Patents
Literature
324 results about "Timing margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Timing margin is an electronics term that defines the difference between the actual change in a signal and the latest time at which the signal can change in order for an electronic circuit to function correctly. It is used in the design of digital electronics.
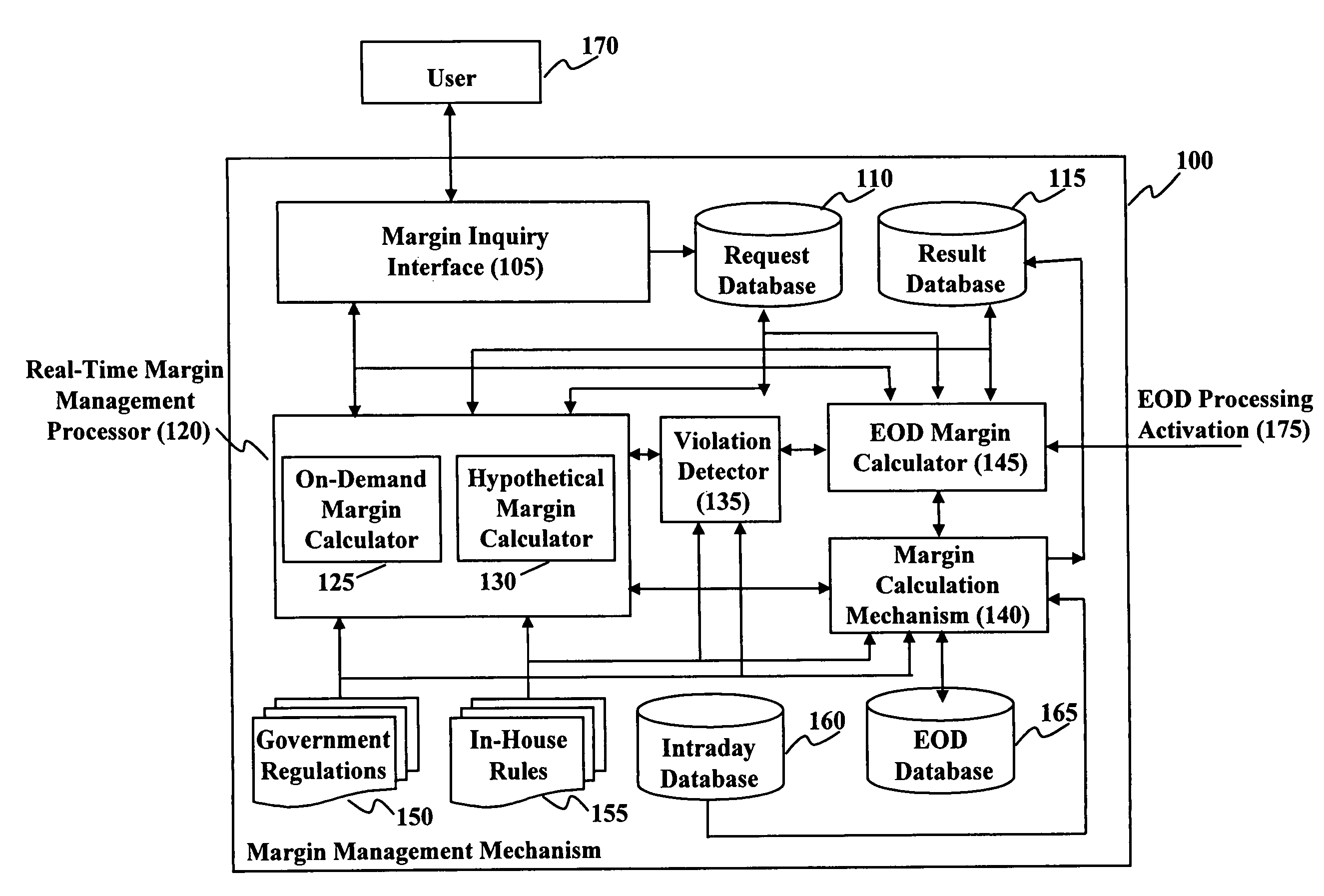
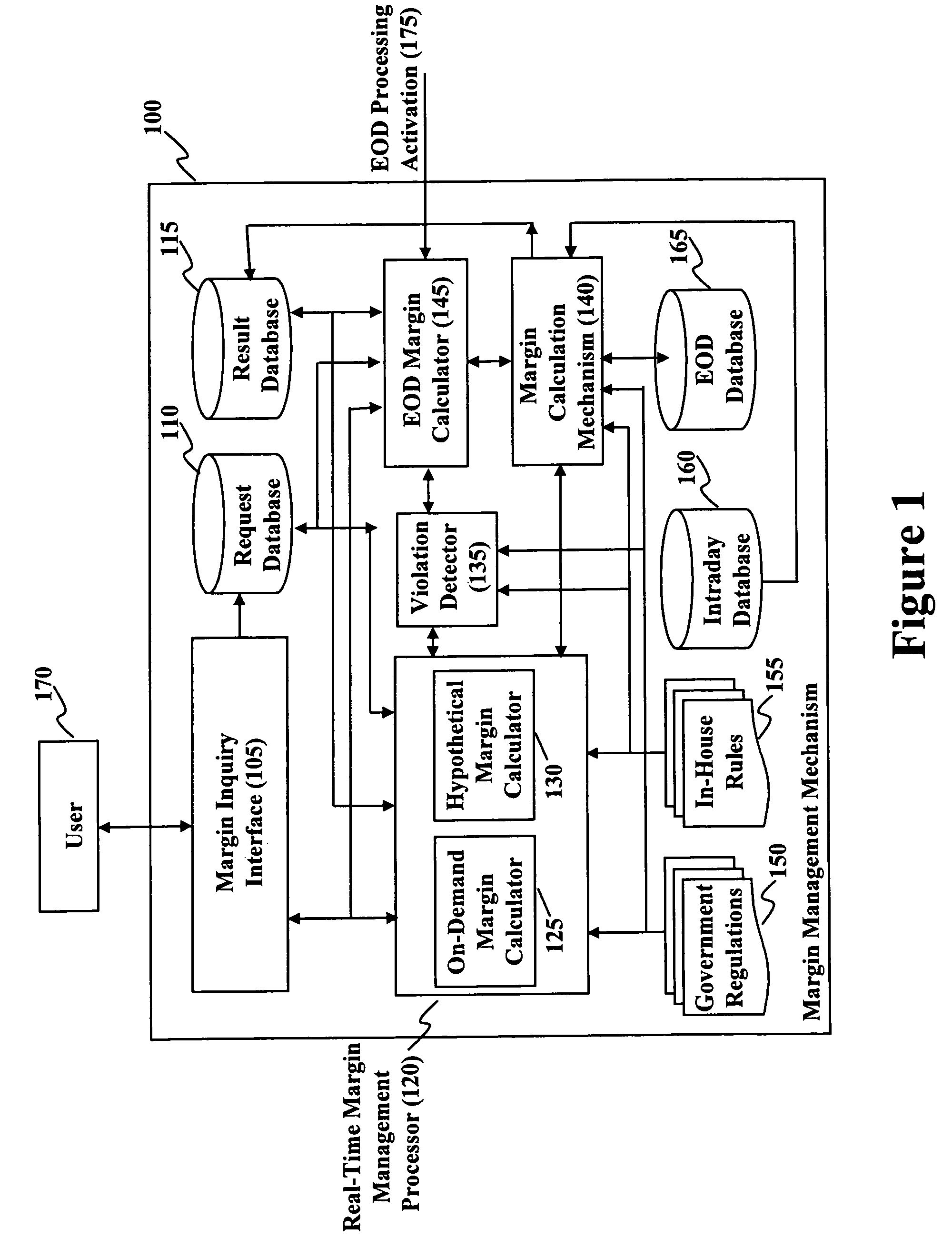
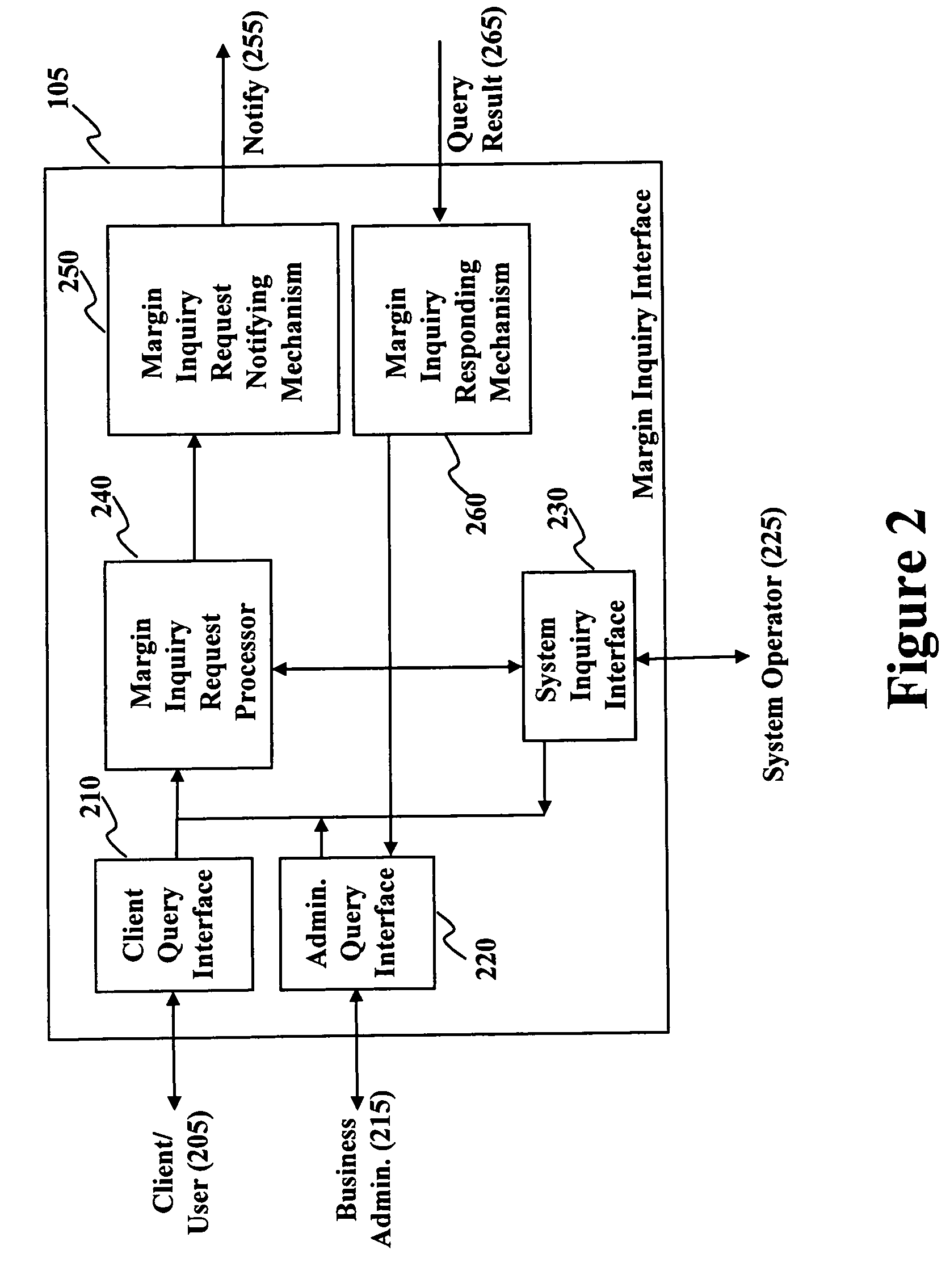
Method and system for real time margin calculation
Owner:UBS BUSINESS SOLUTIONS AG
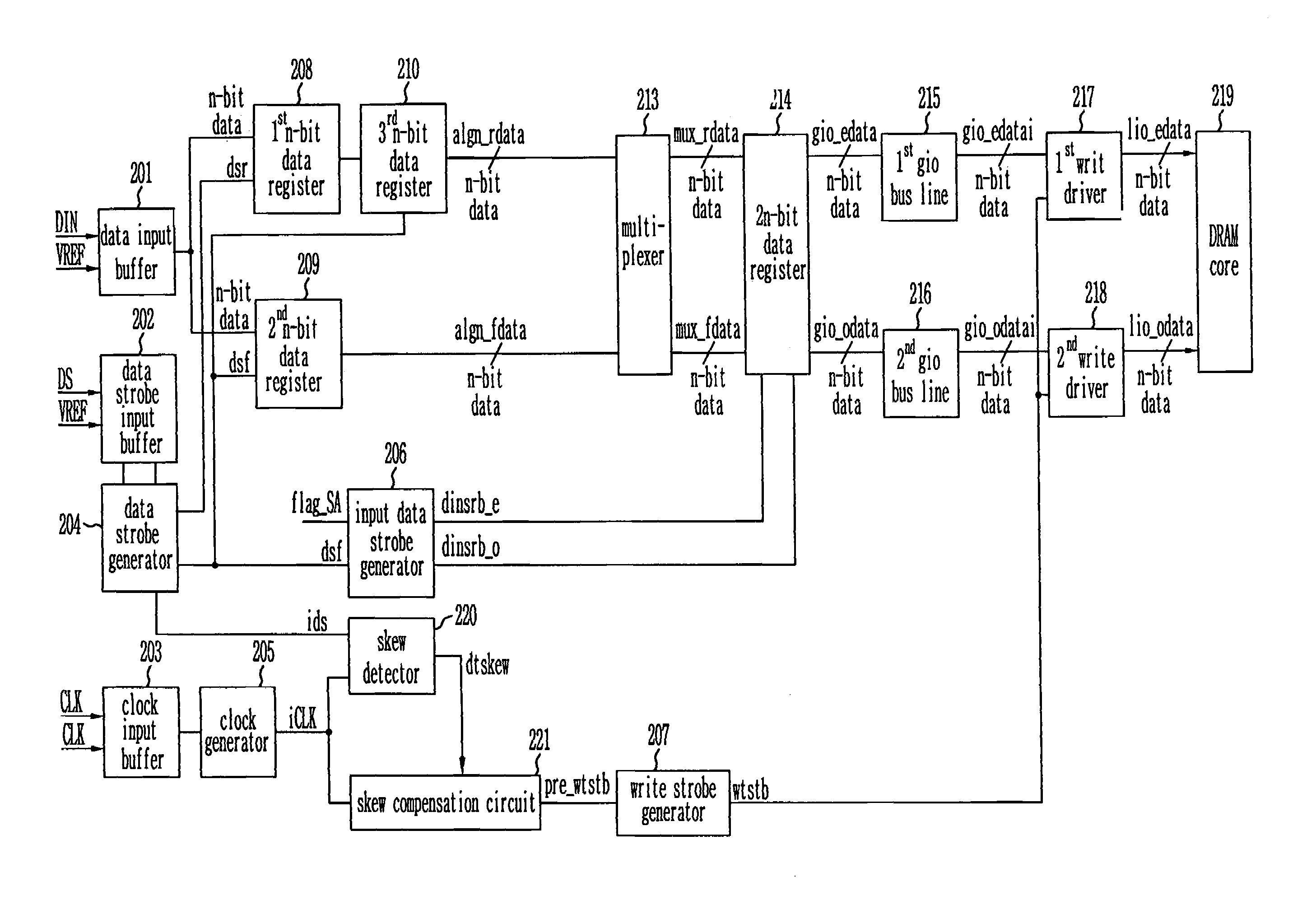
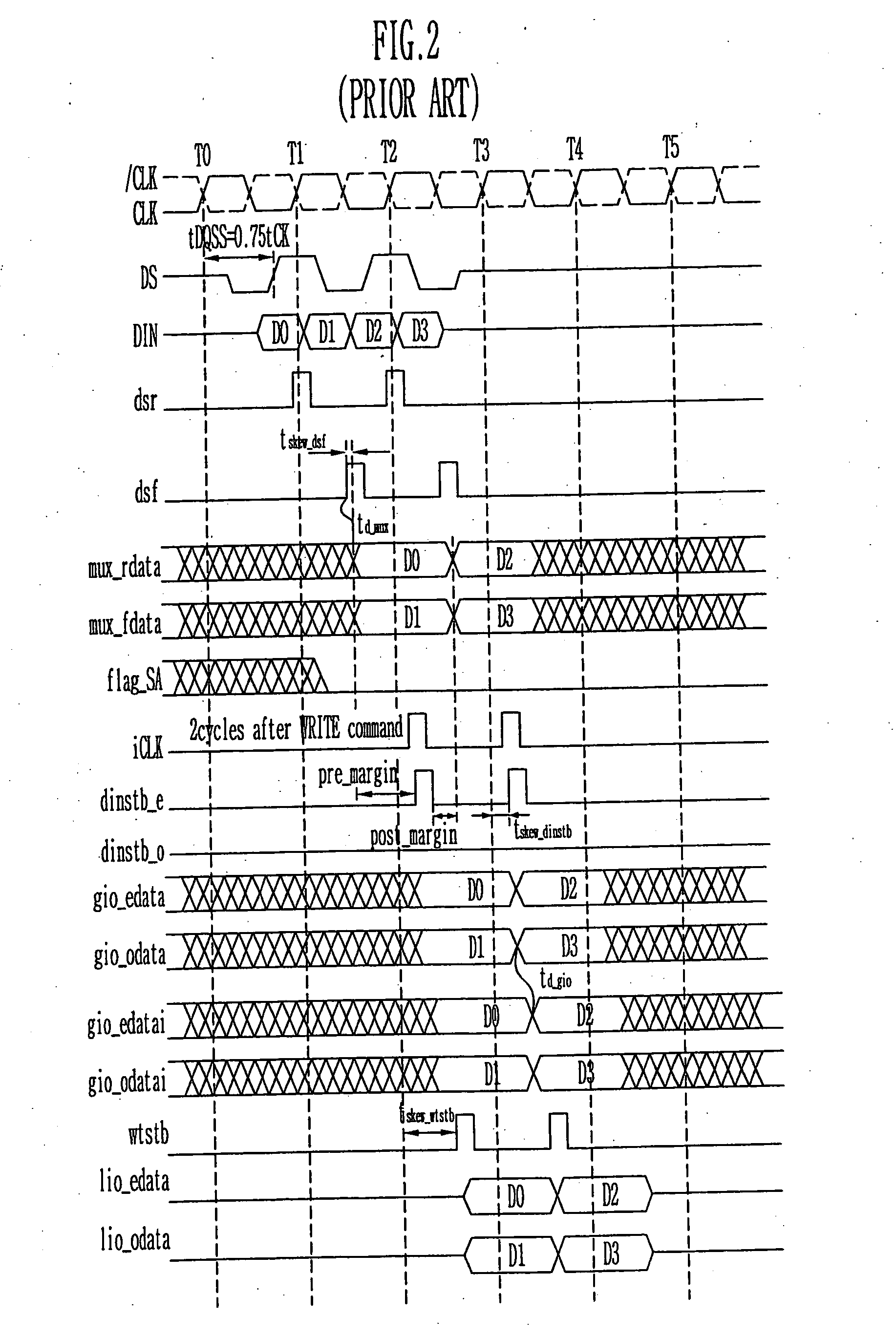
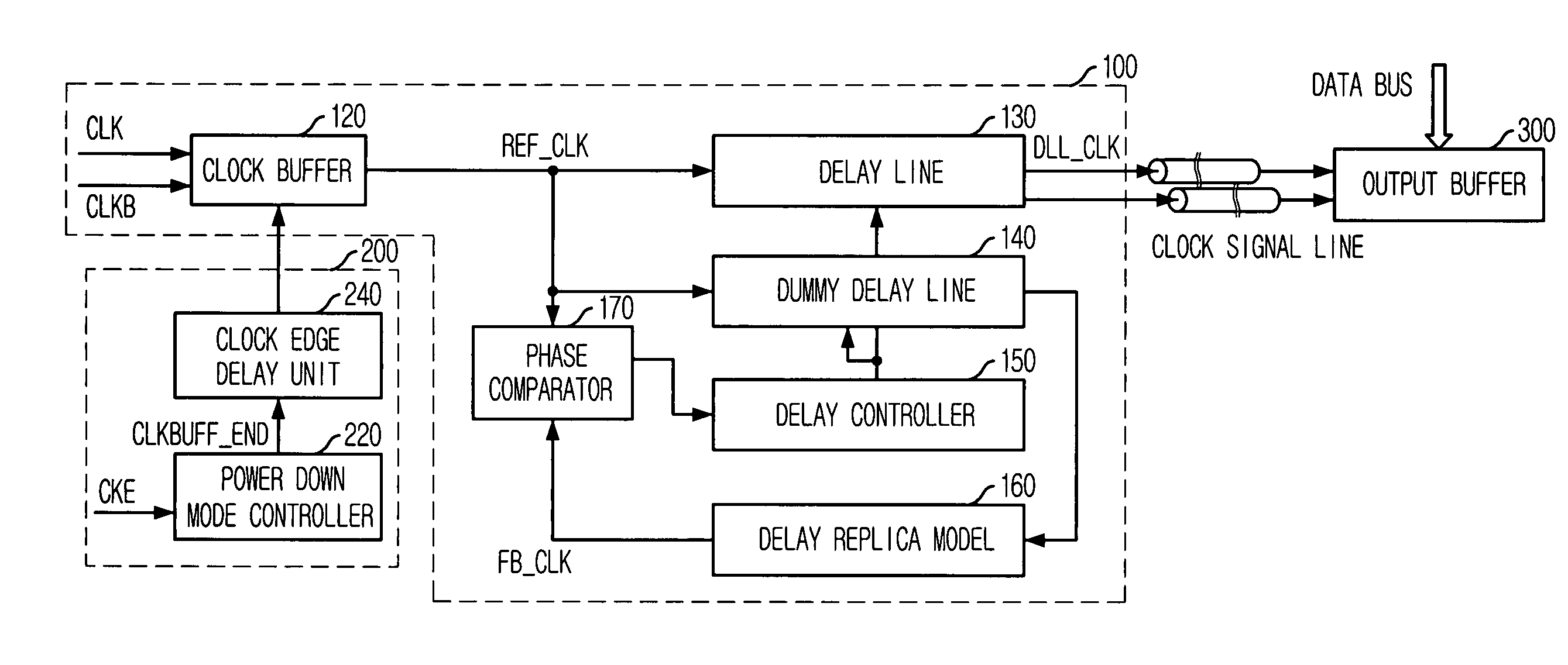
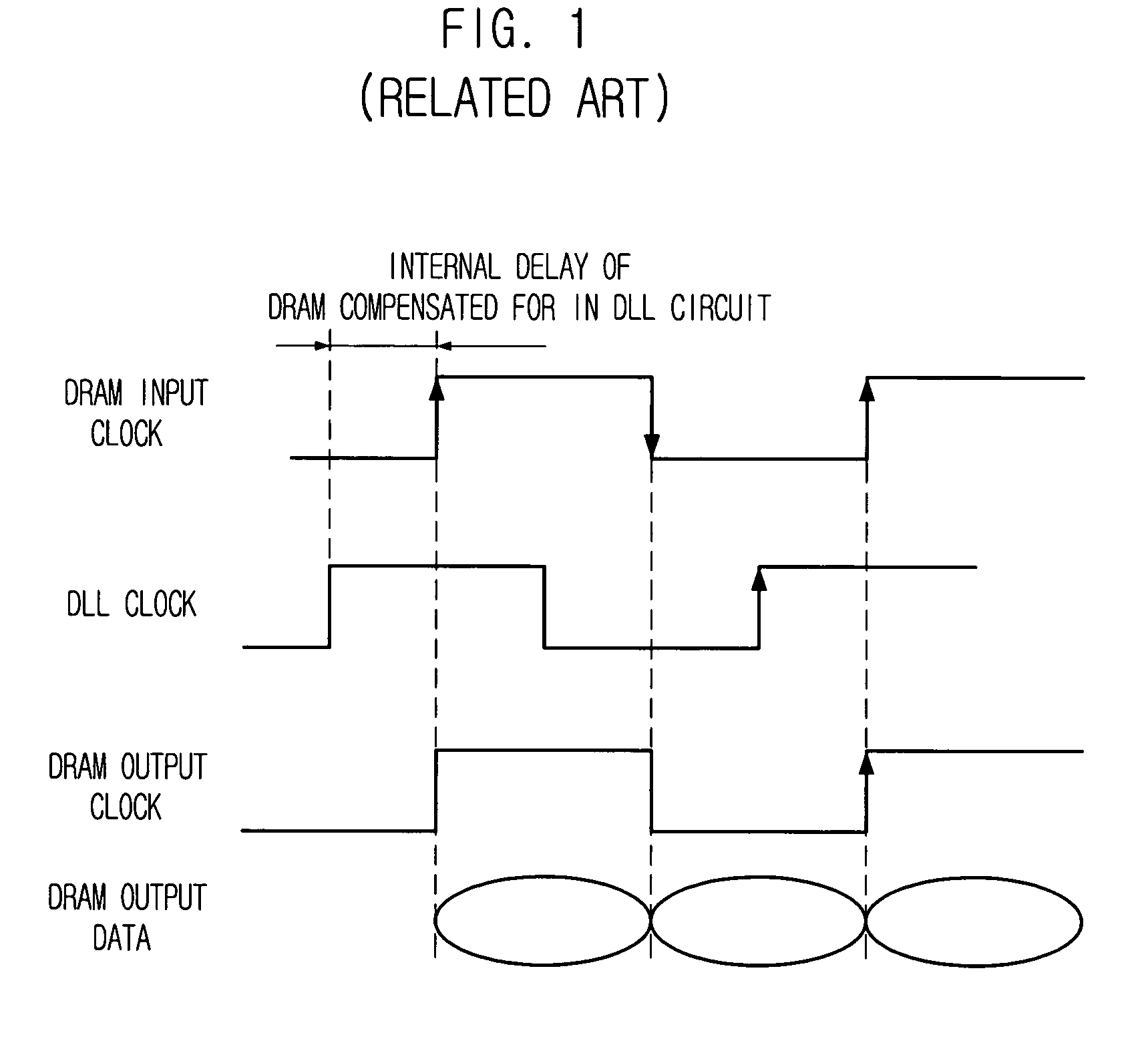
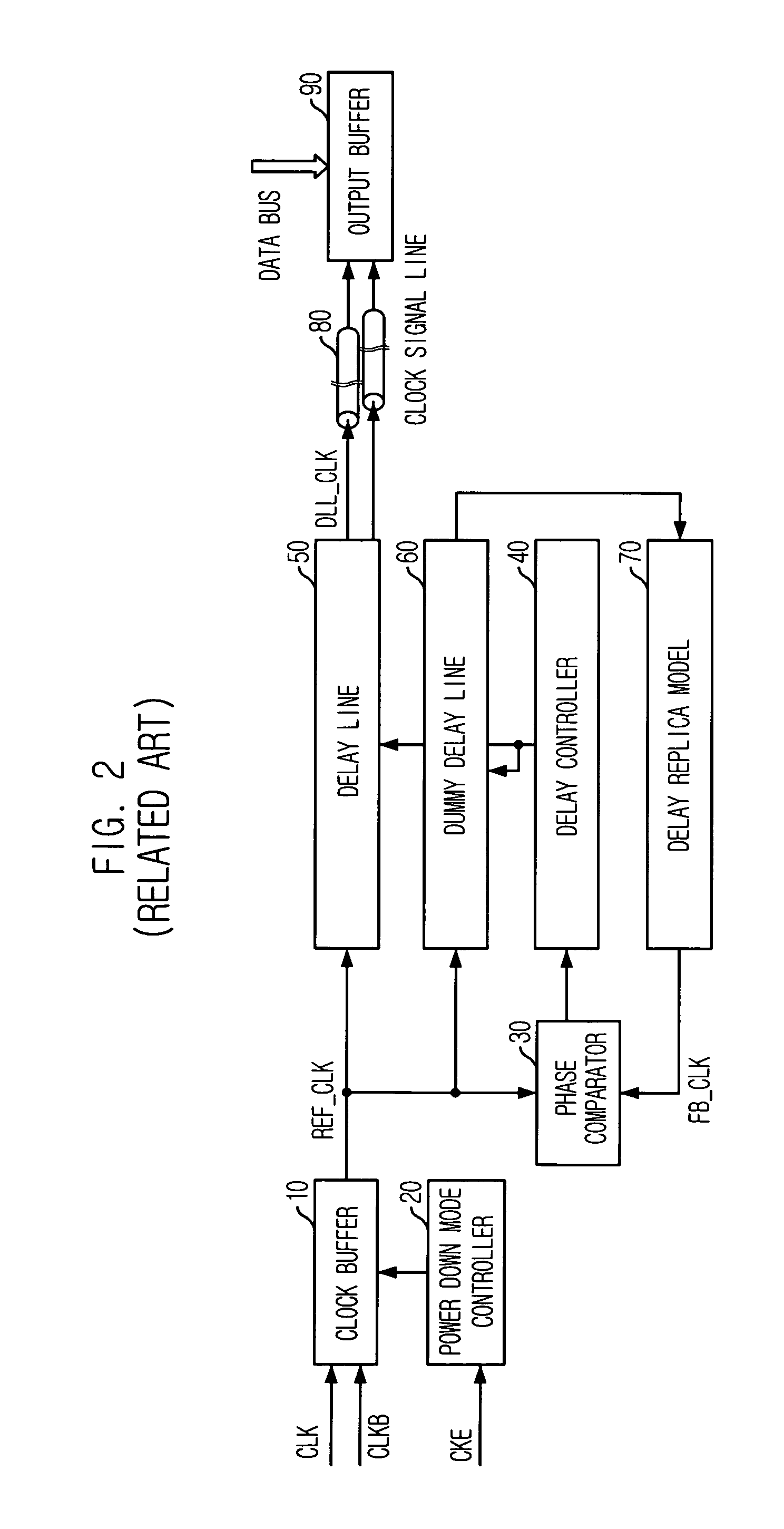
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS7042799B2Guaranteed uptimeTiming marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
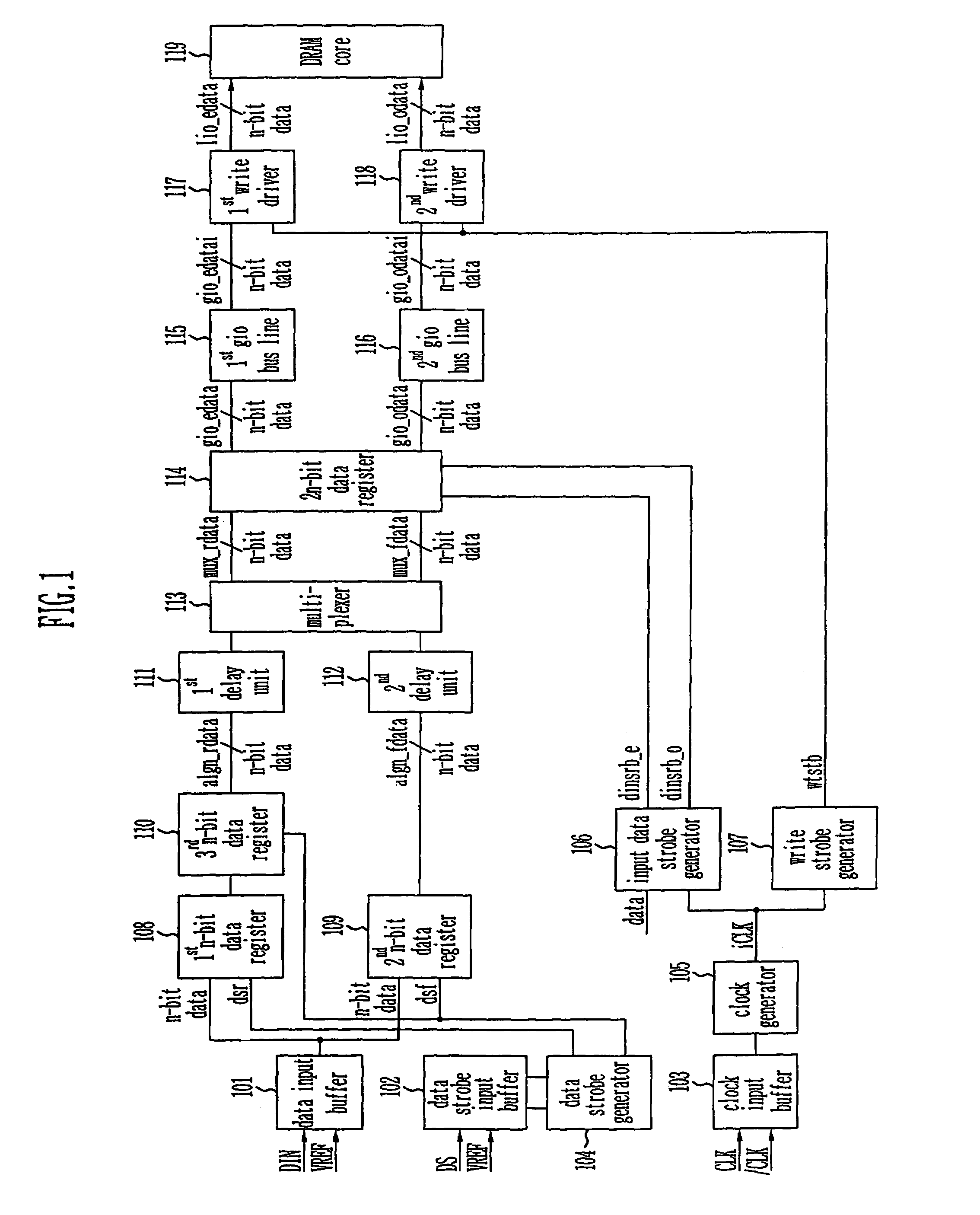
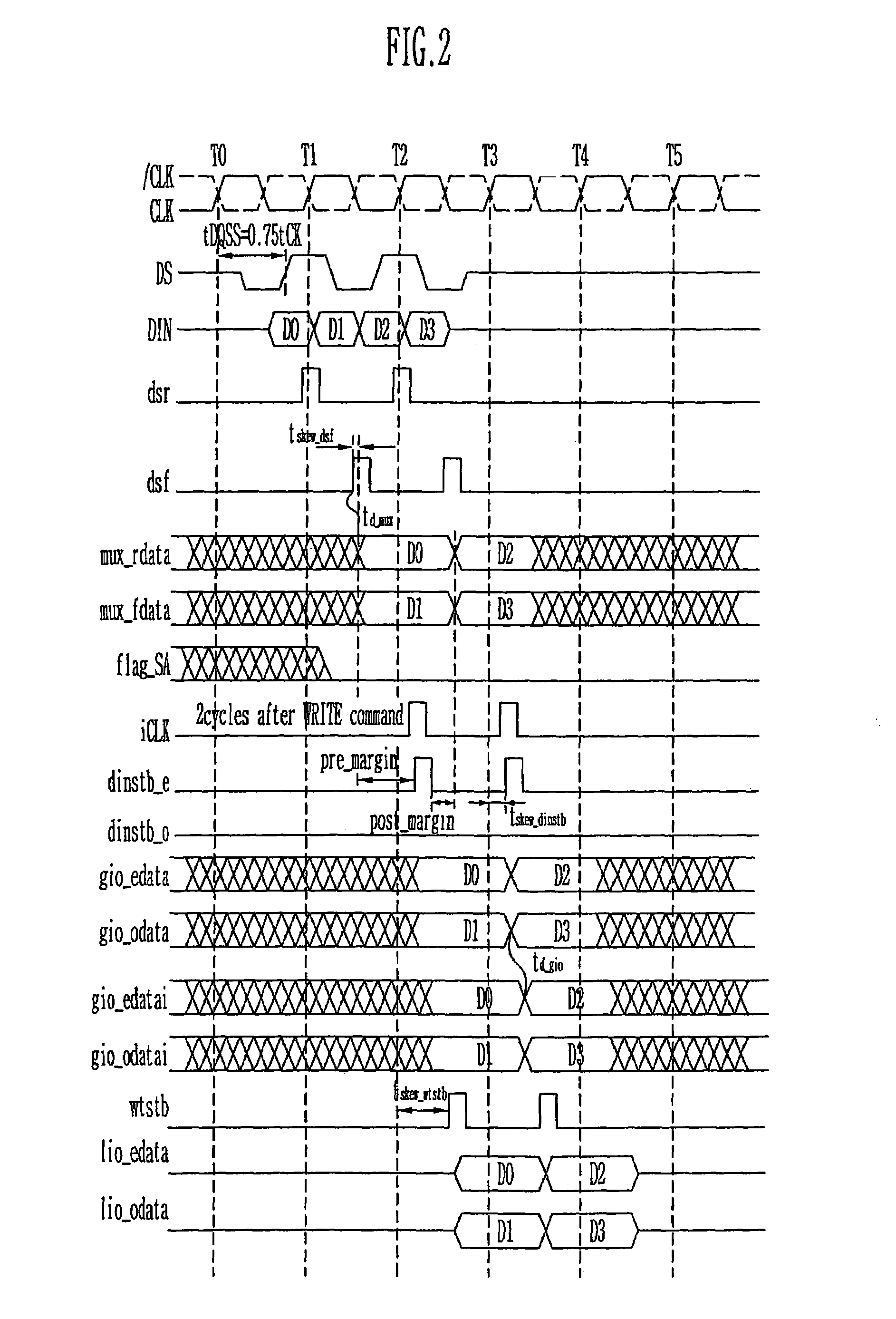
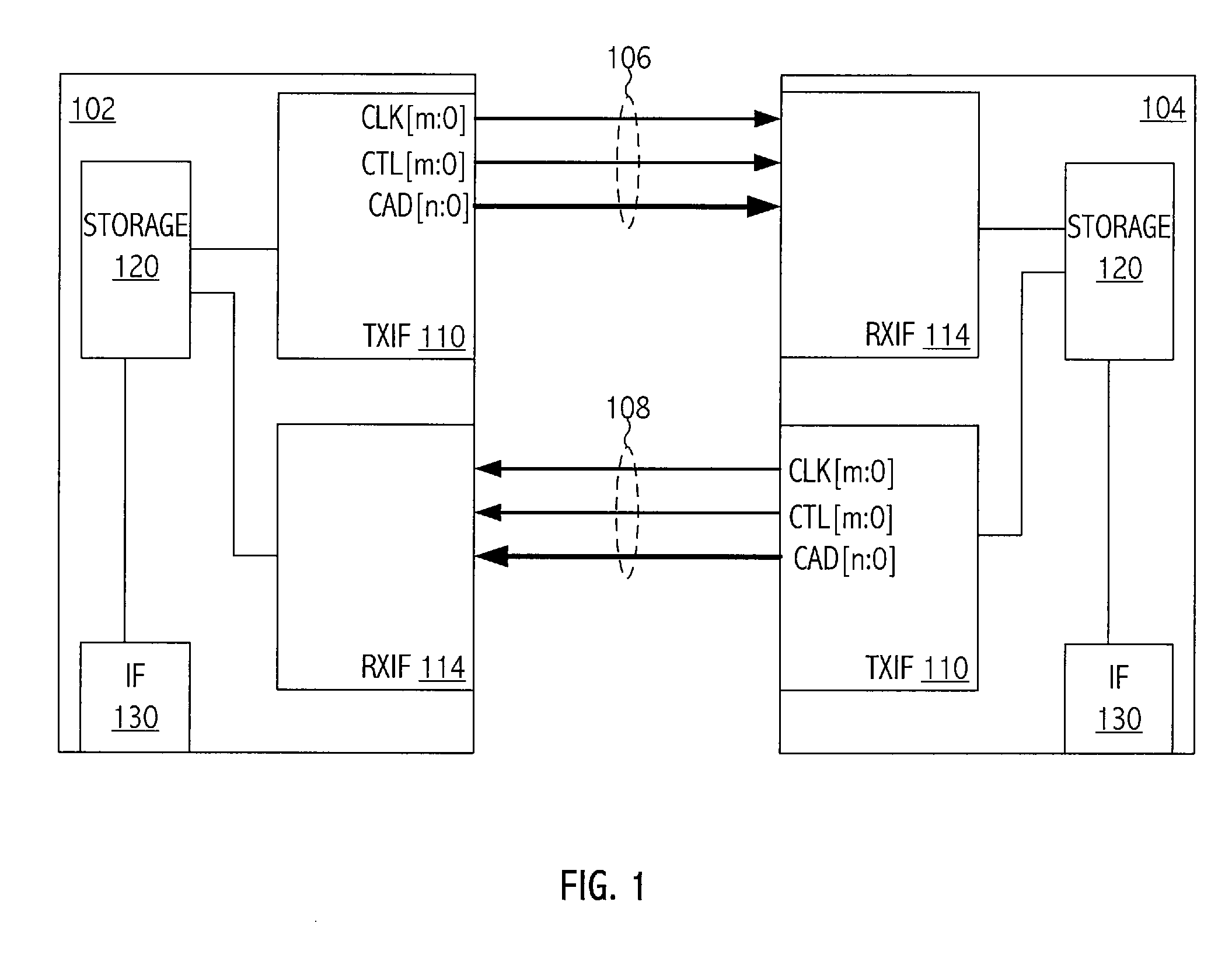
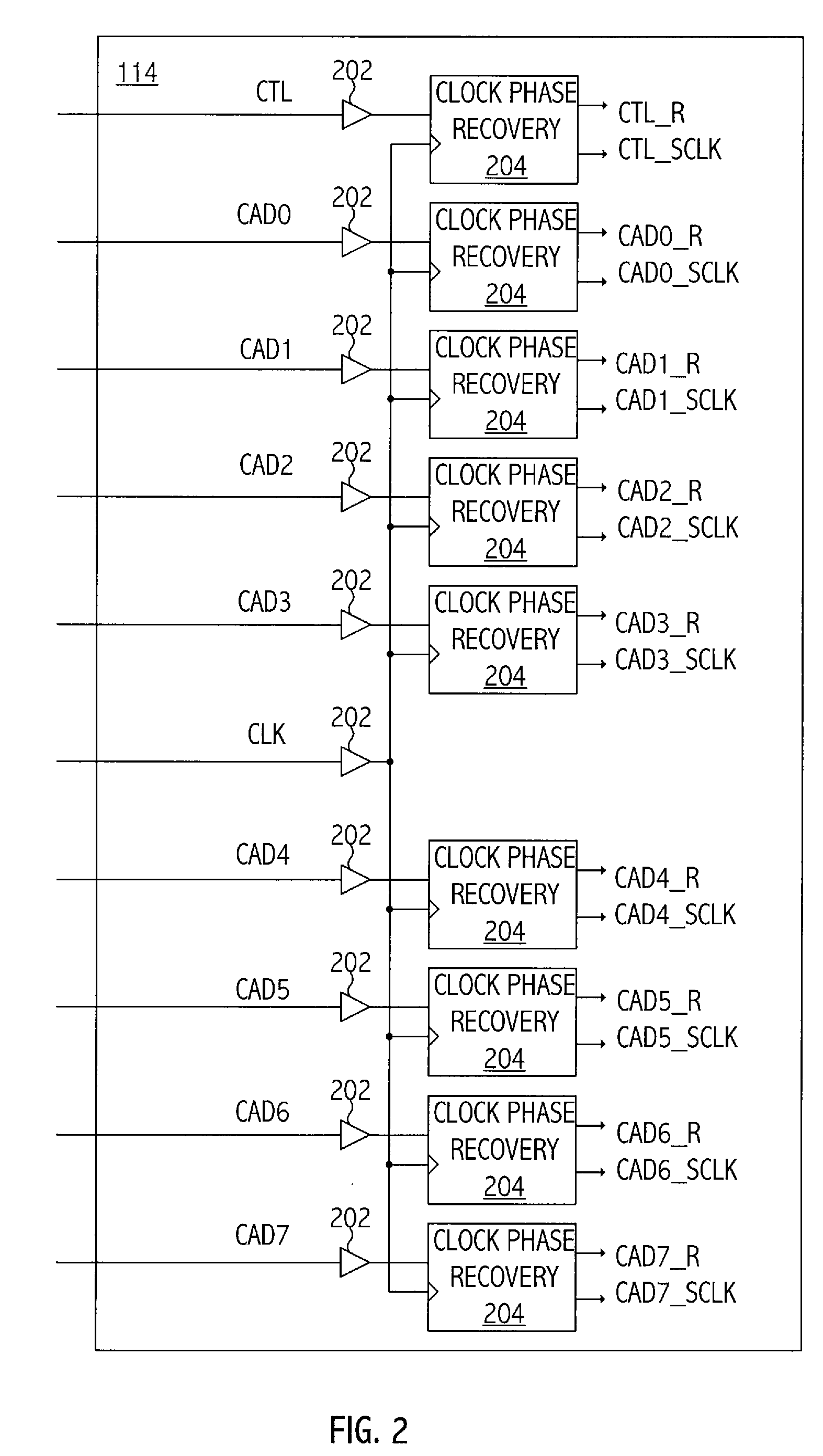
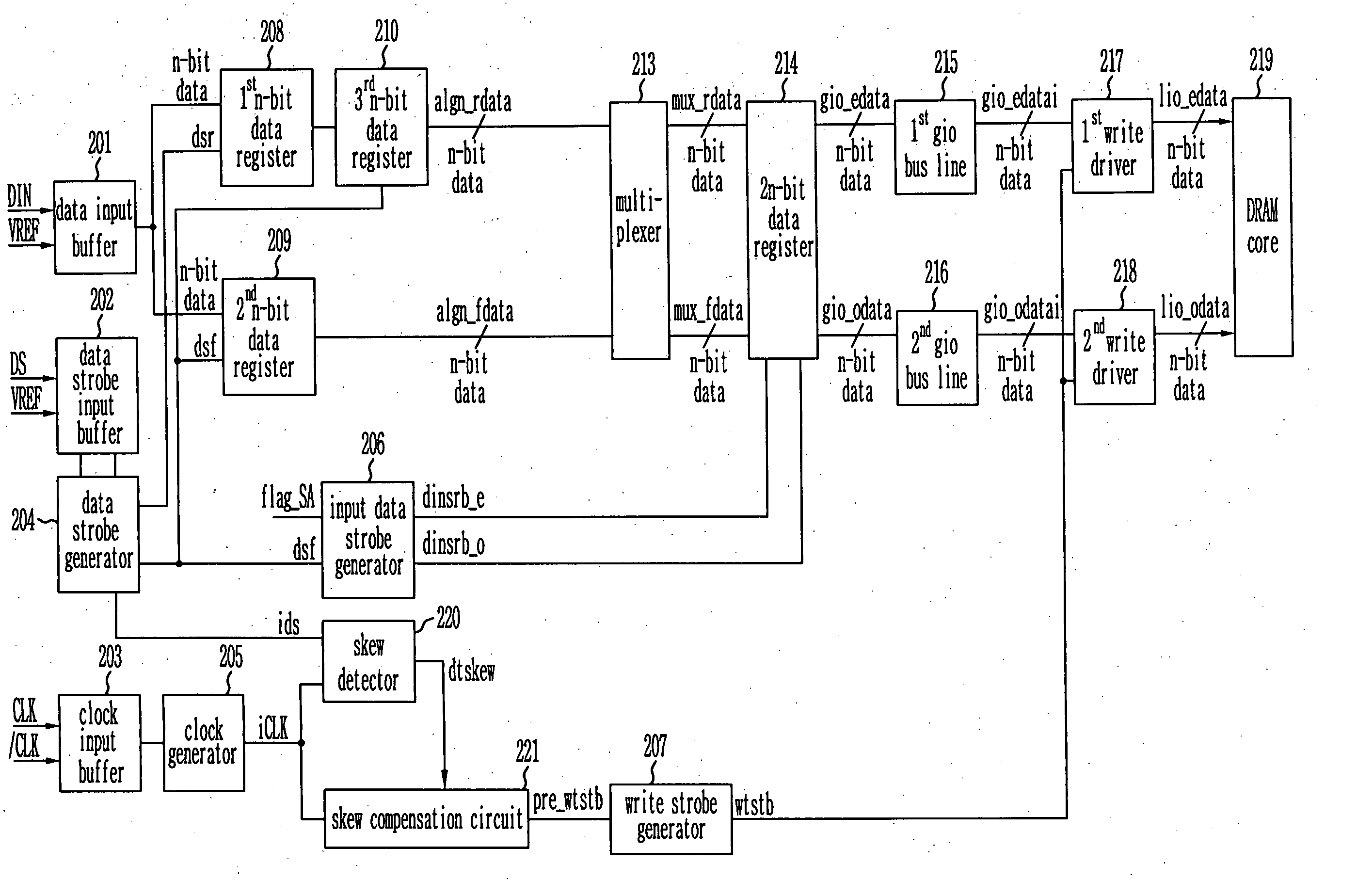
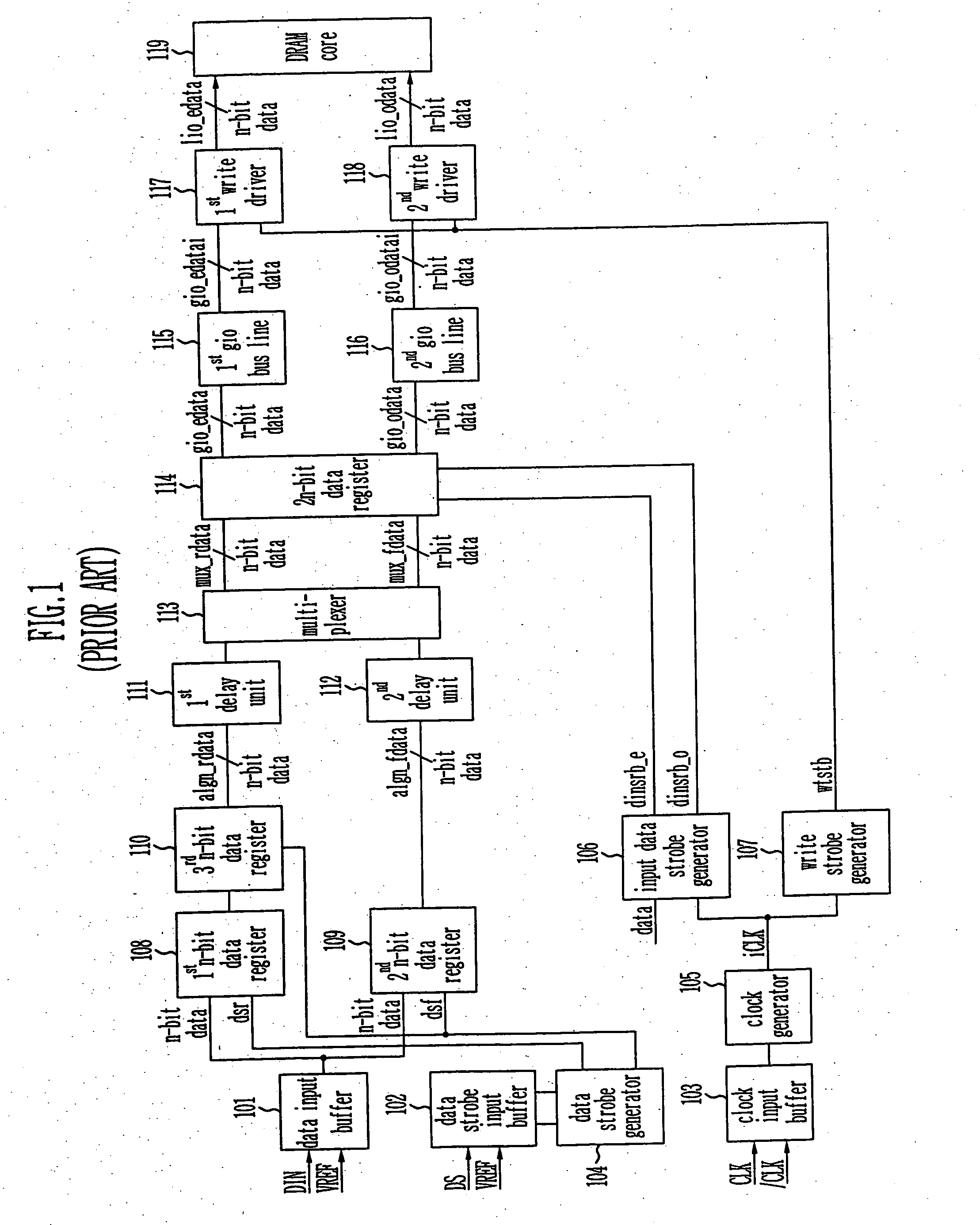
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Data transfer method and electronic device
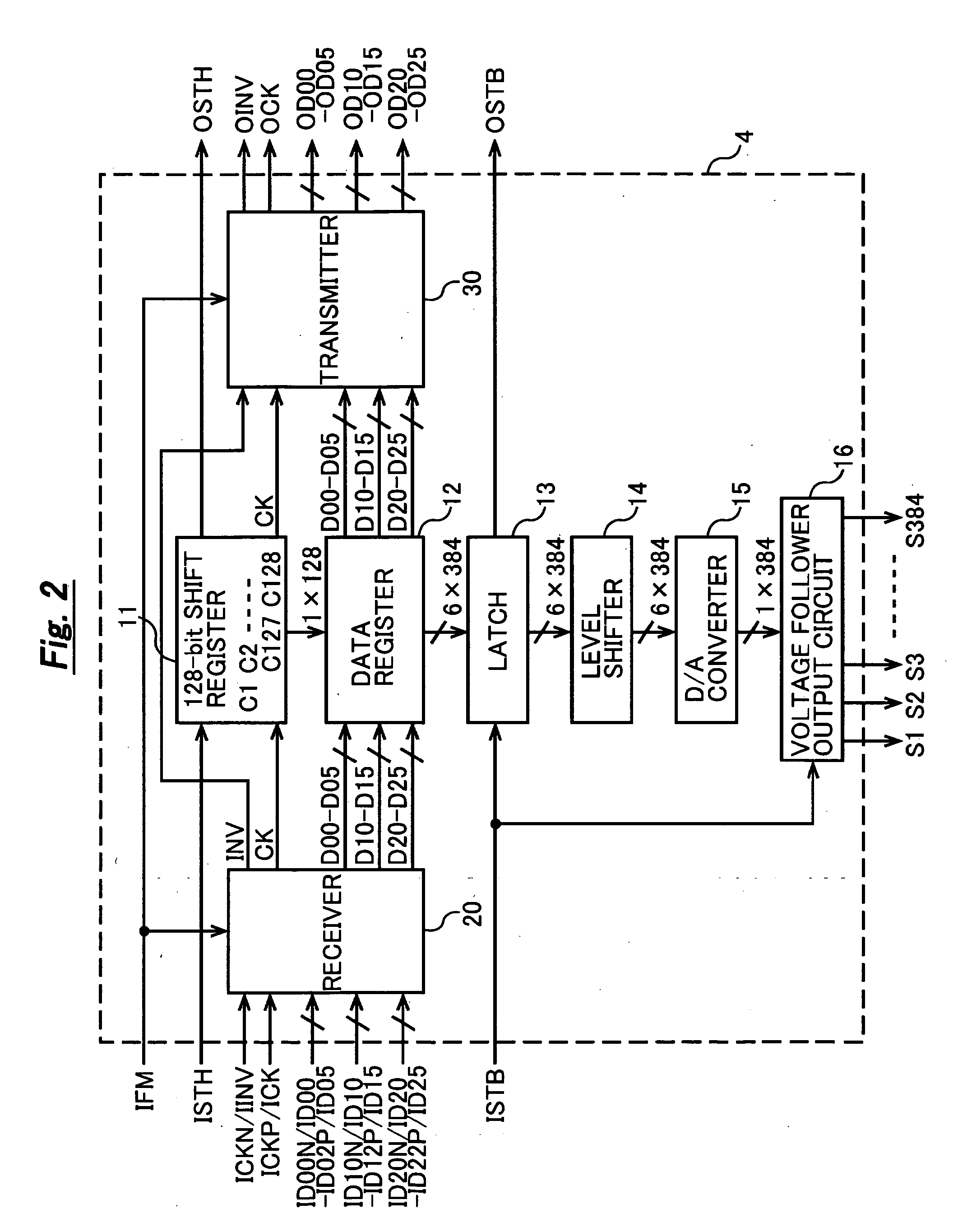
ActiveUS20050219189A1Large amplitudeObtaining adequateCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCMOSTiming margin
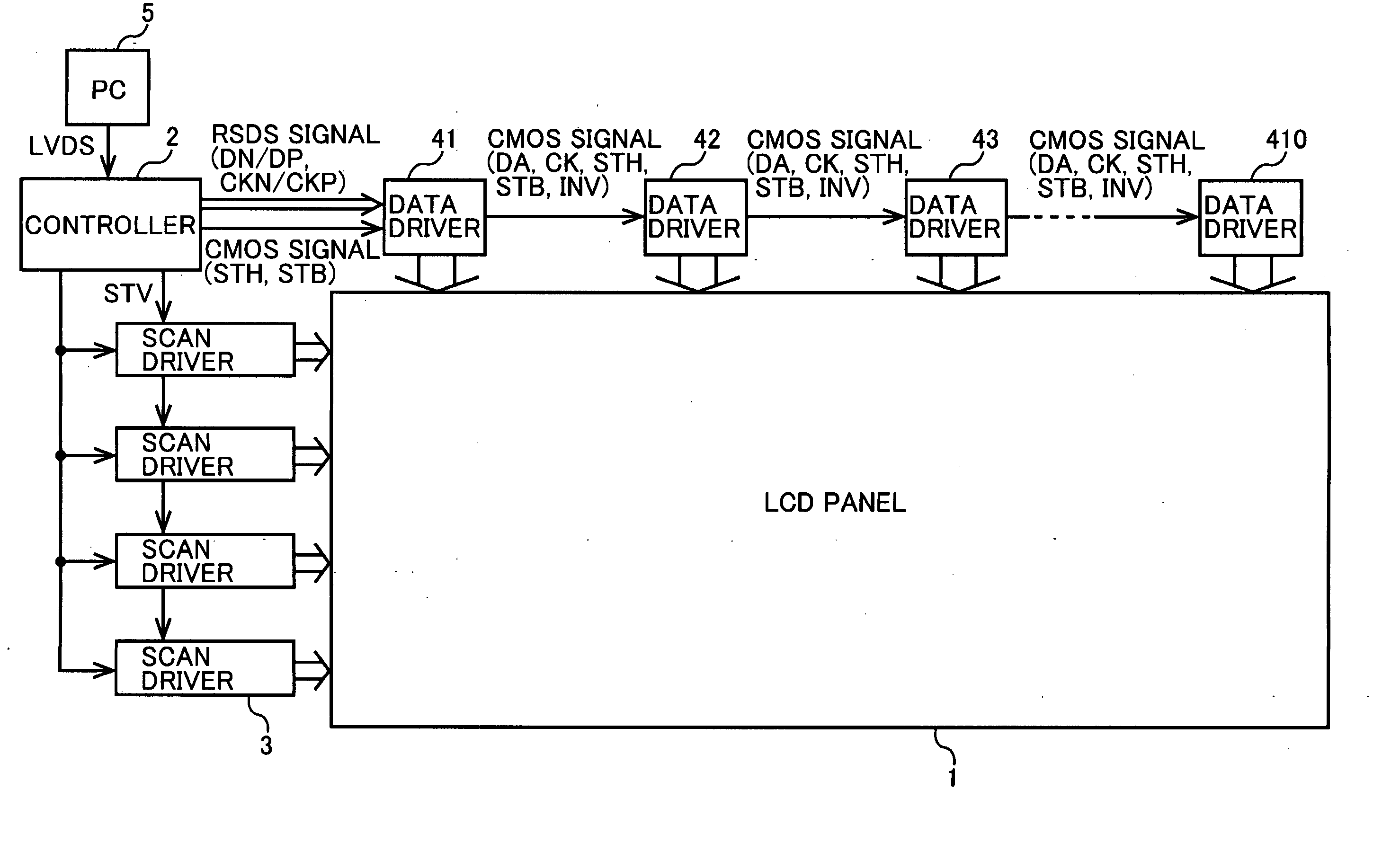
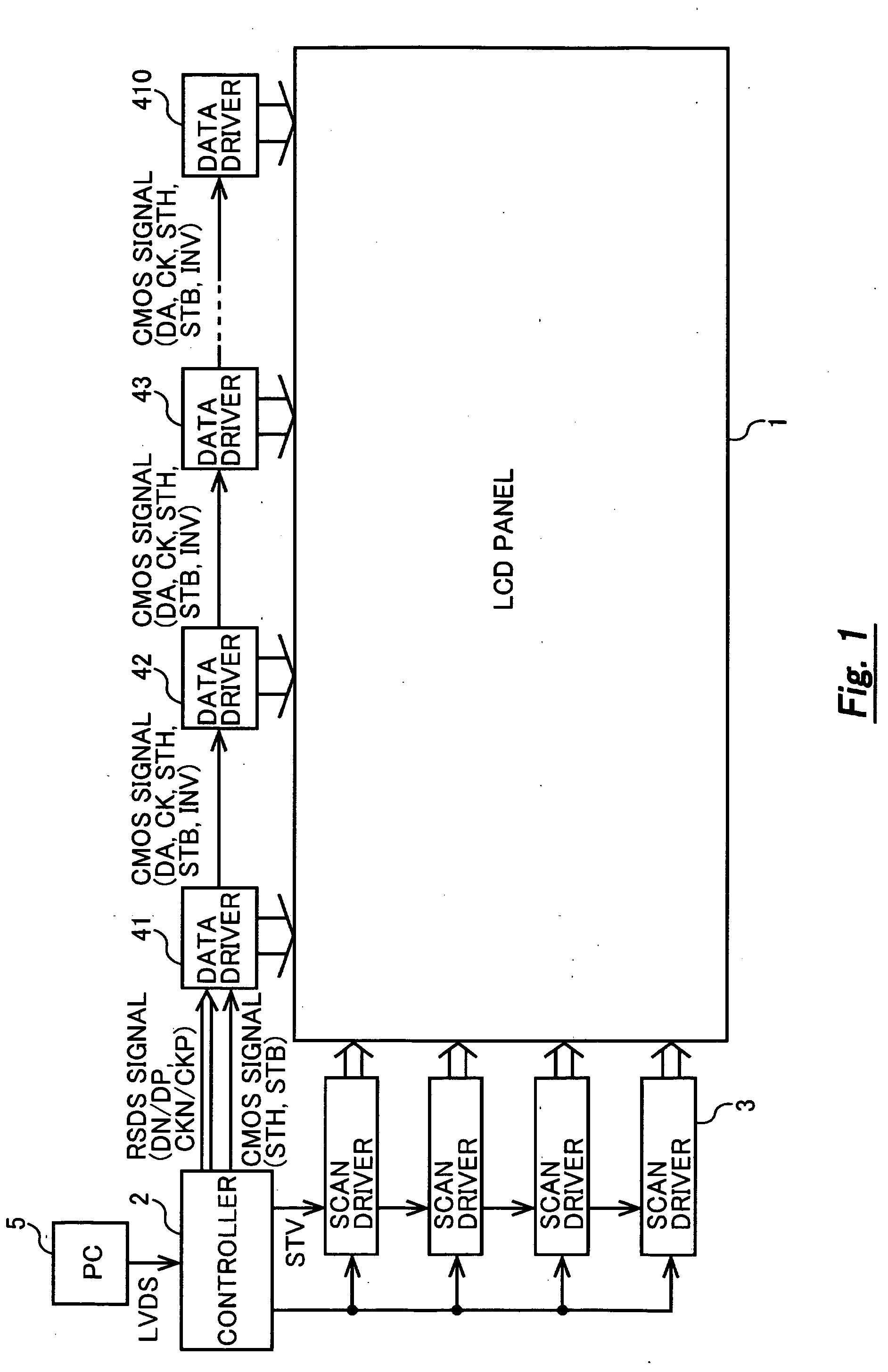
The present invention provides a liquid-crystal display device that is able to reduce EMI, current consumption, and so forth in an interchip transfer of display data, a timing signal, and so forth and to provide an appropriate timing margin. In an interchip transfer of display data, a timing signal, and so forth that uses a plurality of data drivers, a certain data driver is used as a data driver. When the data driver is used in a first stage, an internal receiver is made to function as an RSDS receiver by fixing the IFM terminal at the “H” level. The received RSDS signal constitutes a CMOS signal that has been divided into two by the receiver and is output by the transmitter. Here, a data inversion signal is generated and output by the transmitter. When the data driver is used in the second or subsequent stage, the internal receiver is made to function as a CMOS receiver by fixing the IFM terminal at the “L” level. The received CMOS signal is output after being subjected to inversion control by means of the data inversion signal by the receiver and transmitter.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
