Patents
Literature
904results about "Voltage/current interference elimination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
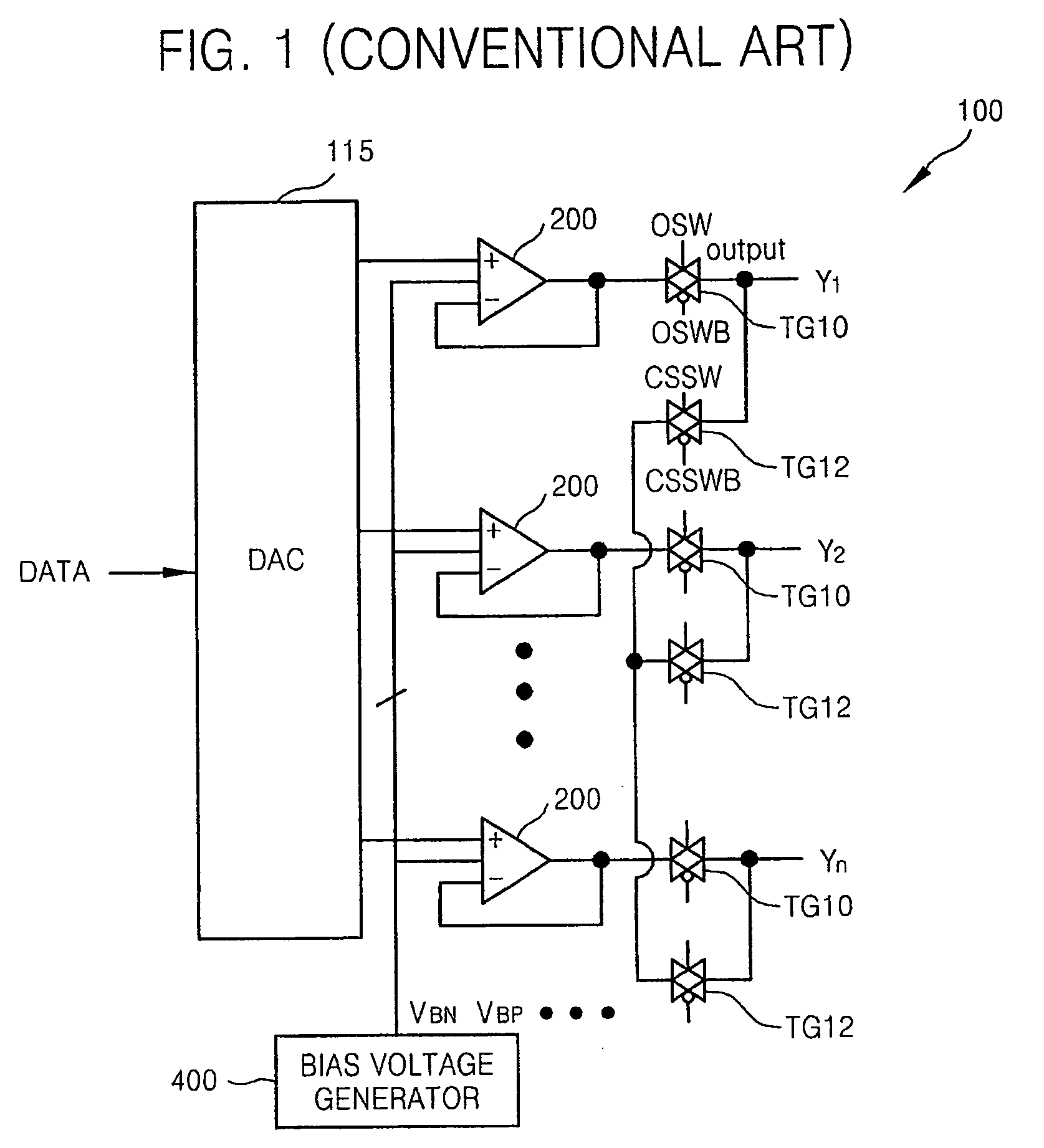
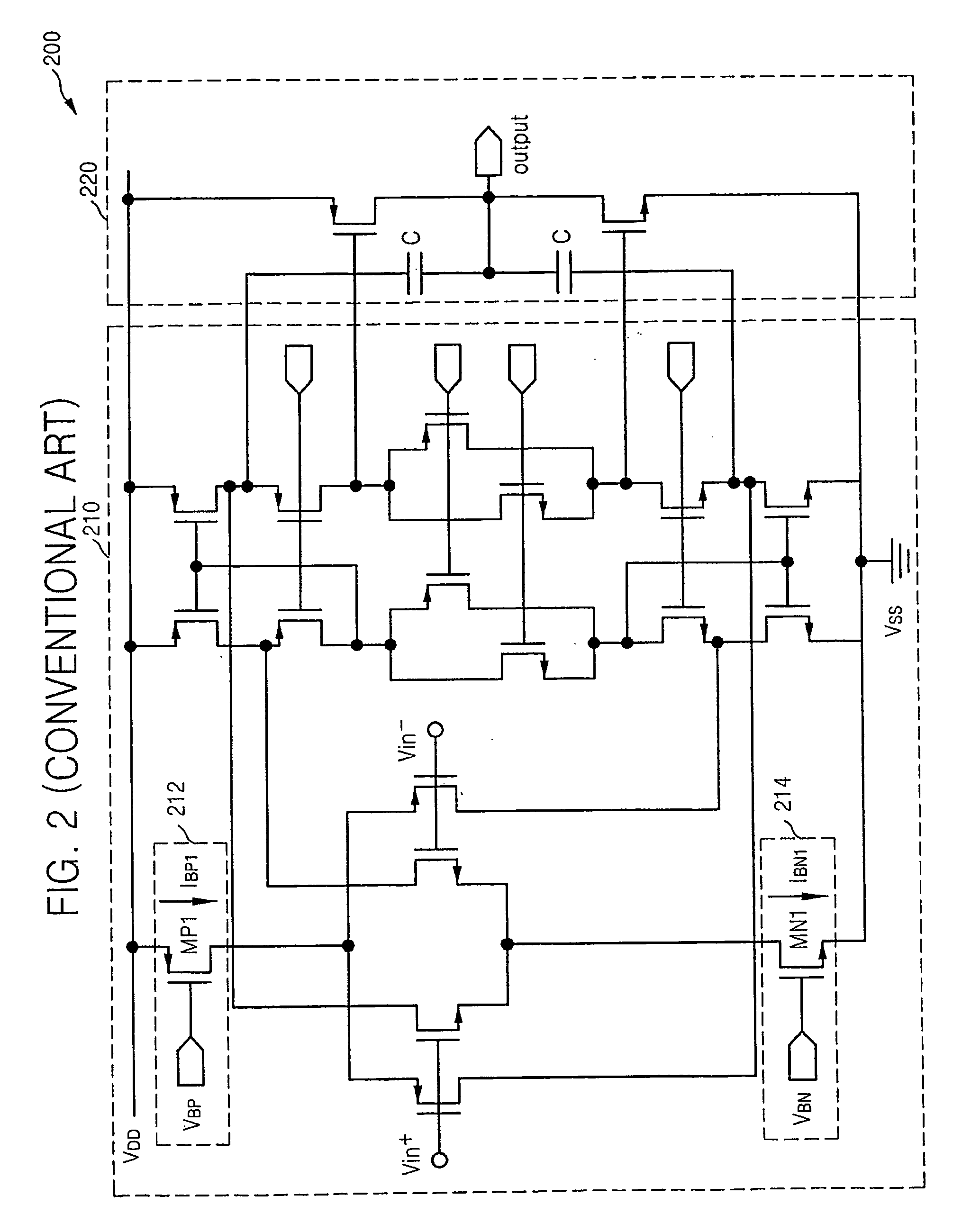
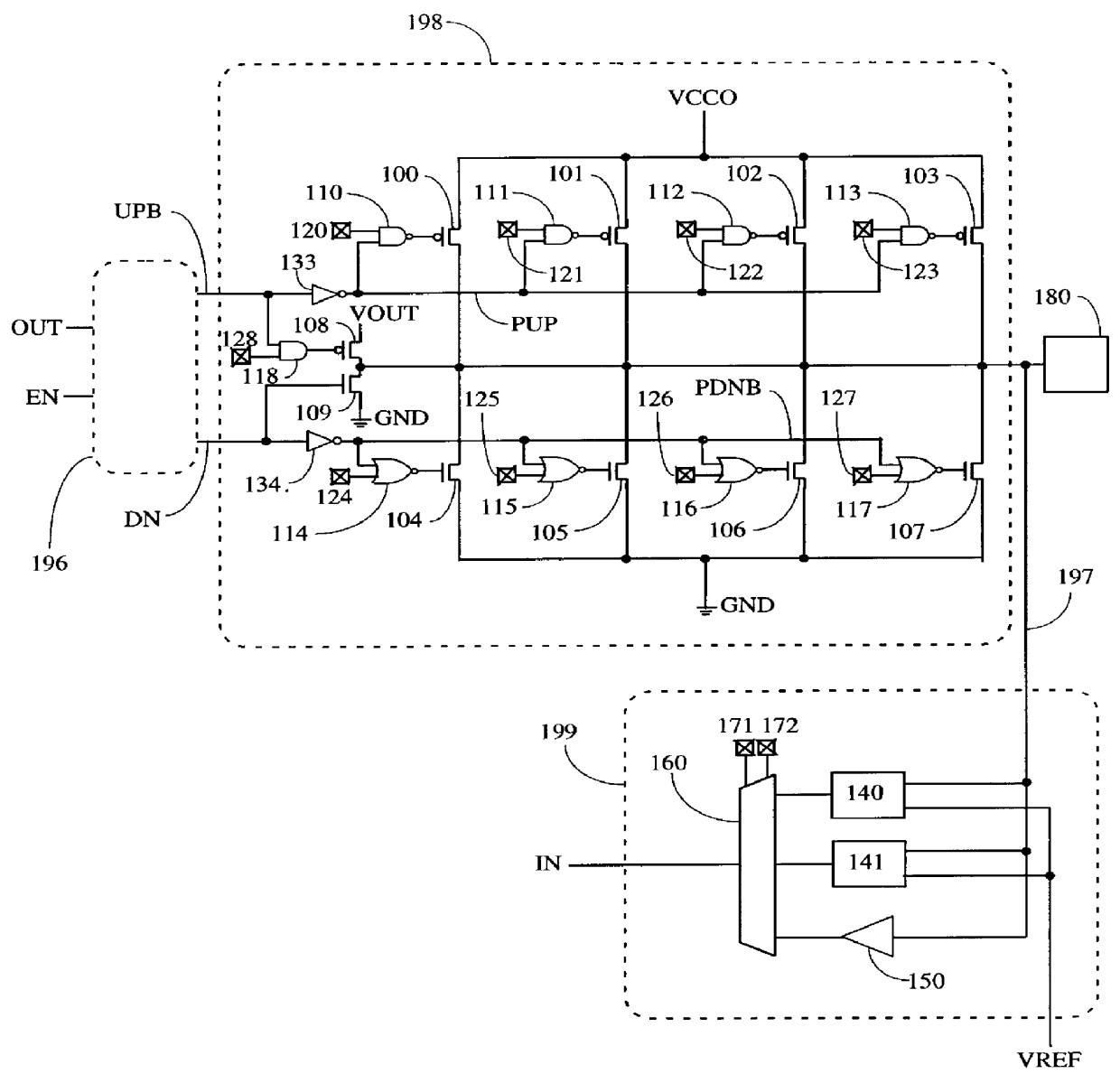
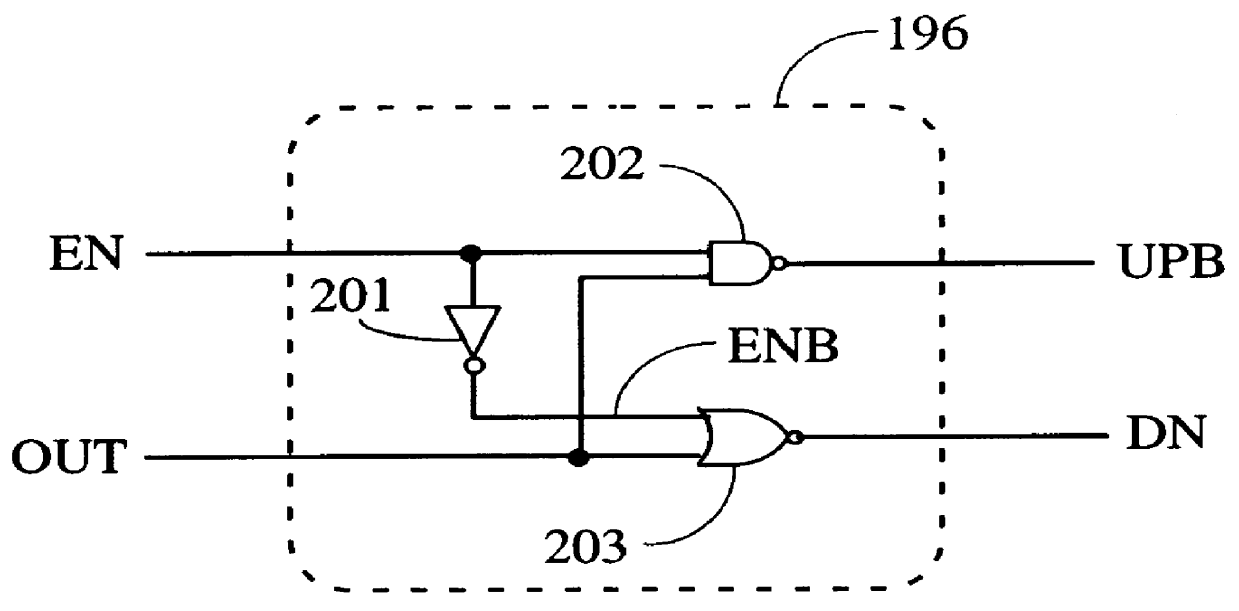
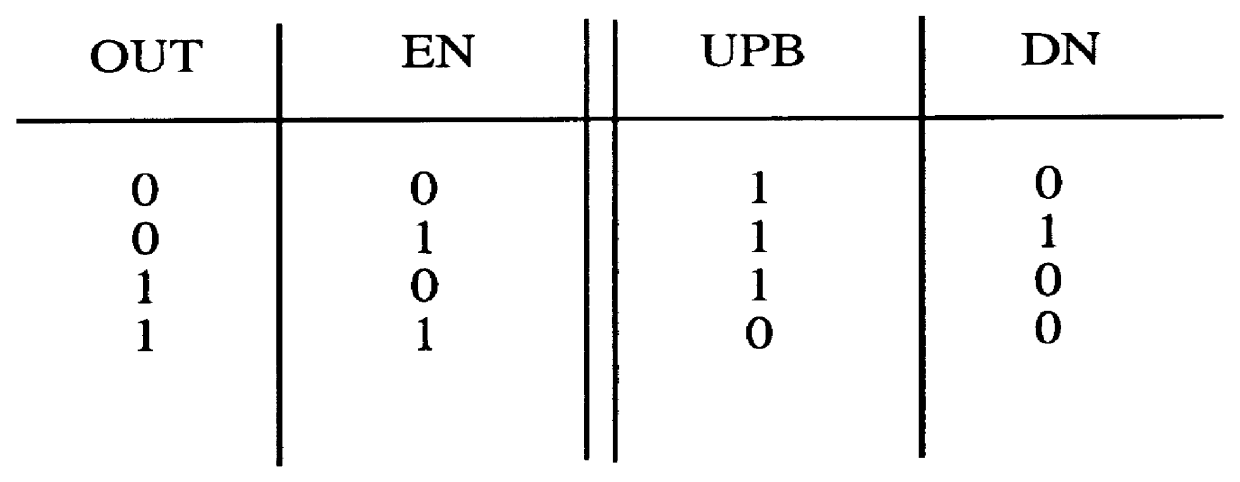
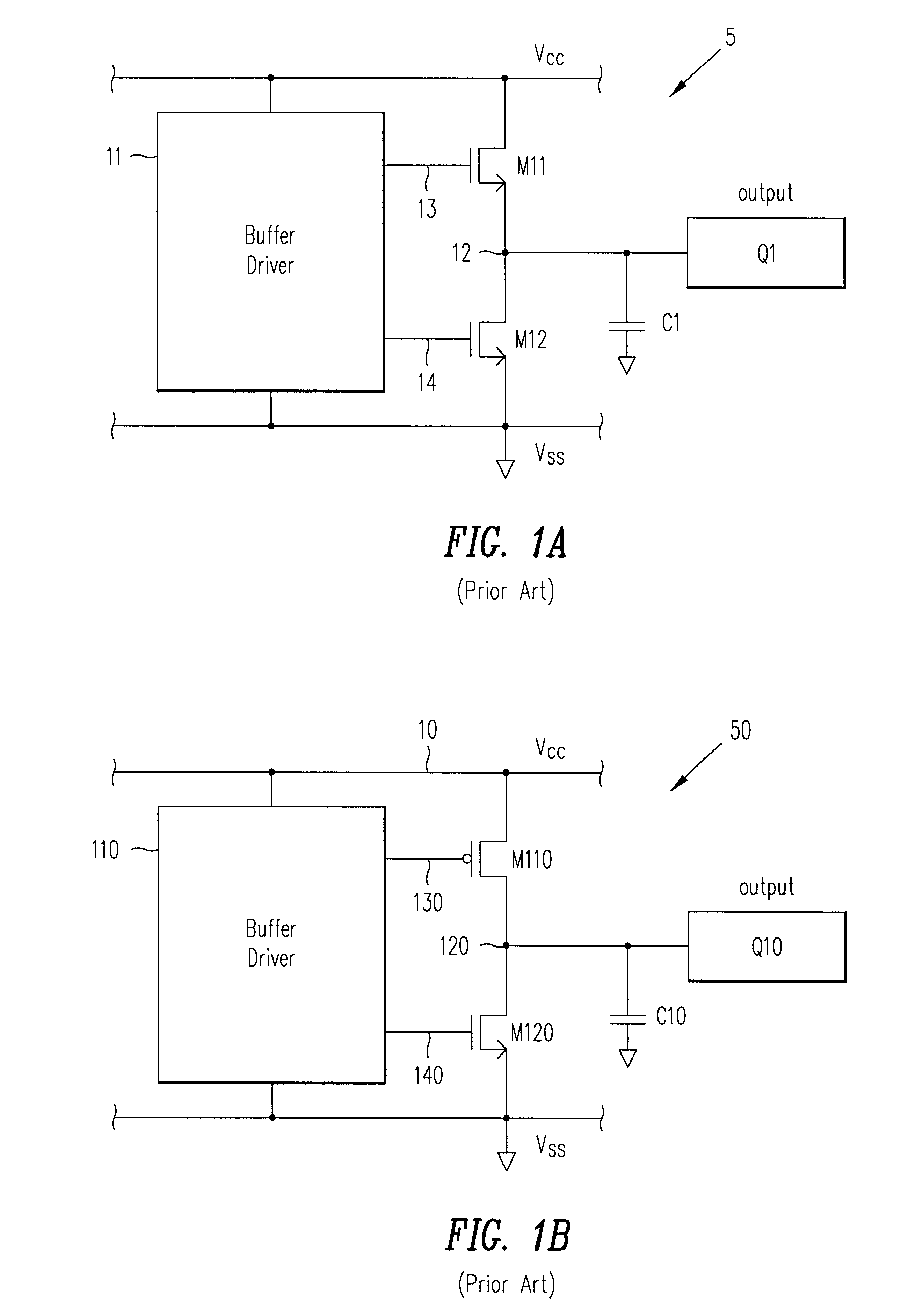
Method and apparatus for an output buffer with dynamic impedance control
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
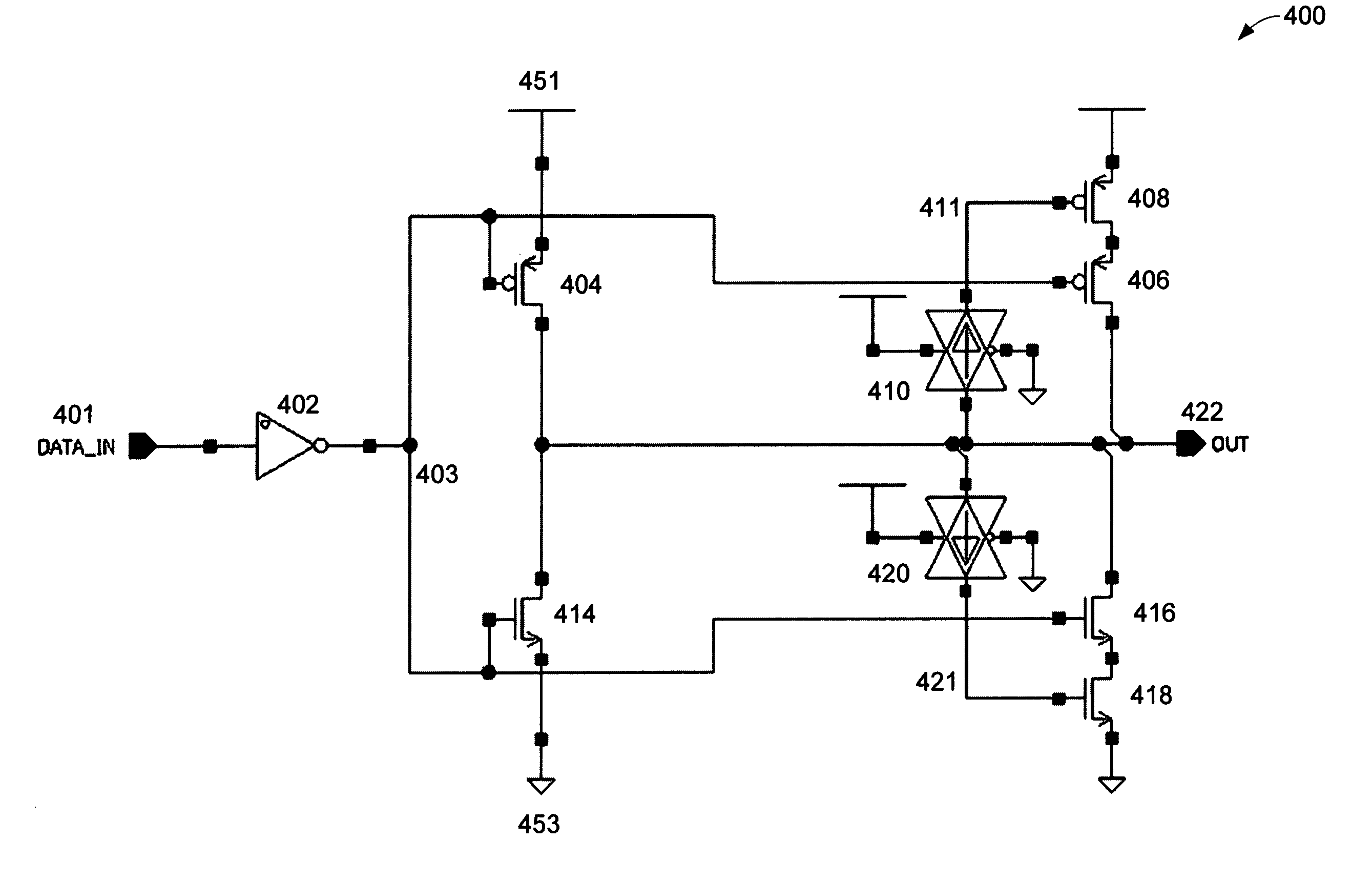
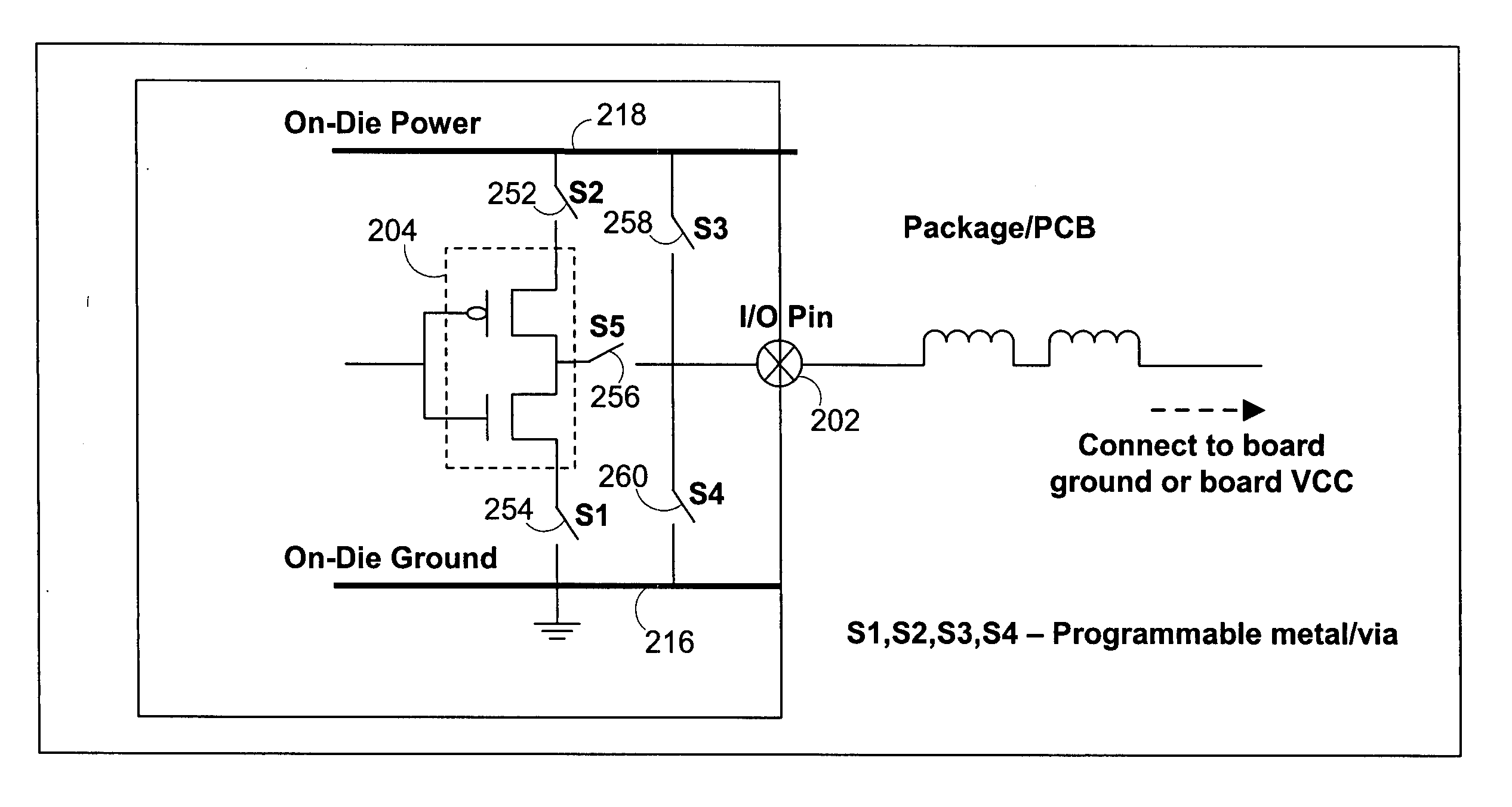
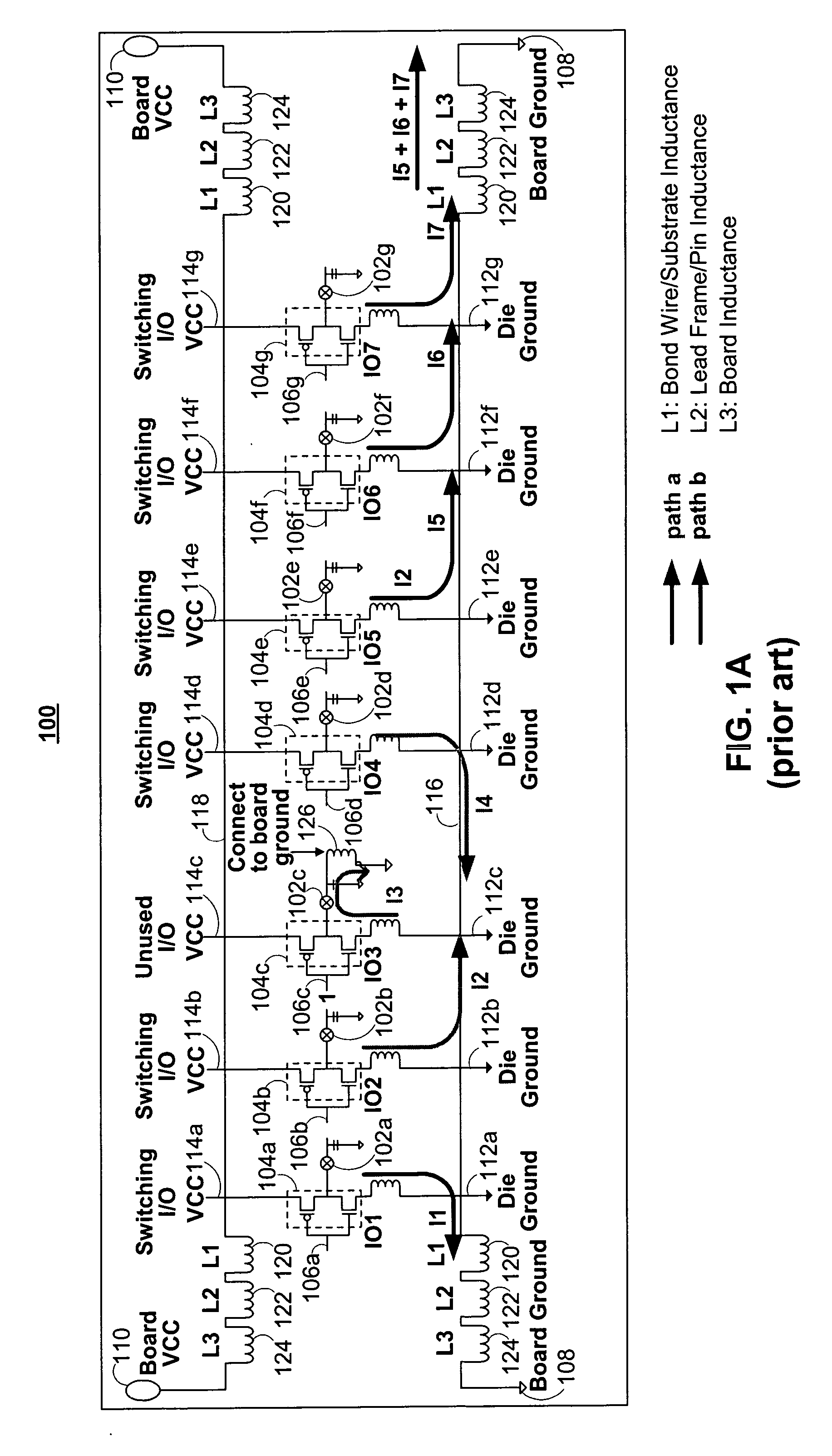
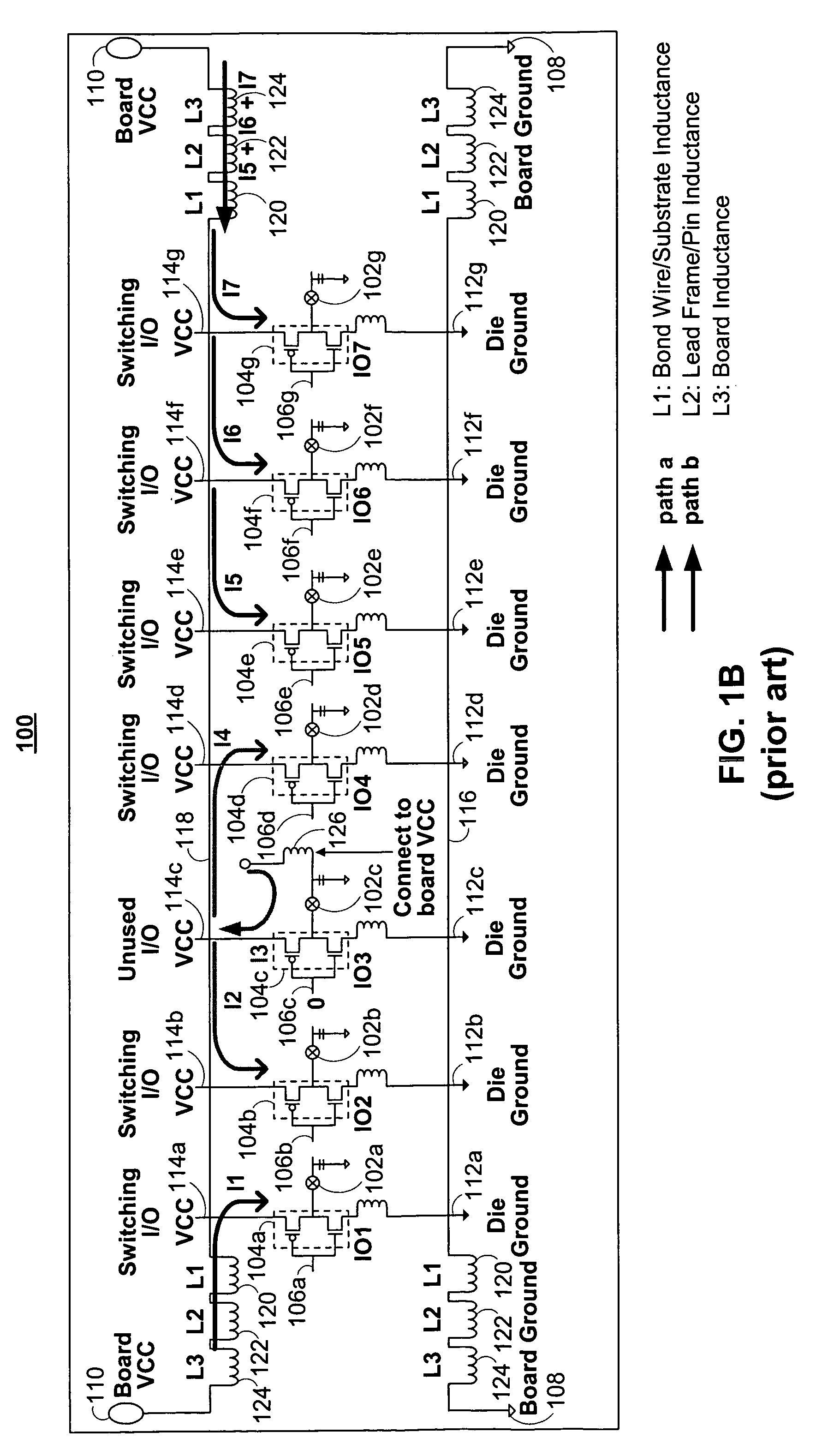
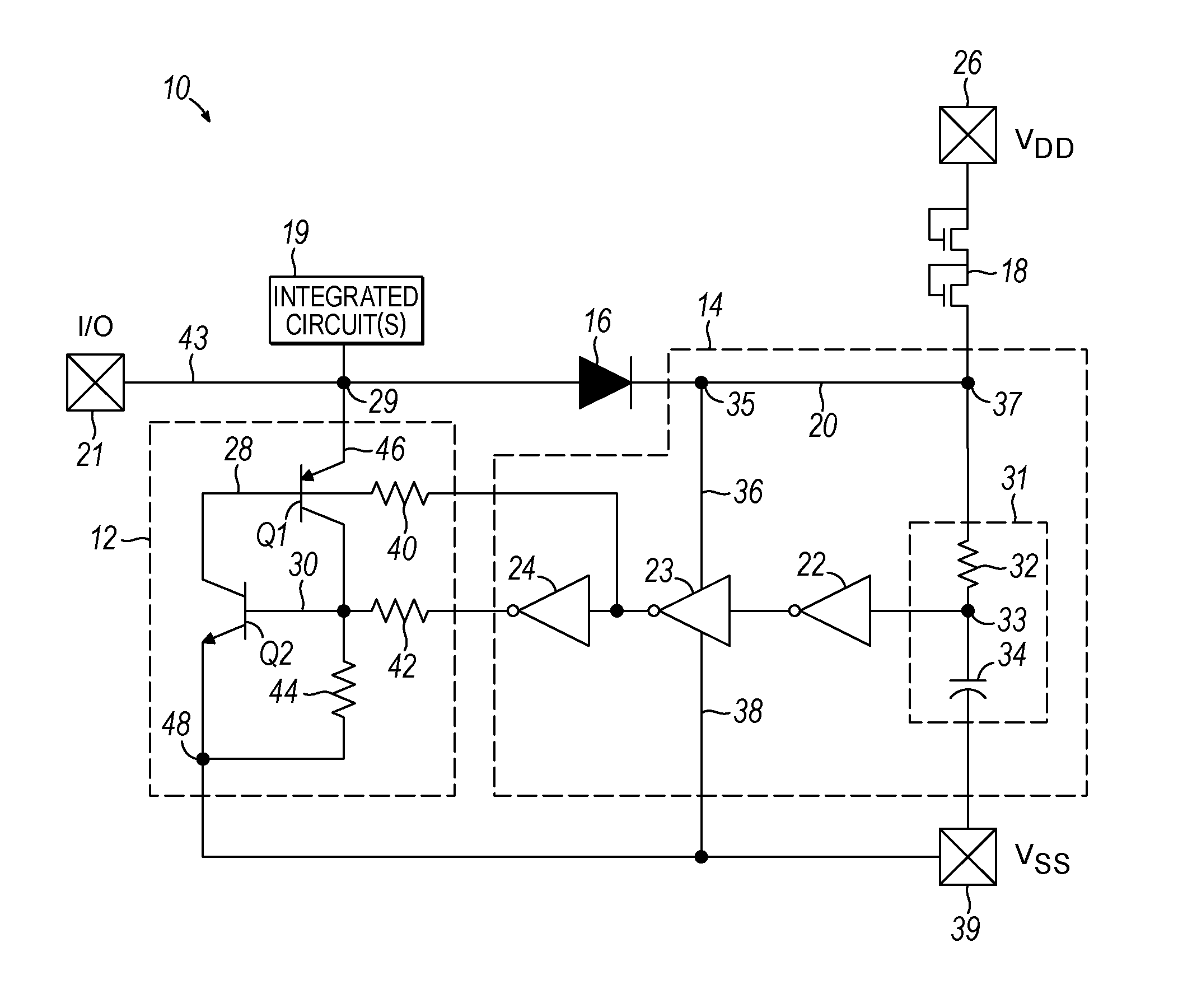
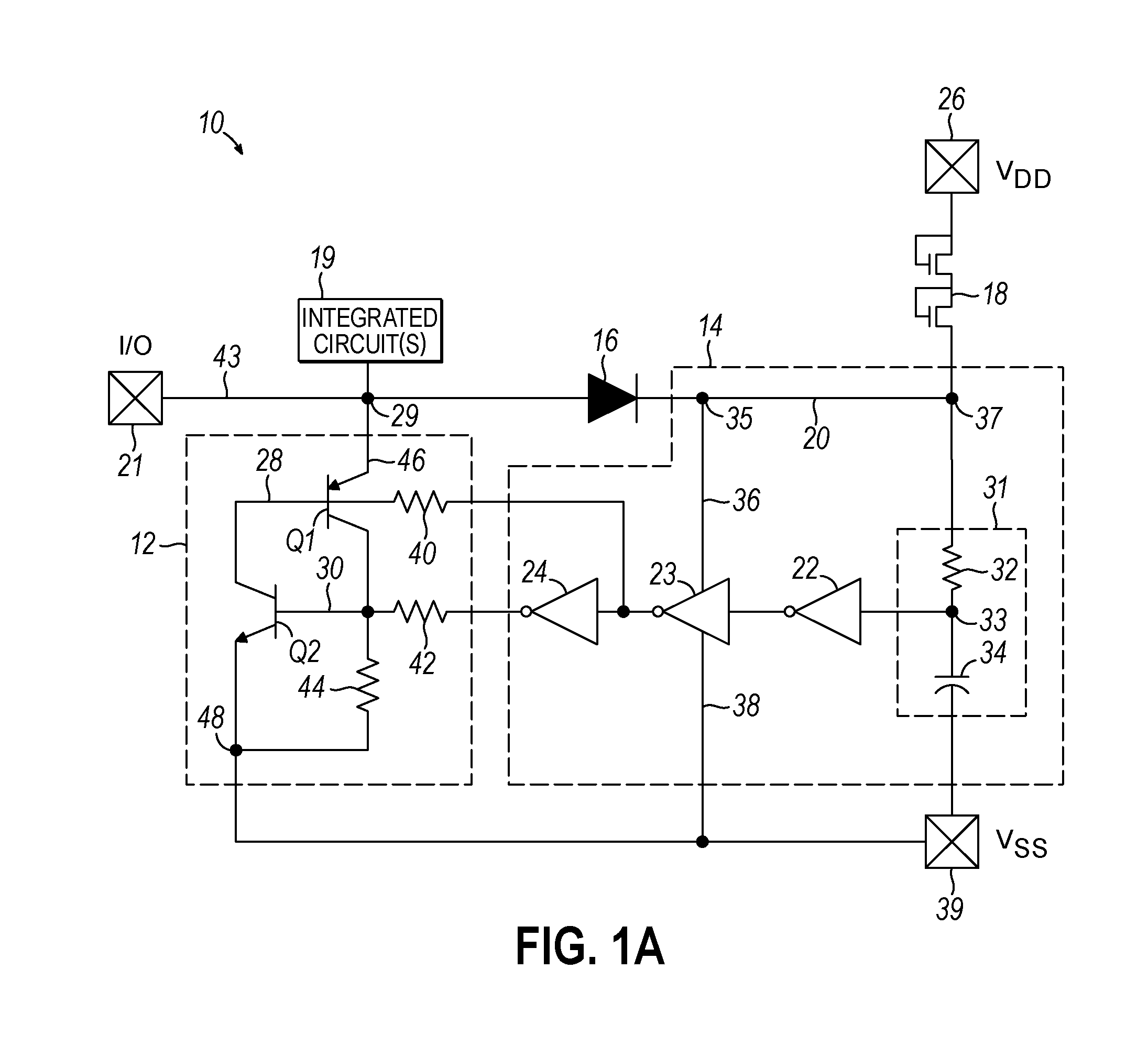
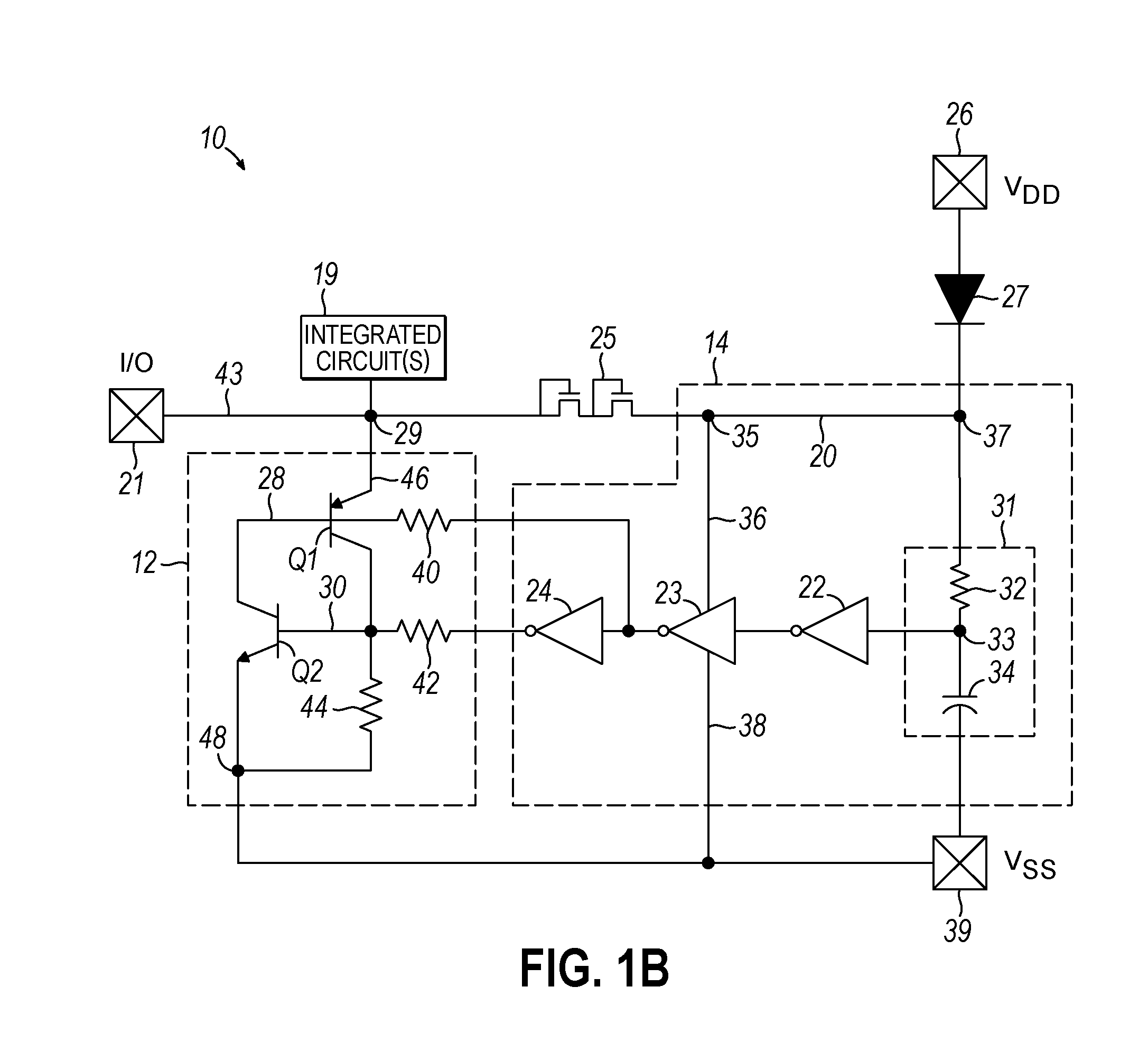
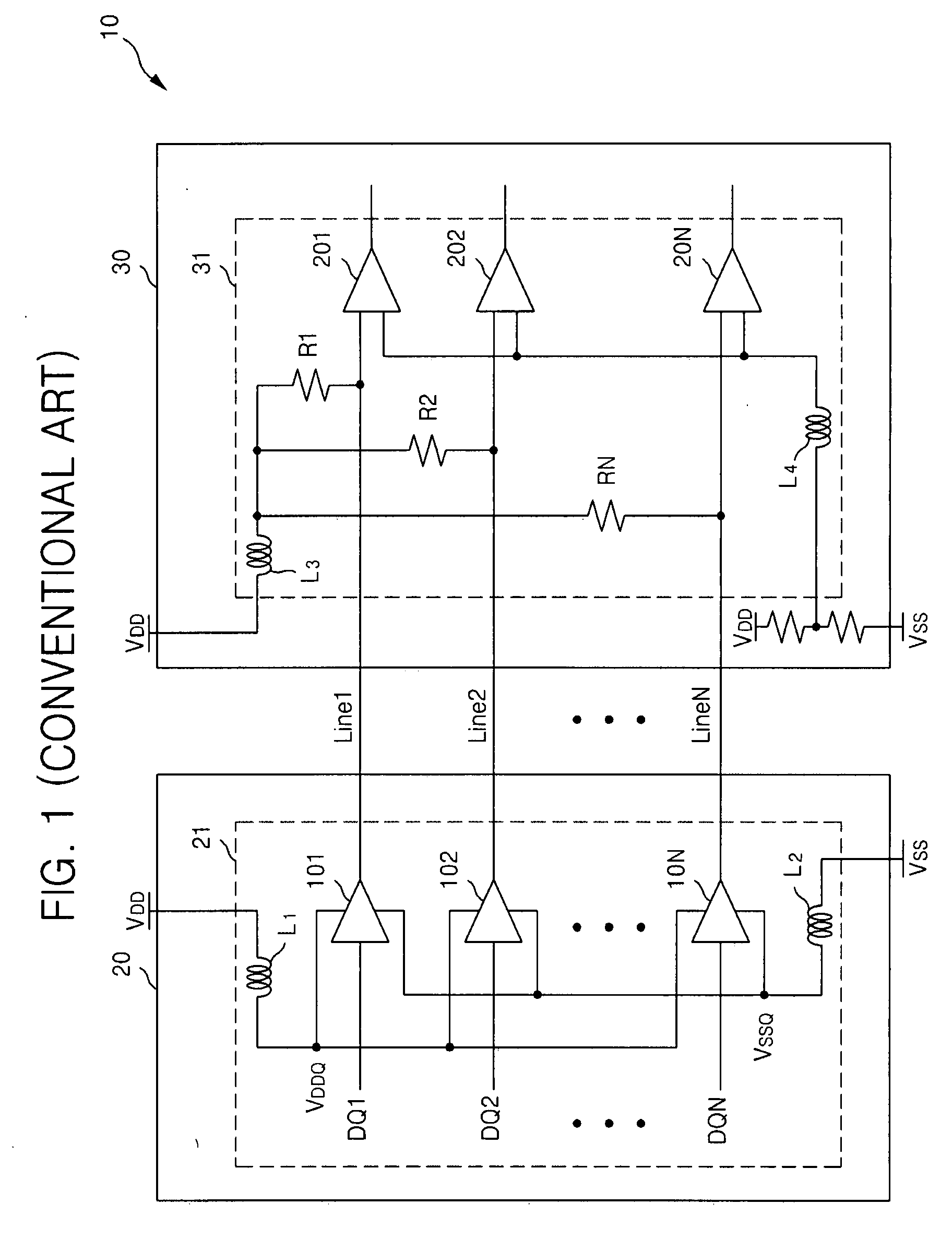
I/O circuitry for reducing ground bounce and VCC sag in integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS20070007991A1Reducing ground bounceReduce ground bounceElectronic switchingHeating/cooling contact switchesGround bounceEngineering
Methods and circuitry for reducing ground bounce and VCC sag effects in integrated circuit (“IC”) devices is provided. In particular, a via-programmable design for I / O circuitry in IC devices is provided. The via-programmable I / O circuitry is used to disconnect I / O pin driver circuitry from and create a substantially direct connection between unused I / O pins and the ground and / or VCC signals of an IC device to reduce ground bounce and VCC sag, respectively.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
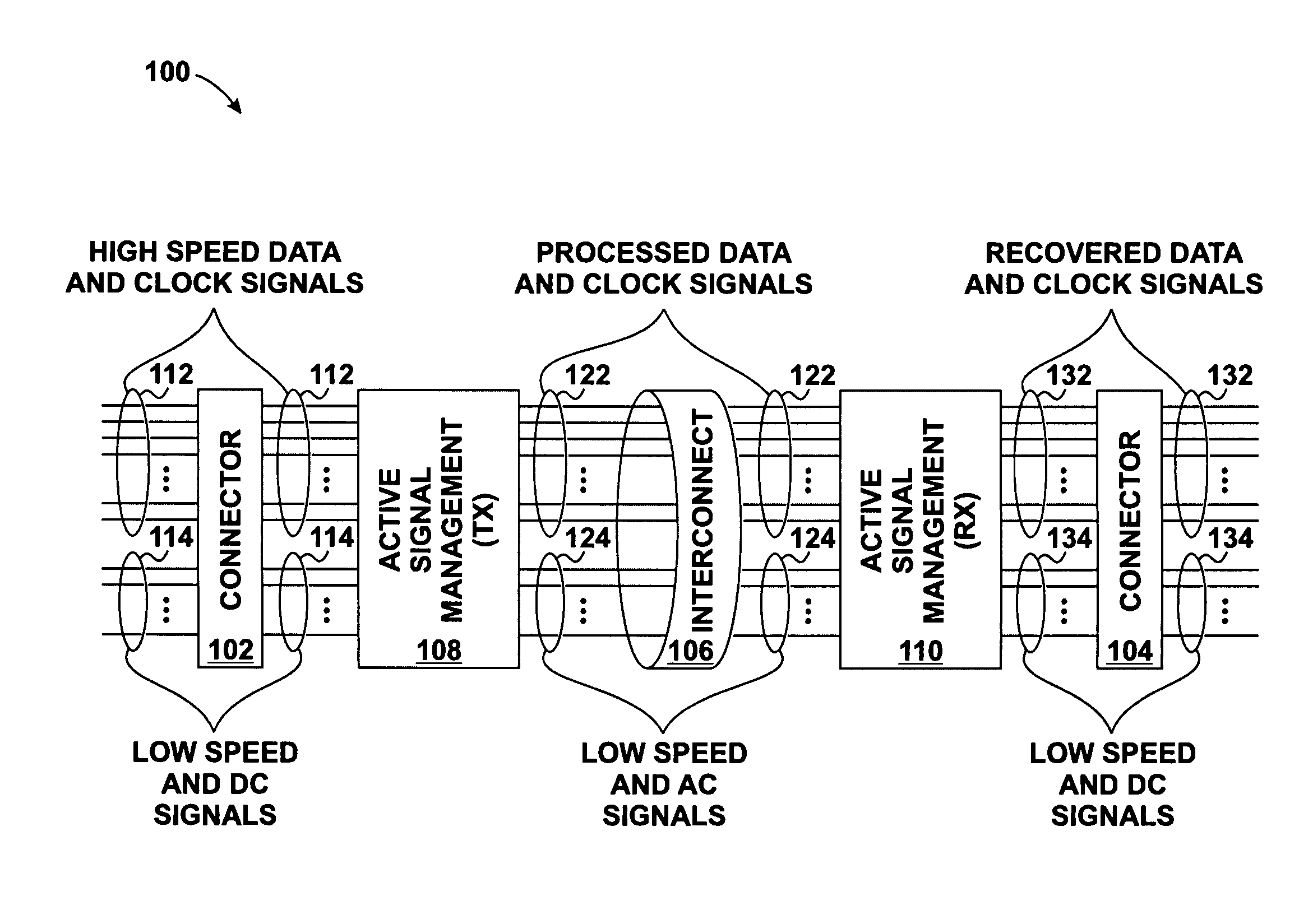
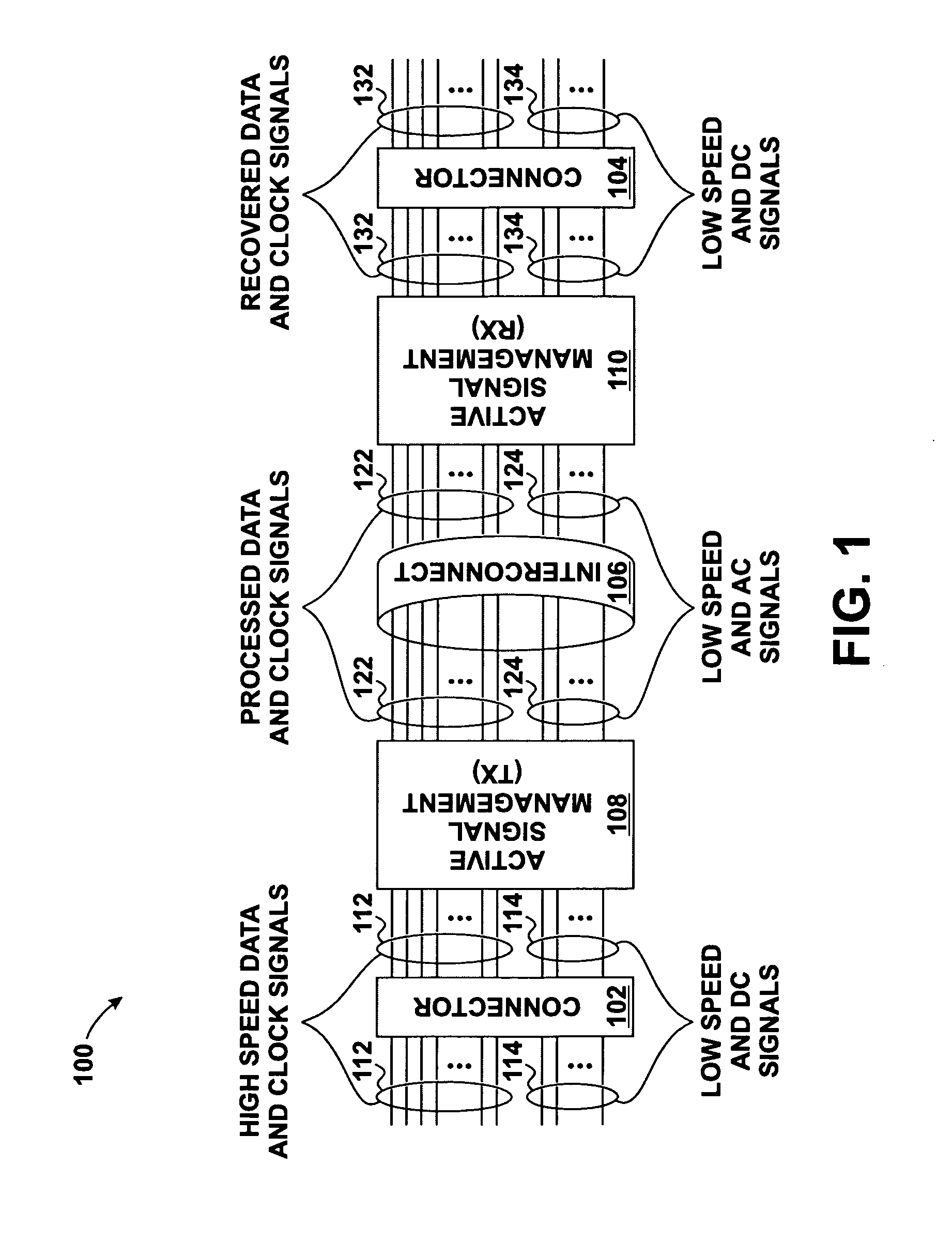
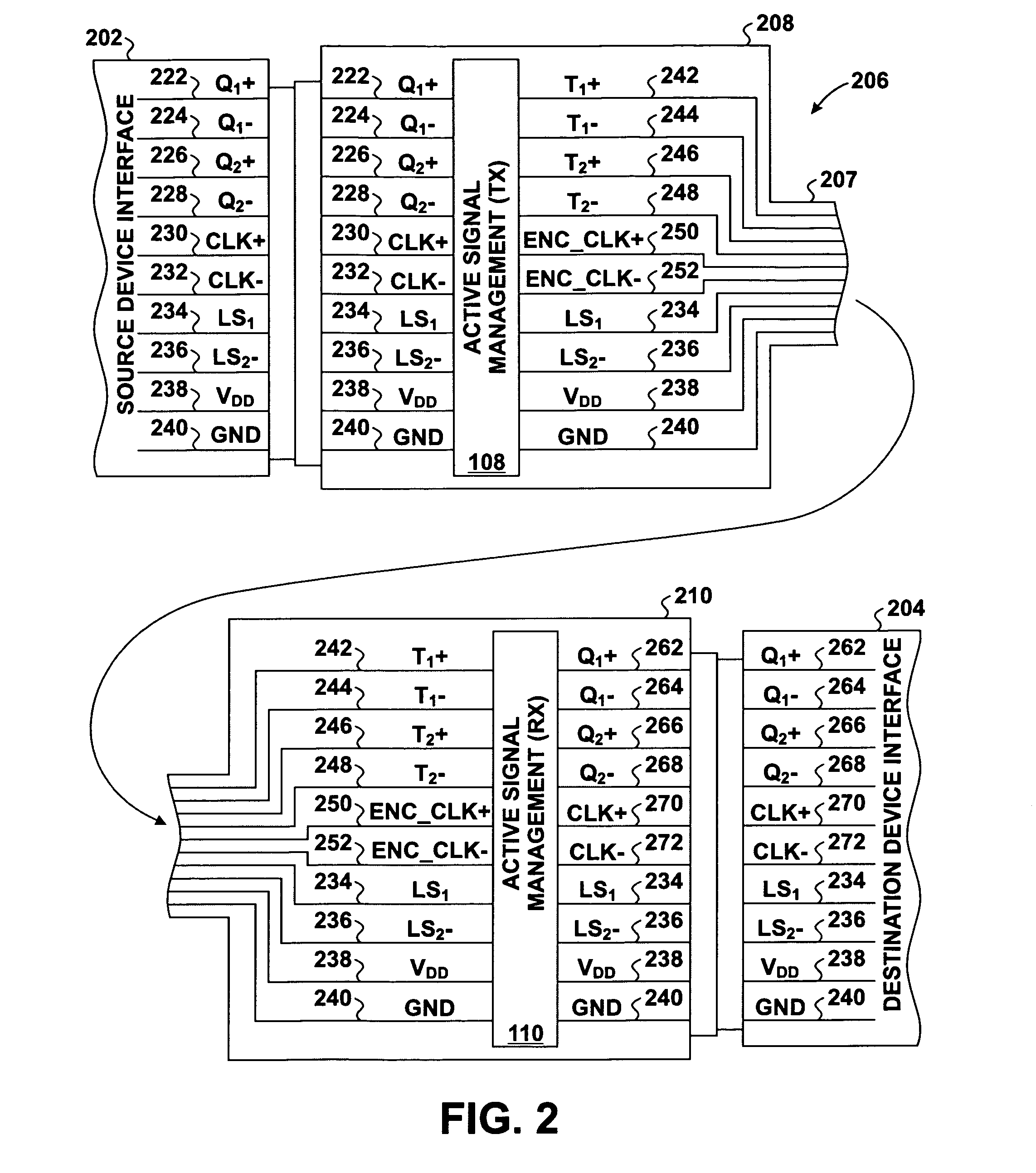
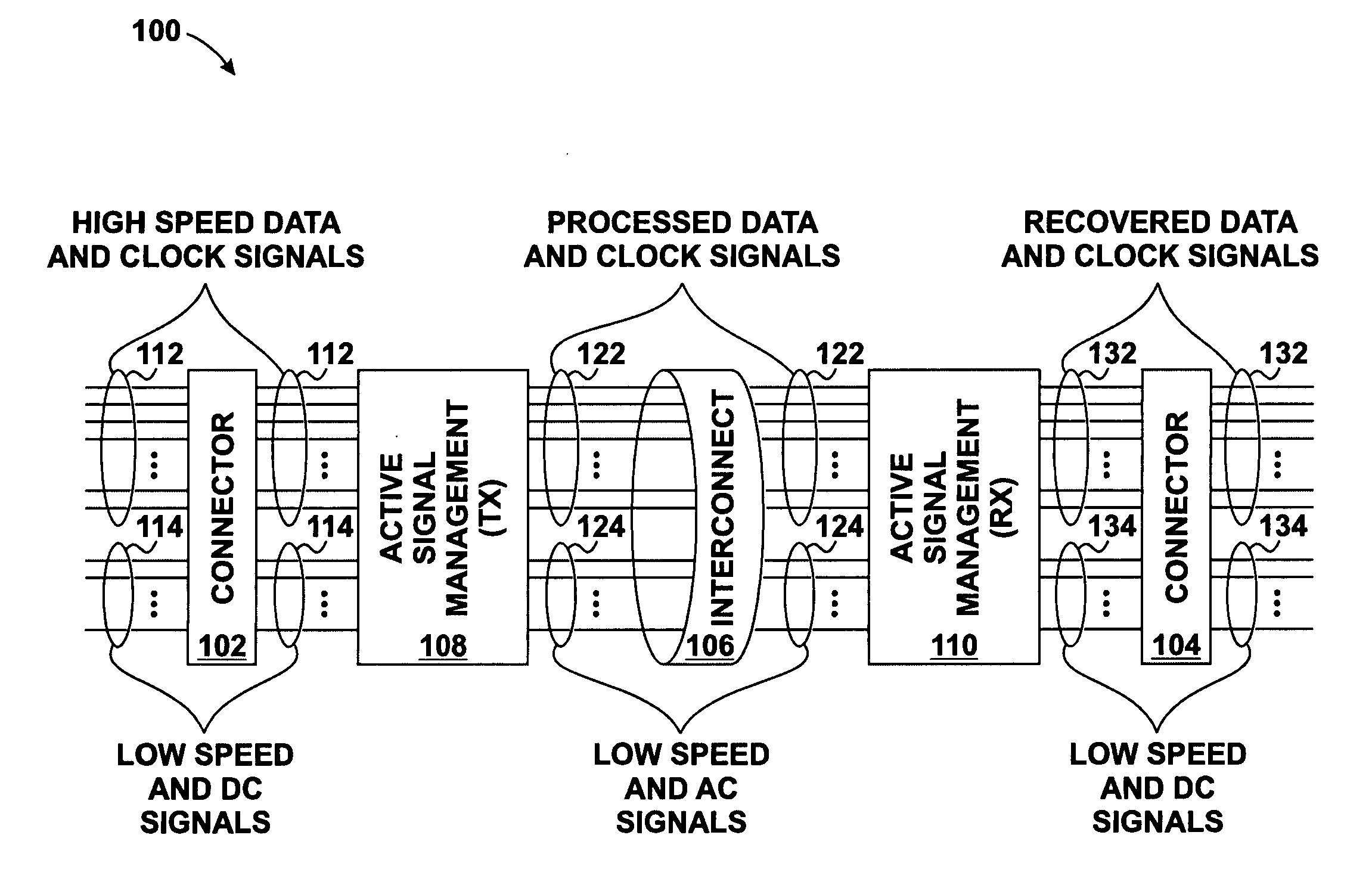
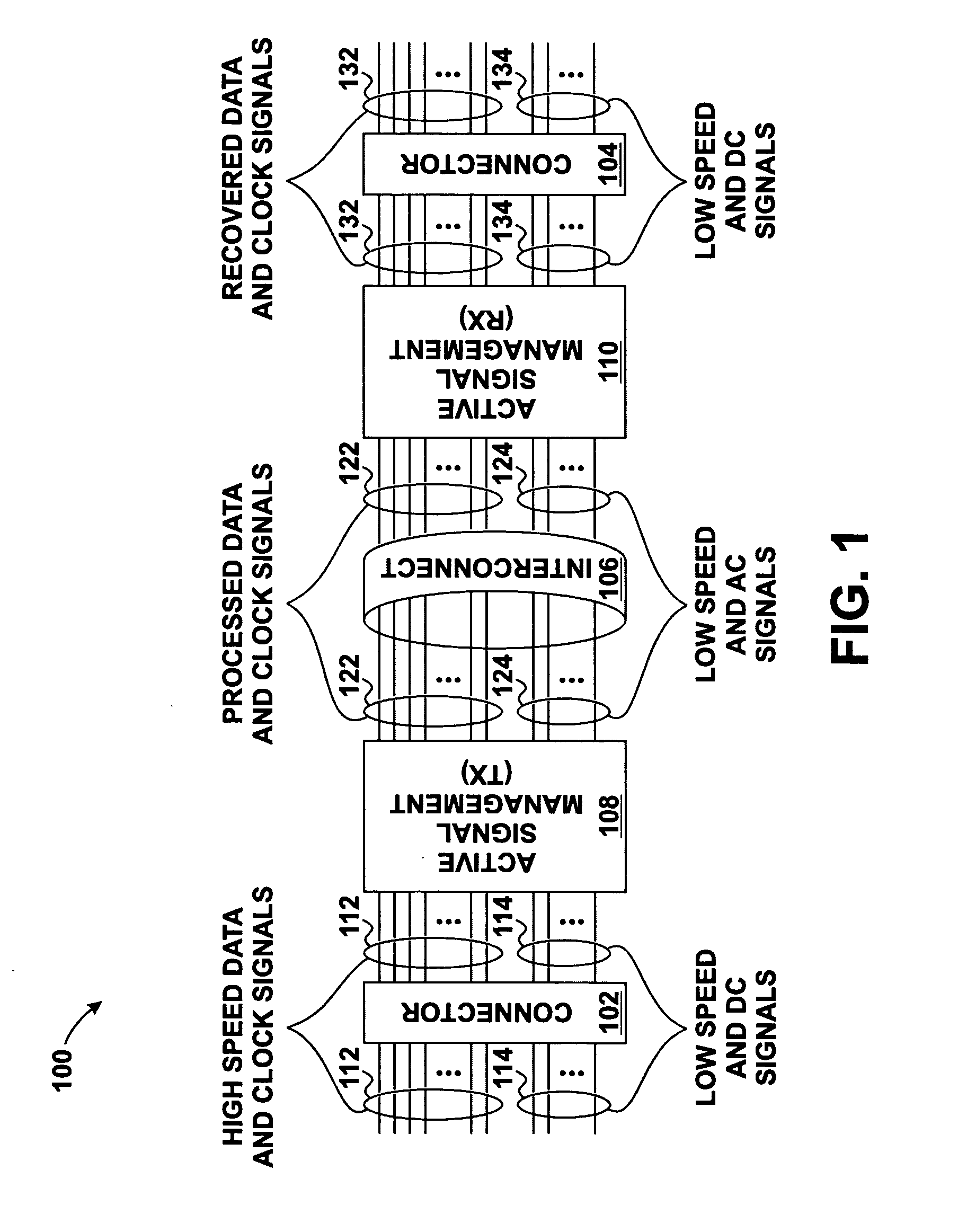
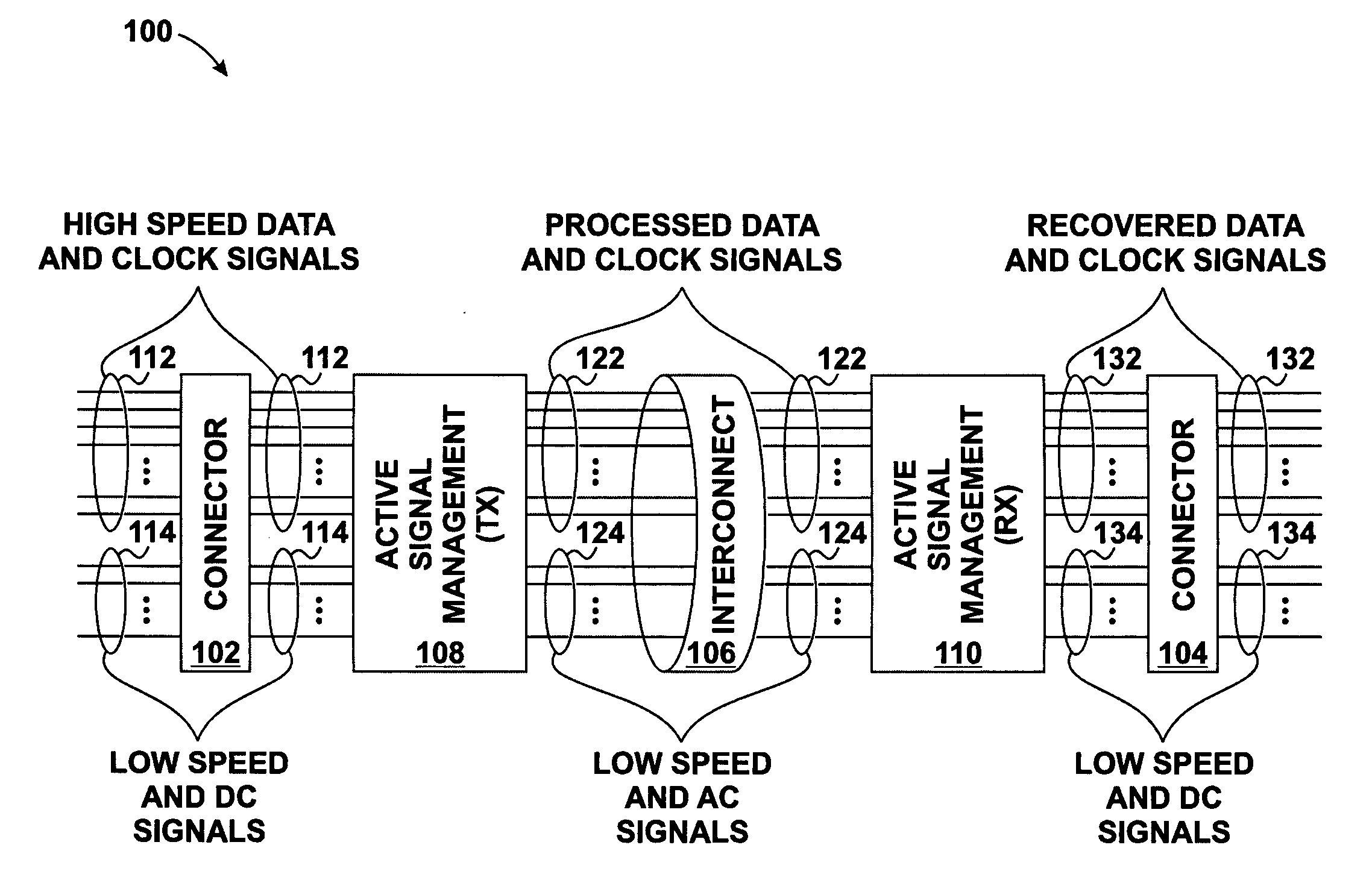
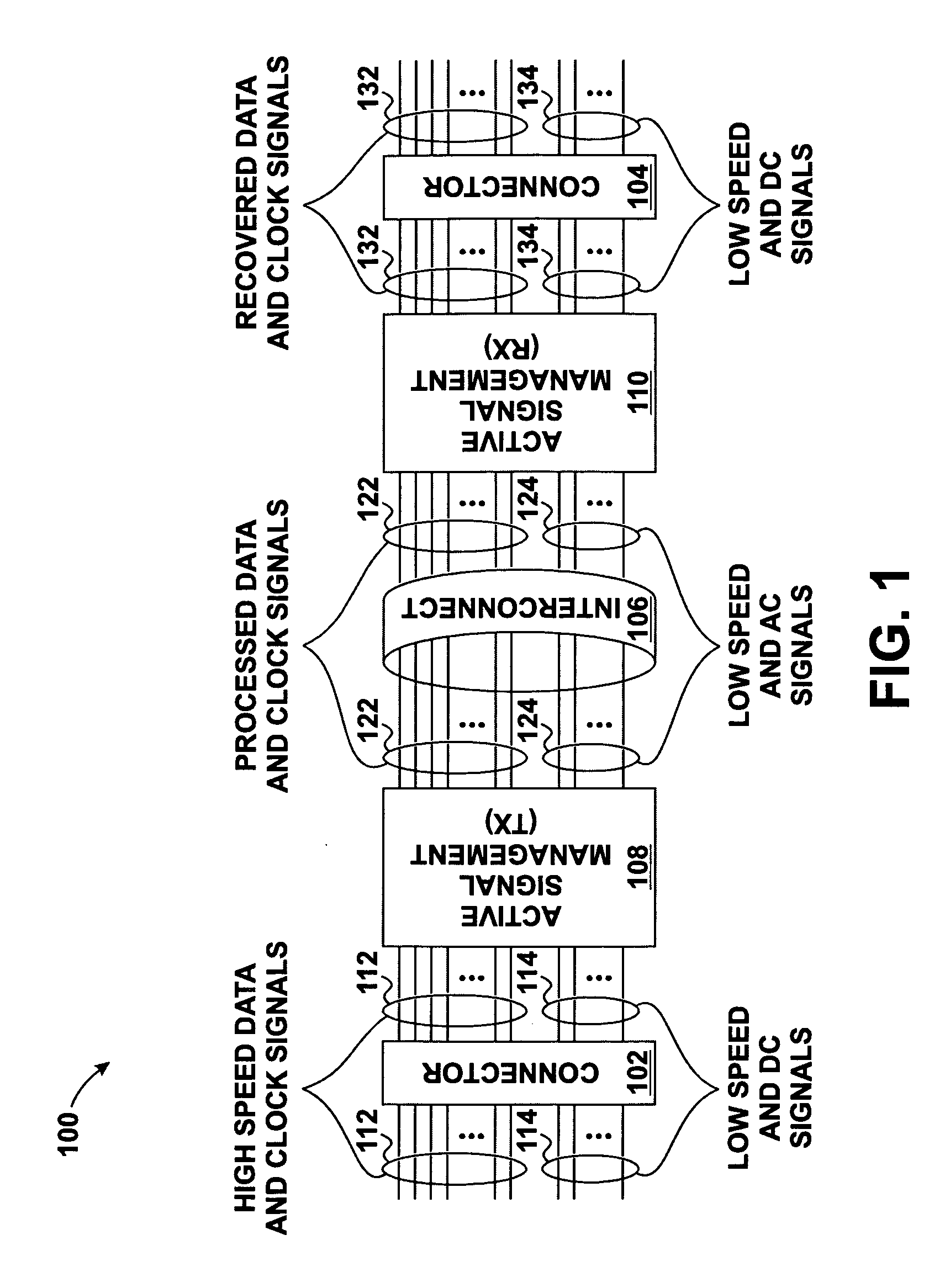
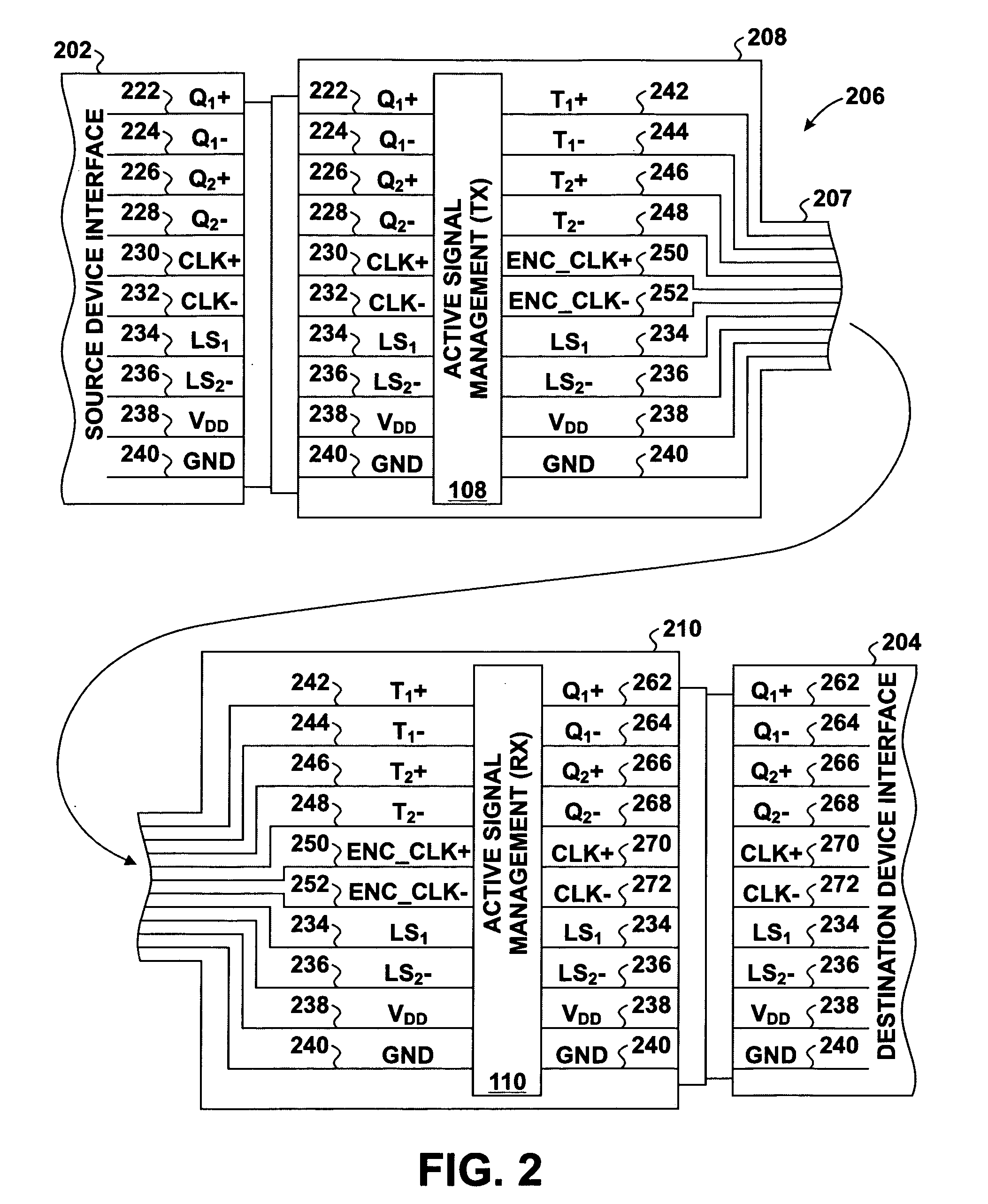
Skew management in cables and other interconnects
InactiveUS20070206643A1Channel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionManagement processEngineering
