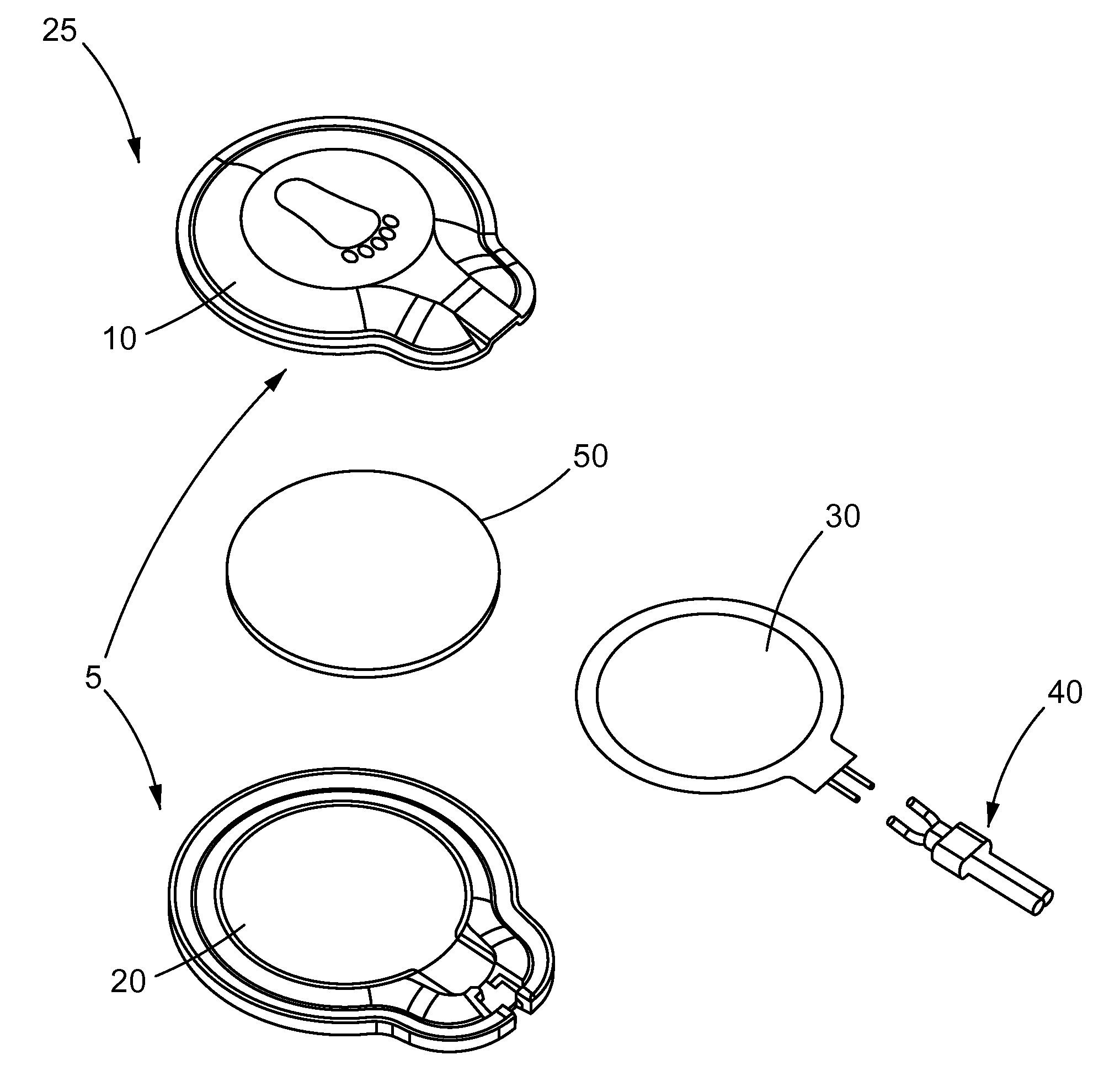
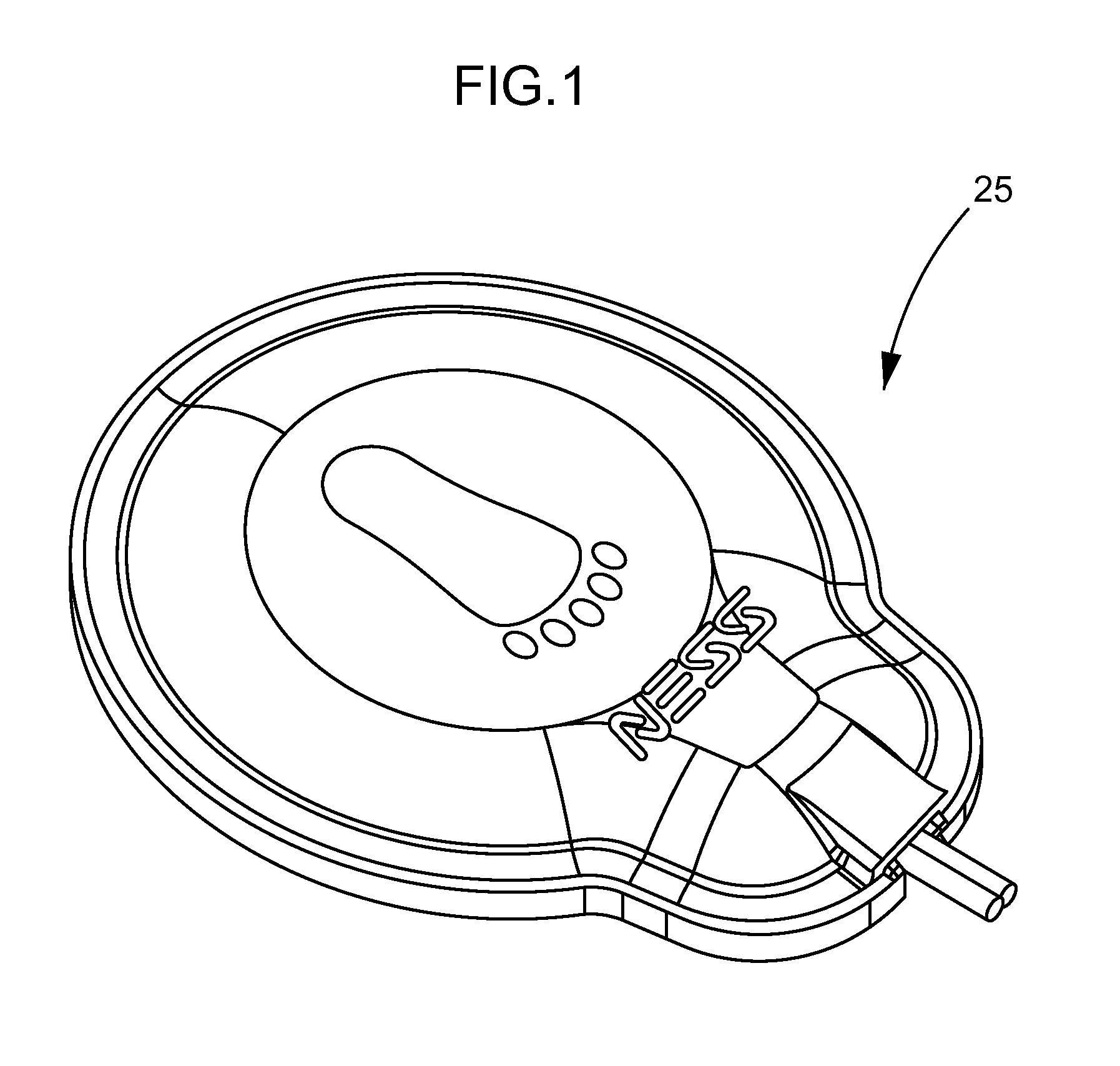
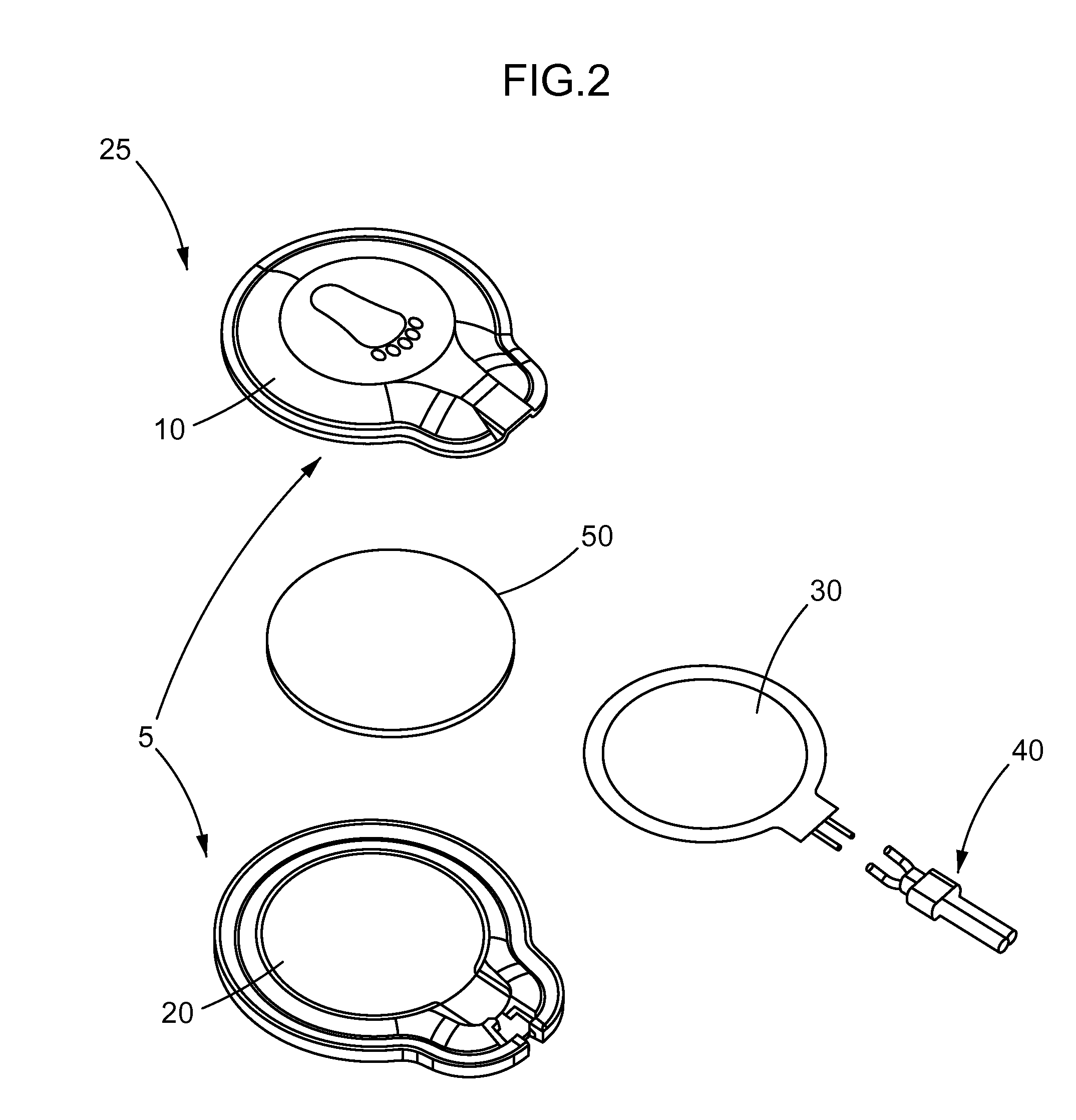
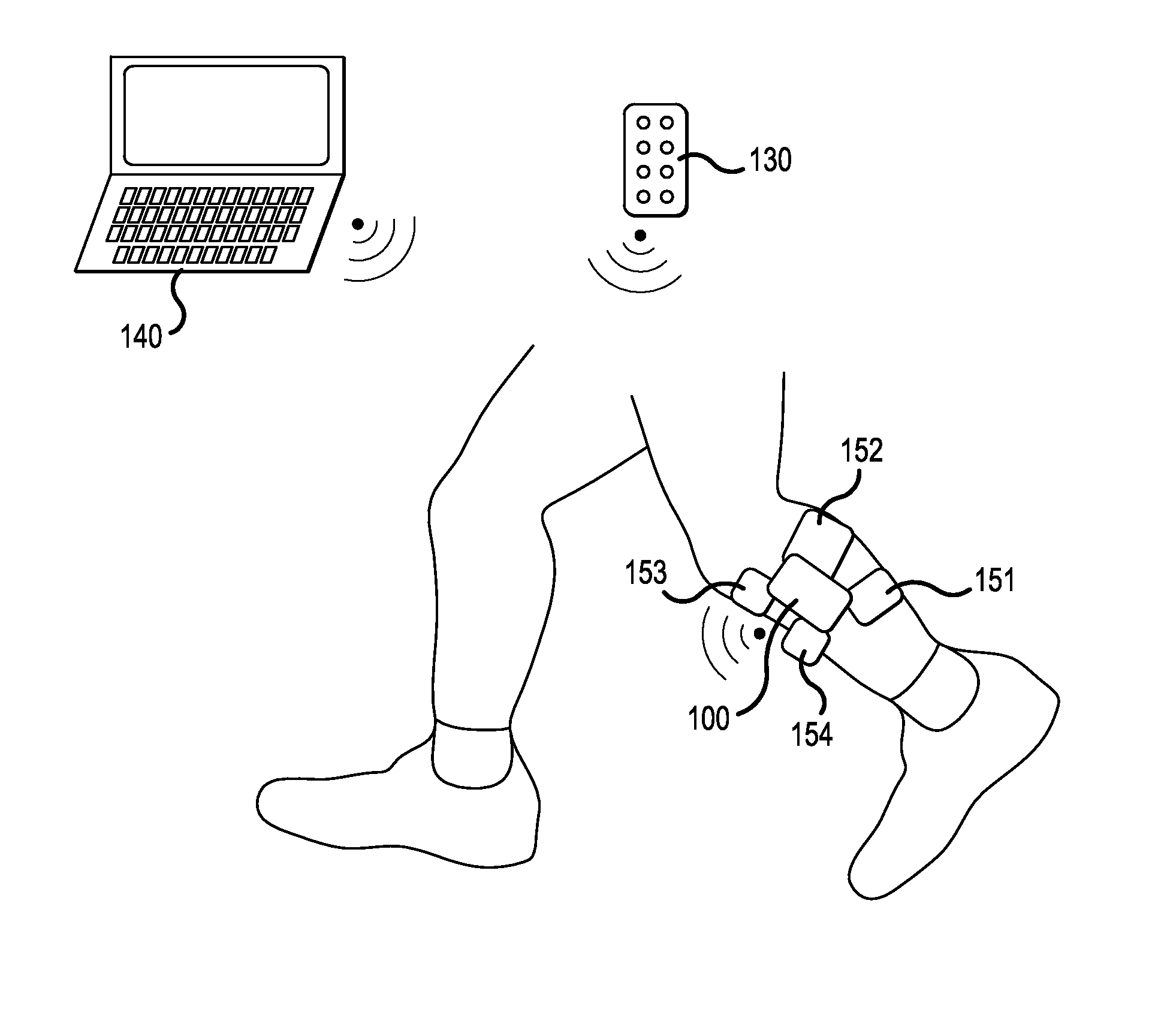
Patents
Literature
247 results about "Functional electrical stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
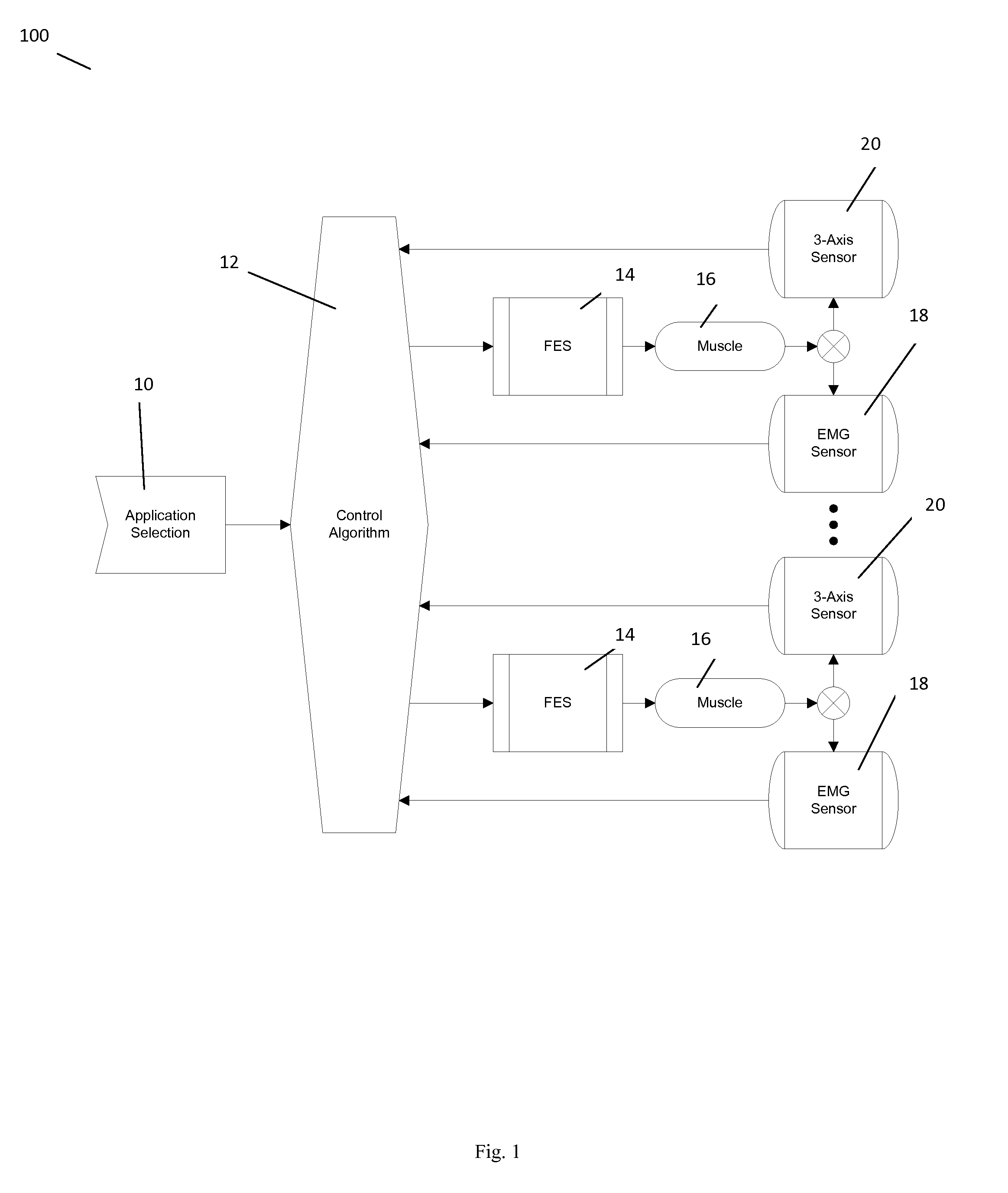
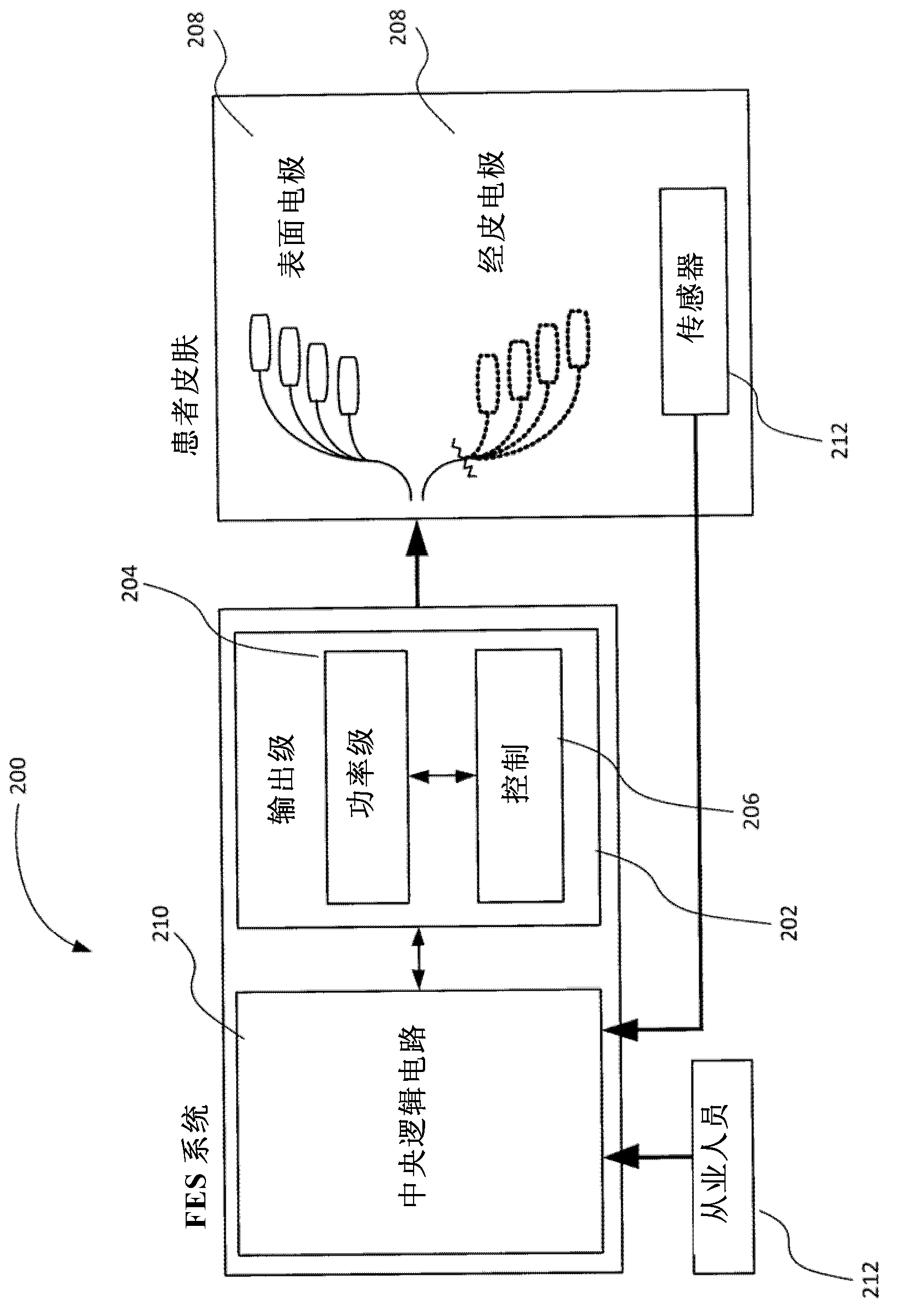
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a technique that uses low-energy electrical pulses to artificially generate body movements in individuals who have been paralyzed due to injury to the central nervous system. More specifically, FES can be used to generate muscle contraction in otherwise paralyzed limbs to produce functions such as grasping, walking, bladder voiding and standing. This technology was originally used to develop neuroprostheses that were implemented to permanently substitute impaired functions in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), head injury, stroke and other neurological disorders. In other words, a person would use the device each time he or she wanted to generate a desired function. FES is sometimes also referred to as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES).
