Patents
Literature
482 results about "Clock tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
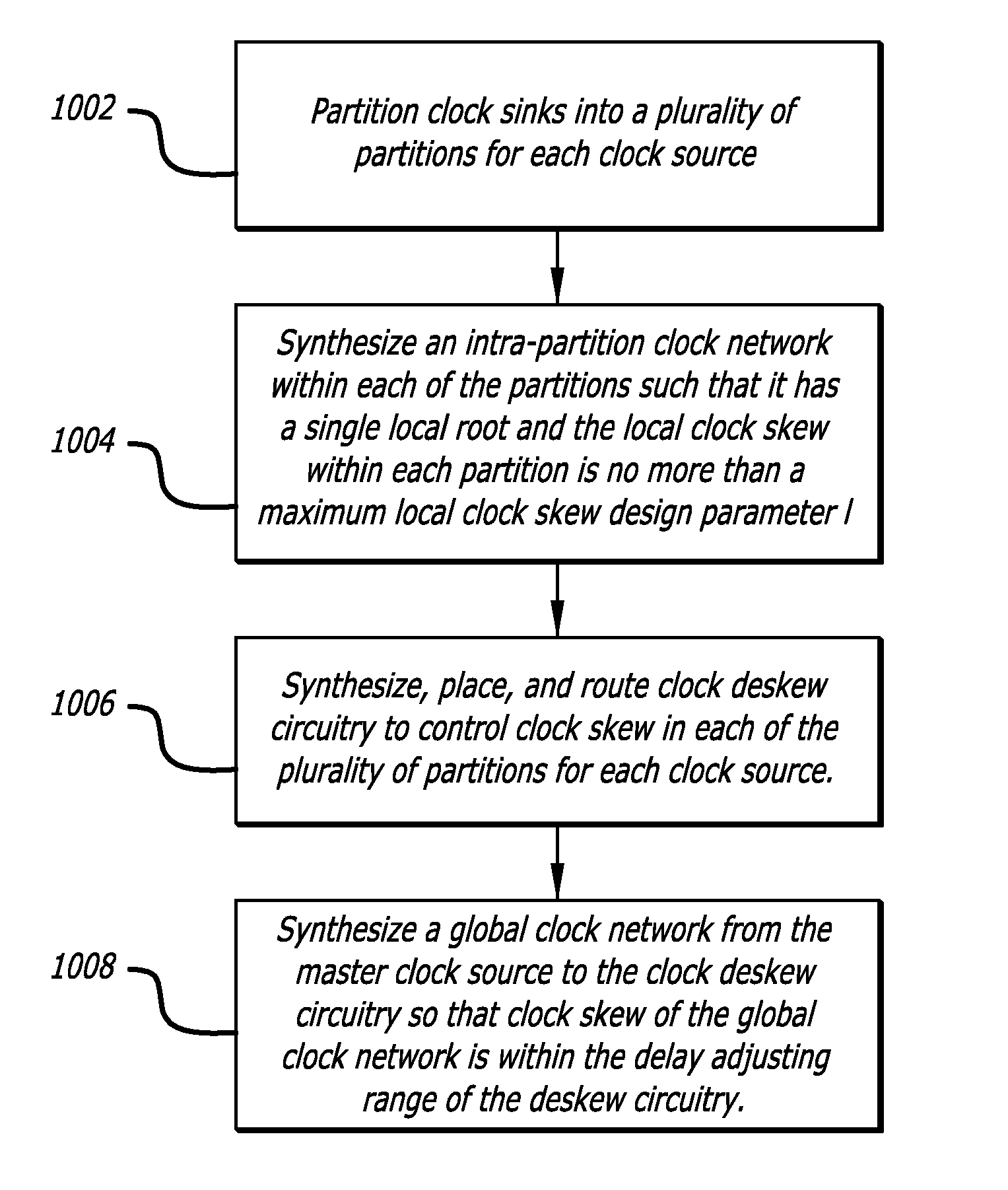
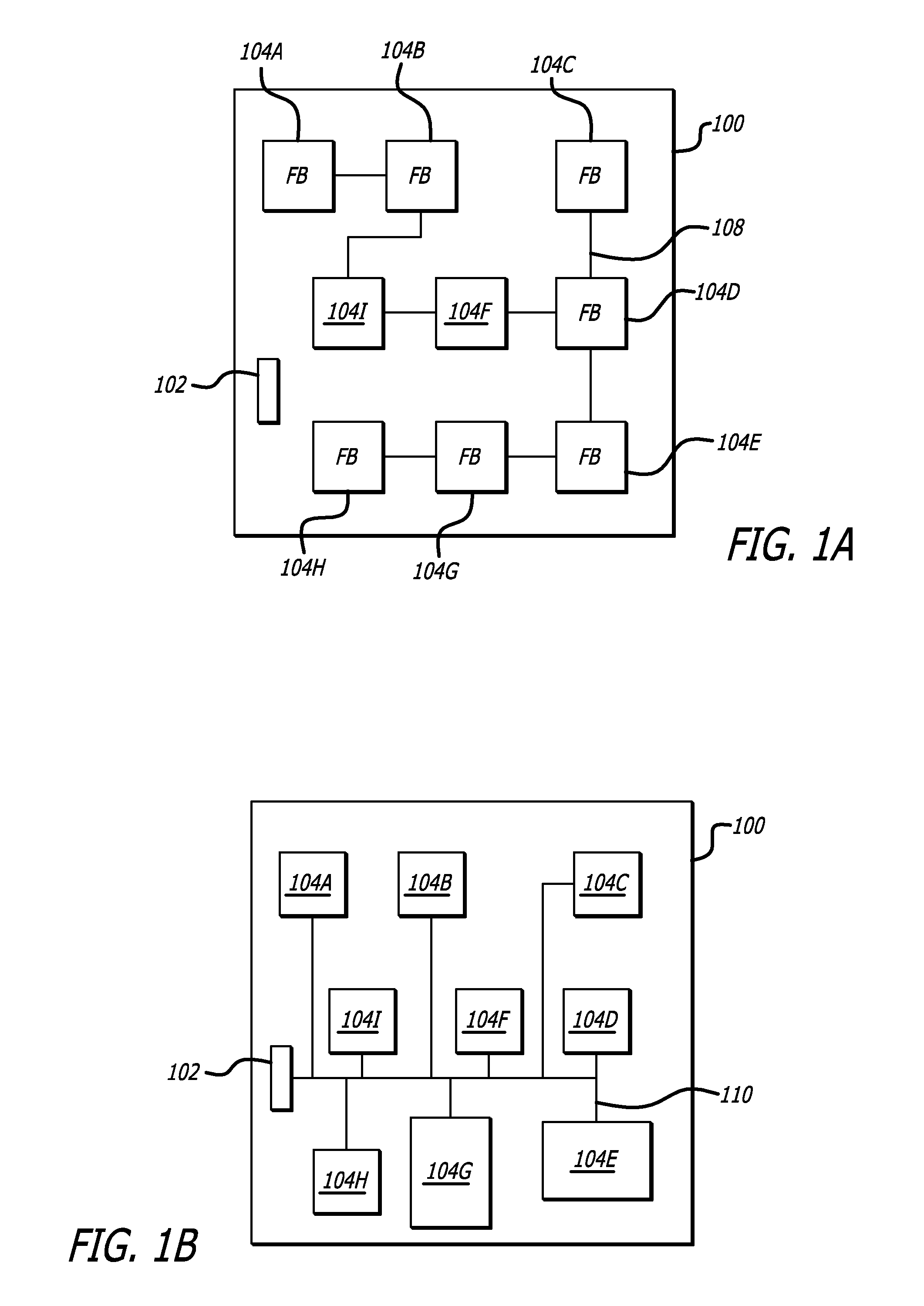
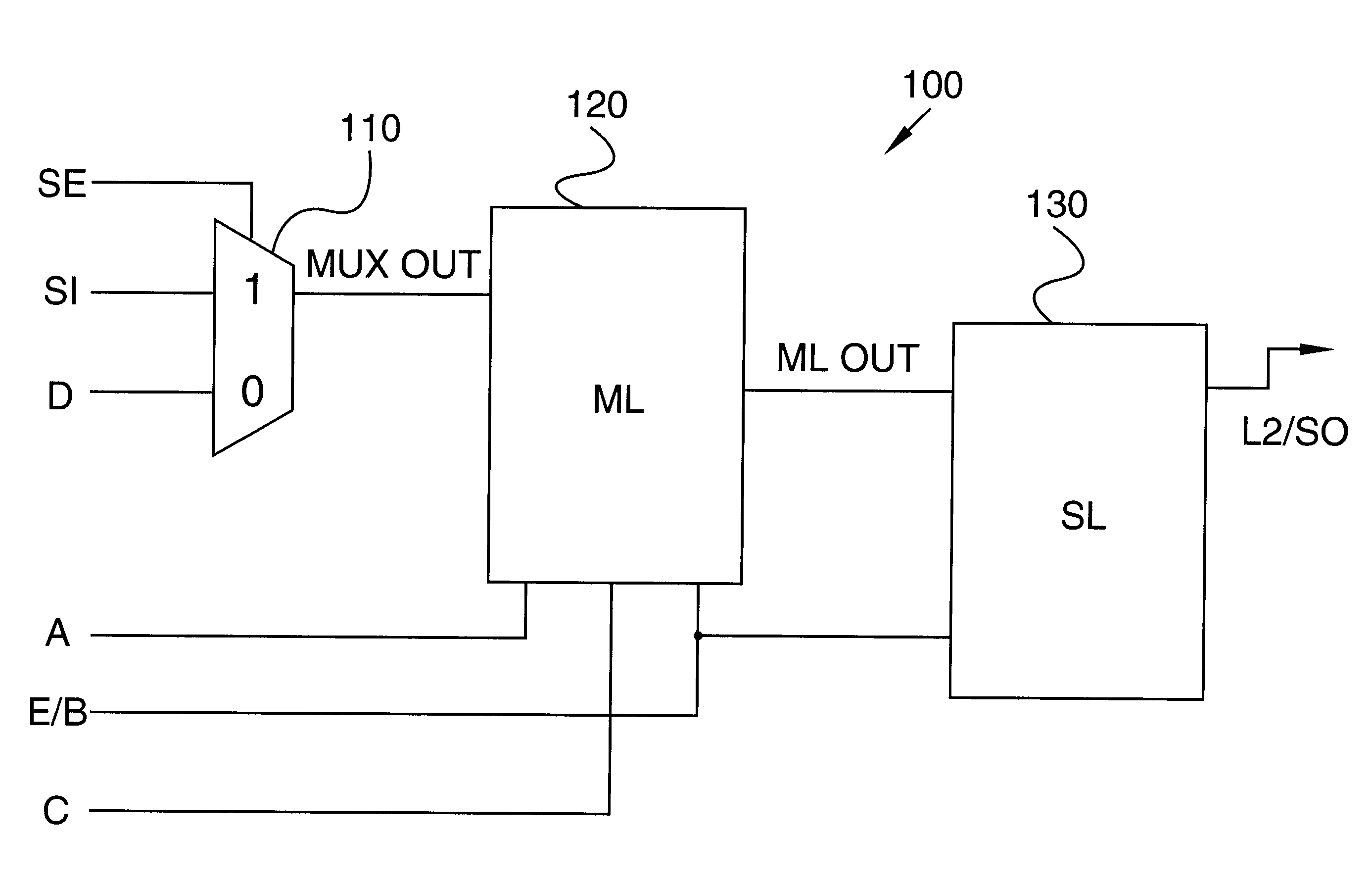
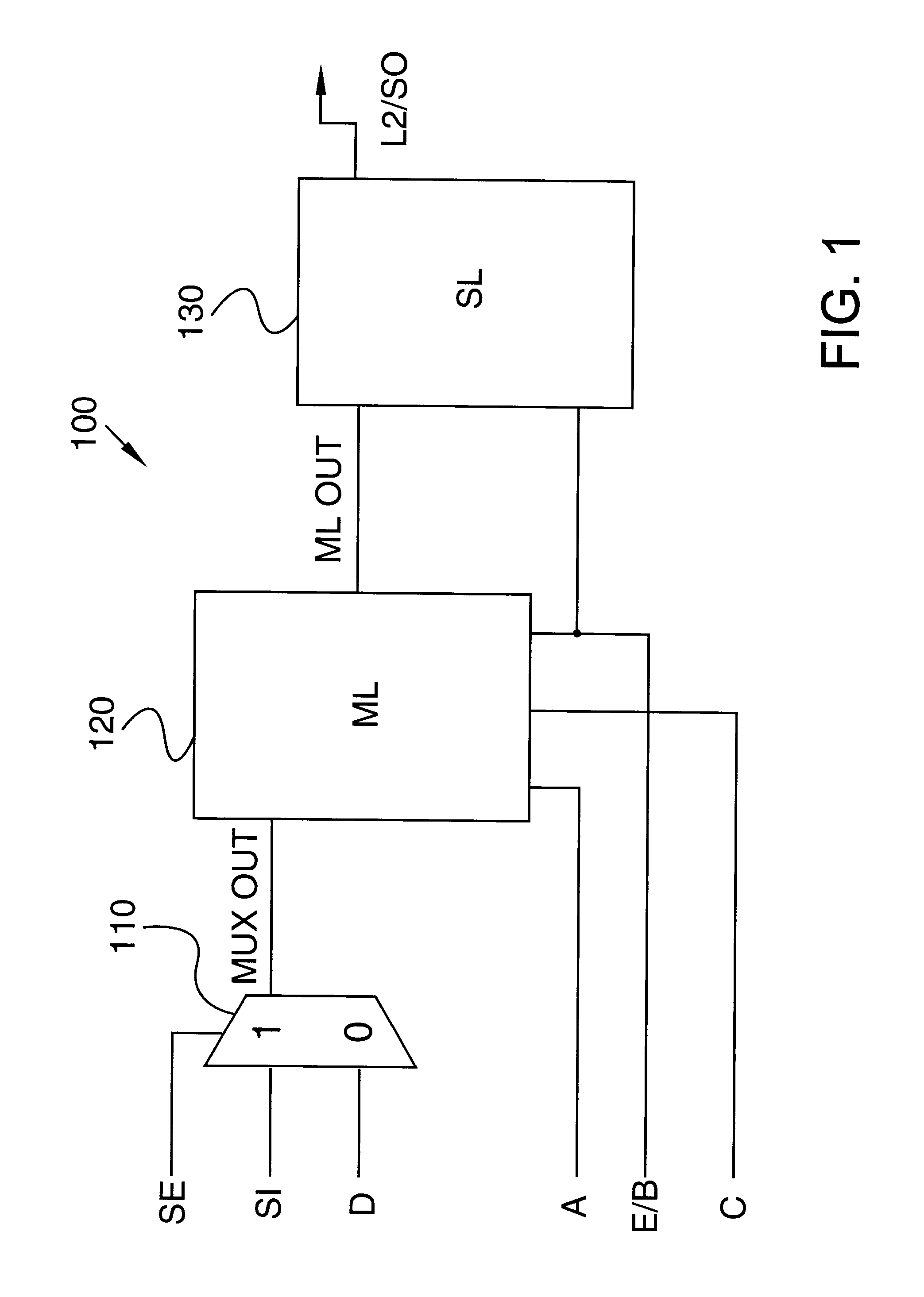
Automatic synthesis of clock distribution networks
ActiveUS8205182B1Minimize and control clock skewMinimize controlCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationClock treeDistribution networks
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for designing an integrated circuit is disclosed. The method includes automatically partitioning clock sinks of an integrated circuit design into a plurality of partitions; automatically synthesizing a clock tree from a master clock generator into the plurality of partitions to minimize local clock skew within each of the plurality of partitions; and automatically synthesizing clock de-skew circuitry into each of the plurality of partitions to control clock skew between neighboring partitions.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
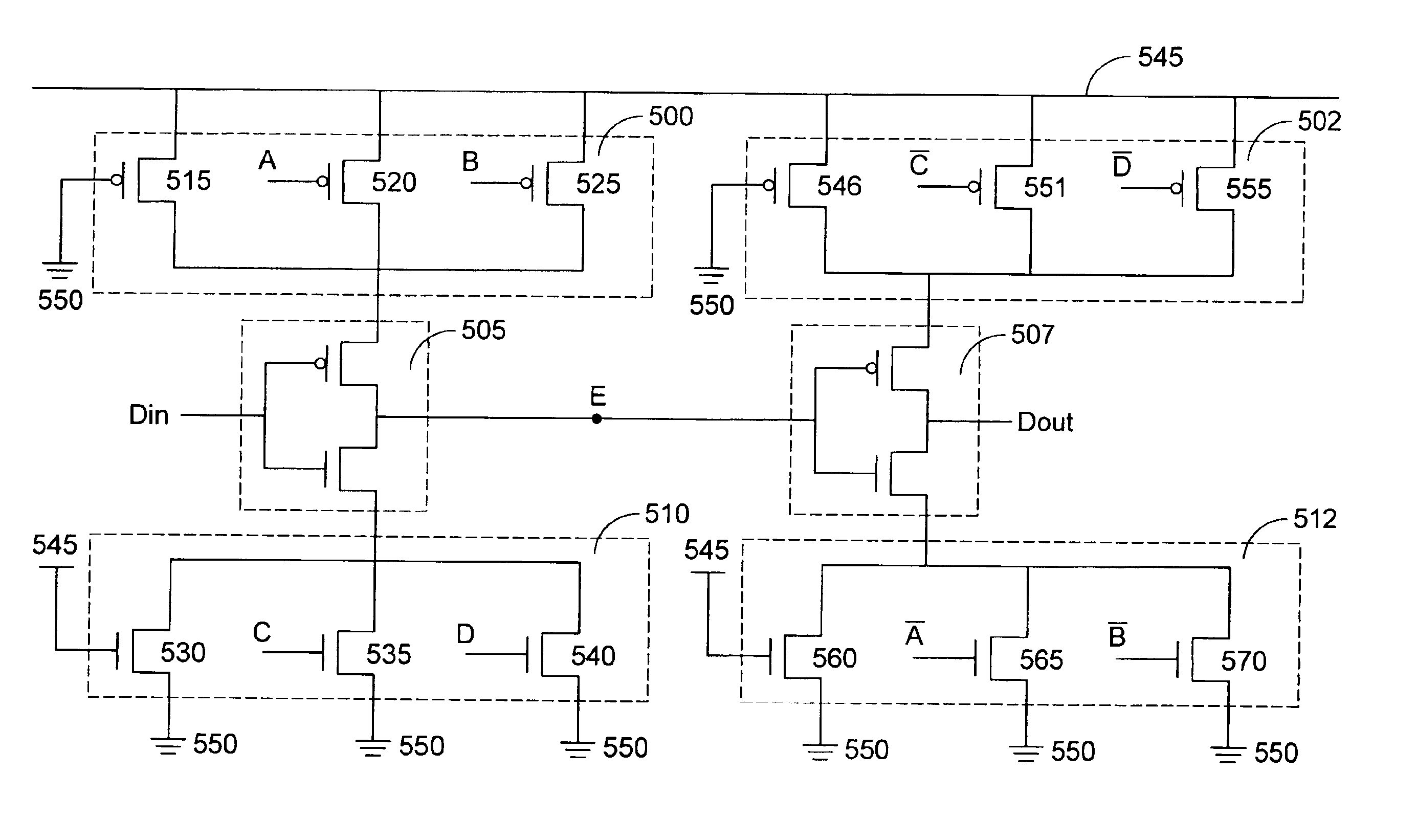
Duty-cycle adjustable buffer and method and method for operating same
ActiveUS6897696B2Increase the number ofContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationElectric pulse generatorClock treeEngineering
A duty-cycle adjustable buffer and a method for operating such buffer can be applied to a clock tree circuit for providing an adjustable duty cycle. The duty-cycle adjustable buffer includes a first inverter and a second inverter connected with each other in series. Each of the first inverter and the second inverter includes a plurality of controlled current charging paths and a plurality of controlled current discharging paths, wherein at least one controlled current charging path and at least one controlled current discharging path of the first inverter and the second inverter are conducted. The timing of the rising edge and falling edge of a clock signal is dynamically adjusted so as to dynamically altering the duty cycle of the clock signal.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
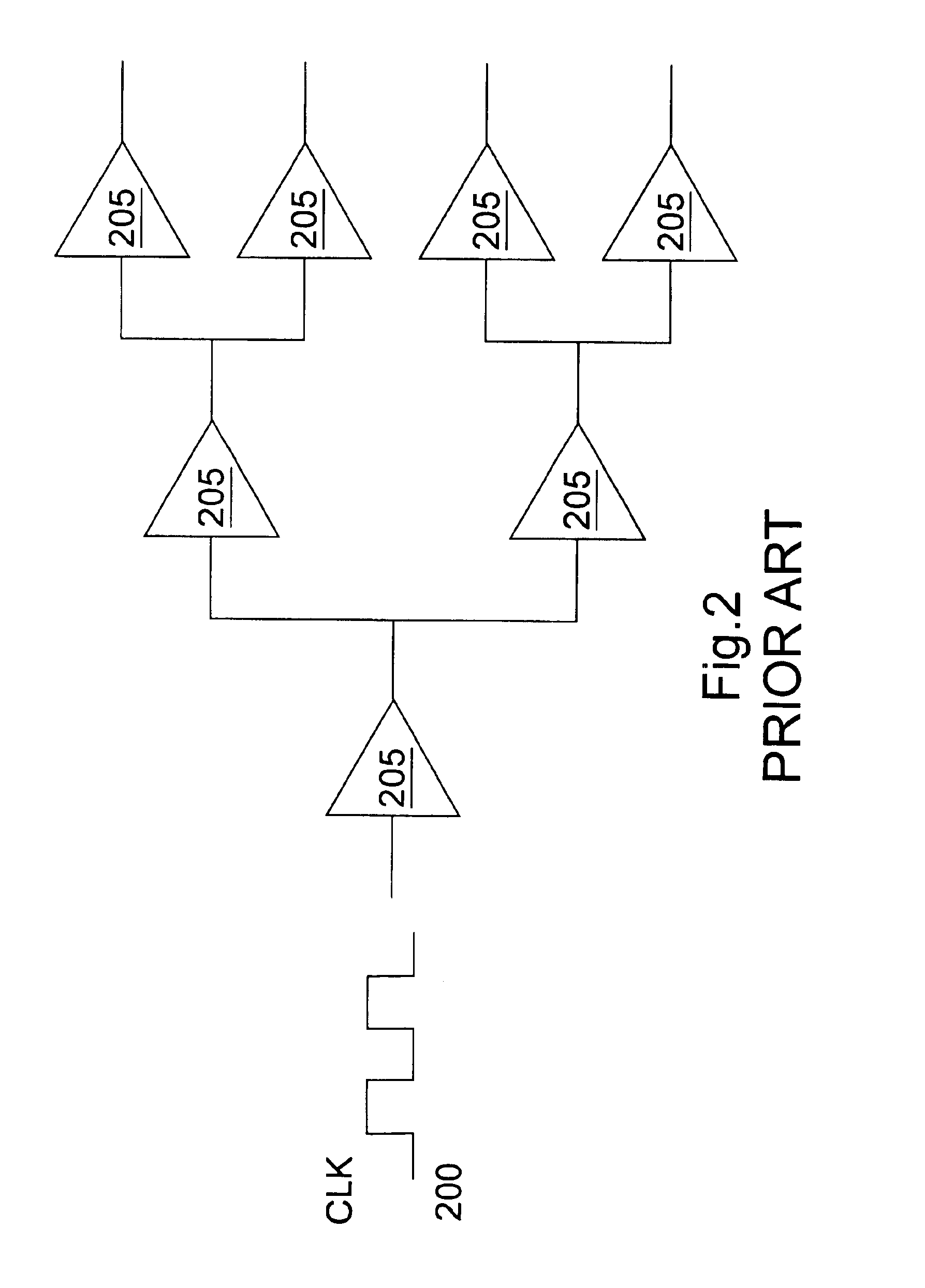
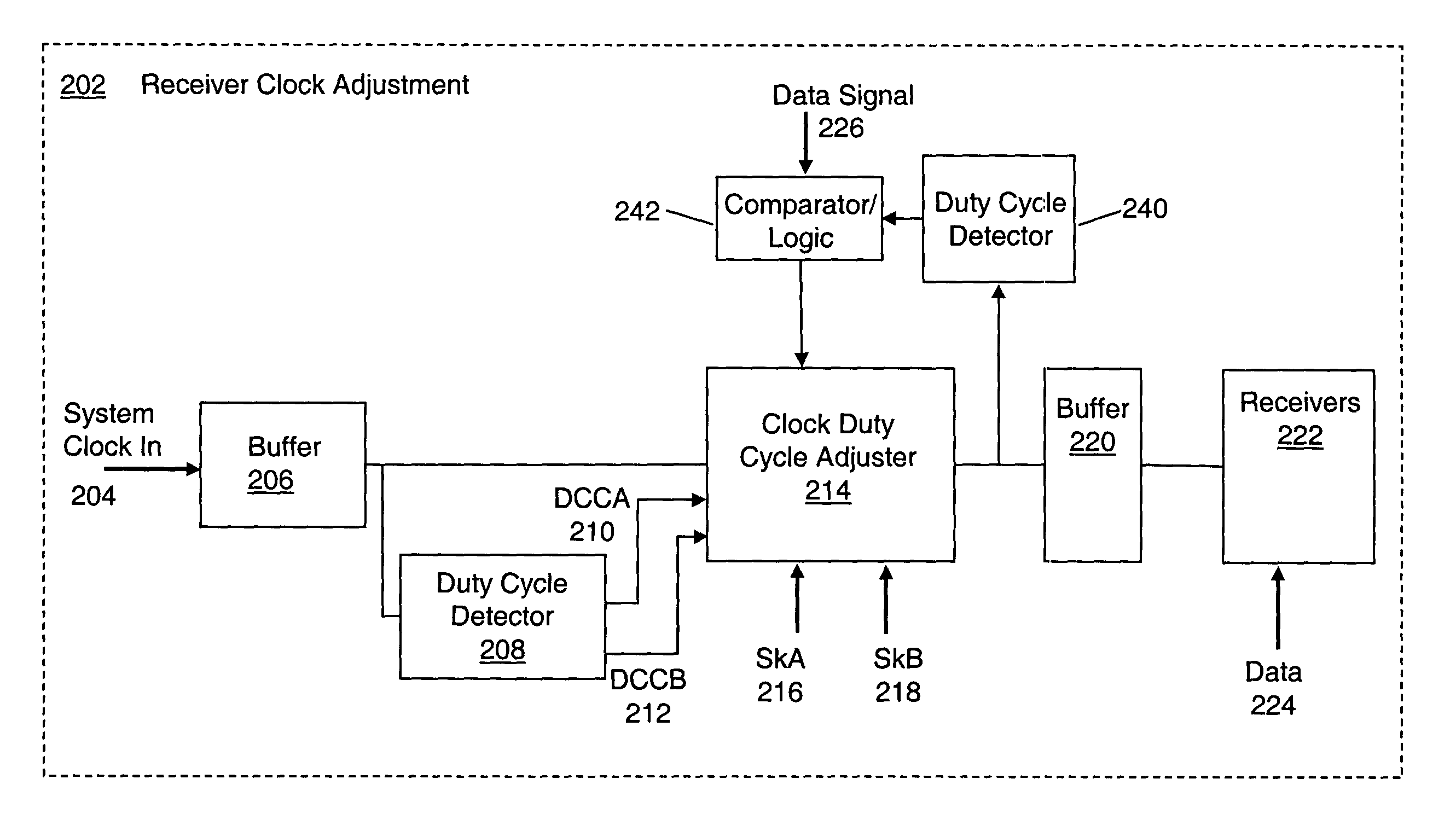
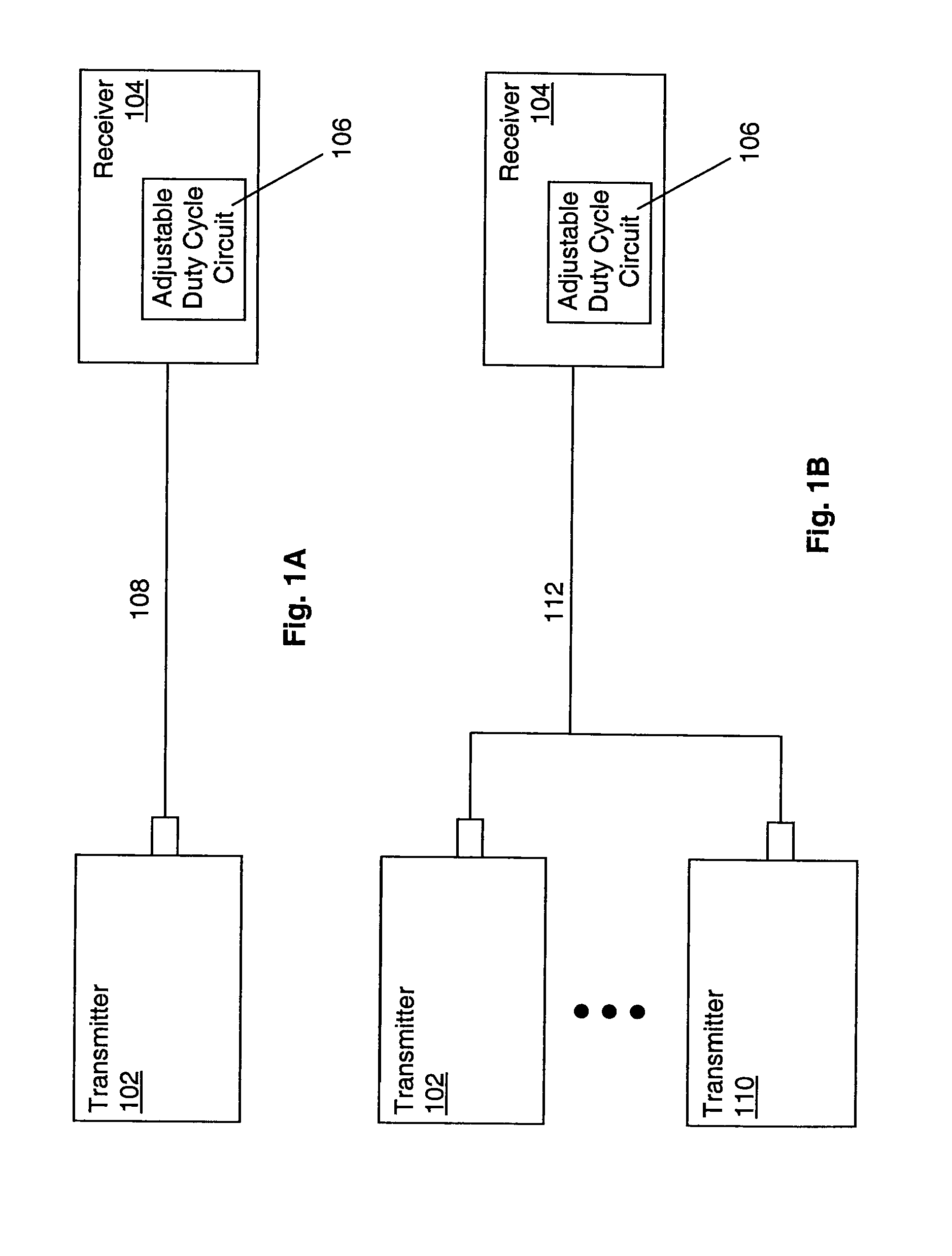
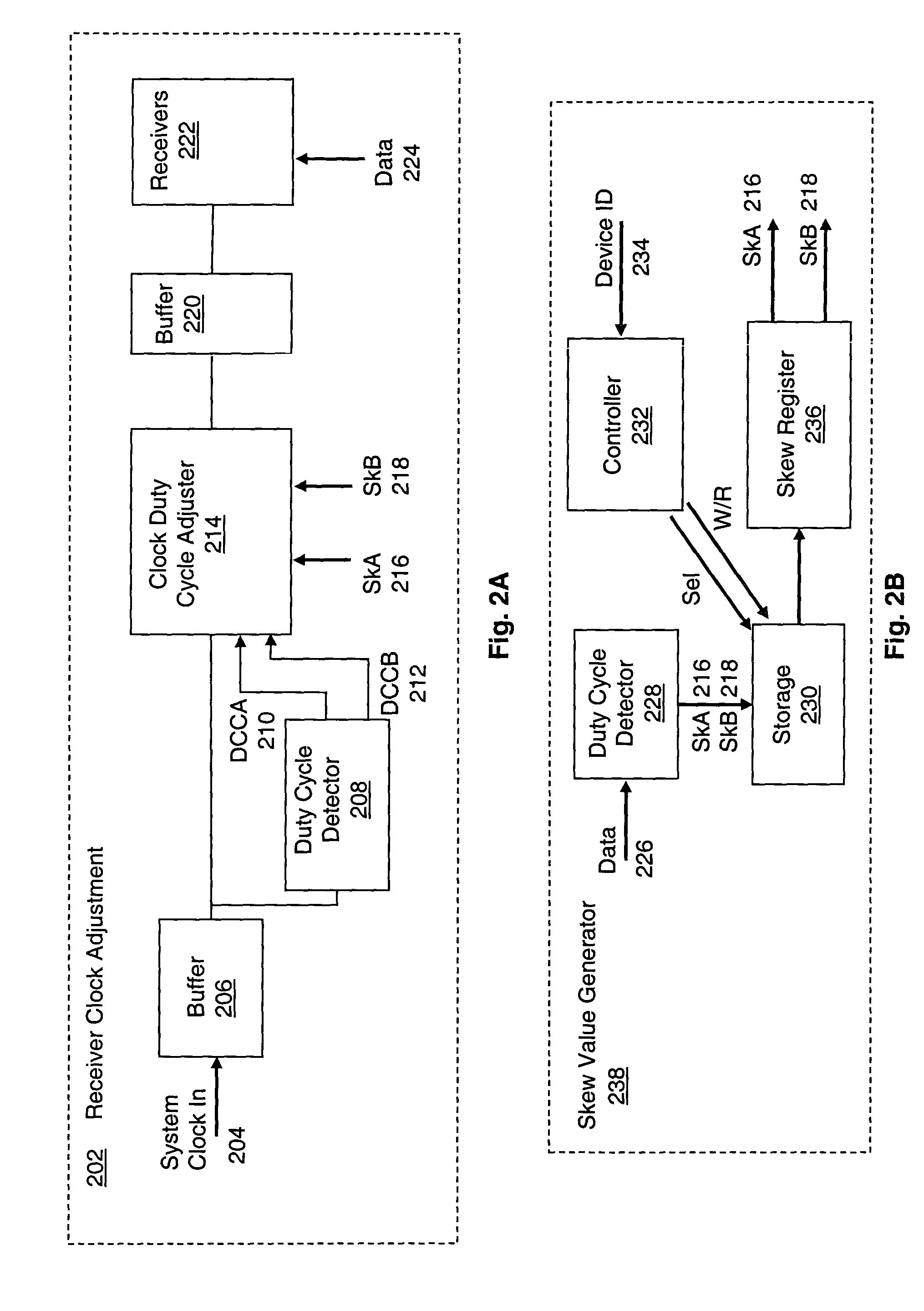
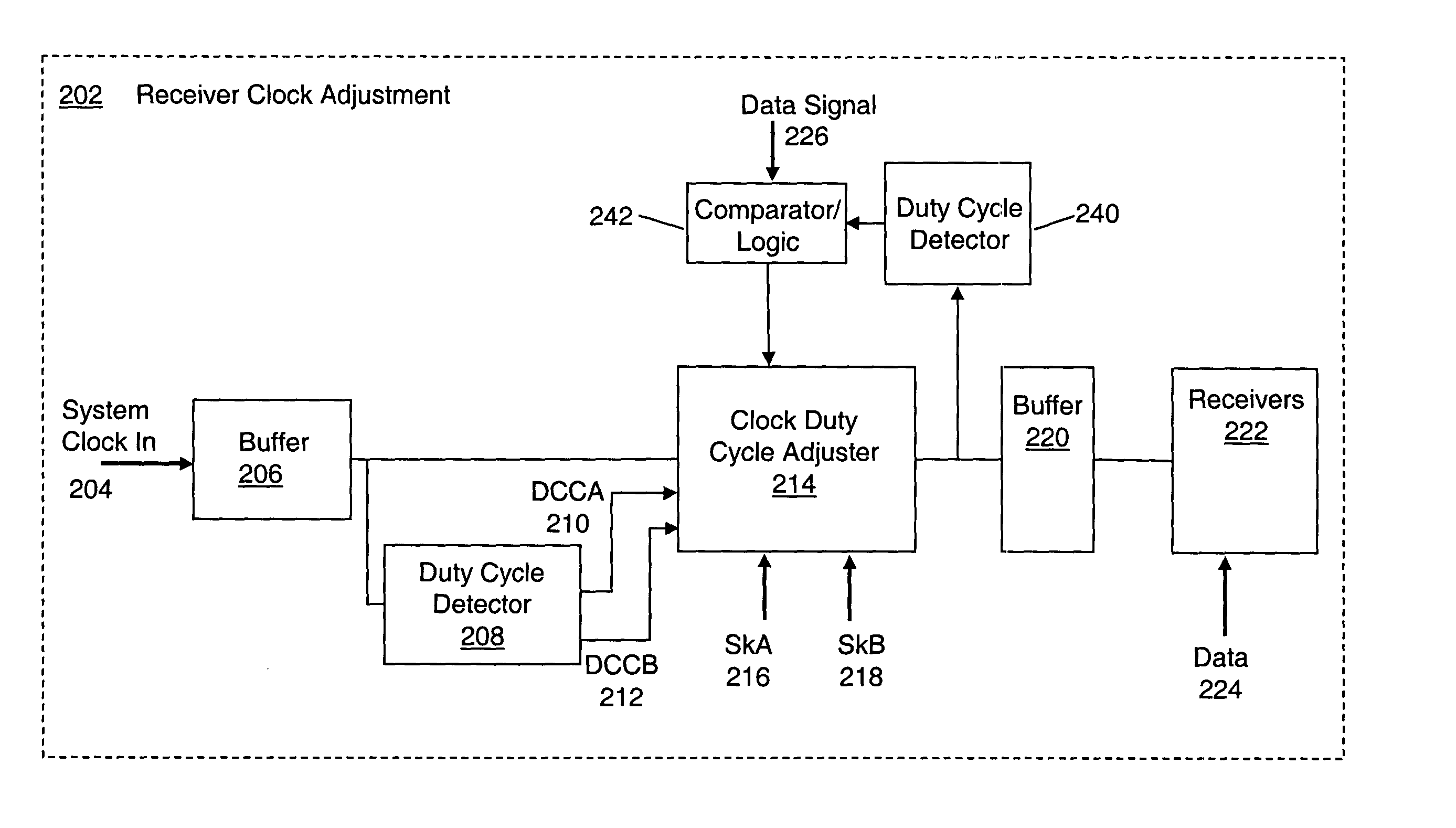
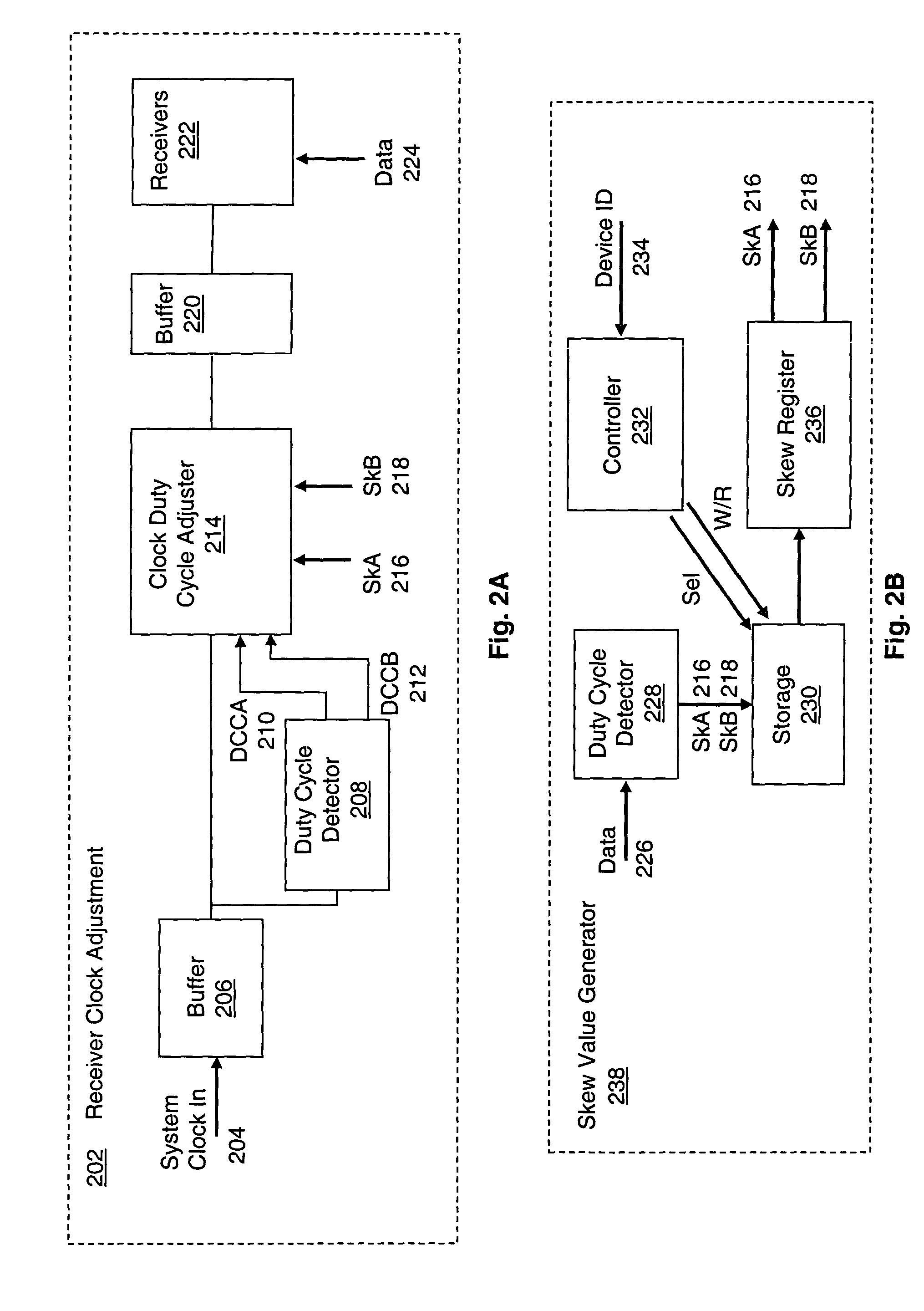
System and method for adaptive duty cycle optimization
A system and method for configuring a receiver such that the duty cycle of the receiver clock accurately matches the duty cycle of the data signal received. This adaptive system and method calibrates a receiver's duty cycle to optimize the receiver timing margin for different data signal types and different slave devices. In one embodiment, a duty cycle correction circuit matches the receiver clock to a predetermined duty cycle. The receiver clock is then configured to have a duty cycle skewed from the predetermined duty cycle based on the specific data signal received. In a receiver system utilizing a clock tree, individual branches of the clock tree are configured to have respective duty cycles skewed to match the duty cycle of a data signal received from a specific transmitting device.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
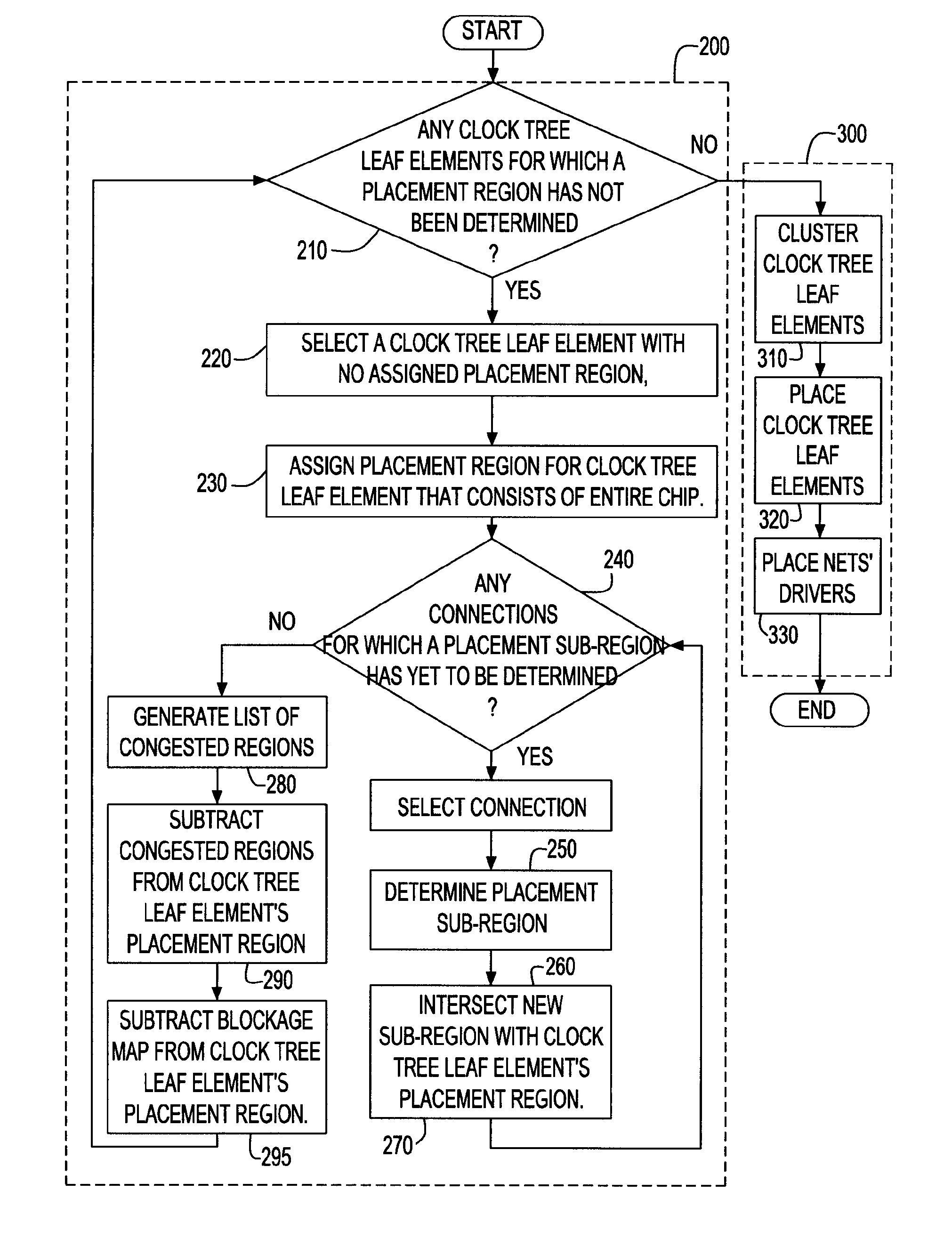
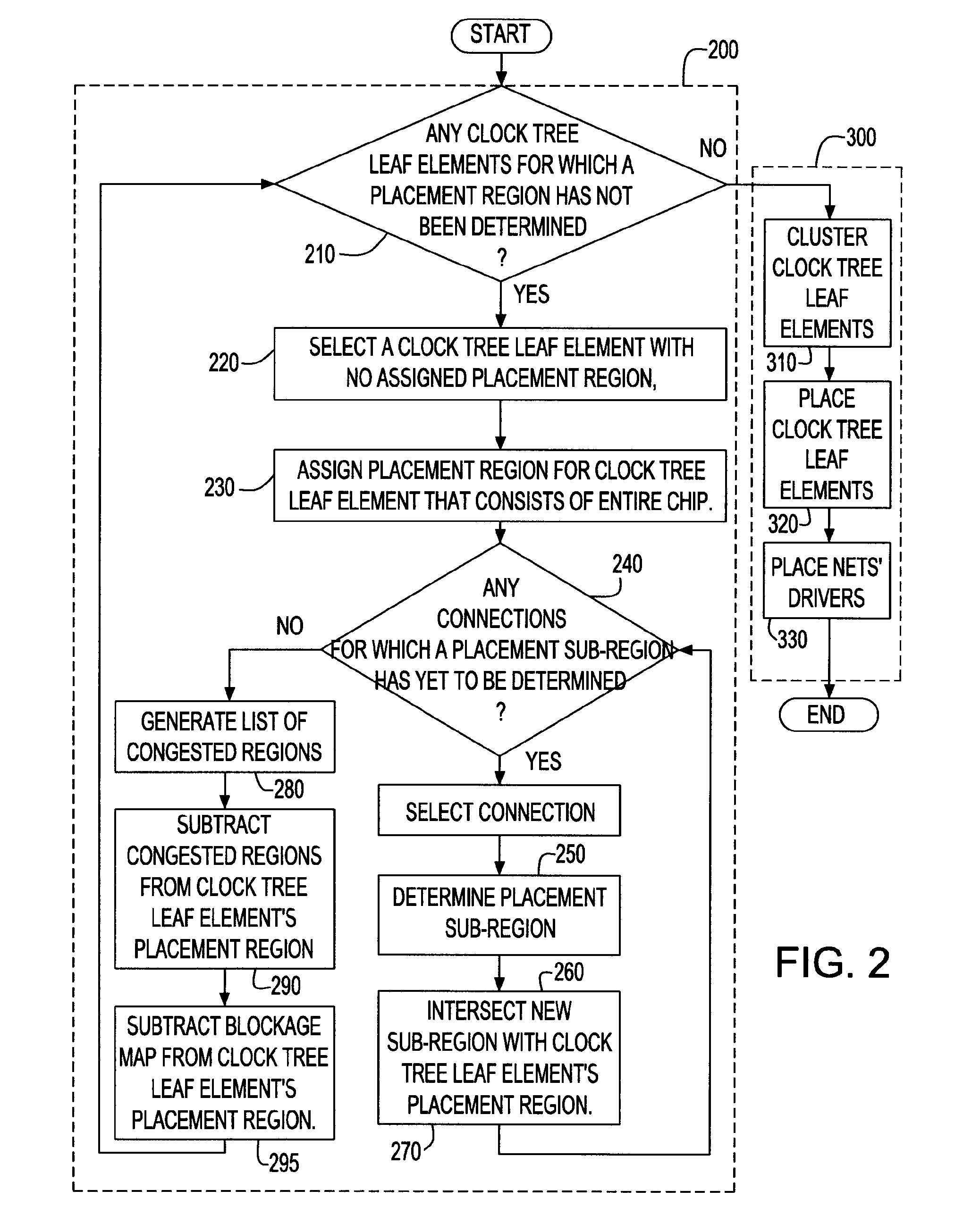
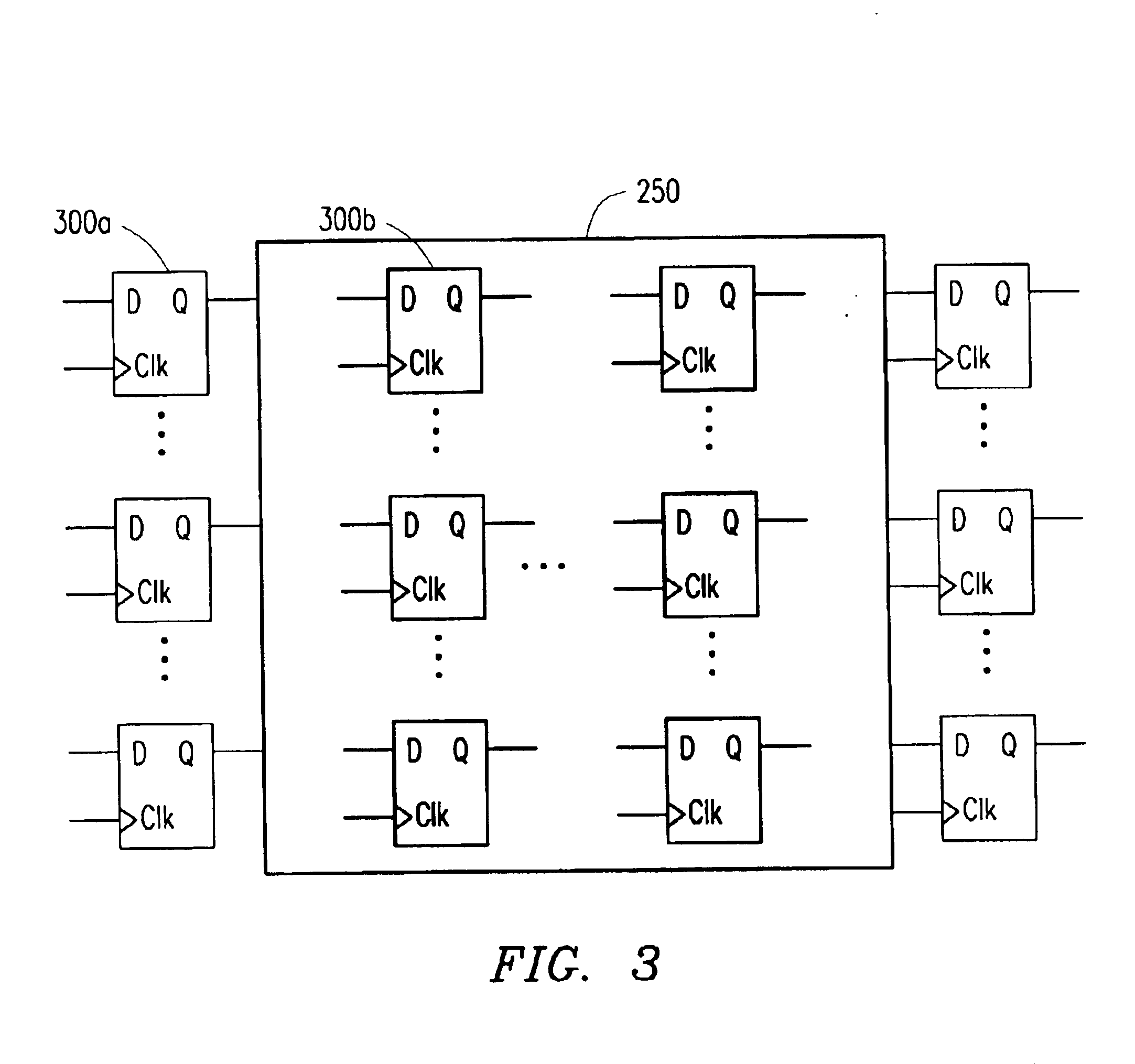
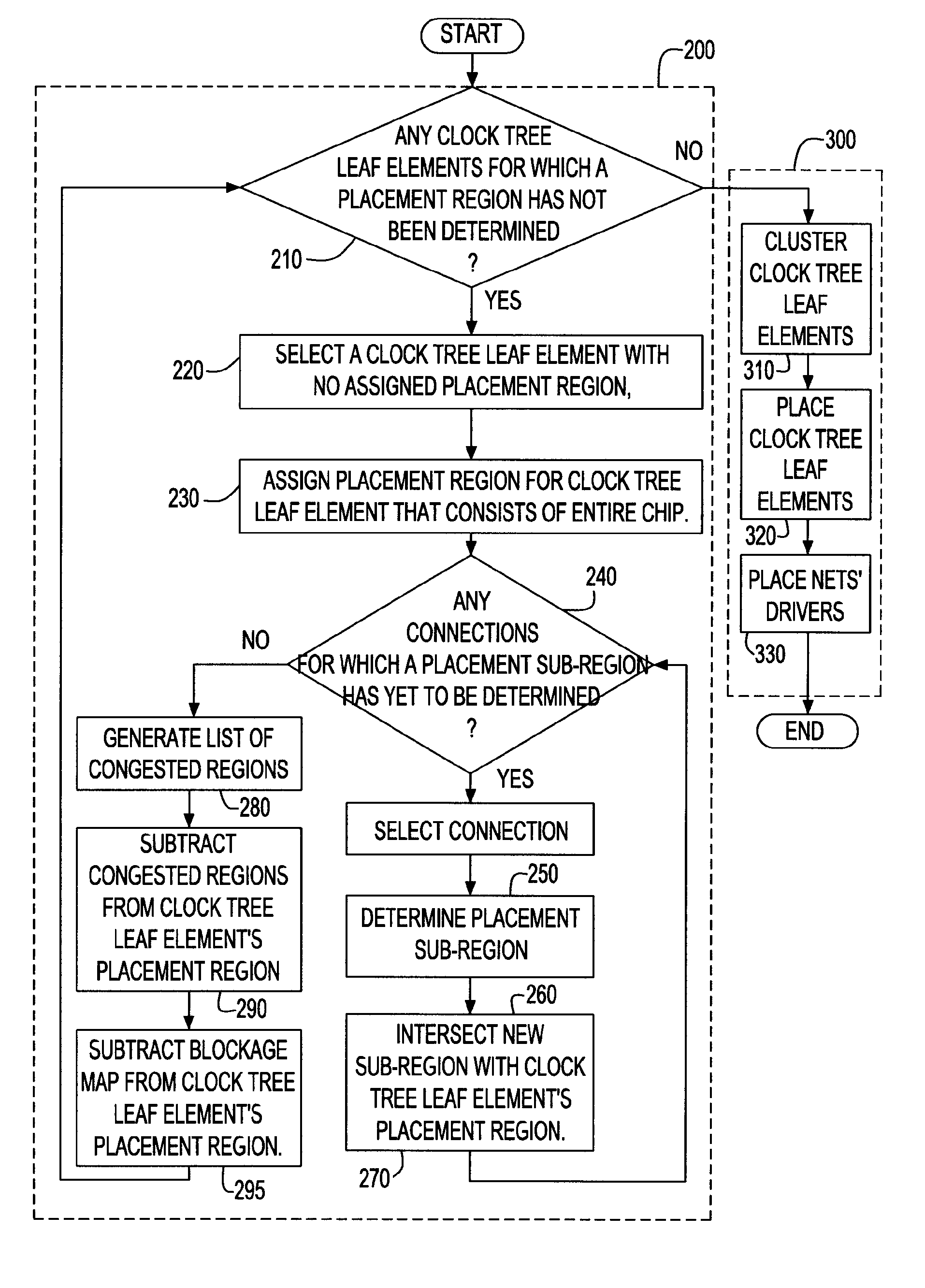
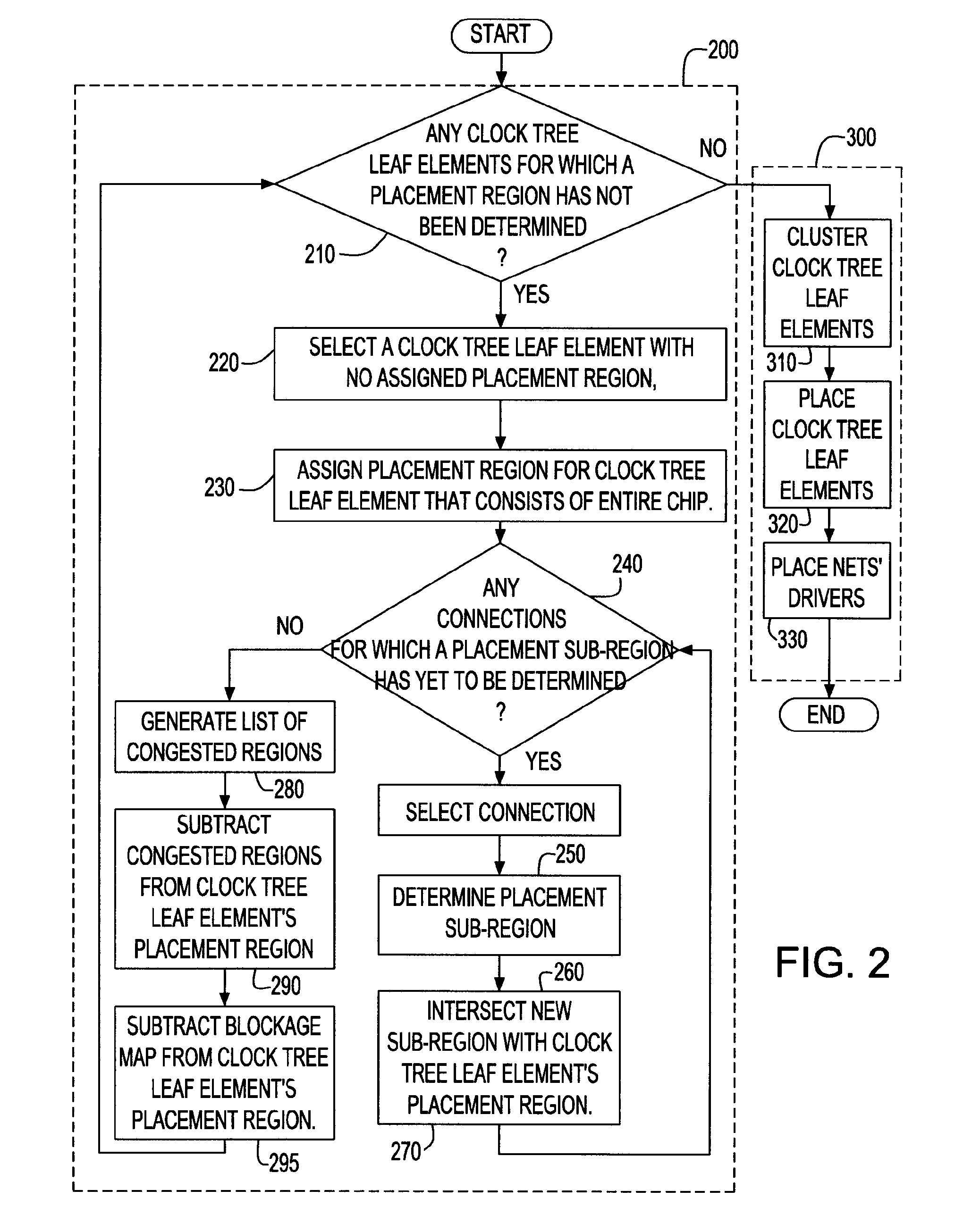