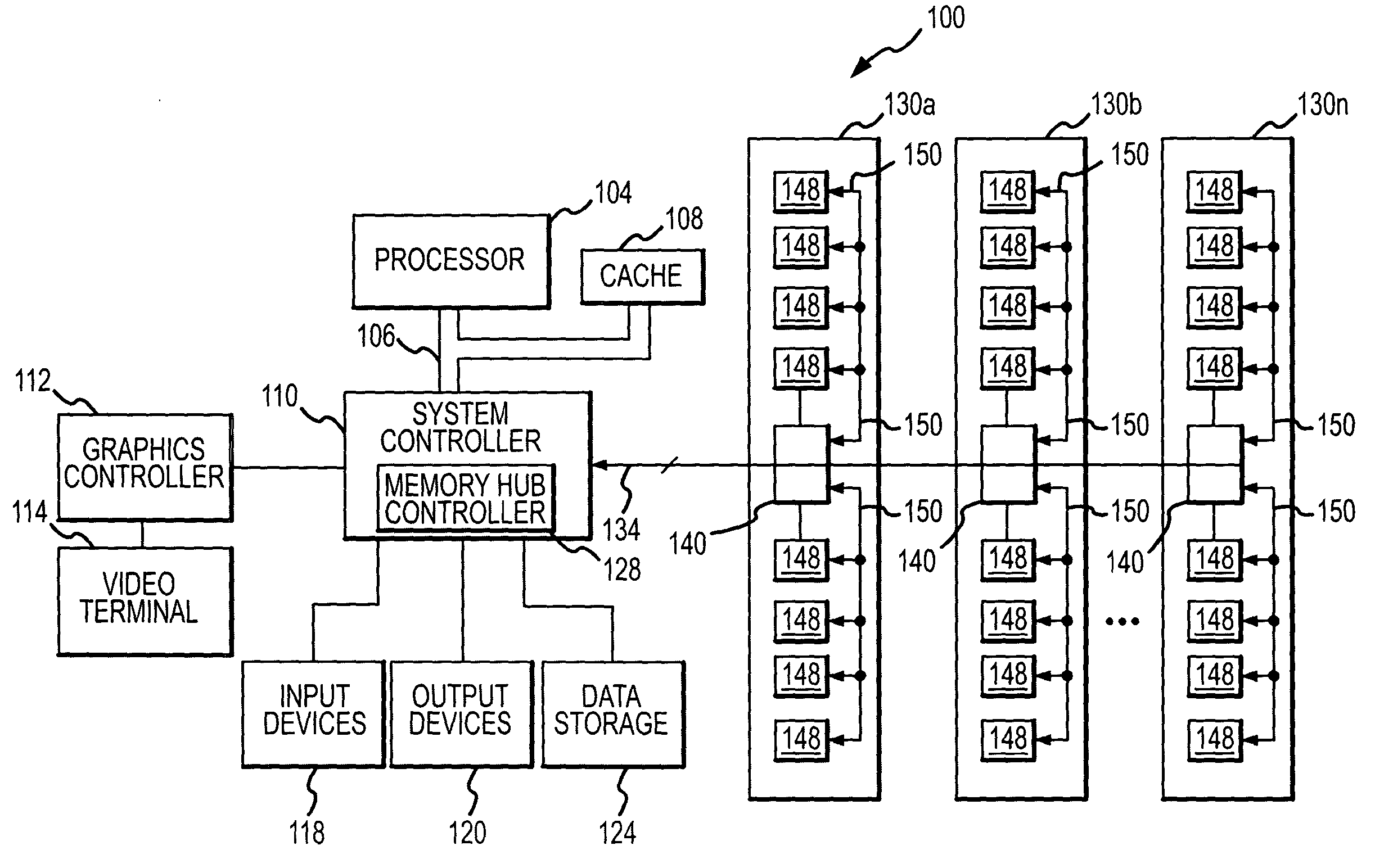
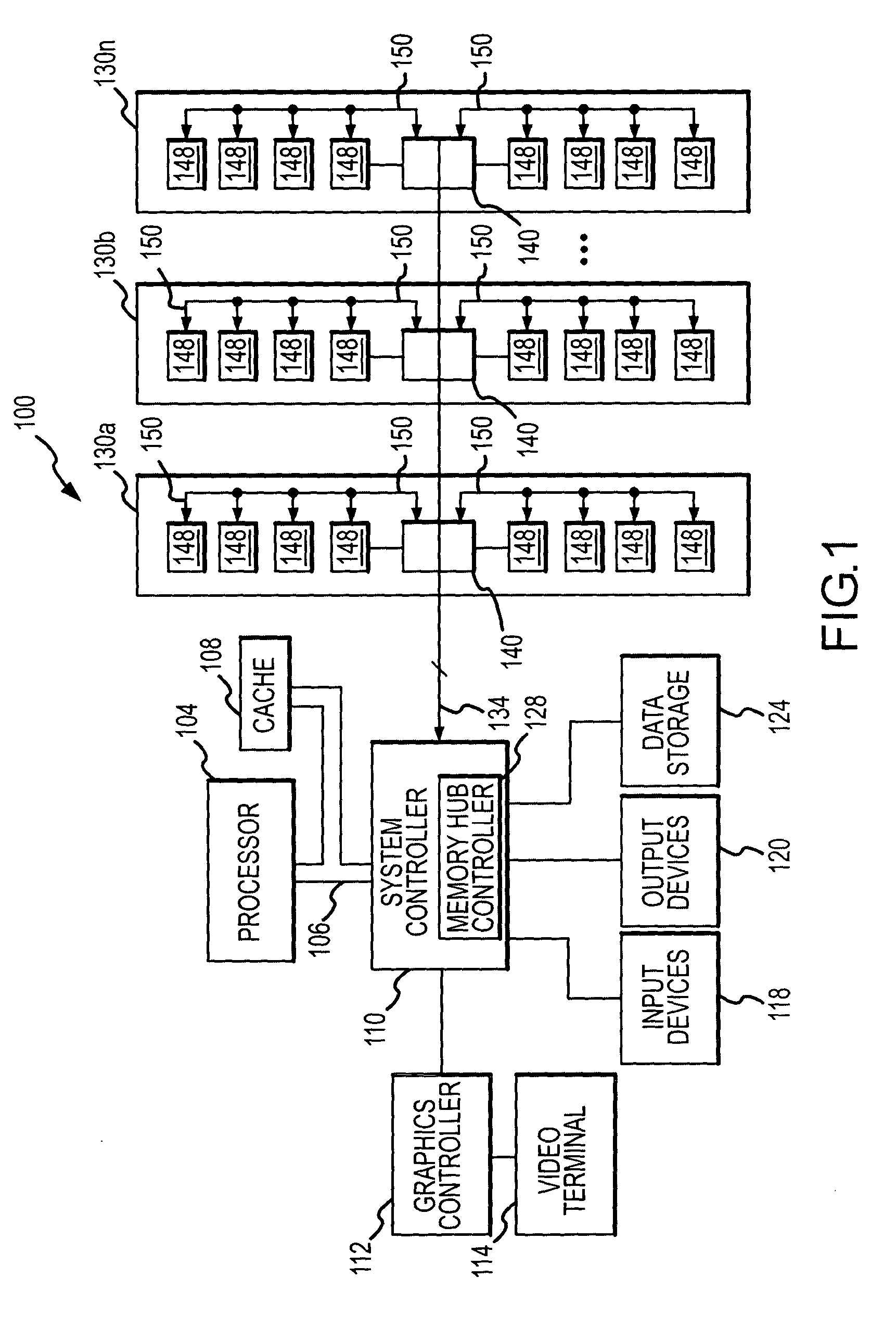
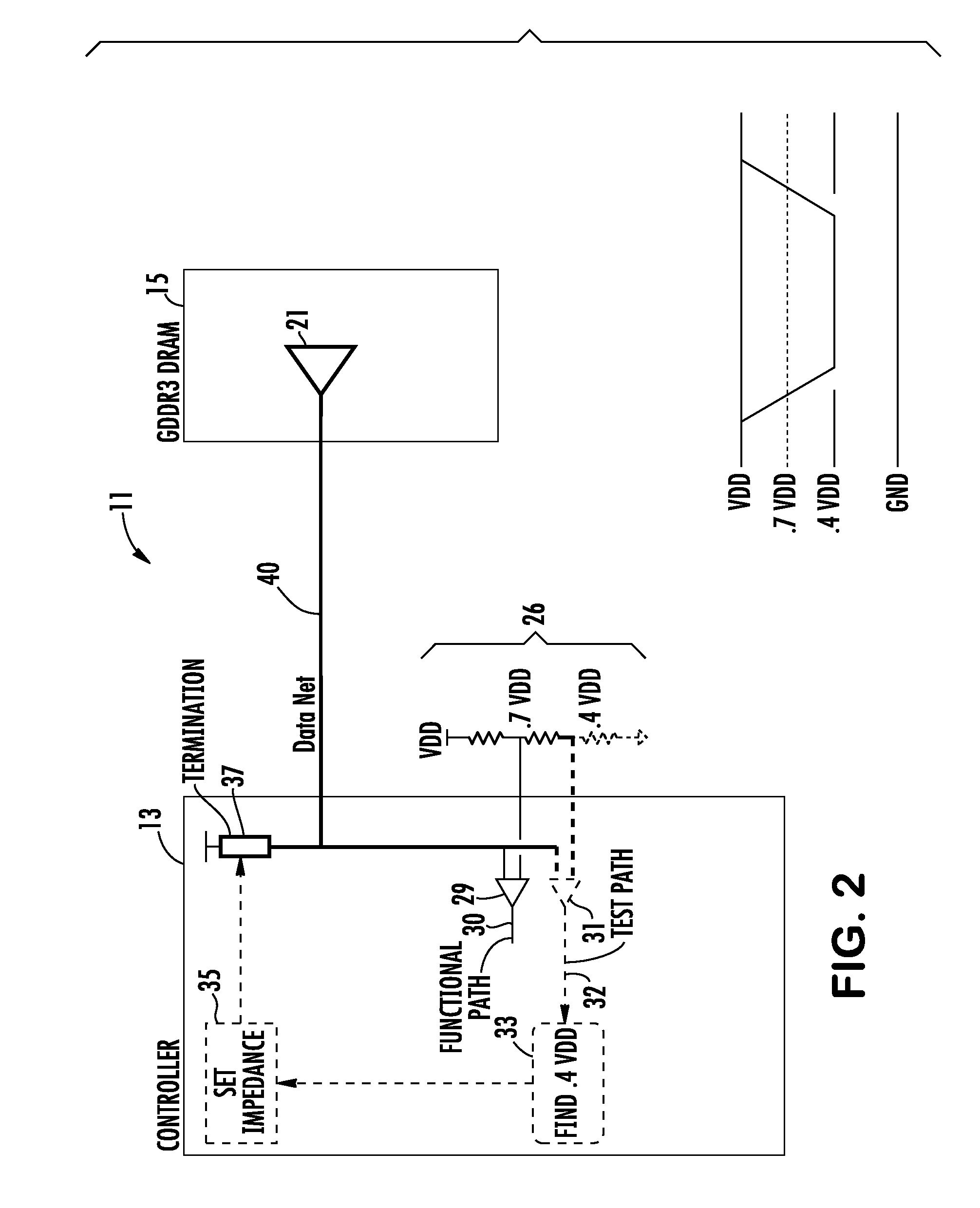
System and method for on-board timing margin testing of memory modules
InactiveUS20050060600A1Increase computing speedElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionOn boardCrossover switch
A memory module includes several memory devices coupled to a memory hub. The memory hub includes several link interfaces coupled to respective processors, several memory controller coupled to respective memory devices, a cross-bar switch coupling any of the link interfaces to any of the memory controllers, a write buffer and read cache for each memory device and a self-test module. The self-test module includes a pattern generator producing write data having a predetermined pattern, and a flip-flop having a data input receiving the write data. A clock input of the flip-flop receives an internal clock signal from a delay line that receives a variable frequency clock generator. Read data are coupled from the memory devices and their pattern compared to the write data pattern. The delay of the delay line and frequency of the clock signal can be varied to test the speed margins of the memory devices.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
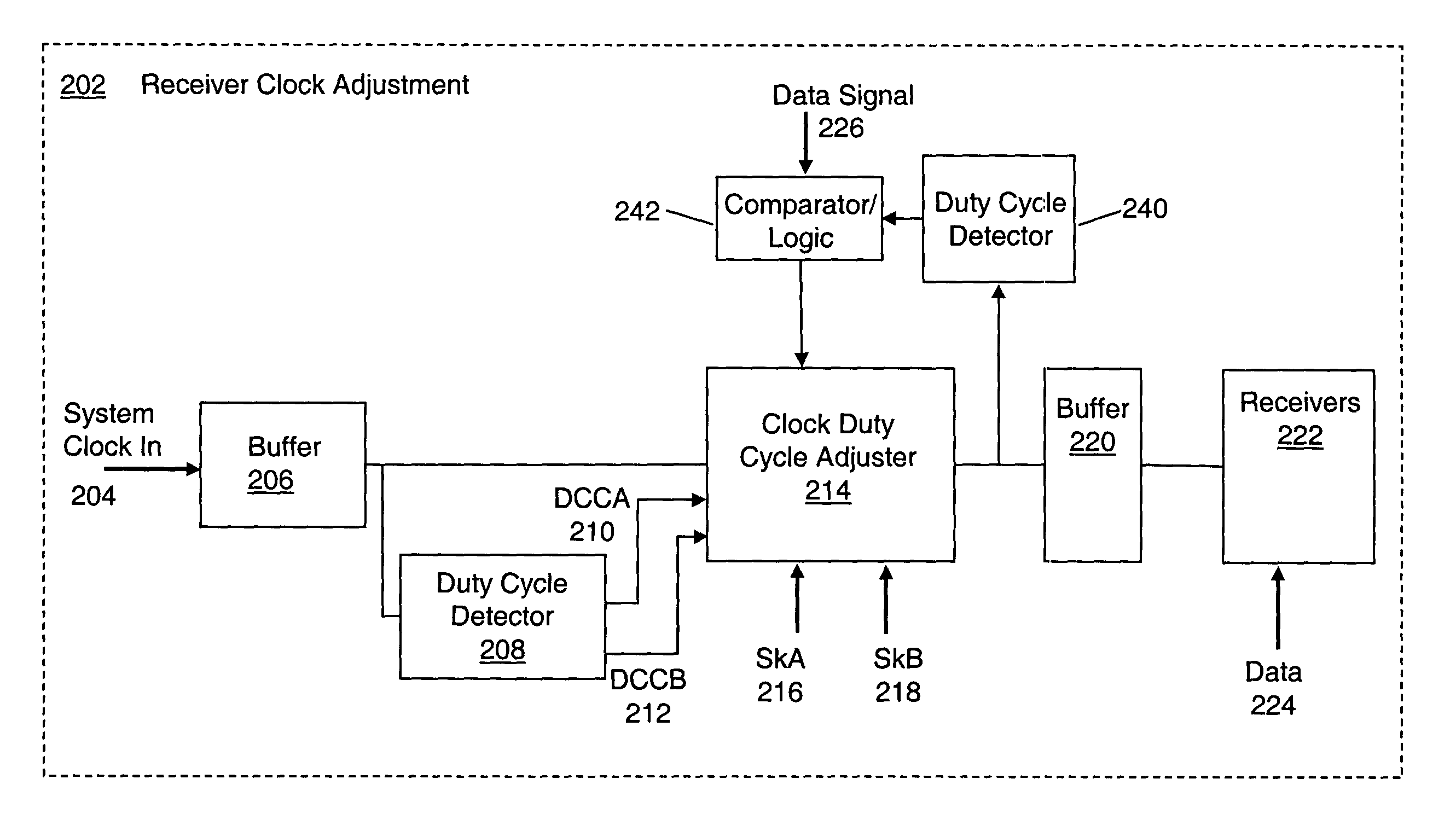
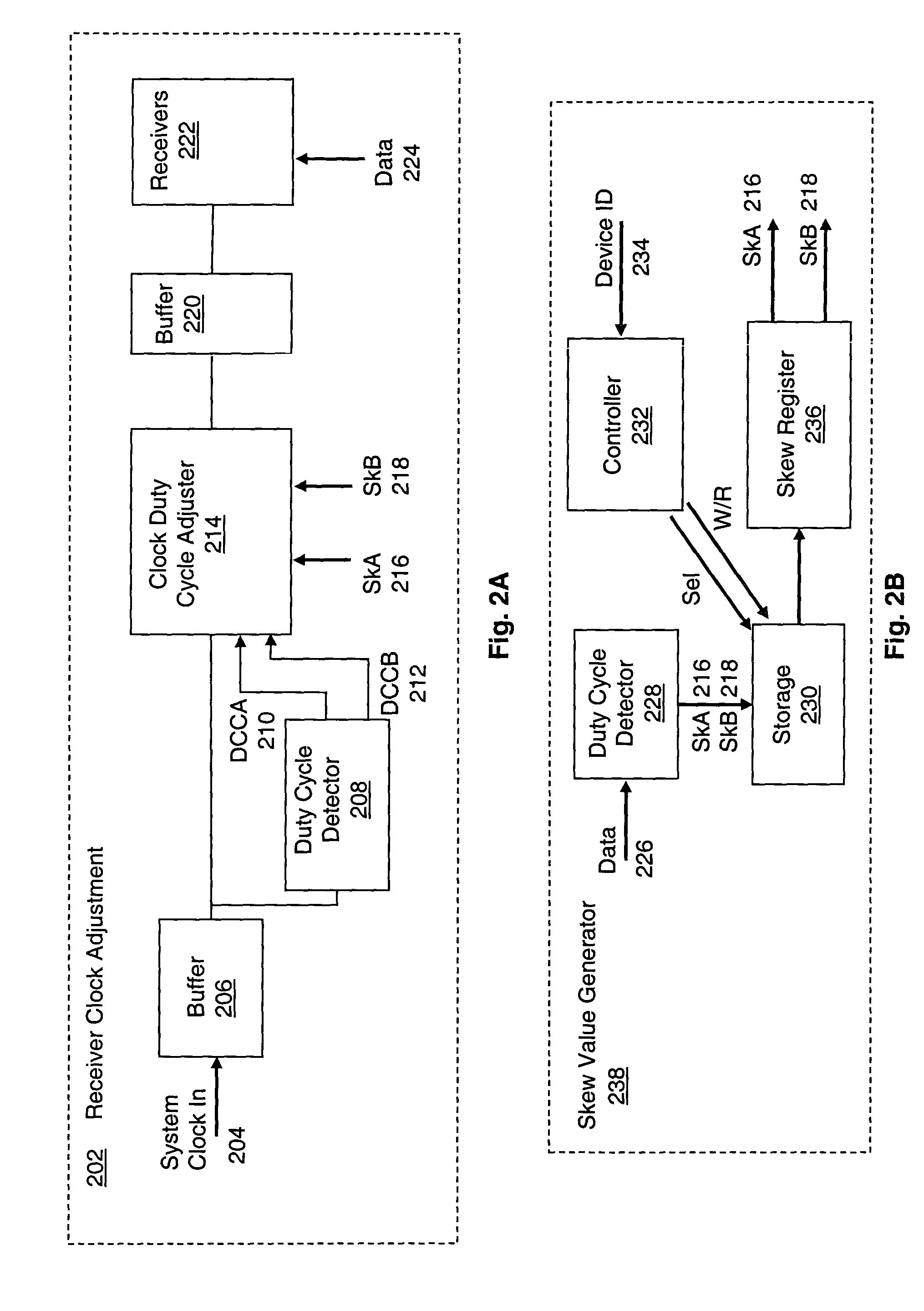
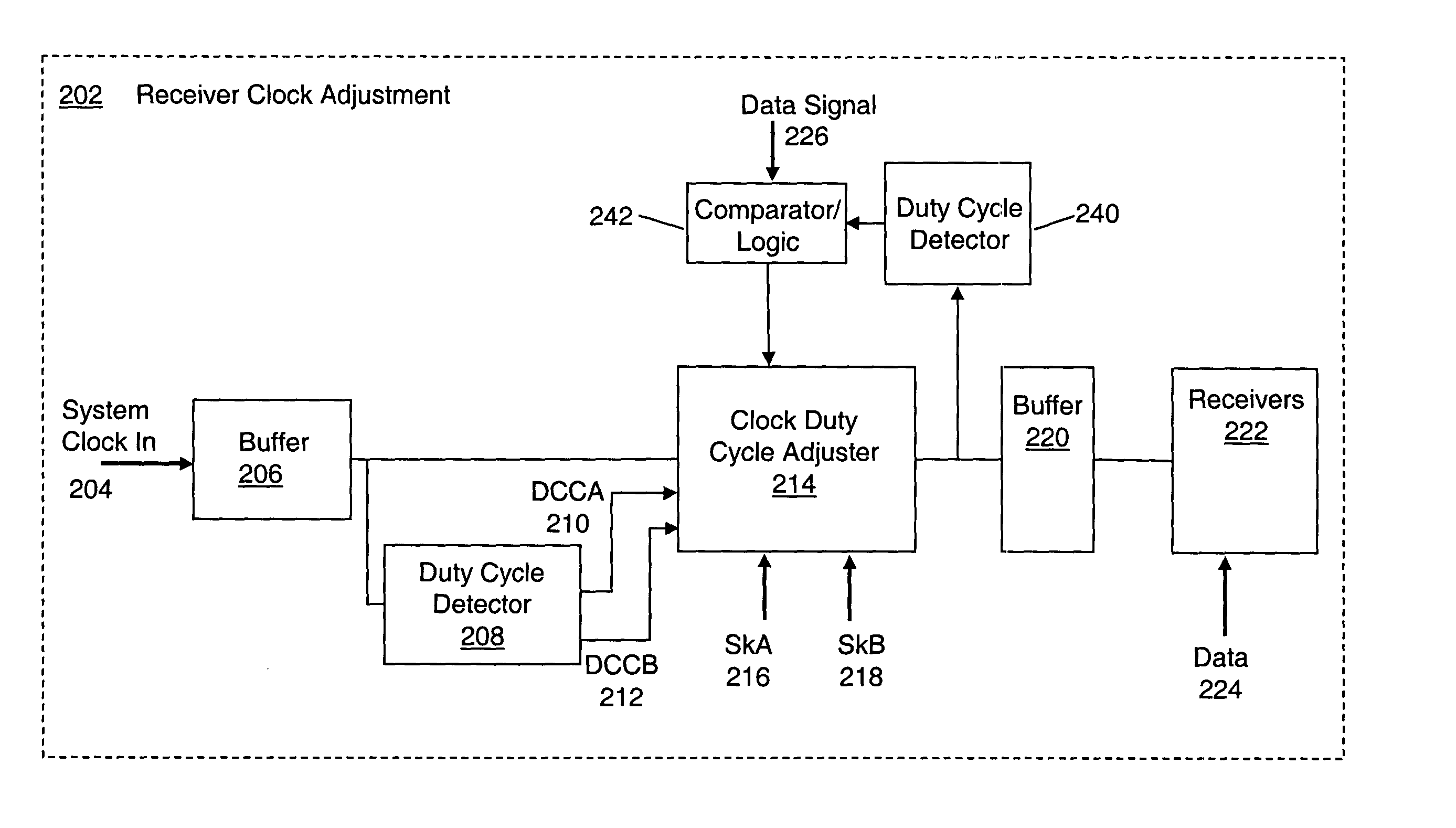
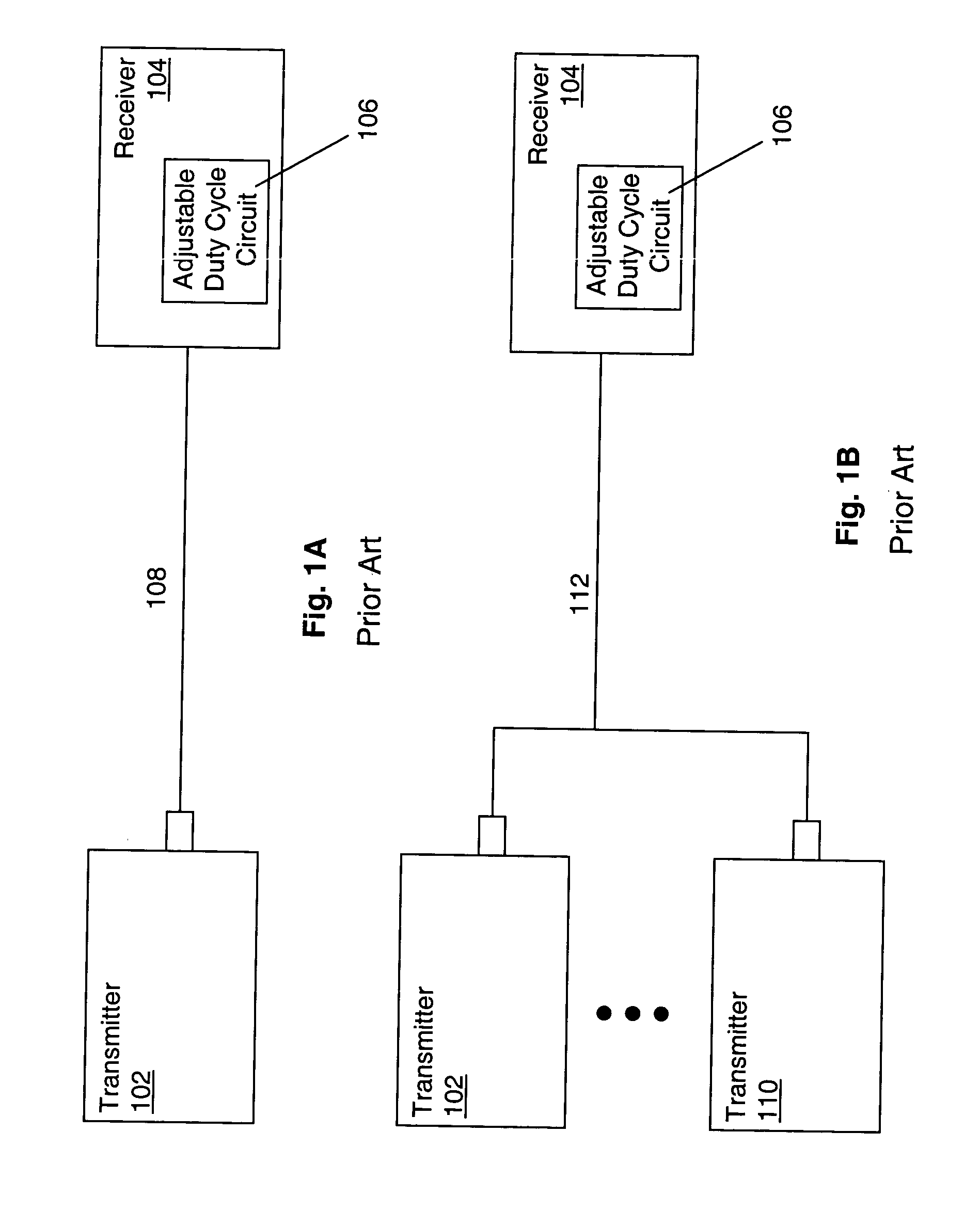
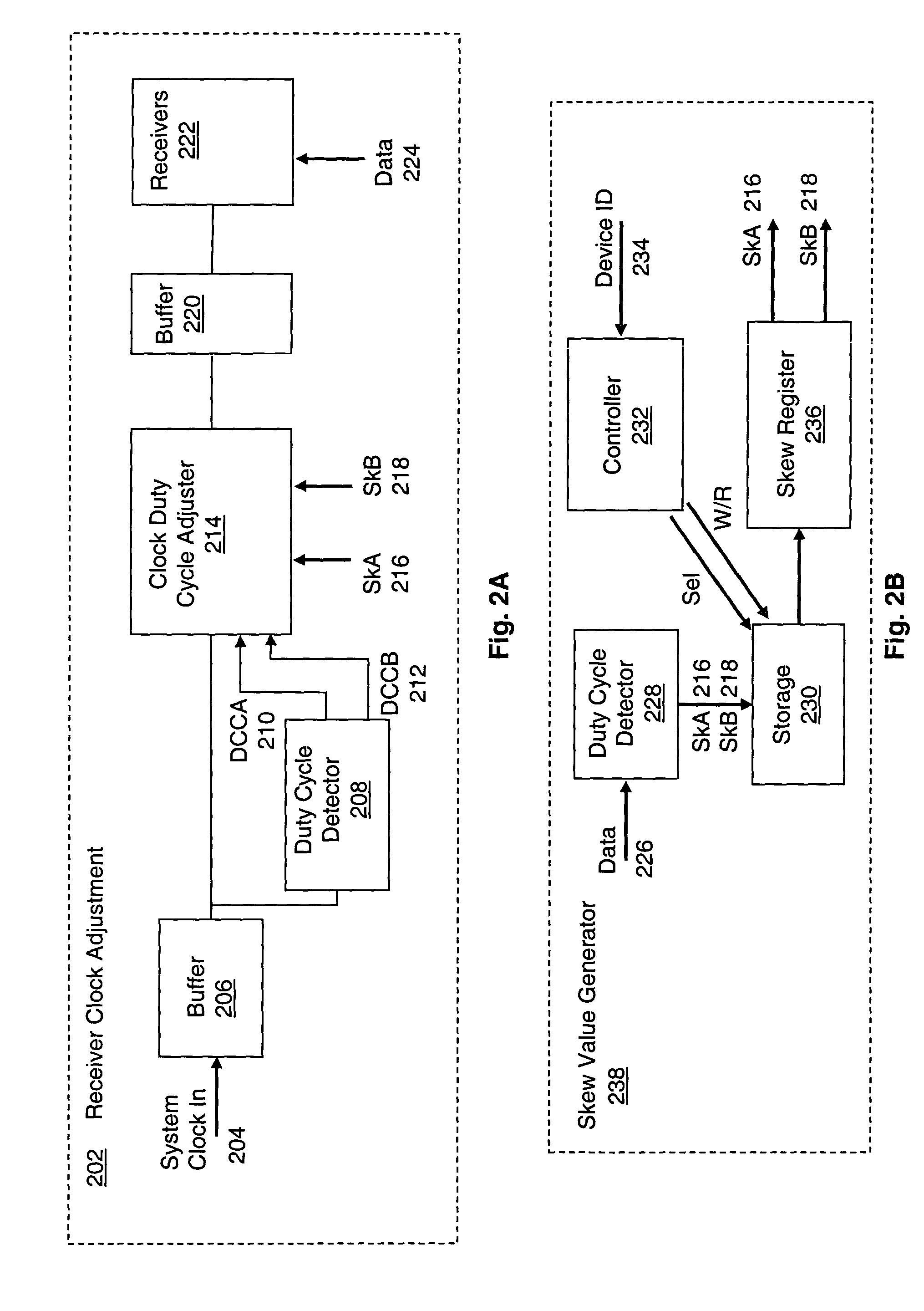
System and method for adaptive duty cycle optimization
A system and method for configuring a receiver such that the duty cycle of the receiver clock accurately matches the duty cycle of the data signal received. This adaptive system and method calibrates a receiver's duty cycle to optimize the receiver timing margin for different data signal types and different slave devices. In one embodiment, a duty cycle correction circuit matches the receiver clock to a predetermined duty cycle. The receiver clock is then configured to have a duty cycle skewed from the predetermined duty cycle based on the specific data signal received. In a receiver system utilizing a clock tree, individual branches of the clock tree are configured to have respective duty cycles skewed to match the duty cycle of a data signal received from a specific transmitting device.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
