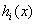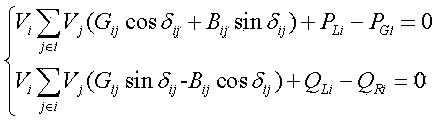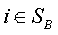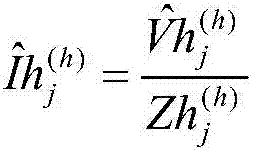Patents
Literature
41 results about "Node (circuits)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering, a node is any point on a circuit where the terminals of two or more circuit elements meet. In circuit diagrams, connections are ideal wires with zero resistance, so a node may consist of the entire section of wire between elements, not just a single point. According to Ohm's law, V = IR, the voltage across any two points of a node with negligible resistance is V=IR=I·0=0, showing that the voltage at every point of a node is the same.
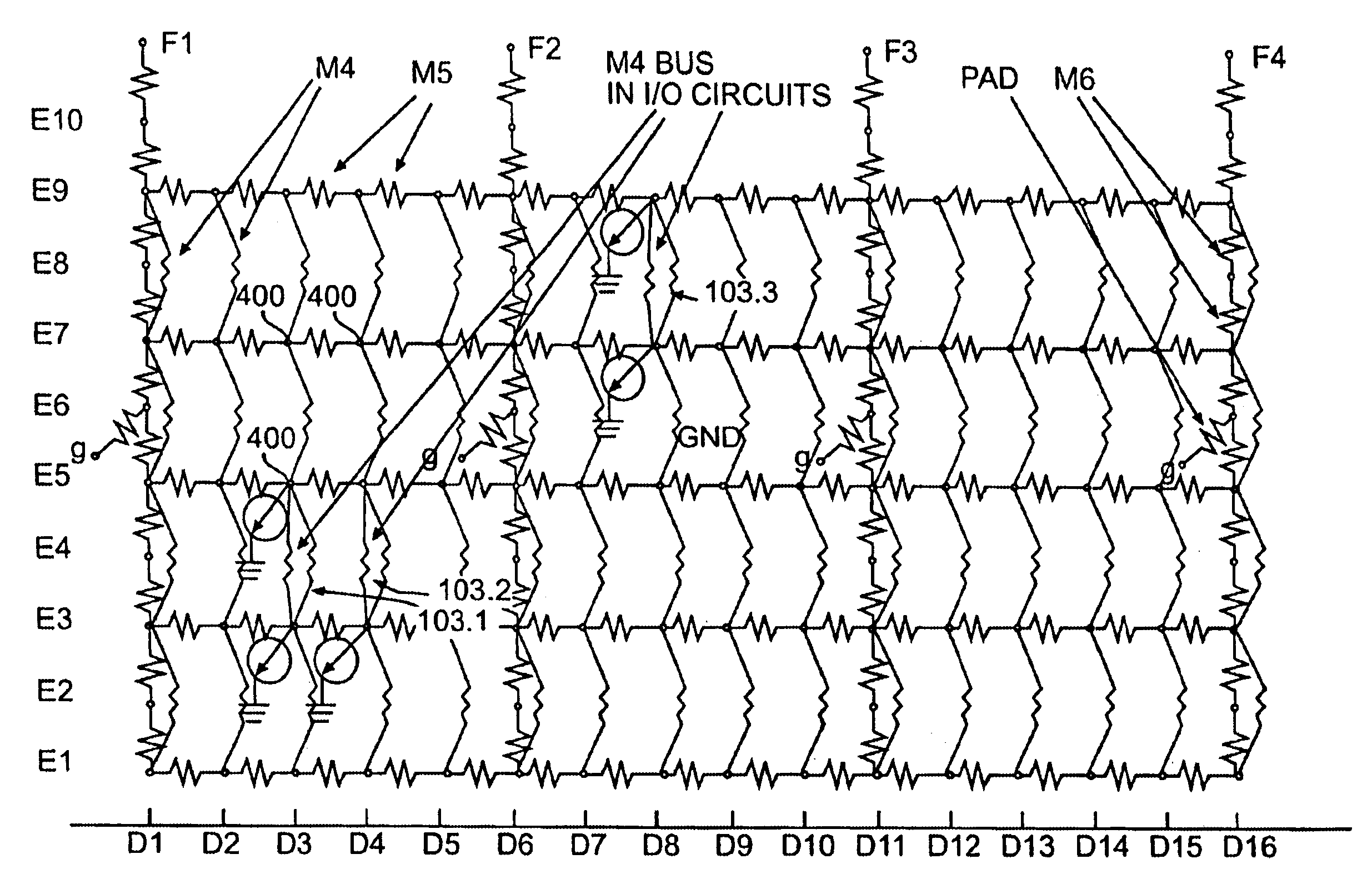
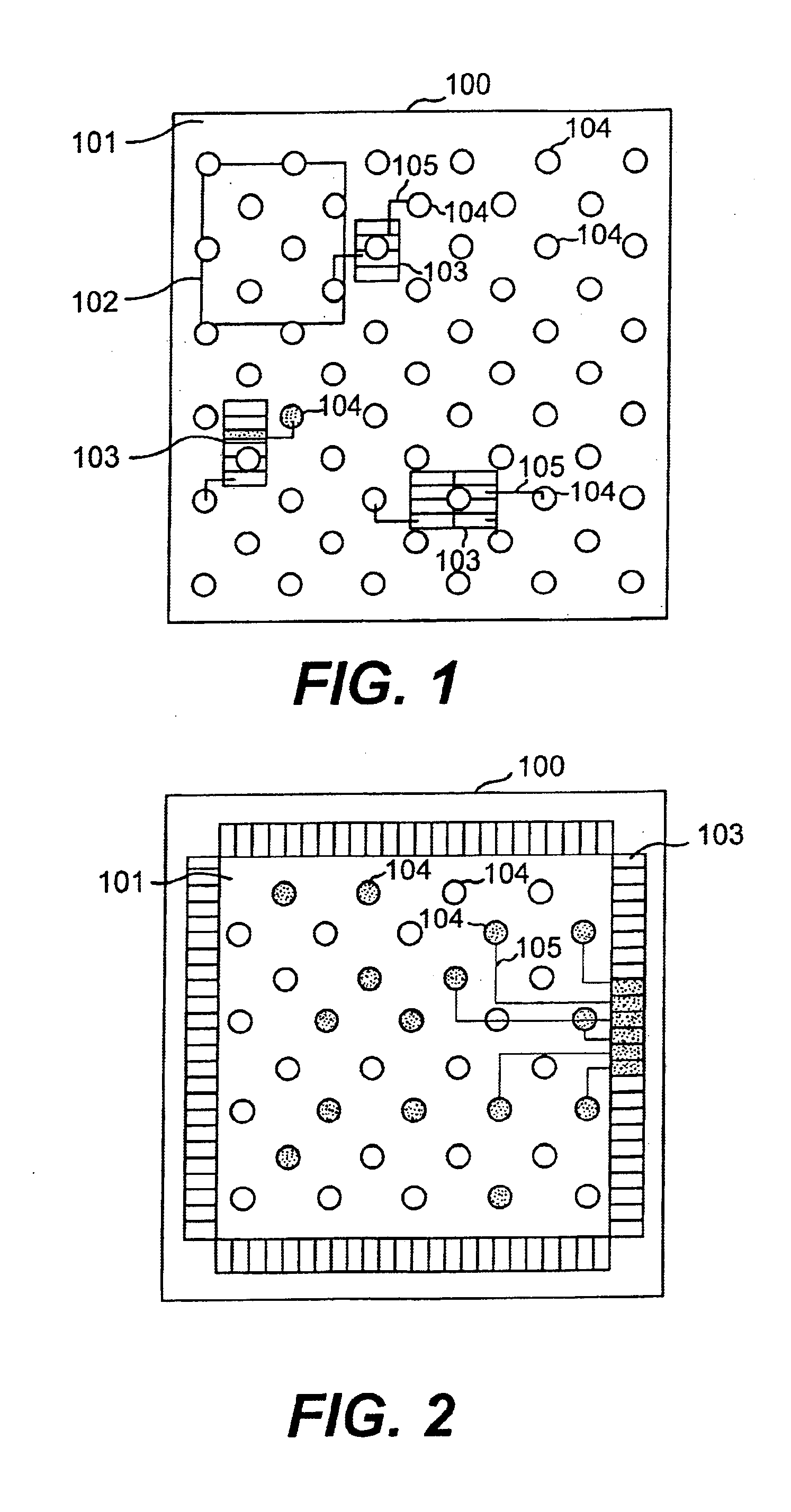
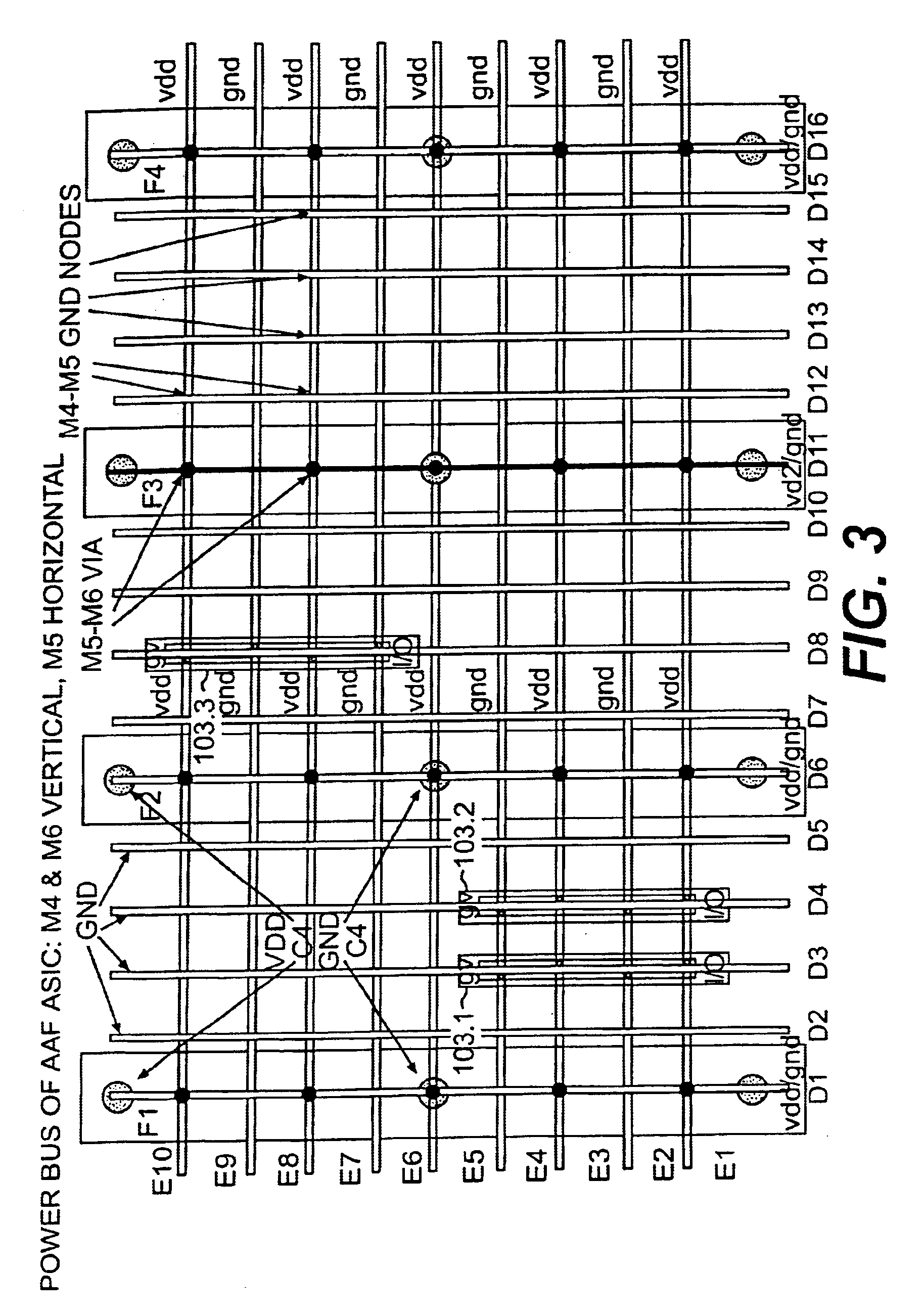
Method of power distribution analysis for I/O circuits in ASIC designs
InactiveUS6868374B1Improve accuracyShorten analysis timeAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsComputer aided designElectrical resistance and conductanceAverage current
A method and system for testing the compliance of a distribution of I / O circuits in a semiconductor chip with voltage (IR) and electromigration (EM) limits. Maximum and average currents for the I / O circuits are calculated. A resistance model for the power distribution network of the chip is created, and the I / O circuit currents are indexed to corresponding nodes in the resistance model. Average current demand of the logic circuitry of the chip is also calculated and indexed to nodes in the resistance model. The resistance model with indexed currents is then solved to determine voltages at the nodes. The voltages are checked for compliance with IR and EM limits, and a report is produced. If violations of the IR and EM limits are detected, the placement of the I / O circuits in the power distribution network may be revised to bring the design into compliance with IR and EM requirements.
Owner:IBM CORP
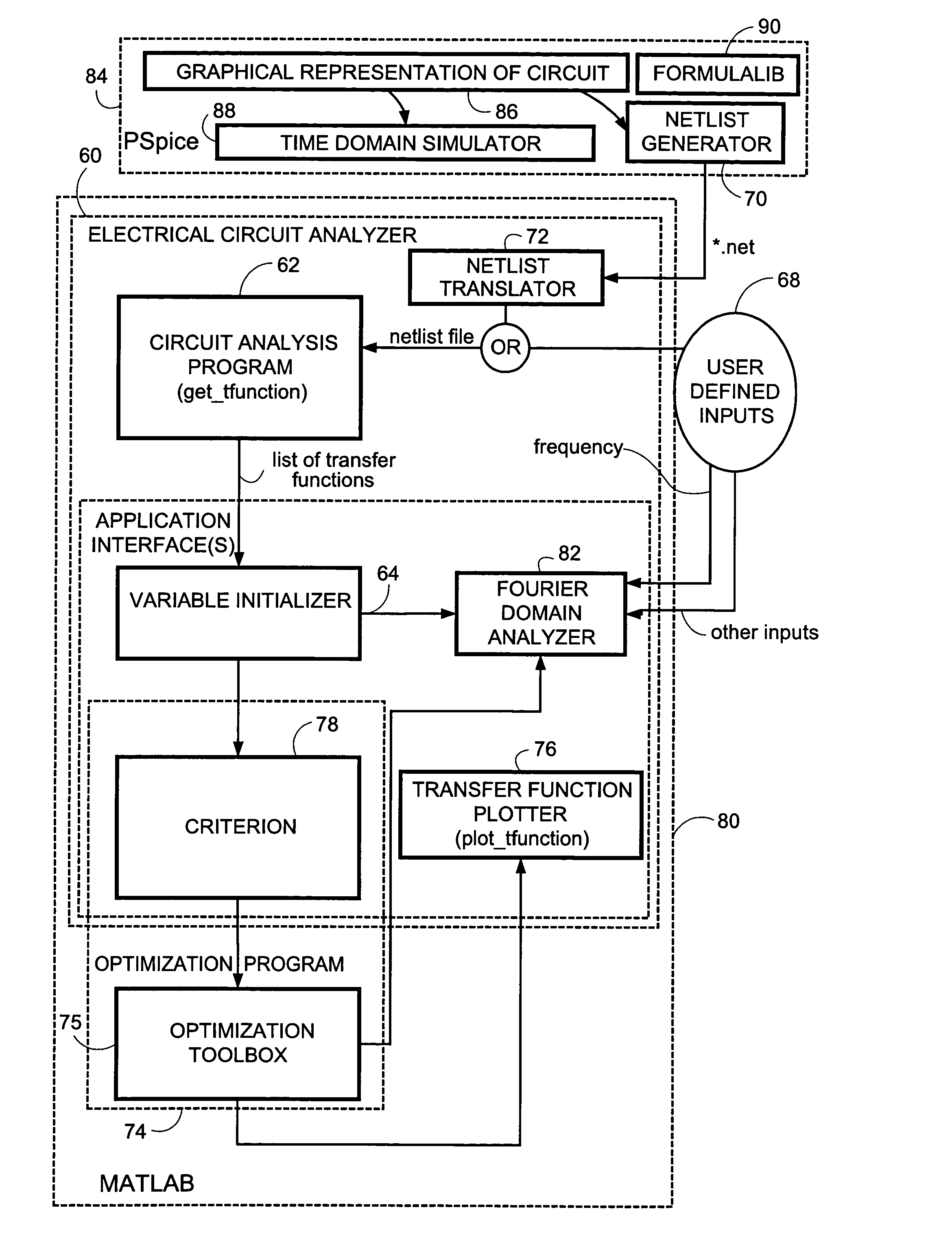
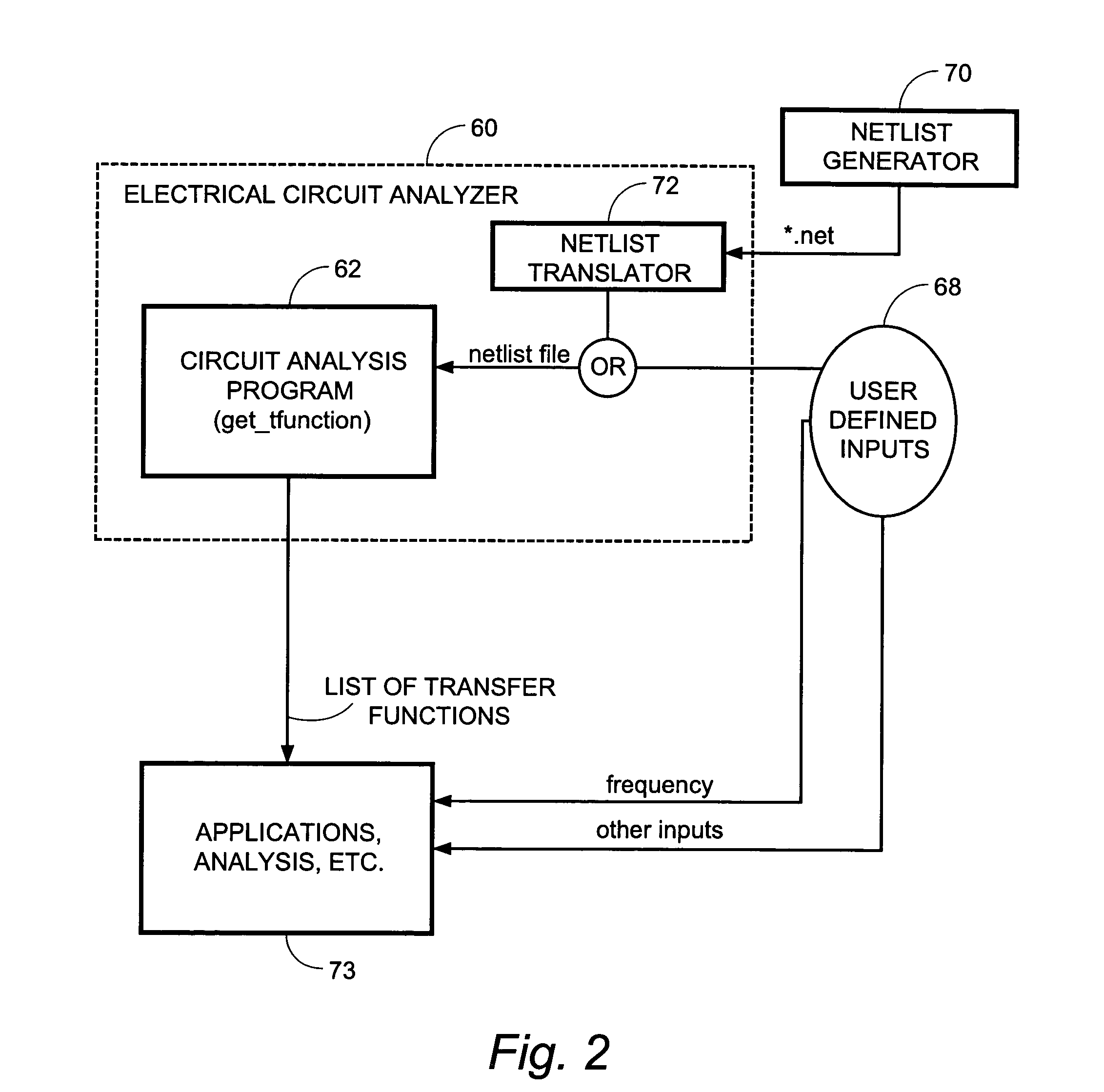
Symbolic analysis of electrical circuits for application in telecommunications
InactiveUS20050027491A1Reduce sizeEasy to interpretAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsTelecommunication applicationLoading coil
Analysis of an electrical circuit is performed using a computer program product (60) and a method. In accordance with the program and the method, a electrical circuit analyzer generates an admittance matrix for an electrical circuit which is being analyzed. The admittance matrix includes symbolic expressions rather than numerical expressions for at least some components of the electrical circuit. The electrical circuit analyzer linearly and algebraically solves an equation system including the admittance matrix for analyzing at least a part of the electrical circuit. The electrical circuit analyzer uses symbolic computation to solve the equation system including the admittance matrix for analyzing at least a part of the electrical circuit. The equation system including the admittance matrix can be solved in various types of analyses, including (1) determining a transfer function between specified nodes of the electrical circuit; and (2) optimizing a component of the electrical circuit. The electrical circuit analyzer sets up the admittance matrix Y by following a set of “rules”. Special rules are provided for certain telecommunications components, such as multi-winded transformers, loading coils, line-drivers, analogue cables, and filters. Inclusion of these special rules for telecommunications components enables the electrical circuit analyzer to be more applicable to telecommunications circuits than conventional analyzers. In accordance with a block / subcircuit matrix approach, an overall circuit is divided into plural subcircuits. In such case, the admittance matrix can comprise separate admittance blocks for each of plural subcircuits. Connectivity blocks which represent connectivity between the plural subcircuits are situated on a cross diagonal of the admittance matrix. The admittance matrix can then be conveniently utilized for analyzing at least a part of the electrical circuit. Advantages of this approach include recursively reducing the size of the matrices including the admittance matrix as subcircuits are added to the admittance matrix.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Solving method for transient analysis of power source network based on equivalent circuit
InactiveCN1431704ASave memoryScale upSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransient analysisVlsi physical design
