Patents
Literature
76 results about "Maximum latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
On a stable connection with sufficient bandwidth and minimal latency, VoIP systems typically have a minimum of 20 ms inherent latency and target 150 ms as a maximum latency for general consumer use.
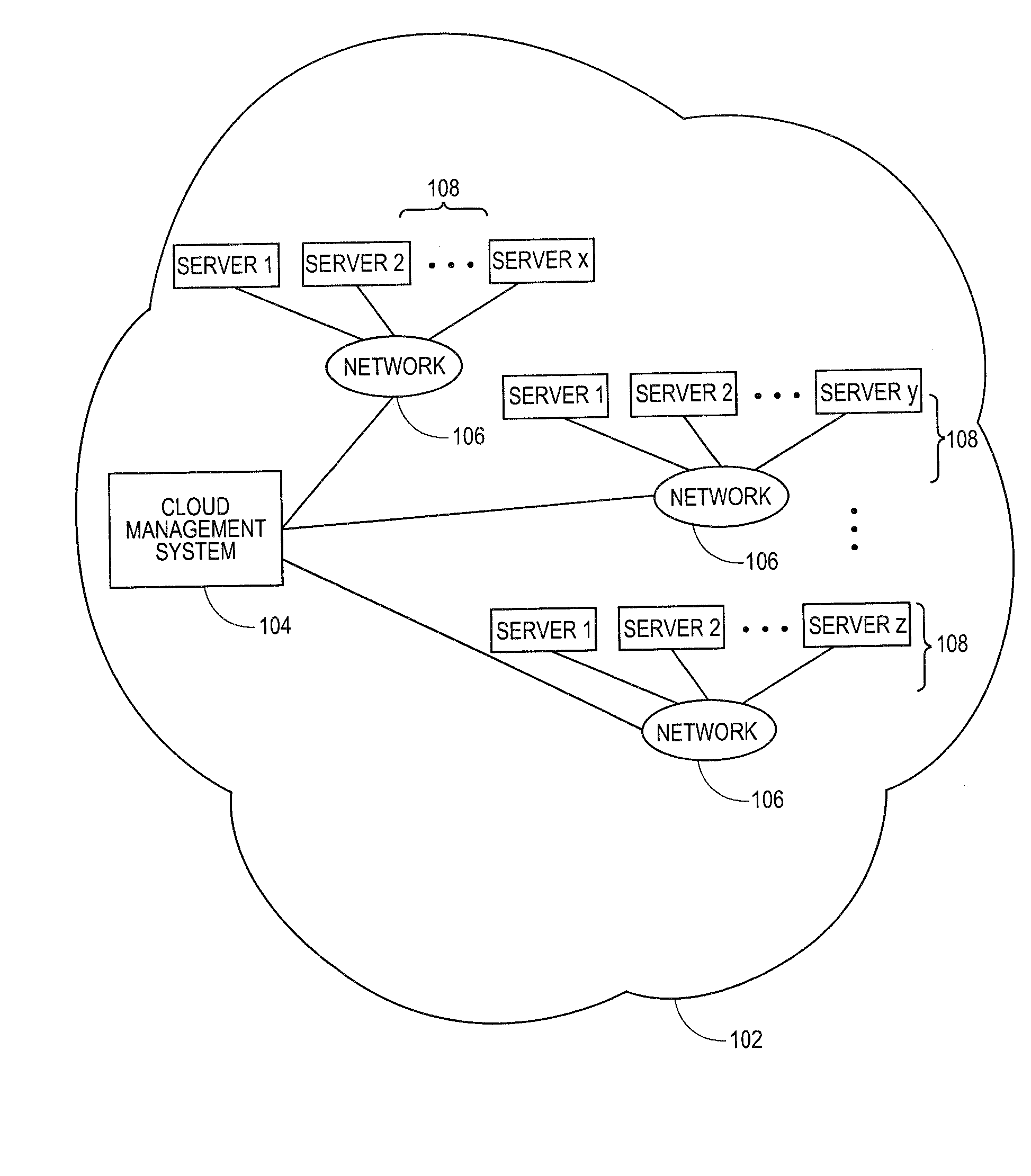
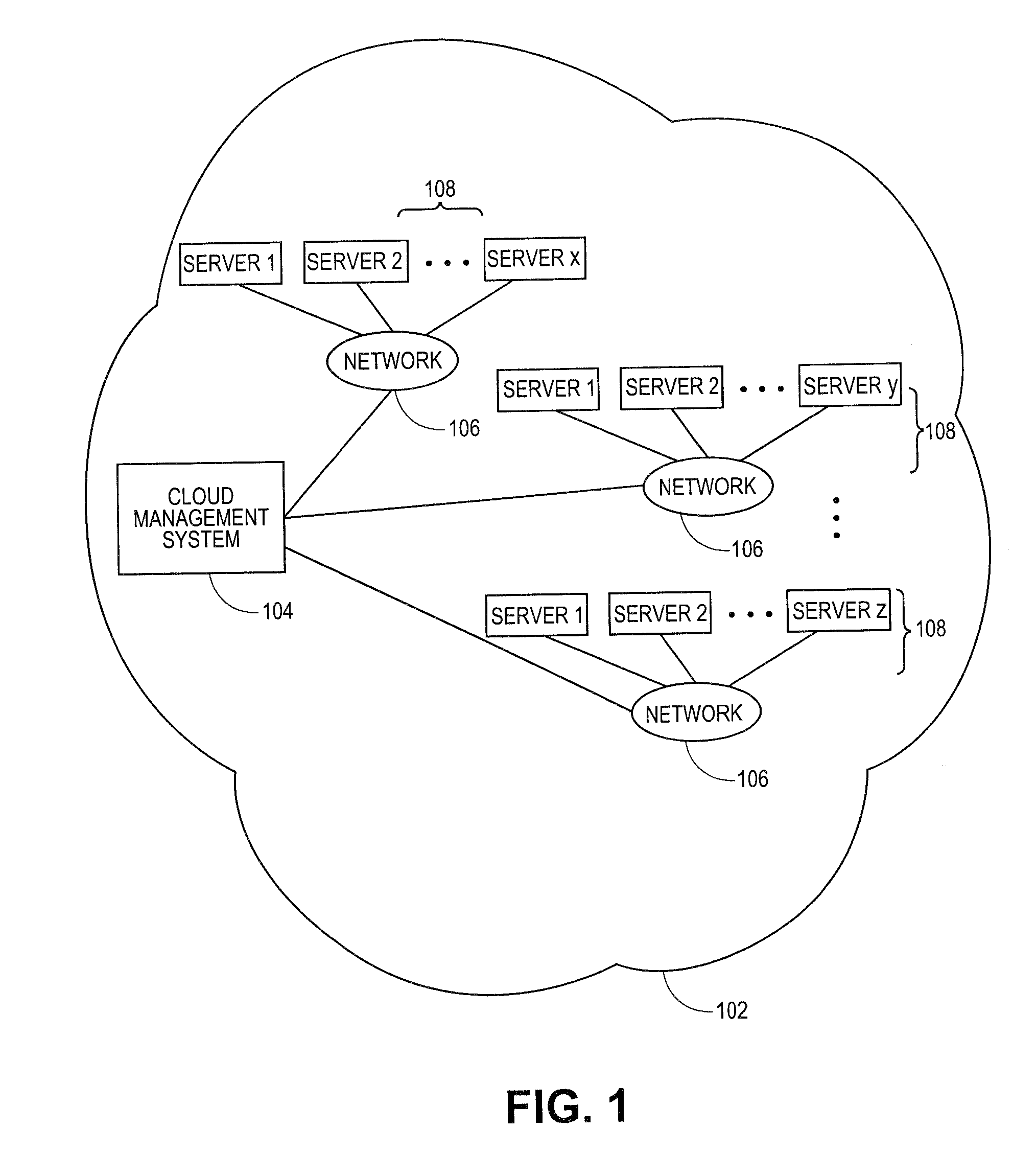
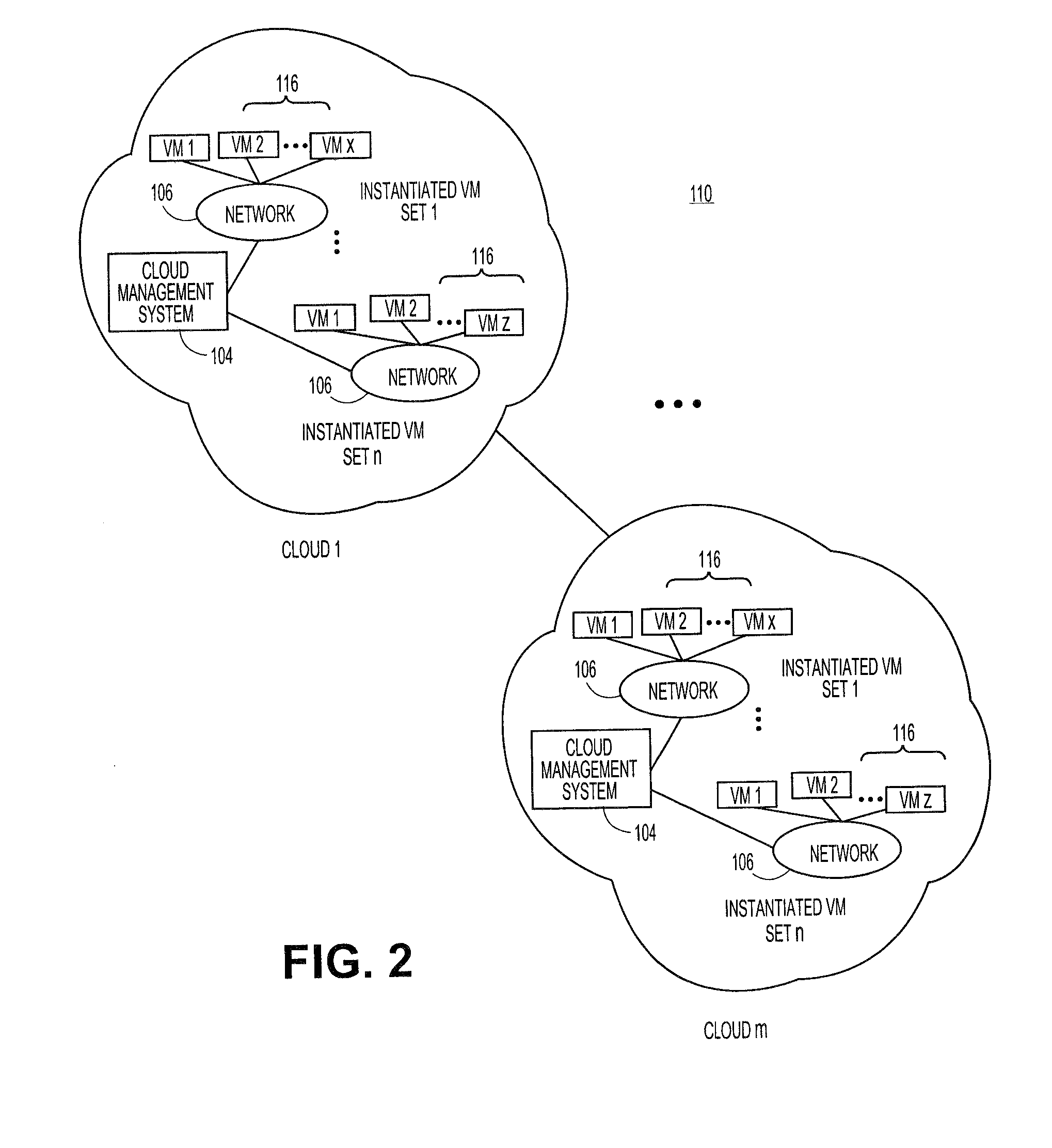
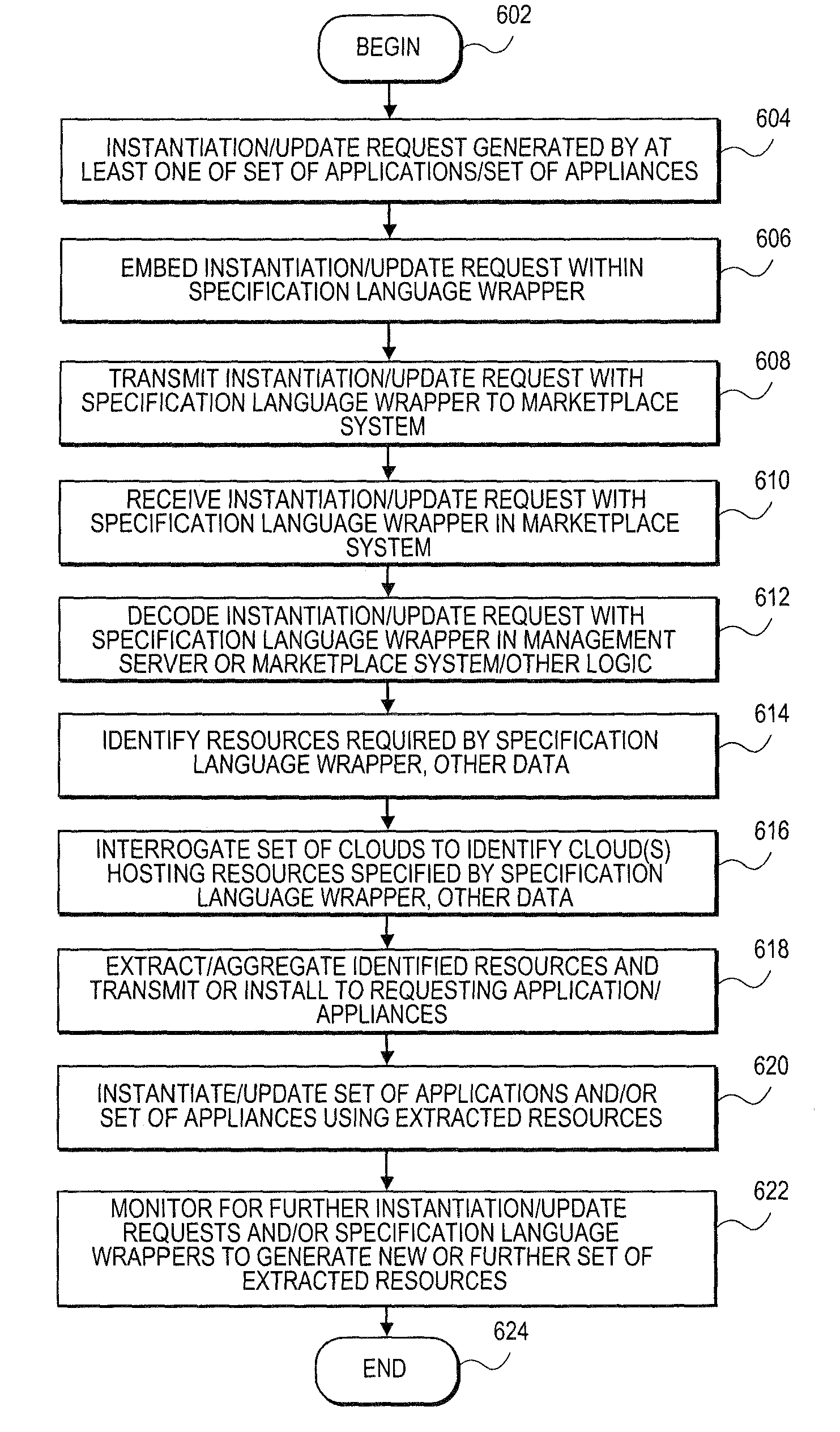
Systems and methods for embedding a cloud-based resource request in a specification language wrapper
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for embedding a cloud-based resource request in a specification language wrapper. In embodiments, a set of applications and / or a set of appliances can be registered to be instantiated in a cloud-based network. Each application or appliance can have an associated set of specified resources with which the user wishes to instantiate those objects. For example, a user may specify a maximum latency for input / output of the application or appliance, a geographic location of the supporting cloud resources, a processor throughput, or other resource specification to instantiate the desired object. According to embodiments, the set of requested resources can be embedded in a specification language wrapper, such as an XML object. The specification language wrapper can be transmitted to a marketplace to seek the response of available clouds which can support the application or appliance according to the specifications contained in the specification language wrapper.
Owner:RED HAT
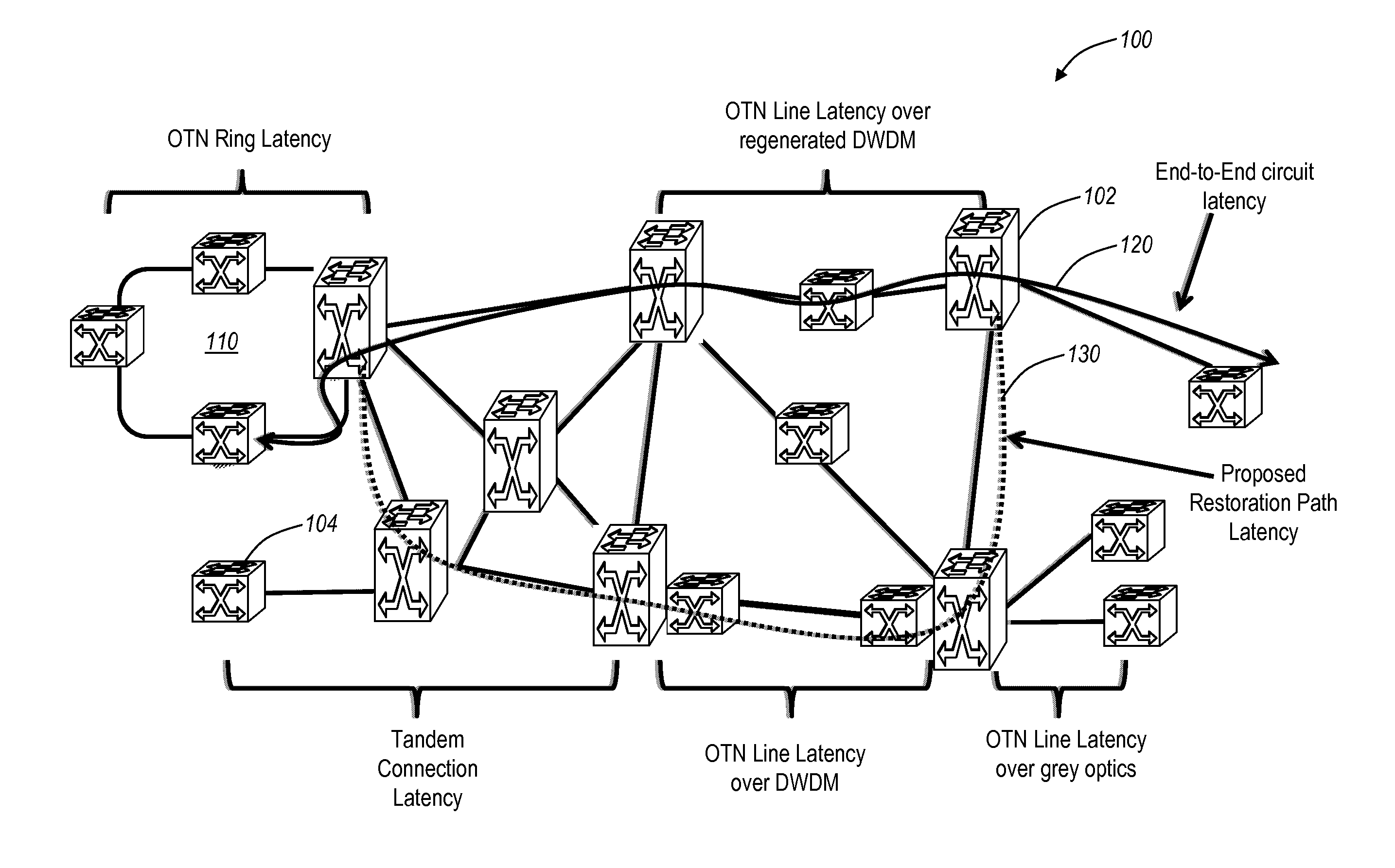
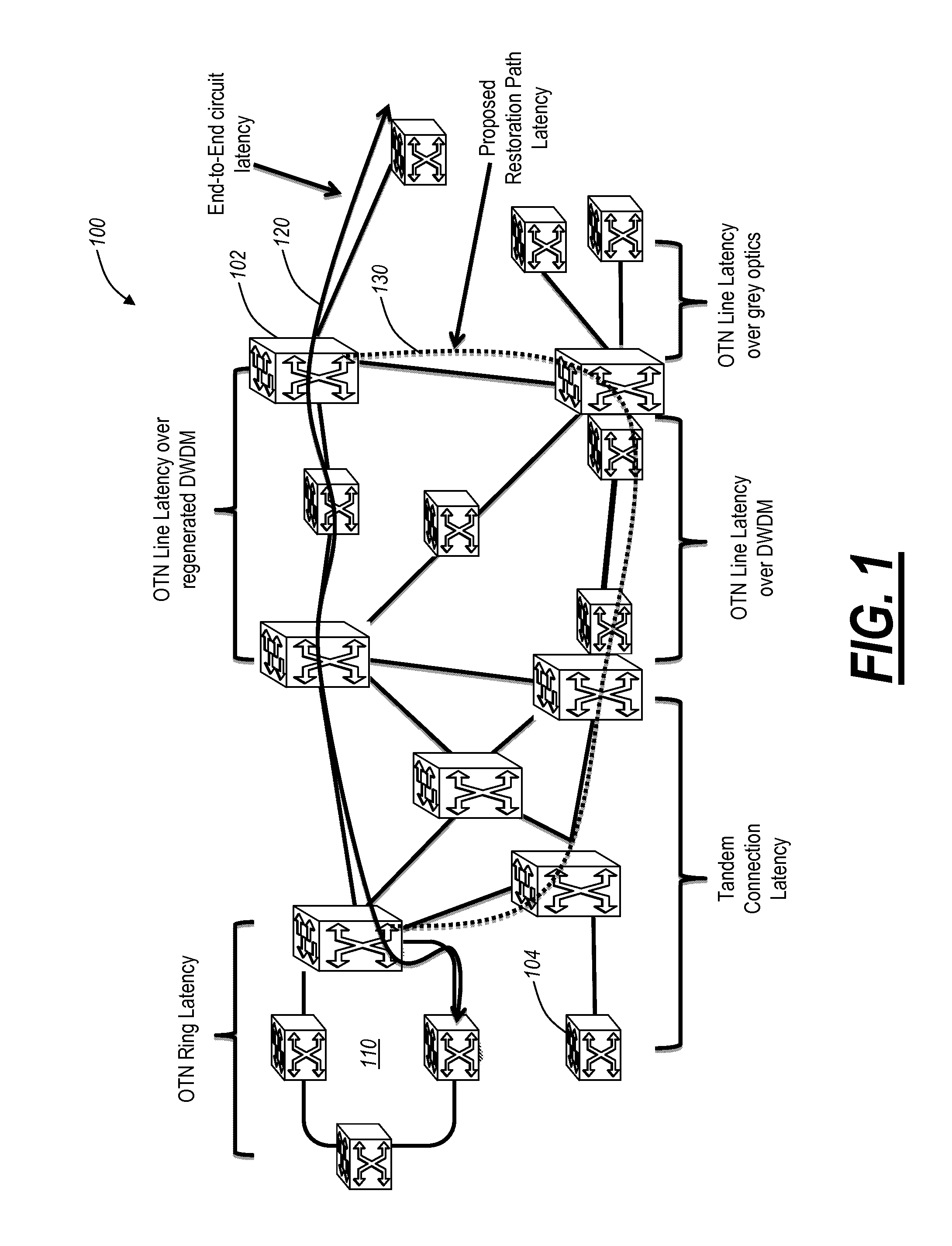
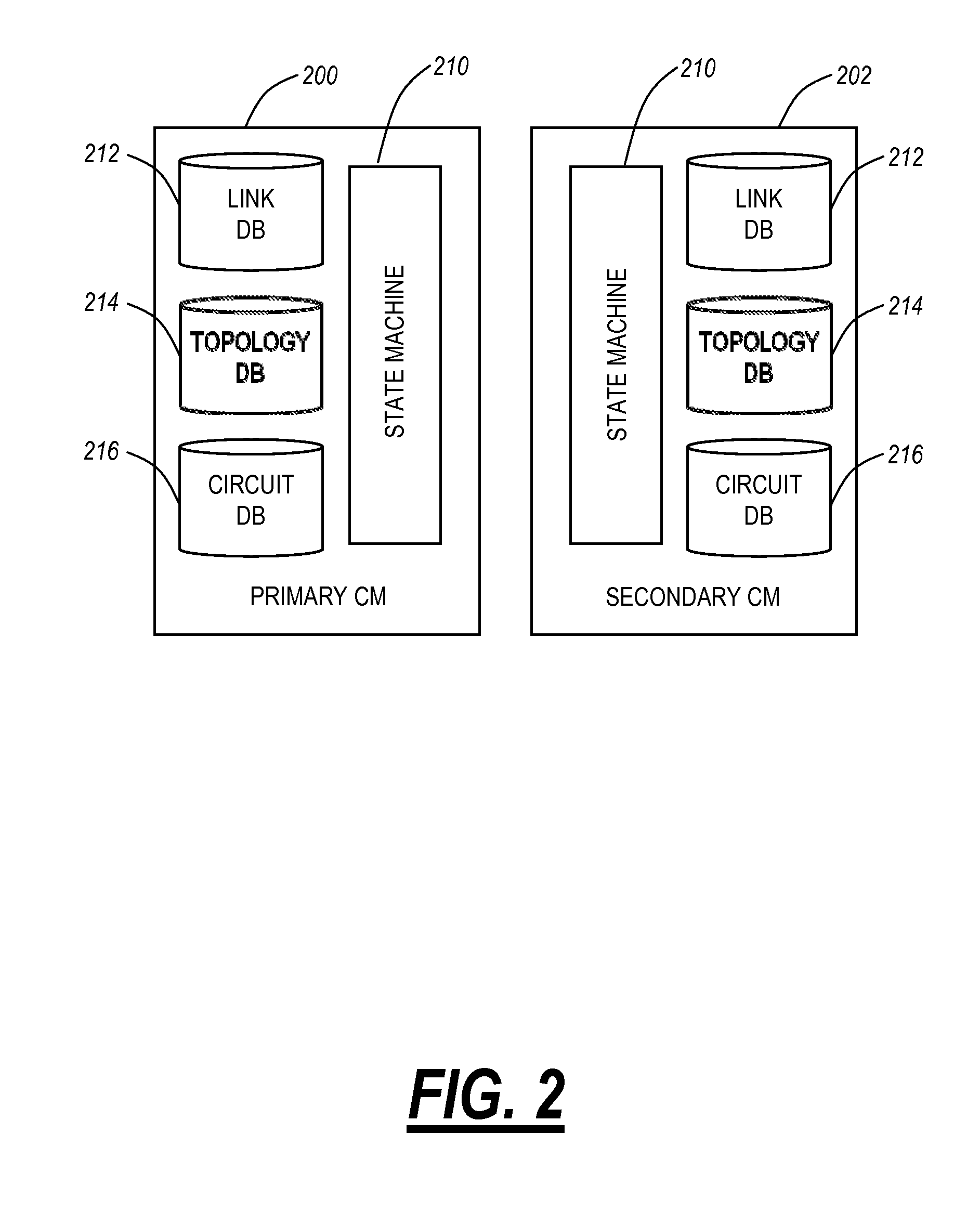
Systems and methods of measuring latency and routing thereon in optical networks
ActiveUS20110170860A1Preventing mesh restorationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNODALMaximum latency
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for making latency measurements and using these measurements in routing in optical networks. In an exemplary embodiment, a method is defined whereby two nodes sharing a line automatically determine whether both nodes are capable of making a latency measurement and then which node will initiate and which node participates in making the latency measurement. In another exemplary embodiment, an on-demand latency measurement may be made between any two arbitrary nodes within a domain. Routing messages may be used to disseminate the latency of links via a signaling and routing protocol. Advantageously, the present invention provides measurement of latency and latency variation of customer circuits (i.e., SNCs) using an in-band, non-intrusive calculation with a high-degree of accuracy. Furthermore, the present invention may consider these calculations for circuit routing based on the latency and circuit acceptance based on maximum latency restrictions.