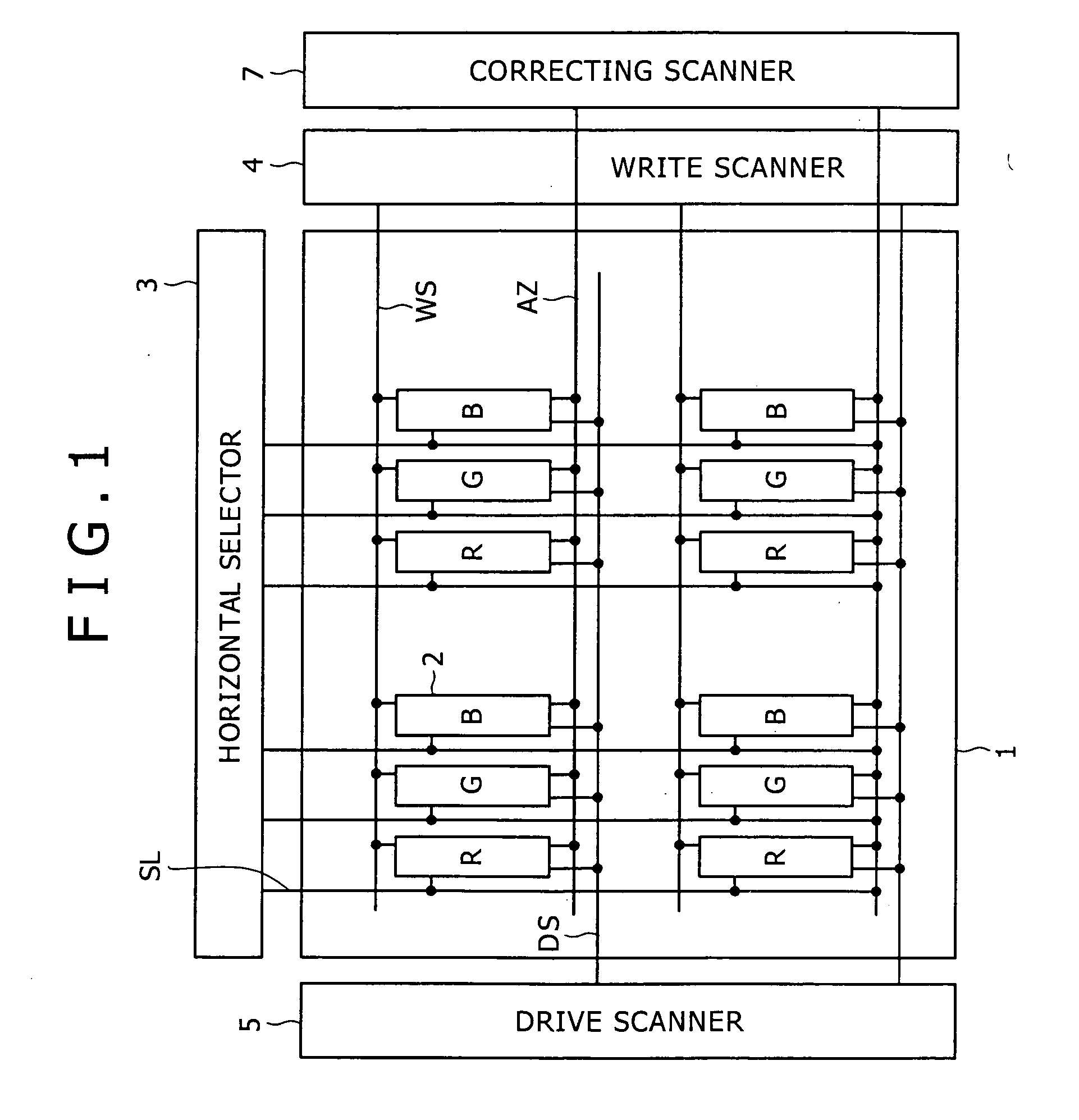
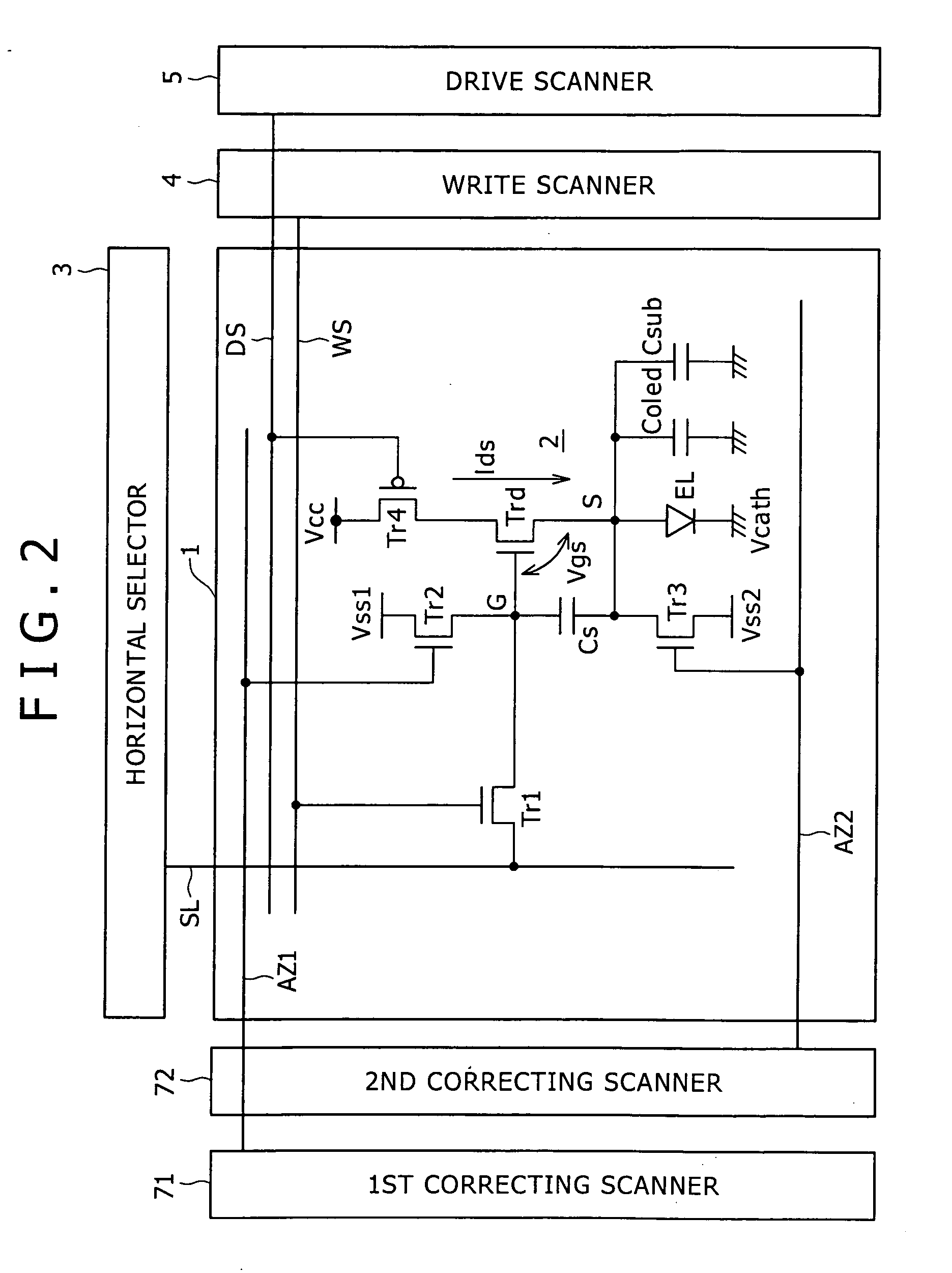
Pixel circuit and display apparatus
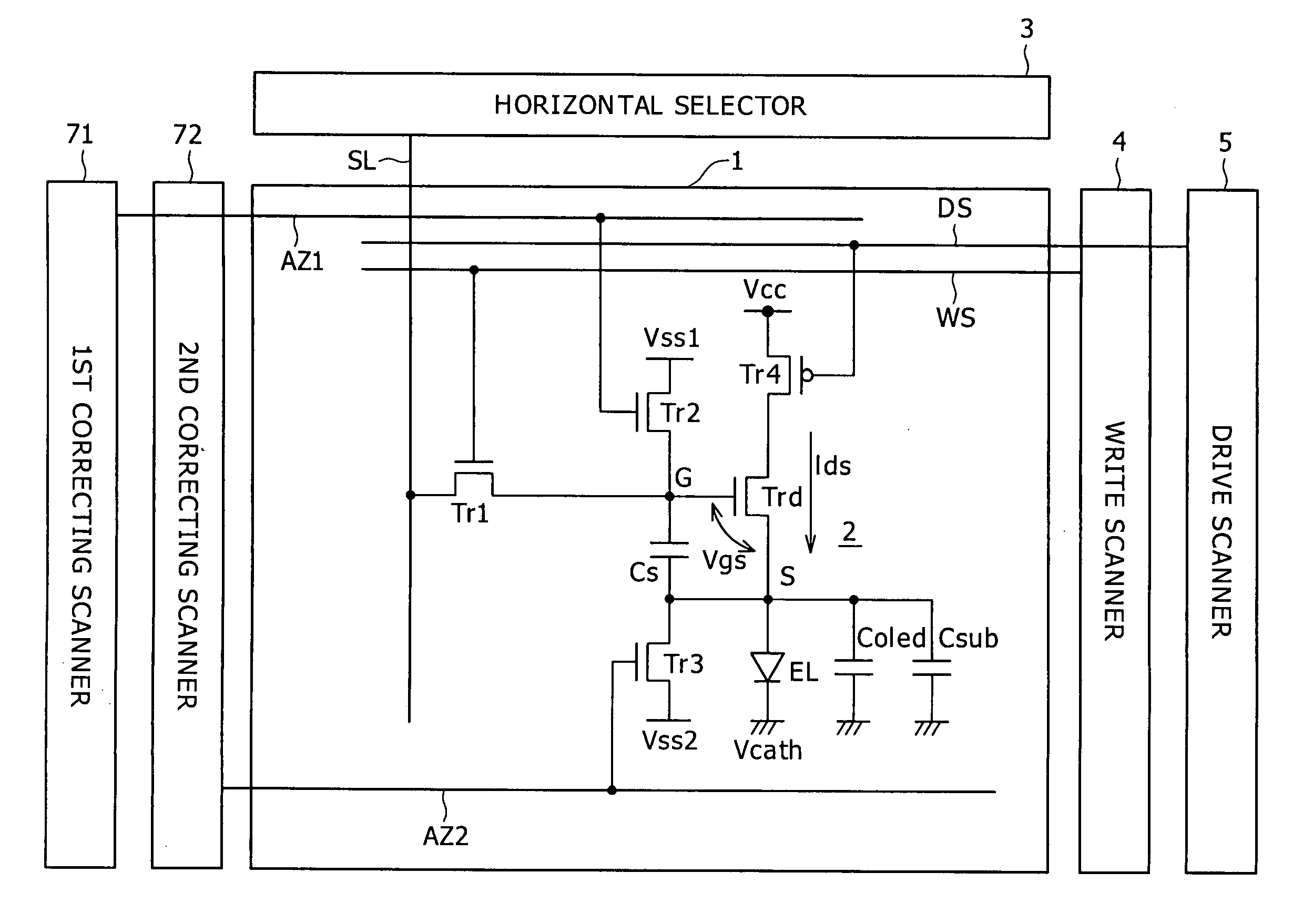
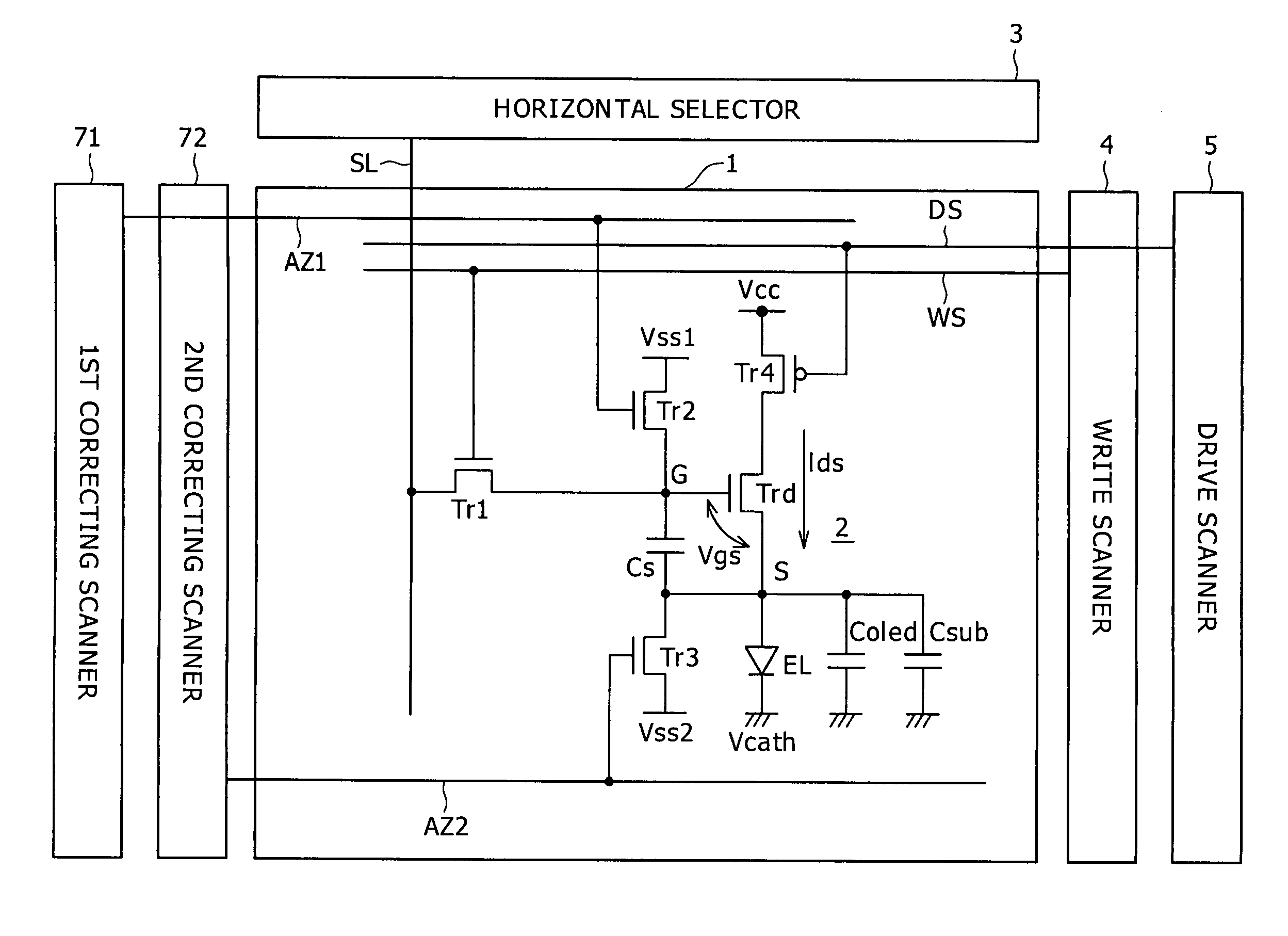
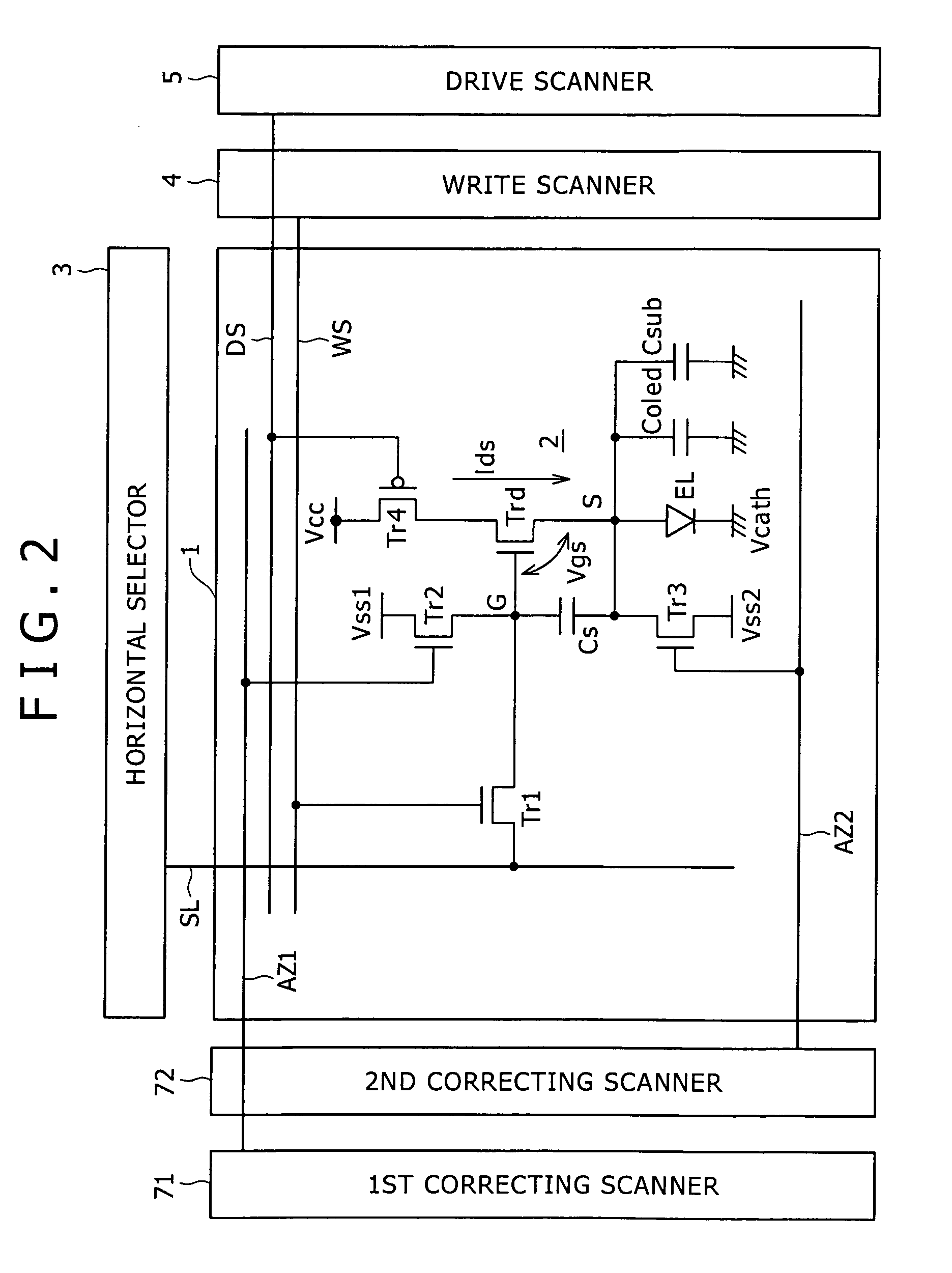
ActiveUS20070152920A1Guaranteed uptimeCorrection for variationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceTiming margin
Disclosed herein is a pixel circuit that includes a correcting section configured to correct the input voltage sampled in the pixel capacitance in order to cancel out the dependency of the output current on the carrier mobility. In the pixel circuit, the correcting section operates depending on the control signal supplied from the scanning line to extract the output current from the drive transistor and introduce the extracted output current into a capacitance of the light-emitting device and the pixel capacitance for thereby correcting the input voltage. The pixel circuit further includes an additional capacitance added to the capacitance of the light-emitting device. In the pixel circuit, portion of the output current extracted from the drive transistor flows into the additional capacitance to give a time margin to operation of the correcting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
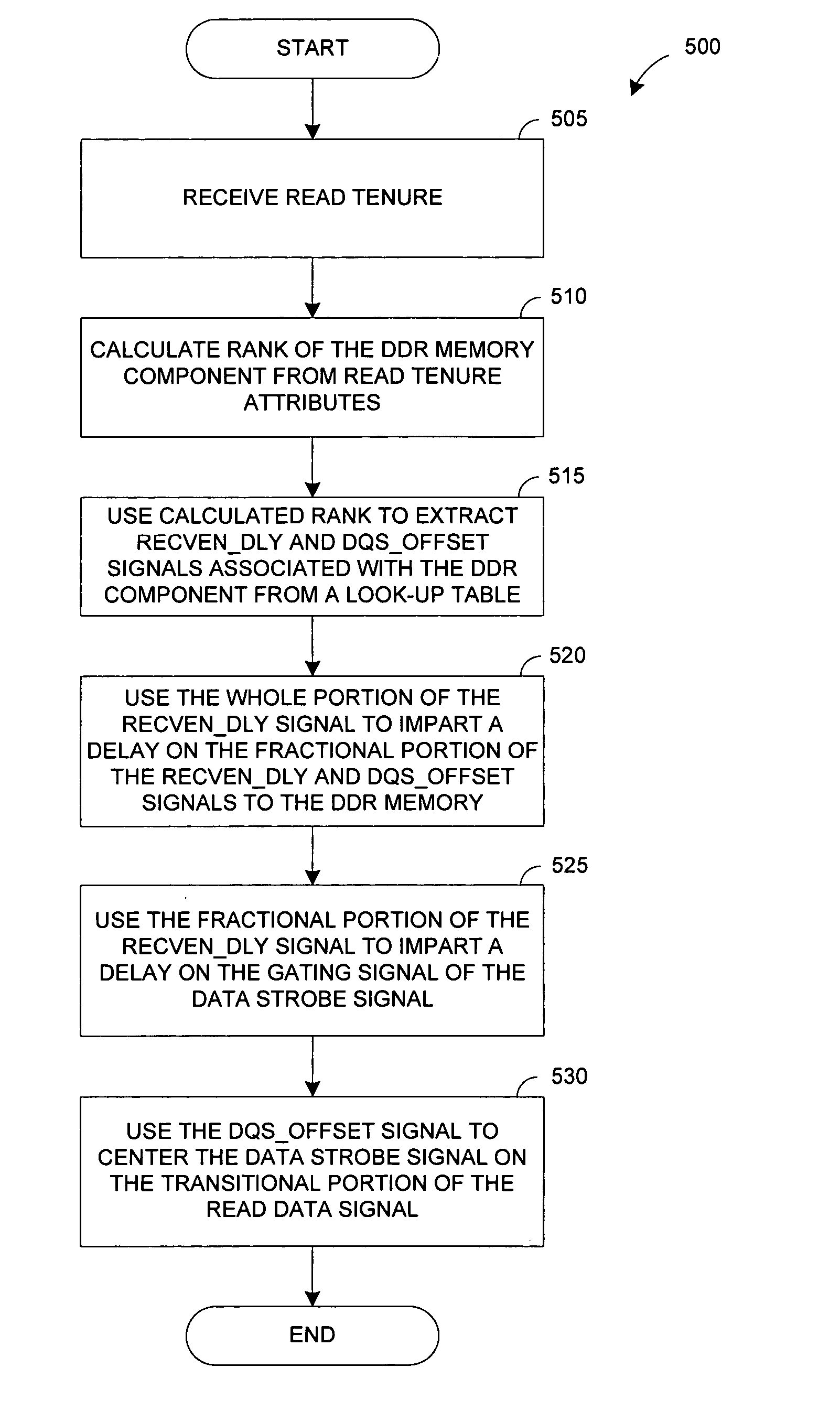
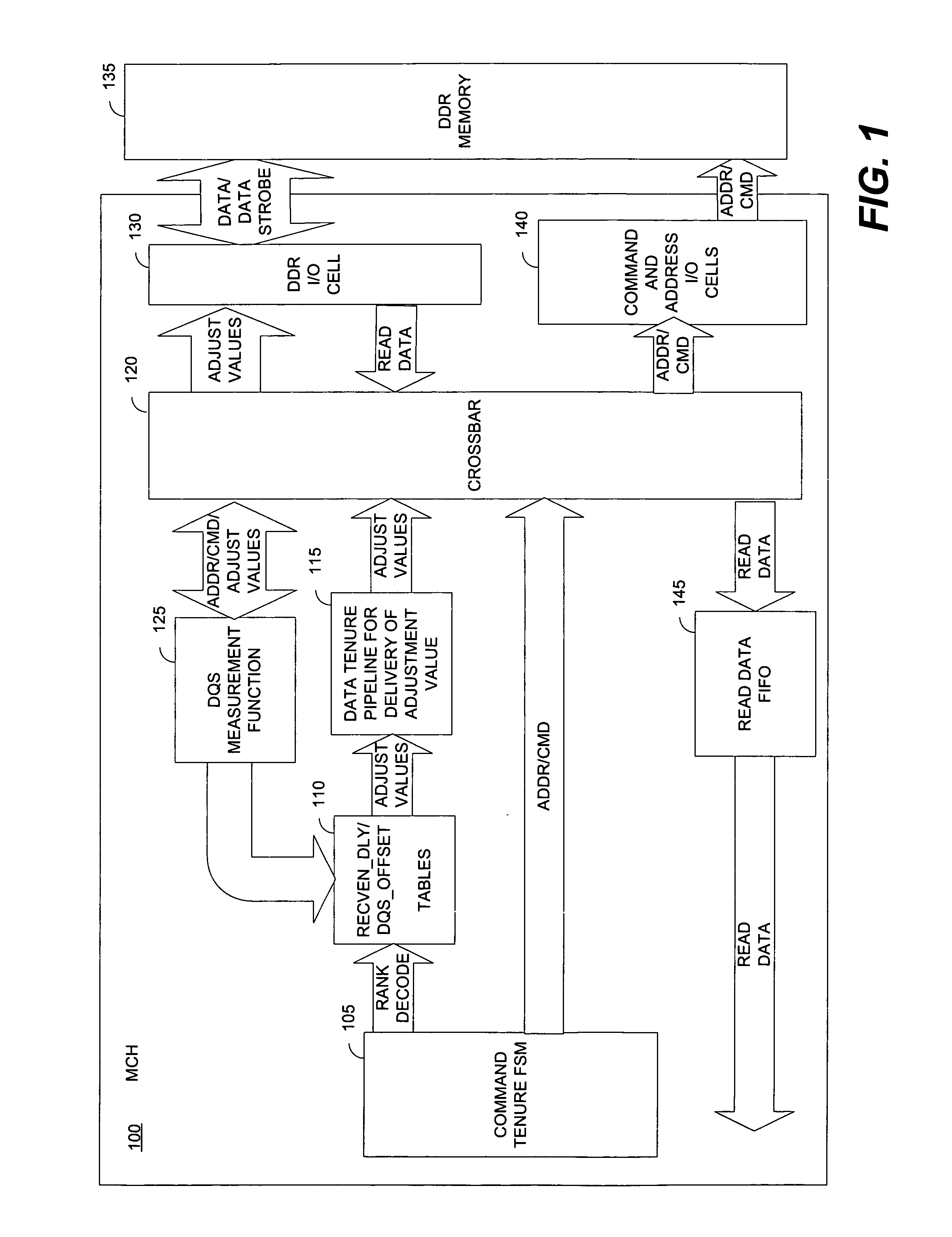
System and method for dynamic rank specific timing adjustments for double data rate (DDR) components
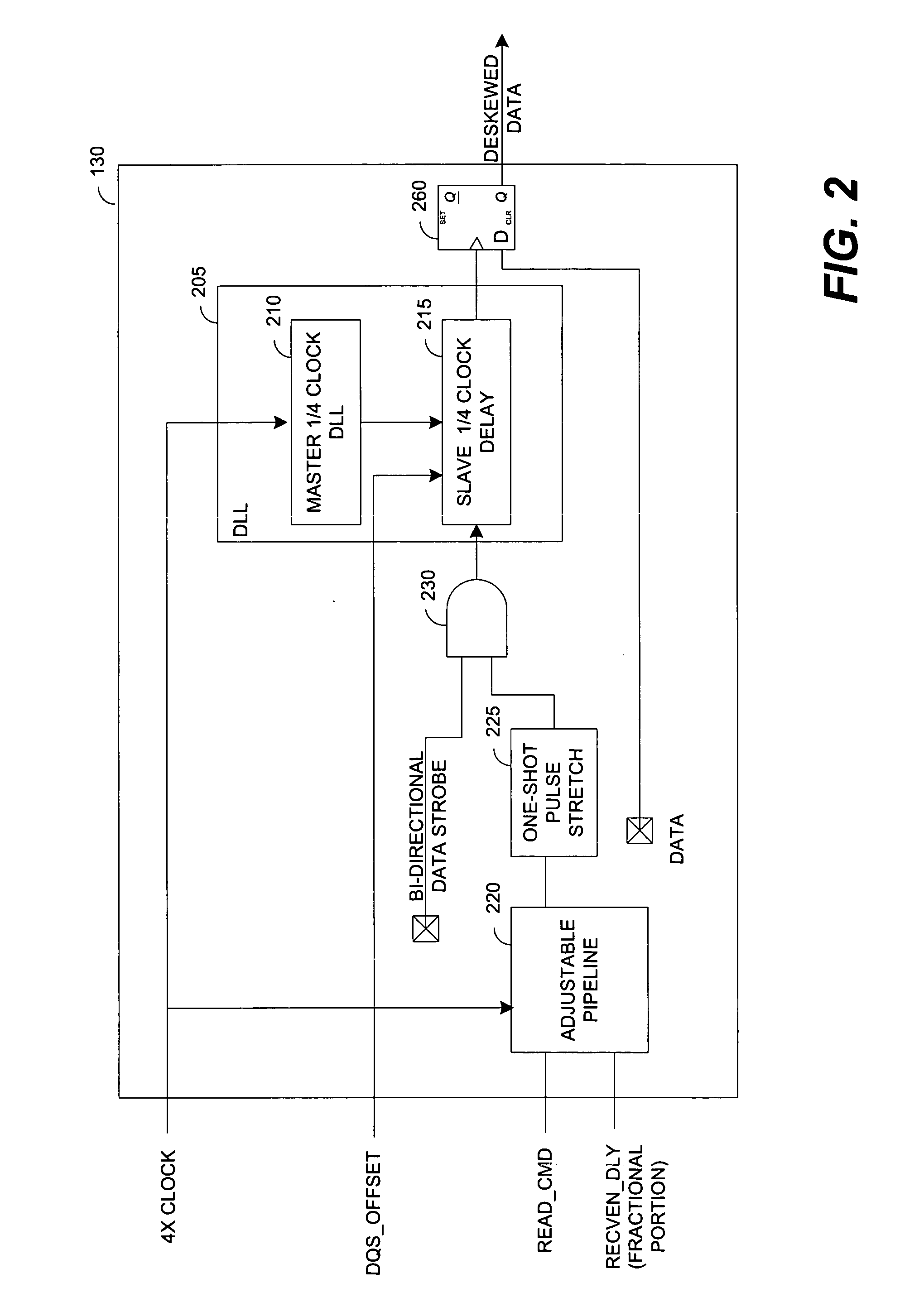
In some embodiments, a system and method for making rank-specific adjustments to the READ tenure parameters of a double data-rate (DDR) memory component to improve the DDR bus timing margins. When a READ tenure is encountered for the DDR memory component, the rank of the DDR memory component is calculated and the value is used to retrieve two adjustment signals, which are specific to the DDR memory component, from the look up table. One of the adjustment signals is used to adjust a gating signal for the data strobe signal of the component. The other adjustment signal is used to fine tune a required ¼ clock delay for the data strobe signal to read the data from the DDR memory component while adjusting for the inherent latency of the DDR memory component. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Pixel circuit and display apparatus
