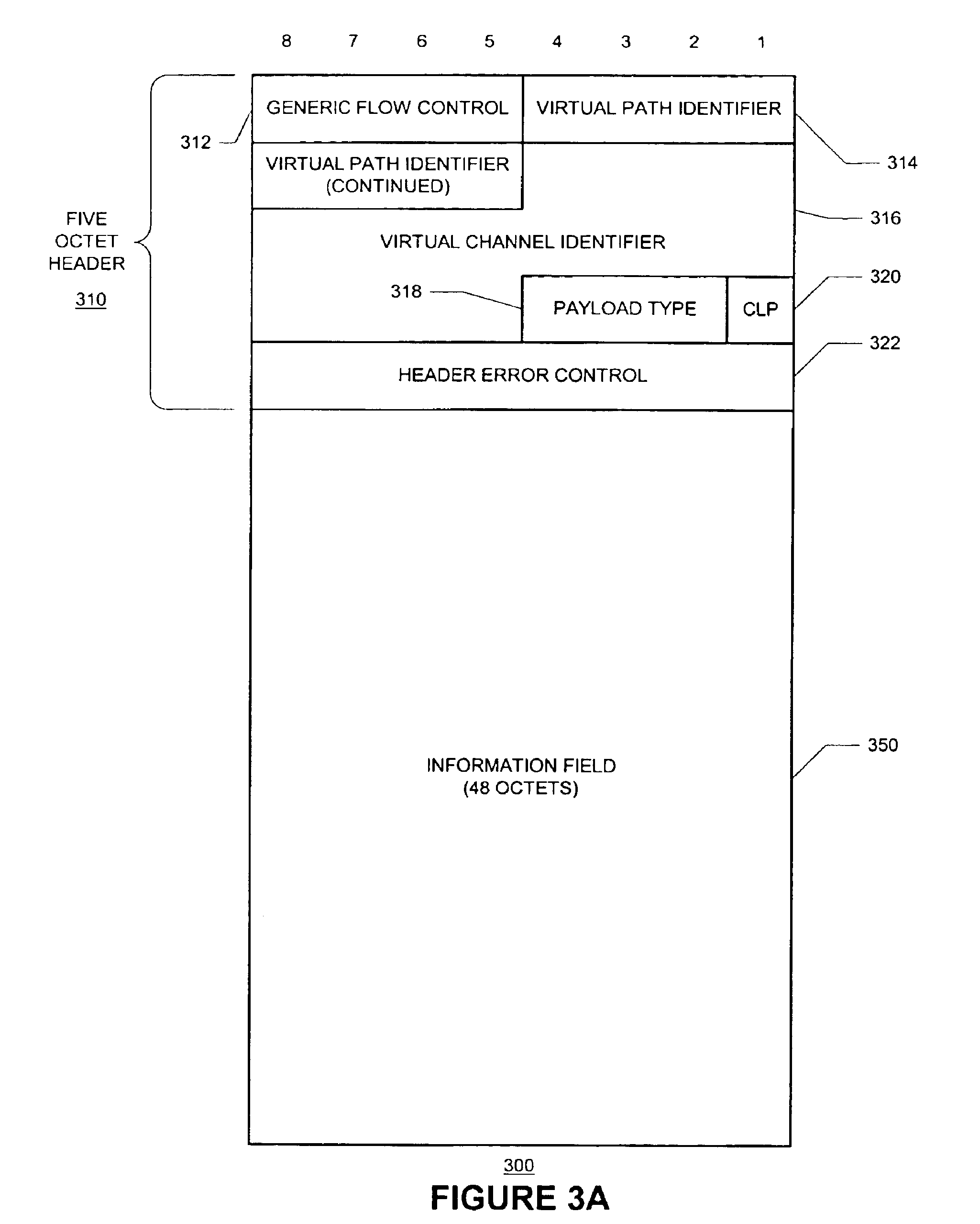
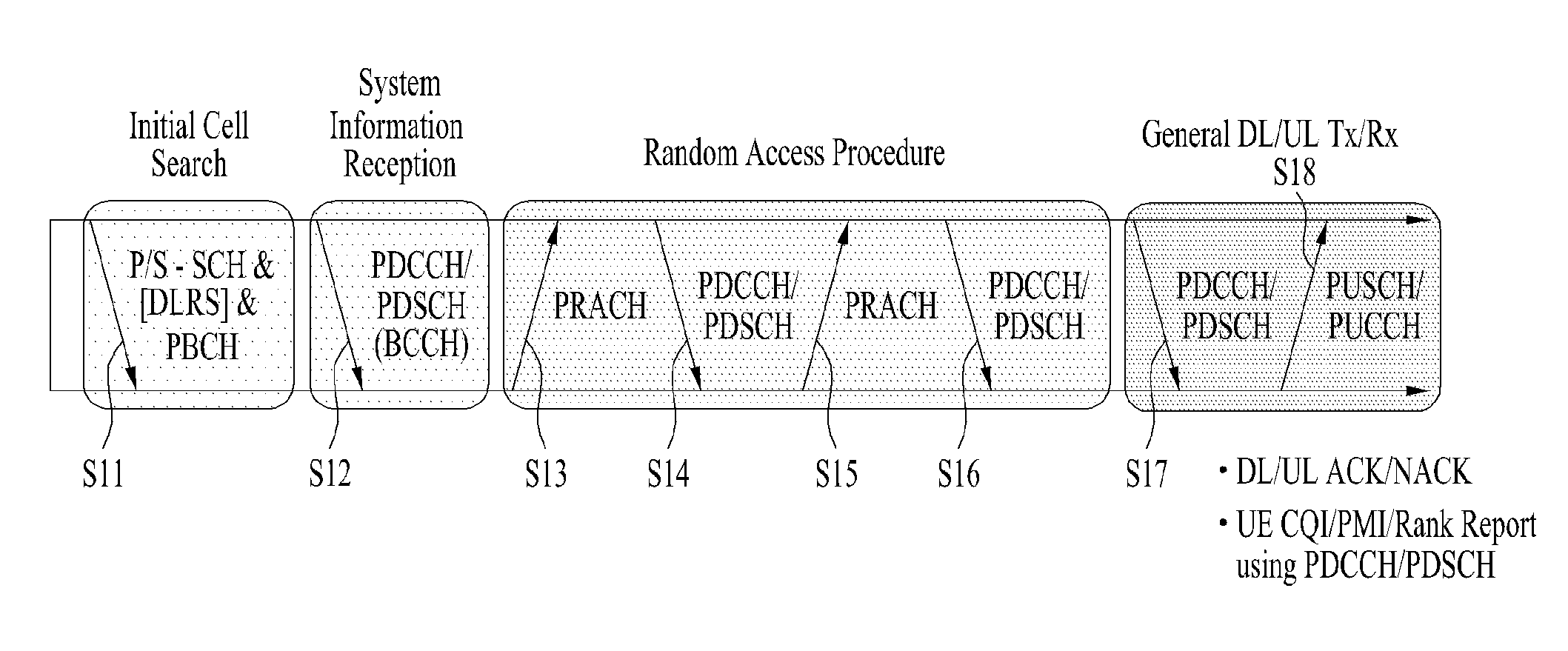
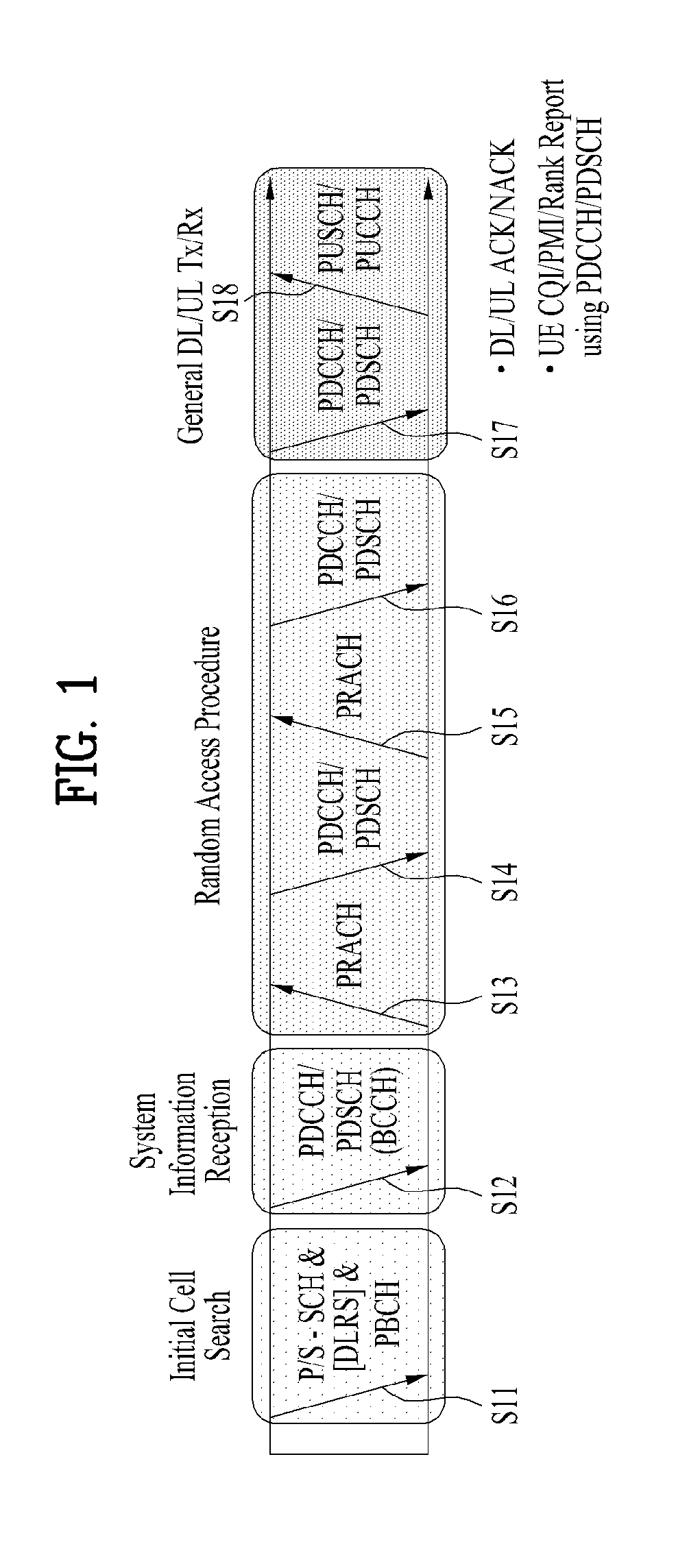
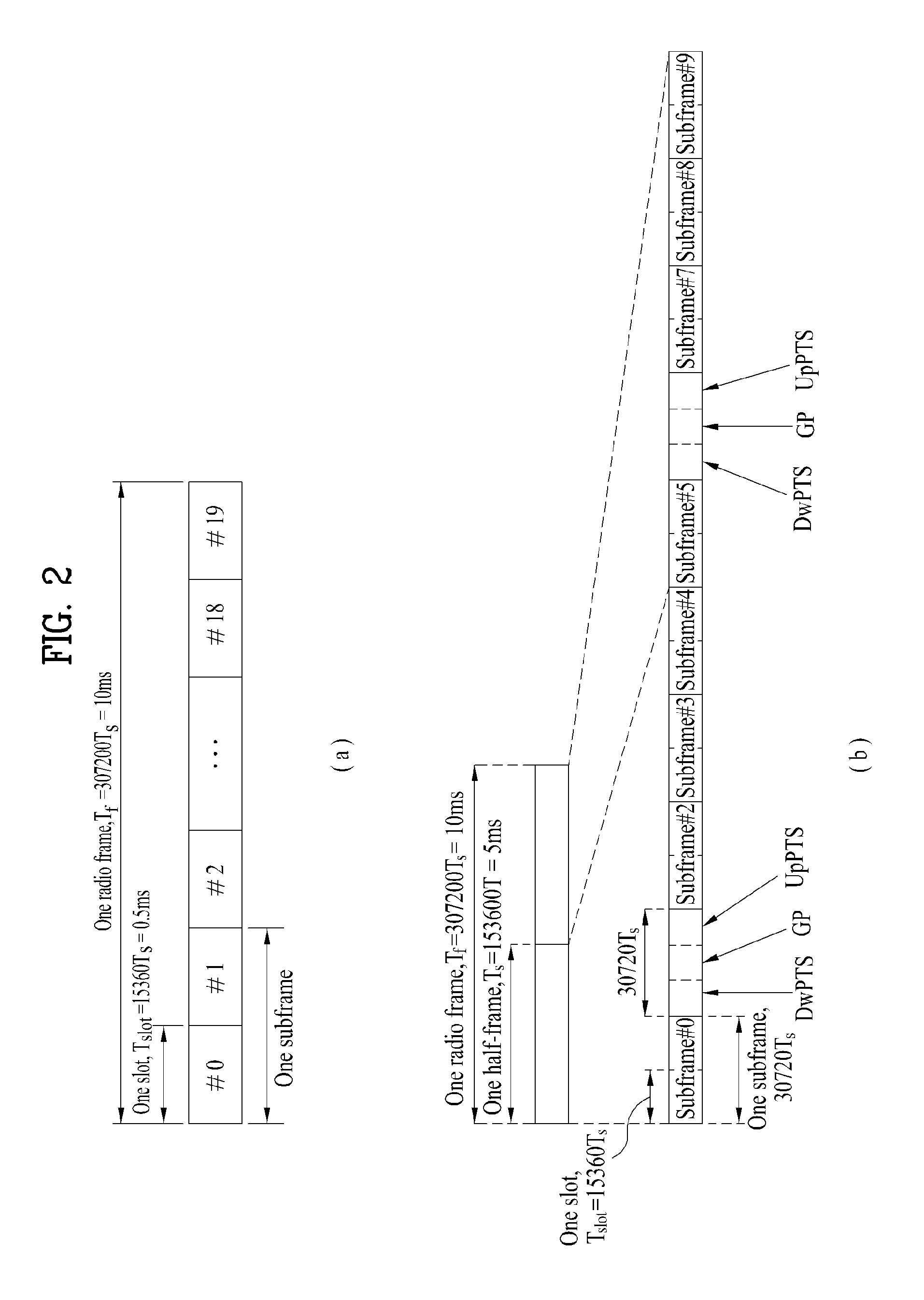
Patents
Literature
104 results about "Cell scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
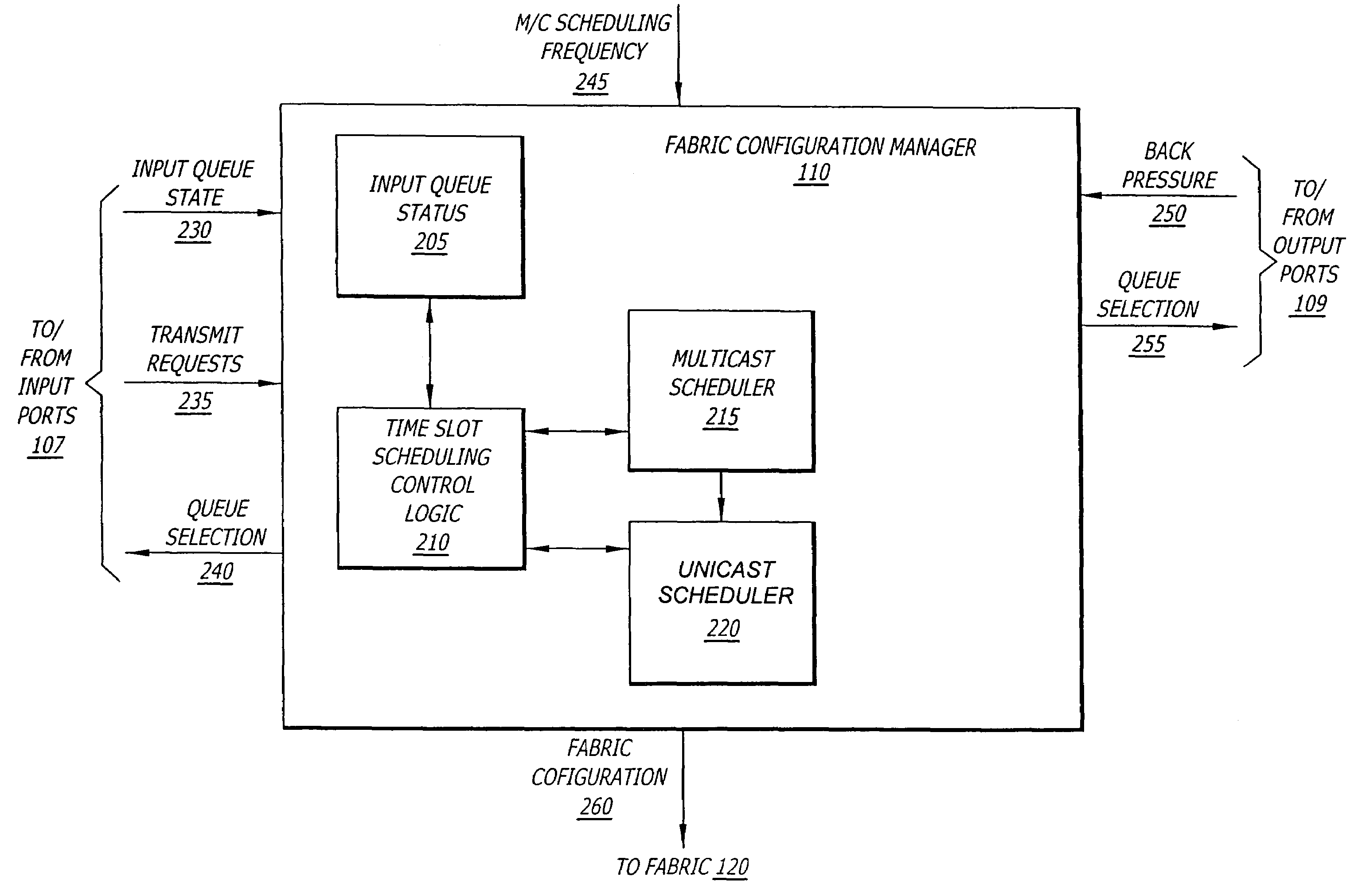
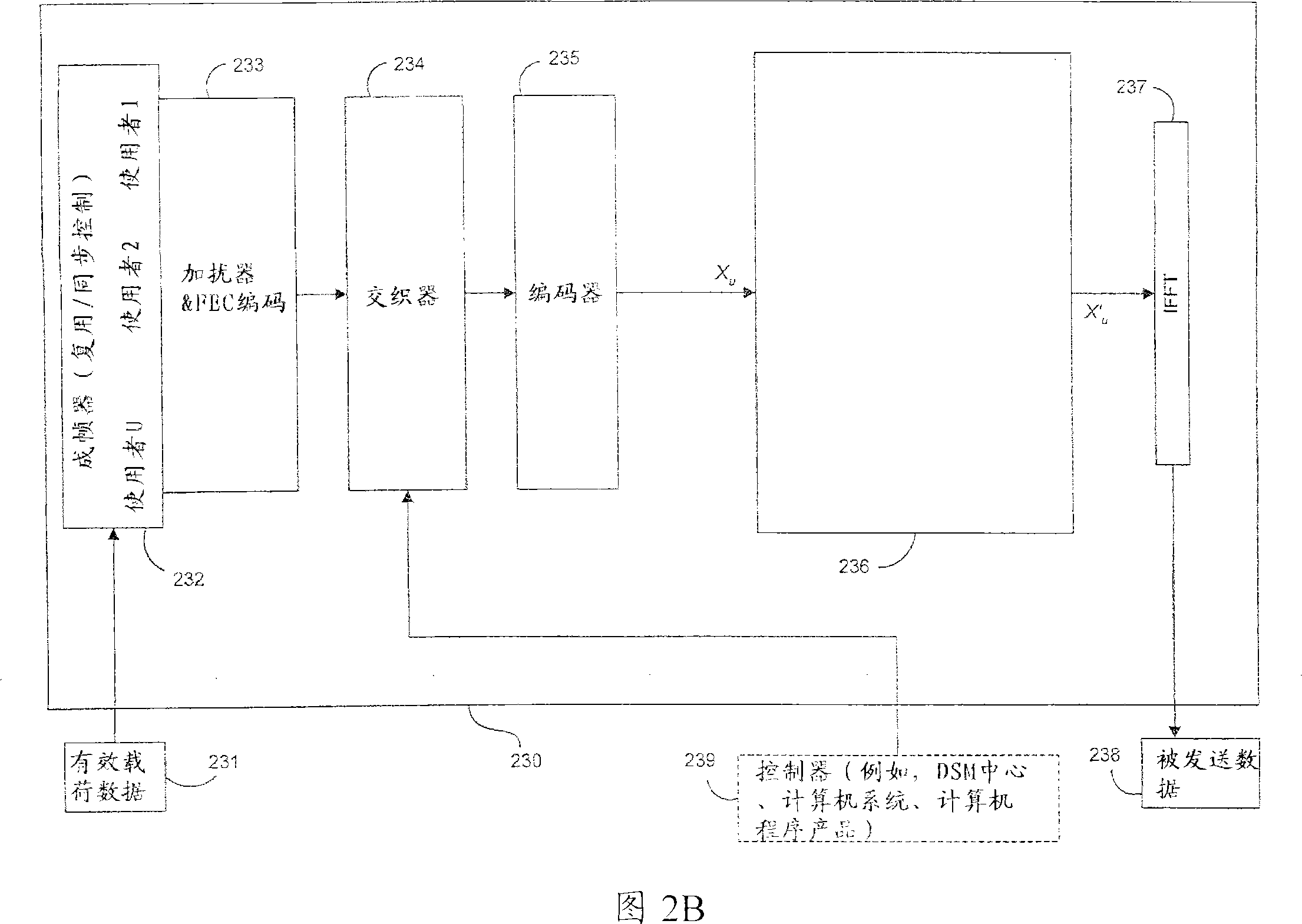
Multicast cell scheduling protocol
InactiveUS6856622B1Convenient ArrangementSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationCell schedulingCircular buffer
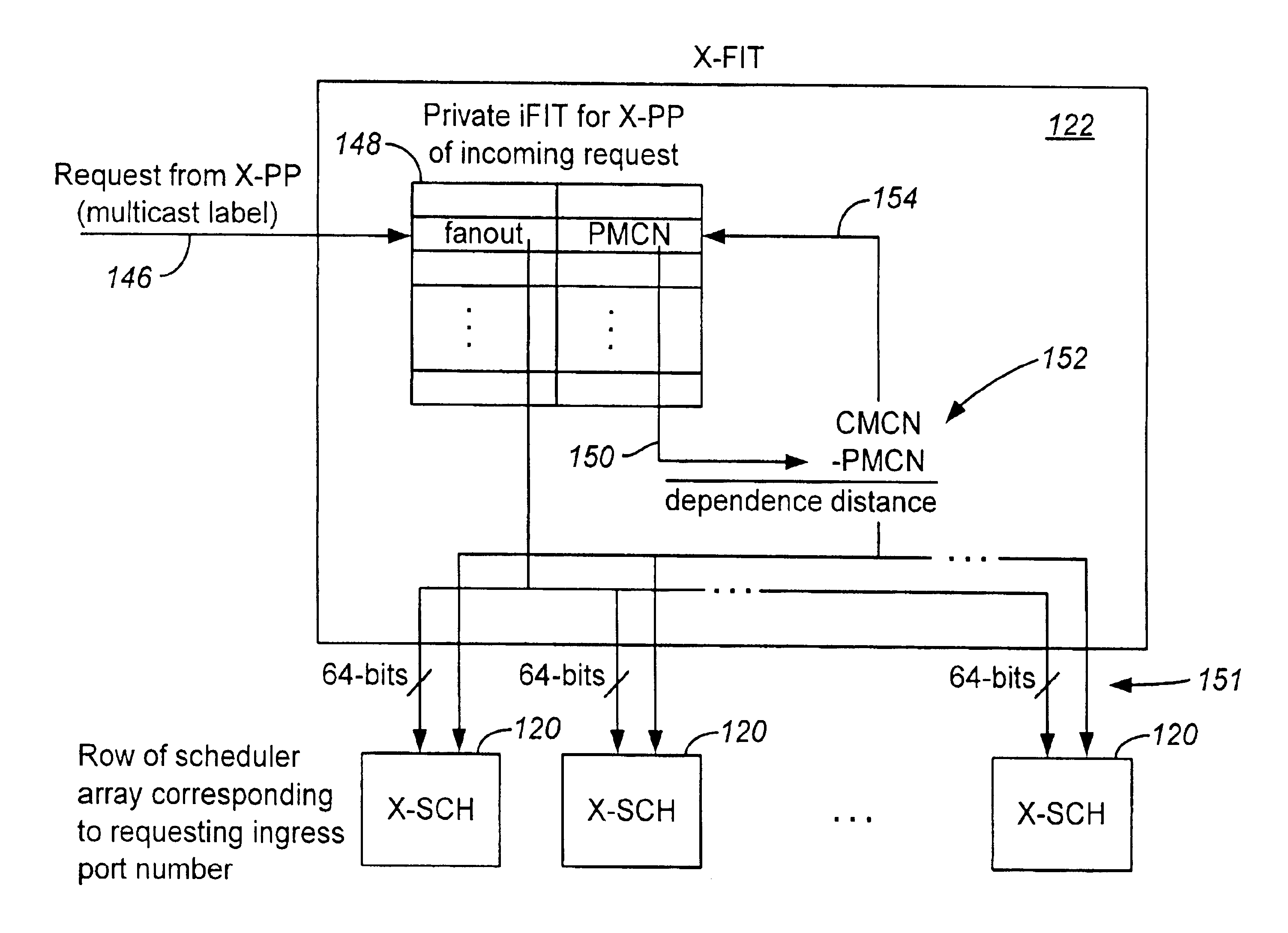
A method of facilitating the scheduling of a first multicast request signal of a series of multicast request signals is disclosed, wherein the first request signal is generated to enable the transmission of a multicast data cell by a source port processor to at least one destination port processor. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the first request signal is received by a roster storage chip associated with a scheduler subsystem. The first request signal has associated therewith a multicast label of a first value and is adapted to schedule transmission of the first multicast cell to the at least one destination port processor at a first time. A roster of the at least one destination port processor to which the first multicast cell is destined is then generated. A dependence distance associated with the first request signal is determined. The dependence distance comprises the numerical value of the difference between a current multicast cell number (CMCN) and a previous multicast cell number (PMCN). The roster and the dependence distance are transmitted to one of the at least one scheduler chips, such transmission causing the roster and the dependence distance to occupy a second tail entry slot of a second circular buffer associated with the one of the at least one scheduler chips. The second tail entry slot has associated therewith a first multicast table index (MTI) comprising a numerical value. The scheduler chip further has associated therewith a head entry slot having associated therewith a second MTI comprising a numerical value. A first numerical parameter comprising the numerical sum of the dependence distance and the first MTI is determined. If the first numerical parameter is higher in value than the second MTI, the first request signal is arbitrated.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
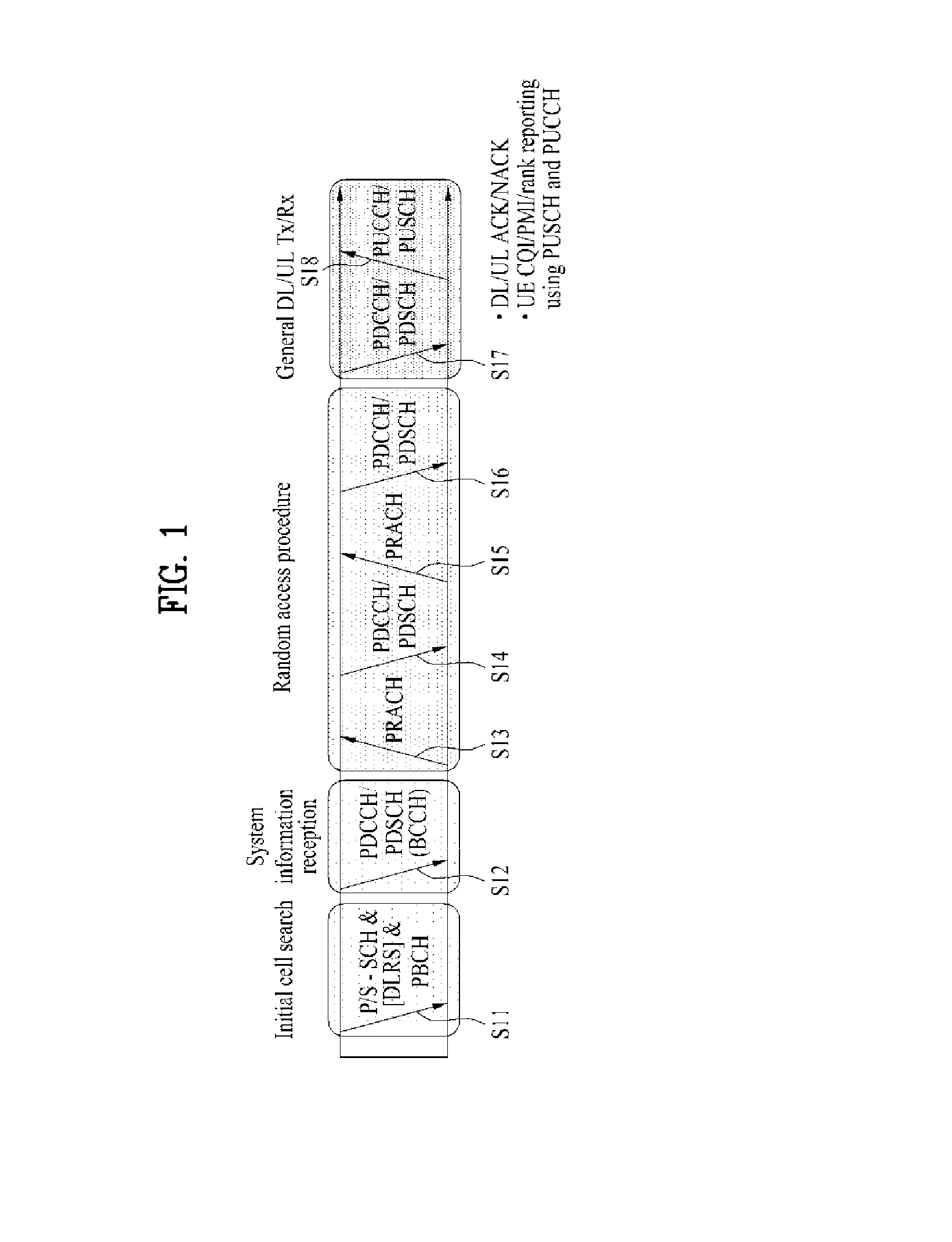
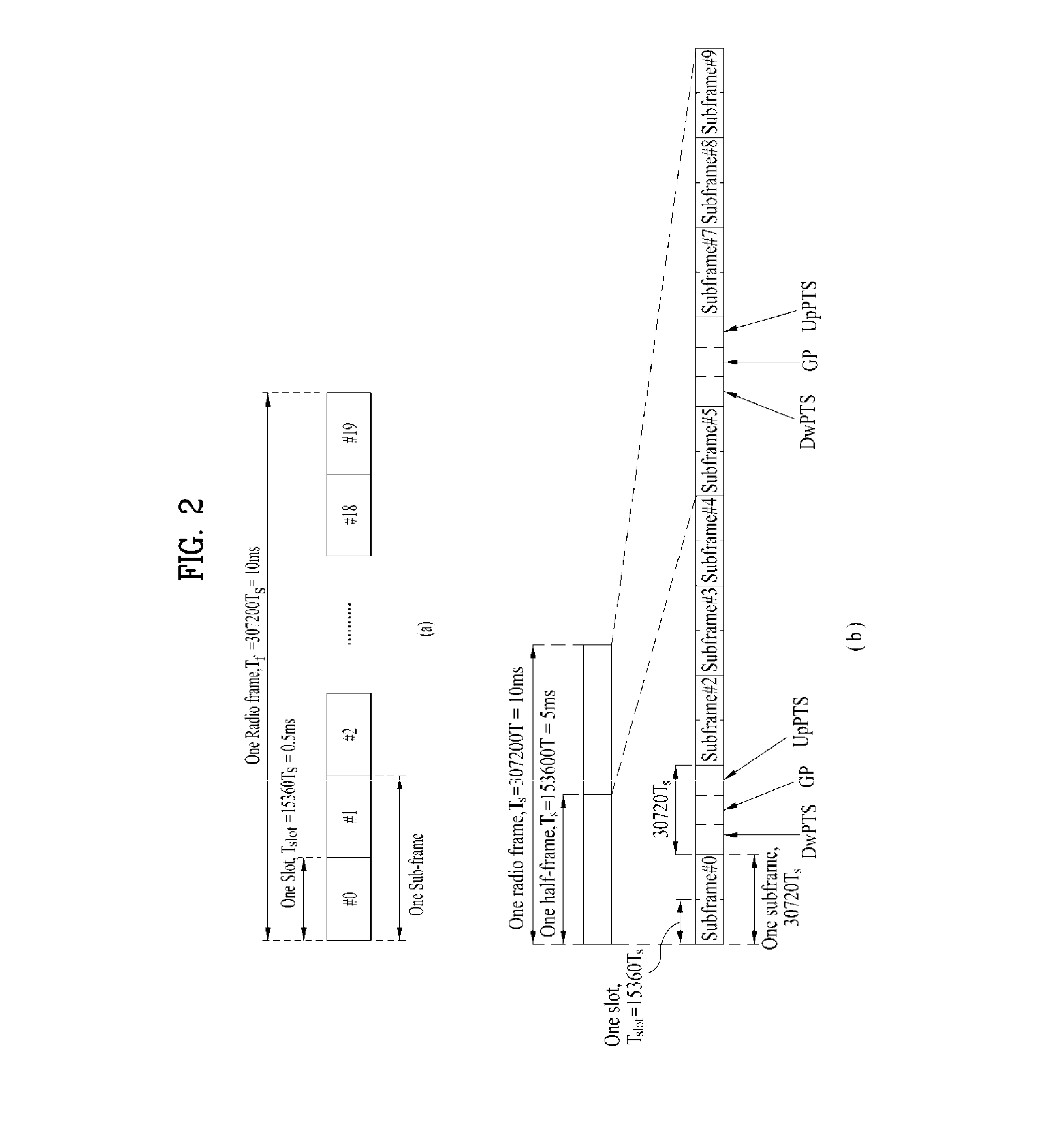
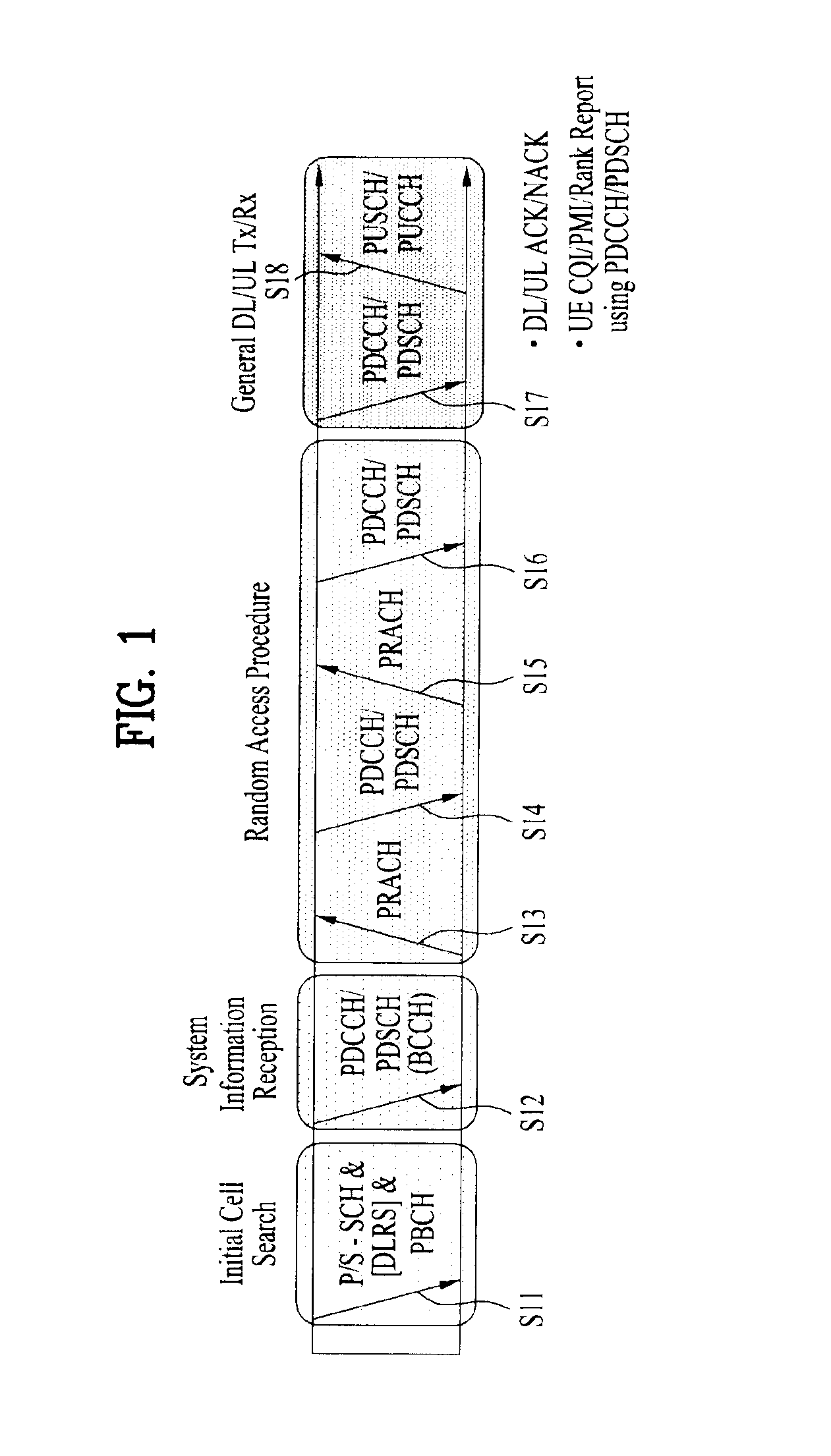
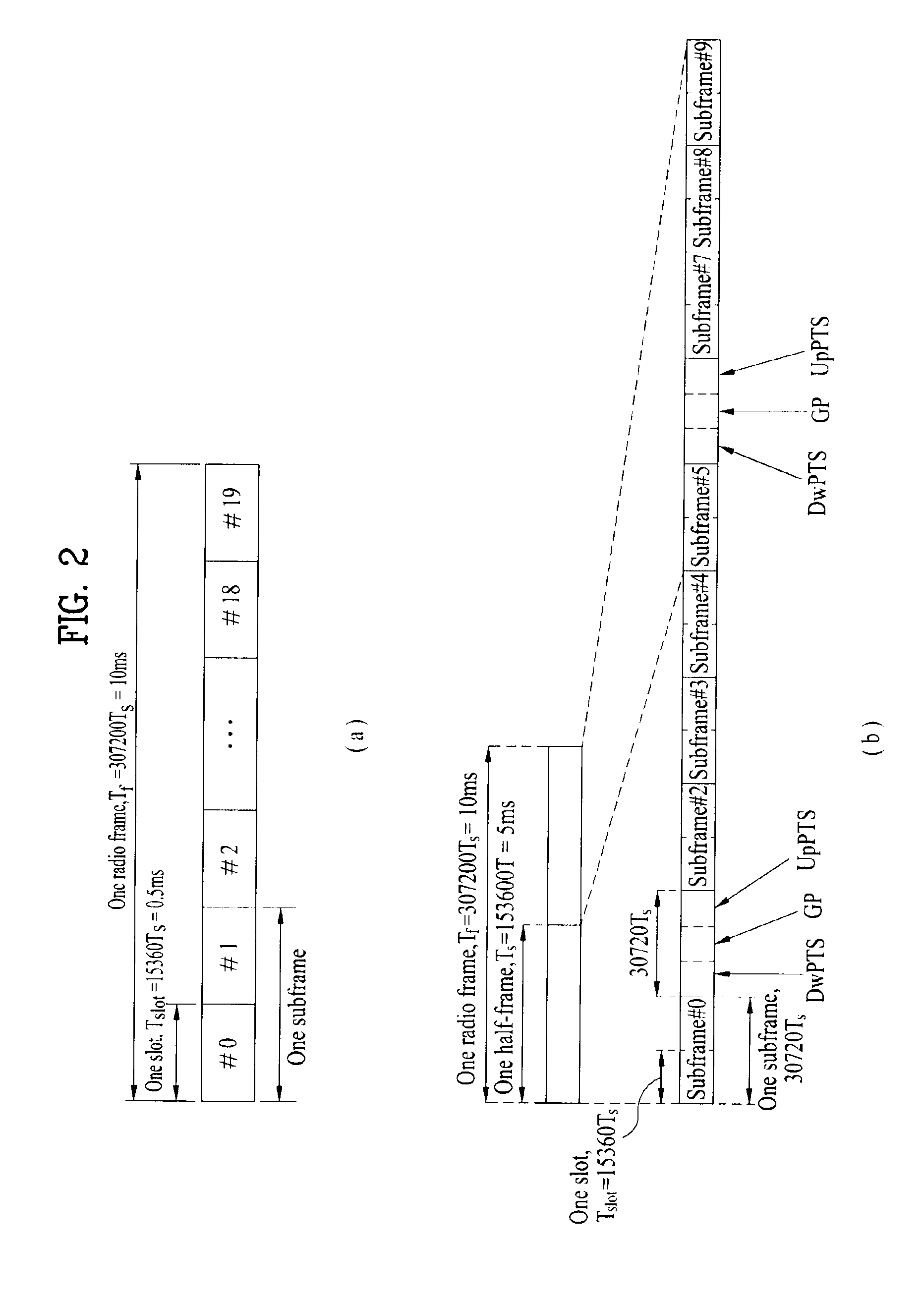
Method for transmitting/receiving data in wireless access system and base station for same
ActiveUS20140029490A1Guaranteed smooth receptionSmooth transmissionError preventionTransmission path divisionCell schedulingUser equipment
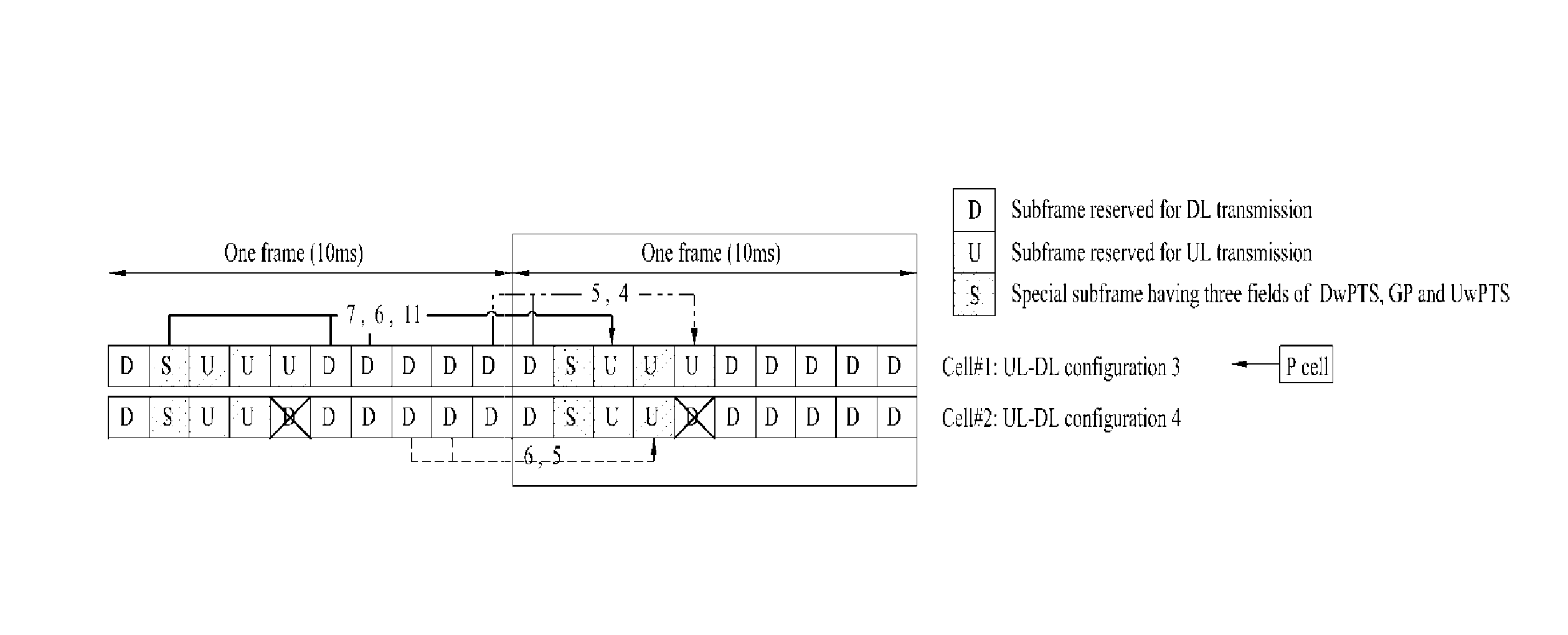
In the present invention, a method for transmitting / receiving data in a wireless access system and a base station for same are disclosed. More particularly, the method comprises the following steps: setting a cell group per at least one cell having an identical uplink-downlink configuration, if a plurality of cells are set to a user equipment; performing via a first cell cross-cell scheduling with regard to a second cell, which belongs to a cell group that is different from that including the first cell, according to the uplink-downlink configuration of the first cell; confirming the occurrence of a collision subframe, in which an uplink subframe and a downlink subframe exist simultaneously in the same time interval, in two cells performing the cross-cell scheduling; and transmitting / receiving data with the user equipment when scheduled in the collision subframe due to the cross-cell scheduling, by modifying a transmission position of the uplink or the downlink according to the cross-cell scheduling.