Transmit-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more active signal management processes to a digital signal at a transmit side of an interconnect. At the receive side of the interconnect, receive-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more corresponding active signal management processes, as appropriate, to the received digital signal to recover the information represented by the original digital signal. The interconnect can include a cable used to transmit the signals between a source device and a destination device, whereby one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry is implemented at a corresponding cable receptacle of the cable. Alternately, one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry can be implemented at a cable adaptor, thereby permitting the use of a passive cable interconnect to transmit the signal.
Owner:XEMI
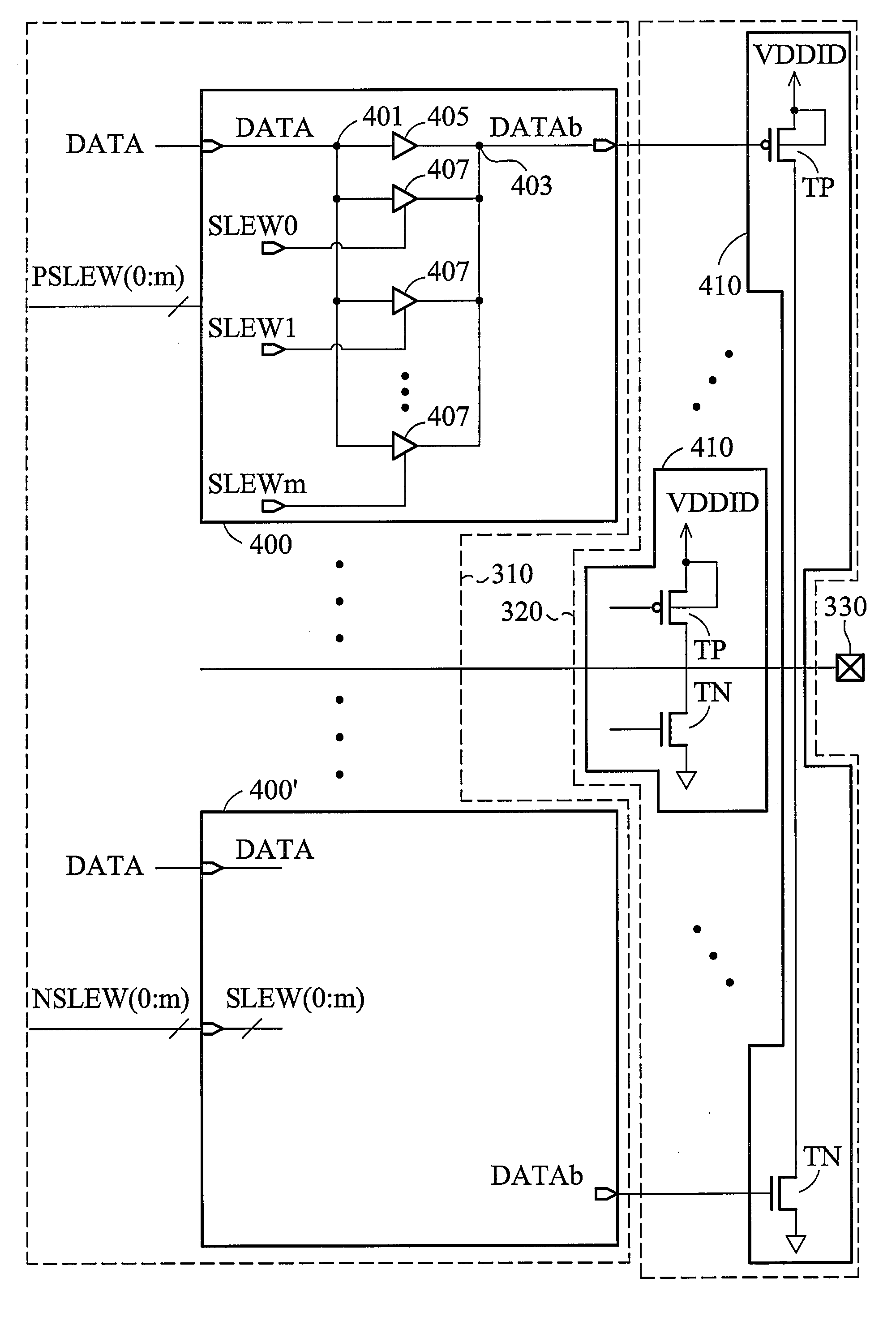
Slew rate controlled circuits
InactiveUS20080106297A1Logic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectronic switchingDriver circuitControl signal
A slew rate controlled output buffer. The slew rate controlled output buffer comprises a pre-driver circuit having a data input node and a data output node and a driver circuit coupled to the output node of the pre-driver circuit. The pre-driver circuit comprises a plurality of inverters connected in parallel, each having an input terminal coupled to the input node and an output terminal coupled to the output node, wherein at least one of the inverters is selectively disabled by a slew rate control signal via a slew rate controller. The driver circuit is driven by an output signal of the pre-driver circuit.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
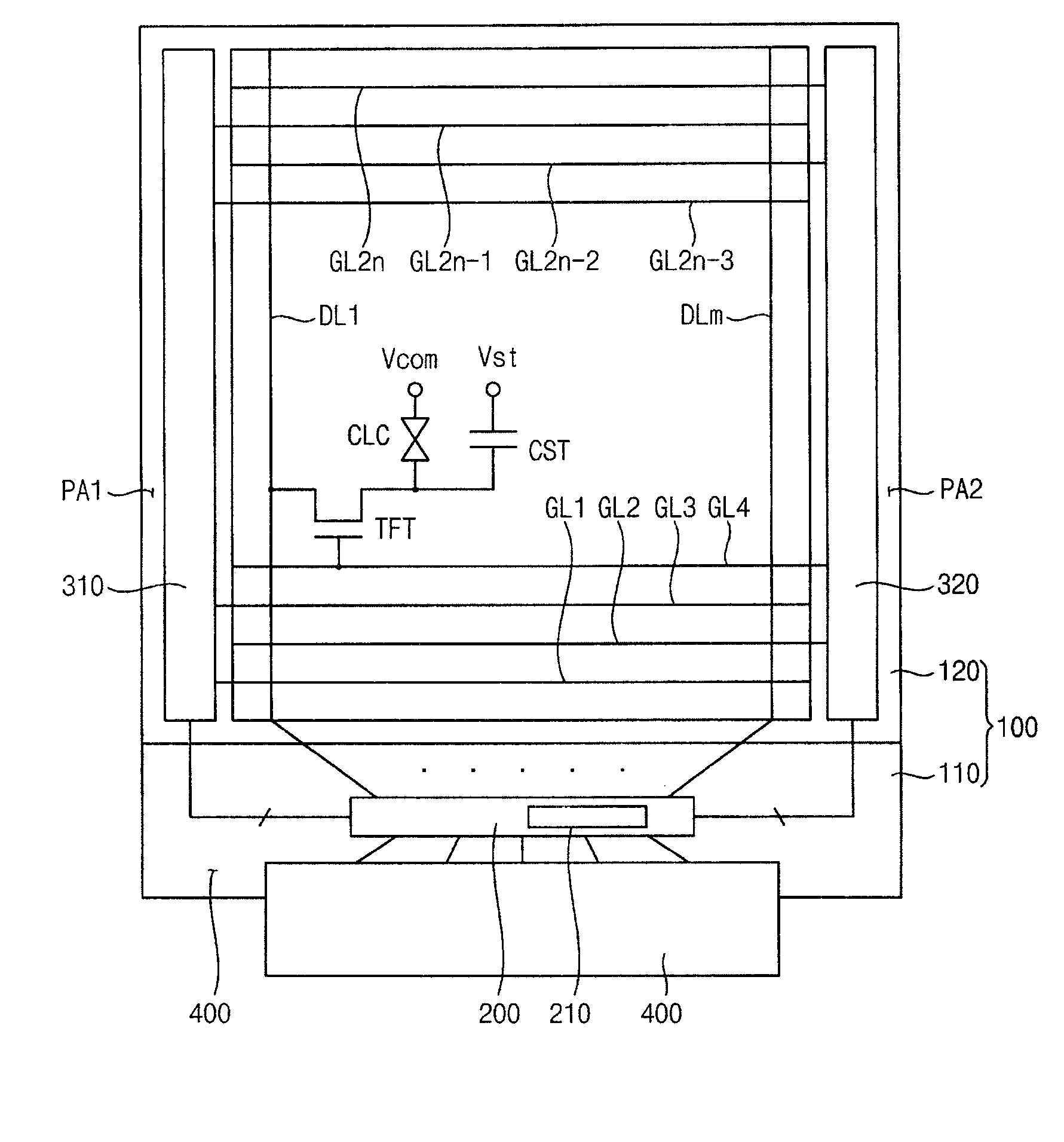
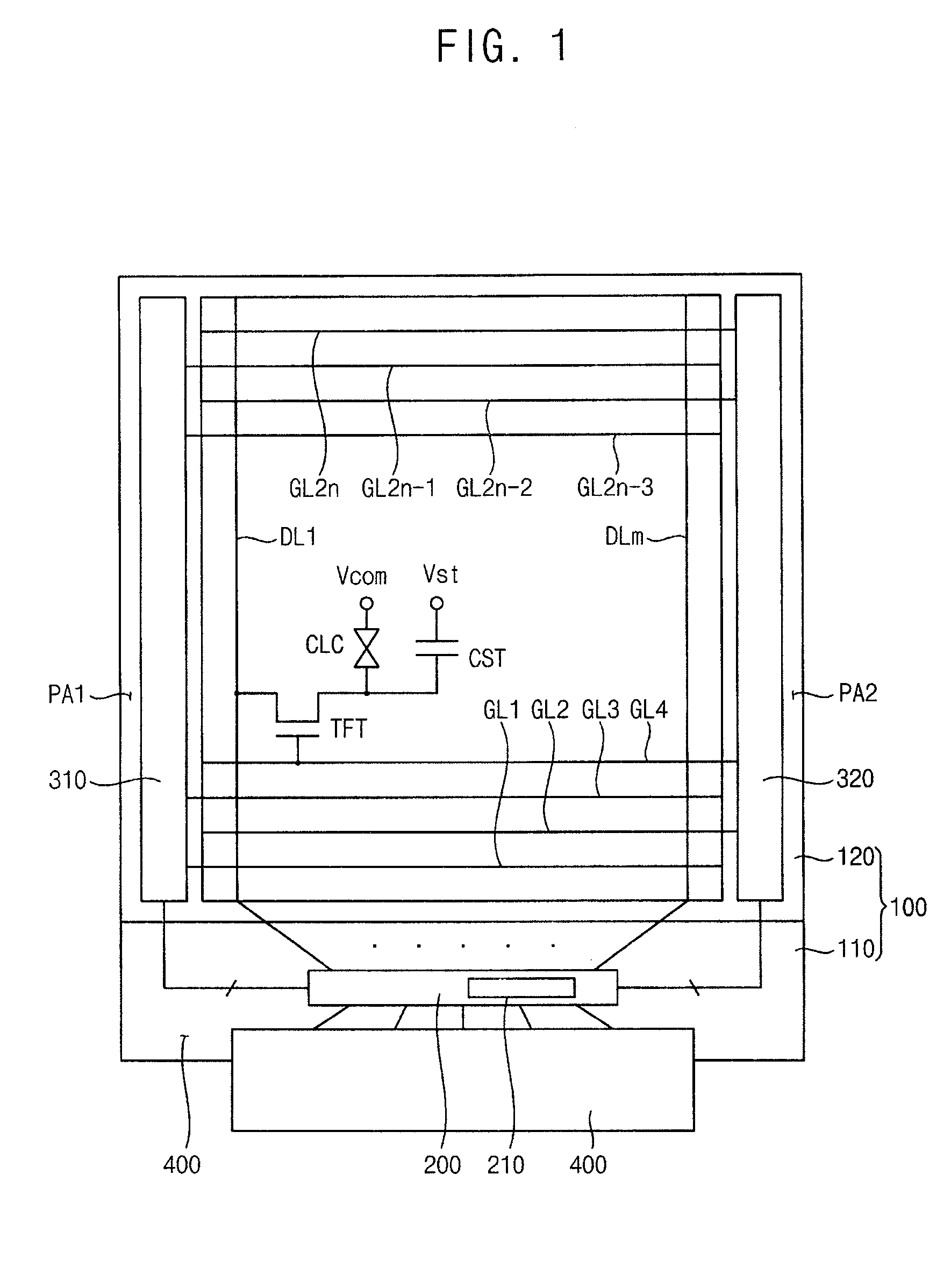
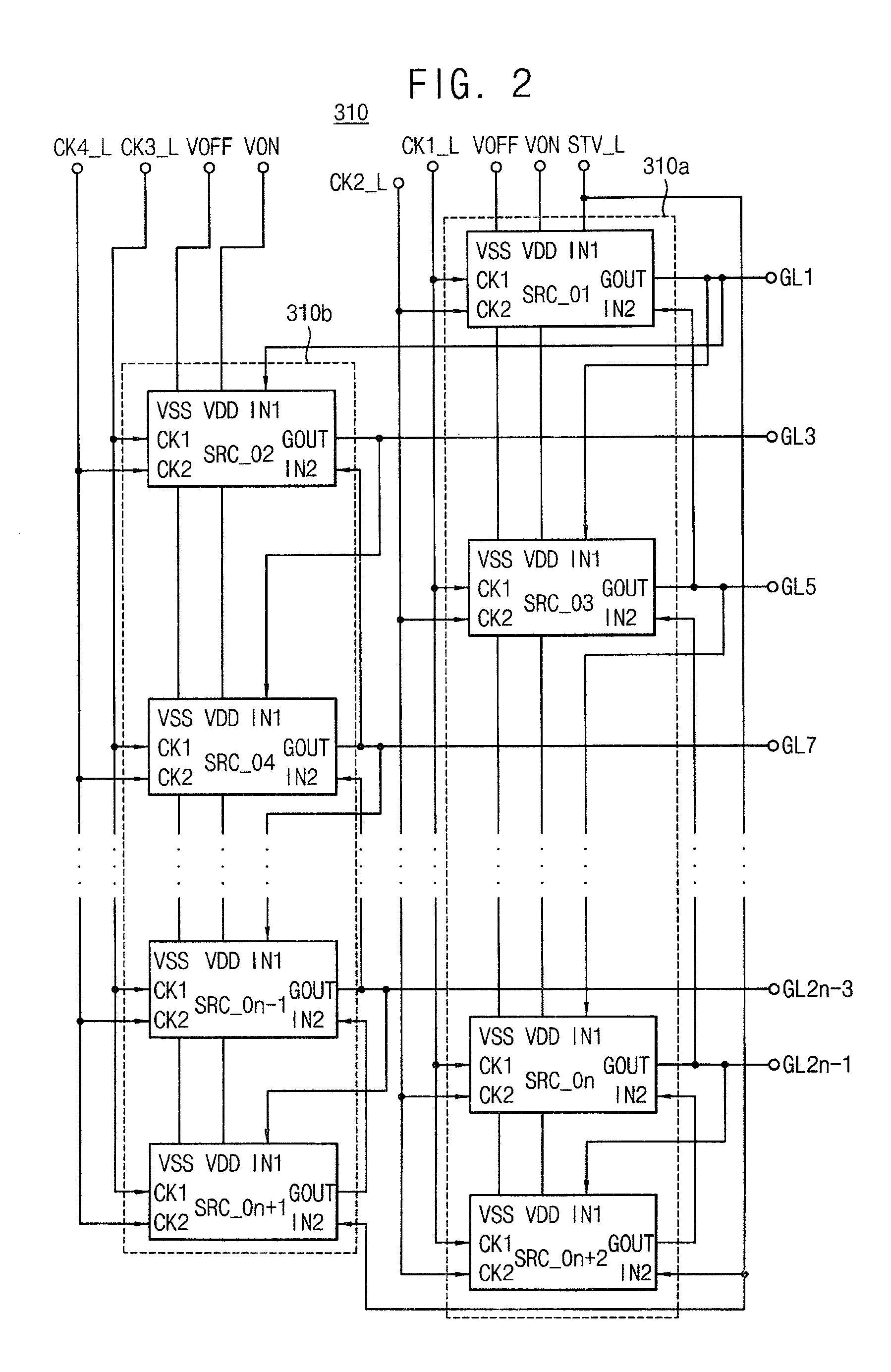
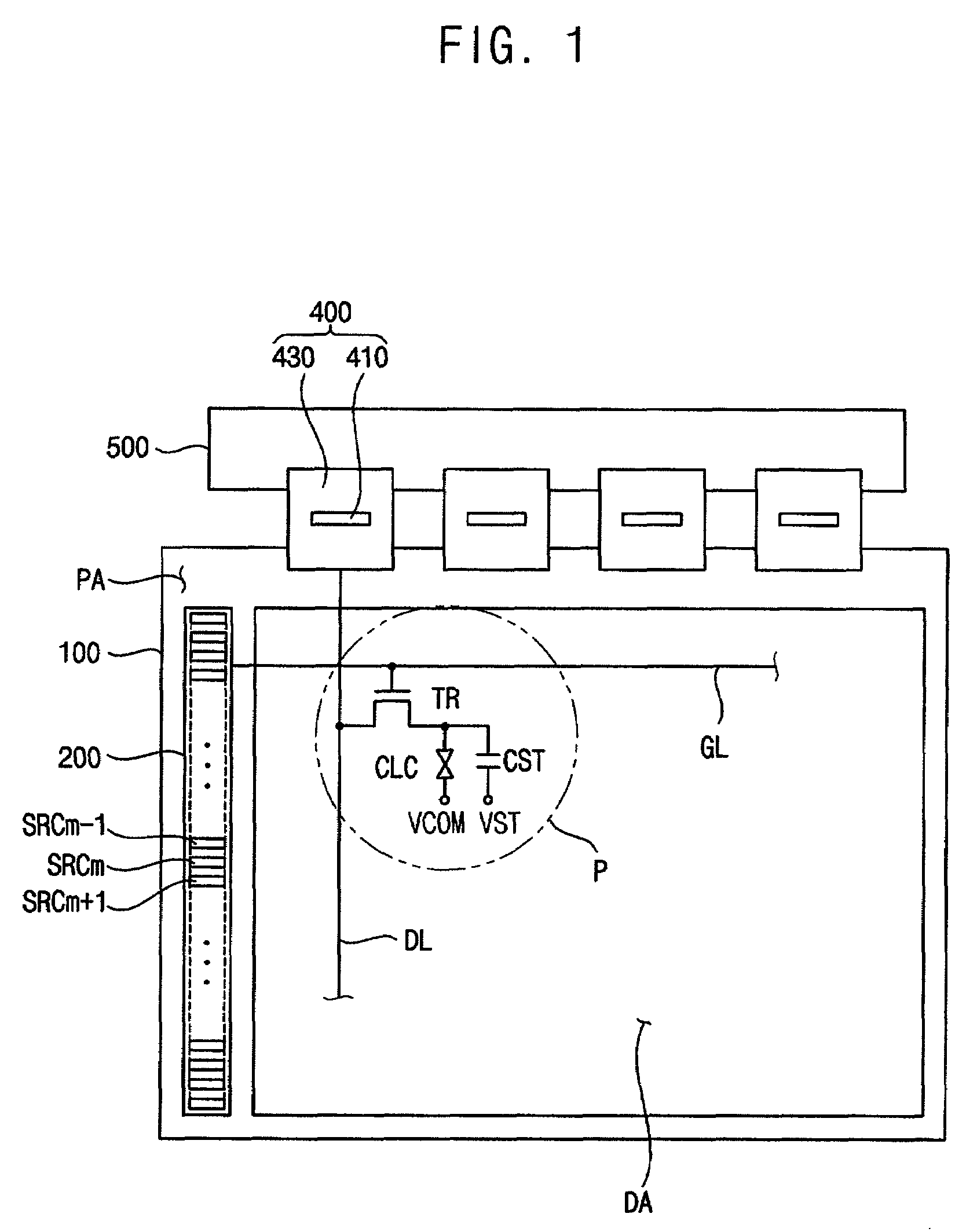
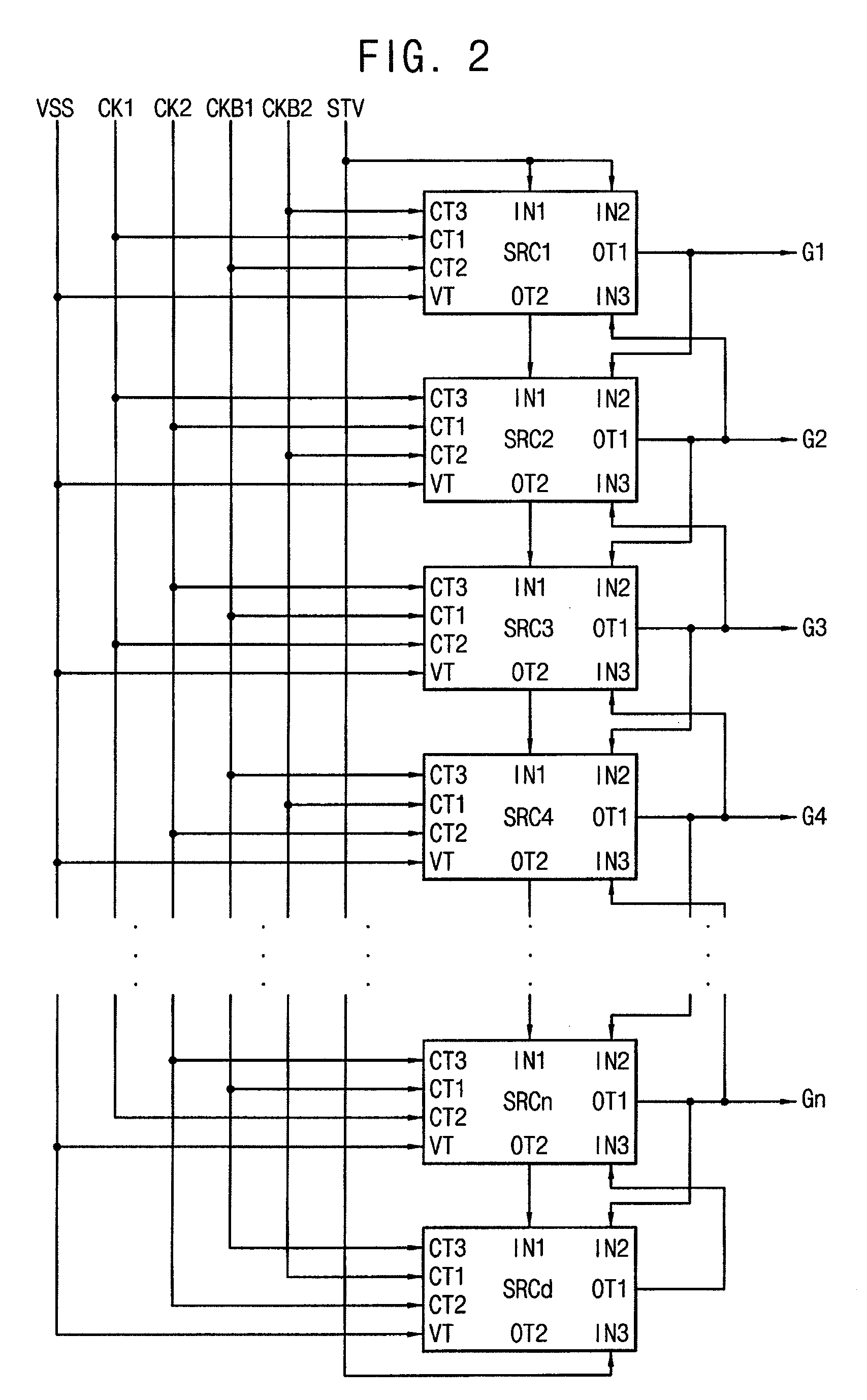
Gate driving circuit and display device having the gate driving circuit
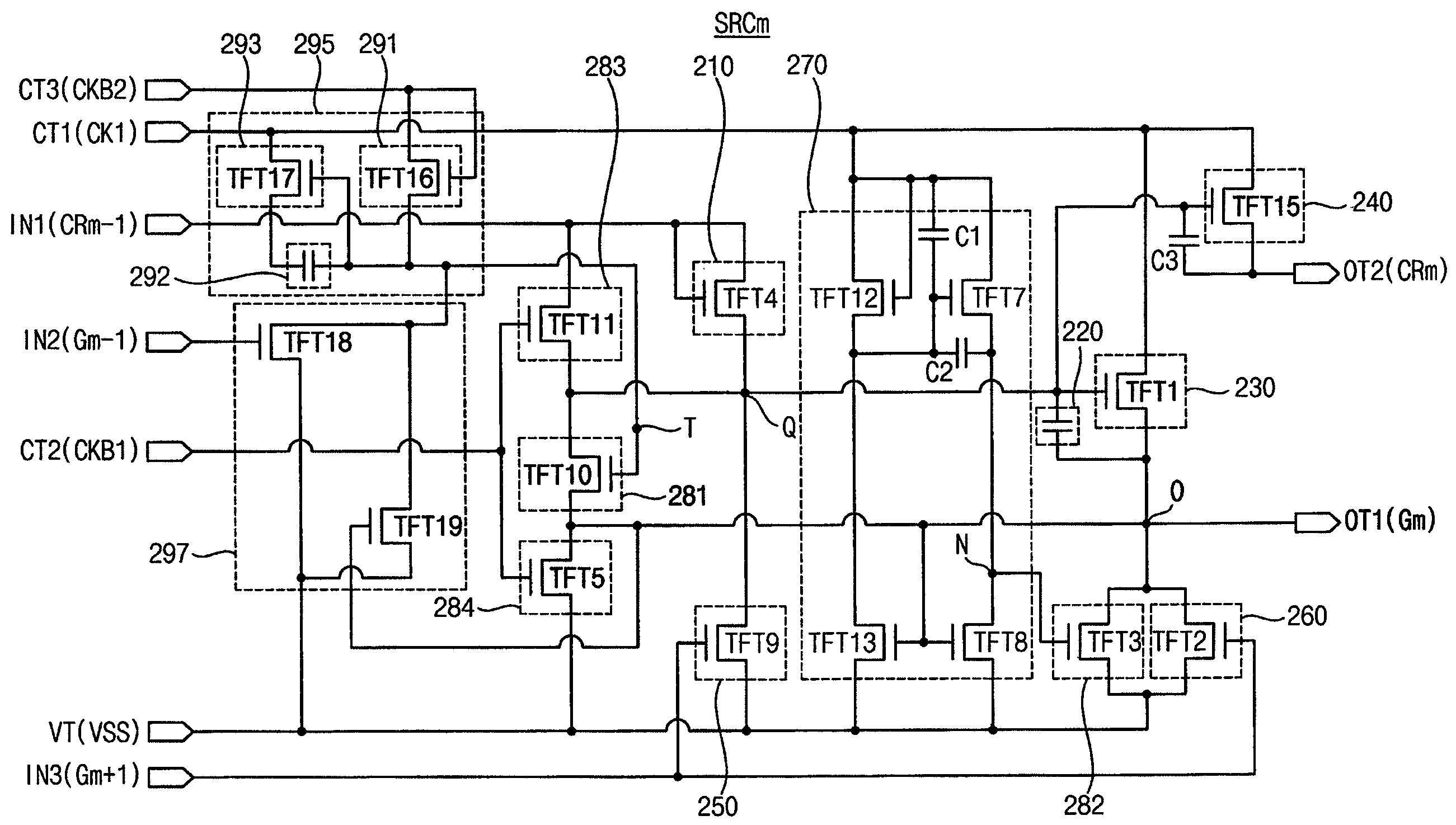
InactiveUS20100164915A1Improve driving reliabilityImprove gate reliabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorTiming marginShift register
