Patents
Literature
49 results about "Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
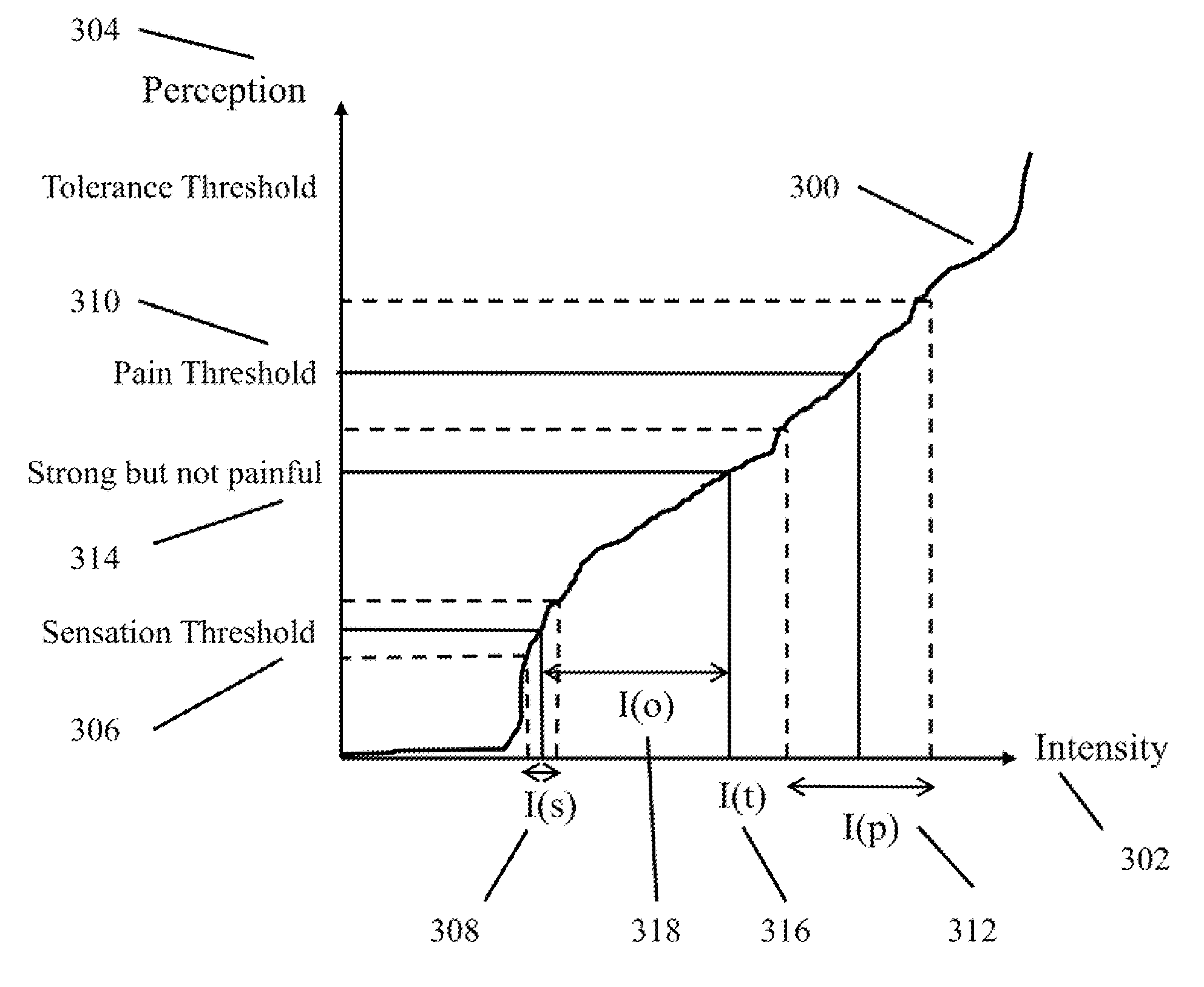
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS or TNS) is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents used for nerve excitation although the term is often used with a more restrictive intent, namely to describe the kind of pulses produced by portable stimulators used to treat pain. The unit is usually connected to the skin using two or more electrodes which are typically conductive gel pads. A typical battery-operated TENS unit is able to modulate pulse width, frequency and intensity. Generally TENS is applied at high frequency (>50 Hz) with an intensity below motor contraction (sensory intensity) or low frequency (<10 Hz) with an intensity that produces motor contraction. While the use of TENS has proved effective in clinical studies, there is controversy over which conditions the device should be used to treat.
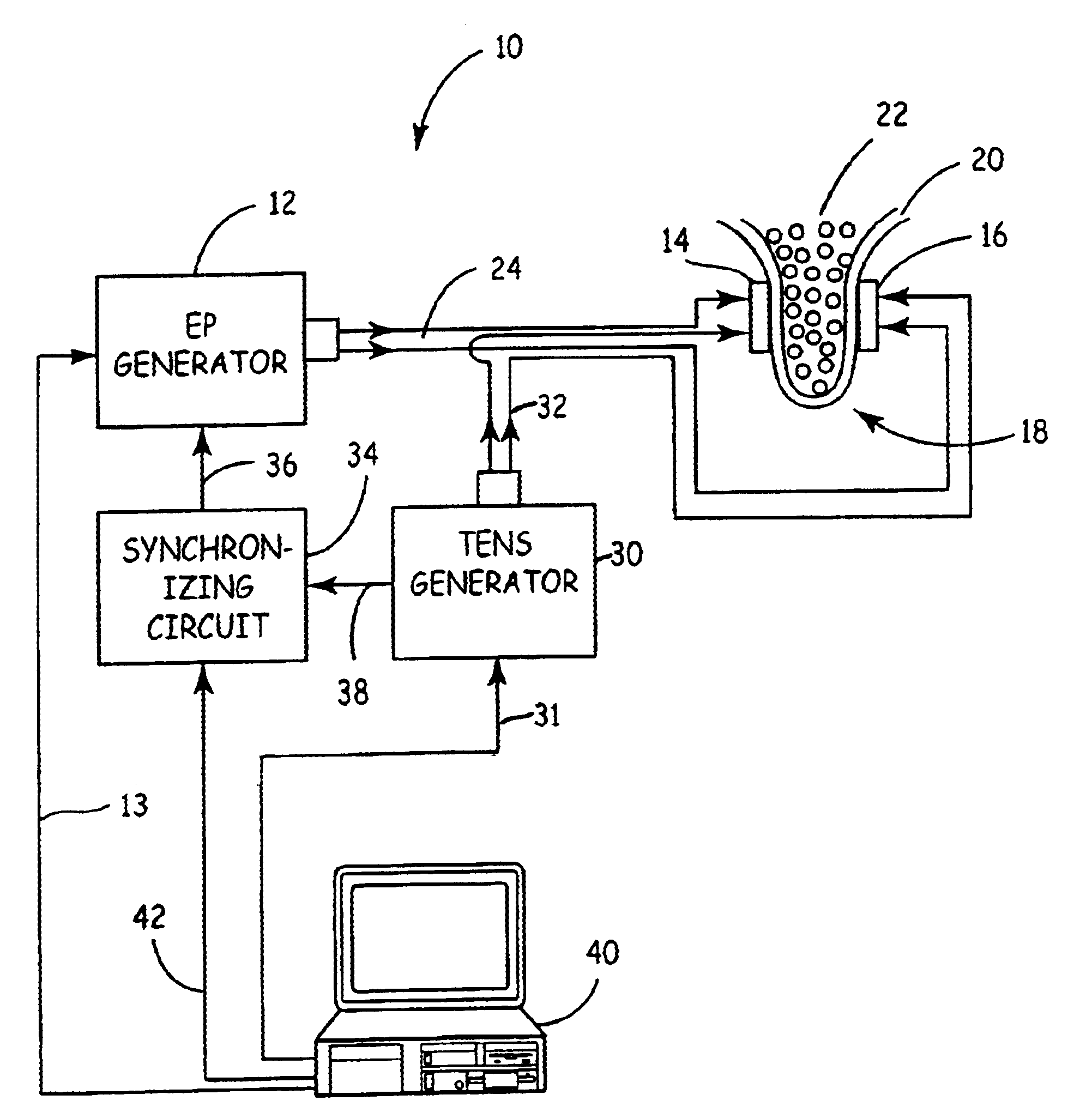
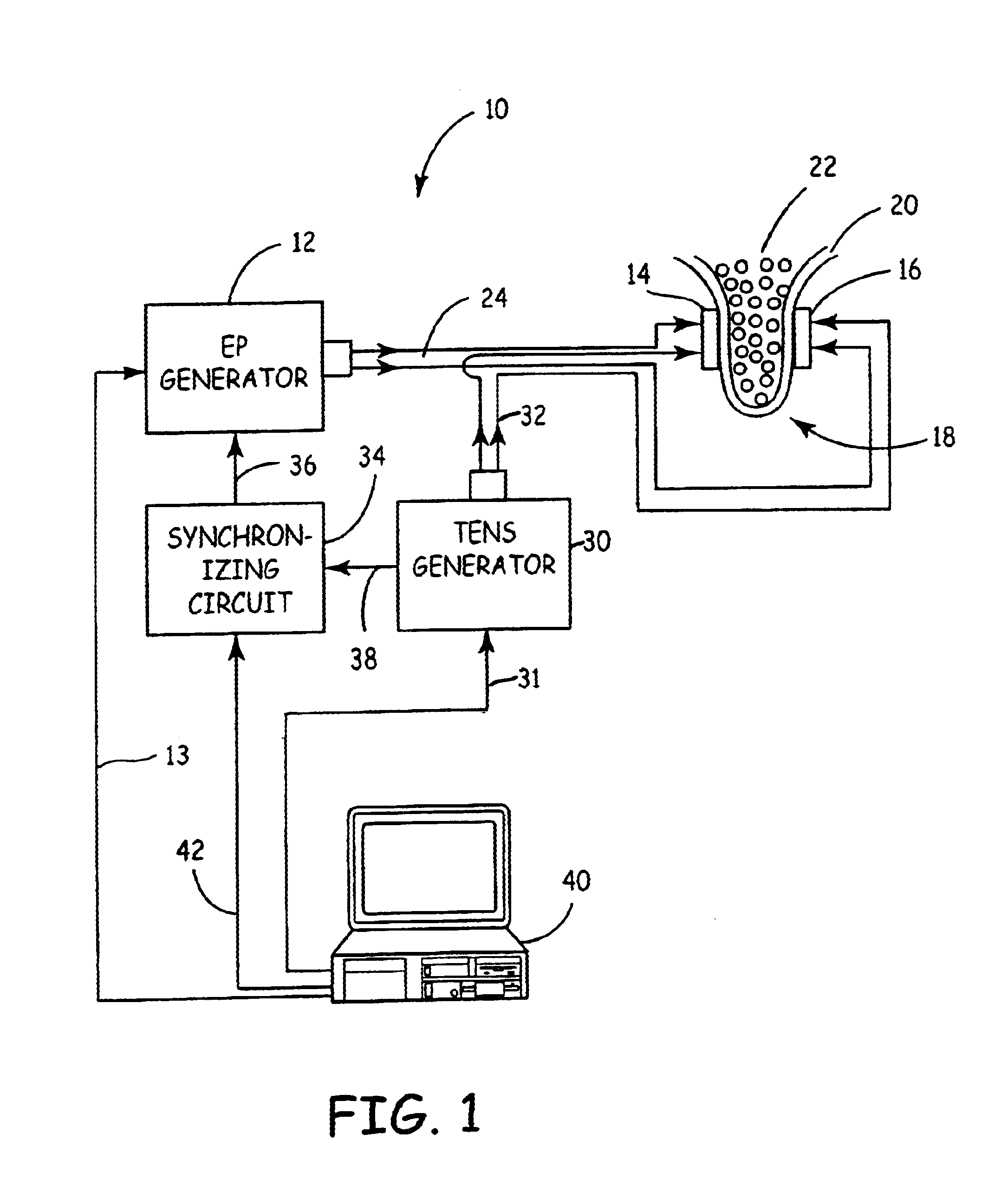
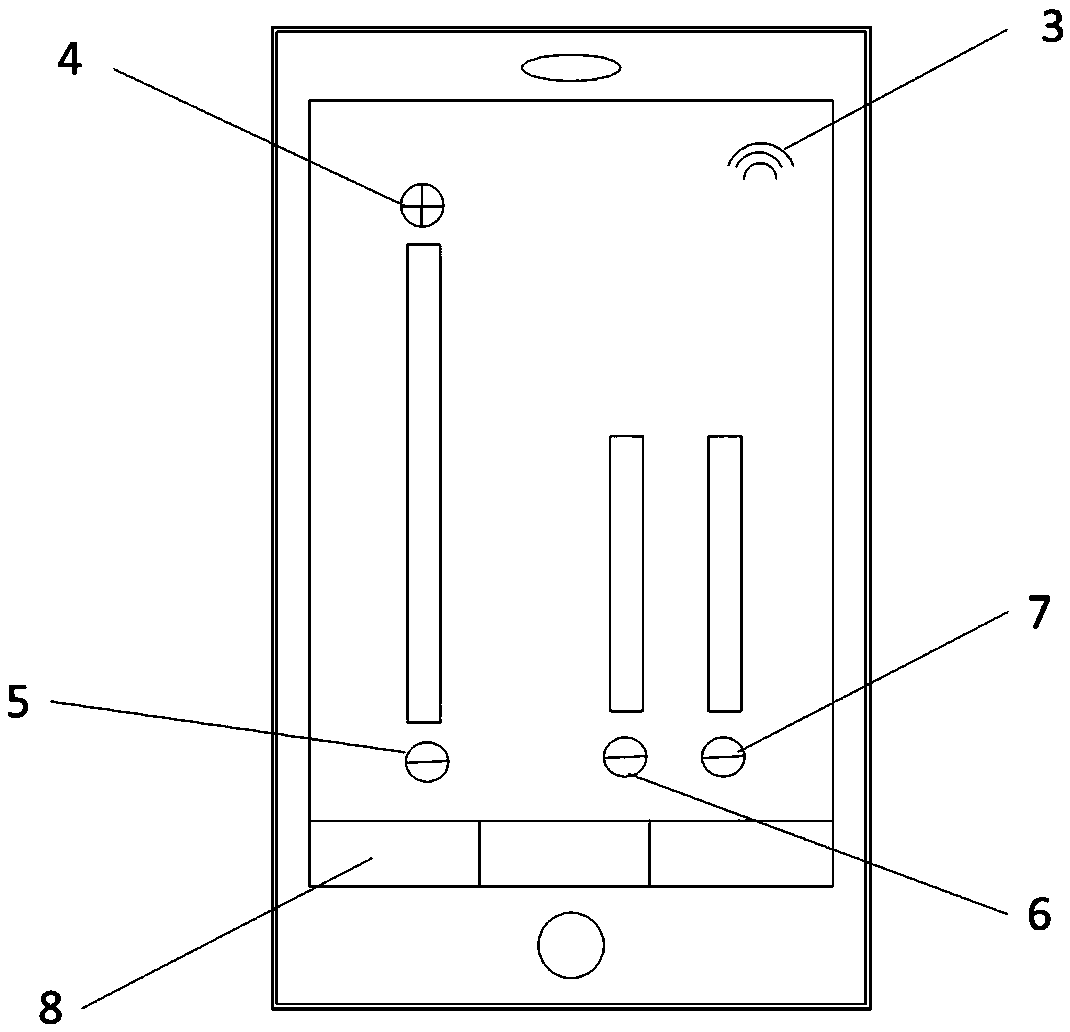
Apparatus and method for reducing subcutaneous fat deposits by electroporation with improved comfort of patients
InactiveUS6697670B2Improve comfortReducing subcutaneous fat depositsElectrotherapyElectricityReduced subcutaneous fat
An apparatus and method for non-invasive treatment in lieu of cosmetic surgery is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a combination of a high and low voltage pulse generators connected to two or more electrodes placed on a treatment site of the patient's body. High voltage pulses, delivered to the electrodes, create an electric field that kills subcutaneous fat cells. Low voltage pulses, delivered to the same or individual electrodes provide transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), blocking the signals of discomfort or pain that may arise from the high voltage pulsing.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Apparatus and method for relieving pain using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20130158627A1Easy and rapid and clinically valid placementMaximize effectivenessExternal electrodesArtificial respirationElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
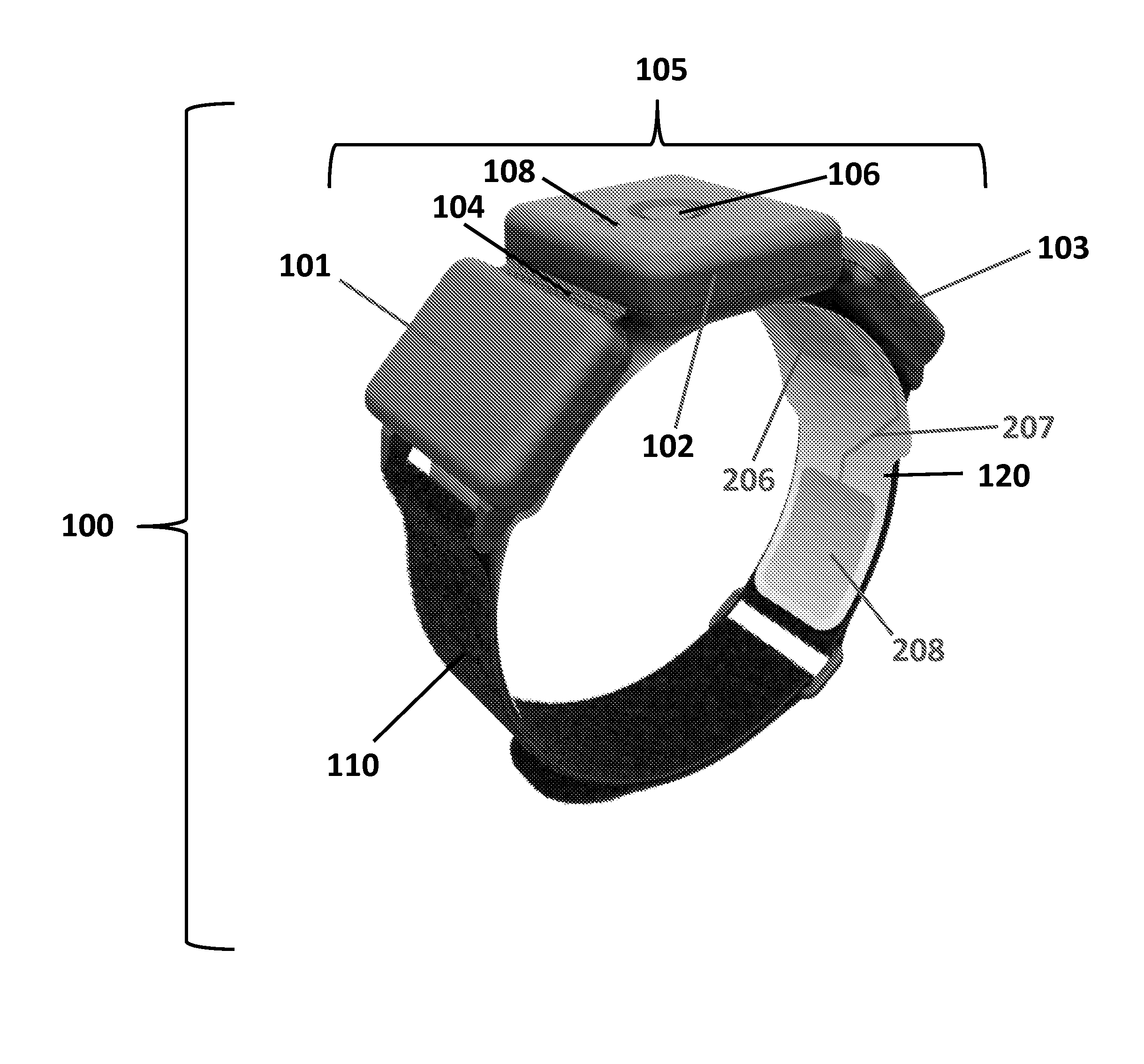
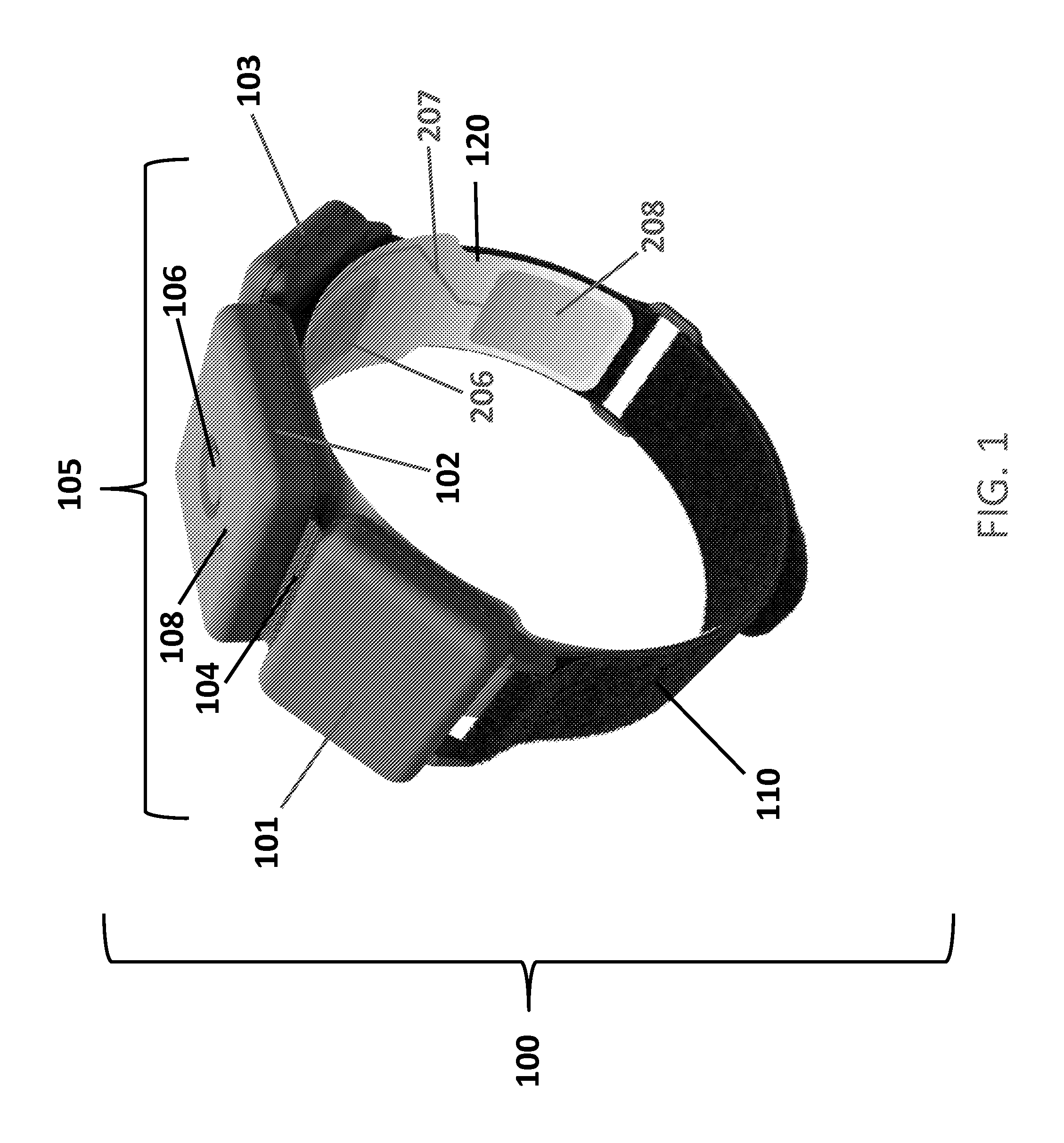
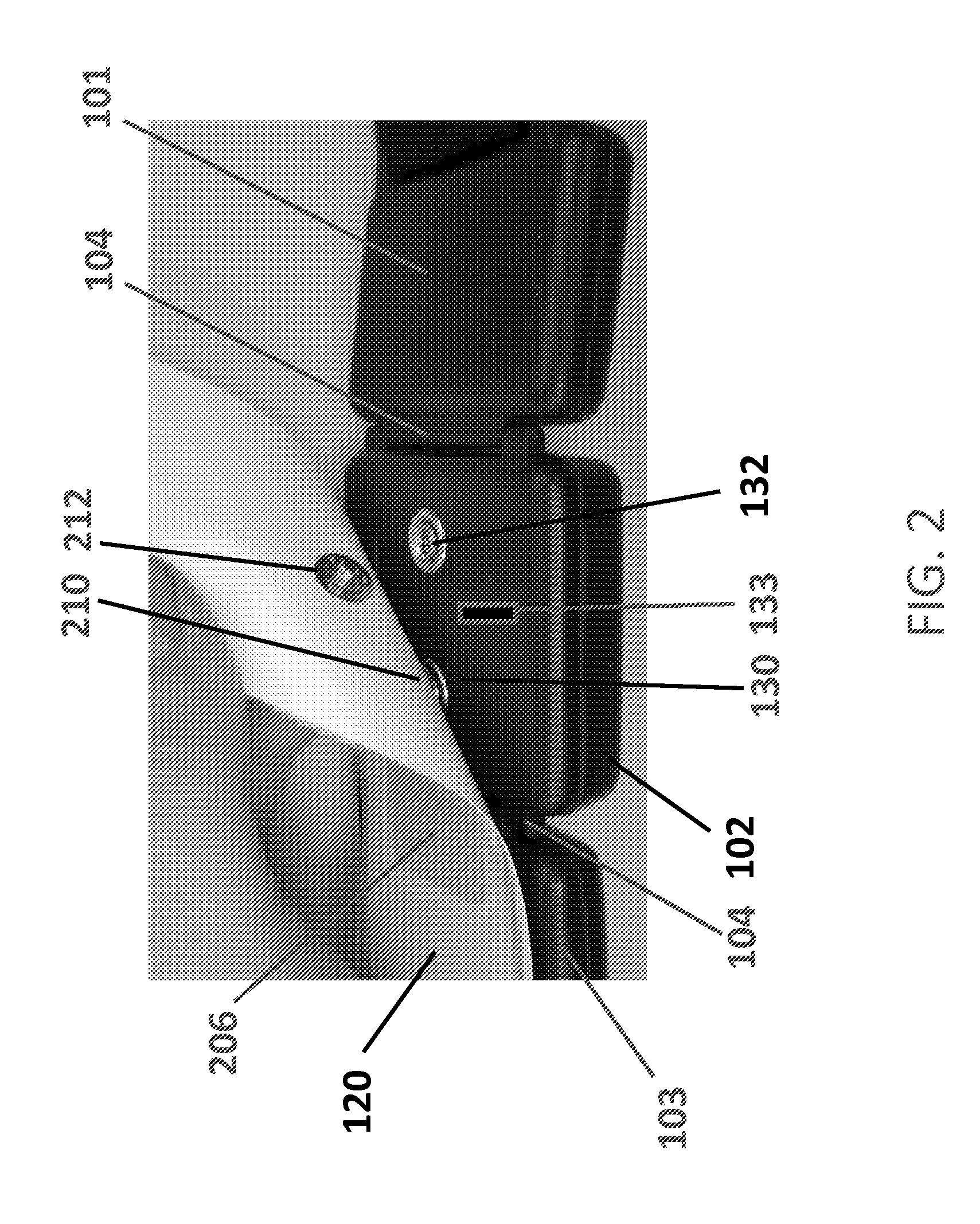
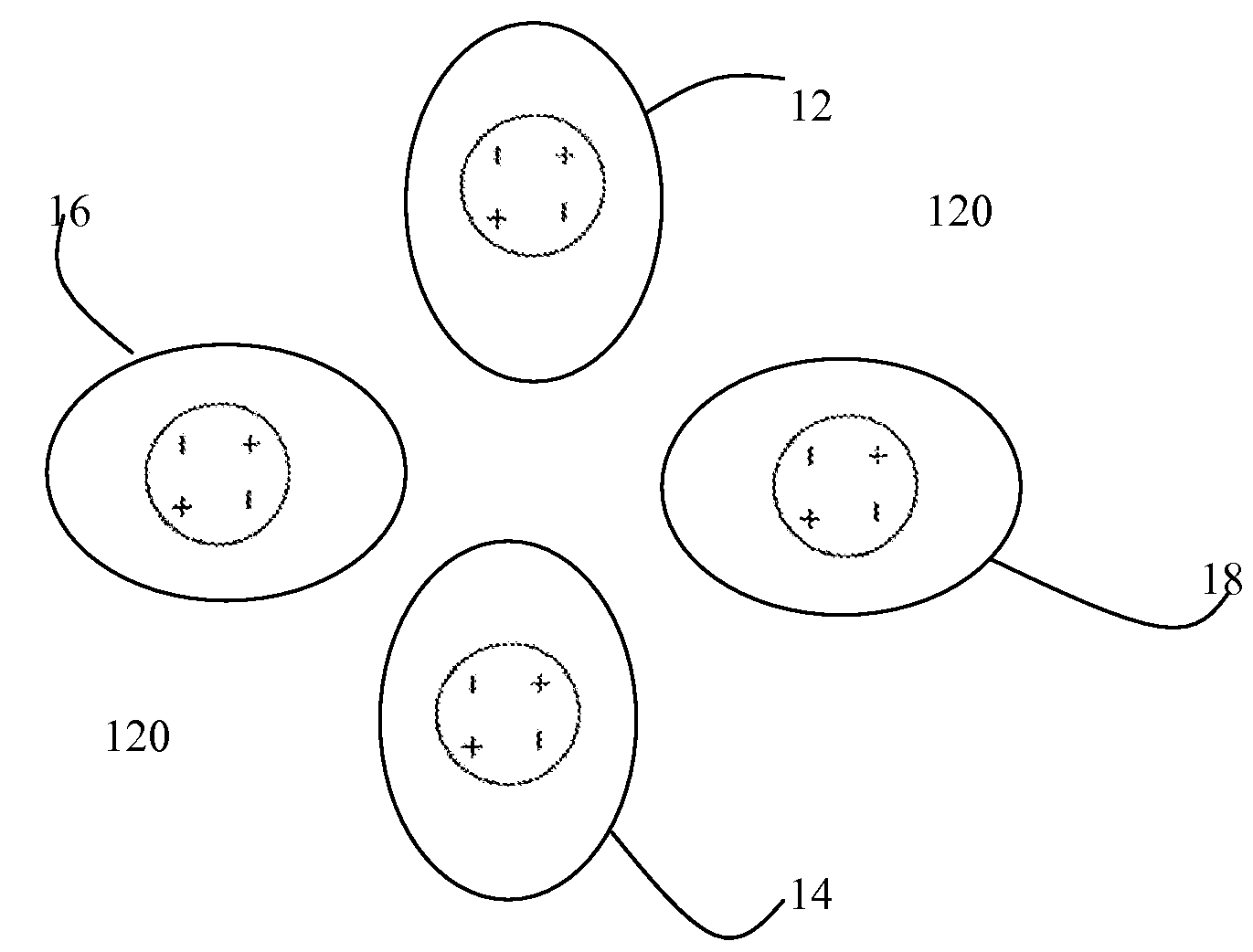
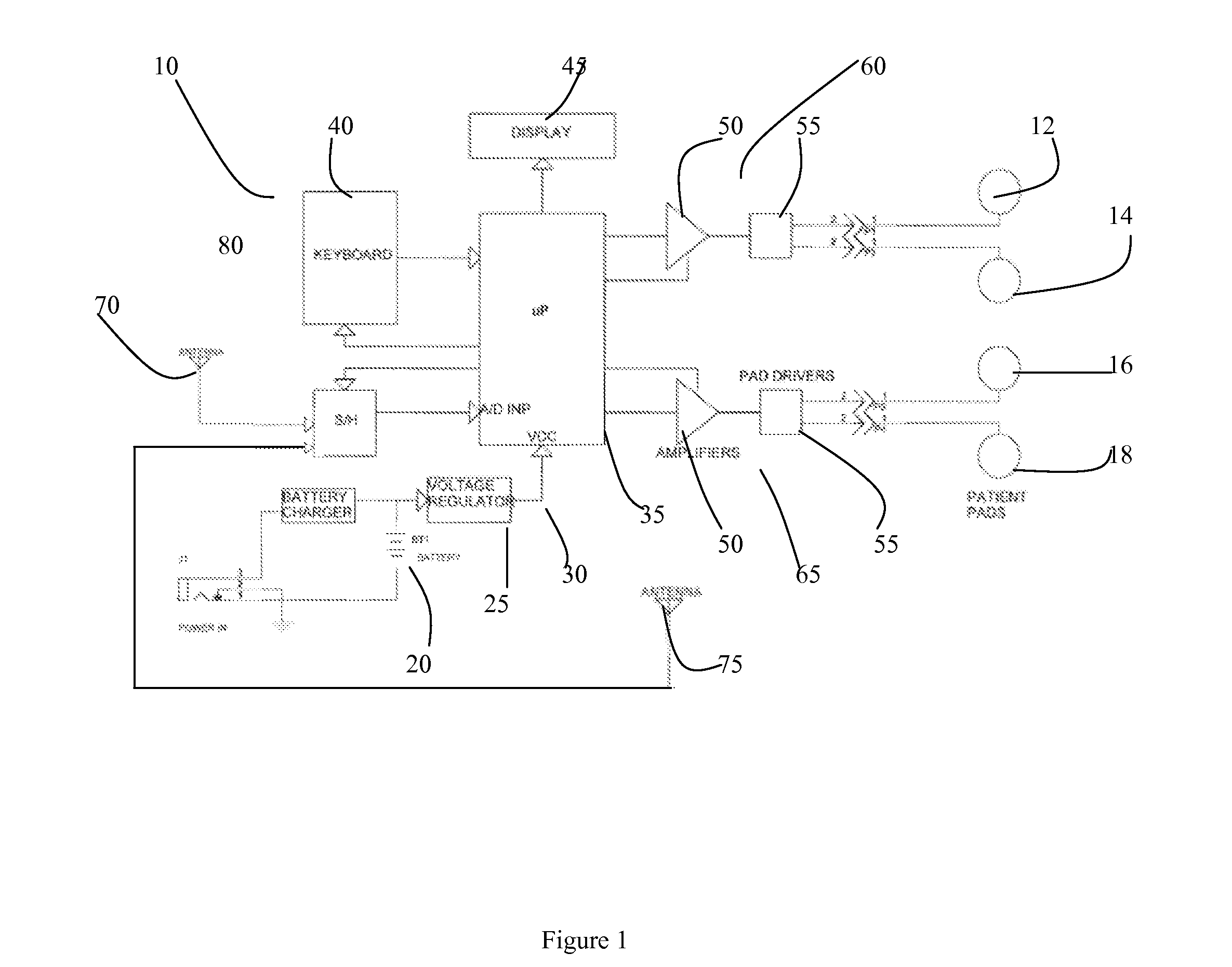
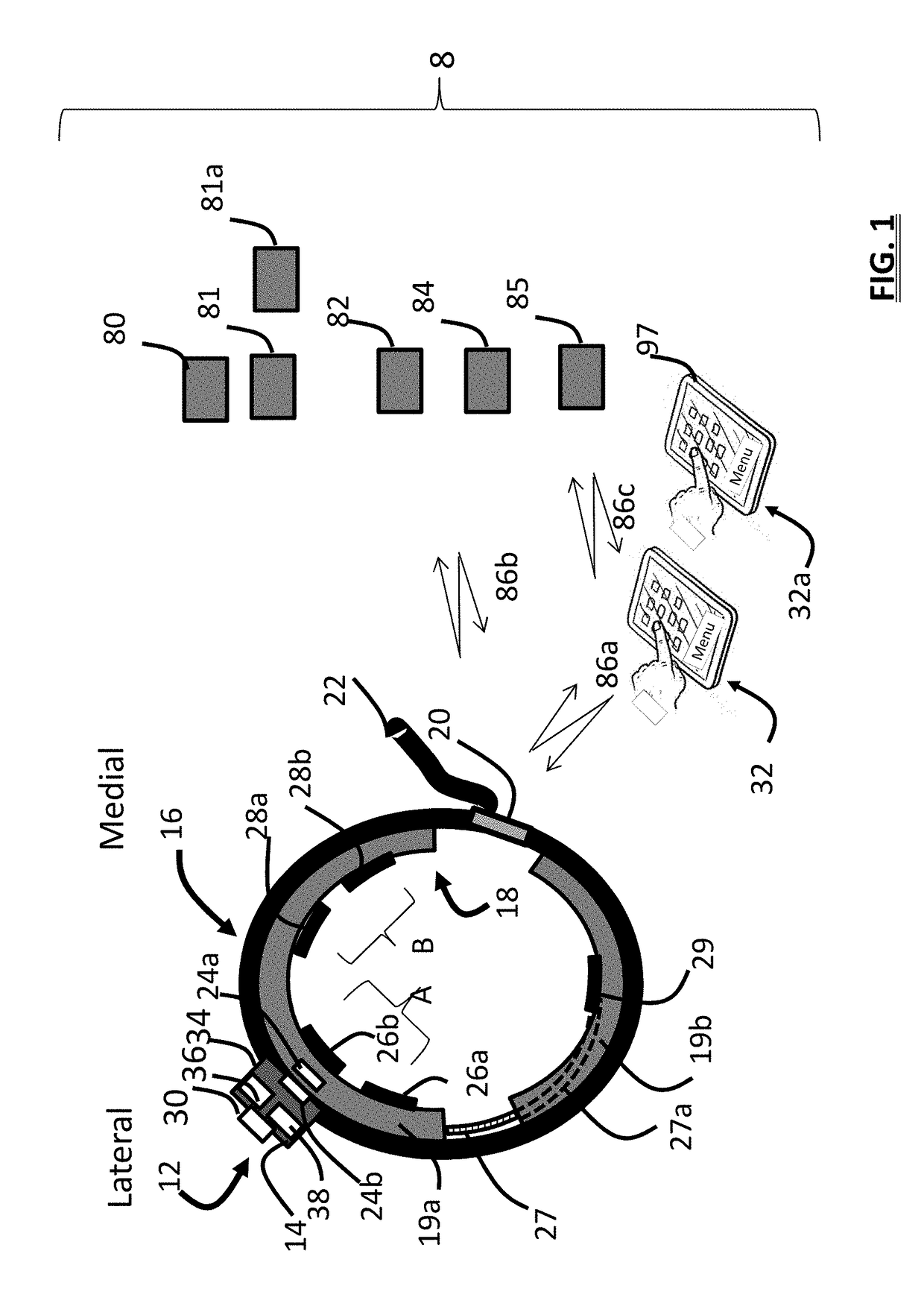
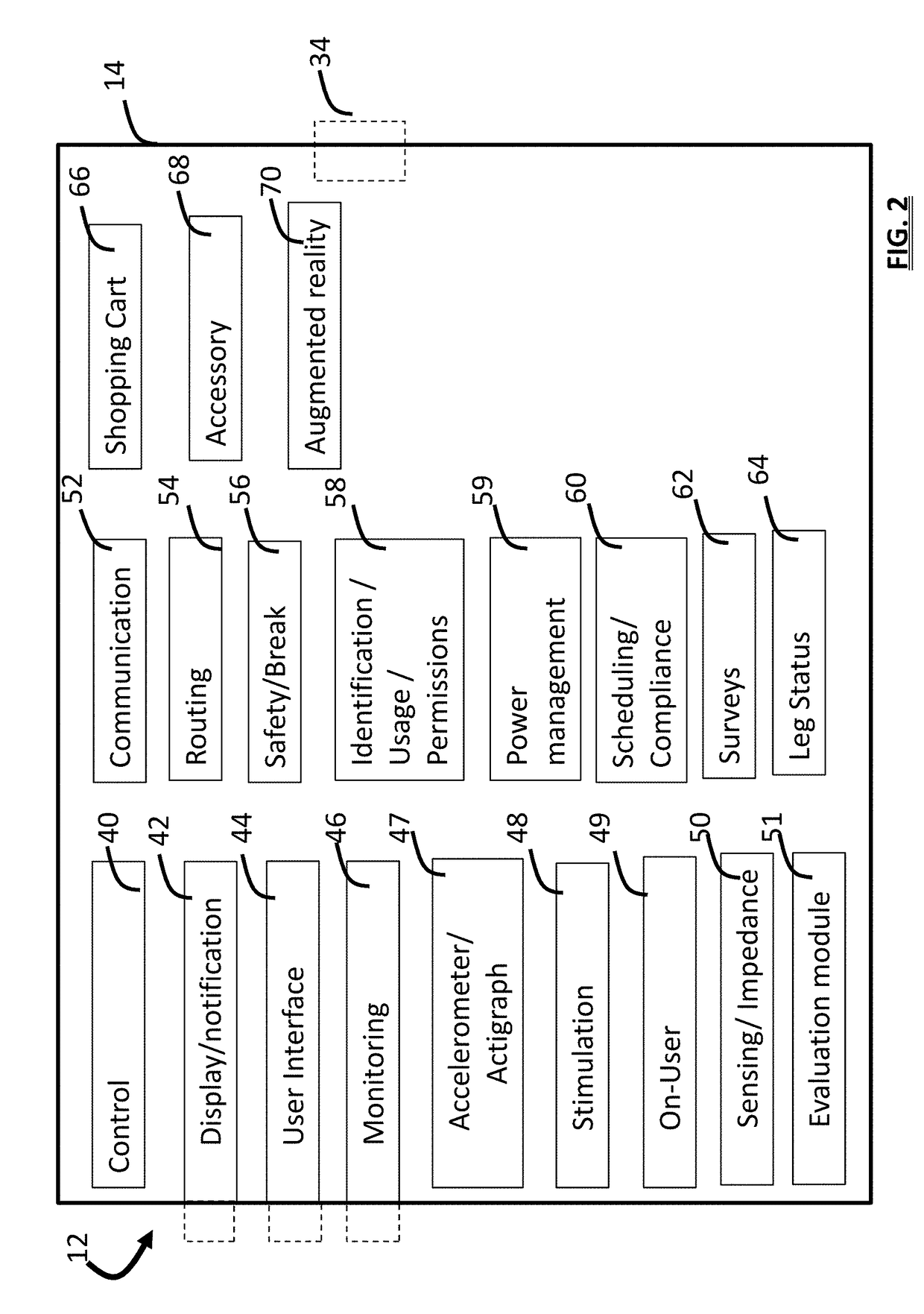
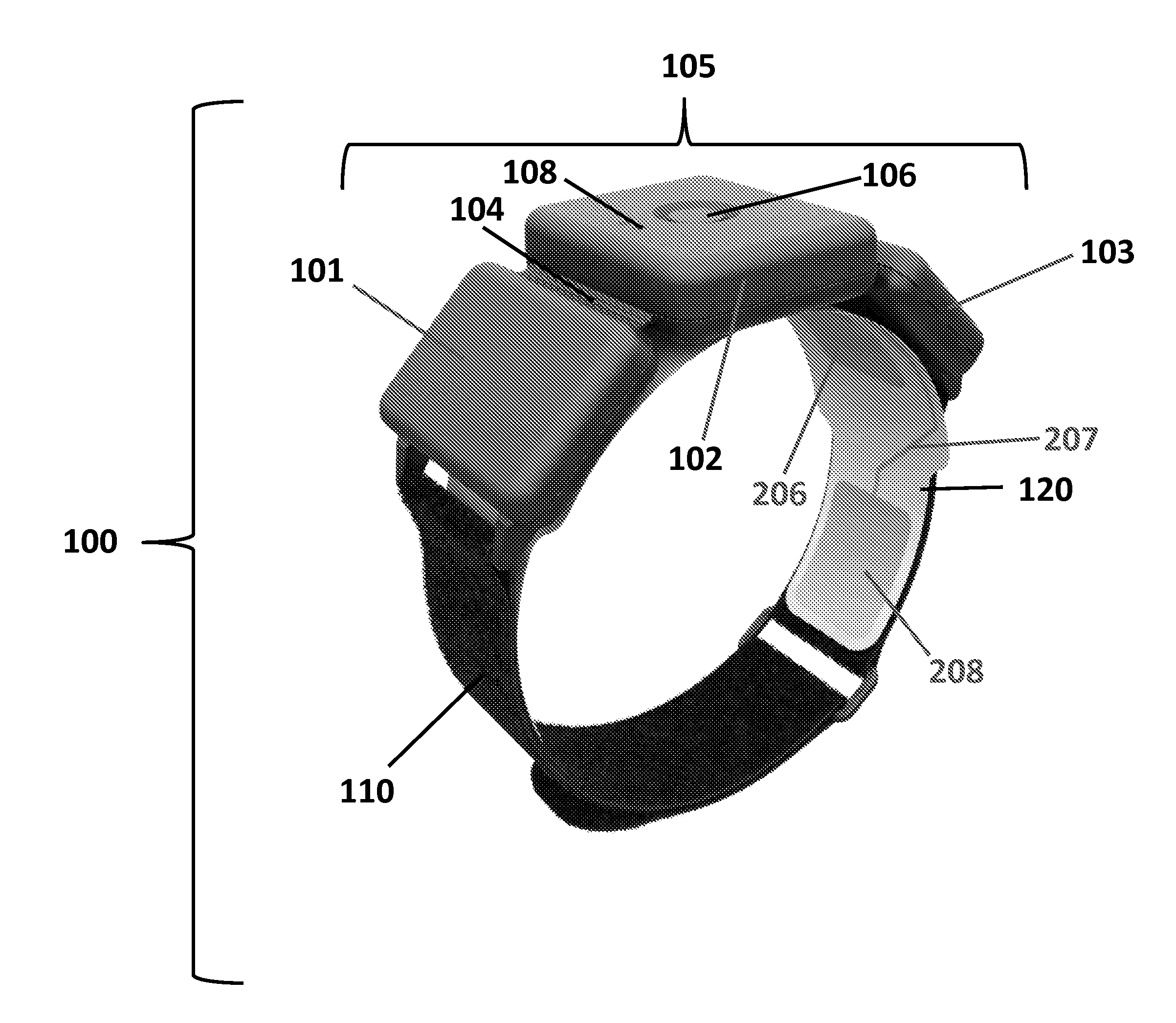
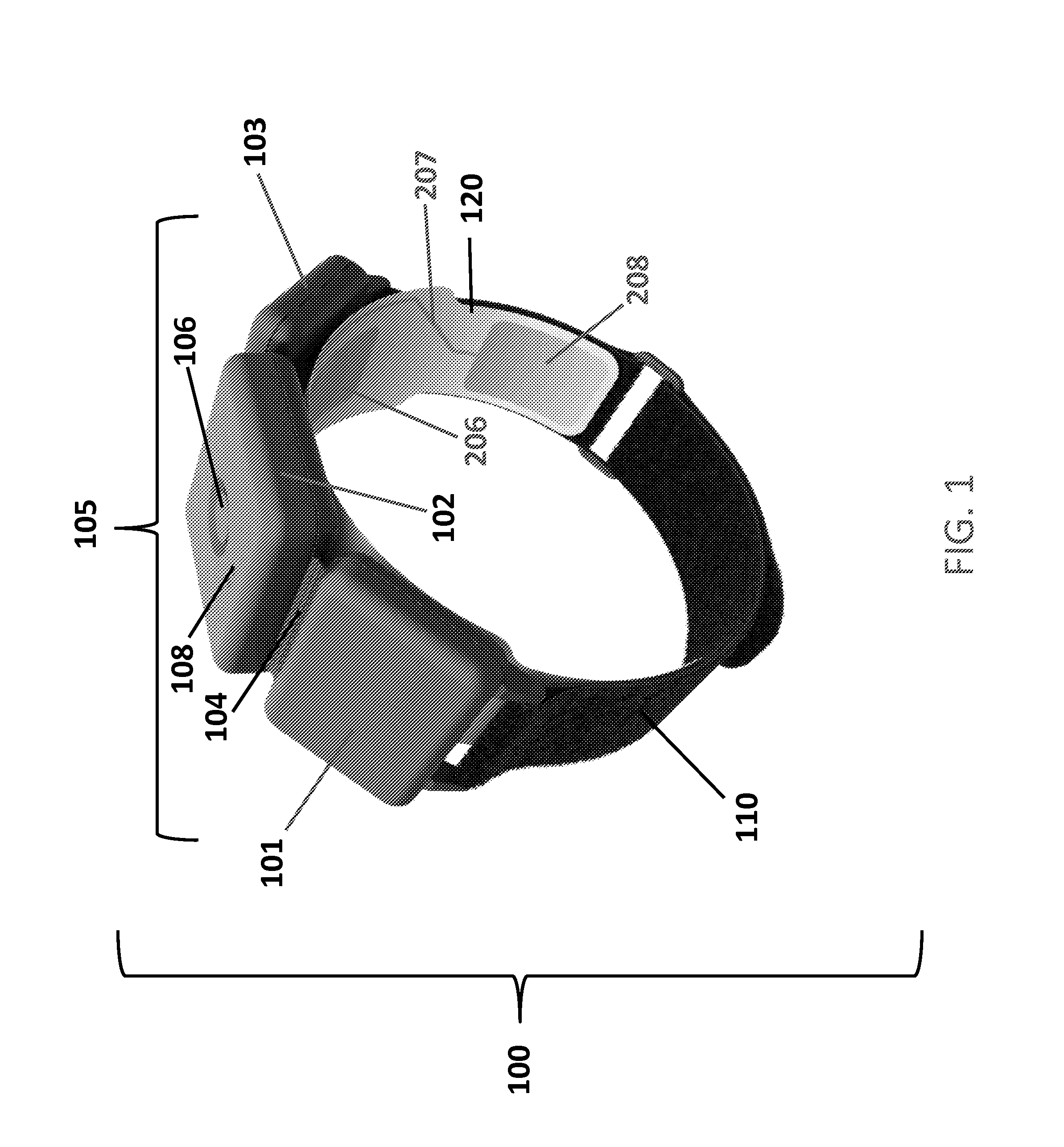
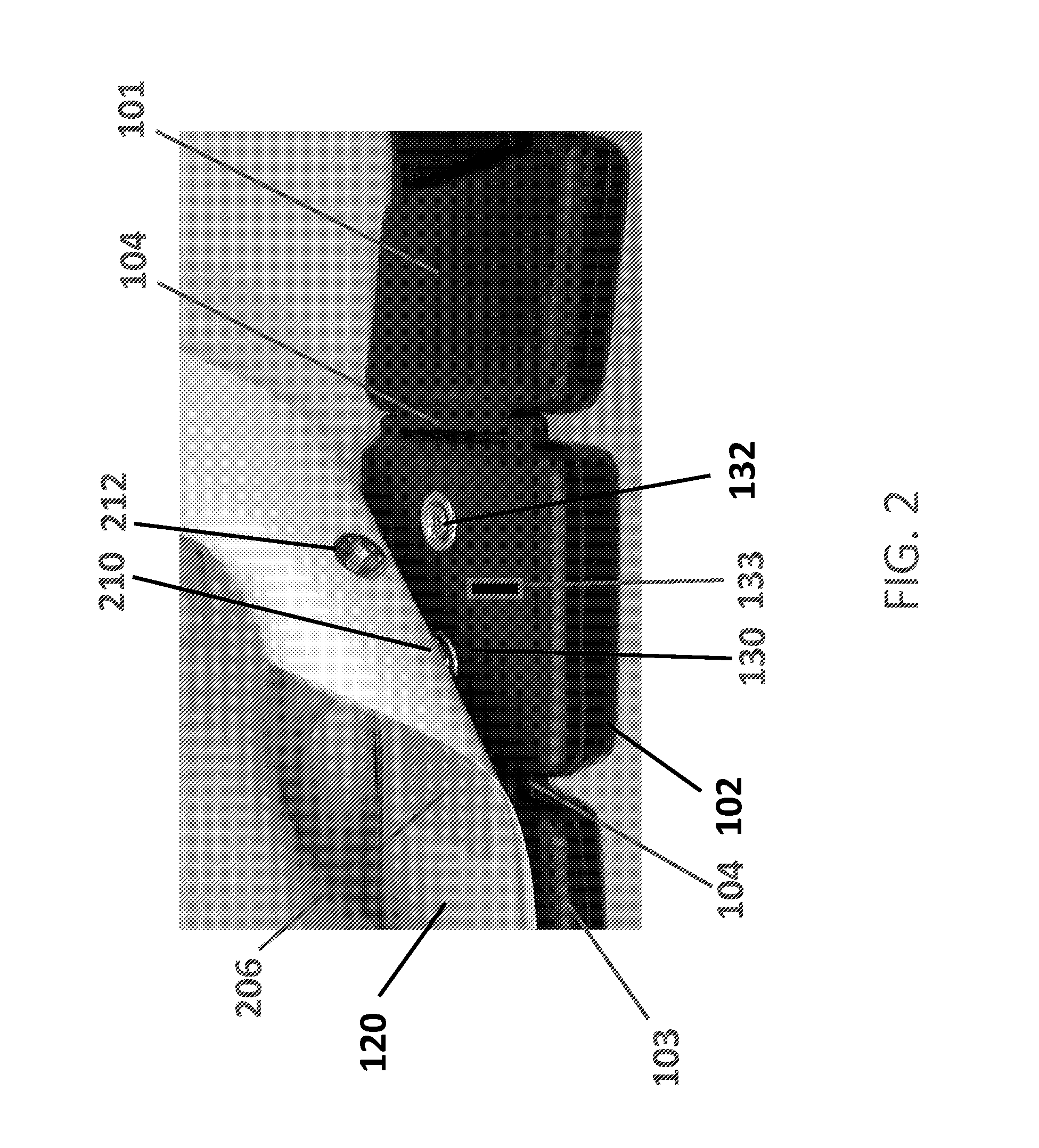
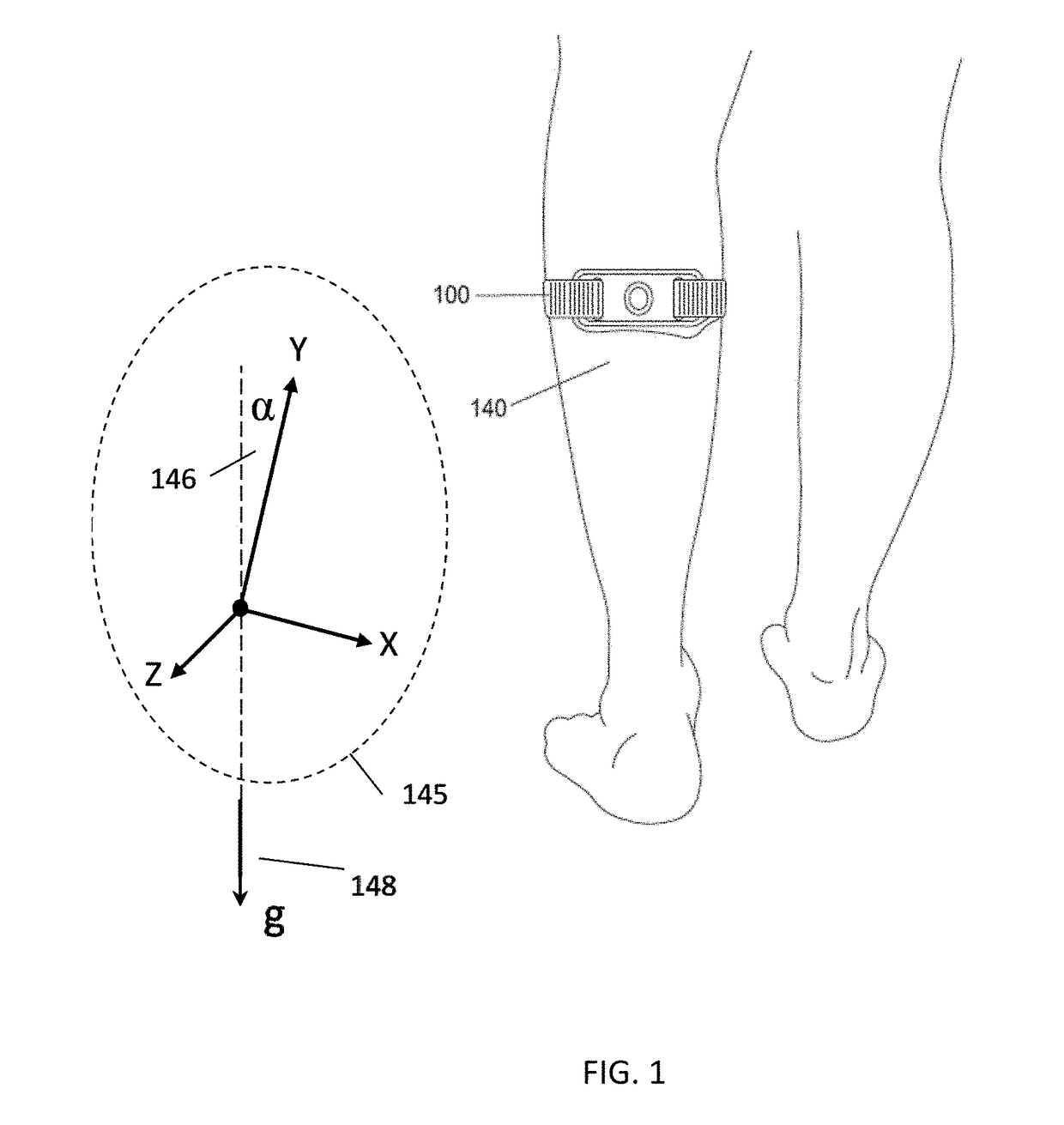
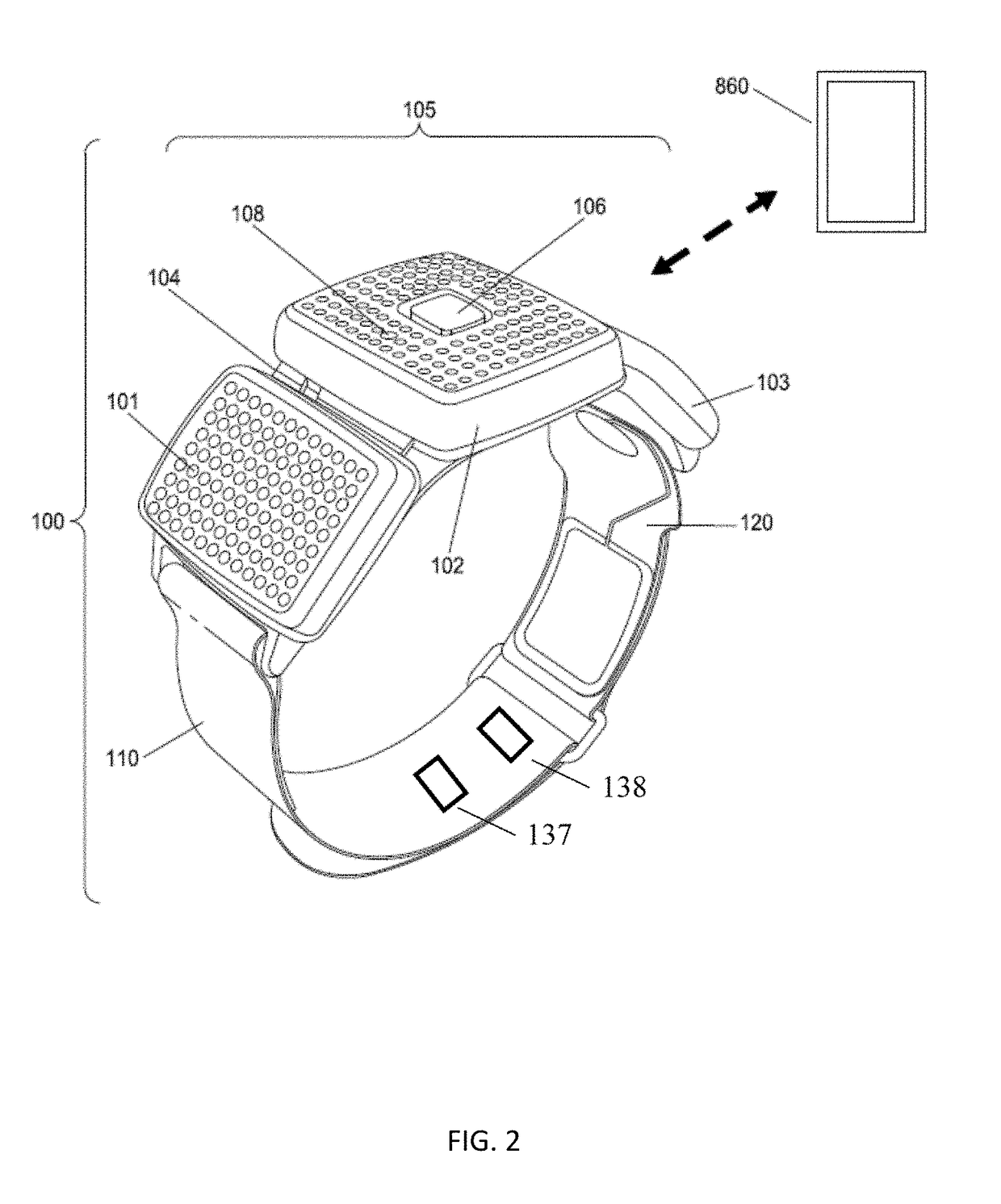
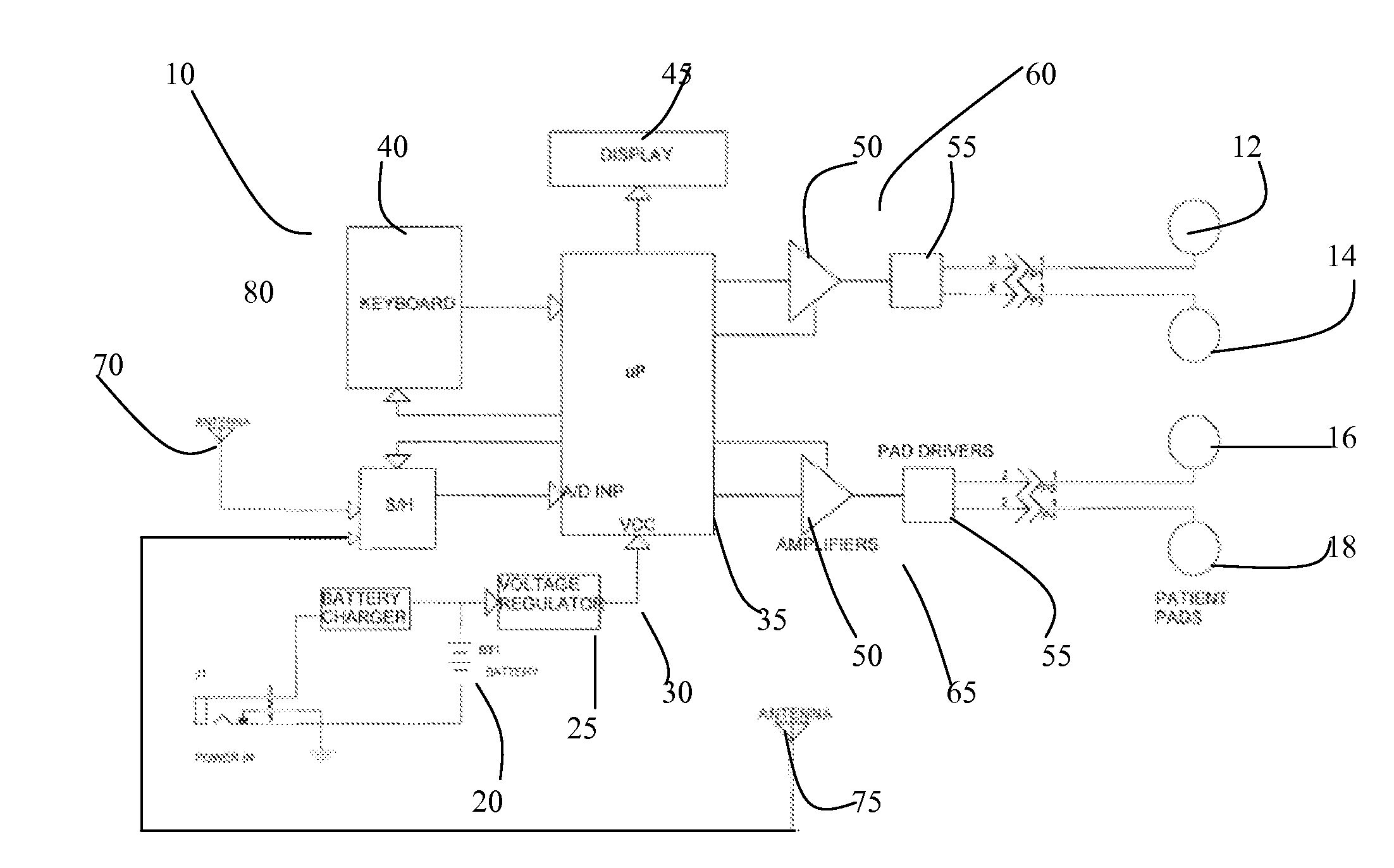
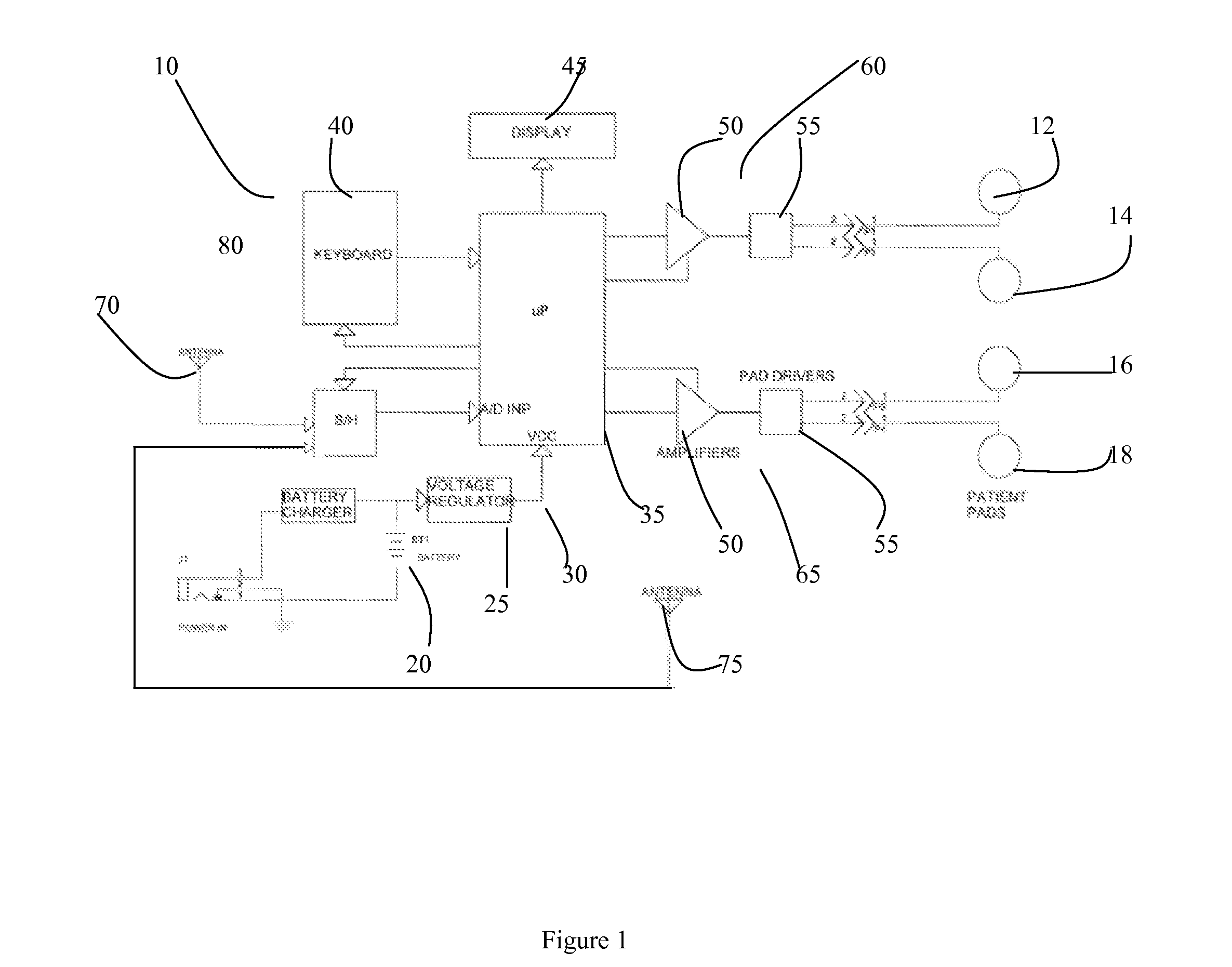
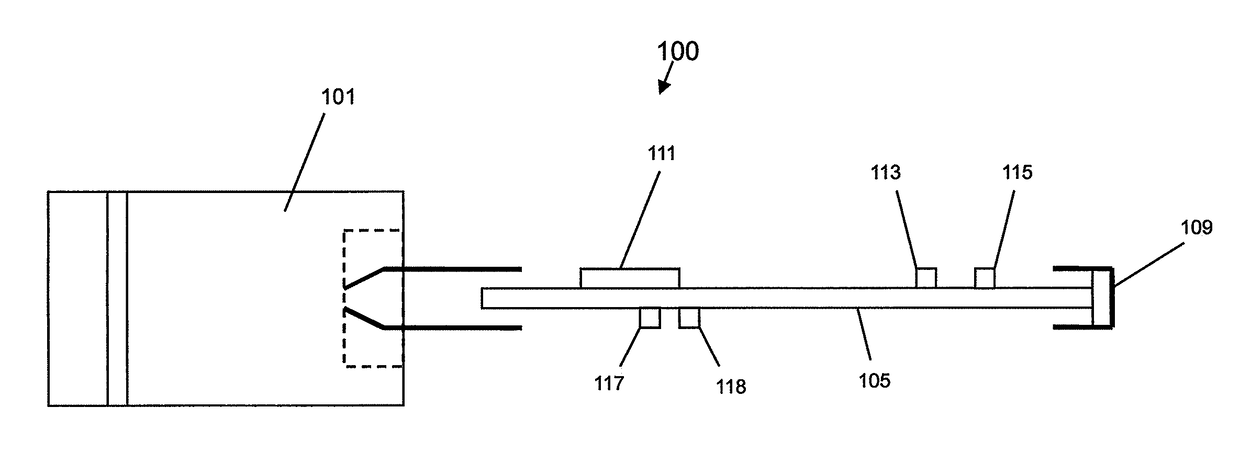
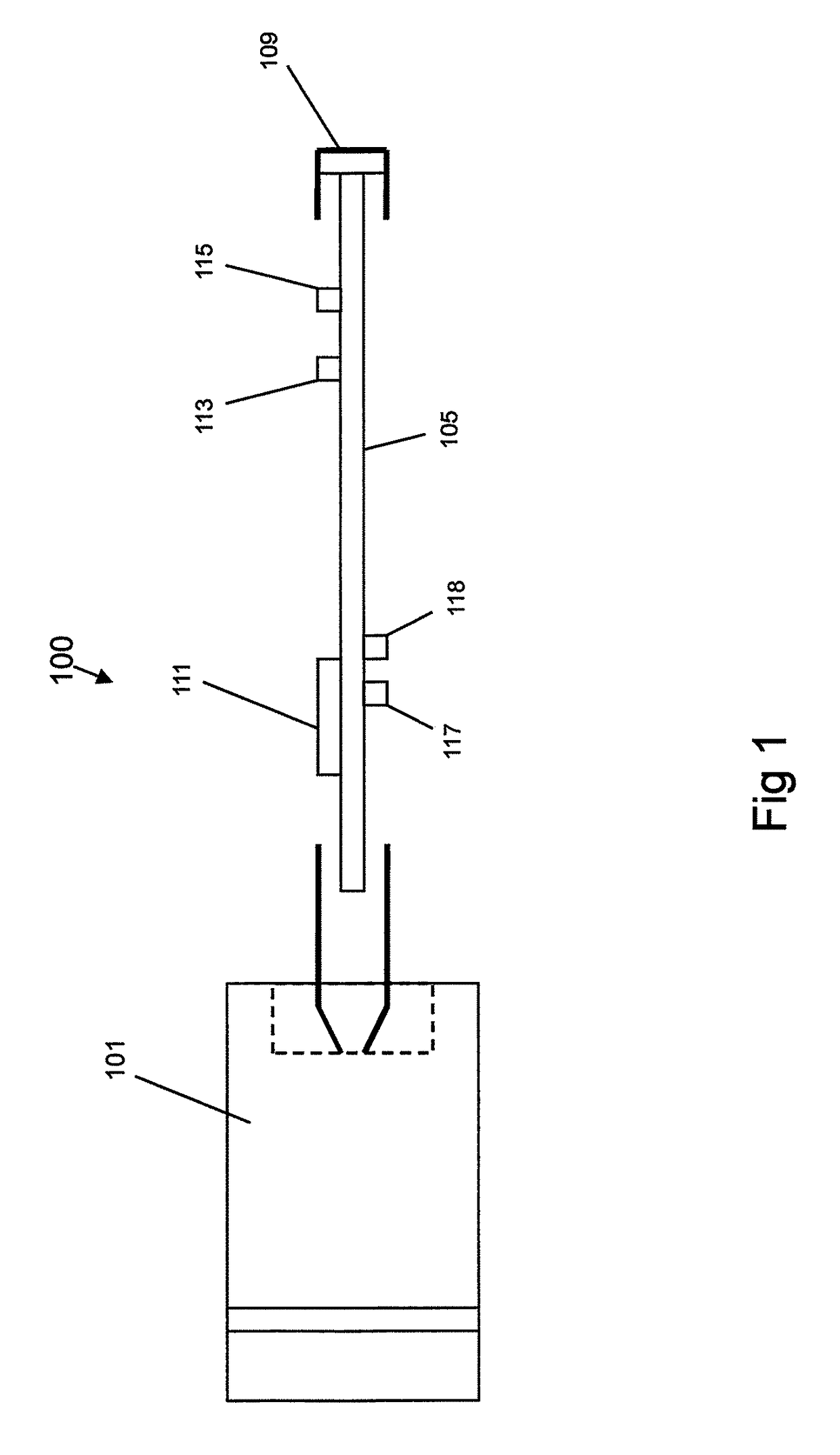
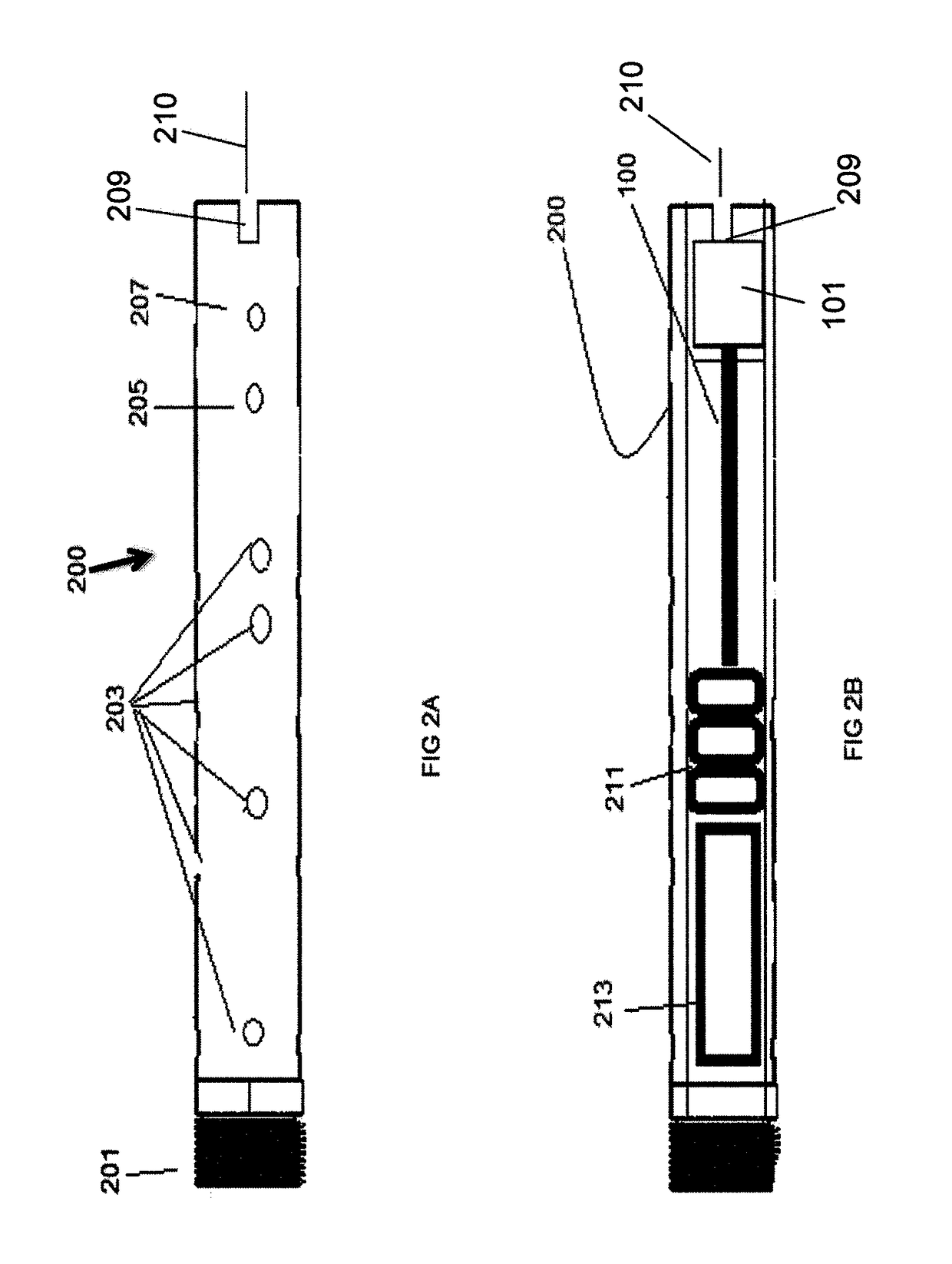
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in humans, comprising a housing; stimulation means mounted within the housing for electrically stimulating nerves; an electrode array releasably mounted to the housing, connectable to the stimulation means, and comprising electrodes for electrical stimulation of nerves; control means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for controlling the stimulation means; monitoring means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for monitoring the stimulation means; user interface means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means for controlling the stimulation means; display means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means and the monitoring means for displaying the status of the stimulations means; and a strap attached to the housing and configured to hold the housing, stimulation means and electrode array at a specific anatomical location to treat pain.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX
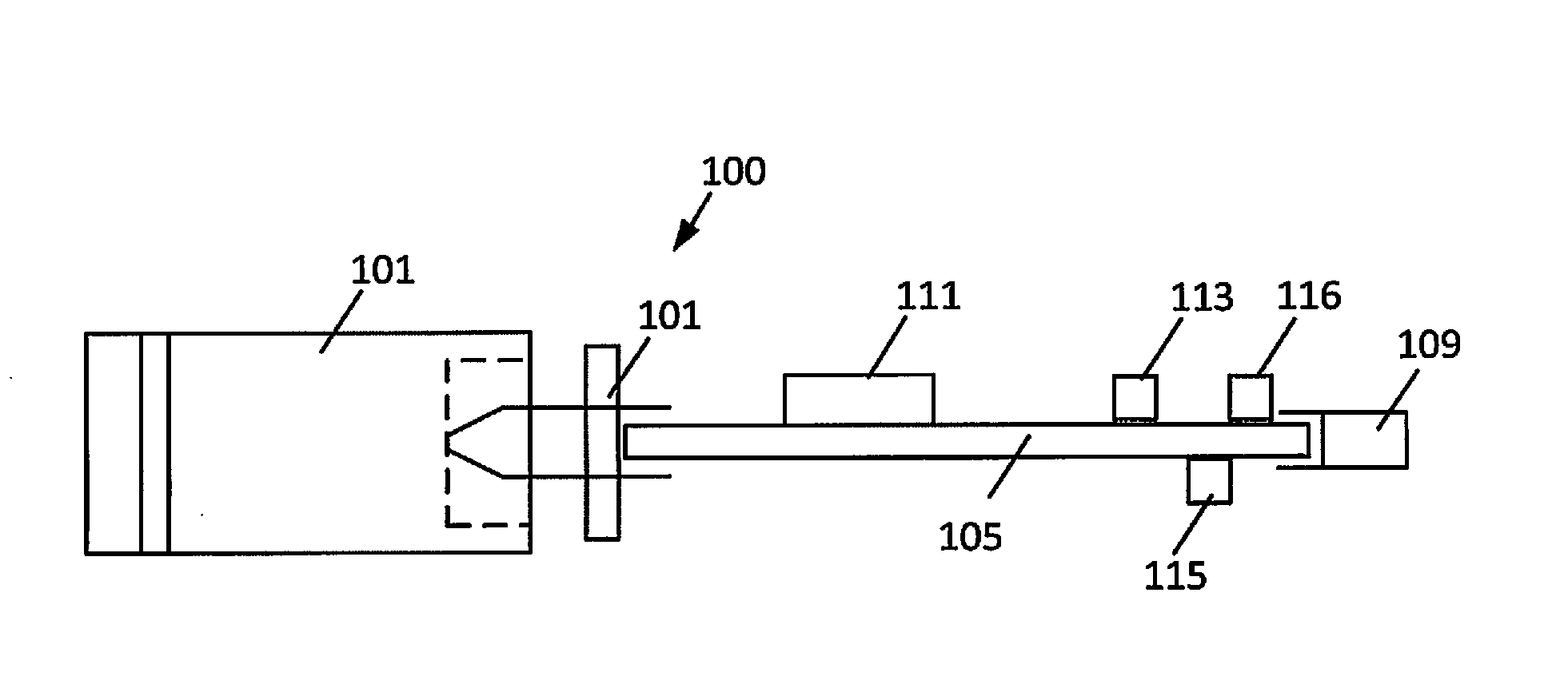
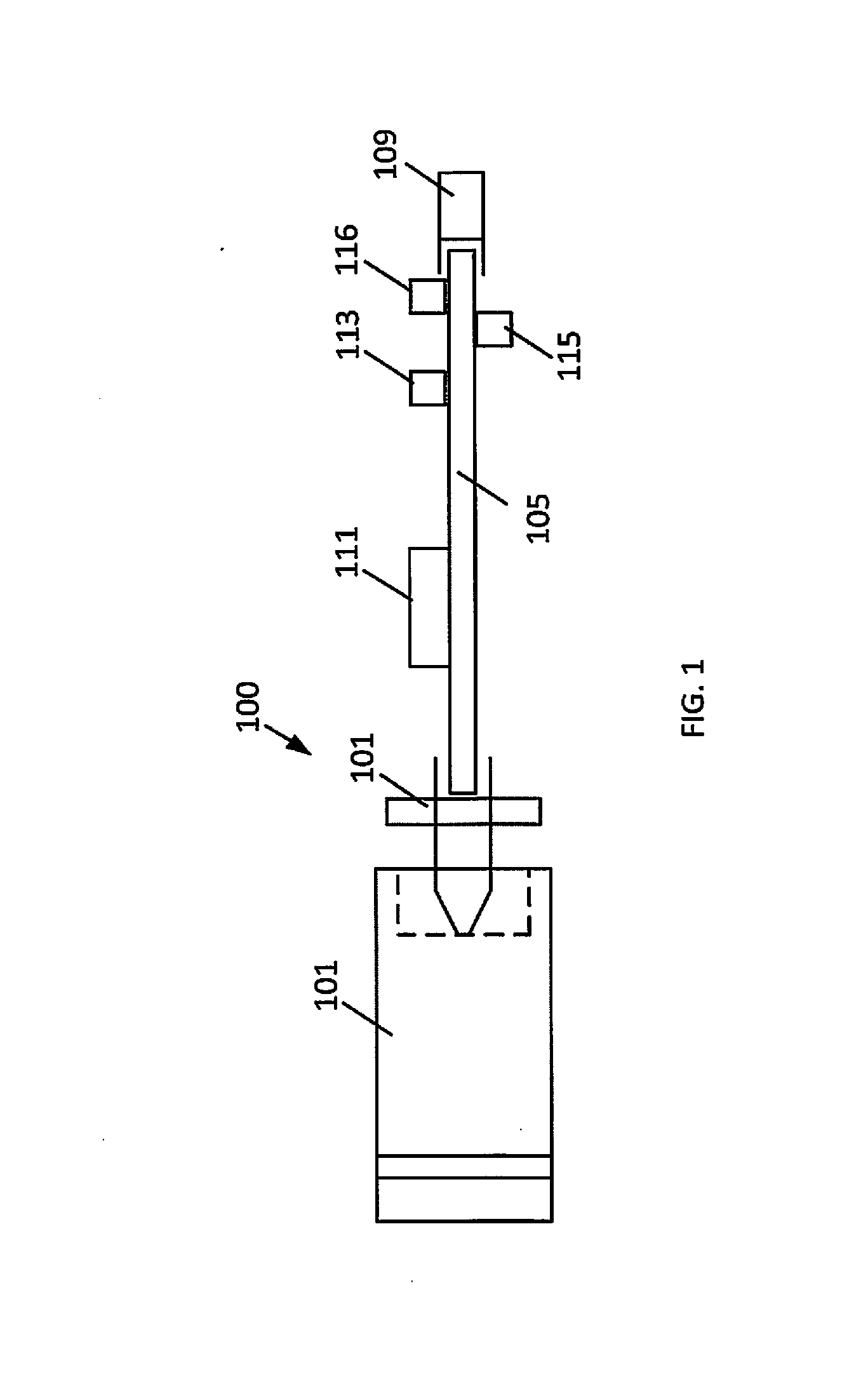
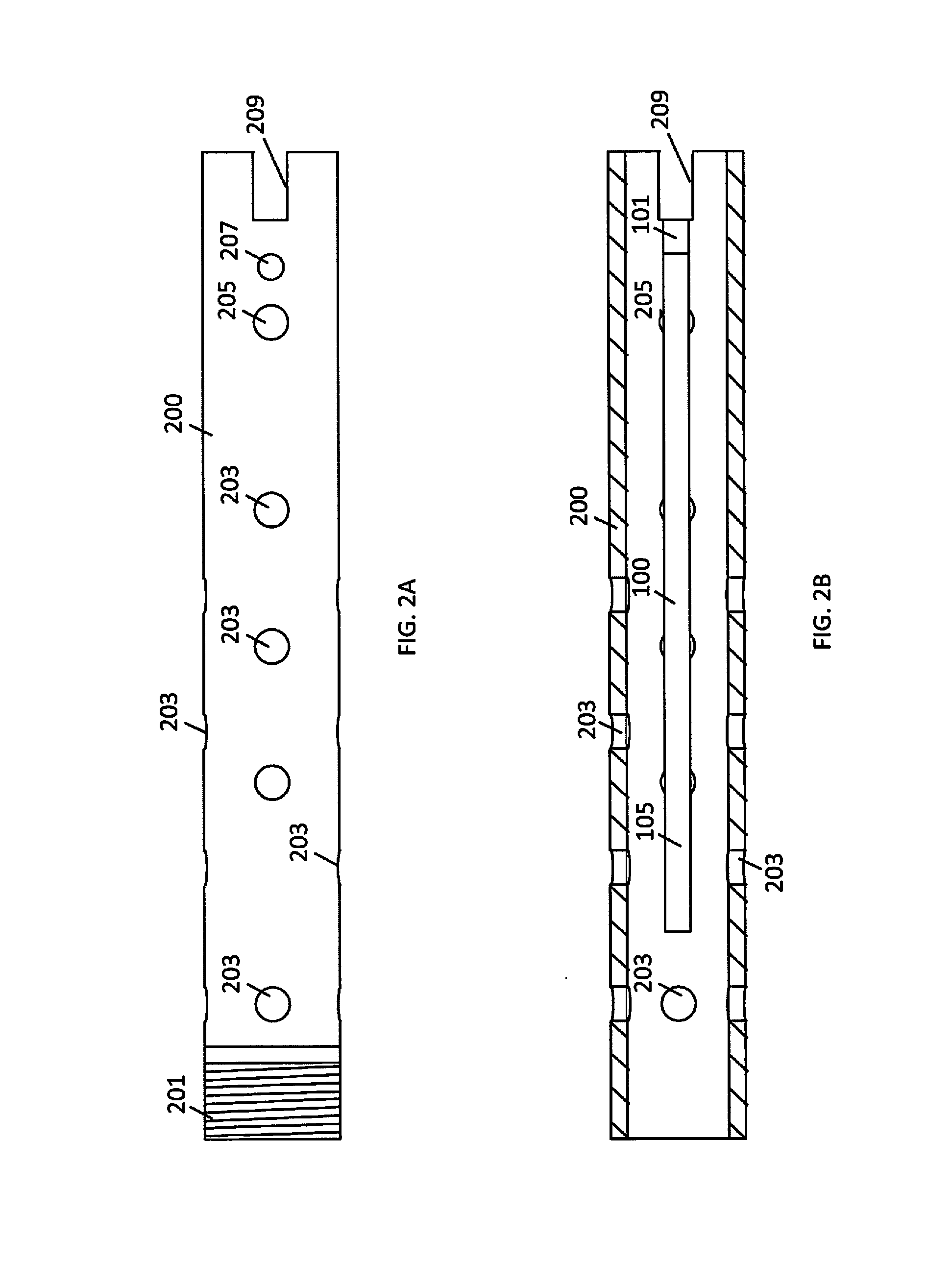
Electromechanical Manipulating Device for Medical Needle and Syringe with Sensory Biofeedback and Pain Suppression Capability