Method of clock tree distribution generation by determining allowed placement regions for clocked elements
InactiveUS20060190899A1Minimize cost functionQuantity minimizationCAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTheoretical computer scienceClock tree
A method, system and program product are described for generating a clock distribution network on an integrated circuit by determining an allowable placement region for each of a set of clock tree leaf elements in the integrated circuit. This allowable placement region is generated by determining and intersecting a set of sub-regions under different constraints, each of which identifies an area in which the clock tree leaf element is placed to satisfy the respective constraint. Constraints for which sub-regions are determined include timing constraints in the form of slacks and congestion constraints. After allowable placement regions have been determined, the clock tree leaf elements are clustered, and each clock tree leaf element is placed at a location within its allowable placement region which minimizes some cost function for that clustering.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
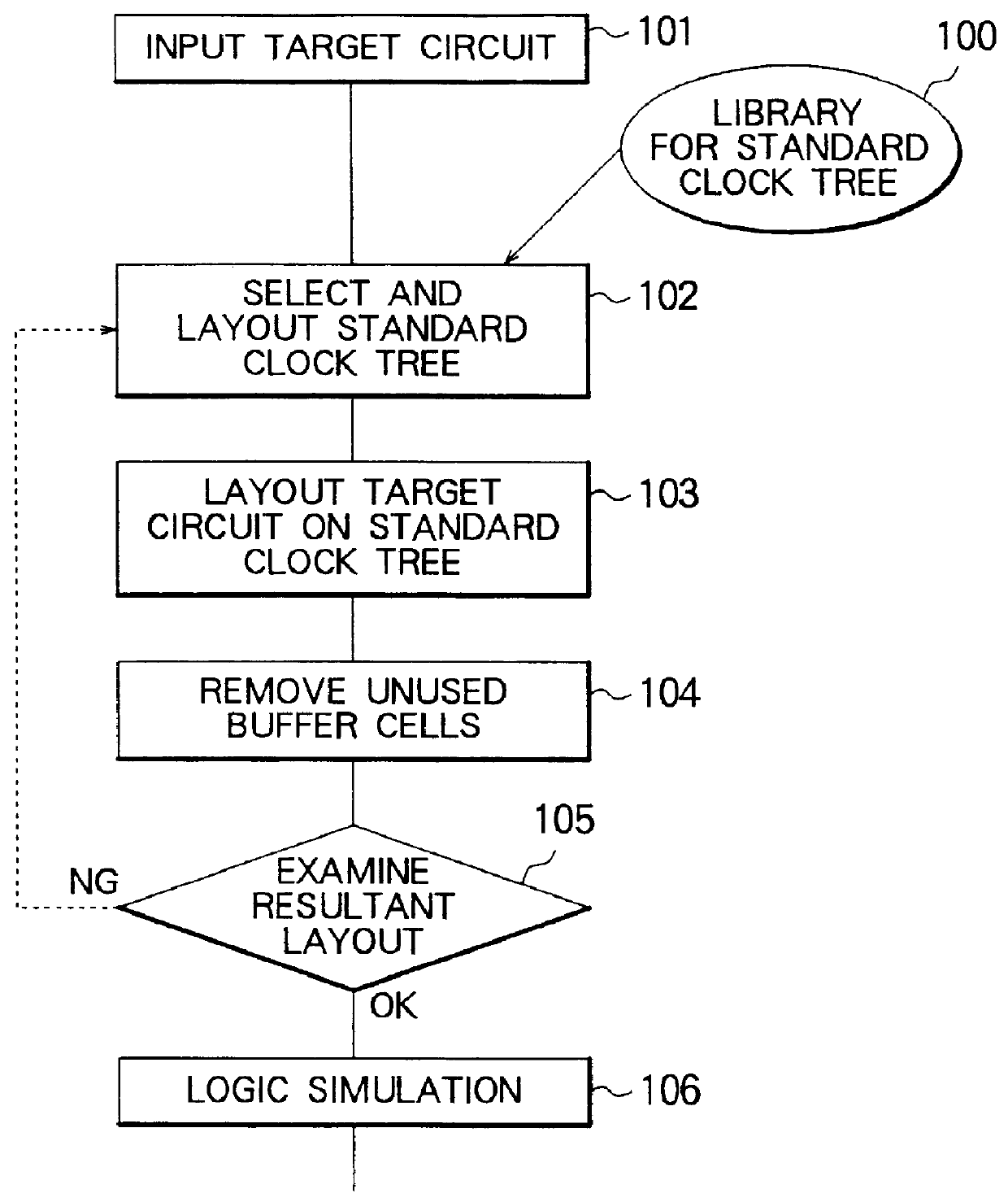
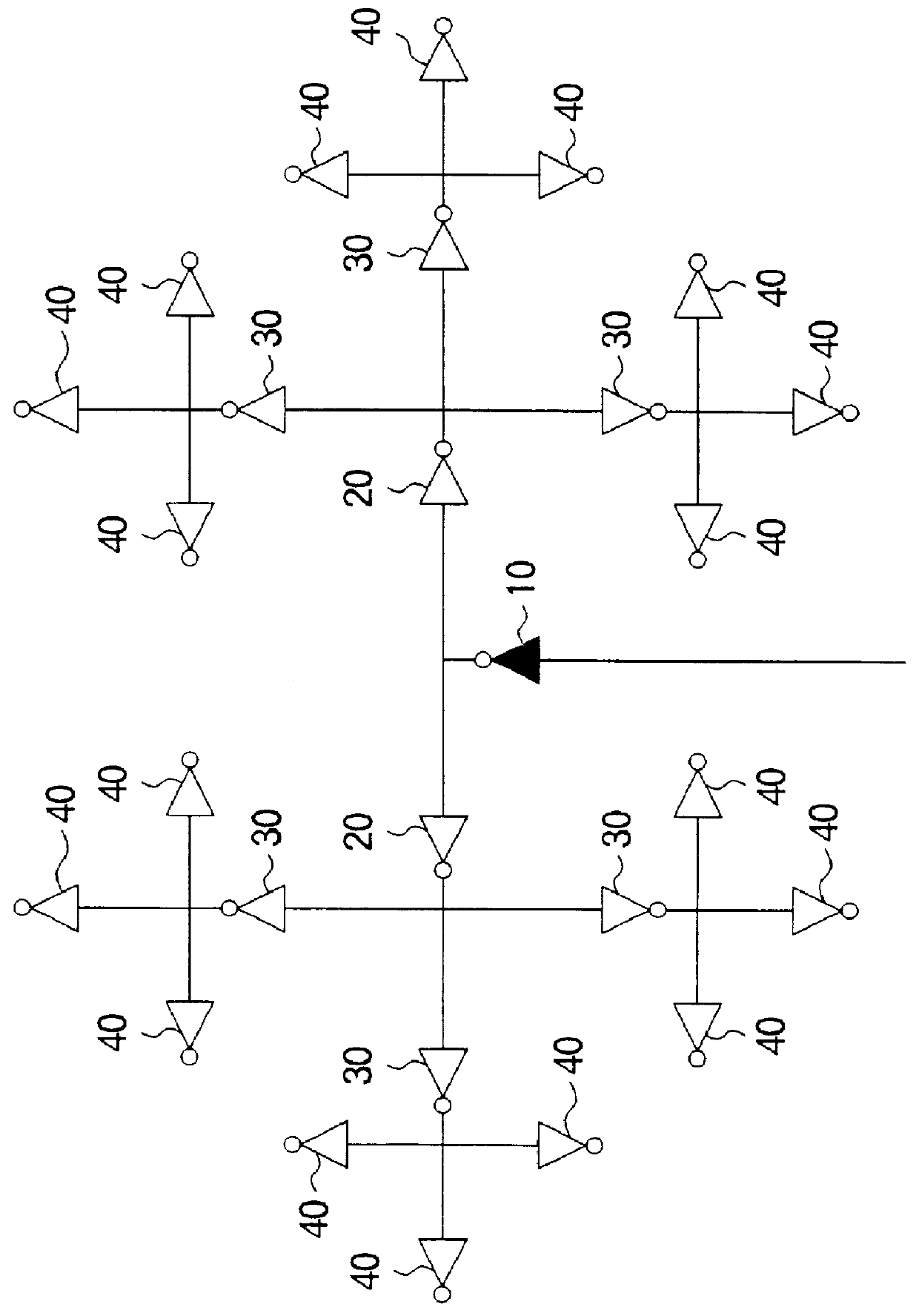
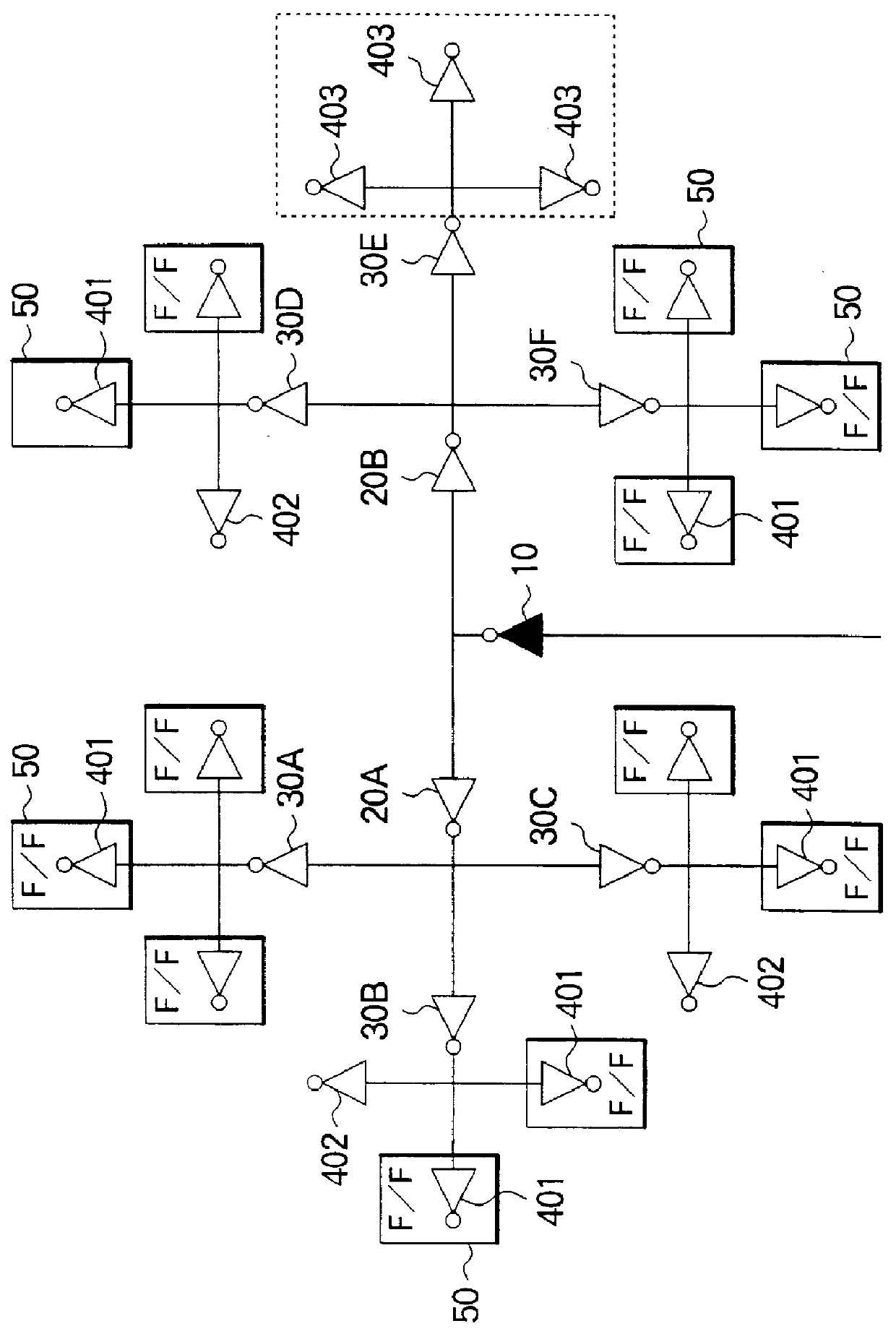
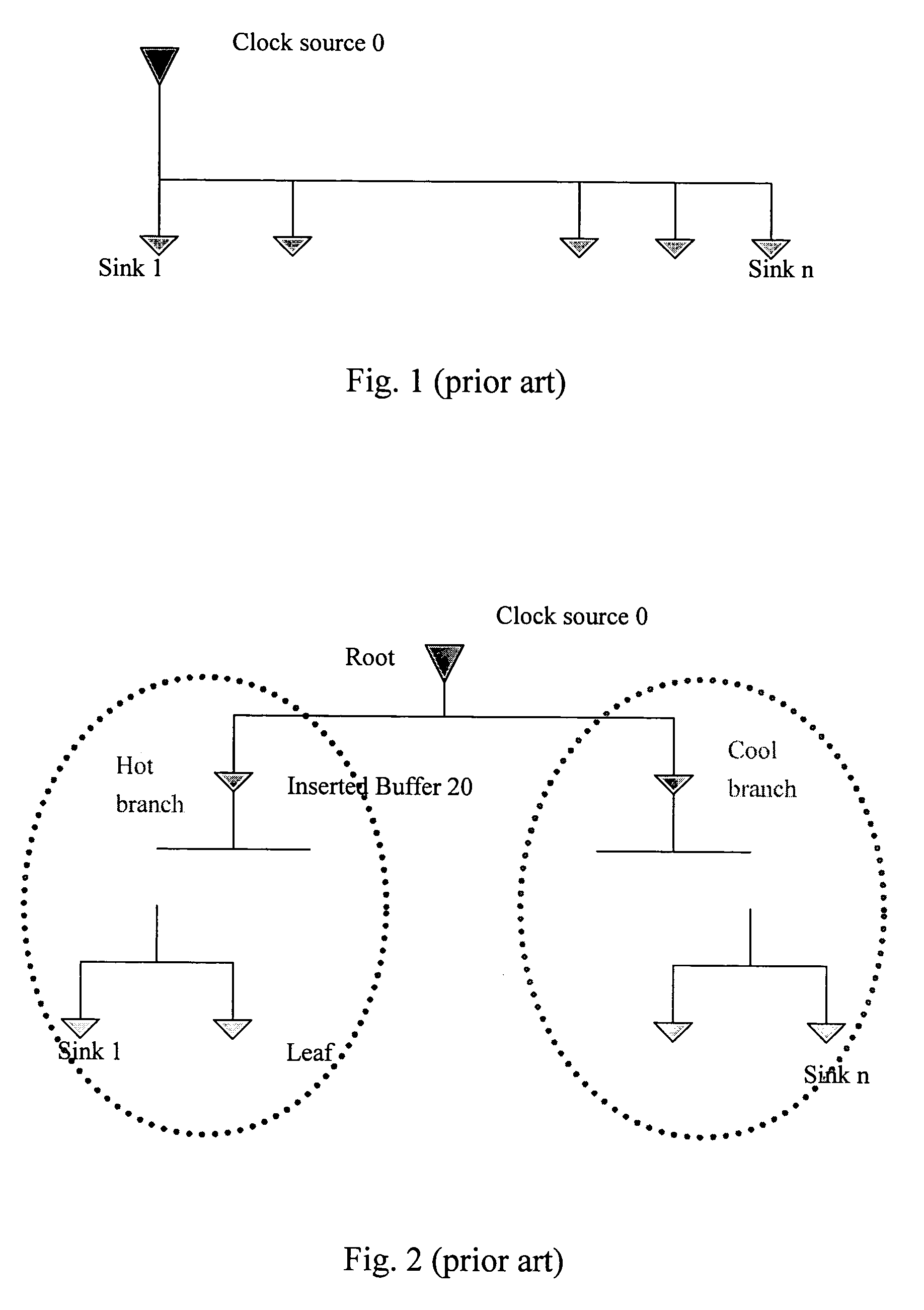
Layout method for a clock tree in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6053950ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWrite bufferClock tree
A clock signal distribution circuit has a clock tree configuration. In the layout of the clock tree, a standard clock tree is prepared having a route buffer, a plurality of intermediate stage buffer cells and a plurality of last stage buffer cells connected in a hierarchical configuration. All of the clock lines have an equal length. If there are no set of flip-flops ina target integrated circuit corresponding to a set of last stage buffer cells, the set of last stage buffer cells are removed as a whole provided there is not other last stage buffer cells connected to a flip-flop.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
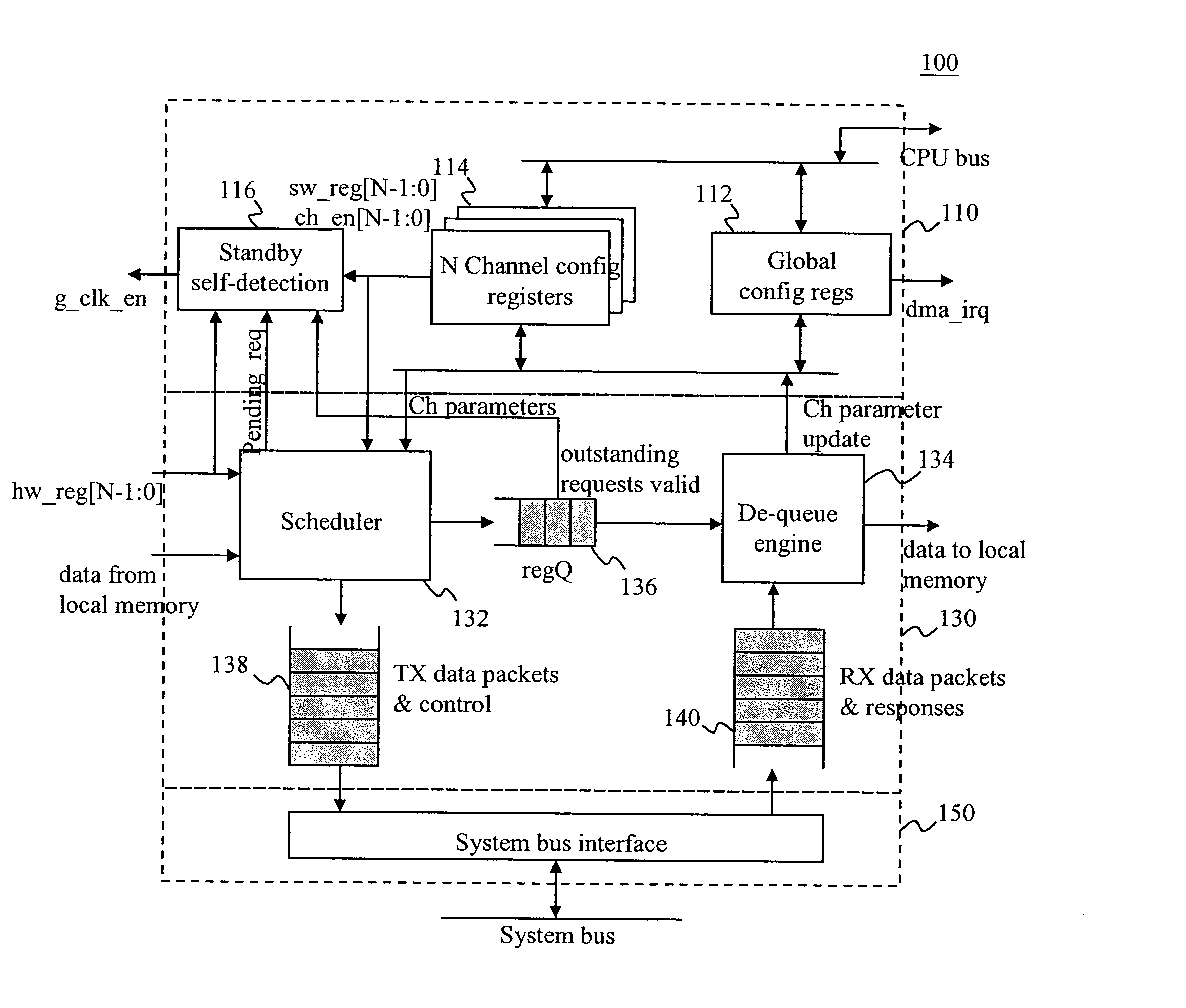
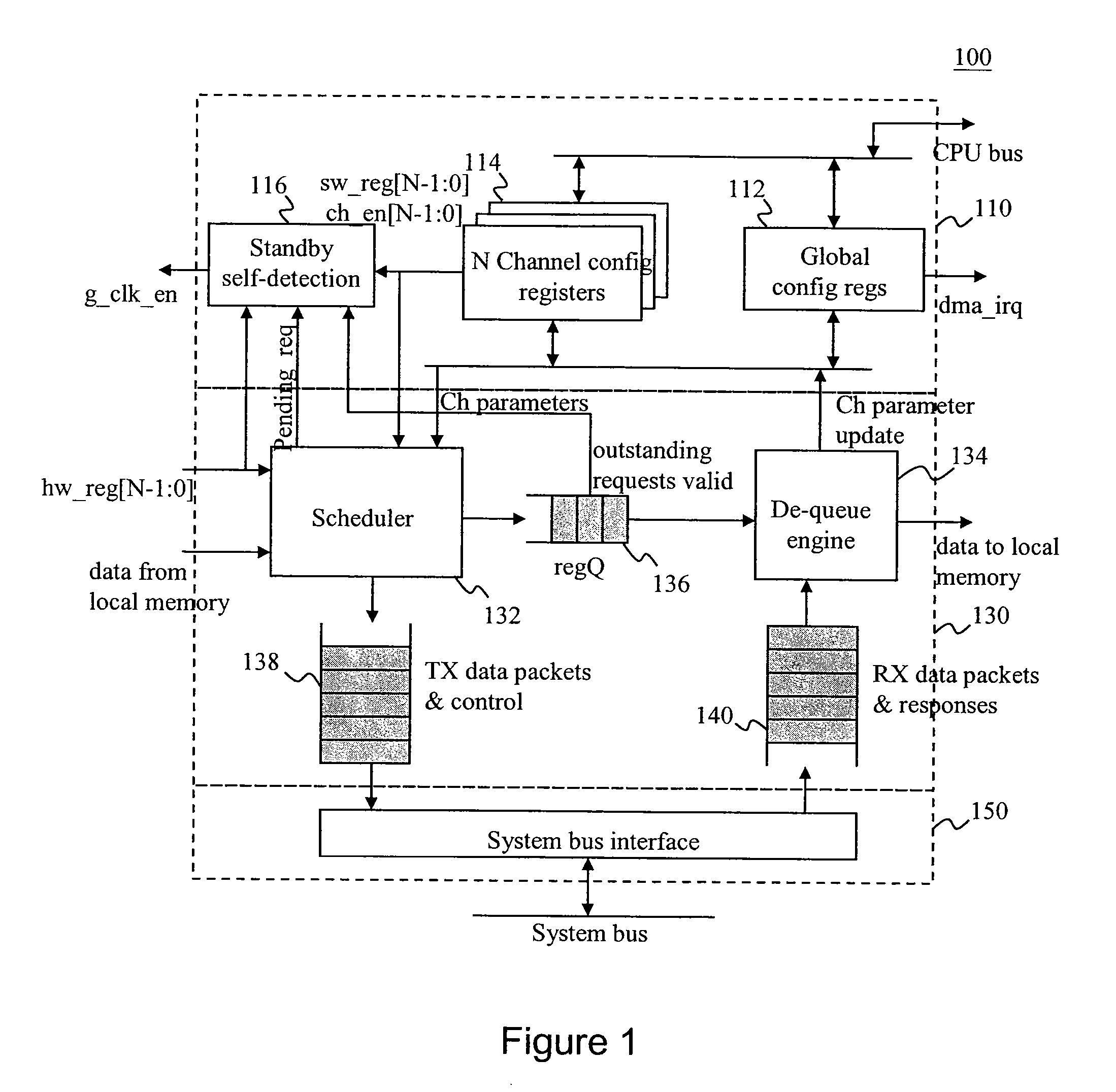
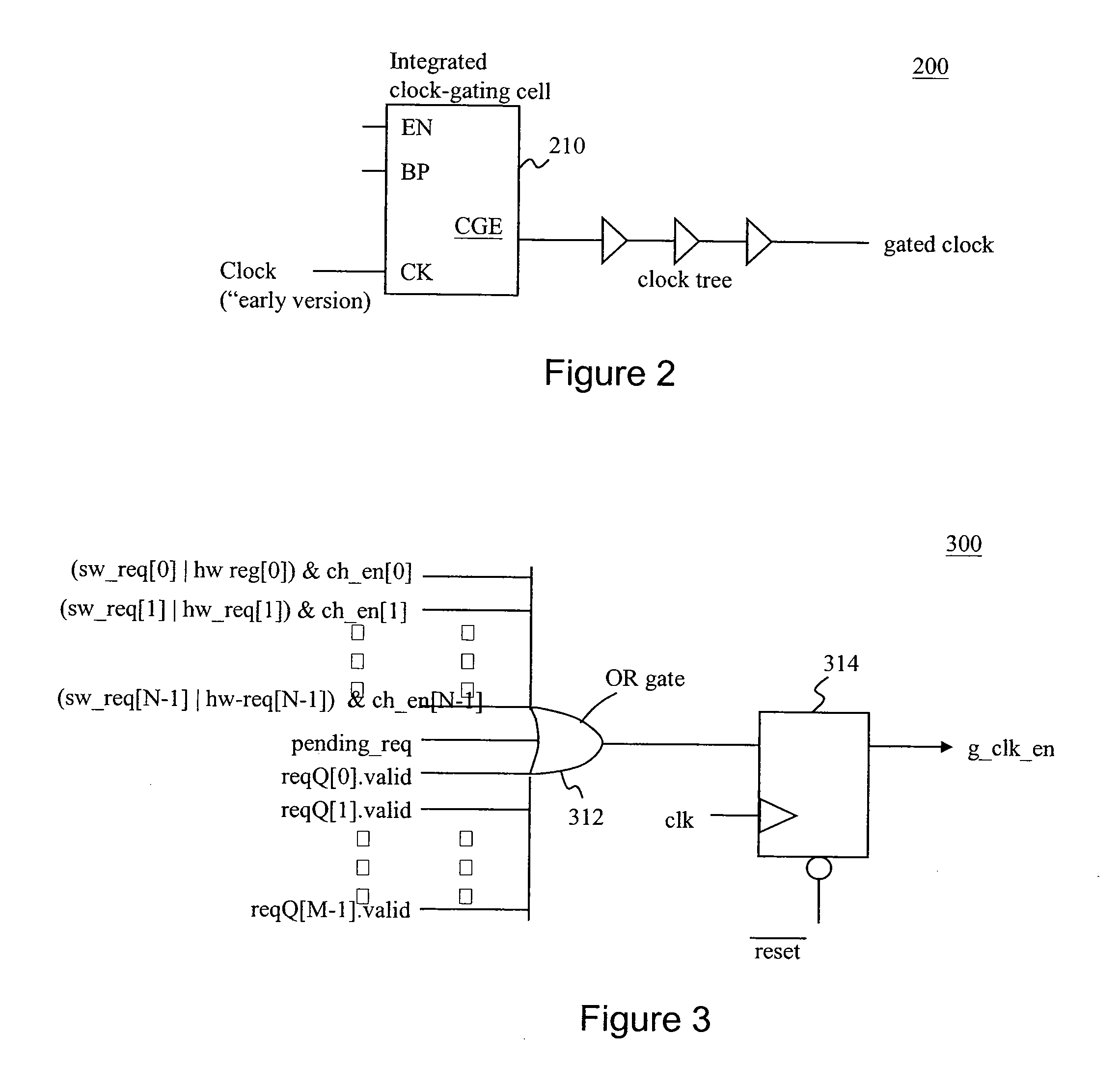
DMA Controller With Self-Detection For Global Clock-Gating Control
InactiveUS20070162648A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingCell schedulingClock tree
A standby self-detection mechanism in a DMA controller which reduces the power consumption by dynamically controlling the on / off states of at least one clock tree driven by global clock-gating circuitry is disclosed. The DMA controller comprises a standby self-detection unit, a scheduler, at least one set of channel configuration registers associated with at least one DMA channel, and an internal request queue which holds already scheduled DMA requests that are presently outstanding in the DMA controller. The standby self-detection unit drives a signal to a global clock-gating circuitry to selectively turn on or off at least one of the clock trees to the DMA controller, depending on whether the DMA controller is presently performing a DMA transfer.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
System and method for adaptive duty cycle optimization
