Patents
Literature
709results about How to "Increase pain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
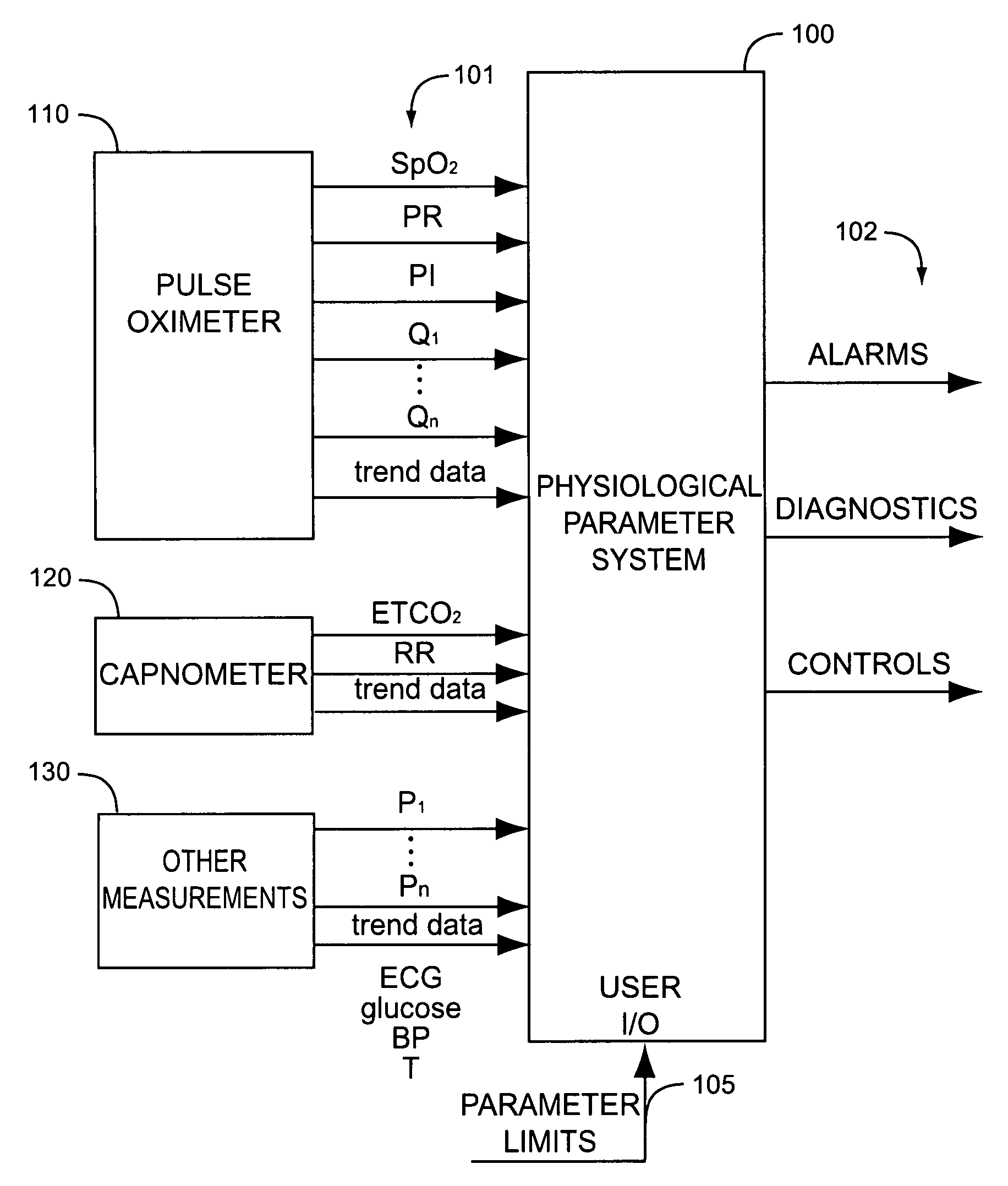
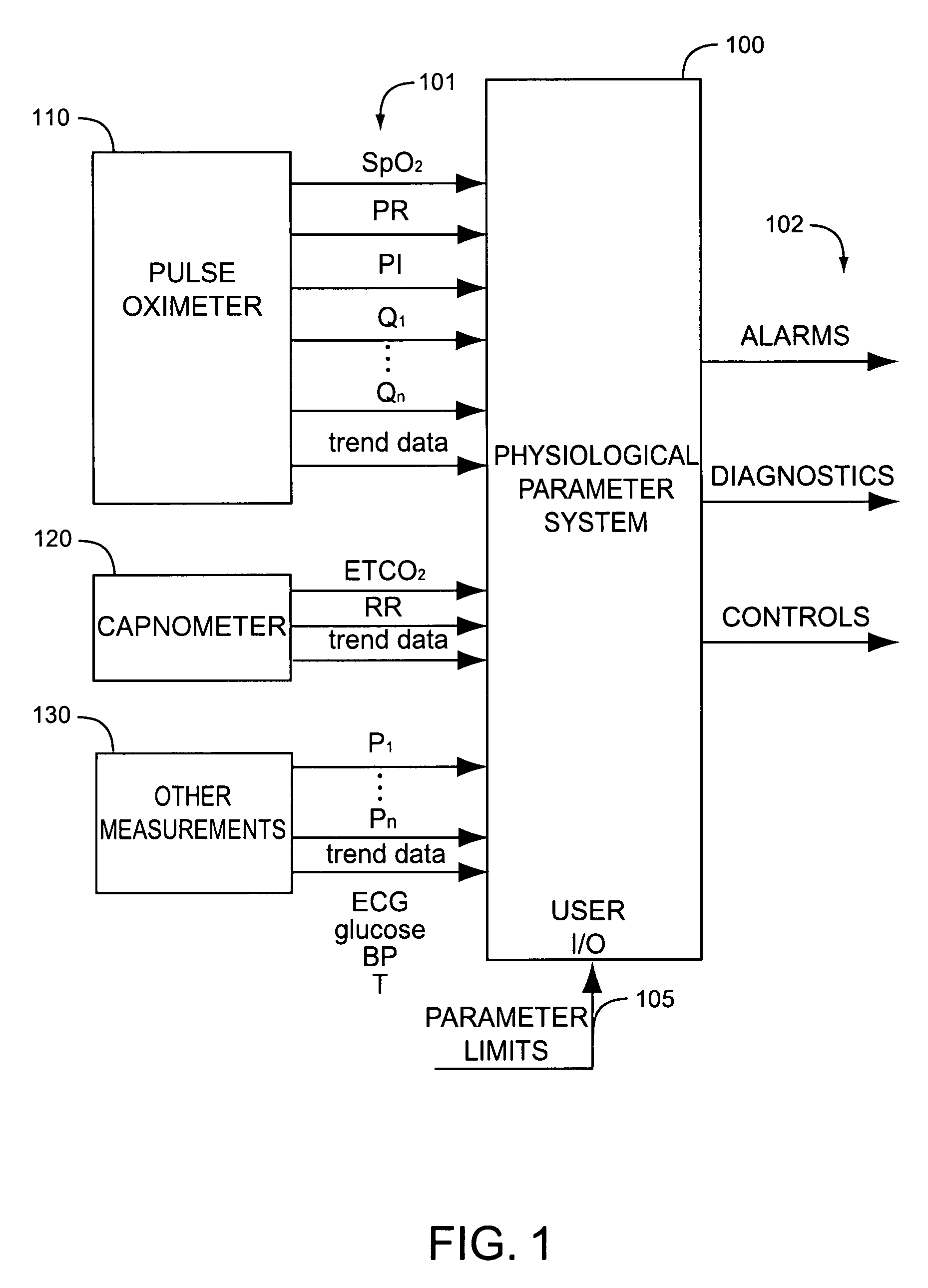
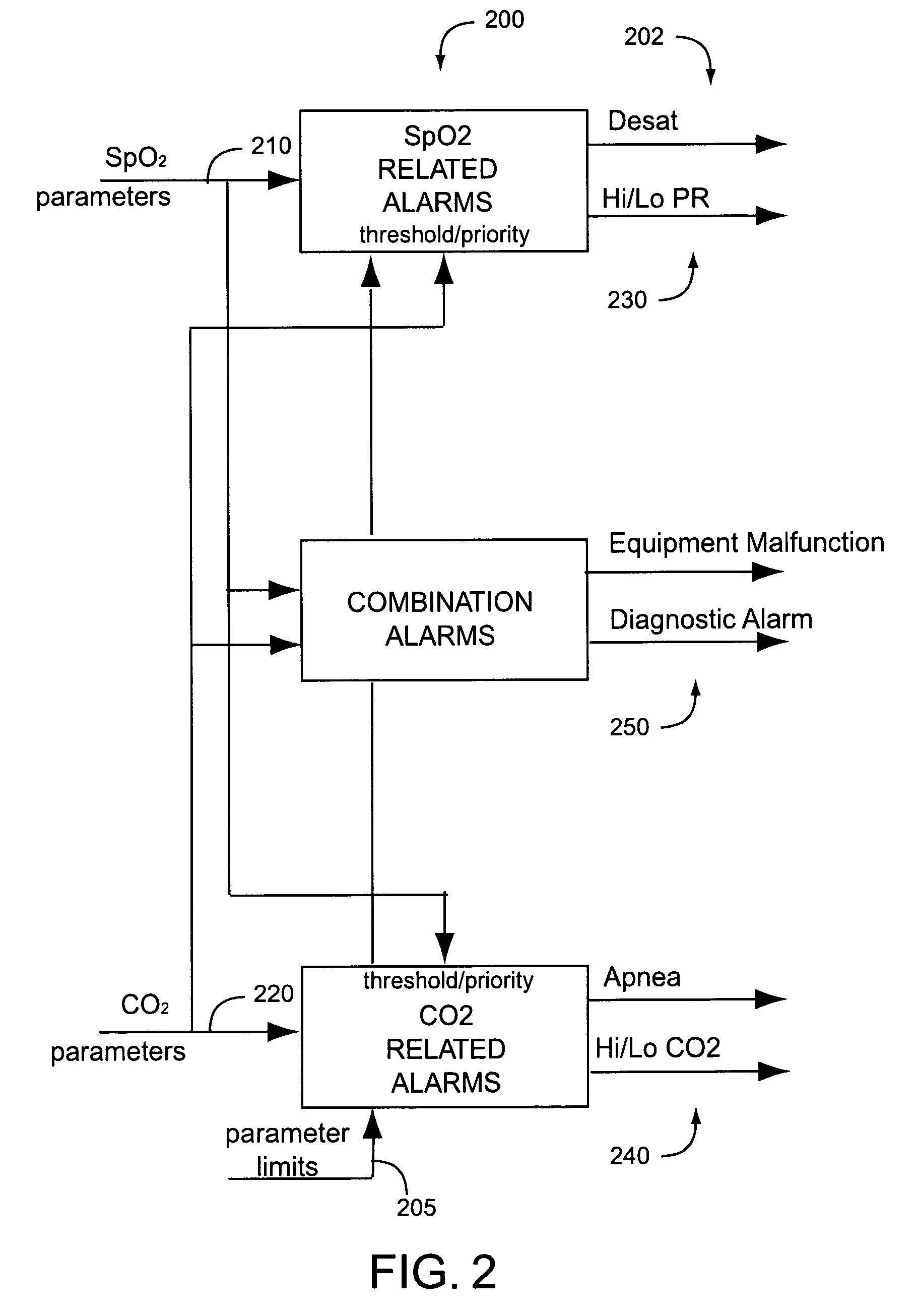
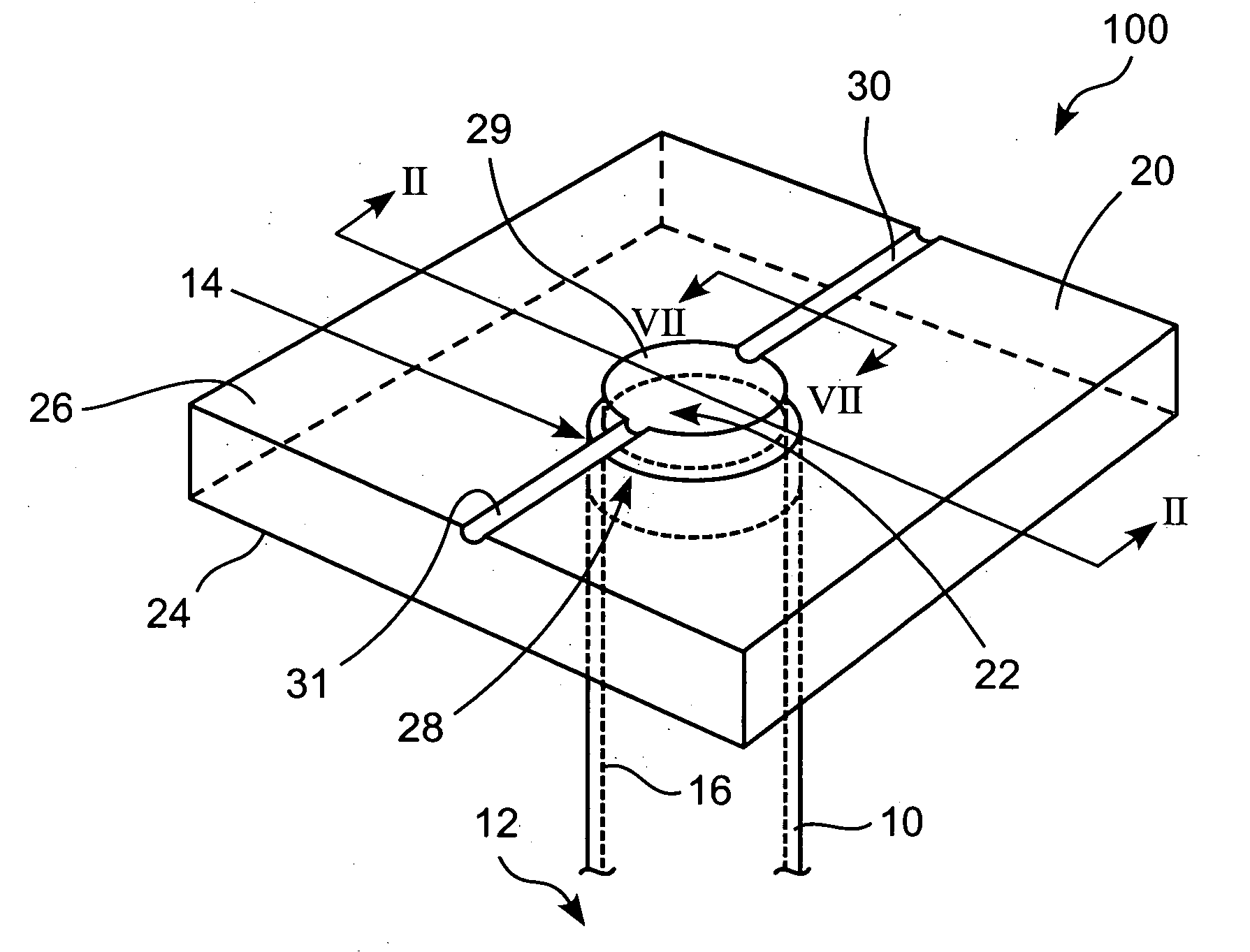
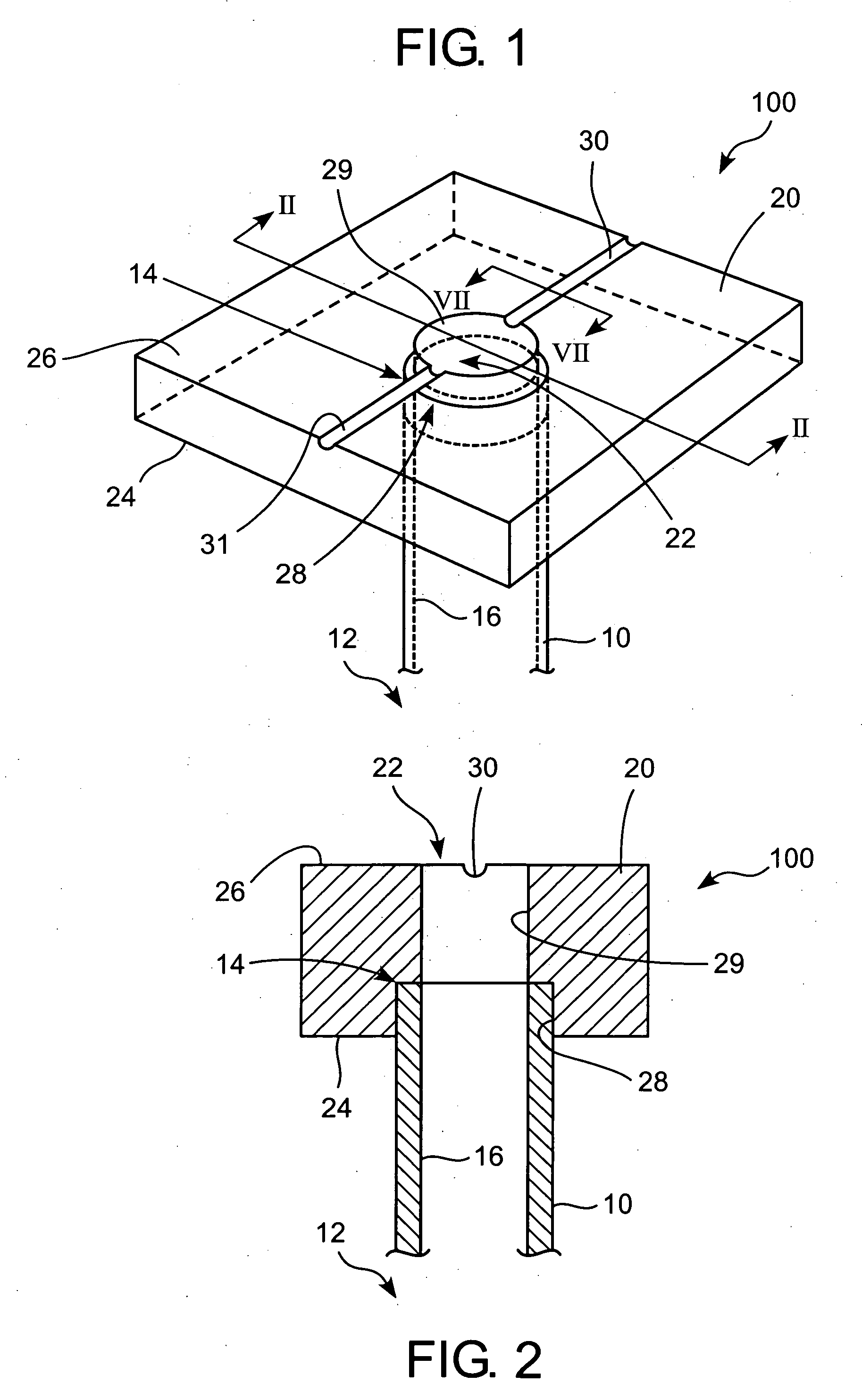
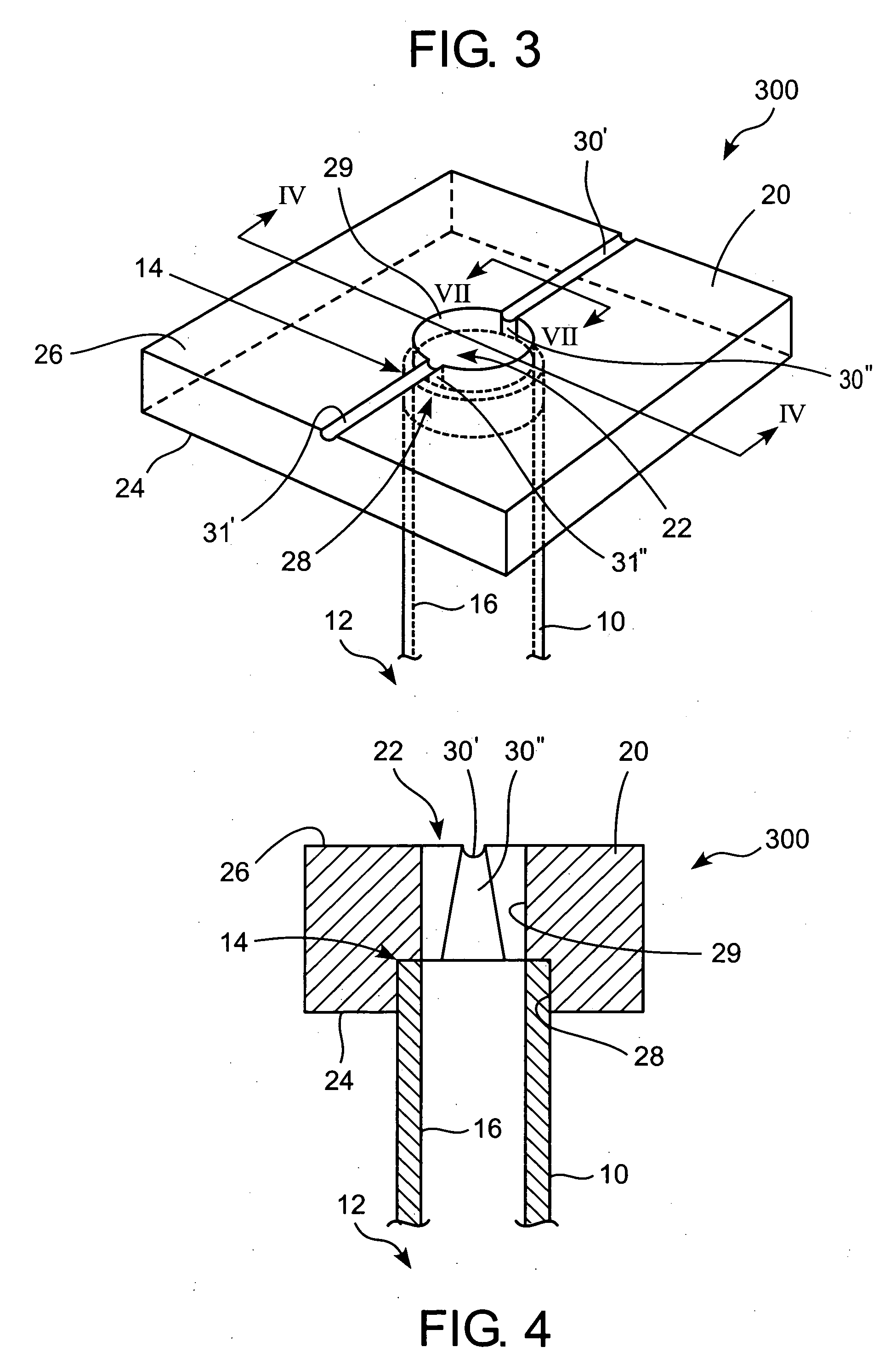
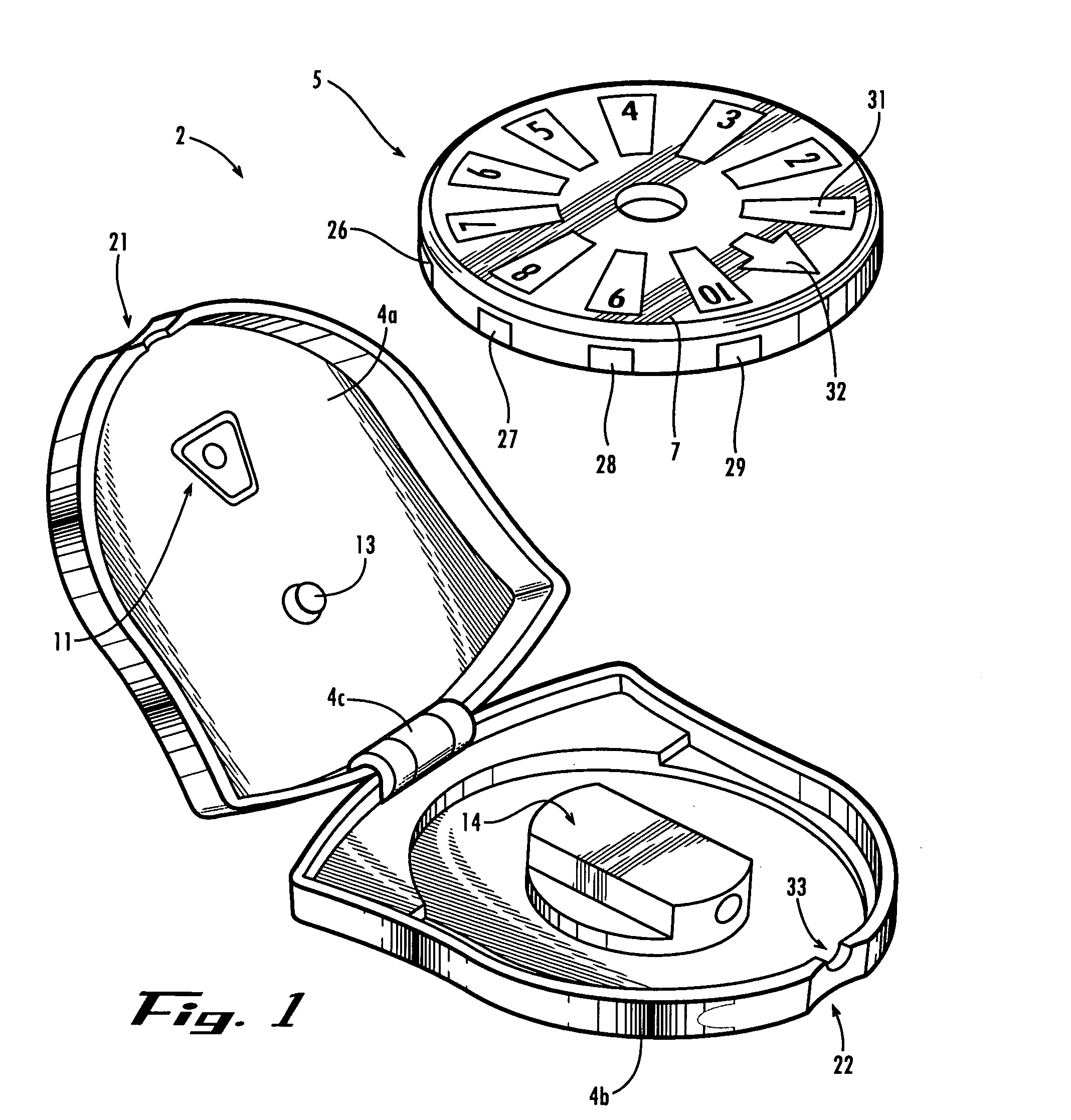
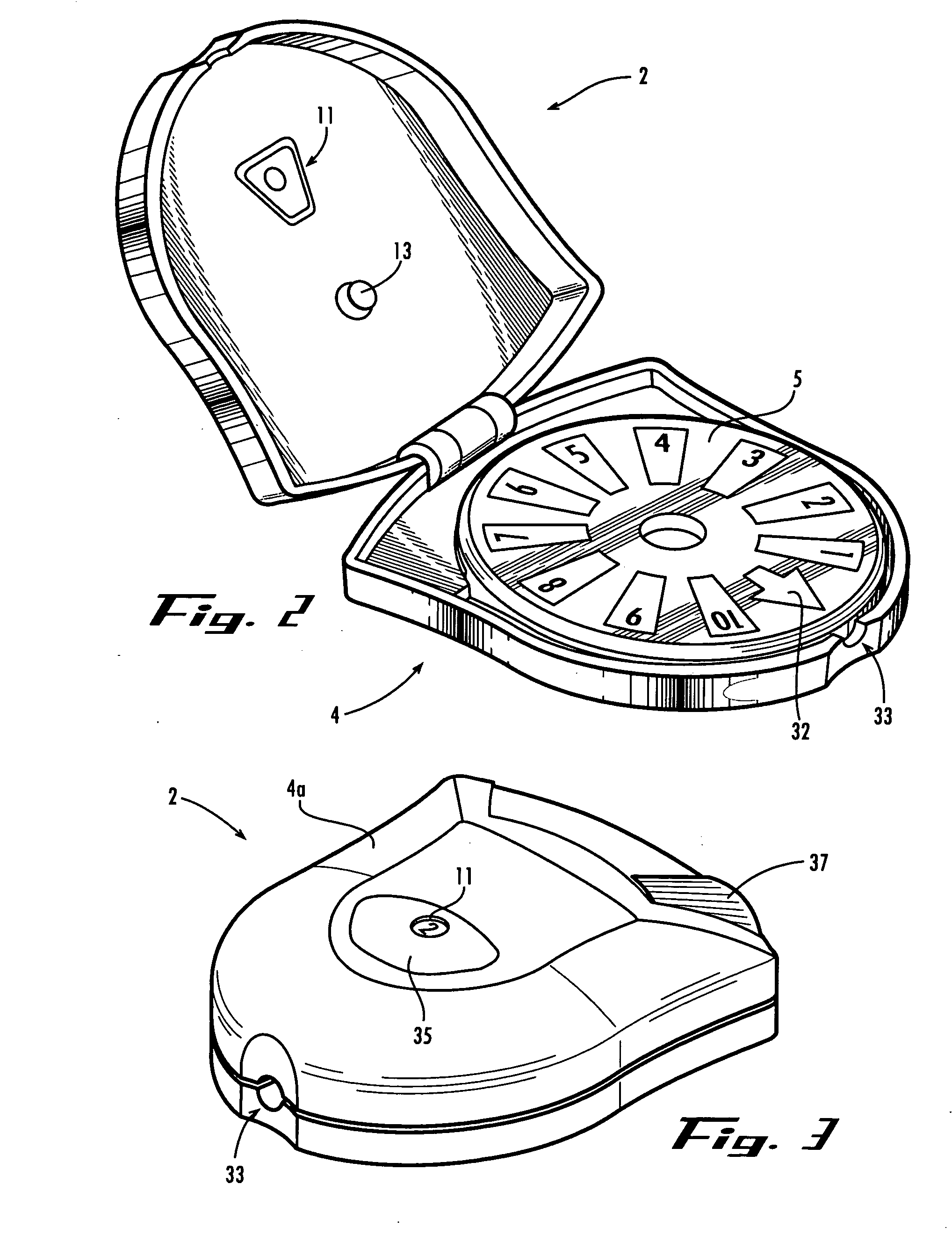
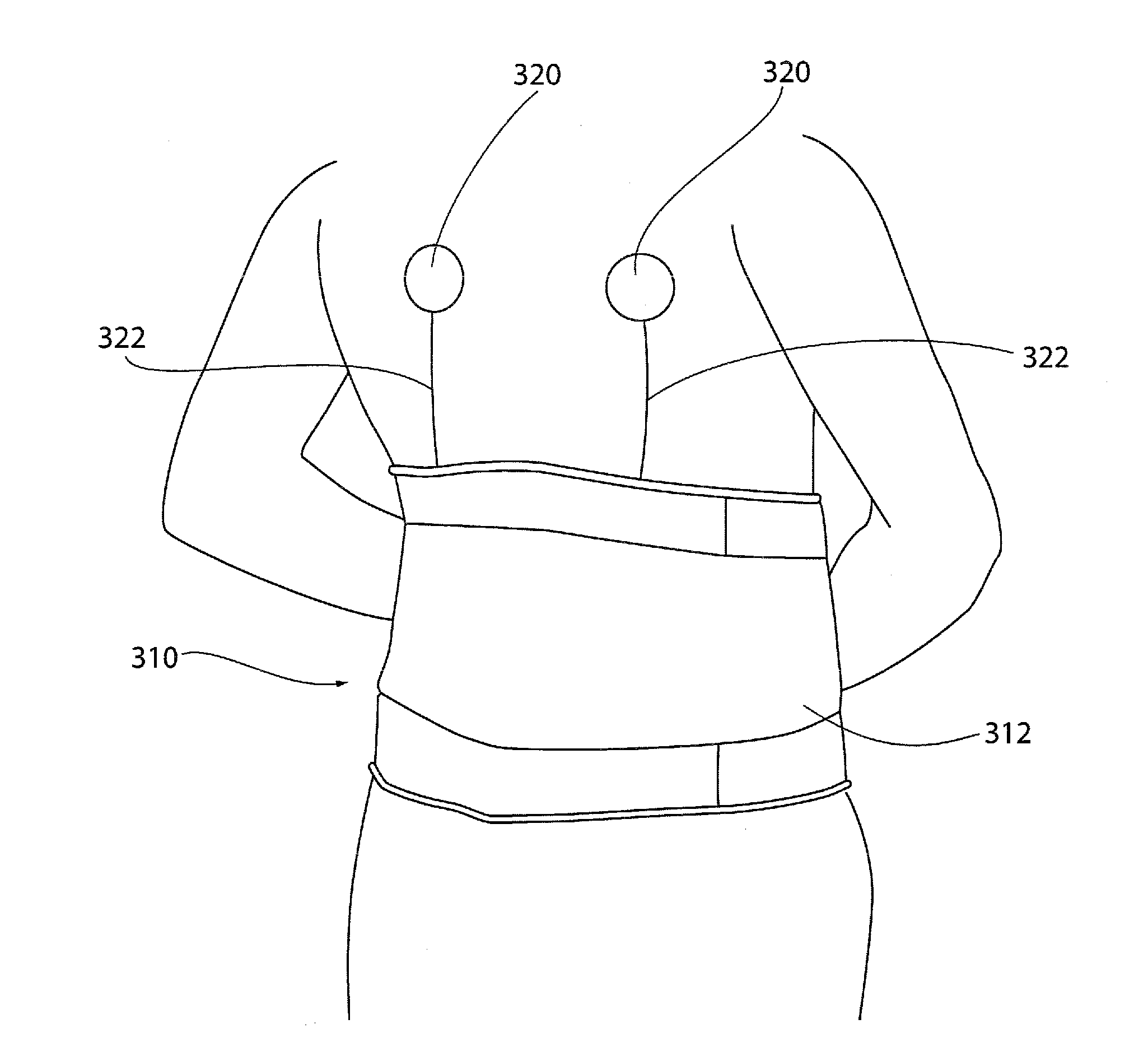
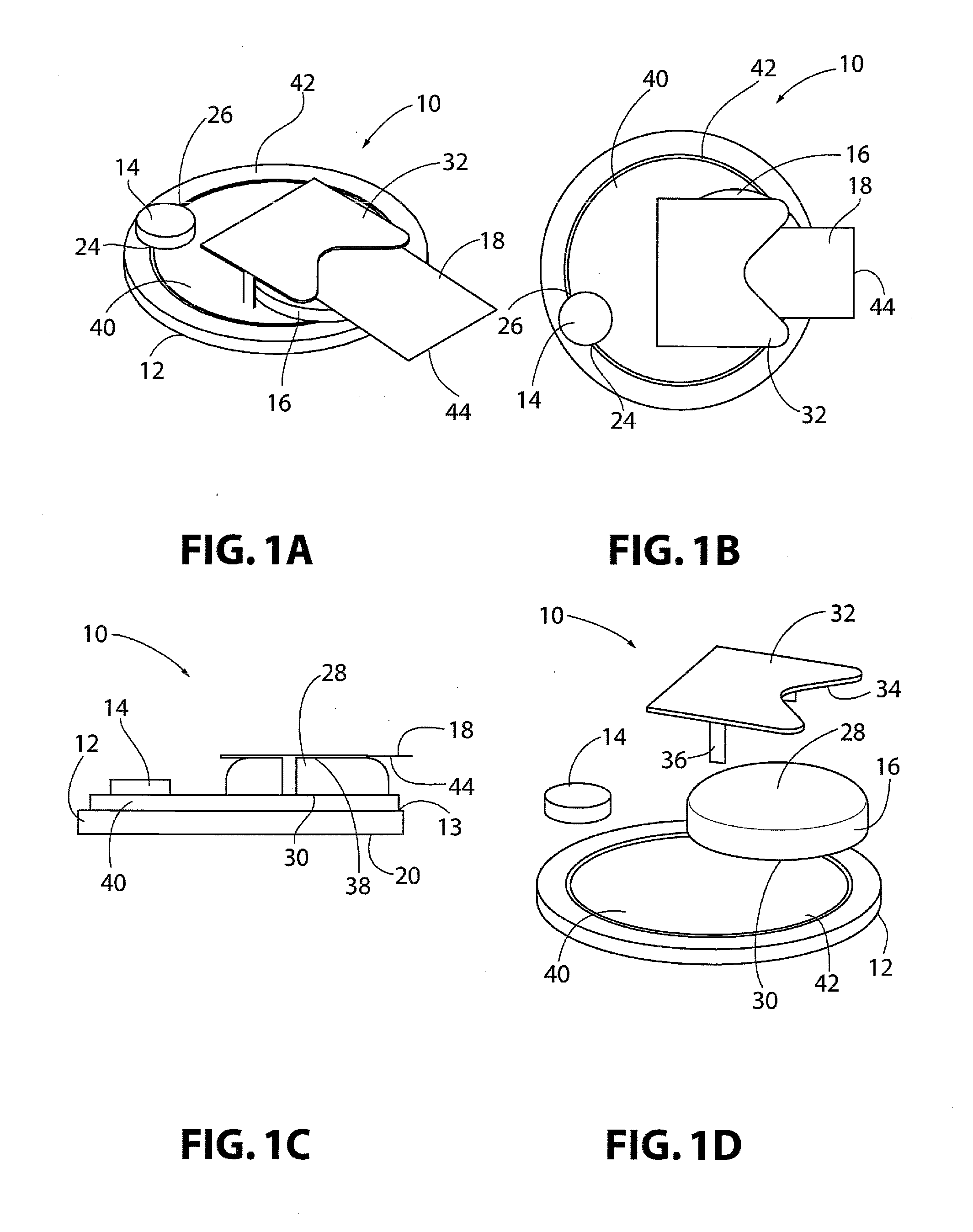
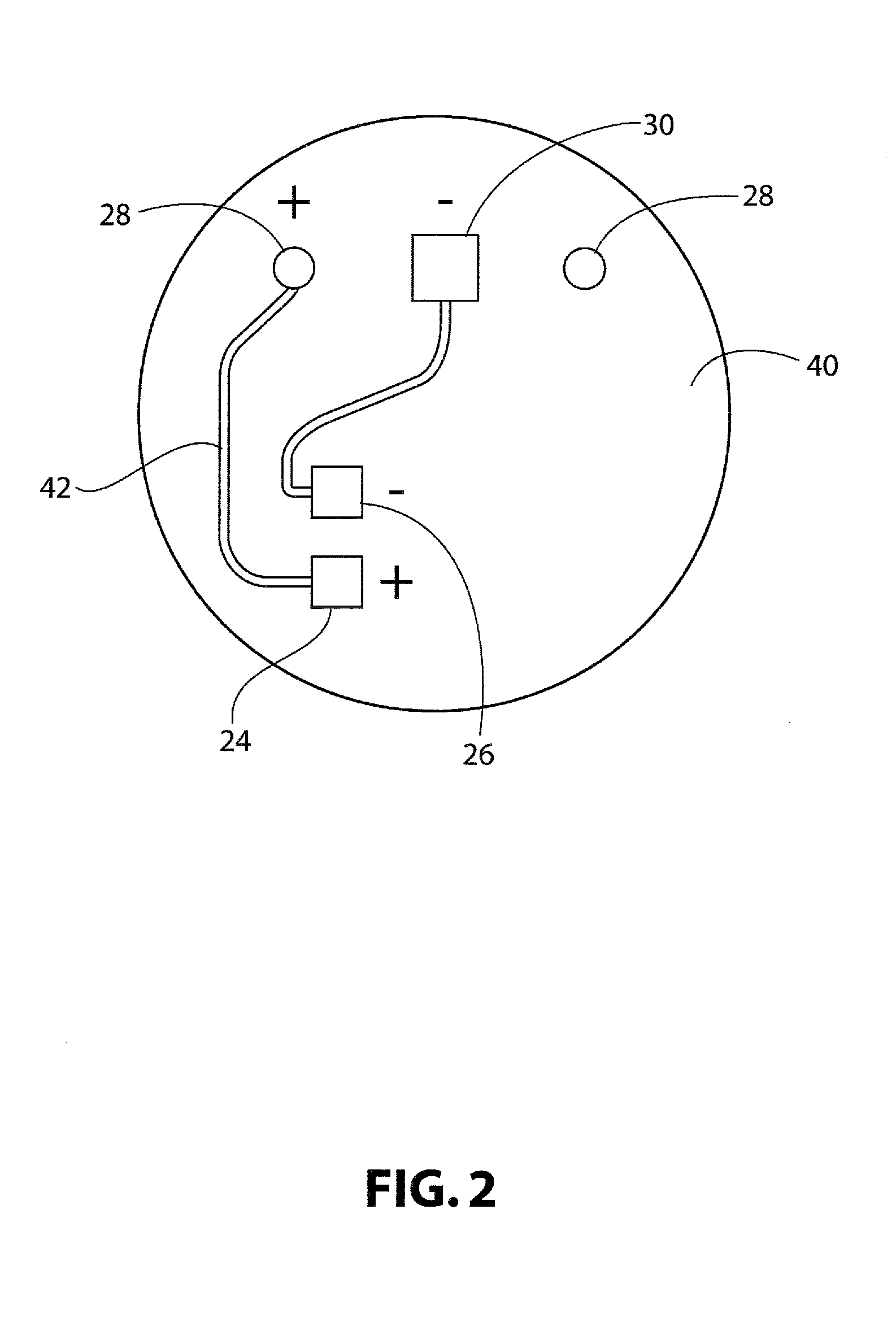
Physiological parameter system
ActiveUS7415297B2Powerful patient condition assessment toolGreat confidenceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineering
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
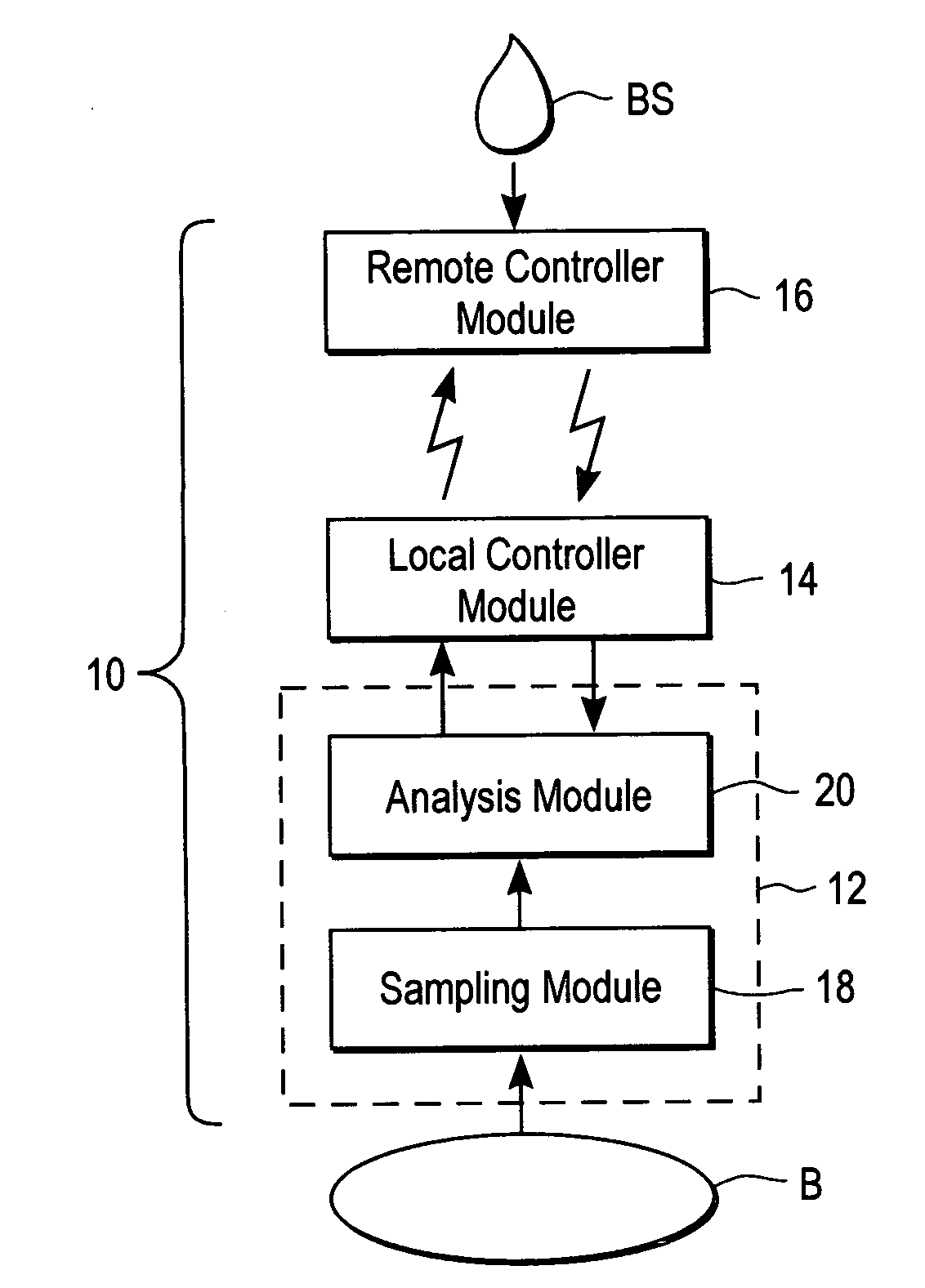
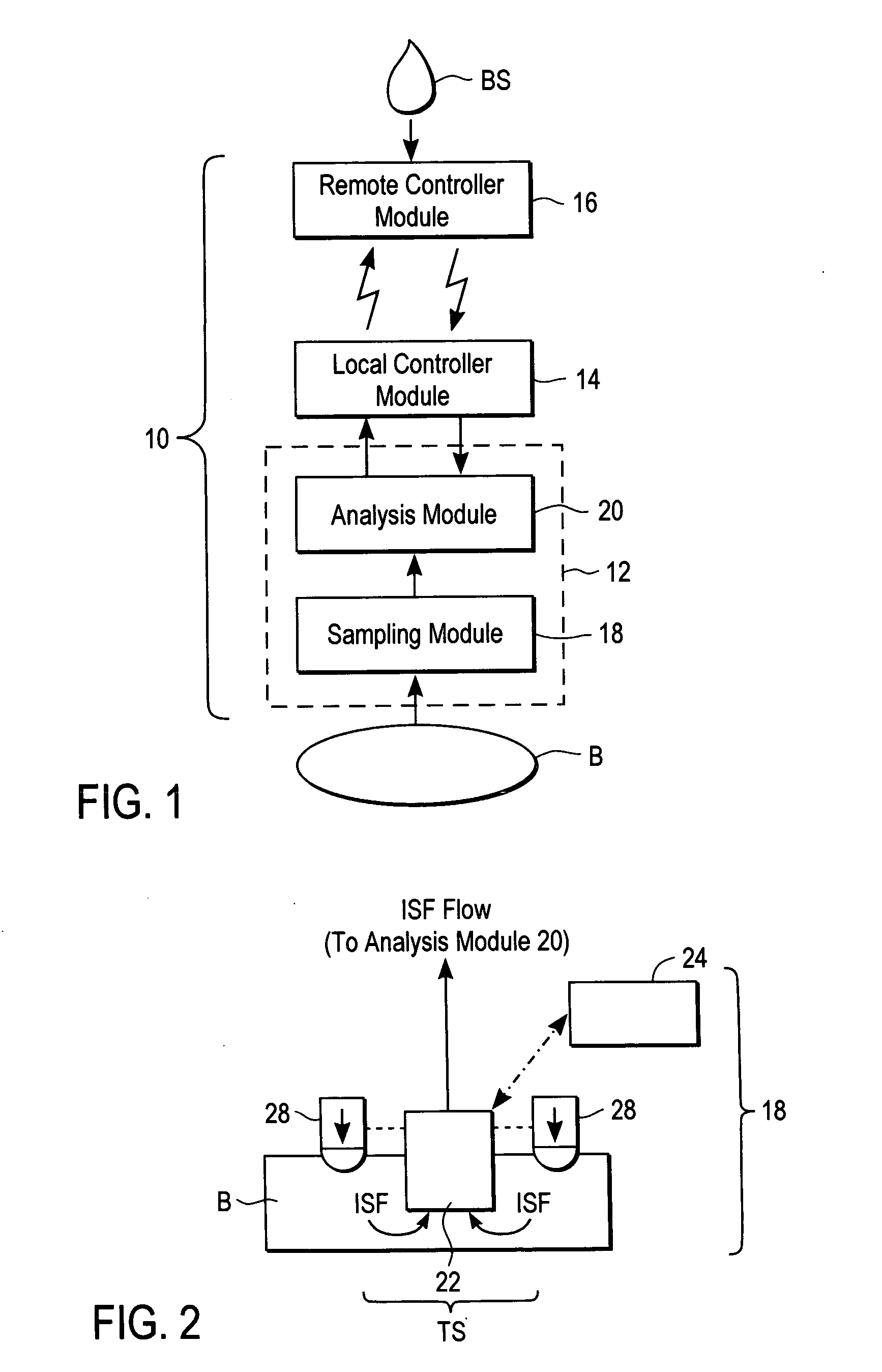
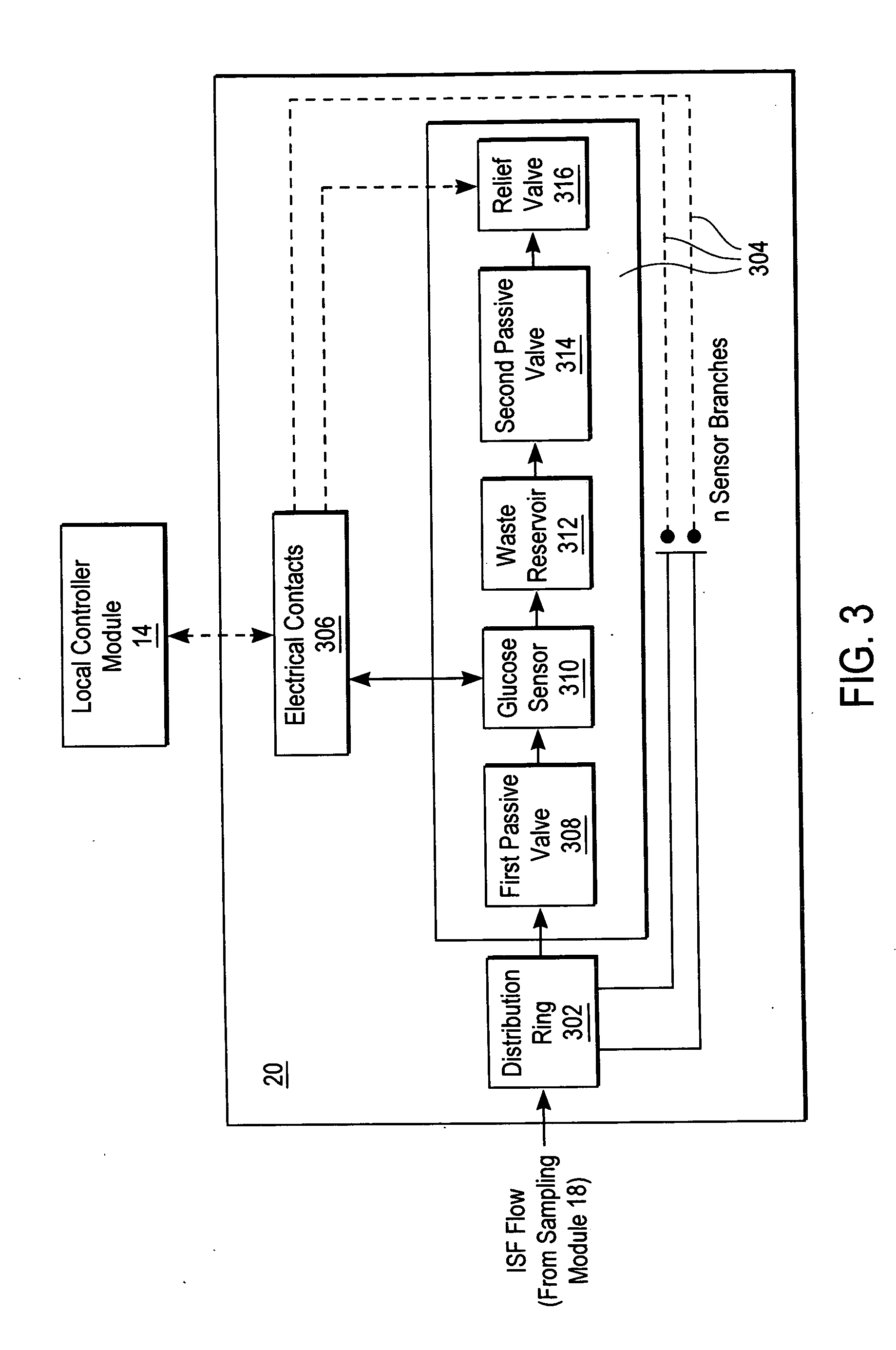
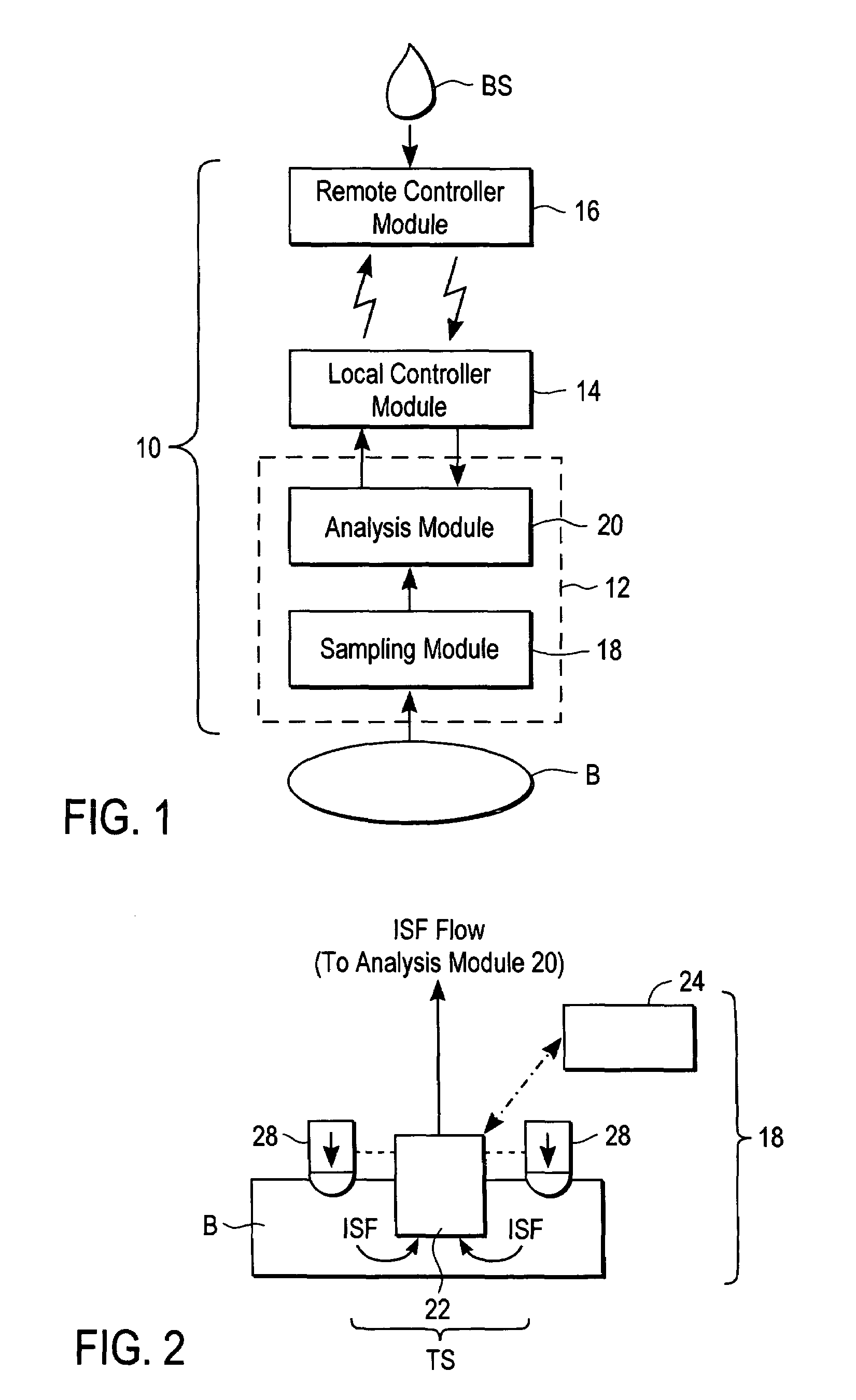
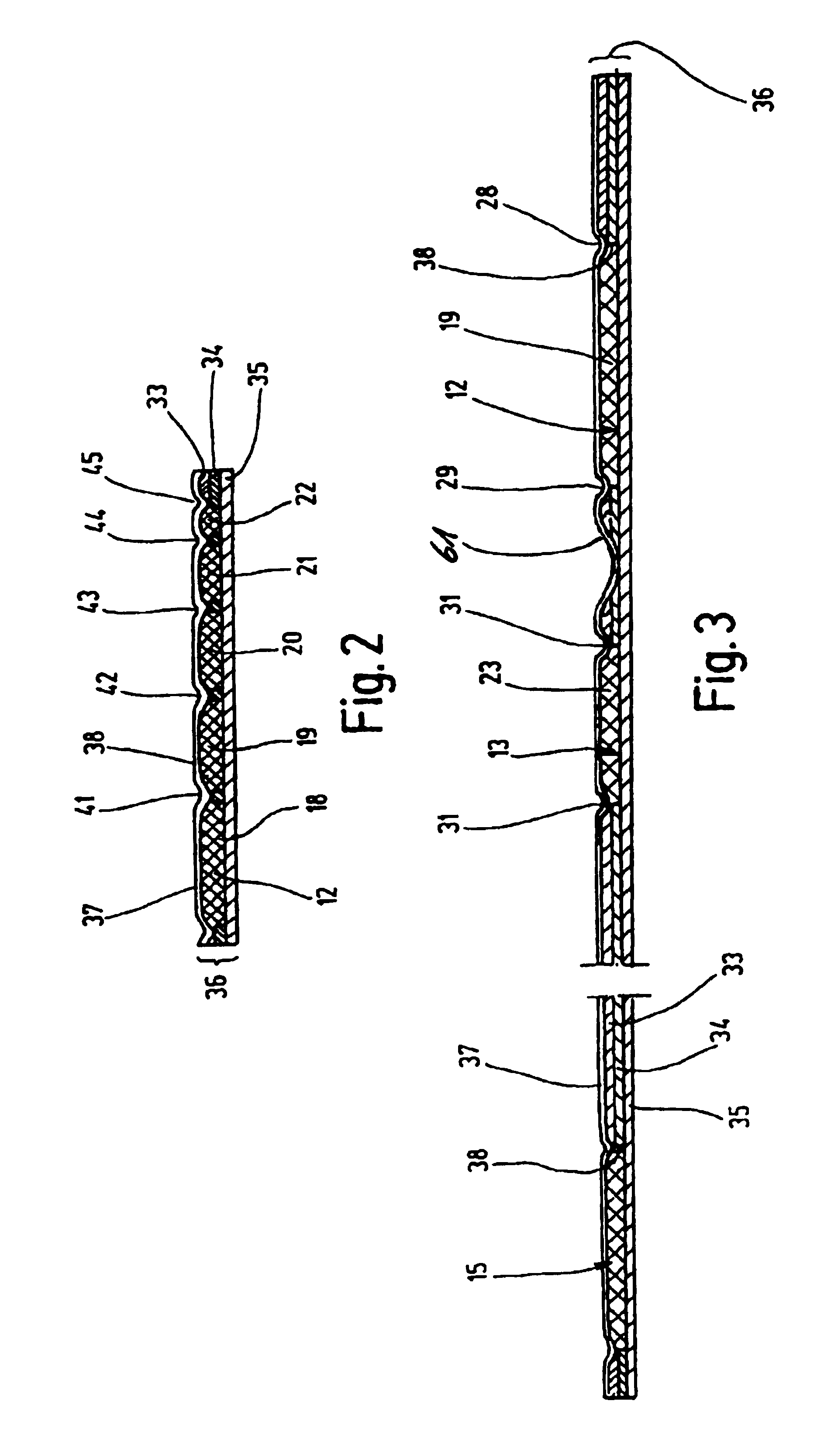
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
ActiveUS20040249253A1Easy to useLittle painWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteElectronic communication
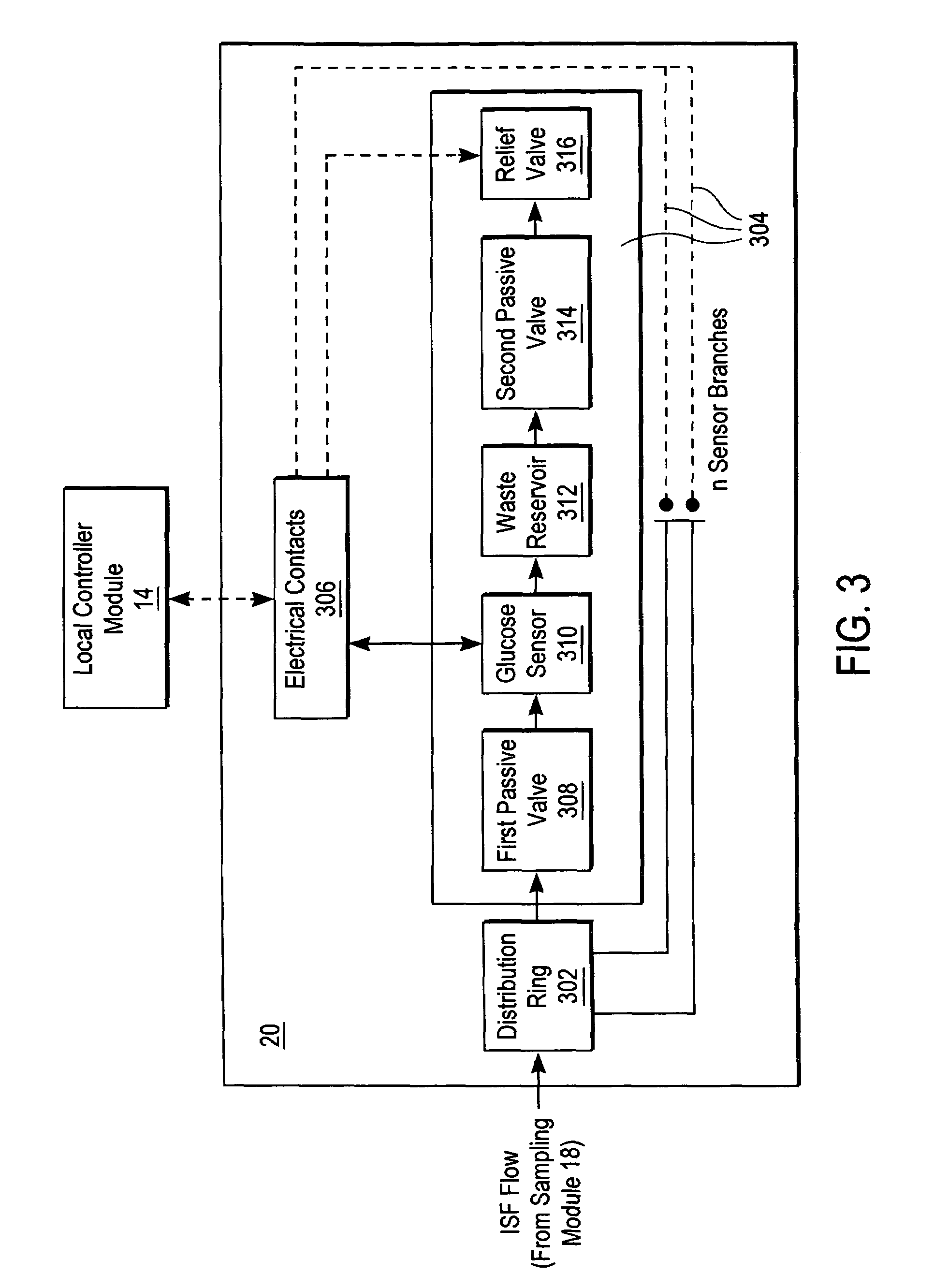
A system for extracting a bodily fluid sample (e.g., an interstitial fluid [ISF] sample) and monitoring an analyte therein includes a disposable cartridge and a local controller module. The disposable cartridge includes a sampling module adapted to extract a bodily fluid sample and an analysis module adapted to measure an analyte (e.g., glucose) in the bodily fluid sample. The local controller module is in electronic communication with the disposable cartridge and is adapted to receive and store measurement data from the analysis module. An ISF extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating and residing in a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, extracting an ISF sample therefrom. The device also includes a pressure ring(s) adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site. The device is configured such that the pressure ring(s) is capable of applying pressure in an oscillating manner whereby an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member is mitigated. A method for extracting ISF includes providing an ISF fluid extraction device with a penetration member and a pressure ring(s). Next, a user's skin layer is contacted by the pressure ring(s) and penetrated by the penetration member. An ISF sample is then extracted from the user's skin layer while pressure is being applied in an oscillating manner by the pressure ring(s). The oscillating pressure mitigates an ISF glucose lag of the extracted ISF sample extracted.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Devices, systems and methods for extracting bodily fluid and monitoring an analyte therein
ActiveUS7258673B2Little painSlight discomfortWithdrawing sample devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsAnalyteD-Glucose
