Method for preparing tiny mesoporous silica drug sustained-release material
A technology of silica and slow-release materials, which is applied in the field of material processing and can solve problems such as non-display
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
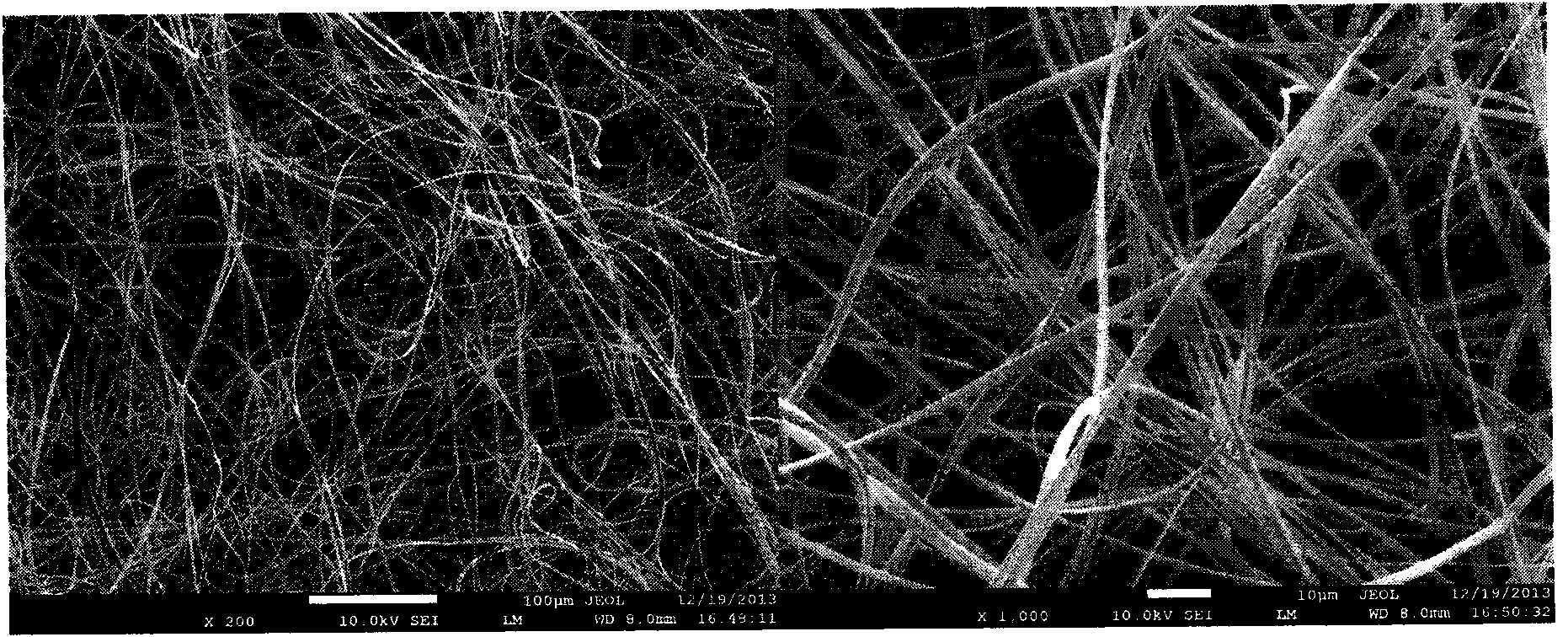
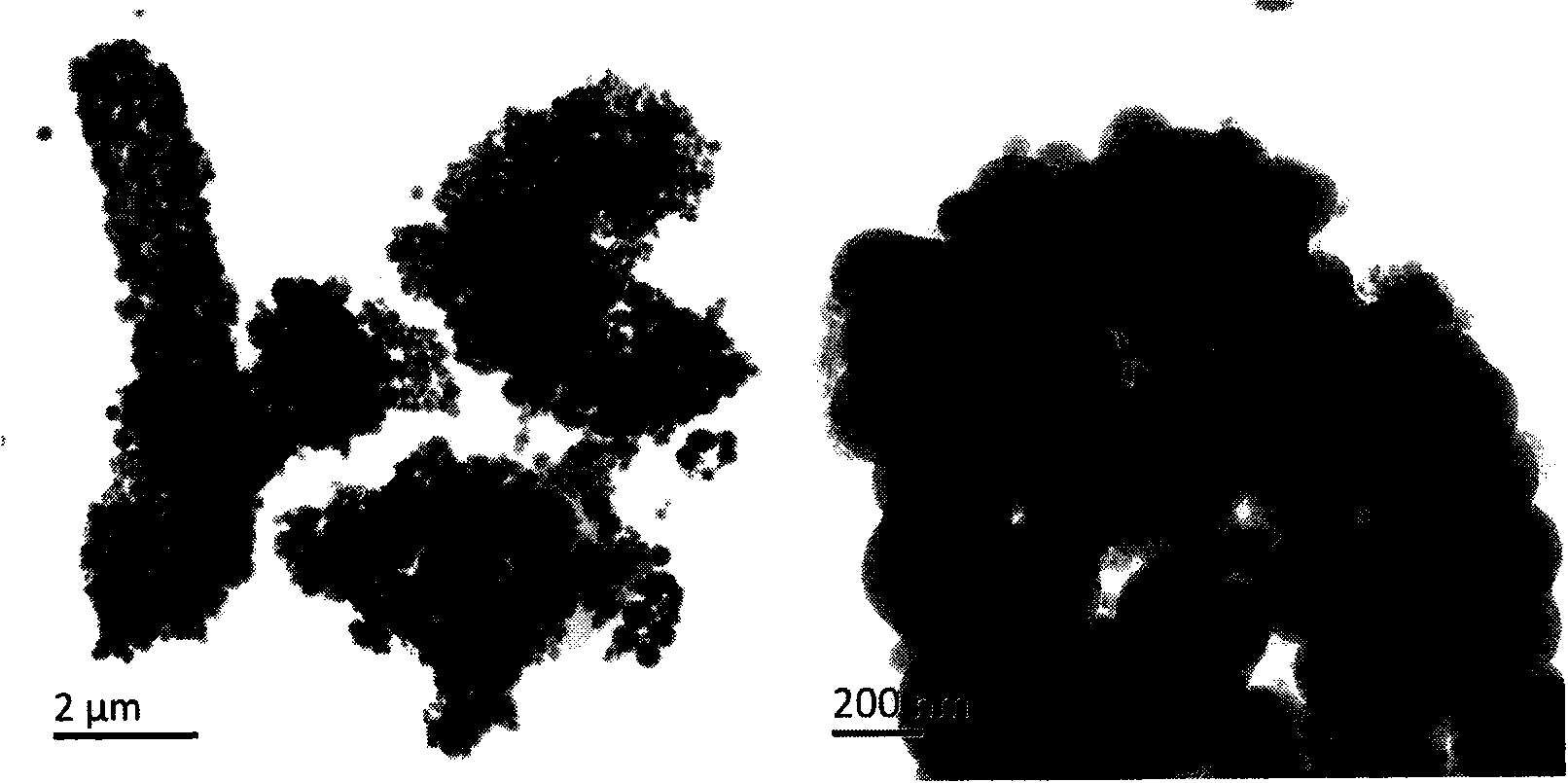
[0040] Prepare 18wt% cellulose acetate solution. Fill the above solution into a syringe fitted with a metal needle. Connect the positive electrode of the high-voltage power supply to the needle, and the ground electrode to the aluminum film on the collector plate. Adjust the voltage to 20kV, the distance between the needle head and the collecting plate to 20cm, and the liquid feeding speed to 5mL / h, etc., to prepare cellulose acetate electrospun fibers with a diameter of several microns, see attached figure 1 .
[0041] Weigh 0.1 g of cellulose acetate for electrospinning at room temperature, add 45 mL of deionized water and 15 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 0.03 mmol of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and then add 0.12 mL of ammonia water as a catalyst. The above mixed solution was dispersed for 30 minutes with an ultrasonic disperser. Let it stand for another 10 minutes to allow CTAB and CAMF to reach adsorption equilibrium. Then 0.6 mL of TEOS dispersed with absolute ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A 14 wt% cellulose acetate solution was prepared. Fill the above solution into a syringe fitted with a metal needle. Connect the positive electrode of the high-voltage power supply to the needle, and the ground electrode to the aluminum film on the collector plate. Adjust the voltage to 10kV, the distance between the needle and the collecting plate to 10cm, and the liquid feeding speed to 1mL / h, etc., to prepare cellulose acetate electrospun fibers with a diameter of several hundred nanometers. image 3 .