A system and method for configuring a receiver such that the duty cycle of the receiver clock accurately matches the duty cycle of the data signal received. This adaptive system and method calibrates a receiver's duty cycle to optimize the receiver timing margin for different data signal types and different slave devices. In one embodiment, a duty cycle correction circuit matches the receiver clock to a predetermined duty cycle. The receiver clock is then configured to have a duty cycle skewed from the predetermined duty cycle based on the specific data signal received. In a receiver system utilizing a clock tree, individual branches of the clock tree are configured to have respective duty cycles skewed to match the duty cycle of a data signal received from a specific transmitting device.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
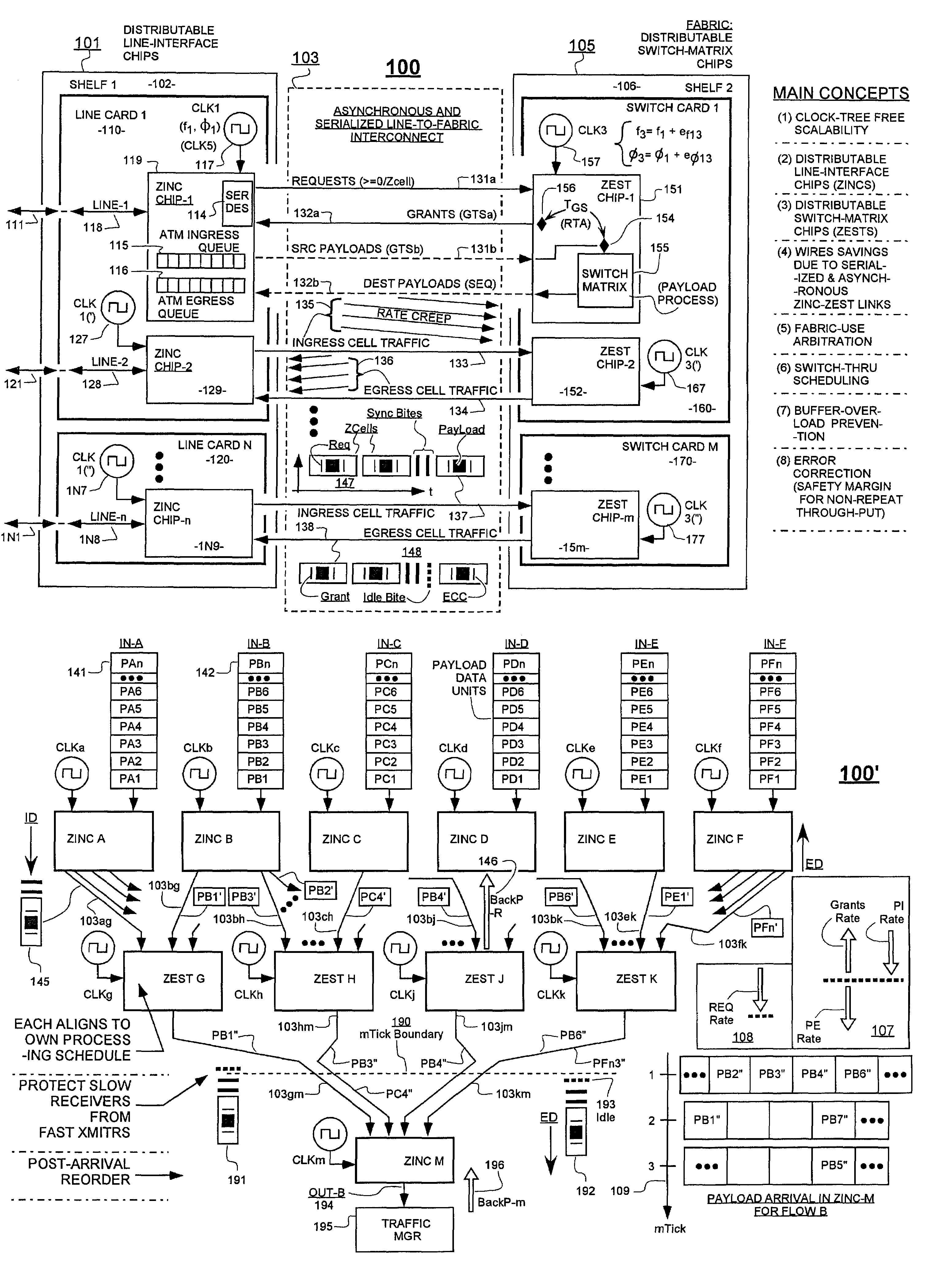
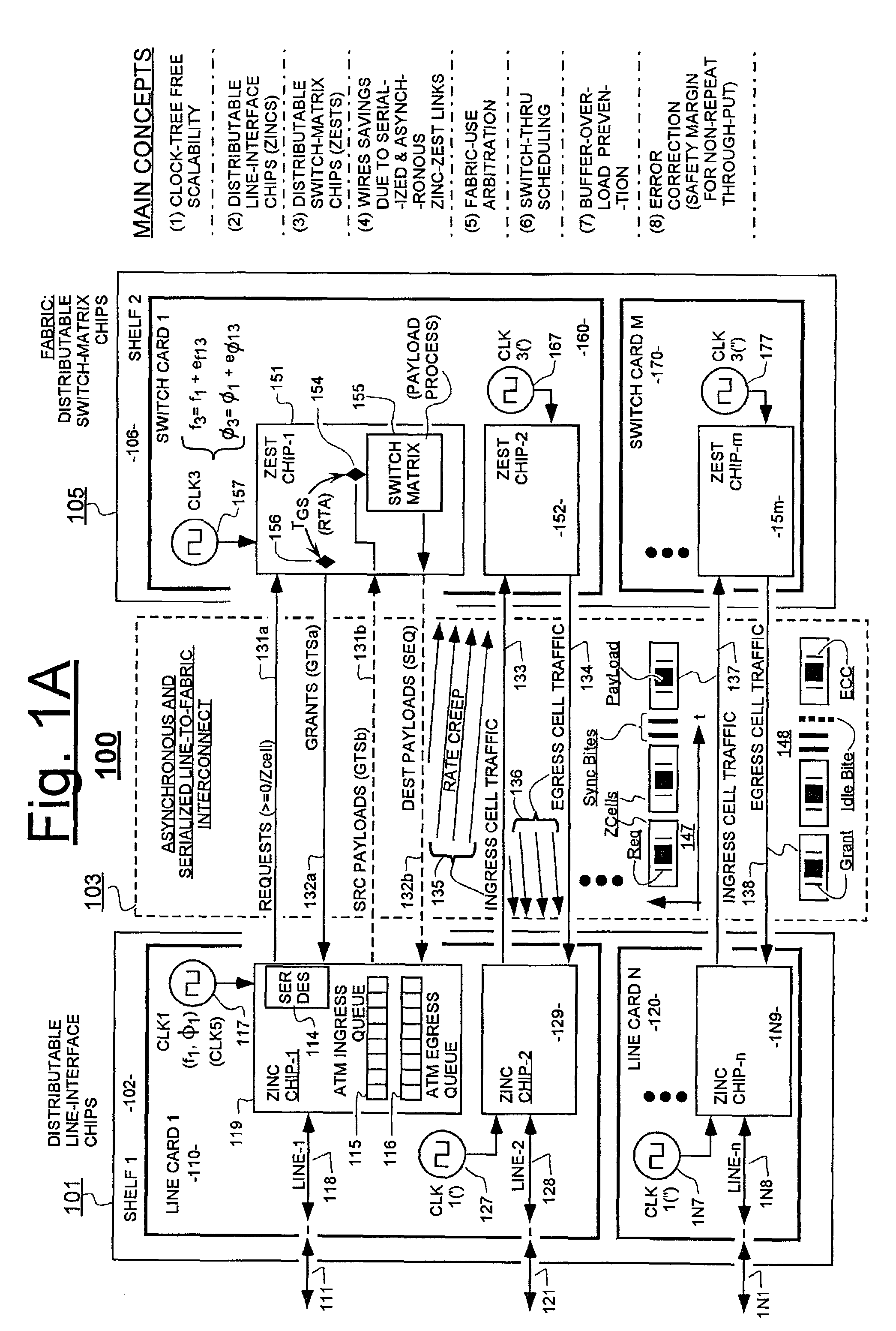
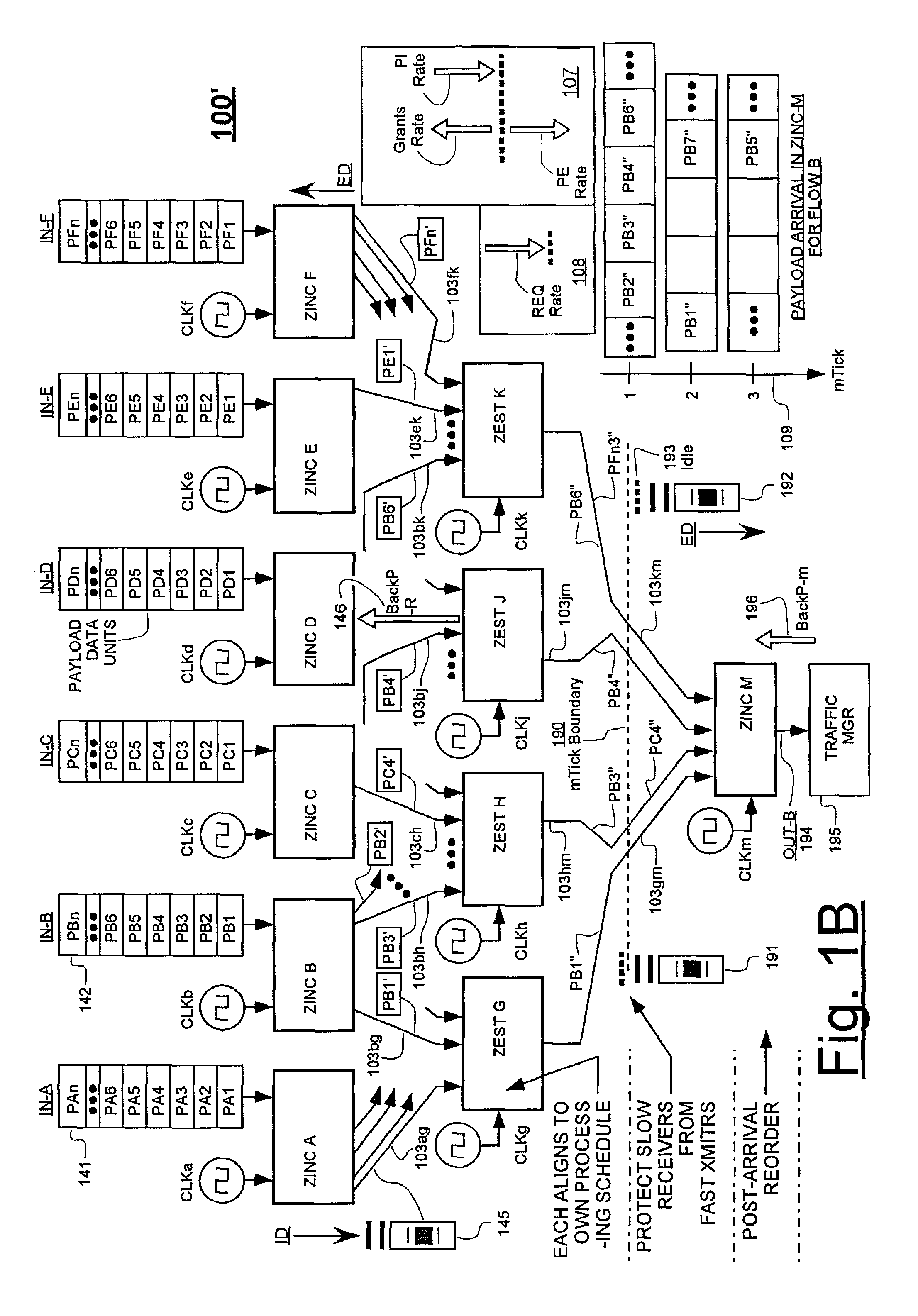
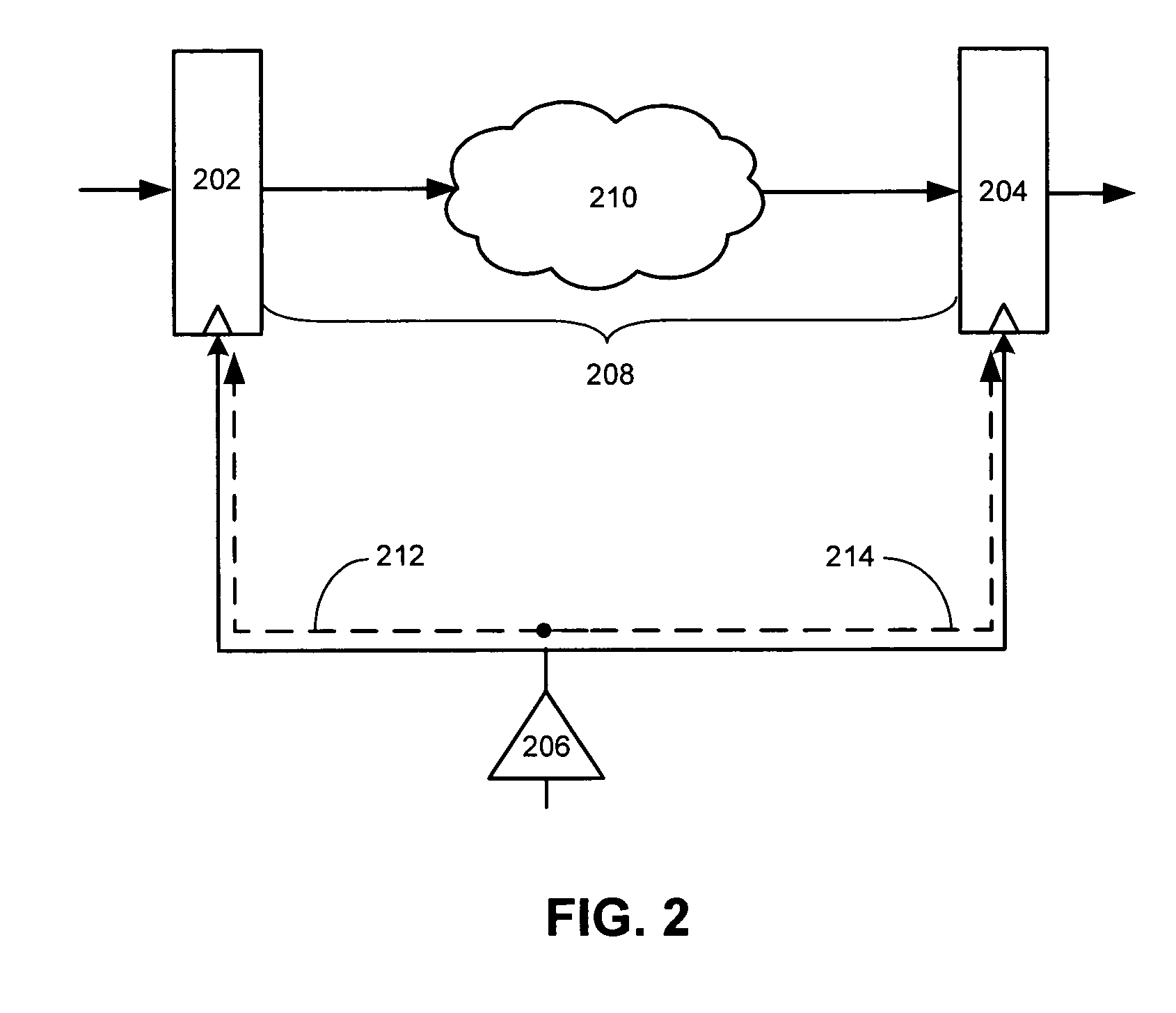
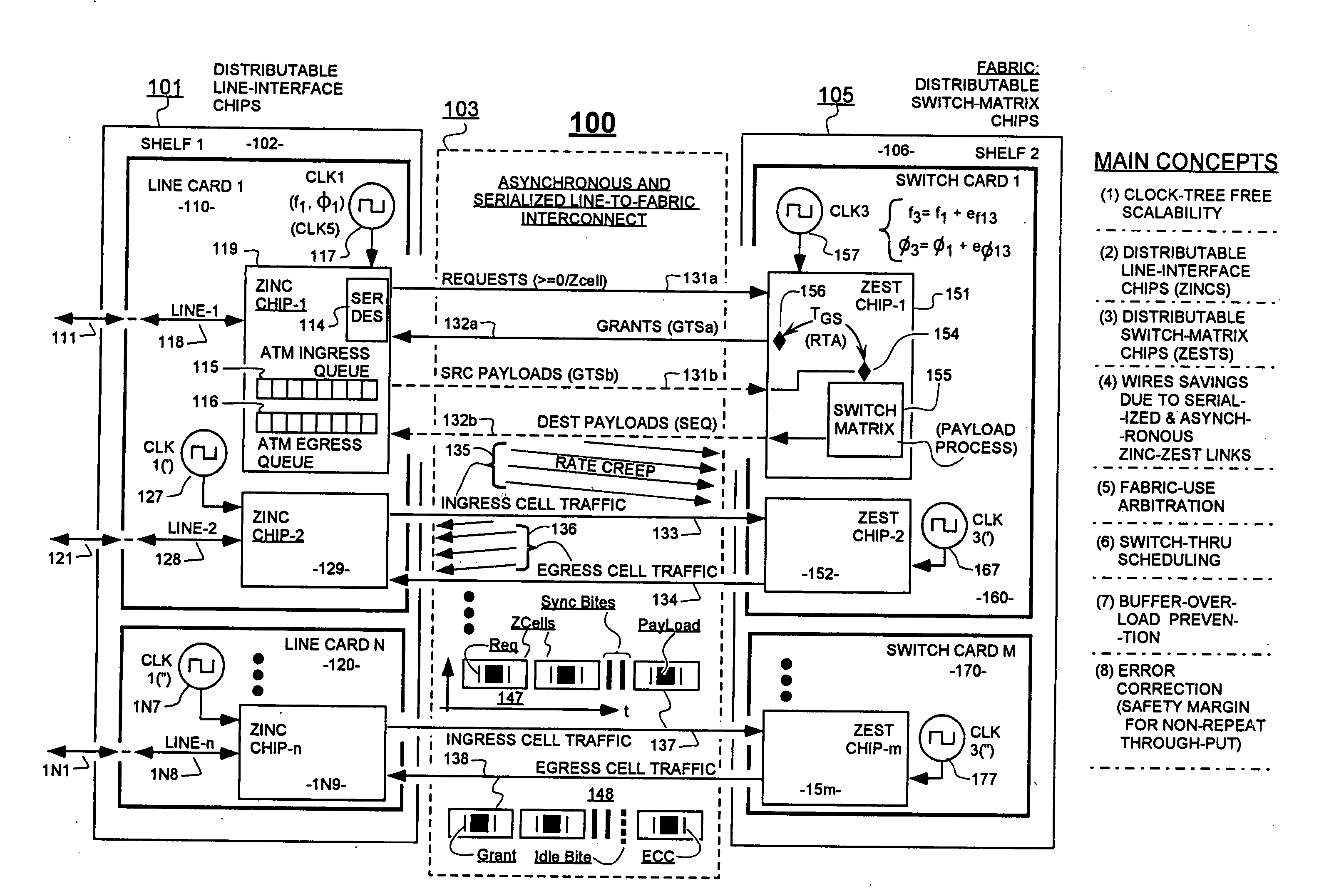
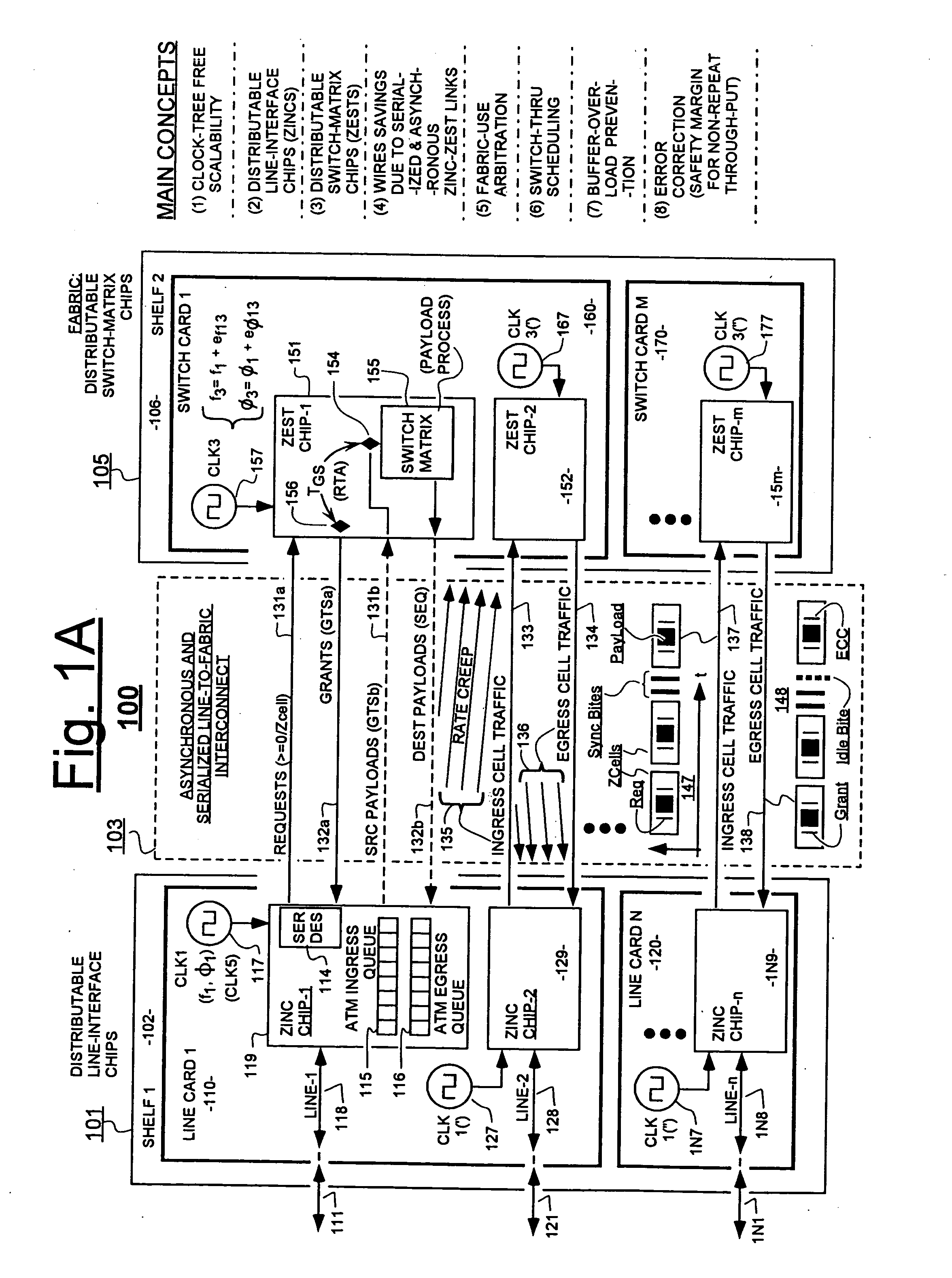
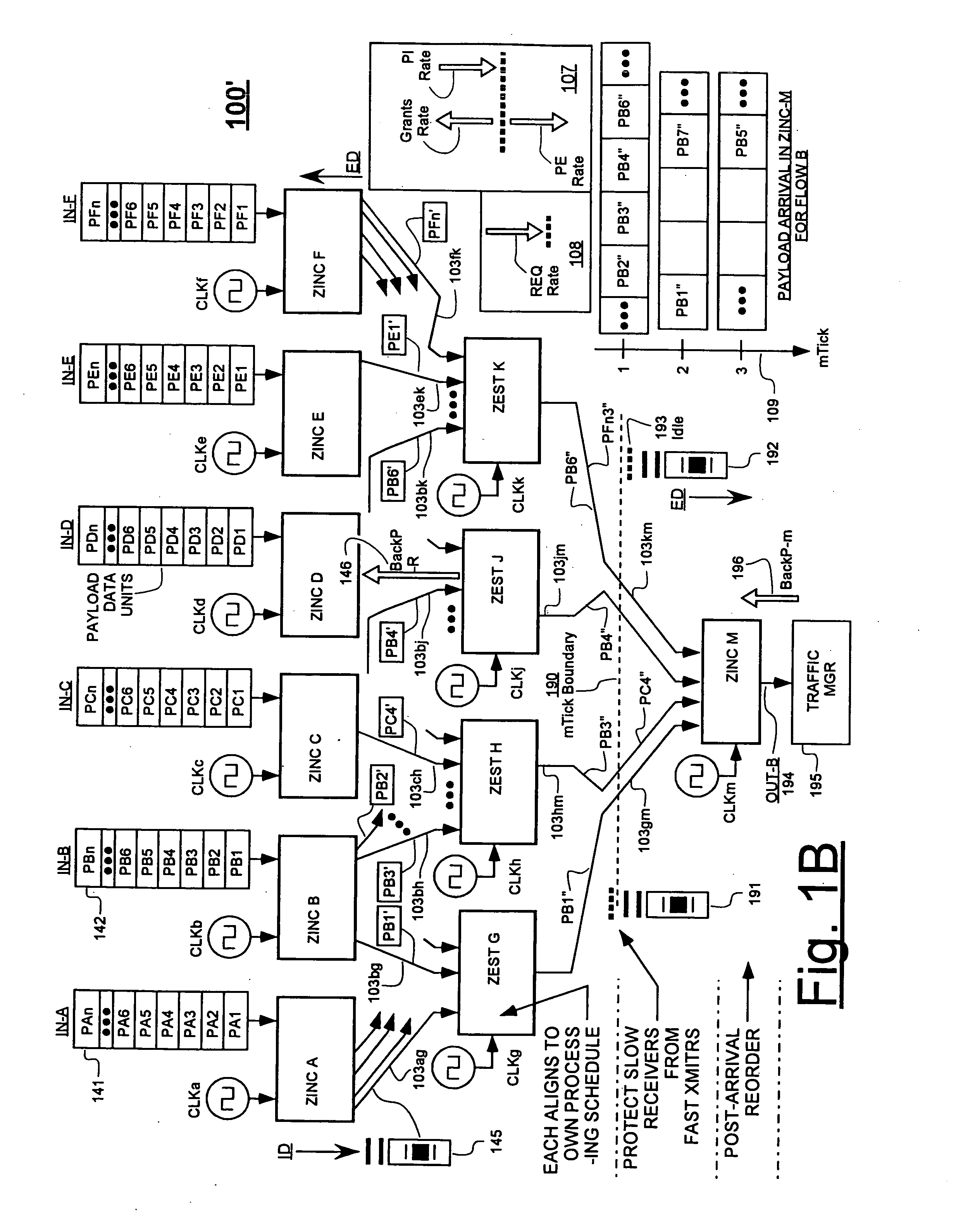
Variably delayable transmission of packets between independently clocked source, intermediate, and destination circuits while maintaining orderly and timely processing in one or both of the intermediate and destination circuits
InactiveUS7181485B1Increase in sizeLarge in speedMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsData packLine card
In a system having independently-clocked job-performing circuits (e.g., payload processors) and independently-clocked job-ordering circuits (e.g., request and payload suppliers), coordinating mechanisms are provided for coordinating exchanges between the independently-clocked circuits. The coordinating mechanisms include those that use transmitted time-stamps for scheduling contention-free performances within the job-performing circuits of requested jobs. The coordinating mechanisms additionally or alternatively include static and dynamic rate constraining means that are configured to prevent a faster-clocked one of the independently-clocked circuits from overwhelming a more slowly-clocked other of the independently-clocked circuits. In one implementation, independently-clocked telecommunication-shelves house a distributed set of line cards and switch cards. An asynchronous interconnect is provided between the independently-clocked shelves for carrying job requests and payload data between the distributed line cards and the distributed switch cards. The multi-shelf system is scalable and robust because additional or replacement line and switch cards may be inserted into one or another of the independently-clocked shelves as desired and because a unified clock-tree is not needed for synchronizing activities within the interconnected, but independently clocked shelves.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Low power LSSD flip flops and a flushable single clock splitter for flip flops
This invention reduces power in flip flop apparatuses by providing flip flop apparatuses that have fewer clock trees than prior art flip flops yet still support some or all of the Level Sensitive Scan Design (LSSD) functionality. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, one clock tree is used instead of two to provide lower power, and less switching devices in clocks splitters are used, which also provides lower power. Additionally, a flushable single clock splitter is provided that allows one clock tree to be used up to the flushable single clock splitter and provides two clocks on the output of the flushable single clock splitter. This saves some power yet still allows for dual clock flip flop designs.
