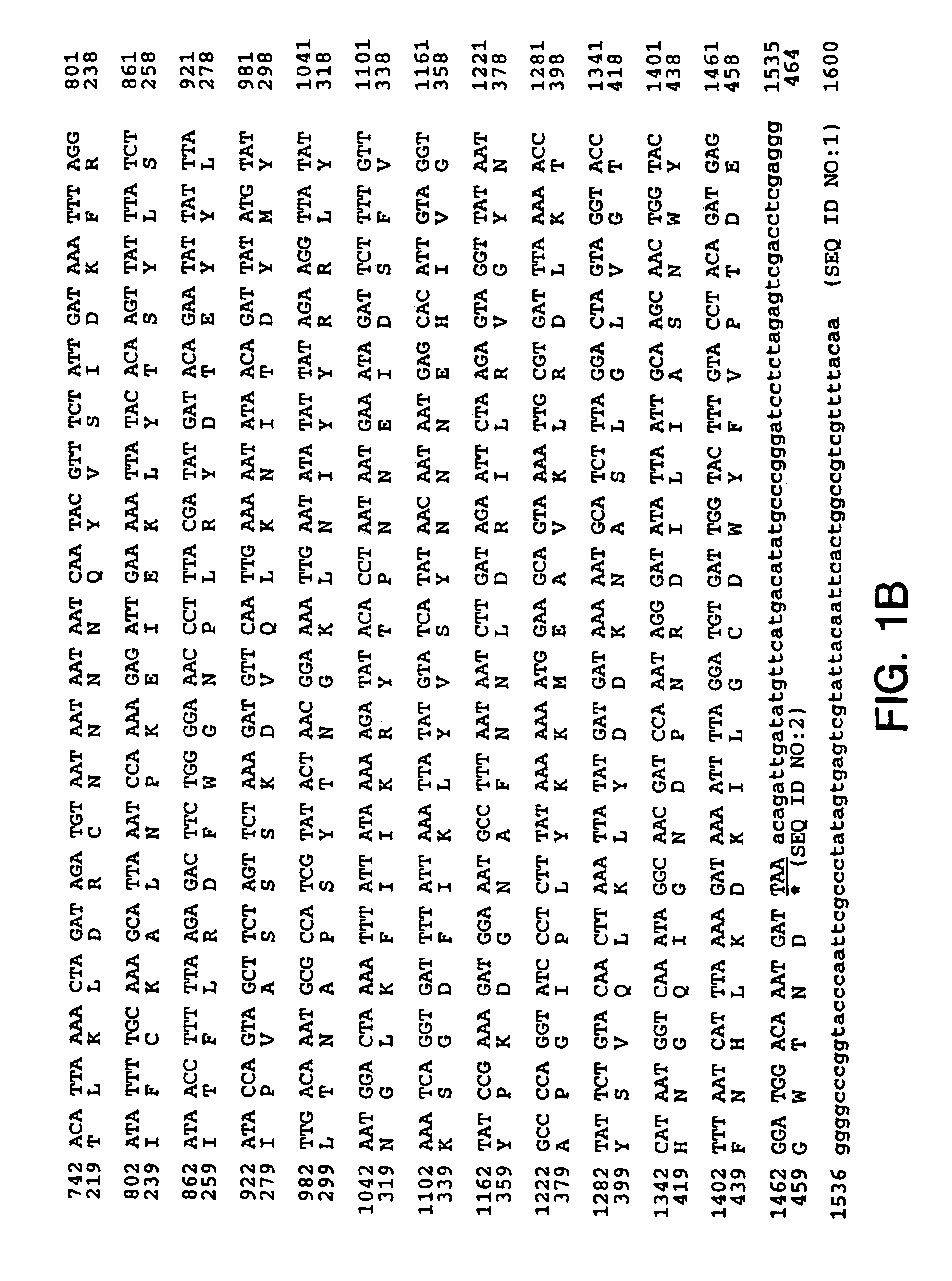
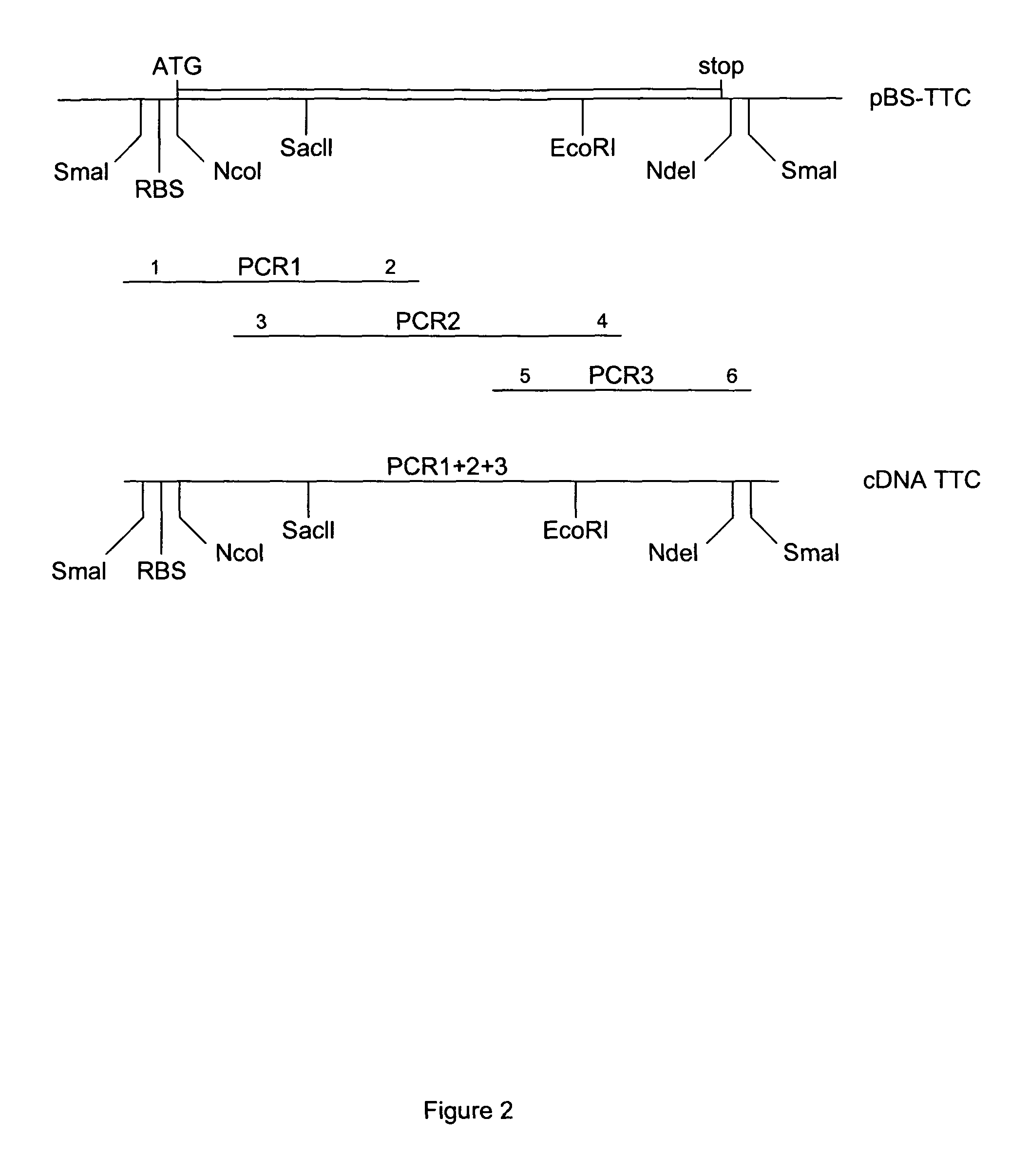
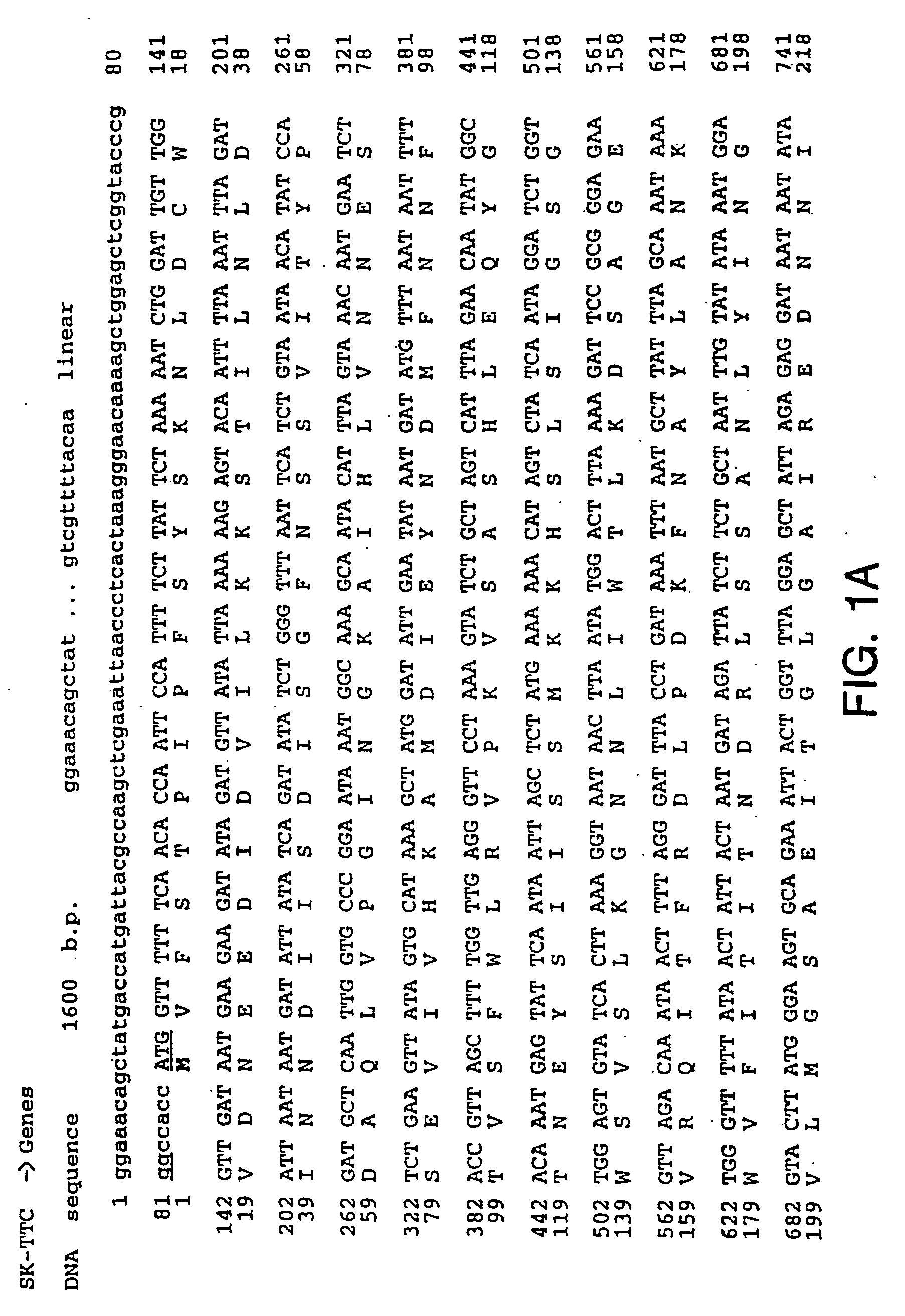
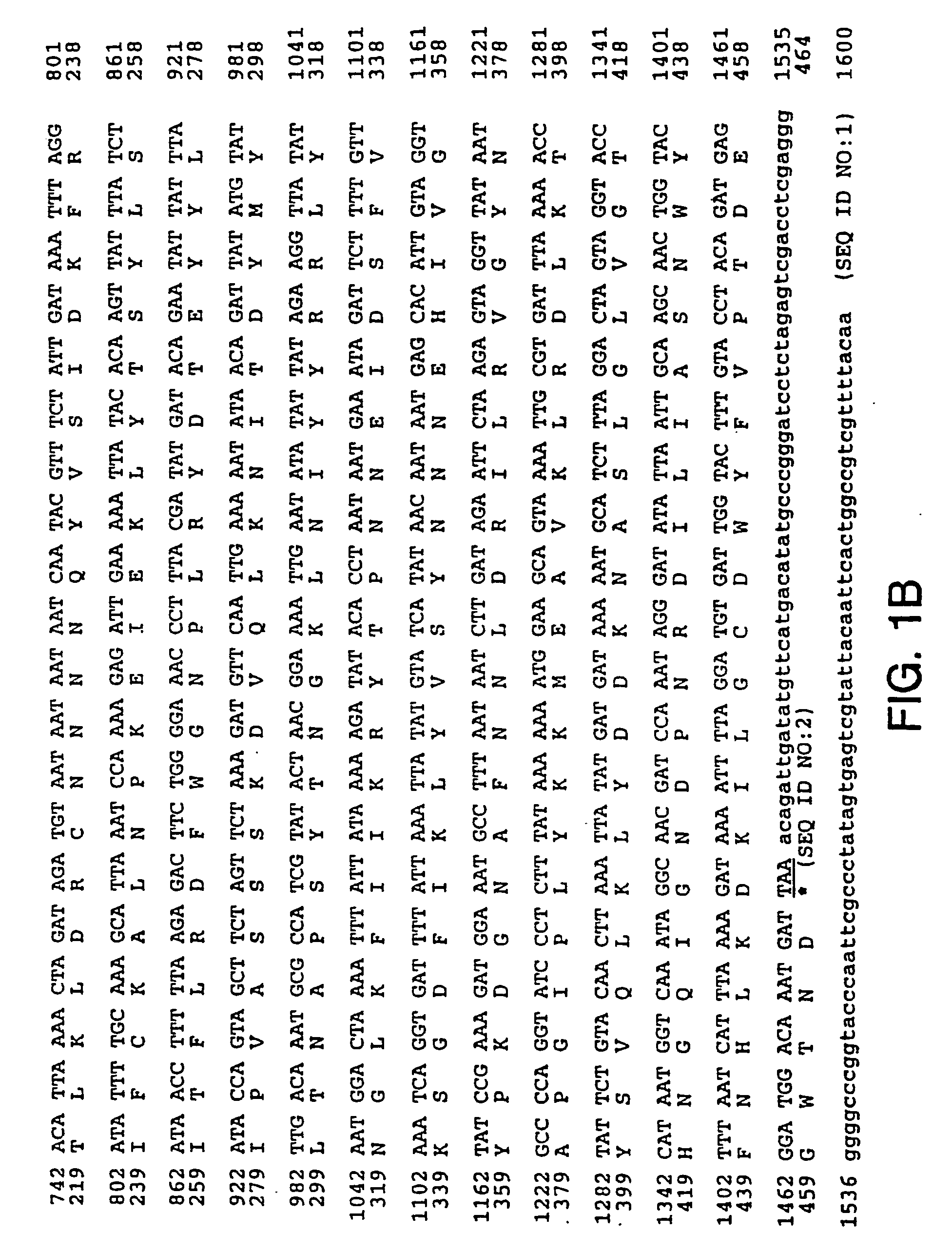
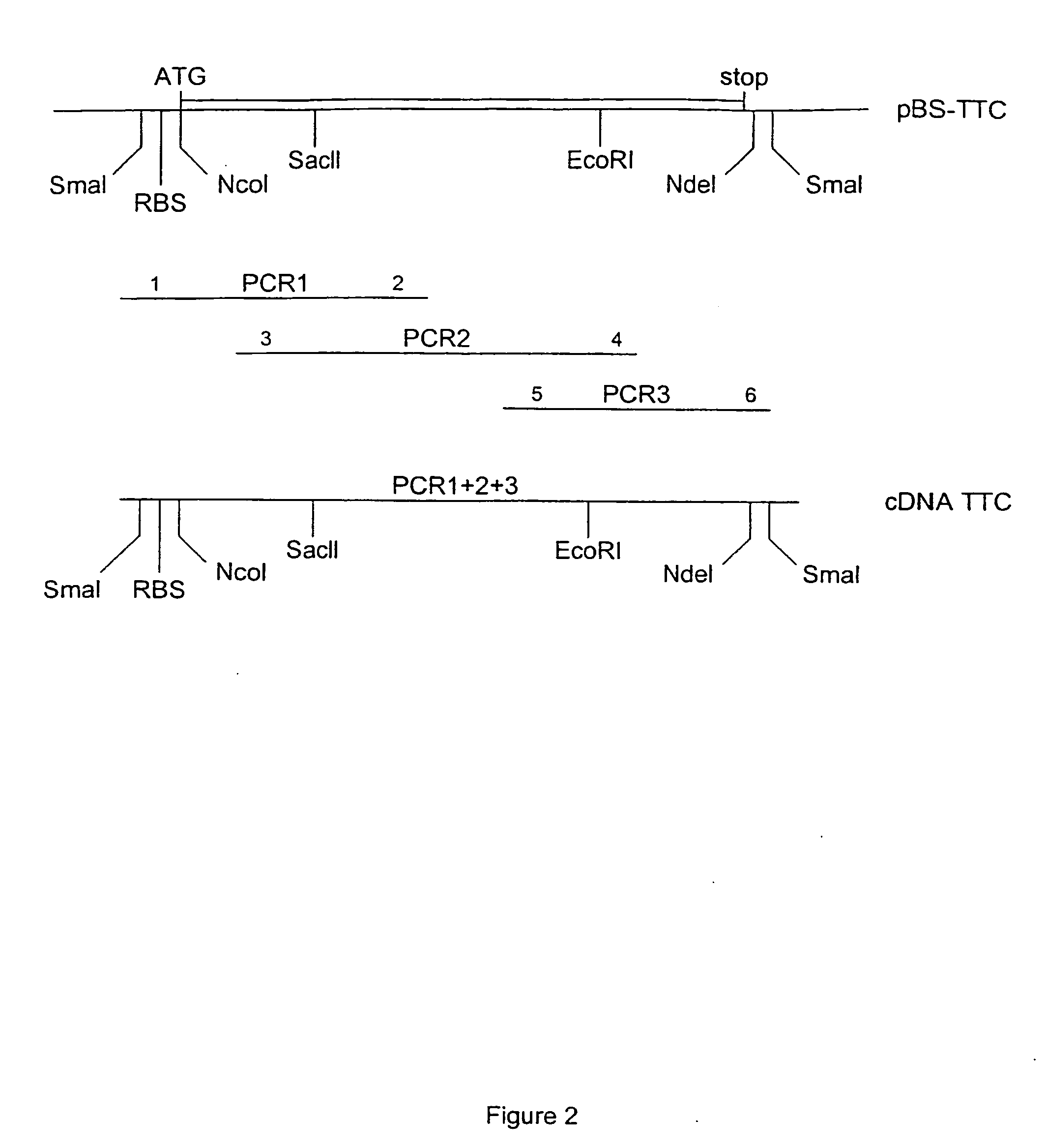
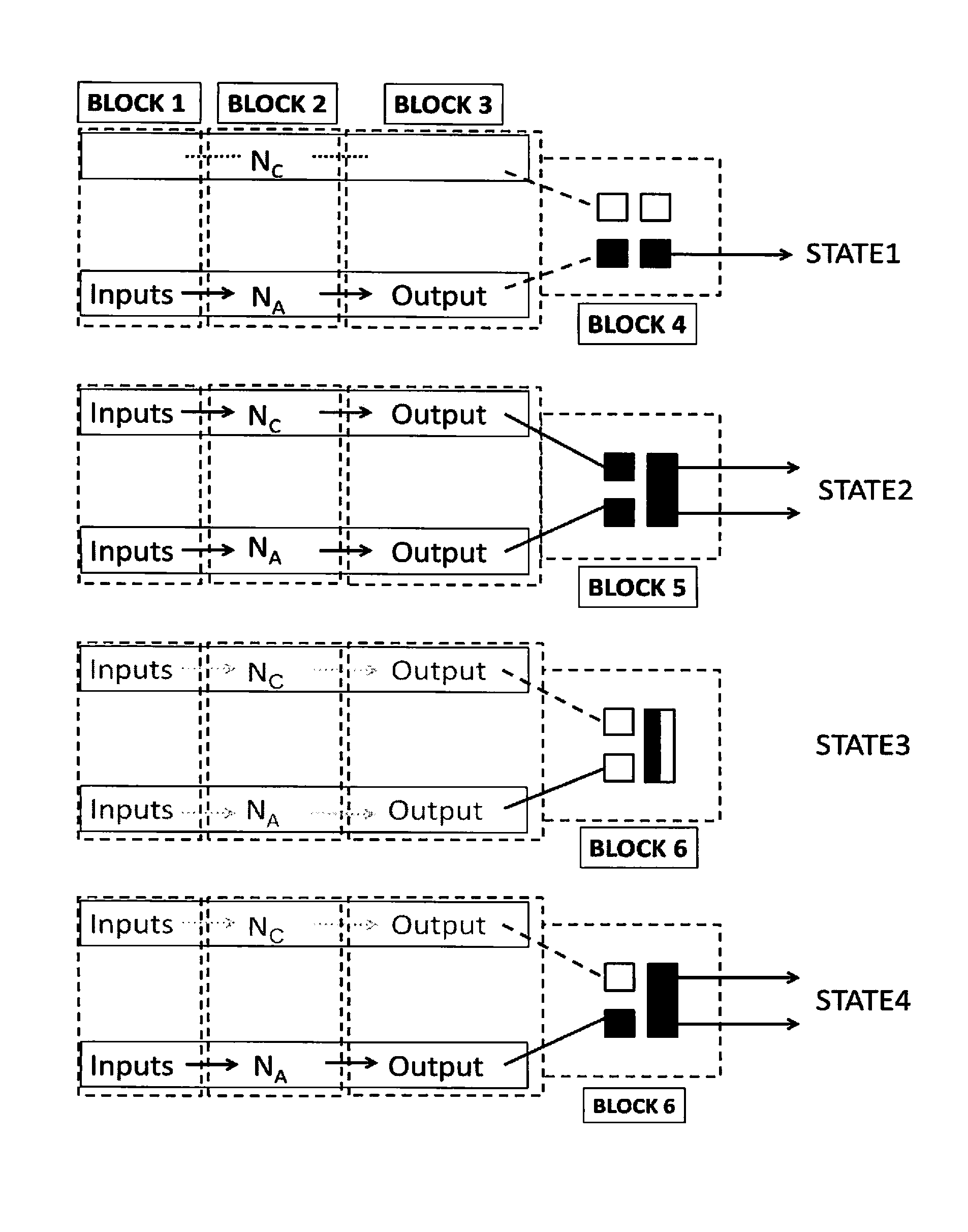
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Synapsis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
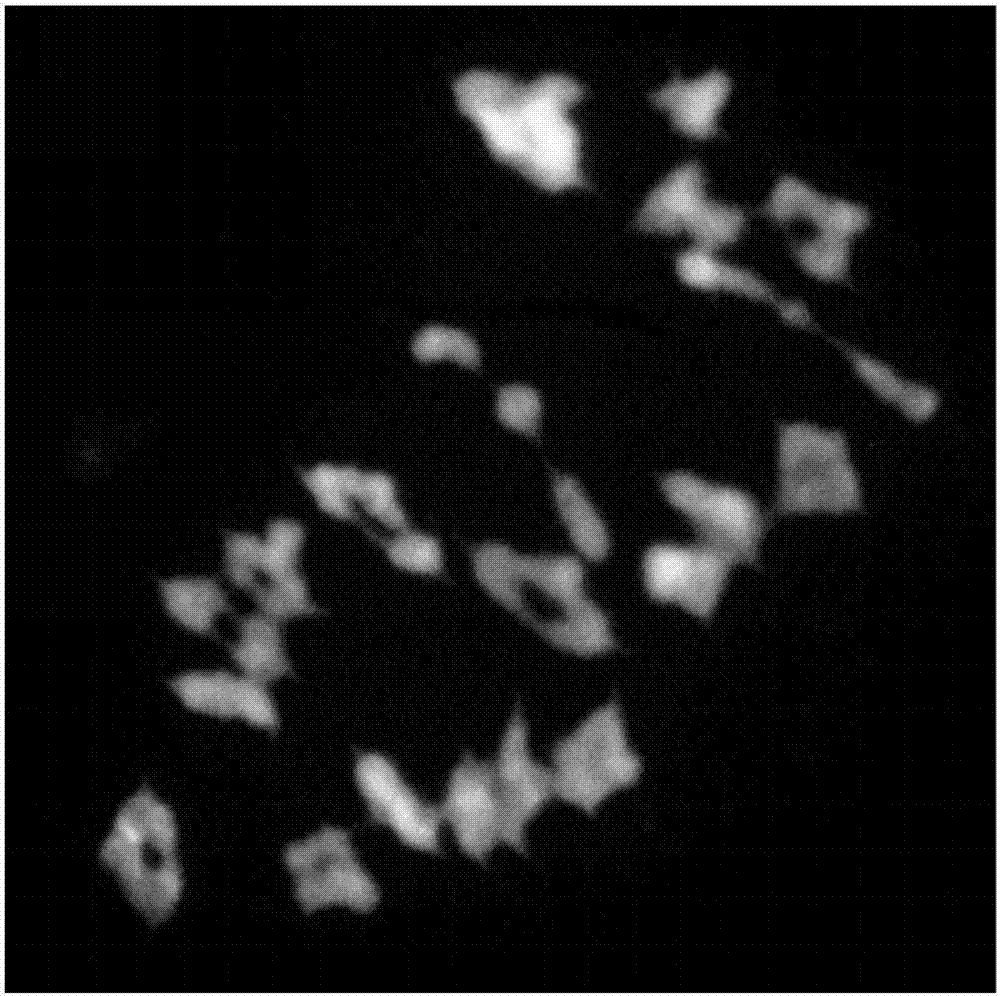
Synapsis (also called syndesis) is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of meiosis. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. These end-membrane complexes then migrate, assisted by the extranuclear cytoskeleton, until matching ends have been paired. Then the intervening regions of the chromosome are brought together, and may be connected by a protein-RNA complex called the synaptonemal complex. Autosomes undergo synapsis during meiosis, and are held together by a protein complex along the whole length of the chromosomes called the synaptonemal complex. Sex chromosomes also undergo synapsis; however, the synaptonemal protein complex that holds the homologous chromosomes together is only present at one end of each sex chromosome.