A gate driving circuit includes a first shift register and a second shift register for driving odd gate lines. The first shift register includes a first plurality of cascade-connected stages that sequentially output a plurality of first gate signals. A first stage of the first shift register receives a first vertical start signal. The second shift register includes a second plurality of cascade-connected stages to sequentially output a plurality of second gate signals. The first stage of the second shift register receives an output signal of the first stage of the first shift register as its vertical start signal. A data charging rate may be improved by ensuring the timing margin of each gate signal, so that the driving reliability of the gate driving circuit may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
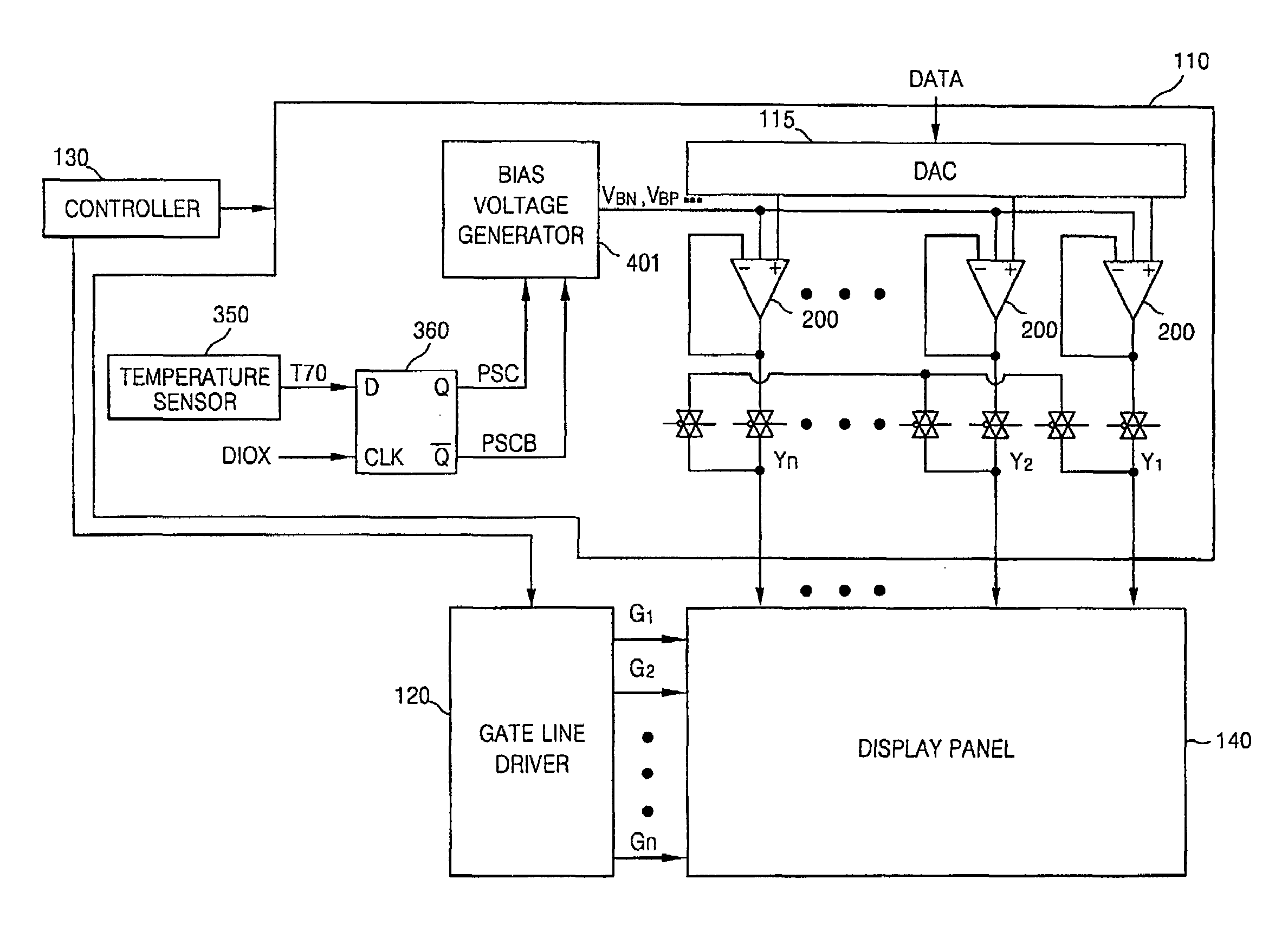
Source line driver and method for controlling slew rate according to temperature and display device including the source line driver
InactiveUS20080278473A1Lower conversion rateCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorVoltage generatorTemperature control
A source line driver and method for controlling a slew rate according to temperature and a display device including the source line driver are provided. The source line driver includes a temperature sensing unit configured to sense a temperature, compare the sensed temperature with a reference temperature, and generate a comparison result as a control signal; and a bias voltage generator configured to output a plurality of bias voltages whose voltage levels are controlled in response to the control signal. Accordingly, the slew rate of an output buffer is controlled based on the sensed temperature, so that false operation caused by heat generated in the source line driver and display panel can be prevented when the temperature is increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
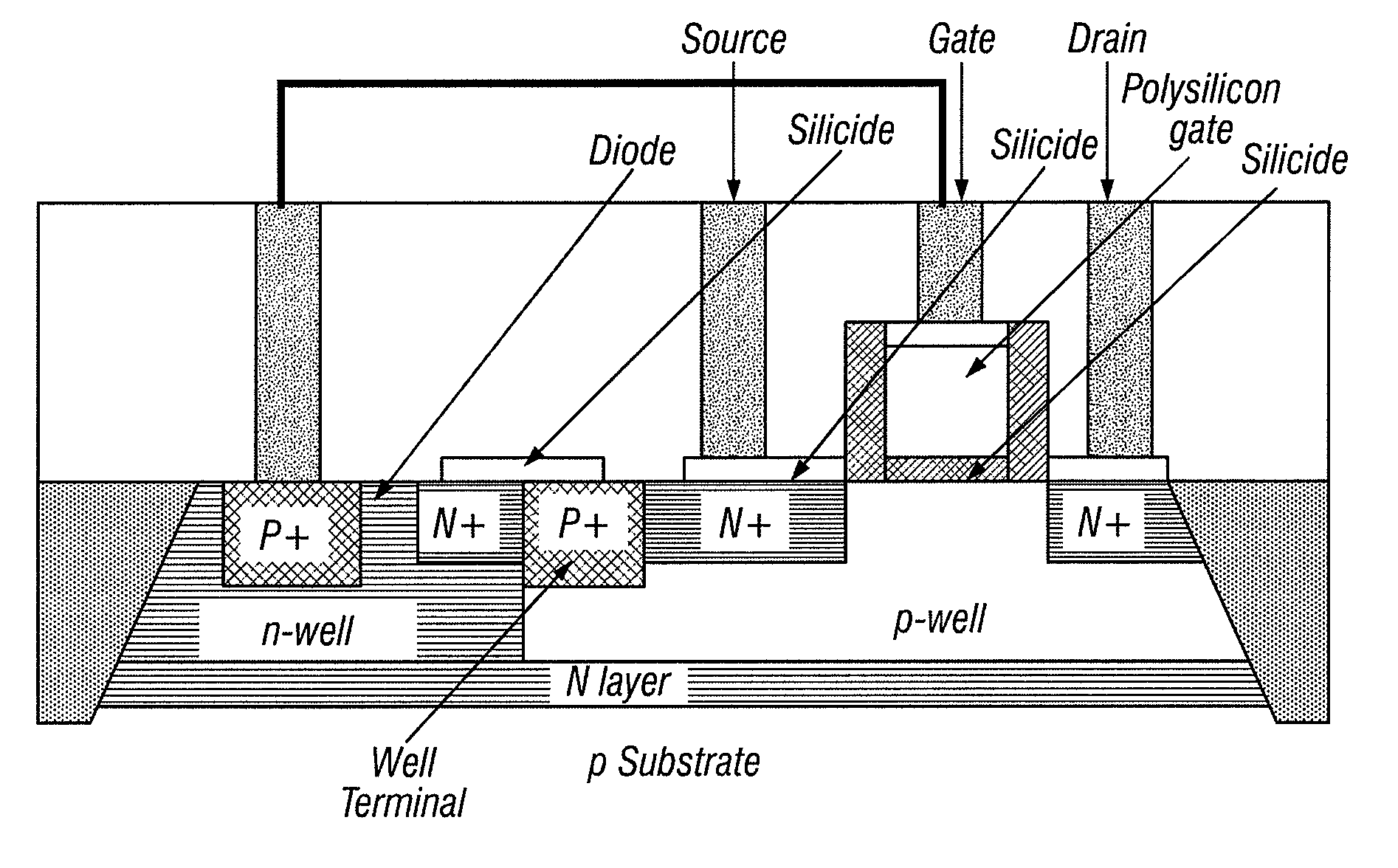
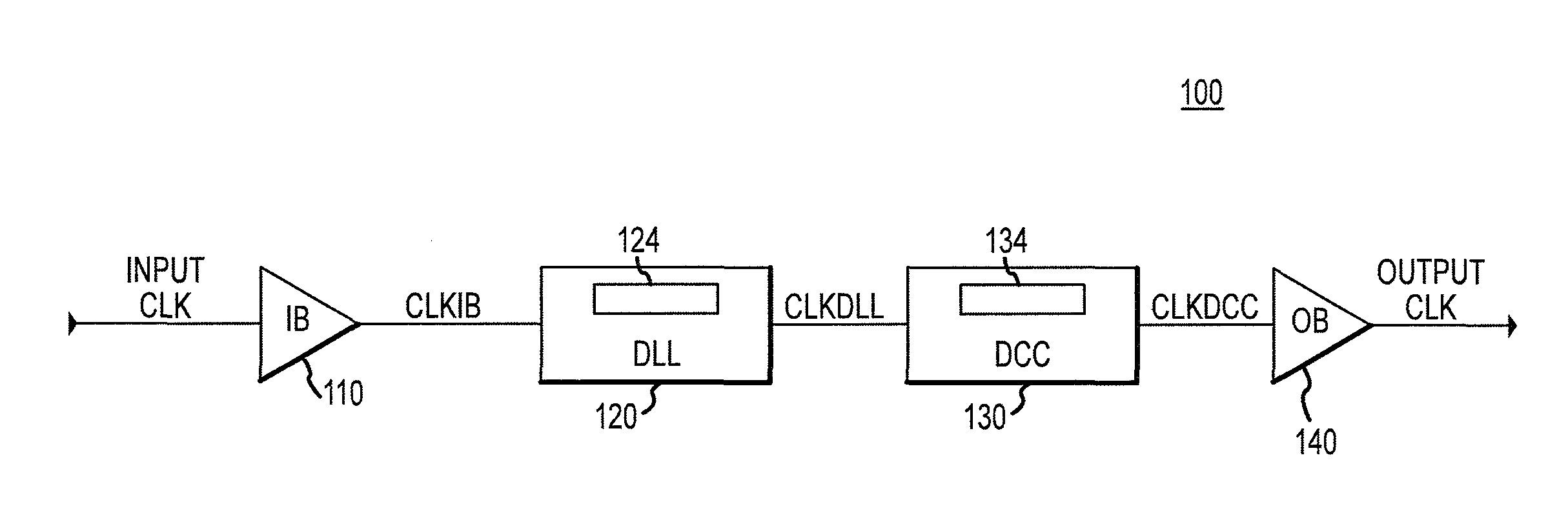
Apparatus and method for improving drive-strength and leakage of deep submicron MOS transistors
InactiveUS7683433B2Increase drive strengthReduce leakage currentTransistorInput/output impedence modificationCMOSEngineering