The method belongs to the routing design area in VLSI physical design. The characters of the method of using computers to solve the set of linear equations are as follows. Based on the features of that the power wire / ground, wire network of the application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) contains a great lot of the chain topology, the parameters R, L, C and the current source in the RLC circuit are equivalent to the nodes at the two ends of the chain. The set of linear equations is listed for the equivalent circuits composed of the nodes at the two ends of all chains. Then, the magnitudes of voltage of the mergered nodes in all chains are determined. The method has the advantages of fast and saving the memory. The scale of the chips to be treated is posible to be enlarged and the precision meets the demand.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fault management system for a communications network
ActiveUS7251754B2Error detection/correctionSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsAccess networkCopper wire
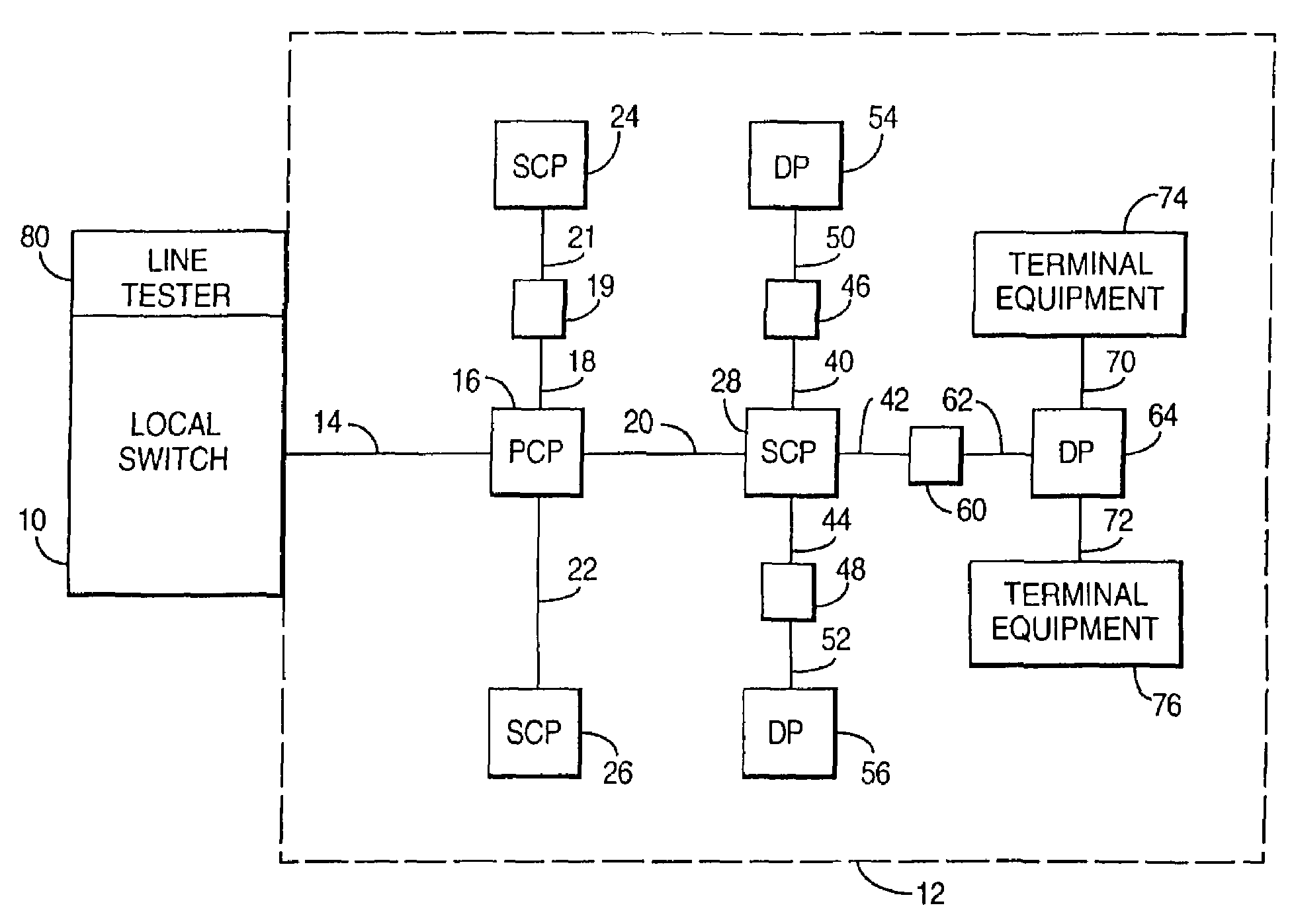
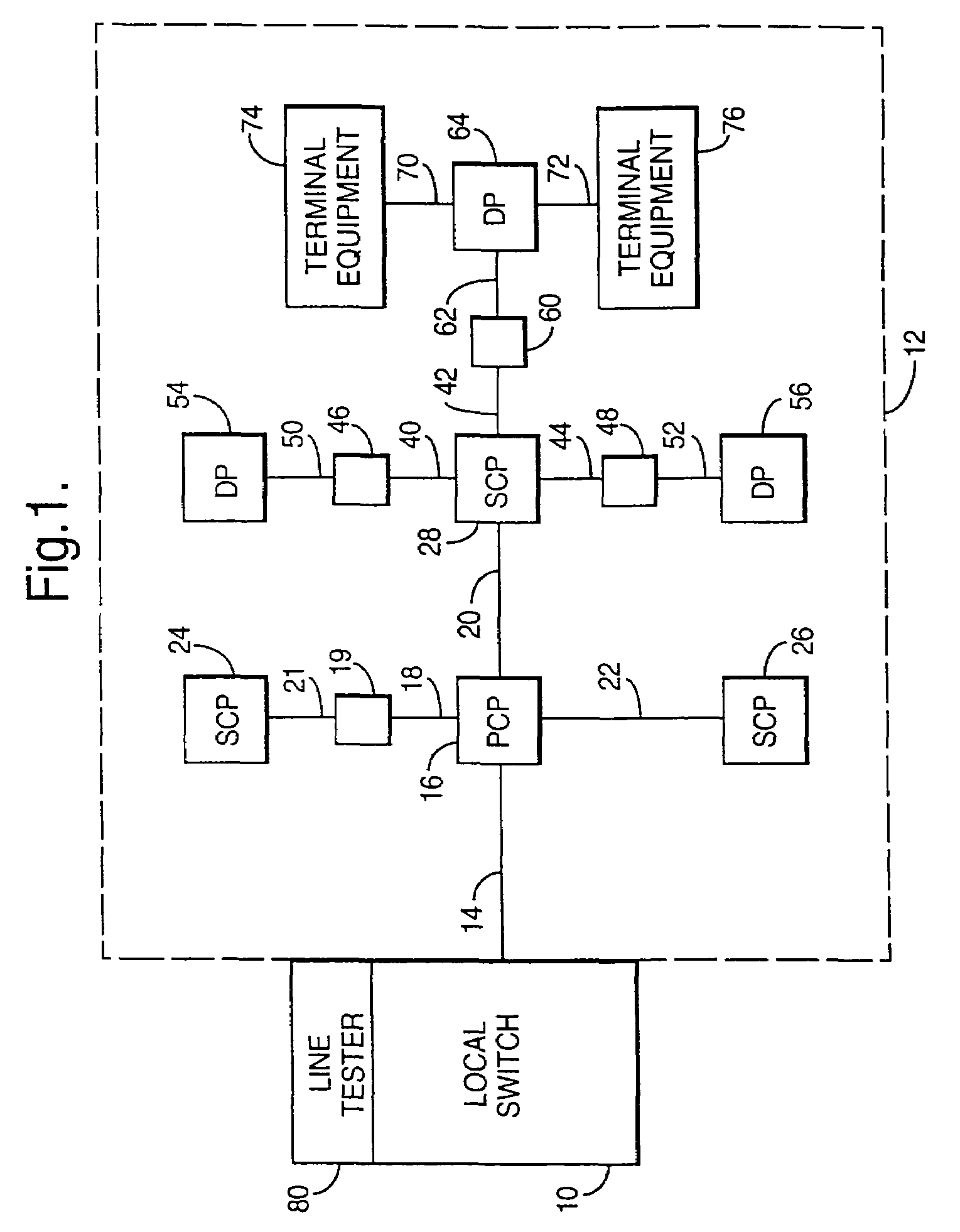
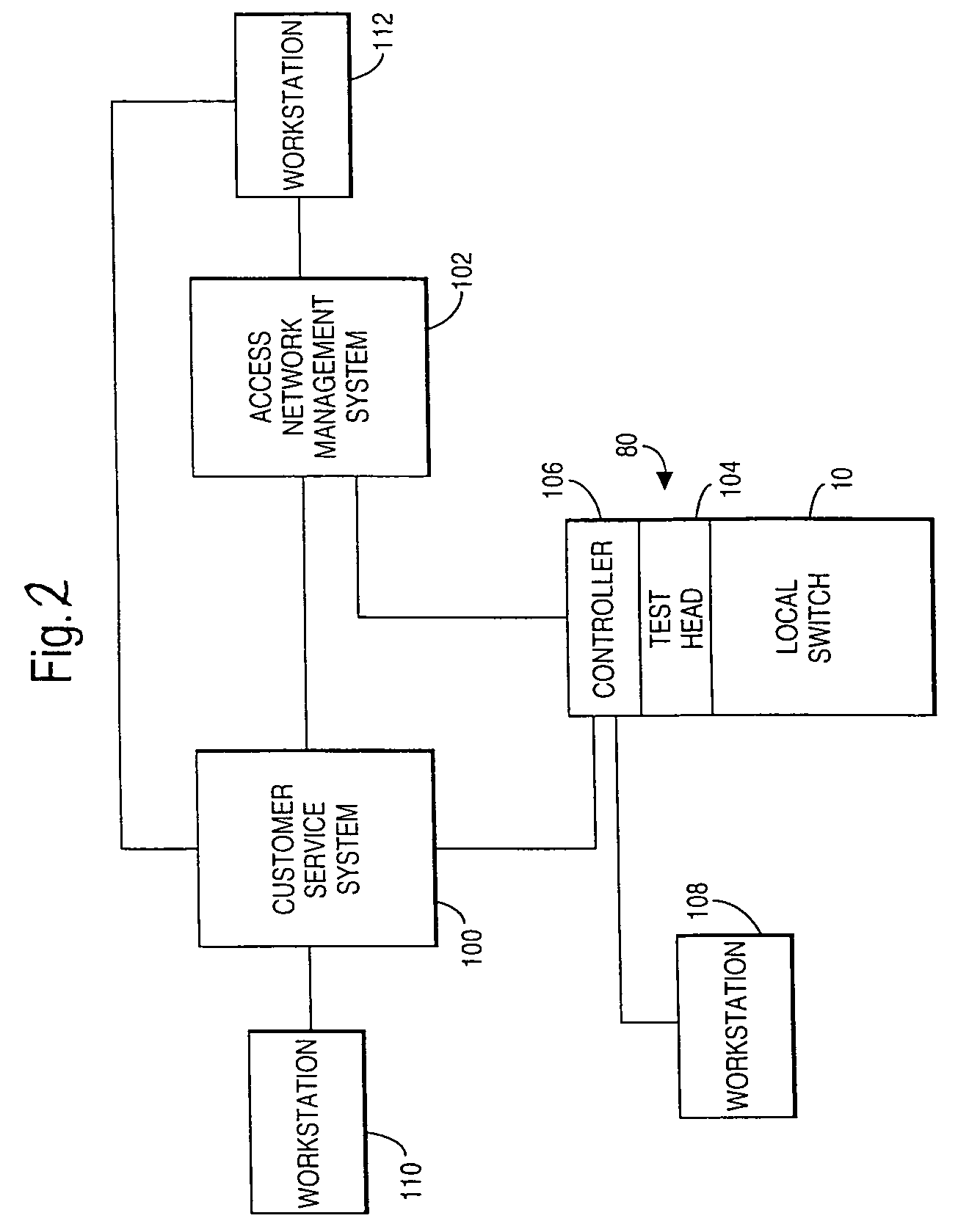
A fault management system is directed to the access network part of a communications network where terminating lines in the form of pairs of copper wires extend from a local switch through a series of nodes to terminal equipment provided for user of the network. Each night, a test head performs a series of tests on each of the terminating lines. The results of the tests are transmitted to an access network management system where they are analyzed with respect to a set of parameters to identify characteristics that would indicate that a fault is likely to occur on the associated circuit within a predetermined period e.g. 1 year. Further analysis can then be carried out to establish the probability of the fault actually occurring and / or whether the potential fault analyzed is going to occur in either the underground or the over-ground part of the network. Further analysis determines relative costs of repair for circuits or network elements in which faults or potential faults have been identified.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
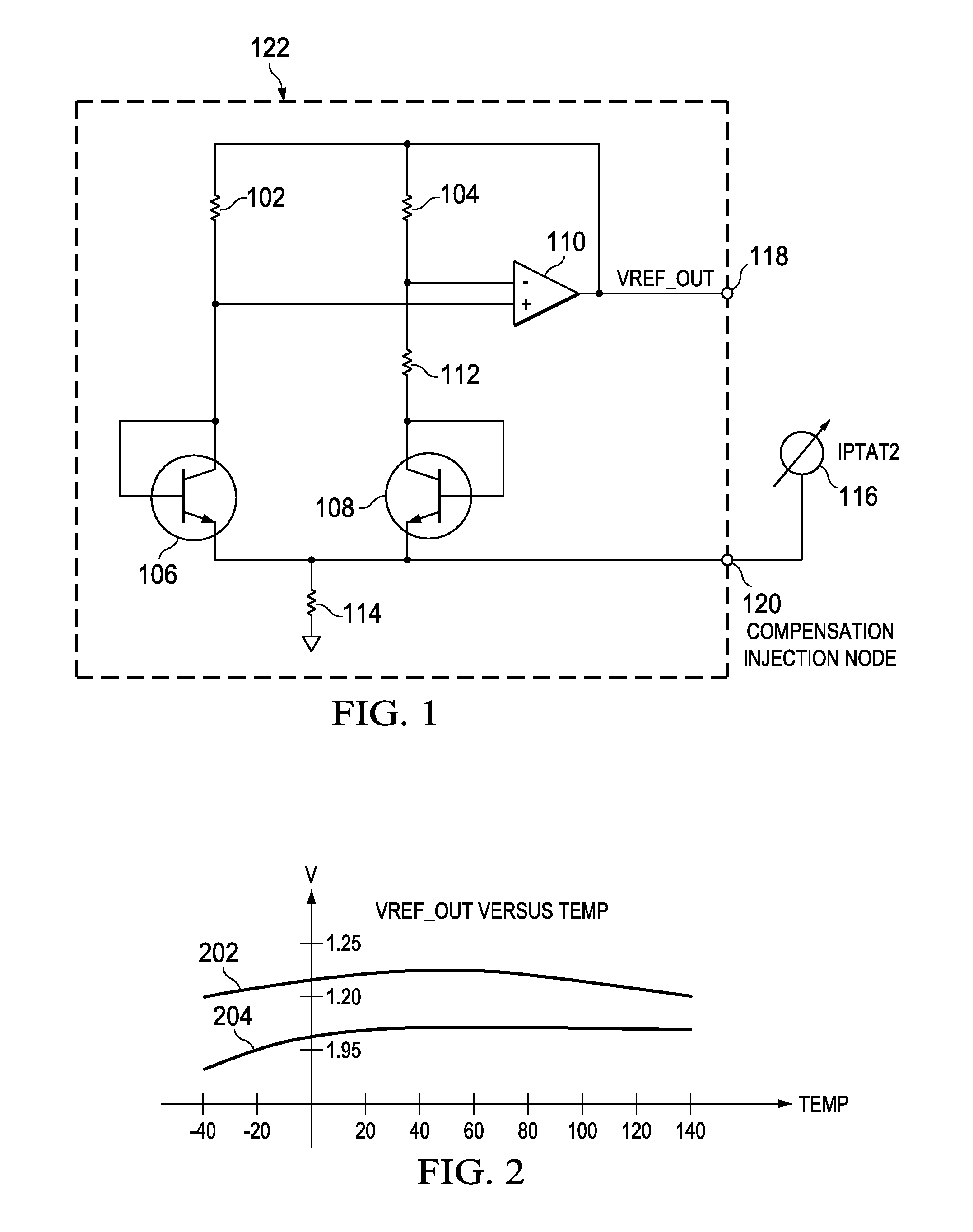
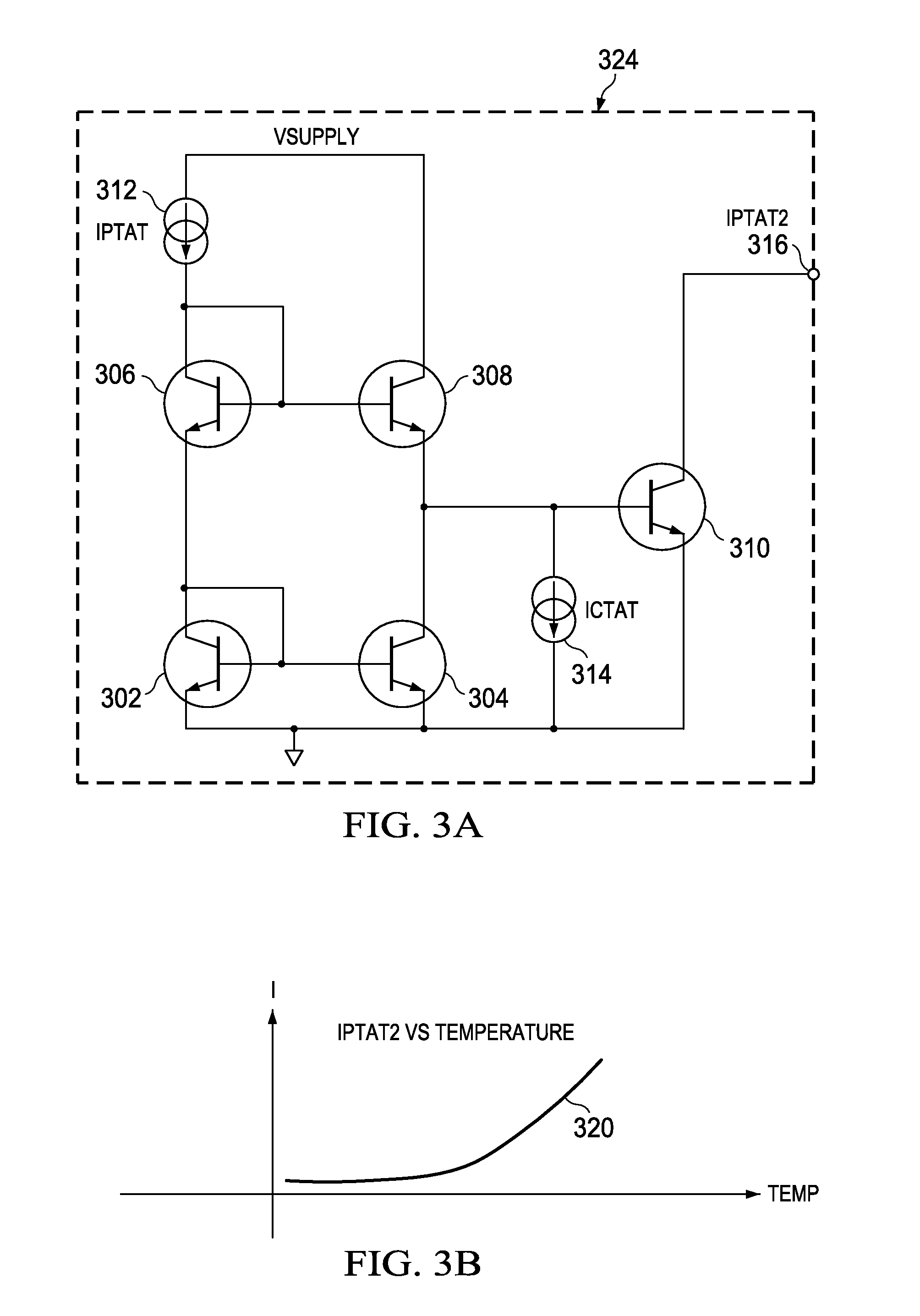
Method and circuit for curvature correction in bandgap references with asymmetric curvature
ActiveUS20080164938A1Easy to correctIncrease temperatureElectric variable regulationRelative magnitudeLogit
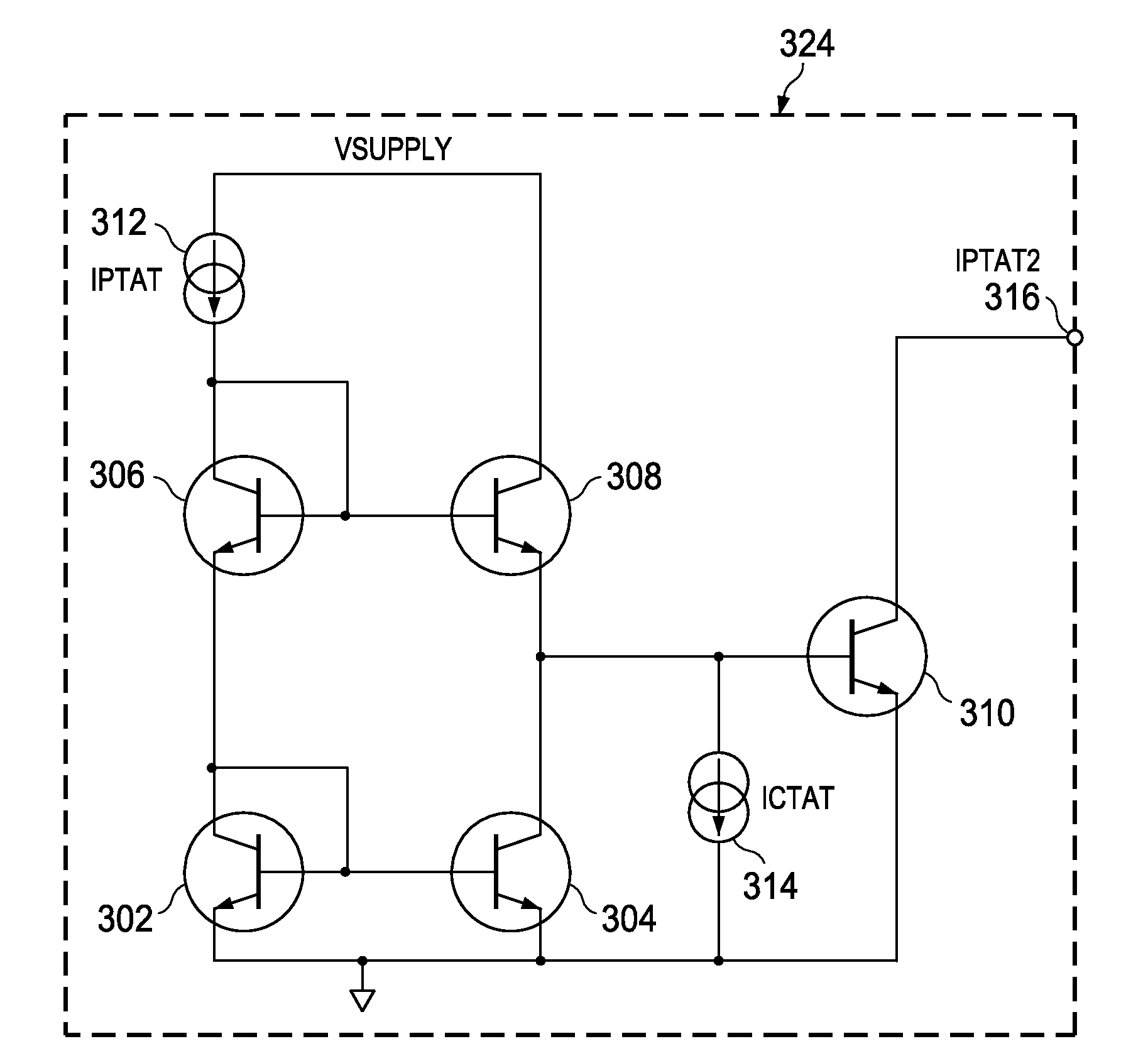
A non-linear correction current ICTAT2 (current complementary to the square of absolute temperature) is generated from a current IPTAT (current proportional to absolute temperature) and a current ICTAT (current complementary to absolute temperature), both modified in a circuit having a topology and components which capitalize on the logarithmic relationship between transistor collector current and base-emitter voltage. The resulting ICTAT2 current (current complementary to the square of absolute temperature) is injected into a node of a bandgap reference circuit to compensate for non-linear temperature effects on output voltage. A more general correction circuit generates both IPTAT2 and ICTAT2, and applies each to a respective multiplier which, in a preferred embodiment, is a current DAC configured as a multiplier. Control inputs CTL1 and CTL2 to respective multipliers set the amplitudes of the modified IPTAT2 and ICTAT2 output currents, which are then summed to generate the compensating current Icomp which is injected to the appropriate node in the bandgap reference circuit as described above. By adjusting the relative amplitudes of the IPTAT2 and ICTAT2 currents, a wide range of compensating current versus voltage curves is produced, allowing the optimization of a wide range of bandgap reference circuits. An optimal value for CTL1 is determined by holding CTL2 constant, then measuring curvature at a plurality of CTL1 values. That CTL1 value closest to the interpolated value at which curvature is minimized is then used.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Extension cone method capable of sensing real-time situation of power distribution network
InactiveCN103729537AEasy to handleImprove rationalitySpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudeData pack