ActiveUS20140142507A1Facilitate actionDistract patientAutomatic syringesInfusion needlesBattery state of chargeDistraction
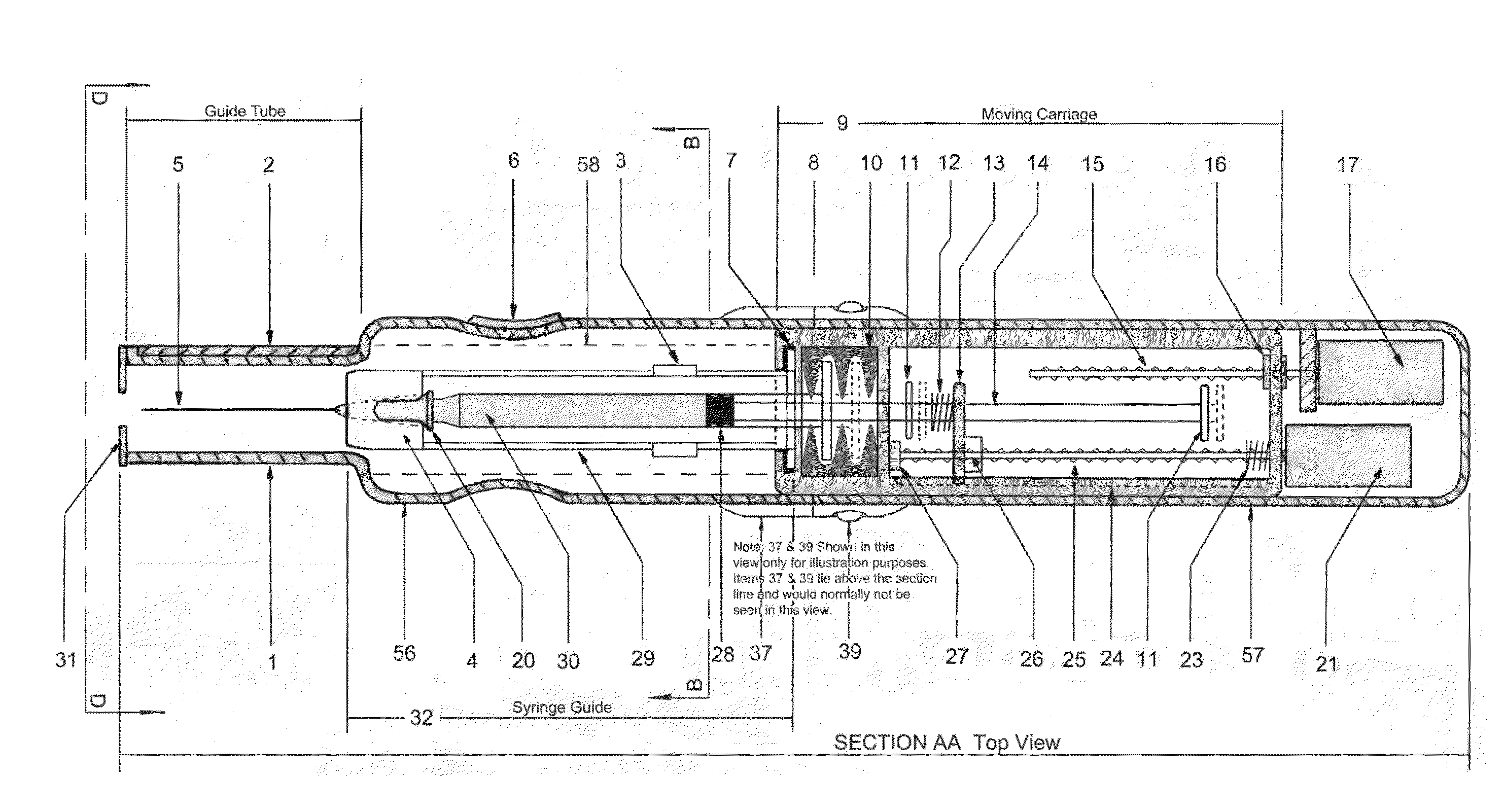
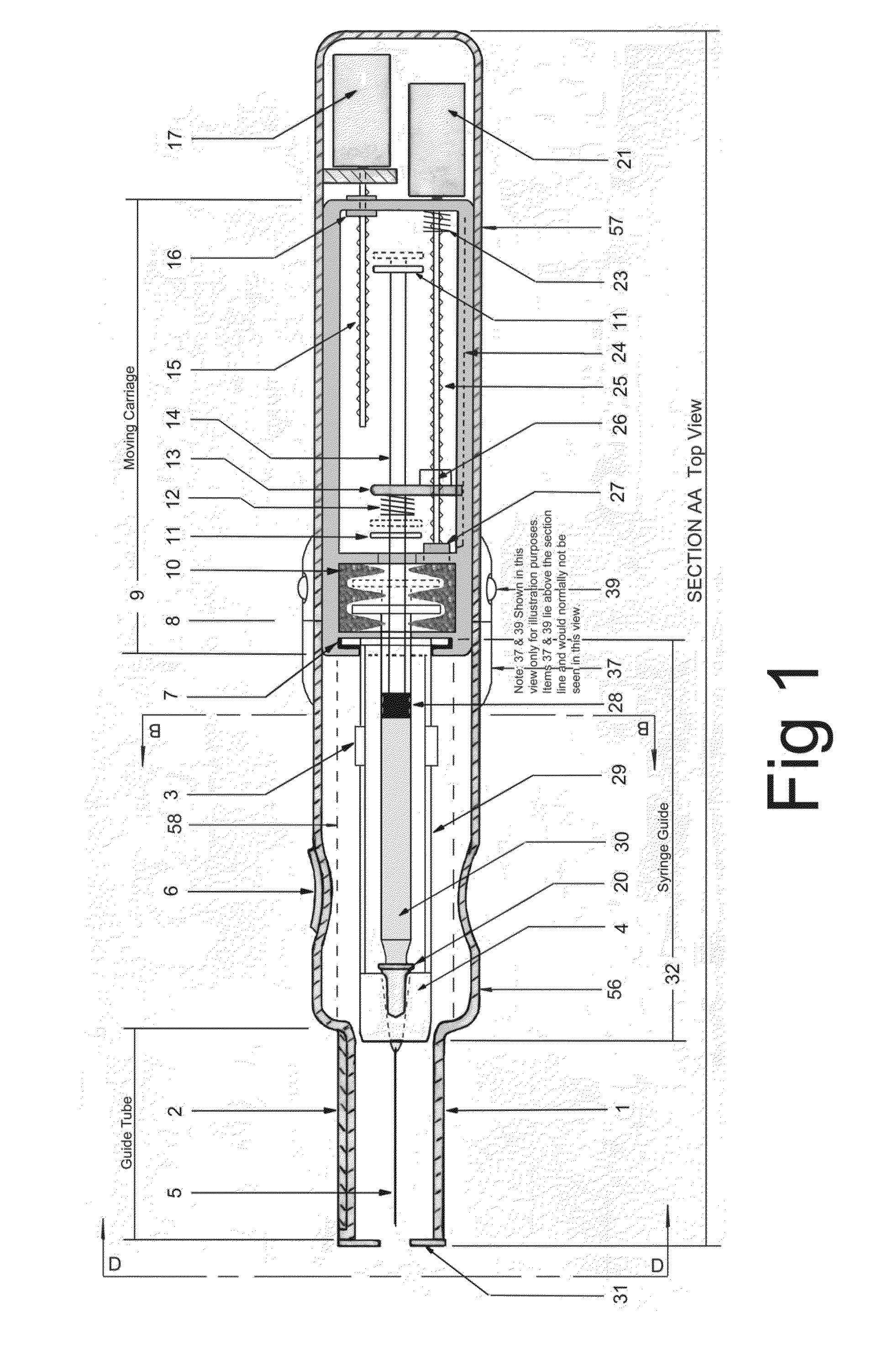
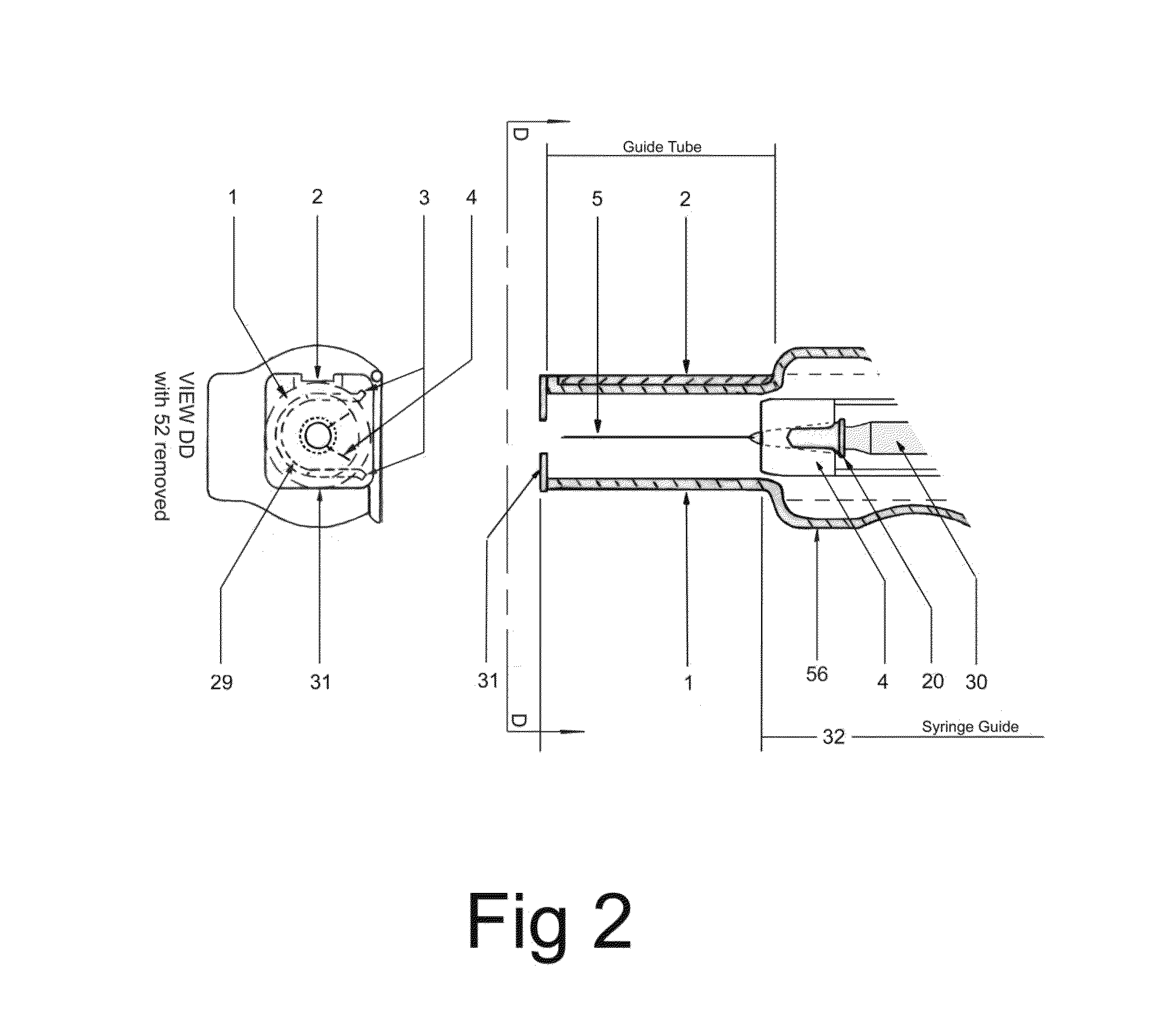
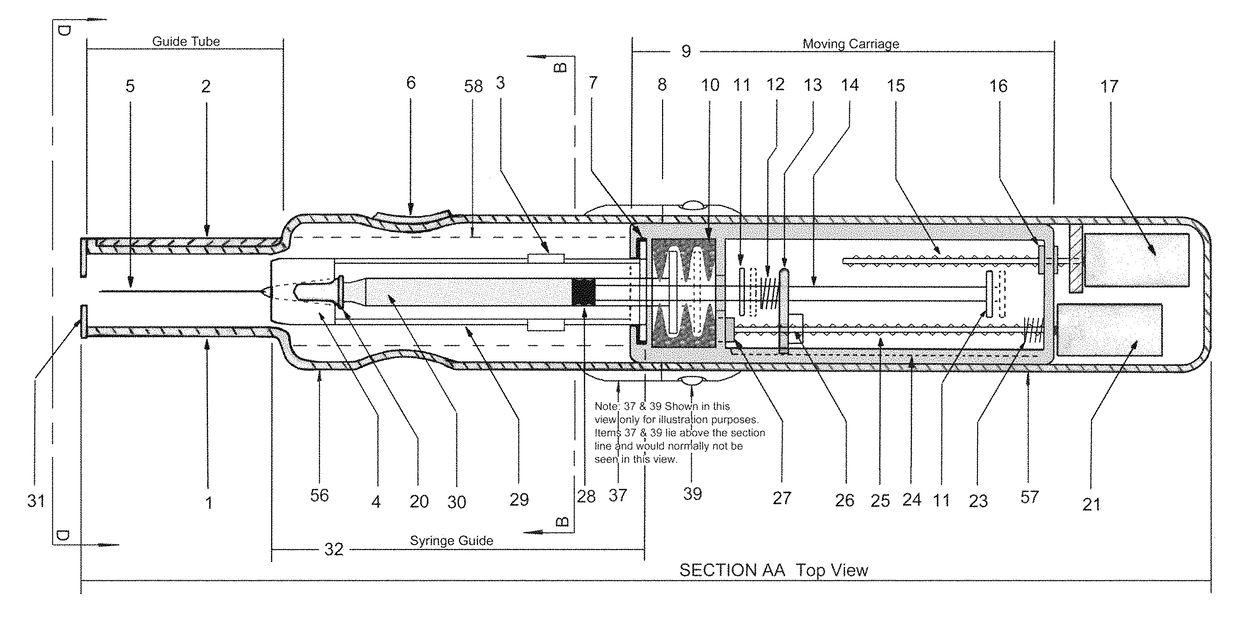
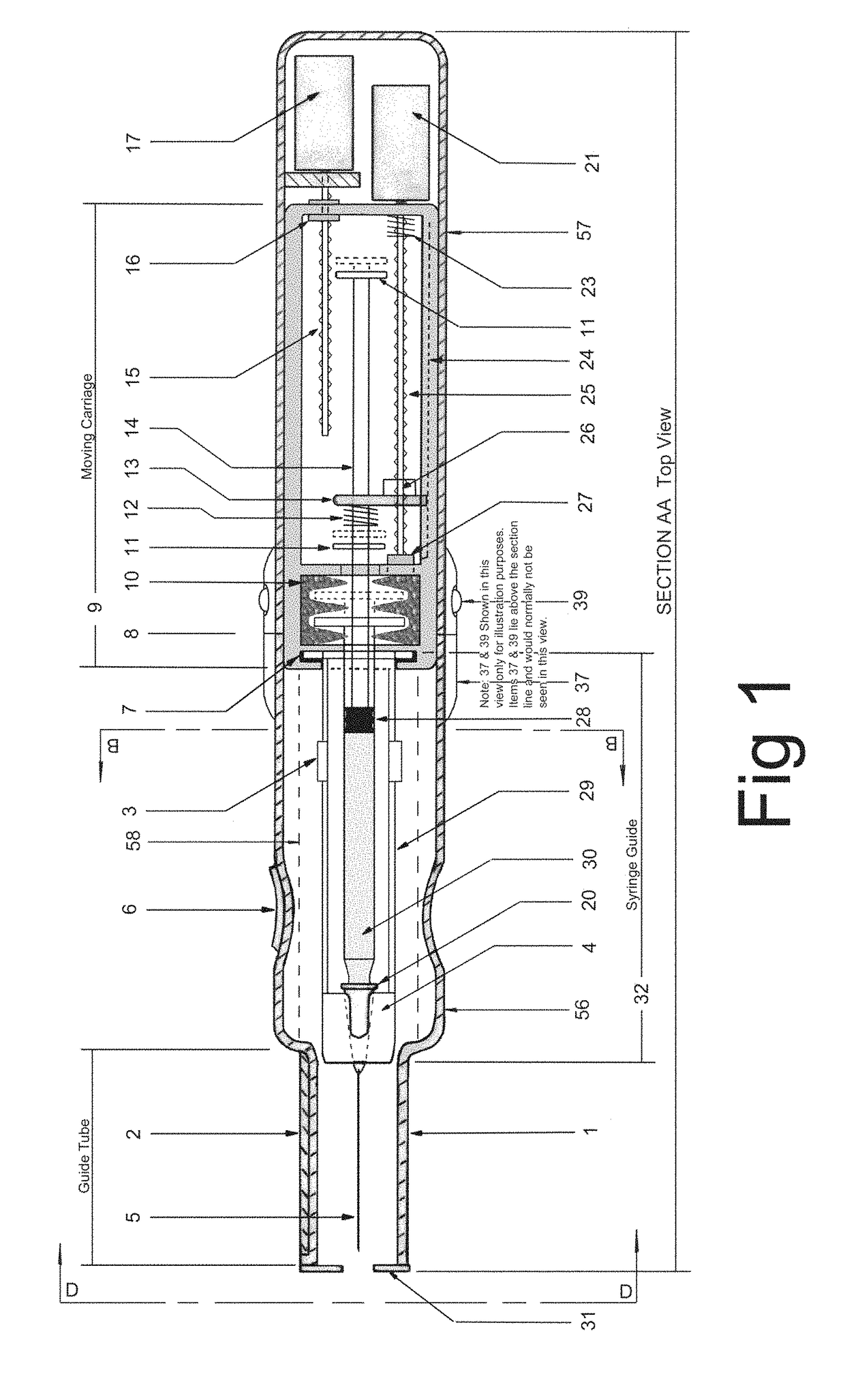
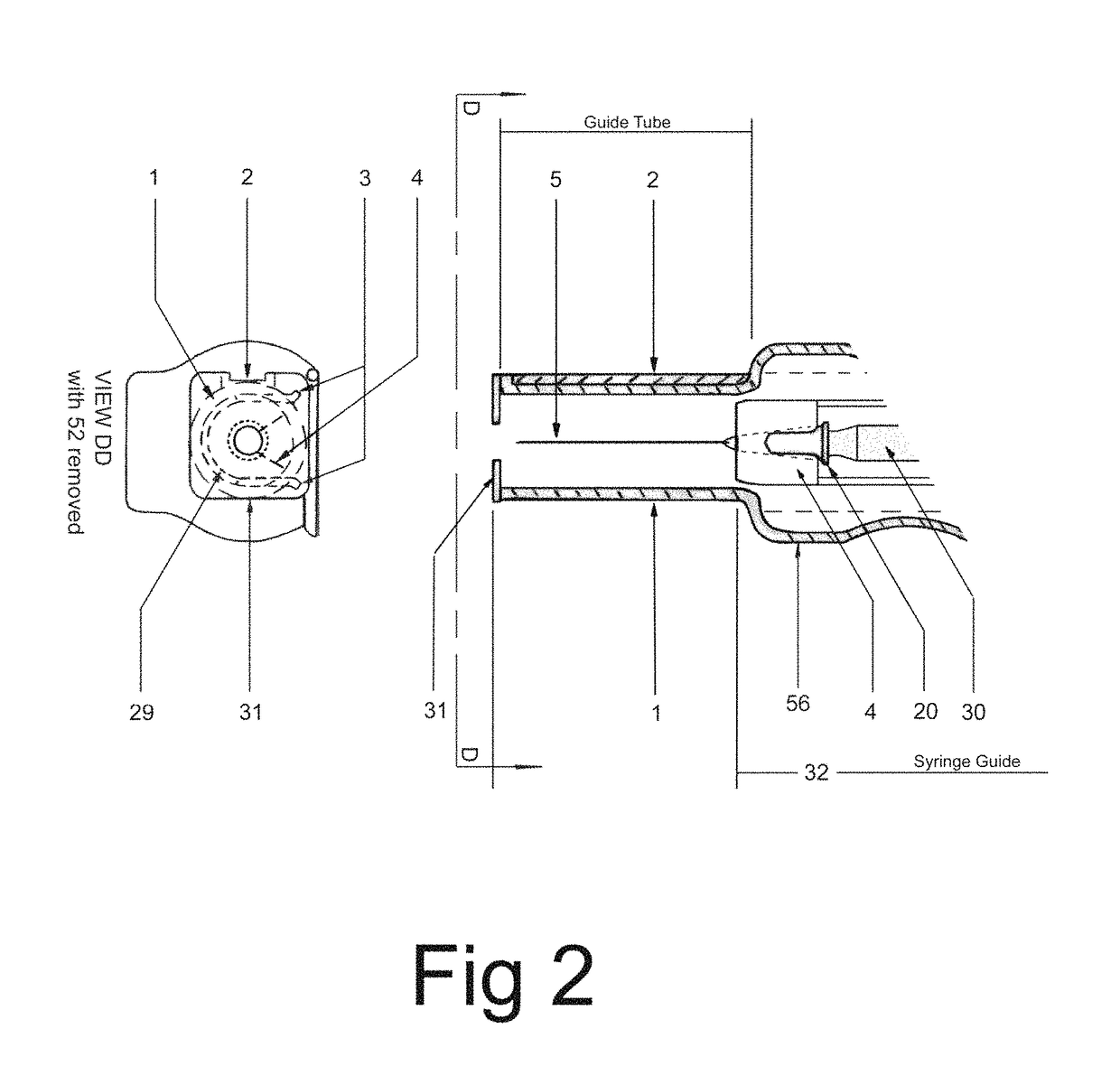
In an aspect, a medication delivering injector which includes a housing having opposing proximal and distal ends and an accessible internal cavity for inserting and removing a medicament container such as a syringe. The injector is designed to hold and manipulate a medication delivery device such as a large variety of standard and non-standard medical syringes with fixed or attached needles, assembled such that centrally located is a cylinder containing a liquid medicament and attached either permanently or removably to the distal end of the cylinder, is a hypodermic needle or cannula in fluidic communication with the cylinder. The needle can be from one-half inches to one-and-one-half inches in length in the illustrated embodiment and other sizes are possible by changes in scale of the injector. At the proximal end of the cylinder is an opening with an inserted seal or bung with an attached rod thus constituting a plunger. The central medicament containing cylinder could also be a standard medicament cartridge. Hereinafter, both are referred to as a “syringe”. A lid or access cover which, in an open position permits insertion and removal of the syringe into / from the housing in a horizontal fashion thus providing ease of loading. The syringe is inserted with the needle end toward the distal end of the housing and the plunger toward the proximal end of the housing. A movable carriage is disposed in the proximal end of the housing and slides in the axial direction forwards and rearwards such that a syringe, whose proximal end is gripped by the carriage, so moves with the carriage such that the needle exits the housing at the distal end of the housing and pierces the tissue of the patient prior to dispensing of the medicament, and then is retracted after the medicament has been dispensed by retraction of the carriage. Attached to the carriage is an actuator which pushes on the syringe plunger causing the medicament contained within the syringe cylinder to be dispensed through the needle into the patient's tissue. In one embodiment suitable for both removable needle and fixed needle syringes, the proximal end of the syringe including the syringe finger flange is gripped by an elastomeric flange grip which resides within the carriage, while the syringe distal end resides in and is supported by a “syringe guide” which is attached to the carriage and thus moved with it. In another embodiment which is so made to accommodate syringes with removable needles and their safe disposal, the syringe flange at the proximal end of the cylinder is gripped by an elastomeric flange grip which resides in the carriage as described above, while the syringe distal end is supported by a needle which resides in a removable disposable needle shield. The needle guide is biased toward the carriage and thus, the syringe body is compressed and guided as the carriage moves forward and rearward.Both the movement of the carriage and the actuator are controlled by servo motors which are controlled by electronics and a microcontroller so operating such that speeds and accelerations are controlled smoothly and gently so as to avoid the stop / start motion of motors controlled by limit switches and simple electronics or the vibration and abruptness such as result from injectors powered by compressed springs or gas. Furthermore, the forces are adaptive to the loads imposed and the requirements necessary for the proper dispensation of medicaments with high viscosity or sensitivity to shear forces.The housing, approximately midway between proximal and distal ends, is affixed by a hinge such that the device can be folded in half to provide for a more compact device to be stored and transported.On the distal end of the housing are electrical sensor pads in communication with the microcontroller such that contact with the patient's skin and the angle at which the injector