Owner:CIENA
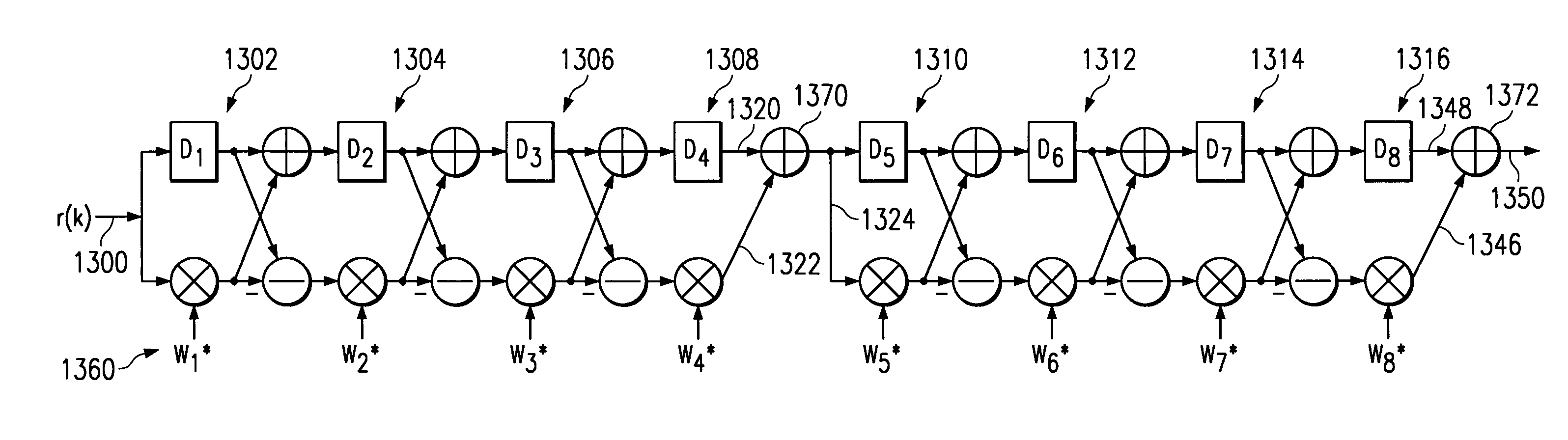
Reduced complexity primary and secondary synchronization codes with good correlation properties for WCDMA
InactiveUS7039036B1Reduce circuit complexityReduce areaTime-division multiplexMultiplex code generationMaximum latencyComputer science
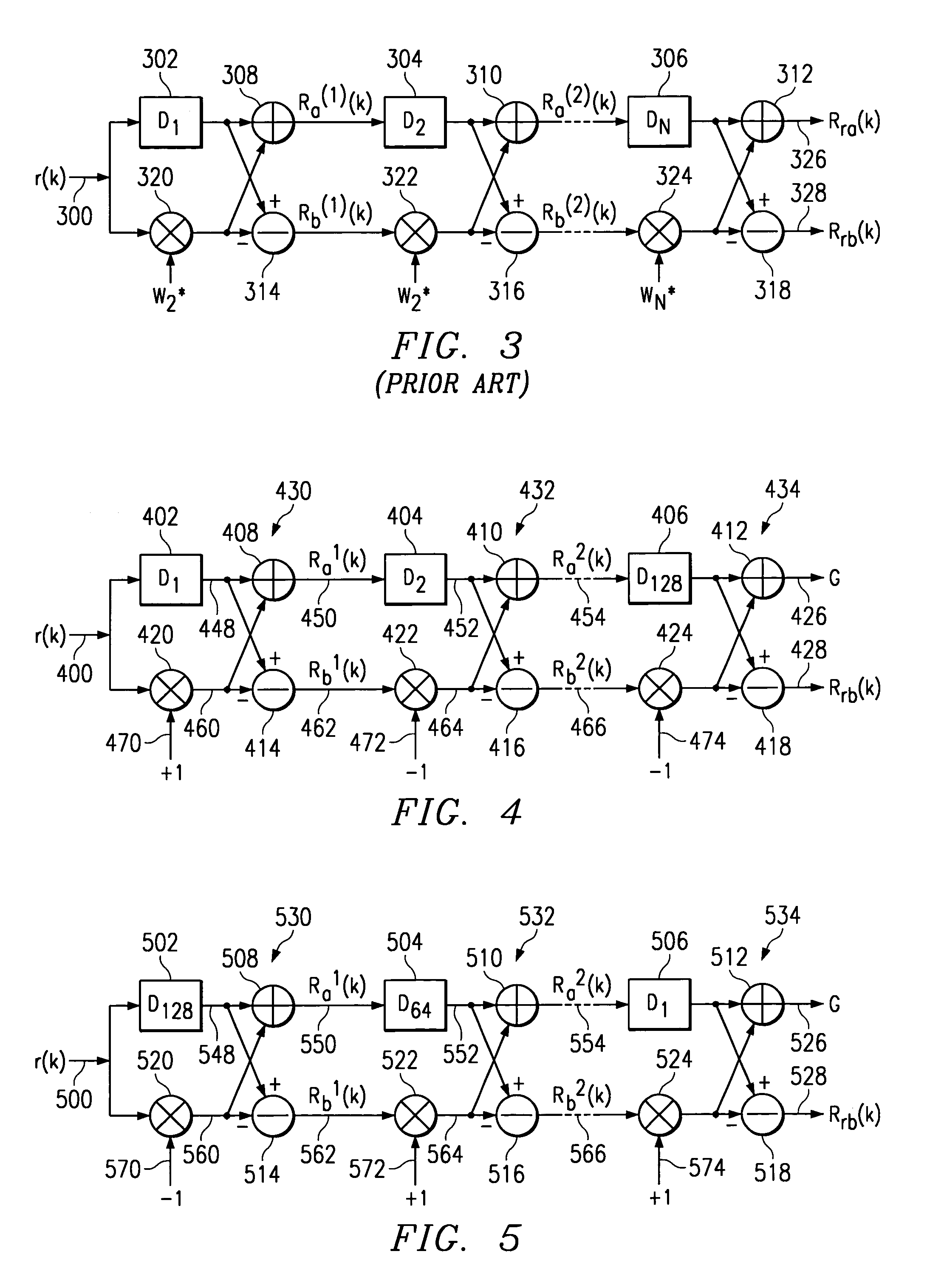
A circuit for processing binary sequences is designed with a plurality of stages (530–534) coupled to provide plural signal paths (526,528). Each stage includes respective signal paths (550,562) for a first Ra1(k) and a second Rb1(k) data sequence. Each stage further includes a respective delay circuit (502) having a different delay from said respective delay circuit of each other stage (504,506) of the plurality of stages. A stage having a greatest delay (502) precedes other stages (504,506) in the plurality of stages of at least one of the plural signal paths.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
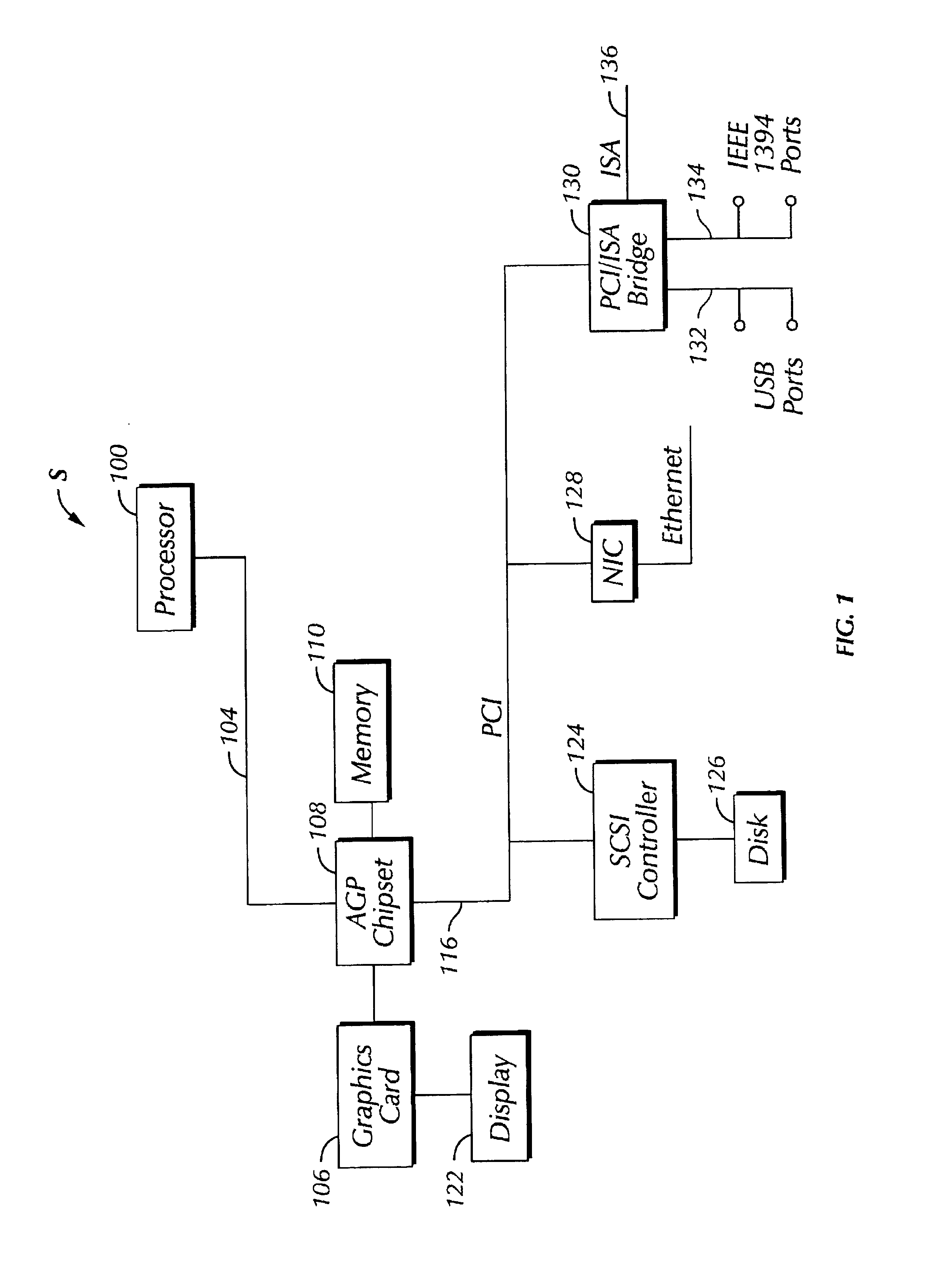
Communication link with isochronous and asynchronous priority modes coupling bridge circuits in a computer system
InactiveUS6151651ASignificant latencyMinimum throughputHybrid switching systemsElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A computer system includes a first processor integrated circuit. A first bridge integrated circuit is coupled to the processor via a host bus. The computer system includes an interconnection bus that couples the first bridge circuit to a second bridge circuit. The interconnection bus provides a first transfer mode for asynchronous data and a second transfer mode for isochronous data. The interconnection bus provides for a maximum latency and a guaranteed throughput for asynchronous and isochronous data.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Broadband switching system
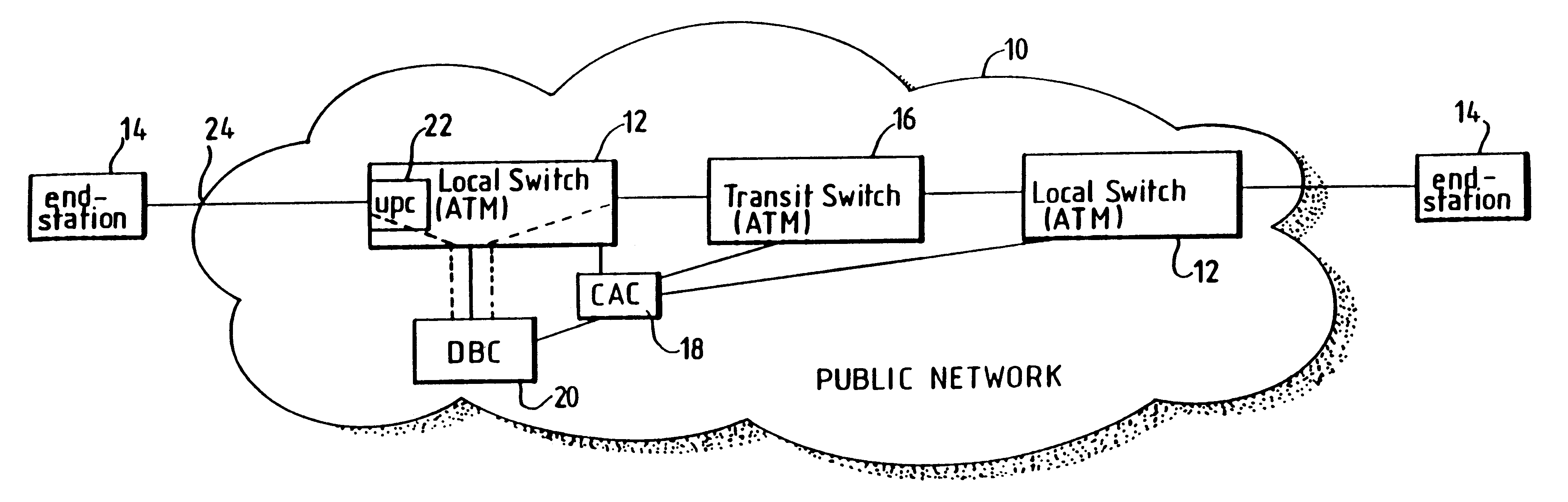
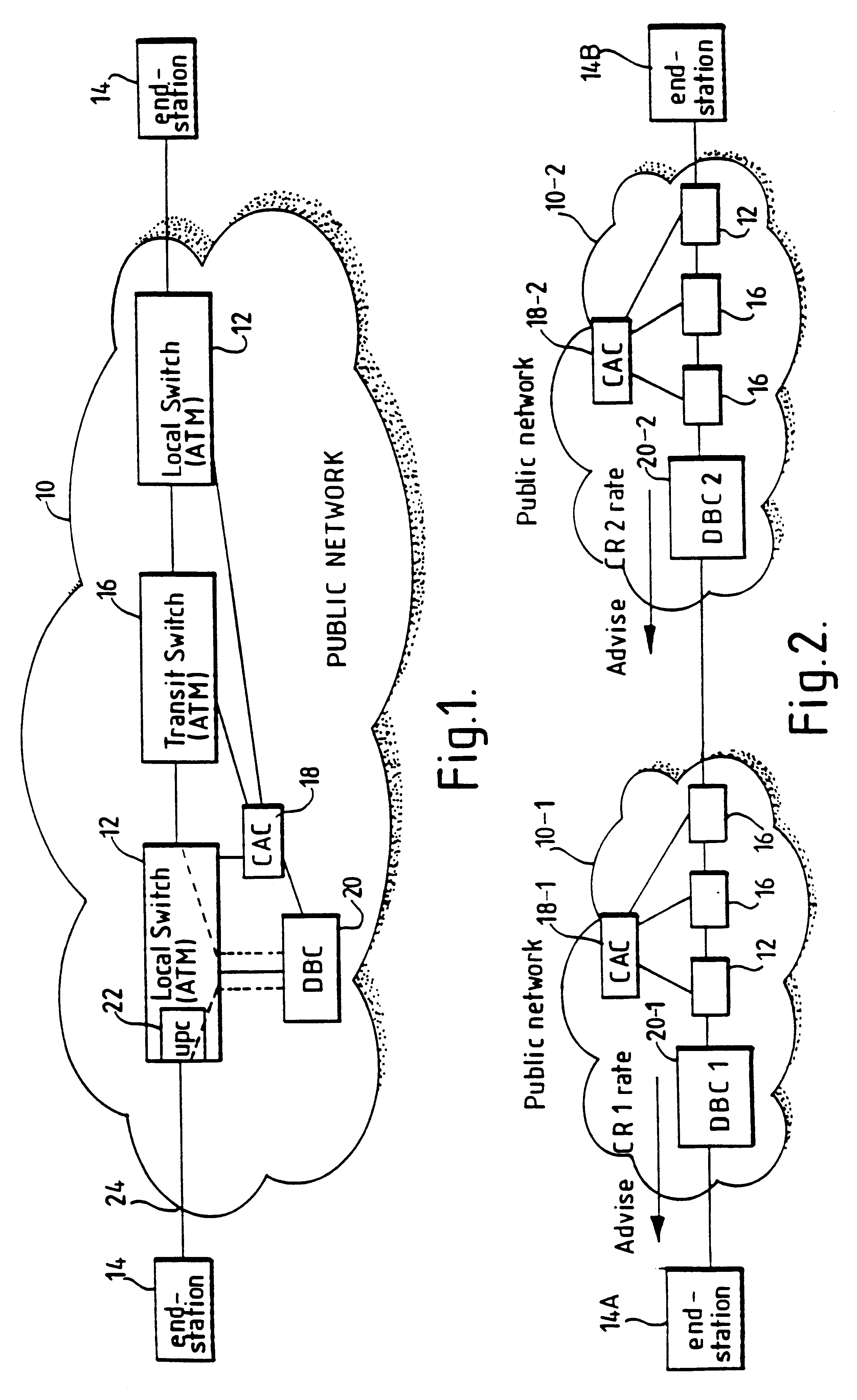
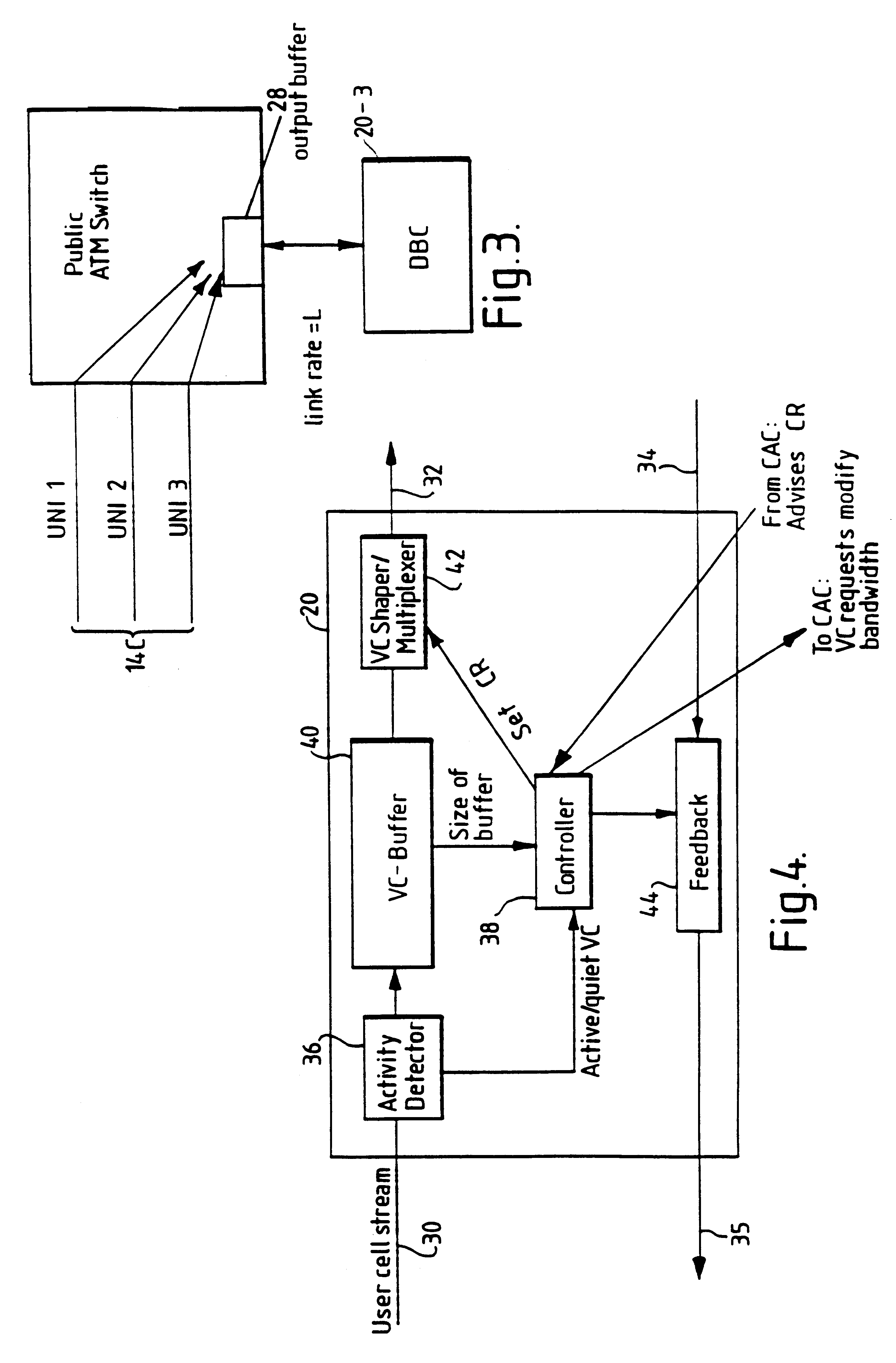
In a broadband switching system for the switching of asynchronously transferred cells of data, a dynamic bandwidth controller (DBC) controls the application of data cells to an input port of the system. Data cells are supplied by a number of transmitting end-systems. When an end-system begins transmitting data cells, the DBC detects the presence of incoming cells and requests bandwidth from a connection admission control (CAC) forming part of the system. The switching system stores a table associating a number of signal sources connected to the ingress with respective predetermined transmission bandwidths and, preferably also, maximum delay times. When arrival of cells from one of the sources at the input port is detected, the DBC sends a request signal for the relevant predetermined bandwidth to the CAC and delays transmission of the cells until at least the predetermined bandwidth is allocated. This delay is typically effected by sending a cell rate indicator signal back to the input port for placing the source in a halt mode. If no allocation of bandwidth has occurred before the respective maximum delay time, bandwidth is allocated by robbing bandwidth form other signal sources.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method and communication system for data exchanging data between users of a bus system
InactiveUS7260609B2Latency periodSimple initializationData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemNormal case
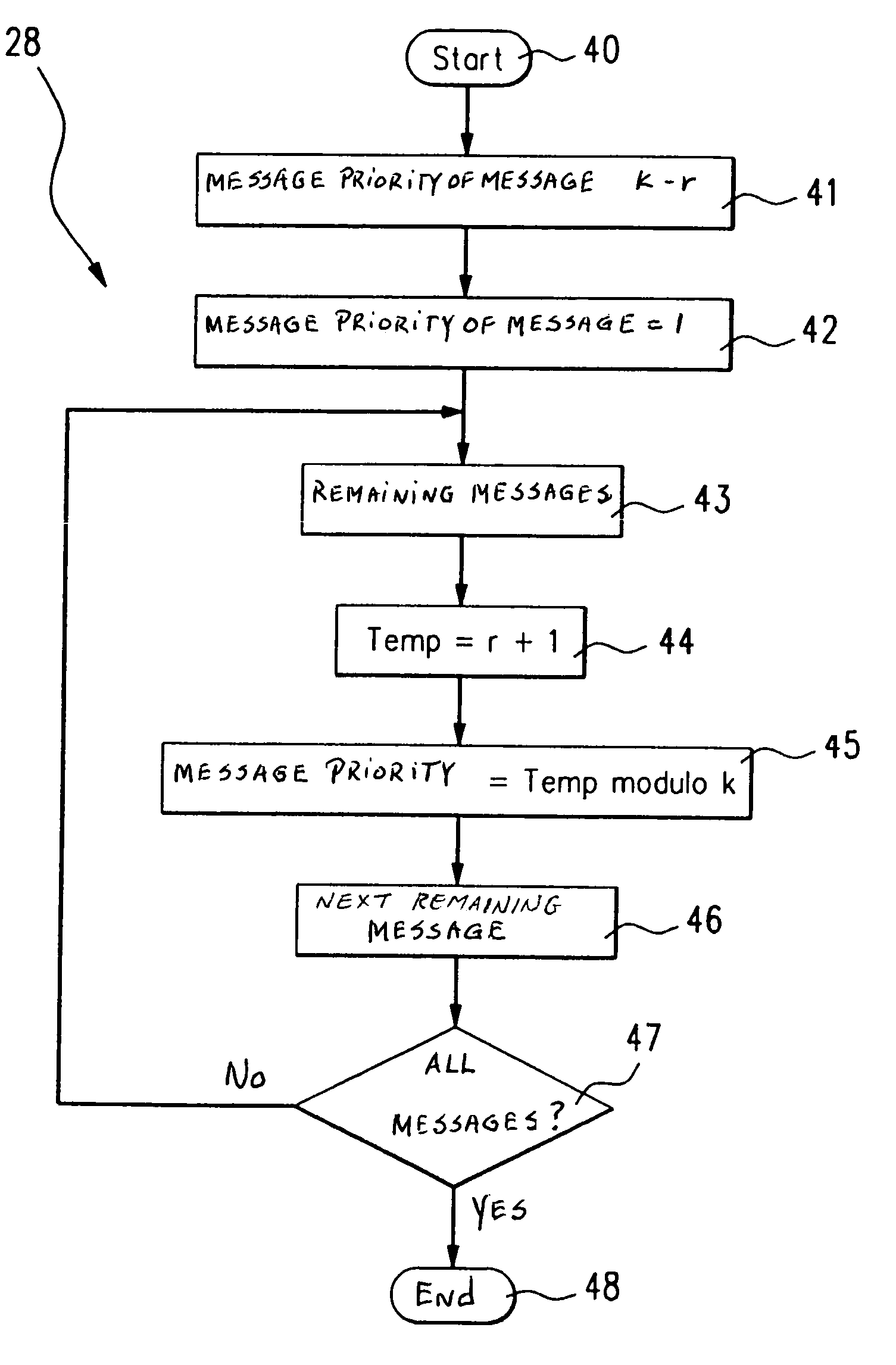
The present invention provides a method and a communications system for the exchange of data between at least two users who are in contact with one another using a bus system. The data are included in messages which are transmitted by users over the bus system. A specifiable priority is assigned to each message. In order to achieve, in the normal case, a high probability of a short latency period (t) of a message to be transmitted, and to be able to guarantee, in the worst case, a maximum latency period (tmax), it is provided that the priorities assigned to the messages be dynamically modified during the operation of bus system. Preferably, the set of all messages is subdivided into equivalence classes, and a priority is assigned to each equivalence class. During the operation of the bus system, the priorities of the messages are dynamically modified within an equivalence class, and the priorities of the equivalence classes are dynamically modified.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