ActiveUS7659872B2Guaranteed uptimeUnified operationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceTiming margin
Disclosed herein is a pixel circuit that includes a correcting section configured to correct the input voltage sampled in the pixel capacitance in order to cancel out the dependency of the output current on the carrier mobility. In the pixel circuit, the correcting section operates depending on the control signal supplied from the scanning line to extract the output current from the drive transistor and introduce the extracted output current into a capacitance of the light-emitting device and the pixel capacitance, thereby correcting the input voltage. The pixel circuit further includes an additional capacitance added to the capacitance of the light-emitting device. In the pixel circuit, a portion of the output current extracted from the drive transistor flows into the additional capacitance to give a time margin to operation of the correcting section.
Owner:SONY CORP
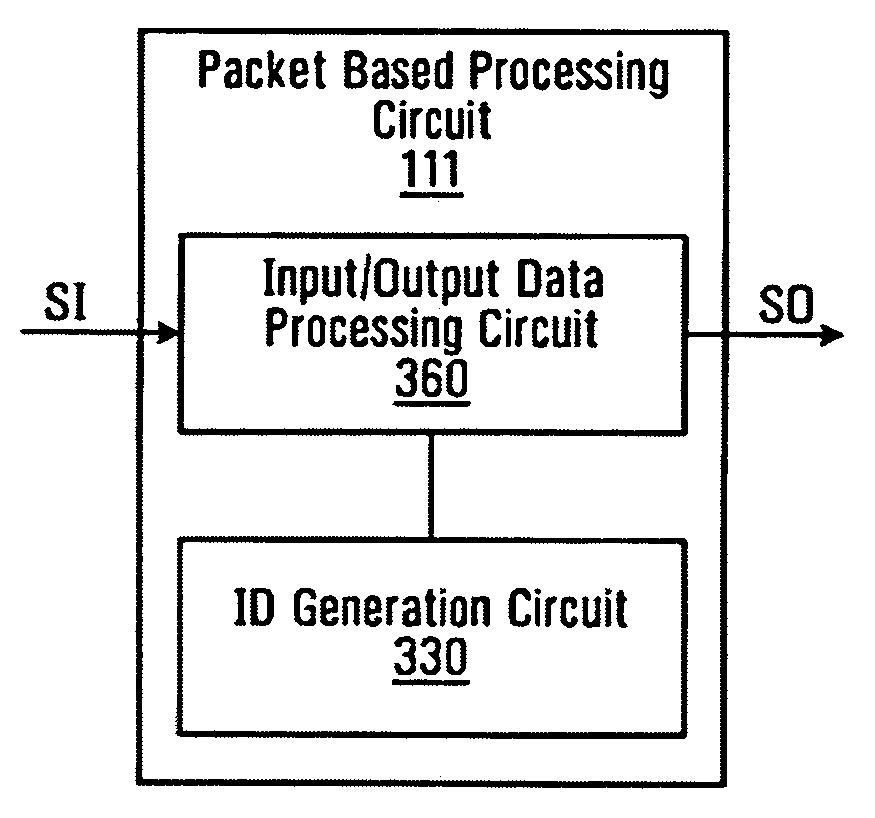
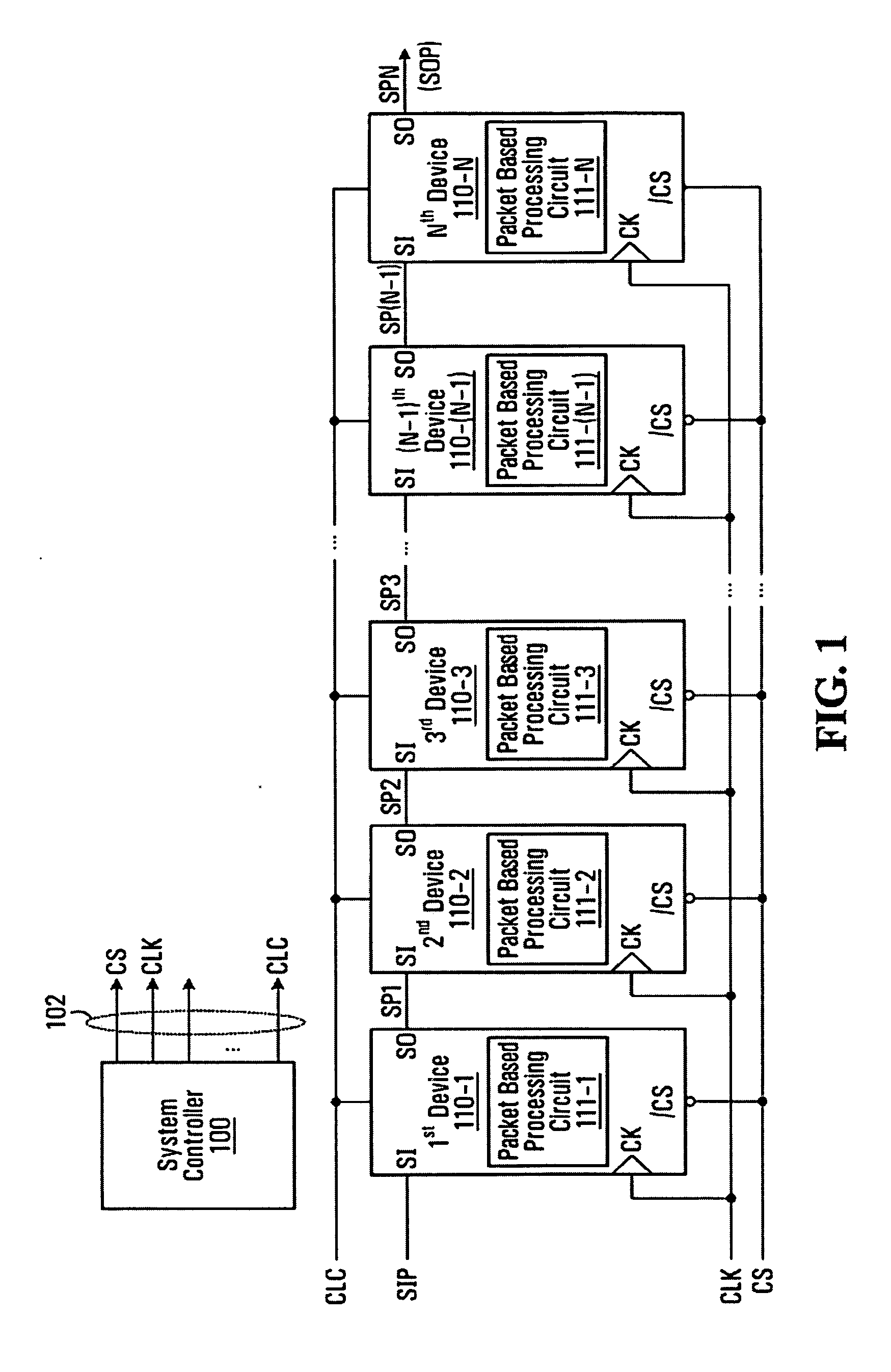
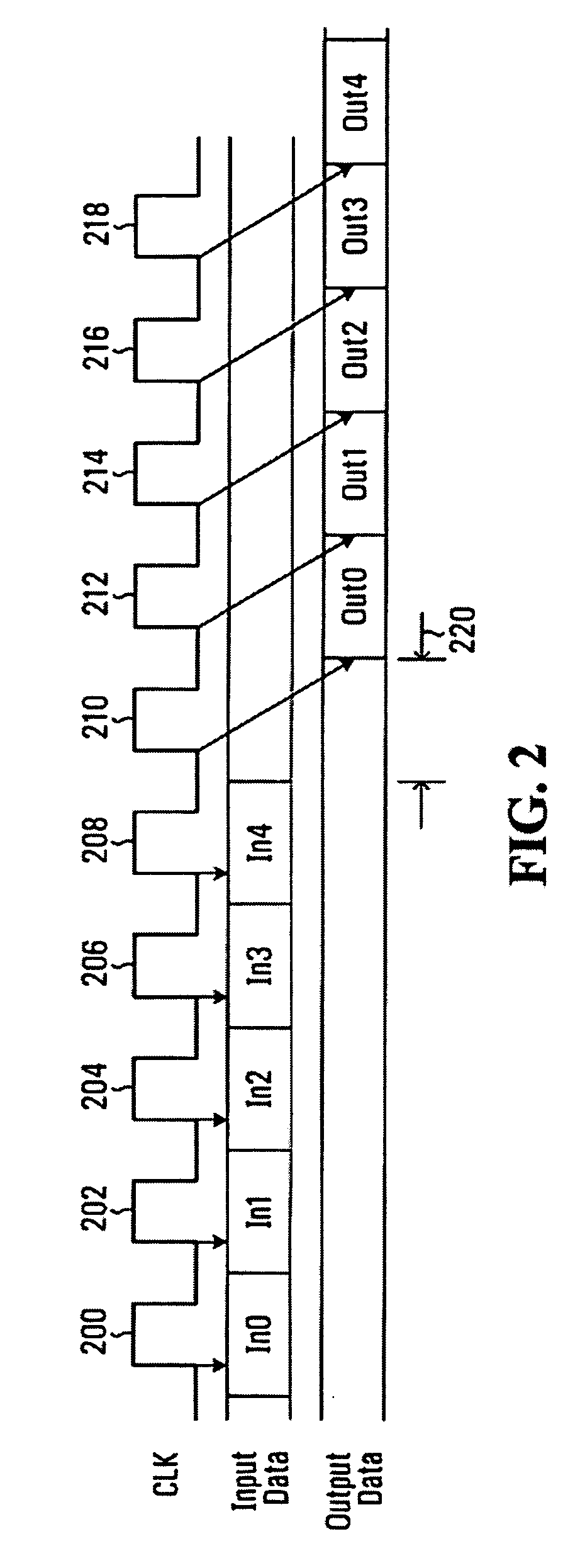
Packet based ID generation for serially interconnected devices
InactiveUS20080080492A1High bandwidthLess interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsTiming marginClock synchronization
Various memory devices (e.g., DRAMs, flash memories) are serially interconnected. The memory devices need their identifiers (IDs). Each of the memory devices generates IDs for neighboring memory devices. The IDs are generated synchronously with clock. Command data and previously generated ID data are synchronously registered. The registered data is synchronously output and provided as parallel data for calculation of a new ID for the neighboring device. The calculation is an addition or subtraction by one. The IDs are generated in a packet basis by interpreting serial packet-basis commands received at the serial input in response to clocks. A clock latency is controlled in response to the interpreted ID and the clock. In accordance with the controlled clock latency, a new ID is provided in a packet basis. In high frequency generation applications (e.g., 1 GHz), two adjacent devices connected in daisy chain fashion are guaranteed enough time margin to perform the interpretation of packet commands.