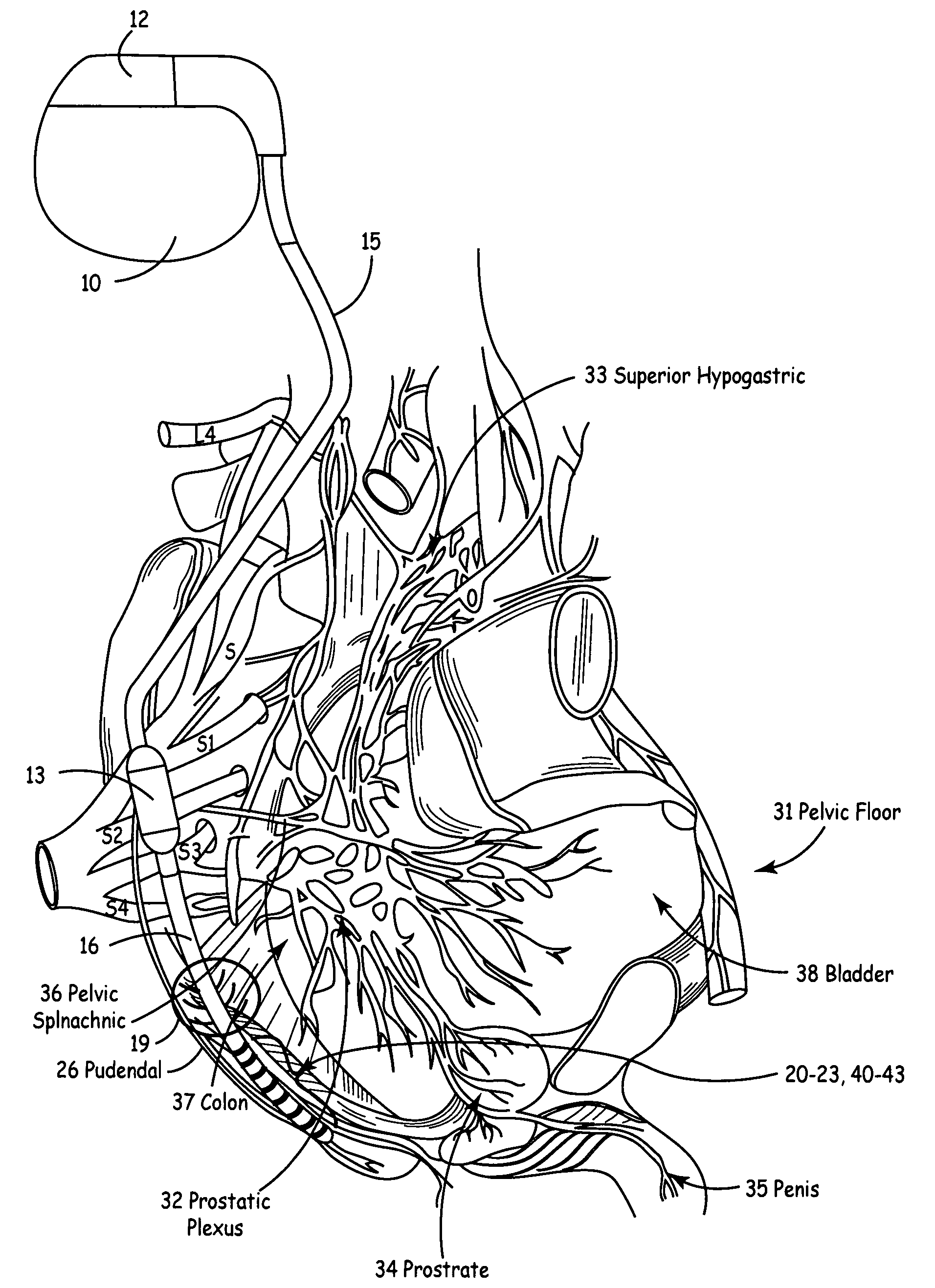
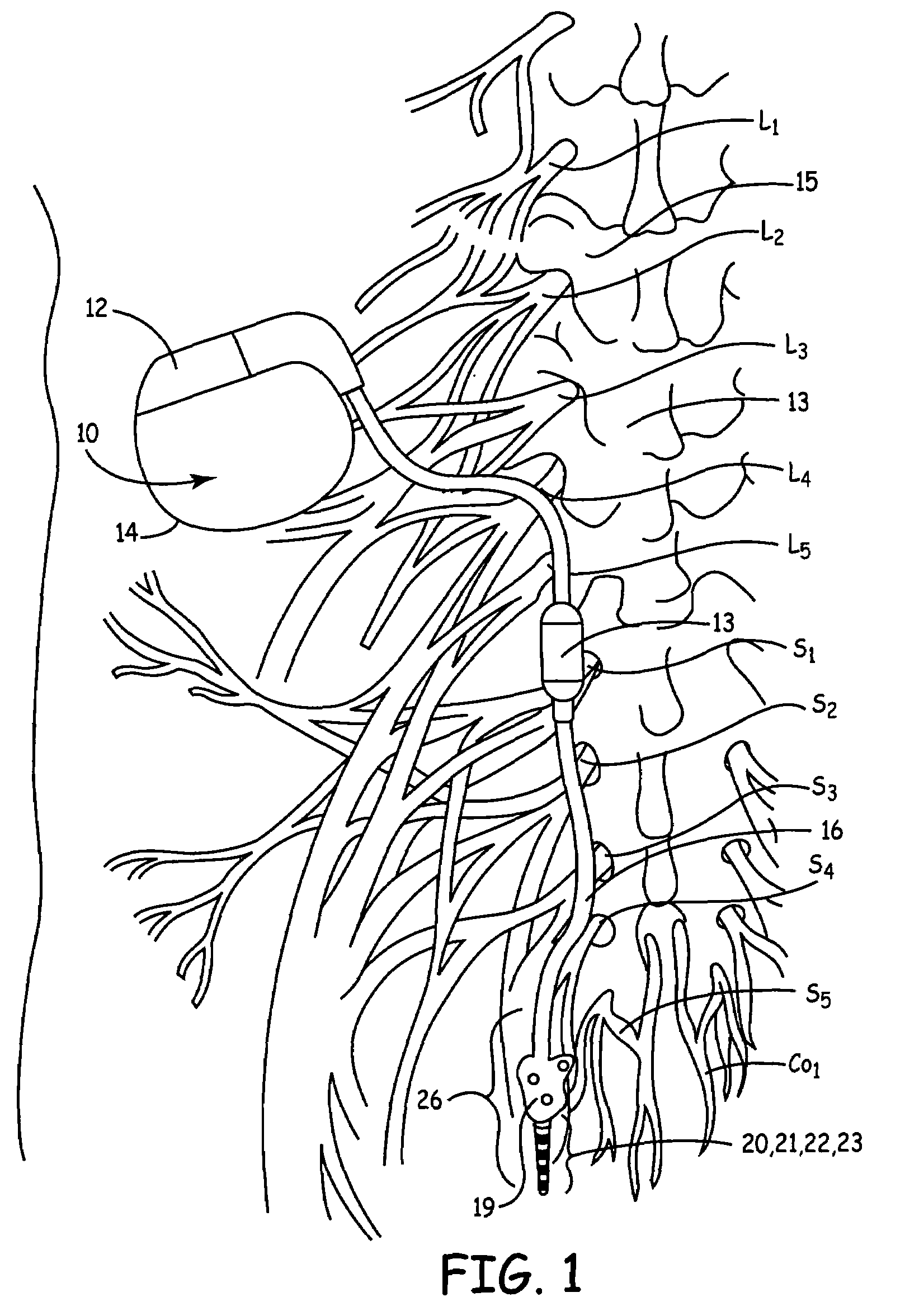
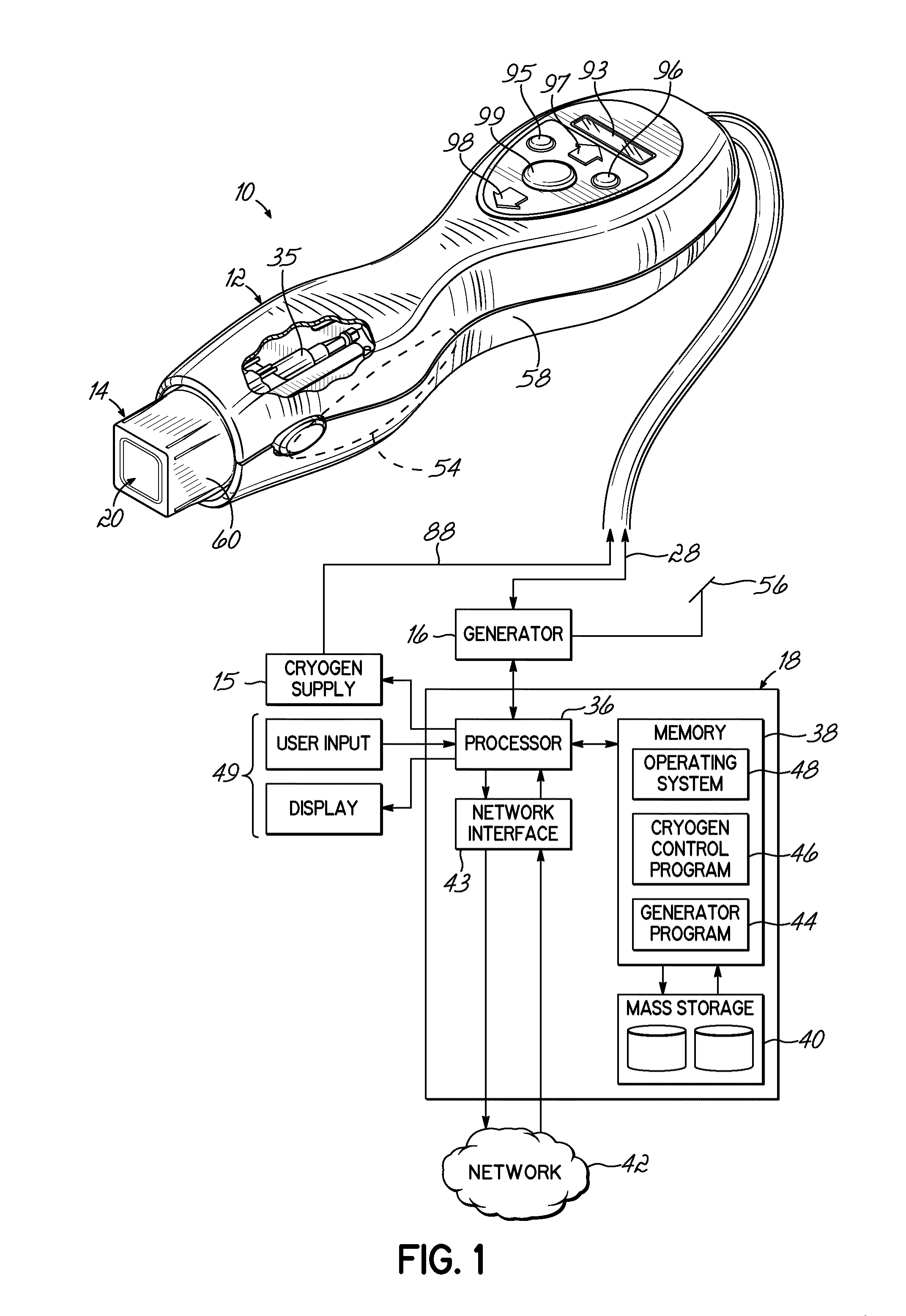
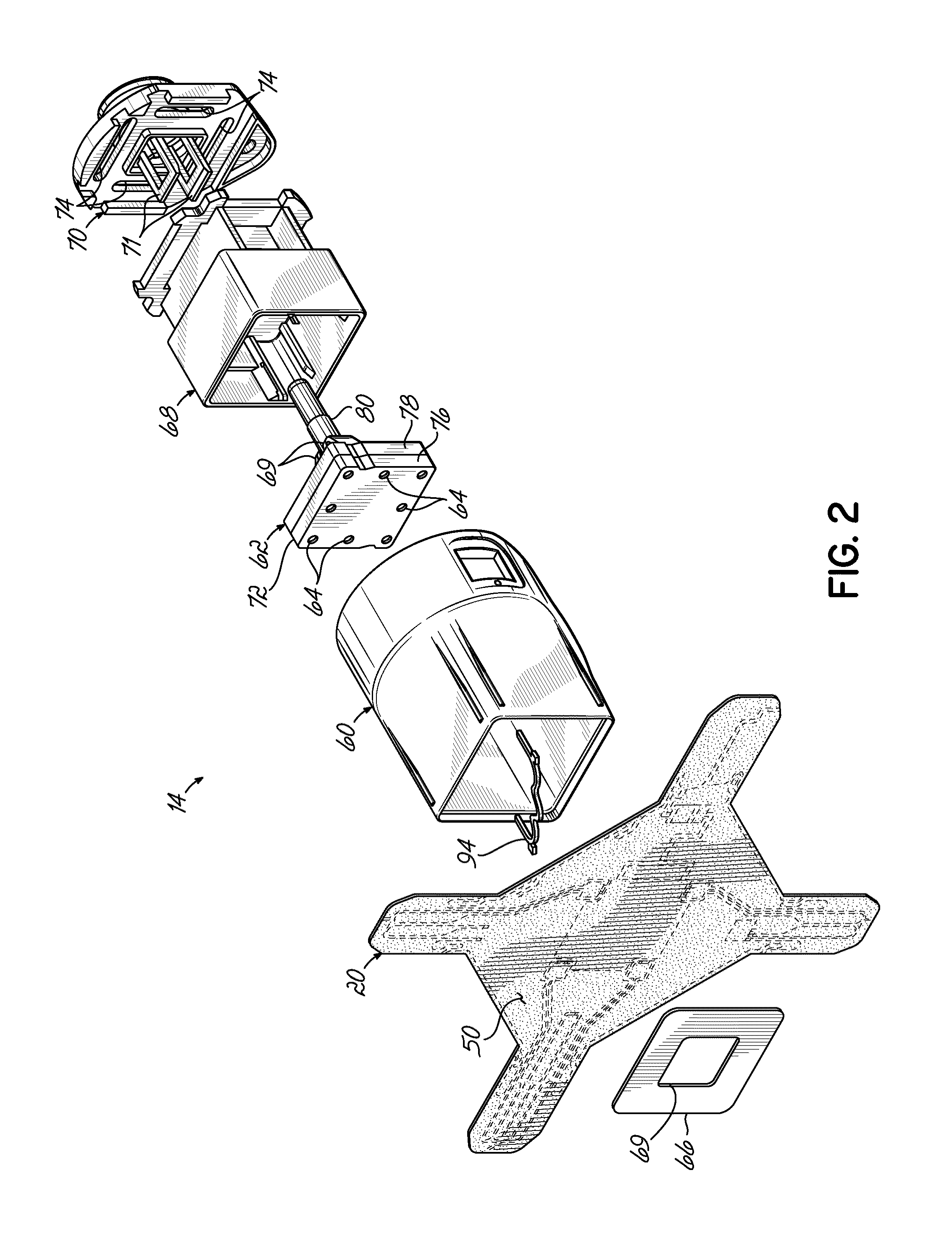
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS7328068B2Undesirable side effects of sacral nerve stimulation may be avoided or minimizedUndesirable side-effectDigestive electrodesGenital electrodesDiseaseProstatalgia
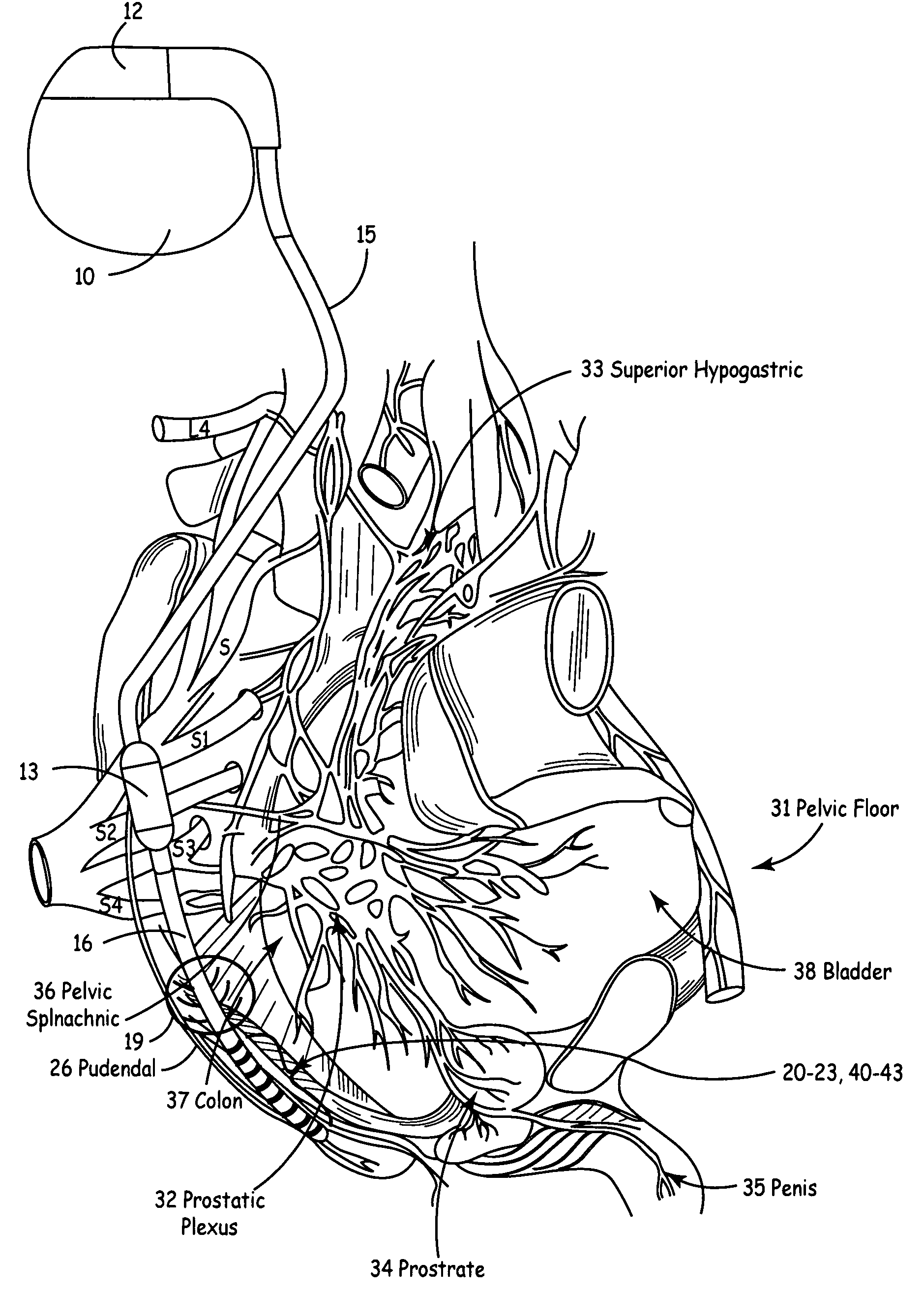
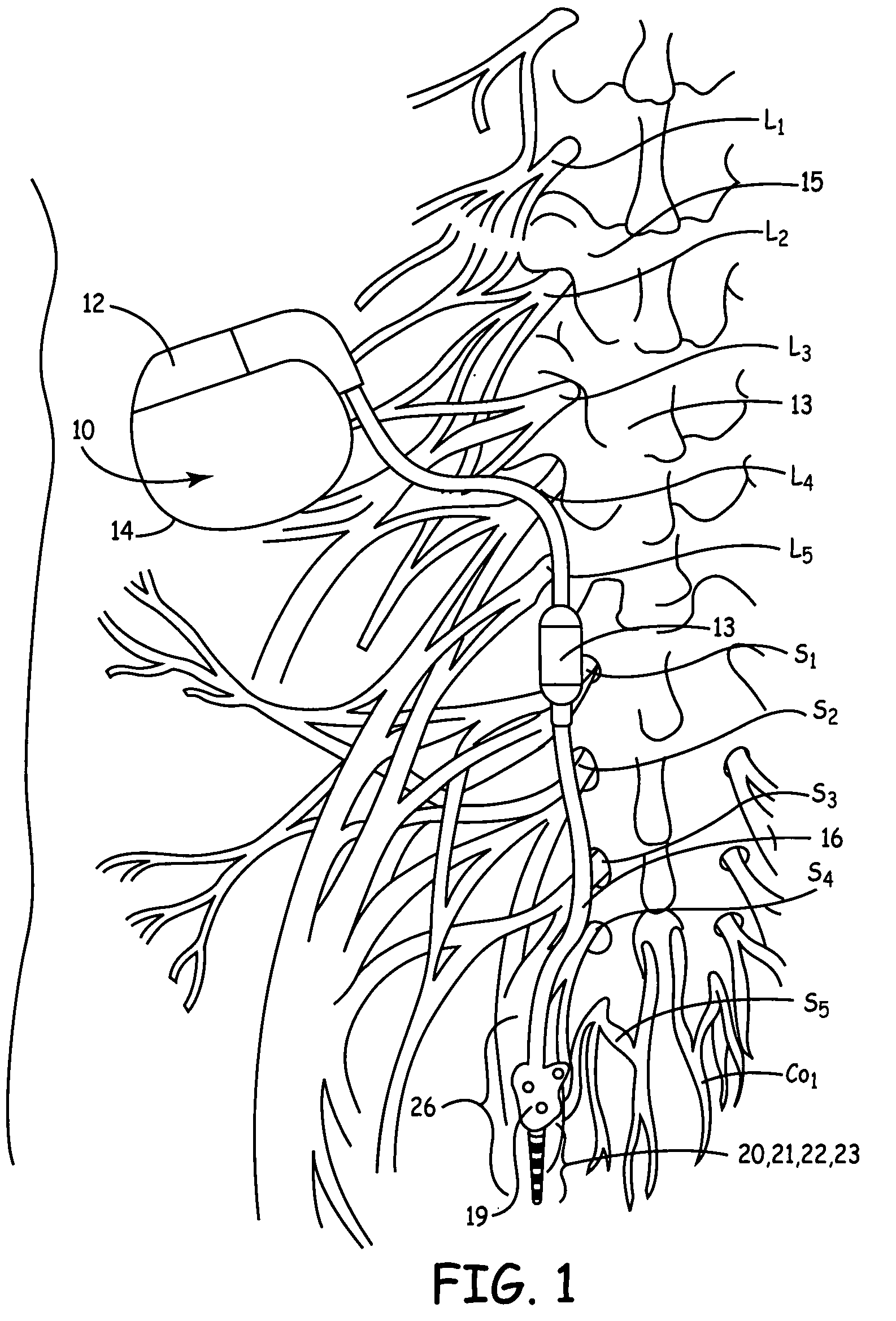
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
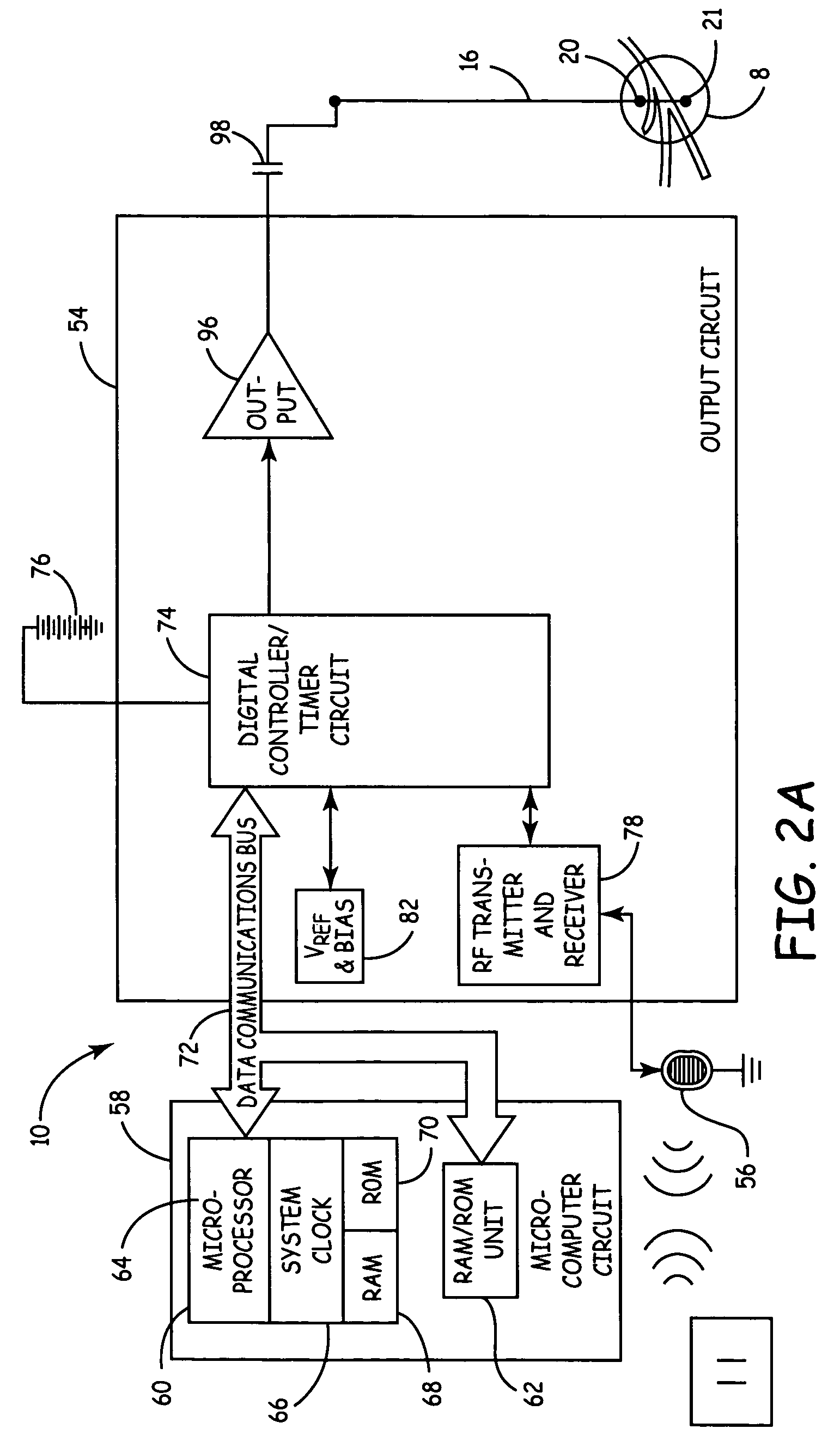
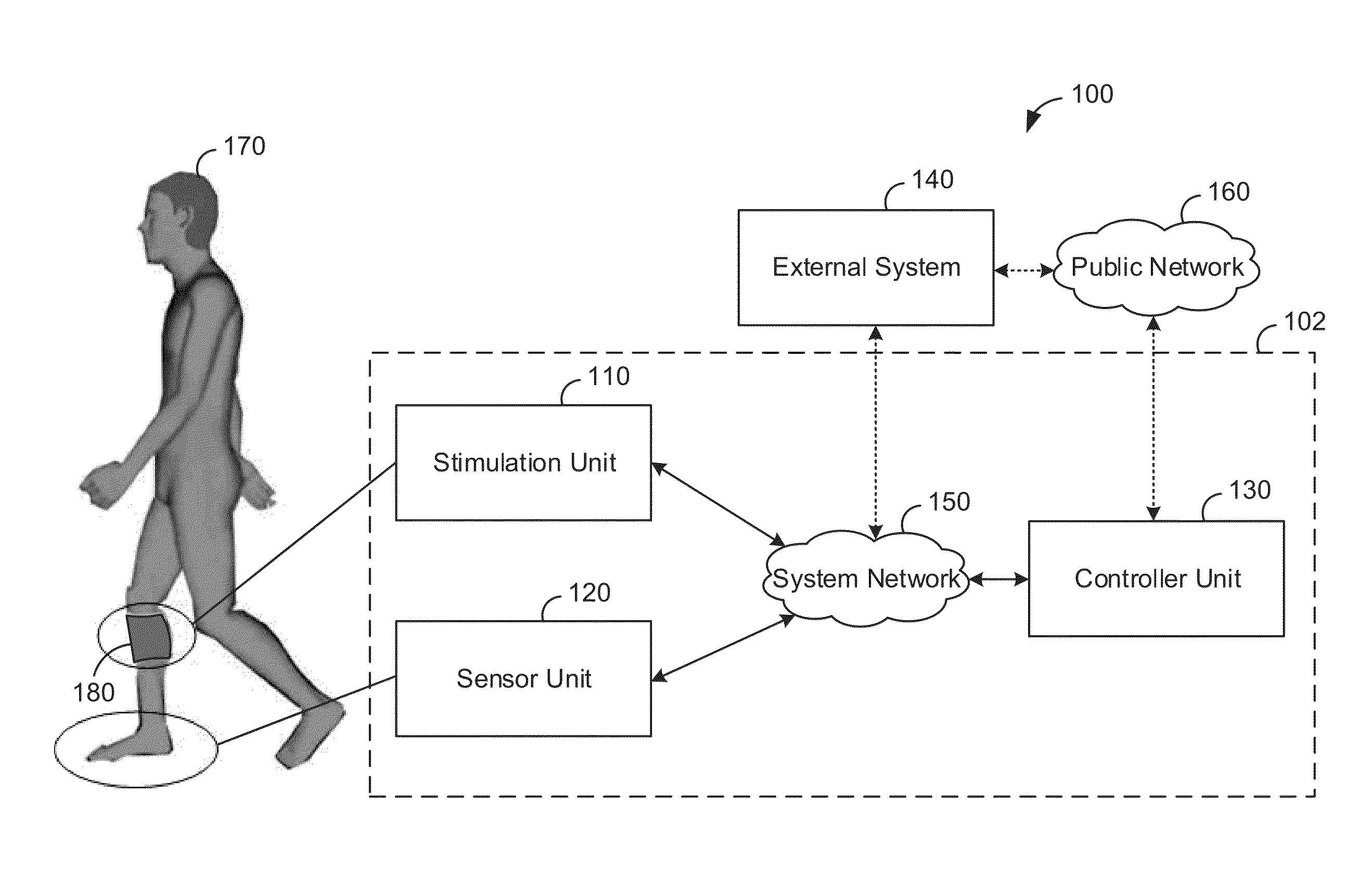
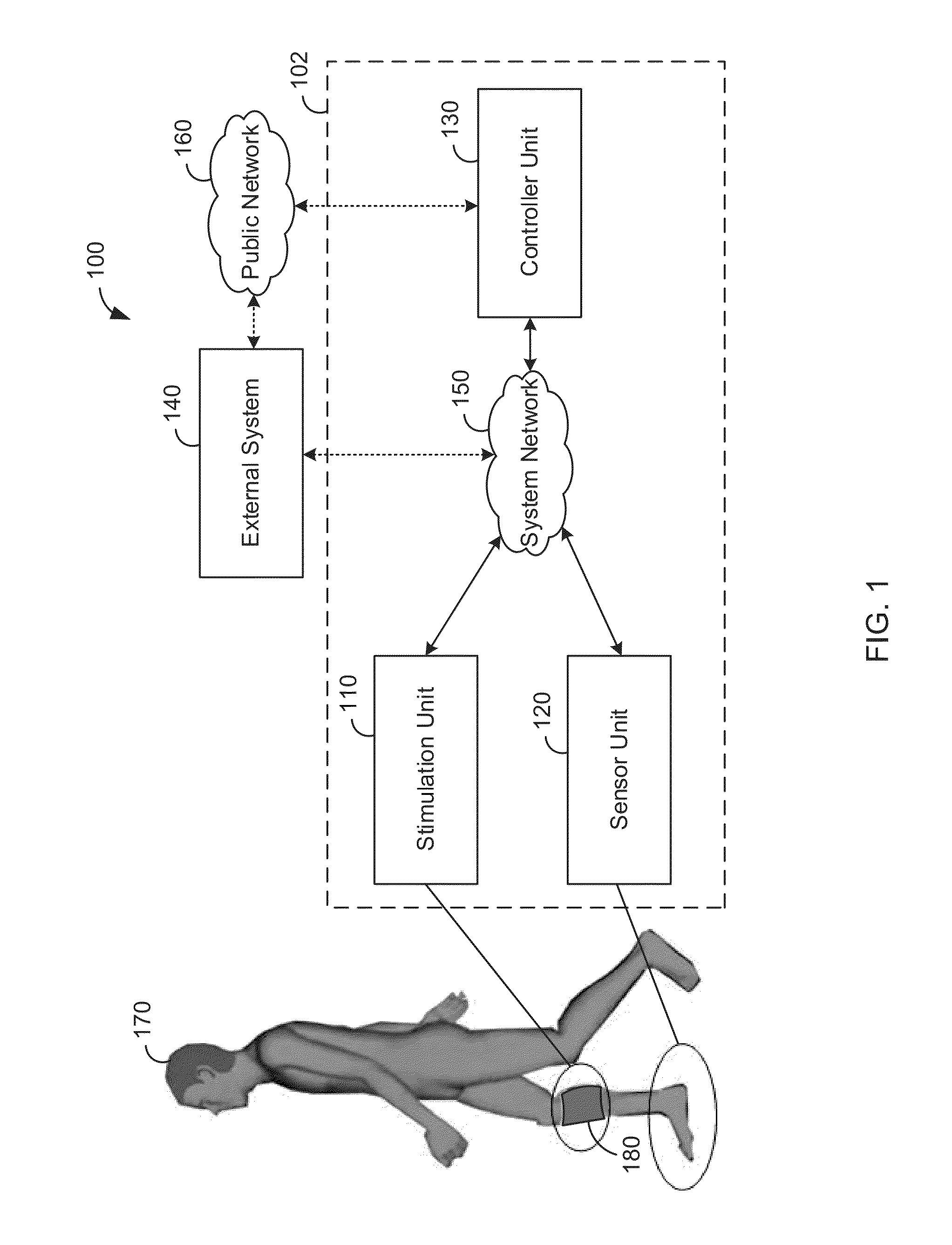
Universal closed-loop electrical stimulation system
ActiveUS20130123568A1Restore motor functionReduce hyperlipidemiaElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNervous systemClosed loop
A universal closed-loop functional electrical stimulation system comprising at least one electrode assembly adapted to deliver an electrical stimulation signal to the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, or muscles of a user, a sensor system adapted to detect a mechanical response to a muscle stimulation signal of at least one muscle associated with a muscle group stimulated through the nervous system or proximate to the electrode assembly. An electrical stimulation device operably coupled to at least one electrode assembly and the sensor system, the electrical stimulation device including a control system to automatically receive feedback from at least one characteristic of the muscle from the detected muscle response and adjust at least one parameter of the muscle stimulation signal in real-time and in response thereto and a programmed microprocessor for controlling said electrical stimulation and receiving input from said sensor system.