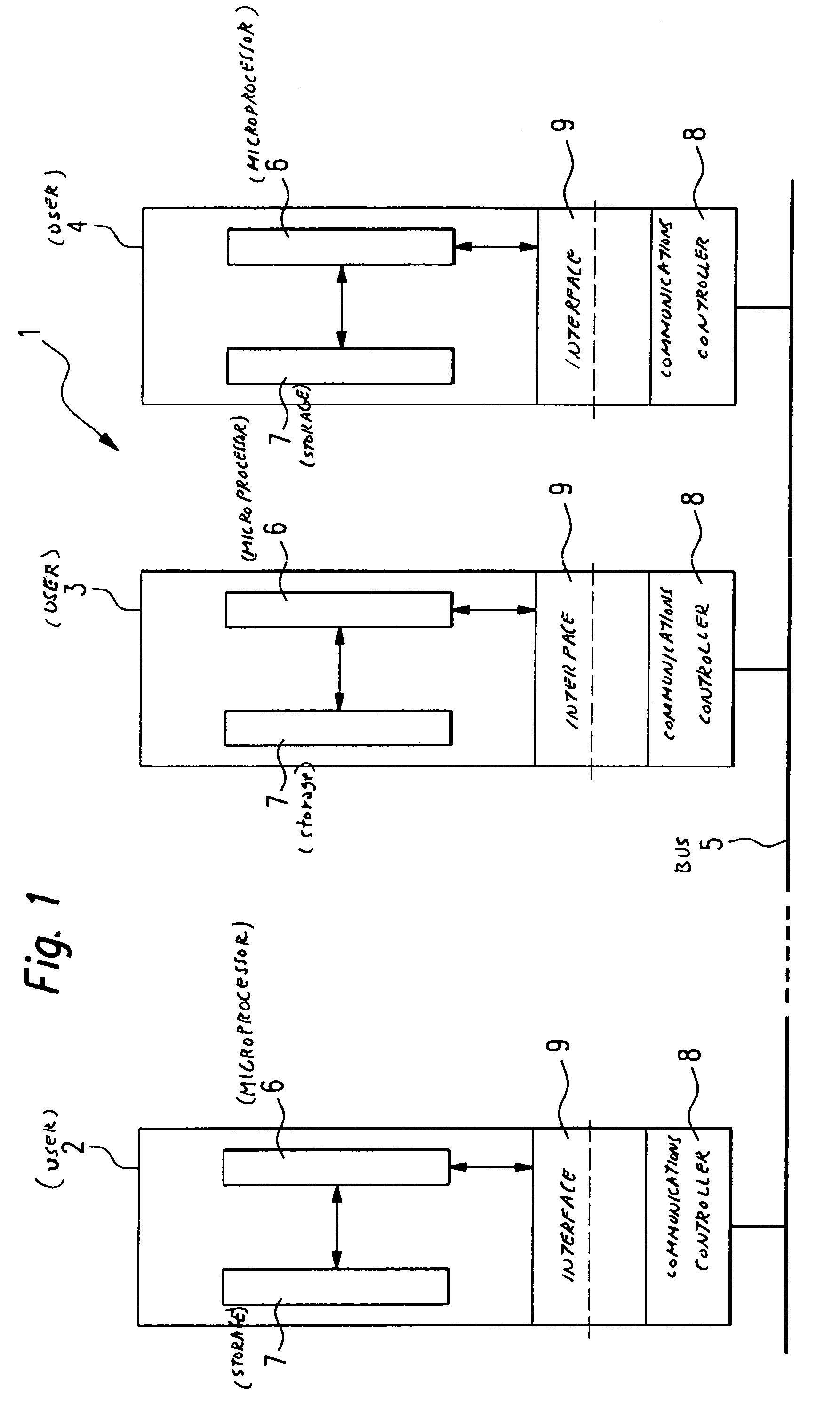
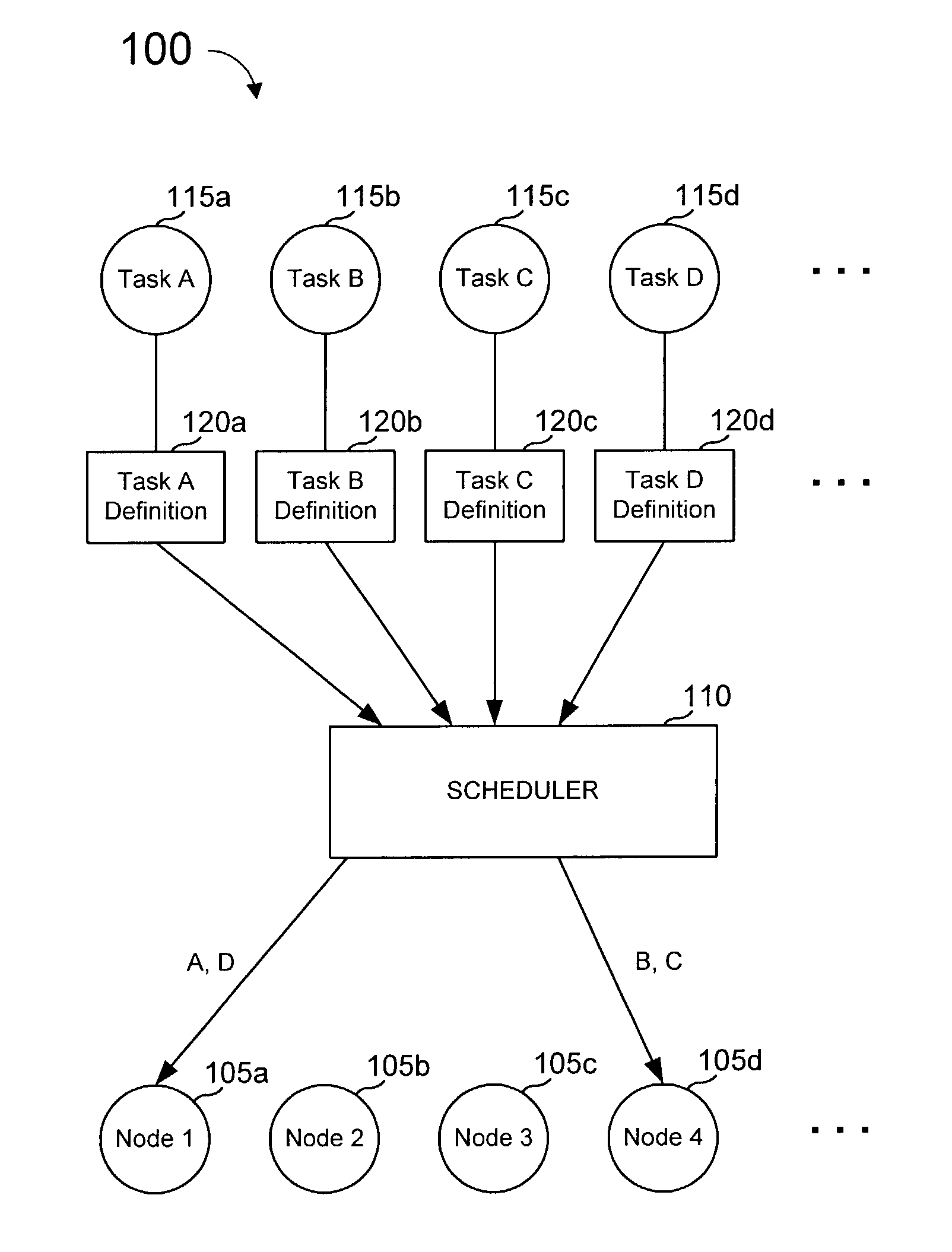
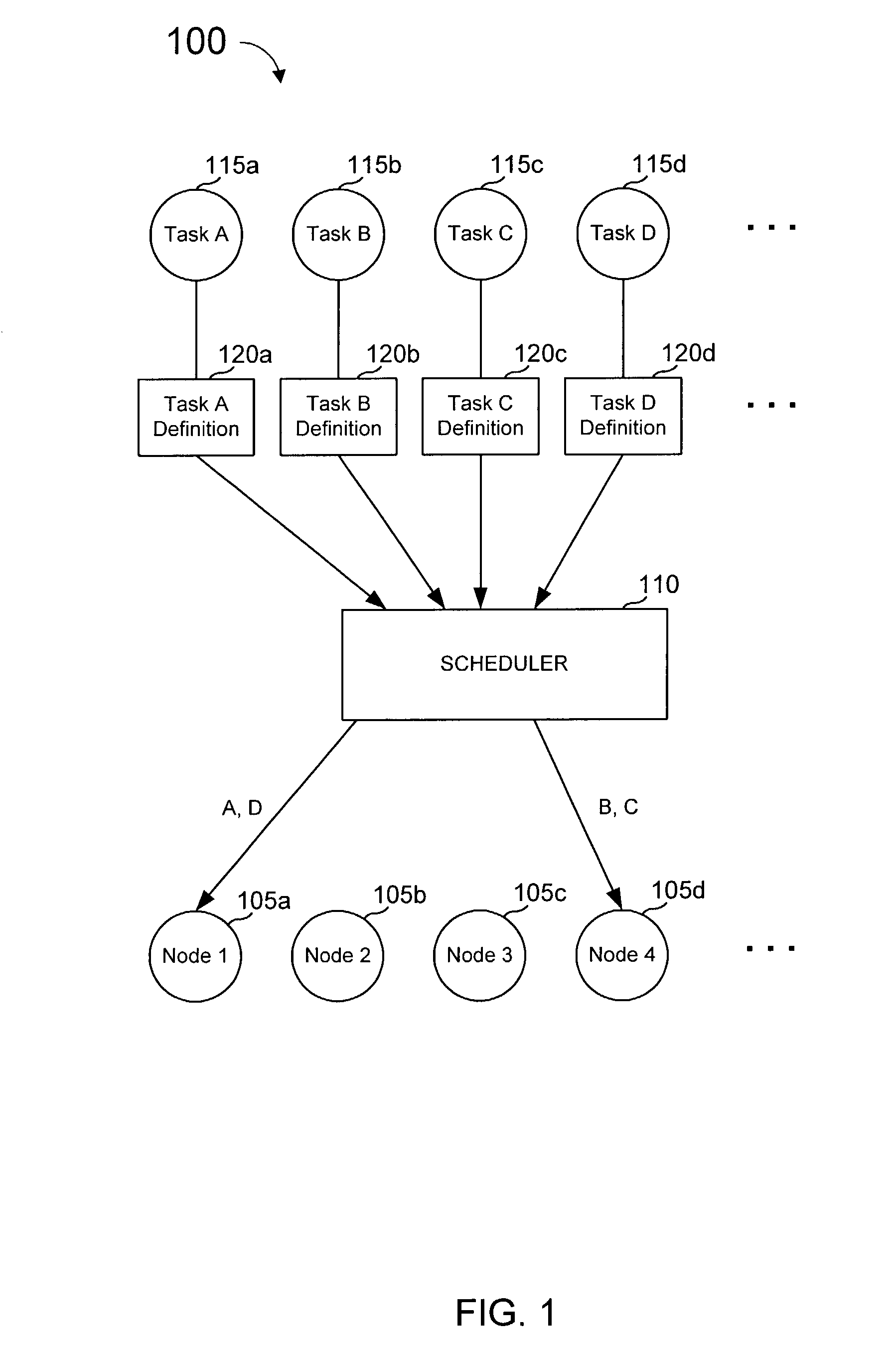
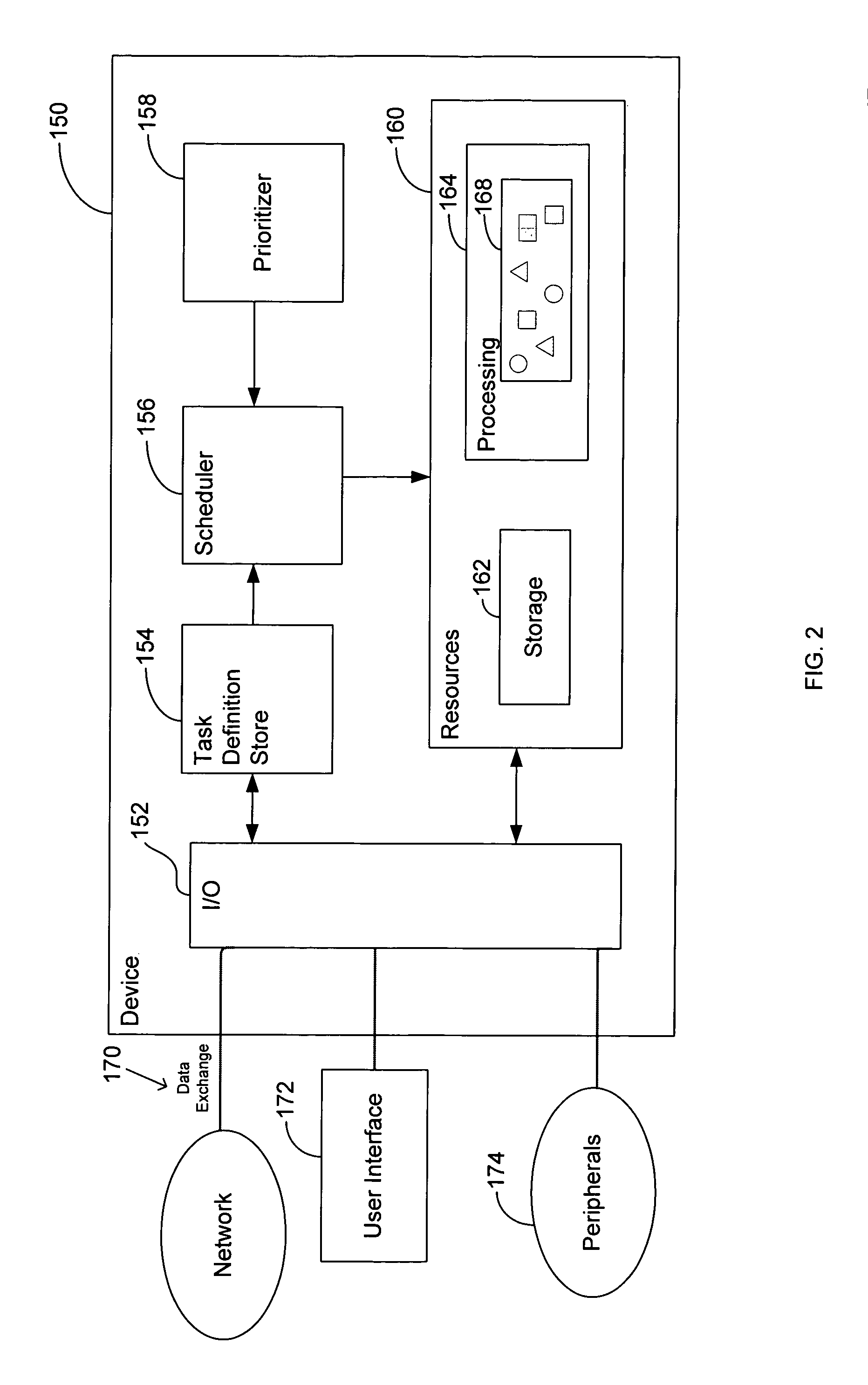
Task definition for specifying resource requirements
ActiveUS8108656B2Resource allocationGeneral purpose stored program computerTask completionMaximum latency
Task definitions are used by a task scheduler and prioritizer to allocate task operation to a plurality of processing units. The task definition is an electronic record that specifies researching needed by, and other characteristics of, a task to be executed. Resources include types of processing nodes desired to execute the task, needed amount or rate of processing cycles, amount of memory capacity, number of registers, input / output ports, buffer sizes, etc. Characteristics of a task include maximum latency tome, frequency of execution of a task, communication ports, and other characteristics. An exemplary task definition language and syntax is described that uses constructs including other of attempted scheduling operations, percentage or amount of resources desired by different operations, handling of multiple executable images or modules, overlays, port aliases and other features.
Owner:CORNAMI INC
Method and system for improving the quality of real-time data streaming
InactiveUS20110058554A1Quality improvementData switching by path configurationReal-time dataData stream
A method for improving quality of real time data streaming over a network. The network includes a plurality of nodes. A source node in the plurality of nodes transmits a real time data packet to a destination node in the plurality of nodes. First, the source node obtains maximum latency information about the data packet of a data frame. The source node stores information about the maximum latency in the data packet. Then, the source node and zero or more intermediate nodes route the data packet from the source to the destination such that the data packet reaches the destination before the maximum latency expires. Each intermediate node, updates the maximum latency of a packet by subtracting the time spent by the packet at the intermediate node from the maximum latency value received along with the packet.
Owner:JAIN PRAVAL +1
System for optimizing latency in an avb network
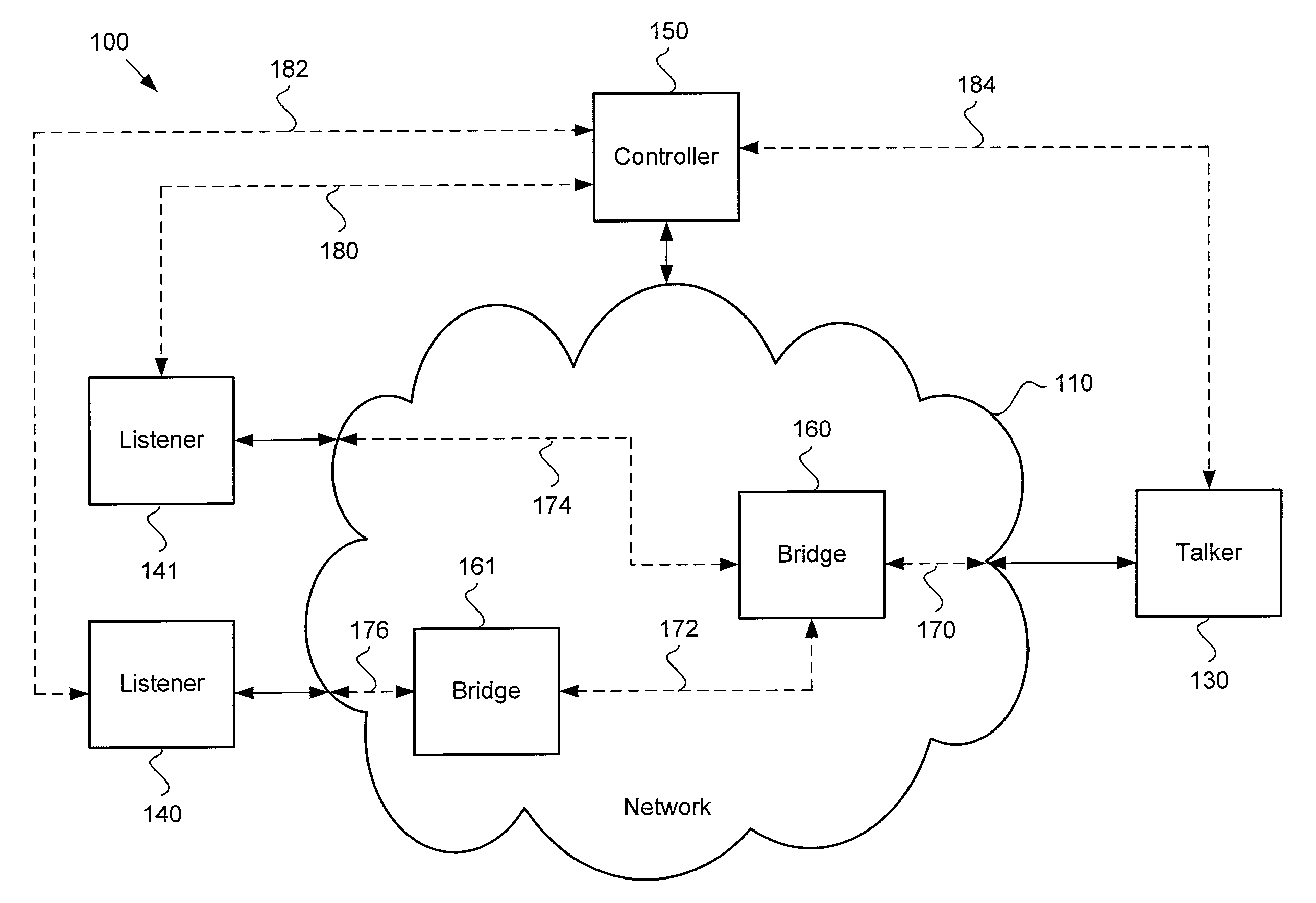
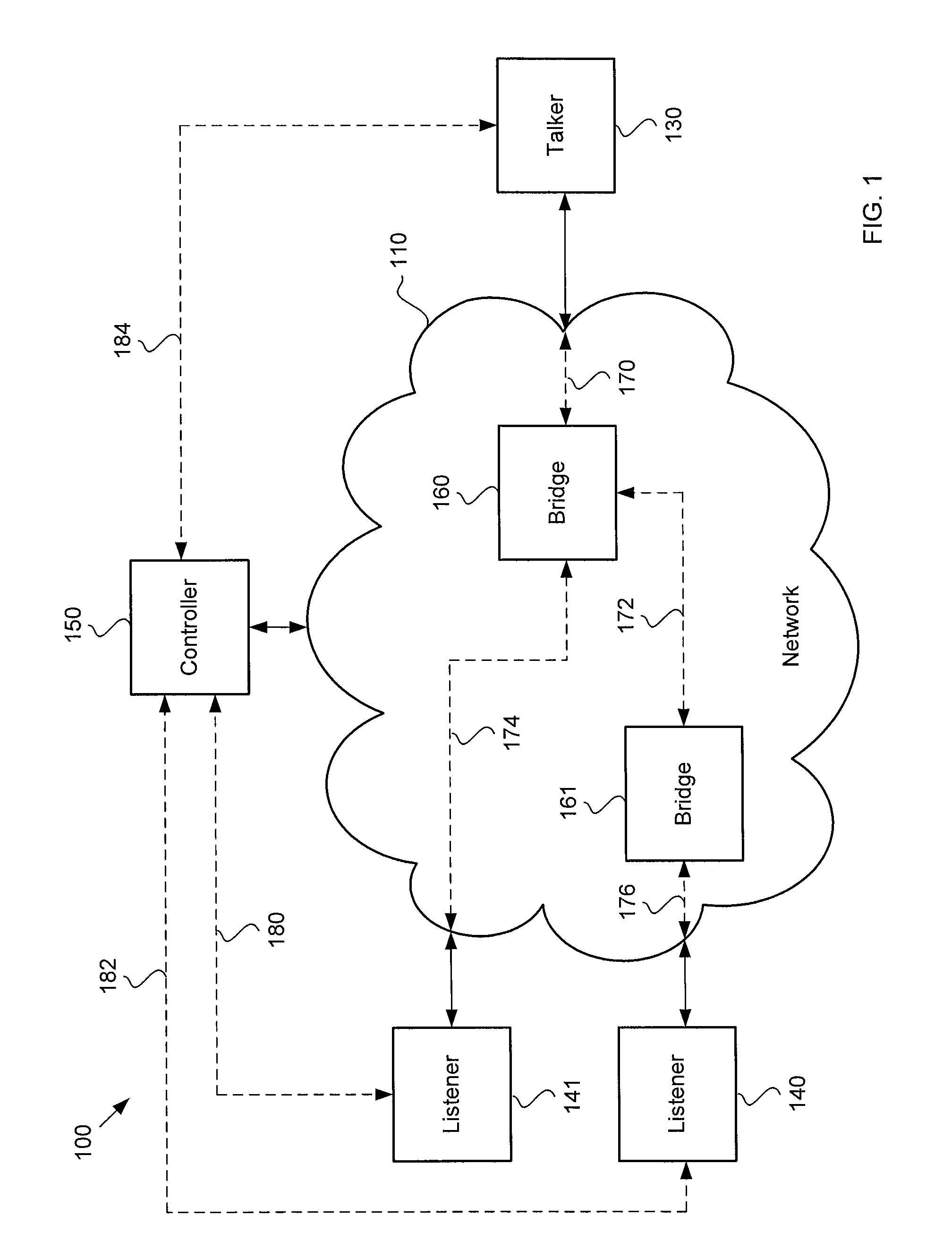
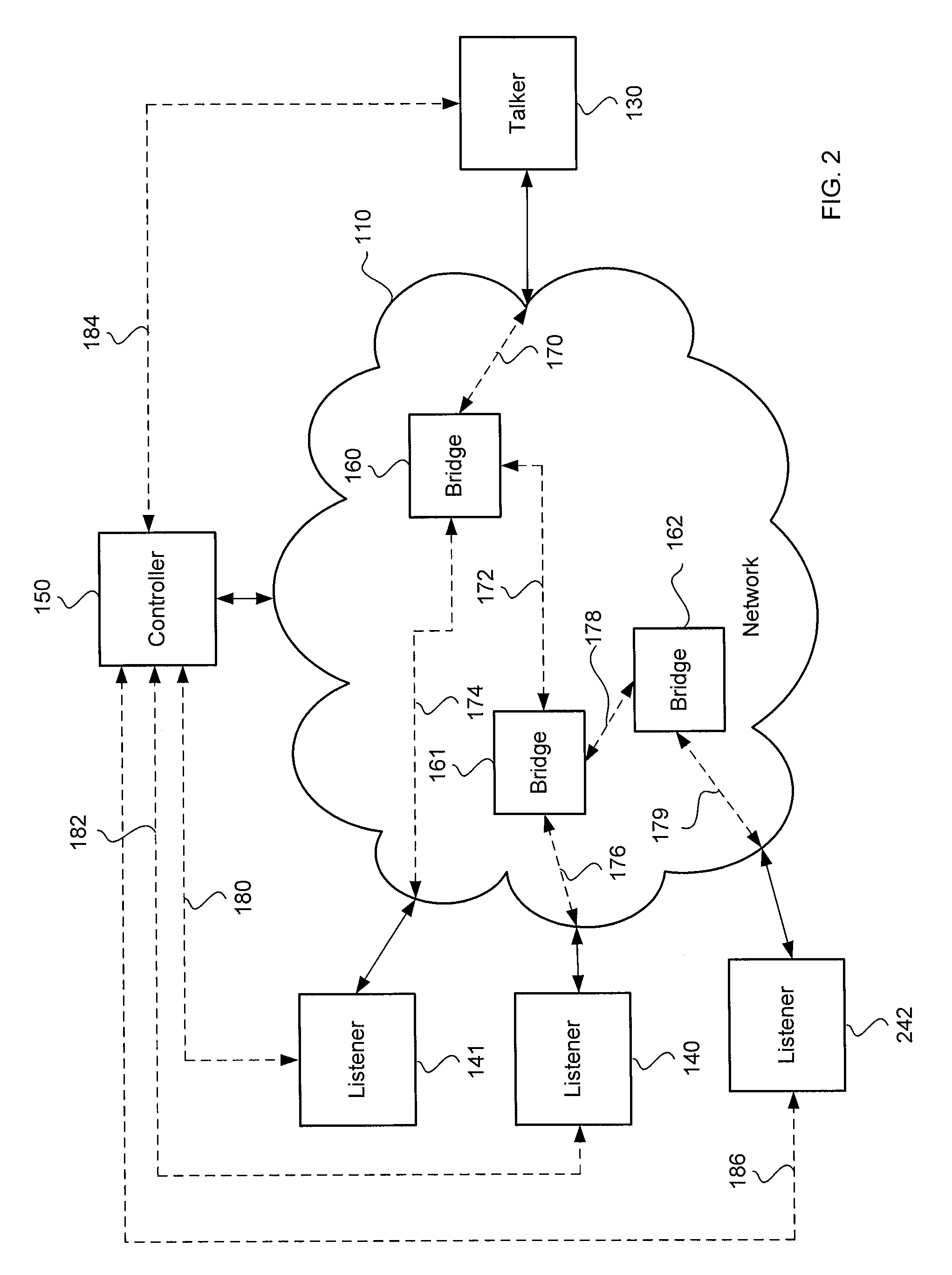
ActiveUS20130138800A1Digital computer detailsSelective content distributionData streamMaximum latency
A network communication system includes a talker that may communicate a data stream having an optimal presentation time to a plurality of listeners over a network, such as an Ethernet Audio / Video Bridging network. The optimal presentation time may be determined by a maximum latency among a plurality of latencies for connections between the talker and the listeners. A controller may communicate with the listeners to determine the maximum latency. The controller may also provide the maximum latency to the talker and the listeners. The talker may determine the optimal presentation time based on the maximum latency. The listeners may allocate an optimum amount of resources to buffer the data stream before the data in the data stream is presented.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
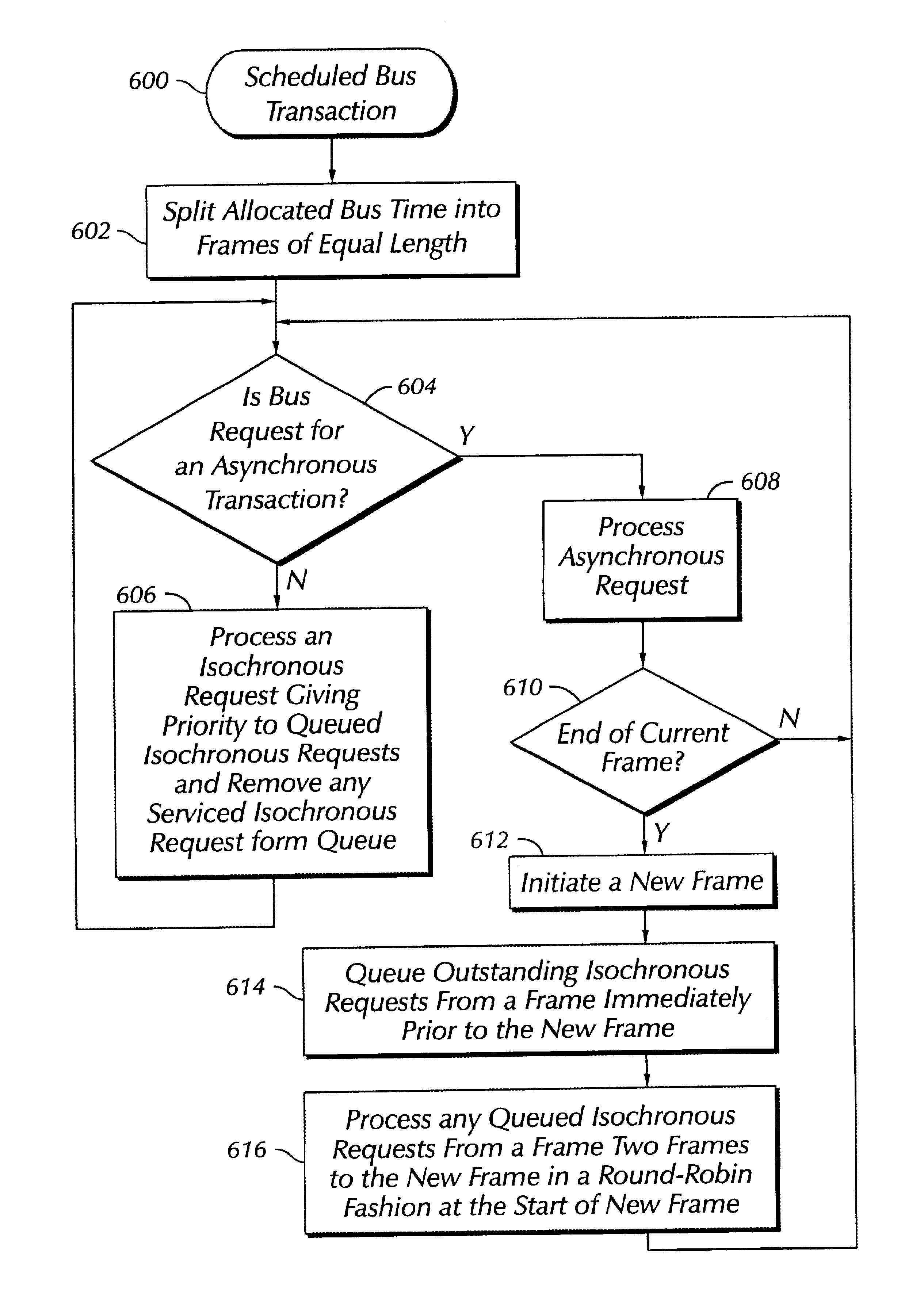
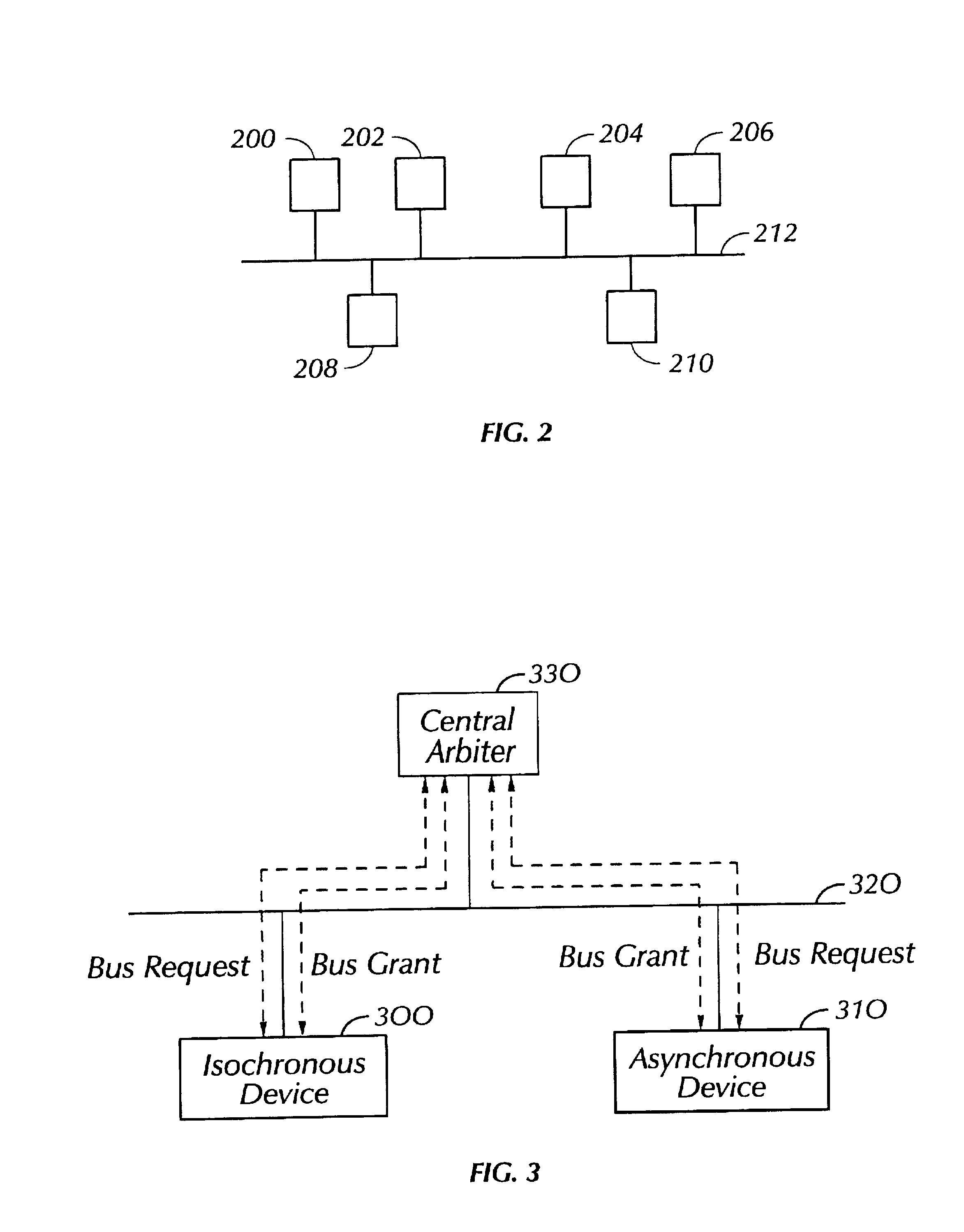
Priority mechanism for scheduling isochronous and asynchronous transactions on a shared bus
A plurality of asynchronous and isochronous transactions on a shared bus are scheduled such that asynchronous latency is minimized while providing a maximum latency for isochronous transactions. This is accomplished by splitting an allocated shared bus time into frames of equal length. When a bus request is received the technique determines whether the bus request in a current frame is for an asynchronous transaction or an isochronous transaction. If an asynchronous transaction bus request exists it is processed, otherwise an isochronous transaction bus request is processed. Bus requests for an isochronous transaction are queued if received while an asynchronous transaction is currently being processed. Asynchronous transactions are given priority until a current frame time has ended. In one embodiment, at the start of a new frame (which becomes the current frame) any queued isochronous transactions are processed before asynchronous transactions of the current frame are given priority. In another embodiment, queued isochronous transactions are only processed at the start of a new frame if they are from two frames prior to the new frame.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