Owner:ROSEDALE DYNAMICS LLC
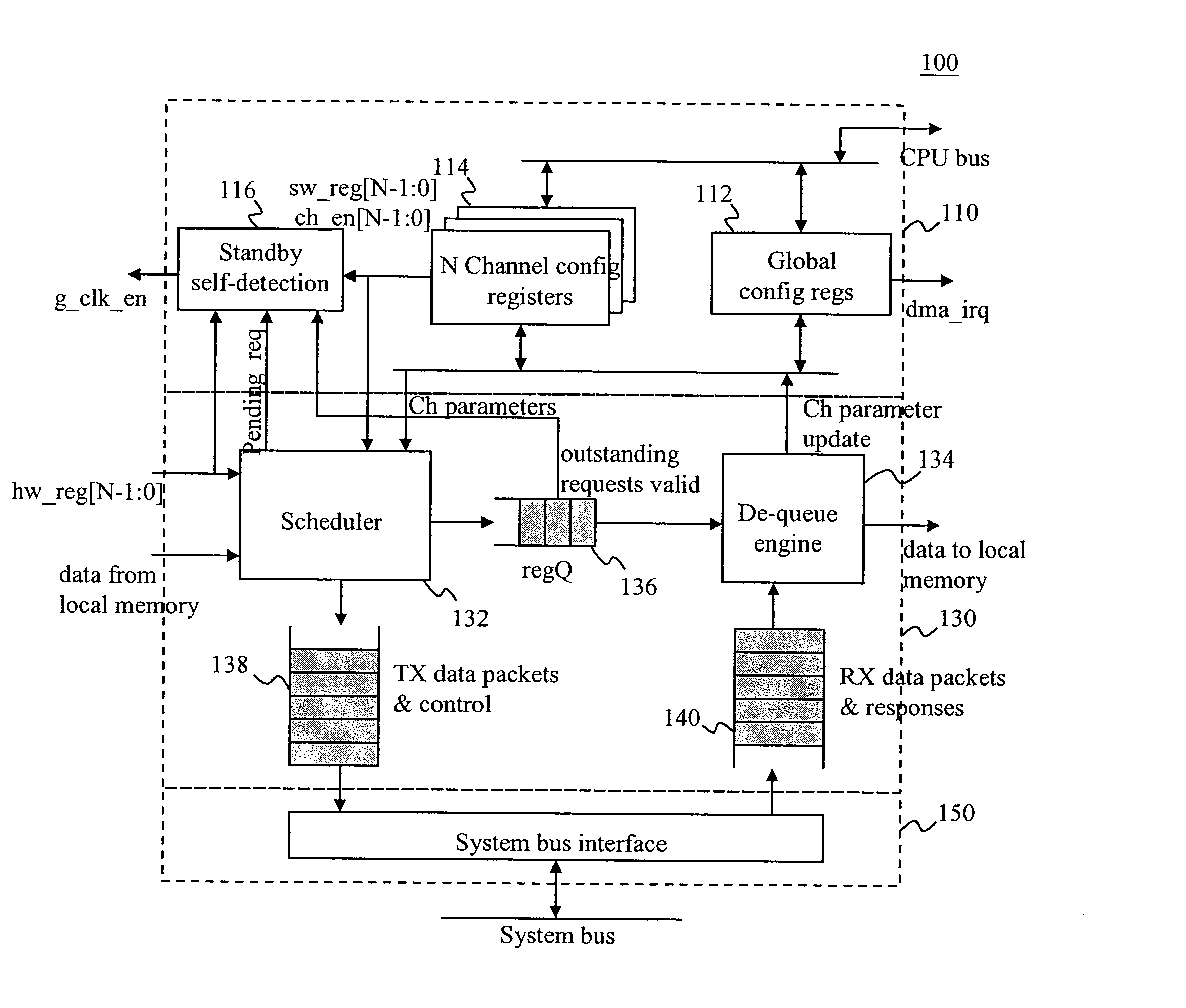
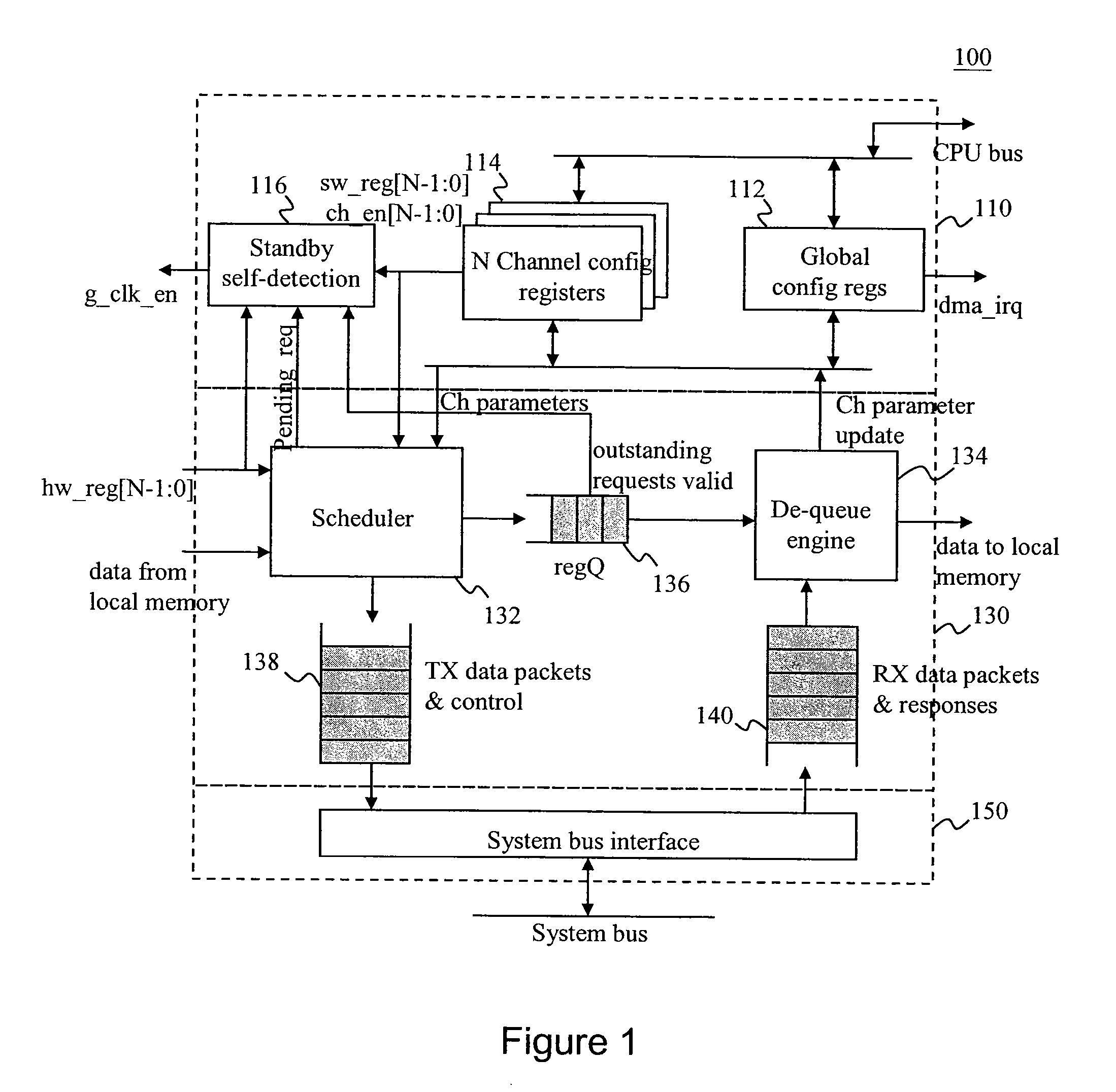
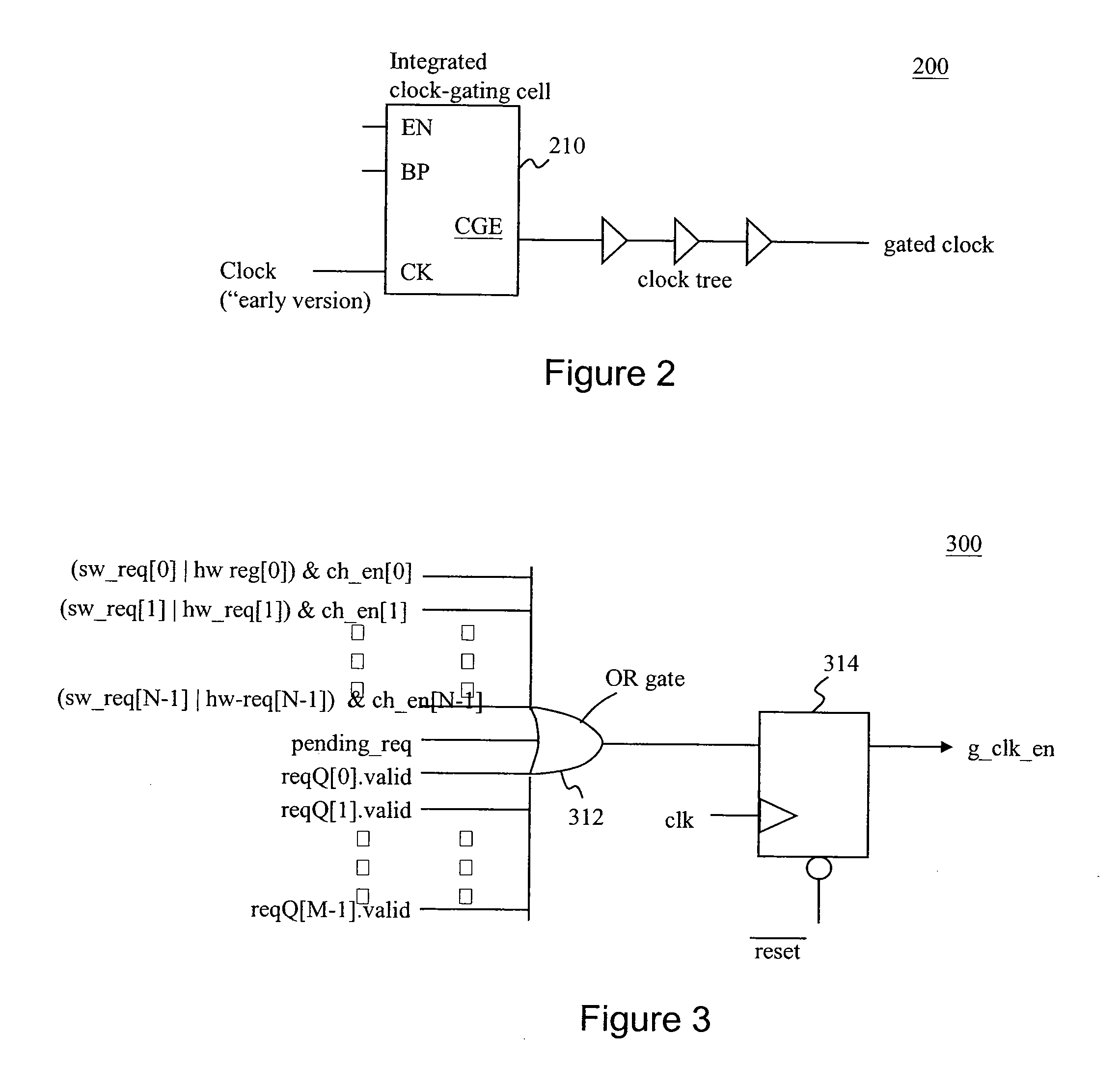
DMA Controller With Self-Detection For Global Clock-Gating Control
InactiveUS20070162648A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingCell schedulingClock tree
A standby self-detection mechanism in a DMA controller which reduces the power consumption by dynamically controlling the on / off states of at least one clock tree driven by global clock-gating circuitry is disclosed. The DMA controller comprises a standby self-detection unit, a scheduler, at least one set of channel configuration registers associated with at least one DMA channel, and an internal request queue which holds already scheduled DMA requests that are presently outstanding in the DMA controller. The standby self-detection unit drives a signal to a global clock-gating circuitry to selectively turn on or off at least one of the clock trees to the DMA controller, depending on whether the DMA controller is presently performing a DMA transfer.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
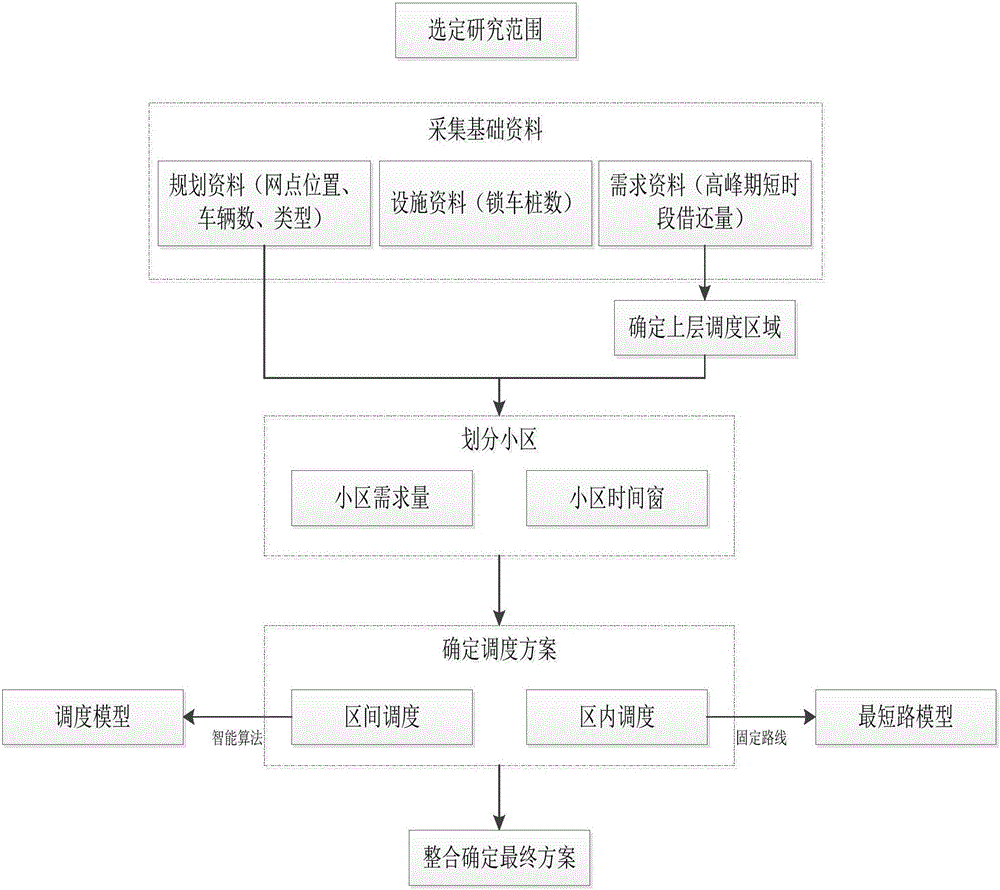
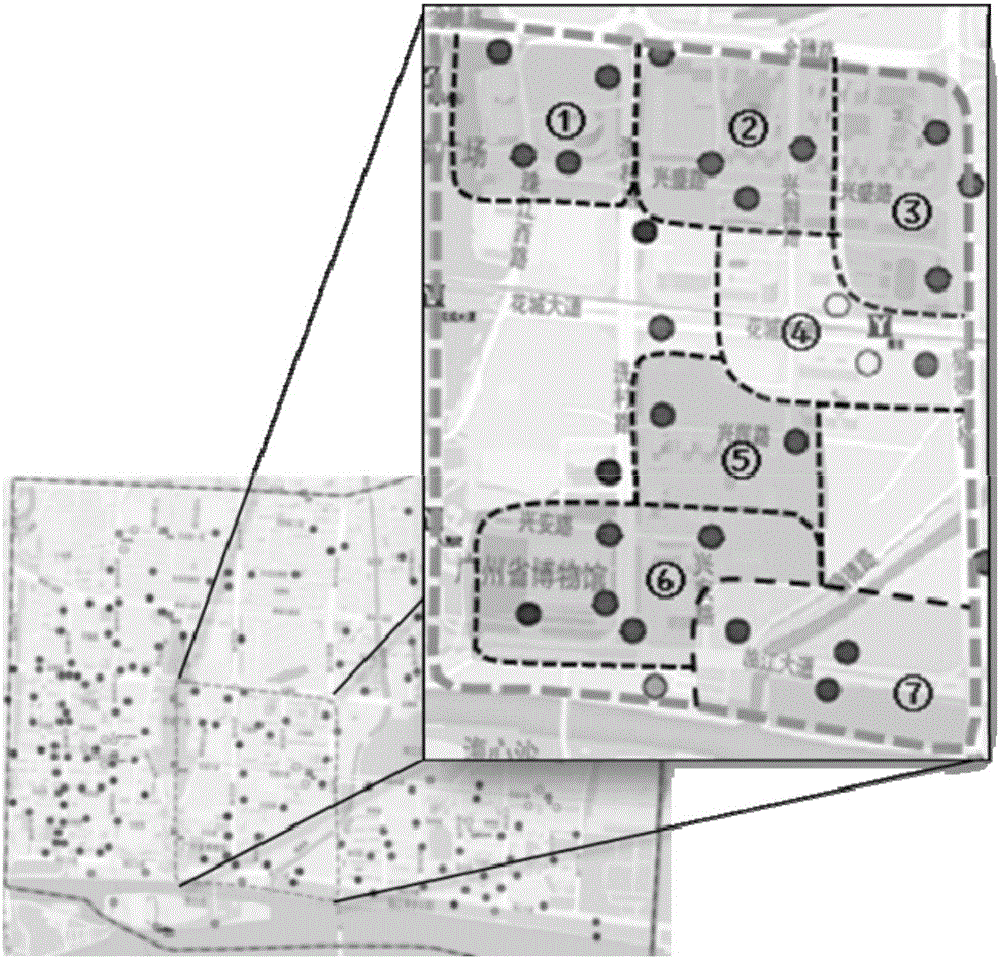
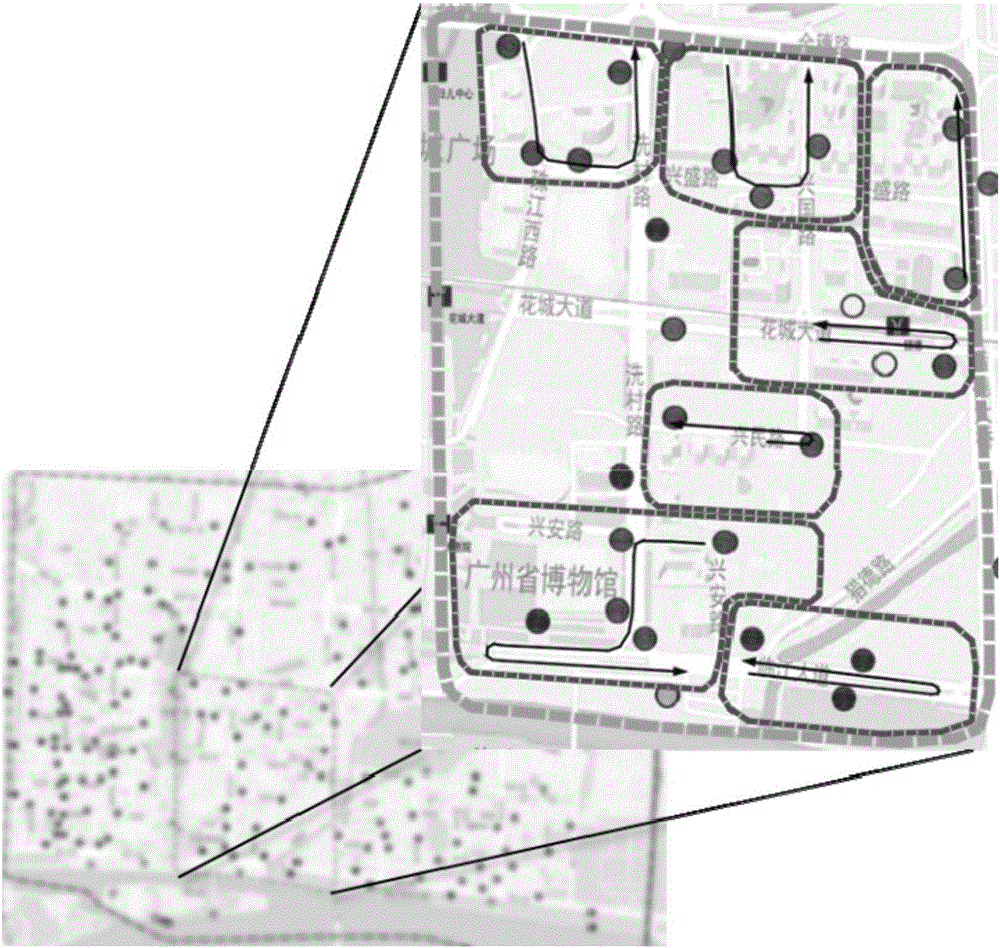
Public bicycle peak time scheduling method based on multilevel partition
InactiveCN105719083AReduce scheduling blindnessShorten the timeBuying/selling/leasing transactionsResourcesCell schedulingTime windows
The invention discloses a public bicycle peak time scheduling method based on multilevel partition. The public bicycle peak time scheduling method is characterized in that 1), a research range can be selected, and base materials can be acquired; 2) an upper layer scheduling area can be determined, and the relation between the rental station bicycle locking pile number and the borrowing and returning demand can be analyzed, and the surrounding rental stations can be brought into the scheduling area by the degree of the bicycle flowing correlation of different rental stations, until the upper layer scheduling area is the public bicycle peak time main flowing range; 3) cell distribution can be carried out in the scheduling area, and according to the rental station peak time operation data, the cells can be divided and numbered by combining the clustering analysis and the artificial adjusting method; 4) the inter-cell scheduling scheme can be determined; 5) the cell fixed scheduling scheme can be determined; and 6) the peak time integrated scheme can be made by combining the inter-cell scheduling scheme and the cell scheduling scheme. The scheduling areas can be divided in a targeted manner by adopting the layered scheduling method, and the scheduling schemes can be determined according to the demand and the time window, and the scheduling blindness caused by the wide distribution of the peak time demands can be reduced effectively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
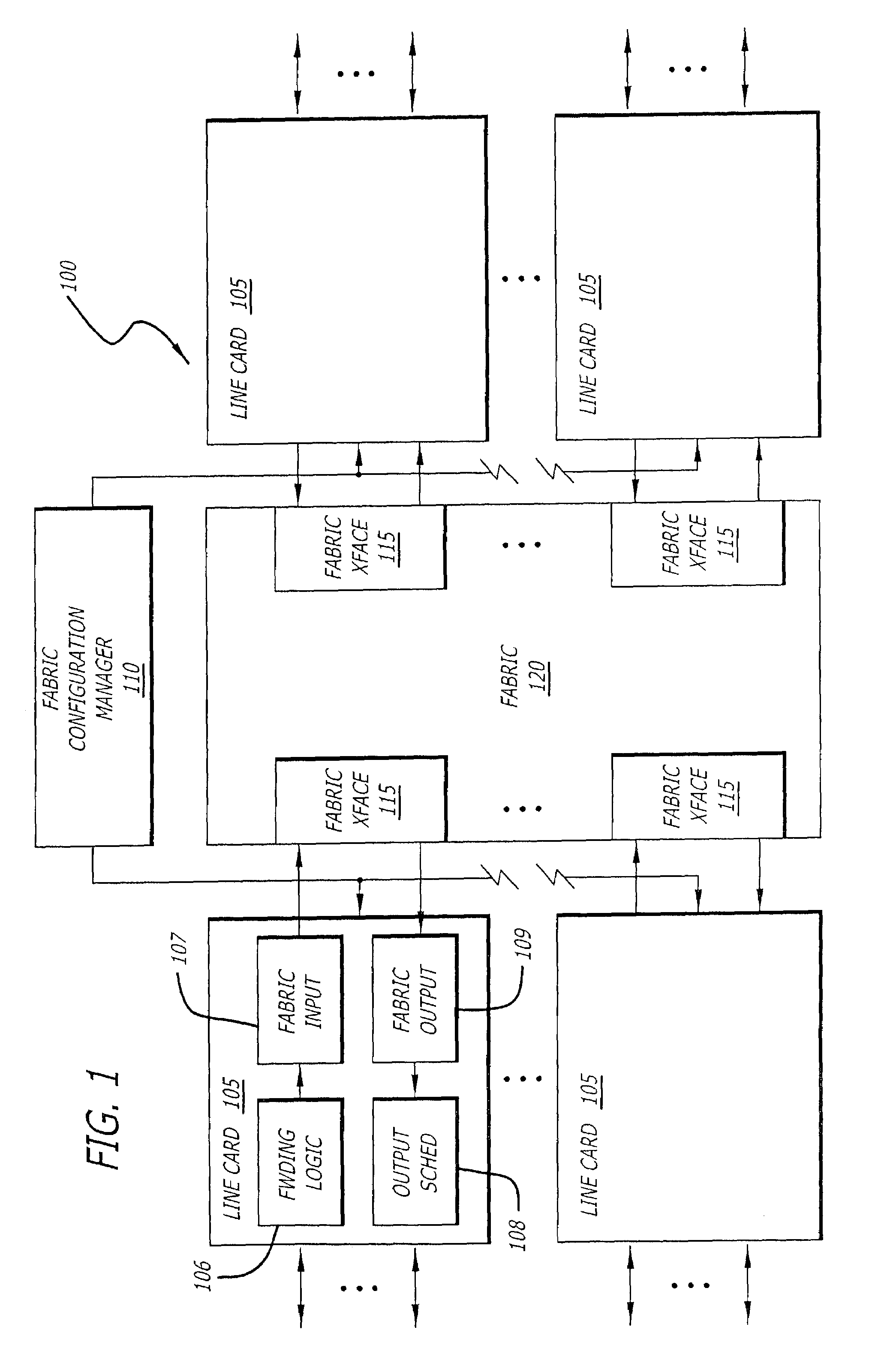
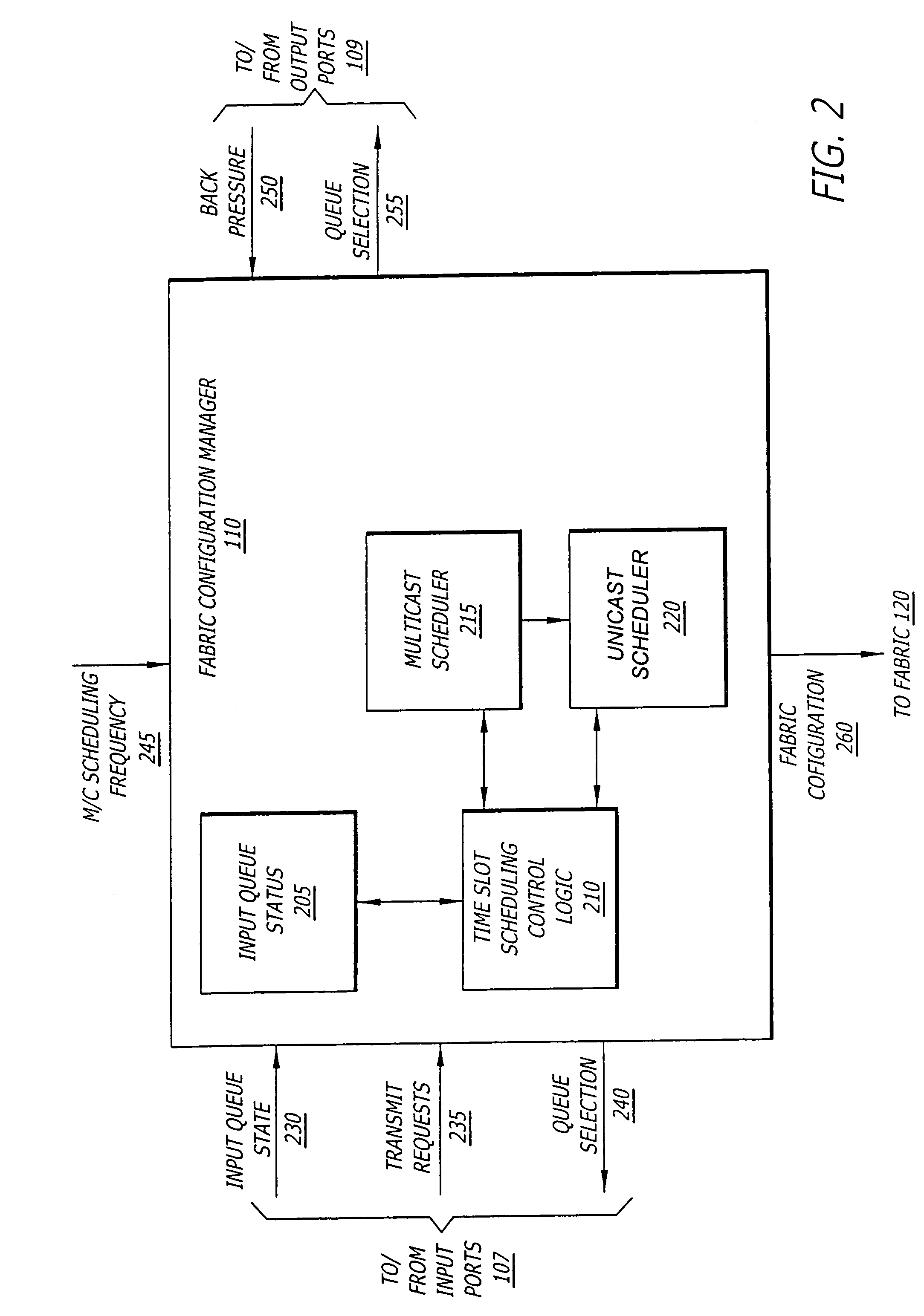
Multicast and unicast scheduling for a network device