Owner:HAMILTON MARILYN J +1
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudenal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS20050113877A1Reduce traumaAvoid damageDigestive electrodesArtificial respirationDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
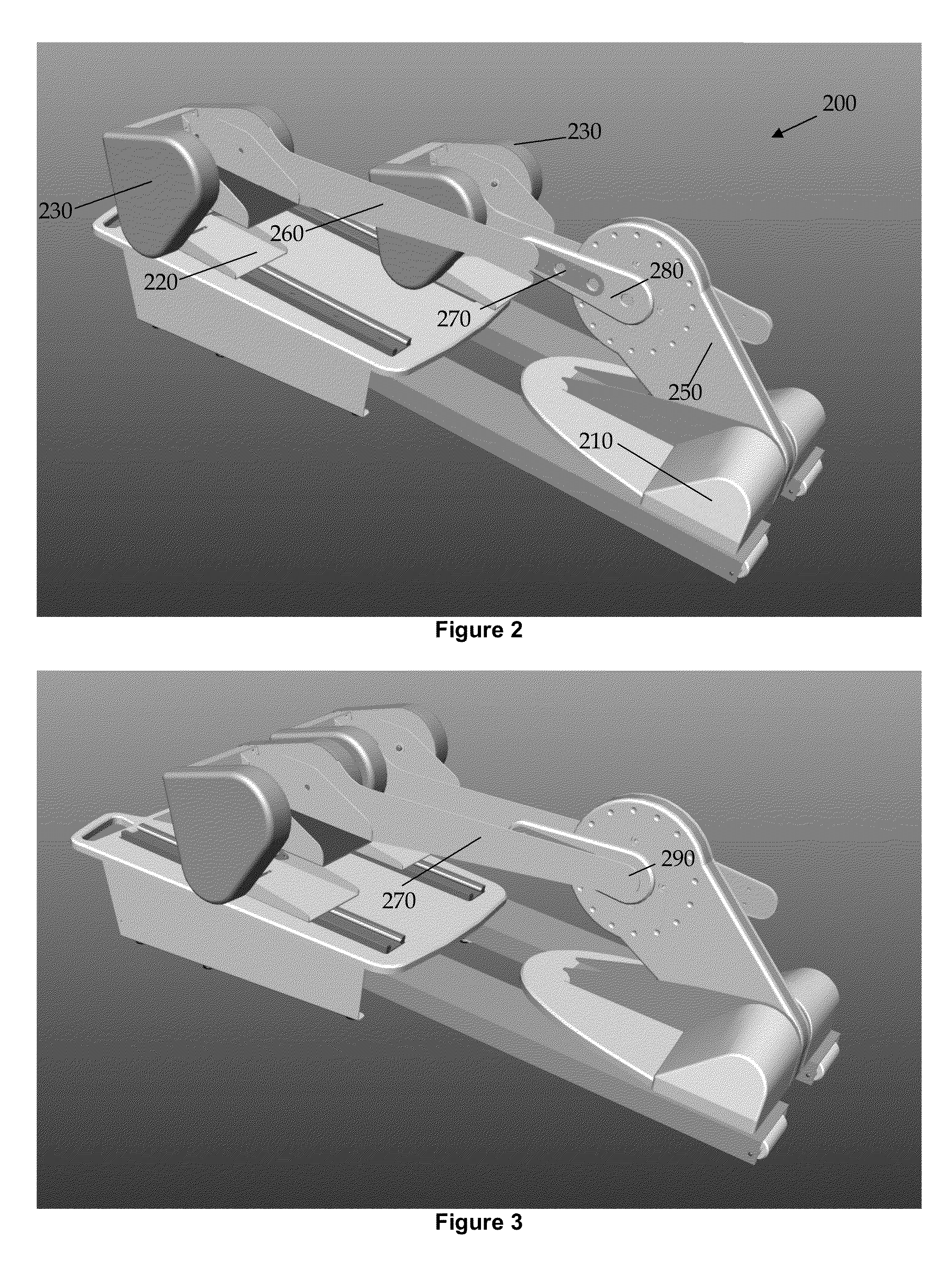
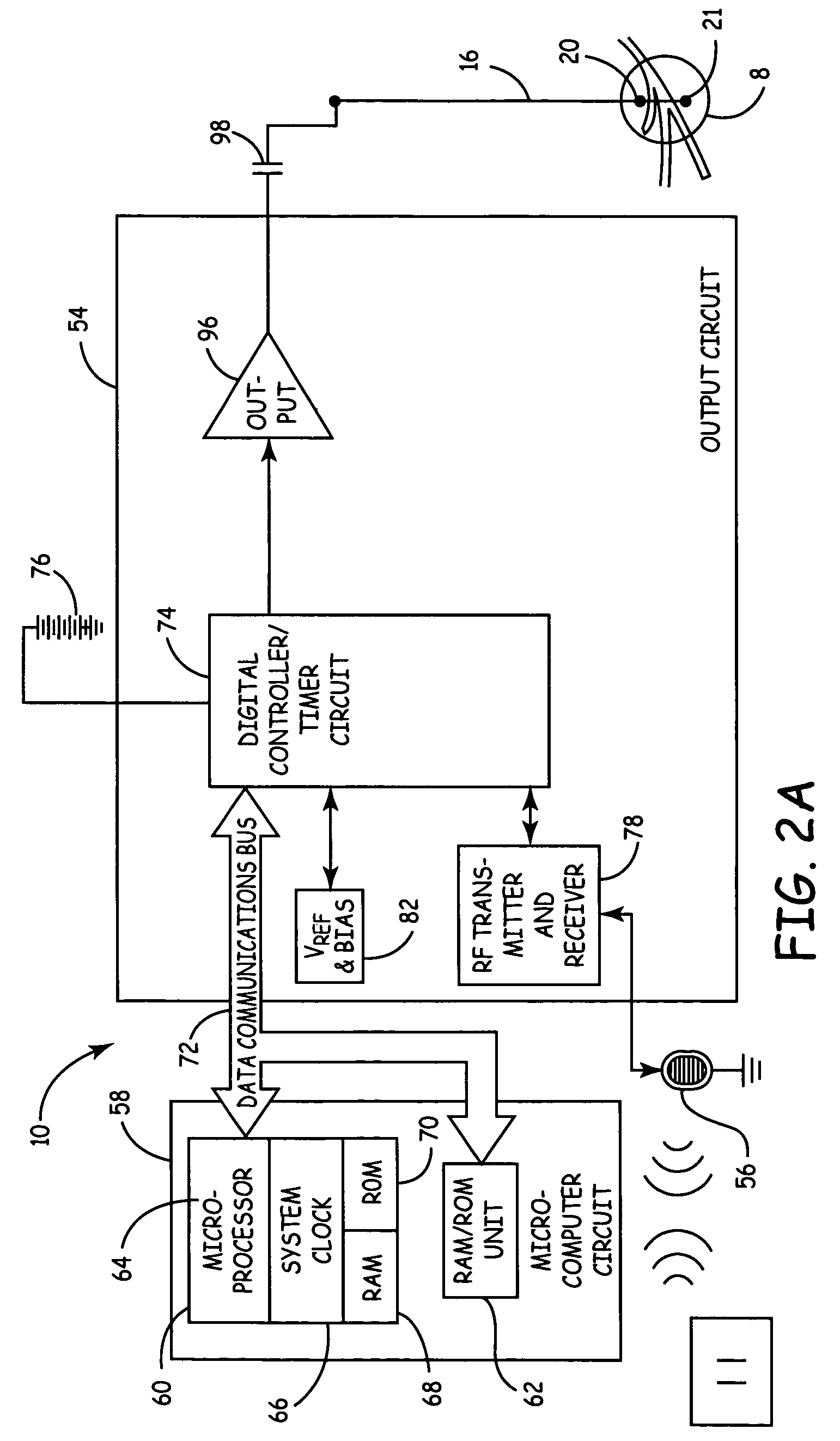
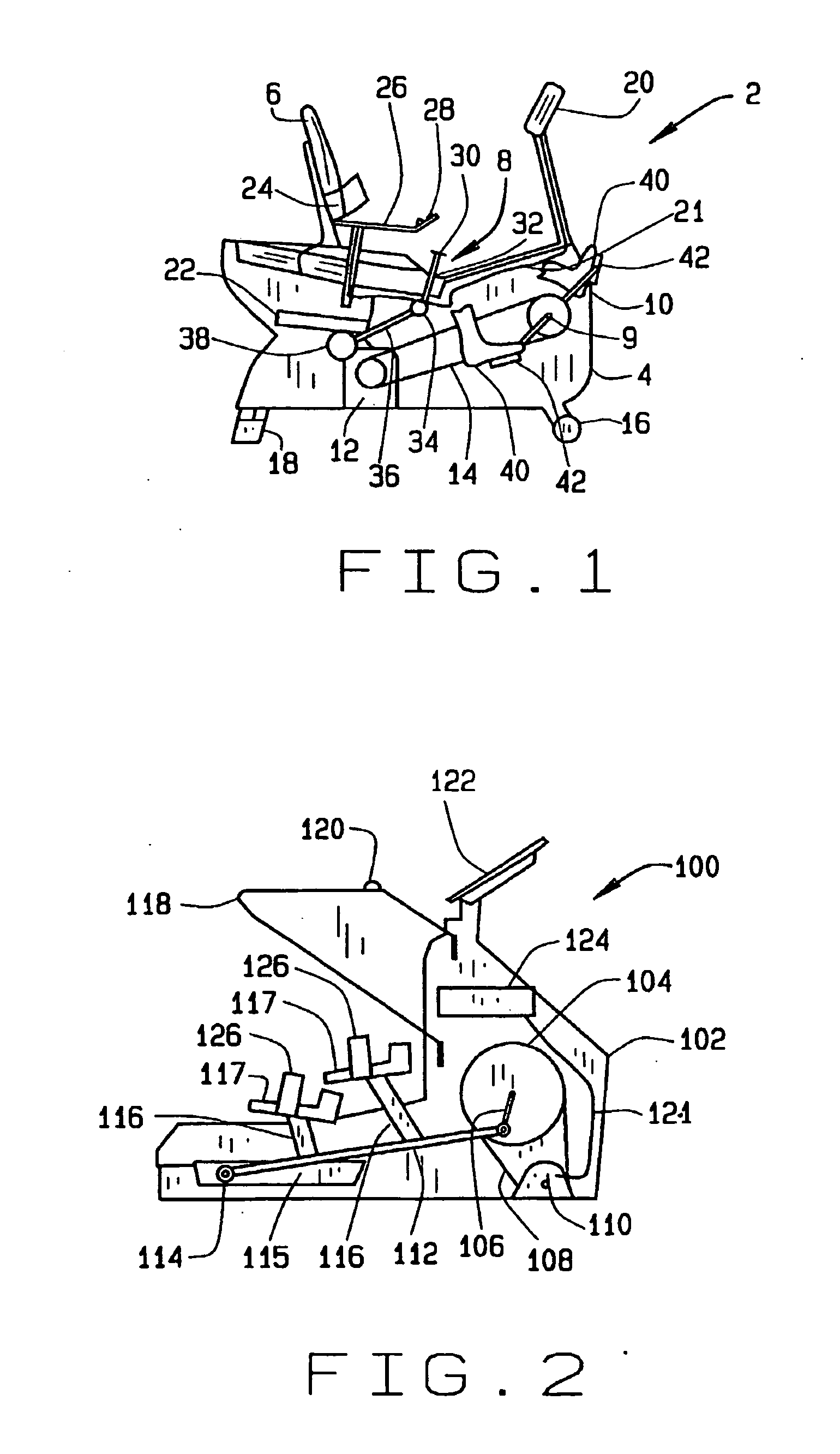
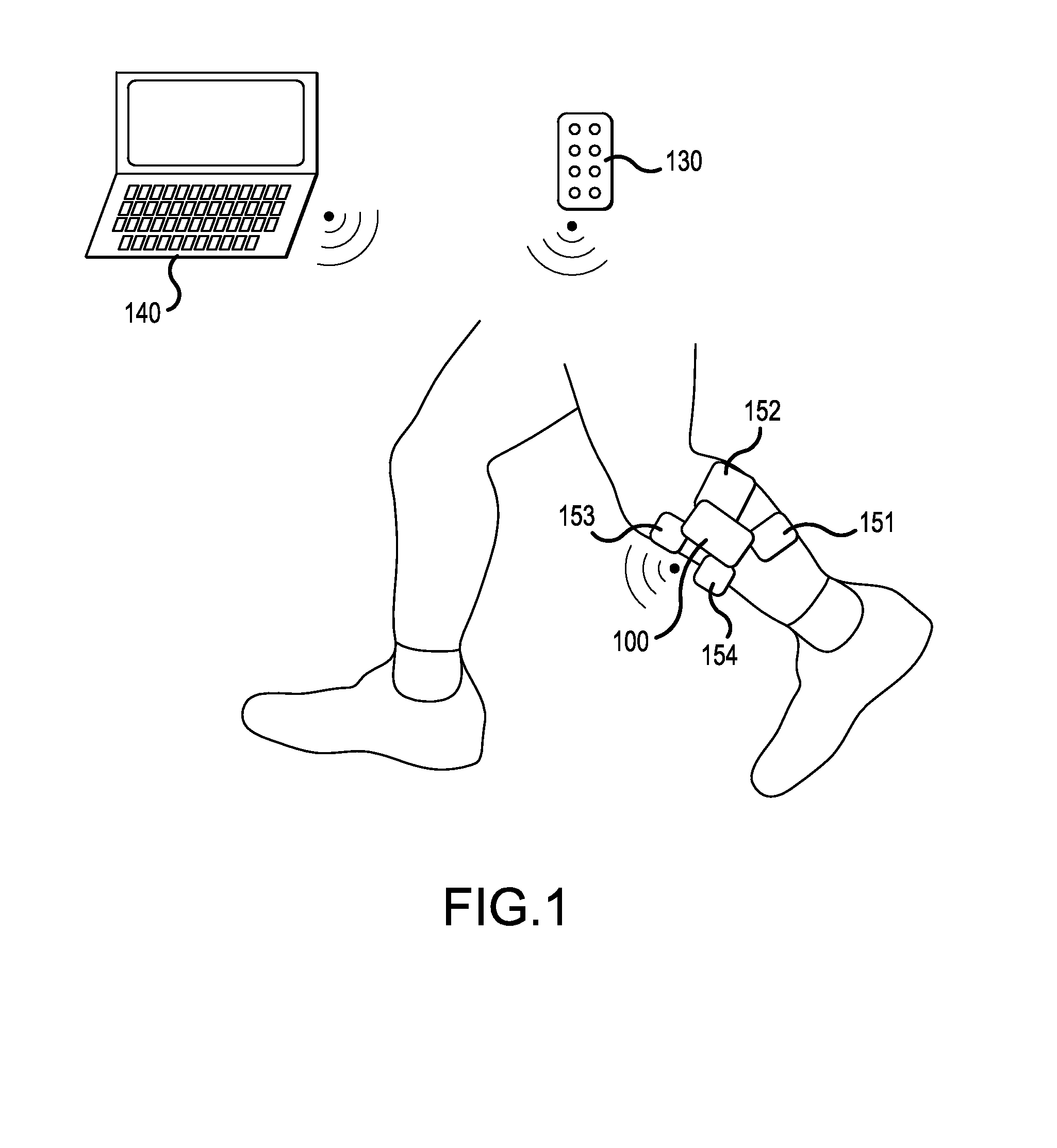
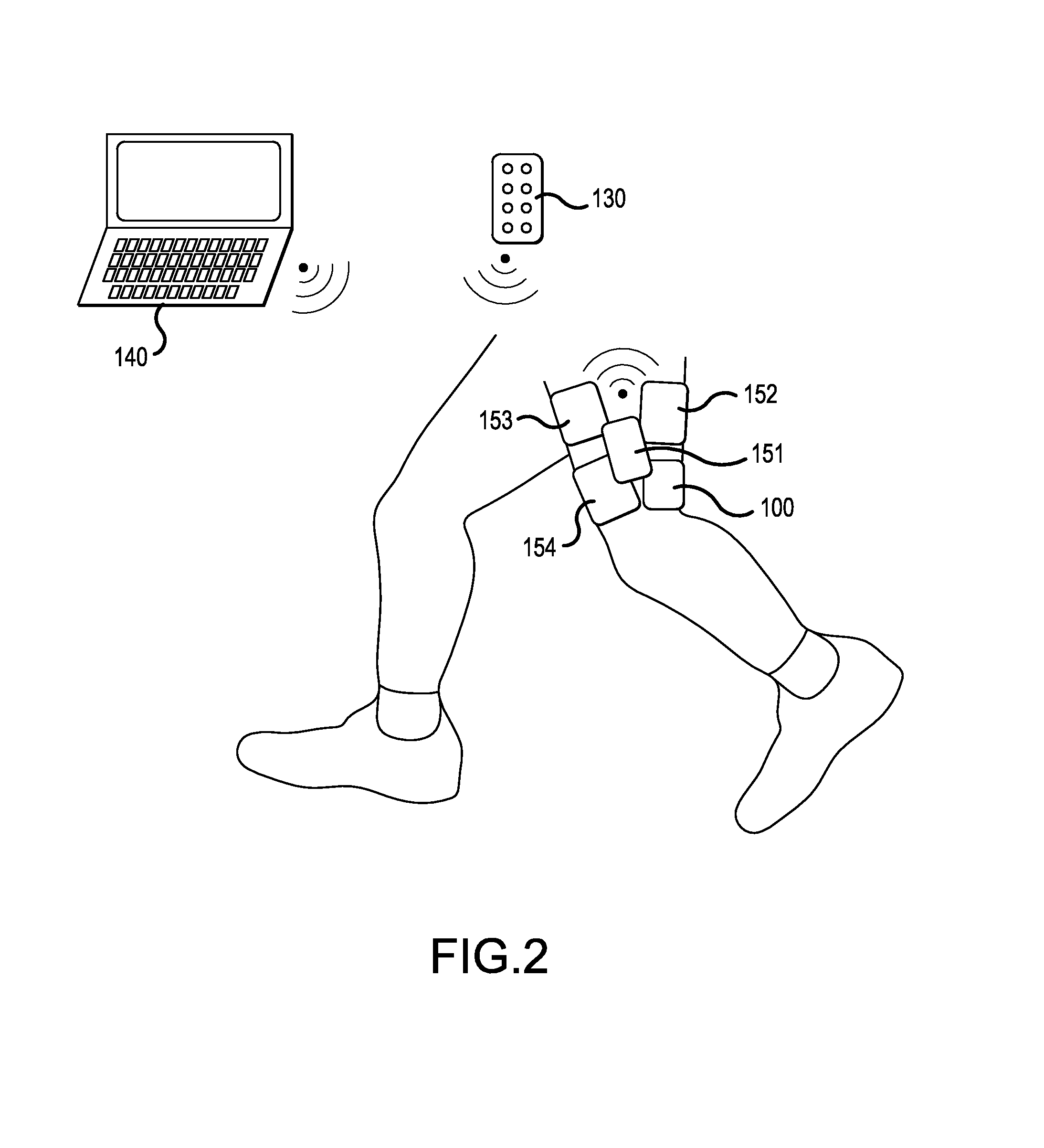
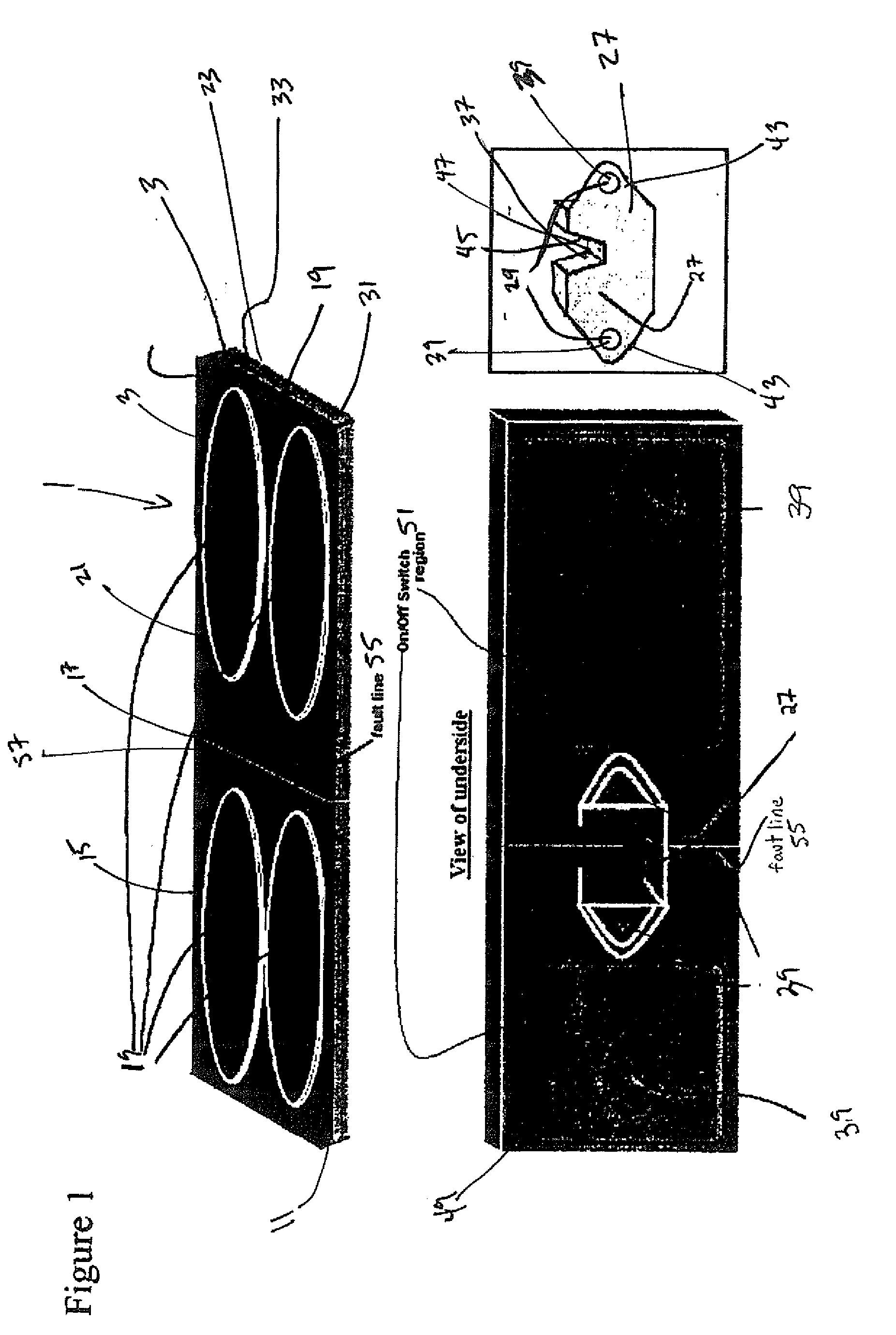
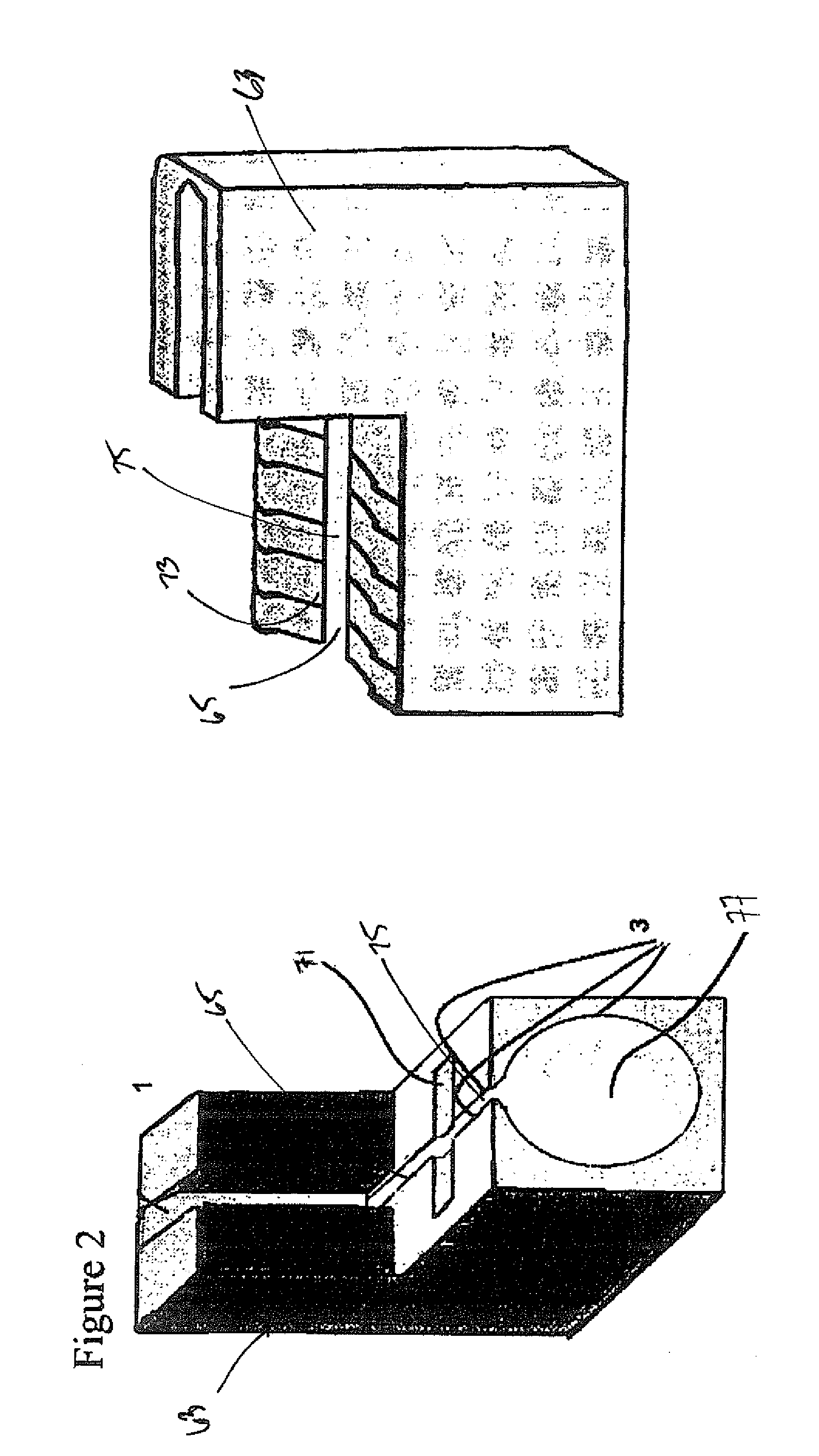
Functional electrical stimulation system
ActiveUS7162305B2Assisted rehabilitationExternal electrodesArtificial respirationElectricityDocking station
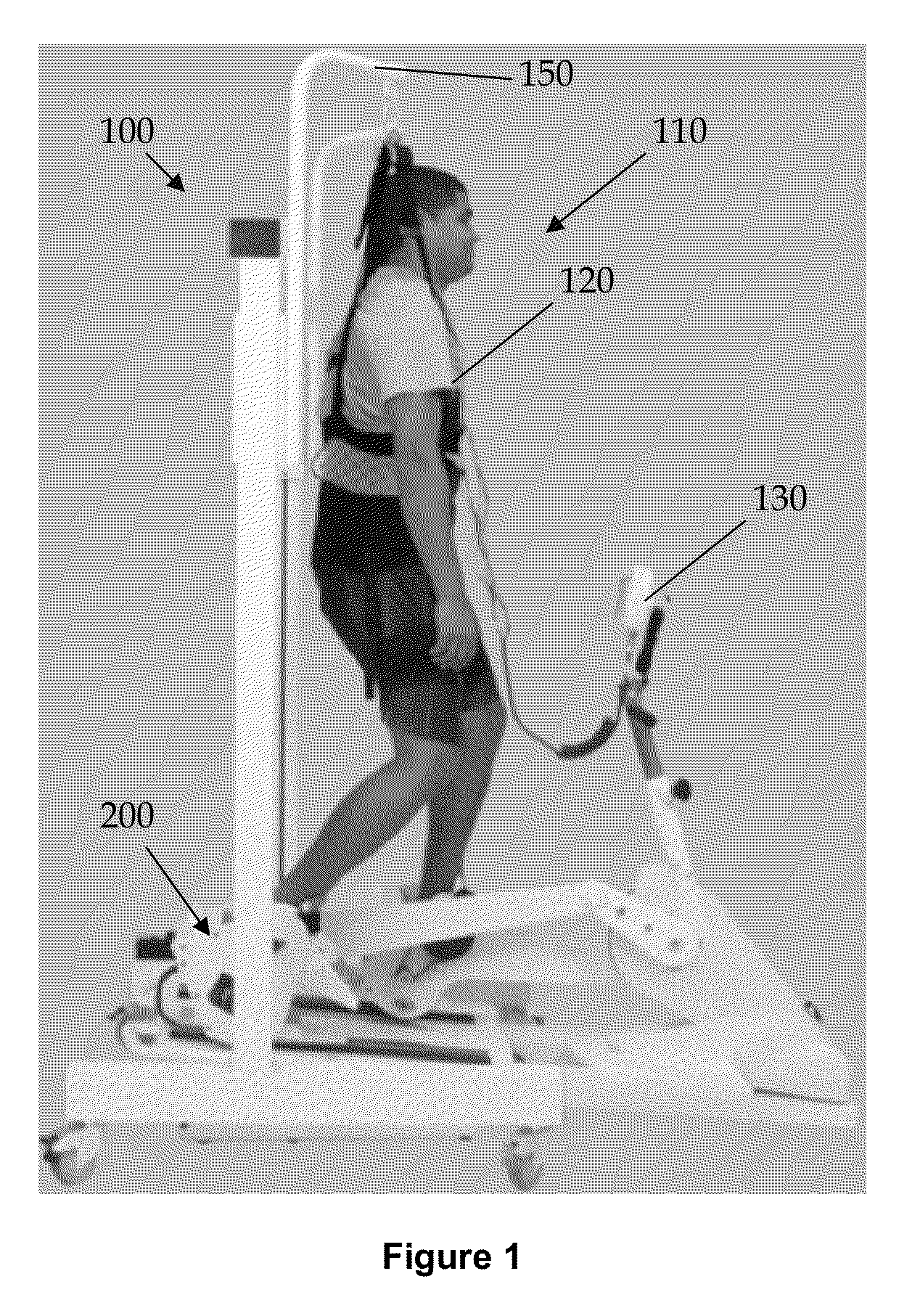
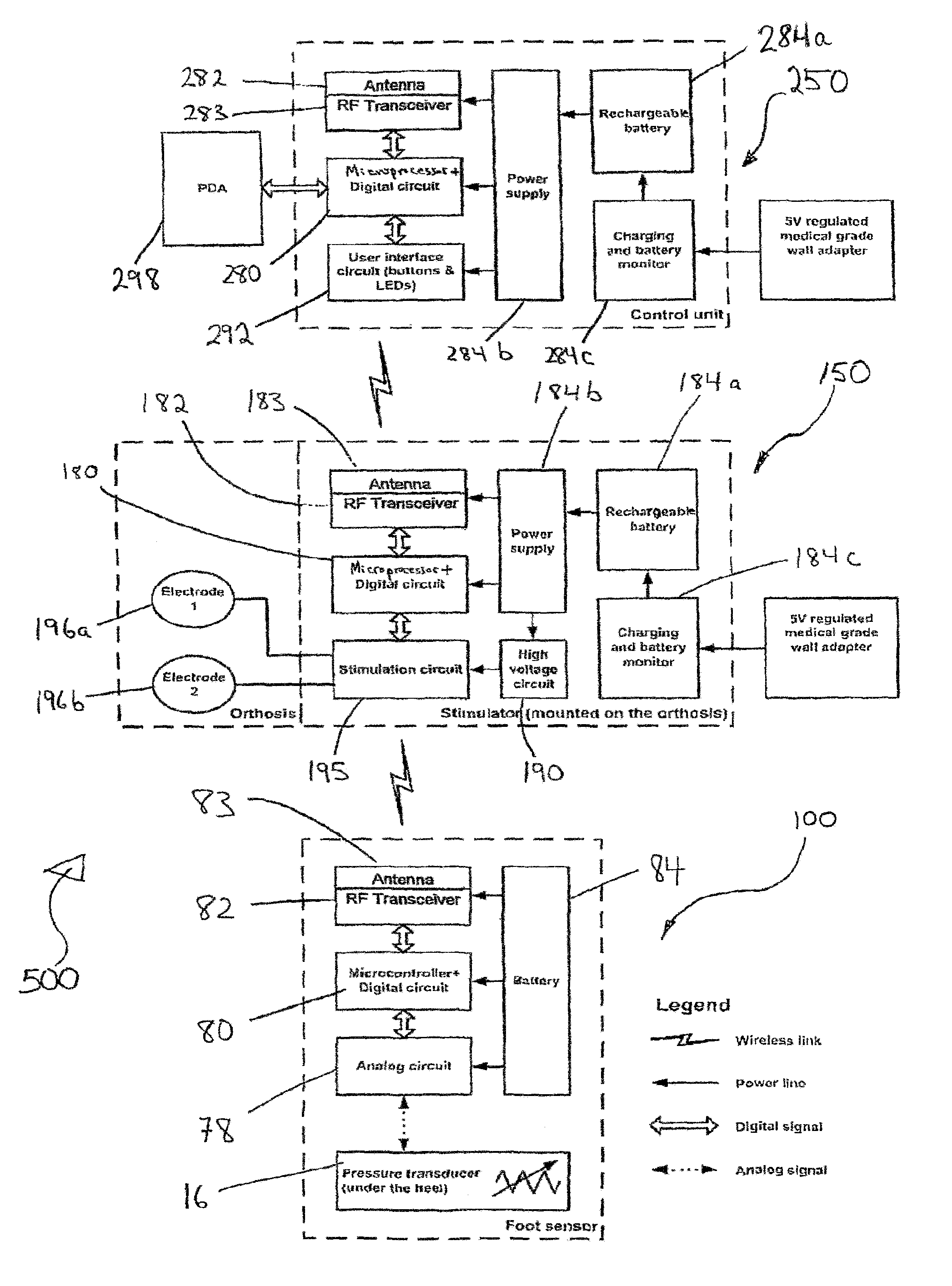
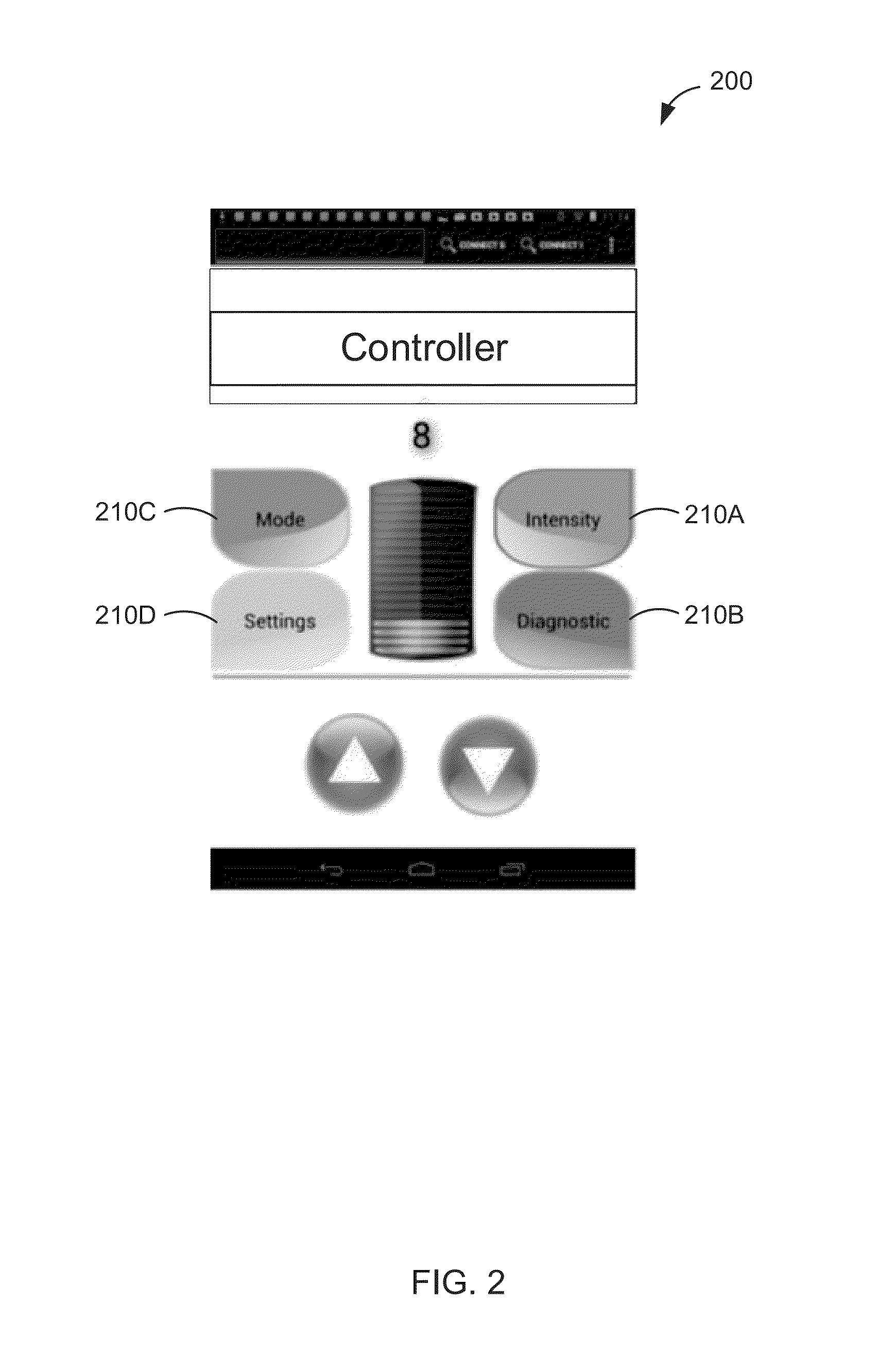
An electrical stimulation device for a body part of a person comprises an orthotic with sensor and electrodes and a controller. The controller receives a sensor signal, compares the sensor signal to a threshold value and generates an electrical output from the electrodes if the sensor signal exceeds the threshold value. A docking station facilitates connection of the electrodes and sensors to a computer. The docking station including a first processor for measuring values of the sensor signal and the electrical outputs and a second processor for generating electrical outputs on the electrodes.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
System for functional electrical stimulation
An exercising system and method for the treatment and rehabilitation of the paralyzed muscles of the legs. Stimulators and sensors are implanted in several of the main muscle groups of the legs. A computerized controller uses wireless signals for communications with the implanted stimulators and sensors. The person receiving the treatment sits on an exercise machine such as a stationery bicycle, a leg press, a rowing machine or other leg exercising machine. The controller determines the position of the legs and transmits a series of commands to the stimulators to provide functional electrical stimulation (FES) to the muscles of the legs, which move the legs in a cyclical or reciprocating manner, such as that needed to pedal a bicycle. Using data provided by the implanted sensors, the controller is able to adjust the stimulation commands sent to the muscles of the legs to control the amount of force exerted by the foot, to limit user fatigue and to keep the foot in a neutral position on the pedal or footrest. Users of the system who are partially paralyzed in the legs can receive an implanted EMG sensor and the controller can synchronize the stimulation of their paralyzed leg muscles with the user's own voluntary activation of their leg muscles.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Method and apparatus for promoting nerve regeneration in paralyzed patients
InactiveUS20060247095A1Lower Level RequirementsLevel of function riseClubsElectrotherapyElectro stimulationNerves regeneration
In one aspect the present disclosure provides a method of rehabilitating a person who has suffered central nervous system damage including the steps of providing exercise equipment capable of exercising a person's limbs, providing functional electrical stimulation to the person's limbs to be exercised in order to operate the exercise equipment, increasing the level of functional electrical stimulation; decreasing a resistance provided by the exercise equipment or providing assistance to maintain an acceptable speed of the exercise equipment as the person's muscles tire; finally completely removing functional electrical stimulation to the person's limbs and providing assistance to maintain an acceptable speed of the exercise equipment; and continuing passive exercise of the person's limbs for a period of time greater than two minutes. Also provided are apparatuses to carry out the method.
