Patents
Literature
131 results about "Client–server model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
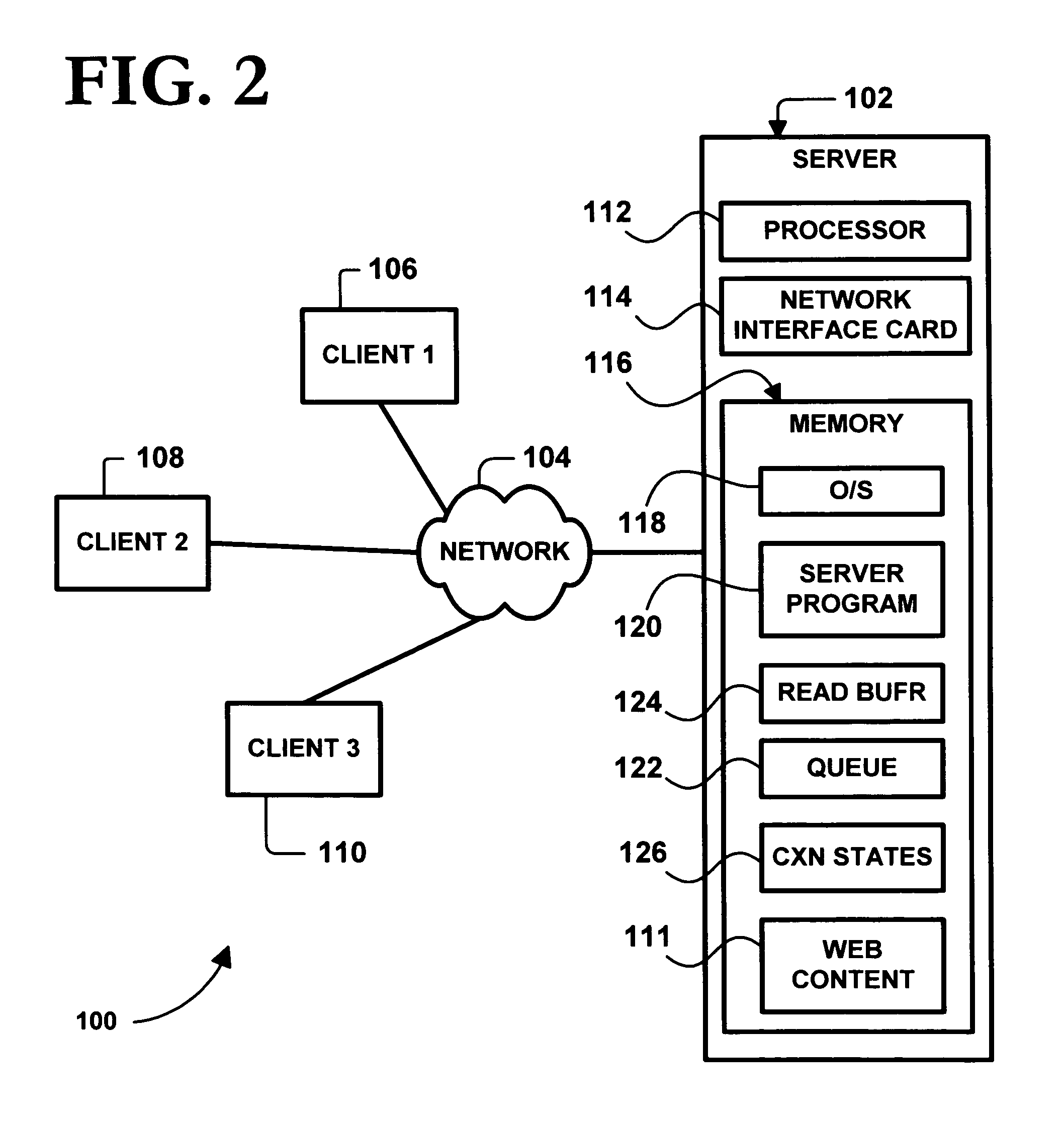
Client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters, called clients. Often clients and servers communicate over a computer network on separate hardware, but both client and server may reside in the same system. A server host runs one or more server programs, which share their resources with clients. A client does not share any of its resources, but it requests content or service from a server. Clients therefore initiate communication sessions with servers, which await incoming requests. Examples of computer applications that use the client–server model are Email, network printing, and the World Wide Web.
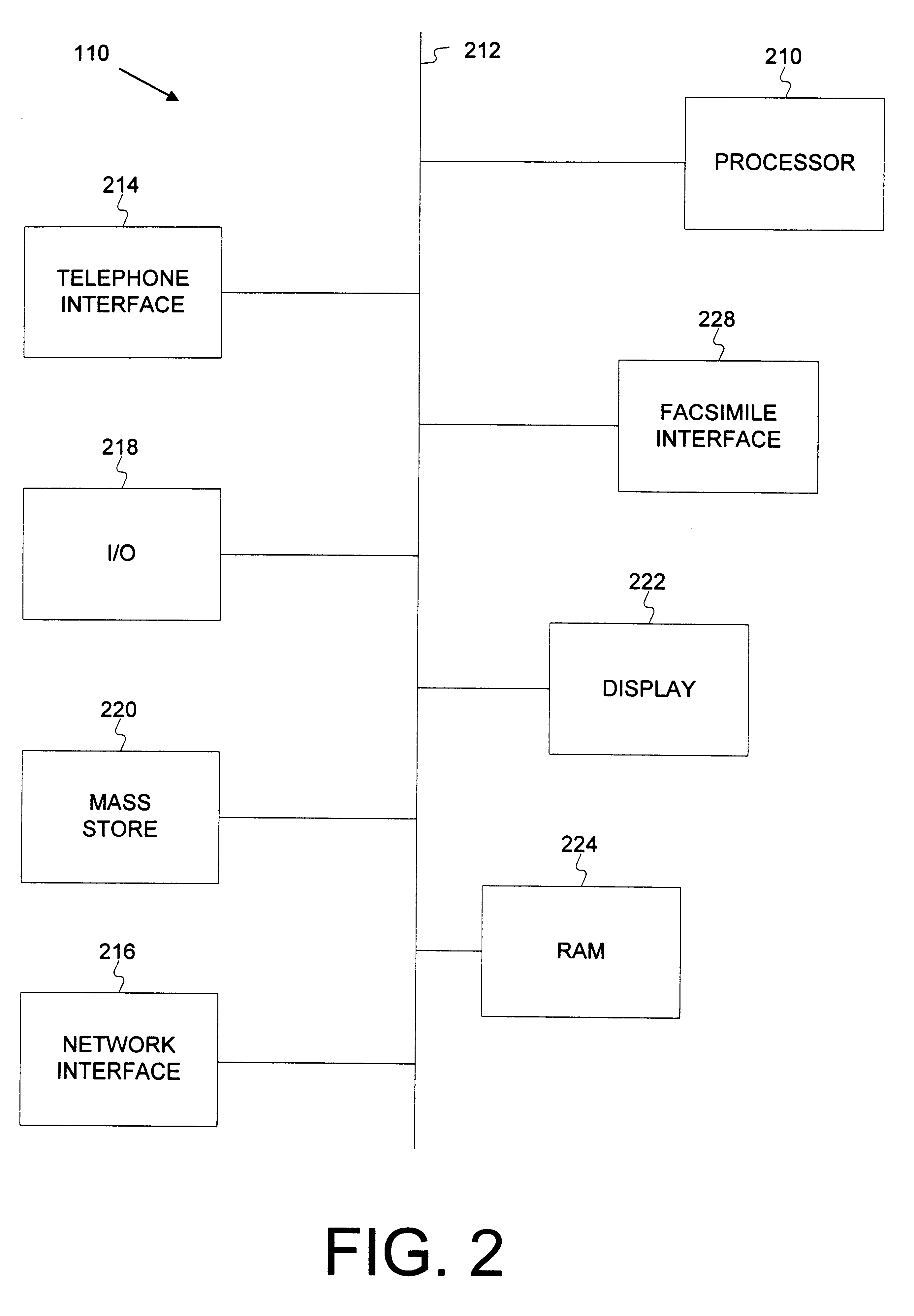
Dynamic content conversion
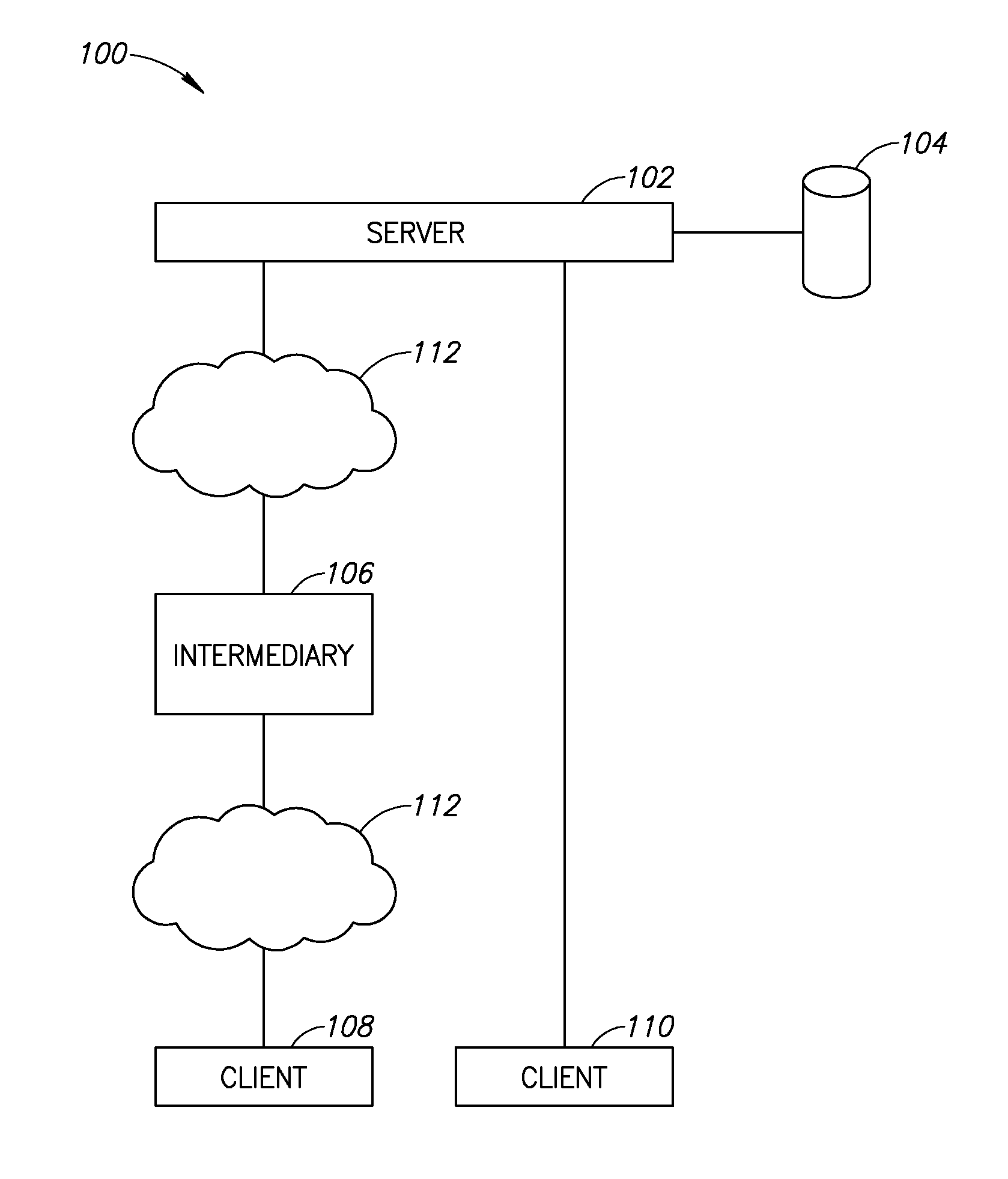
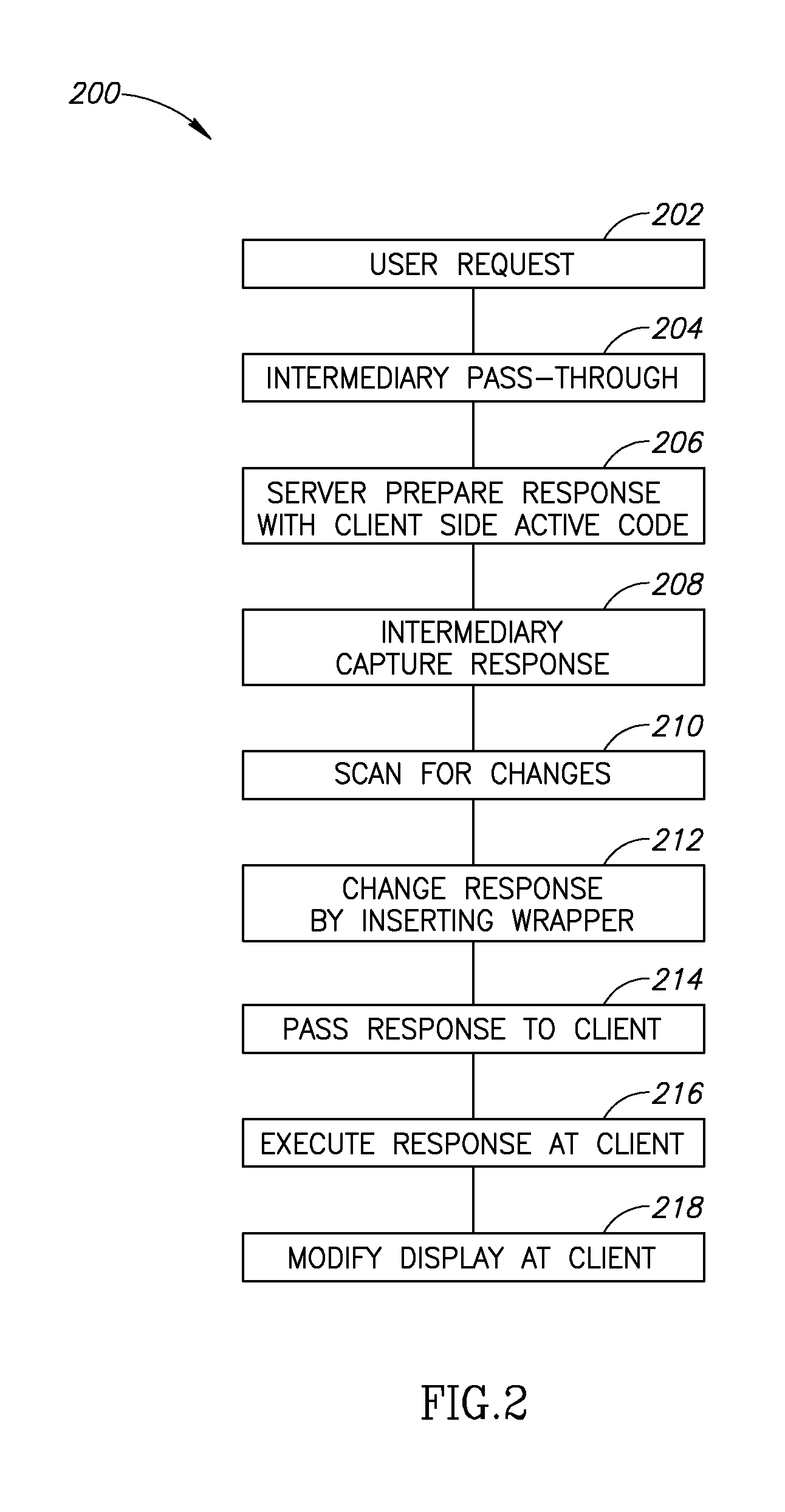
ActiveUS20090083369A1The process is simple and fastDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsDisplay deviceClient-side
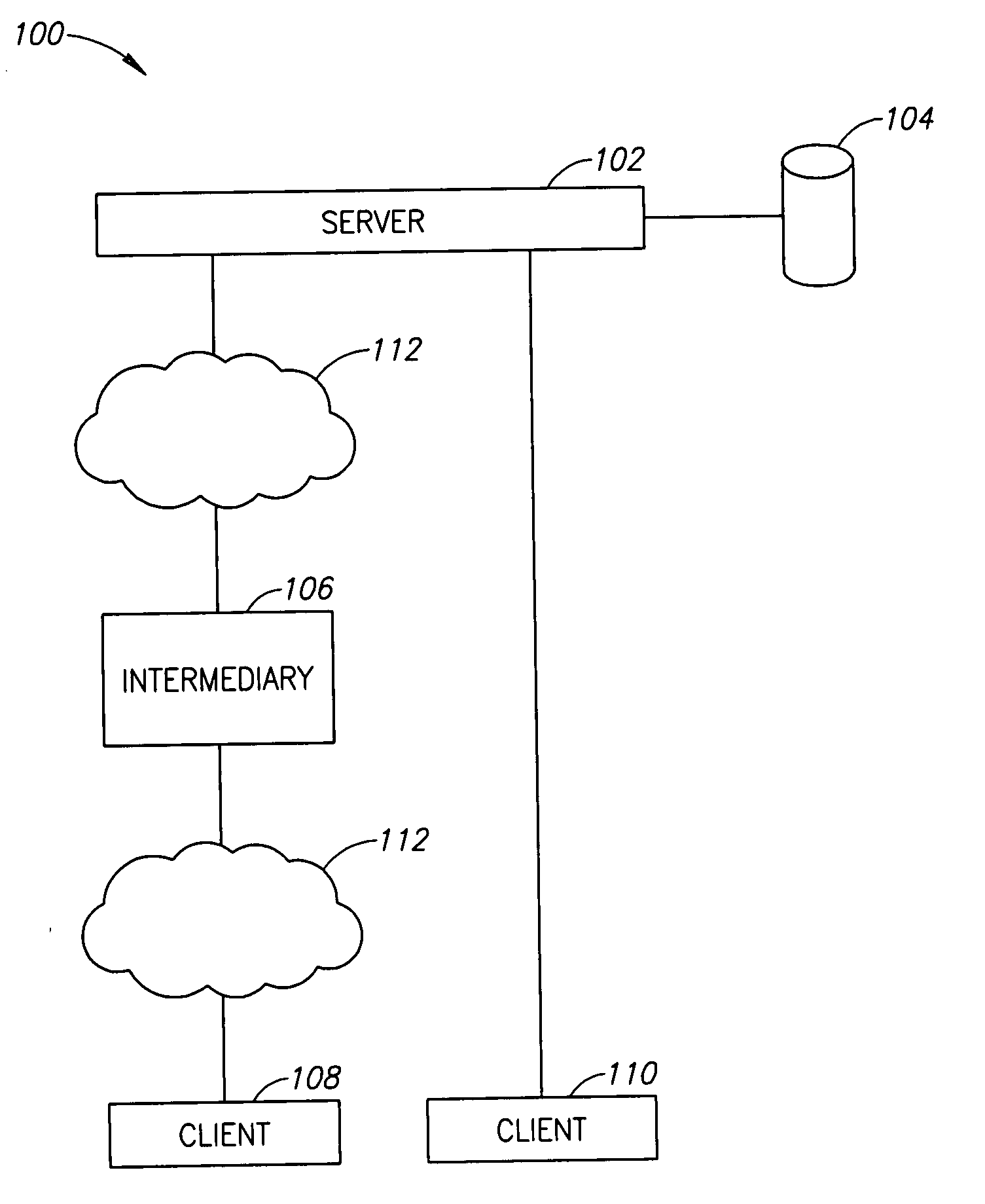
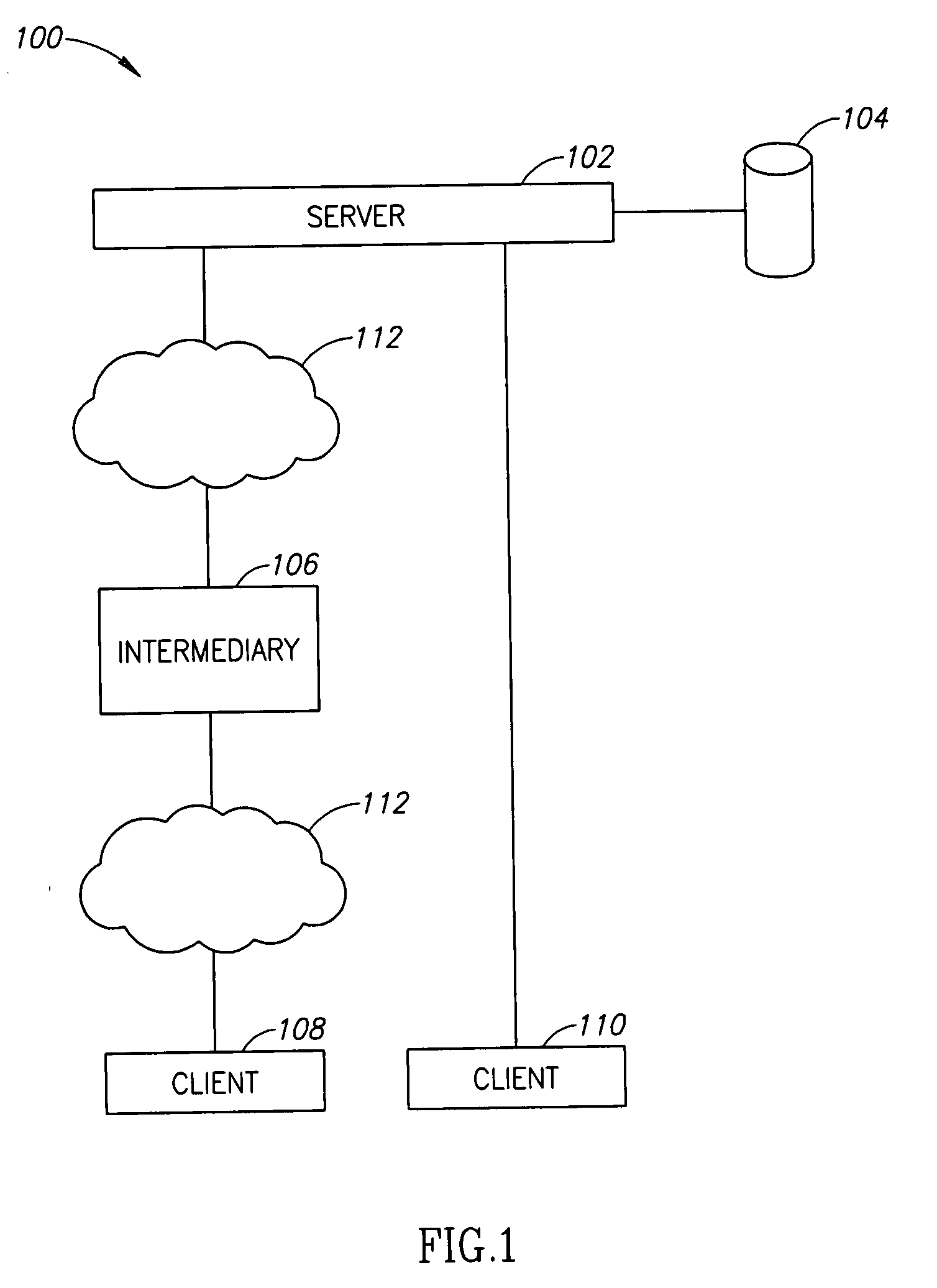
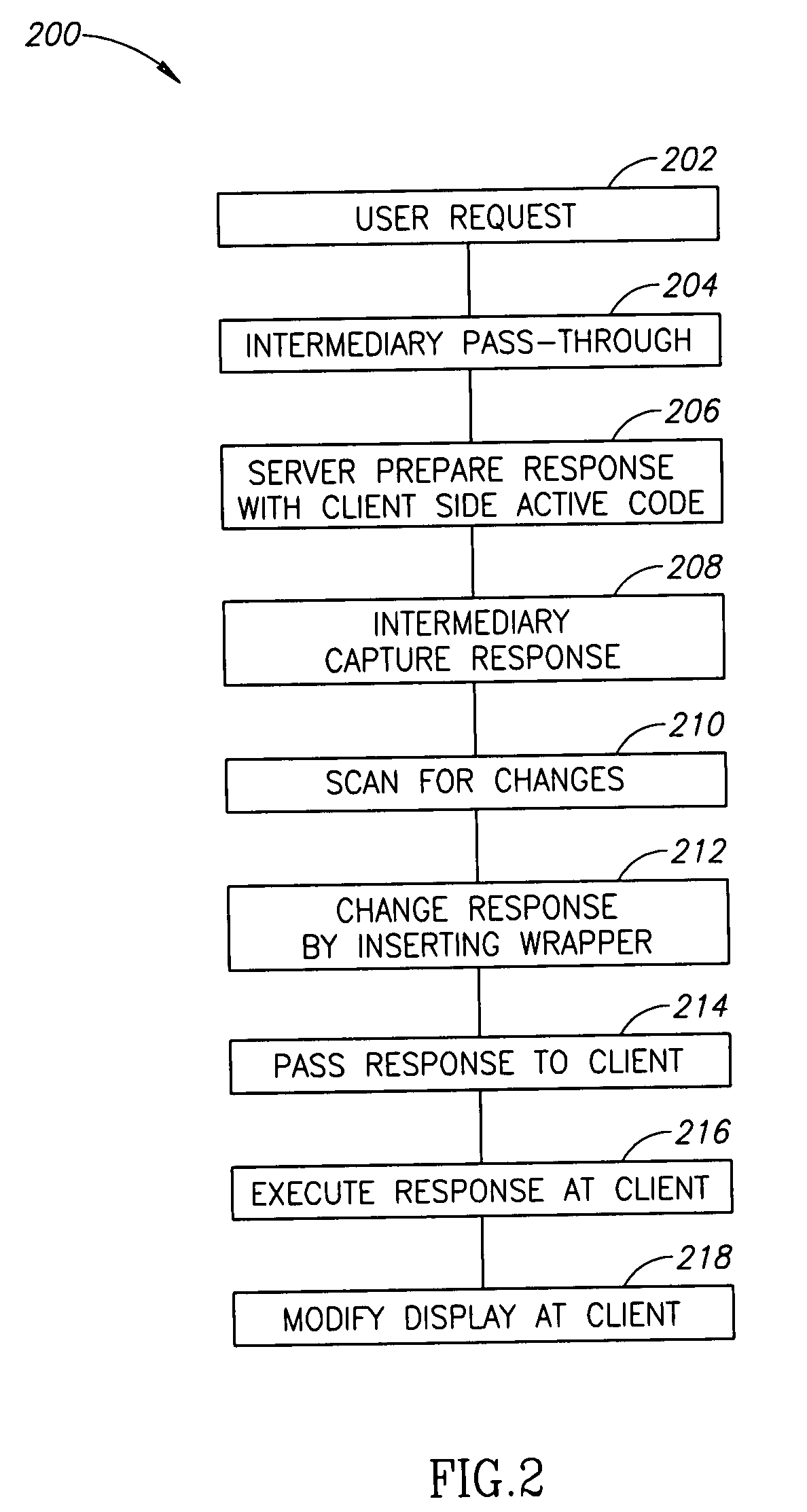
A method of display modification in a client server web system, comprising, intercepting, by a web intermediary, a response to a client request, sent by a server in response to the request, the response including client side active content adapted to execute at a browsing software on a client computer; replacing at least one display-related code section in said response by a wrapper section that includes code for modification of at least one display element and code for executing the original display-related code section; and executing said wrapper section as client side active content at said client to generate a display, modified from a display that would have been generated by executing the response.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Meta-data based method for local cache utilization
ActiveUS20050138176A1Lower the volumeDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsServer agentClient-side
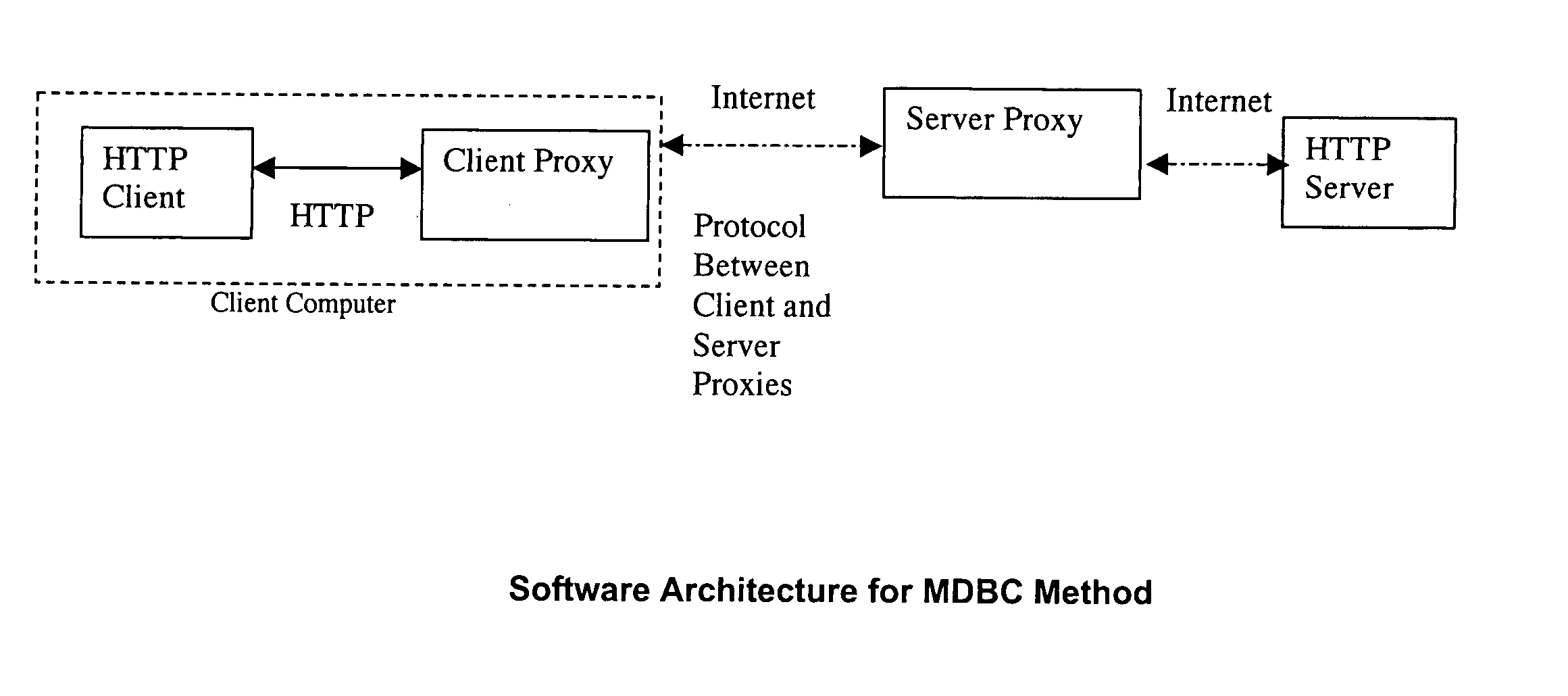
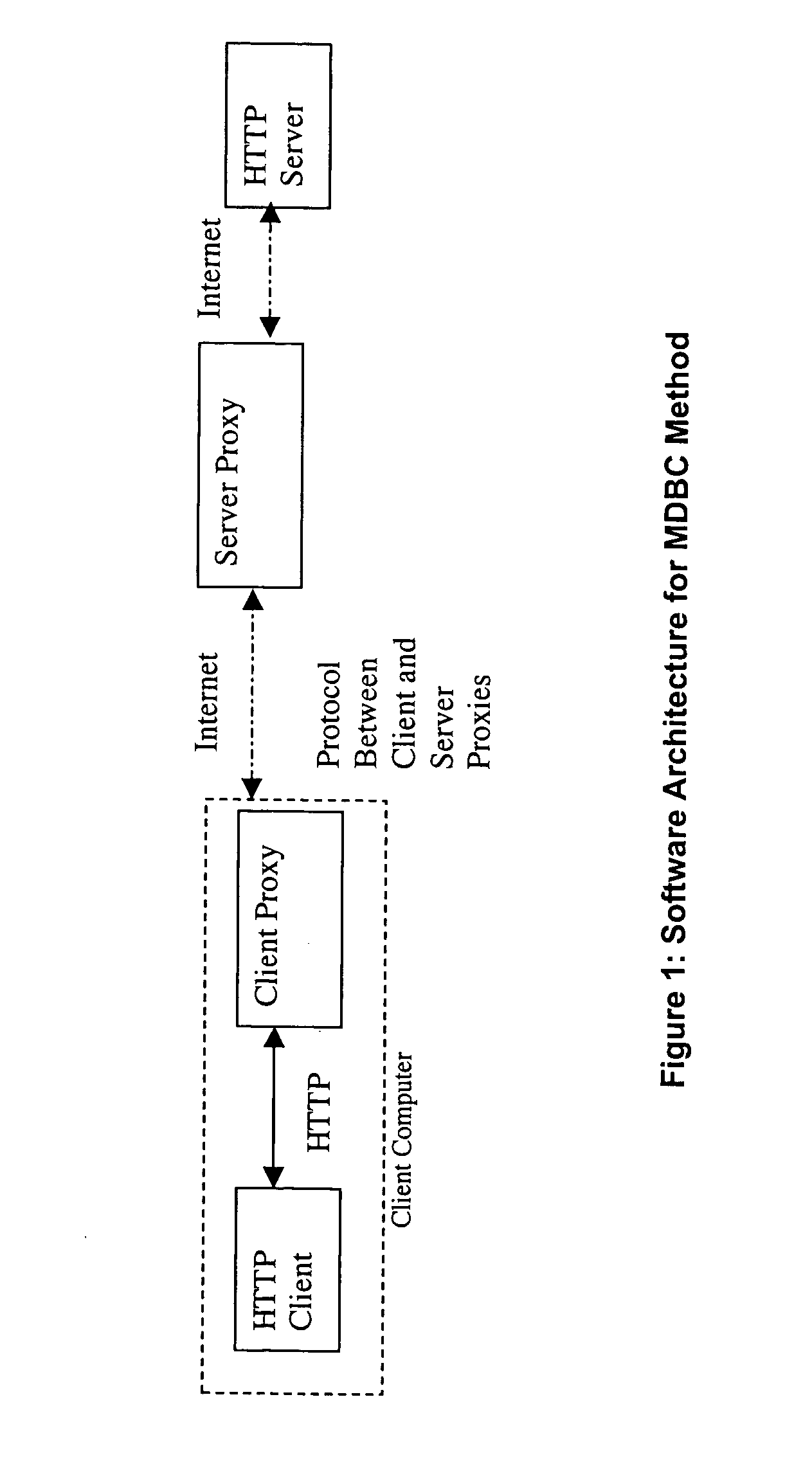
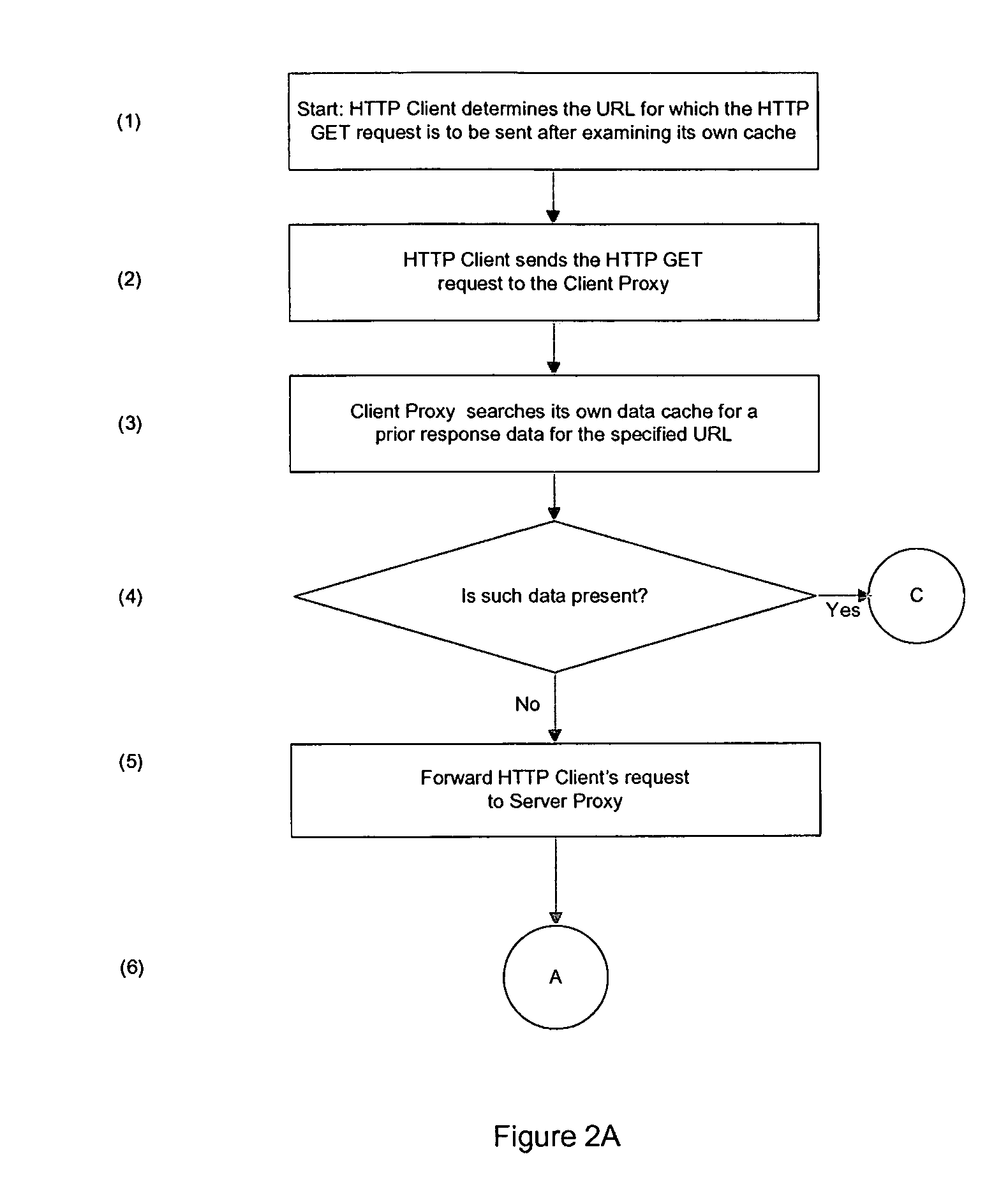
A system and method for caching data and verifying cached data using a client-server model and meta-data. In particular, a client proxy and a server proxy are in communication with each other and with the client and the server, respectively; client proxy meta-data and server proxy meta-data related to the data cached by the client proxy and server proxy, respectively, are calculated and communicated between the client proxy and the server proxy; and the client proxy meta-data and the server proxy meta-data are compared to determine a cache hit or miss.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Apparatus and method for reception and transmission of information using different protocols
