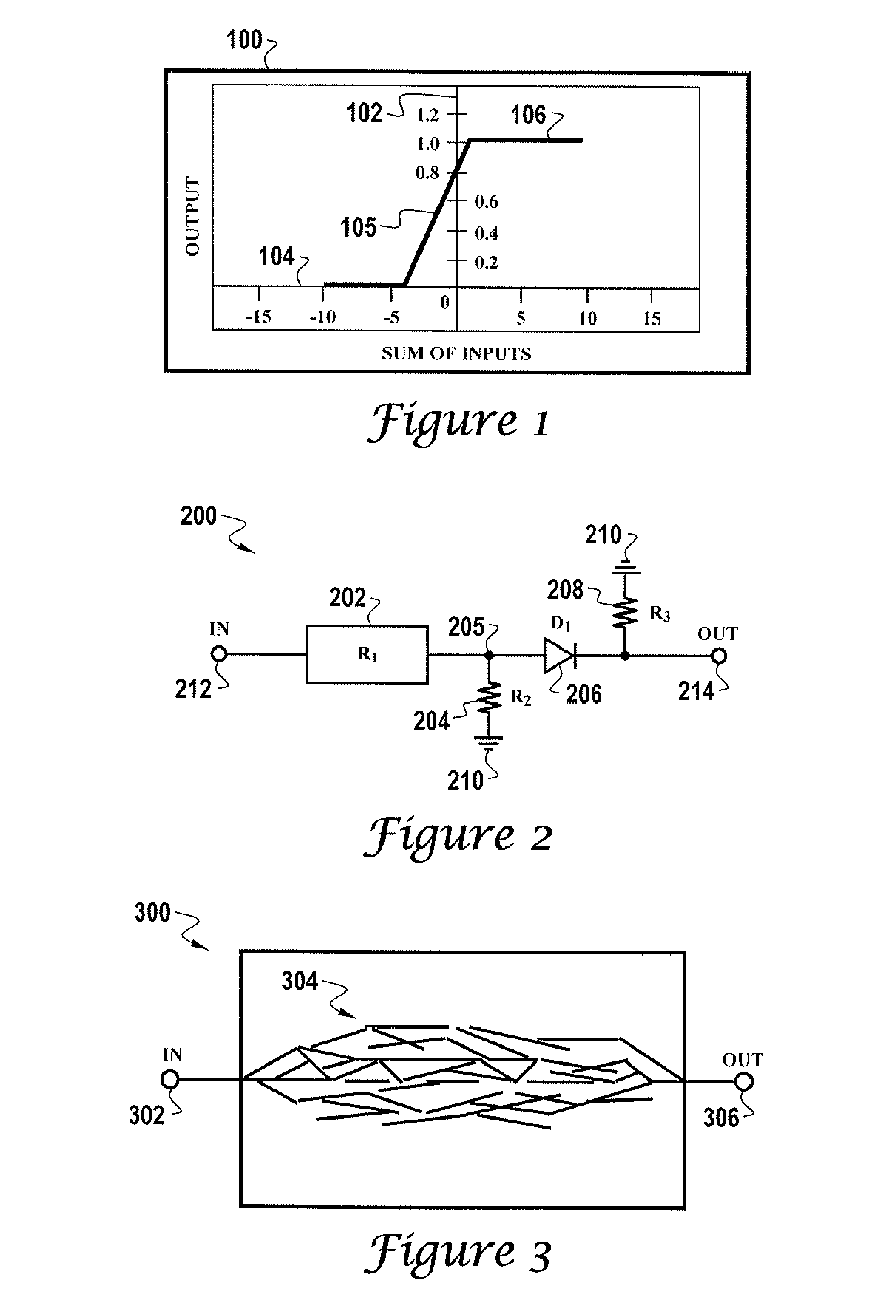
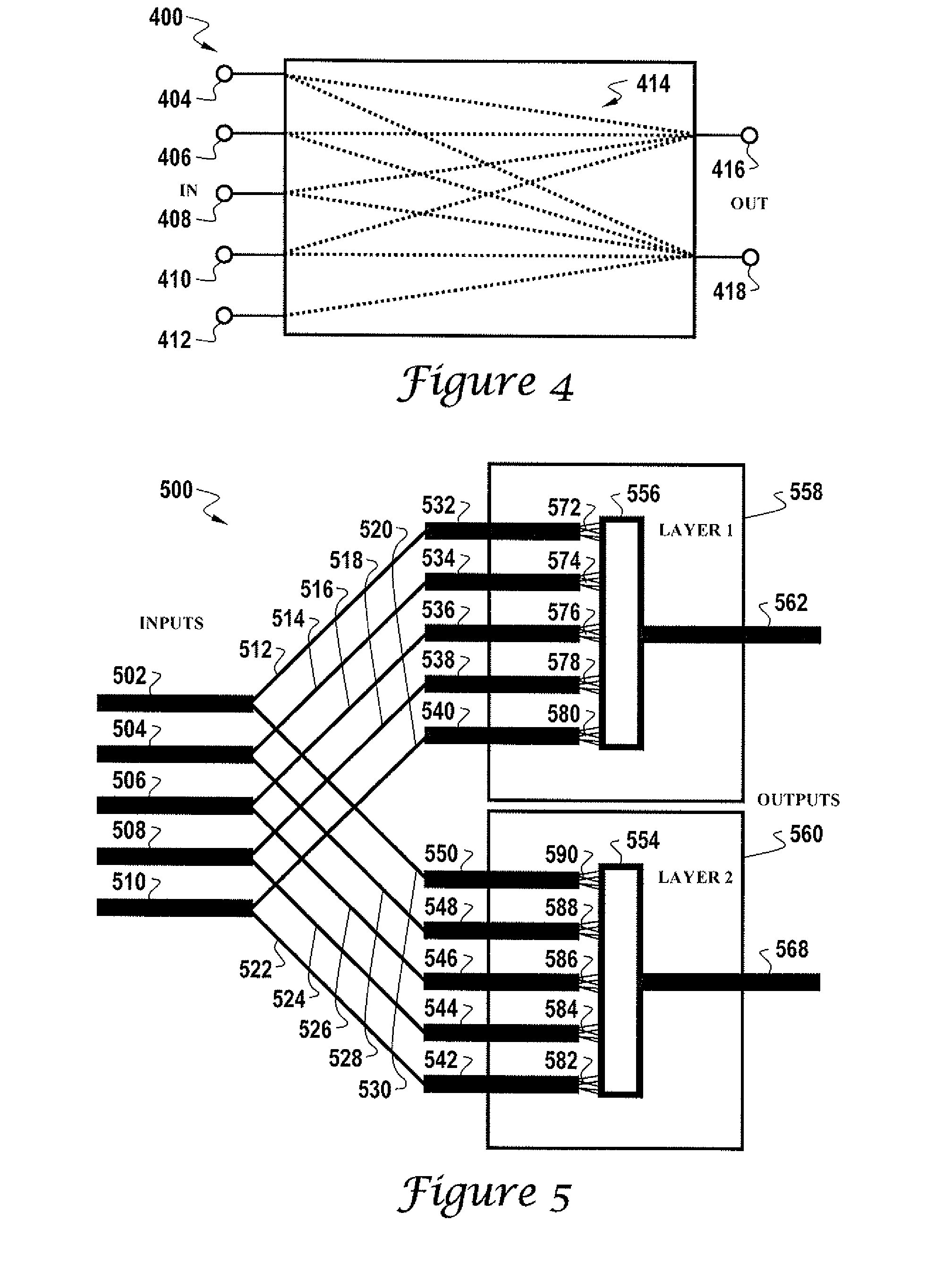
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Synapse structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
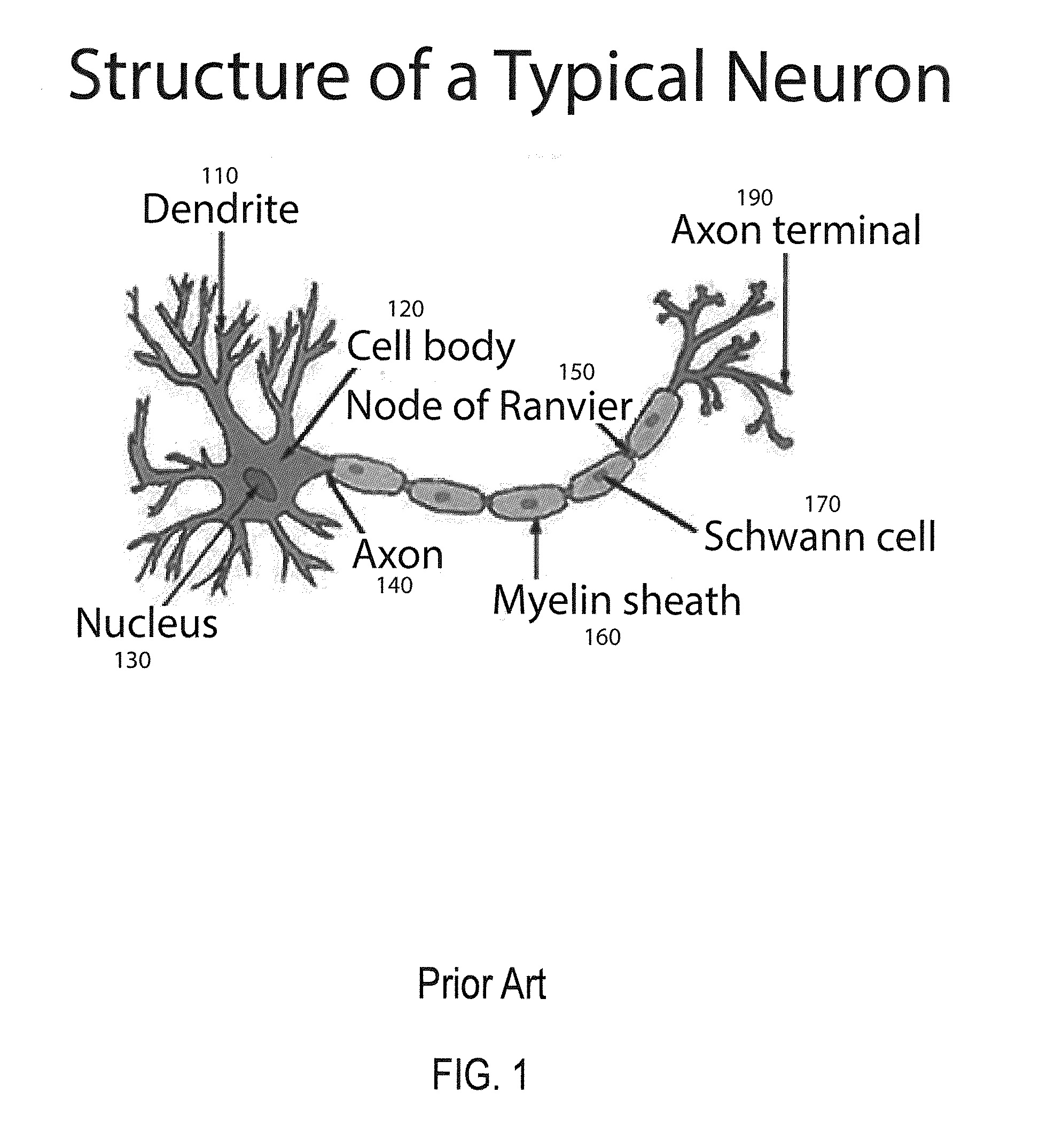
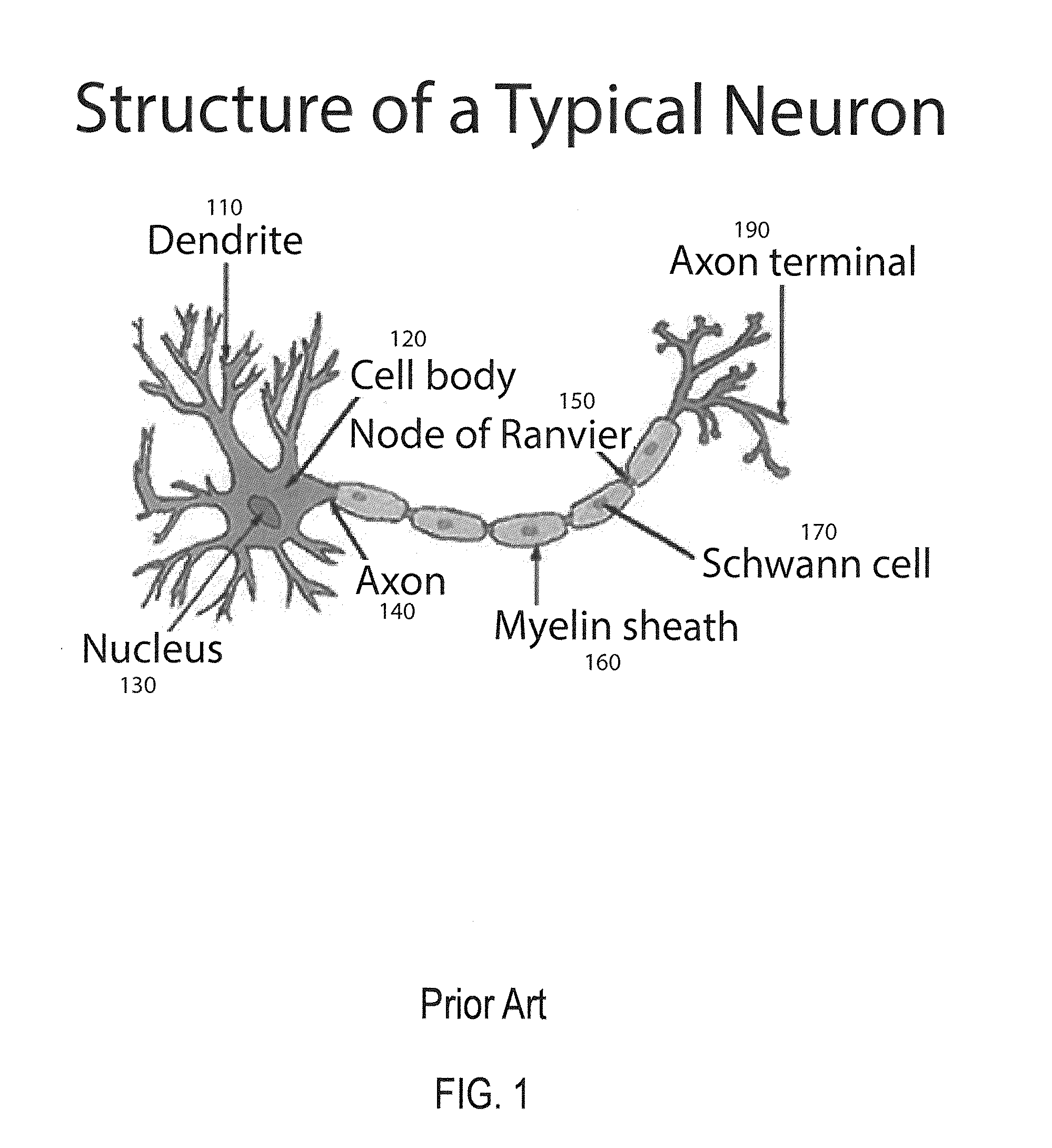
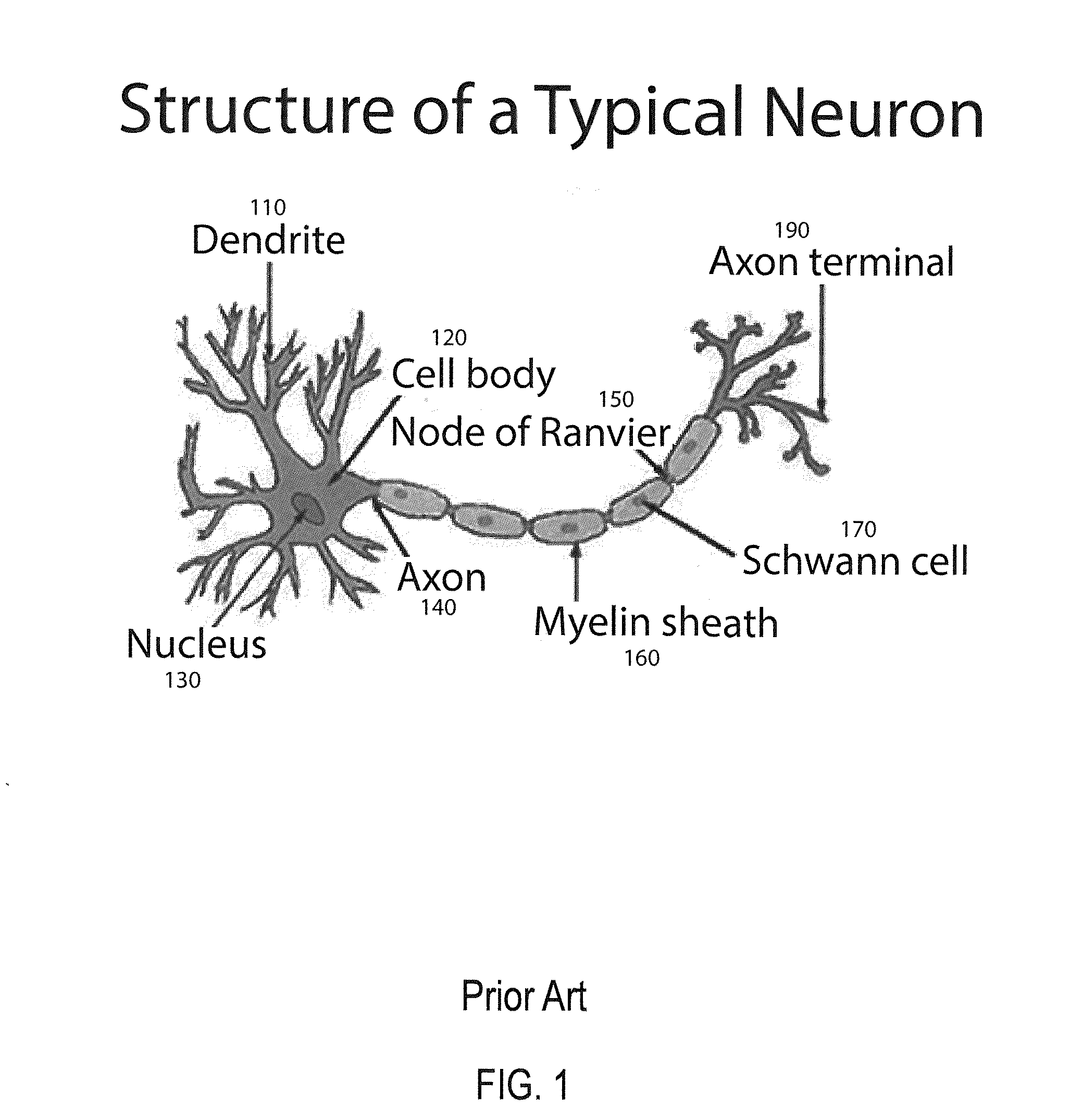
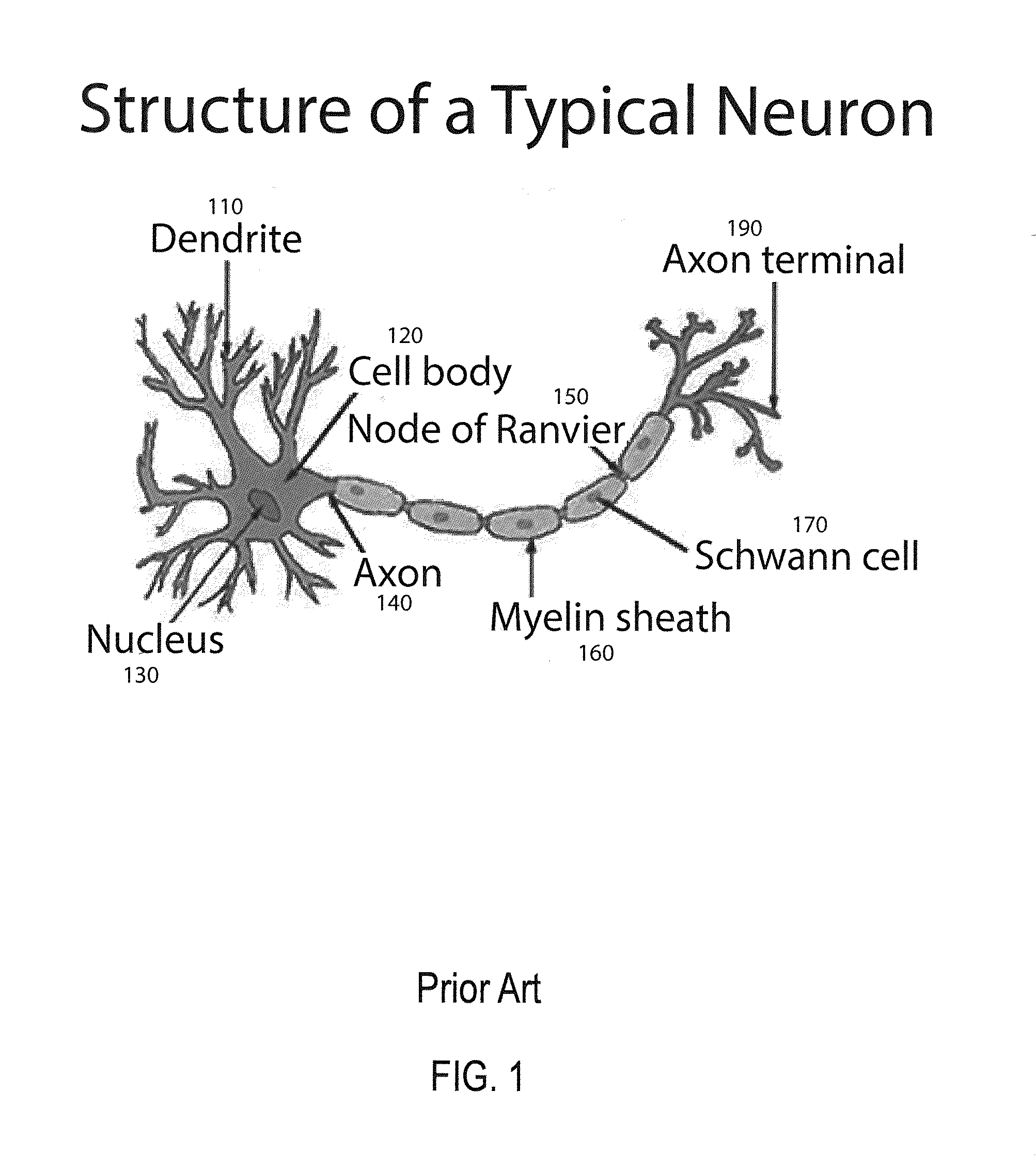
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target efferent cell.
Apparatus comprising artificial neuronal assembly
ActiveUS20100241601A1Augment sensory awarenessDigital computer detailsDigital dataVisual cortexRetina
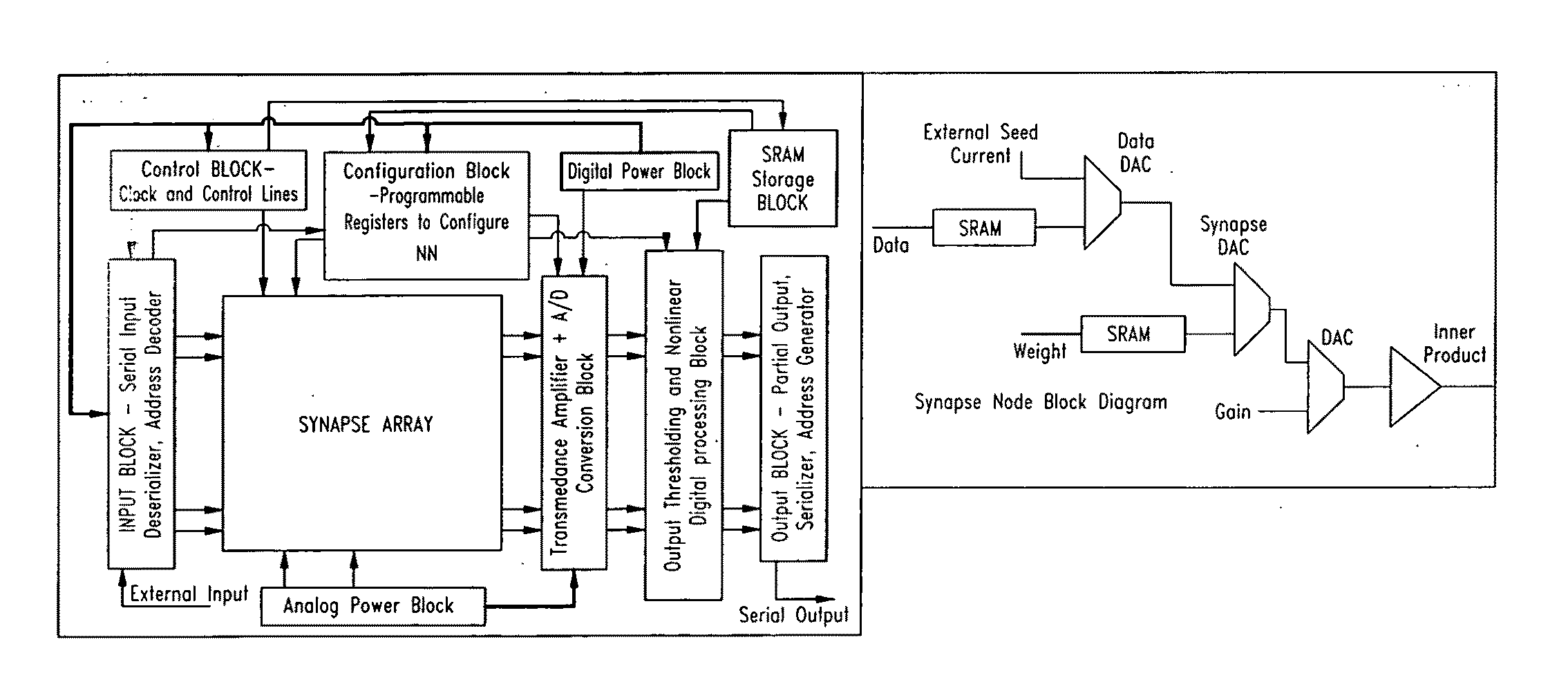
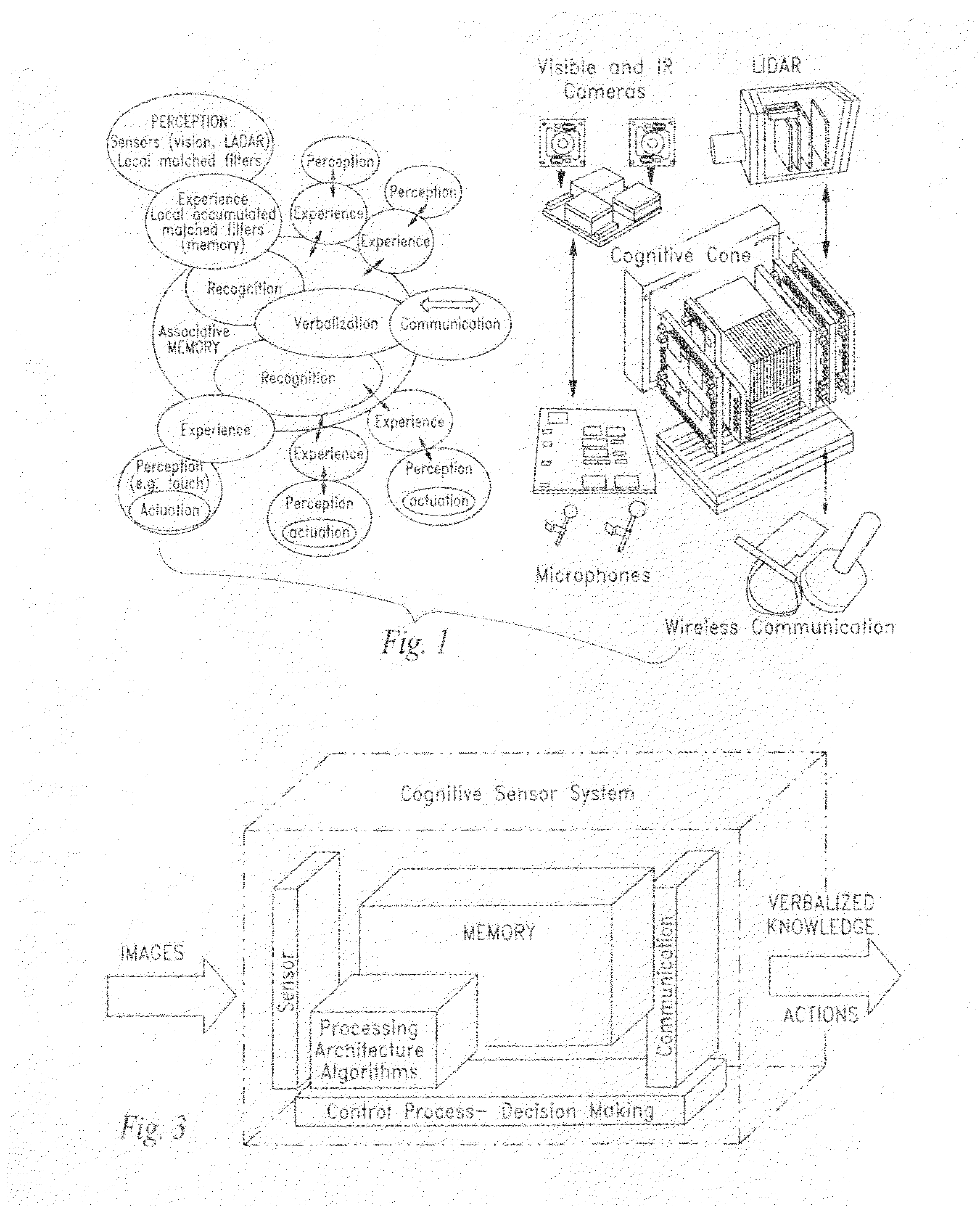
An artificial synapse array and virtual neural space are disclosed.More specifically, a cognitive sensor system and method are disclosed comprising a massively parallel convolution processor capable of, for instance, situationally dependent identification of salient features in a scene of interest by emulating the cortical hierarchy found in the human retina and visual cortex.
