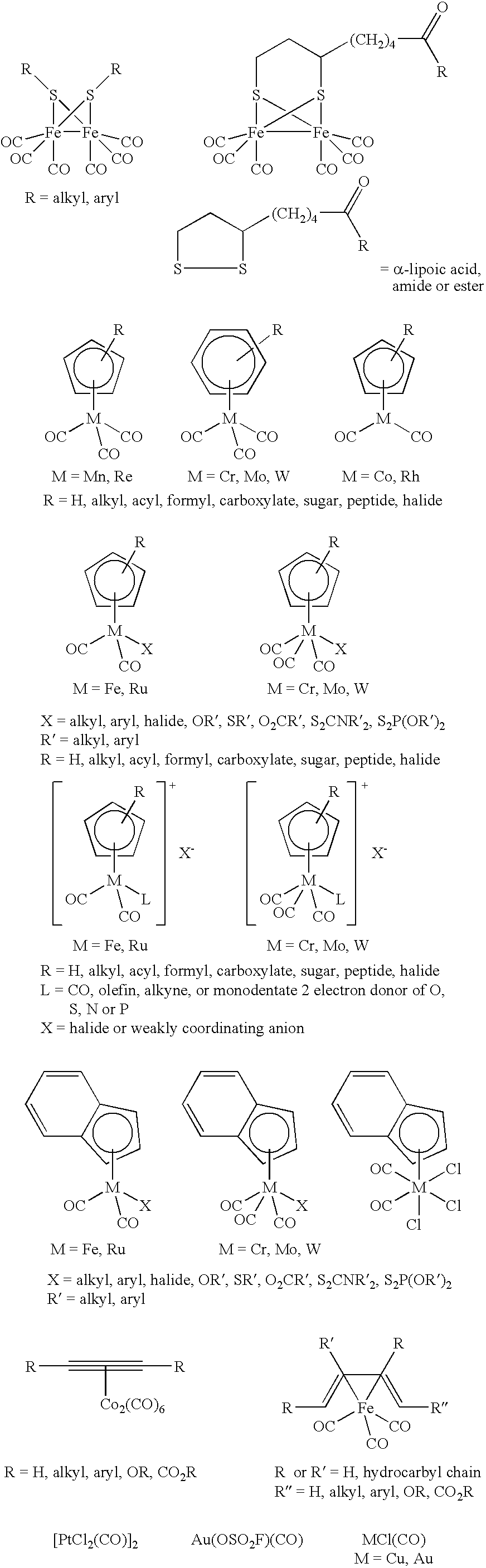
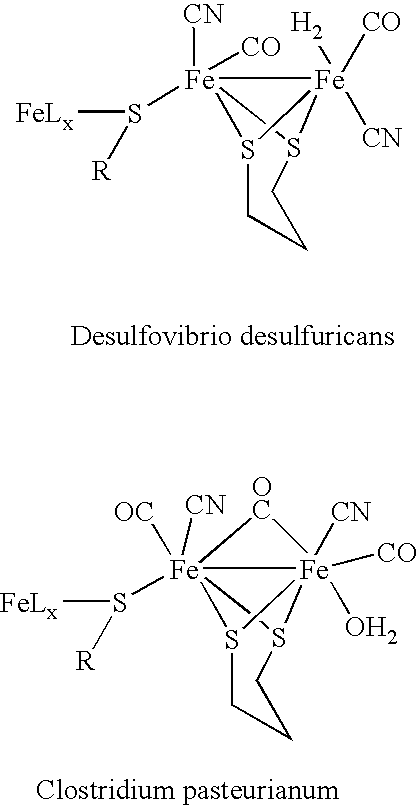
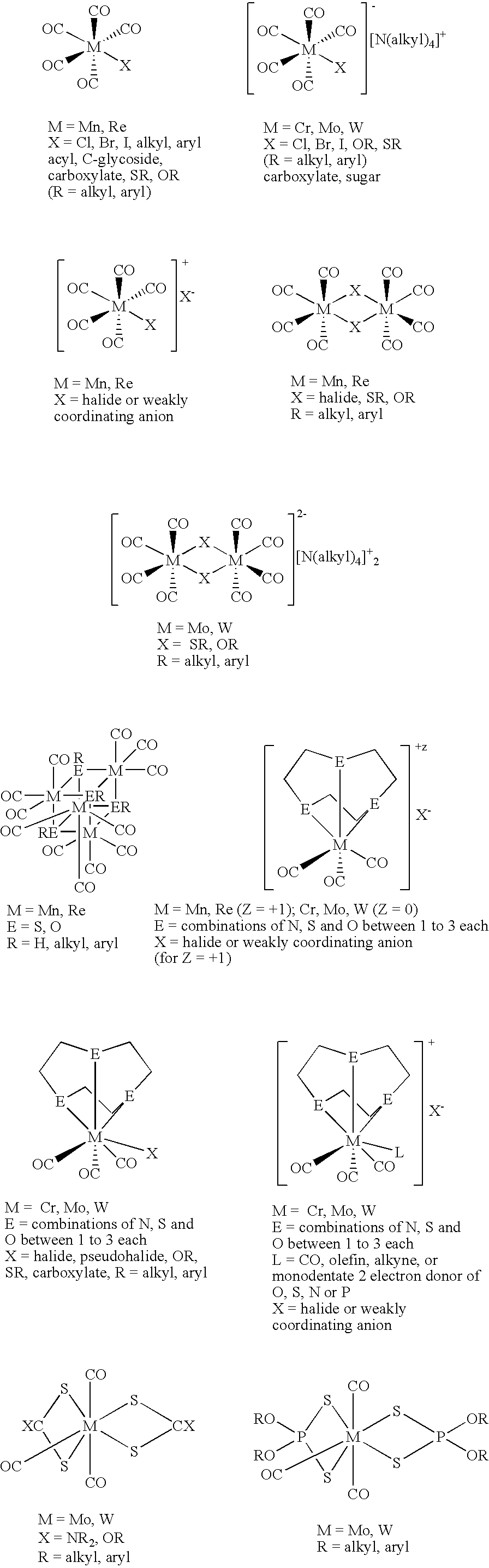
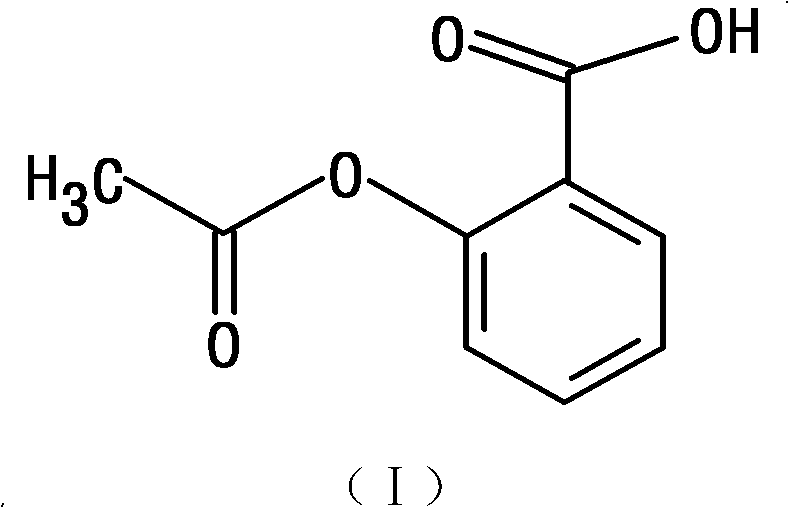
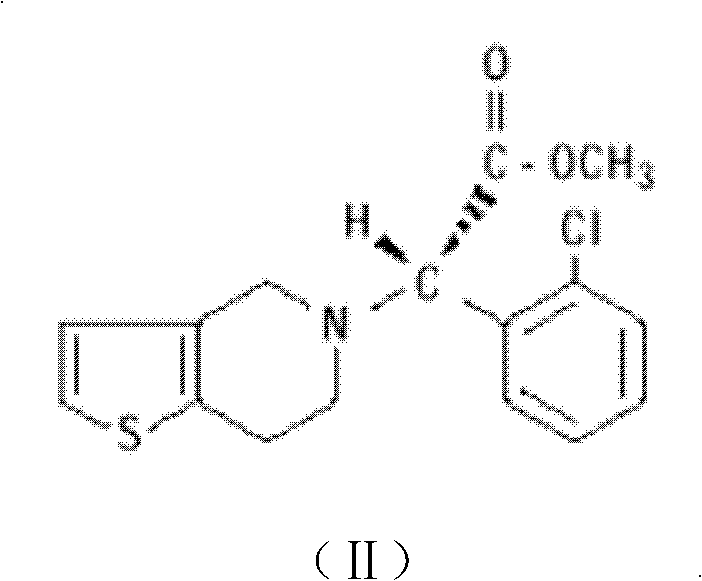
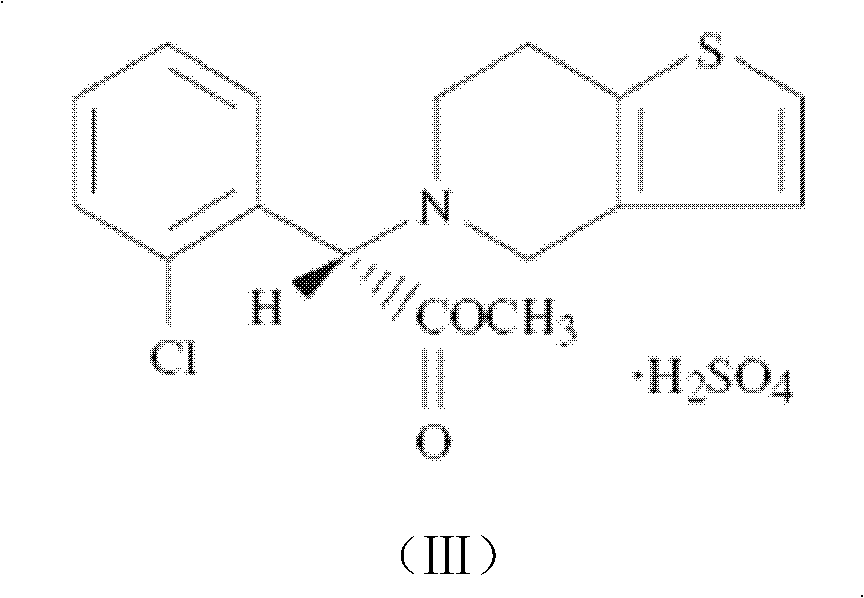
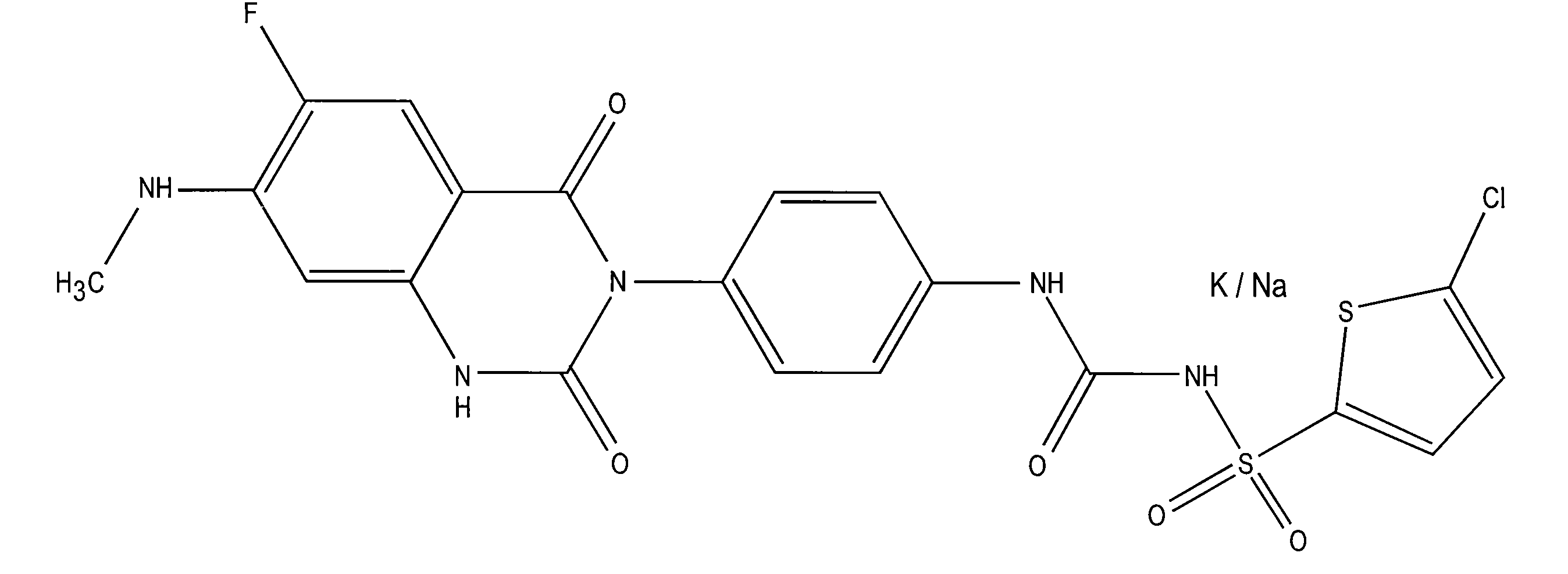
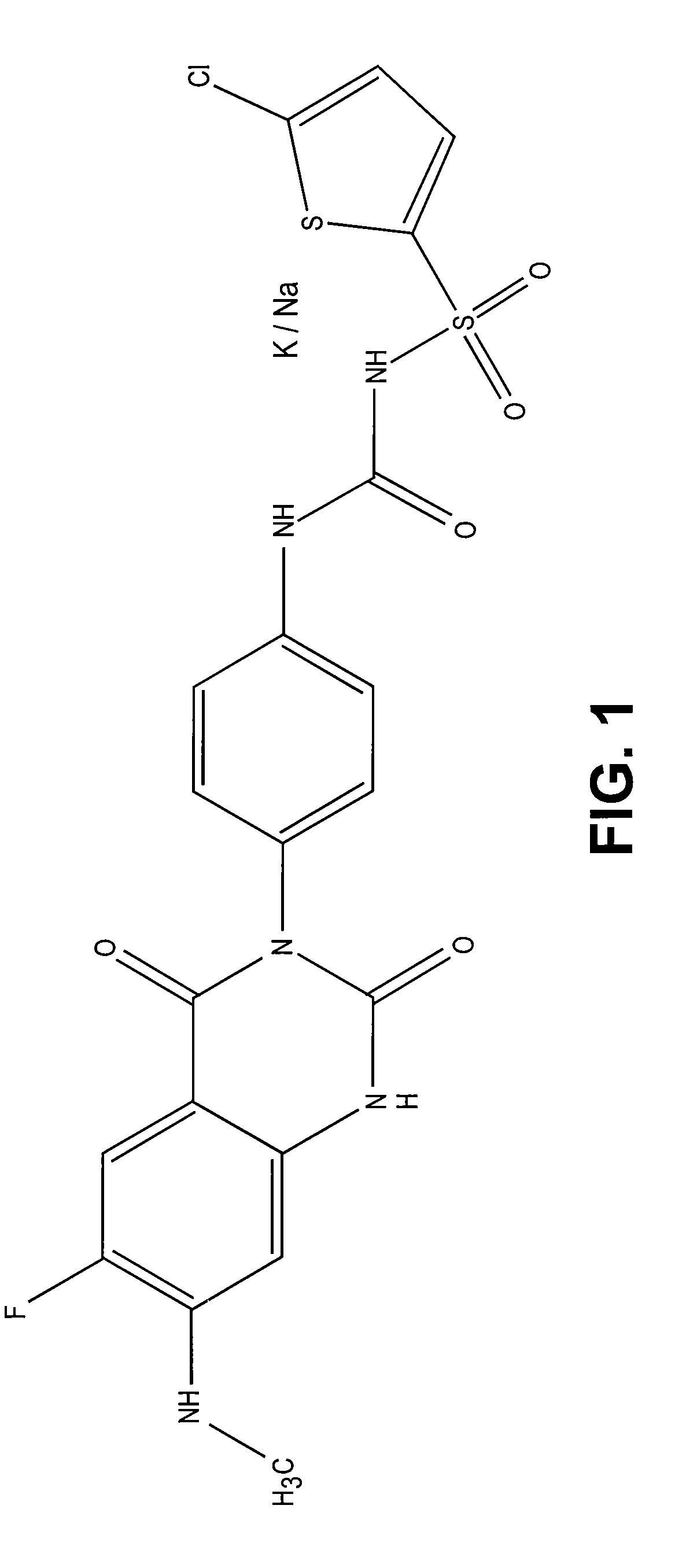
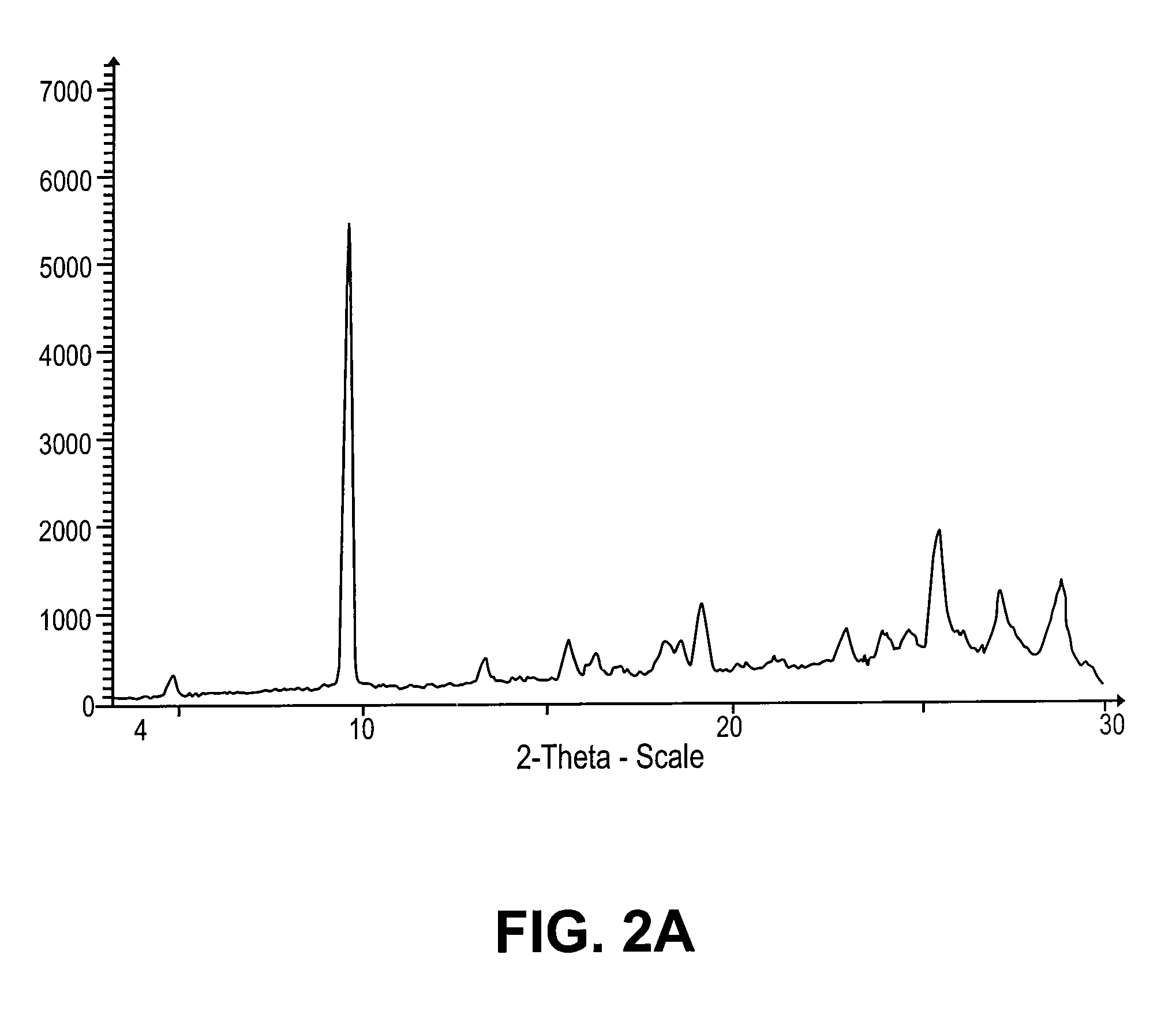
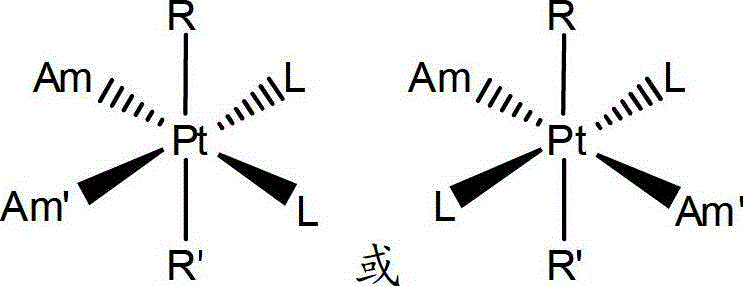
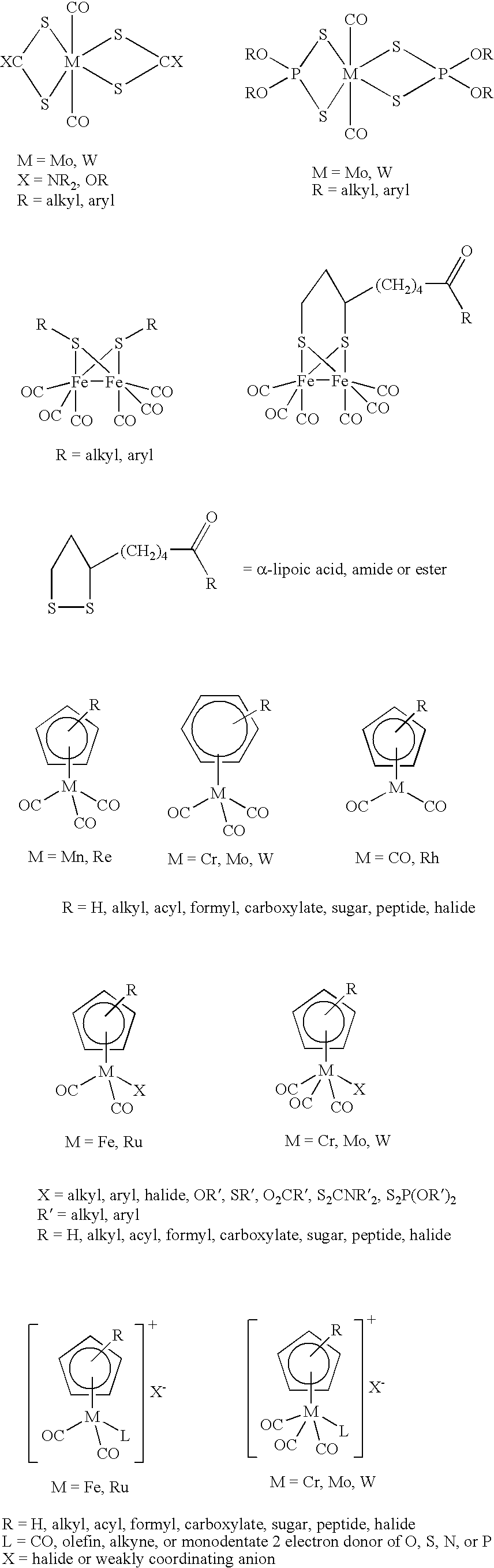Patents
Literature
193 results about "O-acetylsalicylic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
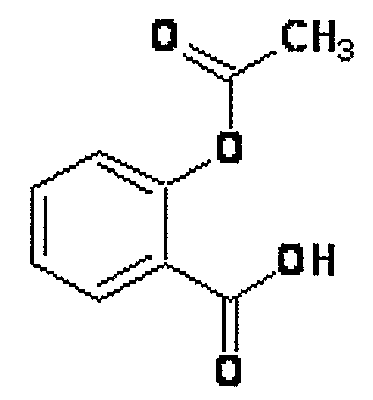
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a medication used to treat pain, fever, or inflammation.
Topical dermal anaesthetic
A liquid composition applied transdermally for relief of pain comprising alcohol in an amount by weight of about 57 to about 91 percent; glycerin in an amount by weight of about 1 to about 12 percent; an analgesic agent in an amount by weight of about 2 to about 28 percent, the analgesic agent comprising a derivative of salicylic acid; methylsulfonylmethane in an amount by weight of about 0.02 to 5 percent; and emu oil in an amount by weight of about 0.01 to 3 percent, the liquid composition permeating skin to relieve pain. The composition further comprising, as an additional feature, aloe vera in an amount by weight of at least about 0.05 percent and having an amount by weight of about 0.05 to 4 percent. The composition features transdermal pain relief such that a patient can apply the analgesic agent directly to an area of pain without such side effects as stomach irritation which is normally associated with aspirin. The composition may be sprayed or rolled directly onto the painful area. Because of the unique formula, the composition is safe to vital internal organs, requires no mixing before use, and is shelf stable for marketing purposes.