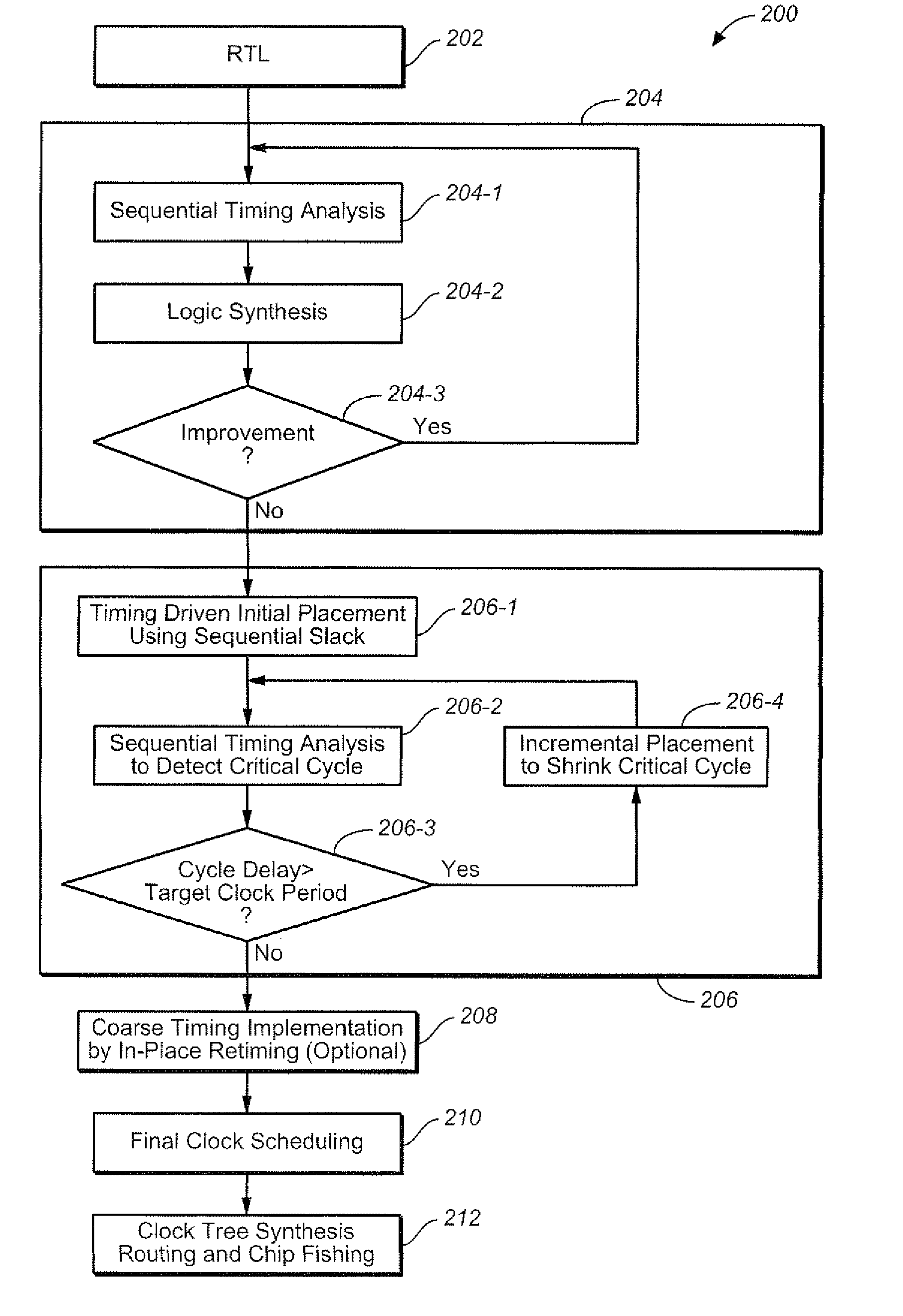
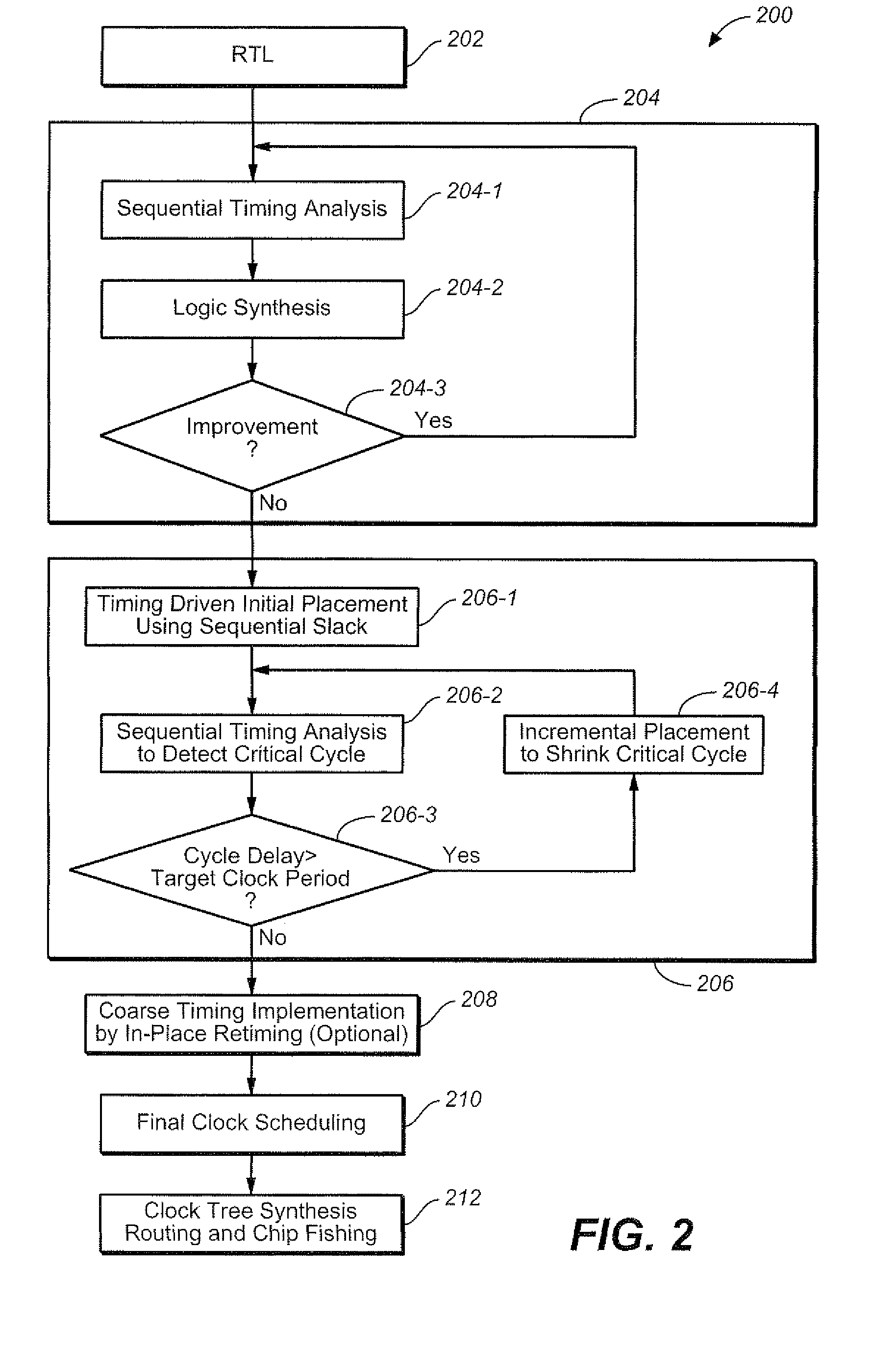
Optimizing integrated circuit design through use of sequential timing information
InactiveUS7743354B2Increase flexibilityEasy to implementCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTiming marginMaximum latency
A method is provided that includes: determining a minimum clock cycle that can be used to propagate a signal about the critical cycle in a circuit design; wherein the critical cycle is a cycle in the design that has a highest proportionality of delay to number of registers; determining for a circuit element in the circuit design, sequential slack associated with the circuit element; wherein the sequential slack represents a minimum delay from among respective maximum delays that can be added to respective structural cycles of which the circuit element is a constituent, based upon the determined limit upon clock cycle duration; using the sequential slack to ascertain sequential optimization based design flexibility throughout multiple stages of a design flow.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
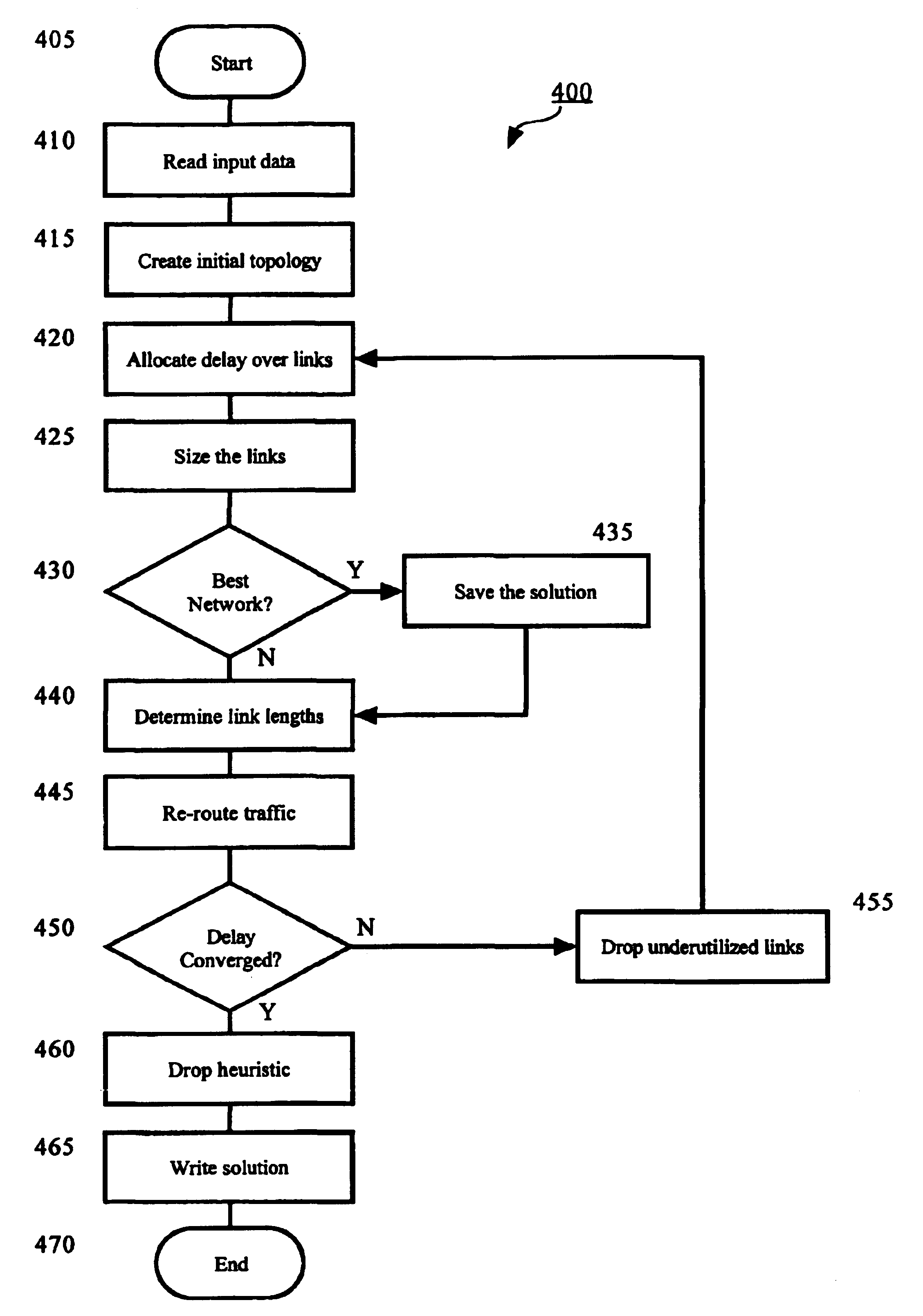
Apparatus and method for designing a network
InactiveUS6934259B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityMaximum latency
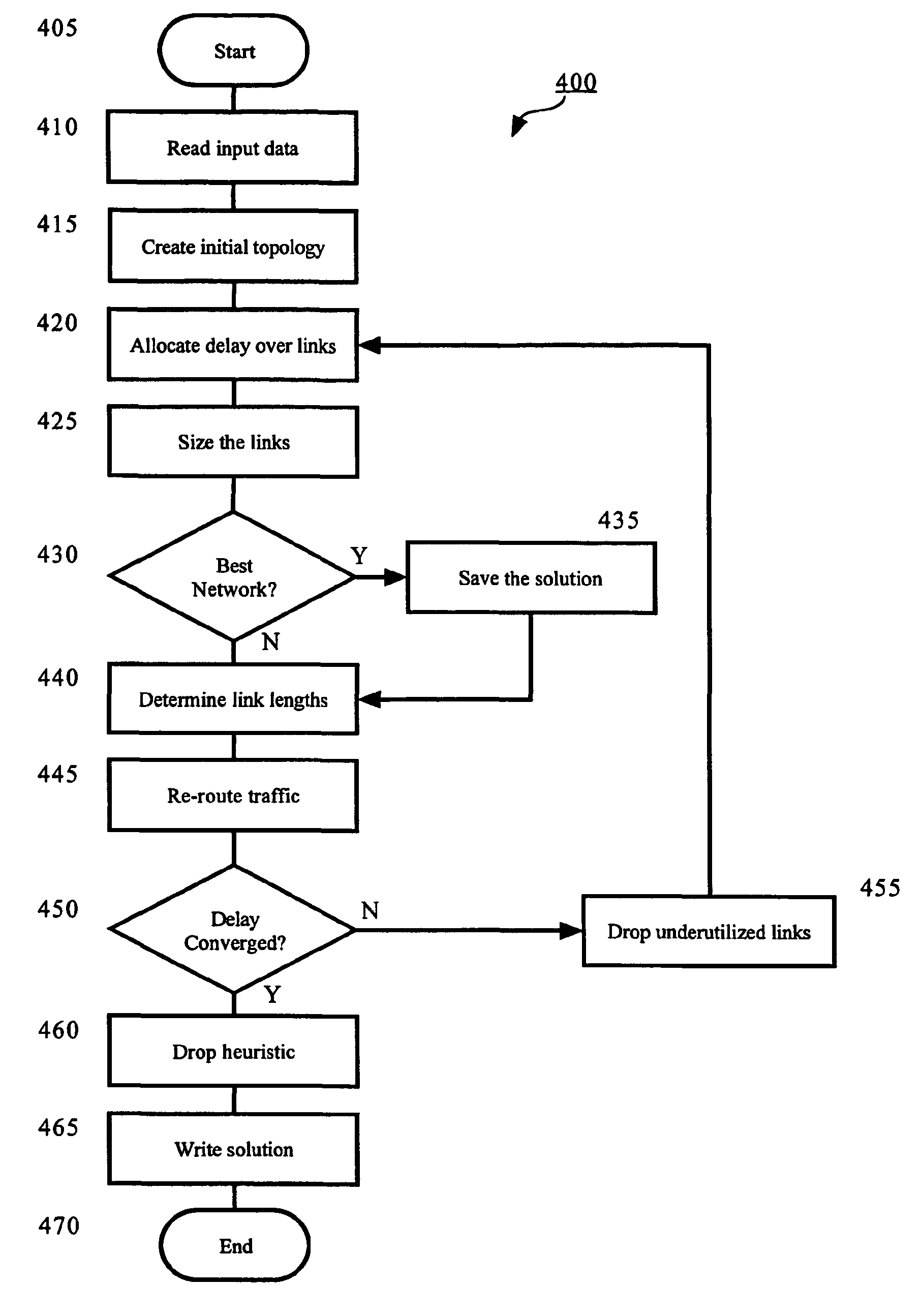
An apparatus and method for designing a network are disclosed. The network is designed wherein nodes originate and terminate traffic to keep delay related to node-to-node delay-sensitive communication below a specified threshold. The method obtains an initial network topology including links and traffic routing based on a volume of traffic, allocates a maximum delay to each link in the network topology in proportion to the square root of an imputed cost for each link, sizes a bandwidth required for each link based on a current traffic routing and at least one of a maximum delay allocated to the link, determines link lengths and reroutes traffic according to shortest paths with respect to the determined link lengths.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Process for the transmission of data by a multi-user, point to multi-point digital data transmission system
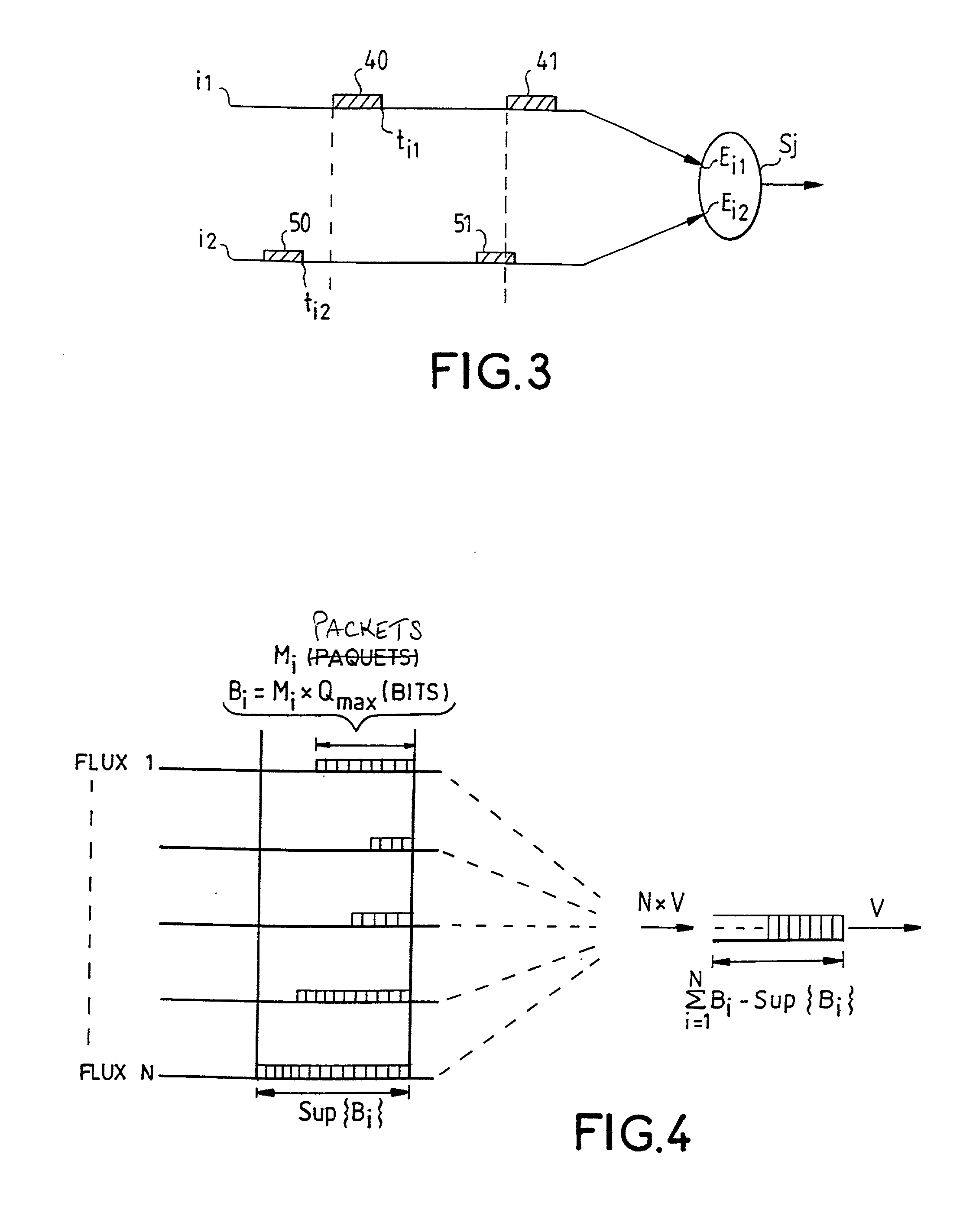
ActiveUS20050018703A1Maintain qualitySpeed up the processSpecial service provision for substationError preventionDigital dataQuality of service
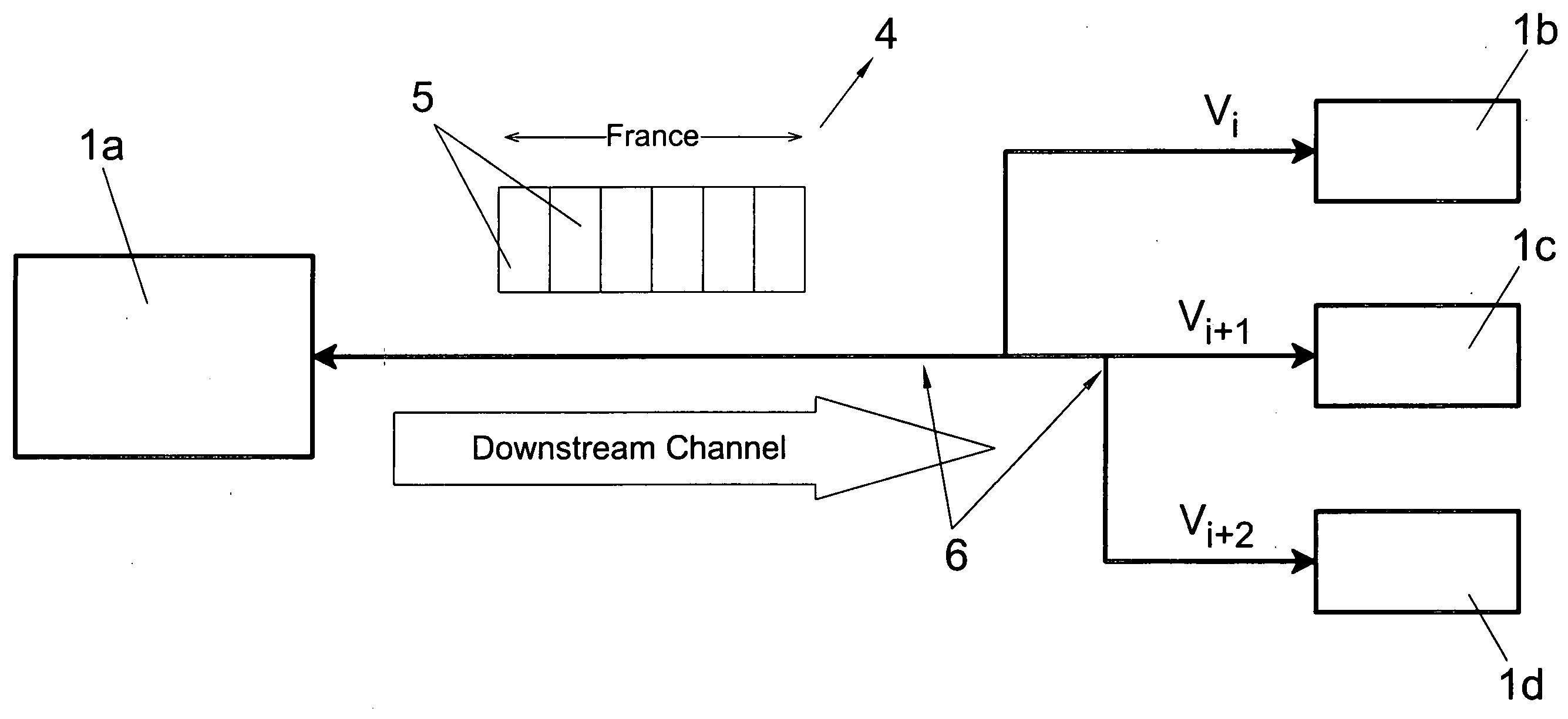
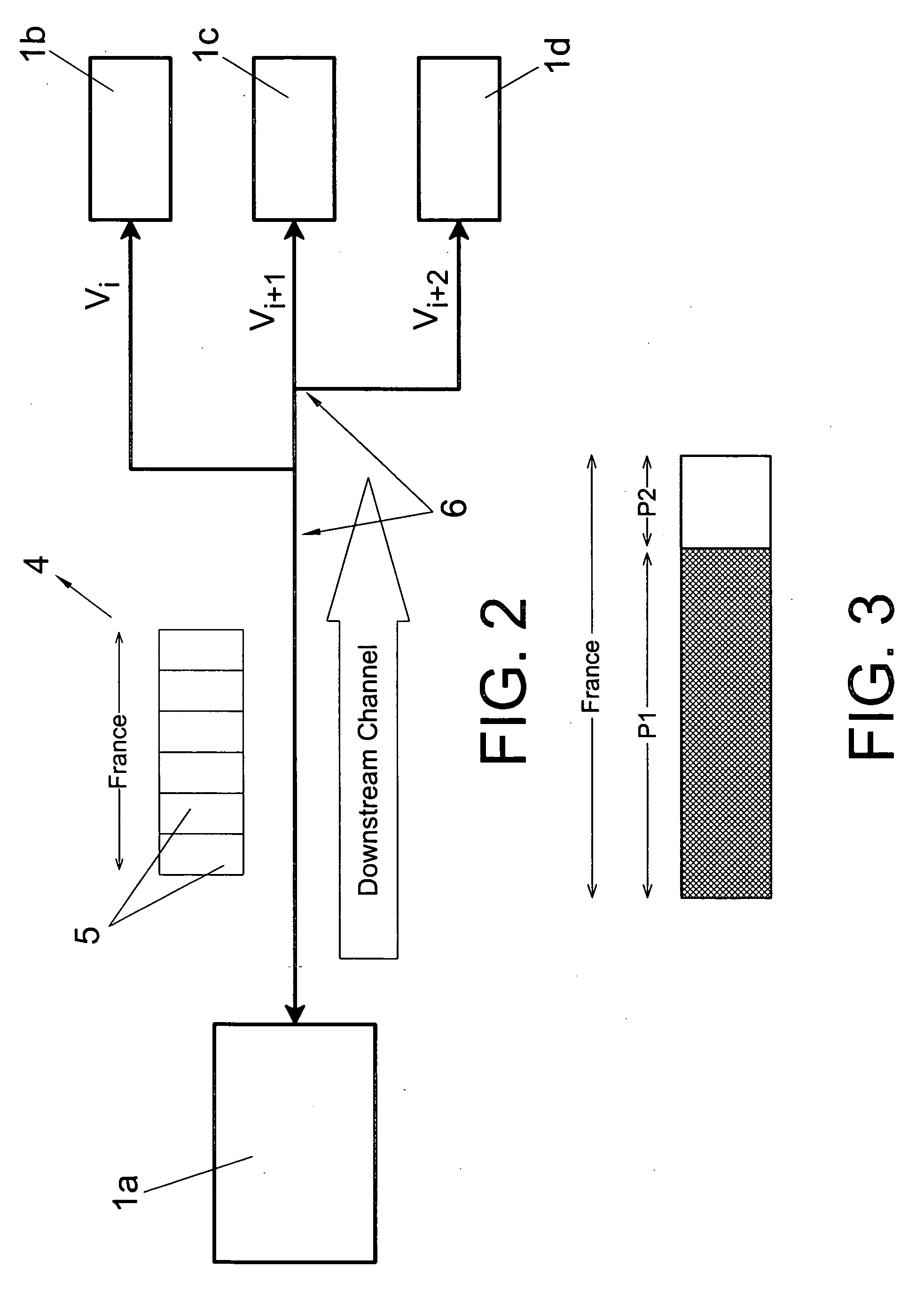
The invention relates to a data transmission method for a multi-user, multipoint-to-multipoint digital data transmission system involving a plurality of pieces of user equipment (1) which are bidirectionally connected via a physical means (6). The inventive method can be used to establish various communications from a piece of user equipment (1a) to different pieces of destination user equipment (1b-1d) at different speeds, while maintaining the bandwidth and maximum latency values required by each of the pieces of destination user equipment (1b-1d). Said method consists in sending multiple information frames (4) from a piece of equipment (1a) to a multitude of pieces of destination user equipment (1b-1d) at different speeds. Moreover, using the percentage reserve of the frame, the invention provides a quality of service based on that required by the piece of user equipment and supplies a criterion for dynamically assigning the packets which are sent to each piece of user equipment in the frame, grouping or dividing the packets to be sent.
Owner:MAXLINEAR HISPANIA S L U
Sequential equivalence checking for asynchronous verification
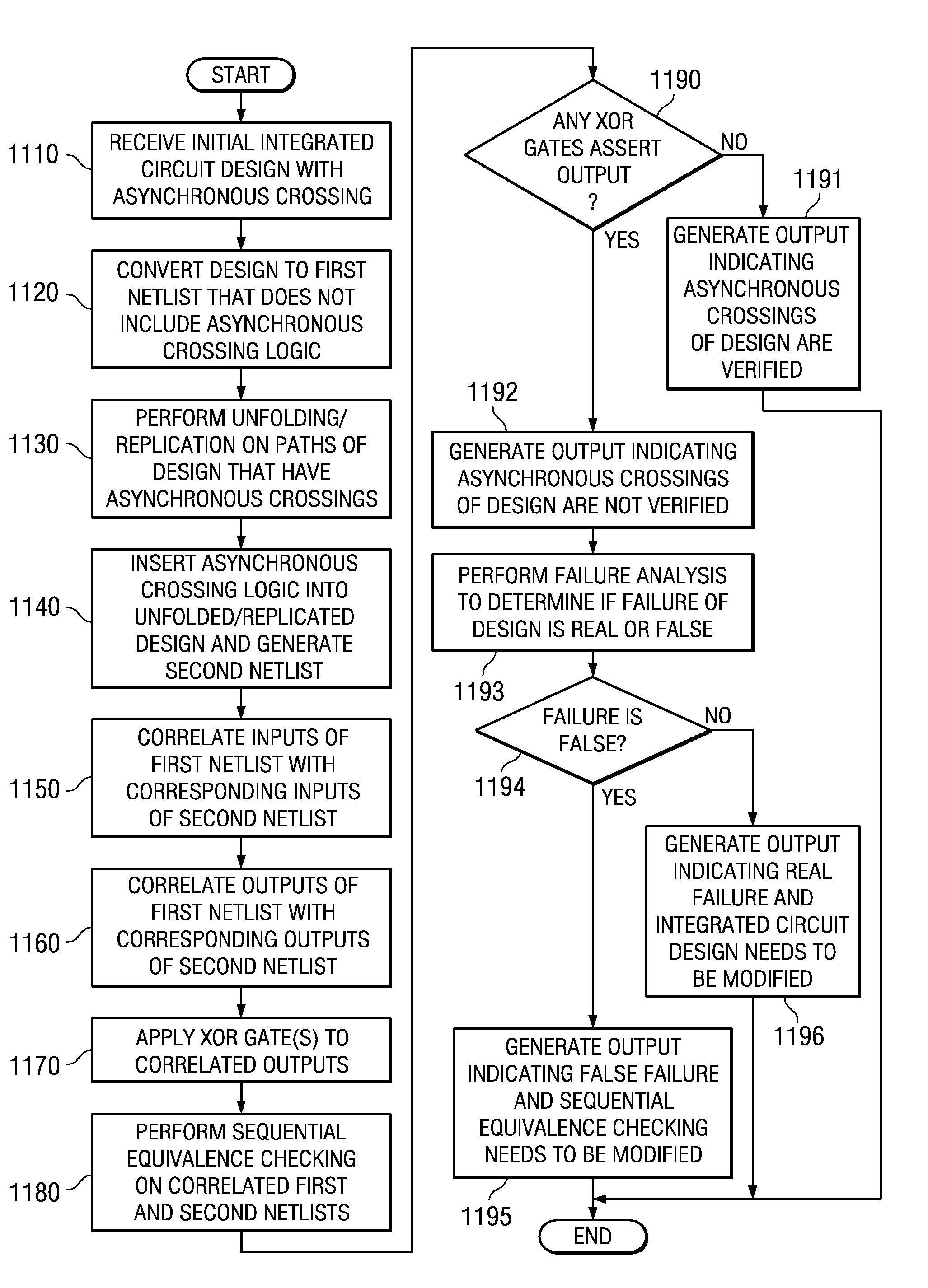
ActiveUS7882473B2Component separationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusMaximum latencyArrival time