Owner:PFG IP +1
Adaptive neural network utilizing nanotechnology-based components
Methods and systems for modifying at least one synapse of a physicallelectromechanical neural network. A physical / electromechanical neural network implemented as an adaptive neural network can be provided, which includes one or more neurons and one or more synapses thereof, wherein the neurons and synapses are formed from a plurality of nanoparticles disposed within a dielectric solution in association with one or more pre-synaptic electrodes and one or more post-synaptic electrodes and an applied electric field. At least one pulse can be generated from one or more of the neurons to one or more of the pre-synaptic electrodes of a succeeding neuron and one or more post-synaptic electrodes of one or more of the neurons of the physical / electromechanical neural network, thereby strengthening at least one nanoparticle of a plurality of nanoparticles disposed within the dielectric solution and at least one synapse thereof.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
Neuromorphic Circuit
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to neuromorphic circuits containing two or more internal neuron computational units. Each internal neuron computational unit includes a synchronization-signal input for receiving a synchronizing signal, at least one input for receiving input signals, and at least one output for transmitting an output signal. A memristive synapse connects an output signal line carrying output signals from a first set of one or more internal neurons to an input signal line that carries signals to a second set of one or more internal neurons.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for providing real-time monitoring of an artifical neural network
ActiveUS20150106316A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesProcessor registerMulti dimensional
A circuit element of a multi-dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such circuit elements, (wherein a circuit element may be digital), a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension to form linked columns and rows of neuron / synapse circuit elements. In one embodiment, the rows and columns of circuit elements have read registers that are linked together by signal lines and clocked and controlled so as to output columnar data to an output register when a neuron / synapse data value is stored in the read register.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
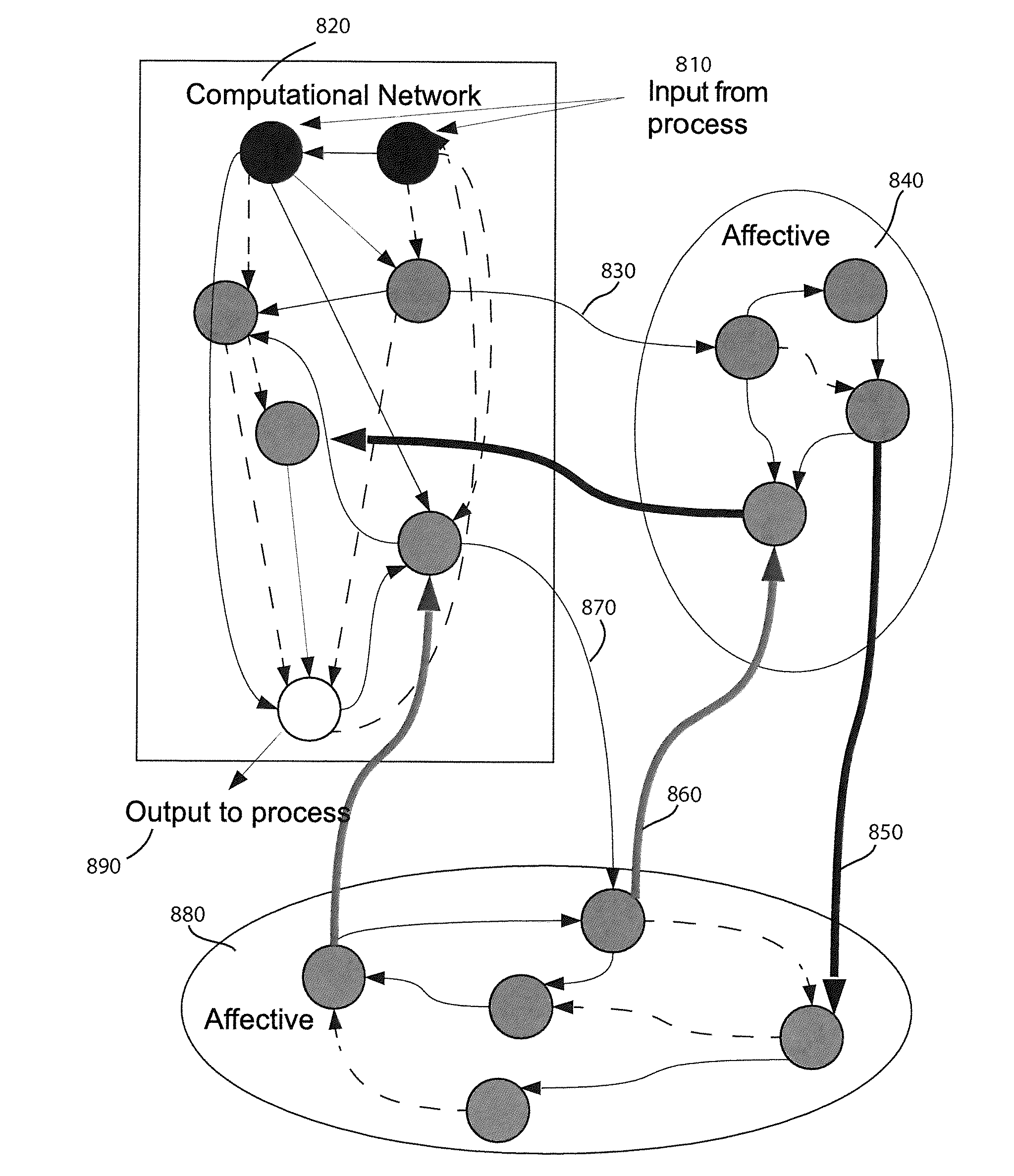
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network
ActiveUS20150106310A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataComputational neuroscienceAnomaly detection
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture (NIDA) for an artificial neural network is disclosed. The method comprises constructing, in one embodiment, an artificial neural network embodiment in a multi-dimensional space in memory such that a neuron is connected by a synapse to another neuron. The neuron and the synapse each have parameters and have features of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Furthermore, crossover and mutation are employed to select children of parents. Through learning, an initial network may evolve into a different network when NIDA is applied to solve different problems of control, anomaly detection and classification over selected time units. The apparatus comprises in one embodiment a computational neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with at least one affective network coupled to receive input data from an environment and to output data to the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Methods of administering vectors to synaptically connected neurons
InactiveUS20050032219A1Specific deliveryExcessive deliveryBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTreatment effectPrimary motor neuron
The present invention relates generally to efficient delivery of viral vectors to cells of the CNS, particularly useful in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and motor neuron diseases. The invention involves selecting a first population and a second population of synaptically connected neurons, wherein a therapeutic polypeptide is to be expressed in said second population of neurons; and administering rAAV virions comprising a therapeutic gene to said first subpopulation of neurons of said subject such that the rAAV virions are transported across a synapse between synaptically connected neurons. In another aspect the present invention also comprises the use of rAAV virions carrying a transgene in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of a disease in a subject, wherein a first population and a second population of synaptically connected neurons are selected and a therapeutic polypeptide is to be expressed in said second population of neurons; and a medicament comprising recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virions is delivered to said first population of neurons of the subject, wherein said virions comprise a nucleic acid sequence that is expressible in transduced cells to provide a therapeutic effect in the subject, and wherein said rAAV virions are capable of transducing a synaptically connected neurons.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
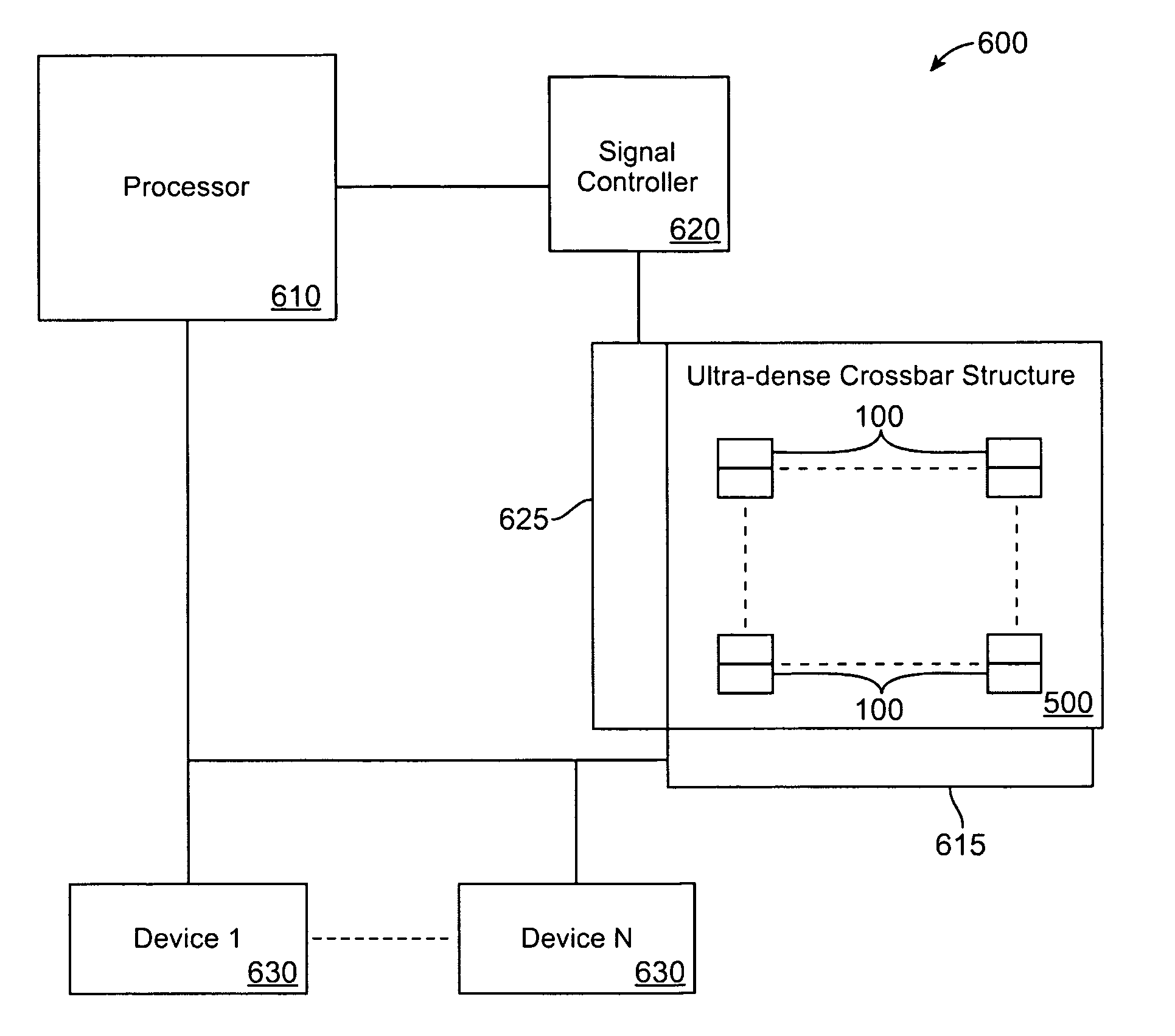
Producing spike-timing dependent plasticity in an ultra-dense synapse cross-bar array
ActiveUS20110153533A1Increasing and decreasing conductanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpike-timing-dependent plasticityUltra dense