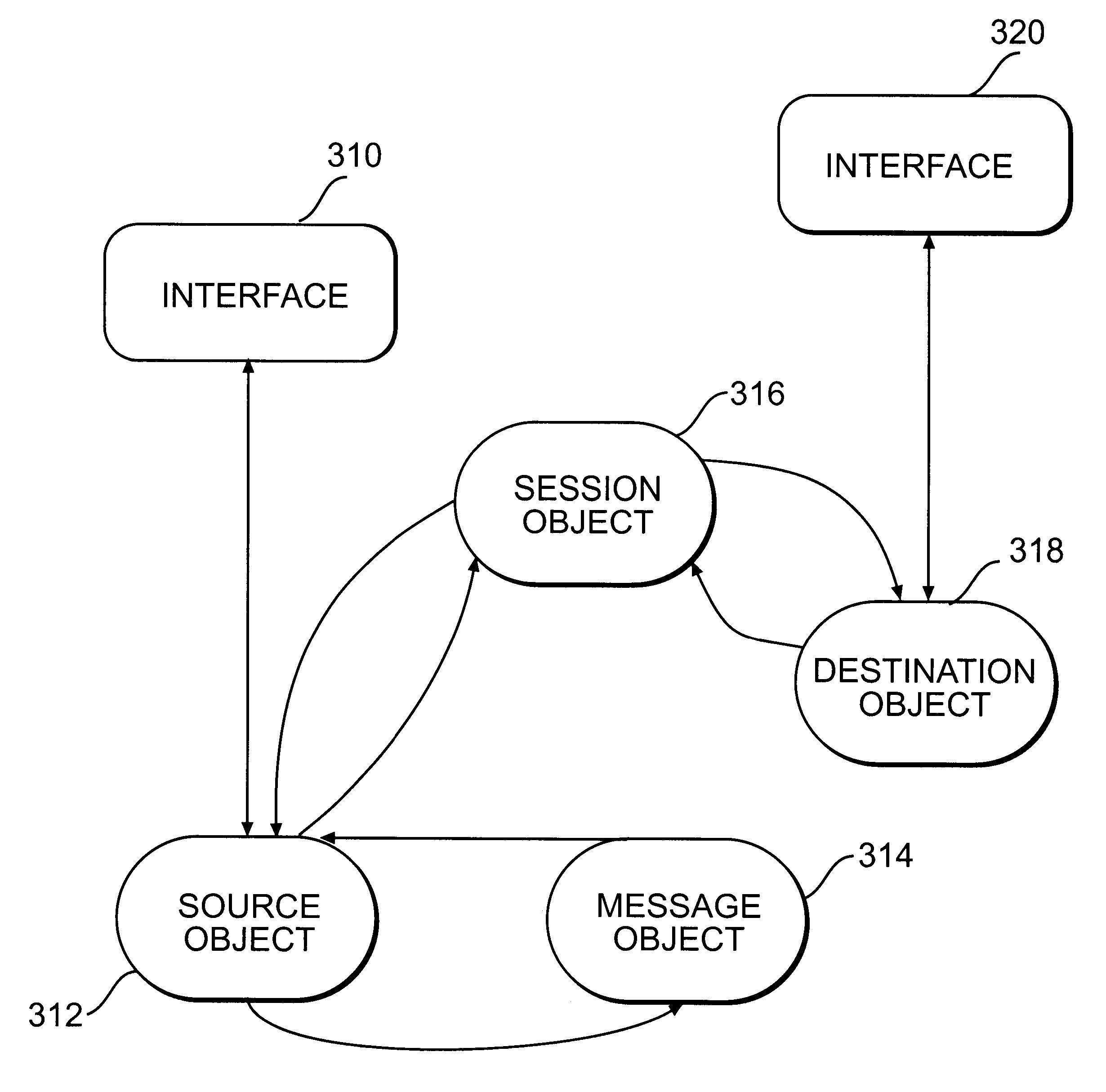
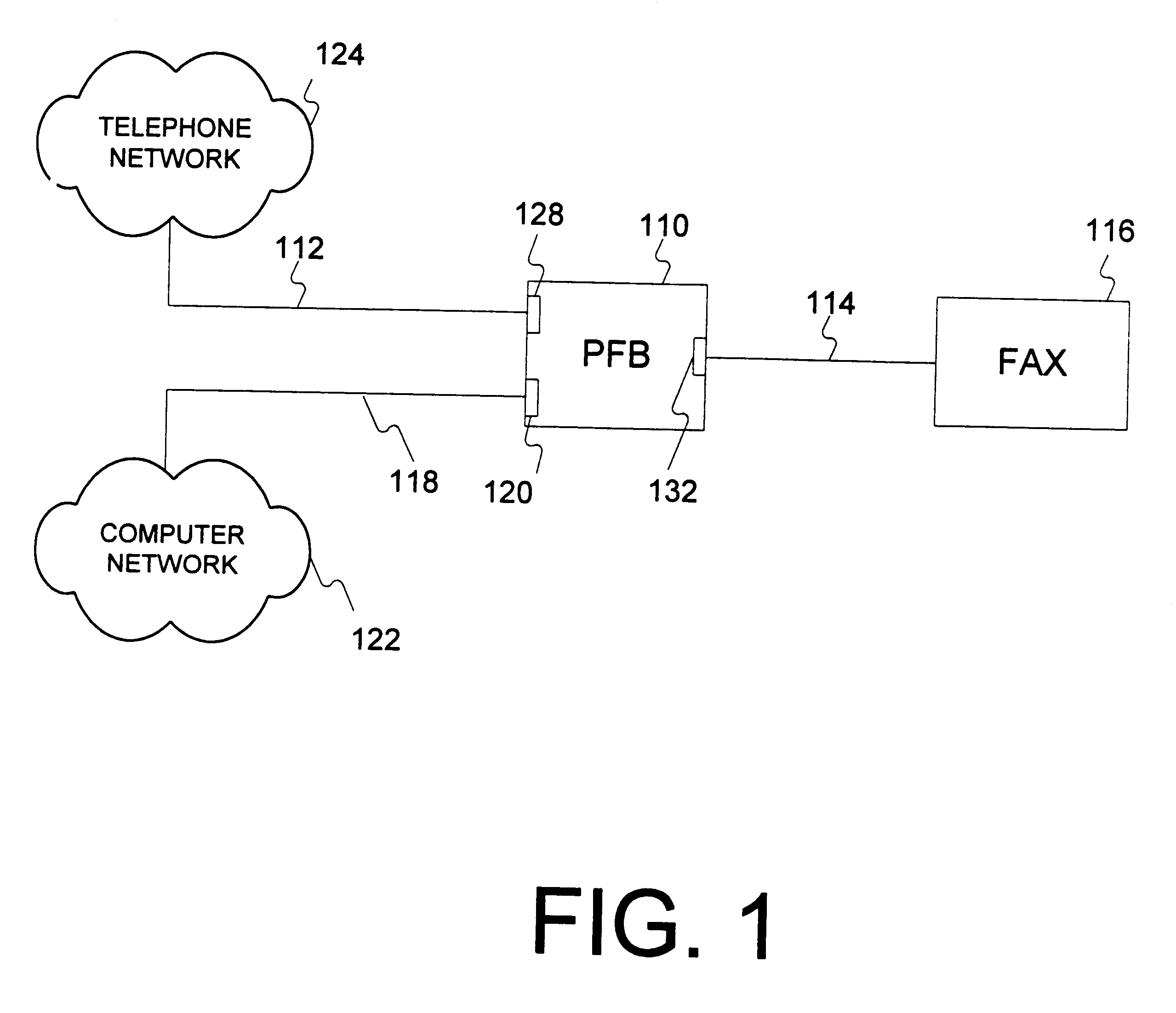
A Protocol Fax Box (PFB) receives information, determines destinations for the information, and converts the information protocol and data, if necessary, for transmission to the destinations. The PFB has plural interfaces from which it receives and sends data. Upon receiving information on one of its interfaces, the PFB creates a set of objects for handling the transfer of the information from the incoming interface to an outgoing, or destination, interface. A source object handles the incoming communication, a session object handles destination determination, and a destination object handles protocol conversion from the source interface to the destination interface. The session object also logs information regarding each session. The PFB may use a client server model to download information as needed from a network, or have processing be performed on the network.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
System and method for obtaining improved search results and for decreasing network loading
InactiveUS6195654B1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideClient–server model
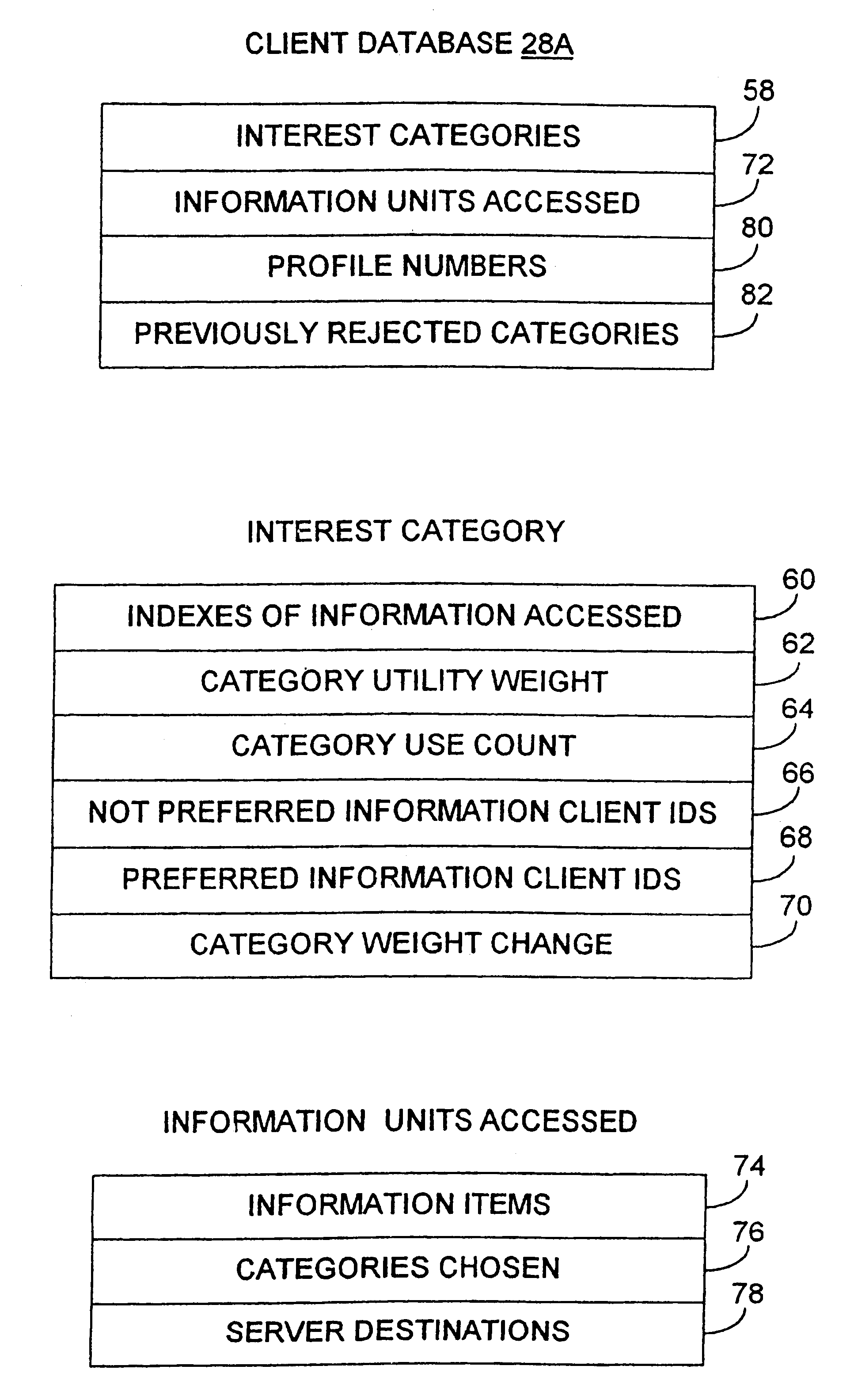
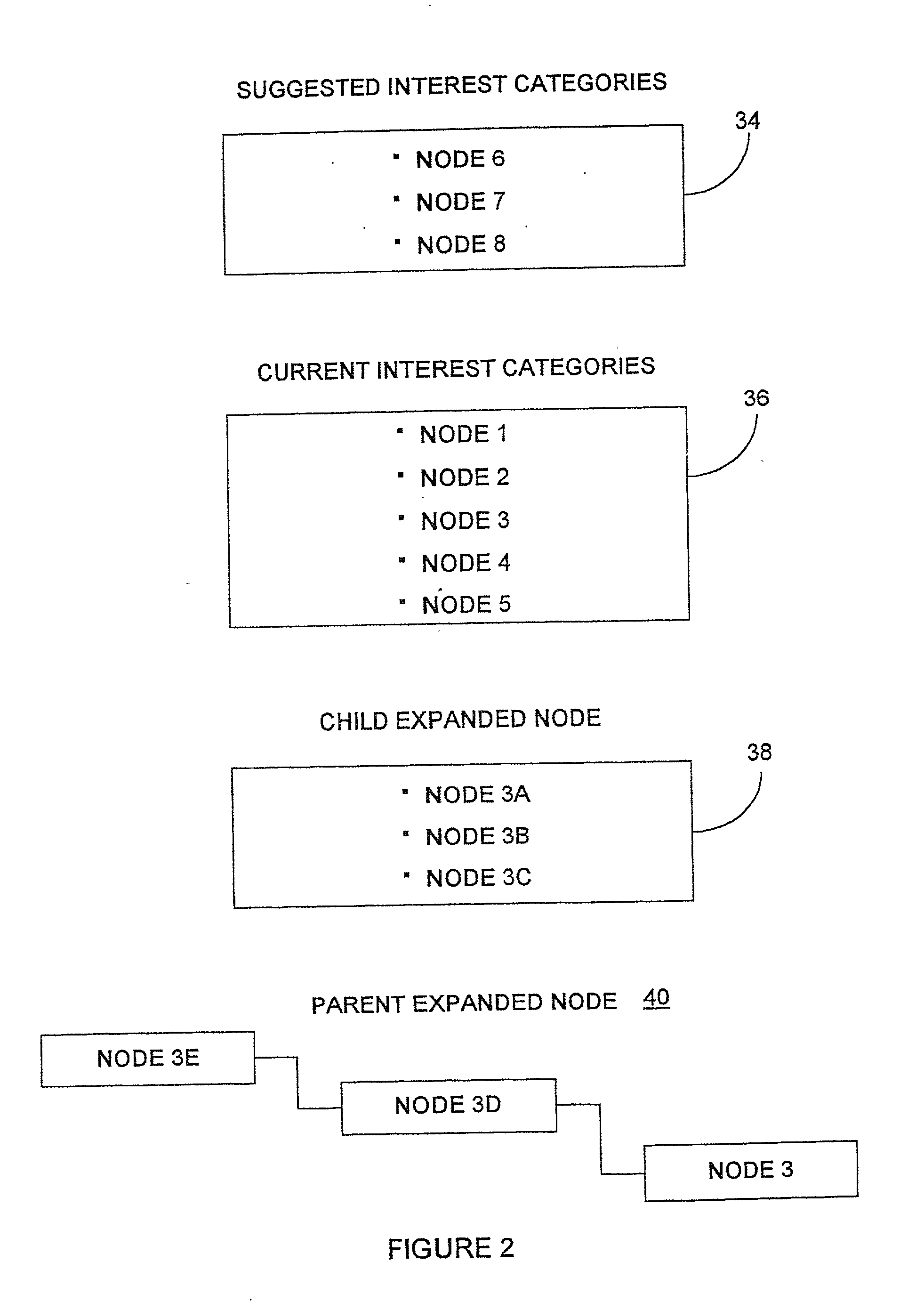
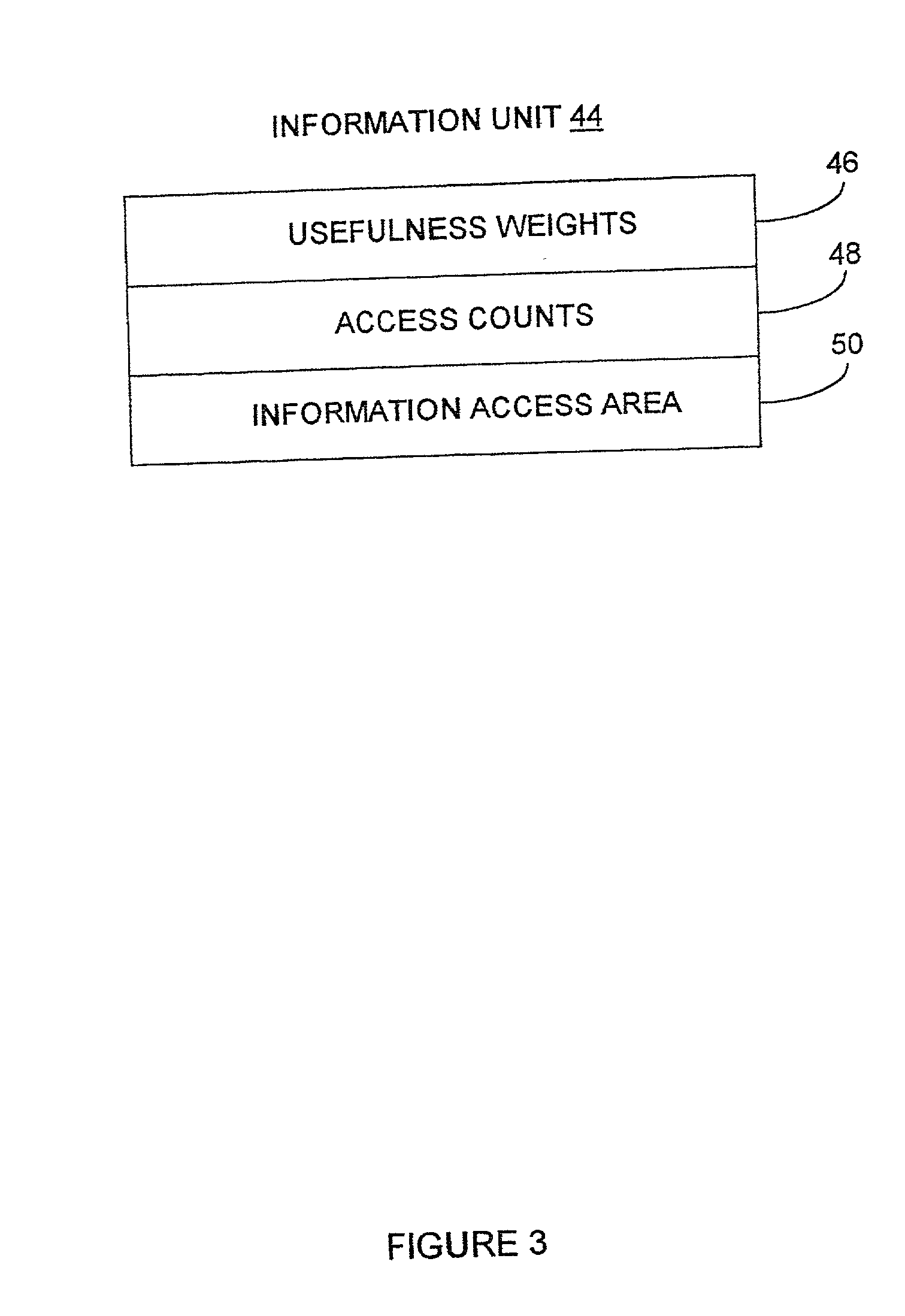
A networked information sharing model is described. The network described comprises a client-server model or a client only model. There exists a shared information database, a shared category database, a shared interest profile database and a shared client enhancement database, each of which is continually and dynamically updated. The shared category database contains categories of interests, within which are weighted and marked information units. Weights are arrived at by empirical use. Marks are maintained to distinguish where the information came from and to access information according to client source preference. The shared interest profile contains a set of profiles which clients are associated with. Useful client categories within profiles are offered when requested. A shared client enhancement list is maintained to identify and weight useful sources of information. A client specific database is maintained with client categories, preferred information sources, weights and weighted information access history. This database is used in conjunction with the shared databases to provide intelligent information sharing.
