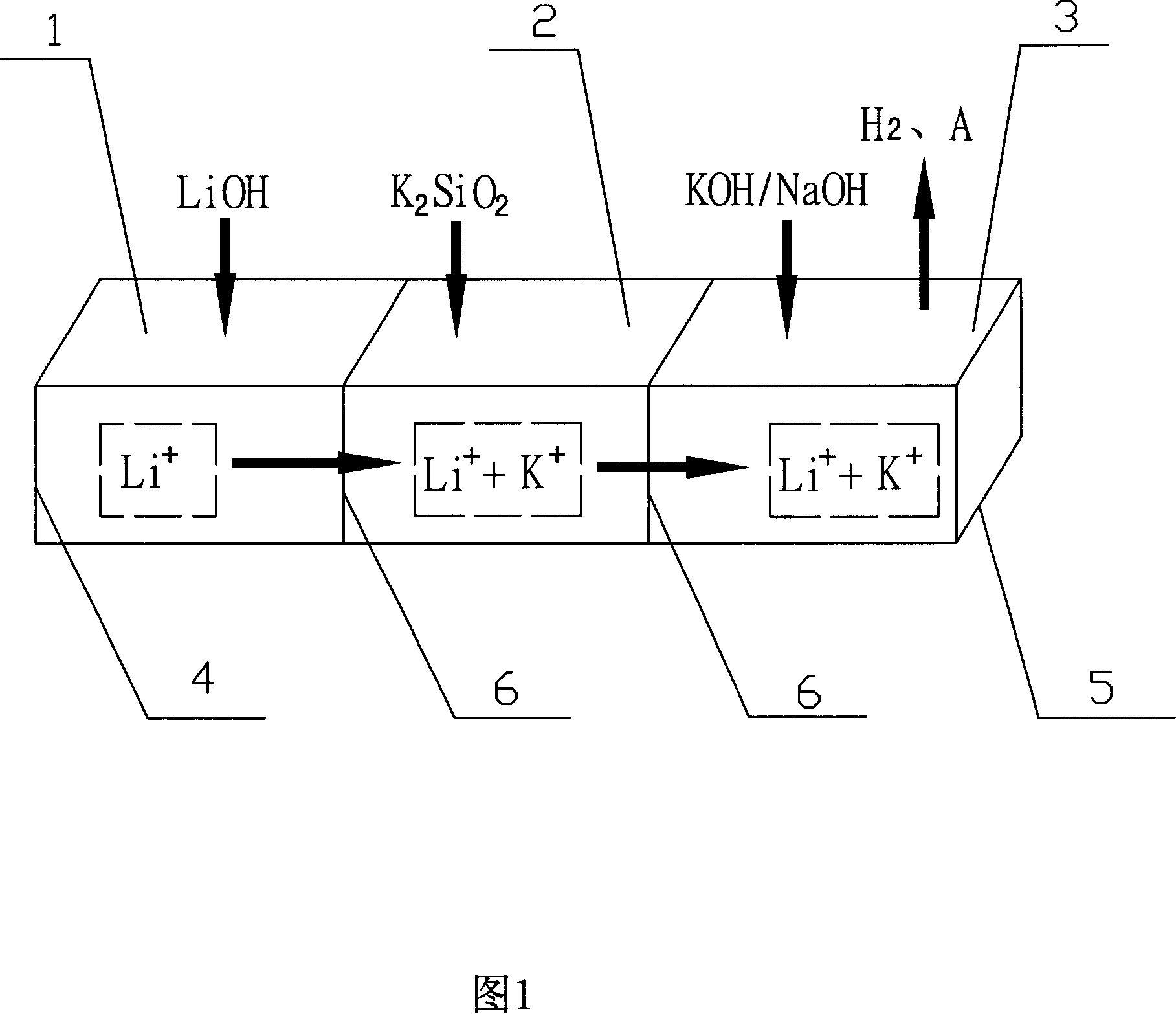
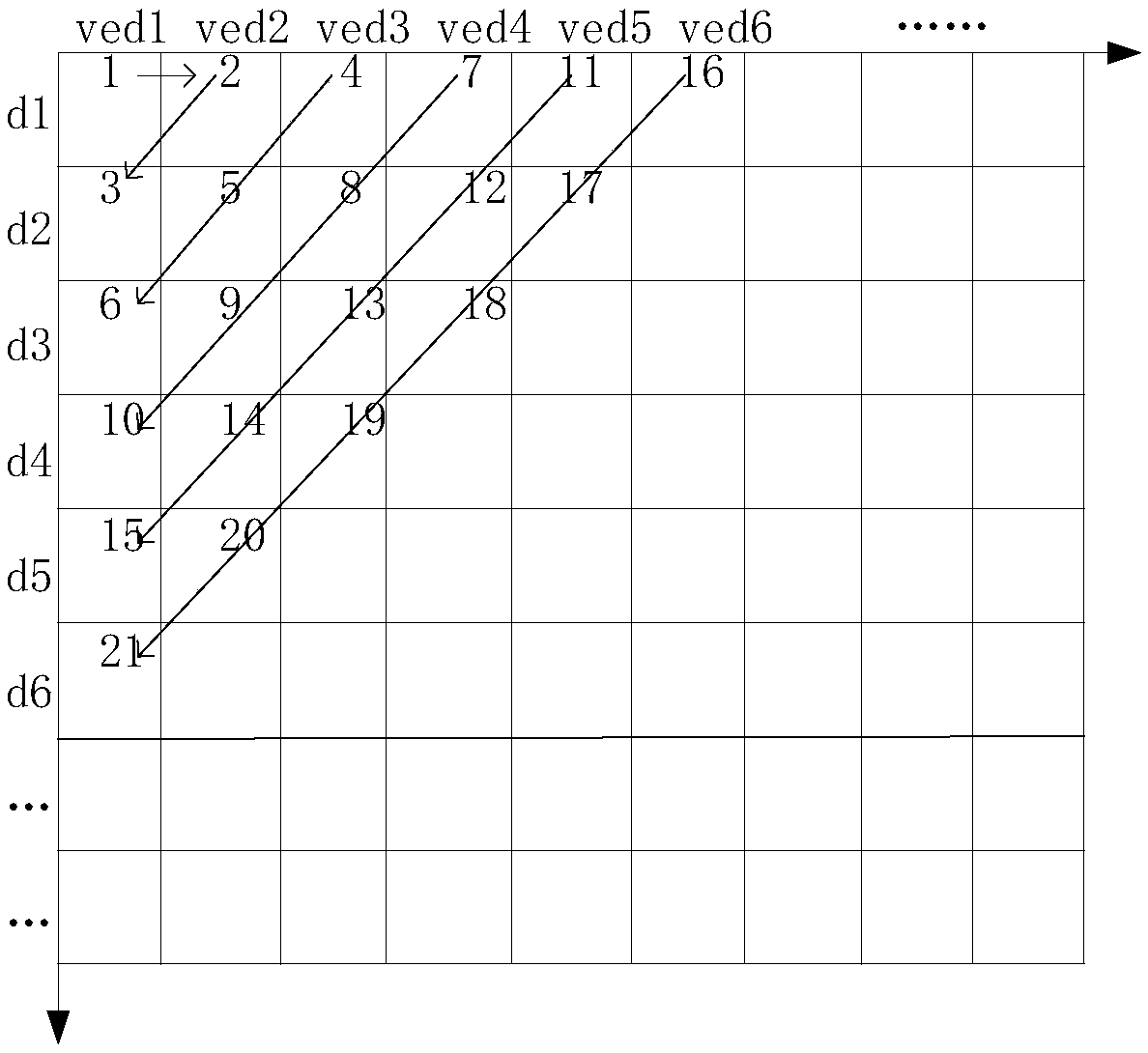Patents
Literature
73 results about "Effective date" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An effective date or as of date is the date upon which something is considered to take effect, which may be a past, present or future date. This may be different from the date upon which the event occurs or is recorded.
