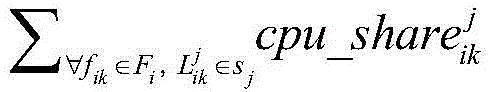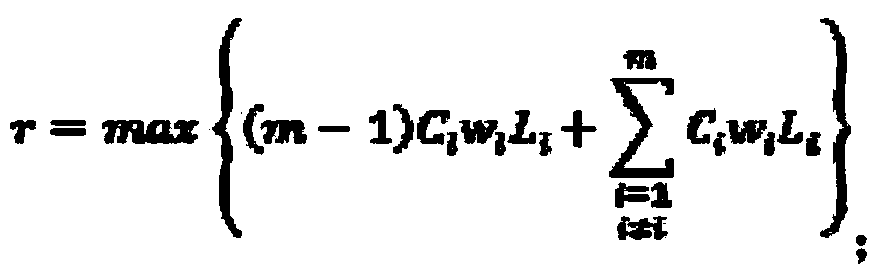Patents
Literature
87 results about "Weighted round robin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
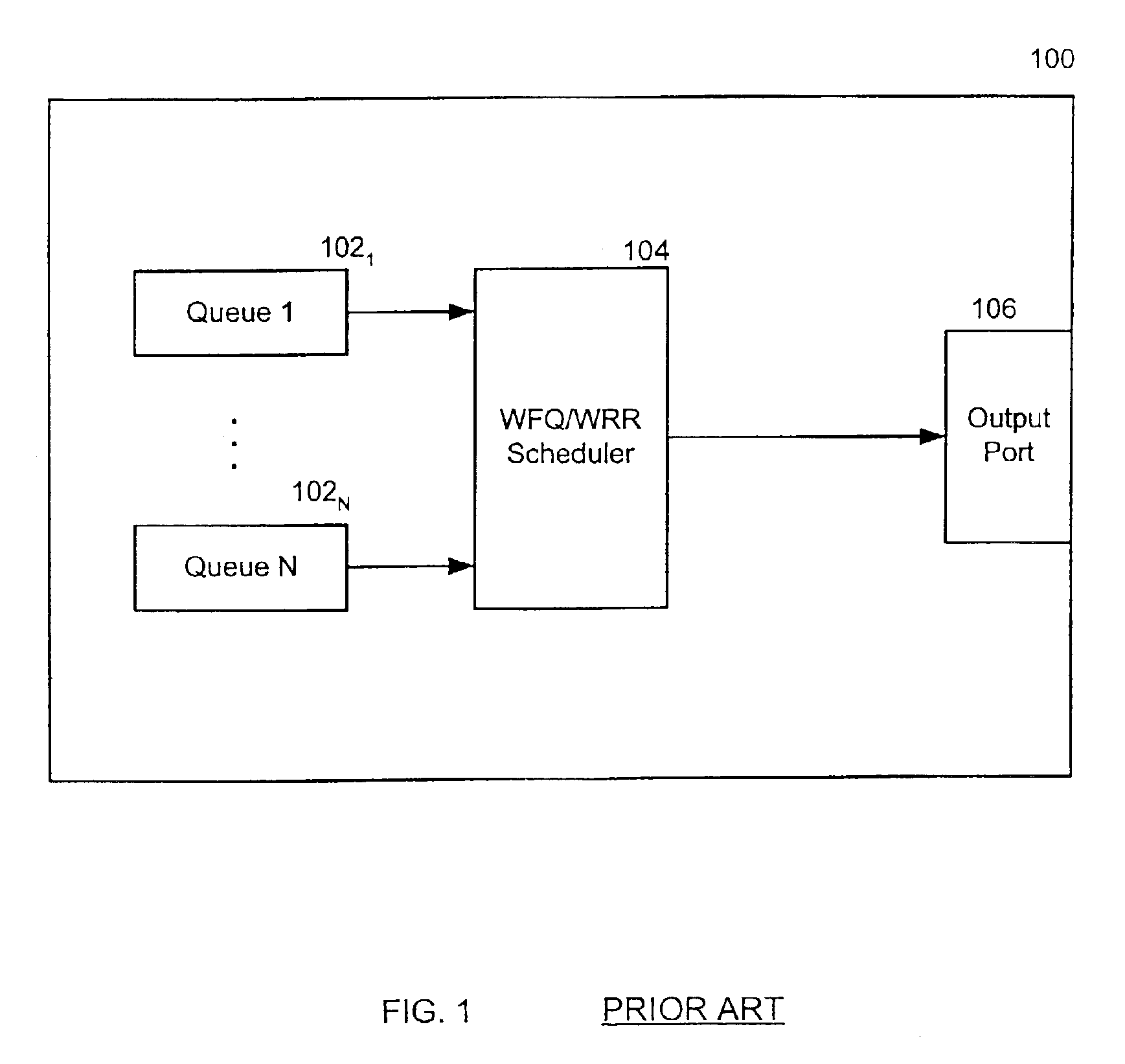
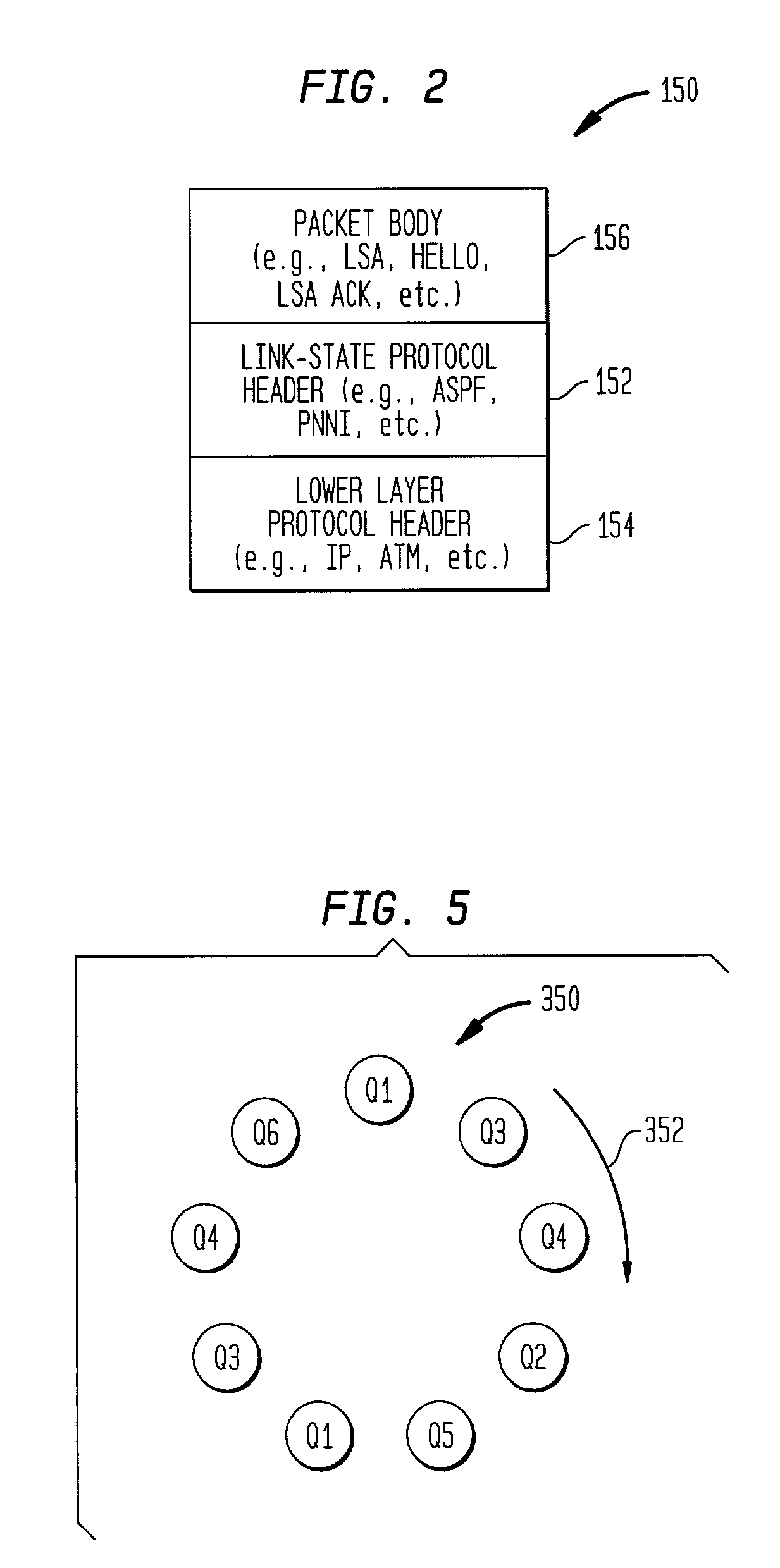
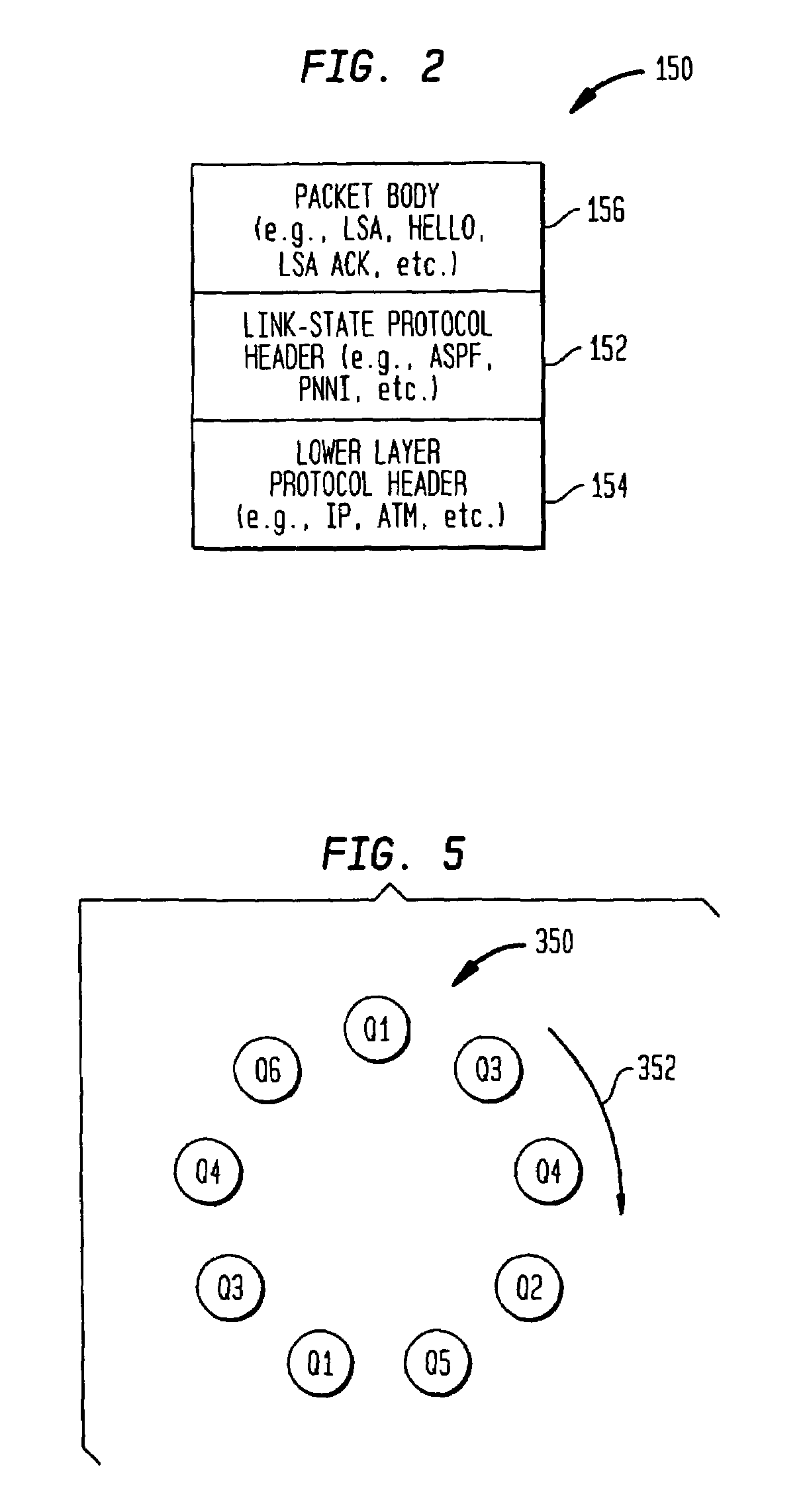
Weighted round robin (WRR) is a network scheduling discipline. Each packet flow or connection has its own packet queue in a network interface controller. It is the simplest approximation of generalized processor sharing (GPS). While GPS serves infinitesimal amounts of data from each nonempty queue, WRR serves a number of packets for each nonempty queue. The number of packets served is in proportion to the assigned weight and in inverse proportion to the size of the packets.
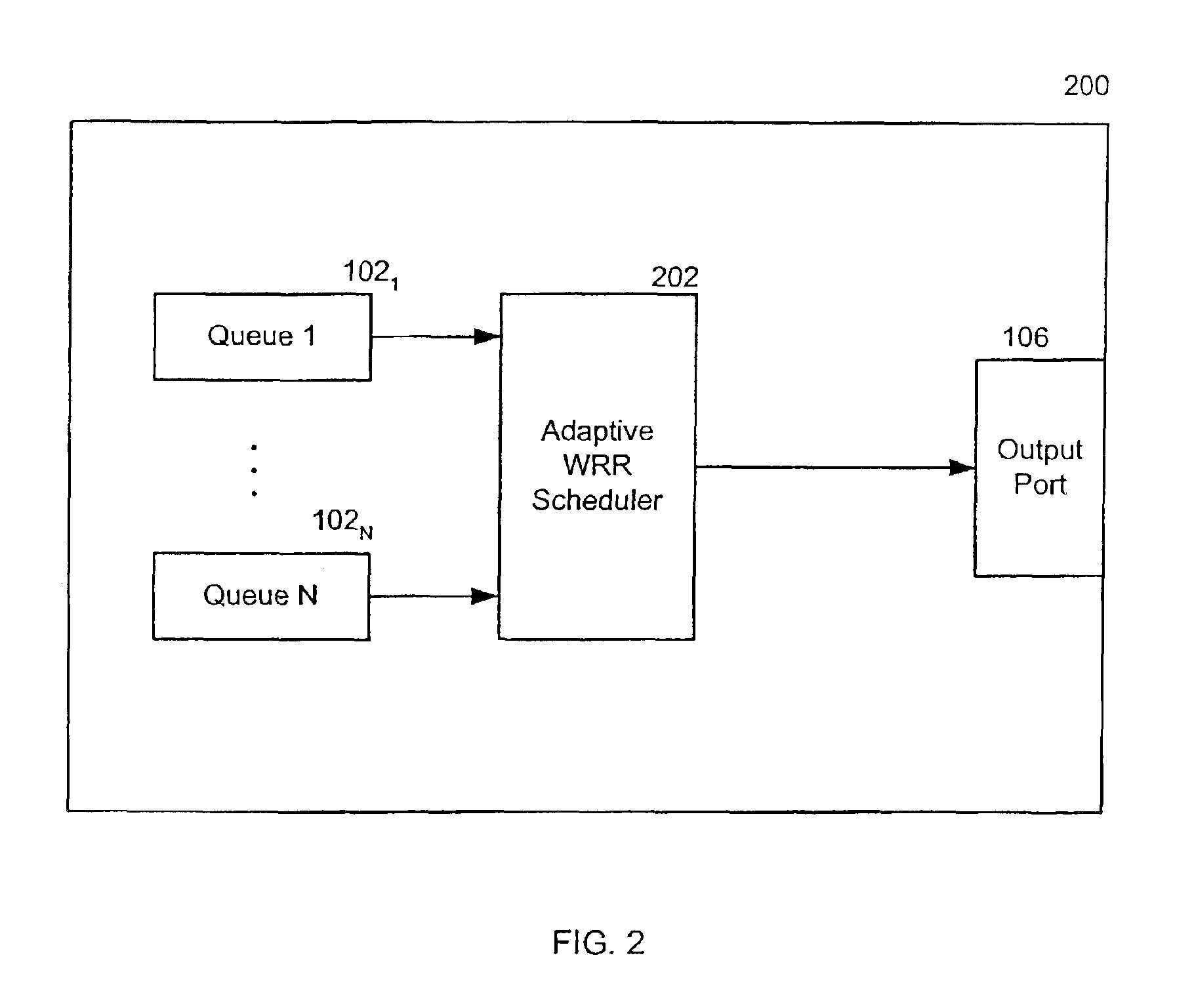
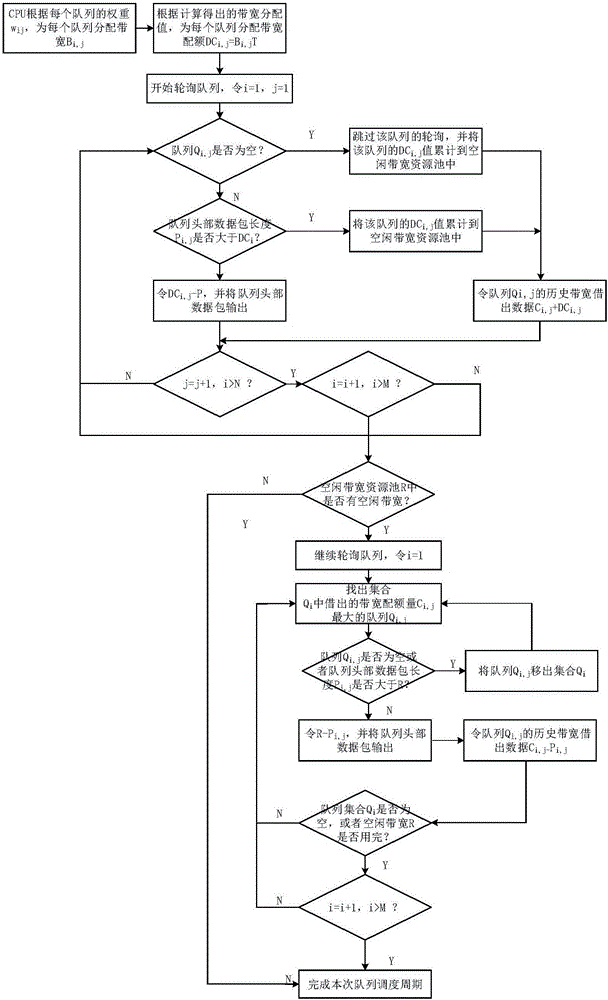
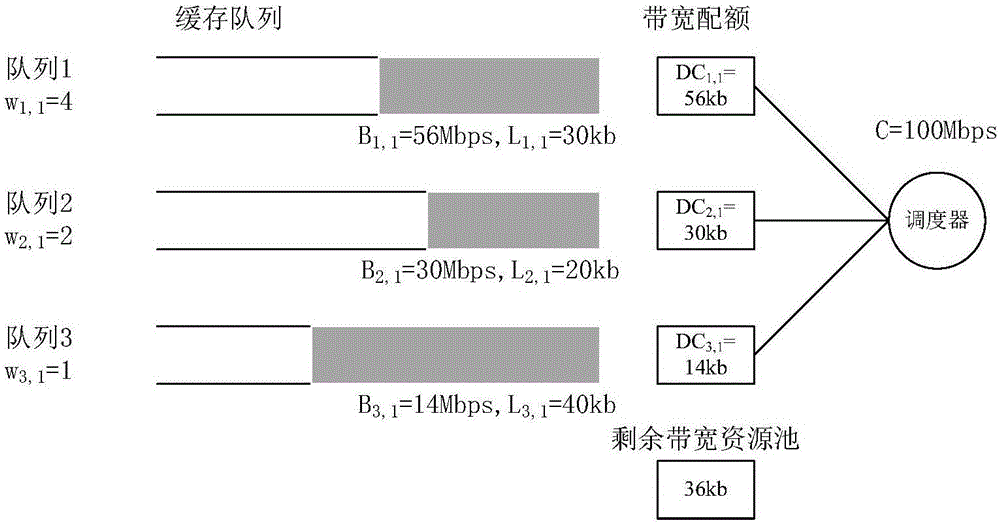
Dynamic weighted round robin queuing
InactiveUS6438135B1Improve performanceData switching by path configurationNetwork packetDistributed computing
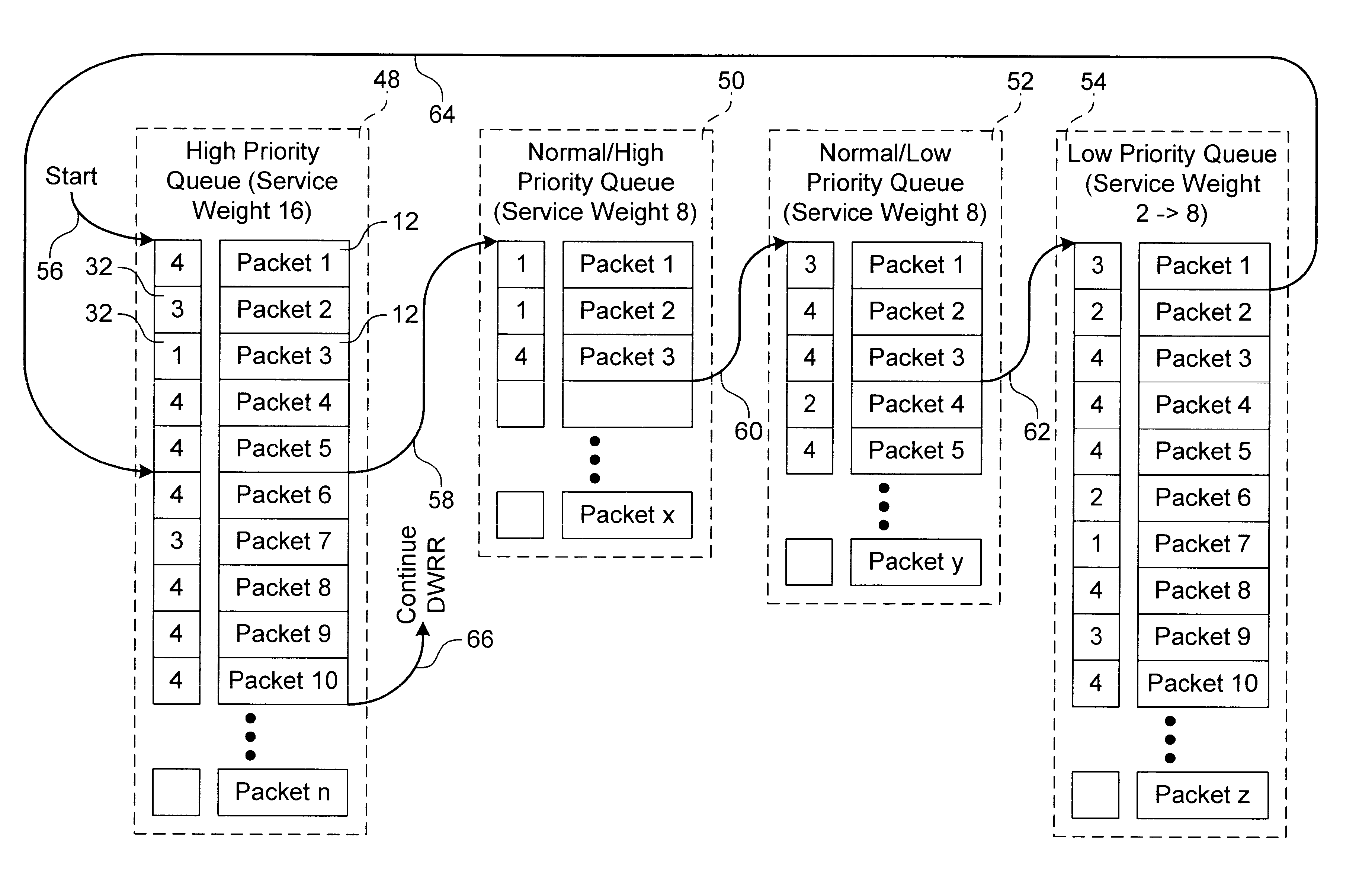
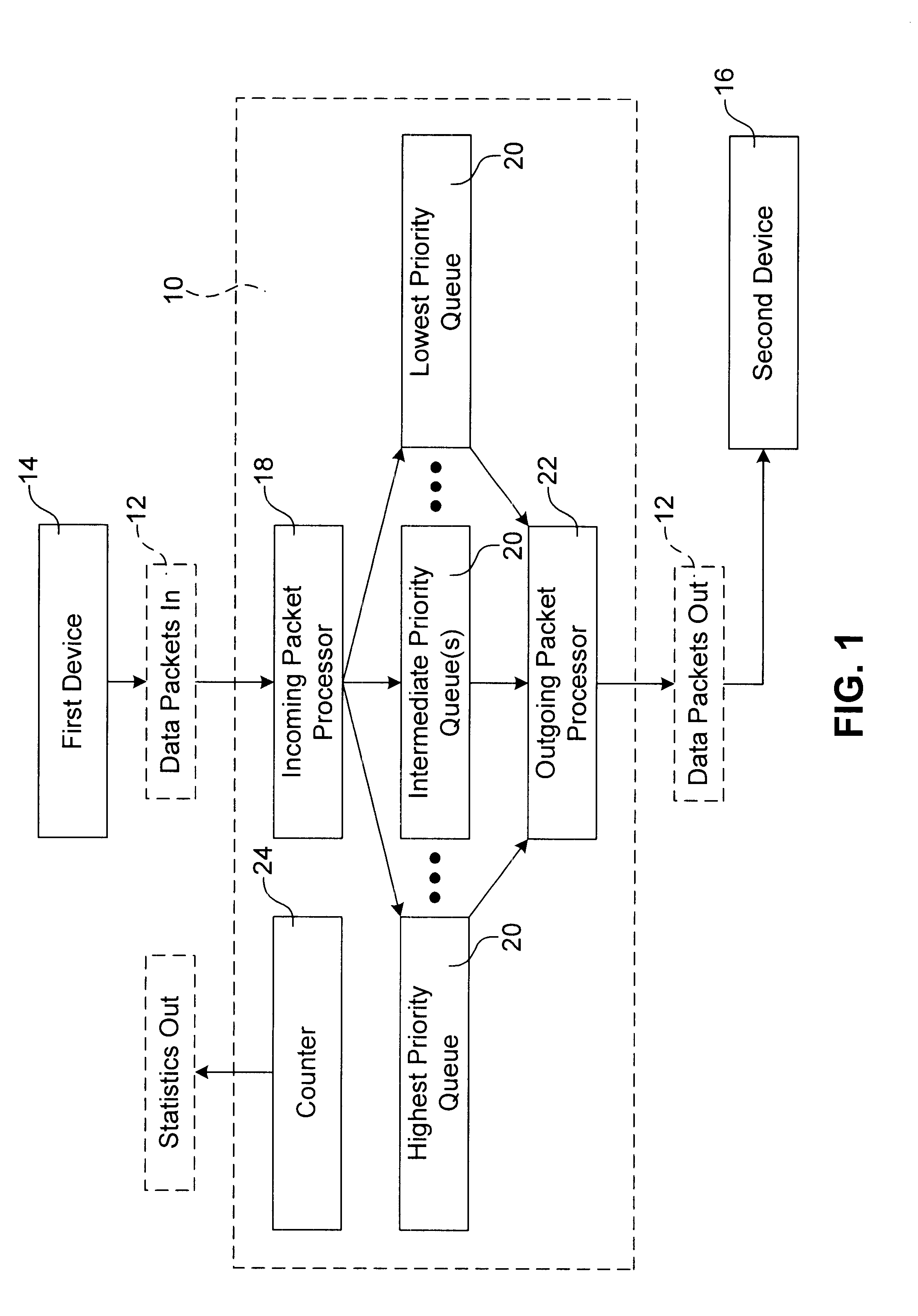
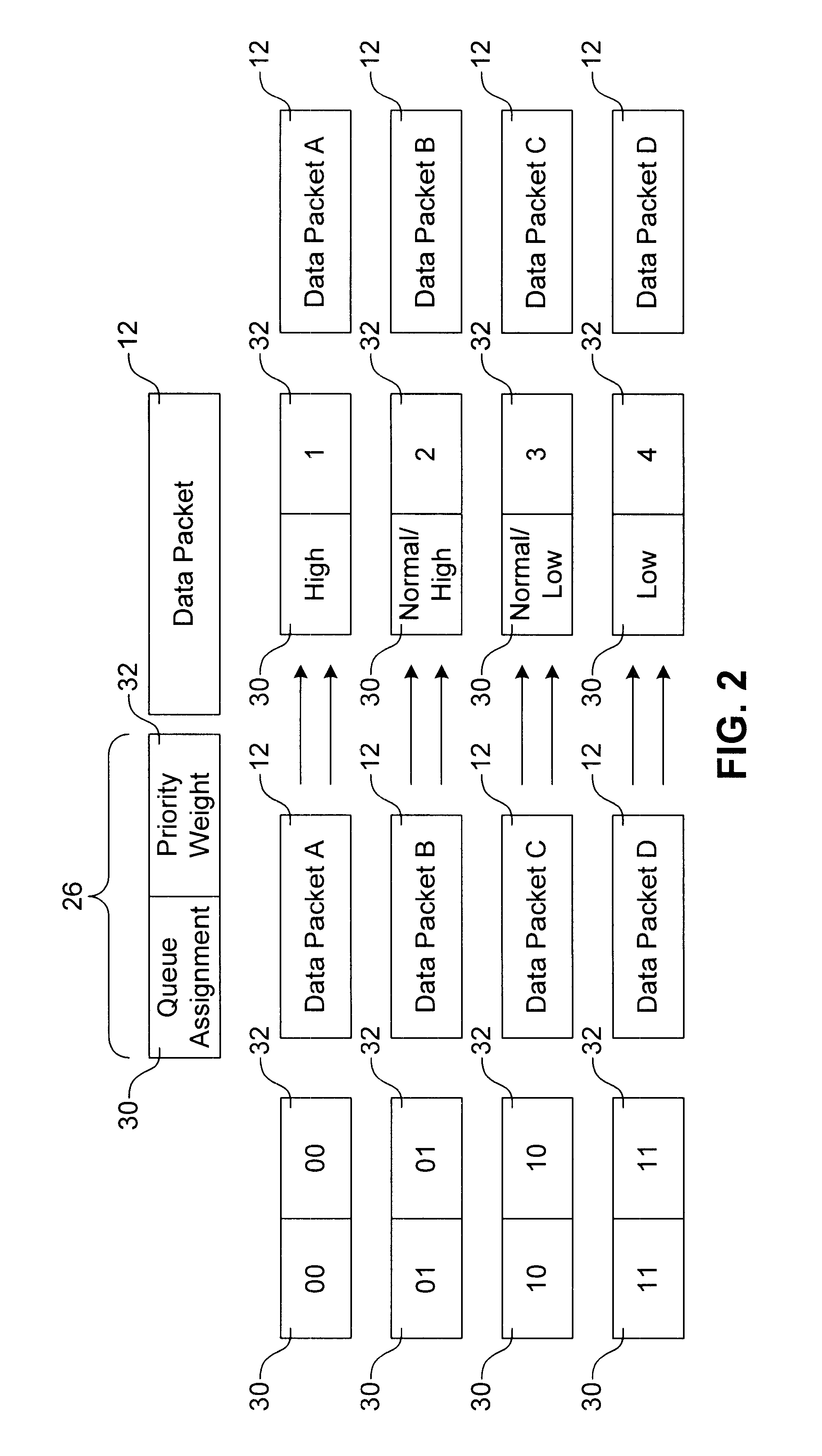
A method for transmitting a plurality of data packets through a network. Each data packet is assigned to one of a plurality of priority queues and each priority queue has a service weight. A priority weight is assigned to each of the data packets and each priority weight has a value. Data packets are delivered from one of the priority queues until a service satisfied condition is met. The service satisfied condition is met when a combination of the values of the priority weights for each of the delivered data packets is equal to or is greater than the service weight assigned to the priority queue. A queuing switch for implementing this method is also discussed. The queuing switch includes an incoming data packet processor and a plurality of priority queues.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
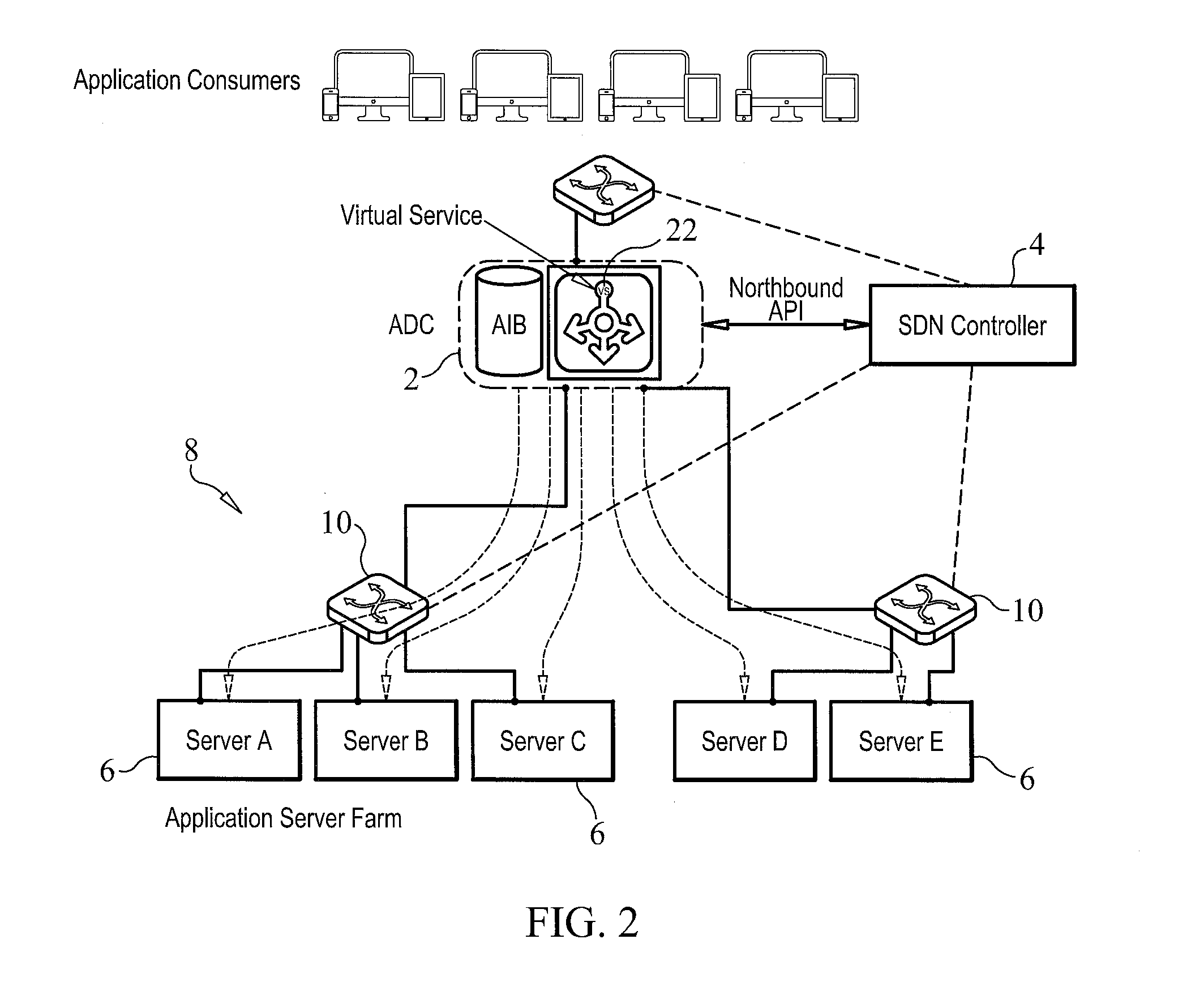
Adaptive load balancer and methods for intelligent data traffic steering
ActiveUS20150358236A1Alleviate and avoid data congestionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
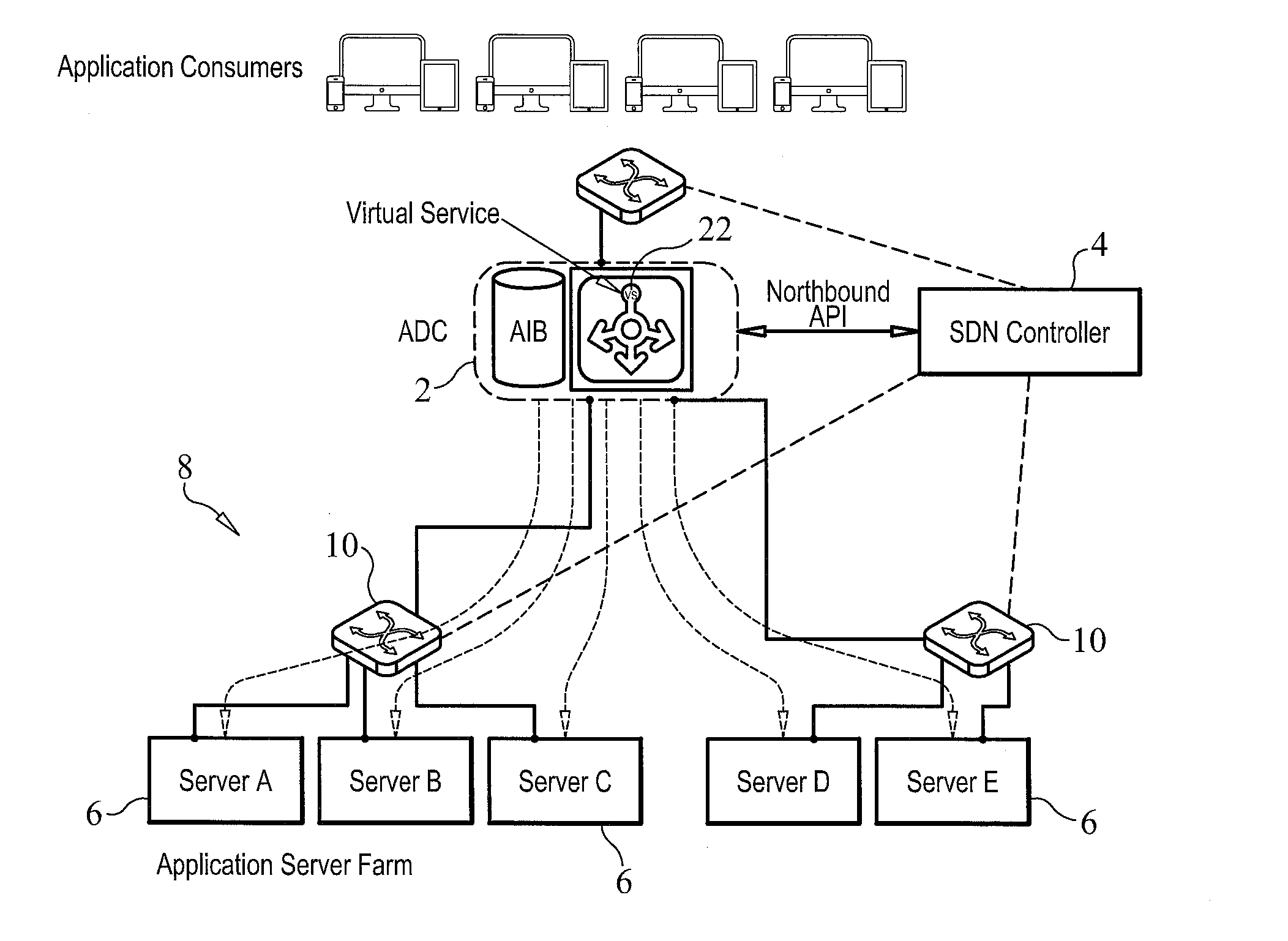