An apparatus and method of manufacture for metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors is disclosed. Devices in accordance with the invention are operable at voltages below 2V. The devices are area efficient, have improved drive strength, and have reduced leakage current. A dynamic threshold voltage control scheme comprised of a forward biased diode in parallel with a capacitor is used, implemented without changing the existing MOS technology process. This scheme controls the threshold voltage of each transistor. In the OFF state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage of the transistor increases, keeping the transistor leakage to a minimum. In the ON state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage decreases, resulting in increased drive strength. The invention is particularly useful in MOS technology for both bulk and silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS. The use of reverse biasing of the well, in conjunction with the above construct to further decrease leakage in a MOS transistor, is also shown.
Owner:SEMI SOLUTIONS LLC
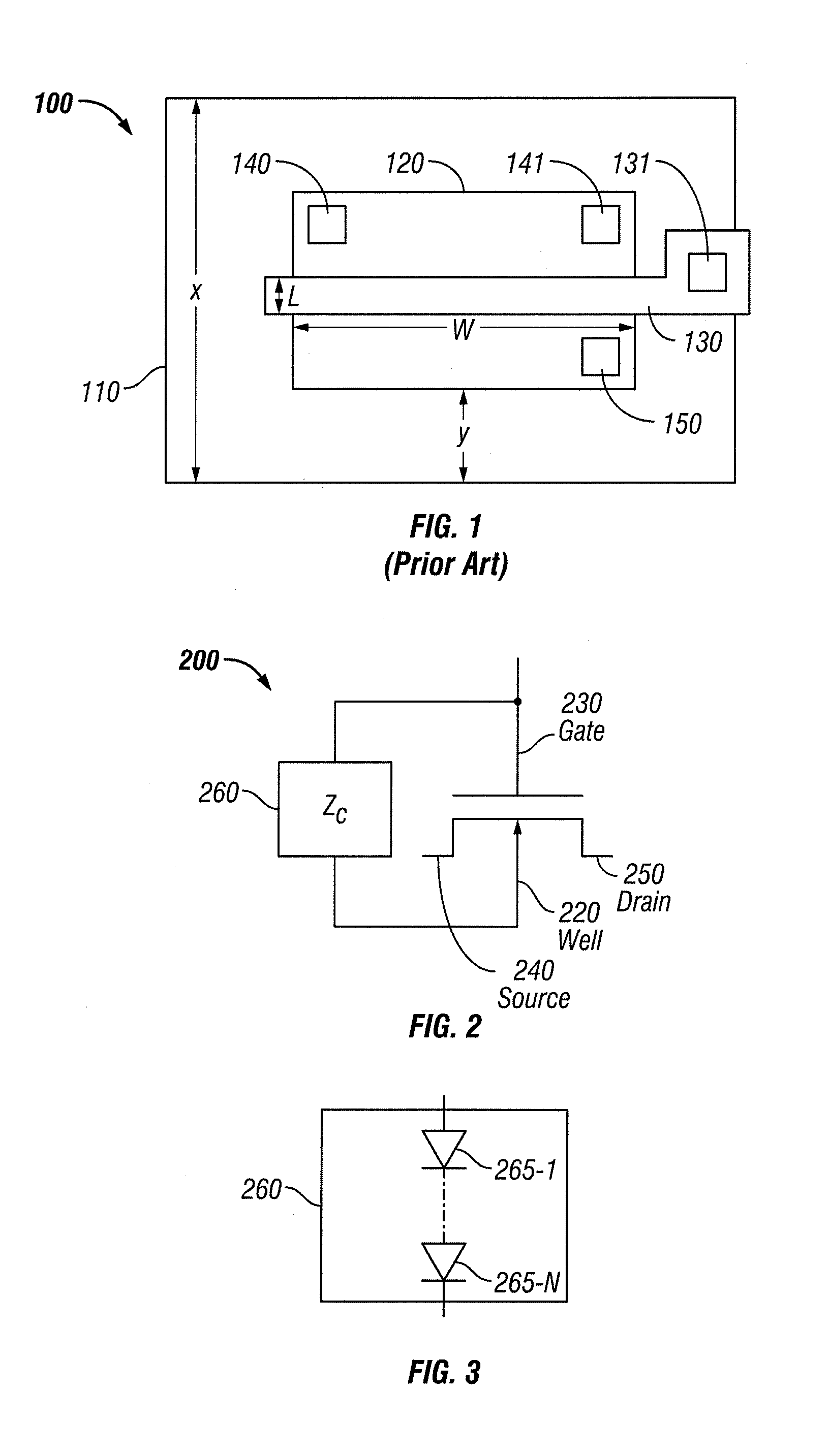
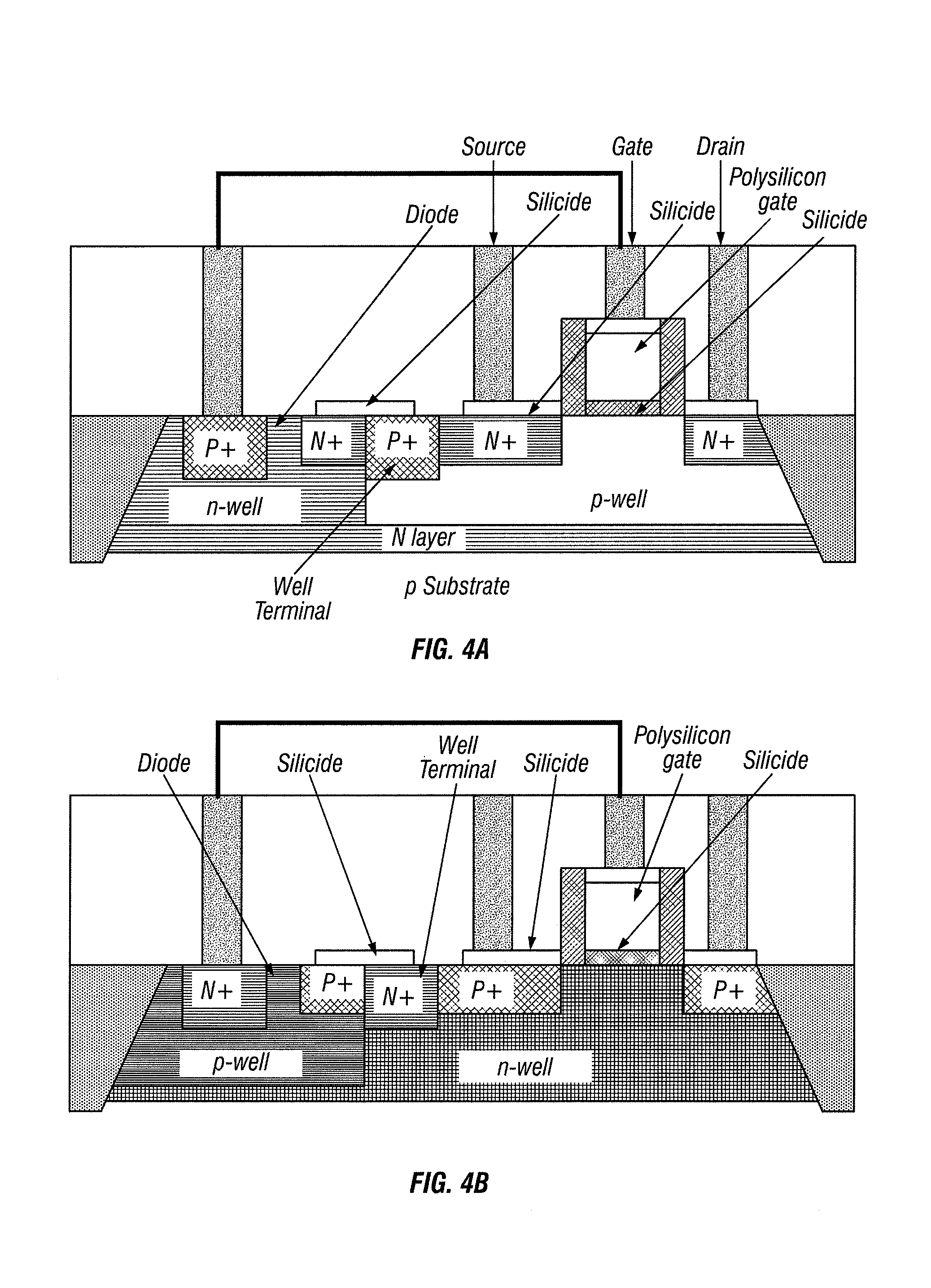
RC-triggered Semiconductor Controlled Rectifier for ESD Protection of Signal Pads
RC-trigger circuits for a semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR), methods of providing electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection, and design structures for a RC-trigger circuit. The RC-trigger circuit is coupled to an input / output (I / O) signal pad by an isolation diode and is coupled to a power supply voltage by a power supply diode. Under normal operating conditions, the isolation diode is reverse biased, isolating the RC-trigger circuit from the input / output (I / O) pad, and the power supply diode is forward biased so that the RC-trigger circuit is supplied with power. The isolation diode may become forward biased during ESD events while the chip is unpowered, causing the RC-trigger circuit to trigger an SCR configured protect the signal pad from ESD into a conductive state. The power supply diode may become reverse biased during the ESD event, which isolates the power supply rail from the ESD voltage pulse.