An interstitial fluid (ISF) extraction device includes a penetration member configured for penetrating a target site of a user's skin layer and, subsequently, residing in the user's skin layer and extracting an ISF sample therefrom and at least three concentrically-arranged pressure rings, each adapted for applying pressure to the user's skin layer in the vicinity of the target site while the penetration member is residing in the user's skin layer. In addition, the ISF extraction device is configured such that (i) the pressure rings apply pressure in an oscillating manner with asymmetric deployment and retraction cycles and (ii) only one of the at least three concentrically-arranged pressure rings is deployed at a time, thereby mitigating an ISF glucose lag of the ISF sample extracted by the penetration member.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures
InactiveUS20070100341A1Reduce painLong-term complicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSmall incisionSpinal locomotion
A dynamic bone stabilization system is provided. The system may be placed through small incisions and tubes. The system provides systems and methods of treating the spine, which eliminate pain and enable spinal motion, which effectively mimics that of a normally functioning spine. Methods are also provided for stabilizing the spine and for implanting the subject systems.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
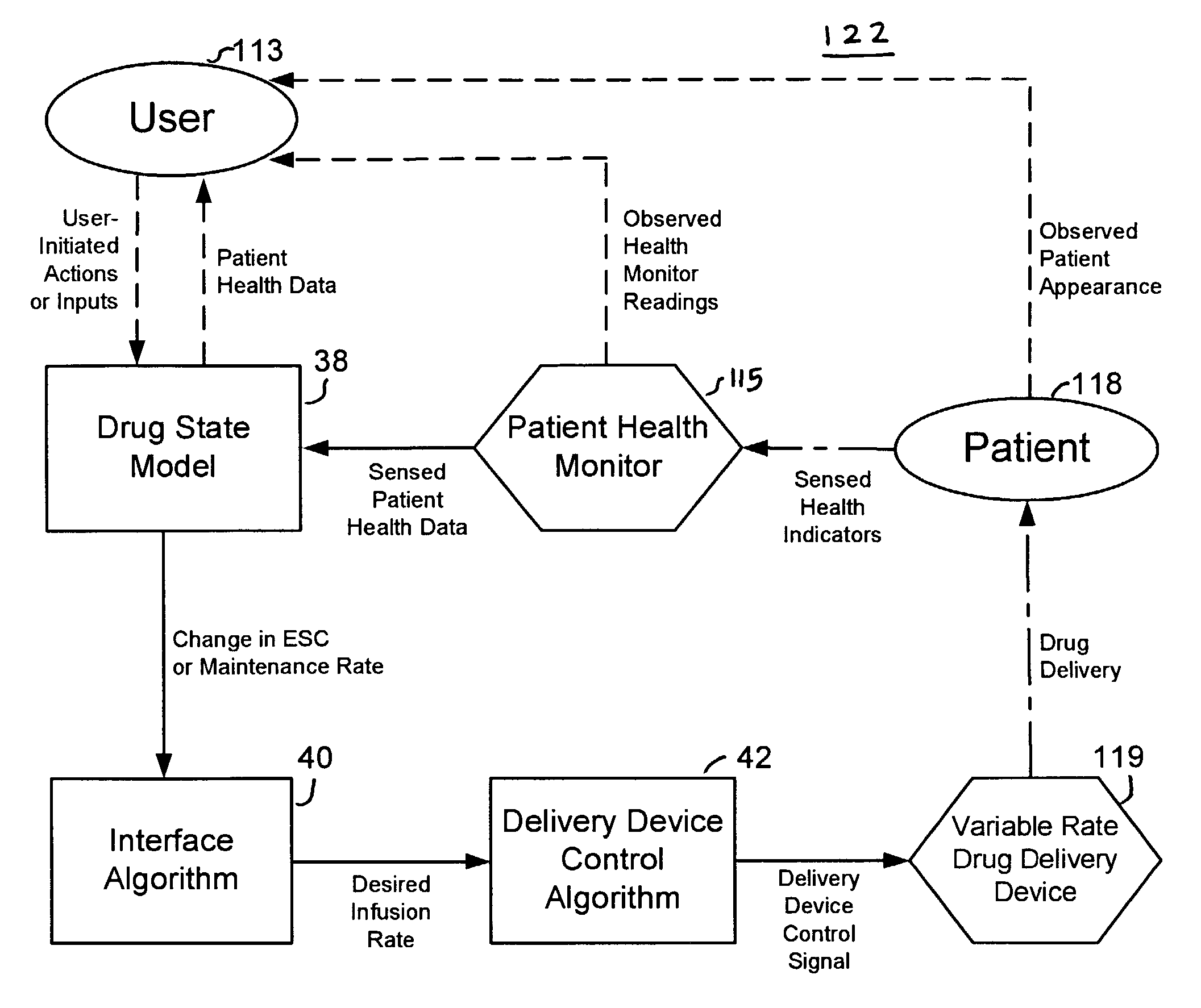
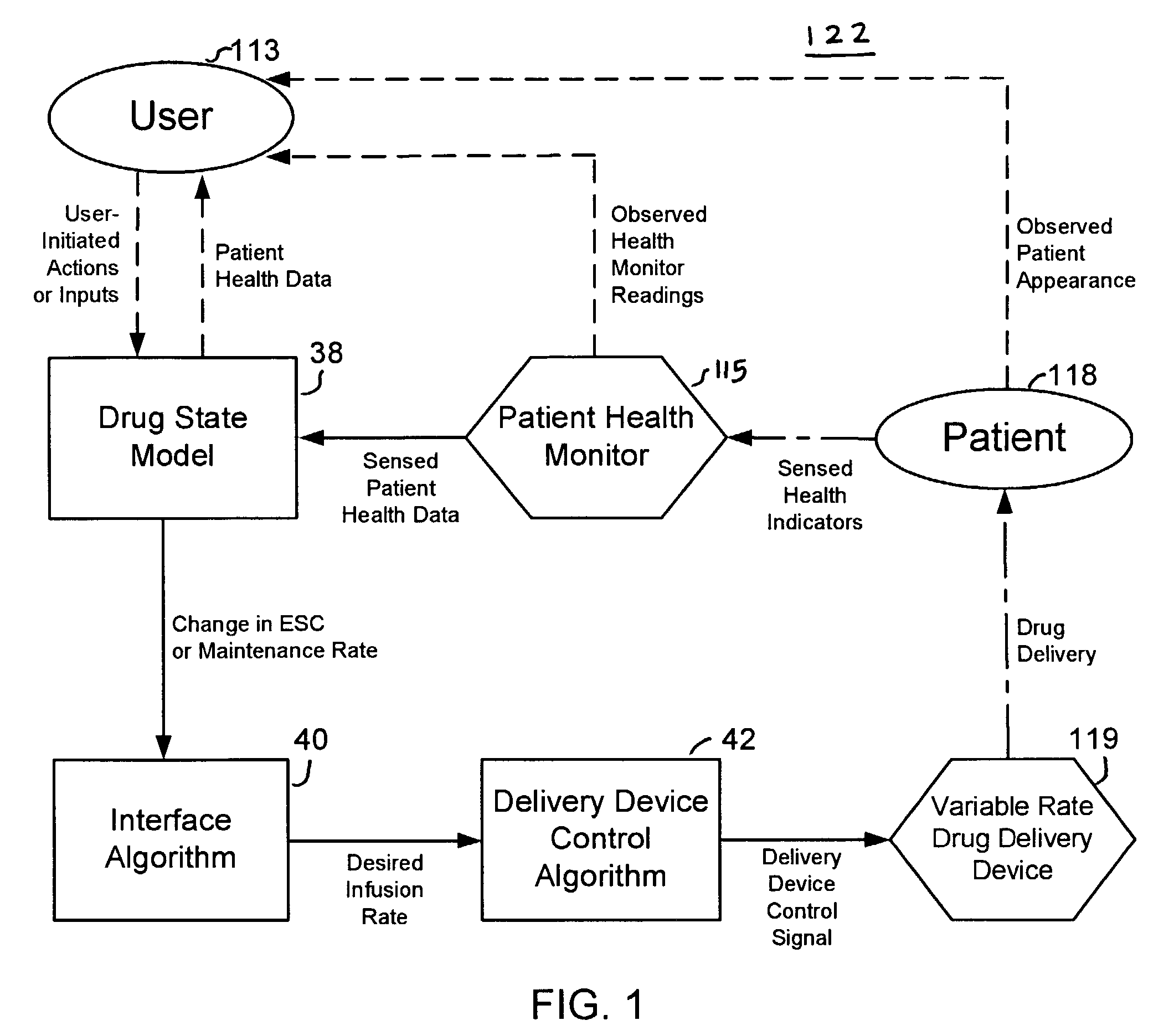
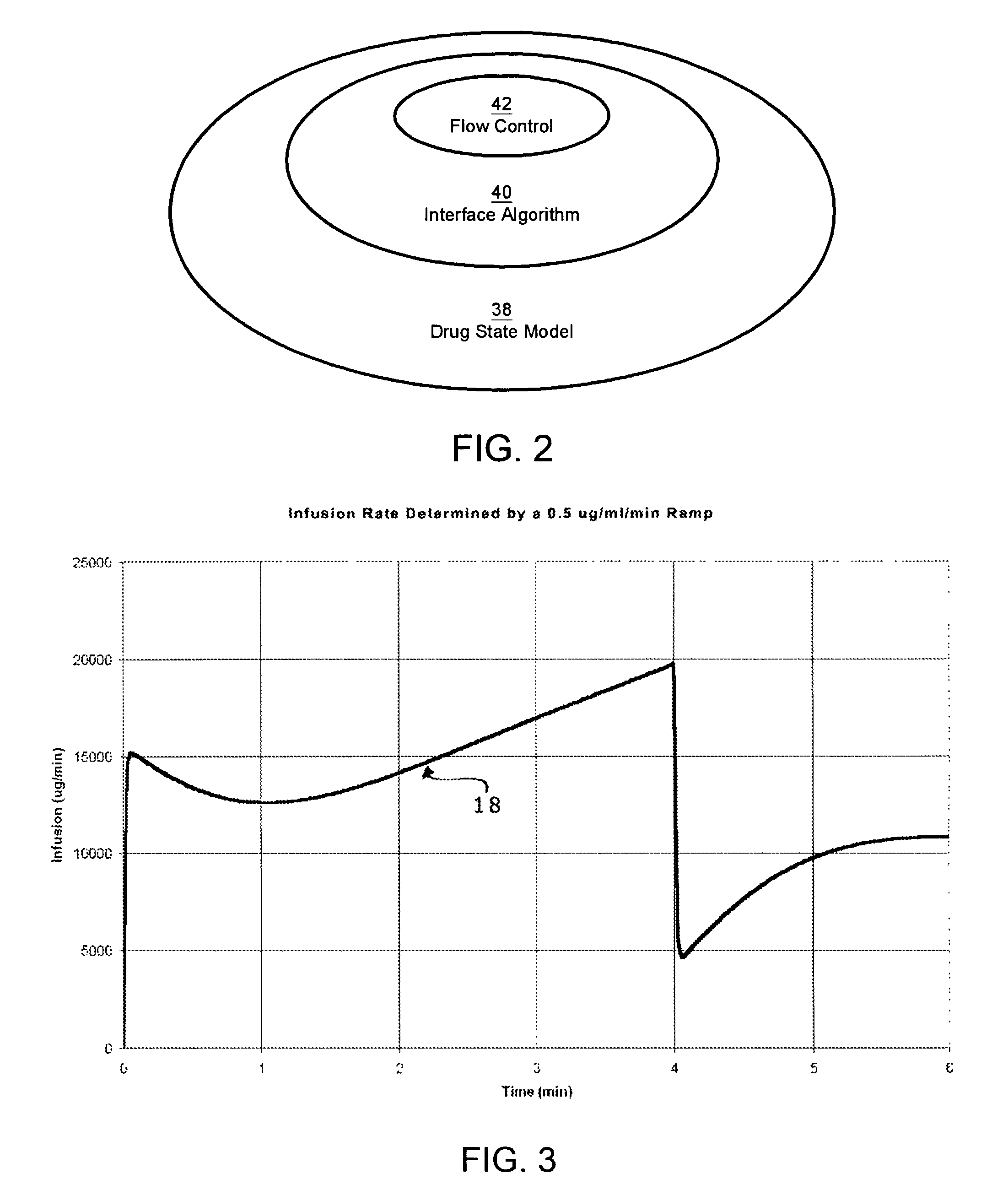
Apparatuses and methods for titrating drug delivery
InactiveUS7229430B2Reduce clinical useSafety managementMedical simulationDrug and medicationsState modelTime profile
A method and apparatus for reducing the workload of titrating drug to effect while leaving clinician users in control of a related procedure is described. A drug delivery device is controlled to achieve a target drug concentration at a selected site in the patient or a predetermined infusion rate waveform. The time profile of the target drug concentration or a predetermined infusion rate waveform is controlled by a drug state model that uses clinical heuristics to implement safe, pre-defined changes in the target drug concentration or infusion rate and user-commanded changes in target drug concentration or infusion rate. The invention allows time to assess the response of the patient to changes in drug level by making small incremental and conservative changes in drug level over time.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
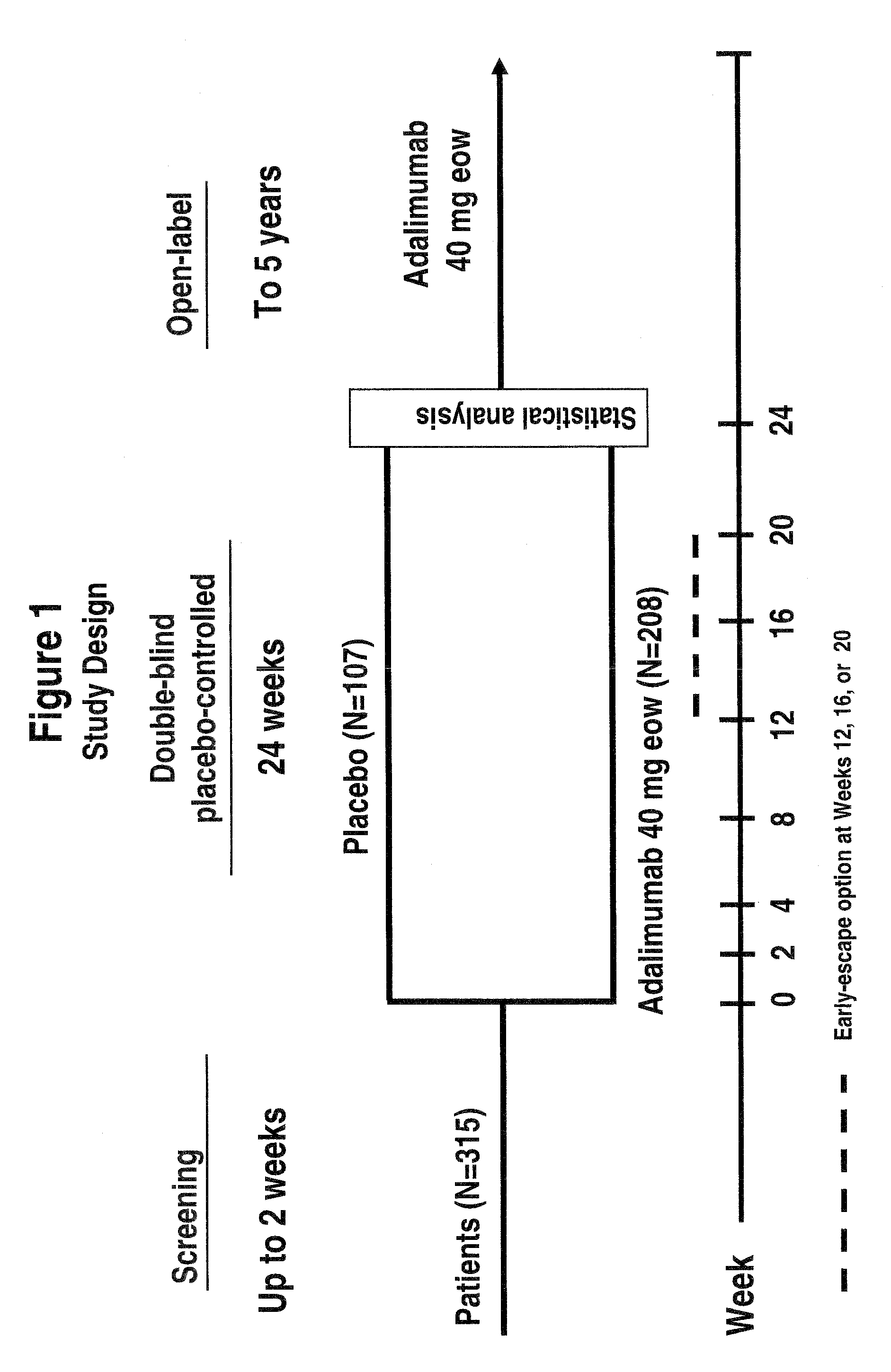
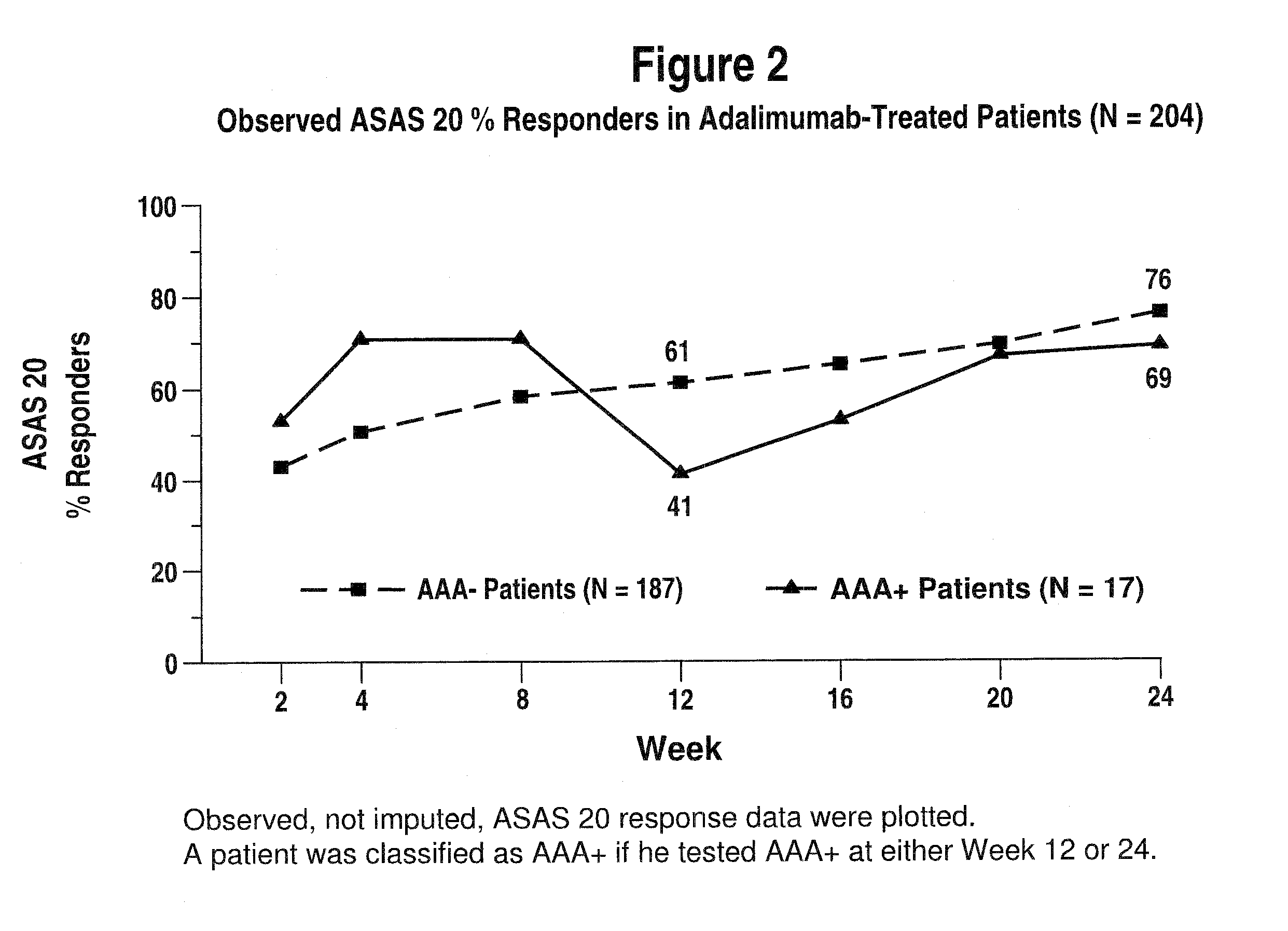
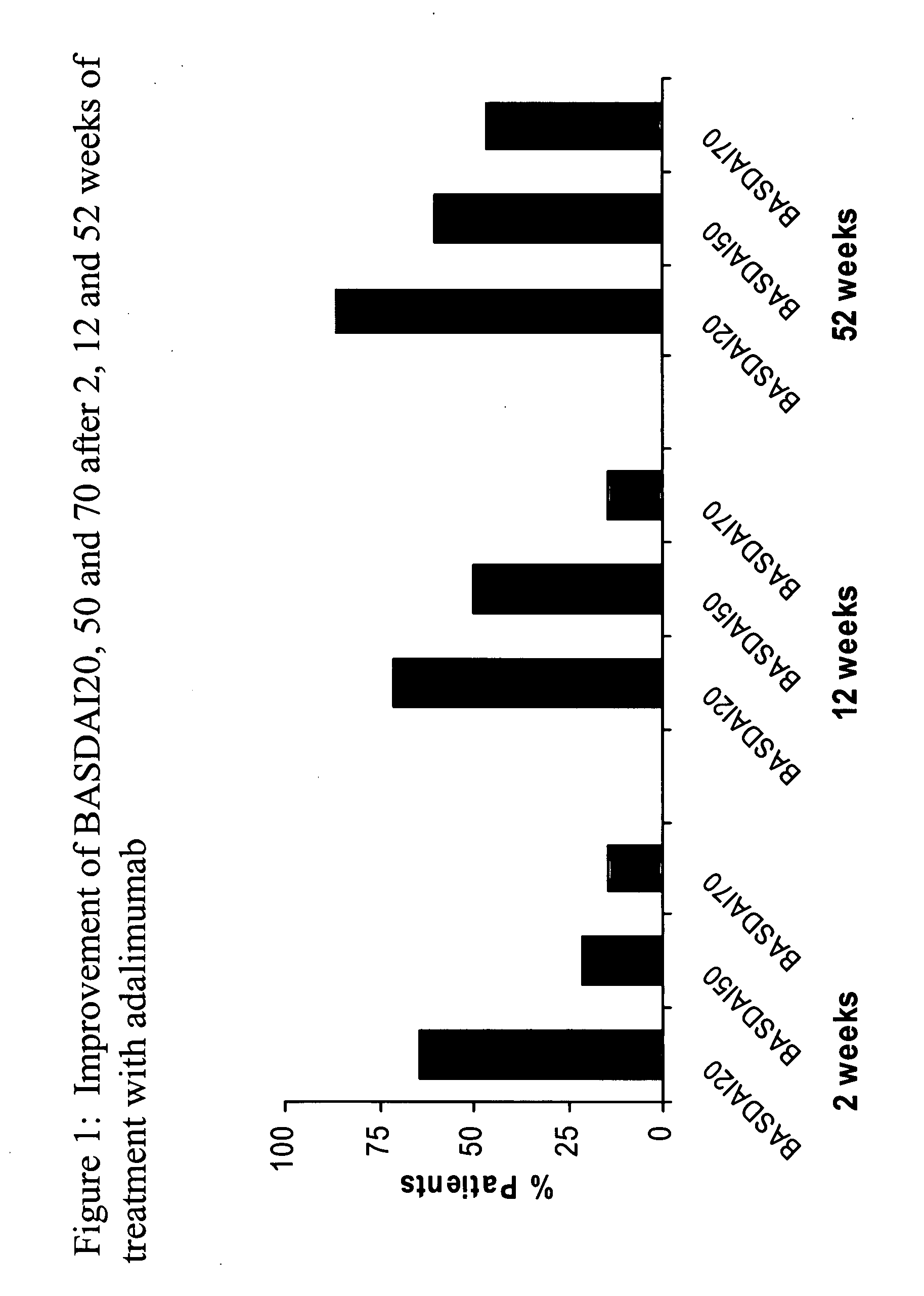
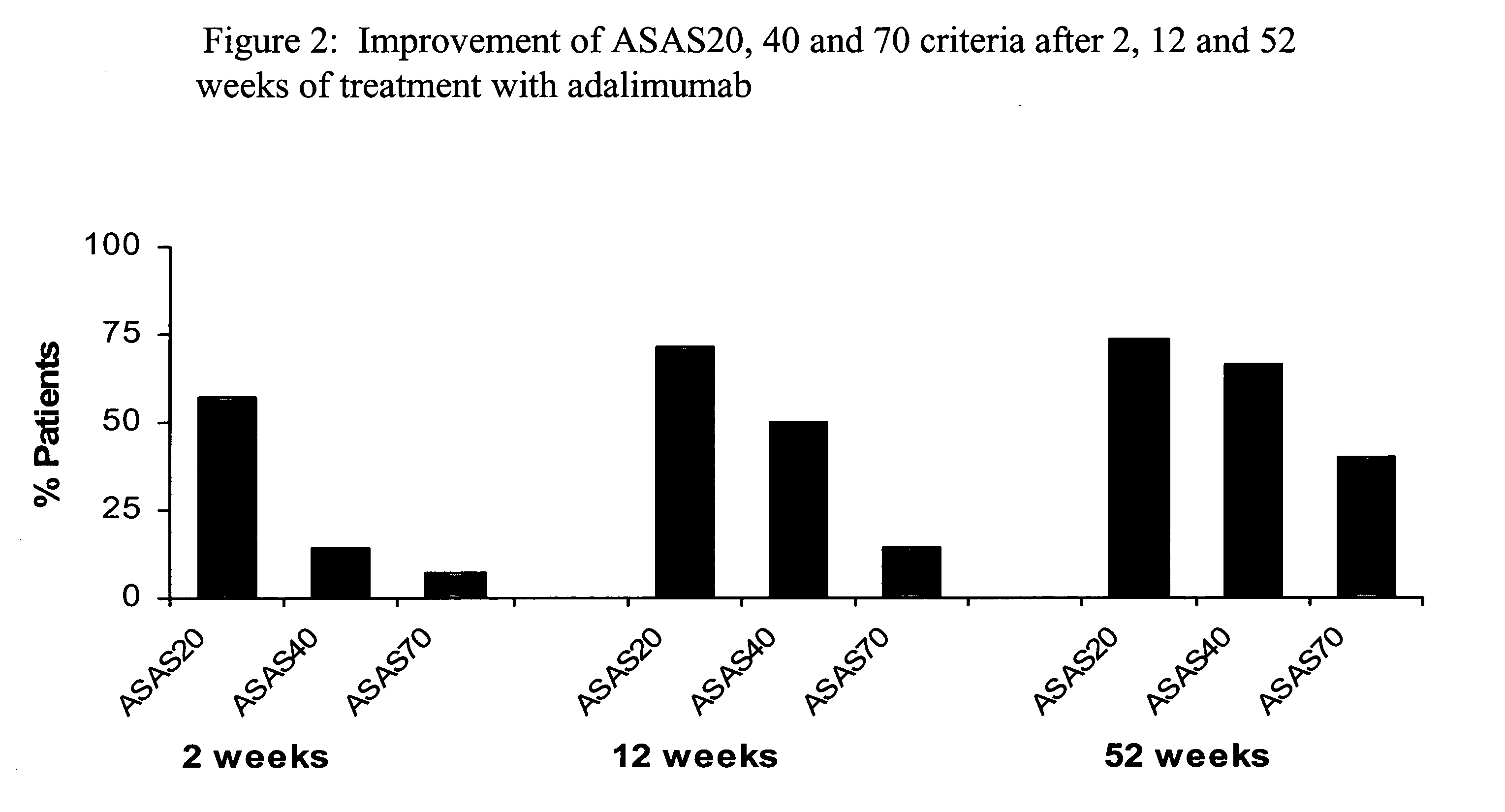
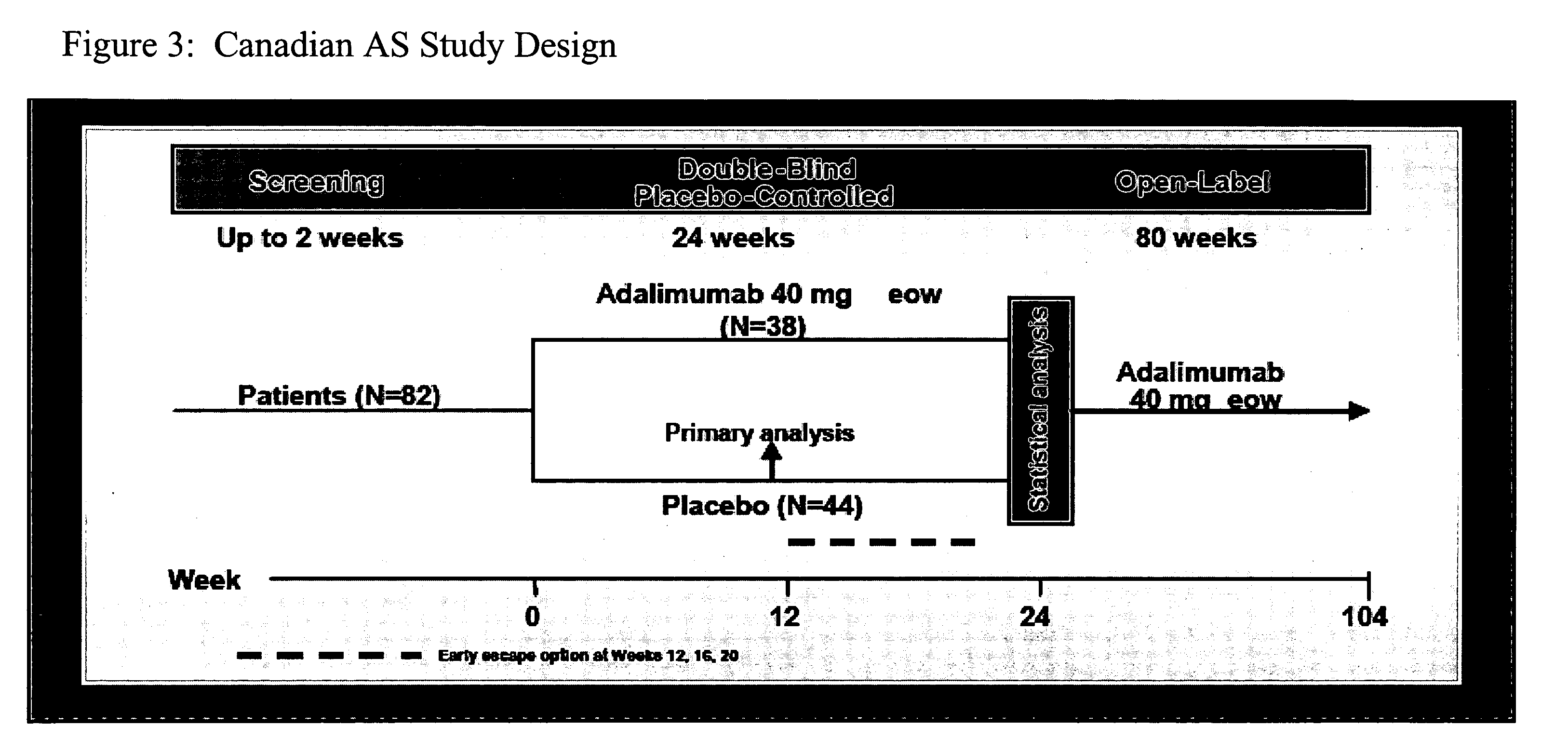
Uses and compositions for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
ActiveUS20090123378A1Treatment safetyImprove fatigueCompounds screening/testingAntibody ingredientsMedicineAnkylosing spondylitis
The invention provides methods, uses and compositions for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The invention describes methods and uses for treating ankylosing spondylitis, wherein a TNFα inhibitor, such as a human TNFα antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, is used to reduce signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis in a subject. Also described are methods for determining the efficacy of a TNFα inhibitor for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis in a subject.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Topical dermal anaesthetic