An adaptive load balancer intelligently steers data traffic through a software defined network (SDN) to which the load balancer is operatively coupled. The network has egress ports to which a plurality of servers is connected. The network has an SDN controller which generates statistical information concerning the network. The adaptive load balancer includes a weighted round robin scheduler module which receives client requests and, based on the statistical information generated by the SDN controller, determines a weight to be attributed to each server of the plurality of servers connected to the network. The adaptive load balancer operates in a passive port mode, a passive path mode, an active path mode and an active path with quality of service (QoS) overlay mode.
Owner:PROGRESS SOFTWARE
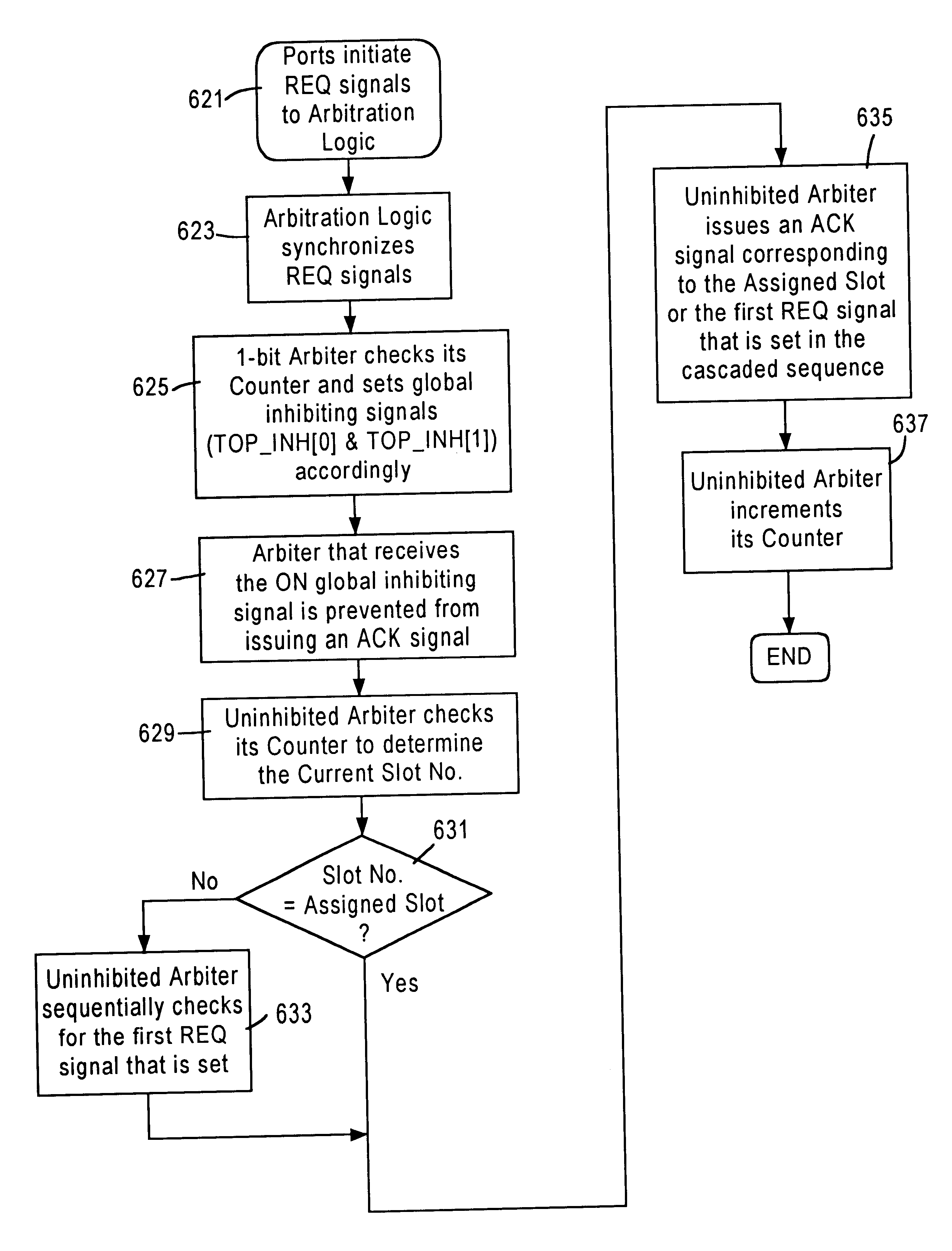
Weighted round robin cell architecture
InactiveUS6563818B1Reduce complexityAvoid signalingMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsNetwork switchComputer science
A network switch configured for switching data frames across multiple ports utilizes an efficient arbiter to store the data frames. Each port possesses queuing logic for requesting a free pointer from a free buffer queue. A multi-level arbitration logic arbitrates all the requests of equal priority from the network switch ports in a round robin scheme. The arbitration logic comprises a plurality of cells that cascaded to output an acknowledgement signal in response to an inhibit signal and a request signal as well as a counter that is incremented upon an asserted acknowledgement signal.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Managing priority queues and escalation in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20040092278A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesStreaming dataLower priority
A method and system for servicing data traffic in wireless local area networks (such as IEEE 802.11 networks) in multiple queues having different levels of priority. These queues include at least a low priority queue for 'best effort' traffic, a medium priority queue for streaming data such as video pictures, and a high priority queue for voice traffic, and are serviced in order of decreasing priority. To prevent the 'best effort' traffic in the low priority queue from being 'starved', a bit is set to indicate when such a condition is likely to occur, and the low priority queue is served first when that bit has been set. Alternatively, low and medium priority traffic is handled on a weighted round-robin basis, and high priority traffic is given strict priority over both. Transmit and receive queues are handled on a rotating priority basis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
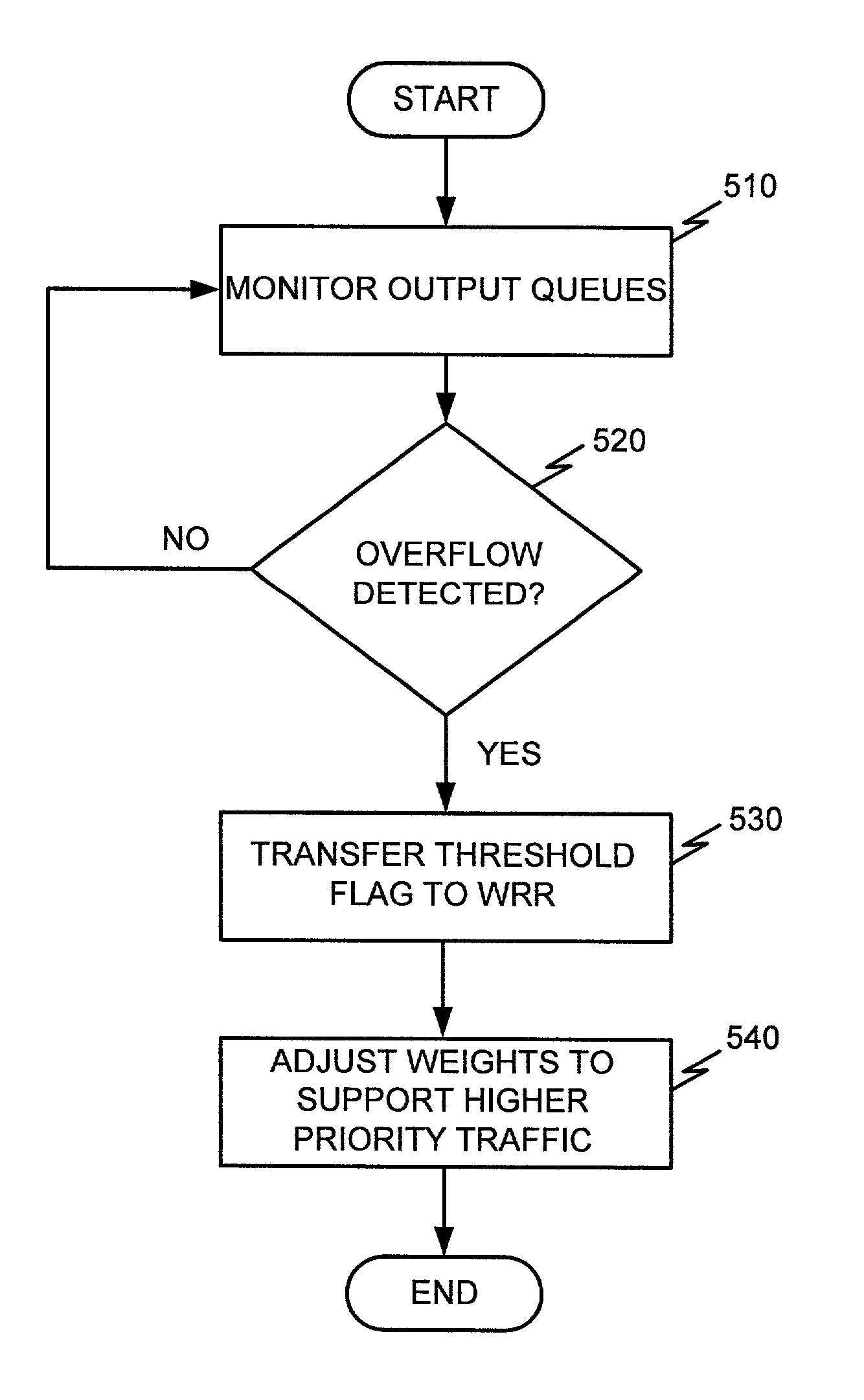
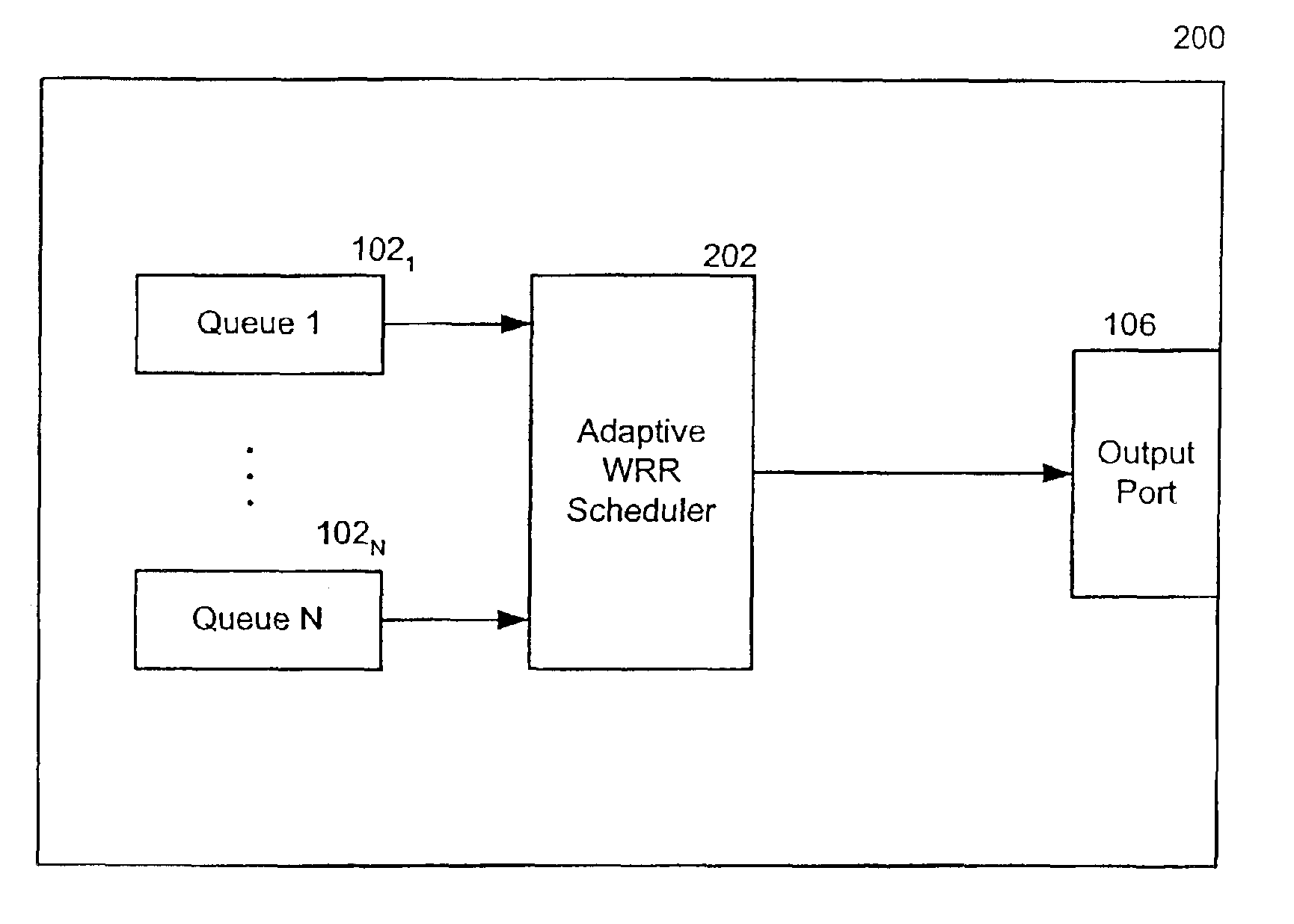
System and method for dynamically updating weights of weighted round robin in output queues
ActiveUS7110359B1Reduce congestionError preventionTransmission systemsWeighted round robinPriority queue
