Patents
Literature
684 results about "Virtual plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
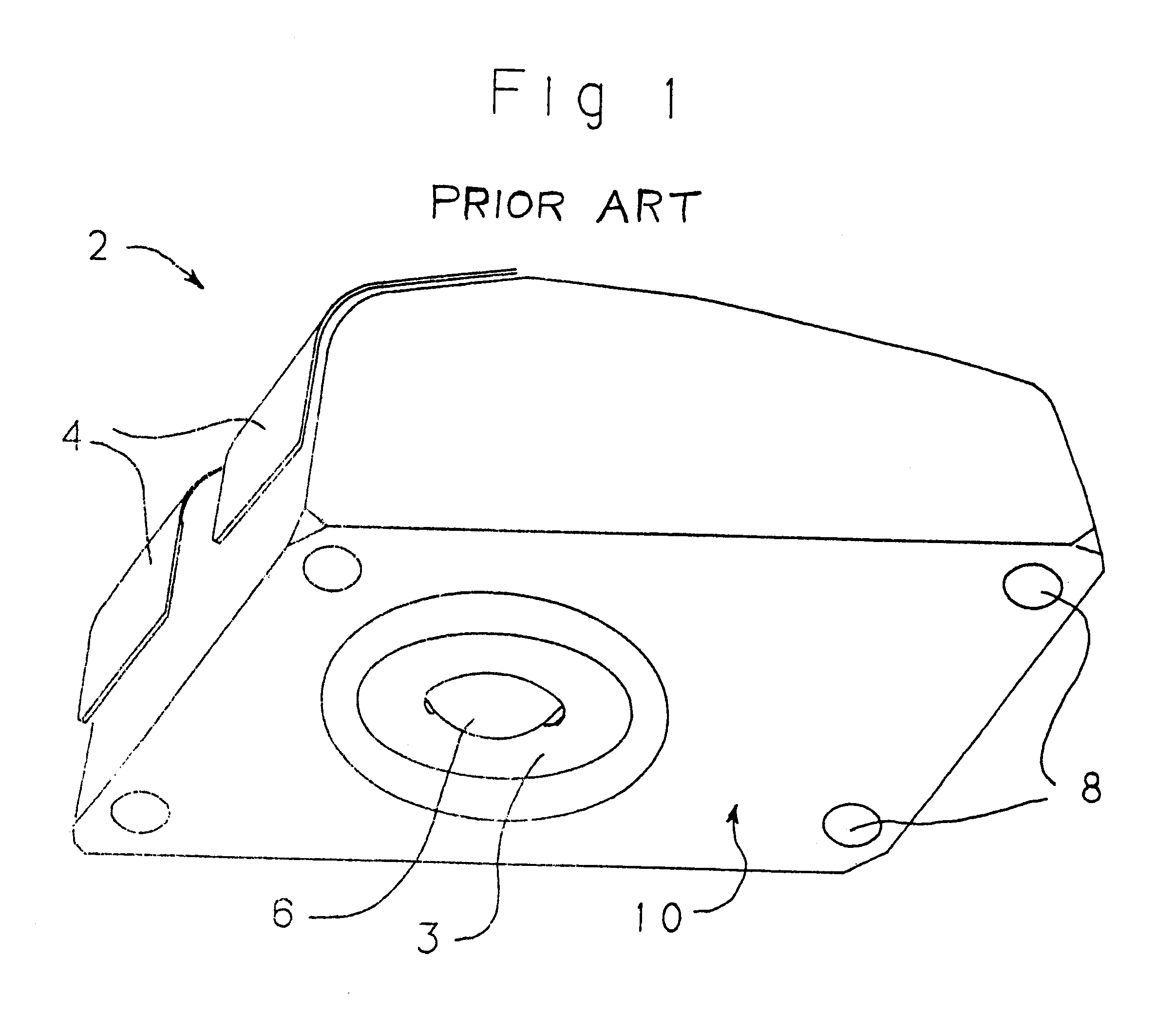
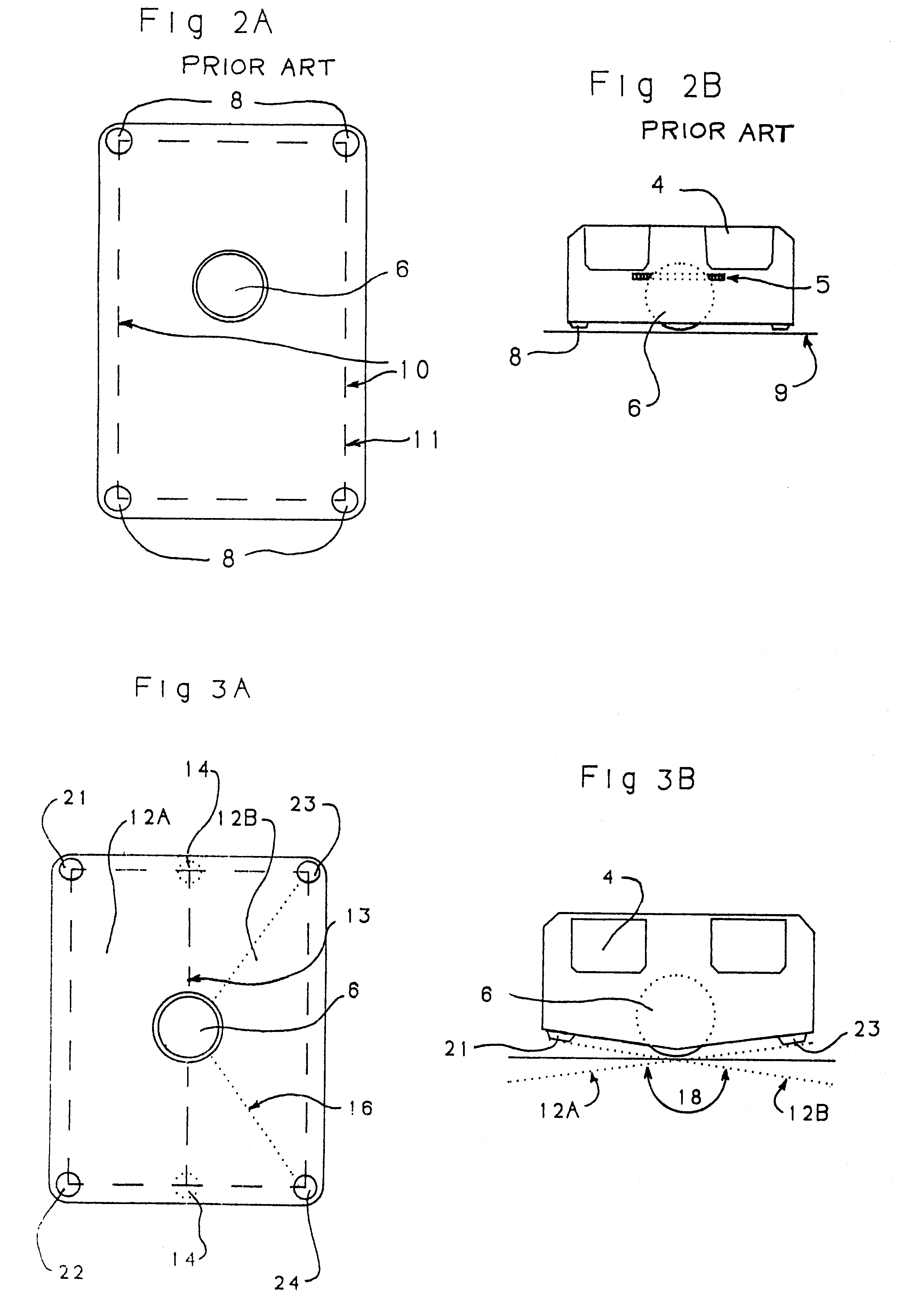
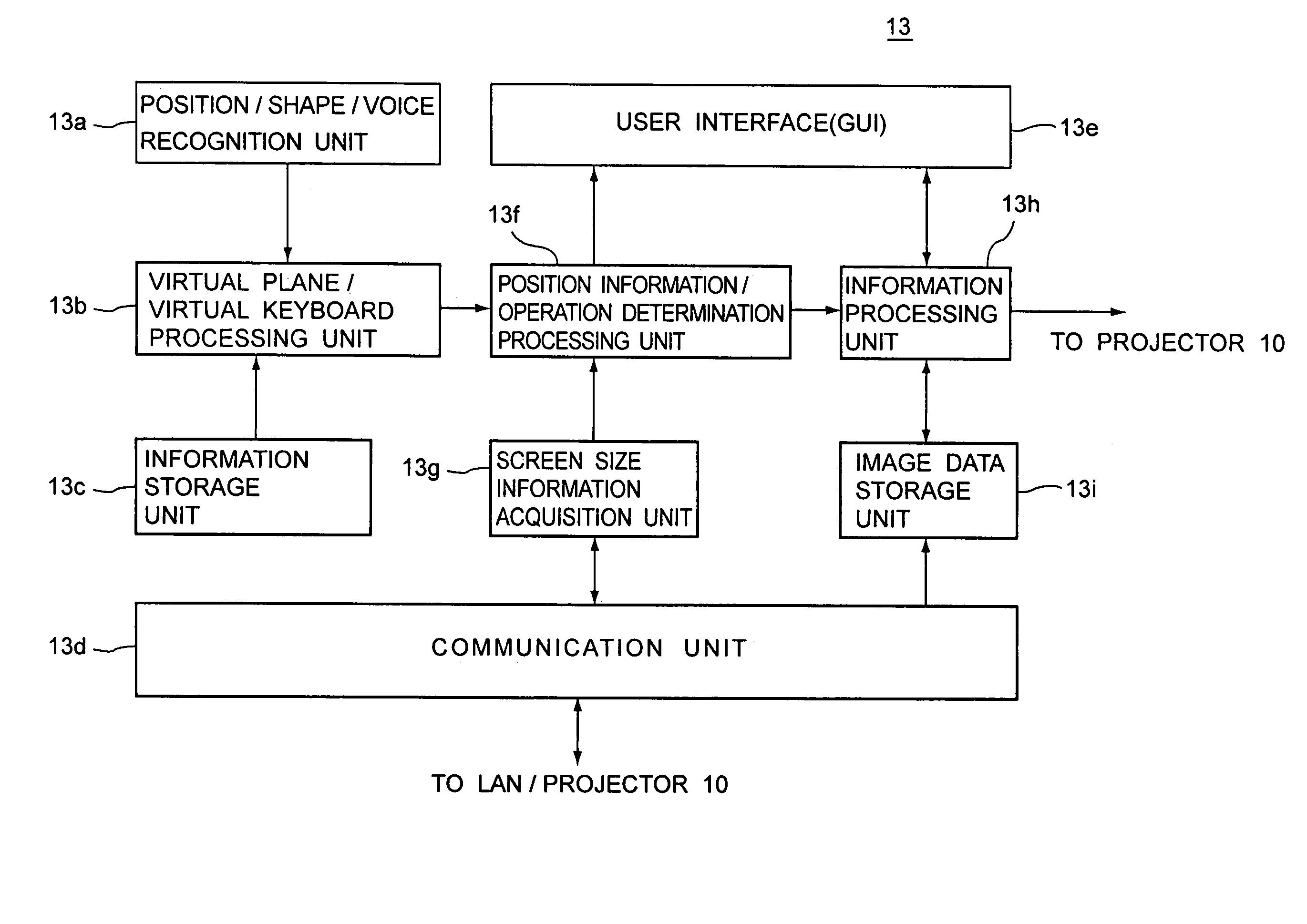
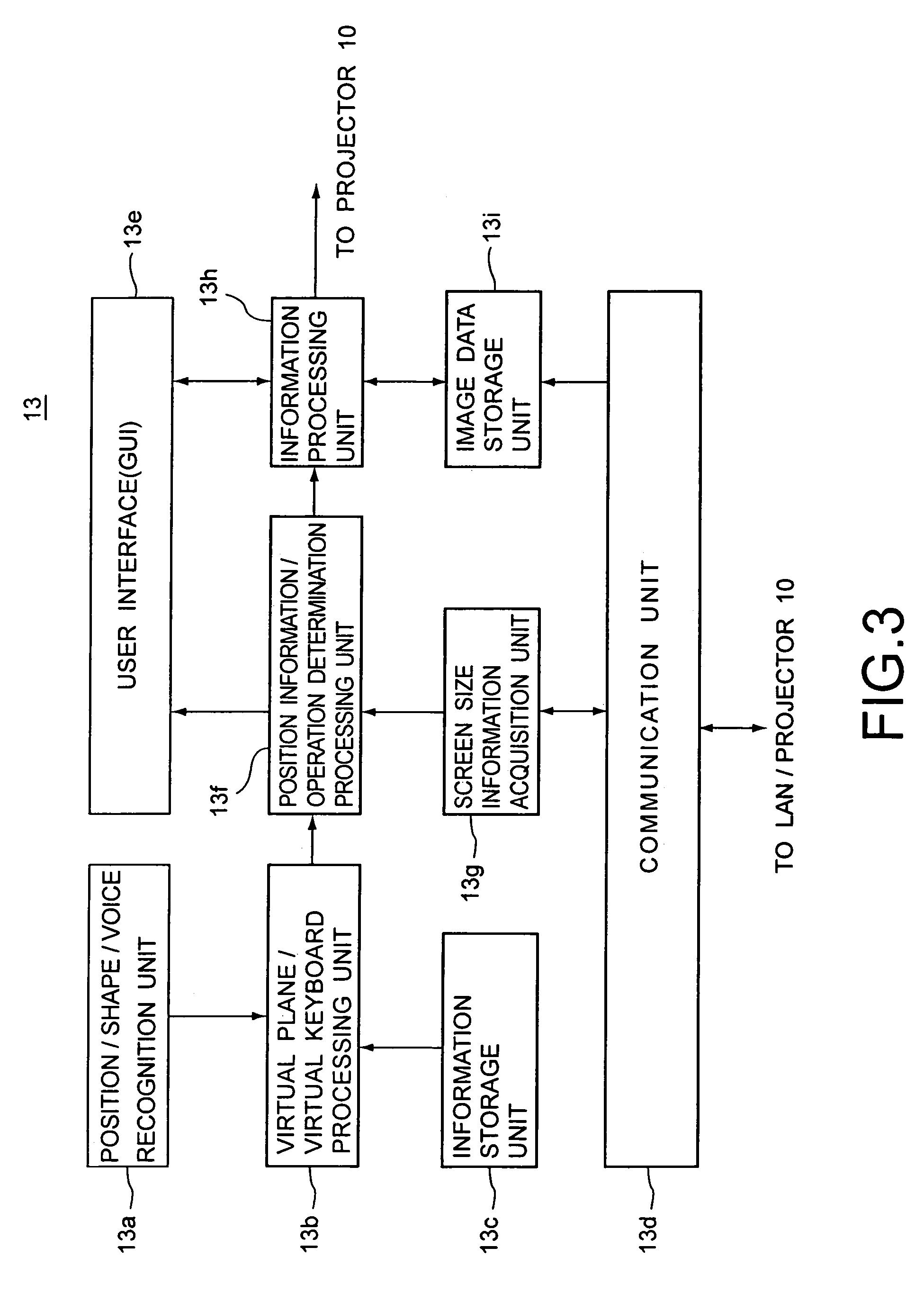
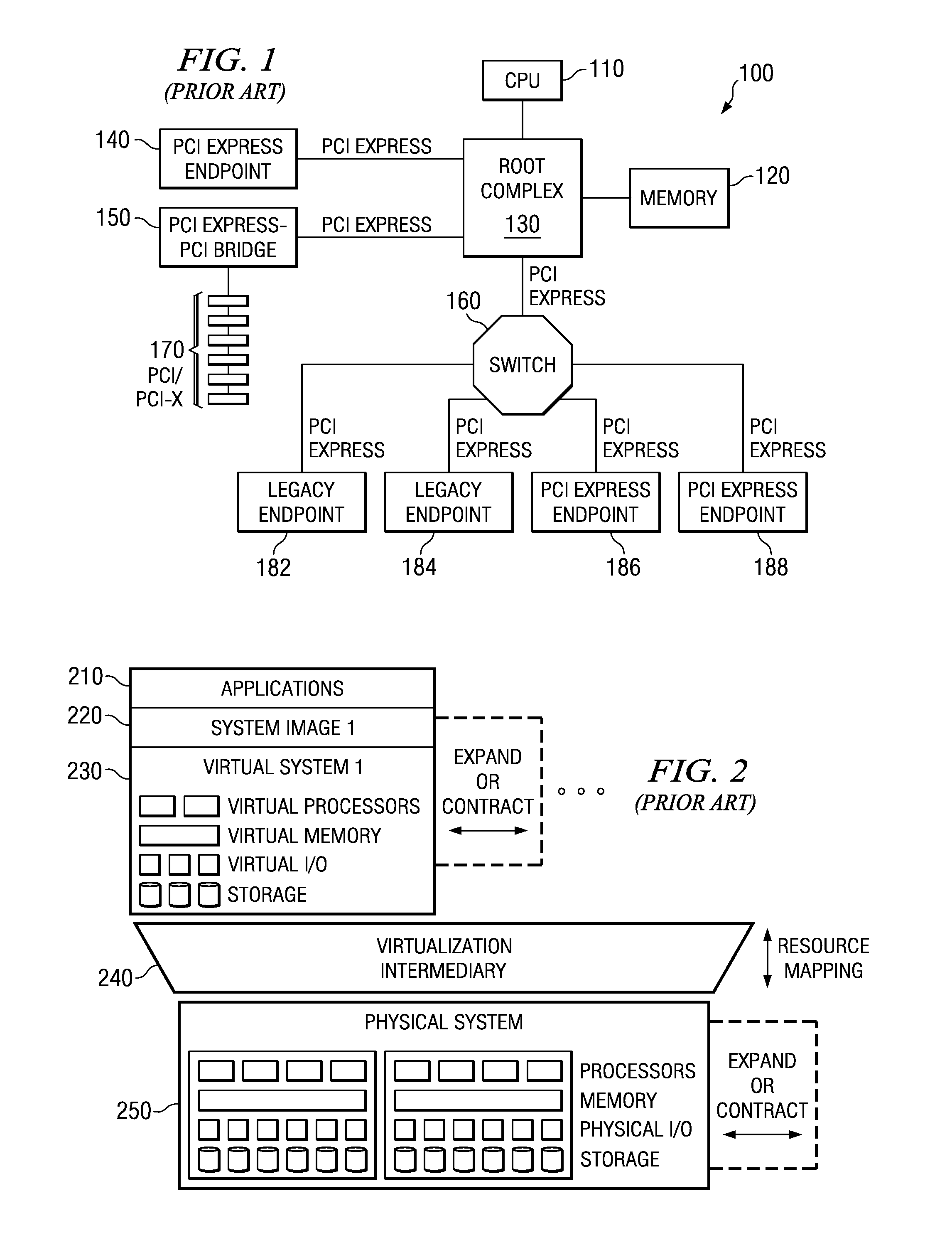
Method and apparatus for controlling user interface of electronic device using virtual plane
ActiveUS20080120577A1Easy to controlEasy to operateInput/output processes for data processingLocation detectionComputer graphics (images)
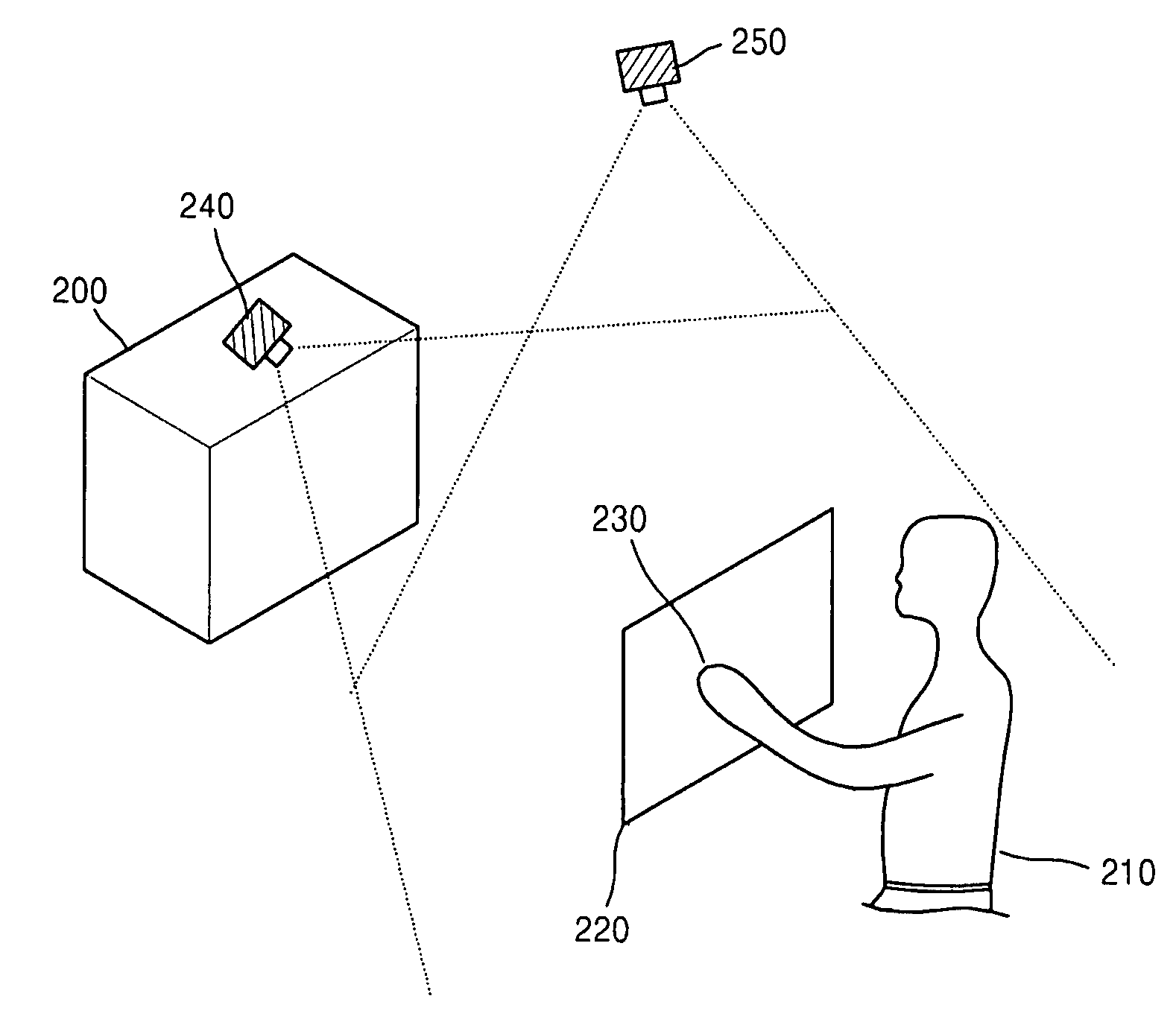
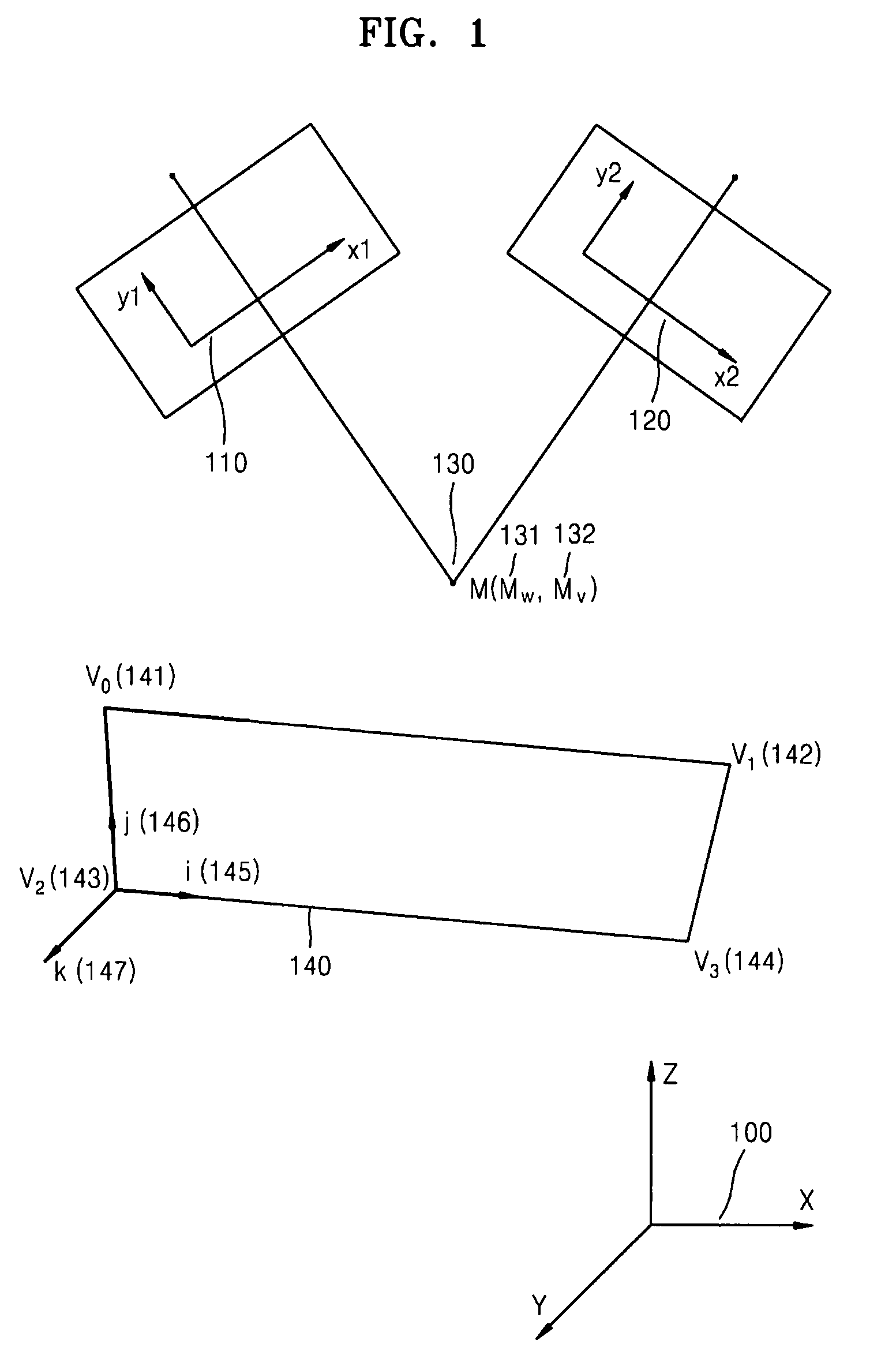
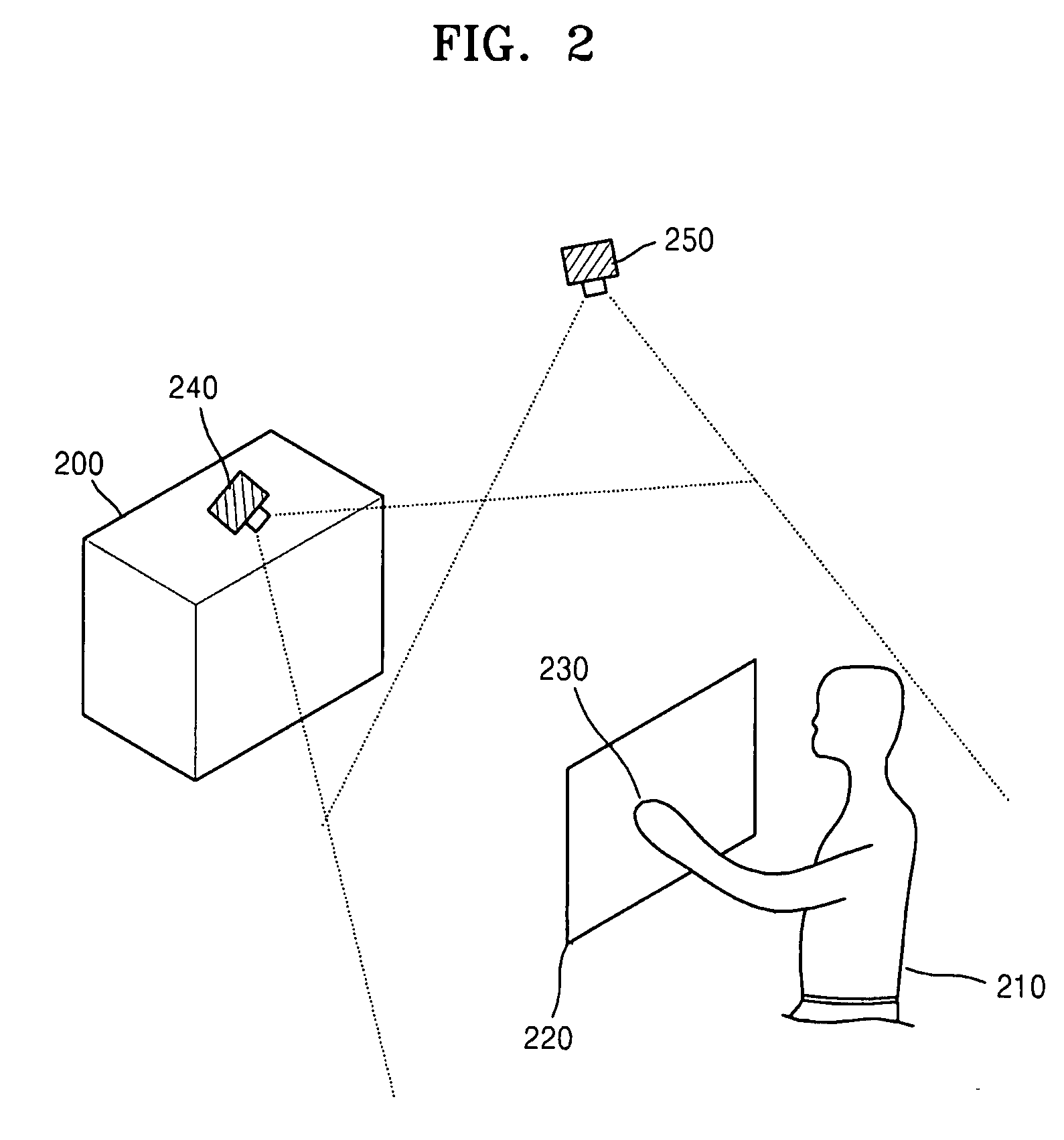
Provided is a method and apparatus for controlling a user interface (UI) of an electronic device by using a specific region of a virtual plane. In the method, the virtual plane is initialized according to spatial coordinates of two or more images detected by using locations of the images displayed in an image display unit of a first image capture device and an image display unit of a second image capture device. Furthermore, the location of a marker is determined and is indicated by a specific image on the virtual plane. Furthermore, a screen pointer corresponding to the marker is displayed at a position where the marker is located in an image display unit corresponding to the virtual plane. Furthermore, a menu of the electronic device is selected which is pointed to by the screen pointer while moving the marker. Accordingly, a user can conveniently control the UI of the electronic device by performing a simple operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lighting device with built-in RF antenna
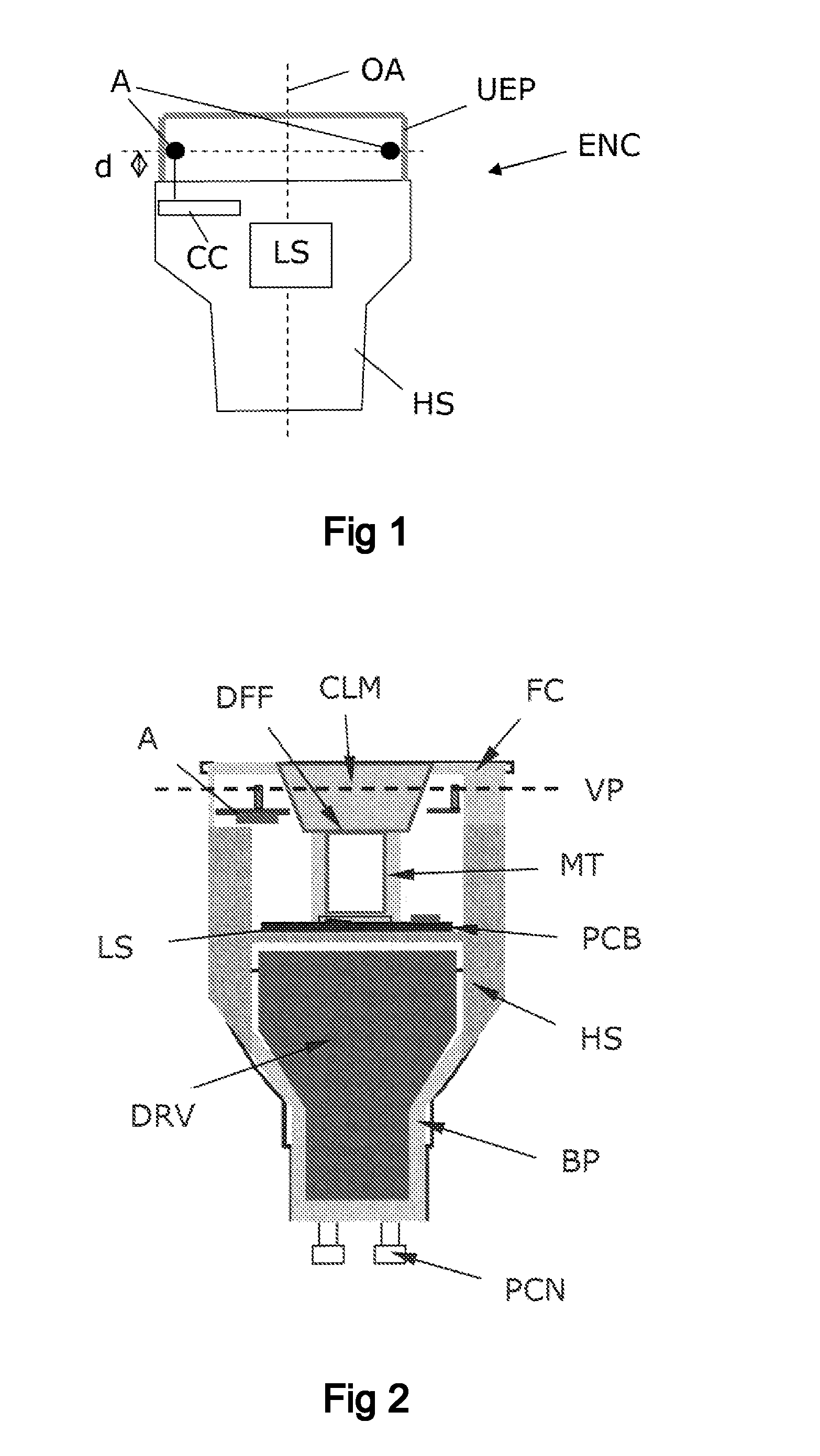
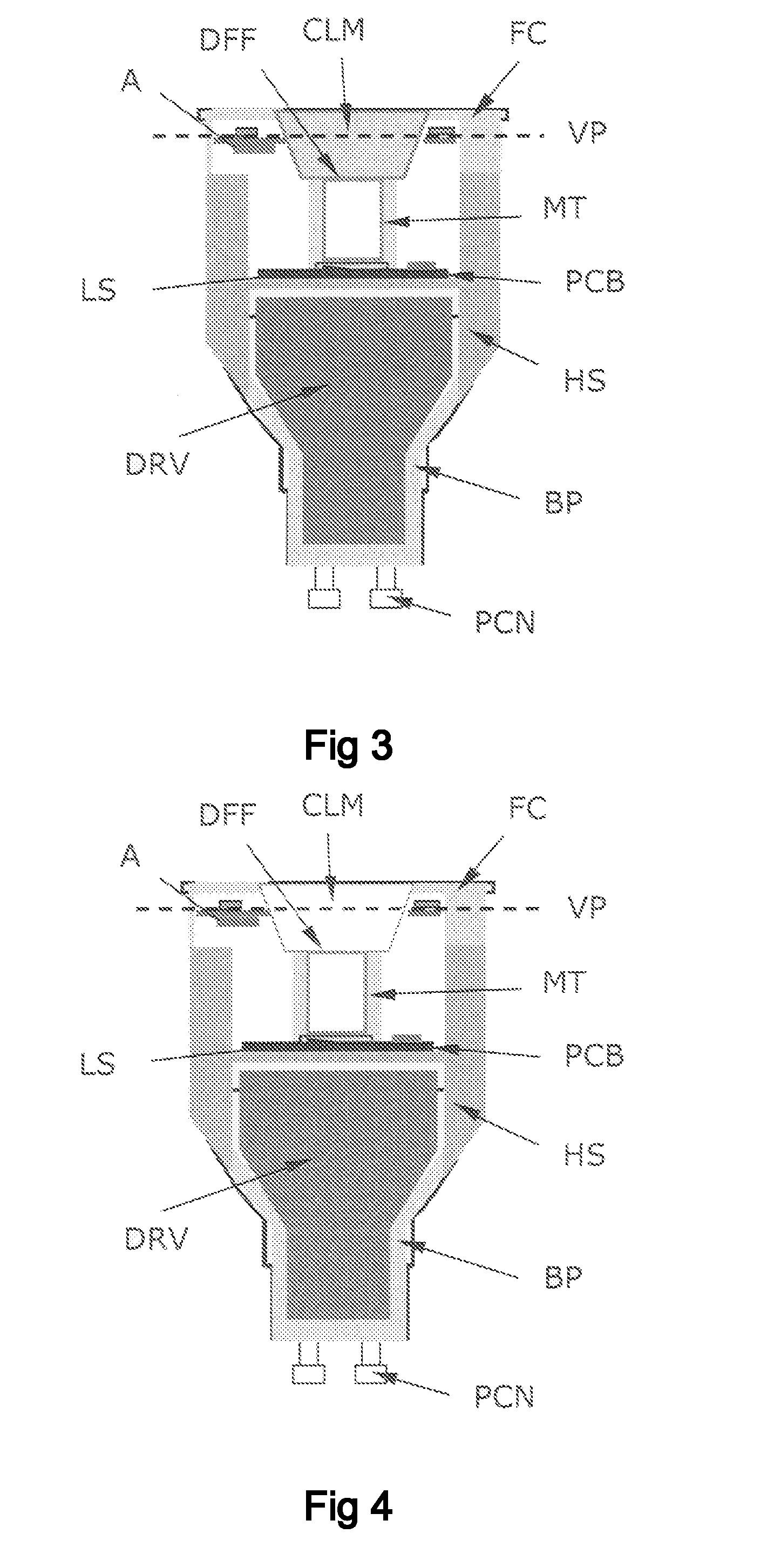
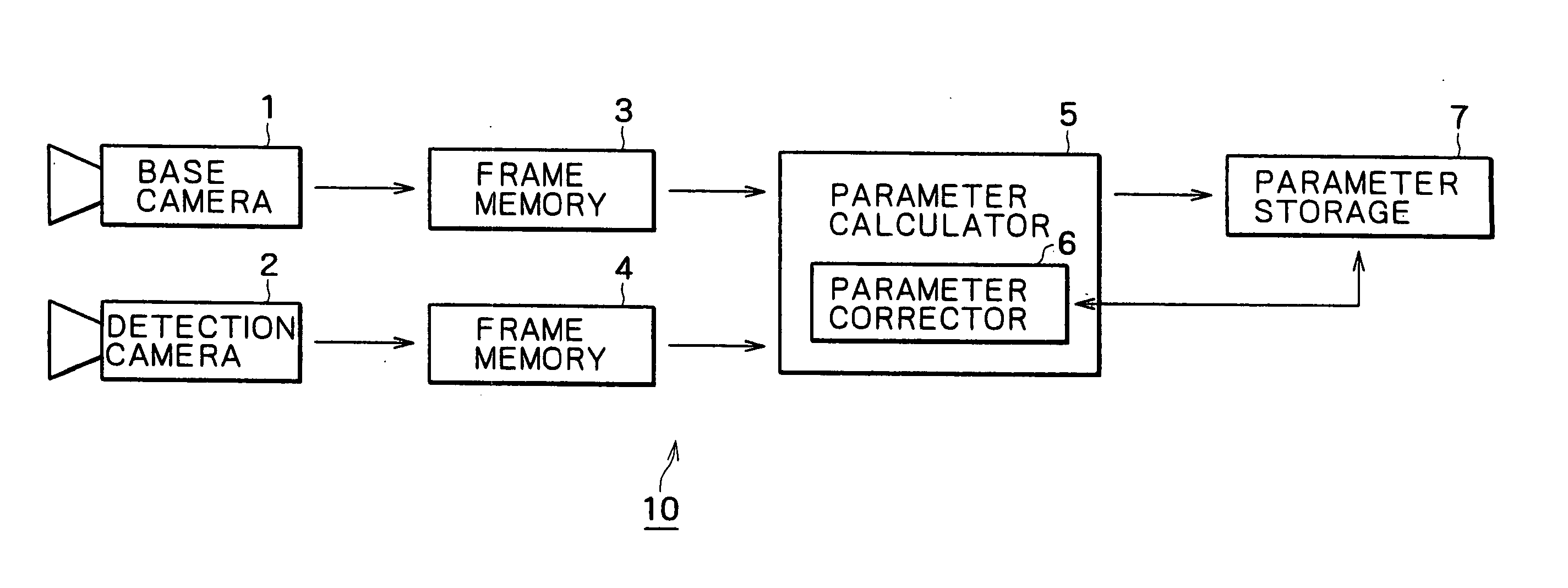
ActiveUS20120274208A1Remove unavoidable heat dissipationSmall sizeLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceRemote controlOptical axis
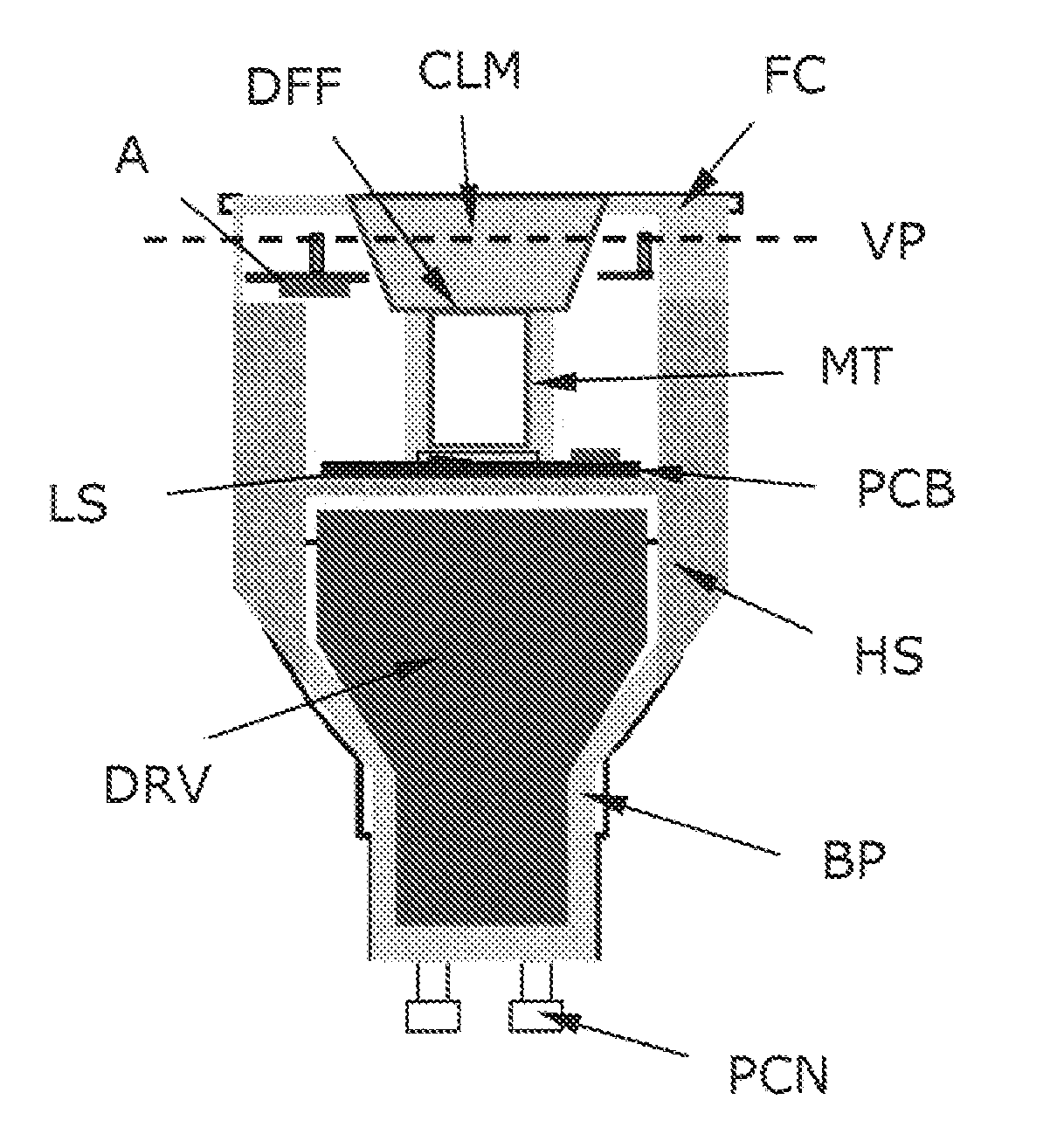
A lighting device, such as a replacement lighting device, comprising a light source (LS), e.g. LEDs, for producing light along an optical axis (OA). A heat sink (HS) made of a material with an electrical resistivity being less than 0.01 Ωm, e.g. a metallic heat sink being a part of the housing, transports heat away from the light source (LS). A Radio Frequency (RF) communication circuit (CC) connected to an an antenna (A) serves to enable RF signal communication, e.g. to control the device via a remote control. Metallic components, including the heat sink (HS), having an extension larger than 1 / 10 of a wavelength of the RF signal are arranged below a virtual plane (VP) drawn orthogonal to the optical axis (OA) and going through the antenna (A). Hereby a compact device can be obtained, and still a satisfying RF radiation pattern can be obtained. The antenna can be a wire antenna or a PCB antenna, e.g. a PIFA or a IFA type antenna. In a special embodiment the antenna is formed on a ring-shaped PCB with a central hole allowing passage of light from the light source. Preferably, the antenna is positioned at least 2 mm in front of the heat sink (HS).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