InactiveUS7519065B2Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationCell schedulingClass of service
A method and apparatus are provided for scheduling unicast and multicast data in an input-queued network device. According to one aspect of the present invention, a combined schedule is created by pipelined staging of multicast and unicast scheduling. Multicast cells are scheduled for transmission among multiple interfaces of a crossbar by performing a multicast cell scheduling cycle for multiple classes of service that are supported by the network device. Then, unicast cells are scheduled for transmission among the interfaces at a lower priority than the previously scheduled multicast cells by performing a unicast cell scheduling cycle for the multiple classes of service using only those interfaces that remain unmatched after completion of the multicast cell scheduling cycle.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
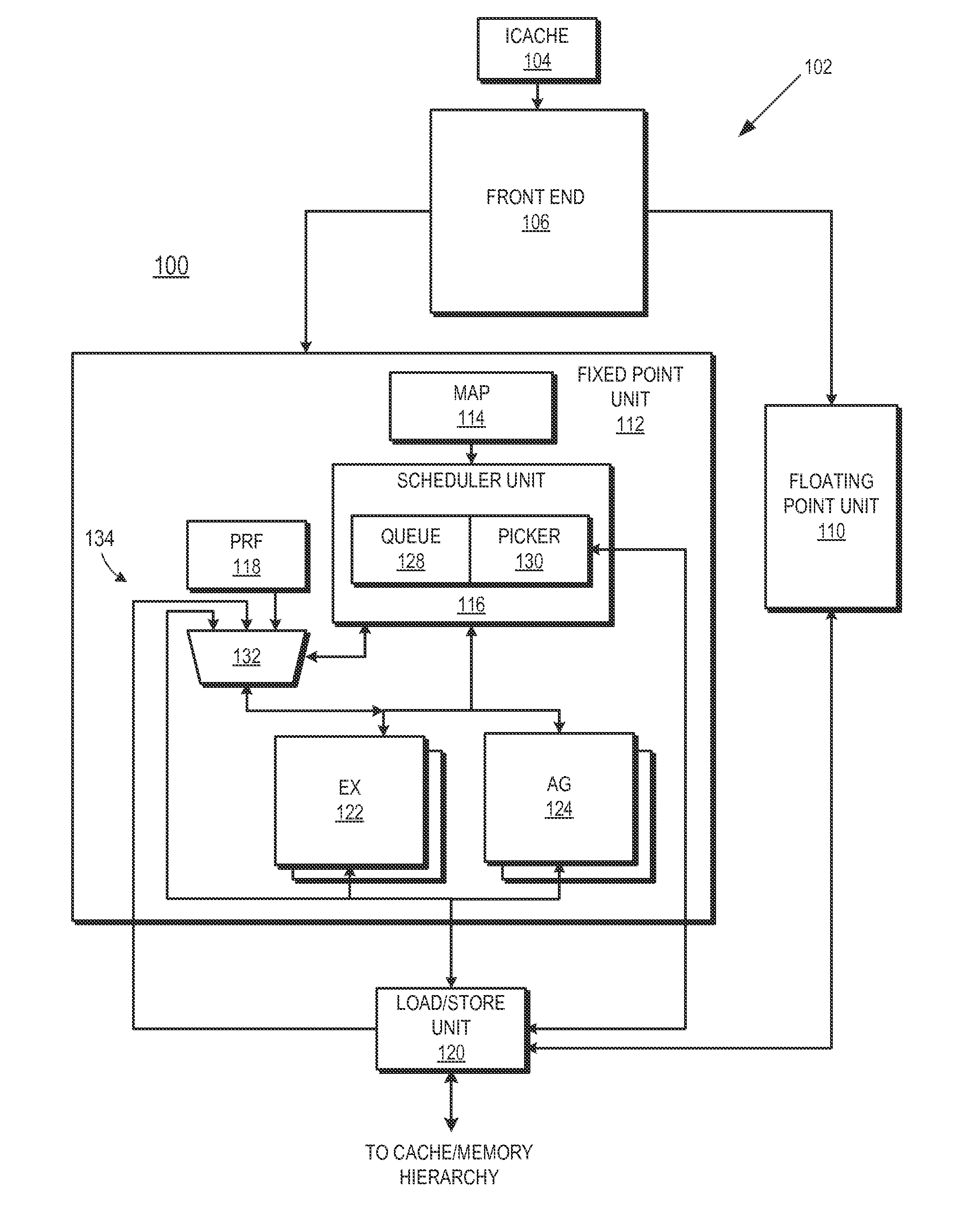
Dependent instruction suppression in a load-operation instruction
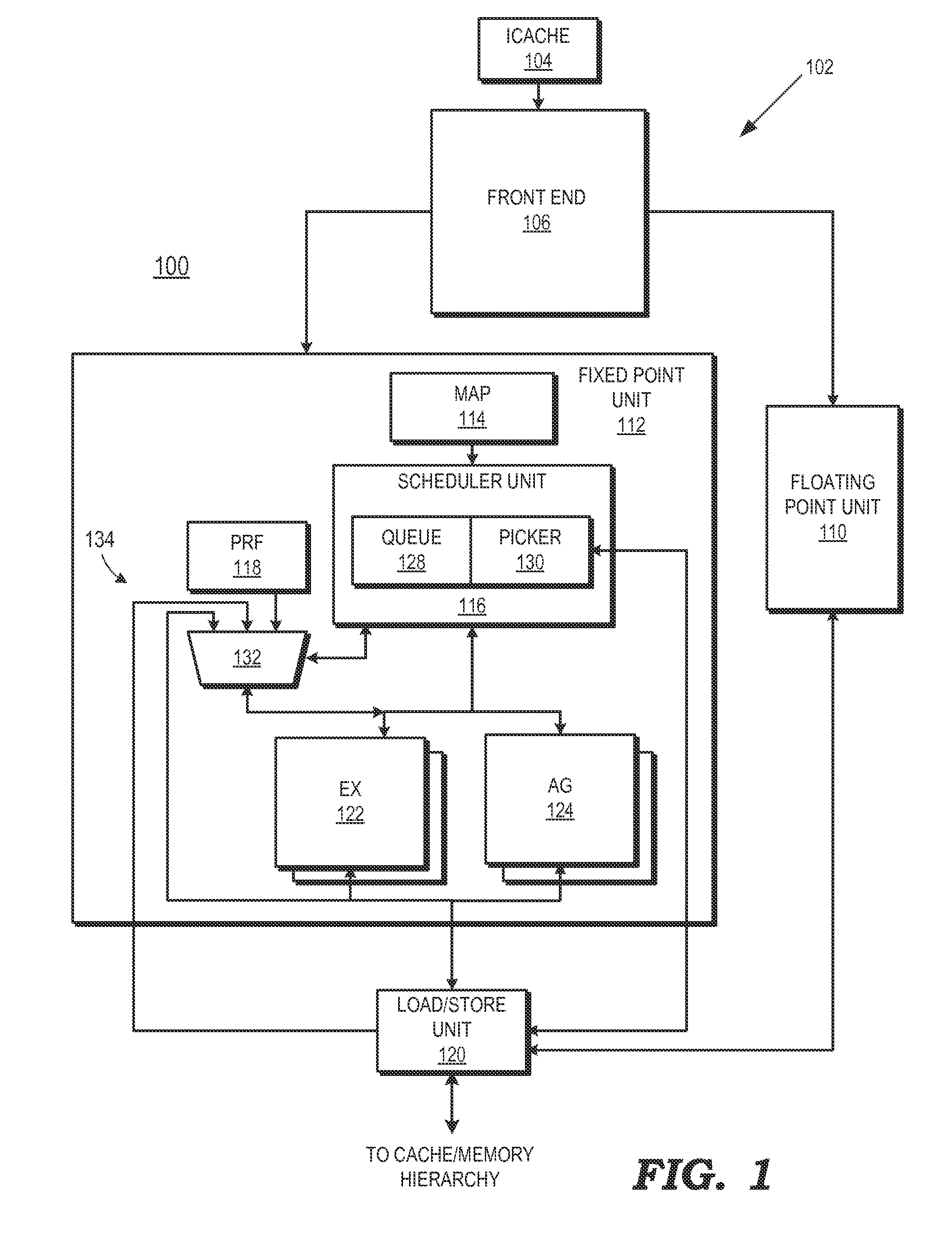
ActiveUS20150026686A1Program initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsCell schedulingExecution unit
A method includes suppressing execution of an operation portion of a load-operation instruction in a processor responsive to an invalid status of a load portion of load-operation instruction. A processor includes an instruction pipeline including an execution unit operable to execute instructions and a scheduler unit. The scheduler unit includes a scheduler queue and is operable to store a load-operation in the scheduler queue. The load-operation instruction includes a load portion and an operation portion. The scheduler unit schedules the load portion for execution in the execution unit, marks the operation portion in the scheduler queue as eligible for execution responsive to scheduling the load portion, receives an indication of an invalid status of the load portion, and suppresses execution of the operation portion responsive to the indication of the invalid status.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Methods and apparatus for switching packets
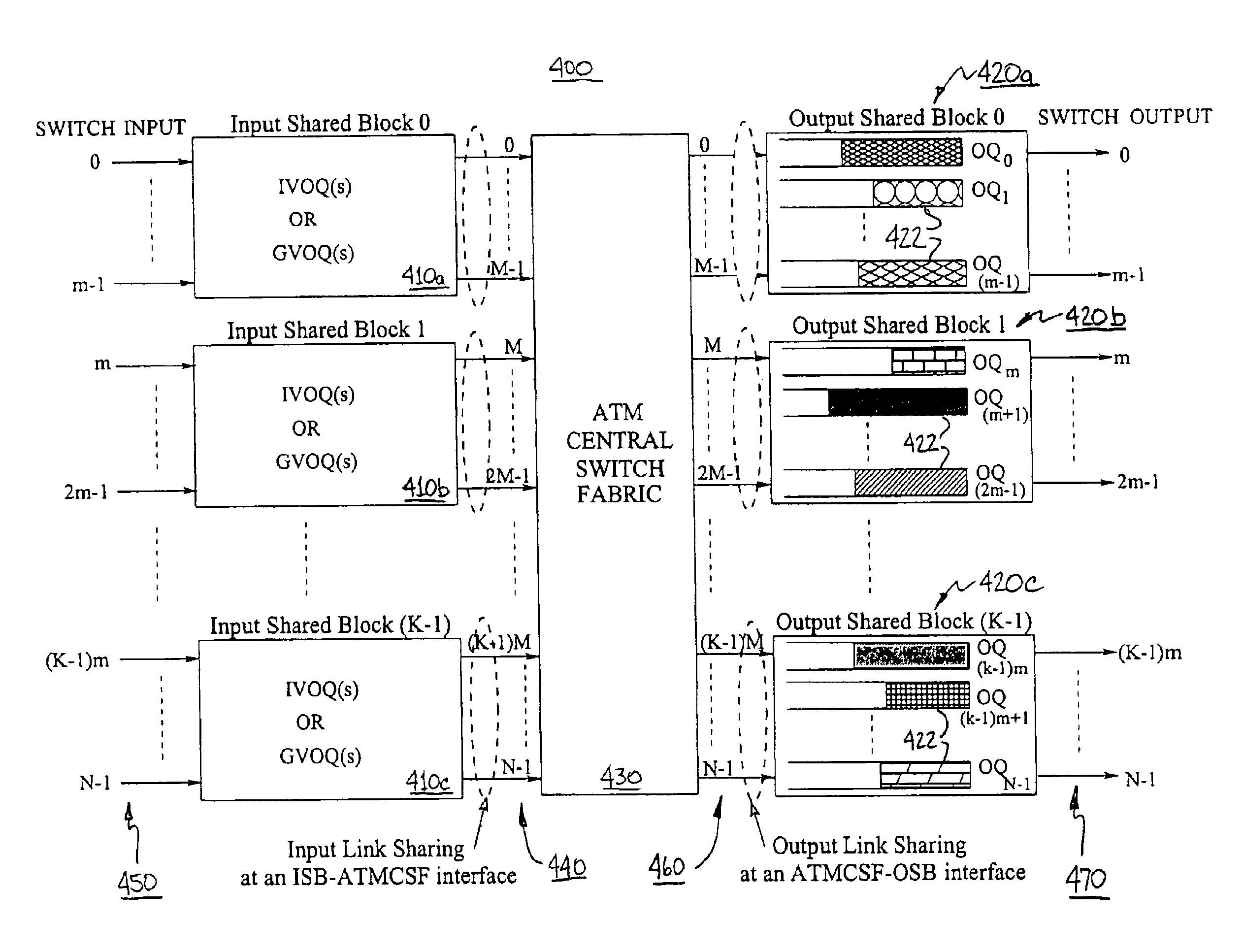
InactiveUS6961342B1Can be highImprove scalabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCell schedulingLarge size
In Switches, switch inputs and outputs may be grouped into (e.g., small) modules called input shared blocks (or “ISBs”) and output shared blocks (or “OSBs”), respectively. Each of the switches includes three (3) main parts: (i) input shared blocks (ISBs); (ii) a central switch fabric (or “ATMCSF”); and (iii) output shared blocks (OSBs). Input link sharing at every ISB-ATMCSF interface and output link sharing at every ATMCSF-OSB interface cooperate intelligently to resolve output contention and essentially eliminate any speedup requirement in central switch fabric. Each of the proposed switches can easily scale to a large size by cascading additional input and output shared blocks (ISBs and OSBs). Instead of using a centralized scheduler to resolve input and output contention, the each of the switches applies a distributed link reservation scheme upon which cell scheduling is based. In one embodiment, a dual round robin dynamic link reservation technique, in which an input shared block (ISB) only needs its local available information to arbitrate potential modification for its own link reservation, may be used.