A network device includes a group of queues, each having a weighted round robin mechanism. The priority queues on a port detect an overflow condition and transfer a flag to the weighted round robin device in response to detecting the overflow condition. The weighted round robin mechanism adjusts the weight associated with one or more of the priority queues in response to receiving the flag and transfers data from the queues based on the adjusted weights.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Servicing output queues dynamically according to bandwidth allocation in a frame environment
InactiveUS6891835B2Reduce in quantityAttenuation bandwidthData switching by path configurationDynamic bandwidth allocationAdaptive weighting
An adaptive weighted round robin scheduling apparatus and method schedules variable-length frame transmissions from a plurality of output queues having different transmission priorities by first allocating, for each queue, a number of bandwidth segments for a bandwidth cycle and a number of transmission opportunities for a round robin cycle, and then processing the queues consecutively in a round-robin fashion, beginning with a highest priority queue, until none of the queues has any bandwidth remaining. More specifically, during each iteration of a round robin cycle, a queue is permitted to transmit a frame if the queue has at least one remaining transmission opportunity, the queue has a frame ready for transmission, and the queue has at least one remaining bandwidth segment, and furthermore the number of transmission opportunities for the queue is decremented by at least one. Upon transmitting a frame, the number of bandwidth segments for the queue is decreased by the number of bandwidth segments in the frame. If a queue has no frame ready for transmission, then the queue may be either penalized, in which case the number of bandwidth segments for the queue is reduced, or forced to forfeit its bandwidth segments, in which case any remaining bandwidth segments are reallocated to other queues and the number of bandwidth segments and the number of transmission opportunities for the queue are set to zero.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
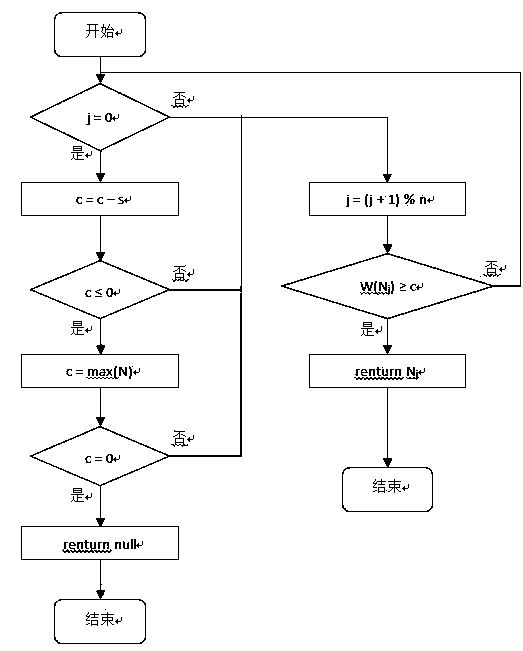
Dynamic weighted round robin scheduling policy method based on priorities
InactiveCN107733689AIncrease profitImprove transmission qualityRadio transmissionData switching networksData streamResource utilization
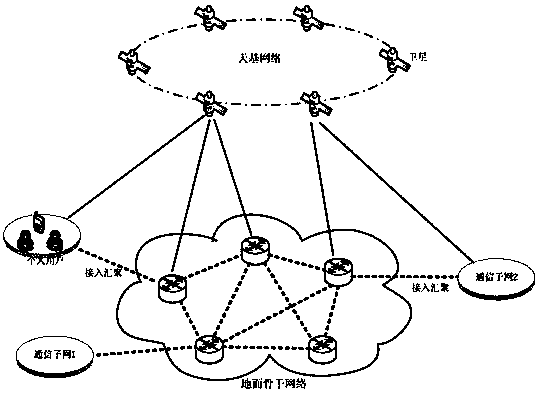
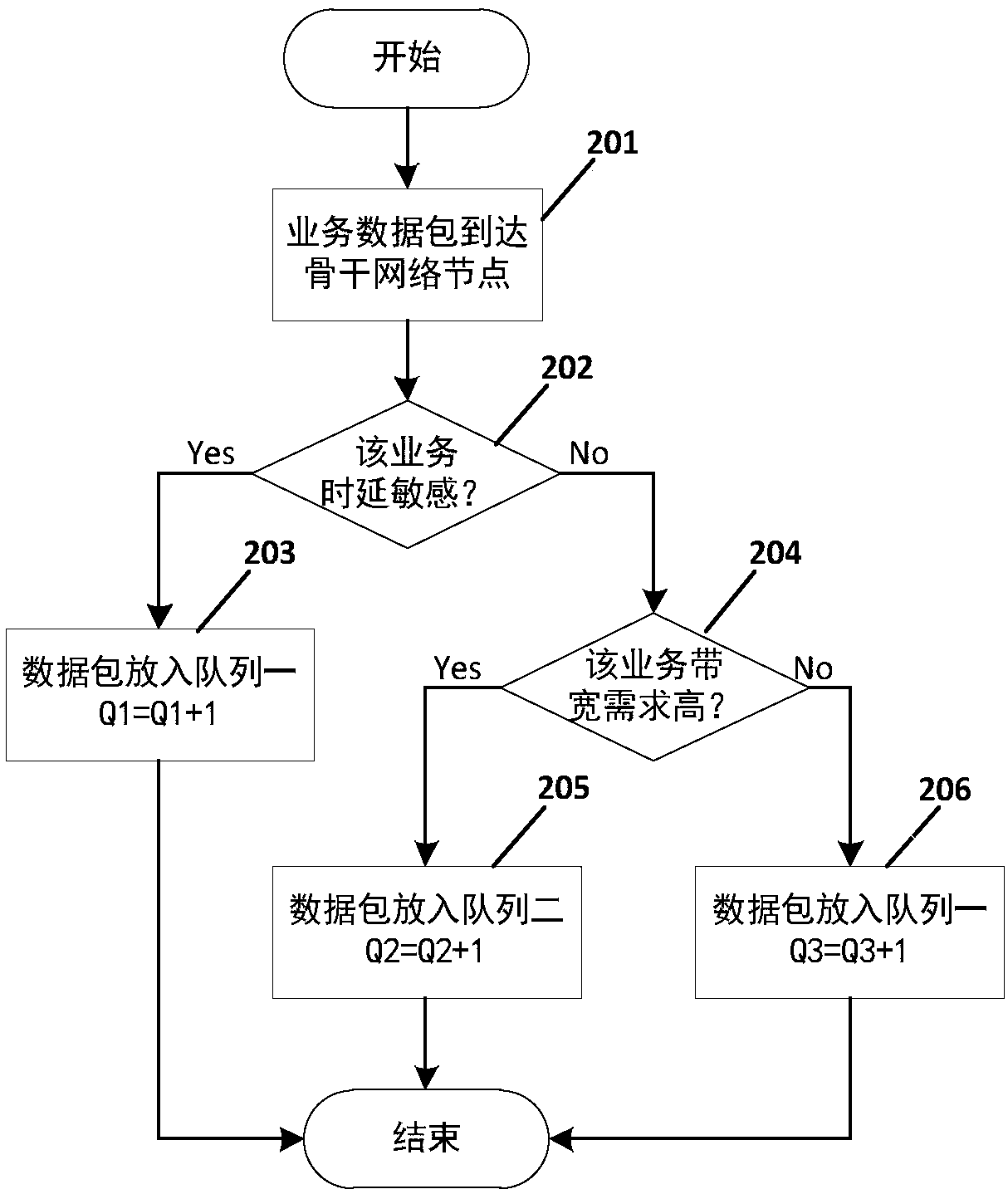
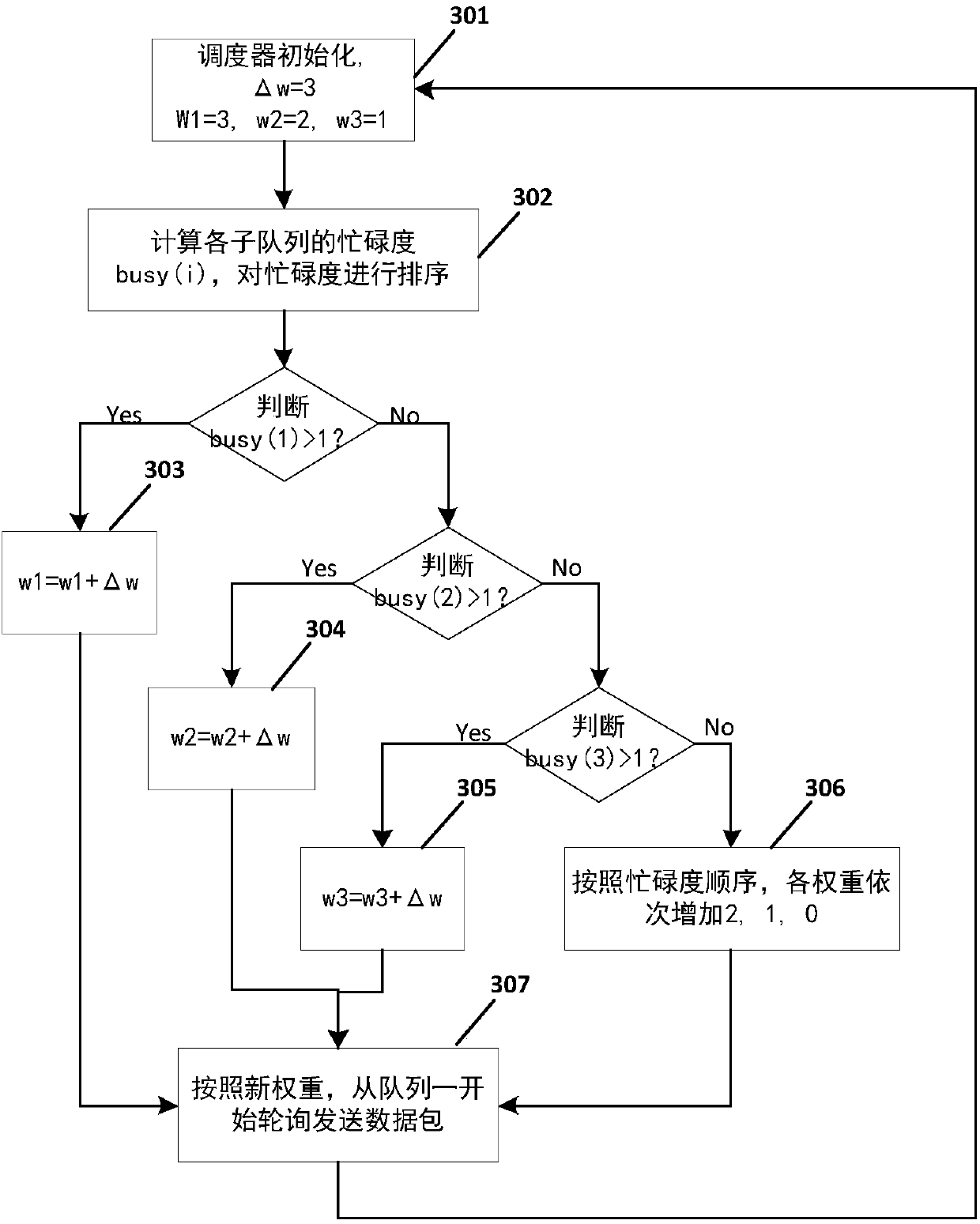