Owner:IBM CORP
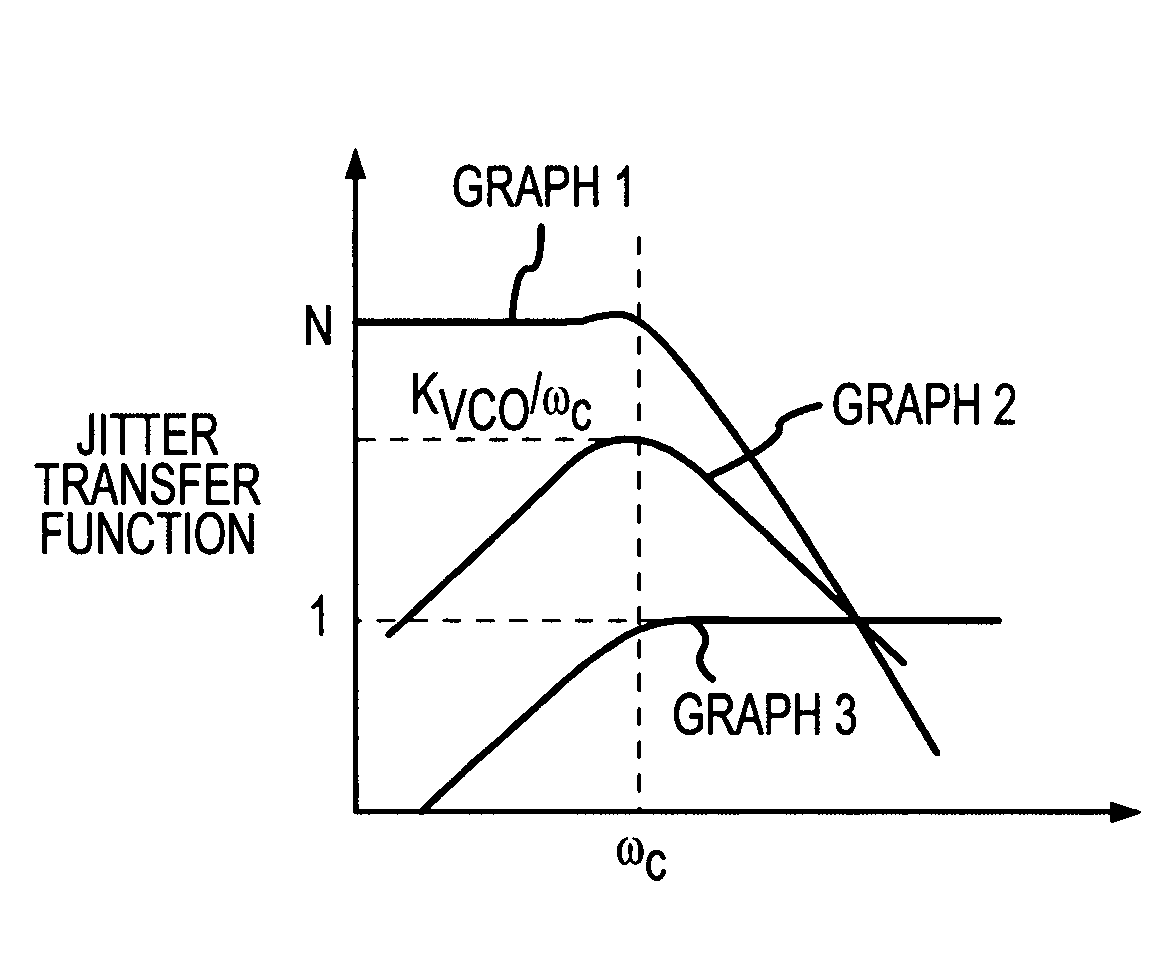
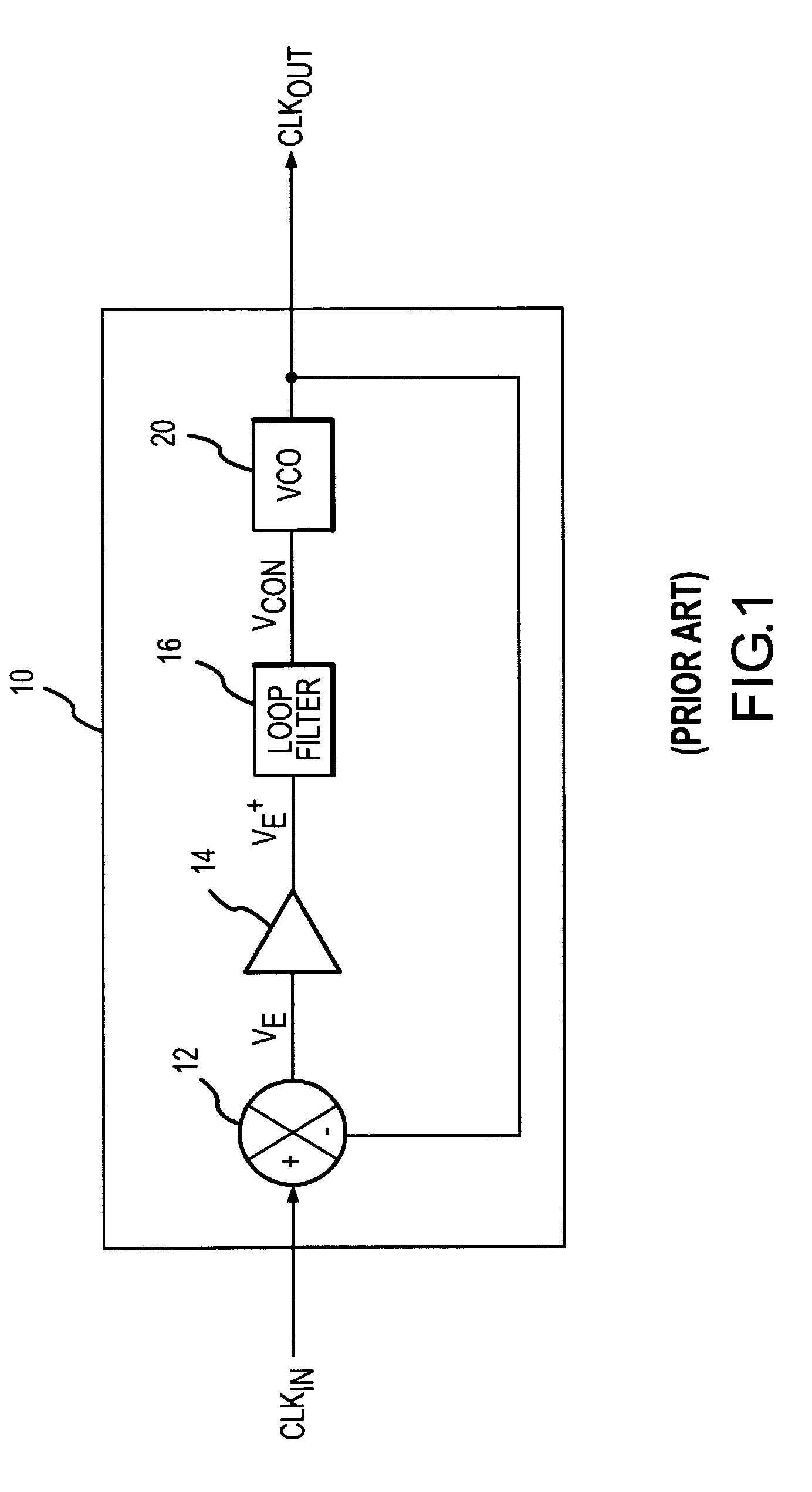
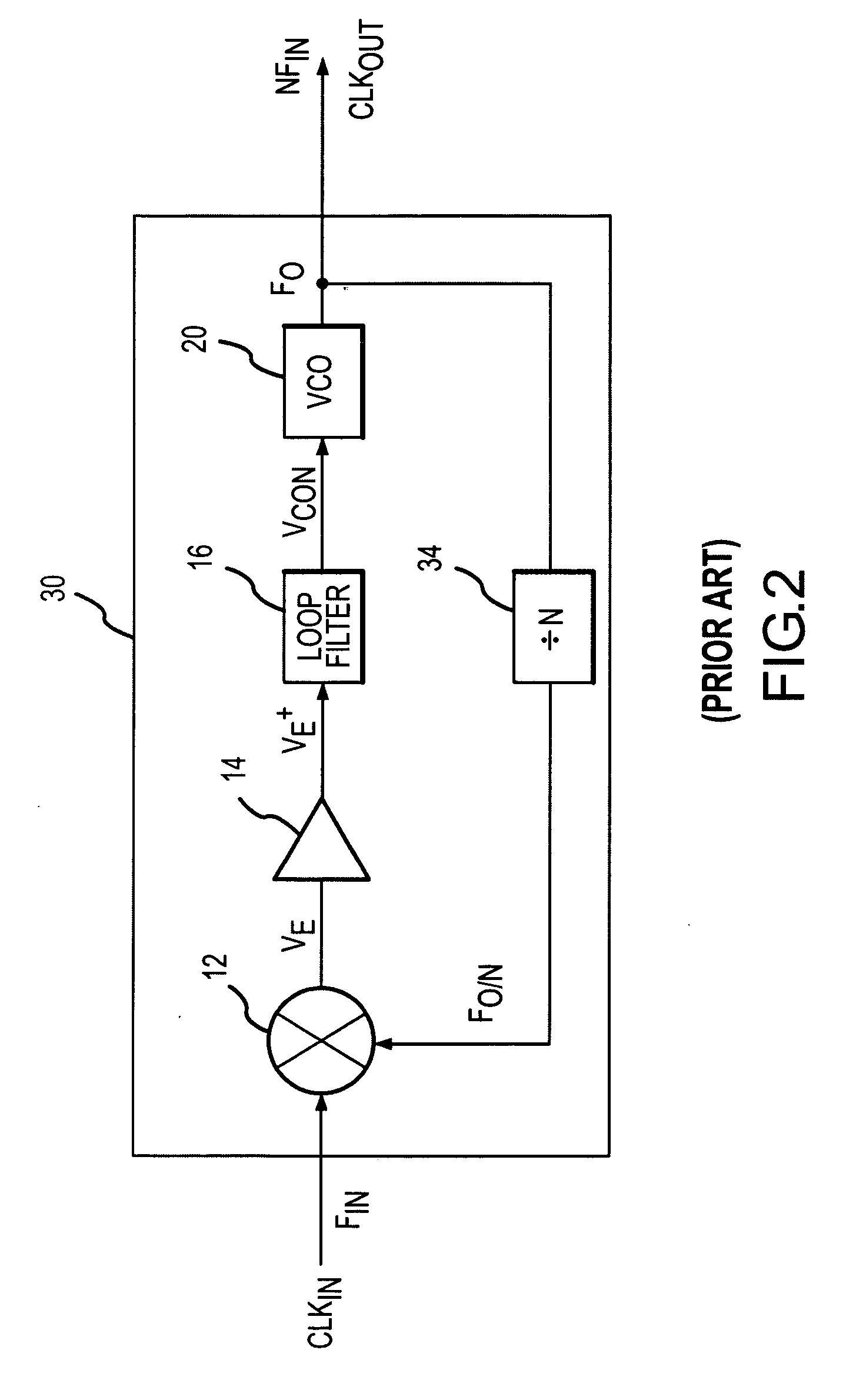
Low power and low timing jitter phase-lock loop and method
A phase-lock loop generates an output clock signal from an input clock signal. The output clock signal is coupled through a clock tree and is fed back to a phase detector, which compares the phase of the output clock signal to the phase of the input clock signal. The output clock signal is generated by a voltage controlled oscillator having a control input coupled to receive an output from the phase detector, and a frequency multiplier coupled to the output of the voltage controlled oscillator. As a result, the CLKOUT signal generated by the frequency multiplier has a relatively high frequency while the voltage controlled oscillator, by operating at a relatively low frequency, uses relatively little power.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
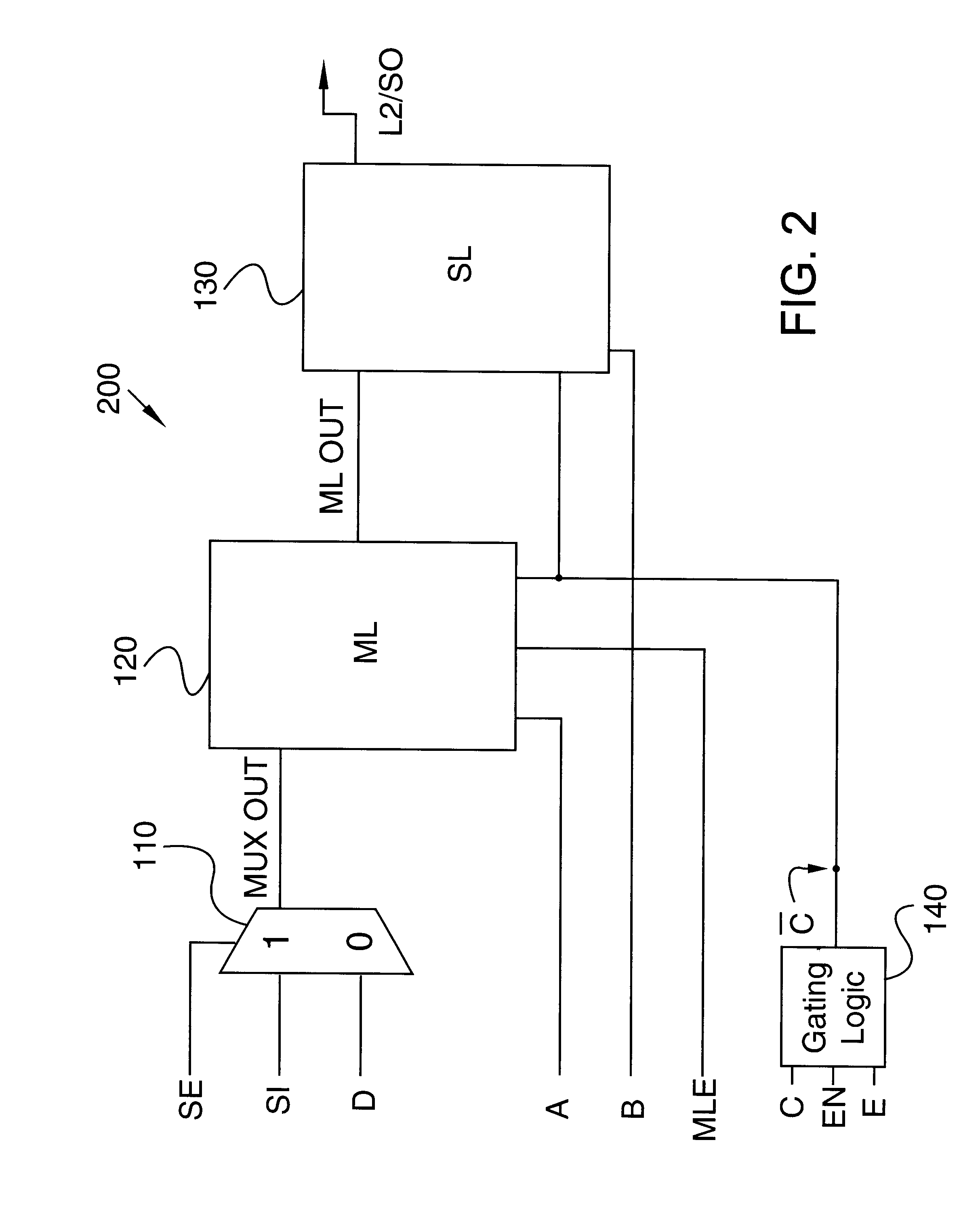
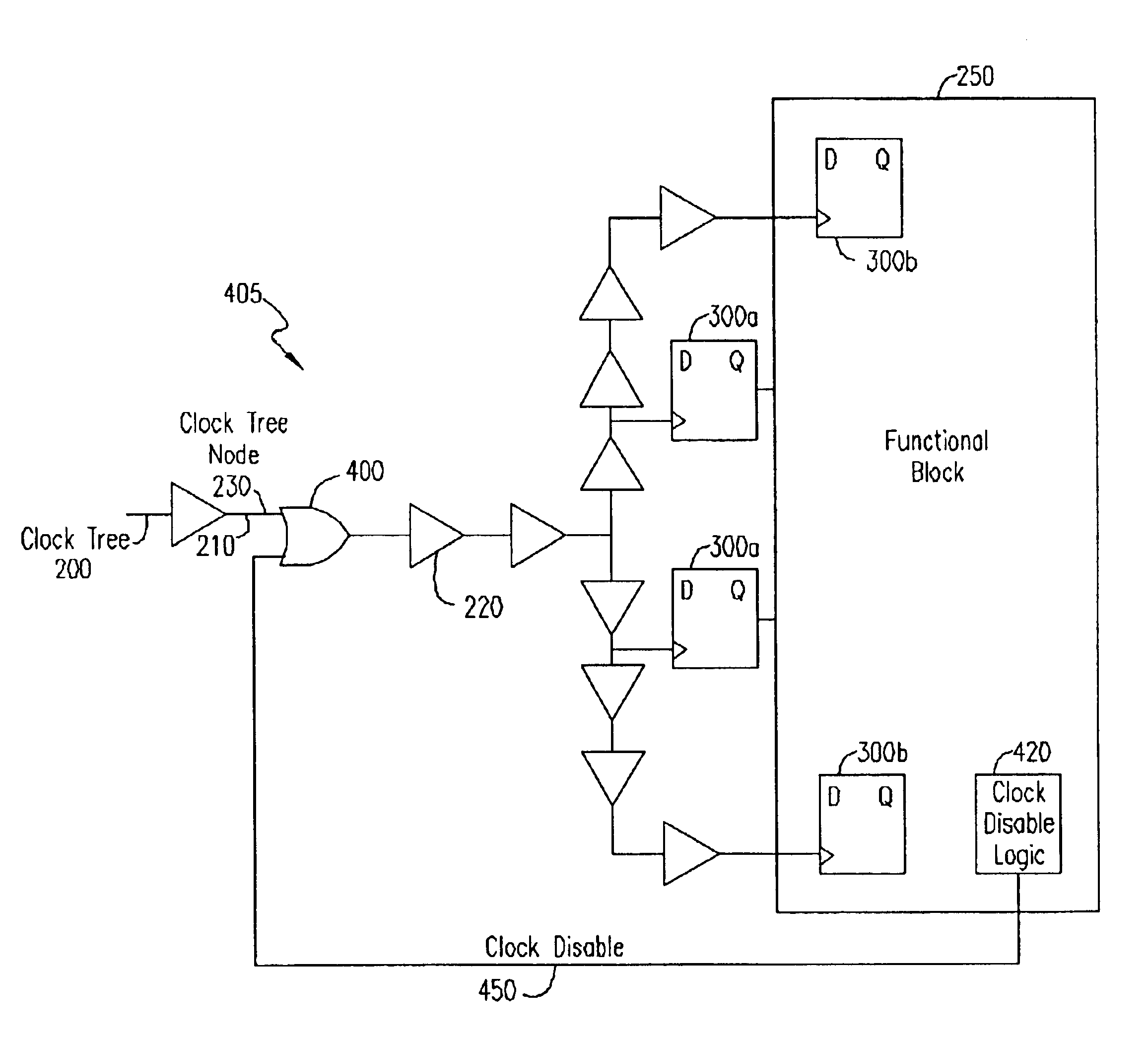
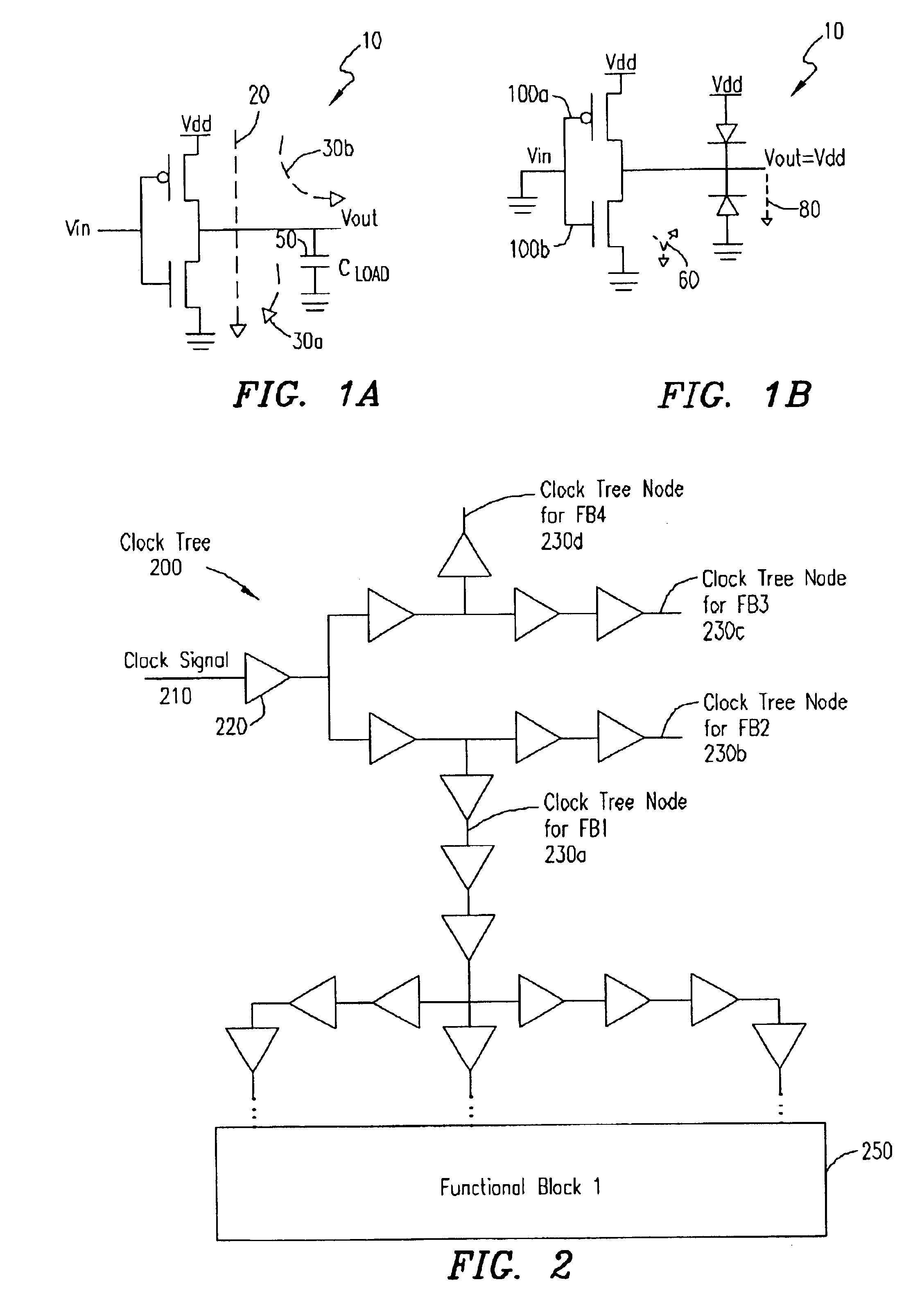
Method and apparatus for clock gating clock trees to reduce power dissipation
ActiveUS6822481B1Reduce power consumptionAvoid switchingEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingClock treeLogic gate
A clock gating circuit reduces the power dissipation in a digital circuit including at least one functional block by gating the clock signal at an input to a clock tree feeding the functional block. The clock gating circuit includes a logic gate that receives a clock signal and a clock disable signal generated by the functional block, and gates the clock signal at the input to the clock tree feeding the functional block. Further, a global signal generator is provided to transmit a global signal to each of the functional blocks to prevent the generation of clock disable signals, when necessary, such as during testing of chips.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Clock tree distribution generation by determining allowed placement regions for clocked elements
InactiveUS7225421B2Minimize cost functionQuantity minimizationCAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTheoretical computer scienceClock tree
A method, system and program product are described for generating a clock distribution network on an integrated circuit by determining an allowable placement region for each of a set of clock tree leaf elements in the integrated circuit. This allowable placement region is generated by determining and intersecting a set of sub-regions under different constraints, each of which identifies an area in which the clock tree leaf element is placed to satisfy the respective constraint. Constraints for which sub-regions are determined include timing constraints in the form of slacks and congestion constraints. After allowable placement regions have been determined, the clock tree leaf elements are clustered, and each clock tree leaf element is placed at a location within its allowable placement region which minimizes some cost function for that clustering.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
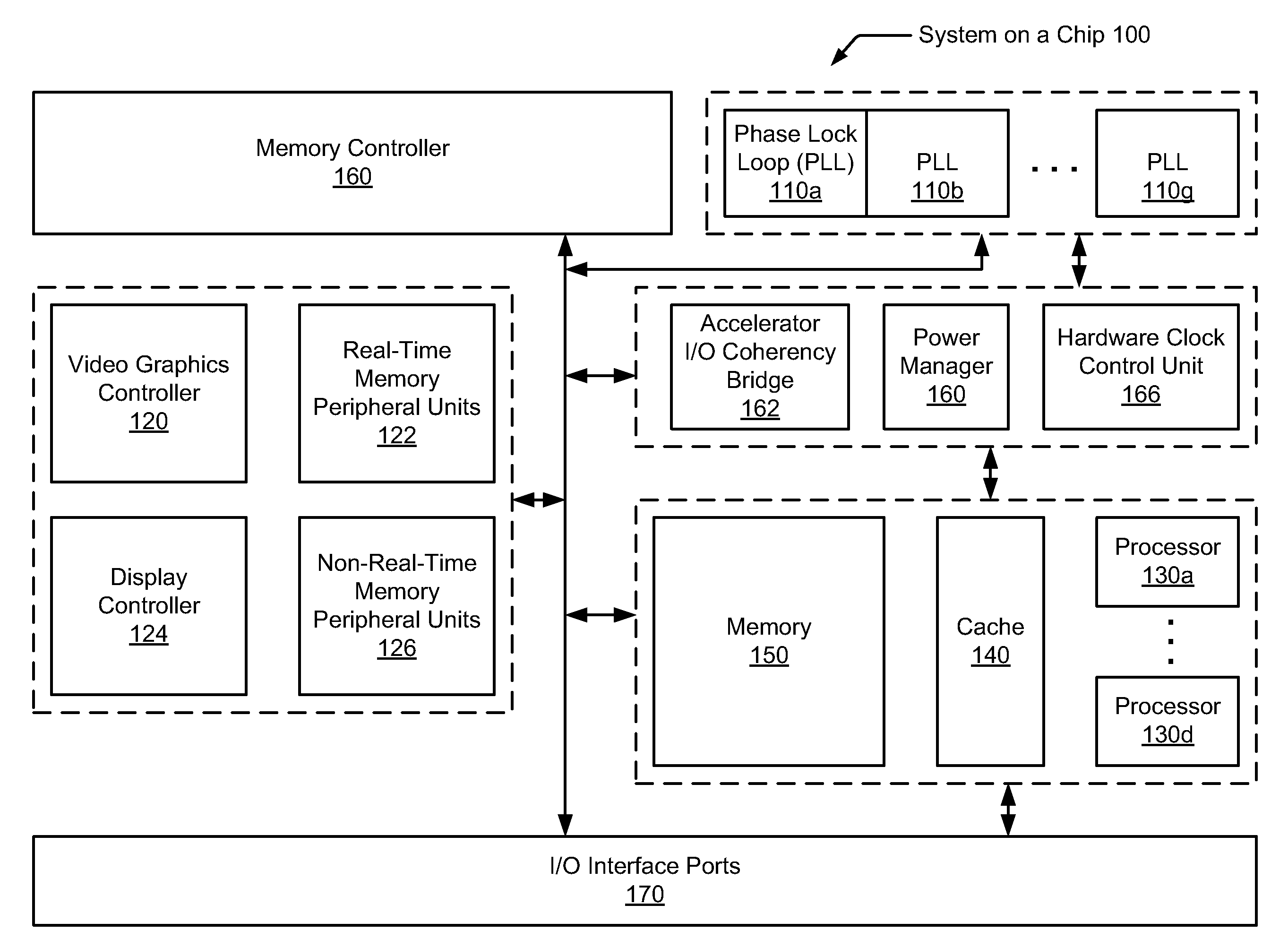
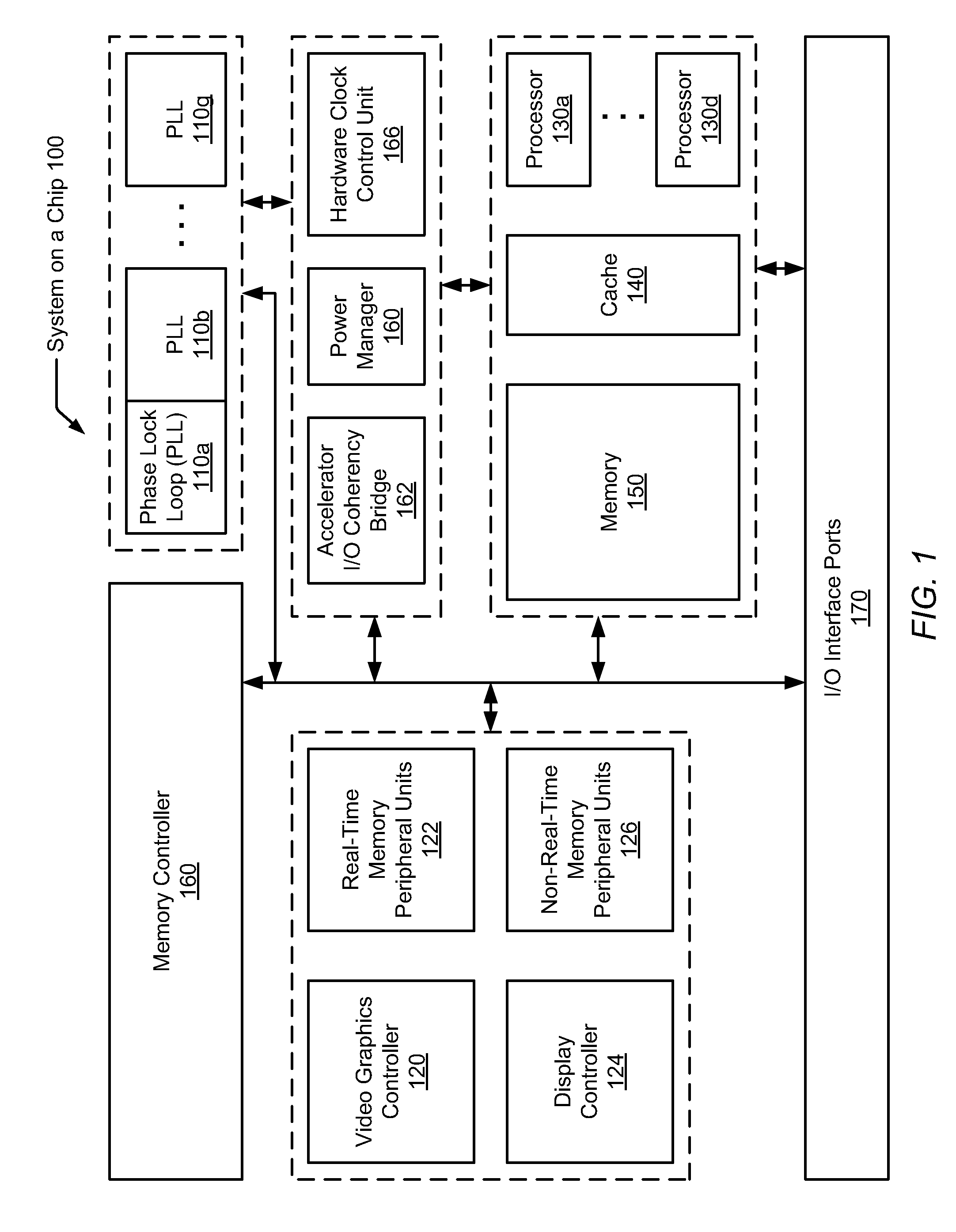
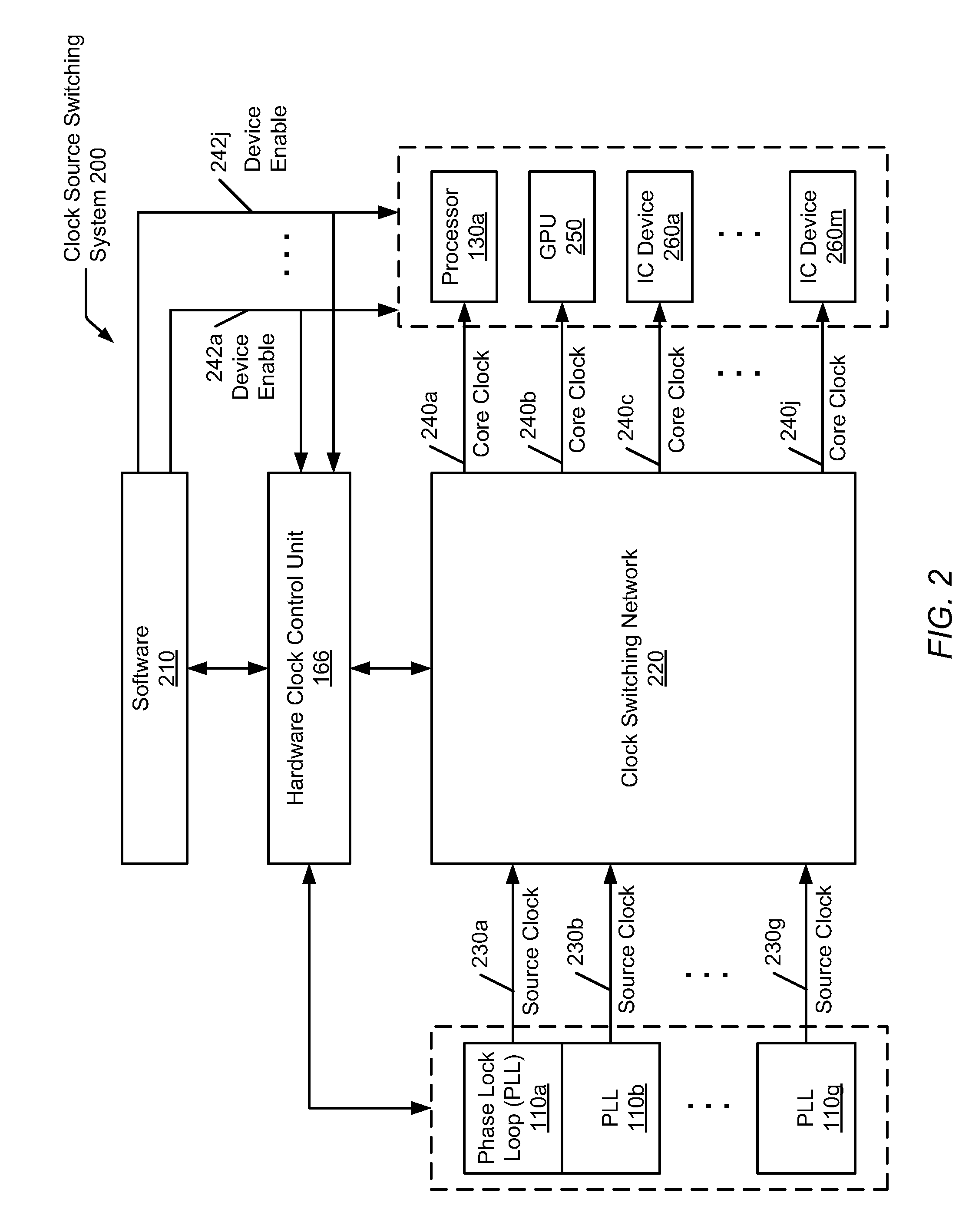
Hardware-based automatic clock gating
A system and method for automatically updating with hardware clock tree settings on a system-on-a-chip (SOC). A SOC includes a hardware clock control unit (HCCU) coupled to a software interface and a clock tree. The SOC also includes multiple integrated circuit (IC) devices, wherein each IC device receives one or more associated core clocks provided by one or more phase lock loops (PLLs) via the clock tree. The HCCU receives a software-initiated request specifying a given IC device is to be enabled. The HCCU identifies one or more core clocks used by the given IC device. For each one of the identified core clocks, the HCCU configures associated circuitry within the clock tree to generate an identified core clock. The HCCU may also traverse the clock tree and disable clock generating gates found not to drive any other enabled gates or IC devices.