Owner:CHARTOLEAUX
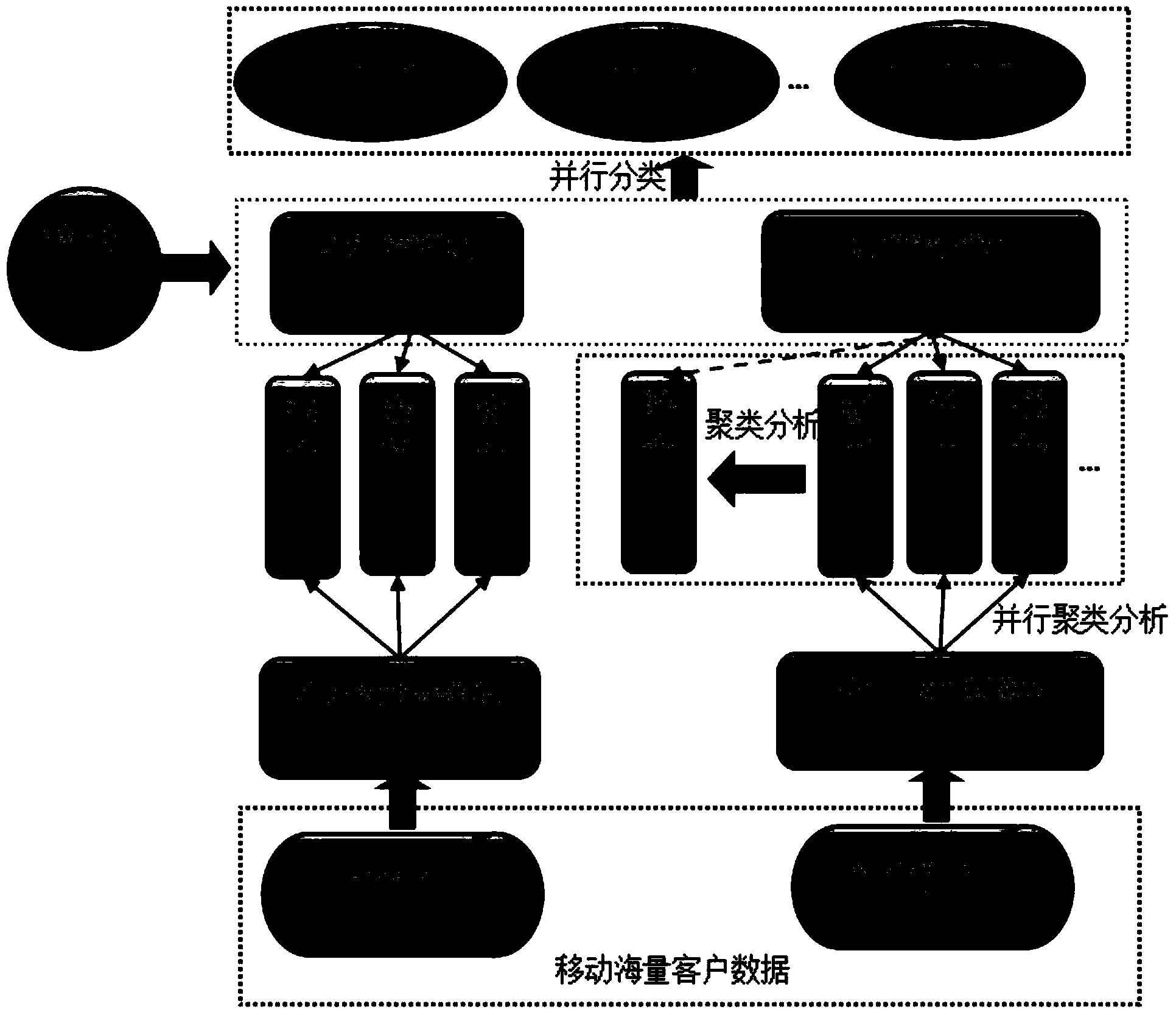
Parallel data mining method for identifying a mass of mobile client bases
ActiveCN103714139AStrong reference valueEfficient data mining analysisMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetPurchasing
The invention discloses a parallel data mining method for identifying a mass of mobile client bases. The parallel data mining method includes the steps of building a client value model and a client behavior model, classifying clients according to the client value model and the client behavior model, popularizing assigned preference services to the clients with the high purchasing power and the high potential purchasing inclination, and then achieving accurate marketing. According to the parallel data mining method, the mass of mobile client bases can be identified, the aspects such as Internet surfing time preferences, Internet surfing place preferences and browsed website preferences of the clients can be identified, and the social group classes of the clients can be accurately judged. Clustering and classifying can be rapidly carried out through the adopted parallel clustering algorithm and the adopted parallel classifying algorithm. By means of the parallel data mining method, different strategies can be formulated for the different client bases by an enterprise, and the important guiding function for profit maximization of the enterprise is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
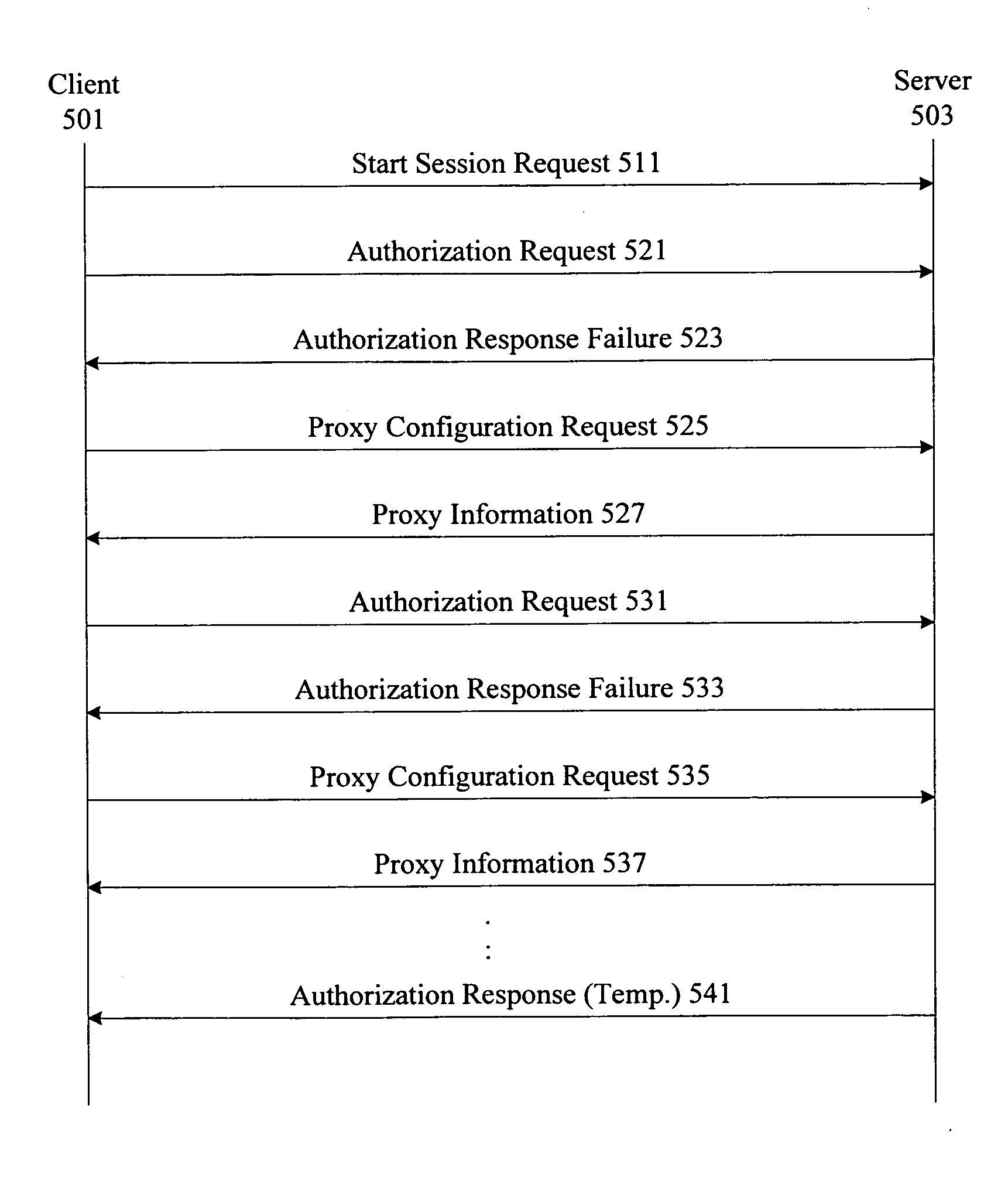
Maintaining session state information in a client server system
InactiveUS20080195740A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationTime informationClient server systems
Techniques and mechanisms are provided for maintaining session state information in a client server system. Session state information such as session state, time stamp information, activity state, counters, etc. are generated and updated by a server. The session state information is sent in encrypted form to a client and the client maintains the encrypted information. The client is not able to decipher or alter the encrypted information. The client sends the encrypted session state information in requests to the server. The server is able to respond intelligently using session state information from the client. Session state information no longer has to be maintained or replicated by session state managers associated with servers.
Owner:MOBITV
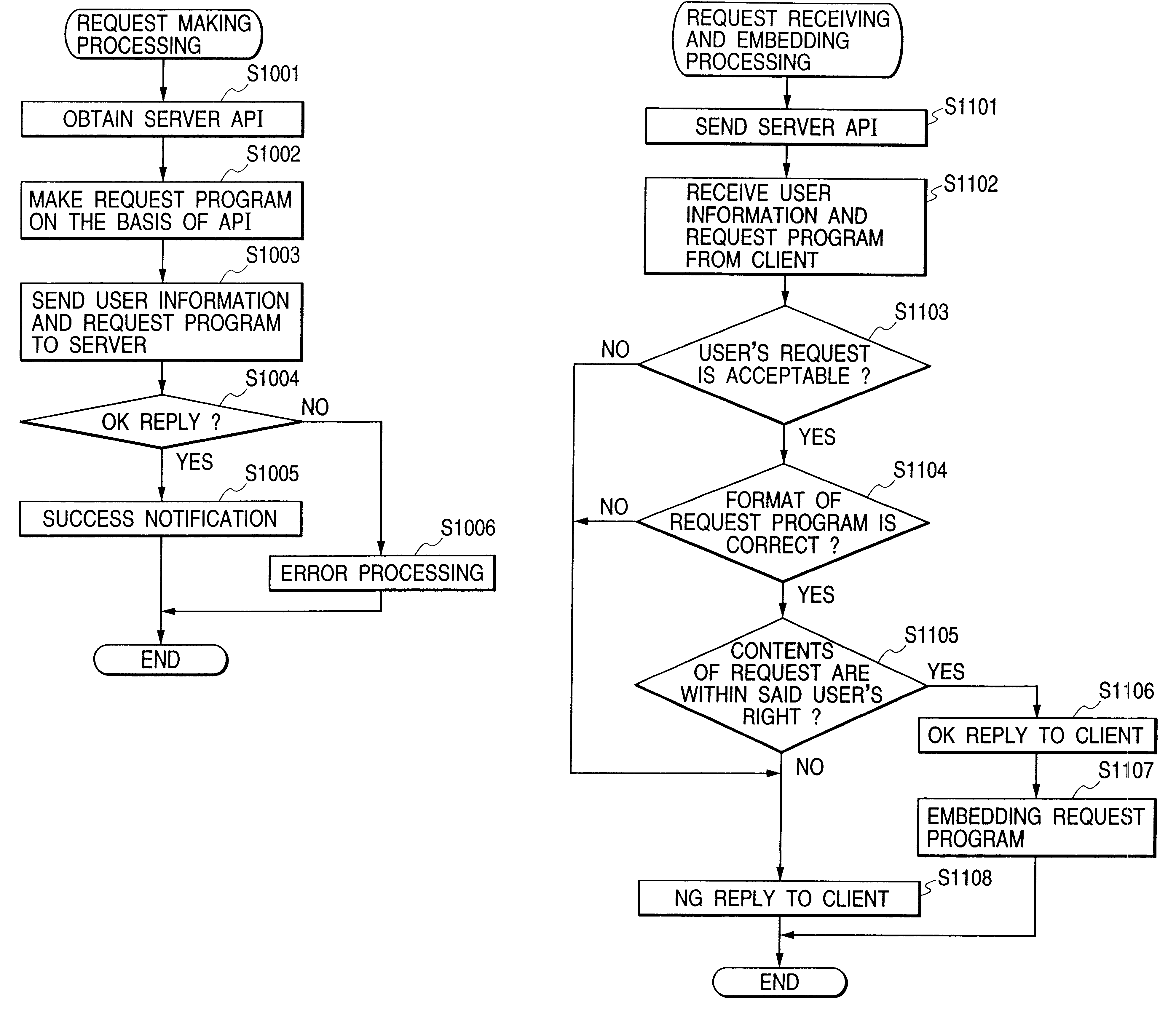
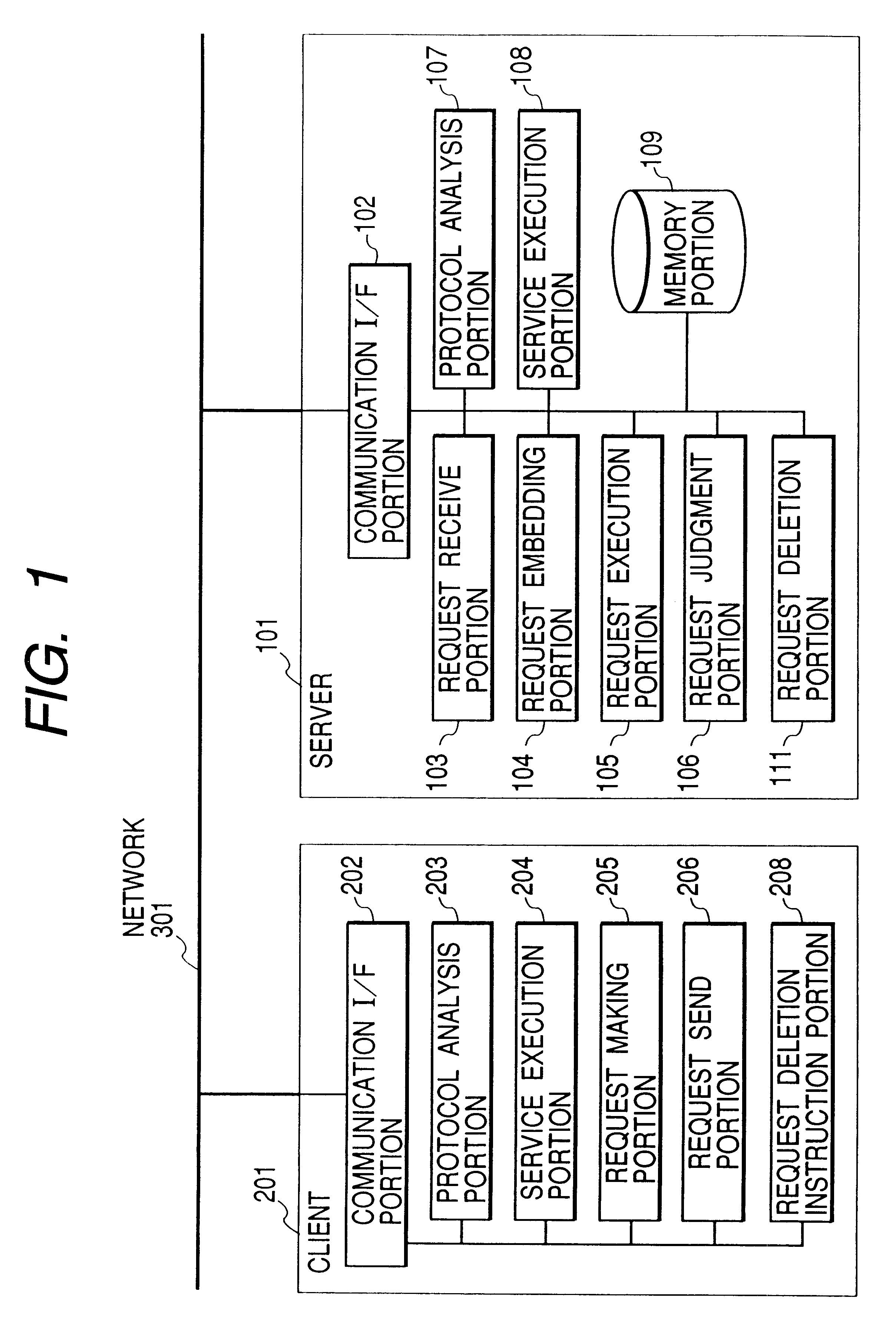
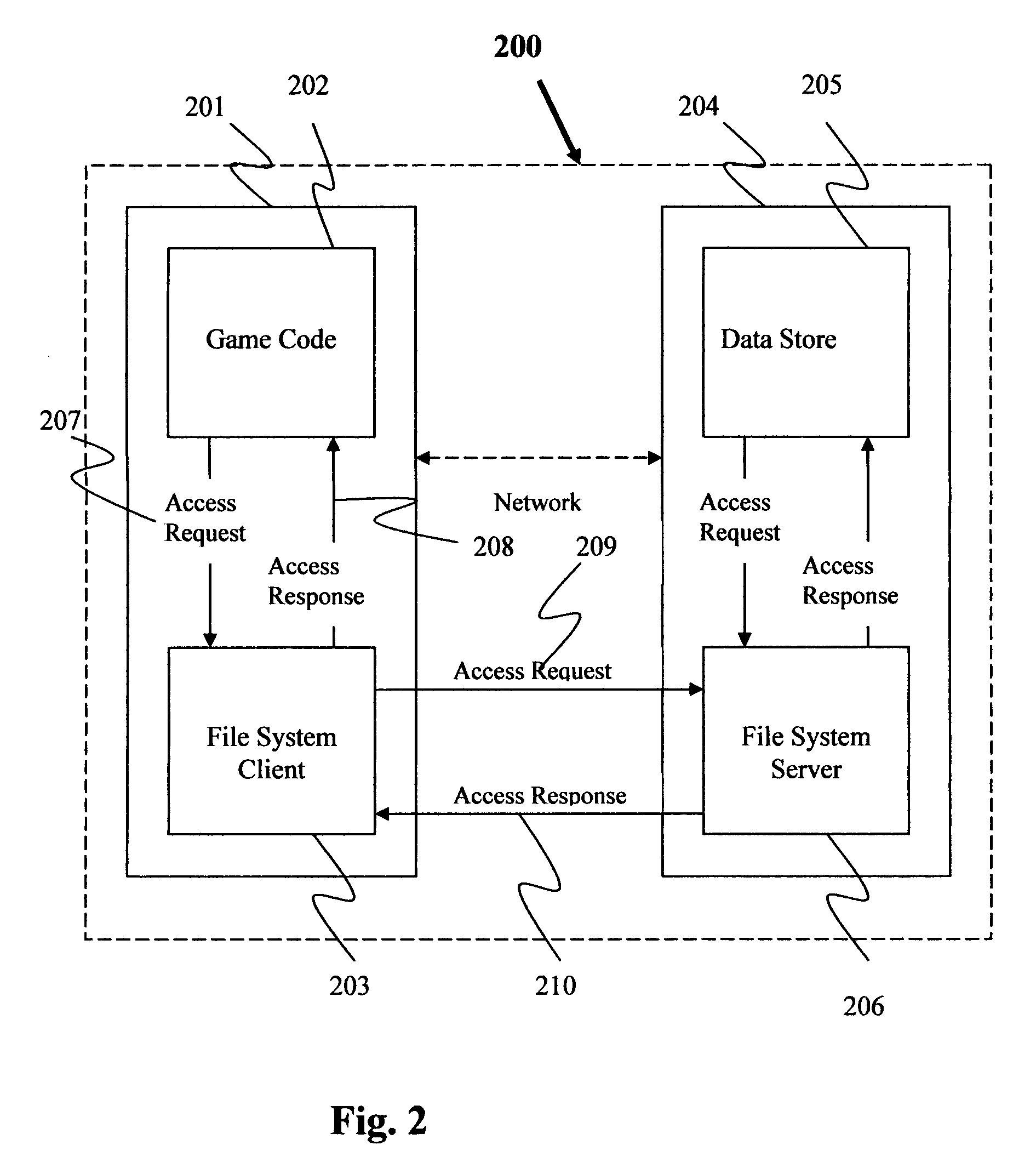
Server, client, client server system, method for controlling them and storage medium therefor
InactiveUS6529943B1Operational securityReduce the burden onDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsClient server systemsClient-side
Part of the functionality and information of a server is published to a client, and the client makes a request based on this information, and before embedding the request from the client into processing, a server determines whether the request is invalid. In addition, before the processing is executed into which the request from the client has been embedded, whether the request is invalid is determined again.This configuration enables a detailed request from the client to be safely embedded into the server's processing and also enables the server and system to be stably operated.