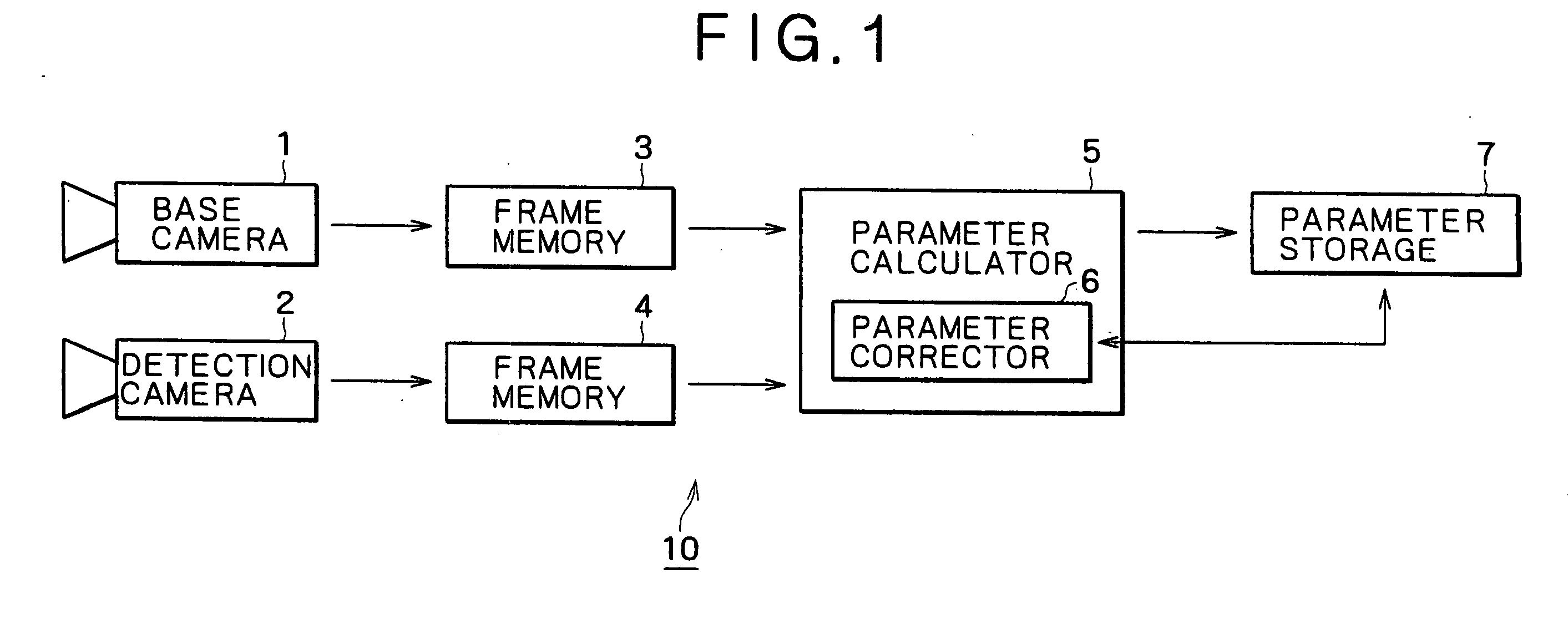
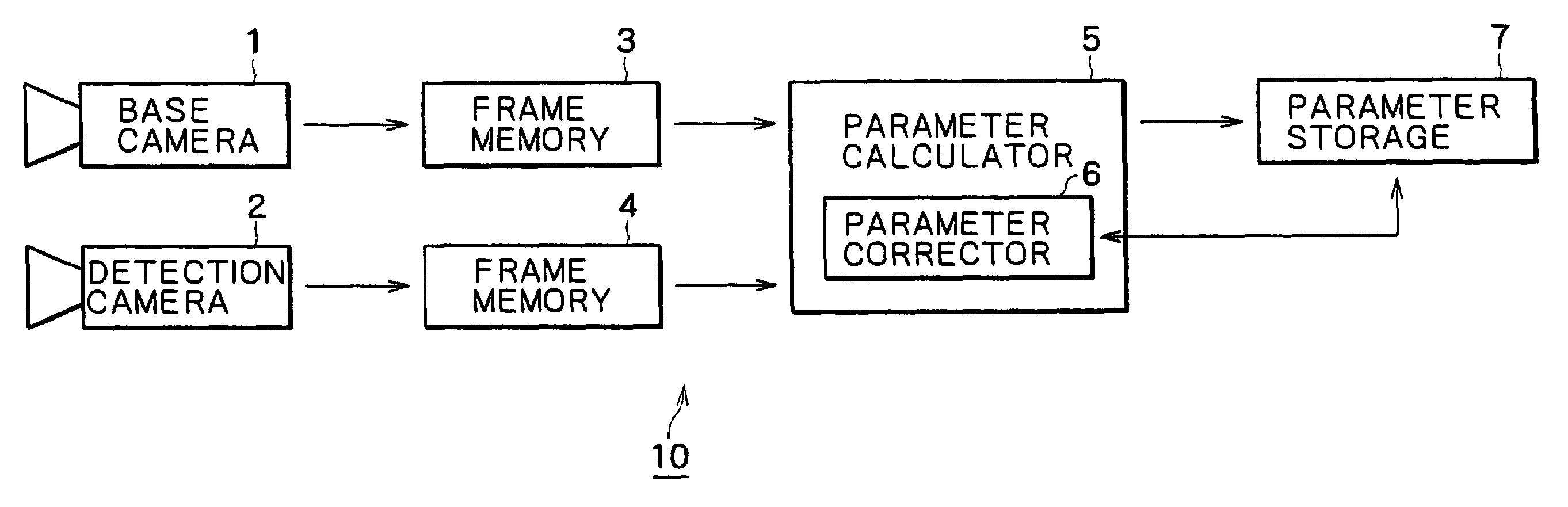
Camera calibration device and method, and computer system
InactiveUS20050185049A1Easy CalibrationEasy to limitImage analysisOptical rangefindersHat matrixCamera lens
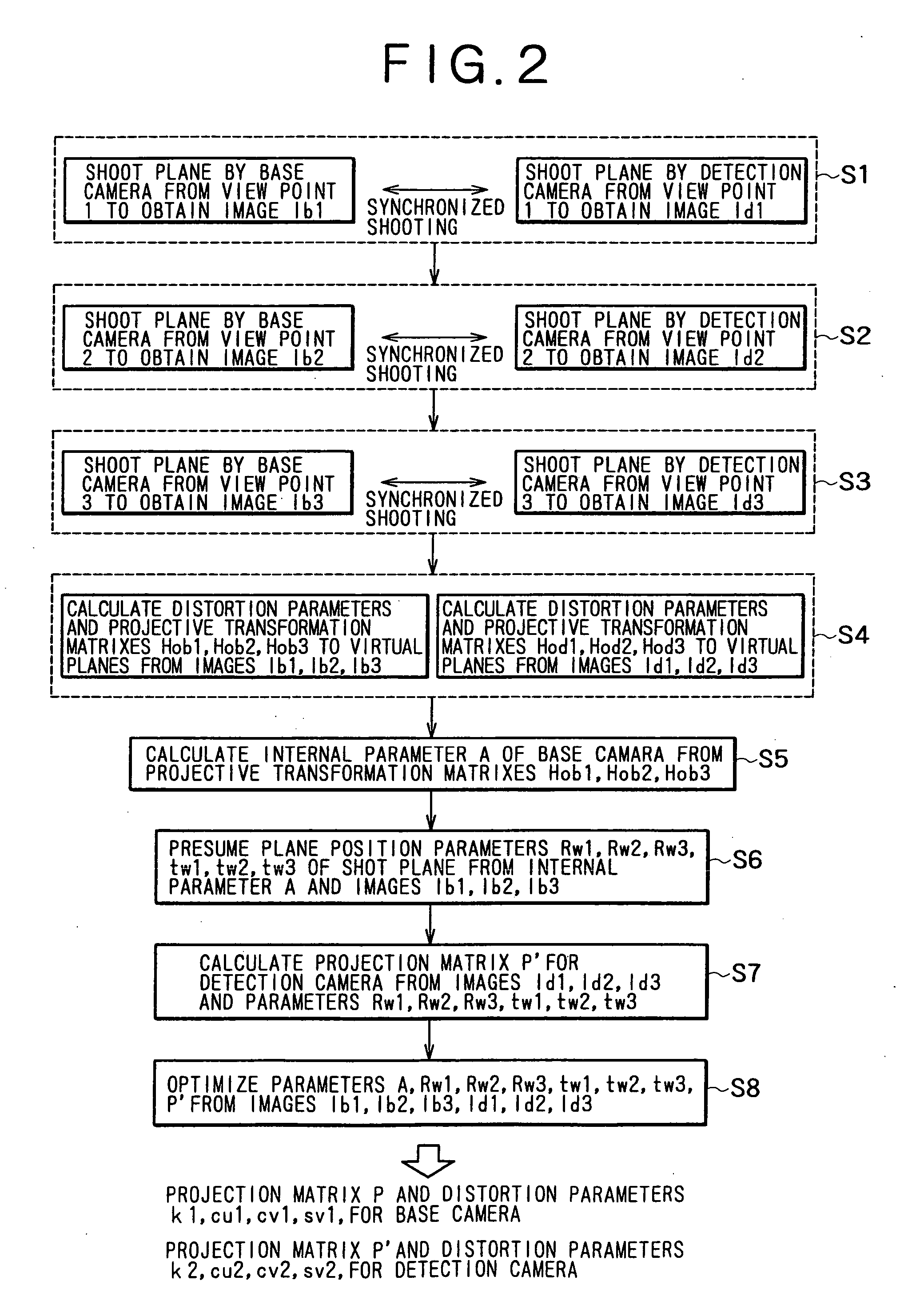
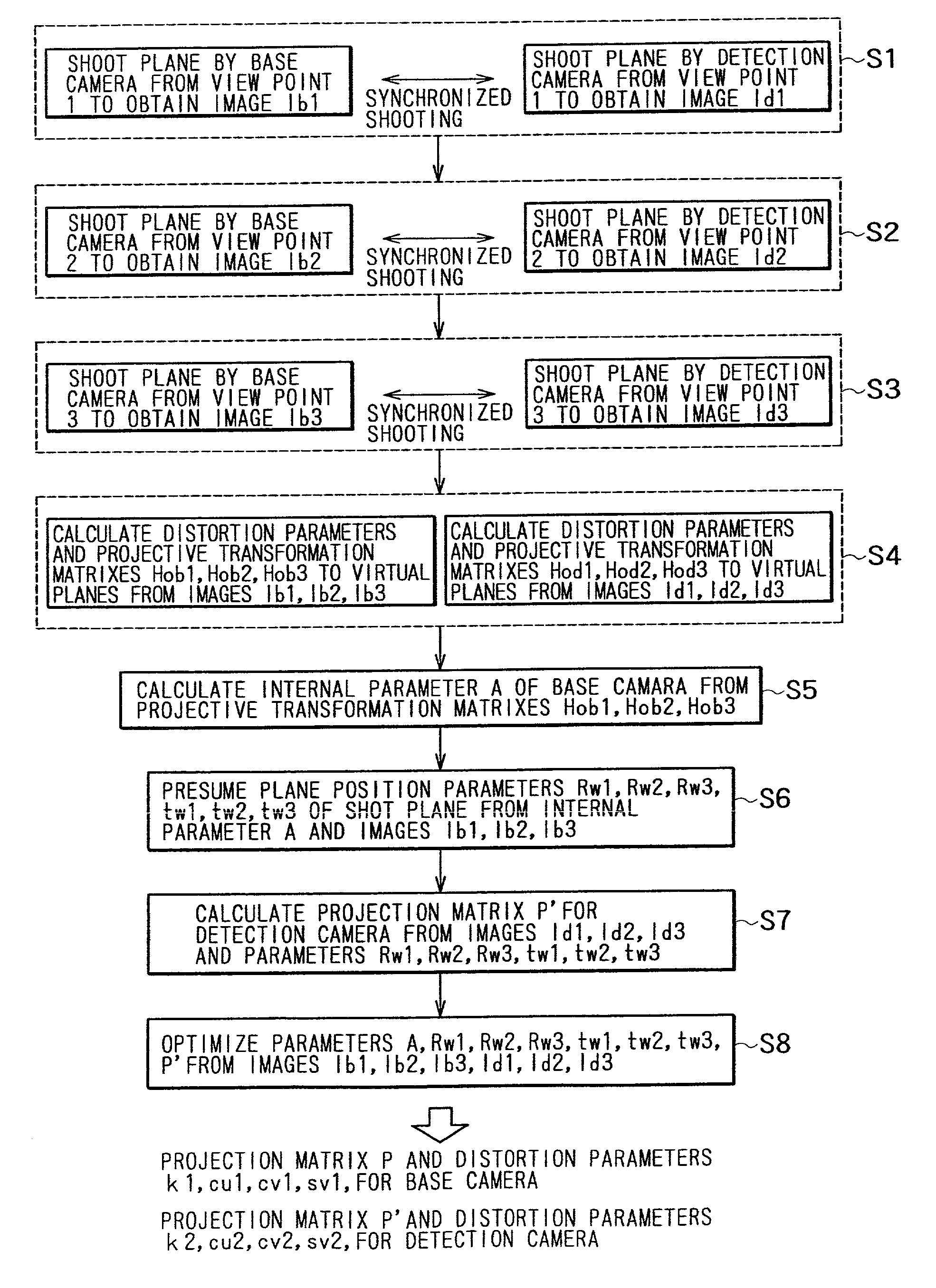
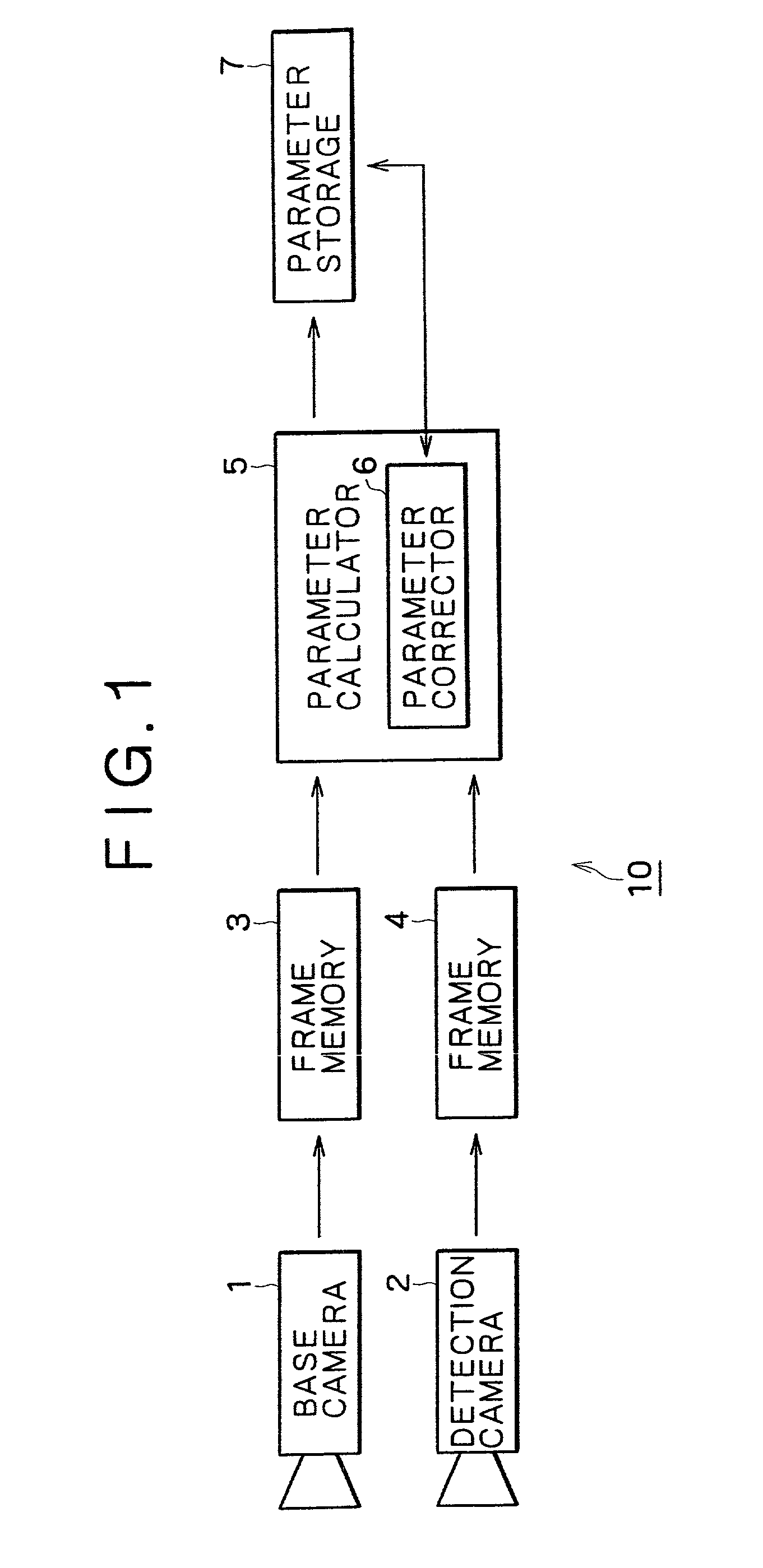
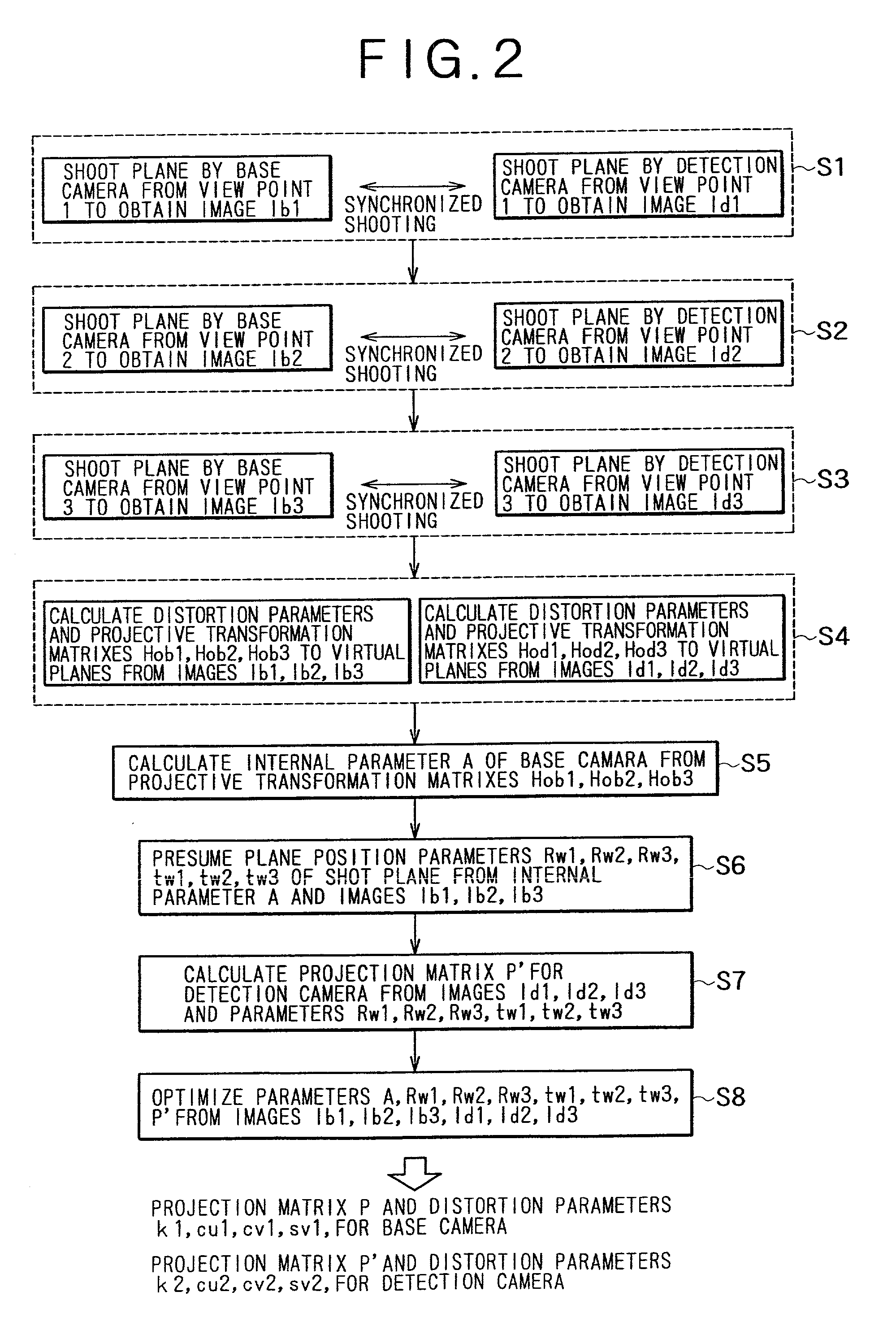
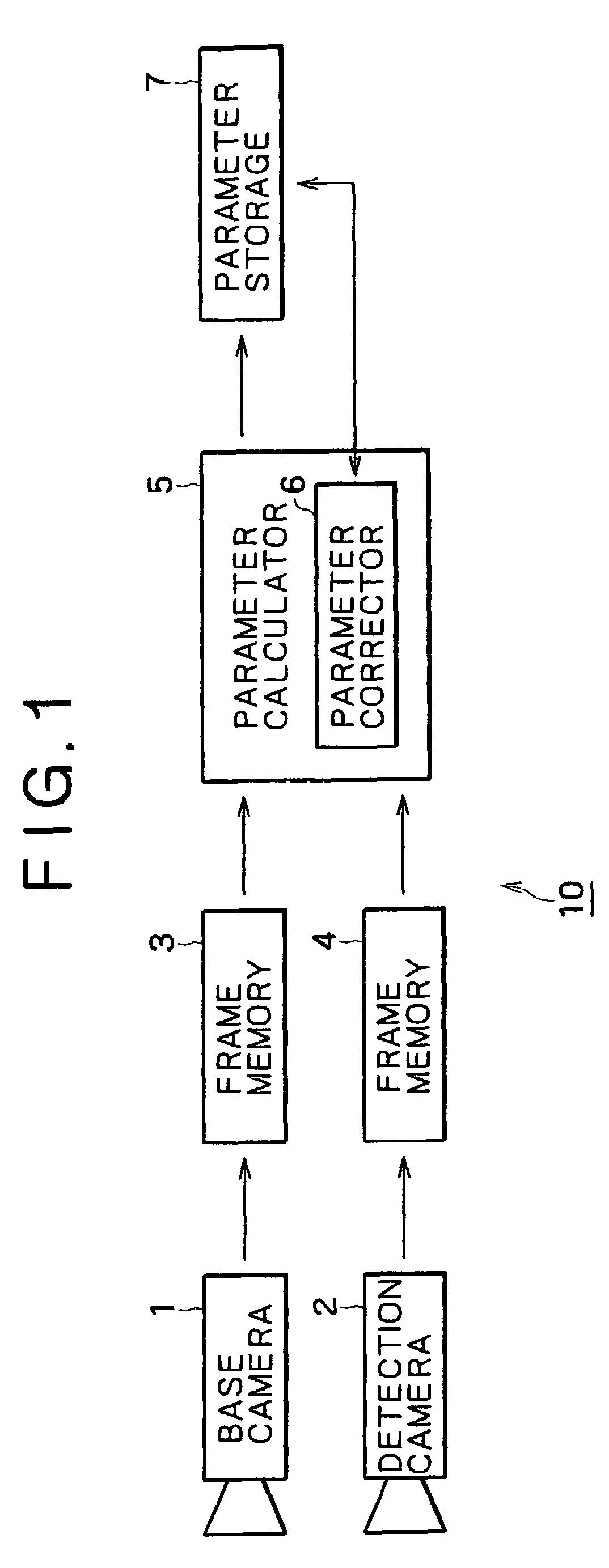
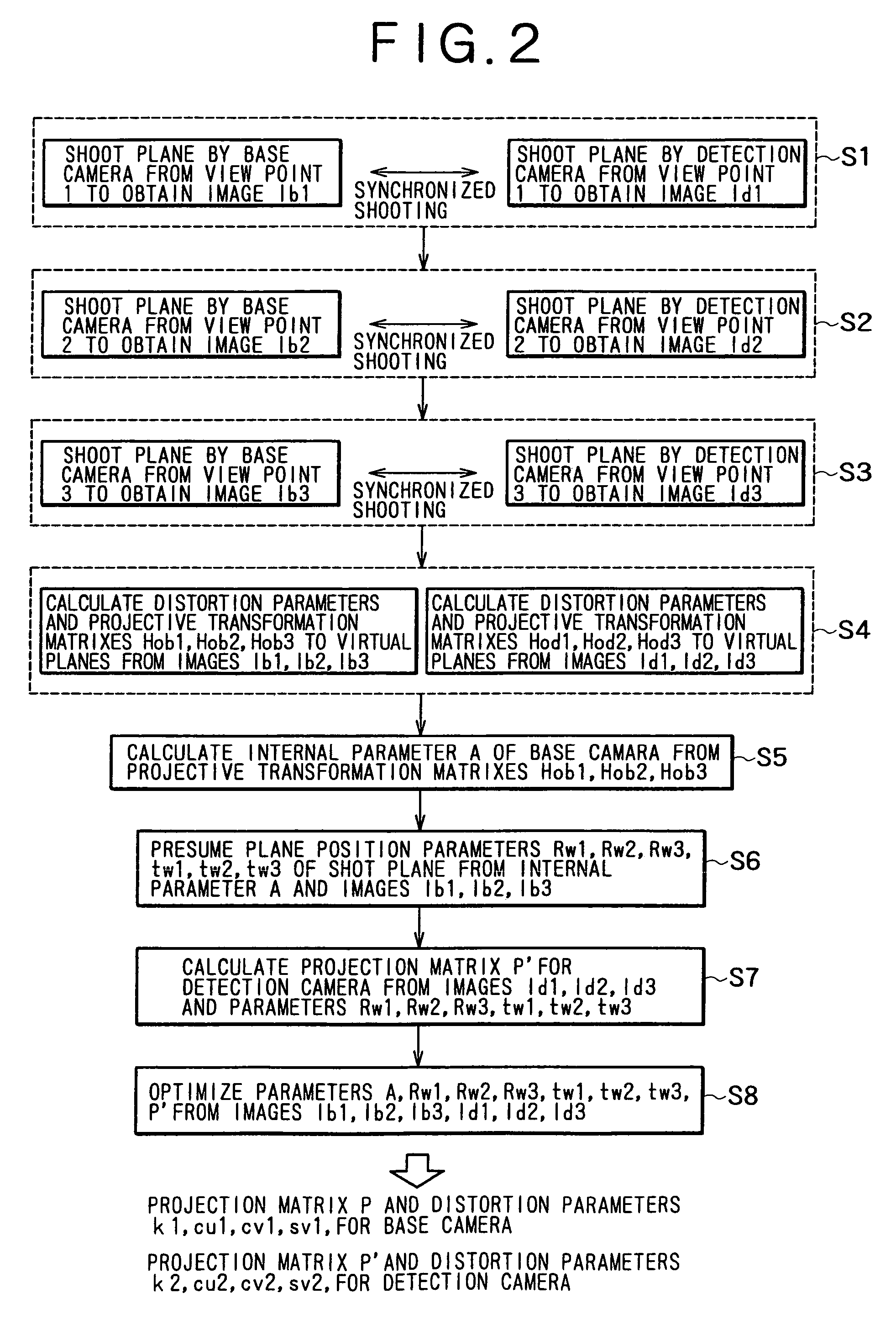
A camera calibration device capable of simply calibrating a stereo system consisting of a base camera and a detection camera. First, distortion parameters of the two cameras necessary for distance measurement are presumed by the use of images obtained by shooting a patterned object plane with the base camera and the reference camera at three or more view points free from any spatial positional restriction, and projective transformation matrixes for projecting the images respectively onto predetermined virtual planes are calculated. Then internal parameters of the base camera are calculated on the basis of the projective transformation matrixes relative to the images obtained from the base camera. Subsequently the position of the shot plane is presumed on the basis of the internal parameter of the base camera and the images obtained therefrom, whereby projection matrixes for the detection camera are calculated on the basis of the plane position parameters and the images obtained from the detection camera. According to this device, simplified calibration can be achieved stably without the necessity of any exclusive appliance.
Owner:SONY CORP
Laser radar for three-dimensional scanning
InactiveUS20120249996A1Applied load reductionReduce loadOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam angleRadar
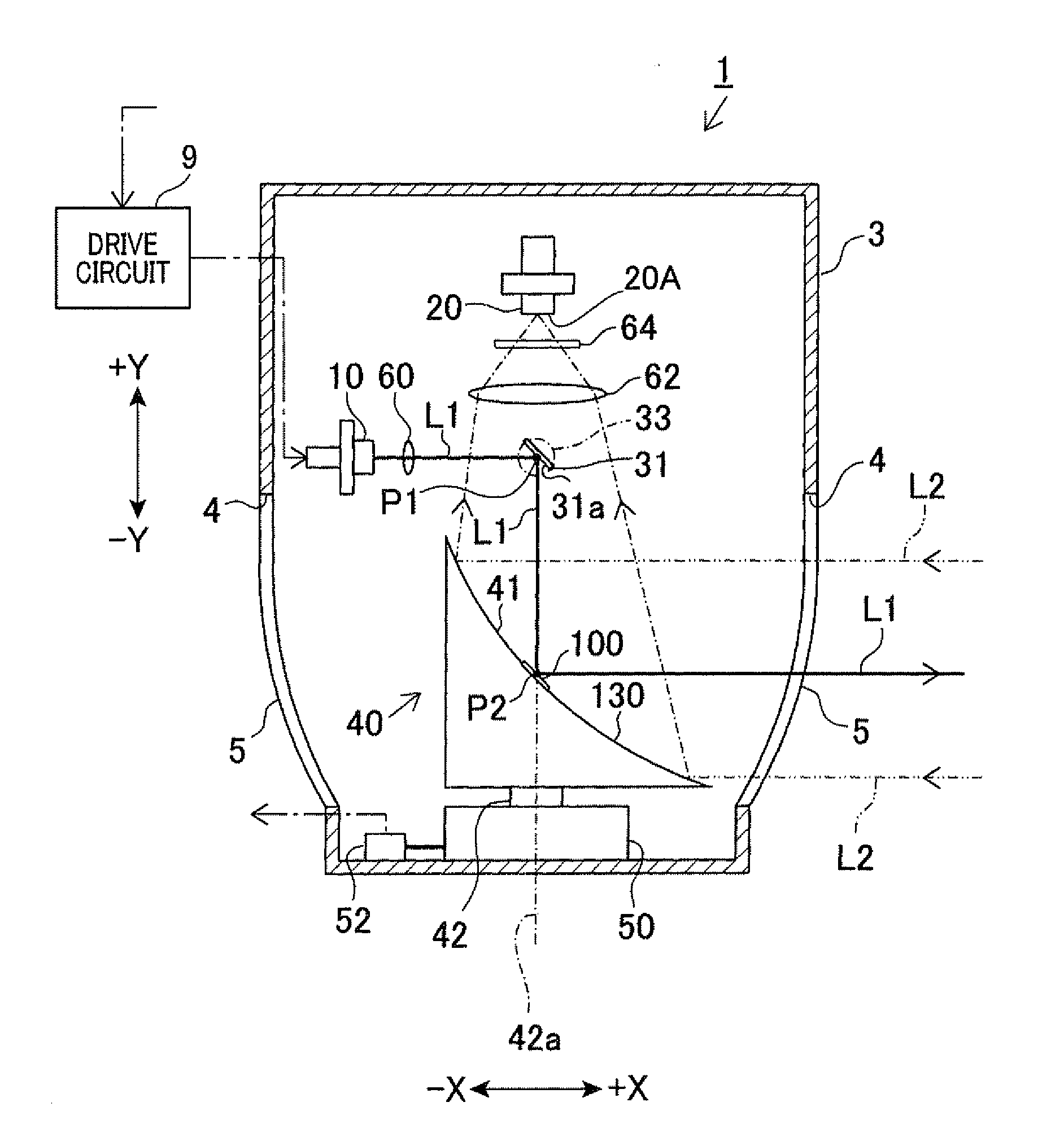
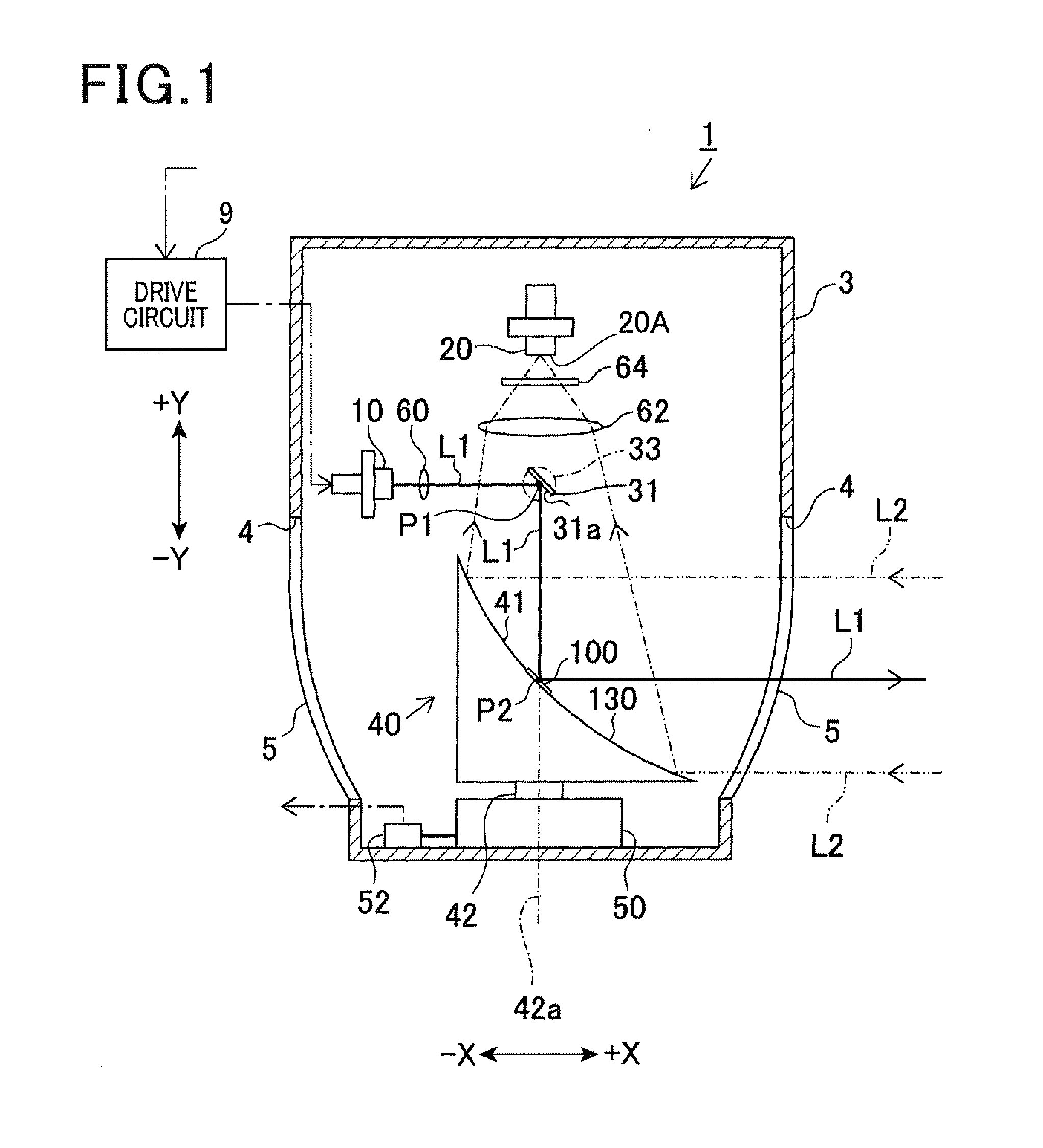
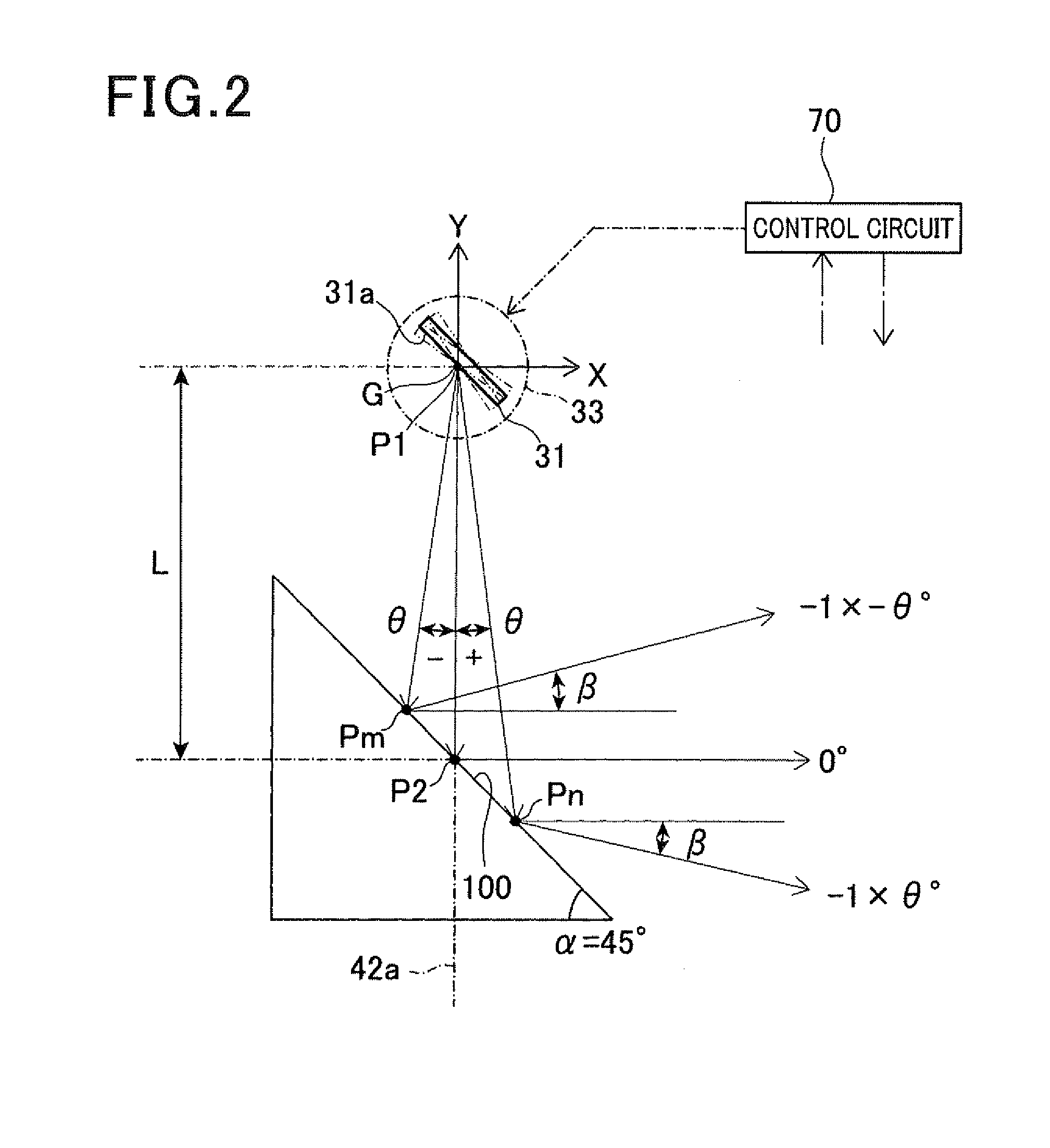
In a laser radar, a first scanning member scans a laser beam in a virtual plane passing through an axis. A control means controls displacements of the first scanning member to change a scan beam angle in the plane. A second scanning member deflects the scanned laser beam and again scans the deflected laser beam toward an external space. A light collecting means collects reflected light. A driving means rotates both the second scanning member and the light collecting means about the axis. The second scanning member has a deflecting surface to deflect the laser beam. The deflecting surface is formed around the axis and has a plurality of reflecting surfaces coaxially arranged centering on the axis. The reflecting surfaces have different inclinations with respect to a horizontal plane perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:DENSO WAVE INC