A liquid composition applied transdermally for relief of pain comprising alcohol in an amount by weight of about 57 to about 91 percent; glycerin in an amount by weight of about 1 to about 12 percent; an analgesic agent in an amount by weight of about 2 to about 28 percent, the analgesic agent comprising a derivative of salicylic acid; methylsulfonylmethane in an amount by weight of about 0.02 to 5 percent; and emu oil in an amount by weight of about 0.01 to 3 percent, the liquid composition permeating skin to relieve pain. The composition further comprising, as an additional feature, aloe vera in an amount by weight of at least about 0.05 percent and having an amount by weight of about 0.05 to 4 percent. The composition features transdermal pain relief such that a patient can apply the analgesic agent directly to an area of pain without such side effects as stomach irritation which is normally associated with aspirin. The composition may be sprayed or rolled directly onto the painful area. Because of the unique formula, the composition is safe to vital internal organs, requires no mixing before use, and is shelf stable for marketing purposes.
Owner:VELTRAN LP
Uses and compositions for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis
InactiveUS20100021451A1Treatment safetyImprove fatigueNervous disorderAntipyreticMedicineAnkylosing spondylitis
The invention provides methods, uses and compositions for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The invention describes methods and uses for treating ankylosing spondylitis, wherein a TNFα inhibitor, such as a human TNFα antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, is used to reduce signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis in a subject. Also described are methods for determining the efficacy of a TNFα inhibitor for treatment of ankylosing spondylitis in a subject.
Owner:WONG ROBERT L
Devices and methods for facilitating fluid transport
ActiveUS20070078358A1Easy to transportShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluid transportEngineering
Arrangements are provided including a base having a bore disposed therein extending from a first surface of the base through a second surface of the base, a fluid transport tube having a first end, a second end opposite the first end, and a lumen having an inner diameter, at least the second end of the tube being received within the bore of the base, and at least one fluid transport enhancing groove having at least a first section disposed in the second surface of the base and in fluid communication with the bore.
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for stabilization of bone structures
InactiveUS7935134B2Relieve stressHigh degreeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBone structuresSmall incision
A dynamic bone stabilization system is provided. The system may be placed through small incisions and tubes. The system provides systems and methods of treating the spine, which eliminate pain and enable spinal motion, which effectively mimics that of a normally functioning spine. Methods are also provided for stabilizing the spine and for implanting the subject systems.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
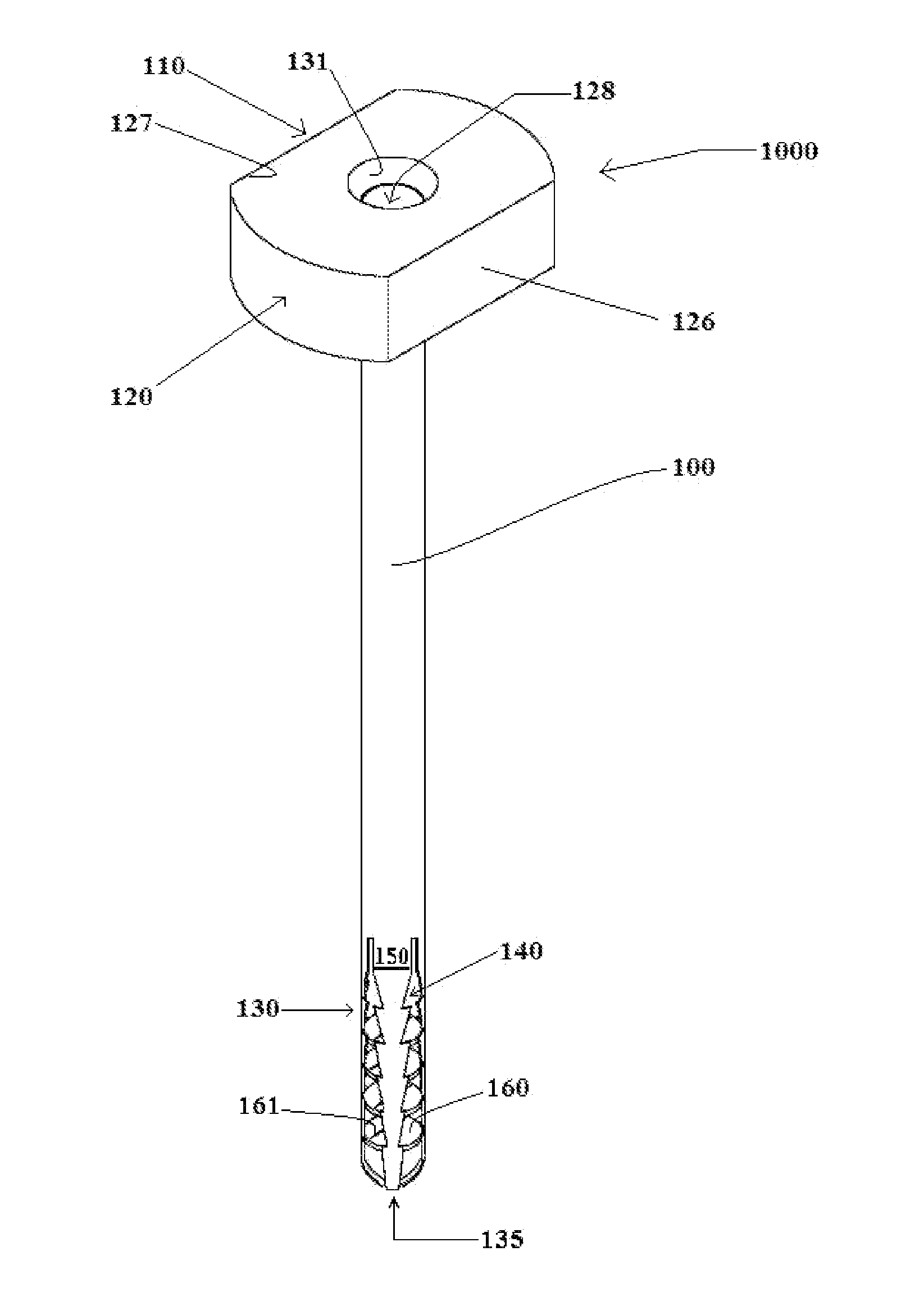
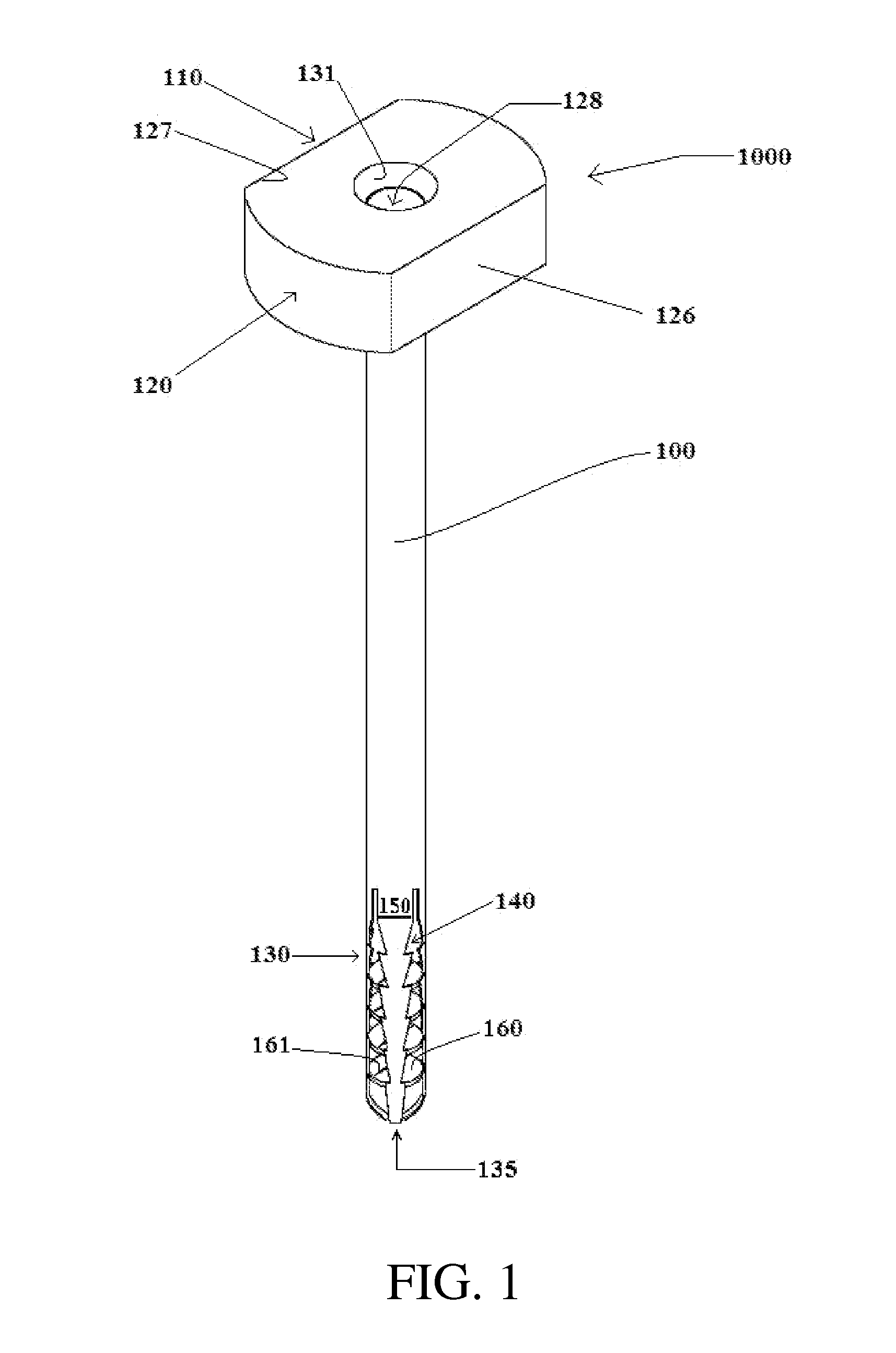