Owner:UZUN NECDET
Method for transmitting/receiving data in a wireless access system and base station for same
ActiveUS20140016519A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionError preventionTransmission path divisionCell schedulingData transmission
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting / receiving data in a Time Division Duplex (TDD) wireless access system supporting multiple cells, and a base station for same. In more detail, on the basis of a multi-cell TDD uplink-downlink configuration, the method includes confirming whether a collision subframe occurs, which is caused when an uplink subframe of a first cell and a downlink subframe of a second cell exists in the same time interval; and performing cross cell scheduling on the second cell through the first cell according to a TDD uplink-downlink configuration of the first cell. When data transmission is scheduled in the collision subframe by cross cell scheduling, by changing the transmission position of an uplink or a downlink according to the cross cell scheduling, the scheduled data are transmitted in the collision subframe.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
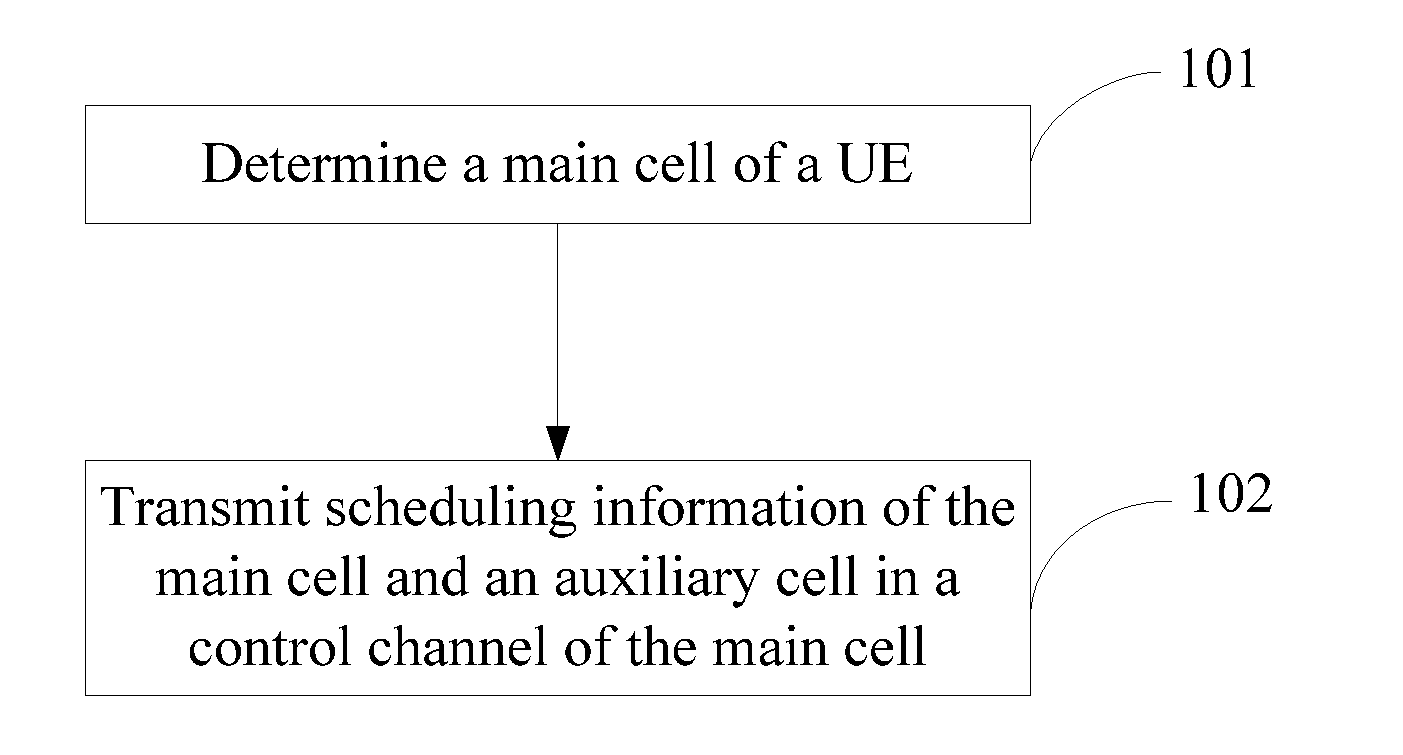
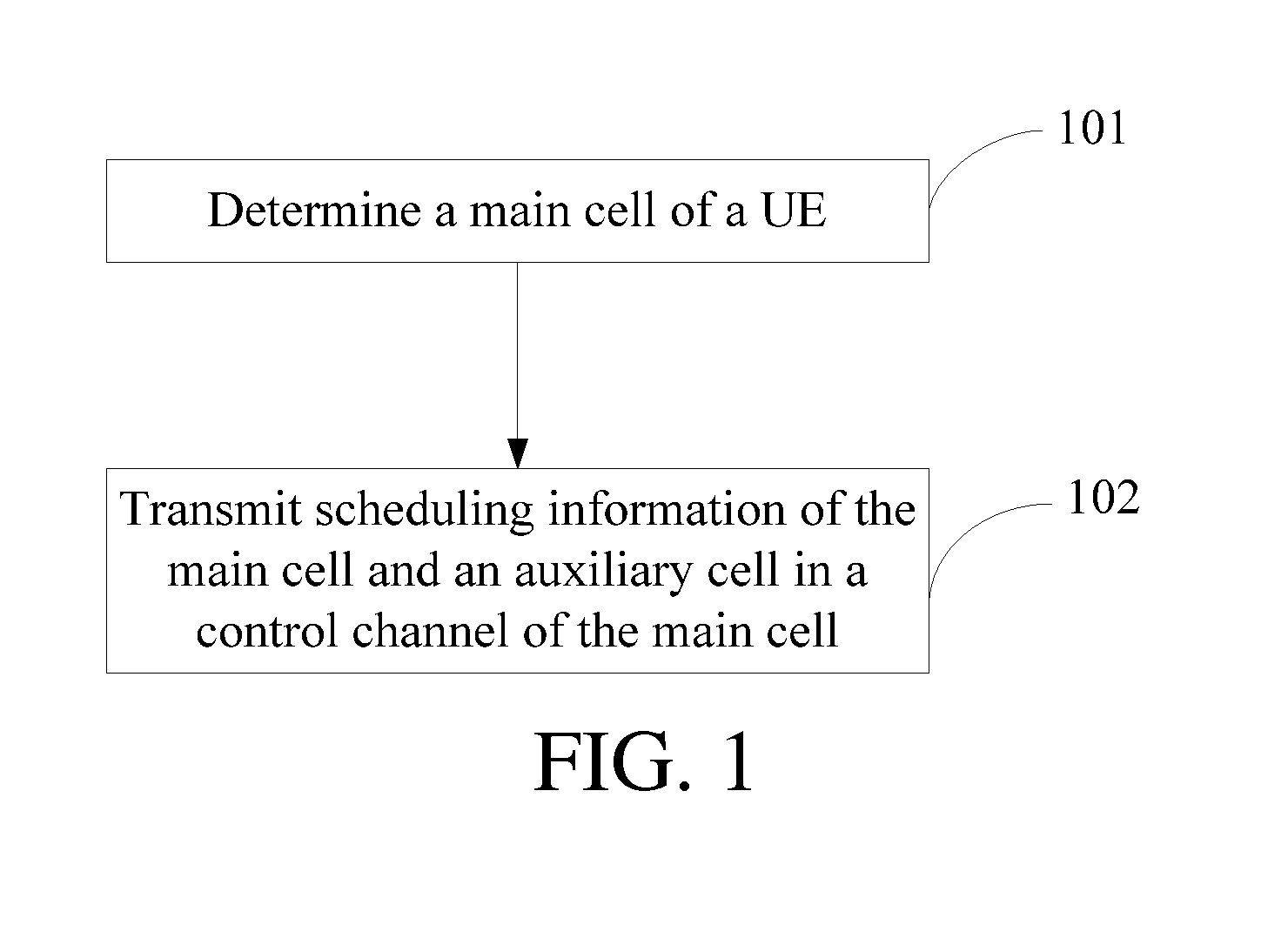
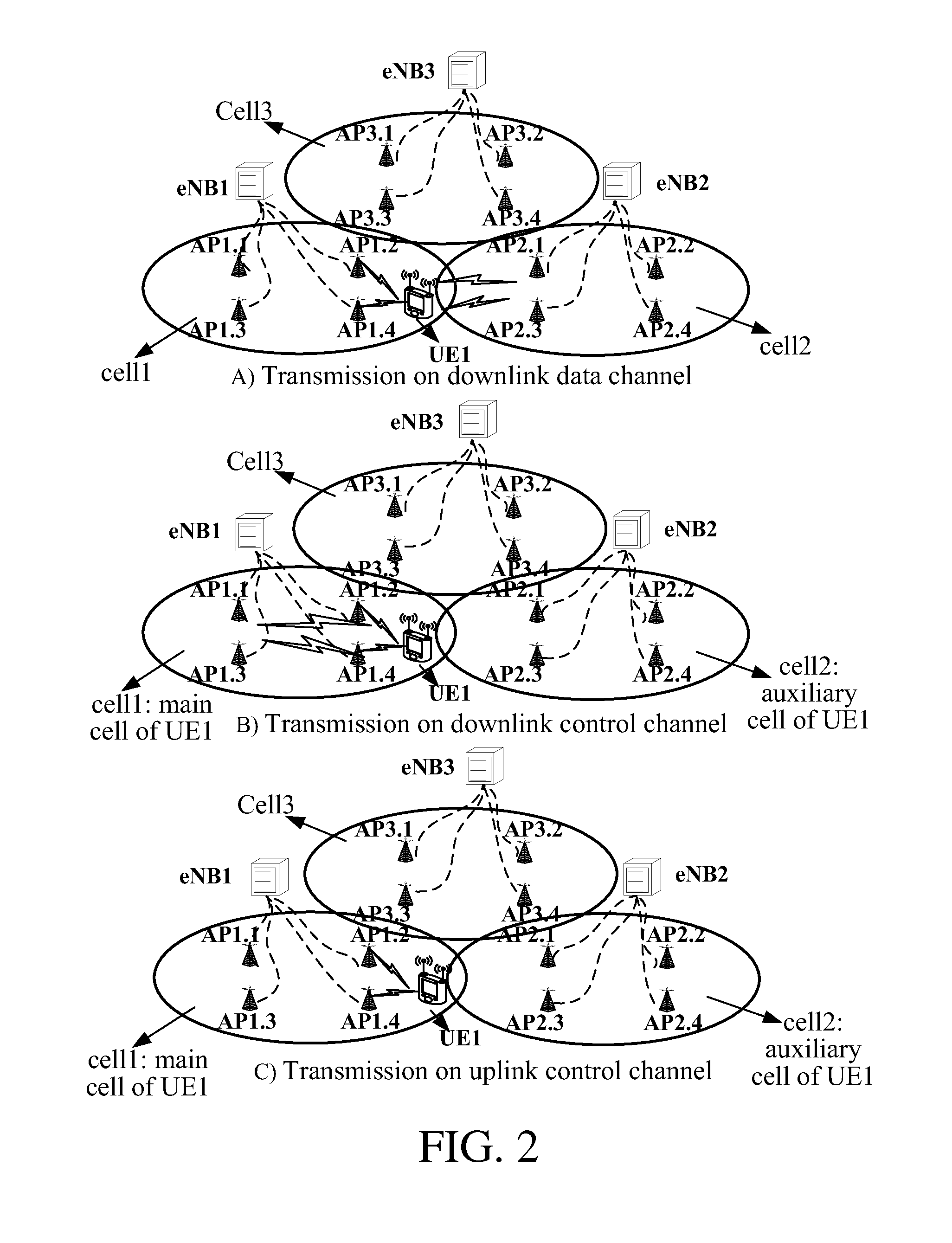
Method, Device and User Equipment for Transmitting Multi-Cell Scheduling Information
ActiveUS20110182200A1Saving detection timeSave powerPower managementError preventionTelecommunicationsCell scheduling
A method, device and user equipment (UE) for transmitting multi-cell scheduling information is provided. When at least two cells are serving the UE, the method for transmitting multi-cell scheduling information includes the following steps: determining a main cell of the UE from the at least two cells; transmitting, in the main cell, the scheduling information of the main cell and an auxiliary cell which are serving the UE.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for transmitting/receiving data in wireless communication system and base station for same
ActiveUS20140050130A1Guaranteed smooth receptionProcess stabilityTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemCell scheduling
In the present invention, a method for transmitting / receiving data in a wireless communication system supporting carrier aggregation / multiple cells and a base station for same are disclosed. More particularly, the method comprises: receiving from the e Node B through a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) of a first cell resource allocation information, which is set as a flag value indicating uplink resource allocation information, when performing cross-cell scheduling on a second cell through a first cell, according to an uplink-downlink configuration of the first cell from a plurality of cells which are set to a user equipment; determining the resource allocation information as a downlink resource allocation information, when the resource allocation information is received from a subframe perspective in which an uplink transmission time is not defined, based on the uplink-downlink configuration of the second cell; receiving the uplink resource allocation information from the e Node B via a physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH), according to the downlink resource allocation information; and transmitting to the e Node B via a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) of the second cell uplink data, according to the uplink resource allocation information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
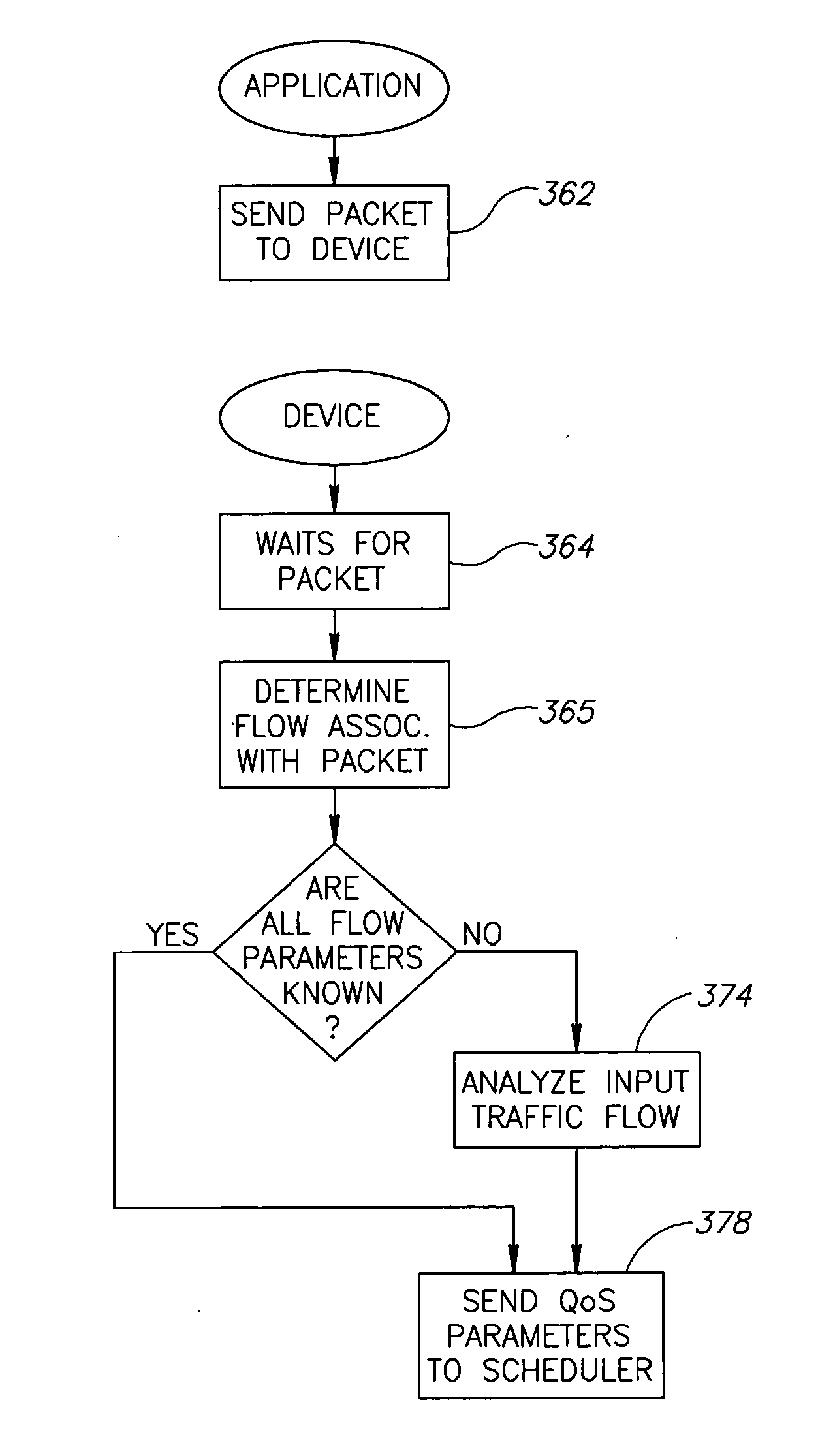
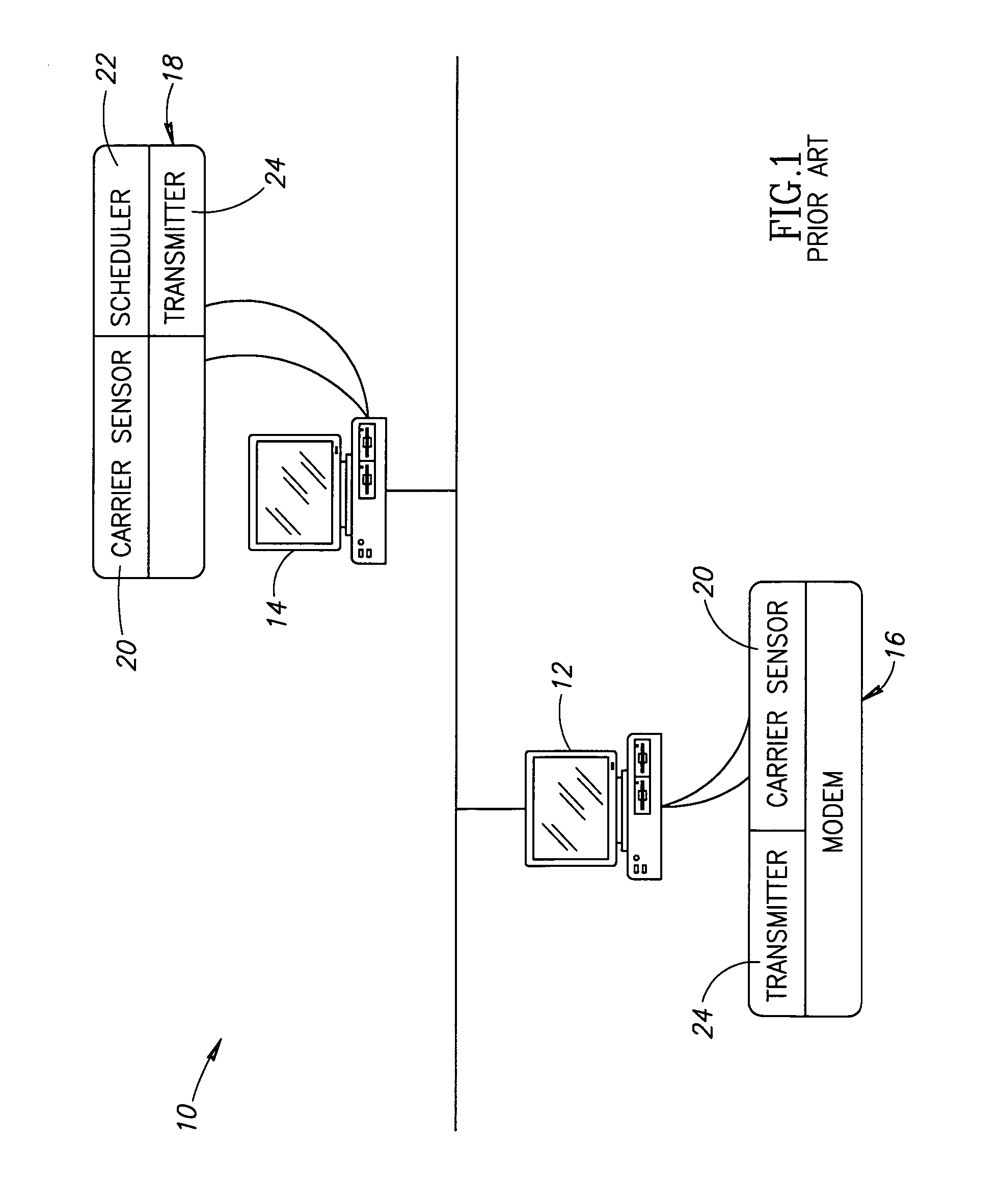
Maximal resource utilization in networks
ActiveUS20060013129A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsResource utilizationCarrier signal
A network device includes a scheduler and a transmitter. The scheduler creates a media access plan (MAP) that has overlapping transmission opportunities and the transmitter transmits the MAP. Another network device includes a carrier sensor and a transmitter. The carrier sensor senses the availability of a network medium for transmission and the transmitter transmits data of a service during an allotted overlapping transmission opportunity if the carrier sensor indicates that the network medium is available. In another embodiment, the network device includes a unit which receives QoS parameters of at least one transmitted service from a QoS parameter determiner and a scheduler. The scheduler creates a MAP for a plurality of services to be transmitted, the scheduler defining the transmission opportunities based on their QoS parameters as received from either the parameter unit or applications providing the services.