Owner:CANON KK
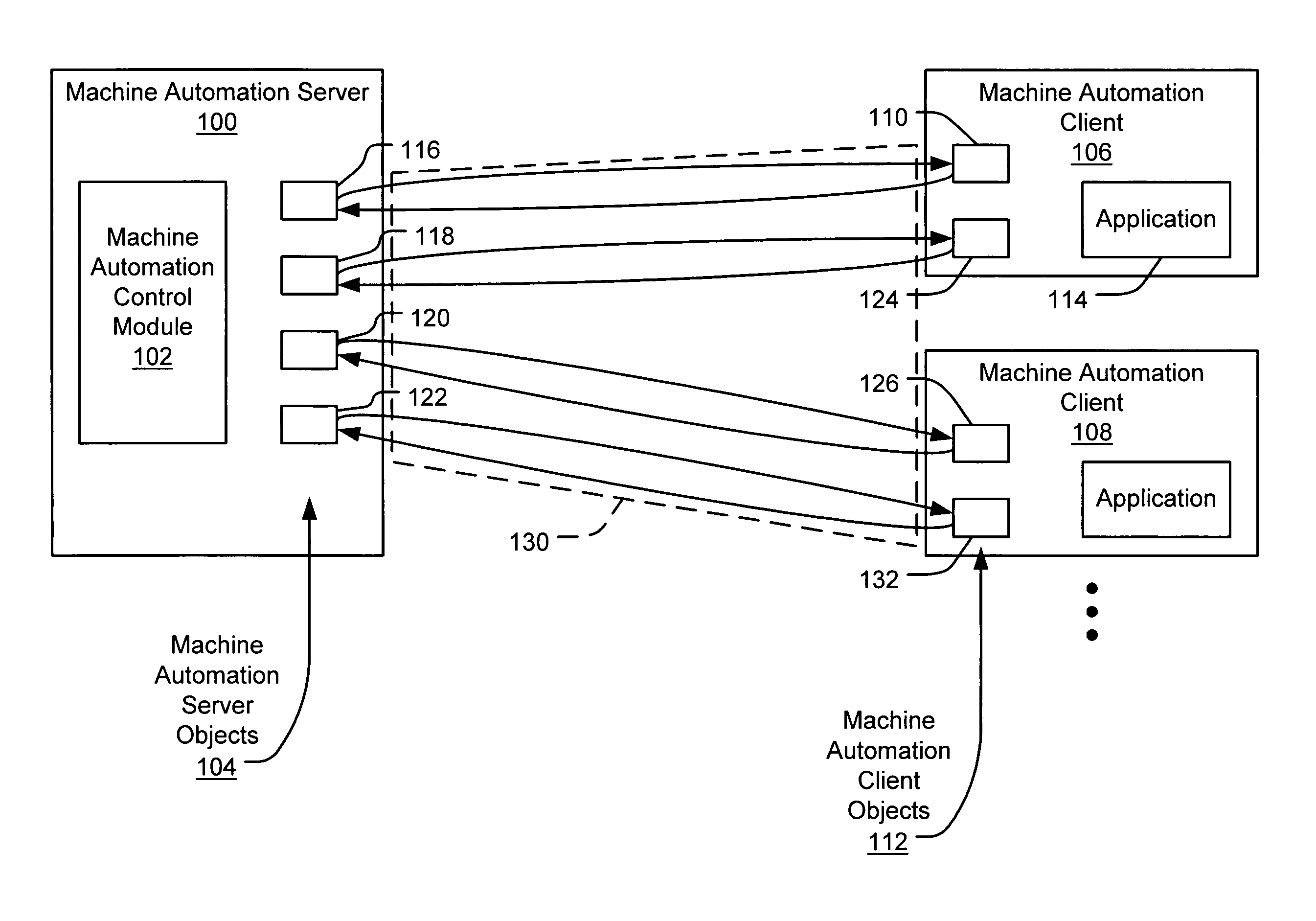
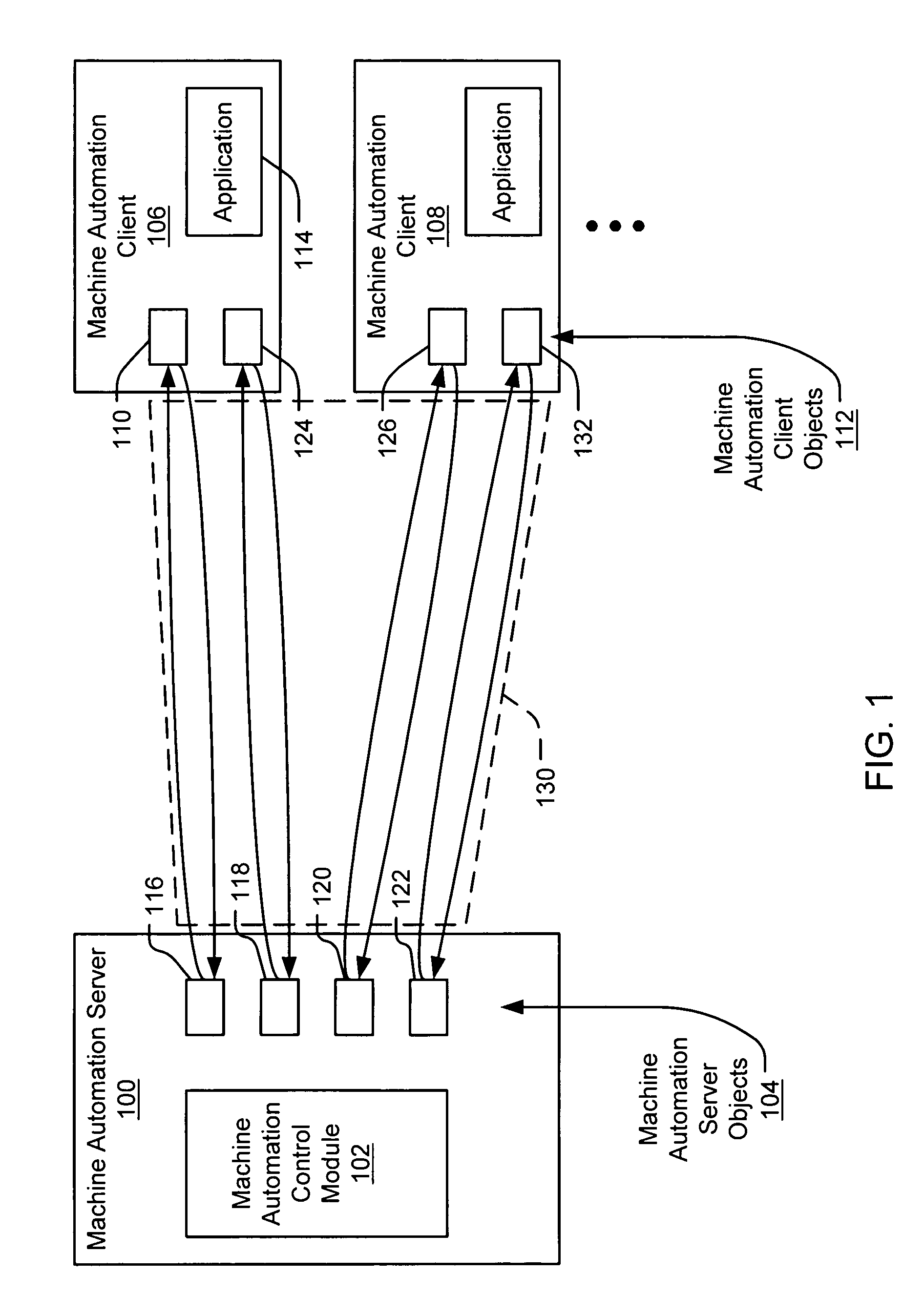
Object-based machine automation method and system
Automation objects are implemented in a client-server model to control operations on one or more client machines from a single machine automation control module, such as a test program. The machine automation control module instantiates machine automation server objects in a server process. The control module can then instruct the server objects to instantiate corresponding machine automation client objects on specified client machines via a connection mechanism. Object-oriented automation classes are provided in a library and may be extended to meet customized requirements of a given testing procedure. Examples of automation objects may include, without limitation, application objects, machine image objects, snapshot objects, file and registry access objects, reboot objects, autologon objects, and command execution objects. Automation objects allow the re-establishment of remote control after the loss of control resulting from a reboot, a relogon, or a disk image restoration, for example. Automation objects may also be used to automate the deployment of software throughout an enterprise.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
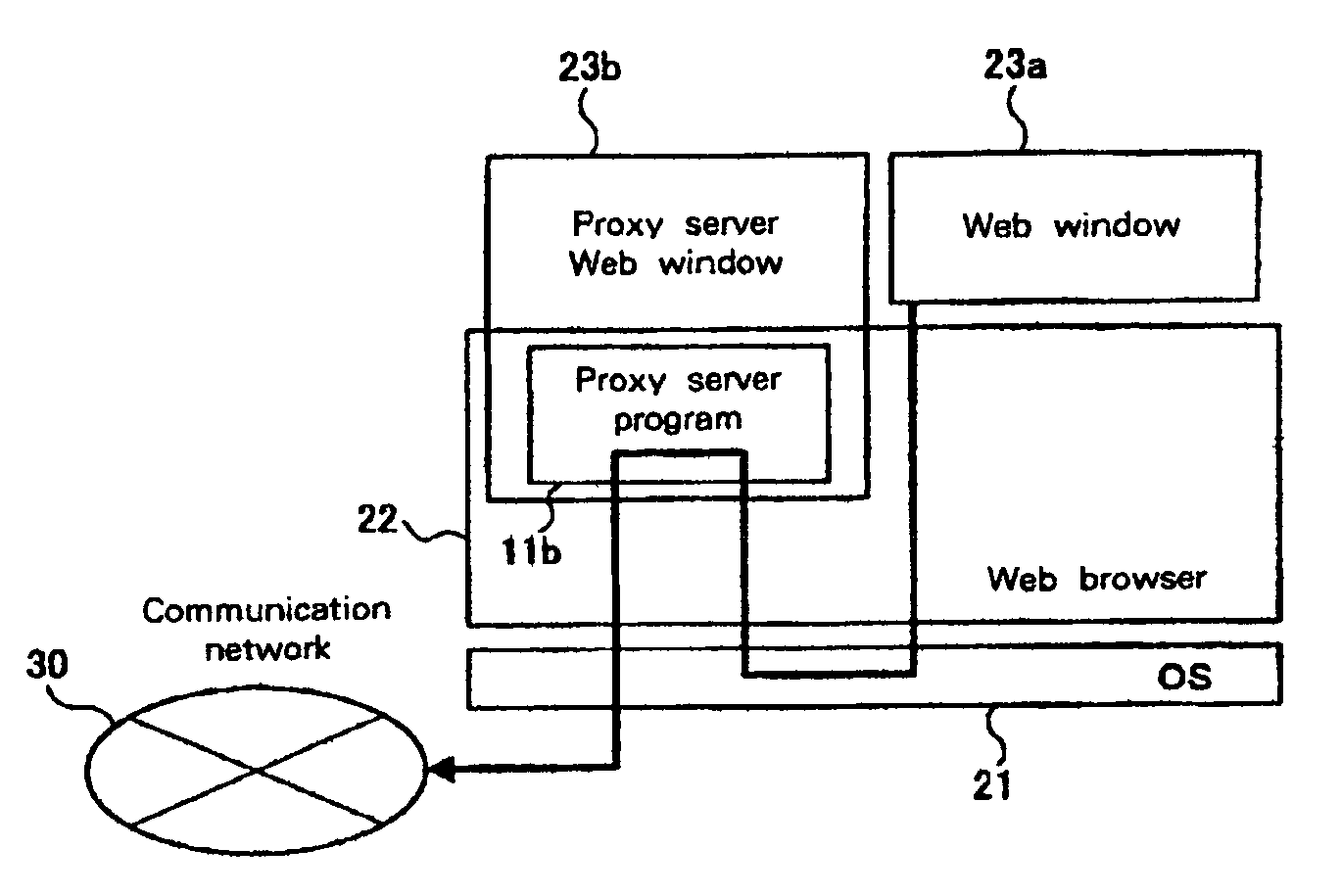
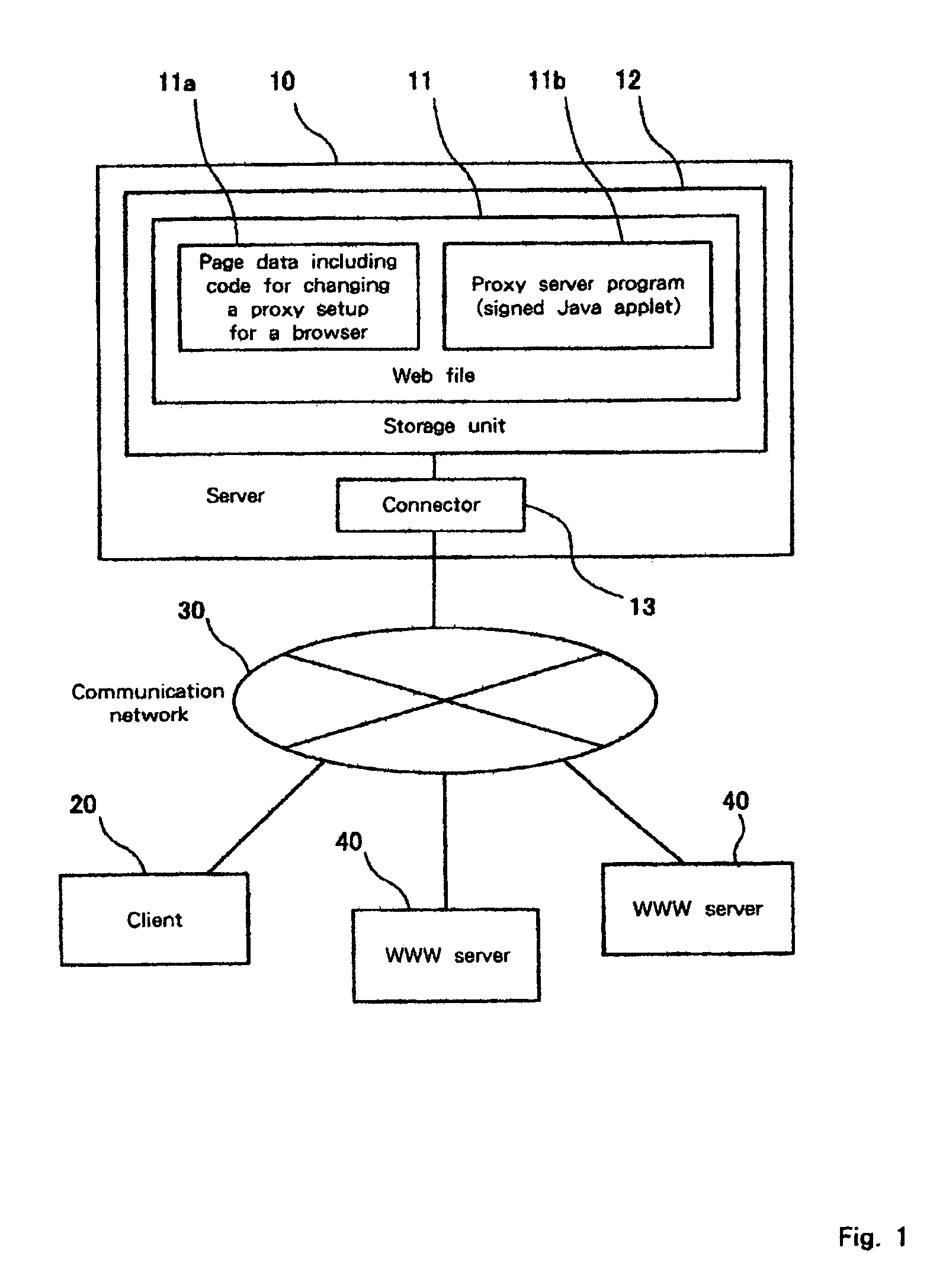
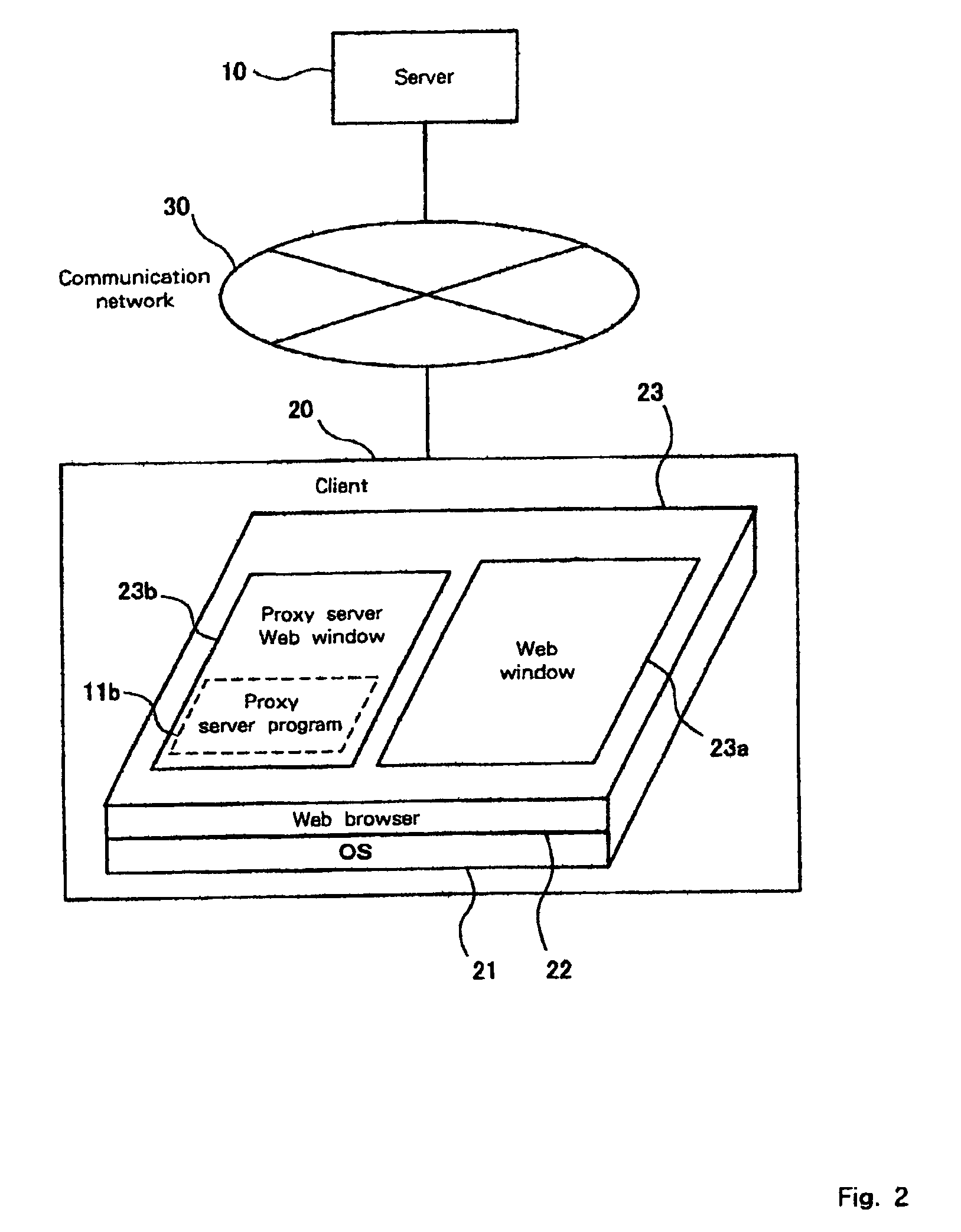
Client server system, server, client, proxy server control method, proxy server function provision method, storage medium and program transmission apparatus
InactiveUS7133904B1Easy to useApplied load reductionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWeb browserClient server systems
A network system comprises: a WWW server 40 for executing a server process; a server 10 for providing a proxy server function; a client 20, which is connected to a communication network 30 for accessing the WWW server 40 and the server 10. The server 10 stores a Web file 11 that includes a proxy server function that can be displayed as a Web page by a Web browser, and that can be read and activated by the Web browser. The client 20 incorporates the Web browser that displays a Web page based on the Web file 11, which is downloaded from the server 10 via the communication network 30. When the Web file 11 is read by the Web browser, the proxy server function of the Web file 11 is initiated.
Owner:IBM CORP
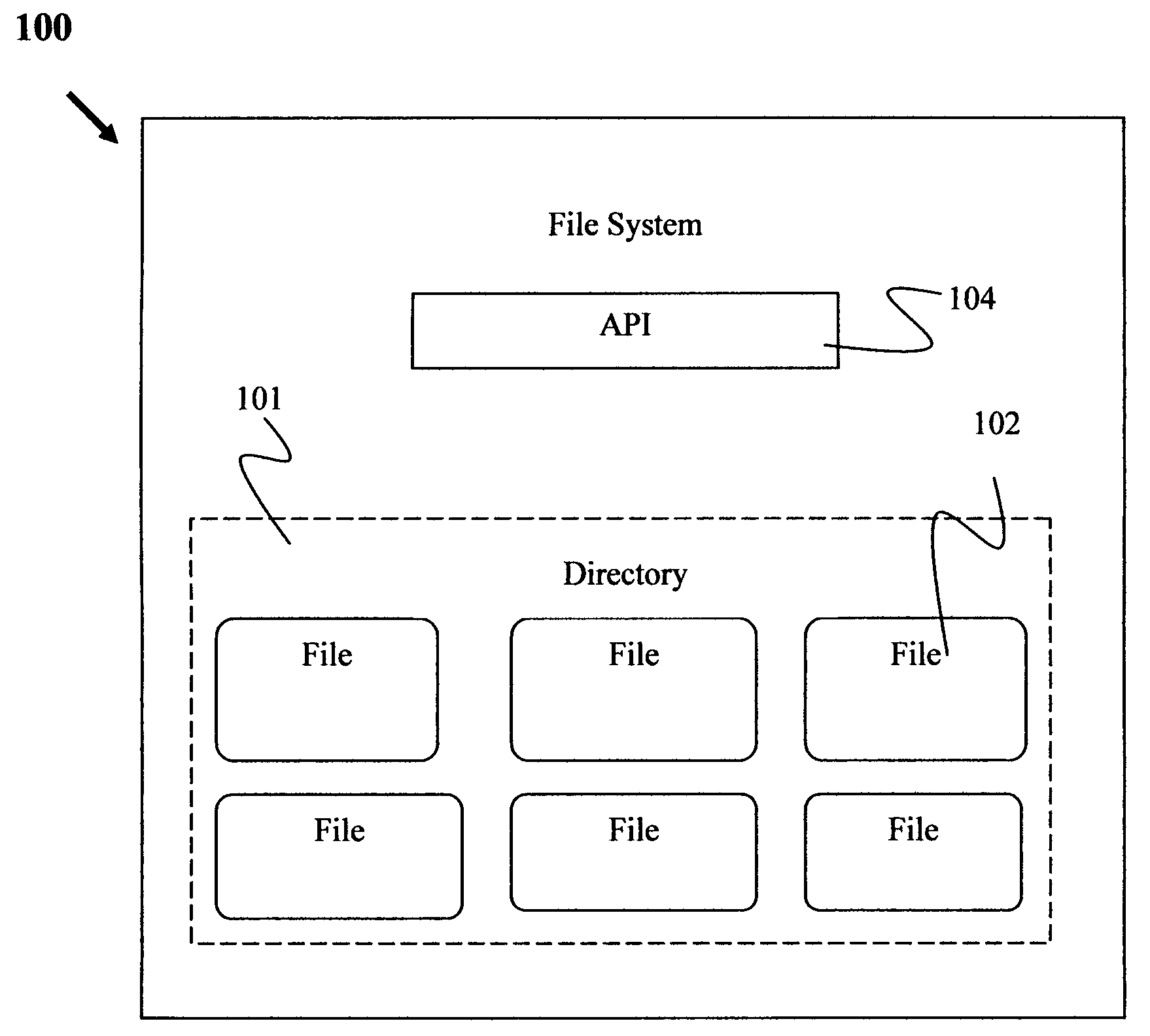
Self-authenticating file system in an embedded gaming device
InactiveUS20080009337A1Digital data protectionApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingOperational systemRemote system
A method and apparatus for pre-load authentication suitable for use with an operating system in an embedded gaming device. A user-space file system that can automatically authenticate its contents is disclosed. The user-space file system can be deployed on a standalone system or using a client-server model such that a remote system server can coordinate with a local client to perform authentication. By moving the authentication into the file system functional block there is additional assurance that any game code or data stored in the file system cannot be accessed without first performing the required authentication.
Owner:MTD GAMING
Client server system
InactiveUS7924451B2Easy to sendWithout causing a user have an uncomfortable feelingMultiple digital computer combinationsClosed circuit television systemsImage resolutionDisplay device
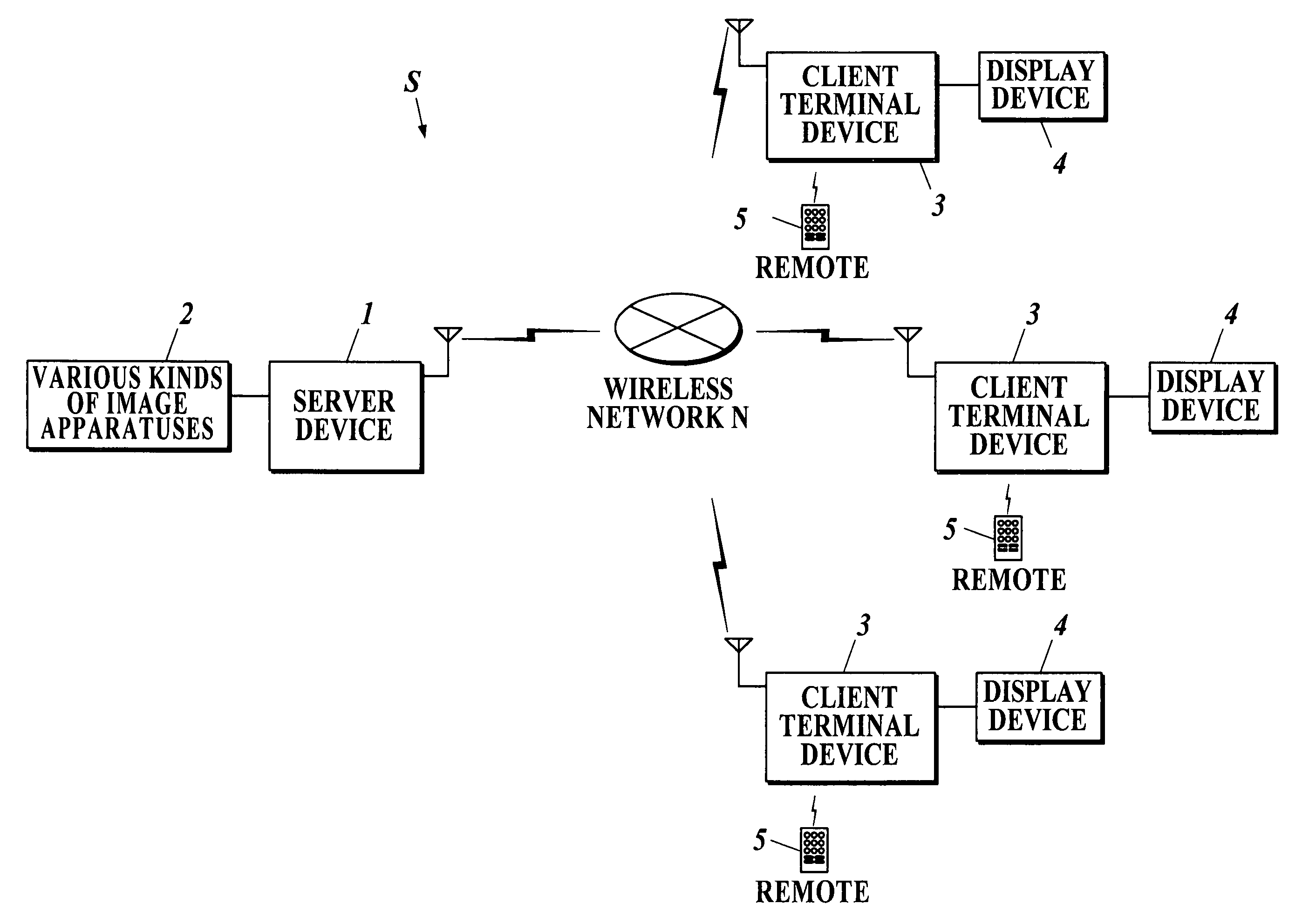
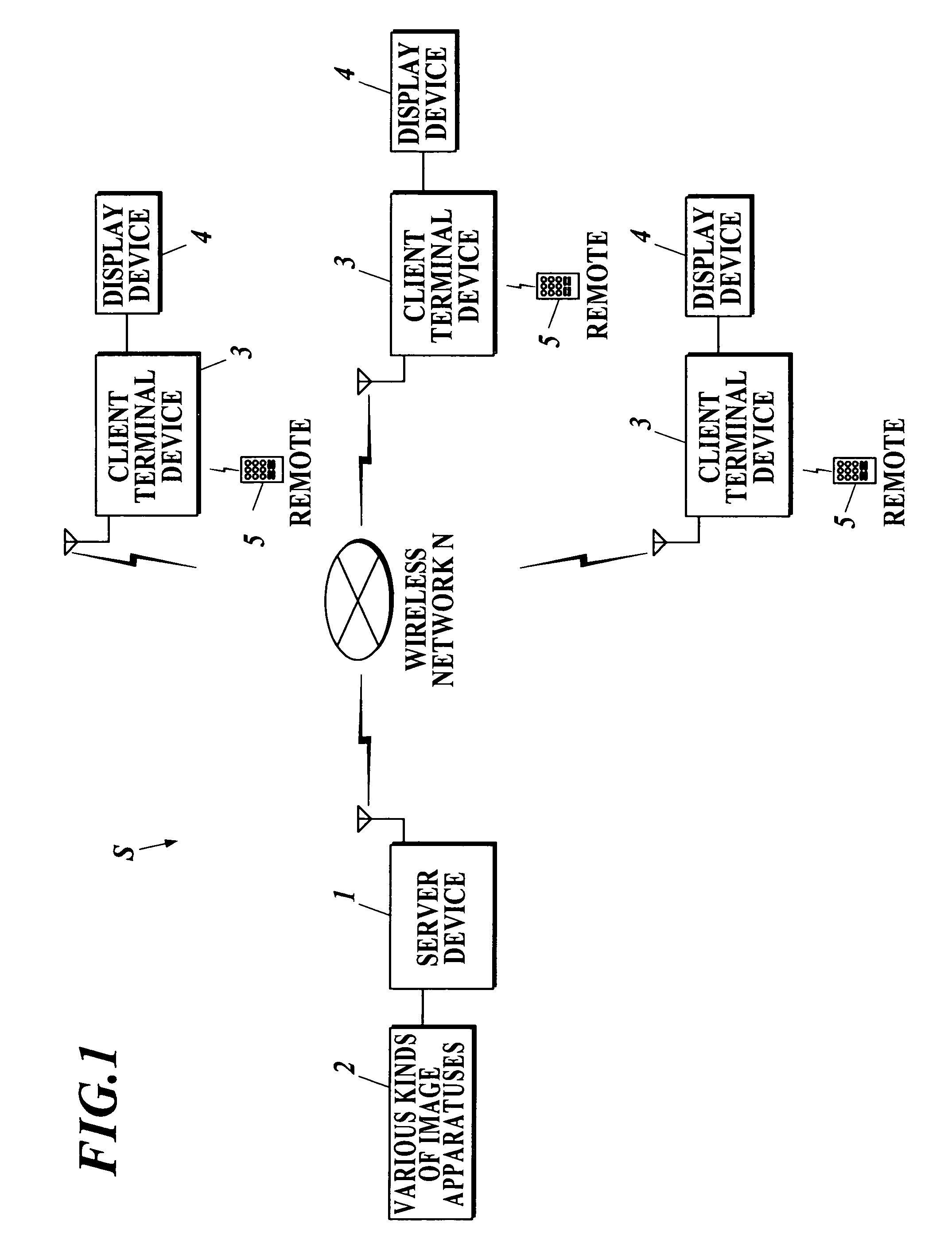
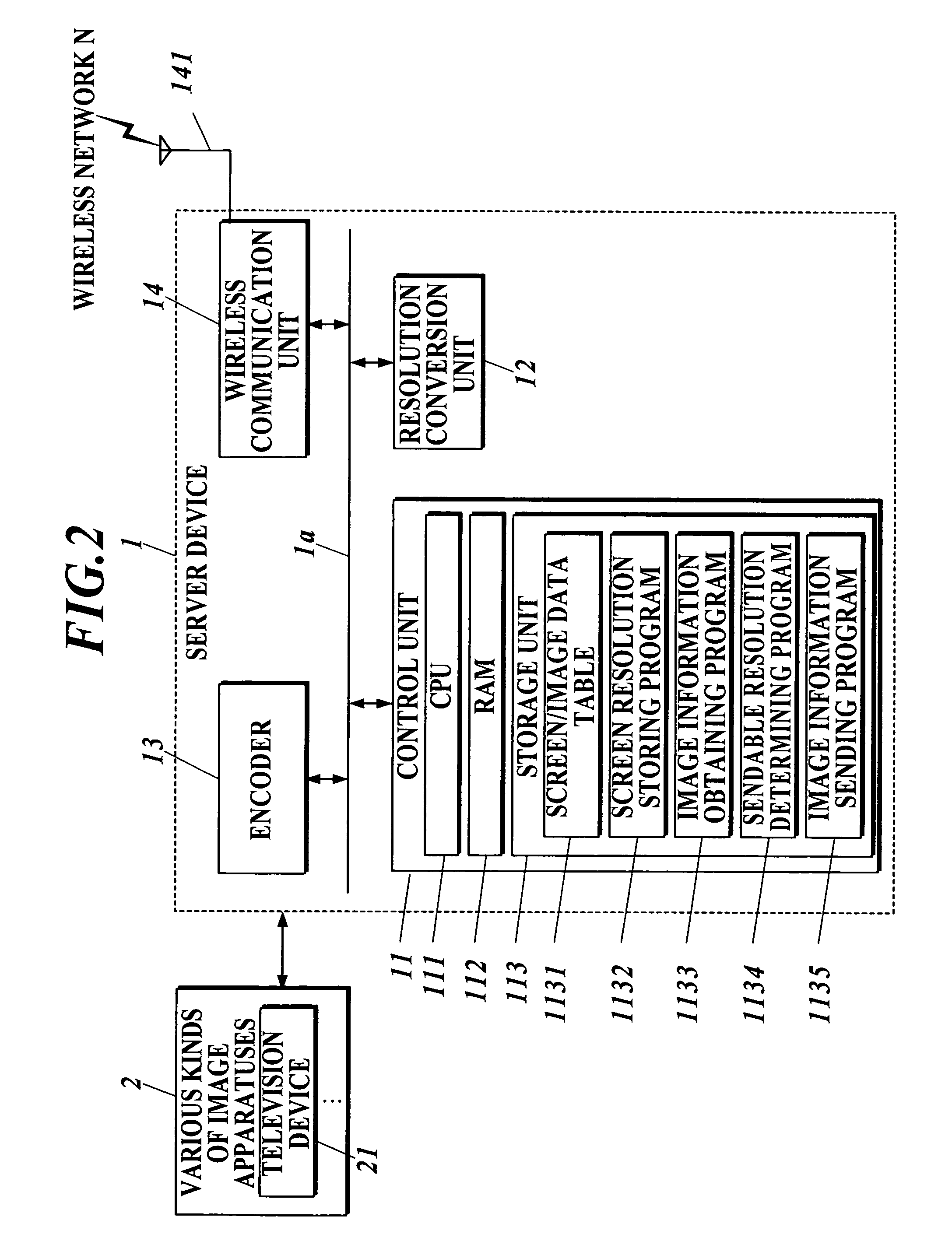
A client server system S includes a plurality of client terminal devices 3 capable to connect with display device 4, whose screen resolution is HD or SD, and a server device which provides image information to the plurality of client terminal devices s through wireless network N. The server device 1 is structured to include a sendable resolution determining program 1134 to make CPU 111 determine whether to convert HD image information into SD image information or not, and an image information sending program 1135 to make the CPU 111 send SD image information attached with SD information to the plurality of client terminal devices 3.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Intelligent networked information sharing
InactiveUS20010005847A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation sharingInformation access
A networked information sharing model is described. The network described comprises a client-server model or a client only model. There exists a shared information database, a shared category database, a shared interest profile database and a shared client enhancement database, each of which is continually and dynamically updated. The shared category database contains categories of interests, within which are weighted and marked information units. Weights are arrived at by empirical use. Marks are maintained to distinguish where the information came from and to access information according to client source preference. The shared interest profile contains a set of profiles which clients are associated with. Useful client categories within profiles are offered when requested. A shared client enhancement list is maintained to identify and weight useful sources of information. A client specific database is maintained with client categories, preferred information sources, weights and weighted information access history. This database is used in conjunction with the shared databases to provide intelligent information sharing.