Embodiments of the invention relate to producing spike-timing dependent plasticity in an ultra-dense synapse cross-bar array for neuromorphic systems. An aspect of the invention includes when an electronic neuron spikes, an alert pulse is sent from the spiking electronic neuron to each electronic neuron connected to the spiking electronic neuron. When the spiking electronic neuron sends the alert pulse, a gate pulse is sent from the spiking electronic neuron to each electronic neuron connected to the spiking electronic neuron. When each electronic neuron receives the alert pulse, a response pulse is sent from each electronic neuron receiving the alert pulse to the spiking electronic neuron. The response pulse is a function of time since a last spiking of the electronic neuron receiving the alert pulse. In addition, the combination of the gate pulse and response pulse is capable increasing or decreasing conductance of a variable state resistor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Stochastic synapse memory element with spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP)
An active memory element is provided. One embodiment of the invention includes a bi-polar memory two-terminal element having polarity-dependent switching. A probability of switching of the bi-polar memory element between a first state and a second state decays exponentially based on time delay and a difference between received signals at the two terminals and a switching threshold magnitude.
Owner:IBM CORP
Artificial synapse chip
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
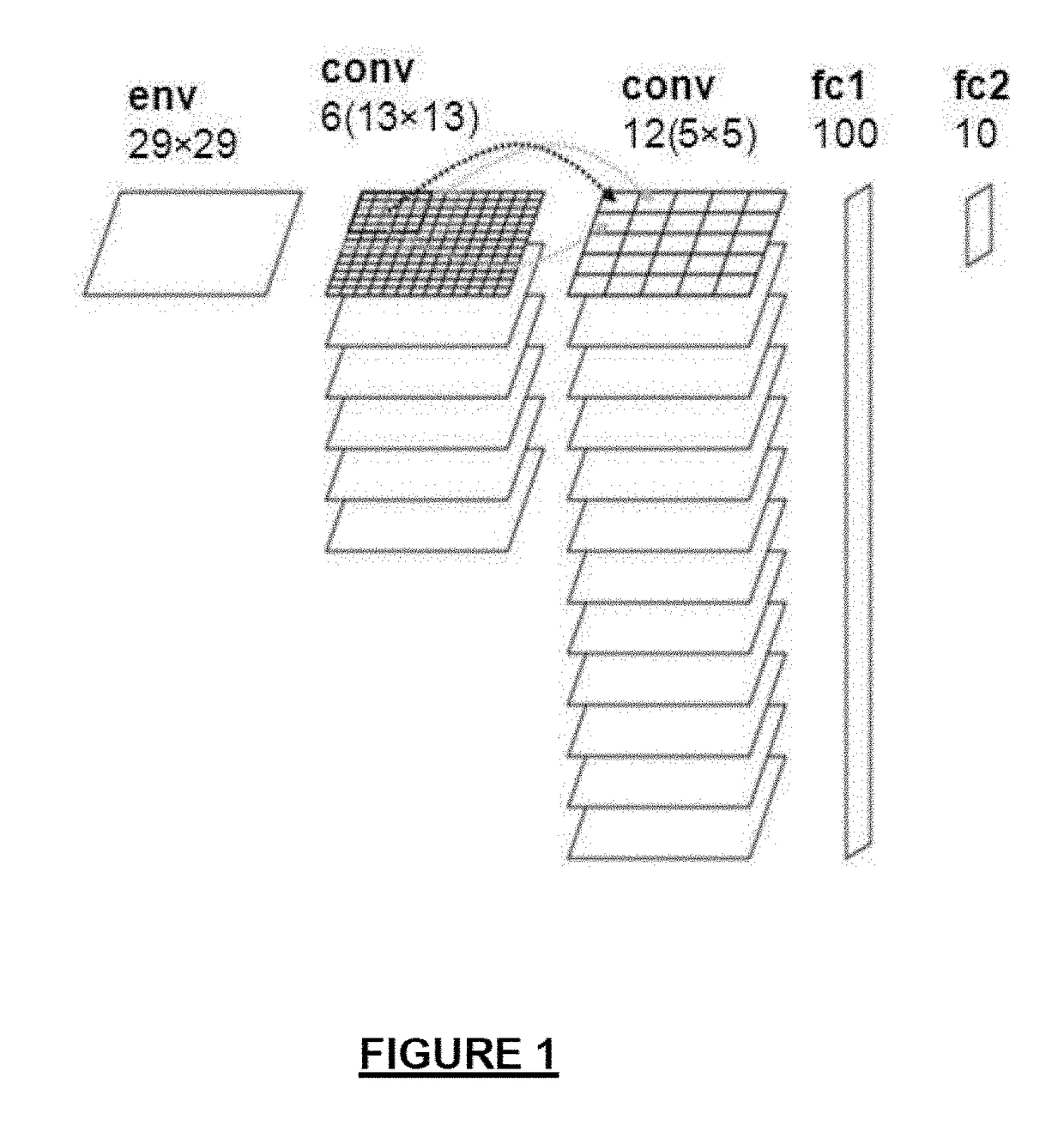
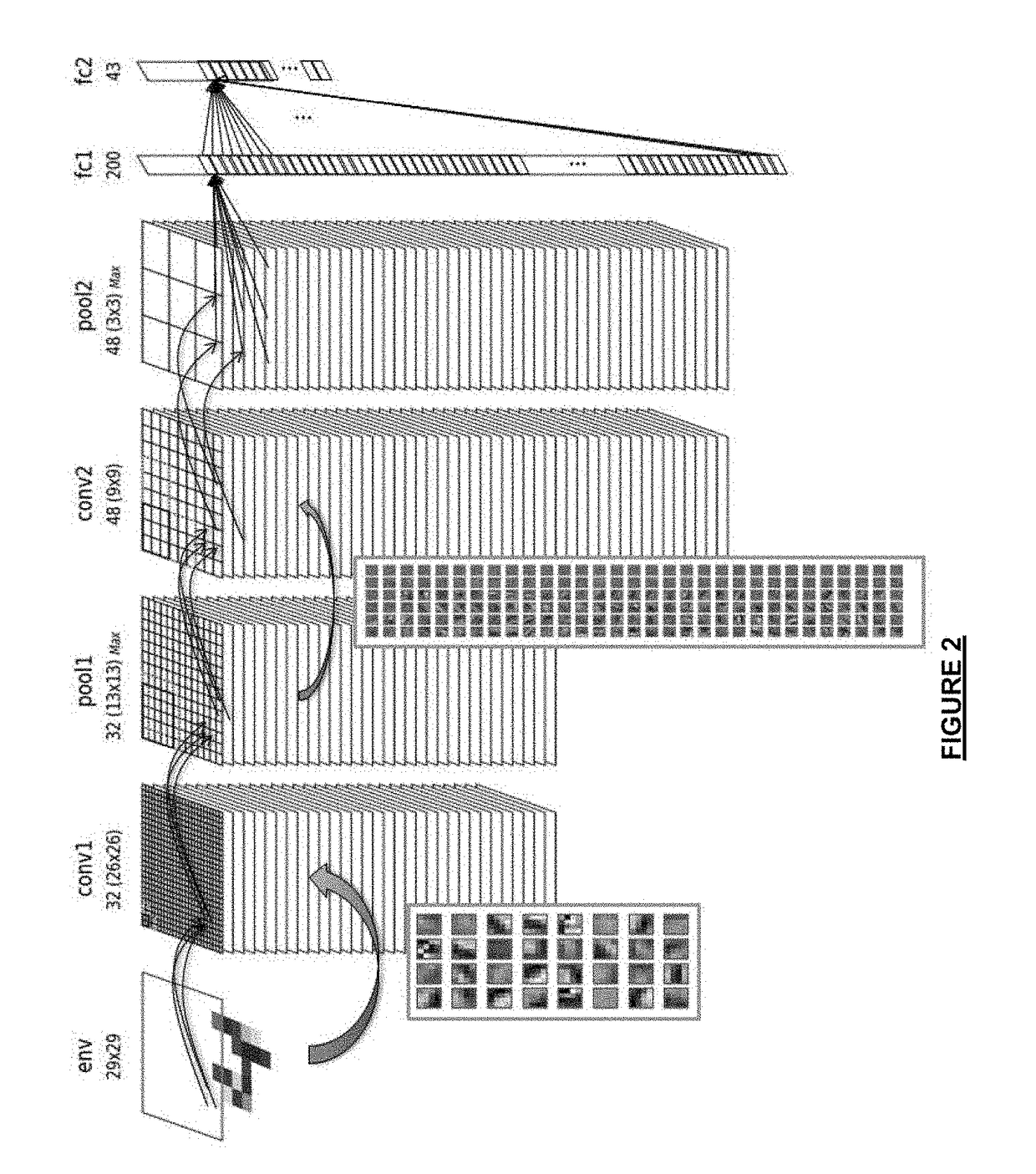
Convolutional neural network
ActiveUS20170200078A1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease speedNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkWeight coefficient
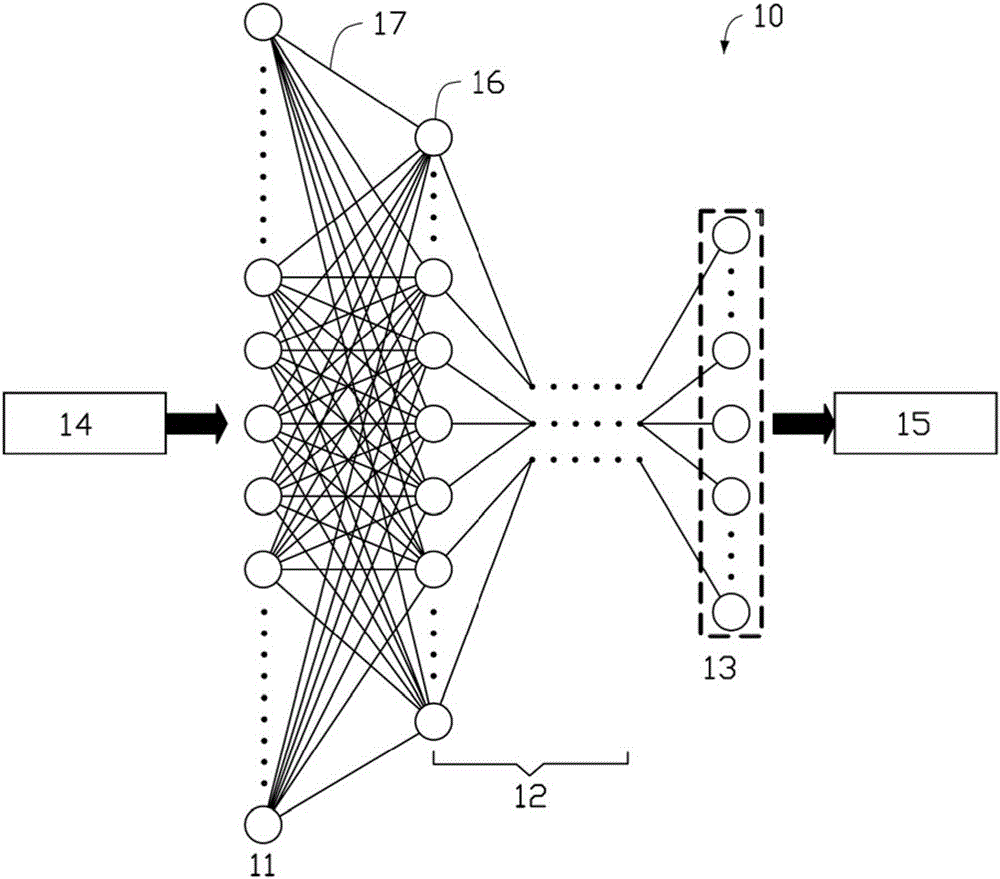
A convolutional neural network comprises a plurality of artificial neurons arranged in one or more convolution layers, each convolution layer comprising one or more output matrices, each output matrix comprising a set of output neurons, each output matrix being connected to an input matrix, comprising a set of input neurons, by artificial synapses associated with a convolution matrix. The convolution matrix comprises the weight coefficients associated with the output neurons of the output matrix, the output value of each output neuron being determined from the input neurons of the input matrix to which the output neuron is connected and the weight coefficients of the convolution matrix associated with the output matrix. Each synapse consists of a set of memristive devices comprising at least one memristive device, each set of memristive devices storing a weight coefficient of the convolution matrix. In response to a change of the output value of an input neuron of an input matrix, the neural network is capable of dynamically associating each set of memristive devices storing a coefficient of the convolution matrix with an output neuron connected to the input neuron. The neural network further comprises an accumulator for each output neuron, the accumulator being configured to accumulate the values of the weight coefficients stored in the sets of memristive devices dynamically associated with the output neuron, the output value of the output neuron being determined from the value accumulated in the accumulator.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method and apparatus for constructing a dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA)
ActiveUS20150106314A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkAnomaly detection
A circuit element of a multi-dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such circuit elements, (wherein a circuit element or component thereof may be analog or digital), a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension, a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension and, optionally, a third destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a third synapse. The DANNA may thus form multiple levels of neuron and synapse circuit elements. In one embodiment, multiples of eight inputs may be selectively received by the circuit element selectively functioning as one of a neuron and a synapse. The dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a special purpose processor for performing one of a control, anomaly detection and classification application and may comprise a first structure connected to a neuroscience-inspired dynamic artificial neural network (NIDA), comprise substructures thereof or be combined with other neural networks.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Feedback artificial neural network training method and feedback artificial neural network calculating system
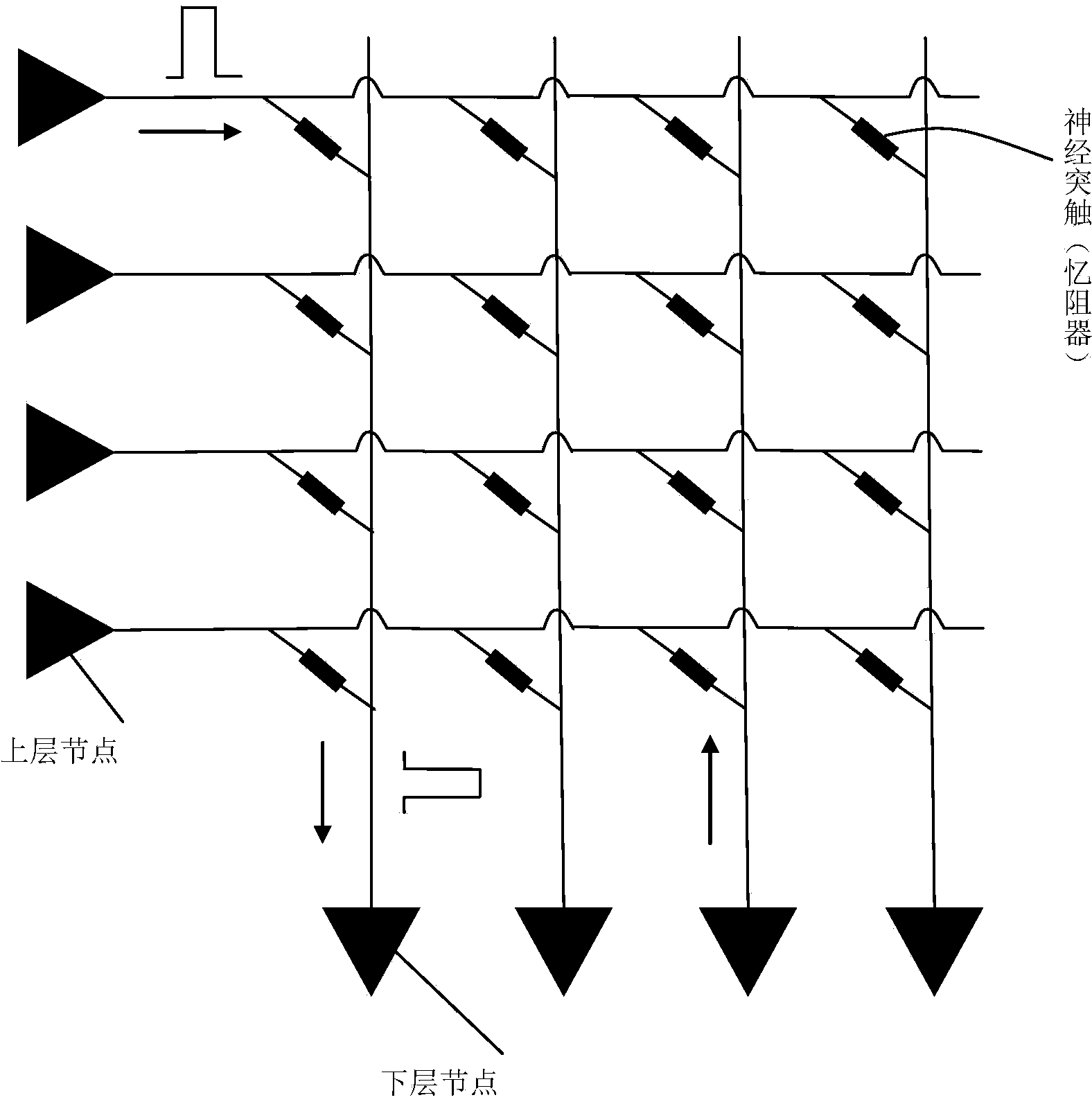
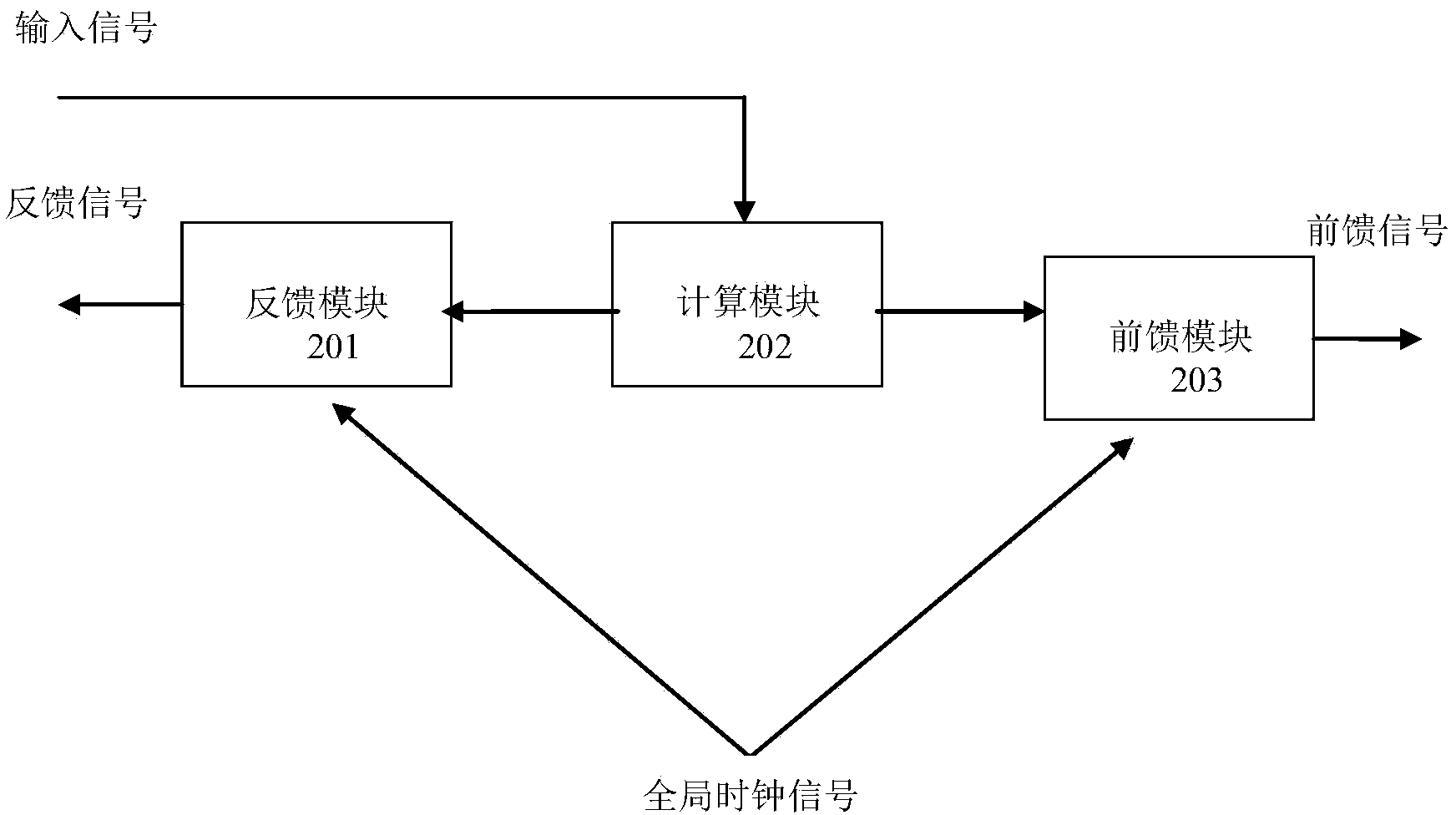
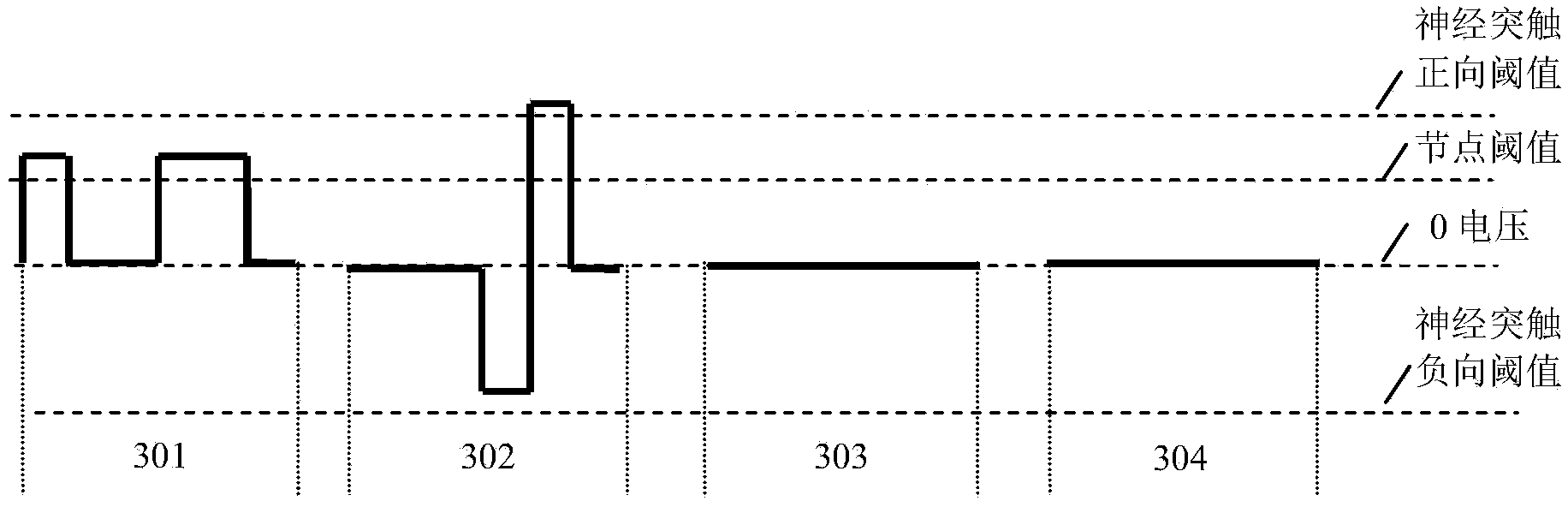
InactiveCN103455843AFast convergenceReduce energy consumptionBiological neural network modelsSynaptic weightNerve network
The invention discloses a feedback artificial neural network training method and a feedback artificial neural network calculating system and belongs to the field of calculation of neural networks. According to the artificial neural network training method, the synapse weight is adjusted according to a feedforward signal and a feedback signal at the two ends of each neural synapse; when the signals at the two ends of each neural synapse are an excitation feedforward signal and an excitation feedback signal respectively, the synapse weight is adjusted to the maximum value; when the signals at the two ends of each neural synapse are a tranquillization feedforward signal and an excitation feedback signal respectively, the synapse weight is adjusted to the minimum value. According to the feedback artificial neural network calculating system, each node circuit comprises a calculating module, a feedforward module and a feedback module and the node circuits are connected through the neural synapses simulated by memristors, and a series of pulse signals are adopted to achieve the feedback artificial neural network training method. An artificial neural network provided by the system and the method is high in rate of convergence, and the artificial neural network calculating system is few in control element, low in energy consumption and capable of being applied to data mining, pattern recognition, image recognition and other respects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
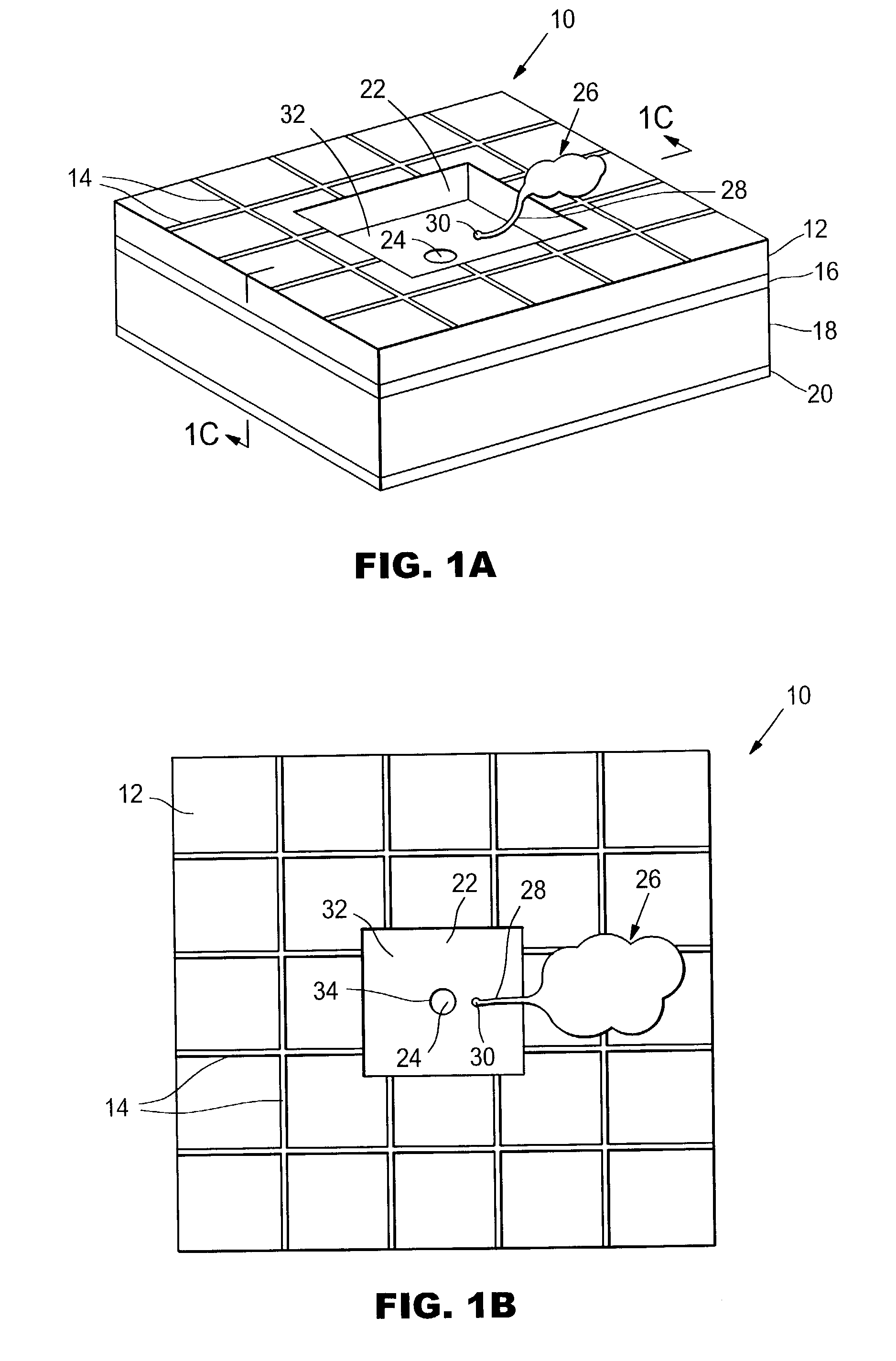
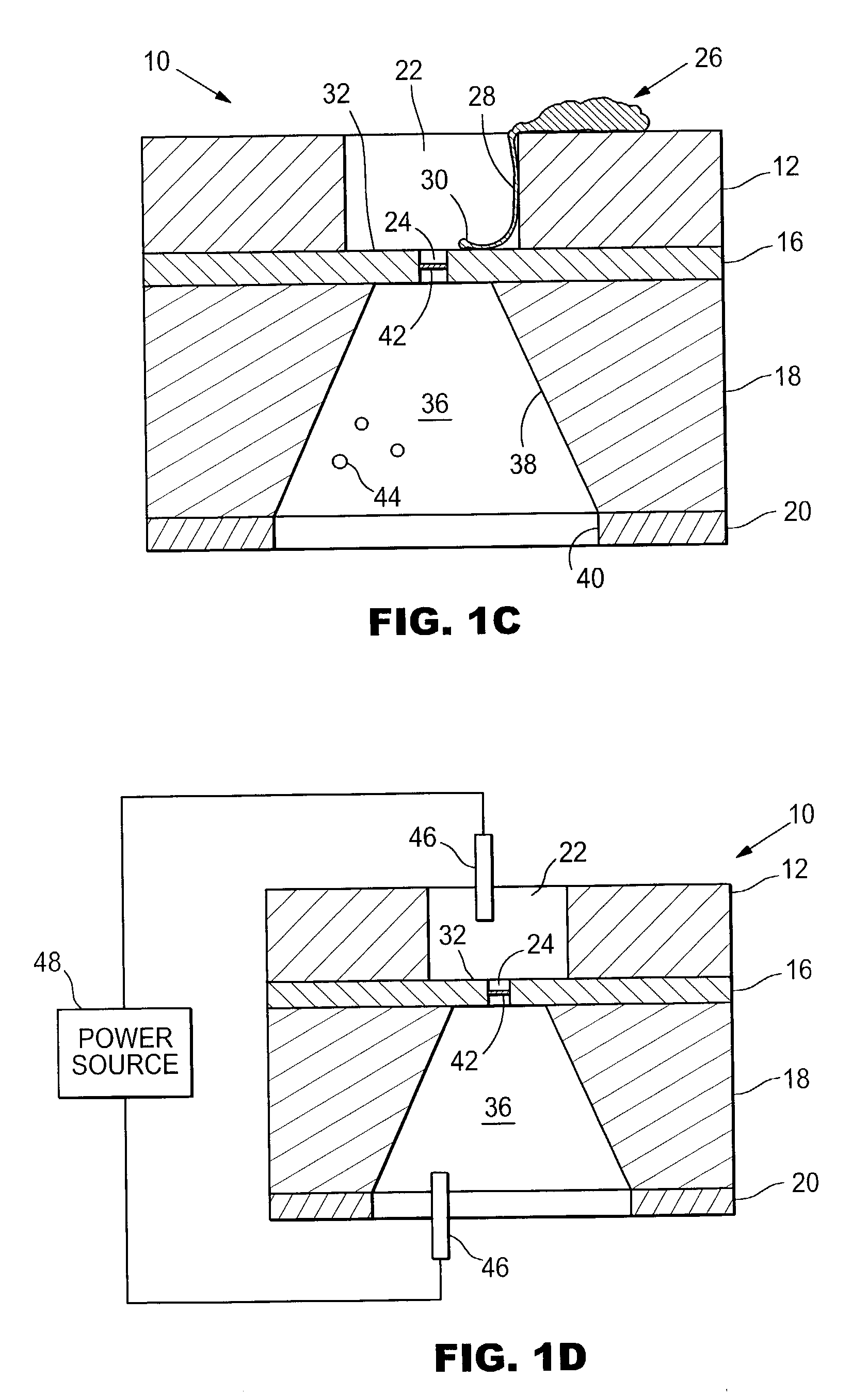