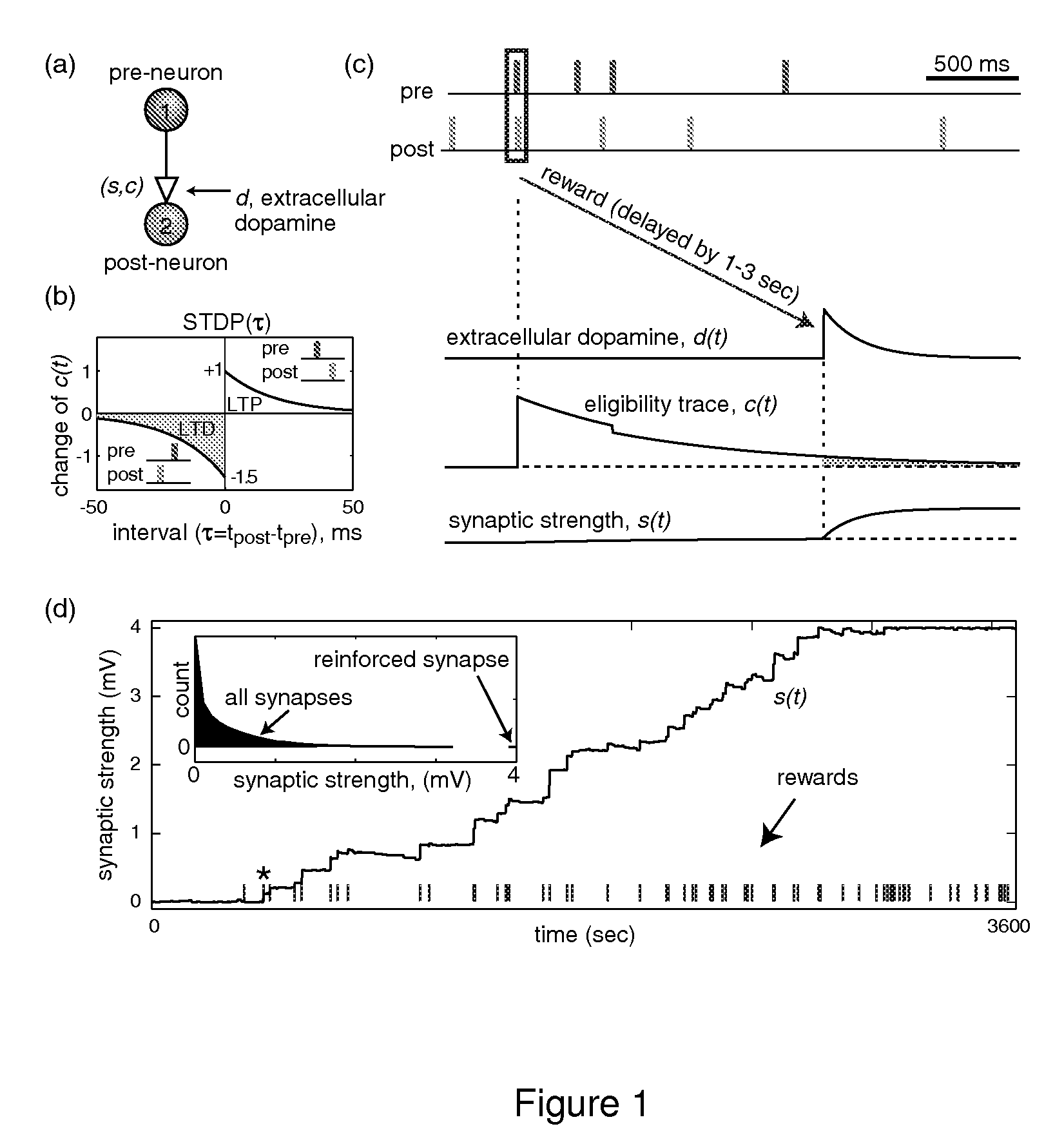
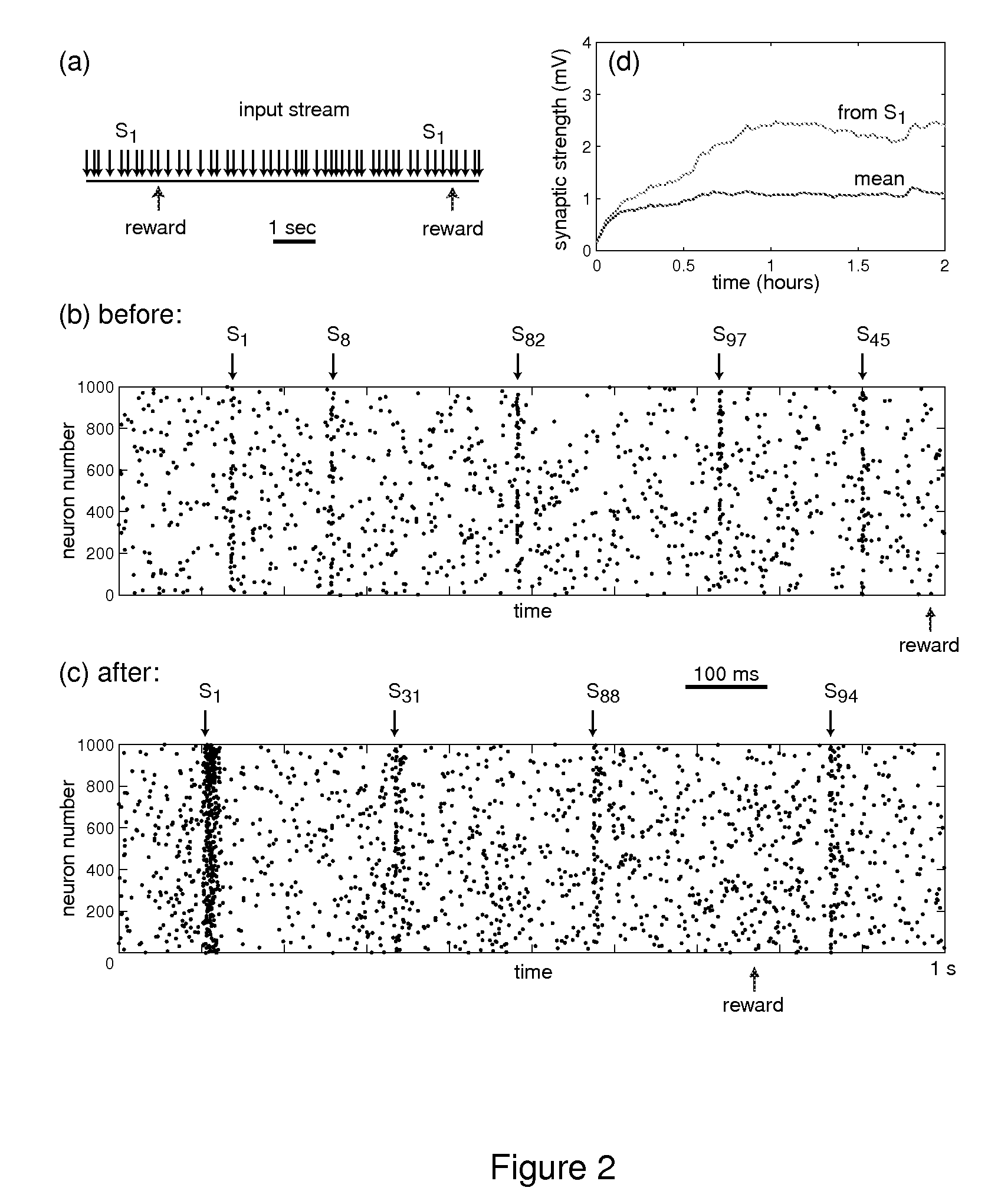
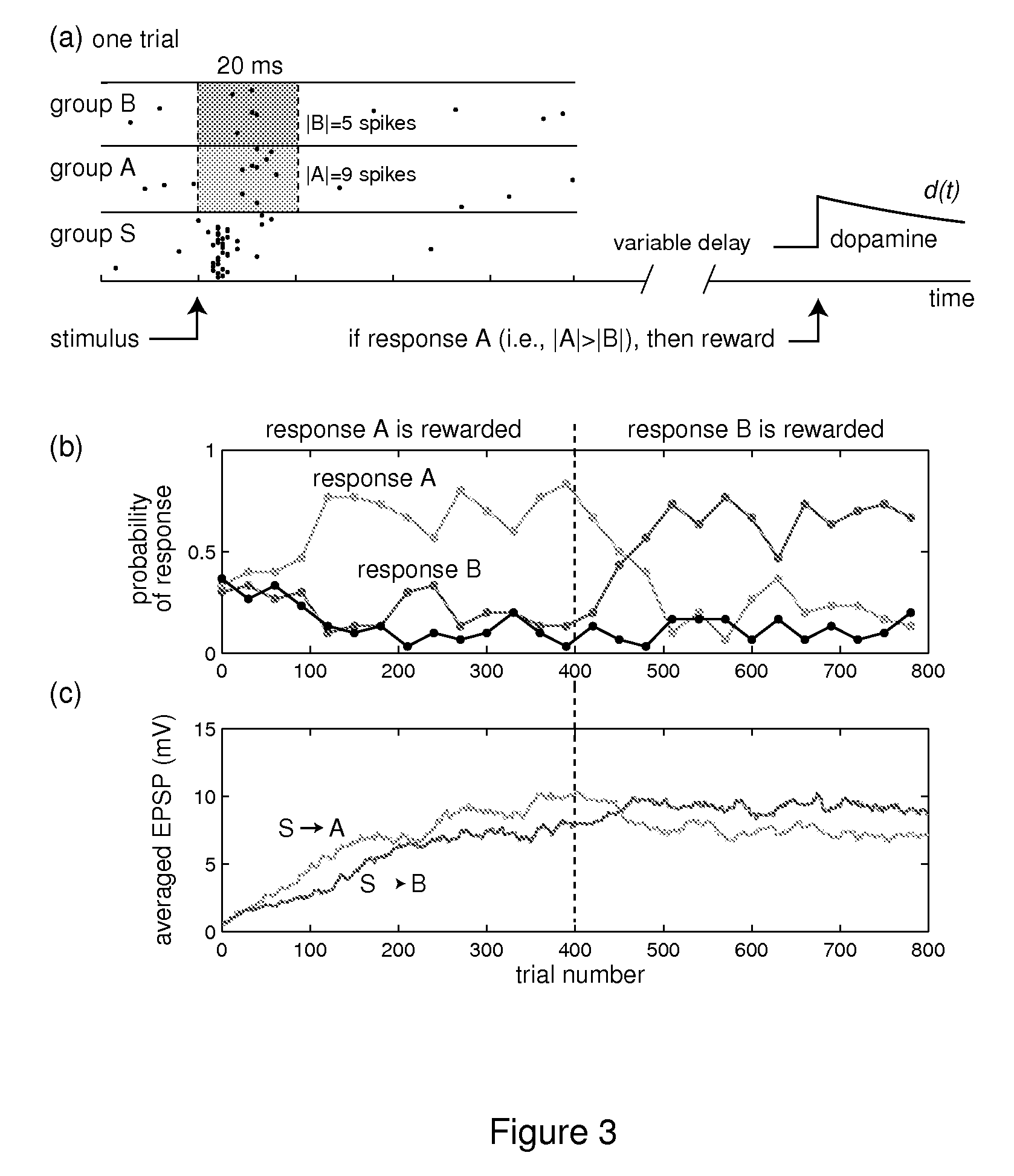
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS20080162391A1Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNerve networkCritical period
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
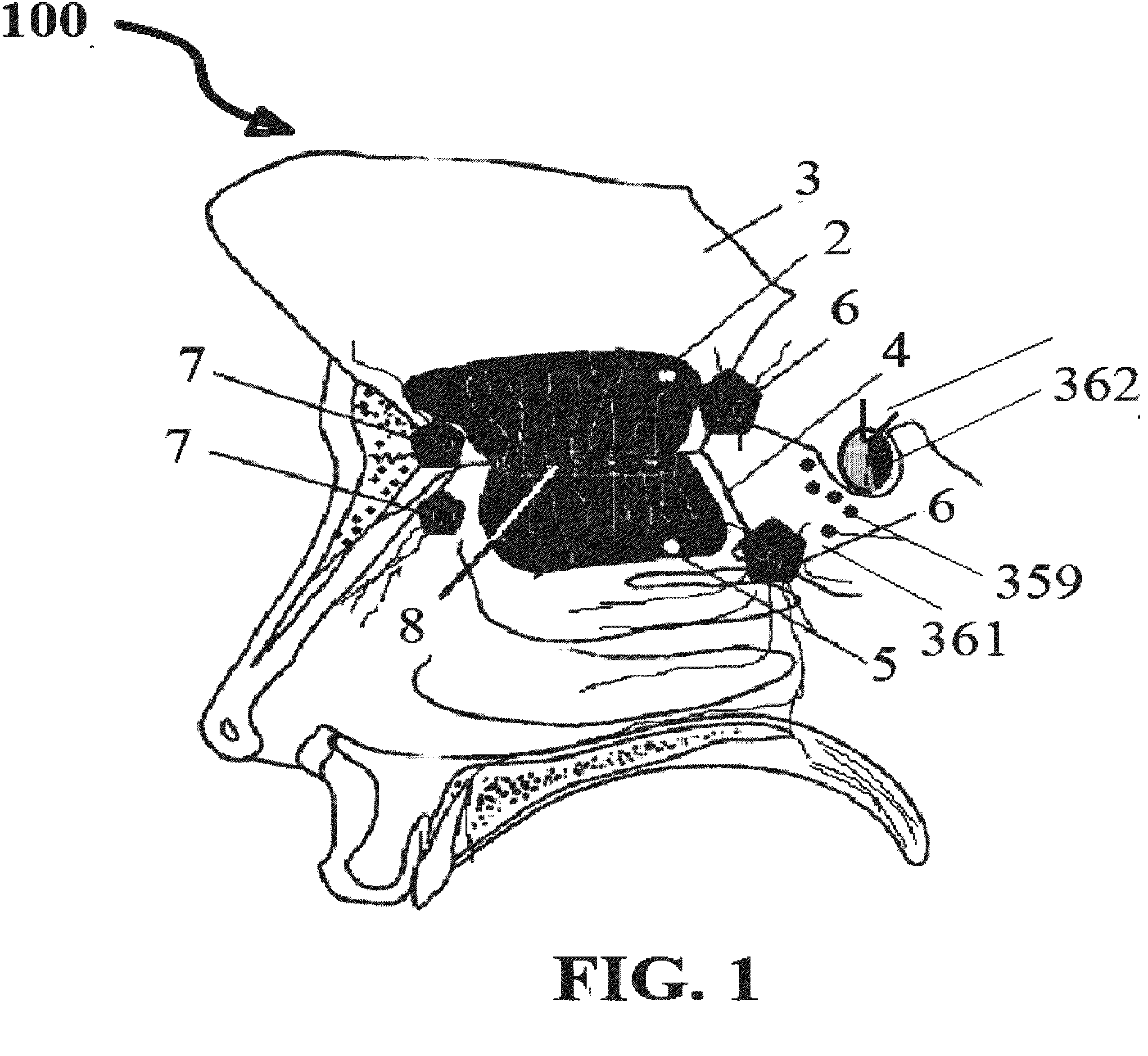
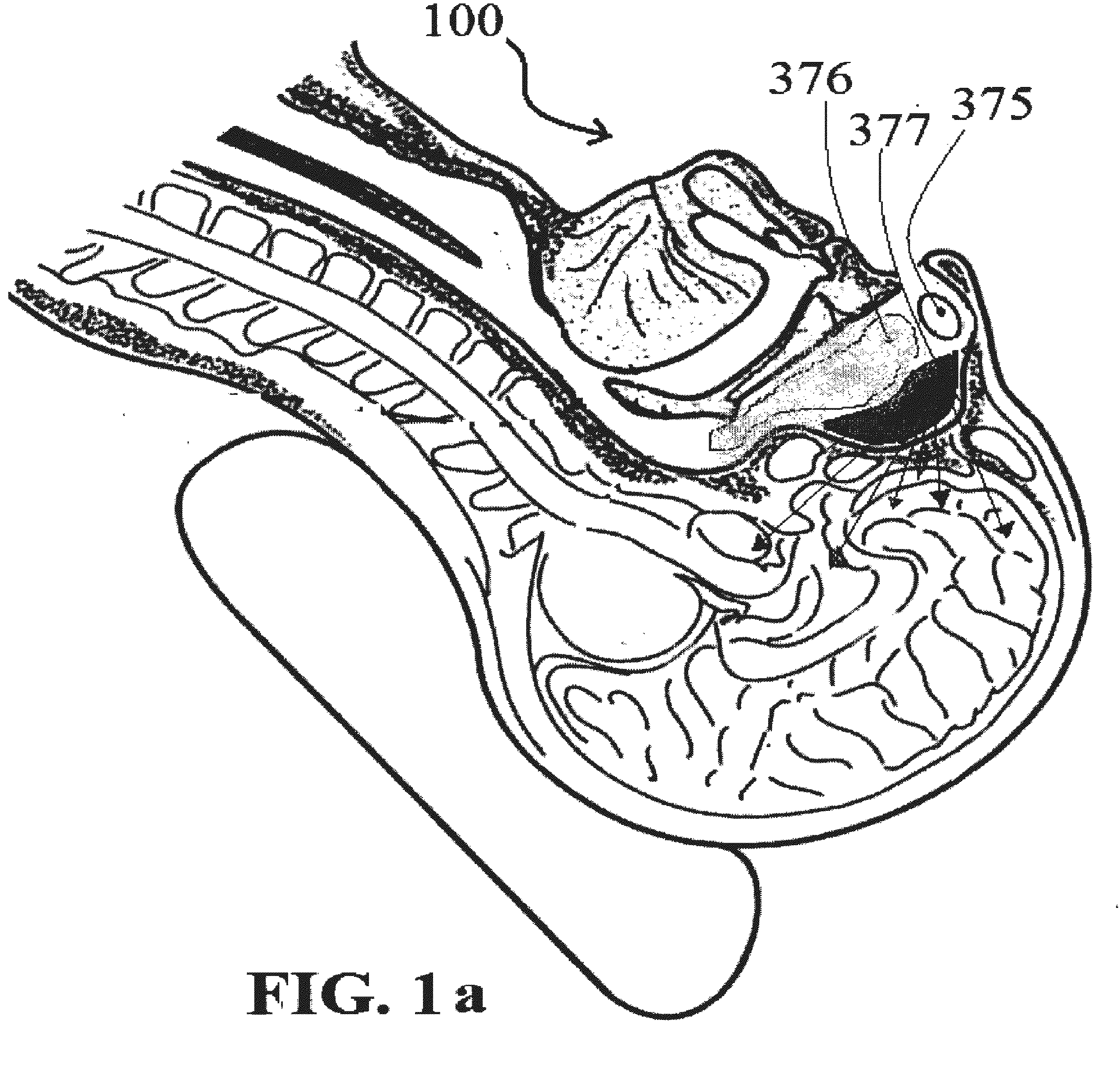
Alzheimer's disease treatment with multiple therapeutic agents delivered to the olfactory region through a special delivery catheter and iontophoresis
InactiveUS20120323214A1Reduce and preventAvoid destructionNervous disorderHead electrodesApoptosisExcitotoxicity
This invention describes the administration of multiple therapeutic agents with insulin in conjunction with bexarotene, ketamine, monoclonal antibodies Etanercept, IGF-1, and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors physostigmine, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Insulin, improves memory; also augments and amplifies the effects of the adjuvant therapeutic agents (paracrine and intracrine effects) and consequently reduces the β amyloid, its soluble precursors, prevents damage to the neuronal skeletal network (taupathy), and blocks glutamate excitotoxicity, reduces brain inflammation, prevents apoptosis, and increases the acetylcholine levels in the neurons and synapses; by using a combination of insulin, bexarotene, ketamine, Etanercept, IGF-1, and physostigmine therapeutic agents. The results are achieved by using the specially designed Iontophoresis incorporated olfactory mucosal delivery (ORE) catheter device located at the olfactory nerves, sphenoid sinus, and adjacent structures described here, to transport the large molecules of therapeutic agents to treat AD delivered to the CNS bypassing BBB from ORE.