Owner:APPLE INC
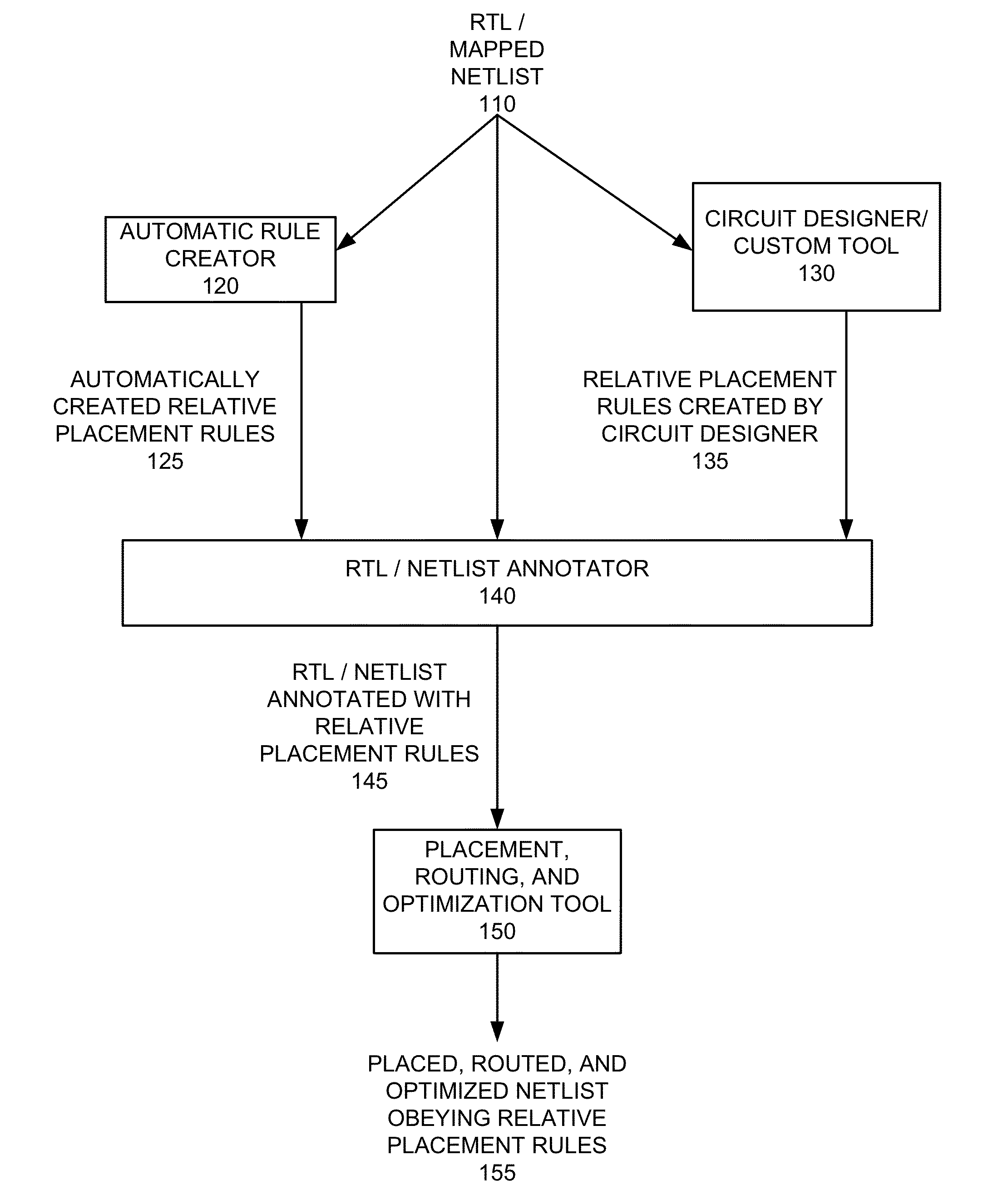
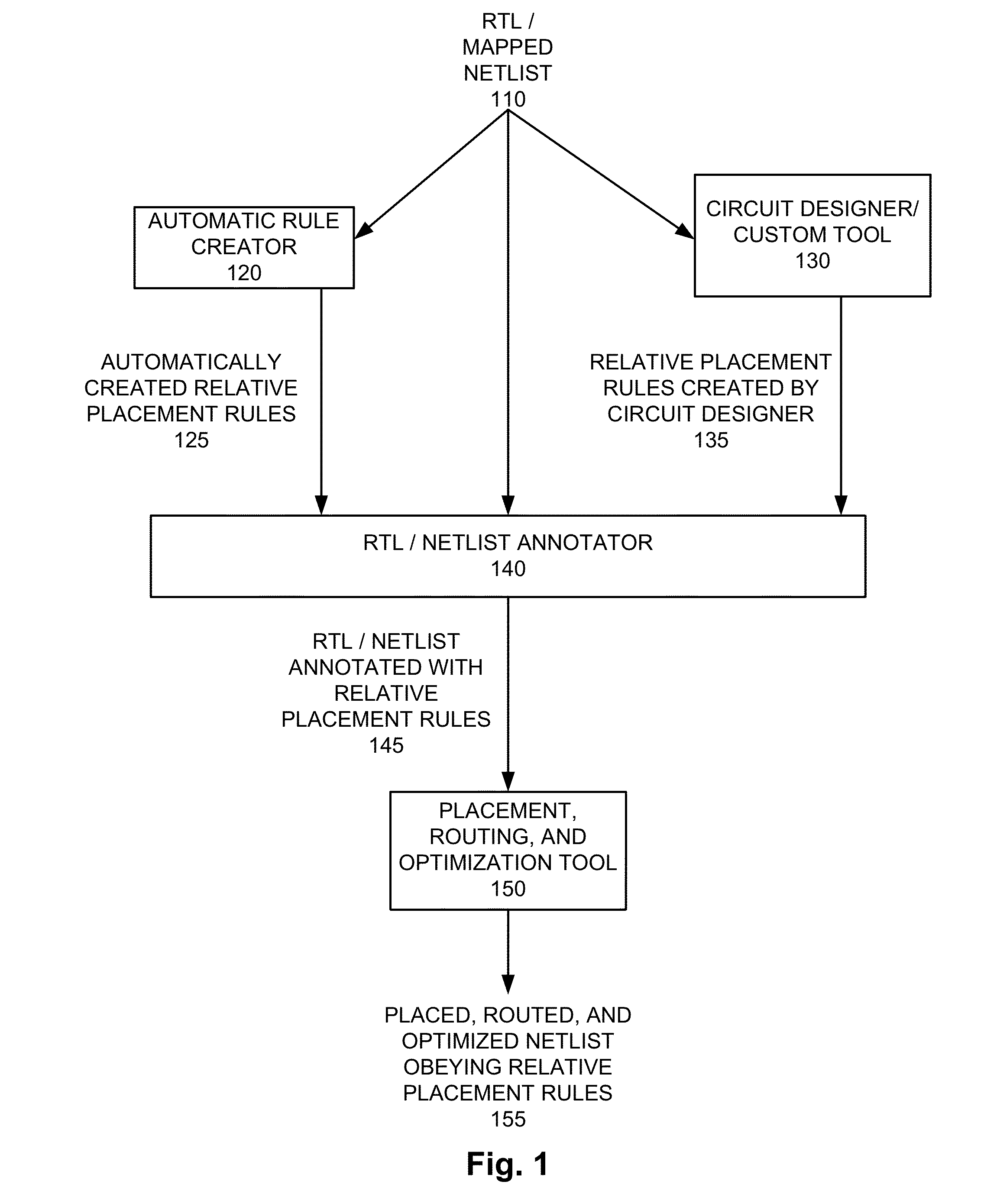
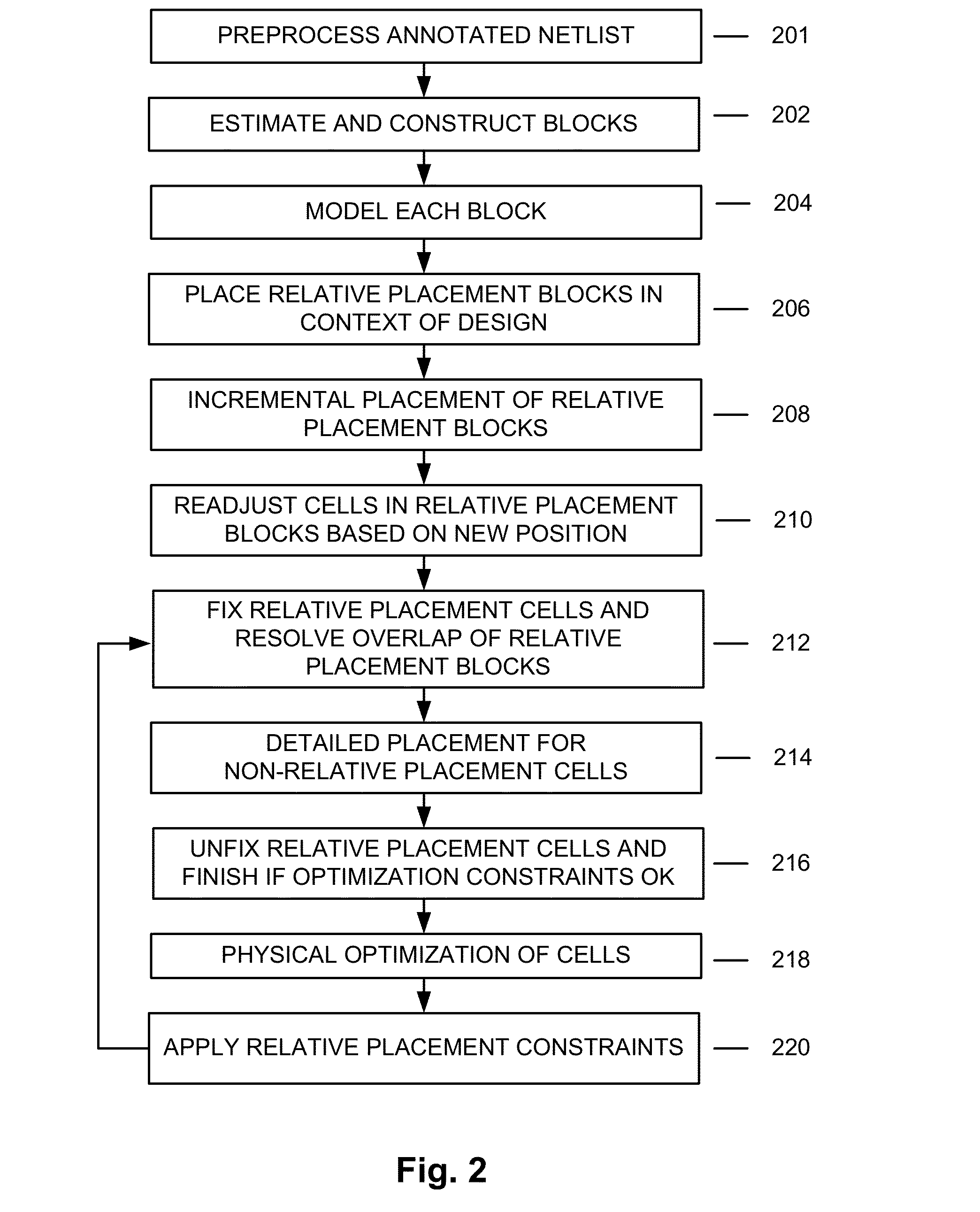
Method and apparatus for automatic relative placement generation for clock trees
ActiveUS20130047127A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceClock tree
Methods and apparatuses are disclosed for automatic relative placement of part of a clock tree in the course of generating a placed, routed, and optimized circuit design.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
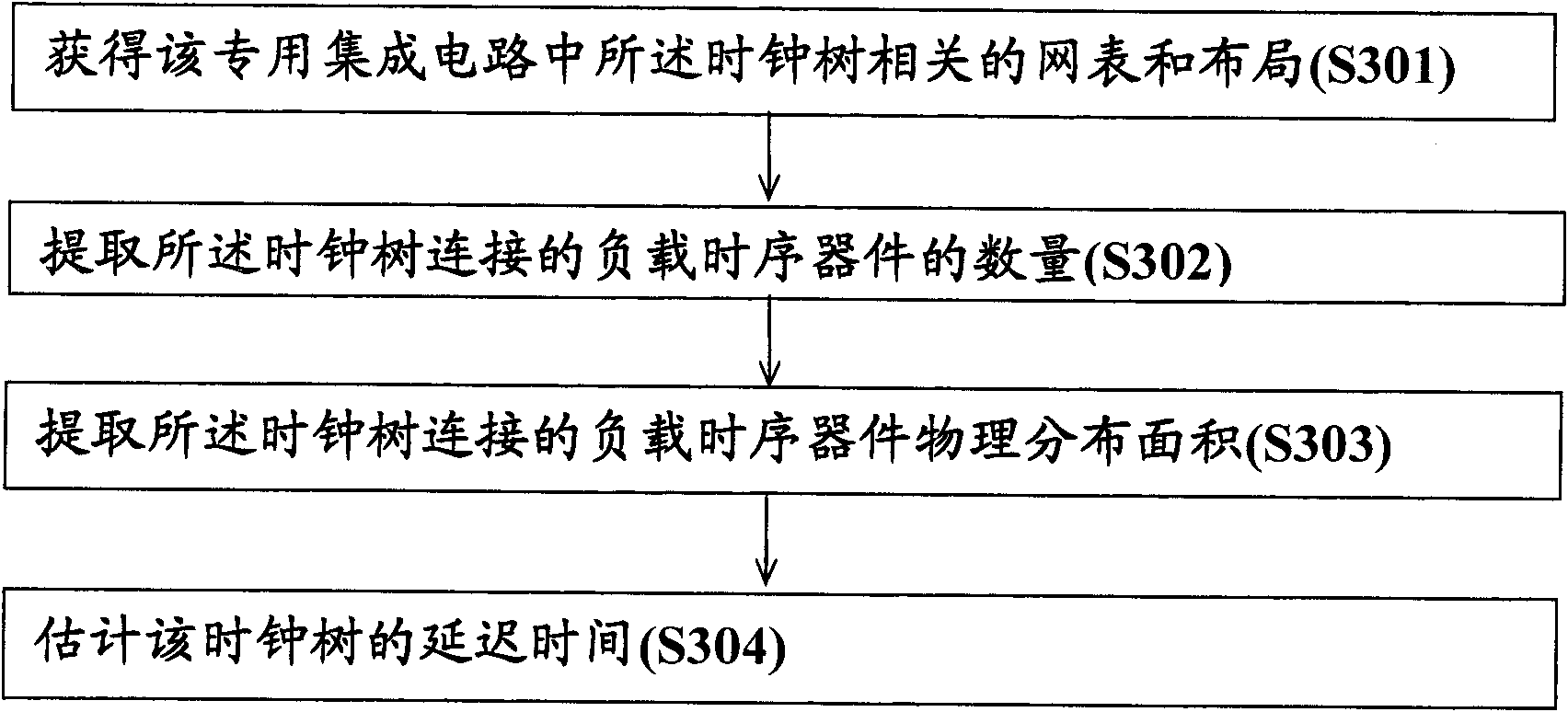
Estimation method and system of clock tree delay time in specified integrated circuit
ActiveCN102169515AShorten design timeImprove design efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsLoad timeEstimation methods
The invention discloses an estimation method and system of clock tree delay time in a specified integrated circuit, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a netlist and a layout relative to the clock tree in the specified integrated circuit; extracting the number of load time sequence apparatuses connected with the clock tree according to the netlist relative to the clock tree; extracting a physical distribution region area of the load time sequence apparatuses connected with the clock tree according to the layout relative to the clock tree; estimating the delay time of the clock tree according to the relation among the number of the load time sequence apparatuses, the physical distribution region area of the load time sequence apparatuses and the clock tree delay time in the historical data of the same process with the specified integrated circuit. An audit flow is reduced to days from weeks by using the improved specified integrated circuit design method, a designer can rapidly find and solve the problem; and therefore, the design time is reduced, and the design efficiency is improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
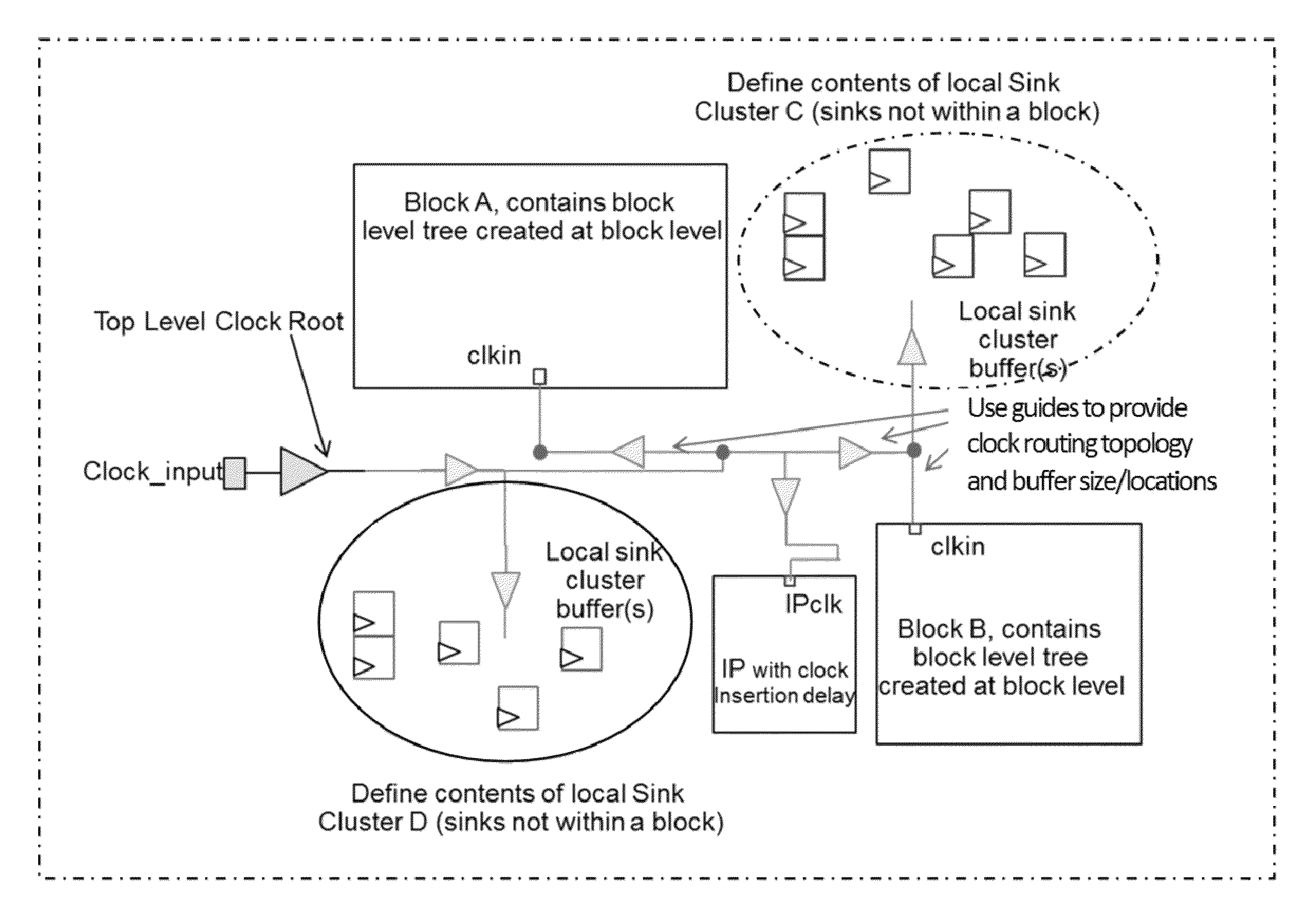
Clock tree generation and routing
ActiveUS8966425B1Ample structureAmple controlComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsClock treeMajorization minimization
A technique generates small scale clock trees using a spine-based architecture (using spine routing) while also using clustered placement. Techniques are used to control clock sink cluster contents in order to minimize clock skew, minimize clock buffer count, and minimize use of routing resources. This approach also provides the user with ample structure and control to customize small efficient clock trees, and can also reduce clock power consumption.