is held against the skin and the steadiness with which the injector is being held can be ascertained. Within the housing are a haptic vibrator and an audio speaker, both producing a vibration which is variable in pitch in such a manner that biofeedback is provided to the injector user as to the pressure, angle and steadiness with which they are holding the injector against the skin. This facilitates the action of injection oneself in the gluteus muscle where visual feedback isn't available to the patient.Multiplexed onto the electrical sensor pads, is a TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) generator which is operational (at the user's choice) just before and during the injection to interrupt or quench the pain of tissue perforation often accompanied with needle injections.Contained on the surface of the housing such as on the access cover, is a display such that user menus, device state, directions, and battery charge status, etc. are displayed. Also contained on the surface of the housing, on the proximal half, are buttons which control the menus and selections that are shown on the display. These selections provide for the user to set such parameters as hypodermic insertion speed and medicament dispensing speeds, the preferred mode of user biofeedback which can include: speech mode (which can be accompanied by musical themes and ringtones, plus variable pitch tone and haptic vibration), MP3 mode (which has speech muted but includes musical ringtones and variable pitch tone and haptic vibration), and haptic mode (which is haptic vibration and audio tone queues needed for injector position biofeedback and readiness), plus mute mode (which provides no audio but the haptic vibration remains), and none, which provides no vibrational biofeedback, yet the display information always remains available.Also contained on the surface of the housing on the distal half, is an “injection initiate” button which causes the sequences required for performance of an injection to occur if said button is “enabled”.Contained within the electronics and its operating program is the ability to audibly play pre-recorded human speech in any language such that: directions in the form of consecutive steps which are required to load the medicament container (syringe) into the device, consecutive steps to perform an injection, steps to remove and properly dispose of parts, to alert of device status and menu choices, etc. can be played through the audio speaker. Also contained within the electronics and program is the ability to play musical ringtones as a distraction during the needle insertion and injection or when a scheduled injection alarm is reached, or calming human voice exhibiting bedside manner during the needle insertion and injection.Also contained within the electronics and software is a real-time clock-calendar which can store a patient's injection schedule and play a musical ringtone as an alarm as each scheduled injection becomes due. Also contained within the electronics and software are the ability to communicate with a personal computer through a USB port, which can also charge the injector's rechargeable battery. The battery in one embodiment, consists of three AAA batteries which can be rechargeable or non-rechargeable. The USB port in combination with an application running on the personal computer, is used to download the injection schedule into the real-time clock-calendar and to download ringtones and musical themes of the user's choice and to download foreign language sets for the pre-recorded human language feature.The injector can be further equipped with the capability to aspirate the tissue by drawing back on the plunger thus creating a vacuum into which fluids will flow. These fluids enter the syringe cylinder where they can be checked for the presence of blood by optical absorption in the red spectrum. This information is useful in the instances where intramuscular injections are to be given with drugs whose ‘Full Prescribing Information’ instructs the patient to aspirate and check for blood in the syringe which indicates that the puncture of a vein has occurred, and if so detected, to abort the injection and then re-inject into a different location.