Mechanisms for performing sequential equivalence checking for asynchronous verification are provided. A first model of the integrated circuit design is provided that has additional logic in it to reflect the possible variance in behavior of the asynchronous crossings. A second model of the integrated circuit design is provided that does not have this asynchronous behavior logic but instead correlates to the simplest synchronous model that is usually used for non-asynchronous functional verification tasks. Sequential equivalence checking is performed to verify that the two models are input / output equivalent. In order to address non-uniform arrival times of bus strands, logic is provided for identifying bus strands that have transitioning bits, determining a representative delay for these strands, comparing the representative delays for all of the bus strands to determine the maximum delay for the entire bus, and applying this maximum delay to one of the models.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
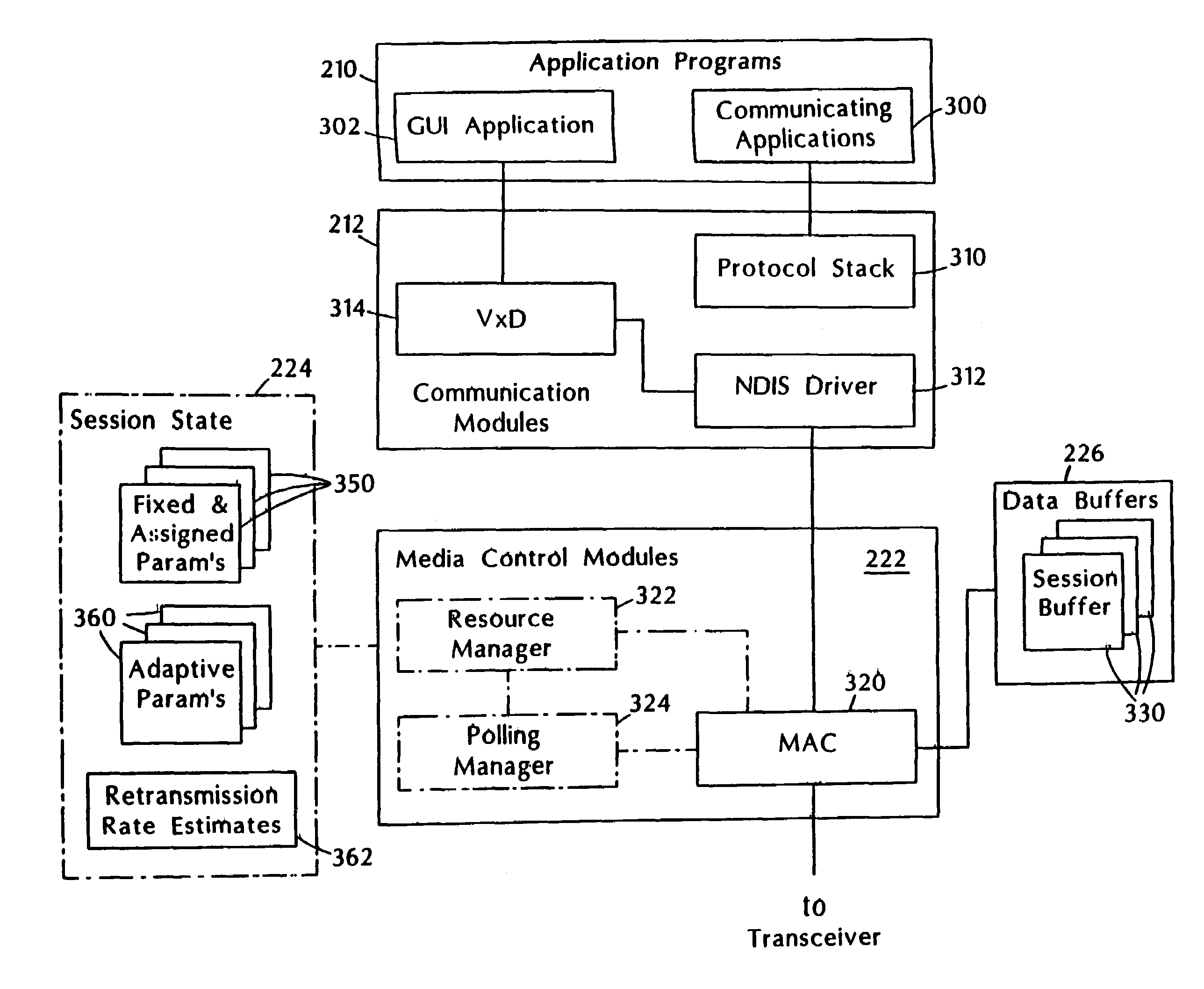
Adaptive media control
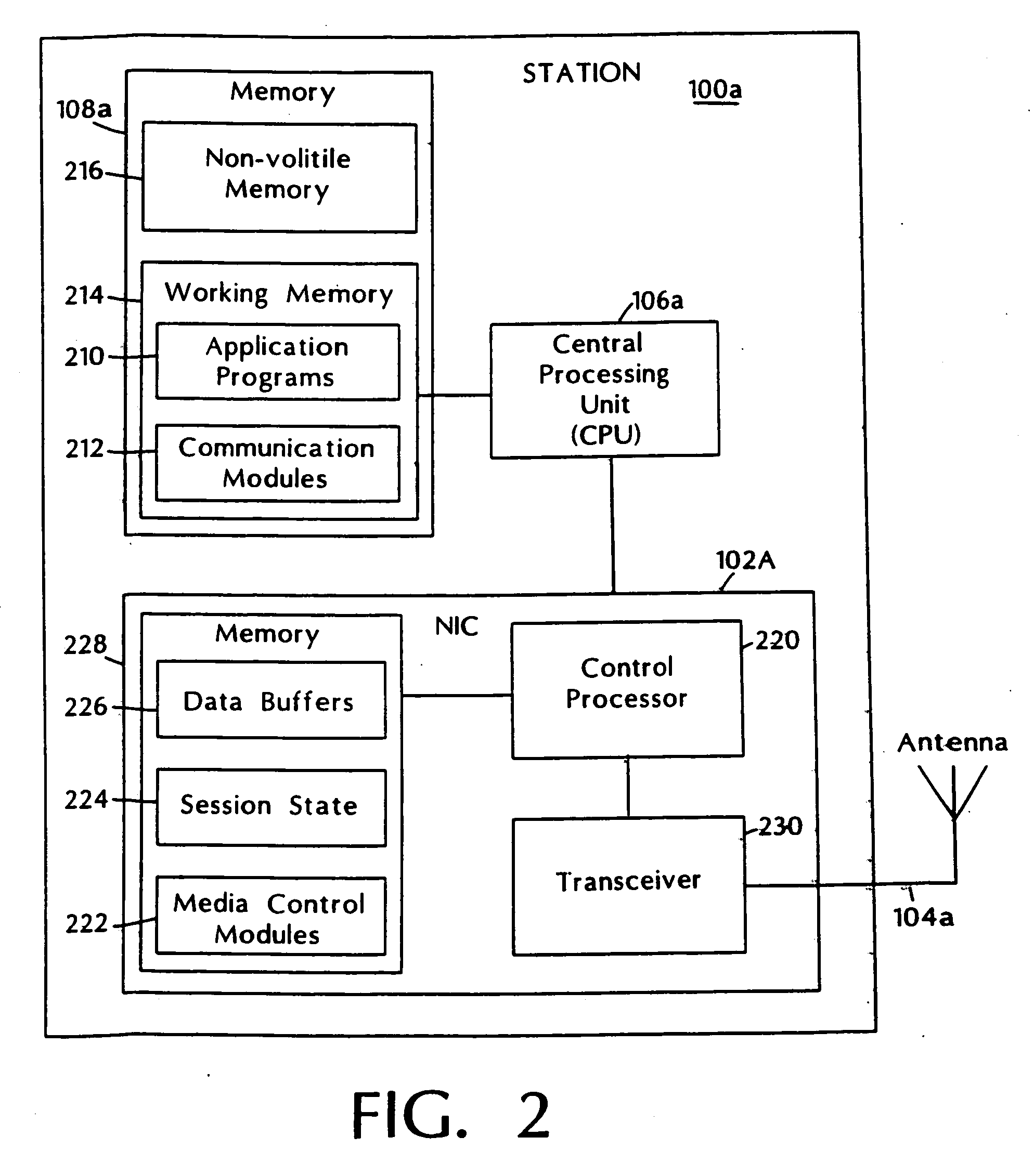
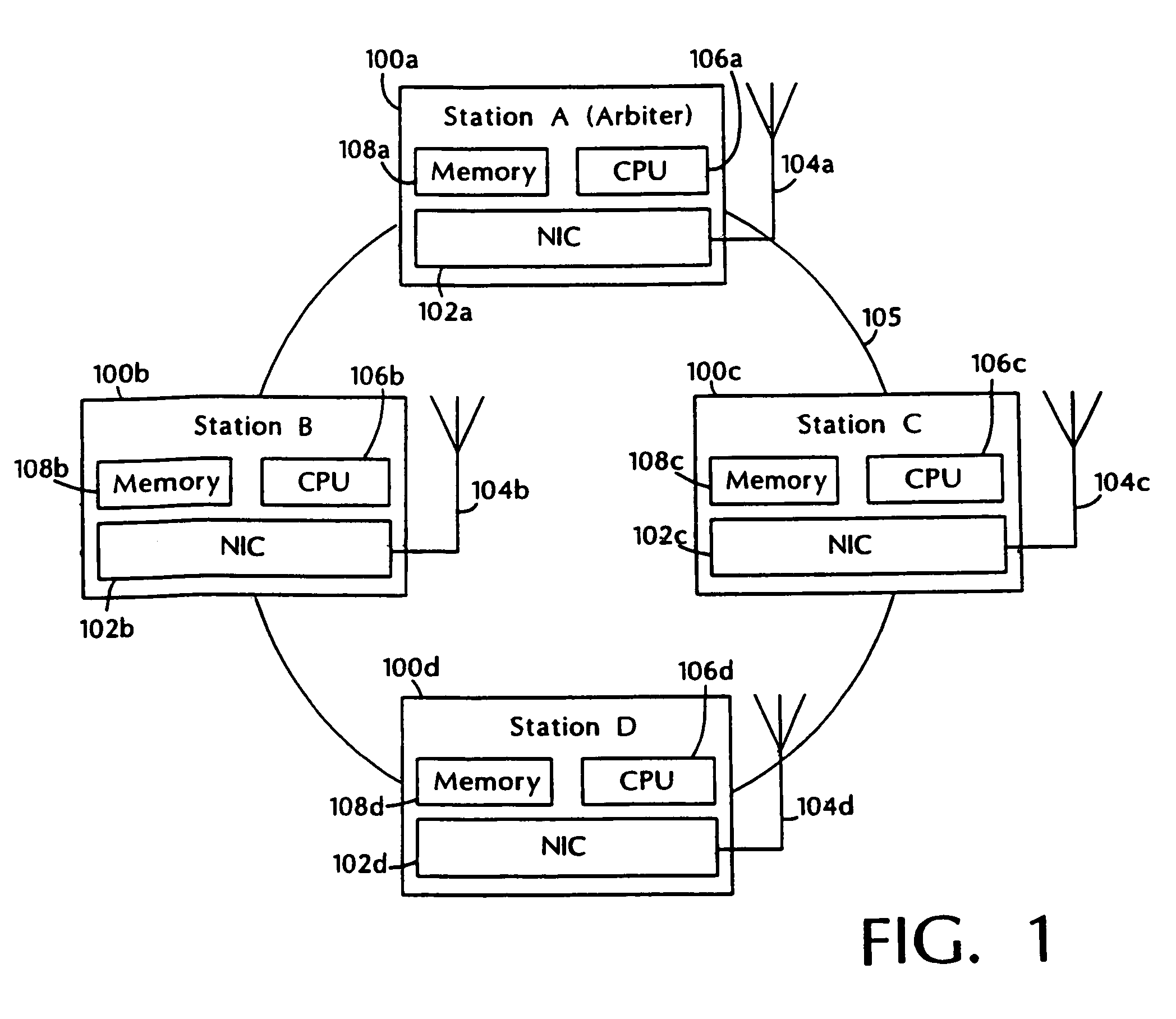
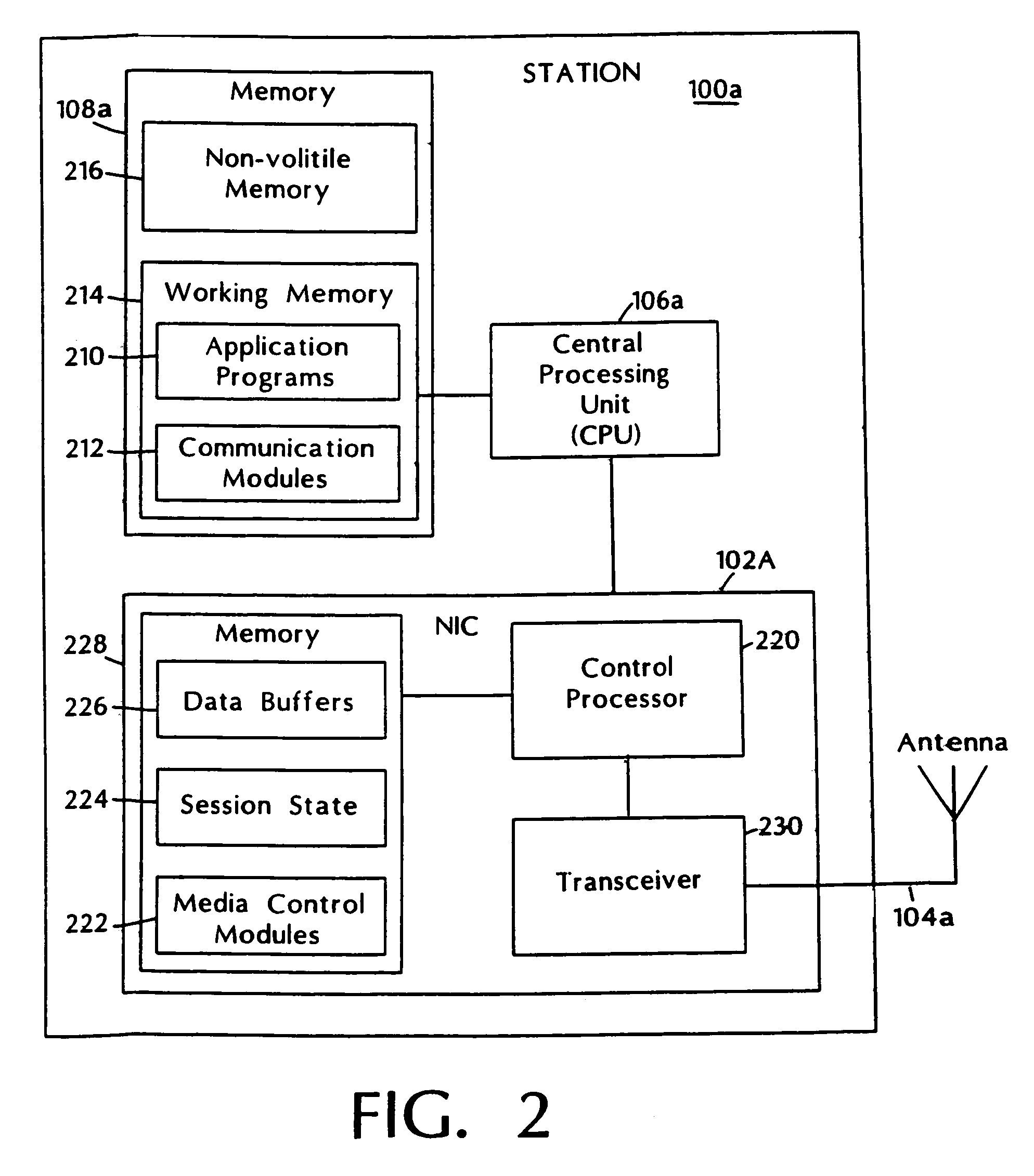
InactiveUS20060262769A1Add supportEasy to useNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexMedia controlsData stream
A media control approach that supports transmission of data streams with QoS requirements, such as minimum throughput or maximum delay, while adapting to the changing characteristics of the transmission medium. The media control approach includes use of a polling manager and a resource manager. The resource manager provides an admission control procedure that prevents admission of sessions that cannot be supported by the system and allocates network resources needed to support admitted sessions. The polling manager uses an efficient “just in time” polling of stations based on their allocated bandwidth or communication rates. Stations that do not use their allocated rates are polled less often than those which use their allocation, thereby increasing the total throughput of the system and providing proper quality of service support for real-time applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) timing driven layout method with timing constraints
ActiveCN102768506AIncrease flexibilityGuaranteed correctnessProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersMaximum latencyLayout
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics, specifically, discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) timing driven layout method with timing constraints. According to the layout method provided by the invention, four types of timing constraints are proposed as follows: a clock period constraint, an input output delay constraint, a specific timing path constraint and a wire network maximum delay constraint. The main idea for processing the four types of timing constraints is to add the information of the timing constraints into a timing analysis step to process the timing constraints as a part of a final cost function. The method provided by the invention can process the timing constraints set by the users, so that the flexibility of an FPGA timing layout algorithm is increased greatly, and simultaneously, the correctness of the layout algorithm also can be guaranteed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
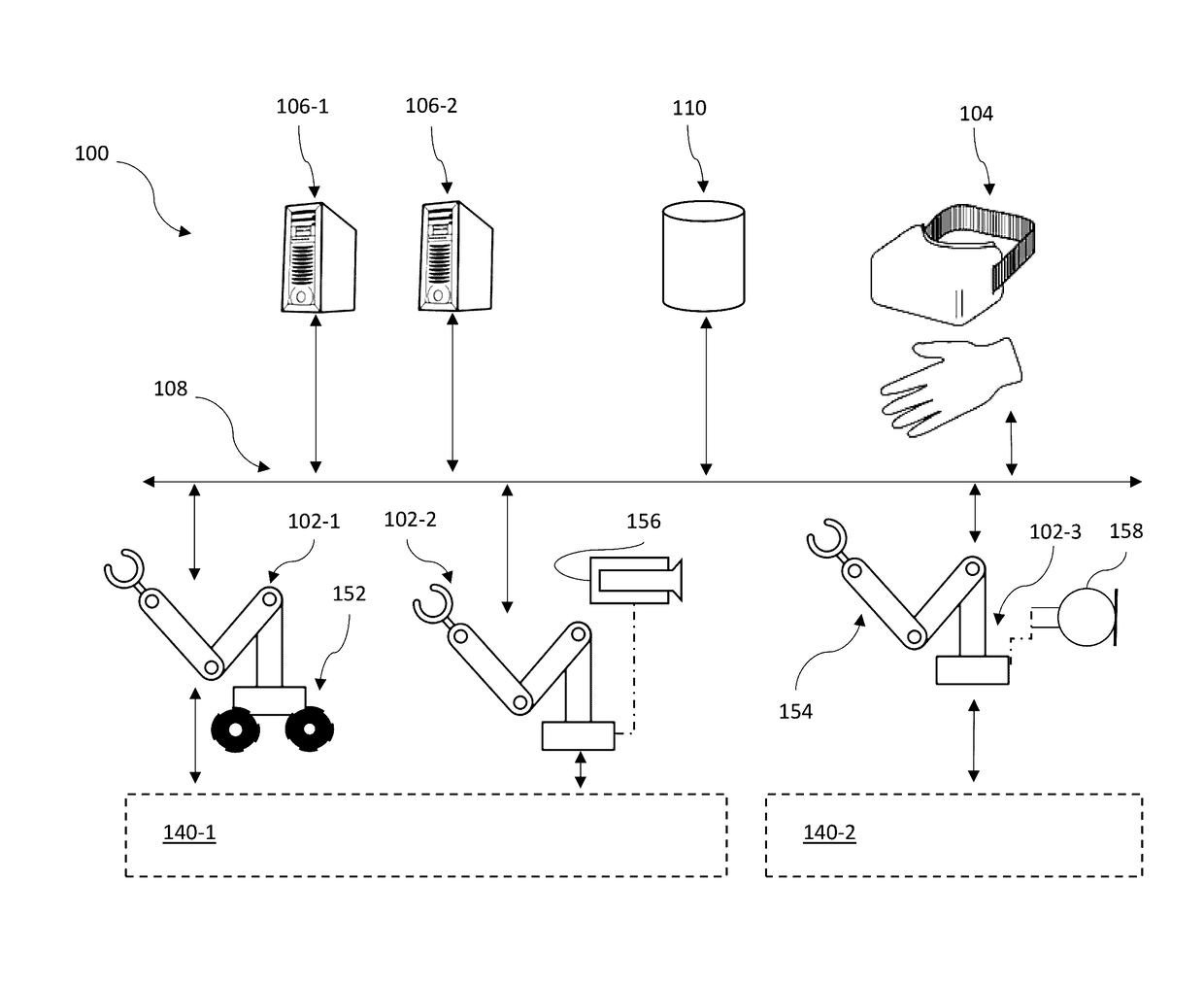
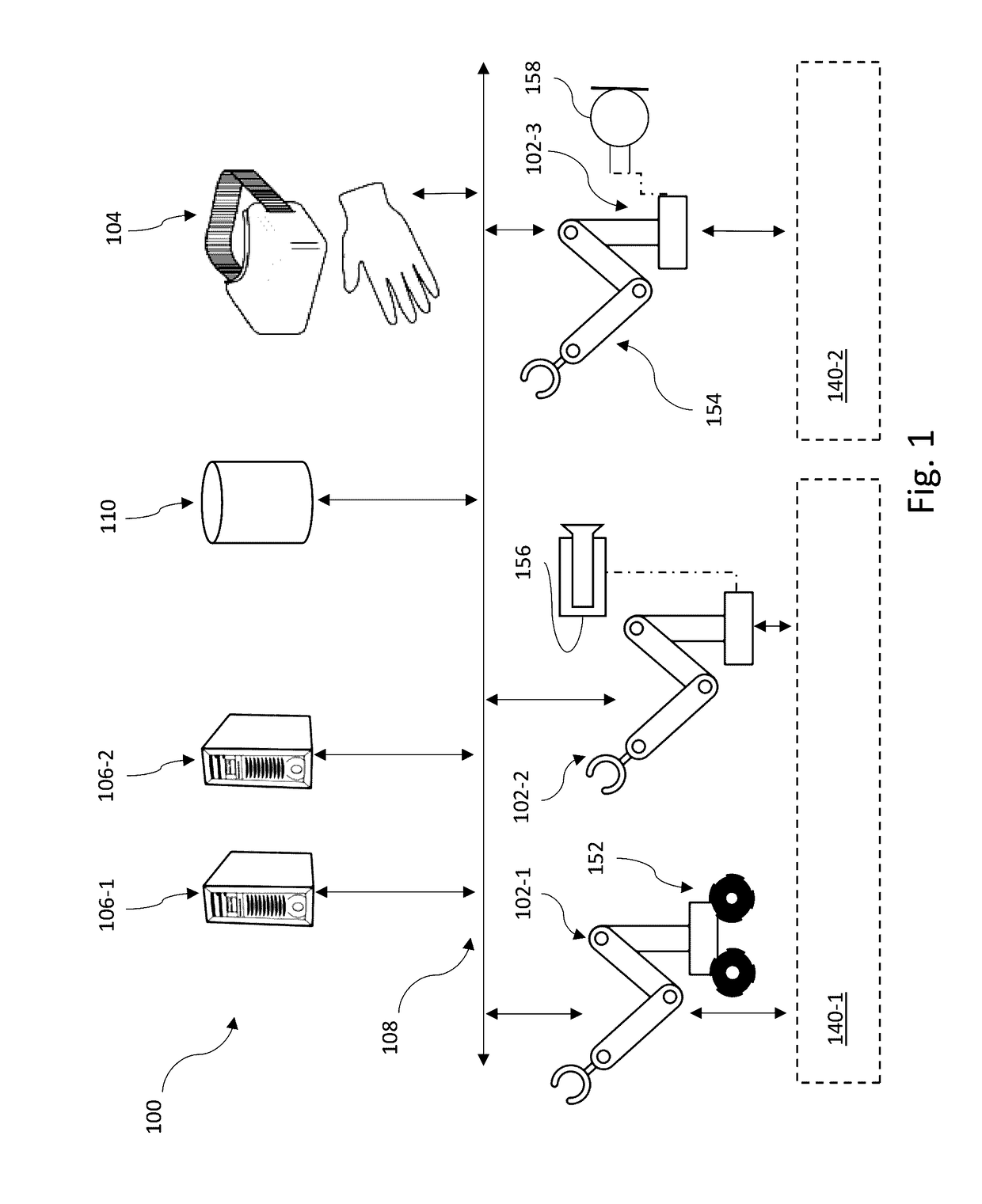
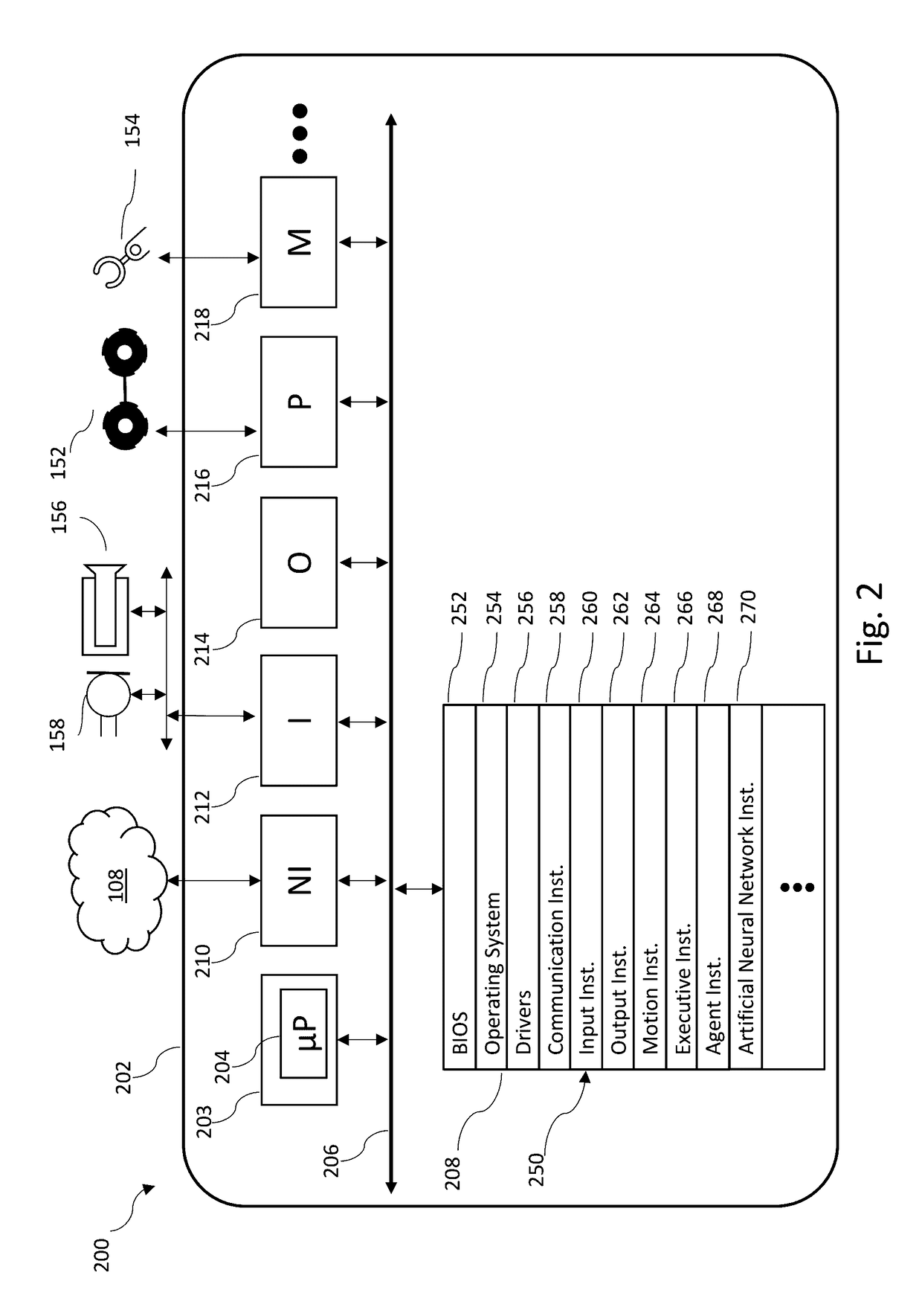
Systems, devices, and methods for distributed artificial neural network computation
ActiveUS20170140259A1Guaranteed LatencyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsMaximum latency
Robots and robotic systems and methods can employ artificial neural networks (ANNs) to significantly improve performance. The ANNs can operate alternatingly in forward and backward directions in interleaved fashion. The ANNs can employ visible units and hidden units. Various objective functions can be optimized. Robots and robotic systems and methods can execute applications including a plurality of agents in a distributed system, for instance with a number of hosts executing respective agents, at least some of the agents in communications with one another. The hosts can execute agents in response to occurrence of defined events or trigger expressions, and can operate with a maximum latency guarantee and / or data quality guarantee.