Owner:PULSIC
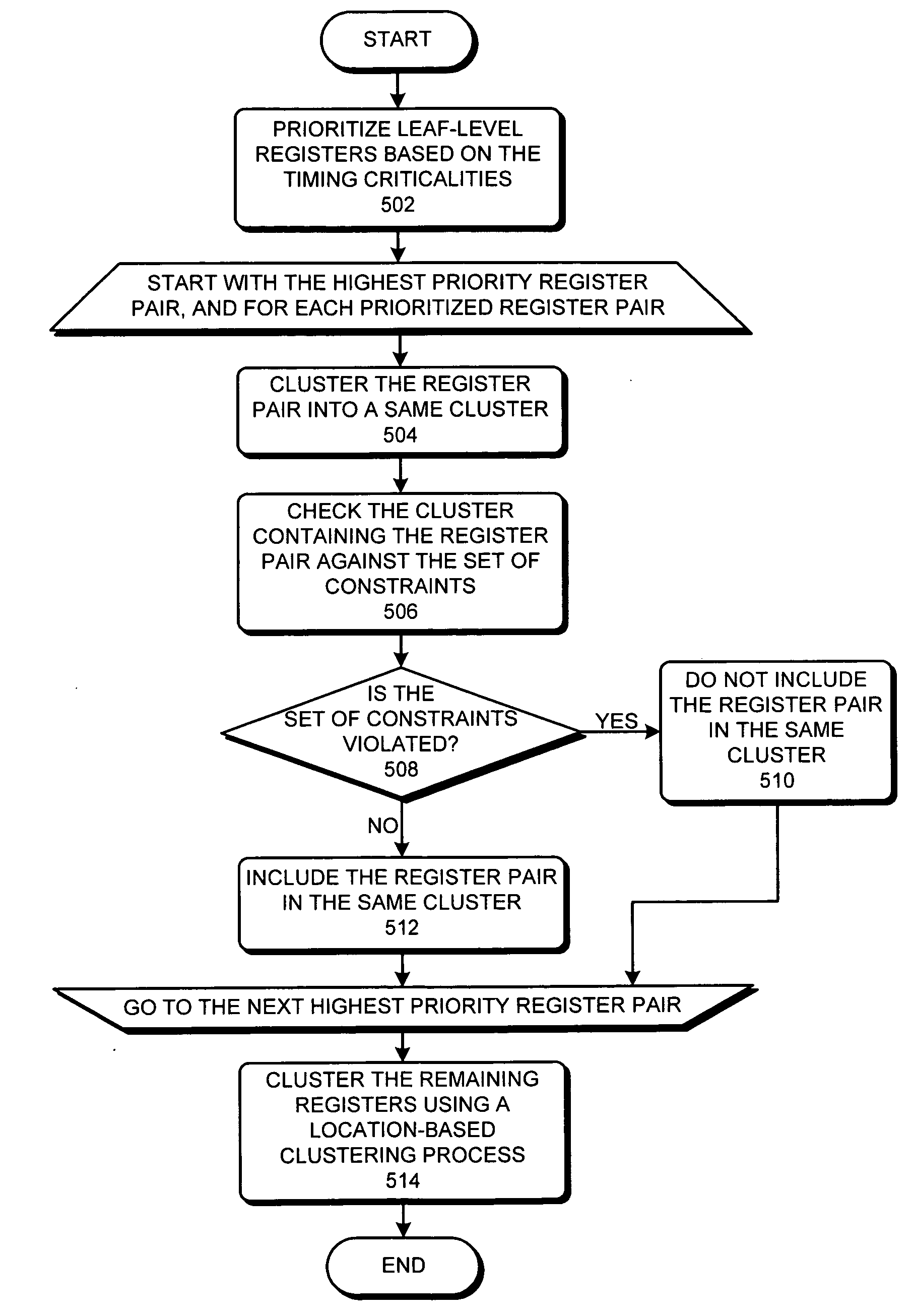
Method and apparatus for generating a variation-tolerant clock-tree for an integrated circuit chip
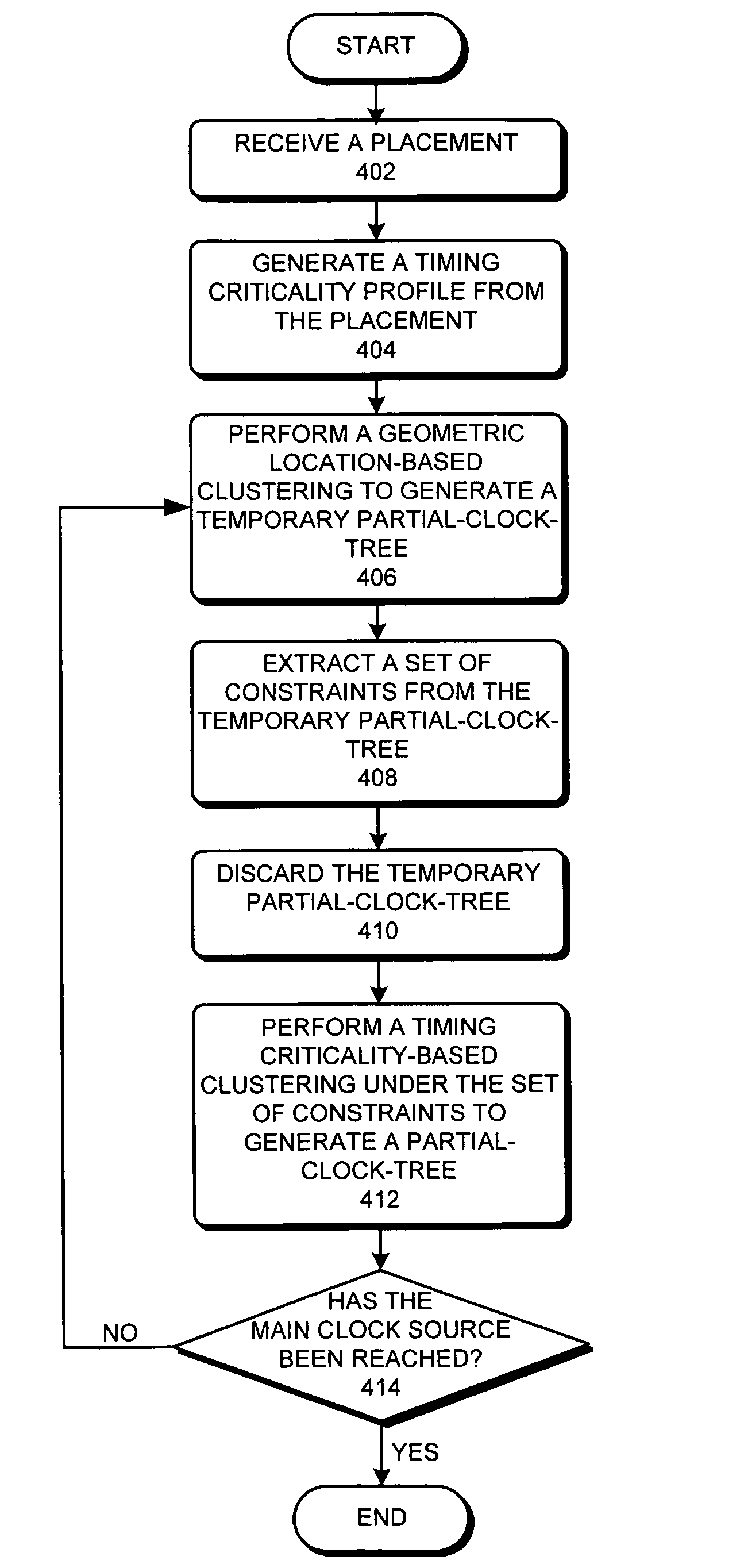
ActiveUS20080168412A1Raise priorityMaximizes inclusionProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcessor registerTime critical
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a process that generates a clock-tree on an integrated circuit (IC) chip. During operation, the process starts by receiving a placement for a chip layout, where the placement includes a set of registers at fixed locations in the chip layout. The process then generates a timing criticality profile for the set of registers, wherein the timing criticality profile specifies timing criticalities between pairs of registers in the set of registers. Next, the process clusters the set of registers based on the timing criticality profile to create a clock-tree for the set of registers. By clustering the registers based on the timing criticality profile, the process facilitates using commonly-shared clock paths in the clock-tree to provide clock signals to timing critical register pairs.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for generating a variation-tolerant clock-tree for an integrated circuit chip
ActiveUS7546567B2Raise priorityMaximizes inclusionProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime criticalConfigfs
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a process that generates a clock-tree on an integrated circuit (IC) chip. During operation, the process starts by receiving a placement for a chip layout, where the placement includes a set of registers at fixed locations in the chip layout. The process then generates a timing criticality profile for the set of registers, wherein the timing criticality profile specifies timing criticalities between pairs of registers in the set of registers. Next, the process clusters the set of registers based on the timing criticality profile to create a clock-tree for the set of registers. By clustering the registers based on the timing criticality profile, the process facilitates using commonly-shared clock paths in the clock-tree to provide clock signals to timing critical register pairs.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Variably delayable transmission of packets between independently clocked source, intermediate, and destination circuits while maintaining orderly and timely processing in one or both of the intermediate and destination circuits
InactiveUS20070130246A1Large in size and speedIncrease volumeMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork packetClock tree
In a system having independently-clocked job-performing circuits (e.g., payload processors) and independently-clocked job-ordering circuits (e.g., request and payload suppliers), coordinating mechanisms are provided for coordinating exchanges between the independently-clocked circuits. The coordinating mechanisms include those that use transmitted time-stamps for scheduling contention-free performances within the job-performing circuits of requested jobs. The coordinating mechanisms additionally or alternatively include static and dynamic rate constraining means that are configured to prevent a faster-clocked one of the independently-clocked circuits from overwhelming a more slowly-clocked other of the independently-clocked circuits. In one implementation, independently-clocked telecommunication-shelves house a distributed set of line cards and switch cards. An asynchronous interconnect is provided between the independently-clocked shelves for carrying job requests and payload data between the distributed line cards and the distributed switch cards. The multi-shelf system is scalable and robust because additional or replacement line and switch cards may be inserted into one or another of the independently-clocked shelves as desired and because a unified clock-tree is not needed for synchronizing activities within the interconnected, but independently clocked shelves.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Methods and apparatus for managing clock skew
An apparatus is disclosed which includes a signal generator providing a first signal having a first frequency; a clock tree operative to propagate the first signal to at least one clock mesh of the apparatus; and a final buffer operative to receive the first signal, provide a second signal having a second frequency, synchronize the second signal with the first signal, and propagate the synchronized second signal to at least one other clock mesh of the apparatus.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC +1
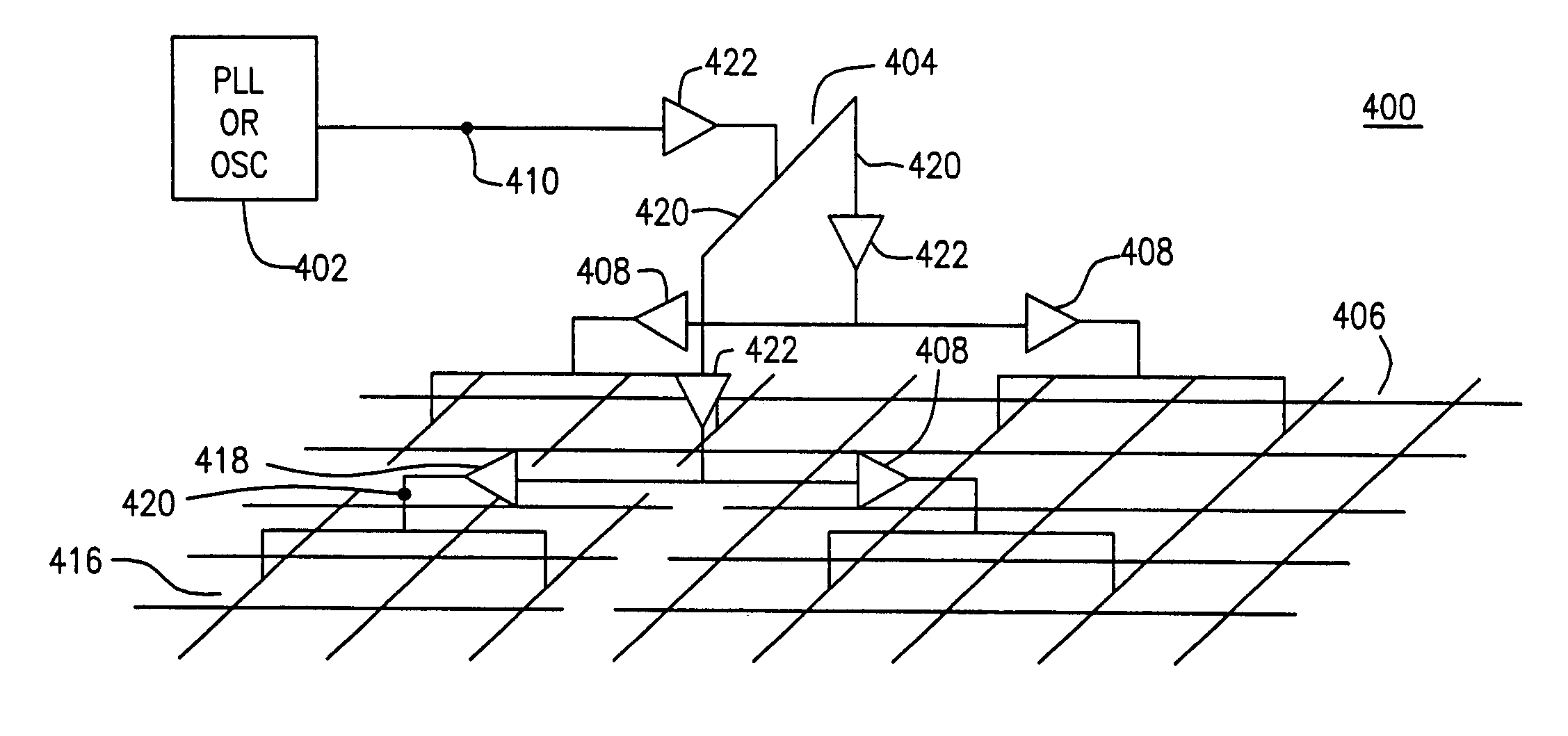
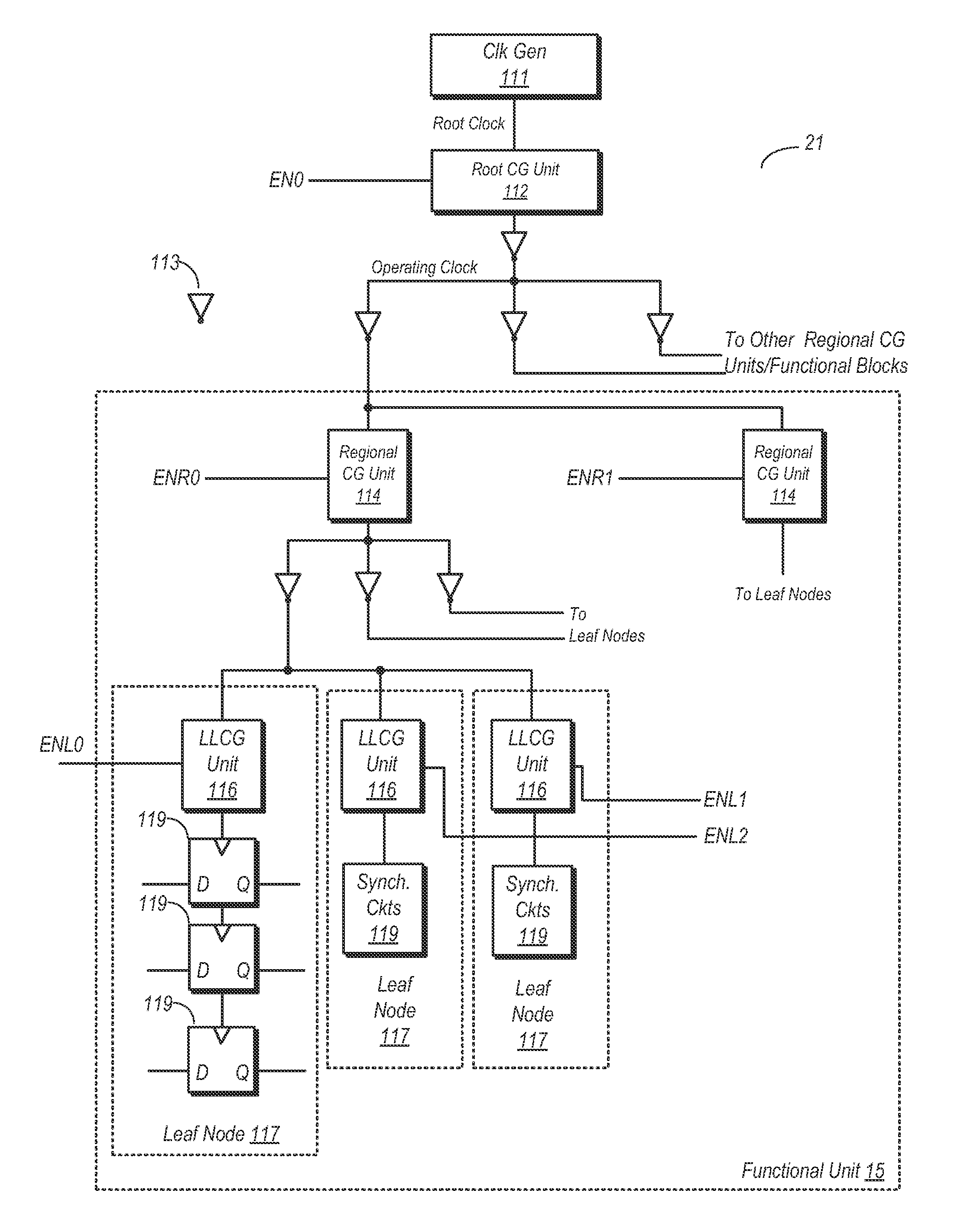
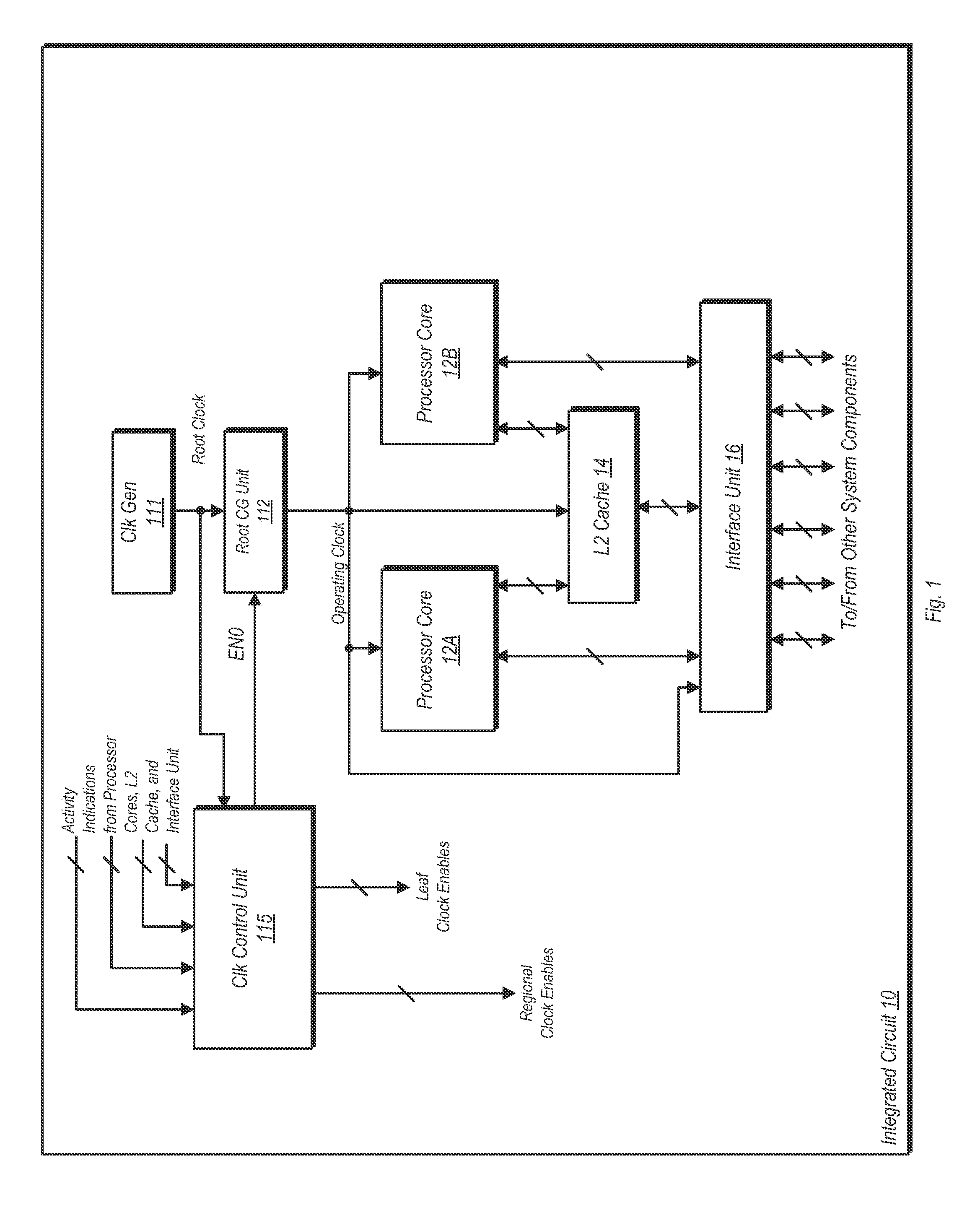
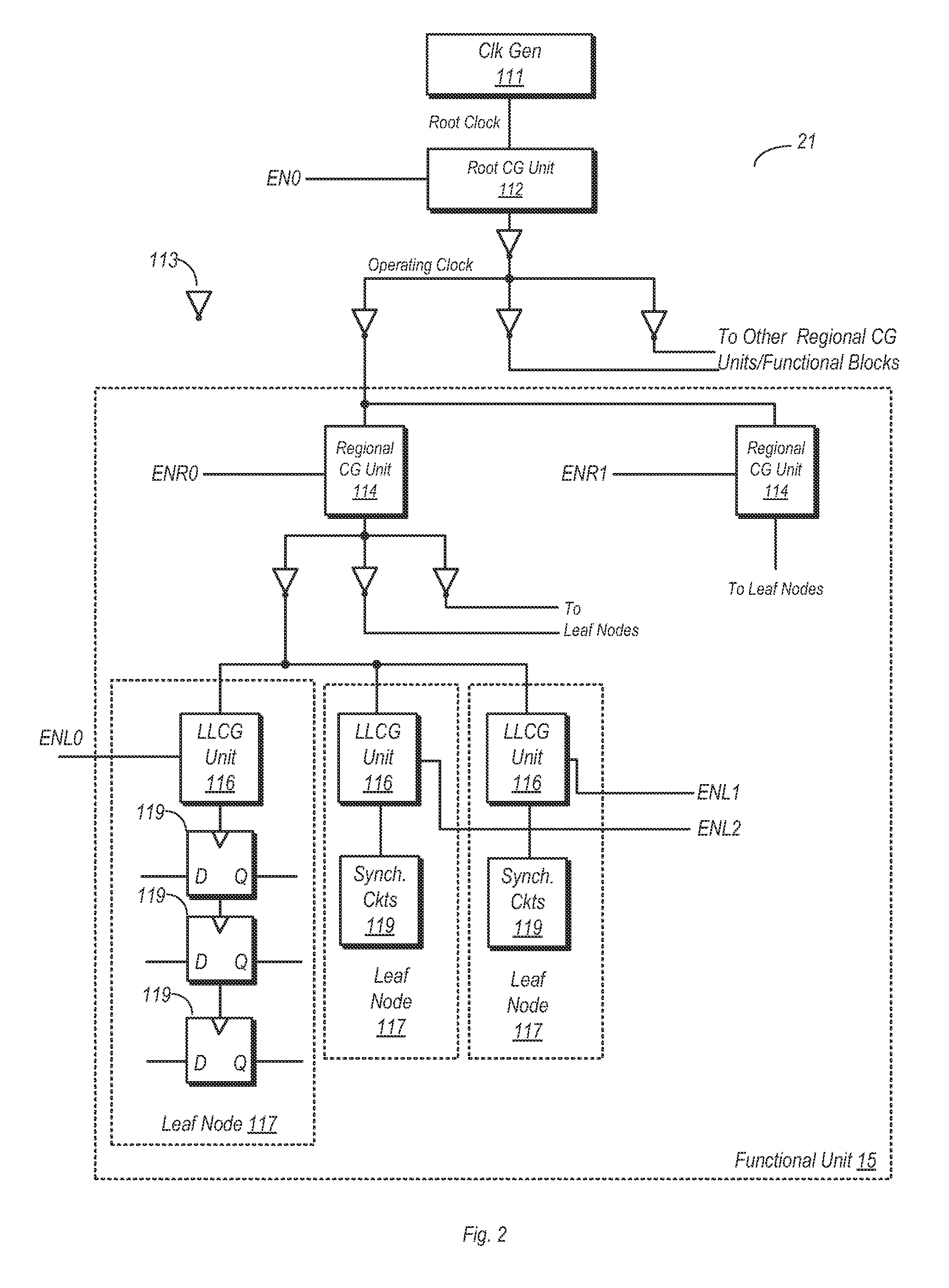
Regional Clock Gating and Dithering
ActiveUS20130191677A1Effective frequency of clock signalSave powerEnergy efficient ICTPower reduction by control/clock signalIdle timeClock tree
A system and method for dithering a clock signal during idle times is disclosed. An integrated circuit (IC) includes a number of functional units and a clock tree. The clock tree includes a root level clock-gating circuit, a number of regional clock-gating circuits, and a number of leaf level clock-gating circuits. The root level clock-gating circuit is coupled to distribute an operating clock signal to the regional clock-gating circuits, while the regional clock-gating circuits are each configured to distribute the operating clock signal to correspondingly coupled ones of the leaf level clock-gating circuits. The IC may further include a control unit configured to monitor activity levels and indications from each of the functional units. The control unit may cause the root clock-gating circuit to dither the clock signal if the IC is idle, wherein dithering includes reducing the duty cycle and the effective frequency of the operating clock signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
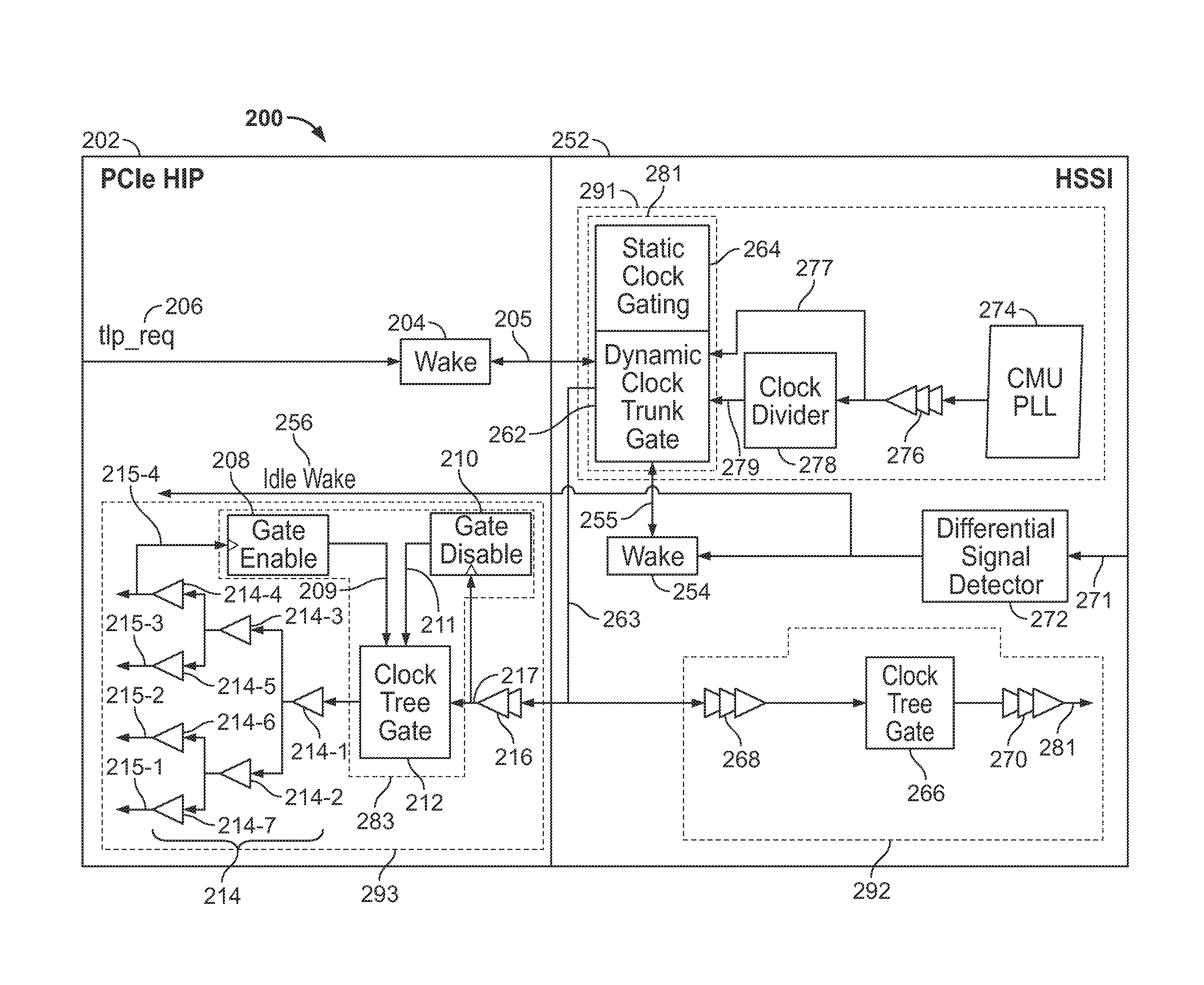
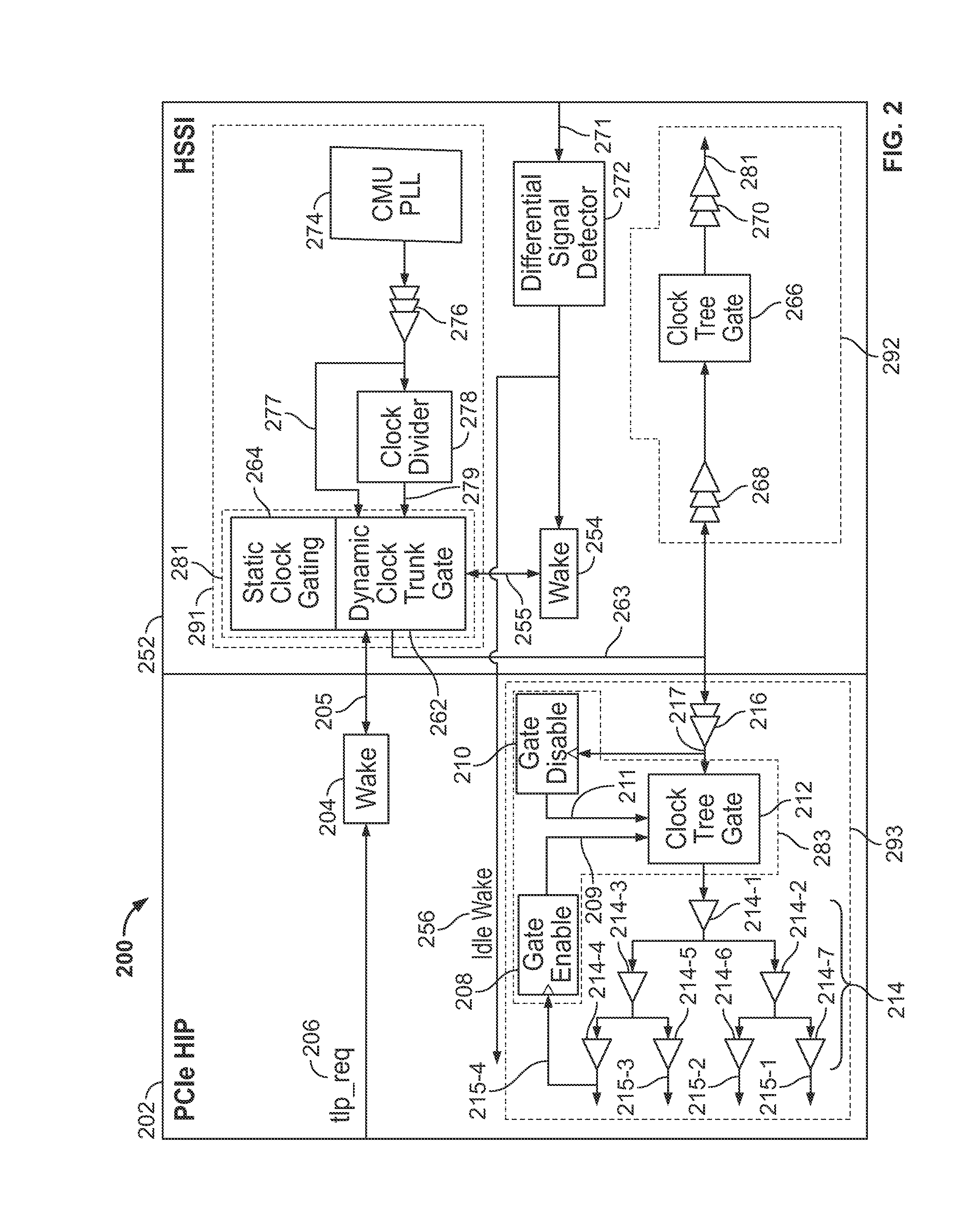
Power management for PCI express
ActiveUS9467120B1Power reduction by control/clock signalPulse automatic controlTransceiverLeaf driver
Systems and methods are provided for managing power of a device coupled with a transceiver module, in communication with a high-speed interface. In one aspect, a dynamic clock trunk tree associated with the transceiver module is controlled by a trunk driver having a first clock tree gate. A dynamic clock leaf tree associated with the device is controlled by a leaf driver having a second clock tree gate. Significant power savings may be achieved, for example, by triggering activation of clock gating mechanisms.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
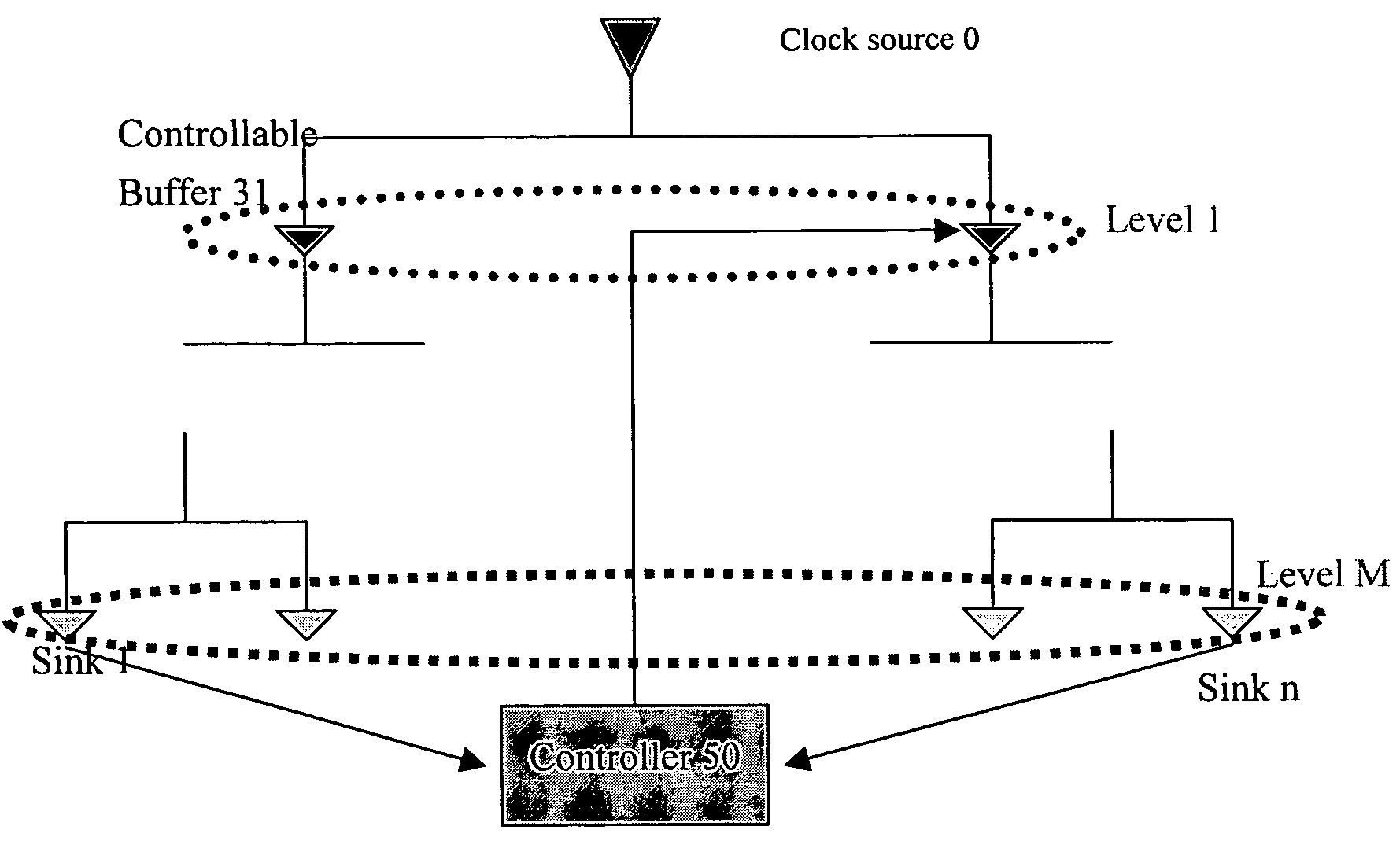
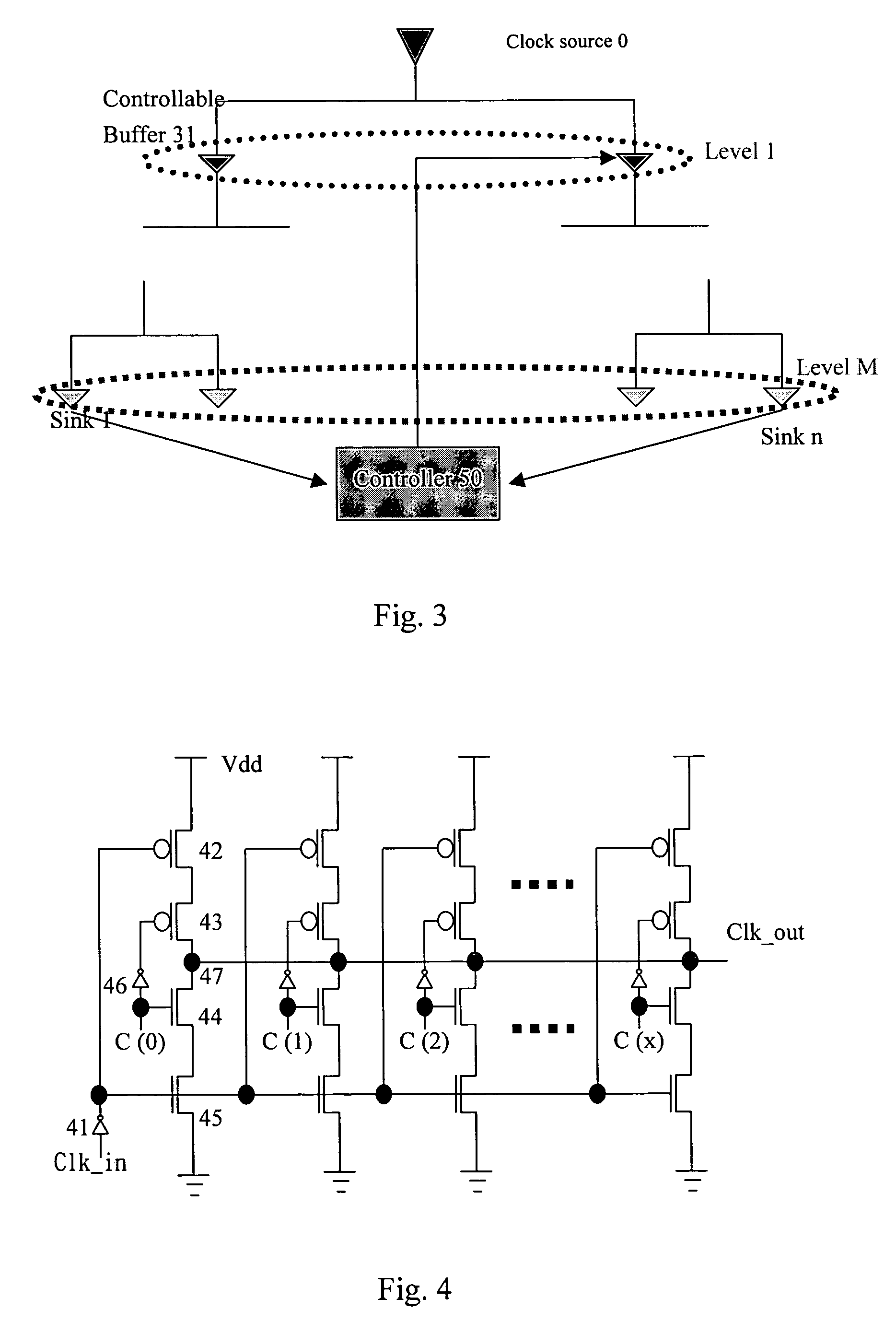
Method for dynamic balancing of a clock tree
InactiveUS7042269B2Excessively generatedSolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorTime delaysClock tree
The present invention provides a method to balance a clock tree dynamically. A controllable buffer is inserted in a specific level of a clock tree, and a controller is provided for adjusting two clocks with different skew by controlling the PMOS / NMOS arrangements in the controllable buffer so as to generate more current for compensating the time delay of slow clock to a sink. This method effectively suppressed the clock skew generated by the voltage drop or the temperature variations in the synchronous logic circuit design.