The invention provides a dynamic weighted round robin scheduling policy method based on priorities. Through utilization of the method, a network resource utilization rate is high, bandwidth resource allocation is fair and network resource scheduling is reasonable and efficient. The method is realized through adoption of the following technical scheme that for data streams of different priorities,the dynamic weighted round robin scheduling policy method based on the priorities comprises a queue management module and a round robin scheduling module; the queue management module divides all business in a network into sub-queues of n priorities; after backbone network nodes receive business data packets, the priorities of the data packets arriving at the backbone network nodes are judged according to QoS demands of the business, and the business data packets are inserted into the corresponding cache sub-queues according to the priorities; the round robin scheduling module carries out periodic round robin; and the busy degree of each sub-queue is calculated according to the current queue lengths Q of the sub-queues, the busy degree is arranged, round robin weight values of the sub-queues are dynamically adjusted according to a busy degree arrangement result, the round robin is carried out on each sub-queue in sequence, and the data packets are sent.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
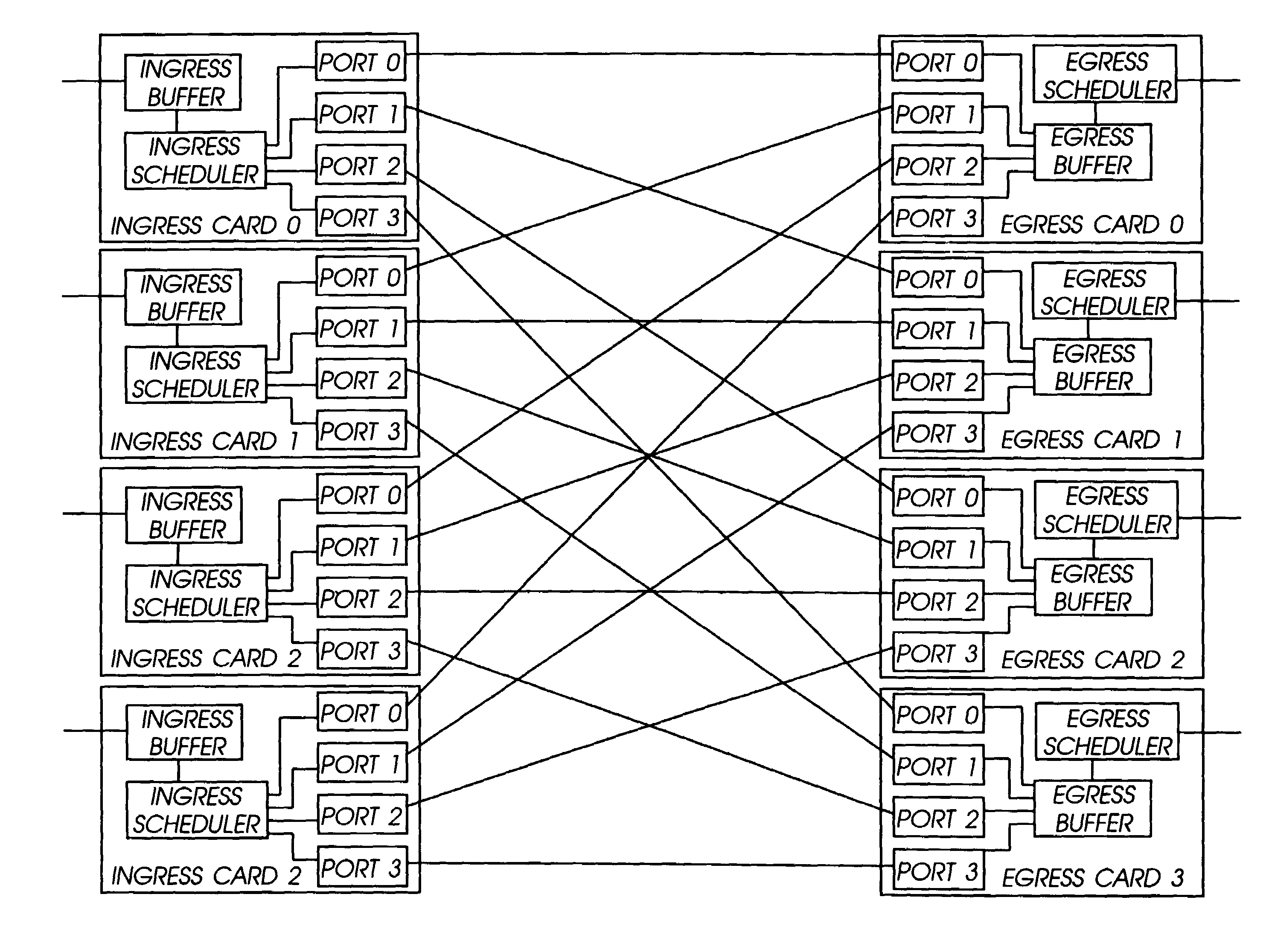
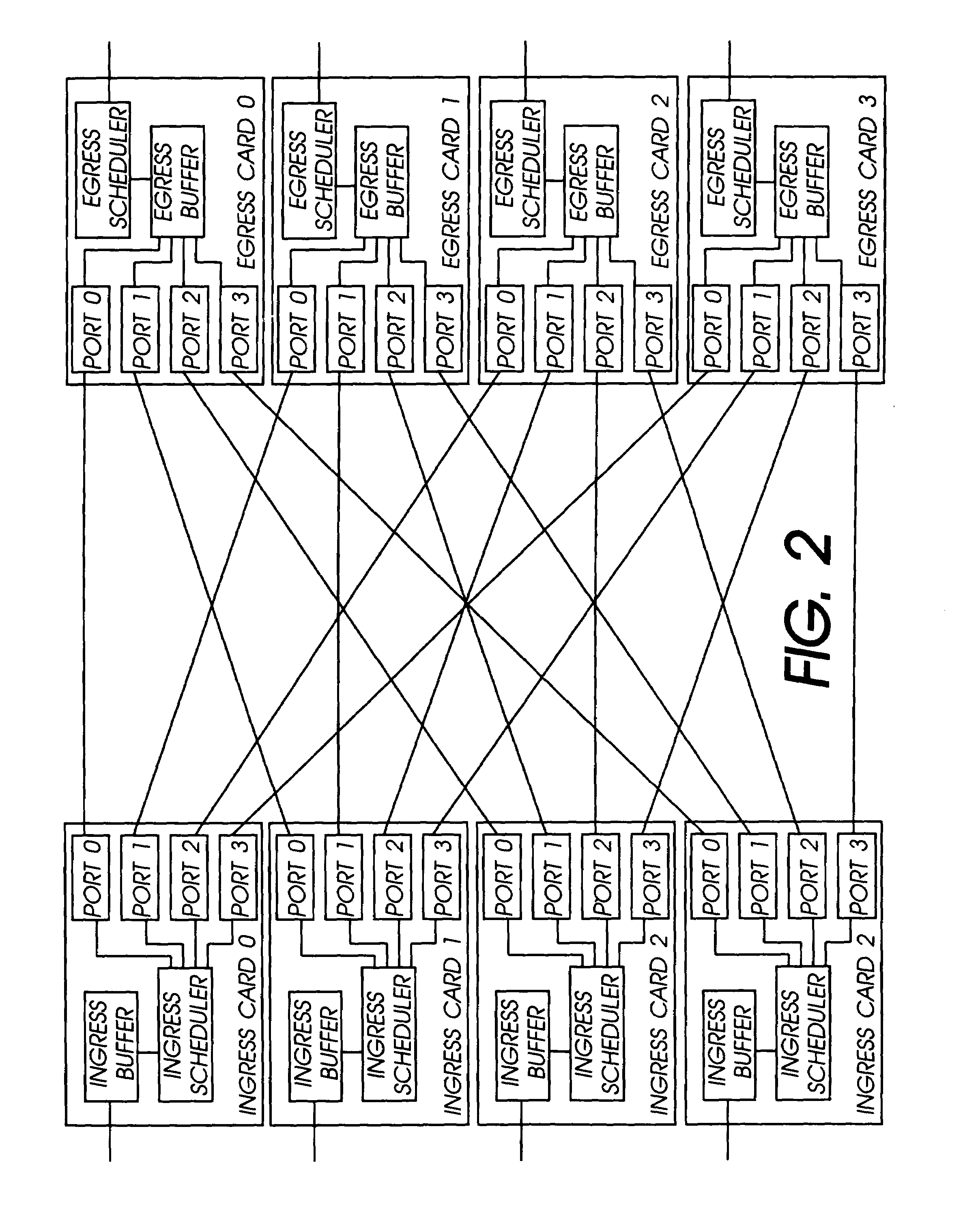
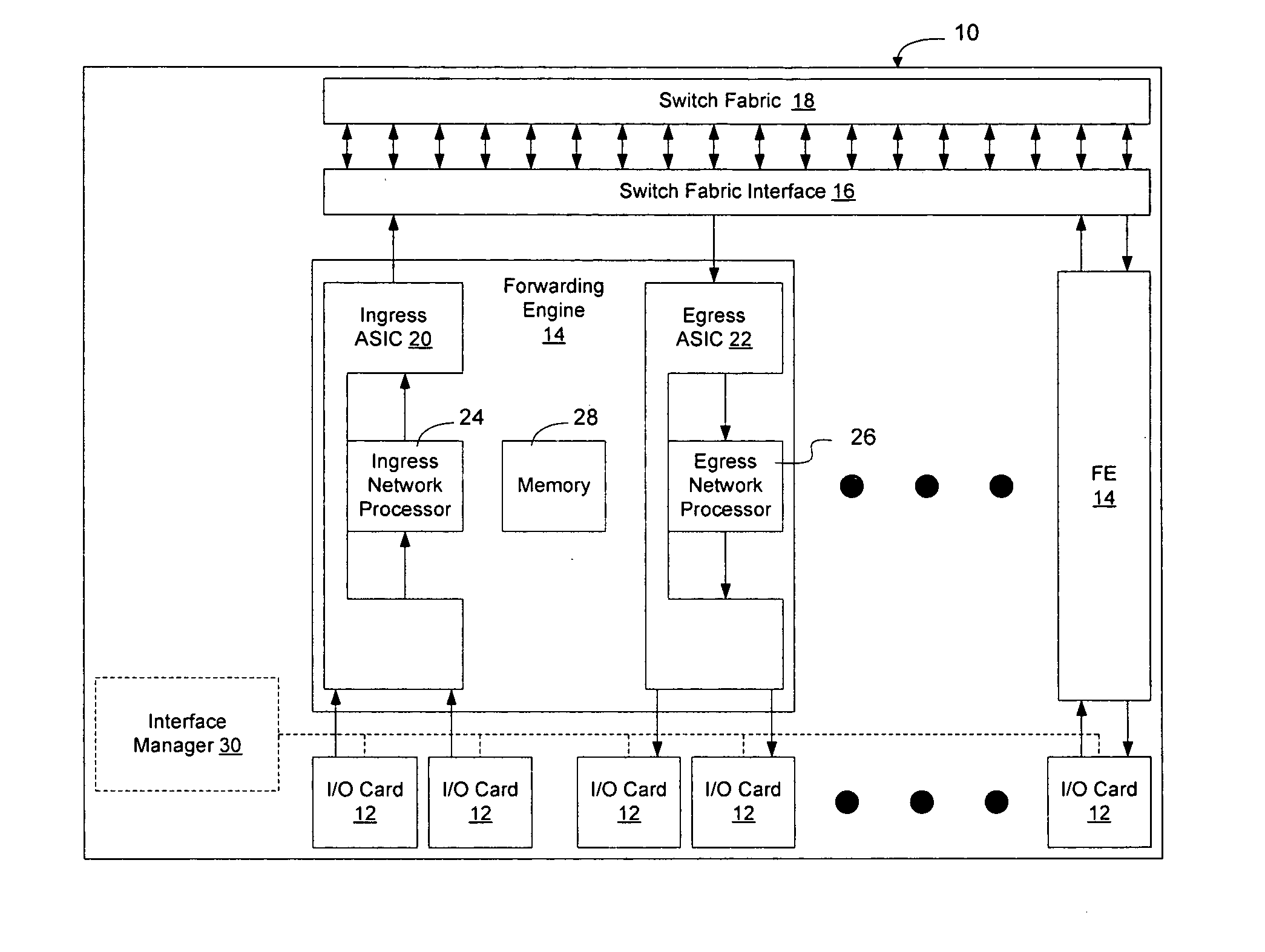
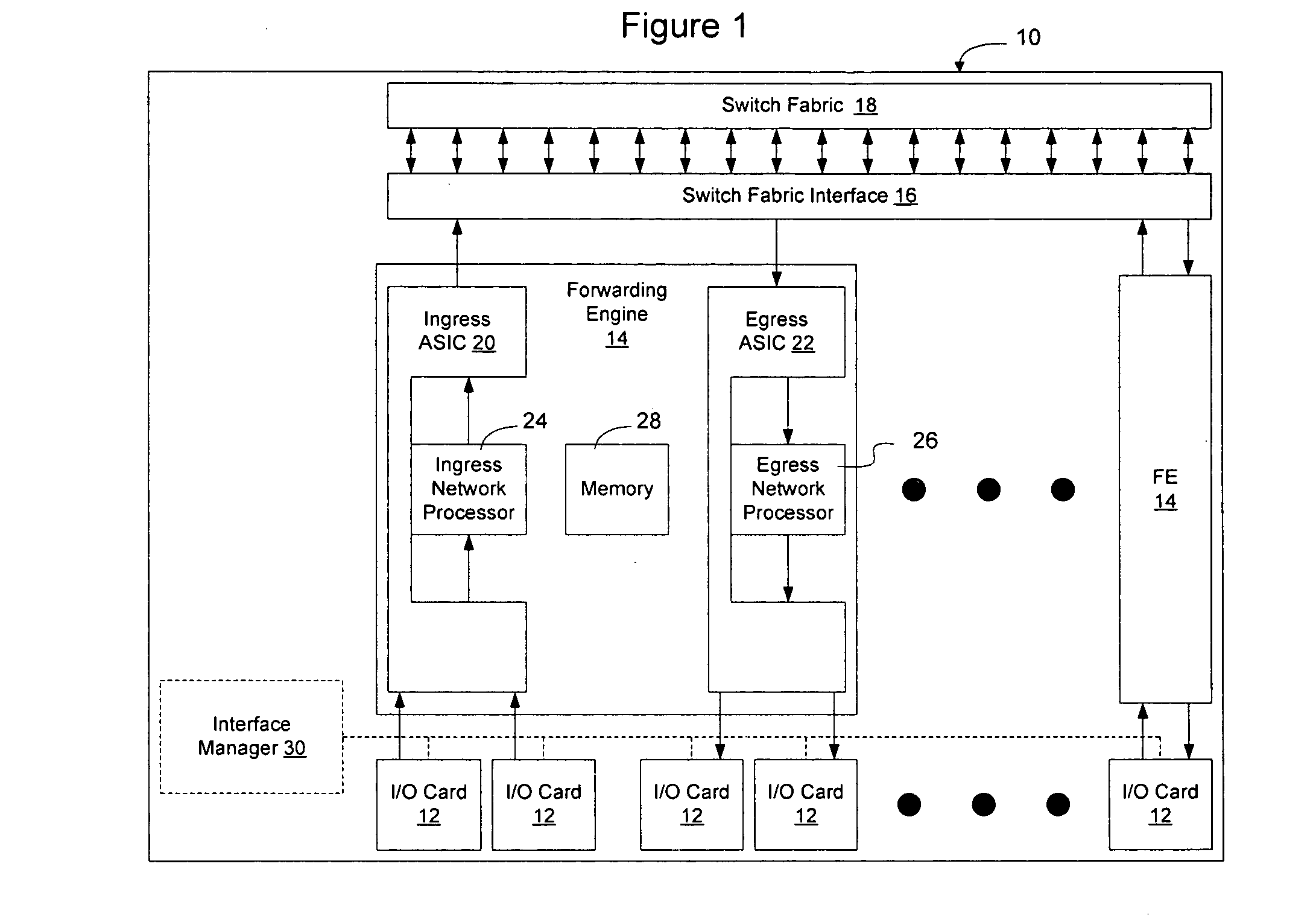
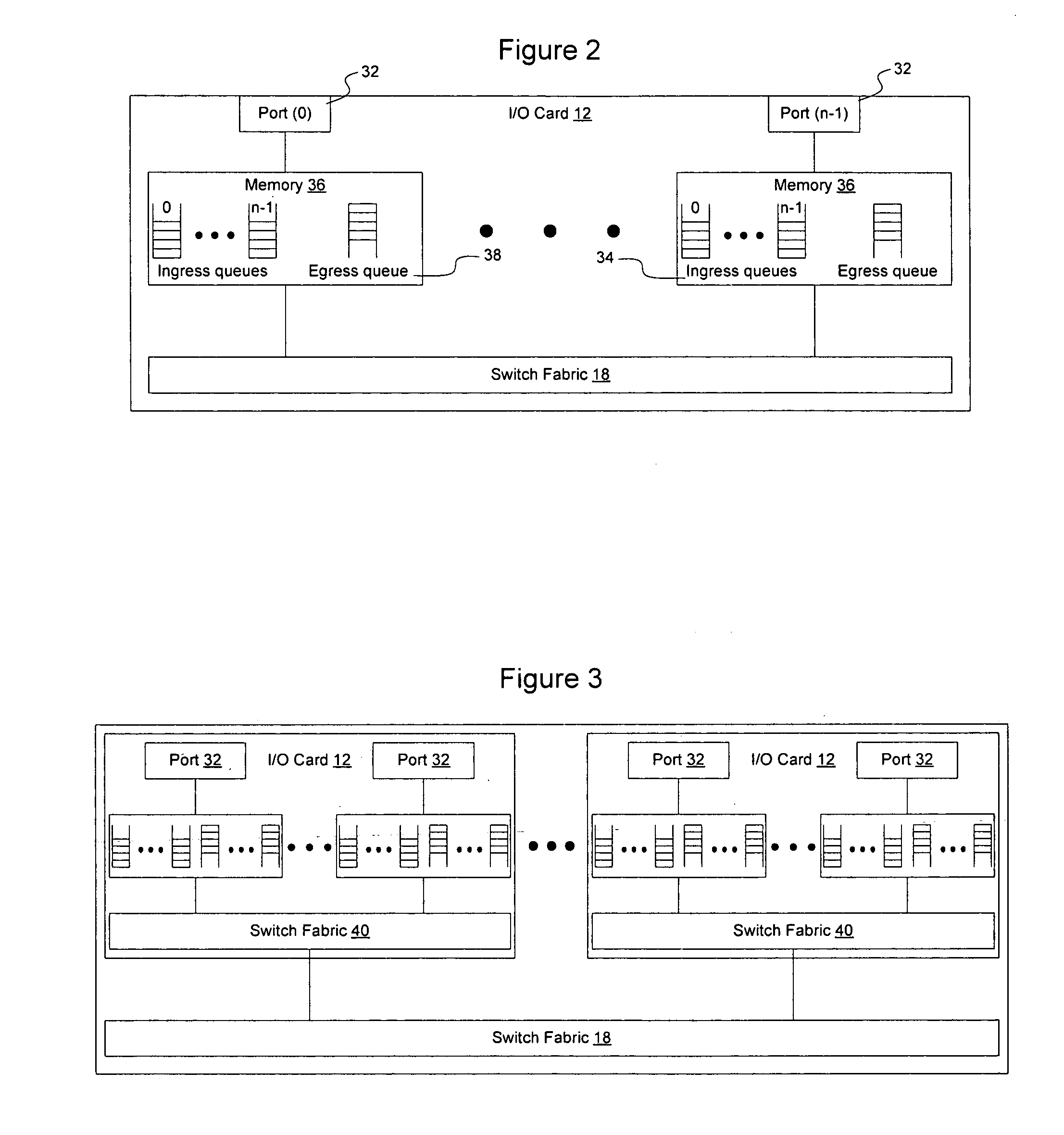
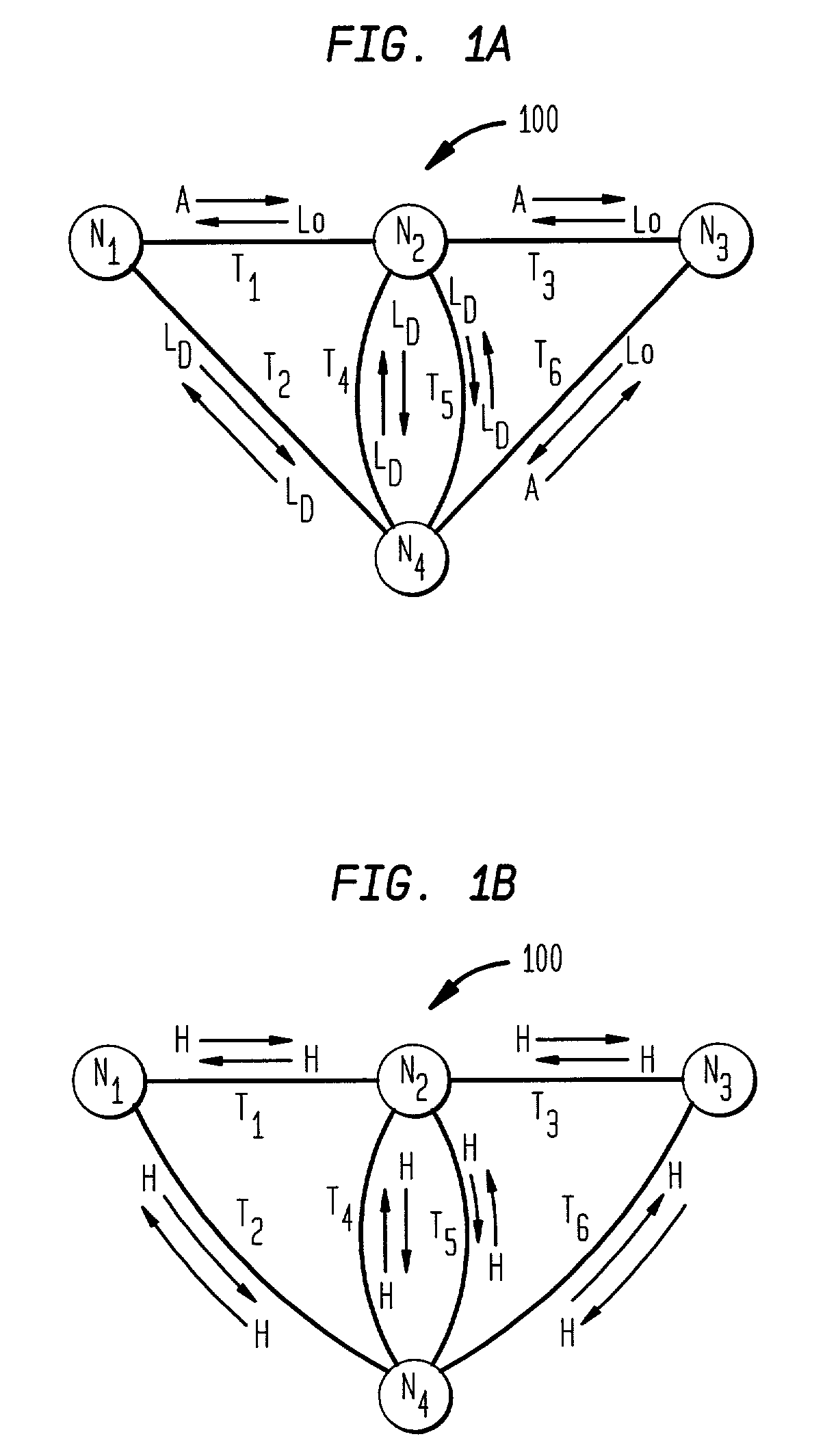
Distributed control of data flow in a network switch
The network switch described herein provides a cell / packet switching architecture that switches between line interface cards across a meshed backplane. In one embodiment, the switching can be accomplished at, or near, line speed in a protocol independent manner. The protocol independent switching provides support for various applications including Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching, Internet Protocol (IP) switching, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) switching, Ethernet switching and frame relay switching. The architecture allows the network switch to provision service on a per port basis. In one embodiment, the network switch provides a non-blocking topology with both input and output queuing and per flow queuing at both ingress and egress. Per flow flow-control can be provided between ingress and egress scheduling. Strict priority, round robin, weighted round robin and earliest deadline first scheduling can be provided.