Owner:INTELLIPEN INC
Apparatus and method for reducing subcutaneous fat deposits by electroporation with improved comfort of patients
InactiveUS20030149451A1Improve comfortLess discomfortElectrotherapyReduced subcutaneous fatTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
An apparatus and method for non-invasive treatment in lieu of cosmetic surgery is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a combination of a high and low voltage pulse generators connected to two or more electrodes placed on a treatment site of the patient's body. High voltage pulses, delivered to the electrodes, create an electric field that kills subcutaneous fat cells. Low voltage pulses, delivered to the same or individual electrodes provide transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), blocking the signals of discomfort or pain that may arise from the high voltage pulsing.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Electrical and magnetic stimulators used to treat migraine/sinus headache, rhinitis, sinusitis, rhinosinusitis, and comorbid disorders
ActiveUS8676324B2Avoid stimulationHeart defibrillatorsMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseMedical disorder
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation devices and magnetic stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of treating medical disorders using energy that is delivered noninvasively by such devices. The disorders comprise migraine and other primary headaches such as cluster headaches, including nasal or paranasal sinus symptoms that resemble an immune-mediated response (“sinus” headaches). The devices and methods may also be used to treat rhinitis, sinusitis, or rhinosinusitis, irrespective of whether those disorders are co-morbid with a headache. They may also be used to treat other disorders that may be co-morbid with migraine or cluster headaches, such as anxiety disorders. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, one or both of the patient's vagus nerves are stimulated non-invasively. In other embodiments, parts of the sympathetic nervous system and / or the adrenal glands are stimulated.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Synthetic traveling wave transcutaneous electrical stimulation device
InactiveUS20060190057A1Increase painImproved discomfort reliefElectrotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationDisplay device
A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device for treating a user's lower back pain or discomfort is provided. The inventive device comprises a stimulation pad with an array of electrodes therein. A controller communicates with the electrodes to energize / de-energize them in a patterned, sequential manner. The patterned actuation of the electrodes in a sequential fashion provides electrical impulses to the patient's skin, simulating a transverse wave motion. The transverse wave motion simulation provides the user with the effect of the electrical stimulation combined with the mechanical tissue stimulation received in traditional massage therapy, resulting in improved pain and discomfort relief. The device may use programs stored in the controller. Alternatively, the user may manually actuate one or more electrodes as well as manually move the electrode actuation to concentrate on a specific lower back region using an electrostatic touch pad or the equivalent. The user may also use voice commands to access the stored programs, move the electrode stimulation region, change the electrode actuation intensity and / or dwell time. The device may store the user's manually-generated routines for repeating when desired. A visual display may provide feedback to the user regarding the electrode actuation position and pattern.
Owner:REESE EDWARD W
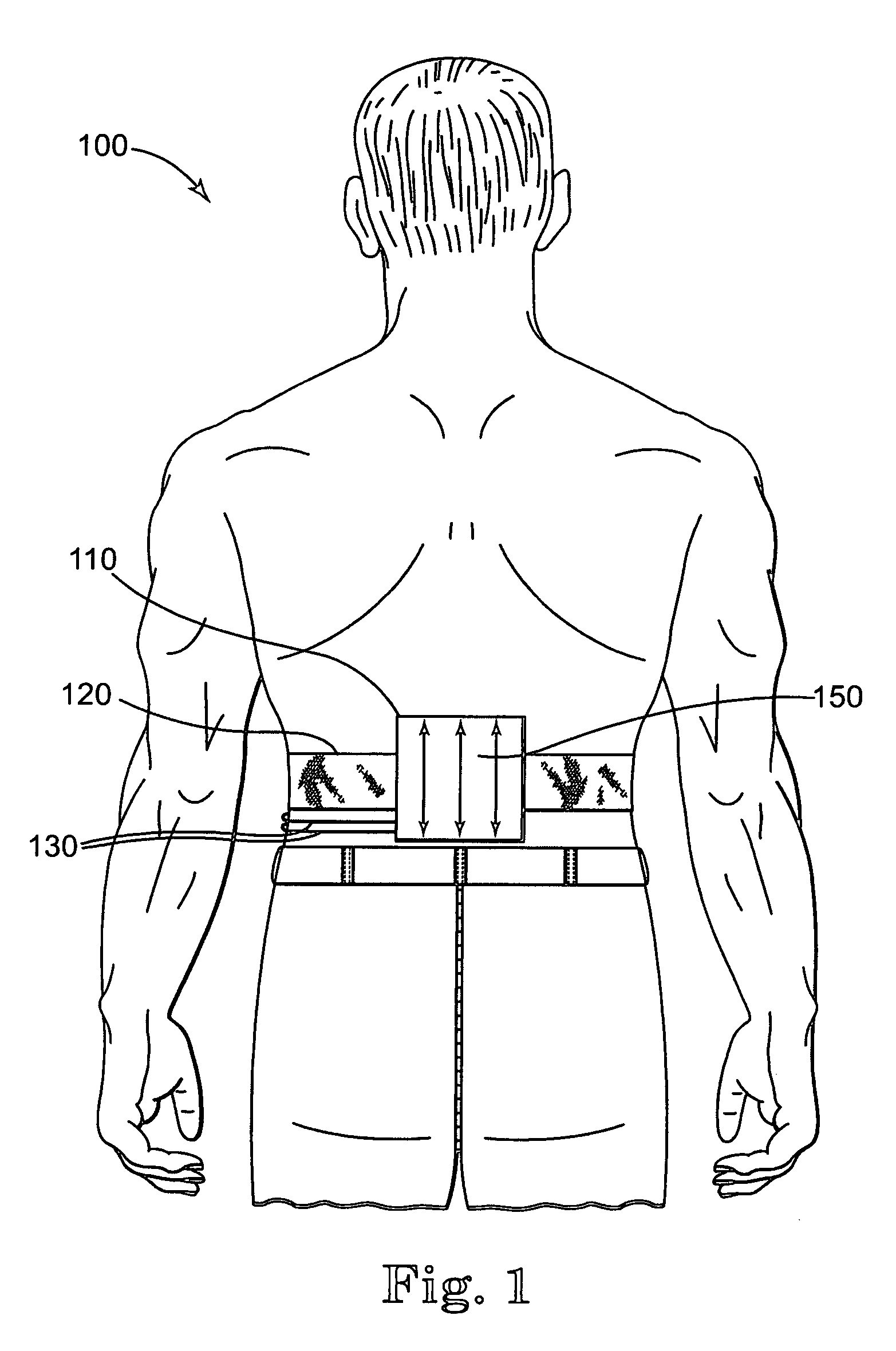
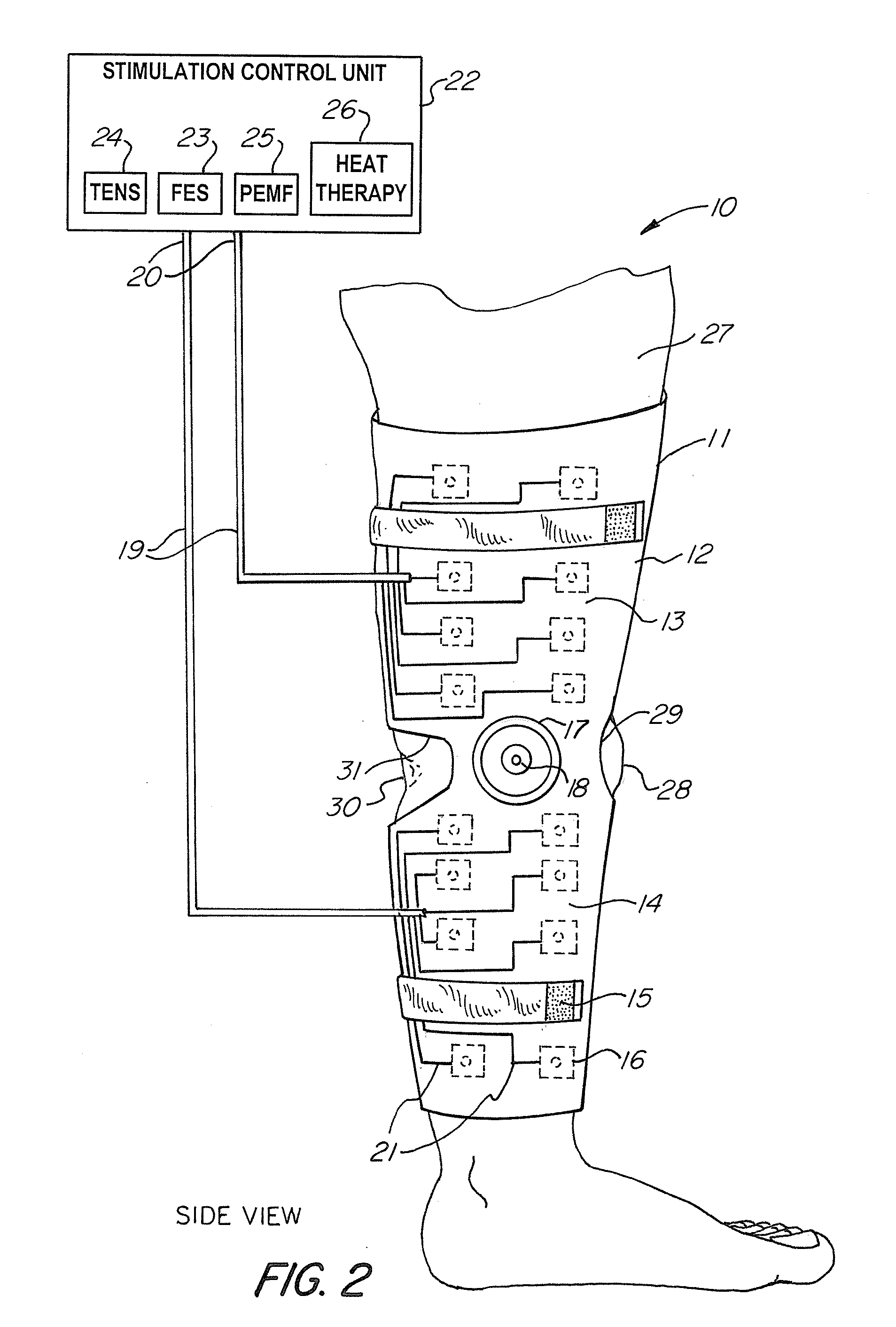
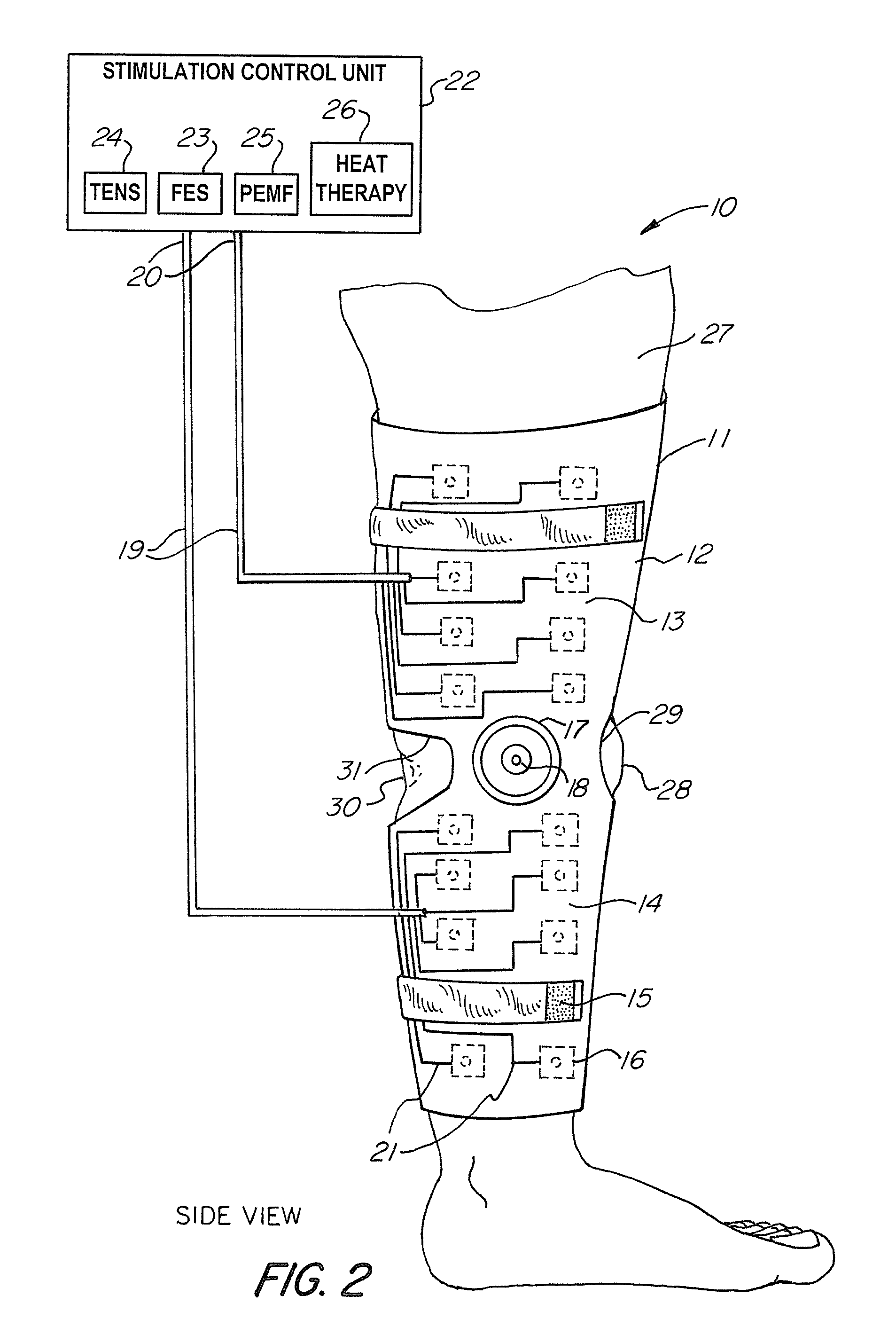
Universal Musculoskeletal Rehab Device (Brace, Sleeve, or Pad) For Electrical Treatment Modalities and Biofeedback Response Monitoring
InactiveUS20130085317A1Convenient treatmentEnhancing rehabilitative treatmentElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyDiseaseInteractive software
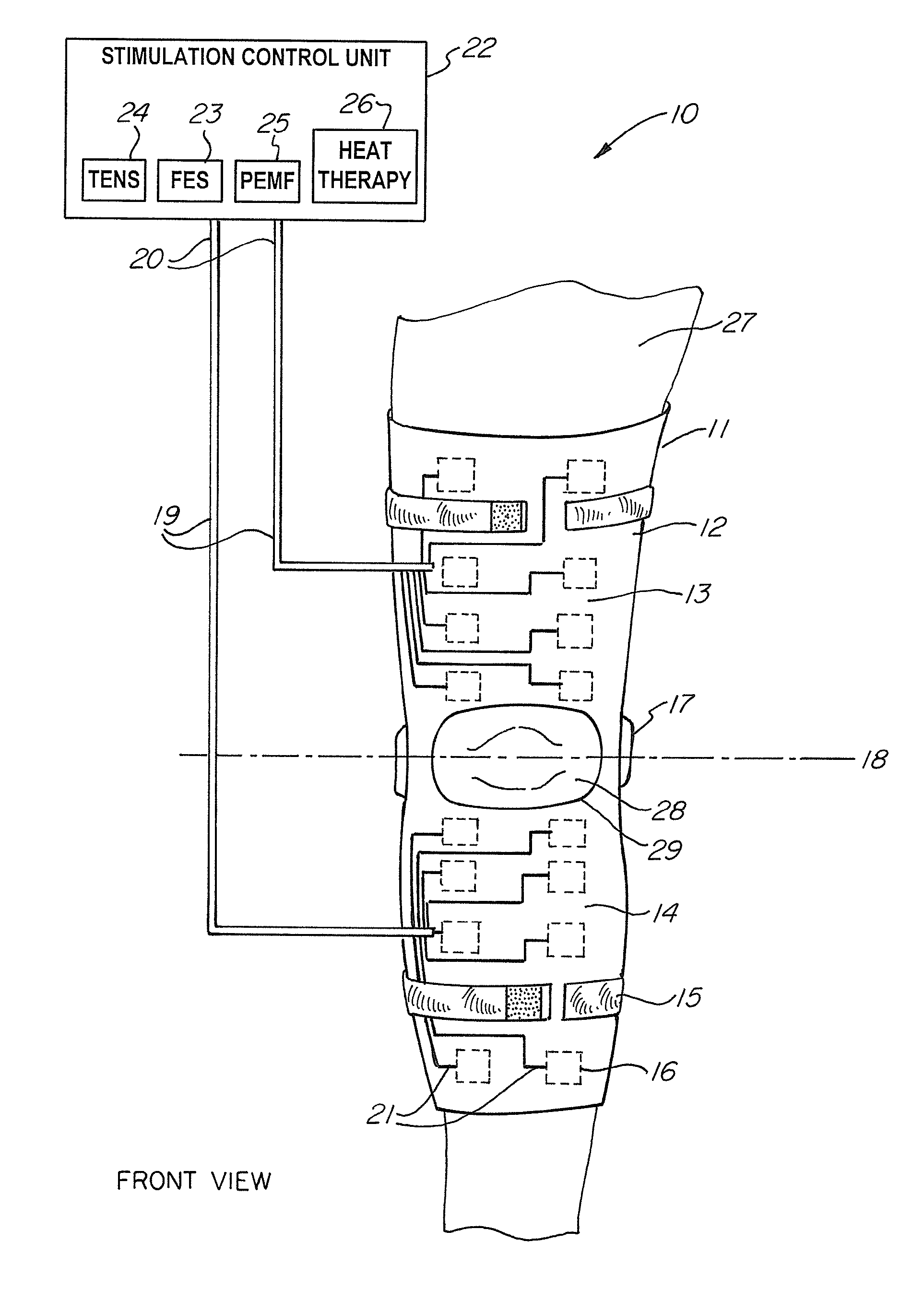
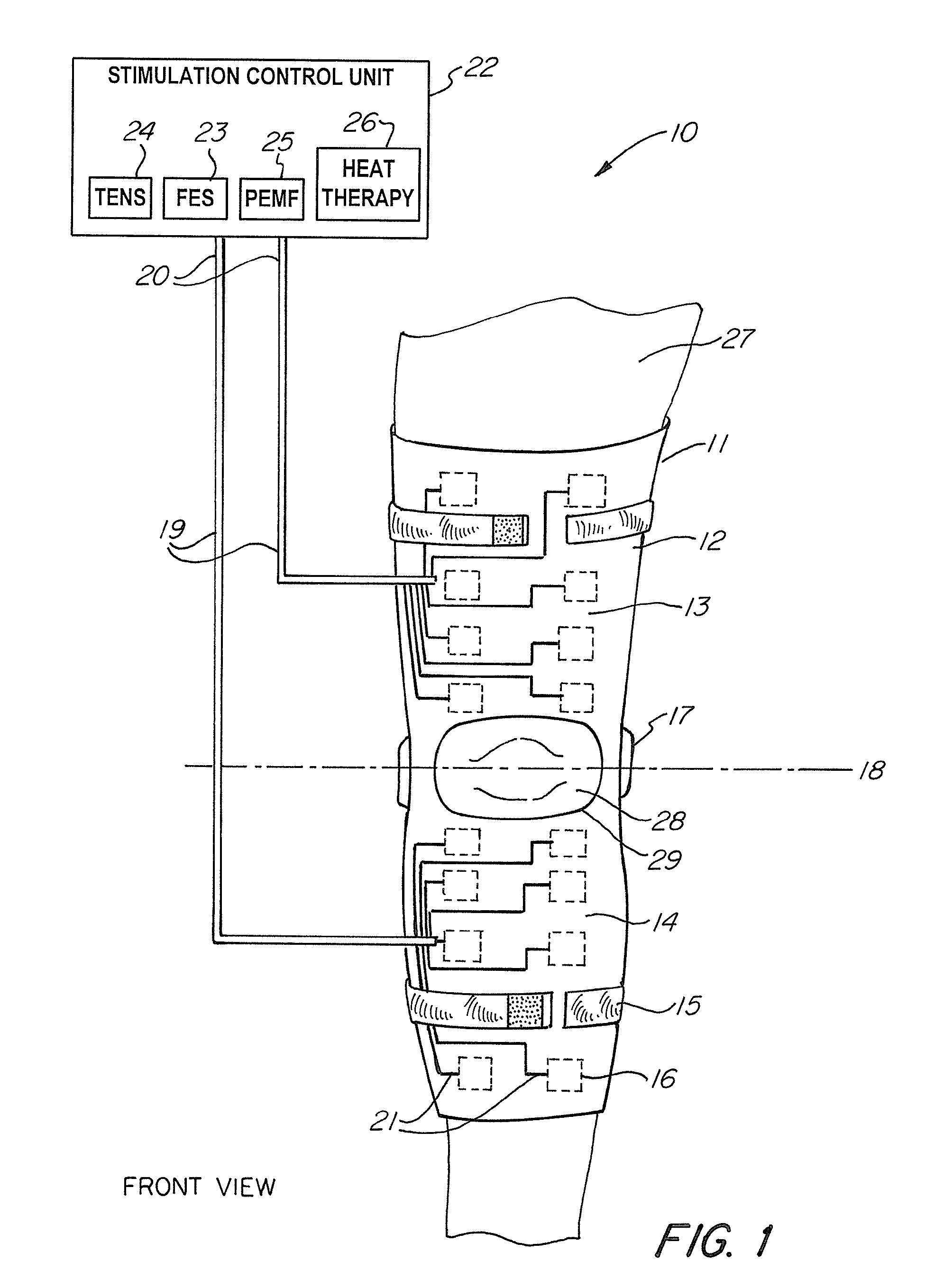
A non-invasive device for assisting the treatment of any kind of musculoskeletal disorder, including but not exclusive of those of joint, limb, and spine disorders, includes a brace, sleeve, flexible pad, or any combination of the three, a plurality of electrodes disposed thereon, wherein the plurality of electrodes transmit at least three electrophysical modalities, and a stimulation control unit having interactive software to establish a controlled sequence of transmission of the at least three electrophysical modalities and communicating the controlled sequence to the electrodes. The at least three electrophysical modalities are chosen from a group consisting of neuromodulating functional electrical stimulation, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation, and heat therapy stimulation. The stimulation control unit also provides feedback data using the electrodes for monitoring and integration with the interactive software to analyze and assess biomechanical, neuromuscular, and neurological responses to the device.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
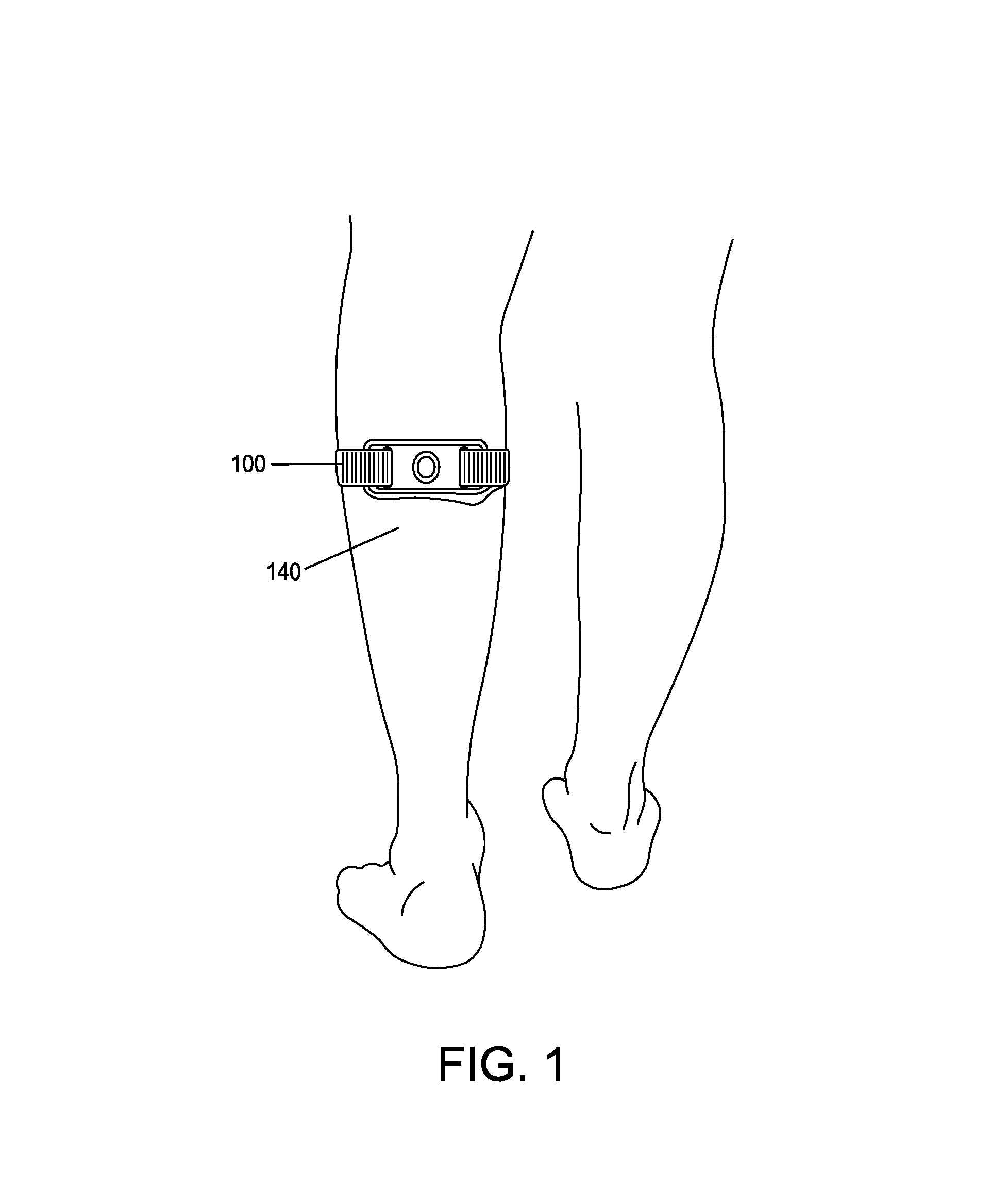
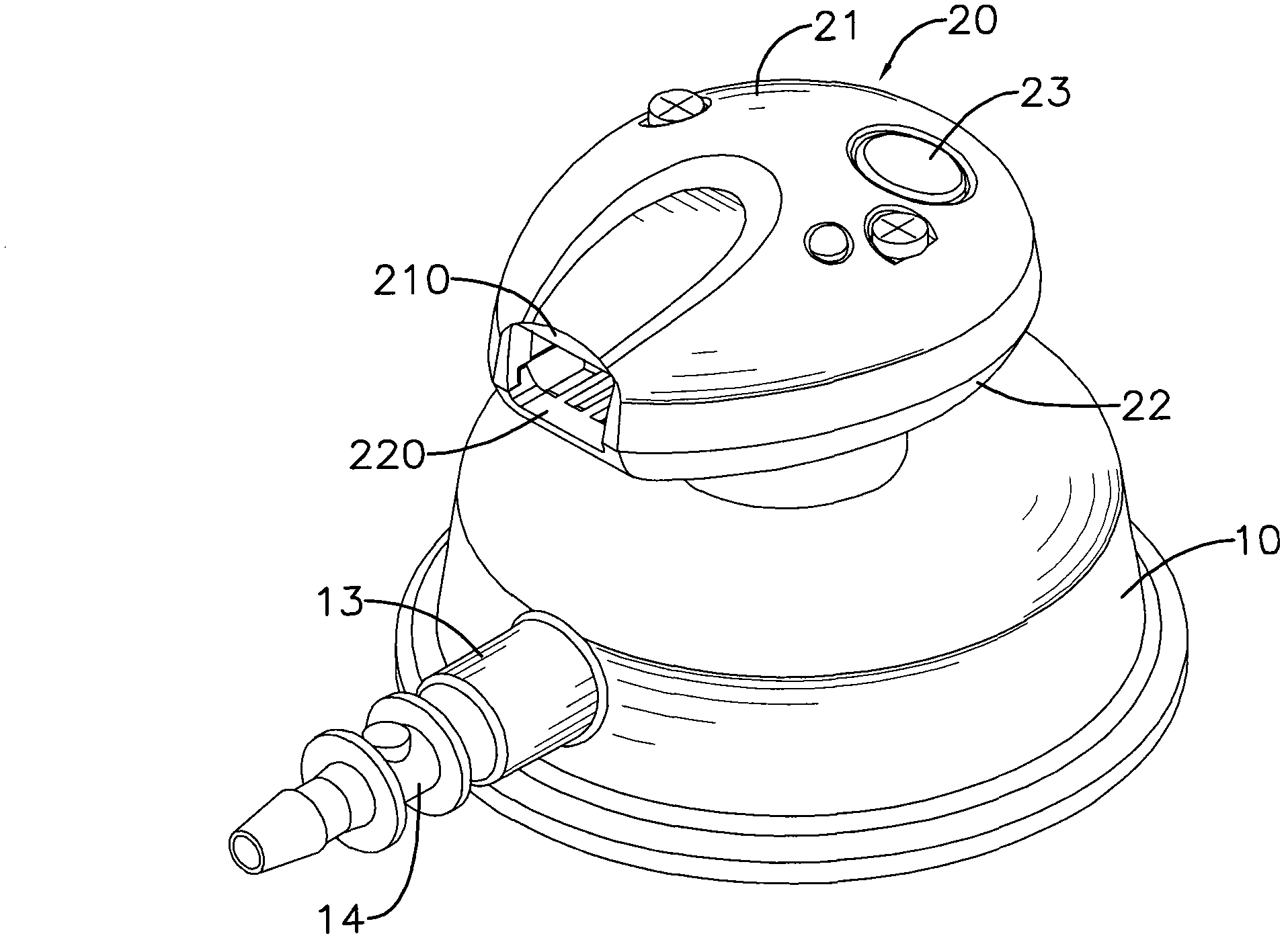
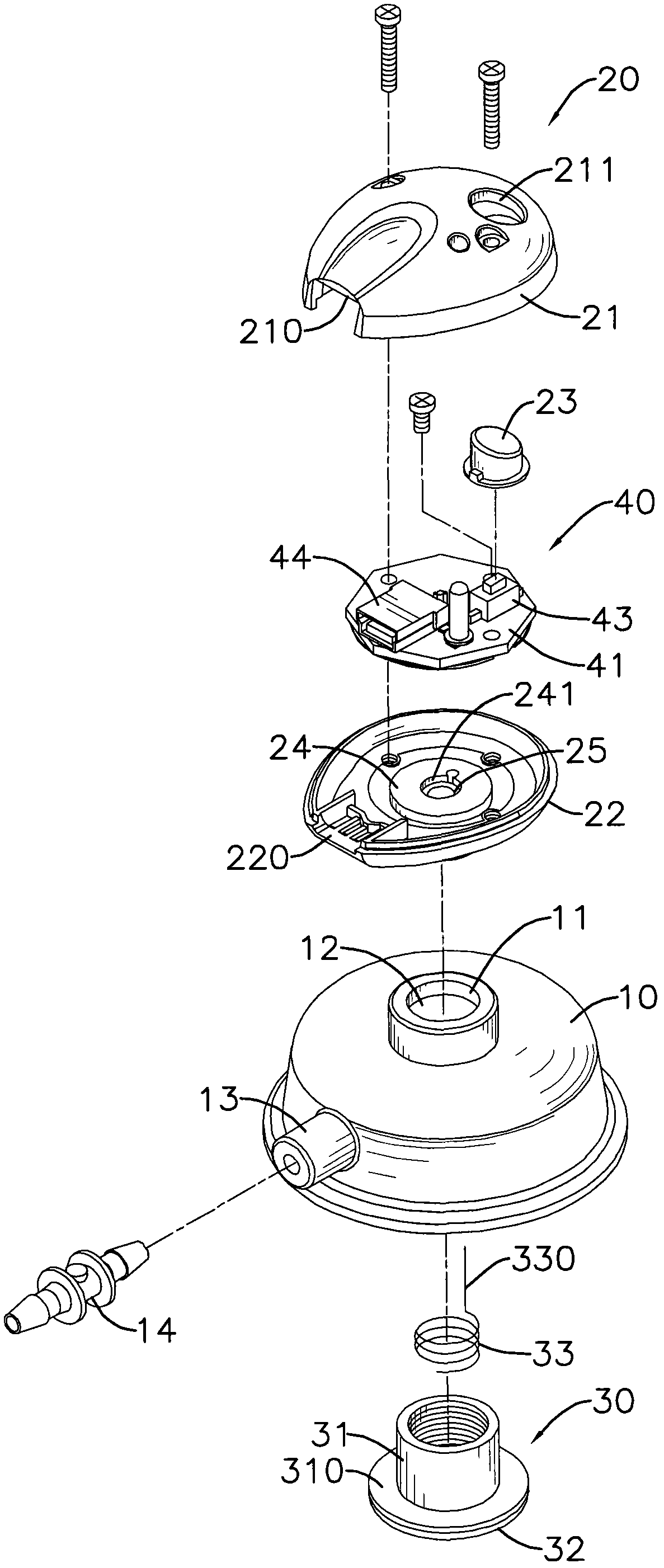
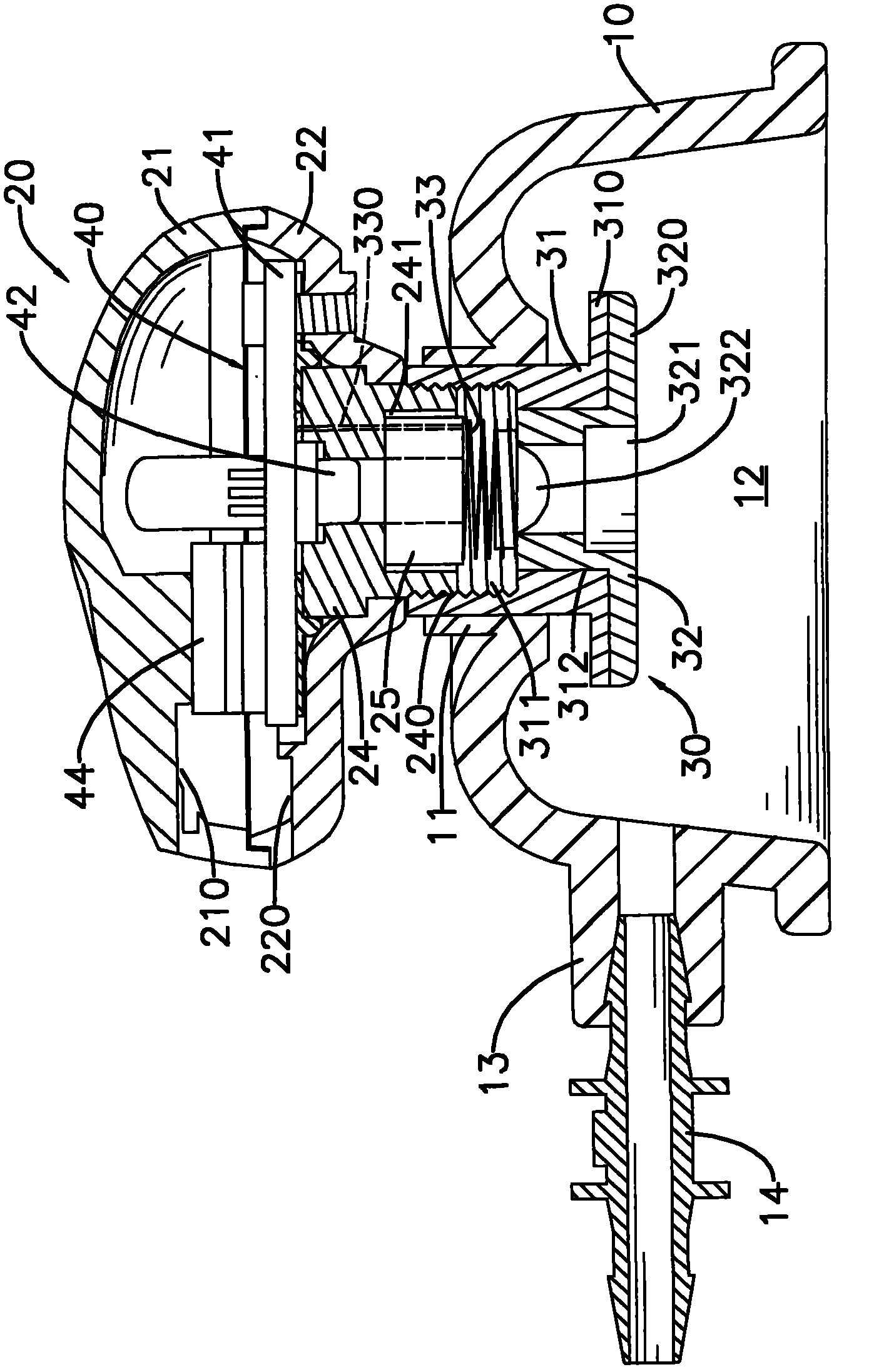
Apparatus and method for relieving pain using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