Artificial synapse chip interface for electronic prosthetic retina
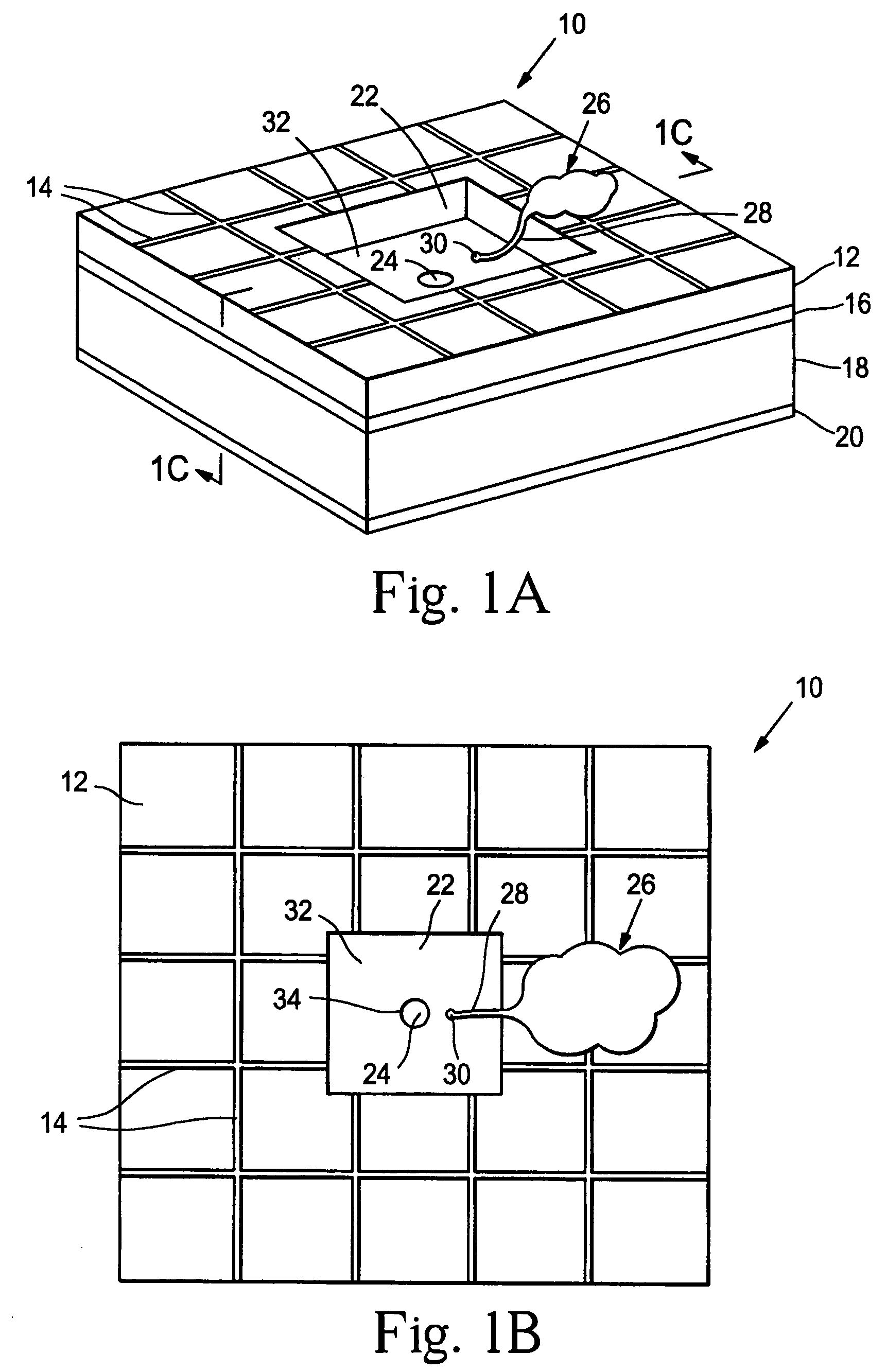
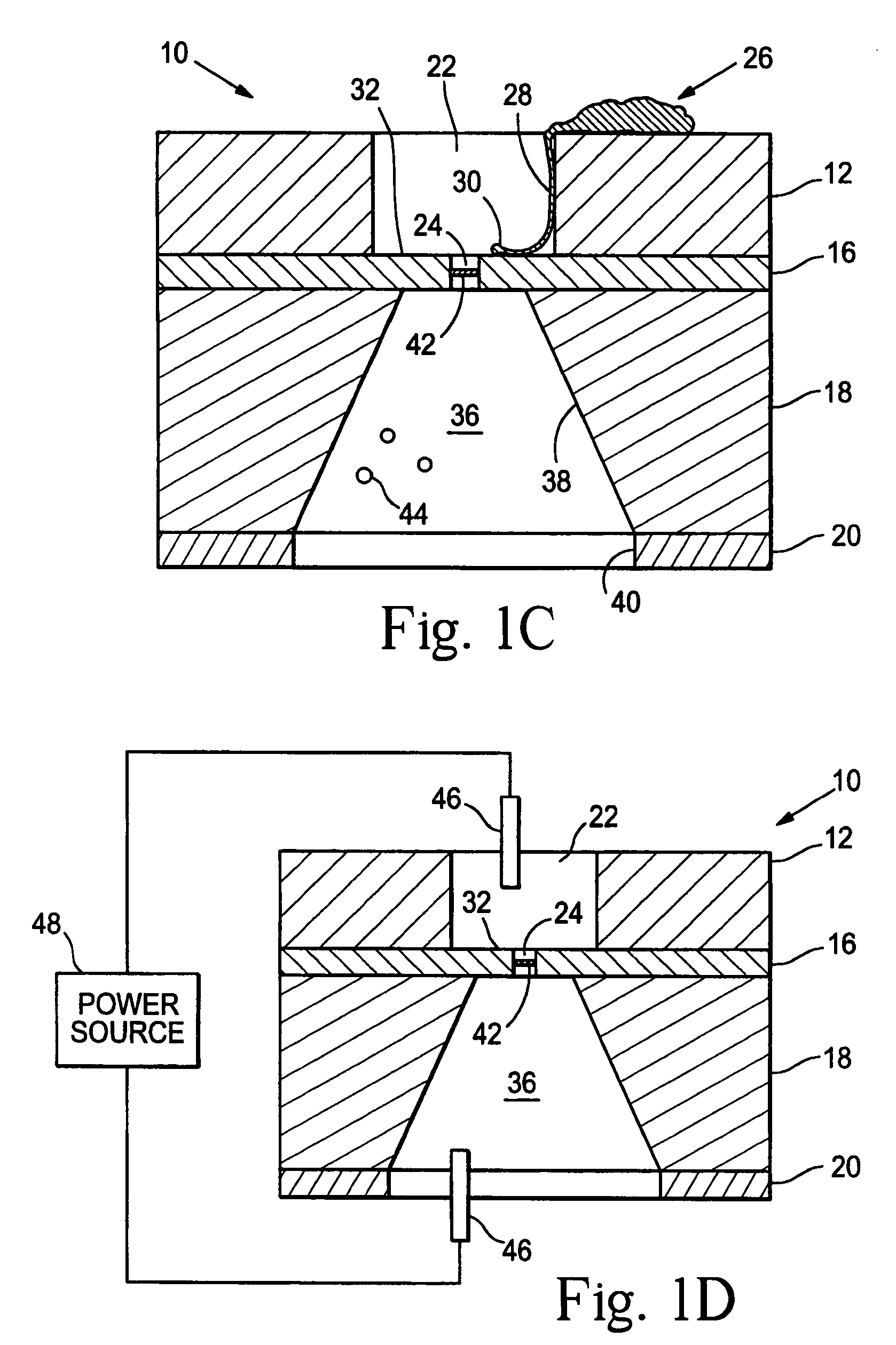
InactiveUS7001608B2Efficient deliveryRecovery functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoElectron
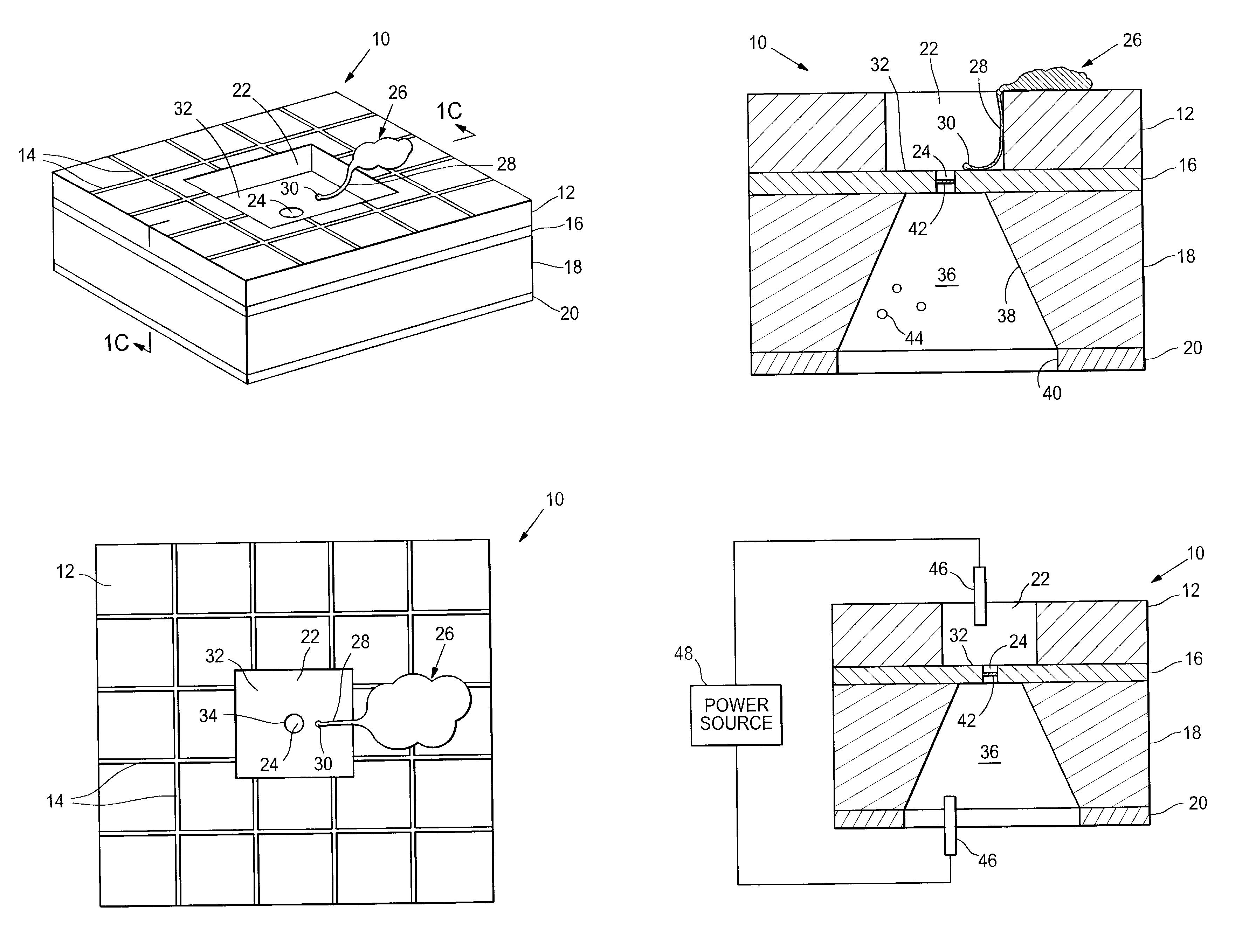
The invention provides microfabricated devices and methods for directing the growth of a cell process to form an artificial synapse. The devices are called artificial synapse chips. The artificial synapse comprises a nanofabricated aperture (about 50–100 nm in size) that connects the cell process to a chemical or electrical means of neuronal excitation. Such an aperture width mimics the length scales of a natural synapse and thus emphasizes the localized spatial relationship between a neuron and a stimulation source. The invention further provides devices and methods for regenerating a nerve fiber into an electrode. The invention thus provides a regeneration electrode that uses a novel neural interface for stimulation and that uses novel surface methods for directing neuronal growth making possible in vivo connection of the devices to neural circuitry in a retina and other anatomical locations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Deep neural network system based on memristor
ActiveCN105224986AIncrease computing speedHigh densityNeural architecturesInformation processingNerve network
The invention provides a deep neural network system based on a memristor, which comprises an input layer, an output layer and multiple hidden layers, wherein the input layer receives an external information input mode, the external information input mode is calculated and converted layer by layer, and an external output result is generated finally by the output layer. A synaptic weight of the deep neural network adopts the memristor for simulation, and the feature that resistance of the memristor changes along with applied electric signals is used to simulate a connection strength behavior of a connection synapse between neural networks. The invention further provides an information processing system for the deep neural network system based on the memristor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for providing random selection and long-term potentiation and depression in an artificial network
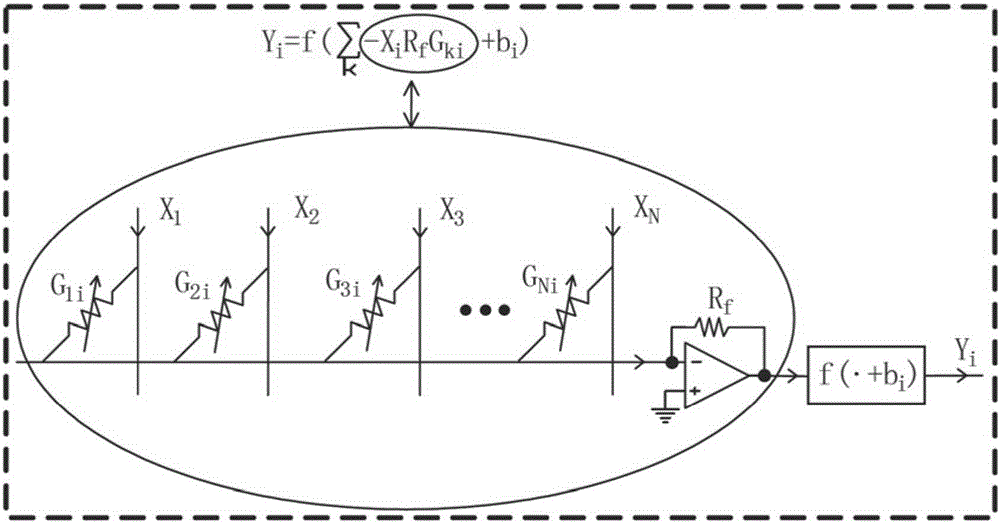
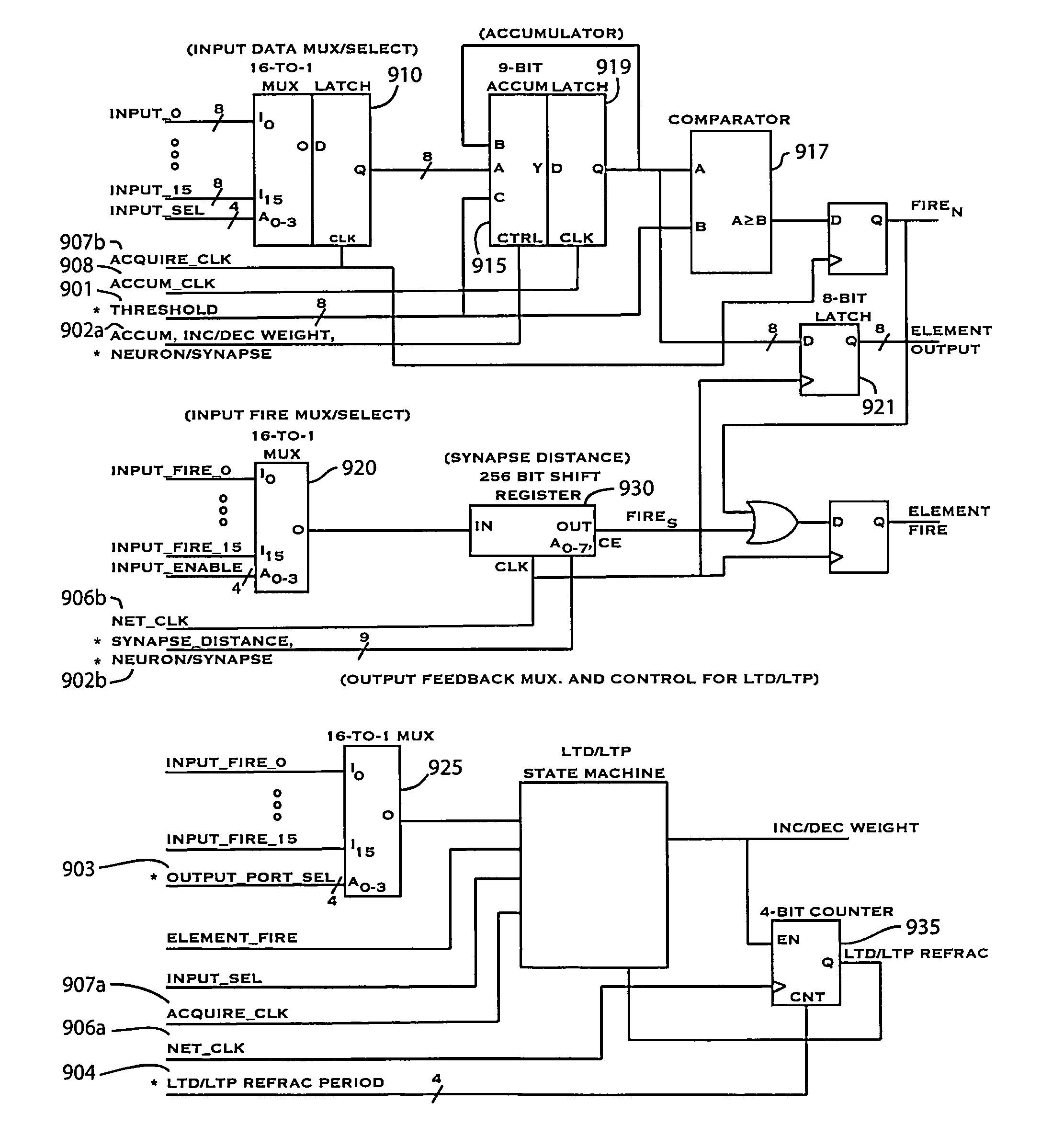
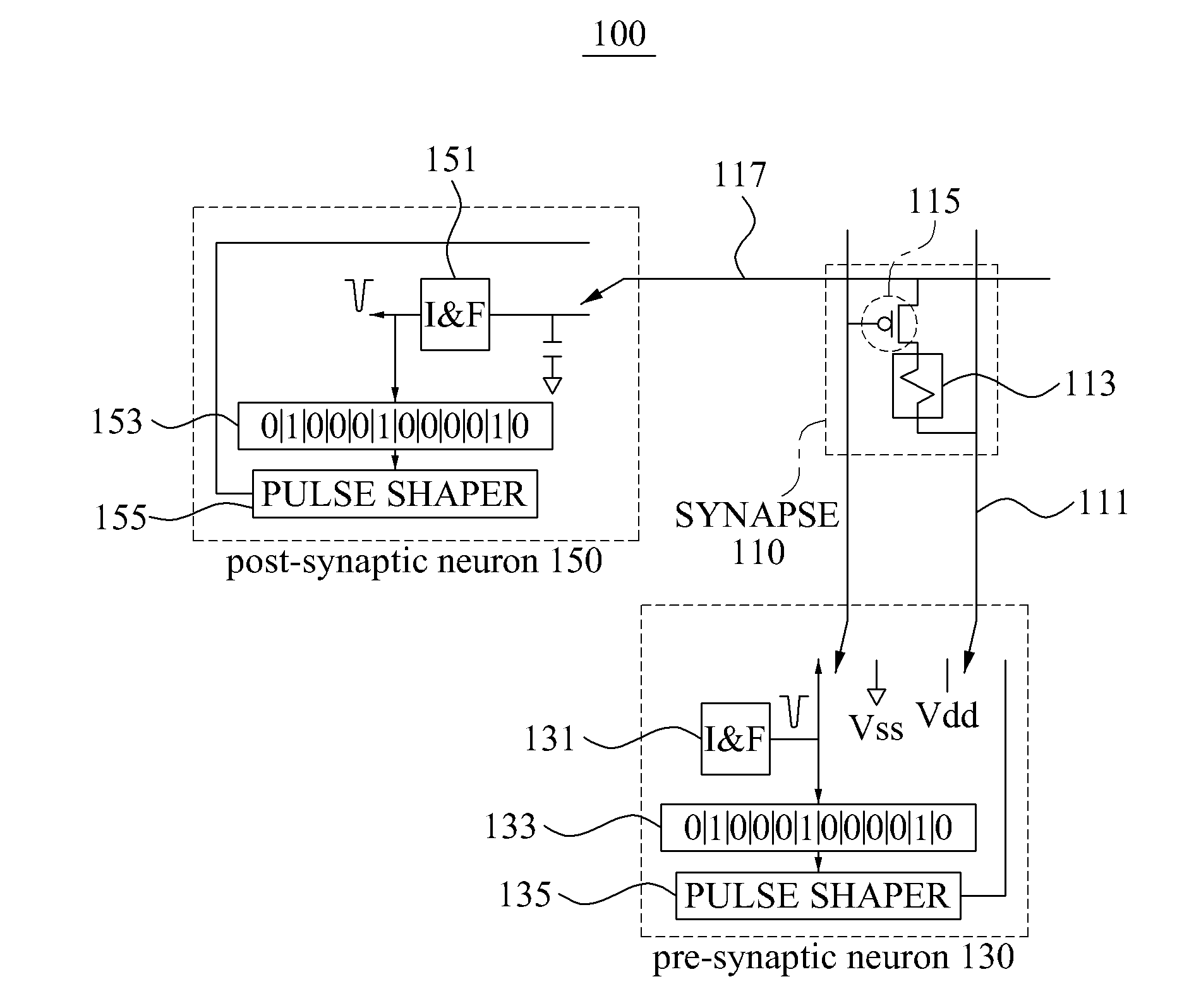
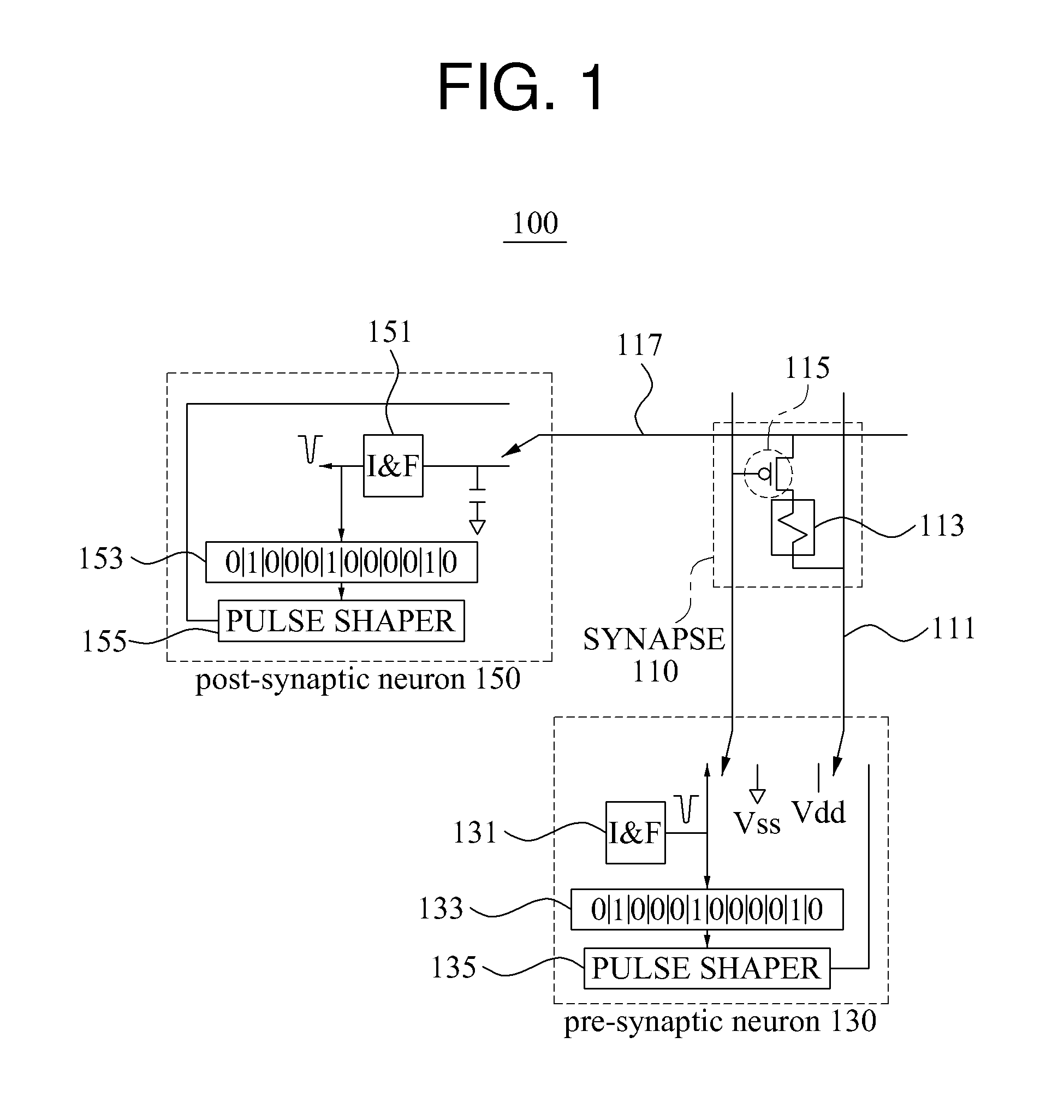
ActiveUS20150106315A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuronSynapse structure
A digital circuit element of a two dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the digital circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such digital circuit elements, a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension, a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension and, optionally, a third destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a third synapse thus forming multiple levels of neuron and synapse digital circuit elements. In one embodiment, multiples of eight inputs may be selectively received by the digital circuit element selectively functioning as one of a neuron and a synapse. The dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may implement long-term potentiation or depression to facilitate learning through the use of an affective system and random selection of input events.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Neuromorphic circuit
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Methods of treating anxiety disorders
Disclosed are methods of treating an anxiety disorder, e.g., obsessive compulsive disorder, in an individual, comprising identifying an individual in need thereof and treating that individual to antagonize opioid receptor activity and to restore normal monoaminergic tone within the synapse.
Owner:OREXIGEN THERAPEUTICS INC
Method and apparatus for modeling a neural synapse function by utilizing a single conventional MOSFET
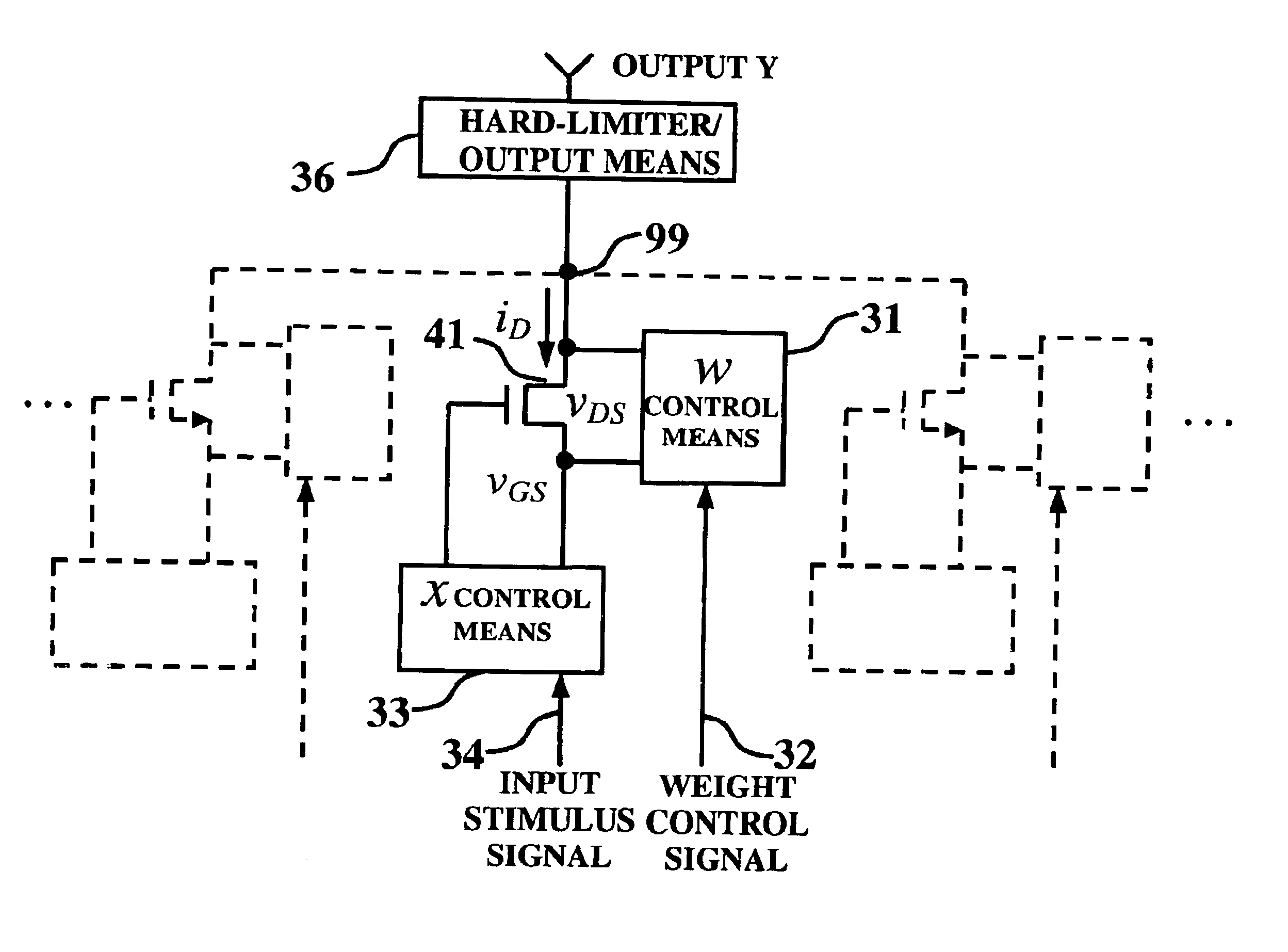
InactiveUS6829598B2Great potentialSimple methodDigital computer detailsDigital storageMOSFETFunctional modeling
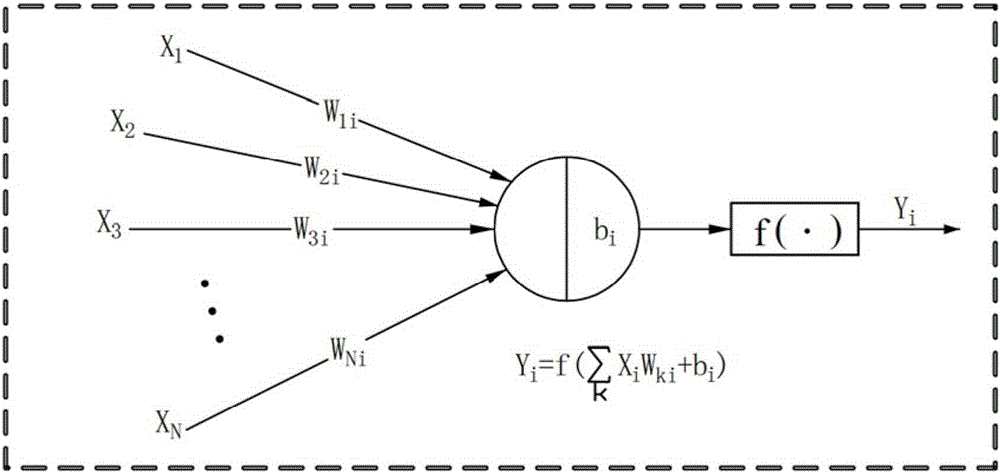
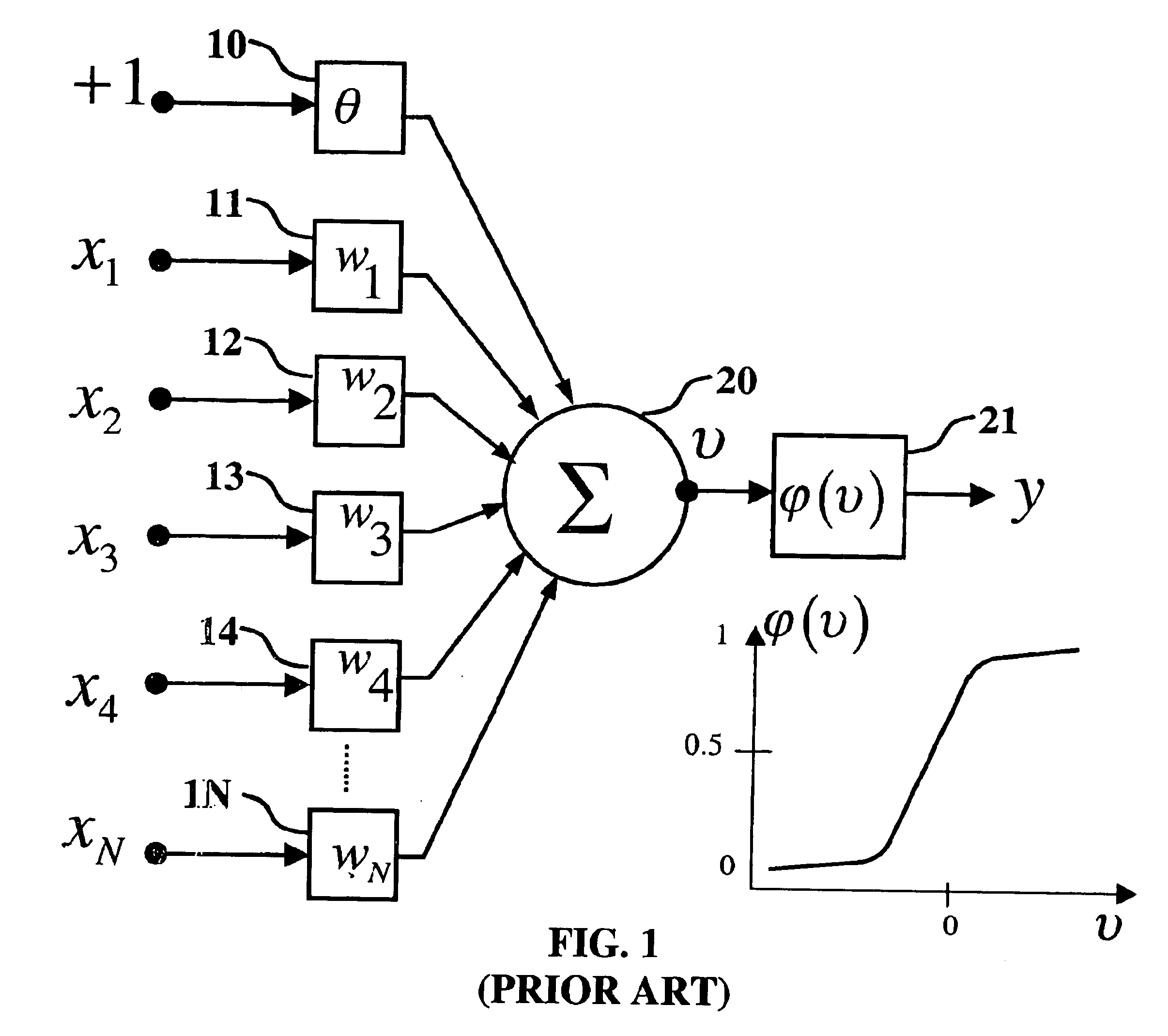
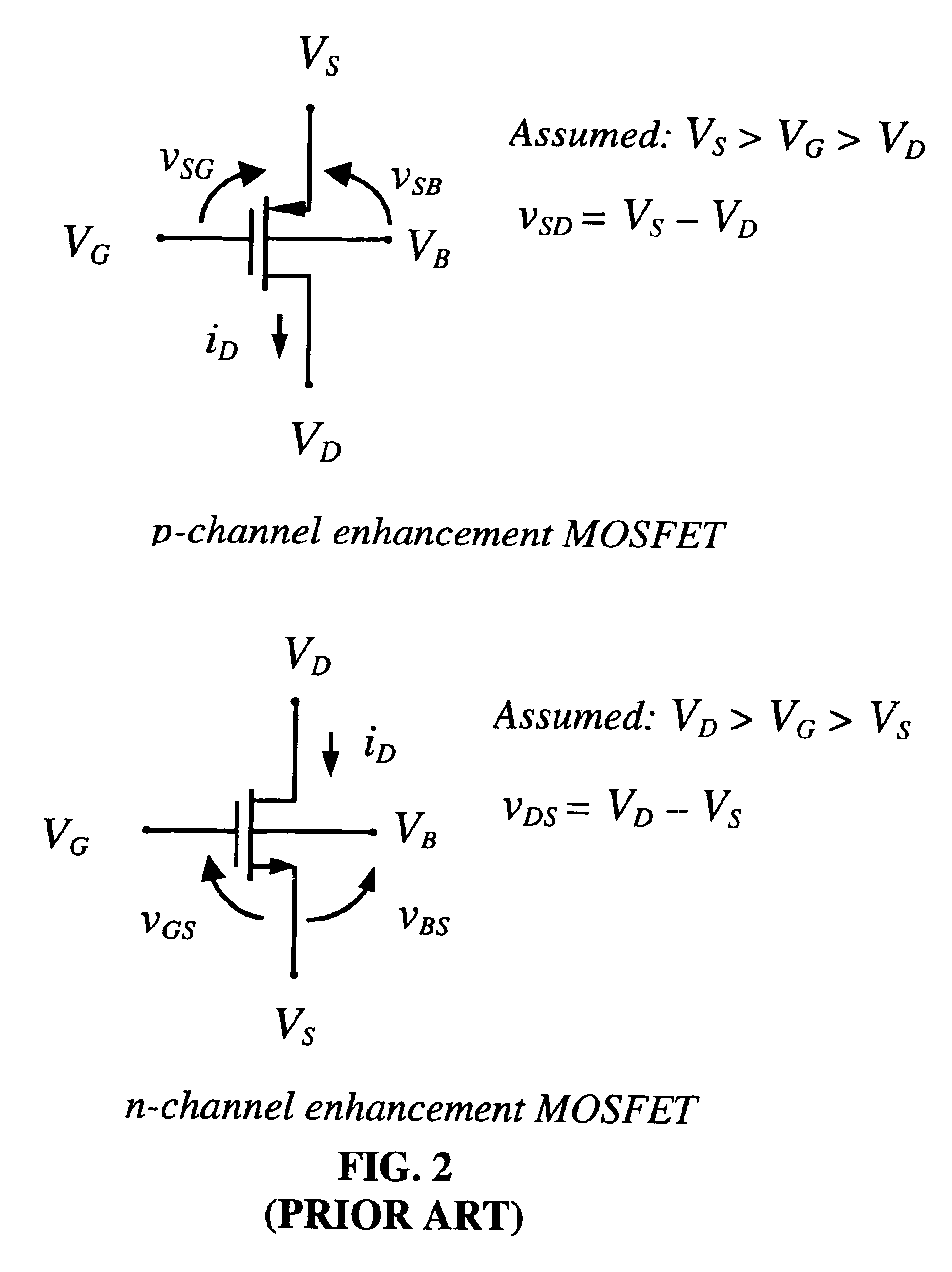
A method and apparatus for modeling a neural synapse function in analog hardware whereby the multiplication function inherent to the operation of a neural synapse is computed by applying a voltage on the gate-source terminals and an independent voltage on drain-source terminals of a MOSFET further using the resultant drain current of the latter device in non-saturation mode as function implementing a computation essentially close to multiplication function between the aforesaid voltages. Analog circuit is provided, capable of generating an output current signal which is proportional in magnitude, within a certain range, to a function computing essentially a sum of weighted input signals-products of corresponding pair of current input signal, and voltage control signal applied to a plurality of inputs thus capable of constructing an artificial neuron model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Synapse for function cell of spike timing dependent plasticity (STDP), function cell of stdp, and neuromorphic circuit using function cell of stdp
ActiveUS20120317063A1Synaptic weight can be decreasedReduce resistanceDigital computer detailsDigital storageSpike-timing-dependent plasticityNeuromorphic circuits
A synapse for a spike timing dependent (STDP) function cell includes a memory device having a variable resistance, such as a memristor, and a transistor connected to the memory device. A channel of the memory device is connected in series with a channel of the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Methods of treating anxiety disorders
Disclosed are methods of treating an anxiety disorder, e.g., obsessive compulsive disorder, in an individual, comprising identifying an individual in need thereof and treating that individual to antagonize opioid receptor activity and to restore normal monoaminergic tone within the synapse.