Concealed lancet cartridge for lancing device
InactiveUS20050033340A1User anxiety can be greatly diminishedIncrease painCatheterSensorsEngineeringLance device
A method and apparatus for reducing user anxiety in the taking of a sample of blood. The apparatus comprises a lancing device that includes a housing and a disposable cartridge. The disposable cartridge is replaceably installed in the housing and includes a plurality of lancets within an outer shell which is effective for keeping the lancets hidden from view during loading and unloading of the disposable cartridge to and from the housing and during use of the lancing device.
Owner:FACET TECH LLC
Microneedle array device and its fabrication method
InactiveUS20060015061A1Simple processLow costSurgeryMicroneedlesElectroplatingBiomedical engineering
A microneedle array device and its fabrication method are provided. The microneedle array device comprises a supporting pad and plural of microneedles. Each microneedle has a top portion with a via thereon, thereby the microfluid may flow in or out. The intersection between the top portion and the inner tube of a microneedle forms a convex needle structure, and is almost perpendicular to the upper surface. For each microneedle, a hollow closed tube is formed between the top portion and the supporting pad. The fabrication method uses the substrates with high transmittance and plural of convex area thereon as the upper and lower caps, and applies a photolithography process to fabricate a microneedle array mold. It then sputters or electroplates metal material on the mold. The microneedle array is formed after having taken off the mold. It is a simple fabrication process.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Synthetic traveling wave transcutaneous electrical stimulation device
InactiveUS20060190057A1Increase painImproved discomfort reliefElectrotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationDisplay device
A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device for treating a user's lower back pain or discomfort is provided. The inventive device comprises a stimulation pad with an array of electrodes therein. A controller communicates with the electrodes to energize / de-energize them in a patterned, sequential manner. The patterned actuation of the electrodes in a sequential fashion provides electrical impulses to the patient's skin, simulating a transverse wave motion. The transverse wave motion simulation provides the user with the effect of the electrical stimulation combined with the mechanical tissue stimulation received in traditional massage therapy, resulting in improved pain and discomfort relief. The device may use programs stored in the controller. Alternatively, the user may manually actuate one or more electrodes as well as manually move the electrode actuation to concentrate on a specific lower back region using an electrostatic touch pad or the equivalent. The user may also use voice commands to access the stored programs, move the electrode stimulation region, change the electrode actuation intensity and / or dwell time. The device may store the user's manually-generated routines for repeating when desired. A visual display may provide feedback to the user regarding the electrode actuation position and pattern.