Owner:EDWA NETWORKS LIMITED LIABILITY
Authentication in a smart thin client server
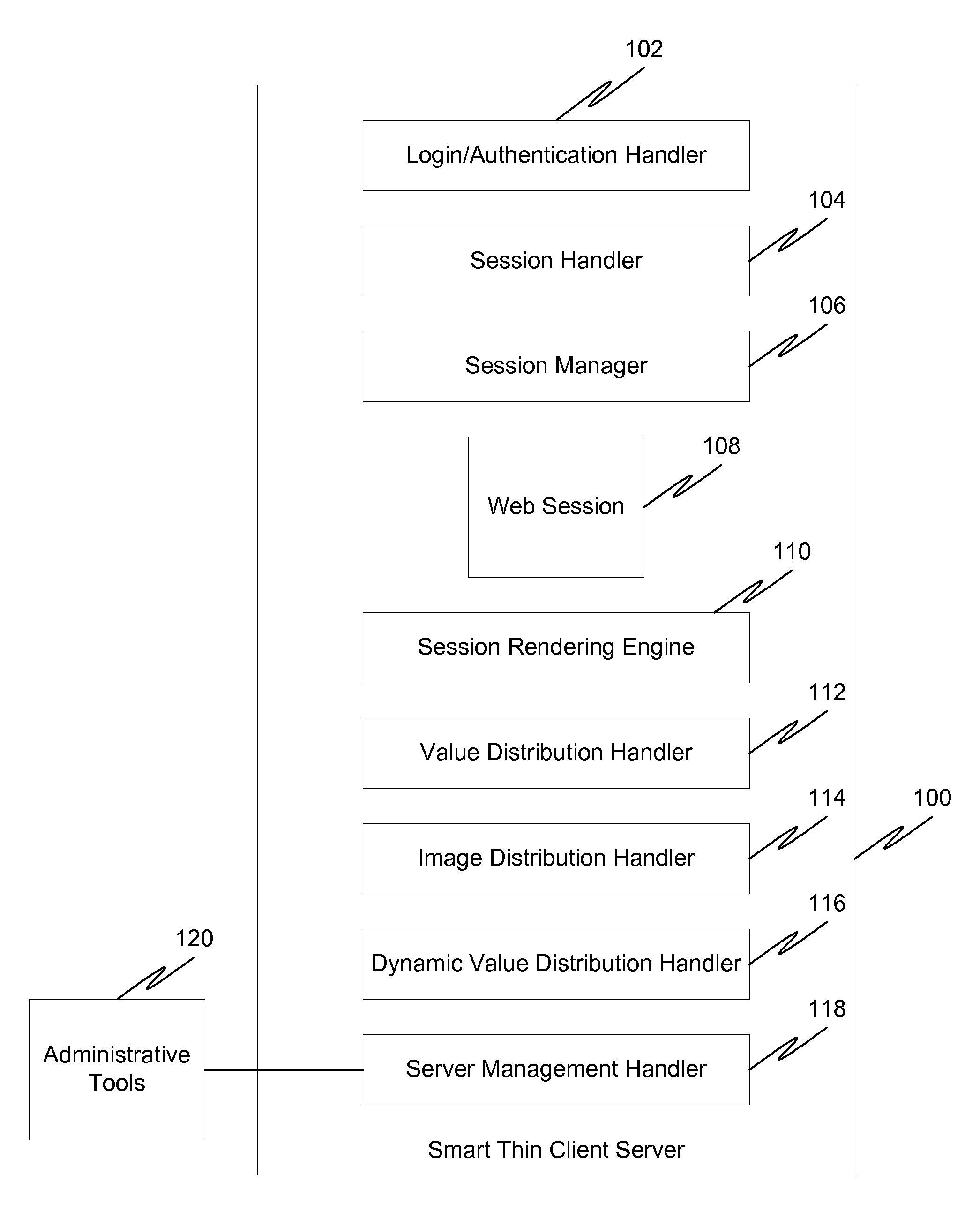
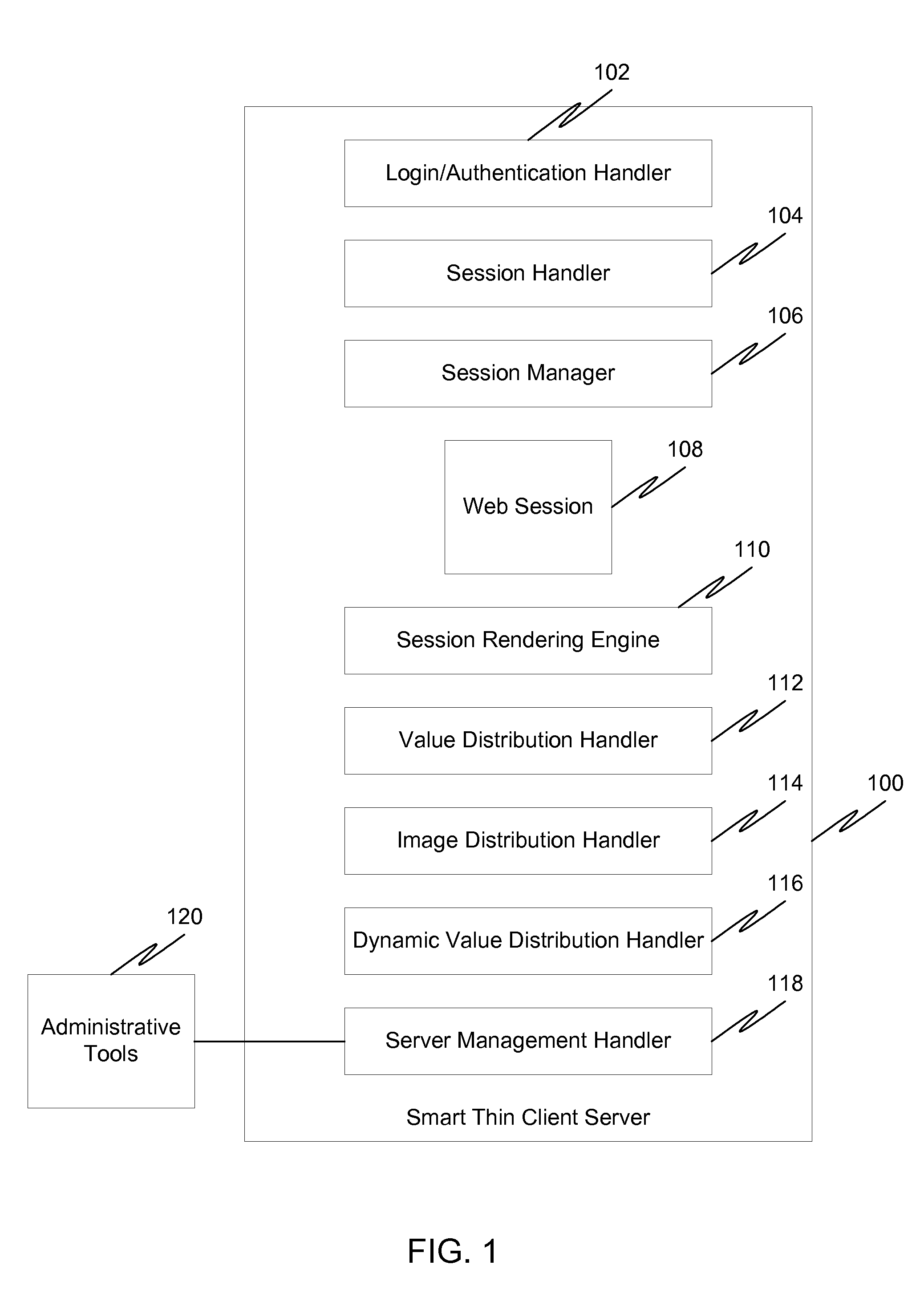
InactiveUS20130042312A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideThin client
In a first embodiment of the present invention, a method for starting a session between a user and a smart thin client server is provided, wherein the smart thin client server permits users to create, manage, and deploy enterprise applications, the method comprising: receiving a request to initiate a session from a user, wherein the request does not include log-in credentials; selecting an anonymous account from a pool of anonymous accounts; obtaining credentials from the anonymous account; and establishing a session for the user using the credentials from the anonymous account.
Owner:MOBILEFRAME
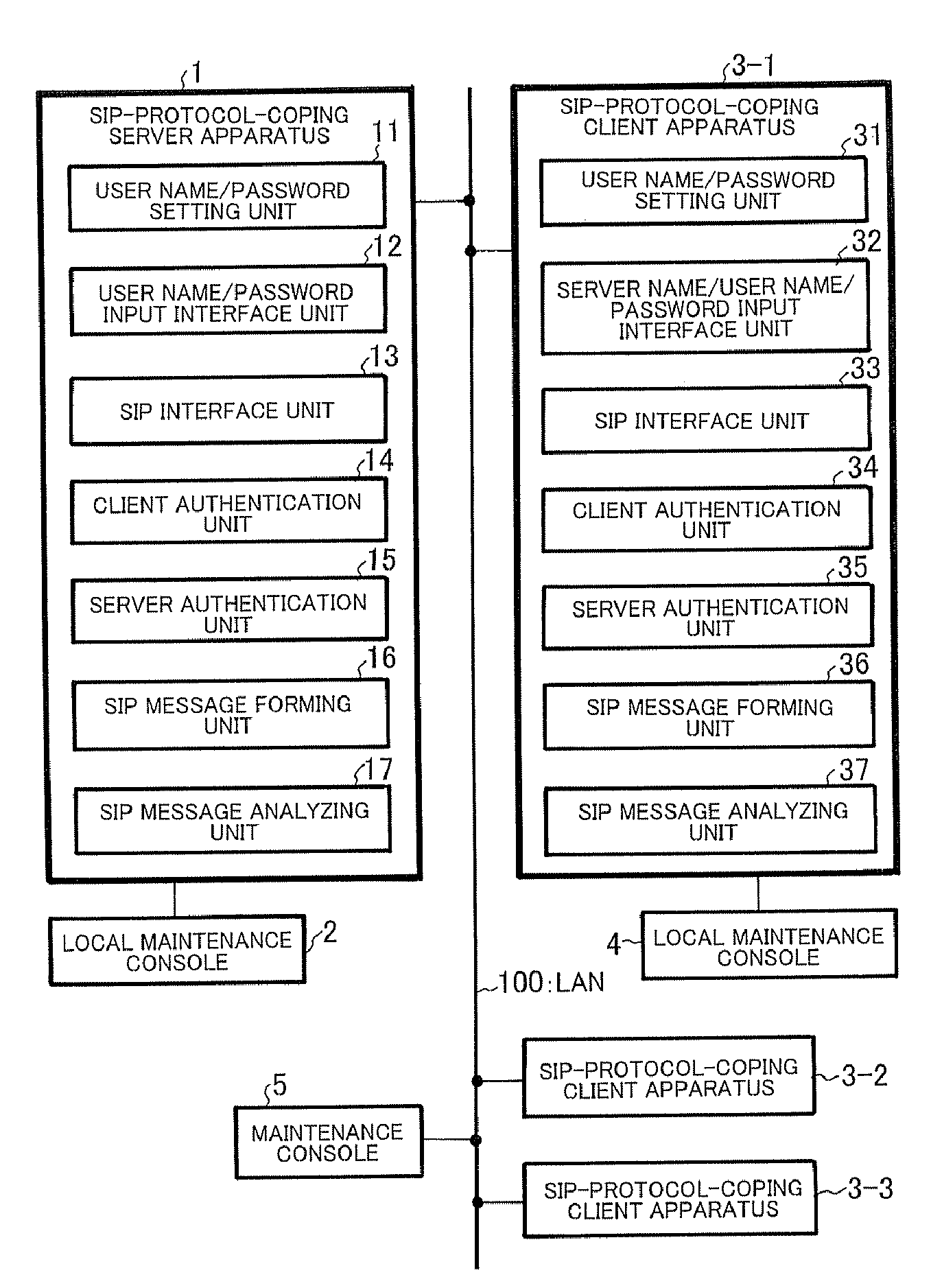
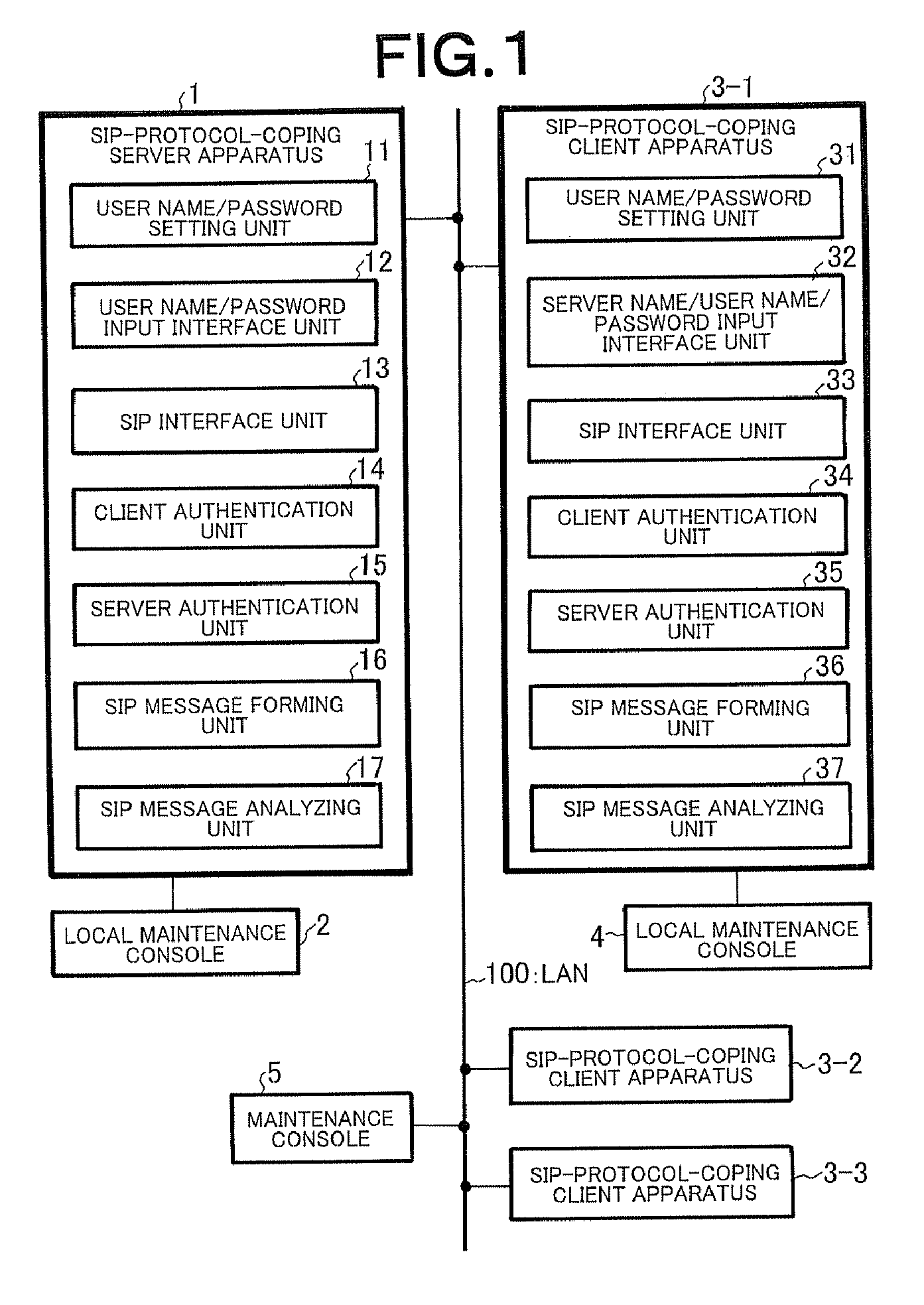
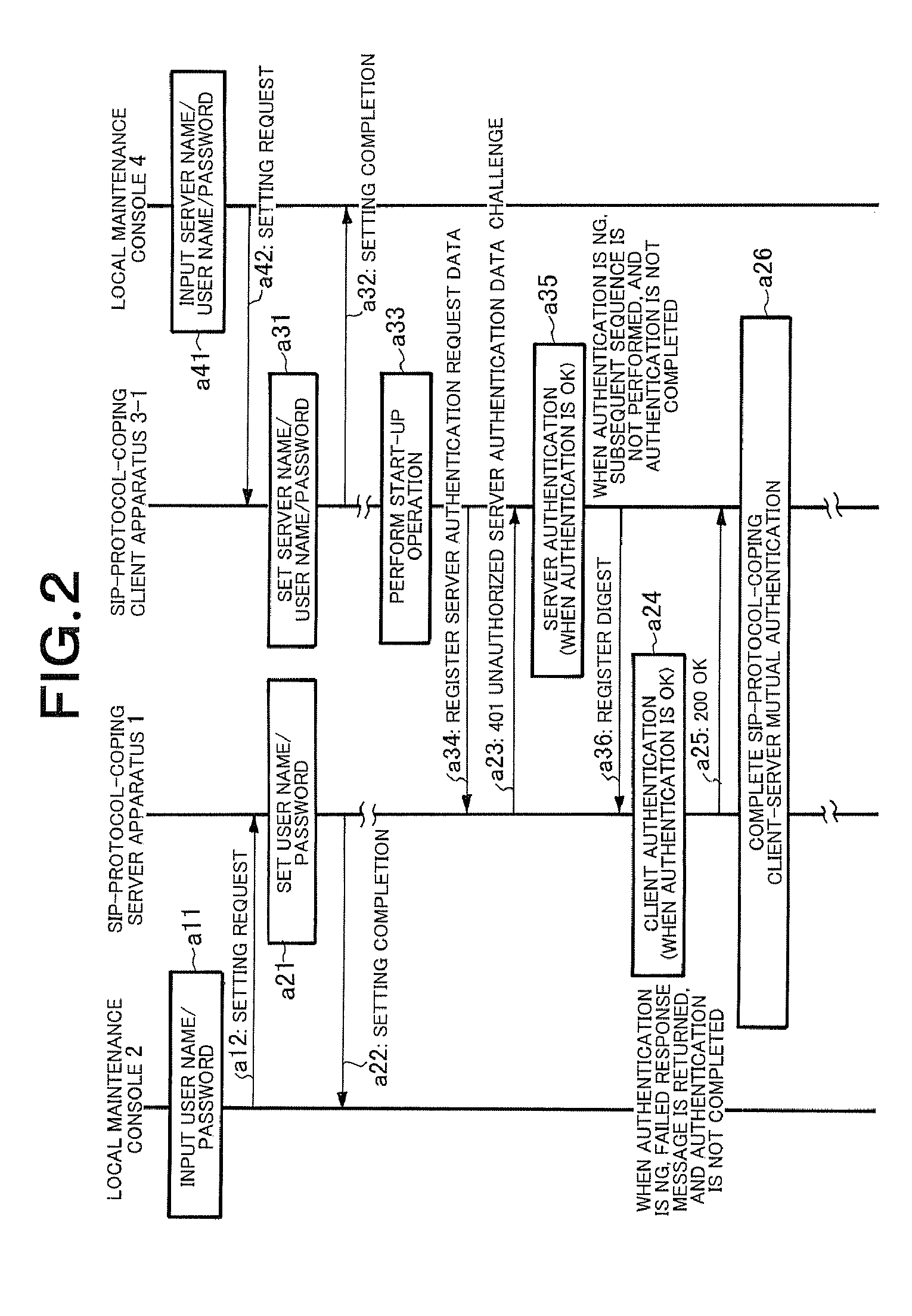
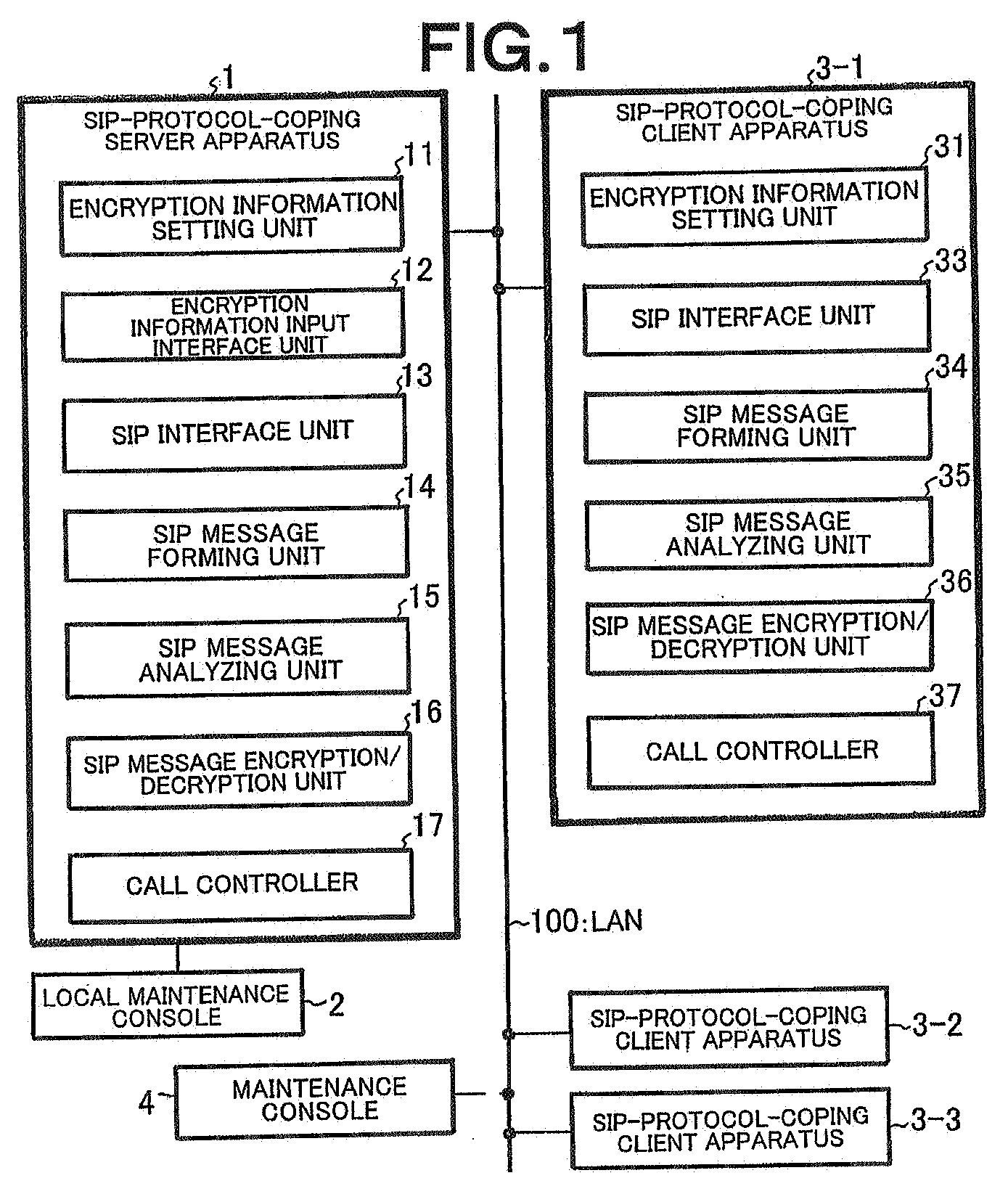
Client server distributed system, client apparatus, server apparatus, and mutual authentication method used therein
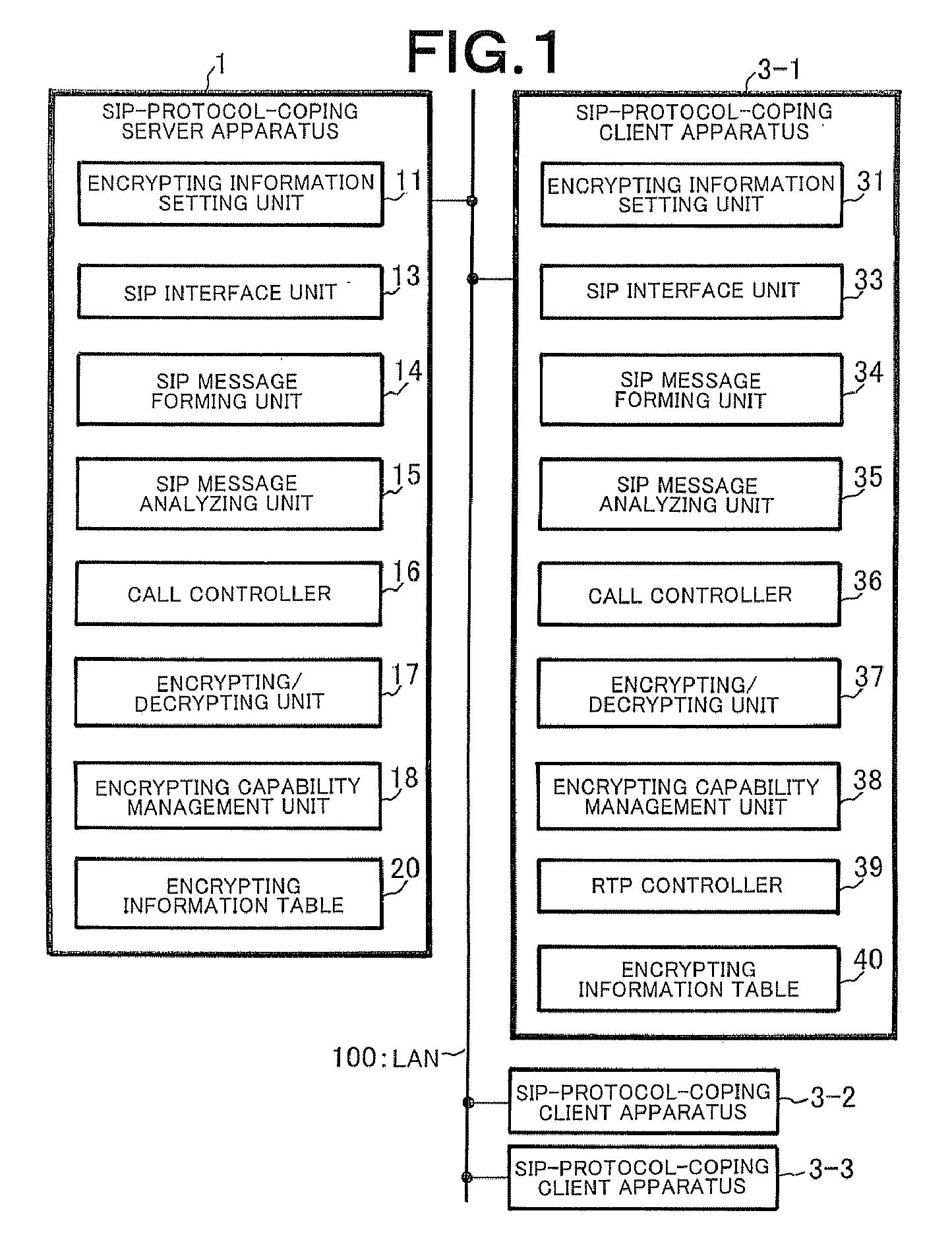
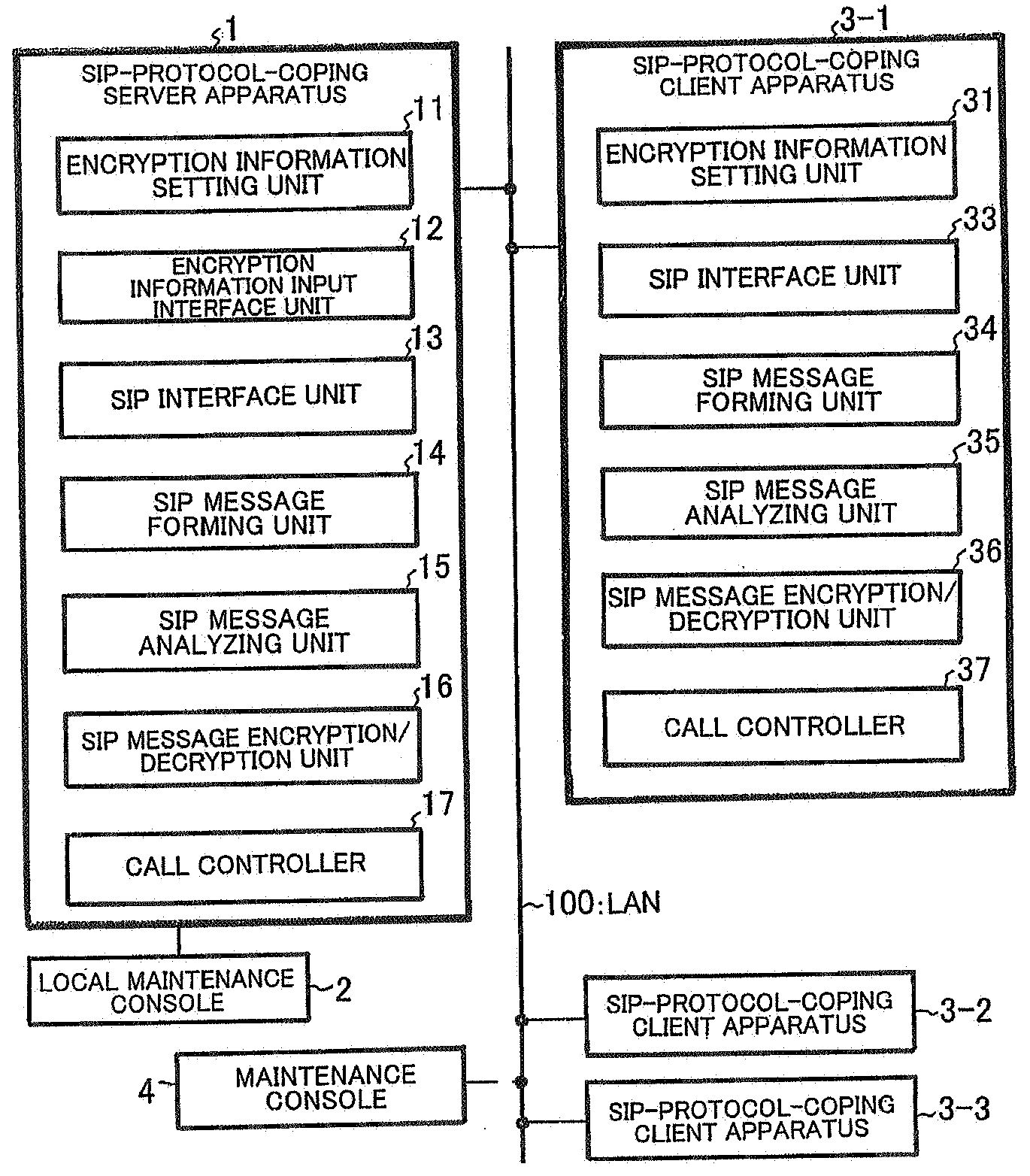
InactiveUS20080028458A1Raise security concernsReduce chanceDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideServer authentication
In a client-server distributed system including an SIP-protocol-coping server apparatus and an SIP-protocol-coping client apparatus, client authentication of the SIP-protocol-coping client apparatus is performed from the SIP-protocol-coping server apparatus by a client authentication unit. In the client-server distributed system, in addition to the client authentication, server authentication of the SIP-protocol-coping server apparatus is performed by a server authentication unit from the SIP-protocol-coping client apparatus. In the client-server distributed system, authentication completion is recognized when the bidirectional authentication is achieved.