Owner:OREXIGEN THERAPEUTICS INC
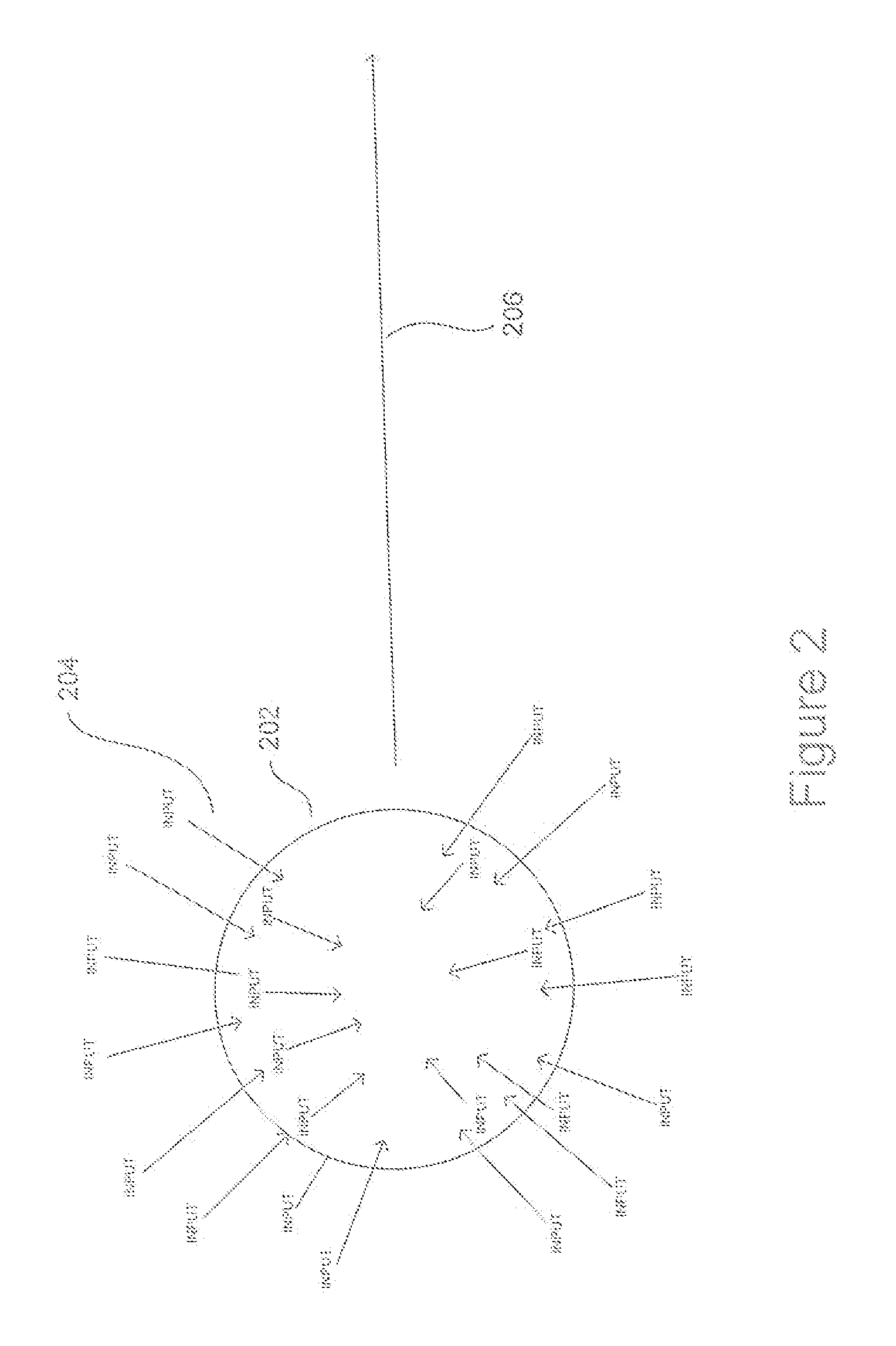
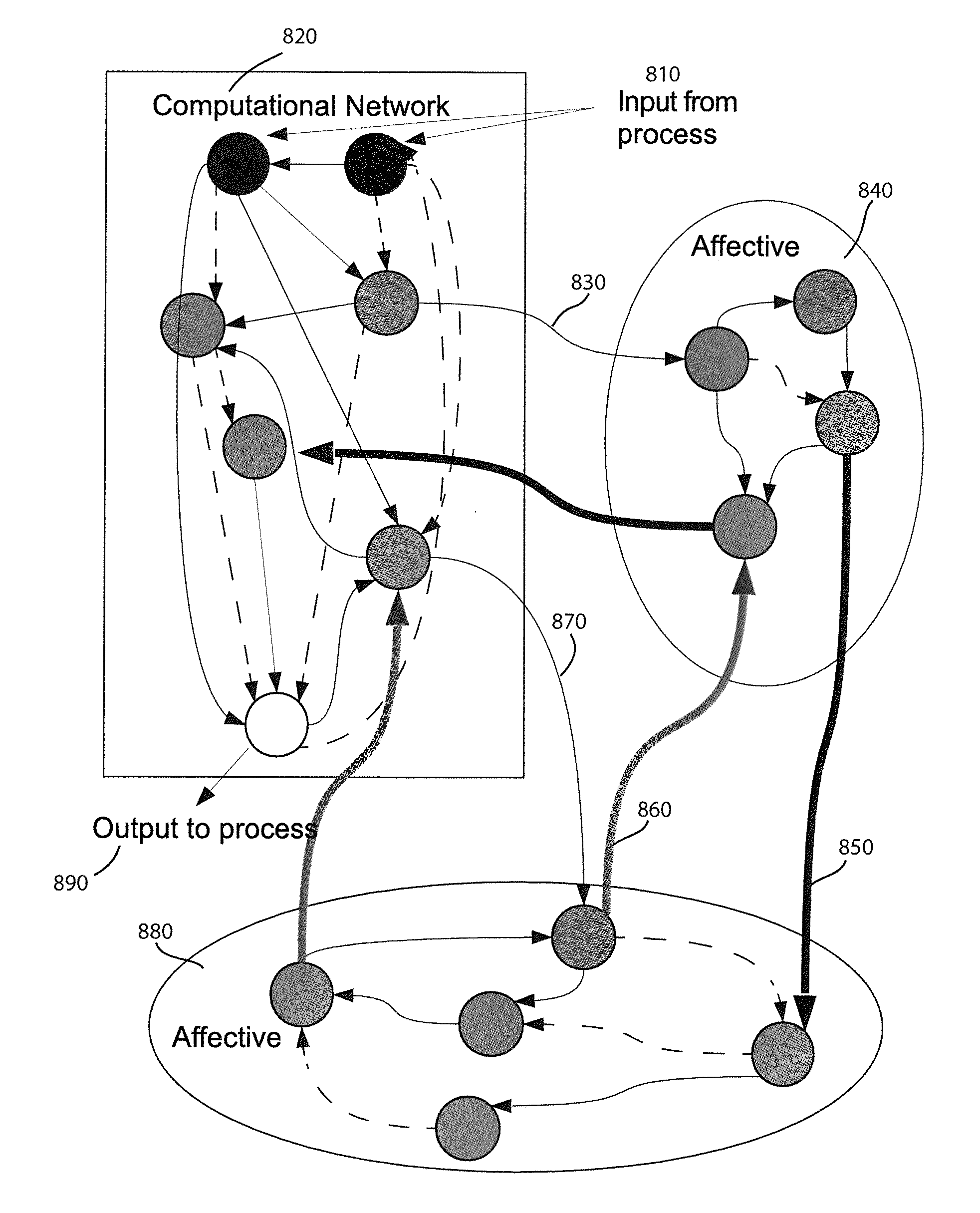
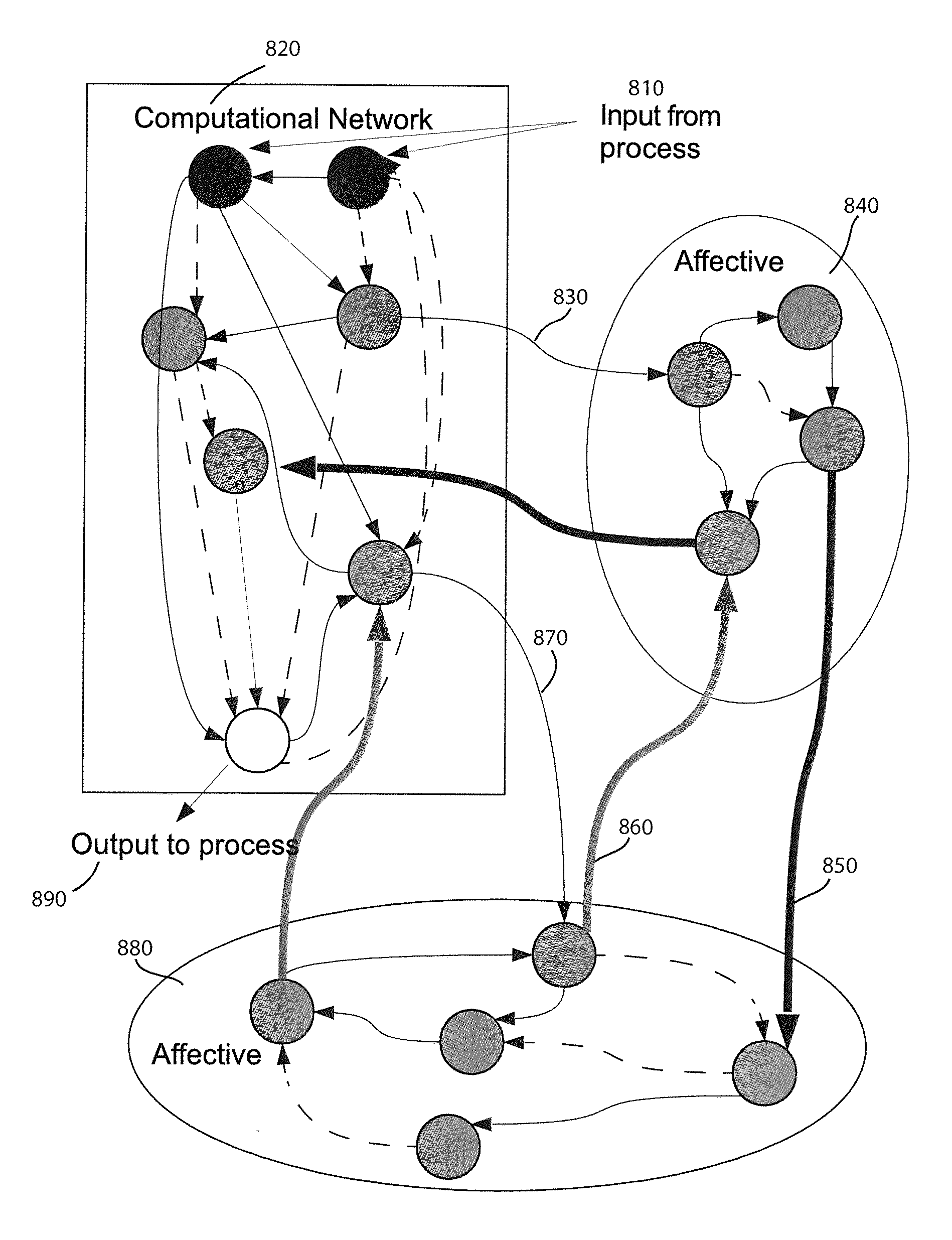
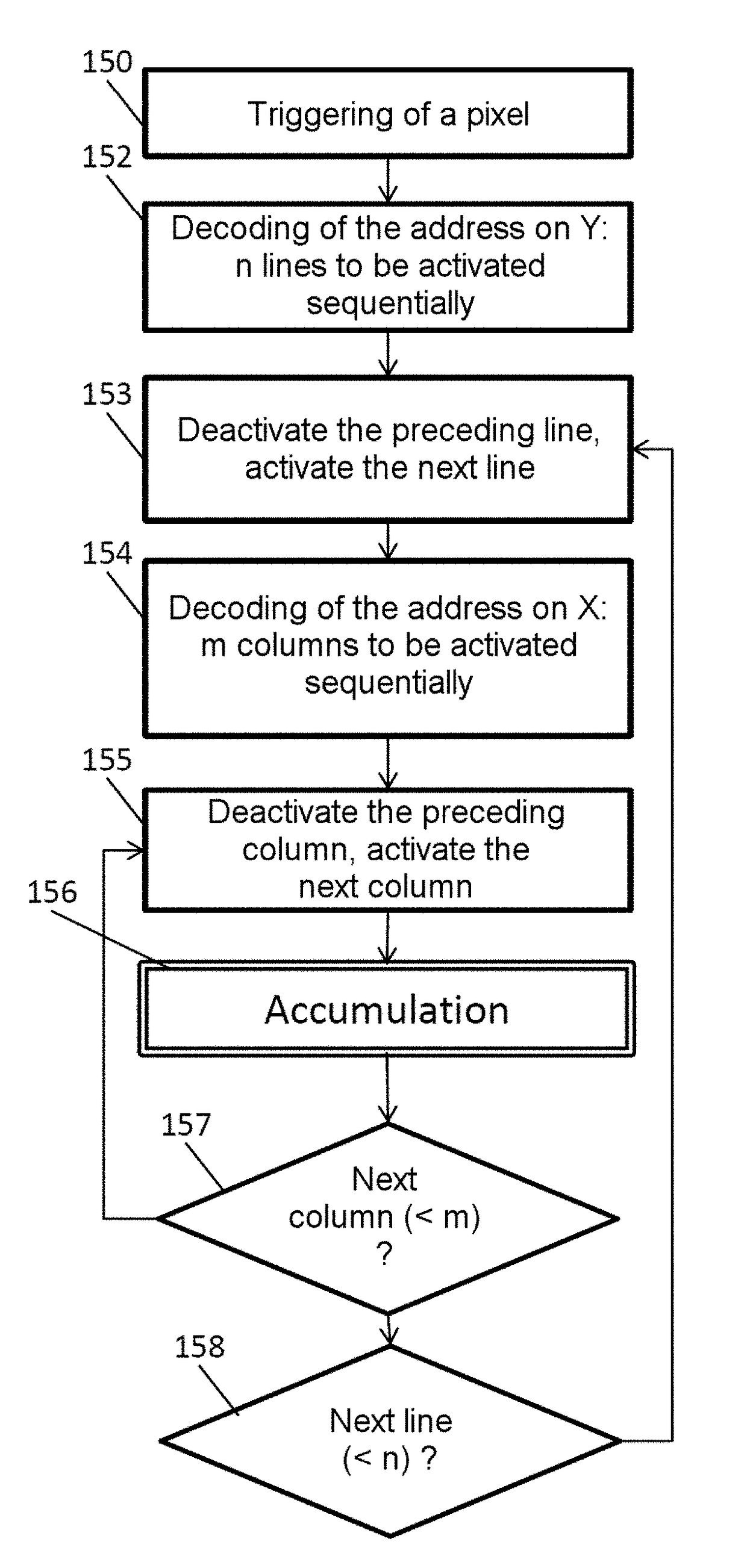
Autonomous Learning Dynamic Artificial Neural Computing Device and Brain Inspired System
ActiveUS20100076916A1Digital computer detailsAnalogue computers for chemical processesInformation processingNervous system
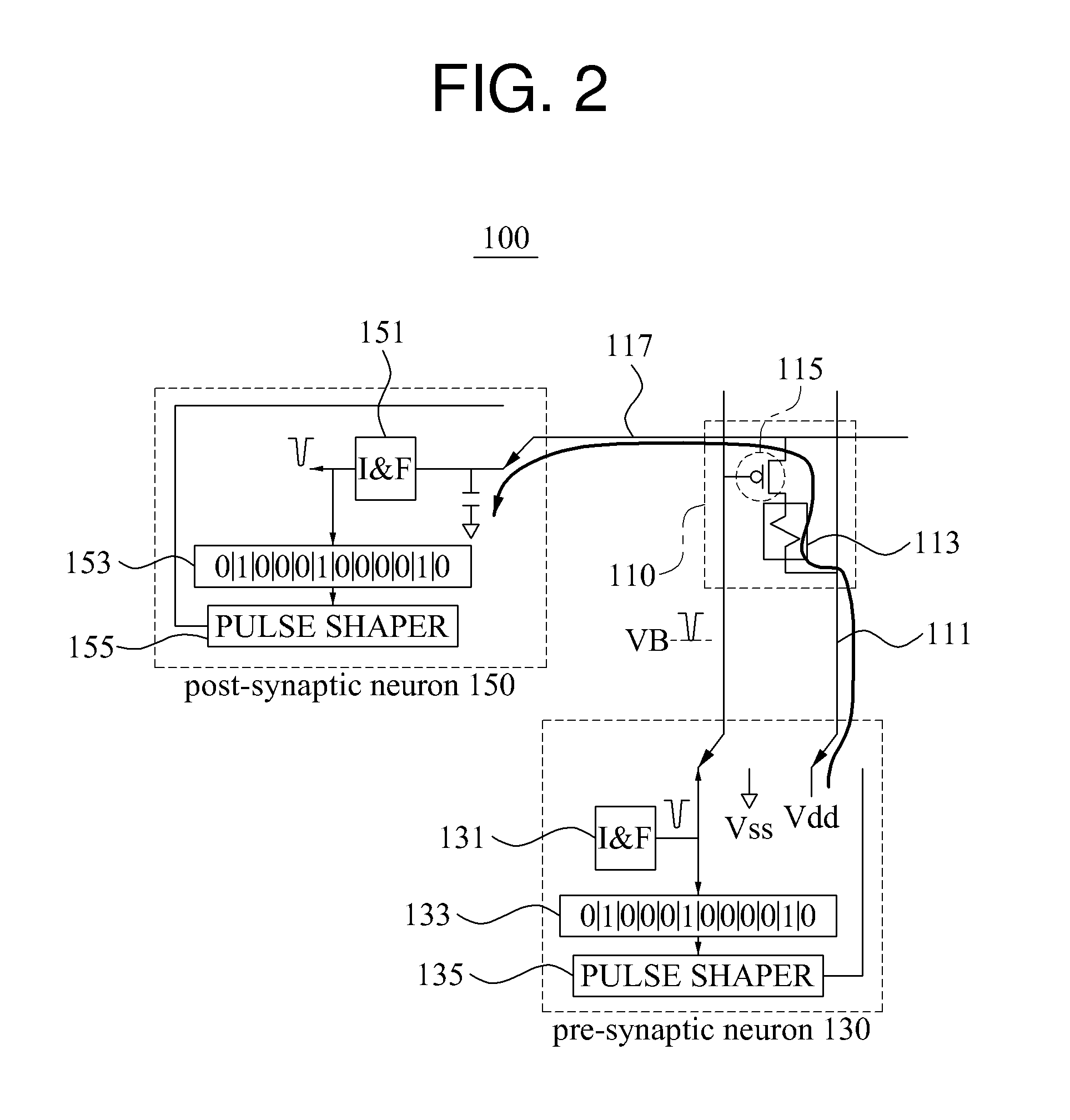
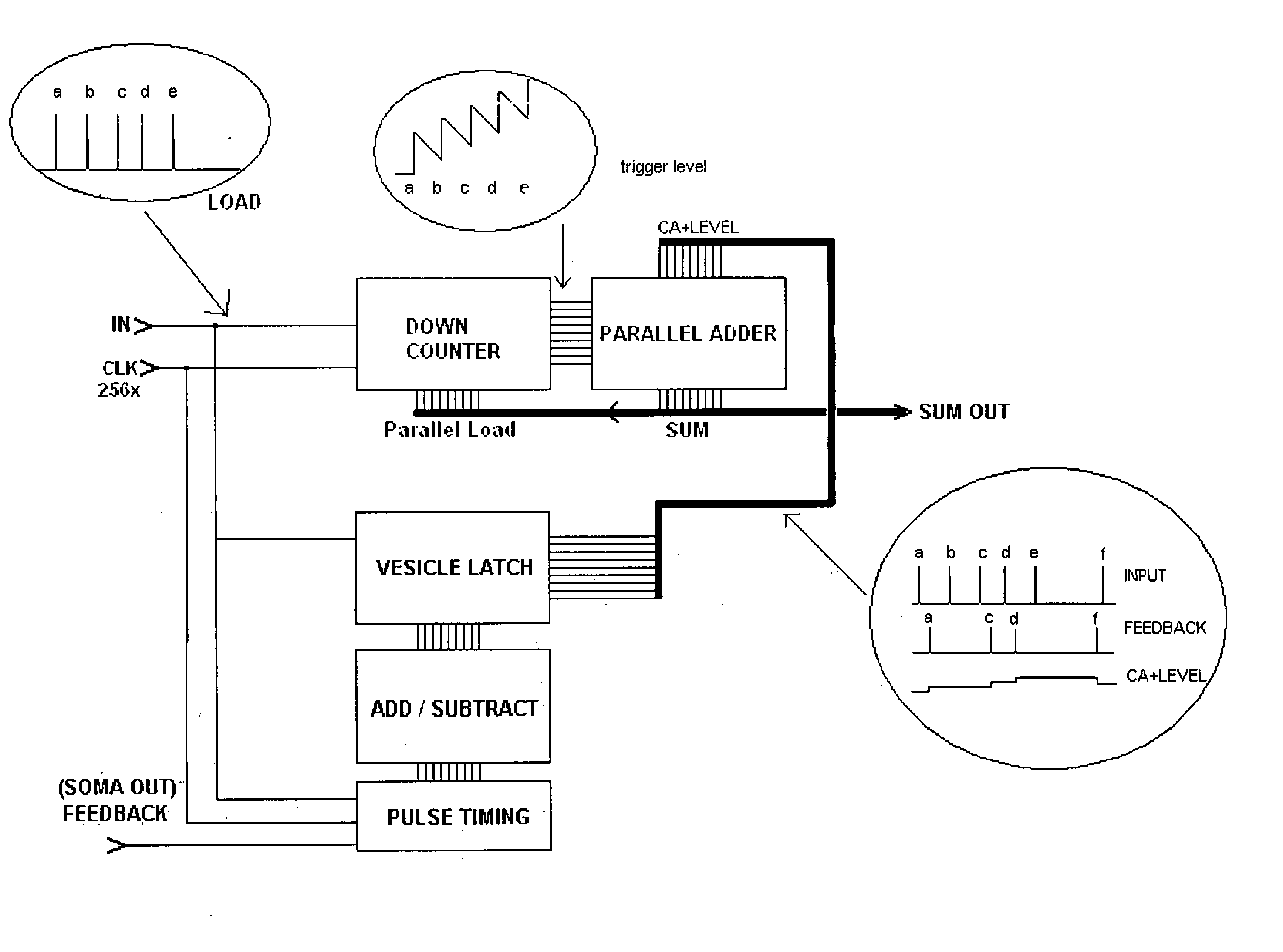
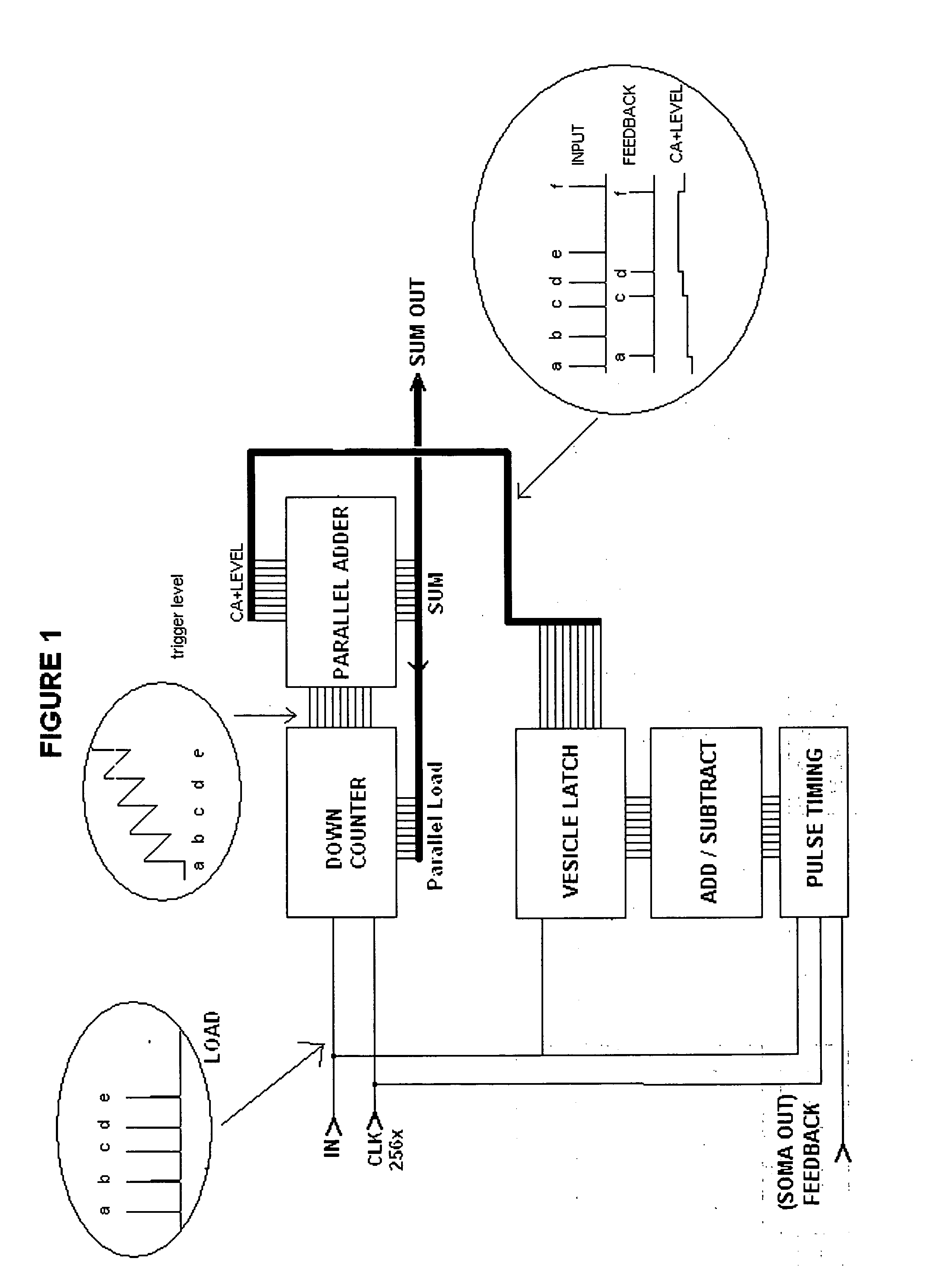
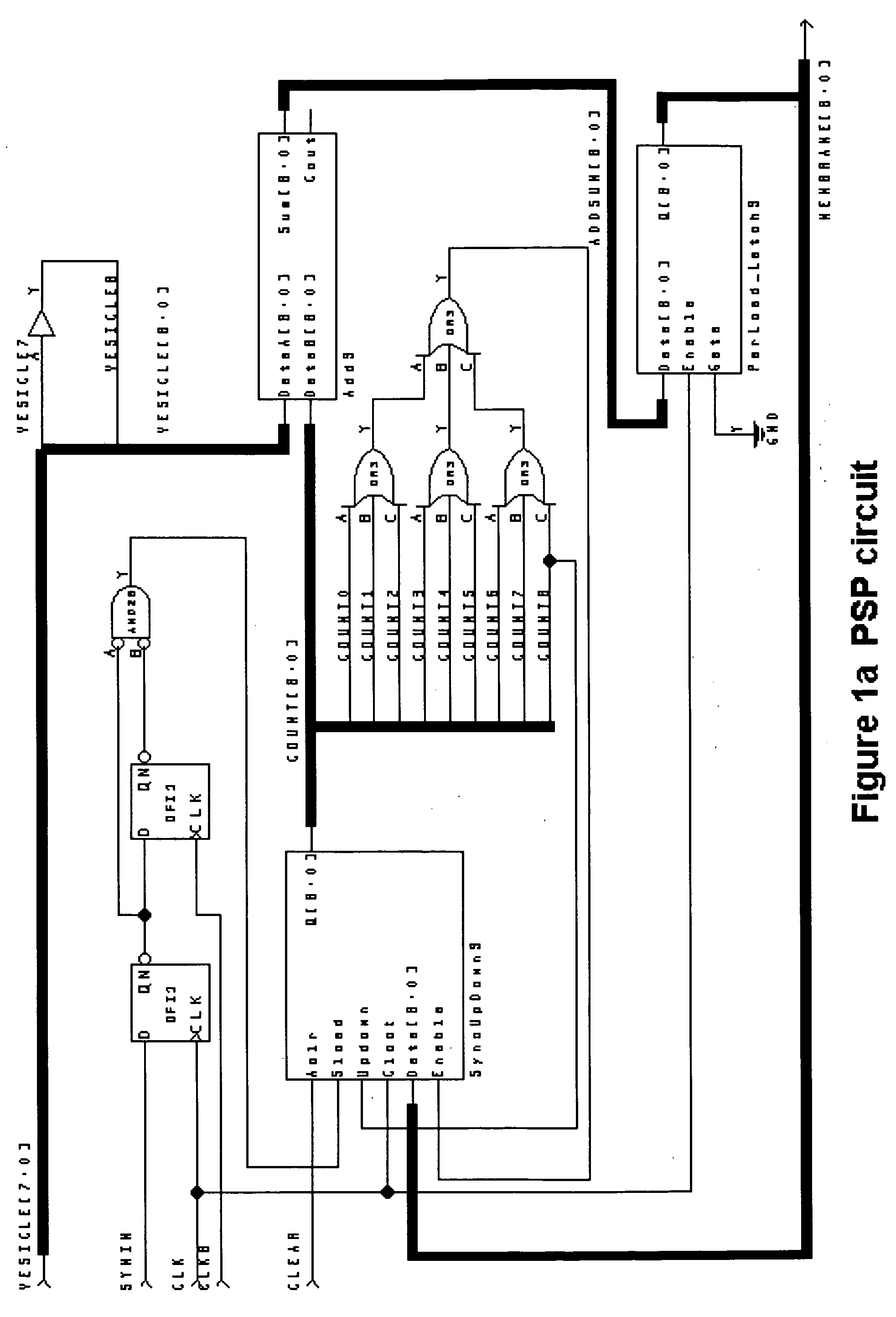
A hierarchical information processing system is disclosed having a plurality of artificial neurons, comprised of binary logic gates, and interconnected through a second plurality of dynamic artificial synapses, intended to simulate or extend the function of a biological nervous system. The system is capable of approximation, autonomous learning and strengthening of formerly learned input patterns. The system learns by simulated Synaptic Time Dependent Plasticity, commonly abbreviated to STDP. Each artificial neuron consisting of a soma circuit and a plurality of synapse circuits, whereby the soma membrane potential, the soma threshold value, the synapse strength and the Post Synaptic Potential at each synapse are expressed as values in binary registers, which are dynamically determined from certain aspects of input pulse timing, previous strength value and output pulse feedback.