Owner:REESE EDWARD W
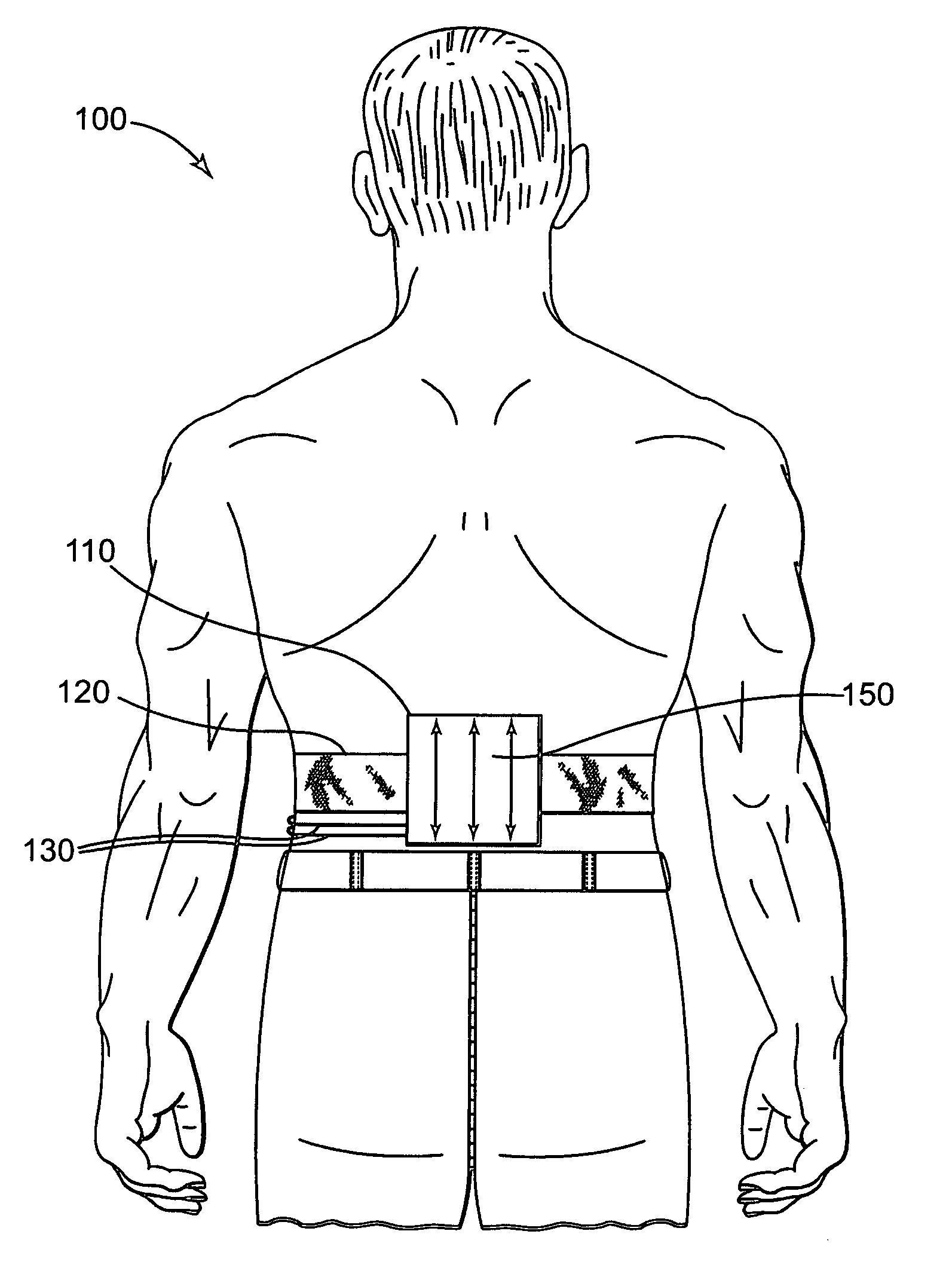
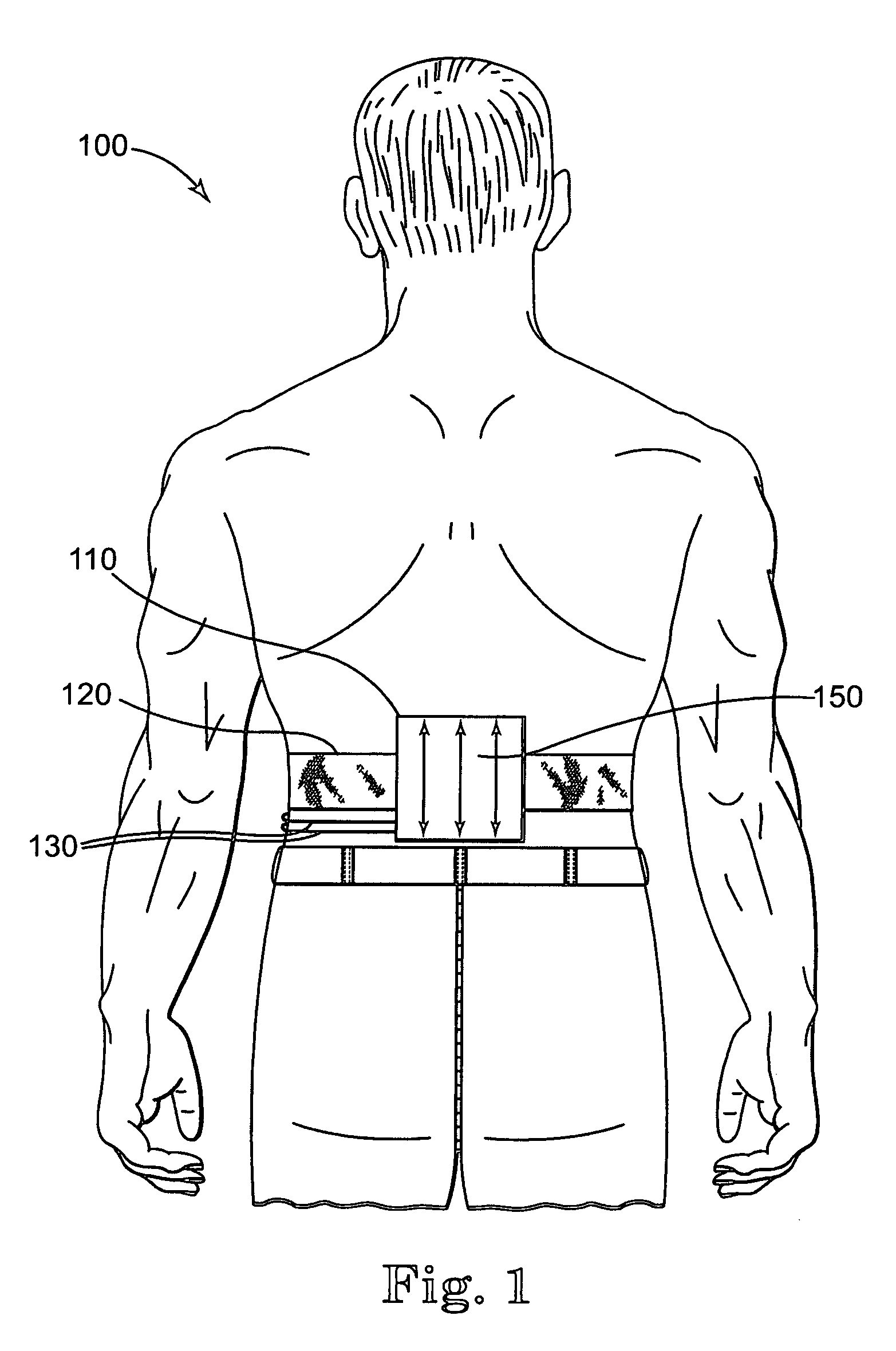
Pain Management Device and System
InactiveUS20130204169A1Improved pain managementImproves wound healingElectrotherapyPneumatic massageElectricityElectrical connection
A vibration device for providing a vibration sensation to a user, the device including: a base; a vibrating element; a power source; and, an actuation mechanism configured to facilitate an electrical connection between the power source and vibrating element, thereby causing the vibrating element to vibrate. A system for providing a vibrating sensation to a user for pain management and a method of manufacturing a vibration device for providing a vibrating sensation to a user are also disclosed.
Owner:ENDETEK
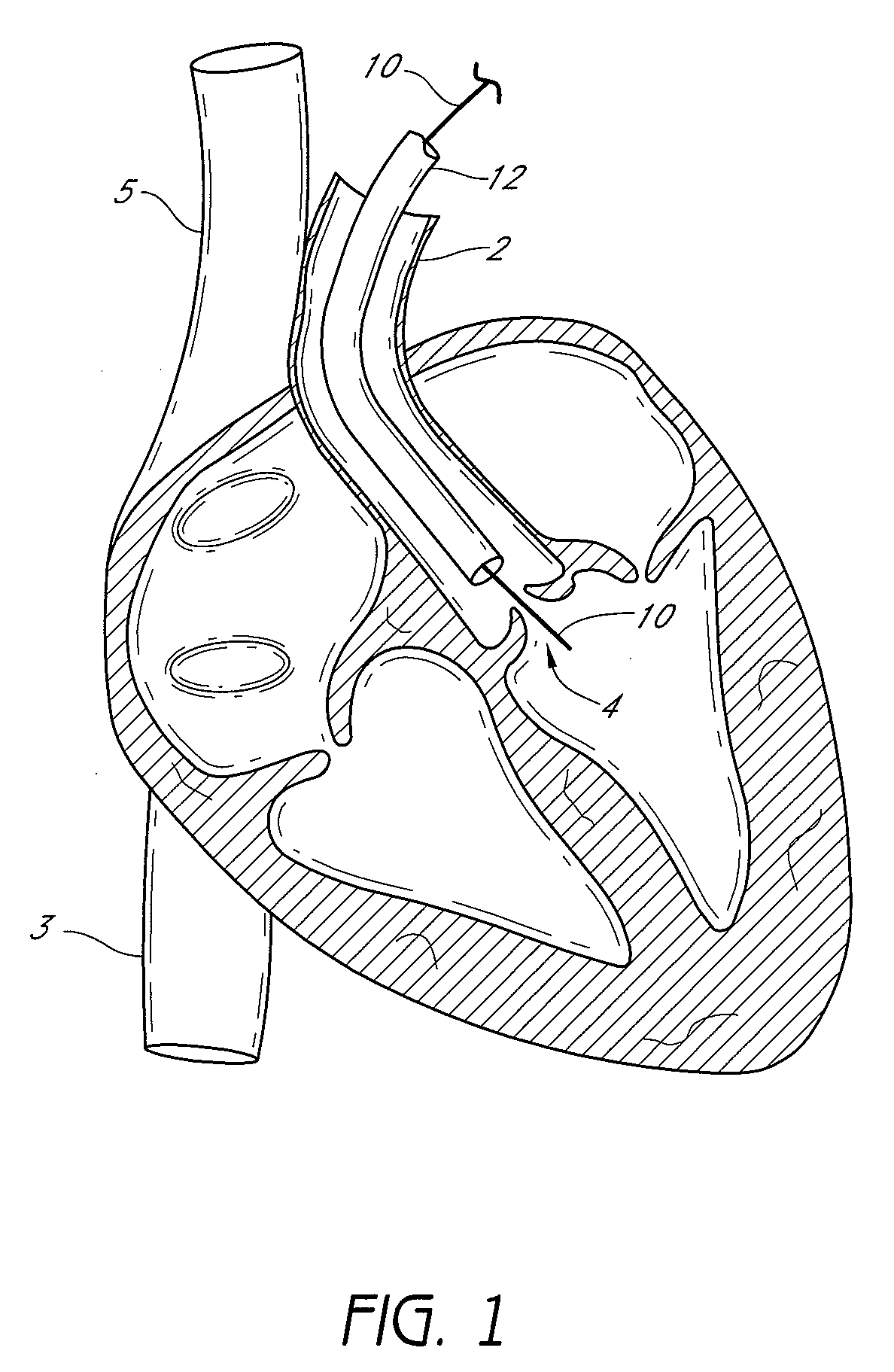
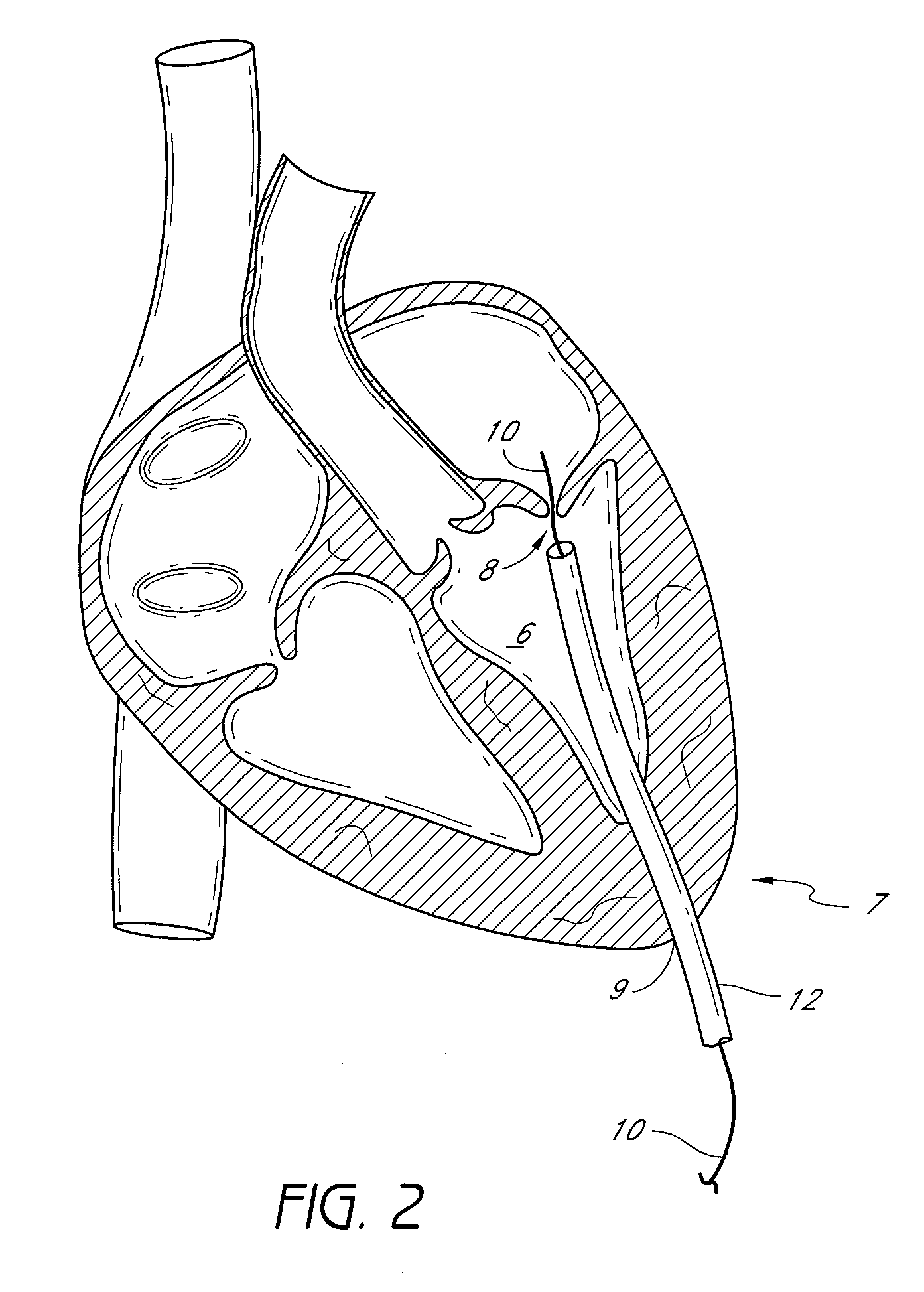
Suturing devices and methods for suturing an anatomic valve
ActiveUS20100030242A1Promote recoveryIncrease painSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgeryAnatomic valve
Owner:PANDORA SELECT PARTNERS +6
Minimally invasive apparatus and method for cleaning endoscope lenses
InactiveUS20140215736A1Time-consume and cumbersomeKeep sizeHollow article cleaningEndoscopesEndoscopeBiomedical engineering
The disposable apparatus for cleaning a distal lens of an endoscope comprises a hollow tube having an open proximal end and an openable distal end and is sized and configured to receive an endoscope therethrough, the apparatus including a plurality of lens cleaning members disposed across an inner diameter of the hollow tube, the cleaning members each including a slit through which the distal lens passes with the lint-free material of the cleaning members wiping across the lens as it passes therethrough.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device and method for obtaining body fluid
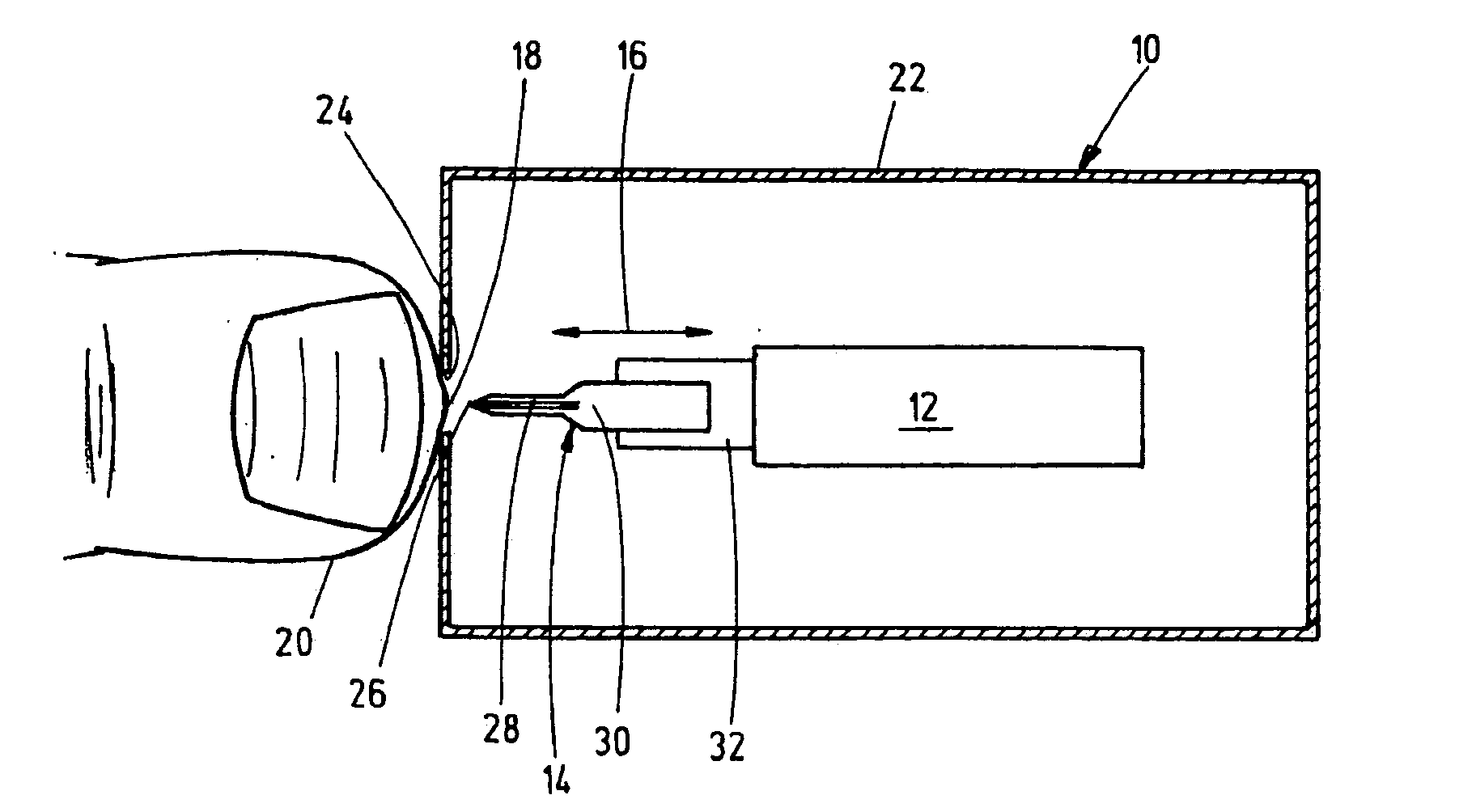
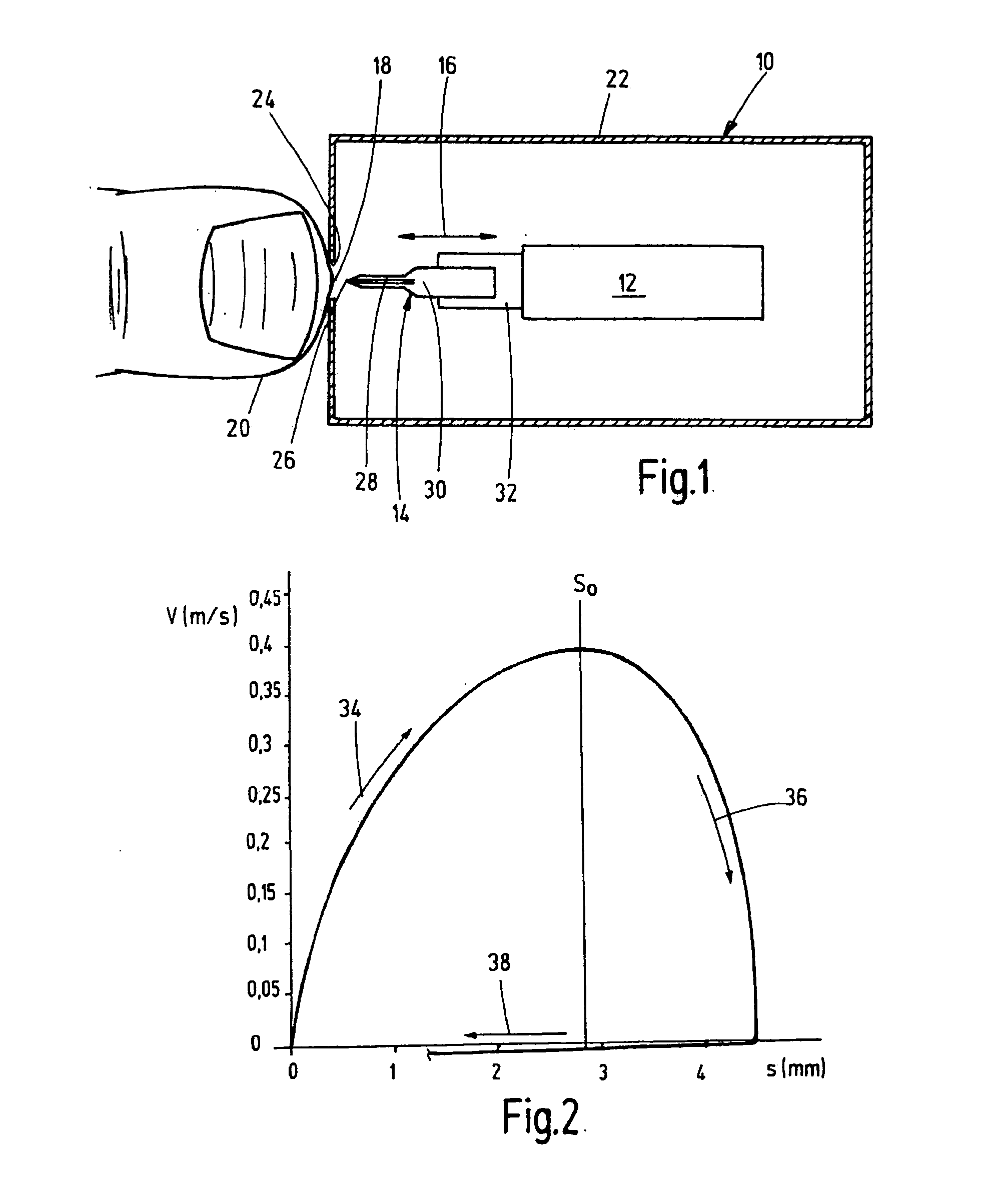
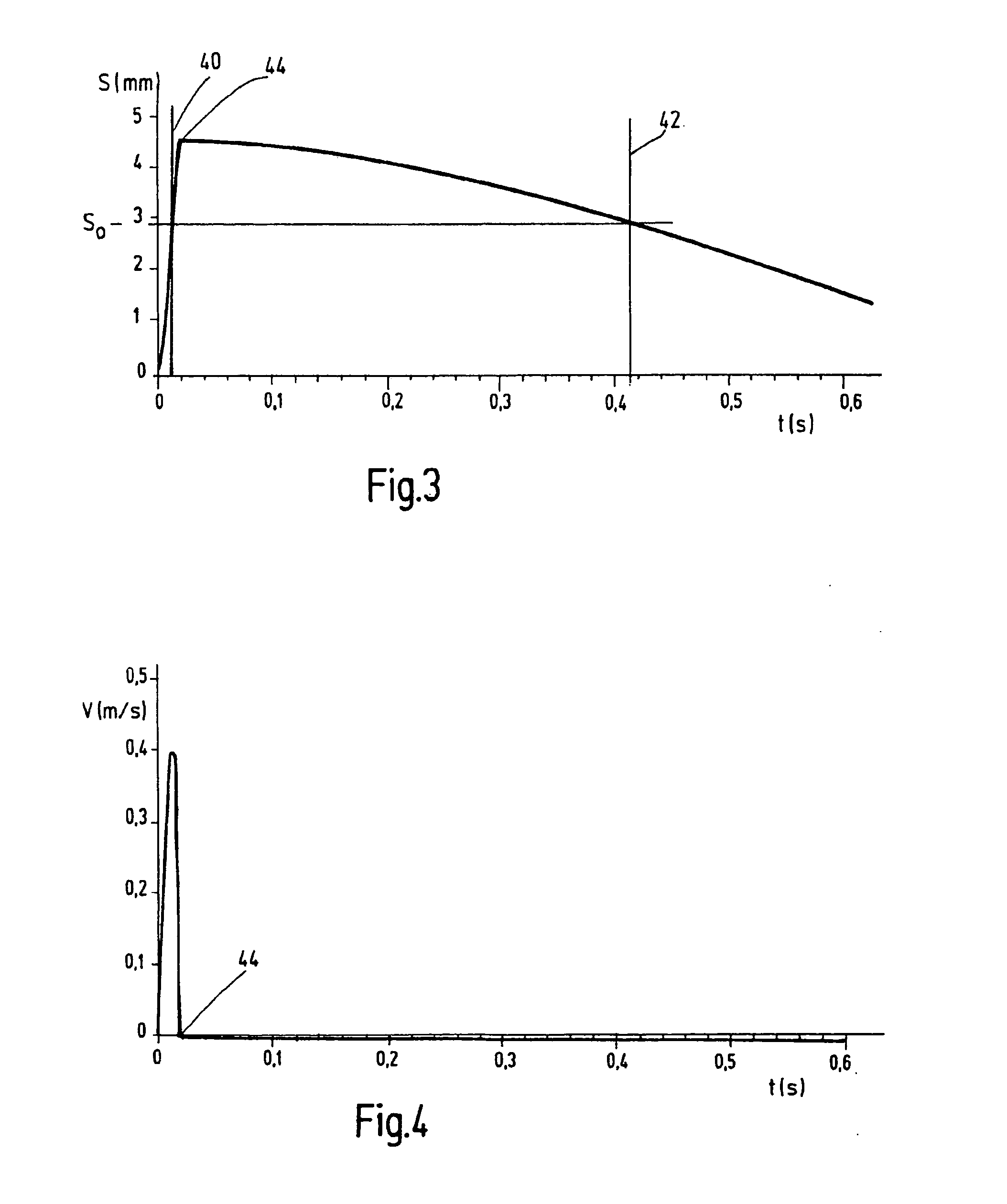
ActiveUS20090024059A1Increased pain sensationSlow speedCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringBody regionBiomedical engineering
A device is disclosed for obtaining body fluid, in particular blood, comprising a lancing element having a tip for puncturing the skin of a body part and an actuator coupled with the lancing element for a forward and backward movement of the lancing element, where the lancing element can be inserted into the skin up to an optionally adjustable puncture position. The actuator is adapted to drive the lancing element forwardly to a penetration speed of at most 0.7 m / s when the lancing element penetrates the skin.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Methods useful for the treatment of pain, arthritic conditions or inflammation associated with a chronic condition
InactiveUS20090298862A1Reduce pain intensityIncrease painBiocideNervous disorderArthritisTreatment pain
Methods, including those for administering novel pharmaceutical compositions, dosage forms containing an opioid active pharmaceutical ingredient, are useful for treating pain, arthritic conditions and / or inflammation associated with a chronic condition, including pain from arthritis and inflammation.