The invention discloses an extension cone method capable of sensing the real-time situation of a power distribution network. According to the extension cone method, an extension cone planning model is established, real-time trend results such as the voltage amplitude value and the phase angle of nodes of the whole network are calculated, and the purpose of sensing the real-time situation of the power distribution network is achieved. The extension cone method comprises the following steps that first, net rack data are read, the net rack data comprise the connection relation of the nodes and branch circuits, real-time data returned by points which are provided with measuring devices and historical loads of points which are not provided with the measuring devices; second, a planning mathematical model is established, the planning mathematical model comprises an objective function model, a trend equation equality constraint, an inequality constraint of node voltages and load nodes; third, secondary cone planning processing is conducted on the trend equation equality constraint, the node voltages, node active power and node reactive power respectively, and state estimation models of an objective function, the equality constraint and the inequality constraint are obtained; fourth, the state estimation models are solved, so that the voltage amplitude of the nodes of the power distribution network and the trend information of the phase angle are obtained, and the purpose for sensing the real-time situation of the power distribution network is achieved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Power system harmonic flow algorithm giving consideration to uncertainty and three-phase unbalance
PendingCN106953331AConvenient and reasonable estimatePolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionTransformerElectric power system
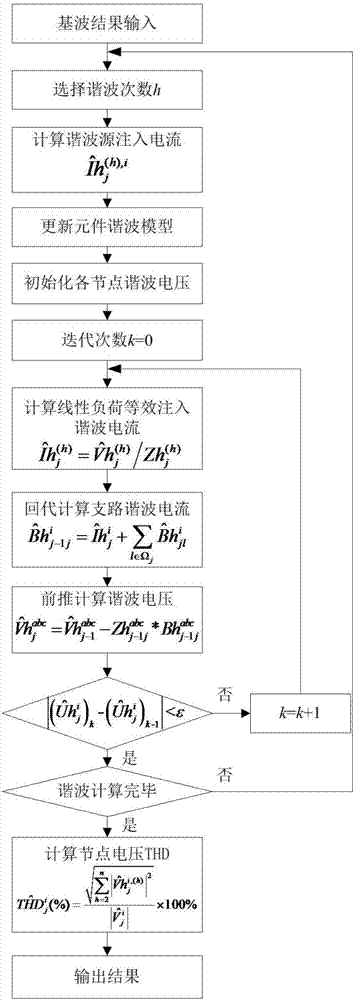
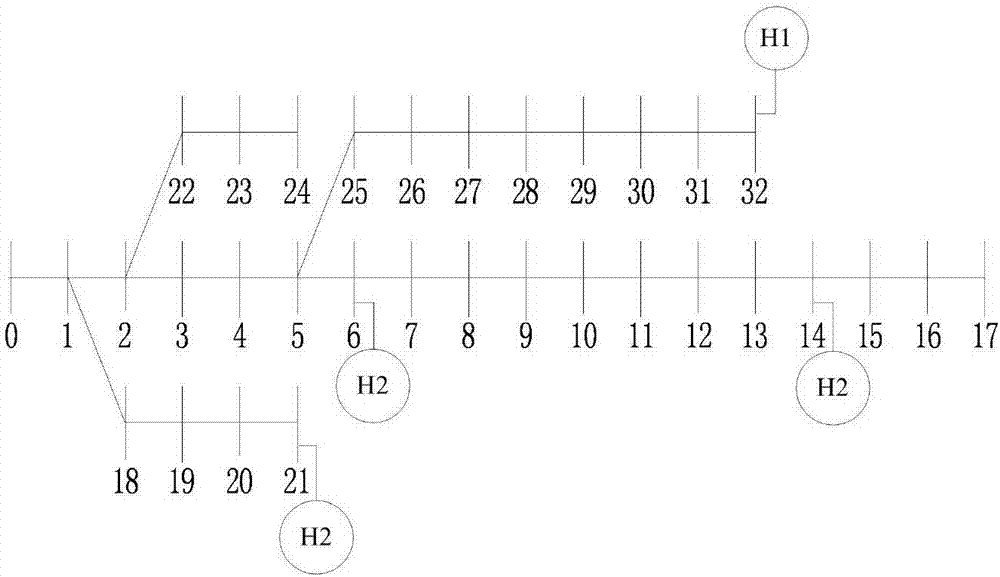
The invention relates to a power system harmonic flow algorithm giving consideration to uncertainty and three-phase unbalance, and the algorithm comprises the steps: selecting a harmonic order h; calculating an h-th order harmonic current value of a harmonic source injection system connected with a nonlinear load node; building an h-th order harmonic model of system elements comprising all circuits and a transformer; initializing a harmonic voltage and phase angle of each node; setting the number of interaction times, and calculating the equivalent injection harmonic current value of each linear load node in each iteration process; solving the sum of the branch harmonic currents from a tail node, and obtaining the harmonic current value of each phase of each branch circuit; sequentially calculating the harmonic voltage values of the nodes from the head end of a feed line to the tail end of the feed line, wherein an iteration ending criterion is that the deviation of the harmonic voltage of each node at each phase relative to the value at the last iteration is less than an allowed value; and solving the distortion rate of the harmonic voltage of each node at each phase according to an obtained fundamental wave voltage value and the value of each harmonic voltage.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Communication bus system operable in a sleep mode and a normal mode
InactiveCN1606725AConfigure selection delayQuick checkVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingNormal modeTransceiver
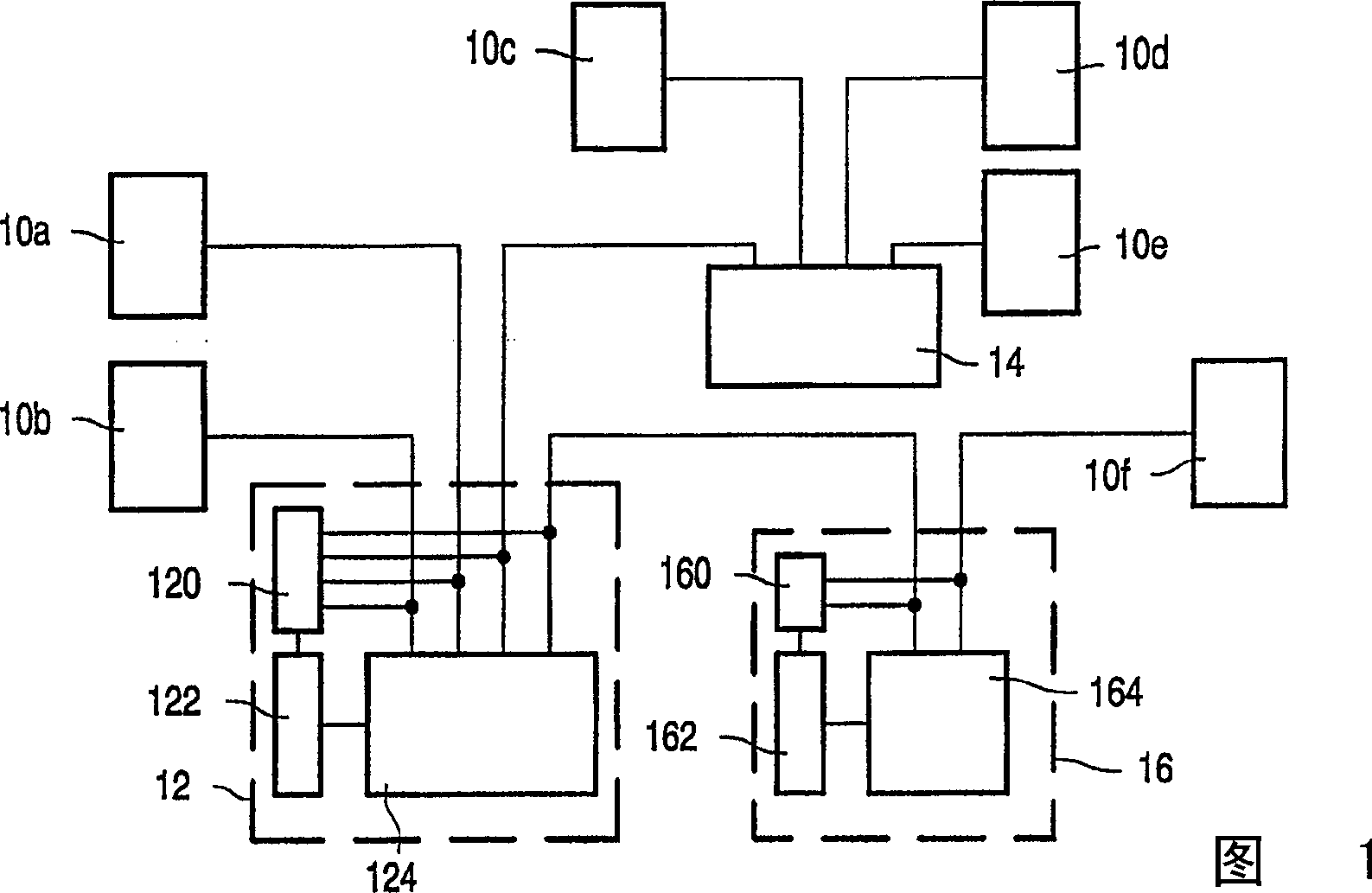
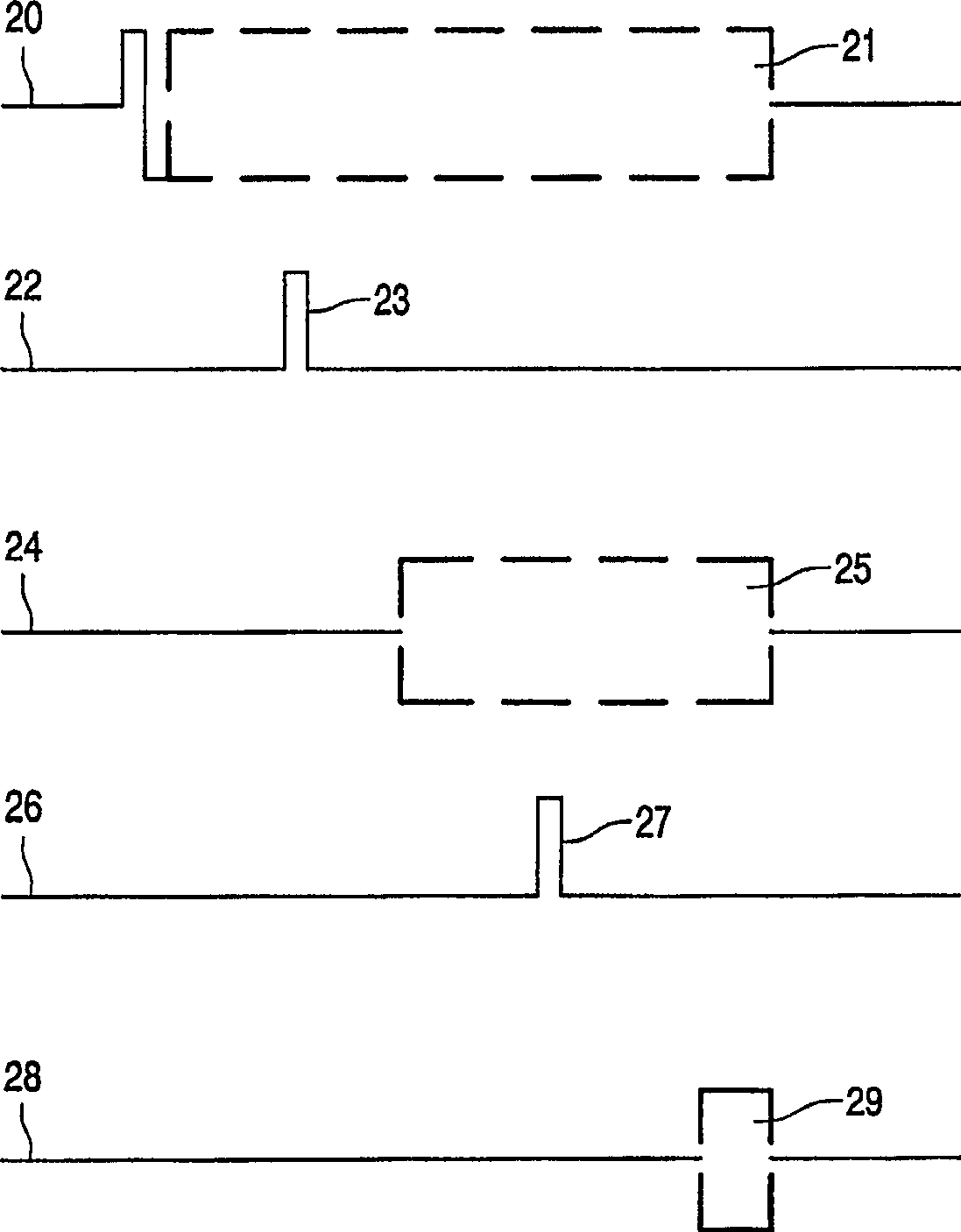
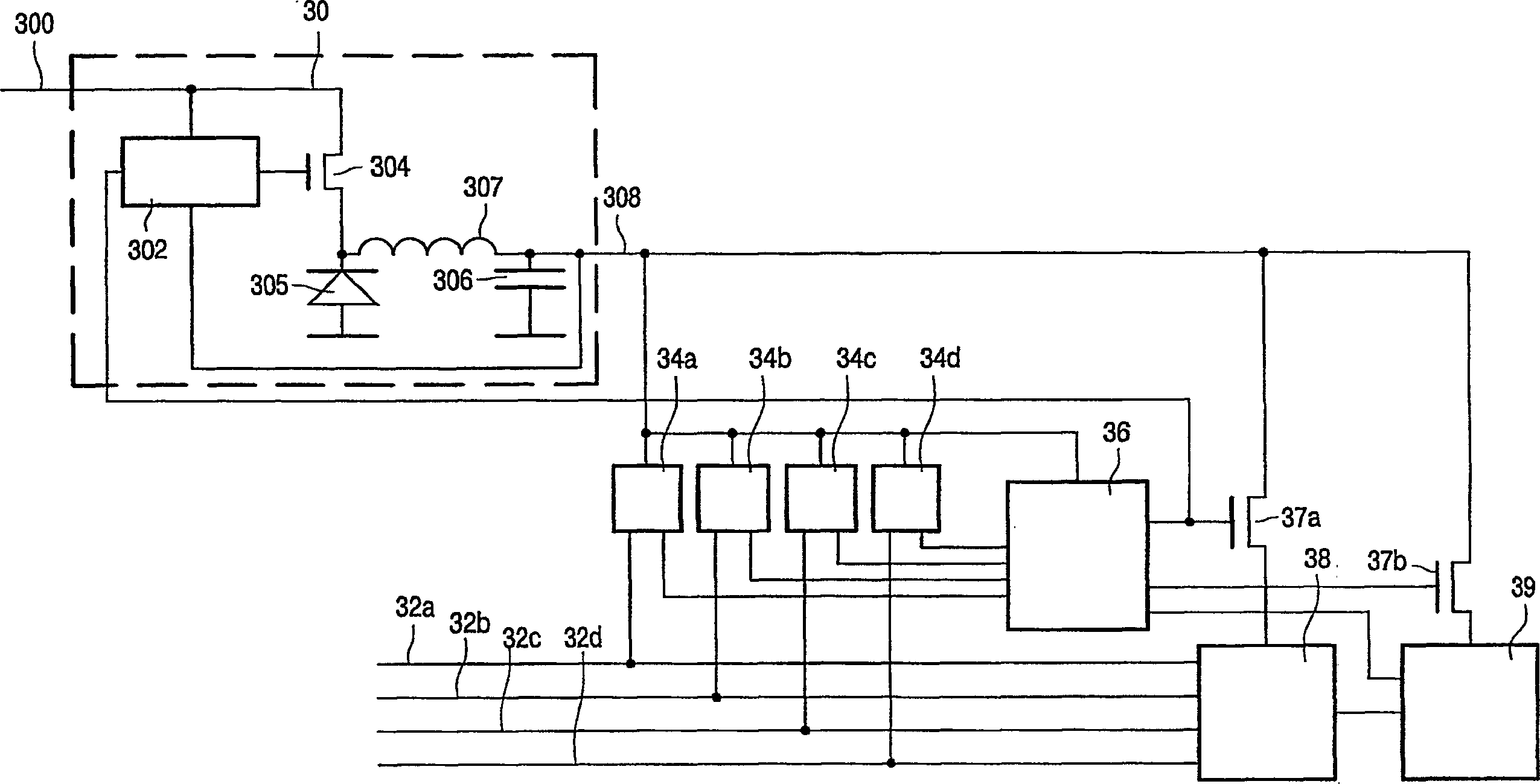
The communication bus system comprises a plurality of node circuits ( 10 a-d) and a relay circuit ( 12, 14, 16 ) coupling the node circuits ( 10 a-d). The relay circuit ( 12, 14, 16 ) has a transceiver circuit ( 124, 164 ) for relaying messages ( 21 ) between the node circuits ( 10 a-d) in a normal mode. The transceiver circuit ( 124, 164 ) is powered down in a sleep mode. A detector circuit ( 120, 160 ) detects an incoming message ( 41 ) when the relay circuit ( 12, 14, 16 ) is in a sleep mode. A mode control circuit ( 122, 162 ) powers up the transceiver ( 124, 164 ) in response to detection of an incoming message ( 21 ). Steps are taken that ensure, in the normal mode, that messages ( 21 ) will not be relayed in unreadable form. The mode control circuit ( 122, 162 ) is arranged to cause the transceiver ( 124, 164 ) to relay a remainder ( 25 ) of the incoming message ( 21 ) after power up. In an embodiment the power needed to transmit the remainder ( 25 ) of the message ( 21 ) is drained from a capacitor ( 306 ) in the power supply ( 30 ) before the power supply ( 30 ) controls the power supply voltage in the normal mode. In another embodiment the detector circuit ( 120, 160 ) temporarily controls the direction of operation of the transceivers ( 124, 164 ) at the start of the normal mode instead of further detectors ( 58 a-d) that normally control the direction of operation in the normal mode.