Owner:WEDGE THERAPEUTICS
Unit, device and method for simulating biological neuron and neuronal synapsis
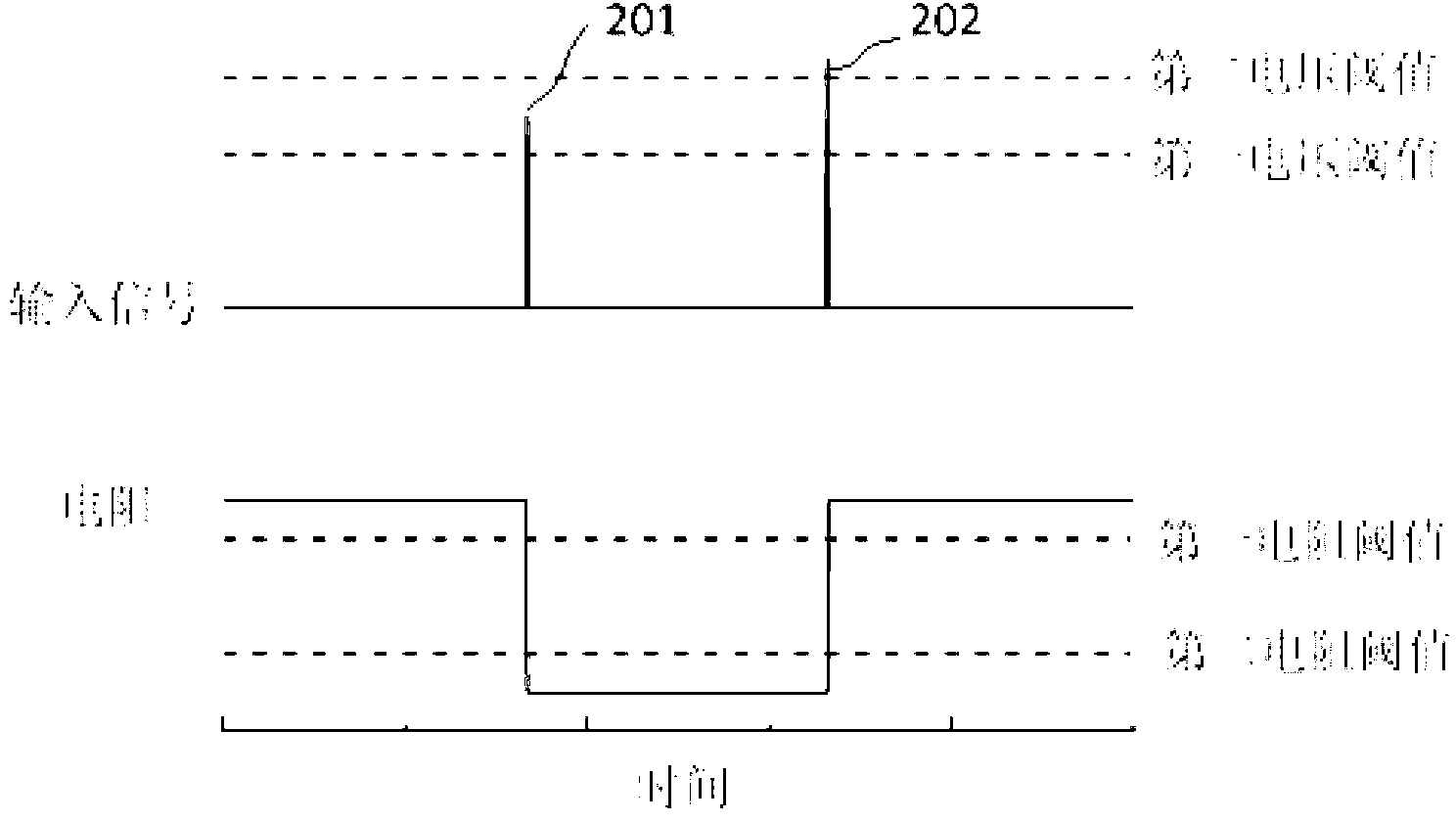
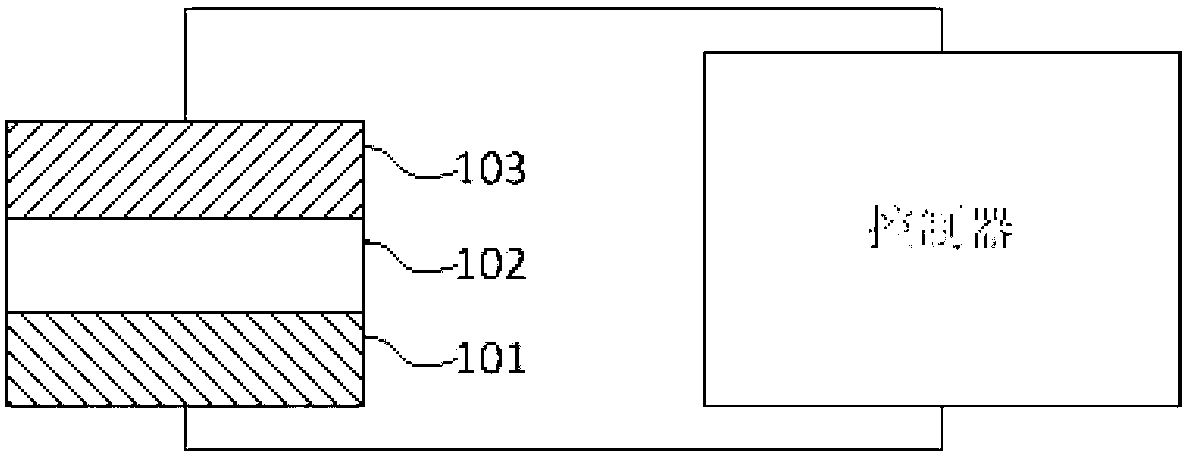
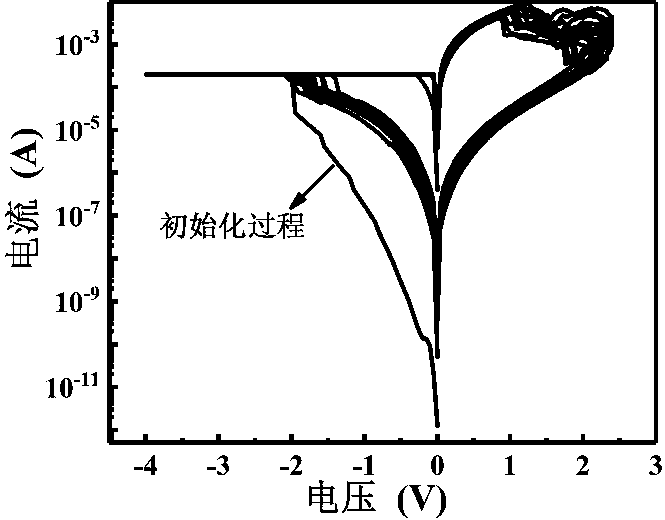
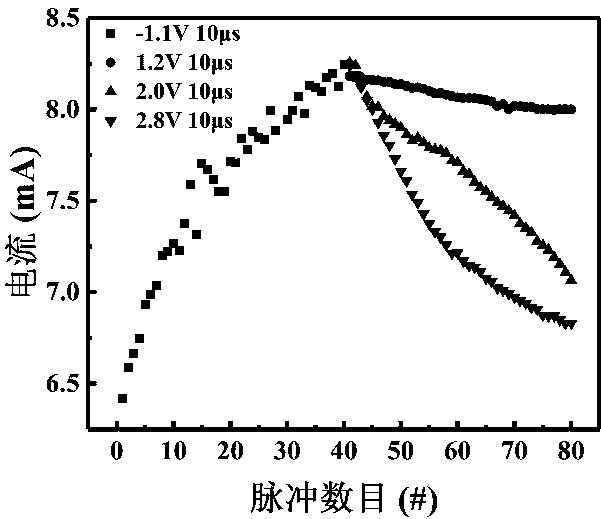
ActiveCN103078054AReduce power consumptionSmall sizeElectrical apparatusNeural architecturesHigh resistanceSynaptic weight
The invention discloses a unit, a device and a method for simulating biological neuron and neuronal synapsis on the basis of chalcogenide compounds. The unit comprises a first electrode layer, a function material layer and a second electrode layer. During the neuron simulation, a device receives the stimulation of one or a plurality of electric pulses, the resistance of the function material is changed into the low resistance state from the high resistance state, the simulated neuron is changed into an excitation state from a resting state, and the threshold value excitation and energy accumulation excitation functions are realized. During the neuronal synapsis simulation, the electric conductance of the function material layer of the device can be gradually changed according to input signals, and the synapsis weight regulating function is realized, the ynapsis weight is changed according to time differences of signals input at two ends, and the STDP (spike timing dependent plasticity) function of synapsis is realized. The basic device forming the artificial neural network can be provided.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Unit, device and method for simulating biological neuronal synapsis
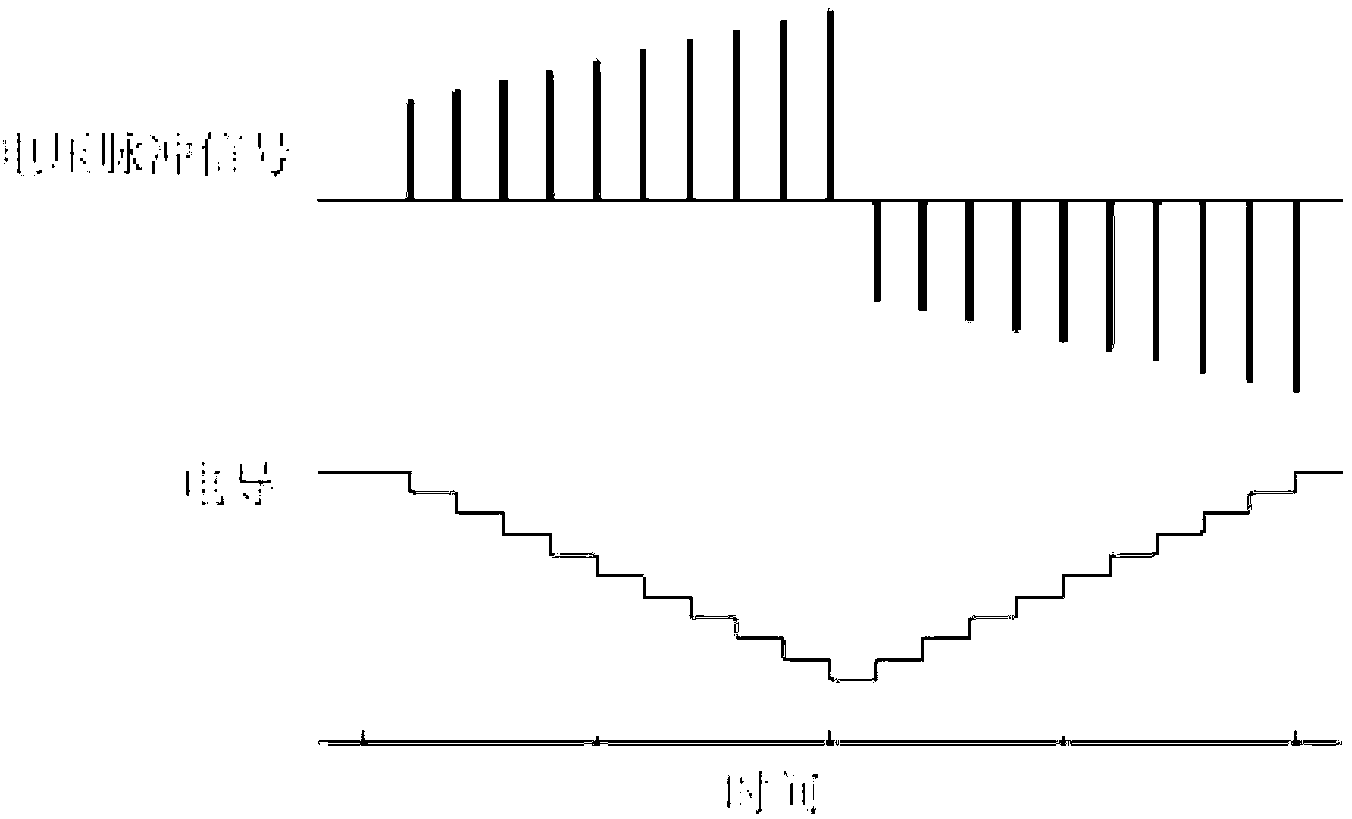
ActiveCN103078055AHighly integratedReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusNeural architecturesSynaptic weightDevice form
The invention discloses a unit, a device and a method for simulating biological neuronal synapsis on the basis of chalcogenide compounds. The unit comprises a first electrode layer, a function material layer and a second electrode layer, wherein the first electrode layer receives first pulse signals, and the second electrode layer receives second pulse signals. A device can change electric conductance simulation synapsis weight changes according to input signals. When the difference value between the frequency of the first pulse signals and the frequency of the second pulse signals is plus or minus, the electric conductance is changed , and the simulation of the pulse frequency dependent synaptic plasticity function of the biological neuronal synapsis is realized. When the signal difference peak value between the first pulse signals and the second pulse signals is plus or minus, the electric conductance is changed, and the simulation of the pulse time dependent synaptic plasticity function of the biological neuronal synapsis is realized. The unit, the device and the method have the advantages that the basic function of the biological neuronal synapsis can be realized on single inorganic devices, the basic device forming the artificial neural network can be provided, and the effects of integration degree improvement and power consumption reduction can be obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
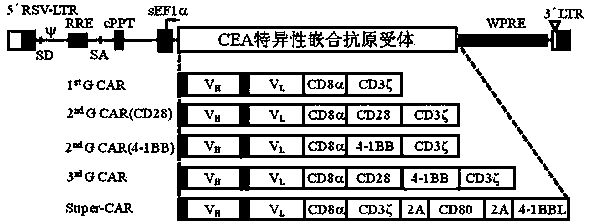
Chimeric antigen receptor, coding gene, expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN104177499AStrong specificityEnhance killing activityDigestive systemAntiviralsAntigenAntigen receptors
The invention discloses a chimeric antigen receptor, a coding gene, an expression vector and application thereof. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises a single chain variable fragment, a CD8 alpha transmembrane domain, a CD3 zeta intracellular signal domain, a first co-stimulator ligand and a second co-stimulator ligand which are in successive tandem connection, wherein the CD8 alpha transmembrane domain is used for connecting the single chain variable fragment to a cell membrane, 2A short peptide is arranged between and in tandem connection with the CD3 zeta intracellular signal domain and the first co-stimulator ligand, and another 2A short peptide is arranged between and in tandem connection with the first co-stimulator ligand and the second co-stimulator ligand. According to the chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention, the 2A short peptide is used to connect the chimeric antigen receptor with the two co-stimulator ligands, so the two co-stimulator ligands are expressed on the surface of an immune cell at the same time; once the chimeric antigen receptor specifically binds with antigen, the two co-stimulator ligands rapidly migrate to synapses formed by the combination of cells, so activity of immune cells is effectively enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI YAKE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
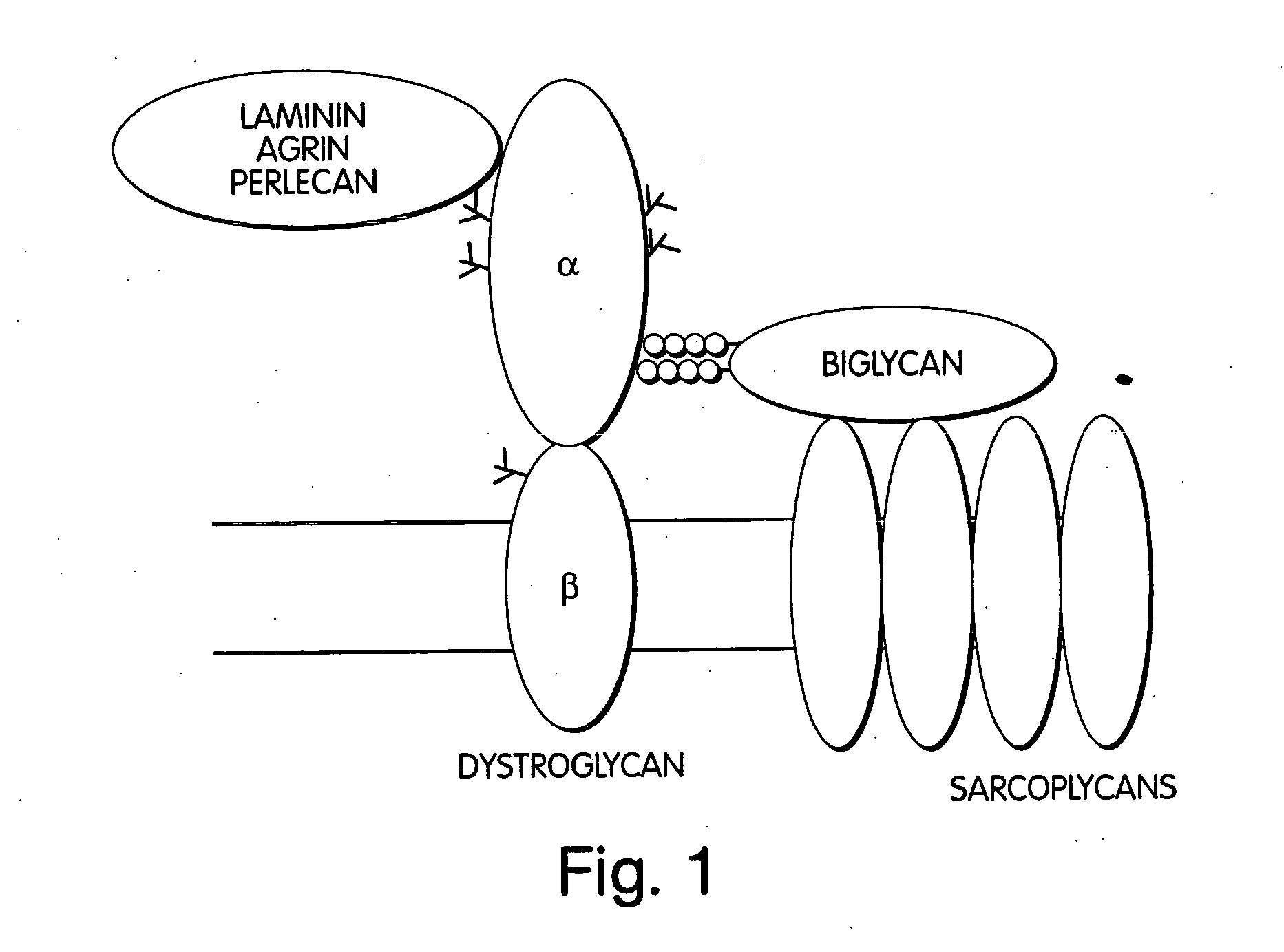
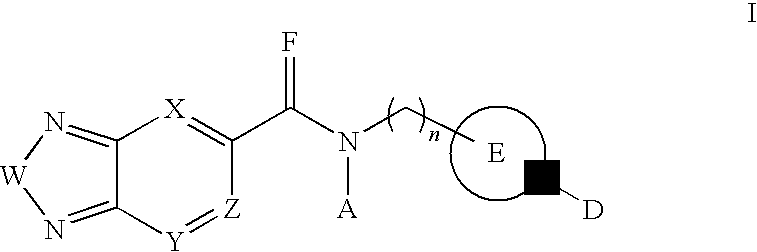
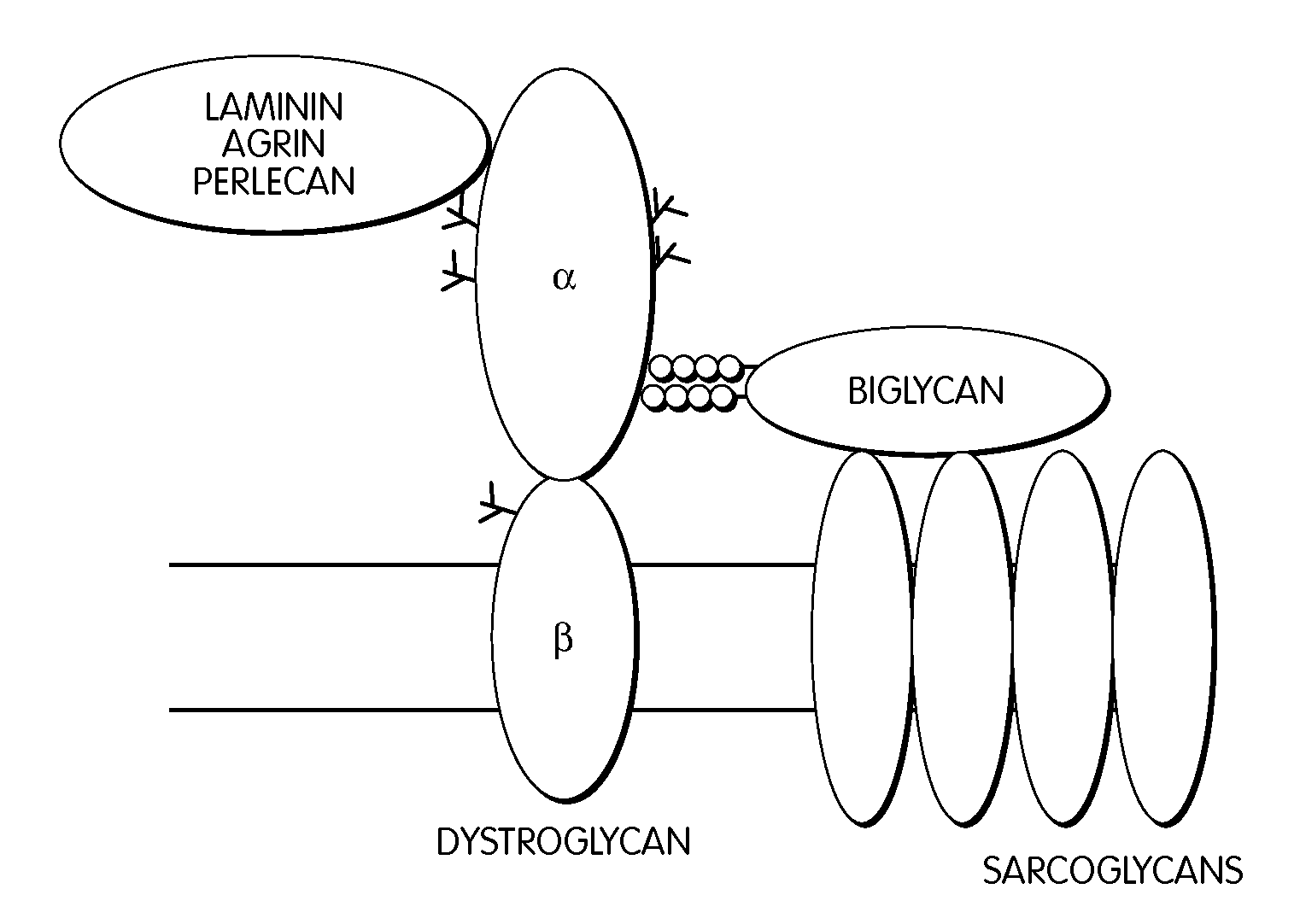
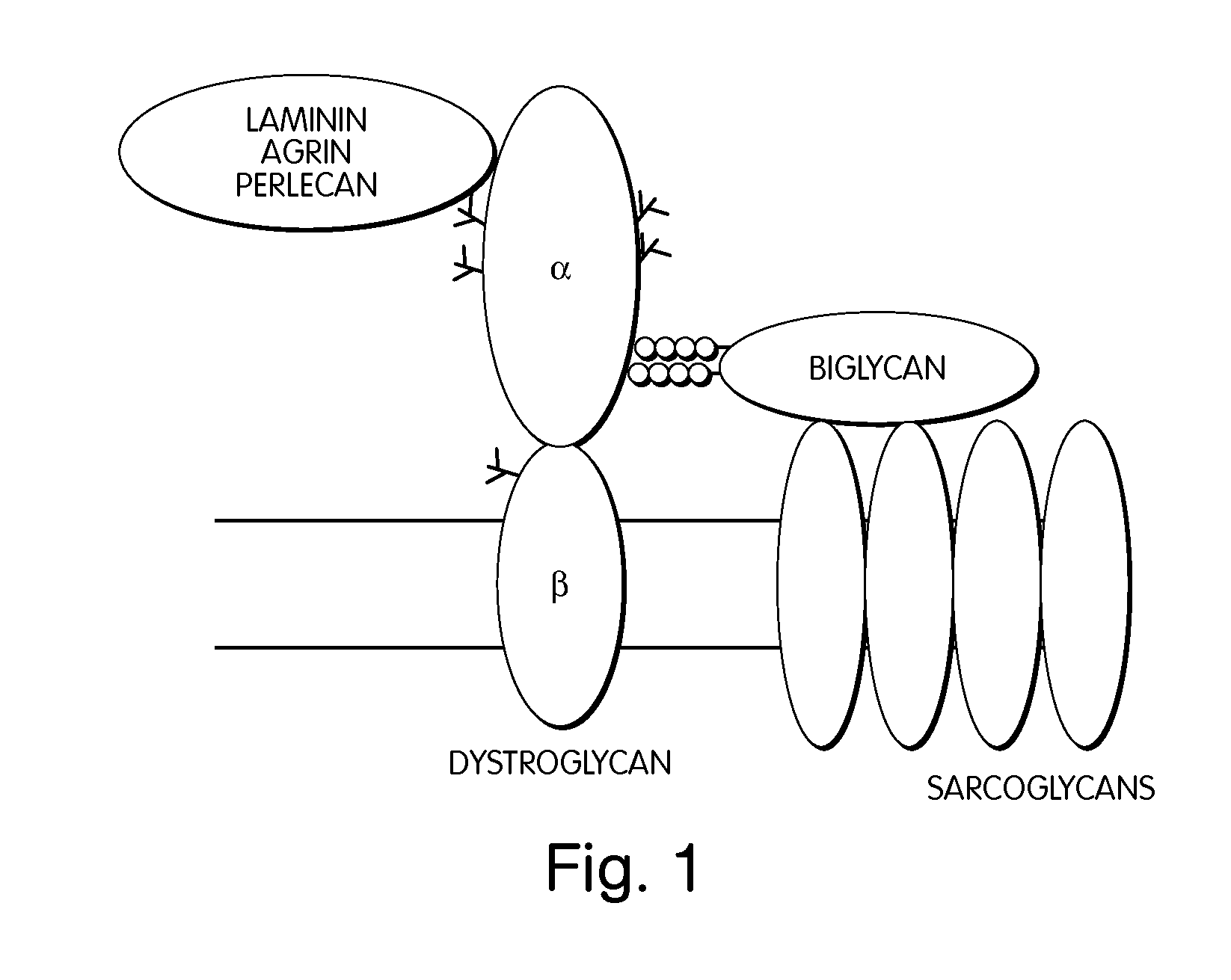
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
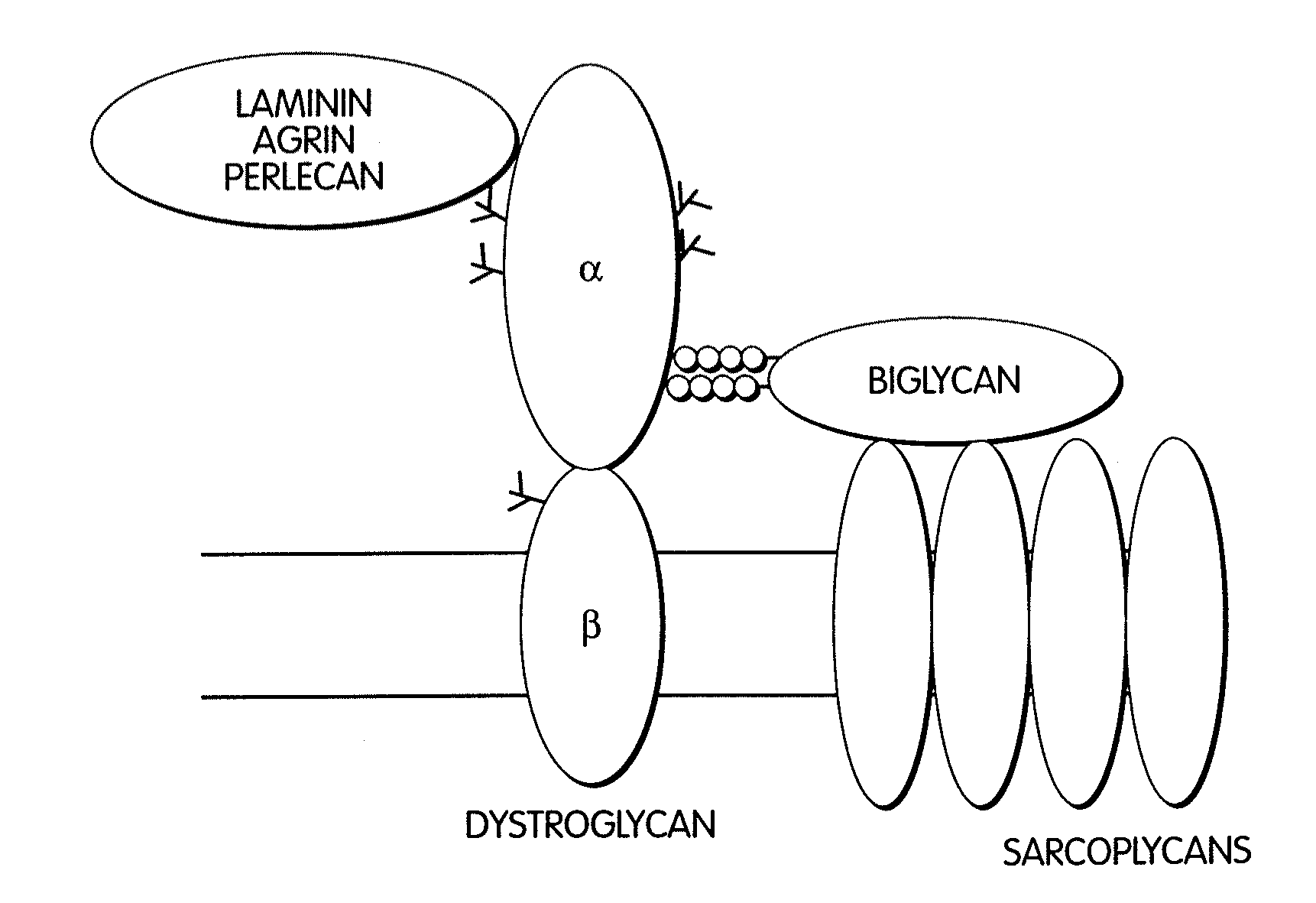
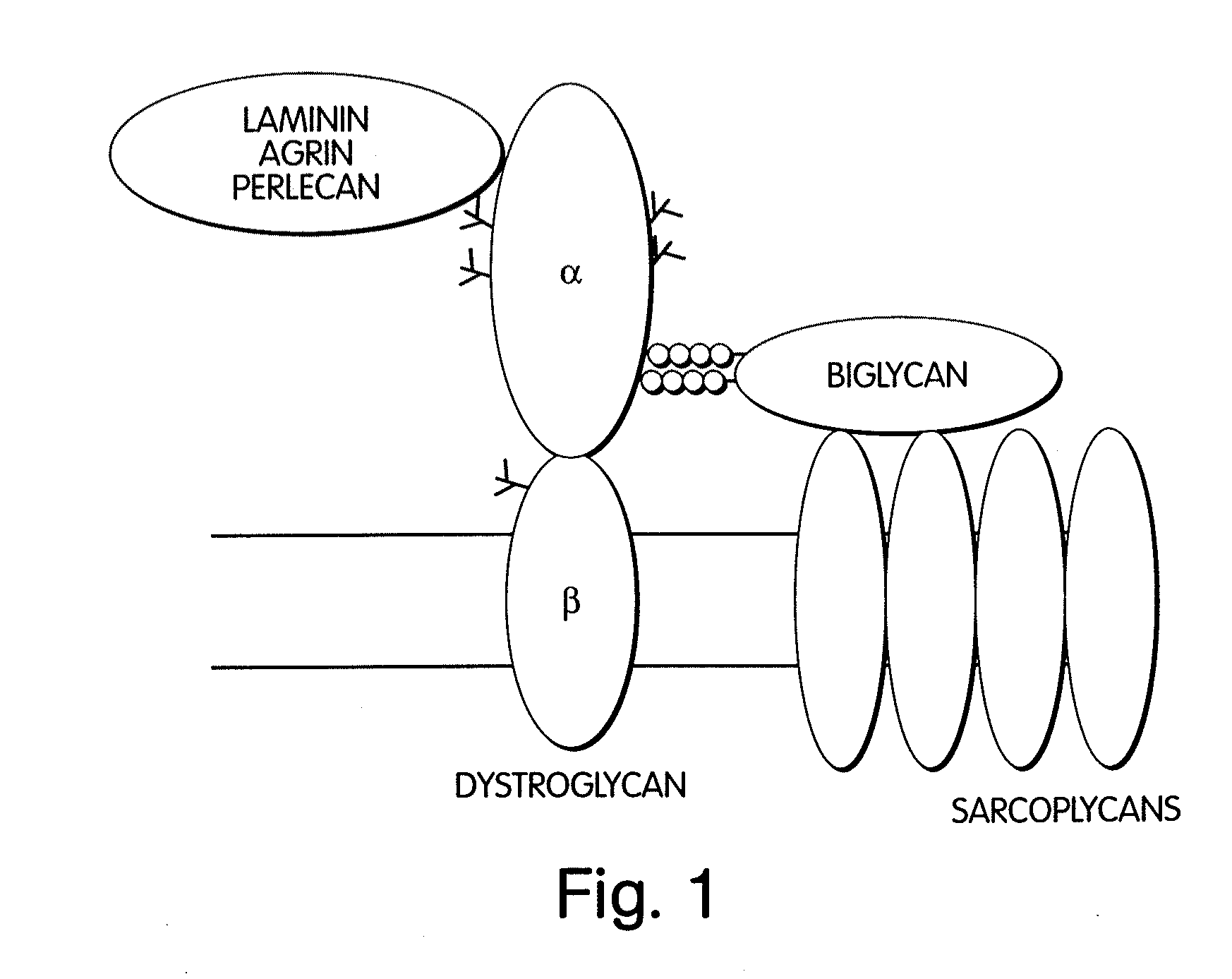
InactiveUS20050059580A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeHormone peptidesSnake antigen ingredientsNervous systemBiglycan
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Examples of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Expandable on-chip back propagation learning neural network with 4-neuron 16-synapse
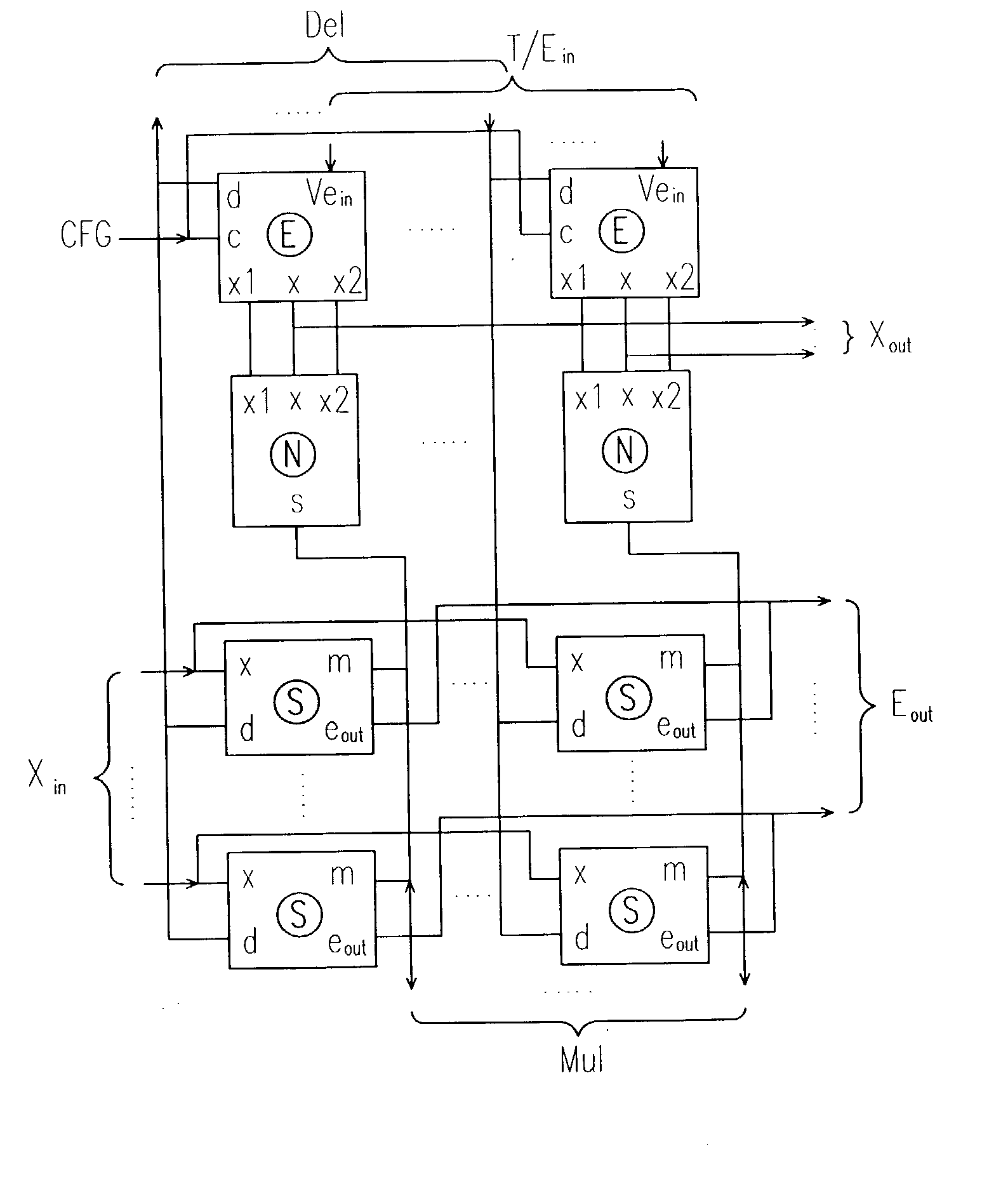
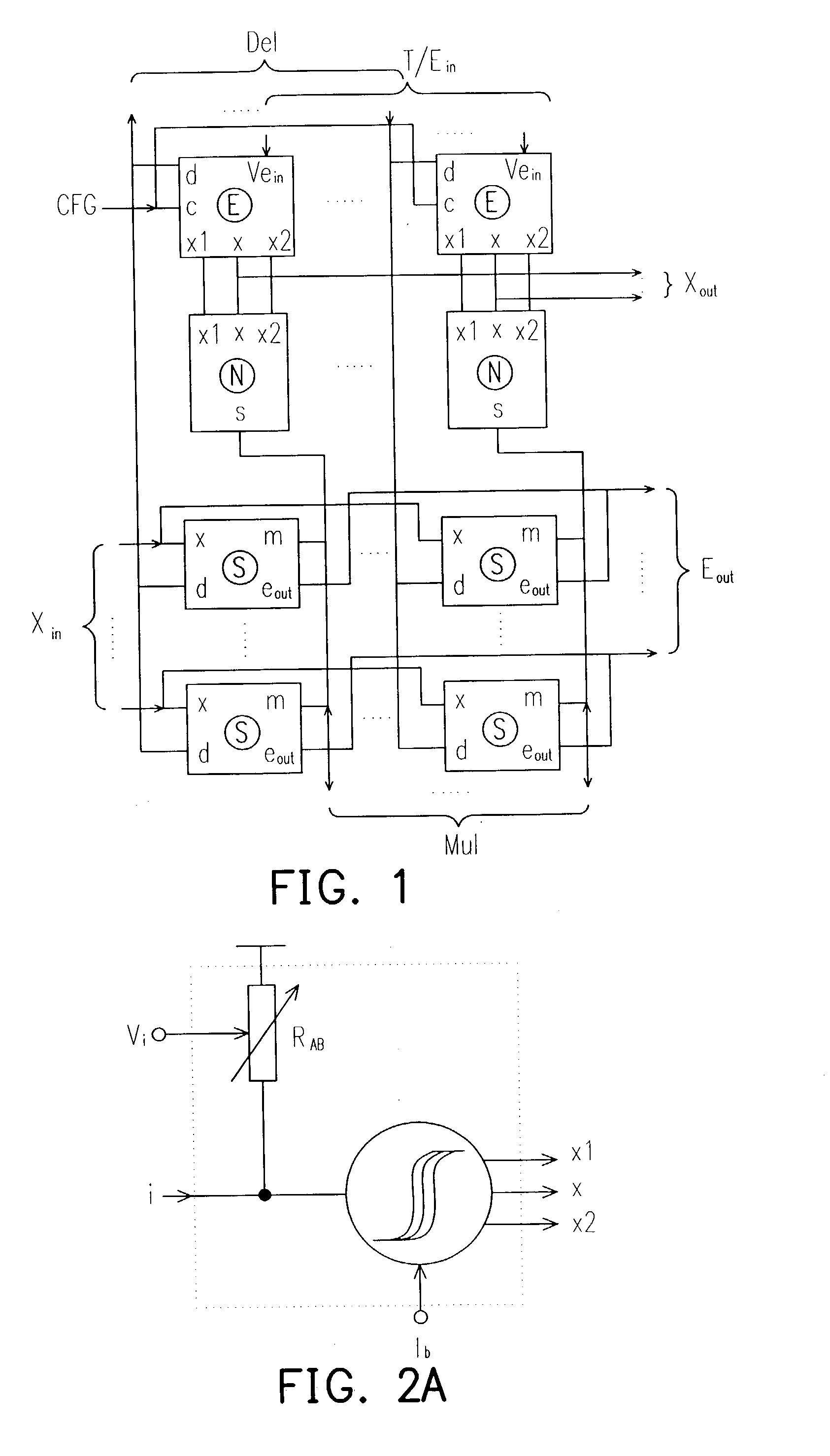
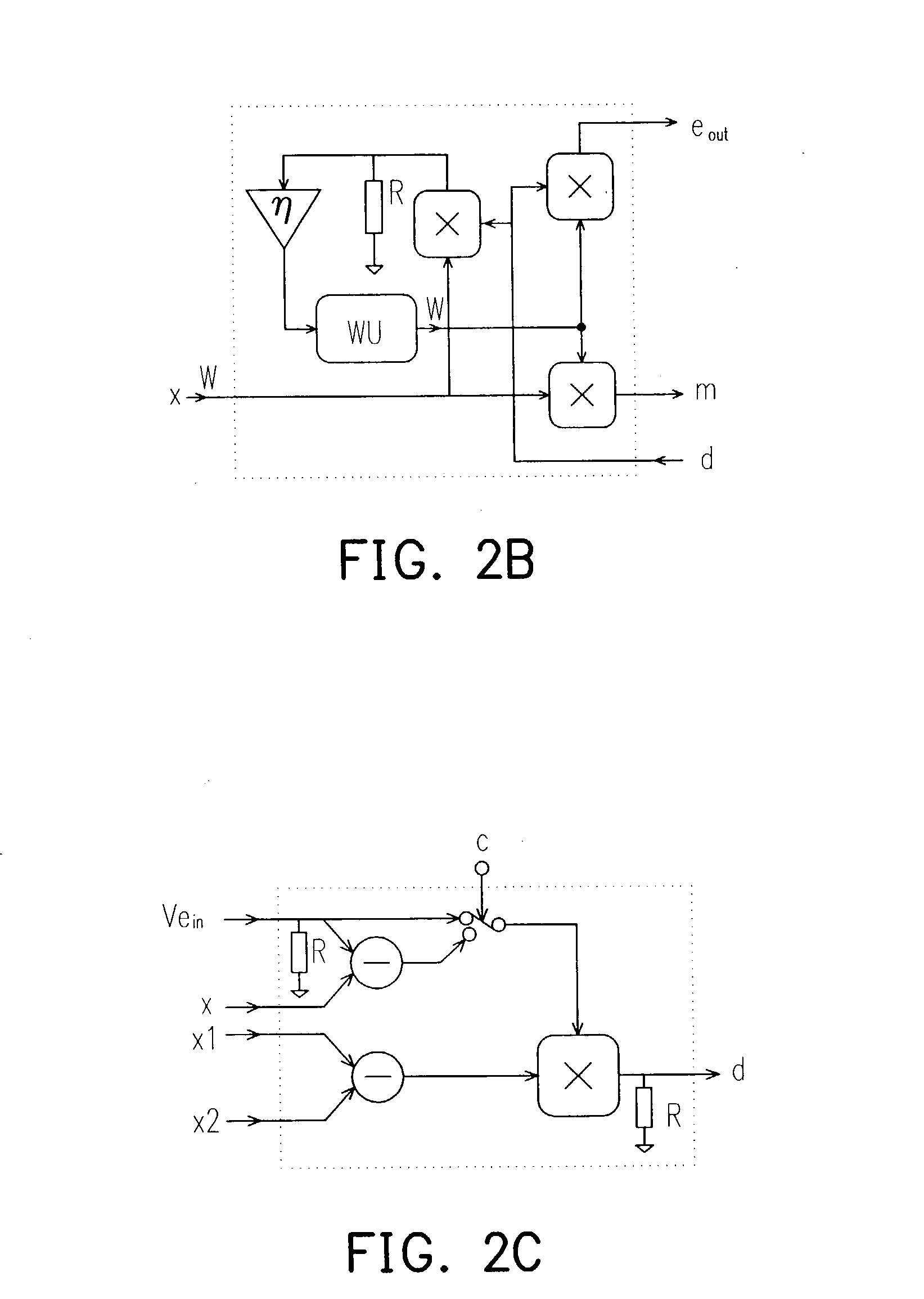
InactiveUS20040083193A1Realize functionImprove performanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkControl signal