Camera calibration device and method, and computer system
InactiveUS6985175B2Simply carrying out camera calibrationImage analysisOptical rangefindersHat matrixCamera lens
A camera calibration device capable of simply calibrating a stereo system consisting of a base camera and detection camera. First, distortion parameters of the two cameras necessary for distance measurement are presumed by the use of images obtained by shooting a patterned object plane with the base camera and the reference camera at three or more view points free from any spatial positional restriction, and projective transformation matrixes for projecting the images respectively onto predetermined virtual planes are calculated. Then internal parameters of the base camera are calculated on the basis of the projective transformation matrixes relative to the images obtained from the base camera. Subsequently the position of the shot plane is presumed on the basis of the internal parameter of the base camera and the images obtained therefrom, whereby projection matrixes for the detection camera are calculated on the basis of the plane position parameters and the images obtained from the detection camera. According to this device, simplified calibration can be achieved stably without the necessity of any exclusive appliance.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image heating apparatus using flexible sleeve
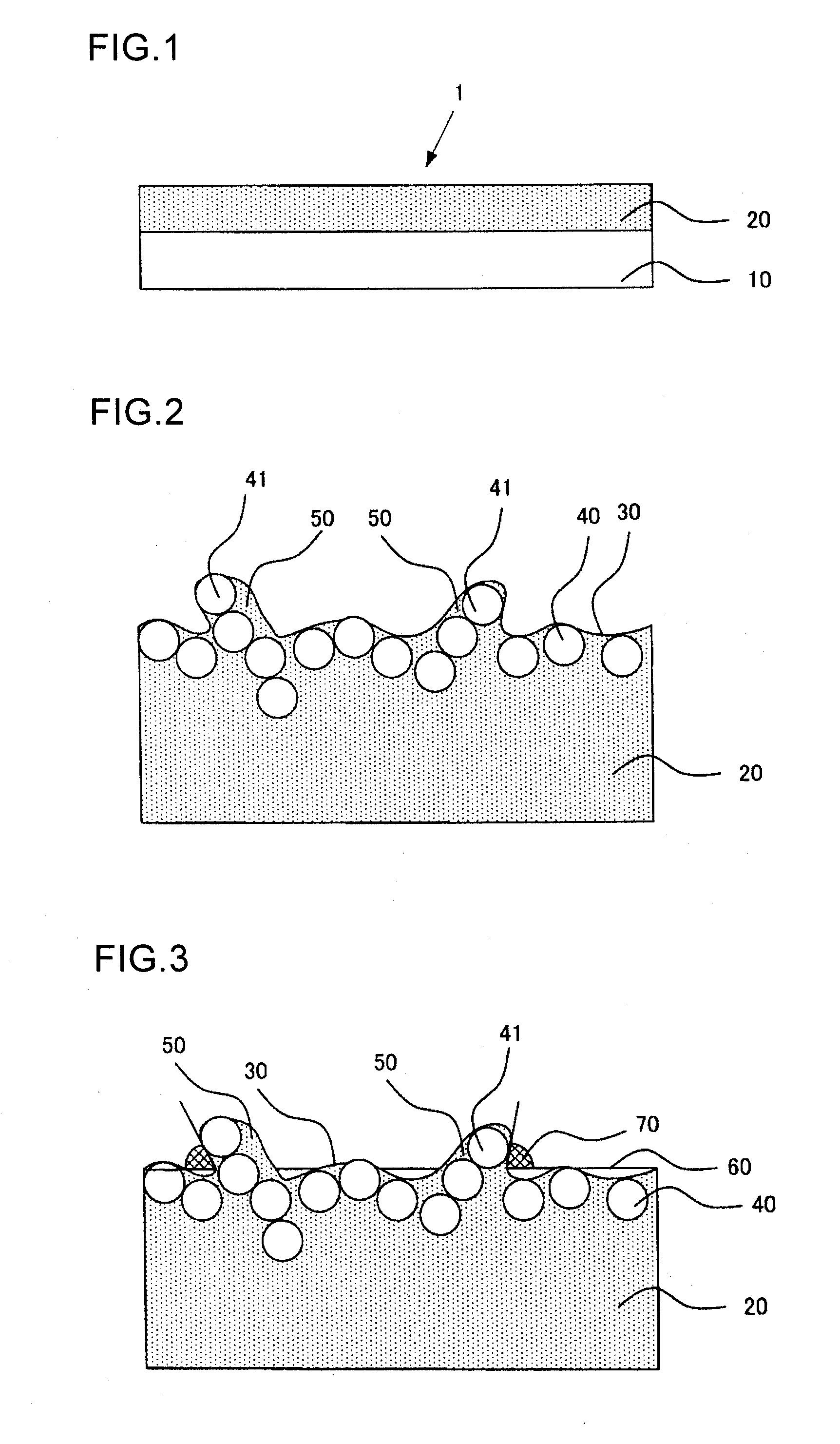
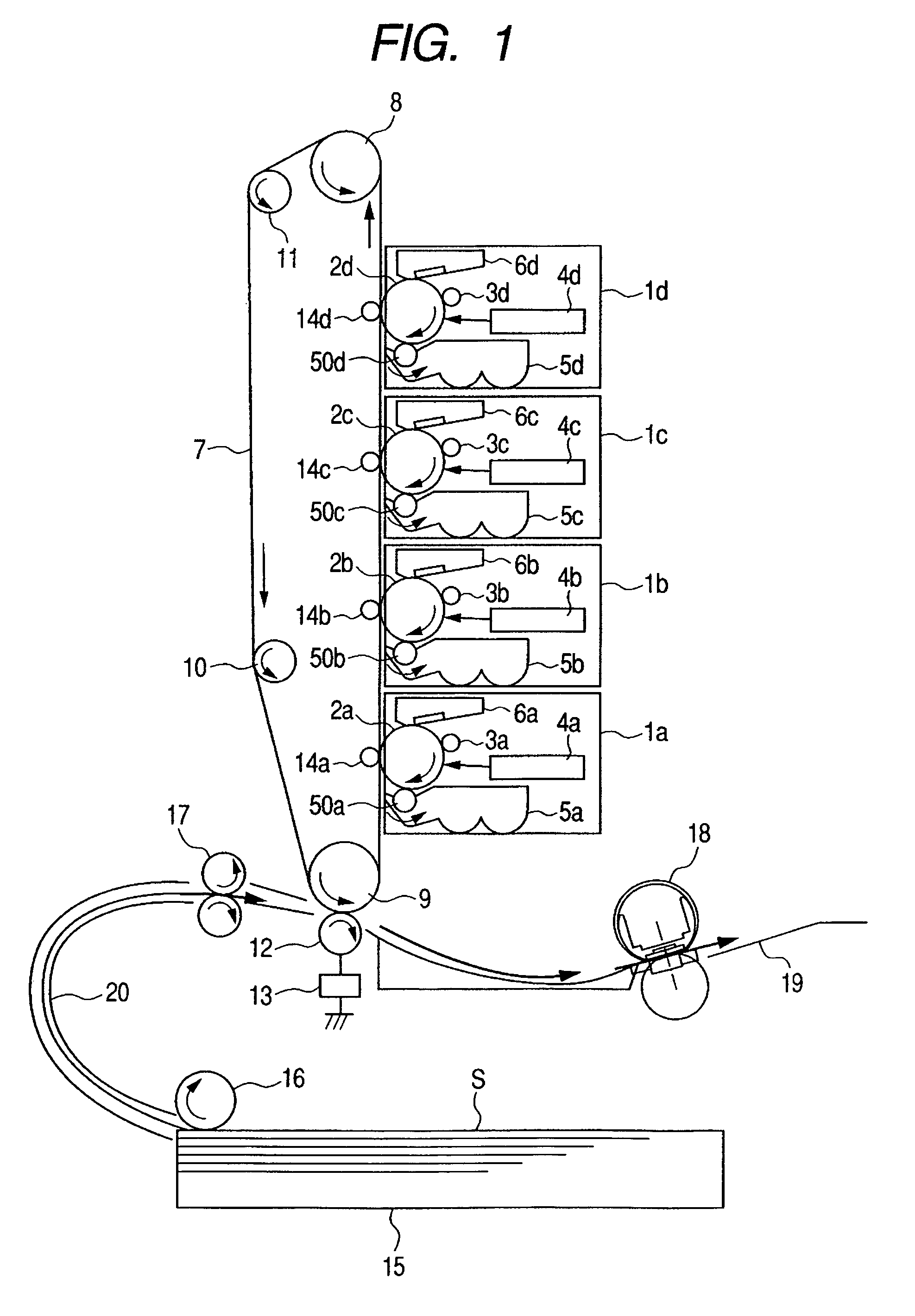
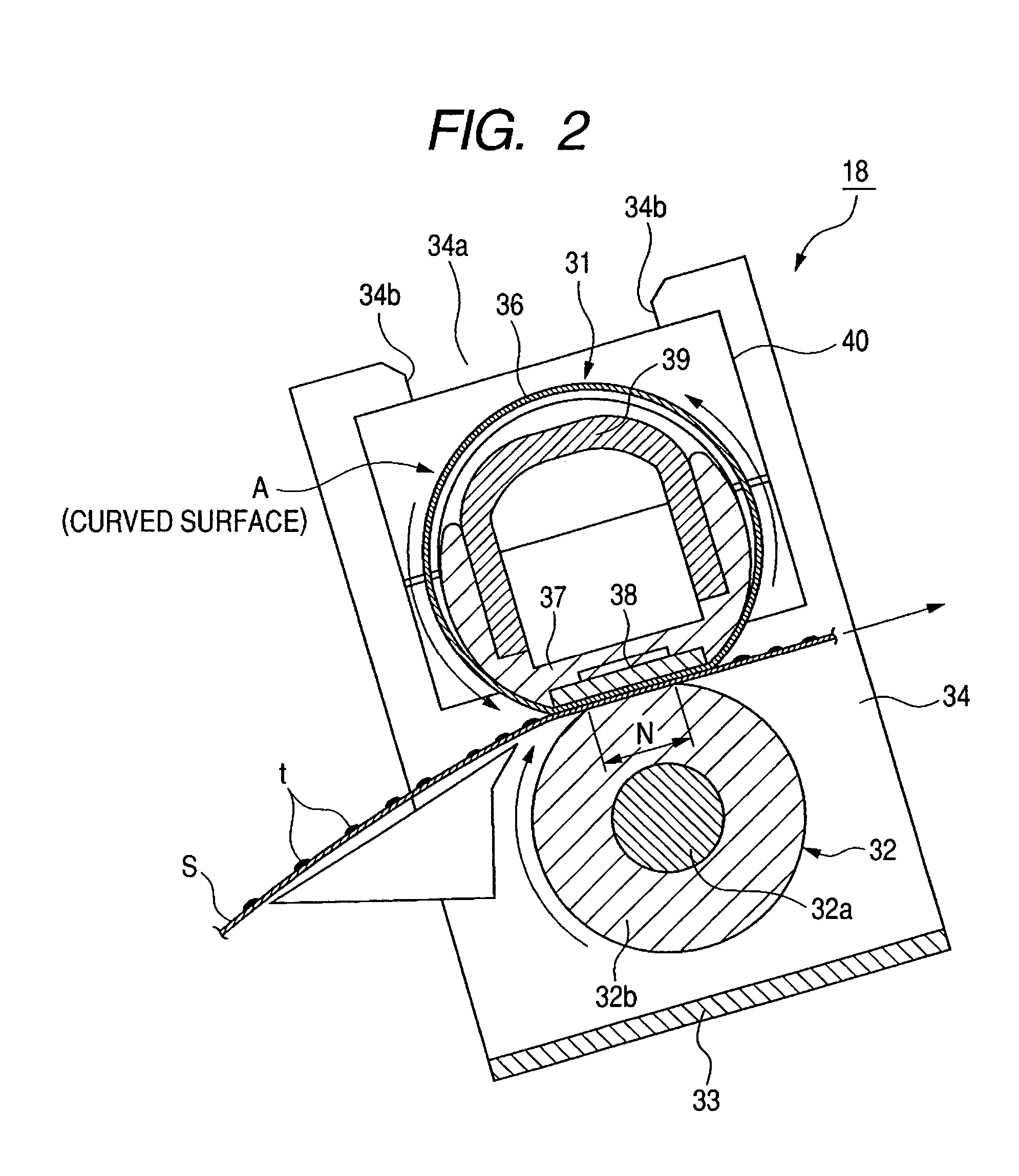
ActiveUS20060233575A1Preventing deterioration of durabilityIncreased durabilityElectrographic process apparatusEdge surfaceEngineering
The image heating apparatus includes a flexible sleeve, a sliding member for sliding on the inner periphery of the sleeve, a back-up member for forming a nip portion together with the sliding member through the sleeve, wherein a recording material for bearing an image is heated while being held and conveyed by the nip portion and a regulation member set by facing the edge surface of the sleeve in the generatrix direction to regulate the movement of the sleeve in the generatrix direction, the regulation surface having a regulation surface with which the edge surface of the sleeve contacts when the sleeve moves in the generatrix direction, wherein the regulation surface of the regulation member has a curved-surface area in which a line when the regulation surface is cut at a virtual plane almost parallel with the nip portion is a curved line expanede toward the edge surface of the sleeve. Thereby, an image heating apparatus is provided which is able to restrain deterioration of the durability of the flexible sleeve.