Owner:NXP BV
Power source system
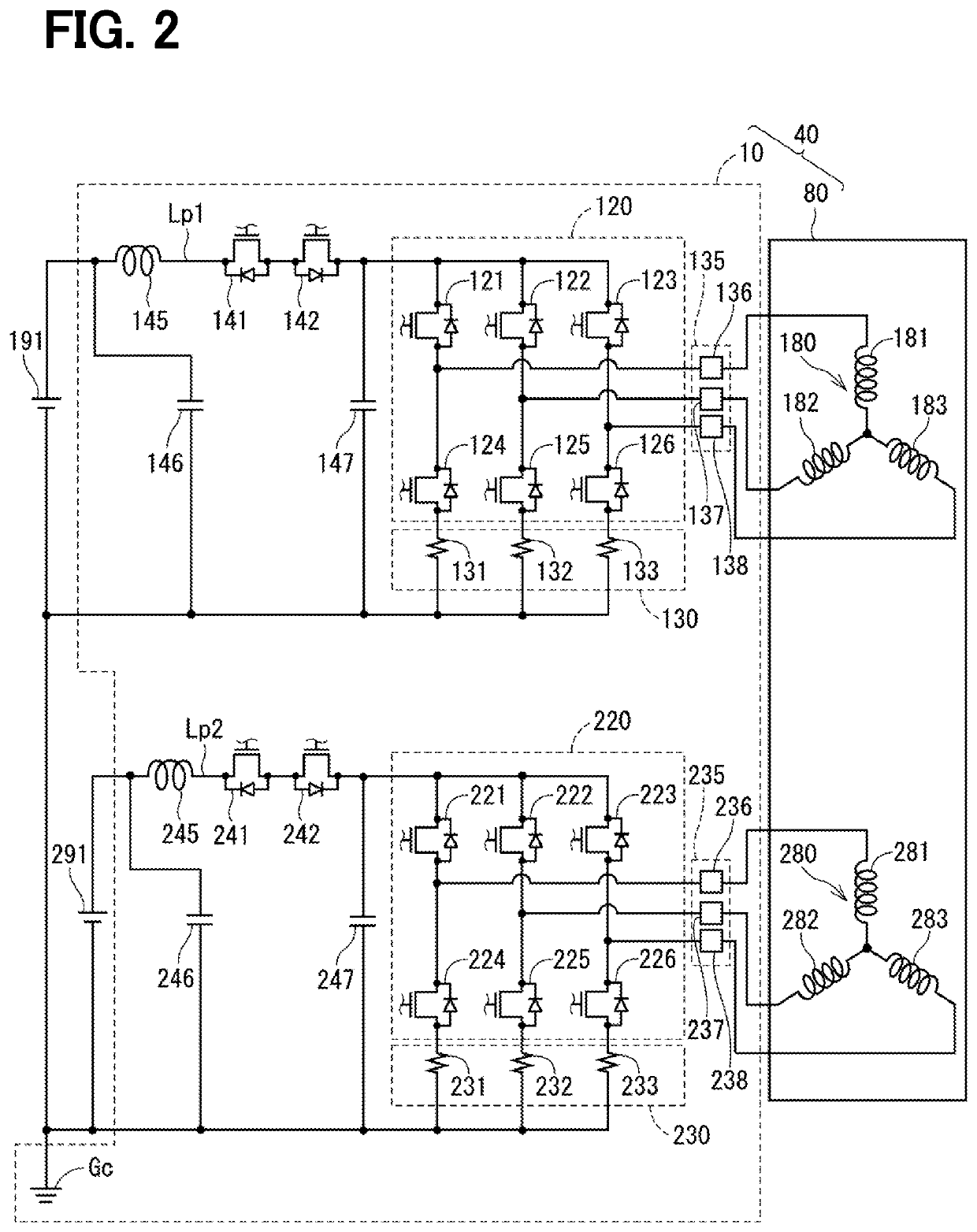
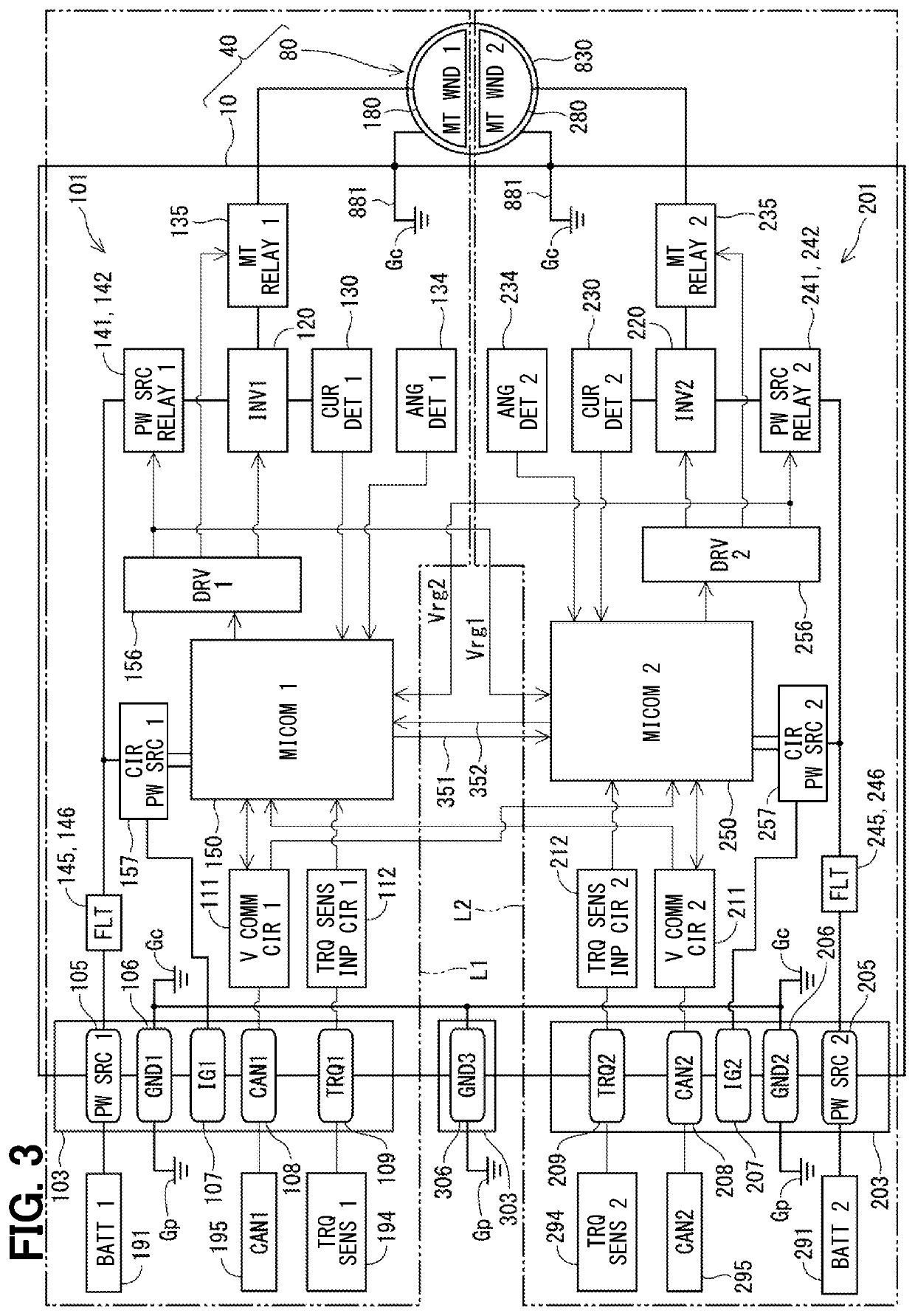
ActiveUS20200391681A1Simple circuit configurationAC motor controlConversion constructional detailsEmbedded systemNode (circuits)
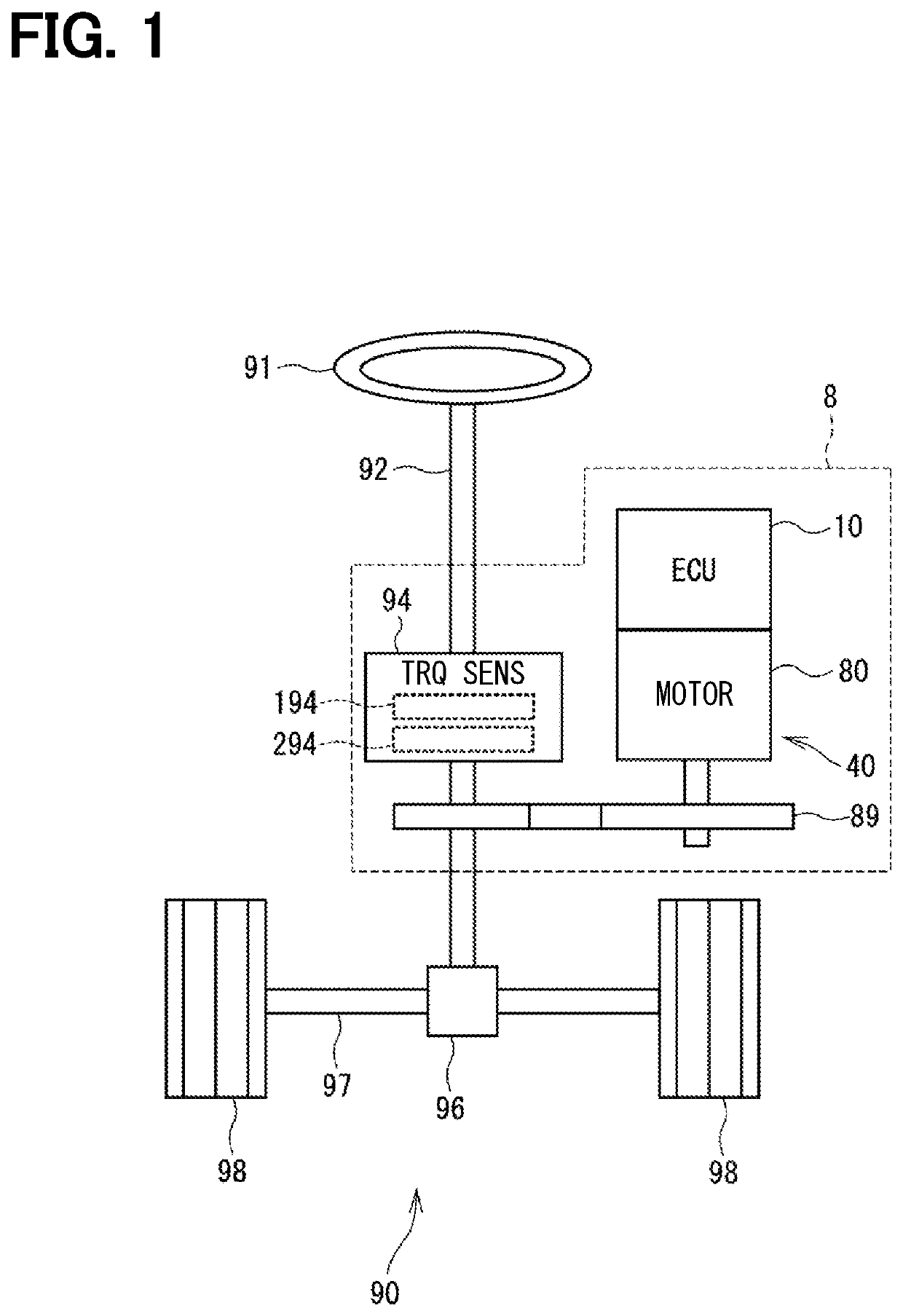
In a power source system, circuit units by the number of systems n or more are respectively connected correspondingly to power sources by the number of n (n is an integer of 2 or more). A common ground is all of the circuit units in common. A ground wiring portion establish node-to-node connection between (n+α) pieces of common ground nodes NC(1) to NC(n+α) provided in the common ground and (n+α) pieces of ground plane nodes NP(1) to NP(n+α) provided on a vehicle body in an independent manner, thereby enabling a simple configuration of redundant circuits that can withstand multipoint failures without separating the ground for each system.
Owner:DENSO CORP
DVD analysis that accounts for delays
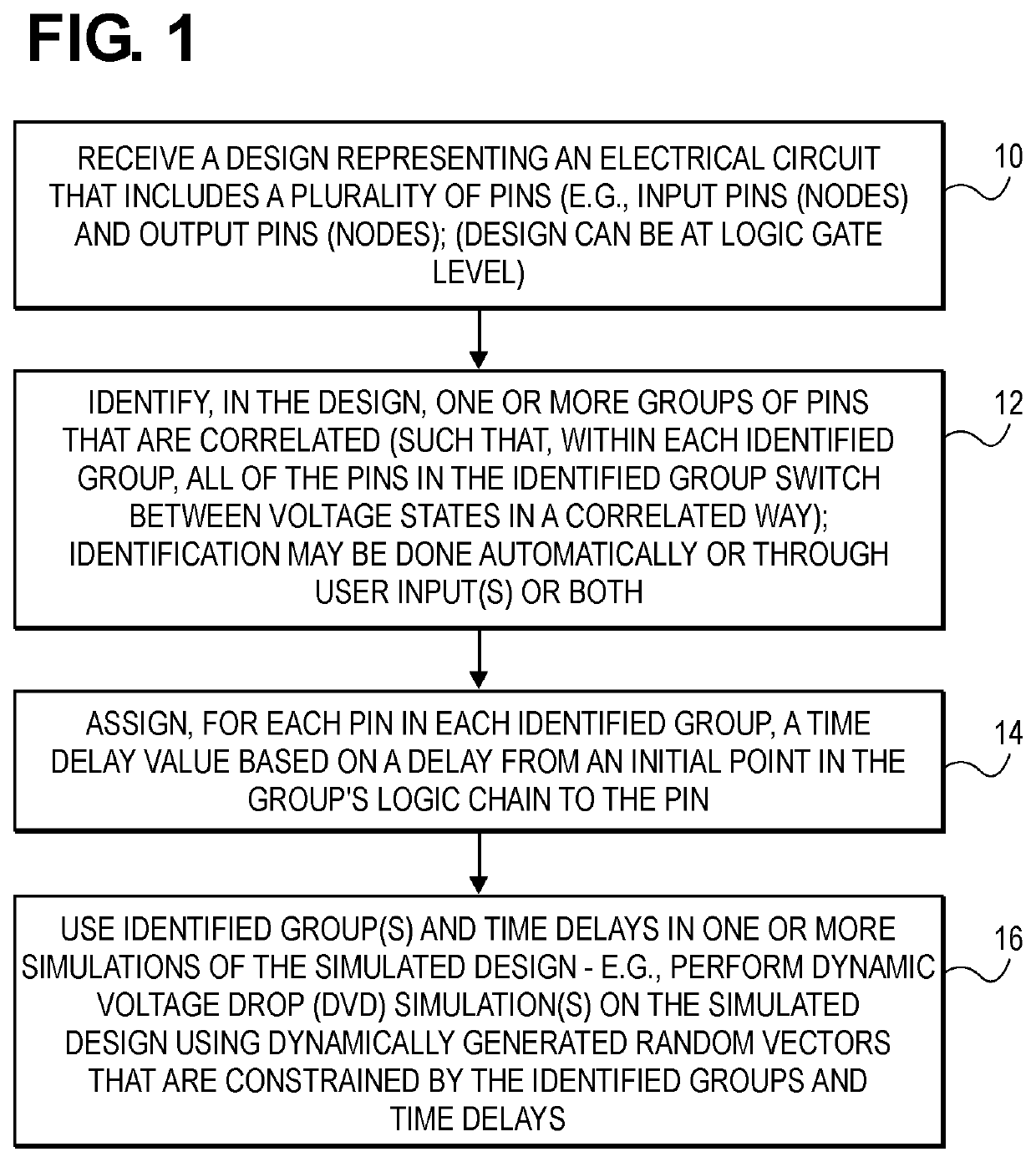
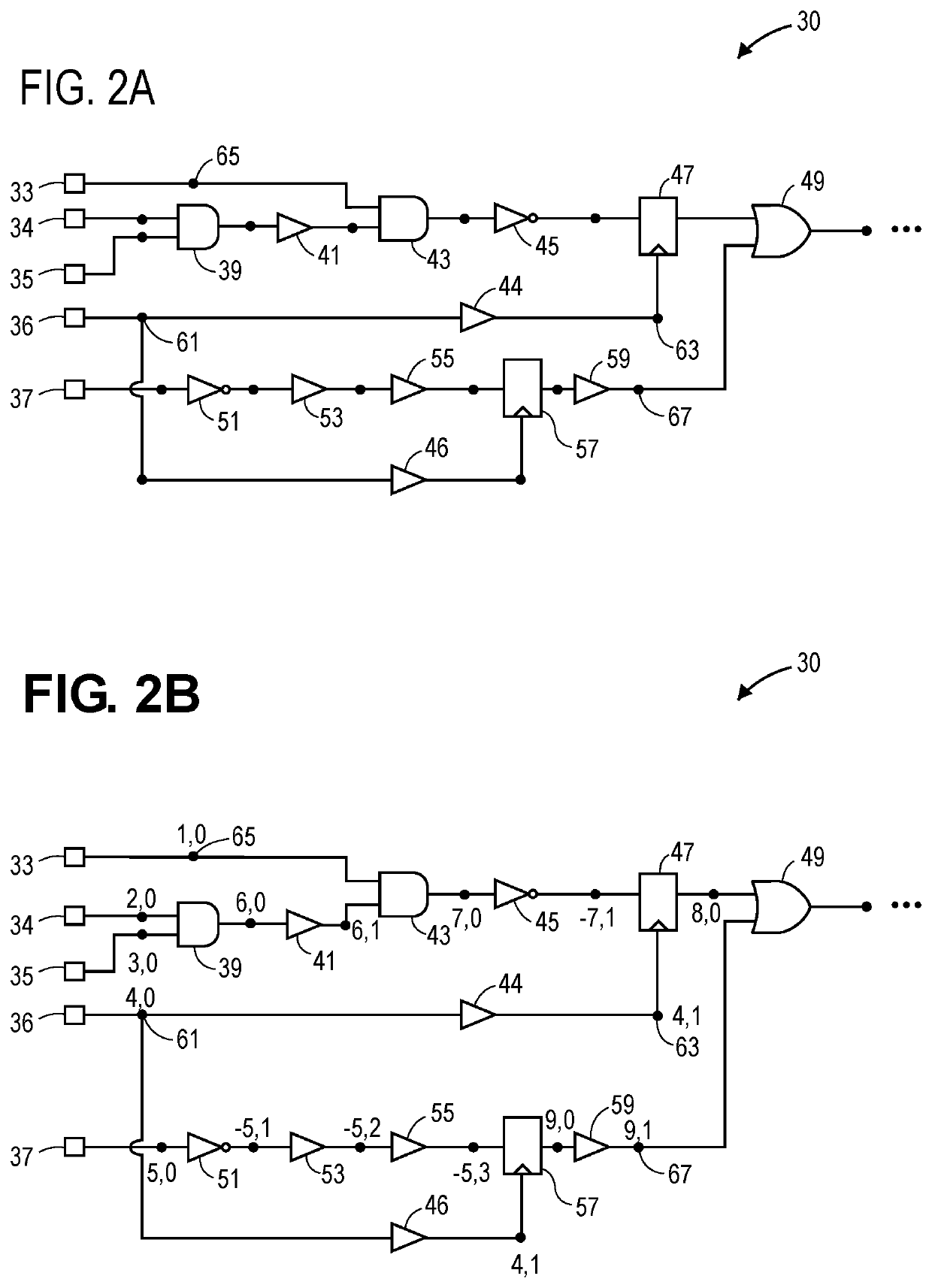
ActiveUS11321513B1Accurately switching timeLimit switching activityComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsTime delaysSoftware engineering
Techniques for computer aided design and engineering of integrated circuits can use group identifiers of correlated signals and time delay values when using vectorless dynamic voltage drop (DVD) simulations and when using other types of simulations or analyses of a circuit design. A method in one embodiment can include the operations of: receiving a design representing an electrical circuit that includes a plurality of pins, the plurality of pins including one or more input nodes or one or more output nodes in the electrical circuit; identifying, in the design, one or more groups of pins that are correlated such that, within each identified group, all of the pins in the identified groups switch between voltage states in a correlated way; assigning, for each pin in each identified group, an identifier for the identified group and a time delay value based on the pin's delay from an initial point in the identified group's logic chain to the pin. The group identifier and the time delay at each pin can limit the switching activities in the DVD simulations to reduce pessimistic results from the simulations. Other methods are described, and data processing systems and machine readable media that cause such systems to perform these methods are also described.
Owner:ANSYS
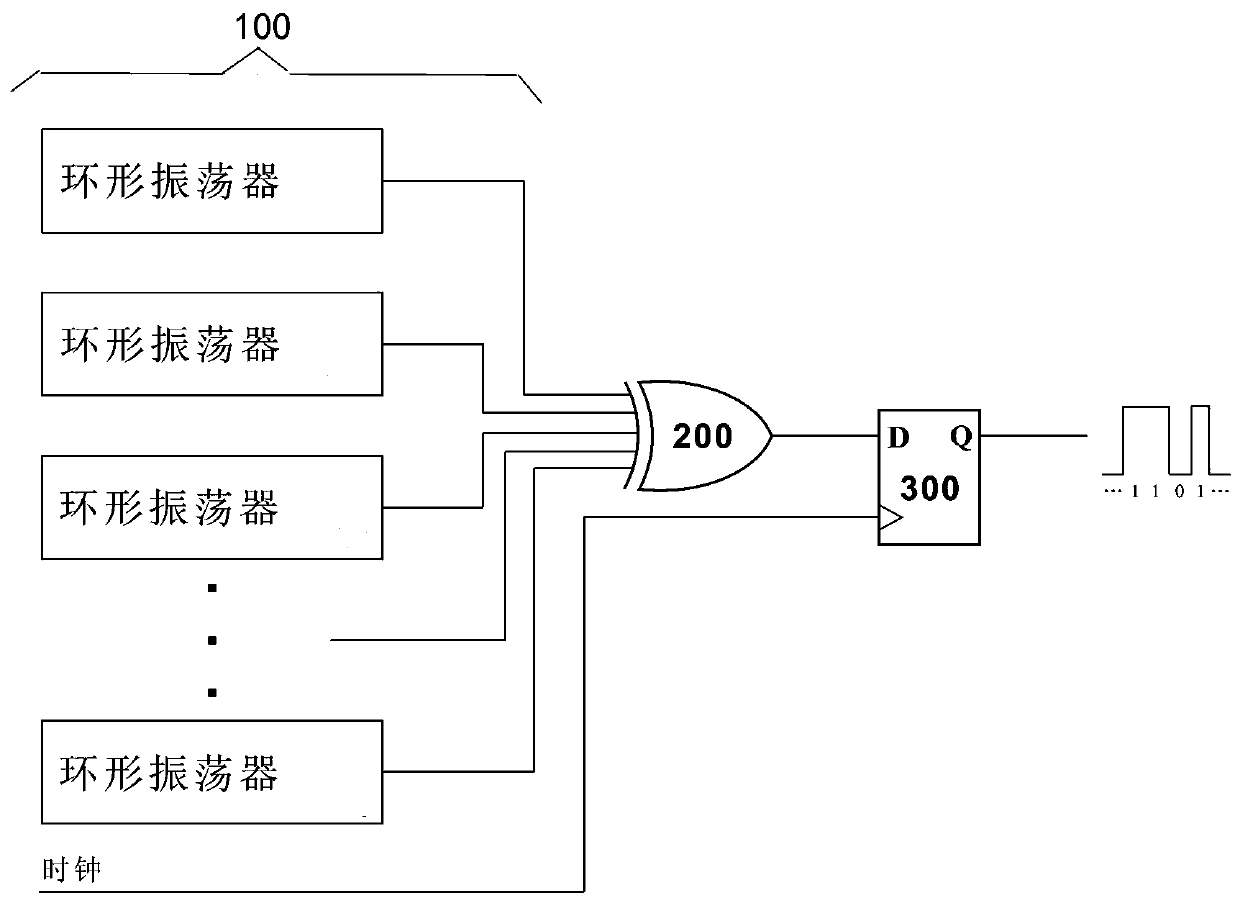
Power consumption and rate adjustable physical random number generation method
ActiveCN110795063ASimple structureEasy to realize integration and miniaturizationRandom number generatorsHemt circuitsControl theory
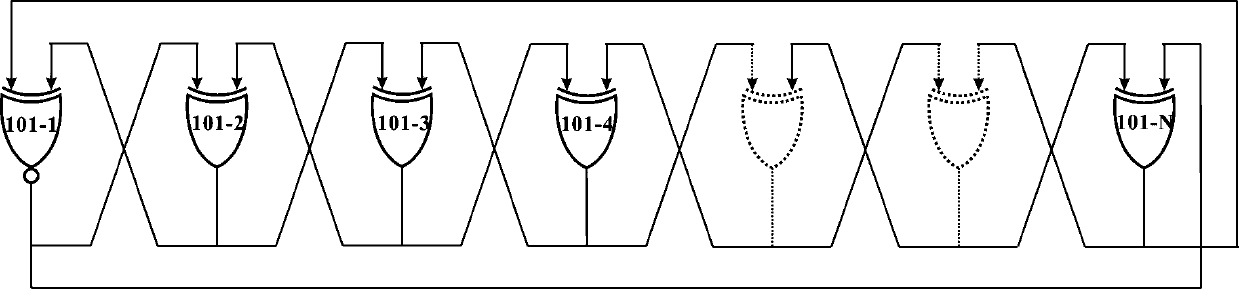
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits, and particularly relates to a power consumption and rate adjustable physical random number generation method. The device comprisesan entropy source module, an entropy sampling module and a clock signal. The entropy source module is composed of M ring oscillators, a node of each ring oscillator serves as signal output at the sametime, and the output of the nodes presents periodic signals and chaotic signals by adjusting the working voltage of the digital logic circuit. The entropy sampling module performs quantitative sampling on output signals in each ring oscillator through a D trigger to generate a random bit sequence. The random bit sequence generates a periodic signal when the digital logic circuit is in a low-voltage state. When the digital logic circuit is in a high-voltage state, a chaotic signal is generated. The oscillation sampling method and the chaotic circuit method are combined, the speed and power consumption of the physical random number generator are controlled by adjusting the voltage, the circuit structure is simple, and integration and miniaturization are easy to achieve.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
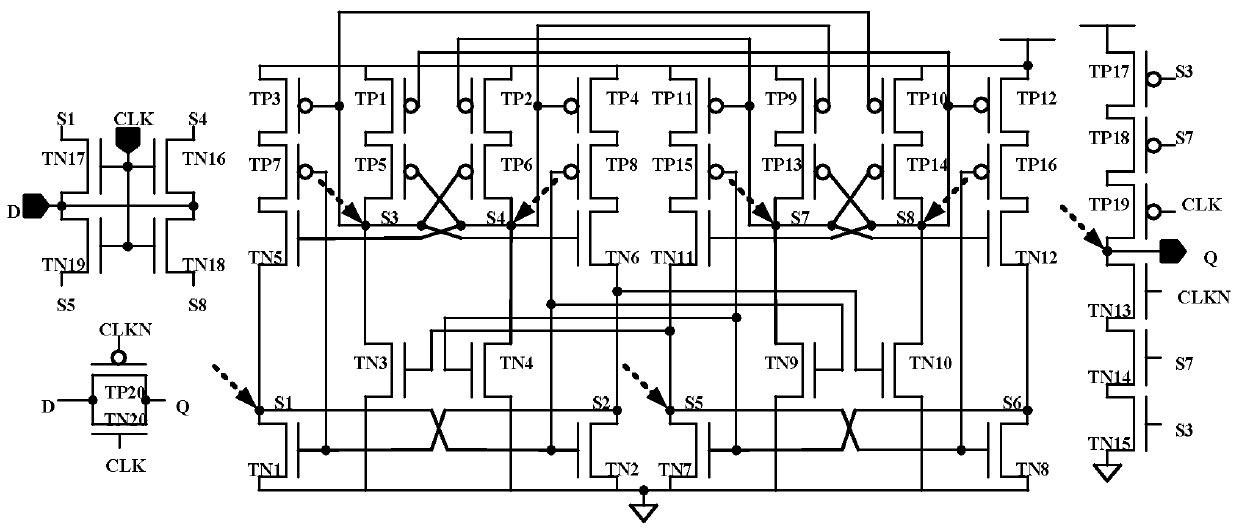
D latch with layout symmetry and resistance to three-node upset
PendingCN111245423AReduce areaSmall propagation delayReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCross connectionCircuit reliability
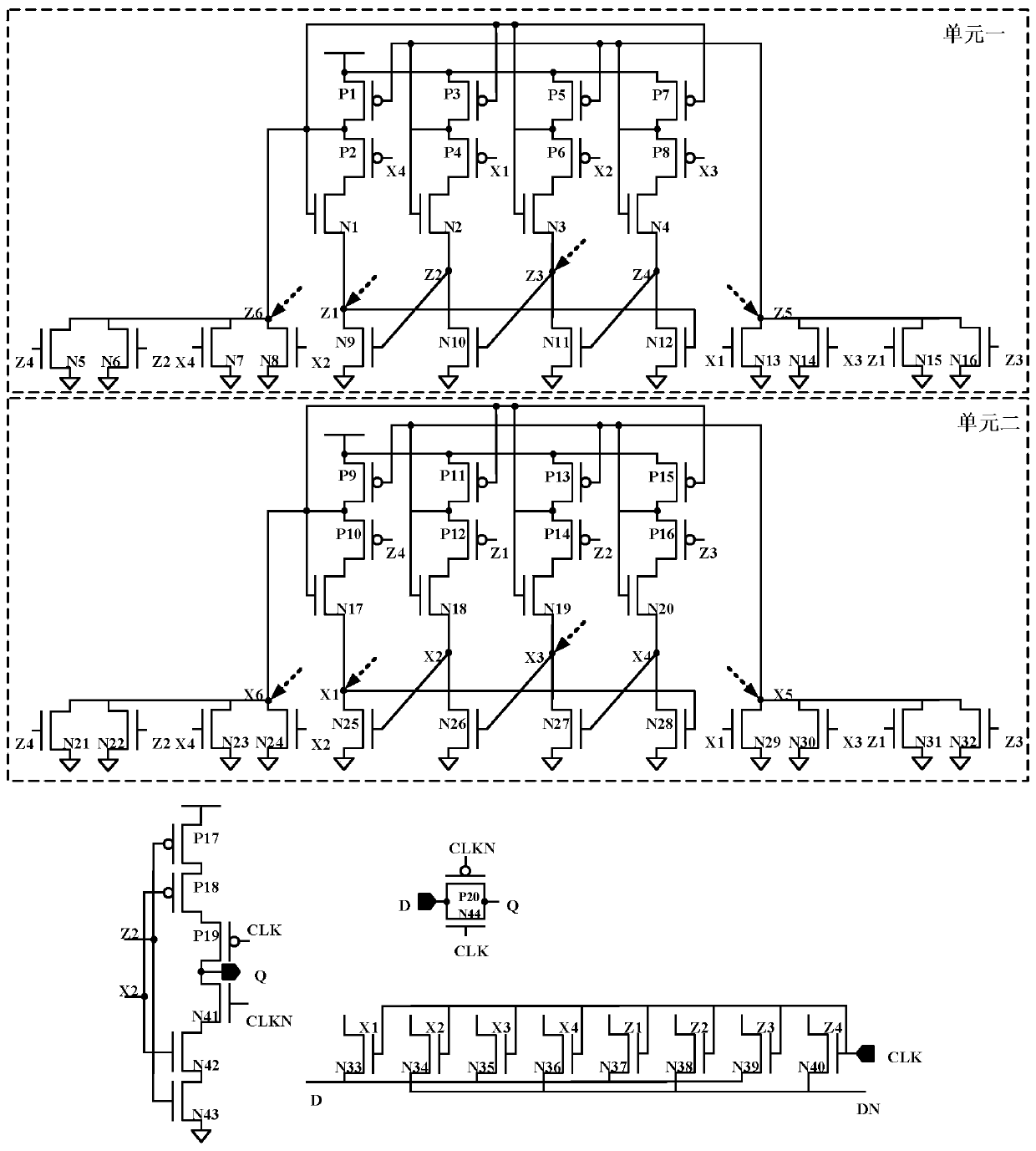
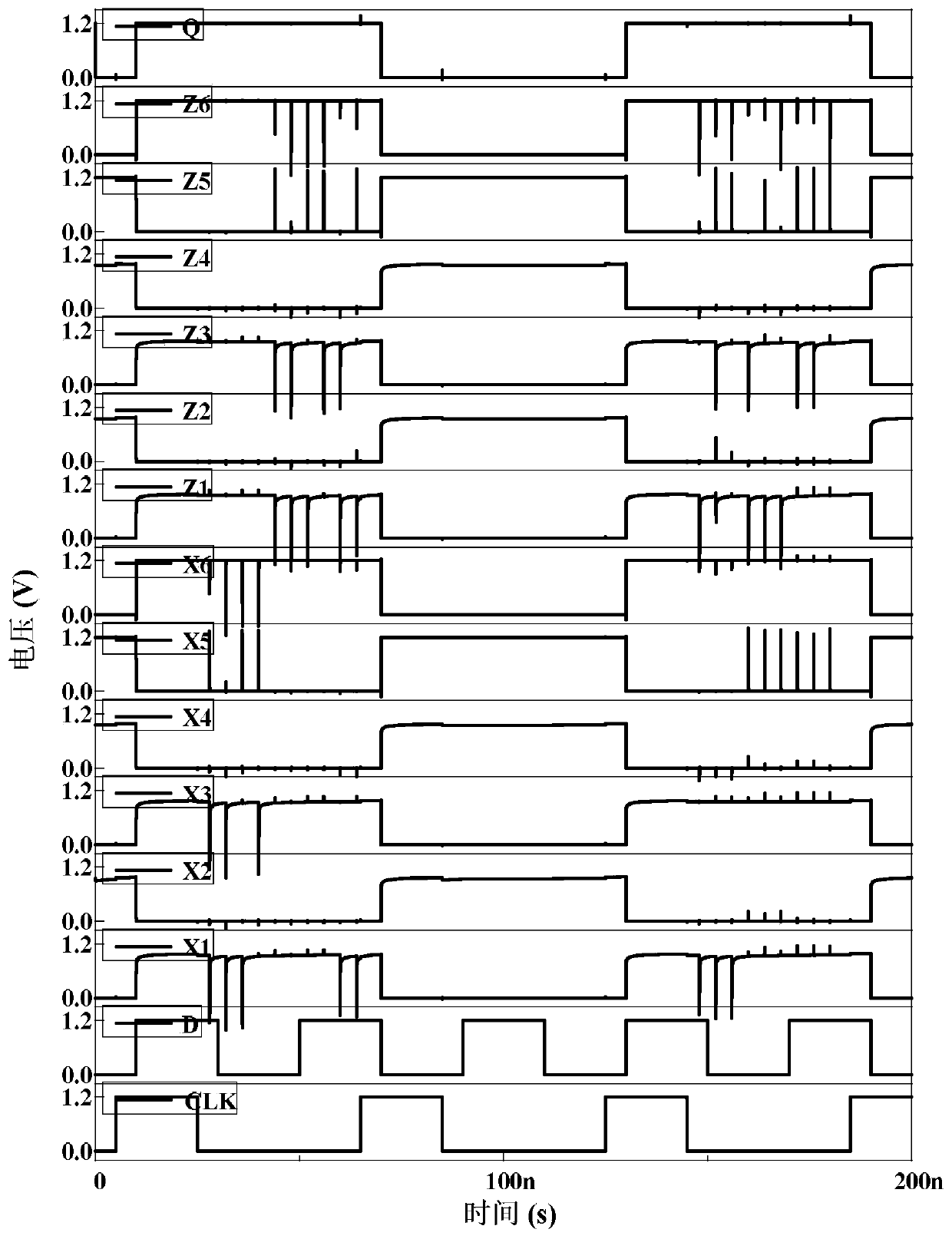
The invention discloses a D latch with layout symmetry and resistance to three-node upset, and belongs to the field of anti-core reinforcement in reliability of integrated circuits. The problems thatan existing anti-three-node-overturn D latch needs to consume more hardware, and is high in power consumption and large in area are solved. The D latch comprises 44 NMOS transistors N1 to N44 and 20 PMOS transistors P1 to P20; and the transistors N1 to N16 and the transistors P1 to P8 form a unit 1, the transistors N17 to N32 and the PMOS transistors P9 to P16 form a unit 2, and the unit 1 and theunit 2 are mirror images of each other in circuit structure. Two units which are connected in a crossed mode are used for achieving recovery of overturning of all the three nodes. The D latch is mainly suitable for medium-low frequency circuits with low power consumption.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