Owner:VELTRAN LP
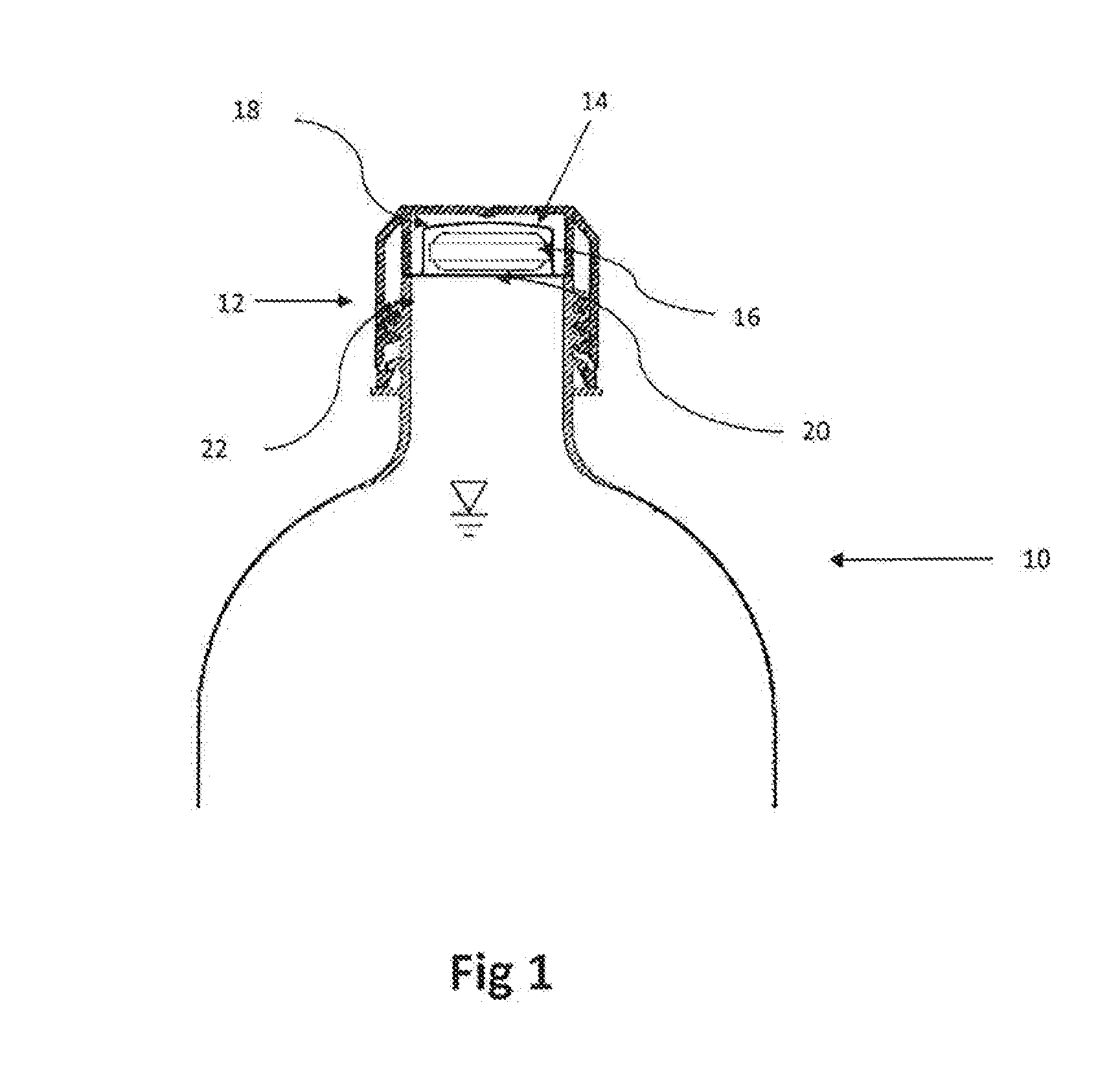
Aqueous Solution of an Analgesic and a Dispenser Therefor
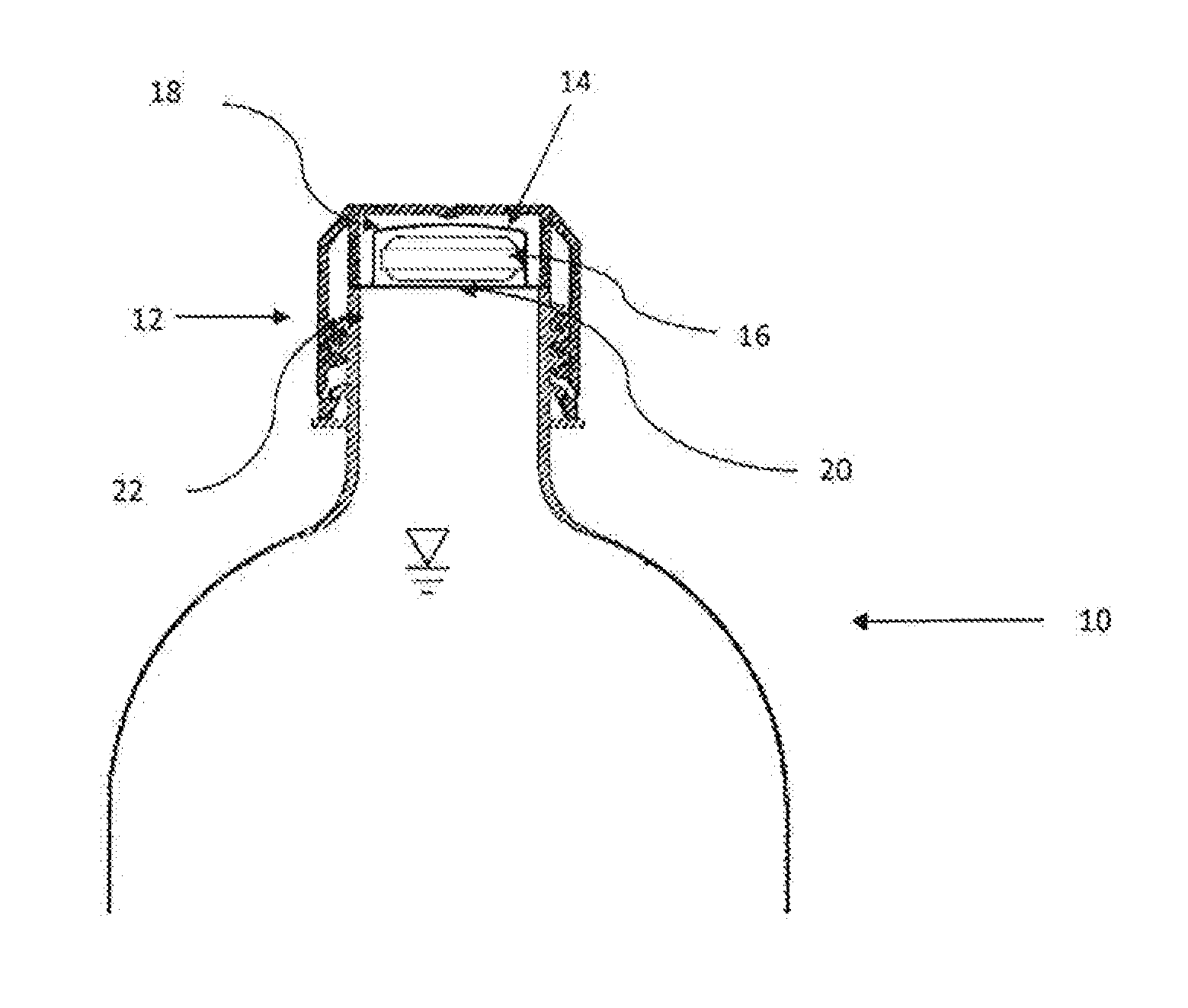
A bottle cap is adapted to retain a quantity of an additive, such as for example aspirin or the like. The additive is retained in an isolated condition within a sealed chamber or within a bladder inside the bottle cap but in fluid communication with the liquid within the bottle, such as water. Means are provided to breech the seal of the chamber or the bladder, thereby releasing some or all of the additive retained within the bottle cap.
Owner:DVORAK STEVEN G MR
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions of drugs such as carbamazepine, celecoxib, olanzapine, itraconazole, topiramate, modafinil, 5-fluorouracil, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, aspirin, flurbiprofen, phenytoin and ibuprofen
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphinic acid, phosphonic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, imine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, S-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, N-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, 0-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +3
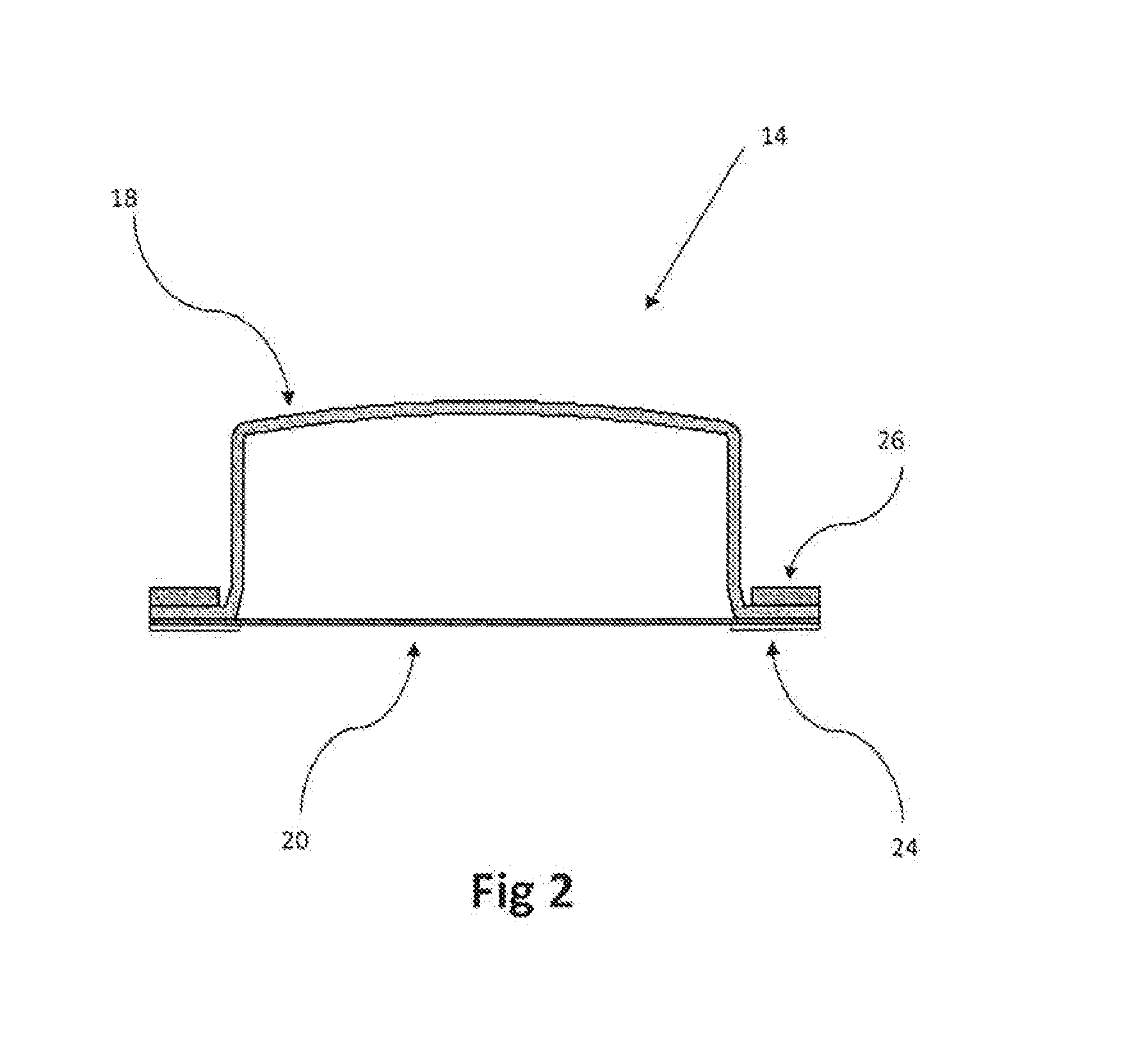
Aqueous solution of an analgesic and a dispenser therefor
A bottle cap is adapted to retain a quantity of an additive, such as for example aspirin or the like. The additive is retained in an isolated condition within a sealed chamber or within a bladder inside the bottle cap but in fluid communication with the liquid within the bottle, such as water. A cap with at least one downward extending protrusion is provided to breech the seal of the chamber or the bladder, thereby releasing some or all of the additive retained within the bottle cap.