Owner:DURECT CORP
Shoe insole for diabetics
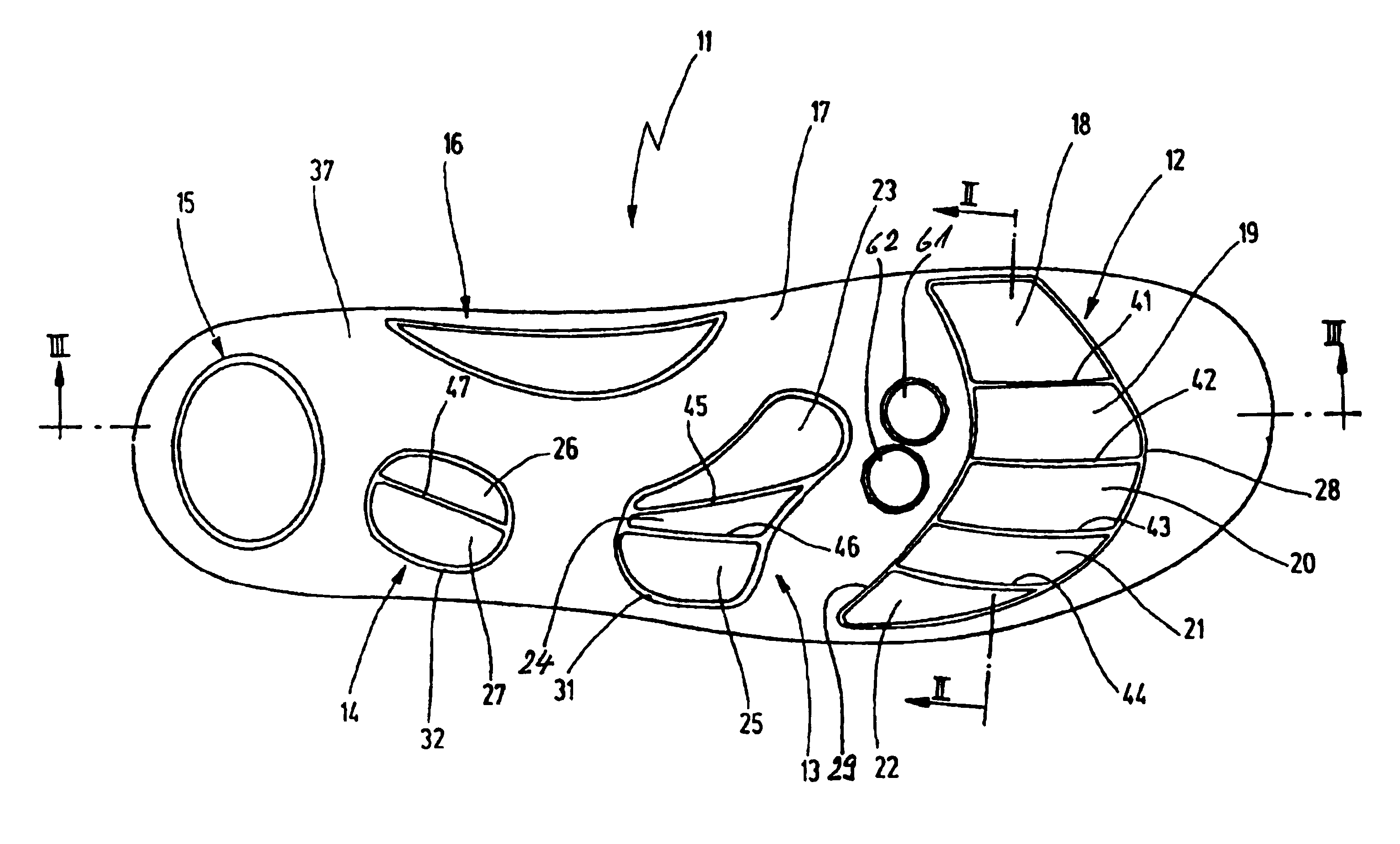
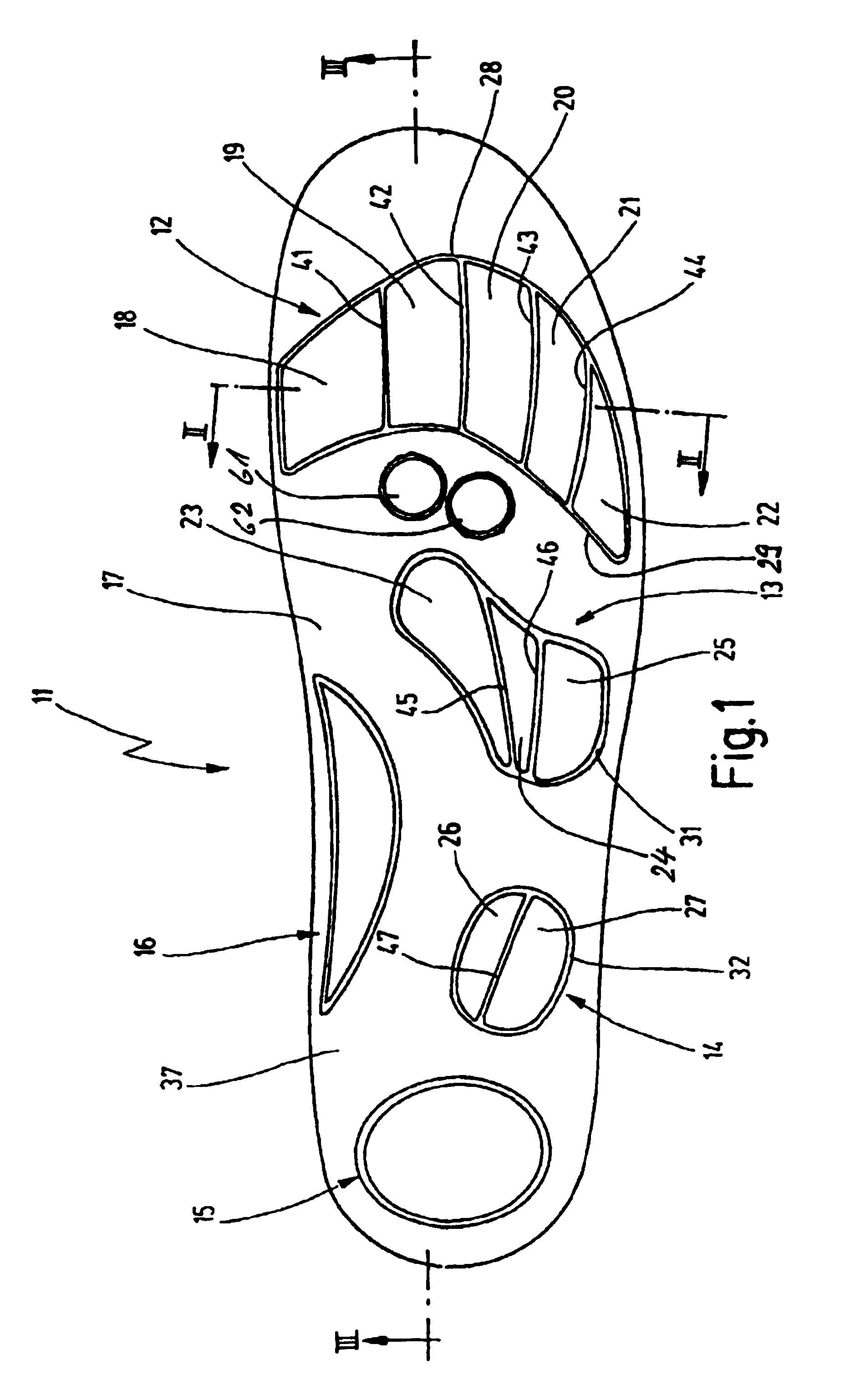
A shoe insole (111) for diabetics is provided with a sole base body (136), a sole covering layer (137) and with a number of cushion-like layers (112, 113, 114, 115, 116) distributed over the surface of the sole. The cushion-like layers consist of at least one first cushion-like layer (112) in the forefoot joint area, a second cushion-like layer (113) in the midfoot / tarsus transition area, and of a third cushion-like layer (114) in the midfoot / heal transition area. These cushion-like layers serving to assist venous blood draining are each subdivided into individual plateau-like areas (118 to 127) that are adjacent in the transversal direction of the sole surface (117) while being separated from one another. The top side of the cushion-like layers also covered by the sole covering layer (137) is raised relative to the level of the top side of the sole base body (136). The aim of the invention is to provide a shoe insole of the aforementioned type that, while providing a lasting assistance of arterial inflow into the foot or foot sole area, has a continuing positive influence on the foot or foot sole areas endangered by a diabetic metabolic condition. To this end, at least one indentation (161, 162) is provided between the first cushion-like layer (112) in the forefoot joint area and the second cushion-like layer (113) in the midfoot / tarsus transition area. Said indentation serves to relieve the pressure on the midfoot bone capitulum(s) and emanates from the top side of the sole base body (136).
Owner:SEITER HANS
Systems and methods for pain treatment using spinal nerve magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS20170259077A1Improved pain reductionReducing overall treatment requiredElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedicineSpinal nerve
Described are methods, devices, and systems for a novel, easy-to-use treatment for pain that does not involve medication. Methods and devices herein use repetitive magnetic fields that desensitize the spinal nerve, thereby affecting transmission of pain signals from the treatment location to the brain.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Orthosis For Range Of Motion, Muscular And Neurologic Rehabilitation Of The Lower Extremities
InactiveUS20130085420A1Maximize effectivenessPrevent muscle wastingBlood stagnation preventionElectrotherapyNervous systemTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
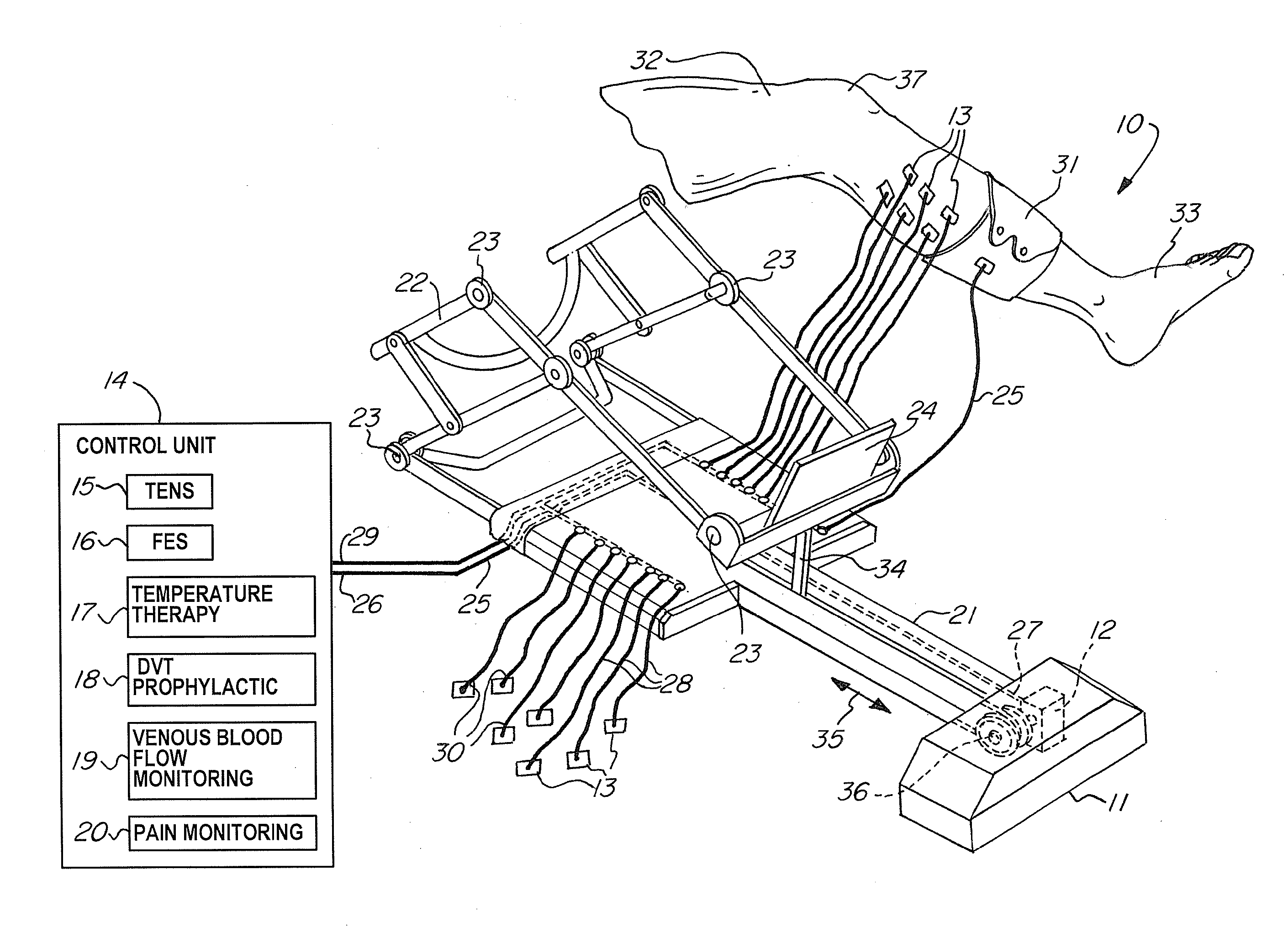
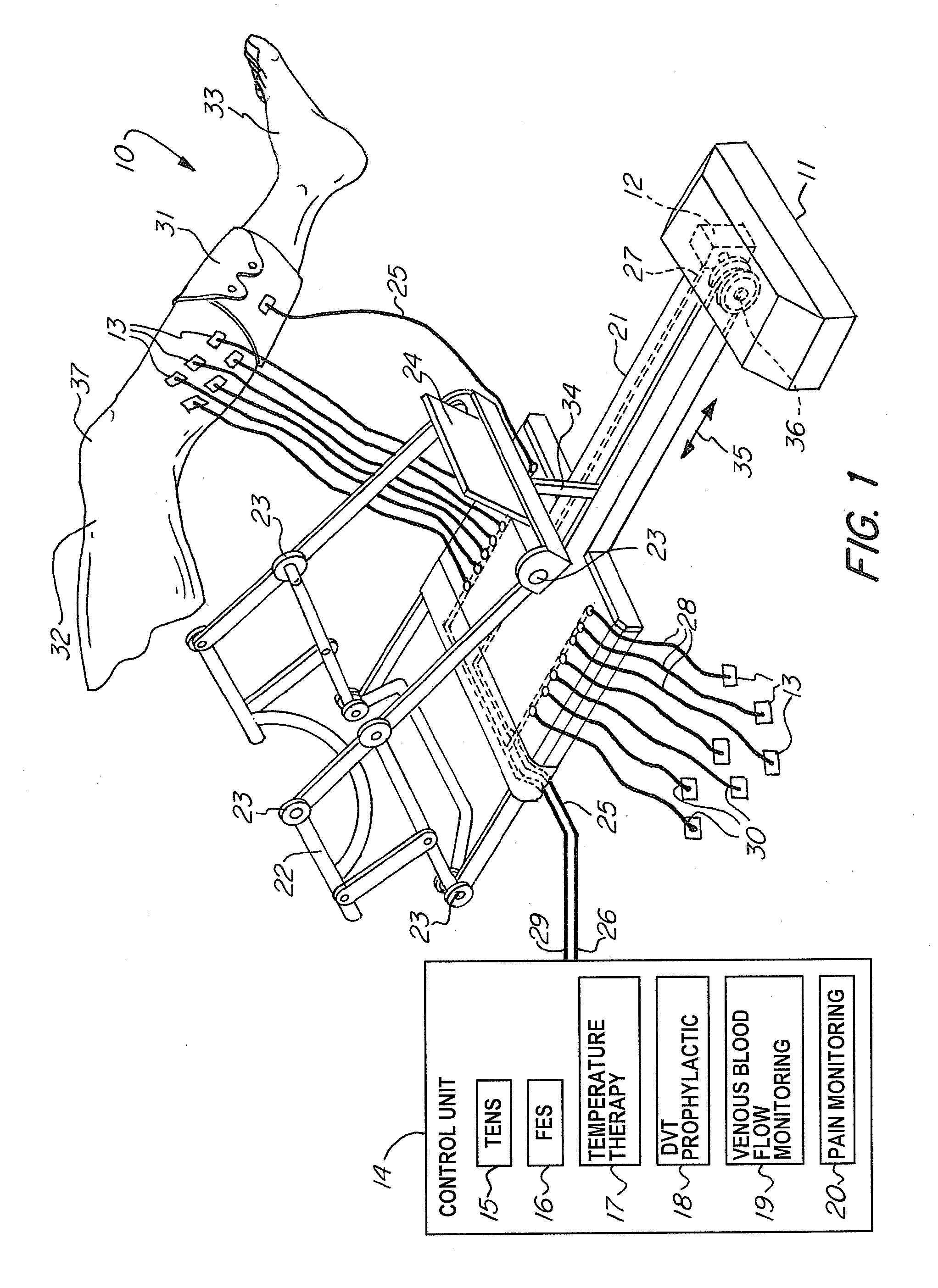
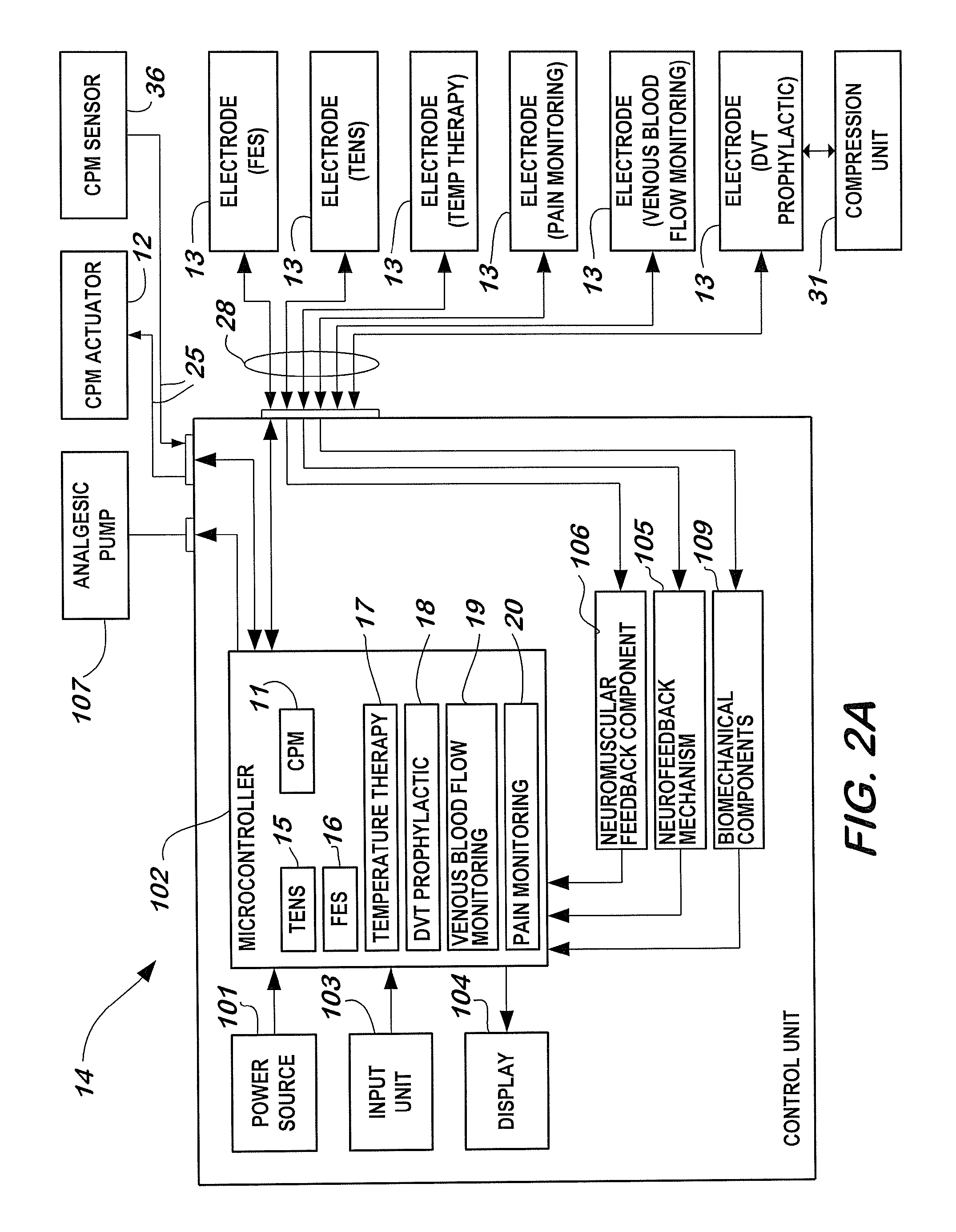
A non-invasive apparatus for rehabilitating a joint, limb, and muscles of a patient recovering from surgery on the joint, includes a continuous passive motion device having at least one support member for supporting the limb, at least one hinge coupled to the at least one support member, and at least one actuator for providing reciprocating motion of the at least one support member about the at least one hinge, a plurality of electrodes transmitting at least four modalities chosen from a group consisting of functional electrical stimulation (FES), transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), temperature therapy stimulation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylactic stimulation, venous blood flow monitoring, and pain monitoring, and a control unit controlling the at least one actuator and the plurality of electrodes according to a coordinated sequence of the reciprocating motion and transmission of the at least four modalities.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
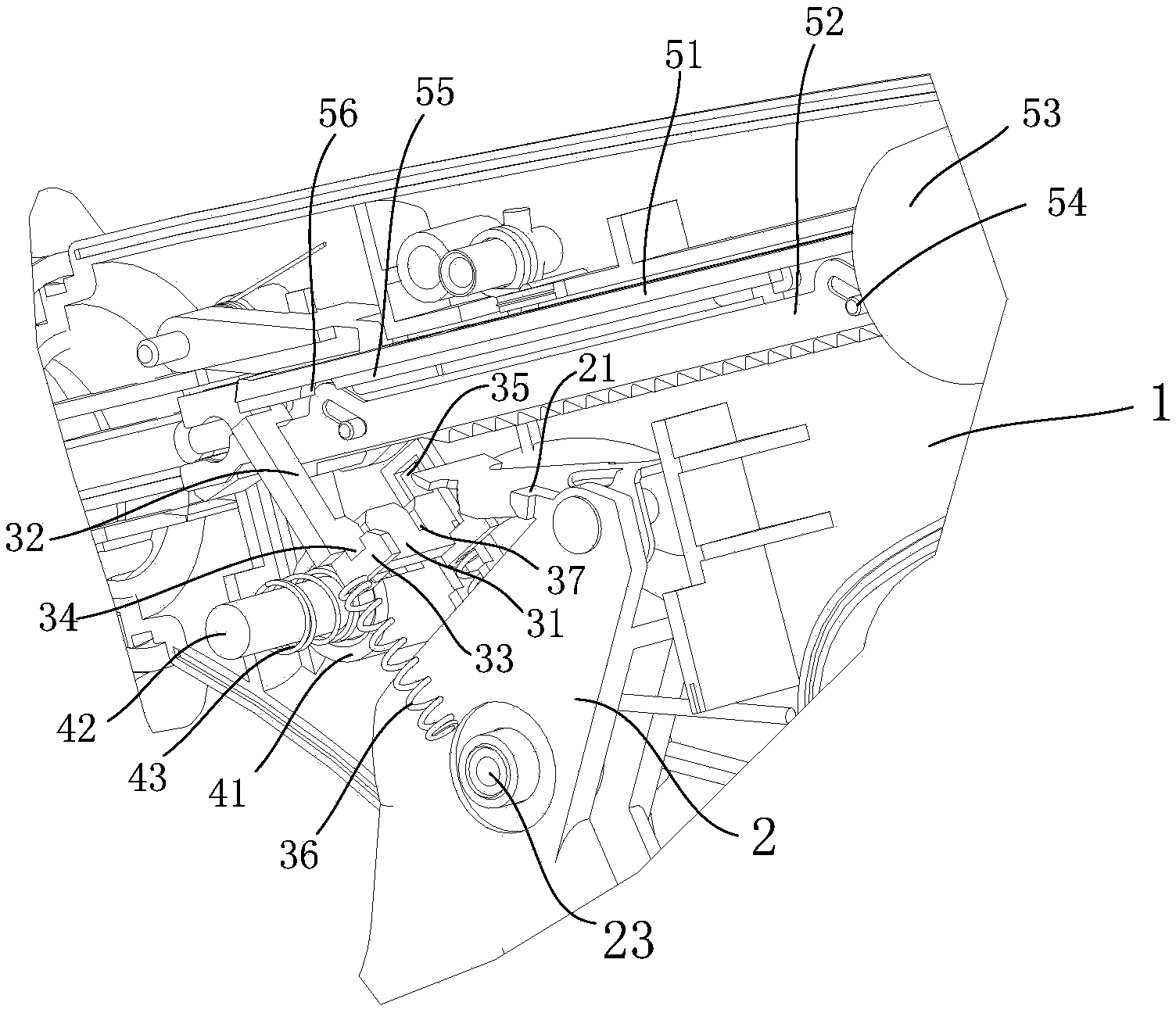
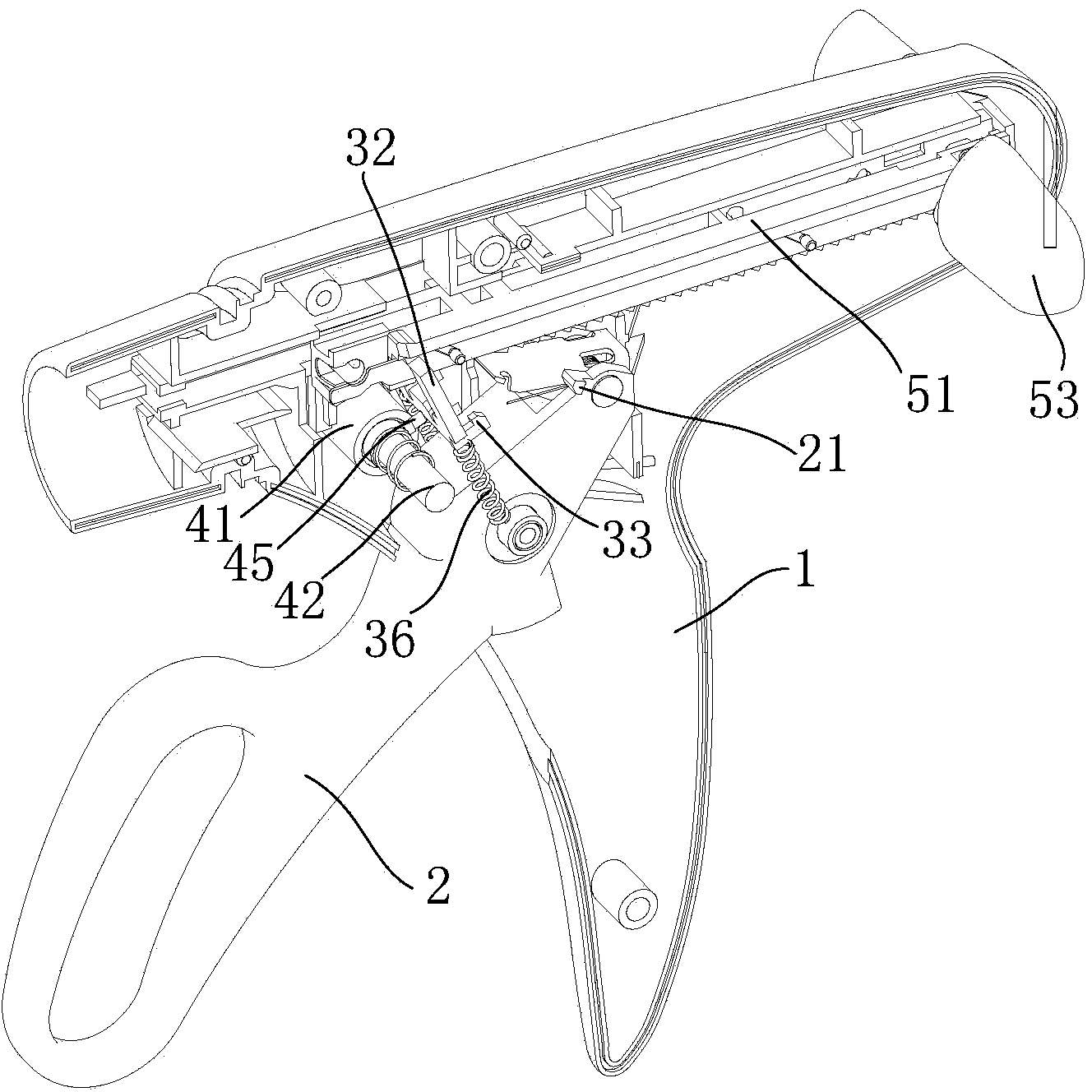
Mistaken-percussion-proof safety mechanism for anastomat and anastomat
The invention provides a mistaken-percussion-proof safety mechanism for an anastomat. The mistaken-percussion-proof safety mechanism for the anastomat comprises a fixed handle and a movable handle, wherein a clamping piece is arranged at the upper part of the movable handle, and a percussion locking mechanism is arranged on the fixed handle at the front side of the movable handle and is matched with the clamping piece; when the movable handle rotates forwards to be closed, the clamping piece is locked by the percussion locking mechanism; an unlocking mechanism for separating the clamping piece from the percussion locking mechanism is also arranged on the fixed handle. The invention also provides an anastomat, which comprises the mistaken-percussion-proof safety mechanism. The movable handle can be locked and cannot automatically reset after being closed for the first time, and the handle is in a closed state, so that the second percussion can be carried out after the handle is unlocked by operating the unlocking mechanism, and thus the failure of operation caused by misjudgment and mistaken percussion of doctors is avoided, and the correctness of operation sequence is ensured; meanwhile, appropriate tissues can be selected to be closed and cut by the doctors through a reset mechanism.