Owner:FORCE10
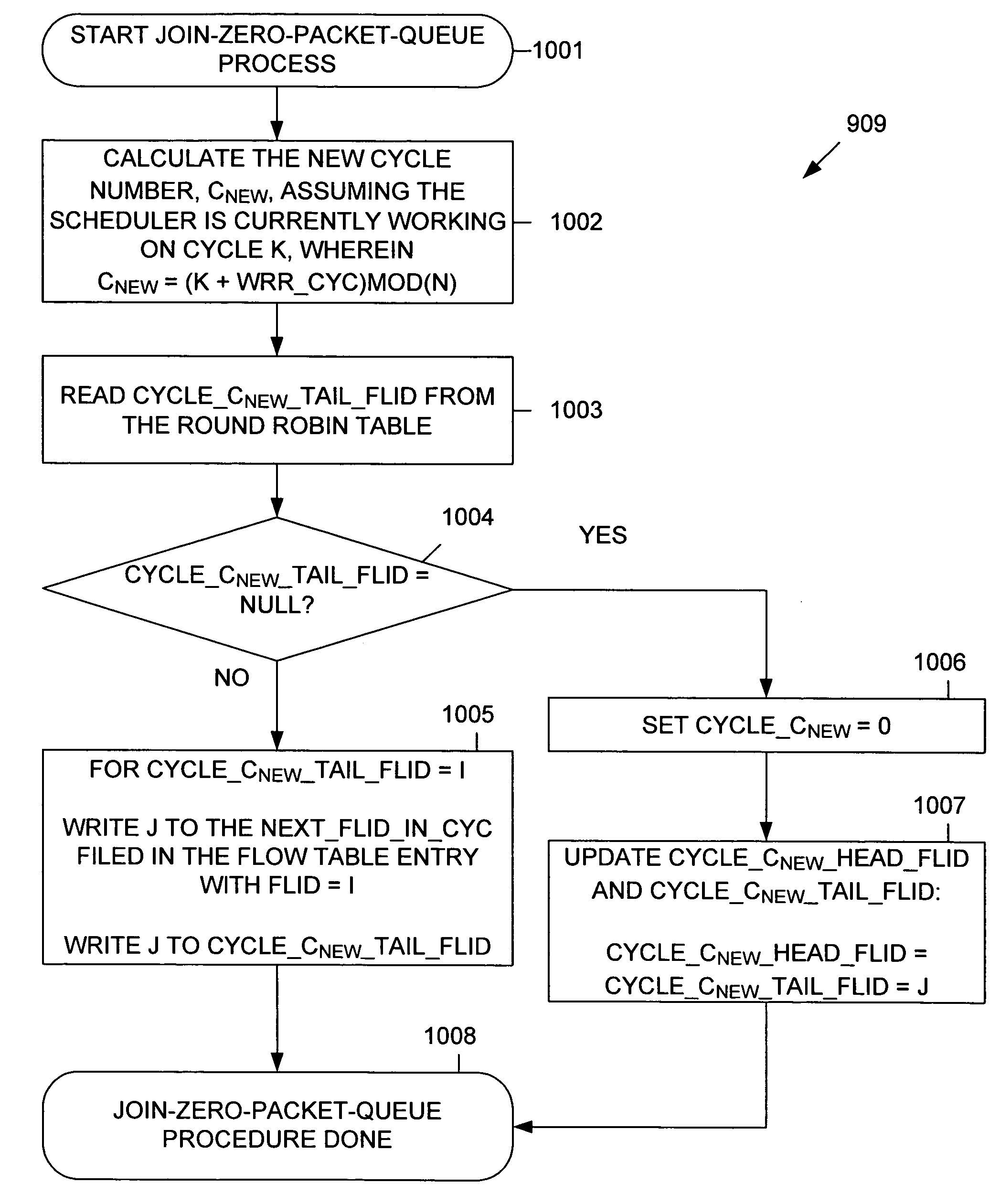
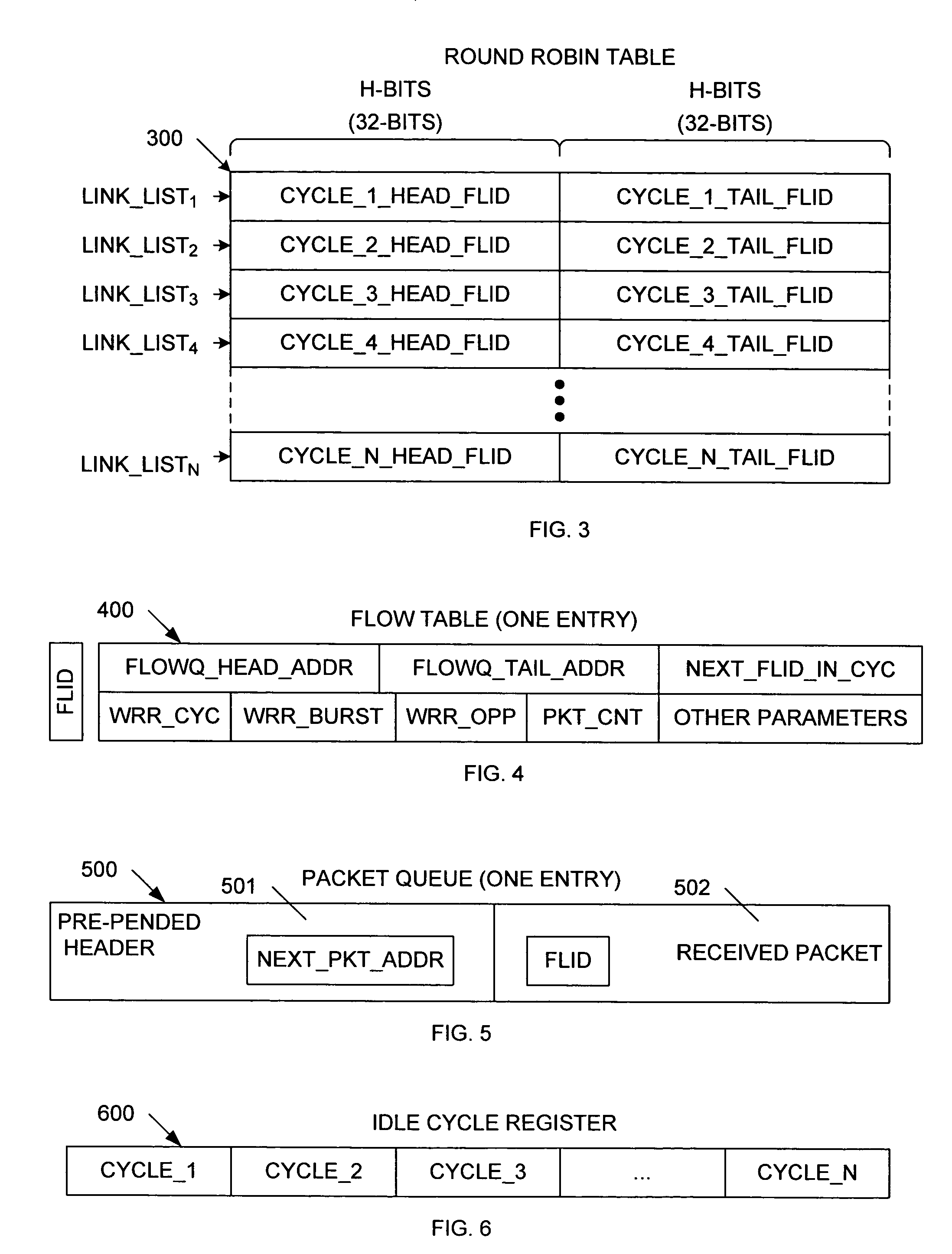
Method of performing weighted round-robin queue scheduling using a dynamic link list and structure for implementing same
InactiveUS20050147034A1Improve processing speedError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingLinked list
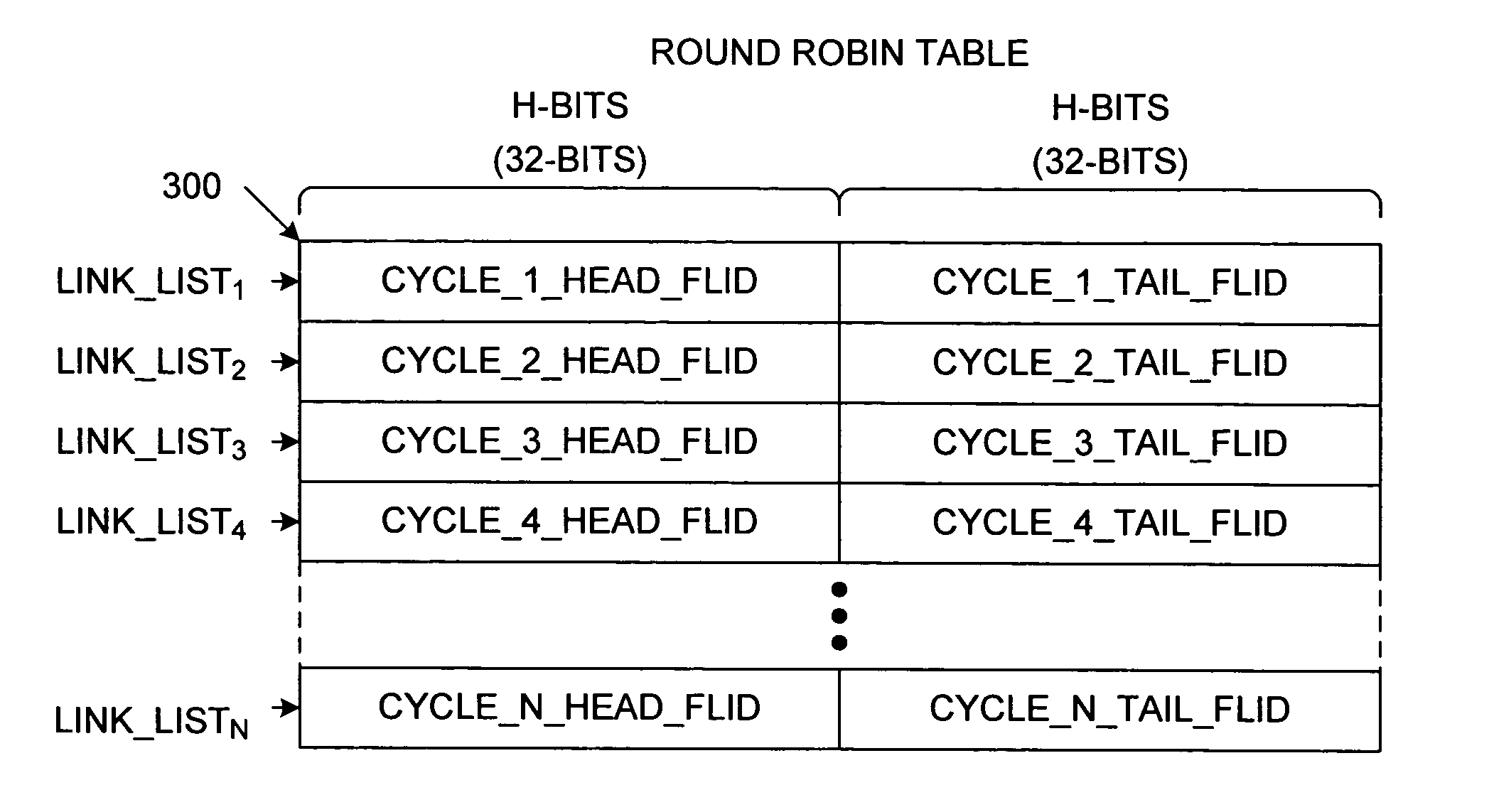
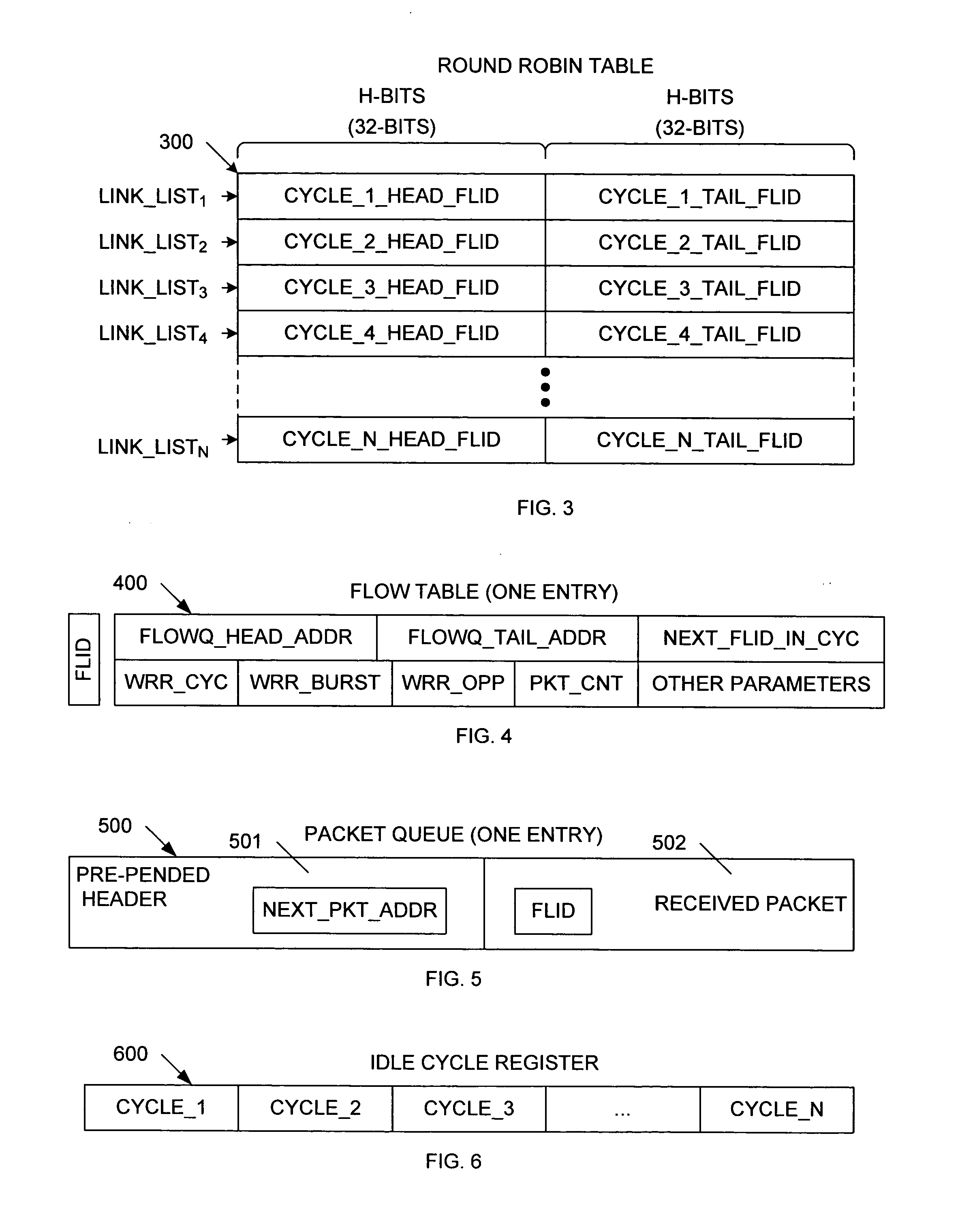
A weighted round-robin scheduler includes a round-robin table that stores a plurality of cycle link lists. Each cycle link list includes a head flow identification (FLID) value identifying a first flow of the cycle link list, and a tail FLID value identifying a last flow of the cycle link list. A flow table is provided having a plurality of flow table entries. Each flow table entry is associated with a corresponding flow. Each flow table entry stores a parameter that identifies the weight assigned to the associated flow. A packet queue is associated with each flow table entry, wherein each packet queue is capable of storing a plurality of packets. The weighted round-robin scheduler also includes an idle cycle register having an idle cycle entry corresponding with each of the cycle link lists, wherein each idle cycle entry identifies the corresponding cycle link list as active or idle.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
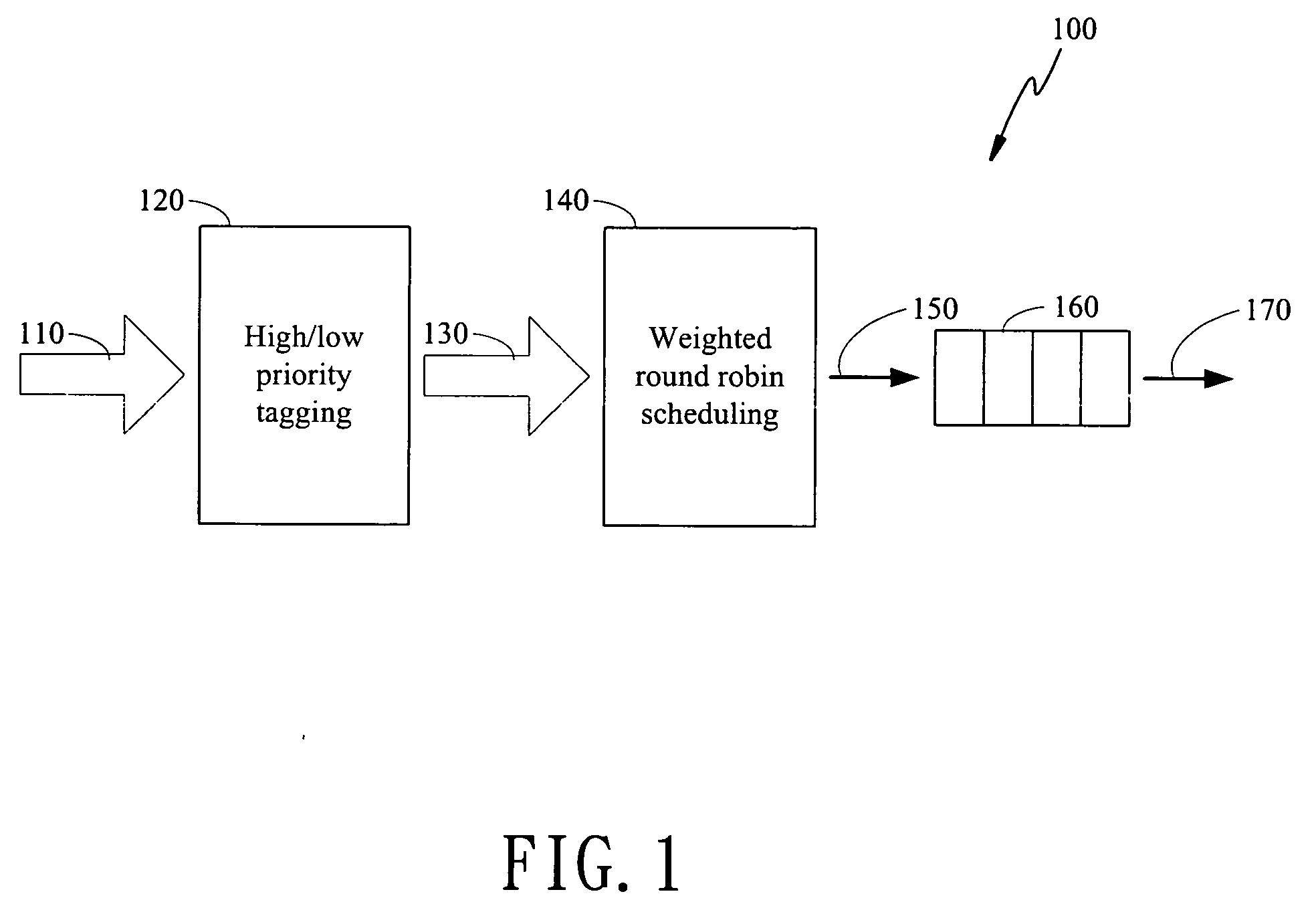
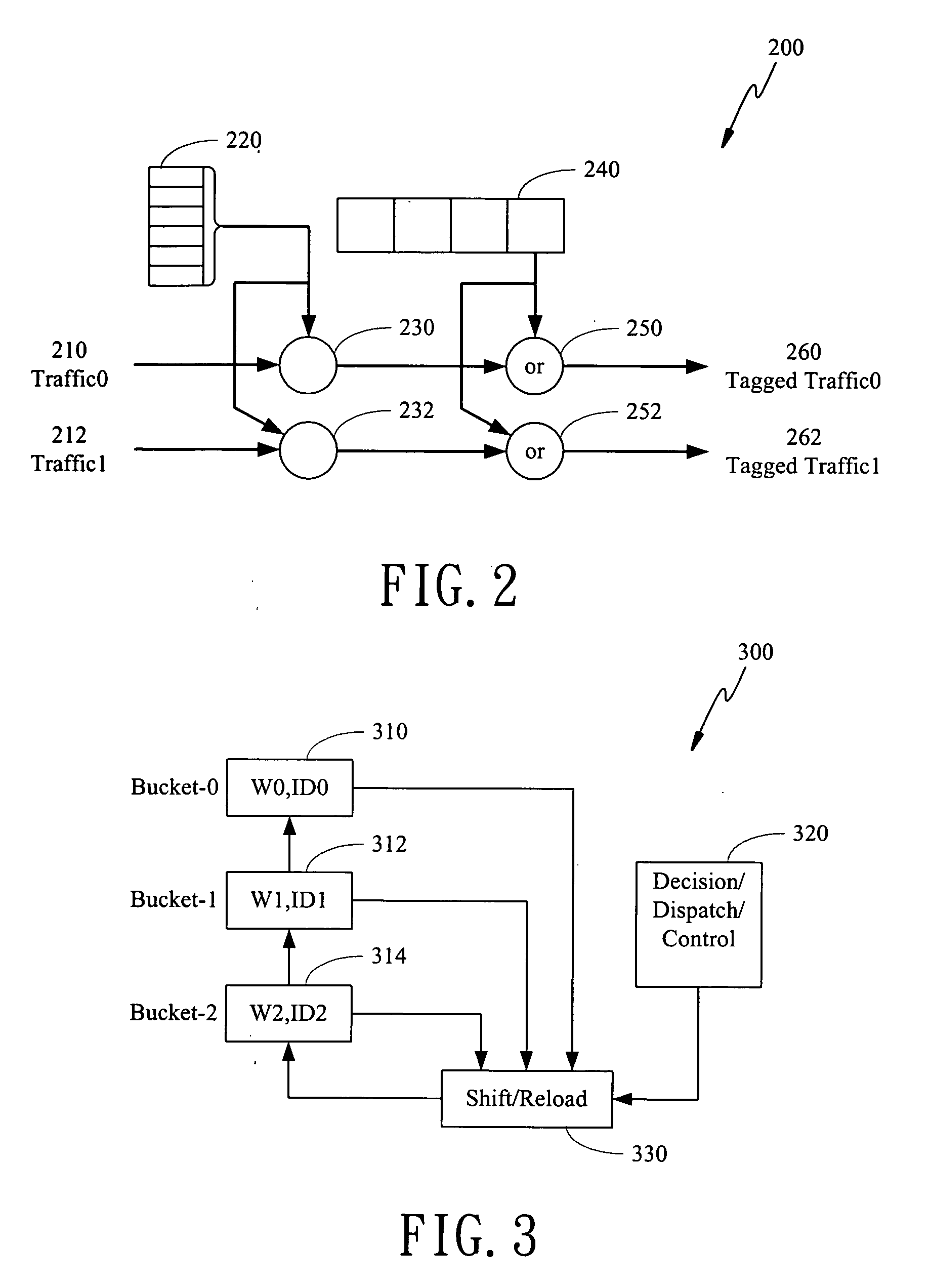
Preemptive weighted round robin scheduler
InactiveUS20060176807A1Error preventionTransmission systemsClassification schemeDistributed computing
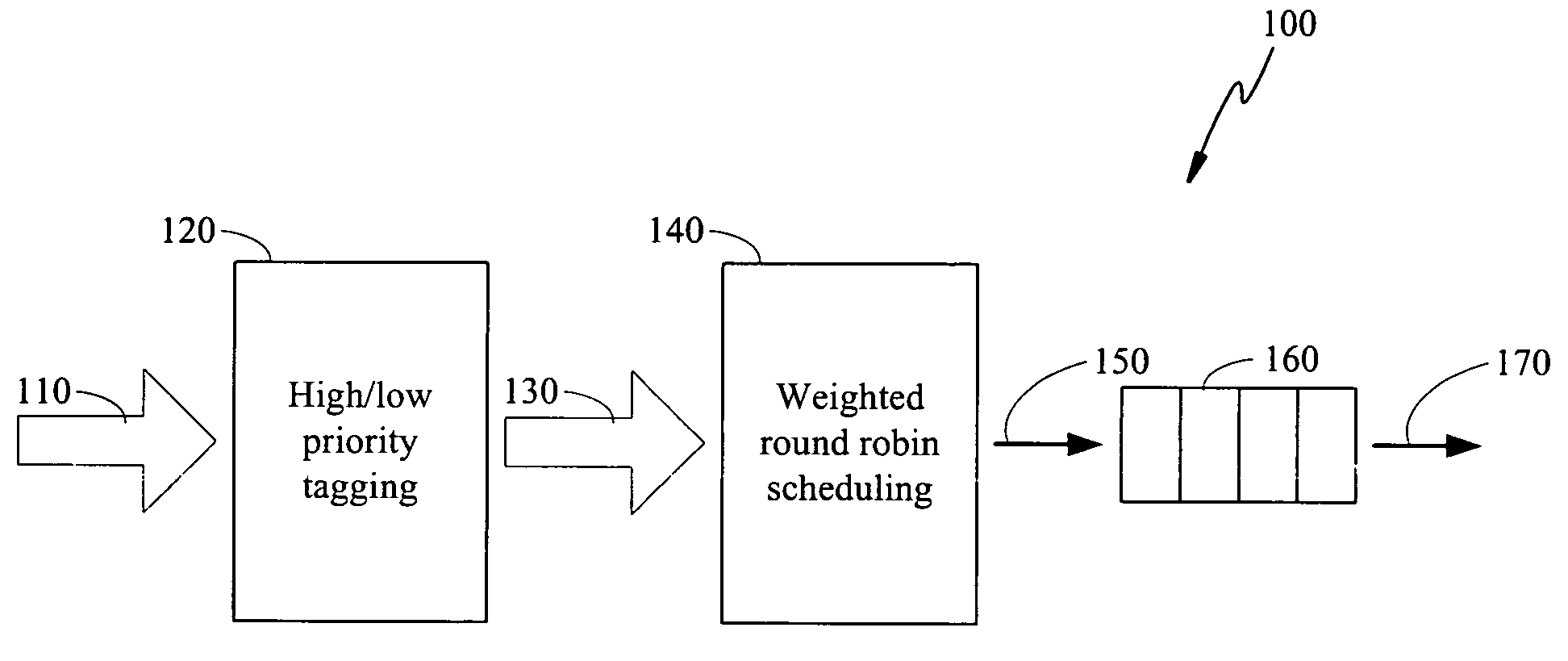
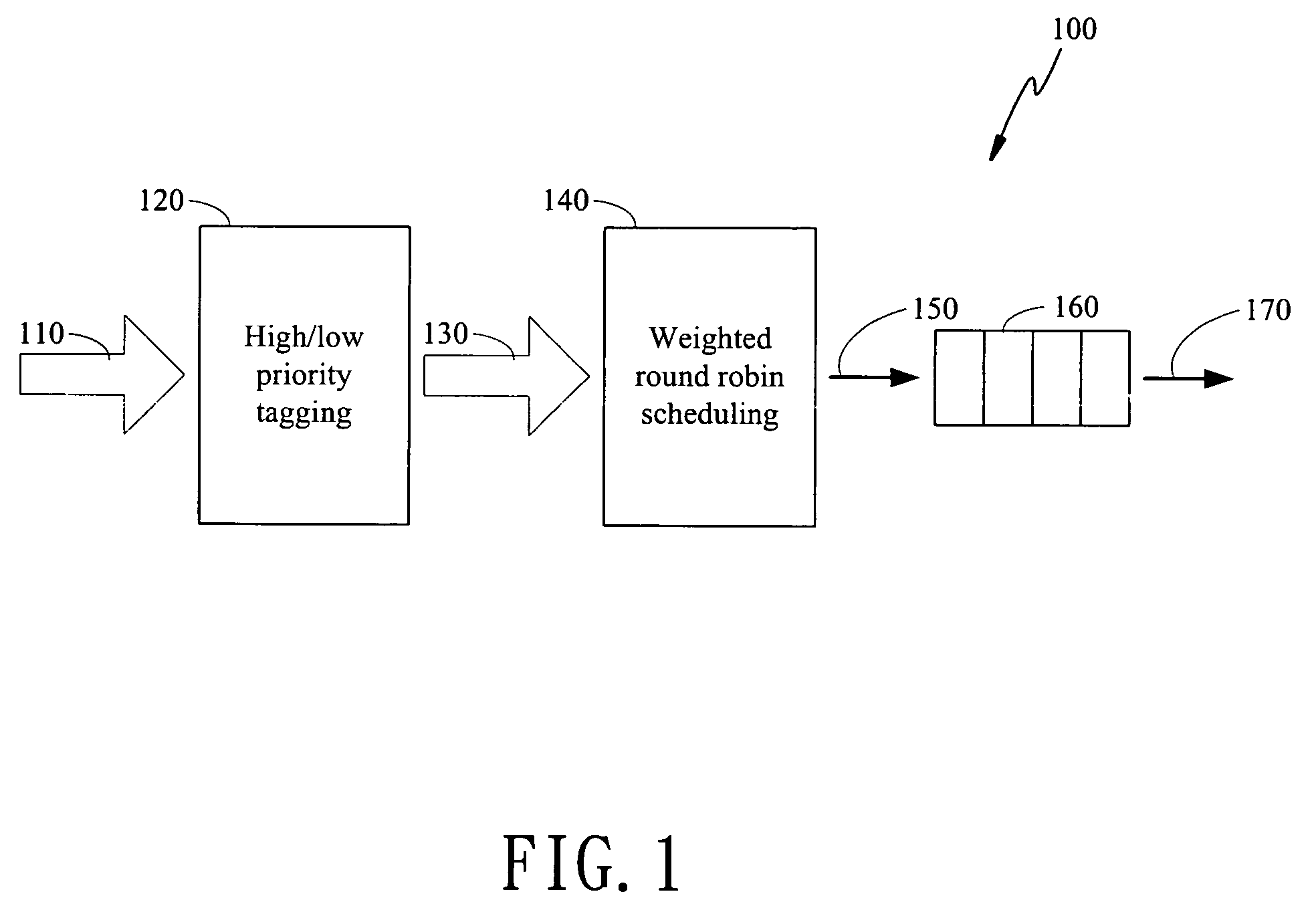
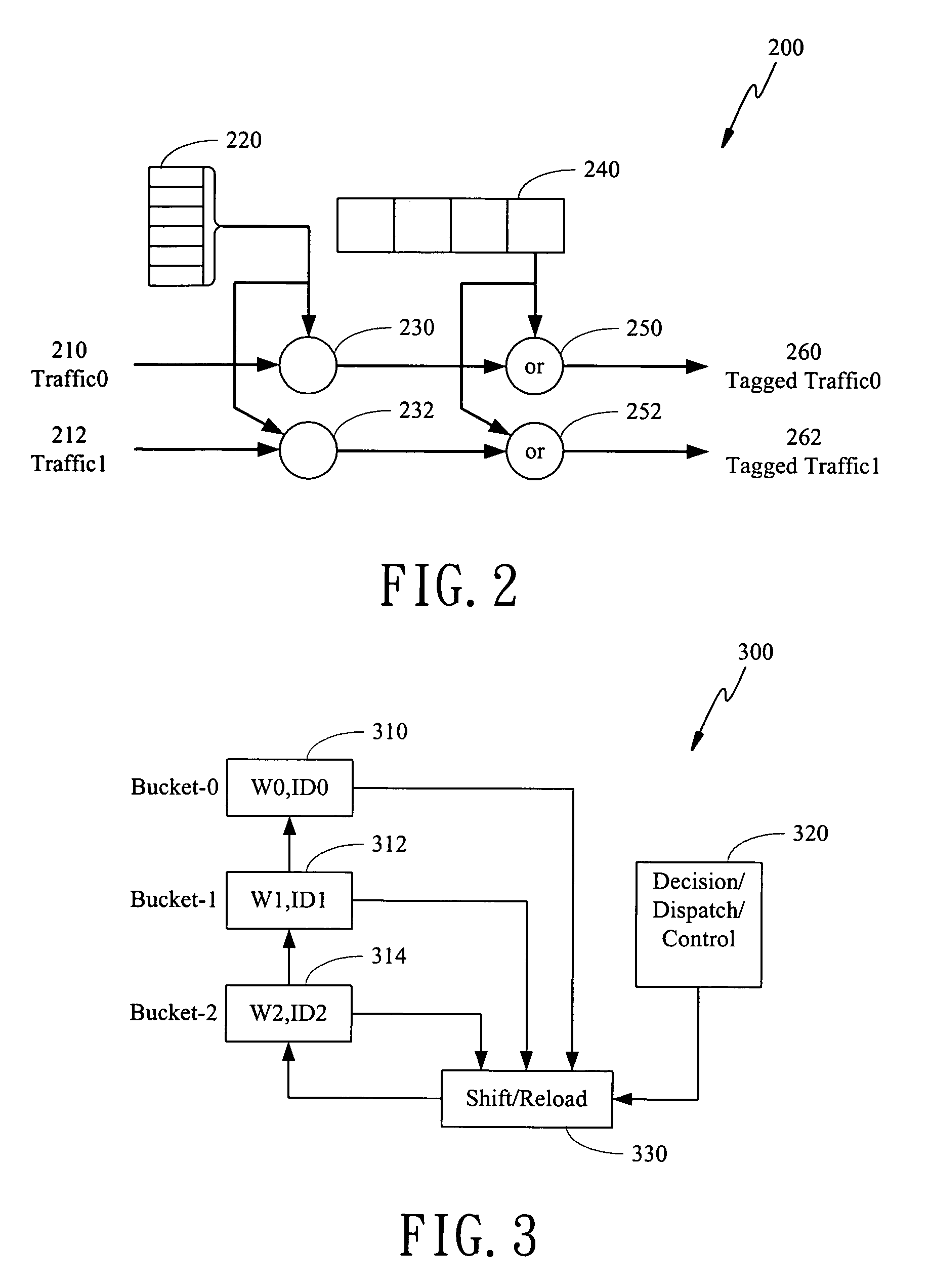
The present invention is to disclose a scheduler which comprising a priority tagging module for receiving a plurality of information chucks, a plurality of output lines, and a WRR (weighted round robin) module. In this regards, each information chucks are tagged with a priority tag by said priority tagging module according to a priority classification scheme. In addition, the WRR module further comprises a bucket list, which has a plurality of buckets, and a control module. Each bucket stores a ticket, which comprises an identification representing one of the plurality of output lines and an associated weight value of the represented output line. Besides, the control module receives the tagged information chucks from the priority tagging module and schedules the tagged information chucks into the plurality of output lines according to a scheduling scheme based on said bucket list.