Owner:CANON KK
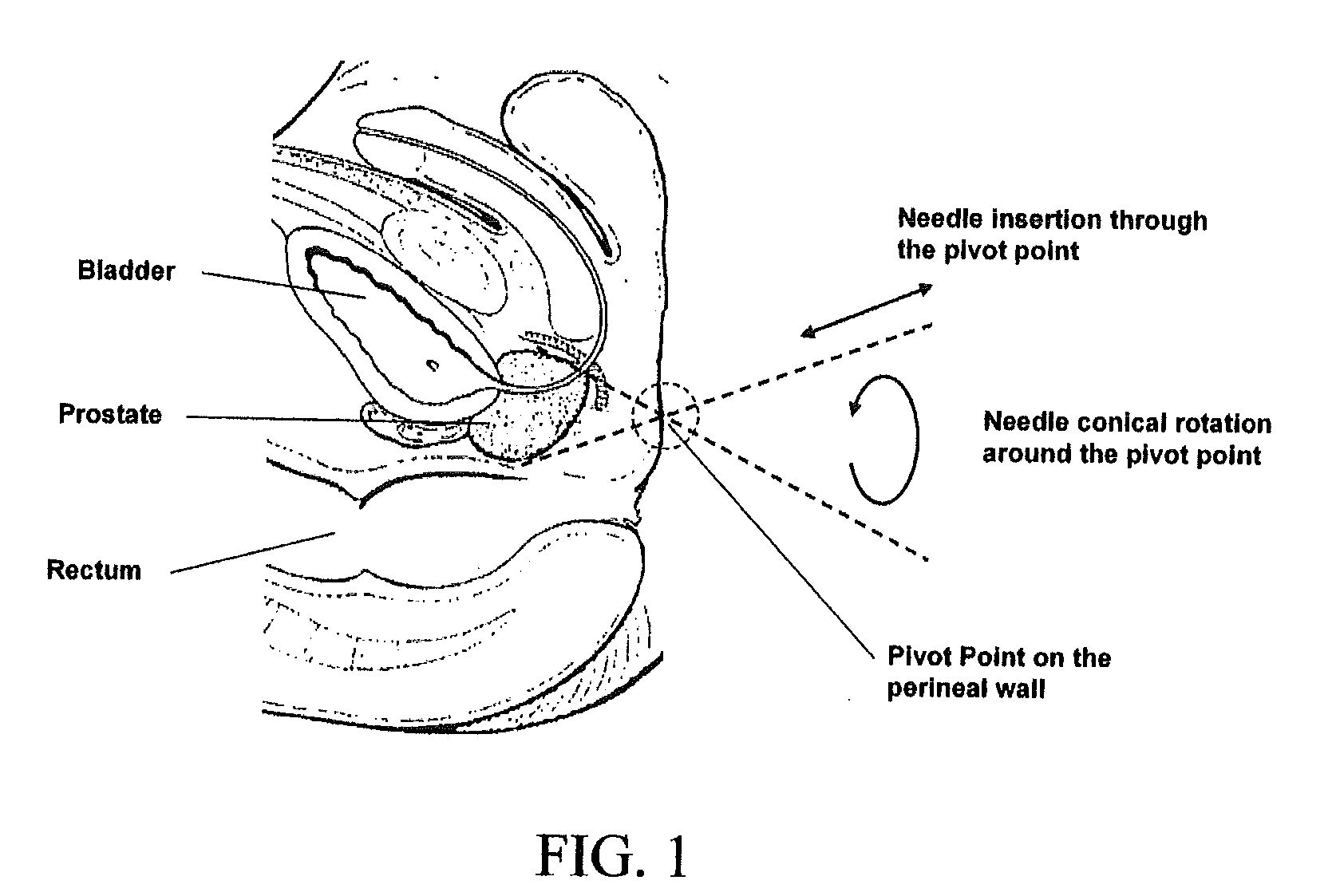
Apparatus and method for motorised placement of needle
InactiveUS20090030339A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingManual insertion
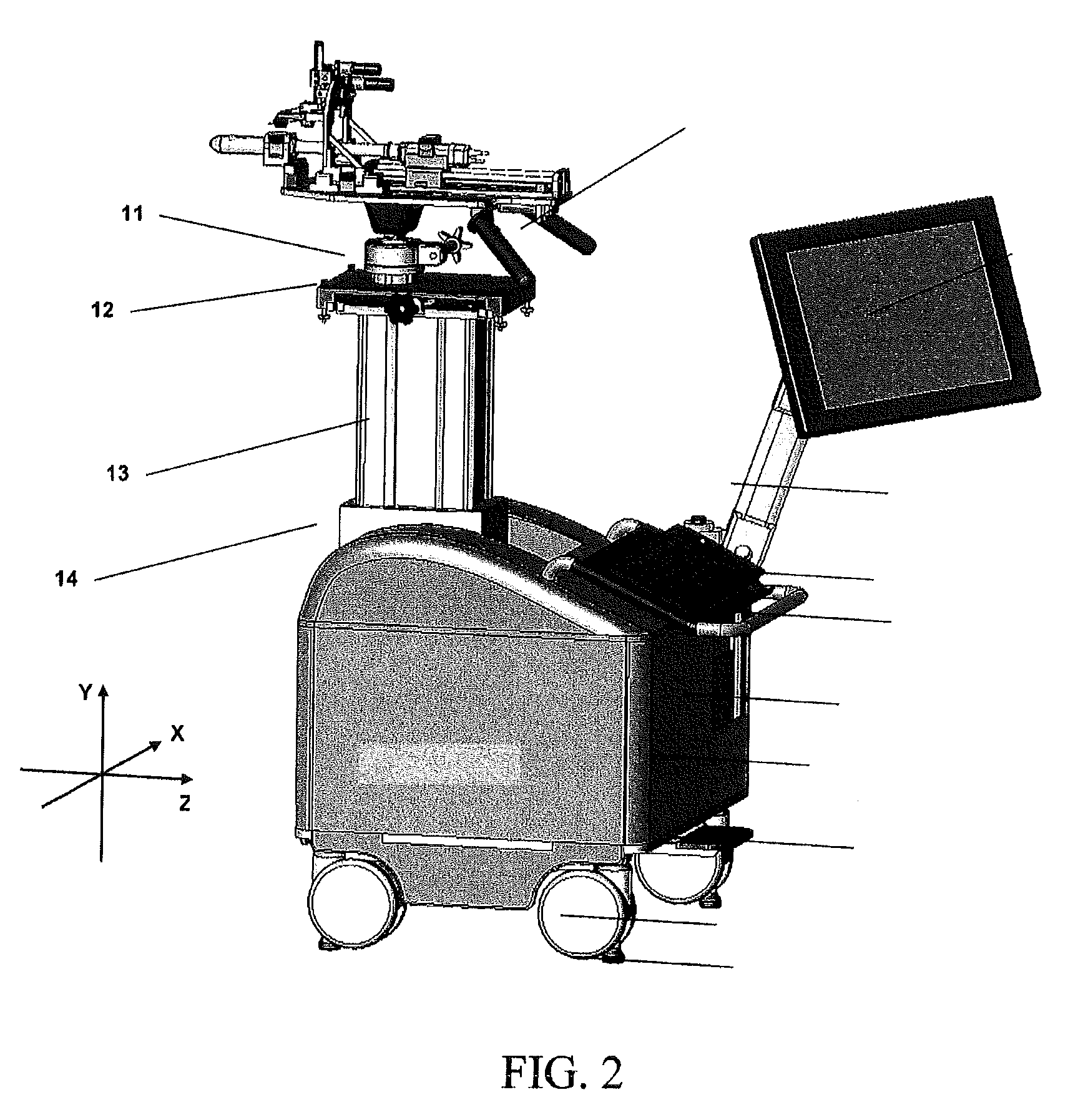
The present invention provides a method and apparatus to insert a needle through a predetermined trajectory and with a predetermined depth, in order to reach a target accurately within soft tissue, under ultrasound imaging guidance. The invention can be applied to carry out, for example, prostate biopsy, or prostate brachytherapy. The apparatus can guide a biopsy needle into defined sites in the prostate gland. A conical approach is used to reach the prostate through one or more pivot points on the perineal wall. The biopsy needle penetrates the patient's skin through the pivot point for multiple cores. The apparatus holds a needle sheath with two ball joints. The orientation of the needle sheath is controlled by locking the front ball joint at the pivot point, and moving the back ball joint on a virtual plane. The biopsy needle is inserted manually through the needle sheath. The depth of the insertion is controlled by the position of the stopper on the biopsy gun holder. Both the orientation and depth stopper are preferably driven by motors.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +1
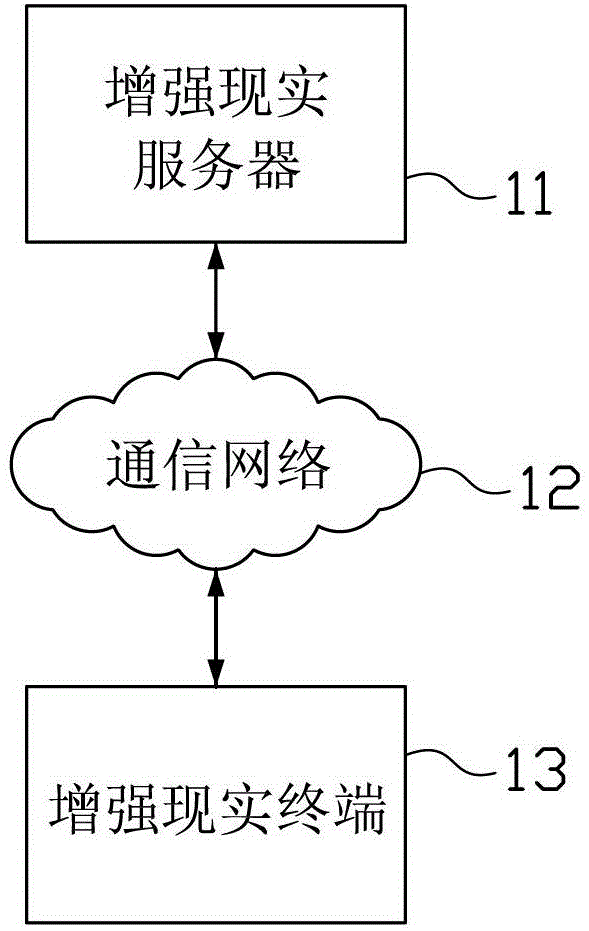
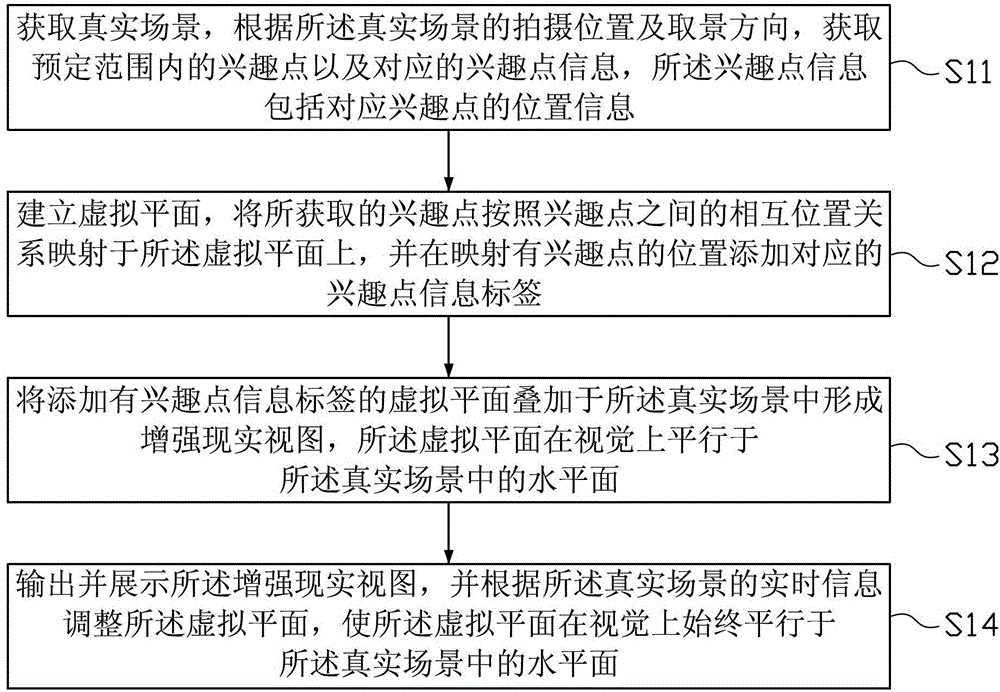
Method and device for realizing augmented reality
ActiveCN104102678AThree-dimensionalLayeredImage data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsTime informationComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a method and a device for realizing augmented reality. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a real scene, and obtaining interest points in a preset range and corresponding interest point information according to a camera site and a viewing direction of the real scene; establishing a virtual plane, mapping the obtained interest points on the virtual plane according to a mutual position relation among the interest points, and adding corresponding interest point information labels at positions, at which the interest points are mapped; forming an augmented reality view by overlaying the virtual plane, to which the interest point information labels are added, in the real scene, wherein the virtual plane is in parallel to a horizontal plane in the real scene based on visual sense; outputting and showing the augmented reality view, and adjusting the virtual plane according to real-time information of the real scene to enable that the virtual plane always is in parallel to the horizontal plane in the real scene based on the visual sense. According to the method and the device for realizing the augmented reality, the distance relation among the interest points and the mutual position relation between the interest points and the users can be more intuitively shown for the users.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Laser radar for three-dimensional scanning
InactiveUS8681319B2Reduce weight and sizeReduce MechanismsOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementBeam angleRadar
In a laser radar, a first scanning member scans a laser beam in a virtual plane passing through an axis. A control means controls displacements of the first scanning member to change a scan beam angle in the plane. A second scanning member deflects the scanned laser beam and again scans the deflected laser beam toward an external space. A light collecting means collects reflected light. A driving means rotates both the second scanning member and the light collecting means about the axis. The second scanning member has a deflecting surface to deflect the laser beam. The deflecting surface is formed around the axis and has a plurality of reflecting surfaces coaxially arranged centering on the axis. The reflecting surfaces have different inclinations with respect to a horizontal plane perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:DENSO WAVE INC
Multiple signaling mouse with faceted surfaces
InactiveUS6369797B1Easy to controlReduce returnsMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser interfaceFacet
A conventional monoplane mouse is constructed to move on a flat surface upon a single plane within which a contained sphere may rotate tangential with the single plane contacting the flat surface. Signal for XY cursor movement are derived from two or more counting sensors positioned at an equator of the rotatable sphere parallel with the single plane. The mouse invention defines two or more facets in the underside housing. The facet mouse can be tilted to one of the exclusive facets and moved on a flat surface to generate XY signals. The facet plane selected by tilt is identified by triggered pressure sensitive switches at each facet plane. The switches also function as undercarriage feet to define the virtual plane of contact to the flat surface. The facet planes in two and four facet embodiments are oriented with the orthogonally placed sphere counting sensors so that the interest of any two opposing facets is parallel with the plane of rotation of one of the counting wheels. A single sphere and counter apparatus can serve all facets, being placed at the intersect of all facets. To aid the hand in applying continuous downward pressure to the mouse onto a preferred facet, a hinged and elevatable palm hood is attached to the top of the mouse. The mouse enables a new user interface beyond the tradition ones of: 1.clicking keys by a finger and 2.whole arm movement of a mouse on an XY surface. By a tilting wrist motion, the user may instantly and continuously toggle 2,4, or more selection assigned to the facets provided.
Owner:MAYNARD JR STUART TYRUS
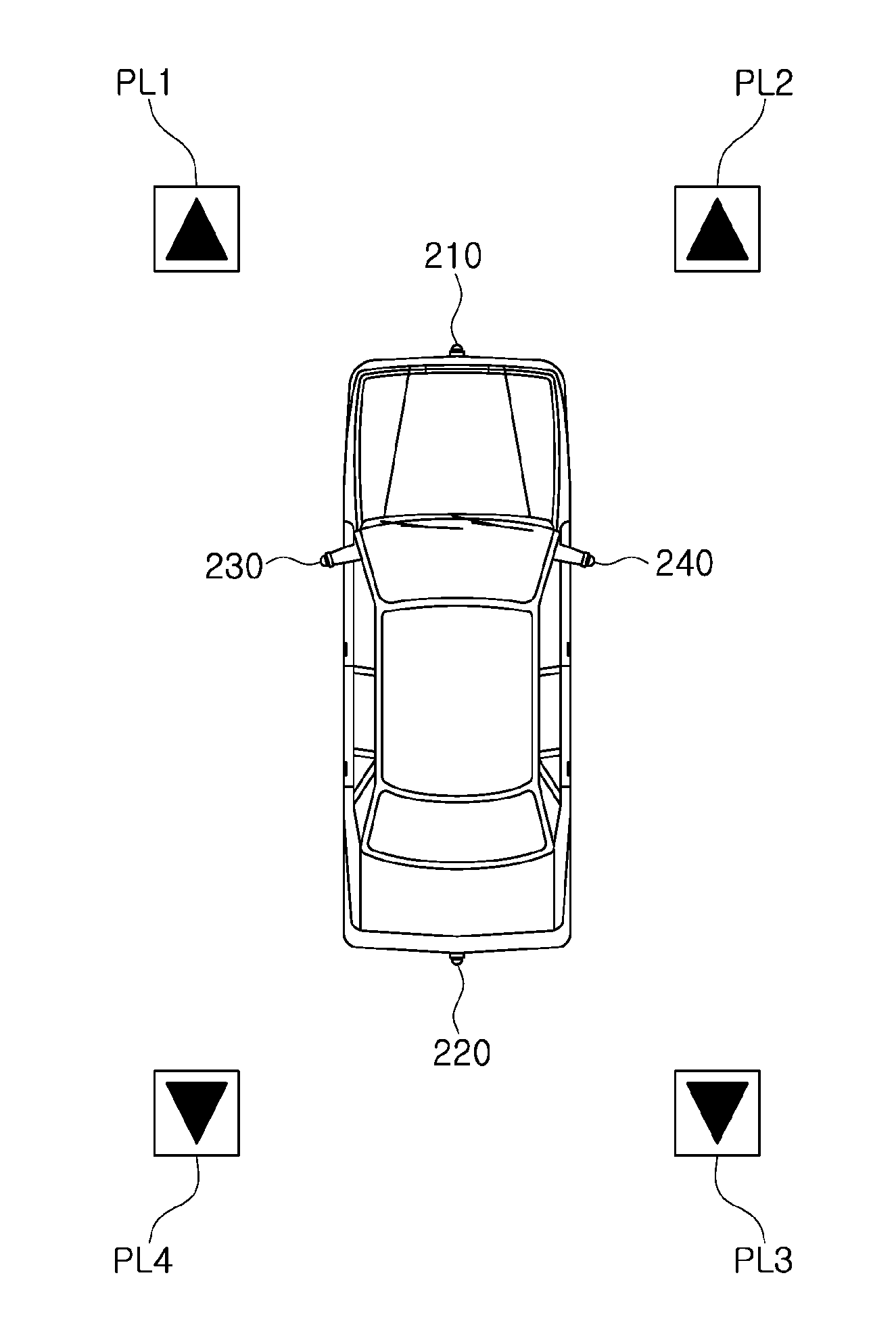
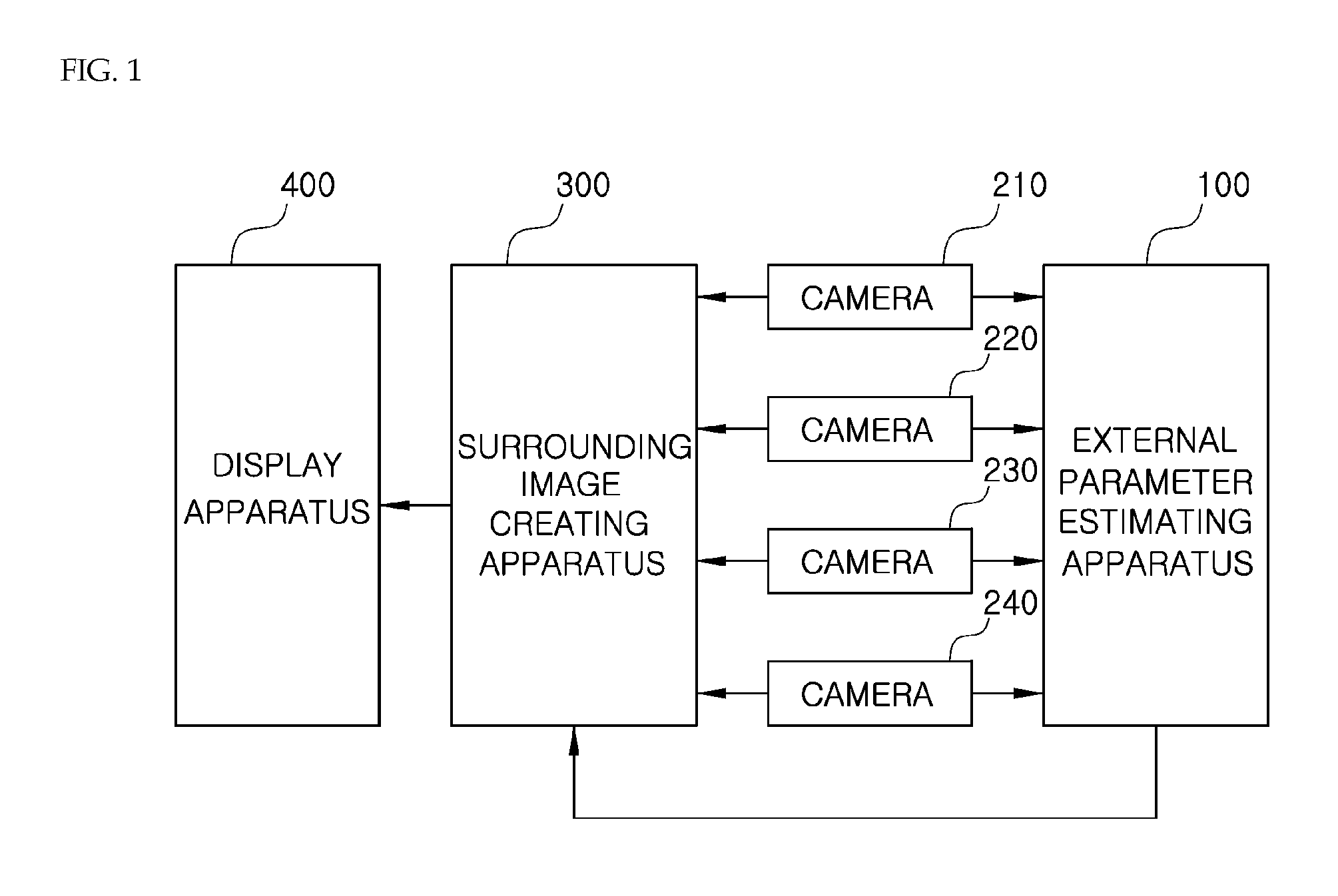
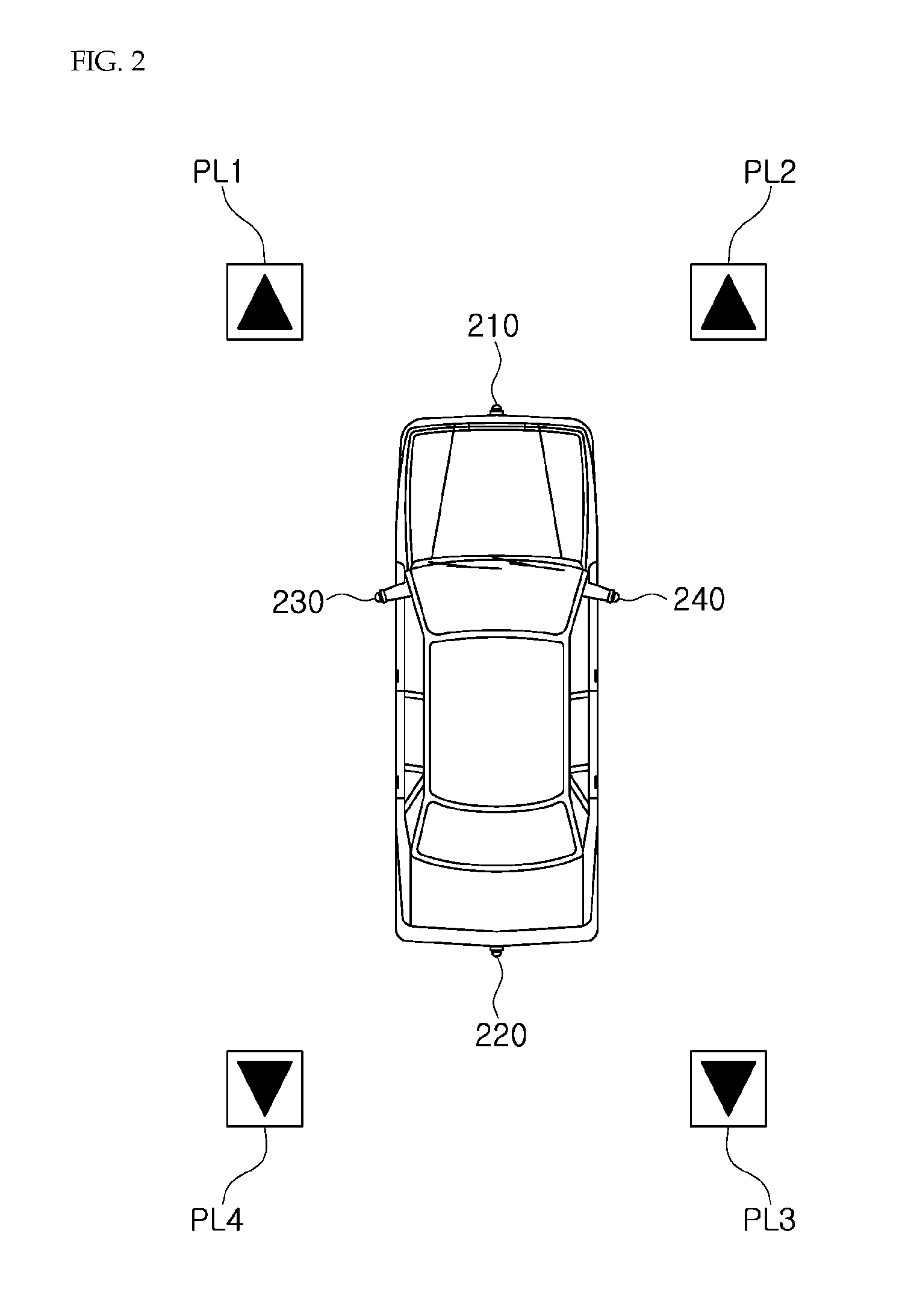
Method and apparatus for creating 3D image of vehicle surroundings
ActiveUS20140347450A1Enhance the imageEasy to adjustGeometric image transformationAnti-collision systemsViewpoints3d image
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for creating a 3D image of vehicle surroundings. The method according to the present invention includes the steps of: mapping images captured by a plurality of cameras installed in a vehicle to a virtual plane defined by a 3-dimensional space model having a container shape with a flat bottom surface and a top surface which has an increasing radius; and creating a view image having a viewpoint of a virtual camera by using the image mapped to the virtual plane. According to the present invention, it is advantageous that an image of vehicle surroundings including surrounding obstacles can be expressed naturally and three-dimensionally. It is also advantageous that an optimal image of vehicle surroundings can be provided by changing the virtual viewpoint according to a traveling state of the vehicle. There is also the advantage that a user can conveniently adjust the viewpoint of the virtual camera.