Owner:MICONVEY TECH CO LTD
Injections
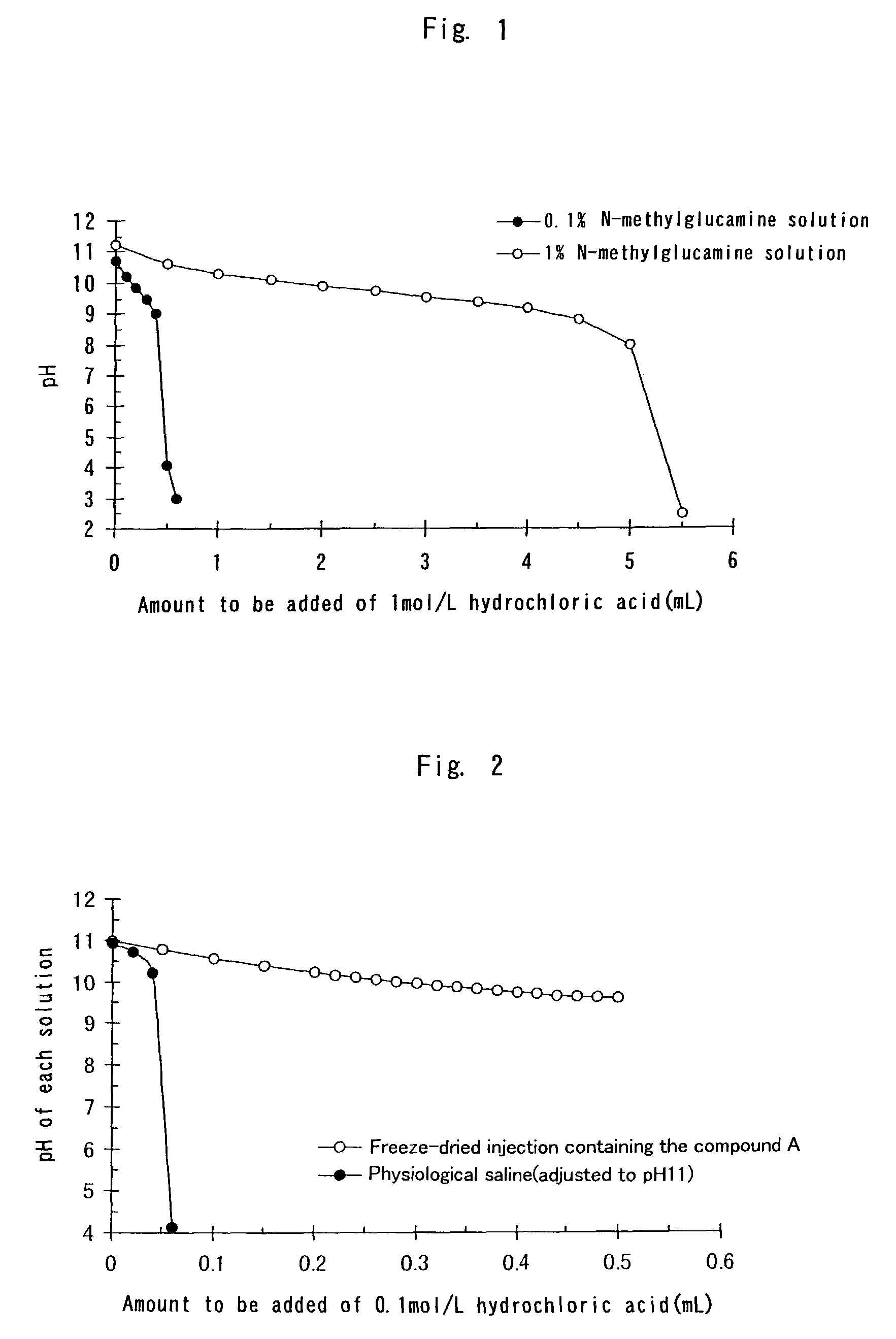
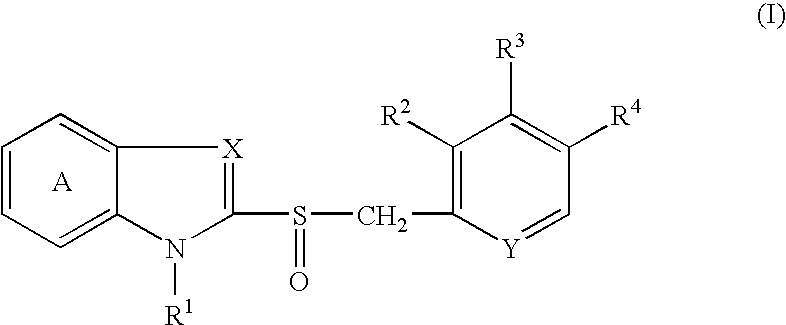
InactiveUS7396841B2Easy to prepareReduce the amount requiredAntibacterial agentsBiocideFreeze-dryingSolvent
An injectable composition comprises a benzimidazole compound having an antiulcer action and a strong alkali (e.g., an alkali metal hydroxide such as sodium hydroxide) in a proportion of about 1 equivalent of the latter relative to 1 mol of the former, and is substantially free from a nonaqueous solvent. The injectable composition may comprise N-methylglucamine, and a saccharide (such as mannitol). The injectable composition may be a freeze-dried preparation. The freeze-dried preparation is dissolvable in or dilutive with a distilled water for injection or an infusion solution without a nonaqueous solvent. The injectable composition is useful as an antiulcer agent.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Formulations of anti-pain agents and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20050256182A1Reduce skin irritationRelieve painBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismSide effectDose sparing
The present invention relates to novel anti-pain formulations and methods of their delivery. Anti-pain agents delivered in accordance with the methods of the invention have an improved clinical utility and therapeutic efficacy relative to other drug delivery methods, including oral, intramuscular and subcutaneous delivery. The methods of the present invention provide benefits and improvements over conventional drug delivery methods including dose sparing, increased drug efficacy, reduced side effects.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Transesophageal echocardiography visual simulation system and method
ActiveCN101916333AGood clinical simulation trainingRealize attitude data collectionCosmonautic condition simulationsSpecial data processing applicationsBiomedical engineeringSonification
The invention discloses a transesophageal echocardiography visual simulation system, comprising an intelligent phantom, a heart ultrasonic image stimulation and acquisition device, a computer connected with the heart ultrasonic image stimulation and acquisition device and a transesophageal ultrasonic probe attitude data acquisition device, wherein, the heart ultrasonic image stimulation and acquisition device is used for stimulating and acquiring heart ultrasonic images, and transmitting the acquired heart ultrasonic images to the computer; when the heat ultrasonic image stimulation and acquisition device acquires the heart ultrasonic images, the transesophageal echocardiography probe attitude data acquisition device and a sensor are used for synchronously acquiring probe attitude data of the heat ultrasonic image stimulation and acquisition device, and transmitting the acquired probe attitude data to the computer; and the computer is used for analyzing, processing and visually displaying the received heart ultrasonic images and the probe attitude data.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV +1
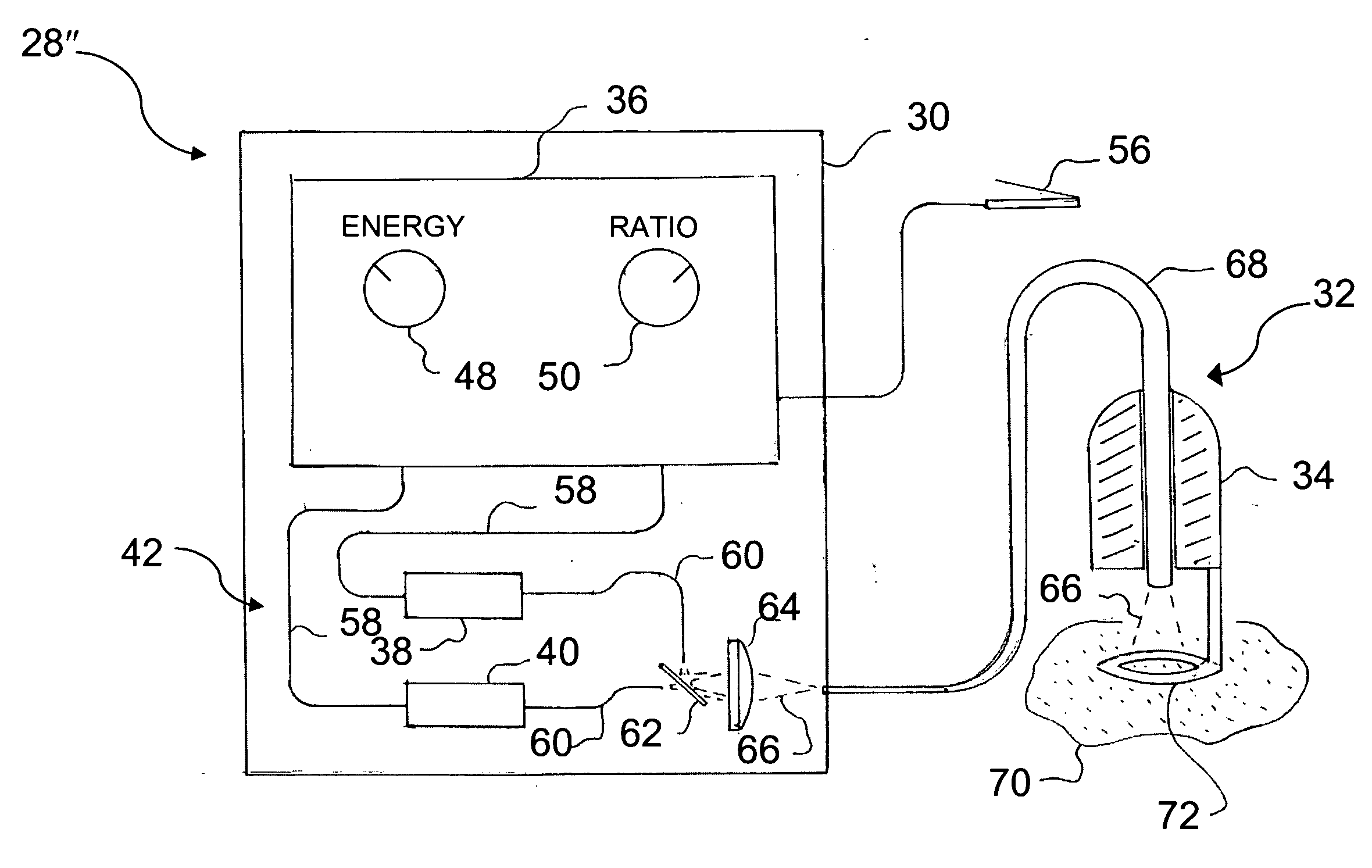
Light beam wavelength mixing for hair removal
InactiveUS20070270785A1Safe and effective methodSafe and effective and apparatusSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyMedicineLight beam
A light based treatment method and apparatus removes unwanted hair from a target region of skin. The treatment method uses multiple wavelength bands of light or radiation. The ratio of the energies of the wavelength bands is selected according to a skin parameter, e.g., skin type, which can be differentiated by the amount of melanin in the skin. The treatment method can provide safe and effective permanent hair removal for any skin type.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