Owner:SIGMA DESIGNS ISRAEL S D I
Pipelined maximal-sized matching cell dispatch scheduling
InactiveUS7006514B2Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsCell schedulingSufficient time
A Pipelined-based Maximal-sized Matching (PMM) scheduling approach for input-buffered switches relaxes the timing constraint for arbitration with a maximal matching scheme. In the PMM approach, arbitration may operate in a pipelined manner. Each subscheduler is allowed to take more than one time slot for its matching. Every time slot, one of them provides the matching result. The subscheduler can adopt a pre-existing efficient maximal matching algorithm such as iSLIP and DRRM. PMM maximizes the efficiency of the adopted arbitration scheme by allowing sufficient time for a number of iterations. PMM preserves 100% throughput under uniform traffic and fairness for best-effort traffic.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
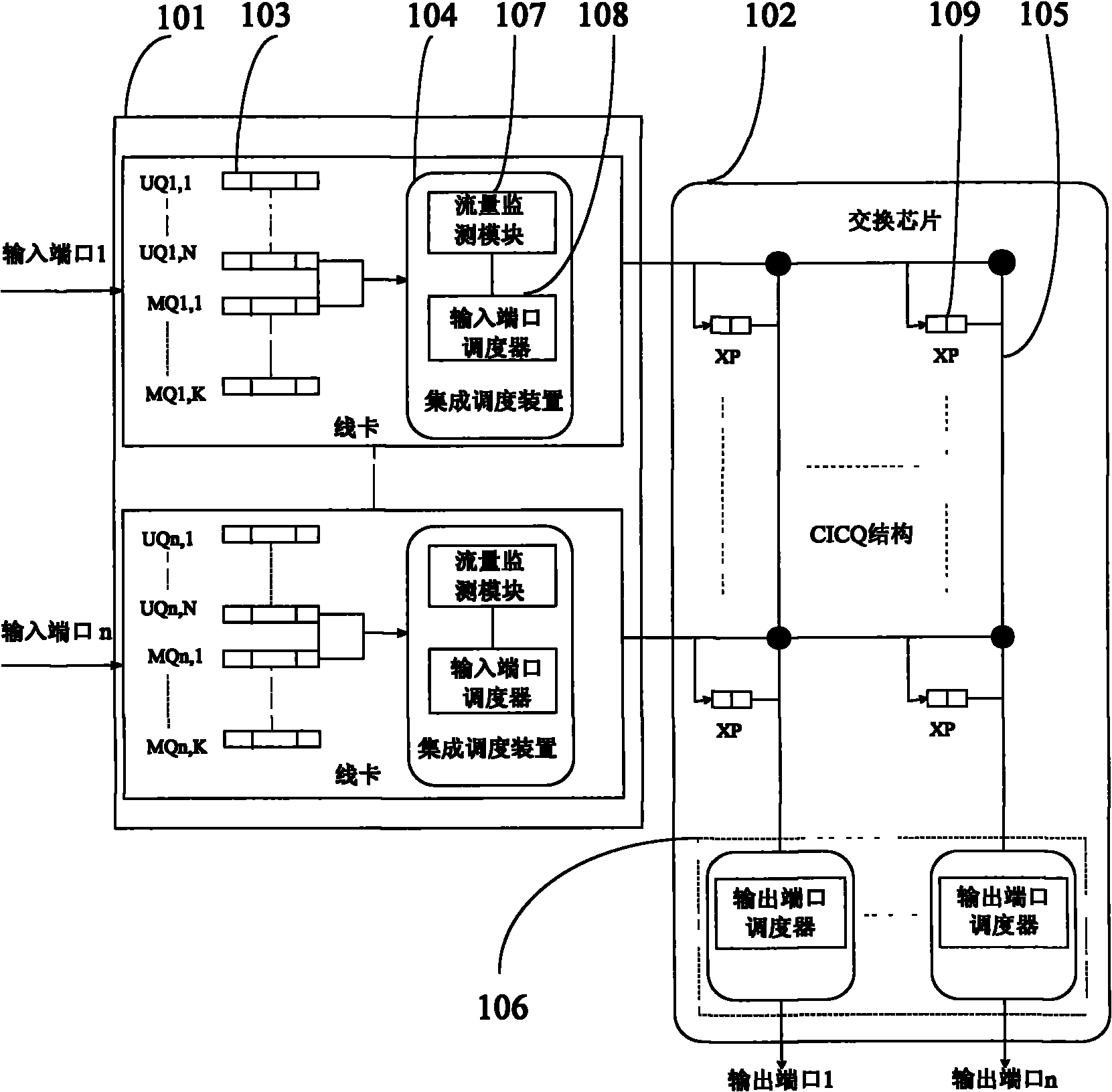
Unicast and multicast integrated scheduling device, exchange system and method
InactiveCN101902390AFair serviceImprove throughputSpecial service provision for substationTraffic capacityCell scheduling
The invention provides a unicast and multicast integrated scheduling device comprising a flow monitoring module and an input port scheduler. The invention further provides a unicast and multicast integrated scheduling exchange system which comprises an integrated scheduling device and an exchange chip. The invention also provides a unicast and multicast integrated scheduling method, comprising the following steps: obtaining the flow ratio information of a unicast queue and a multicast queue in input port flow; according to the flow ratio information of the unicast queue and the multicast queue in the input port flow, determining the time slot ratio of the unicast queue and the multicast queue; obtaining the state information cached by an intersection and the cell scheduling request information; and according to the time slot ratio of the unicast queue and the multicast queue, the state information cached by the intersection and the cell scheduling request information, scheduling the unicast cell and the multicase cell. The embodiment of the invention can greatly improve system throughput rate.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
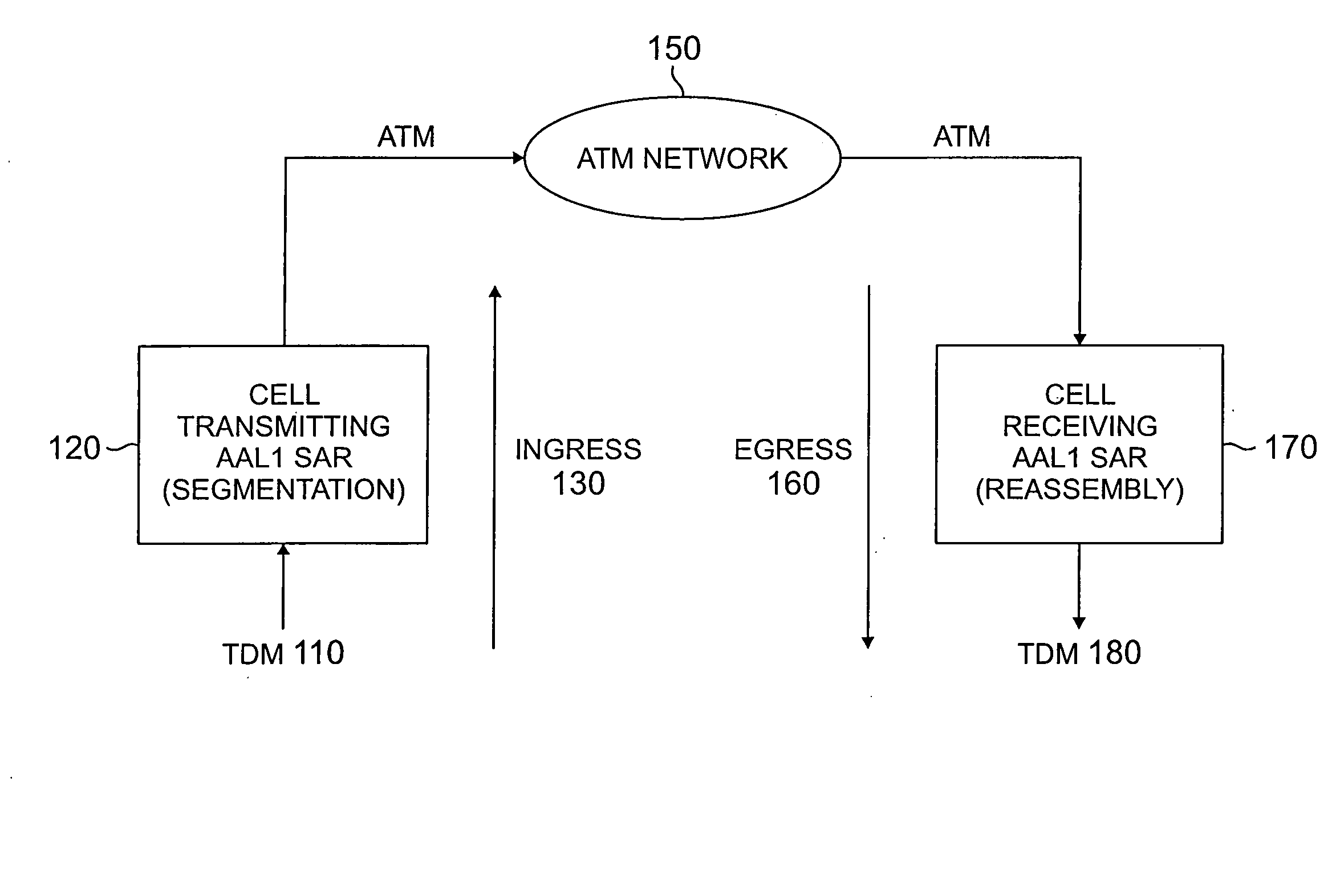
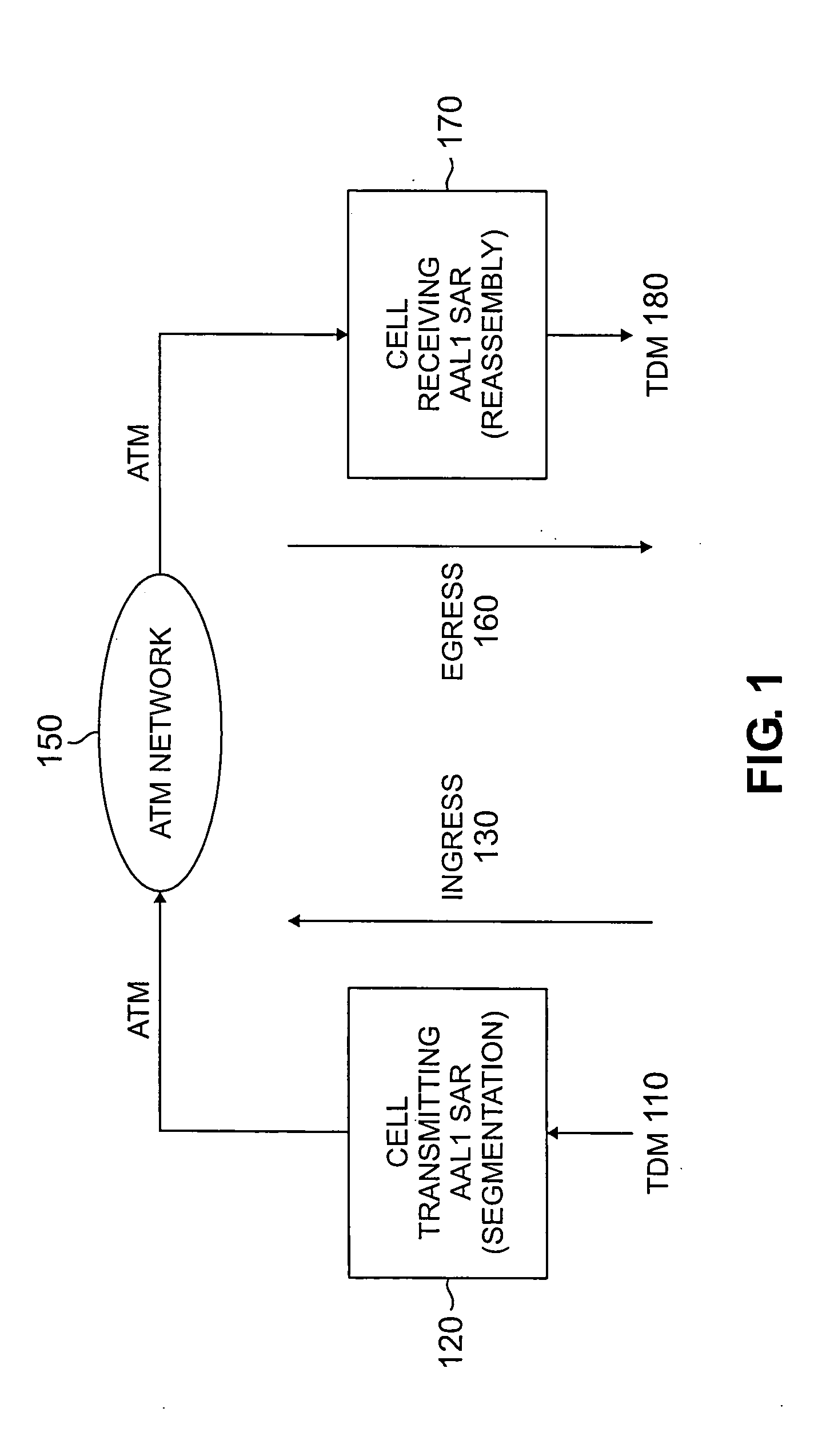
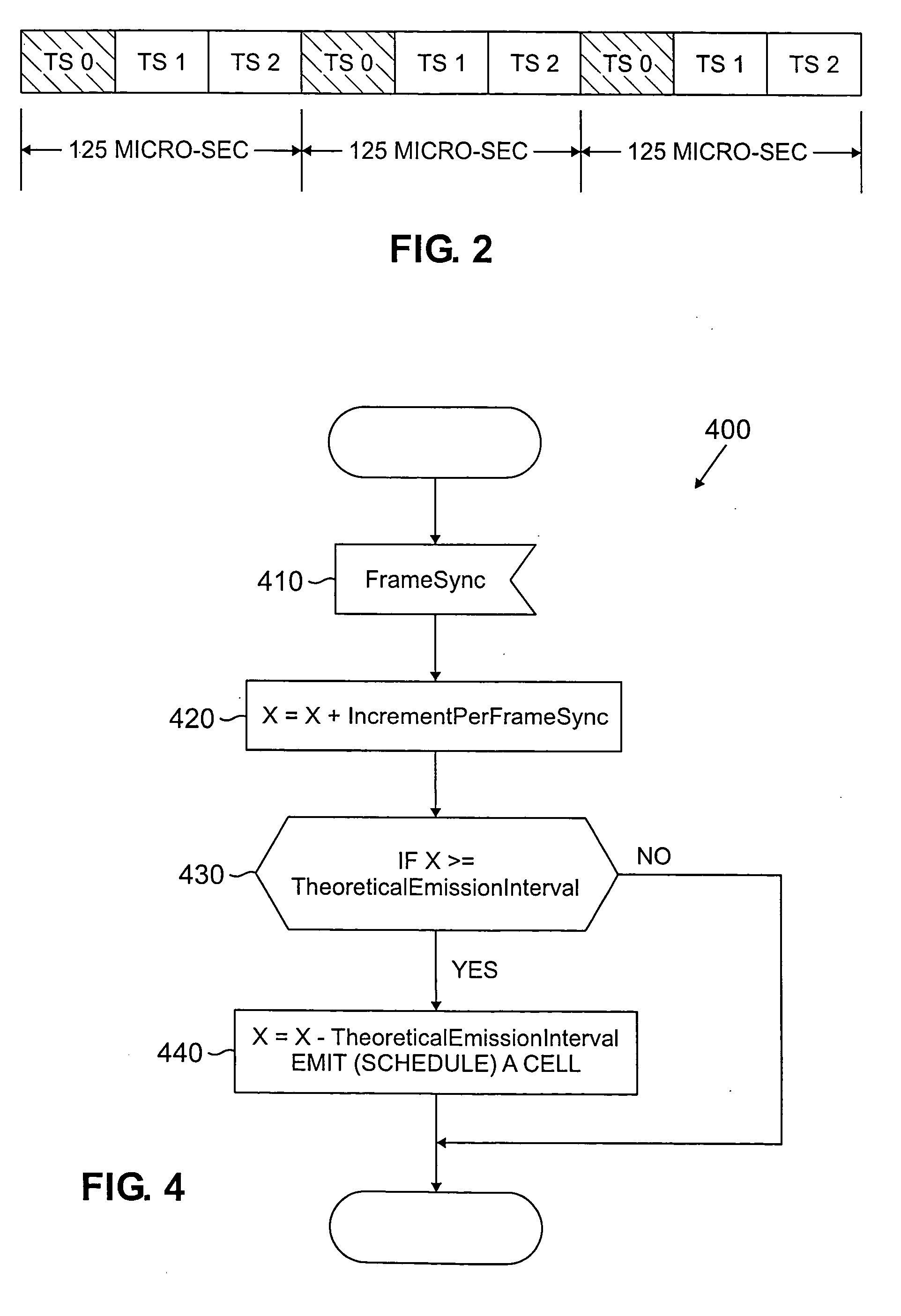
Method and apparatus for ATM adaptation layer staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling
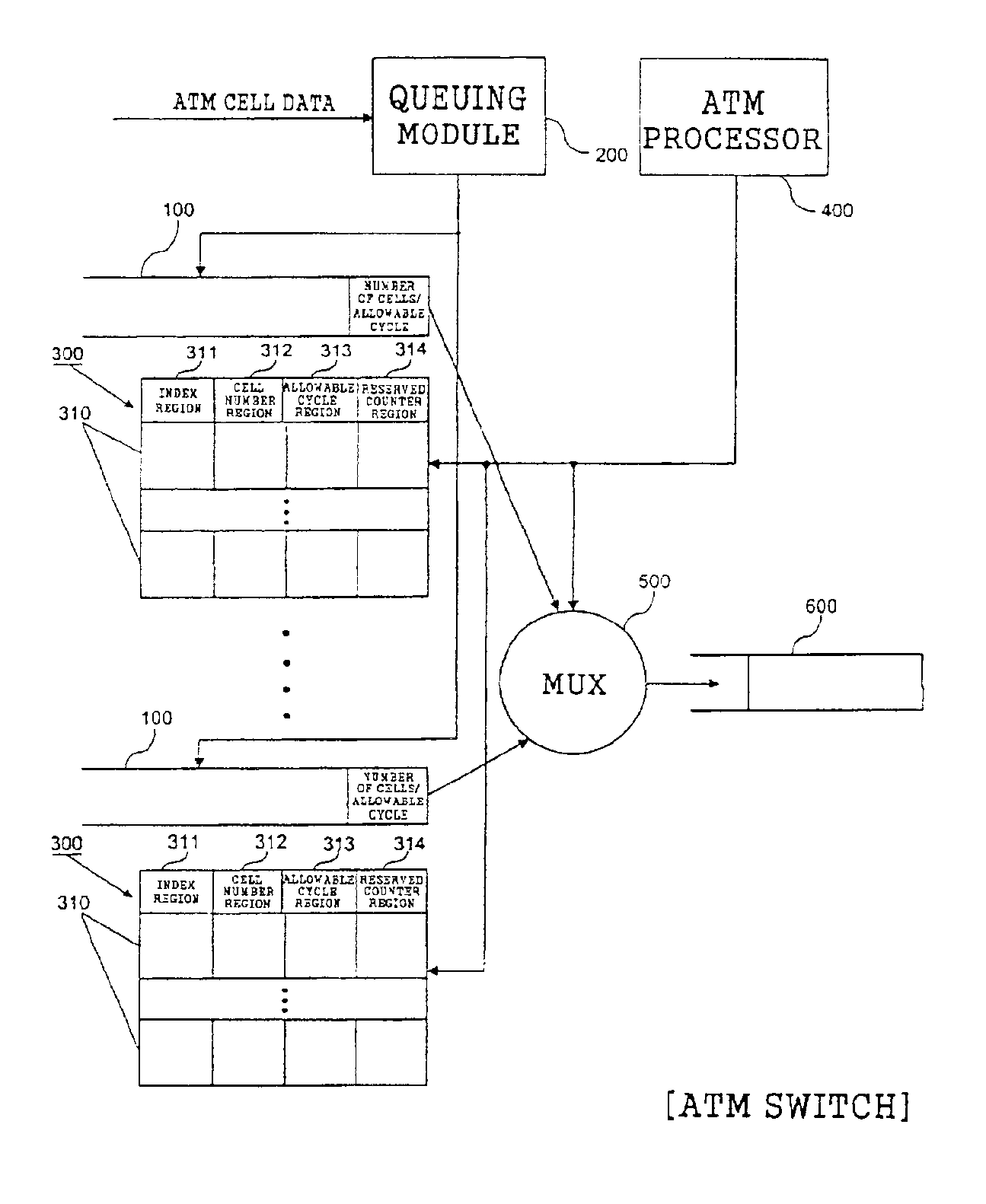
A method and apparatus are disclosed for ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) staggered constant bit rate cell scheduling. Cells from a plurality of virtual circuits are scheduled. Each of the virtual circuits have a transmission characteristic and each of the plurality of virtual circuits are classified into one of a plurality of stagger groups based on similar transmission characteristics. For each frame synchronization, a cell is transmitted from a given virtual circuit until a predefined cell threshold is exceeded for the stagger group containing the given virtual circuit. A Cell Delay Variation of each of the virtual circuits will not exceed a given time interval. A scheduler can be allocated for each connection or for each period.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
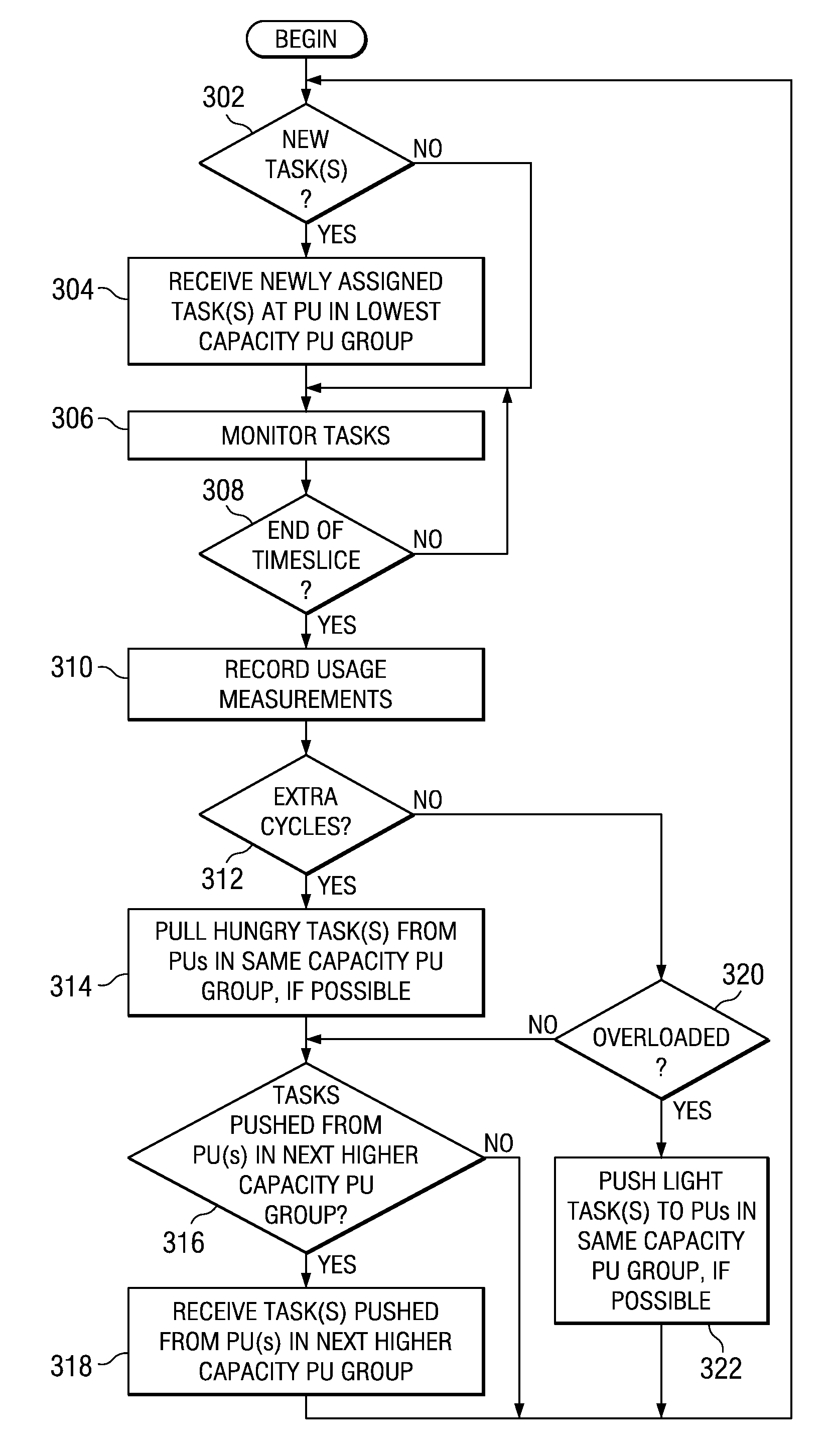
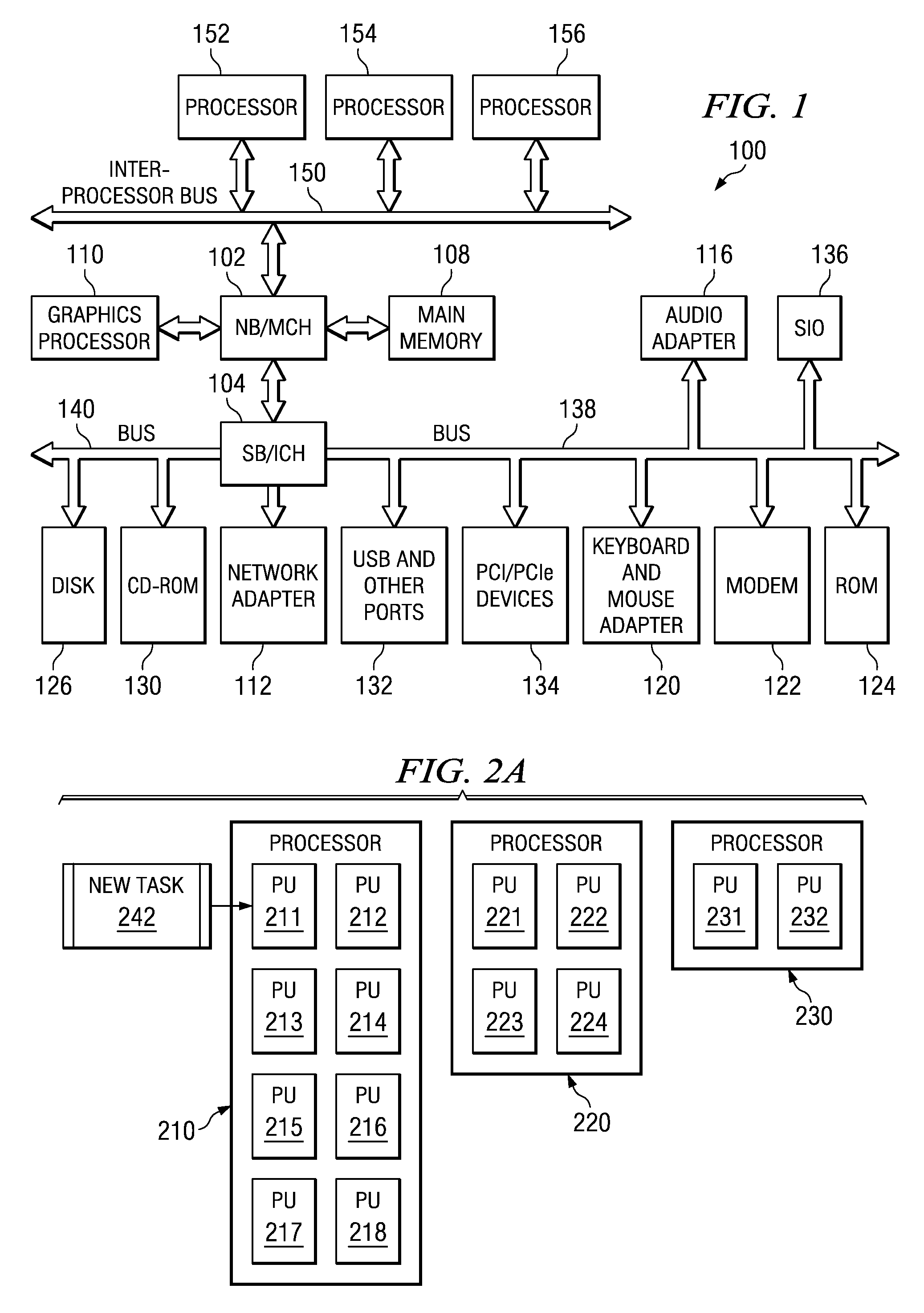
Scheduling tasks across multiple processor units of differing capacity
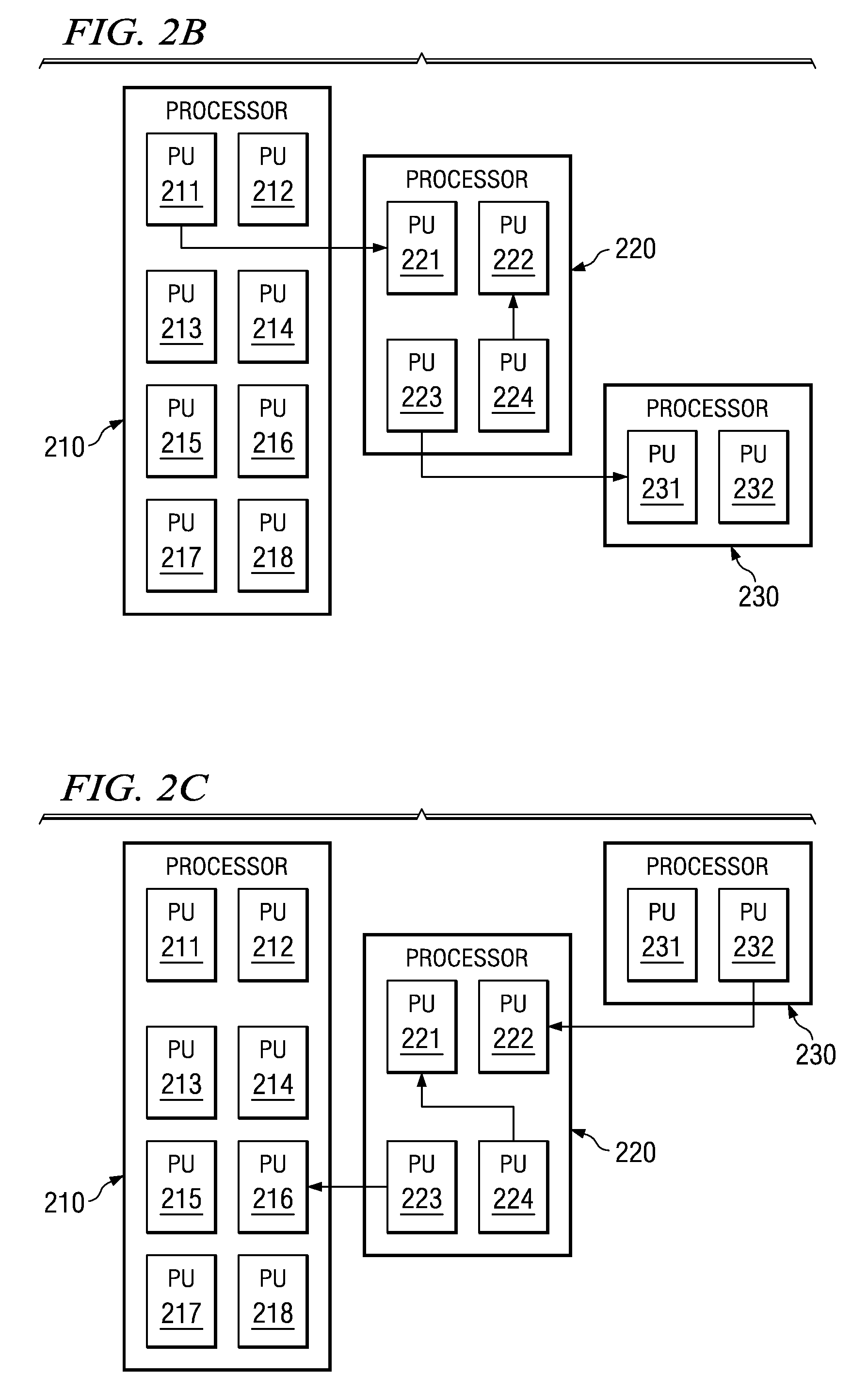
ActiveUS20080320487A1Large capacityMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsCell schedulingMulti processor
A mechanism is provided for scheduling tasks across multiple processor units of differing capacity. In a multiple processor unit system with processor units of disparate speeds, it is advantageous to have the most processing-intensive tasks run on the processor units with the highest capacity. All tasks are initially scheduled on the lowest capacity processor units. Because processor units with higher capacity are more likely to have idle time, these higher capacity processor units may pull one or more tasks onto themselves from the same or lower capacity processor units. A processor unit will attempt to pull tasks that utilize a larger percentage of the timeslice. When a higher capacity processor unit is overloaded or near capacity, the higher capacity processor unit may push tasks to processor units with the same or lower capacity. A processor unit will attempt to push tasks that utilize a smaller percentage of the timeslice.