Owner:RUMMERFIELD PATRICK
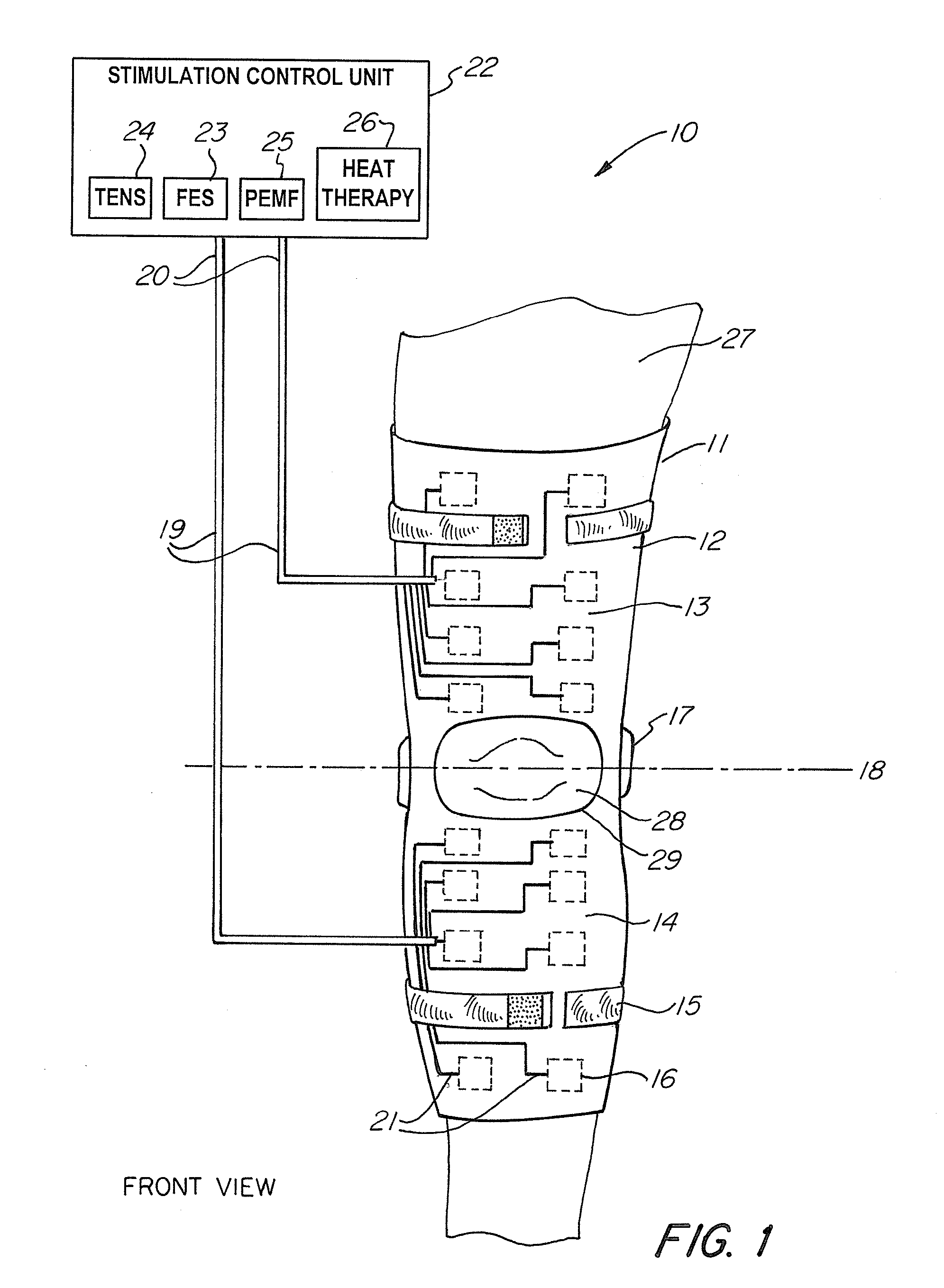
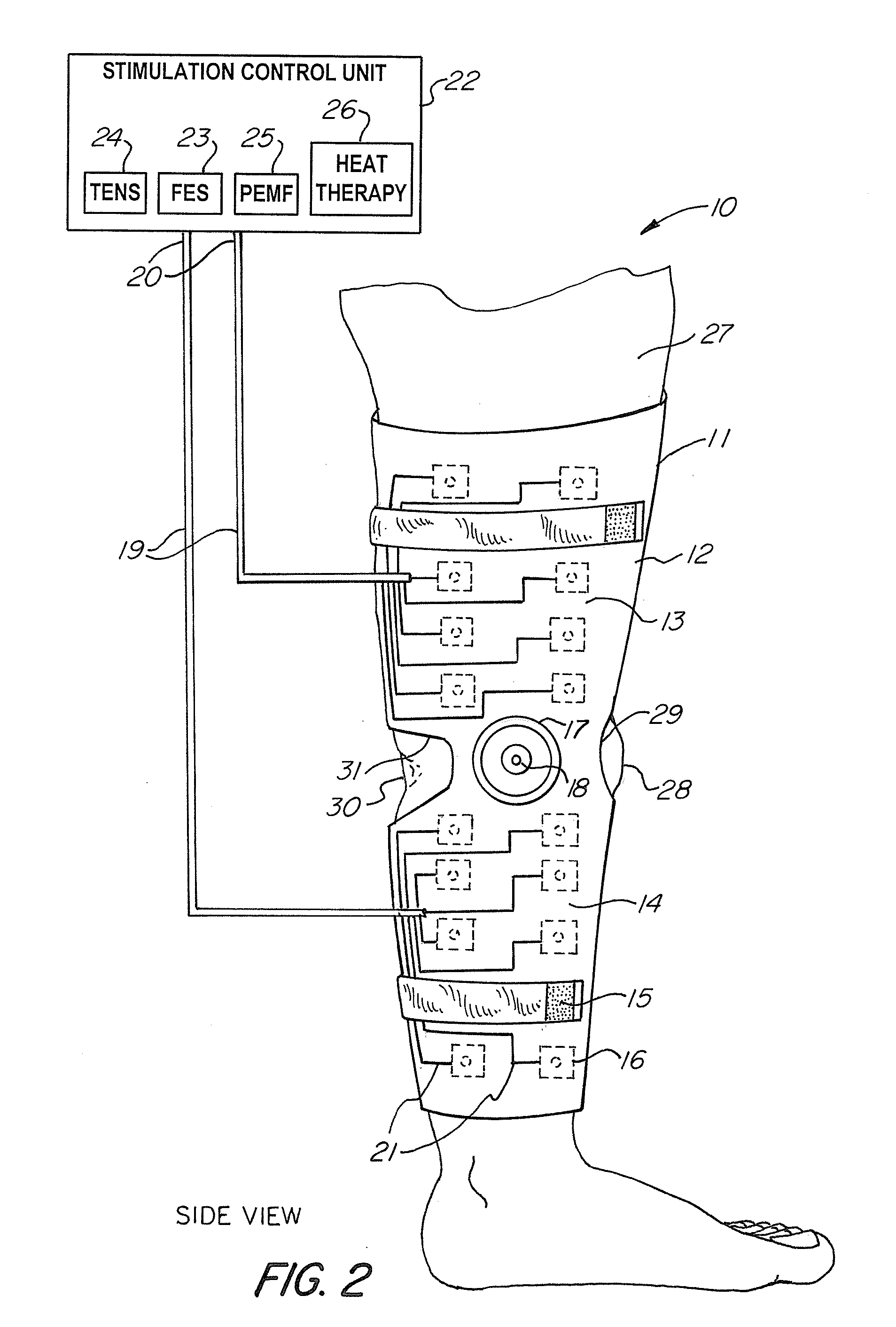
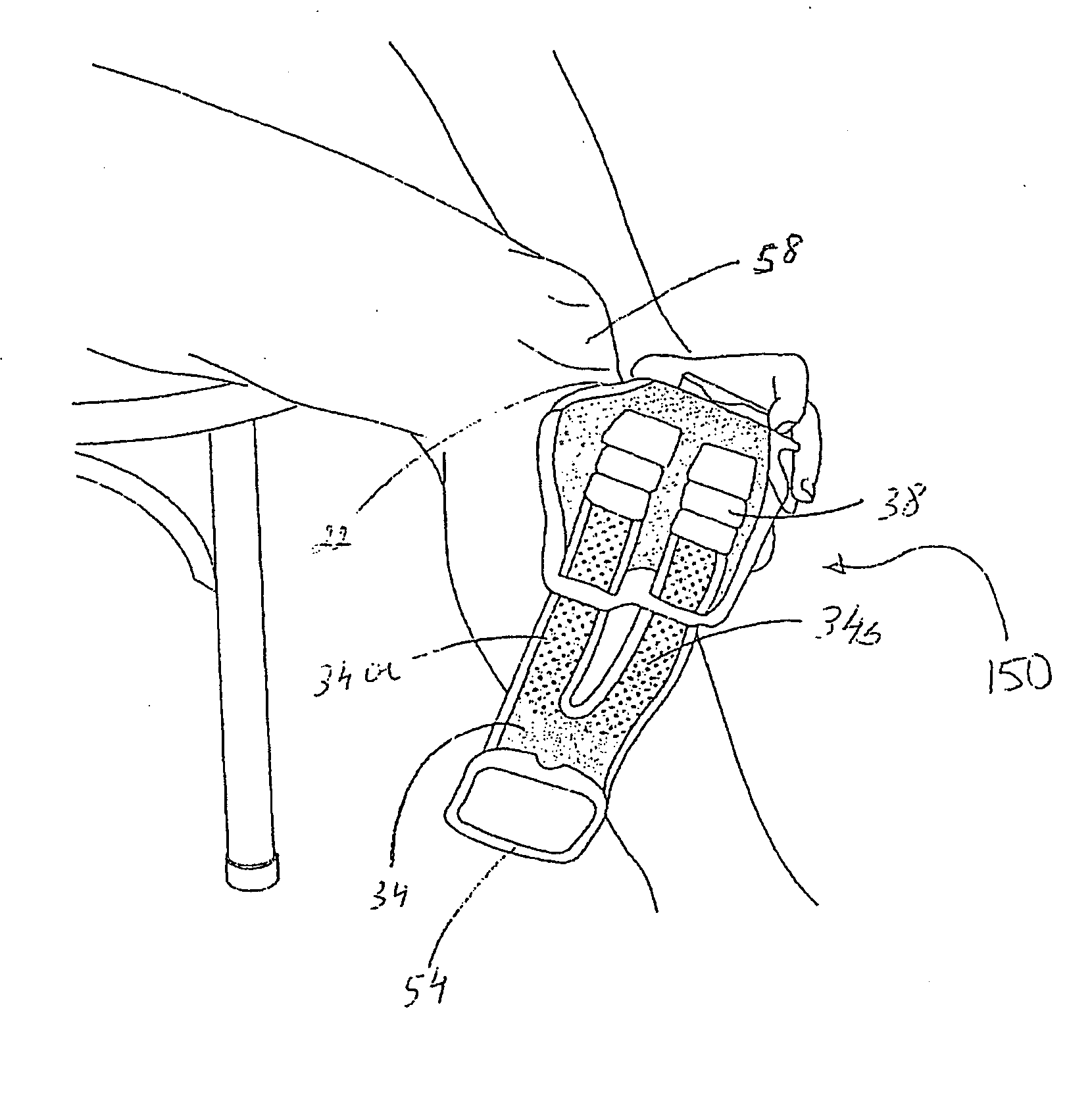
Universal Musculoskeletal Rehab Device (Brace, Sleeve, or Pad) For Electrical Treatment Modalities and Biofeedback Response Monitoring
InactiveUS20130085317A1Convenient treatmentEnhancing rehabilitative treatmentElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyDiseaseInteractive software
A non-invasive device for assisting the treatment of any kind of musculoskeletal disorder, including but not exclusive of those of joint, limb, and spine disorders, includes a brace, sleeve, flexible pad, or any combination of the three, a plurality of electrodes disposed thereon, wherein the plurality of electrodes transmit at least three electrophysical modalities, and a stimulation control unit having interactive software to establish a controlled sequence of transmission of the at least three electrophysical modalities and communicating the controlled sequence to the electrodes. The at least three electrophysical modalities are chosen from a group consisting of neuromodulating functional electrical stimulation, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation, and heat therapy stimulation. The stimulation control unit also provides feedback data using the electrodes for monitoring and integration with the interactive software to analyze and assess biomechanical, neuromuscular, and neurological responses to the device.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
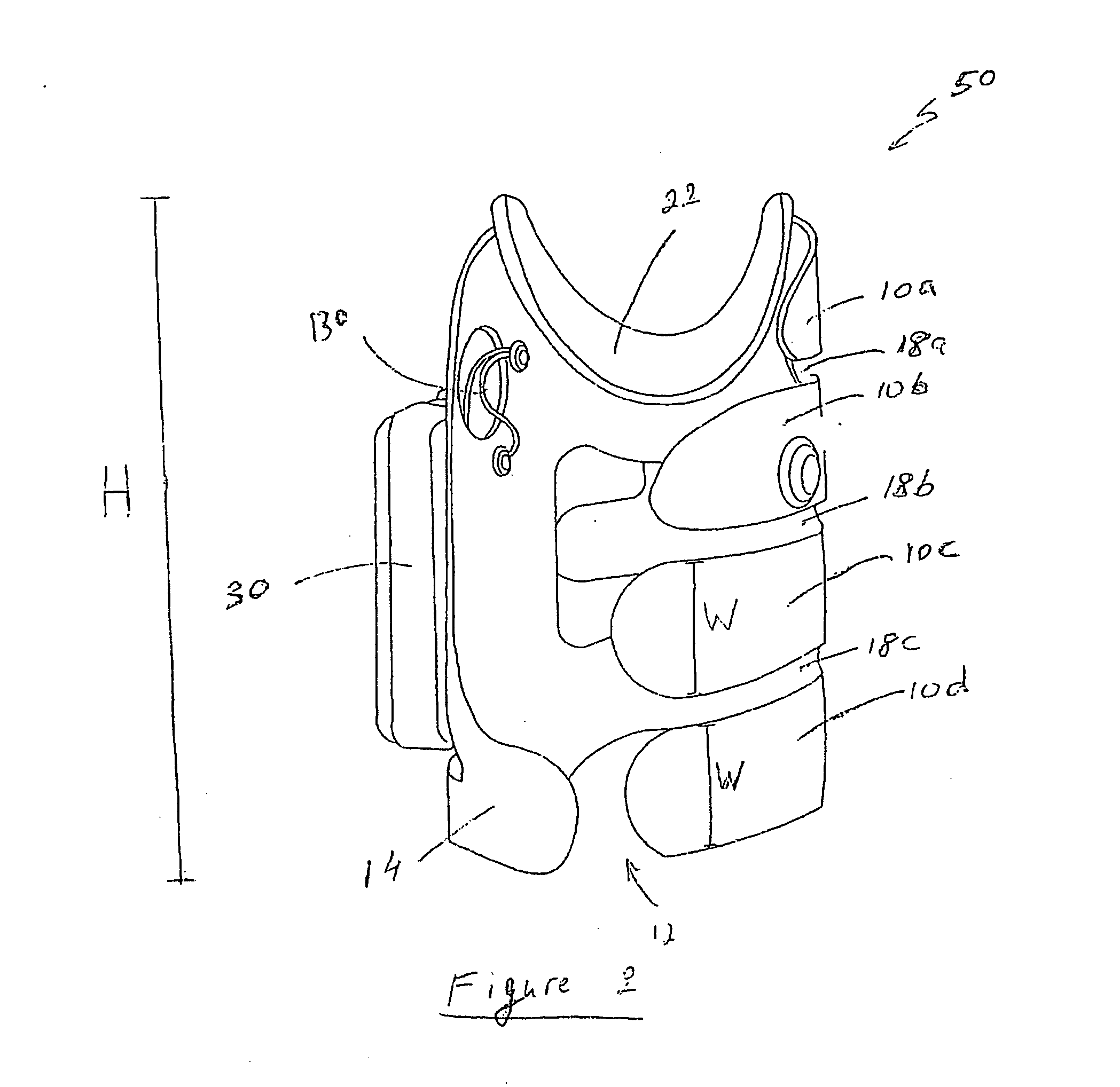
Orthosis for a gait modulation system
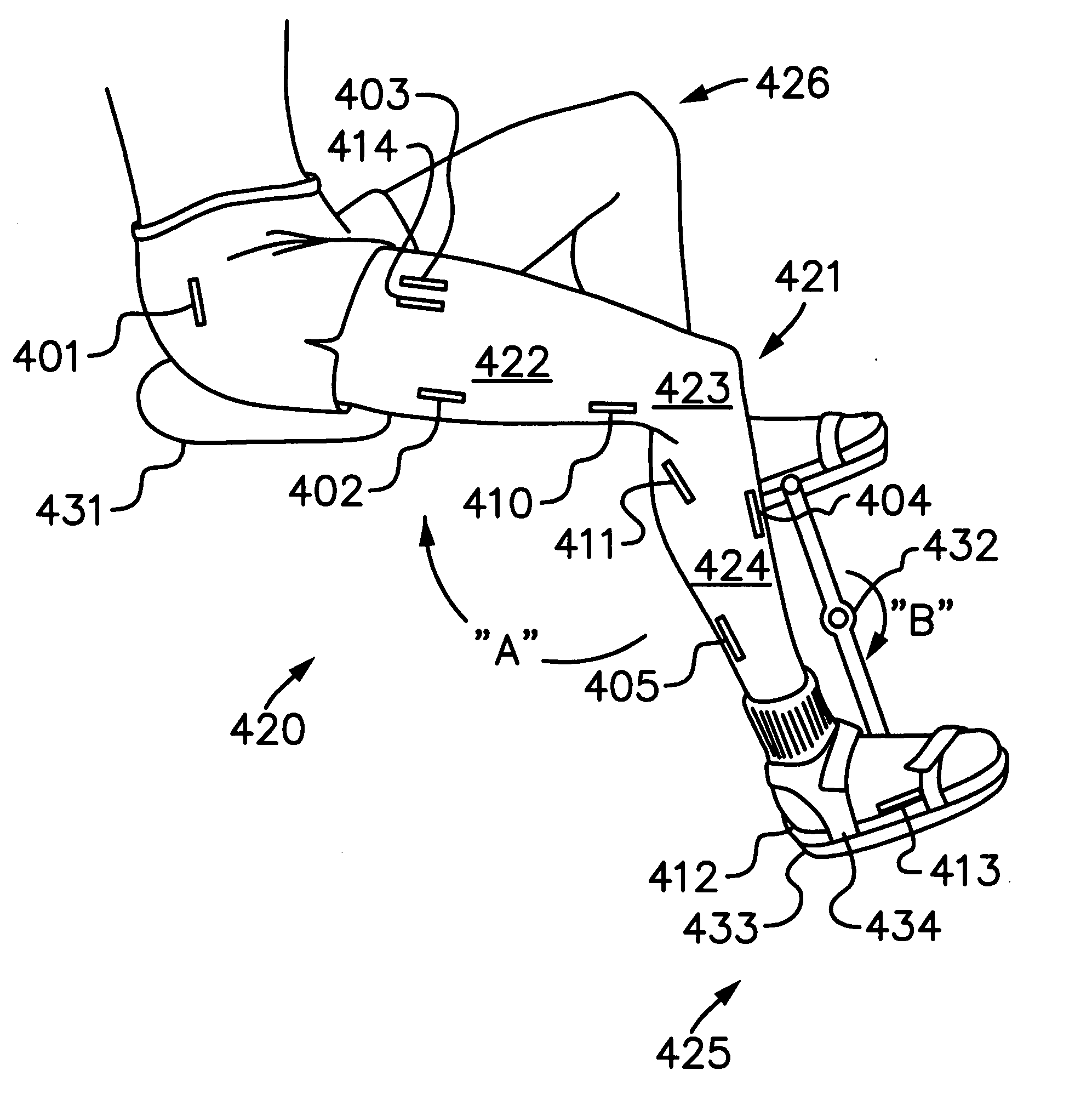
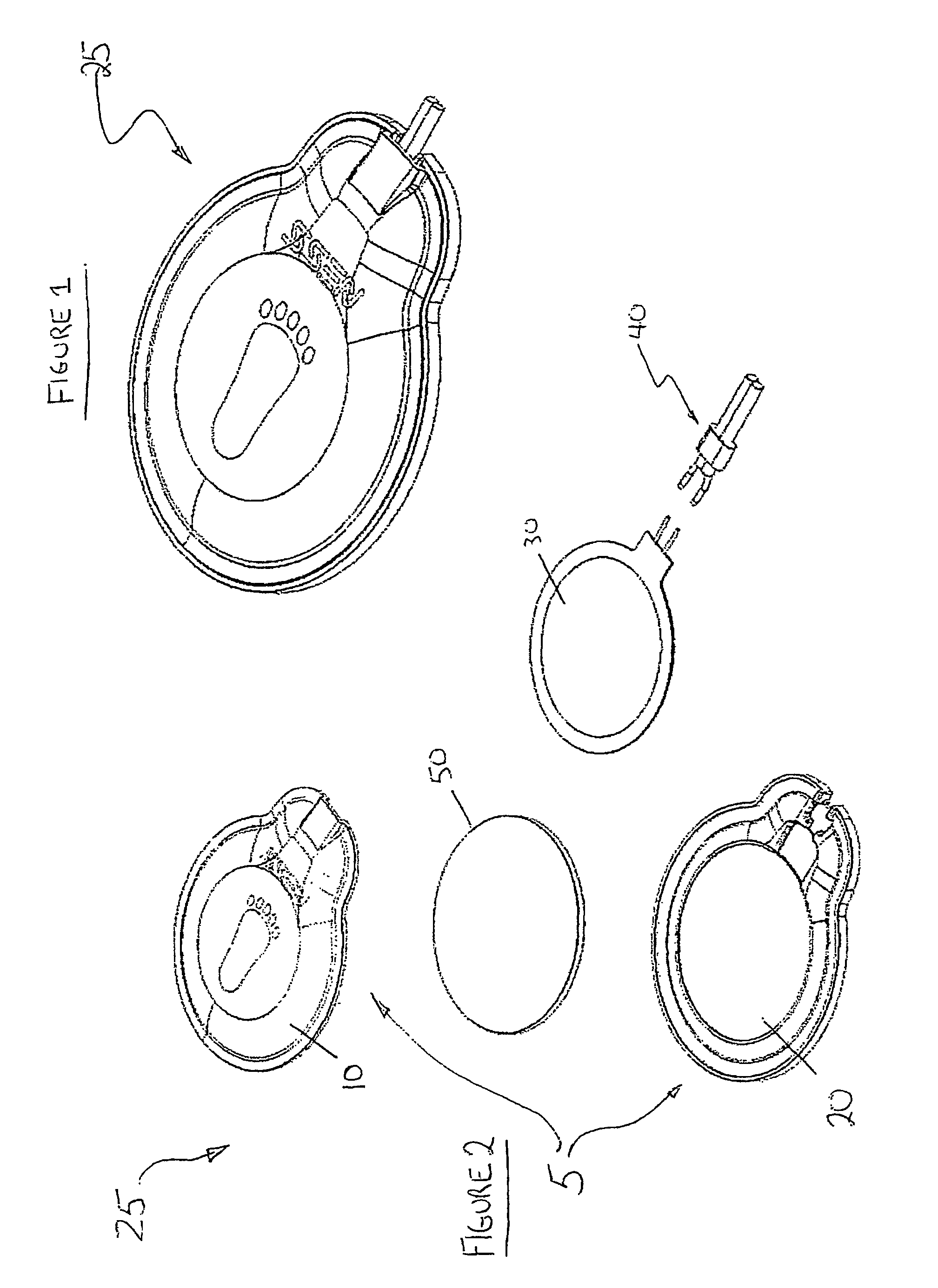
A functional electrical stimulation (FES) orthosis for FES to a limb segment, including: (a) a semi-rigid, self-retaining C-shaped frame, the frame configured to substantially envelop the limb segment, the frame including a first flexible and elongated circumferentially retaining element and at least a first and a second opposing flexible and elongated circumferentially retaining elements disposed on the circumferentially opposite side of the frame, the first retaining element and the first opposing retaining element forming a pair of opposing retaining elements, and (b) a surface electrical stimulation electrode for contacting at least one stimulation point on a surface of the limb segment, associated with, and supported by, the frame, the surface electrode for electrically associating, via the frame, with a neuroprosthetic stimulator unit, so as to provide FES, wherein the opposing retaining elements are configured to be radially spring-loaded towards a center of the frame, such that in donning the orthosis around the limb segment, the limb segment applies a counter-pressure from within the frame, against the opposing retaining elements, such that the orthosis is firmly and fixedly self-retained in a pre-determined position on the surface.
Owner:VIDACARE +1
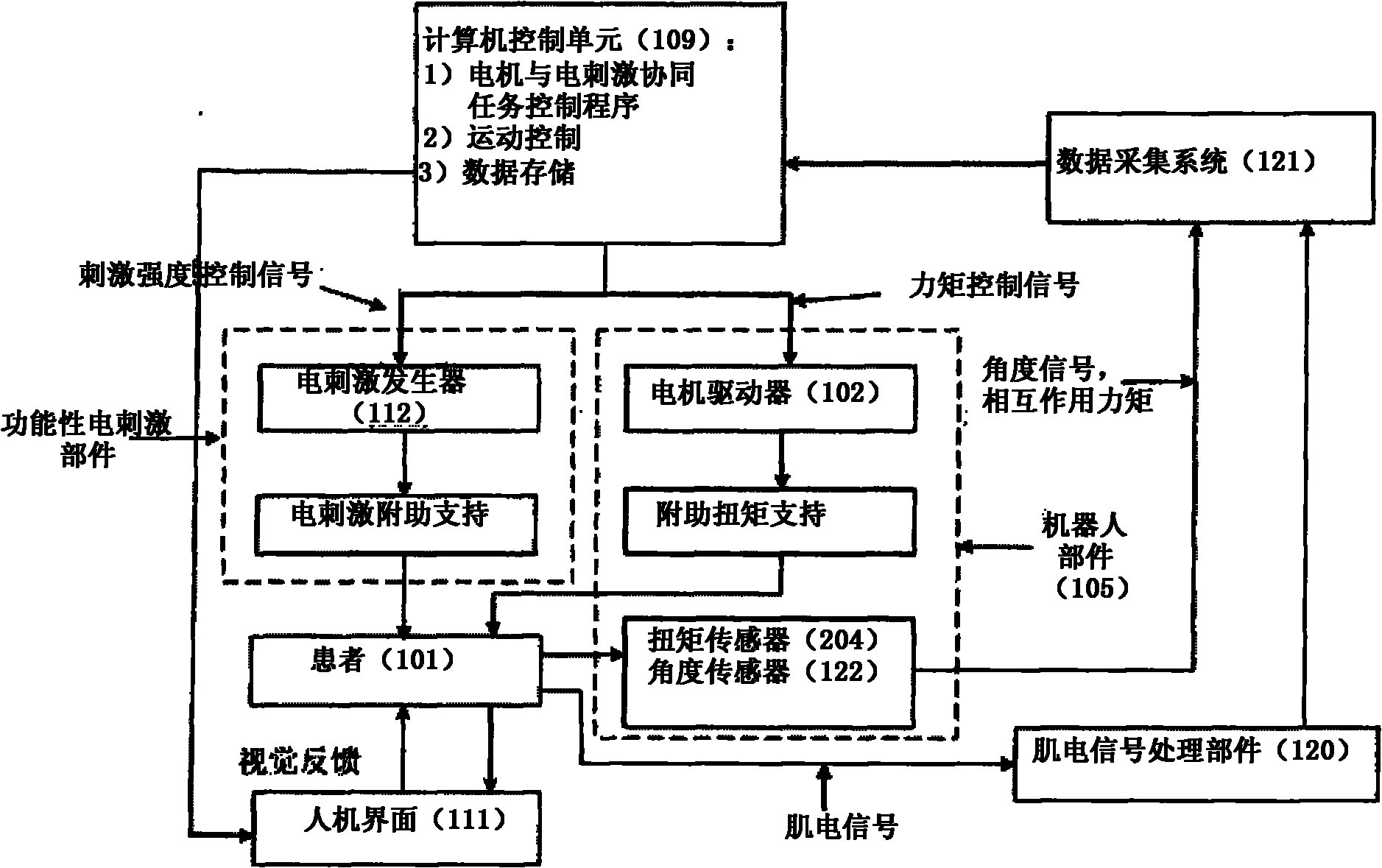
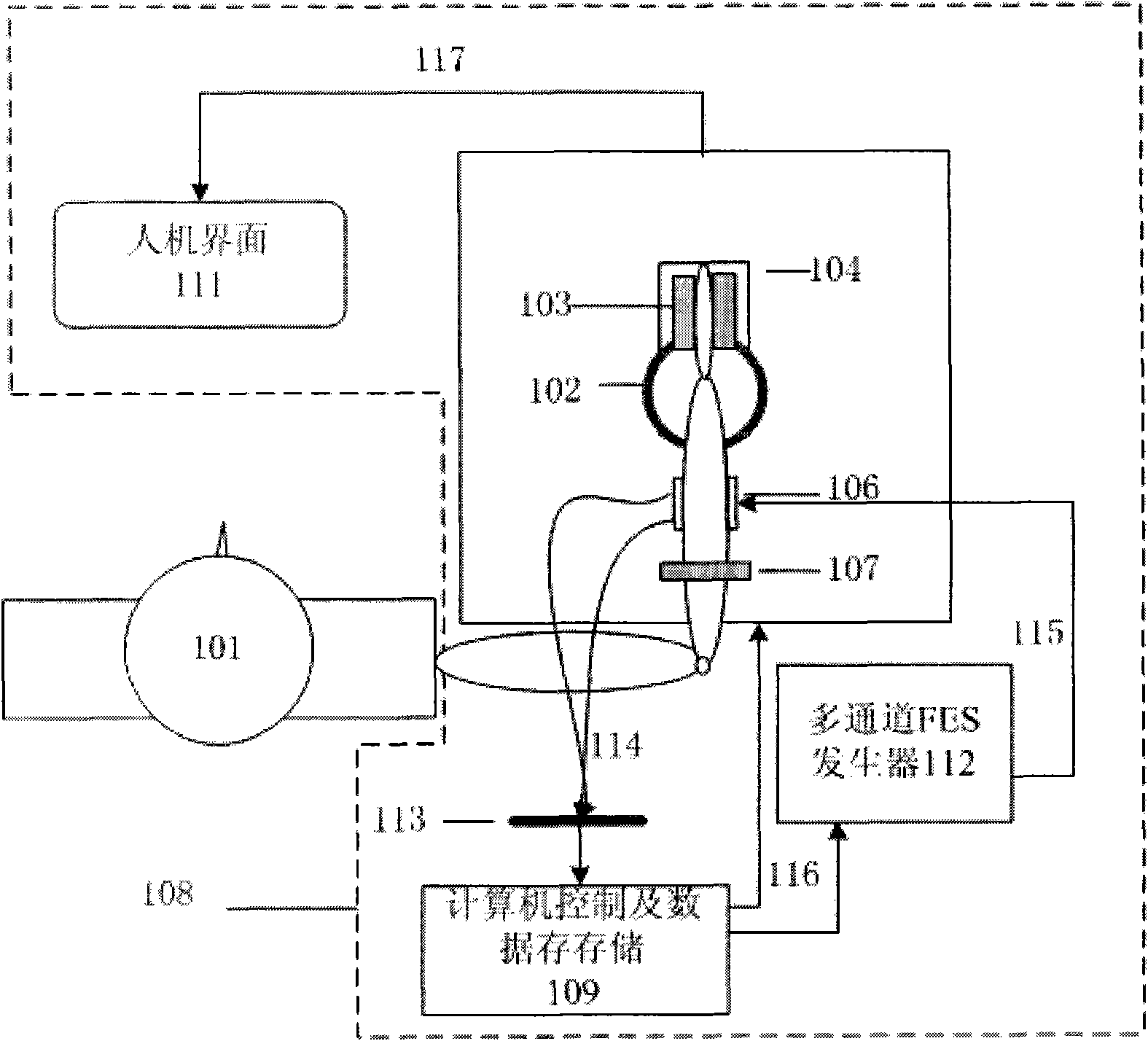
Rehabilitation training system and method combined with functional electric stimulation and robot
ActiveCN101961527AEffective rehabilitationExpand the scope of activitiesGymnastic exercisingDiagnostic recording/measuringKnee JointEngineering
The invention provides rehabilitation training system and method combined with functional electric stimulation and a robot. The system comprises a functional electric stimulation part, a robot part and a control unit which is respectively connected with the functional electric stimulation part and the robot part, wherein the control unit is used for receiving bioelectric signals and controlling the functional electric stimulation part and the robot part at real time according to the mode of adjustable auxiliary proportion of the functional electric stimulation part and the robot part or the mode of adjustable tracking error so that the functional electric stimulation part can stimulate the corresponding muscle groups of a joint of a patient and the robot part can provide a joint auxiliary torque for the patient. The invention can be applied to progressive interactive rehabilitation of elbow joints, wrist joints, knee joints, ankle joints and shoulder joints and can help patients carry out active rehabilitation training in an improved movement space, thereby greatly accelerating the recovery of movement function of joints of affected sides.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Orthosis for a gait modulation system
A functional electrical stimulation (FES) orthosis for FES to a limb segment, including: (a) a semi-rigid, self-retaining C-shaped frame, the frame configured to substantially envelop the limb segment, the frame including a first flexible and elongated circumferentially retaining element and at least a first and a second opposing flexible and elongated circumferentially retaining elements disposed on the circumferentially opposite side of the frame, the first retaining element and the first opposing retaining element forming a pair of opposing retaining elements, and (b) a surface electrical stimulation electrode for contacting at least one stimulation point on a surface of the limb segment, associated with, and supported by, the frame, the surface electrode for electrically associating, via the frame, with a neuroprosthetic stimulator unit, so as to provide FES, wherein the opposing retaining elements are configured to be radially spring-loaded towards a center of the frame, such that in donning the orthosis around the limb segment, the limb segment applies a counter-pressure from within the frame, against the opposing retaining elements, such that the orthosis is firmly and fixedly self-retained in a pre-determined position on the surface.