Owner:IBM CORP
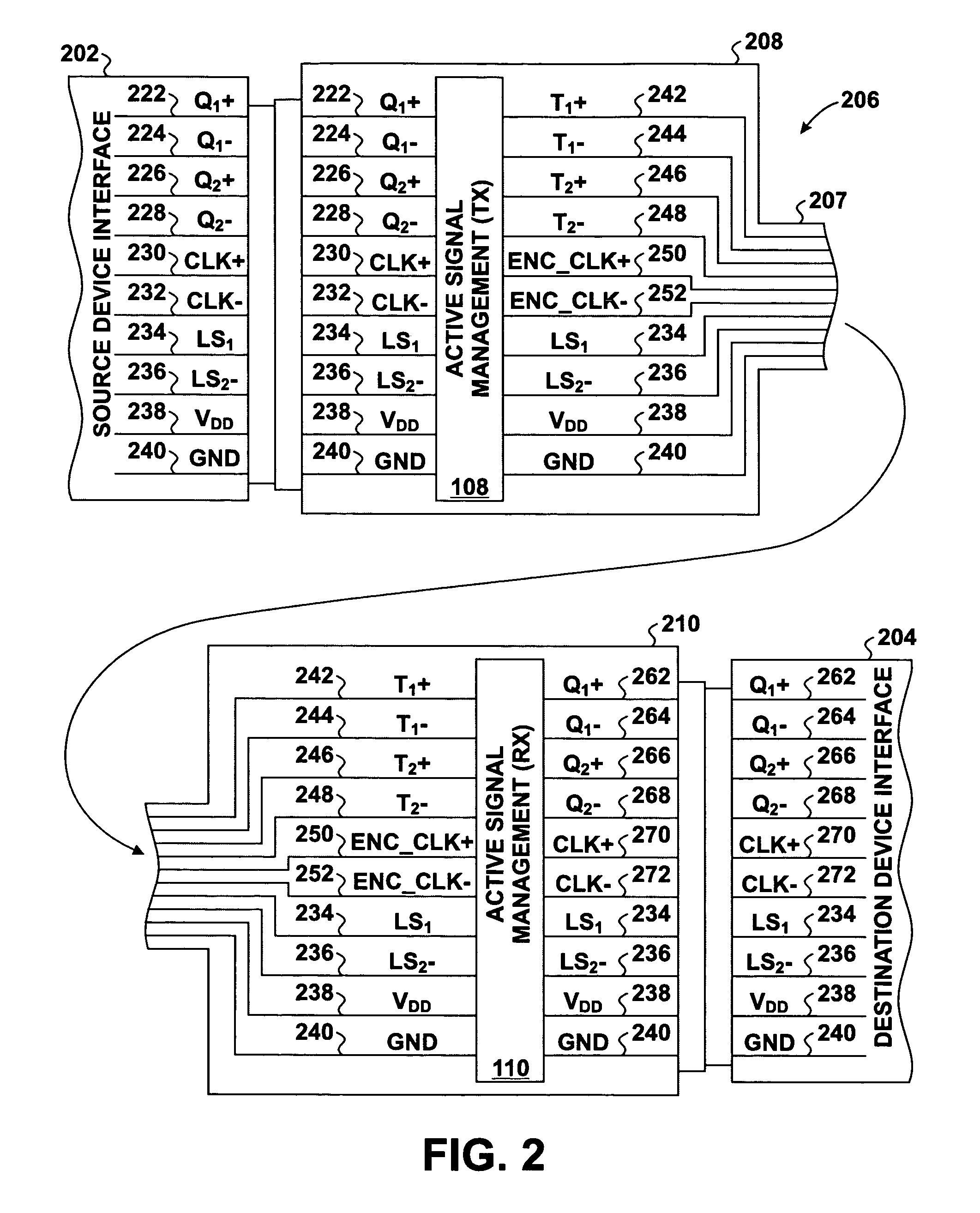
Method and apparatus for conversion between quasi differential signaling and true differential signaling
InactiveUS20070103204A1Channel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionDifferential signalingManagement process
Transmit-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more active signal management processes to a digital signal at a transmit side of an interconnect. At the receive side of the interconnect, receive-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more corresponding active signal management processes, as appropriate, to the received digital signal to recover the information represented by the original digital signal. The interconnect can include a cable used to transmit the signals between a source device and a destination device, whereby one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry is implemented at a corresponding cable receptacle of the cable. Alternately, one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry can be implemented at a cable adaptor, thereby permitting the use of a passive cable interconnect to transmit the signal.
Owner:XEMI
Encoding and deserialization-serialization for digital signals
InactiveUS20070206641A1Channel dividing arrangementsParallel/series conversionManagement processEngineering
Transmit-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more active signal management processes to a digital signal at a transmit side of an interconnect. At the receive side of the interconnect, receive-side active signal management circuitry applies one or more corresponding active signal management processes, as appropriate, to the received digital signal to recover the information represented by the original digital signal. The interconnect can include a cable used to transmit the signals between a source device and a destination device, whereby one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry is implemented at a corresponding cable receptacle of the cable. Alternately, one or both of the transmit-side active signal management circuitry and the receive-side active signal management circuitry can be implemented at a cable adaptor, thereby permitting the use of a passive cable interconnect to transmit the signal.
Owner:XEMI
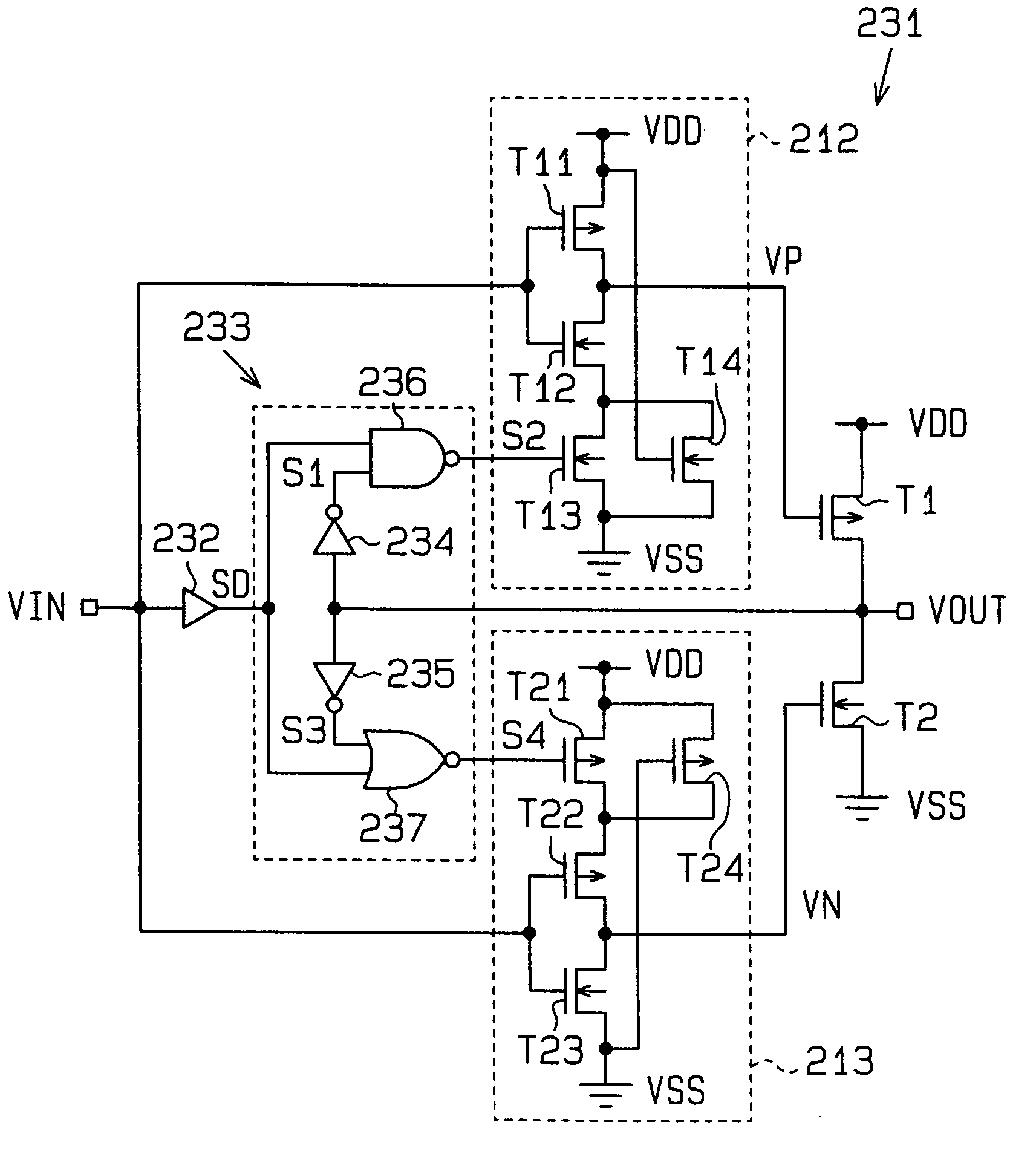
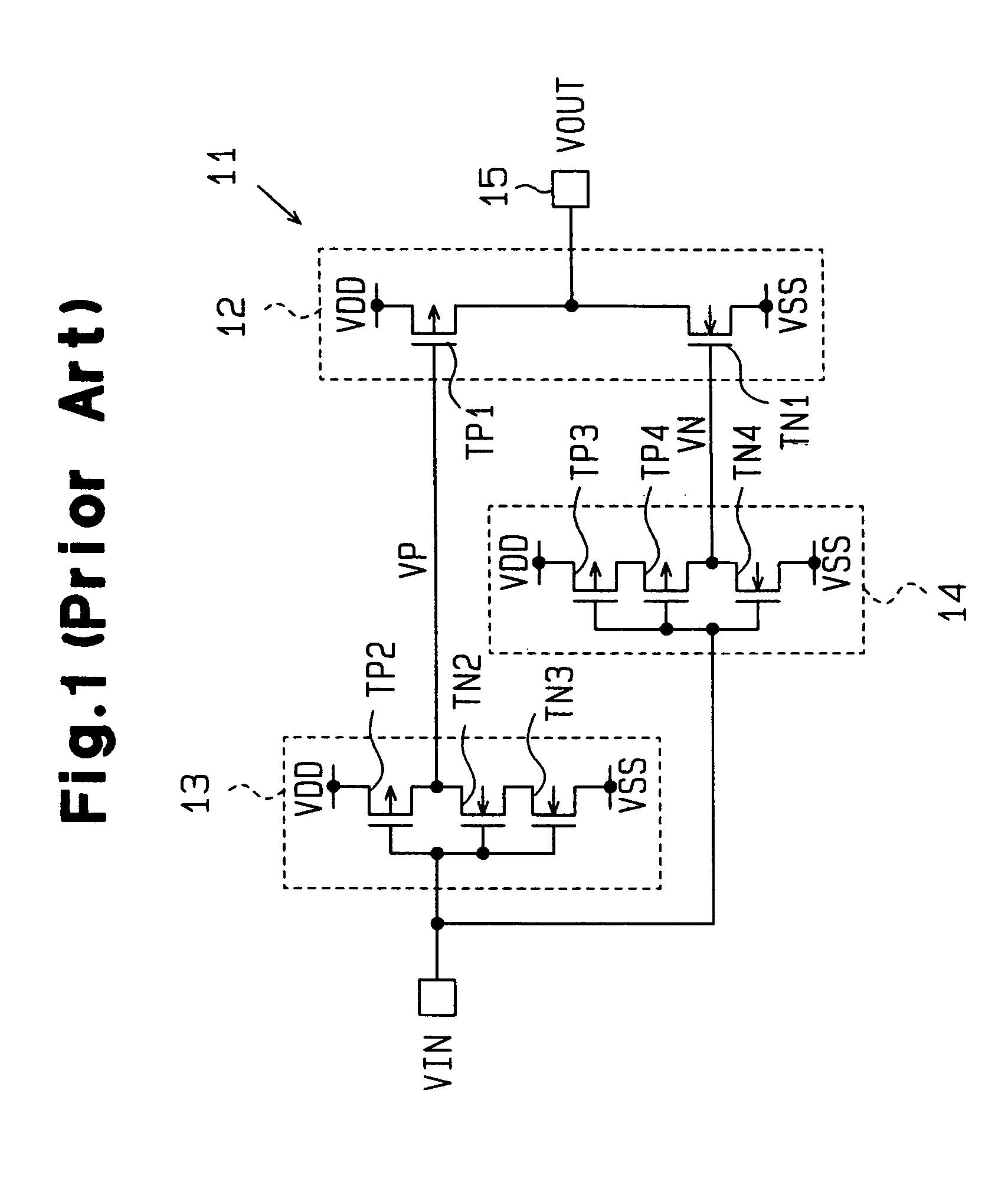
Output buffer circuit and control method therefor
InactiveUS7053660B2Less variationLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectronic switchingDriver circuitControl signal
An output buffer includes a first drive circuit that receives an input signal having a sharp waveform and generates an output signal that has a gentle waveform. A second drive circuit is connected to the first drive circuit at an output terminal and has a lower impedance than the first drive circuit. A delay circuit is also connected to the output terminal and generates a delayed output signal. A first control circuit is connected between the delay circuit and the second drive circuit and receives the input signal and the delayed output signal and generates a first control signal used to drive the second drive circuit.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Switch driver with slew rate control
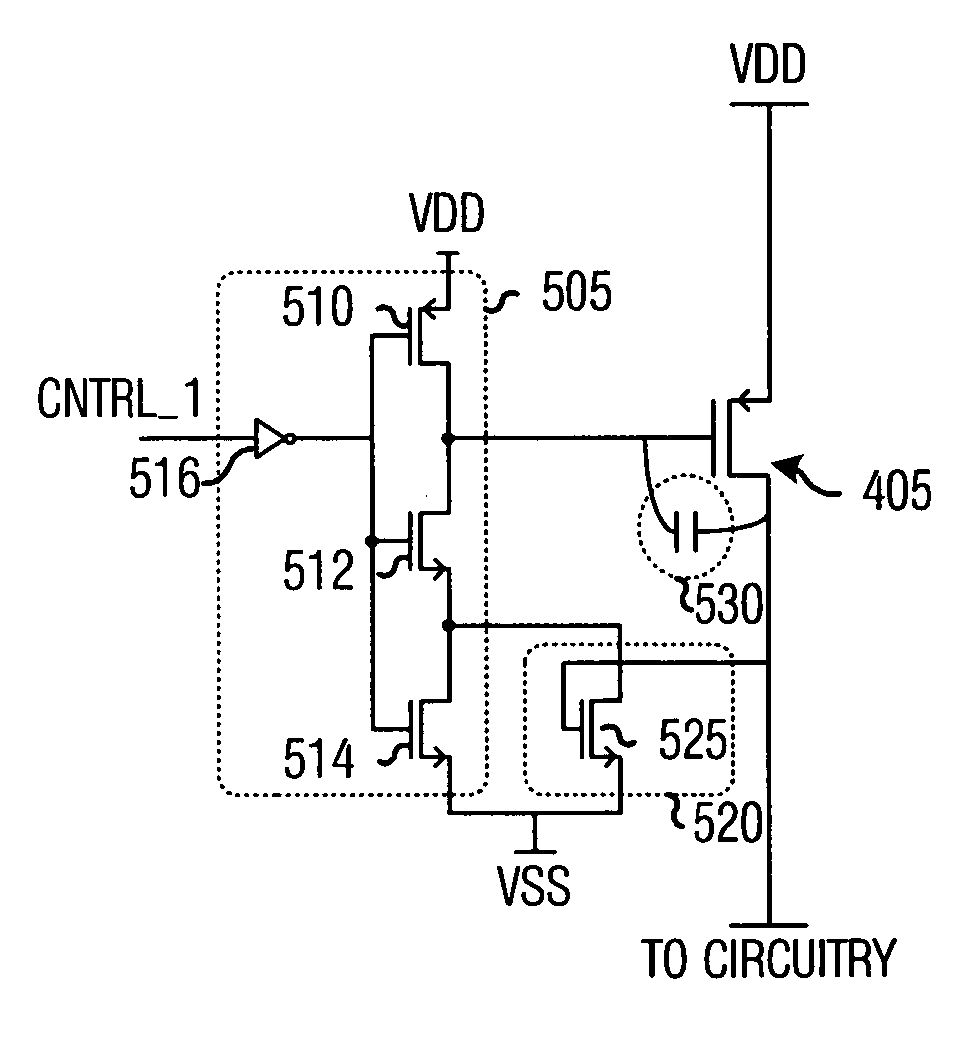
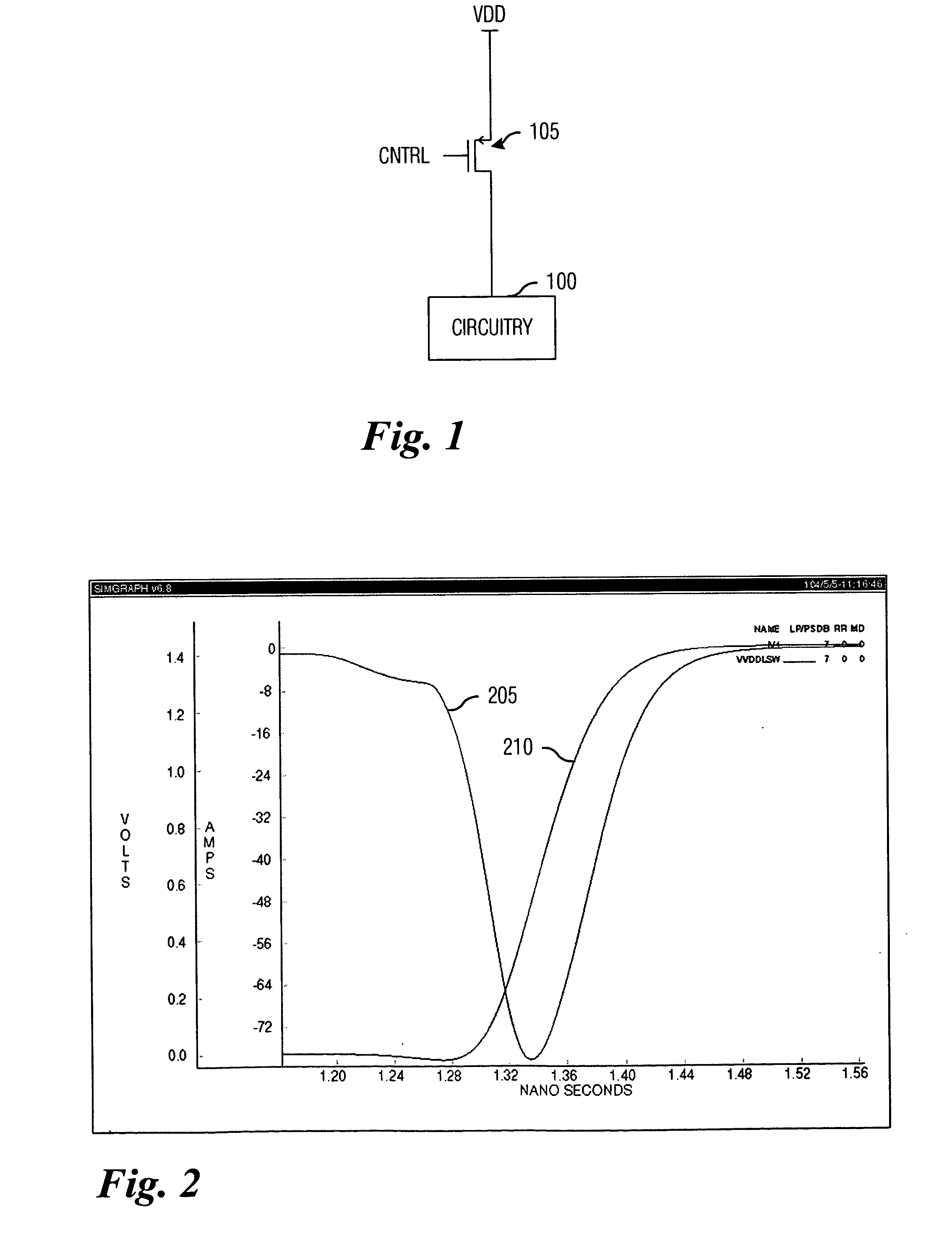
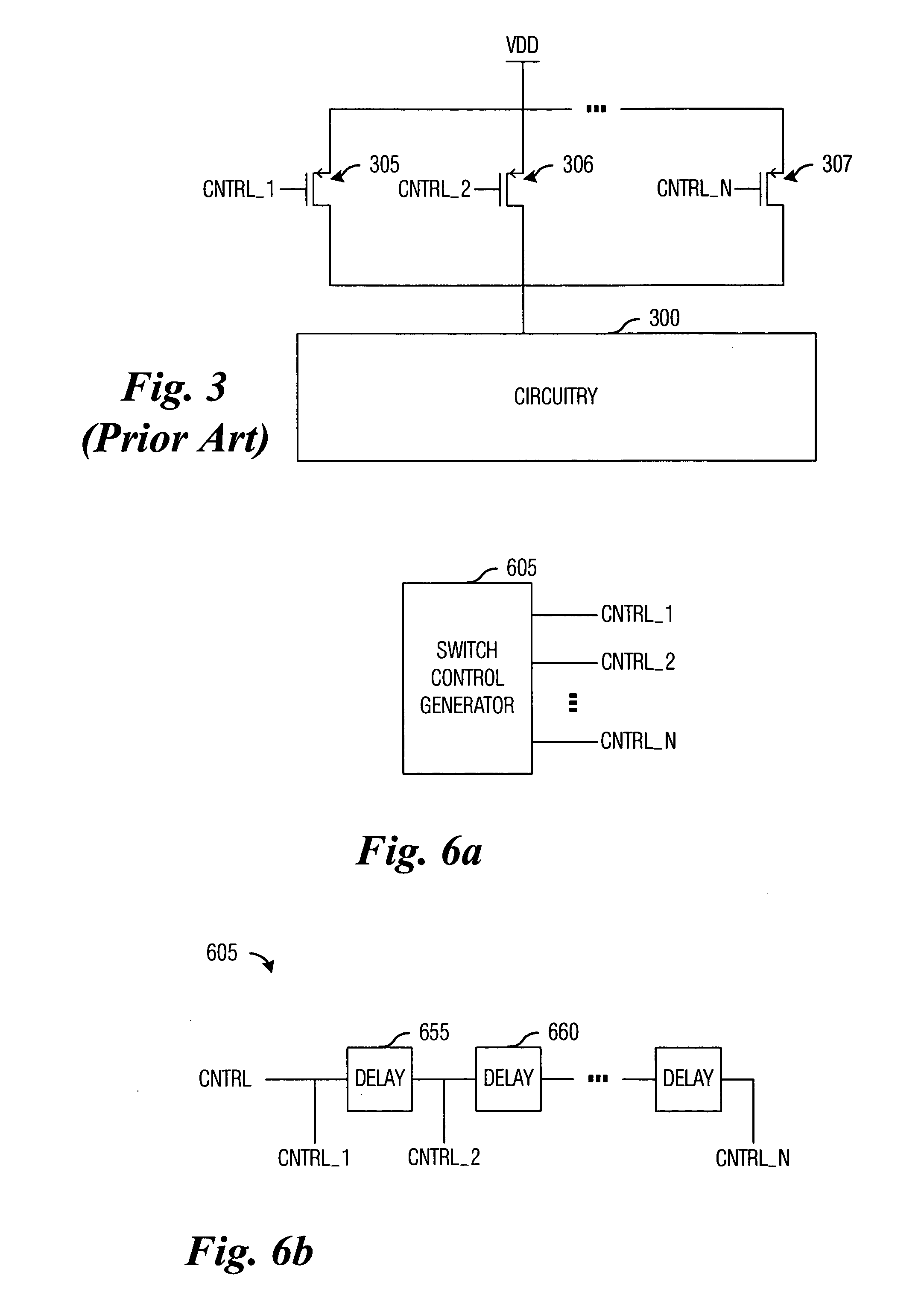
ActiveUS20060033551A1Total current dropReduced magnitudePower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic switchingDriver circuitCapacitance
System and method for providing power to circuitry while avoiding a large transient current. A preferred embodiment comprises a distributed switch (such as switch arrangement 400) with a plurality of switches (such as switch 405) coupling a power supply to the circuitry. Each switch is individually controlled by a control signal and is turned on sequentially. Also coupled to each switch is a pre-driver circuit (such as pre-driver circuit 410). The pre-driver circuit comprises a potential adjust circuit (such as potential adjust circuit 505) that rapidly adjusts a voltage potential at the switch and a rate adjust circuit (such as the rate adjust circuit 520) that accelerates the power ramp-up across the switch once transient currents are no longer a concern. Adjusting the voltage potential so that the switch operates in a saturation mode increases an effective capacitance across the switch and thereby retarding the power ramp-up across the switch.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