Owner:BRAINCHIP INC
Synapse circuit and neuromorphic system including the same
ActiveUS20140358834A1Digital computer detailsDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A synapse circuit to perform spike timing dependent plasticity (STDP) operation is provided. The synapse circuit includes a memristor having a resistance value, a transistor connected to the memristor, and the transistor configured to receive at least two input signals. The resistance value of the memristor is changed based on a time difference between the at least two input signals received by the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
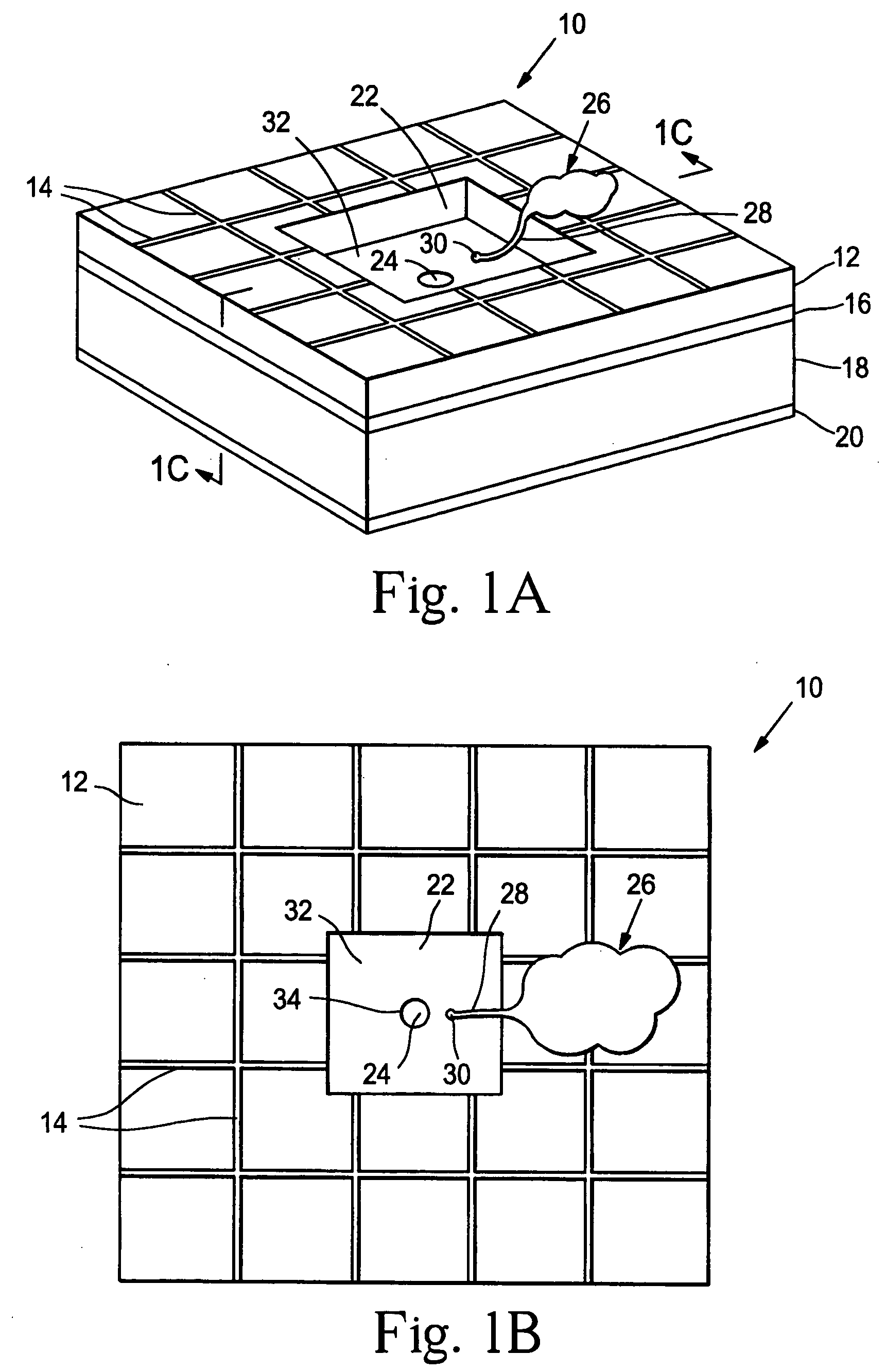
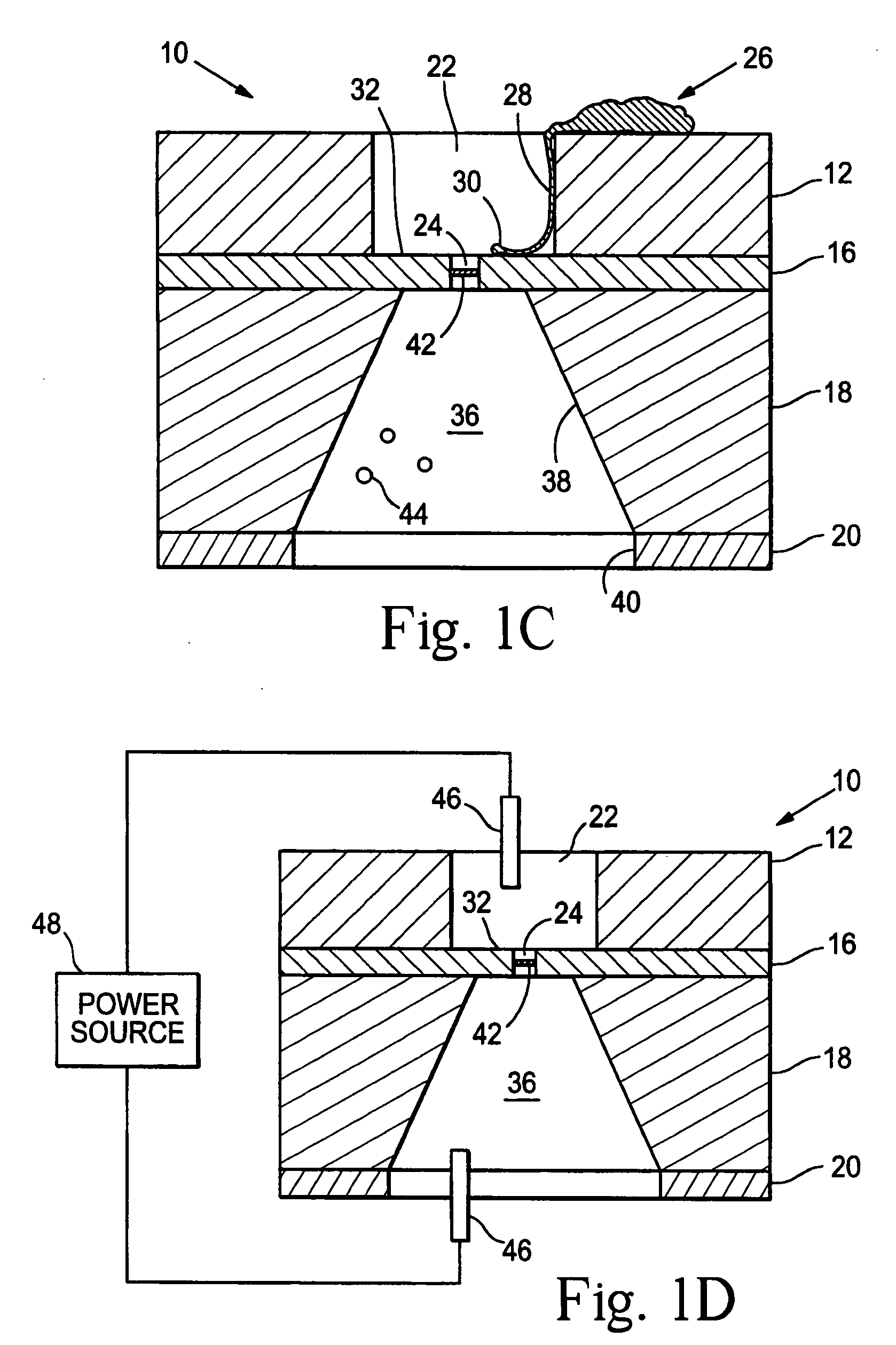
Artificial synapse chip
Devices and methods are provided for administering a fluid to a neuronal site. The device comprises a reservoir, an aperture in fluid connection to the reservoir, and electrical means for moving to the fluid to or through the aperture. The electrical means may take the form of electroosmotic force, piezoelectric movement of a diaphragm or electrolysis of a solution. The electrical means may be external to the host, implanted in the host or may be photodiodes activated by light, particularly where the neuronal site is associated with the retina.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
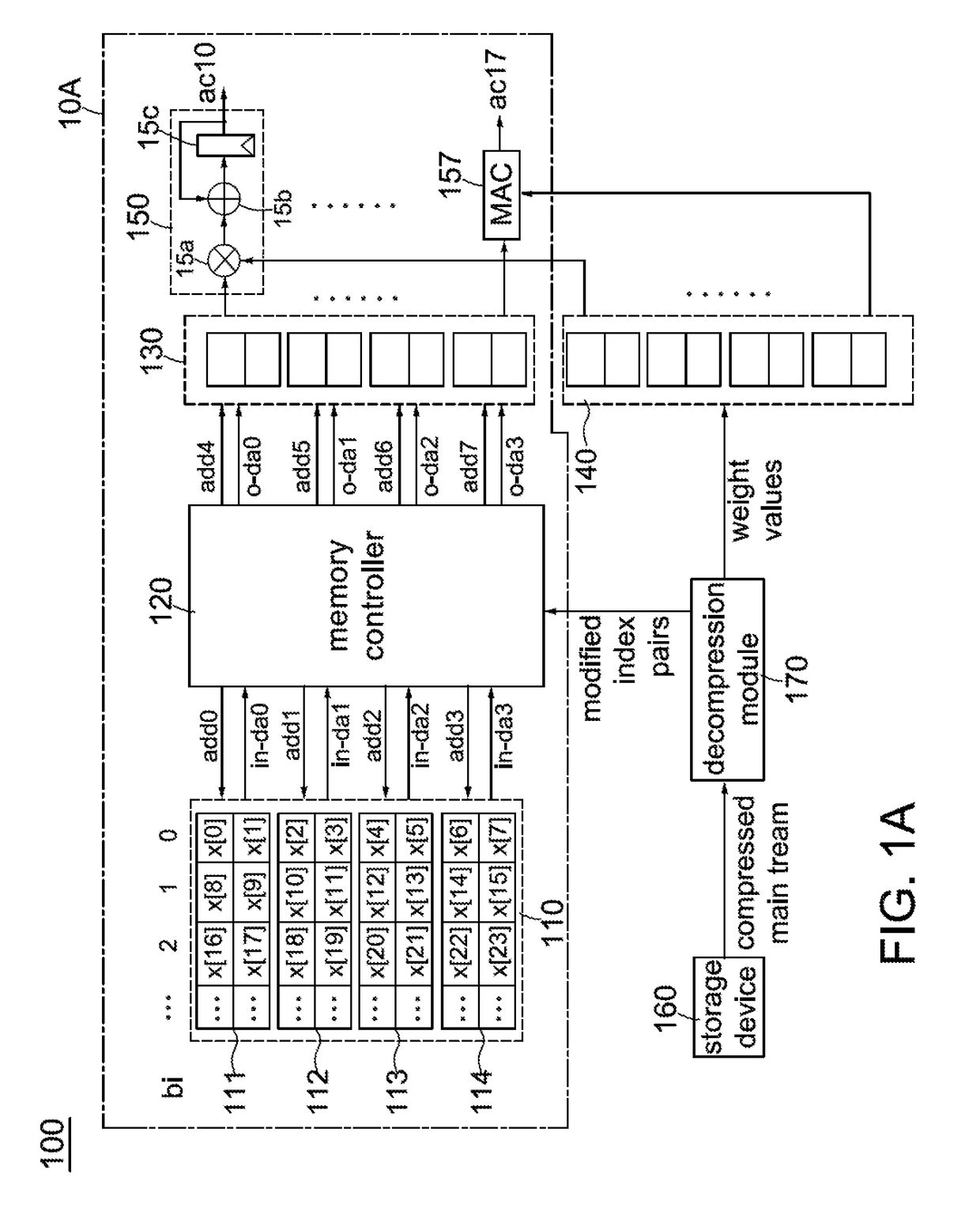
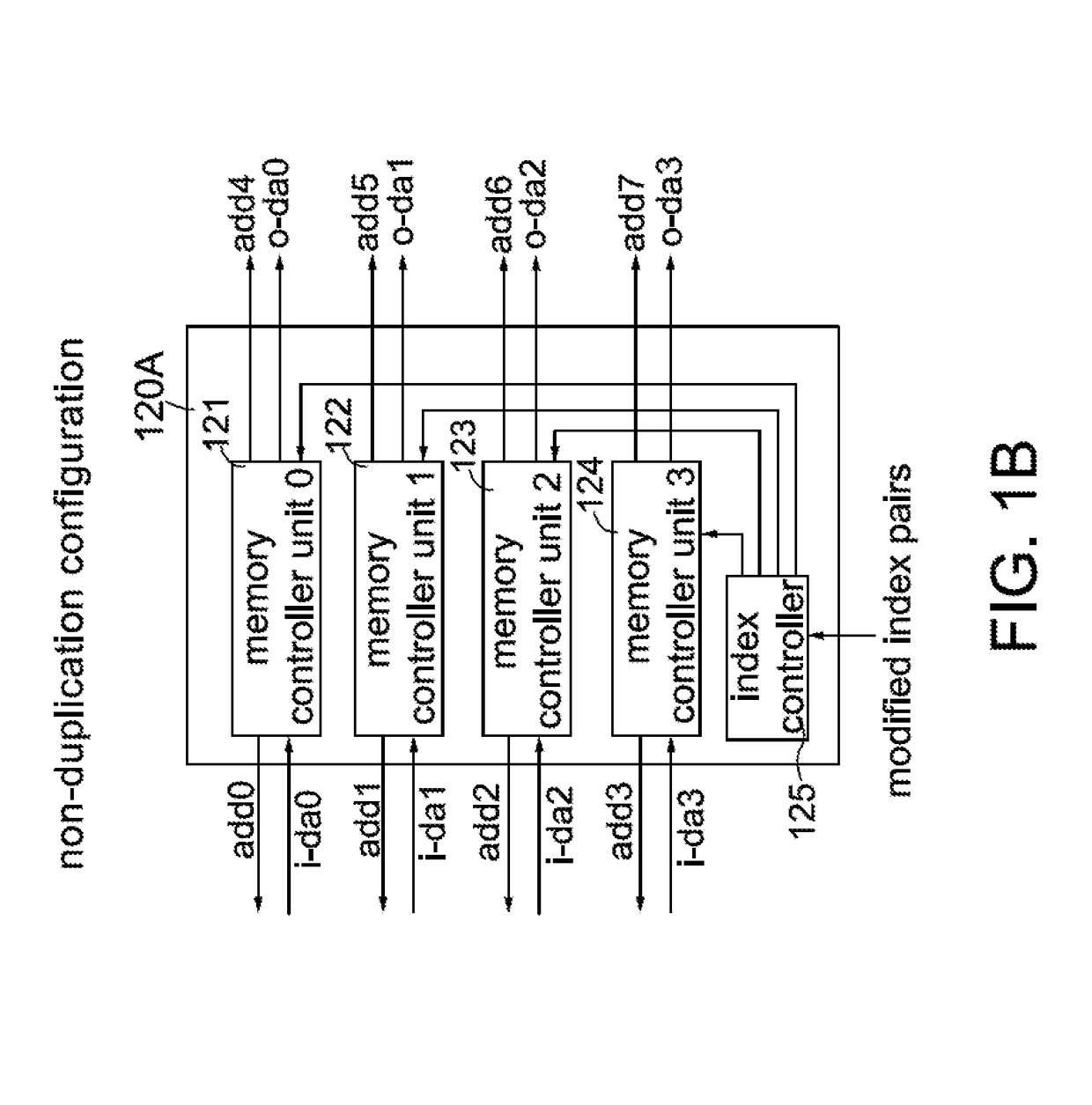
Method for matrix by vector multiplication for use in artificial neural network
ActiveUS20190012296A1Maximizing MAC hardware utilizationMaximize utilizationDigital data processing detailsCode conversionAlgorithmIndex compression
A method for matrix by vector multiplication, applied in an artificial neural network system, is disclosed. The method comprises: compressing a plurality of weight values in a weight matrix and indices of an input vector into a compressed main stream; storing M sets of synapse values in M memory devices; and, performing reading and MAC operations according to the M sets of synapse values and the compressed main stream to obtain a number M of output vectors. The step of compressing comprises: dividing the weight matrix into a plurality of N×L blocks; converting entries of a target block and corresponding indices of the input vector into a working block and an index matrix; removing zero entries in the working block; shifting non-zero entries row-by-row to one of their left and right sides in the working block; and, respectively shifting corresponding entries in the index matrix.