Owner:IBM CORP
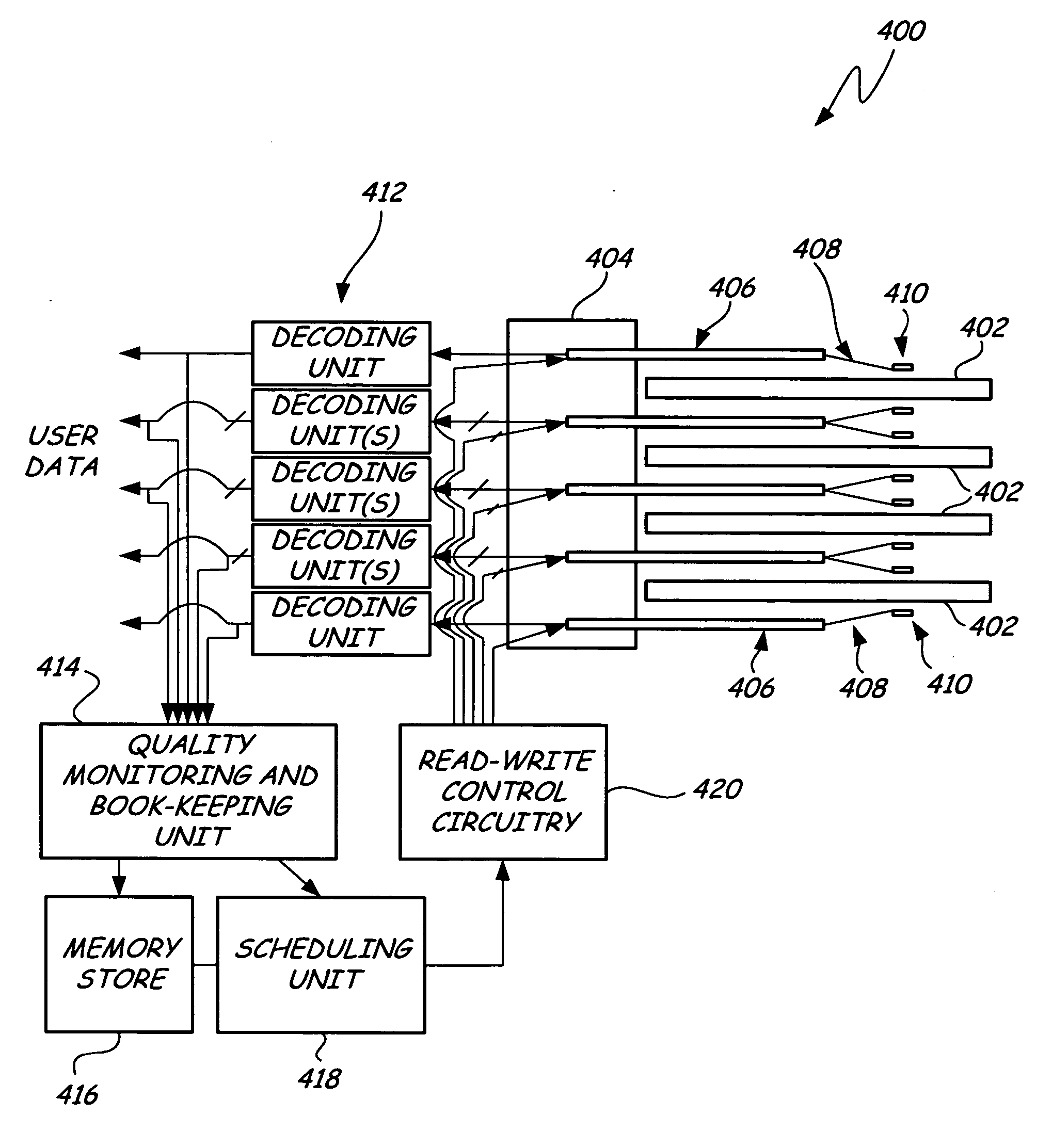
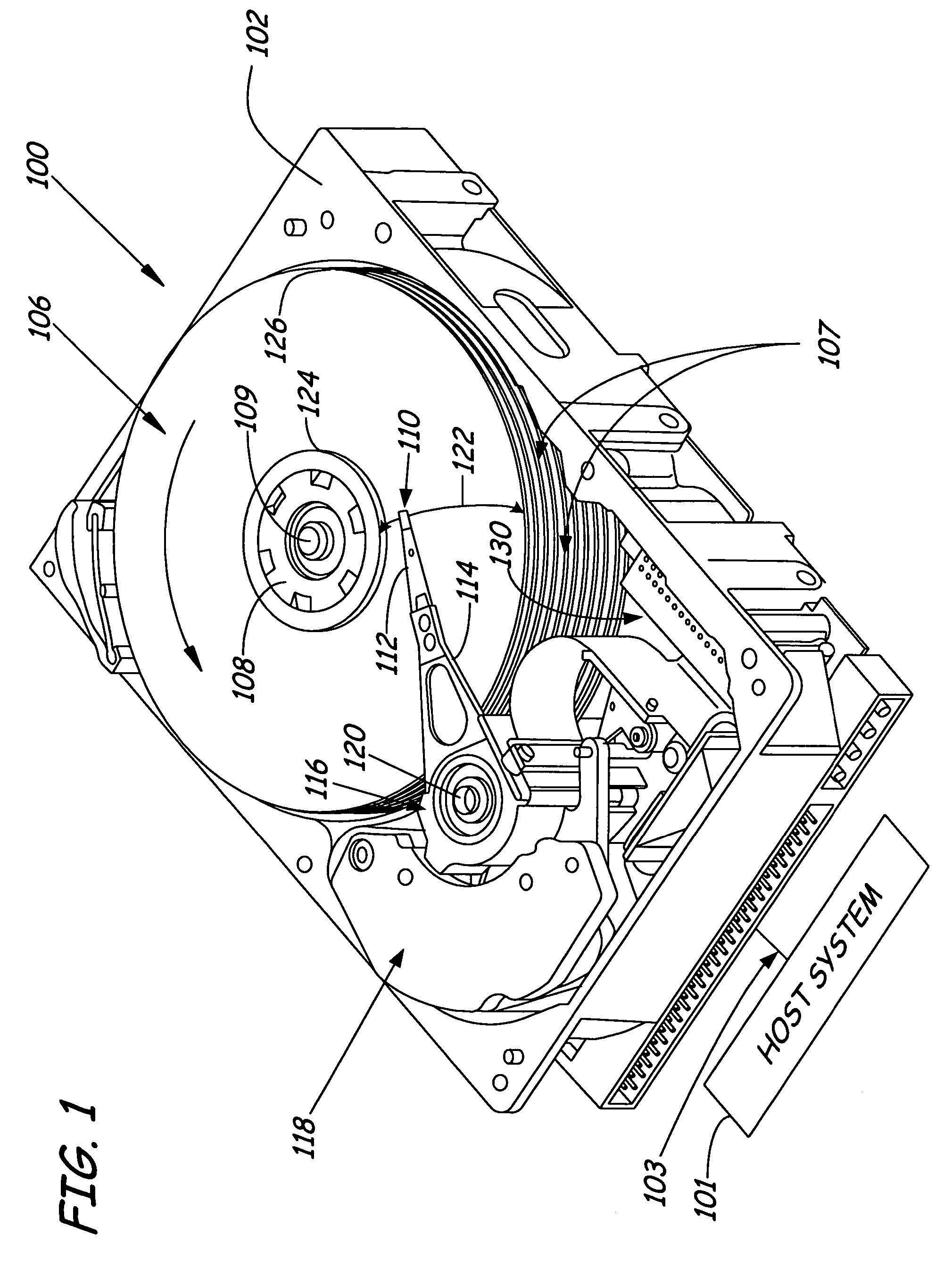
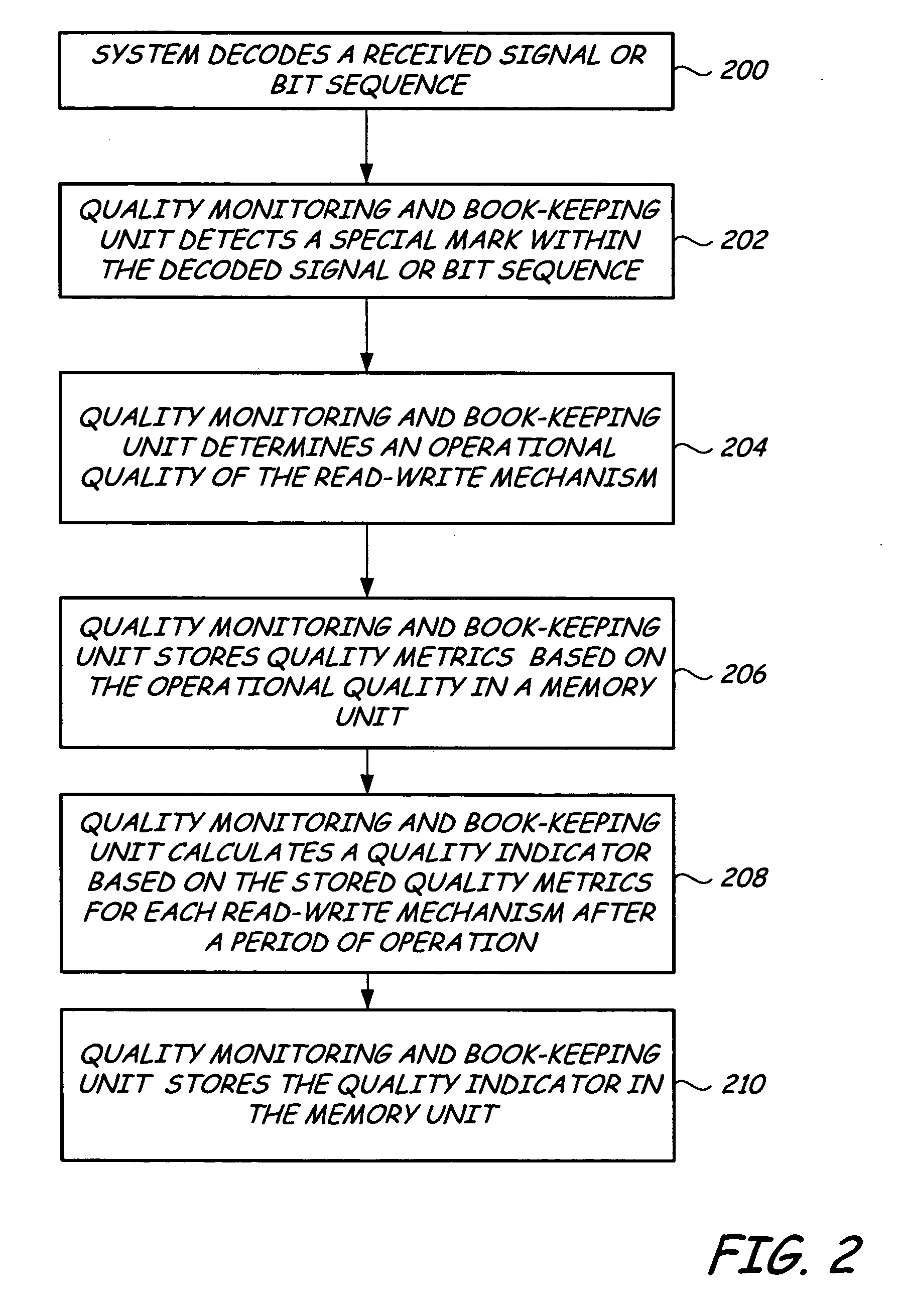
System and method for drive-side guarantee of quality of service and for extending the lifetime of storage devices
InactiveUS20060215290A1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageQuality of serviceCell scheduling
A storage device has a storage medium, a plurality of read-write mechanisms, a quality monitoring and book-keeping unit and a scheduling unit. The plurality of read-write mechanisms is coupled to the storage medium. The quality monitoring and book-keeping unit is coupled to the plurality of read-write mechanisms and is adapted to monitor at least one performance parameter associated with each read-write mechanism during operation. The scheduling unit is coupled to the quality monitoring and book-keeping unit. The scheduling unit is adapted to rank each of the plurality of read-write mechanisms according to the at least one performance parameter and to responsively schedule use of a read-write mechanism according to its rank.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
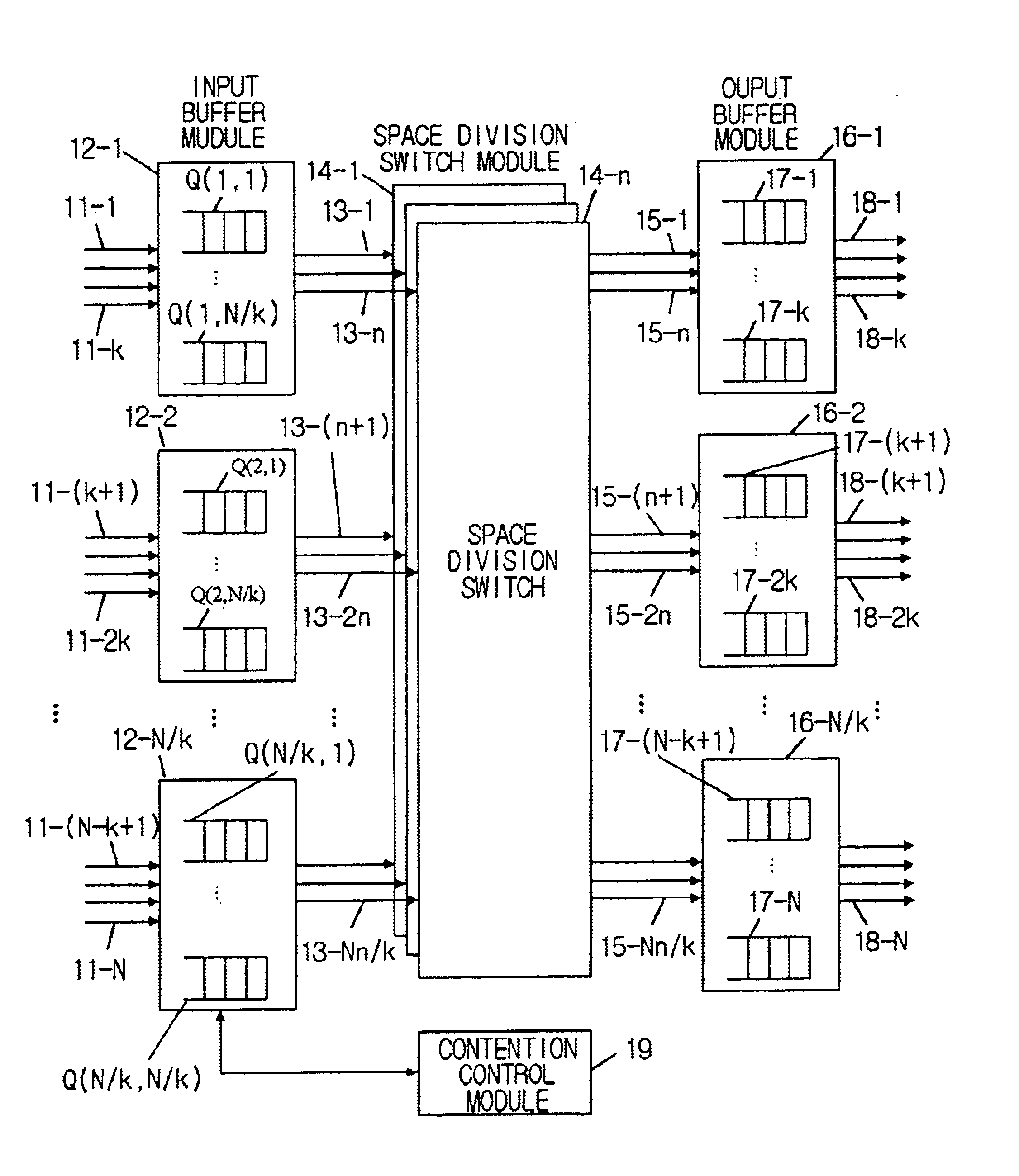
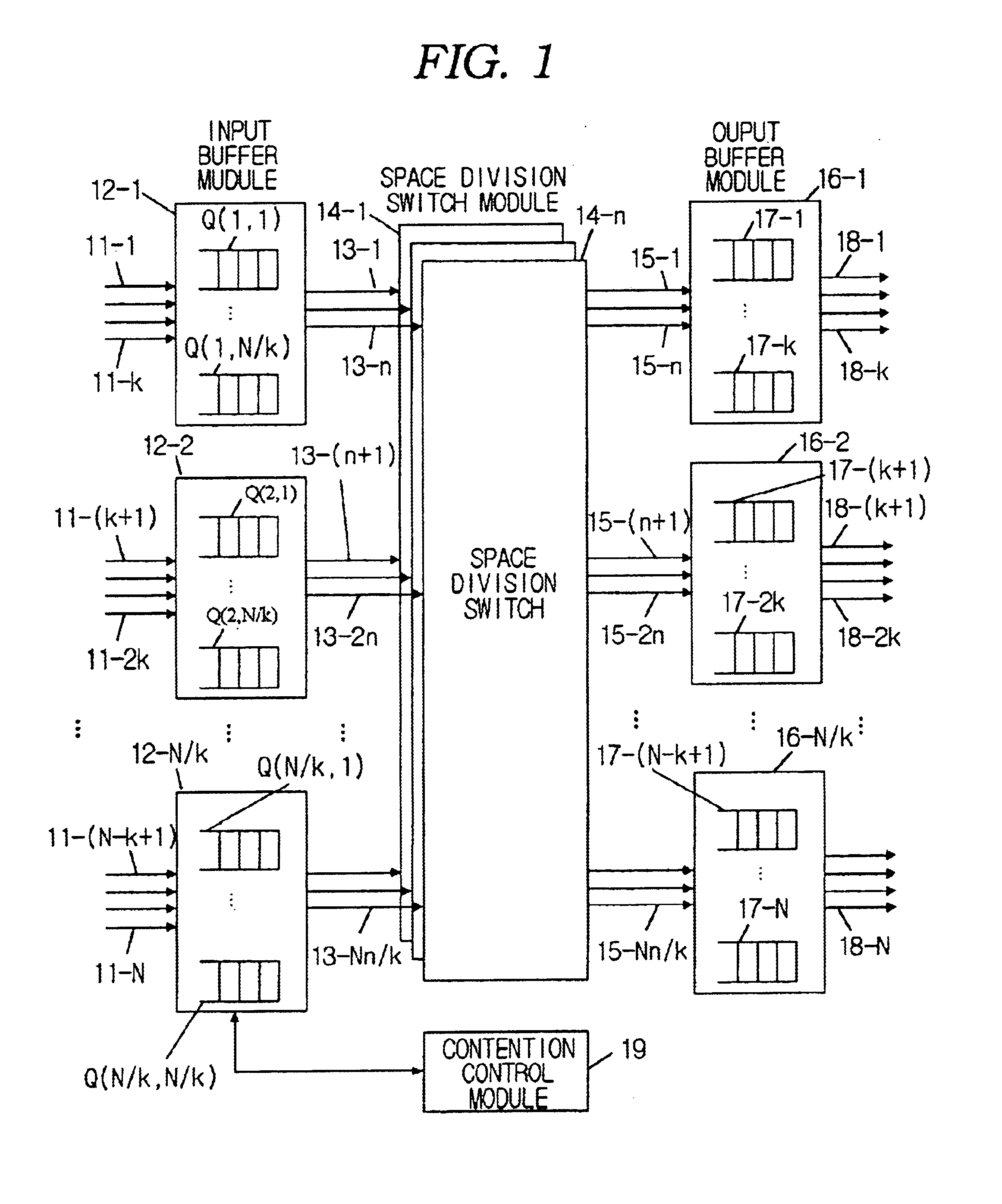
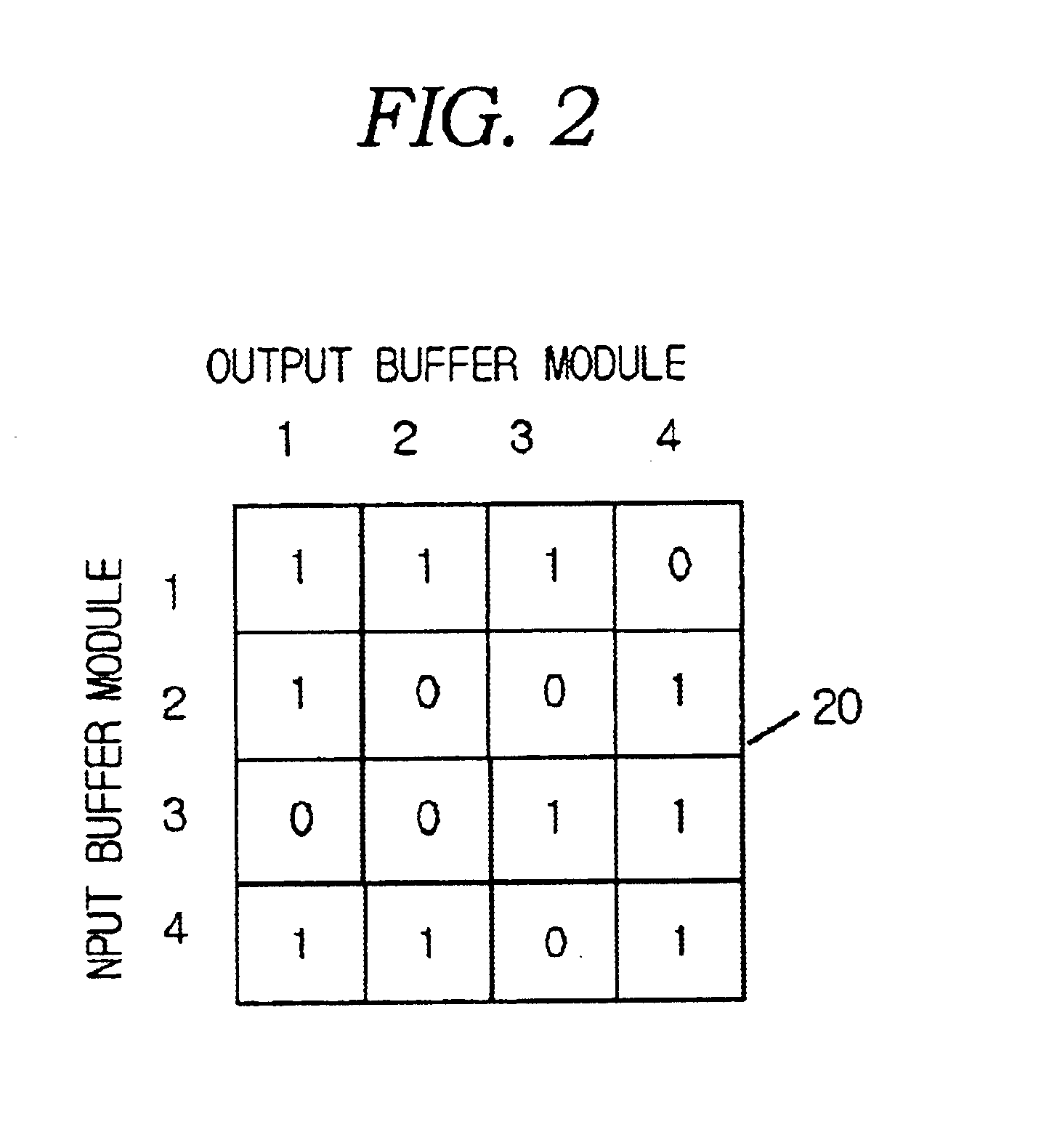
Cell scheduling method of input and output buffered switch using simple iterative matching algorithm
InactiveUS6904047B2Guaranteed high speed operationImprove matchMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCell schedulingFifo queue
A method for scheduling an input and output buffered ATM or packet switch and, more particularly, to a method for cell-scheduling an input and output buffered switch that is adapted to a high-speed large switch is provided. The input and output buffered switch has multiple switching planes, and its structure is used to compensated for decreasing performance of the input buffered switch resulting from HOL (head-of-line) blocking of the input buffered switch. The input and output buffered switch consists of input buffer modules grouping several input ports and output ports and output buffer modules, and each input buffer module has several FIFO queues for the associated module output buffer modules. In the input and output buffered switch having multiple switching planes, cell scheduling is carried out using a simple iterative matching (SIM) method. The SIM method consists of three operations, those are, request operation, grant operation, and accepting operation, and in the SIM method, the operations are iteratively carried out several times in one cell period, thereby matching efficiency can be increased. Each input buffered module determines simultaneously multiple FIFO queues served in one cell period, so that the SIM method with multiple selection ability has higher speed operations and better performance than conventional scheduling methods.
Owner:KT CORP +1
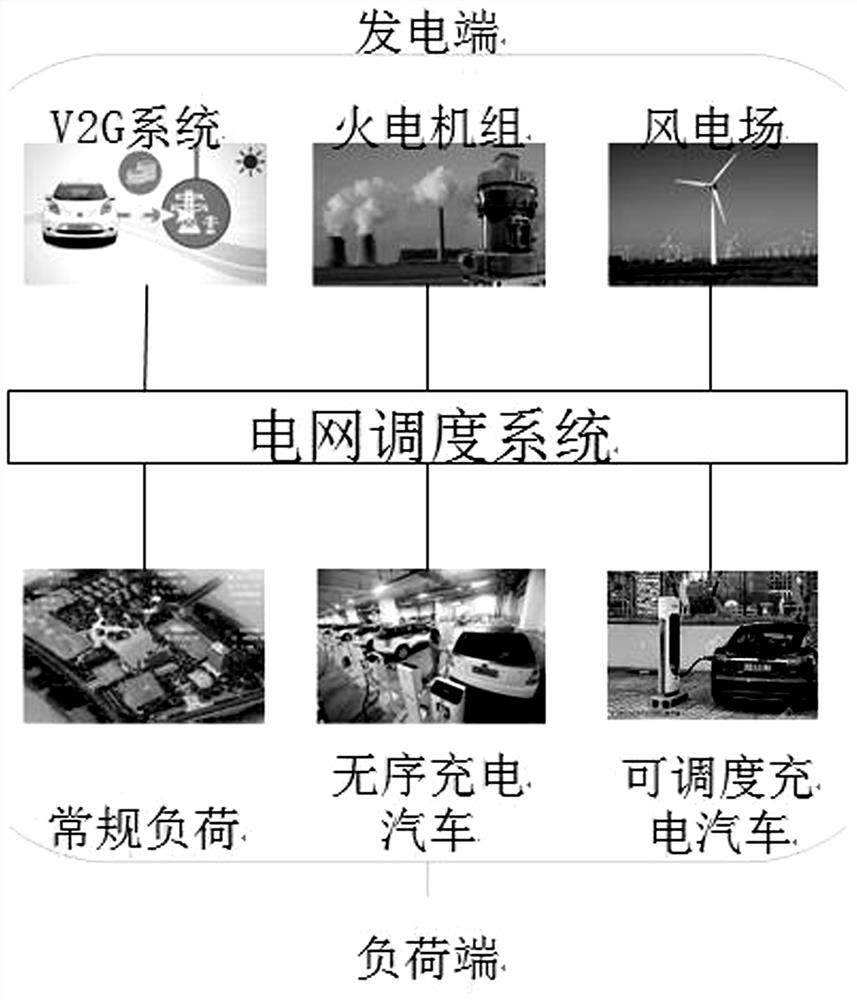
Intelligent power grid deep learning scheduling method considering schedulable electric vehicle fast/slow charging and discharging forms
ActiveCN111626527AComprehensive treatmentReduce start-stop costsForecastingElectric vehicle charging technologyCell schedulingLoad forecasting
The invention discloses an intelligent power grid deep learning scheduling method considering schedulable electric vehicle fast / slow charging and discharging forms, belongs to the field of regional intelligent power grid operation, and aims to perform power supply power optimal distribution by taking total operation cost as an objective function in a day-ahead scheduling stage. In the intra-day pre-scheduling stage, load fluctuation and a day-ahead scheduling plan are simulated to serve as input samples of the deep learning network, prediction data generated through simulation are input into aregional intelligent power grid model in the intra-day pre-scheduling stage, and controllable unit scheduling data in the scheduling plan in the model training stage serve as output samples of the deep learning network. An intra-day scheduling model of the regional smart grid is trained based on the deep learning network through the input sample and the output sample to acquire a predicted valueof the load at the next scheduling moment through ultra-short-term prediction. The predicted value and the day-ahead scheduling plan are inputted into an intra-day scheduling model of the regional smart power grid to obtain an intra-day scheduling value of the controllable unit. The method solves the problems that errors exist in prediction of distributed power supplies, electric vehicles and loads of a regional smart power grid, and intra-day economic dispatching of the regional smart power grid is difficult to achieve.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for controlling the transmission of cells across a network
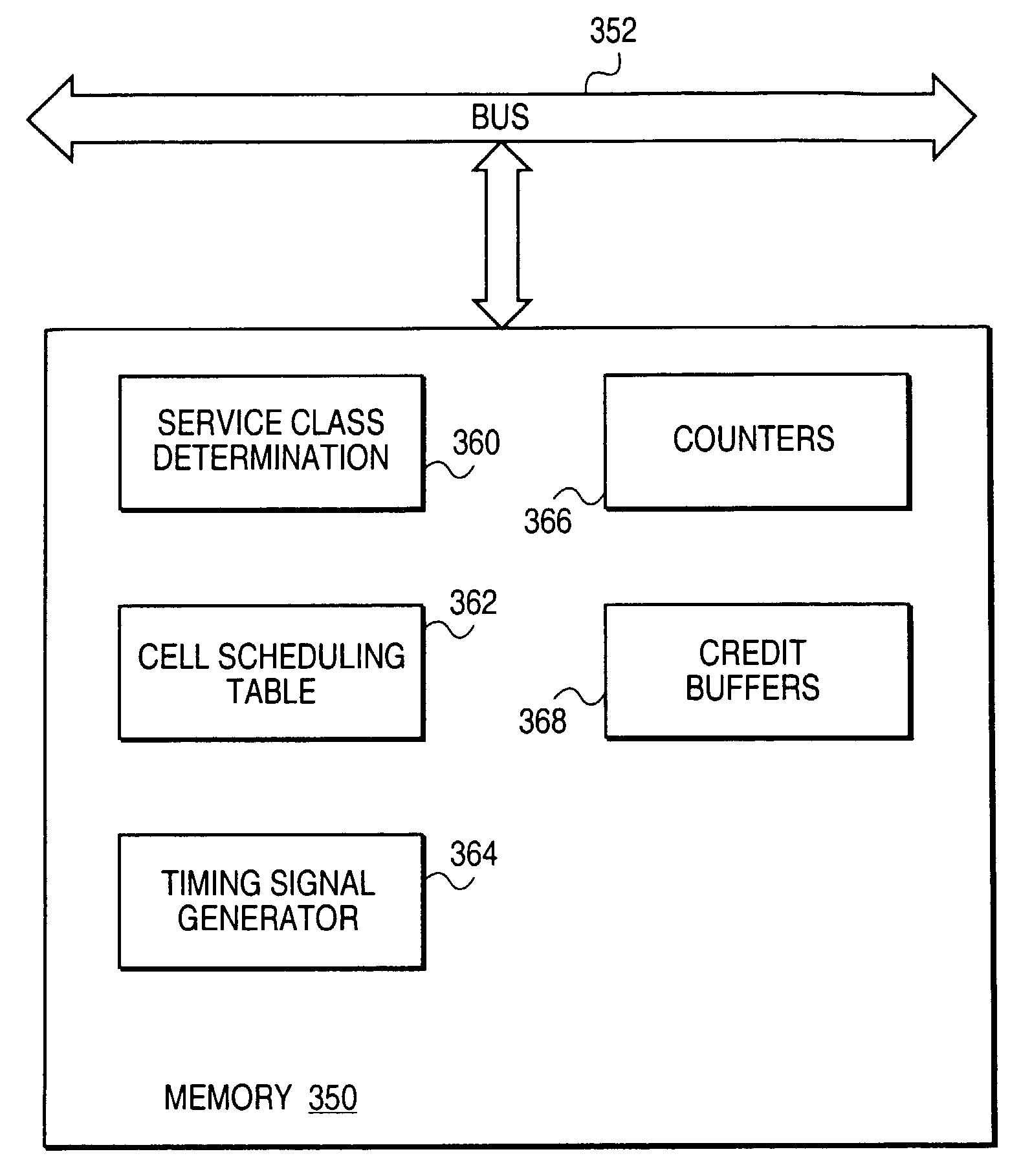
InactiveUS7436767B1Reduce processing loadReducing timer interruptsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCell schedulingPeak value
A Multiservice Access Concentrator (MAC) provides traffic shaping by allocating at least one cell stream to at least one cell slot of a cell scheduling table. A cell slot and a corresponding cell stream are designated in response to a cell interrupt signal generated following cell transmission. At least one counter and at least one credit buffer are maintained, and a service class of the designated cell stream is determined. The size of the credit buffer is determined by a maximum burst cell size (MBC) of the corresponding cell stream and virtual circuit (VC). A cell of the designated cell stream is transmitted in response to the determined service class and a count of the at least one counter and contents of the at least one credit buffer. Therefore, cells are transmitted based on cell credits. A virtual circuit (VC) builds cell credit based on the sustained cell rate (SCR) of the VC. Cell credit is consumed as cells are transmitted. If no data is queued or transmitted, the cell credit builds to a maximum burst cell size (MBC). When data is queued again and credit is available, cell transmissions may burst to the peak cell rate (PCR) until credit is exhausted. Cell transmission timing is controlled using the cell interrupt signal, wherein the cell interrupt signal emulates a clock signal.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
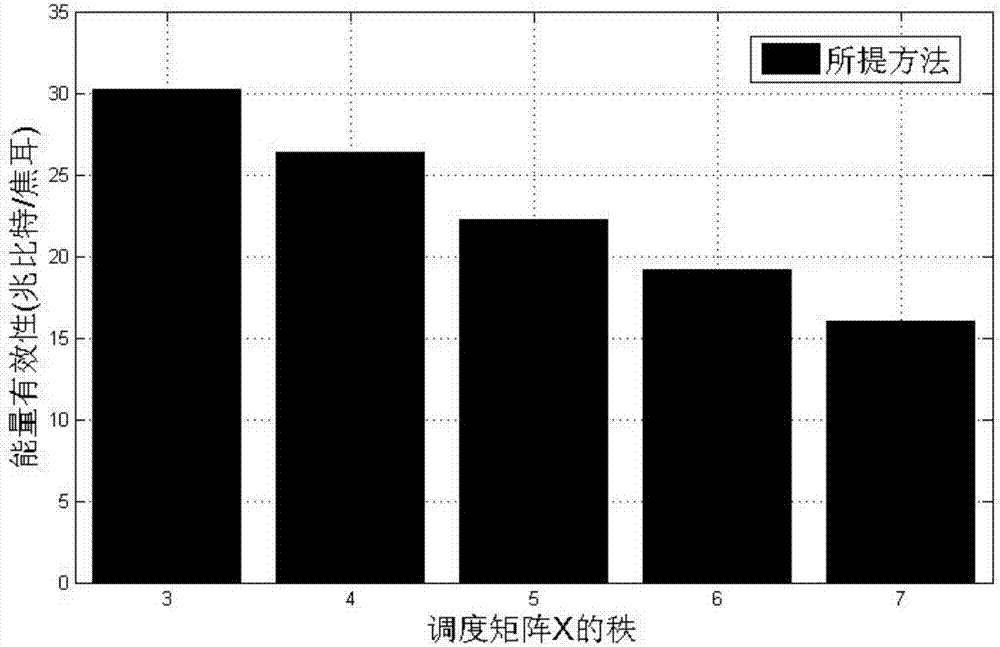