A expandable neural network with on-chip back propagation learning is provided in the present invention. The expandable neural network comprises at least one neuron array containing a plurality of neurons, at least one synapse array containing a plurality of synapses, and an error generator array containing a plurality of error generator. An improved Gilbert multiplier is provided in each synapse where the output is a single-ended current. The synapse array receives a voltage input and generates a summed current output and a summed neuron error. The summed current output is sent to the input of the neuron array where the input current is transformed into a plurality of voltage output. These voltage output are sent to the error generator array for generating a weight error according to a control signal and a port signal.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS7923015B2Easy to transportEasy to operateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCell biologyTetanus Toxins
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Di-substituted amides for enhancing glutamatergic synaptic responses
InactiveUS20100120764A1Stable baselineIncrease amplitudeBiocideNervous disorderSIDS - Sudden infant death syndromeCentral sleep apnea
This invention relates to compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods for use in the prevention and treatment of cerebral insufficiency, including enhancement of receptor functioning in synapses in brain networks responsible for basic and higher order behaviors. These brain networks, which are involved in regulation of breathing, and cognitive abilities related to memory impairment, such as is observed in a variety of dementias, in imbalances in neuronal activity between different brain regions, as is suggested in disorders such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, respiratory depression, sleep apneas, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and affective or mood disorders, and in disorders wherein a deficiency in neurotrophic factors is implicated, as well as in disorders of respiration such as overdose of an alcohol, an opiate, an opioid, a barbiturate, an anesthetic, or a nerve toxin, or where the respiratory depression results form a medical condition such as central sleep apnea, stroke-induced central sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea, congenital hypoventilation syndrome, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, sudden infant death syndrome, Rett syndrome, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury, Cheney-Stokes respiration, Ondines curse, Prader-Willi's syndrome and drowning. In a particular aspect, the invention relates to compounds useful for treatment of such conditions, and methods of using these compounds for such treatment.
Owner:CORTEX PHARMA
Treatment of muscular dystrophies and related disorders
InactiveUS20110053854A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSynapseDisease
The invention provides, among other aspects, compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of collagen VI; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); and disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
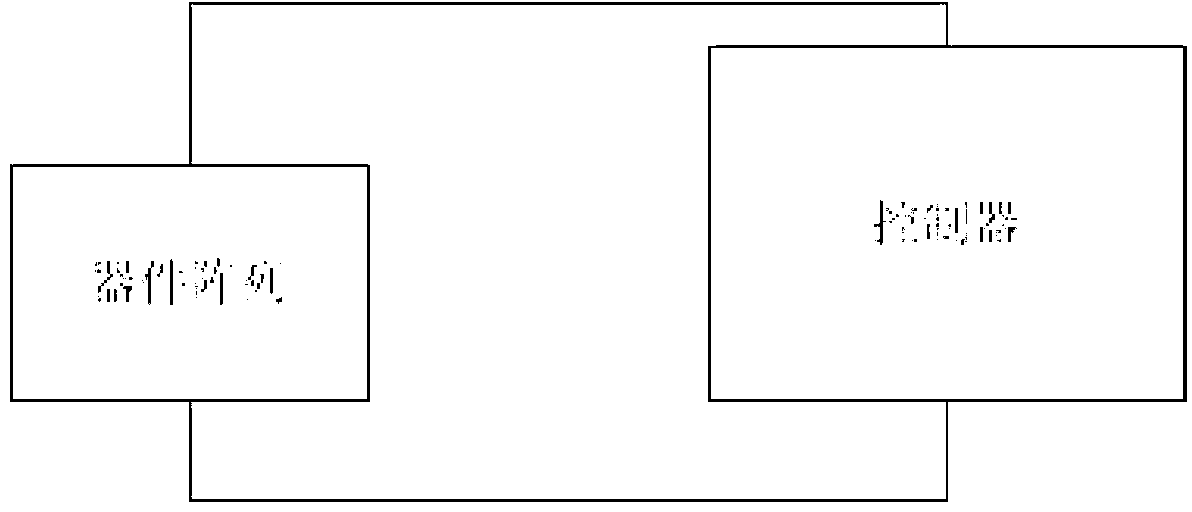
Neuromorphic synapses
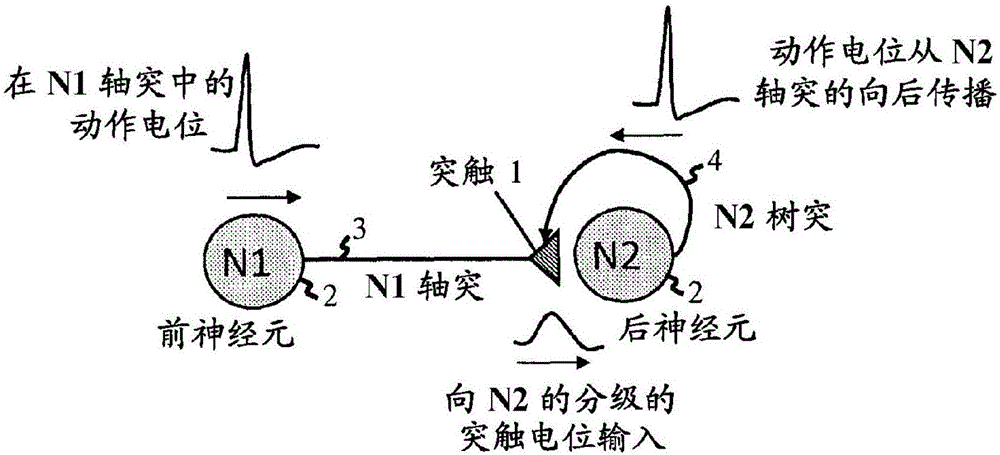
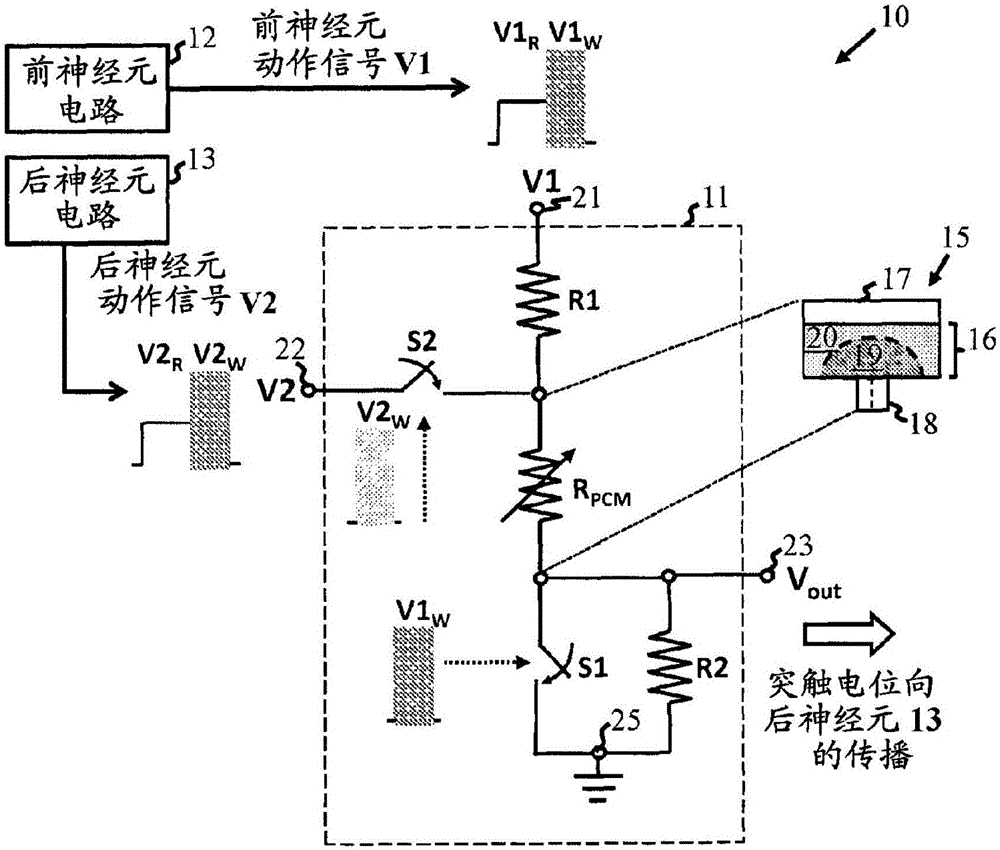
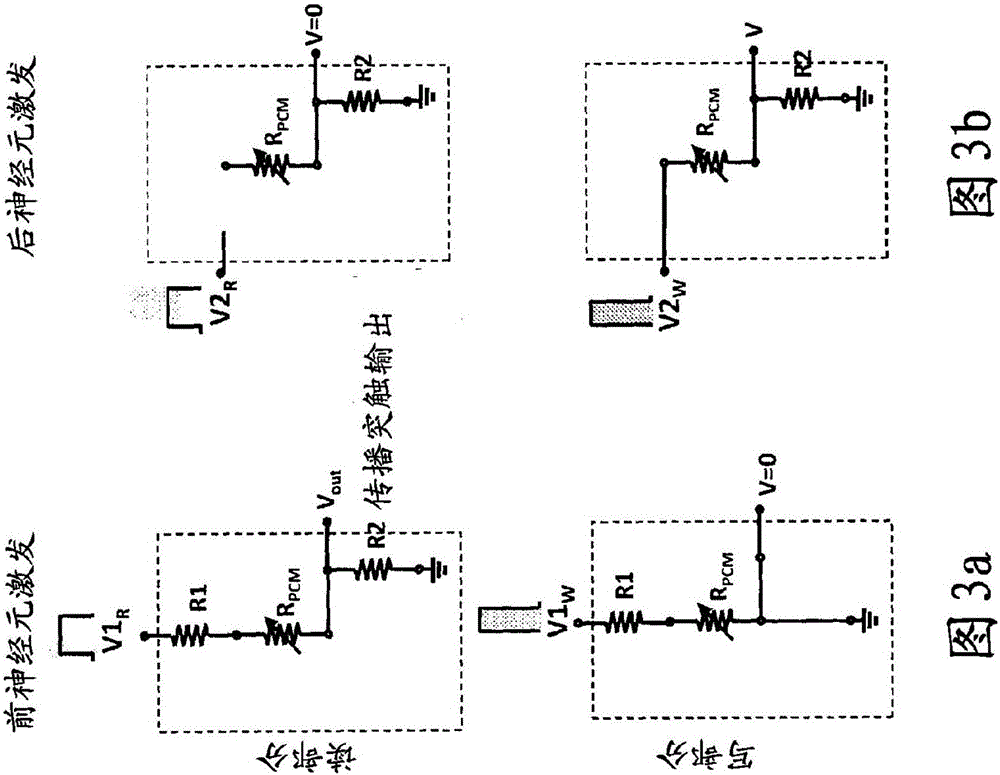
A neuromorphic synapse (11) comprises a resistive memory cell (15) connected in circuitry having first and second input terminals (21,22).These input terminals (21,22) respectively receive pre-neuron and post-neuron action signals, each having a read portion and a write portion, in use. The circuitry also has an output terminal (23) for providing a synaptic output signal which is dependent on resistance of the memory cell (15).The circuitry is operable such that the synaptic output signal is provided at the output terminal (23) in response to application at the first input terminal (21) of the read portion of the pre-neuron action signal,and such that a programming signal,for programming resistance of the memory cell (15), is applied to the cell (15) in response to simultaneous application of the write portions of the pre-neuron and post-neuron action signals at the first and second input terminals (21,22) respectively. The synapse (11) can be adapted for operation with identical pre-neuron and post-neuron action signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
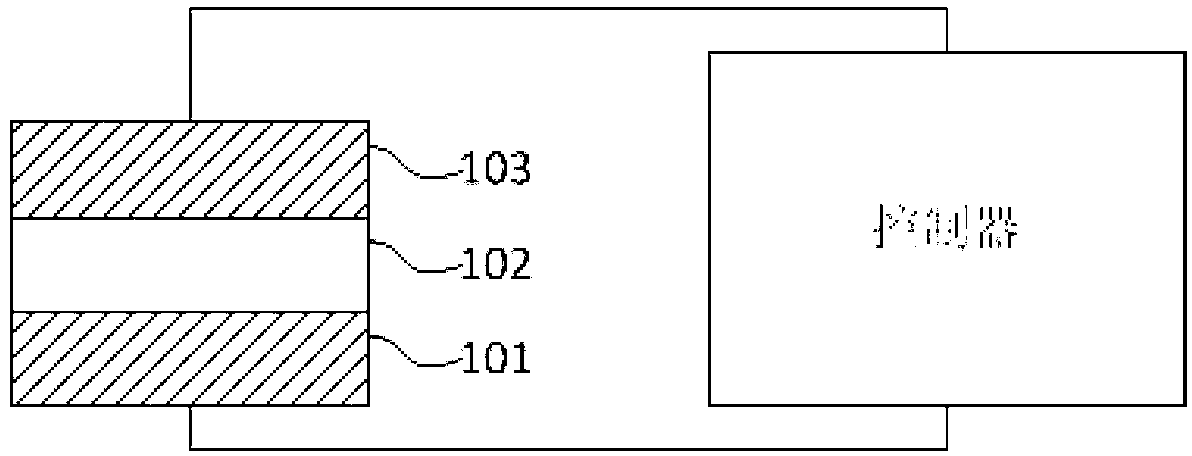
Inorganic-organic/inorganic hybrid dual-layer nano-film memristor for simulating nerve synapses, and preparation method of memristor
ActiveCN109904316AGood simulation of synapse bionic functionIncrease choiceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSynapseAtomic layer deposition
The invention discloses an inorganic-organic / inorganic hybrid dual-layer nano-film memristor for simulating nerve synapses, and belongs to the cross field of semiconductor microelectronic devices andartificial intelligence. A molecular layer deposition technology and an atomic layer deposition technology are utilized to prepare the inorganic-organic / inorganic hybrid dual-layer nano-film memristorwith a good nerve synapse simulation bionic function; and the adopted molecular layer deposition and atomic layer deposition technologies can be compatible with a microelectronic process and are suitable for large-scale integration. The memristor comprises a substrate, a bottom electrode, a memristor functional layer and a top electrode in sequence from bottom to top, wherein the memristor functional layer consists of two layers of nano-stack structure film materials including a lower-layer inorganic-organic hybrid film and an upper-layer metal oxide film.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