Owner:DVORAK STEVEN G MR
Methods of treatment of patients at increased risk of development of ischemic events and compounds hereof
InactiveUS20130040898A1Impair thrombus formationIncreased riskElcosanoid active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsBeta blockerPlatelet inhibitors
The present invention relates to compounds for treatment that protects the endothelium, prevents pathologic thrombus formation in the microcirculation and preserves platelet number and function and thus may be related to treatment or prevention of ischemic events in patients with cardiovascular disease. The present invention is particularly useful for patients having or being at increased risk of development of an ischemic event such as an acute myocardial infarction and / or no-reflow phenomena and / or ischemia-reperfusion injury by administration of agent(s) modulating and / or preserving endothelial integrity. The compounds may be administered in combination with standard treatment of acute cardiovascular ischemic events such as Platelet inhibitors such as aspirin (ASA), Thienopyridins, GPIIb / IIIa inhibitors), Parenteral anticoagulants such as unfractioned heparin (UFH), bivalirudin, enoxaparin, and fondaparinux, Verapamil, Adenosine, Sodium nitroprusside, Nitroglycerin, Epinephrine, Beta-blockers and surgical methods such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), PCI with thrombus aspiration, PCI with stents.
Owner:THROMBOLOGIC
Blister pack for a container
InactiveUS20130186779A1Burst strengthClosure with auxillary devicesRigid containersEngineeringBlister pack
The present invention relates to a blister pack sealed to the neck of a container and adapted to fit under the container lid forming a seal, said blister pack containing a liquid soluble material such as dissolvable aspirin. When force is applied to the blister pack, the base, which is comprised of a rupturable material, breaks and allows the liquid soluble material to be mixed with the liquid in the container. The blister pack remains as a seal for the container until it is desired that the user remove the blister pack for access to the container. The user can then re-seal the container using the container lid.
Owner:KAMBOURIS AMBROSIOS
Method for treating a mammal by administration of a compound having the ability to release CO, compounds having the ability to release CO and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