[0046] Weigh 0.1 g of cellulose acetate for electrospinning at room temperature, add 30 mL of deionized water and 30 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 0.3 mmol of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and then add 0.9 mL of ammonia water as a catalyst. The above mixed solution was dispersed for 30 minutes with an ultrasonic disperser. Let it stand for another 10 minutes to allow CTAB and CAMF to reach adsorption equilibrium. Then 0.06 mL of TEOS dispersed with absolute ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A 9wt% cellulose acetate solution was prepared. Fill the above solution into a syringe fitted with a metal needle. Connect the positive electrode of the high-voltage power supply to the needle, and the ground electrode to the aluminum film on the collector plate. Adjust the voltage to 30kV, the distance between the needle and the collecting plate to 15cm, and the liquid feeding speed to 2mL / h, etc., to prepare cellulose acetate electrospinning with a diameter of submicron, see attached Figure 5 .
[0051] Weigh 0.1 g of cellulose acetate for electrospinning at room temperature, add 15 mL of deionized water and 45 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 0.01 mmol of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, and then add 0.09 mL of ammonia water as a catalyst. The above mixed solution was dispersed for 30 minutes with an ultrasonic disperser. Let it stand for another 10 minutes to allow CTAB and CAMF to reach adsorption equilibrium. Then 0.2 mL of TEOS dispersed with absolute ethanol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com