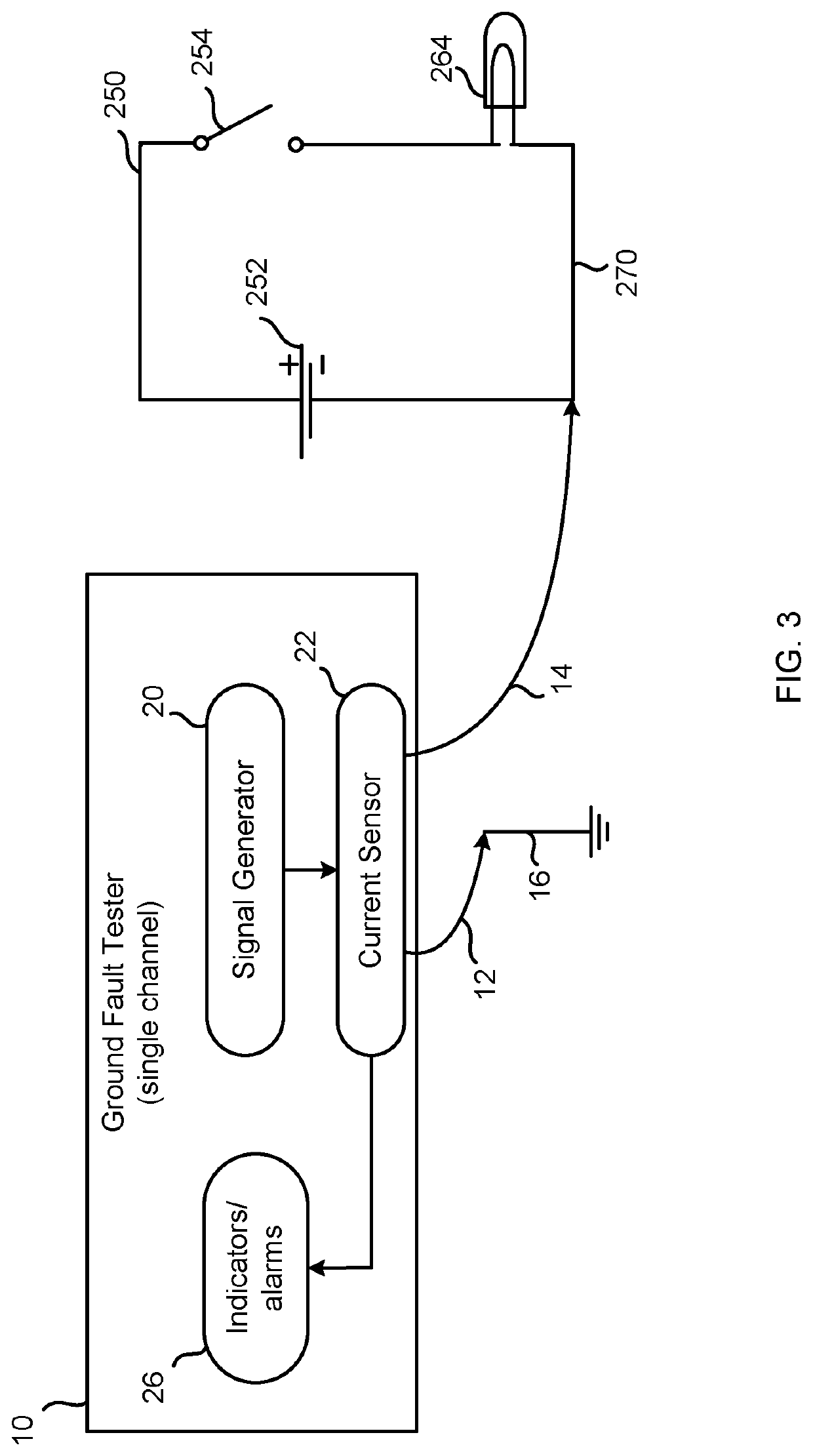
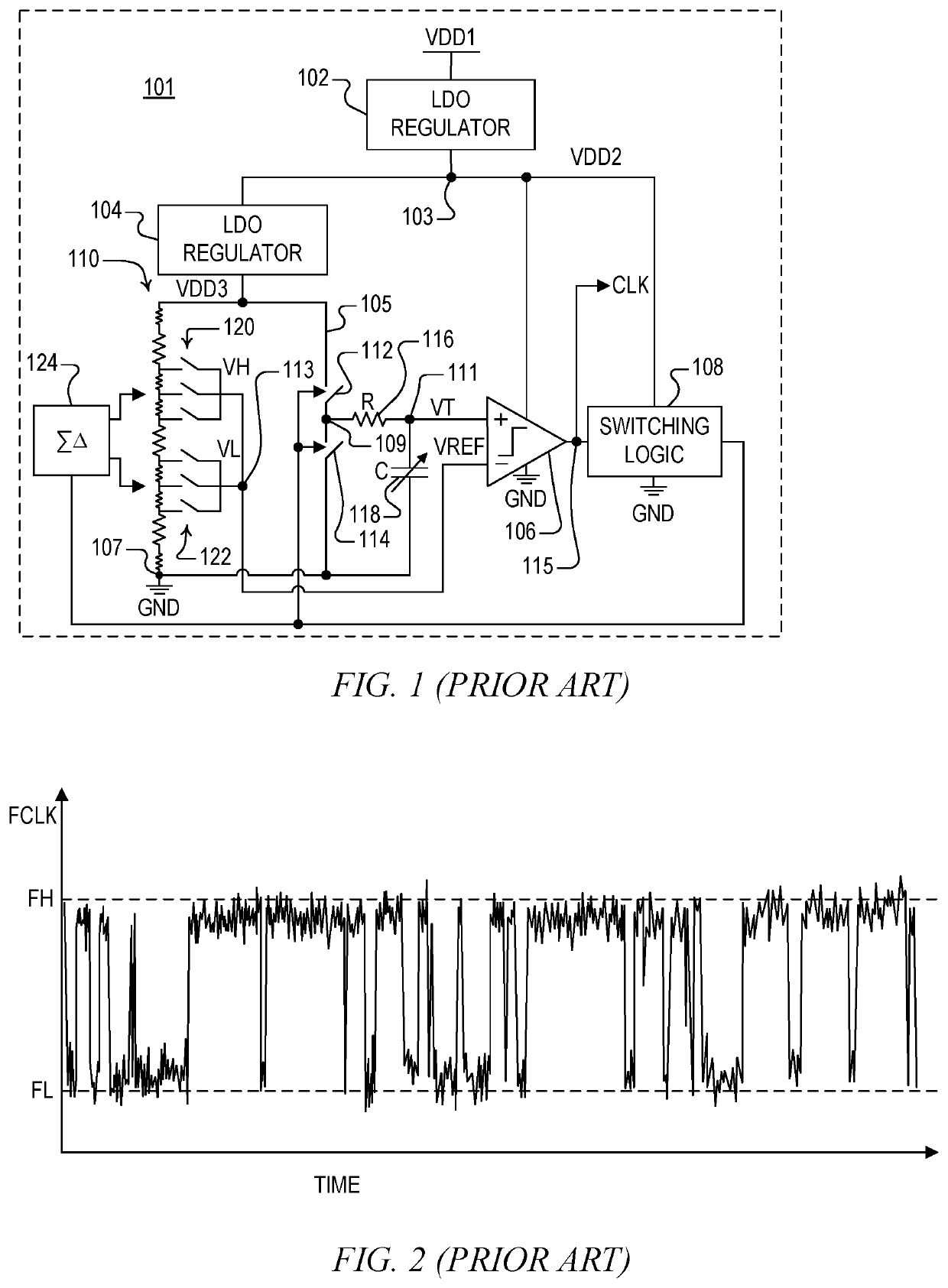
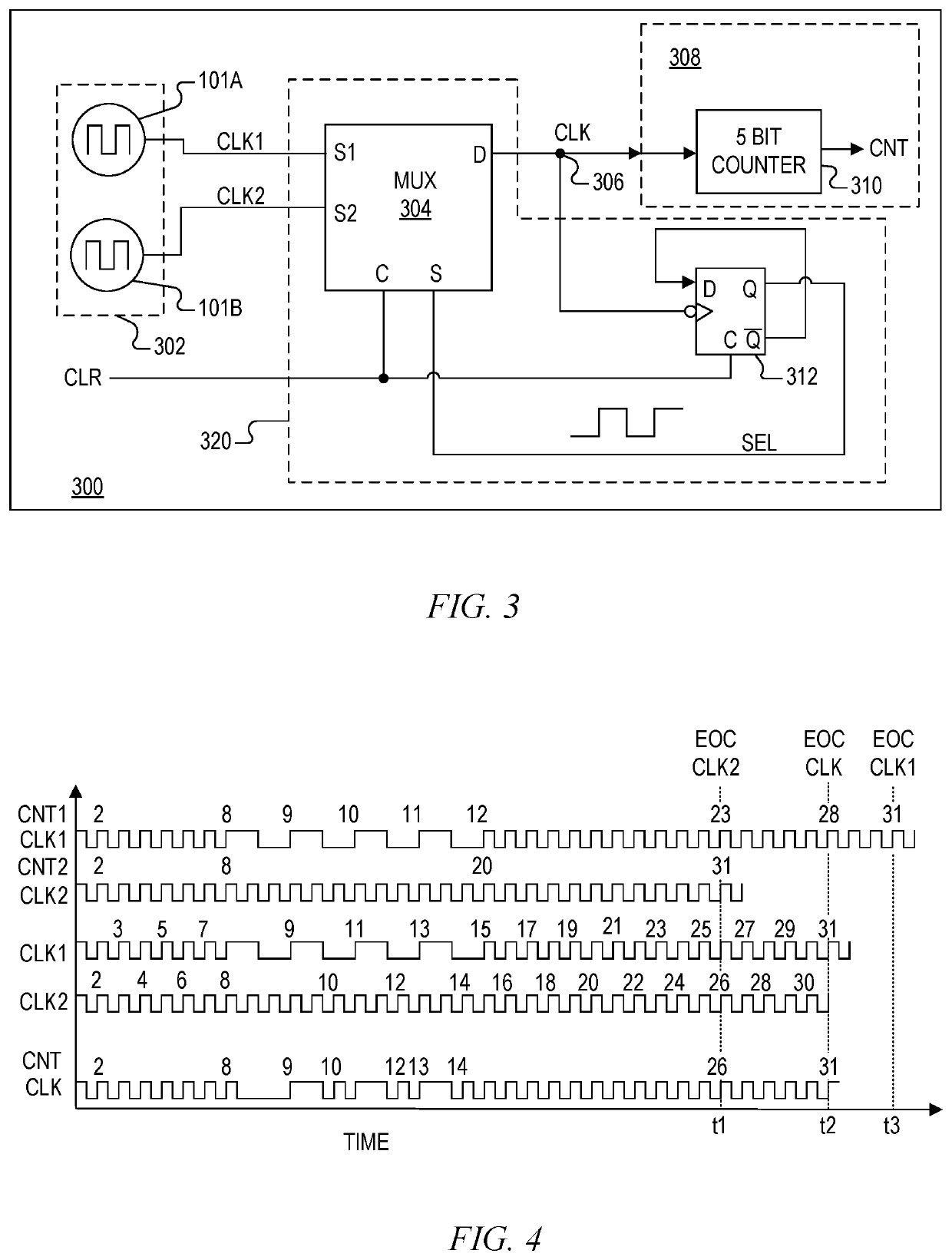
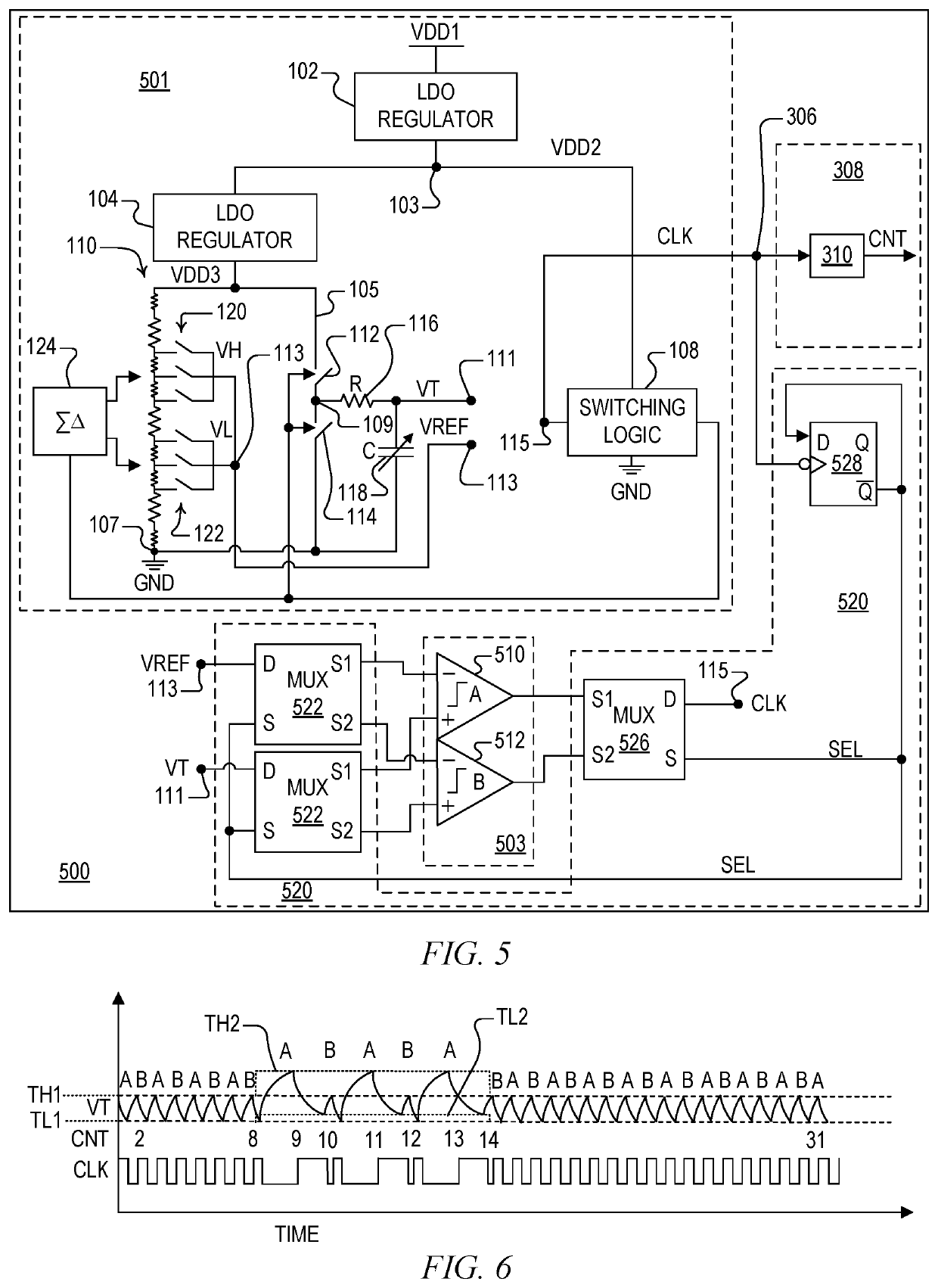
Multichannel ground fault tester
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
System and method of duplicate circuit block swapping for noise reduction
ActiveUS20200191849A1Reduce noiseNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNode (circuits)Hemt circuits
An integrated circuit including at least one circuit node, multiple duplicate circuit blocks integrated on the integrated circuit in close proximity with each other, each including at least one device that is susceptible to random telegraph noise (RTN), and a switch circuit that swaps electrical coupling of the duplicate circuit blocks, one at a time, to the at least one circuit node in sequential cycles of a clock signal. The duplicate circuit blocks may be large functional blocks, such as an oscillator or a comparator or the like, or limited to circuits including RTN susceptible devices, such as differential pairs or the like. Each duplicate circuit block may include any number of connections for coupling to corresponding circuit nodes. The swapping may further include chopping in which multiple inputs are swapped with each other while multiple outputs are swapped with each other in consecutive clock cycles.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
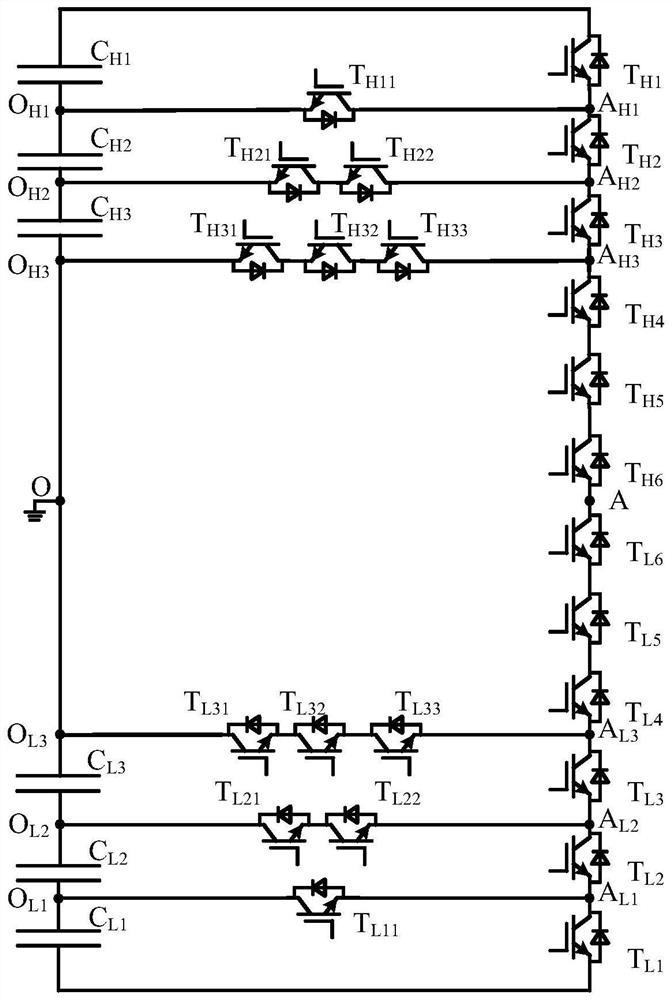
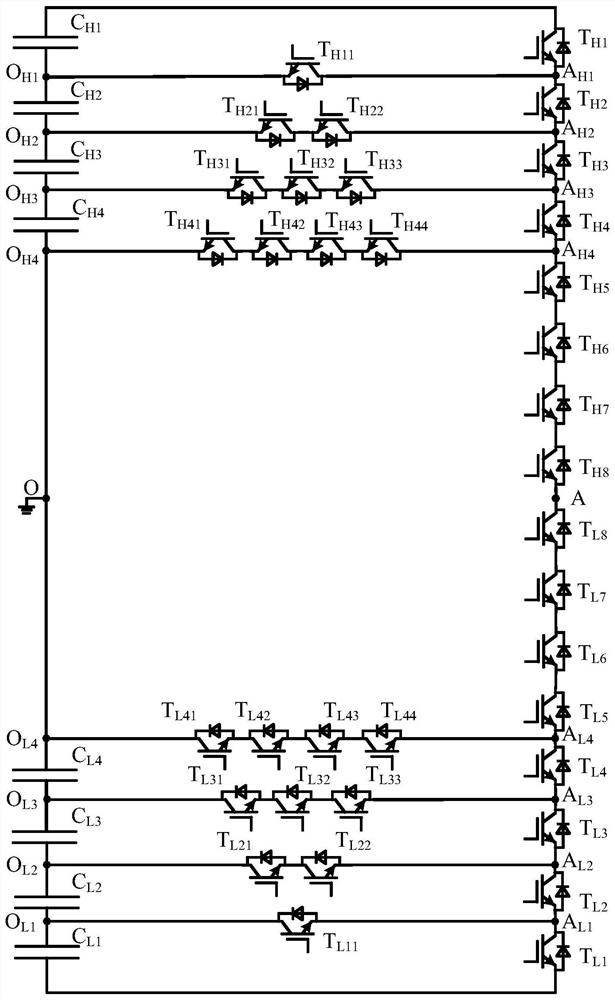
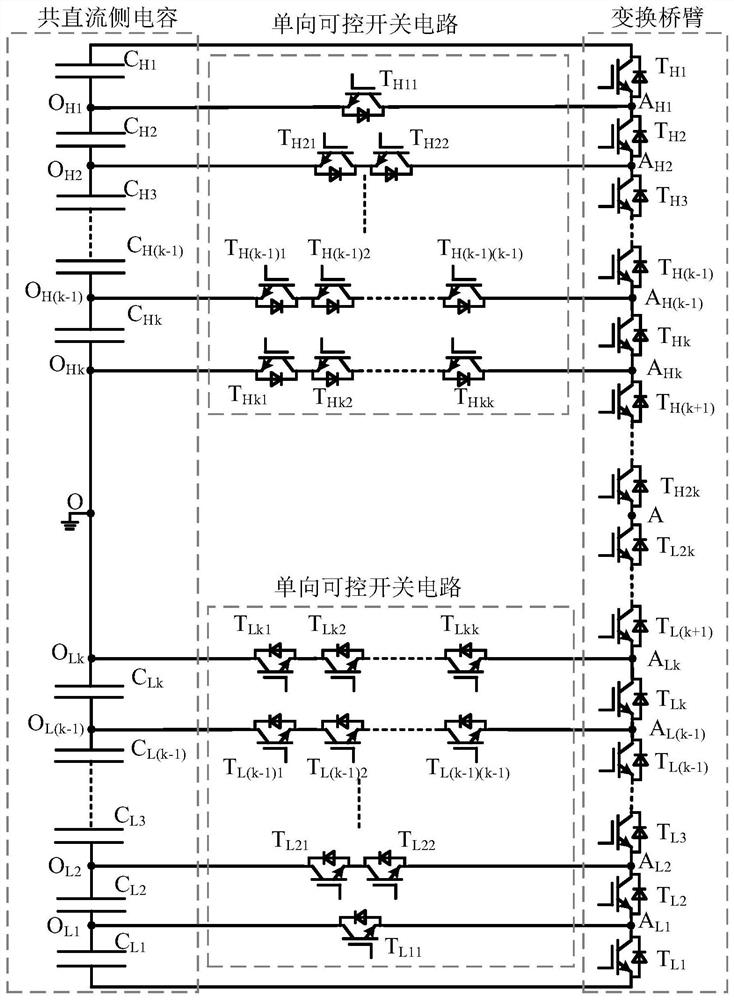
A Multilevel Converter with Common DC Side Capacitors
The invention relates to a novel multilevel converter with a common direct current side capacitor. When 2k+j (k is a positive integer, j is equal to 1 or 2) level is output, the common direct currentside capacitor is formed by connecting (2k+j-1) voltage equalization capacitors in series; any bridge arm is formed by connecting 2(2k+j-1) switches composed of a controllable power device with an anti-parallel diode; 2k layers are provided in nodes between the voltage equalization capacitors; k forward and reverse switch branch circuits are respectively extracted from two ends to the middle part;the other ends of the branch circuits are connected to corresponding layers, from two ends to the middle part, of the node between the bridge arms, wherein the ith branch circuit is formed by connecting i switches in series (i= 1,2...k). When j is equal to 1, the k forward and reverse switch branch circuits have a common connection point, and the switches can only retain the anti-parallel diodes;or the two branch circuits are connected in series, the two ends are respectively connected to a middle point of the common direct current side capacitor and the bridge arms. According to the novel multilevel converter with the common direct current side capacitor, the number of devices used in the multilevel converter is decreased and the size and complexity of the system are reduced. In a multi-phase equilibrium system, the capacitance required by the multilevel converter is significantly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Dynamic Component Matching in Integrated Circuits
ActiveCN110892238BThermometer detailsProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsNode (circuits)Hemt circuits
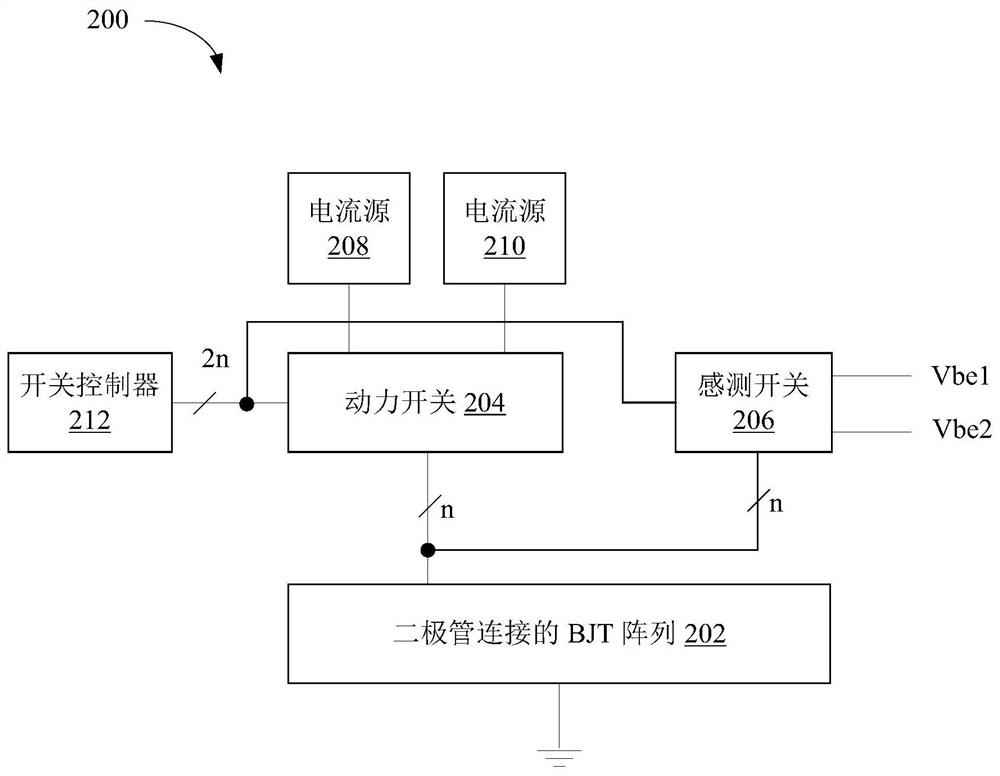
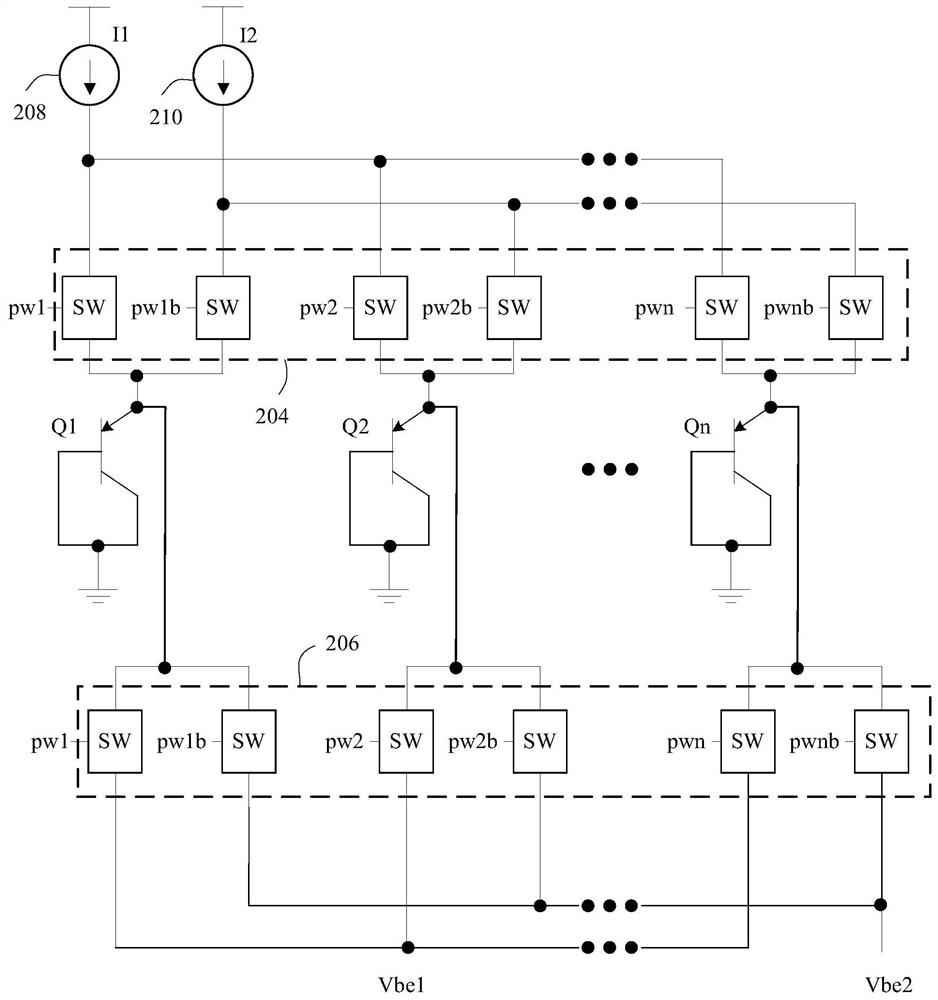
An example dynamic element matching (DEM) circuit includes: a plurality of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) (202), each of the plurality of BJTs having a base terminal and a collector terminal coupled to electrical ground; a plurality of power switch pairs (204), each power switch pair coupled to an emitter of a respective one of the plurality of BJTs; a plurality of sensing switch pairs (206), each sensing switch pair being respectively coupled to a plurality of BJTs The emitter of each of the BJTs, the first switch of each sense switch pair is coupled to the first node (Vbel), and the second switch of each sense switch pair is coupled to the second node (Vbe2); a first current source (208) coupled to the first switch in each power switch pair; and a second current source (210) coupled to the second switch in each power switch pair .
Owner:XILINX INC
Dual-node-upset-resistant D latch applied to high-frequency circuit