Several classes of in vivo carbon monoxide-releasing compounds are useful for the treatment and / or prevention of diseases, such as chronic inflammatory, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, and of diseases with a strong inflammatory component, such as atherosclerosis, stroke, coronary disease, and Alzheimers disease. The in vivo carbon monoxide-releasing compounds can be attached to known drug vectors and / or known anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin.
Owner:ALFAMA INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO DE PRODUTOSFARMACEUTICOS LDA
Method for treating a mammal by administration of a compound having the ability to release CO, compounds having the ability to release CO and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
Several classes of in vivo carbon monoxide-releasing compounds are useful for the treatment and / or prevention of diseases, such as chronic inflammatory, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, and of diseases with a strong inflammatory component, such as atherosclerosis, stroke, coronary disease, and Alzheimers disease. The in vivo carbon monoxide-releasing compounds can be attached to known drug vectors and / or known anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin.
Owner:ALFAMA INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO DE PRODUTOSFARMACEUTICOS LDA
Auxiliary container for physical association with conventional medication container
InactiveUS20030111467A1Eliminating potentially damaging exposurePreventing loss and exposurePharmaceutical containersTable equipmentsAspirinImmediate release
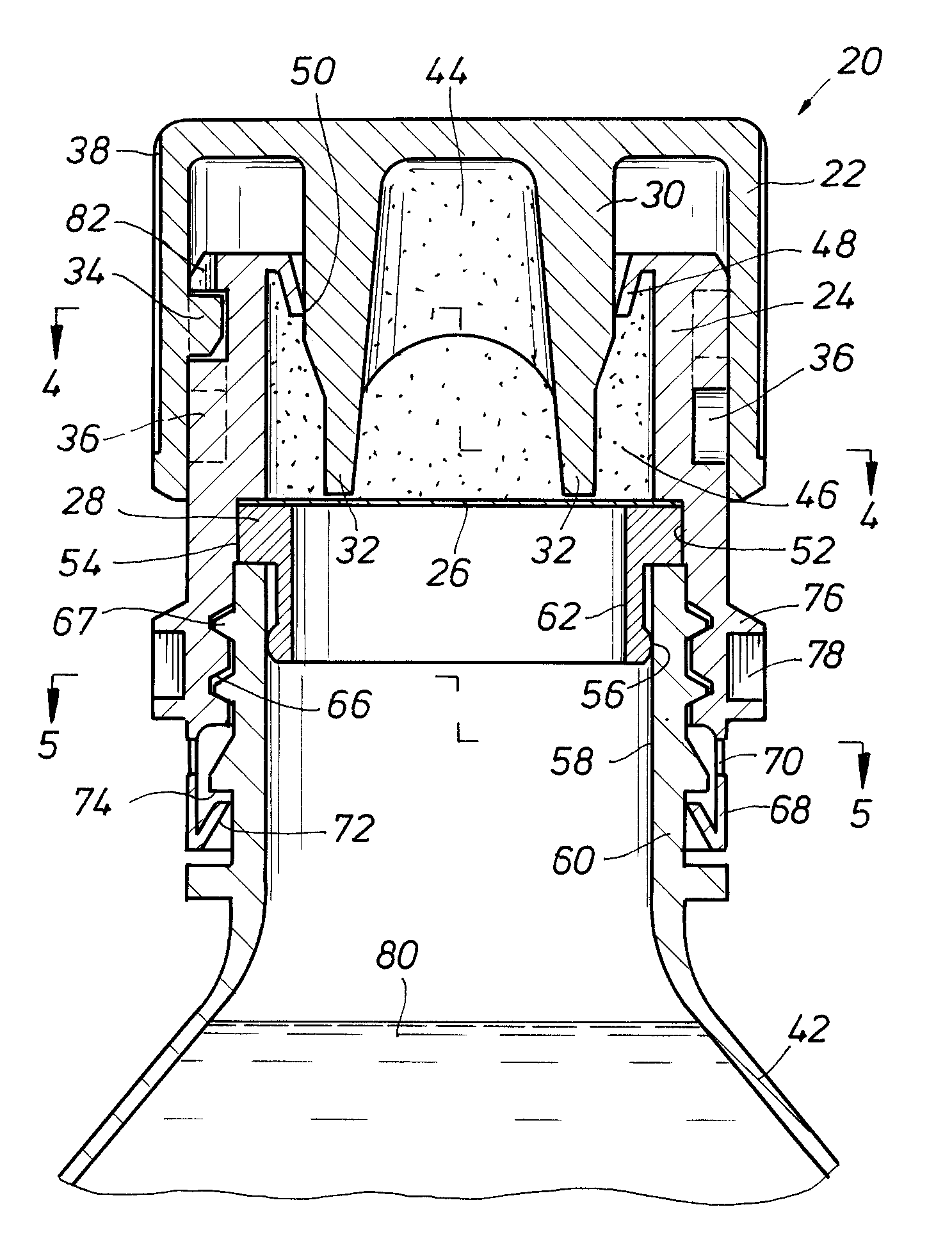
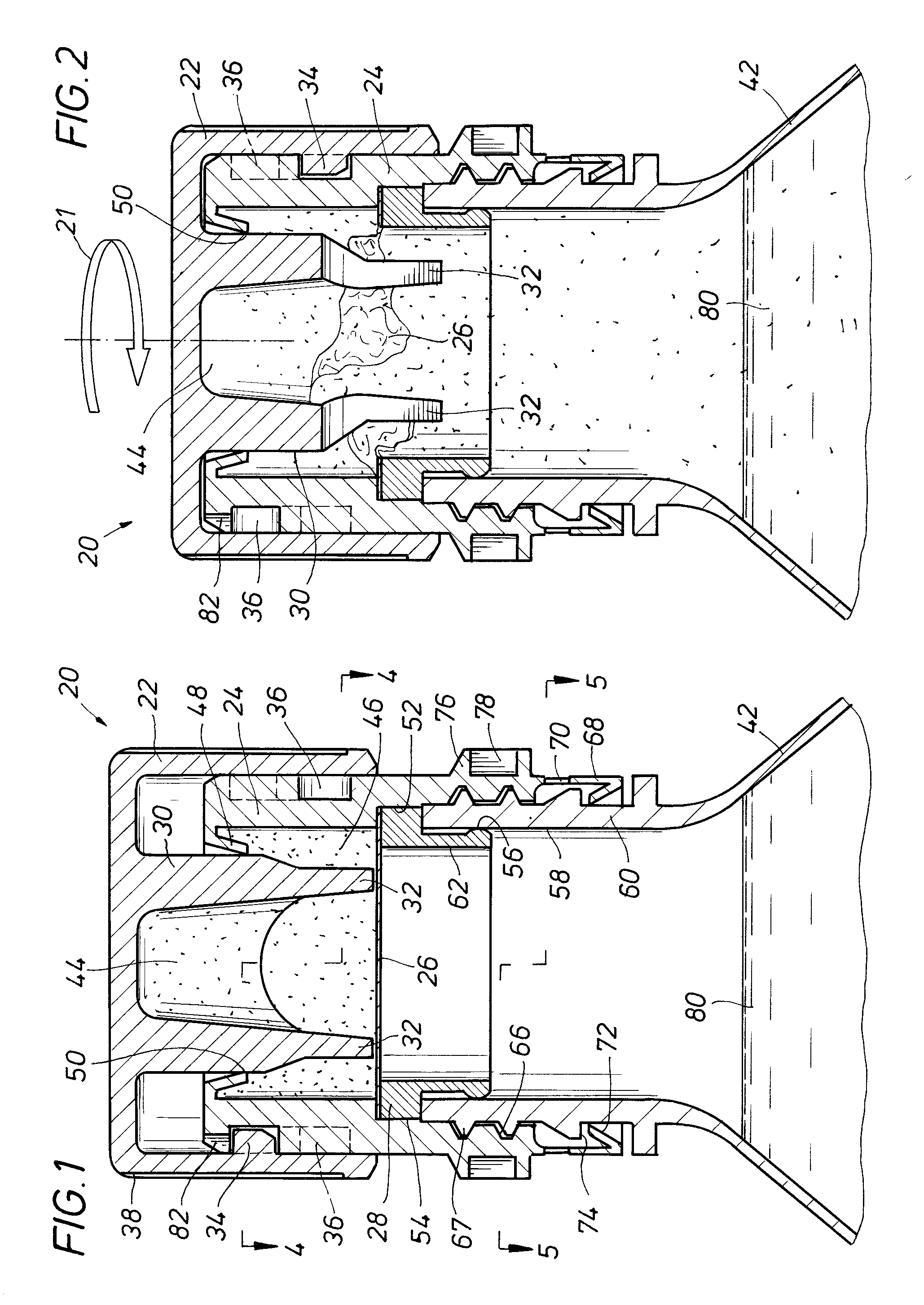
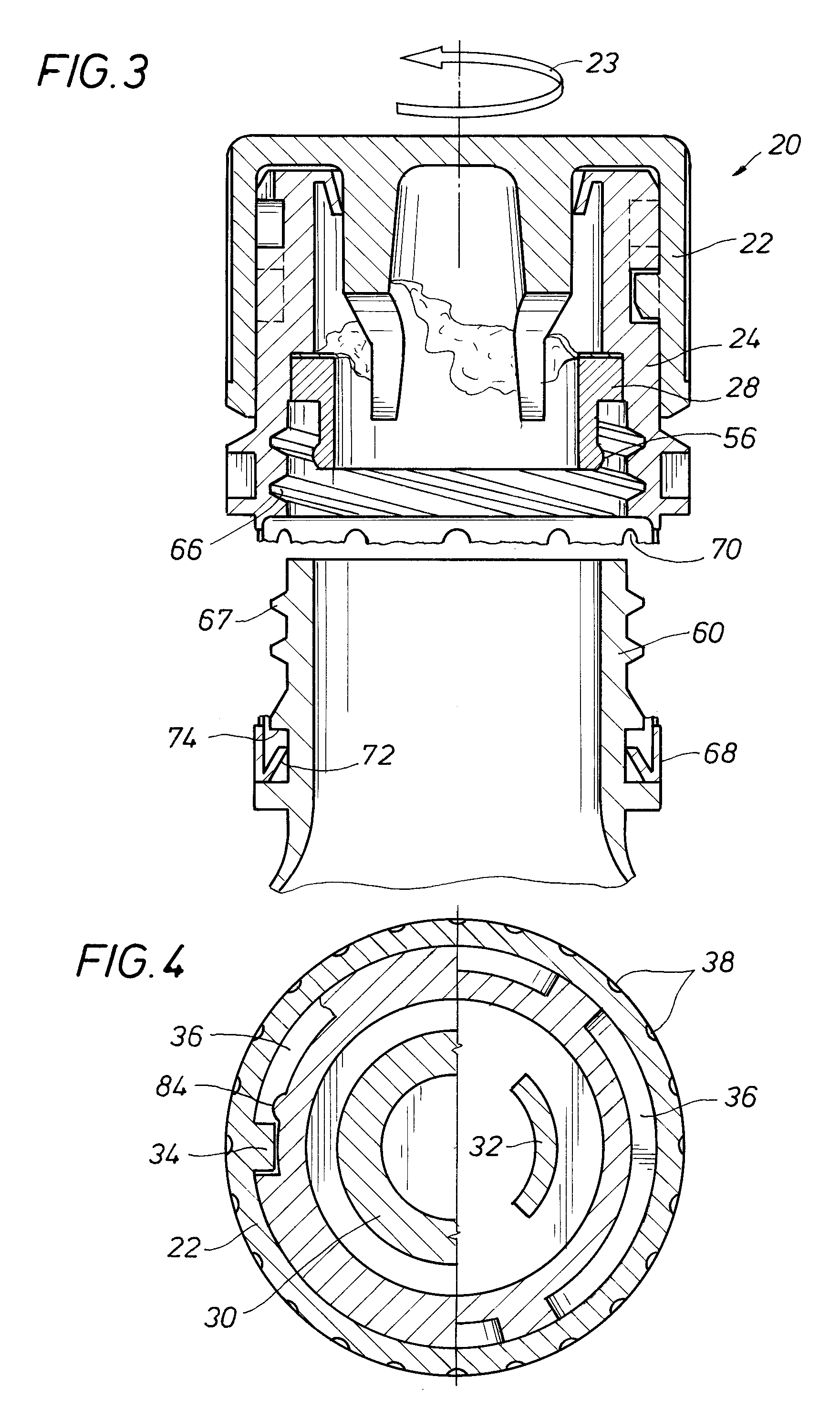
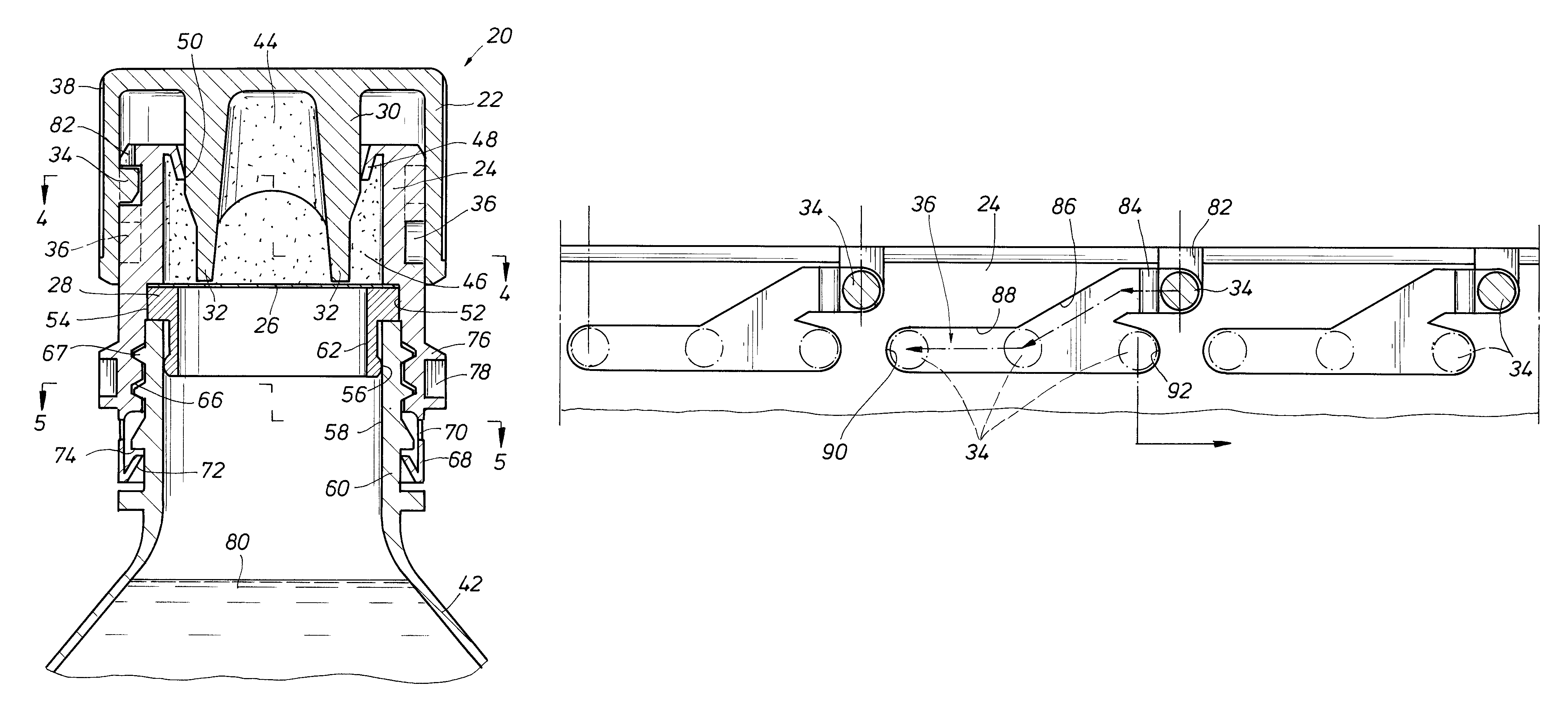
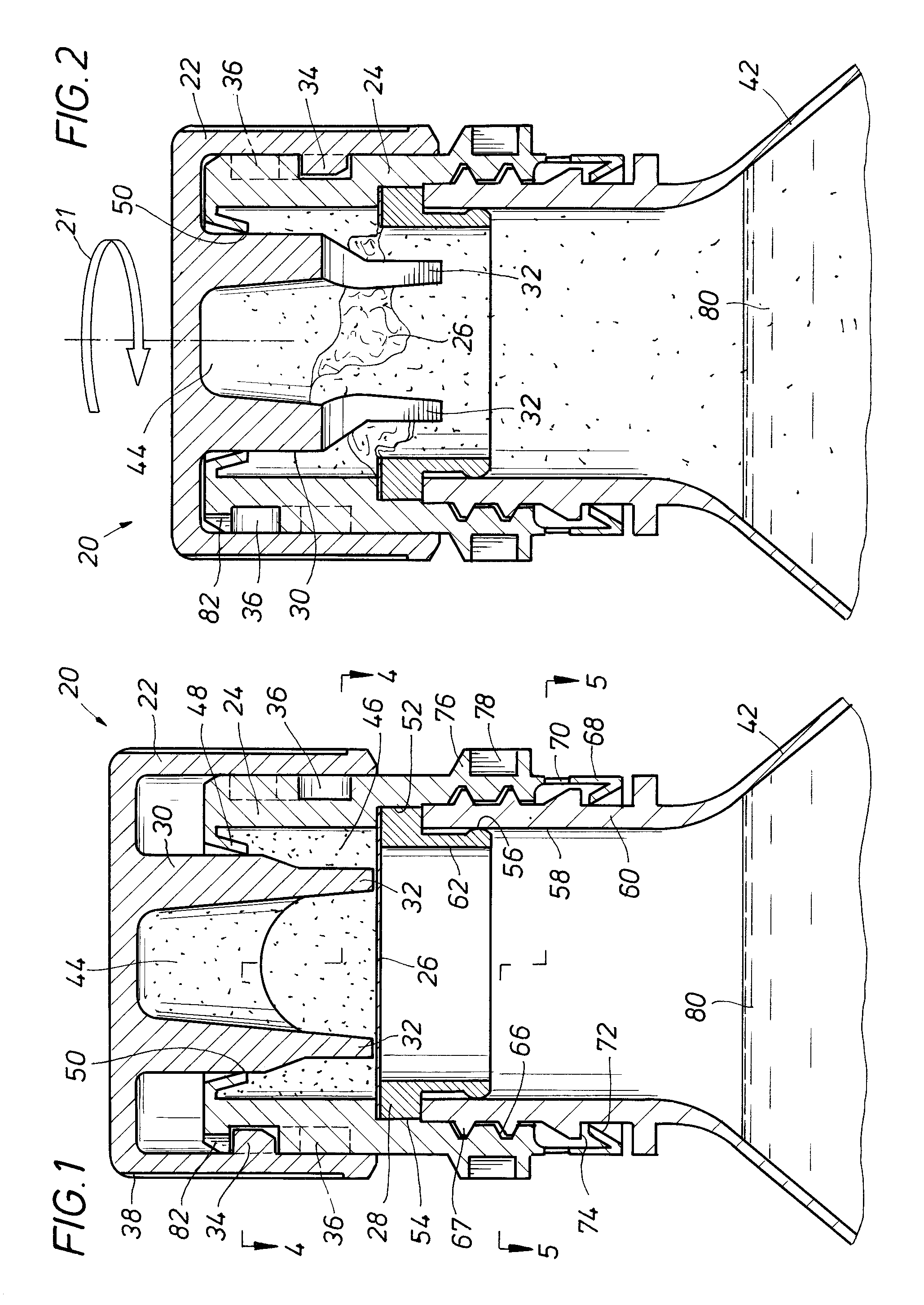
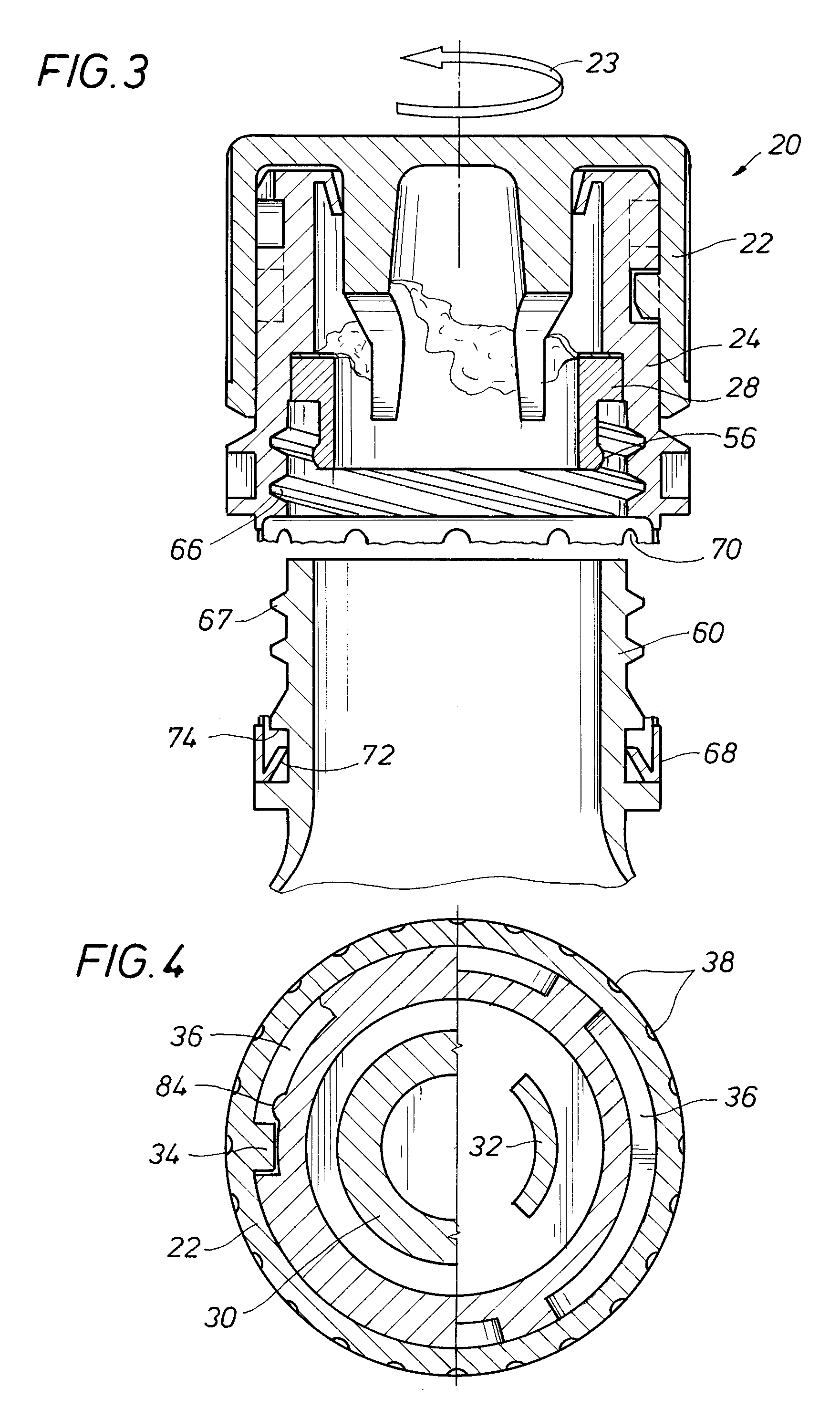
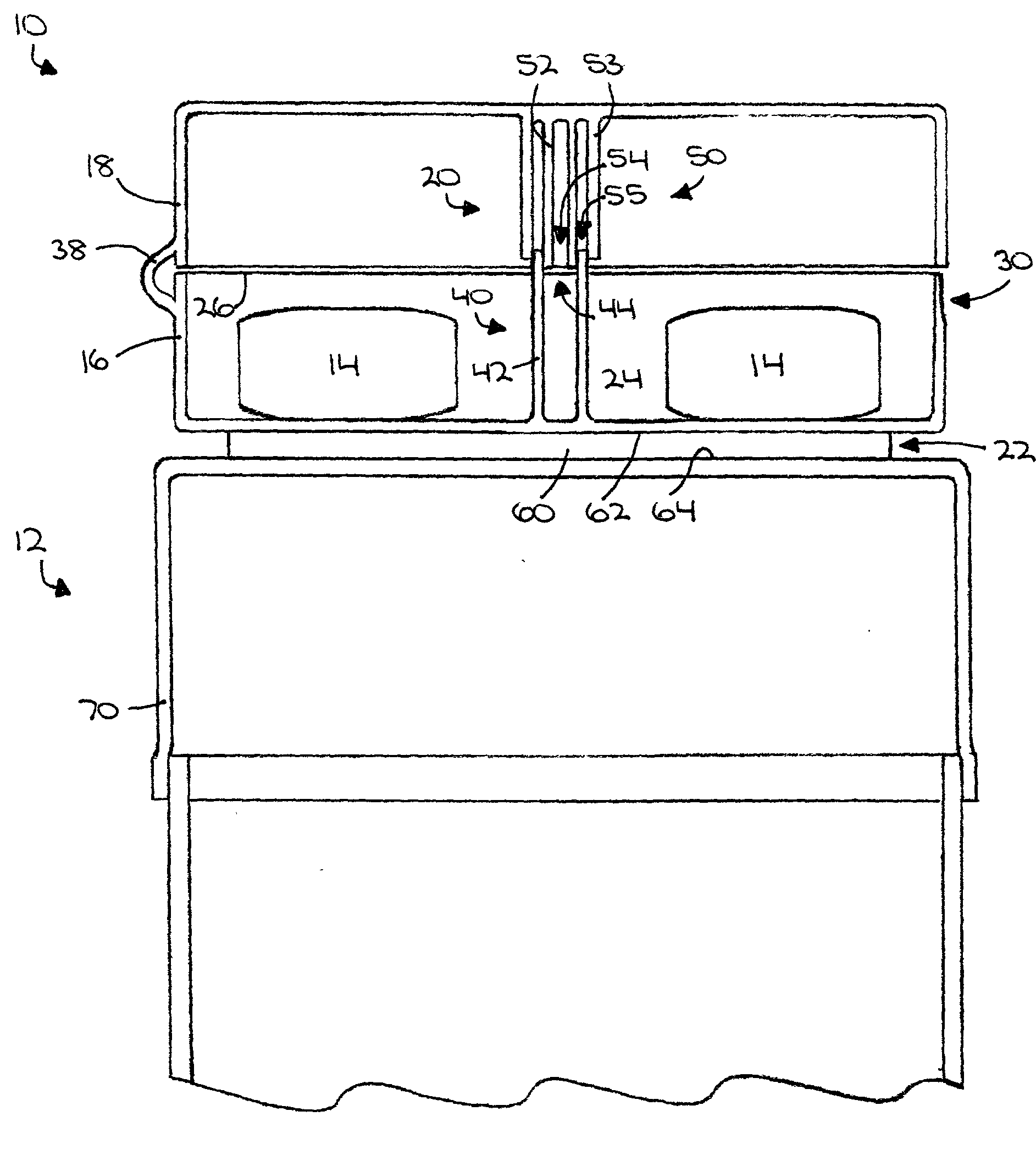
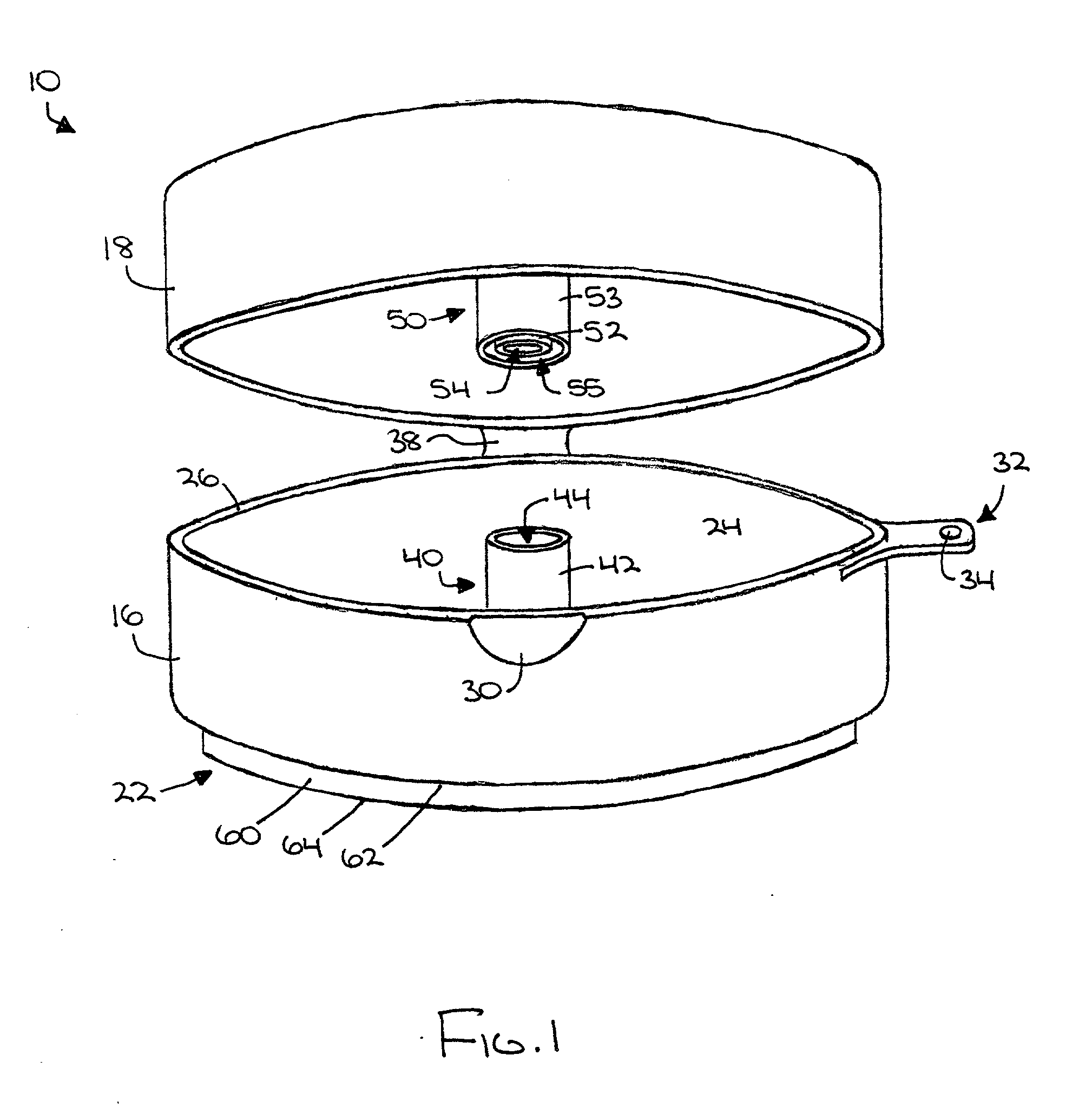
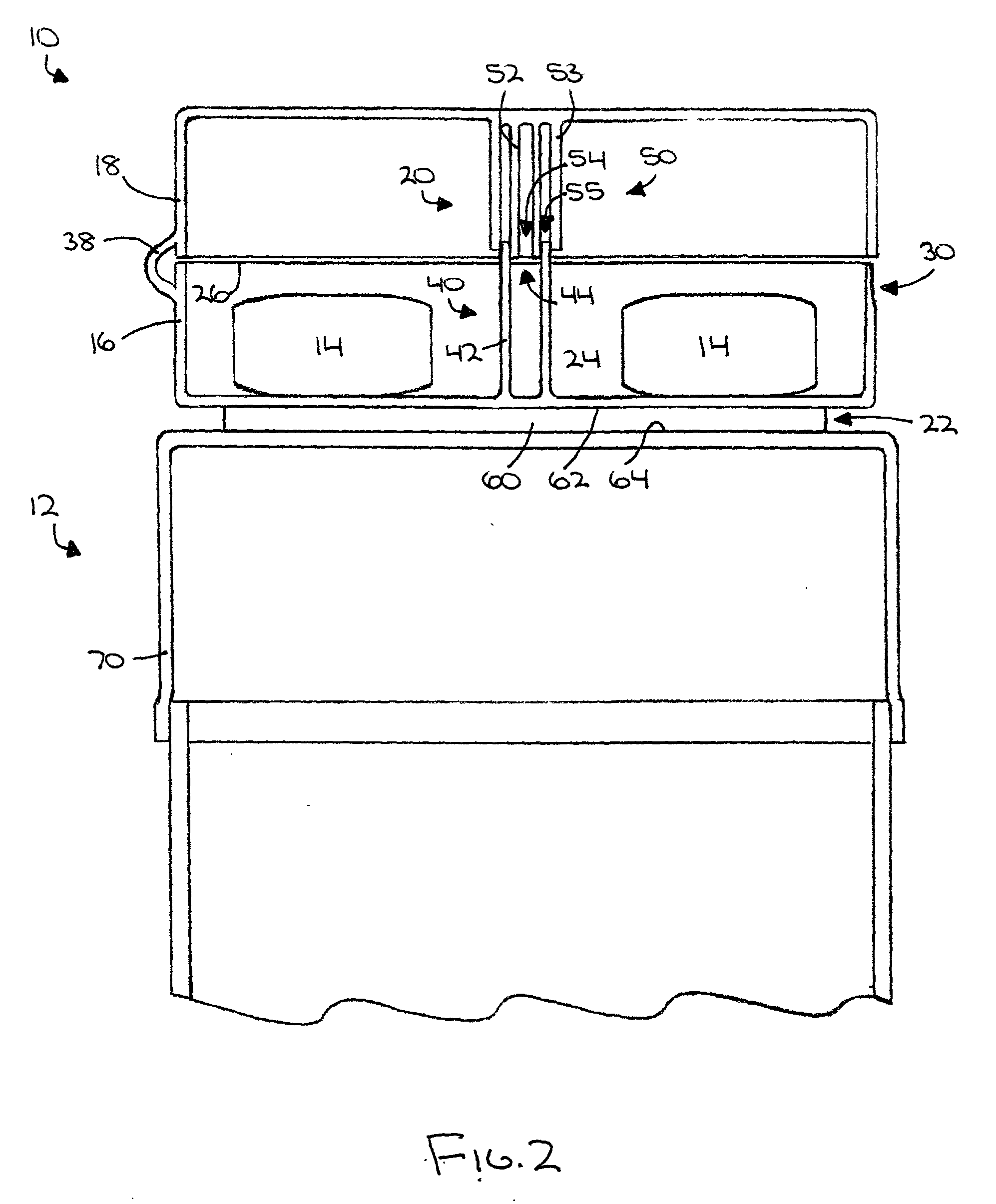
An auxiliary container (10) adapted for unintrusive coupling with a conventional medication container (12), such as pill bottle, cream tube, or spray can, wherein the auxiliary container (10) provides an independent storage space (26) which does not require breaking a seal of, removing, or replacing an existing lid (70) or cap of the conventional container (12). In one contemplated use, for example, the auxiliary container (10) is used to store small doses of a supplementary medication (14), such as aspirin, in close association with a primary medication (e.g., a heart medicine such as nitroglycerine), such that both are conveniently available and accessible for immediate use. In a preferred first embodiment, the auxiliary container (10) broadly comprises a body (16); a lid (18); a closure mechanism (20); and a coupling mechanism (22).