ActiveUS8948876B2Easy and rapid and clinically valid placementMinimize interferenceExternal electrodesArtificial respirationElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in humans, comprising a housing; stimulation means mounted within the housing for electrically stimulating nerves; an electrode array releasably mounted to the housing, connectable to the stimulation means, and comprising electrodes for electrical stimulation of nerves; control means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for controlling the stimulation means; monitoring means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for monitoring the stimulation means; user interface means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means for controlling the stimulation means; display means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means and the monitoring means for displaying the status of the stimulations means; and a strap attached to the housing and configured to hold the housing, stimulation means and electrode array at a specific anatomical location to treat pain.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX INC
Detecting cutaneous electrode peeling using electrode-skin impedance
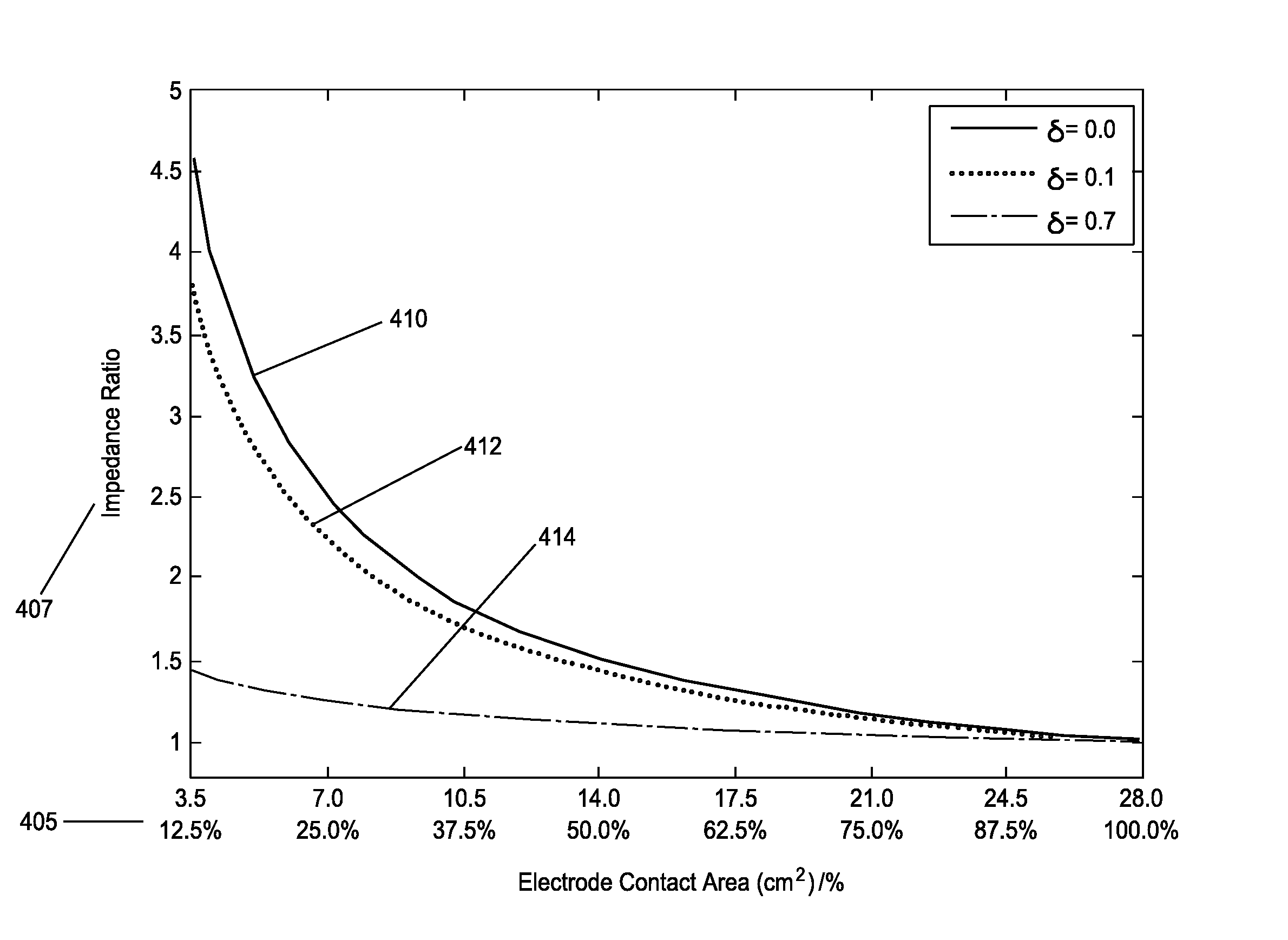
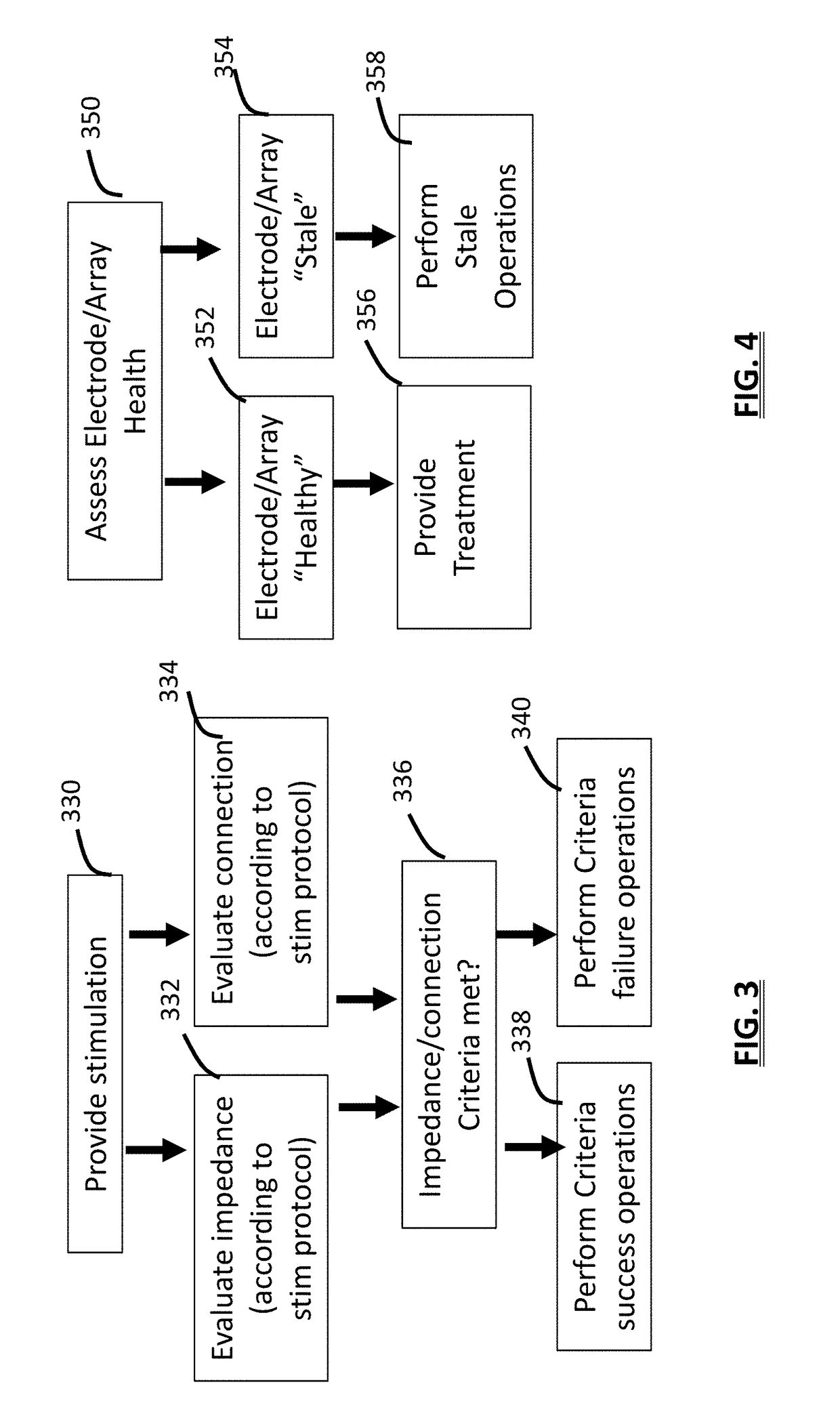
ActiveUS9474898B2Reduce riskContinuous measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in a user, the apparatus comprising:stimulation means for electrically stimulating at least one nerve;an electrode array connectable to said stimulation means, said electrode array comprising a plurality of electrodes for electrical stimulation of the at least one nerve, said electrodes having a pre-formed geometry and known electrode-skin contact area size when in complete contact with the user's skin;monitoring means electrically connected to said stimulation means for monitoring the impedance of the electrical stimulation through said electrode array; andanalysis means for analyzing said impedance to estimate a change in the electrode-skin contact area.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX INC
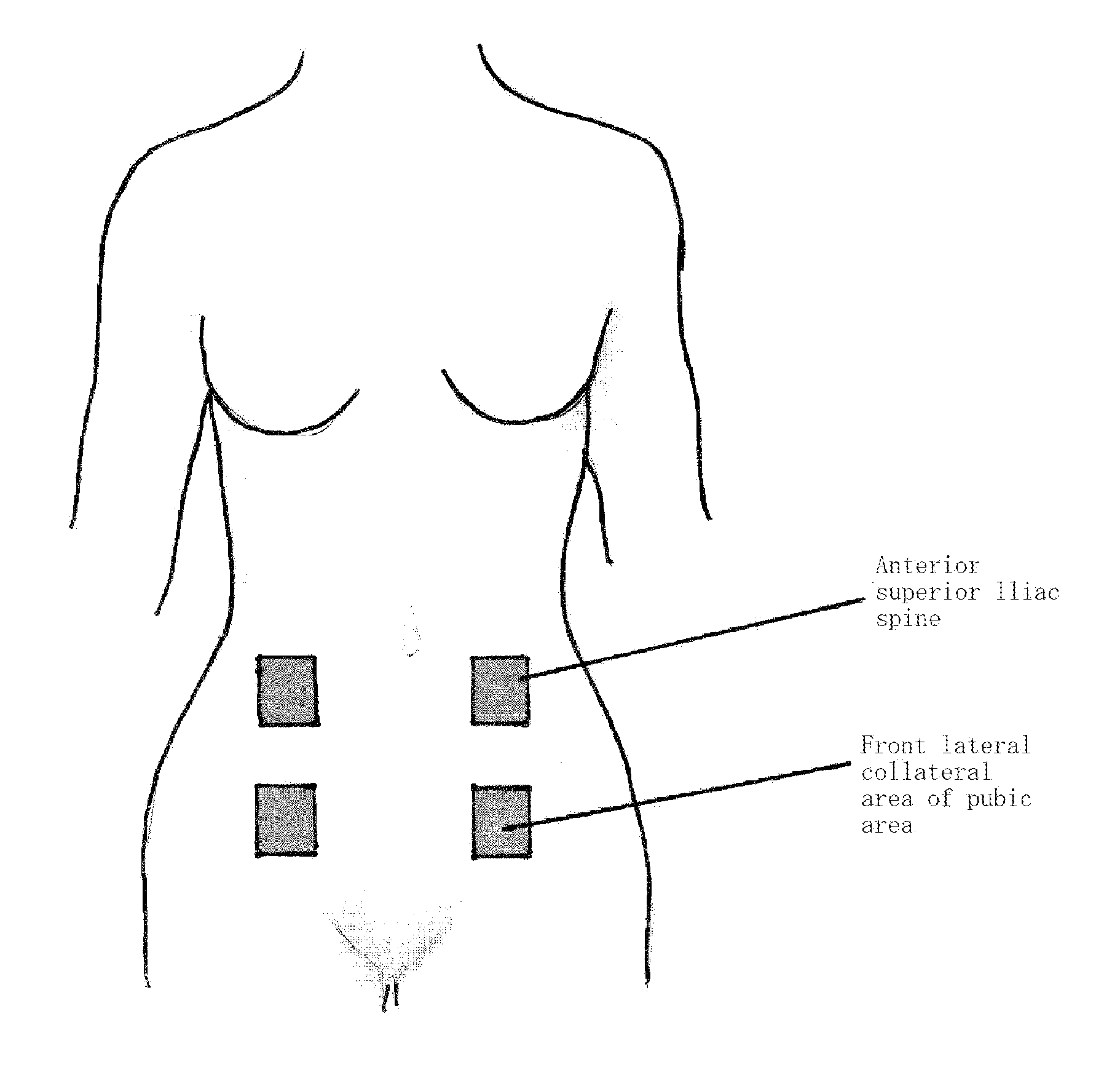
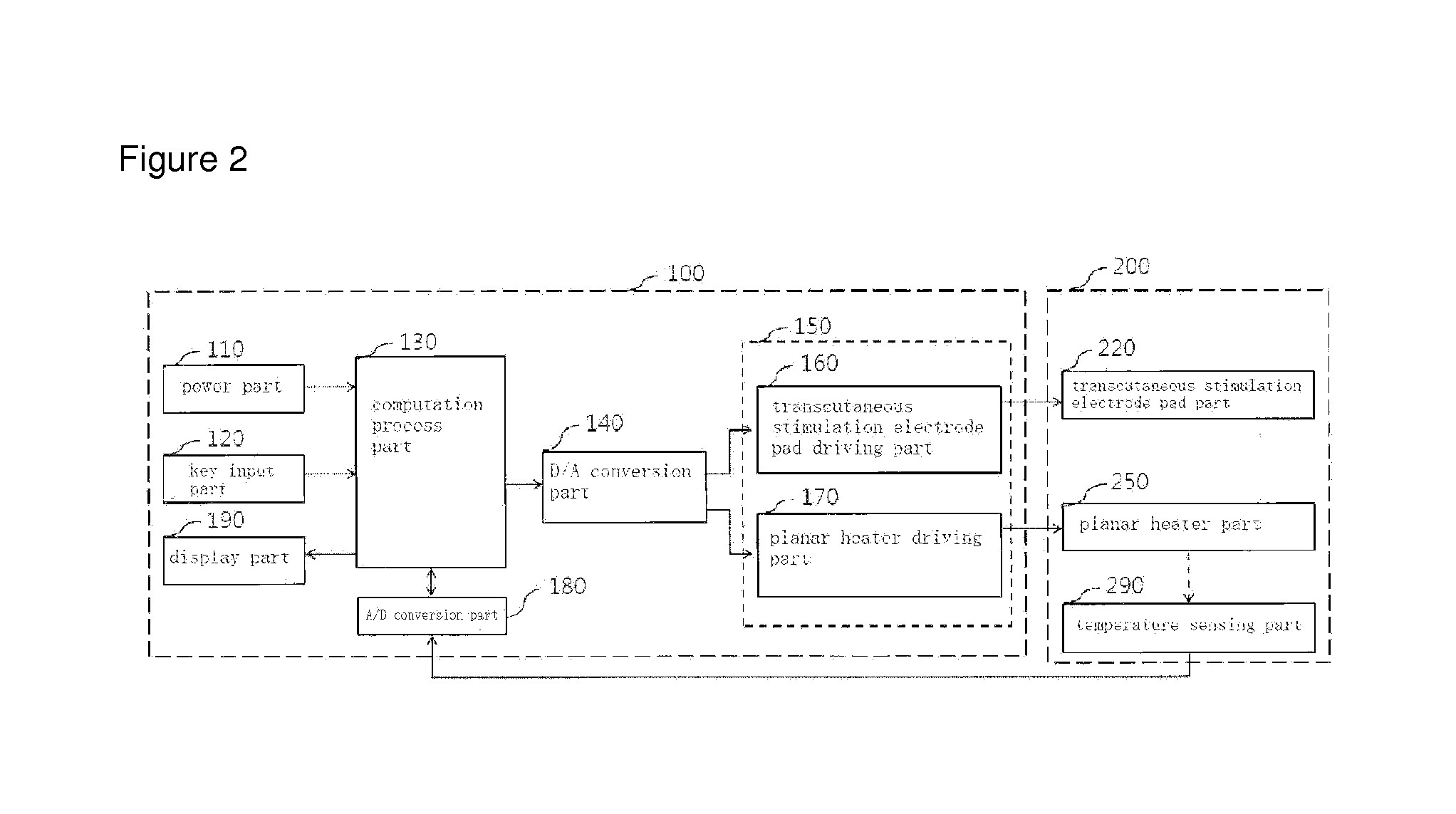
Portable combined stimulation device for alleviating menstrual pain
ActiveUS20120109233A1Alleviate menstrual painEffectively alleviatedElectrotherapyTherapeutic coolingThermal stimulationTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
The present invention relates to a portable device for alleviating menstrual pain through transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and thermal stimulation. More particularly, the present invention relates to a portable device for alleviating menstrual pain by applying transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation to the abdominal and back area of a user through the use of a planar heart embedded in the stimulating electrode pad. The stimulating electrode pad is a patch type one which is attachable / detachable to / from any body part with menstrual pain. The portable device for alleviating menstrual pain in the public area of the user according to the present invention comprises, a menstrual pain alleviating unit and a main body unit. The menstrual pain alleviating unit includes a transcutaneous stimulating electrode pad portion provided with a transcutaneous stimulating electrode to apply transcutaneous stimulation to the abdominal or back area of the user, and a planar heater portion provided with a planar hater to apply thermal stimulation to the abdomen of the user. The main body unit includes a power portion for supplying power to the menstrual pain alleviating unit, and an operation processing portion for generating a transcutaneous stimulating electrode control signal for controlling the transcutaneous stimulating electrode pad portion and a planar heater control signal for controlling the planar heater portion. The menstrual pain alleviating unit further includes a temperature sensing portion provided with a temperature sensor mounted on the planar heater portion to sense the temperature of the planar heater portion, and an A / D converting portion for converting the signal output from the temperature sensing portion into a digital signal.
Owner:LEE WON JOON +3
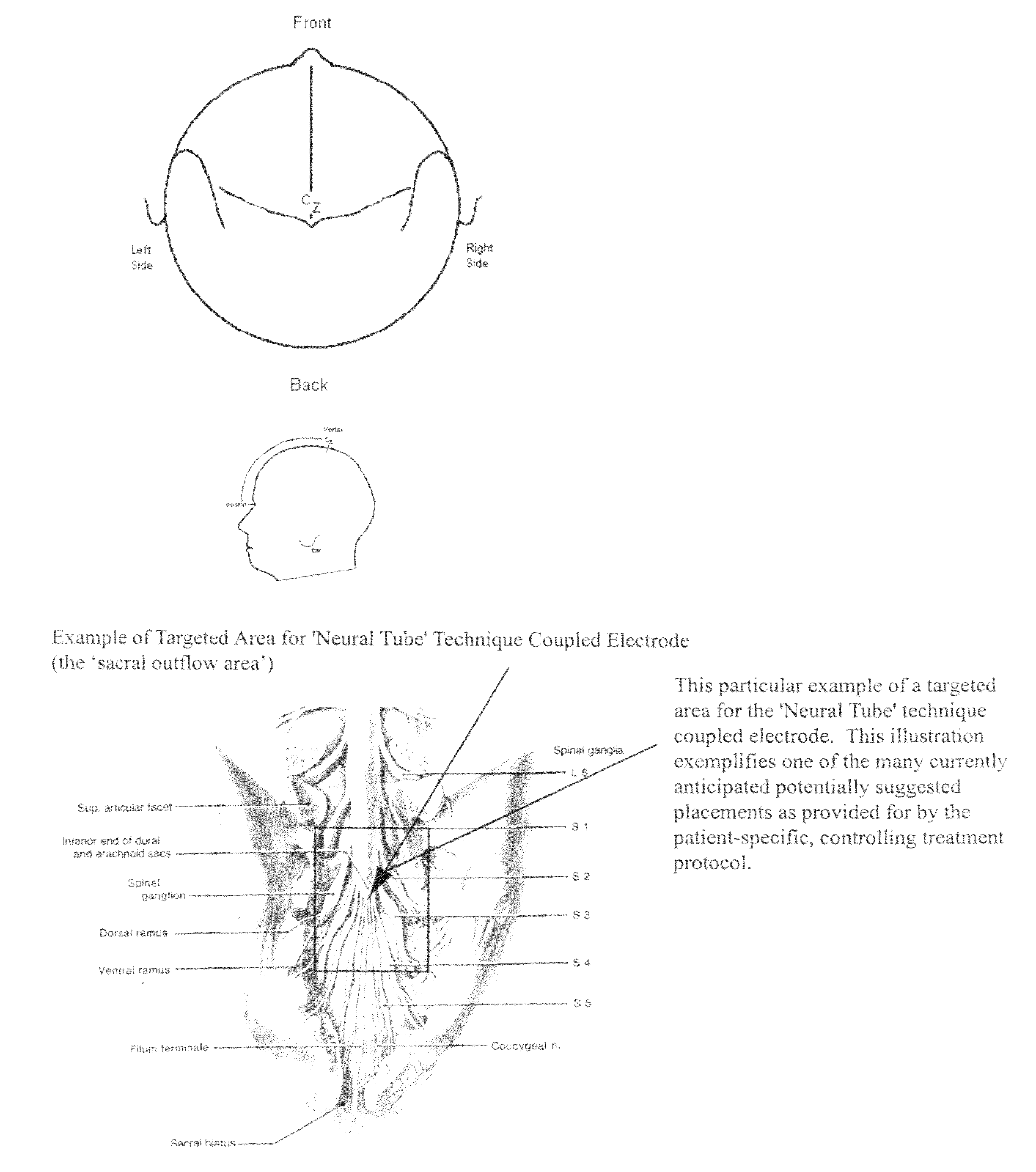
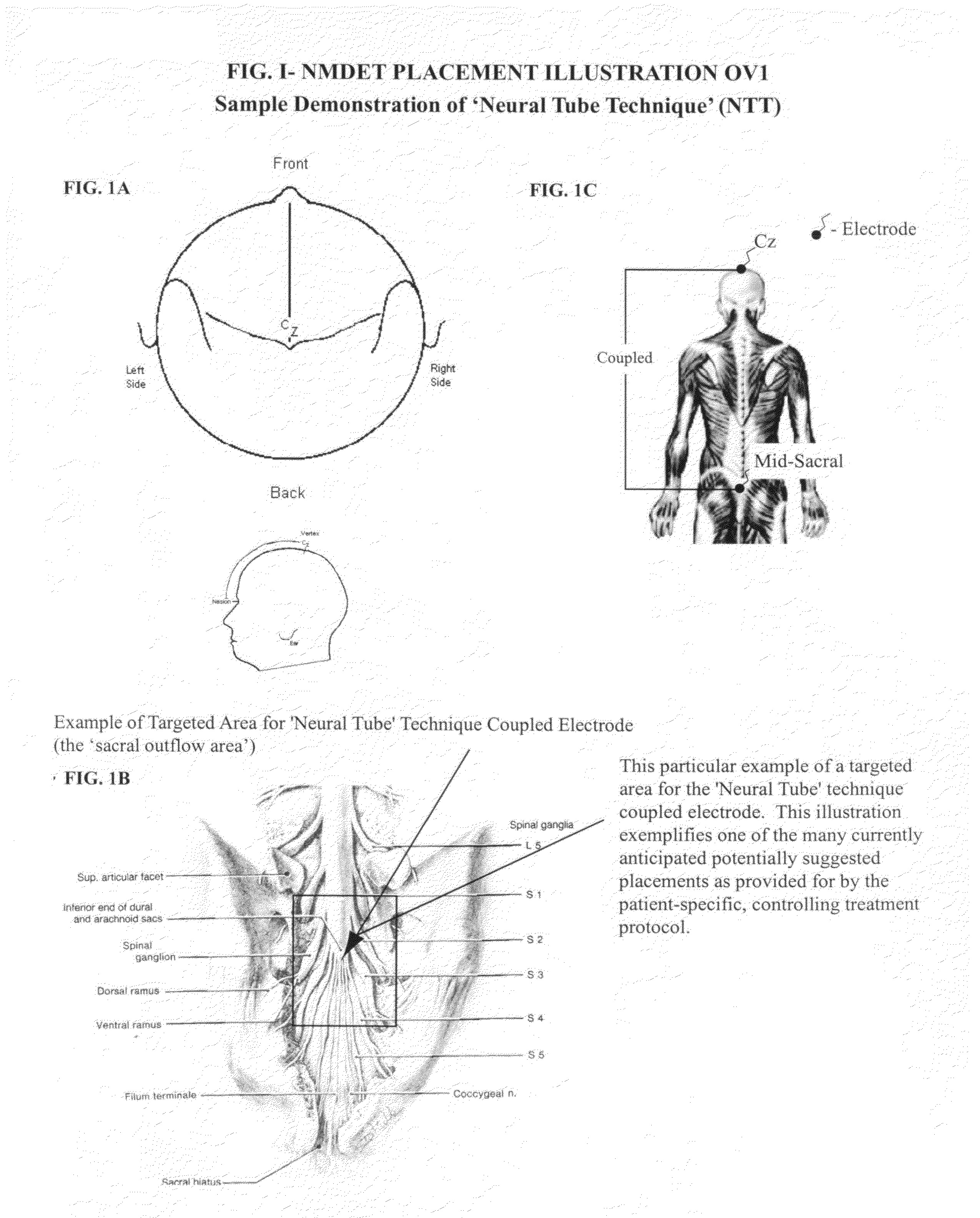
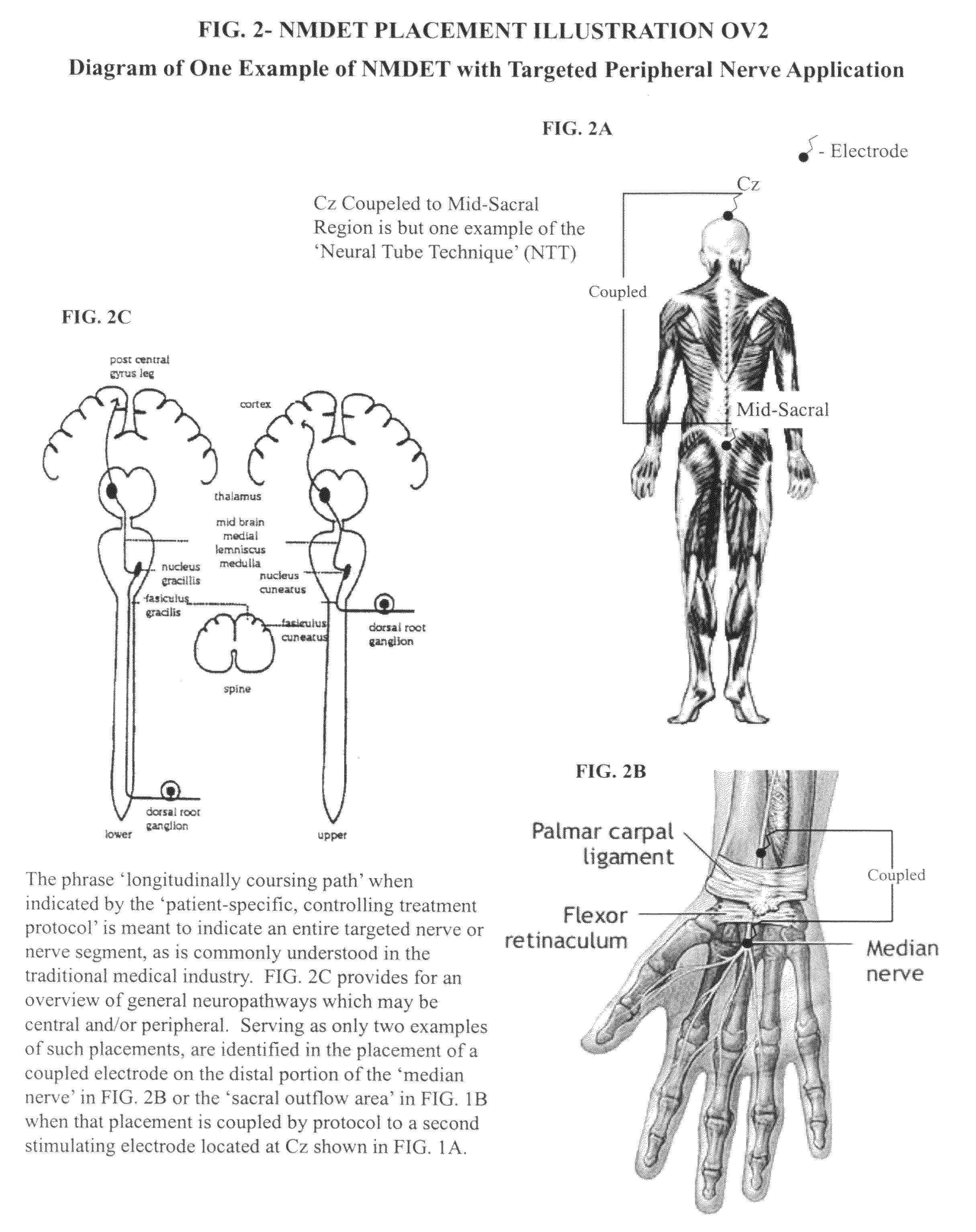
Coupled neuraxial mesoscopic desynchronization electrostimulation therapy (cNMDET) method
ActiveUS8428738B2Add supportIncrease capacityElectrotherapyElectrode placementTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
This novel therapeutic (reparative, etiotropic not merely symptomatolytic) electrostimulatory method hereinafter referred to as Coupled Neuraxial Mesoscopic Desynchronization Electrostimulation Therapy (cNMDET) is comprised of a varied combination of progressively sequenced electrode placements and its clinically targeted areas which are comprised of the CNS [regions of the brain and spinal cord including, but not limited to, the underlying clinicopathologic mechanisms of the ANS] and clinically involved components of the PNS variably coupled in such a manner as to apply this therapeutic electrostimulation (reparative modulation) along the coursing path (longitudinally) of the targeted neural pathway over a segment and / or in its entirety, as well as, the utilization of patterned applications for involved joints, muscles, fascia, ligaments, tendons and areas involved in inflammatory processes of clinical significance accomplished through the application of, preferably, but not limited to, Coupled Neuraxial Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (cNTENS) and Coupled Neuraxial Transcranial Direct Stimulation (ctDCSn).