PendingCN111200429AReduce areaReduce power overheadReliability increase in field effect transistorsCircuit reliabilityNuclear power
The invention discloses a dual-node-upset-resistant D latch applied to a high-frequency circuit, which belongs to the field of anti-core reinforcement in reliability of integrated circuits. The problems that a traditional D latch resistant to charge sharing needs to consume more hardware and is large in power consumption and area, and the reinforcement performance is seriously affected due to moresensitive nodes are solved. The D latch comprises 20 NMOS transistors N1 to N20 and 12 PMOS transistors P1 to P12, and only 32 transistors are needed to construct the D latch, so that the area andthe power consumption overhead of the D latch are reduced. An input signal D can be directly transmitted to the output end of an output signal D through the transmission gates constructed by the transistors N20 and P12, so that the transmission delay is reduced. The D latch provided by the invention is suitable for being applied to high-frequency circuits, and is particularly suitable for aerospace, aerospace flight, nuclear power stations and the like with nuclear radiation effects.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Node load short-circuit self-isolation circuit and method and multi-split circuit
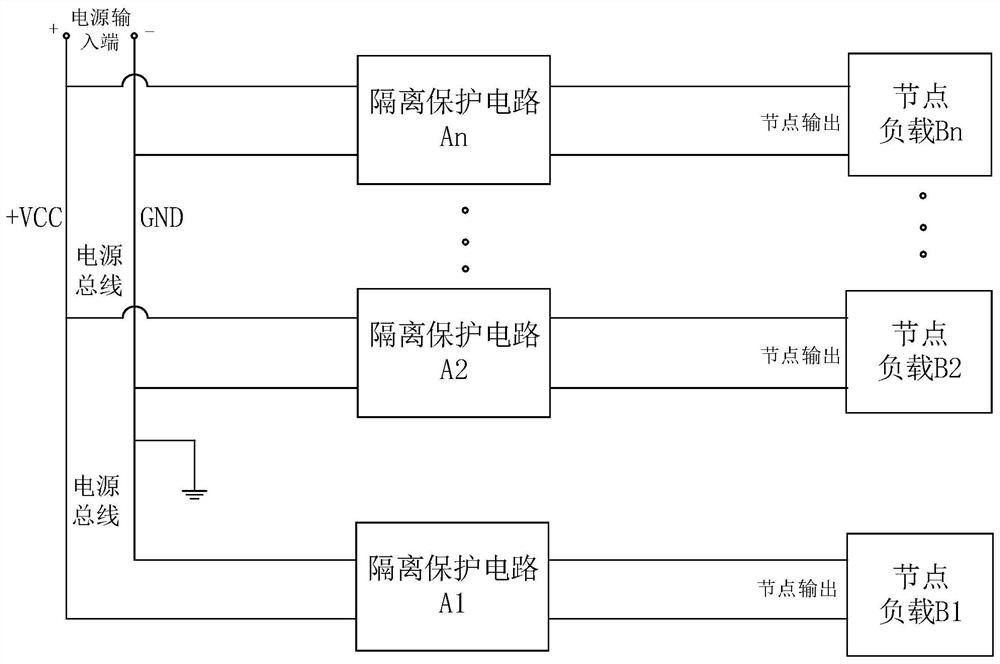
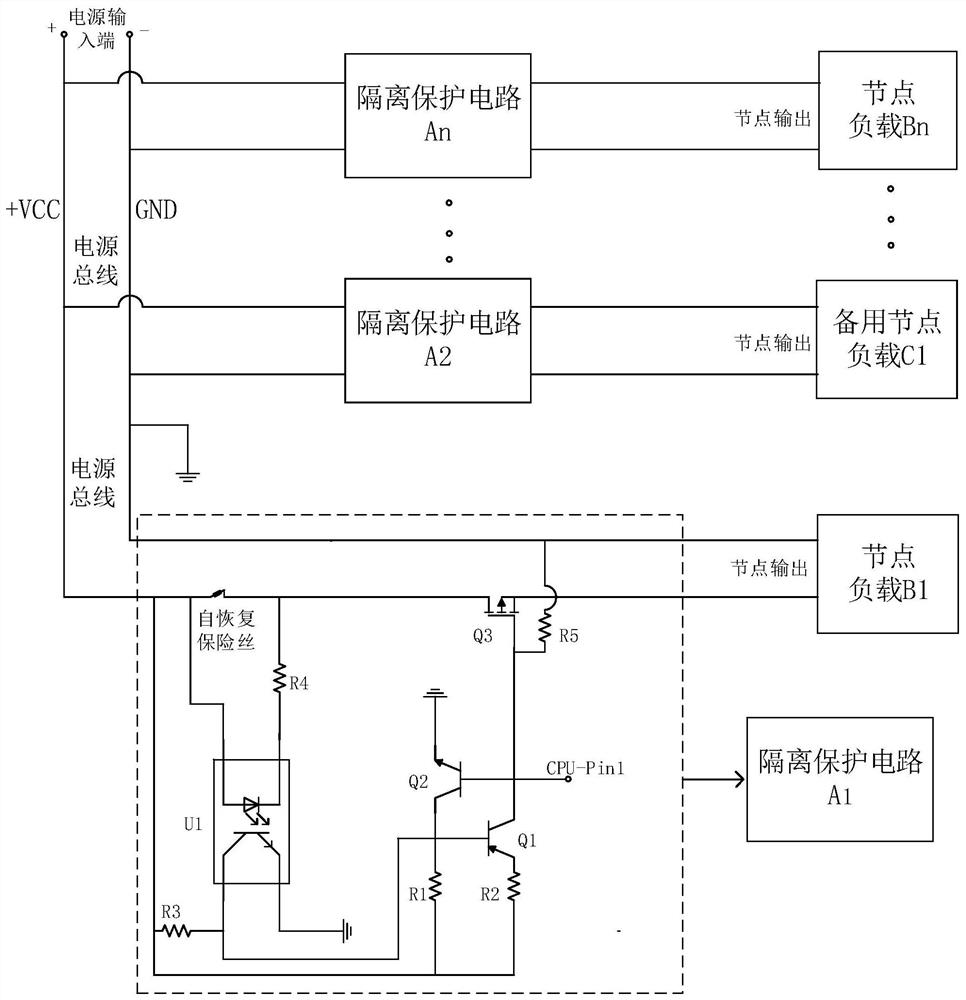
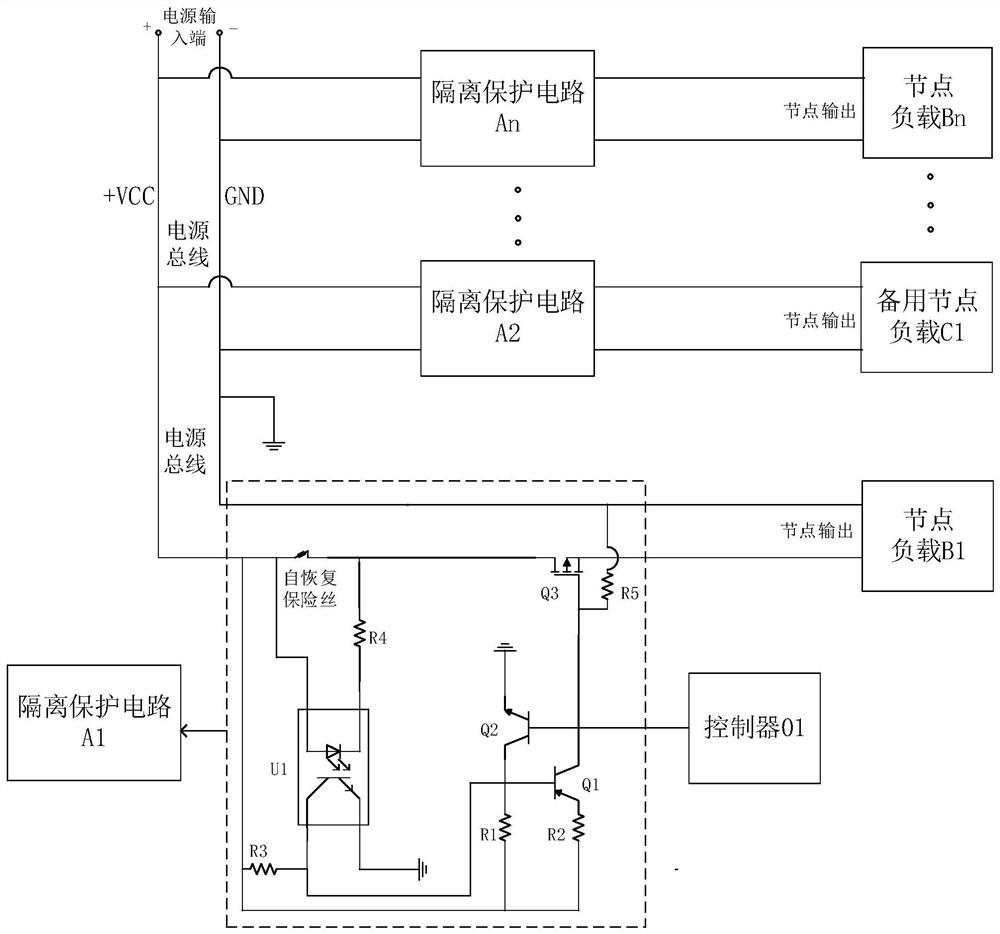
ActiveCN113141287AAchieve isolationEffective isolationEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionBus networksNode (circuits)Engineering
The invention relates to a node load short-circuit self-isolation circuit, a node load short-circuit self-isolation method and a multi-split circuit. The node load short-circuit self-isolation circuit comprises a power bus and at least one node load arranged on the power bus; isolation protection circuits in one-to-one correspondence with the node loads are also arranged between the node loads and the power bus; and the isolation protection circuit is used for monitoring whether the node load connected with the isolation protection circuit is short-circuited or not, and when the node load is short-circuited, the node load is isolated from the power bus. According to the node load short-circuit self-isolation circuit, when a certain node load is short-circuited, the load node can be effectively isolated from a power bus so as to protect output of other loads from being affected, complete isolation of a fault node is achieved, and the phenomenon of false triggering or dysfunction of the controller due to short circuit of the node load is avoided.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Low-redundancy charge sharing resistant D latch for high frequency circuit applications
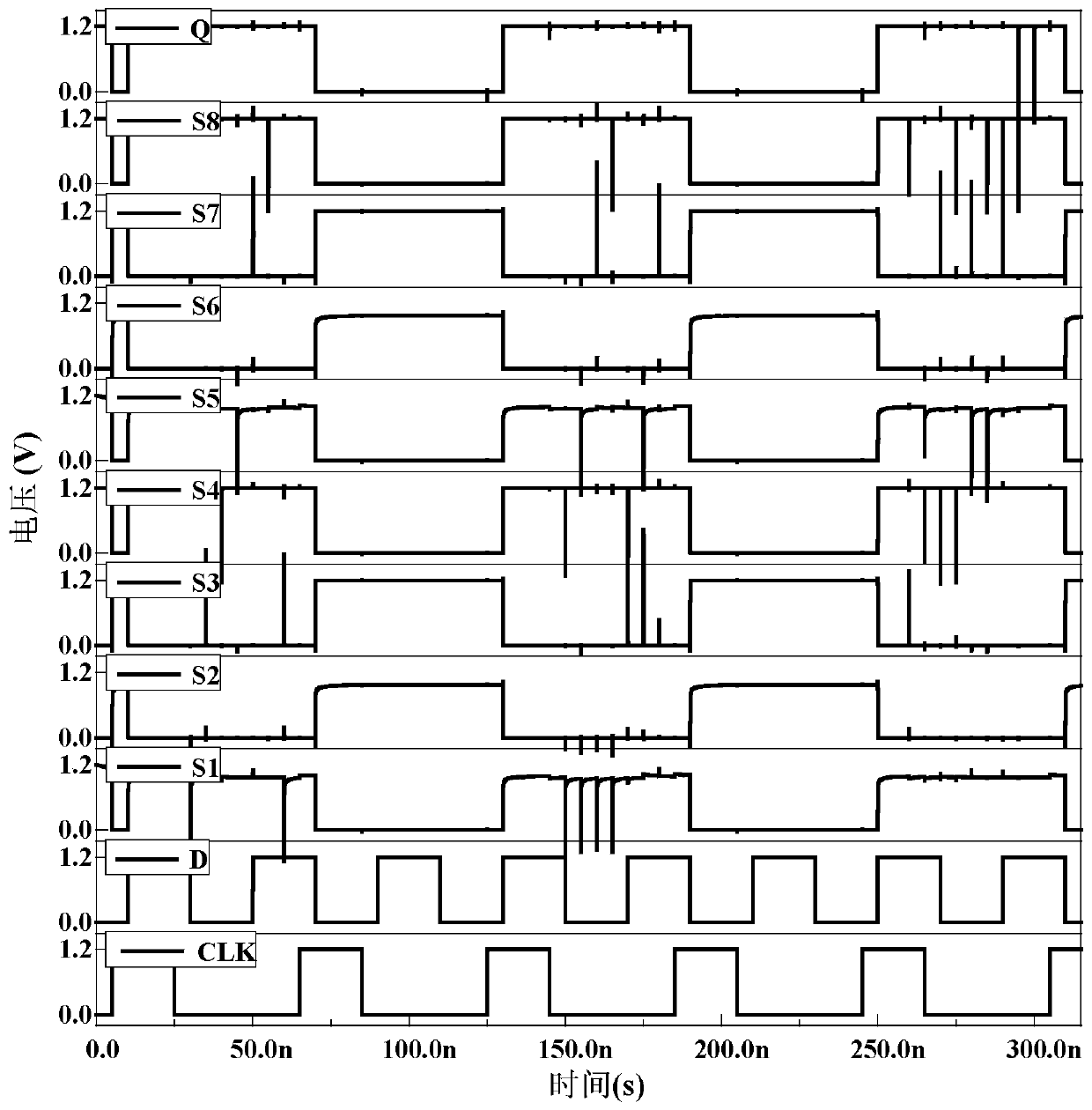
ActiveCN111010163AReduce power consumptionOverall small sizeReliability increase in field effect transistorsCircuit reliabilityNode (circuits)
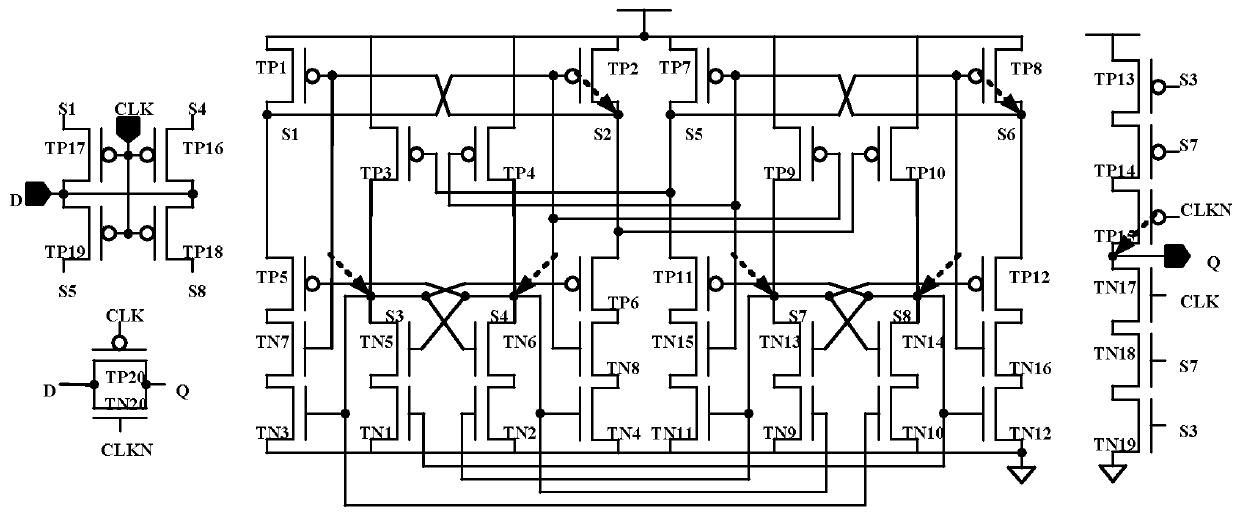
The invention discloses a low-redundancy D latch capable of resisting charge sharing for high-frequency circuit application, and belongs to the field of radiation hardening in integrated circuit reliability. The problems of high hardware overhead, large layout area, high power consumption and long transmission time of an anti-charge sharing D latch reinforced by adopting multimode redundancy in the prior art are solved; a transistor TP1 is connected with a node S8, a transistor TP2 is connected with a node S7, a transistor TP9 is connected with a node S4, and a transistor TP10 is connected with a node S3. Such a connection mode is beneficial for the transistors TP1 and TN3, the transistors TP2 and TN4, the transistors TP9 and TN9, and the transistors TP10 and TN10 not to be influenced on or off at the same time as much as possible. And the recovery time after the node is overturned is reduced as much as possible, and the influence on the whole circuit system can also be reduced as muchas possible. The low-redundancy charge sharing resistant D latch is mainly applied to high-frequency circuits.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Power source system
Owner:DENSO CORP
Anti-charge sharing D latch for high frequency circuit application
ActiveCN110995236APromote recoveryReduce power consumptionVoltage/current interference eliminationCircuit reliabilityNode (circuits)