Owner:MILLENIUM MARKETING GROUP
Method of treatment with coadministration of aspirin and prasugrel
InactiveUS20080108589A1Strong inhibitory activityShort incubation periodSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideAspirinMedicine
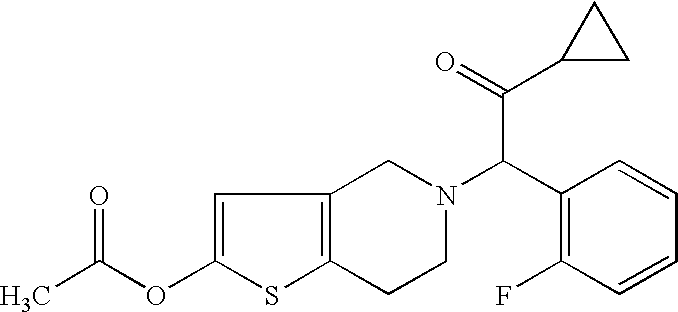
A method for the prevention of diseases caused by thrombus or embolus. The method is to separately administer 2-acetoxy-5-(α-cyclopropylcarbonyl-2-fluorobenzyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and aspirin, in their pharmacologically effective amounts, to a warm-blooded animal.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD +1
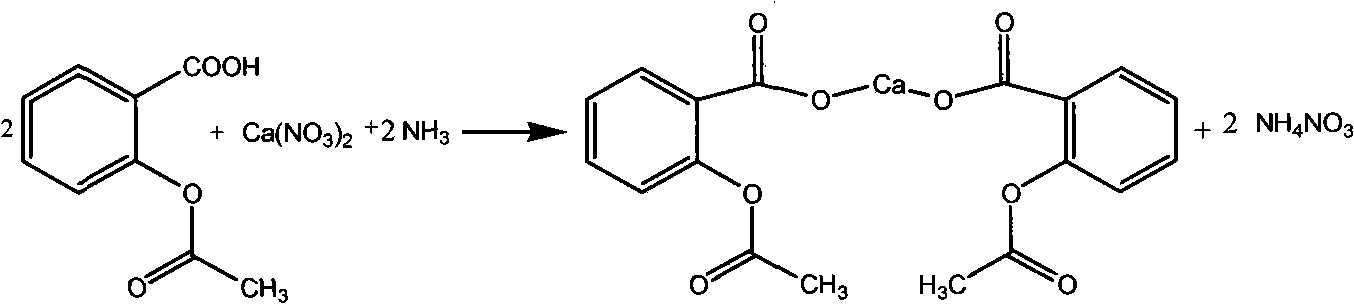
Preparation method of carbasalate calcium
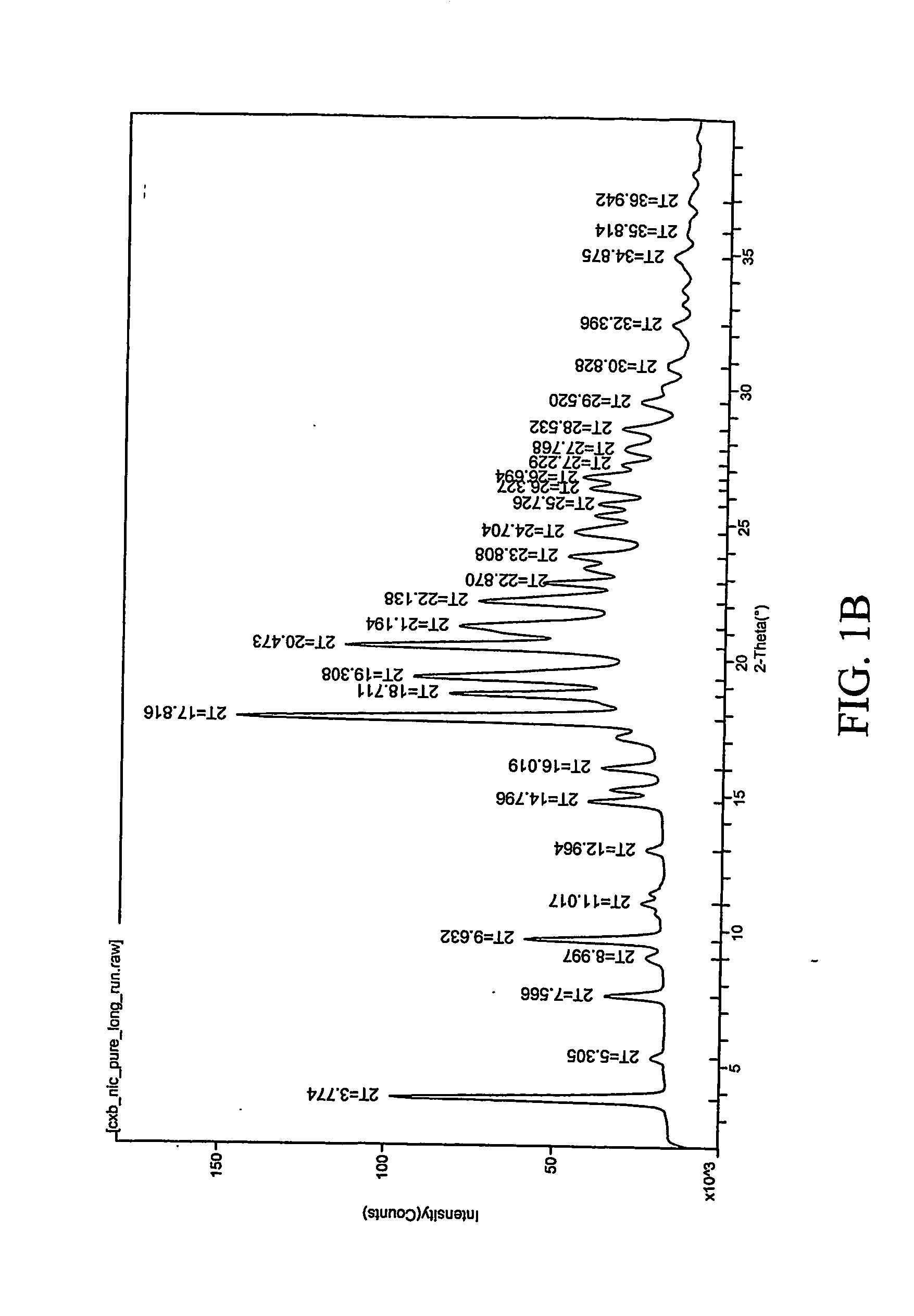
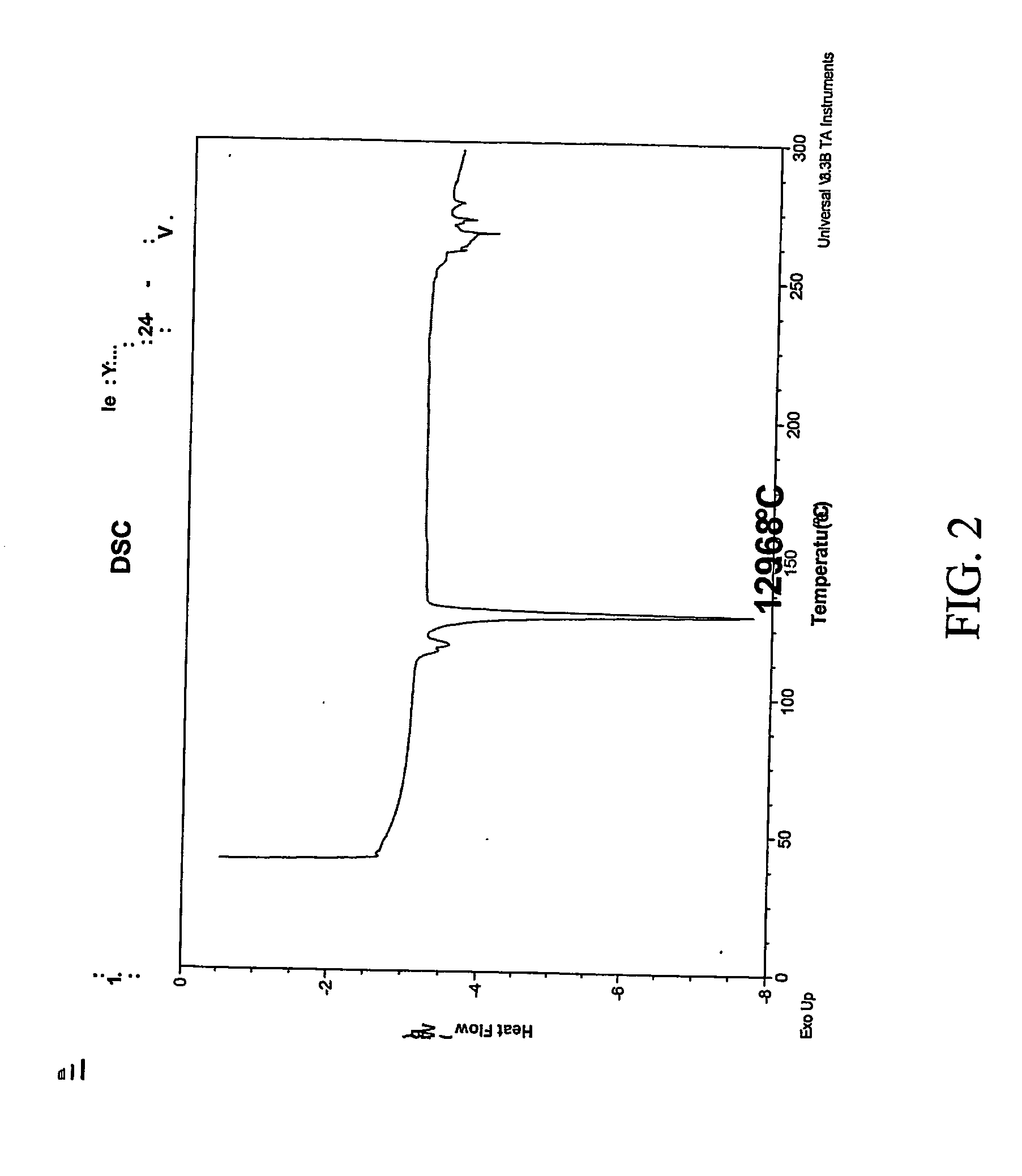
ActiveCN101575305ASolve problems that cannot be complexedOvercome securityUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationDissolutionO-acetylsalicylic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of carbasalate calcium, comprising the following steps of: according to parts by weight, adding 4 to 6 parts of methanol or ethanol solvent in a dissolution kettle, heating up to 30 DEG C to 40 DEG C, adding 1 part of aspirin, 1.1 parts of urea and 1.05 parts of calcium nitrate in sequence, heating and stirring for fully dissolution, then filtering to a reaction kettle; after the filtrate is cooled to 0 DEG C to 5 DEG C, introducing an ammonia solution of the methanol or ethanol and stirring, keeping the temperature below 10 DEG C till the pH value of the reaction system reaches neutral; keeping stirring, heating up to 40 DEG C to 45 DEG C, conducting crystallization and centrifugation, drying and packaging, and then obtaining the finished product. The preparation method uses the methanol or ethanol as single solvent, solves the problems of poor safety performance, high production cost, difficult recycling of solvent and the like caused by the adoption of the mixed solvent of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and ethanol in the prior art; the preparation method has the advantages of concise production process, low production cost and good safety performance; and the yield can reach 95 to 96 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGXIAO CHEM
Device and methods for identifying and treating aspirin non-responsive patients
InactiveUS20060160165A1Reduce post-acute myocardial infarction (AMI) cardiovascular eventIncreased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingO-acetylsalicylic acidMedicine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying and treating subjects in need of antithrombotic therapies but who are not responsive to aspirin.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
High shear process for aspirin production
InactiveUS20090005592A1Simple reaction conditionsIncrease ratingsOrganic compound preparationRotary stirring mixersAspirinEmulsion
Use of a high shear mechanical device in a process for production of acetyl salicylic acid, by contacting acetic anhydride with salicylic acid in a high shear device. The disclosed process makes possible a decrease in mass transfer limitations, thereby enhancing production of acetyl salicylic acid. A system for production of acetyl salicylic acid is also provided in which a reactor is configured to receive the output from a high shear device, which is configured to receive, via one or more inlets, acetic anhydride, and salicylic acid and generate a fine dispersion or emulsion of reactants.