Owner:VIDACARE +1
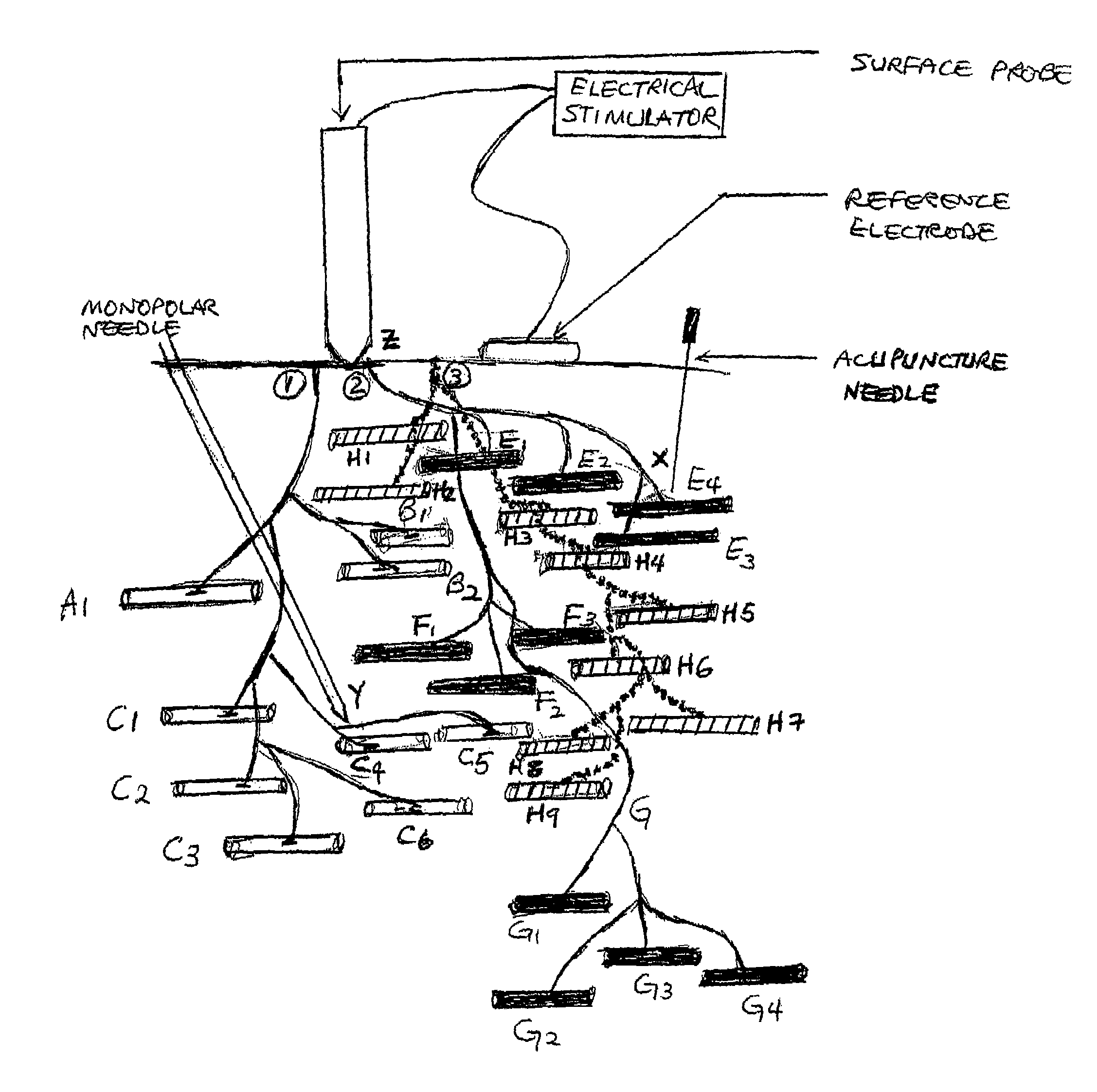
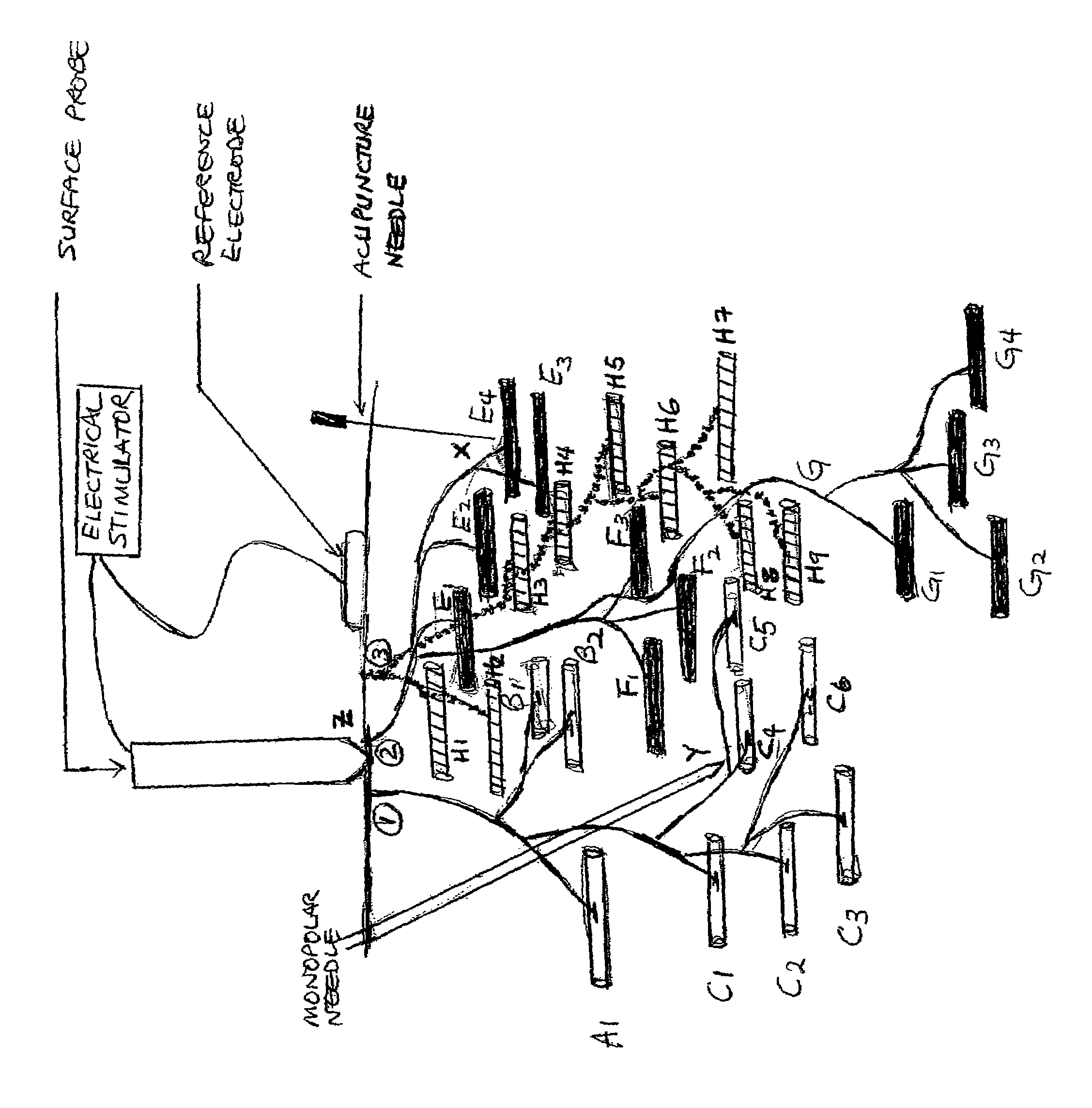
Intramuscular stimulation therapy using surface-applied localized electrical stimulation
ActiveUS7725193B1Improve efficiencyIncrease and prolong resultant pain reliefElectrotherapyAcupunctureFunctional electrical stimulationNeedle electrode
A modality of electrical twitch obtaining intramuscular stimulation pain relief therapy utilizes a surface probe with a conductive tip to apply surface electrical stimulation of relatively high voltage locally and focally to muscle motor points and regions of adjacent motor end plate zones. The surface-applied electrical stimulation through intact skin readily facilitates the elicitation of forceful twitch responses from muscle fibers associated with the stimulated motor points and motor end plate zones, without requiring needle penetration into the patient's flesh. Rapid movement between multiple treatment sites is possible allowing treatment of a larger number of muscle motor point areas in afflicted muscles and more muscles to be treated in a single treatment session. The therapeutic effect of the twitches increases with the force and number of the twitches. In addition, since physical insertion of the needle electrode is totally unnecessary, patients experience little to no pain during and after the procedure, and the risk of repetitive stress injury to the therapist is reduced. Additionally, significantly less skill is required to effectively elicit pain relieving twitch responses, thus facilitating training of medical and para-medical personnel to perform the procedure.
Owner:JUS JAS
Functional electrical stimulation systems
ActiveUS20150080979A1Reduce the risk of fallingElectrotherapyContact operating partsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
A gait modulation system including: (a) a sensor device including a sensor adapted for associating with at least one lower limb of the patient, the sensor for transducing at least one parameter related to a gait of the patient, so as to obtain gait data related to the gait, and (b) a muscle stimulator including: (i) an electrical stimulation circuit, the circuit adapted to supply an electrical stimulation output to an electrode array for performing functional electrical stimulation of at least one muscle of the lower limb, and (ii) a microprocessor, operatively connected to the at least one sensor, the microprocessor adapted for: receiving a stream of gait information based on the gait data; processing the gait information, and controlling the stimulation output based on the processing of the gait information, and wherein the microprocessor is further adapted to identify a failure in the stream of gait information, and to consequently control the electrical stimulation circuit to deliver a fail-safe stimulation output over a portion of a duration of the failure.
Owner:BIONESS NEUROMODULATION
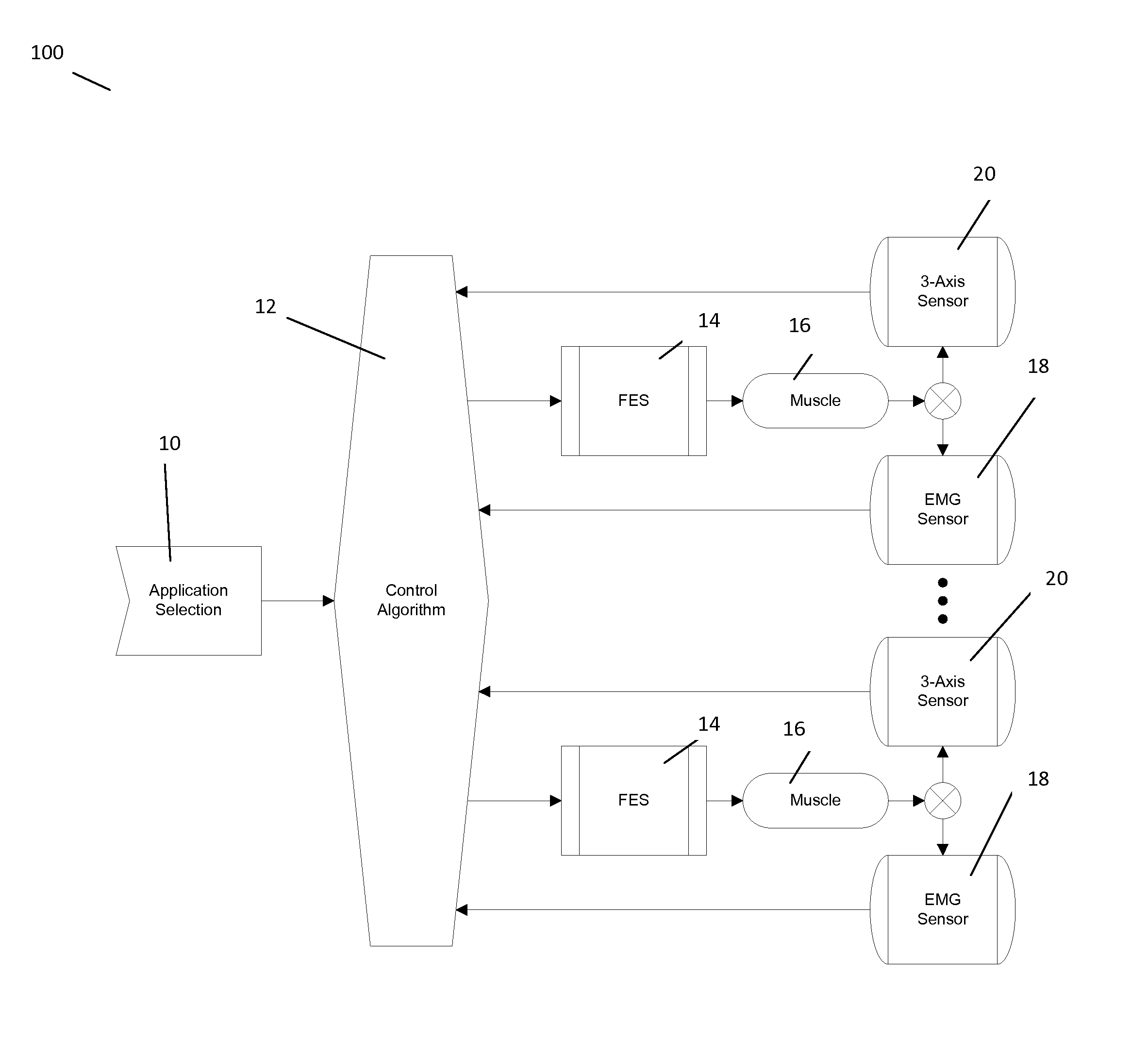
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) method and system to improve walking and other locomotion functions
ActiveUS20140128939A1Avoid spreadingImprove comfortElectrotherapyInertial sensorsPresent methodMuscle contraction
A method and system which provides wireless, noninvasive electrical stimulation to different muscle groups to allow the user to conduct physical activities, such as walking, by stimulating various muscle groups in the body at the correct times of activation or by stimulating muscle groups in a simulation mode when standing, sitting or lying down, whereby walking is not required to stimulate the various muscle groups. The system provides a small portable wearable system which utilizes available software, including Bluetooth technology, to provide electrical nerve stimulating pulses with low current, minimal phase charge which is controlled remotely and induce desired muscle contraction with increased comfort for the user. The present method and system applies electrical stimulation with accurate timing, based on a three-dimensional motion sensor, as a trigger to initiate stimulation and which is adapted to turn itself on and off when not walking.
Owner:GOOD SAMARITAN HOSPITAL
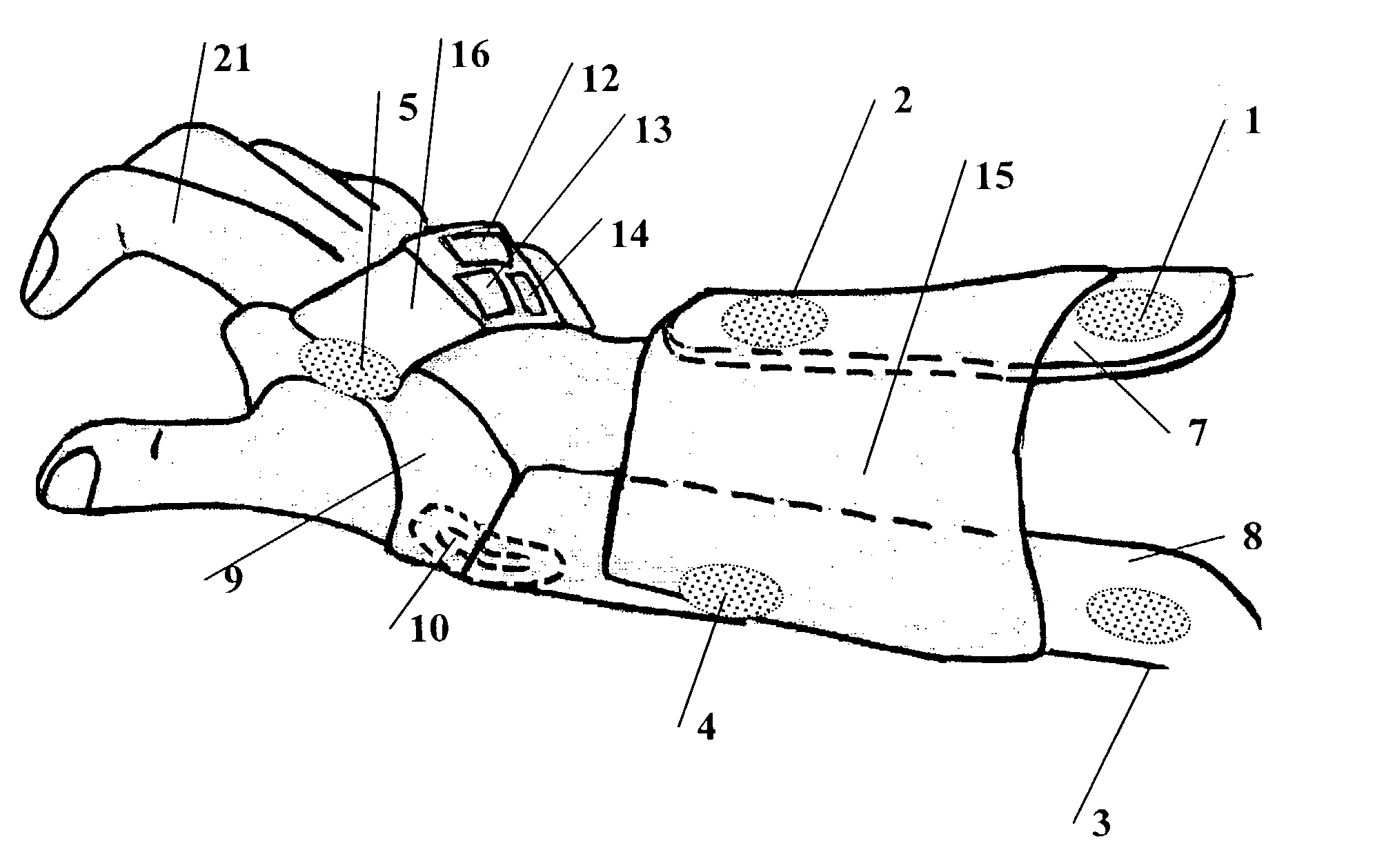
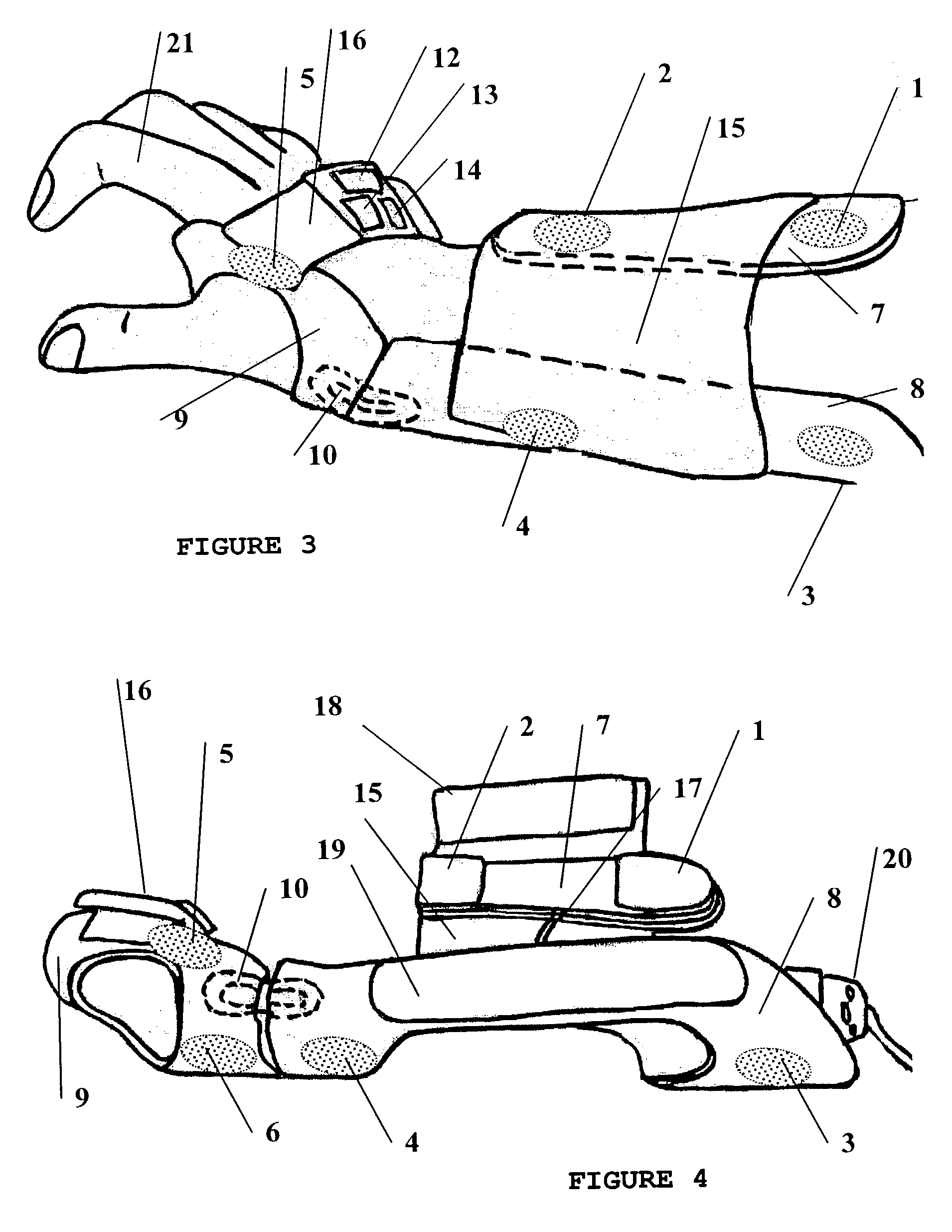
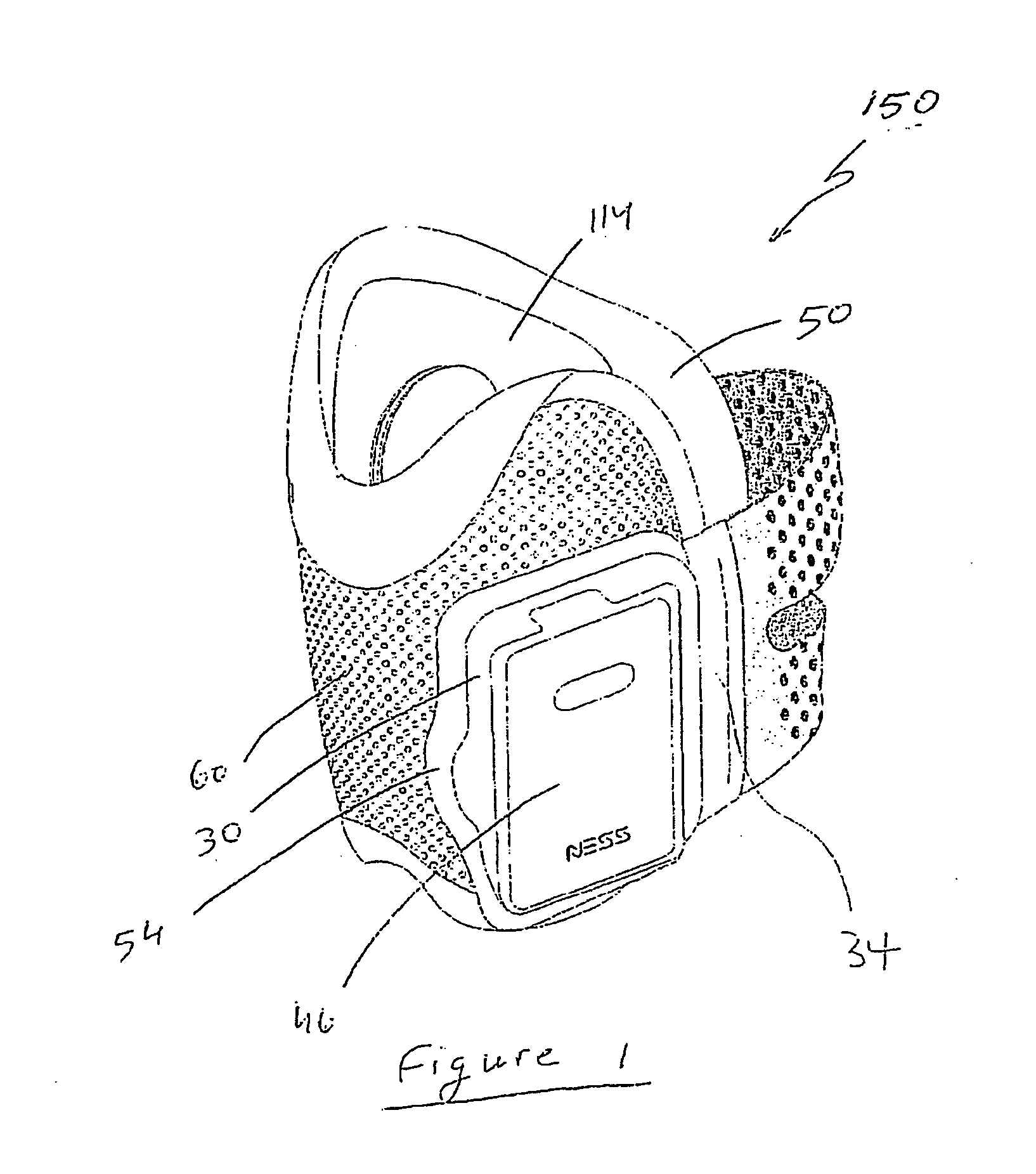
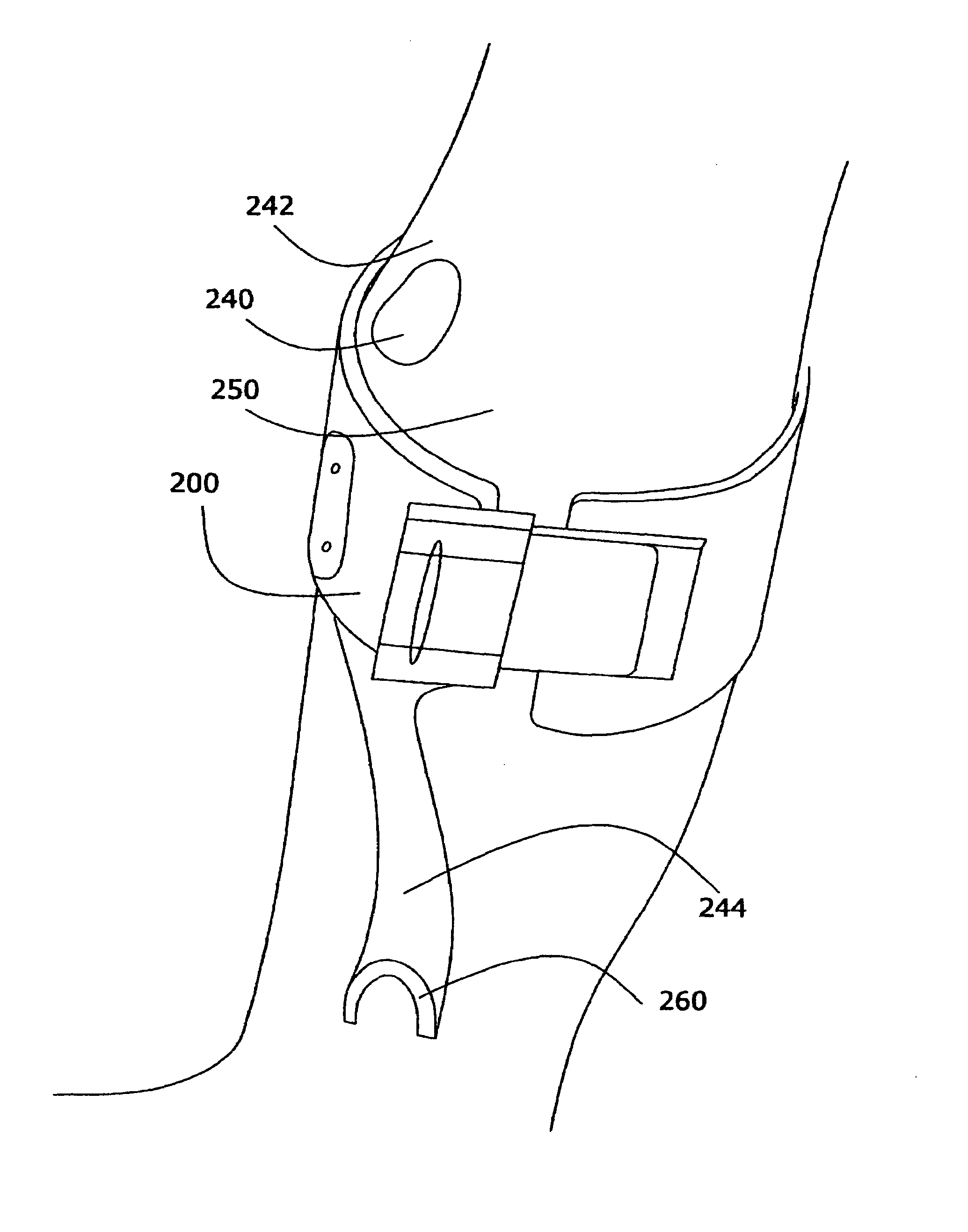
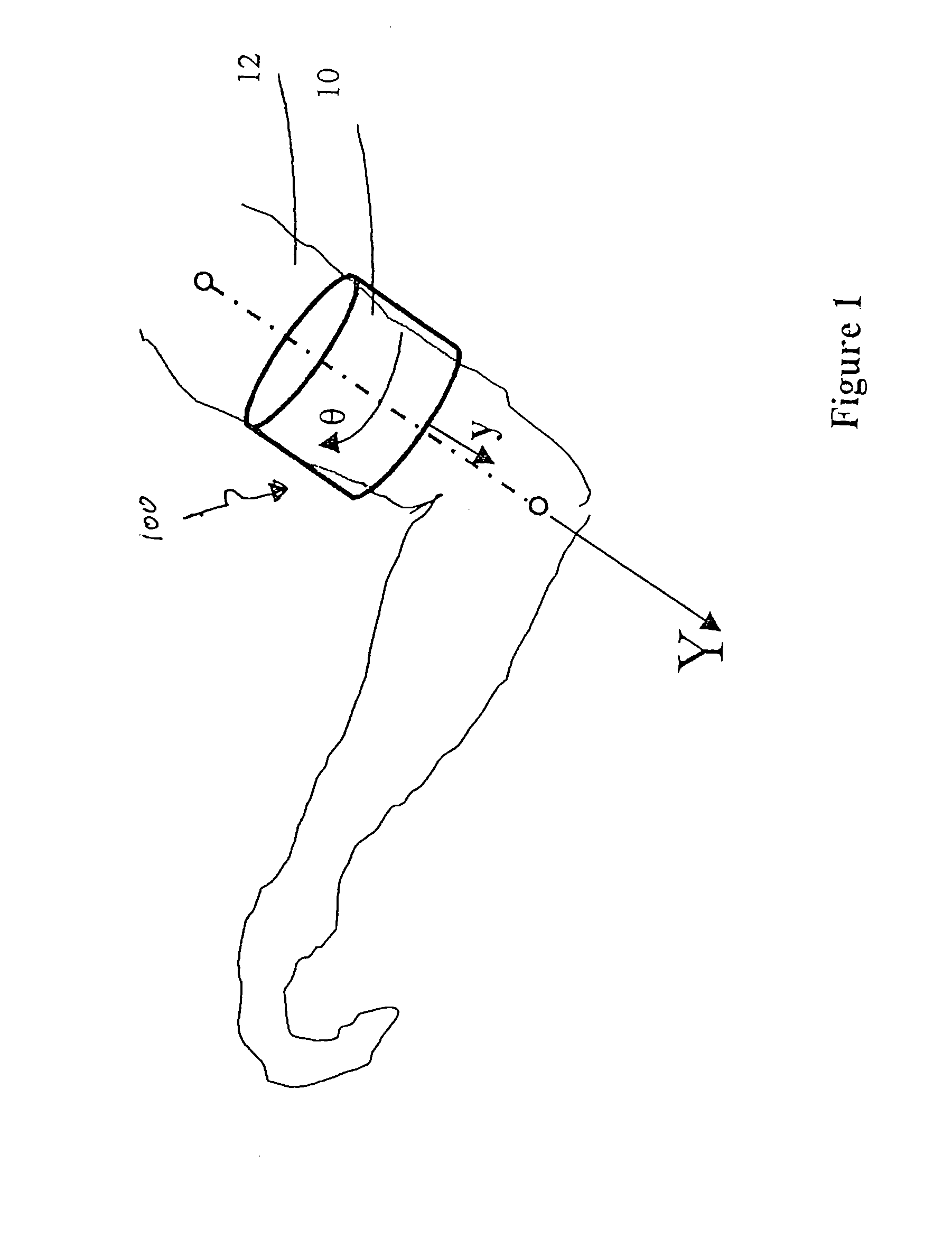
Surface neuroprosthetic device having a locating system
InactiveUS7337007B2Accurate and facile and repeatable positioningEasy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionApparel holdersElectricityProsthesis
A surface neuroprosthetic device for functional electrical stimulation (FES) having a locating system for locating the device on to a limb segment of a user, and a method therefor, the device including: (a) an at least semi-rigid exoskeleton shell for encompassing at least a portion of the limb segment; (b) at least one electrical stimulation electrode operatively connected with the shell, for making electrical contact with a surface of the limb segment, so as to effect FES of at least one muscle of the limb segment; and (c) a locator, operatively connected with the shell, for determining a positioning of the shell relative to the limb segment, such that the electrode is positioned near an activating point, the locator including: (i) means for determining rotational positioning of the exoskeleton shell on the limb segment, and (ii) means for determining longitudinal positioning of the exoskeleton shell on the limb segment.