Owner:BEYOND I CO LTD
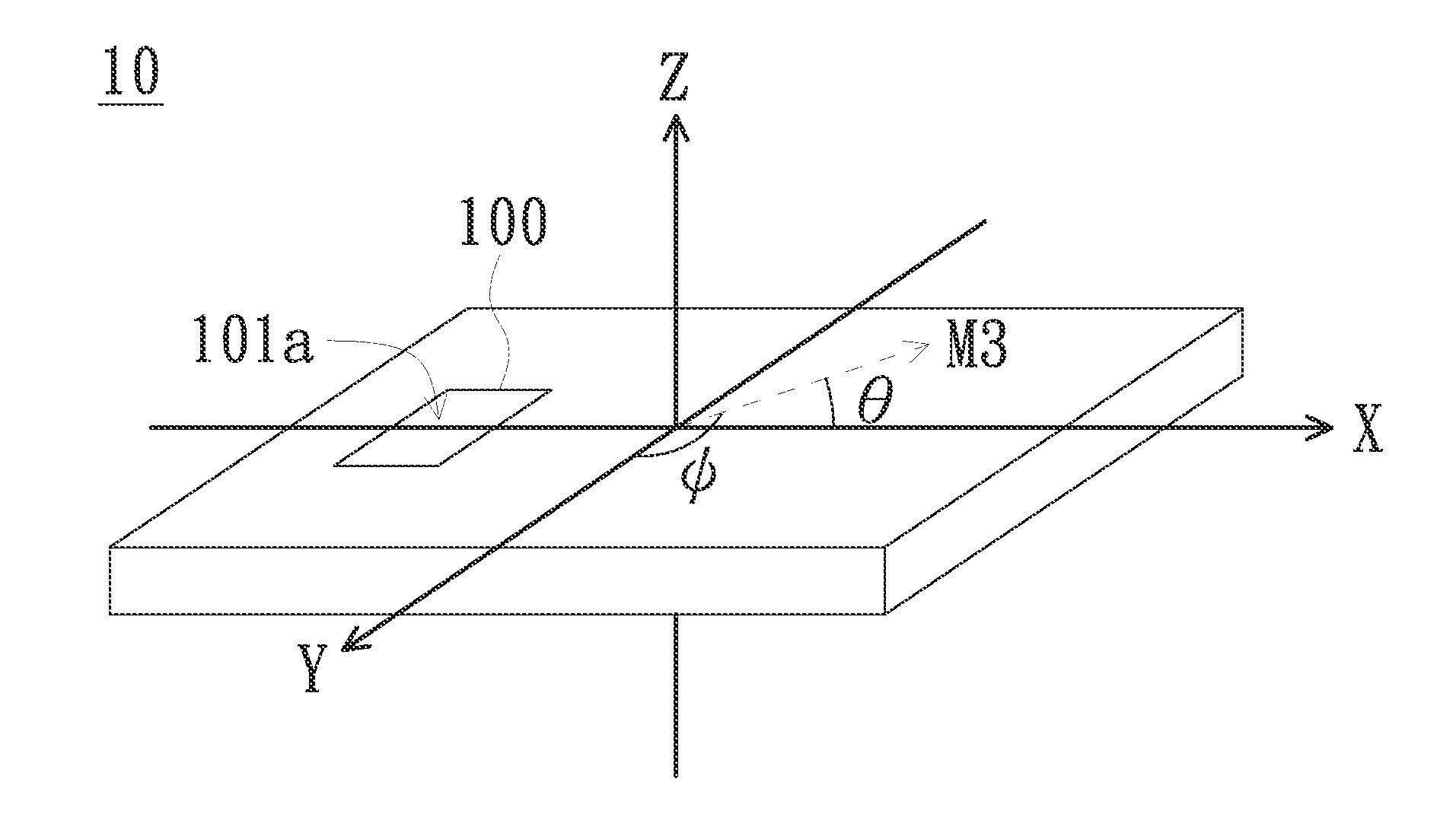
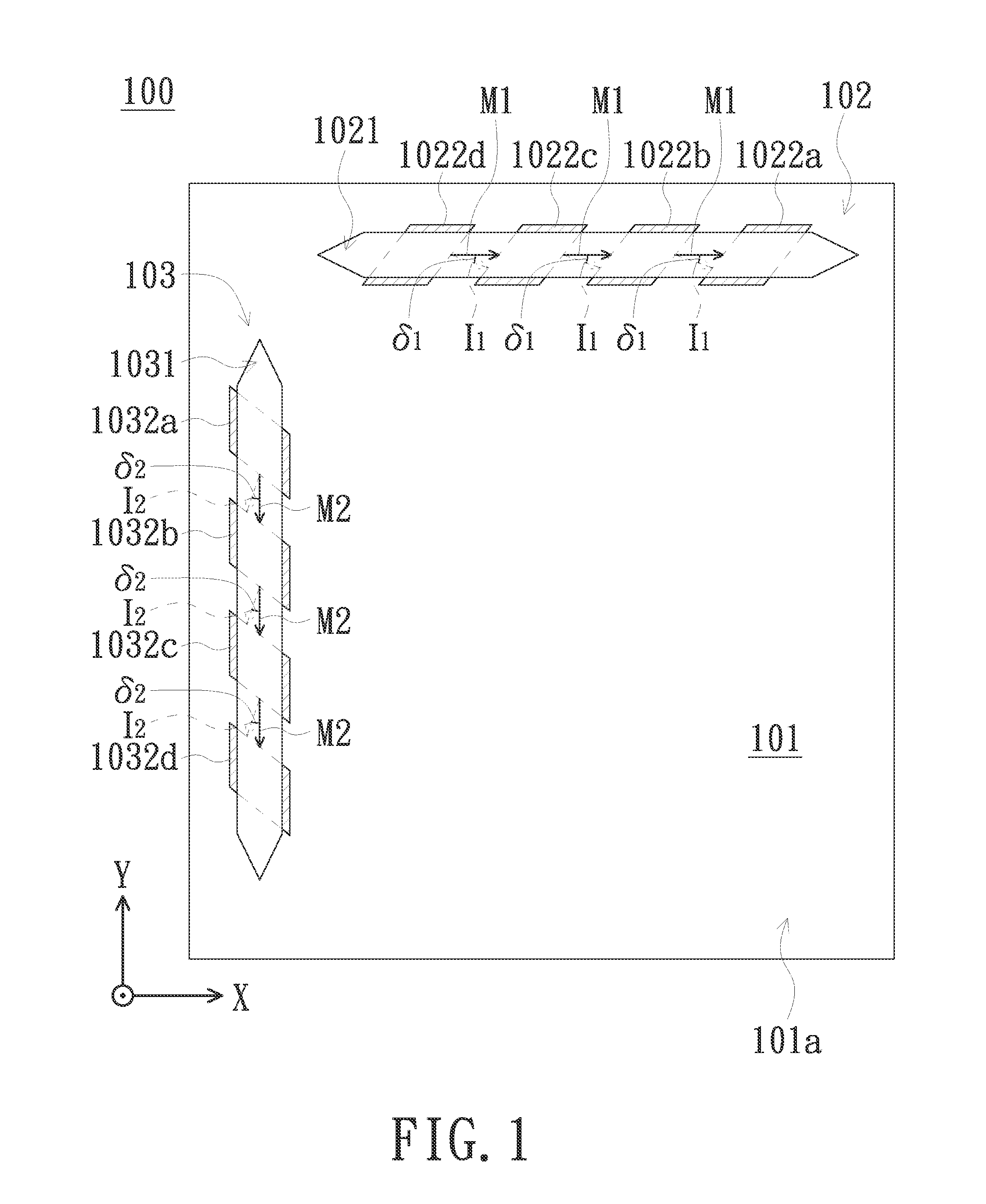
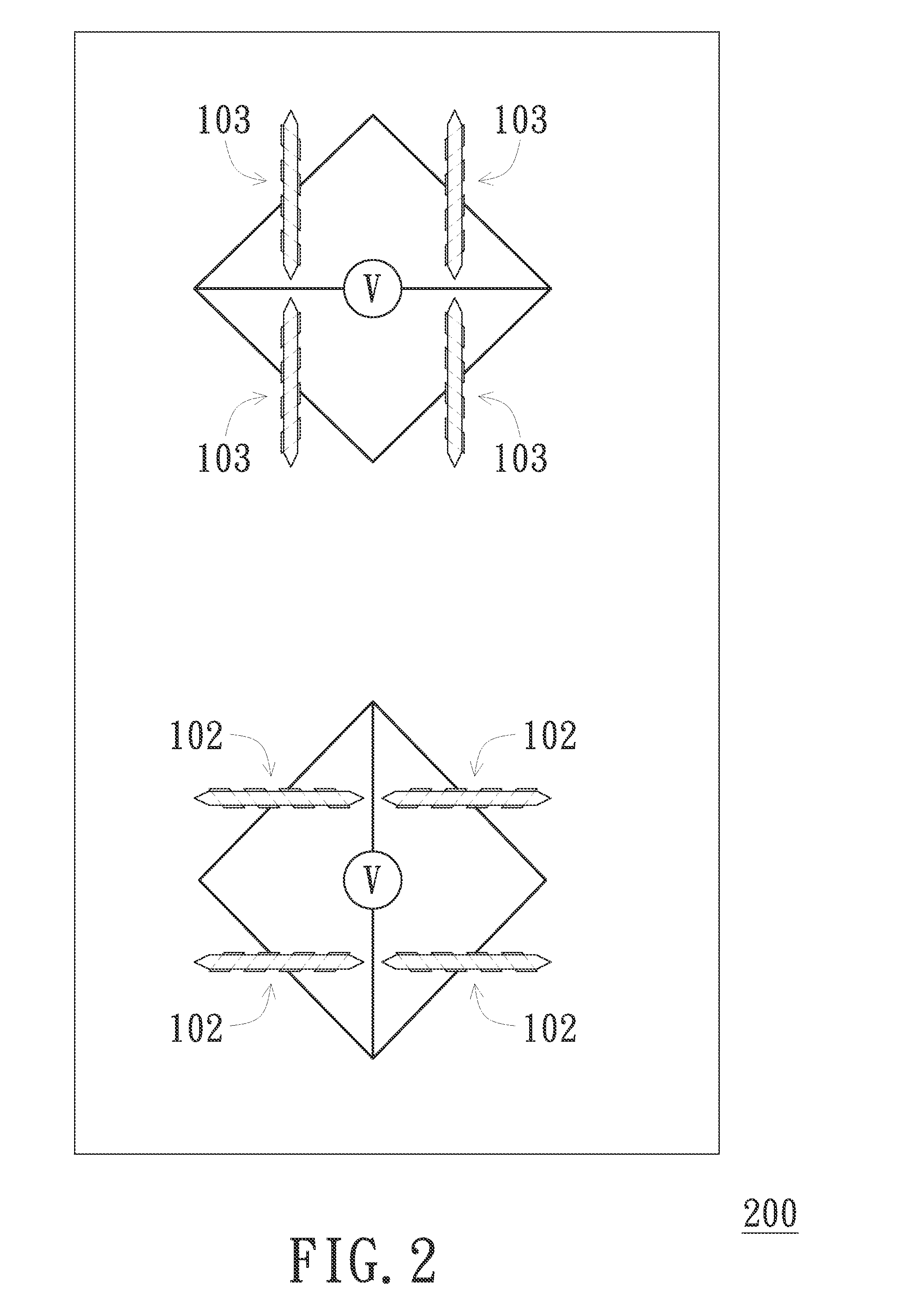
Magnetic-Field Sensing Method
InactiveUS20150128431A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce yieldThree-component magnetometersCompassesClassical mechanicsMagnetic field
A magnetoresistive sensing device is provided. A first sensed magnetic-field component in parallel with the x-axis and a second sensed magnetic-field component in parallel with the y-axis of an external magnetic field forming a first inclination angle with the x-axis and a second inclination angle with the y-axis are determined. A virtual plane is defined so as to render a magnetic-field component perpendicular to the virtual plane of the external magnetic field is essentially zero. The first inclination angle and the second inclination angle are adjusted with reference to the virtual plane. An x-axis magnetic-field component in parallel with the x-axis, a y-axis magnetic-field component in parallel with the y-axis and a z-axis magnetic-field component in parallel with the z-axis of the external magnetic field are estimated according to the adjusted first inclination angle, the adjusted second inclination angle, the first sensed magnetic-field component and the second sensed magnetic-field component.
Owner:VOLTAFIELD TECH
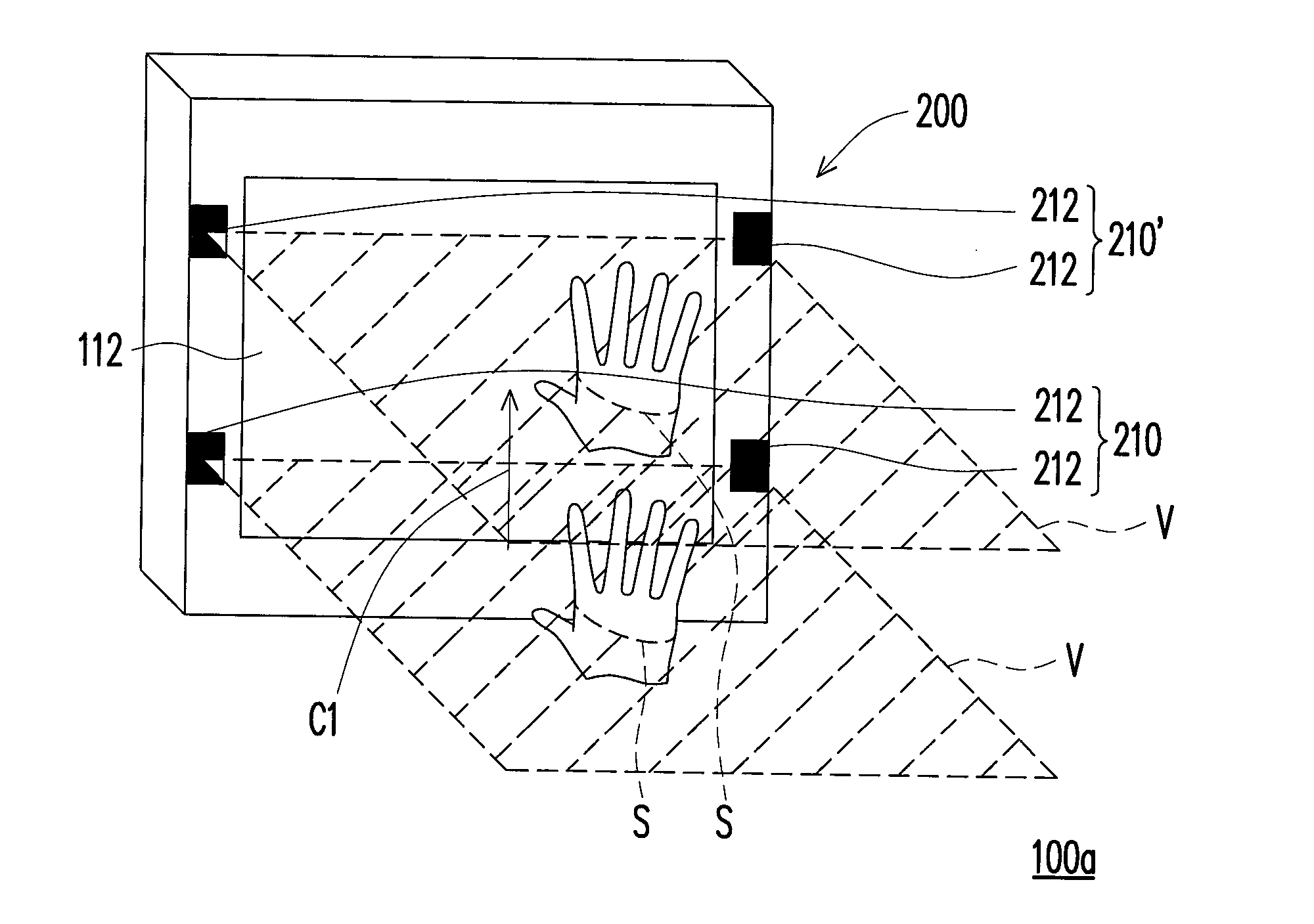
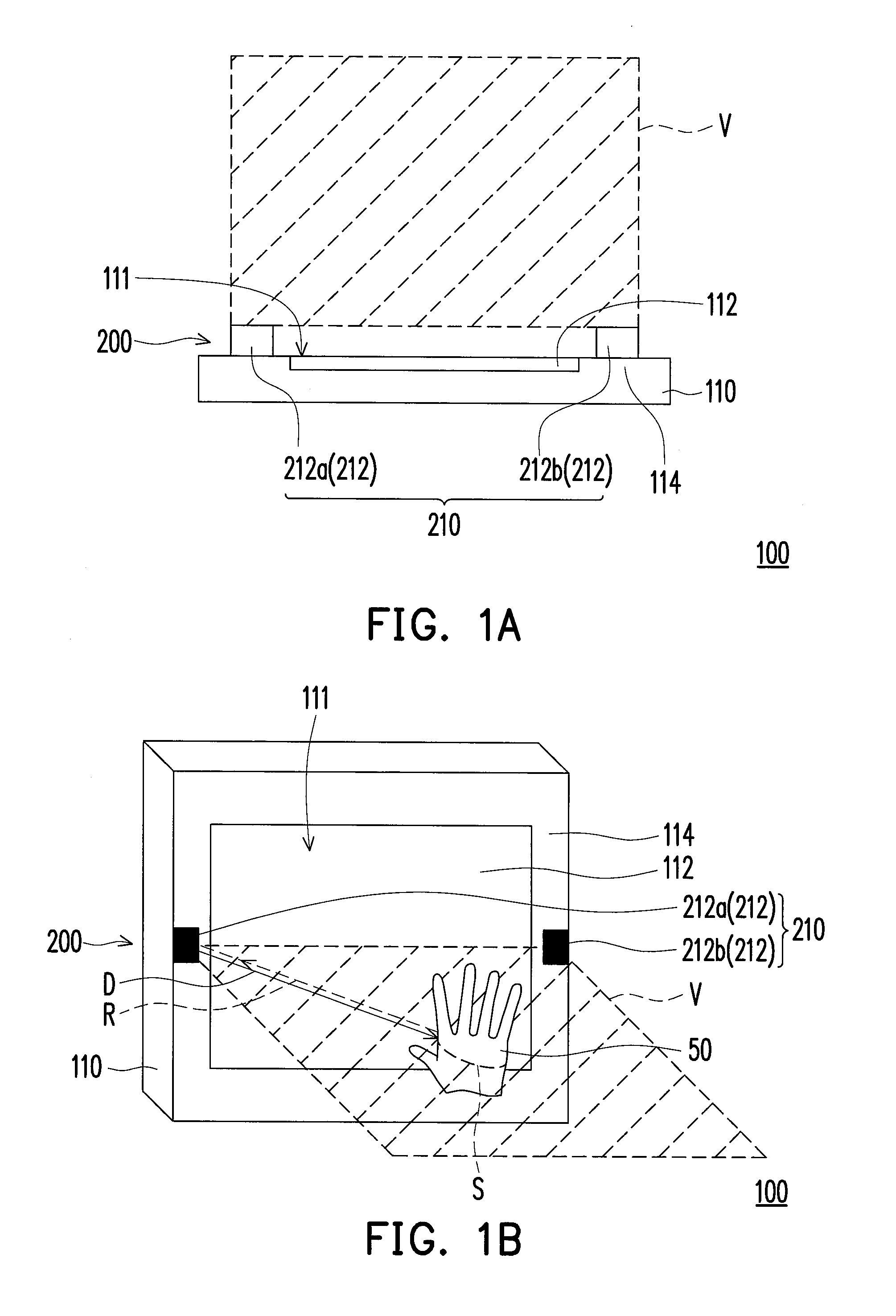
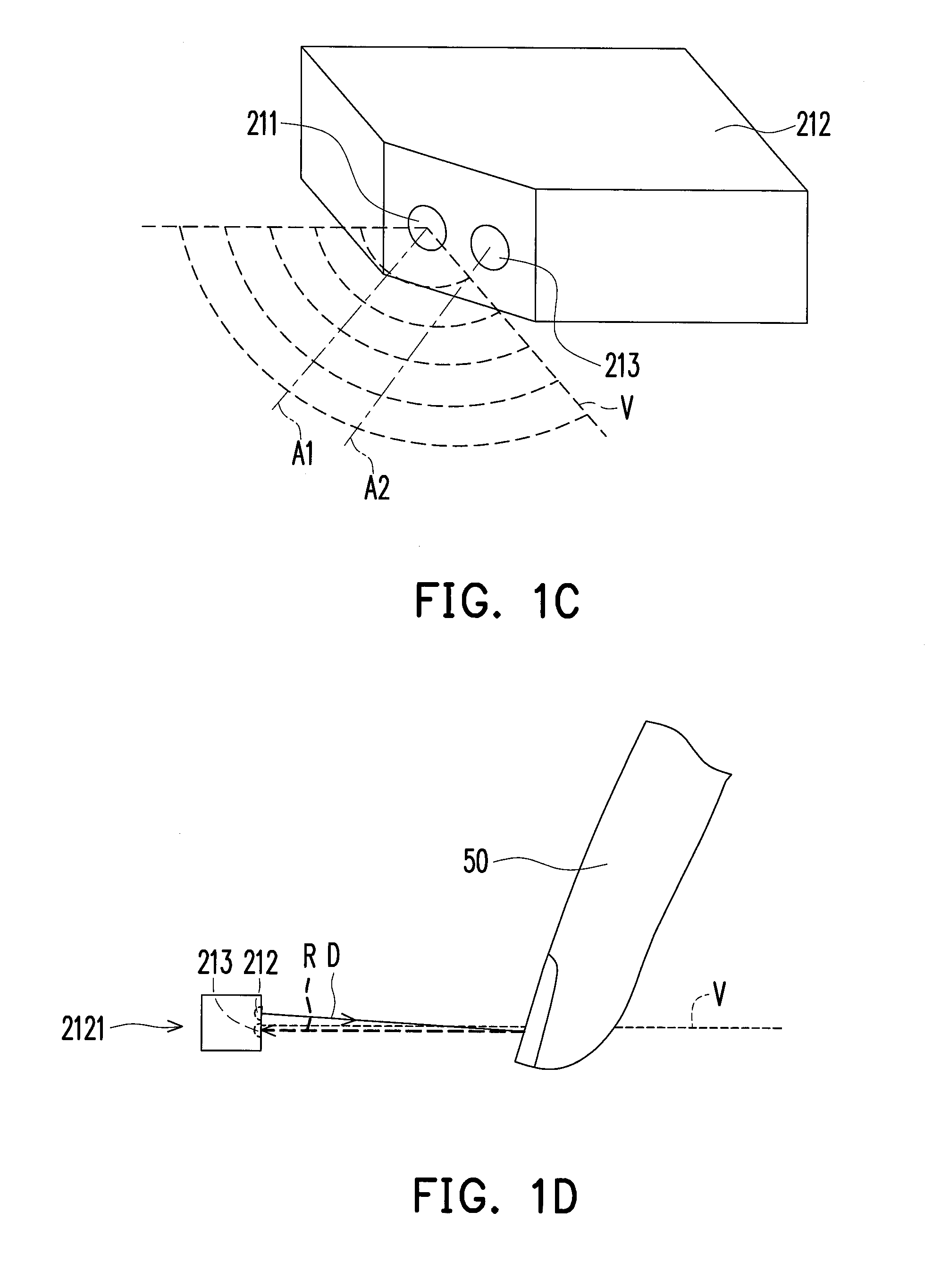
Gesture sensing apparatus, electronic system having gesture input function, and gesture determining method
InactiveUS20130257736A1Efficient gesture sensingLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectronic systemsComputer science
A gesture sensing apparatus configured to be disposed on an electronic apparatus is provided. The gesture sensing apparatus includes at least one optical unit set disposed beside a surface of the electronic apparatus and defining a virtual plane. Each of the optical unit set includes a plurality of optical units, and each of the optical units includes a light source and an image capturing device. The light source emits a detecting light towards the virtual plane. The virtual plane extends from the surface toward a direction away from the surface. The image capturing device captures an image along the virtual plane. When an object intersects the virtual plane, the object reflects the detecting light in the virtual plane into a reflected light. The image capturing device detects the reflected light to obtain information of the object. An electronic system having a gesture input function is also provided.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
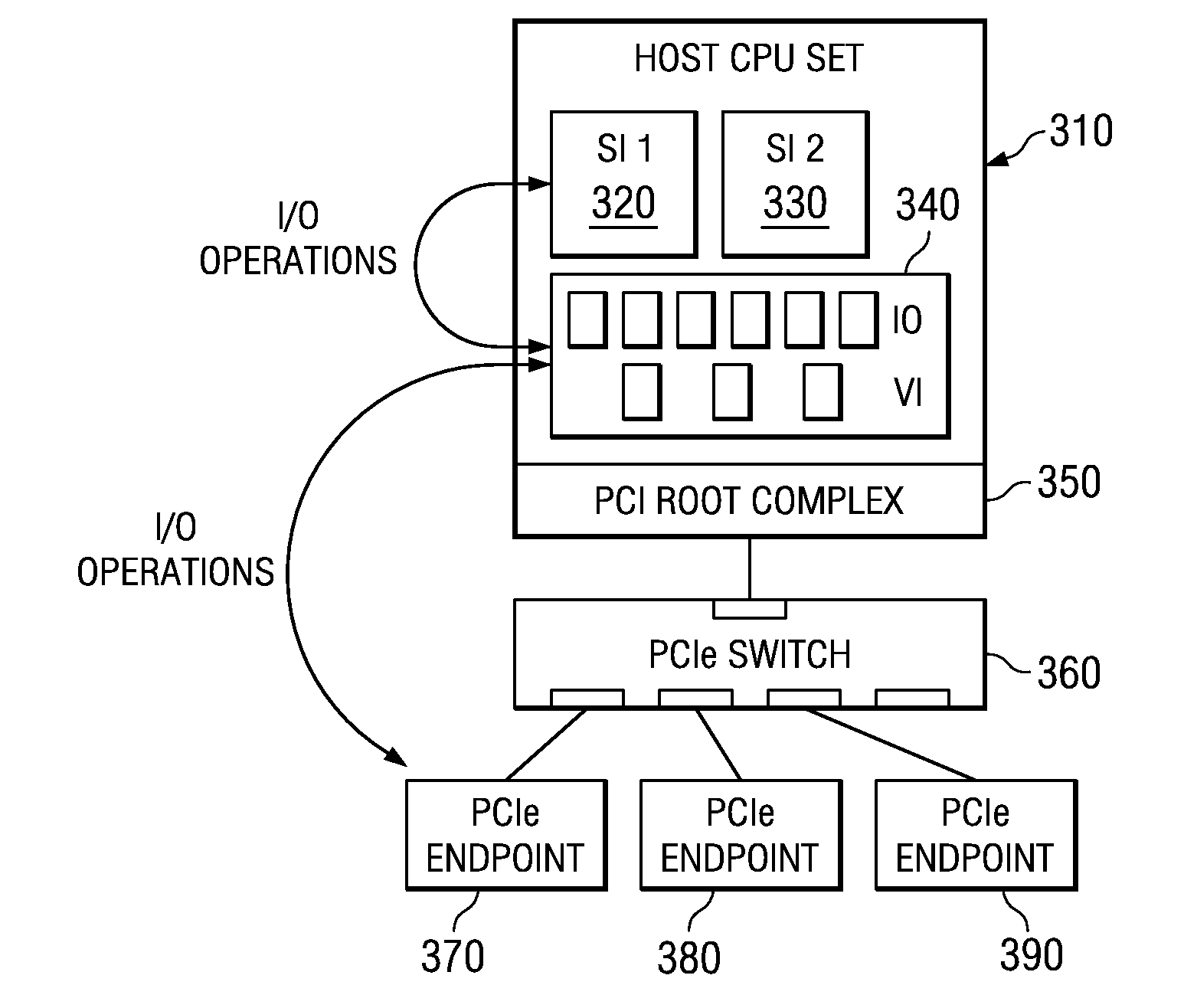
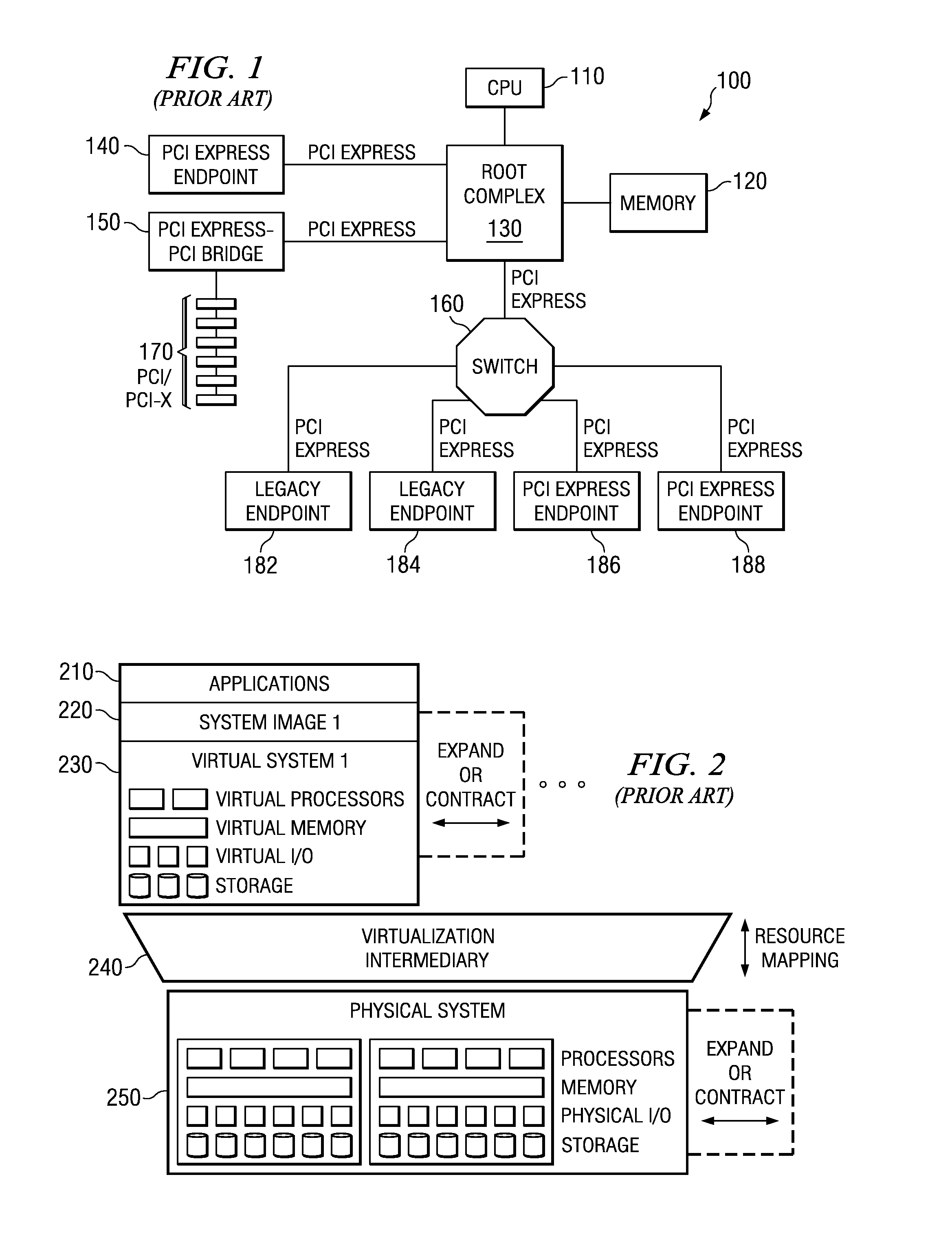
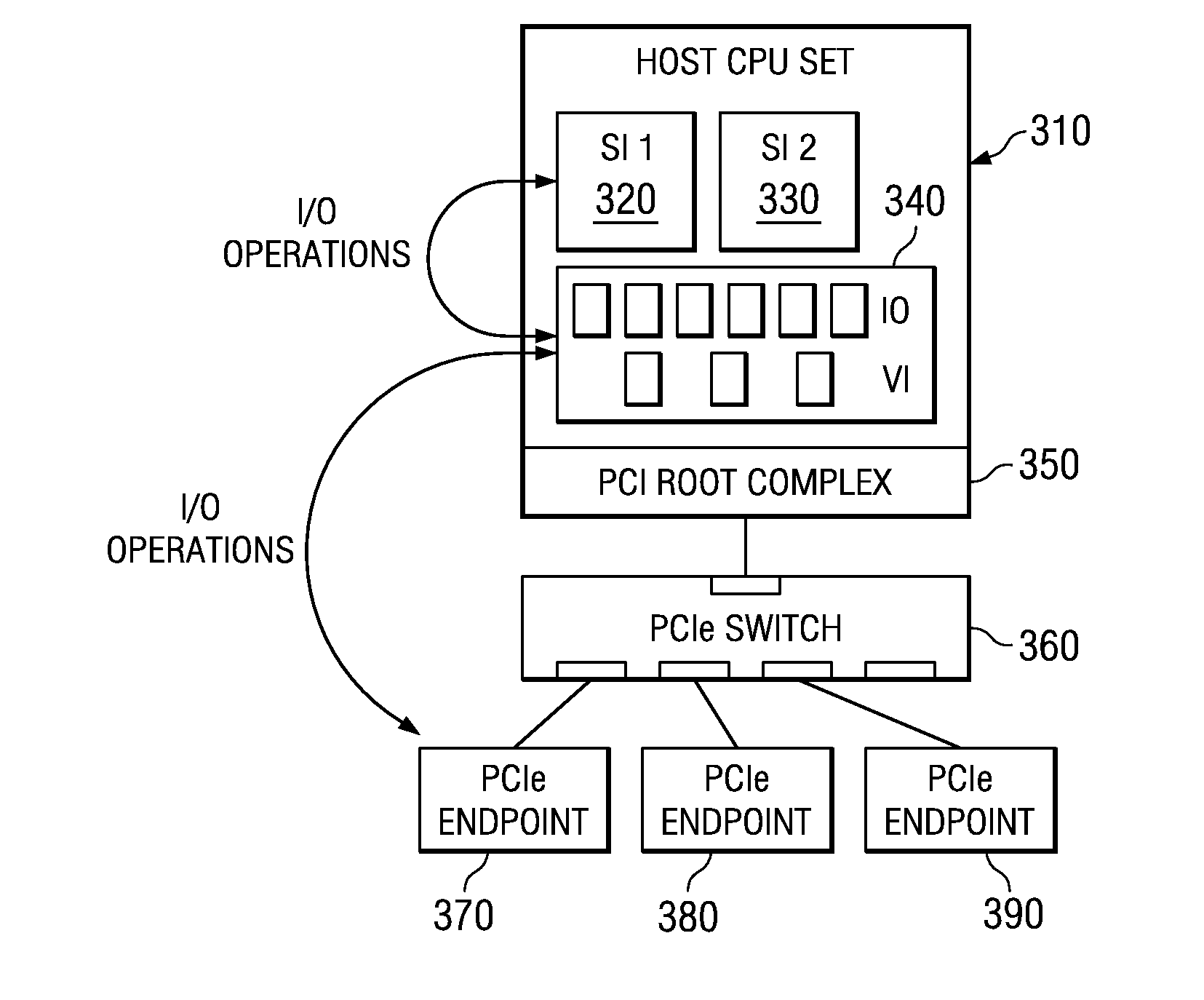
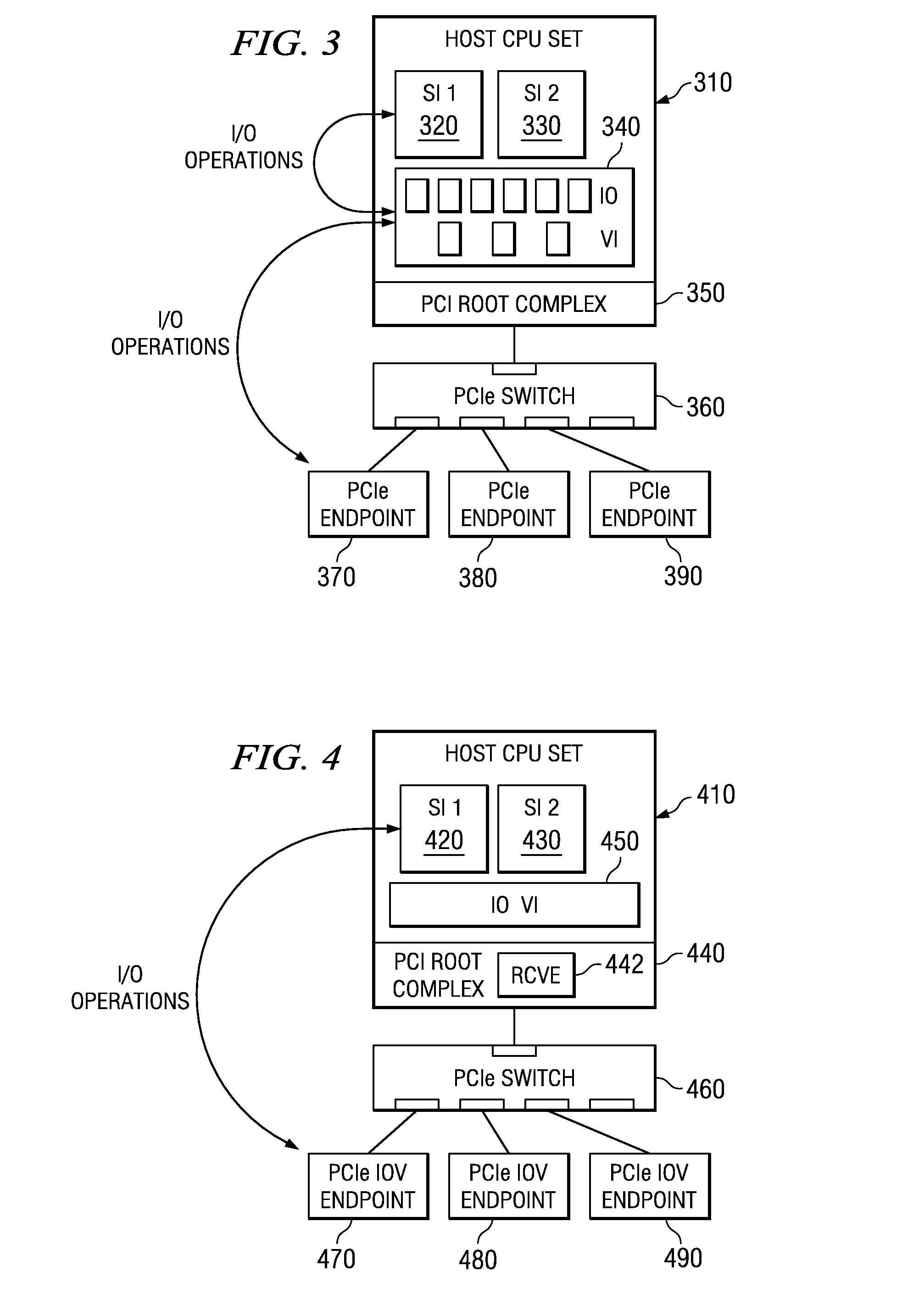
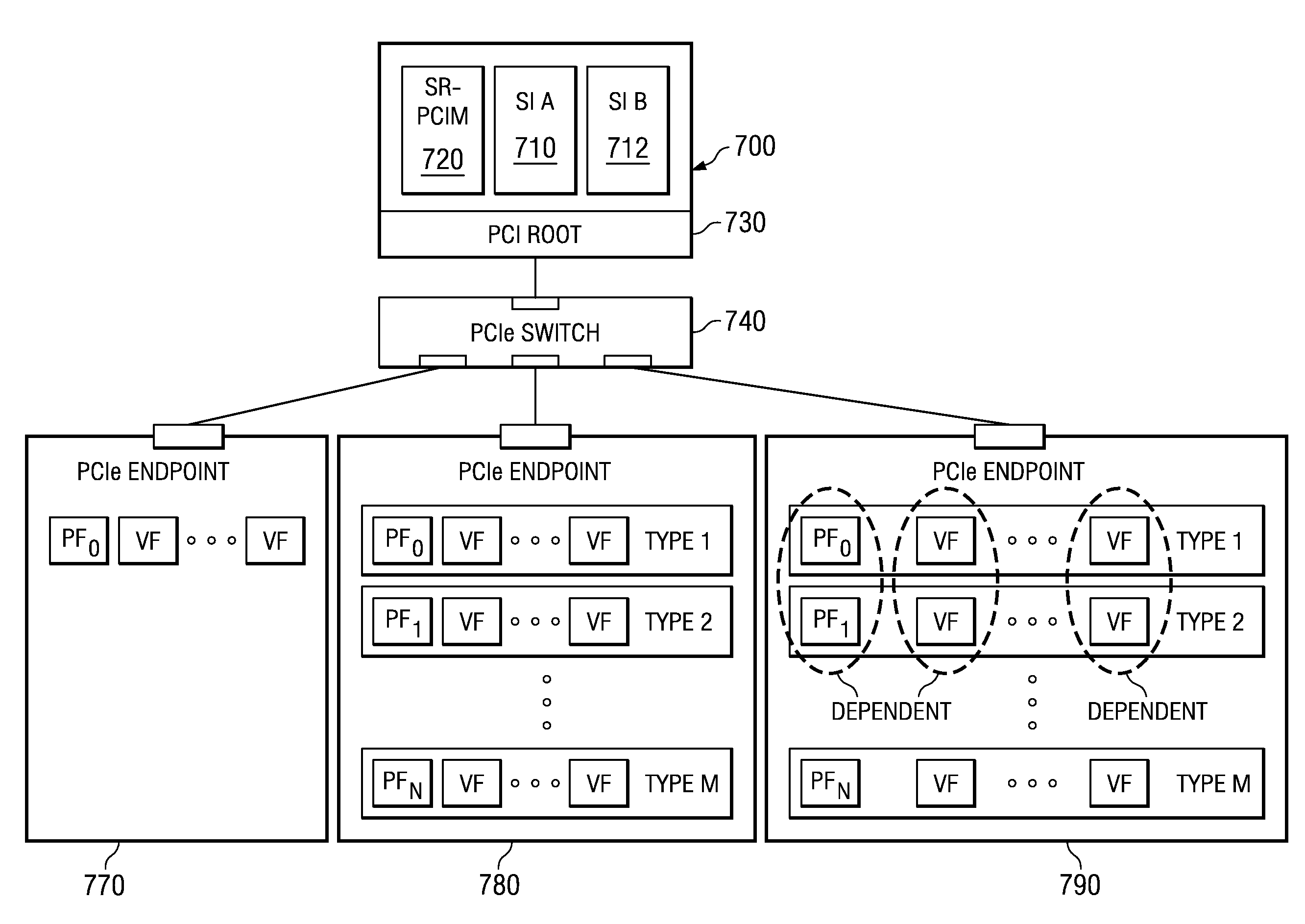
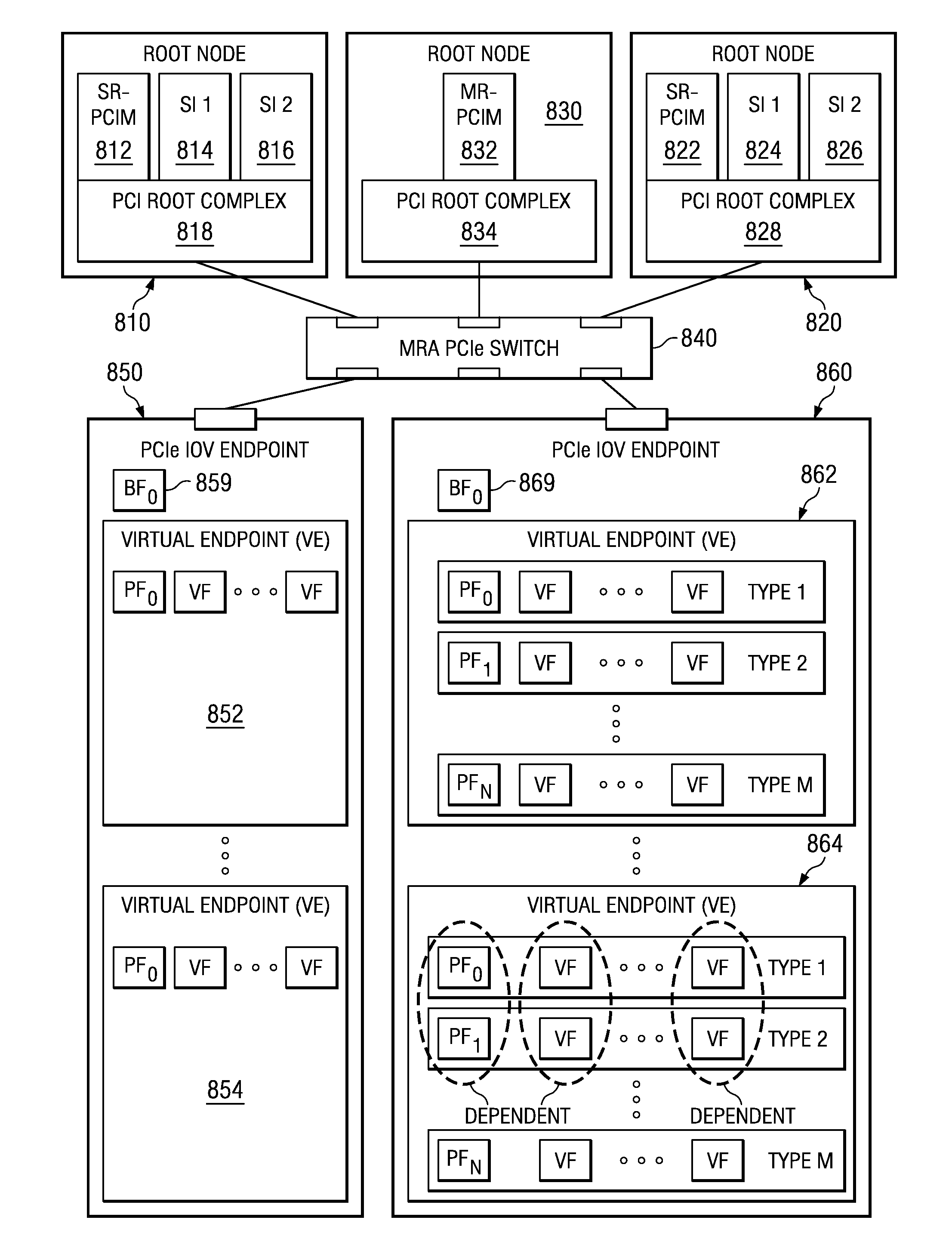
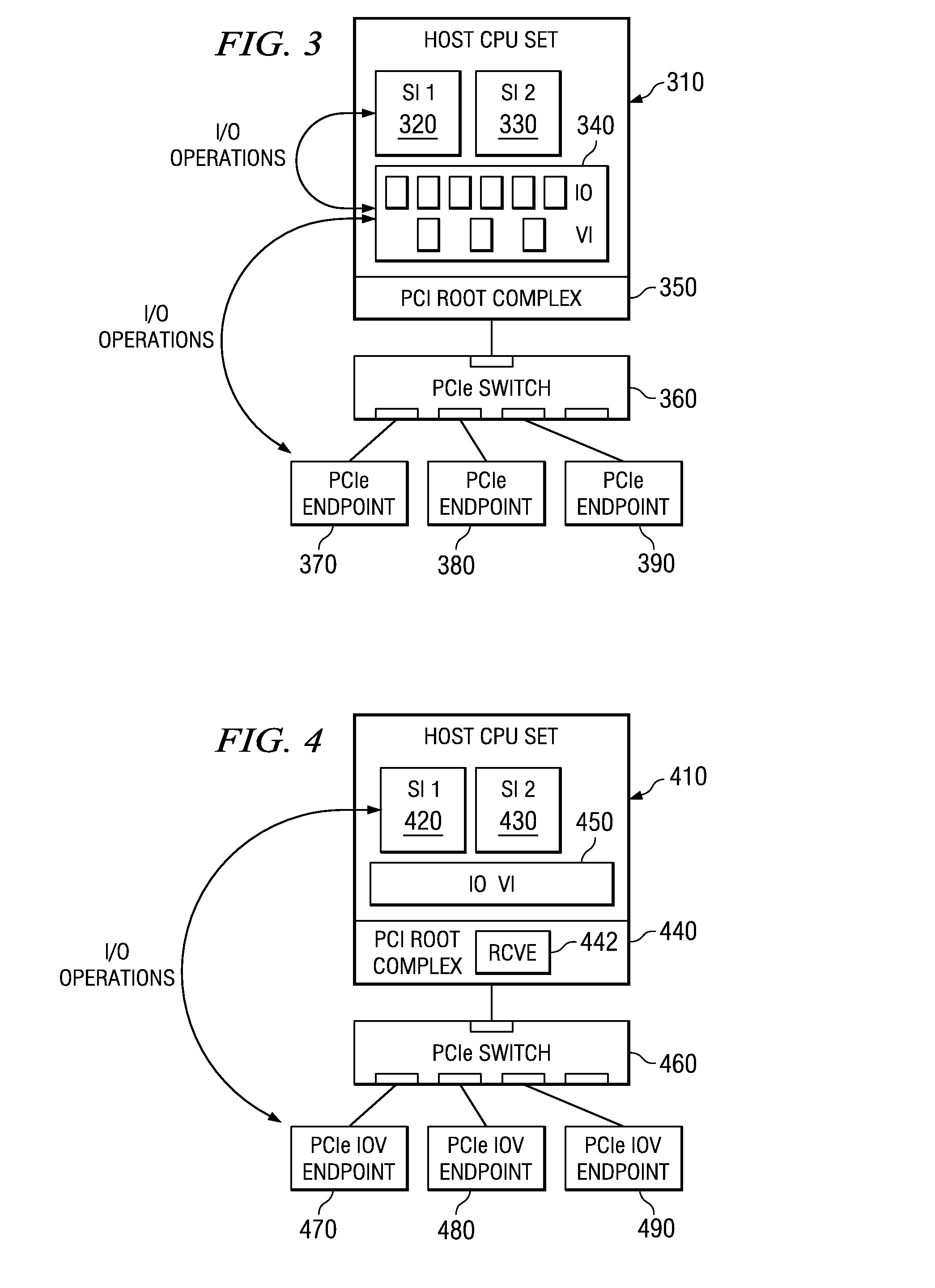
System and method for migration of a virtual endpoint from one virtual plane to another
InactiveUS20080147943A1Data switching by path configurationMemory systemsVirtualizationApplication software
A system and method for migration of a virtual endpoint from one virtual plane to another are provided. With the system and method, when a management application requests migration of a virtual endpoint (VE) from one virtual plane (VP) to another, a fabric manager provides an input / output virtualization intermediary (IOVI) with an interrupt to perform a stateless migration. The IOVI quiesces outstanding requests to the virtual functions (VFs) of the VE, causes a function level reset of the VFs, deconfigures addresses in intermediary switches corresponding to the VP, and informs the fabric manager that a destination migration is requested. The fabric manager sends an interrupt to the destination IOVI which performs a function level reset of the destination VFs and reprograms the intermediary switches with the addresses of the destination VP. The destination VFs may then be placed in an active state.
Owner:IBM CORP
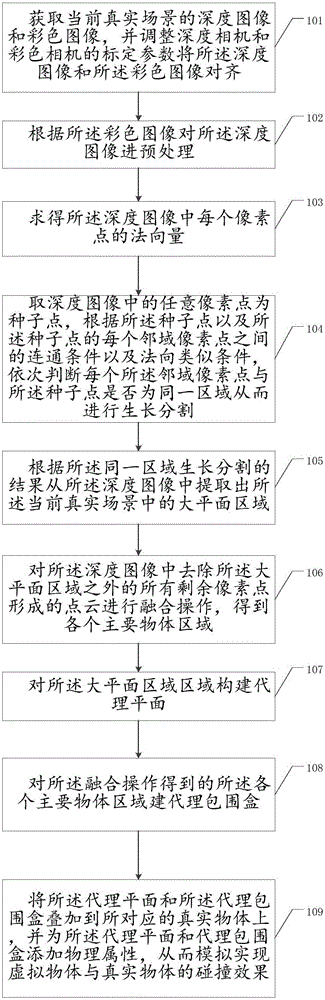
Depth image partitioning and agent geometry based virtual and real collision interaction method and apparatus
InactiveCN105046710AGood virtual reality interaction effectImage enhancementImage analysisColor imagePoint cloud
A depth image partitioning and agent geometry based virtual and real collision interaction method and apparatus are disclosed. The application discloses a method for realizing collision interaction of a virtual object and a real object by partitioning a scene in a depth image and constructing agent geometries based on a partitioning result. Firstly, color image information and depth image information of a current real scene are obtained; secondly, normal information in the depth image and connectivity are taken as criterions, the depth image is subjected to regional partitioning with a regional growth method, and on this basis, a main plane region in the scene is identified by utilizing a plane judgment technology of a Gaussian image; thirdly, other point cloud regions except the main plane region are subjected to fusion processing to obtain other main object regions in the scene; fourthly, constructing a virtual plane for an identified main plane and constructing a bounding box for a partitioned object; and finally, superposing the agent geometries onto the real object, endowing the real object with physical attributes, and realizing collision interaction of the virtual object and the real object by simulation. The depth image partitioning method disclosed by the application is quick, effective and more realistic in virtual and real interaction effect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Display Device