Owner:OCADO INNOVATION
Adaptive media control
InactiveUS7460514B2Add supportEasy to useNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexMedia controlsData stream
A media control approach that supports transmission of data streams with QoS requirements, such as minimum throughput or maximum delay, while adapting to the changing characteristics of the transmission medium. The media control approach includes use of a polling manager and a resource manager. The resource manager provides an admission control procedure that prevents admission of sessions that cannot be supported by the system and allocates network resources needed to support admitted sessions. The polling manager uses an efficient “just in time” polling of stations based on their allocated bandwidth or communication rates. Stations that do not use their allocated rates are polled less often than those which use their allocation, thereby increasing the total throughput of the system and providing proper quality of service support for real-time applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
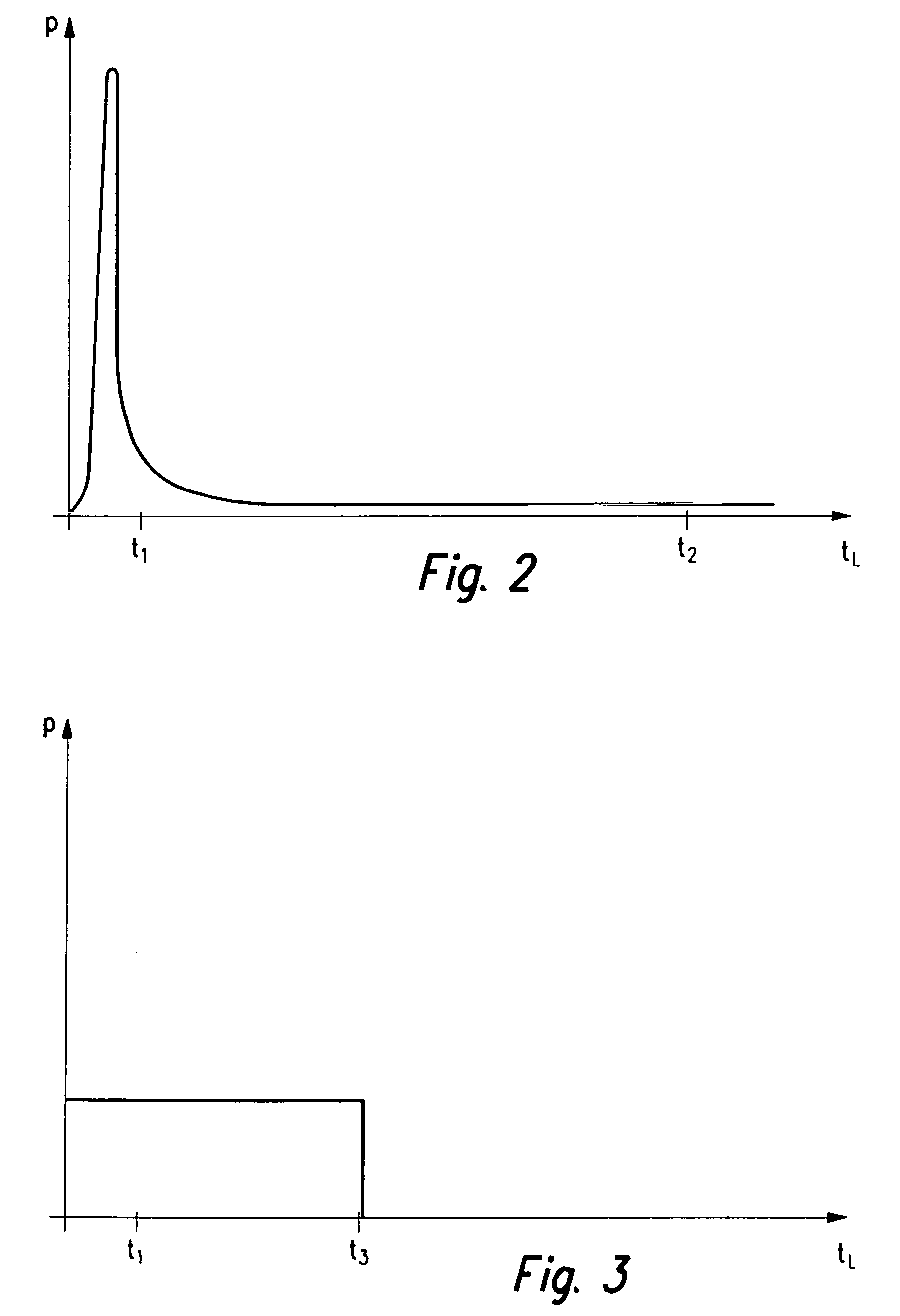
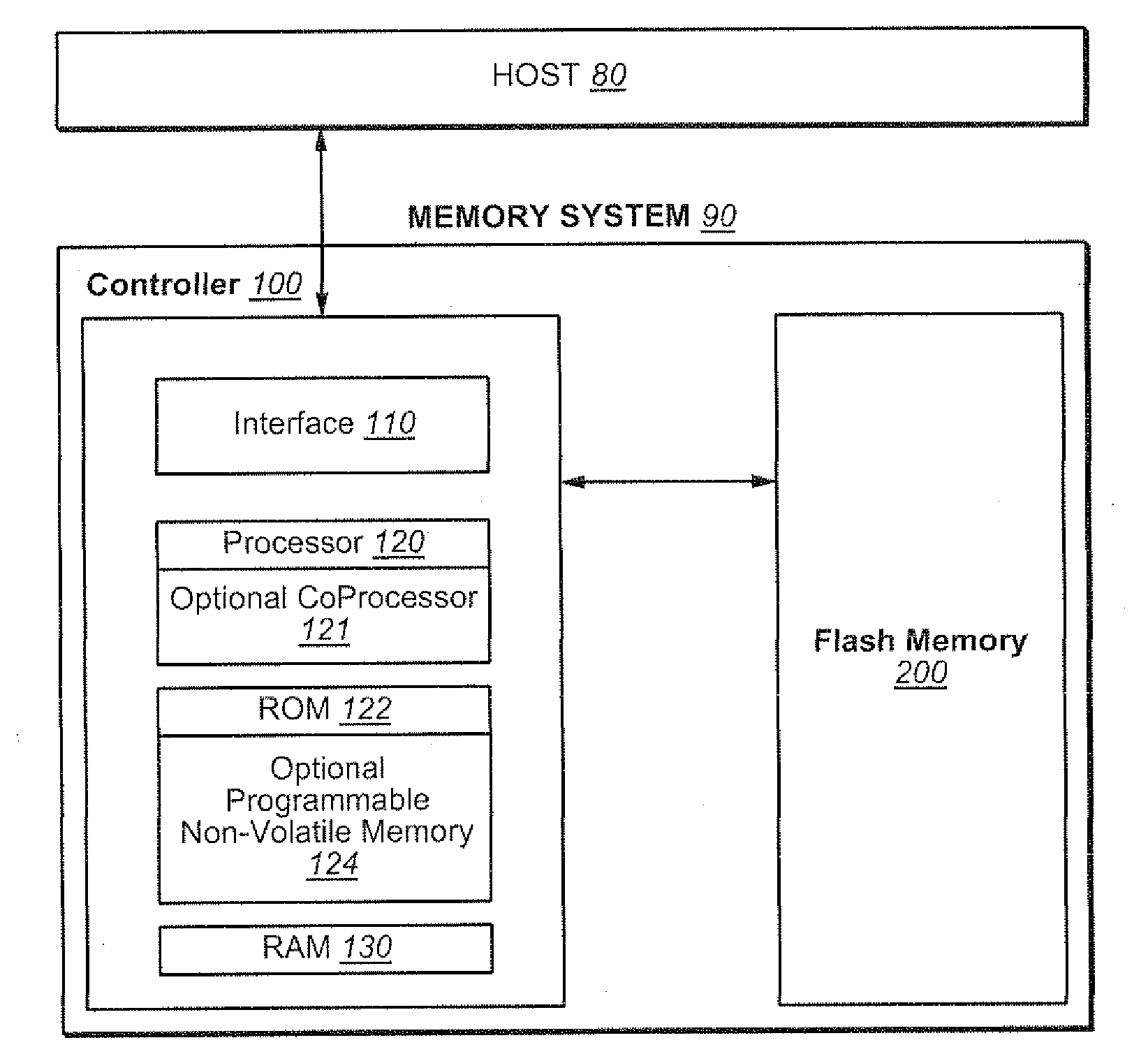
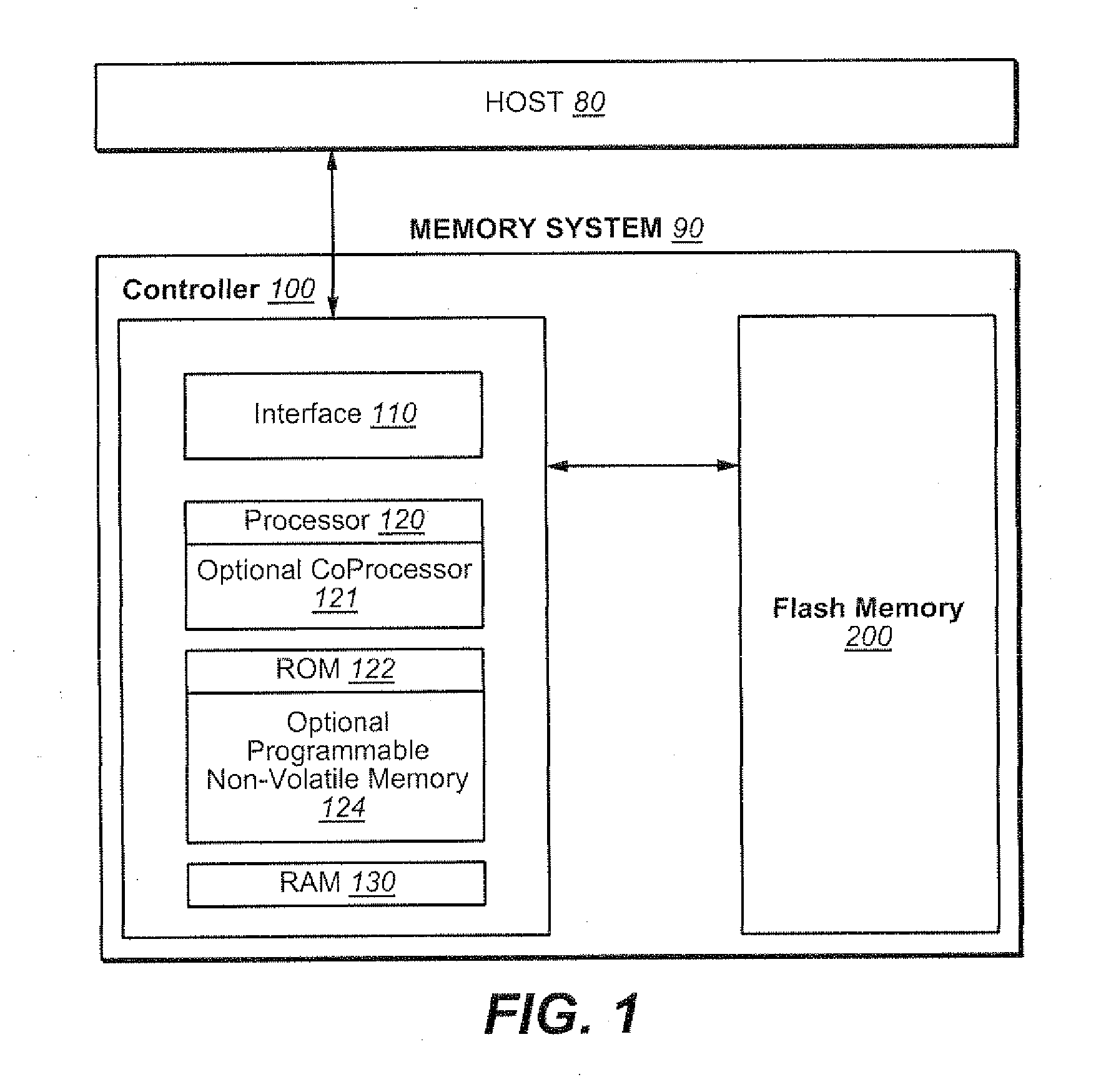
Use of Guard Bands and Phased Maintenance Operations to Avoid Exceeding Maximum Latency Requirements in Non-Volatile Memory Systems
ActiveUS20110320685A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMaximum latencyControl data
Techniques are presented for performing maintenance operations, such as garbage collection, on non-volatile memory systems will still respecting the maximum latency, or time-out, requirements of a protocol. A safety guard band in the space available for storing host data, control data, or both, is provided. If, on an access of the memory, it is determined that the guard band space is exceeded, the system uses a recovery back to the base state by triggering and prioritising clean-up operations to re-establish all safety guard bands without breaking the timing requirements. To respect these timing requirements, the operations are split into portions and done in a phased manner during allowed latency periods.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
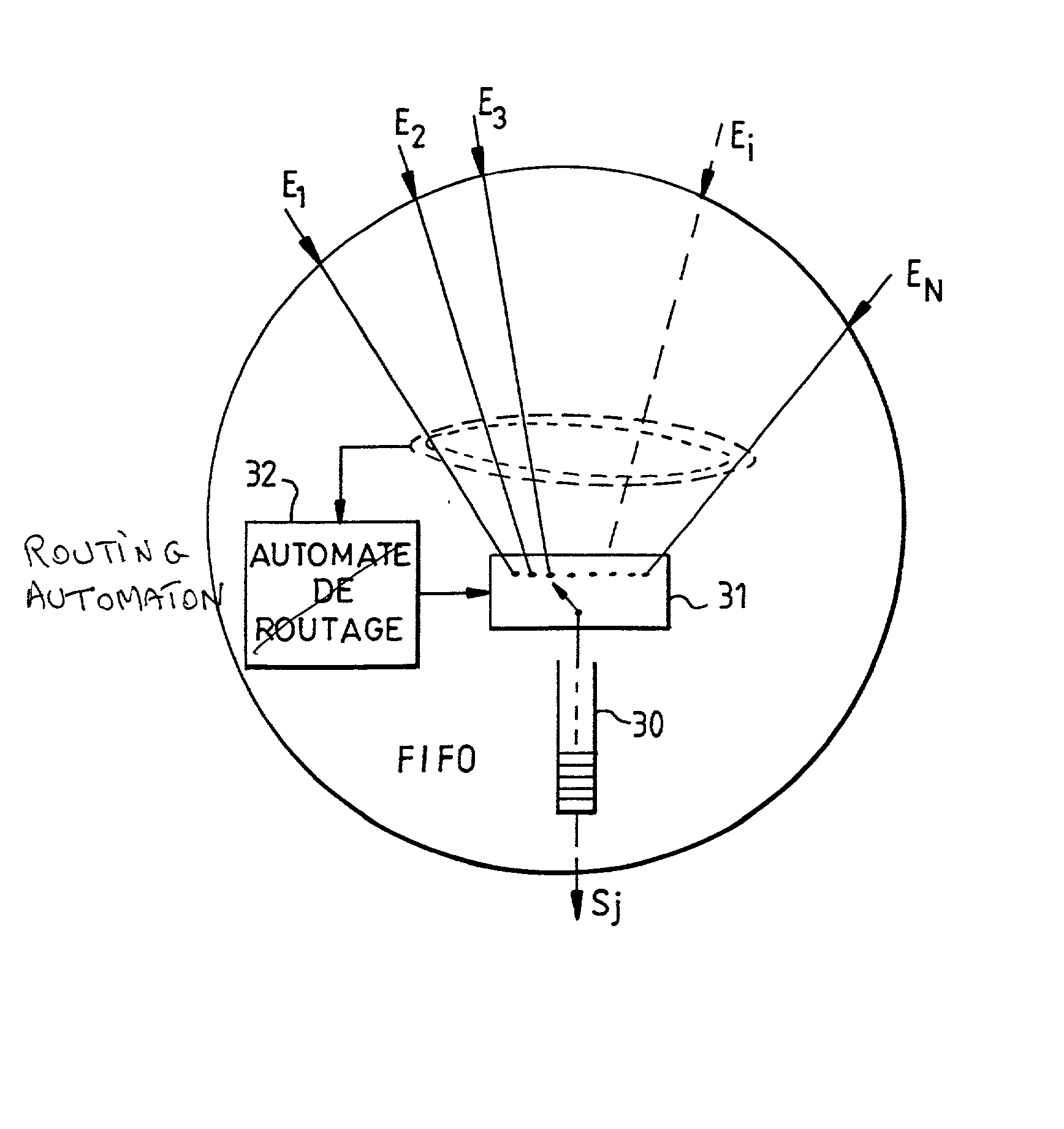
Time based packet scheduling and sorting system
Methods and systems for controlling scheduling in a packet switching node in a network are provided which enable the scheduling of packets from different sources in an earliest deadline first order. The packets are assigned timestamp deadlines and placed in input queues. The timestamps are determined according to maximum delay or minimum throughput quality of service requirements specified for the packets. The packets are scheduled in the earliest deadline first order in an output packet store. The packet closest to its timestamp deadline is selected from the output packet store by using an index.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Systems and methods of measuring latency and routing thereon in optical networks
ActiveUS8774232B2Preventing mesh restorationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNODALMaximum latency
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for making latency measurements and using these measurements in routing in optical networks. In an exemplary embodiment, a method is defined whereby two nodes sharing a line automatically determine whether both nodes are capable of making a latency measurement and then which node will initiate and which node participates in making the latency measurement. In another exemplary embodiment, an on-demand latency measurement may be made between any two arbitrary nodes within a domain. Routing messages may be used to disseminate the latency of links via a signaling and routing protocol. Advantageously, the present invention provides measurement of latency and latency variation of customer circuits (i.e., SNCs) using an in-band, non-intrusive calculation with a high-degree of accuracy. Furthermore, the present invention may consider these calculations for circuit routing based on the latency and circuit acceptance based on maximum latency restrictions.