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
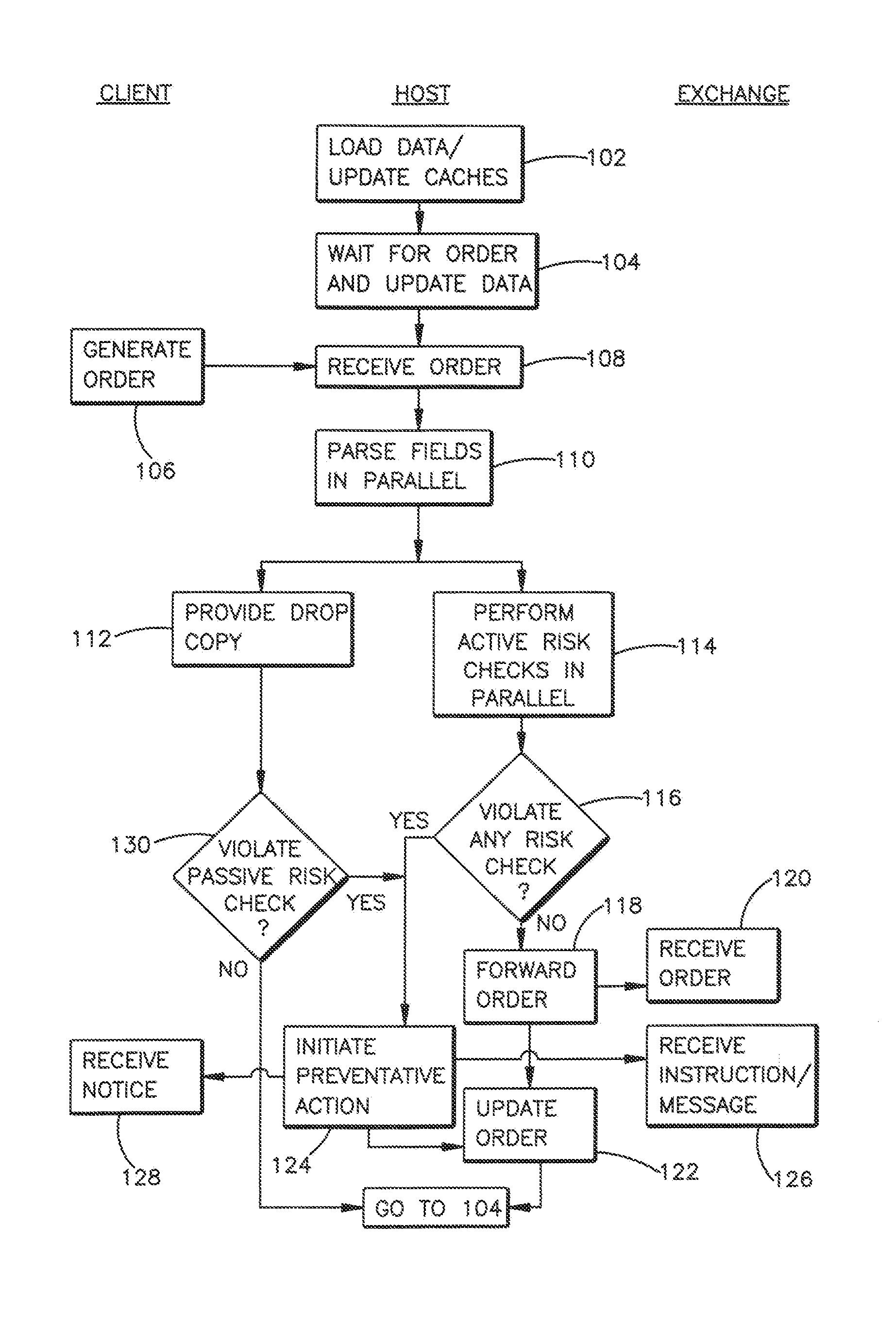
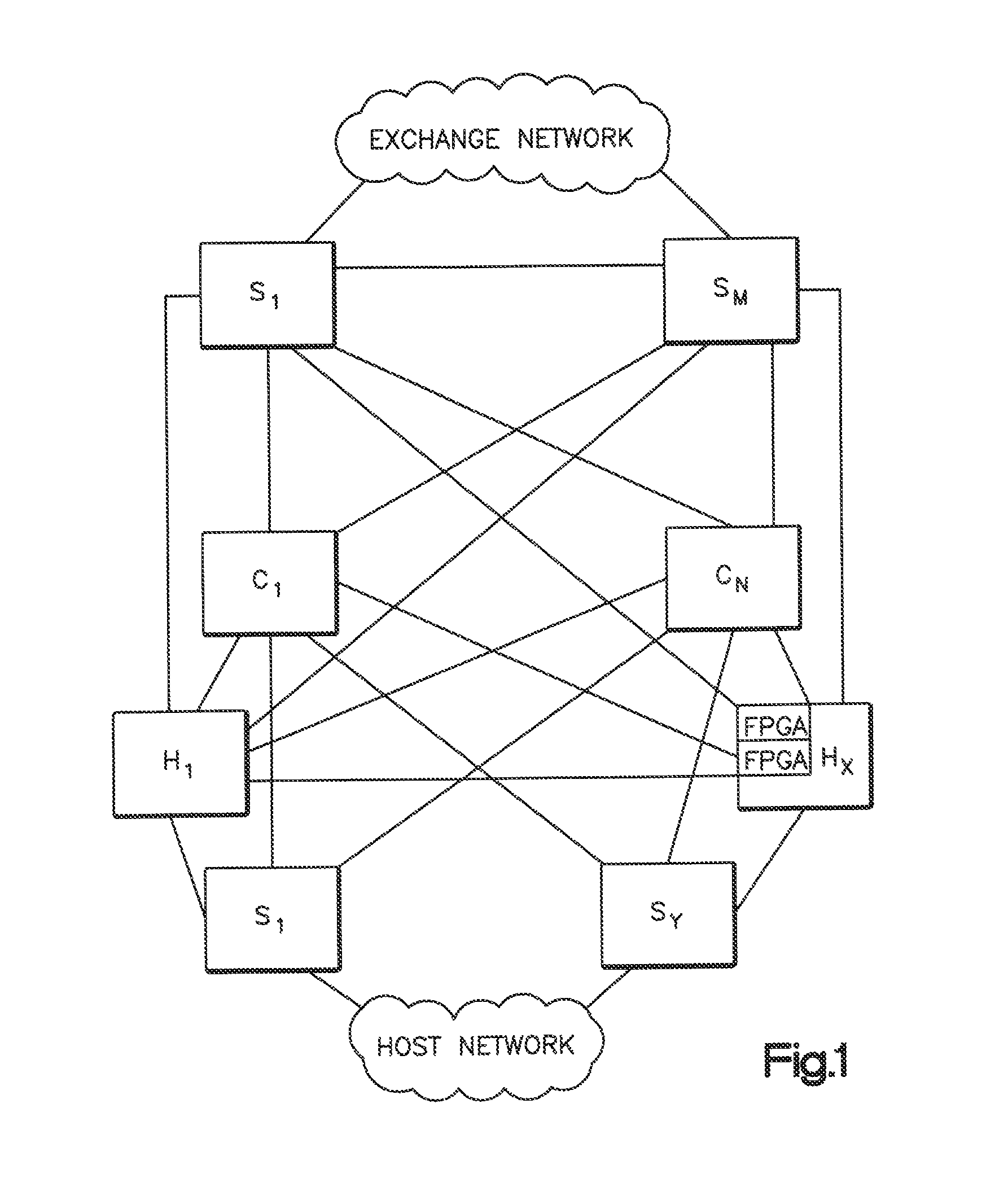
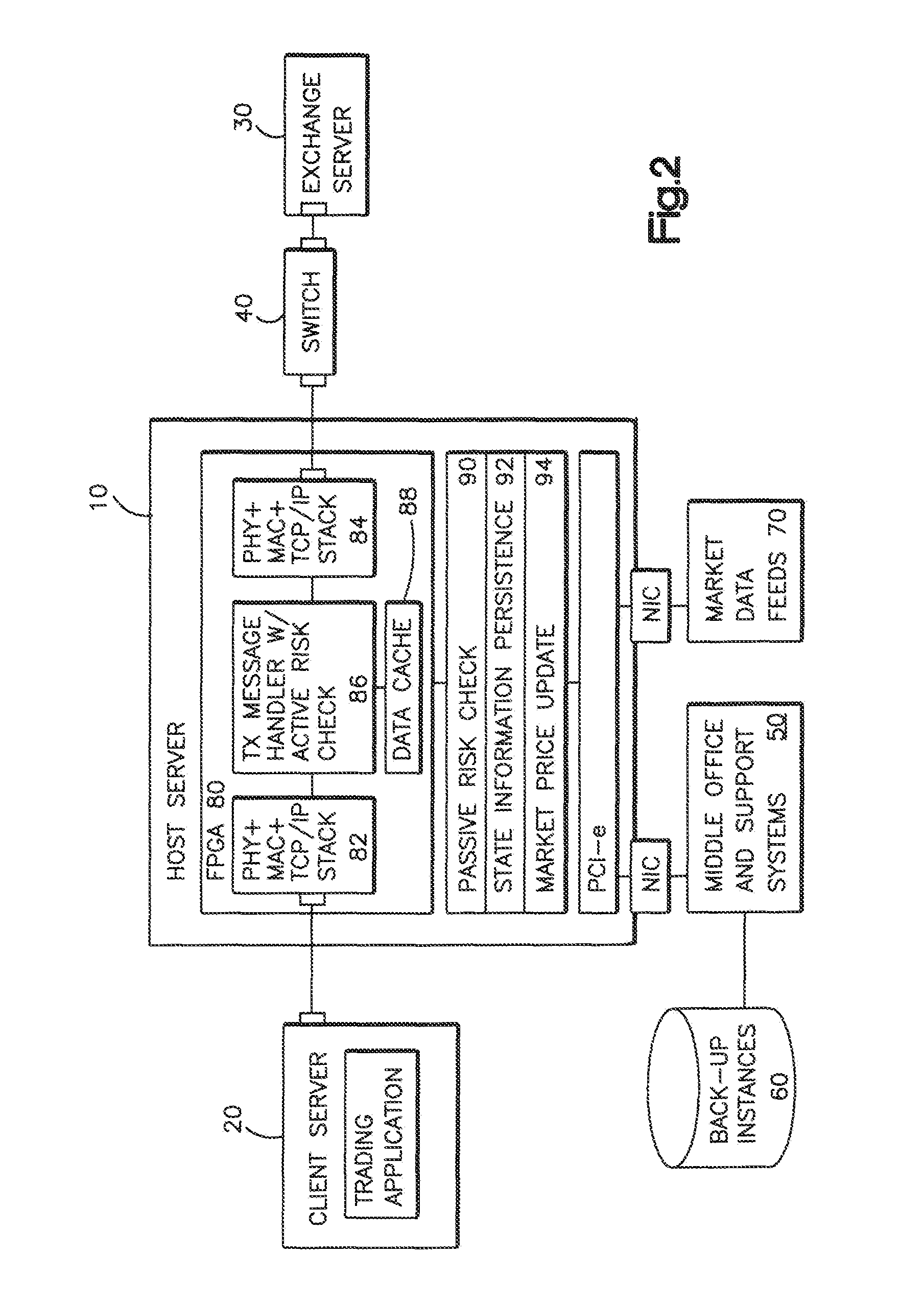
Validating an electronic order transmitted over a network between a client server and an exchange server with a hardware device
Methods and systems for performing risk checks on electronic orders for securities. According to one embodiment, the method comprises performing risk checks on an electronic order for a security, the electronic order being issued from a client computer to an exchange computer via a network, wherein a risk check engine is logically interposed between the client computer and the exchange computer on the network. According to the illustrative method, at the risk check engine, the electronic order is received and parsed into one of more fields and data within the fields is identified at a network layer. The risk check engine performs one or more risk checks on the data using a processing element at the network layer. If the risk checks are passed, the risk check engine permits the electronic order to be transmitted to the exchange computer. If one or more of the risk checks are violated, the risk check engine rejects the order.
Owner:FRIEDMAN SETH GREGORY
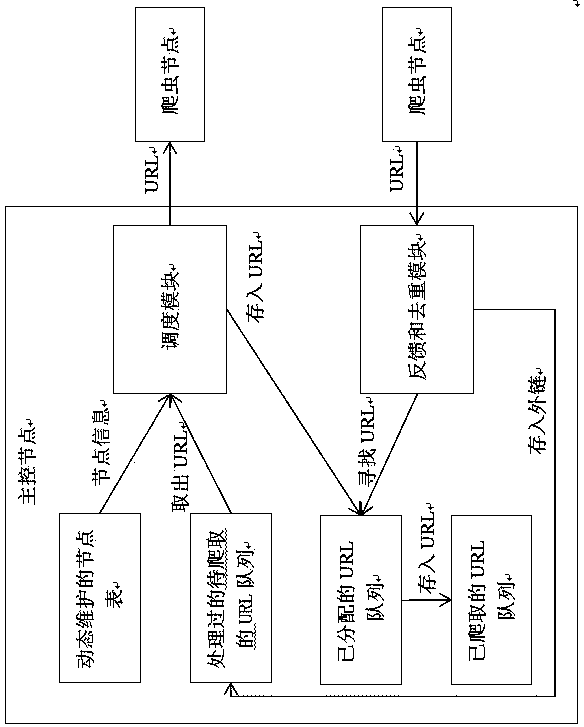
Distributed crawler task scheduling method based on weighted round-robin algorithm
ActiveCN103870329ALoad balancingFlexible scalabilityProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationFault toleranceExtensibility
A distributed crawler task scheduling method based on a weighted round-robin algorithm at least includes the following steps: (1) according to different scales, network crawlers are divided into five types of crawlers, i.e. a stand-alone multi-thread crawler, a homogeneous centralized crawler, a heterogeneous centralized crawler, a small-scale distributed crawler and a large-scale distributed crawler; (2) a master-slave architecture is deployed; (3) when a crawler node is connected to a master node for the first time, the master node gives an initial weight to the crawler node; (4) according to the scheduling algorithm based on weighted round-robin, the master node continuously chooses a crawler node and assigns a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) task to be crawled to the crawler node; (5) each time when a URL task is crawled by a crawler node, a result is returned to the master node, and the weight of the crawler node is updated by the master node, and the like. The distributed crawler scheduling policy based on the weighted round-robin algorithm, which is put forward by the invention, is designed for small-scale distributed crawlers and can ensure the load balance of each crawler node and ensure that crawler nodes have flexible scalability and fault tolerance.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Client server, intelligent terminal, online game system and method
InactiveCN101741653AReduce loadMaintain fairnessData switching by path configurationSpecial data processing applicationsClient-sideComputer science
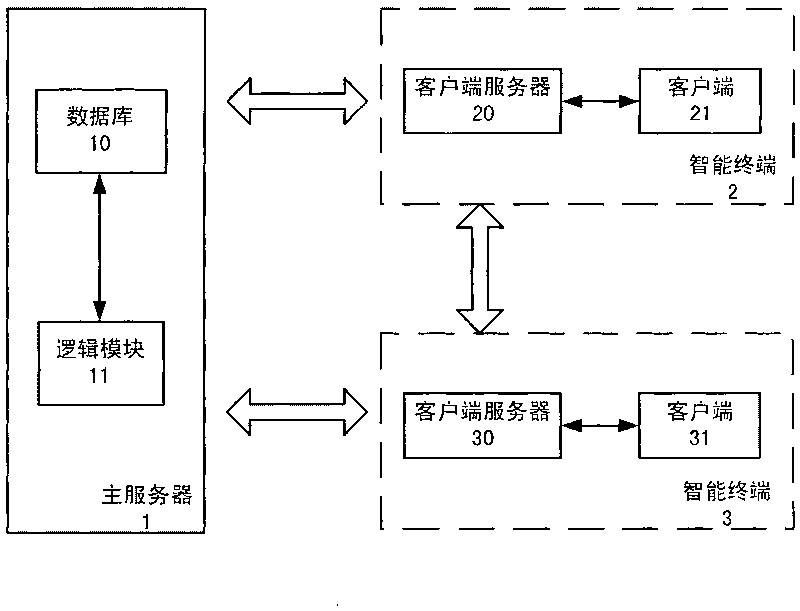
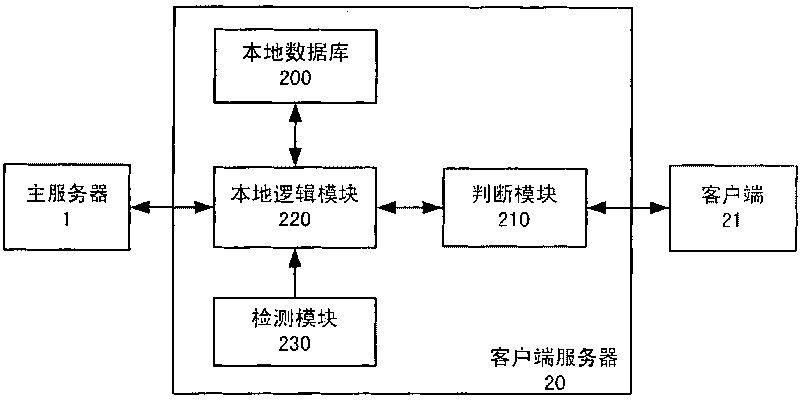
The invention relates to a client server, an intelligent terminal, an online game system and a method, wherein the client server communicates with a client and a main server and comprises a local database, an adjustment module and a local logic module; the local database is used for storing information from the client; the adjustment module is used for judging whether a request from the client can be processed locally at the client serve; and the local logic module is used for processing the request from the client when the judgment module judges that the request from the client can be processed locally at the client serve, and is also used for synchronizing the information stored in the local database to the main server. The invention can be used to relieve the load of the main server of an online game and prevent plug-in and other cheating means.