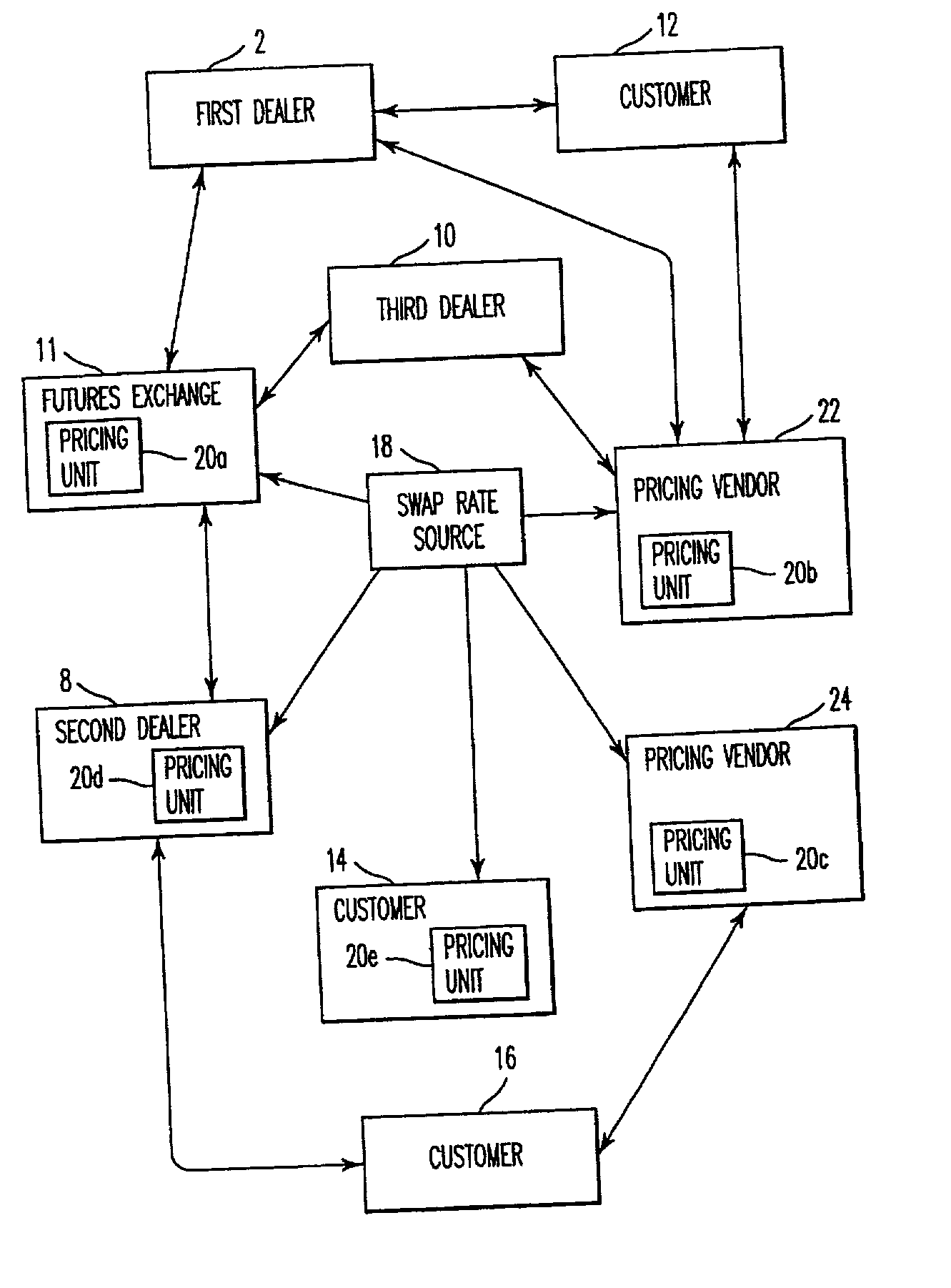
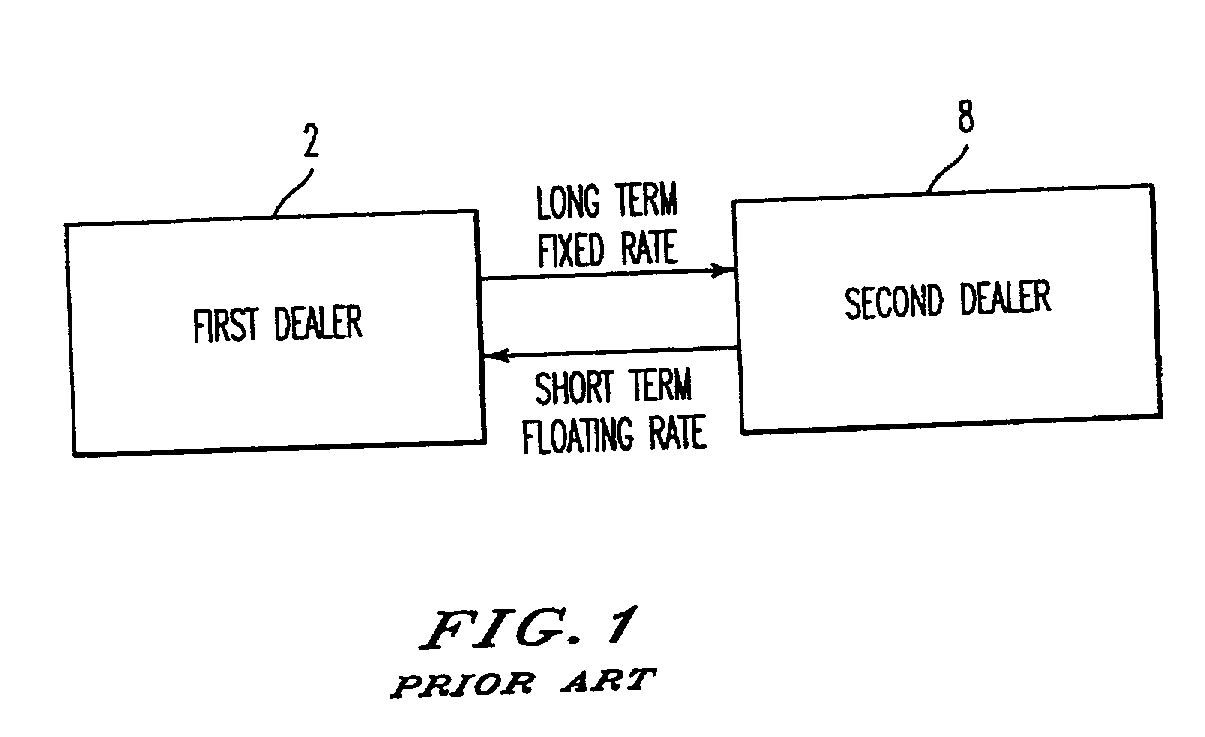
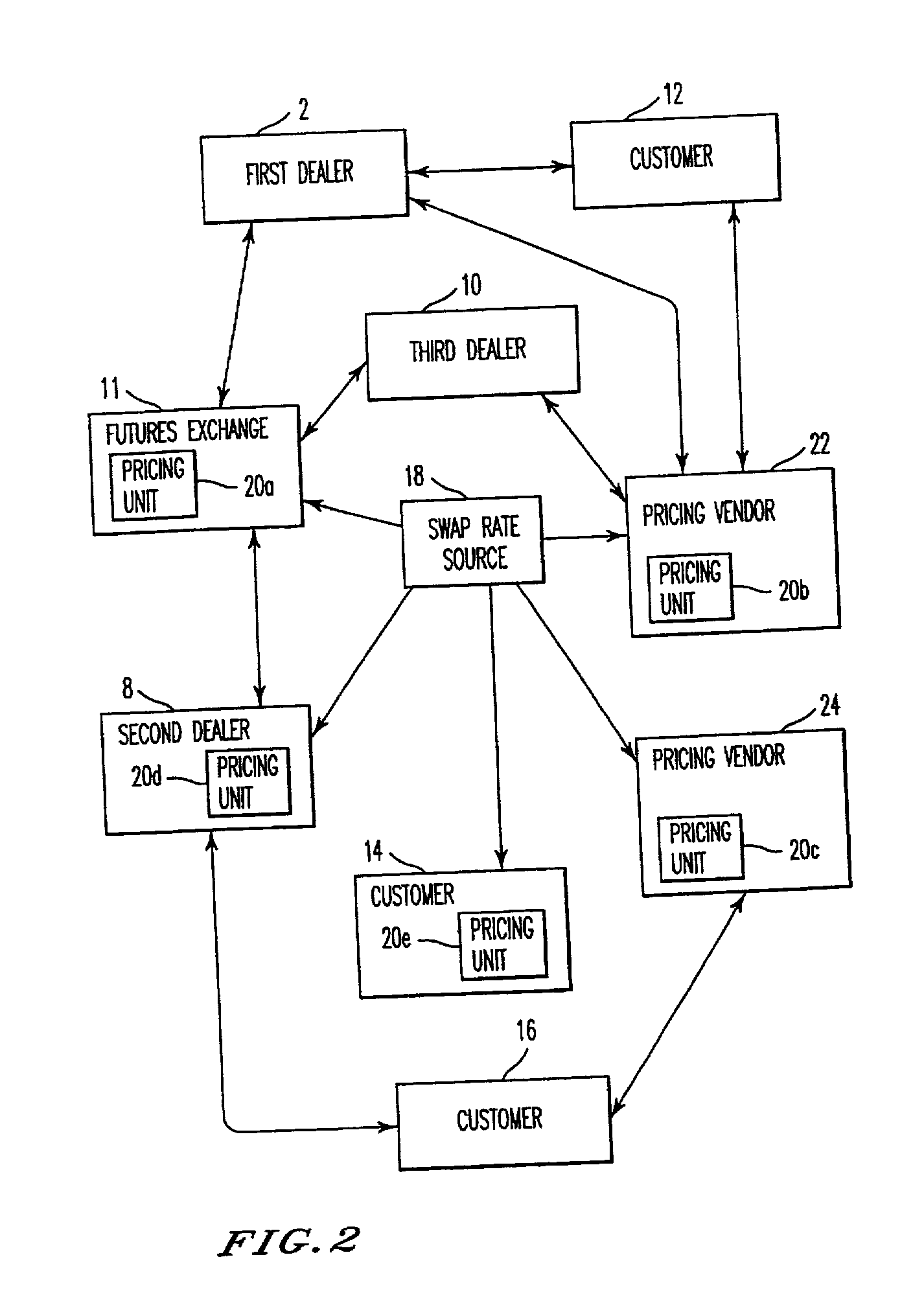
Method, system, and computer program product for trading interest rate swaps
InactiveUS20020010670A1Transparent pricingReduce management costsFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentEffective date
A method, system, computer program product, and data structure for trading in which a standardized contract is traded. The contract obligates a buyer and a seller to settle the contract based on a price of the contract at a first effective date. The contract is traded through an exchange that guarantees payment to the buyer of any amount owed to the buyer from the seller as a result of the contract and that guarantees payment to the seller of any amount owed to the seller from the buyer as a result of the contract. The price of the contract is determined based on preselected notional cash flows discounted by at least one point on an interest rate swap curve obtained from a preselected swap rate source.