Owner:CIENA
Method of reserving resources with a maximum delay guarantee for multi-hop transmission in a distributed access wireless communications network
ActiveUS20090092105A1Improve data transfer rateSpectrum efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMulti hop relayComputer network
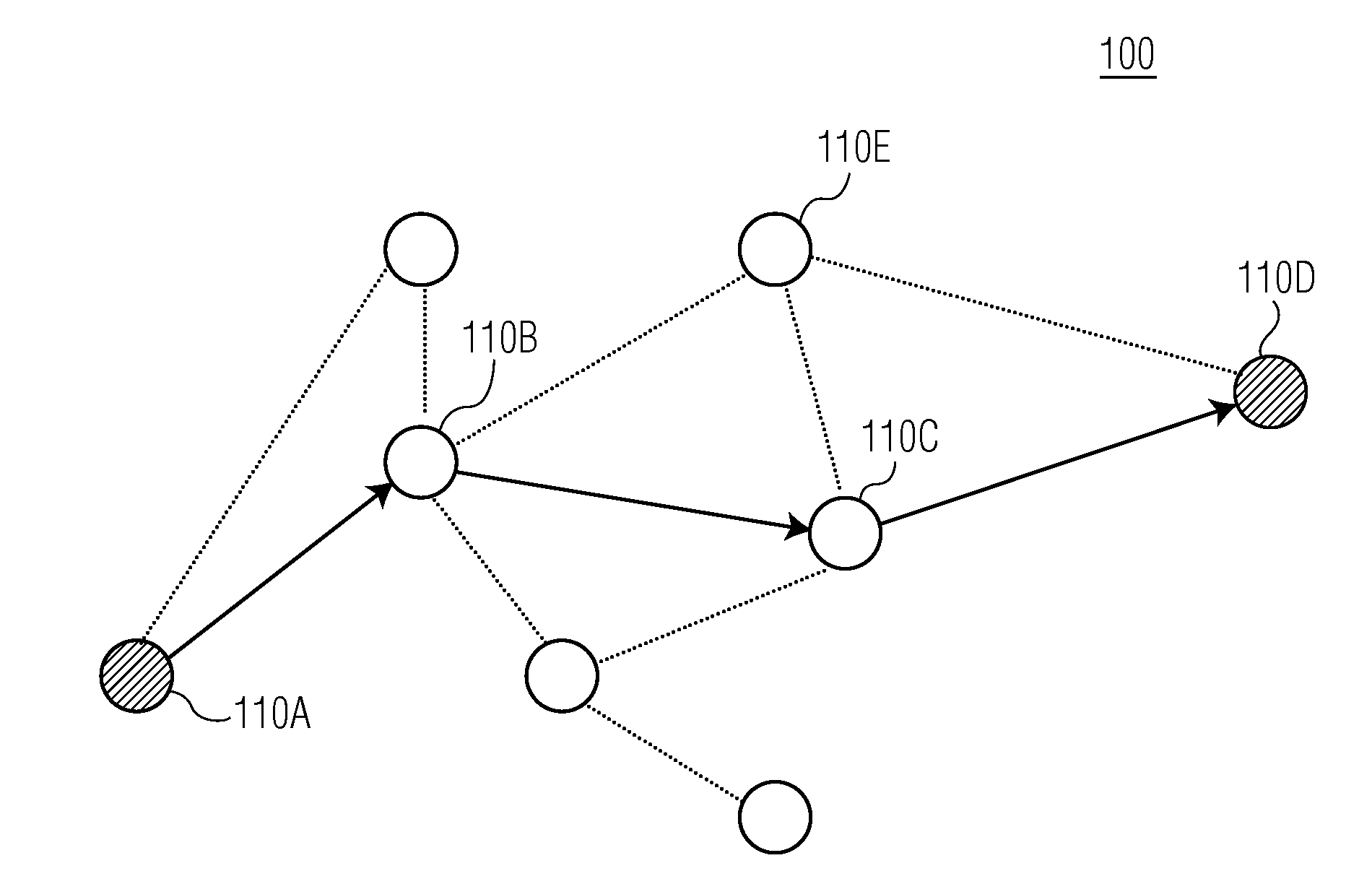
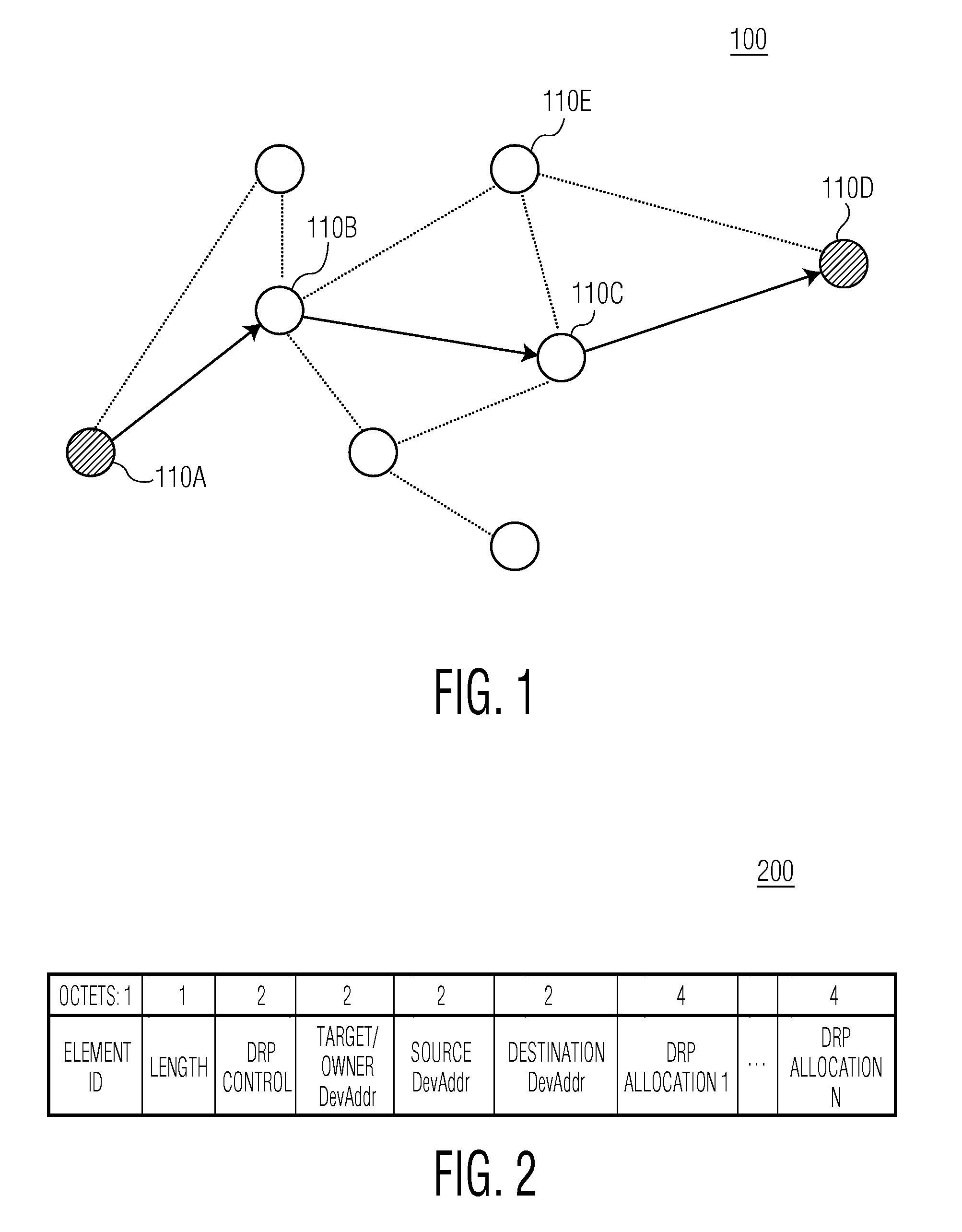
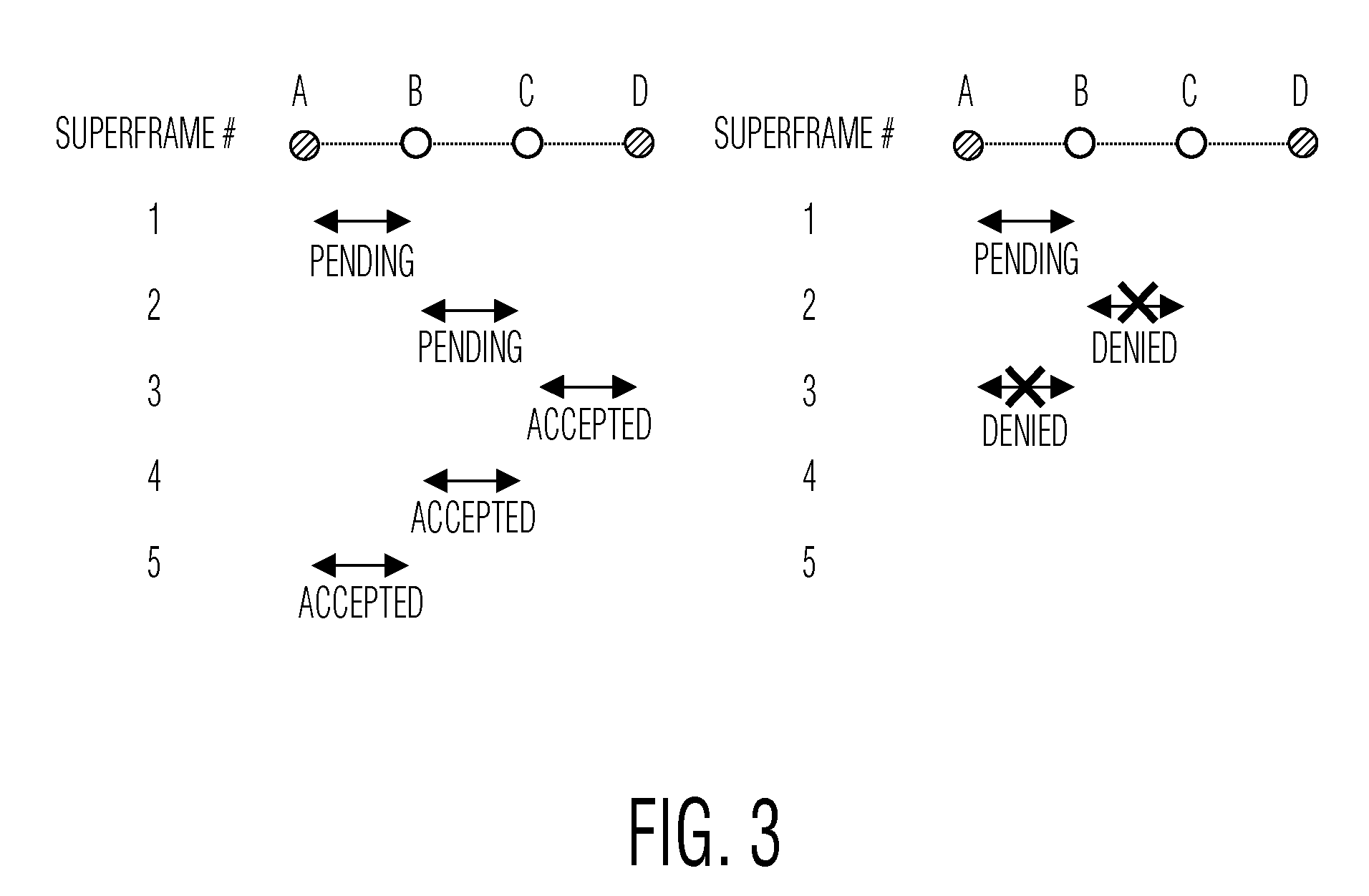
In a communication network (100), a method (400) of reserving X slots (610) for transmitting data from a source device (110A) to a destination device (110D) via multi-hop relay includes sending a first hop reservation request from the source device (110A) to a second device (110), for transmitting data from the source device to the destination device. The first hop reservation request identifies the source device, the destination device, and X proposed slots (610) to be reserved for the first hop. The source device then receives a first message, addressed to the source device from the second device, indicating that the first hop reservation request is pending and that the X slots proposed by the source device have been reserved by the second device. Later, the source device receives a subsequent message indicating whether a final hop reservation request has been accepted by the destination device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optimizing buffer latency in a streamed packet delivery session
InactiveUS6937603B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSingle sessionPacket loss
A method of optimizing the buffer latency in a streaming application for delivering streamed packets over a network. The packet delays are dynamically recorded for forming a histogram of the frequencies of occurrence associated with each delay. The histogram is updated plural times during a single session. A optimal latency is obtained from the updated histogram at which the packet loss percentage is within a predetermined amount and the optimal latency is less than a allowable maximum delay required by the application. The size of the buffer is thus adjusted.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for setting parameters and determining latency in a chained device system
ActiveUS20090138570A1Short response timeSignificant latencyMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingMaximum latencyMaster controller
A storage system and method for setting parameters and determining latency in a chained device system. Storage nodes store information and the storage nodes are organized in a daisy chained network. At least one of one of the storage nodes includes an upstream communication buffer. Flow of information to the storage nodes is based upon constraints of the communication buffer within the storage nodes. In one embodiment, communication between the master controller and the plurality storage nodes has a determined maximum latency.
Owner:SPANSION LLC +1
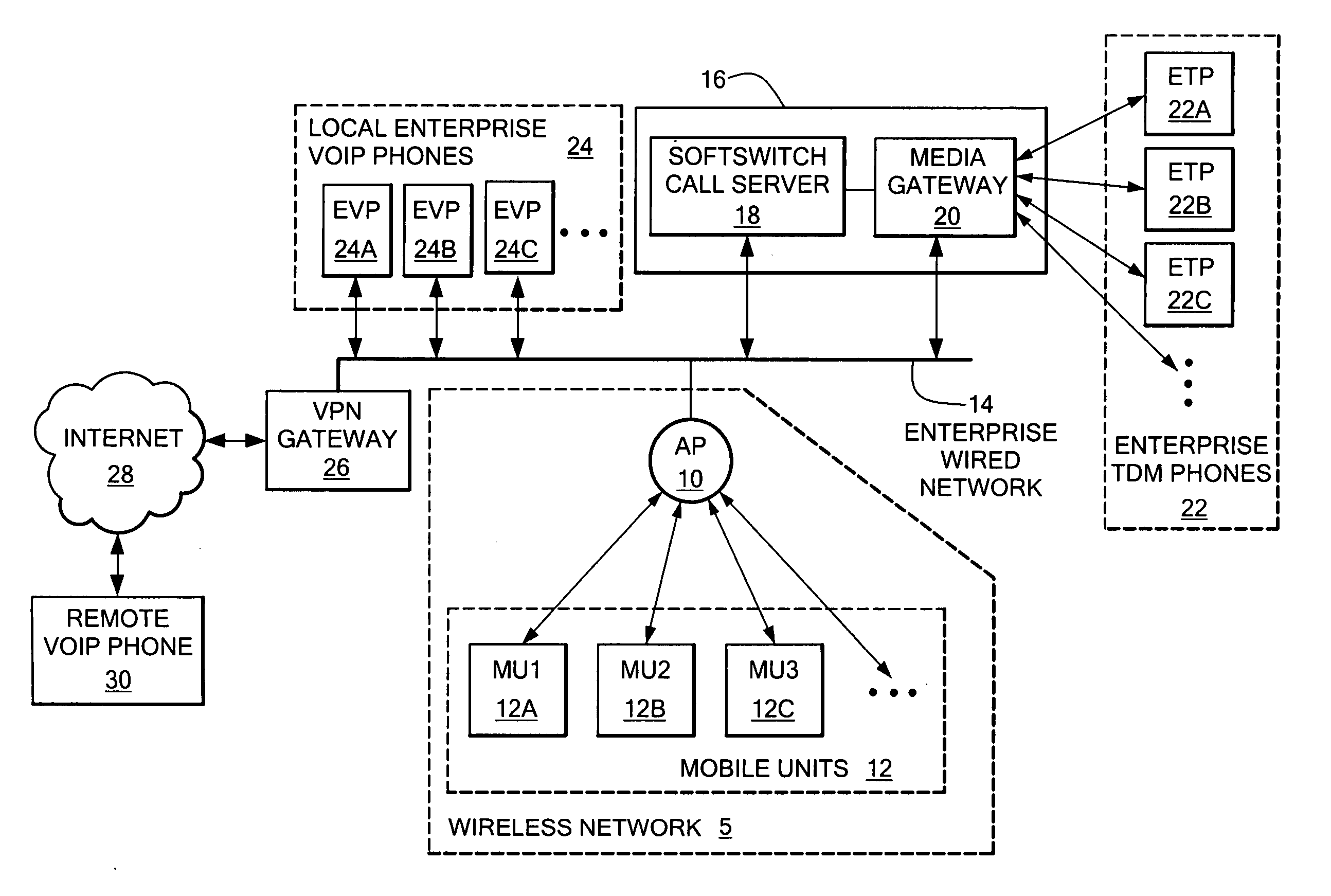
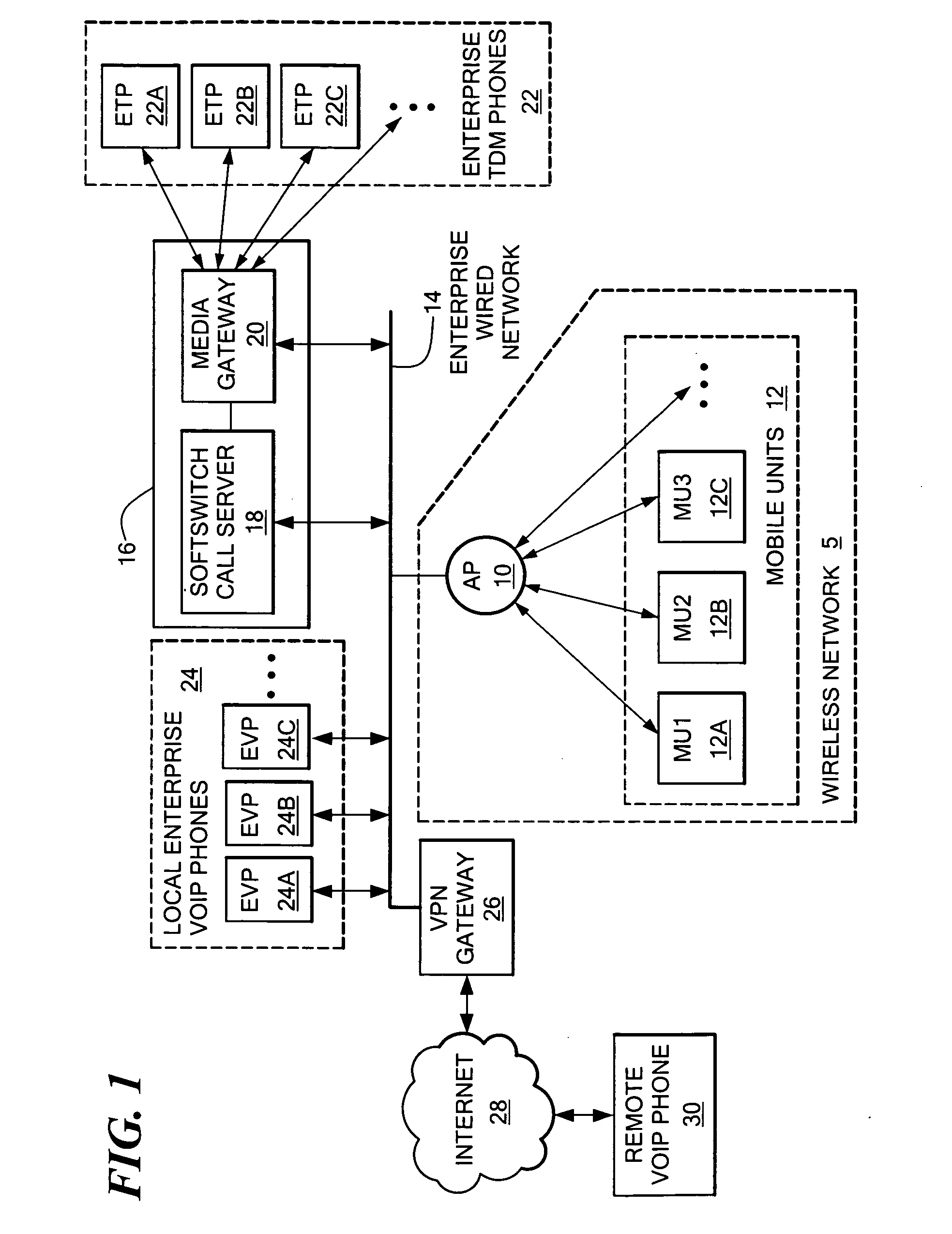
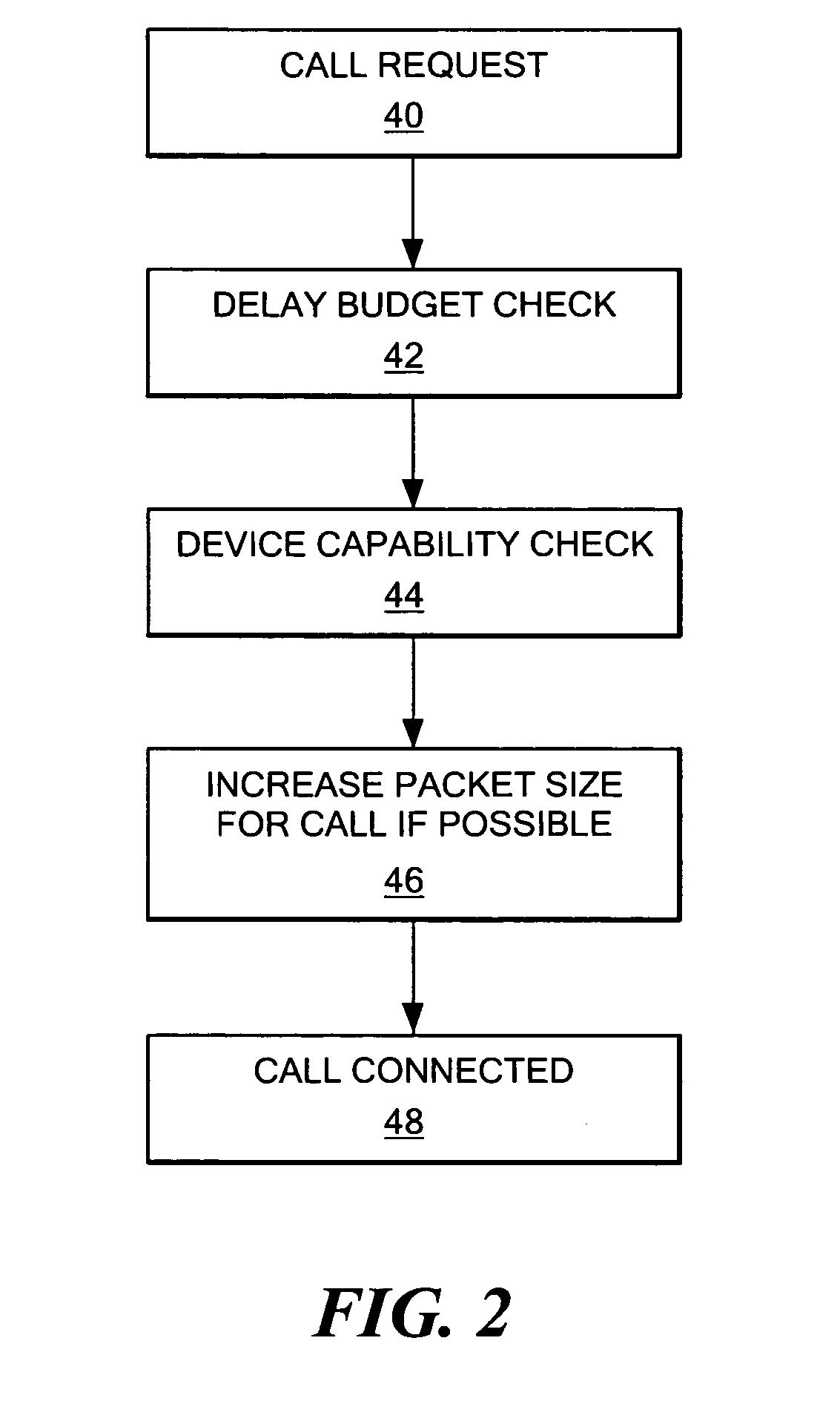
System and method for increasing call capacity for a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050226219A1Increase access capacityIncrease delayInterconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementTotal delayMaximum latency
A system for increasing the call capacity of an access point in a WLAN, allowing the number of WLAN phones that can be supported to be increased. The system determines whether a maximum total voice path delay would be exceeded if the packetization delay is increased for packets in a call. In the event that the packetization delay can be increased without the total delay exceeding the maximum delay, the disclosed system increases the size of packets used in the call, if all participating devices can process the increased packet size. The maximum delay may be predetermined, and reflect a maximum delay that cannot be exceeded without adversely impacting the voice quality of a call. If the two end points for a call are determined to be physically “local” to each other, packetization delay for the call may be increased based on the assumption that the increased packetization delay will not decrease the voice quality of the call.
