Distributed crawler task scheduling method based on weighted round-robin algorithm
A technology of weighted round-robin and task scheduling, applied in the field of network search, can solve the problem that the crawling ability cannot keep up with the growth rate of information on the Internet, and achieve flexible scalability and fault tolerance, good scalability, and ensure load balance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
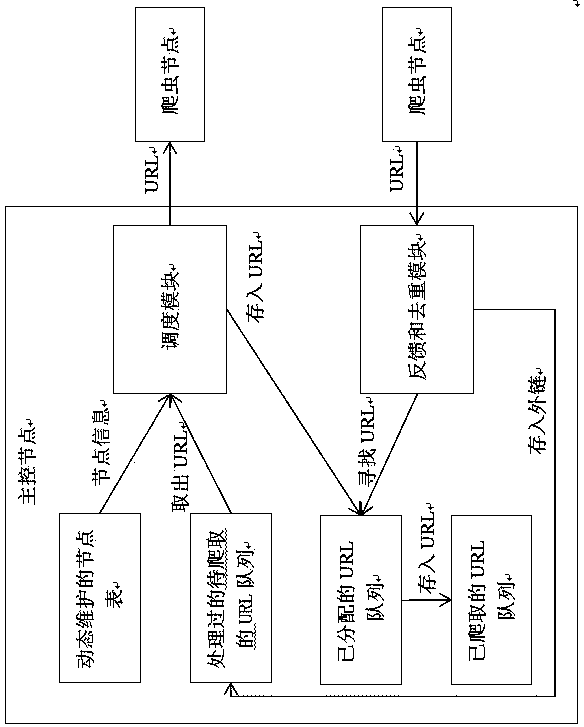
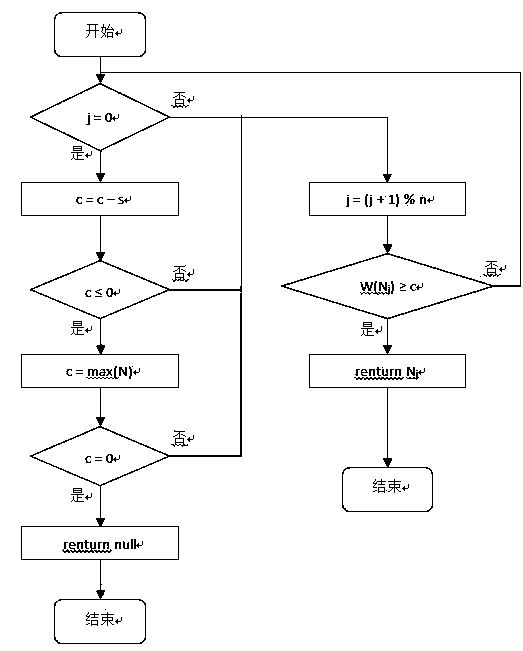
[0036] The present invention adopts a master-slave crawler architecture. In the master control node, there is a node table, three URL queues, a scheduling module and a crawler feedback module. The node table records the information of each crawler node, including node number, weight, etc. It must be dynamically updated to keep in line with the actual crawler nodes. The timing of its dynamic update can be every time the crawler node performs a URL task feedback, or it can be performed once every certain time, which can be set according to the specific situation. The scheduling module first takes out a URL from the URL queue to be crawled, then takes out the information of each node from the node table, and selects a crawler node for scheduling, assigns the URL to the crawler node, and stores the URL in the Allocated URLs are in the queue. And when a crawler node completes the crawling work of a URL, the crawler feedback module queries the URL in the allocated URL queue, delet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com