Owner:PRINCETON TECH CORP
Scan test design method, scan test circuit, scan test circuit insertion cad program, large-scale integrated circuit and mobile digital equipment
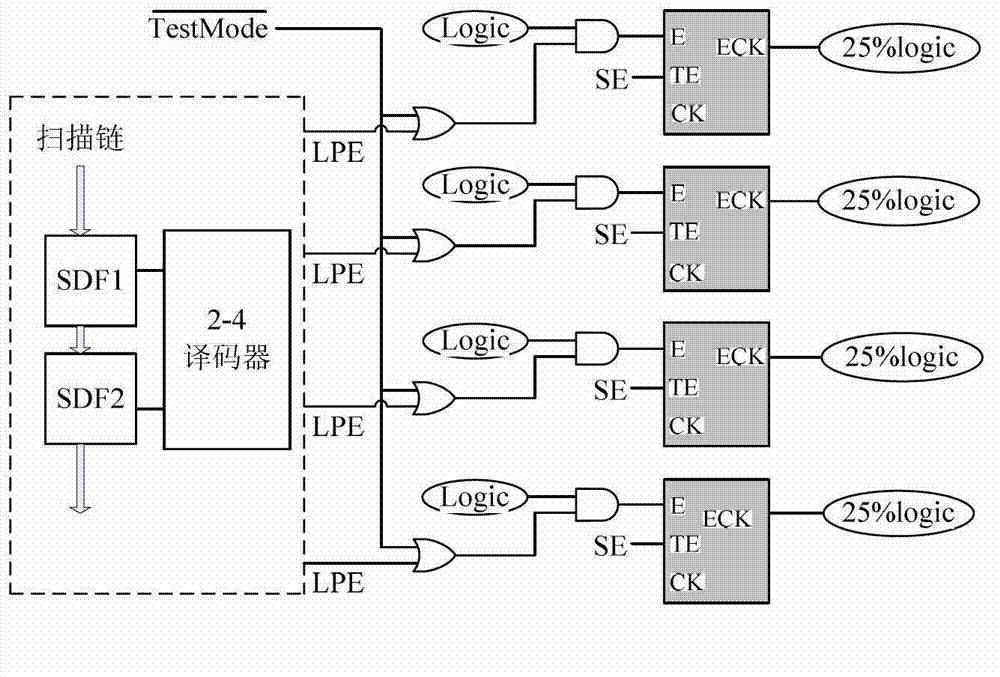
InactiveUS20060282727A1Little design reversionImprove battery lifeDigital circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareTest designShift register
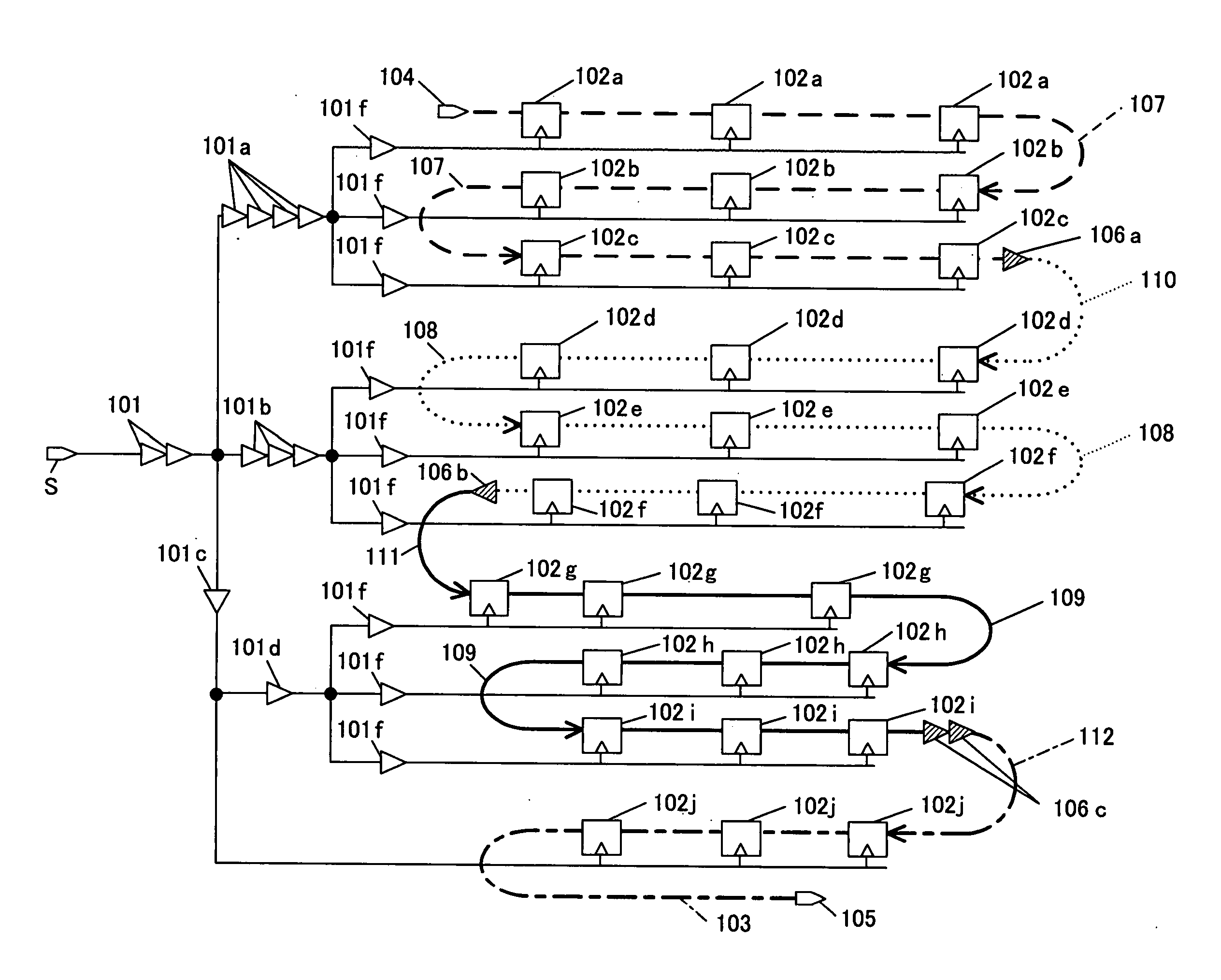
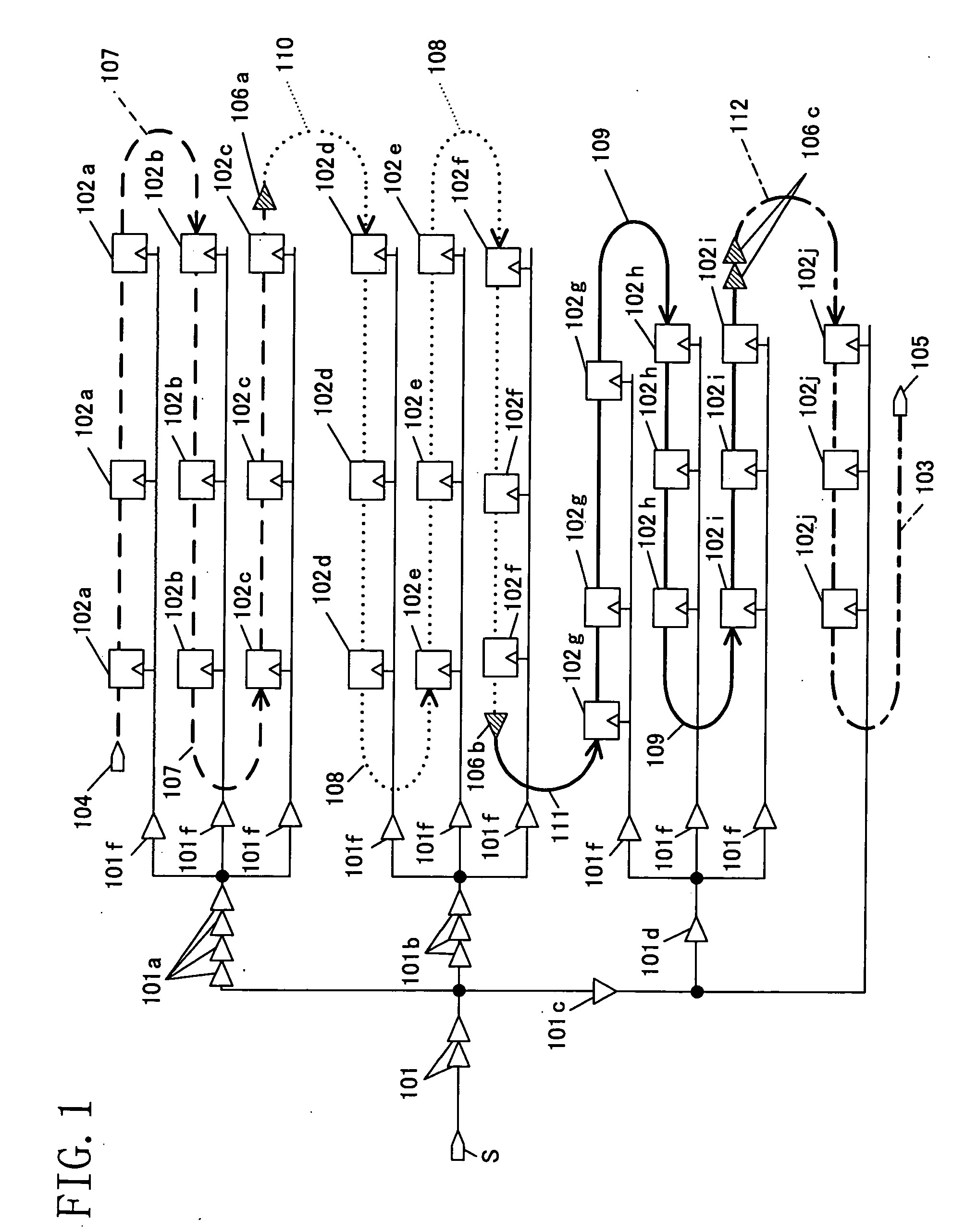
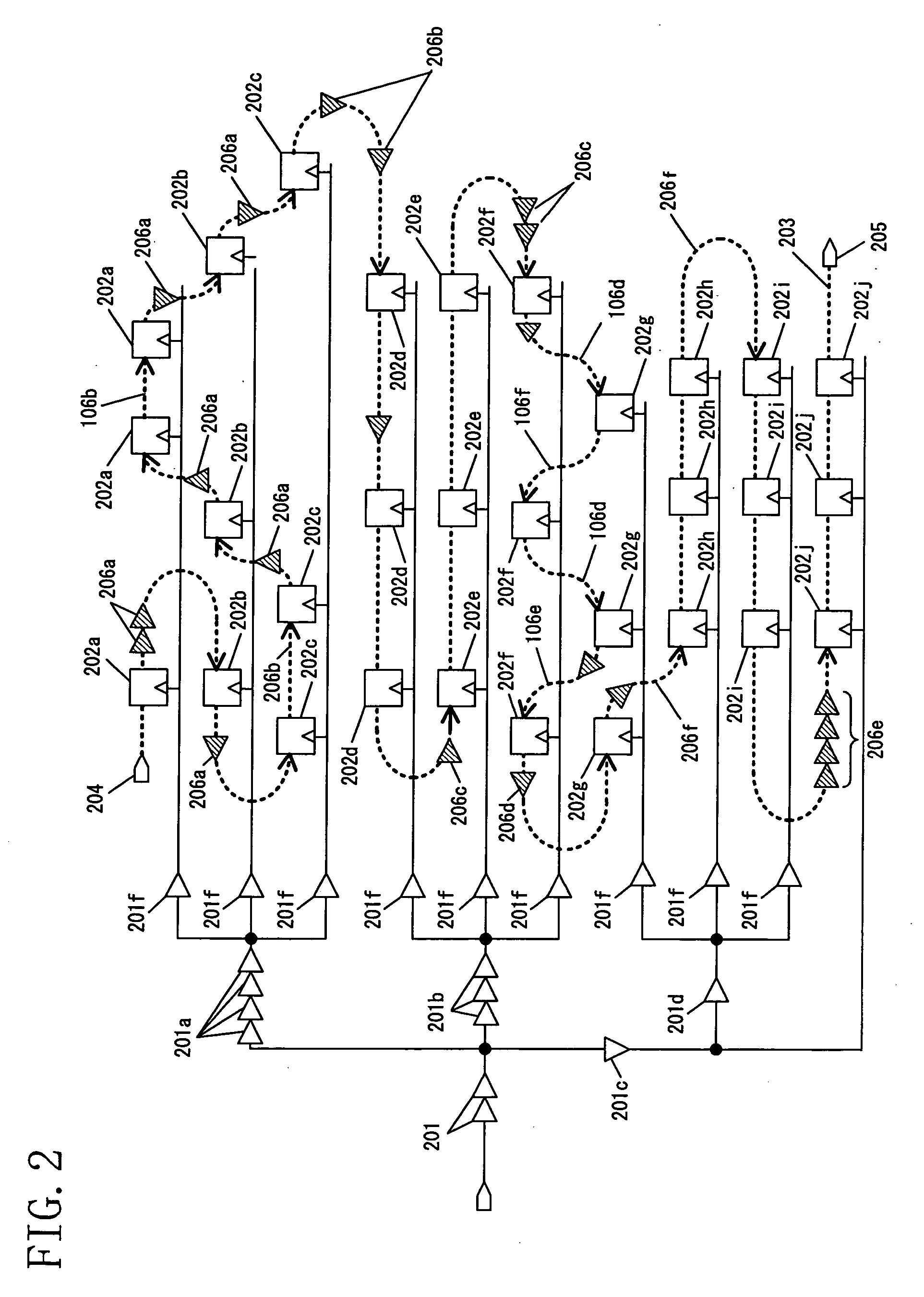
In scan test circuit design, a plurality of flipflop circuits (102a, 102b or 102c) driven with each of final-stage elements 101f of a clock tree T are connected in series, to form a sub-scan chain. Also, sub-scan chains smallest in the relative difference in the number of stages of delay elements existing from the clock supply point S of the clock tree T (i.e., sub-scan chains different by one stage) are connected to each other. Further, sub-scan chains are connected so that data shift be made from a flipflop circuit larger in clock delay to a flipflop circuit smaller in clock delay. This reduces the number of delay elements inserted in data lines of a shift register for hold time guarantee in shift operation of the scan shift register, and suppresses power consumption.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
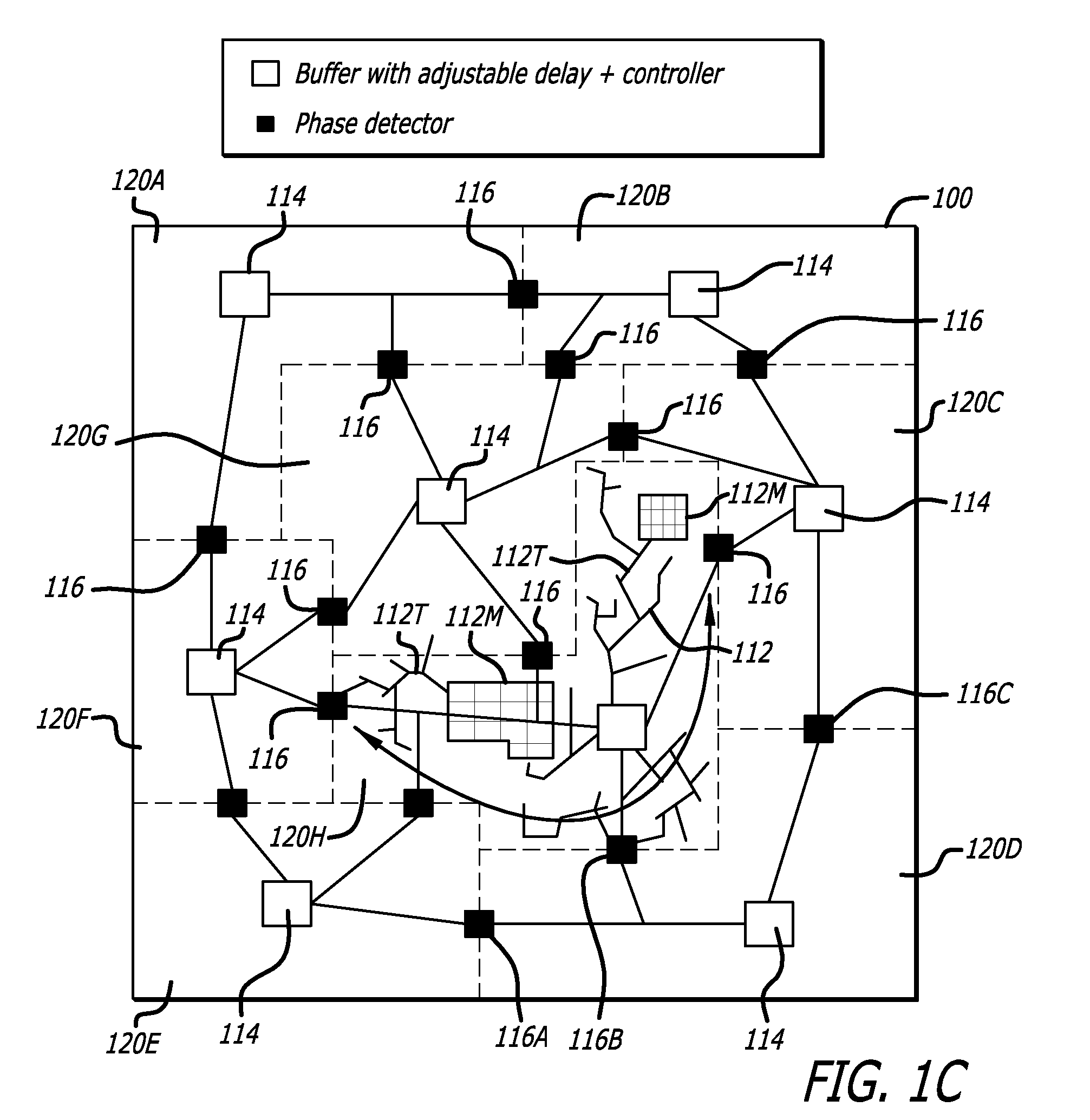
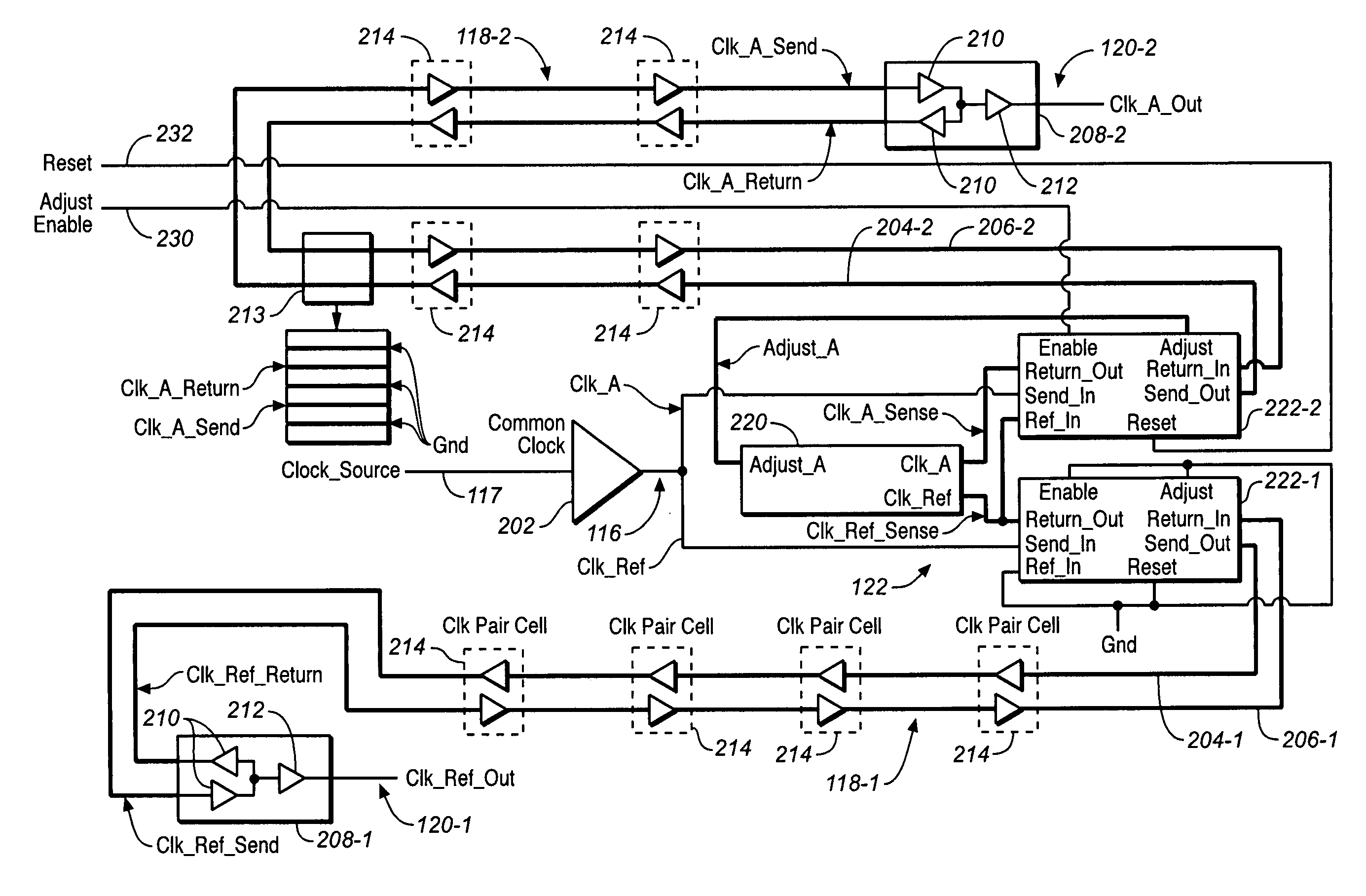
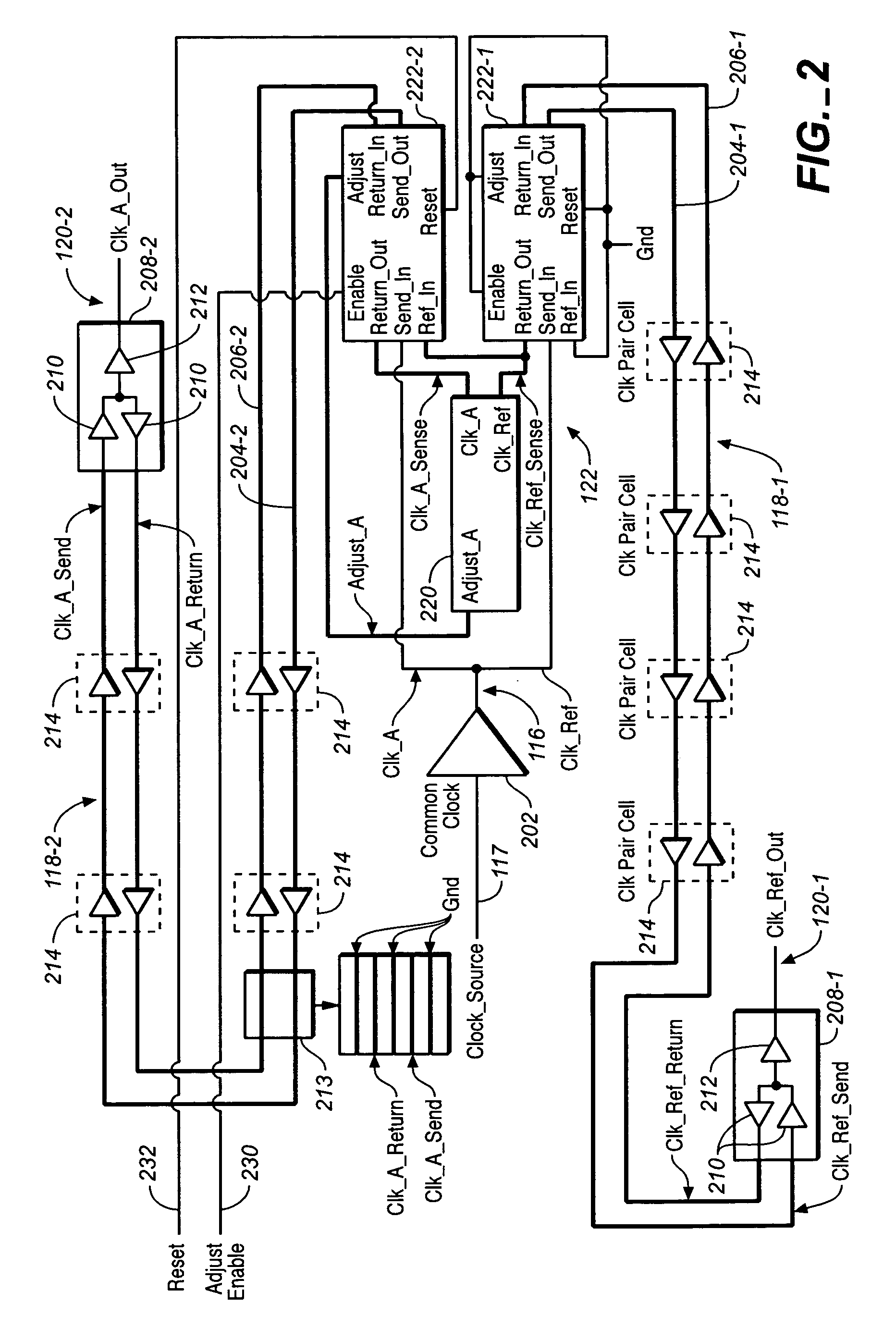
Chip level clock tree deskew circuit
A signal deskew circuit is provided, which includes first and second signal branches, each branch extending between a start location and a respective end location. Each signal branch includes a send path and a return path, which have substantially the same propagation delays. An adjustable delay buffer is coupled in the send and return paths of a first of the signal branches and has a delay, which is adjustable based on a respective adjust signal. A skew sensor coupled to the return paths of the first and second signal branches, which generates the respective adjust signal for the adjustable delay buffer based on a phase difference between signals on the return paths of the first and second signal branches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for balancing a clock tree
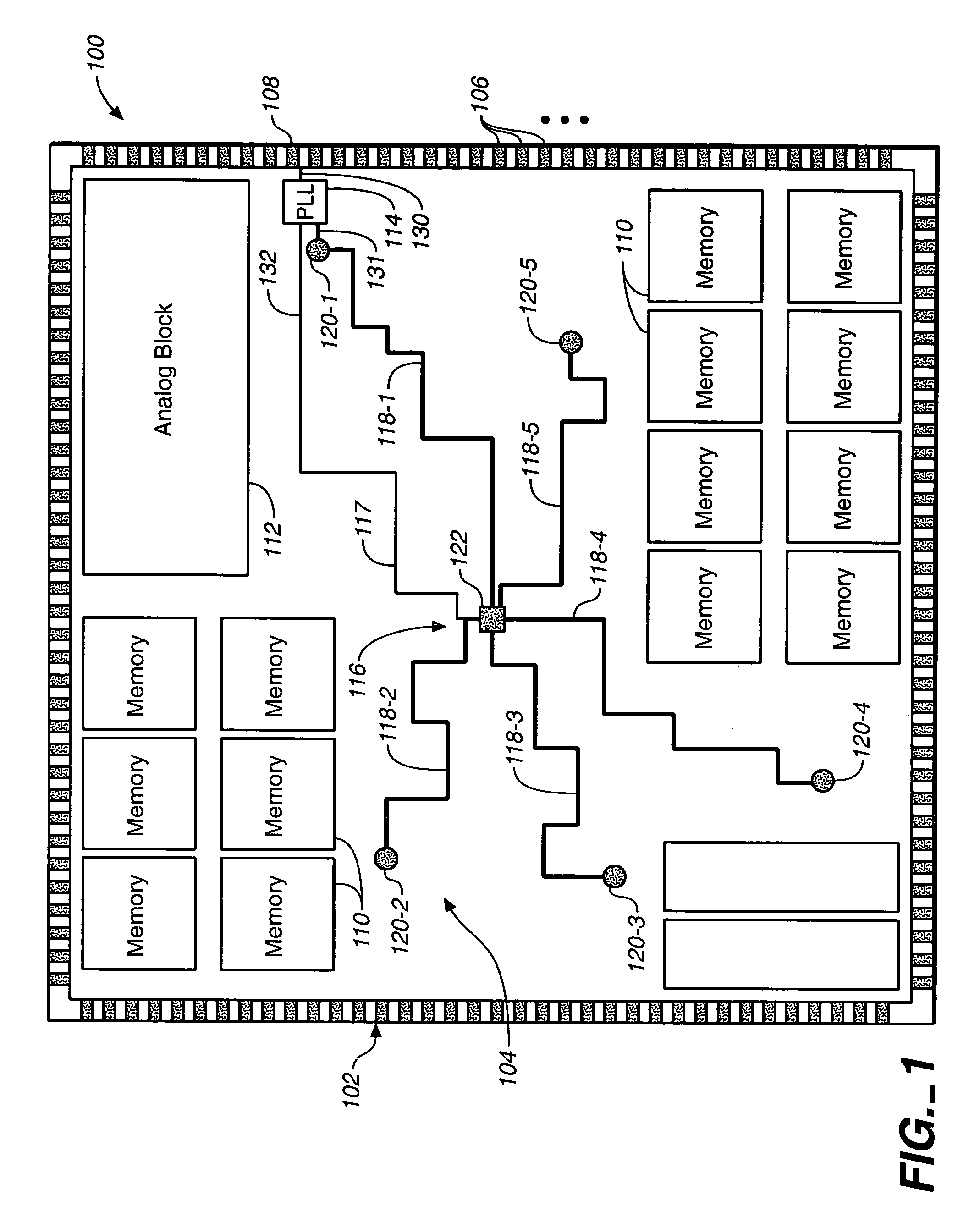
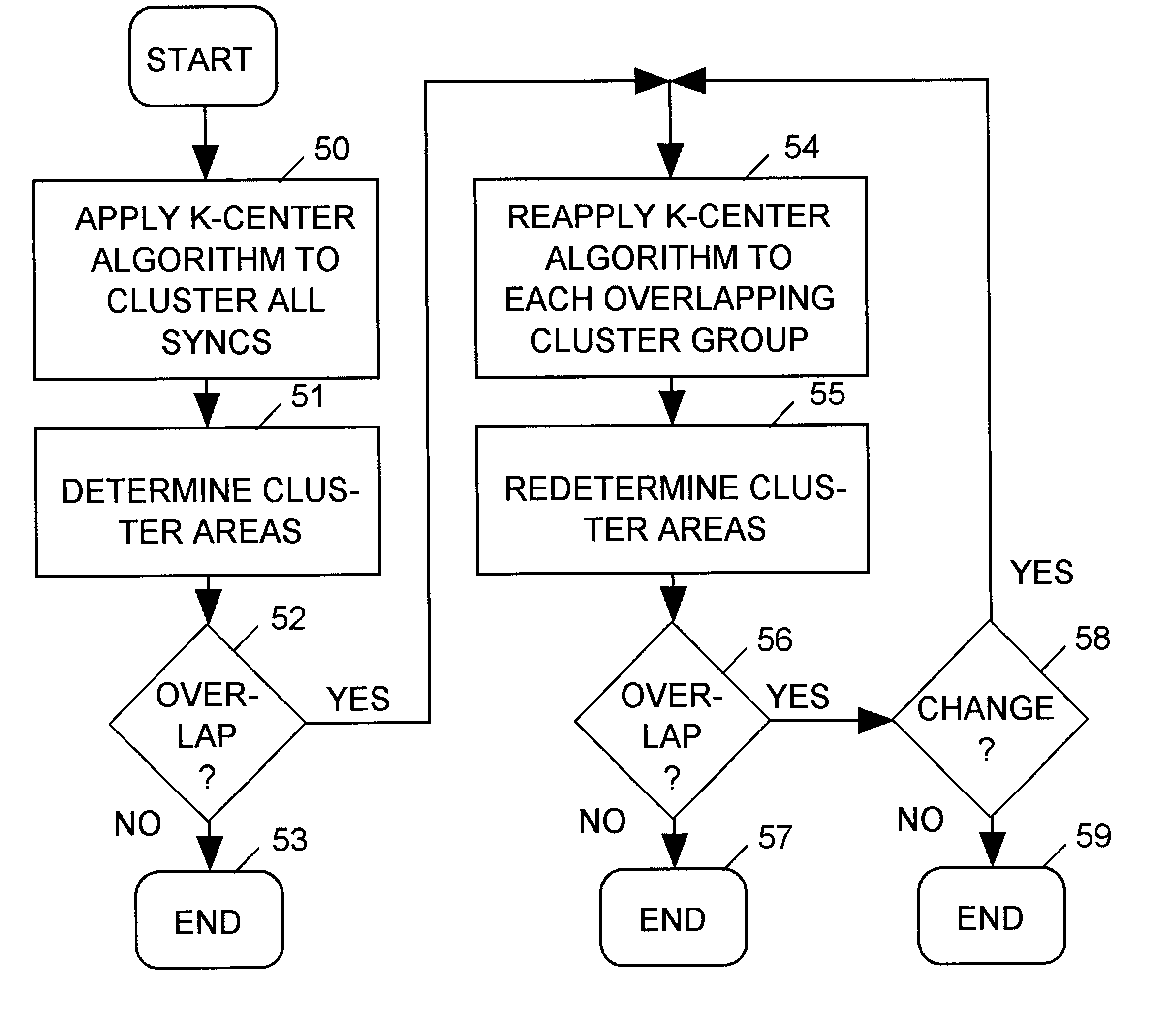
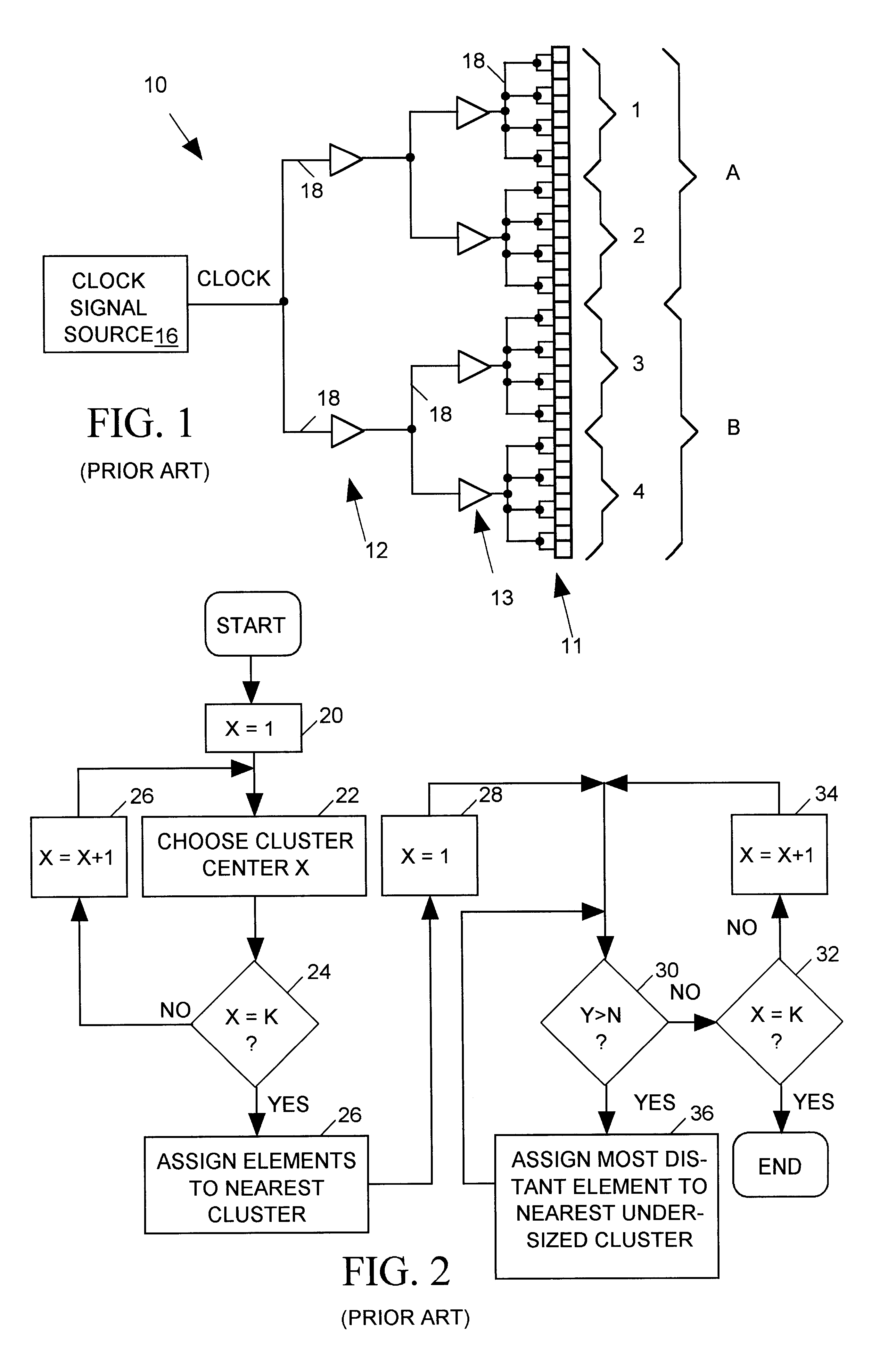
In an integrated circuit (IC) design, a set of KxN clocked IC devices ("syncs") such as flip-flops and latches are organized into K clusters of N syncs each, with each cluster being clocked by a separate clock tree buffer. An improvement to a conventional "K-center" method for assigning syncs to clusters is disclosed. The improved method, which reduces the separation between syncs within the clusters, initially employs the conventional K-center method to preliminarily assign the KxN syncs to K clusters having N syncs per cluster. The improved method thereafter ascertains boundaries of rectangular areas of the IC occupied by the separate clusters. When areas of any group of M>1 clusters overlap, the K-center meth is repeated to reassign the set of MxN syncs included in e M overlapping clusters to a new set of M clusters. The new set of M clusters are less likely to overlap.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Optimization method of capturing power consumption in scan test
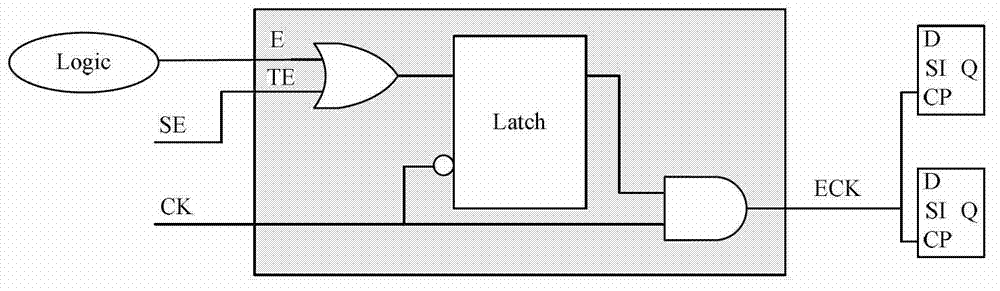
InactiveCN103091620AReduce capture power consumptionElectronic circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsTest designTest vector
The invention discloses an optimization method of capturing power consumption in a scan test. The optimization method of capturing power consumption in the scan test comprises the following steps: generating a netlist with a scan chain; grouping gating control clock units; designing a power constrain unit; combining with the generated netlist with the scan chain, conducting chip layout design which comprises a floorpan, a layout, a clock tree sythesis and wiring; reading a gate-level netlist with a scan structure, a process library, a timing sequence constrain file and a test protocol into an automatic test vector generating tool after the chip layout design is completed, conducting testability design rule checking, and generating a test vector; and conducting gate-level simulation to the test vector generated. By means of the optimization method of capturing the power consumption in the scan test, the capturing power consumption in a test process can be reduced significantly, the reduction of coverage or the sharp increase of the quantity of test vectors is not generated, changing of a test design process is needless, and realization is easy.