Owner:爱思开电讯投资(中国)有限公司
Data writing method and server network card
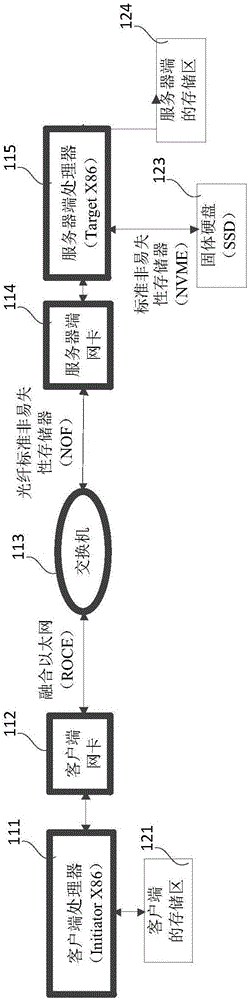
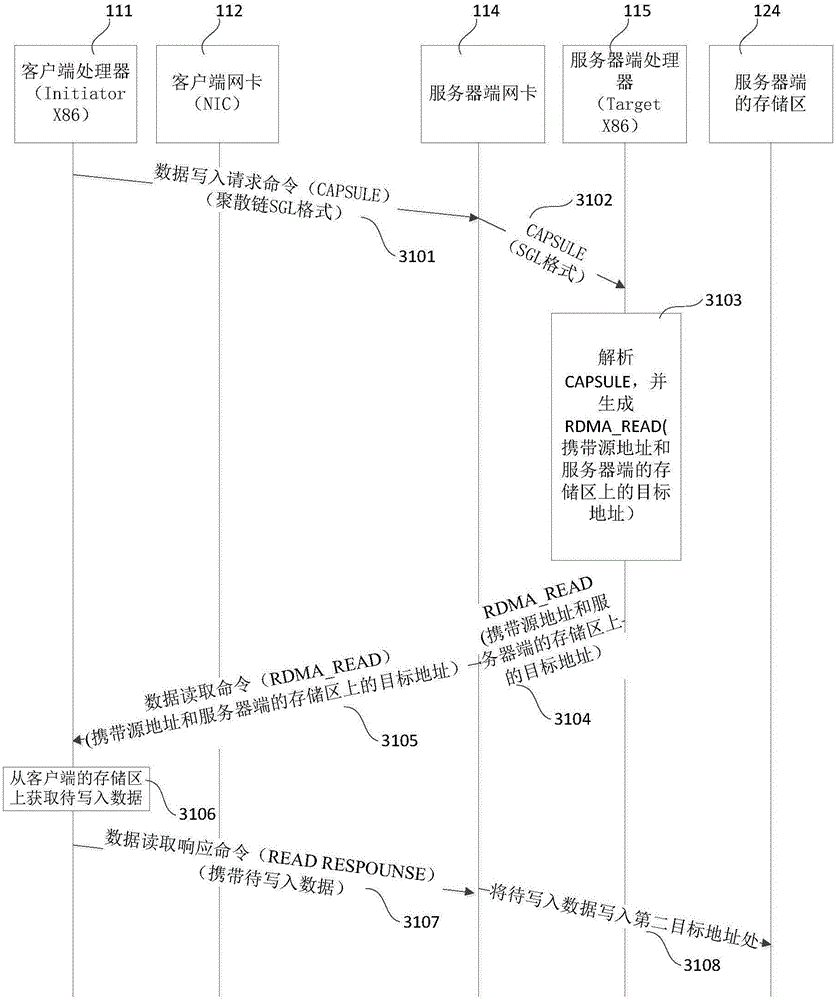
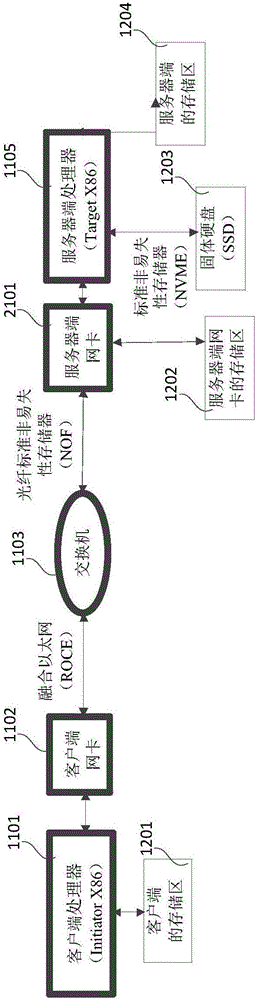
ActiveCN106210041AReasonable planningEfficient solutionInterprogram communicationTransmissionClient-sideNetwork interface controller
The embodiments of the invention relate to the technical field of communications, and particularly relate to a data writing method and a relevant device for reducing the time delay of the data writing process. In the embodiments, after a server network card receives a data writing request command sent by a client server, on the one hand, the server network card directly analyzes the data writing request command, and returns a first data reading command to a client processor, so as to store data to be written into a storage area of the server network card; and on the other hand, the server network card transmits the data writing request command to the server, so that when a second data reading command returned by the server is received, the data to be written can be directly transmitted from the storage area of the server network card to a storage area pointed by a second target address.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Client server distributed system, server apparatus, client apparatus, and inter-client rtp encrypting method used for them
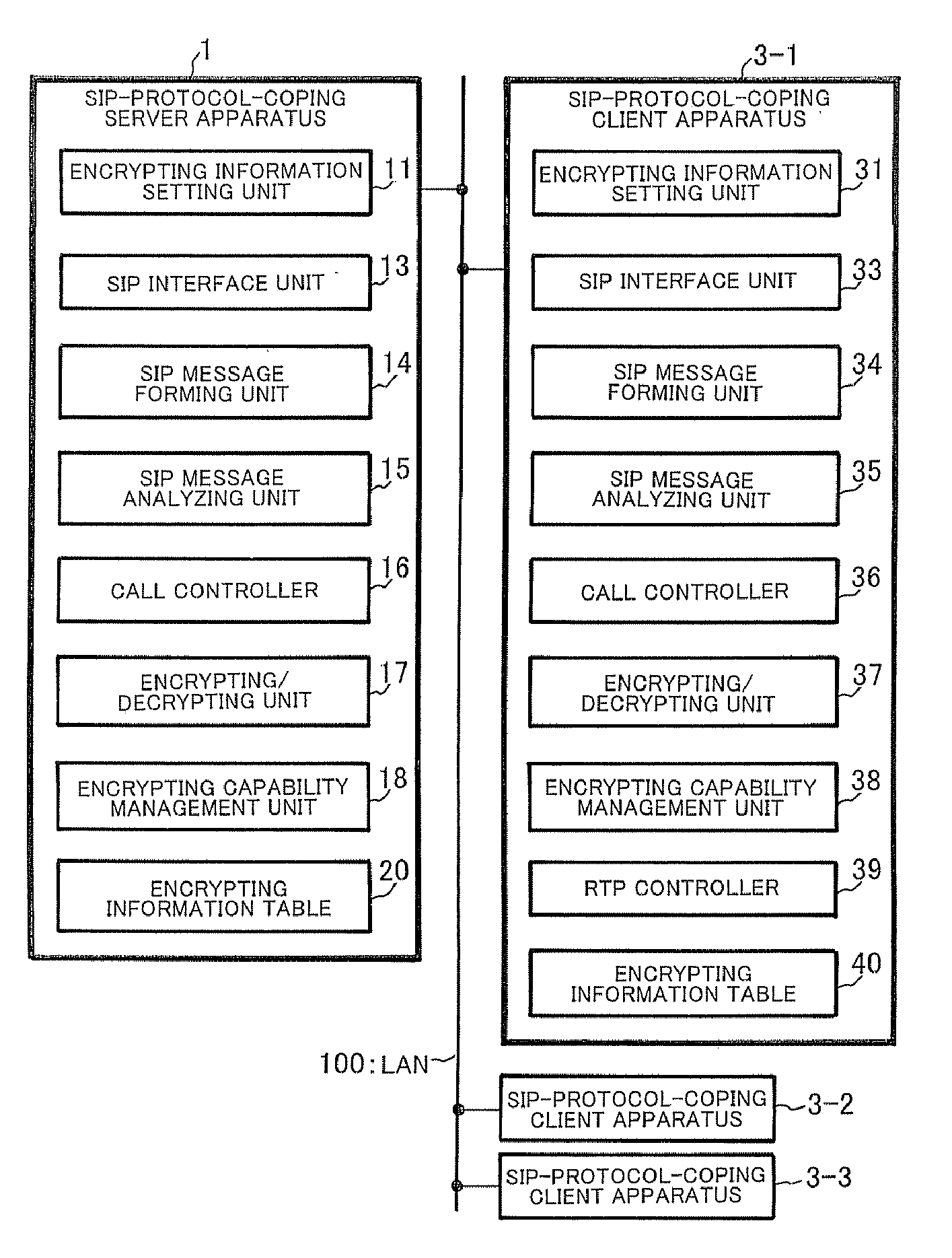
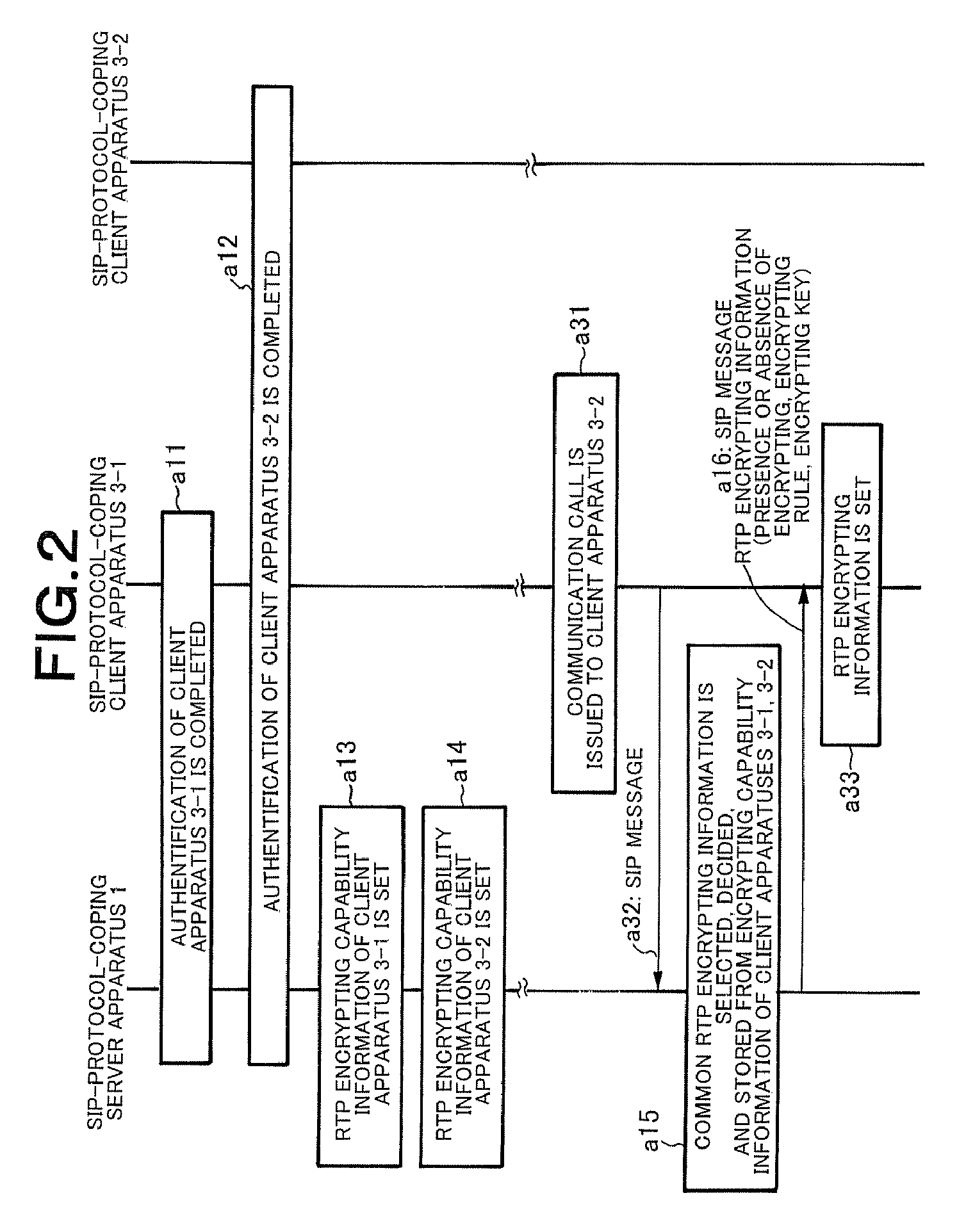
ActiveUS20080025516A1Low costImprove security featuresKey distribution for secure communicationProgram controlCapability managementManagement unit
When an SIP interface unit of a server apparatus receives an SIP message for call connection from a client apparatus and an SIP message analyzing unit can confirm that the SIP message is normal, a call controller recognizes that an RTP communication is carried out between the client apparatus and another client apparatus and instructs an encrypting capability management unit to determine RTP encrypting information which is used between the client apparatuses. The encrypting capability management unit determines the RTP encrypting information between these client apparatuses based on the instruction. With this arrangement, there can be provided a client-server distributed system that can realize an encrypting security function without requiring a certificate authentification function at a low cost in order to deliver an encrypting key as well as without necessity of holding or managing a certificate and preparing an authenticating server in a system.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
System for aborting response to client request if detecting connection between client server is closed by examining local server information
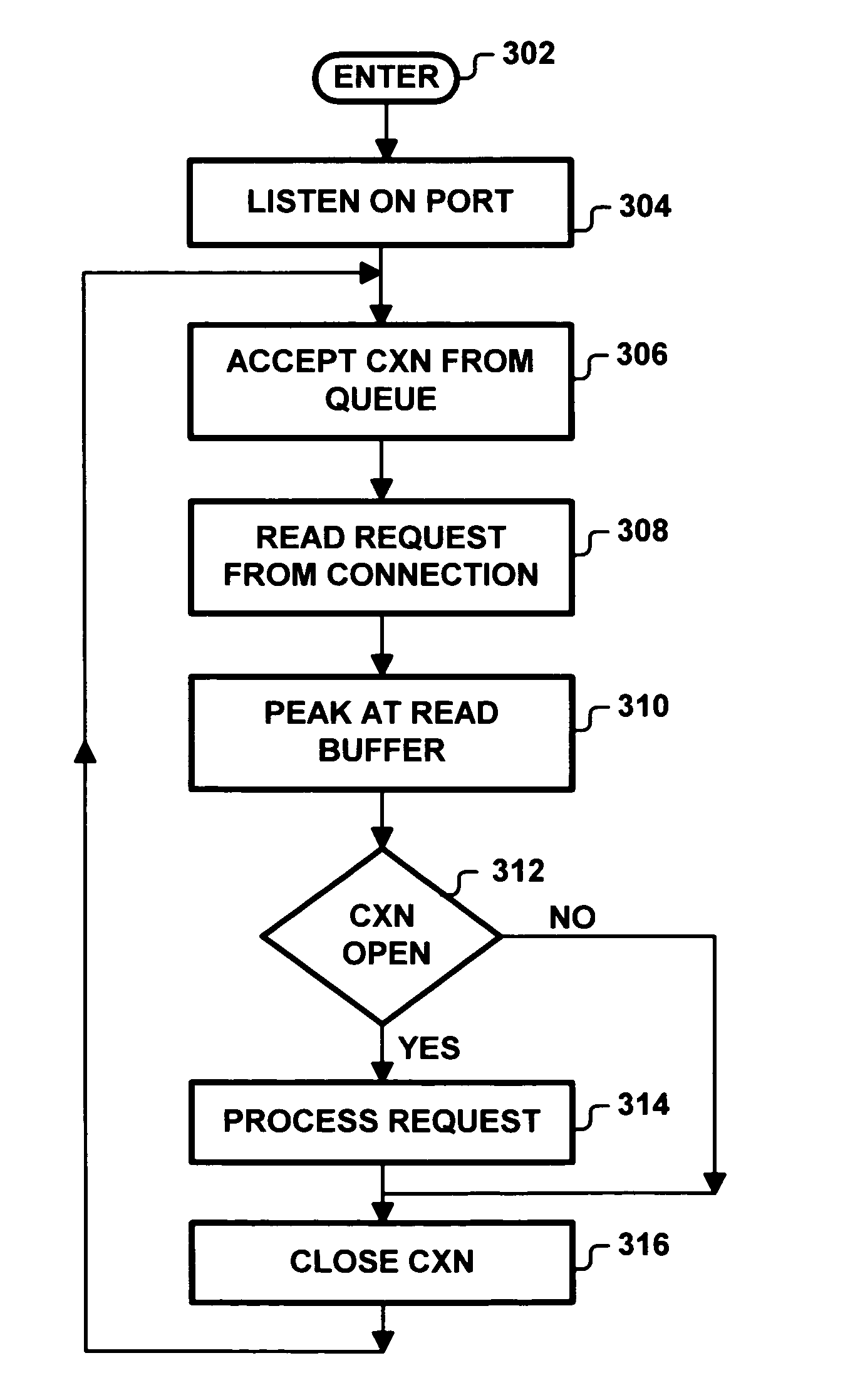
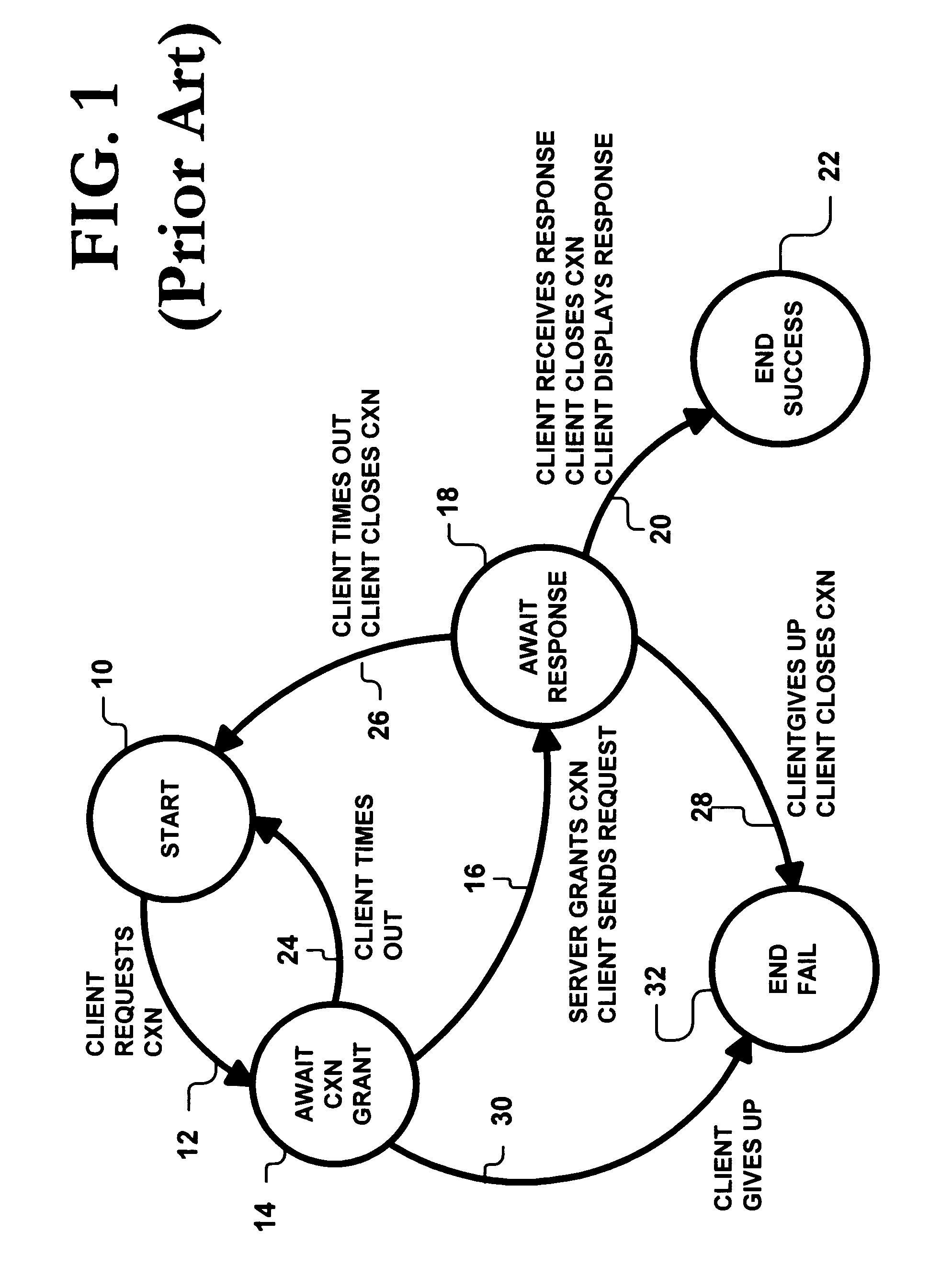
InactiveUS7376741B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlClient-sideClient–server model
An HTTP server is programmed to detect timed-out client requests by inferring states of its client-server connections. These connections, being full-duplex, can each be viewed as including a client-to-server channel and a server-to-client channel. The state of the server-to-client channel can be inferred by examining local server information to determine whether the client-to-server channel is still established. The server processes a request by a client if the inferred state indicates that the server-to-client channel is still established, and the server terminates the client request if the inferred state indicates that the server-to-client channel is no longer established. Consequently, the server does not expend resources by processing timed-out or dead client requests.
Owner:HTC CORP
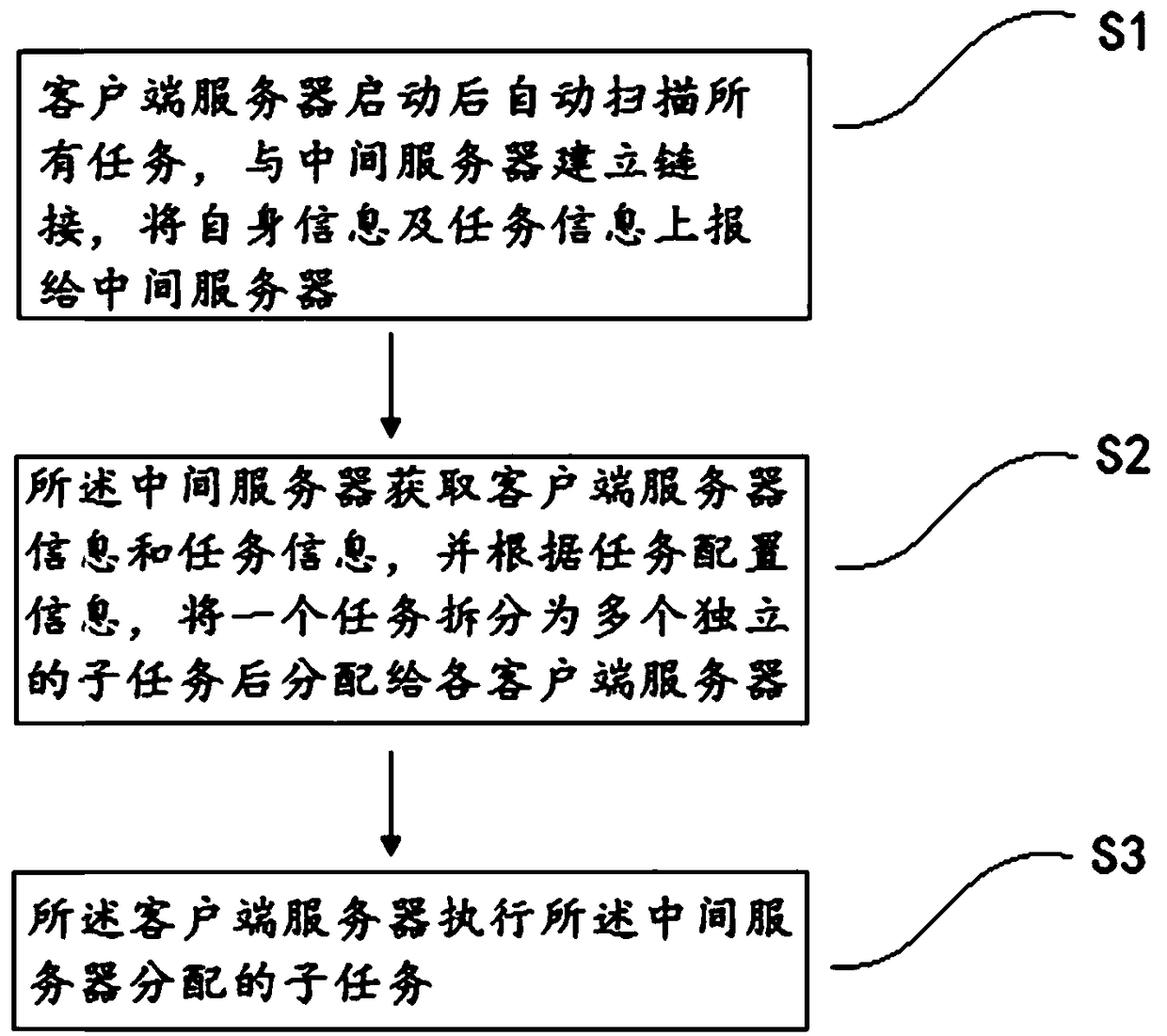
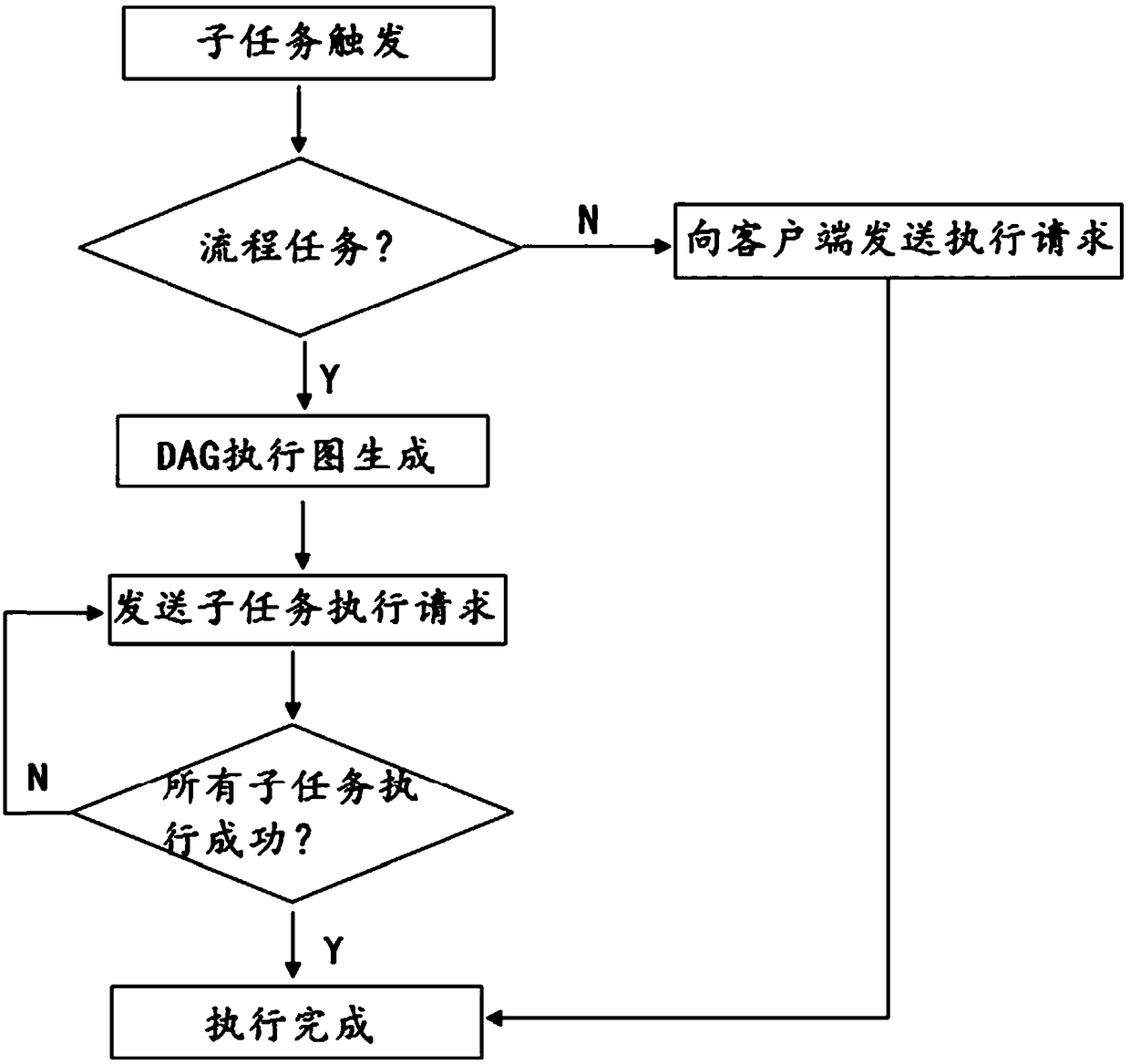
A distributed task scheduling method and system
ActiveCN108958920AEasy to manageImplement parallel schedulingProgram initiation/switchingClient-sideParallel scheduling
The invention discloses a distributed task scheduling method and system, belonging to the computer technical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, after the client server starts up, alltasks are automatically scanned, a link is established with the intermediate server, and self-information and task information are reported to the intermediate server; S2, that intermediate server obtains the client server information and the task information, and splits a task into a plurality of independent sub-tasks according to the task configuration information, and distribute the task to each client server; S3, the client server executes the sub-tasks assigned by the intermediate server. Through integration of the task scheduling engine in the intermediate server, the dependency relationship of the tasks are conveniently managed. Through the intermediate server, a task is divided into several independent sub-tasks, and the client server is called to execute the assigned task items in parallel to achieve parallel scheduling.