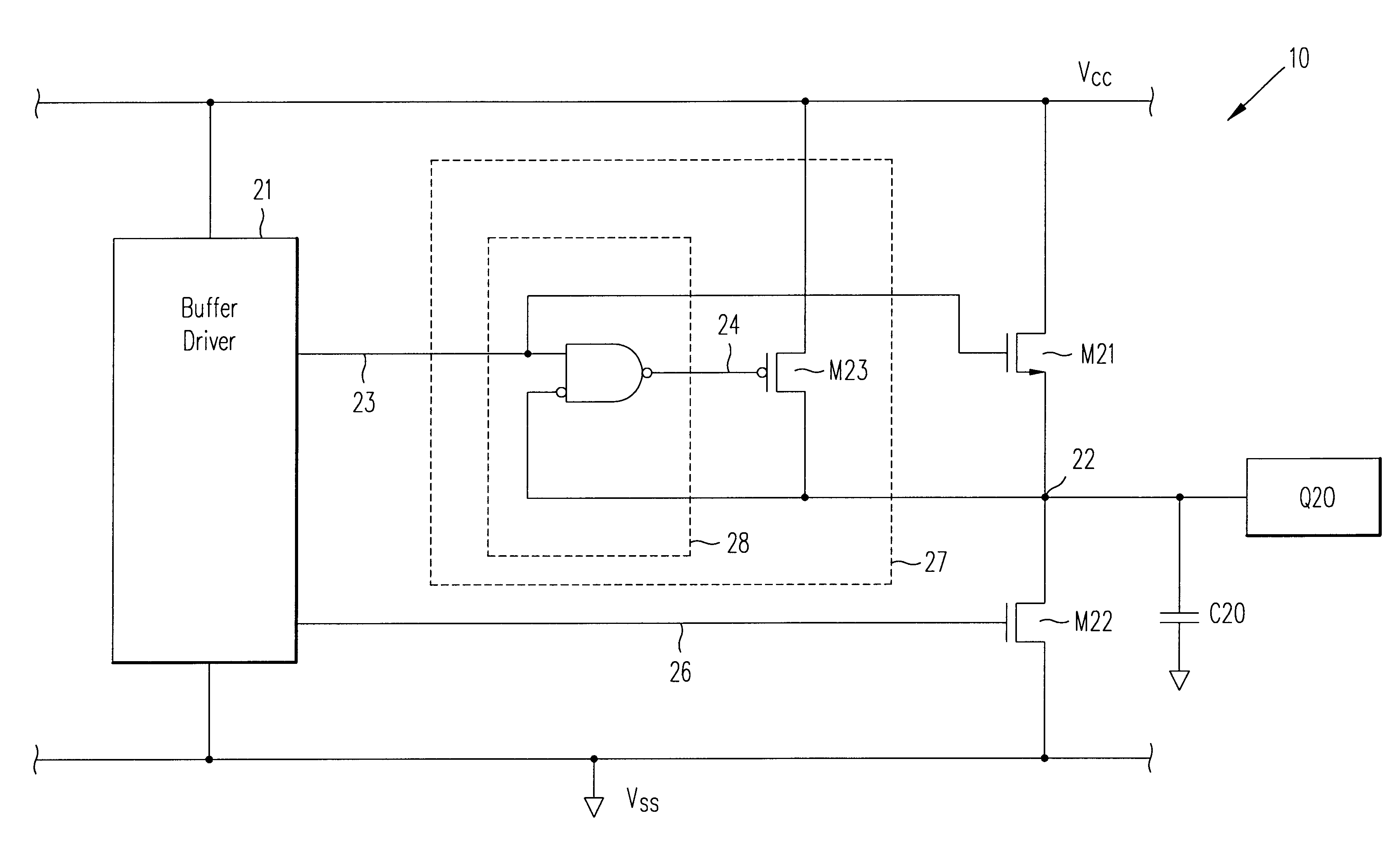
Semiconductor device and information processing system
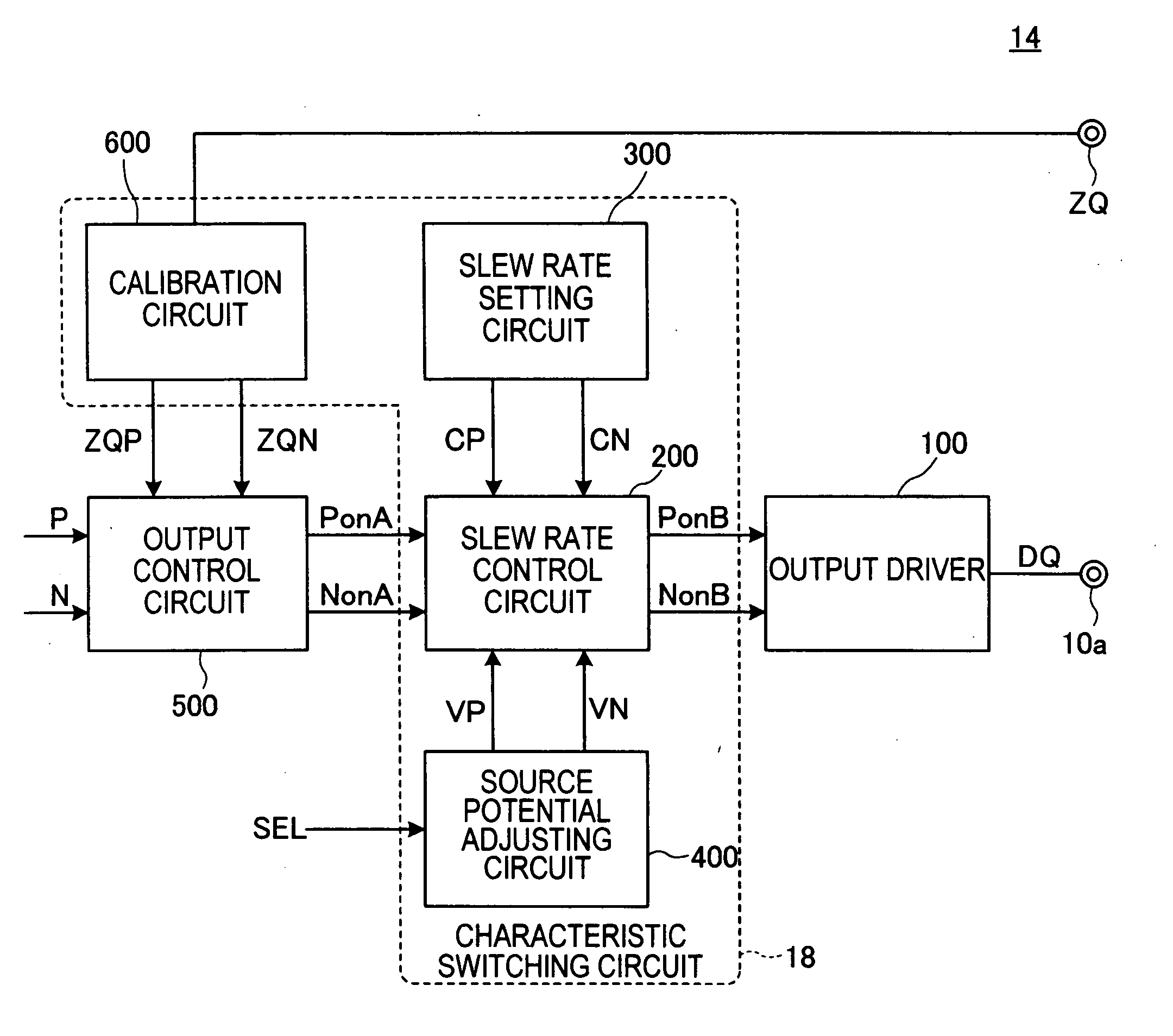
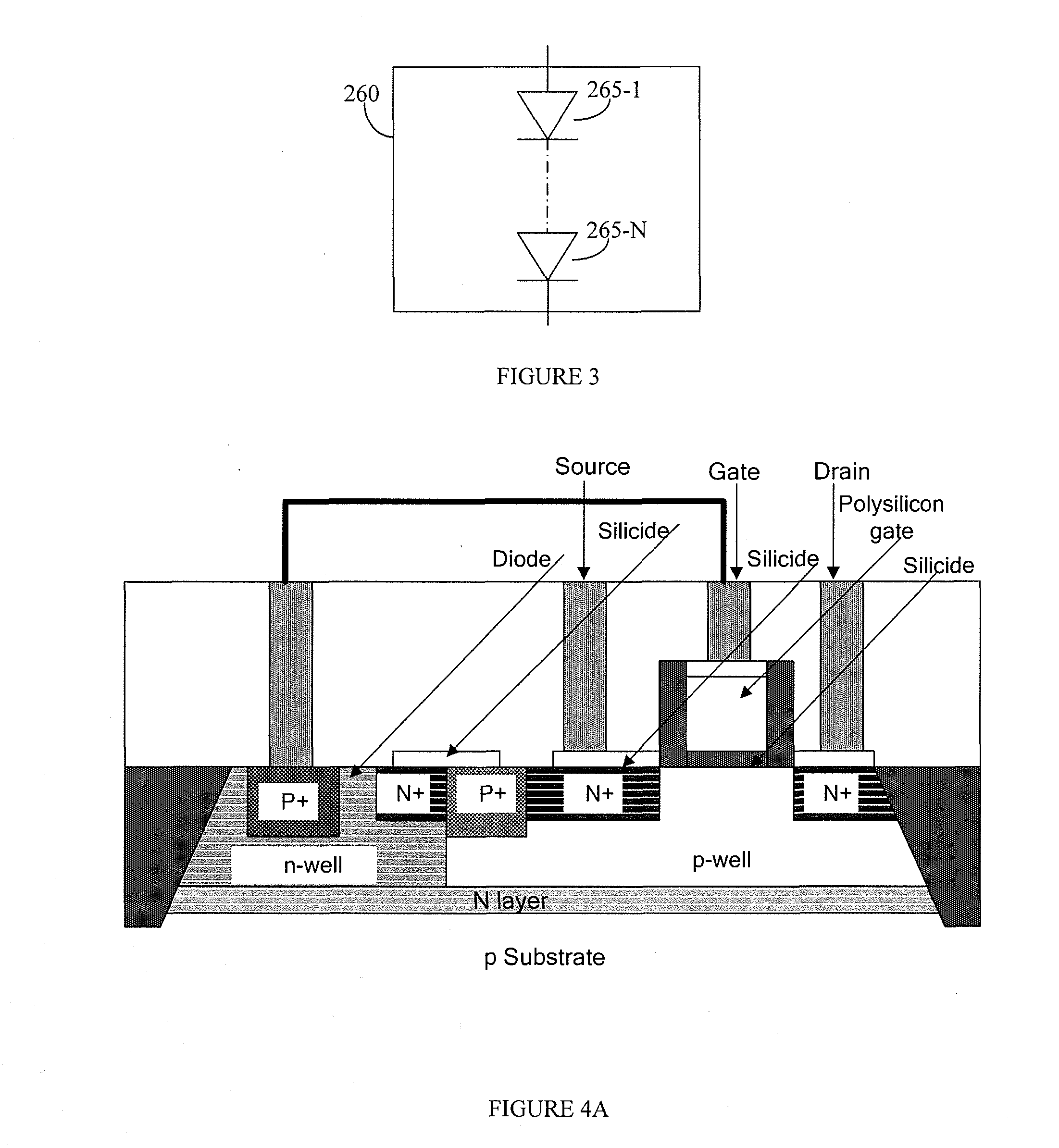
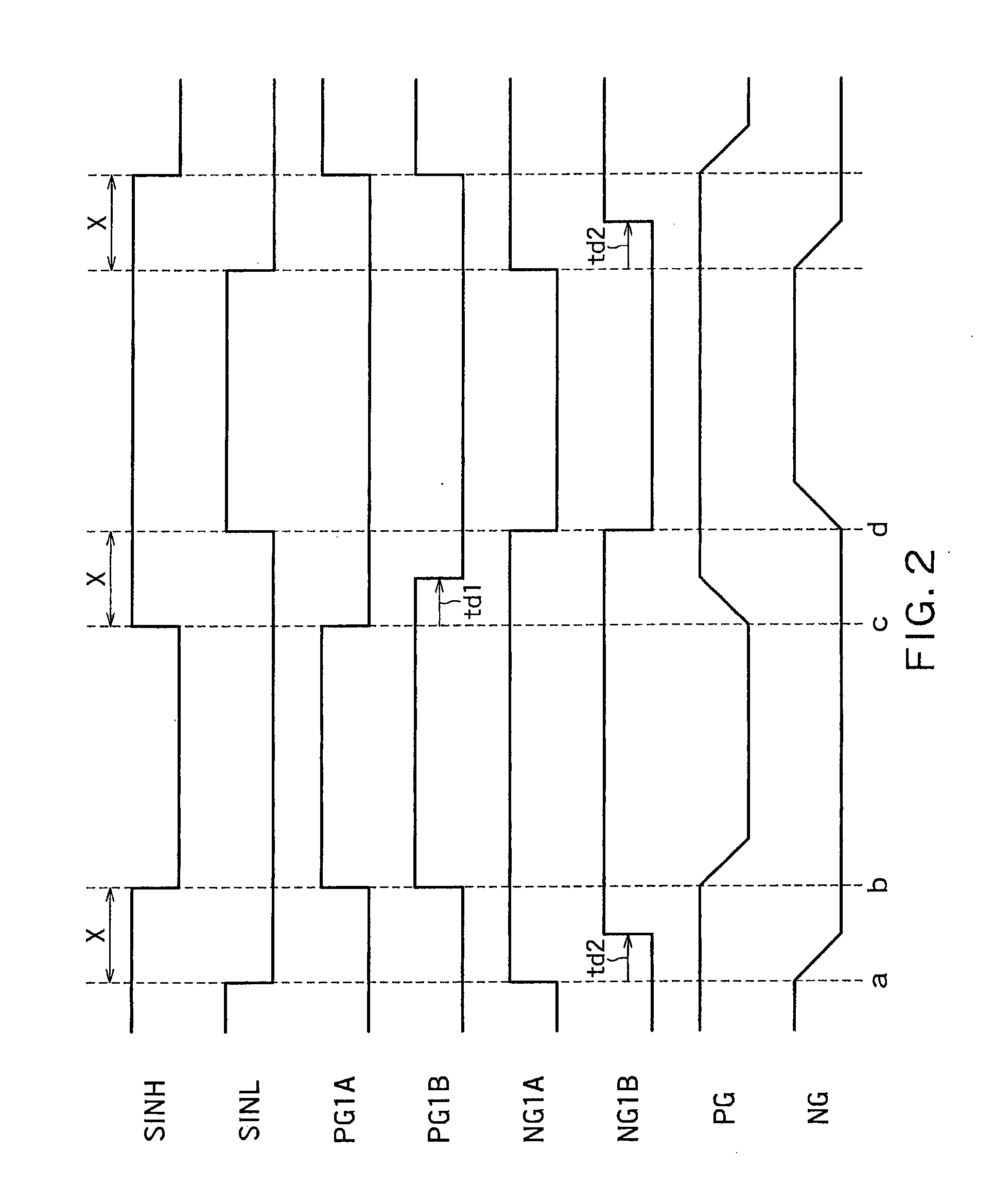
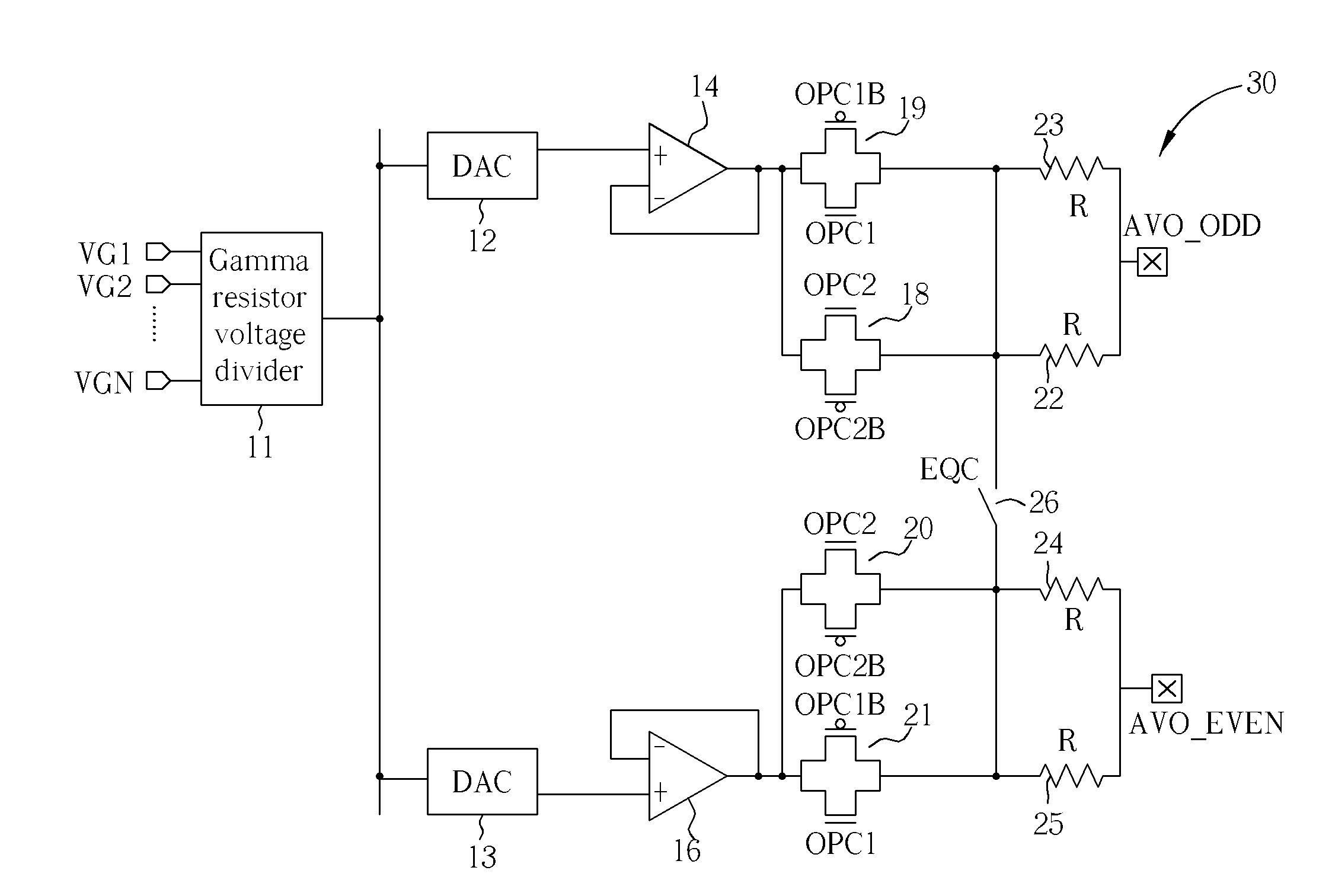
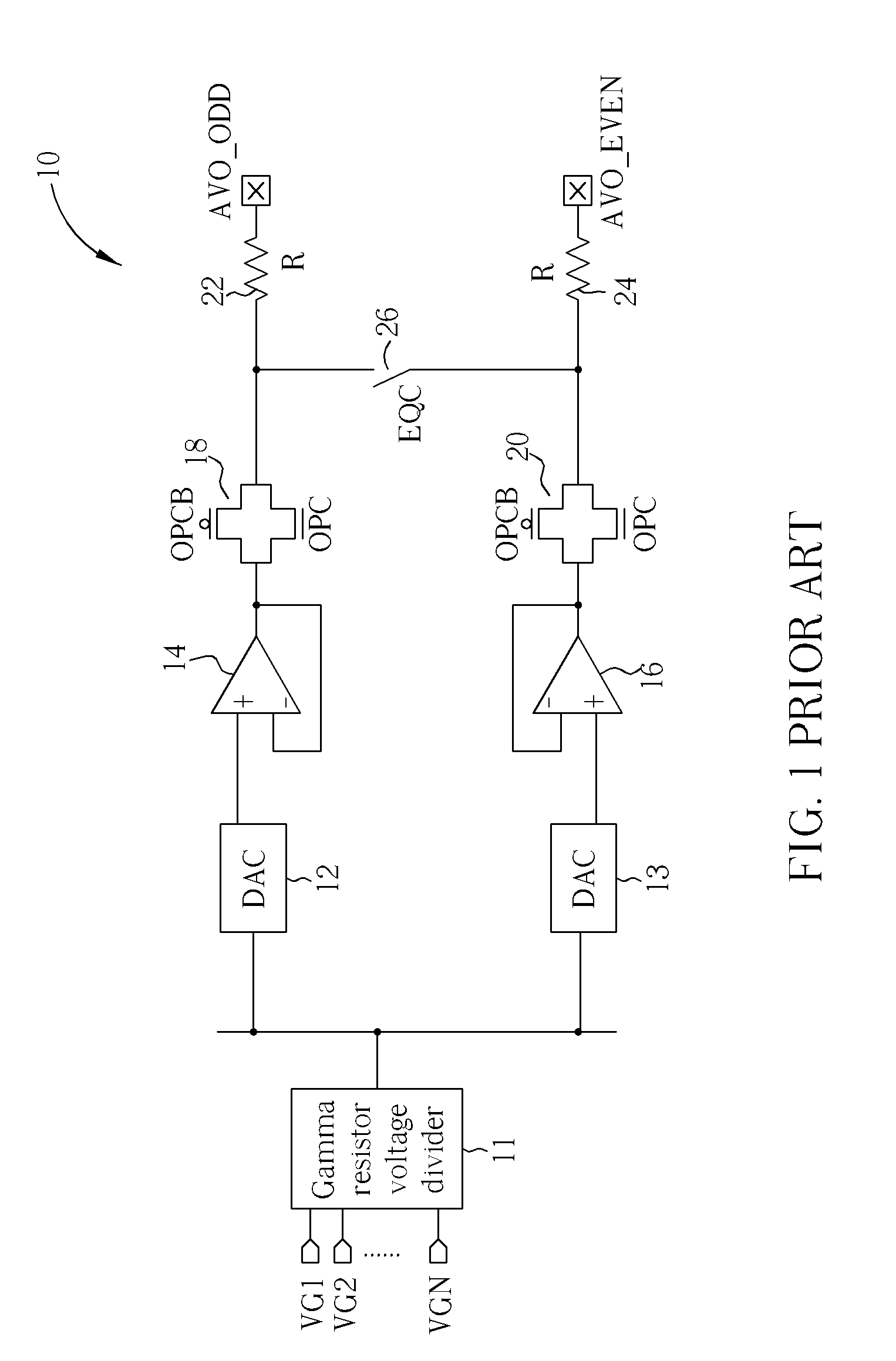
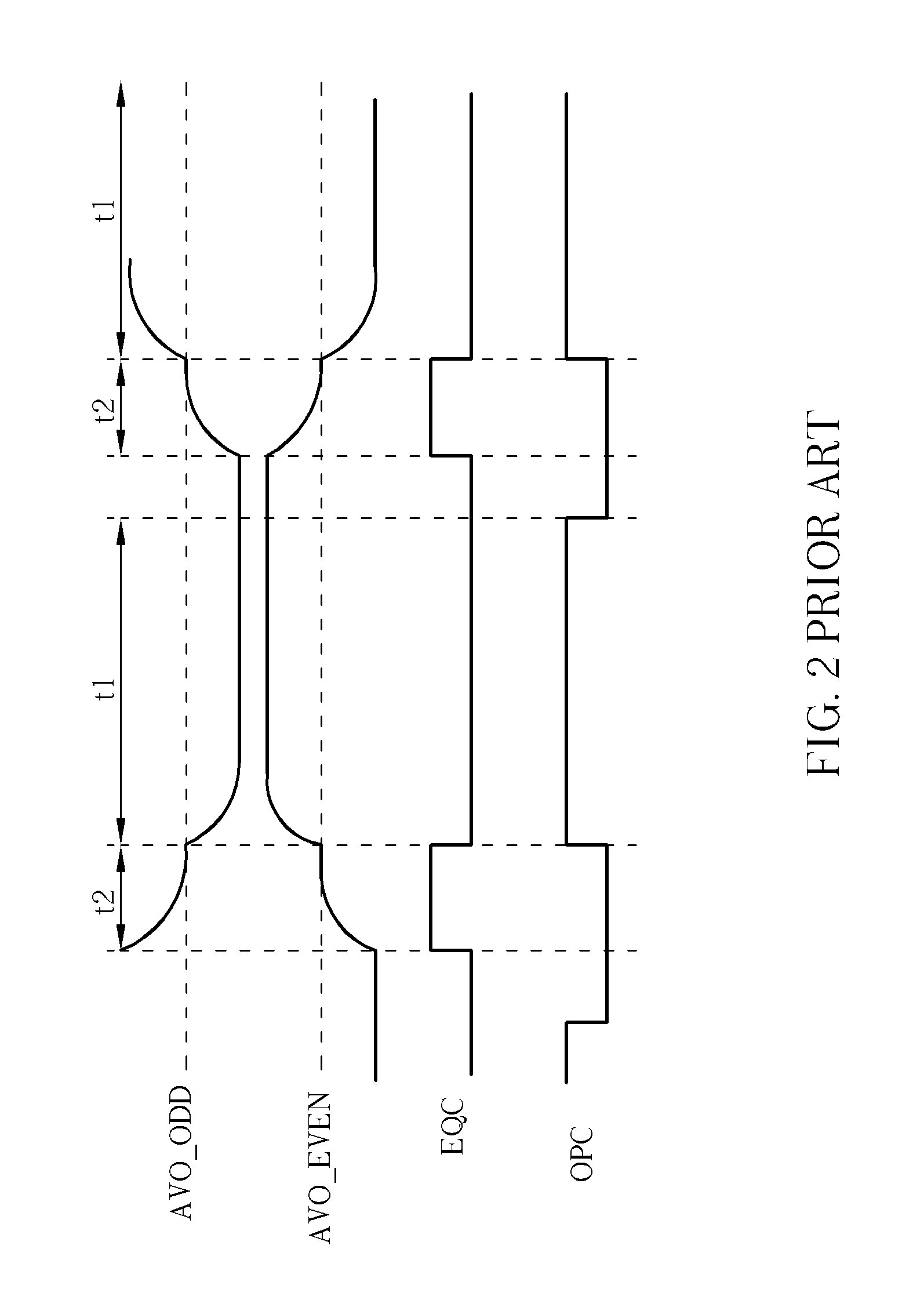
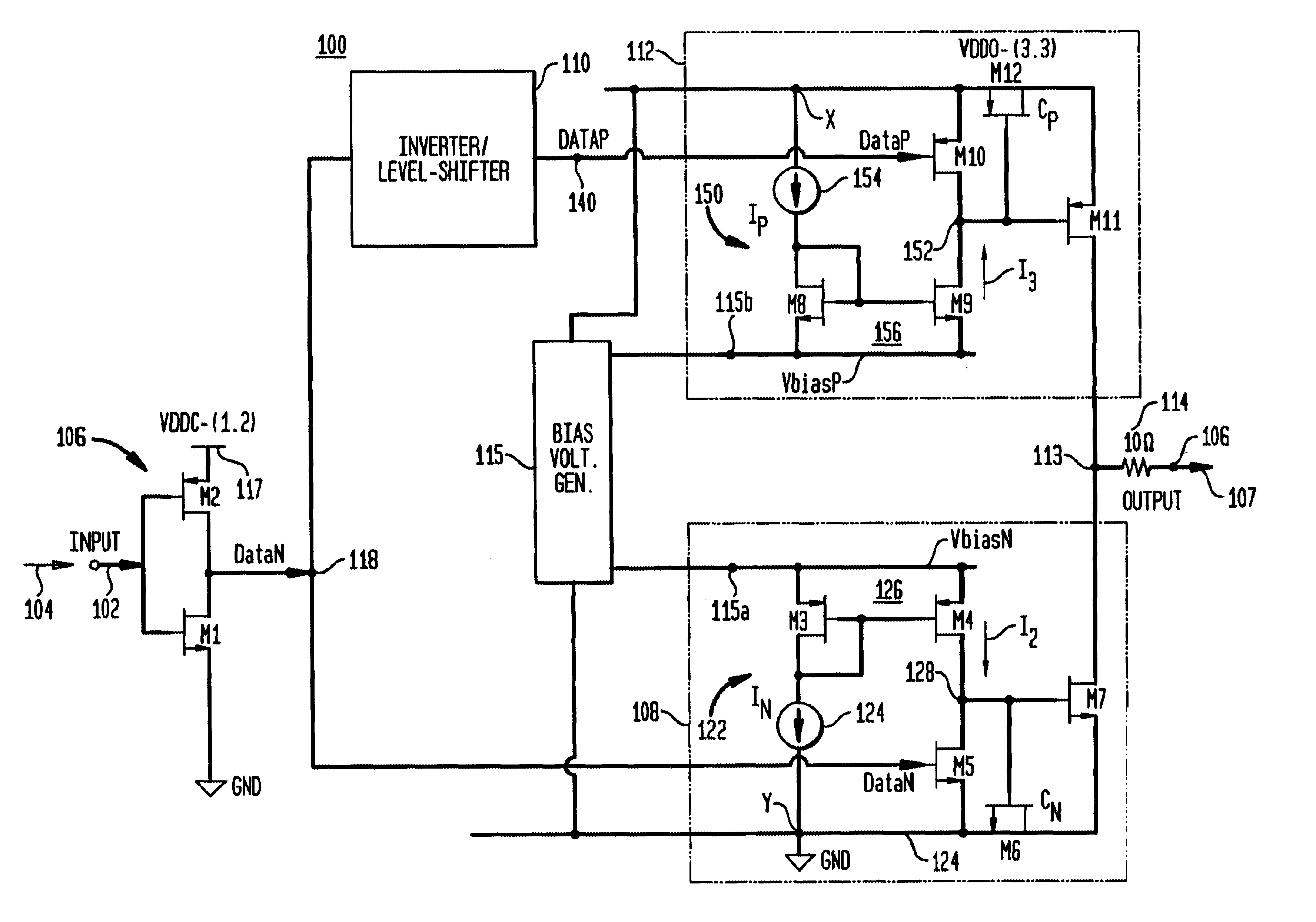
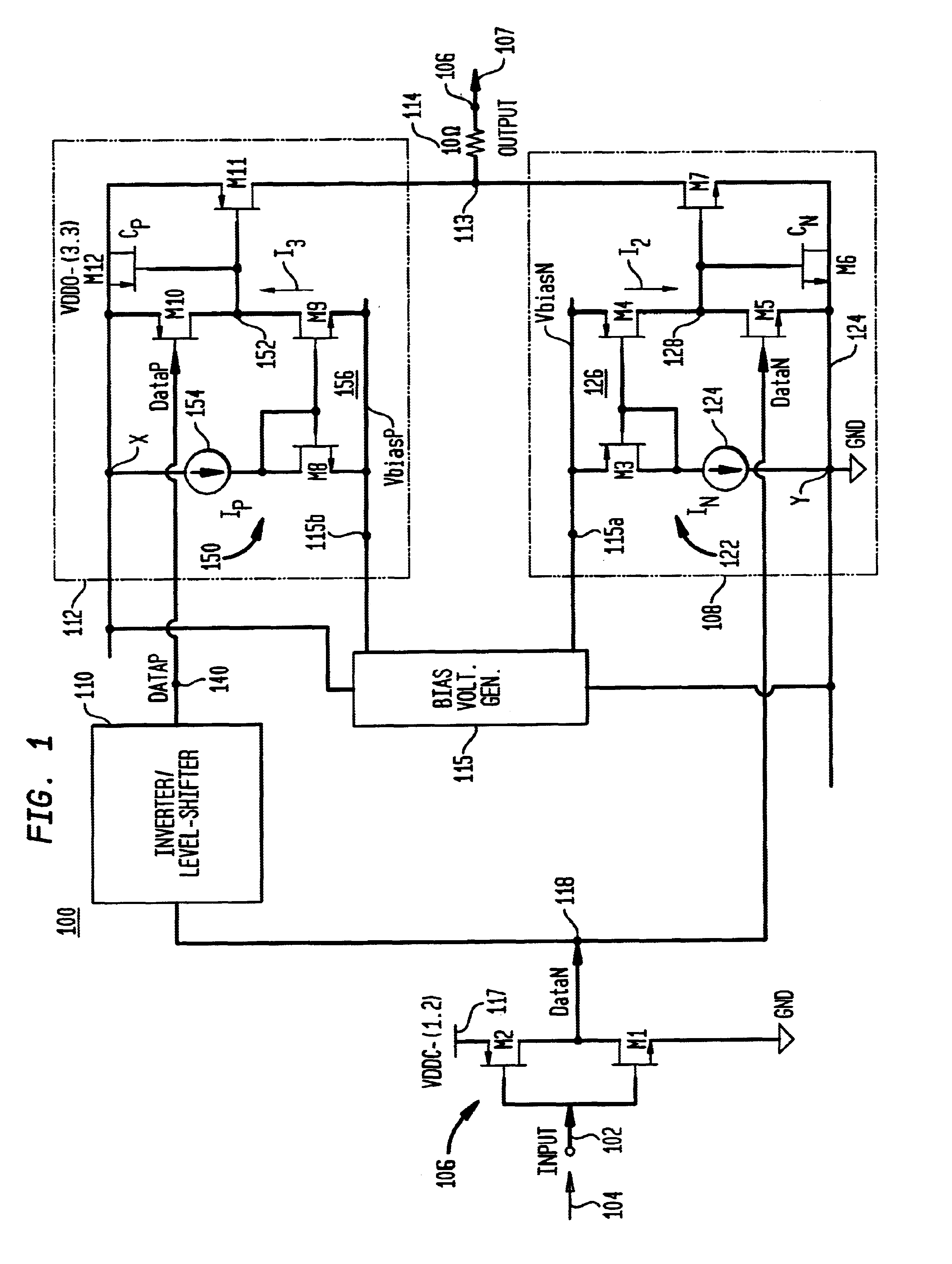
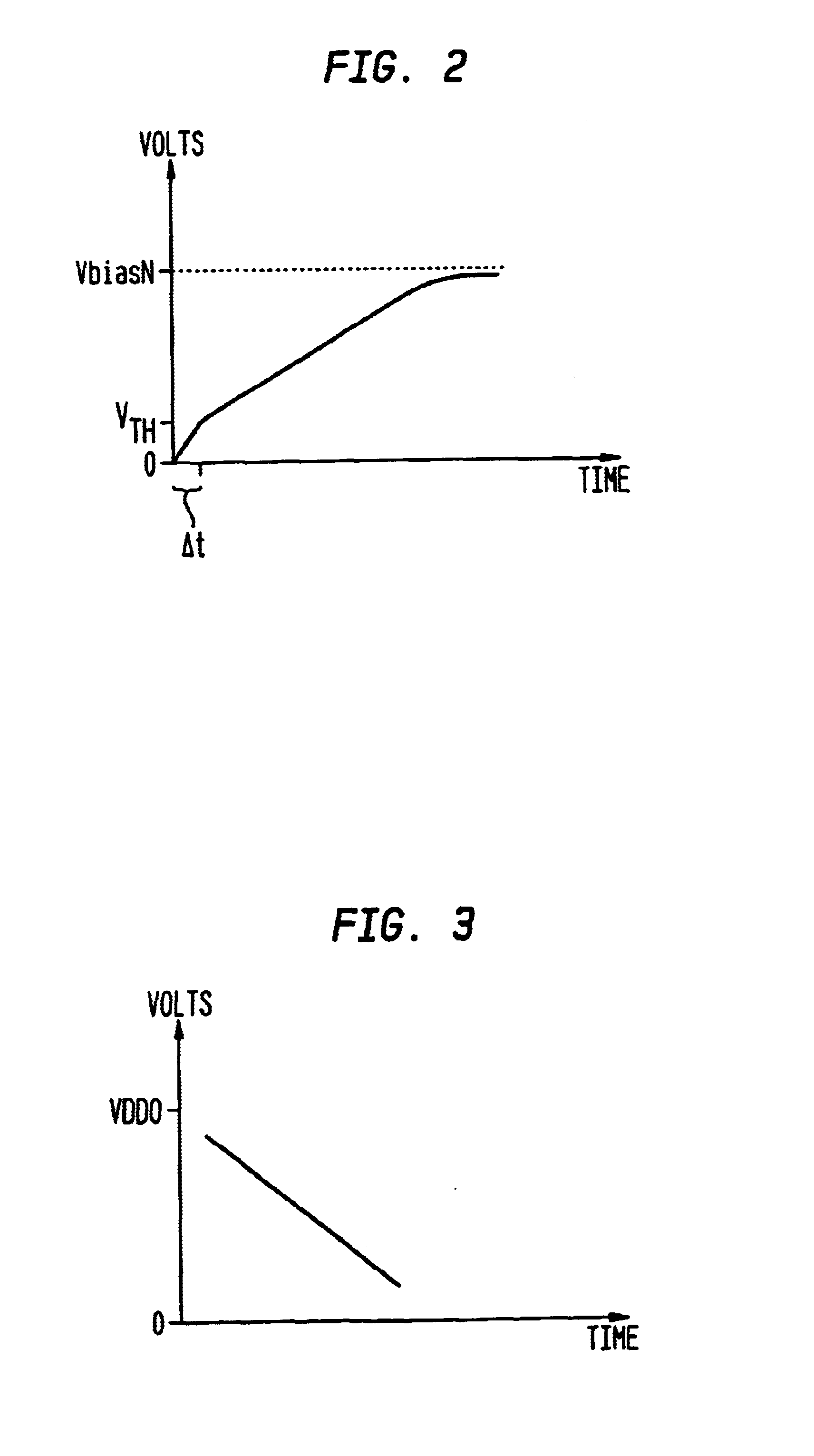
ActiveUS20110109361A1Reduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorVoltage/current interference eliminationPower semiconductor deviceInformation processing
The semiconductor device includes an output driver and a characteristic switching circuit that switches characteristics of the output driver. The characteristic switching circuit mutually matches a rising time and a falling time of an output signal output from the output driver, when a power voltage supplied to a power line is a first voltage, with a rising time and a falling time of the output signal output from the output driver, when the power voltage supplied to the power line is a second voltage. As a result, an increase in an influence of a harmonic component or a crosstalk when the power voltage is reduced does not occur. Moreover, because a receiving condition on a receiver side does not change even when the power voltage is reduced, signal transmission and reception can be performed correctly irrespective of the power voltage.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Low-leakage level shifter with integrated firewall and method
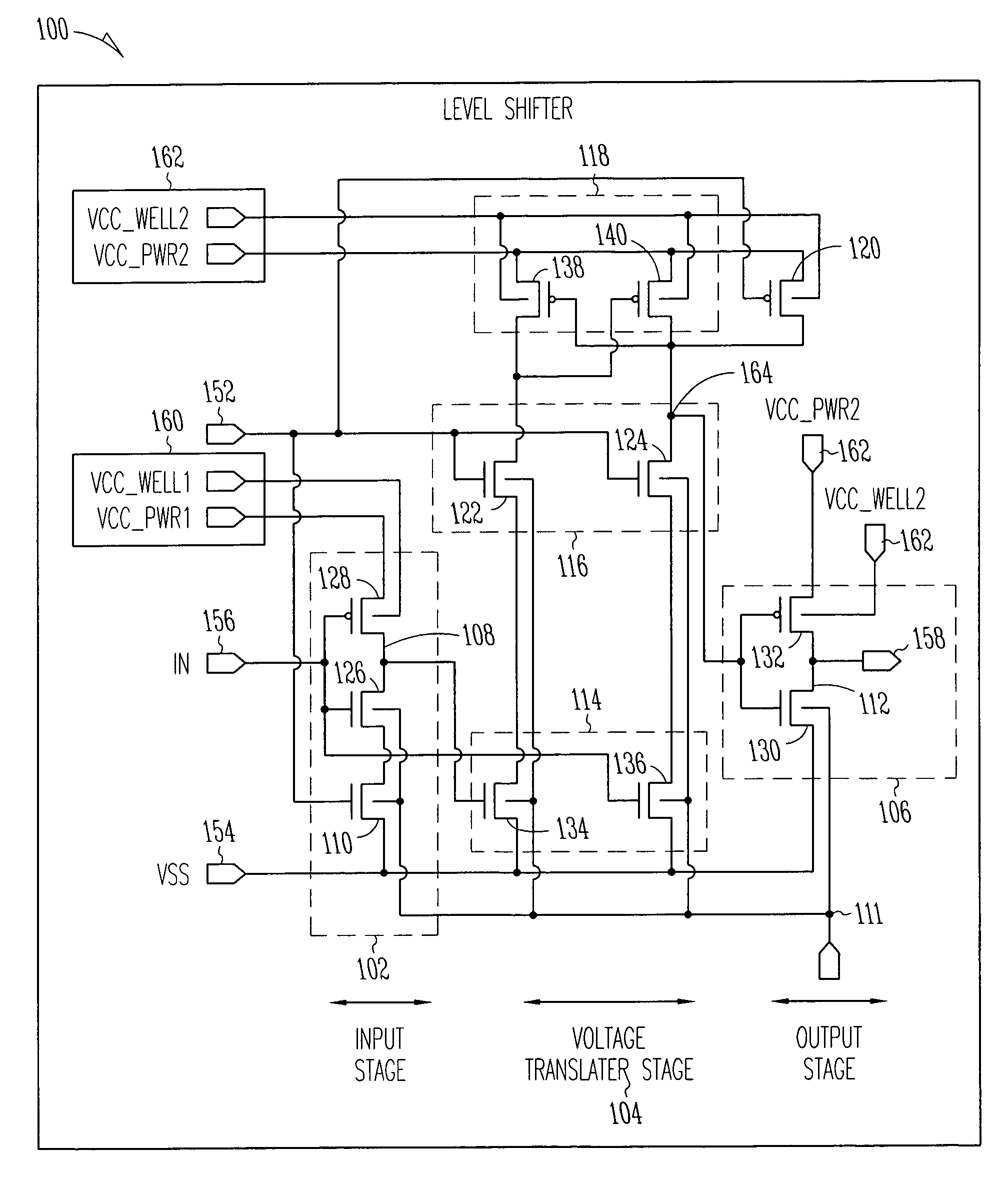
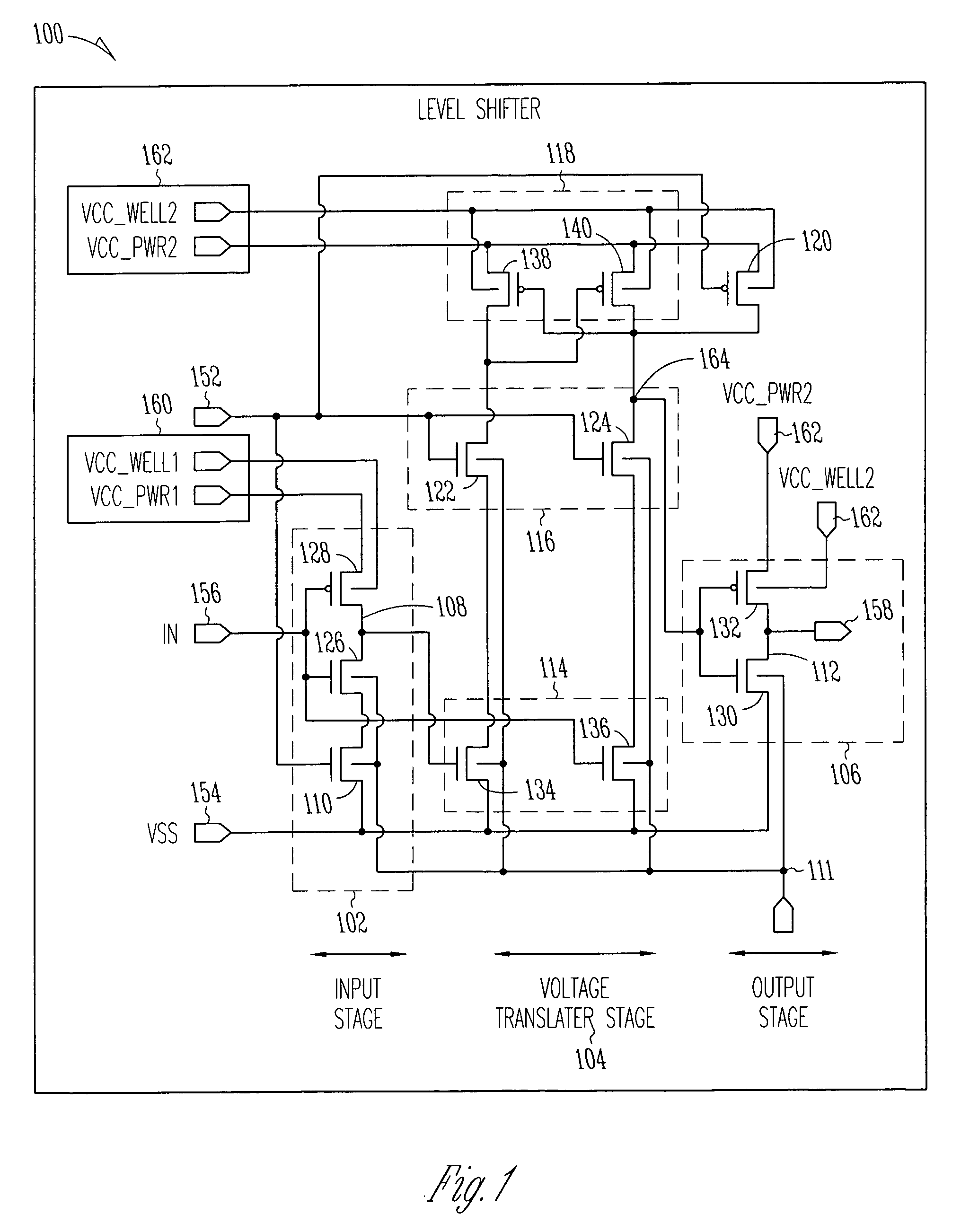
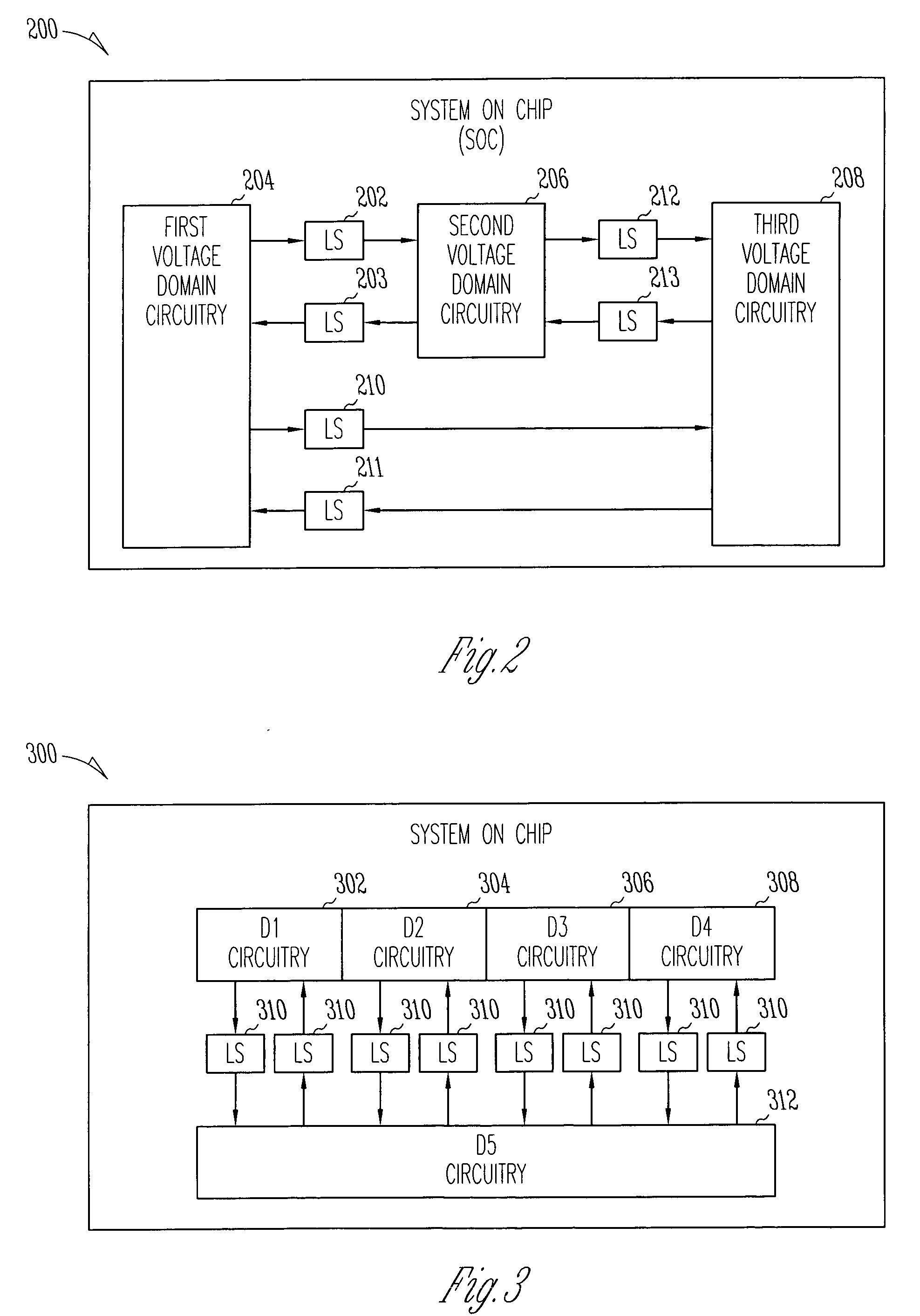
ActiveUS20050285623A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsPower reduction by control/clock signalVoltage referenceLow leakage
A level shifter may reduce leakage current and provide firewall protection between circuits of different voltage domains when one voltage domain is in a standby mode. The level shifter may either couple or decouple input circuitry from a reference voltage in response to a firewall enable signal, may translate signals between a first voltage domain and a second voltage domain when the firewall enable signal is deasserted, and may generate an output signal having a predetermined one of either a high or low state when the firewall enable signal is asserted.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
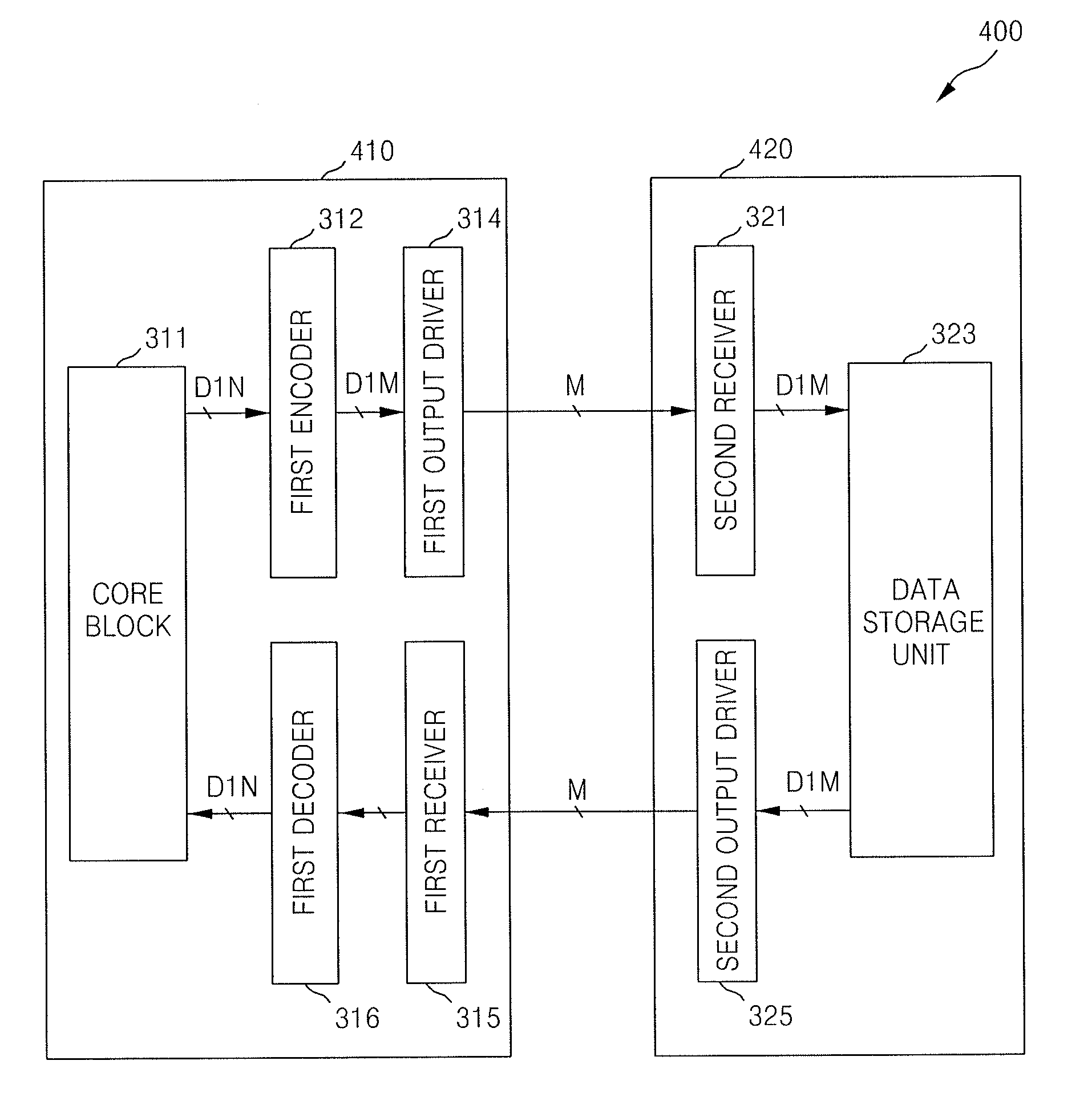
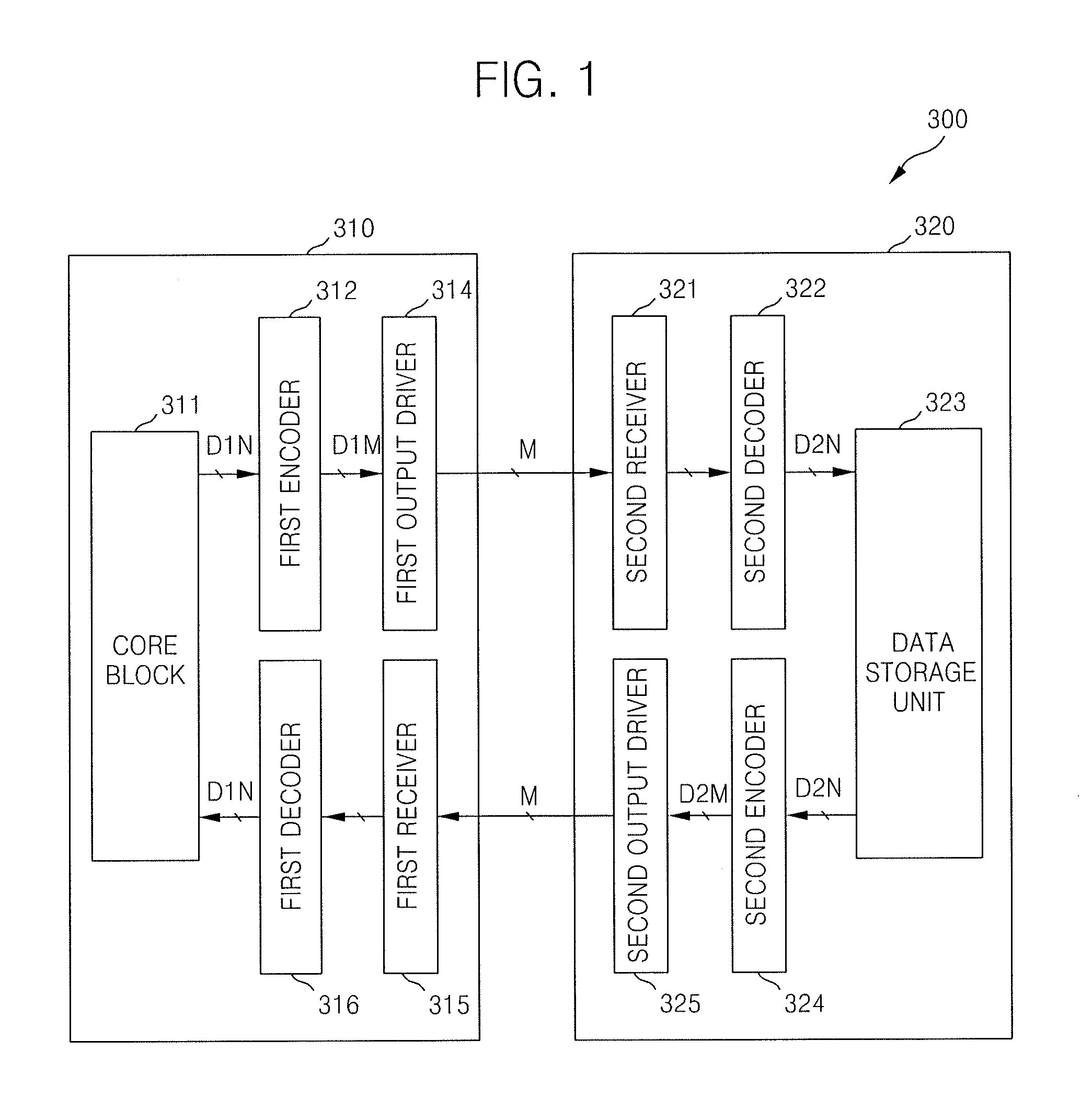
Semiconductor devices, a system including semiconductor devices and methods thereof
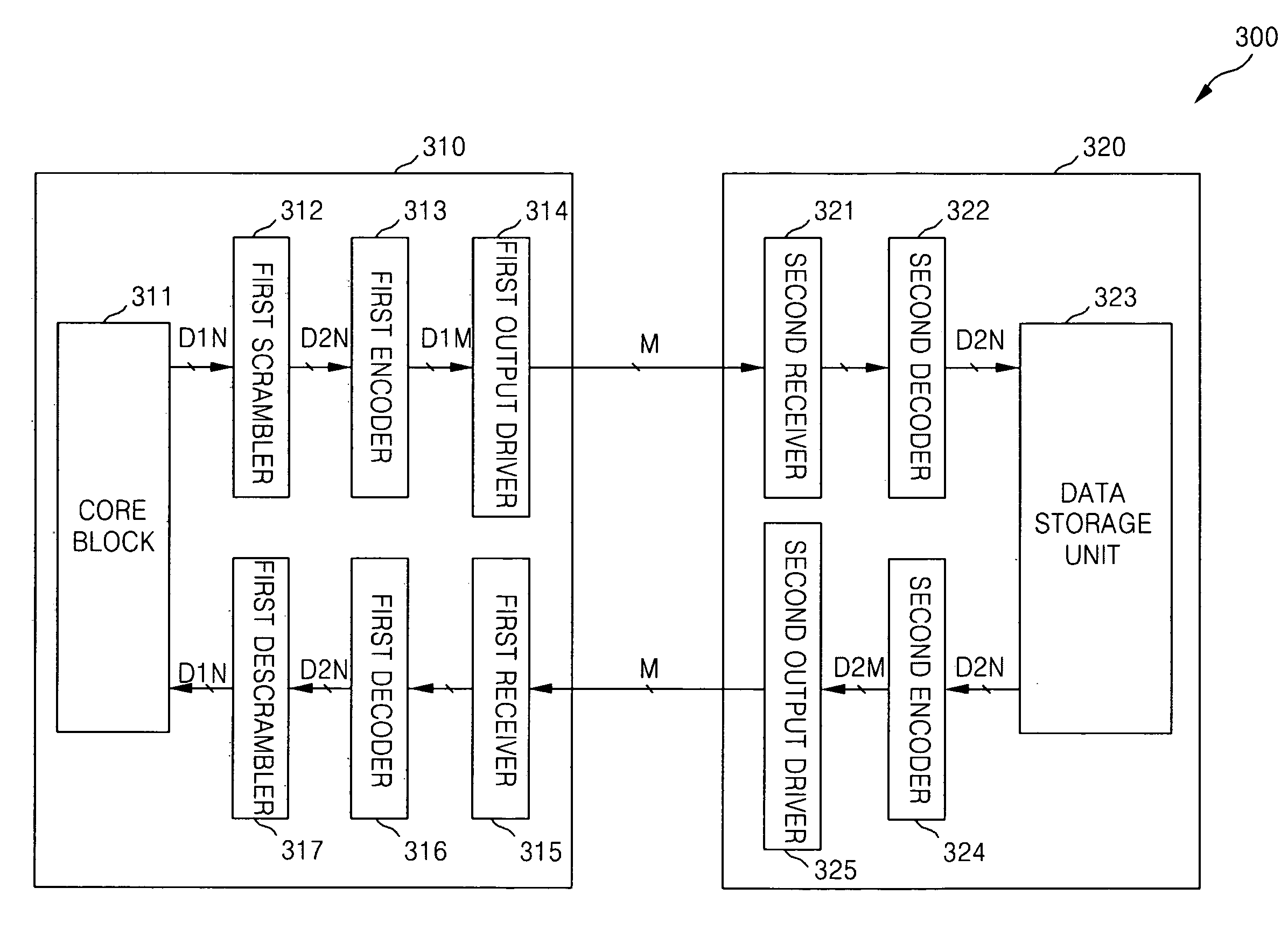
ActiveUS20070290902A1Reduce noiseData representation error detection/correctionChannel dividing arrangementsElectrical conductorOriginal data
Semiconductor devices, a system including said semiconductor devices and methods thereof are provided. An example semiconductor device may receive data scheduled for transmission, scramble an order of bits within the received data, the scrambled order arranged in accordance with a given pseudo-random sequence. The received data may be balanced such that a difference between a first number of the bits within the received data equal to a first logic level and a second number of bits within the received data equal to a second logic level is below a threshold. The balanced and scrambled received data may then be transmitted. The example semiconductor device may perform the scrambling and balancing operations in any order. Likewise, on a receiving end, another semiconductor device may decode the original data by unscrambling and unbalancing the transmitted data. The unscrambling and unbalancing operations may be performed in an order based upon the order in which the transmitted data is scrambled and balanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Supply-state-enabled level shifter interface circuit and method