Owner:JIANGSU SEUIC TECH CO LTD
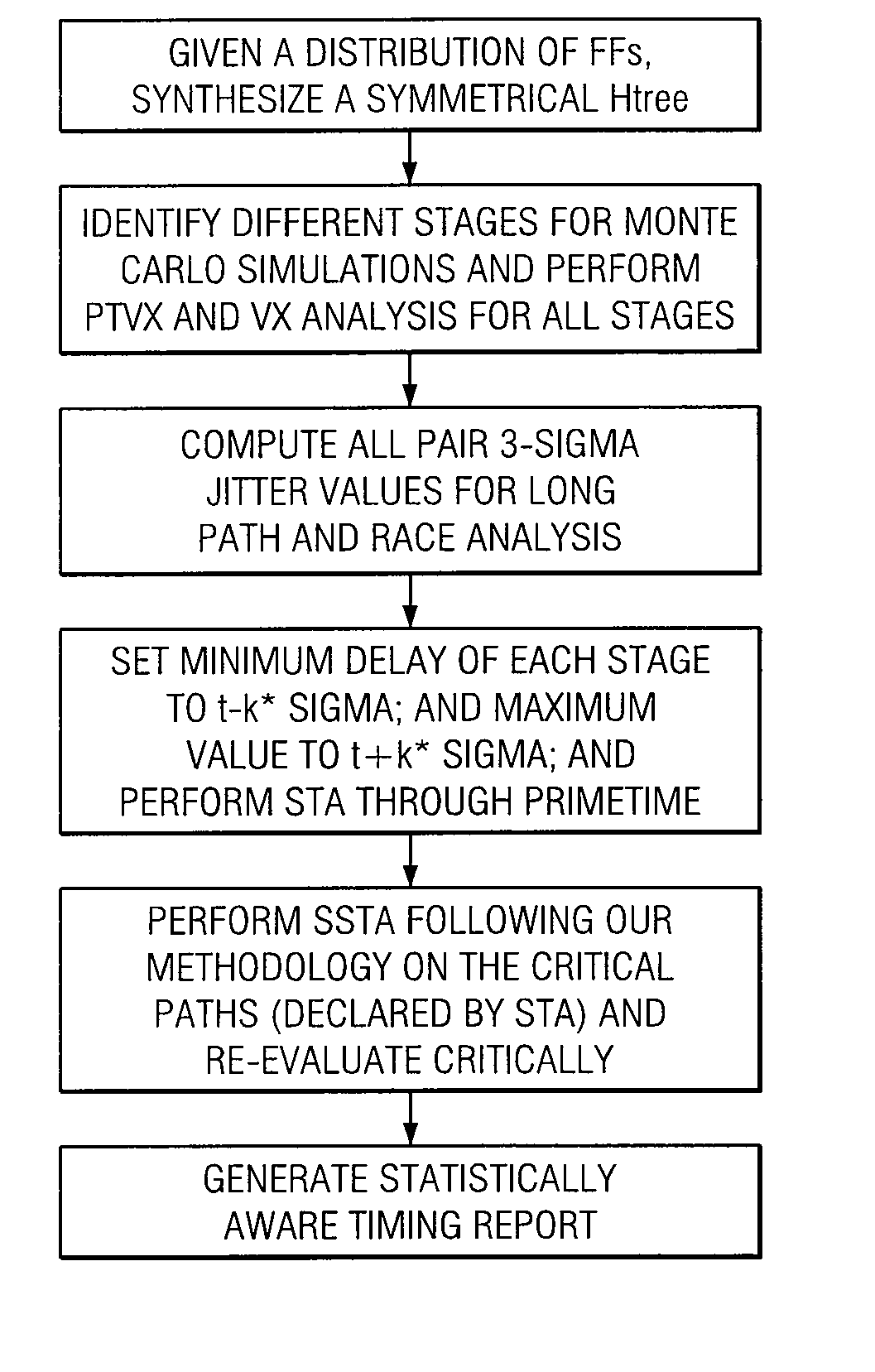
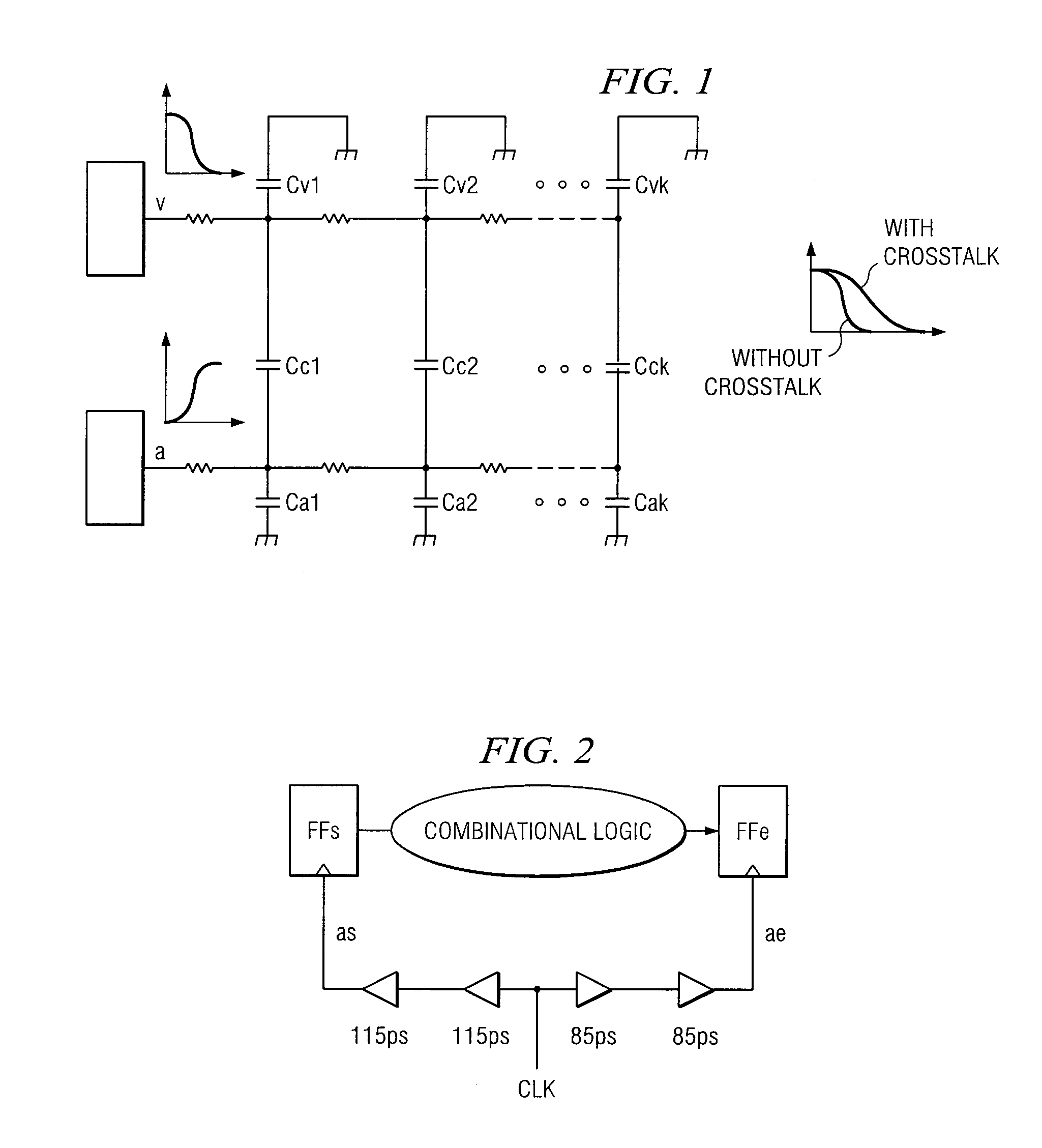
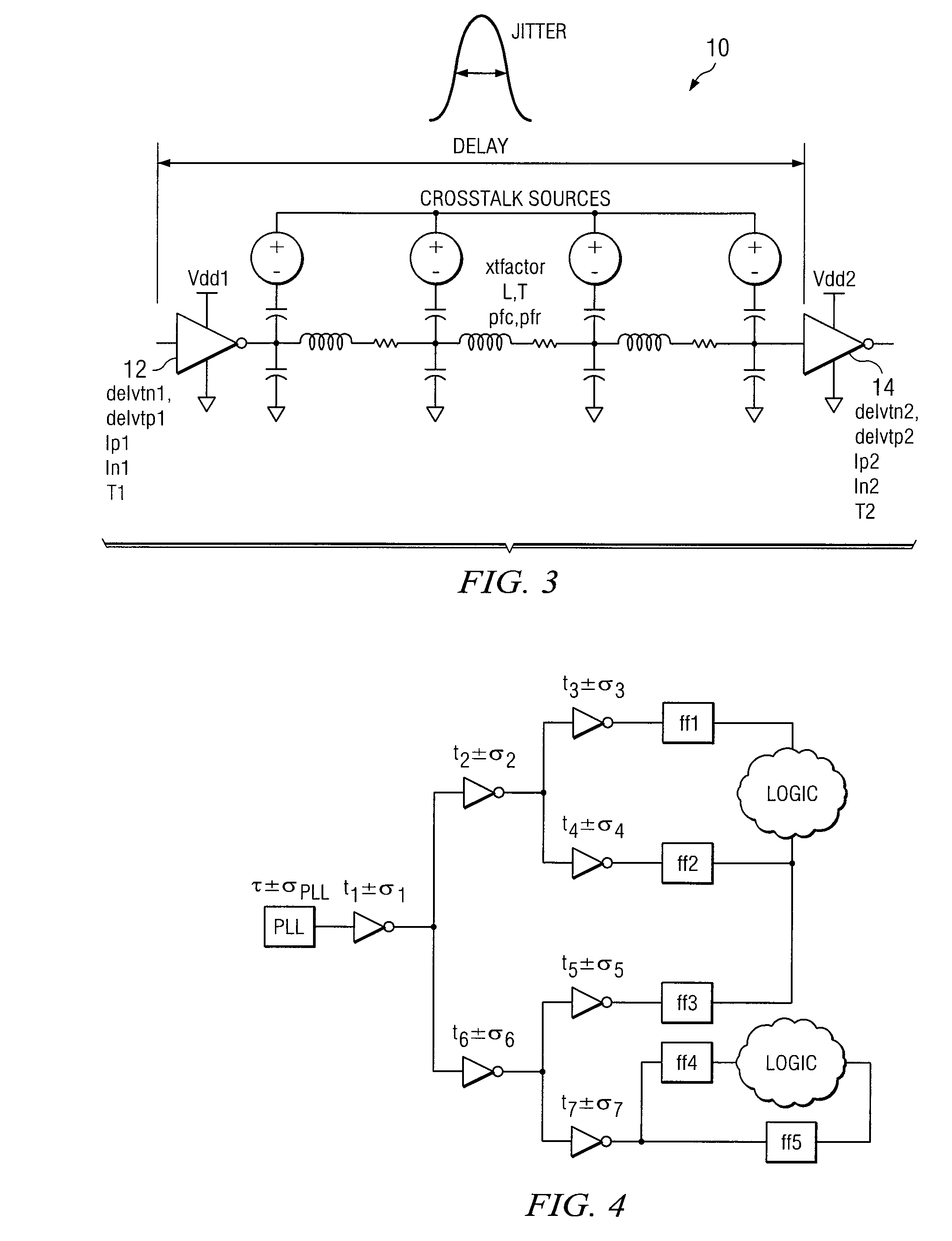
Estimating Jitter In A Clock Tree Of A Circuit And Synthesizing A Jitter-Aware And Skew-Aware Clock Tree
InactiveUS20060288320A1CAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsTheoretical computer scienceClock tree
In one embodiment, a method for computing jitter in a clock tree includes dividing a clock tree into a plurality of stages and computing jitter in one or more of the stages according to a model of at least a portion of a circuit associated with the clock tree. The model includes a representation of each source of jitter in the circuit. The method also includes, to compute jitter associated with a path or a pair of paths in the clock tree, statistically combining the jitter in each of the stages of the path or the pair of paths in the clock tree with each other. In one embodiment, to efficiently compute jitter and to achieve zero clock skew, a method synthesizes a symmetrical clock tree of a circuit in which corresponding stages in all paths from a root of the clock tree to sinks of the clock tree exhibit approximate electrical equivalence to each other.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
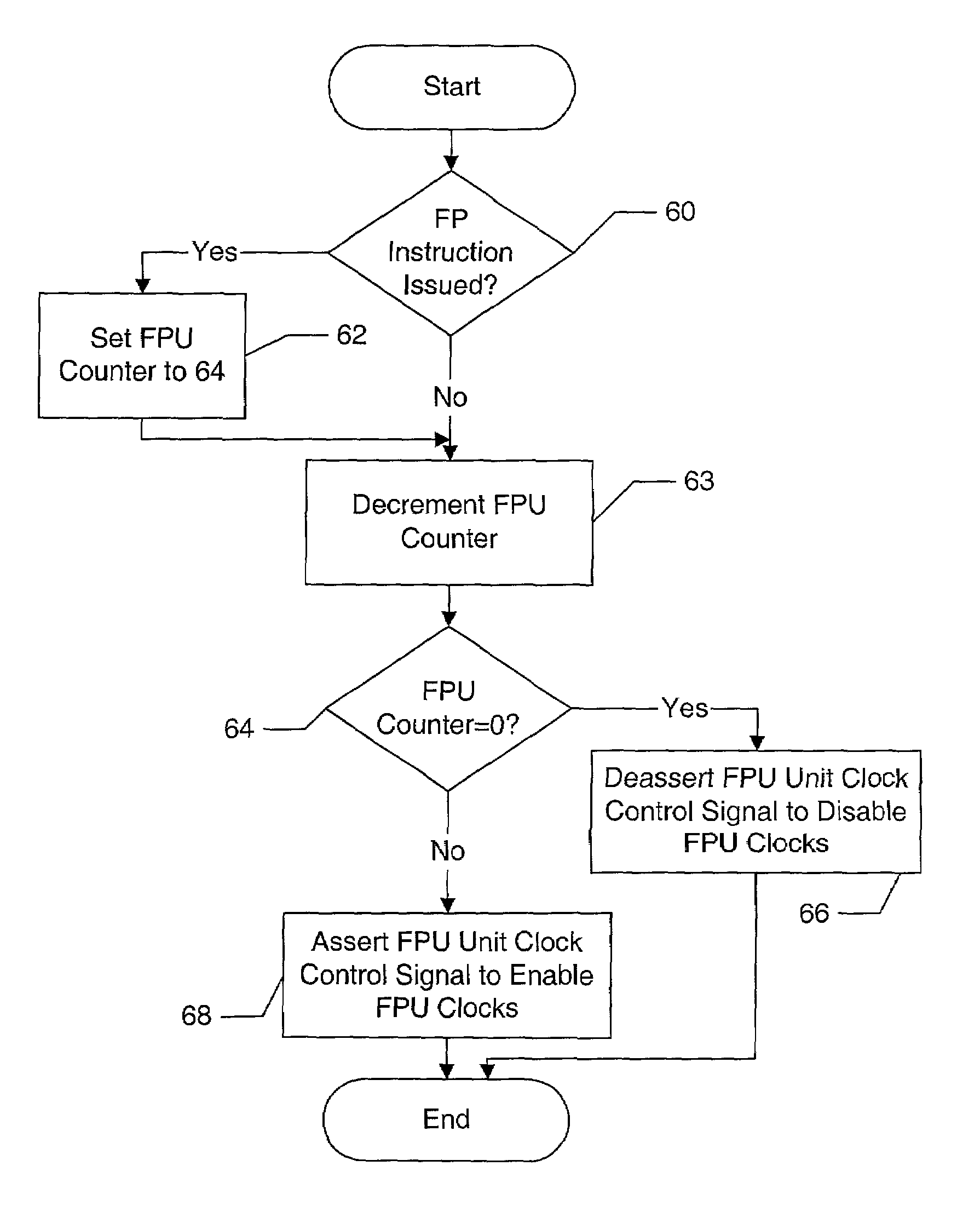
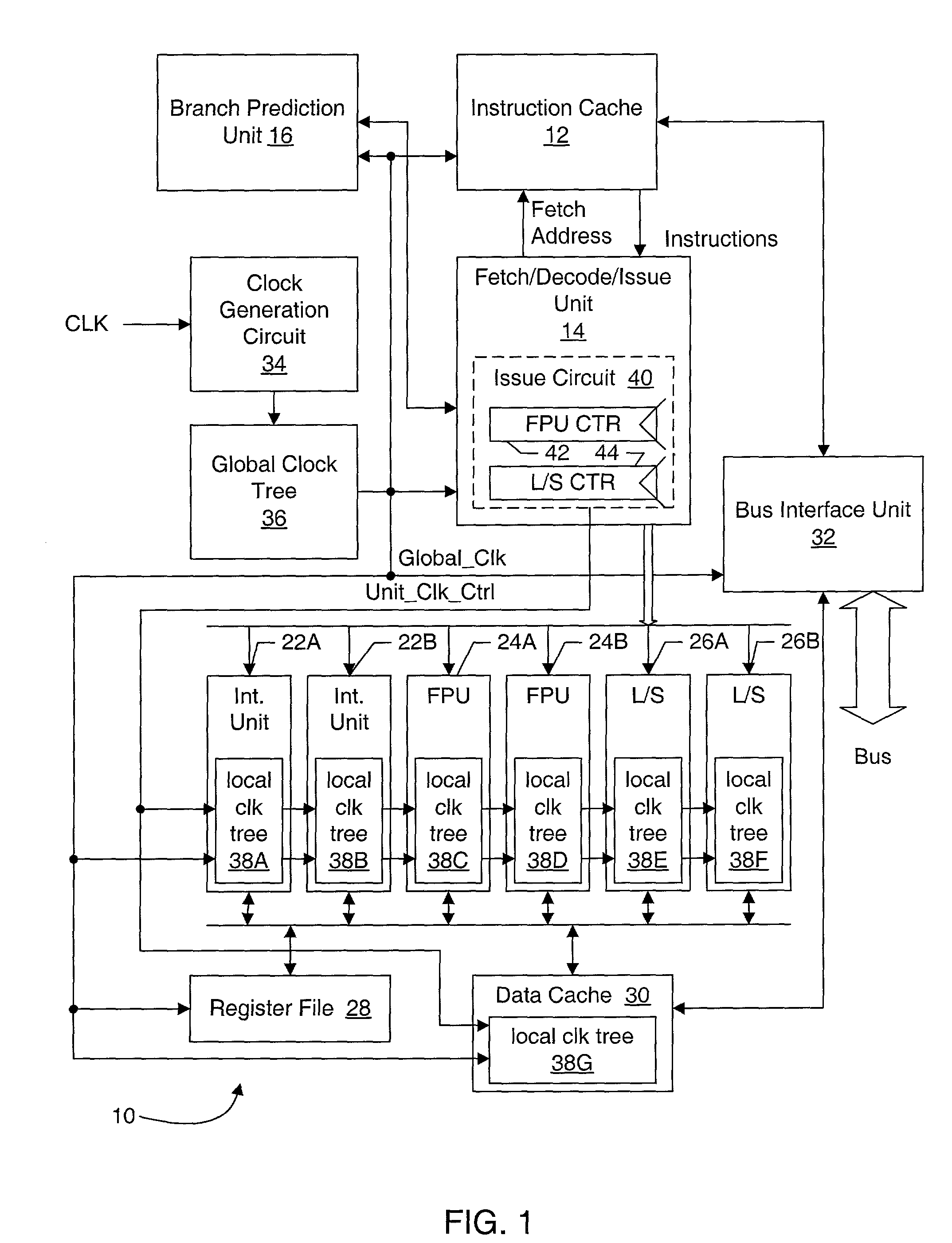
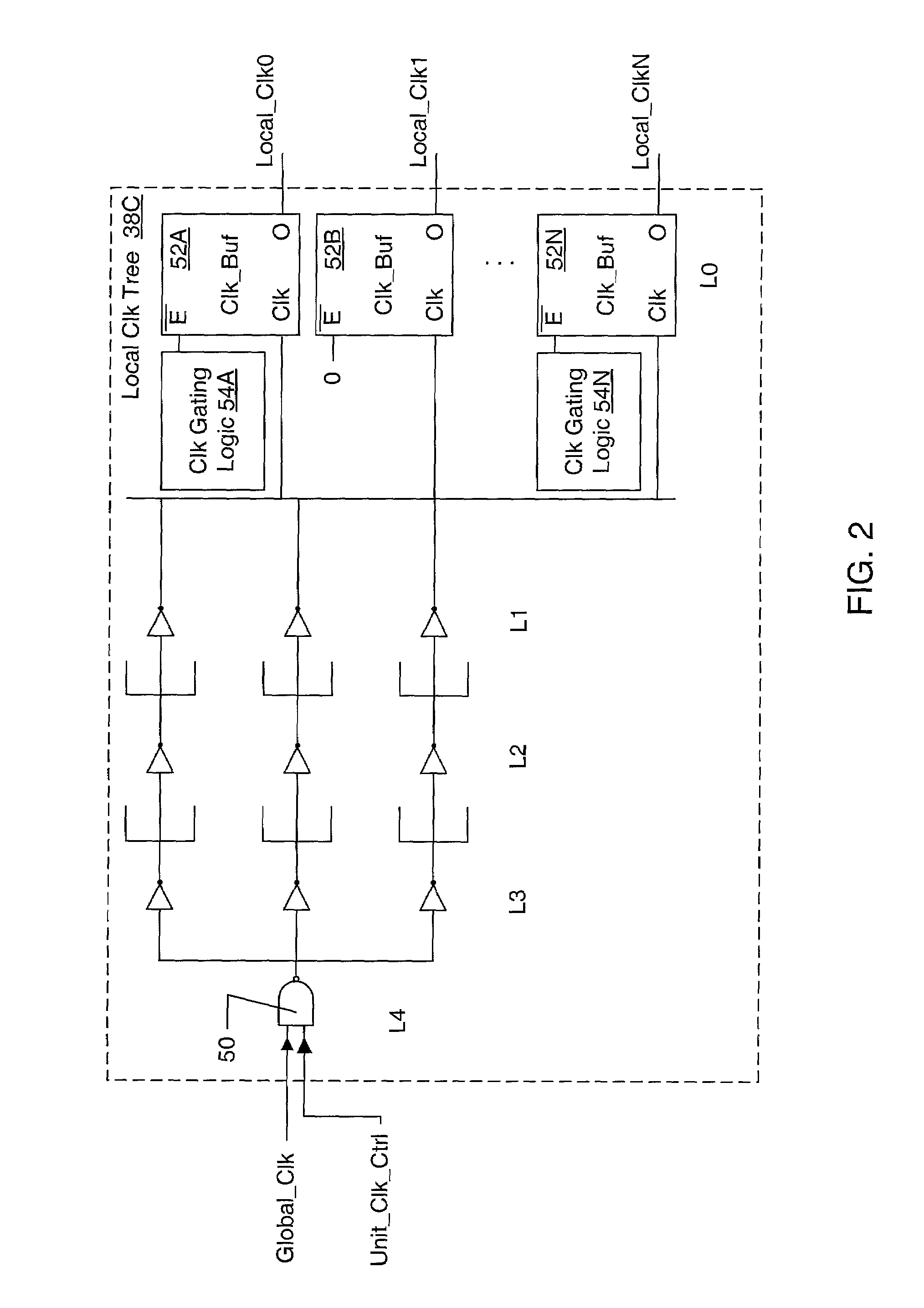
Clock gating of sub-circuits within a processor execution unit responsive to instruction latency counter within processor issue circuit
A processor may include an execution circuit, an issue circuit coupled to the execution circuit, and a clock tree for clocking circuitry in the processor. The issue circuit issues an instruction to the execution circuit, and generates a control signal responsive to whether or not the instruction is issued to the execution circuit. The execution circuit includes at least a first subcircuit and a second subcircuit. A portion of the clock tree supplies a plurality of clocks to the execution circuit, including at least a first clock clocking the first subcircuit and at least a second clock clocking the second subcircuit. The portion of the clock tree is coupled to receive the control signal for collectively conditionally gating the plurality of clock, and is also configured to individually conditionally gate at least some of the plurality of clocks responsive to activity in the respective subcircuits of the execution circuit. A system on a chip may include several processors, and one or more of the processors may be conditionally clocked at the processor level.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
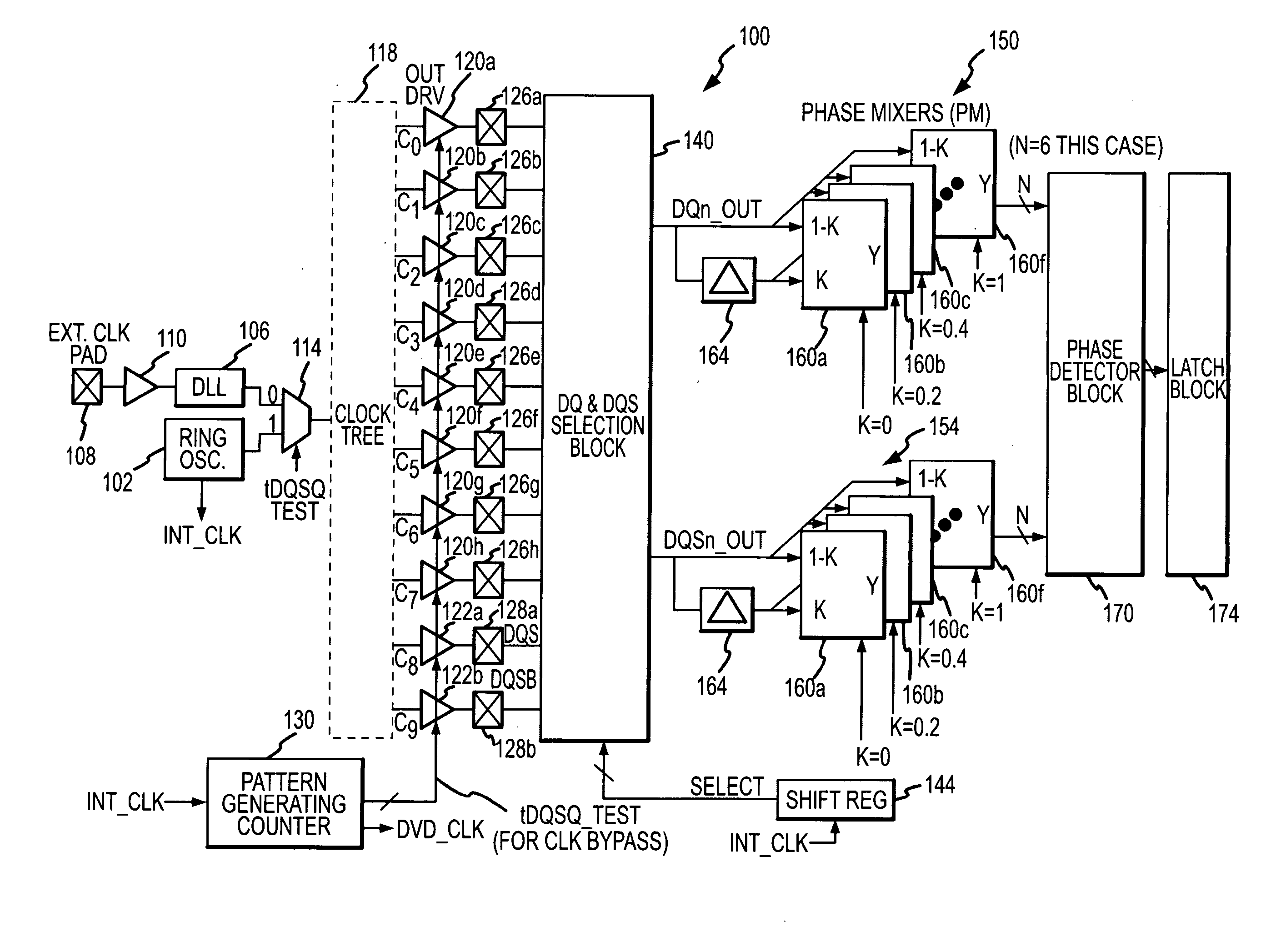
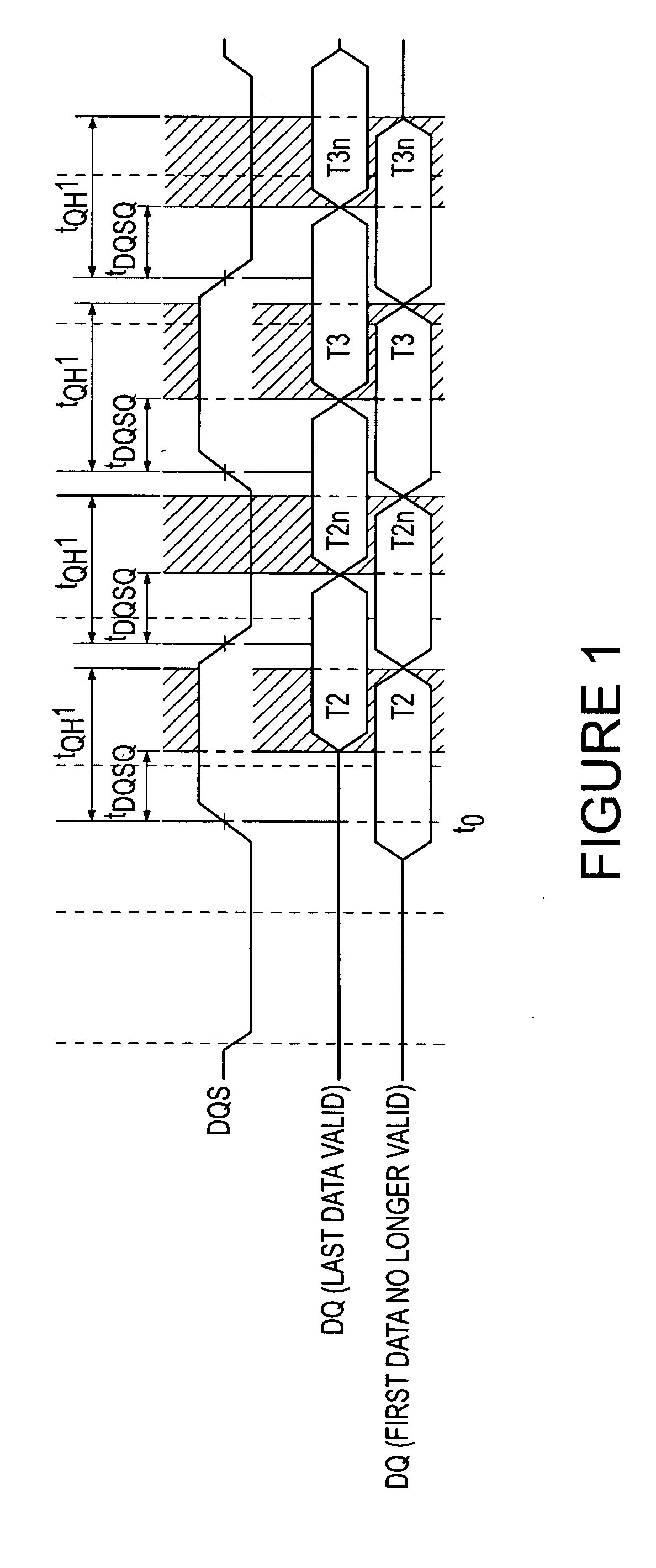
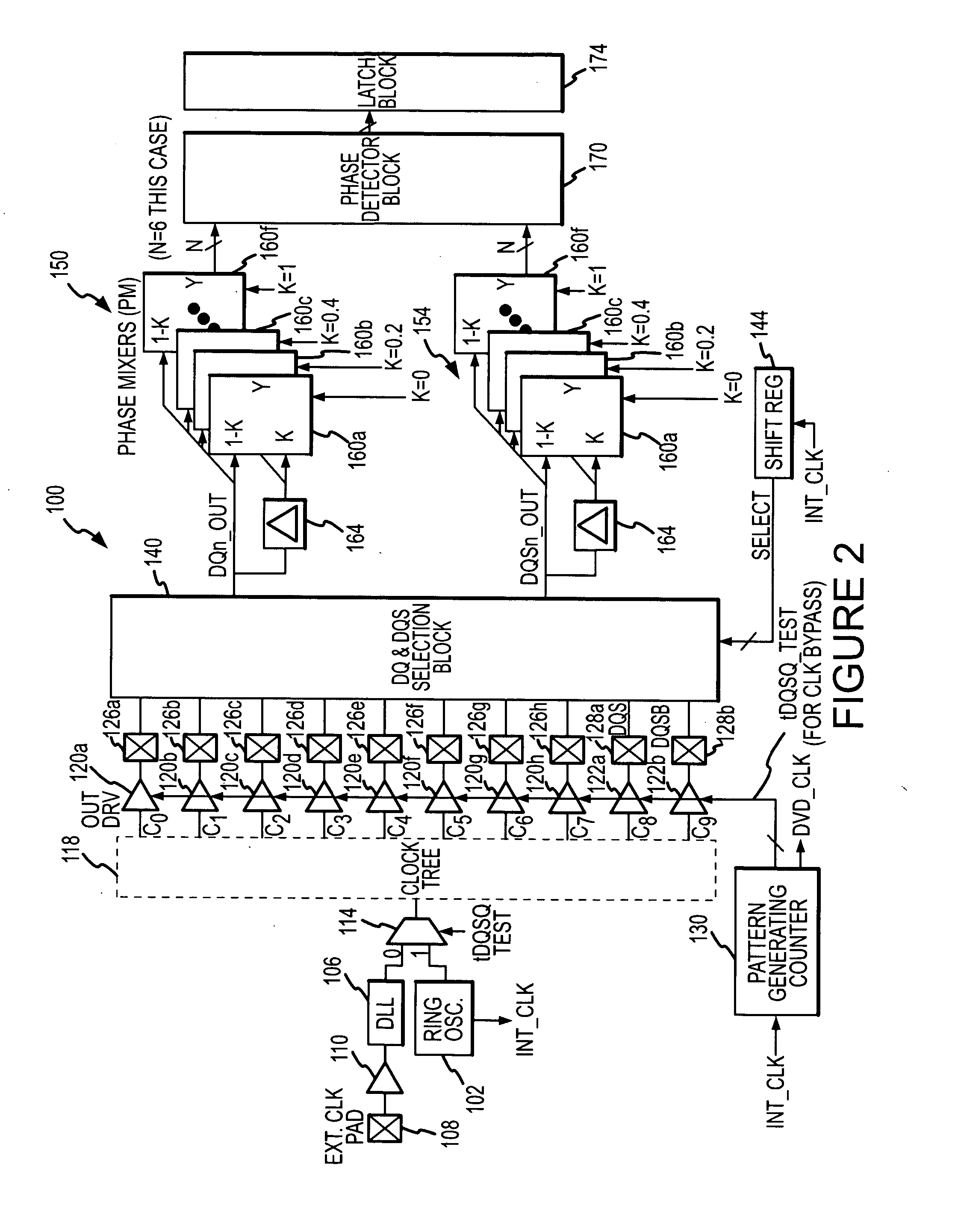
Built-in system and method for testing integrated circuit timing parameters
A built-in self-test system for a dynamic random access memory device using a data output register of the memory device to apply test signals to data bus terminals and a data strobe terminal of the memory device responsive to respective clock signals. The clock signal are generated by a test system oscillator and coupled through a clock tree of the memory device. The test system further includes a selector that sequentially selects each of the test signals applied to the data bus terminals and applies the selected test signal to a multi-phase generator. The multi-phase generator delays the selected signal by different time to generate a set of delayed signals. The phases of the delayed signals are compared to the test signal applied to the data strobe terminal to determine the delay of the compared signals relative to each other, thereby determining the timing parameter.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com