Owner:HRD CORP
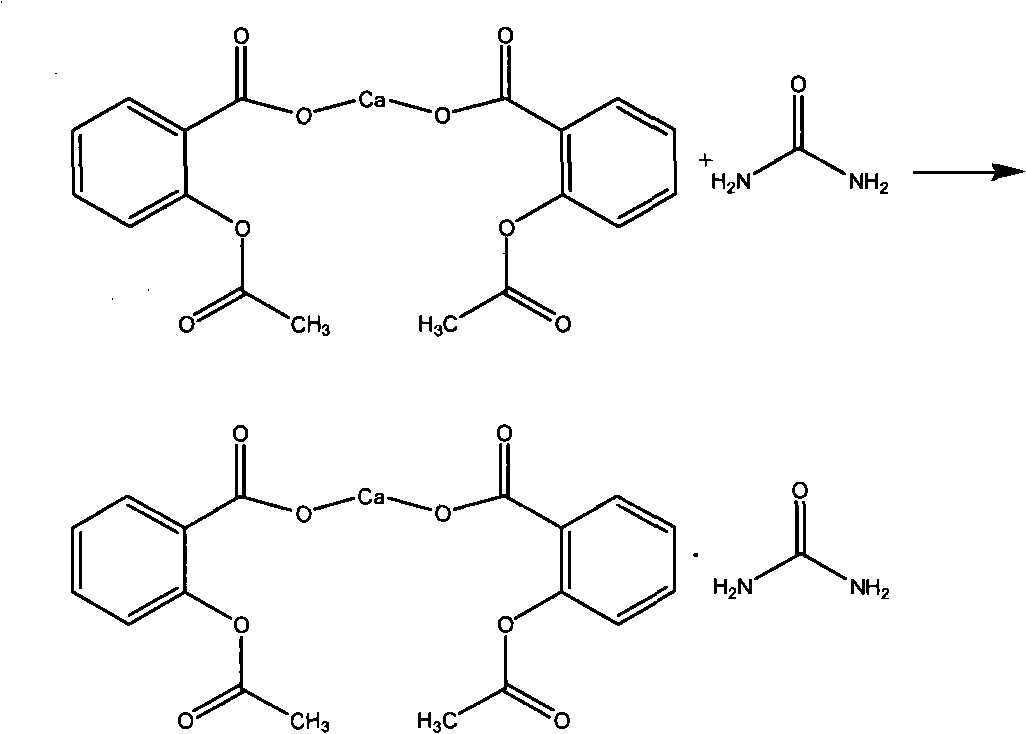
Preparation method of carbasalate calcium
ActiveCN102924335AHigh product contentImprove stabilityUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationAlcoholFiltration
The invention relates to a preparation method of carbasalate calcium. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dispersing aspirin, calcium nitrate and urea into alcohol, adding ammonia water under a stirring condition at 0-5 DEG C, then heating up to 25-35 DEG C, and reacting for 2-2.5 hours; and (2) cooling the reaction solution obtained in step (1) to 0-5 DEG C, standing for growing crystals, and then performing suction filtration and drying to obtain carbasalate calcium. The preparation method of arbasalate calcium is characterized by high product content, low content of impurities (related substances), good stability, concise process and low production cost; and the requirement on equipment is lowered, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:QILU ANIMAL HEALTH PROD +1
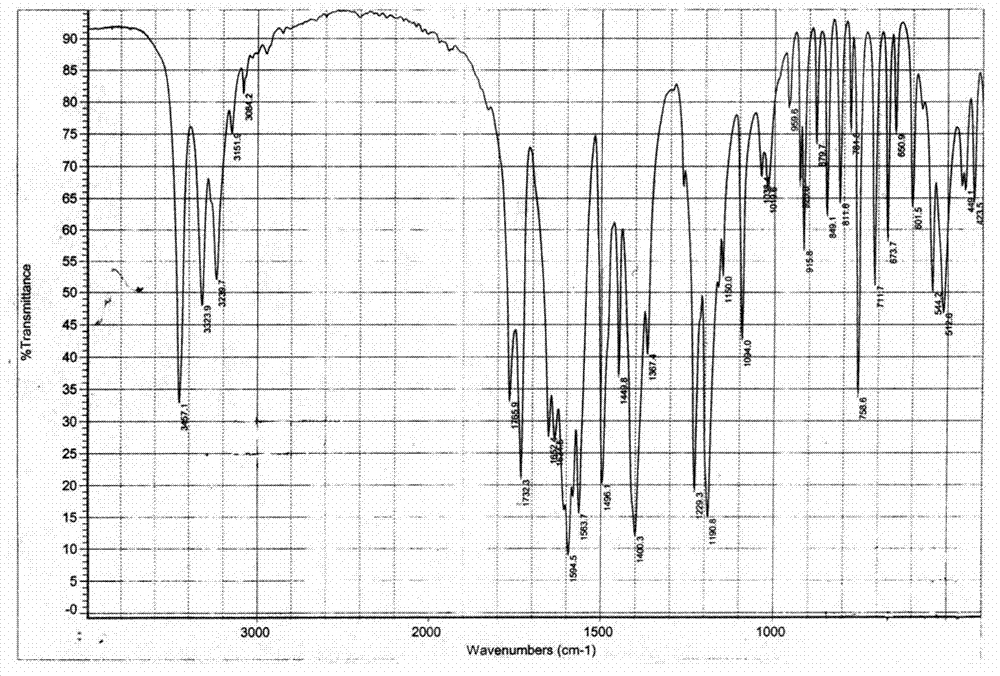
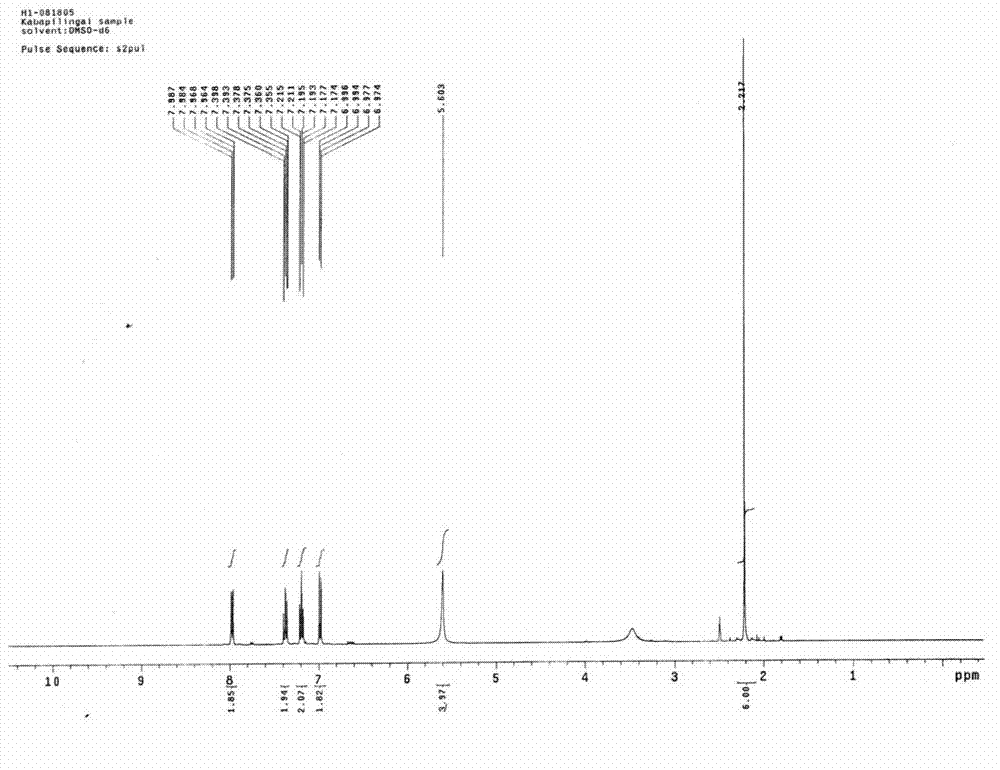
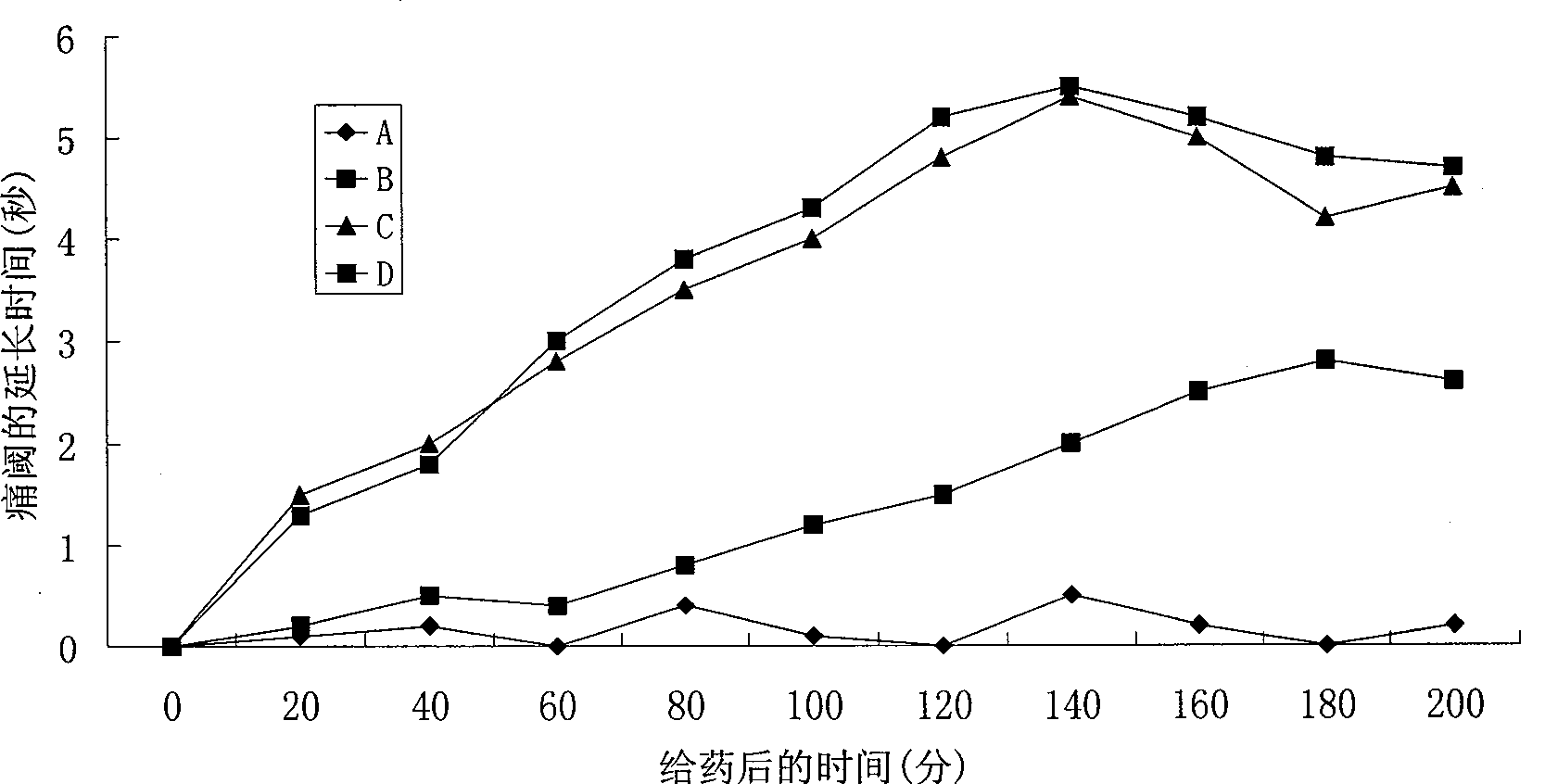
Use of salt of an acetylsalicylic acid for the treatment of viral infections
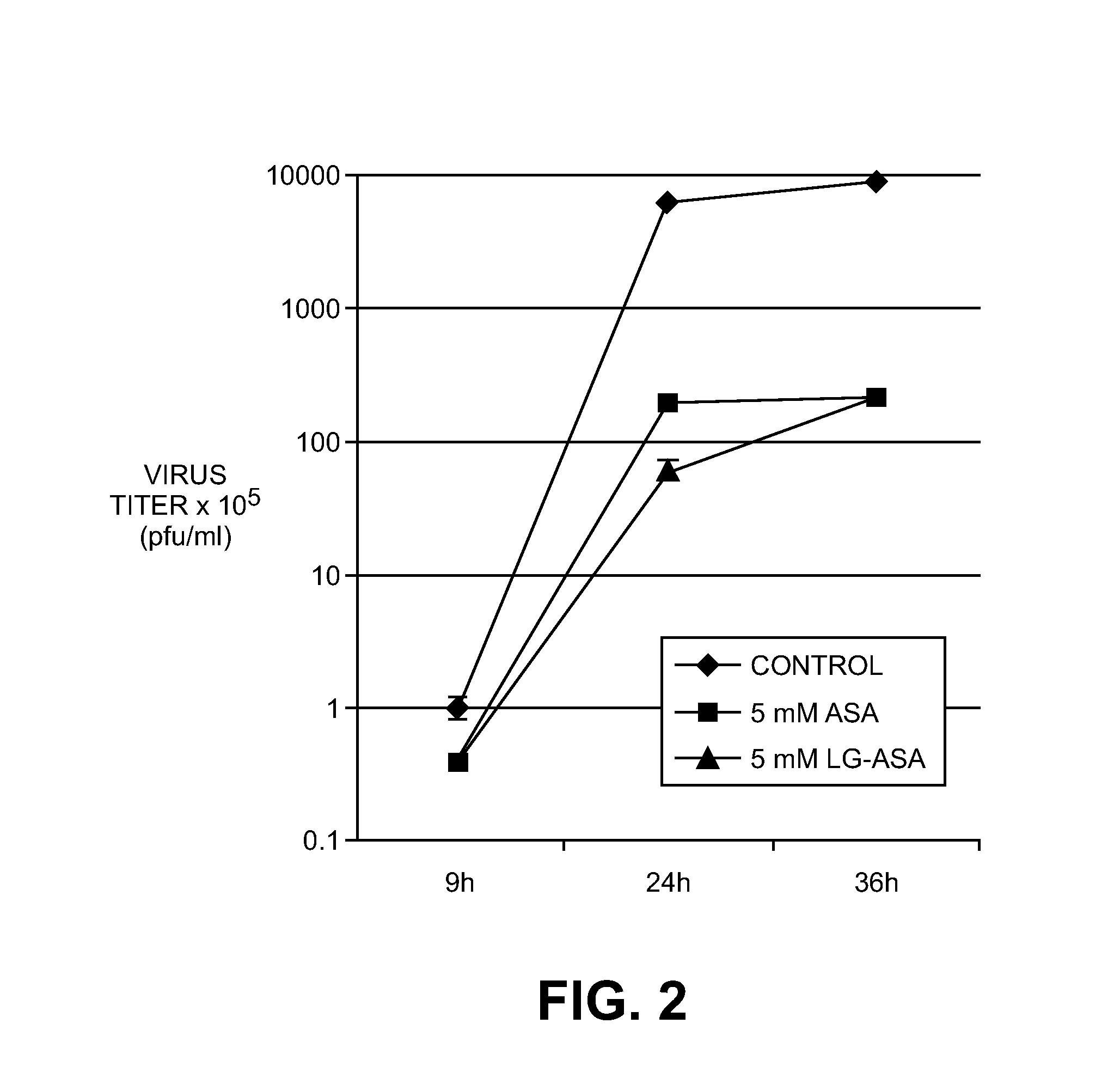
ActiveUS20120017892A1Improve toleranceReliably avoids riskCompounds screening/testingBiocideO-acetylsalicylic acidViral infection
The invention relates to a method of use of a composition comprising a salt of the o-acetylsalicylic acid with a basic amino acid for producing a pharmaceutical composition for the prophylaxis or treatment of viral infections of humans or of animals, in particular mammals and birds.
Owner:ASPIAIR GMBH
Detecting method for accurate risk early warning and accurate drug use of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and specific primer
ActiveCN106893783AStrong specificityReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinSingle strand
The invention discloses a detecting method for accurate risk early warning and accurate drug use of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and a specific primer. The invention provides a specific primer for detecting SNP site of drug resistance of the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, which comprises a primer group 1 and a primer group 2; the primer group 1 is composed of primer pair 1-primer pair 13; a primer group 2 is composed of single stranded extended primer 1- single stranded extended primer 13; the method can efficiently detect and complete the accurate early warning of the attack of the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and the accurate drug use after being attacked, namely, four kinds of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease early warning with huge health risk and accurate drug use of four clinical common drugs (aspirin, nitroglycerin, warfarin, and clopidogrel) for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:李爱娟
Method for preparing tiny mesoporous silica drug sustained-release material
InactiveCN104030296AFast release rateSilicaPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAspirinDrug release rate
The invention provides a method for preparing a tiny mesoporous silica drug sustained-release material and a tiny mesoporous hollow tubular silicon dioxide material obtained through the method. The drug loading capacity, calculated through a TG method, of the tiny mesoporous hollow tubular silicon dioxide material for aspirin model drugs is 15%, the sustained-release stage is the time of six hours of the initial stage of an experiment, and the drug releasing rate is high; after six hours, the stage of release balancing is achieved, and the amount of balanced release is 73.6%.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
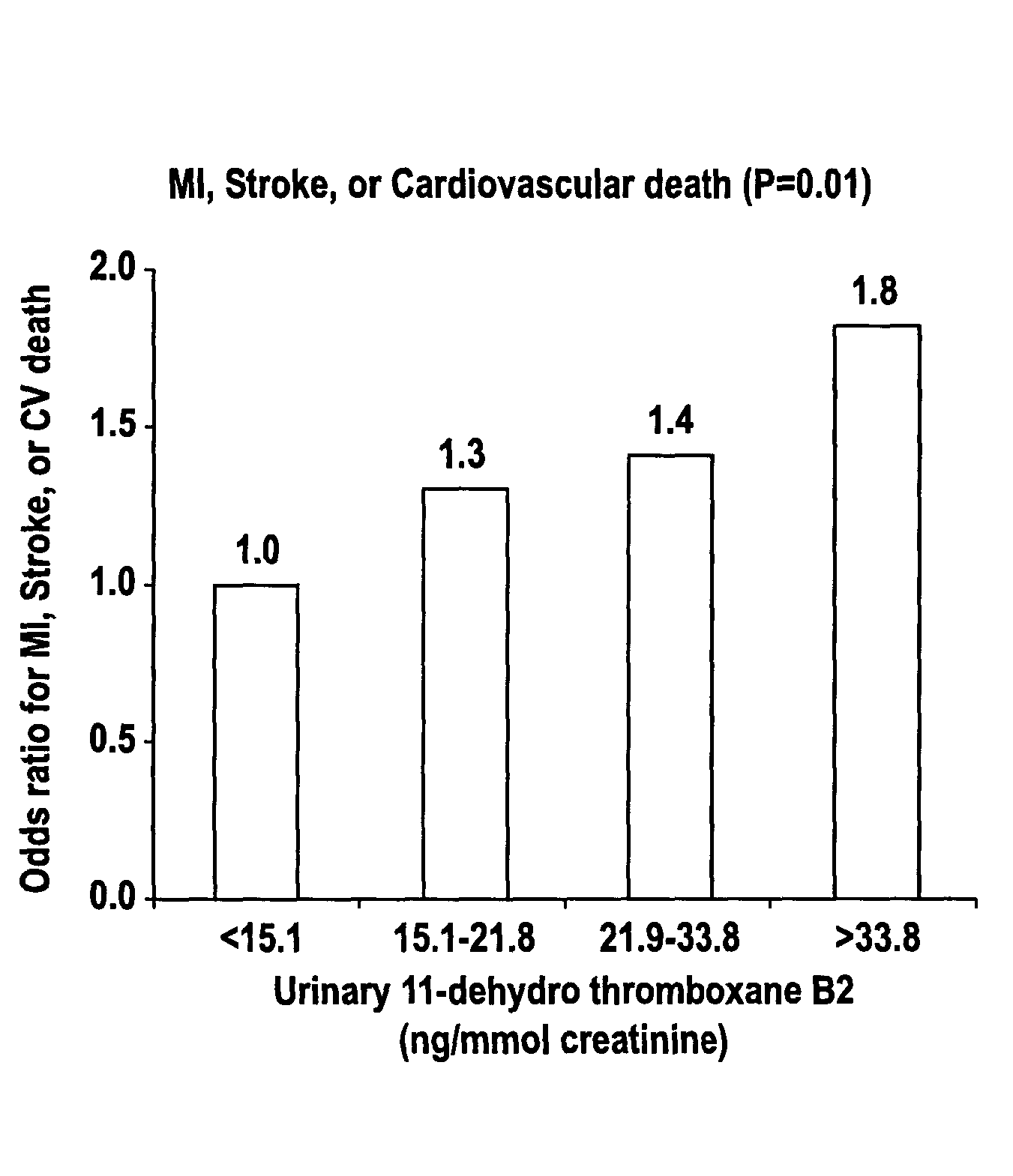
Method for predicting cardiovascular events
InactiveUS7081347B2Accurate predictorIncreased cardiovascular riskBiocideOrganic chemistryAspirinBacteriuria
A method for assessing aspirin resistance and relative risk of a cardiovascular event in a patient taking aspirin is provided. The concentration of 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2 in a urine sample is measured and compared to a set of standardized quartile concentrations. A concentration of urinary 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2 that falls within the second, third, or fourth quartile is indicative of aspirin resistance and an elevated risk of a recurrent cardiovascular event.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Method and system for stabilization of arachidonic acid for use in platelet function assay
InactiveUS7205115B2Quick fixReduce oxidation rateTissue/virus culture apparatusBiological testingAntioxidantOxygen
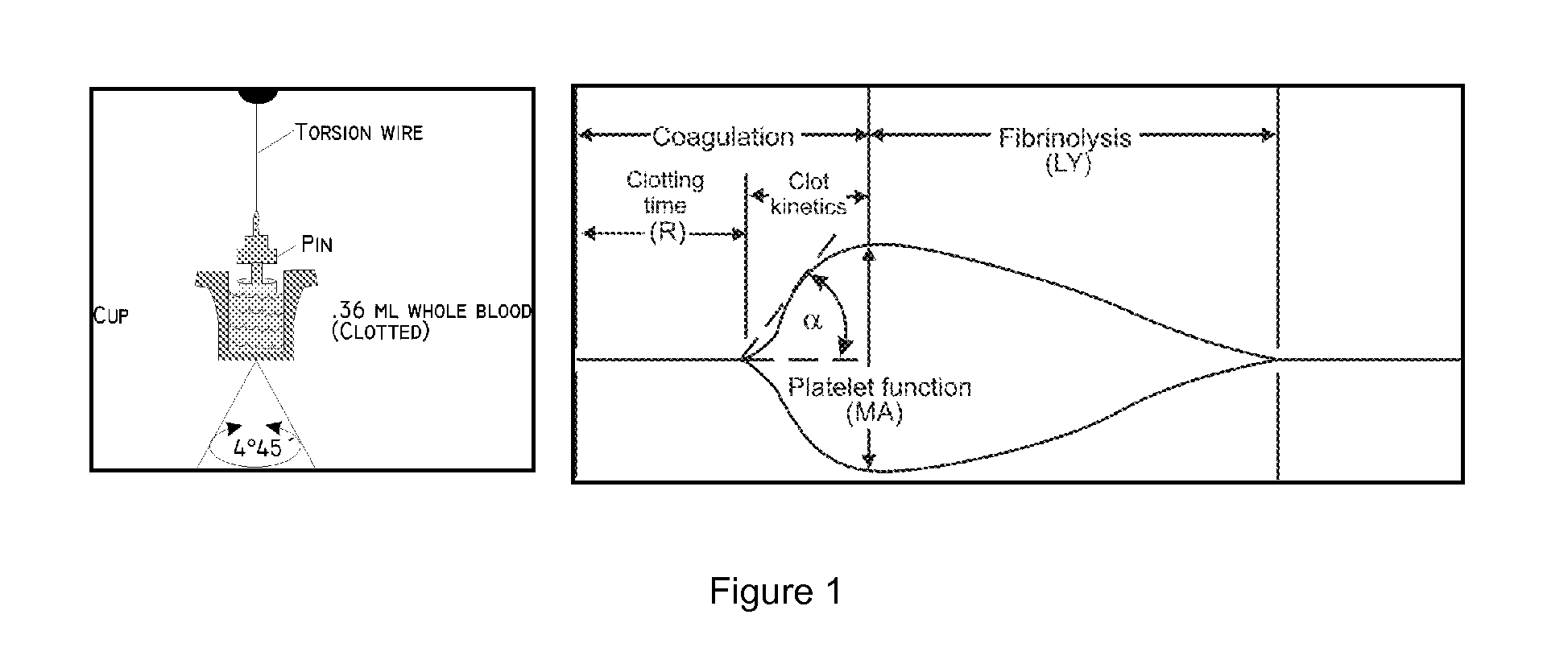
Methods and systems for rapidly determining the level of platelet inhibition in whole blood, due to aspirin usage, with a single use arachidonic based assay device that can be stored at room temperature is provided. A lyophilized assay reagent that contains arachidonic acid at sufficient concentration to maximally activate platelets is utilized. An antioxidant within the same lyophilized assay reagent reduces the oxidation rate of arachidonic acid but does not interfere with platelet function. An oxygen absorber within the single use assay device packaging creates an inert environment within a short period of time after package is sealed. The assay device can have a housing with a plurality of channels and a common blood sample introduction port coupled to each of a channel of the plurality of channels. The assay device can also include a lyophilized assay reagent that contains arachidonic acid at sufficient concentration to maximally activate platelets.