Owner:ZHONGAN ONLINE P&C INSURANCE CO LTD
Dynamic content conversion
ActiveUS20120023160A1The process is simple and fastMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDisplay deviceClient-side
A method of display modification in a client server web system, comprising, intercepting, by a web intermediary, a response to a client request, sent by a server in response to the request, the response including client side active content adapted to execute at a browsing software on a client computer; replacing at least one display-related code section in said response by a wrapper section that includes code for modification of at least one display element and code for executing the original display-related code section; and executing said wrapper section as client side active content at said client to generate a display, modified from a display that would have been generated by executing the response.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
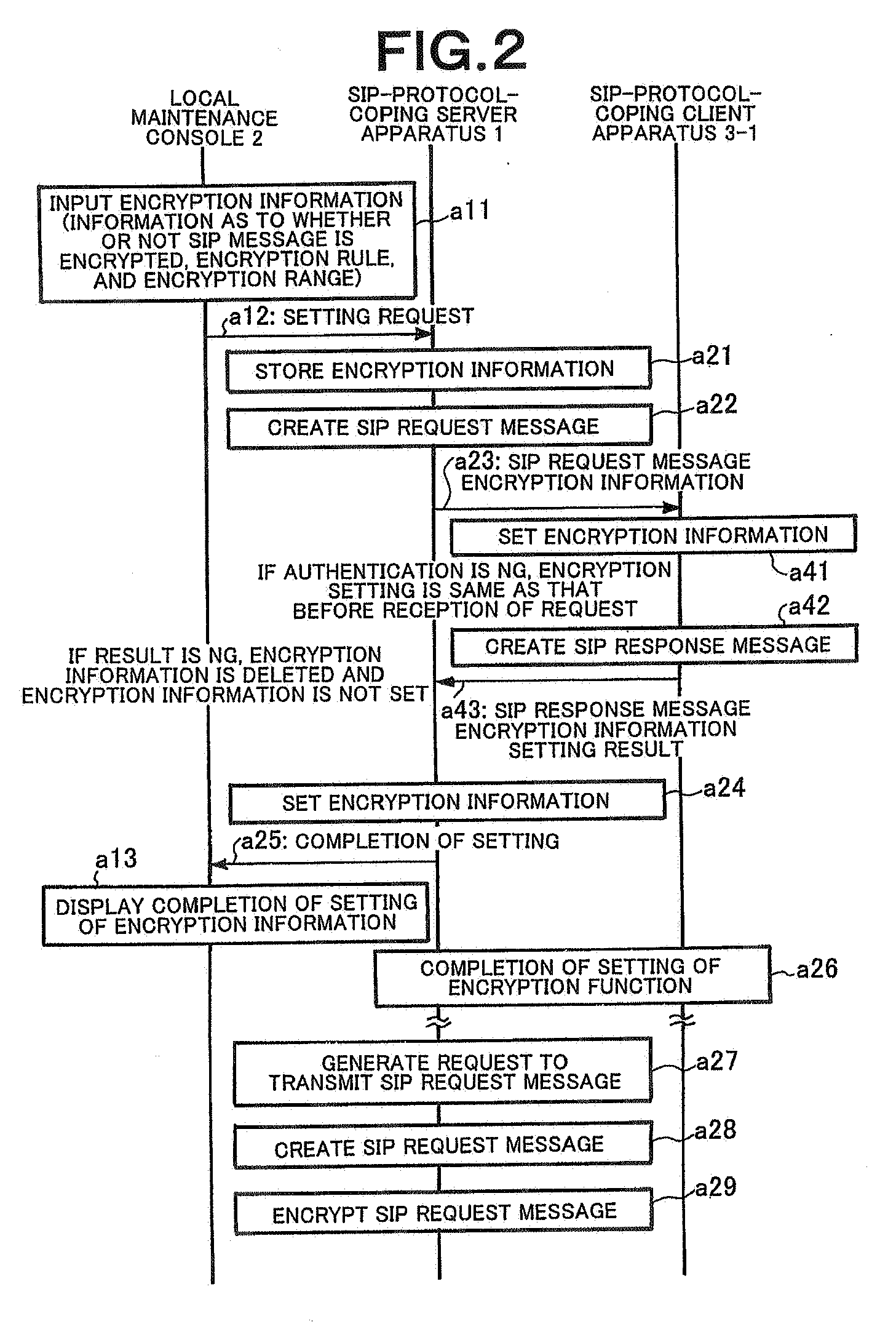
Client server distributed system, client apparatus, server apparatus, and message encryption method used therefor
ActiveUS20080028204A1Low costStrengthen encryption security functionSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareClient-side
When encryption information including an encryption rule, an encryption range, and an encryption key is input to a server apparatus from a local maintenance console in advance, the server apparatus stores the encryption information in an encryption information setting unit, creates an SIP request message including the encryption information, and transmits the SIP request message to a client apparatus. The client apparatus receives the SIP request message including the encryption information. If confirming normality of the encryption information, the client apparatus sets the encryption information therein. After completion of a setting of the encryption information, the client apparatus transmits a notification of the completion of the setting of the encryption information to the server apparatus. Upon receiving the notification of the completion of the setting of the encryption information, the server apparatus acknowledges the completion of the setting of the encryption information, sets the encryption information therein, transmits the notification of the completion of the setting of the encryption information to the local maintenance console, and causes the local maintenance console to display the completion of the setting of the encryption information.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
Migration tool for implementing desktop virtualization
At least a method and a system for migrating a plurality of endpoint computing devices of an organization are described herein. User applications, data, and settings are migrated from a plurality of endpoint computing devices of the organization into a client server operating environment employing a thin client implementation. A server may execute software for deploying the thin client implementation. By way of creating a personalized virtualization disk for each endpoint computing device, migration to a thin client virtualized desktop implementation may be easily performed by the organization without modification, change, or loss of user installed applications, personalized settings, and user data.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Client server system, information processing apparatus and control method therefor, and program for executing the control method
InactiveUS7619765B2Good printabilityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsInformation processingComputer module
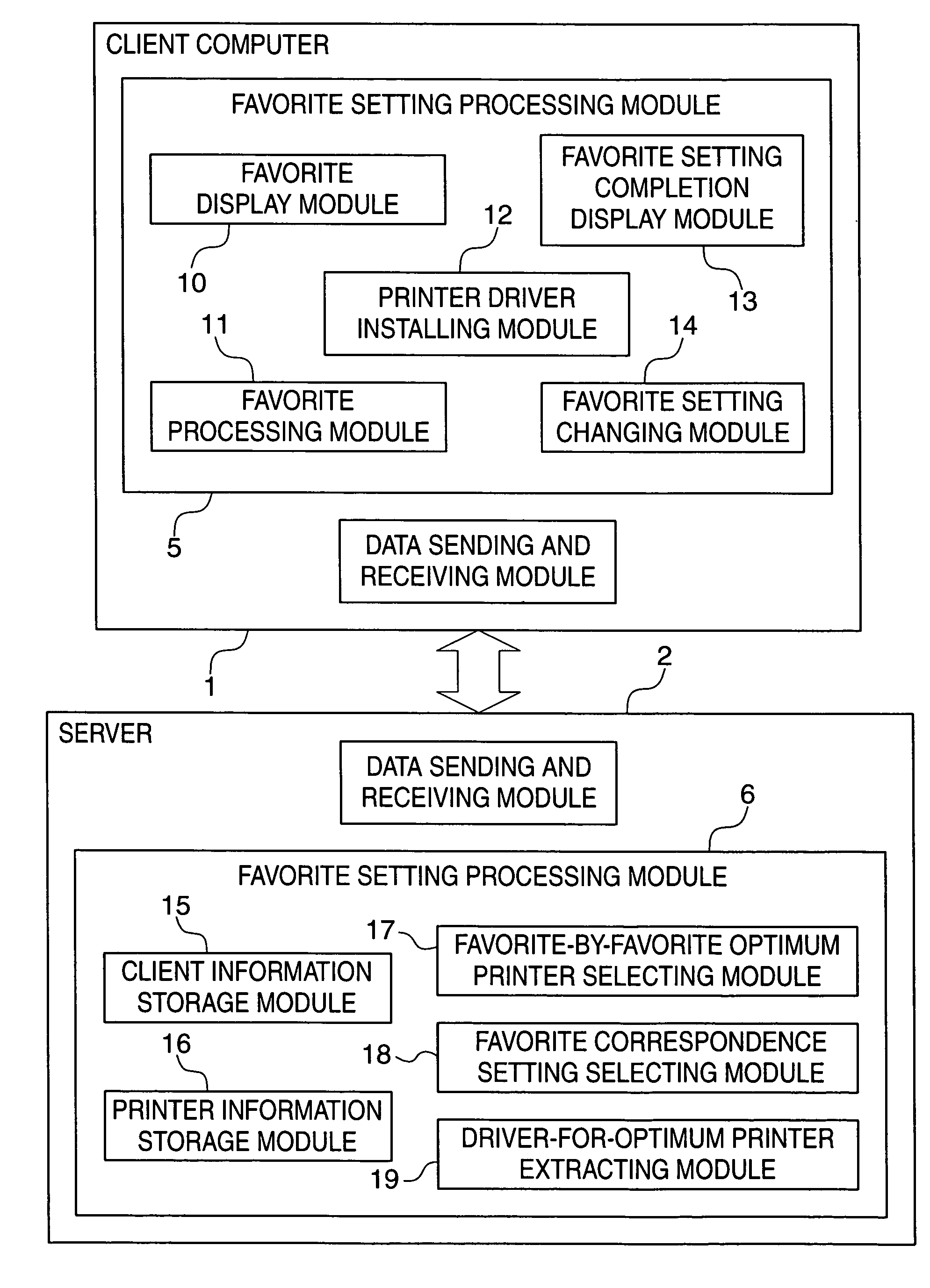
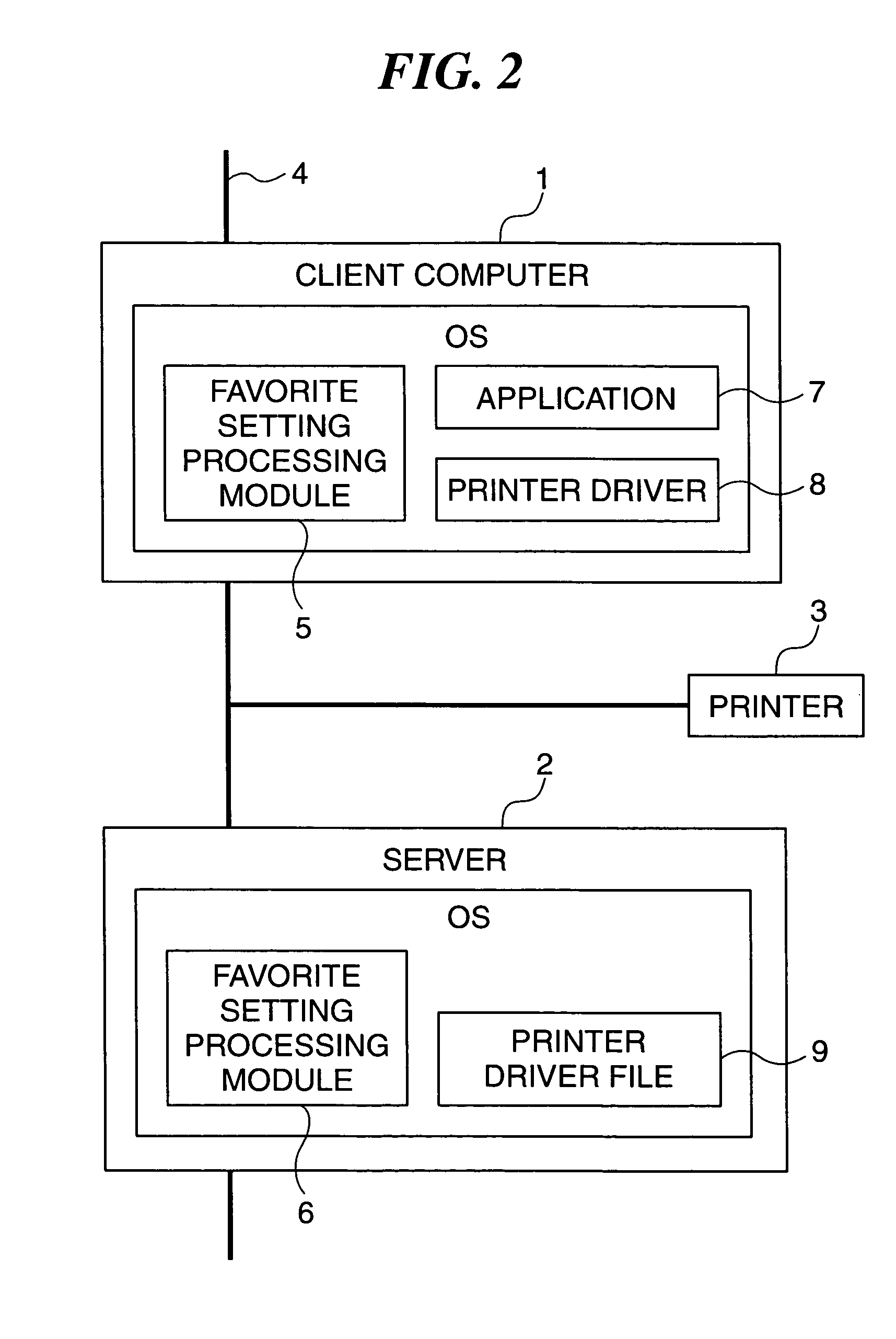
A client server system which enables the user of a client computer to obtain the optimum printing result only by designating desired print settings, and to perform printing according to common print settings even if printers are modified or a new printer is added on a network. A favorite display module displays a print setting designating screen relating a printer. A data sending and receiving module transmits the print settings designated on the print setting designating screen by a user and an ID of a client computer to a server. A data sending and receiving module receives a printer driver adapted to the printer and print setting information from the server. A favorite setting changing module changes print settings of the printer driver according to the print setting information sent from the server. A favorite setting completion display module indicates that the changing of the print settings has been completed.
Owner:CANON KK
Client server and method for full process monitoring on function text of client server
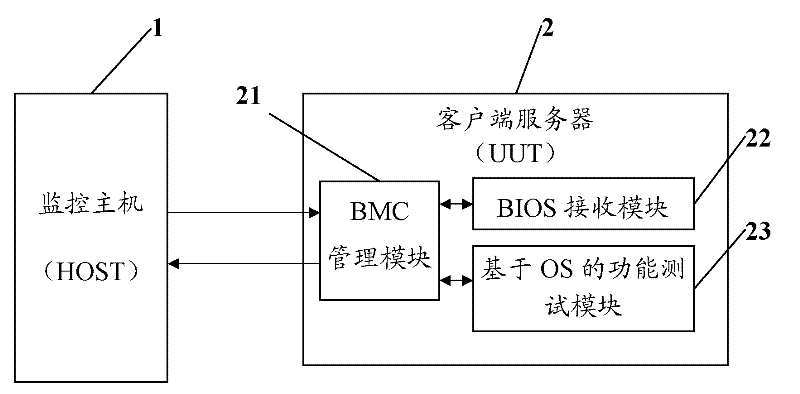
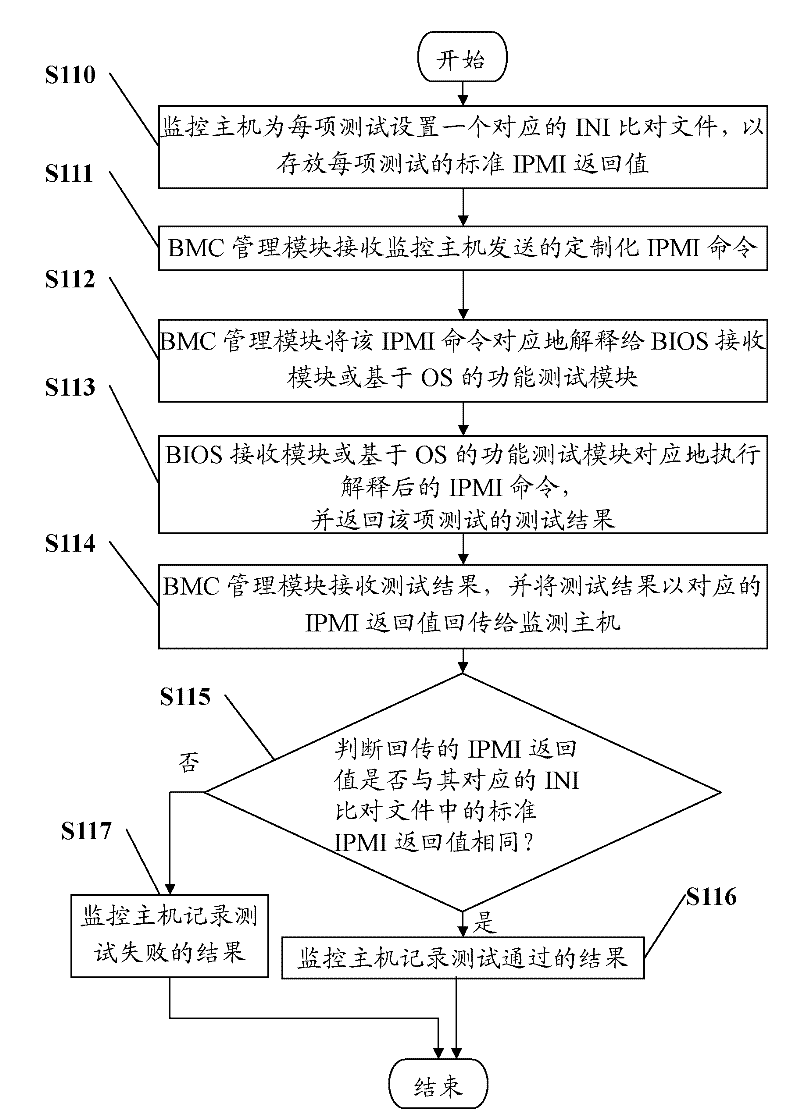
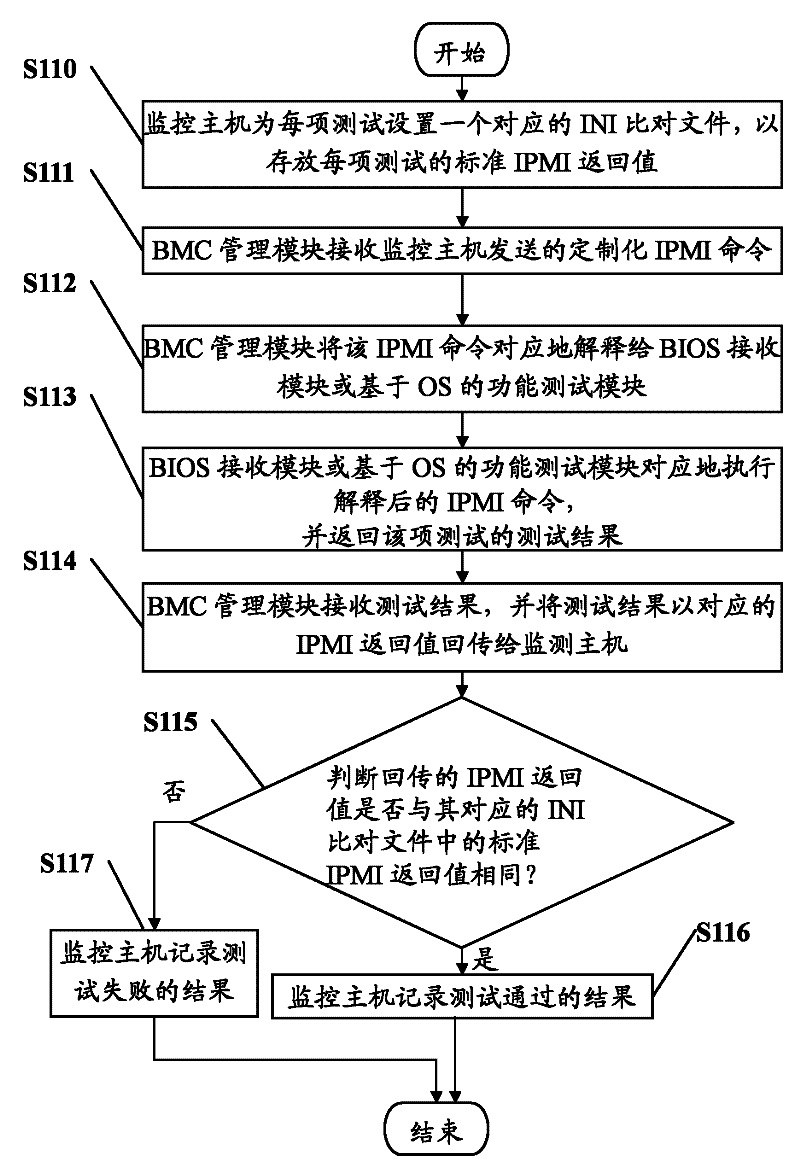
InactiveCN102244591ADetecting faulty hardware by remote testData switching networksIntelligent Platform Management InterfaceFunctional testing
The invention discloses a method for full process monitoring on function text of a client server. The method comprises the following steps that: a BMC (baseboard management controller) management module receives a customized IPMI (intelligent platform management interface) command transmitted by a monitoring host; the IPMI command is correspondingly explained for the client server, a BIOS receiving module or a function test module based on an OS (operating system); the BIOS receiving module or the function test module based on OS correspondingly executes the explained IPMI command, and returns back a test result; and the BMC management module obtains the test result, and returns back the test result as a corresponding IPMI return value to the monitoring host. The invention further provides a client server. With the method and the client server, the test process of the client server can be fully monitored.
Owner:淮南东正电子科技有限公司
Client server system and method for executing an application utilizing distributed objects
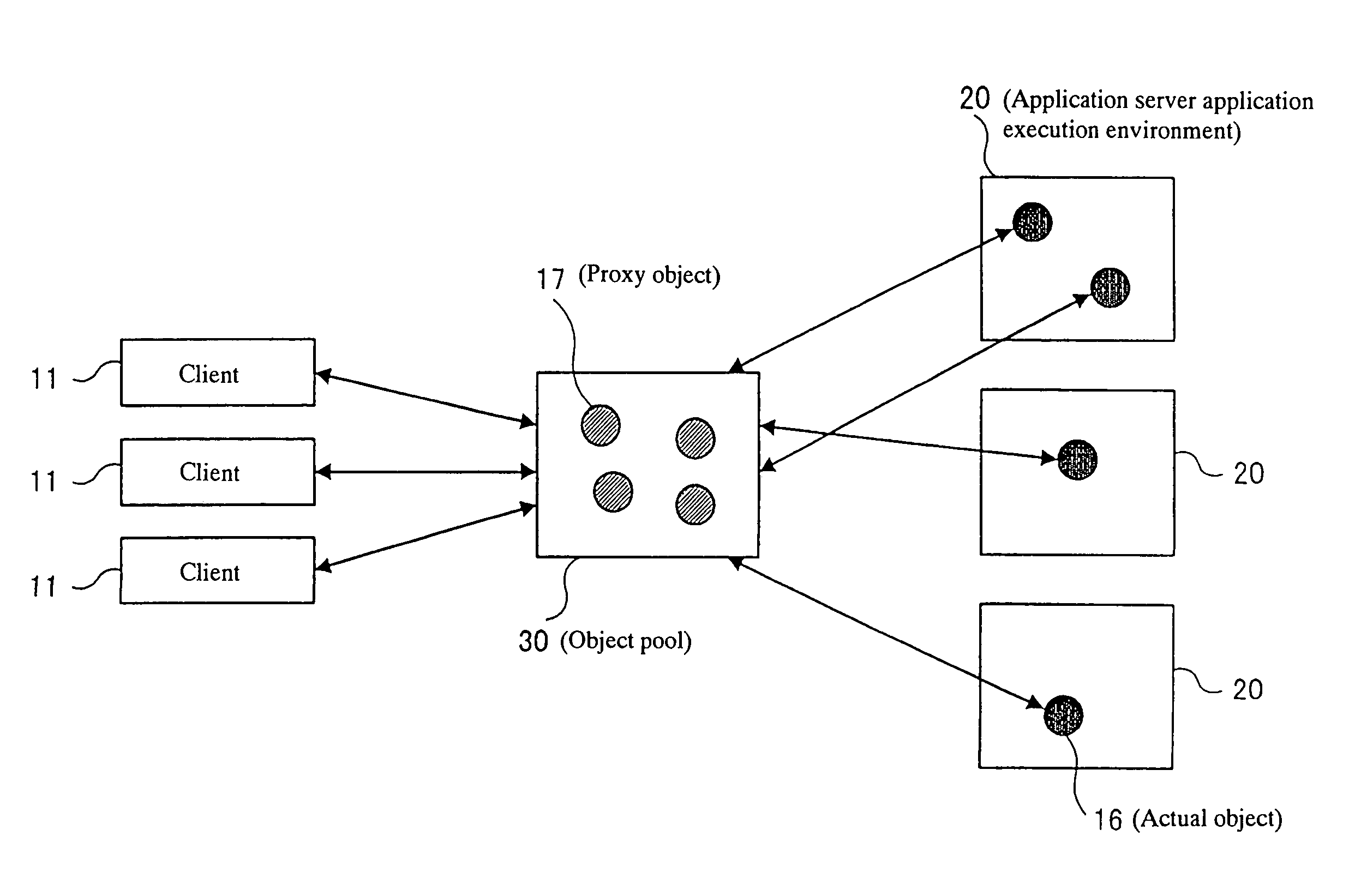
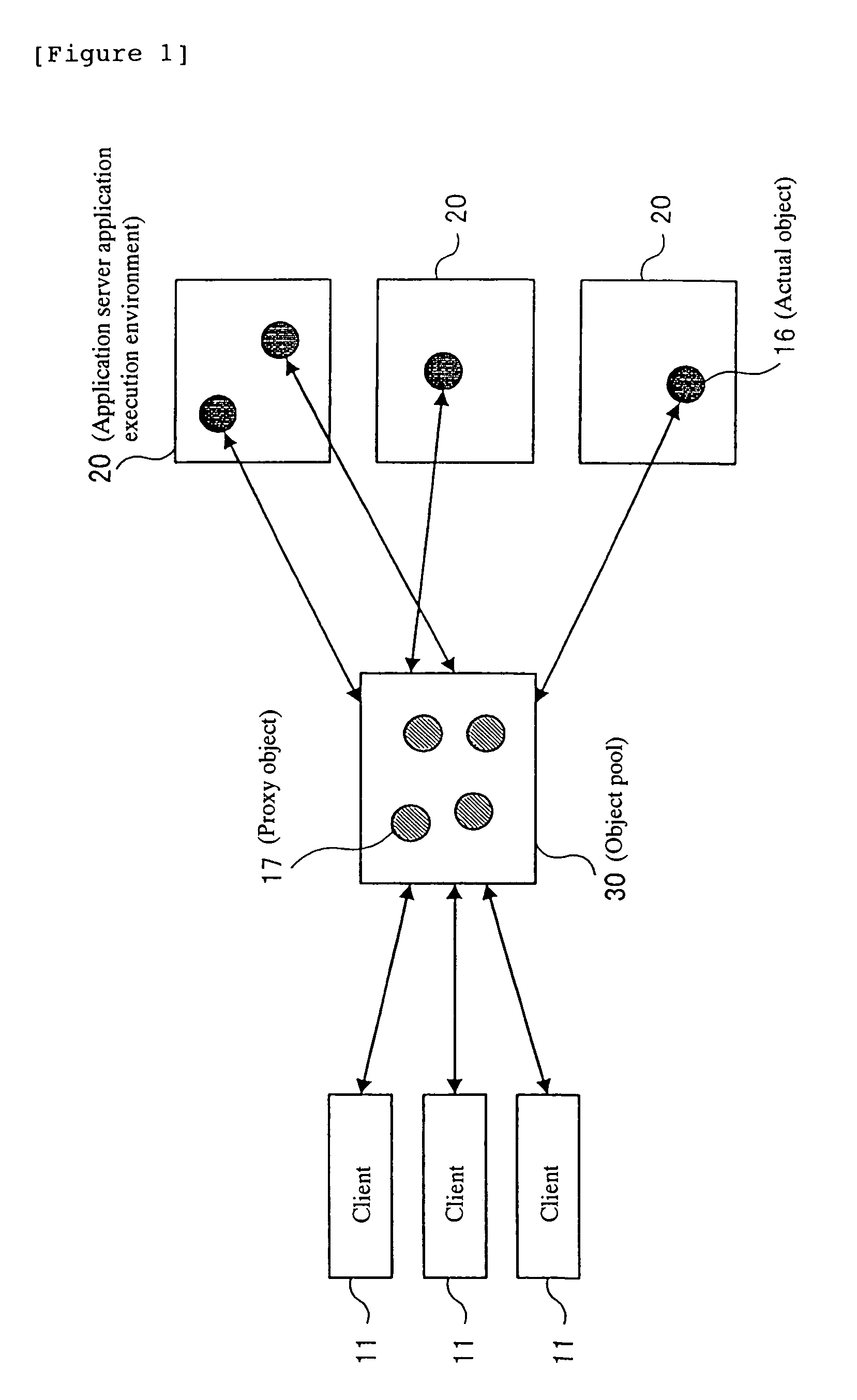
InactiveUS7398313B1Short response timeIncrease profitMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverDistributed object
A client connected to a communication network performs an access request to an object. An application server performs an application by an actual object according to the client request. An object pool connected to the client and the application server pools a proxy object corresponding to the actual object and holds the actual object management information. The application server notifies the object pool of an event according to the status change of the application. The object pool automatically updates the actual object management information according to the notification of the event from the application server.
Owner:IBM CORP
Client server system and devices thereof
ActiveUS20040025020A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsEffective dateClient server systems
A client server system and devices thereof, which perform a distributed processing while performing access control. when a client device demands a job of the server device, the server device outputs an authentication demand message to an authentication server via a network. The authentication device performs authentication of a user taking account of an effective range of authentication information and effective dates and returns results of authentication to the server device via the network. The server device implements the demanded job in accordance with the results of authentication.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
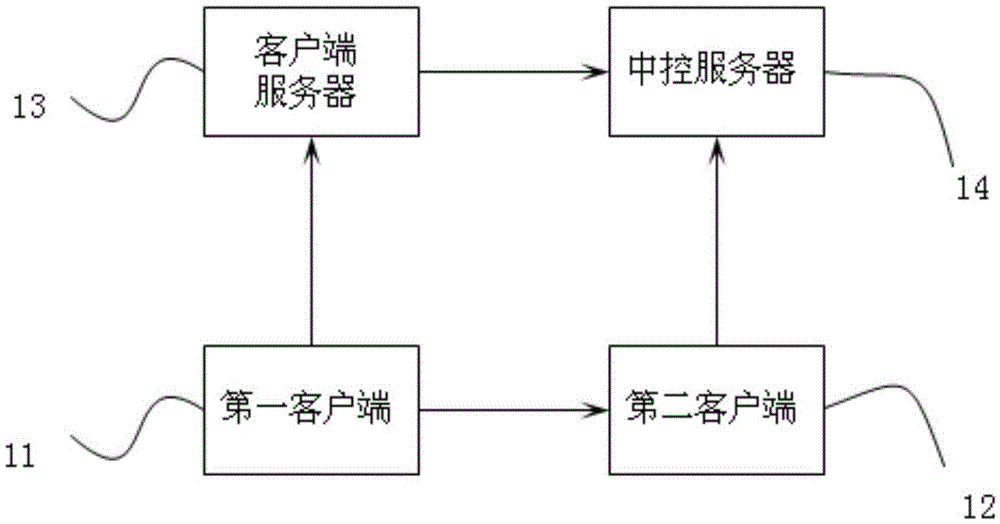
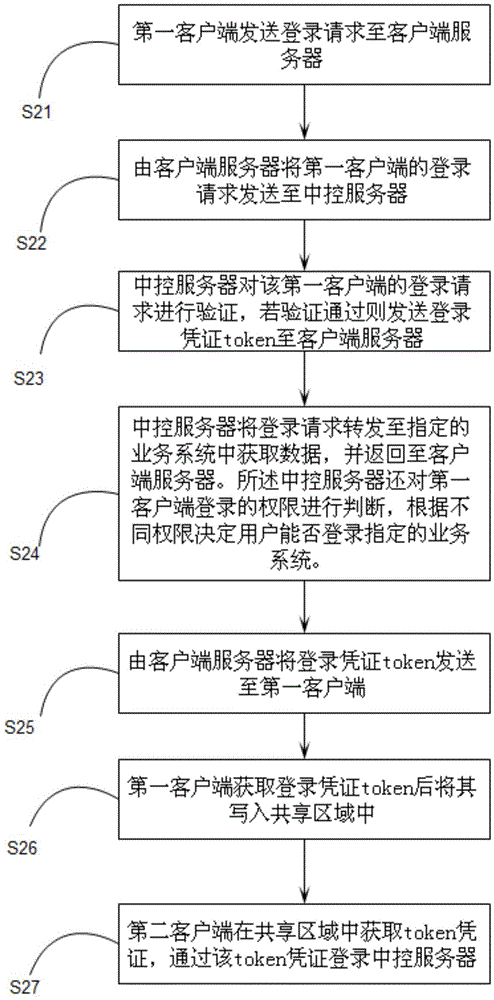
Client login method and system through regional information sharing
The invention relates to a client login method through regional information sharing. The method comprises the following steps: a first client sending a login request to a client server; the client server sending the login request of the first client to a center control server; the center control server verifying the login request of the first client, sending a login credential token to the client server after verifying; the client server sending the login credential token to the first client; the first client writing the login credential token in a sharing region after acquiring the same; a second client acquiring the token credential in the sharing region, and logining the center control server through the token credential. Through the login mode provided by the invention, the same account can login a plurality of terminals without repeatedly inputting the account and the password; the operation of a user is more convenient, and the security of the login account is guaranteed. The invention further relates to a login system for realizing above login method.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DUOYI NETWORK TECH
Online retailer platform based on ORM framework
The invention discloses an online retailer platform based on an ORM framework, comprising a purchase management server, a development management server, a client server, a distributed type transaction coordination server and a central processing server. The purchase management server is responsible for purchase information and performs classification management on the purchase data; the development management server performs development management on the online retailer platform; the client server presents information related to the product to the client according to search contents of the client; the distributed type transaction establishes a server state list which collects the operation states of the purchase management server, the development management server and the client server; the central processing server dynamically distributes the functions of the purchase management server, the development management server and the client server according to the operation state uploaded by the distributed transaction coordination server; and the development management server is based on the ORM frame structure. The online retailer platform based on ORM framework based on the ORM framework realizes the purpose that all servers of the online retailer platform operate equally.
Owner:GUANGXI JIAZHIBAO NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com