The invention discloses an anti-charge sharing D latch for high-frequency circuit application, which belongs to the field of anti-radiation reinforcement in integrated circuit reliability. The problems of large hardware overhead, multiple sensitive nodes, high power consumption, long transmission time and long recovery time of an anti-charge sharing D latch applied to a high-frequency circuit aresolved. The gate of a transistor TN1 is connected to a node S8, the gate of a transistor TN2 is connected to a node S7, the gate of a transistor TN9 is connected to a node S4, and the gate of a transistor TN10 is connected to a node S3. Due to the above connection mode, the recovery time after overturning can be reduced, the transistors TP3 and TN1, TP4 and TN2, TP9 and TN9, and TP10 and TN10 areensured not to be influenced at the same time as much as possible, so that the overturned node can be recovered quickly, and the system can recover to a normal working state in a very short time. Therefore, the anti-charge sharing D latch for high-frequency circuit application is mainly applied to high-frequency circuits.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
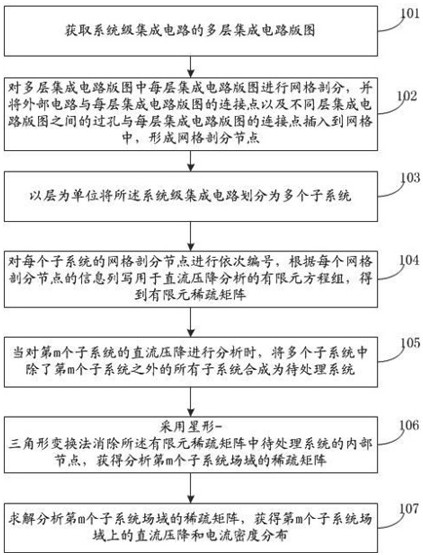
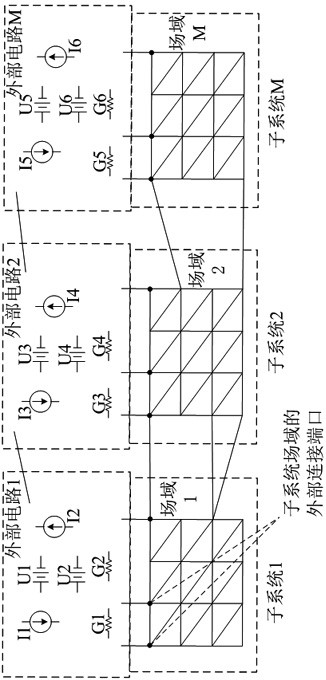
A DC voltage drop analysis method and system for a system-level integrated circuit
ActiveCN112307710BEliminate internal nodesAccurate analysisComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsHemt circuitsControl theory
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
Fault managment system for communications network
There is described a method of operating a fault management system for an access network which forms part of a communications network. In the access network, terminating lines in the form of pairs of copper wires extend from a local switch (10) through a series of nodes to terminal equipment provided for user of the network. The fault management system includes a test head (104) and an access network management system (102). Each night, the test head (104) performs a series of tests on each of the terminating lines. The results of the tests are transmitted to the access network management (102). The test results are then analysed with respect of a set of parameter to identify characteristics that would indicate that a fault is likely to occur on the associated circuit within a predetermined period e.g. 1 year. Further analysis can then be carried out to establish the probability of the fault actually occurring and / or whether the potential fault analysed is going to occur in either the underground or the over-ground part of the network. Further analysis determines the relative costs of repair for circuits or network elements in which faults or potential faults have been identified.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
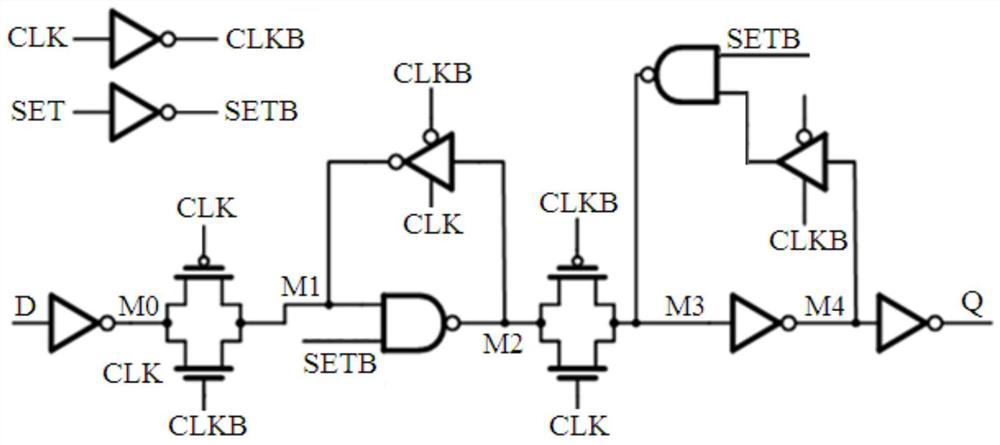
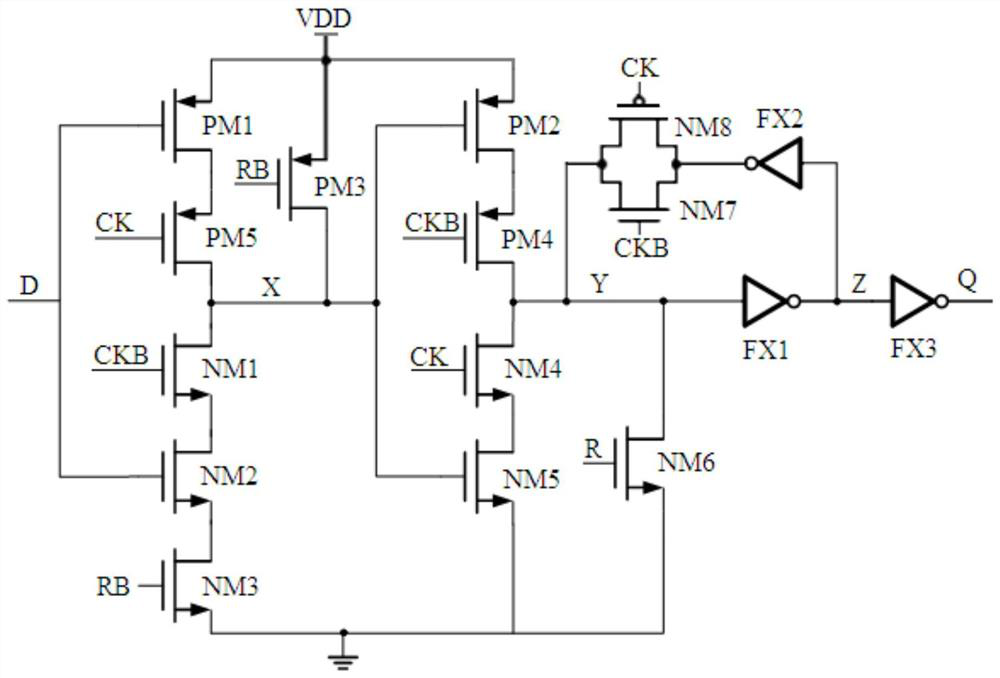
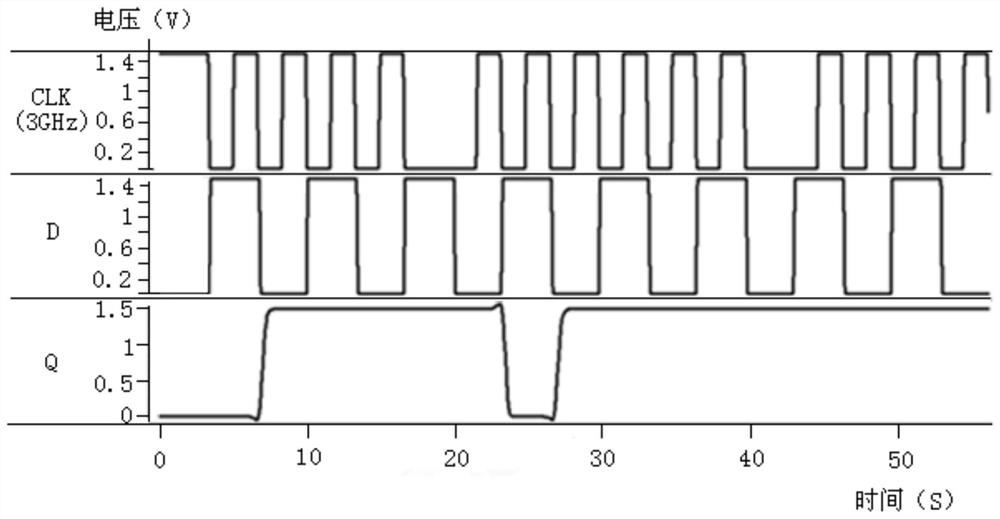
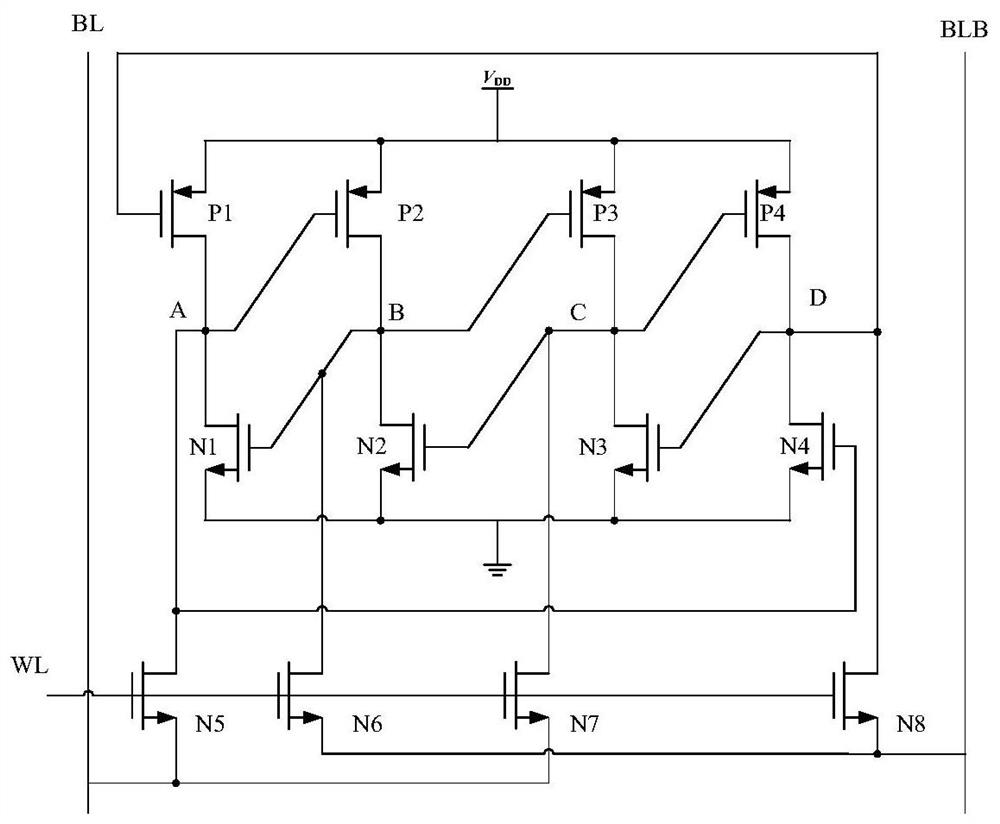
c 2 mos trigger
ActiveCN109088618BReduce in quantityReduce leakagePulse generation by bipolar transistorsNode (circuits)Software engineering
The invention discloses a C 2 MOS flip-flops, including: five PMOS transistors, eight NMOS transistors and three inverters; when the clock signal CK is at a high level, the state of node X is collected to node Y, and passed through the first inverter and the second inverter The three inverters are transmitted to the output terminal Q, and the feedback loop does not work at this time; when the clock signal CK is low, the state of the input node D is collected to the node X, and the first inverter, the second inverter 1. The feedback loop composed of the seventh NMOS transistor and the eighth NMOS transistor maintains the state of the node Y, so that the output state of the output terminal Q remains unchanged. The invention can make the circuit run in the high-speed digital circuit and maintain the integrity of the data.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
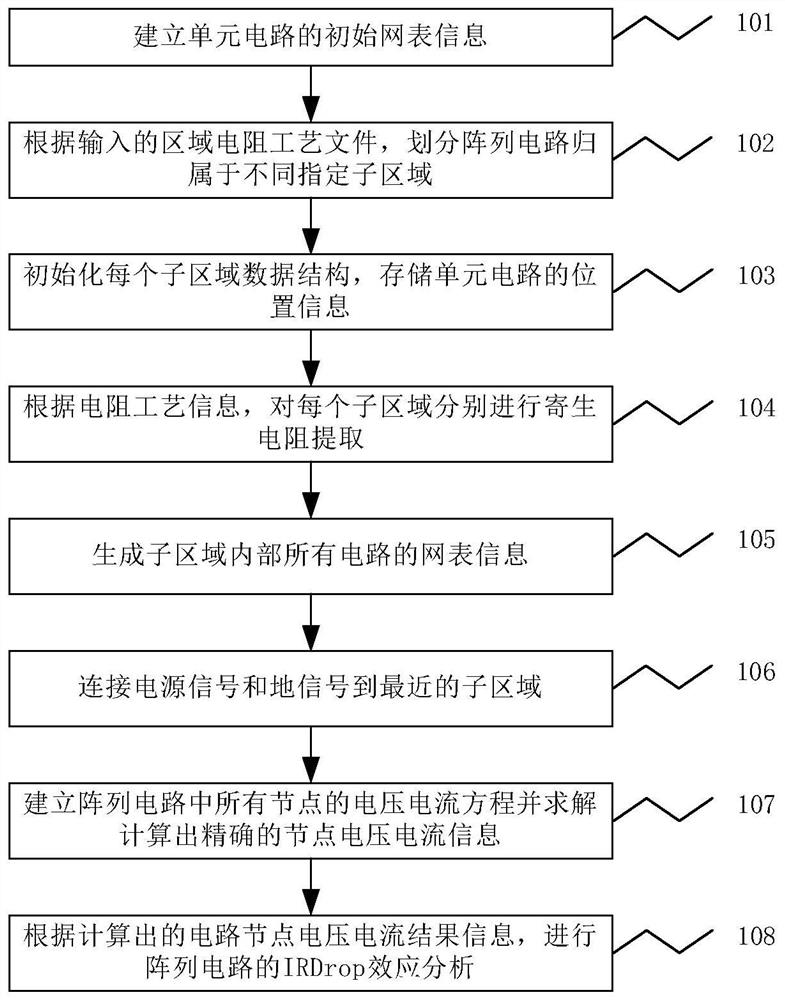
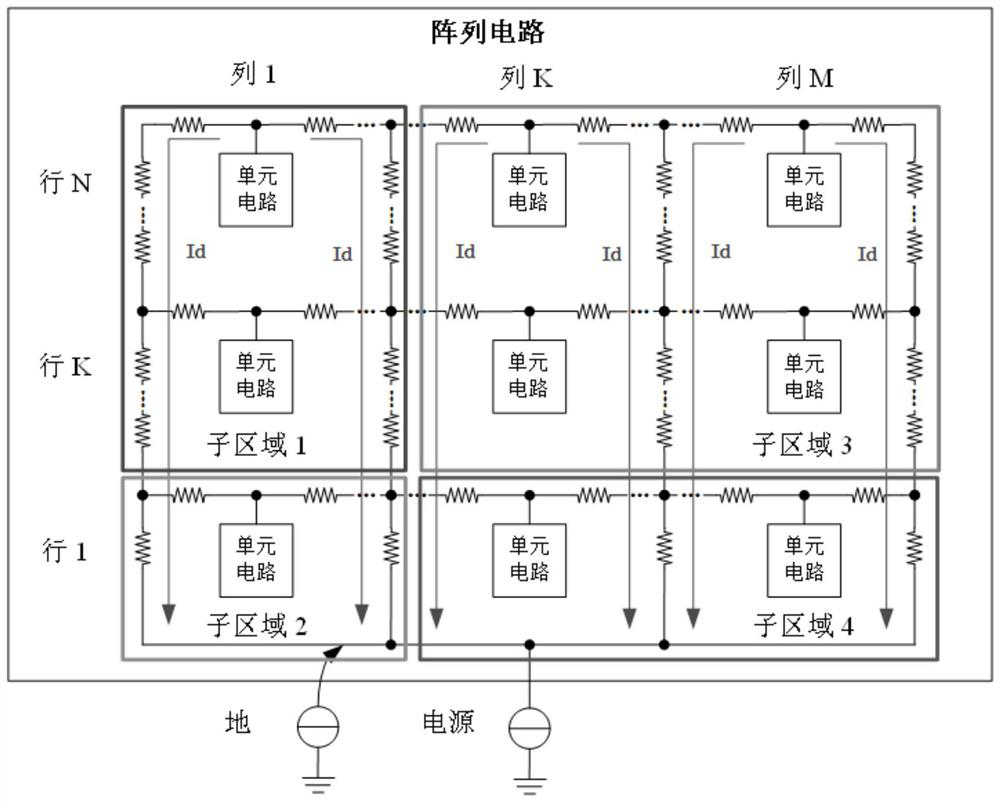
IRDrop simulation method for large-scale array circuit
PendingCN114186528AAccurate calculationComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceNode (circuits)
A precise IRDrop simulation method for a large-scale array circuit comprises the following steps: 1) dividing the array circuit to belong to different specified sub-regions according to an input region resistance process file; 2) initializing the data structure of the sub-region, and storing the position information of all unit circuits covered by the sub-region; 3) respectively extracting parasitic resistance of each sub-region; 4) generating netlist information of all circuits in the sub-region; 5, voltage and current equations of all nodes in the array circuit are established, node voltage and current information is solved and calculated, and IRDrop effect analysis is carried out on the array.According to the accurate IRDrop simulation method for the large-scale array circuit, an accurate IRDrop simulation result can be provided for circuit designers, and the influence brought by the IRDrop effect is accurately analyzed.