Owner:NOVACHIPS CANADA
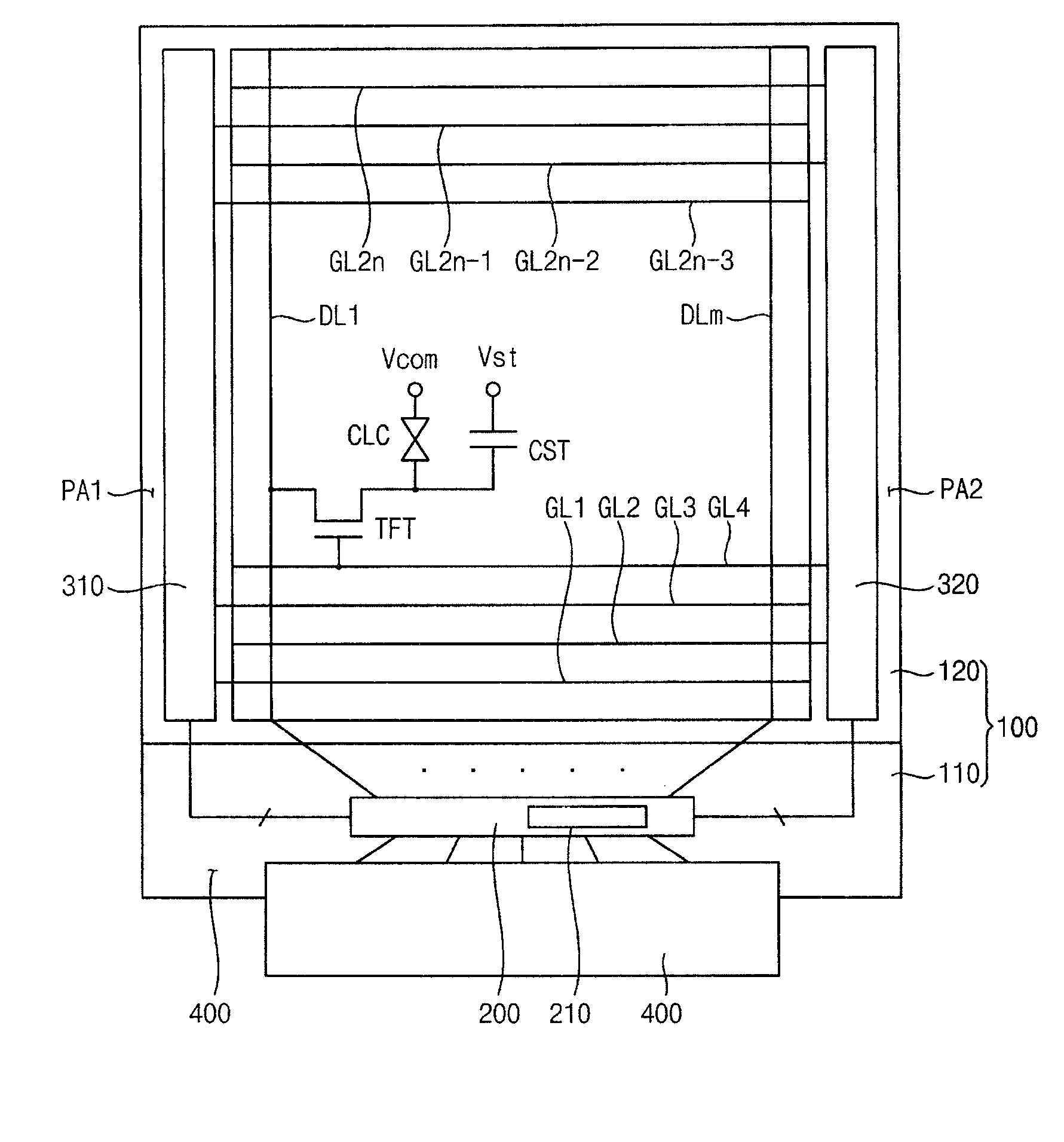
Gate driving circuit and display device having the gate driving circuit
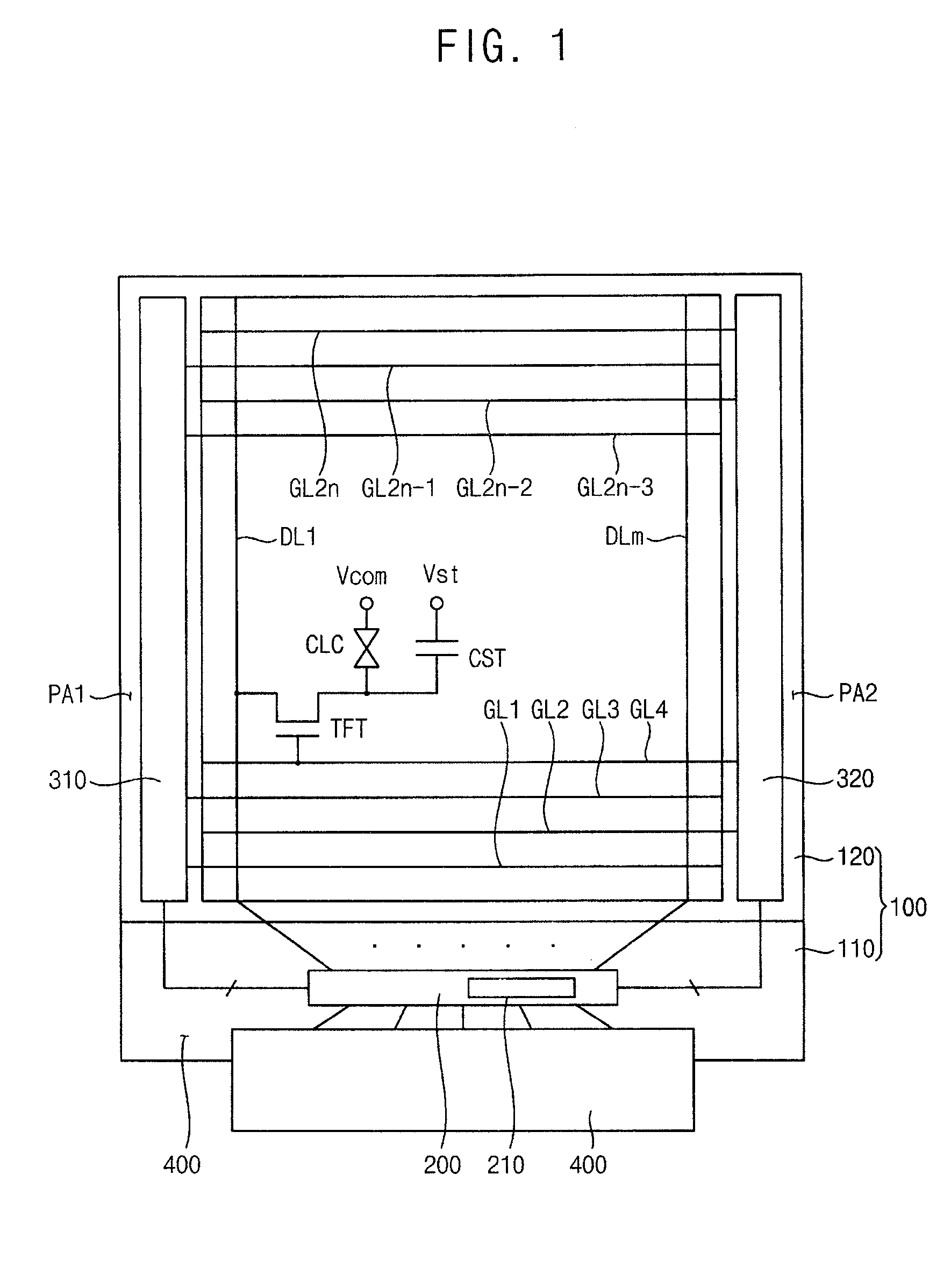
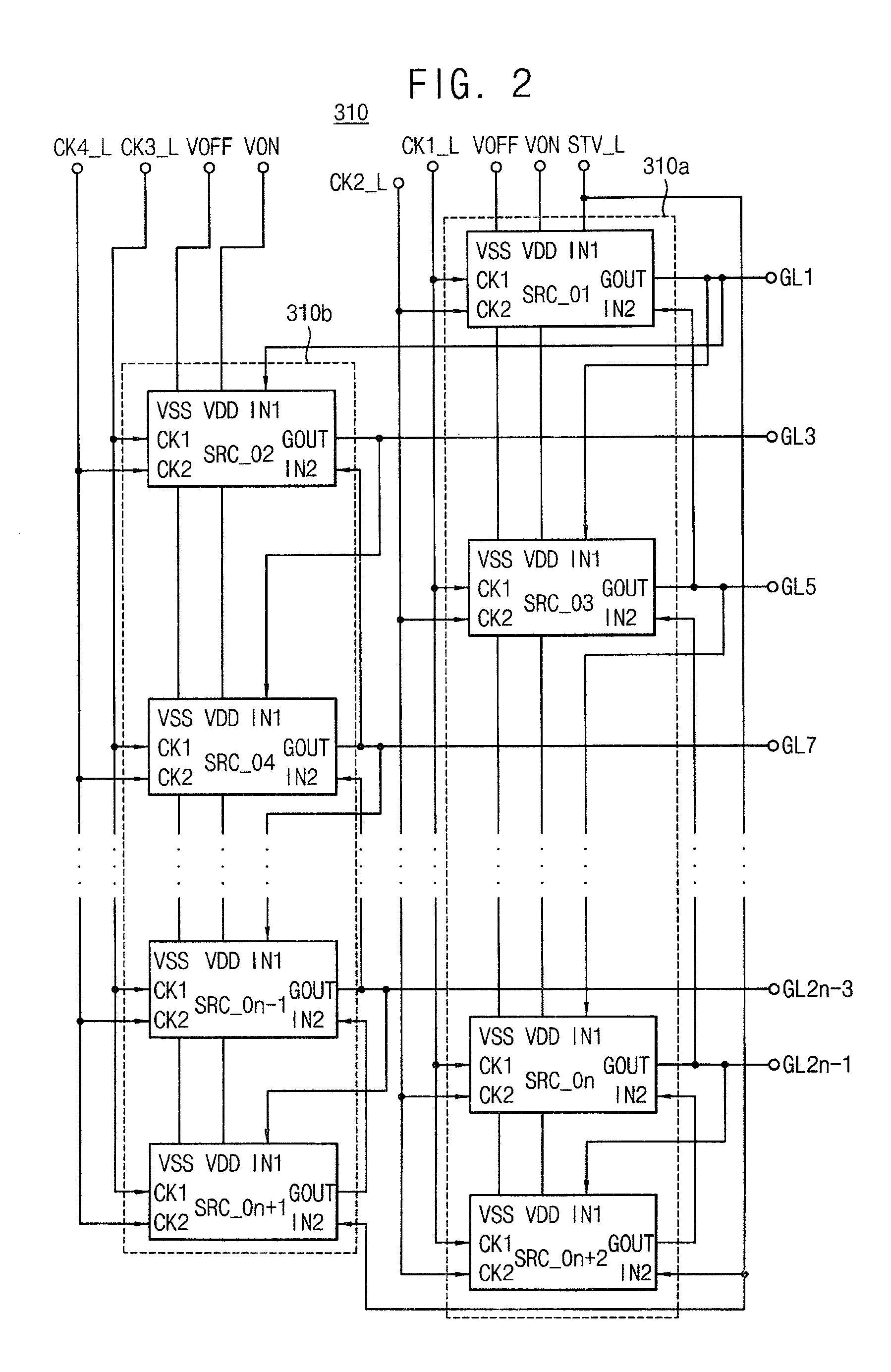
InactiveUS20100164915A1Improve driving reliabilityImprove gate reliabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorTiming marginShift register
A gate driving circuit includes a first shift register and a second shift register for driving odd gate lines. The first shift register includes a first plurality of cascade-connected stages that sequentially output a plurality of first gate signals. A first stage of the first shift register receives a first vertical start signal. The second shift register includes a second plurality of cascade-connected stages to sequentially output a plurality of second gate signals. The first stage of the second shift register receives an output signal of the first stage of the first shift register as its vertical start signal. A data charging rate may be improved by ensuring the timing margin of each gate signal, so that the driving reliability of the gate driving circuit may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
System and method for adaptive duty cycle optimization
A system and method for configuring a receiver such that the duty cycle of the receiver clock accurately matches the duty cycle of the data signal received. This adaptive system and method calibrates a receiver's duty cycle to optimize the receiver timing margin for different data signal types and different slave devices. In one embodiment, a duty cycle correction circuit matches the receiver clock to a predetermined duty cycle. The receiver clock is then configured to have a duty cycle skewed from the predetermined duty cycle based on the specific data signal received. In a receiver system utilizing a clock tree, individual branches of the clock tree are configured to have respective duty cycles skewed to match the duty cycle of a data signal received from a specific transmitting device.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
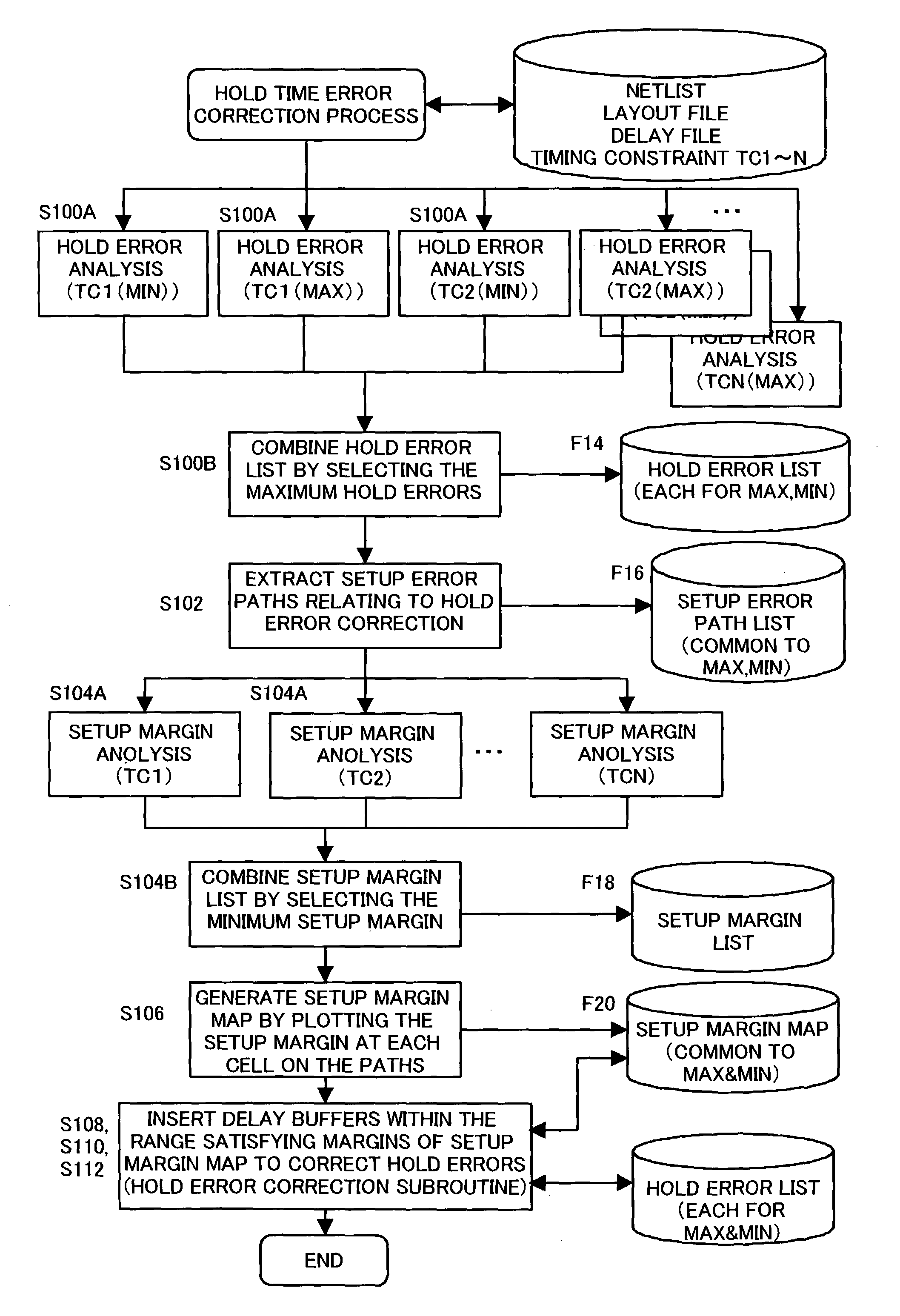
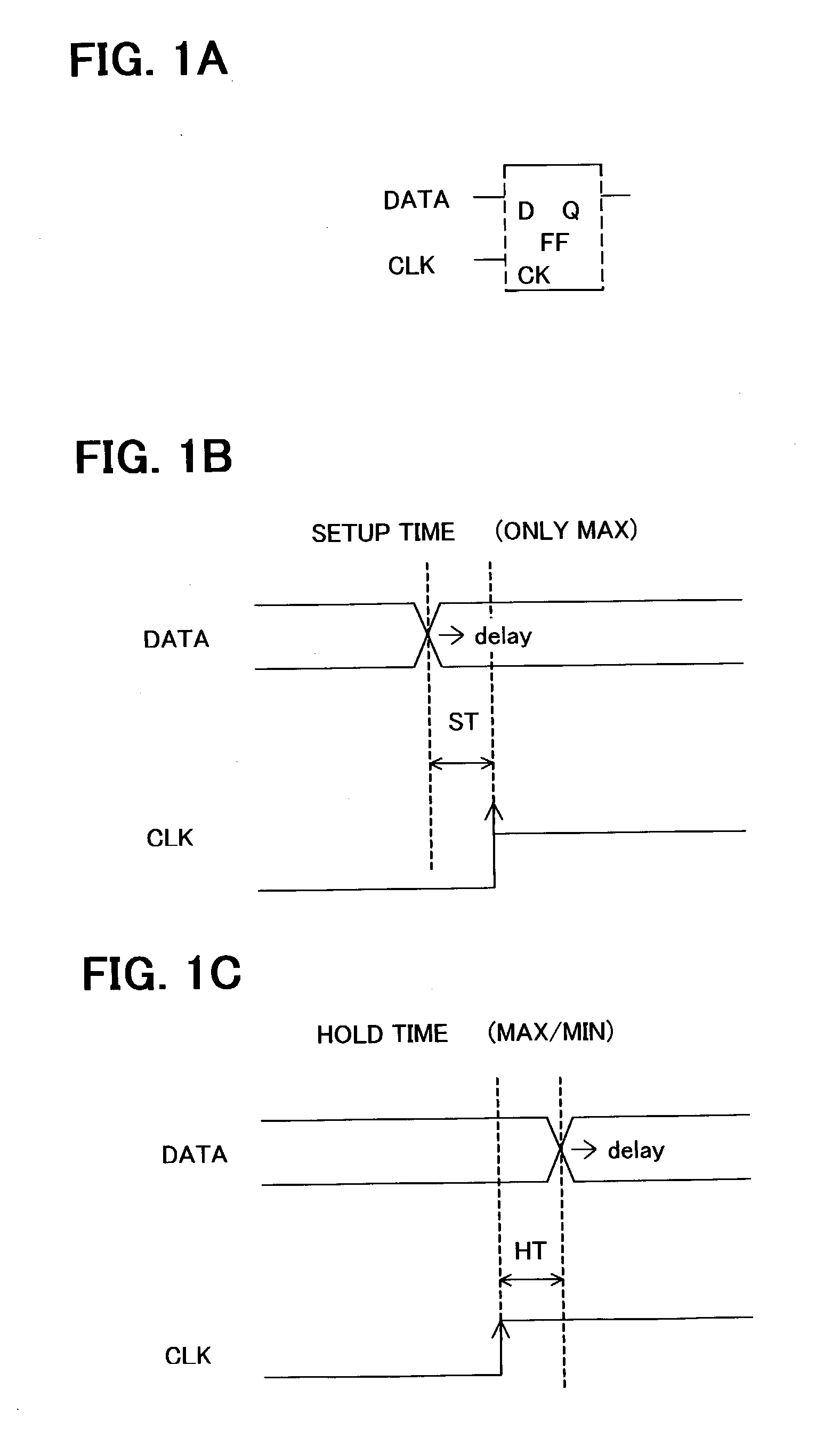
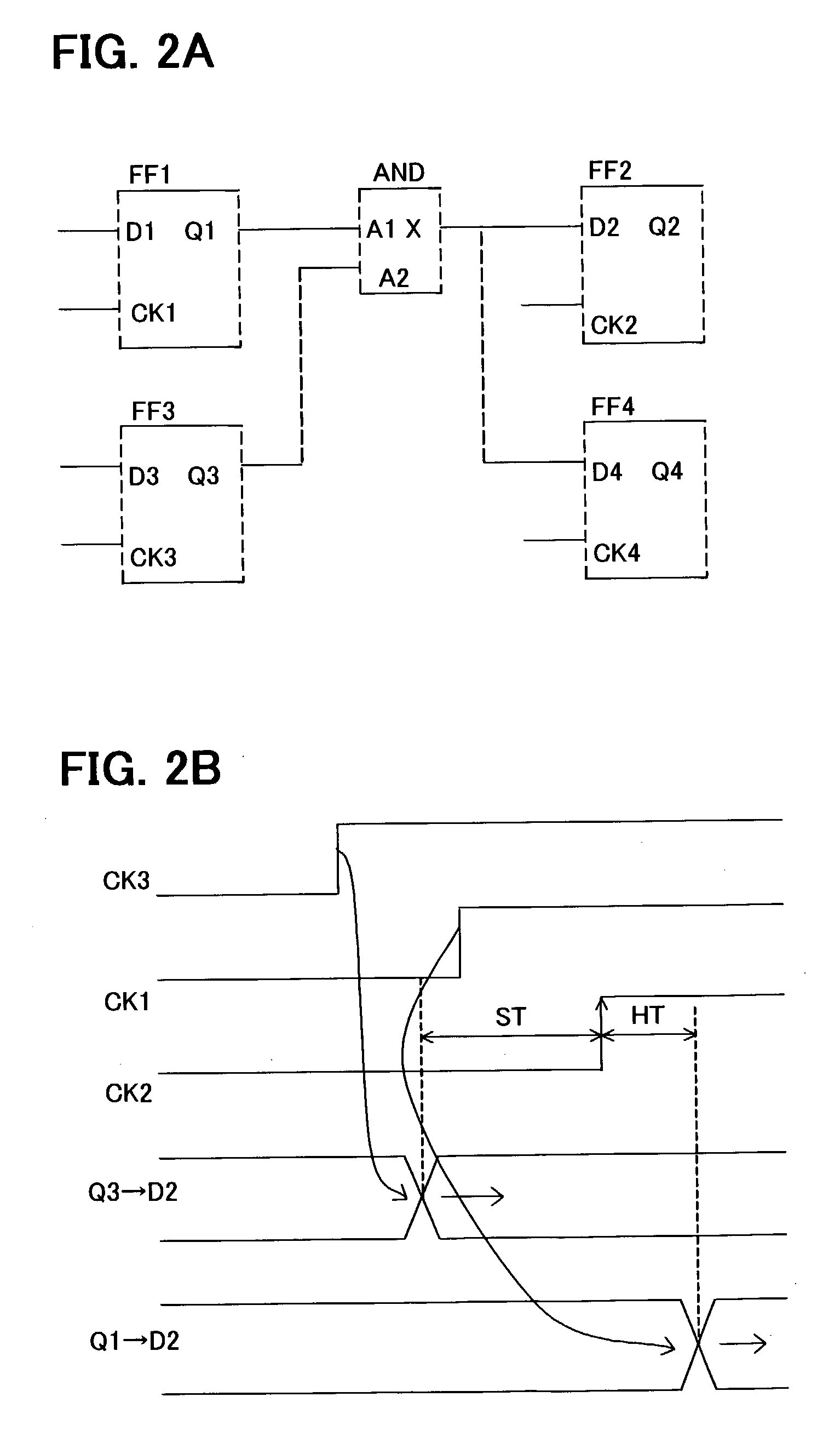
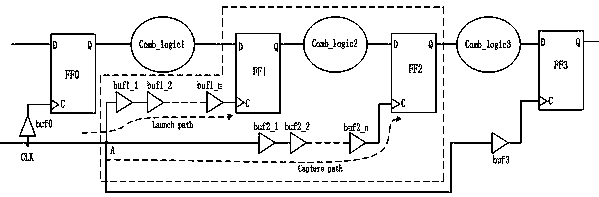
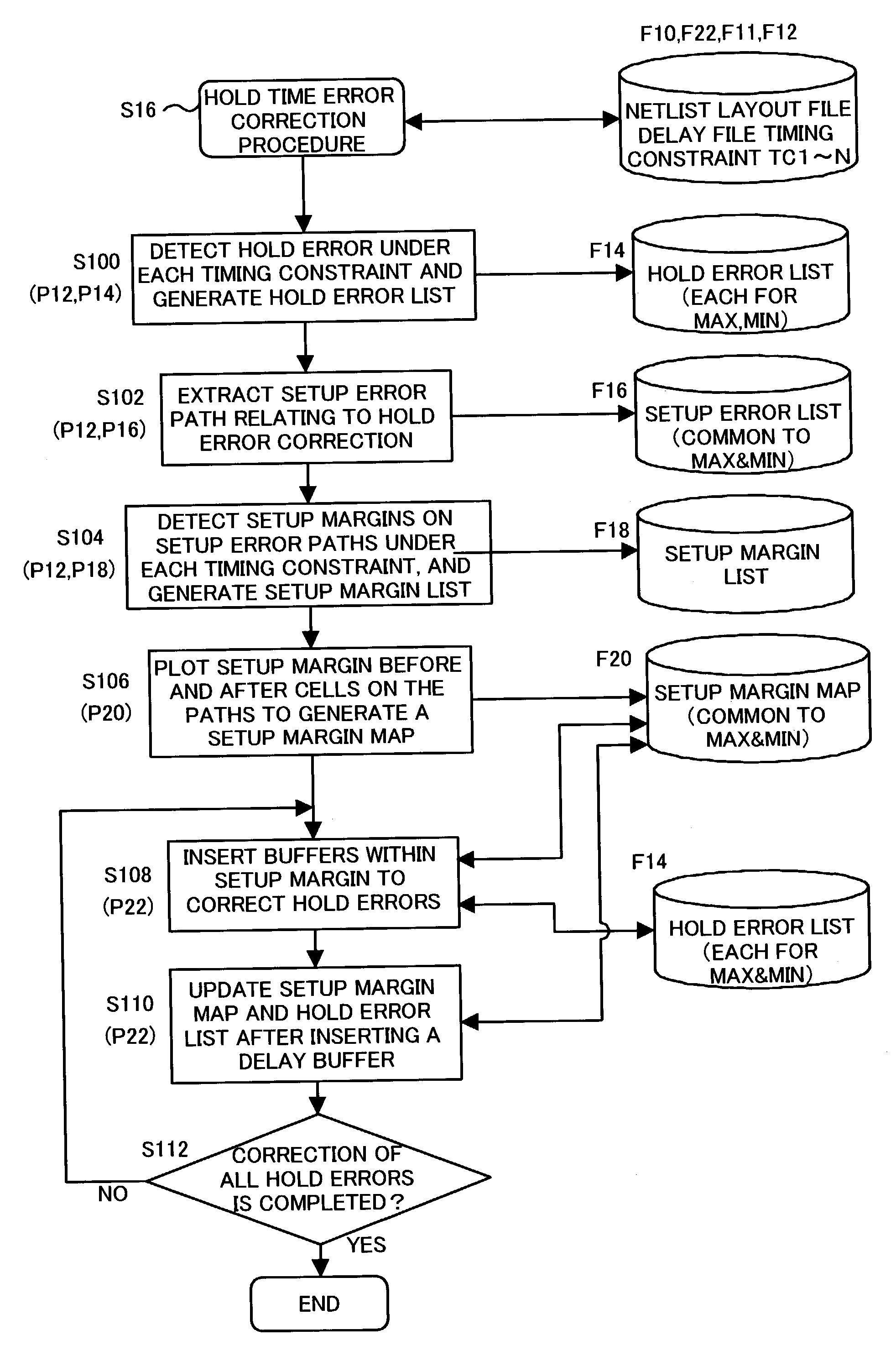
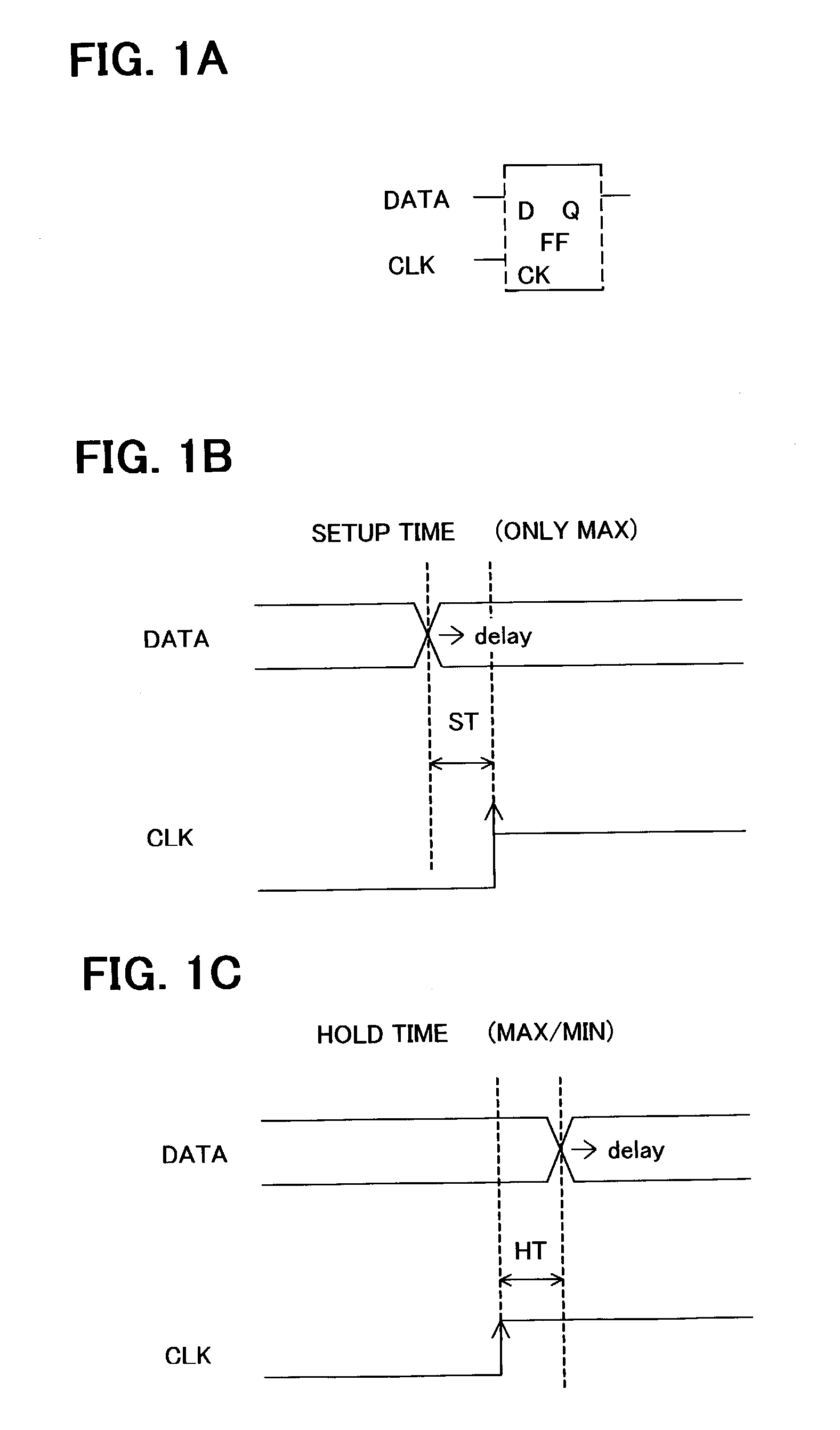
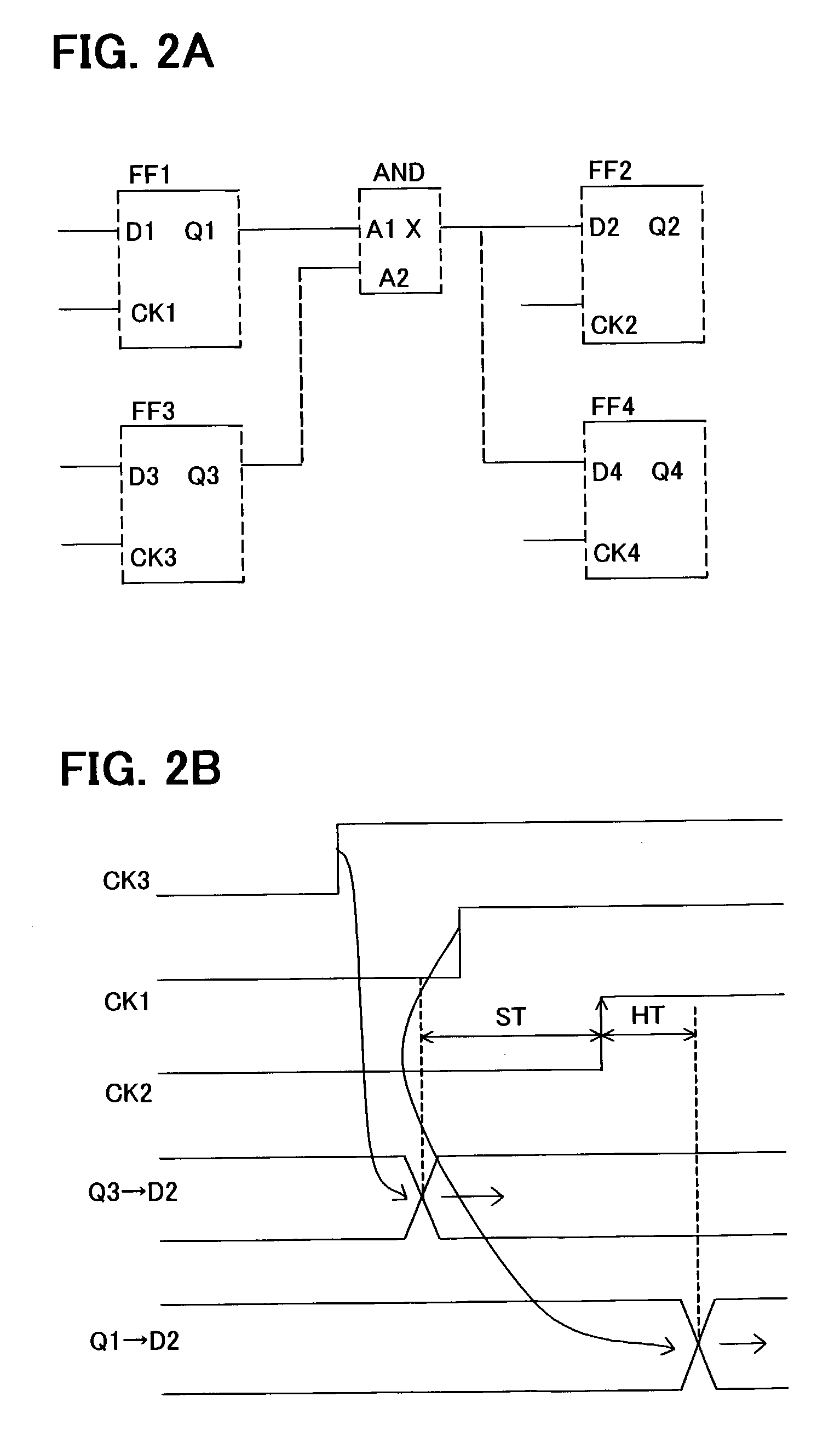
Hold time error correction method and correction program for integrated circuits
A hold time error list, having for each hold time error path a hold time error value satisfying plural timing constraints, and more specifically a maximum hold time error value for each of timing constraints, as well as a setup time margin map allocating to path a setup time margin satisfying plural timing constraints for each setup time error path, and more specifically minimum value of setup time margins for the same path for each timing constraint, are generated. Also, referring to this setup time margin map, delay buffers, which reduces or eliminates hold time error of hold error list, and a delay of which is within the range of delay amounts and positions equal to or lower than the setup time margin, are inserted. Referring to the setup time margin map, it is possible to insert delay buffer to correct hold time error without causing new setup time errors.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
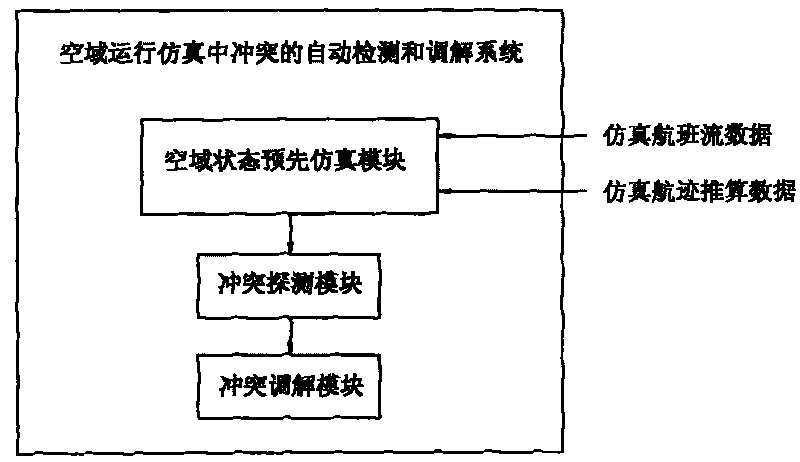
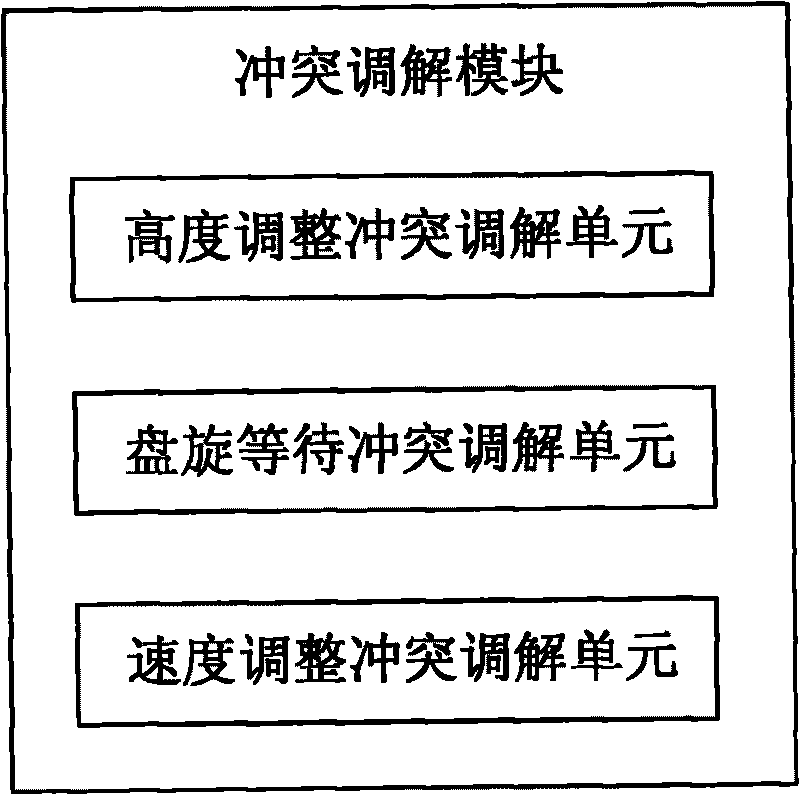
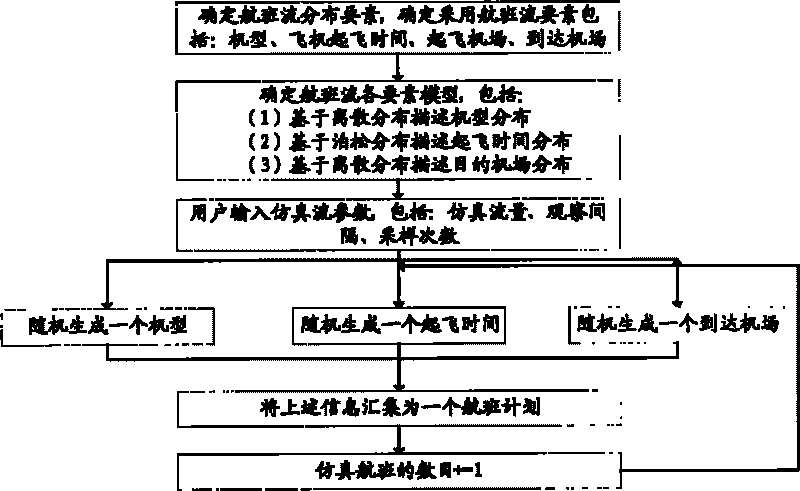
System and method for automatically detecting and reconciling conflicts in airspace operation simulation
ActiveCN101694752AMeet the complexity requirementsEasy to detectForecastingAircraft traffic controlTiming marginComputer science
The invention discloses a system and a method for automatically detecting and reconciling conflicts in airspace operation simulation. The system comprises an airspace pre-simulating module, a conflict detecting module and a conflict reconciling module, wherein the airspace pre-simulating module is used for detecting the operation condition of a simulated airspace in a future period; the conflict detecting module is used for detecting the conflict condition of flying flow in the airspace at a certain point of time; and the conflict reconciling module is used for reconciling detected flying conflicts within a required and allowed time margin of reconciling time. The system realizes the automatic detection and processing of flying conflicts in the airspace simulation operation by simple algorithm and enables the airspace simulation to be closer to real operation condition of the airspace, thereby providing an assistant decision-making means for scientific assessment and planning of airspace operation.