ActiveUS20140354714A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceVIRTUAL PIXEL
A display device is provided. The display device comprises a display comprising a plurality of pixels arranged in a display plane. The display device is configured to determine a virtual plane at which a long-sighted user of the display device who is looking at the display sees sharp. Further, the display device is configured to determine a first contiguous group of pixels of the display which are located within a first optical path from a first virtual pixel of the virtual plane to an eye of the long-sighted user, and to determine a second contiguous group of pixels of the display which are located within a second optical path from a second virtual pixel of the virtual plane to the eye of the long-sighted user.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Operation recognition system enabling operator to give instruction without device operation
InactiveUS7343026B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTime segmentImaging data
An operation recognition system including an object to be operated, at least one camera, a processor, and a controller. At least one camera is configured to acquire image data of an operator in a predetermined period of time, and a processor is configured to perform recognition processing on the acquired image data. Upon processing the image data, the processor is configured to define a virtual plane in between the object to be operated and the operator. The processor is configured to then perform a process to determine if a predetermined part of the operator penetrates the virtual plane based on the recognition processing. Based on this determination, the controller is configured to control the object to be operated.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Camera calibration device and method, and computer system
InactiveUS7023473B2Simply carrying out camera calibrationImage analysisOptical rangefindersCamera lensHat matrix
A camera calibration device capable of simply calibrating a stereo system consisting of a base camera and a detection camera. First, distortion parameters of the two cameras necessary for distance measurement are presumed by the use of images obtained by shooting a patterned object plane with the base camera and the reference camera at three or more view points free from any spatial positional restriction, and projective transformation matrixes for projecting the images respectively onto predetermined virtual planes are calculated. Then internal parameters of the base camera are calculated on the basis of the projective transformation matrixes relative to the images obtained from the base camera. Subsequently the position of the shot plane is presumed on the basis of the internal parameter of the base camera and the images obtained therefrom, whereby projection matrixes for the detection camera are calculated on the basis of the plane position parameters and the images obtained from the detection camera. According to this device, simplified calibration can be achieved stably without the necessity of any exclusive appliance.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Spread illuminating apparatus
ActiveUS20050243575A1Avoid scratchesReduce pressureMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePoint lightLight guide
A side light type spread illuminating apparatus comprises: a light conductive plate having a plurality of prisms formed on a light exit surface thereof, point light sources; and a prism sheet disposed on the light conductive plate, wherein the prisms have respective circular arc configurations with a common curvature in cross section taken along a line orthogonal to the direction the prisms extend, and are arrayed such that distances each defined between apexes of adjacent two of the prisms differ irregularly from one another within a range of 10 to 200 μm, and such that overall tangential angles at respective ends of the prisms vary irregularly within a range of 40 to 70 degrees, and wherein the respective ridges of the prisms are located on a common virtual plane, whereby the prism sheet are supported evenly by all of the prisms of the light conductive plate.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Light-emitting apparatus and illuminating apparatus
InactiveUS20050236628A1Increase light intensityReduce in quantityPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsFluorescenceEngineering
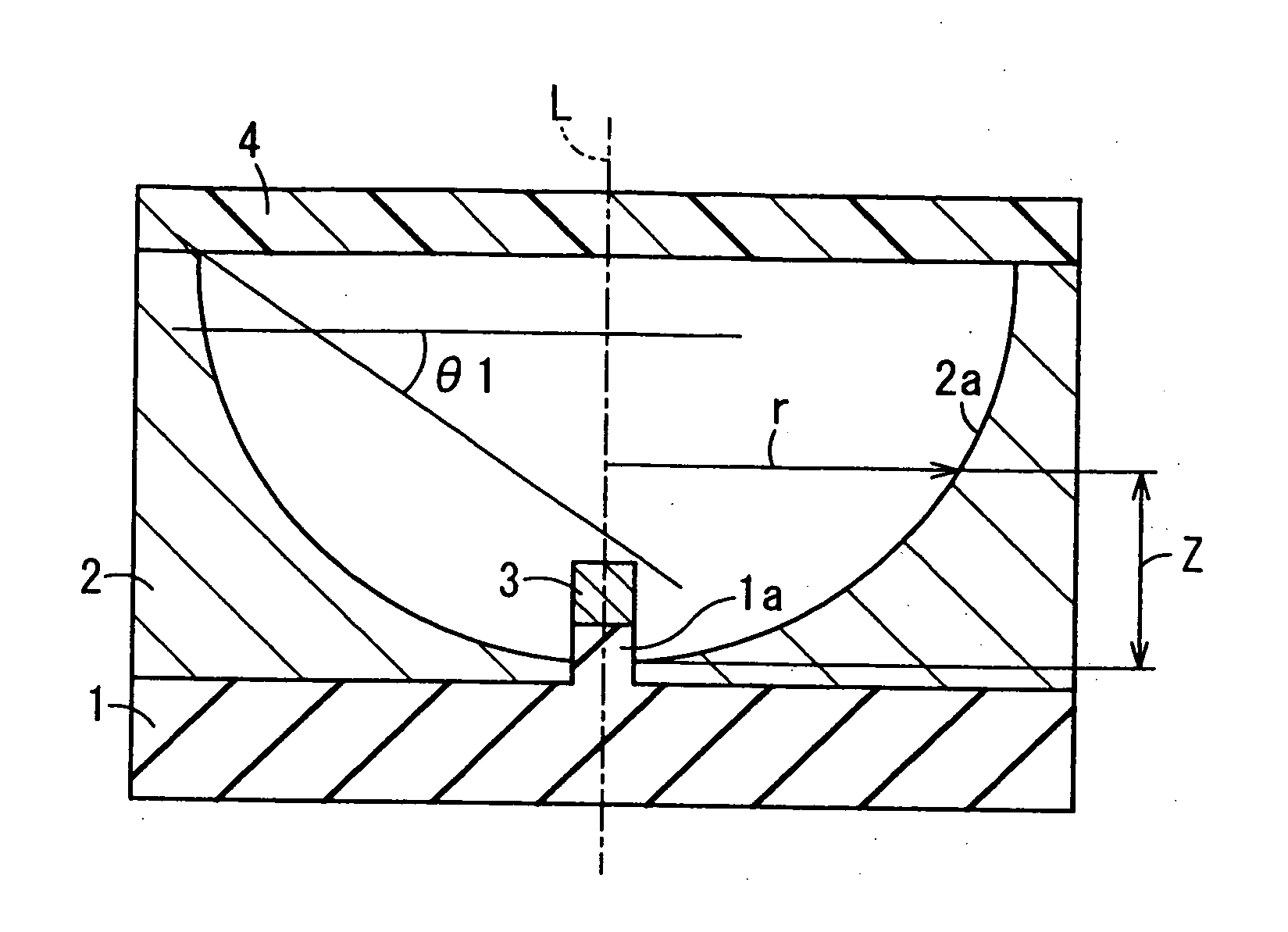
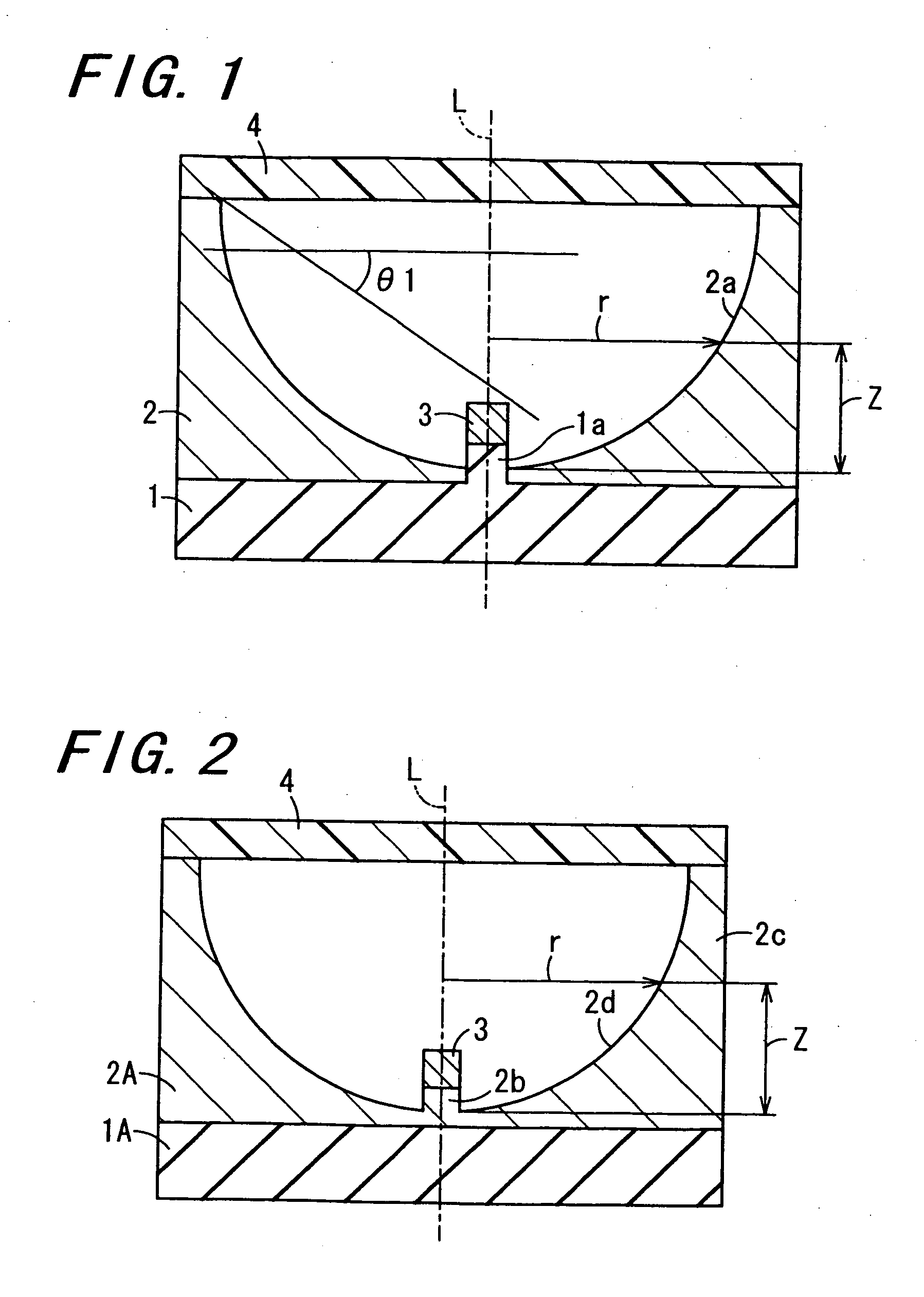
A light-emitting apparatus includes a light-emitting element, a base body, a reflection member and a fluorescent material layer. A cross section of the inner surface of the reflection member cut by a virtual plane including a virtual axis penetrating a center of the inner surface and perpendicular to the upper principal surface of the base body has a sectional profile defined by a curved line expressed by the following formula, and the inner surface of the reflection member is a curved surface obtained by rotating the curved line about the virtual axis: Z=(cr2) / [1+{1−(1+k)c2r2}1 / 2] (where −10≦k≦−0.001, 0.001≦c≦10). An angle θ1 which is made by an upper surface of the fluorescent material layer and a line which connects one corner of a light-emitting portion of the light emitting element with an uppermost position of the inner surface and is tangent to the one corner, is given as θ1≧90°−sin−1 (1 / n1)
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Migration of a virtual endpoint from one virtual plane to another