Owner:成都华大九天科技有限公司
An Automatic Node Removal Method for Approximate Computation of Circuits
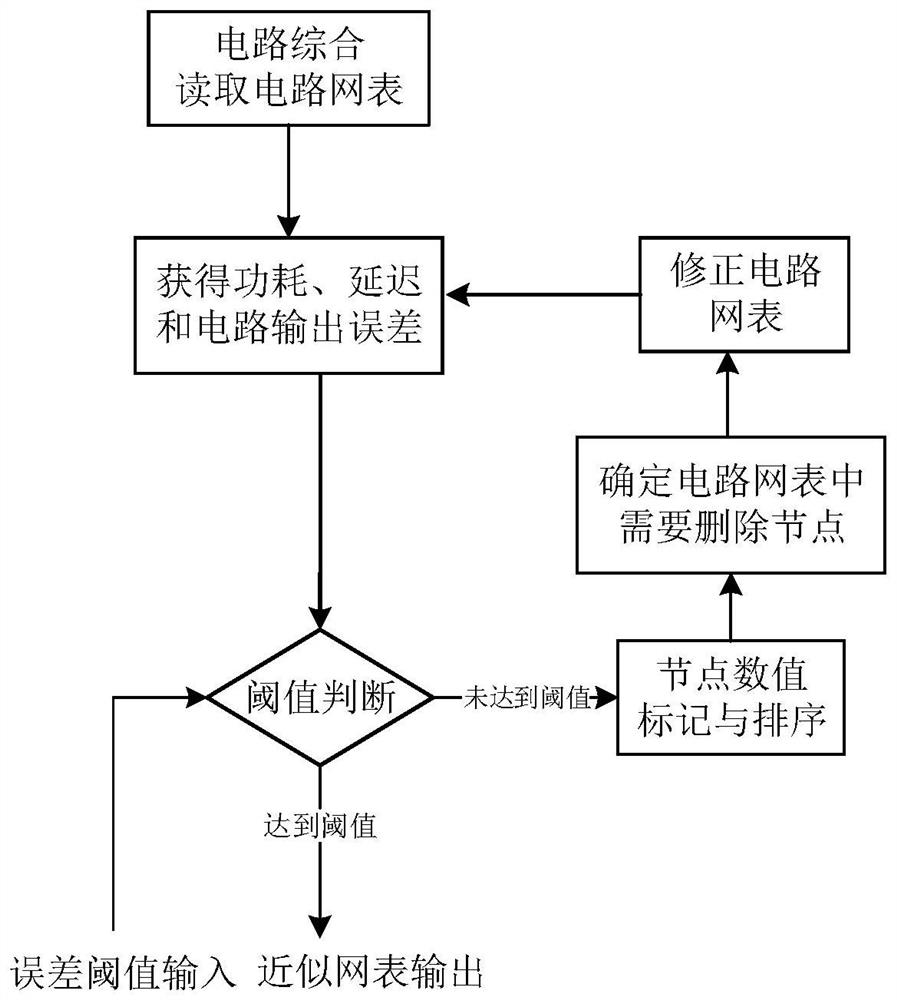
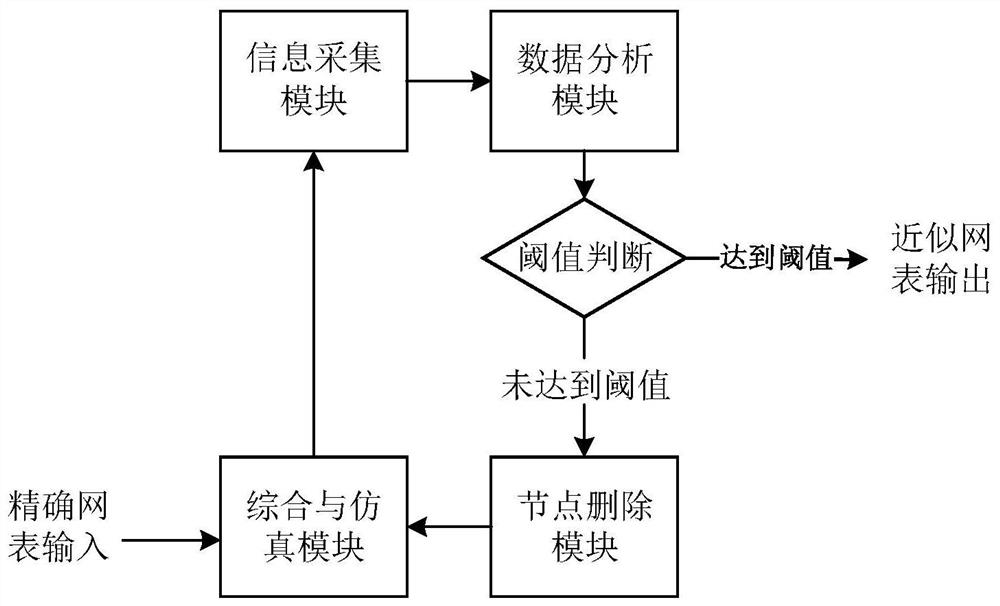
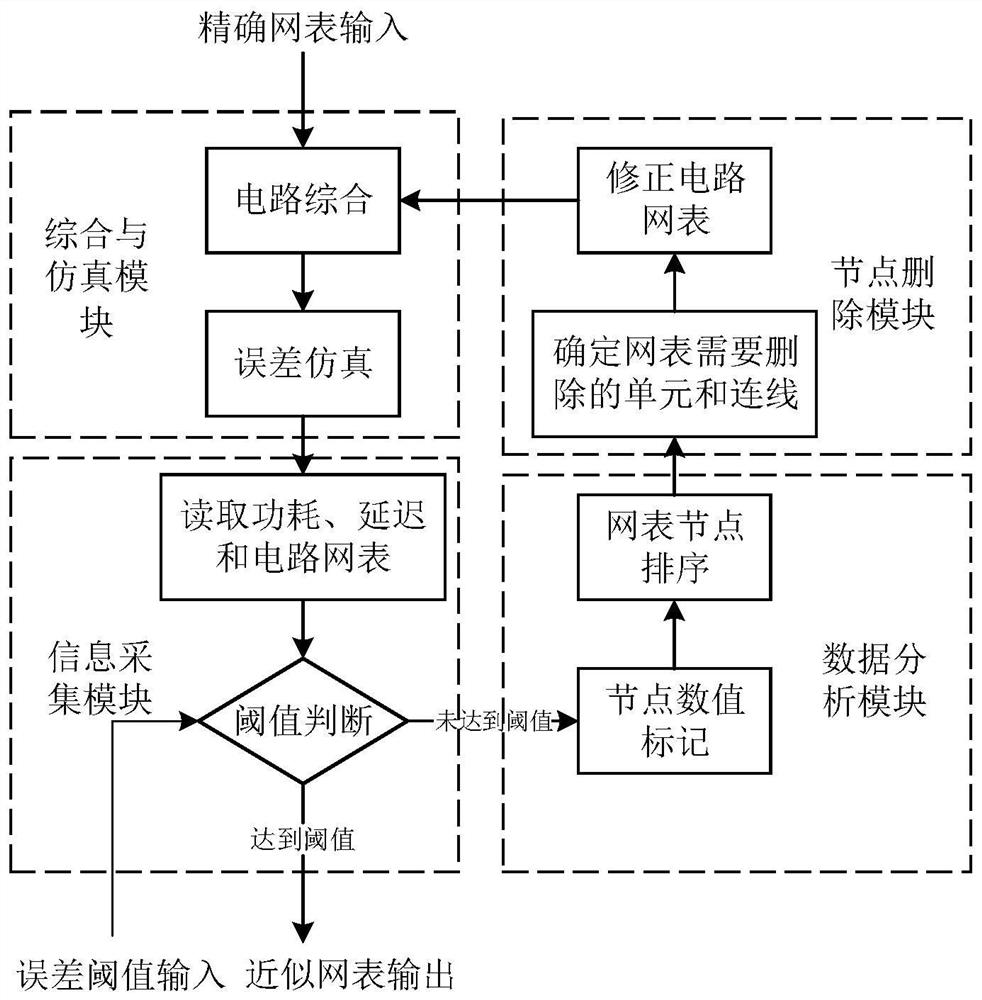
InactiveCN107862132BEasy to controlImprove design efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsNode (circuits)Algorithm
The invention relates to an automatic node deletion method for circuit approximate calculation, which belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits. Synthesize the circuit that needs approximate calculation to obtain the circuit netlist and obtain the power consumption and delay information in the circuit netlist, and obtain the circuit output error through simulation; if the error reaches the threshold, the circuit netlist is output, if not, the circuit netlist is separately Each node in the table is deleted one by one to obtain the power consumption change value, delay change value and output error change value of the circuit when each node is deleted; calculate the power consumption change value and delay change value of each node when the node is deleted The ratio to the output error change value is marked on each node, and the nodes in the circuit netlist are sorted in the order of the ratio from high to low; delete the node with the highest ratio and the affiliated node that is only used to generate the node, and the node will be deleted Synthesize the final circuit netlist to generate a new circuit netlist and return to the first step. The invention has the characteristics of high efficiency, high precision and low error.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Integrated circuit resistance extraction method based on parallel algorithm
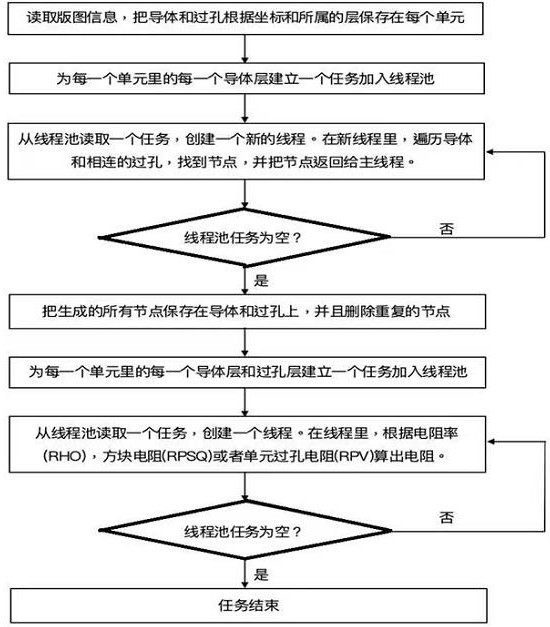
The invention relates to a thread processing method in the field of integrated circuits, in particular to an integrated circuit resistance extraction method based on a parallel algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, reading layout information, and storing all conductors in corresponding units according to coordinates of the conductors or via holes and layers to which the conductors or via holes belong; step 2, firstly, establishing a thread pool, and establishing a task adding thread pool for each conductor layer of each unit; then, starting threads according to the thread number configured by a user, and performing the following operations on each thread: step two, taking out a task from a thread pool; step 2, traversing all conductors in the task, and creating nodes at places in contact with other conductors or via holes; step 2, returning the created nodes and conductors or via holes corresponding to the nodes to the host process; and step 3, all the threads run to the end, all the nodes are stored in the conductor, and the repeated nodes are deleted.
Owner:青岛展诚科技有限公司
Terminal resistance circuit, chip and chip communication device
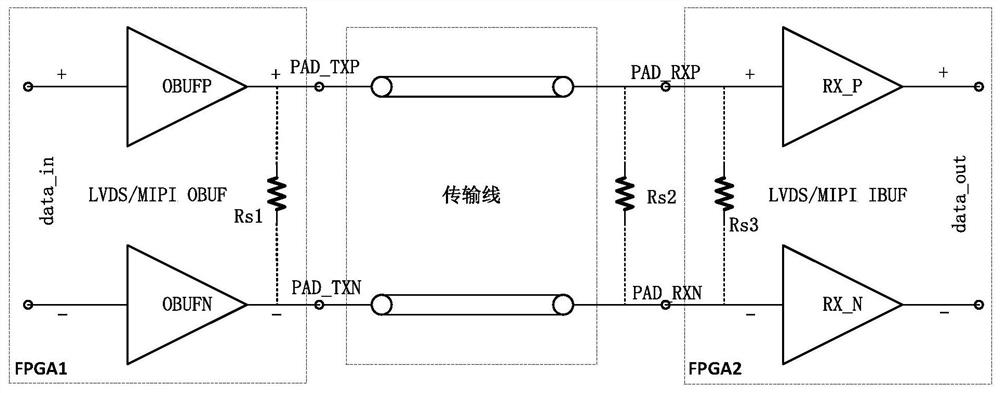
ActiveCN112731828AImprove stabilityAvoid working abnormallyProgramme controlComputer controlResistive circuitsNode (circuits)
The embodiment of the invention discloses a terminal resistance circuit, a chip and a chip communication device, and relates to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits. The terminal resistance circuit is applied to a high-speed differential I / O pair of a chip, the high-speed differential I / O pair comprises a first interface and a second interface, the terminal resistance circuit comprises two resistance circuits and a control circuit, one ends of the two resistance circuits are electrically connected with the first interface after the two resistance circuits are connected in series, and the other ends of the two resistance circuits are electrically connected with the second interface after the two resistance circuits are connected in series, a target node is arranged on the wire between the two resistance circuits, and the two resistance circuits are symmetrically arranged relative to the target node; and the control circuit is electrically connected with the two resistance circuits respectively and is used for controlling the two resistance circuits to be in an off state in the power-on process of the chip. According to the invention, the problem of abnormal system operation caused by short circuit of the two I / Os in the power-on process of the chip can be avoided, and the working stability of the chip is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN PANGO MICROSYST CO LTD
A kind of anti-dual-node flipping latch
ActiveCN108055032BImprove reliabilitySmall area overheadLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsReliability increase in field effect transistorsNode (circuits)Hemt circuits
An embodiment of the present application provides an anti-dual-node inversion latch, which relates to the technical field of integrated circuits. The latch includes: the latch has a storage node A, a storage node B, a storage node C, and a storage node D. Storage node E, storage node F, storage node G; the latch further has: a first cross-coupling structure; a second cross-coupling structure; a third cross-coupling structure; a fourth cross-coupling structure; a fifth cross-coupling structure structure; sixth cross-coupling structure; seventh cross-coupling structure; eighth cross-coupling structure; ninth cross-coupling structure. The technical problem that the latch in the prior art cannot achieve anti-double-node inversion in a small-area circuit structure is solved, so that the latch provided by the present application can improve the ability of the digital integrated circuit to resist single-event inversion under harsh conditions. , The technical effect of anti-dual node flipping, high reliability and low area overhead.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
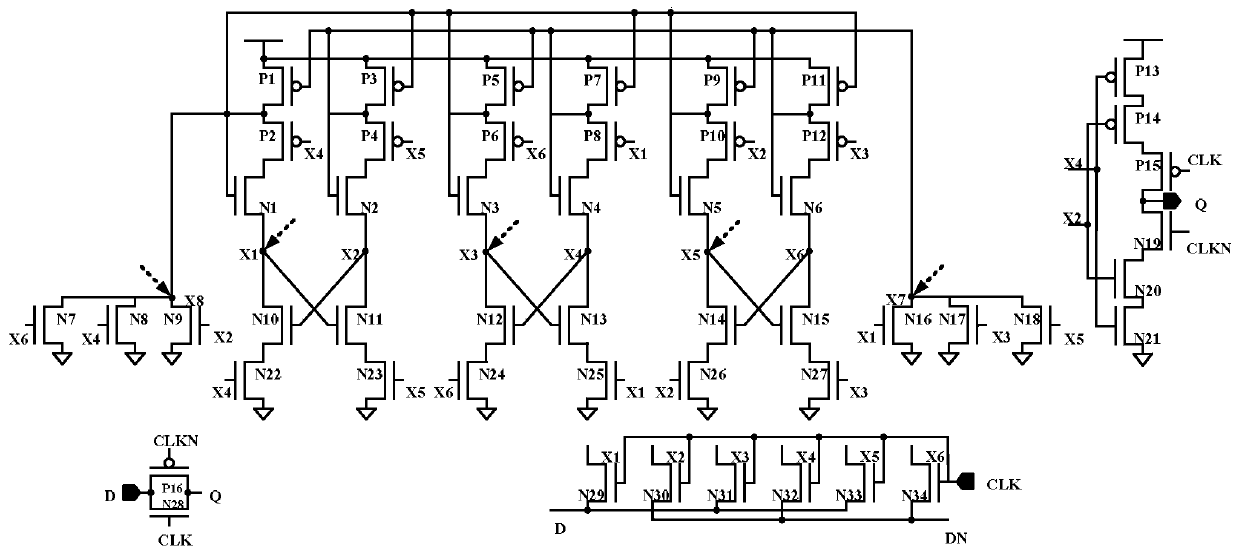
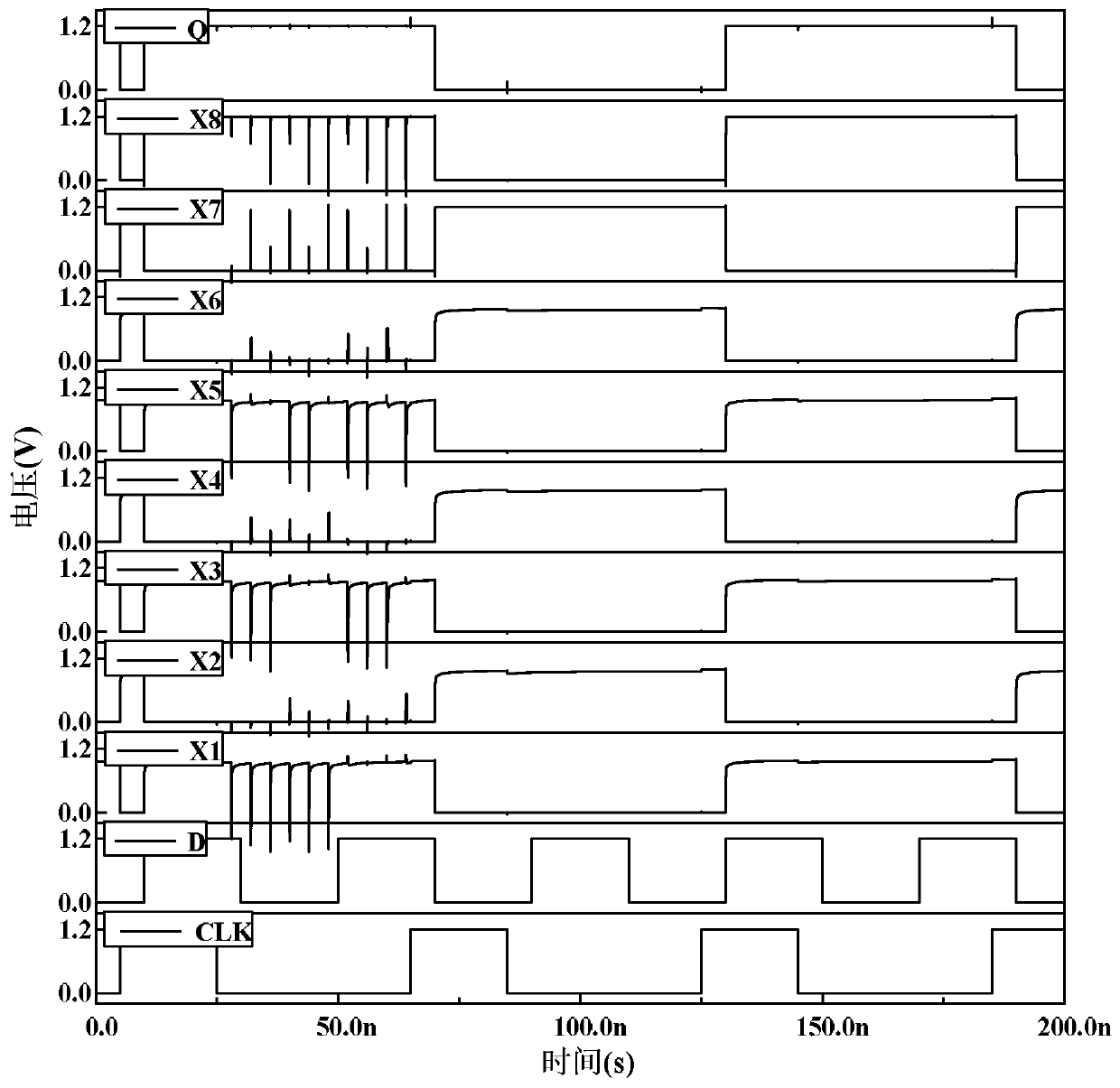
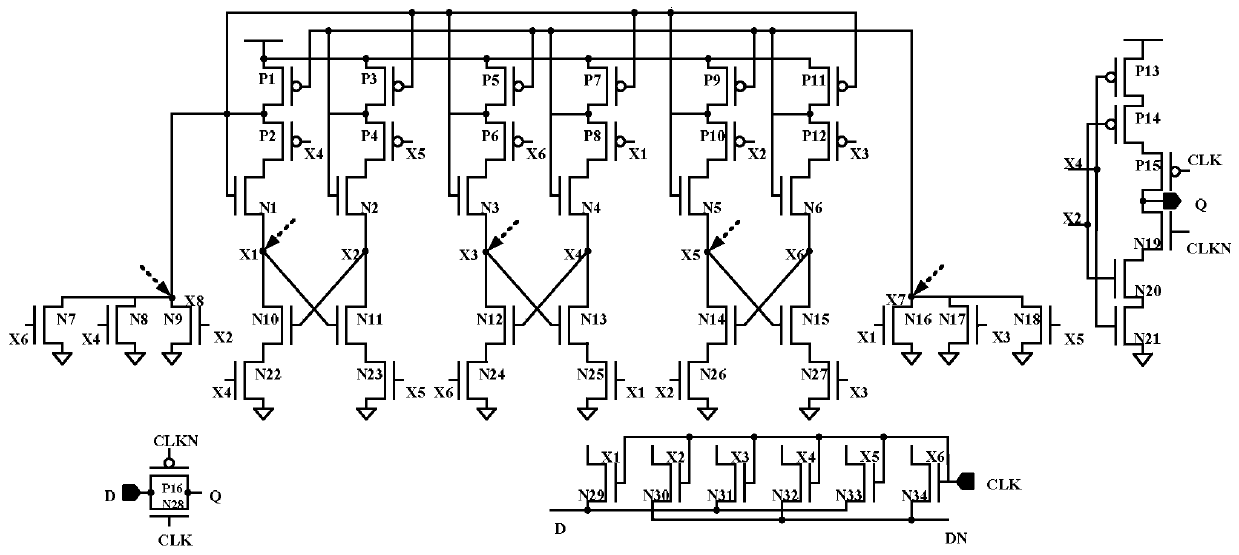
Three-node overturning resistant D latch for high-frequency circuit application
InactiveCN111147064AReduce the number of sensitive nodesReduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalNode (circuits)Circuit reliability
The invention discloses a three-node overturning resistant D latch for high-frequency circuit application, and belongs to the field of anti-nuclear reinforcement in integrated circuit reliability. Theproblems that a traditional D latch resisting three-node overturning needs to consume more hardware, and is high in power consumption, long in transmission path and large in transmission delay are solved. The D latch comprises 34 NMOS transistors N1 to N34 and 16 PMOS transistors P1 to P16, according to the invention, the NMOS transistors are connected in series and stacked for construction, thestacking mode can effectively reduce the problem of electric leakage caused by threshold loss, and protection of quick recovery of three-node overturning is realized. And some nodes are connected by adopting a principle of nearby connection, so that connected metal wires are shorter and symmetrical, the layout area is small, and the communication performance is better and the recovery time is shorter. The invention is mainly applicable to high-frequency circuits.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com