Owner:AVIATION DATA COMM +1
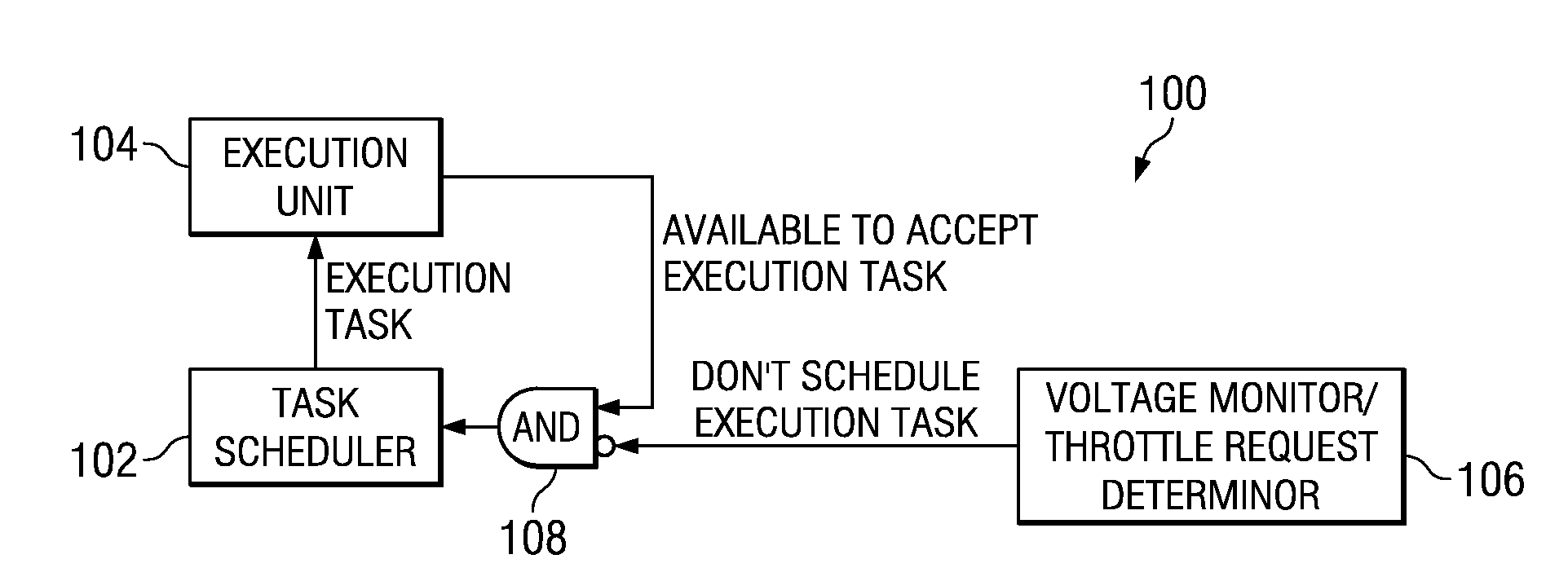
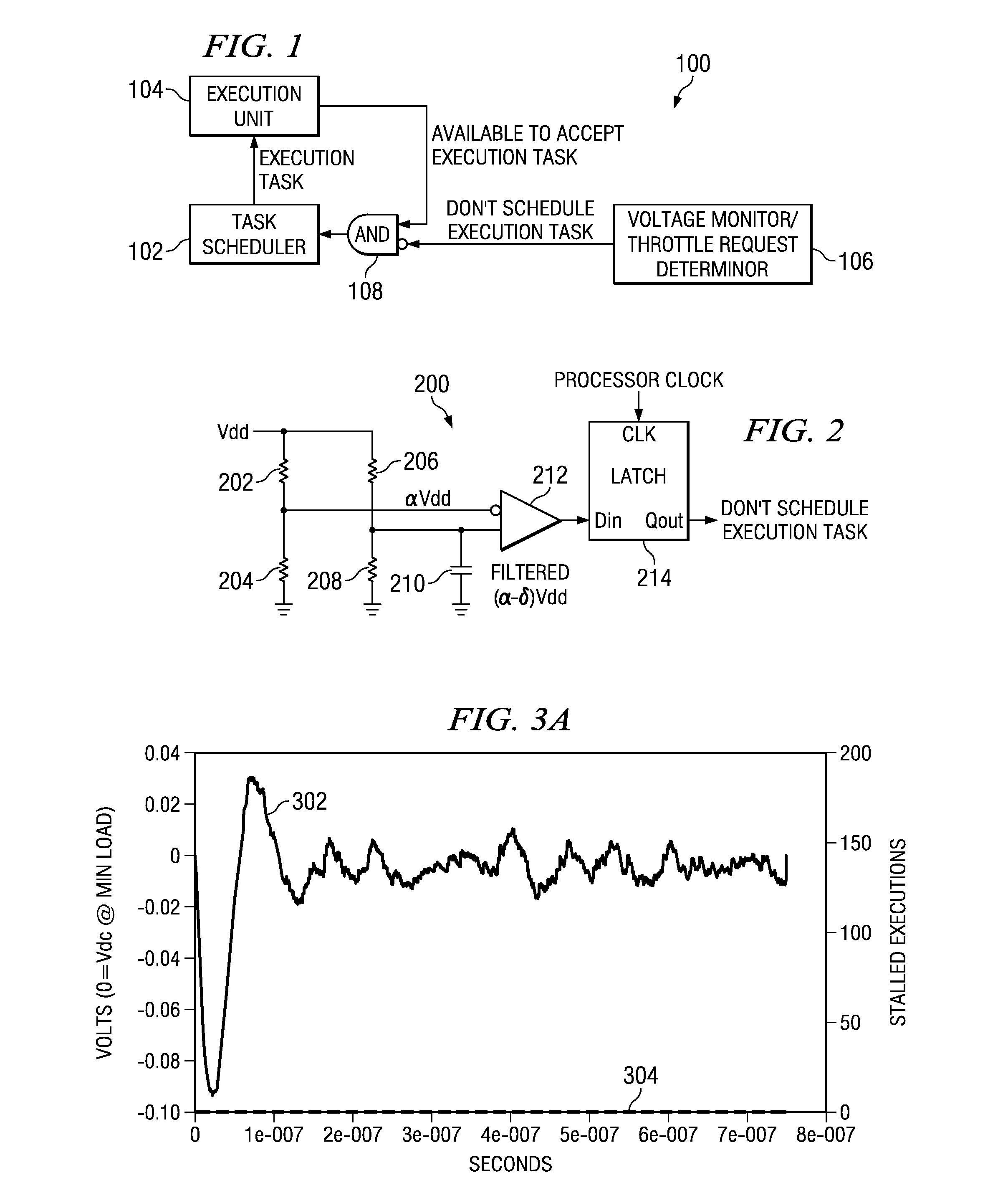
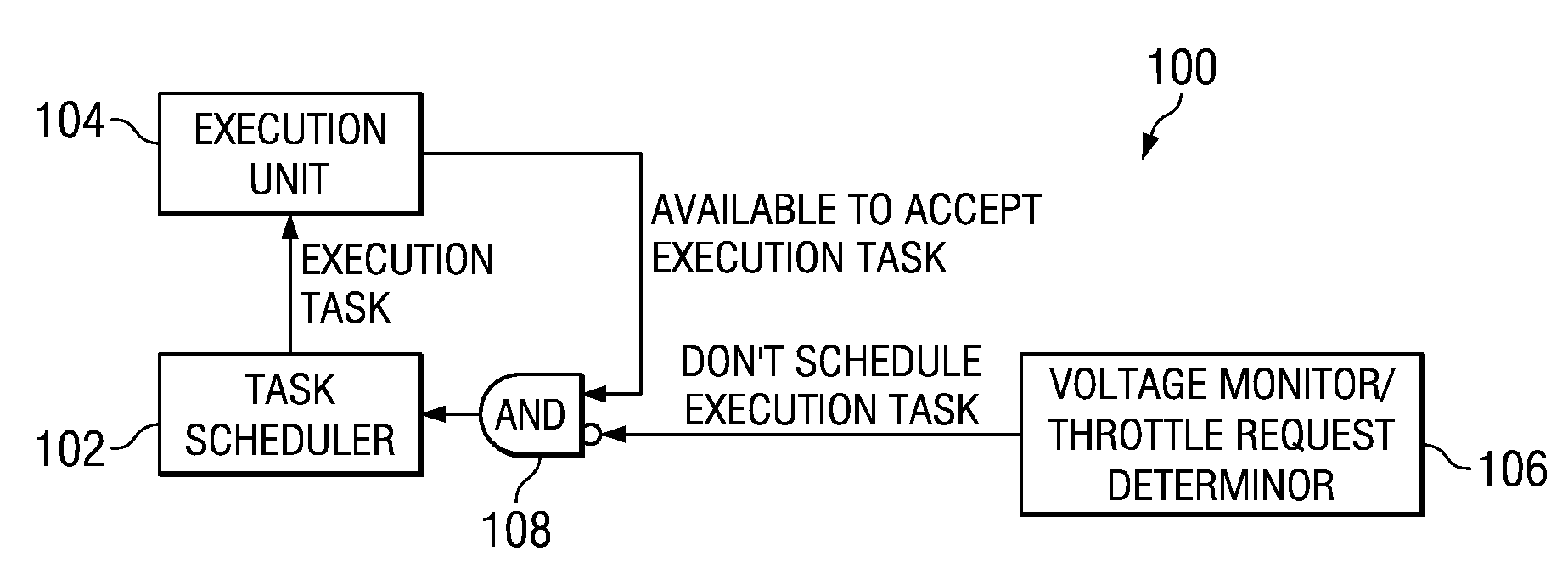
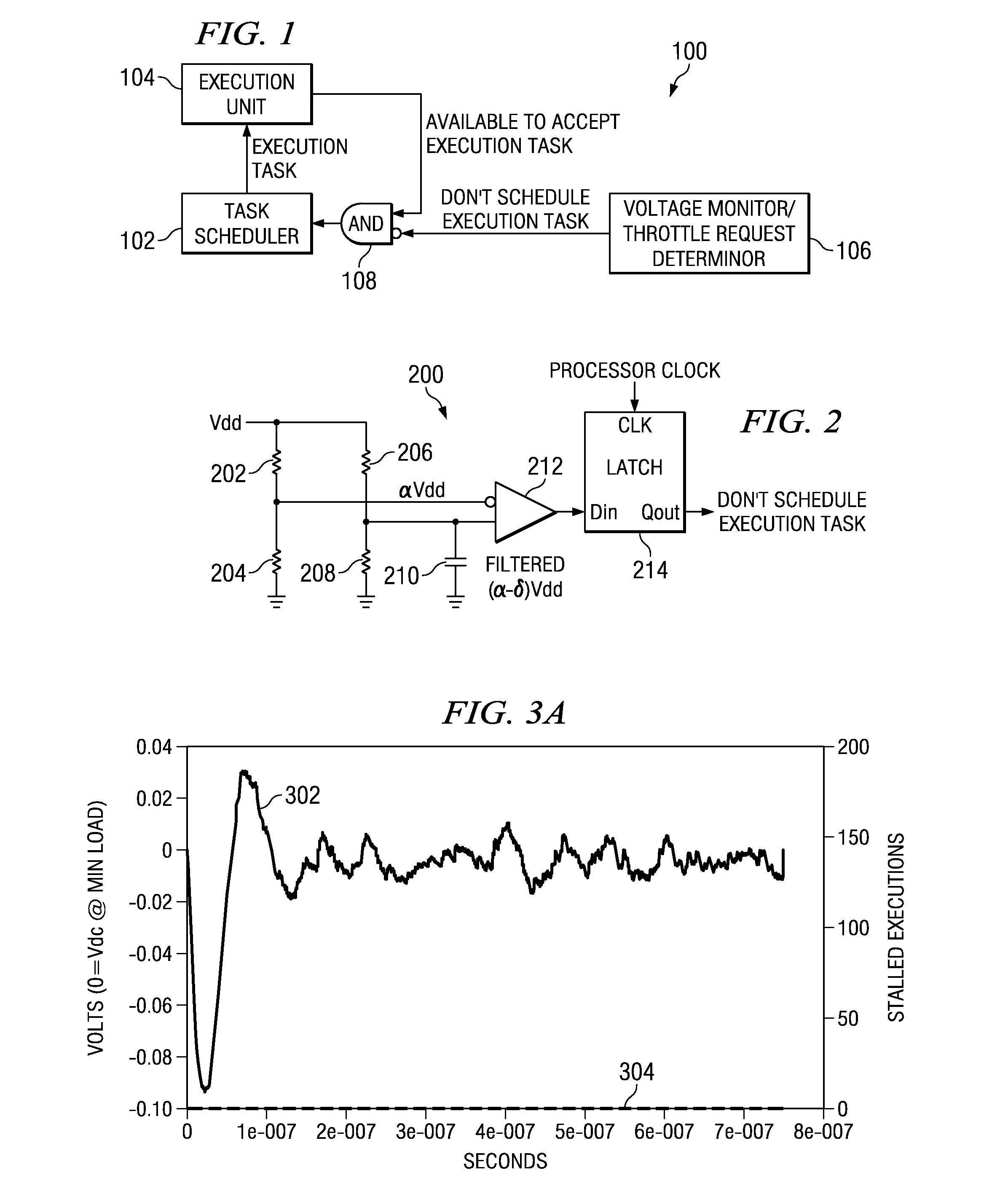
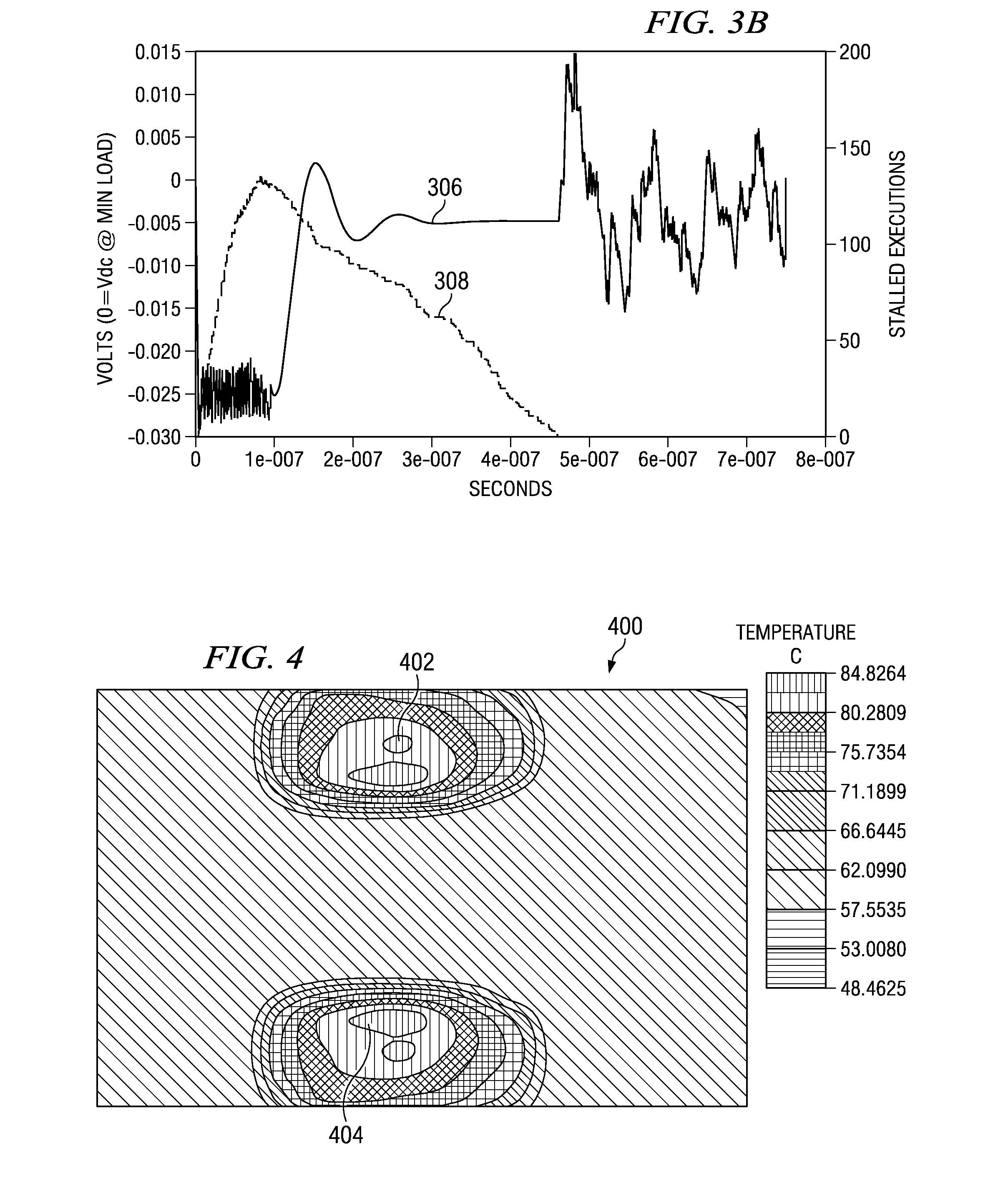
Application of Multiple Voltage Droop Detection and Instruction Throttling Instances with Customized Thresholds Across a Semiconductor Chip
InactiveUS20090063065A1Energy efficient ICTCurrent/voltage measurementTiming marginSemiconductor chip
A method and system for applying multiple voltage droop detection and instruction throttling instances with customized thresholds across semiconductor chips. Environmental parameters are detected for various locations on a chip, and timing margins are determined for each location on the chip. An acceptable voltage droop for each location is determined based on the environmental parameters and the timing margins for the corresponding location. A droop threshold is then determined for each location based on the corresponding acceptable voltage droop determined for the corresponding location.
Owner:IBM CORP
Stacked capacitor memory
InactiveUS20070183191A1Reduce chip areaLess complicated to fabricateSolid-state devicesDiodeEngineeringMulti port
Stacked capacitor memory is realized, wherein a capacitor stores data and a diode serves as an access device instead of MOS transistor, the first terminal is connected to a word line, the second terminal is connected to the first electrode of the capacitor which serves as a storage node while the second electrode is connected to a plate line, the third terminal is floating, and the fourth terminal is connected to a bit line. When write, the storage node is charged or not, depending on the conducting state of the diode which is controlled by the bit line. When read, the diode also serves as a sense amplifier to detect whether the storage node is forward bias or not, and it sends binary data to a latch device wherein includes a current mirror and a feedback loop which cuts off the current path after latching, thus it reduces active current, minimizes data pattern sensitivity, and also rejects coupling noise. And dummy rows and columns generate replica delay signals which guarantee timing margin and reduce cycle time. And its applications are extended to single port, multi port and content addressable memory. In addition, the memory cells are formed in between the routing layers, which memory cells can be stacked over the transistor or another capacitor memory cell.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
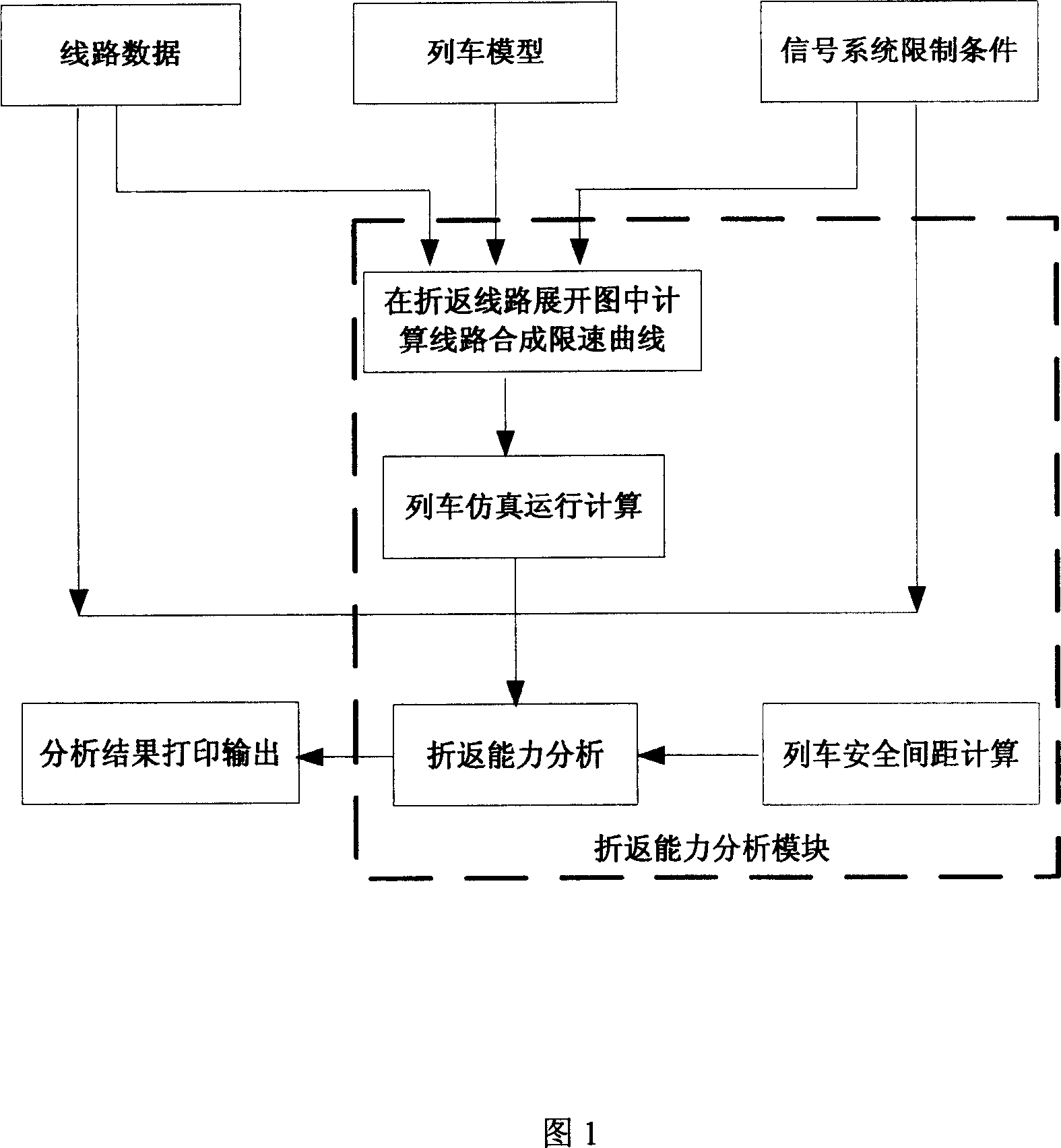
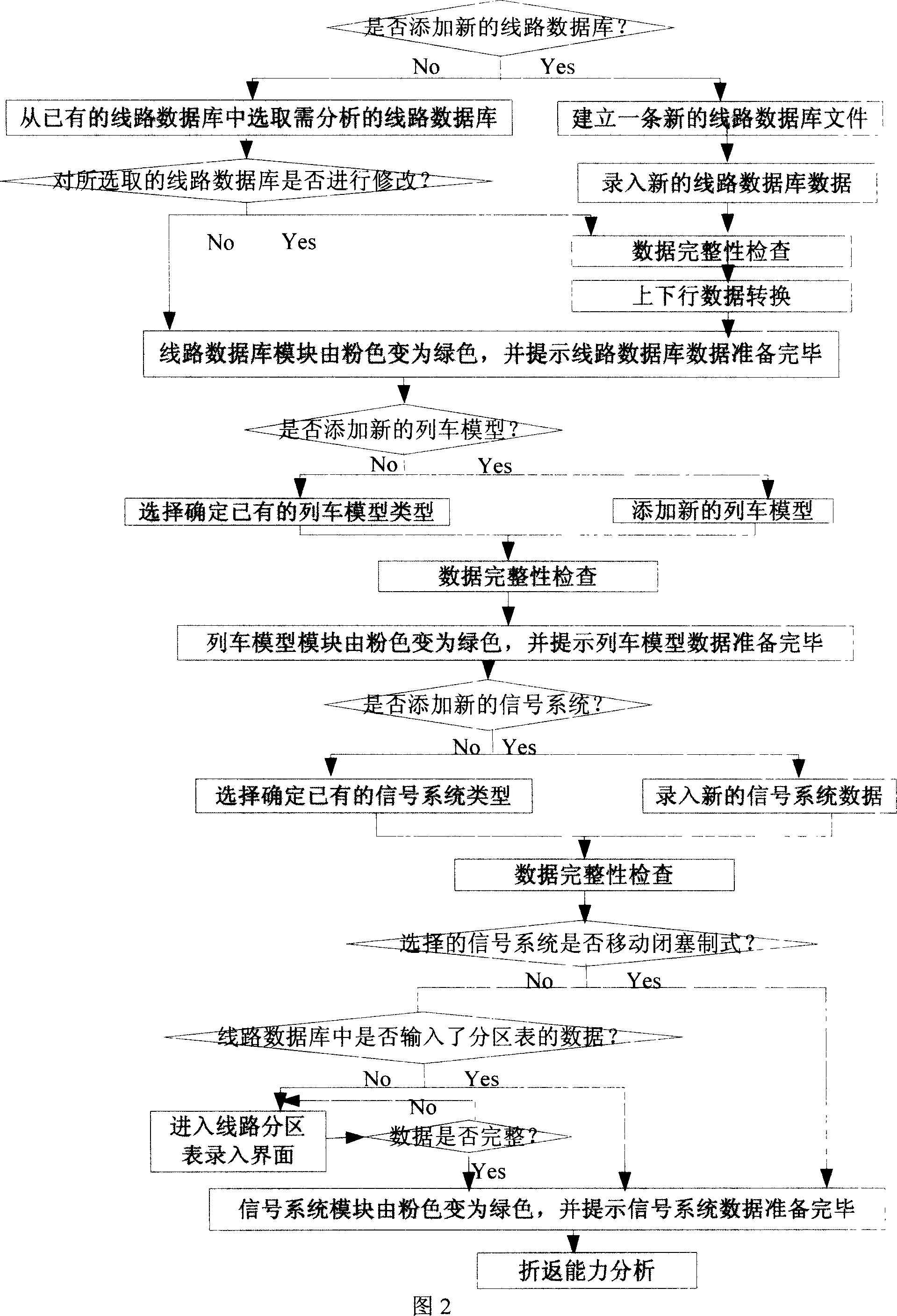
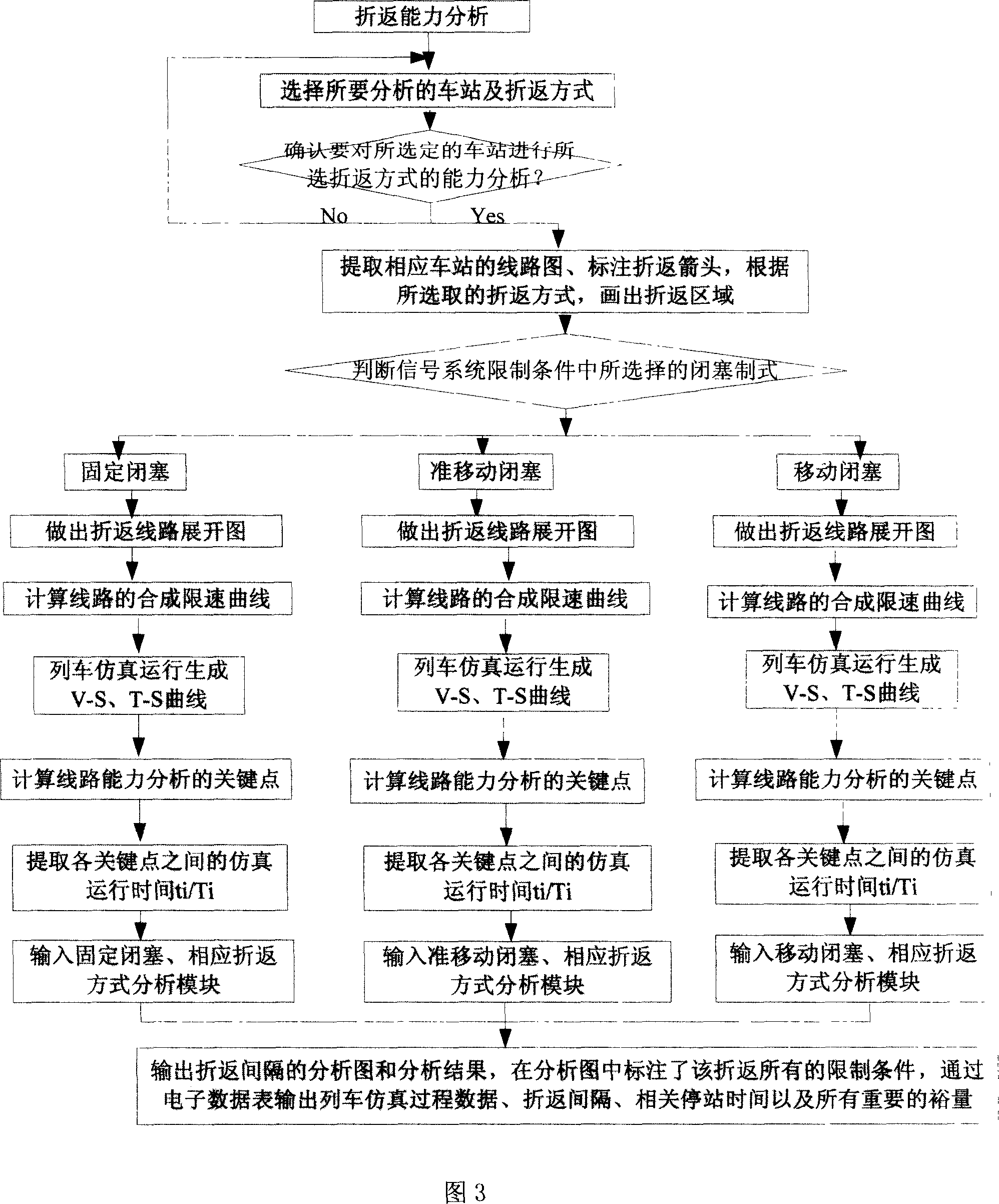
City track traffic line turning-back capacity analysis method
ActiveCN101025766AThe process of analysis and calculation is intuitive and simpleClose to real operating conditionsRailway traffic control systemsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringBack regions
The invention is a method for analyzing the turning-back capacity of rail traffic lines, adopting simplified line layout and simplified train running time-distance sketch map to analyze constraints between trains: by setting a margin for each constraint, not only able to obtain turning-back interval but also able to obtain the margin of each constraint; listing the constraints according to the stay time in station and the stay time in turning-back region, thus not only able to obtain the current adopted time margins of the stay time in station and the stay time in turning-back region; the running time ti / Ti of train at each key point is extracted by a method of generating line synthesis speed limiting curve on the development diagram of turning-back lines, generating V-S and T-S curves by computer simulation. And the analyzing method is simple and visual, not only improving analyzing completeness and accuracy but also largely reducing workload of analyzers by computer simulation.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
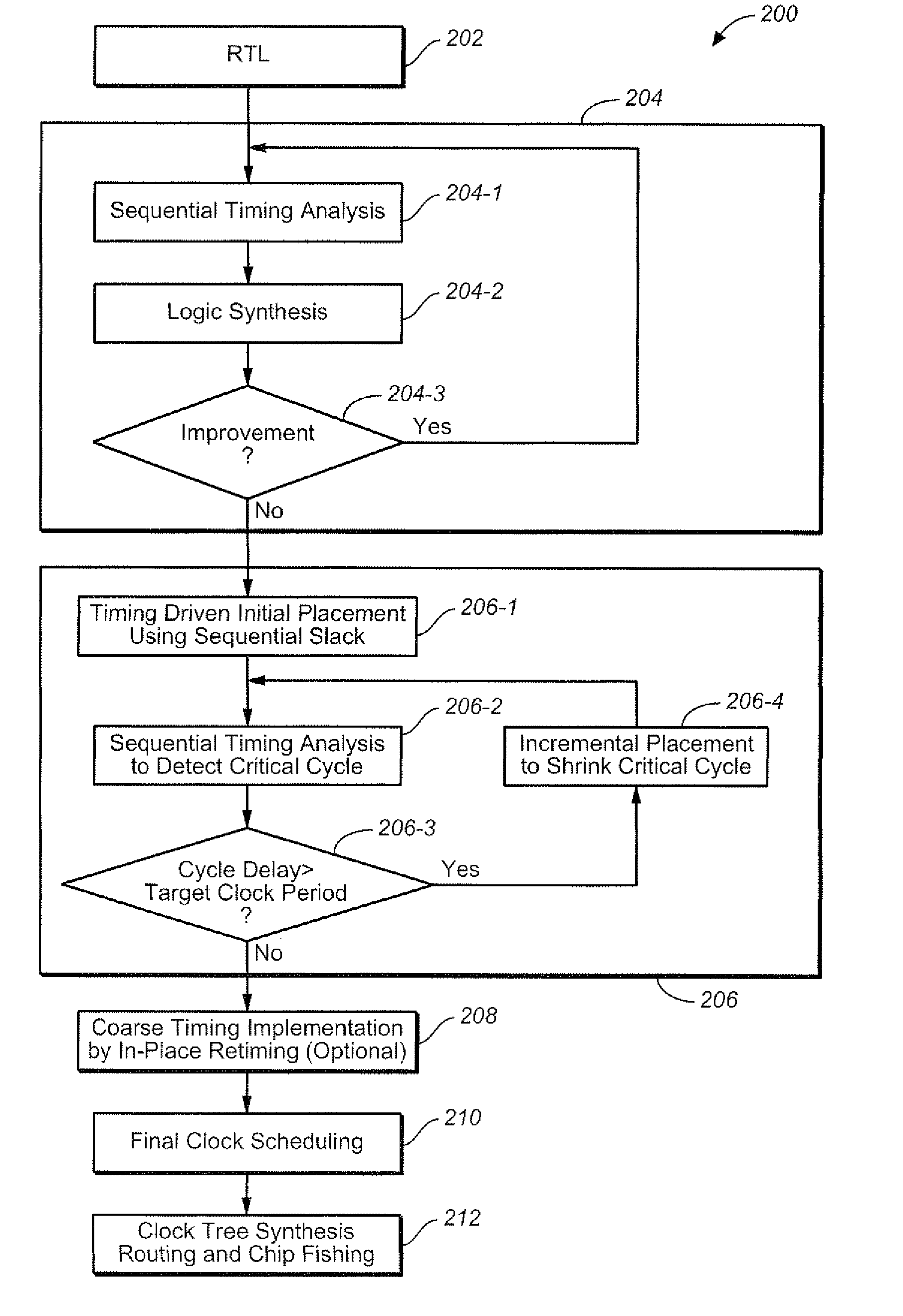
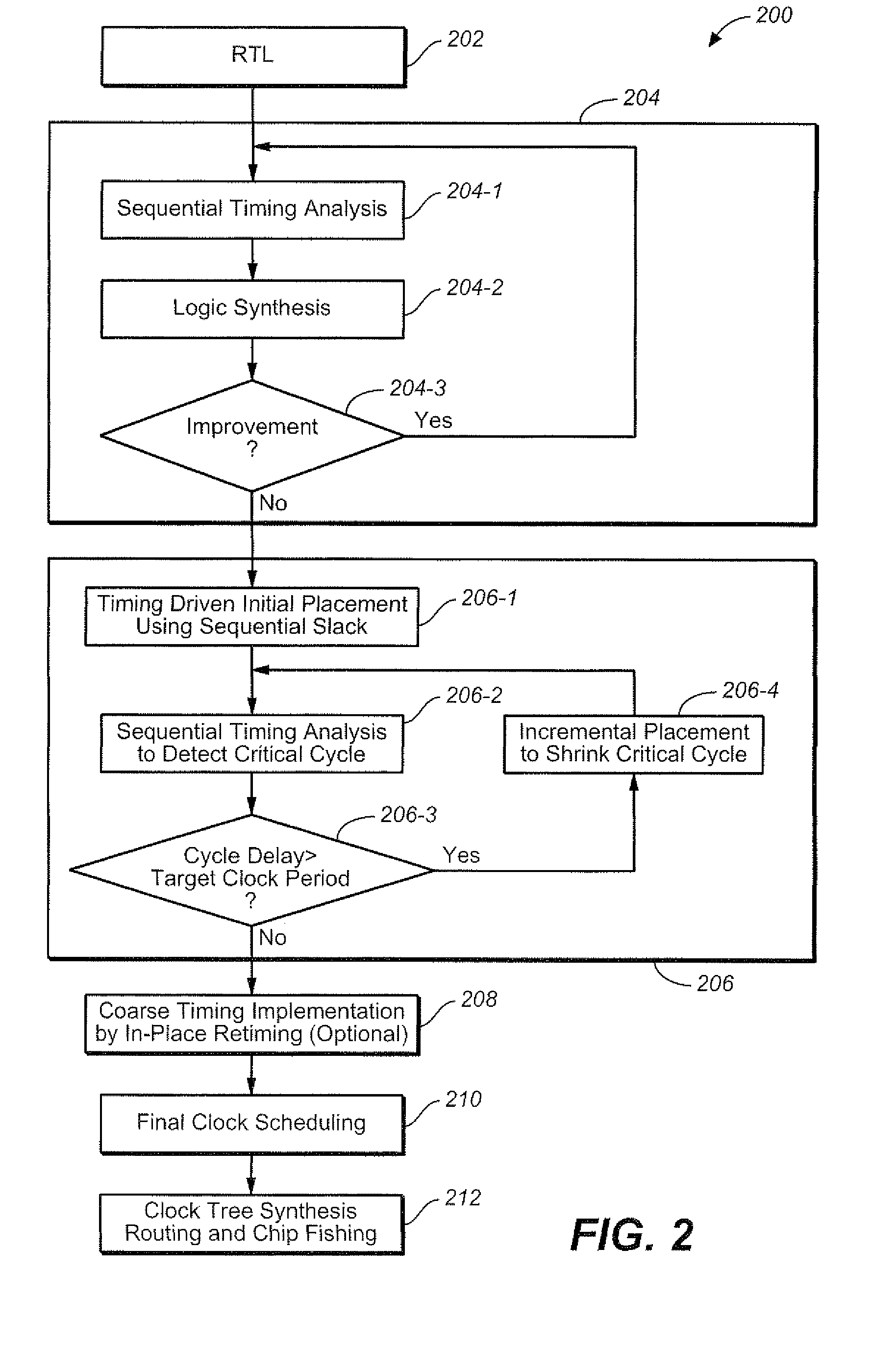
Optimizing integrated circuit design through use of sequential timing information
InactiveUS7743354B2Increase flexibilityEasy to implementCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTiming marginMaximum latency
A method is provided that includes: determining a minimum clock cycle that can be used to propagate a signal about the critical cycle in a circuit design; wherein the critical cycle is a cycle in the design that has a highest proportionality of delay to number of registers; determining for a circuit element in the circuit design, sequential slack associated with the circuit element; wherein the sequential slack represents a minimum delay from among respective maximum delays that can be added to respective structural cycles of which the circuit element is a constituent, based upon the determined limit upon clock cycle duration; using the sequential slack to ascertain sequential optimization based design flexibility throughout multiple stages of a design flow.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Transmitter voltage and receiver time margining
ActiveUS20070230513A1Analog circuit testingError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunication interfaceTiming margin
A technique for characterizing a communications interface includes determining a voltage margin and a timing margin of the interface based on data sampled by a sampling device of a receiver of the interface. In at least one embodiment of the invention, a method for determining margin associated with a receiver circuit of an integrated circuit includes periodically sampling a signal over a time period by a receiver sampling circuit of the receiver circuit to generate a sampled version of the signal. The method includes incrementally varying a value of the parameter associated with the signal. The varying of the parameter is through a range of values of the parameter over the time period. The method includes determining a margin value of the receiver circuit associated with the parameter based, at least in part, on the sampled version of the signal.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS20050141331A1Stable data write operationGuaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Application of Multiple Voltage Droop Detection and Instruction Throttling Instances with Customized Thresholds Across a Semiconductor Chip
InactiveUS20090063884A1Energy efficient ICTElectronic circuit testingTiming marginSemiconductor chip
A method and system for applying multiple voltage droop detection and instruction throttling instances with customized thresholds across semiconductor chips. Environmental parameters are detected for various locations on a chip, and timing margins are determined for each location on the chip. An acceptable voltage droop for each location is determined based on the environmental parameters and the timing margins for the corresponding location. A droop threshold is then determined for each location based on the corresponding acceptable voltage droop determined for the corresponding location.