Devices and methods of low frequency magnetic stimulation therapy
InactiveUS20170312536A1Function increaseImprove cognitive functionElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectricityMedicine
Described herein, in certain embodiments, are devices and methods for modulating the electrical activity of a brain in a targeted manner using a weak magnetic field, generally field with a strength of less than about 100 Gauss. The magnetic field is varied over time in a periodic manner, generally with a frequency tuned to specifically affect one of the intrinsic frequencies of the brain, optionally the alpha frequency. The “Low Field Magnetic Stimulation” devices and methods described herein modulate the electrical activity of a brain without requiring medication. Methods and devices described herein gently “tune” the brain and affect mood, focus, and cognition of human subjects.
Owner:NEOSYNC
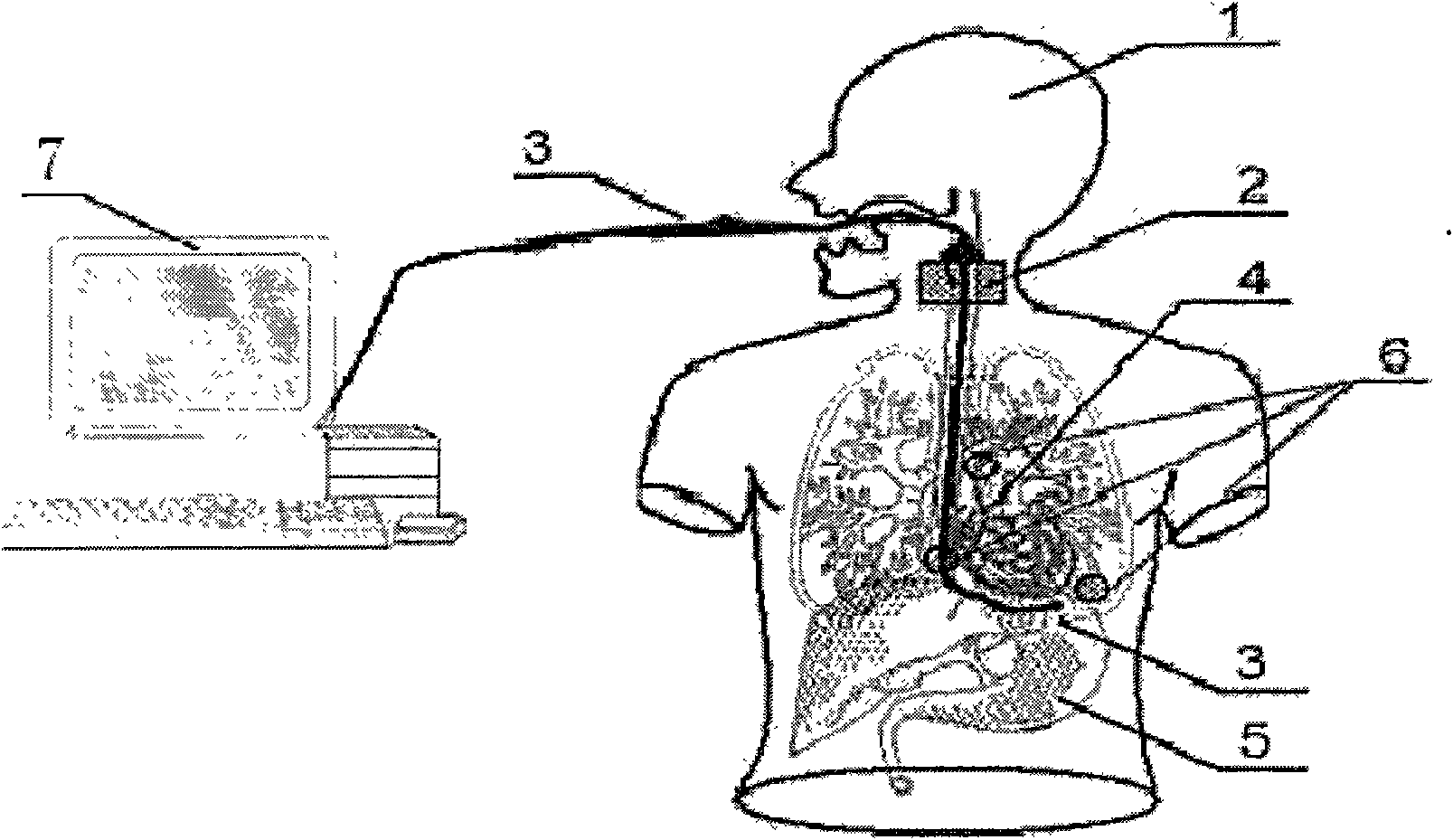
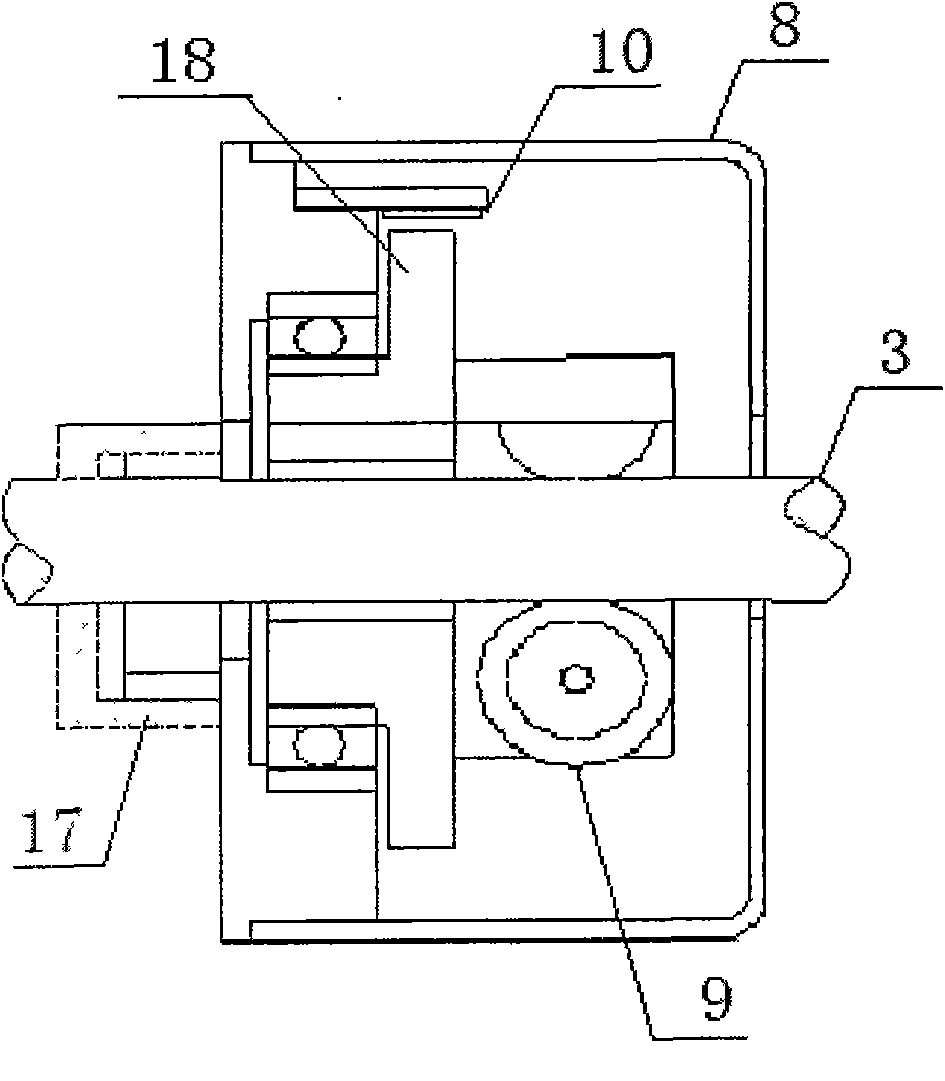
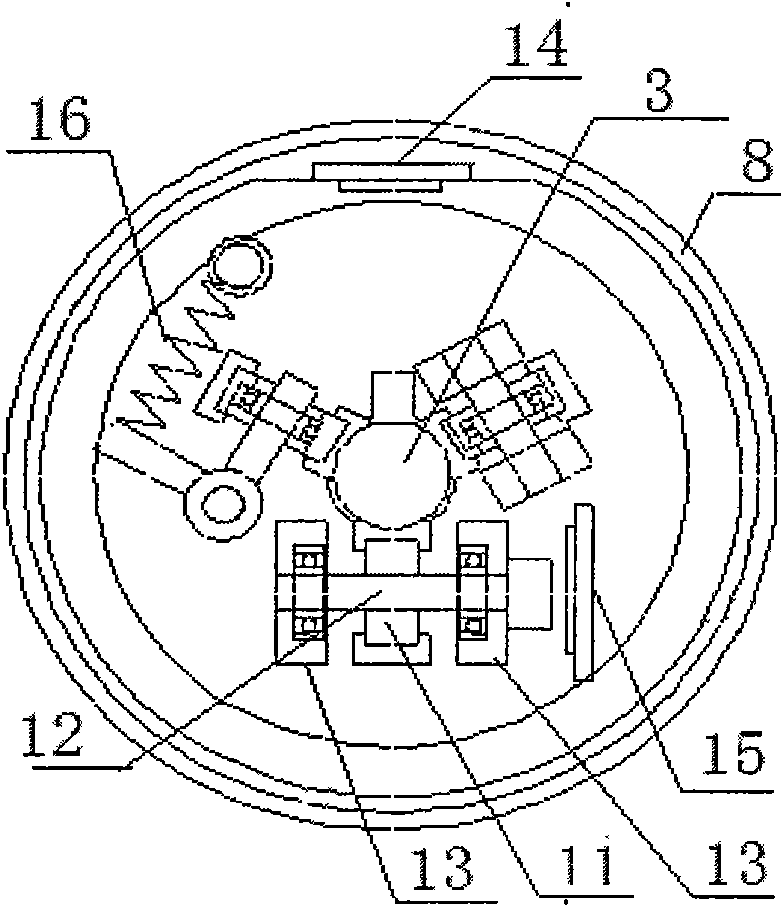
Physiological parameter system
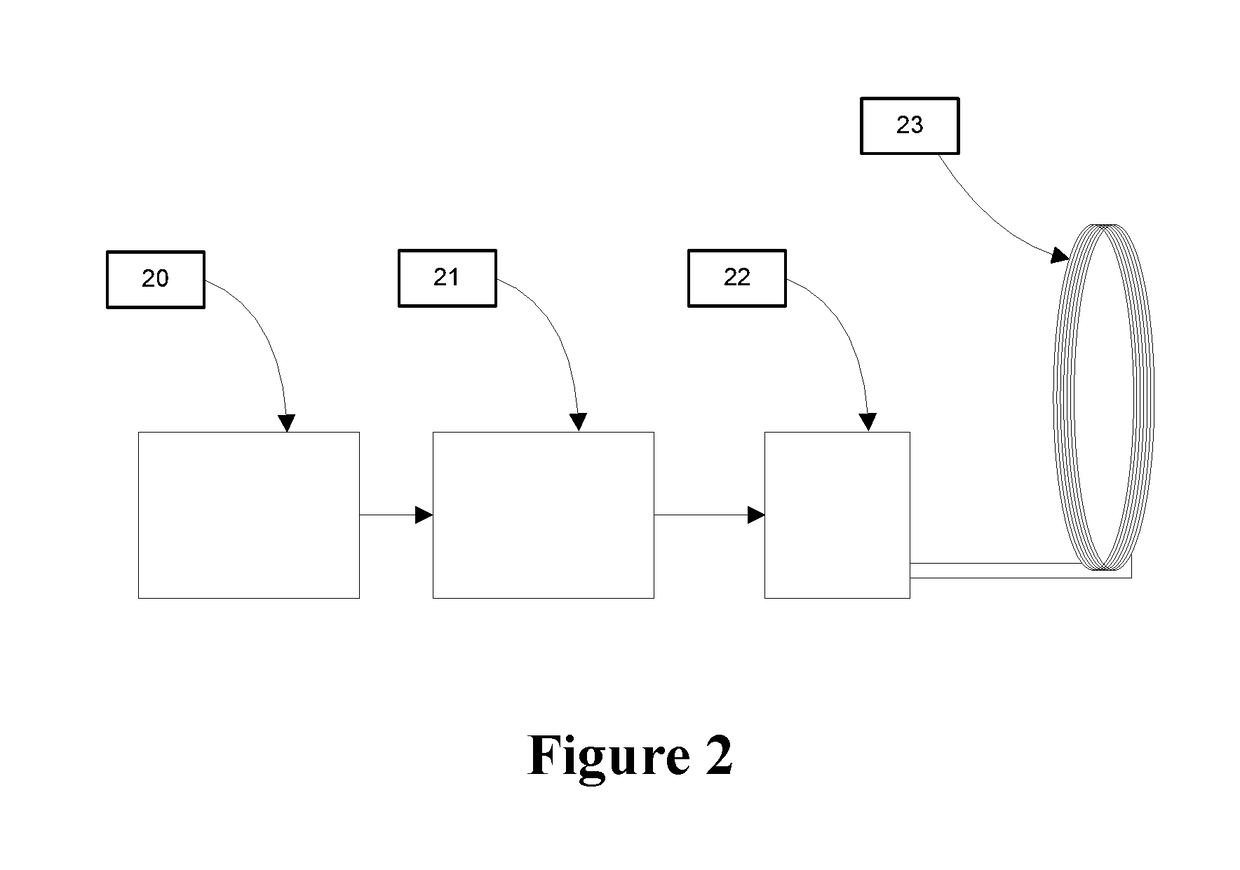
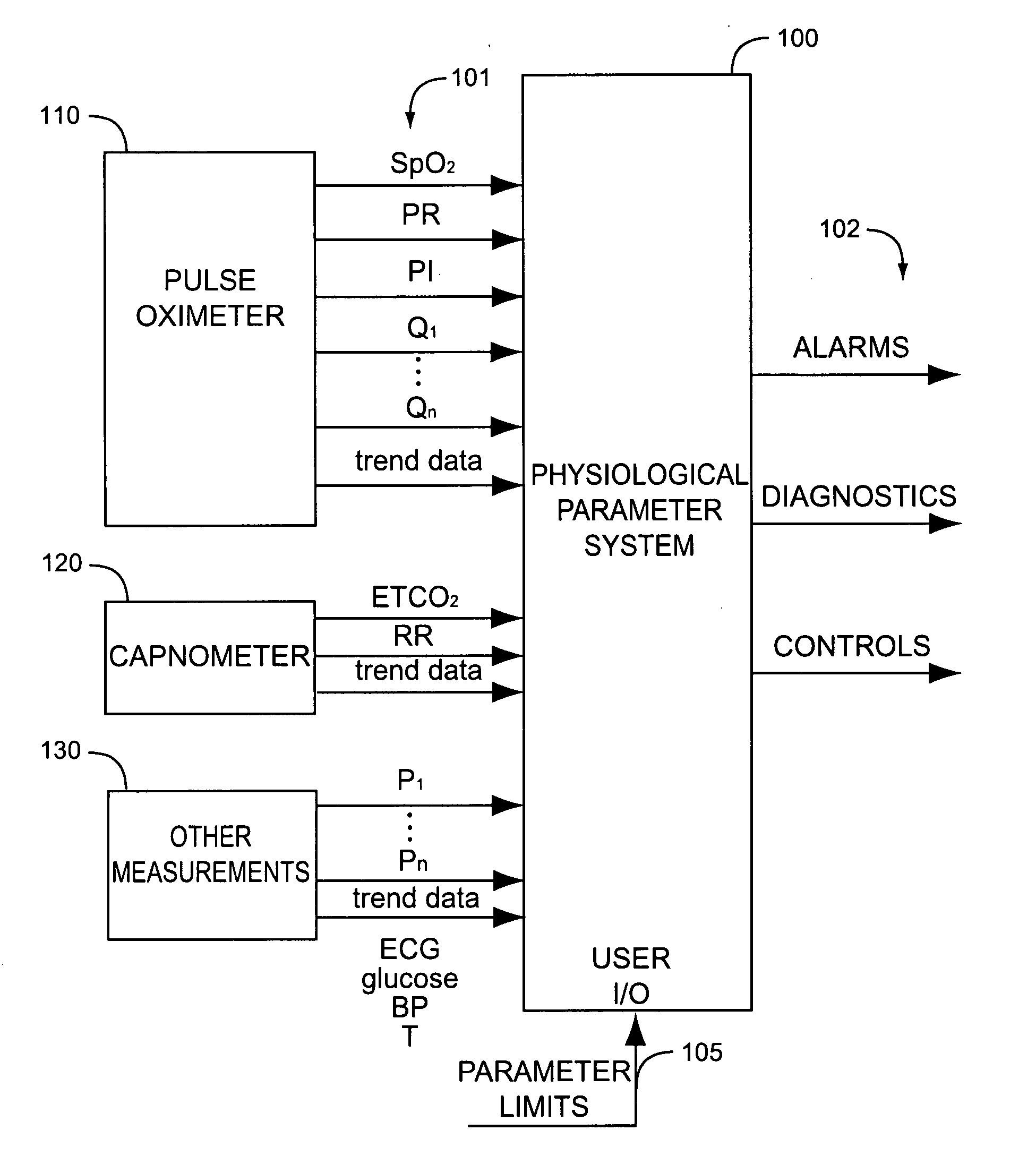
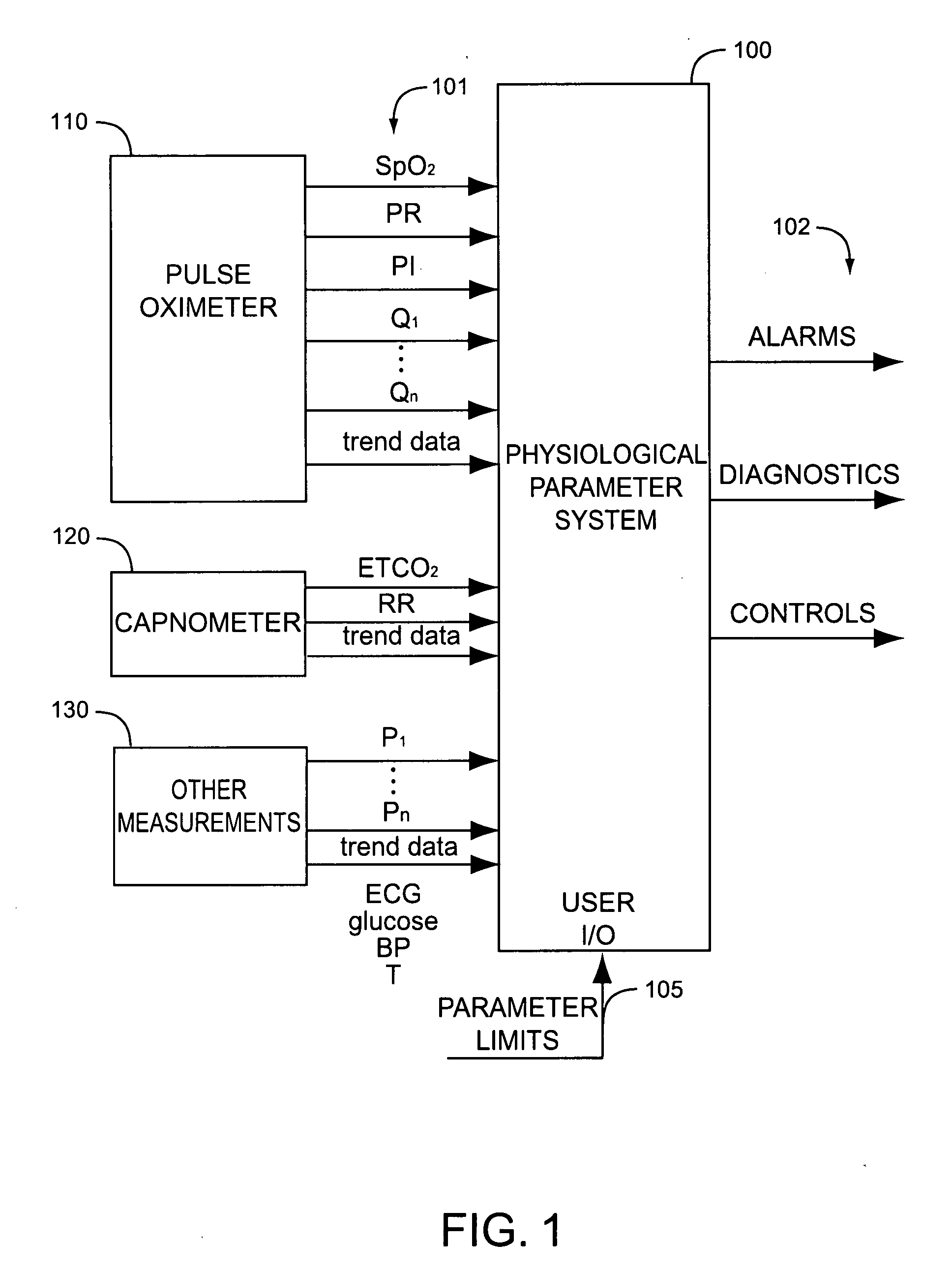
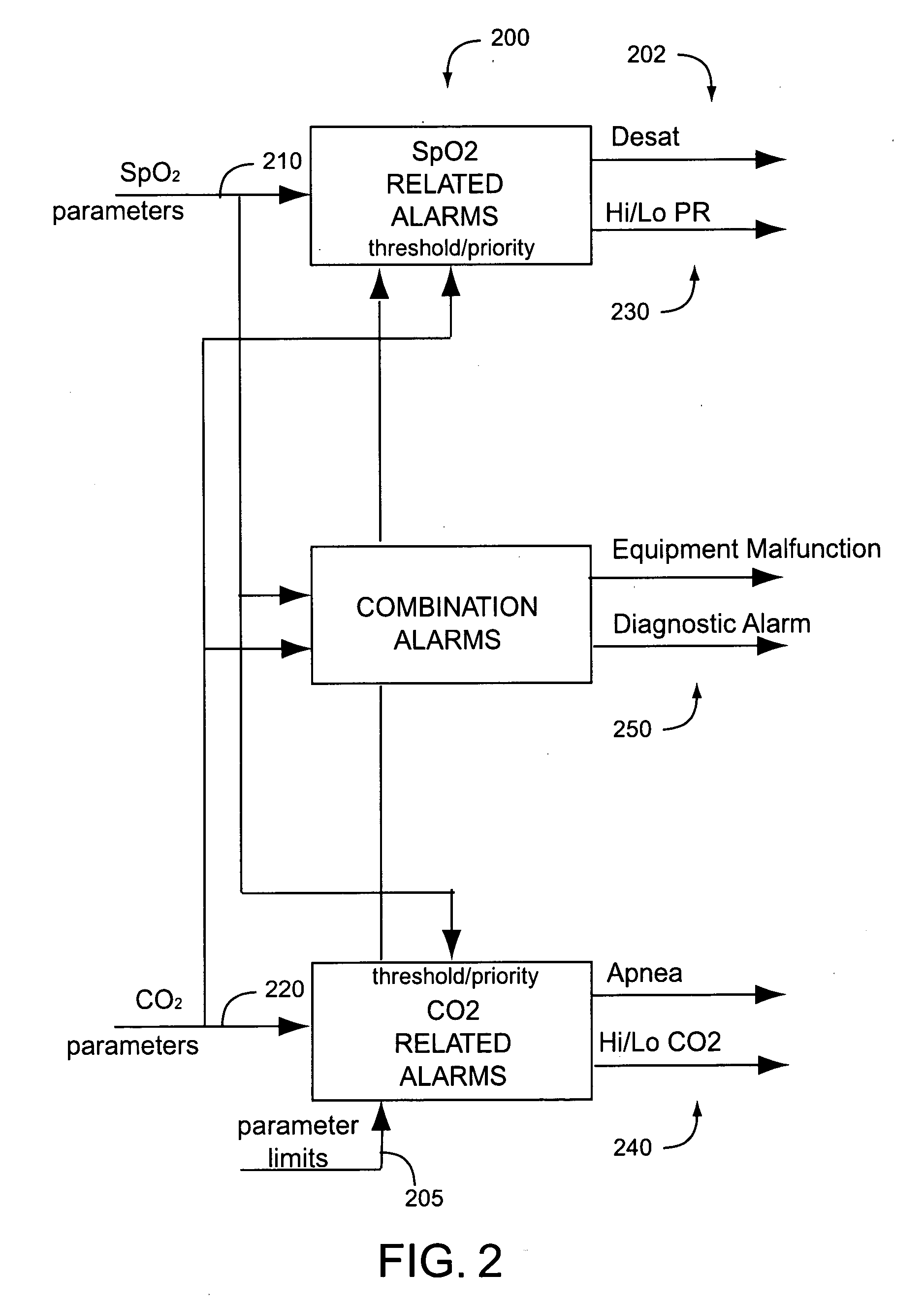
A physiological parameter system has one or more parameter inputs responsive to one or more physiological sensors. The physiological parameter system may also have quality indicators relating to confidence in the parameter inputs. A processor is adapted to combine the parameter inputs, quality indicators and predetermined limits for the parameters inputs and quality indicators so as to generate alarm outputs or control outputs or both.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Spinous process fixation plate and minimally invasive method for placement
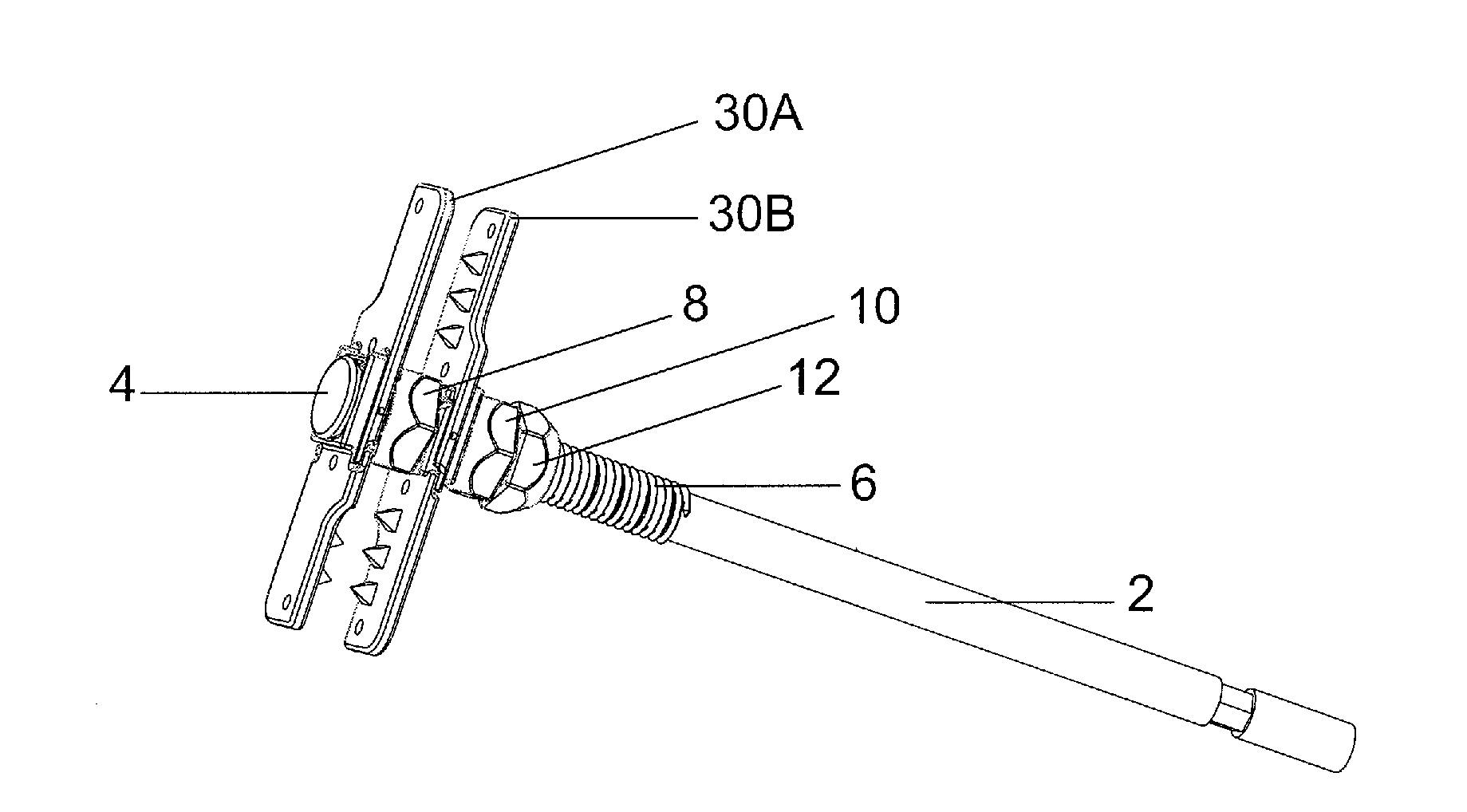
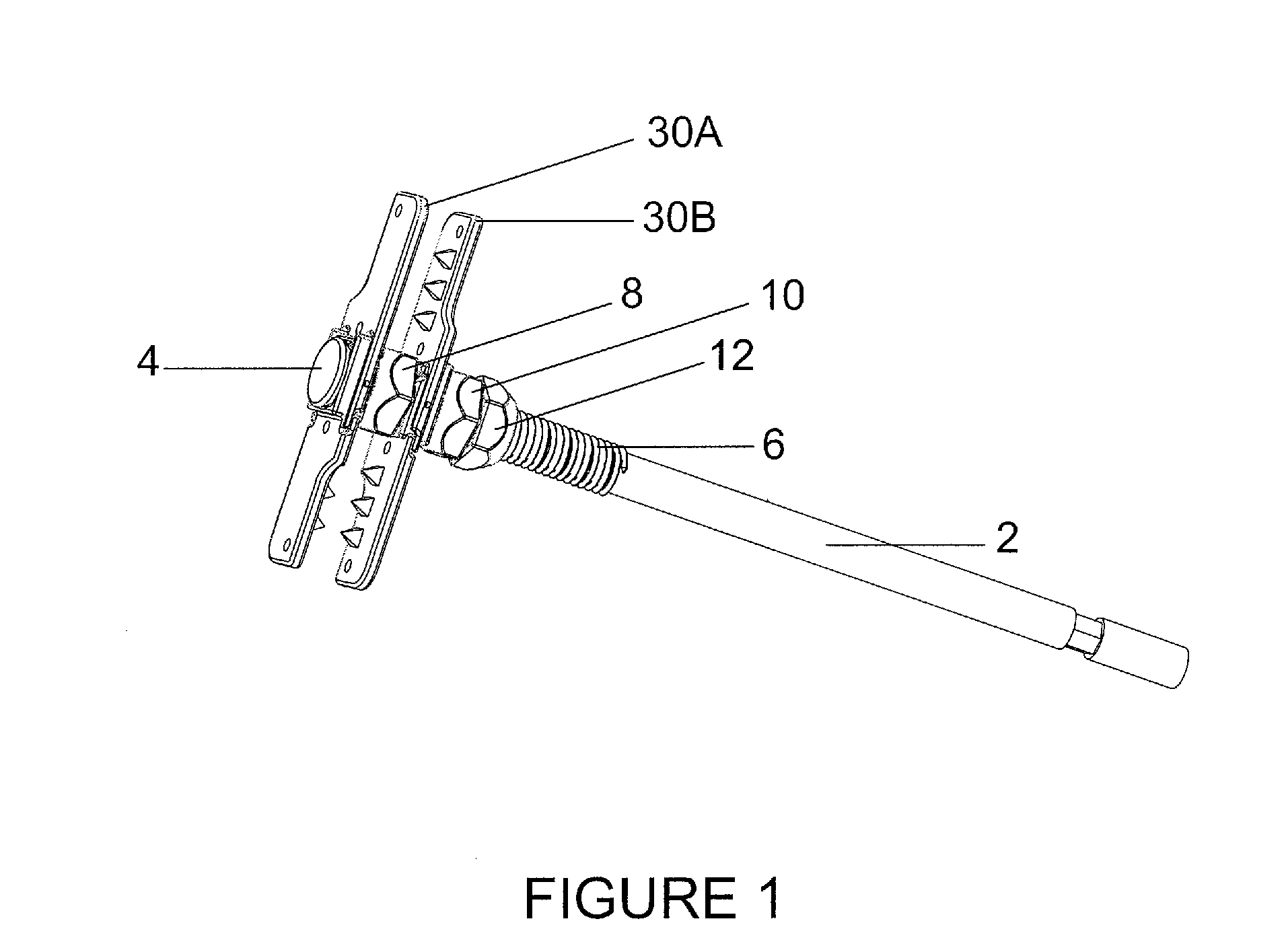
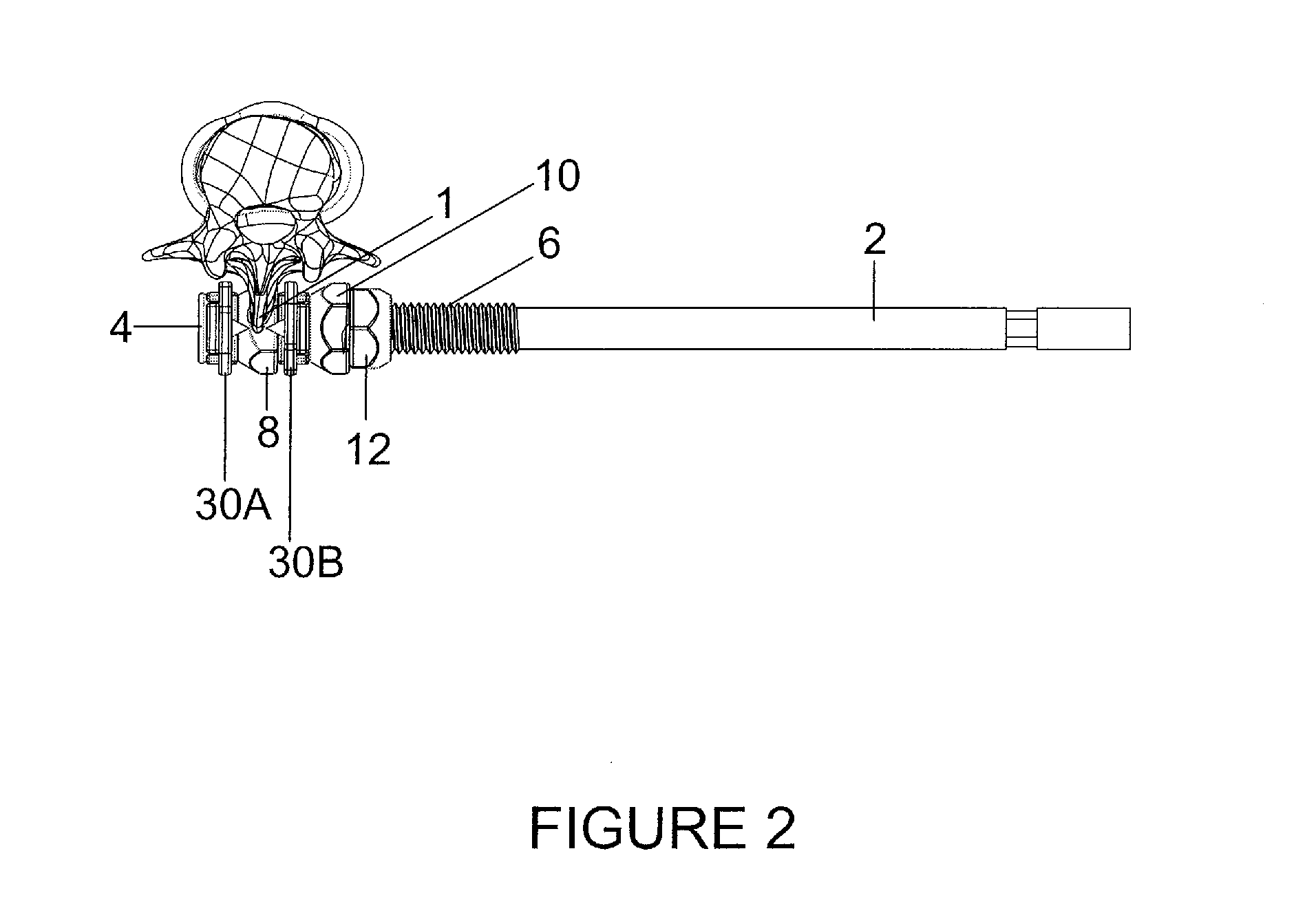
ActiveUS20110087285A1Shorten operation timeShorten the timeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMinimally invasive proceduresEngineering
The invention is directed to a laterally inserted spinous process plating device and a method for installing the device using a minimally invasive procedure. The device includes a partially threaded bolt as well as a contralateral and ipsilateral fixation plates, a deployment nut, a lag nut and a locking nut. Each fixation plate includes a pair of wing portions that are pivotally connected to one another to facilitate installation. The each of the fixation plates includes anchoring elements.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
Medicament for treating allergic rhinitis
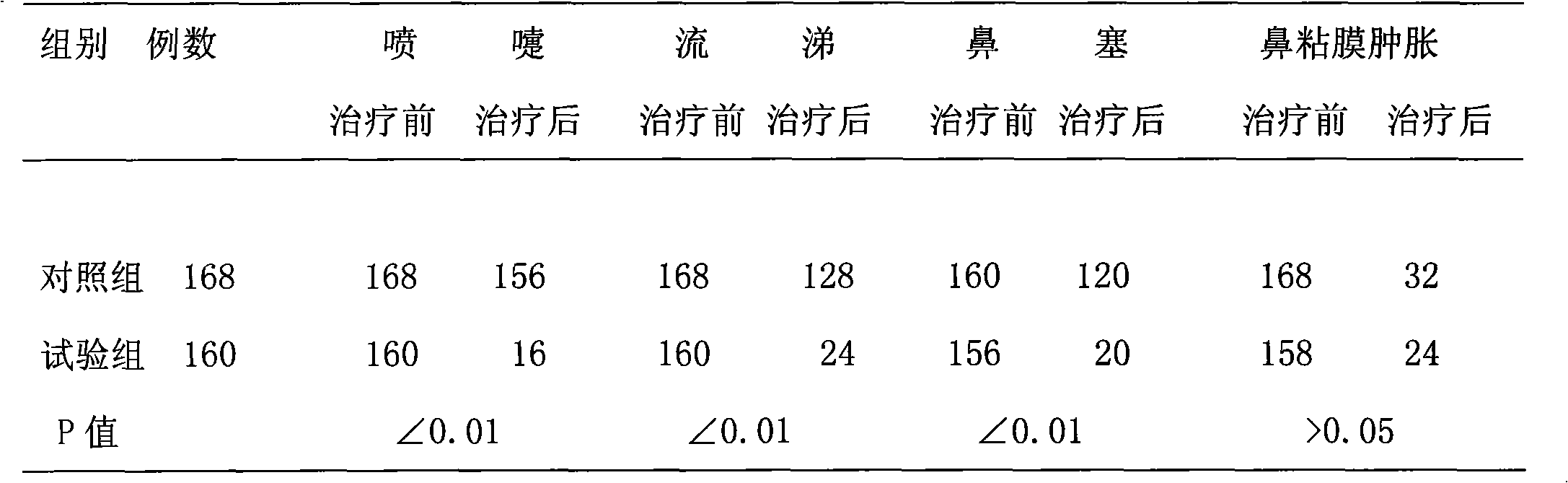
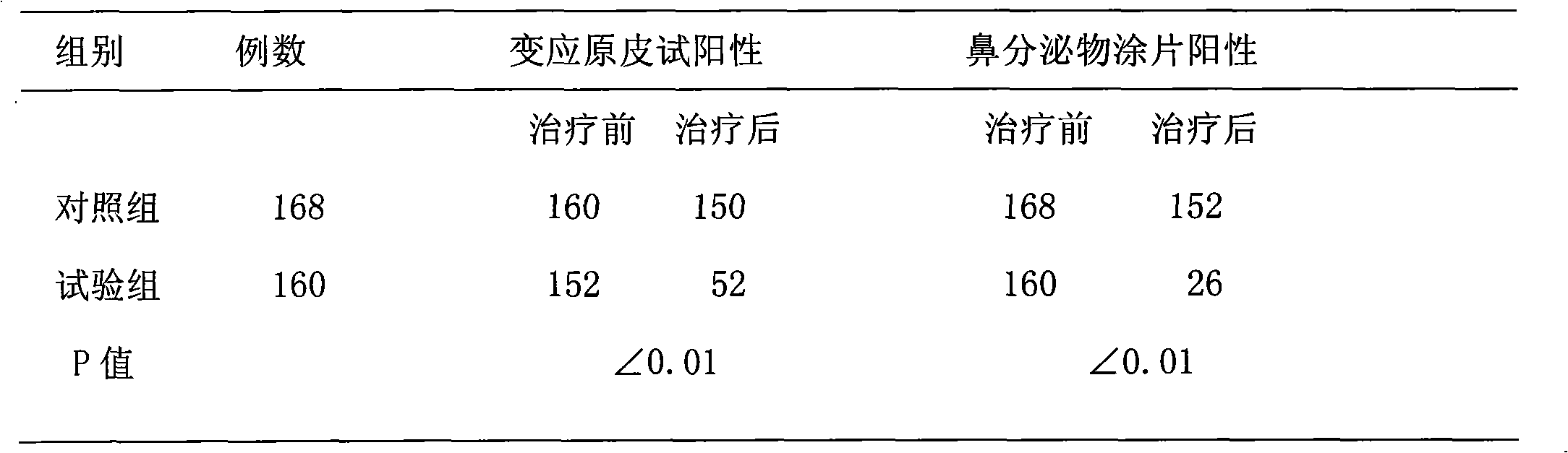
InactiveCN101991649AGood treatment effectEasy to useHydroxy compound active ingredientsRespiratory disorderWestern medicineTreatment effect
The invention provides a medicament for treating allergic rhinitis, belonging to a medicament using traditional Chinese medicines as effective ingredients. The medicament for treating allergic rhinitis is prepared from the raw materials of milkvetch roots, small centipeda herbs, asarum, violet magnolia, cocklebur fruits, angelica roots, borneol, sesame oil and liquid paraffin. The medicament has good treatment effect, is convenient for use, overcomes the defects of long treatment course, great pain, high expense, more complications, easy relapse and the like of Western medicine treatment, and also overcomes the defects of slow effect taking, inconvenient use and the like of traditional Chinese pills, oral decoctions, patches and the like.
Owner:成新莲
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com