Mechanisms for migration of a virtual endpoint from one virtual plane to another are provided. With these mechanisms, when a management application requests migration of a virtual endpoint (VE) from one virtual plane (VP) to another, a fabric manager provides an input / output virtualization intermediary (IOVI) with an interrupt to perform a stateless migration. The IOVI quiesces outstanding requests to the virtual functions (VFs) of the VE, causes a function level reset of the VFs, deconfigures addresses in intermediary switches corresponding to the VP, and informs the fabric manager that a destination migration is requested. The fabric manager sends an interrupt to the destination IOVI which performs a function level reset of the destination VFs and reprograms the intermediary switches with the addresses of the destination VP. The destination VFs may then be placed in an active state.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Optical sheet and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100124631A1High hardnessIncrease resistanceProjectorsSynthetic resin layered productsAcute angleHardness
The main object of the present invention is to provide an optical sheet having excellent abrasion resistance and hardness, and a method for producing the same. The present invention provides an optical sheet in which a hard coat layer is provided on one surface of a substrate, wherein the hard coat layer comprises a cured product of a curable resin composition for a hard coat layer, which comprises reactive inorganic fine particles and a binder component, and wherein fine protrusions are provided on an interface on the side opposite to the substrate side of the hard coat layer, in which the minimum angle of each of the fine protrusions making angles with a virtual plane that is parallel to the hard coat layer is an acute angle. The present invention also provides a method for producing the optical sheet, comprising the steps of: forming a coating by applying a curable resin composition for a hard coat layer to one surface of a substrate, which composition comprising reactive, irregularly shaped silica fine particles and a binder component, and forming a hard coat layer and fine protrusions by curing the coating while or after preventing that the long axes of the reactive, irregularly shaped silica fine particles are each oriented in a direction planar to a virtual plane.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
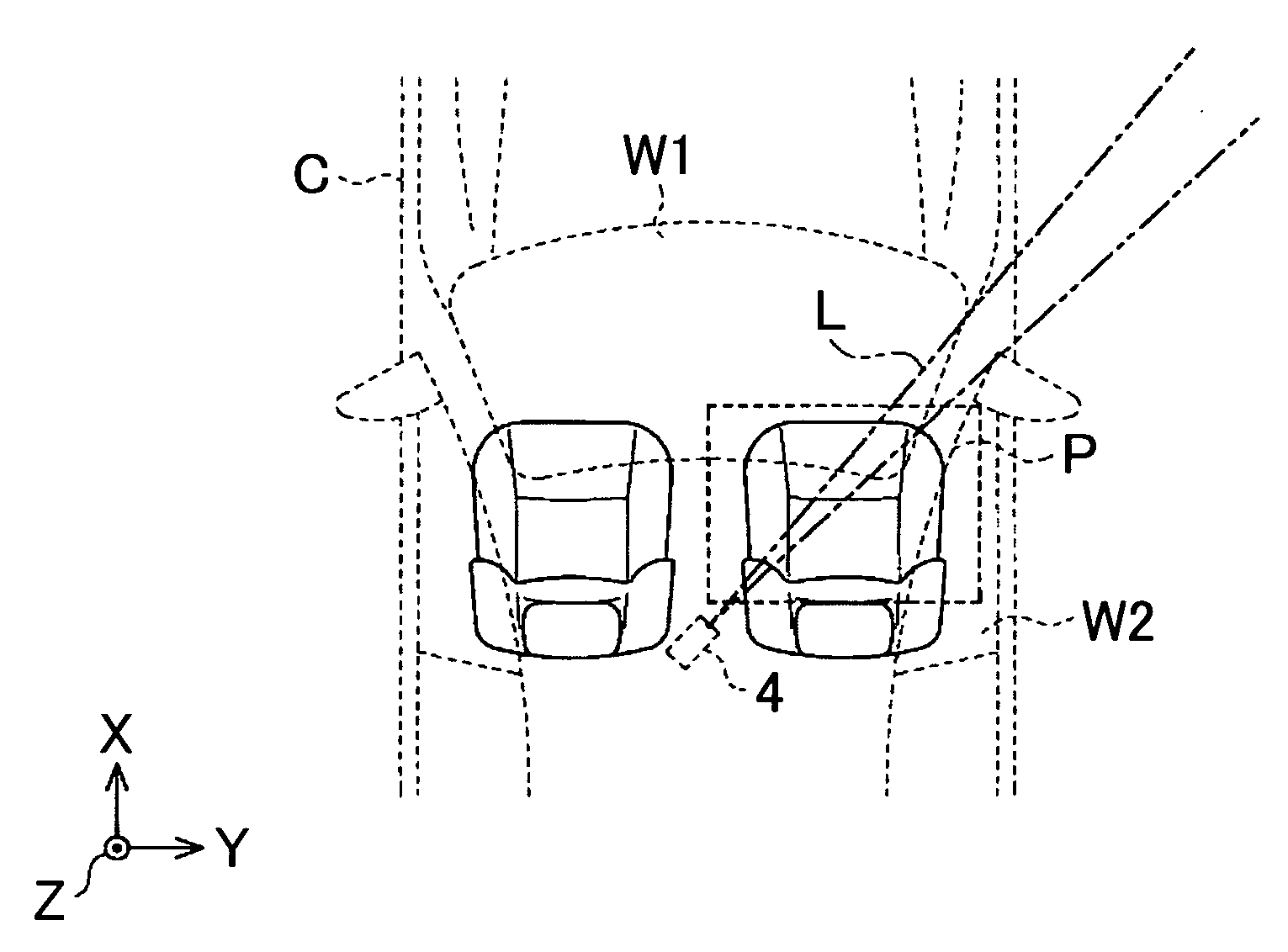
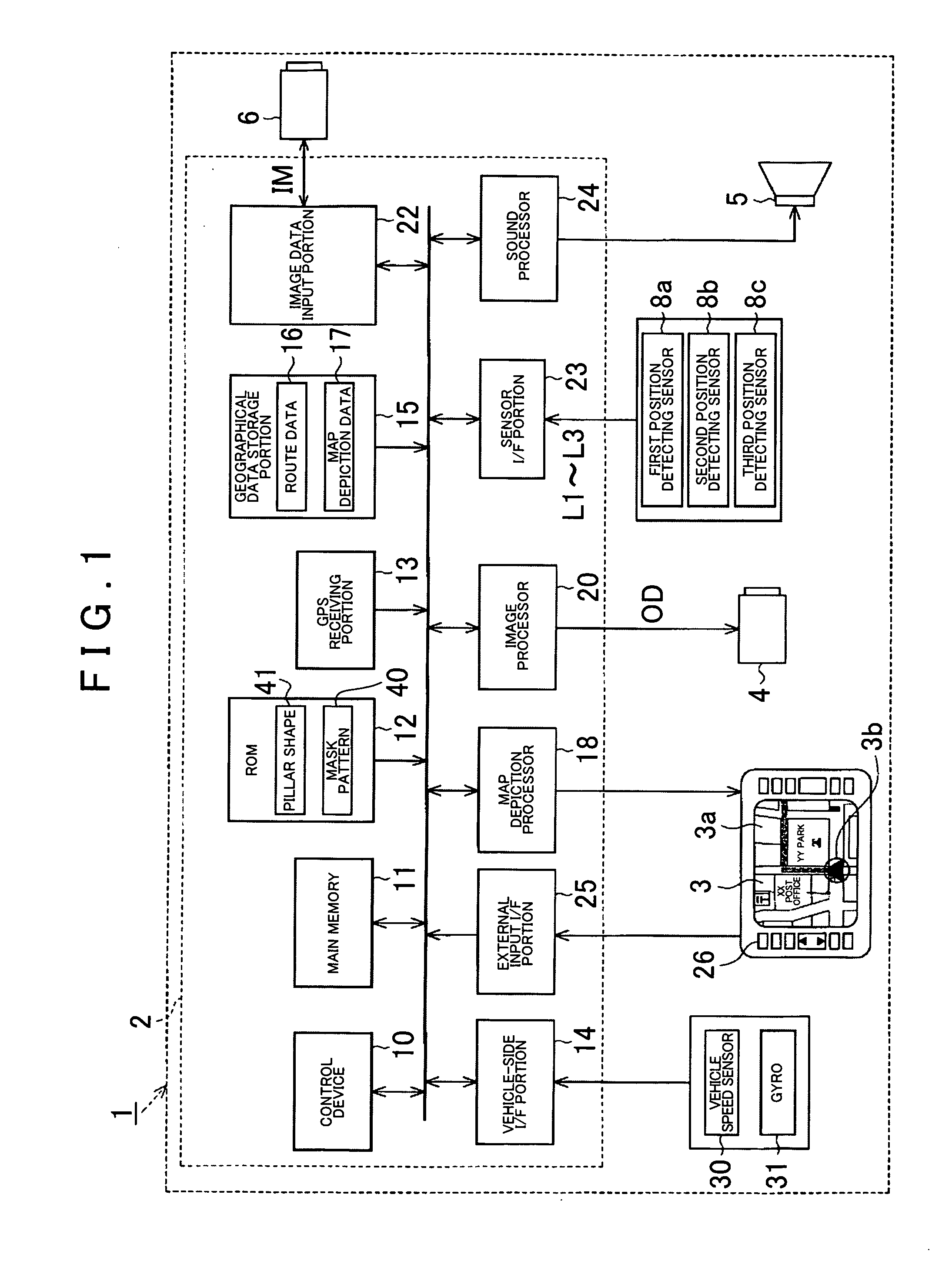
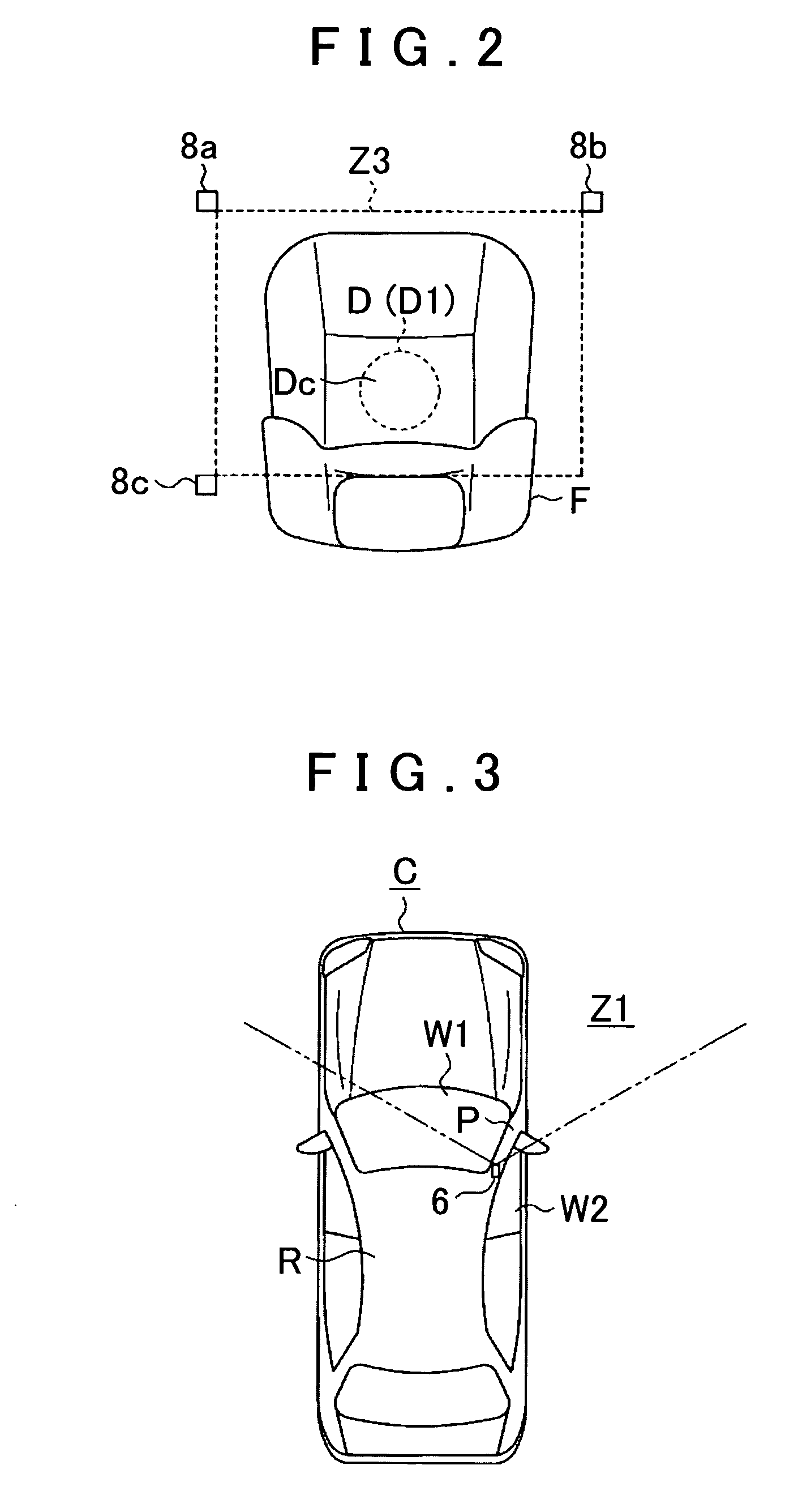
Driving support method and driving support device
ActiveUS20080204557A1Improve continuityReduces area not displayedColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsComputer graphics (images)Image plane
A driving support device uses a camera mounted on a vehicle for imaging a blind spot area created by a pillar of the vehicle and displays an image taken by the camera on the interior surface of the pillar. A virtual plane passing through boundaries of the blind spot area is set, and an image plane of the camera is set at a predetermined position where a non-displayed area or an excess area, created by deviation between the virtual plane and the image plane of the camera, is reduced. Image data input from the camera is subjected to coordinate transformation on the virtual plane, and an image corresponding to the blind spot area created by the pillar is displayed on the interior surface of the pillar, based on the image data subjected to coordinate transformation on the virtual plane.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Information processing apparatus and method, program for executing said method, and storage medium storing said program
InactiveUS20050093860A1Effective informationSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingInformation processingComputer graphics (images)
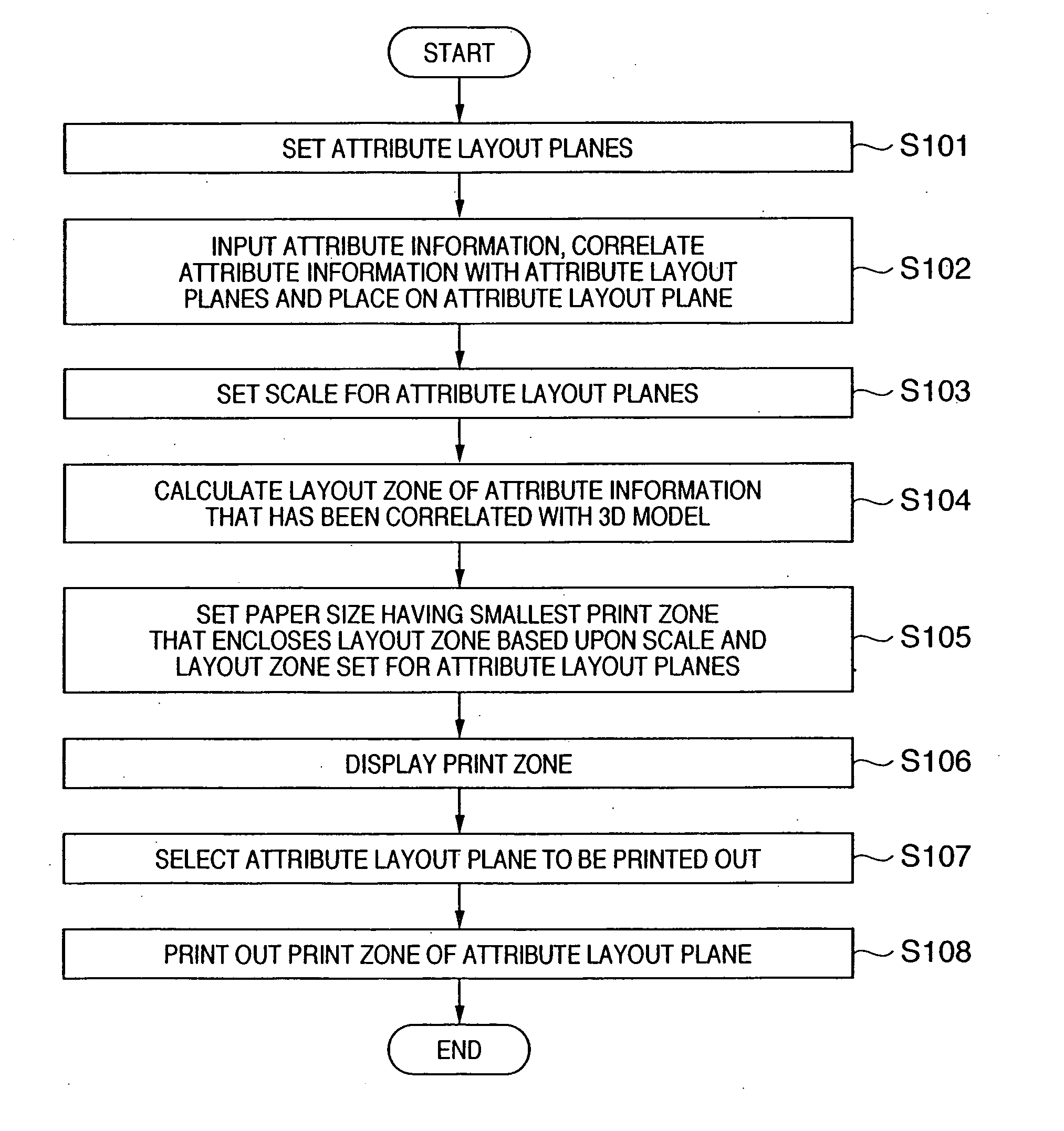
Disclosed is an information processing apparatus having display means for virtually displaying planes, in which attribute information concerning a three-dimensional model is laid out, in three-dimensional space identical with that of the three-dimensional model, and output means, which is responsive to a direct designation by designating means of a plane displayed by the display means, for outputting print data of the three-dimensional model and of the attribute information as viewed from a normal-line direction of the virtual plane designated. The information processing apparatus (a 3D-CAD apparatus, for example) prints drawings more efficiently.
Owner:CANON KK
Image heating apparatus using flexible sleeve
An image heating apparatus includes a flexible sleeve, a sliding member for sliding on the inner periphery of the sleeve, and a back-up member for forming a nip portion together with the sliding member through the sleeve. A recording material for bearing an image is heated while being held and conveyed by the nip portion, and a regulation member is set by facing the edge surface of the sleeve in the generatrix direction to regulate the movement of the sleeve in the generatrix direction, the regulation member having a regulation surface with which the edge surface of the sleeve contacts when the sleeve moves in the generatrix direction. The regulation surface of the regulation member has a curved-surface area in which a line when the regulation surface is cut at a virtual plane almost parallel with the nip portion is a curved line expanded toward the edge surface of the sleeve. Thereby, an image heating apparatus is provided which is able to restrain deterioration of the durability of the flexible sleeve.