Owner:ACCUMETRICS INC
Applications of koumine in preparing medicament for treating chronic ache
ActiveCN101322705AAnalgesic effect is effectiveLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderIndometacinTolerability
The invention discloses the application of koumine to the preparation of medicines for treating chronic pains and belongs to the application of gelsemium alkaloid monomer. The analgesic experiments of the koumine on chronic pains of animals prove that the koumine has potent dose-dependent analgesic effect, the analgesic potency is superior to that of the classical antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs which are aspirin and indomethacin, the therapeutic index of the koumine is much higher than that of the total alkaloids of gelsemium, the koumine possibly has no tolerance, no addiction and little side effect, which indicates that the koumine has potent and low-toxicity analgesic effect, the mechanism of action of the koumine is possibly different from those of clinically common opium analgesics or aspirin analgesics, the koumine and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof have the application of preparing of the medicines for treating chronic pains and have no serious disadvantages of the clinically common analgesics and can be developed into a novel analgesic which has potent analgesic effect in treating chronic pains such as inflammatory pain, neuropathic pain, cancer pain and the like, has no tolerance and addiction and little side effect, thus the koumine has bright industrialization prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Novel Nsaids Possessing a Nitric Oxide Donor Diazen-1-Ium-1,2-Diolate Moiety
InactiveUS20080214646A1Prevent or ameliorate gastrointestinal upsetBiocideOrganic chemistryEster prodrugRadiation equivalent dose
This invention provides a prodrug that help arthritis patients without increasing cardiovascular and gastrointestinal risk. A novel group of hybrid nitric oxide-releasing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NO-NSAIDs), moiety attached via a one -carbon methylene spacer to the carboxylic acid group of the traditional NSAIDs aspirin, ibuprofen and indomethacin were synthesized. The ester prodrugs showed equipotent anti-inflammatory activities in vivo to that of the parent aspirin, ibuprofen and indomethacin. The simultaneous release of parent drug and nitric oxide from the NO- prodrugs constitutes a potentially beneficial property for the prophylactic prevention of thrombus formation and adverse cardiovascular events such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Data acquired in an in vivo ulcer index (UI) assay showed that this group of ester prodrugs in which no lesions were observed when compared to the parent drugs at equivalent doses. Accordingly, these hybrid NO-NSAID prodrugs possessing a diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate moiety, represents a new approach for the rational design of anti-inflammatory drugs with reduced gastric ulcerogenicity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Oral enteric preparation containing Grel drugs and aspirin
The invention relates to a novel oral enteric preparation which is composed of 0.1-1000mg of Grel drugs, or medically acceptable salts, ester or derivatives, 37.5-325mg of aspirin and at least one medically acceptable load, wherein the Grel drugs, or medically acceptable salts, esters or derivatives are clopidogrel, prasugrel, brilinta, sarpogrelate, ozagrel, anagrelide, pamicogrel, or medically acceptable salts, ester or derivatives, preferably, clopidogrel sulfate. The oral enteric preparation is used for curing acute coronary syndrome (ACS), angor pectoris, stroke, myocardial infarction or cardia cerebrovascular diseases of patients. According to the oral enteric preparation, adverse reactions such as functional gastrointestinal disorders, nausea, vomit, gastritis, concealed hemorrhage, ulcer exacerbation and gastrointestinal bleeding caused by strong stimulus of aspirin to stomach can be avoided.
Owner:王定豪
Compositions and methods for reducing hepatotoxicity associated with drug administration and treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and associated cirrhosis
InactiveUS20090239831A1Improve efficiencyEnhancing armamentariumBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsActive agentHigh doses
The present invention relates to the discovery that acetylsalicylic acid (ASA or aspirin), salicylic acid (SA) and related salicylate esters and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, when coadministered in effective amounts with a drug or other bioactive agent which typically (in the absence of the salicylate compound) produces significant hepatotoxicity as a secondary indication, will substantially reduce or even eliminate such hepatotoxicity. Favorable therapeutic intervention results from the use of the present invention having the effect of reducing hepatotoxicity associated with the administration of certain drugs and other bioactive agents and in certain instances of allowing the administration of higher doses of a compound which, without the coadministration, would produce hepatotoxicity which limits or even negates the therapeutic value of the compound. The invention also relates to methods of reducing the likelihood of a patient at risk for non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD), including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), or treating NAFLD or NASH including primary NASH, NASH secondary to liver transplantation (NASH post-liver transplantation) or cirrhosis represent alternative aspects of the present invention.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Intravenous and oral dosing of a direct-acting and reversible p2y12 inhibitor
InactiveUS20090048216A1Inhibits thrombosis formationInhibits propagationBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsAspirinOral medication
The invention provides methods and compositions for rapid and reversible inhibition of platelet aggregation in human subjects in need thereof by administering compounds of the formula:alone or in combination with a second agent which can be aspirin or a thrombolytic agent.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Anti-cancer medicinal aspirin platinum complex and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102942594AInhibit apoptosisInhibition of replicationGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectO-acetylsalicylic acid
The invention discloses an anti-cancer medicinal aspirin platinum complex and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of coordinating amine or heterocyclic amine on a platinum atom through a coordinated N atom and the coordination function of the platinum, introducing halogen or hydroxyl, carboxylate radical or substituted carboxylate radical through the coordination function, and oxidizing the platinum atom into tetravalent platinum, connecting aspirin molecular axially to form tetravalent platinum complex with one aspirin molecular single substitute or two aspirin molecular double substitutes axially. As the tetravalent state of the platinum is relatively inert, the toxic side effect on organs is small, and moreover, the uptake route of drug is changed, the anticancer activity of the drug is improved, the anti-tumor activity which is same to or even more excellent than that of cis-platinum is realized, and the killing function to the drug resistant cells is good. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in structure, low in cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Positively charged water-soluble prodrugs of aspirin