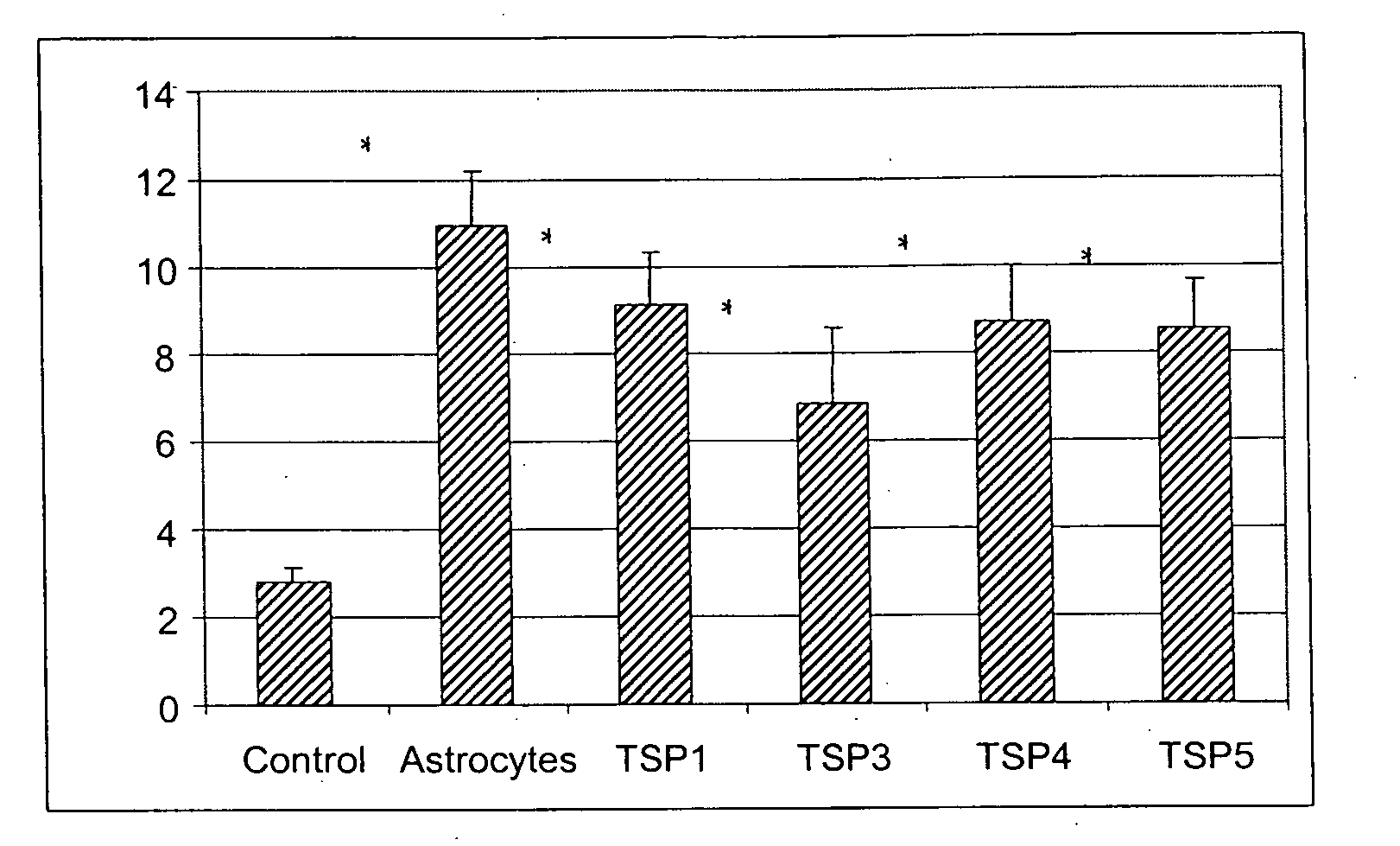
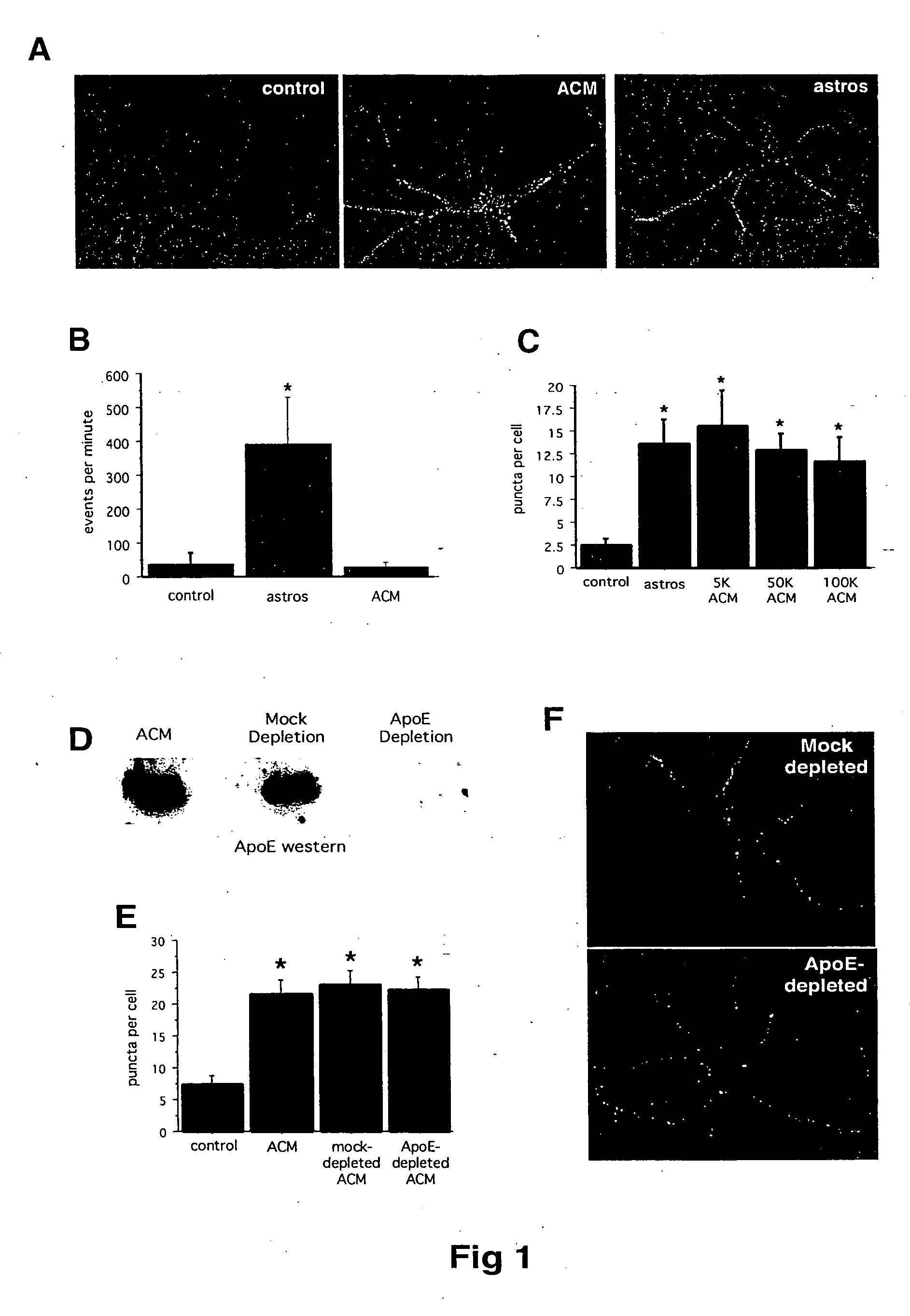
Modulation of synaptogenesis
InactiveUS20060019880A1Synaptogenesis is enhancedNervous disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsSynaptogenesisEmbryonic brain
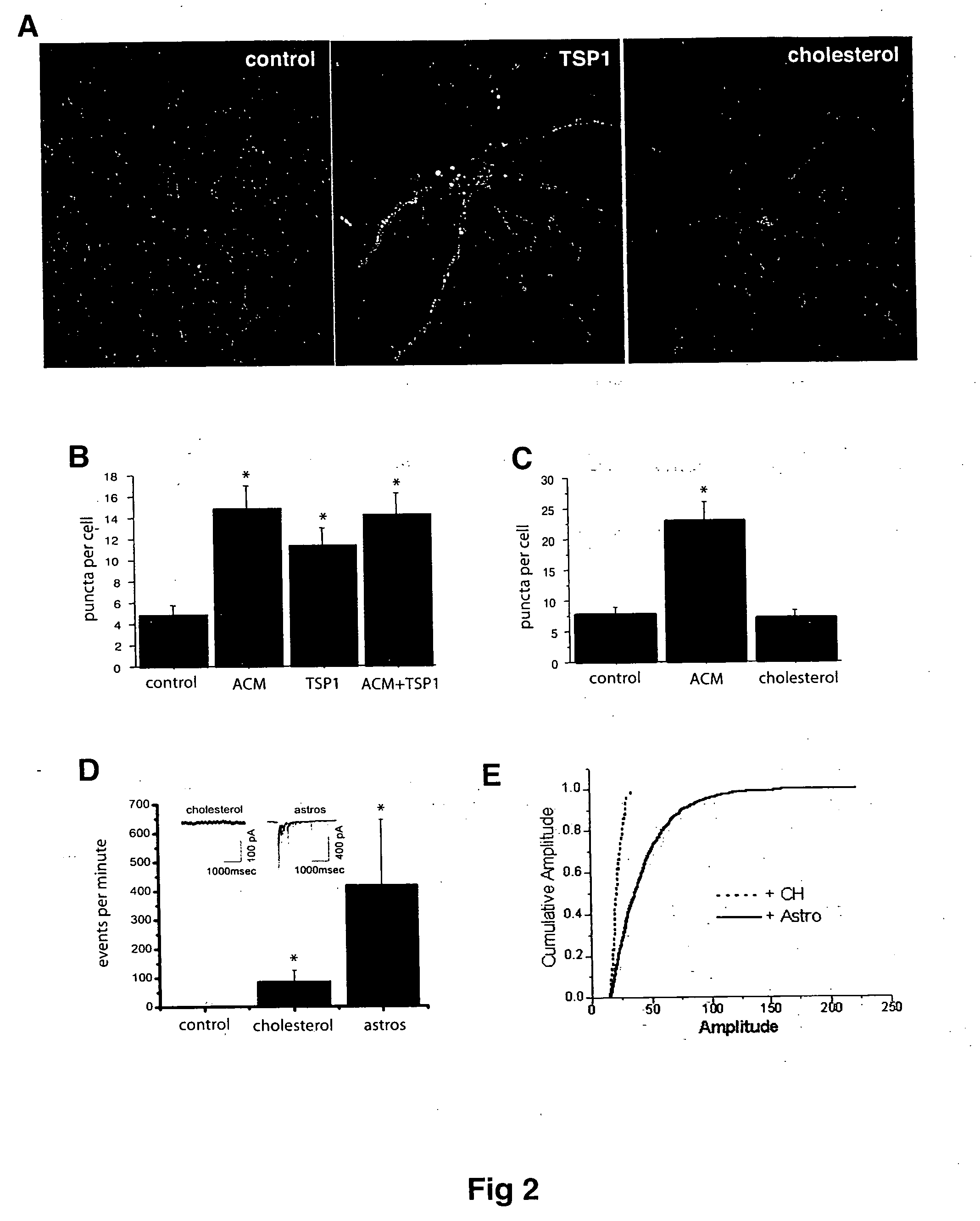
Soluble proteins, e.g. thrombospondins, can trigger synapse formation. Such proteins are synthesized in vitro and in vivo by astrocytes, which therefore have a role in synaptogenesis. These thrombospondins are only expressed in the normal brain exactly during the period of developmental synaptogenesis, being off in embryonic brain and adult brain but on at high levels in postnatal brain. Methods are provided for protecting or treating an individual suffering from adverse effects of deficits in synaptogenesis, or from undesirably active synaptogenesis. These findings have broad implications for a variety of clinical conditions, including traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, and other conditions where synapses fail to form or form inappropriately. Synaptogenesis is enhanced by contacting neurons with agents that are specific agonists or antagonists of thrombospondins. Conversely, synaptogenesis is inhibited by contacting neurons with inhibitors or antagonists of thrombospondins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
InactiveUS20100130405A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeCompound screeningNervous disorderBiglycanBecker's muscular dystrophy
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Example of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS20050060761A1Easy to transportEasy to operateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologic markerFragment C tetanus toxin
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
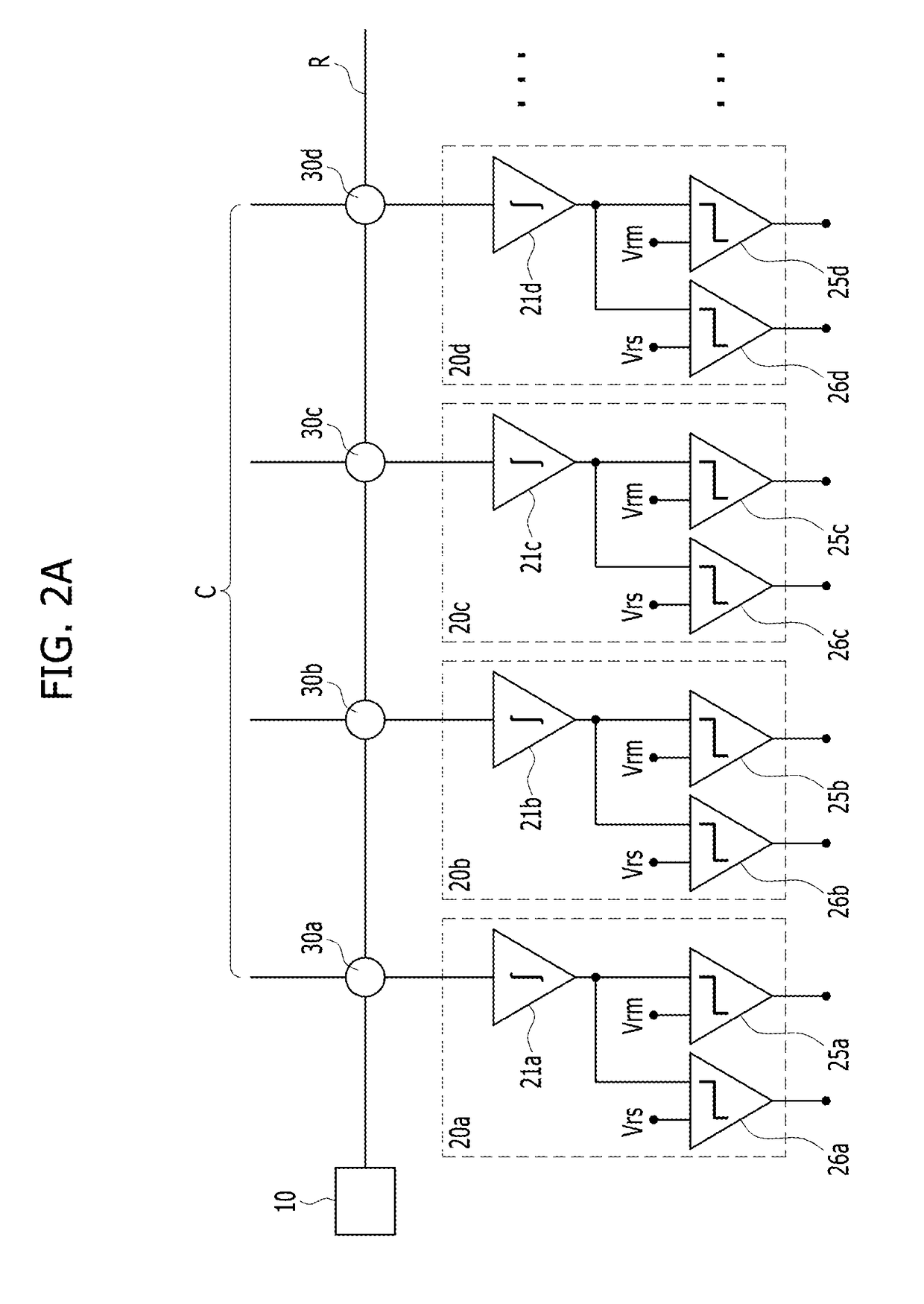
Neuromorphic device including post-synaptic neurons having a comparator for deciding quasi-learned synapses
ActiveUS20170193353A1High voltage levelNeural architecturesPhysical realisationIntegratorEngineering
A neuromorphic device may include: a pre-synaptic neuron; a plurality of post-synaptic neurons; and a plurality of synapses electrically connected to the pre-synaptic neuron and electrically connected to the plurality of post-synaptic neurons. Each of the post-synaptic neurons may include: an integrator; a main comparator having a first input port connected to an output port of the integrator; and a first sub comparator having a first input port connected to the output port of the integrator.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Stdp-based learning method for a network having dual accumulator neurons
A method for unsupervised learning of a multilevel hierarchical network of artificial neurons wherein each neuron is interconnected with artificial synapses to neurons of a lower hierarchical level and to neurons of an upper hierarchical level. The method includes at a neuron the steps of integrating inference spikes from the interconnected neurons of the lower hierarchical level both in a first and a second accumulators using the same synaptic weights; when the first accumulator reaches a first threshold, generating a learning spike, resetting the first accumulator, triggering synaptic conductance modification in accordance with a spike-timing dependent plasticity rule and delivering the learning spike as an inhibitory signal to other neurons in the same hierarchical level; when the second accumulator reaches a second threshold, generating an inference spike, delivering the generated inference spike to the interconnected neurons of the upper hierarchical level, resetting the second accumulator and possibly delivering the inference spike as an inhibitory signal to other neurons in the same hierarchical level.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
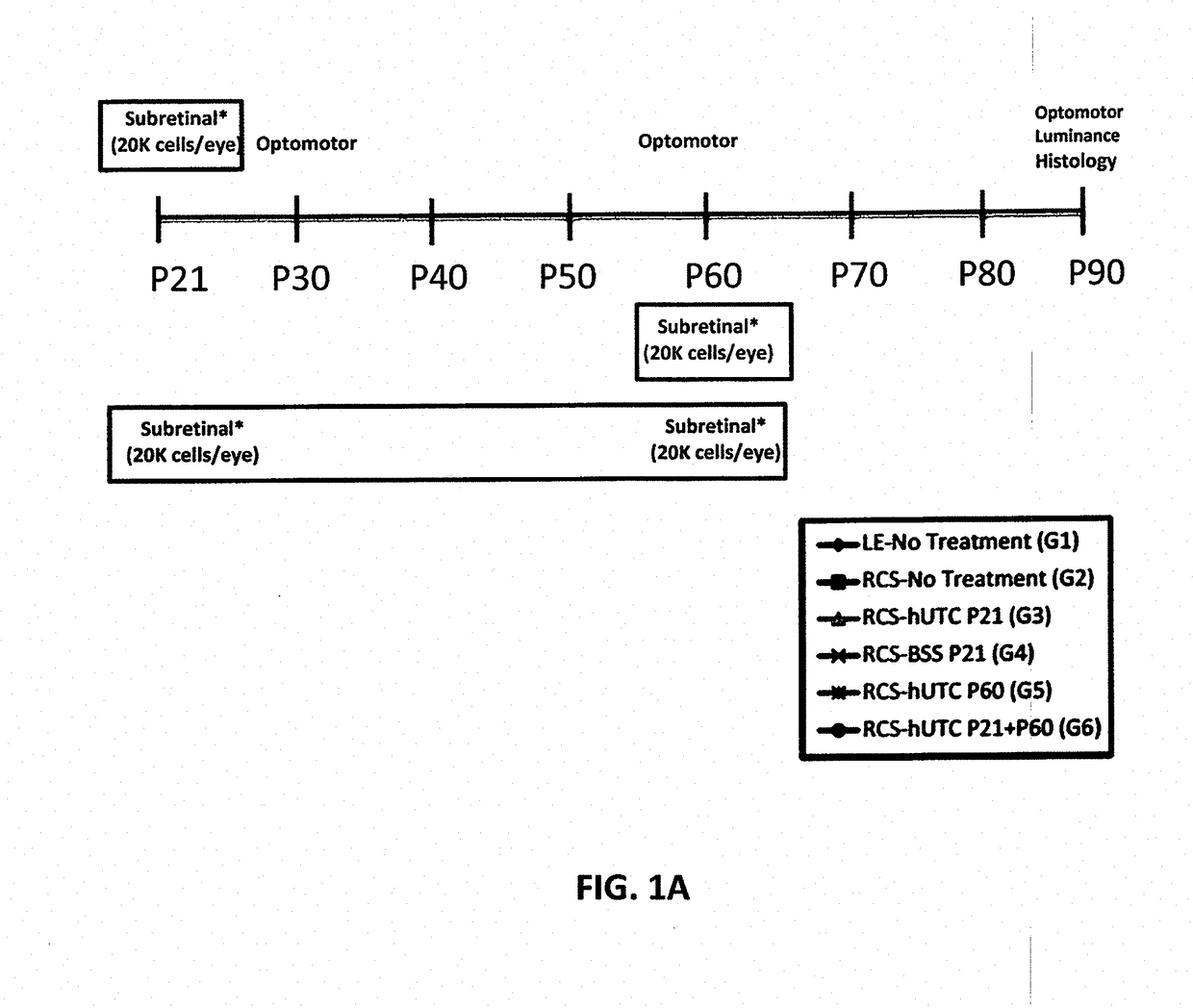
Method of modulating müller glia cells
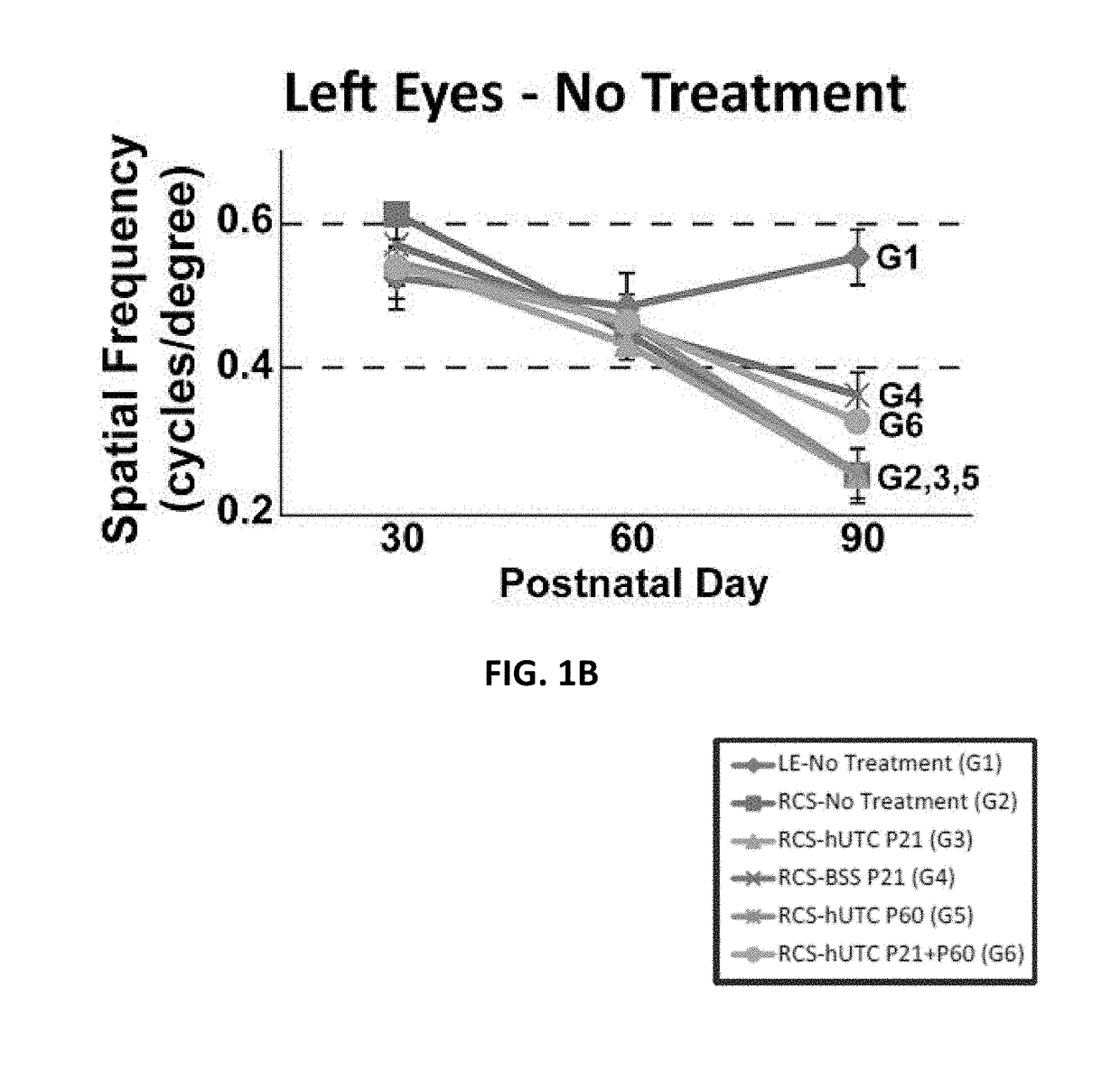
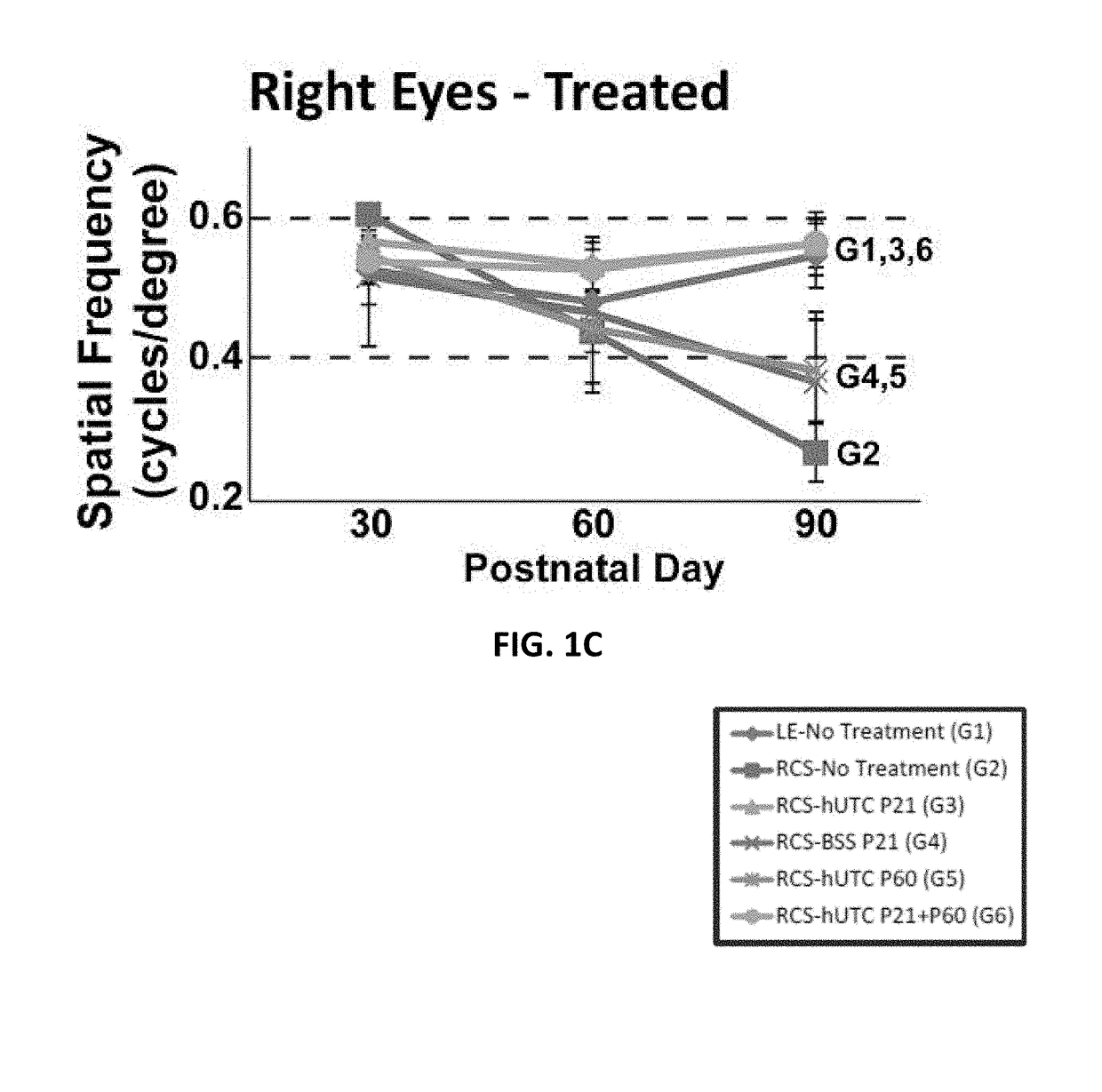
Methods and compositions for treating ophthalmic disease, in particular retinal degeneration, including modulating Müller glia, restoring retinal synaptic connectivity and forming α2δ1-containing synapses, using postpartum-derived cells are disclosed.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Construction method of in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
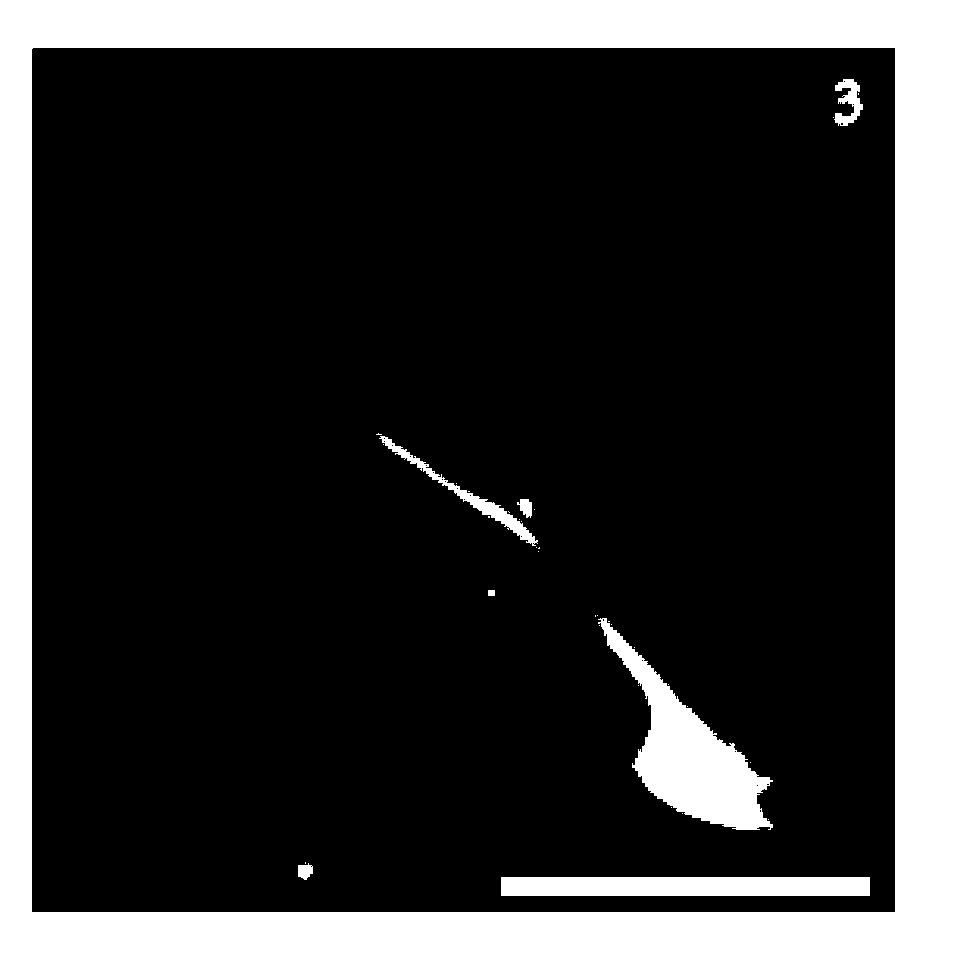
InactiveCN102994450AAvoid interferencePrecise determinantsNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUltrastructureScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses a construction method of an in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting in-vitro neonatal rat cortical neurons; (2) selecting in-vitro rat mesenchymal stem cells; (3) pre-processing the in-vitro rat mesenchymal stem cells, and inoculating in the neonatal rat cortical neurons for co-culture; and (4) after the co-culture, treating the rat mesenchymal stem cells and the neonatal rat cortical neurons by a light microscope, a fluorescence microscope, an atomic force microscope and a scanning electron microscope; and determining an in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation and a growth tendency, an interaction and formation of a synapsis-like structure between the cortical neurons and the mesenchymal stem cells on an ultrastructure. The construction method disclosed by the invention provides a simplified in-vitro model for the mesenchymal stem cell transplantation; meanwhile, the synapsis-like structure formed in the model provides an in-vitro evidence of a structure integration mechanism for the mesenchymal stem cell injury mechanism.