Owner:VALENCIA ANDREW D
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and method of using same
ActiveUS20080207985A1Avoid problemsElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationPulsed DC
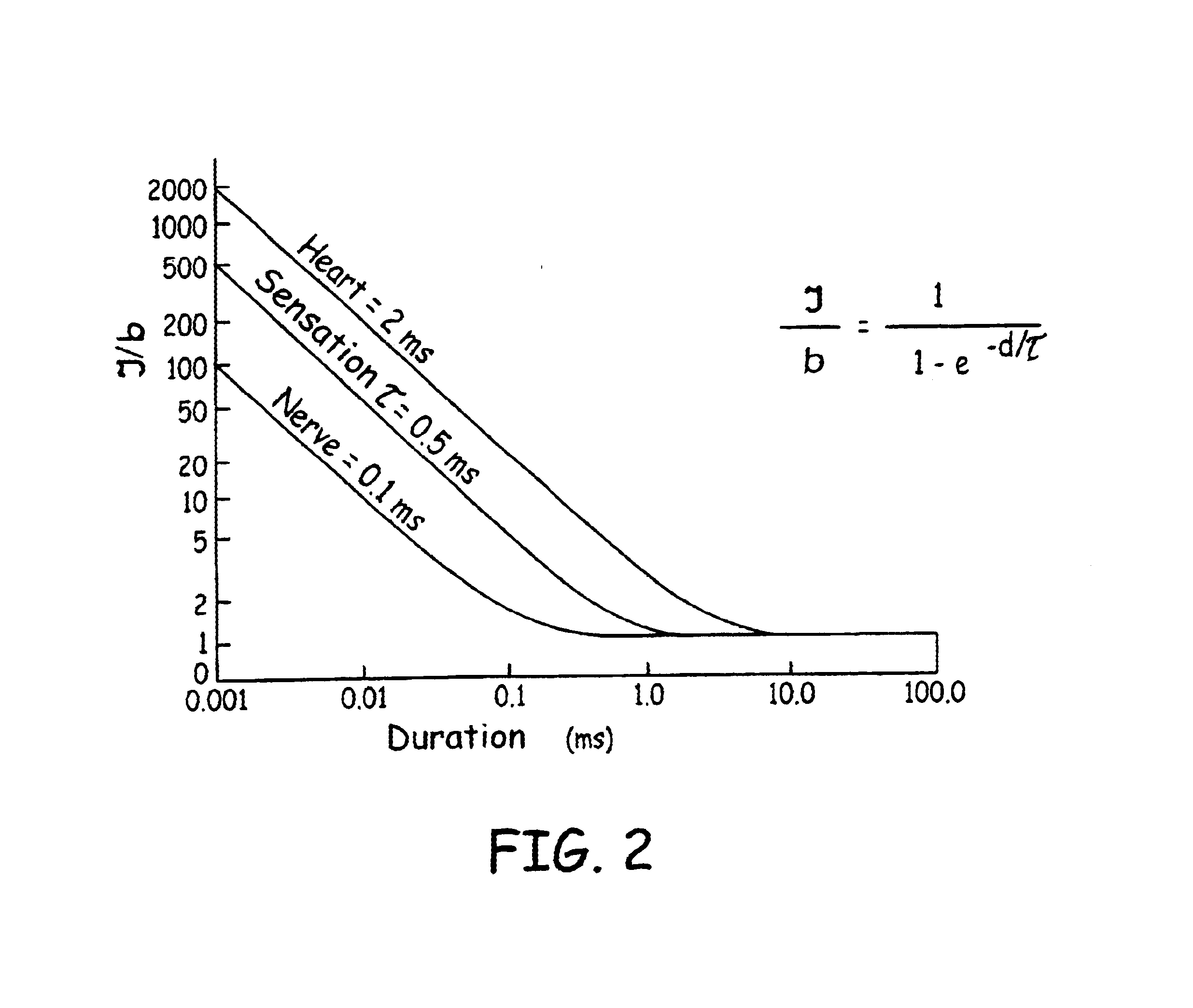
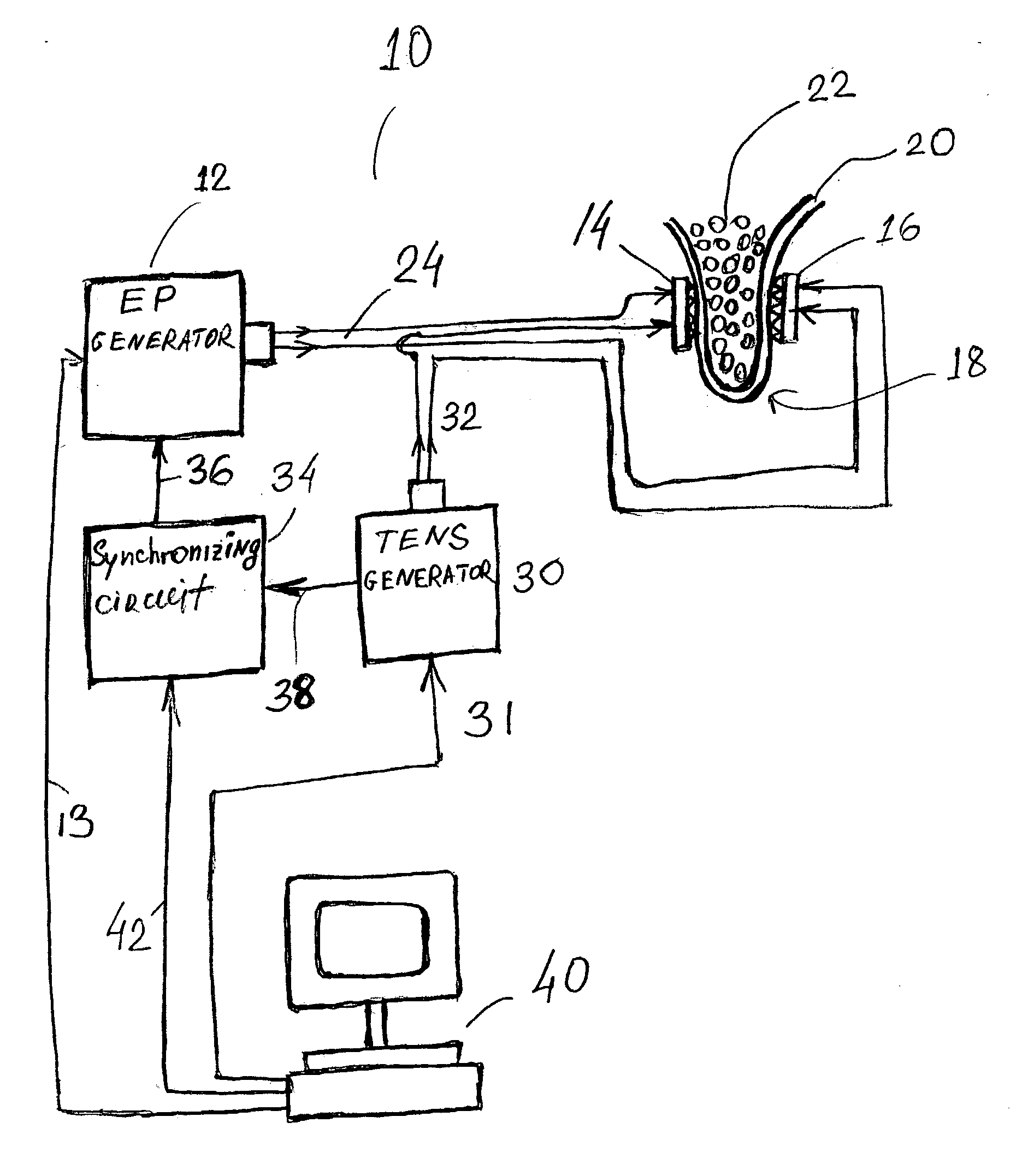
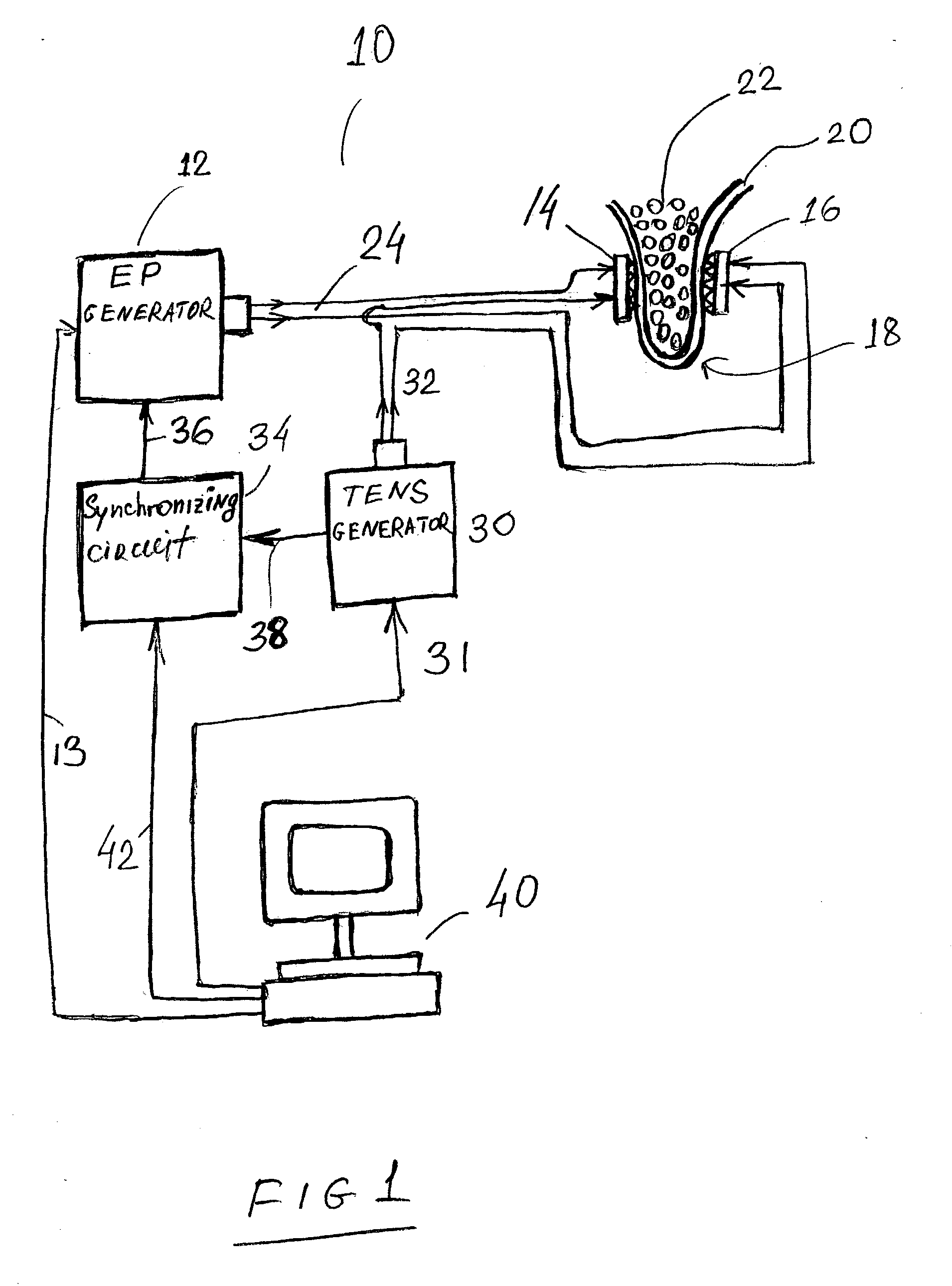
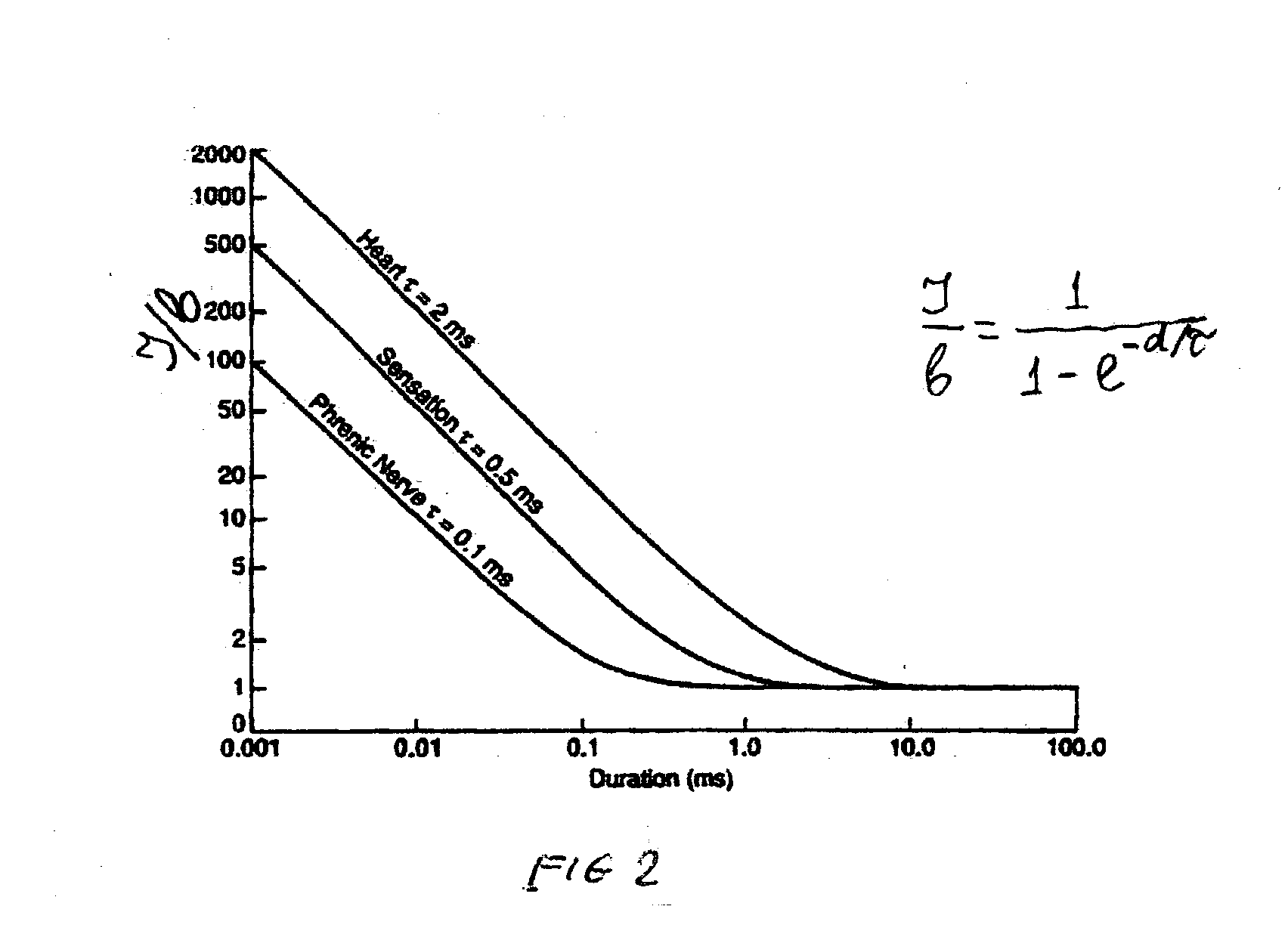
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and associated methods to produce analgesia in a mammal by providing an electrical nerve stimulus utilizing a pulsed input of low level electrical current, wherein the level of current is measurable with the measurements utilized to at least adjust the strength of the current according to selected parameters. Additionally, the use of magnets to produce a magnetic field to further control chronic and acute pain. In exemplary implementations, the apparatus maintains continuous monitoring of the electrical characteristics of TENS at the site of input and output, and the electrical input can be modified during treatment to obtain desired electrical input. More particularly the disclosure relates to an electromagnetic apparatus incorporating pulsed direct current, two or more electrodes, and at least two dipole antennas wherein the dipole antenna circuits receive and analyze signal from the dipole antennas, using the information from signal analysis within the methods for producing analgesia in mammals. The strength of the current that the patient is receiving at the targeted site as the actual field is measured by the dipole antennas and adjustment is not dependent on subjective measurements to ascertain whether the proper amplitude, frequency and pulse duration are being applied.
Owner:WILSON SPENCE L
Systems and methods for providing patient signaling and contingent stimulation
ActiveUS20190001135A1Reduced user satisfactionStimulation can be inconvenientElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityRegimen
Systems and methods provide notification to a user about pending neurostimulation or ongoing neurostimulation using a variety of notification signals and obtaining a user response to the notification using a variety of methods by which the user response is provided. Systems using implanted neurostimulation devices, external neurostimulators which provide transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, or both provide responsive and scheduled therapy regimens that include ecosystem support for augmenting user compliance when treating symptoms, conditions, or disorders. The system is also to assist the user through assessment protocols for improved customization of stimulus regimen attributes such as stimulation protocol parameter values, electrode montages, user surveying, and compliance contingent operations.
Owner:EBT MEDICAL INC
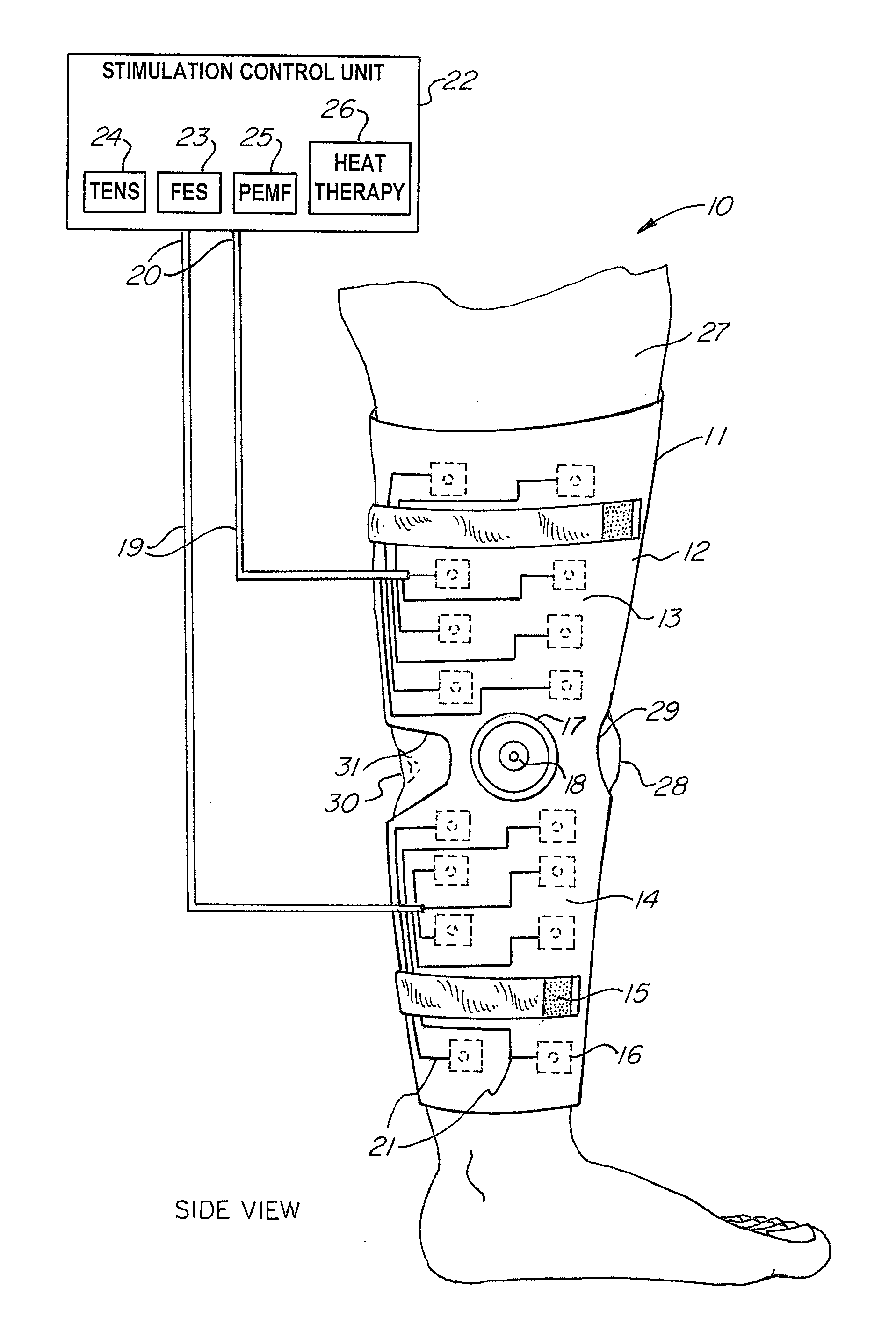
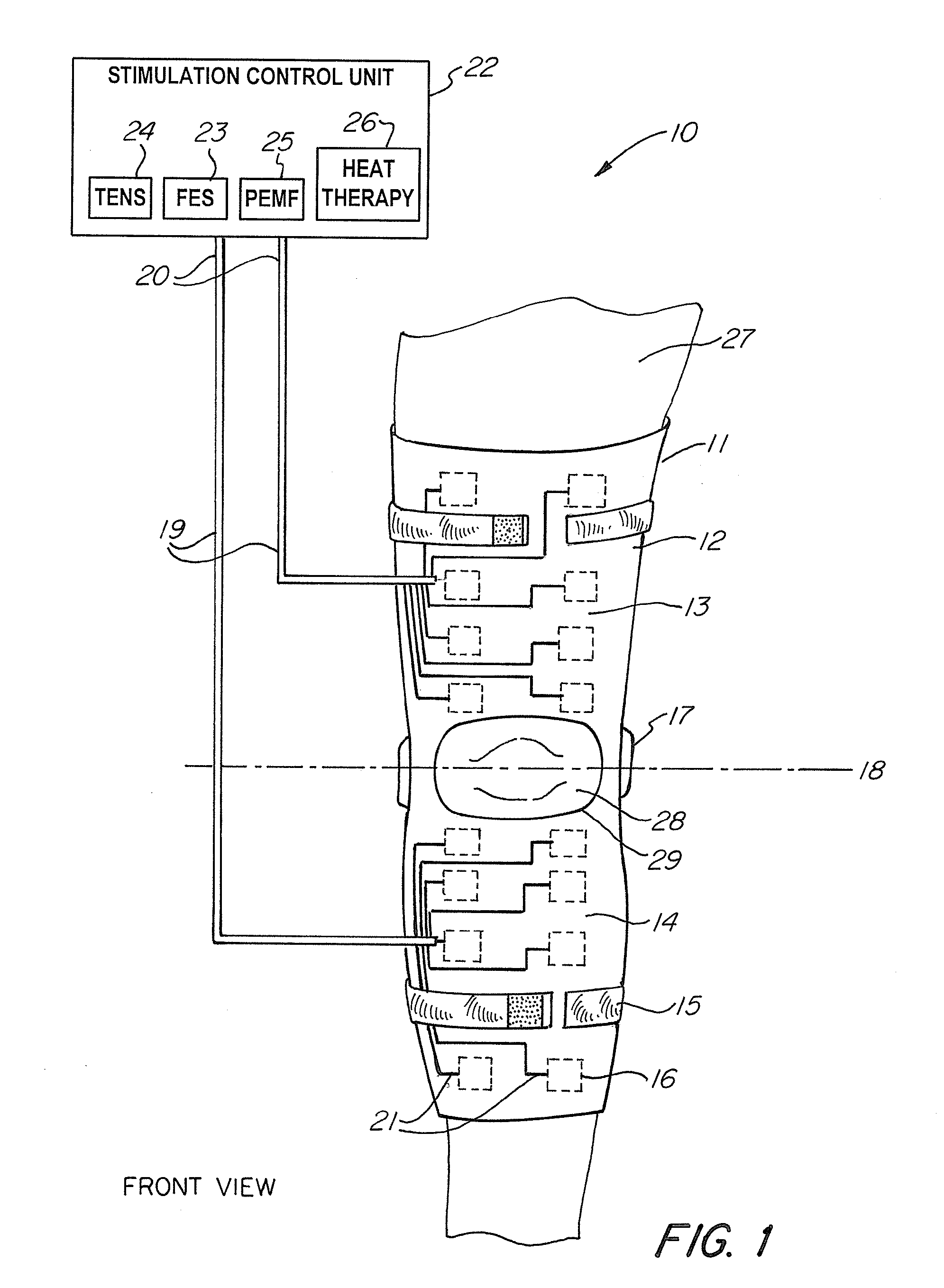
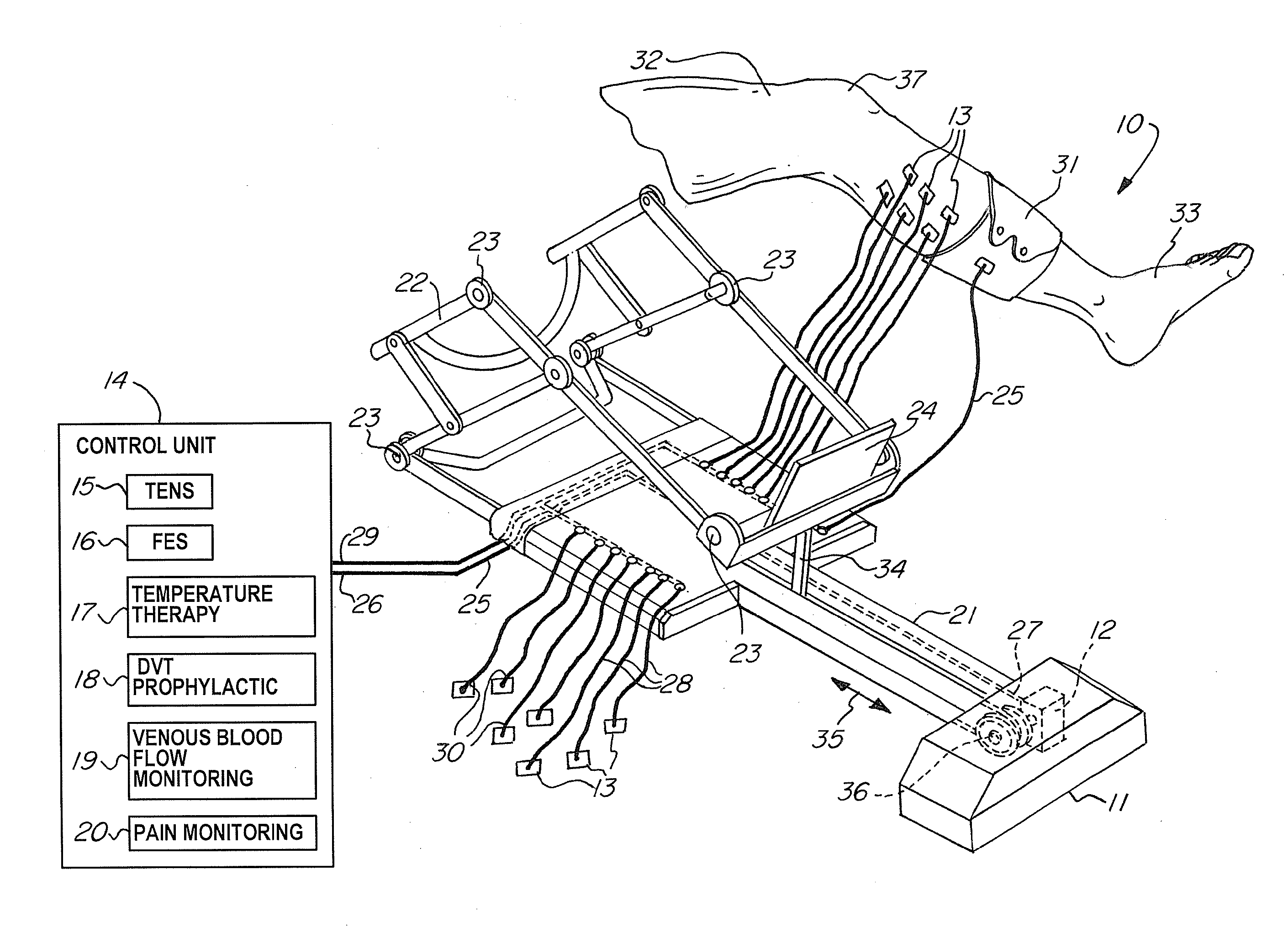
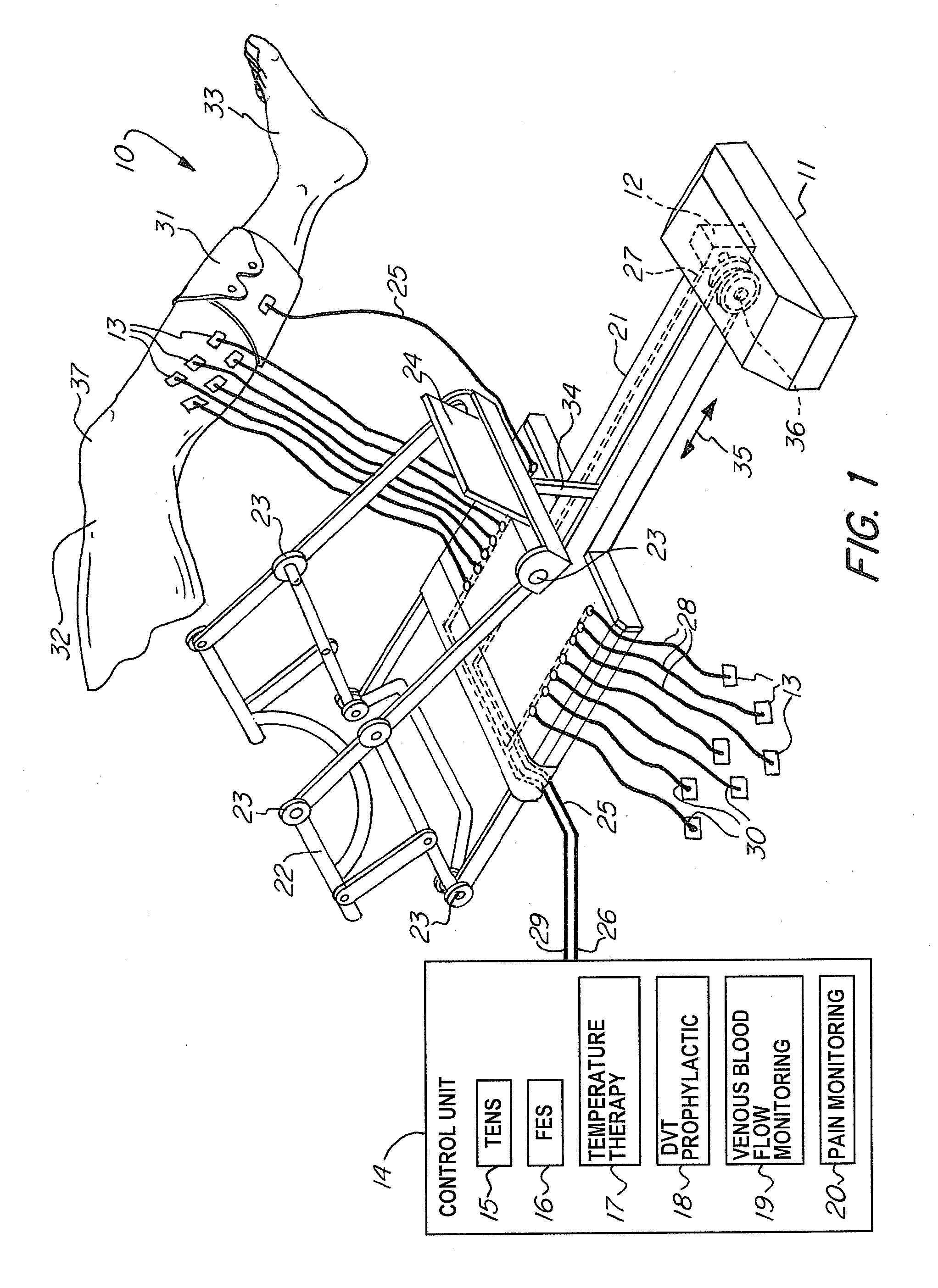
Orthosis For Range Of Motion, Muscular And Neurologic Rehabilitation Of The Lower Extremities
InactiveUS20130085420A1Maximize effectivenessPrevent muscle wastingBlood stagnation preventionElectrotherapyNervous systemTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
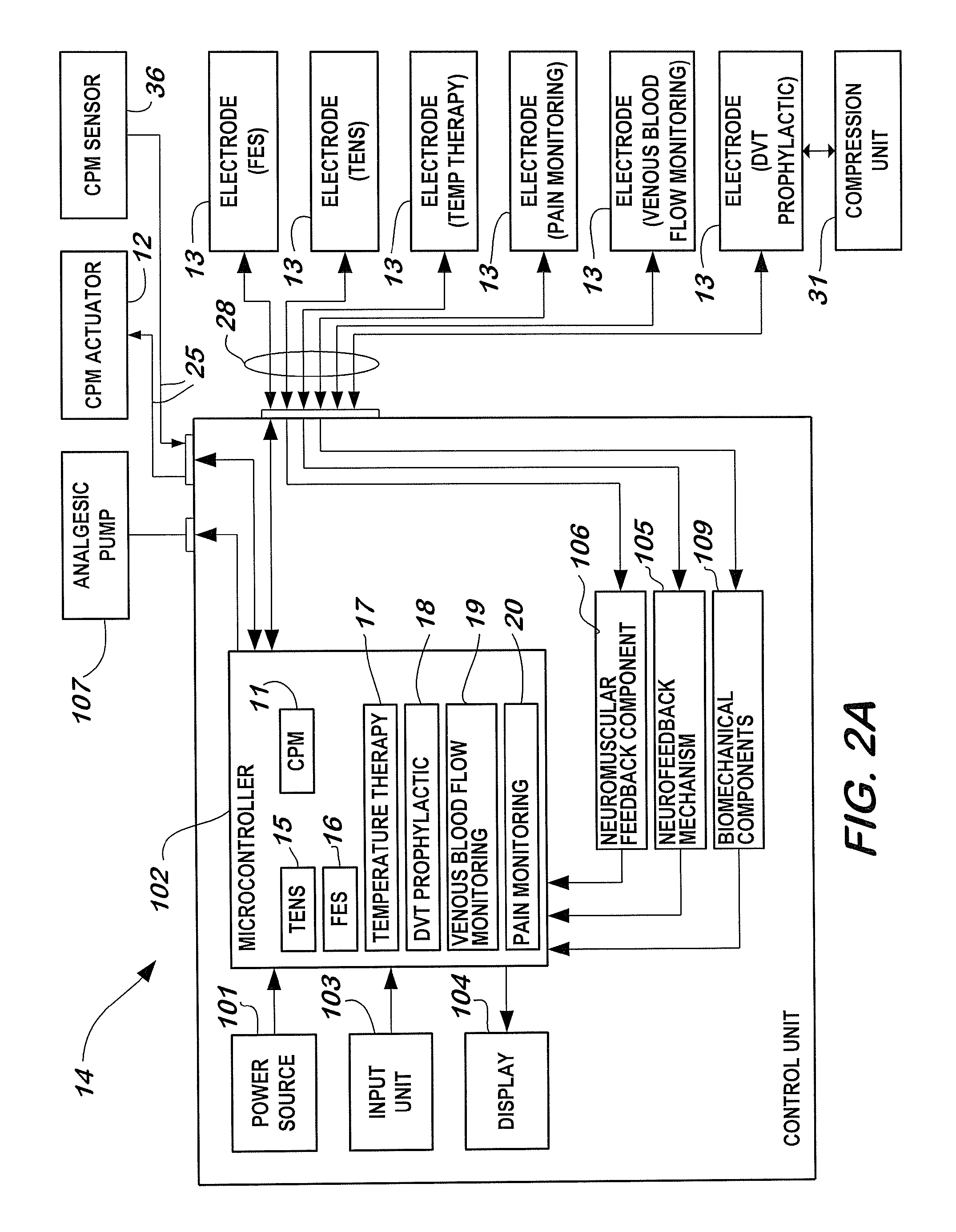
A non-invasive apparatus for rehabilitating a joint, limb, and muscles of a patient recovering from surgery on the joint, includes a continuous passive motion device having at least one support member for supporting the limb, at least one hinge coupled to the at least one support member, and at least one actuator for providing reciprocating motion of the at least one support member about the at least one hinge, a plurality of electrodes transmitting at least four modalities chosen from a group consisting of functional electrical stimulation (FES), transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), temperature therapy stimulation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylactic stimulation, venous blood flow monitoring, and pain monitoring, and a control unit controlling the at least one actuator and the plurality of electrodes according to a coordinated sequence of the reciprocating motion and transmission of the at least four modalities.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
Firearm training apparatus and method
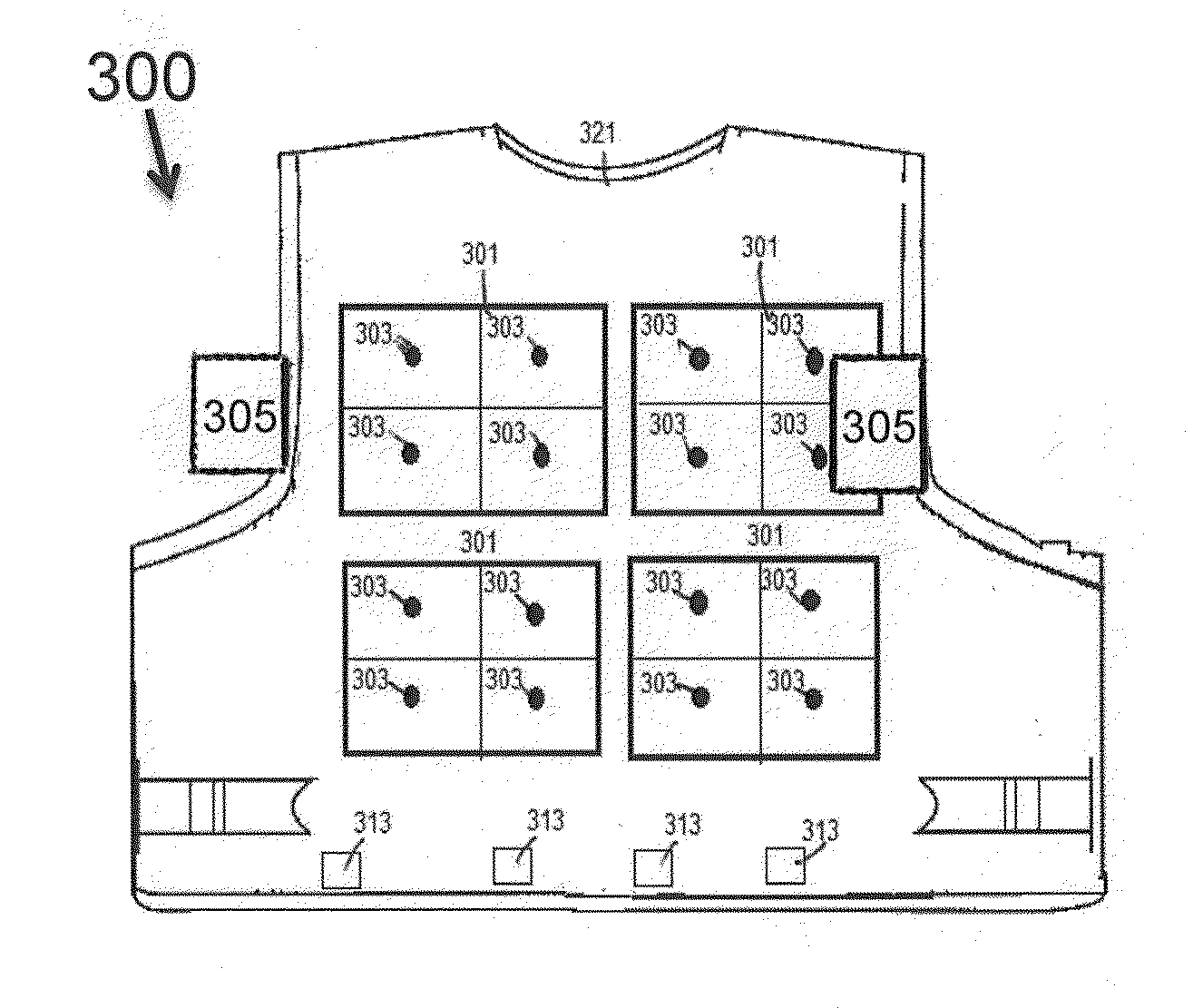
ActiveUS20150354922A1Deterioration of learned skillLacking in target accuracyFiring/trigger mechanismsAiming meansElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
A firearm training apparatus and method provides simulated weapon realism that places higher priority to shot placement by using a culminated laser beam with specific target areas to achieve marksmanship accuracy. Trainee shooters can visually observe hits by an LED in the target area and hear an alarm sound when another trainee is hit. Stress and reaction to stress is achieved through the use of a TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) units in vests worn by the trainees. Greater realism is achieved by eliminating special safety equipment required with projectile systems, and focus on weapon accuracy and firing characteristics.