InactiveCN101484415AFast in vivo penetrationAvoid side effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderSolubilityDisease
The novel positively charged prodrugs of acetylsalicylic acid and its analogues in the general formula(1) 'Structure 1' were designed and synthesized. The compounds of the general formula(1) 'Structure 1' indicated above can be prepared from functional derivatives of ASA or its analogues,(for example acid halides or mixed anhydrides), by reaction with suitable alcohols, thiols, or amines. The positively charged amino groups of these pro-drugs not only largely increases the solubility of the drugs, but also bonds to the negative charge on the phosphate head group of membranes and push the pro-drug into the cytosol. The experiment results suggest that the pro-drug, diethylaminoethyl acetylsalicylate.AcOH, diffuses through human skin -400 times faster than acetylsalicylic acid itself and -100 times faster than ethyl acetylsalicylate. In plasma, 80% of these pro-drugs can change back to the drug in a few minutes. The pro-drugs can be used medicinally in treating any aspirin-treatable conditions in humans or animals and be administered not only orally, but also transdermally for any kind of medical treatments and avoid most of the side effects of aspirin, most notably GI disturbances such as dyspepsia, gastroduodenal bleeding, gastric ulcerations, and gastritis. Controlled transdermal administration systems of the prodrug enable the aspirin in the blood to reach constantly optimal therapeutic blood levels to increase effectiveness and reduce the side effects of aspirin.
Owner:于崇曦 +1
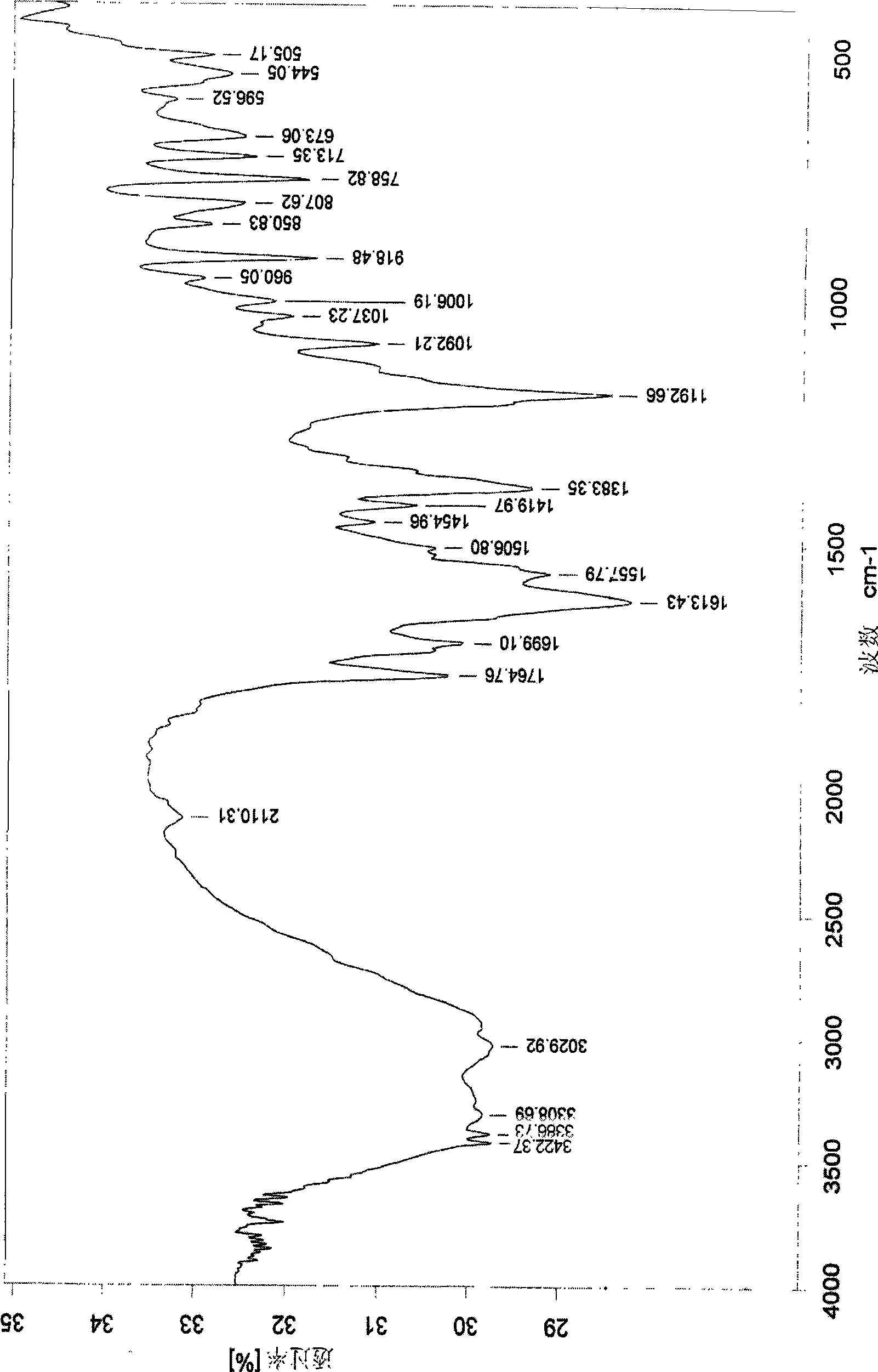
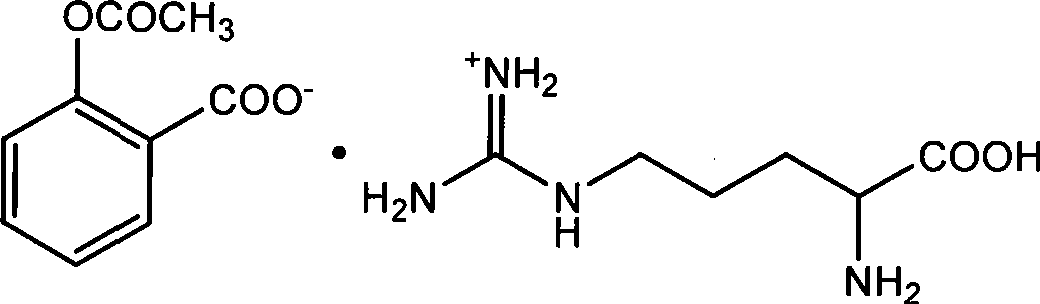
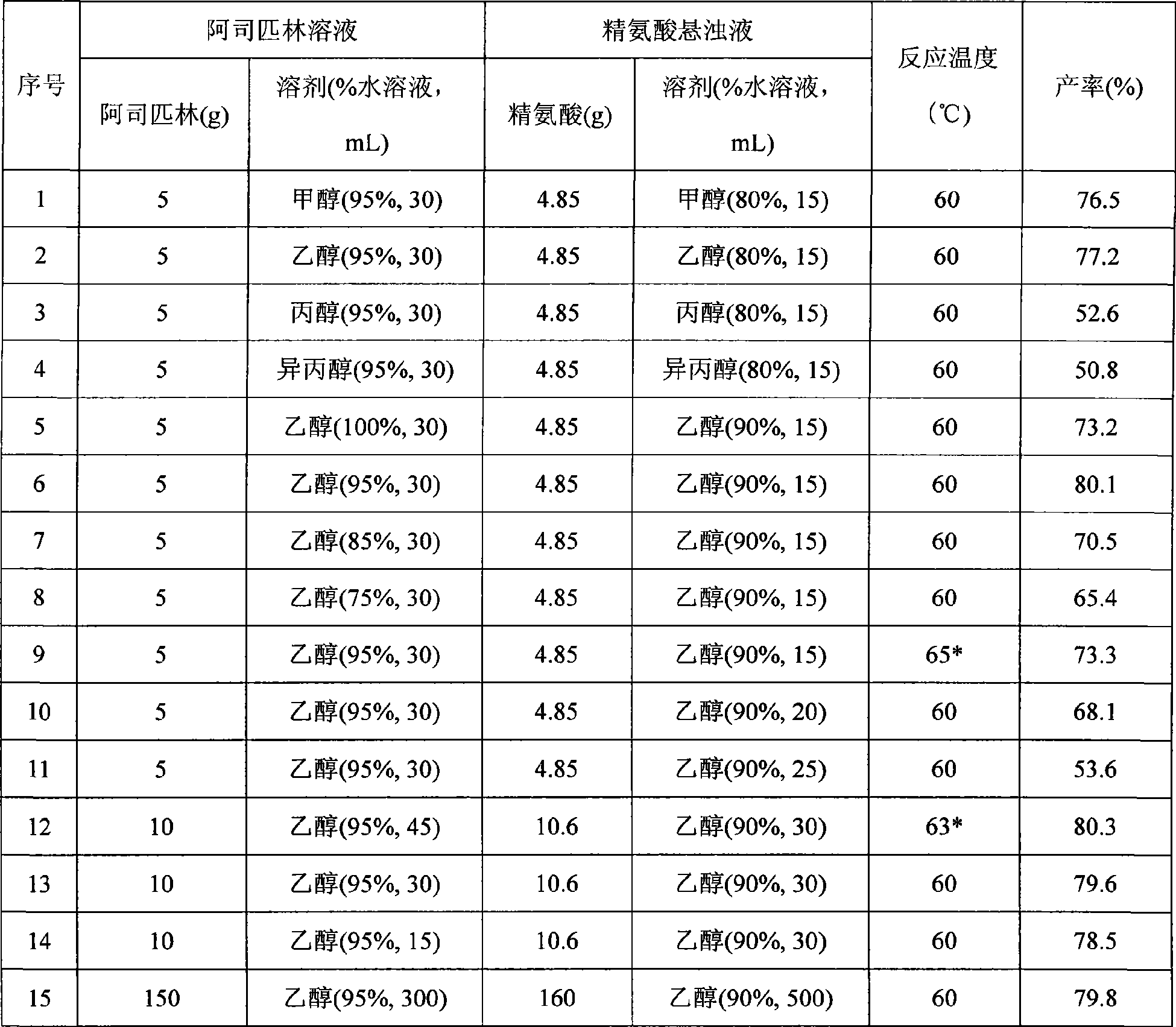
Preparation of arginine acetylsalicylate
InactiveCN101486644ASimple reaction conditionsReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryAspirinArginine
The invention relates to a preparation method of aspirin arginine. The method is characterized in that: aspirin and arginine as reactants respectively dissolve in linear chain or branched aliphatic alcohol solvents with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, under two-phase stirring, the aspirin alcoholic solution is dripped into the arginine alcoholic suspension, at room temperature and under normal pressure, the reaction takes place to generate aspirin arginine crystals; the aspirin arginine is obtained through the filtration and drying of the crystals; and the molar ratio is as follows: aspirin: arginine is 1:1 to 1.1. The method has simple and feasible production technique, short flow, low cost, high yield and good product quality.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
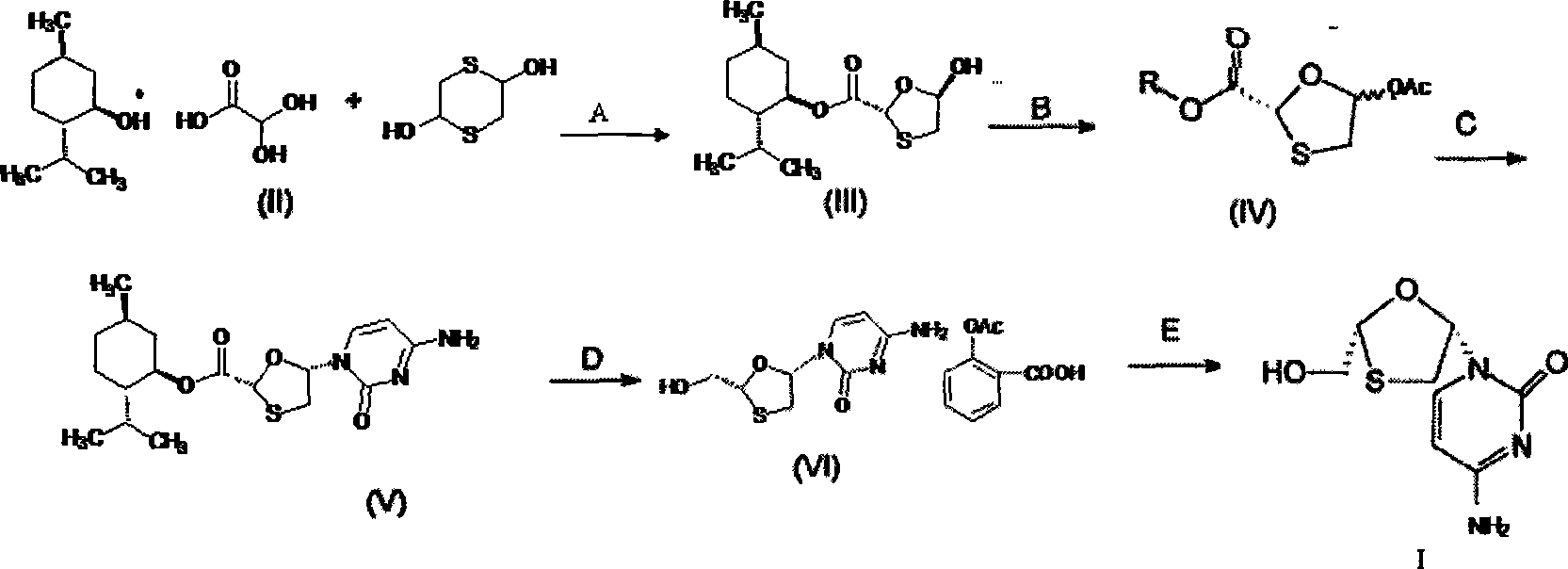
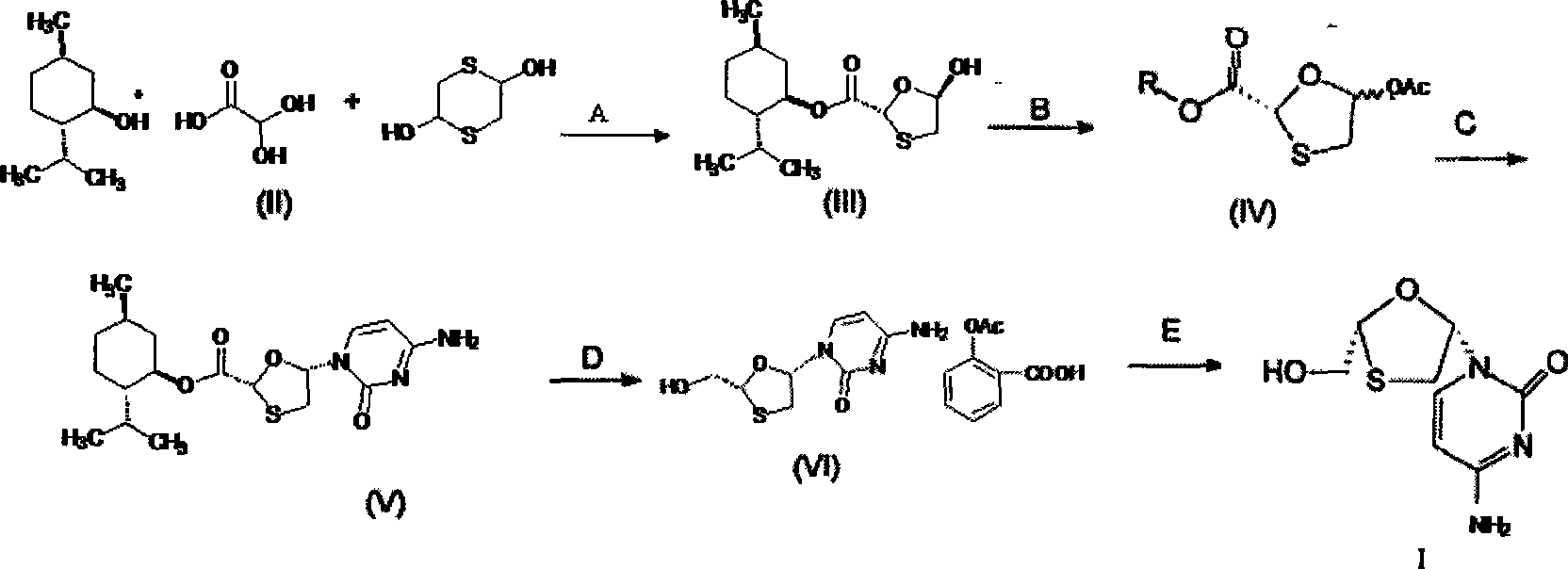
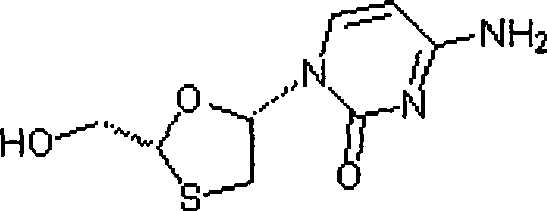
Lamivudine diastereoselective synthesis method
A lamivudine diastereoselective synthesis method, which takes chiral auxiliary agent L-menthol as the initial material, synthesizes trans-5-hydroxyl-1, 3-oxygen thiacyclopentane-2-carboxylic acid-(1'R, 2'S, 5'R) menthol ester under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid, choose triethanolamine to obtain trans-isomer trans-5-hydroxyl-1, 3-oxygen thiacyclopentane-2-carboxylic acid-(1'R, 2'S, 5'R) menthol ester, and let the trans-isomer to react with acylating agent to obtain trans-5-acetoxy-1, 3-oxygen thiacyclopentane-2-carboxylic acid-(1'R, 2'S, 5'R) menthol ester, glycosidate with cytosine under the action of alkali to obtain 5S-cytosine-1'-radical-1, 3-oxygen thiacyclopentane-2-carboxylic acid-(1'R, 2'S, 5'R) menthyl ester, and then deoxidize with a deoxidizer, and salifying with aspirin, to ionize and liberate lamivudine. Since triethanolamine is added as in the course of reaction interconverting agent, the yield of lamivudine is increased greatly. Aspirin is added in the course of reaction, so that the lamivudine forms an aspirin salt that has poor water solubility, and therefore can effectively separate and liberate lamivudine from the medium.
Owner:湖南千金湘江药业股份有限公司
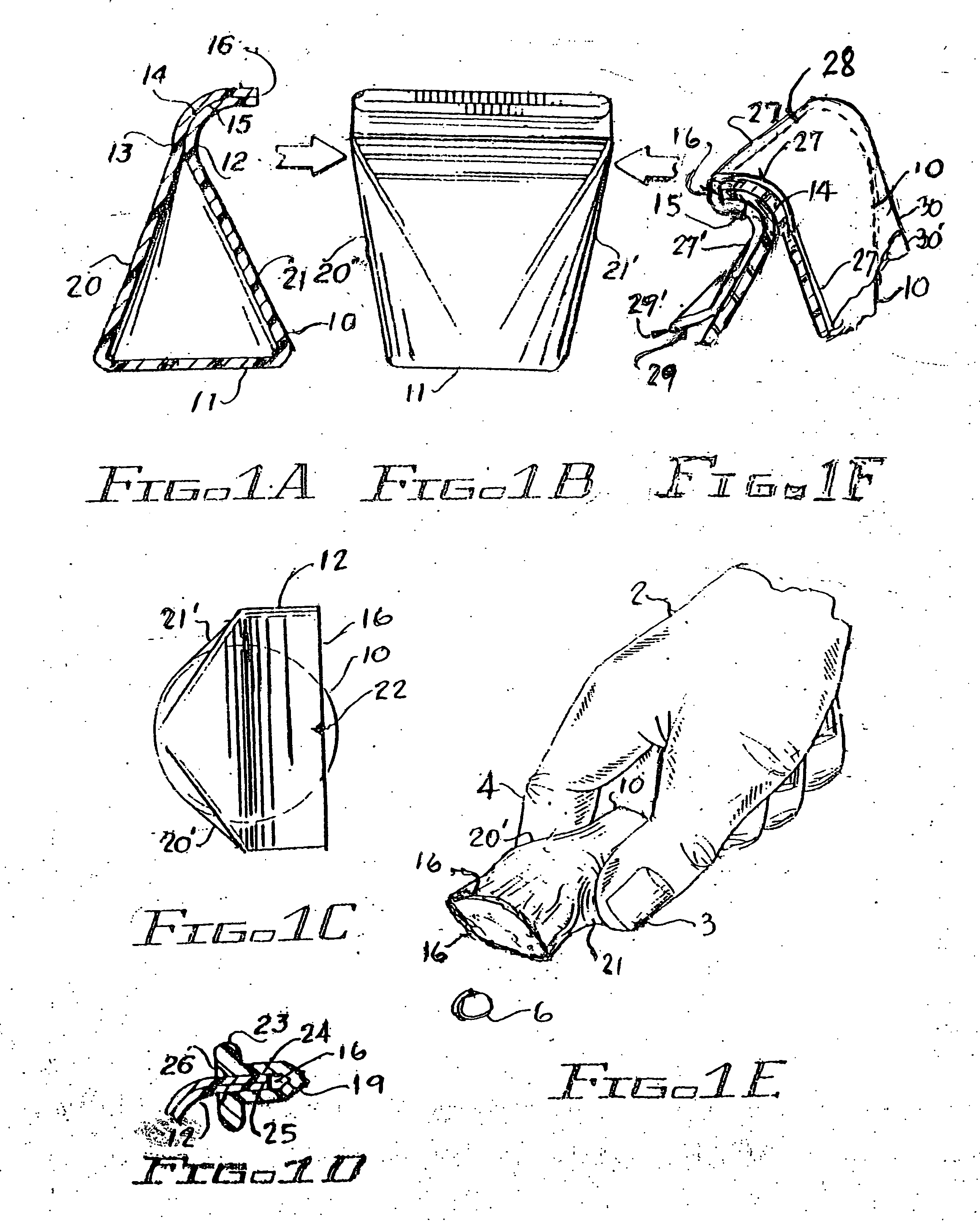
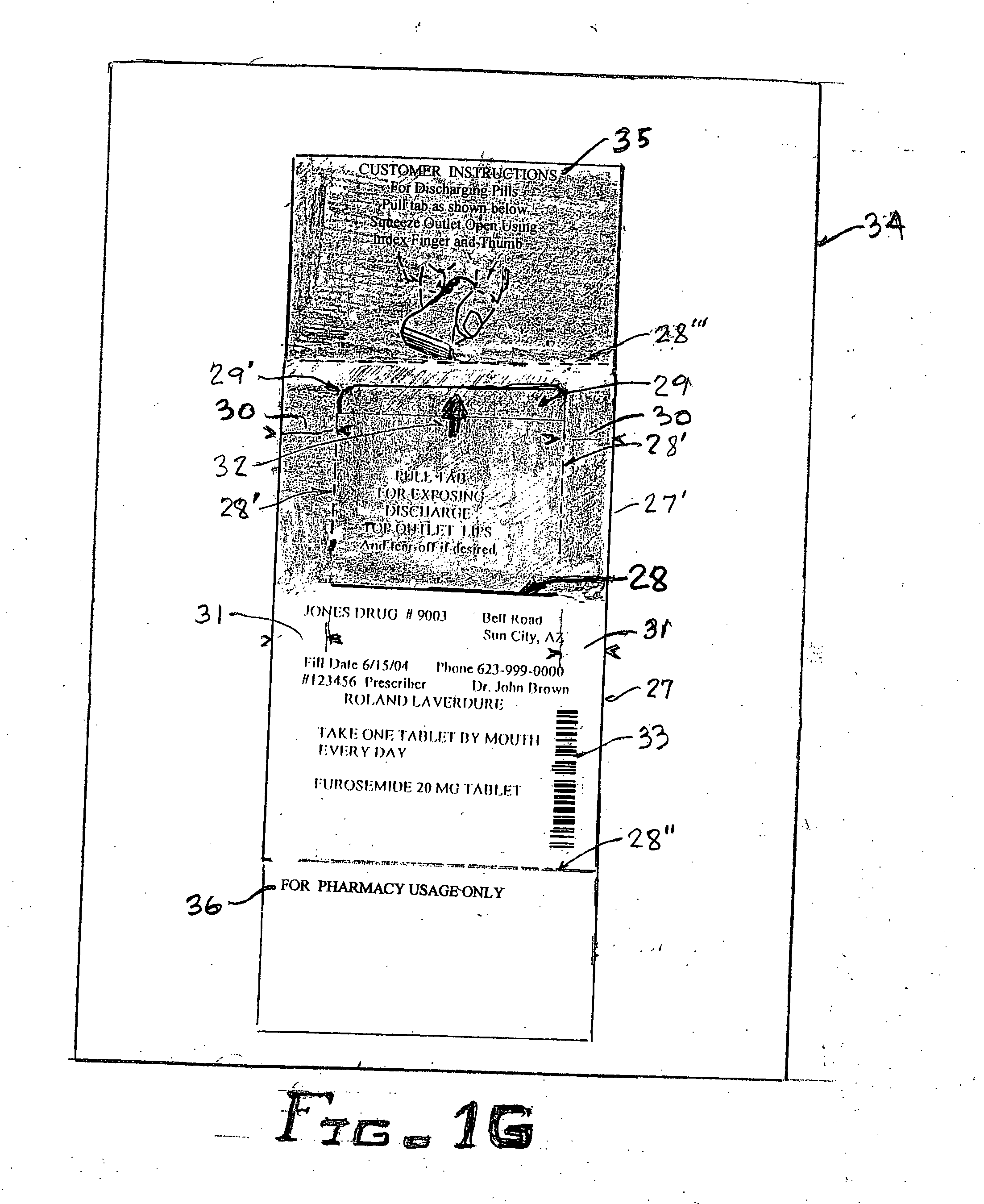
LID-LESS, squeeze-to-open, self-closing, pill-box
An improved hand held thermoplastic multi-purpose lid-less airtight container, that can be squeezed open by the same hand for dispensing when up-ended, and automatically self-closes upon release of the manual squeeze effort, thus restricting exposure to contaminants, bugs, germs etc. and removal of contents by others; depending upon its ultimate usage, said container may be provided with a suitable tamper evident closure as follows: 1 / for pharmacies when filling prescription pills a child resistant tamper evident protection closure is made simply by overlapping the elongated curved slotted outlet of said lid-less container with the self-adhesive prescription paper label presently used by pharmacies for tear-off by the customer 2 / for other than prescription filling, a simple tack-weld at the closure outlet lips for separation by the customer's initial squeeze to open operation 3 / for purchase by the customer for temporary storage of vitamins, drugs, aspirin, usually kept in pockets or purses for quick withdrawal, of the likes of Bayer aspirin towards possibly warding off heart attacks.
Owner:LAVERDURE ROLAND J A
Method using choline type deep-eutectic solvent to catalyze to synthesize aspirin
InactiveCN106928055AThe synthesis method is simpleLow melting pointOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSide effectAcetic anhydride
The invention belongs to the technical field of green organic synthesis chemistry, and particularly relates to a method using a choline type deep-eutectic solvent to catalyze to synthesize aspirin. The method comprises the following steps of adding the choline type deep-eutectic solvent, salicylic acid and acetic anhydride into a reaction container; heating to react for 15 to 40min at the temperature of 70 to 80 DEG C; purifying a crude product after reaction, so as to obtain the aspirin. The method using the choline type deep-eutectic solvent to catalyze to the synthesize aspirin has the advantages that the operation is simple, the reaction condition is mild, the side effect is small, and the environment-friendly effect is realized; when the deep-eutectic solvent is prepared, the utilization rate of atoms is 100%; the purifying of the deep-eutectic solvent is not needed, the deep-eutectic solvent can be recycled, the green chemical development requirement is met, and the wide industrial production application prospect is realized.
Owner:NANYANG INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com