Owner:RETI CORP
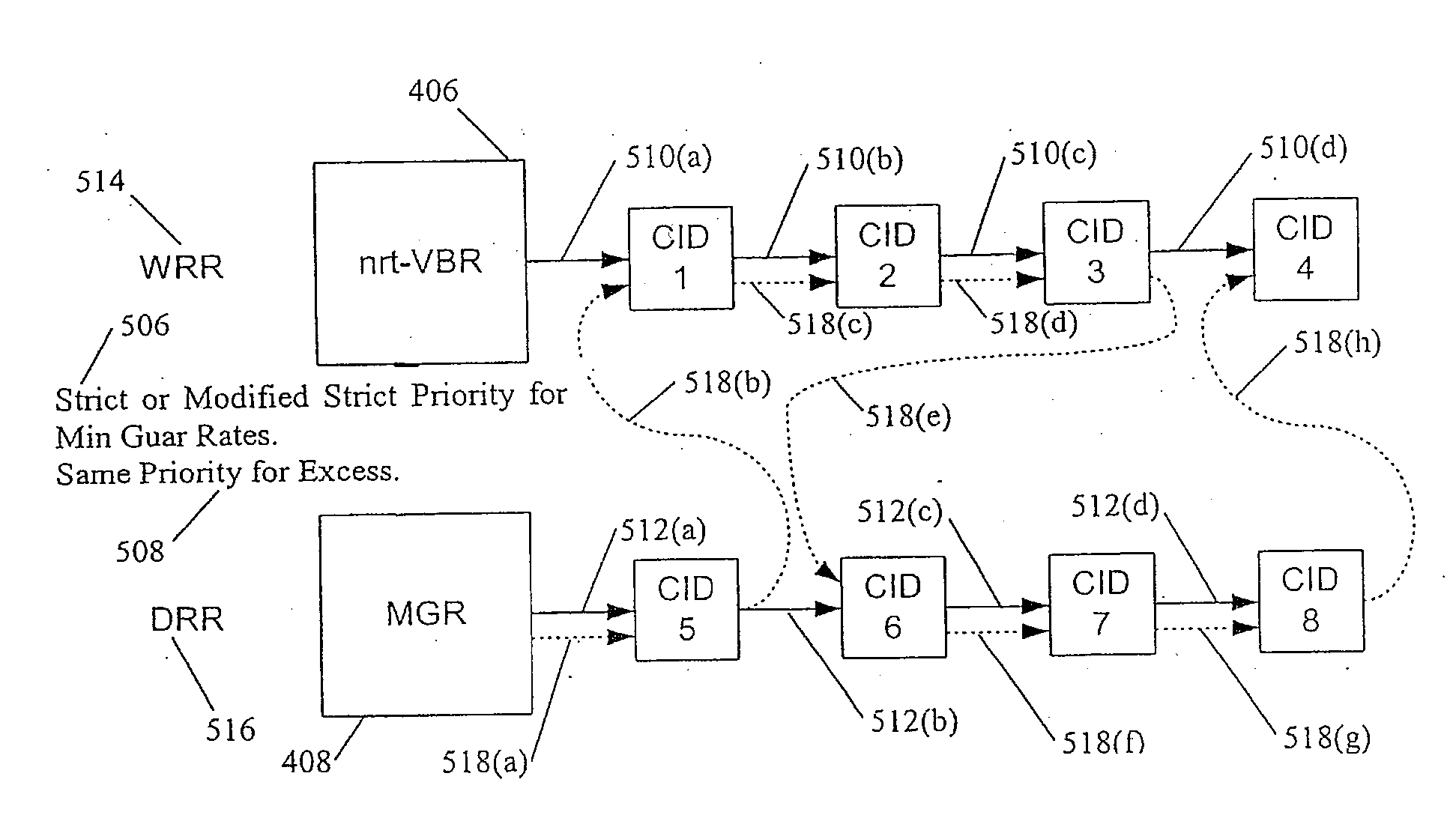
Scheduling Method and System for Communication Systems That Offer Multiple Classes of Service
InactiveUS20070153690A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeficit round robinCommunications system
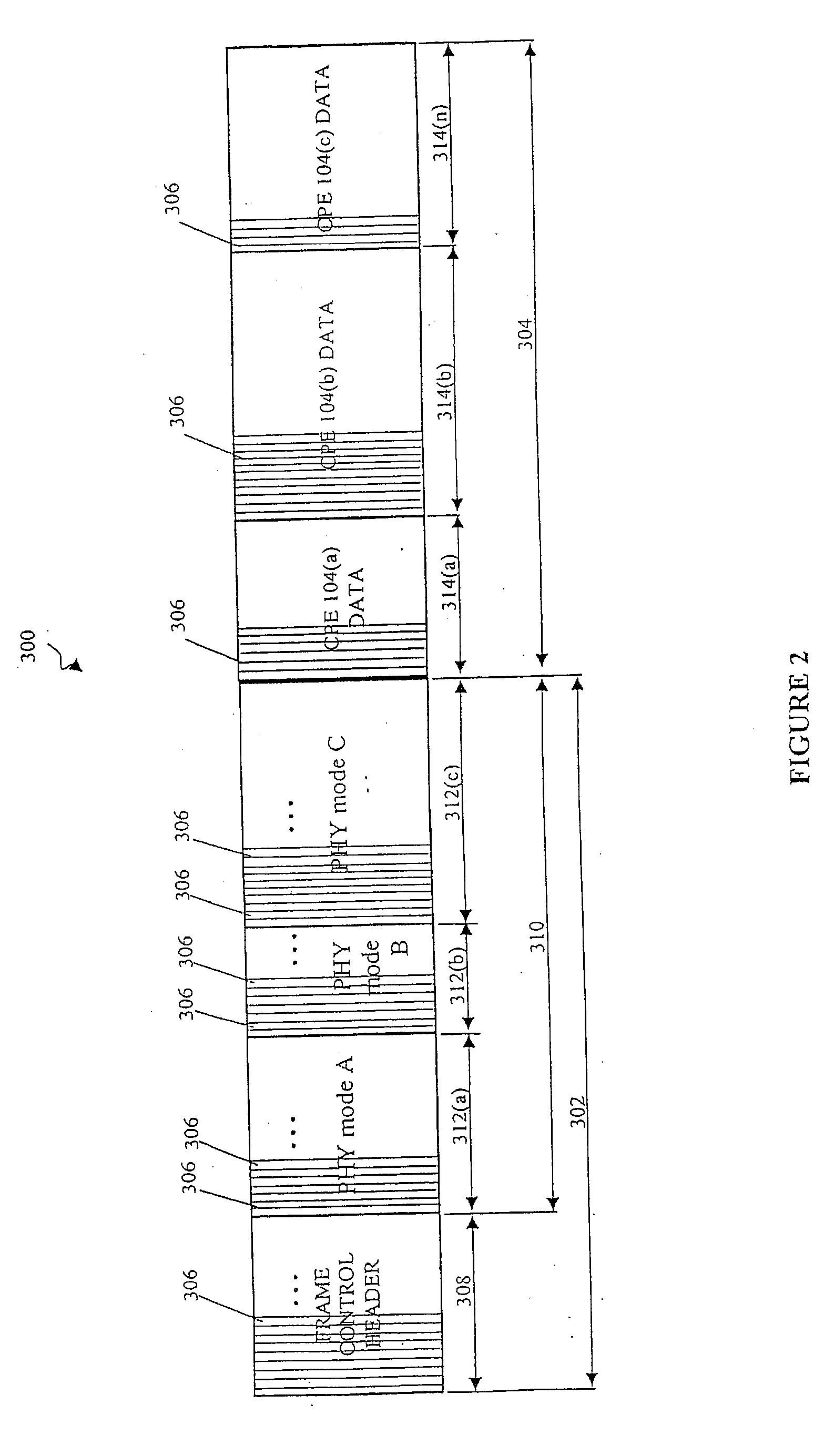
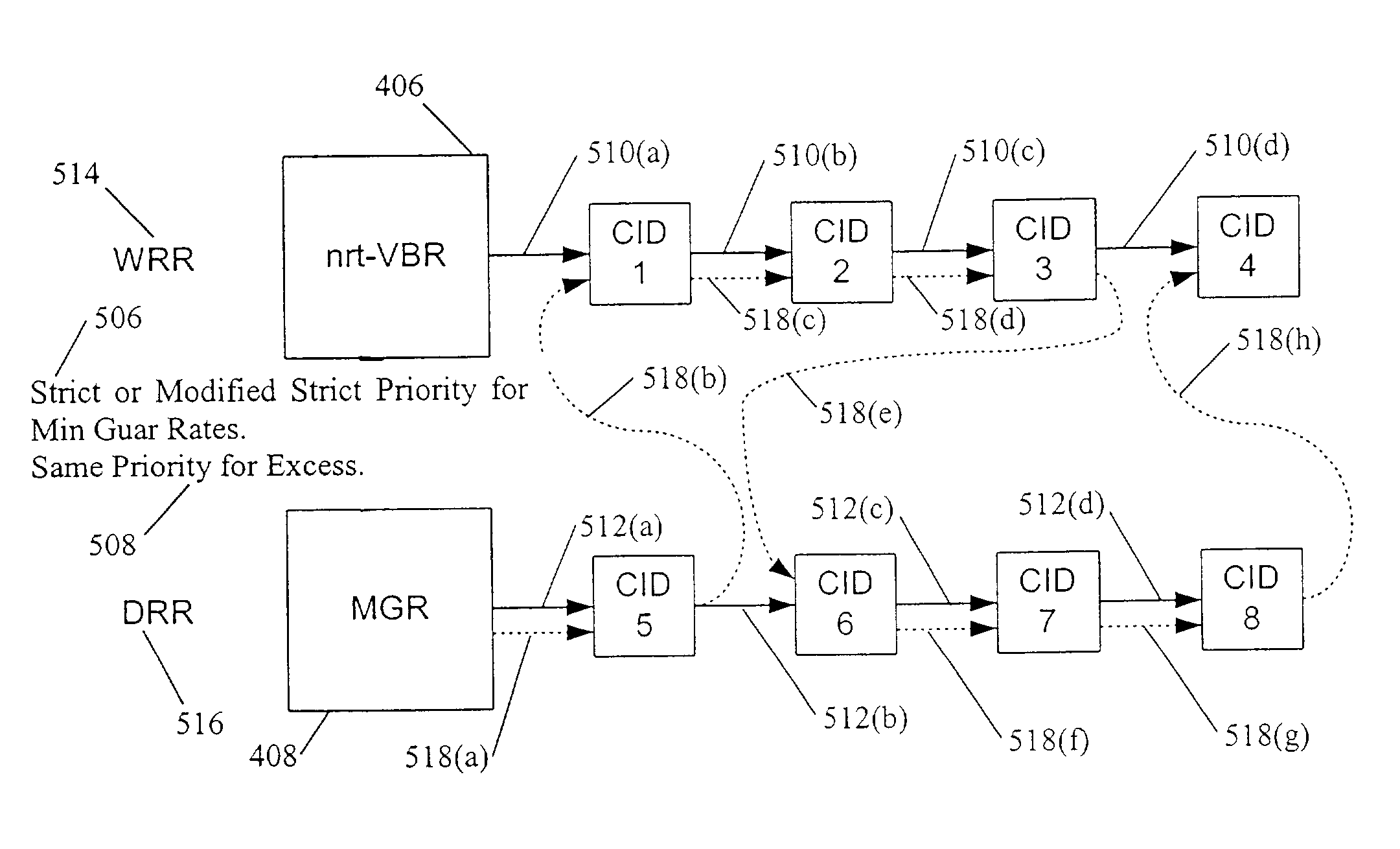
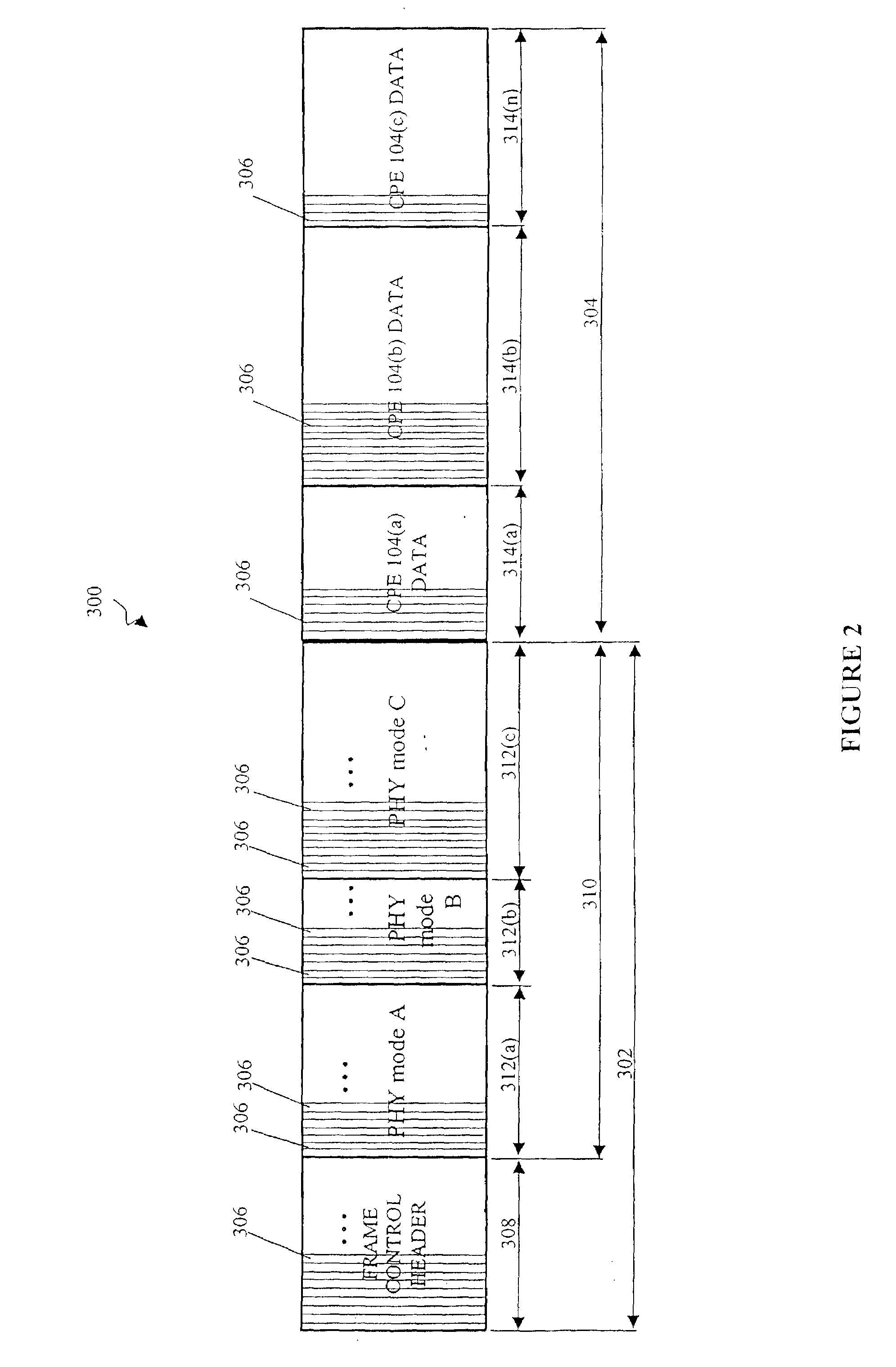
A method and system for prioritizing connection data that is associated with different classes of service for transmission in a frame based communication system. These classes of service can include CBR, nrt-VBR, MGR, and UBR traffic. One embodiment of the scheduling method and system uses hierarchical round-robin (HRR) with deficit round-robin (DRR). In this embodiment, the scheduling method and system guarantees minimum rates of nrt-VBR and MGR traffic to the connections. The excess bandwidth is then fairly allocated between the existing connections and their classes of service. For example, the excess is allocated for UBR traffic and for the excess demands of the nrt-VBR and MGR connections. In one embodiment, the scheduling method and system allocates the excess bandwidth in a frame to the existing connections using weighted round robin to differentiate between different classes of service. In one embodiment, excess allocation to nrt-VBR and MGR connections is rolled back into the deficit counters for the minimum guaranteed rates of nrt-VBR and MGR connections.
Owner:GAMEHANCEMENT LLC +1
Scheduling method and system for communication systems that offer multiple classes of service
ActiveUS7177275B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityDeficit round robin
A method and system for prioritizing connection data that is associated with different classes of service for transmission in a frame based communication system. These classes of service can include CBR, nrt-VBR, MGR, and UPR traffic. One embodiment of the scheduling method and system uses hierarchical round-robin (HRR) with deficit round-robin (DRR). In this embodiment, the scheduling method and system guarantees minimum rates of nrt-VBR and MGR traffic to the connections. The excess bandwidth is then fairly allocated between the existing connections and their classes of service. For example, the excess is allocated for UBR traffic and for the excess demands of the nrt-VBR and MGR connections. In one embodiment, the scheduling method and system allocates the excess bandwidth in a frame to the existing connections using weighted round robin to differentiate between different classes of service. In one embodiment, excess allocation to nrt-VBR and MGR connections is rolled back into the deficit counters for the minimum guaranteed rates of nrt-VBR and MGR connections.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Method and apparatus for implementing scheduling algorithms in a network element
InactiveUS20050259574A1Overcomes drawbackAccurate schedulingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeficit round robinAnticipatory scheduling
Device-wide performance guarantees may be implemented in a network element using a pull forwarding scheme by using separate proceses on the network element communicating via handshake signals to enable coordination between the aspects of the network element. One class of processes execute at the ingress queues, a second class of process execut at junction points, and a final class of processes execute at the egress ports. The combination of these separate processes leads to the correct scheduling of frames in a device-wide manner as if there were a centralized scheduler with complete information about all queued frames. As a result, the performance guarantees of the intended scheduling algorithm are preserved and are provided in a device-wide manner. The scheduling algorithms that are supported include round-robin, deficit round robin, negative deficit round robin, weighted round robin, and strict priority.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Preemptive weighted round robin scheduler
InactiveUS7430207B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer moduleDistributed computing
Owner:RETI CORP
Ethernet cache exchanging and scheduling method and apparatus
This invention provides one Ethernet exchange buffer and transfer method, which comprises the following steps: receiving data pack from input end; cutting data pack into certain length signal element by cut unit; storing signal element into central memory unit; adopting equal time lag transfer through end and line transfer unit and turning output end by each time lag; adopting run require or transfer of different lines at one output end; after getting transfer, reading signal element from common central buffer unit and the data pack resets the signal element sent to the linkage. This invention also provides one Ethernet exchange buffer and transfer device.
Owner:WUHAN FIBERHOME NETWORKS
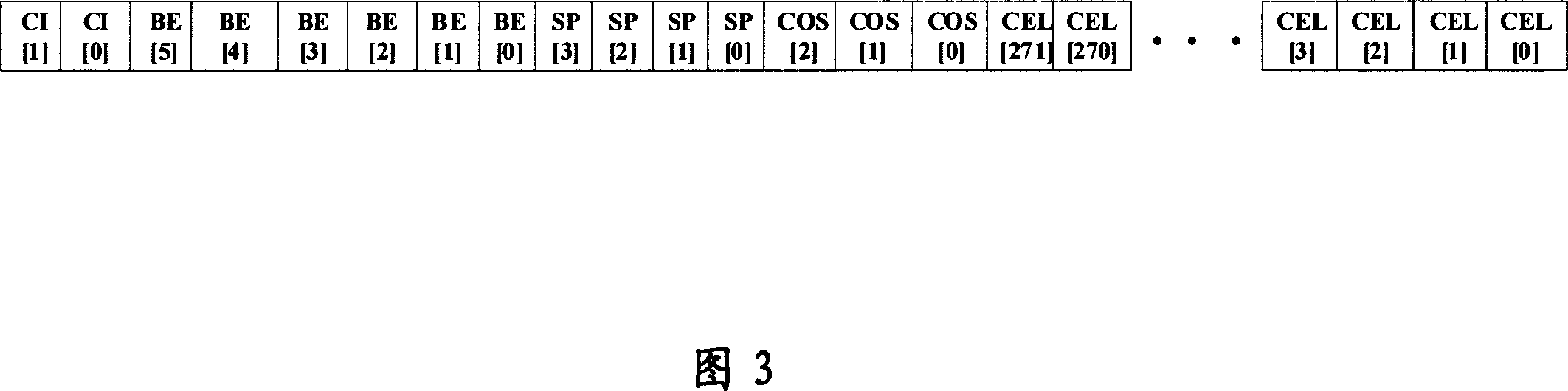
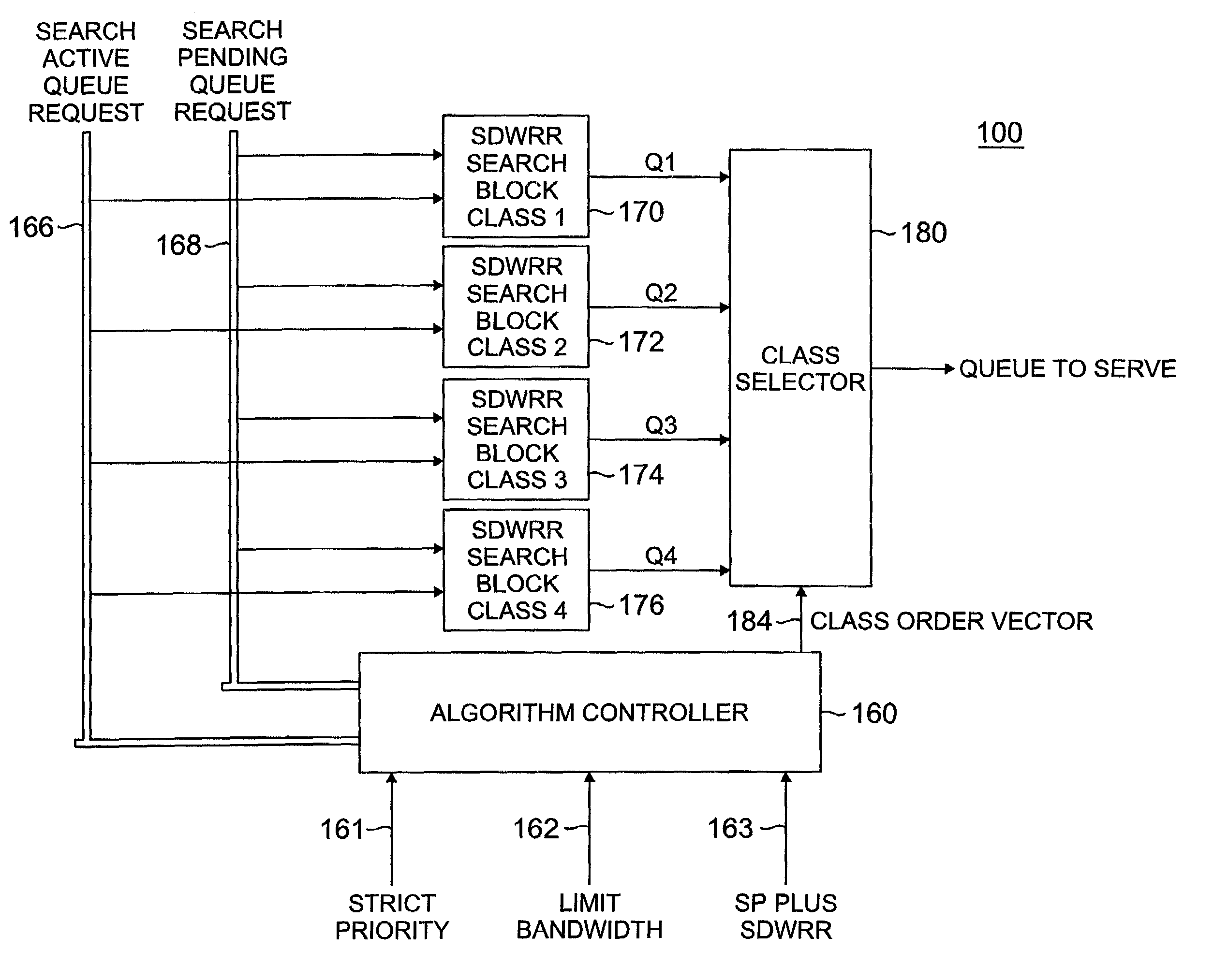
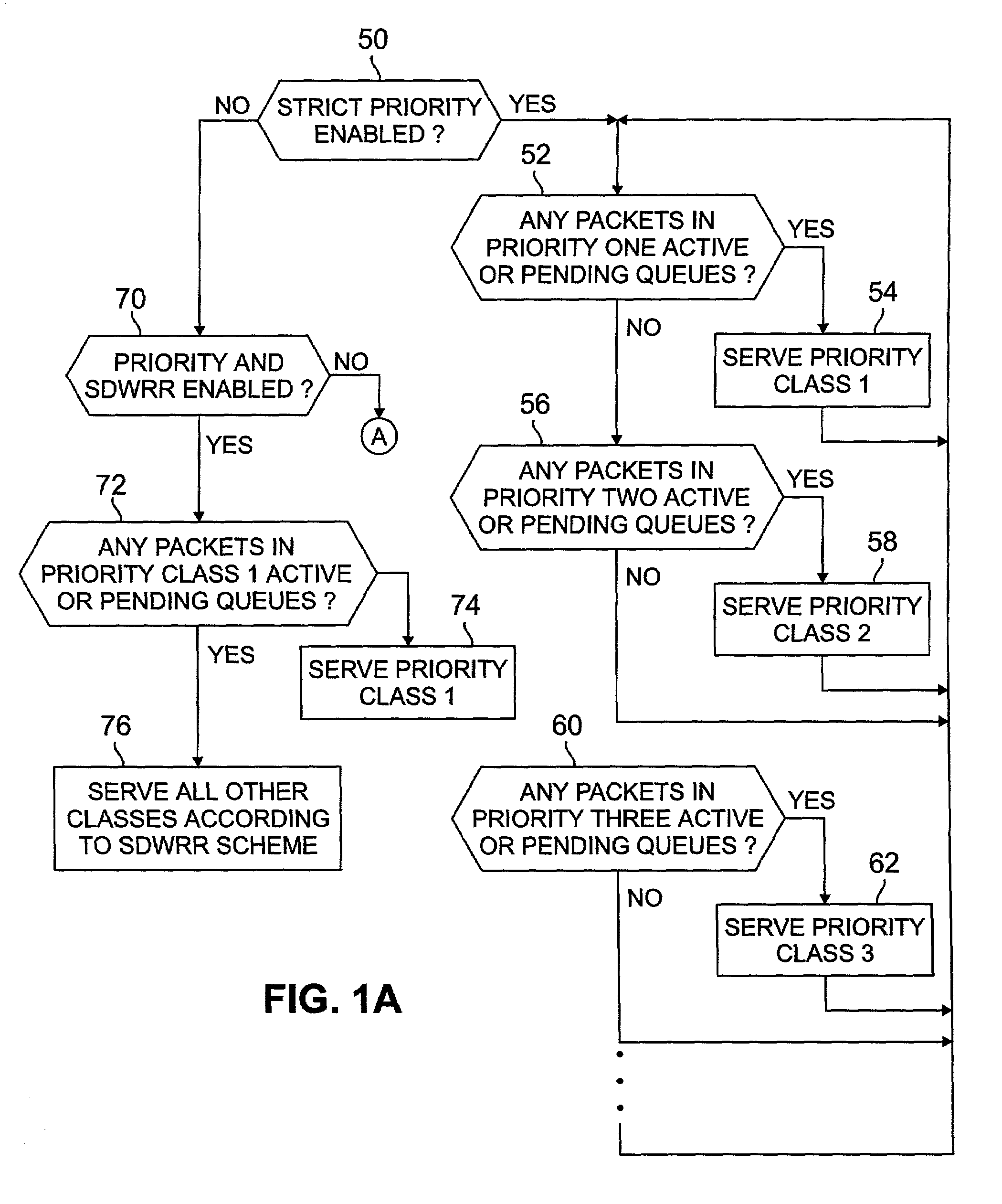
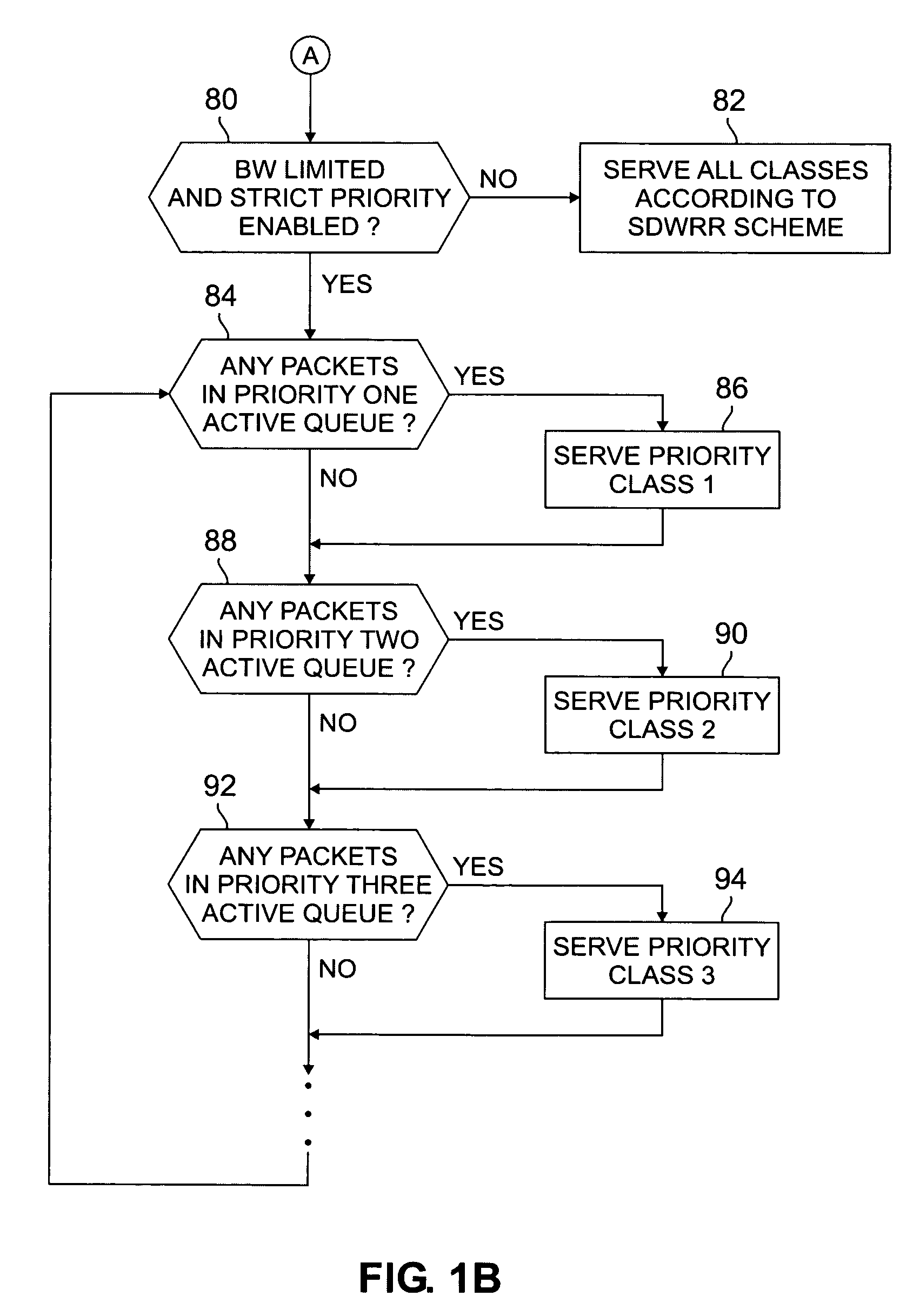
Method and apparatus for providing multiple data class differentiation with priorities using a single scheduling structure
InactiveUS7159219B2Reduced space requirementsSimplifies design verification processError preventionTransmission systemsData classDistributed computing
A scheduler for shared network resources implementing a plurality of user selectable data scheduling schemes within a single hardware device. The schemes include strict priority, priority for one class plus smooth deficit weighted round robin for the other classes, bandwidth limited strict priority and smooth deficit weighted round robin for all user classes. The network operator selects one of the four schemes by enabling or disabling certain bits in the hardware device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
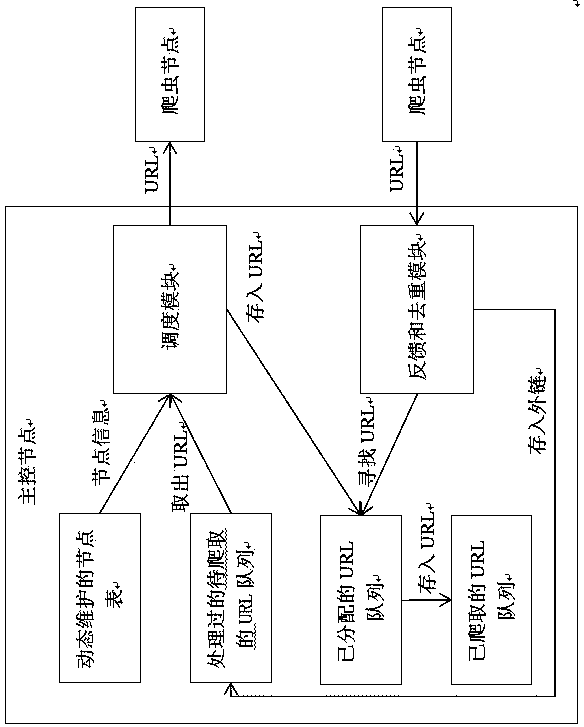
Distributed crawler task scheduling method based on weighted round-robin algorithm
ActiveCN103870329ALoad balancingFlexible scalabilityProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationFault toleranceExtensibility
A distributed crawler task scheduling method based on a weighted round-robin algorithm at least includes the following steps: (1) according to different scales, network crawlers are divided into five types of crawlers, i.e. a stand-alone multi-thread crawler, a homogeneous centralized crawler, a heterogeneous centralized crawler, a small-scale distributed crawler and a large-scale distributed crawler; (2) a master-slave architecture is deployed; (3) when a crawler node is connected to a master node for the first time, the master node gives an initial weight to the crawler node; (4) according to the scheduling algorithm based on weighted round-robin, the master node continuously chooses a crawler node and assigns a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) task to be crawled to the crawler node; (5) each time when a URL task is crawled by a crawler node, a result is returned to the master node, and the weight of the crawler node is updated by the master node, and the like. The distributed crawler scheduling policy based on the weighted round-robin algorithm, which is put forward by the invention, is designed for small-scale distributed crawlers and can ensure the load balance of each crawler node and ensure that crawler nodes have flexible scalability and fault tolerance.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
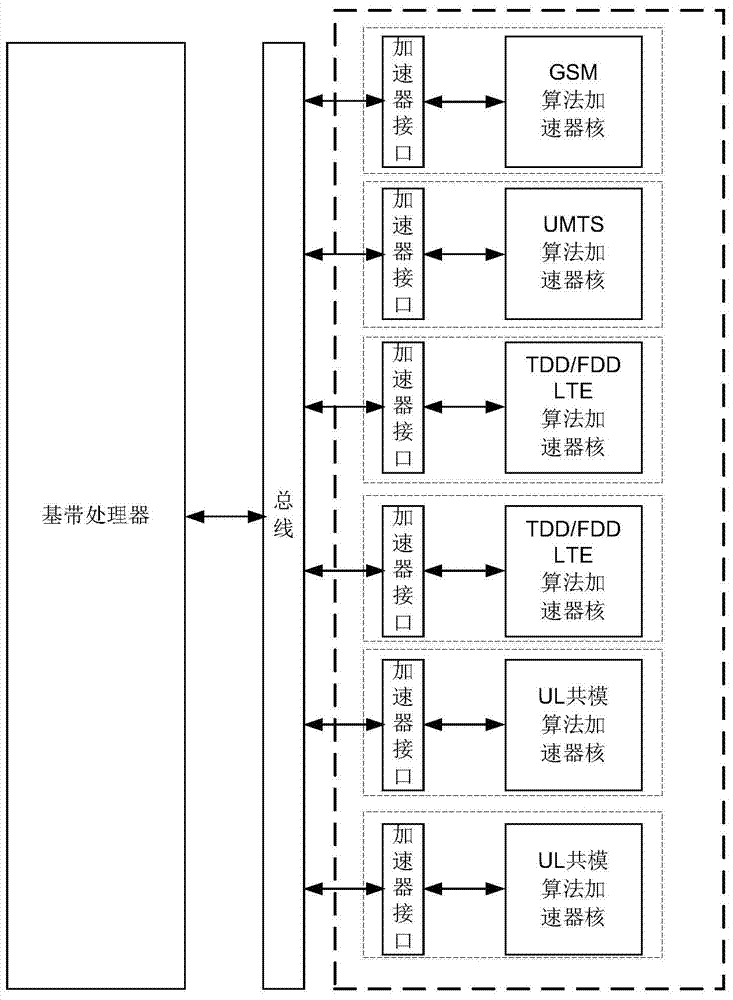
Hardware accelerator and chip