Owner:姜晓丹 +1
Method for inducing neuroblastoma cells to be differentiated to nerve cells
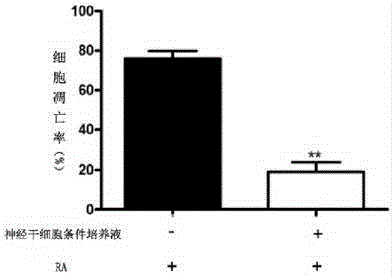
ActiveCN105176929AInhibit apoptosisPromote maturityNervous system cellsNerve cellsNeuroblastoma cell
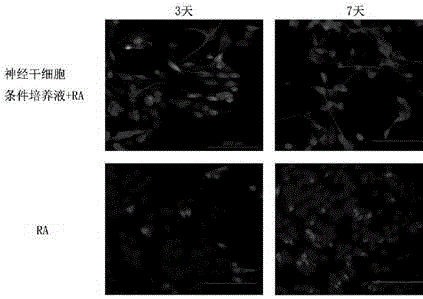
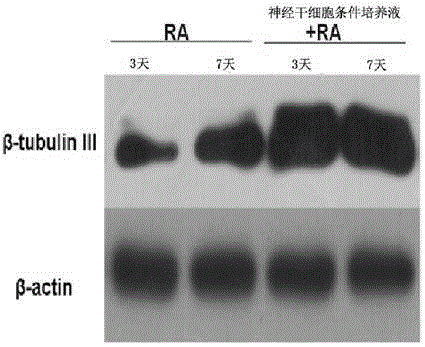
The invention relates to the cell transdifferentiation technology in the field of cell research, in particular to a method for inducing neuroblastoma cells to be differentiated to nerve cells. The neuroblastoma cells are cultured for 3-7 days through an inducing culture medium, and then the nerve cells are obtained; the inducing culture medium is obtained by adding retinoic acid to a neural stem cell condition culture solution to 10 micrometers; a complete culture medium including a DMEM / F12 basic cukture mediam, B27, bFGF, EGF, heparn sodium, L-glutamine and mycillin is used for culturing the neural stem cells, the complete culture medium is replaced by a half after culturing is conducted for three days, and the replaced culture solution is the neural stem cell condition culture solution. By means of the method, the differentiation efficiency is improved, and the maturity of the cells and growth of neural synapses of nerve cells are also improved. The cell apoptosis in SH-SY5Y treated through RA can be inhibited.
Owner:SHANDONG QILU STEM CELL ENG
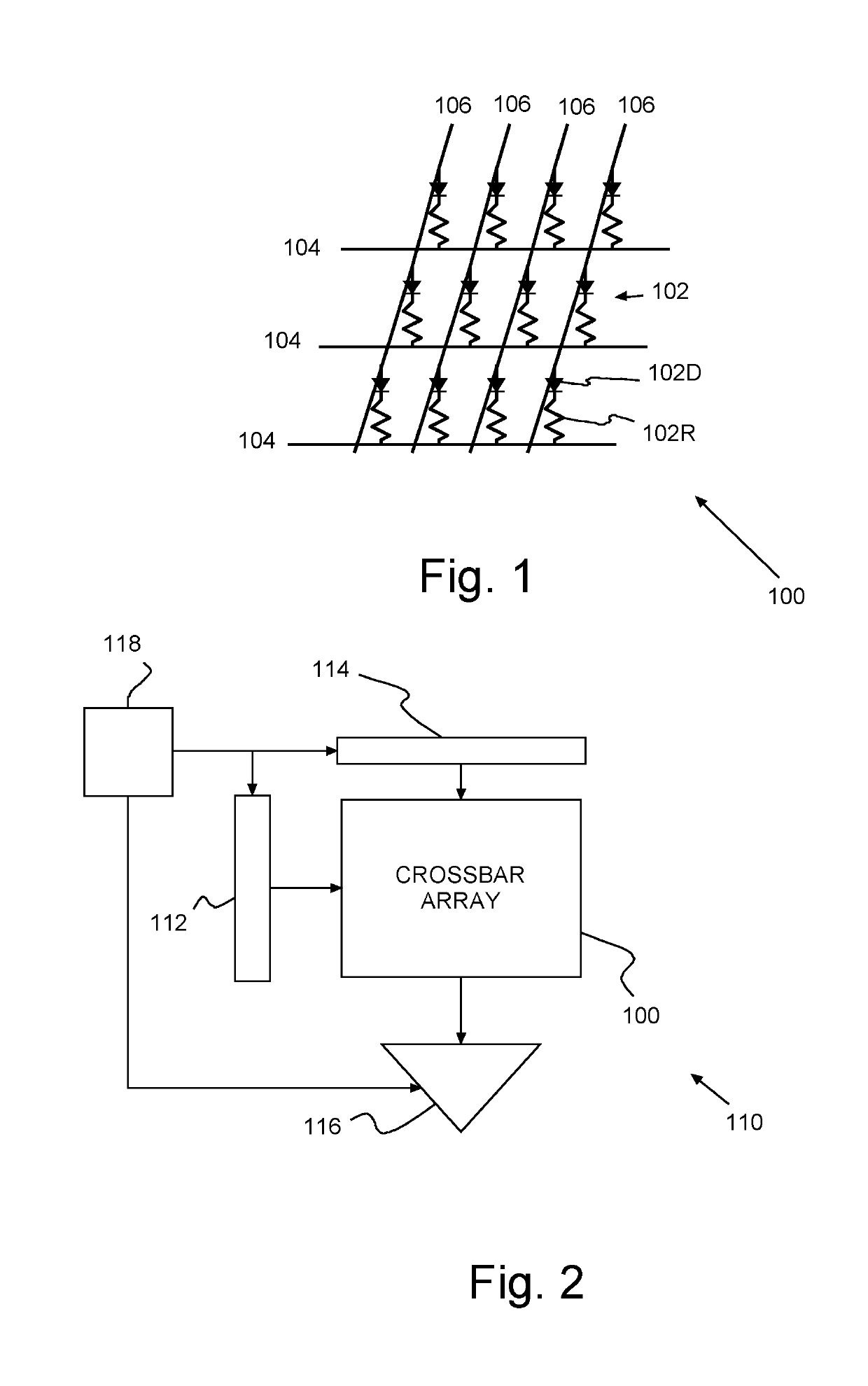
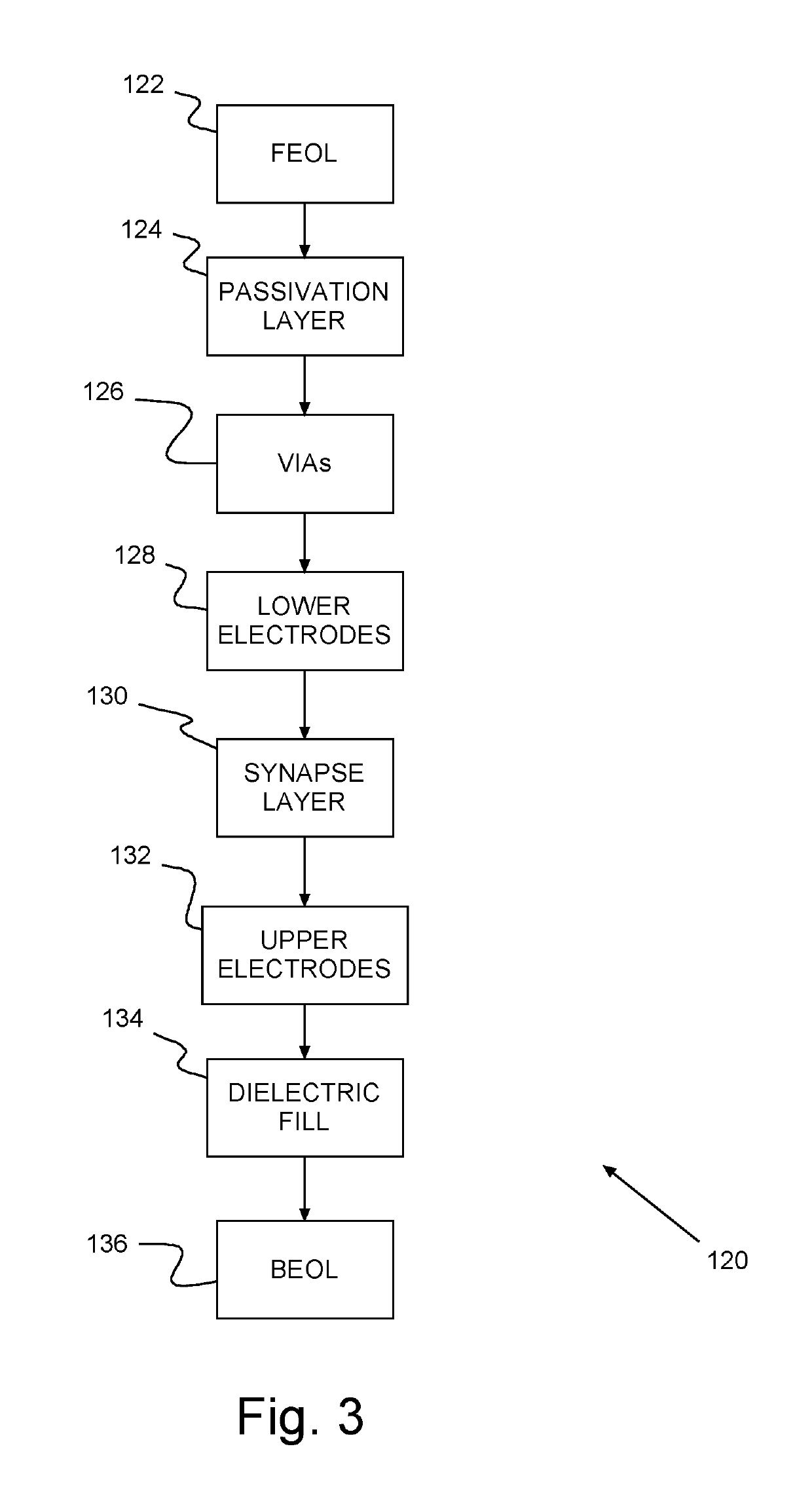
Synaptic crossbar memory array
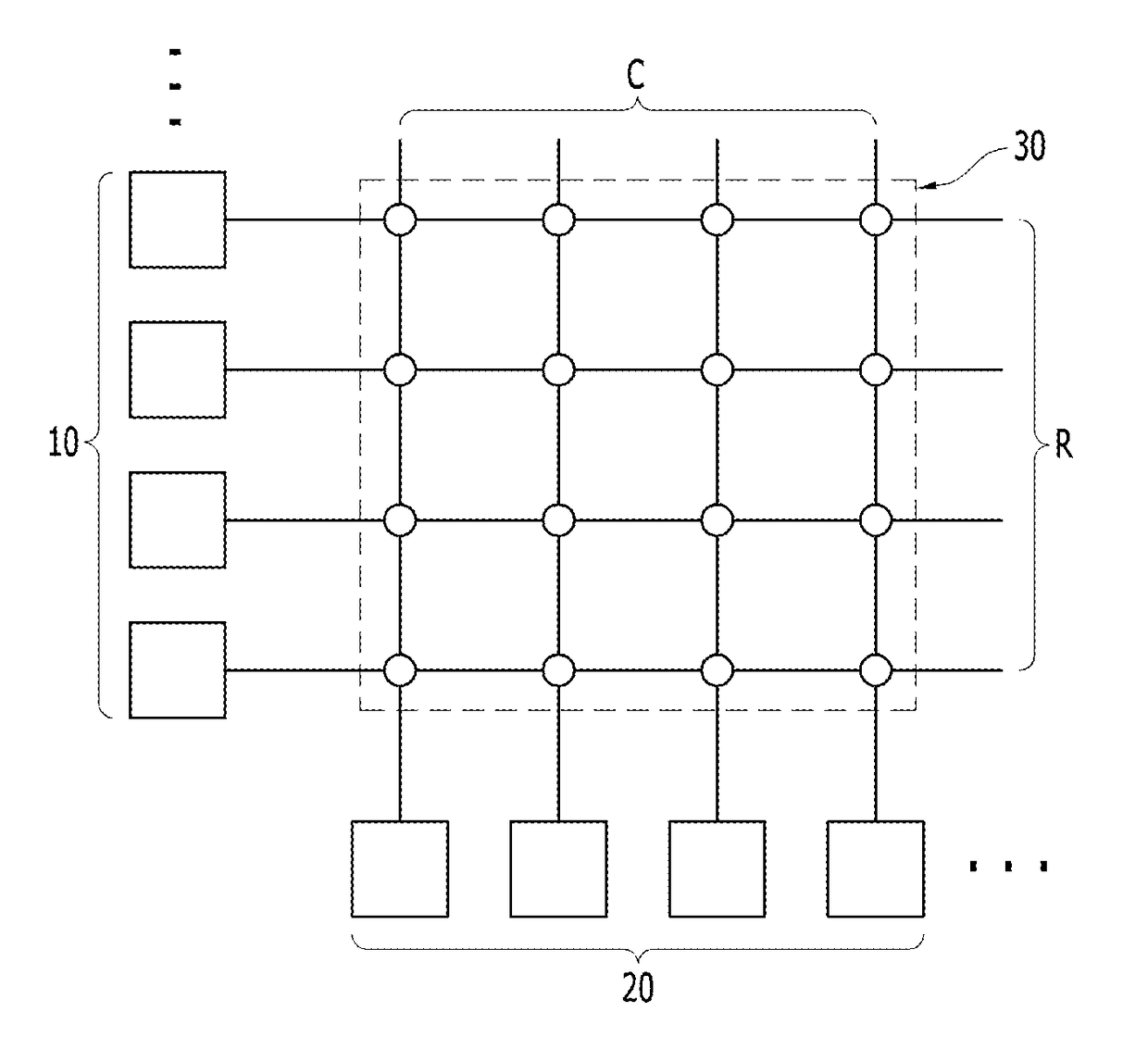
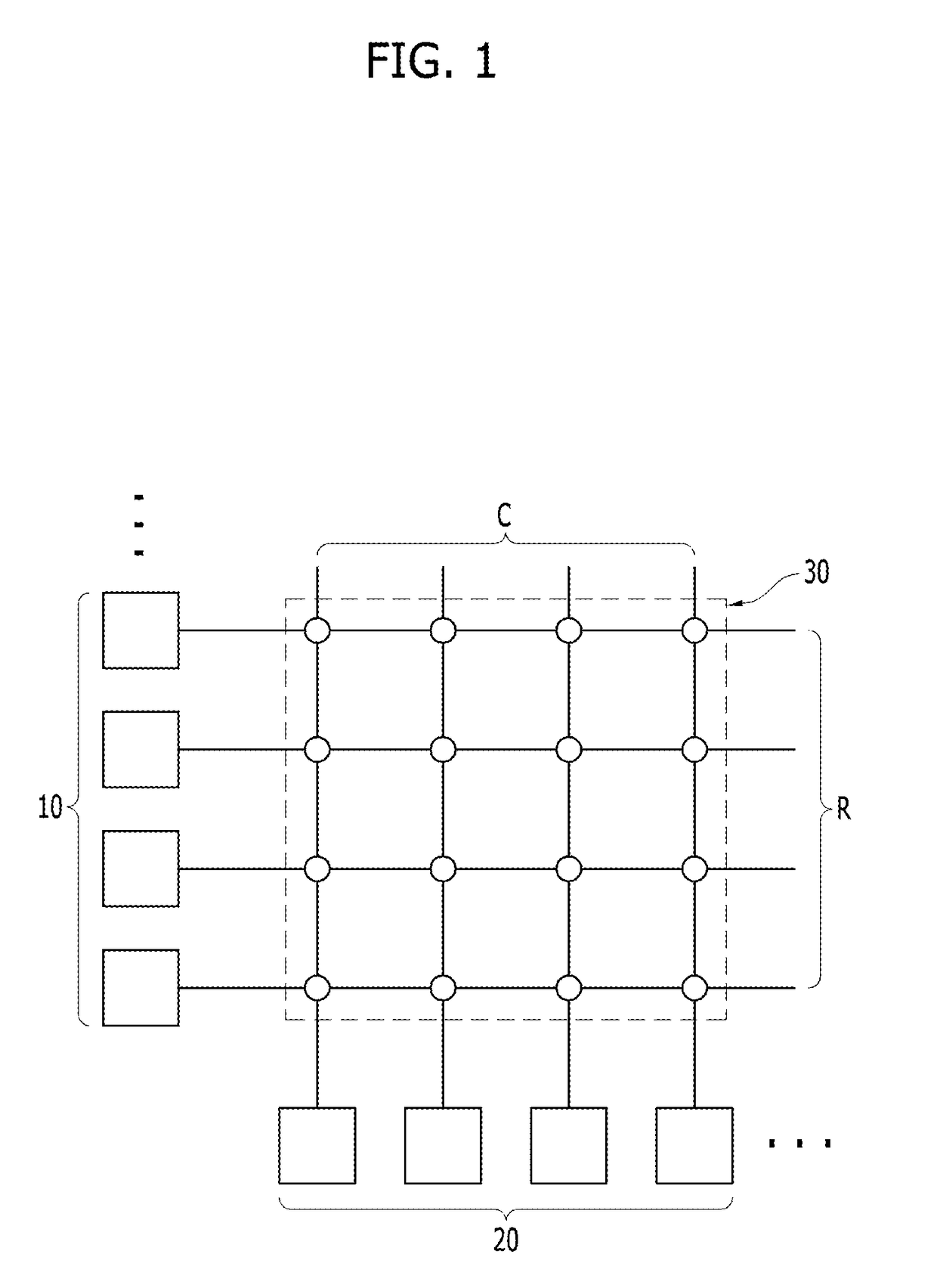
ActiveUS20190164597A1Wide rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSynapse structure
A method of forming an Integrated Circuit (IC) chip, the IC chip and an on-chip synaptic crossbar memory array. Chip devices are formed on a surface of a semiconductor wafer. A connective layer is formed above the chip devices. A bottom electrode layer is formed on the connective layer. A neuromorphic synapse layer is formed above the bottom electrode layer with each synapse on a bottom electrode. Upper electrodes are formed above the synapses and orthogonal to bottom electrode lines. Each synapse being beneath an upper electrode where the upper electrode crosses a bottom electrode. Upper electrodes are refractory metal and the bottom electrodes are copper, or vice versa.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-color in-situ hybridization method for rapidly analyzing and detecting triticeae plant chromosome configuration
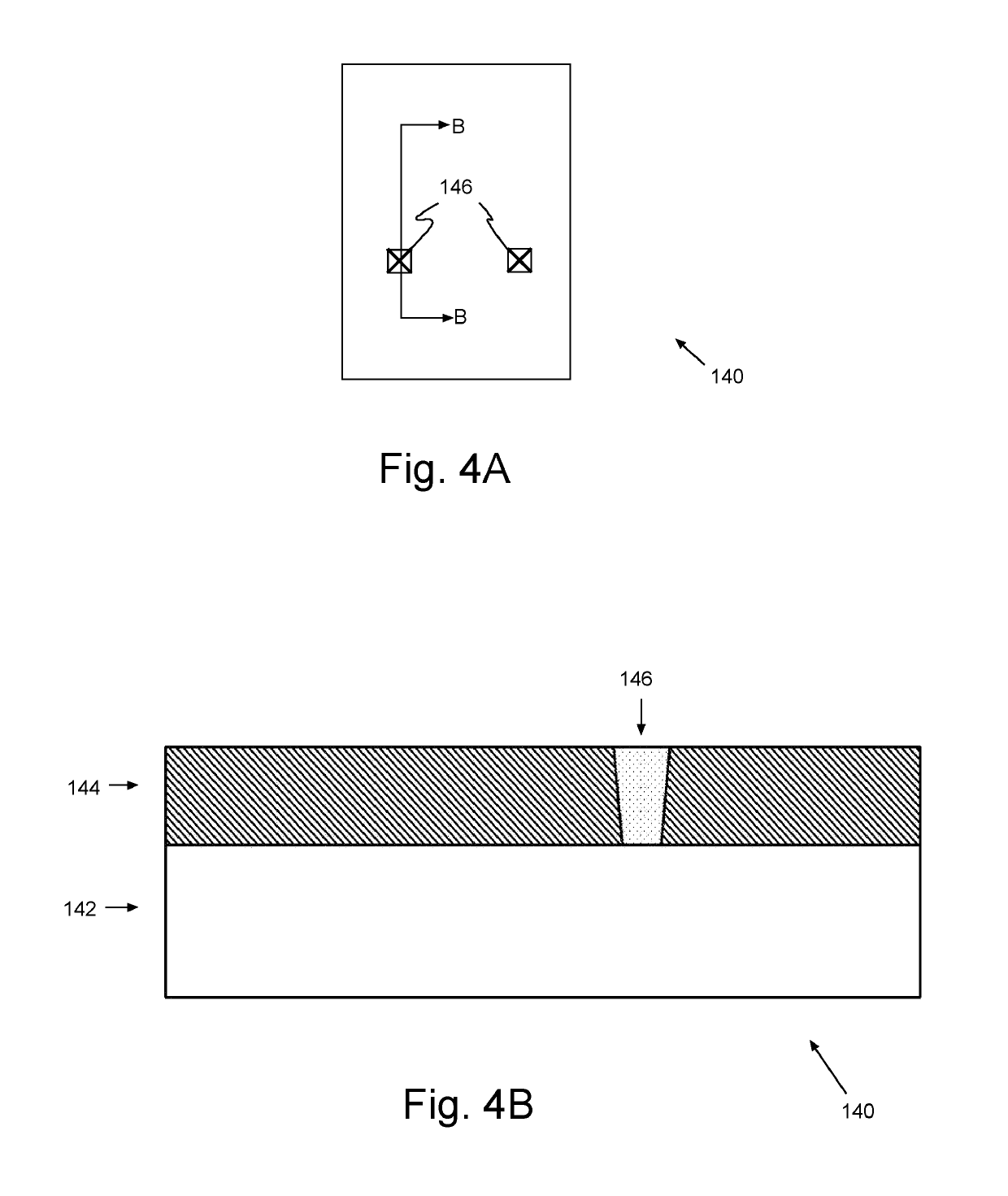
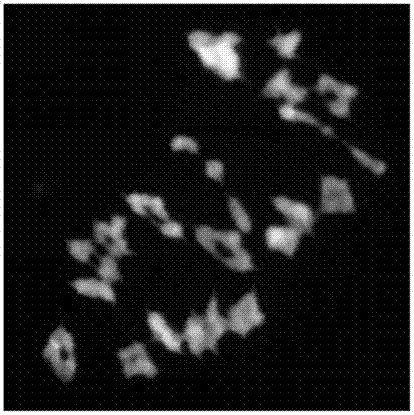
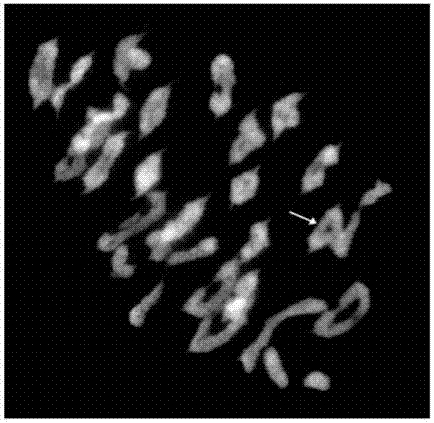
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and especially relates to a multicolor in-situ hybridization method for rapidly analyzing and detecting triticeae plant chromosome configuration. The method is characterized in that mc-GISH is used for analysis of a chromosome pairing behavior during a pollen blast cell meiosis process, one-time hybridization can effectively identify the chromosome pairing condition during a meiosis process of triticeae at different genomes, and the method provides a powerful tool for analyzing a genetic relationship between the different genomes of triticeae, and especially for identifying the synapsis and pairing behaviors between different genomes of artificial created polyploid species.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
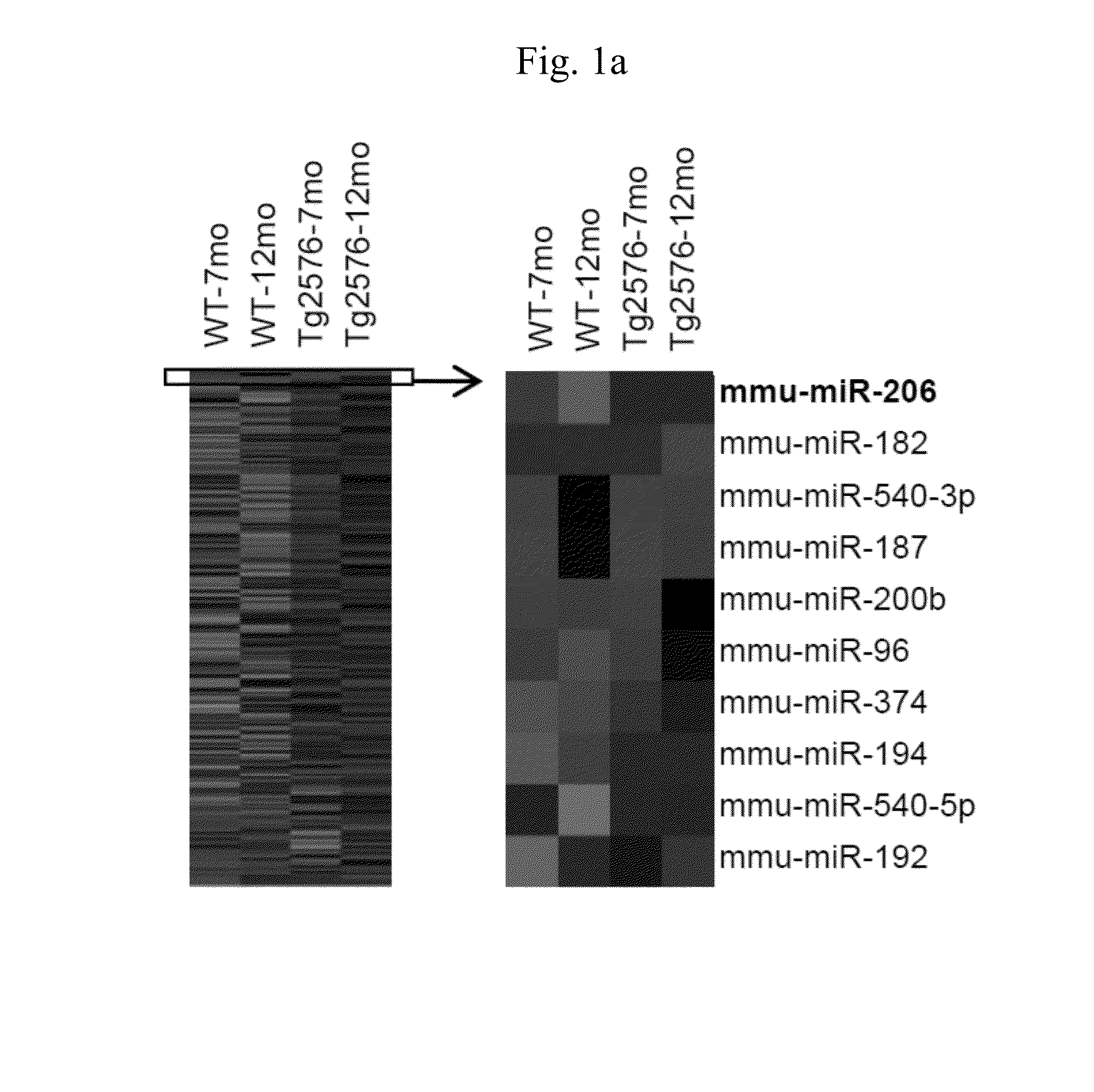