Owner:BIONESS NEUROMODULATION
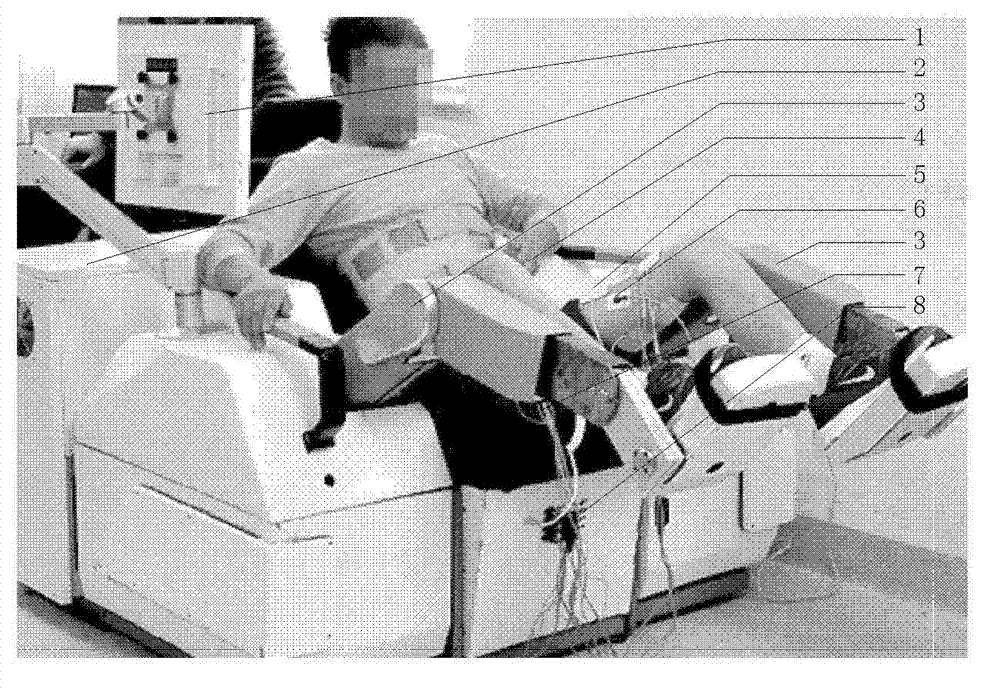
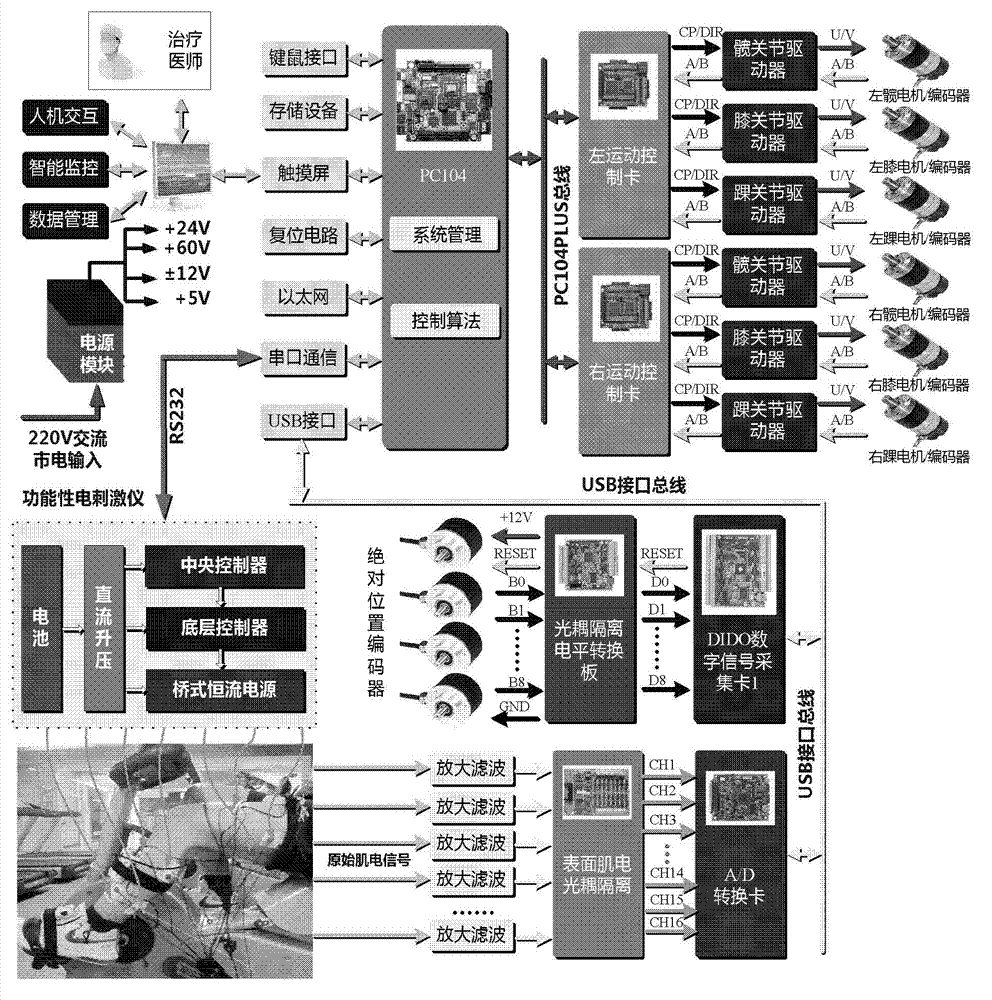
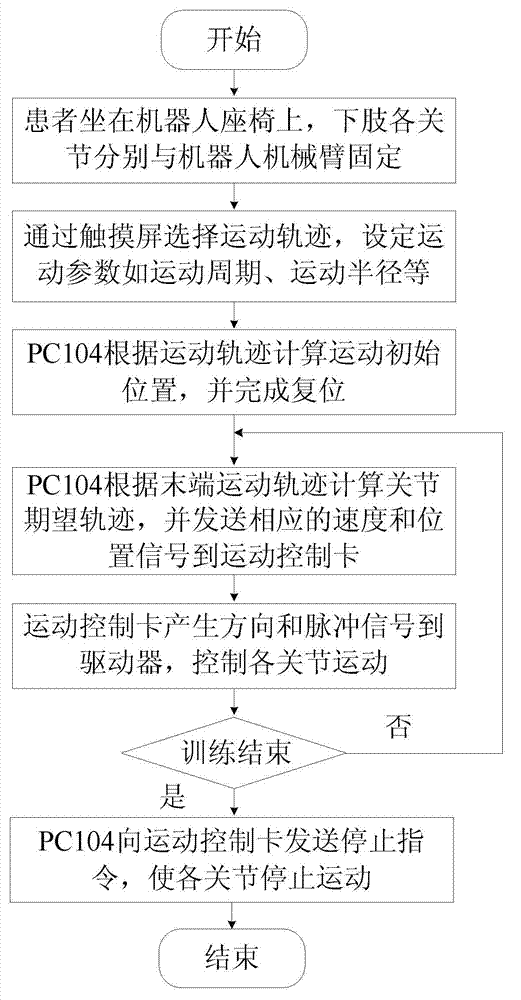
Sitting and lying type lower limb rehabilitation robot
ActiveCN102727361AIncrease motivationWith surface electromyography signal acquisitionGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesPhysical Therapy ModalityOccupational therapy
The invention discloses a sitting and lying type lower limb rehabilitation robot, which can respectively carry out a passive training, an assisted training or an active training according to the damage degree or the rehabilitation stage of a patient. The robot comprises a seat, a mechanical arm, a main industrial control box, a man-machine interaction interface, an electrical stimulation handheld switch, an electrical stimulation electrode plate, an electromyographic signal acquisition electrode plate, a functional electrical stimulation instrument and an electromyographic signal acquisition industrial control box. During the passive training, the lower limb of the patient is trained according to a set movement locus; during the assisted training, the main muscle group of the lower limb of the patient is applied with electrical stimulation pulse; according to the movement locus of a tail end, the electrical stimulation pulse is subjected to sequential control to finish the assisted training; during the active training, the electromyographic signal of the corresponding muscle of the patient is collected; and according to different control algorithms, the patient drives robot to realize the active training. According to the sitting and lying type lower limb rehabilitation robot disclosed by the invention, the traditional physical therapy, occupational therapy and kinesitherapy are organically combined, so that the patient rehabilitation effect can be effectively improved, and the desire of the patient to actively participate is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
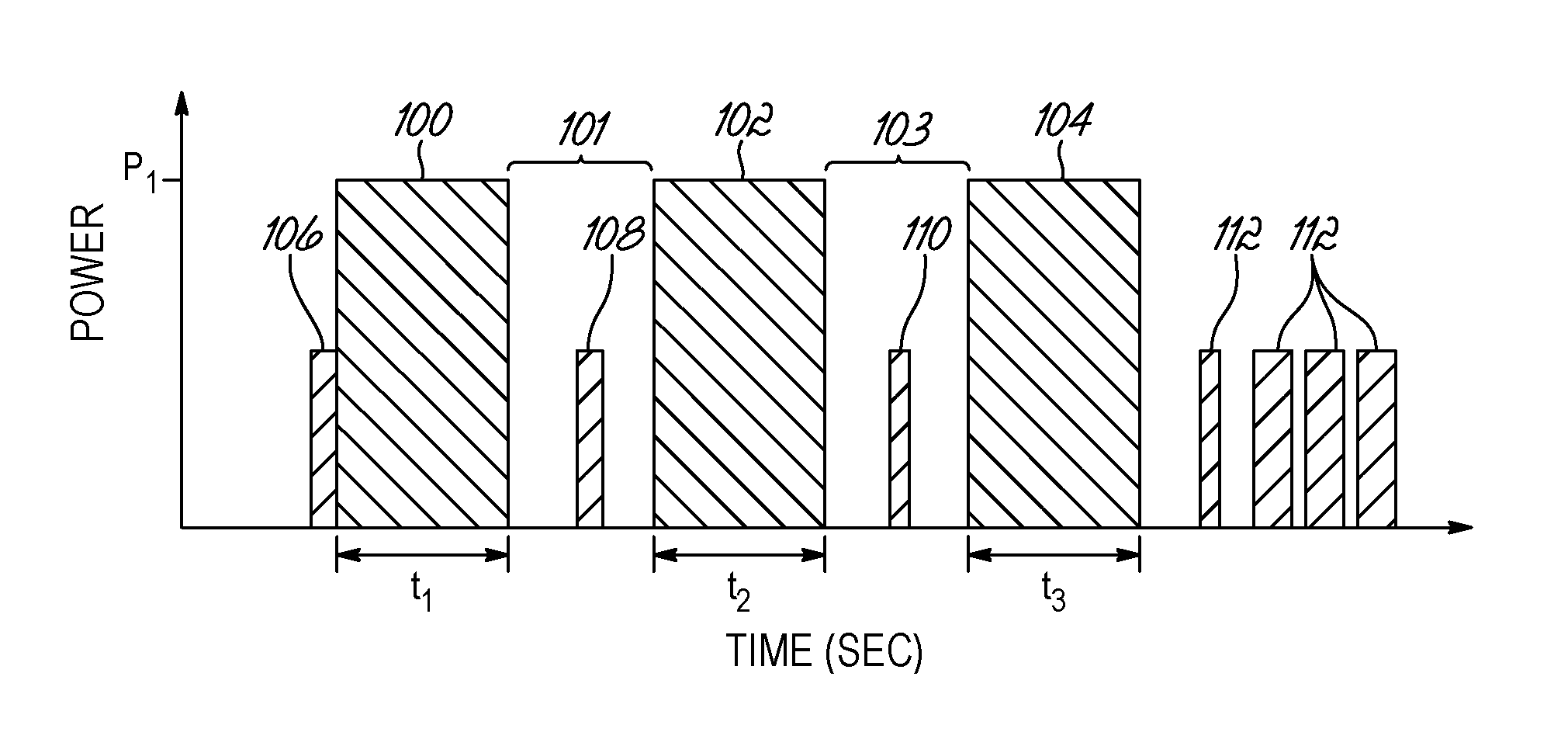
Tissue treatment systems with high powered functional electrical stimulation and methods for reducing pain during tissue treatments
Methods, apparatus, and systems for transcutaneously treating tissue located beneath a skin surface with electromagnetic energy delivered from a treatment electrode. A portion of the treatment electrode is contacted with the skin surface. While maintaining the contact between the portion of the treatment electrode and the skin surface, the electromagnetic energy is delivered from the treatment electrode in a plurality of power pulses through the skin surface to the tissue over a treatment time with a time gap between each consecutive pair of the pulses to lower a level of pain perceived by a patient.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
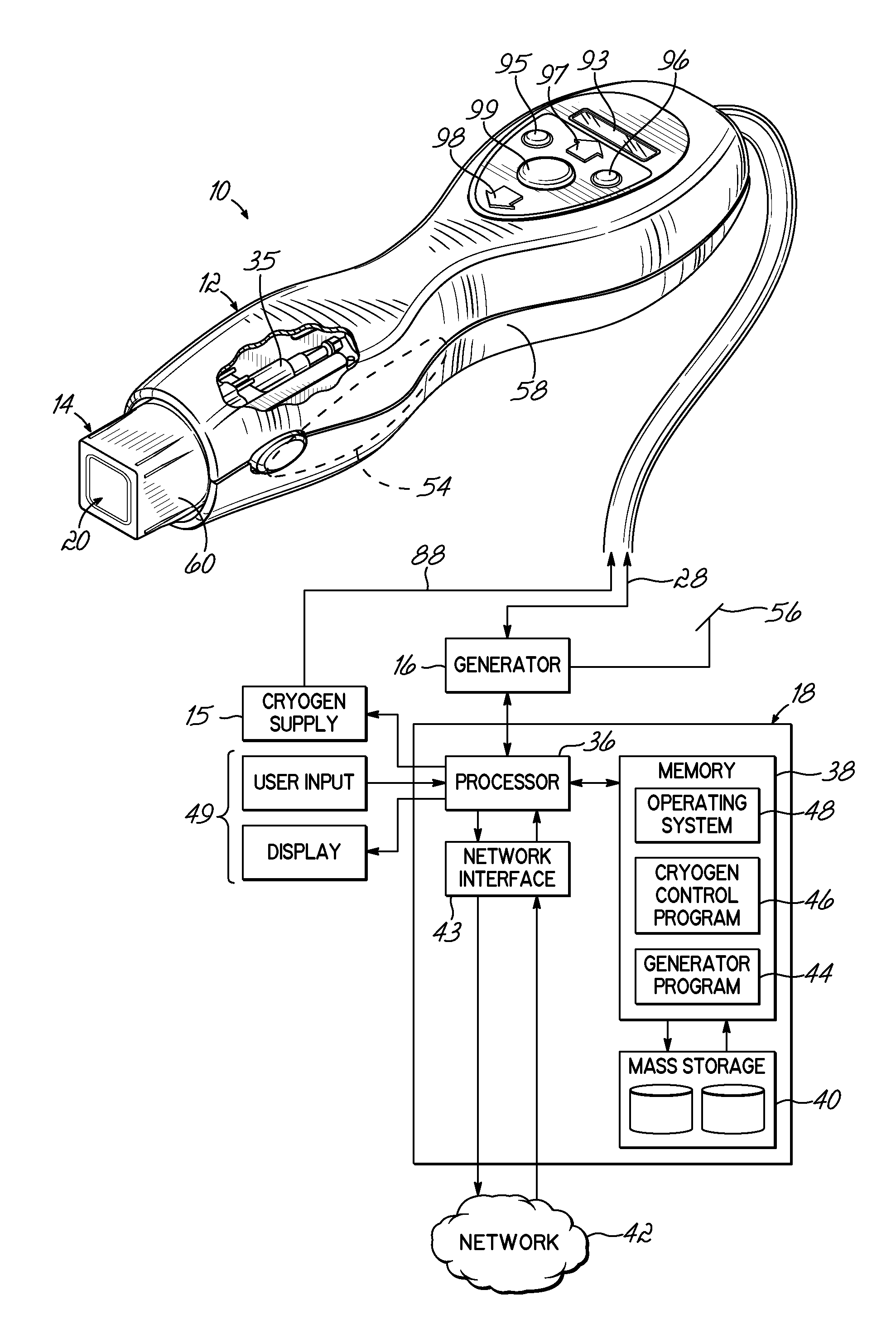
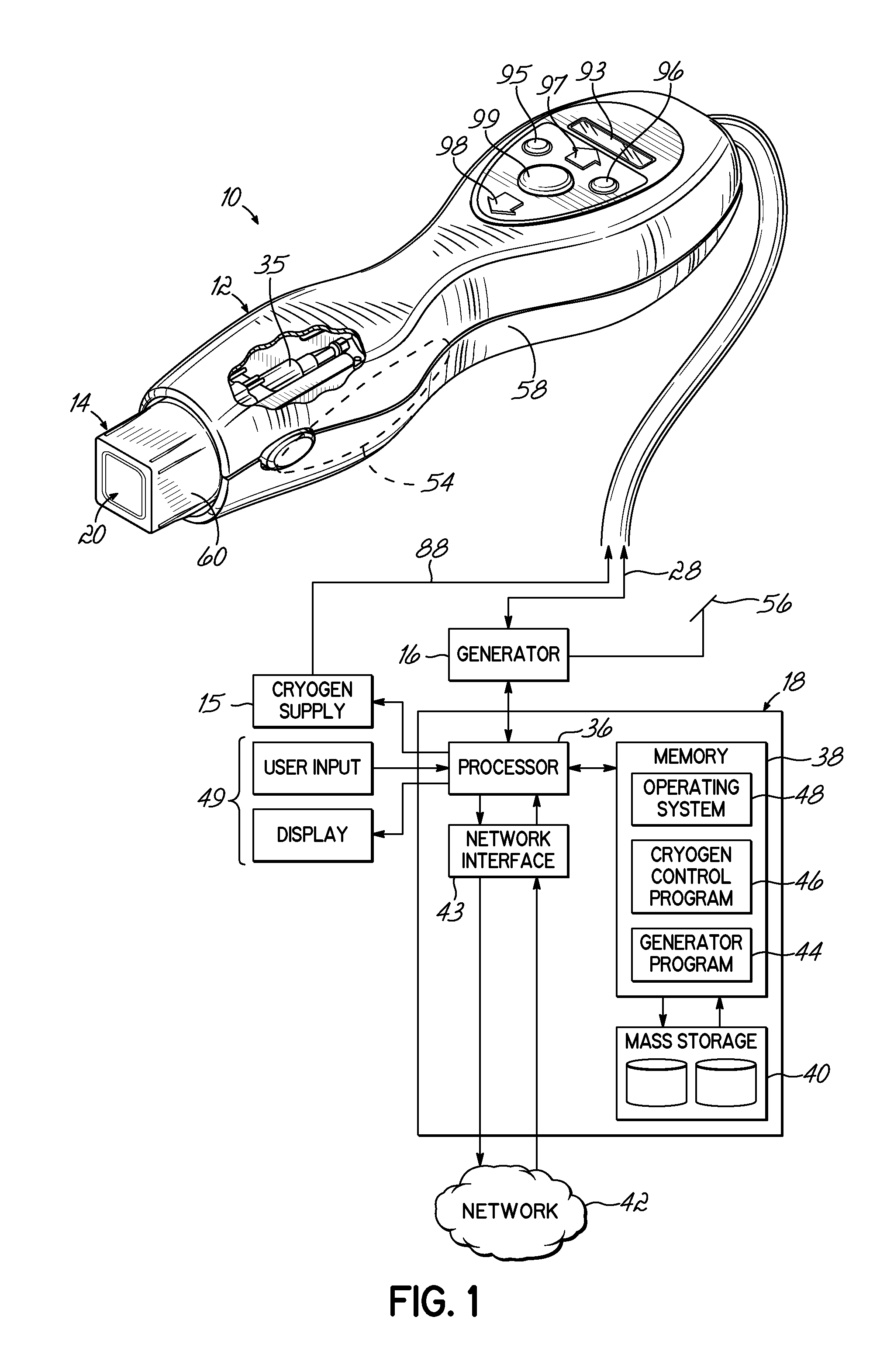
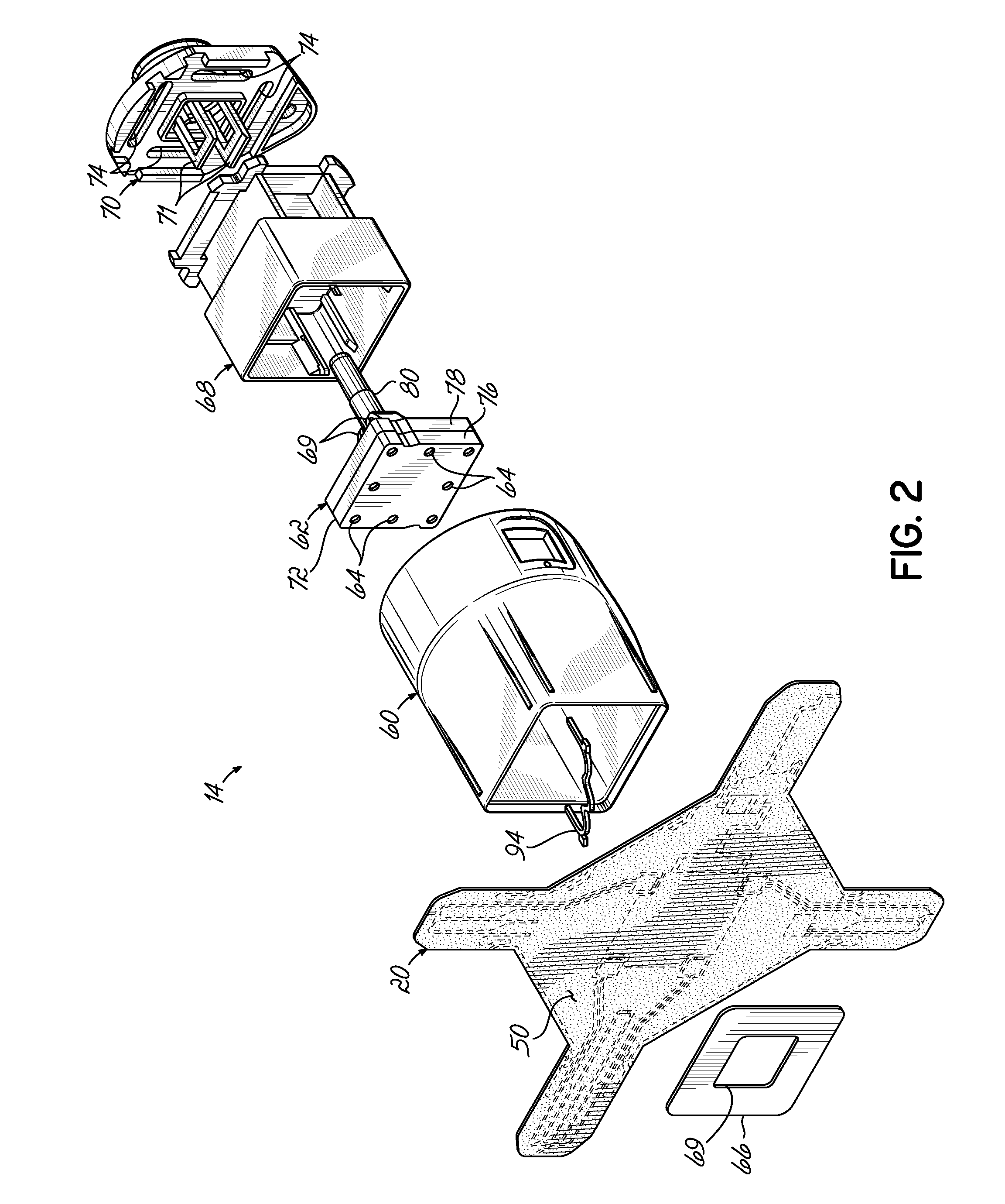
Motorized Functional Electrical Stimulation Step and Stand Trainer
A functional electrical stimulation step and stand system comprising two footplates (left and right) connected to a primary drive motor that cause the footplates to move in a reciprocal motion. The footplates are further connected to corresponding servos, which allow for control of the movement of the footplate with respect to an axis. system comprises an electrical stimulation control unit. The stimulation step and stand system further comprises a control unit that has electrical stimulation leads connected to electrodes that deliver an electrical impulse to a patient's muscles. In a further embodiment, the control unit has one or more wireless stimulators.
Owner:RESTORATIVE THERAPIES
Functional electrical stimulation systems
ActiveUS8788049B2Reduce the risk of fallingElectrotherapyContact operating partsElectricityFunctional electrical stimulation
A gait modulation system including: (a) a sensor device including a sensor adapted for associating with at least one lower limb of the patient, the sensor for transducing at least one parameter related to a gait of the patient, so as to obtain gait data related to the gait, and (b) a muscle stimulator including: (i) an electrical stimulation circuit, the circuit adapted to supply an electrical stimulation output to an electrode array for performing functional electrical stimulation of at least one muscle of the lower limb, and (ii) a microprocessor, operatively connected to the at least one sensor, the microprocessor adapted for: receiving a stream of gait information based on the gait data; processing the gait information, and controlling the stimulation output based on the processing of the gait information, and wherein the microprocessor is further adapted to identify a failure in the stream of gait information, and to consequently control the electrical stimulation circuit to deliver a fail-safe stimulation output over a portion of a duration of the failure.
Owner:BIONESS NEUROMODULATION
Tremor reduction systems suitable for self-application and use in disabled patients
InactiveUS20100174342A1Reduce tremorReliable and accurate mannerElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSlow MovementFunctional electrical stimulation
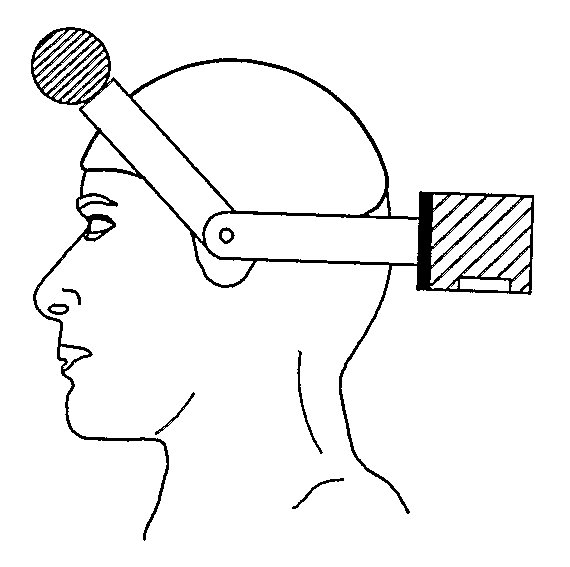
Apparatus for tremor reduction including a sensor for sensing muscle movements, a stimulation / recording electrode unit for providing Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) to a muscle, the stimulation / recording electrode unit including a filter for filtering around a tremor frequency to ignore slow movements and high frequency noise associated with the muscle movements that were sensed, and a processor for generating a set of relationships of muscle response to the FES, called FES-muscle-response relationships, and for selecting a new FES for application to the muscle in accordance with acquired knowledge of the FES-muscle-response relationships. An apparatus and a helmet for effecting proper alignment and application of a stimulation / recording electrode to a patient's arm and neck region, respectively, are also described.