Owner:FORCE TRAINING SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for relieving pain using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20150148865A1Easy and rapid and clinically valid placementMinimize interferenceExternal electrodesArtificial respirationElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in humans, the apparatus comprising:a housing;stimulation means mounted within the housing for electrically stimulating nerves;an electrode array releasably mounted to the housing and connectable to the stimulation means, the electrode array comprising a plurality of electrodes for electrical stimulation of nerves;control means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for controlling at least one characteristic of the stimulation means;monitoring means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the stimulation means for monitoring at least one characteristic of the stimulation means;user interface means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means for controlling the stimulation means;display means mounted to the housing and electrically connected to the control means and the monitoring means for displaying the status of the stimulations means; anda strap attached to the housing;wherein the strap is configured to hold the housing, stimulation means and electrode array at a specific anatomical location to treat pain.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX INC
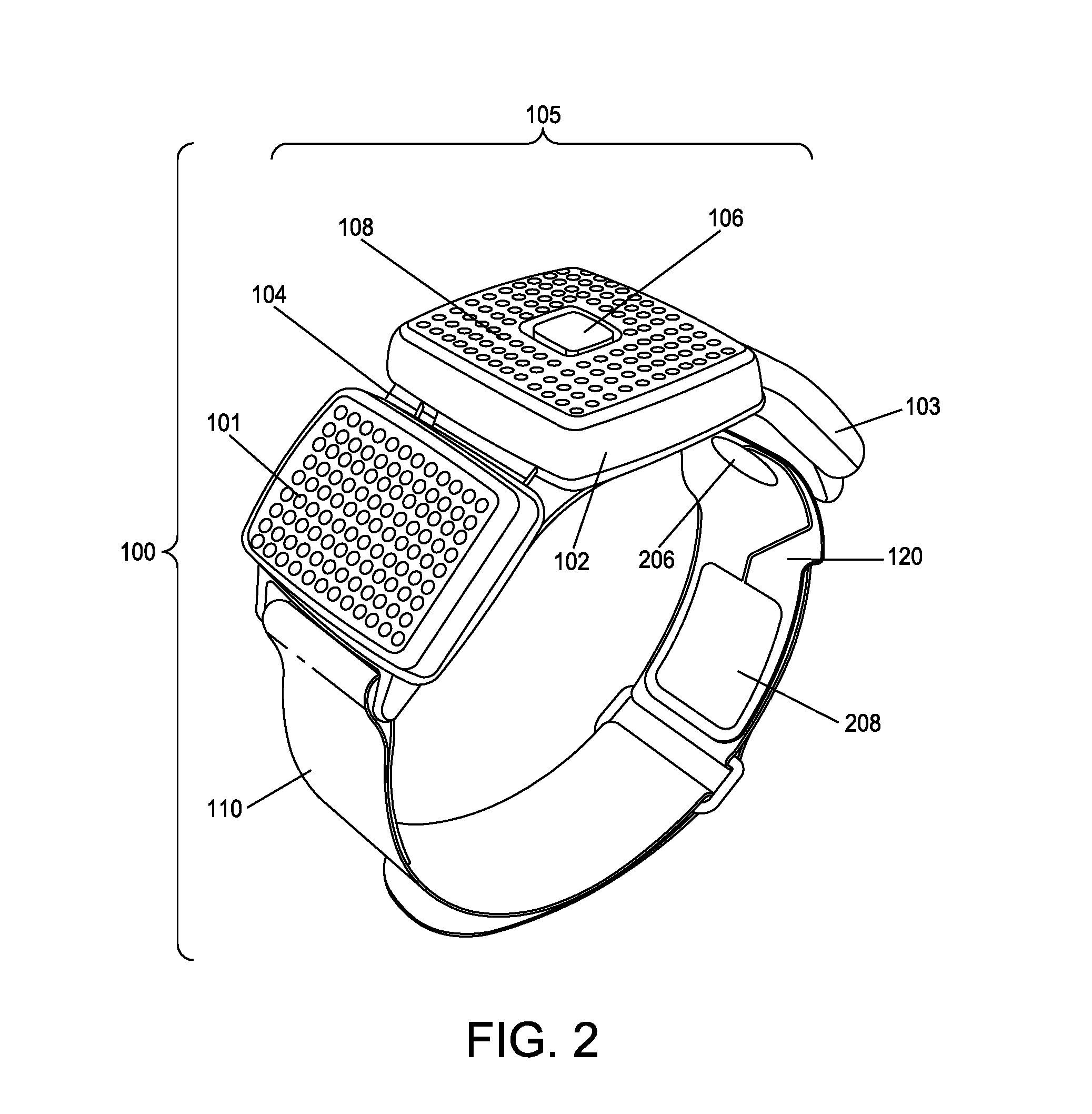
Apparatus and method for activity monitoring, gait analysis, and balance assessment for users of a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device
PendingUS20180132757A1Minimize interferenceContinuously balanceInertial sensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
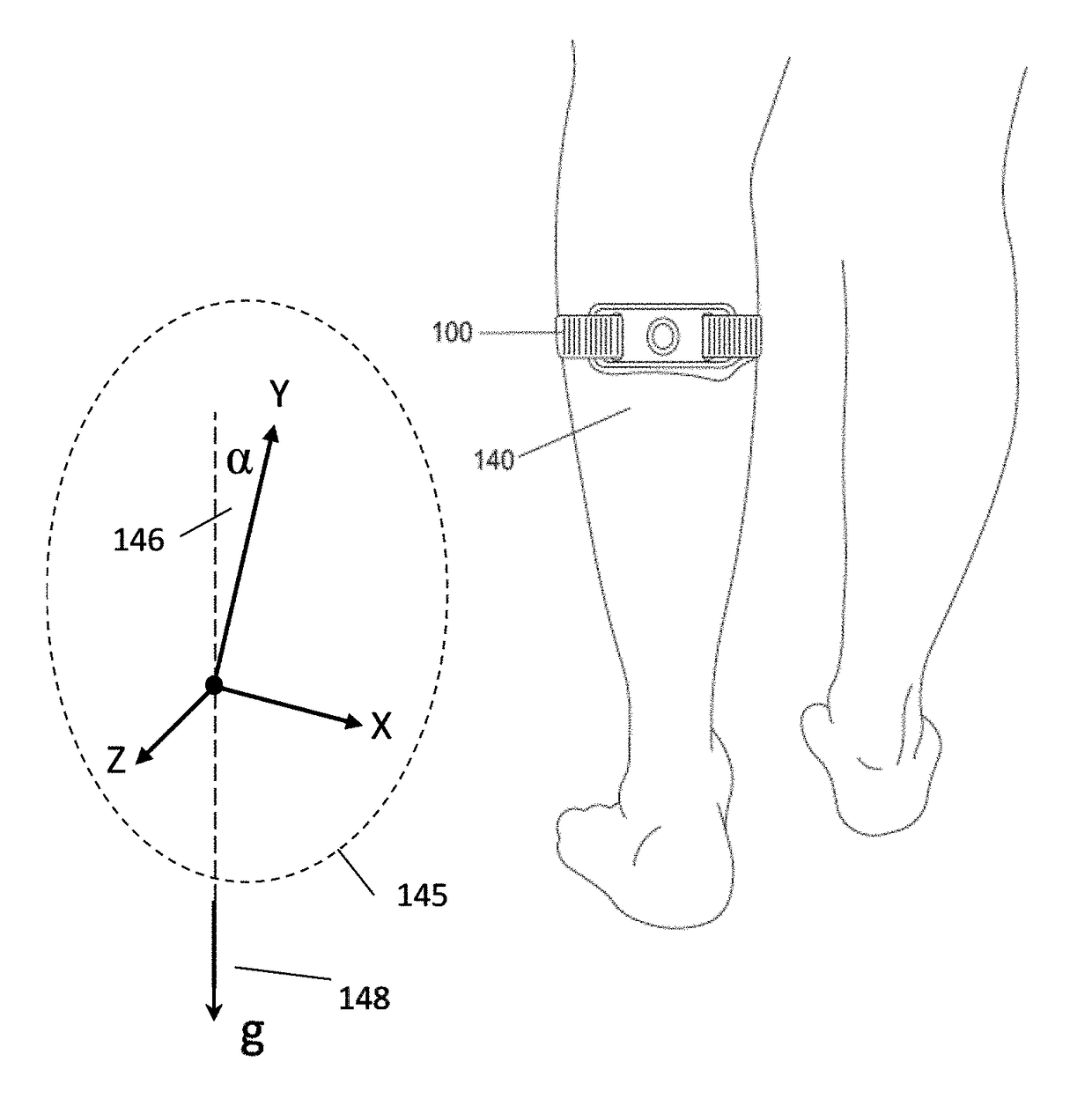
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in a user, the apparatus comprising: a housing; an application unit for providing mechanical coupling between the housing and the user's body; a stimulation unit mounted to the housing for electrically stimulating at least one nerve with at least one stimulation pulse during a therapy session; and a determination unit mounted to the housing and configured to perform at least one of: (i) determining an activity level of the user; (ii) determining a gait characteristic of the user; (iii) determining a balance function of the user; and (iv) determining apparatus placement position on the user.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX INC
Universal musculoskeletal rehab device (brace, sleeve, or pad) for electrical treatment modalities and biofeedback response monitoring
InactiveUS8560077B2Convenient treatmentGood curative effectExternal electrodesMagnetotherapyDiagnostic Radiology ModalityDisease
A non-invasive device for assisting the treatment of any kind of musculoskeletal disorder, including but not exclusive of those of joint, limb, and spine disorders, includes a brace, sleeve, flexible pad, or any combination of the three, a plurality of electrodes disposed thereon, wherein the plurality of electrodes transmit at least three electrophysical modalities, and a stimulation control unit having interactive software to establish a controlled sequence of transmission of the at least three electrophysical modalities and communicating the controlled sequence to the electrodes. The at least three electrophysical modalities are chosen from a group consisting of neuromodulating functional electrical stimulation, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation, and heat therapy stimulation. The stimulation control unit also provides feedback data using the electrodes for monitoring and integration with the interactive software to analyze and assess biomechanical, neuromuscular, and neurological responses to the device.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
Cupping cup with phototherapy device and electrotherapy device
InactiveCN102648989ARadiation therapySuction devicesTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationLight treatment
The invention relates to a cupping cup with a phototherapy device and an electrotherapy device. The cupping cup is mainly characterized in that a close end controller is arranged on a cup; the cup is in a hollow clock shape and has elasticity; a negative pressure chamber is formed in the cup; a contact electrode is arranged in the negative pressure chamber; an air nozzle communicated with the negative pressure chamber is formed on the peripheral wall of the cup, and is connected with an air sucking pump through an air delivery pipe; a phototherapy module is arranged on the close end controller, correspondingly stretches into the cup, and is arranged between the contact electrode in the cup; and when the cup is placed on a special acupuncture point of a human body and starts to suck air, the cup can be adsorbed on the special acupuncture point, and at the time, the contact electrode is in contact with skin so as to carry out transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), while the phototherapy module simultaneously emits laser light to irradiate on the special acupuncture point so as to carry out laser acupuncture, so that the cupping cup can be used for carrying out cupping, laser acupuncture and TENS at the same time.
Owner:UNITED INTEGRATED SERVICES
Electrical and magnetic stimulators used to treat migraine/sinus headache, rhinitis, sinusitis, rhinosinusitis, and comorbid disorders
ActiveUS20160361540A9Avoid stimulationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedical disorderDisease
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation devices and magnetic stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of treating medical disorders using energy that is delivered noninvasively by such devices. The disorders comprise migraine and other primary headaches such as cluster headaches, including nasal or paranasal sinus symptoms that resemble an immune-mediated response (“sinus” headaches). The devices and methods may also be used to treat rhinitis, sinusitis, or rhinosinusitis, irrespective of whether those disorders are co-morbid with a headache. They may also be used to treat other disorders that may be co-morbid with migraine or cluster headaches, such as anxiety disorders. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, one or both of the patient's vagus nerves are stimulated non-invasively. In other embodiments, parts of the sympathetic nervous system and / or the adrenal glands are stimulated.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Electromechanical manipulating device for medical needle and syringe with sensory biofeedback and pain suppression capability
ActiveUS9849252B2Facilitate actionDistract patientAutomatic syringesInfusion needlesDistractionBattery state of charge
In an aspect, a medication delivering injector which includes a housing having opposing proximal and distal ends and an accessible internal cavity for inserting and removing a medicament container such as a syringe. The injector is designed to hold and manipulate a medication delivery device such as a large variety of standard and non-standard medical syringes with fixed or attached needles, assembled such that centrally located is a cylinder containing a liquid medicament and attached either permanently or removably to the distal end of the cylinder, is a hypodermic needle or cannula in fluidic communication with the cylinder. The needle can be from one-half inches to one-and-one-half inches in length in the illustrated embodiment and other sizes are possible by changes in scale of the injector. At the proximal end of the cylinder is an opening with an inserted seal or bung with an attached rod thus constituting a plunger. The central medicament containing cylinder could also be a standard medicament cartridge. Hereinafter, both are referred to as a “syringe”. A lid or access cover which, in an open position permits insertion and removal of the syringe into / from the housing in a horizontal fashion thus providing ease of loading. The syringe is inserted with the needle end toward the distal end of the housing and the plunger toward the proximal end of the housing. A movable carriage is disposed in the proximal end of the housing and slides in the axial direction forwards and rearwards such that a syringe, whose proximal end is gripped by the carriage, so moves with the carriage such that the needle exits the housing at the distal end of the housing and pierces the tissue of the patient prior to dispensing of the medicament, and then is retracted after the medicament has been dispensed by retraction of the carriage. Attached to the carriage is an actuator which pushes on the syringe plunger causing the medicament contained within the syringe cylinder to be dispensed through the needle into the patient's tissue. In one embodiment suitable for both removable needle and fixed needle syringes, the proximal end of the syringe including the syringe finger flange is gripped by an elastomeric flange grip which resides within the carriage, while the syringe distal end resides in and is supported by a “syringe guide” which is attached to the carriage and thus moved with it. In another embodiment which is so made to accommodate syringes with removable needles and their safe disposal, the syringe flange at the proximal end of the cylinder is gripped by an elastomeric flange grip which resides in the carriage as described above, while the syringe distal end is supported by a needle which resides in a removable disposable needle shield. The needle guide is biased toward the carriage and thus, the syringe body is compressed and guided as the carriage moves forward and rearward.Both the movement of the carriage and the actuator are controlled by servo motors which are controlled by electronics and a microcontroller so operating such that speeds and accelerations are controlled smoothly and gently so as to avoid the stop / start motion of motors controlled by limit switches and simple electronics or the vibration and abruptness such as result from injectors powered by compressed springs or gas. Furthermore, the forces are adaptive to the loads imposed and the requirements necessary for the proper dispensation of medicaments with high viscosity or sensitivity to shear forces.The housing, approximately midway between proximal and distal ends, is affixed by a hinge such that the device can be folded in half to provide for a more compact device to be stored and transported.On the distal end of the housing are electrical sensor pads in communication with the microcontroller such that contact with the patient's skin and the angle at which the injector is held against the skin and the steadiness with which the injector is being held can be ascertained. Within the housing are a haptic vibrator and an audio speaker, both producing a vibration which is variable in pitch in such a manner that biofeedback is provided to the injector user as to the pressure, angle and steadiness with which they are holding the injector against the skin. This facilitates the action of injection oneself in the gluteus muscle where visual feedback isn't available to the patient.Multiplexed onto the electrical sensor pads, is a TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) generator which is operational (at the user's choice) just before and during the injection to interrupt or quench the pain of tissue perforation often accompanied with needle injections.Contained on the surface of the housing such as on the access cover, is a display such that user menus, device state, directions, and battery charge status, etc. are displayed. Also contained on the surface of the housing, on the proximal half, are buttons which control the menus and selections that are shown on the display. These selections provide for the user to set such parameters as hypodermic insertion speed and medicament dispensing speeds, the preferred mode of user biofeedback which can include: speech mode (which can be accompanied by musical themes and ringtones, plus variable pitch tone and haptic vibration), MP3 mode (which has speech muted but includes musical ringtones and variable pitch tone and haptic vibration), and haptic mode (which is haptic vibration and audio tone queues needed for injector position biofeedback and readiness), plus mute mode (which provides no audio but the haptic vibration remains), and none, which provides no vibrational biofeedback, yet the display information always remains available.Also contained on the surface of the housing on the distal half, is an “injection initiate” button which causes the sequences required for performance of an injection to occur if said button is “enabled”.Contained within the electronics and its operating program is the ability to audibly play pre-recorded human speech in any language such that: directions in the form of consecutive steps which are required to load the medicament container (syringe) into the device, consecutive steps to perform an injection, steps to remove and properly dispose of parts, to alert of device status and menu choices, etc. can be played through the audio speaker. Also contained within the electronics and program is the ability to play musical ringtones as a distraction during the needle insertion and injection or when a scheduled injection alarm is reached, or calming human voice exhibiting bedside manner during the needle insertion and injection.Also contained within the electronics and software is a real-time clock-calendar which can store a patient's injection schedule and play a musical ringtone as an alarm as each scheduled injection becomes due. Also contained within the electronics and software are the ability to communicate with a personal computer through a USB port, which can also charge the injector's rechargeable battery. The battery in one embodiment, consists of three AAA batteries which can be rechargeable or non-rechargeable. The USB port in combination with an application running on the personal computer, is used to download the injection schedule into the real-time clock-calendar and to download ringtones and musical themes of the user's choice and to download foreign language sets for the pre-recorded human language feature.The injector can be further equipped with the capability to aspirate the tissue by drawing back on the plunger thus creating a vacuum into which fluids will flow. These fluids enter the syringe cylinder where they can be checked for the presence of blood by optical absorption in the red spectrum. This information is useful in the instances where intramuscular injections are to be given with drugs whose ‘Full Prescribing Information’ instructs the patient to aspirate and check for blood in the syringe which indicates that the puncture of a vein has occurred, and if so detected, to abort the injection and then re-inject into a different location.
Owner:INTELLIPEN INC
Wearable transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation dysmenorrhea therapeutic instrument
InactiveCN108744275AReduce the problem of poor treatment effectReduce volumeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationTreatment effectTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
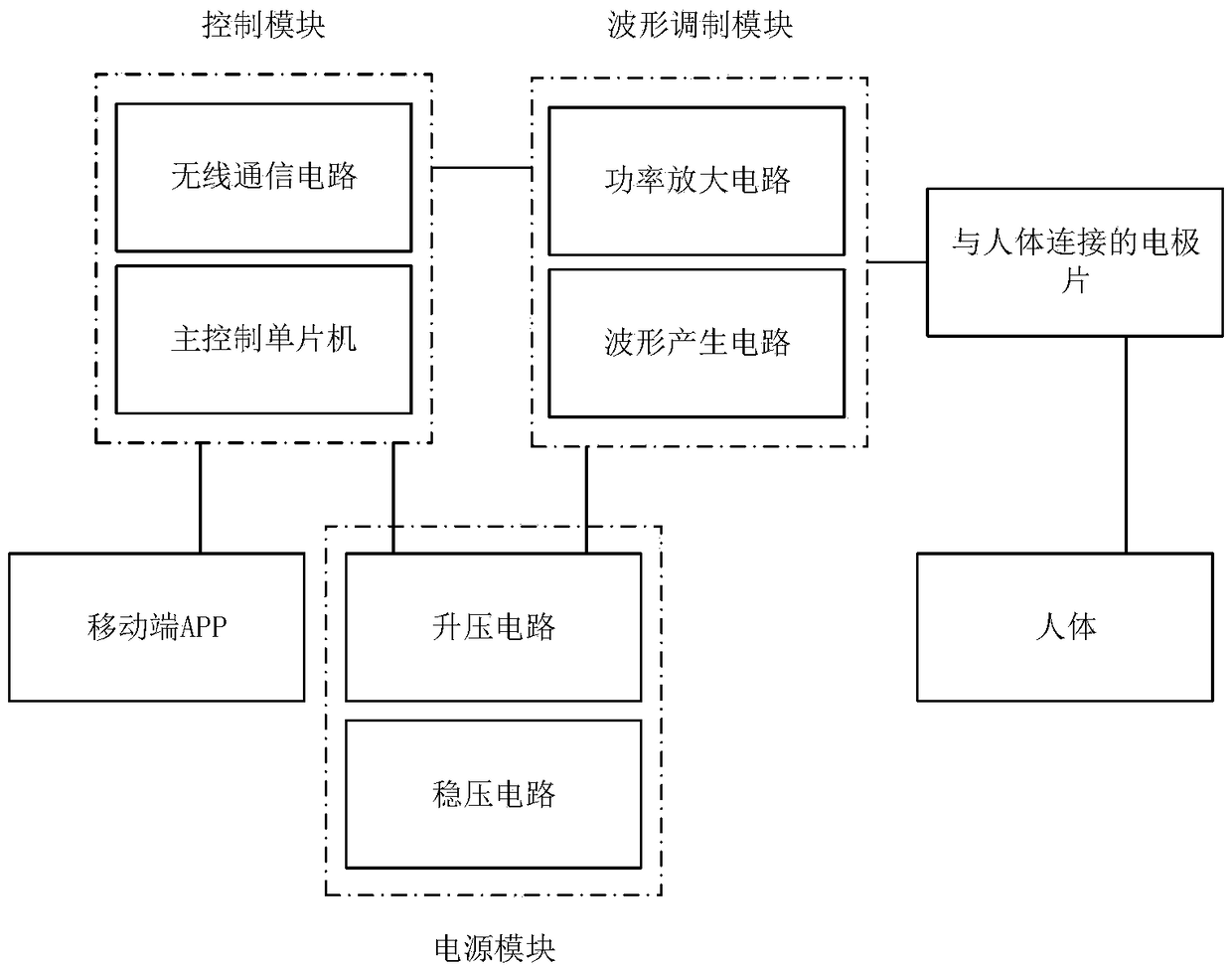
The invention discloses a wearable transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) dysmenorrhea therapeutic instrument comprising: a power module, a control module, a waveform modulation module, anelectrode piece connected to a human body and a mobile terminal APP. The power module supplies power to each module of the system. The control module determines a therapeutic prescription by interacting with the mobile terminal APP, and controls the waveform modulation module to generate a stimulation pulse which acts on the human body through the electrode module connected to the human body. Thepower module includes a boosting circuit and a voltage stabilizing circuit. The control module includes a wireless communication circuit and a main control SCM. The waveform modulation module includes a power amplification circuit and a waveform generation circuit. The wearable TENS therapeutic instrument can generate a plurality of prescription waveforms, has high waveform generation efficiencyand accurate waveforms, has an intensity adjustment function, achieves a good therapeutic effect in combination with various current therapies, has a wearable design and a user-friendly interface, andis very easy to operate.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Firearm training apparatus and method
InactiveUS20130309633A1Deterioration of learned skillGreat realismAiming meansTraining adaptationElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
A firearm training apparatus and method provides simulated weapon realism that places higher priority to shot placement by using a culminated laser beam with specific target areas to achieve marksmanship accuracy. Trainee shooters can visually observe hits by an LED in the target area and hear an alarm sound when another trainee is hit. Stress and reaction to stress is achieved through the use of a TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) units in vests worn by the trainees. Greater realism is achieved by eliminating special safety equipment required with projectile systems, and focus on weapon accuracy and firing characteristics.