Owner:MOSLER WARREN B +2
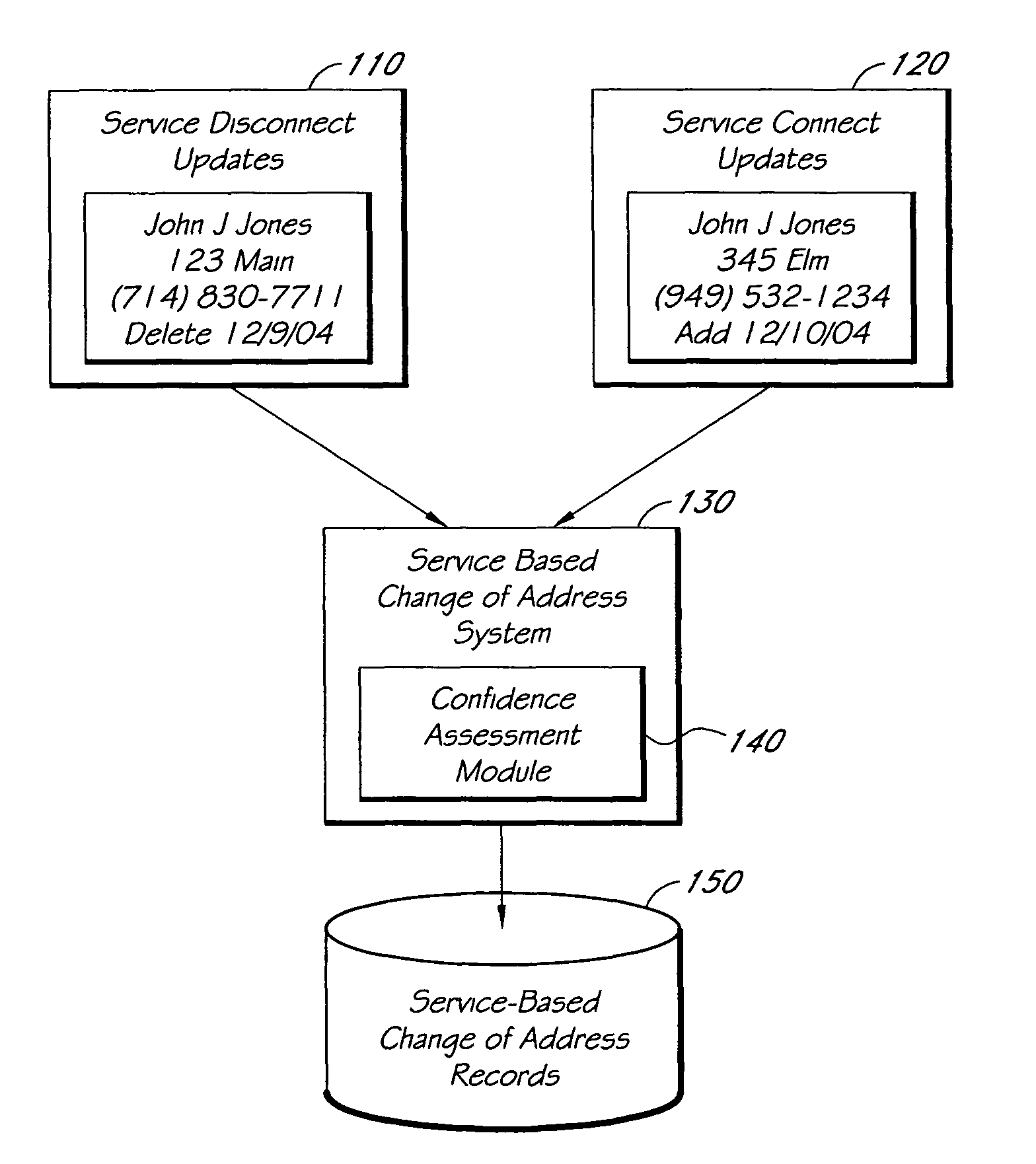