ActiveUS9257973B1Avoid it happening againInhibit currentLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsElectric pulse generatorLevel shiftingNormal level
An enable circuit receives an input enable signal that is referenced to a first voltage and generates a level-shifted output enable signal referenced to a second voltage. Bias control circuitry prevents shoot-through currents during ramping of the first voltage and from causing indeterminate logic levels of the level-shifted output enable signal. An enabled level-shifting circuit receives an input logic signal that is referenced to the first voltage and generates a level-shifted output logic signal referenced to the second voltage. Enable circuitry operates in response to the level-shifted output enable signal to enable normal level-shifting operation while the first and second voltages are at normal operating levels and prevents shoot-through currents in the enabled level-shifting circuit from causing indeterminate levels of the level-shifted output logic signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
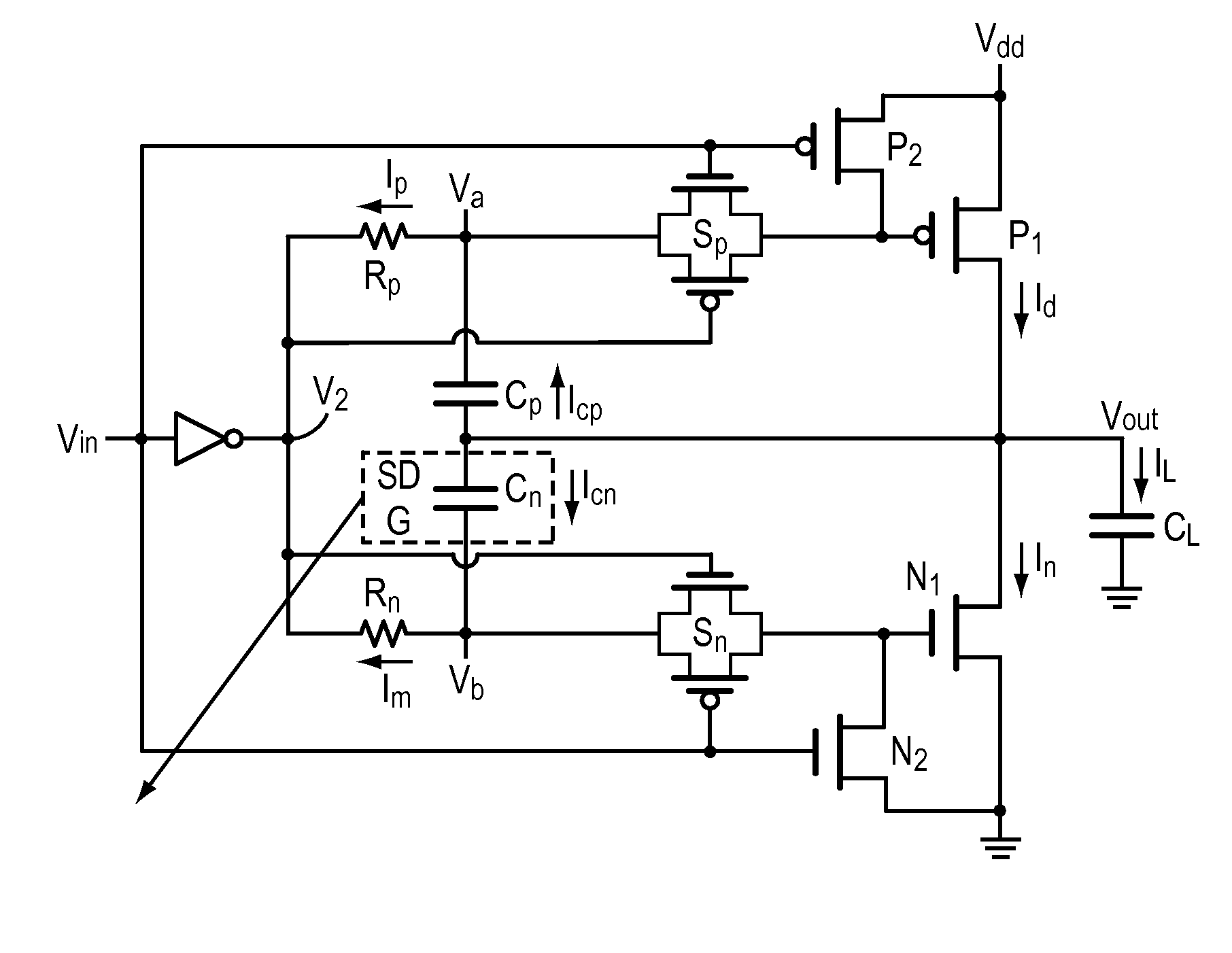
Low speed, load independent, slew rate controlled output buffer with no DC power consumption
InactiveUS7924066B2Improve degradation rateShorten the timePower consumption reductionElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLow speed
An output buffer utilizes capacitive feedback to control the output slew rate largely independent of load capacitance. The invention slows the rising and falling slew rates and via a capacitance feedback reduces the effect of load capacitance on slew rate, and uses no DC current. Transistor switches are employed to isolate and reduce noise and interaction among the circuit components and functions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Technique for operating a delay circuit
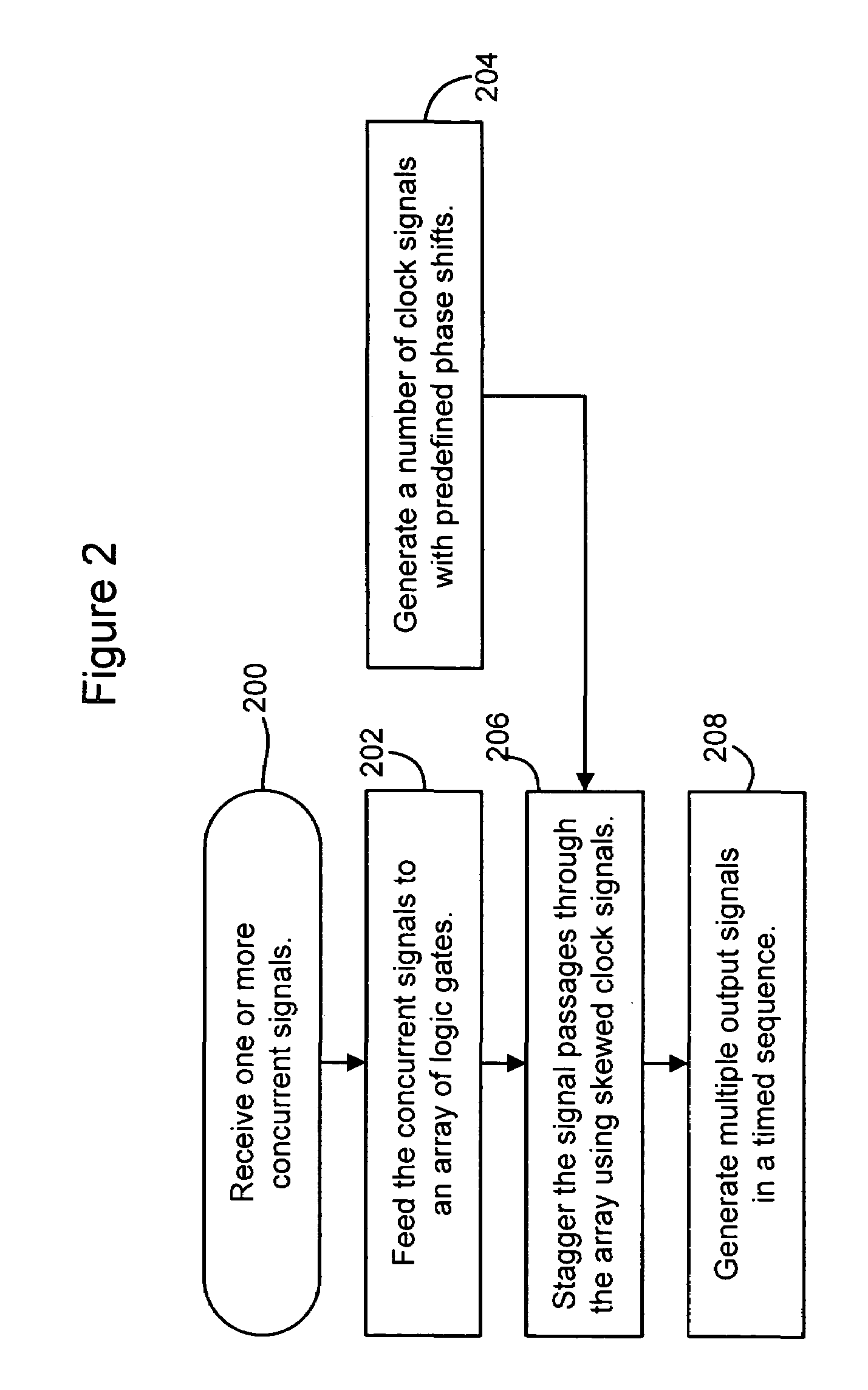
A technique for operating a delay circuit is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized by a delay circuit comprising a plurality of data paths. The delay circuit may receive a signal. The delay circuit may also stagger transmissions of the signal through the plurality of data paths. The delay circuit may additionally generate a plurality of signals based on the staggered transmissions. Each of the plurality of data paths in the delay circuit may comprise at least one of an inverter, a logic gate, a flip-flop, a latch, a register, or a resistor-capacitor (RC) delay element.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Apparatus and Method for Improving Drive-Strength and Leakage of Deep Submicron MOS Transistors
InactiveUS20070069306A1Increase drive strengthReduce leakage currentTransistorInput/output impedence modificationCMOSEngineering
An apparatus and method of manufacture for metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors is disclosed. Devices in accordance with the invention are operable at voltages below 2V. The devices are area efficient, have improved drive strength, and have reduced leakage current. A dynamic threshold voltage control scheme comprised of a forward biased diode in parallel with a capacitor is used, implemented without changing the existing MOS technology process. This scheme controls the threshold voltage of each transistor. In the OFF state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage of the transistor increases, keeping the transistor leakage to a minimum. In the ON state, the magnitude of the threshold voltage decreases, resulting in increased drive strength. The invention is particularly useful in MOS technology for both bulk and silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS. The use of reverse biasing of the well, in conjunction with the above construct to further decrease leakage in a MOS transistor, is also shown.