Owner:IBM CORP
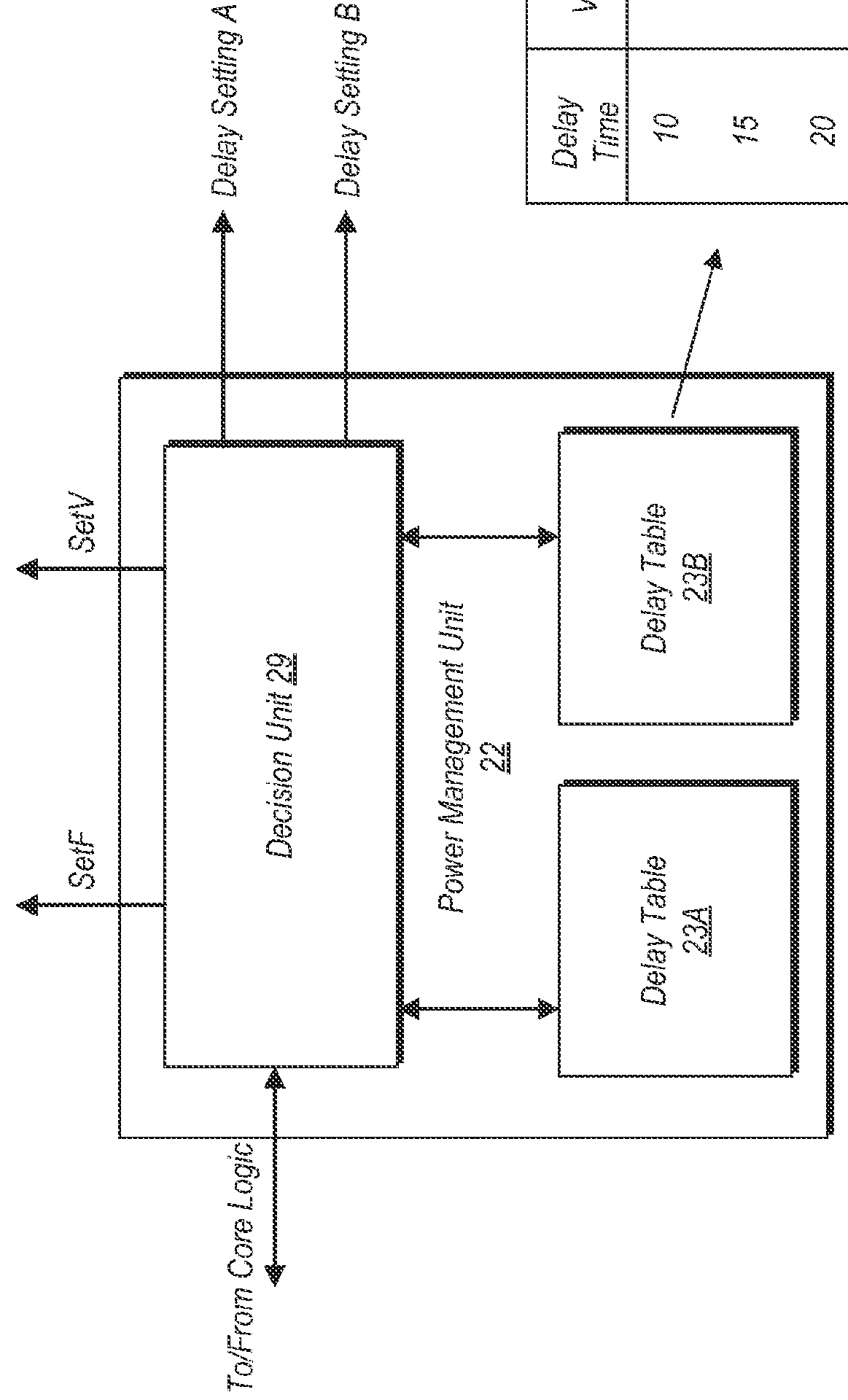
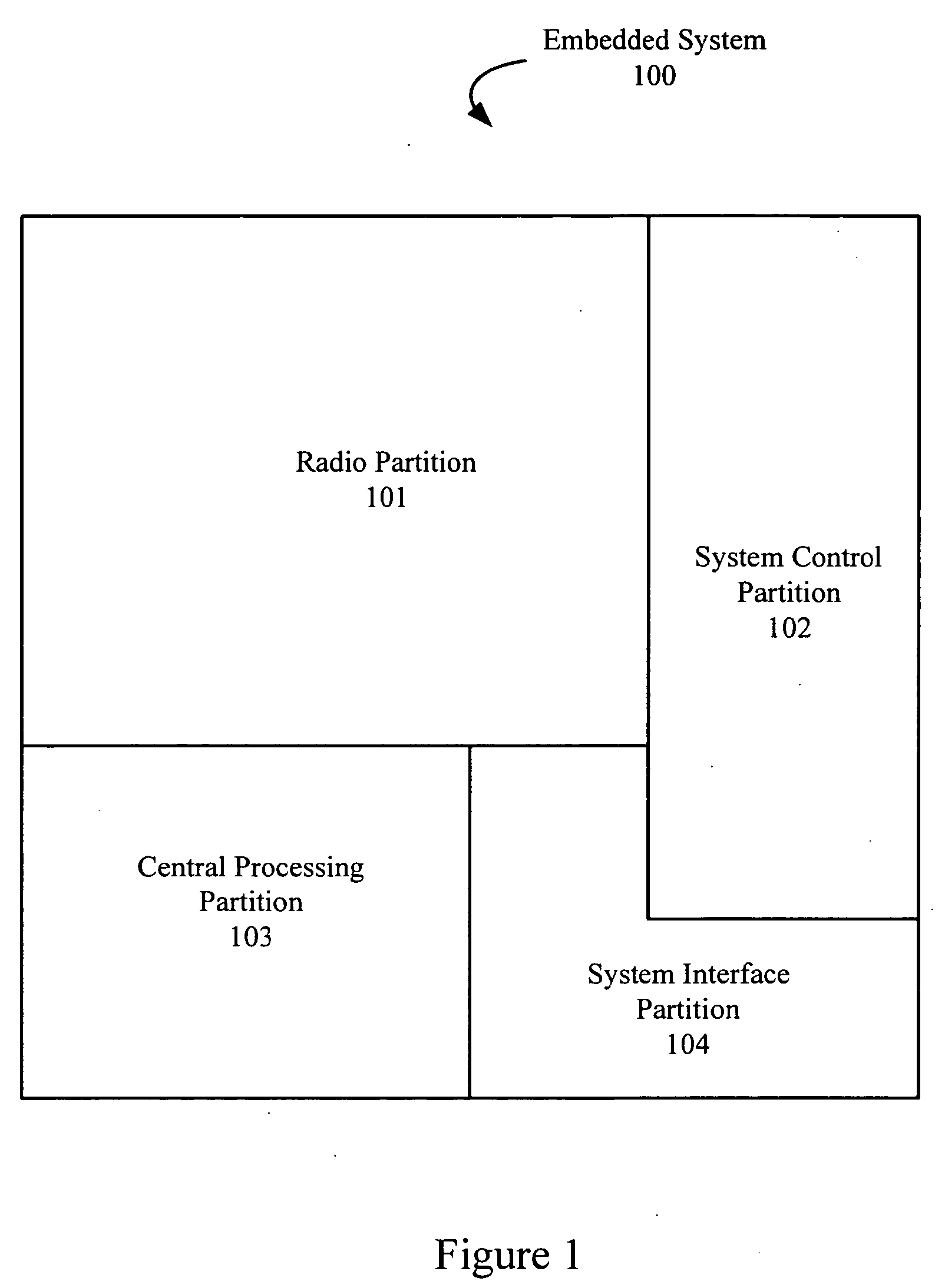
Reducing power consumption in embedded systems by controlling voltage based on system state and partition designation
ActiveUS7257723B2Minimum consumptionReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTiming marginCritical path method
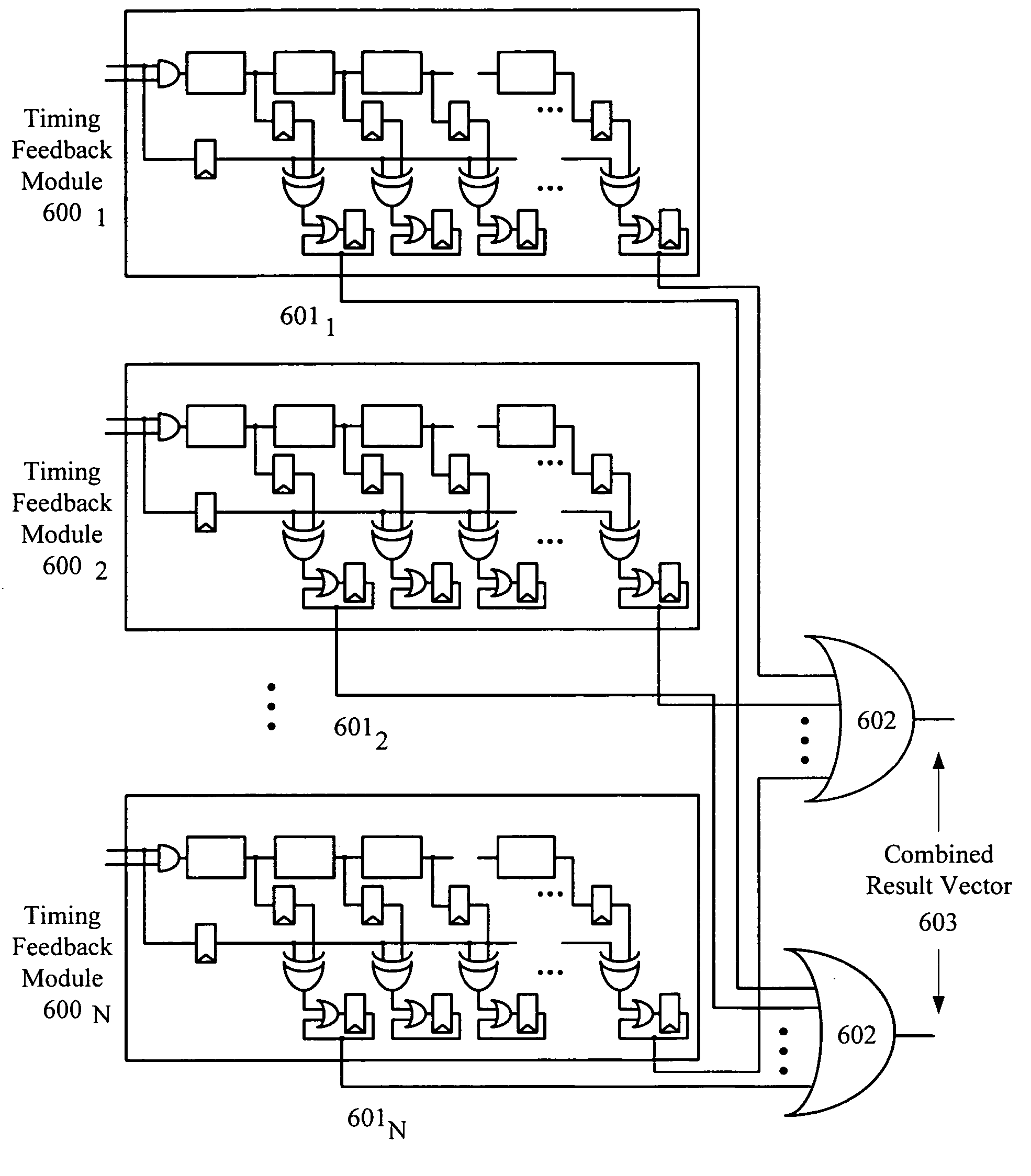
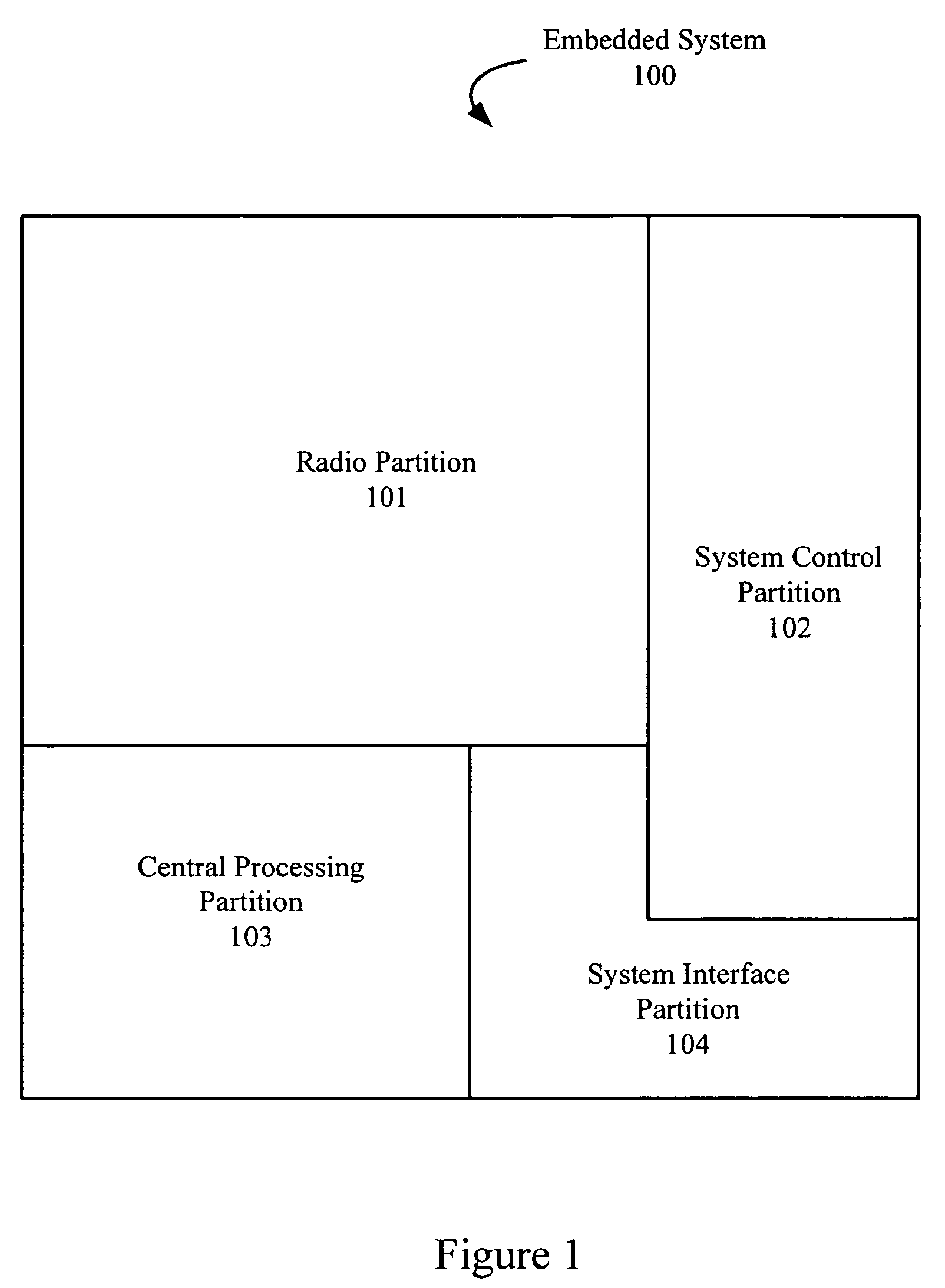
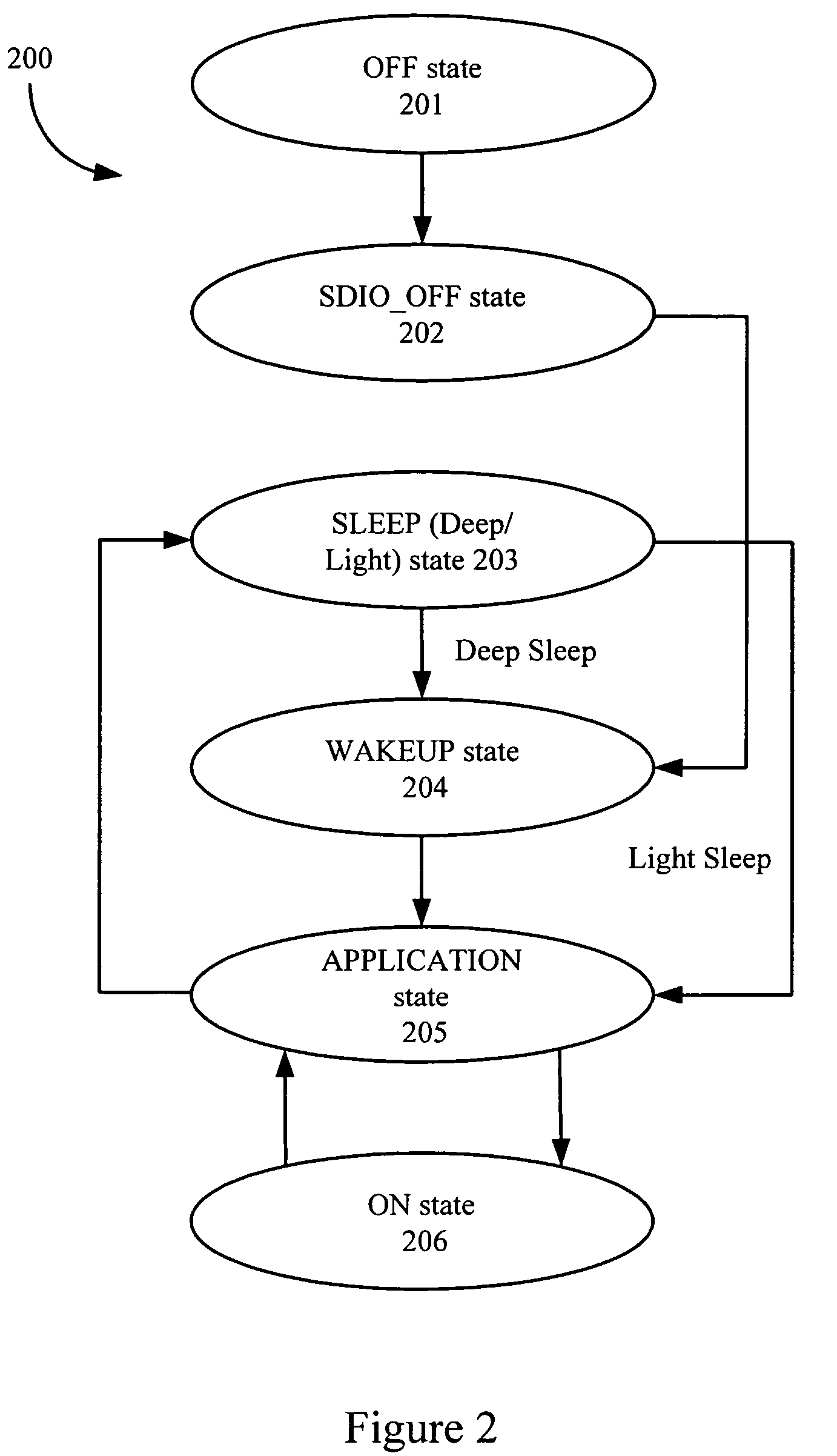
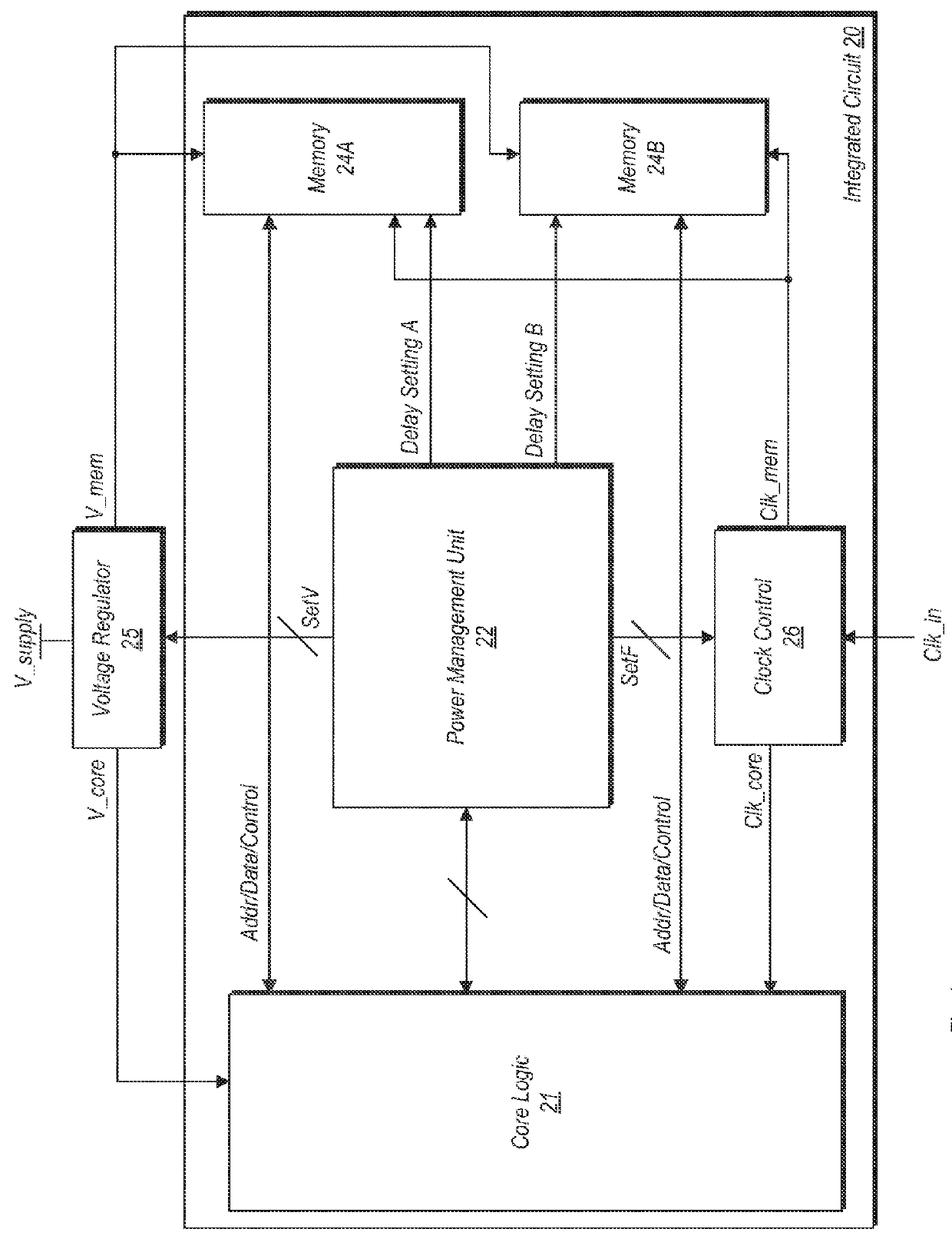
An embedded system optimally operates with minimal power consumption without sacrificing performance. Power consumption can be reduced by independently and dynamically controlling multiple power partitions, wherein components within a partition can have the same power profile. States of operation can be programmably defined in a table and enforced using hardware. Voltages in the table can be dynamically updated during a runtime of the system using a timing feedback module, which is connected to a critical path in a partition. The timing feedback module can output a vector that indicates the timing margin for that critical path. Using this timing margin, software can increase or decrease the voltage to optimize power consumption of that partition.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
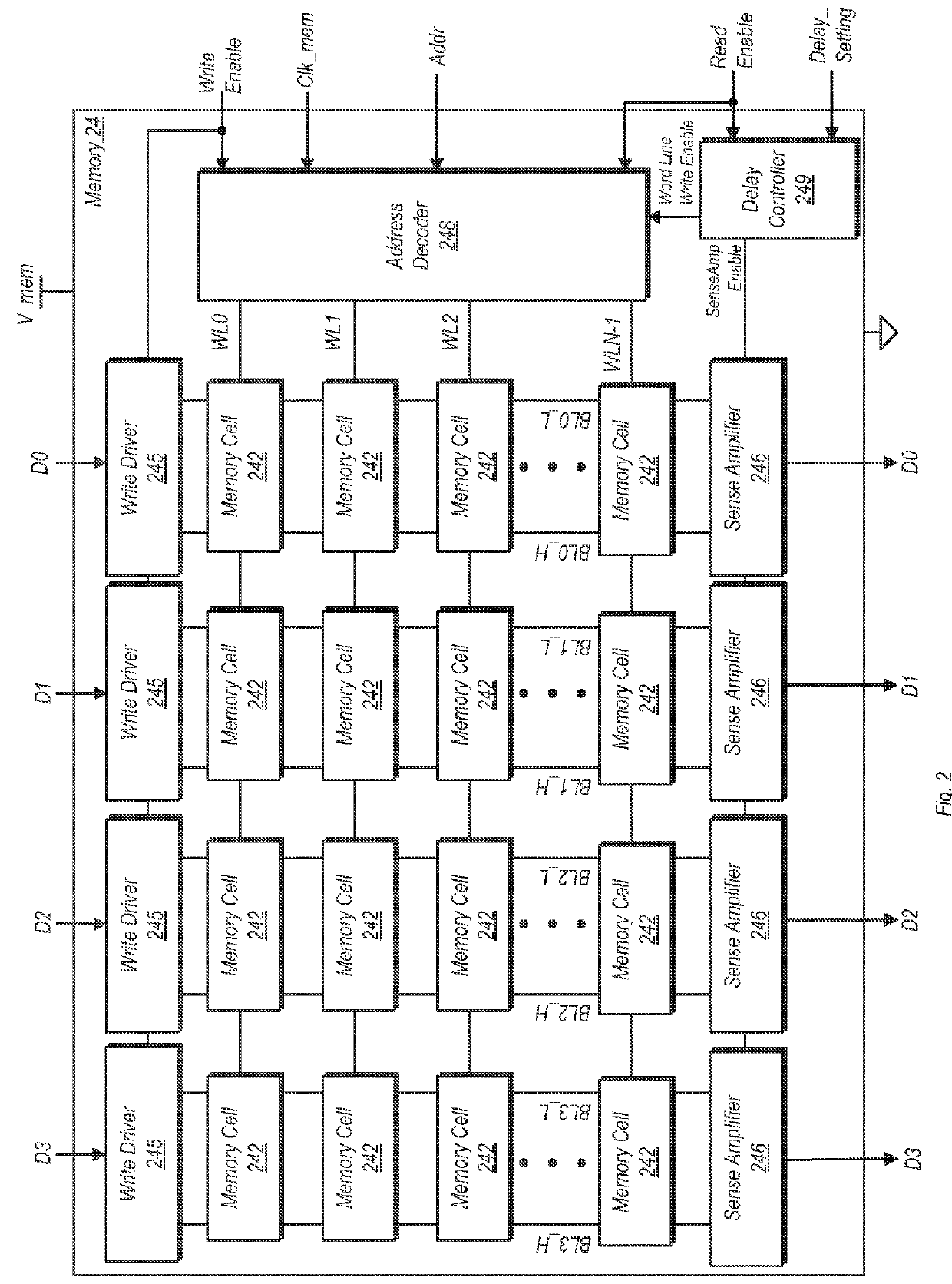
Memory Read Timing Margin Adjustment
ActiveUS20120117402A1Improve performanceReduce latencyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTiming marginOperating point
An apparatus and method for changing the extra margin adjustment (EMA) for a memory is disclosed. A control unit may access a table responsive to an indication of a change of operating point. The table includes a number of different delay times, each of which corresponds to a particular operating point. The control unit may select the delay time that corresponds to the new operating point to which the memory operation is being changed. The control unit may further convey an indication of the selected delay time to the memory, thereby causing the memory to operate according thereto.
Owner:APPLE INC
Reducing power consumption in embedded systems by controlling voltage based on system state and partition designation
ActiveUS20060156045A1Efficiency tuningMinimum consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementTiming marginConfigfs
An embedded system optimally operates with minimal power consumption without sacrificing performance. Power consumption can be reduced by independently and dynamically controlling multiple power partitions, wherein components within a partition can have the same power profile. States of operation can be programmably defined in a table and enforced using hardware. Voltages in the table can be dynamically updated during a runtime of the system using a timing feedback module, which is connected to a critical path in a partition. The timing feedback module can output a vector that indicates the timing margin for that critical path. Using this timing margin, software can increase or decrease the voltage to optimize power consumption of that partition.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
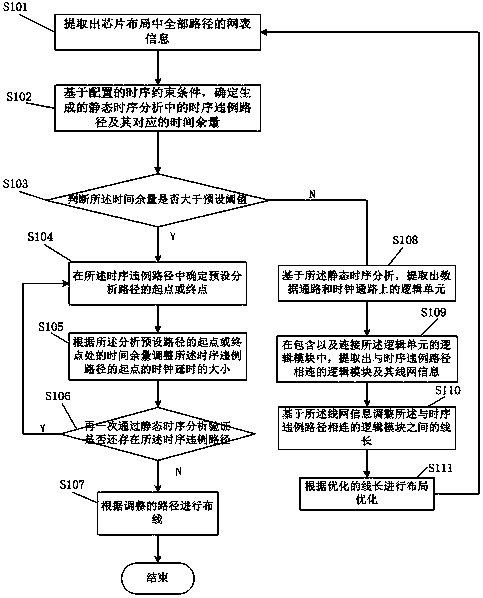
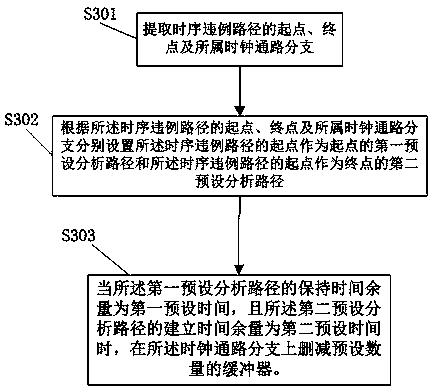
A time sequence repairing method based on time headroom
ActiveCN109583103ASmall design areaIncrease working frequencySpecial data processing applicationsTiming marginStatic timing analysis
The invention provides a time sequence repairing method based on time headroom, which comprises the following steps: step 1, extracting netlist information of all paths in a chip layout, and then entering a step 2; Step 2, determining a time sequence violation path in the generated static time sequence analysis and a corresponding time margin based on the configured time sequence constraint condition, and then entering a step 3; Step 3, judging whether the time margin is greater than a preset threshold value or not, if so, determining a starting point or an end point of a preset analysis pathin the time sequence violation path, and adjusting the magnitude of the clock delay of the time sequence violation path; Otherwise, analyzing based on the static time sequence; The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting logic units on a data path and a clock path according to a preset time sequence violation path, further extracting logic modules connected with the time sequenceviolation path and line network information of the logic modules, adjusting the line length between the logic modules connected with the time sequence violation path, performing optimized layout according to the optimized line length, and then returning to the step 1. The design area of the chip is reduced, and the working frequency of the chip is improved.