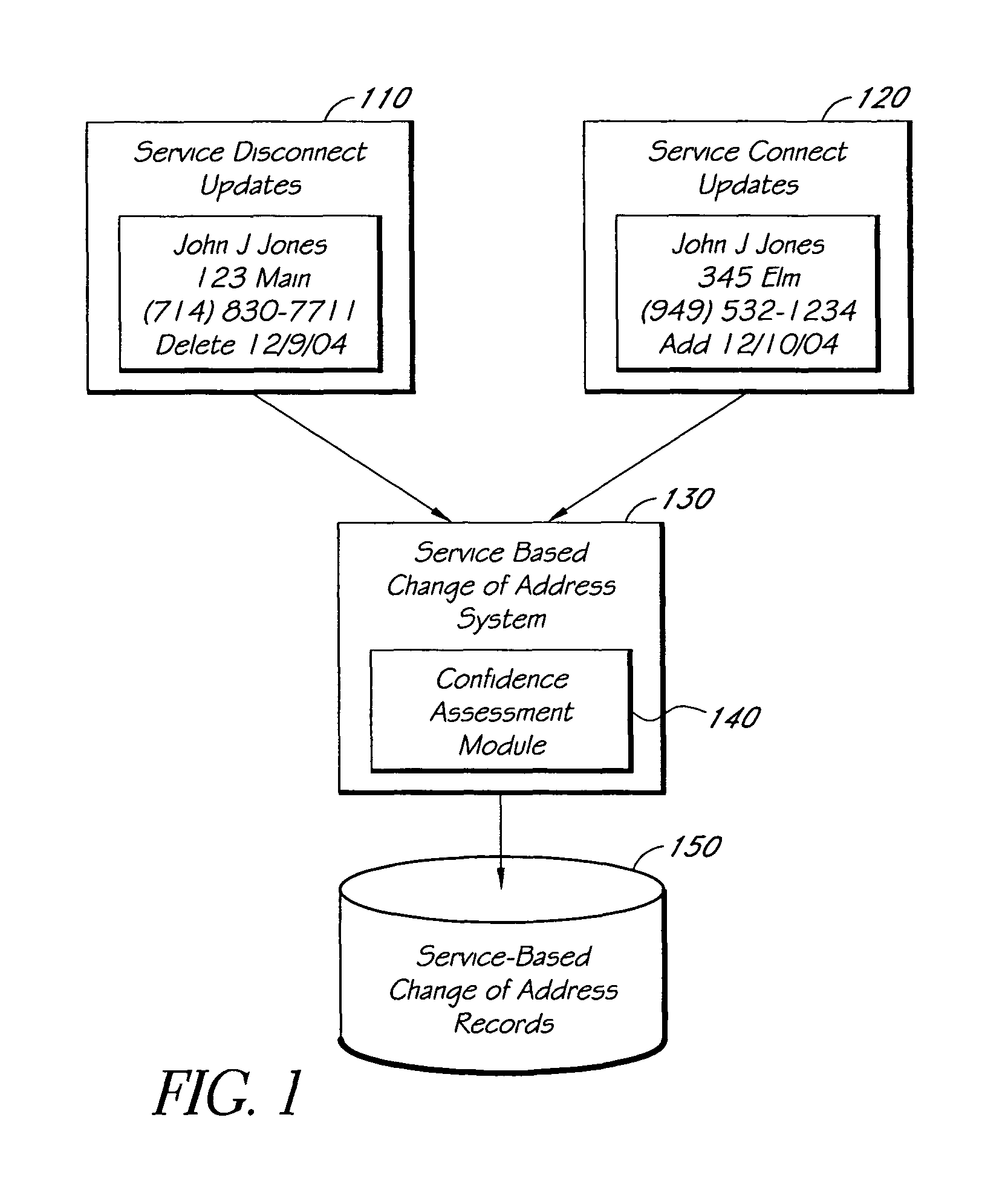