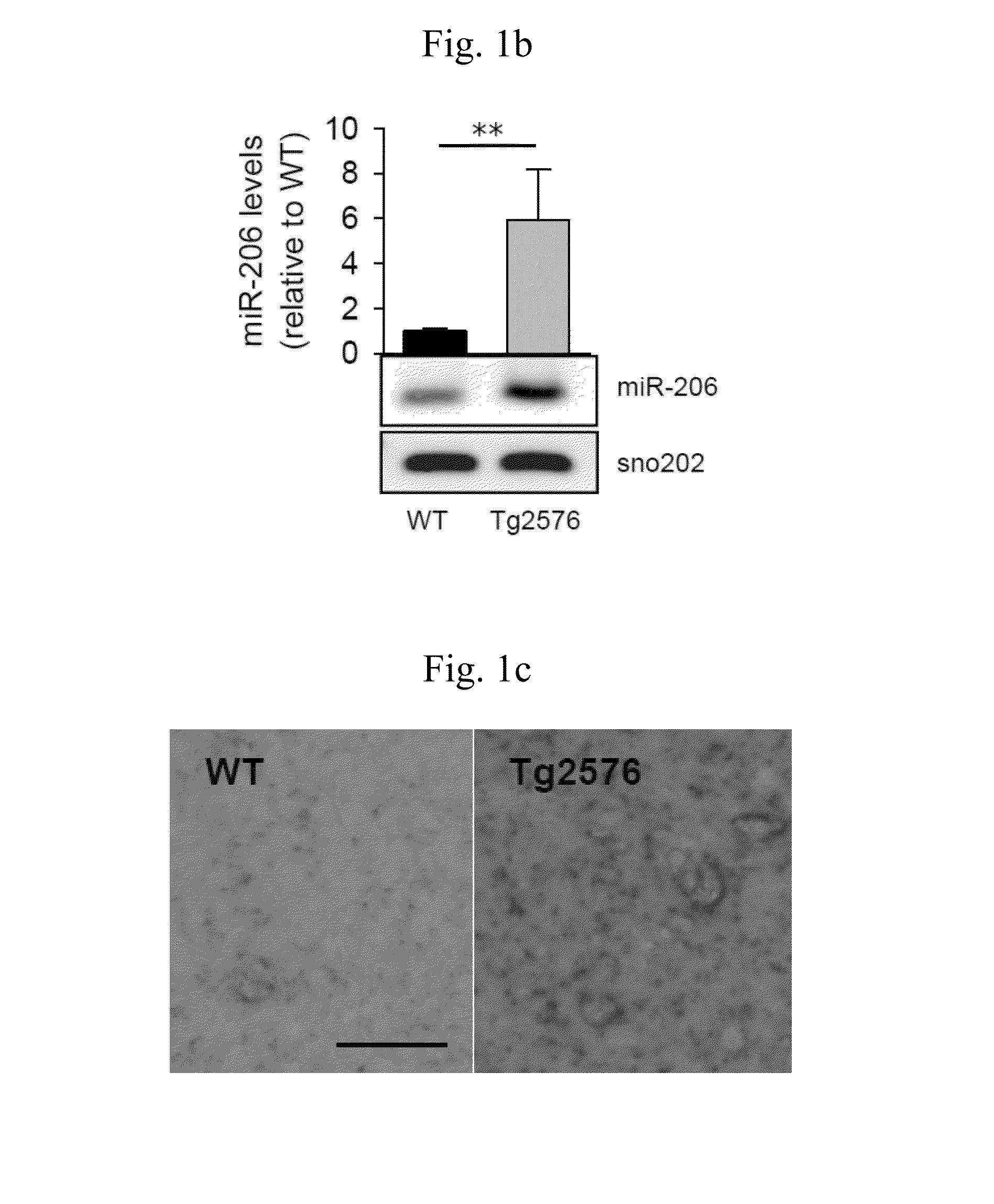
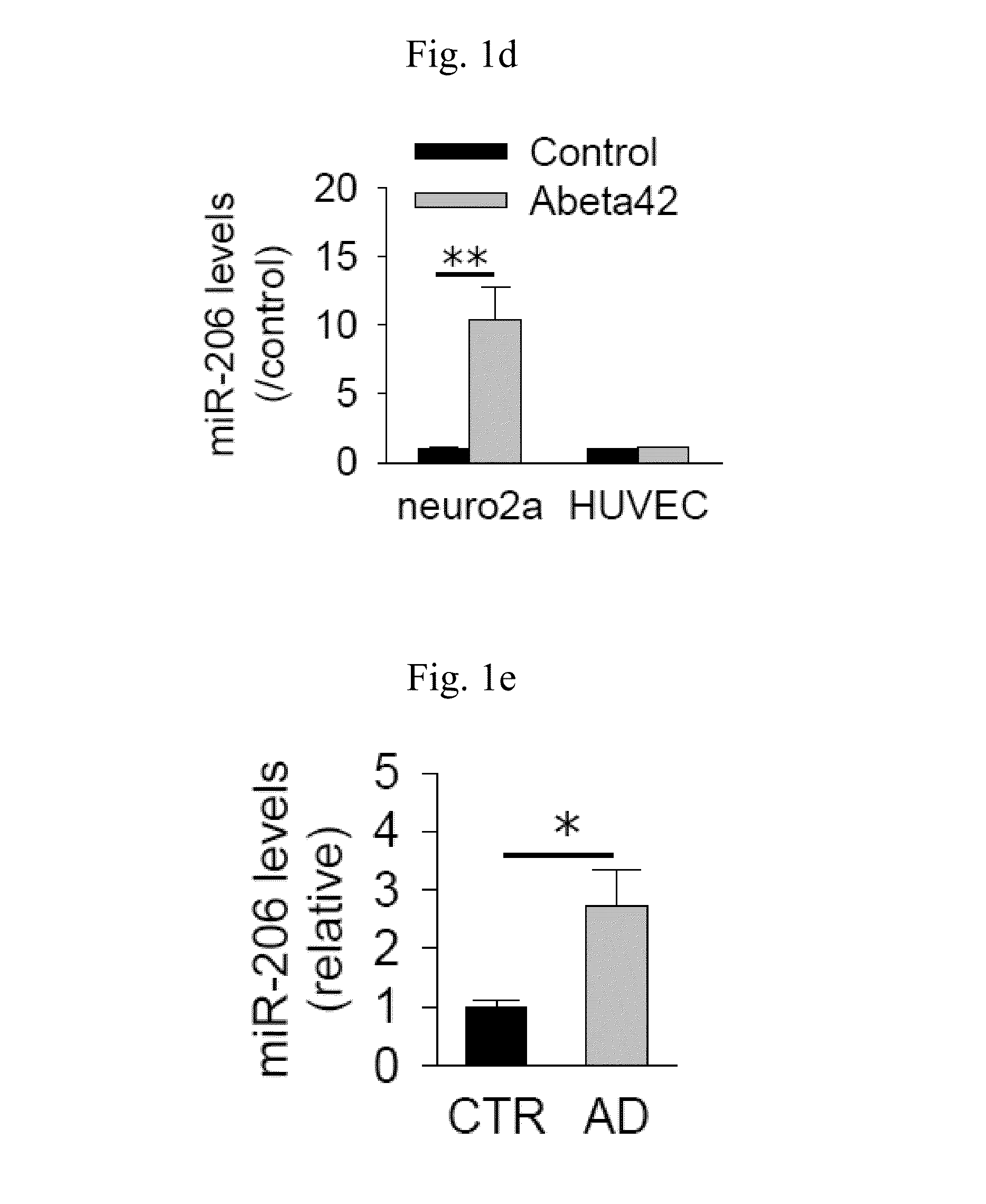
Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting miRNA
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases by targeting a specific miRNA. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit for diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. A miR-206 target found in the present invention, which is highly expressed in both animal models of Alzheimer's disease and human brain samples, is a substantial treatment target selected without artifact errors. An antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention as an inhibitor for miR-206 suggests a successful result in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting miRNA. The antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention inhibits the function of miR-206 to greatly increase the levels of BDNF and IGF-1 and to increase the regeneration of synapses, thereby treating neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
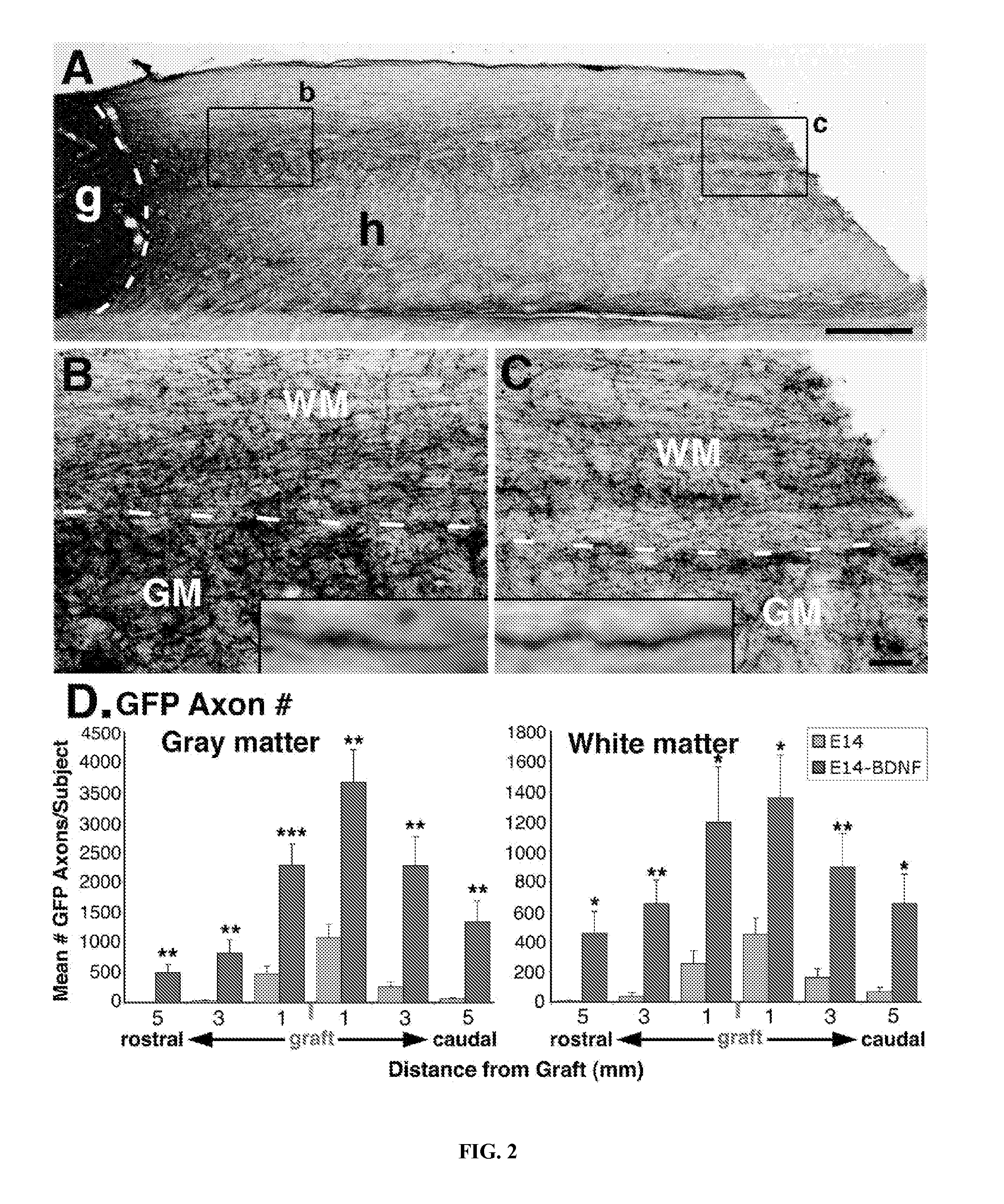
Methods for Use of Neural Stem Cell Compositions for Treatment of Central Nervous System Lesions
ActiveUS20140308256A1Promote growthConducive to survivalBiocideNervous disorderNervous systemCentral nervous system lesion
Methods for inducing non-embryonic lesioned central nervous system neurons to survive, integrate, extend axons over long distances, induce intra-lesion ingrowth of neurons into the lesion from host tissue and form synapses in vivo. Pluripotent neural stem cells are grafted into the lesioned CNS tissue within a tissue adhesive suspension, optionally in the presence of growth factors. No modification of the neuronal regenerative inhibitory environment of the CNS is necessary.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Biological agents active in central nervous system
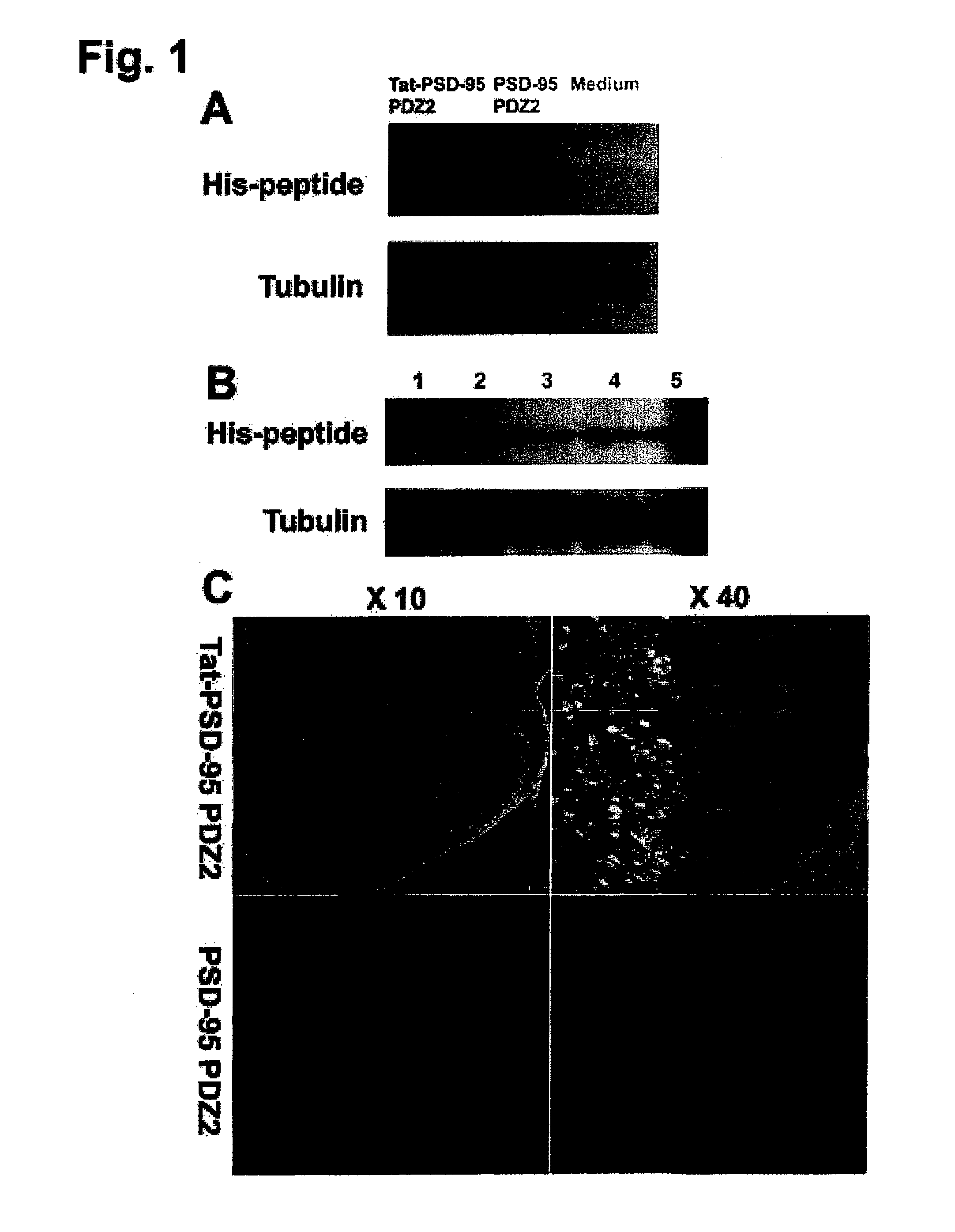
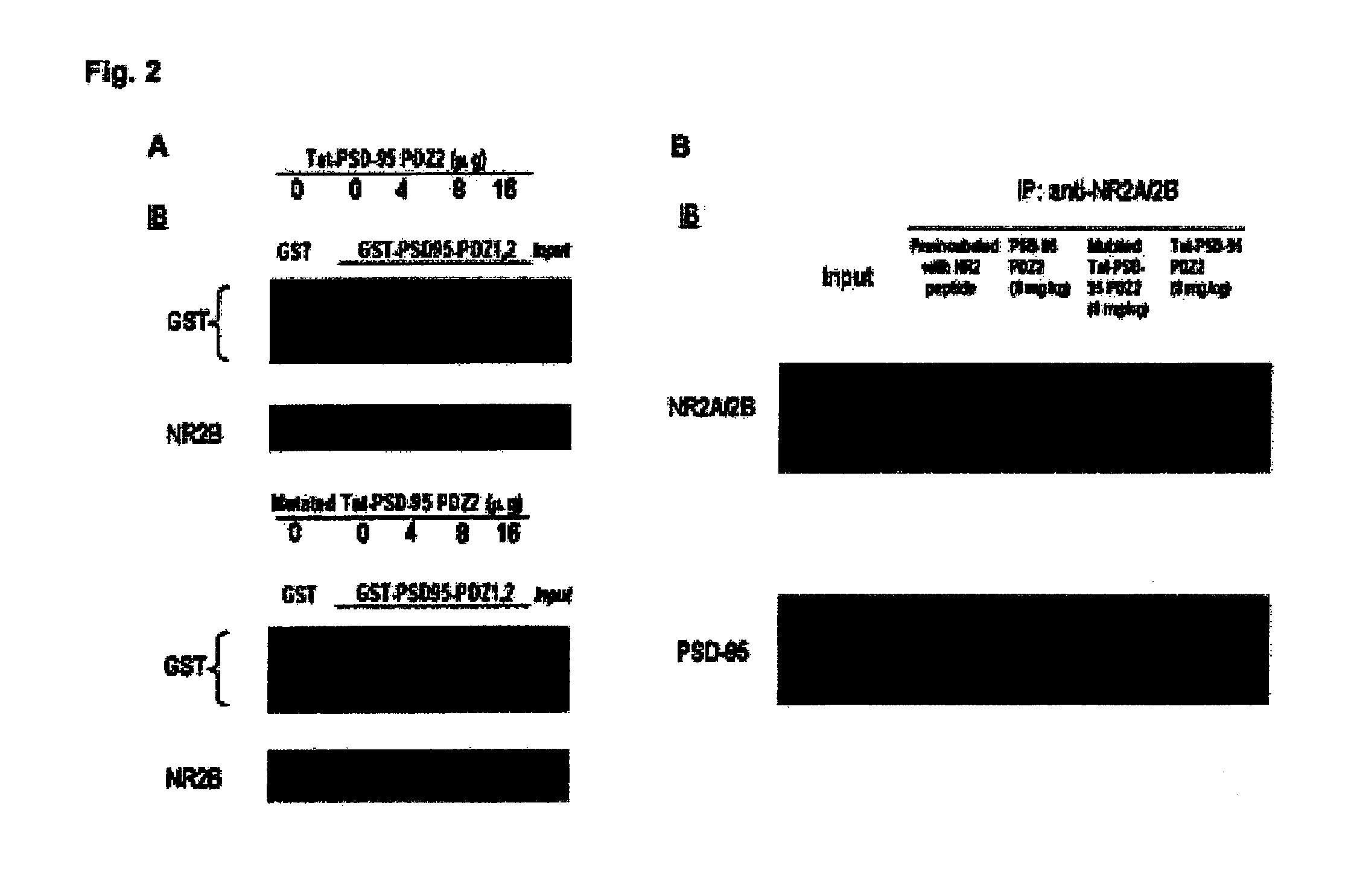
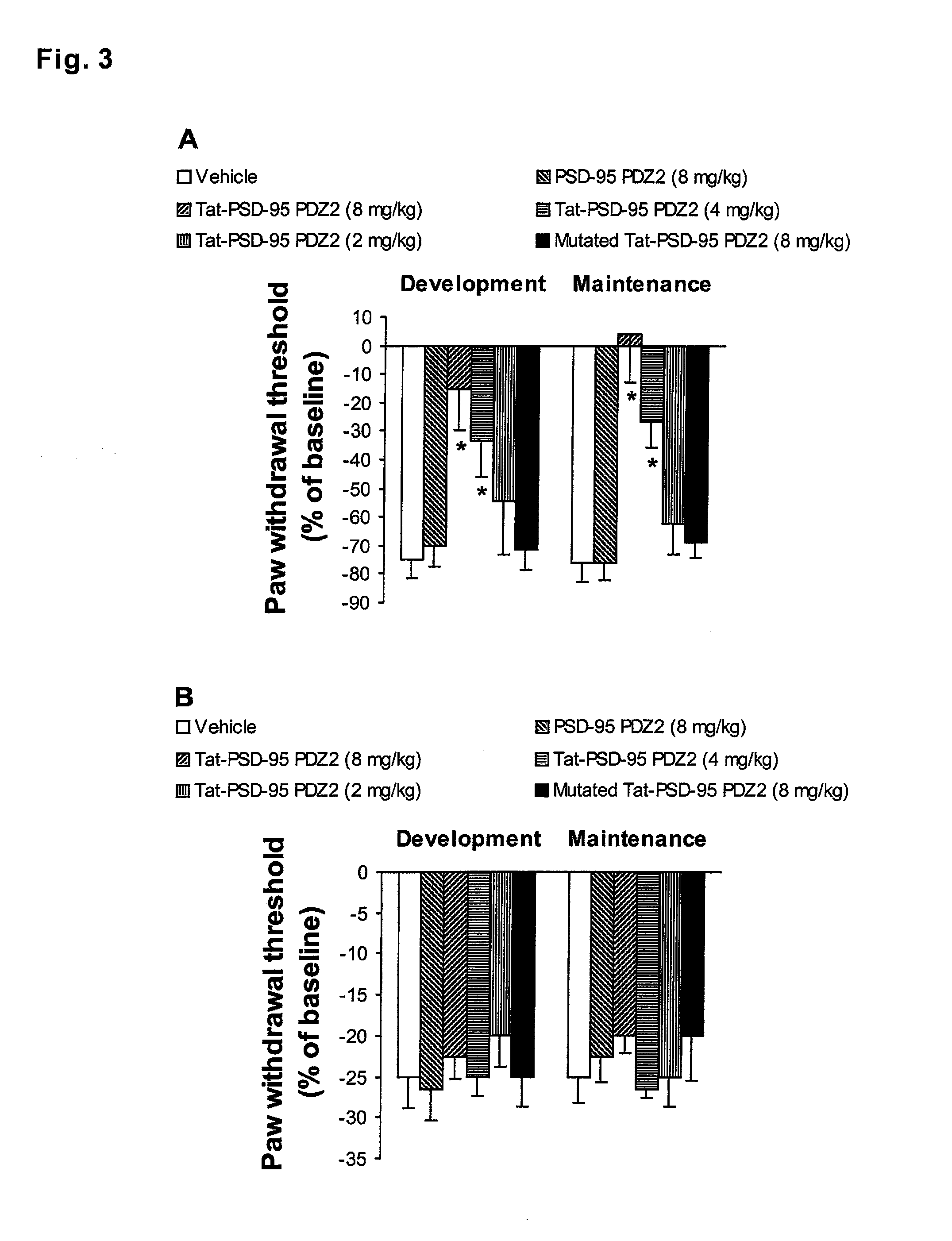
InactiveUS20100204100A1Relieving acute or chronic pain in a humanTreating and preventing allodynia and hyperalgesiaPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderIn vivoIndividual animal
Cell-permeant fusion peptides Tat-PDZ can dose-dependently reduce the threshold for anesthesia. PDZ domain-mediated protein interactions at synapses in the central nervous system play an important role in the molecular mechanisms of anesthesia. Moreover, Tat-PDZ cell-permeant fusion peptides are delivered intracellularly into neurons in the central nervous system subsequent to intraperitoneally injection. By in vitro and in vivo binding assays, we found that the Tat-PDZ dose-dependently inhibited the interactions between NMDARs and PSD-95. Furthermore, behavior testing showed that animals given Tat-PDZ exhibited significantly reduced established inflammatory pain behaviors compared to vehicle-treated group. Our results indicate that by disrupting NMDAR / PSD-95 protein interactions, the Tat-PDZ cell-permeable fusion peptides provide a new approach for inflammatory pain therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Use of drugs that activate p2y receptors to enhance synaptogenesis
The present invention encompasses compositions and methods that activate P2Y receptors for the increased production of new synapses in the central nervous system. The formulations of the invention may be administered to a healthy subject or to a subject in need thereof to restore synapses.