Owner:AMICRO SEMICON CORP
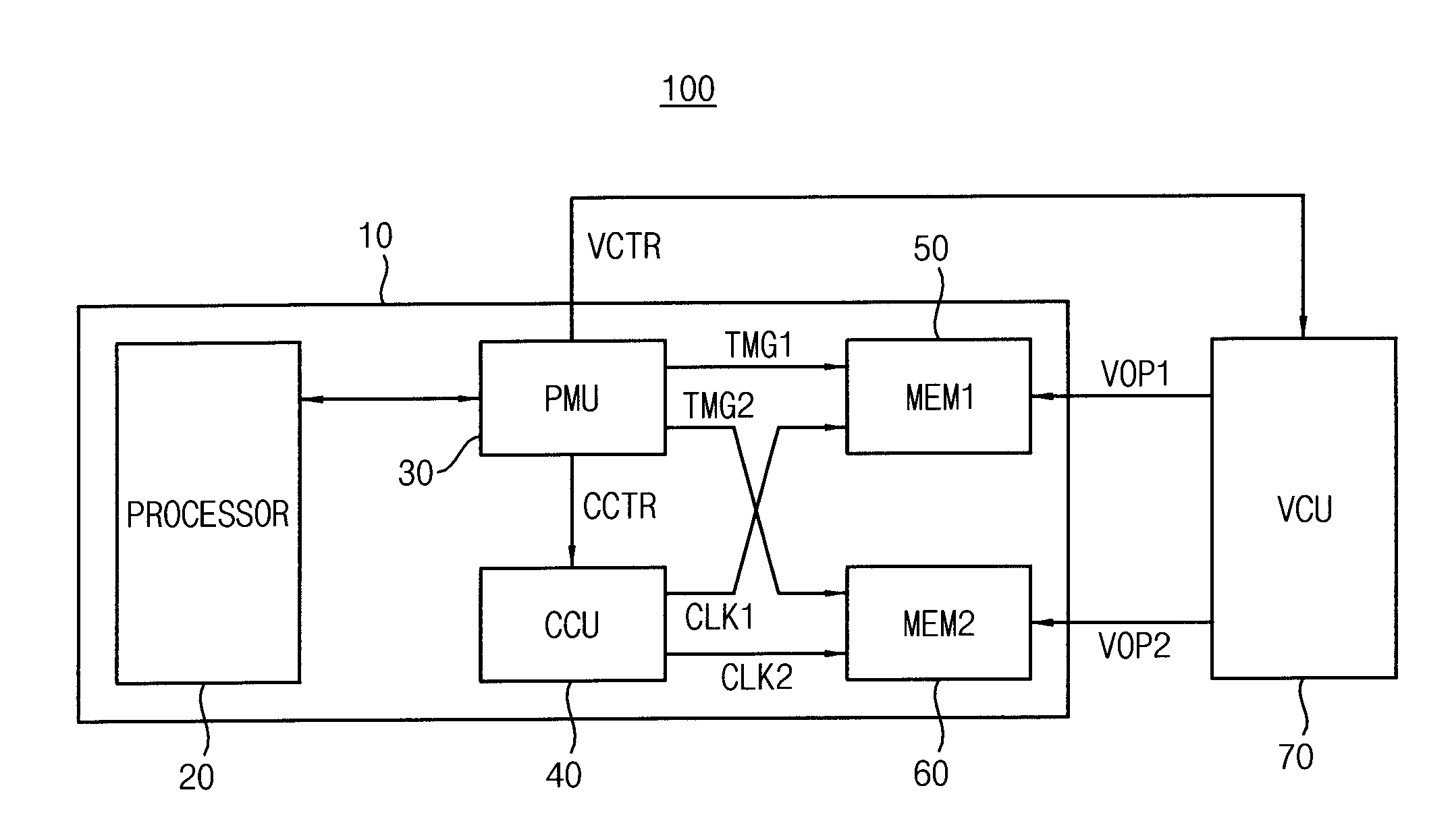
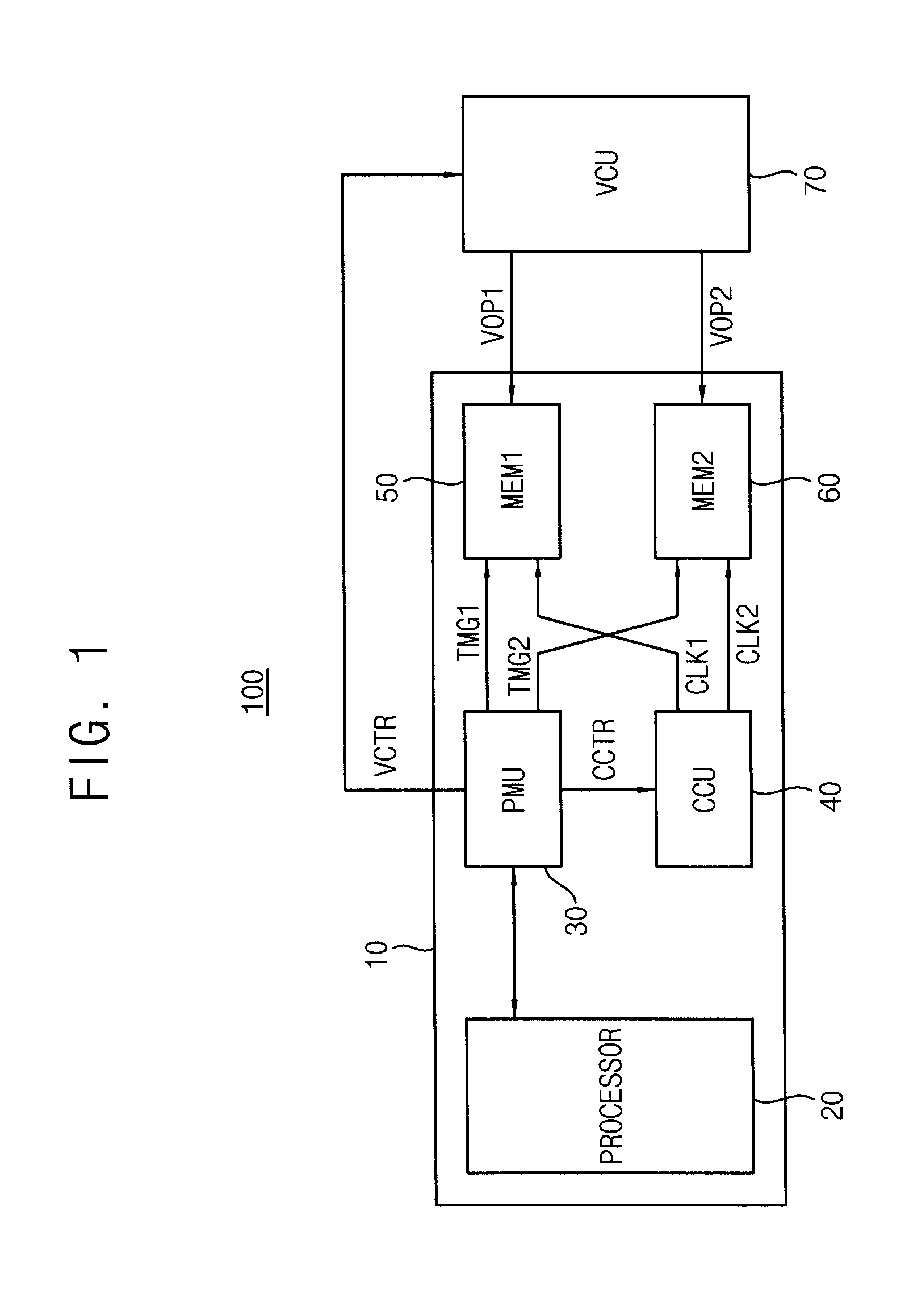
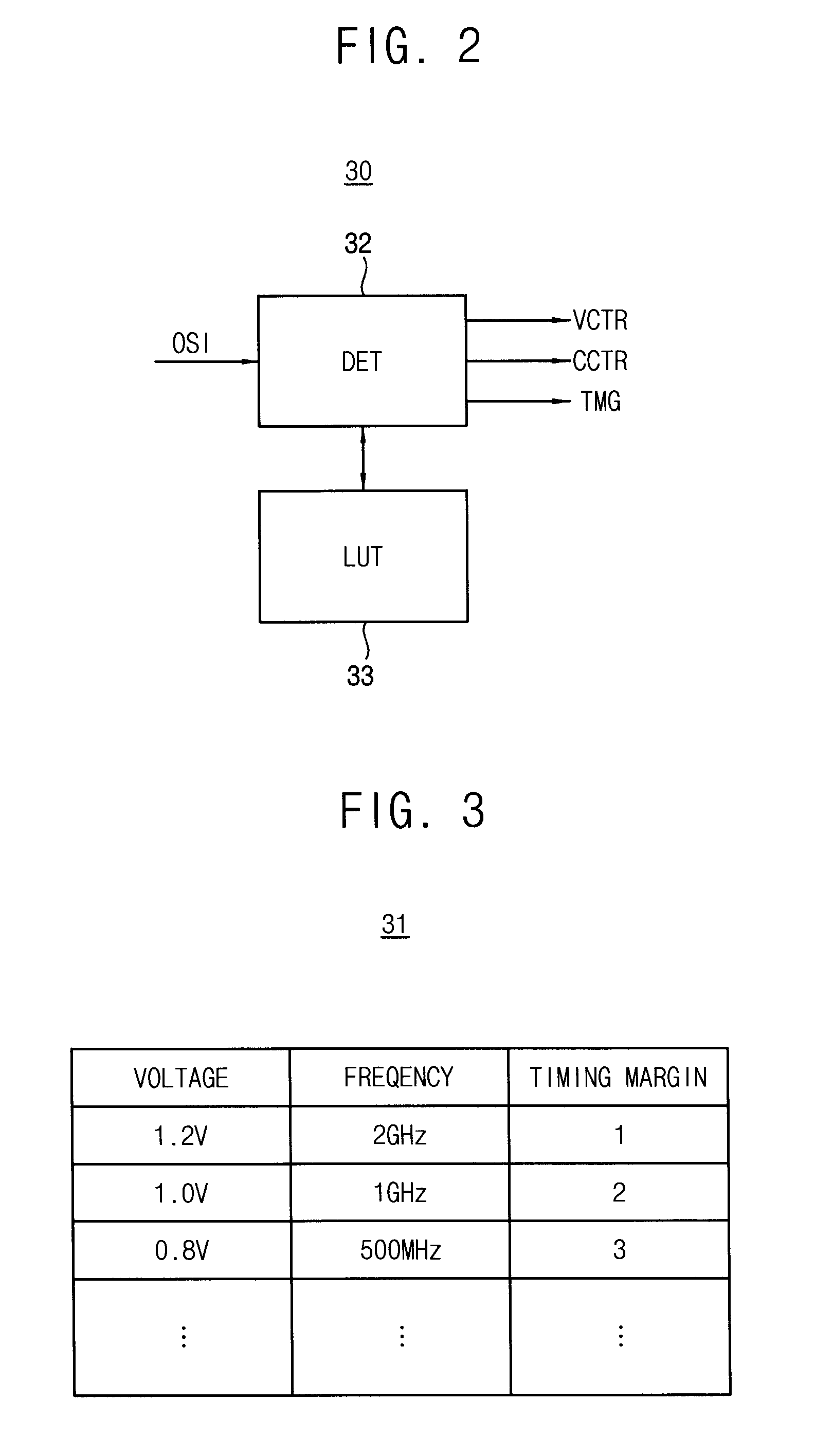
Memory device of adaptively calibrating timing margin and integrated circuit including the same
ActiveUS20150287444A1Reduce operating frequencyExtension of timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginSelf adaptive
An integrated circuit, a method of controlling an operation timing of a memory device, an application processor, and a power manager are provided. The application processor includes: a power manager configured to determine a first operating power level, from among a plurality of operating power levels, to determine a first timing margin corresponding to the first operating power level, to generate a first gray code signal indicating the first timing margin, and to output the first gray code signal; and a first memory device configured to adjust an operation timing according to the first timing margin indicated by the first gray code signal, wherein the power manager is configured to provide the first operating power level to the first memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
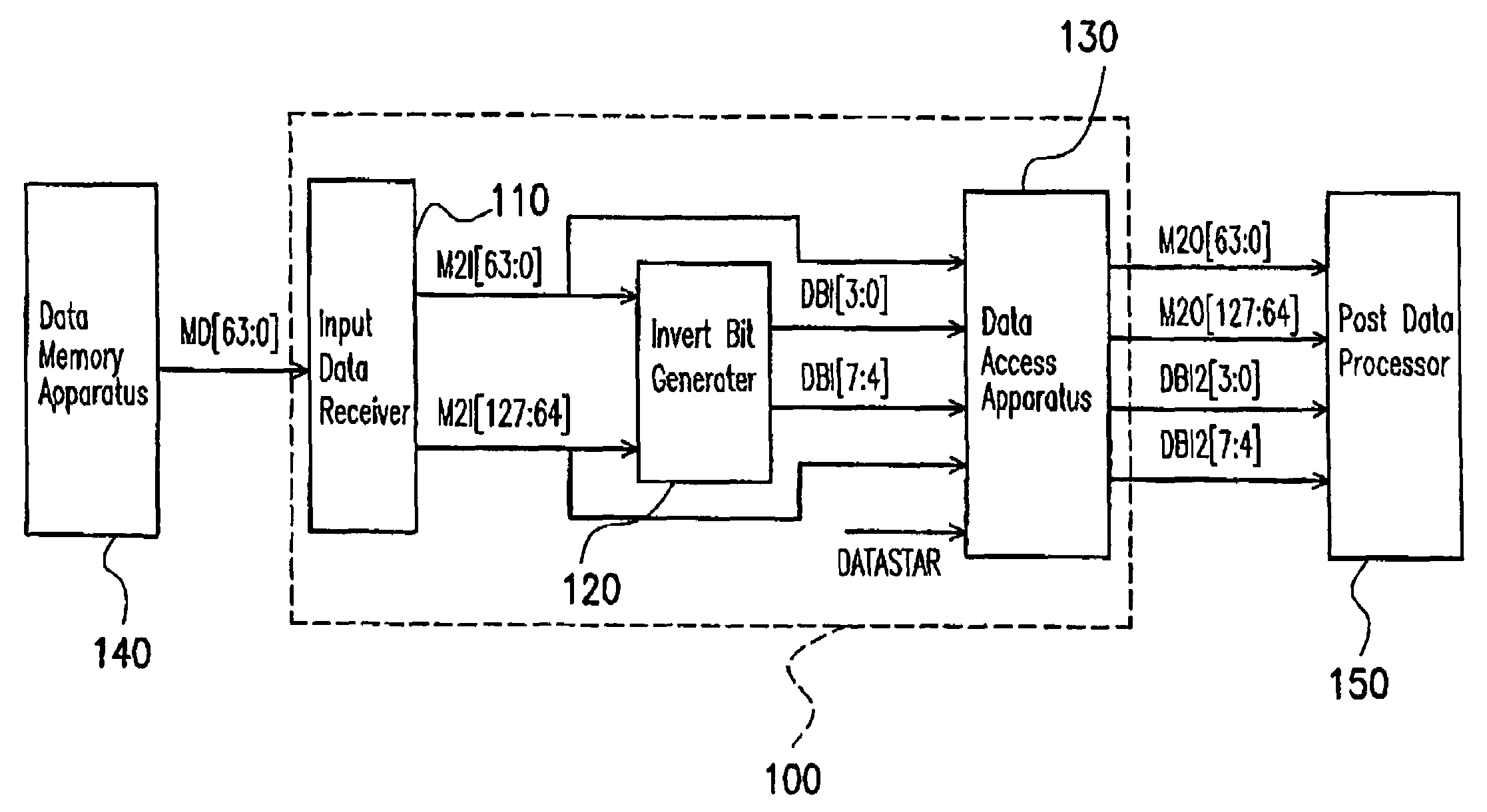
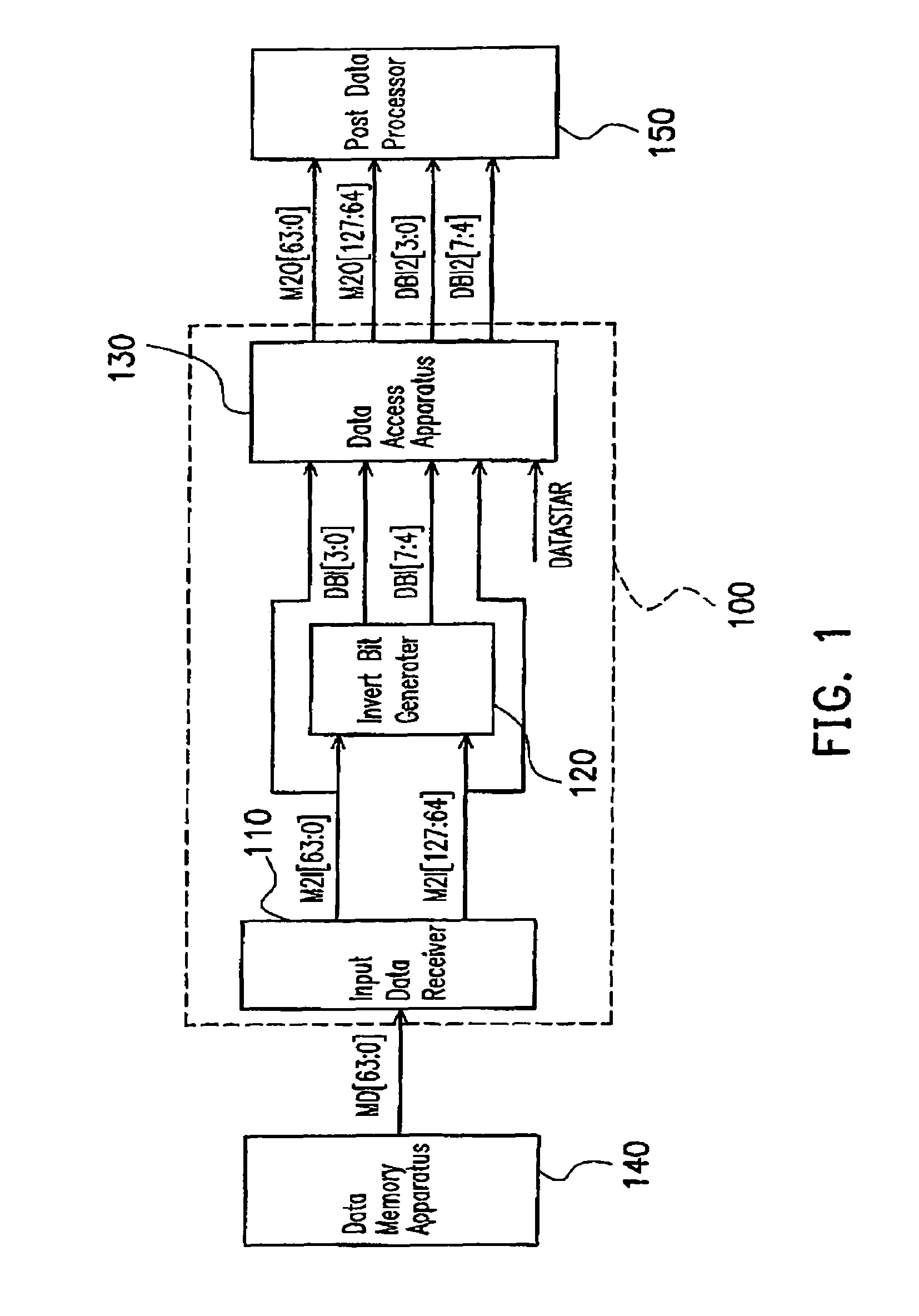
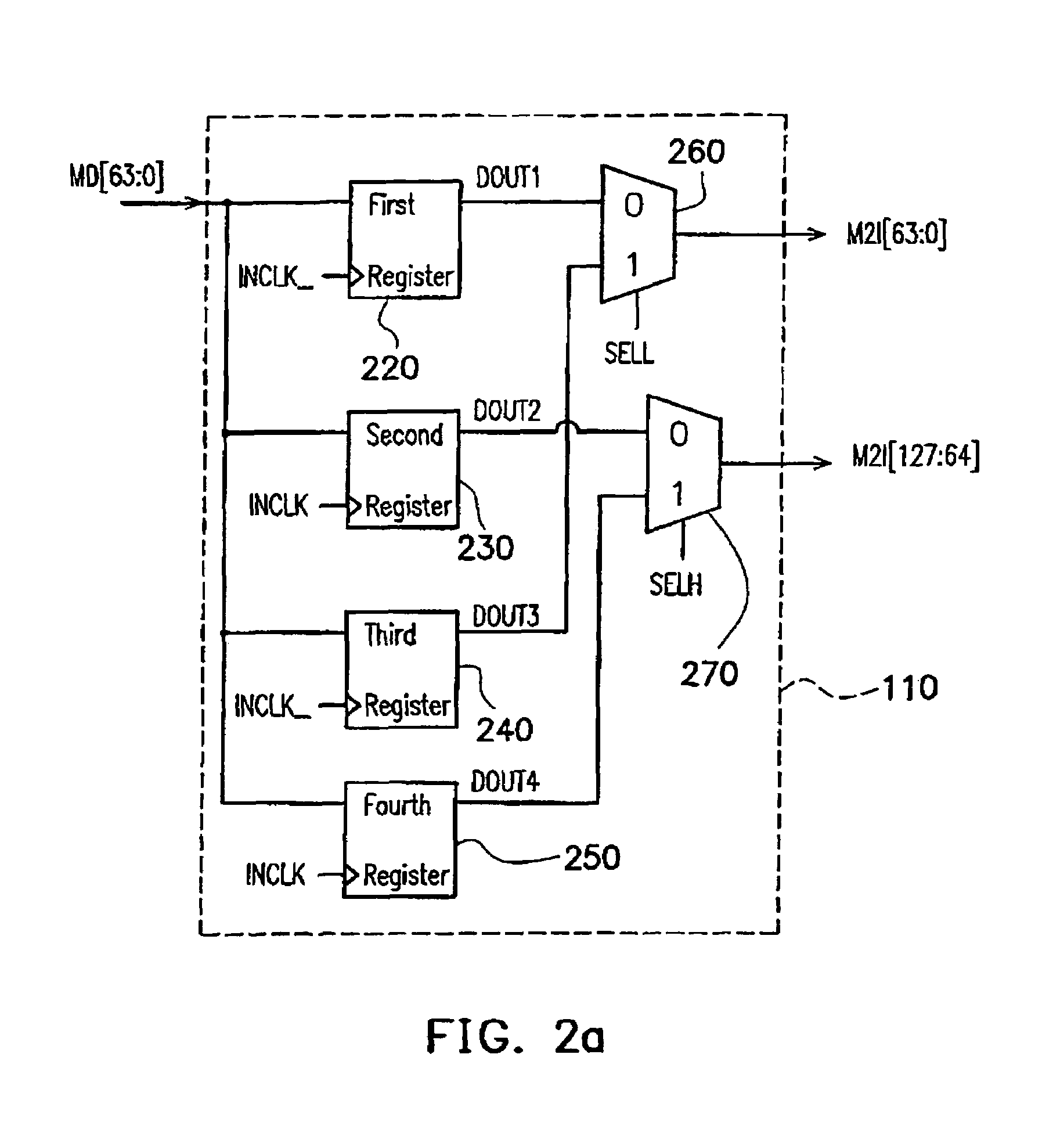
Data memory controller that supports data bus invert
InactiveUS7082489B2Extension of timeReduce variationEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingTiming marginFrequency reduction
The present invention provides a data memory controller that supports for the invert of data bus. Data transmitted from a memory is received in a chip set, which further transmits the data to a data processing apparatus. While receiving the memory data, the chip set doubles the bandwidth and reduces the frequency, such that the time margin for processing data is increased. In addition, after outputting data to the data processing apparatus, a first frame of data is compared to bus idle state to further reduce frequency of data invert and power consumption.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
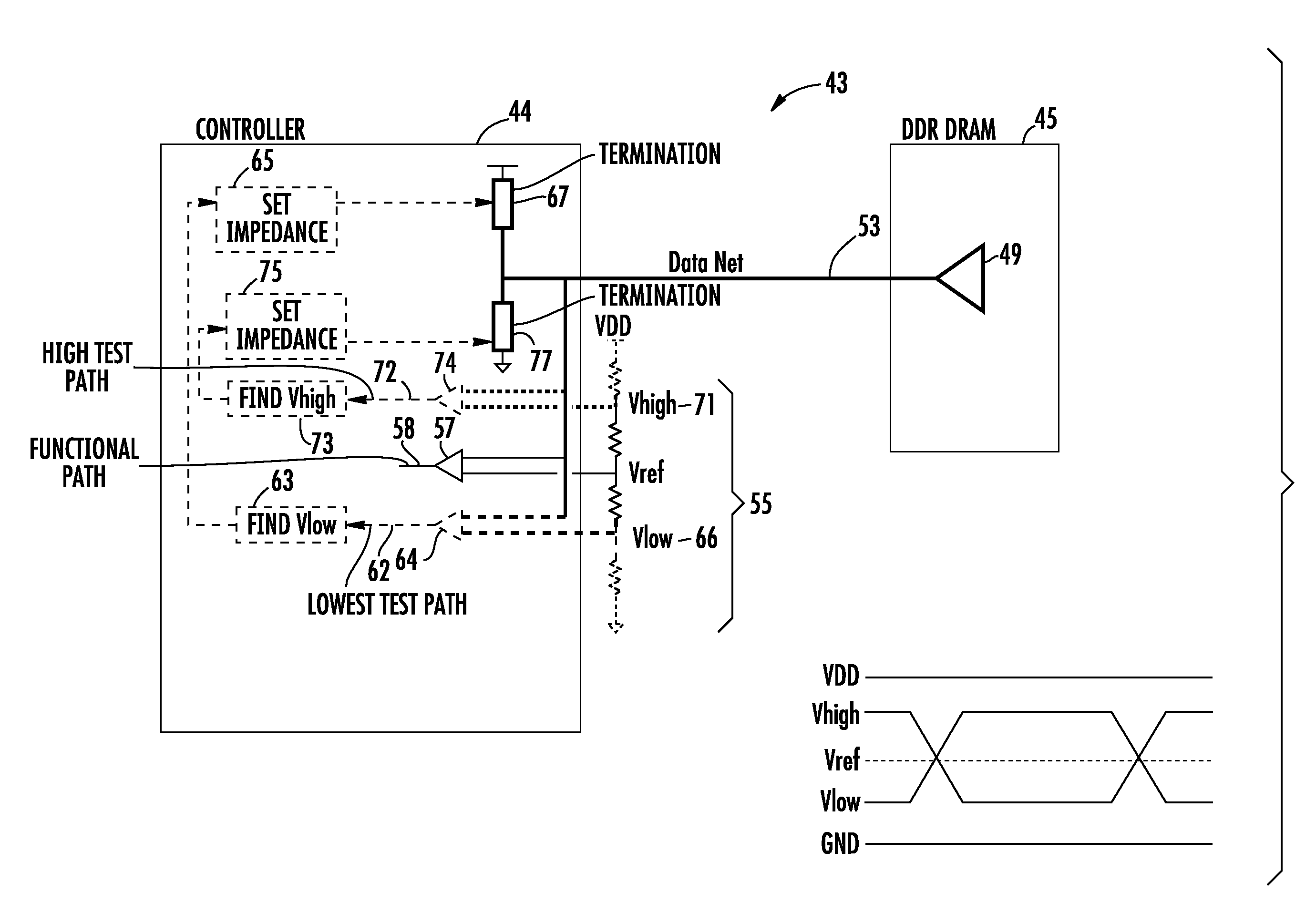
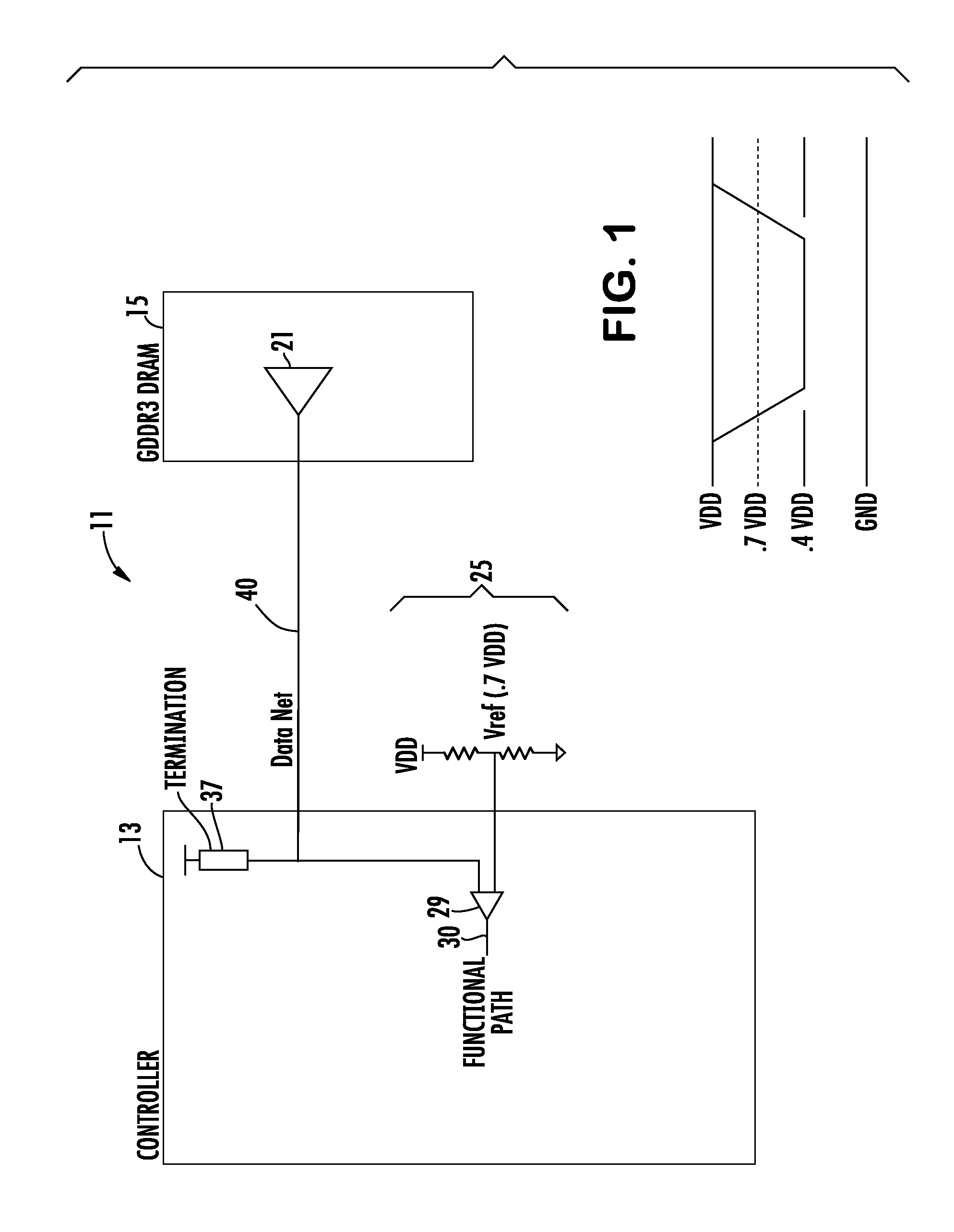
Setting Controller Termination in a Memory Controller and Memory Device Interface in a Communication Bus
InactiveUS20100192000A1Reduce mismatchImprove Timing MarginVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringTiming marginCoupling
Owner:IBM CORP
Hold time error correction method and correction program for integrated circuits
InactiveUS6990646B2Hold time errorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designTiming marginTime error
A hold time error list, having for each hold time error path a hold time error value satisfying plural timing constraints, and more specifically a maximum hold time error value for each of timing constraints, as well as a setup time margin map allocating to path a setup time margin satisfying plural timing constraints for each setup time error path, and more specifically minimum value of setup time margins for the same path for each timing constraint, are generated. Also, referring to this setup time margin map, delay buffers, which reduces or eliminates hold time error of hold error list, and a delay of which is within the range of delay amounts and positions equal to or lower than the setup time margin, are inserted. Referring to the setup time margin map, it is possible to insert delay buffer to correct hold time error without causing new setup time errors.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Delay locked loop circuit
A DLL circuit and a synchronous memory device perform stable operation in a power down mode although the entry and exit into / from the power down mode is repeated rapidly. The synchronous memory device operates in a normal mode and a power down mode. A delay locked loop (DLL) generates a DLL clock having frozen locking information when exiting the power down mode. A controller precludes phase update operation of the DLL when a predetermined time passes after entering the power down mode to thereby obtain a time margin for a phase update operation undertaken in the normal mode.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
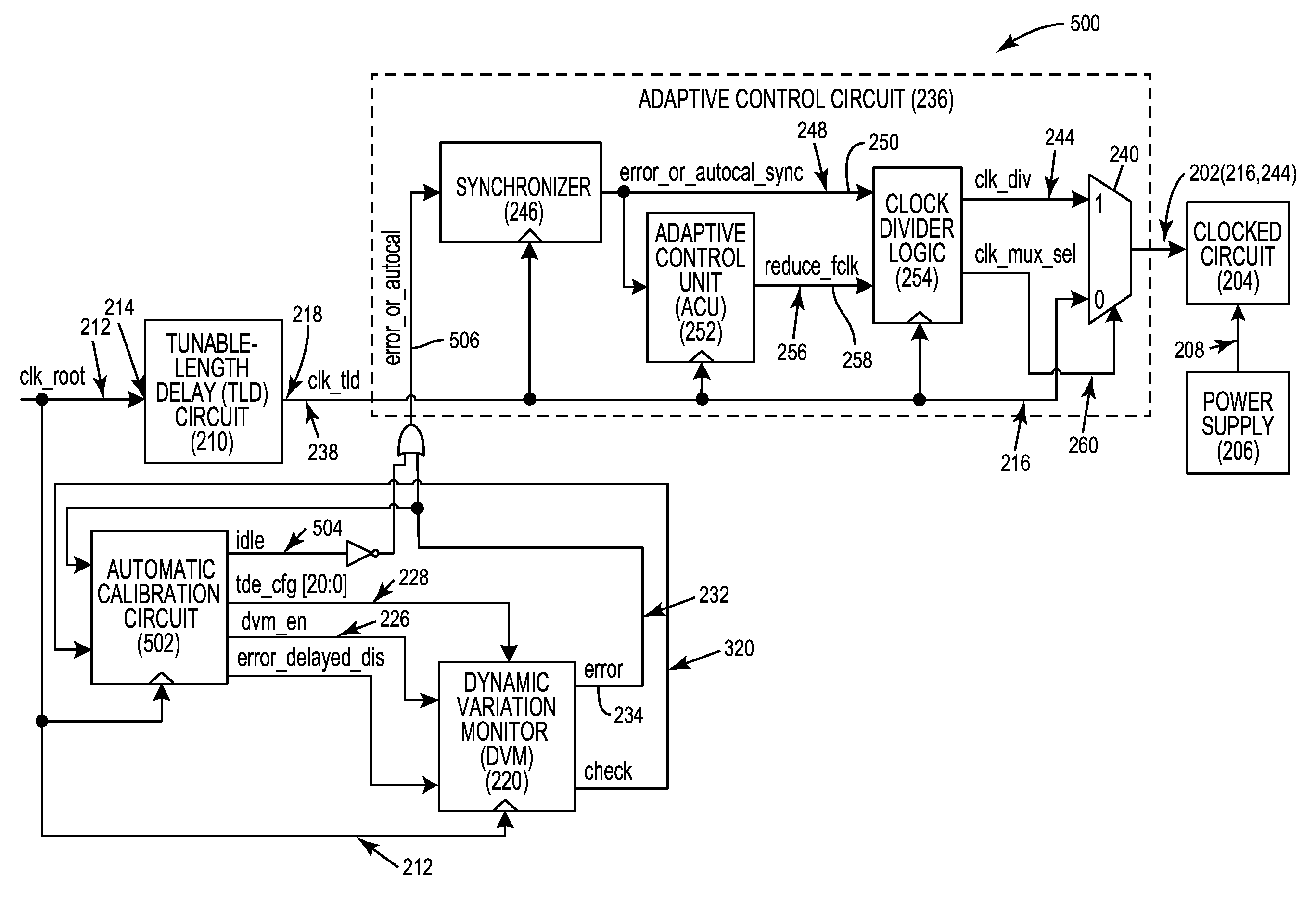
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems
ActiveUS9413344B2Costly overheadCostly timeContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationSingle output arrangementsTiming marginDistribution system
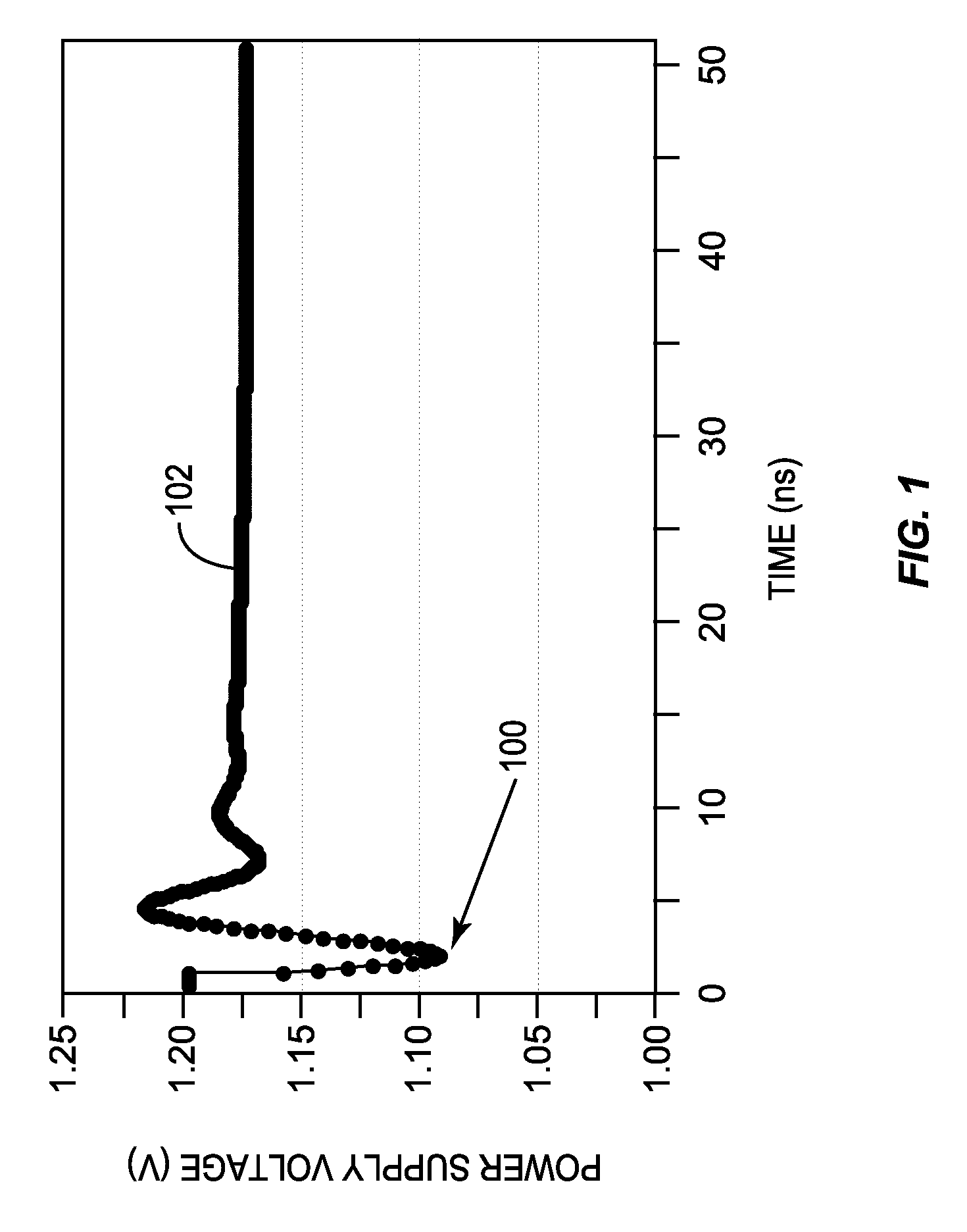
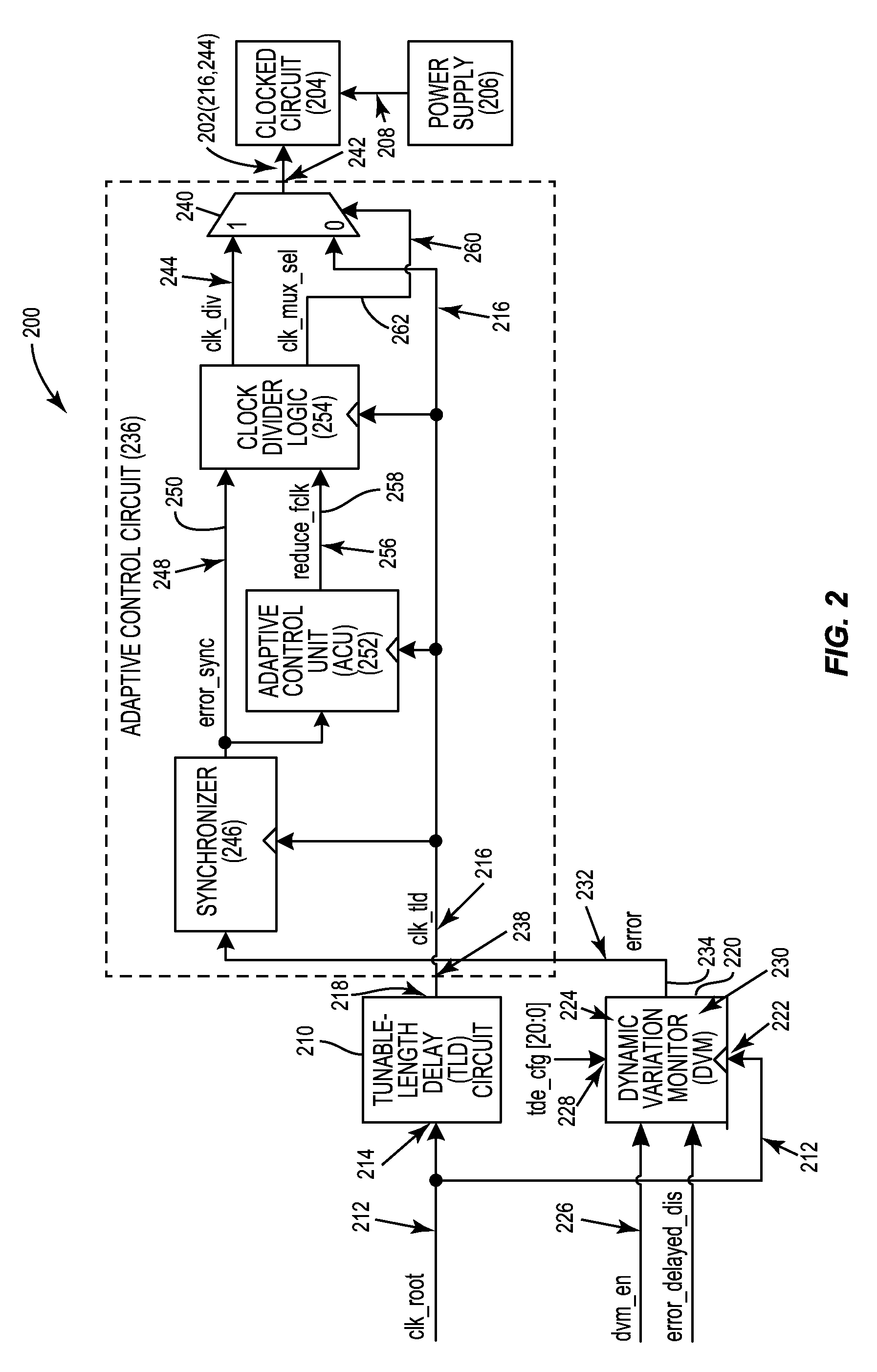
Automatic calibration circuits for operational calibration of critical-path time delays in adaptive clock distribution systems, and related methods and systems, are disclosed. The adaptive clock distribution system includes a tunable-length delay circuit to delay distribution of a clock signal provided to a clocked circuit, to prevent timing margin degradation of the clocked circuit after a voltage droop occurs in a power supply supplying power to the clocked circuit. The adaptive clock distribution system also includes a dynamic variation monitor to reduce frequency of the delayed clock signal provided to the clocked circuit in response to the voltage droop in the power supply, so that the clocked circuit is not clocked beyond its performance limits during a voltage droop. An automatic calibration circuit is provided in the adaptive clock distribution system to calibrate the dynamic variation monitor during operation based on operational conditions and environmental conditions of the clocked circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com