Owner:CANON KK
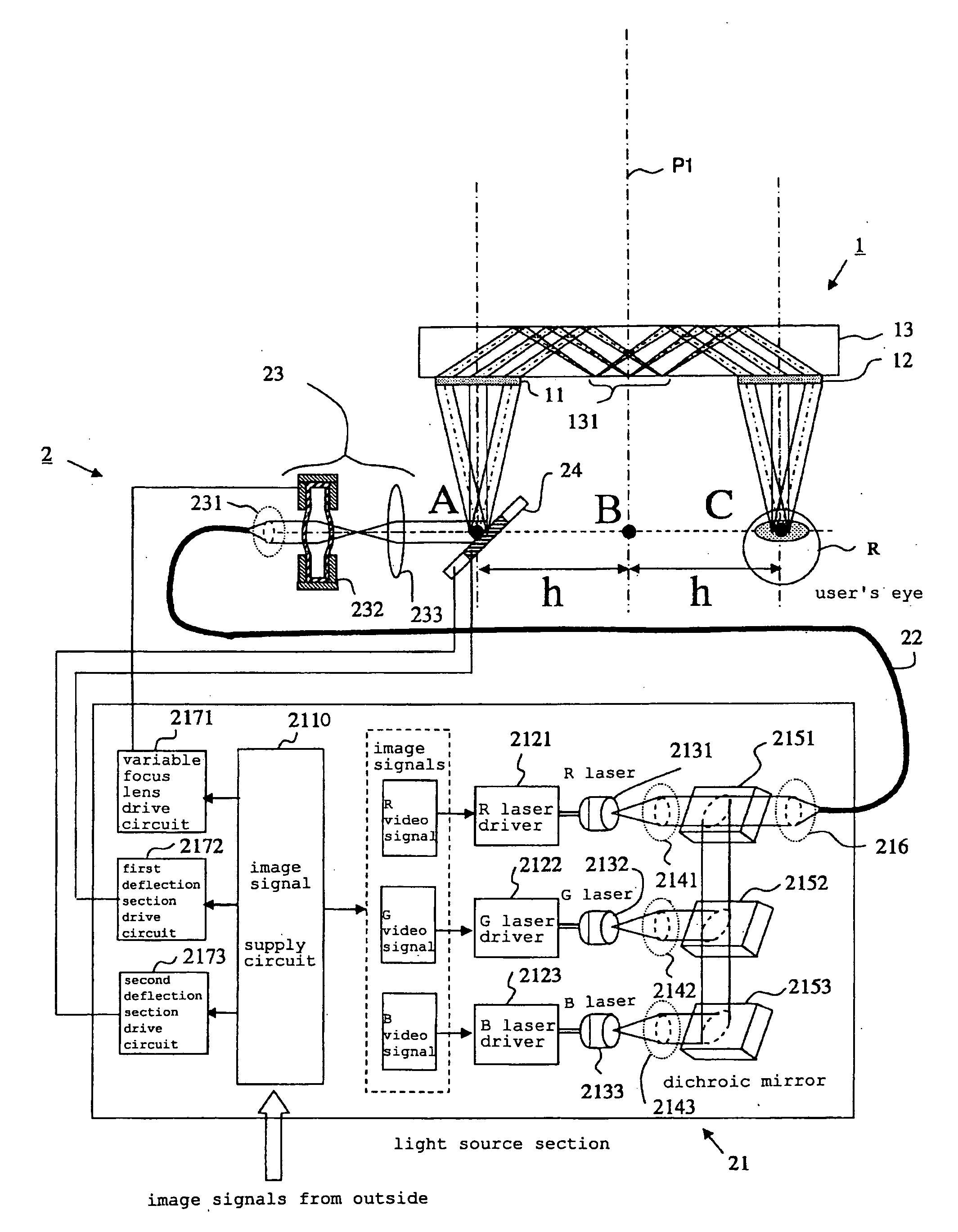
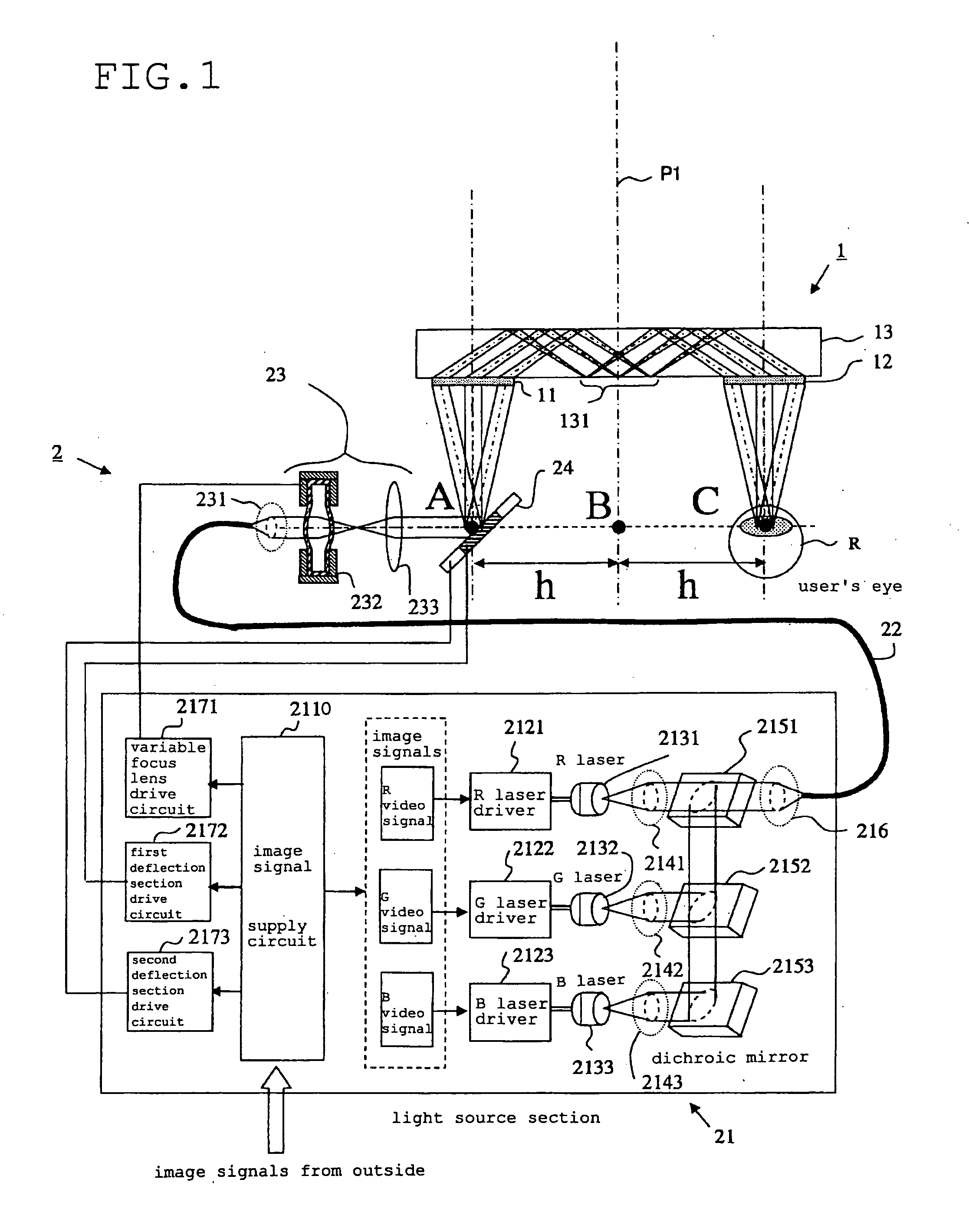
Optical system for light flux transfer, and retinal scanning display using such an optical system
InactiveUS20090190094A1Reduce generationDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideDisplay device
The present invention provides an optical system that can reduce the occurrence of aberration, and a scanning retinal display that uses such an optical system. A first diffraction section and the second diffraction section are attached to a light guiding section in a state separated from each other. The first diffraction section diffracts light flux that is incident on it, to be incident on the light guiding section. The light guiding section guides light flux that has been diffracted by the first diffraction section to the second diffraction section using reflection inside the light guiding section. The second diffraction section re-diffracts light flux that has been guided by the light guiding section and output externally of the light guiding section. The first diffraction section, the light guiding section, and the second diffraction section are substantially symmetrical, either side of a virtual plane between the first diffraction section and the second diffraction section.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
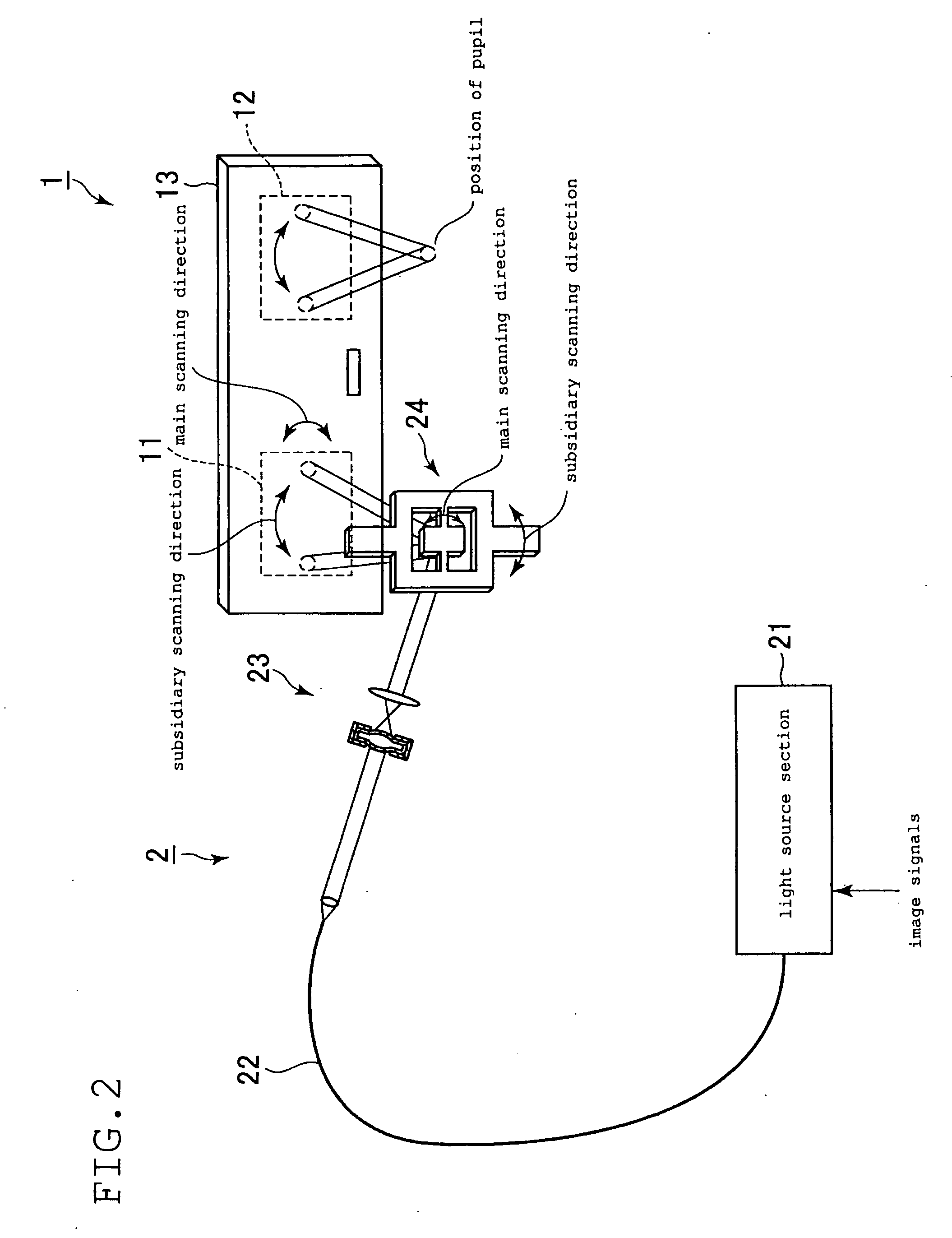
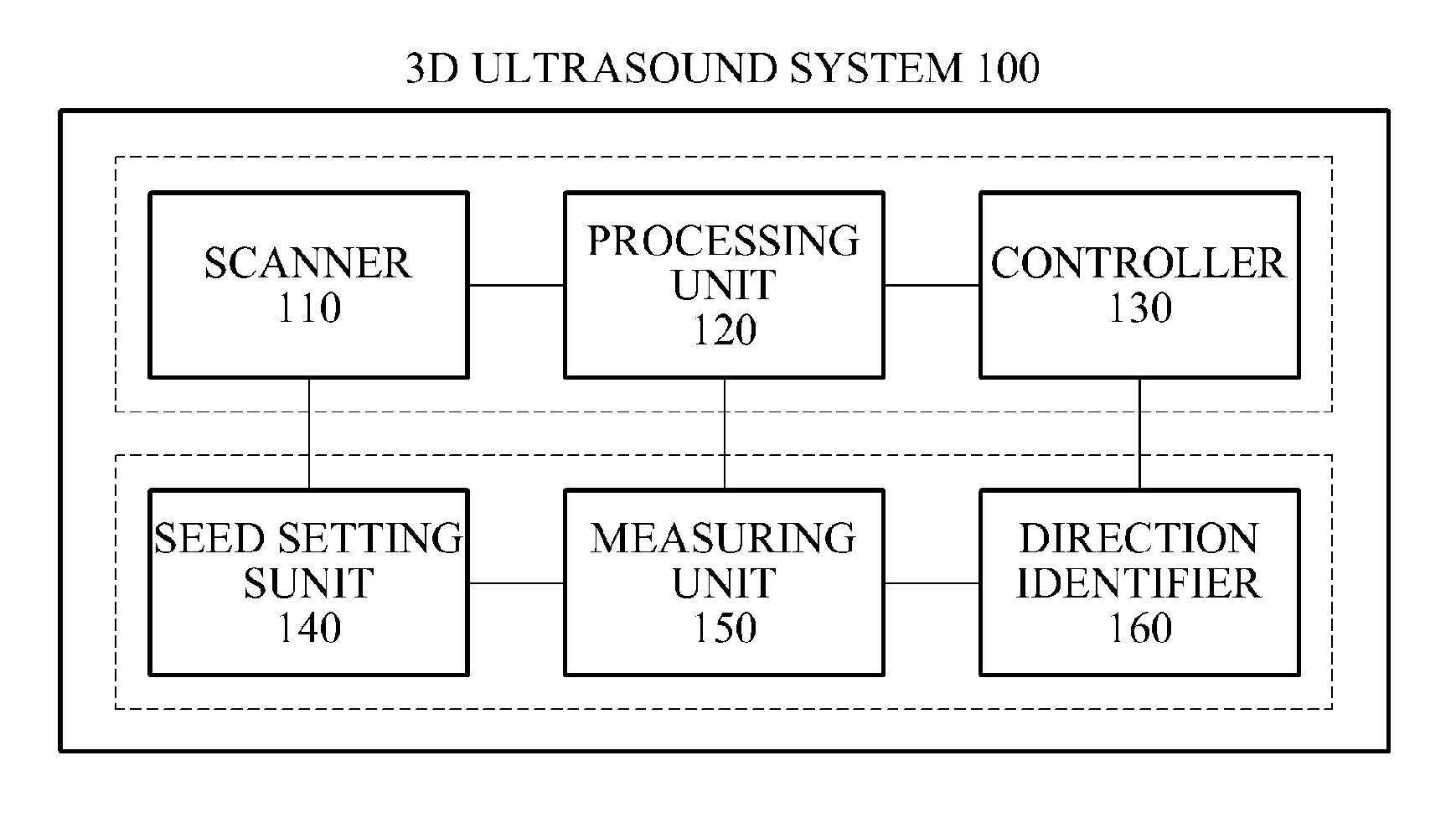
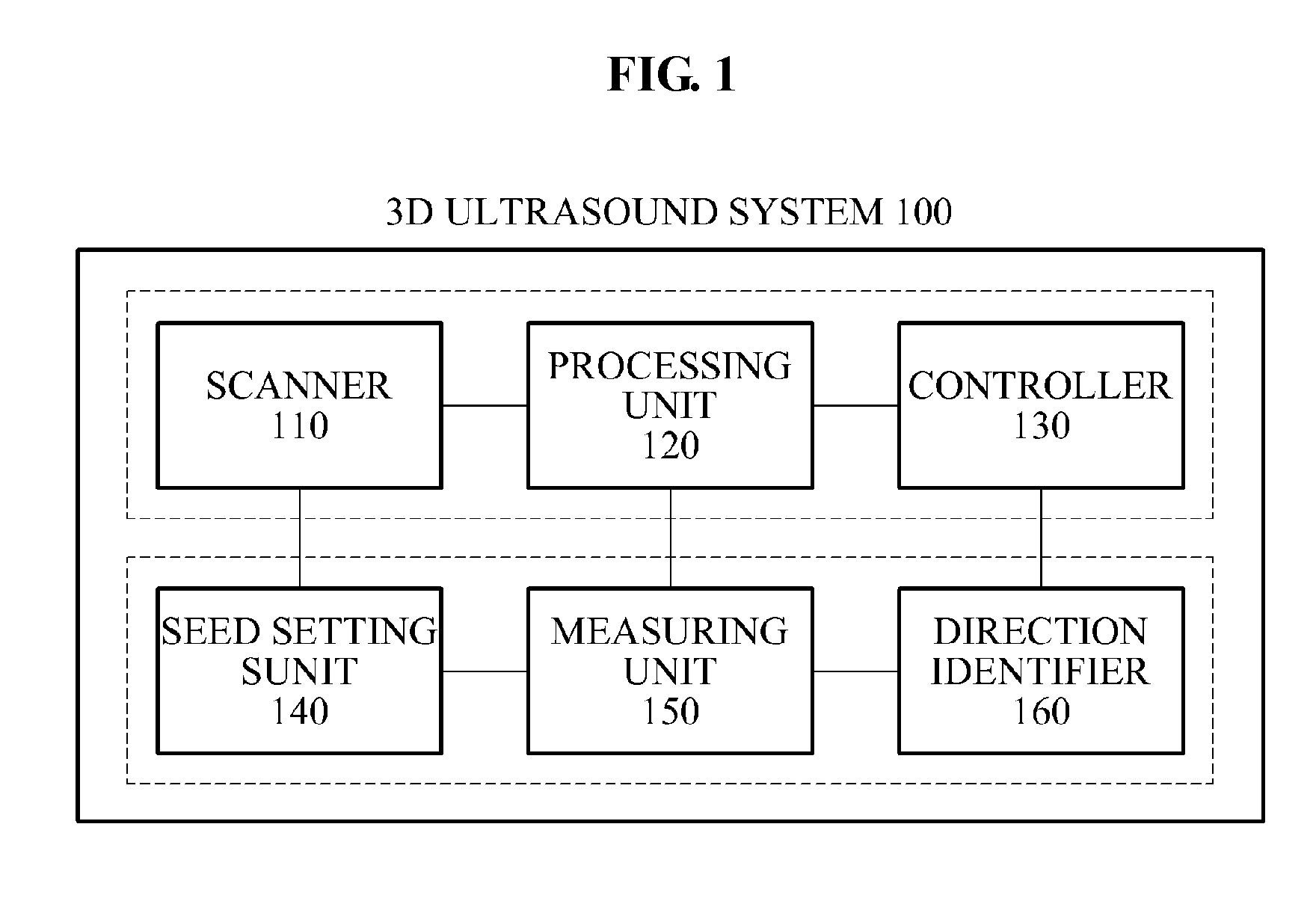
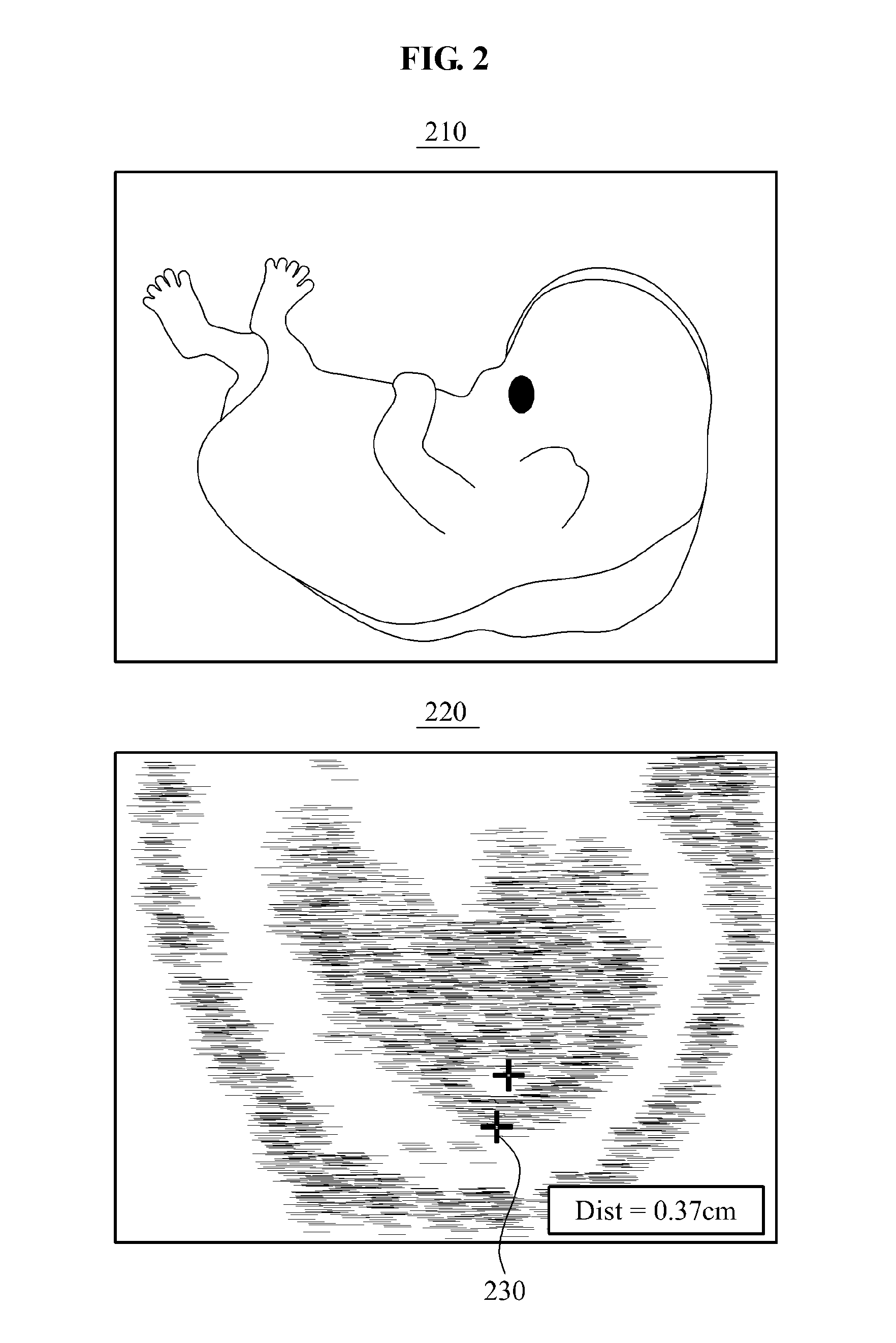
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound system for scanning object inside human body and method for operating 3D ultrasound system
ActiveUS20110224546A1View accuratelyAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationImaging data
Provided is a three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound system and a 3D ultrasound system operating method that may obtain 3D ultrasound data with respect to an object inside a human body to determine an accurate sagittal view. The 3D ultrasound system may include a scanner to generate ultrasound data including image data generated by scanning an object inside a human body, a processing unit to detect a center point of the object from the generated ultrasound data, and to generate, on the ultrasound data, a virtual plane on which the detected center point is placed, and a controller to rotate the ultrasound data based on the image data included in the virtual plane and to determine a sagittal view with respect to the object.
Owner:SAMSUNG MEDISON
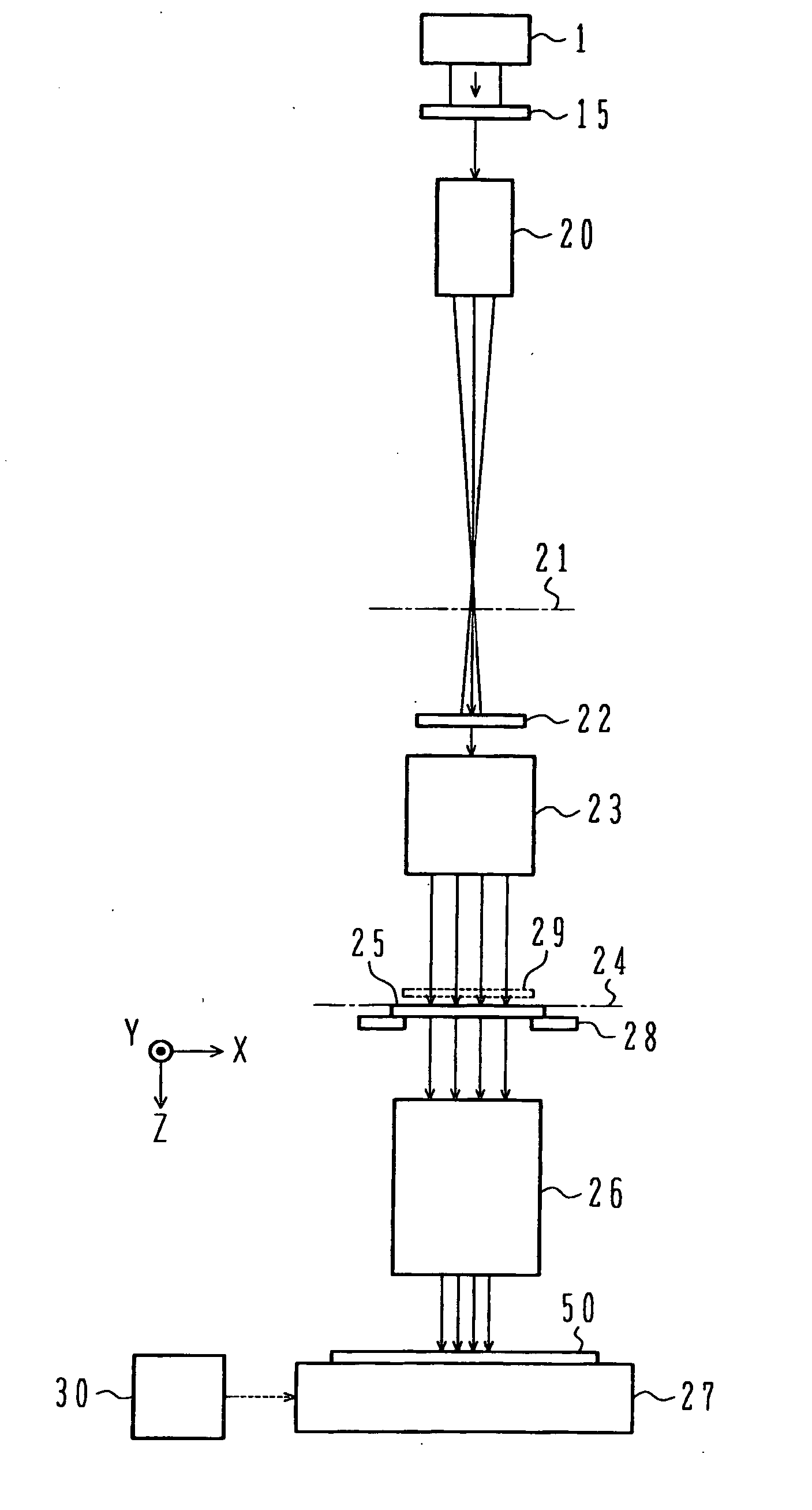
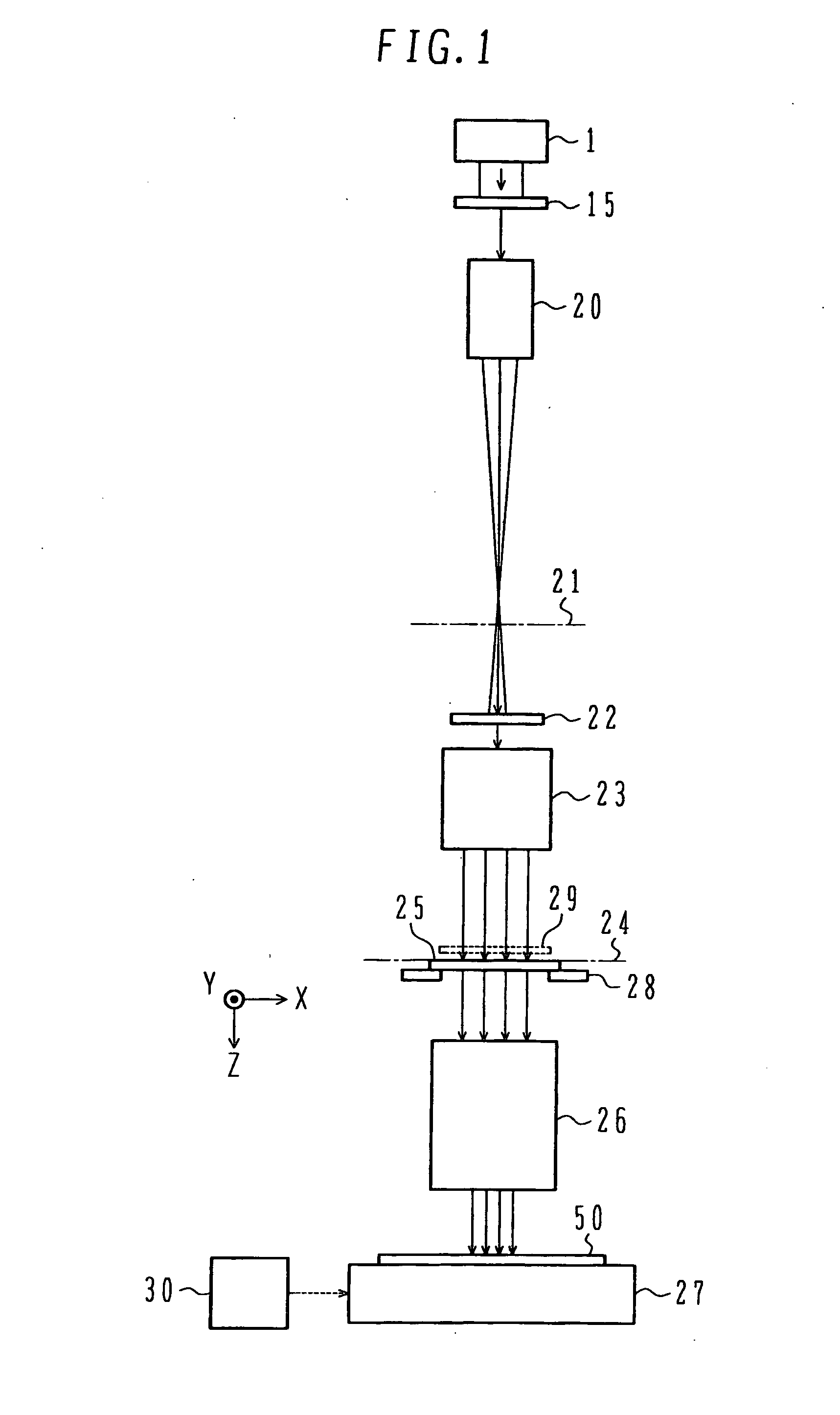
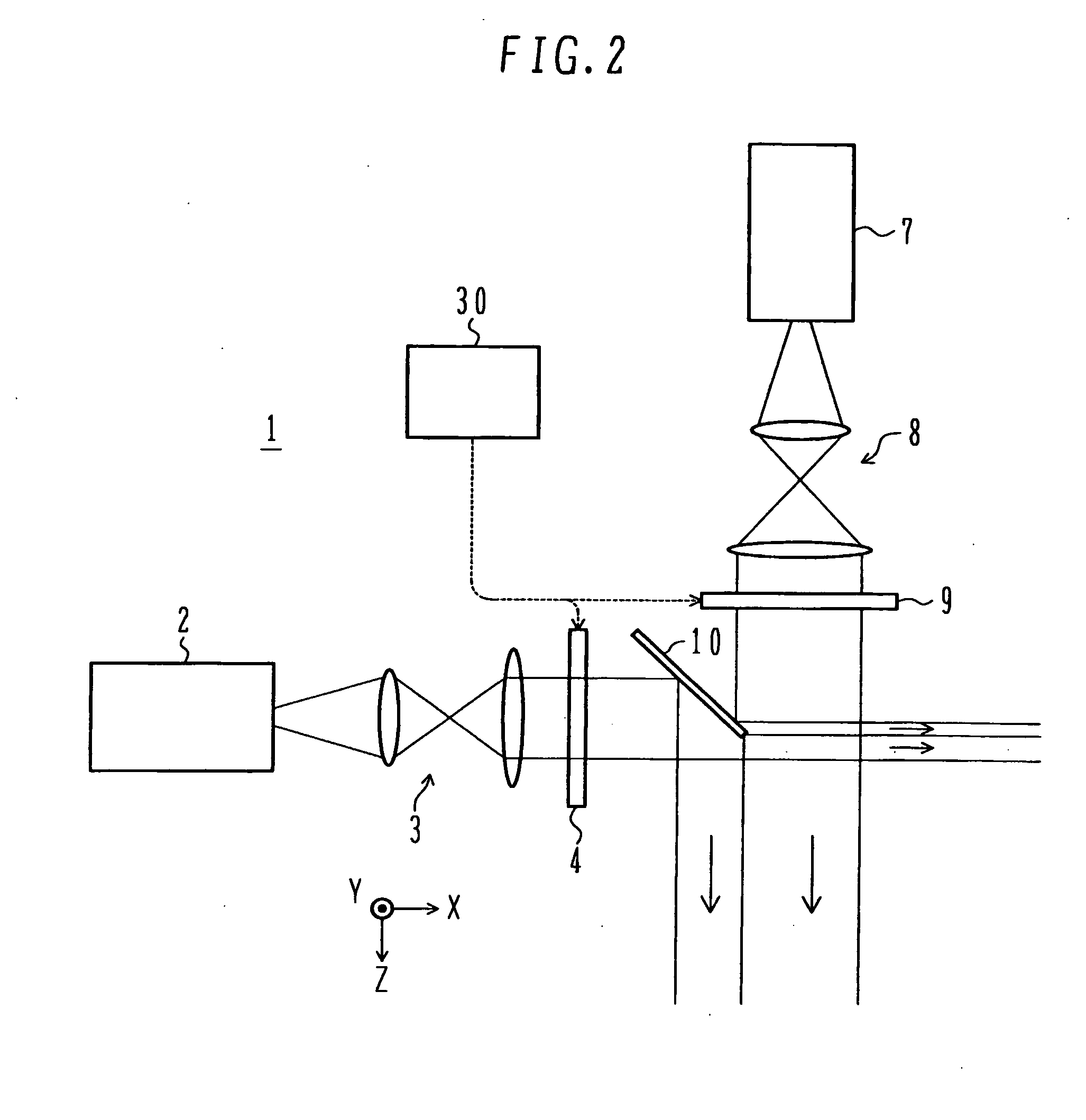
Laser beam irradiation apparatus and pattern drawing method
InactiveUS20060289412A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptoelectronicsIrradiation
A laser source emits a laser beam. A diffractive optical element is disposed at a position which the laser beam emitted from the laser source is incident on. The diffractive optical element splits the incident laser beam into laser beams. The laser beams are incident on a first zoom lens system. The first zoom lens system focuses the incident laser beams onto a first virtual plane.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
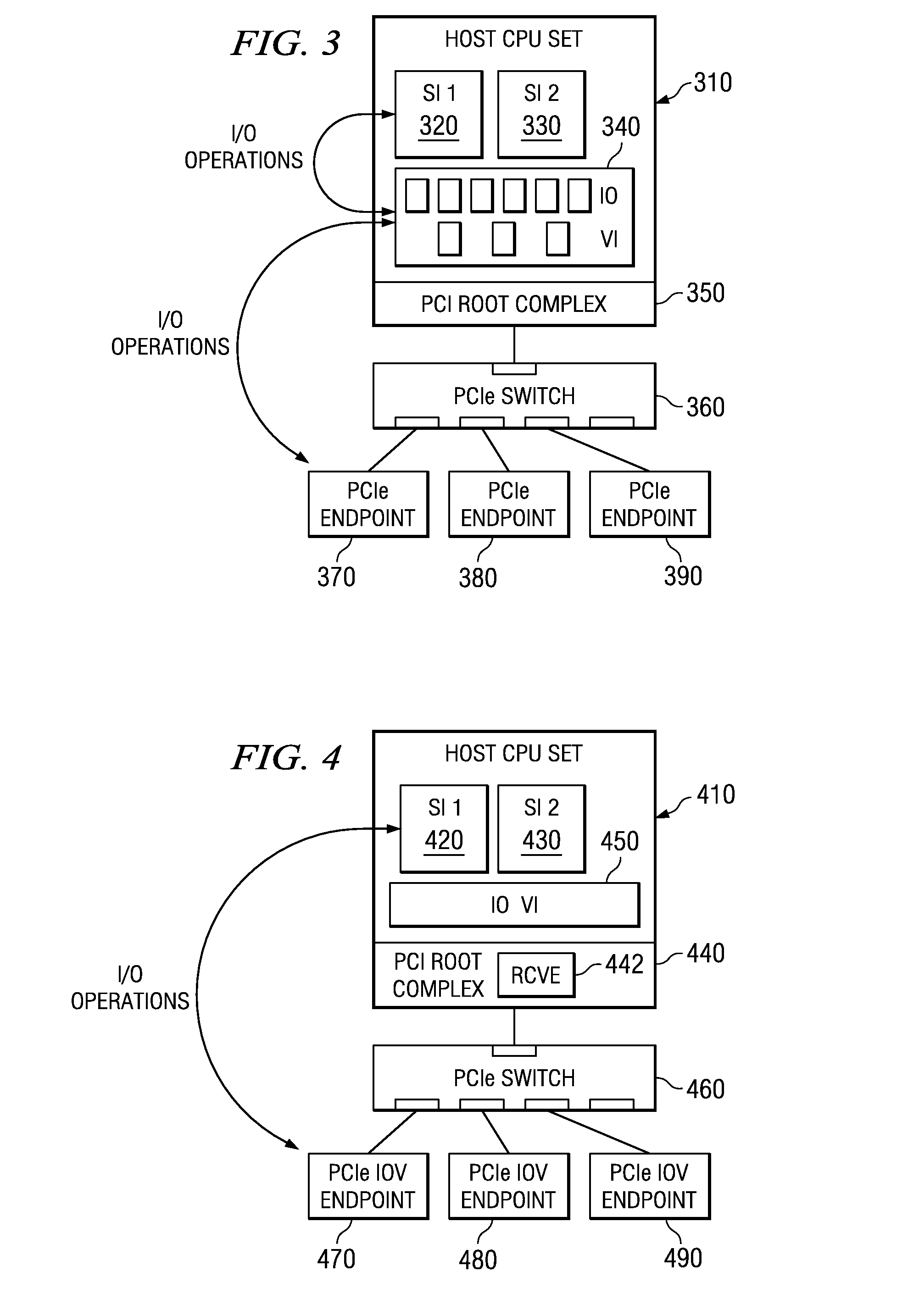
Hot-plug/remove of a new component in a running PCIe fabric
InactiveUS7836238B2Component plug-in assemblagesInput/output processes for data processingComputer scienceData structure
Mechanisms for hot-plug / remove of a new component in a running communication fabric, such as a PCIe fabric, are provided. With these mechanisms, the addition of a new component in the fabric is detected and an event is sent to a multiple root fabric configuration manager. The multiple root fabric configuration manager gathers information about the new component and updates its I / O component tree structure in its configuration data structure to include the new component. The new component may then be utilized via the updated configuration data structure. When a component is to be removed, the multiple root fabric configuration manager receives an event indicating the component to be removed, determines which branches of the tree structure are affected by the removal, and updates its configuration data structure accordingly to remove the component and its associated components from the virtual plane of the removed component.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com