Owner:BACK BAY SCI
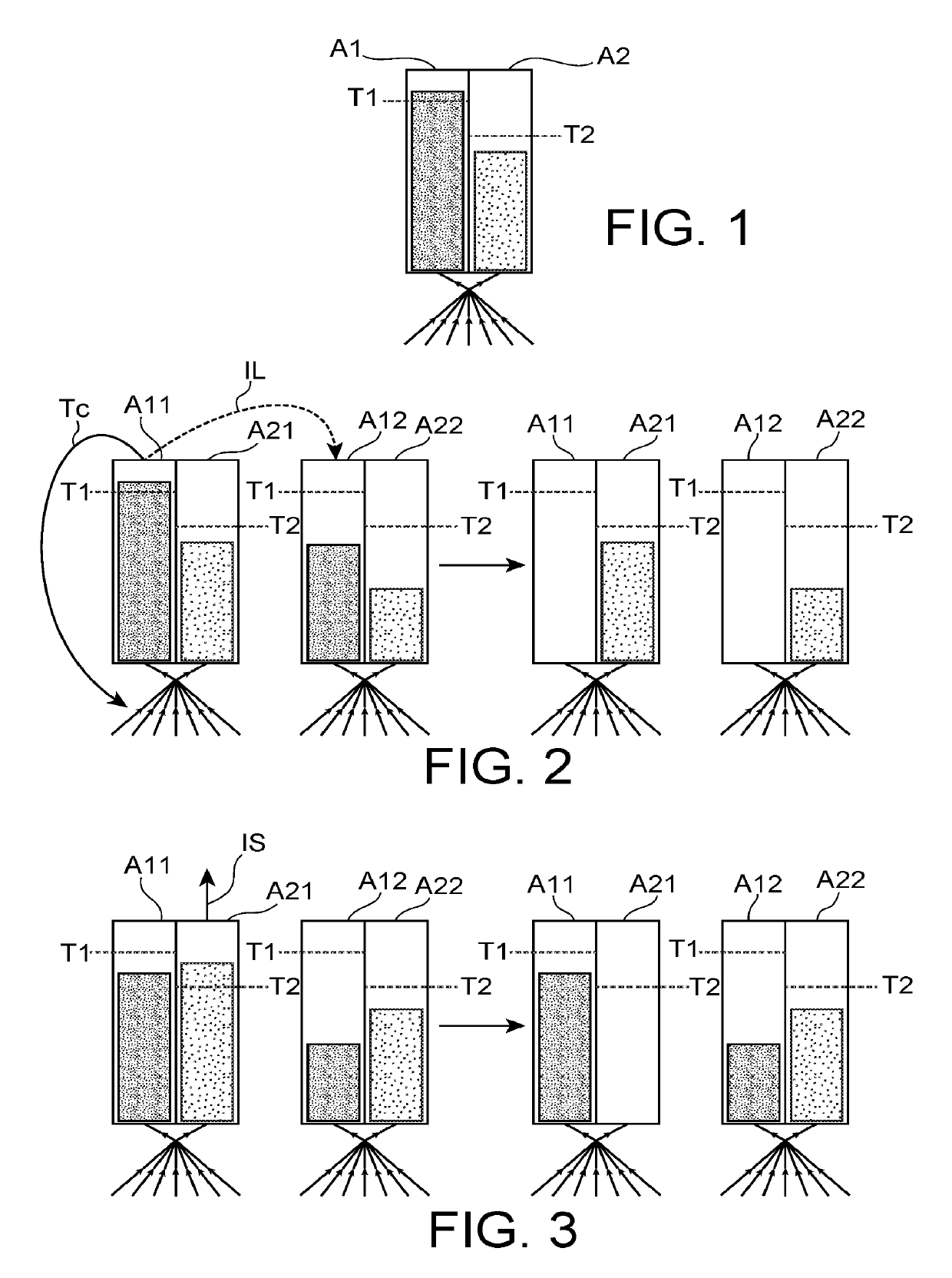
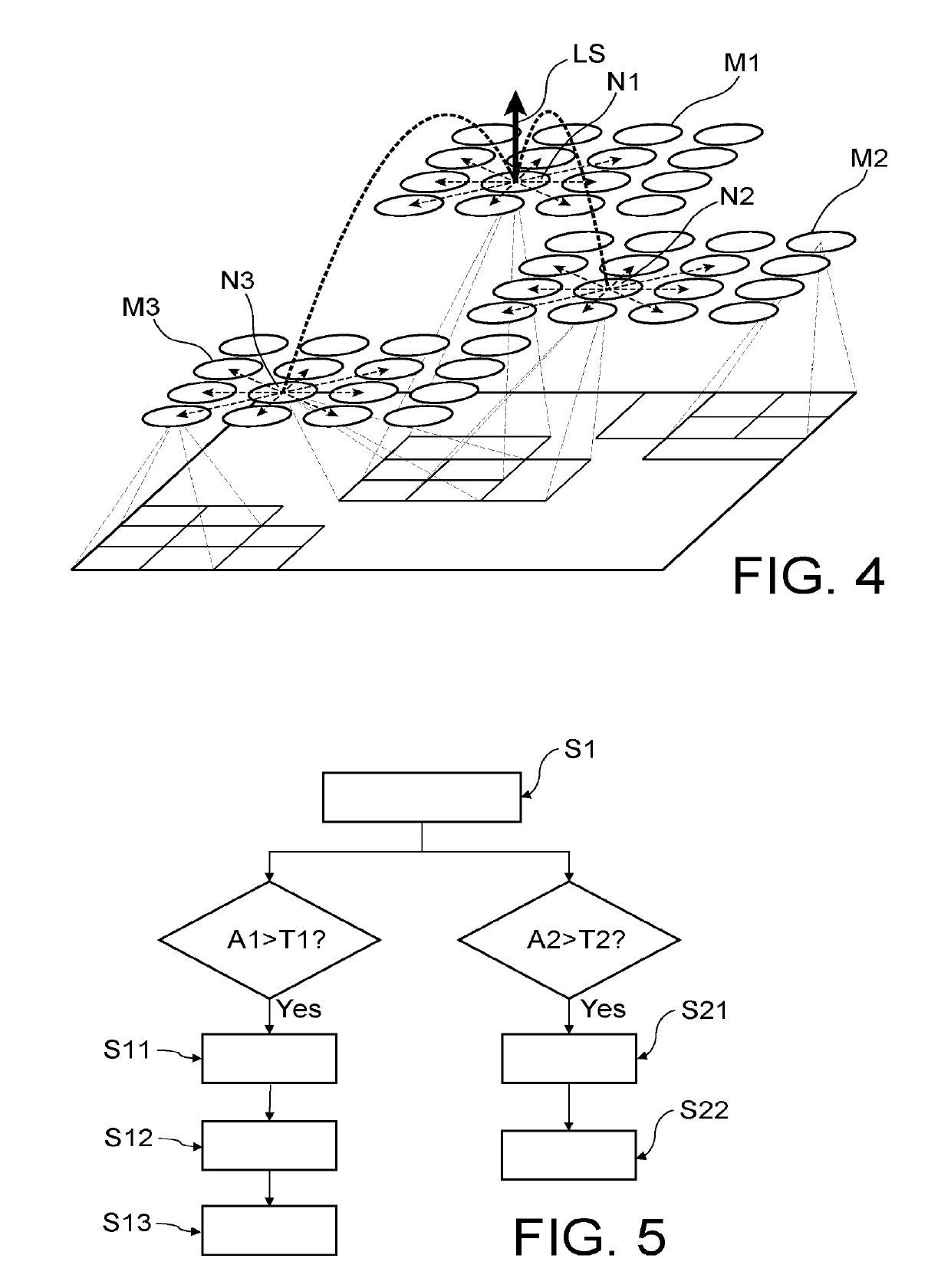
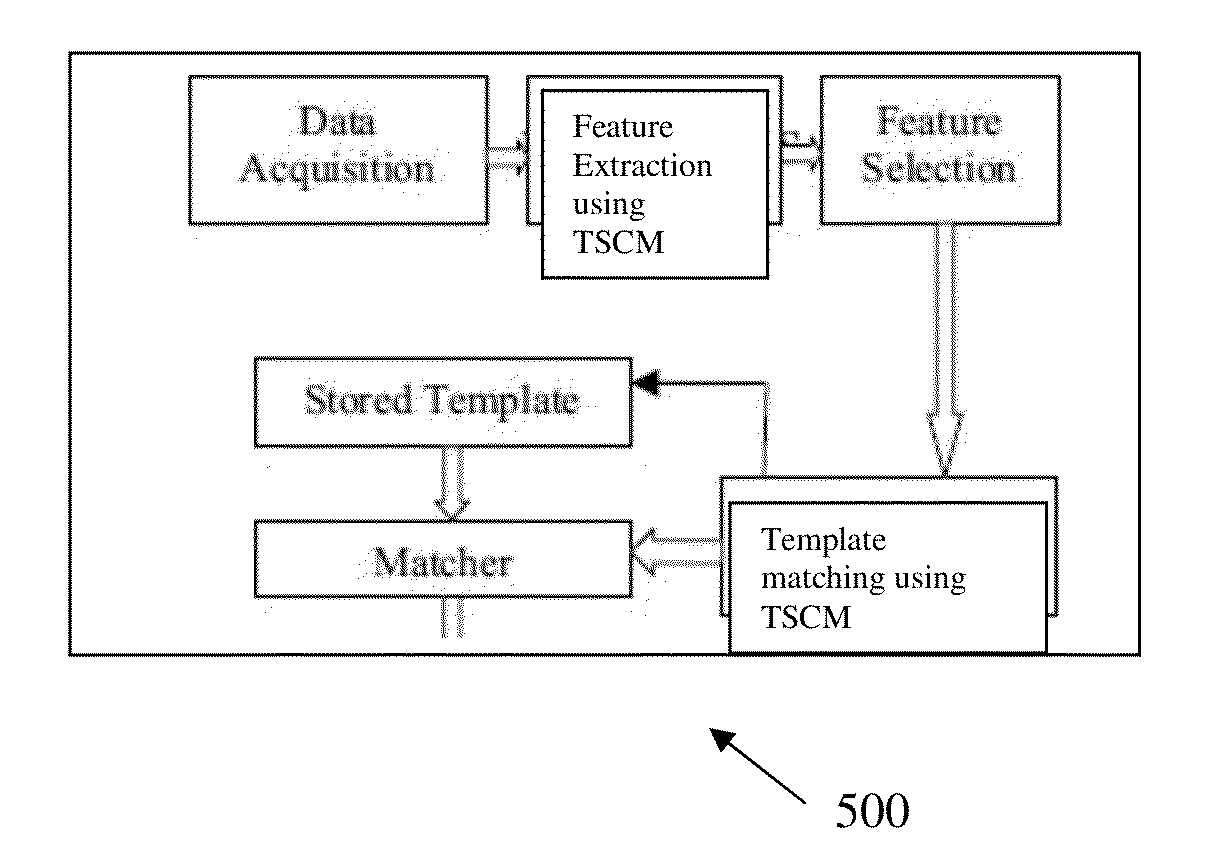
Time series classifying memory, systems and methods
A time series classifying memory includes an enumerated group of synapses. Each synapse of the group has a junction including pre-synaptic emitters communicating with post synaptic receptors. A single pathway is input to each synapse of the group, and when innervated, stimulates the junctions. Each successive synapse has successively more post synaptic receptors according to a fixed ratio. At each junction, quanta of neurotransmitter emitted from the emitters bind with available receptors. When all the receptors at a junction have been bound, the junction goes refractory. The synapse adjacent to the last junction to go refractory is marked. During a training mode the mark is a Long Term Potentiation (LTP) mark. During a live mode the mark is a Short Term Potentiation (STP) mark. The input is classified upon successful correlation of the LTP mark with the STP mark. A clock operable with synaptic matrix models this process.
Owner:BRECKENRIDGE JOHN L
Methods for direct visualization of active synapses
InactiveUS20070092449A1Easy to transportEasy to operateDisease diagnosisIn-vivo testing preparationsBiologic markerFragment C tetanus toxin
A method for visualizing an active synapse wherein said method comprises: (a) exposing cells forming the active synapse to a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein; and (b) visualizing the biomarker; wherein the accumulation of the biomarker into dendritic spines of the cells allows visualization of an active synapse. Also, a method for screening molecules capable of modulating synapse activity is provided. A kit useful for the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease comprises a biomarker comprising at least fragment C of tetanus toxin and a reporter protein.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
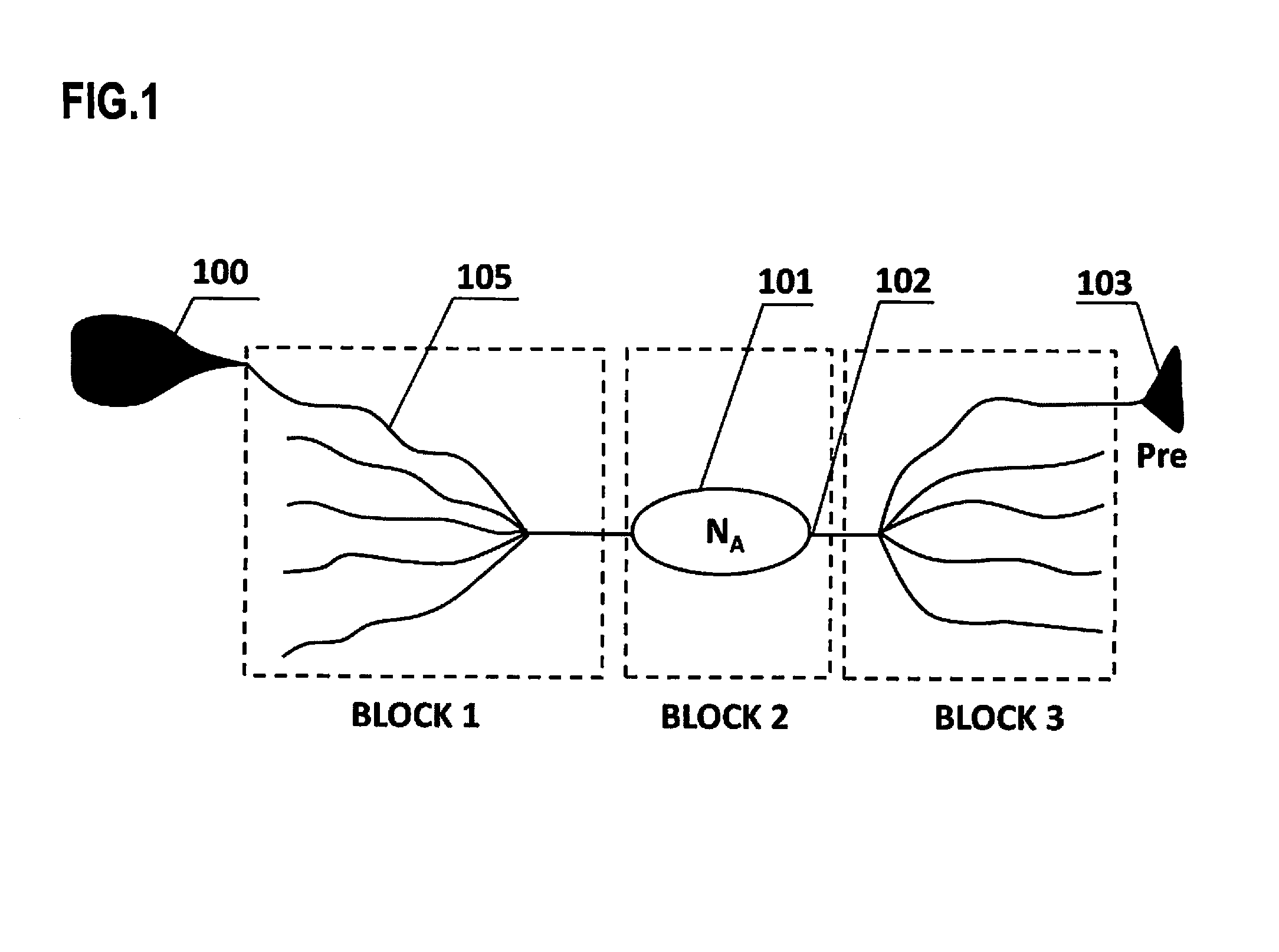
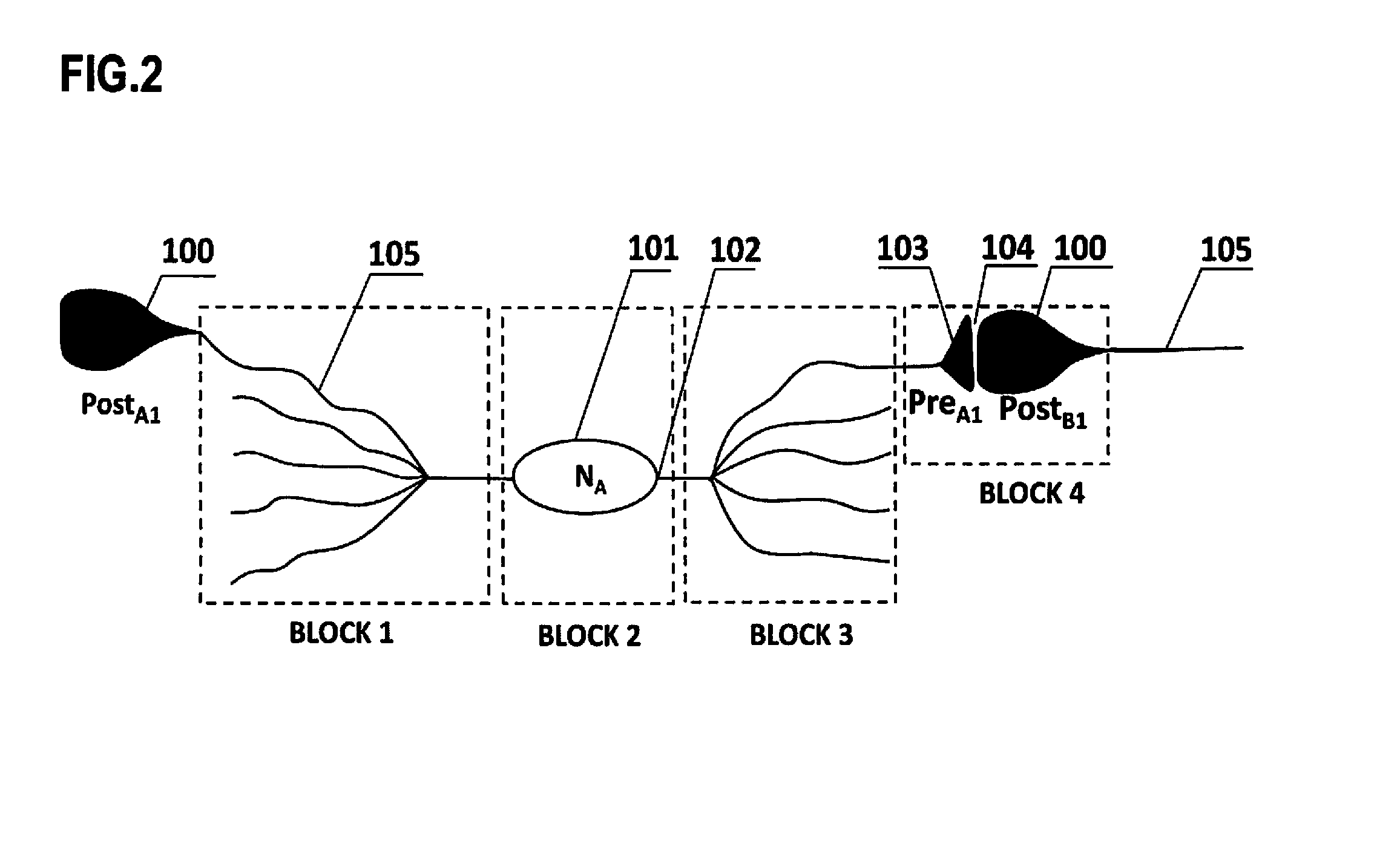
Artificial neural circuit forming re-activatible functional link between the postsynaptic terminals of two synapses
An electronic neuronal circuit system to model the interaction between the postsynaptic terminal of a first synapse between two neurons and the postsynaptic terminal of a second synapse between two neurons includes comparators to model the presynaptic neurons of the synapses, plurality of three diodes connected to the comparators to model synapses, an AND gate and latch to model the formation of functional link between the postsynaptic terminals, and timer-controlled latches for controlling the life-span of the inter-postsynaptic functional link, durations of re-activation of inter-postsynaptic functional link and flow of activity through the output postsynaptic dendritic terminals.
Owner:VADAKKAN KUNJUMON ITTIRA
Culture media for neurons, methods for preparing the culture media, and methods for culturing neurons
InactiveUS6376238B1Overcome problemsImprove survivabilityBiocideCulture processHigh cellMicrobiology
The present invention is directed to a culture medium for neurons prepared by adding albumin to a culture supernatant obtained from a culture of primary astroglial cells in a trophic medium supplemented with insulin and transferrin. The culture medium of the present invention makes it possible to culture central nerve cells consistently. When nerve cells are cultured at a low cell density, excellent neurite extension is obtained, and synapses are formed rapidly. On the other hand, when nerve cells are cultured at a high cell density, long-term stability of cells that have formed neuronetworks can be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com