Owner:BOSTON LEON +1
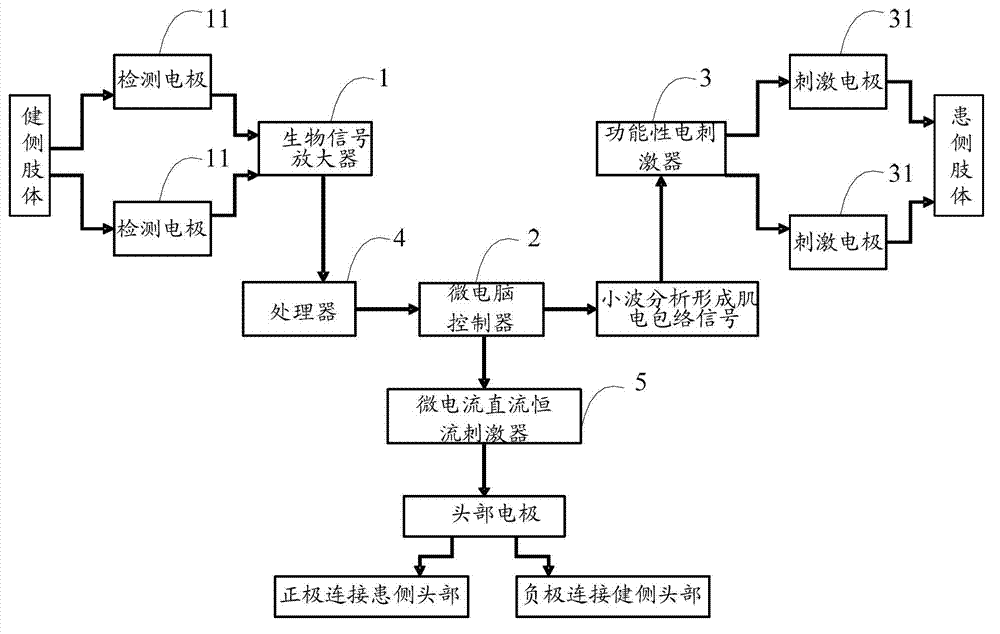
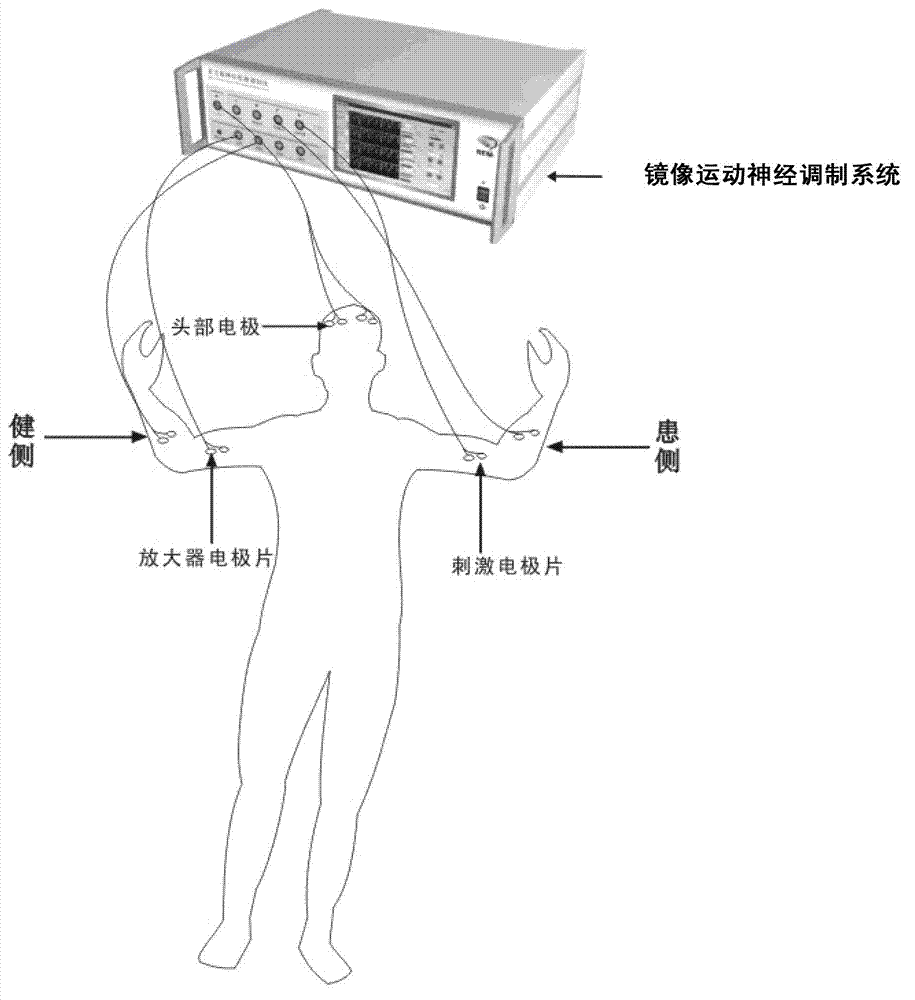
Mirror movement neuromodulation system
ActiveCN102886102AImprove plasticityPromote recoveryArtificial respirationMirror movementsTranscranial direct-current stimulation
The invention discloses a mirror movement neuromodulation system, which comprises a plurality of lead biological signal amplifiers, a microcomputer controller, a plurality of lead functional electric stimulators and a micro-current direct-current constant-current stimulator. The principle that functional electric stimulation and transcranial direct-current electric stimulation techniques and mirror movement neurons participate in movement control is applied comprehensively, the biological signal amplifiers, the functional electric stimulators for simulating integrated electromyography envelope signal control, and the micro-current direct-current constant-current stimulator are integrated through the microcomputer controller, myoelectric activity envelope signals are generated by processing myoelectric signals of a plurality of muscle groups which move functionally by using an uninjured side limb, and the plurality of functional electric stimulators are modulated and controlled, so that the same mirror action is generated by the plurality of muscle groups of an injured limb on an opposite side according to uninjured side myoelectric information, brain functional regulation and reconstruction are realized, the plasticity of neuronal synapsis and the recovery of neurological functions are facilitated, and the treatment effect of sports rehabilitation is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGZHI TECH
Functional electrical stimulation system
An electrical stimulation device for a body part of a person comprises an orthosis with sensor and electrodes and a controller. The controller receives a sensor signal, compares the sensor signal to a threshold value and generates an electrical output from the electrodes if the sensor signal exceeds the threshold value. The controller comprises a calibration module for determining an initial resting position of the body part.
Owner:TONG KAI YU +2
Noninvasive electrical stimulation system for standing and walking by paraplegic patients
InactiveUS20110040349A1Increase independenceEasy to operateElectrotherapyArtificial respirationClosed loopPrimary motor neuron
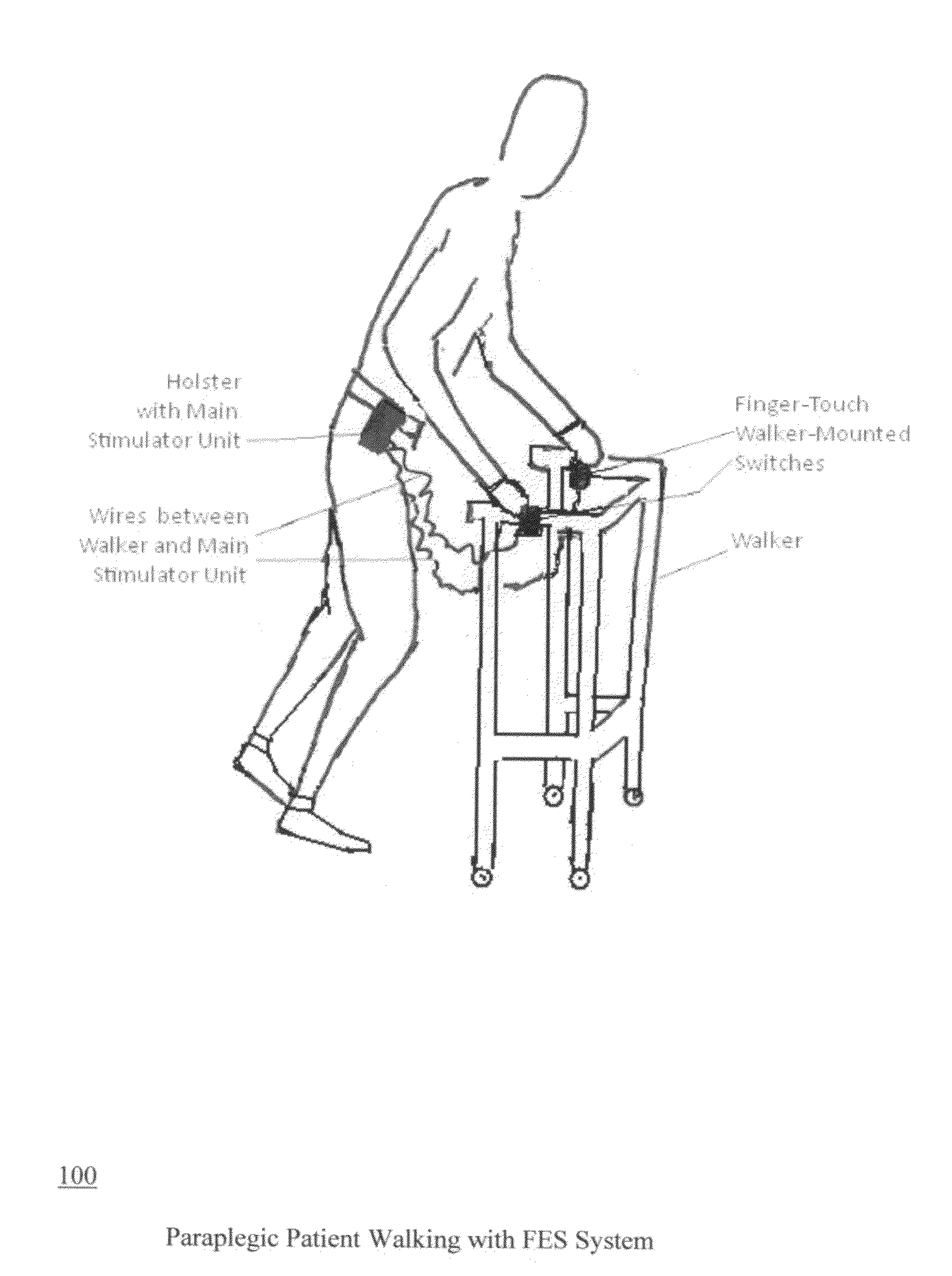
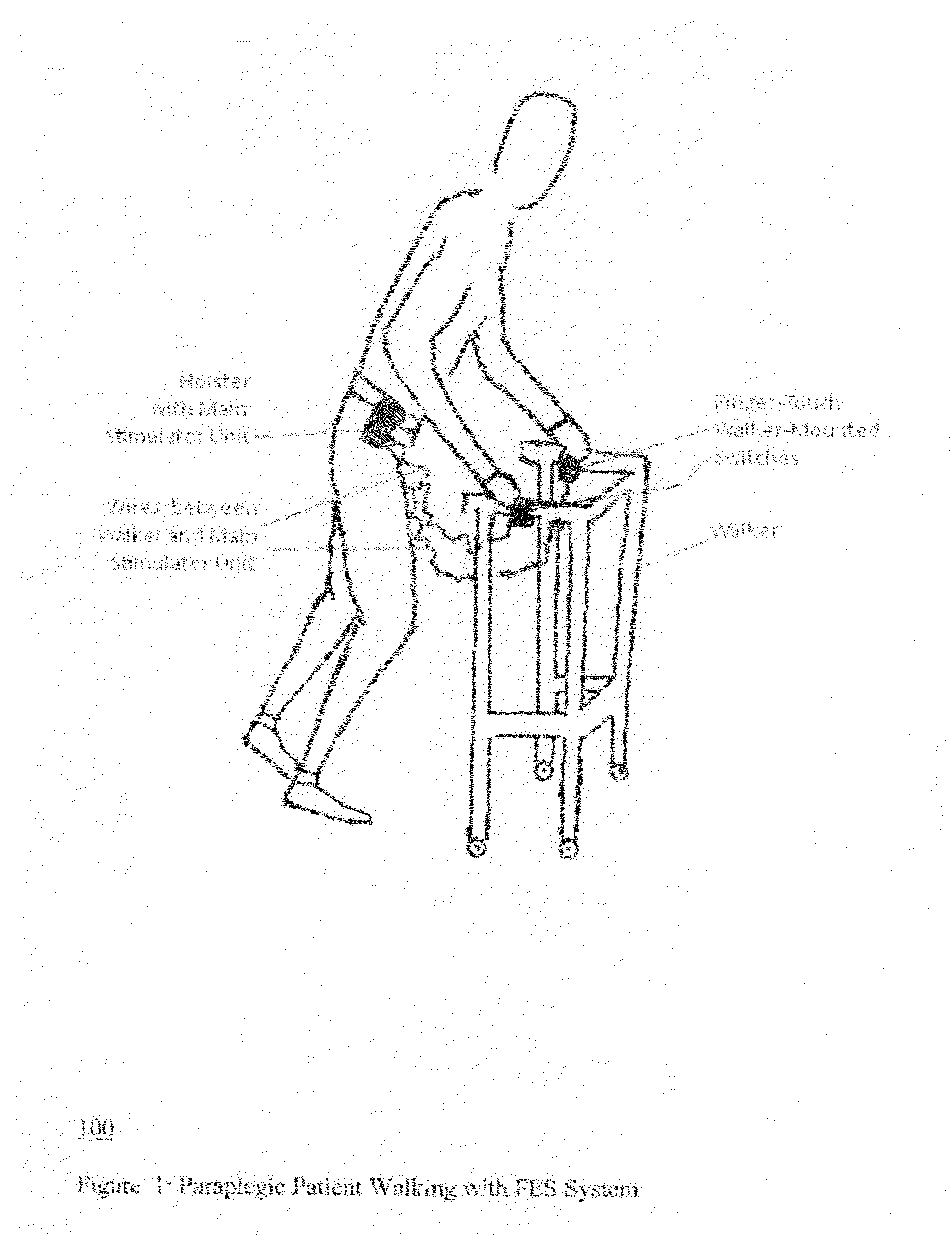
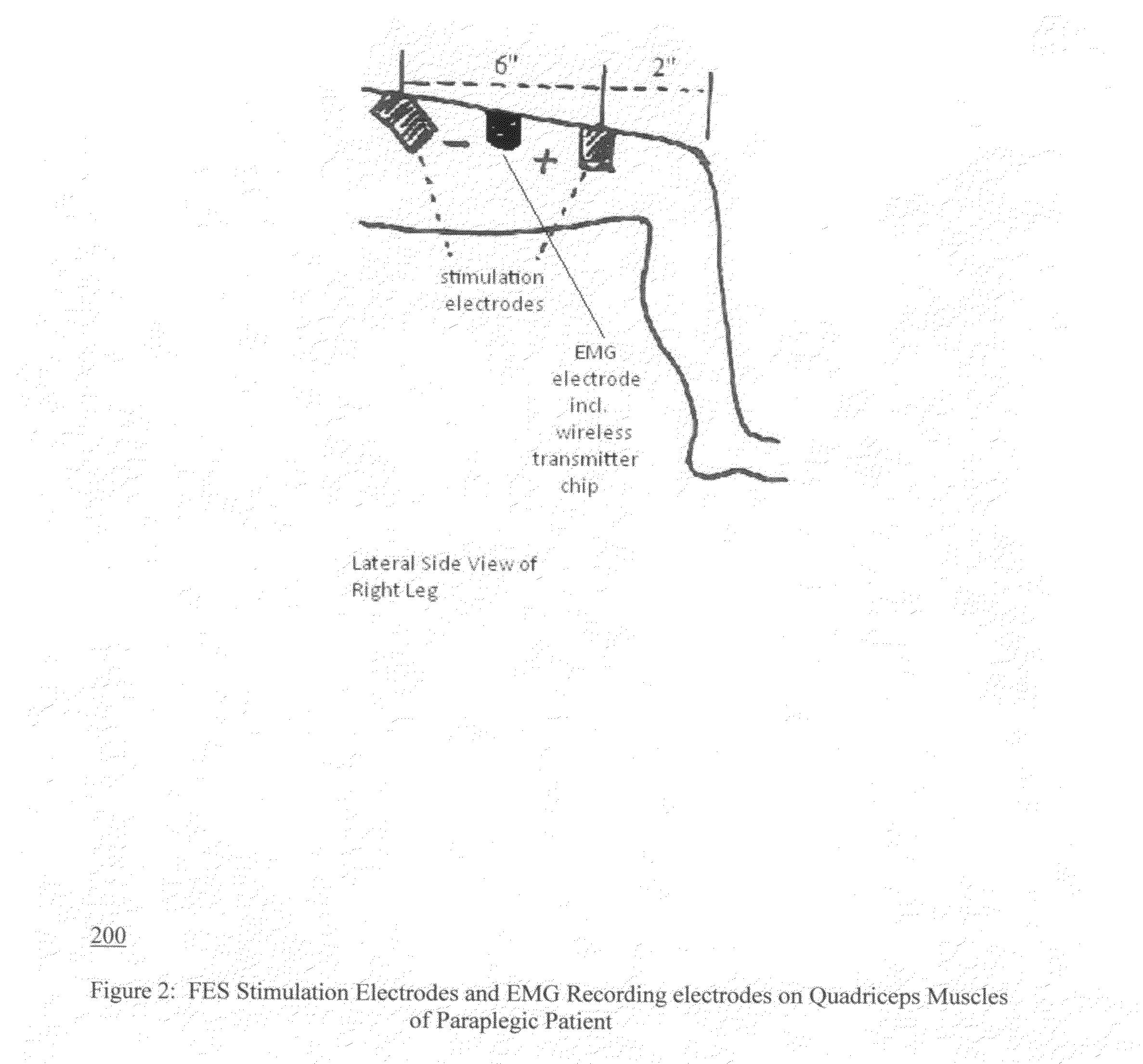
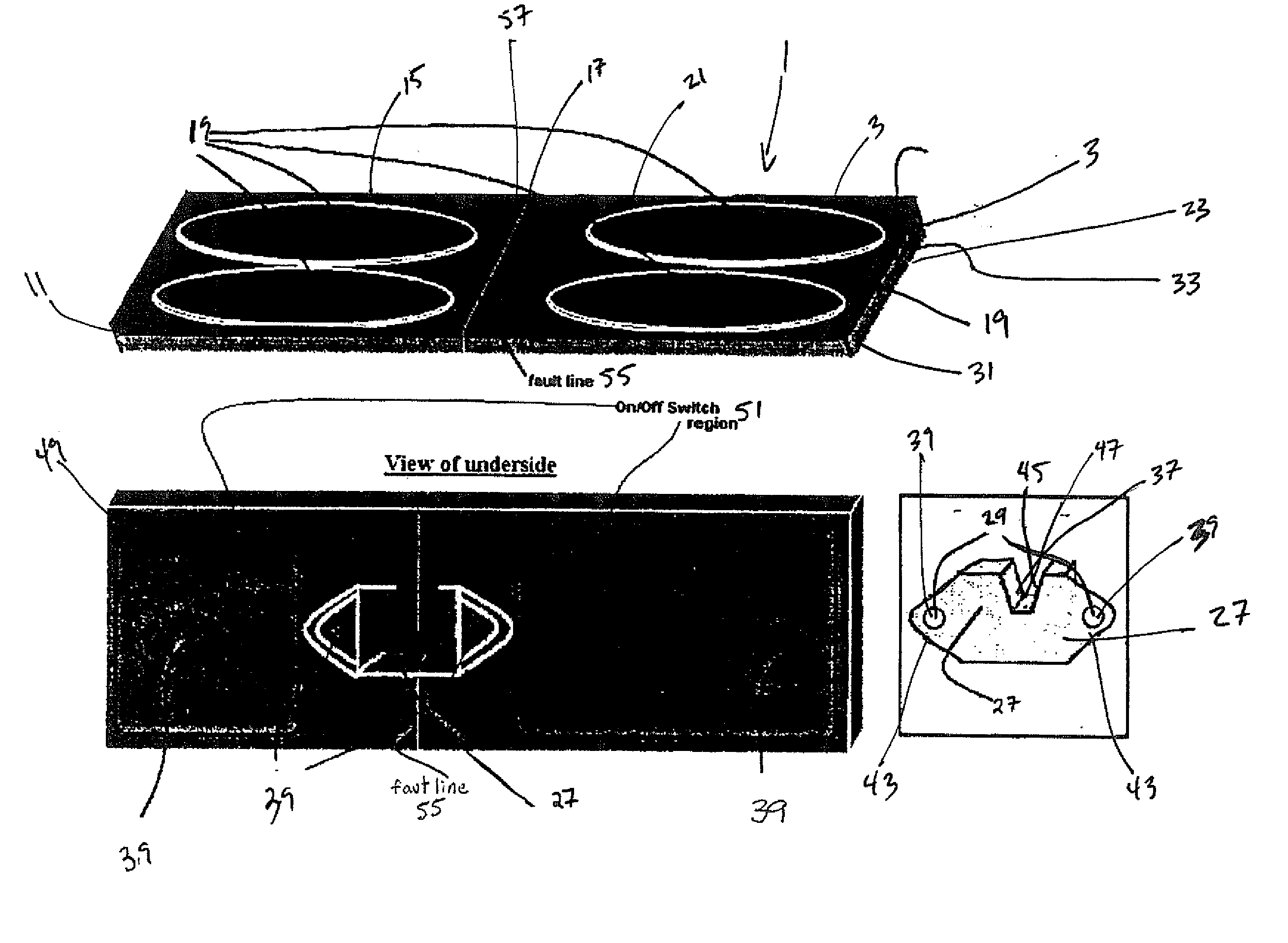
The present invention is concerned with functional electrical stimulation (FES) of paraplegics having spinal cord injuries (SCI), especially for the purpose of walking, where stimulation is applied to motor neurons below the level of the SCI. Specifically, the invention is concerned with FES in closed-loop where closed loop operation is provided by wireless feedback by EMG signals recorded via noninvasive surface EMG electrodes. No wire connections are required between the EMG electrodes and a signal processor (SP) for providing the feedback signal to the SP. Also, no wire feedback is required to send timing information from the stimulation signal generator to blocking circuits, in cases where such circuits are required to protect the wireless transmitters of the feedback information from being damaged by the stimulation pulses. Wireless operation is facilitated by miniature chips (receivers and transmitters), such as used in the Bluetooth technology. Hence, the paraplegic users are not burdened with any wires that are otherwise needed for closed-loop operation and with the need to connect them between the patient's back, legs, and a pocket-borne control box. Furthermore, closed loop operation frees the patients from the need to manually adjust stimulation levels with progression of muscle fatigue.The present invention allows the achieving closed-loop FES without requiring the sharing the same electrode for both stimulation and EMG recording and which requires complex control and non-standard electrodes. The avoidance of electrode-sharing further allows using regular and widely available stimulation electrodes and regular surface EMG electrodes, such as described in Graupe and Kohn: “Functional Electrical Stimulation for Ambulation by Paraplegics”, 1994.In certain realizations of the present invention, the blocking circuit discussed above requires no input from the stimulus signal generator, while such inputs are essential in any electrode-sharing design since pulse level is highest at the stimulation site. Hence, also no wireless receiver is required next to the EMG electrodes and no wireless transmitter is required next to the stimulus signal generator.In certain other realizations, blocking circuits are not required at all.
Owner:GRAUPE DANIEL
Tremor reduction systems suitable for self-application and use in disabled patients
InactiveUS20070123951A1Reduce tremorReliable and accurate mannerElectrotherapyPerson identificationElectricityBand-pass filter
A system and apparatus for enabling independent, highly reliable and accurate self-application of an anti-tremor means by a disabled patient, without requirement for application fixtures, wherein anti-tremor means comprises a single unit, self adhesive stimulation and recording electrode with an integrated supply of energy and a control unit, further comprising an alignment, and application means for applying said anti-tremor means configured to enable independently self application by a severely handicapped patient, wherein system and method for tremor reduction is by means of closed-loop functional electrical stimulation, including a sensor for sensing muscle movements, and Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) apparatus for providing FES to a muscle, the FES apparatus being in communication with the sensor via a band pass filter for filtering around a tremor frequency to ignore slow movements and high frequency noise.
Owner:BOSTON LEON
Electrical stimulation for a functional electrical stimulation system
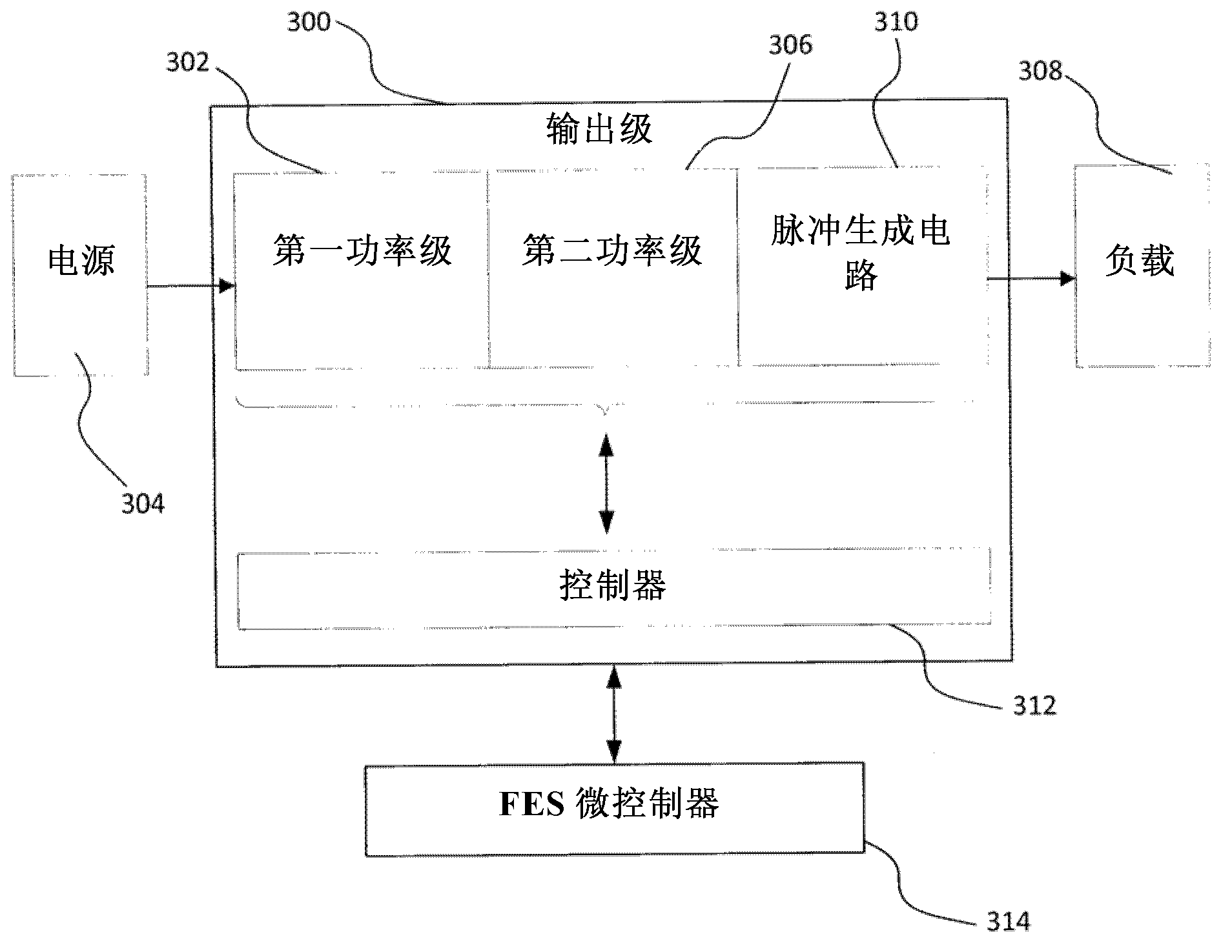
InactiveUS20150100107A1Shortened fall timeElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityControl signal
An electrical stimulation system and method for generating a stimulation signal for at least two electrodes coupled to a body part in a functional electrical stimulation system. One example embodiment includes a controller unit operable for receiving stimulation parameters and a trigger signal, and in response to receiving the trigger signal, outputting control signals based on the stimulation parameters. A voltage conversion module coupled to the unit receives the control signals and converts a supply voltage based on the received control signals. A switch receives the converted supply voltage at a first terminal and outputs a simulation signal at a second terminal. Outputting of the converted supply voltage at the second terminal by the switch is controlled by a driver module based on the received control signals.
Owner:ENSILVER CANADA
Functional electrical stimulation device and system, and use thereof
ActiveCN103052424AElectric pulse generator circuitsExternal electrodesPeriodic alternatingCapacitance
Disclosed herein is a functional electrical stimulation (FES) device and system. In one embodiment, sequential bipolar pulse stimulation may be provided to an area of a living body via one or more electrode leads applied to the area via a FES device comprising a current pulse generating circuit comprising output nodes for operative coupling to the one or more electrode leads, and configured for operative coupling to a voltage supply. The current pulse generating circuit generally comprises positive and negative stimulation paths drawing from the voltage supply to respectively apply positive and negative currents through the area via the one or more electrode leads. In one example, the stimulation paths comprise respective capacitive elements, a capacitance ratio of which dictating, at least in part, an amplitude ratio of the positive and negative currents, wherein periodic alternative activation of the stimulation paths provides the sequential bipolar pulse stimulation. In another example, each path comprises a respective charging element and a respective activation switch, wherein each respective charging element is charged by the voltage supply and discharged upon activation of the respective activation switch to generate positive and negative current pulses respectively, such that a pulse rise time of the positive and negative current pulses is predominantly dictated by a switching speed of each respective switch. Systems and uses for these devices, and FES in general, are also described.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
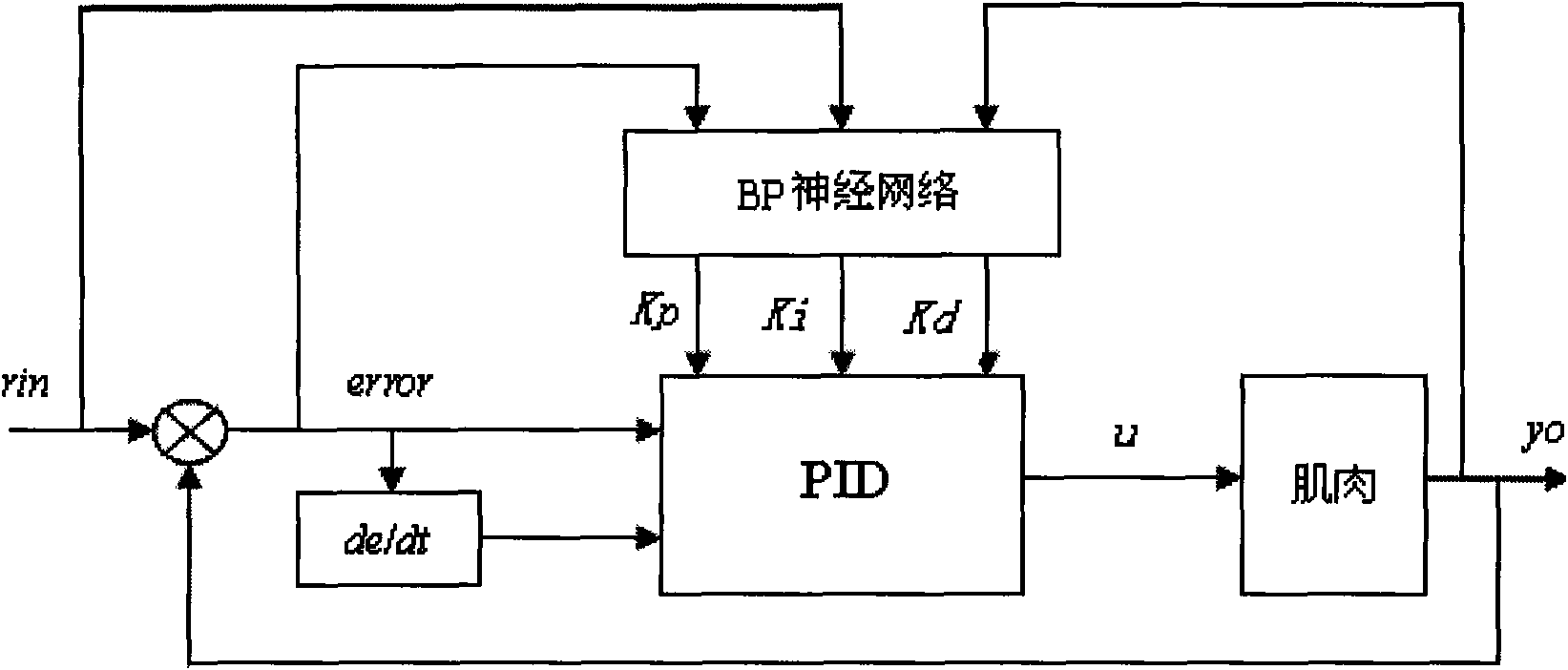
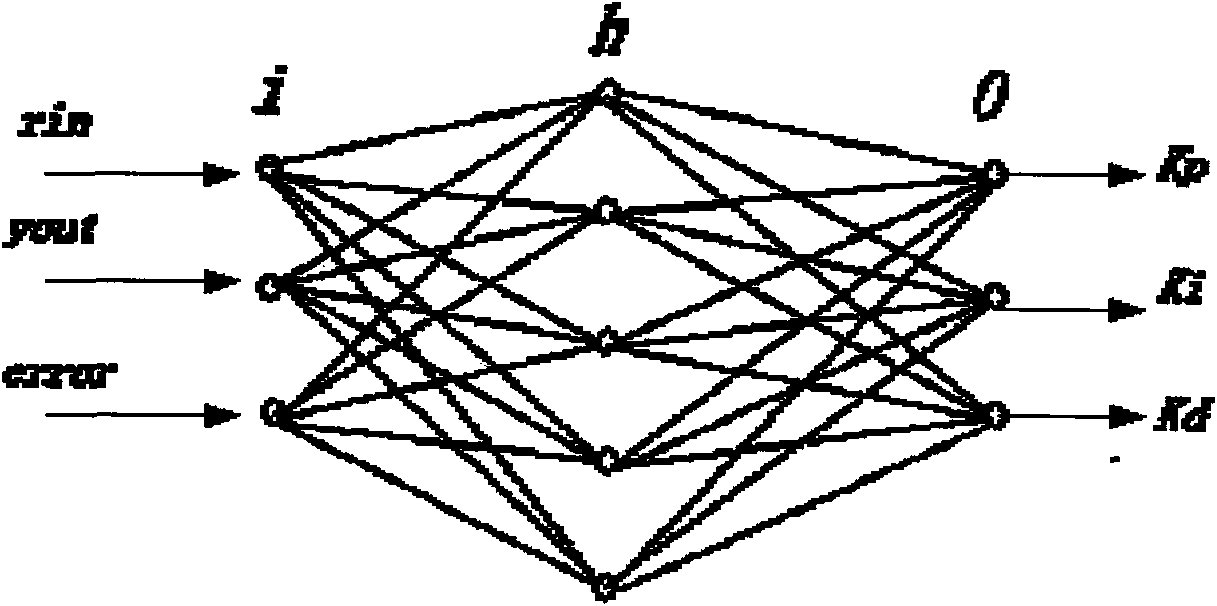
PID-adjusting precise control method of functional electrical stimulation (FES) based on BP neural network
InactiveCN101596338AOptimal Scale FactorOptimize integral coefficientElectrotherapyNeural architecturesElectricityWeight coefficient
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Tissue treatment systems with high powered functional electrical stimulation and methods for reducing pain during tissue treatments
Methods, apparatus, and systems for transcutaneously treating tissue located beneath a skin surface with electromagnetic energy delivered from a treatment electrode. A portion of the treatment electrode is contacted with the skin surface. While maintaining the contact between the portion of the treatment electrode and the skin surface, the electromagnetic energy is delivered from the treatment electrode in a plurality of power pulses through the skin surface to the tissue over a treatment time with a time gap between each consecutive pair of the pulses to lower a level of pain perceived by a patient.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
Tremor reduction systems suitable for self-application and use in disabled patients
InactiveUS7643882B2Reliable and accurate mannerEasy to liftElectrotherapyPerson identificationElectricityBand-pass filter
A system and apparatus for enabling independent, highly reliable and accurate self-application of an anti-tremor means by a disabled patient, without requirement for application fixtures, wherein anti-tremor means comprises a single unit, self adhesive stimulation and recording electrode with an integrated supply of energy and a control unit, further comprising an alignment, and application means for applying said anti-tremor means configured to enable independently self application by a severely handicapped patient, wherein system and method for tremor reduction is by means of closed-loop functional electrical stimulation, including a sensor for sensing muscle movements, and Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) apparatus for providing FES to a muscle, the FES apparatus being in communication with the sensor via a band pass filter for filtering around a tremor frequency to ignore slow movements and high frequency noise.