ActiveCN104503728AAvoid interactionExpected processing capacityProgram controlTransmissionFifo queueInterface circuits
The embodiment of the invention discloses a hardware accelerator and a chip. The hardware accelerator comprises an interface circuit, and an accelerator core which is coupled to the interface circuit; the interface circuit is used for receiving a first task request and decoding the first task request so as to obtain marking information, as well as configuring the first task request into an FIFO array in match with the marking information according to the marking information; a scheduling controller is used for determining a target channel set with at least one second task request to be treated in the n cycle from at least two channel sets, receiving the time parameters fed back by the accelerator core and respectively corresponding to the targeted channel sets, and scheduling the at least one second task request of the targeted channel sets according to the time parameters and the weighted round robin algorithm; the accelerator core is used for responding to the at least one second task request after scheduling. With the adoption of the hardware accelerator, the isolation in the configuration process can be effectively achieved, so that the mutual influence can be avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Managing priority queues and escalation in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS7421273B2Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesStreaming dataLower priority
A method and system for servicing data traffic in wireless local area networks (such as IEEE 802.11 networks) in multiple queues having different levels of priority. These queues include at least a low priority queue for ‘best effort’ traffic, a medium priority queue for streaming data such as video pictures, and a high priority queue for voice traffic, and are serviced in order of decreasing priority. To prevent the ‘best effort’ traffic in the low priority queue from being ‘starved’, a bit is set to indicate when such a condition is likely to occur, and the low priority queue is served first when that bit has been set. Alternatively, low and medium priority traffic is handled on a weighted round-robin basis, and high priority traffic is given strict priority over both. Transmit and receive queues are handled on a rotating priority basis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method of performing weighted round-robin queue scheduling using a dynamic link list and structure for implementing same
InactiveUS7580355B2Improve processing speedError preventionTransmission systemsProcessor registerDistributed computing
A weighted round-robin scheduler includes a round-robin table that stores a plurality of cycle link lists. Each cycle link list includes a head flow identification (FLID) value identifying a first flow of the cycle link list, and a tail FLID value identifying a last flow of the cycle link list. A flow table is provided having a plurality of flow table entries. Each flow table entry is associated with a corresponding flow. Each flow table entry stores a parameter that identifies the weight assigned to the associated flow. A packet queue is associated with each flow table entry, wherein each packet queue is capable of storing a plurality of packets. The weighted round-robin scheduler also includes an idle cycle register having an idle cycle entry corresponding with each of the cycle link lists, wherein each idle cycle entry identifies the corresponding cycle link list as active or idle.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
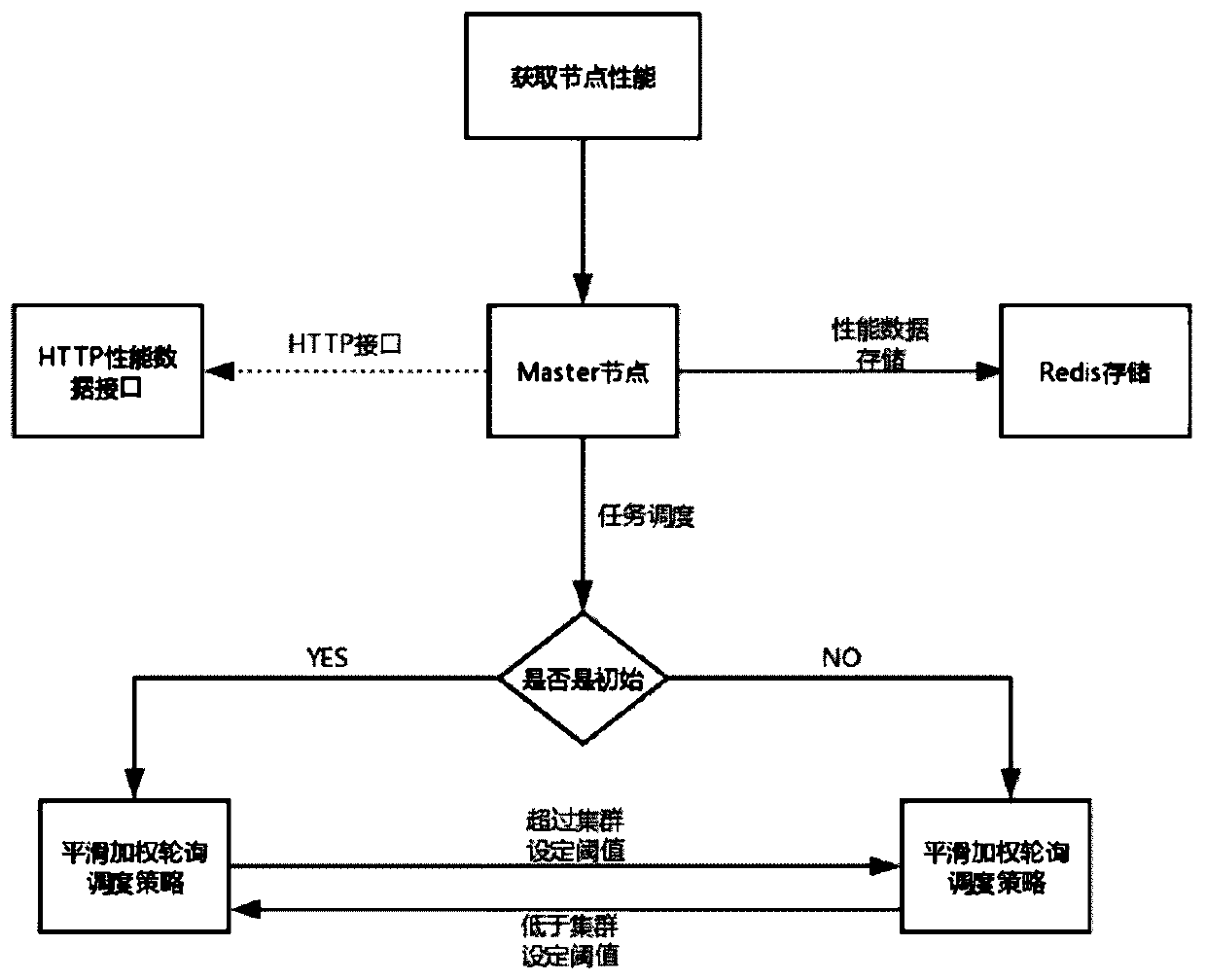
Self-adaptive task scheduler and method
ActiveCN110764912AImprove performanceCompletion time delayResource allocationArtificial lifeCompletion timeData acquisition
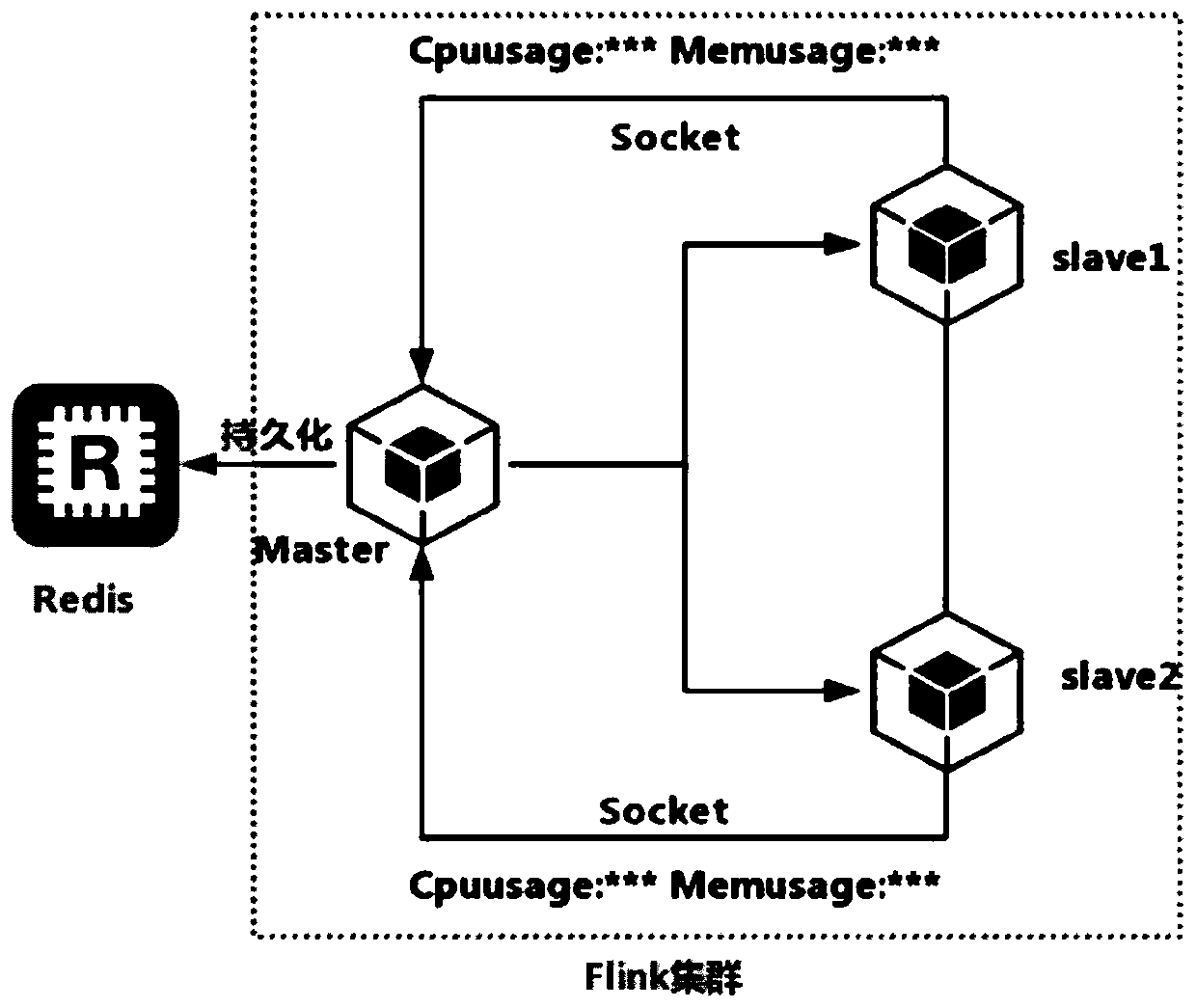
The invention discloses a self-adaptive task scheduler and method, and belongs to the technical field of load balancing scheduling of distributed stream processing systems. The scheduler mainly comprises a performance monitoring data acquisition module, a smooth weighted polling task scheduling module and a task scheduling module based on an ant colony algorithm. According to a method for carryingout task scheduling by adopting the self-adaptive task scheduler, in the task running initial stage, a smooth weighted polling task scheduling algorithm is adopted, tasks are allocated according to the weights of nodes, and the nodes are not continuously selected under the condition that the number of times of selection is not changed. When the load of the cluster exceeds a set threshold value, in order to avoid delaying the overall completion time of the task set, an optimal task allocation scheme is calculated within a certain number of iterations by using a load balancing algorithm based on an ant colony algorithm, and when cluster resources are reduced to below the set threshold value, a smooth weighted polling algorithm is continued to be adopted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
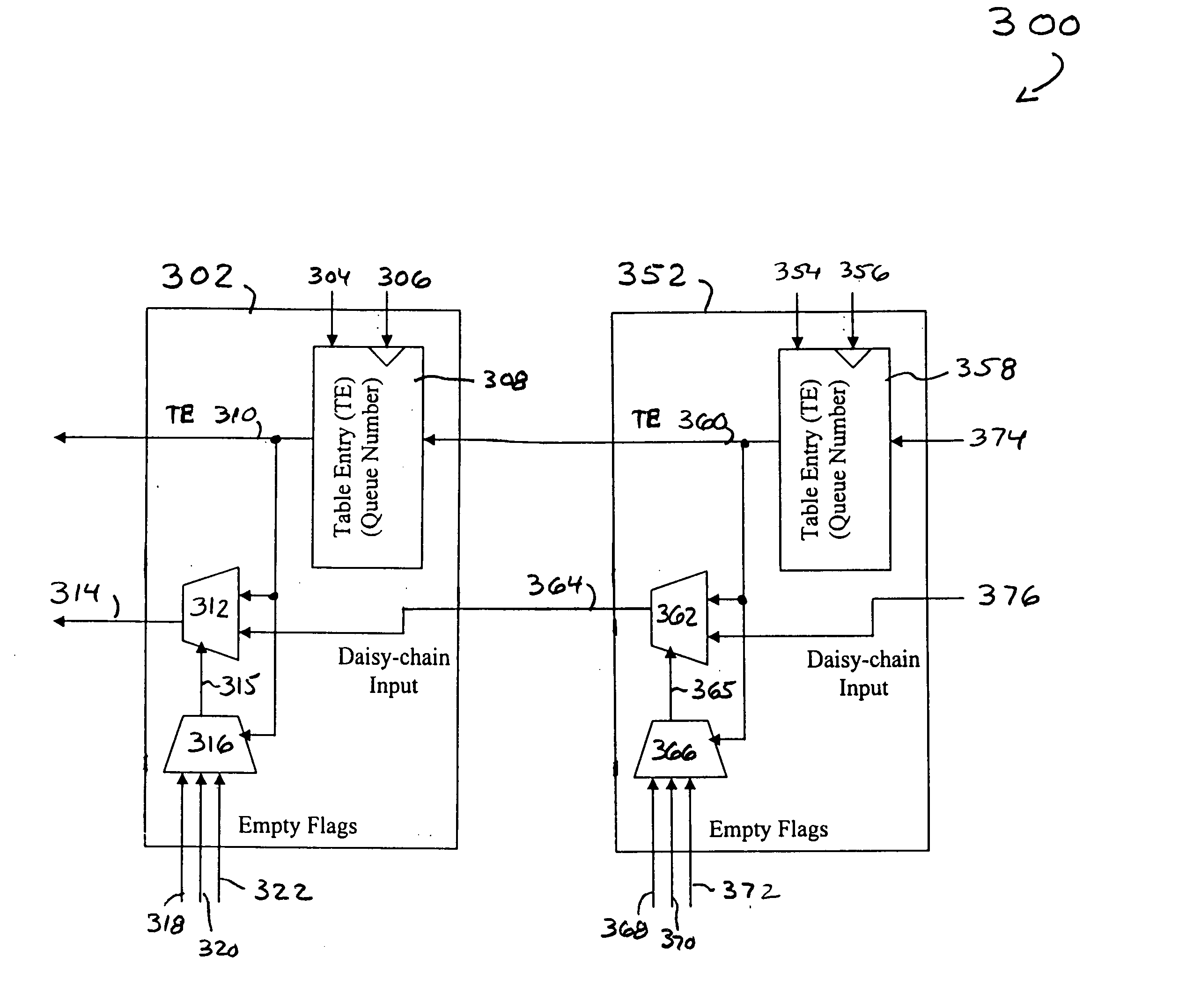
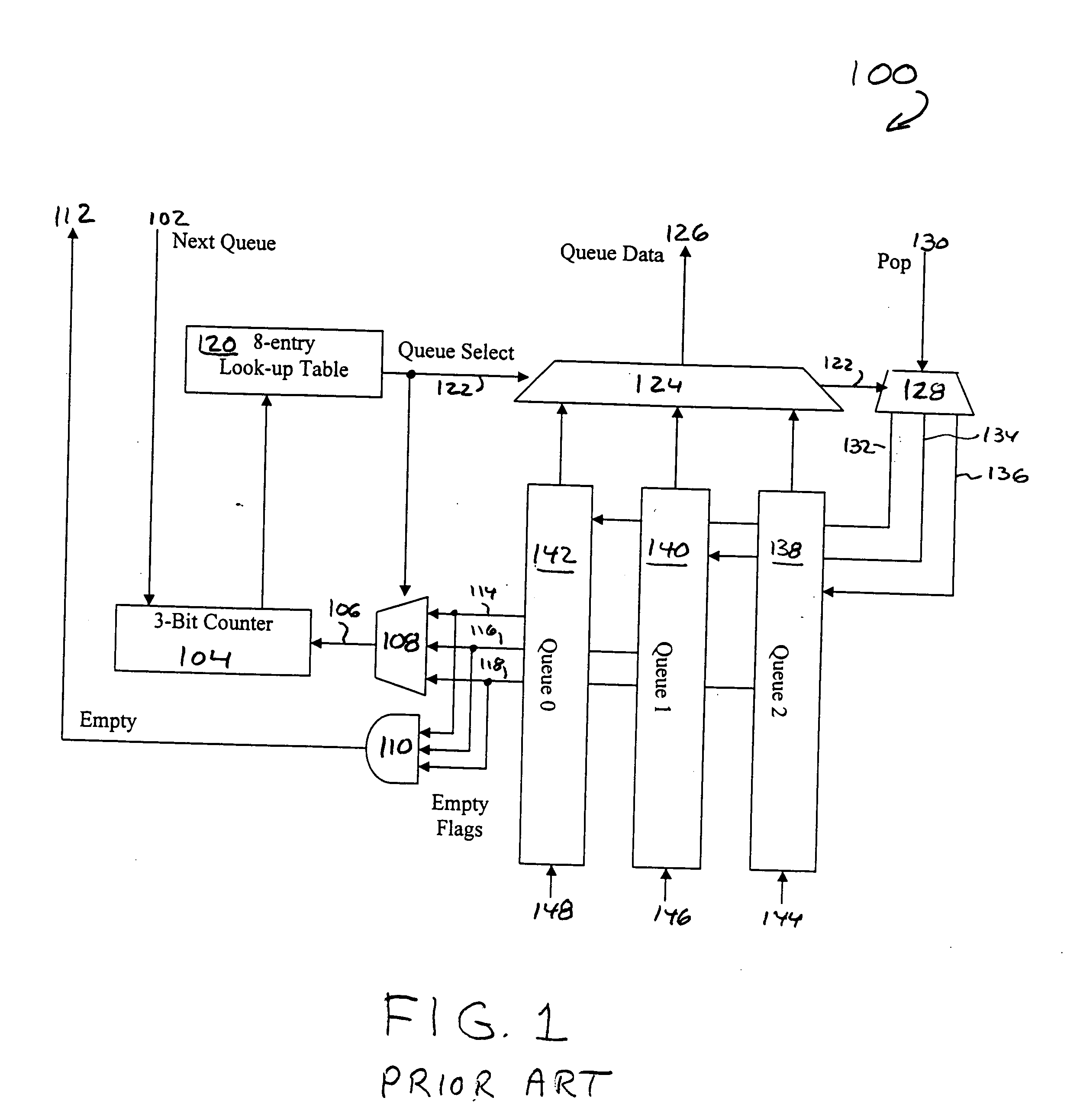
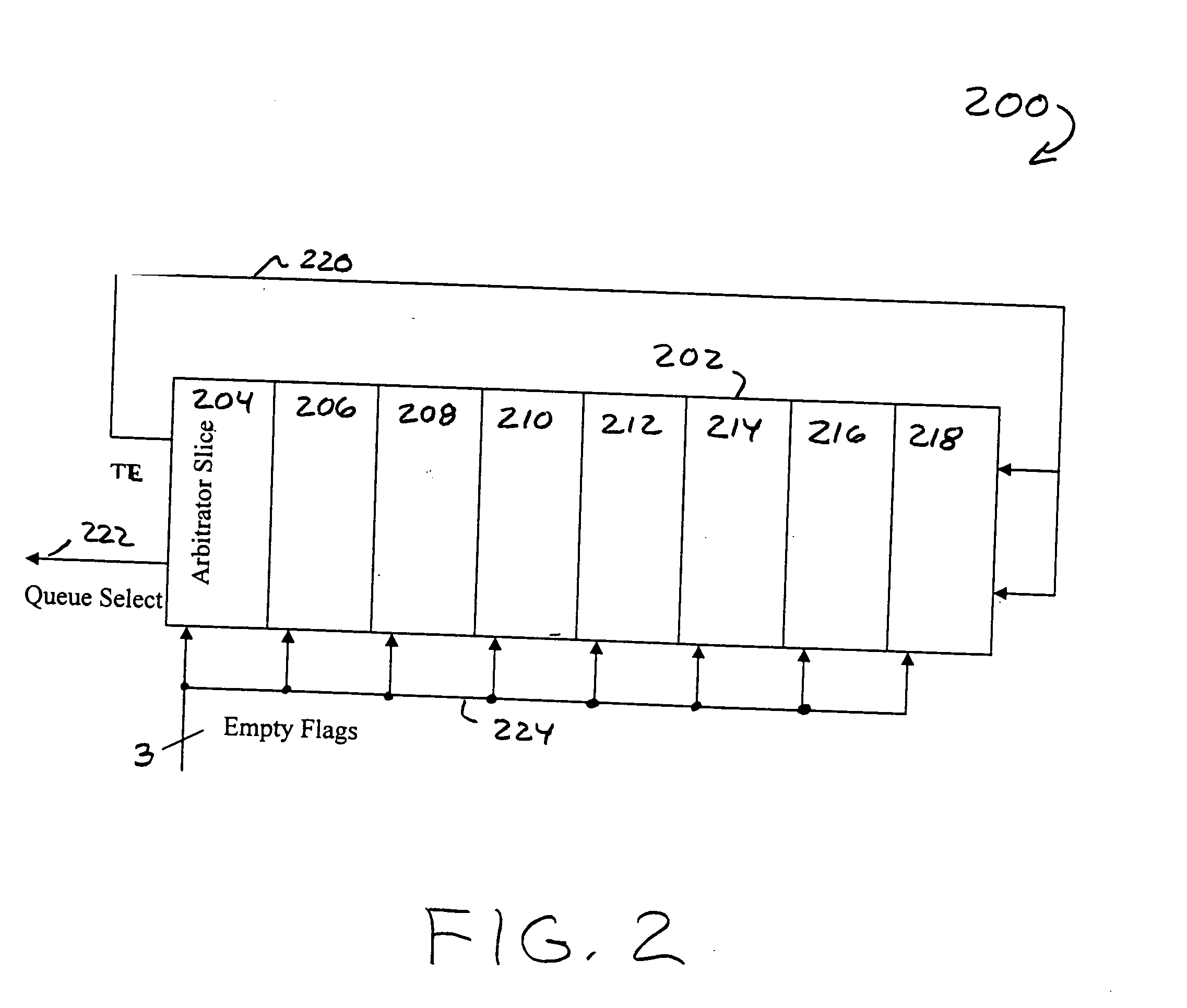
Weighted round-robin arbitrator
ActiveUS20050122982A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiplexerComputer science
A weighted round-robin arbitrator for a plurality of data queue includes an arbitration table comprising a plurality of entries. Each entry represents a time slot for the transmission of one data packet from a selected one of the plurality of data queues. There is one arbitration logic circuit for each of the plurality of entries in the arbitration table. Each arbitration logic circuit includes a first multiplexer receiving an output from a first table entry and an output from a second table entry in the arbitration table. A second multiplexer receives empty flags from each of the data queues, the flags indicating that there is no data to the sent from that queue. An output of the second multiplexer is coupled to a control input of the first multiplexer so that the first table entry value is output from the first multiplexer if the corresponding queue has data to be sent out and the second table entry value is sent out from the first multiplexer if the queue corresponding to that table entry has data to be sent out and the queue corresponding to the first entry has no data to be sent out.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
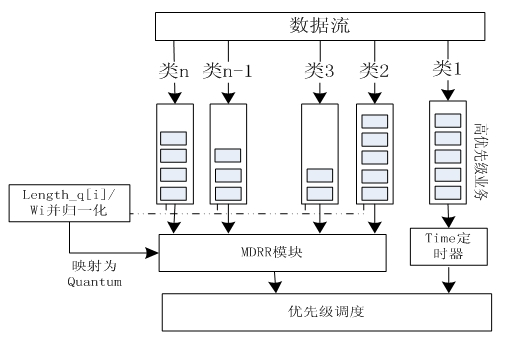
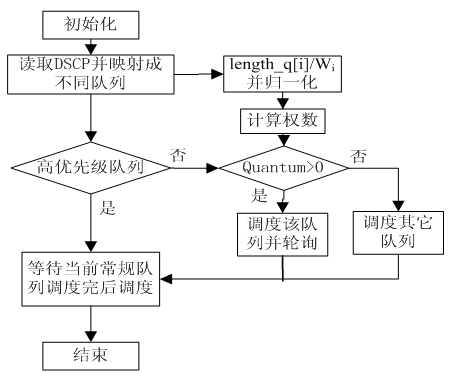
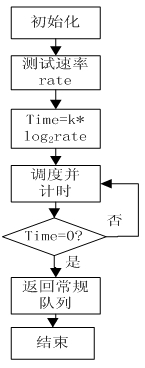
Queue scheduling method based on timer and MDRR
InactiveCN101969409AReduce latencyImprove scheduling abilityData switching networksDifferentiated servicesQueue number
The invention discloses a queue scheduling method based on a timer and MDRR, which is based on a differentiated service model and is mainly composed of three parts of a Time timer, a real-time weight updating algorithm a modified weighted round robin (MDRR) scheduling algorithm, wherein the Time timer is mainly used for controlling the scheduling of a high priority queue, ensures that the queue can obtain higher service quality and ensures fairness in the network; according to the real time situation of the data flow in the queue, the weight parameter in the MDRR scheduling algorithm can be dynamically changed; and when service amount is overlarge, the weight is properly enlarged to ensure effect on other queues is lowered to the minimum. The method realizes the scheduling with configurable support queue number and adjustable rate, and has good expandability and simple operation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for load balancing of Web requests based on operating system virtualization