Owner:BRITISH CAYMAN ISLANDS INTELLIGO TECH INC
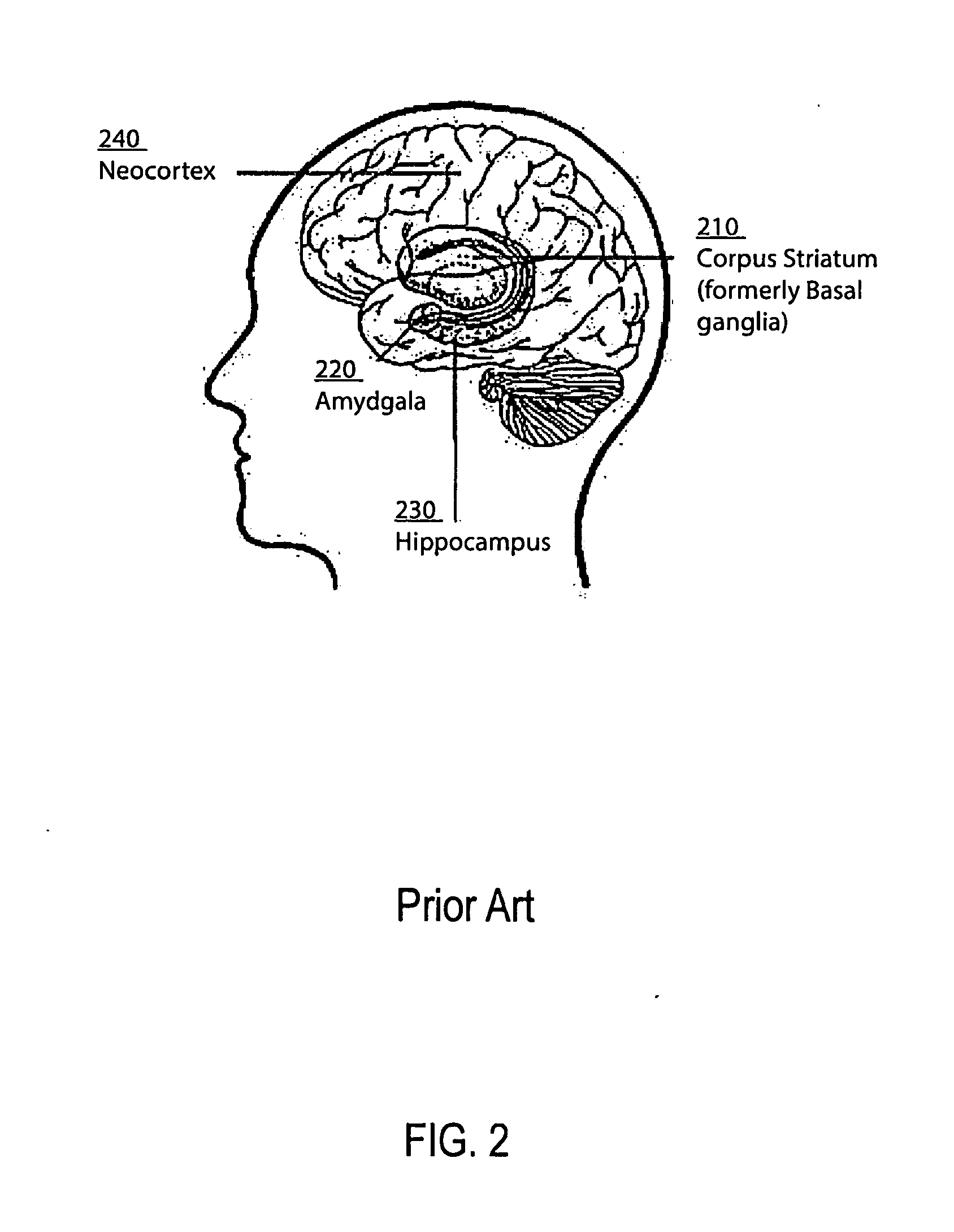
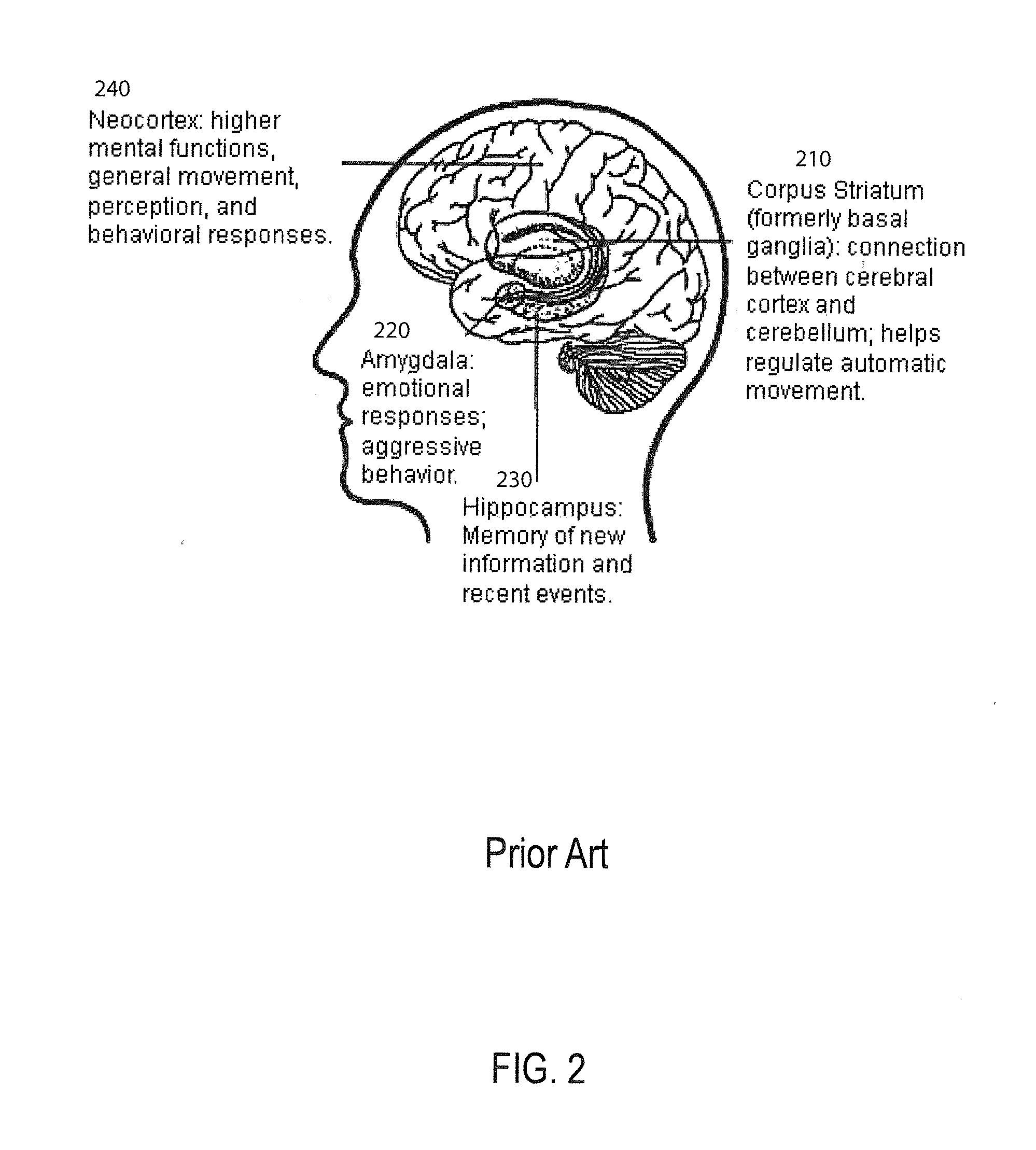
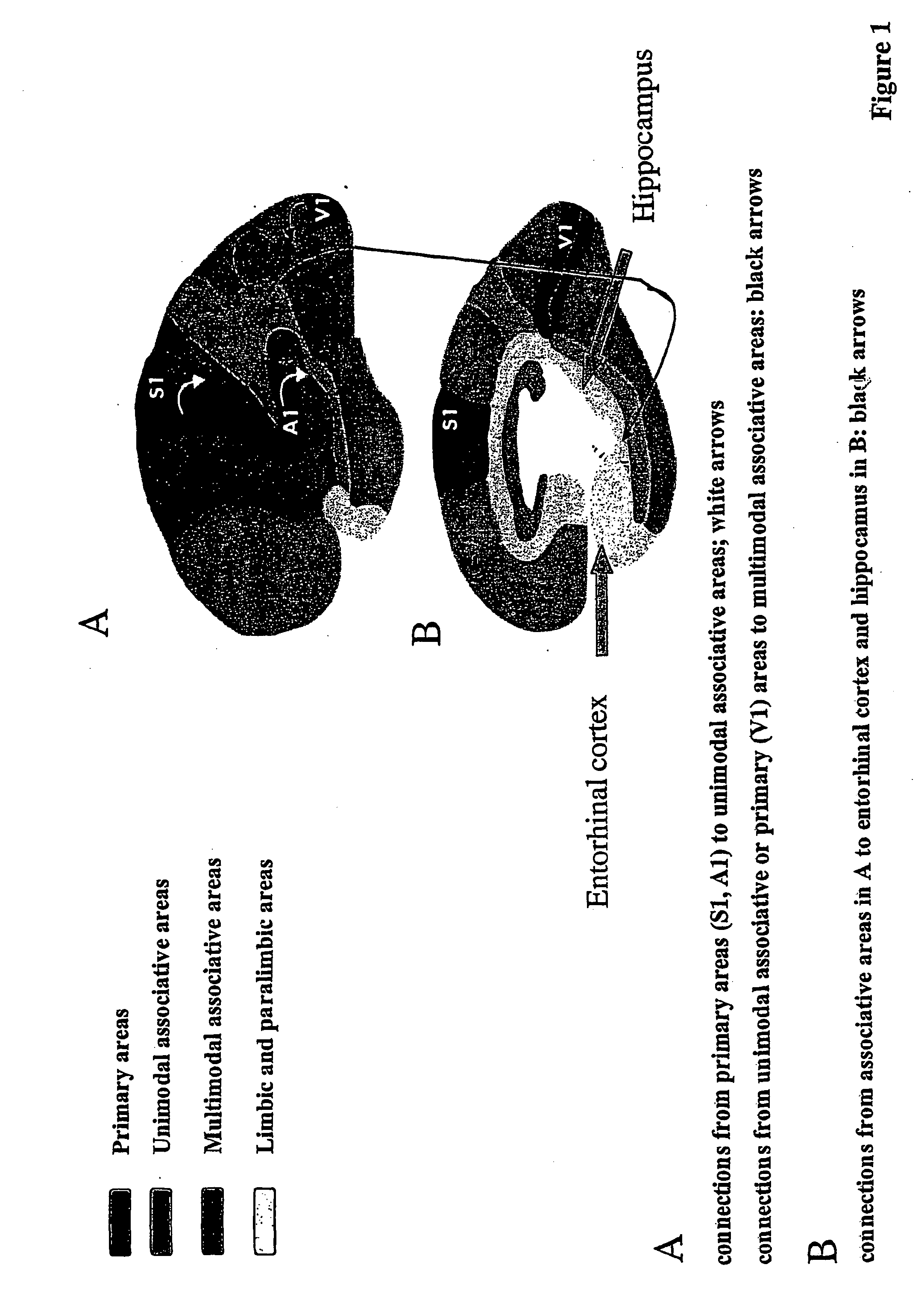
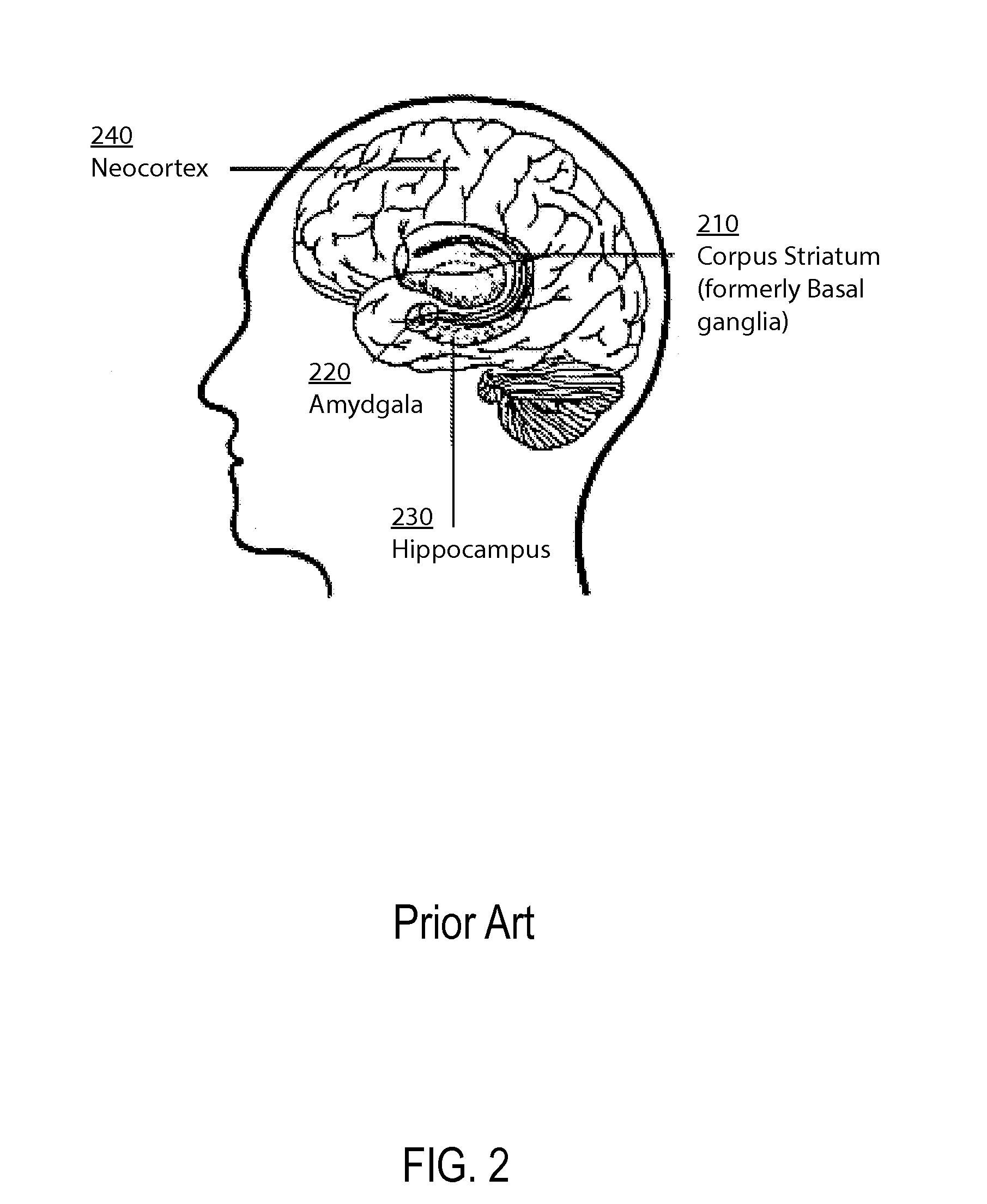
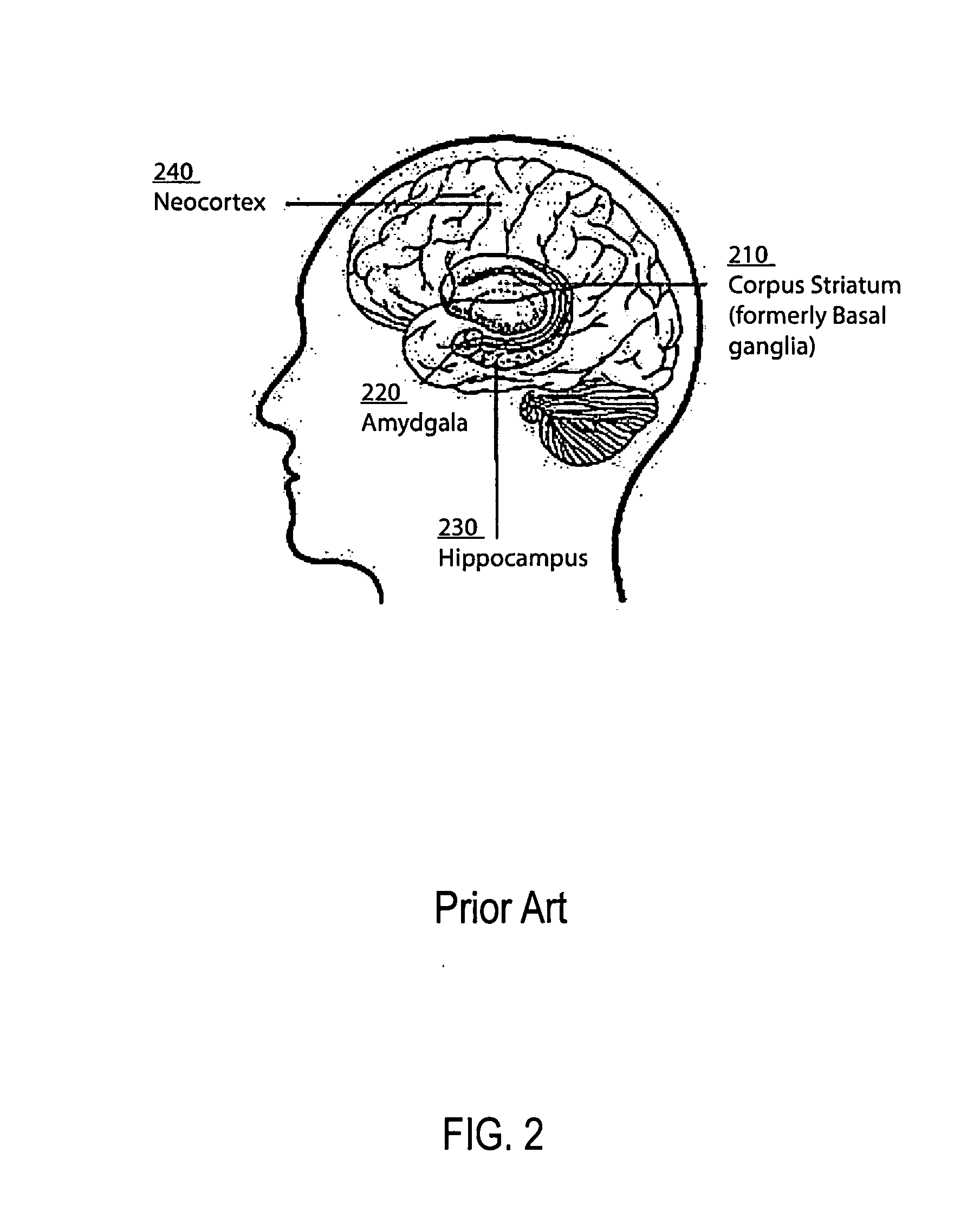
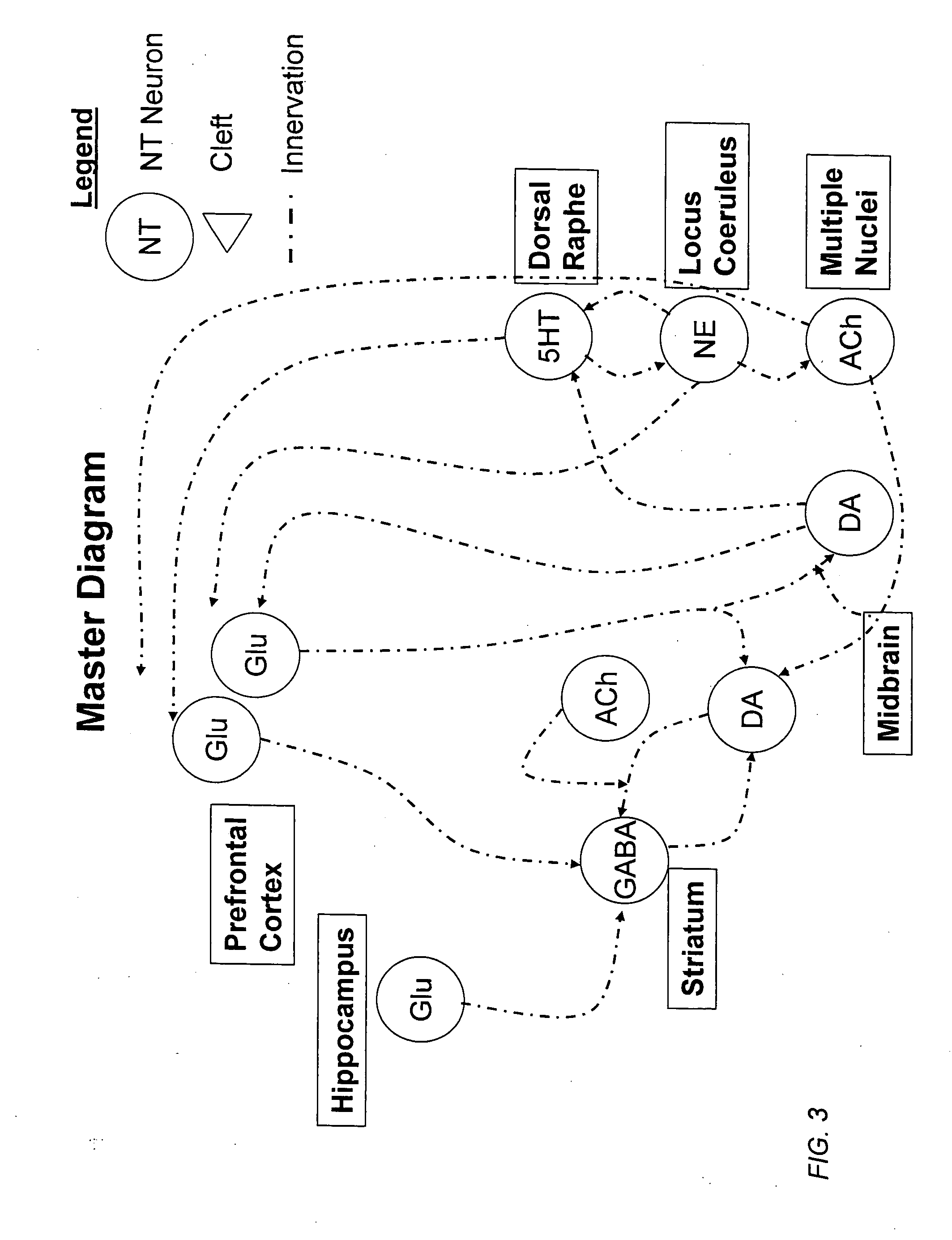
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric & cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20070106479A1Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserHuntingtons chorea
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases. A method is provided for developing a computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain which comprises the steps of identifying data relating to a biological state of a generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex; identifying biological processes related to the data, these identified biological processes defining at least one portion of the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala, and cortex; and combining the biological processes to form a simulation of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. A resulting computer model is of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, comprising code to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, and code to define the mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes. At least two of the biological processes are associated with the mathematical relationships. A combination of the code to define the biological processes and the code to define the mathematical relationships define a simulation of the biological state of the interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Computer executable software code is provided comprised of code to define biological processes related to a biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain including code to define mathematical relations associated with the biological processes. A computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain is provided, comprising a computer-readable memory storing codes and a processor coupled to the computer-readable memory, the processor configured to execute the codes. The memory comprises code to define biological processes related to the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, and code to define mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Methods and compositions for the production of monoclonal antibodies
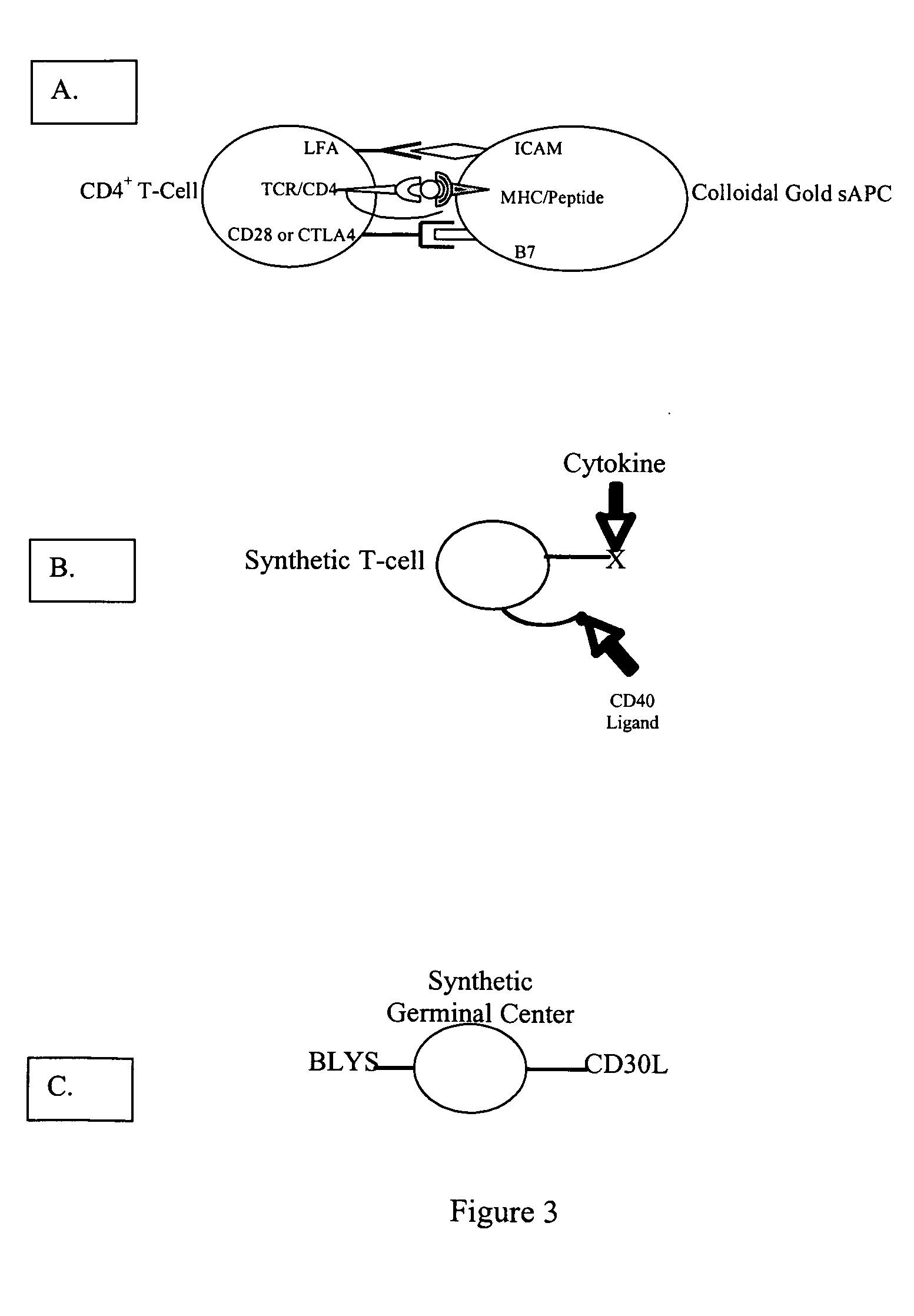
InactiveUS20100068261A1Improve efficiency and specificityPromote absorptionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMonoclonal antibodyImmunological Synapses
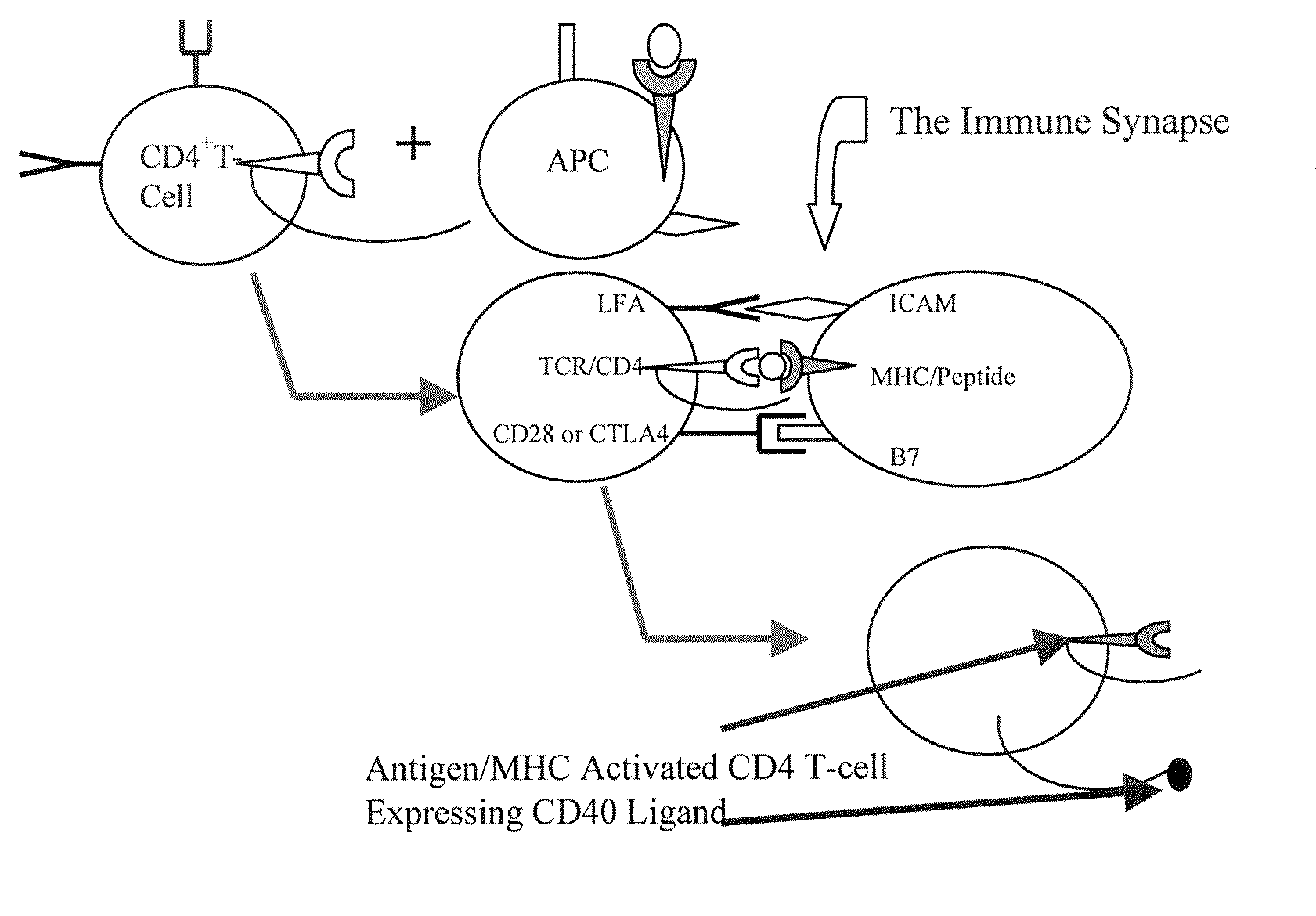
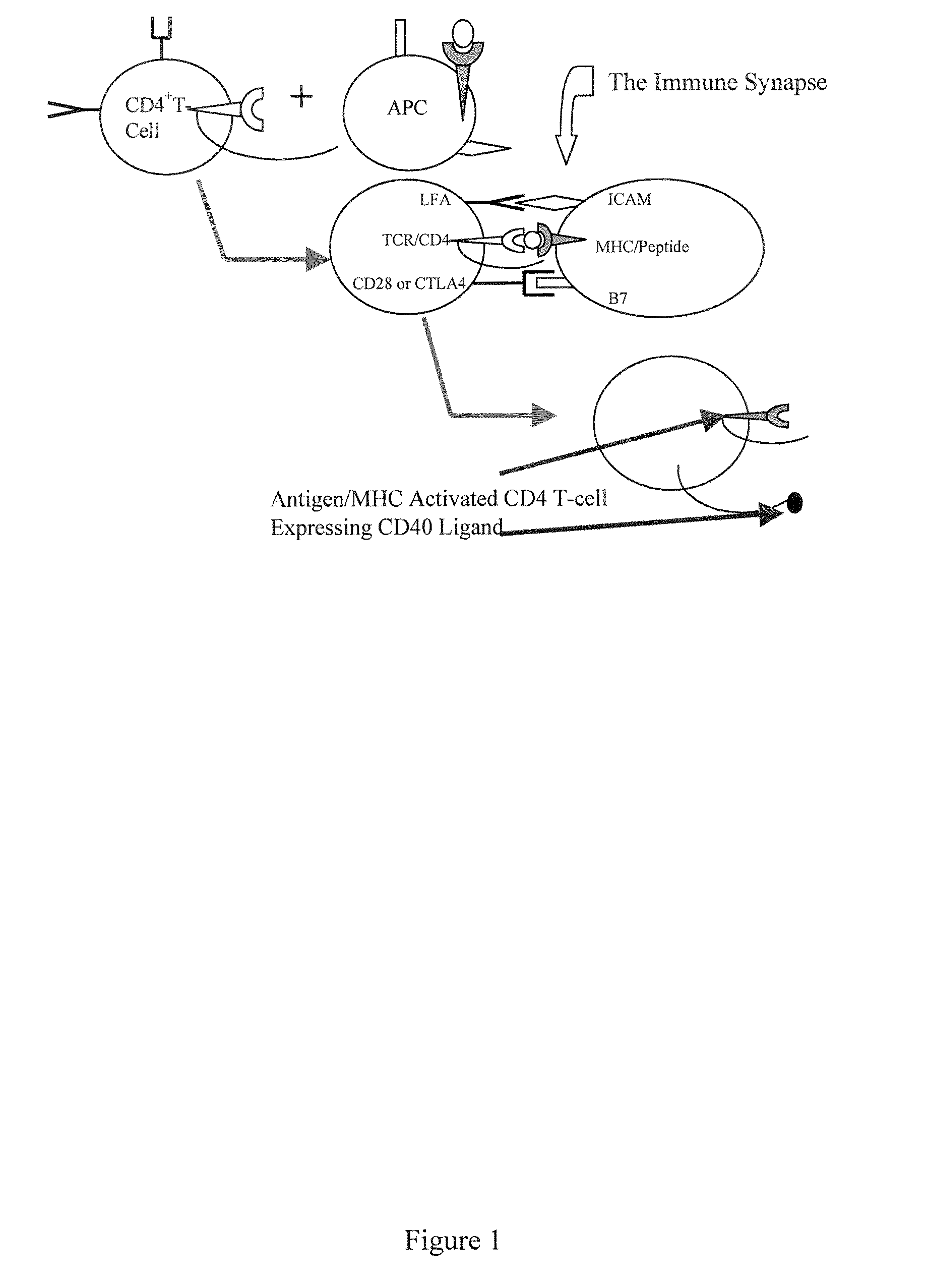
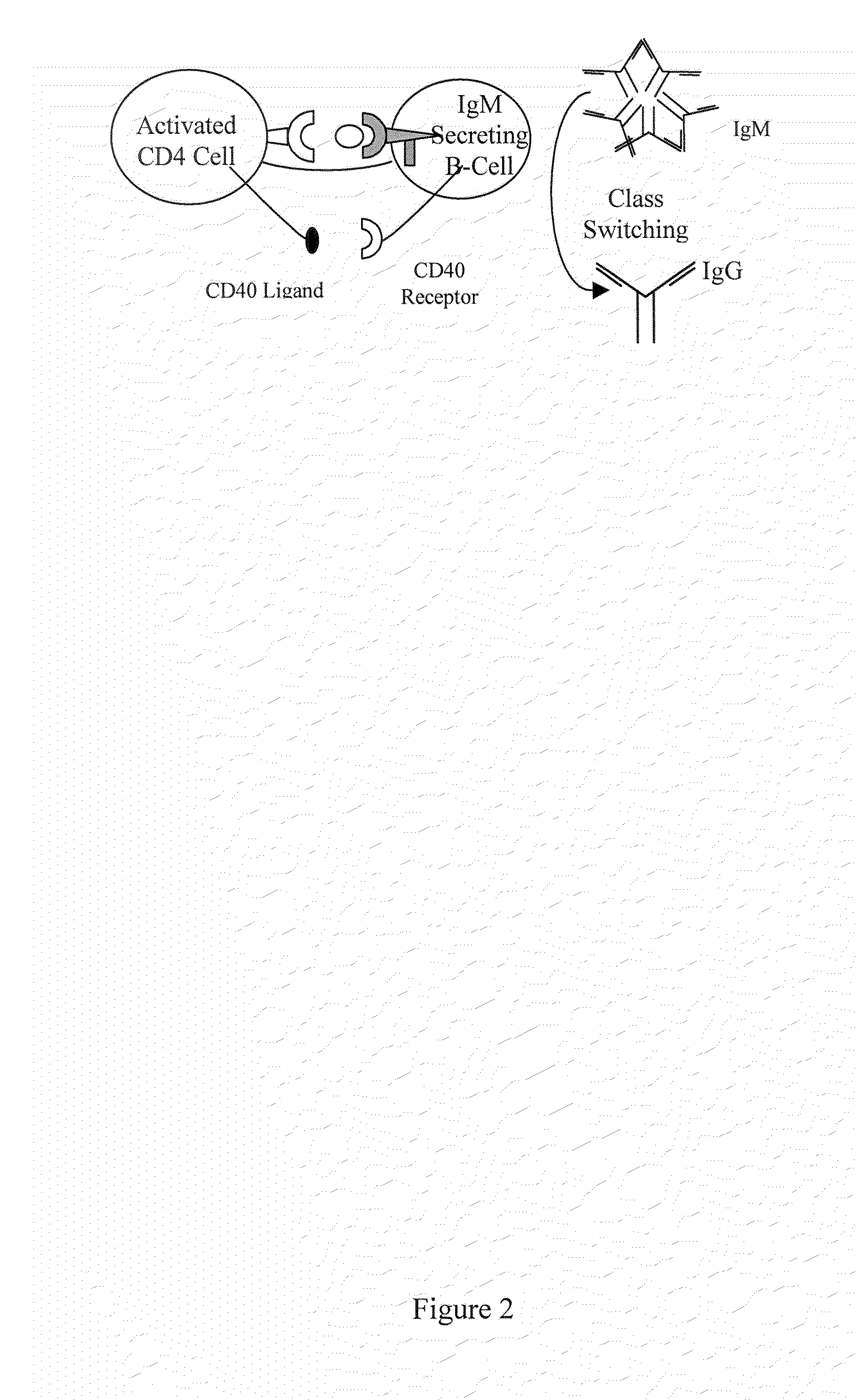