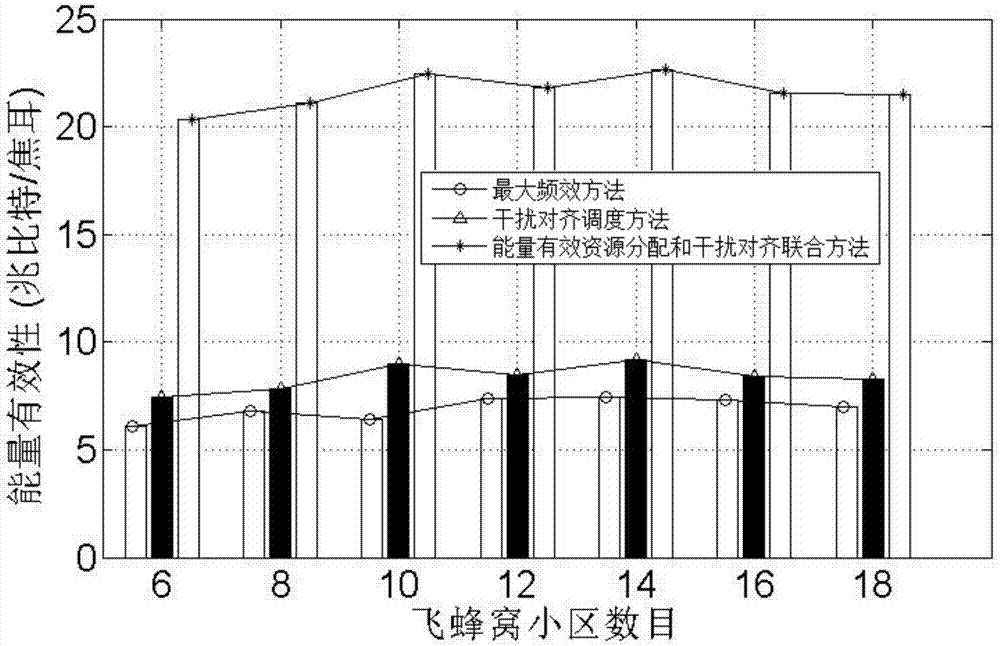
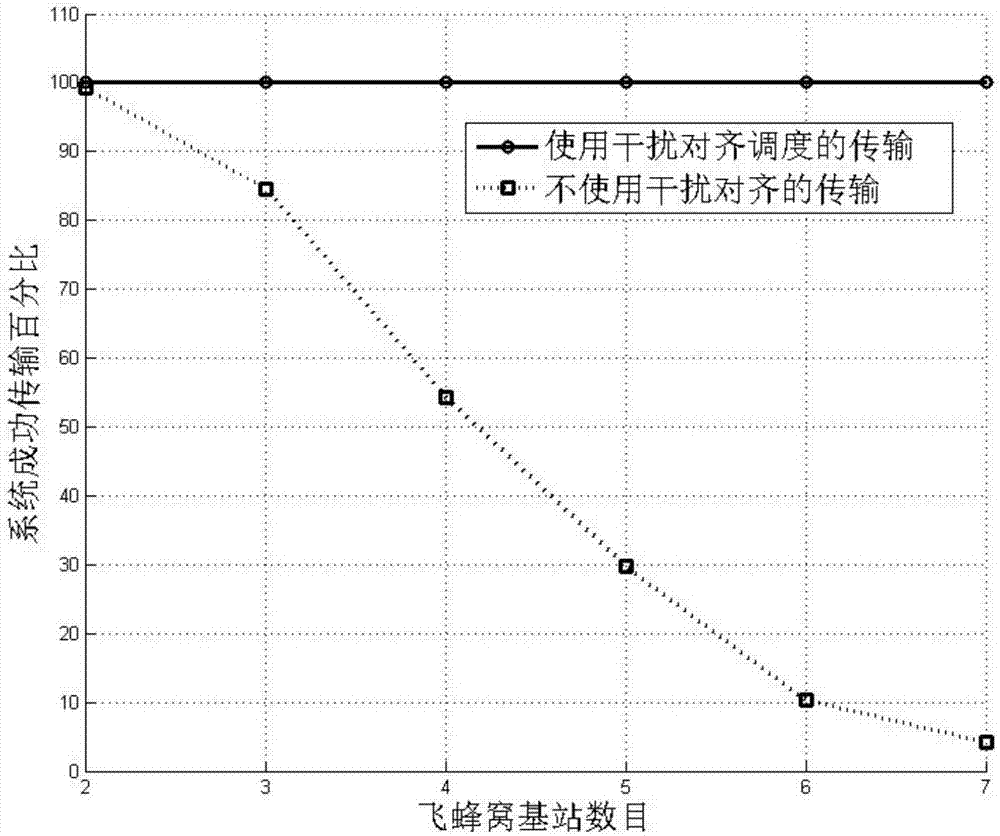
Energy-efficient resource distribution and interference alignment combined method in heterogeneous network
InactiveCN107241799AReduce distractionsImprove energy efficiencyHigh level techniquesWireless communicationCell schedulingCommunications system
The invention provides an energy-efficient resource distribution and interference alignment combined method in a heterogeneous network. The energy-efficient resource distribution and interference alignment combined method in the heterogeneous network comprises a first step of setting various parameters of a communication system in the heterogeneous network; a second step of constructing an energy-efficient resource distribution and interference alignment combined optimization problem in the heterogeneous network based on the lowest rate demand of a macro-cell user, the signal intensity of a femto-cell user, the interference intensity of the femto-cell user, the scheduling constraint of a femto-cell base station and a power constraint condition; a third step of carrying out energy-efficient fast femto-cell scheduling and interference alignment algorithm design; and a fourth step of carrying out energy-efficient iteration power distribution. The fast femto-cell scheduling, the interference alignment algorithm design and the optimal power distribution algorithm are carried out for the energy efficiency problem in the heterogeneous network; the communication performance of the macro-cell users and the femto-cell users is guaranteed, and the energy efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Power dispatching anti-misoperation method and system thereof
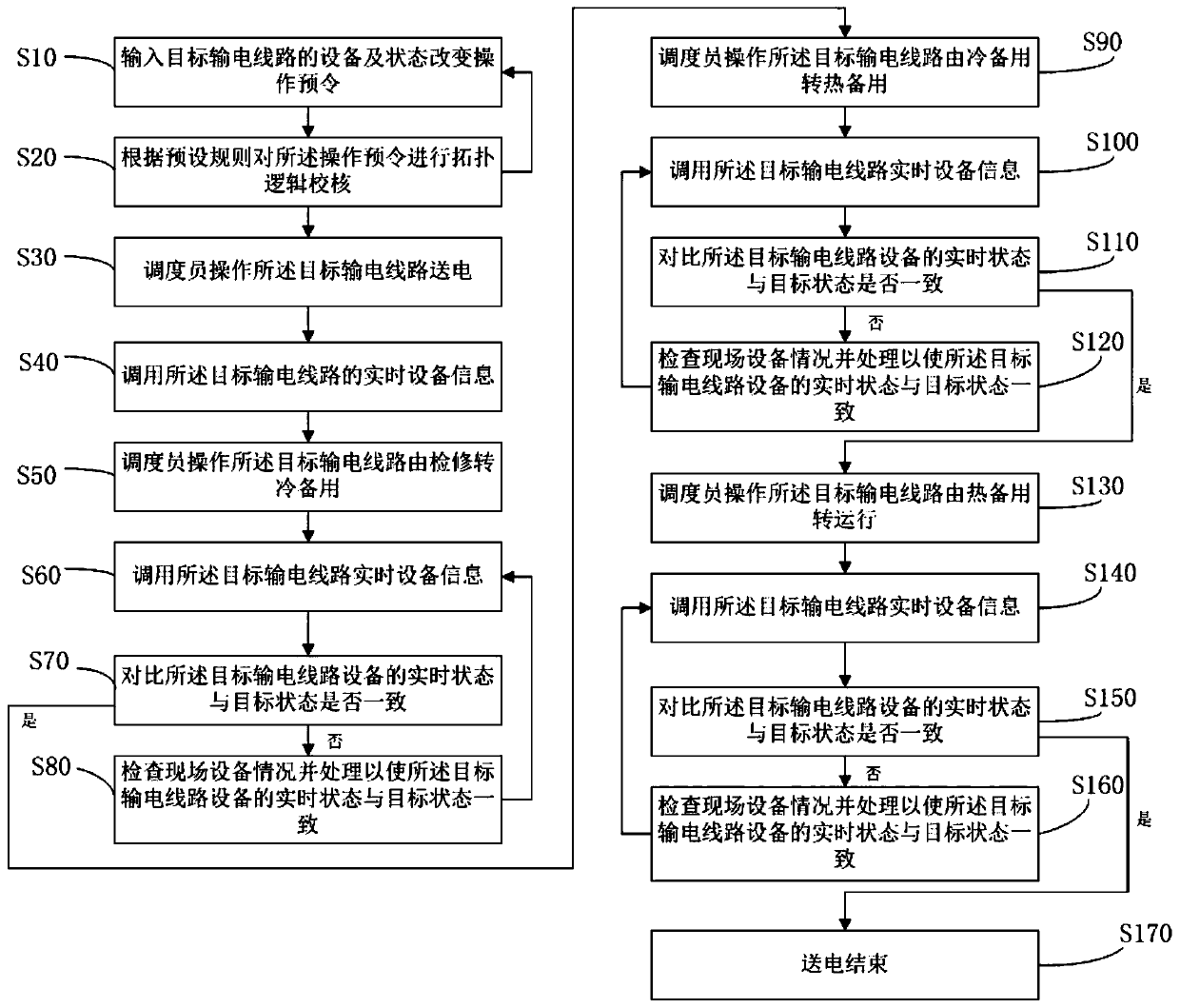
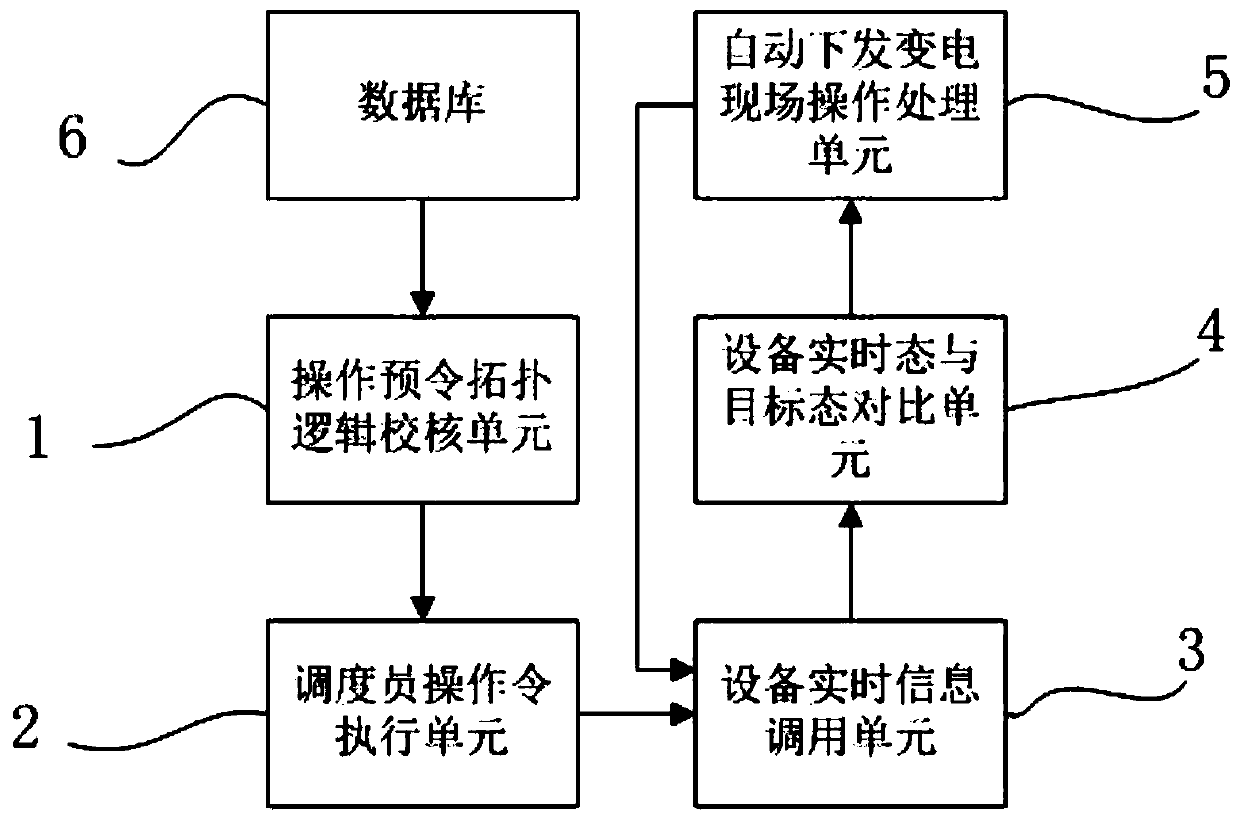
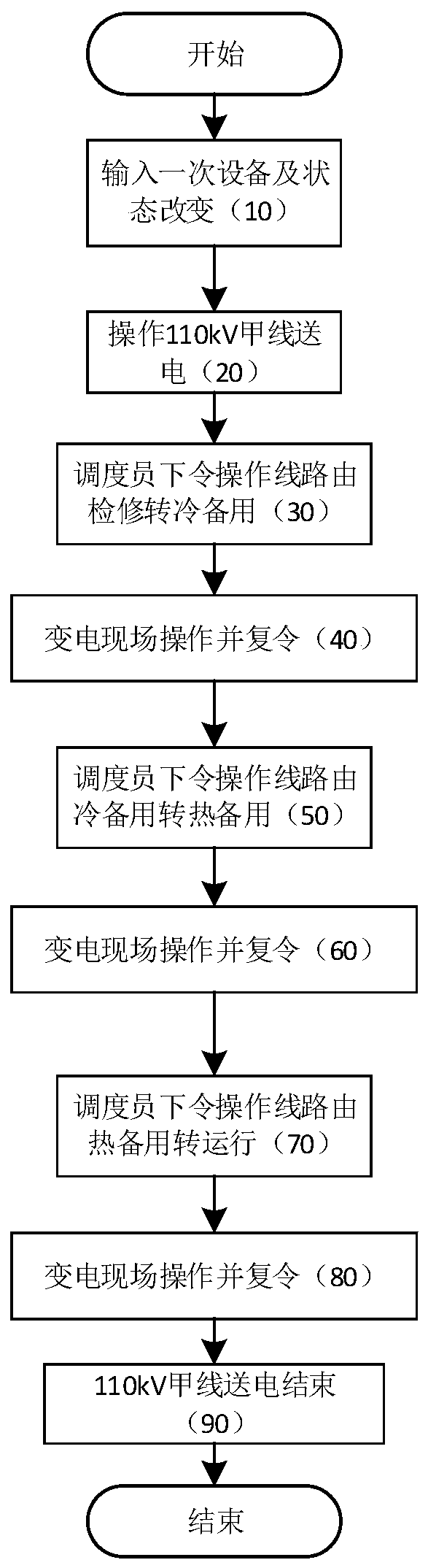
The invention provides a power dispatching anti-misoperation method and a system thereof. The system comprises an operation pre-order topology logic checking unit, a dispatcher operation order execution unit, a device real-time information calling unit, a device real-time state and target state comparison unit and an automatic issuing power transformation field operation processing unit. The method and the system thereof perform topology logic check on the operation pre-order according to the electrical five-prevention rule in the device power transmission stop operation order ordering in thepower dispatching network order issuing, compare the real-time device state and the target device state when the dispatcher operates the transmission device to change the state, and lock the order issuing process when the real-time device state is not consistent with the target device state to form a safety protection system and avoid malicious misoperation.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Apparatus and method for delay bound weighted round robin cell scheduling in asynchronous transfer mode switch
InactiveUS6937601B2Minimize overheadMeet the requirementsData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionCell schedulingDelayed binding
An apparatus and method for DBWRR (Delay Bound Weighted Round Robin) cell scheduling in an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) switch. More particularly, the present invention provides an apparatus and method for DBWRR cell scheduling in a high-speed ATM switch which can meet requirements for a cell transfer delay of real-time traffic in the ATM switch and minimize a processing overhead of the switch.
Owner:USRCOM KOREA
Dynamic minimum-memory interleaving
ActiveCN101204014ACode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesCell schedulingComputer architecture
Minimum-memory-implementation is available with any depth and period in DSL interleaving / deinterleaving, always allowing the minimum amount of memory to be used in both transmitter and receiver without loss of performance or of basic triangular structure, even if the interleaver / deinterleaver parameters change dynamically. A novel cell-scheduling process ensures availability of the minimum amount of memory (or any other desired memory usage) to implement an image of the perfect triangle and works for any co-prime depth and interleaver period. Minimal memory use may be further characterized by a simple off-line method that determines an addressing order for each of the memory cells in a minimum-memory (or other) implementation of an interleaver / deinterleaver according to the invention. Time variation of interleaver depth in operation can be accommodated easily with absolute minimum memory requirement at all time instants.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
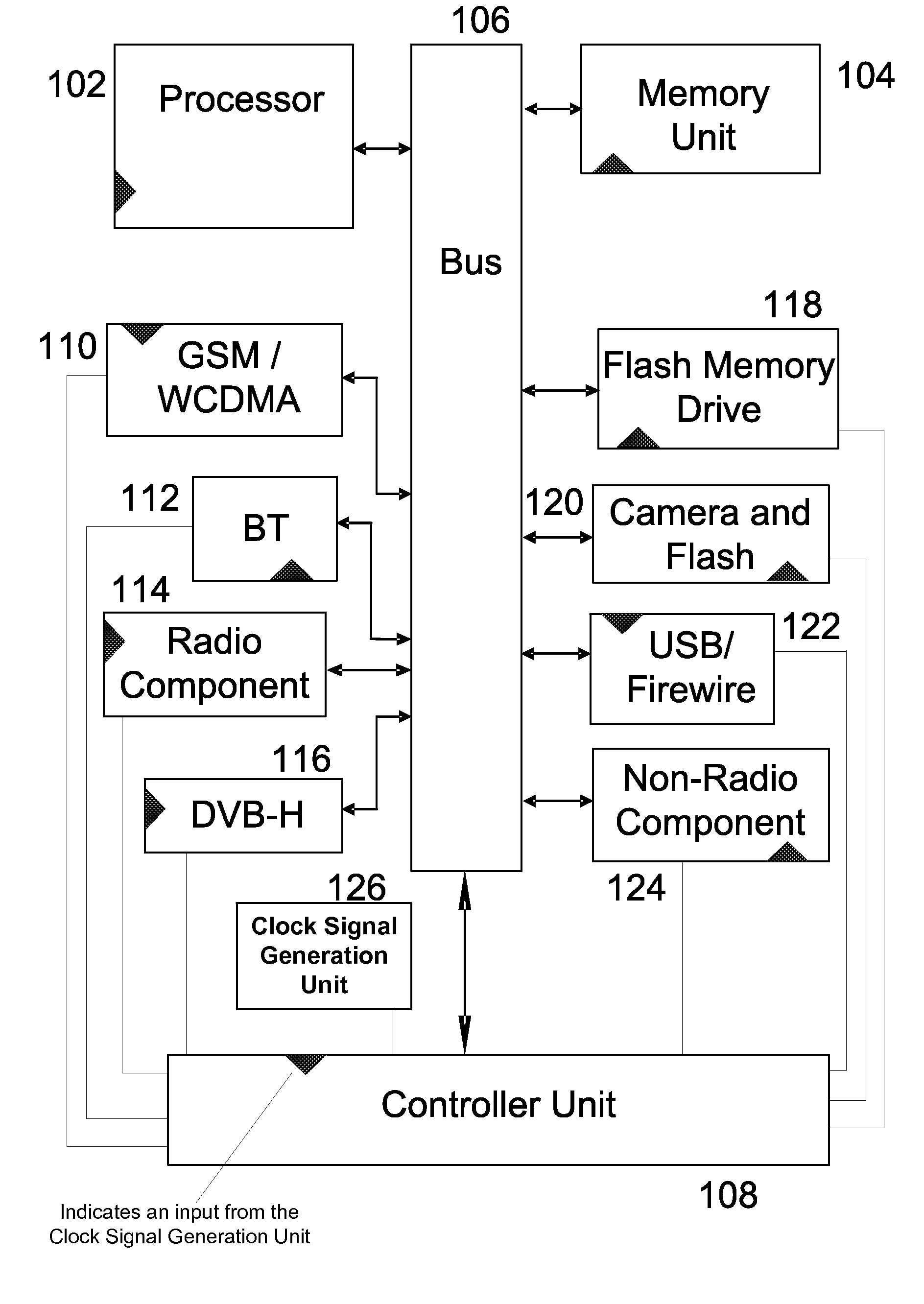
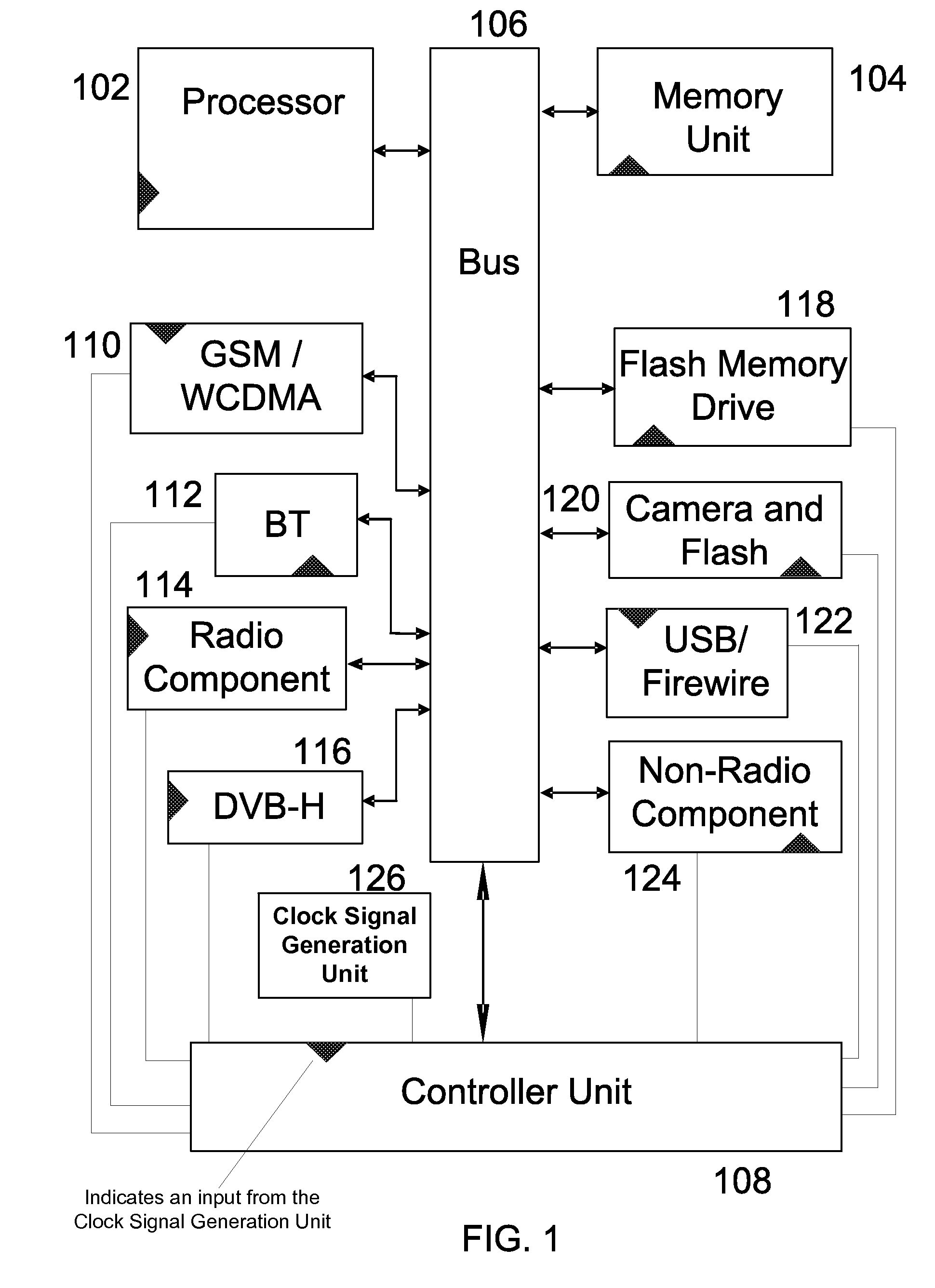
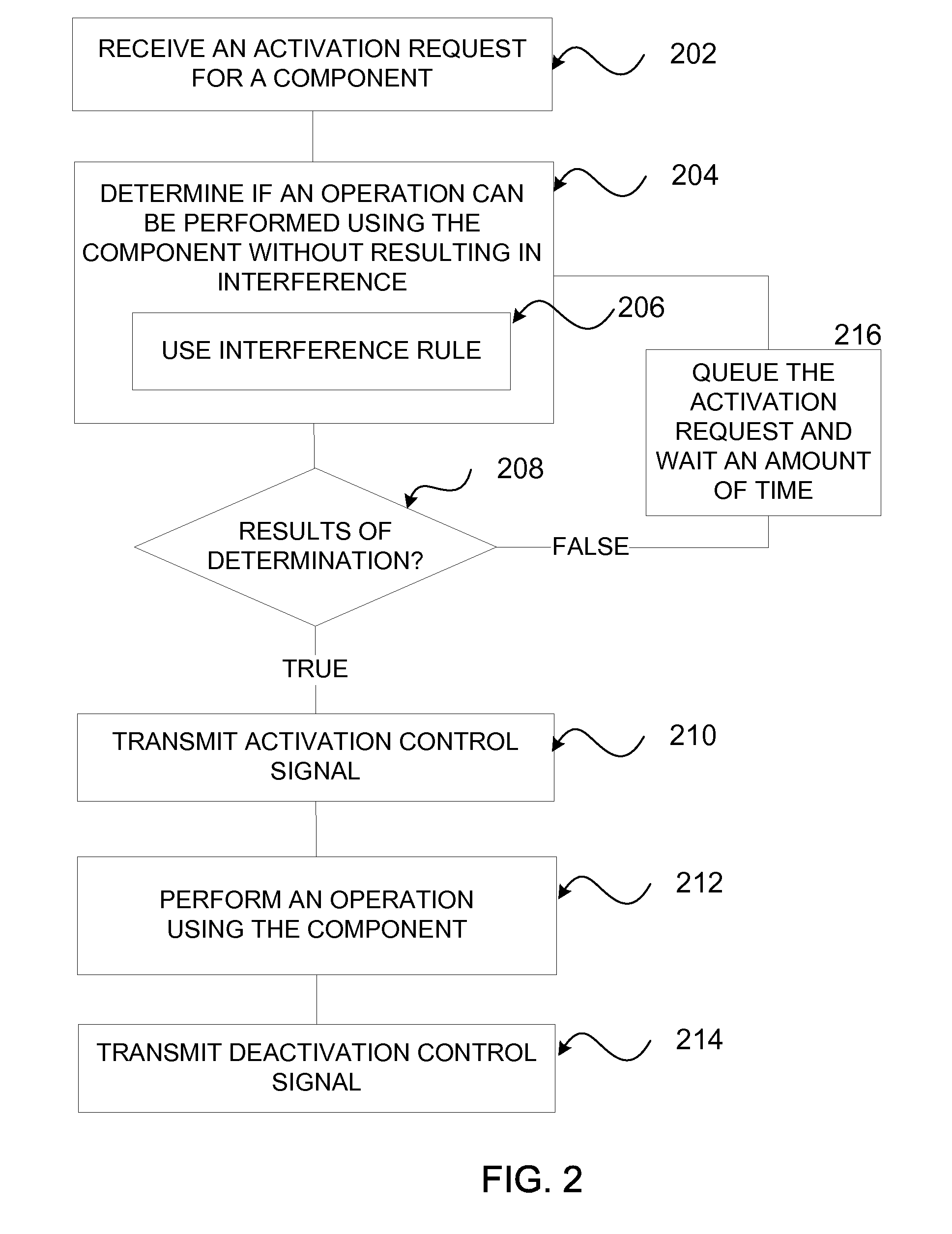
System scheduler for mobile terminals
ActiveUS7626973B2Reduce distractionsTransmission systemsSubstation equipmentEngineeringRadio frequency
Systems and methods that are adapted to avoid radio frequency interference originating from modules, peripherals and interconnects of a mobile terminal that are generating unintentional radiation (e.g. memory cards, camera flashes, data buses etc.) and coupling to the radios of the same mobile terminal are disclosed. The systems may include a controller unit that schedules the operation of the components to avoid concurrent operation of radios and sensitive peripheral devices which may interfere with each other during concurrent operation.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
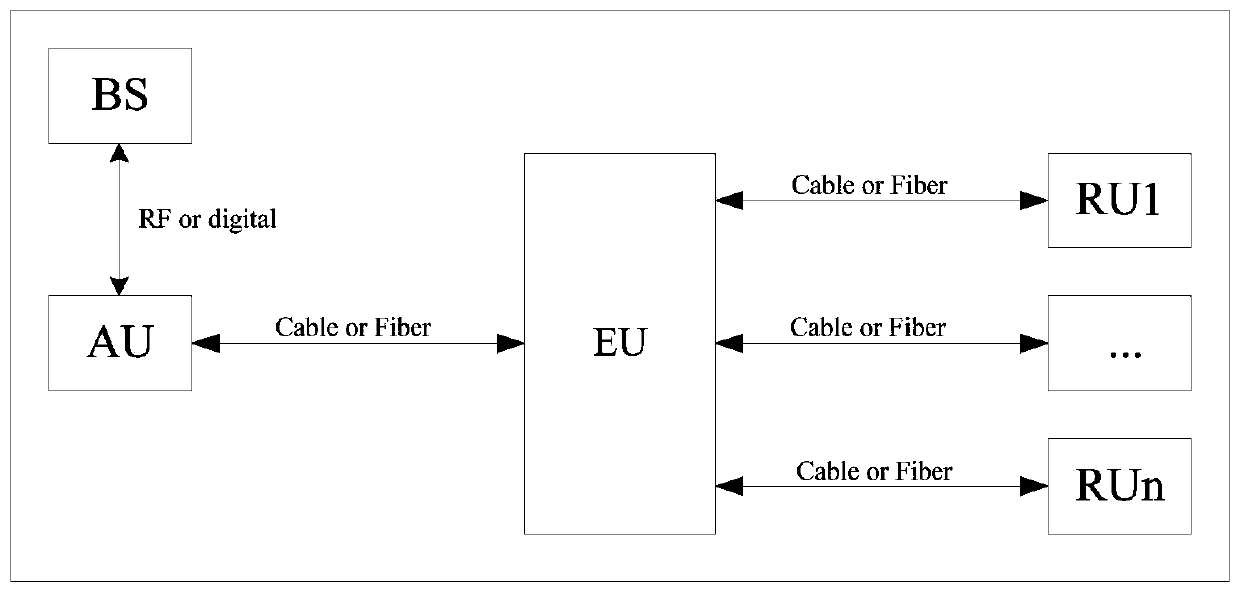
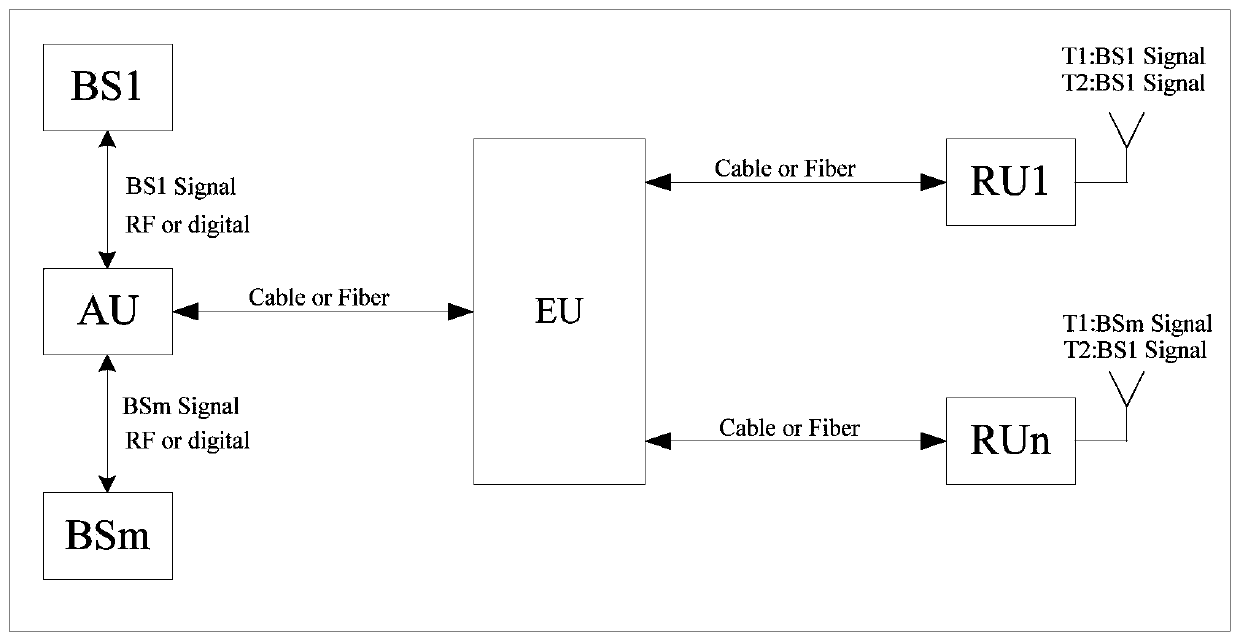
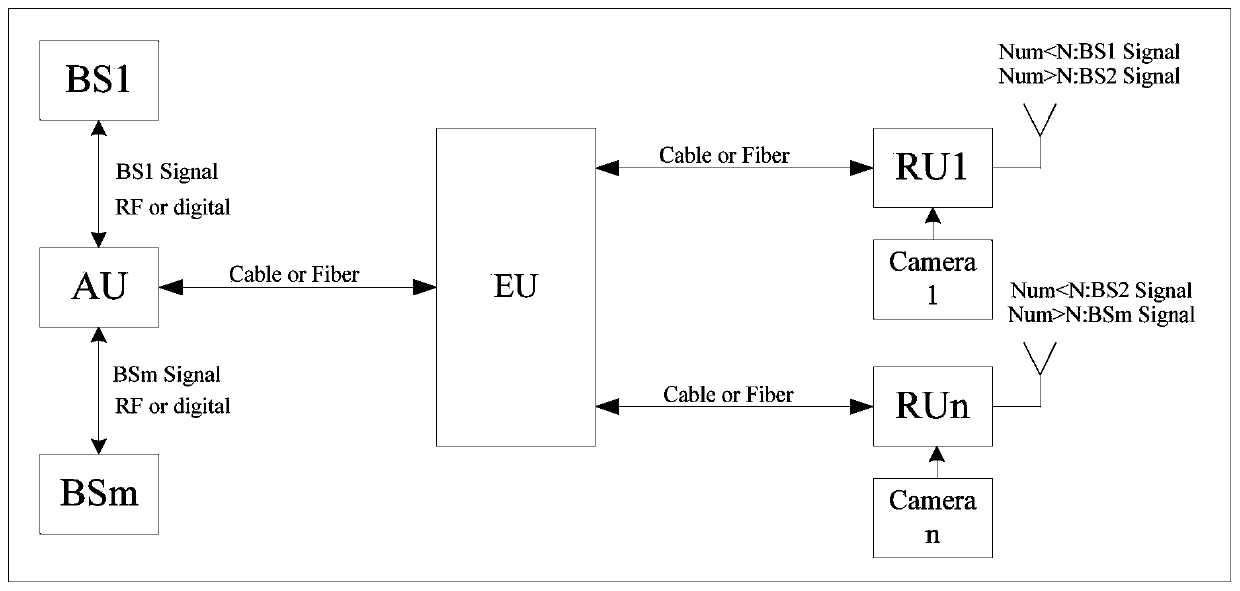
Cell scheduling method, electronic equipment, storage medium and distributed antenna system
ActiveCN111491391AImprove application flexibilityRealize automatic schedulingSite diversityRadio-over-fibreComputer networkCell scheduling