Owner:BOSTON LEON
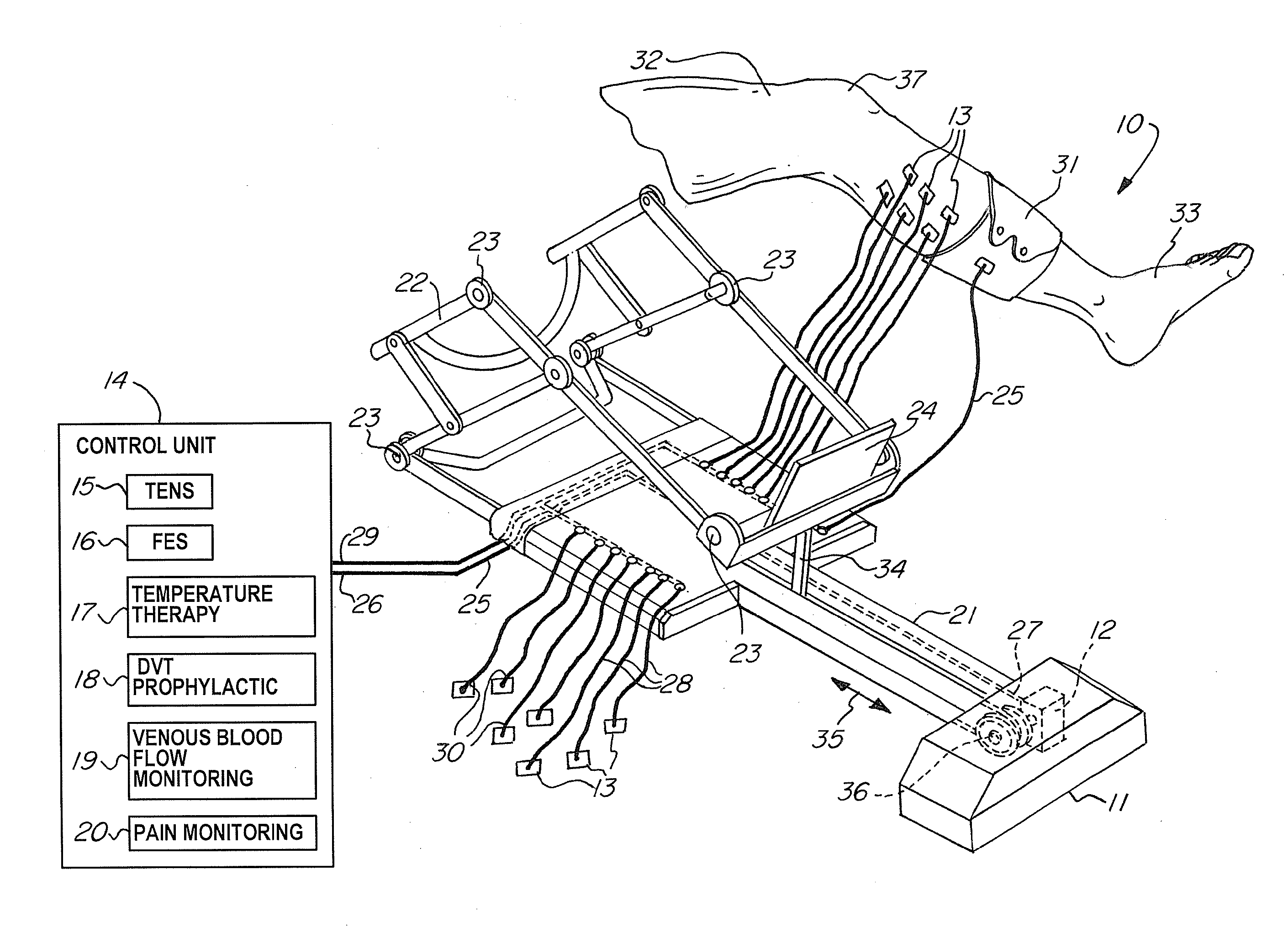
Orthosis For Range Of Motion, Muscular And Neurologic Rehabilitation Of The Lower Extremities
InactiveUS20130085420A1Maximize effectivenessPrevent muscle wastingBlood stagnation preventionElectrotherapyNervous systemTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
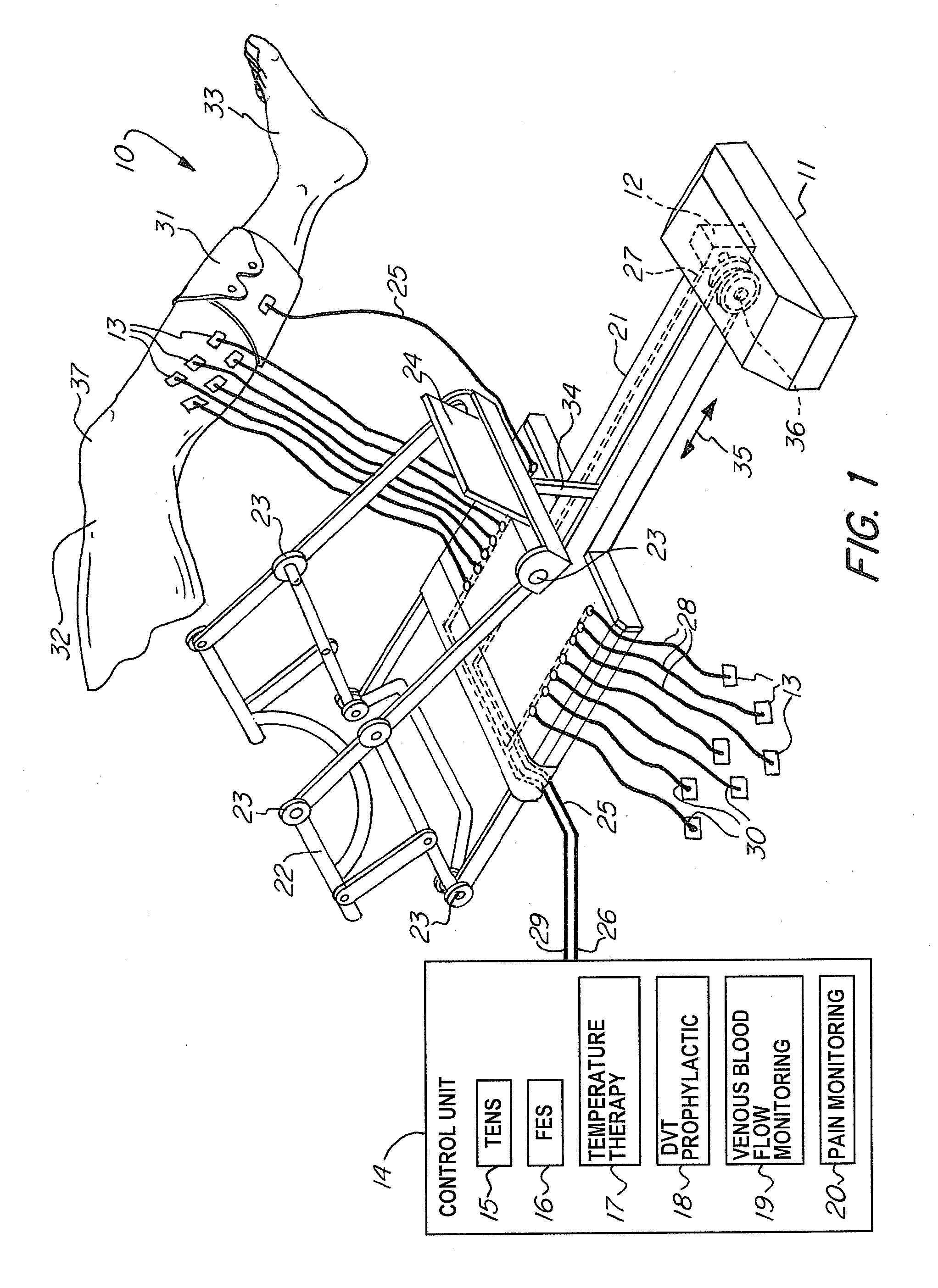
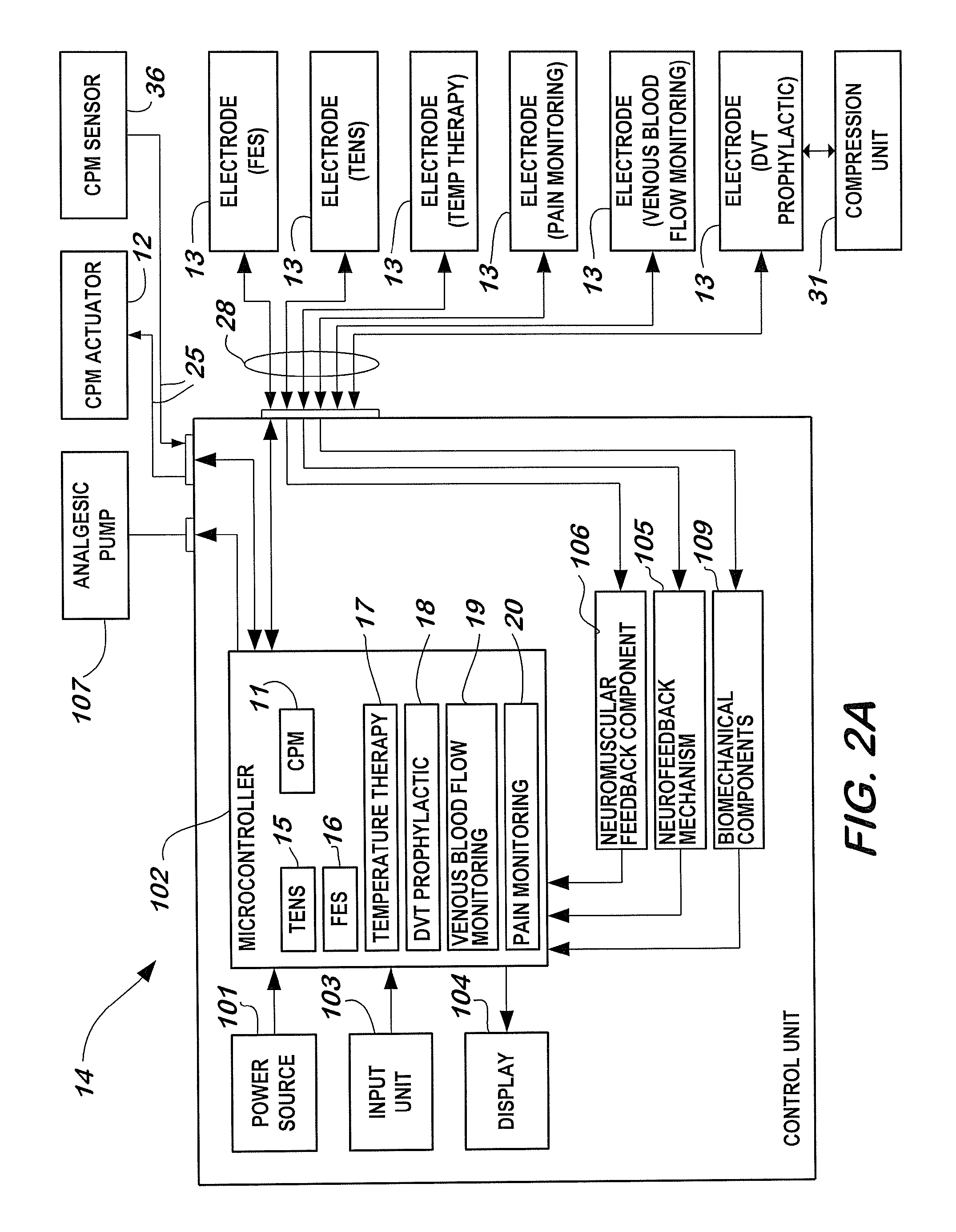
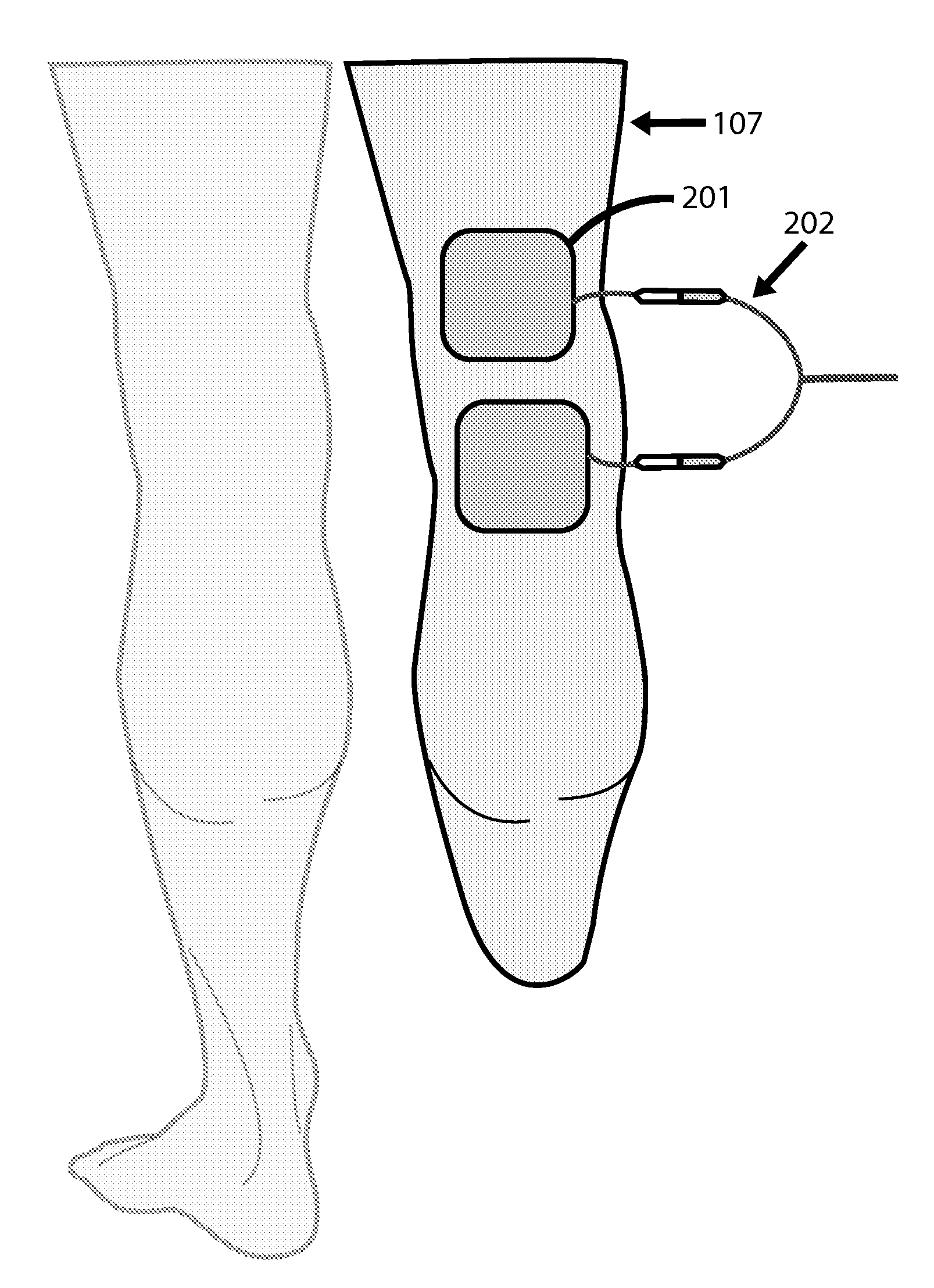
A non-invasive apparatus for rehabilitating a joint, limb, and muscles of a patient recovering from surgery on the joint, includes a continuous passive motion device having at least one support member for supporting the limb, at least one hinge coupled to the at least one support member, and at least one actuator for providing reciprocating motion of the at least one support member about the at least one hinge, a plurality of electrodes transmitting at least four modalities chosen from a group consisting of functional electrical stimulation (FES), transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), temperature therapy stimulation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylactic stimulation, venous blood flow monitoring, and pain monitoring, and a control unit controlling the at least one actuator and the plurality of electrodes according to a coordinated sequence of the reciprocating motion and transmission of the at least four modalities.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
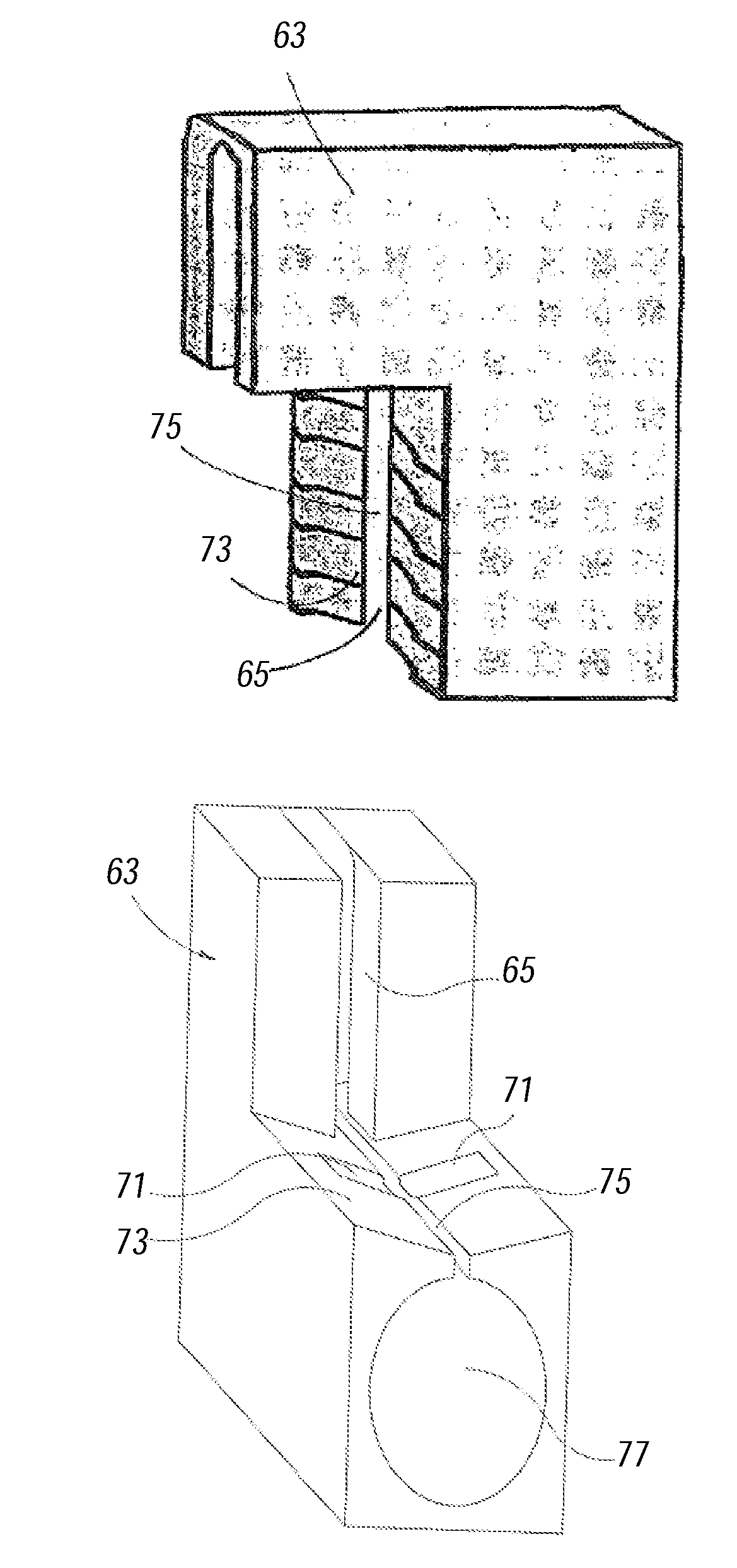
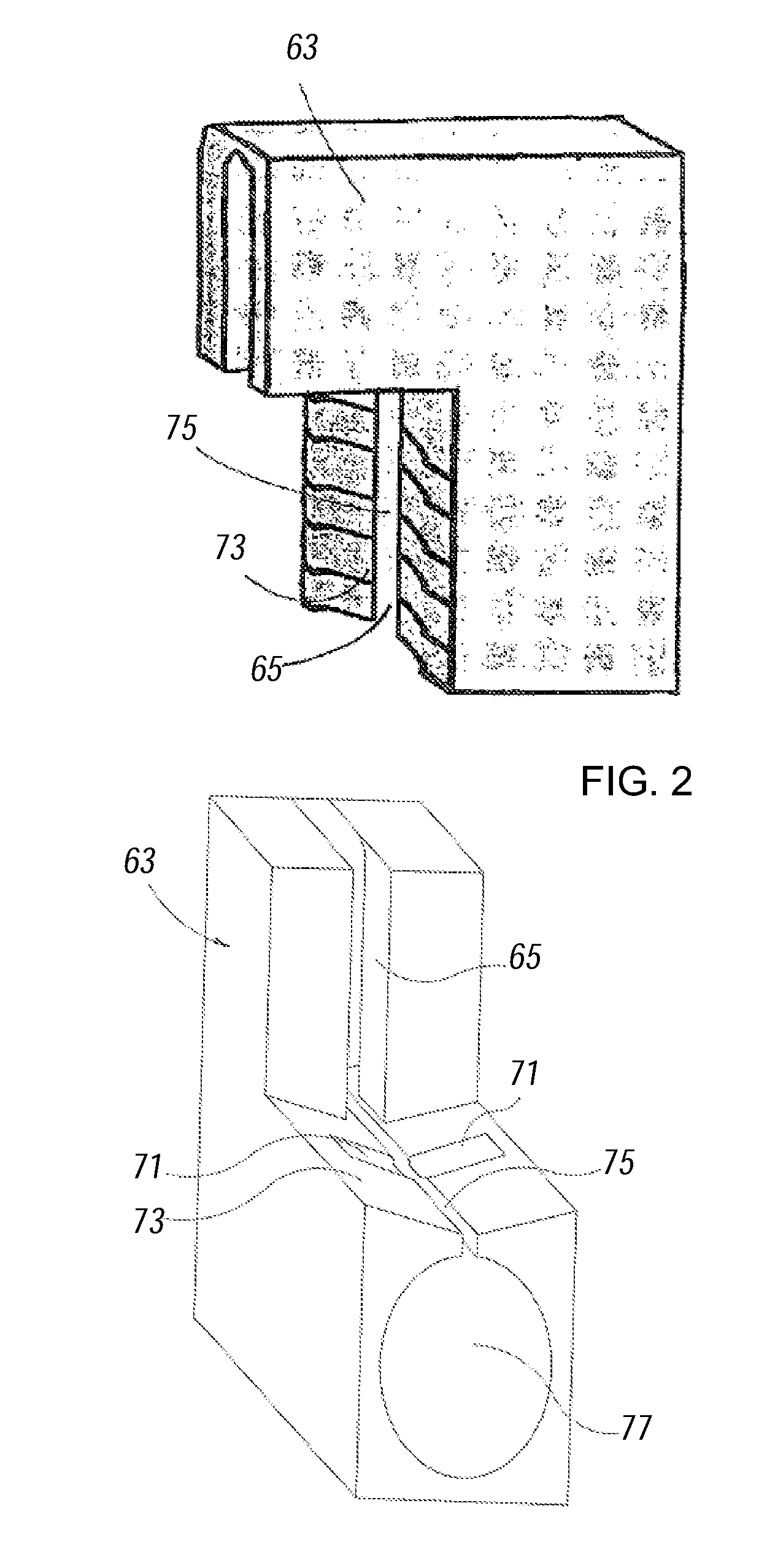
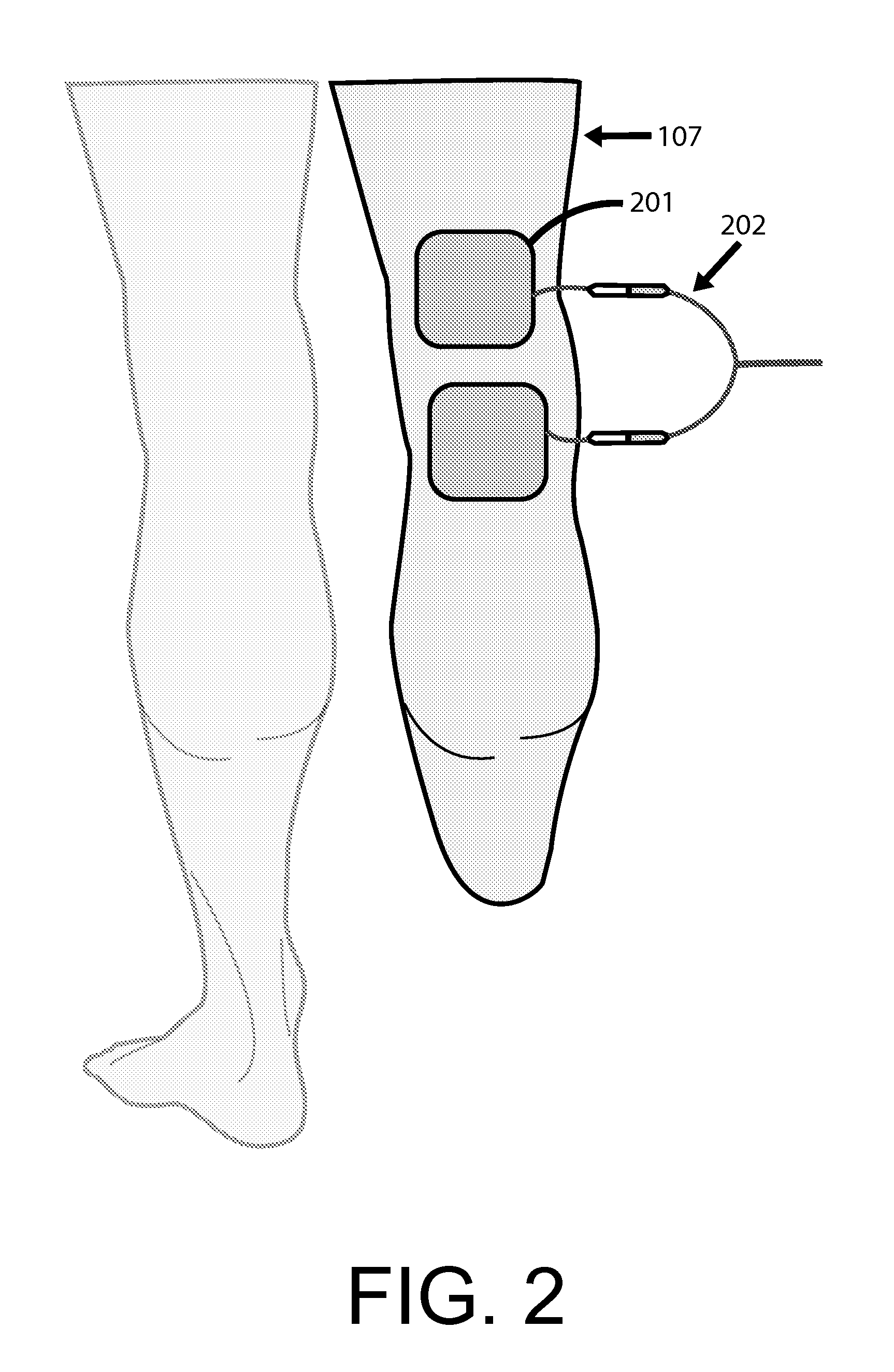
Integration of functional electrical stimulation in prosthetic sockets, liners, and garments for improved amputee care and performance
InactiveUS20100114238A1Relieve stressStress minimizationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationRe educationElectrical conductor
The present disclosure provides a functional electrode stimulation (FES) apparatus for use with prosthetic limbs. FES may provide the benefits of pain management, muscle building, prevention of muscle atrophy, and muscle re-education of residual limb and / or peri-residual limb muscles. The FES apparatus comprises a portable electrical stimulator; means to carry a current between the electrical stimulator and a prosthetic limb liner or socket; a plurality of elastic conductors integrated with the prosthetic limb liner or socket and capable of carrying the current from the means; a plurality of thin planar conductive fabric electrodes capable of carrying the current from the elastic conductors; and a plurality of thin electrodes capable of carrying the current between the thin planar conductive fabric electrodes and the skin of a patient.
Owner:MUCCIO PHILIP EDWARD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com