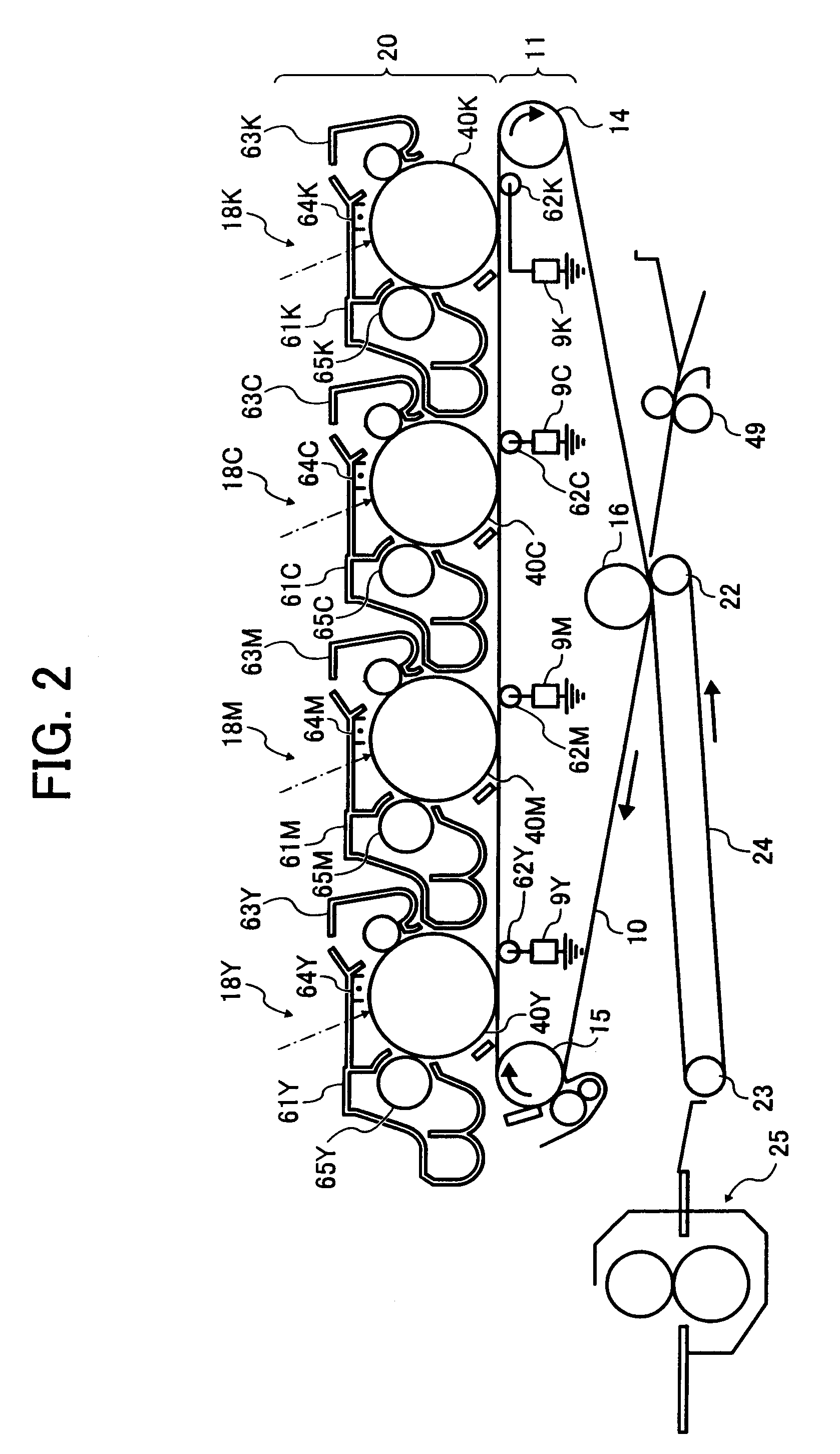
An image forming apparatus includes an image carrier, an endless belt whose front surface contacts the image carrier to form a transfer nip, and a bias applying roller configured to apply a transfer bias to a back surface of the endless belt. An image is formed of a toner having an additive embedded rate of not less than 40 percent and including a mother particle having a binder resin and a colorant, and an external additive. The bias applying roller is located so as to satisfy a relationship, L>(A / 2)+(B / 2)+C, where A is a diameter of the image carrier, B is a diameter of the bias applying roller, C is a thickness of the endless belt, and L is a distance between centers of the image carrier and the bias applying roller on a virtual plane perpendicular to an axis direction of the image carrier.
Owner:RICOH KK
Preparation method of double-layered wall material phase-variable micro capsule
InactiveCN104874339AGood dispersionLow costHeat-exchange elementsMicroballoon preparationCross-linkEmbedding rate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-layered wall material phase-variable micro capsule and in particular relates to a dense double-layered structure which is formed by connecting inner and outer two layers of wall materials by adopting an interface polymerization under the action of a cross-linking agent, wherein the inner and outer layers of the wall materials are prepared by adopting an in-situ polymerization. The preparation method comprises the step of forming the stable double-layered structure under the action of the cross-linking agent with urea formaldehyde as the outer layer wall material and an alkene polymer as the inner layer wall material, wherein the cross-linking agent is an organic micromolecule containing double bonds and hydroxymethyl radical groups. The method is suitable for an organic core material; on the basis that the particle size is uniform and the embedding rate is high, the double-layered wall material phase-variable micro capsule also has the advantages of the hydrophilic performance and not-easily-agglomeration performance of a urea formaldehyde resin micro capsule, is hydrophobic with polymethyl methacrylate and is low in permeability.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com