InactiveCN104902001ALoad balancingAvoid overloaded situationsTransmissionVirtualizationOperational system
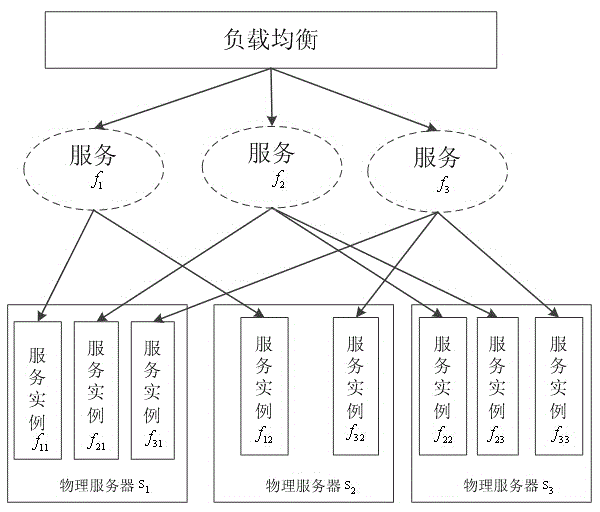
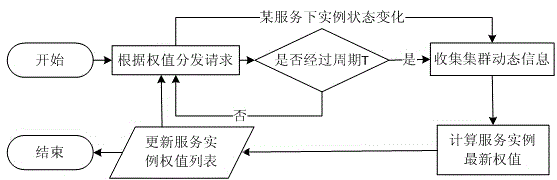
The invention discloses a method for load balancing of Web requests based on operating system virtualization. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, carrying out collection and normalization of server resource information; secondly, collecting dynamic information of a server and service instances; thirdly, computing final weights of service instance copies of all services according to the server resource information and the periodically-collected dynamic information; and lastly, distributing the requests through weighted round robin. According to the method, the phenomenon that the different service instance copies on one server simultaneously receive a large amount of Web requests due to the lower server load to cause the server overload can be effectively avoided, the load balancing between the service instance copies and the server is implemented, the concurrence capacity of a Web cluster system is improved, and the average response time of the requests is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Queue scheduling method based on dynamic weight calculation
ActiveCN104009936AImprove service qualityIncrease flexibilityData switching networksService flowCurrent load
The invention discloses a queue scheduling method based on dynamic weight calculation. The method comprises the steps of receiving data packets, classifying the data packets and storing the data packets in corresponding service queues; reading and measuring the information of data packets in each service queue; calculating the optimal weighted value of each service queue according to the read information of the data packets in each service queue and the maximum return judging criteria; conducting scheduling output on the data packets in the service queues through a weighted round robin scheduler according to the optimal weighted values of the service queues obtained through calculation. According to the method, the weighted values of the data packets in the service queues can be adjusted dynamically according to the bandwidth requirements and time delay requirements of the service flow data packets and the current load condition of the network, fixed allocation of weighted values is achieved effectively for the weighted round robin scheduling algorithm, and flexibility and adaptability are improved greatly. The queue scheduling method based on dynamic weight calculation is applied to the communication field.
Owner:BANGYAN TECH +1
Method and apparatus for integrating guaranteed-bandwidth and best-effort traffic in a packet network
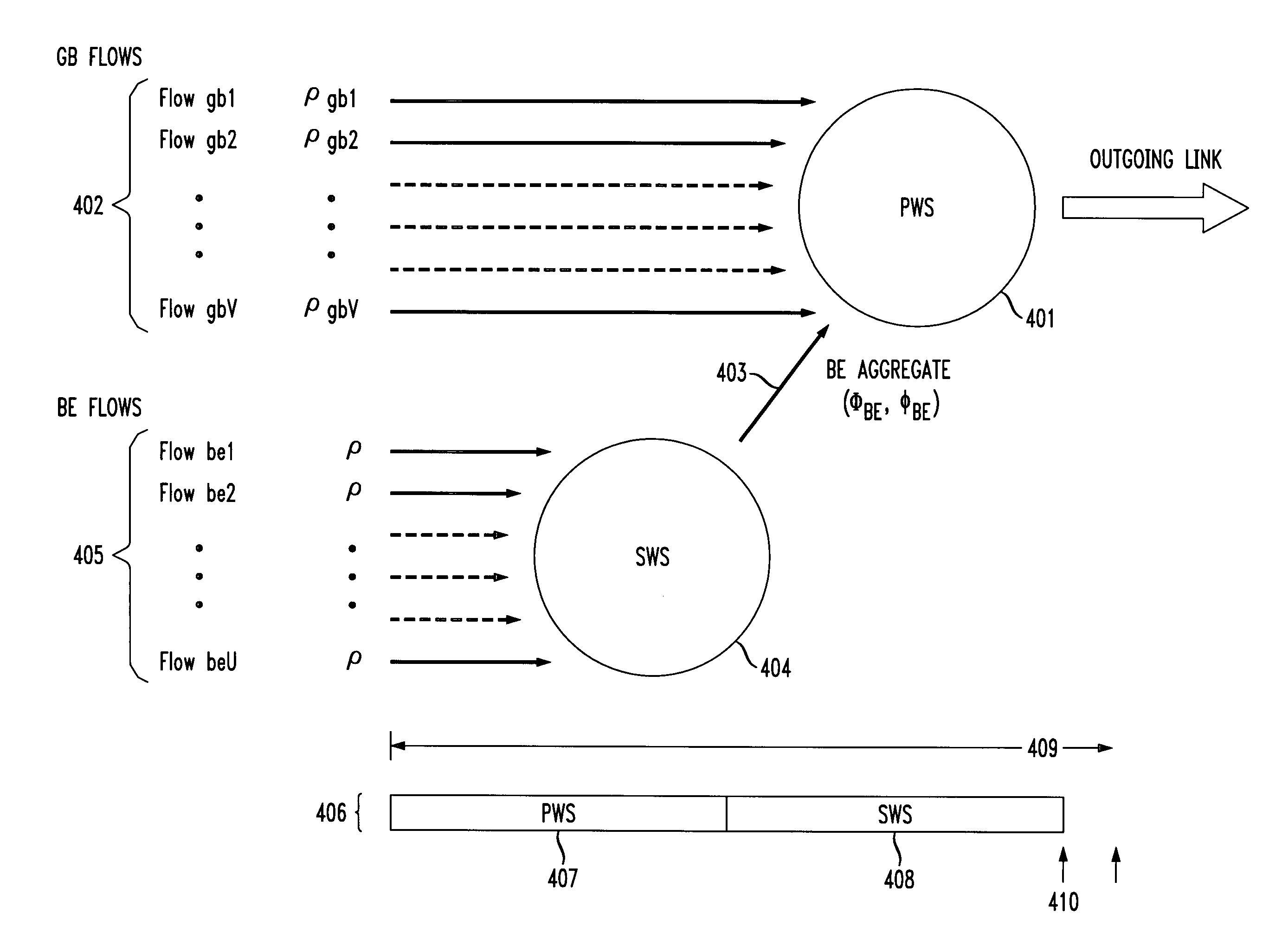
A scheduling apparatus flexibly integrates guaranteed-bandwidth (GB) and best-effort (BE) flows and comprises a combination of a primary weighted-round-robin (WRR) scheduler (PWS) and a secondary WRR scheduler (SWS). The PWS distributes service to the individual GB flows and determines the amount of service that the BE flow aggregate should receive during each frame. The SWS takes care of fairly distributing the service share of the BE aggregate over the individual BE flows. The scheduling apparatus divides the service frame in two subframes. In the first subframe, the PWS fulfills the bandwidth requirements of the GB flows. In the second subframe, the SWS distributes fair service to the BE flows. For each frame, the duration depends on the amount of bandwidth allocated to the GB flows and on the number of GB flows that are backlogged at the beginning of the frame. The amount of bandwidth globally available to BE flows (i.e., the duration of the second subframe) is dynamically adapted to the backlog state of the GB flows, increasing when the GB-flow activity is low, and decreasing when the GB-flow activity intensifies.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Dynamic queue scheduling device and method based on bandwidth borrowing
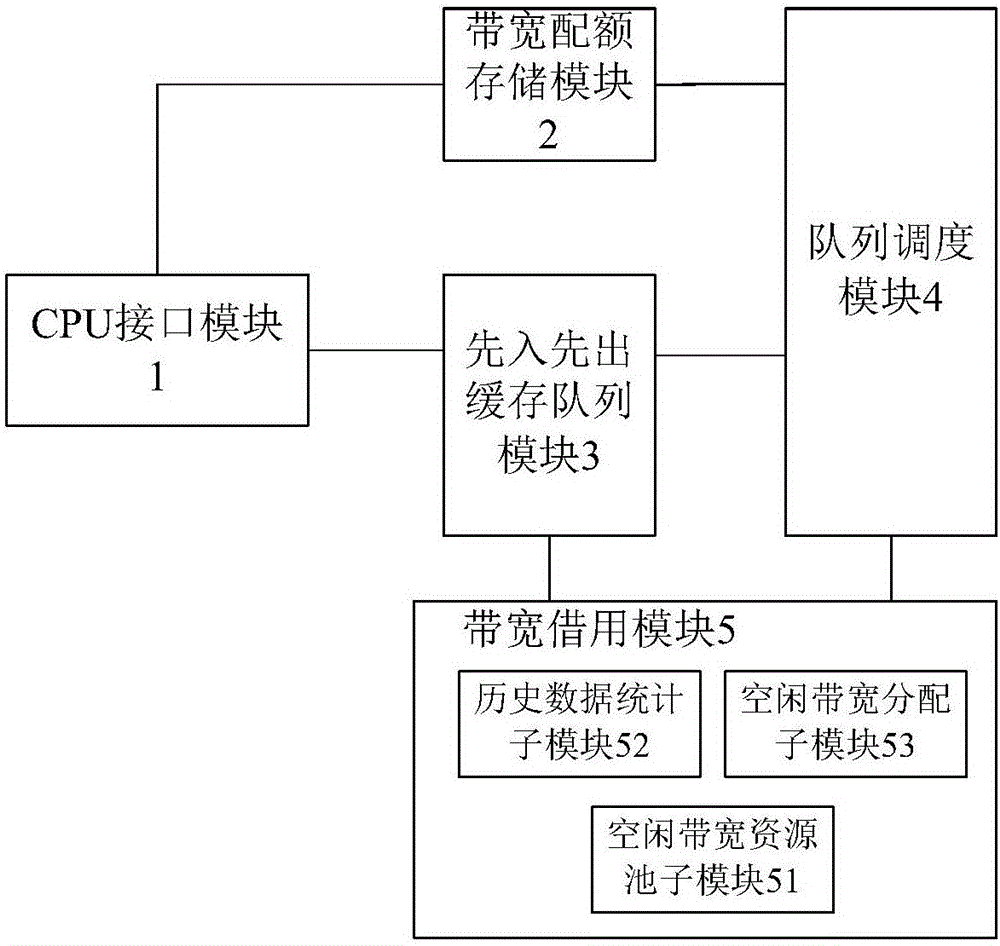
The invention discloses a dynamic queue scheduling device and method based on bandwidth borrowing and mainly solves a problem of low bandwidth utilization rate of an output port in the prior art. An implementation scheme of the invention comprises the following steps of reading a register with a configurable CPU through a CPU interface module (1) to obtain a bandwidth quota which is distributed to each queue; storing a bandwidth quota which is distributed to each first input first output queue through a bandwidth quota storage module (2); buffering a data packet at which each business flow arrives through a first input first output buffer queue module (3); scheduling the queue in a weighted round-robin manner through a scheduler module (4) according to the bandwidth quota which is distributed to each queue; and distributing the unused idle bandwidth quota in one scheduling period to a non-empty queue whose data packet is still not output in the scheduling period by a bandwidth borrowing module (5). According to the device and the method, the packet loss probability of a system is reduced, the utilization rate of the bandwidth resources is improved, and the device and the method can be used for routers and switches in a communication network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Link state network having weighted control message processing
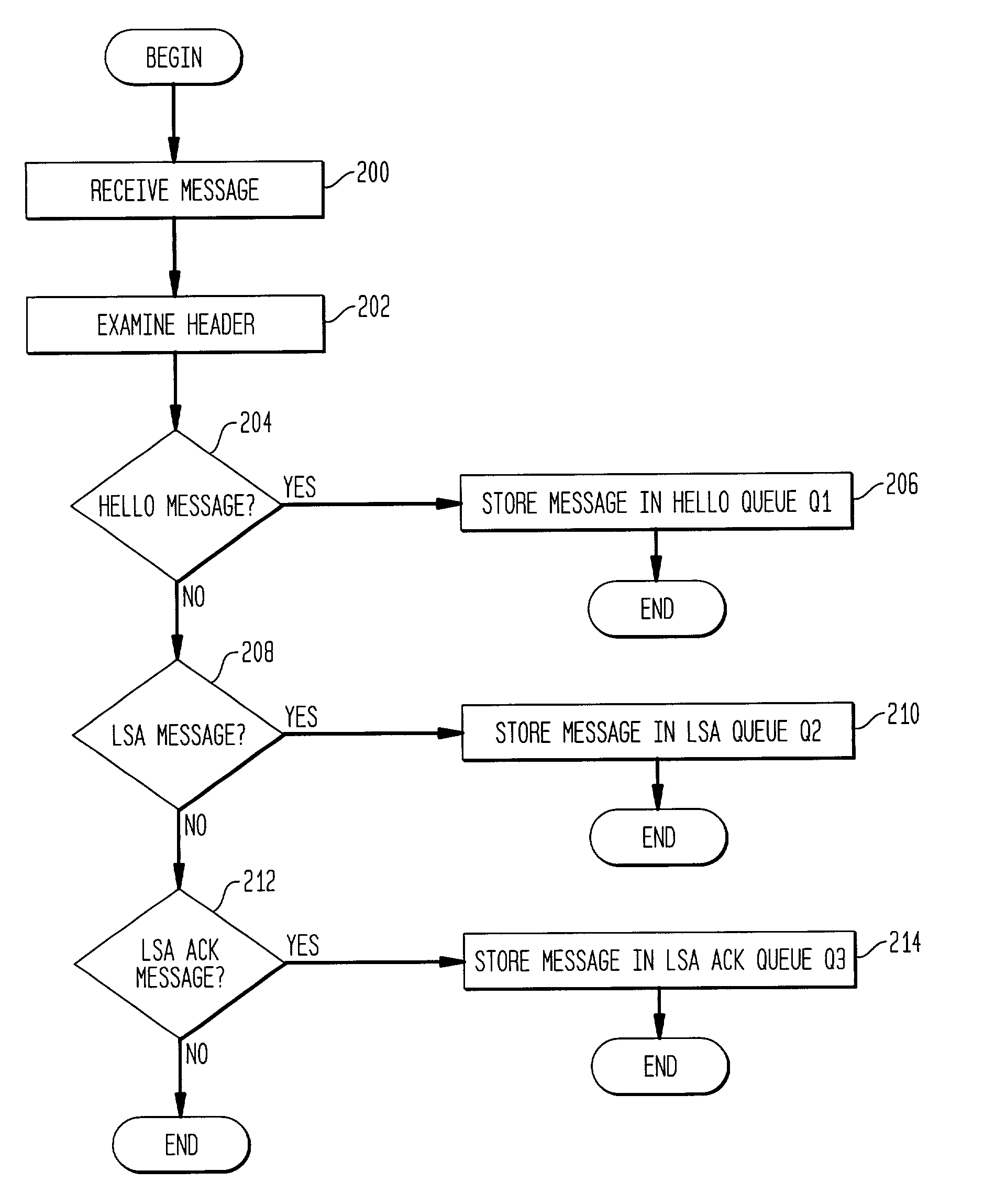
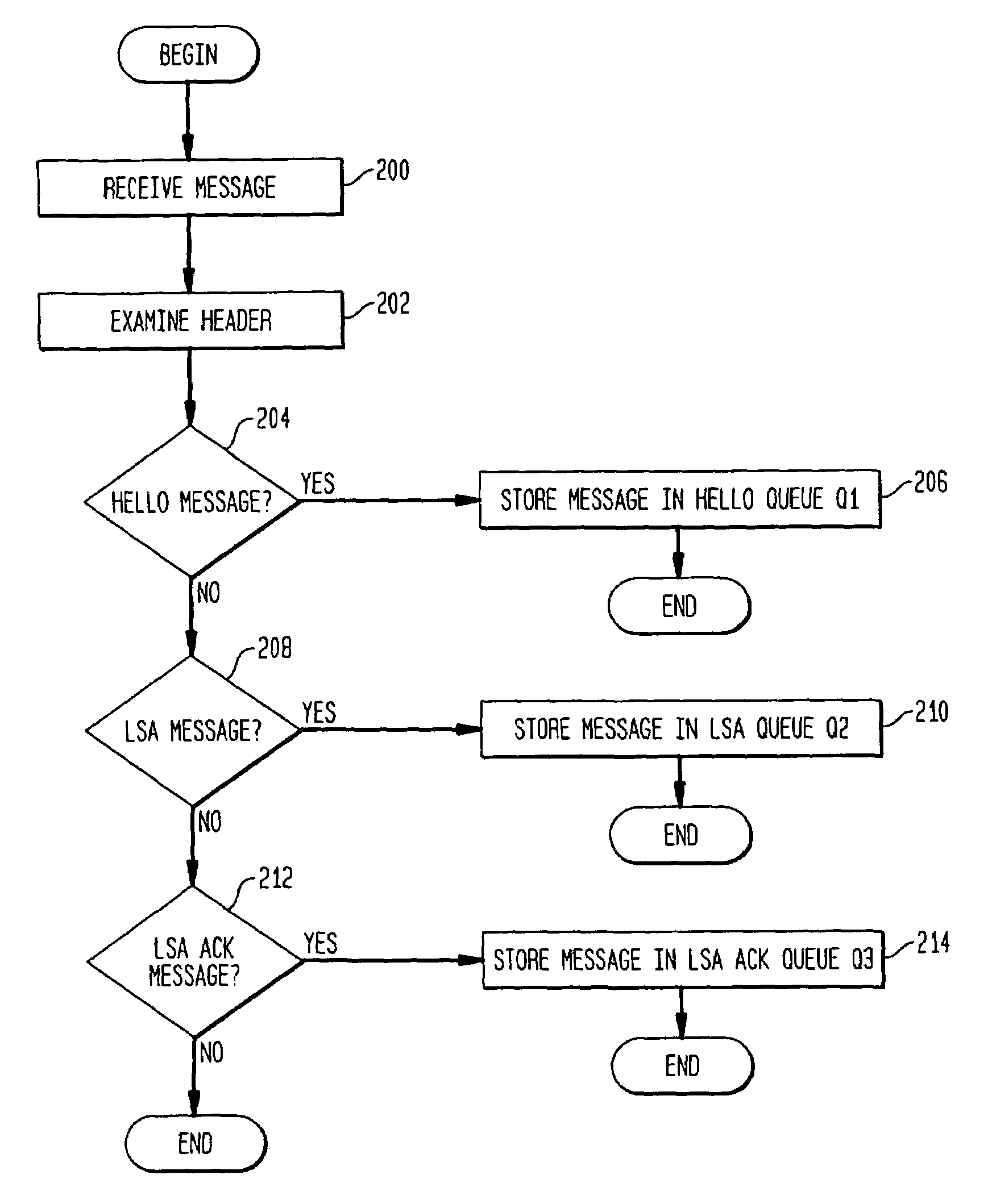
InactiveUS7006441B1Improve reliabilityImprove scalabilityError preventionTransmission systemsMessage queueMessage type
A node in a network running a link-state routing protocol identifies certain routing control messages and stores the identified messages in separate queues. The queues are weighted such that each message type is allotted a predetermined amount of processing overhead to optimize the message processing by a node. In one embodiment, the node processor processes the queued messages in accordance with the entries in a weighted round robin polling table. An upper limit of processing time can be specified for each visit to a particular message queue.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Link state network having weighted control message processing
InactiveUS7548514B1Improve reliabilityImprove scalabilityError preventionTransmission systemsMessage queueMessage type
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Applying backpressure to a subset of nodes in a deficit weighted round robin scheduler
A scheduler in a network element may include a dequeuer to dequeue packets from a set of scheduling nodes using a deficit weighted round robin process, where the dequeuer is to determine whether a subset of the set of scheduling nodes is being backpressured. The dequeuer may set a root rich most negative credits (MNC) value, associated with a root node, to a root poor MNC value, associated with the root node, and set the root poor MNC value to zero, when the subset is not being backpressured, and may set the rich MNC value to a maximum of the root poor MNC value and a root backpressured rich MNC value, associated with the subset, and set the root poor MNC value to a root backpressured poor MNC value, associated with the subset, when the subset is being backpressured.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com