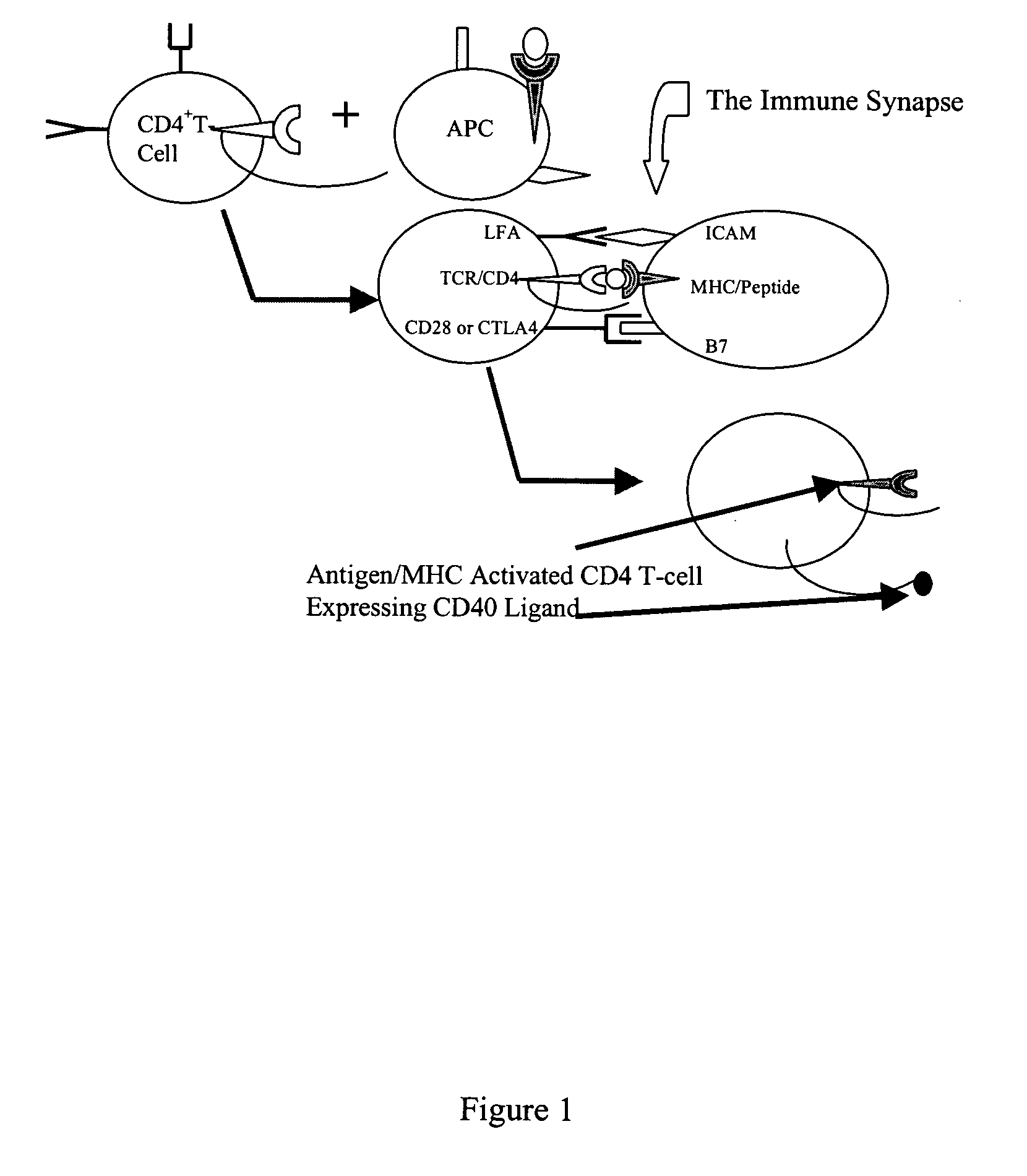
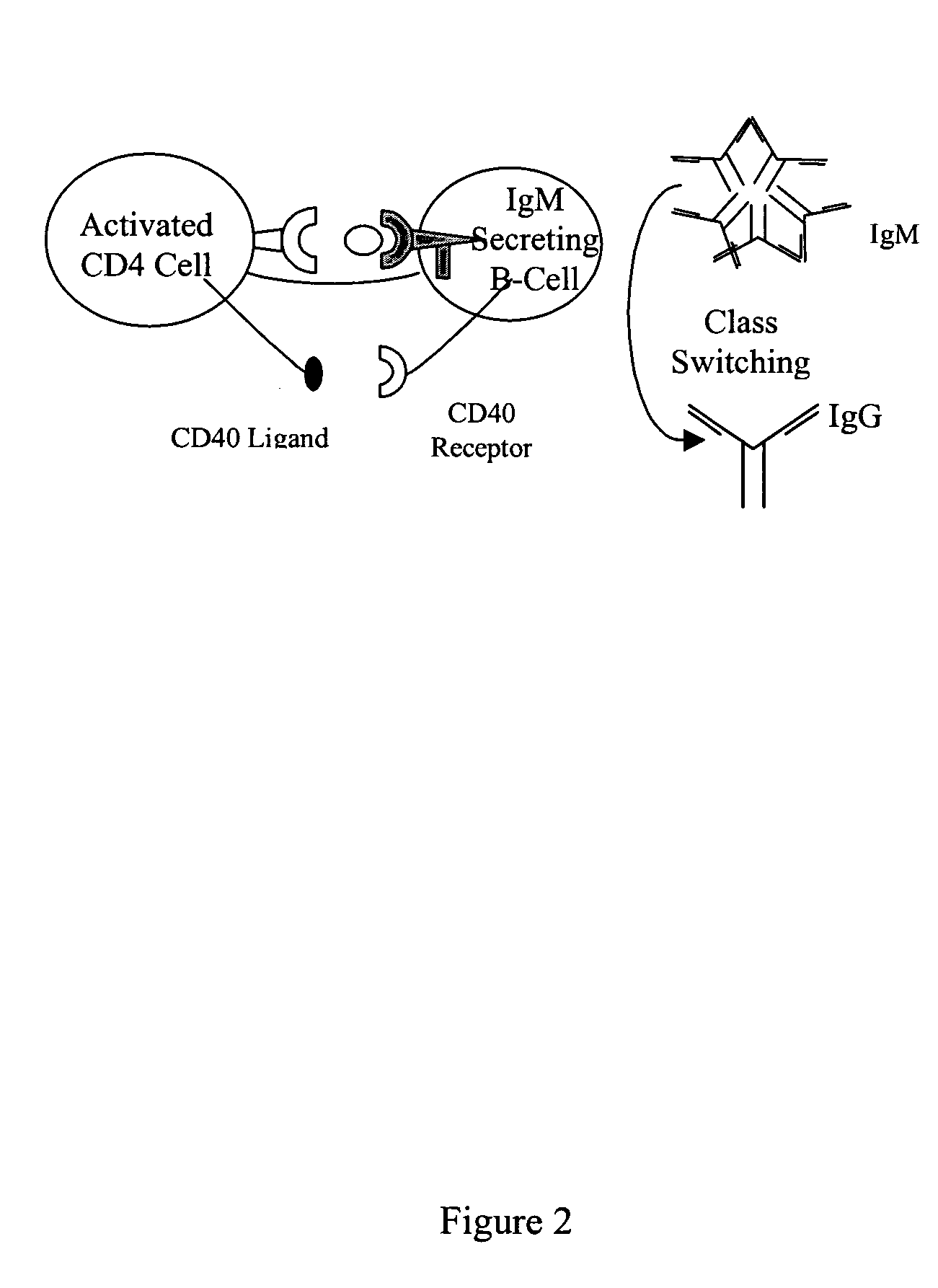
The present invention comprises compositions and methods for making monoclonal antibodies. The present invention further comprises vectors that replicate the immune system components, particularly an antigen-presenting cell (APC) element of the immune synapse. Additionally, the present invention may further comprise synthetic T-cells.
Owner:CYTIMMUNE SCI
Stochastic synapse memory element with spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP)
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
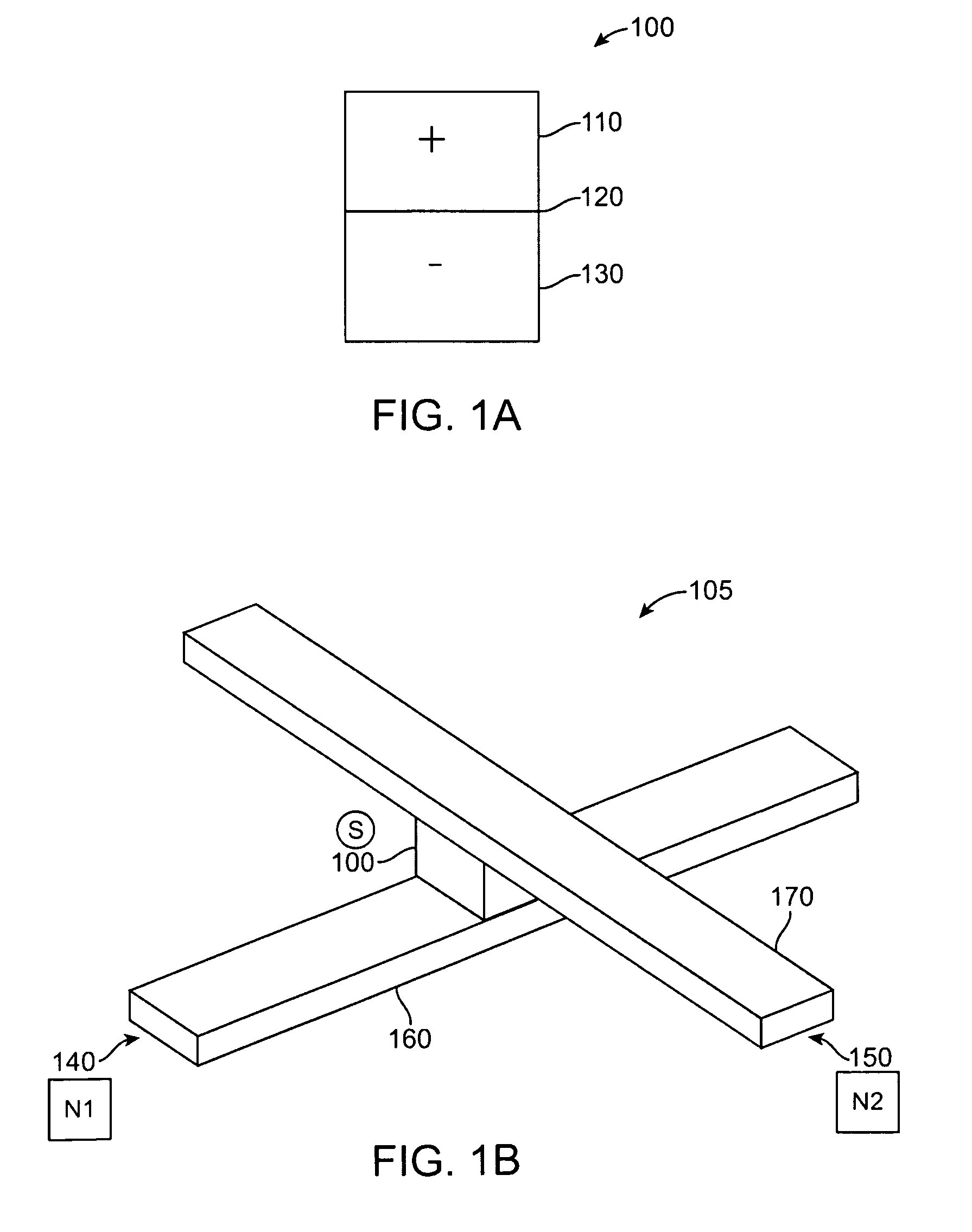
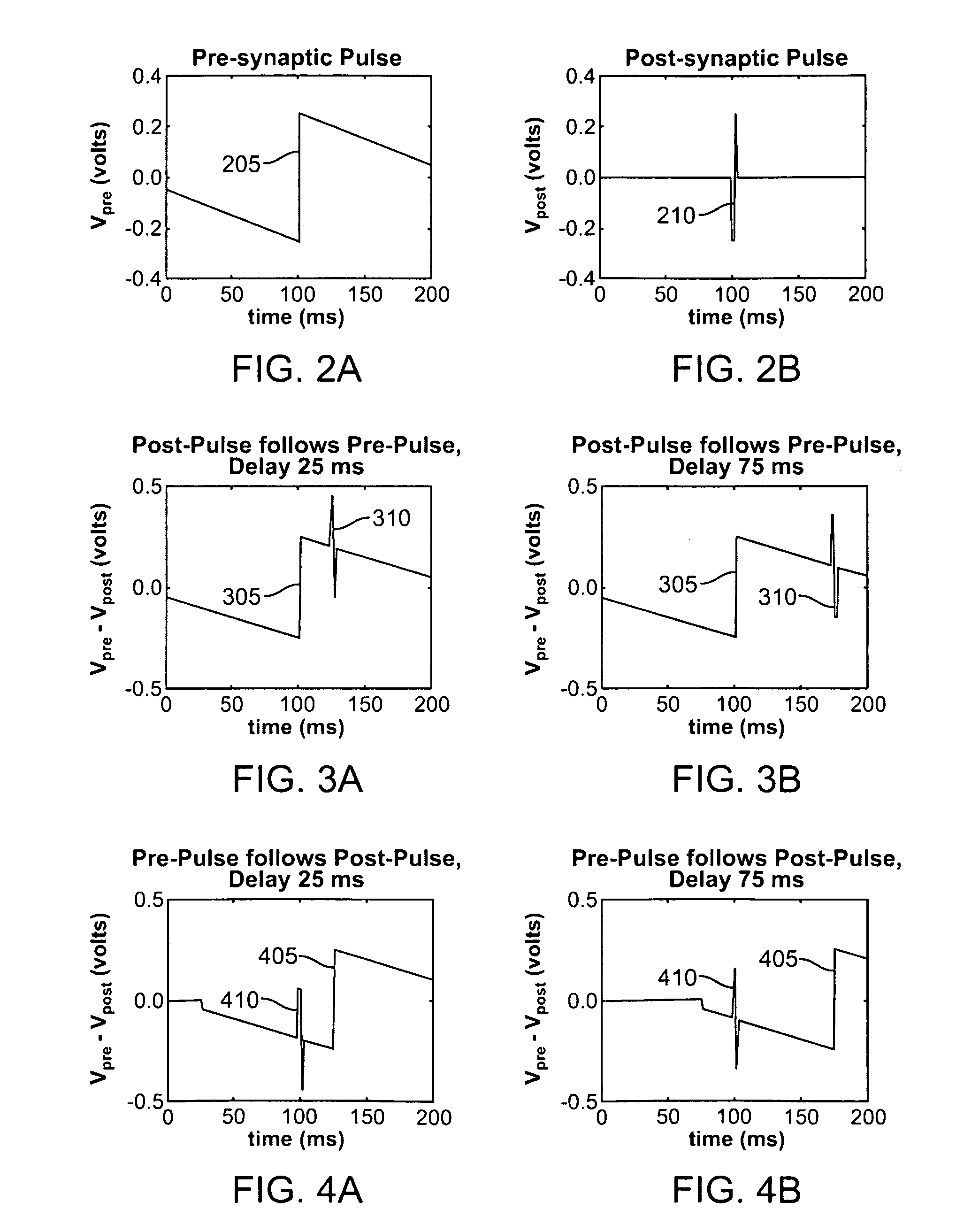
Neuron hardware structure and method of simulating pulse neural network by adopting neuron hardware structure
InactiveCN105719000AReduce occupancyIncreased ability to accommodate neuronsNeural architecturesPhysical realisationHardware structureNODAL
The invention discloses a neuron hardware structure and a method of simulating a pulse neural network by adopting the neuron hardware structure. The neuron hardware structure is characterized in that a neural network is provided, and comprises a plurality of neuron layers, which comprise a plurality of neurons; every neuron comprises a synapse layer, which comprises a plurality of synapses. The above mentioned method is characterized in that 1) the synapse model can be determined; 2) the synapses can be simulated; 3) the neurons can be simulated; 4) the neuron layers can be simulated; 5) the neural network can be simulated. By adopting the neuron hardware structure, the hardware resources occupied by the single neuron node can be reduced. By adopting the neuron hardware structure to simulate the pulse neural network, the simulation time is short, the expandability is good, the hardware resources occupied by the pulse neural network can be reduced, and then the capability of the hardware device accommodating the neurons can be improved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
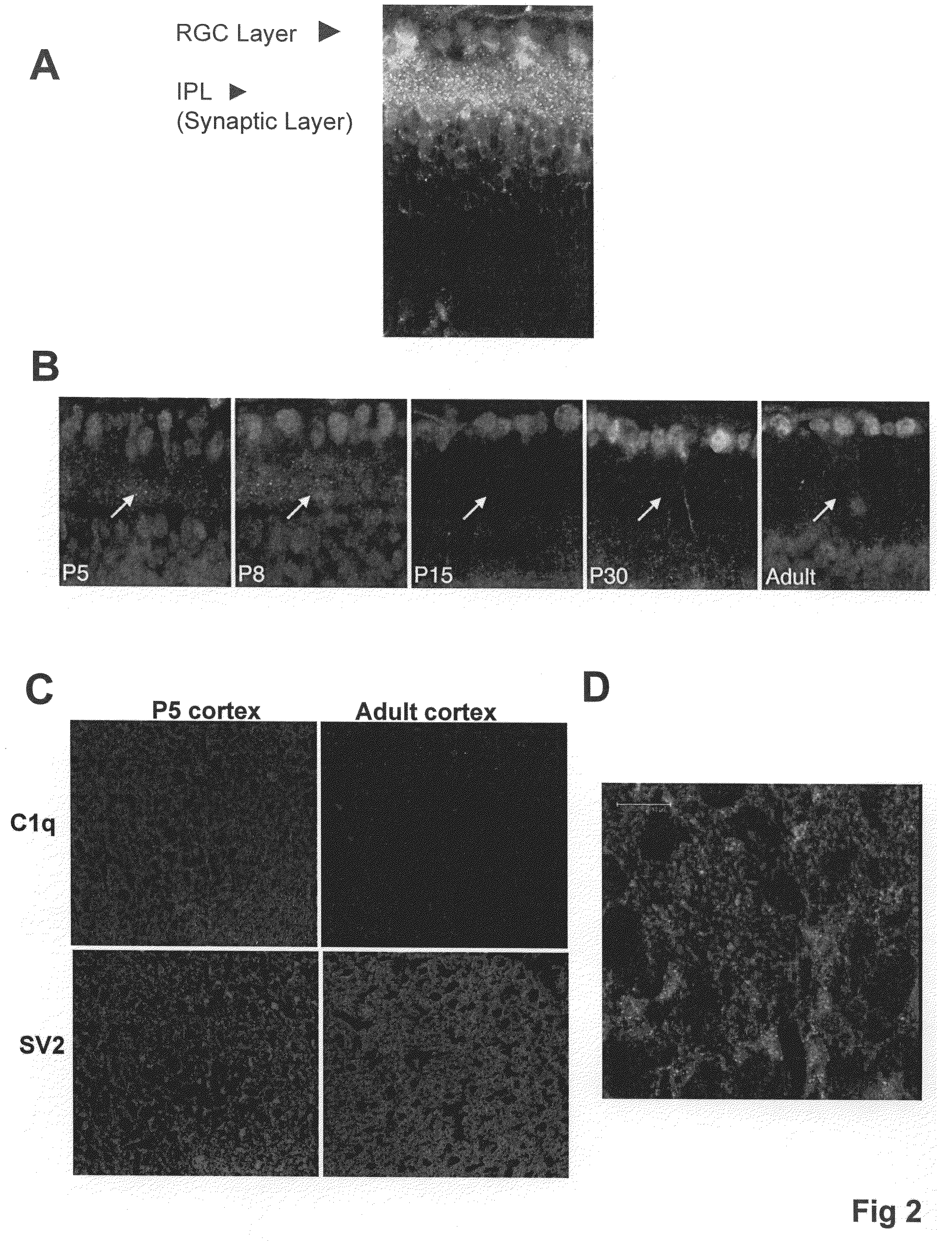
Modulation of synaptic maintenance
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for the production of monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS20050175583A1Improve efficiency and specificityPromote absorptionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryImmunological synapseMonoclonal antibody
The present invention comprises compositions and methods for making monoclonal antibodies. The present invention further comprises vectors that replicate the immune system components, particularly an antigen-presenting cell (APC) element of the immune synapse. Additionally, the present invention may further comprise synthetic T-cells.
Owner:CYTIMMUNE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com