Owner:AVAYA INC
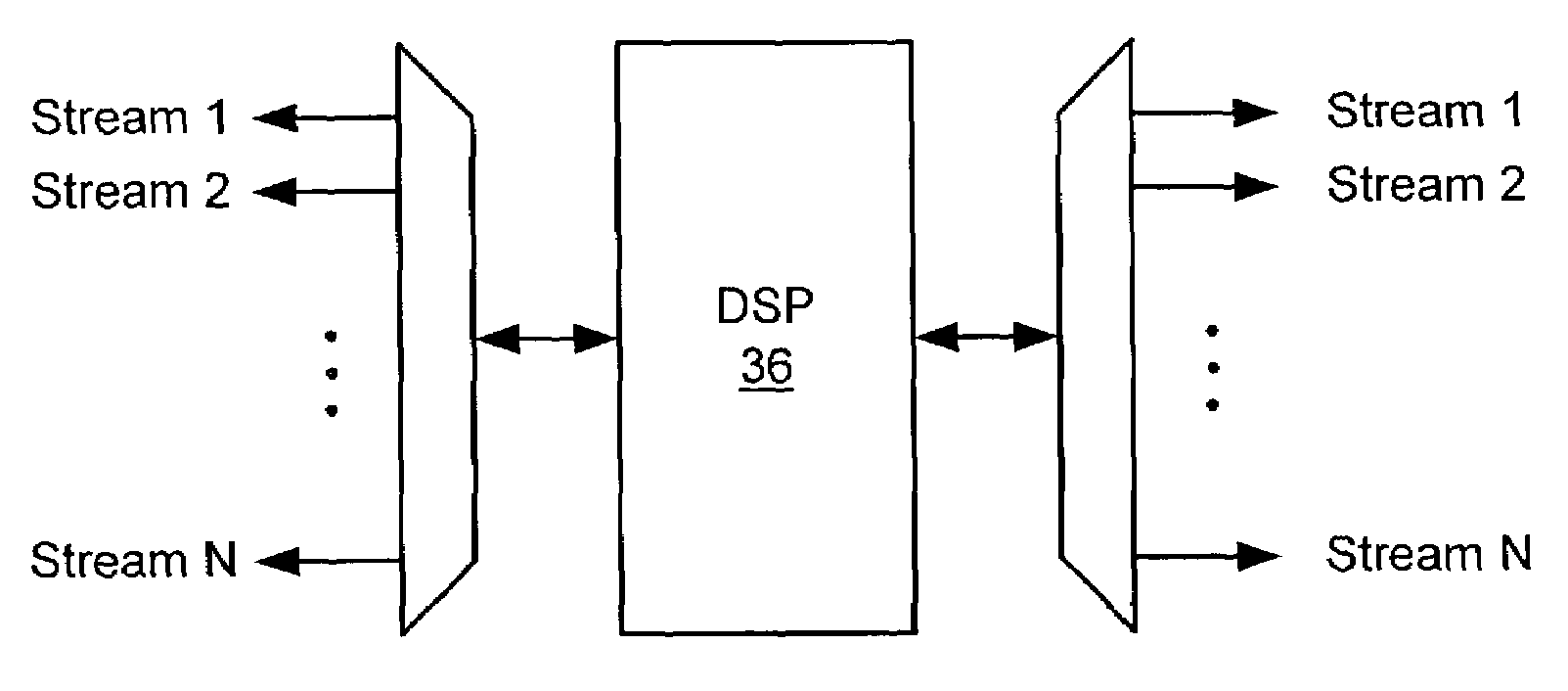
Low-latency packet processor
ActiveUS7330900B2Easy to useMultiprogramming arrangementsData switching by path configurationPacket arrivalMaximum latency
Packets of real-time media streams are processed at a network node such within a desired maximum latency less than the frame interval of the streams. The media streams have respective packet rates all substantially equal to a nominal packet rate and respective packet arrival times that are generally non-deterministic. The streams are assigned to digital signal processors (DSPs), each capable of processing up to a predetermined maximum number of the streams within real-time constraints. The number of streams assigned to each DSP is less than the predetermined maximum number and no greater than the quotient of a desired maximum processing latency less than the frame interval and the DSP processing latency for a single packet. For example, if the desired maximum processing latency is 5 ms. and the processing latency for one packet is 1.6 ms., then only three streams are assigned to a DSP (5 / 1.6˜3), even if the DSP can process many more than 3 streams in real time. The technique can also be applied to groups of streams whose respective packet arrival times are generally deterministic. Different groups can be processed by a DSP without incurring an entire frame interval of latency, potentially resulting in more efficient use of the DSPs.
Owner:DIALOGIC INC
Method for the sizing of a deterministic type packet-switching transmission network
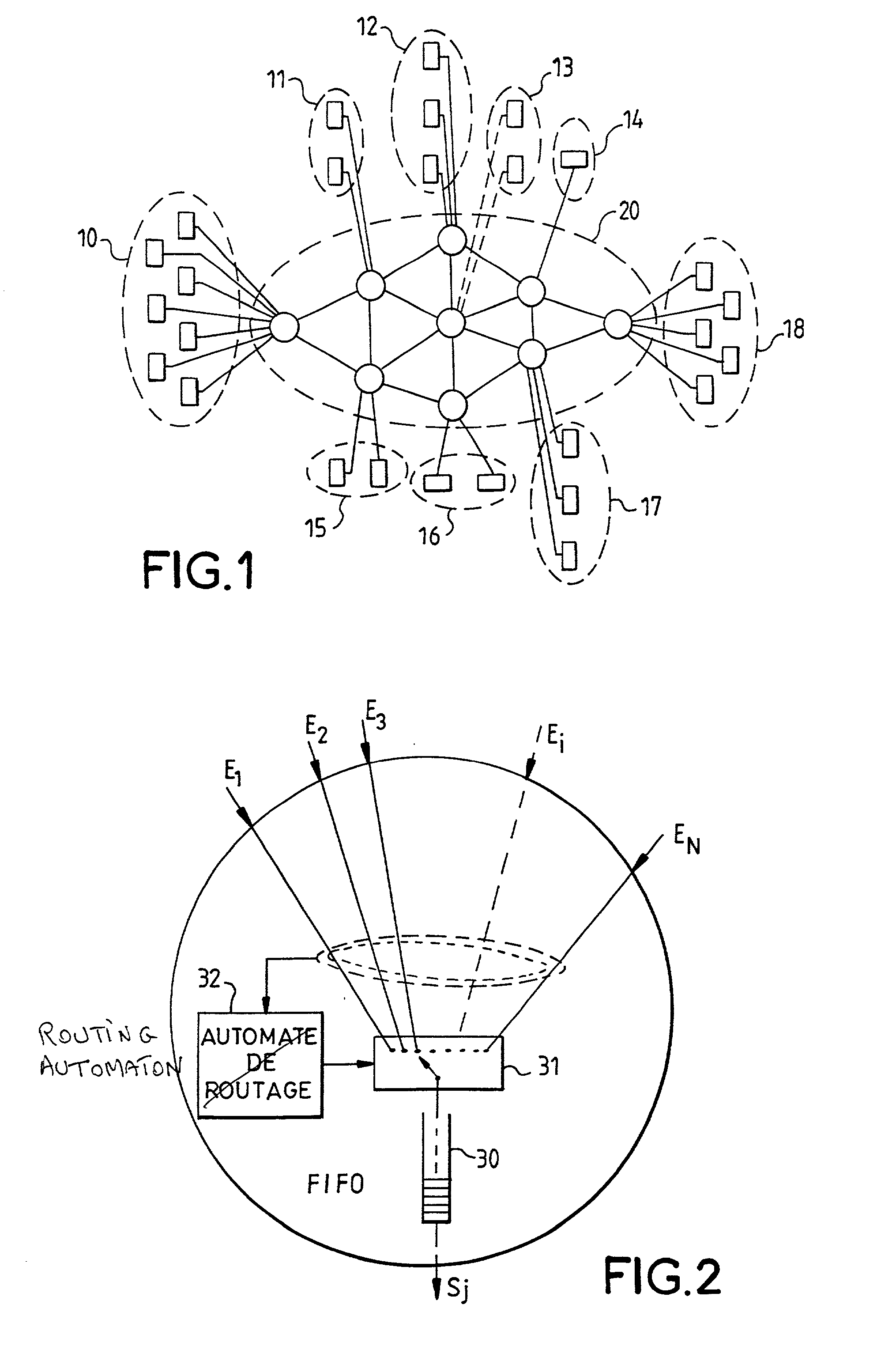
ActiveUS20020122421A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork sizeMaximum latency
Deterministic type packet-switching transmission networks are networks in which the different flows of information follow virtual paths defined in advance for which any change requires a reprogramming of the interconnection nodes. The advantage of determinism is that it makes it easier to estimate the maximum delay time that the packets may undergo during their journey in the network. However, it remains to be verified that the network is appropriately sized for the transmission of the different information flows, with the constraints of maximum delay times and of regularity imposed by the connected items of equipment. A method is proposed here for the sizing of the network. In this method, the verification of compliance with these constraints is based on the determining of the jitter components added by the different interconnection nodes of the network, at their different output ports. This determination is done incrementally, in descending along the virtual paths travelled through by the different information flows.
Owner:THALES SA
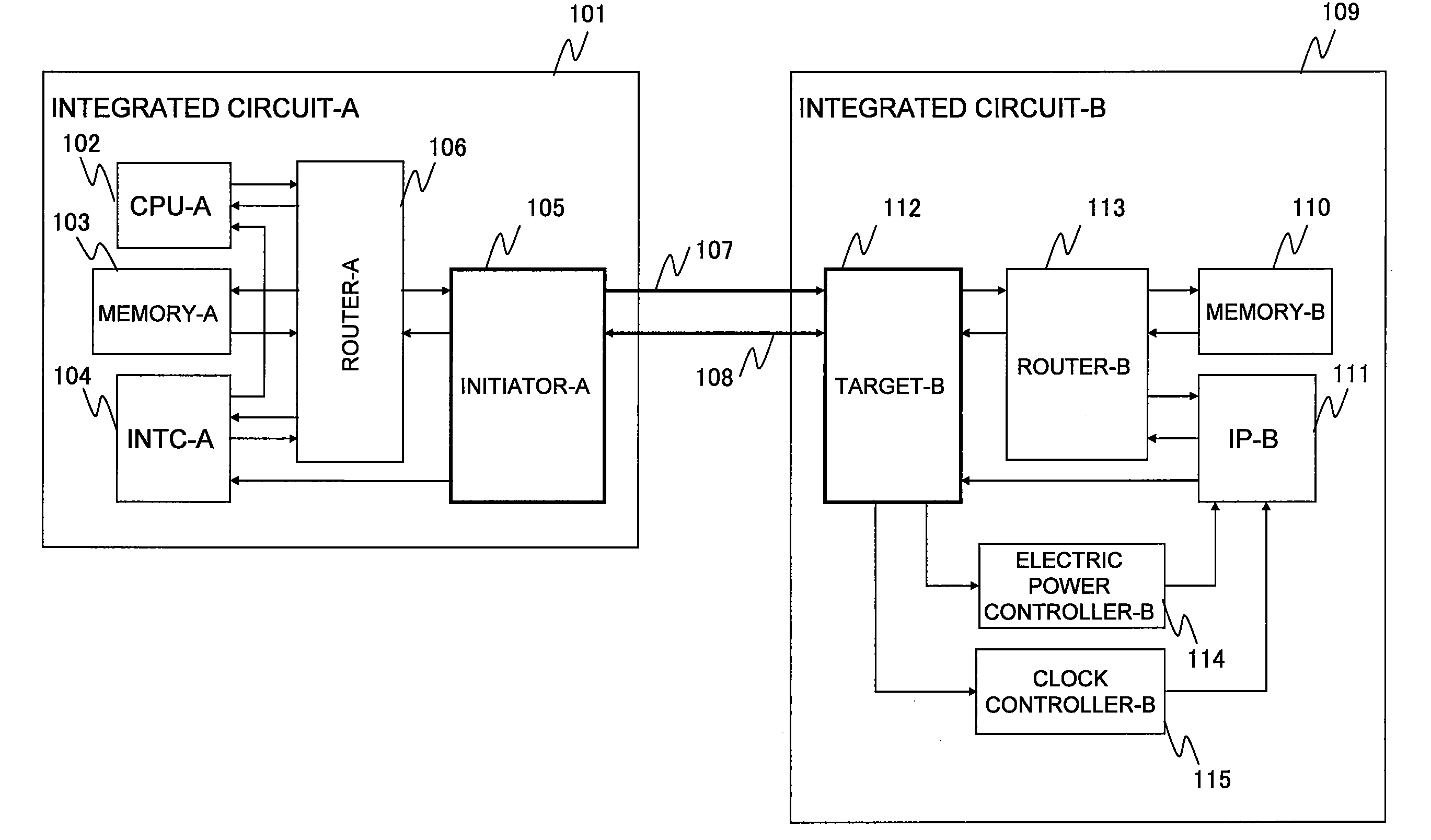
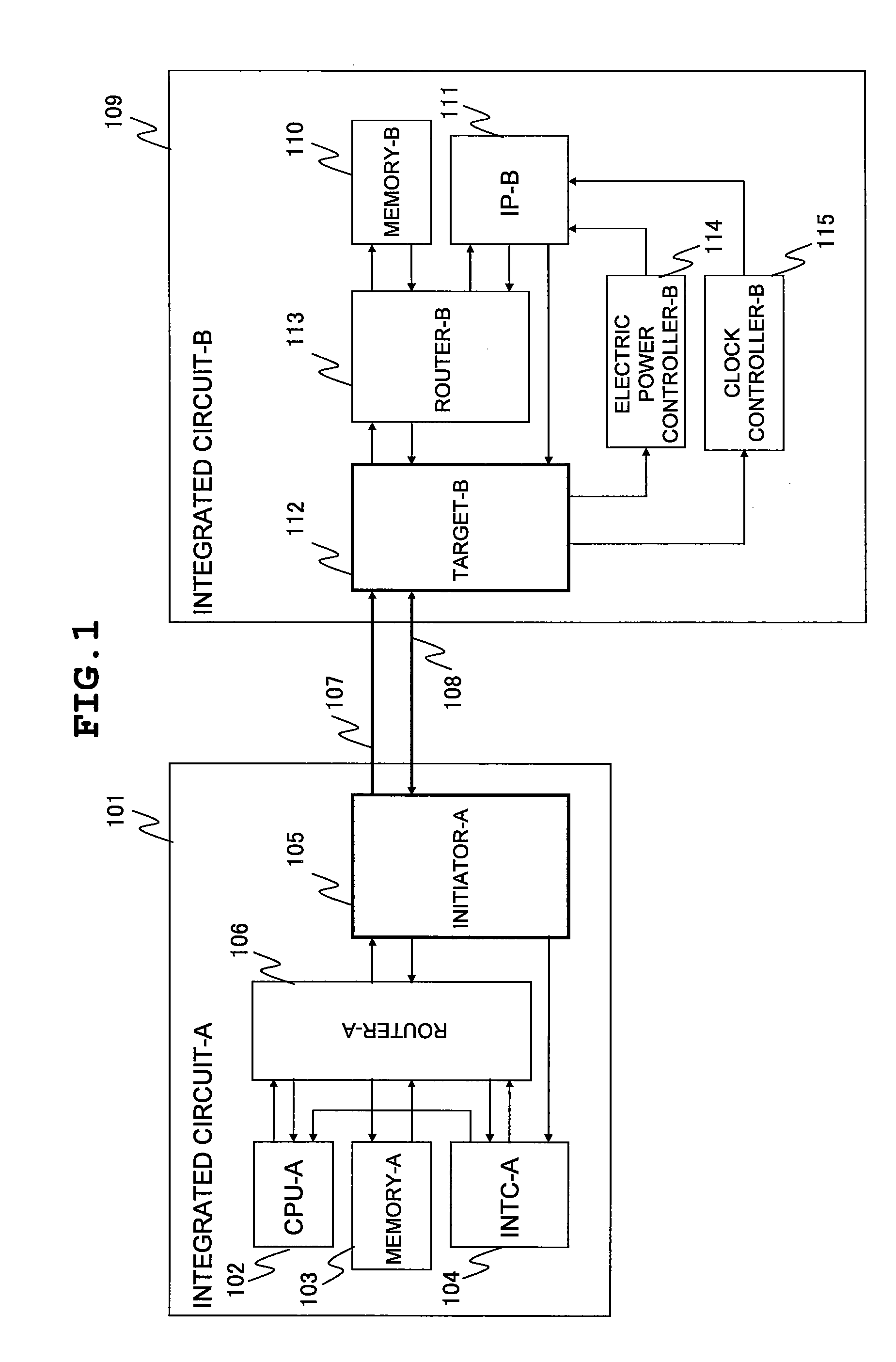
Data processing system
InactiveUS20090059943A1Suppression of latencyReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationData processing systemMaximum latency
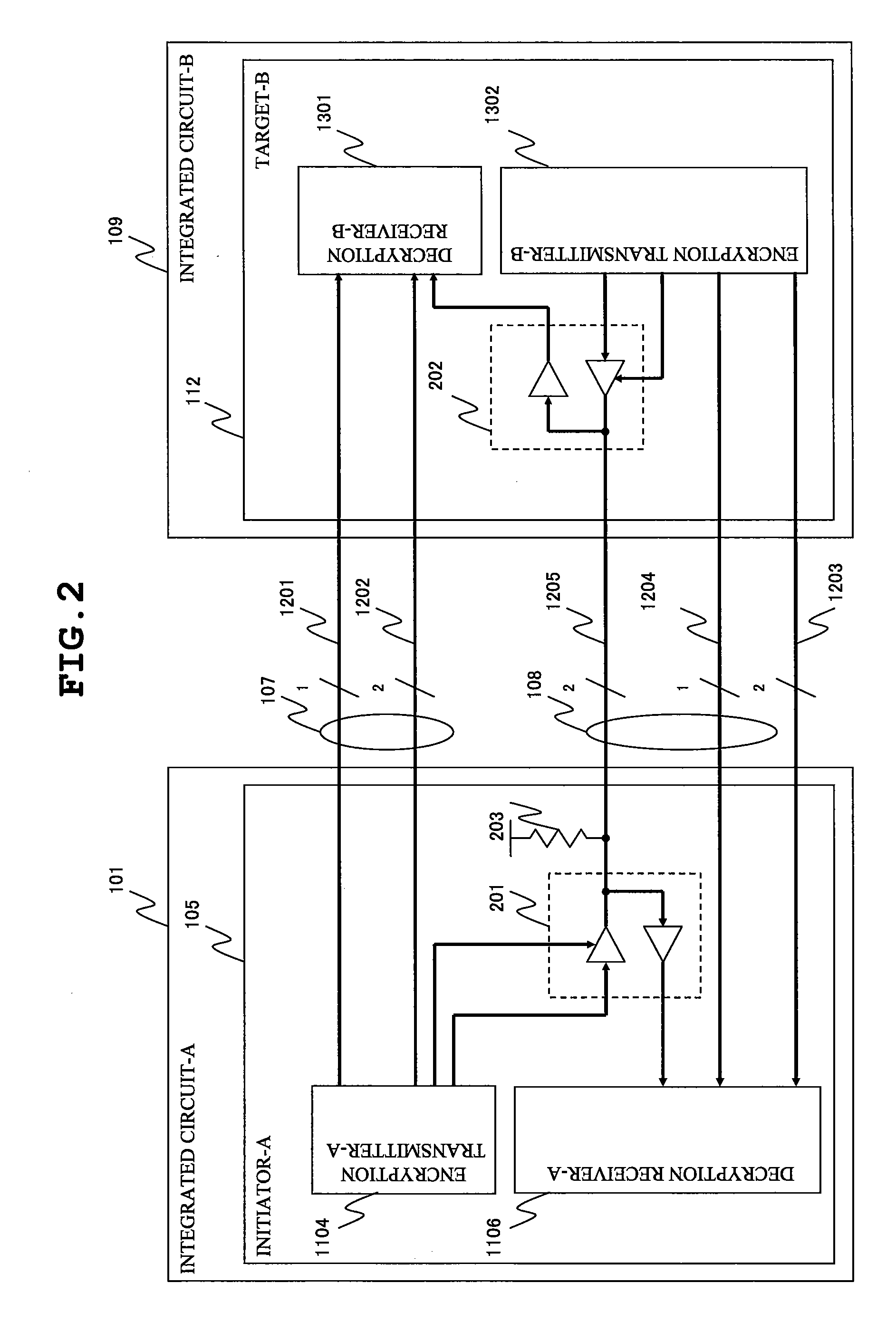
A data processing system enabling an outstanding-based variable flow control is provided. The data processing system includes a first semiconductor integrated circuit possessing an initiator and a second semiconductor integrated circuit possessing a target. The initiator transmits a request packet to the target, the target transmits a response packet to the initiator, and split transaction interface is practiced. The initiator includes an outstanding number counting circuit for counting an outstanding number defined by the difference in number between the request packets transmitted and the response packets received. The request packet transmission number is controlled so that the count value of the outstanding number counting circuit may not exceed the outstanding number to which the target can respond. The outstanding number is dynamically changeable to a suitable number so that the maximum latency from the issue of the request packet to the reception of the response packet is suppressed.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
System and method for designing a network
A system and computer-readable medium for designing a network are disclosed. A network is designed by a system having modules configured to perform steps that generate the network wherein nodes originate and terminate traffic to keep delay related to node-to-node delay-sensitive communication below a threshold. The computer-readable medium stores instructions for controlling a computing device to design the network. The instructions comprise obtaining an initial network topology including links and traffic routing based on a volume of traffic, allocating a maximum delay to each link in the network topology in proportion to a square root of an imputed cost for each of the links, sizing a bandwidth required for each of the links based on a current traffic routing and at least one of a maximum delay allocated to the link, determining link lengths and rerouting traffic according to shortest paths with respect to the determined link lengths.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Embedding a cloud-based resource request in a specification language wrapper
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for embedding a cloud-based resource request in a specification language wrapper. In embodiments, a set of applications and / or a set of appliances can be registered to be instantiated in a cloud-based network. Each application or appliance can have an associated set of specified resources with which the user wishes to instantiate those objects. For example, a user may specify a maximum latency for input / output of the application or appliance, a geographic location of the supporting cloud resources, a processor throughput, or other resource specification to instantiate the desired object. According to embodiments, the set of requested resources can be embedded in a specification language wrapper, such as an XML object. The specification language wrapper can be transmitted to a marketplace to seek the response of available clouds which can support the application or appliance according to the specifications contained in the specification language wrapper.
Owner:RED HAT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com