The invention discloses a cell scheduling method, electronic equipment, a storage medium and a distributed antenna system, the distributed antenna system comprises an access unit, an expansion unit and a plurality of far-end units, and the access unit acquires a plurality of base station signals. The cell scheduling method comprises the following steps: acquiring the number of users in the coverage range of the plurality of far-end units; determining a target far-end unit for starting cell scheduling based on the number of users; determining scheduling information corresponding to the target remote unit; scheduling at least one base station signal from the plurality of base station signals based on the scheduling information; and routing at least one base station signal to the target far-end unit by the extension unit. According to at least one embodiment of the invention, the cell scheduling method, the electronic equipment, the storage medium and the distributed antenna system can achieve the statistics of the number of users in the coverage range of the far-end units, determine whether to start the cell scheduling or not based on the number of users, achieve the scheduling of atleast one base station signal for the far-end units starting the cell scheduling, achieve the automatic scheduling of a plurality of operators and a plurality of cells, and improve the application flexibility of a digital DAS.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
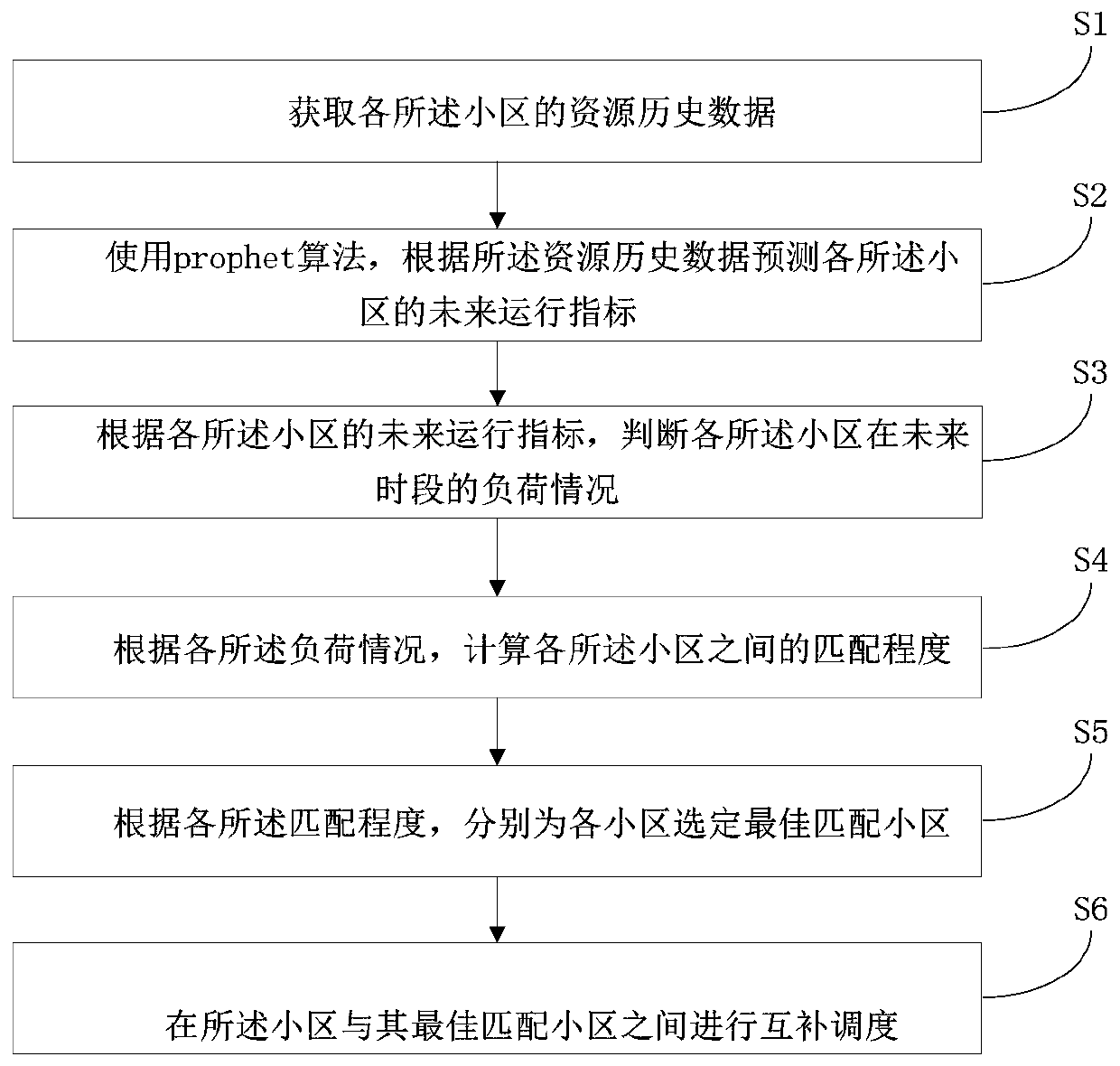
Cell scheduling method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN111132179APrediction is accurateIncrease success rateNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh level techniquesCell schedulingDistributed computing
The invention discloses a cell scheduling method, system and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring resource historical data of each cell, and predicting future operation indexes of the cells by using a prophet algorithm, judging load conditions of the cells in a future time period, calculating matching degrees among the cells, respectively selecting optimal matching cells for the cells, performing complementary scheduling between the cells and the optimal matching cells, and the like. Future operation indexes are predicted by using a prophet algorithm, so that an accurate prediction result can be provided; the optimal matching cell of each cell is determined according to the prediction result, more time exists between each cell and the optimal matching cell of the cell to be in the complementary state, complementary scheduling is carried out between each cell and the optimal matching cell of the cell, the higher success rate can be achieved, and the effect of resource and load balancing is better achieved. The method is widely applied to the technical field of wireless communication.
Owner:广东宜通联云智能信息有限公司
Network-wide inter-cell interference minimization via coordinated multipoint cell scheduling coordination
InactiveCN102460990AReduce distractionsSignal allocationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsInformation transmissionCell scheduling
Network-wide inter-cell interference is reduced by aggregating cells (herein, sub-cells) into Coordinated Multipoint (CoMP) cells, each having a controller. The CoMP cells are divided into sets, similar to a frequency reuse plan. Scheduling information regarding transmissions, scheduled to and from UEs in one set of CoMP cells is transmitted to controllers in sets of neighboring CoMP cells, in advance of the transmissions. Controllers in the receiving sets of CoMP cells schedule transmission to minimize both inter-sub-cell interference and interference with the set of CoMP cells that transmitted the scheduling information, and assuming no interference from other CoMP cells. They then transmit scheduling information to subsequent set(s) of CoMP cells.; The order of scheduling information transmission between sets of CoMP cells may be rotated for fairness The scheduling information may range from bare threshold data indicating at least one transmission, to detailed information such as estimated path gains to each UE.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
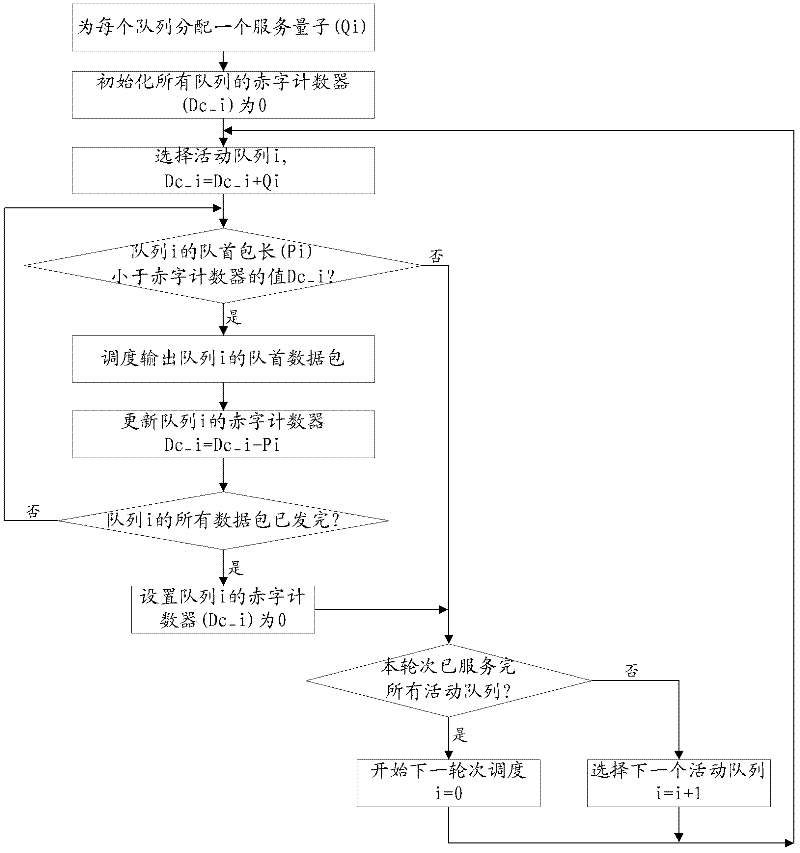
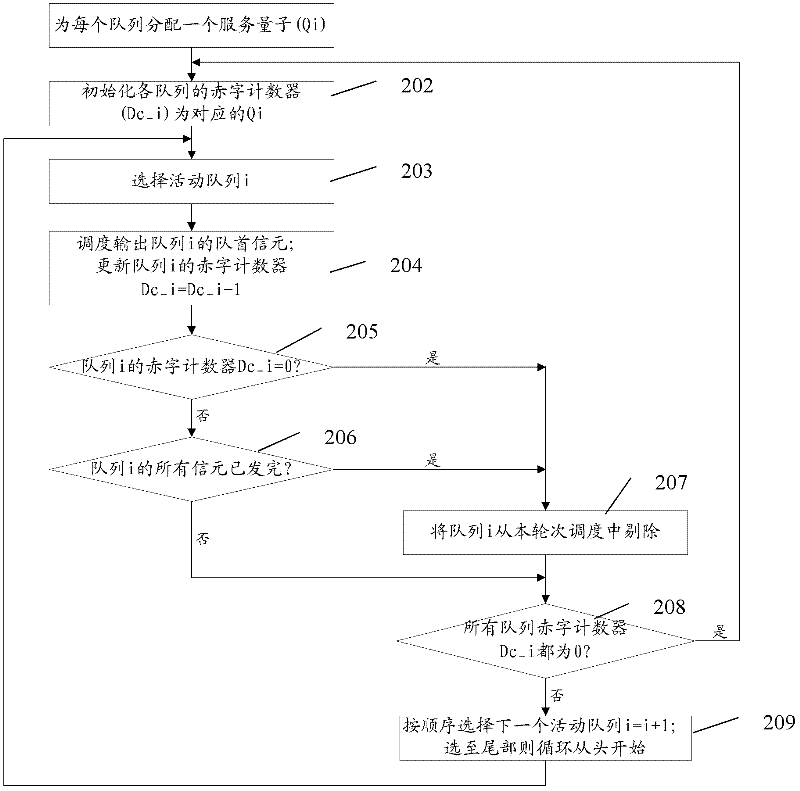
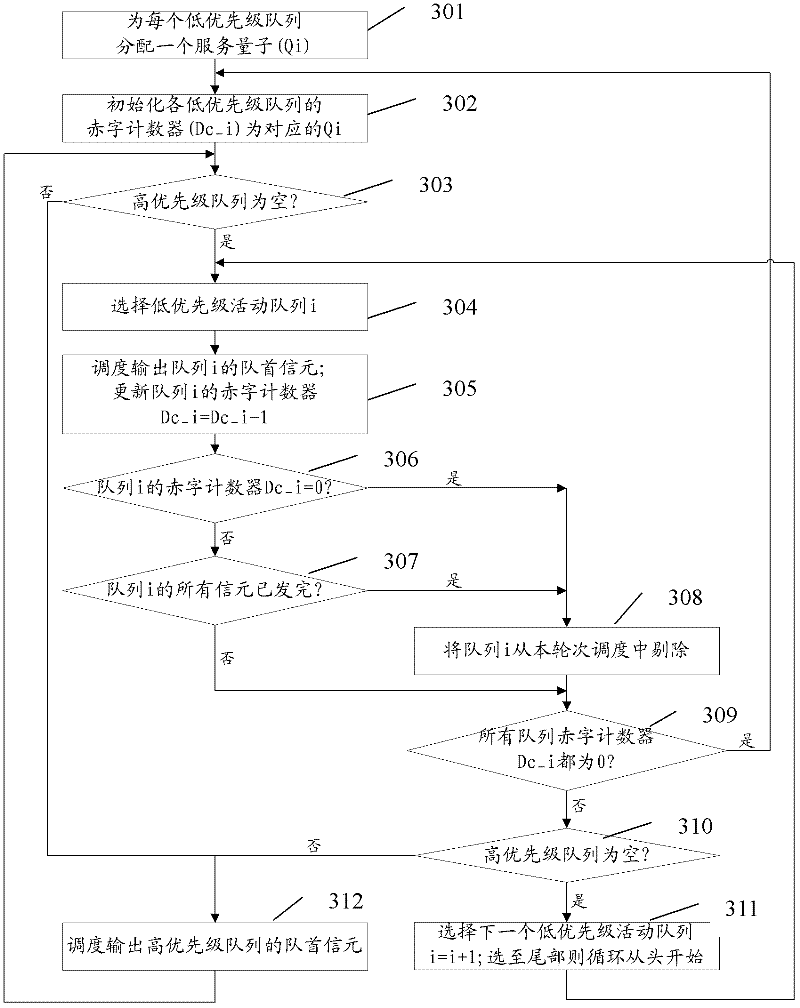
Cell scheduling method and device
ActiveCN102684983ASatisfy the reserved bandwidthSatisfy the principle of fair schedulingStore-and-forward switching systemsCell schedulingFair scheduling
The invention provides a cell scheduling method and device. The cell scheduling method comprises the following steps of: distributing service quantum Qi for each low-priority queue according to reserved bandwidth required by each low-priority queue and initializing a deficit counter value of each low-priority queue to be Qi; when a high-priority queue has cells waiting for scheduling and outputting, scheduling and outputting the cells of the high-priority queue by an outputting and scheduling module according to the highest scheduling priority till the high-priority queue is empty; and when the high-priority queue is empty, carrying out round robin on the cell at the head of each low-priority mobile queue by the outputting and scheduling module. The cell scheduling method and device disclosed by the invention realize fair scheduling and balanced output of the cells.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
DCI generation method, cell scheduling method, system and device, and medium
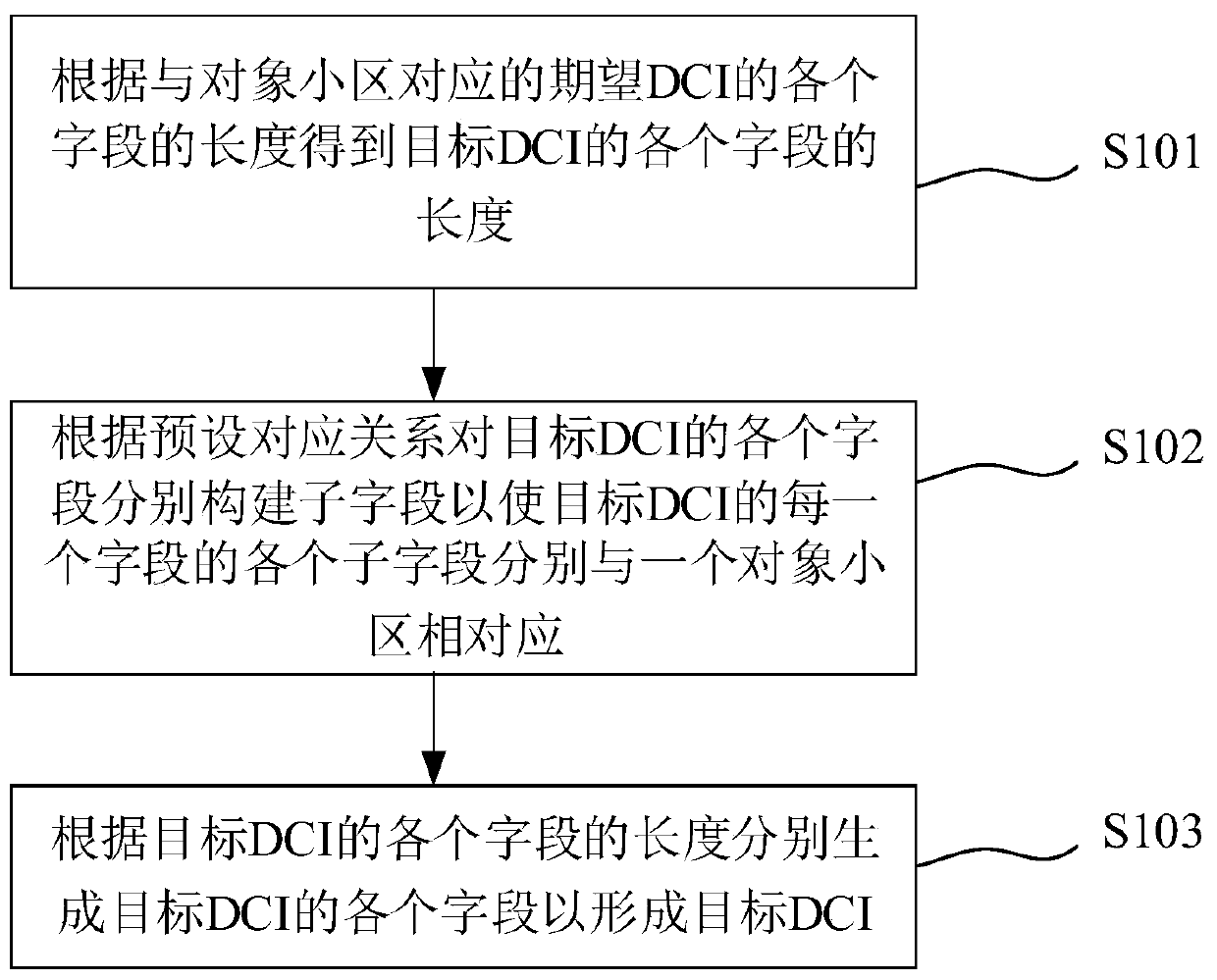
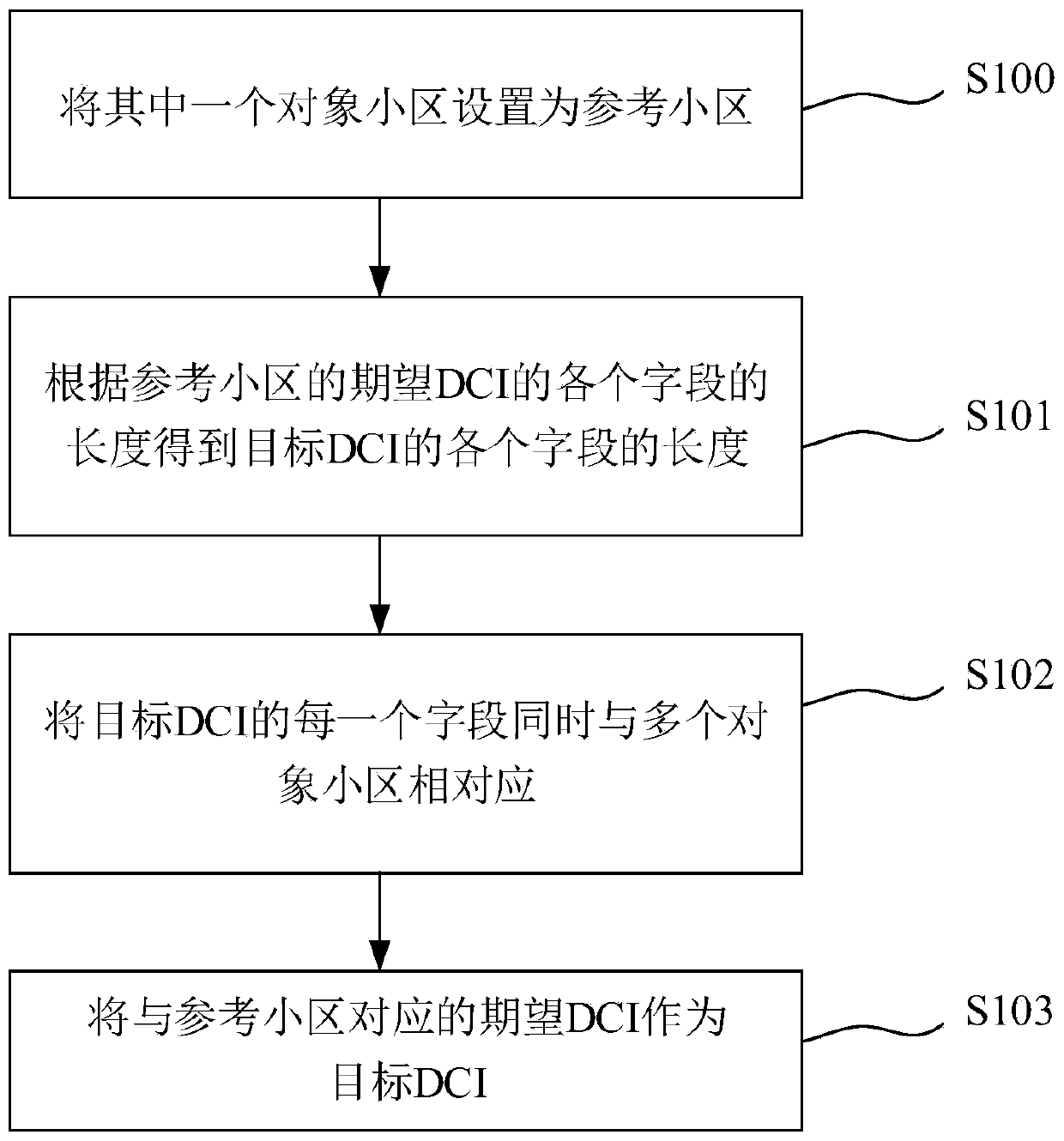
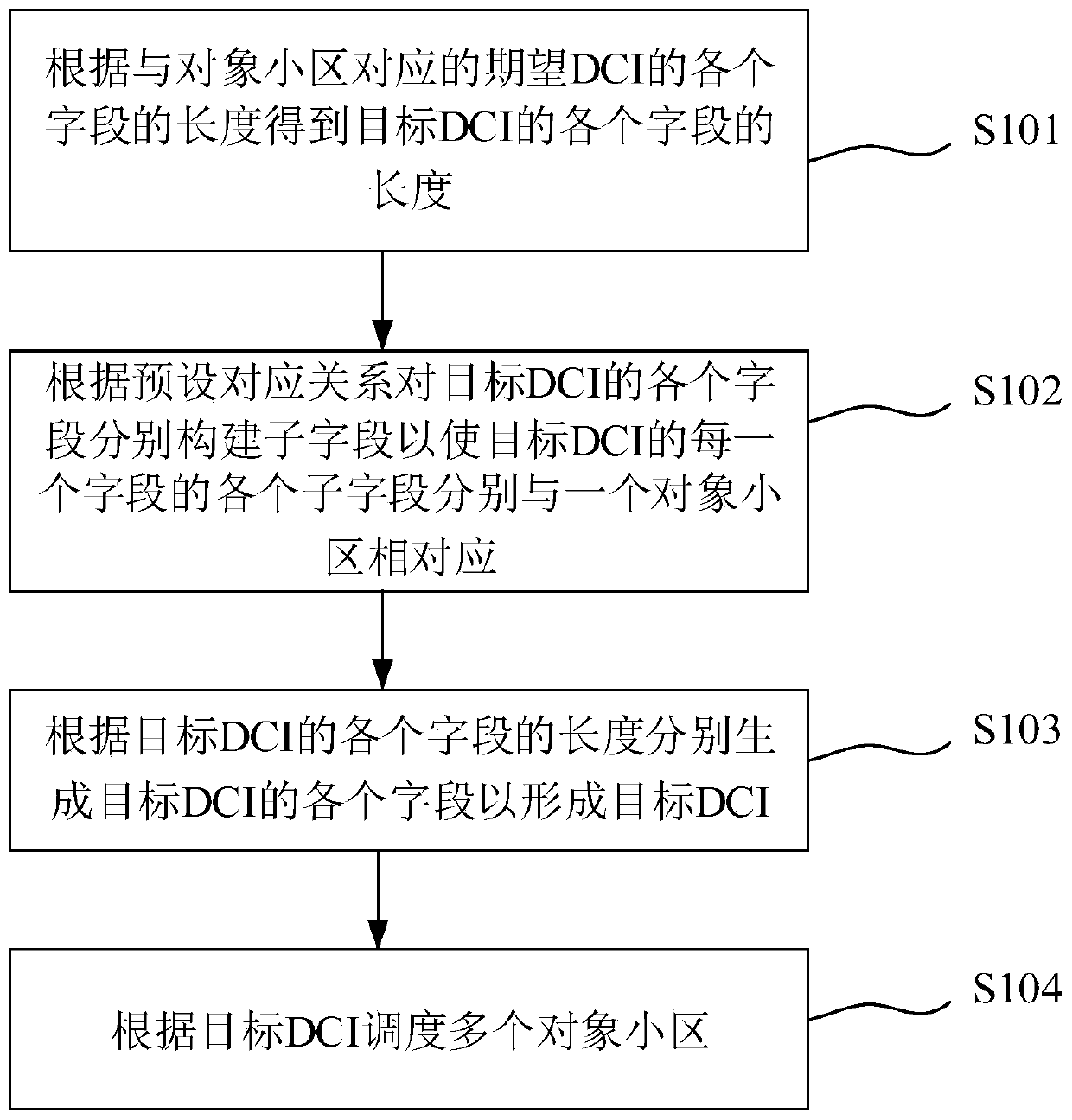
ActiveCN111245586ASave communication resourcesSignal allocationWireless communicationCell schedulingParallel computing
The invention discloses a DCI generation method, a cell scheduling method, system and device, and a medium. The DCI generation method comprises the following steps: obtaining the length of each fieldof a target DCI according to the length of each field of an expected DCI corresponding to object cells, wherein the number of the object cells is not less than two, the expected DCI is the DCI required for separately scheduling each object cell, and the length of each field of the target DCI is the length required for being compatible with the corresponding field of the expected DCI; respectivelyconstructing sub-fields for each field of the target DCI according to a preset corresponding relation so as to enable each sub-field of each field of the target DCI to respectively correspond to one object cell; and generating each field of the target DCI according to the length of each field of the target DCI and the corresponding relation to form the target DCI. According to the invention, one target DCI is compatible with scheduling information of a plurality of cells.
Owner:BEIJING SPREADTRUM HI TECH COMM TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com