Owner:SEMI SOLUTIONS
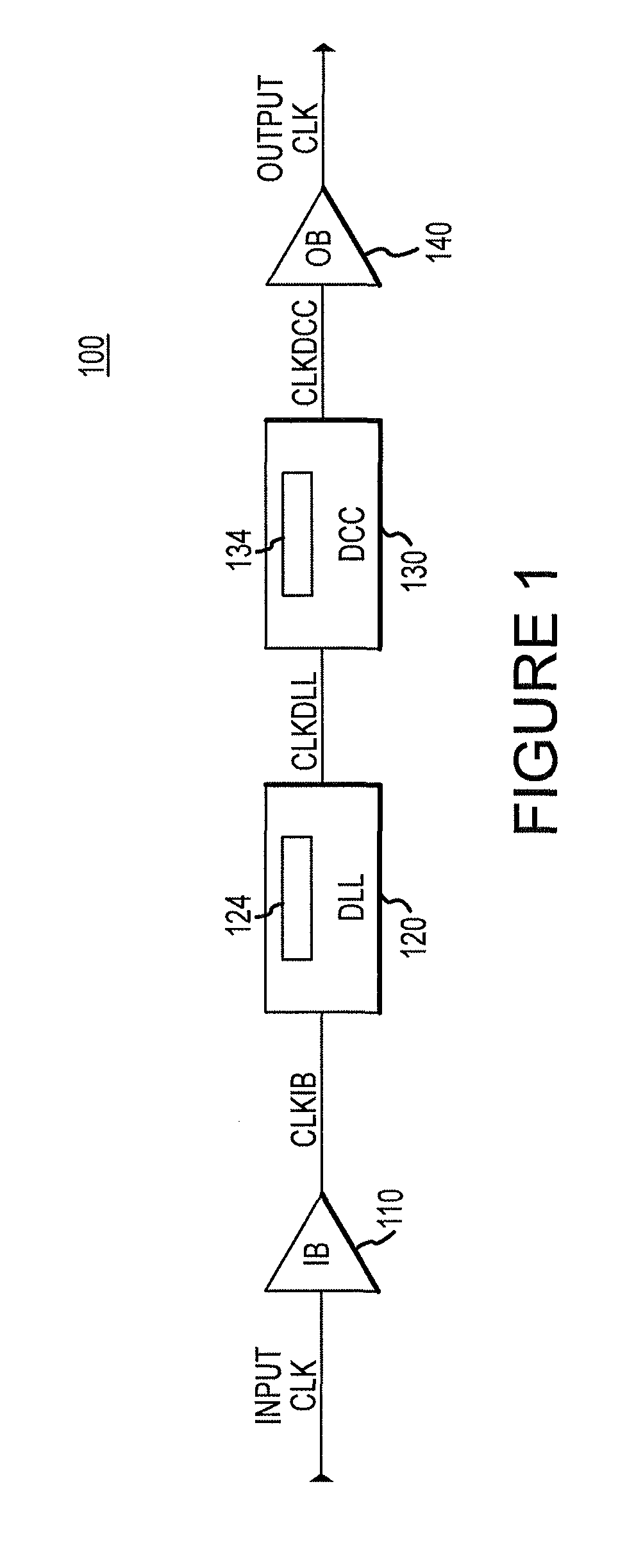
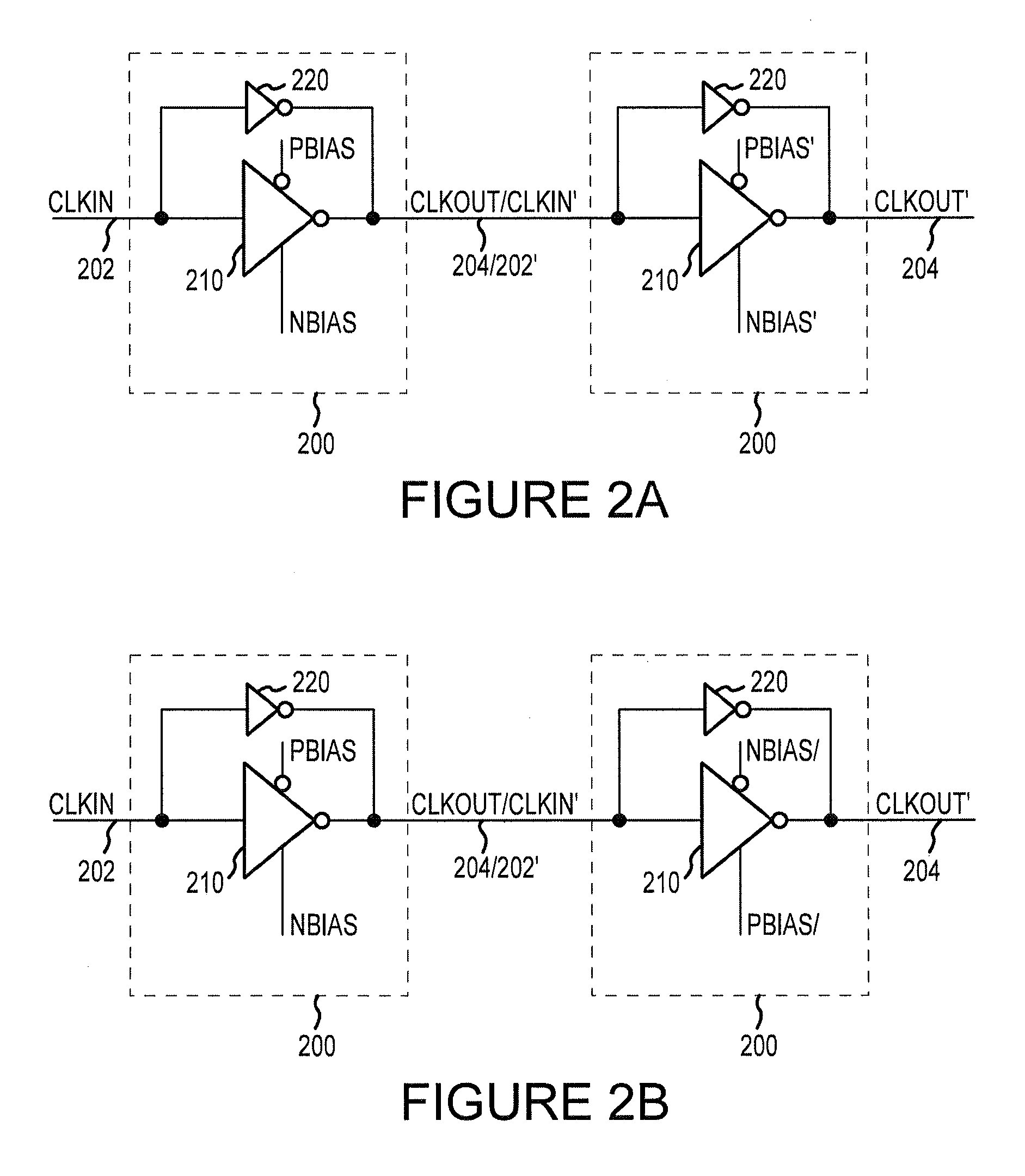
Apparatus and methods for altering the timing of a clock signal
Clock signal timing cells, clock signal timing circuits, clock circuits, memory devices, systems, and method for altering the timing of a clock signal are disclosed. An example method for altering the timing of an output signal provided responsive to an input clock signal includes adjusting a transition of an edge of the output signal from one voltage level to another based at least in part on a bias signal. An example clock signal timing cell includes an inverter and a bias controlled inverter coupled in parallel to the inverter. The bias controlled circuit is configured to provide an output signal wherein a transition of a clock edge of the output signal between first and second voltage levels is based at least in part on a bias signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
FPGA with a plurality of I/O voltage levels
InactiveUS6049227AFlexible pinout assignmentEasily interfaceVoltage/current interference eliminationLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsEngineeringVoltage reference
The invention comprises an FPGA having a plurality of input reference voltages and / or output voltage supplies. In one embodiment, two or more differential amplifiers in the same configurable input buffer use different input reference voltages. According to a second aspect of the invention, the I / O pad line is configurably connected to the input reference voltage line, so that any configurable Input / Output Block (IOB) can be used to supply the input reference voltage. According to a third aspect of the invention, the reference input of an I / O is configurably connected to any of two or more input reference voltage lines. According to another aspect of the invention, a single input reference voltage and / or a single output voltage supply is applied to each IOB, with the IOBs grouped into sets. Each set of IOBs has a separate input reference voltage and / or a separate output voltage supply.
Owner:XILINX INC
Low speed, load independent, slew rate controlled output buffer with no DC power consumption
InactiveUS20100244907A1Reduce slew rate variationImprove degradation ratePower consumption reductionElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLow speed
An output buffer utilizes capacitive feedback to control the output slew rate largely independent of load capacitance. The invention slows the rising and falling slew rates and via a capacitance feedback reduces the effect of load capacitance on slew rate, and uses no DC current. Transistor switches are employed to isolate and reduce noise and interaction among the circuit components and functions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Driver circuit
ActiveUS20130194003A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsVoltage/current interference eliminationDriver circuitControl signal
The driver circuit includes a first controlling circuit that outputs, to a gate of the auxiliary pMOS transistor, a first controlling signal that rises in synchronization with a rising of the first pulse signal and falls after a delay from a falling of the first pulse signal. The driver circuit includes a second controlling circuit that outputs, to a gate of the auxiliary nMOS transistor, a second controlling signal that rises in synchronization with a rising of the second pulse signal and falls after a delay from a falling of the second pulse signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
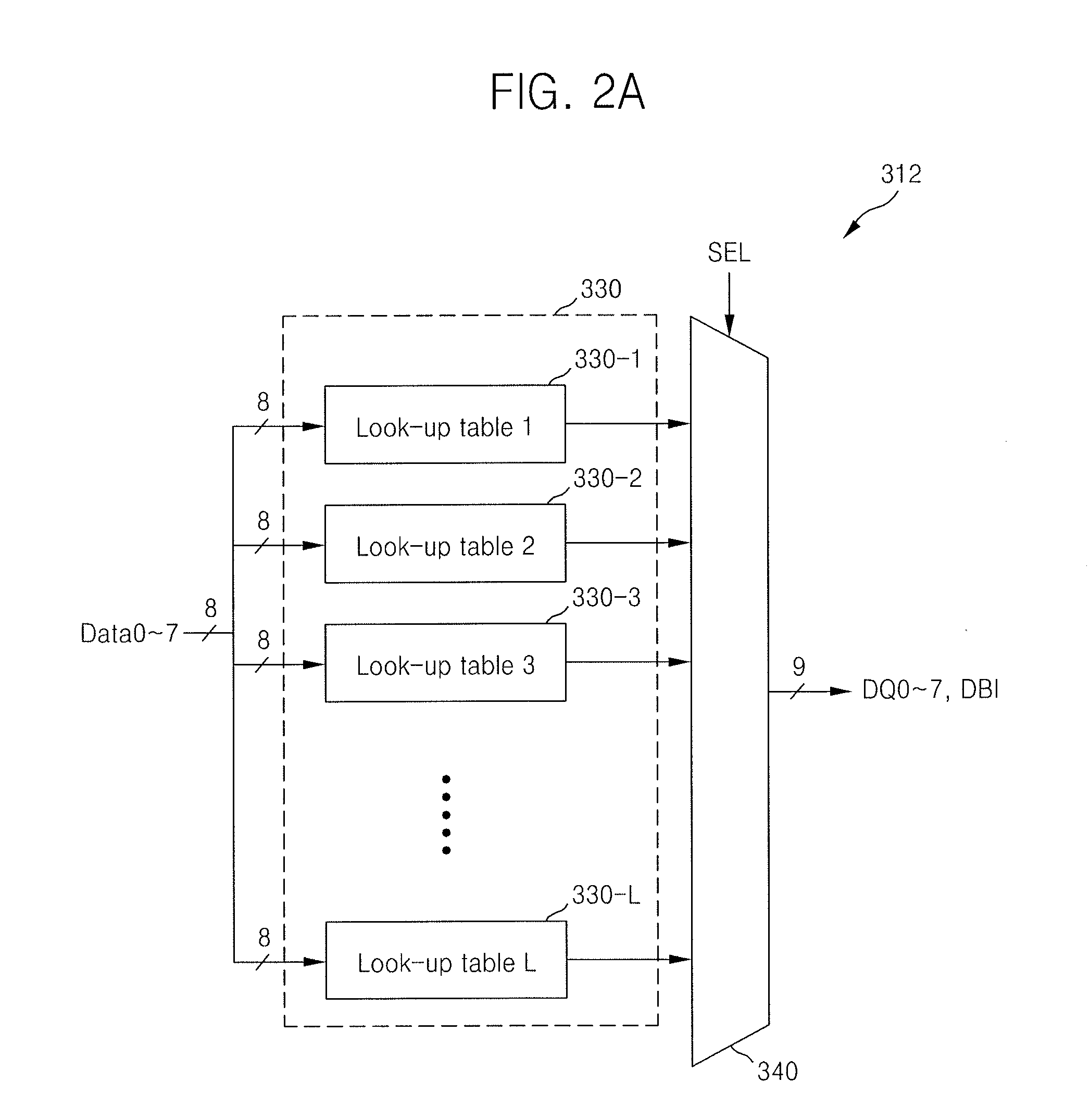
Method and apparatus for parallel data interfacing using combined coding and recording medium therefor
ActiveUS20110156934A1Reduce and minimize noiseCurrent changeChannel dividing arrangementsIndividual digits conversionDevice materialLookup table
A semiconductor device may include a coding lookup table unit including a plurality of coding lookup tables each of which is selected by a respectively selection signal, and a selection unit configured to receive one of N-bit parallel data and extract respective encoded data corresponding to the selection signal and to which the N-bit parallel data is mapped from the coding lookup table unit, and encoded data and extract respective N-bit parallel data corresponding to the selection signal and to which the encoded data is mapped from the coding lookup table unit, wherein N is 2 or an integer greater than 2, and wherein the coding lookup tables respectively store a plurality of coded data patterns that respectively correspond to patterns of the N-bit parallel data and are random temporally and spatially.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Source driver with charge sharing
ActiveUS20090015297A1Improve stabilityImprove drivabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalPower reduction by energy recoveryCharge sharingResistor
A source driver includes four output switches, two resistors, and a charge-sharing switch. The first output switch and the first resistor are coupled in series to a first output channel of the source driver. The second output switch and the second resistor are coupled in series to a second output channel of the source driver. The third output switch is coupled in parallel to the first output switch. The fourth output switch is coupled in parallel to the second output switch. The charge-sharing switch is coupled between the first resistor and the second resistor. The third output switch and the fourth output switch are controlled to adjust the resistance of the output current path of the source driver.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
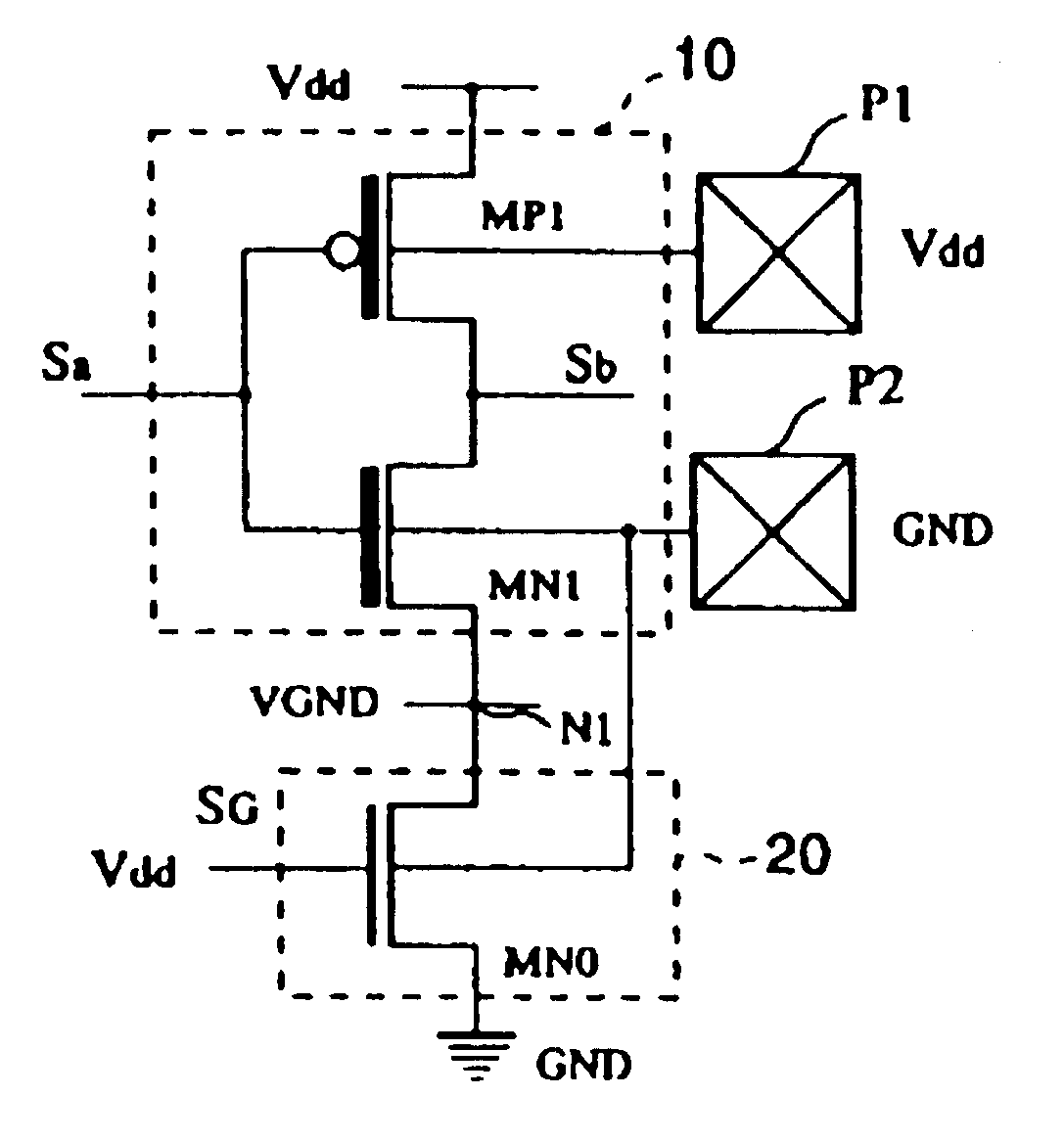
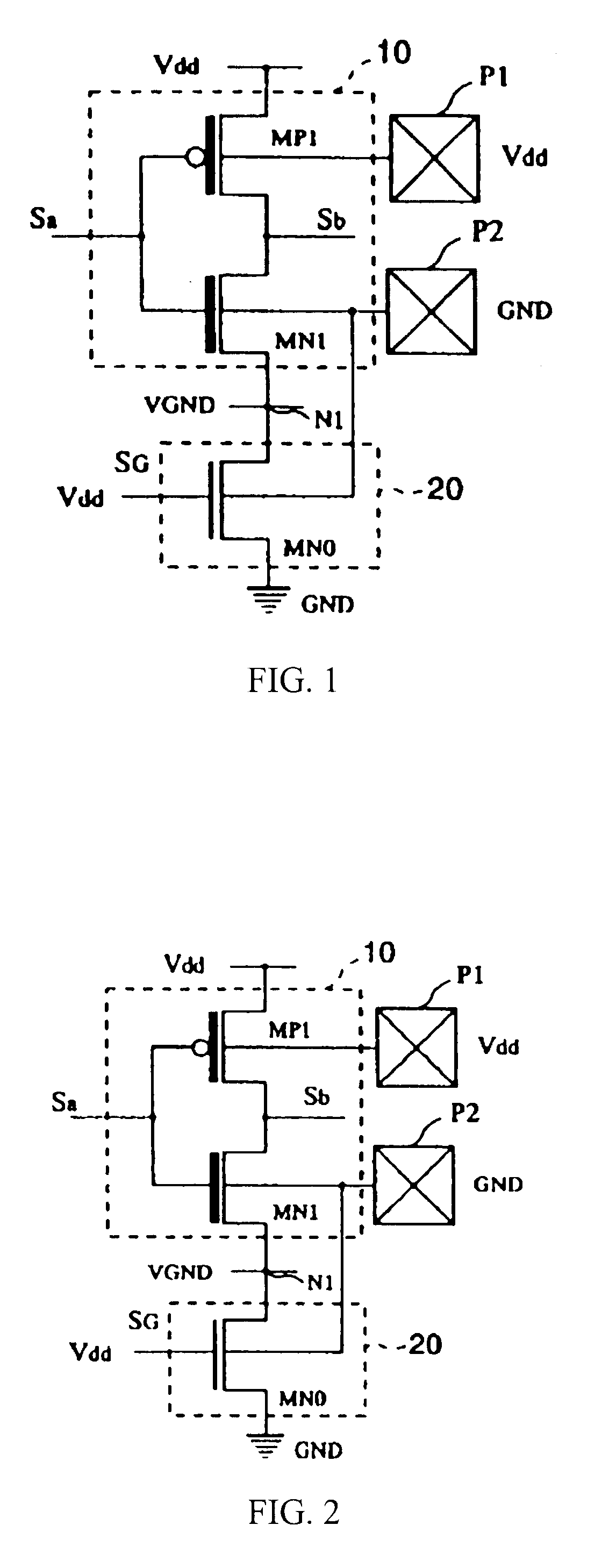
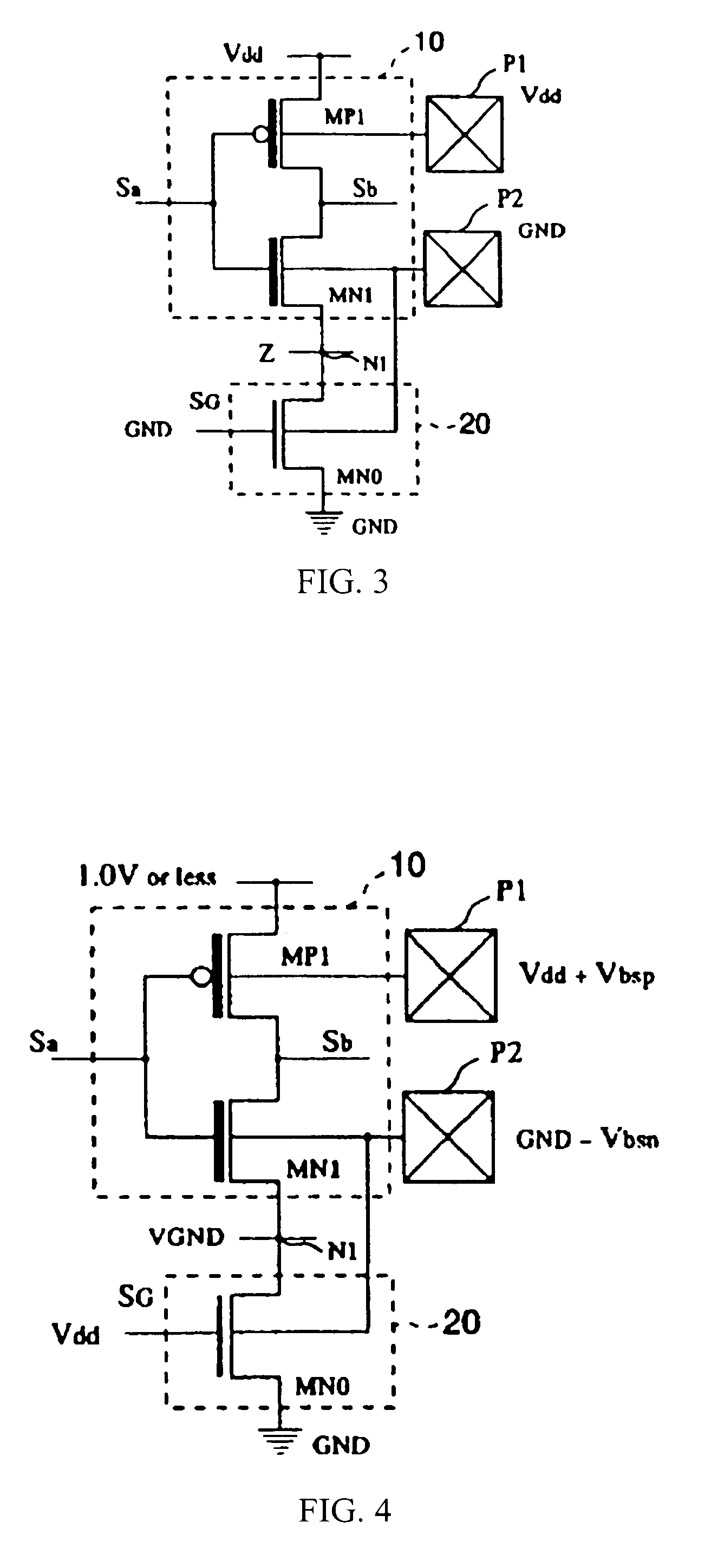
Semiconductor integrated circuit
The objective of this invention is to provide a type of semiconductor integrated circuit which can lessen solution in the circuit area to the minimum necessary level, and can lessen the leakage current in the standby state so as to cut the power consumption, and which allows Iddq test to determine whether it is passed or defective. Logic circuit 10 composed of low threshold voltage transistors and switching circuit 20 composed of transistors having the standard threshold voltage are set. In the operation, the switching circuit is turned ON, and a driving current is fed to logic circuit 10. On the other hand, in the standby mode, the switching circuit is turned OFF, and the path of the leakage current is cut off to lessen generation of the leakage current. In the case of Iddq test, different bulk bias voltages are applied to the channel regions of PMOS transistors and NMOS transistors from an IC tester through pads P1 and P2. In this way, the leakage current can be lessened on a low level, and whether the semiconductor integrated circuit is passed or defective can be judged from the results of the current measurement.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High speed buffer circuit with improved noise immunity
InactiveUS6307399B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionElectronic switchingLow voltageFeedback circuits
In a buffer circuit a pull-up circuit causes an output terminal of the buffer circuit make a transition from a low voltage to a high, and a feedback circuit increases the rate of the transition during the part of the transition when the output terminal moves from the low voltage to a predesignated voltage, the predesignated voltage being a value between but different from the low and high voltages. In another buffer circuit powered by a power supply voltage, a pull-up transistor causes a signal at an output terminal of the buffer circuit make a transition from a low voltage to a high voltage, and a converter circuit converts the power supply voltage to a lower voltage, the lower voltage powering the pull-up transistor.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
High-speed gate driver for power switches with reduced voltage ringing
InactiveUS20140103962A1Reduce the amplitudeDelay premature agingElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorField-effect transistorControl circuit
A fast power switch comprises one or more field-effect transistors, such as pull-up and pull-down transistors, that are coupled to a load. Respective driver electronic circuits for each of the field-effect transistors include parallel first and second drivers with a shared driver output coupled to a gate of the field-effect transistor. The first and second drivers are operative to switch the shared driver output for the appropriate field-effect transistor in response to a transition (e.g., low-to-high or high-to-low) at a driver input terminal. A control circuit enables the stronger second driver in response to a transition at the driver input terminal and subsequently disables the second driver once a transition threshold at the gate of the field-effect transistor(s) is crossed. The weaker first driver is sized to damp reactive energy at the load to minimize ringing.
Owner:SL3J SYST S A R L
Slew rate controlled output buffer
InactiveUS6903588B2Control rateReduce degradationElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceCharge current
An output buffer includes first and second circuit portions coupled between input and output terminals. Each circuit portion includes a capacitive element; an output transistor having a gate coupled to the capacitive element, and a drain that drives a voltage at the output terminal; and a current generator configured to generate a charging current that is directed to the capacitive element responsive to a logic transition at the input terminal, wherein the charging current causes a substantially linear ramp voltage to form at the gate of the output transistor, whereby the ramp voltage controls a slew rate of the output terminal voltage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Gate drive circuit and display apparatus having the same
A gate drive circuit includes m stages cascade connected to one another, each stage respectively outputting one of a plurality of gate signals. An m-th stage includes a pull-up part, a pull-down part, a boost-up part, a first maintenance part and a second maintenance part. The pull-up part outputs a high voltage of a first clock signal at the high voltage of an m-th gate signal. The pull-down part applies a low voltage to an output node of the pull-up part. The boost-up part boosts a voltage charged by an offset second clock signal. The first maintenance part maintains the first node at a low voltage in response to the boosted voltage of the second node. In addition, the second maintenance part maintains the m-th gate signal at the low voltage in response to the high voltage of the first clock signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Popular searches
Oscillations generators Oscillations comparator circuits Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Emergency protective devices Computation using denominational number representation Code division multiplex Pulse manipulation Digital output to display device Non-linear optics Input/output processes for data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com