Owner:FORCE TRAINING SOLUTIONS
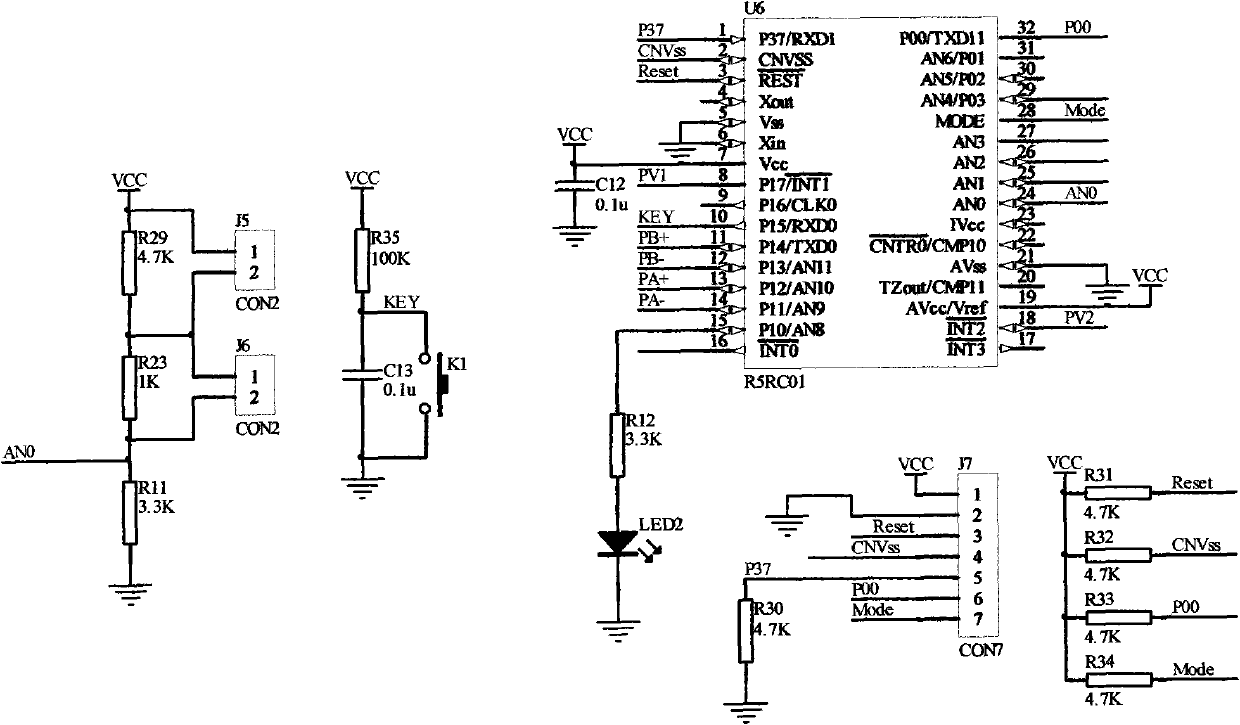
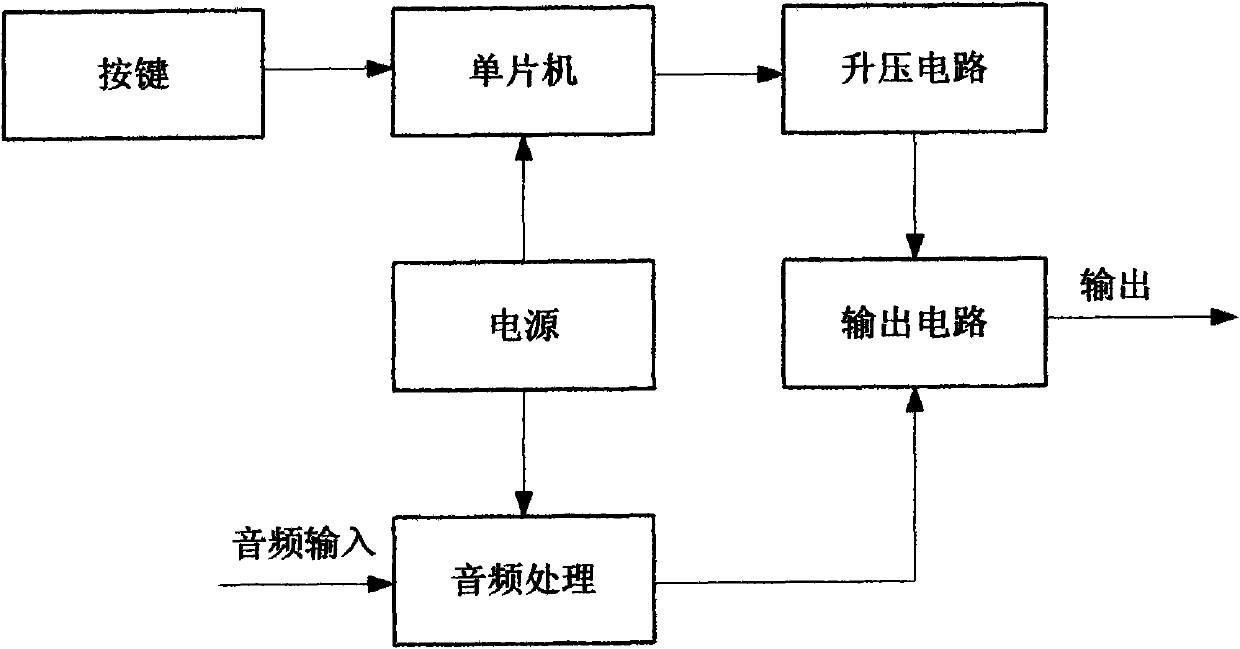
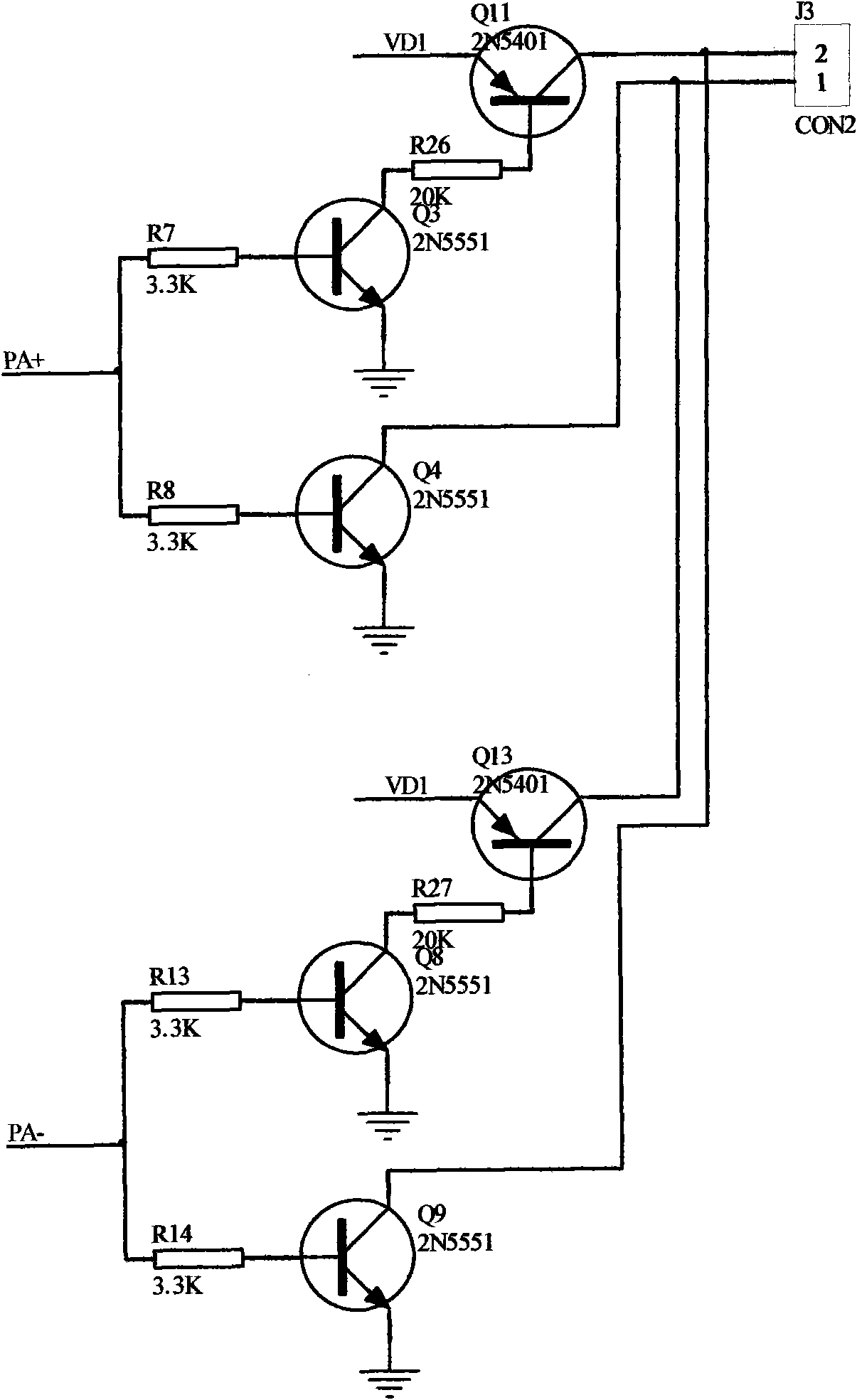
Percutaneou transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation pain therapeutic equipment modulated by music
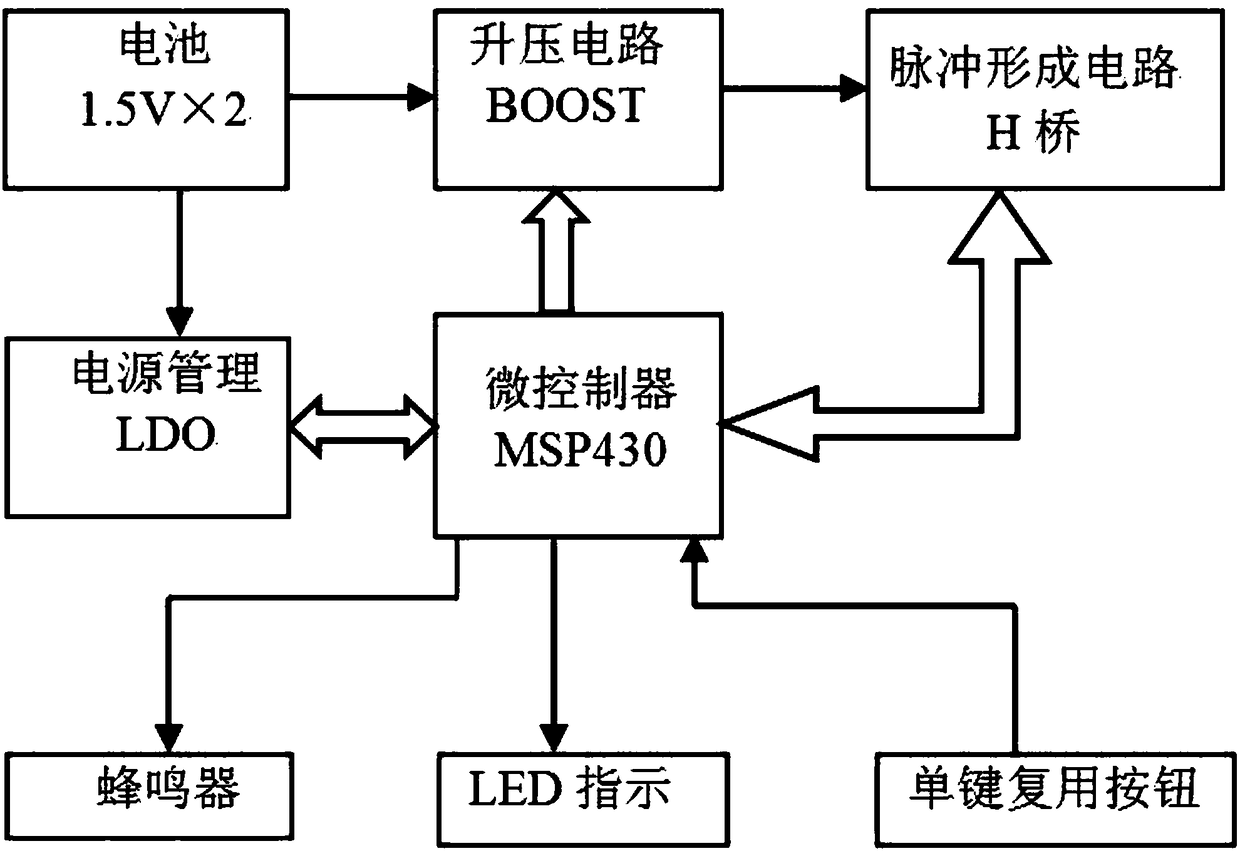
InactiveCN101905060AIn line with the pain treatment conceptReduce demandArtificial respirationMicrocontrollerTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
The invention provides percutaneou transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation pain therapeutic equipment modulated by music, consisting of a machine box, a key circuit, a singlechip circuit, a boosted circuit, an output circuit, a voice frequency processing circuit and a power supply circuit. The therapeutic equipment generates an electrical pulse wave under the control of the singlechip circuit and uses favorite music of a patient output by MP3 to modulate, so that electrophotoluminescence pulse amplitude acting on a human body changes along with strength and weakness of the music, and left and right channels of the music respectively correspond to two path for outputting, so that two path output pulses are different. The synchronously act of a special percutaneou transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) electrical signal and the music selected by the patient improves curative efficacy. The variable stimulation solves adaptability and tolerance of an organism on TENS to the greatest extent, and also realizes the individual demand of analgesia.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
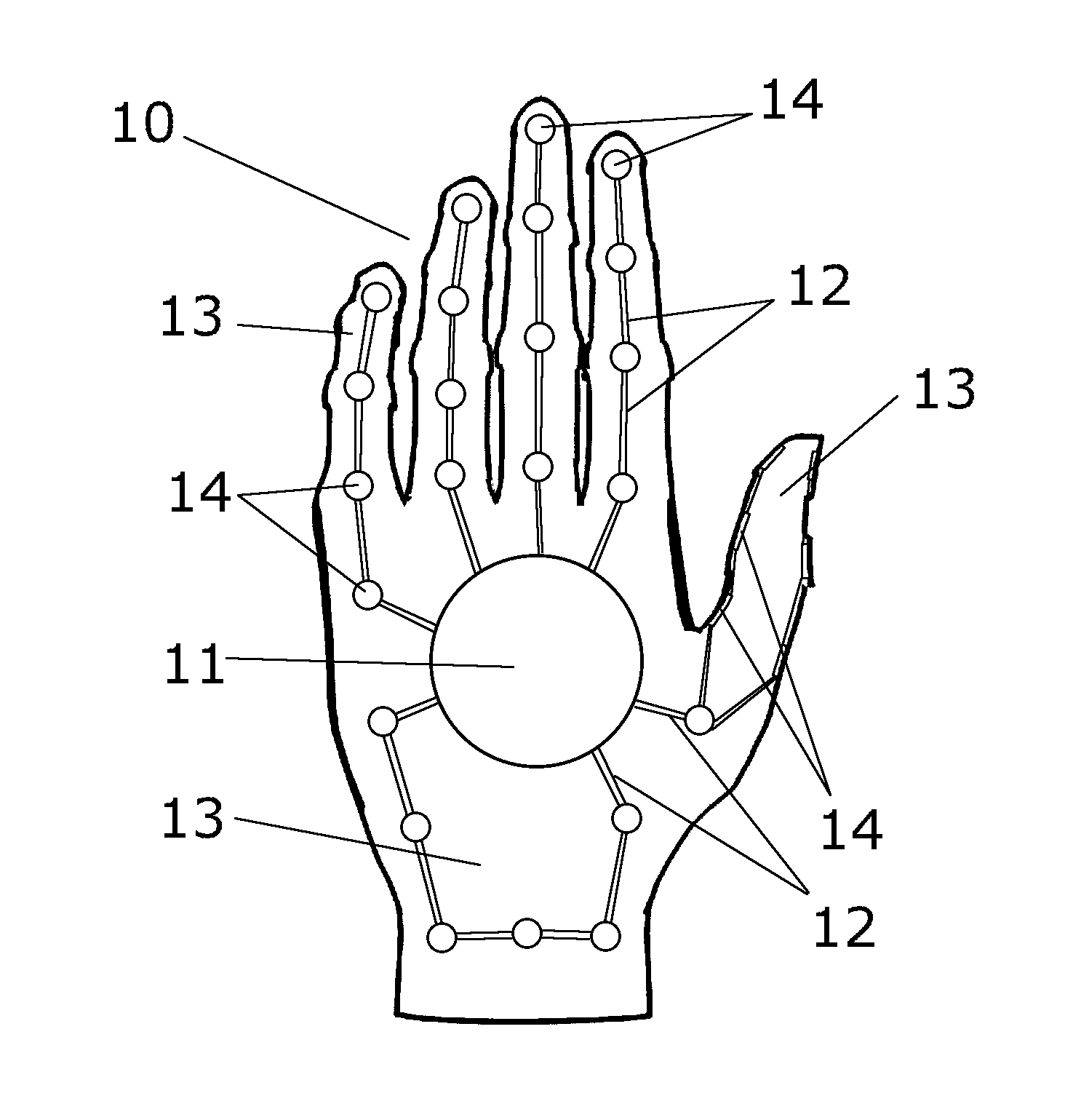
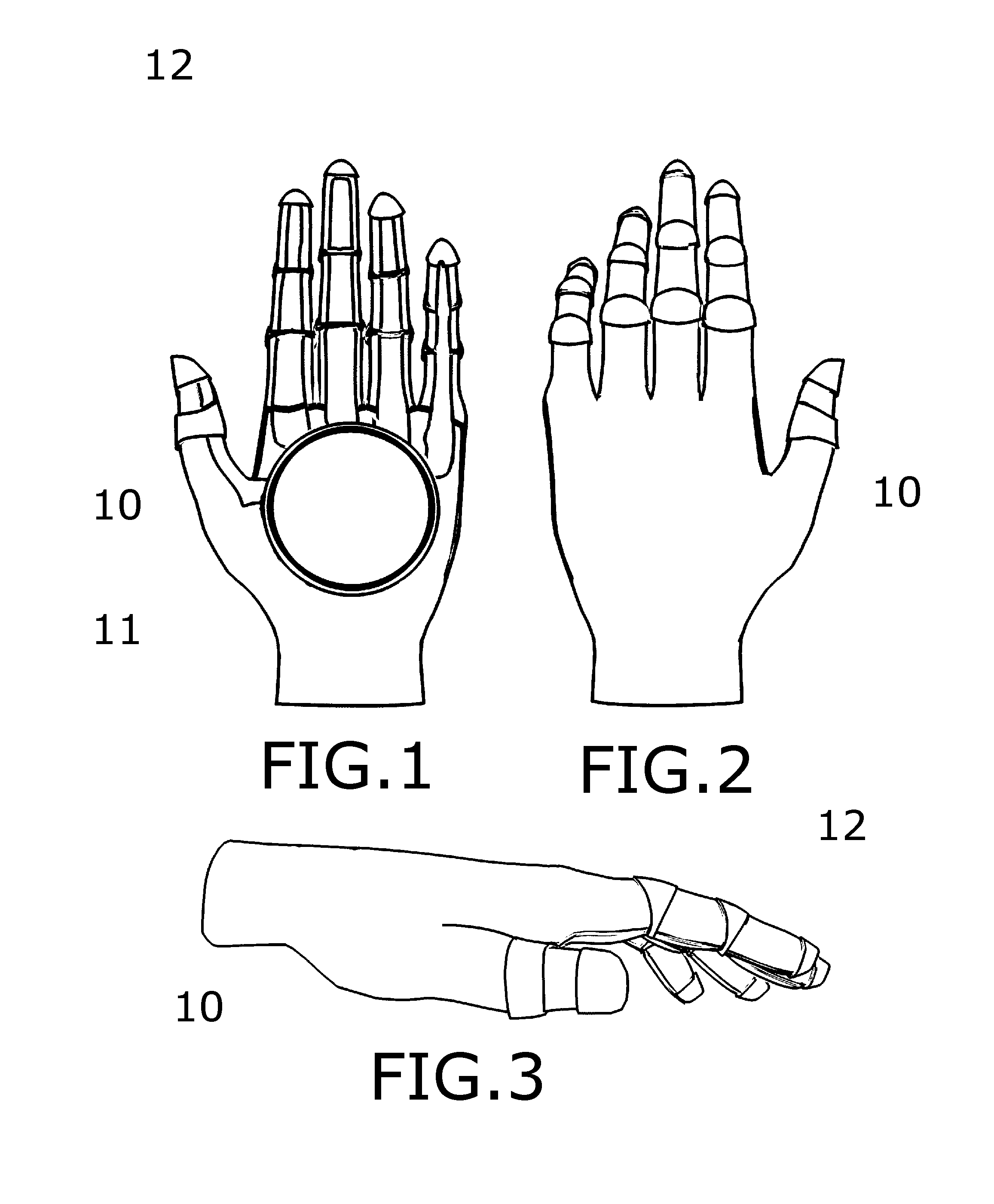
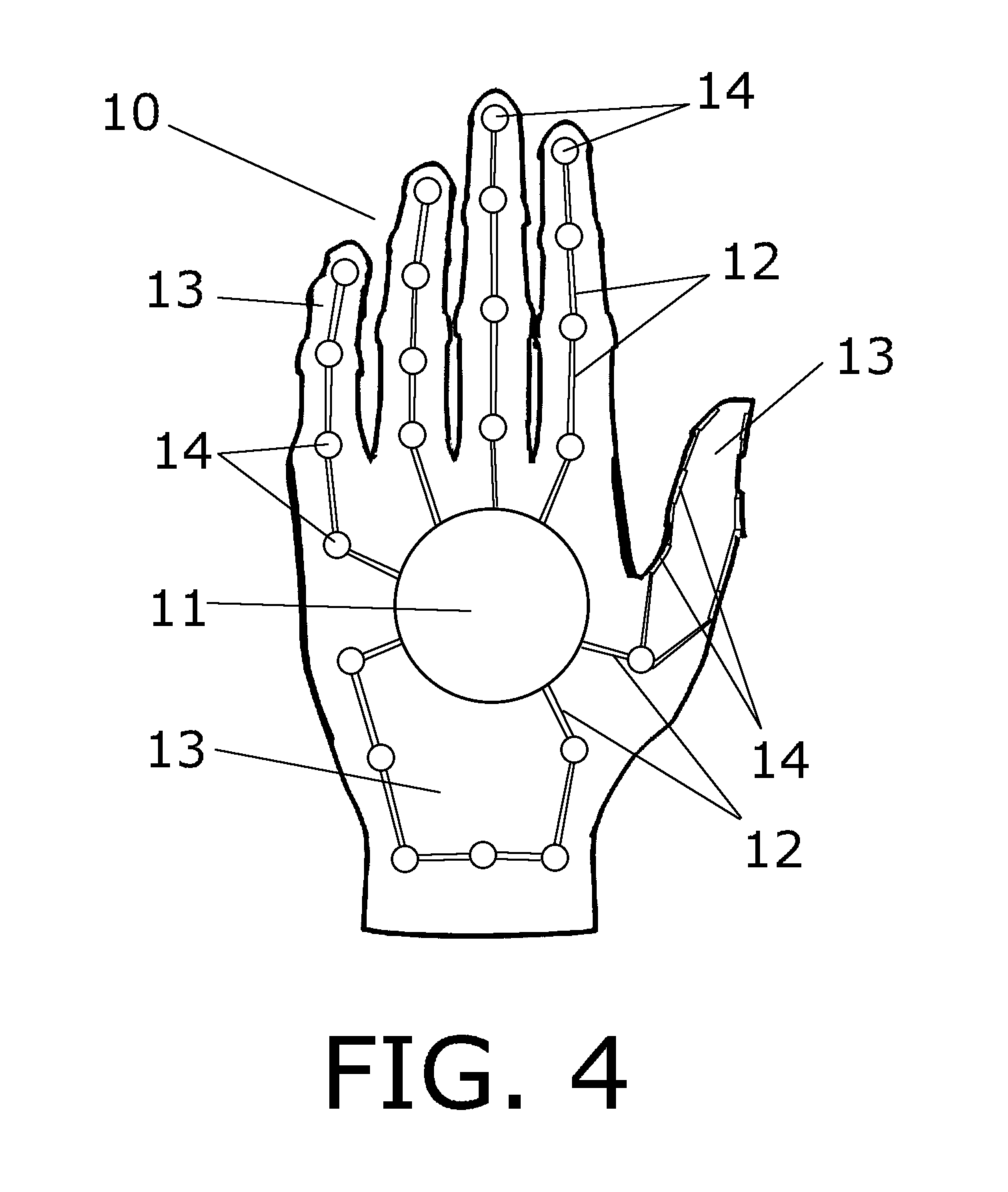
Medical Glove for Electric Stimulation
A medical glove for electrical stimulation provides electrodes, supplying low voltage electric current for the purpose of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) for patients with chronic pain in their hands, or Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) to assist stroke patients in regaining motor skills. The glove is battery-powered, fits tightly on the user's hand, and is preferably manufactured from nylon fabric.
Owner:OSBORNE LARRY
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and method of using same
ActiveUS7706885B2Avoid problemsElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationPulsed DC
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and associated methods to produce analgesia in a mammal by providing an electrical nerve stimulus utilizing a pulsed input of low level electrical current, wherein the level of current is measurable with the measurements utilized to at least adjust the strength of the current according to selected parameters. Additionally, the use of magnets to produce a magnetic field to further control chronic and acute pain. In exemplary implementations, the apparatus maintains continuous monitoring of the electrical characteristics of TENS at the site of input and output, and the electrical input can be modified during treatment to obtain desired electrical input. More particularly the disclosure relates to an electromagnetic apparatus incorporating pulsed direct current, two or more electrodes, and at least two dipole antennas wherein the dipole antenna circuits receive and analyze signal from the dipole antennas, using the information from signal analysis within the methods for producing analgesia in mammals. The strength of the current that the patient is receiving at the targeted site as the actual field is measured by the dipole antennas and adjustment is not dependent on subjective measurements to ascertain whether the proper amplitude, frequency and pulse duration are being applied.
Owner:WILSON SPENCE L
Functional transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device for motor function regulation
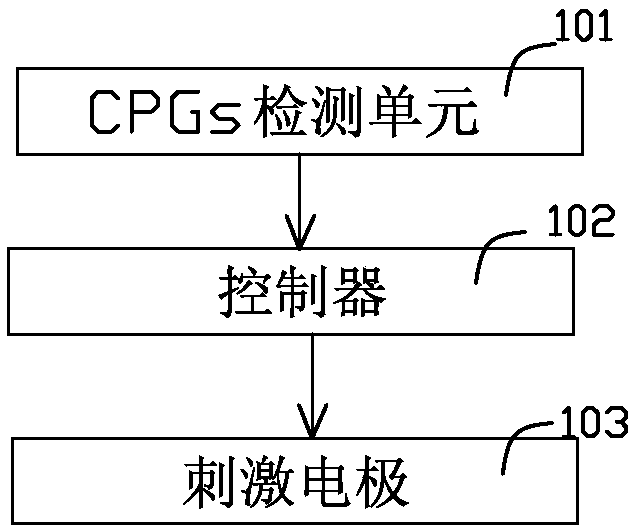
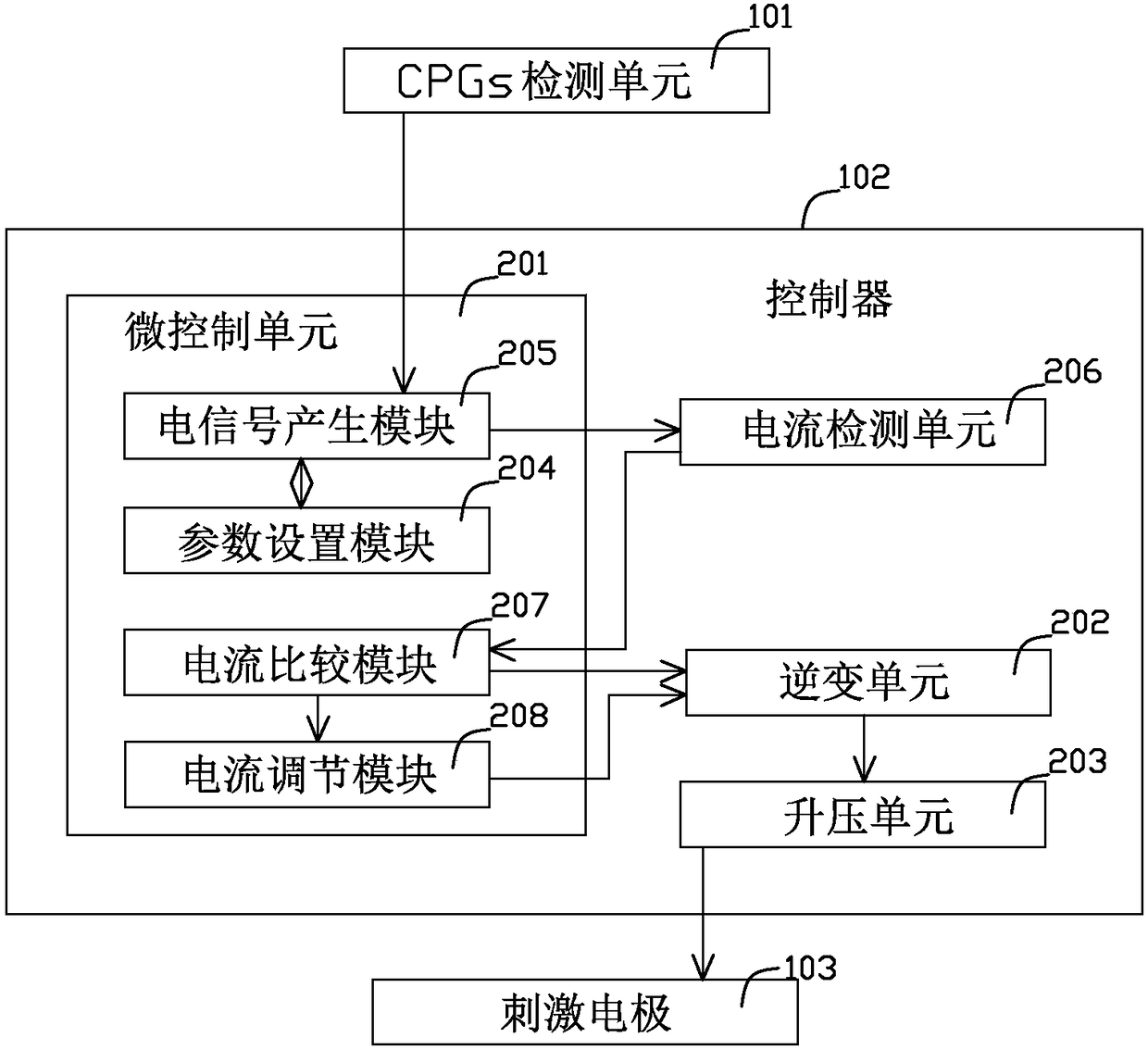
InactiveCN108261607AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionExternal electrodesArtificial respirationTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationSpinal nerve
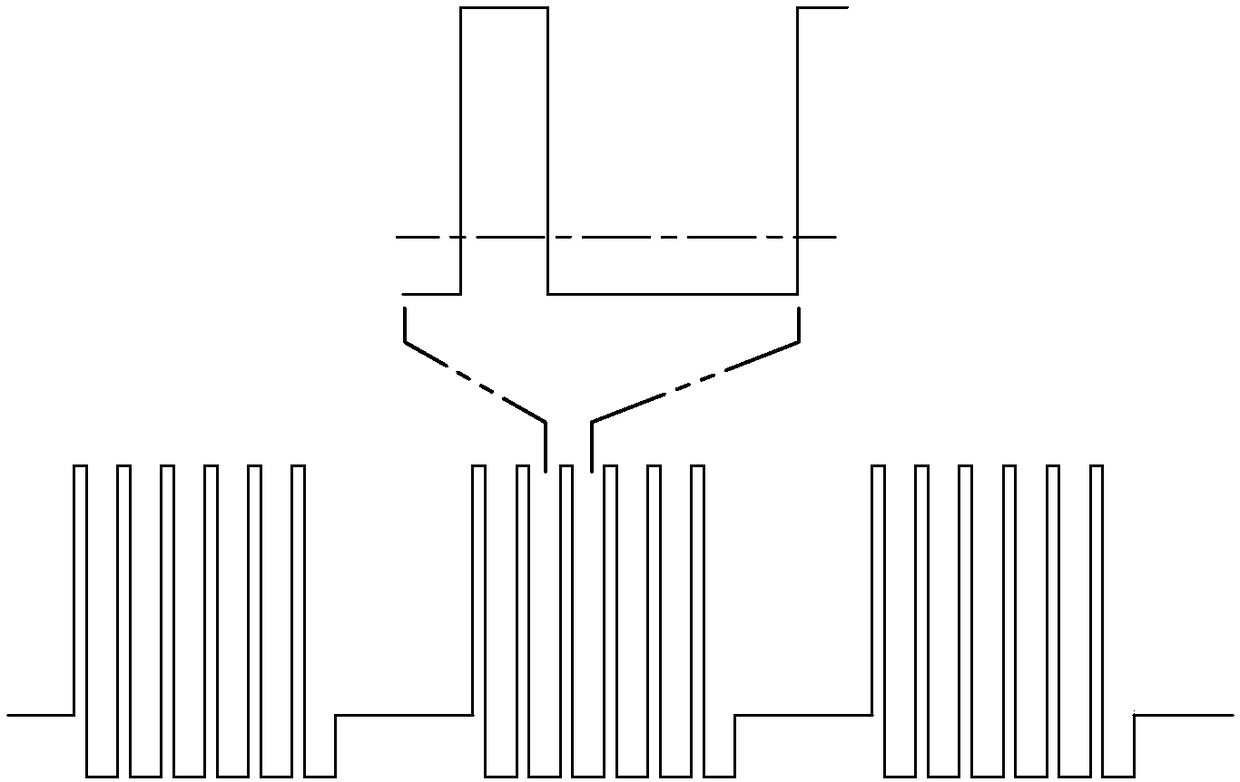
The invention relates to a functional transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device for motor function regulation. The functional transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device comprises a CPGs detection unit, a controller and a stimulating electrode, wherein the CPGs detection unit is used for monitoring electromyographic signals generated by human lower limb CPGs, and sending a signal generation command to the controller after monitoring the electromyographic signals; the controller is used for receiving the signal generation command, generating stimulation current according to preset parameters, and inputting the stimulation current into the stimulating electrode; the stimulating electrode is placed on the skin of the spine of a person to be tested for outputting stimulation waves; the stimulation waves are low-frequency main waves modulated by taking high-frequency bidirectional asymmetric square waves as carrier waves; the CPGs detection unit is used for monitoring the movement trends generated by the human lower limbs so as to produce the electromyographic signals, and the special stimulation waves are generated in time, so that synchronous stimulation is given to the spinal nerves of a user, and a positive incentive is given to the behavior of taking a step forward; the rehabilitation walking training for the lower limbs of the user is promoted.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Firearm training apparatus and method
ActiveUS9759521B2Deterioration of learned skillImprove accuracyFiring/trigger mechanismsAiming meansElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
A firearm training apparatus and method provides simulated weapon realism that places higher priority to shot placement by using a culminated laser beam with specific target areas to achieve marksmanship accuracy. Trainee shooters can visually observe hits by an LED in the target area and hear an alarm sound when another trainee is hit. Stress and reaction to stress is achieved through the use of a TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) units in vests worn by the trainees. Greater realism is achieved by eliminating special safety equipment required with projectile systems, and focus on weapon accuracy and firing characteristics.
Owner:FORCE TRAINING SOLUTIONS
Control system for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation physical headache therapeutic instrument
PendingCN108853722AReduce power consumptionSave electricityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationElectrical impulse
The invention belongs to the headache therapeutic instrument control system technical field and relates to a control system for a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation physical headache therapeutic instrument. The control system comprises a power supply module, a power source voltage regulation module, a power source management module, a controller circuit and a pulse formation circuit; thepower source module is electrically connected with the pulse formation circuit through the power source voltage regulation module; the power source module is electrically connected with the controllercircuit through the power source management module; the controller circuit is electrically connected with the power source voltage regulation module and the power source management module; and the controller circuit is electrically connected with the pulse formation circuit and is used for detecting the pulse formation circuit. The control system for the transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation physical headache therapeutic instrument has the advantages of low power consumption, light and simple design structure, simple operation and high safety, and can assist in saving electric energy and regularly monitor the voltage and current of electric pulses. According to the control system of the invention, the service life of a power source can be prolonged, the frequency of the electric pulses can be changed according to the demand of a user; and working modes of three frequencies are designed, so that the user can conveniently select the working modes.
Owner:陕西诺奕生物医药科技有限公司
Method and system to remotely control a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device
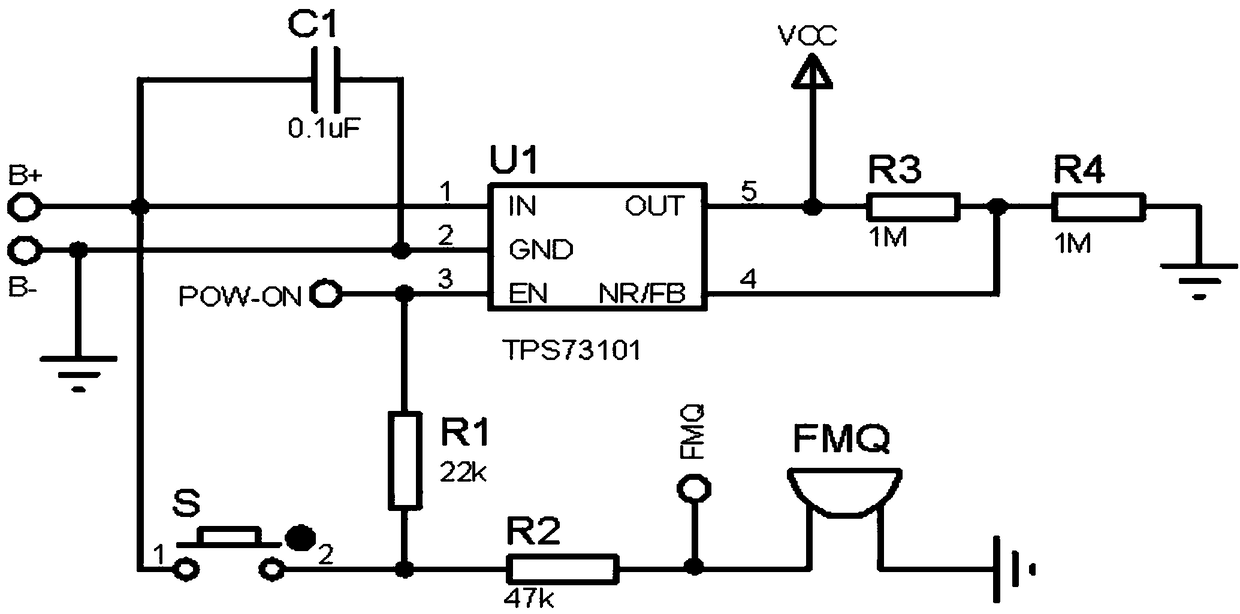
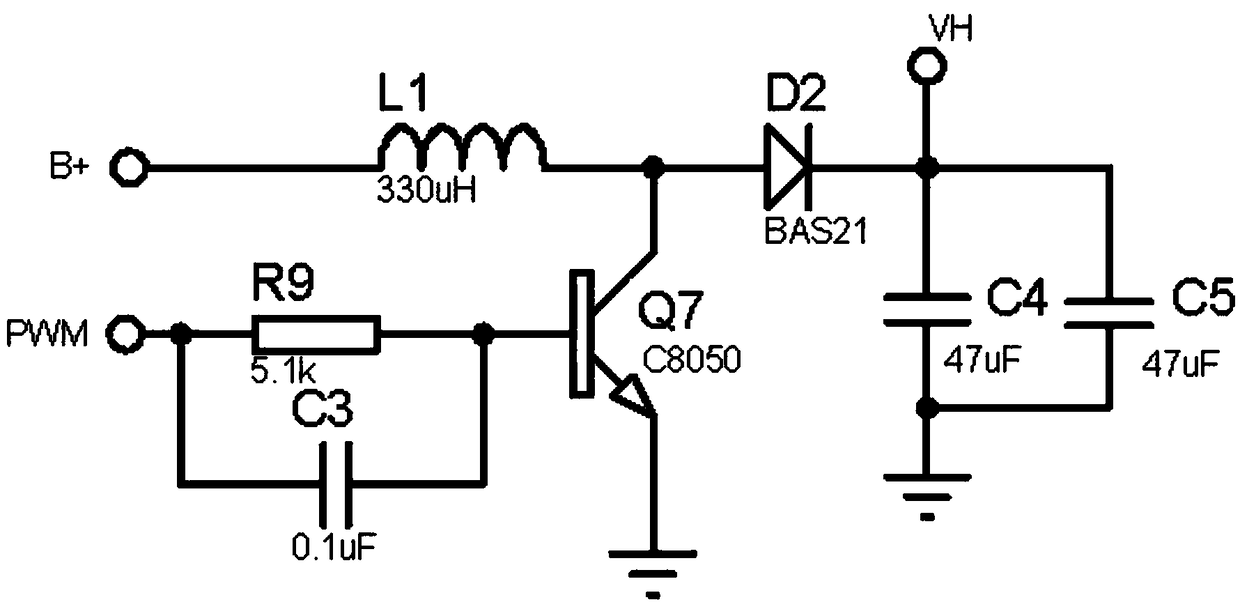
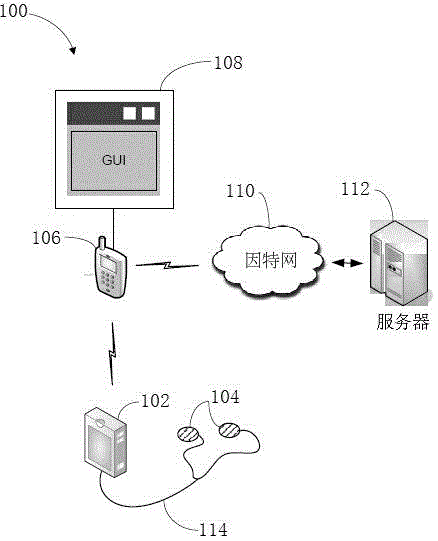
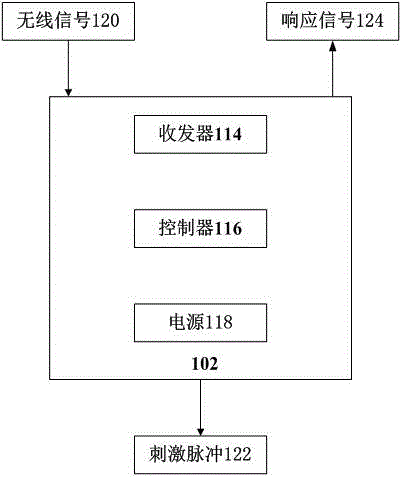
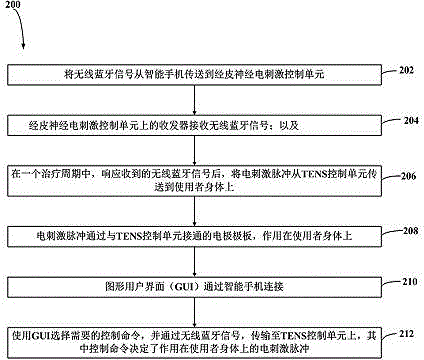
InactiveCN104436429APhysical therapies and activitiesElectrotherapyElectricityGraphical user interface
A system to remotely control a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device is disclosed. The system includes a TENS control unit where a transceiver of the TENS control unit is configured to receive wireless Bluetooth signals transmitted from a smartphone, and to transmit wireless Bluetooth response signals to the smartphone in response to biofeedback from a user's body. The system also includes a controller configured to transmit electrical stimulus pulses during a treatment session in response to receiving the wireless Bluetooth signals, where the controller is configured to modulate pulse width, frequency, intensity, or any combination thereof, of the electrical stimulus pulses. A graphical user interface is accessible using the smartphone and configured for a user to select desired control commands to transmit to the TENS control unit using the wireless Bluetooth signals, where the control commands determine the electrical stimulus impulses that are applied to the user's body.
Owner:扎克·本巴赛特
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com