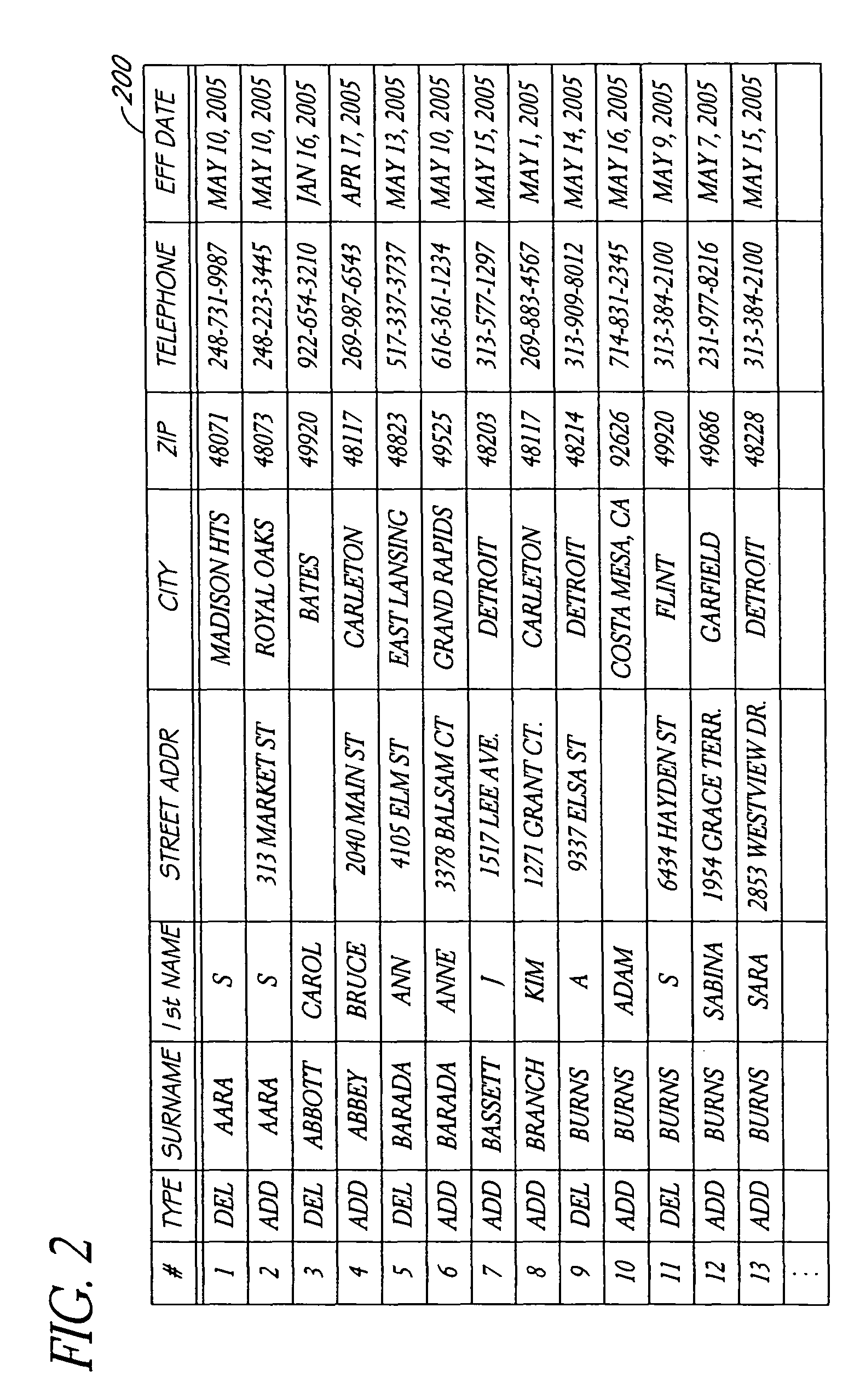
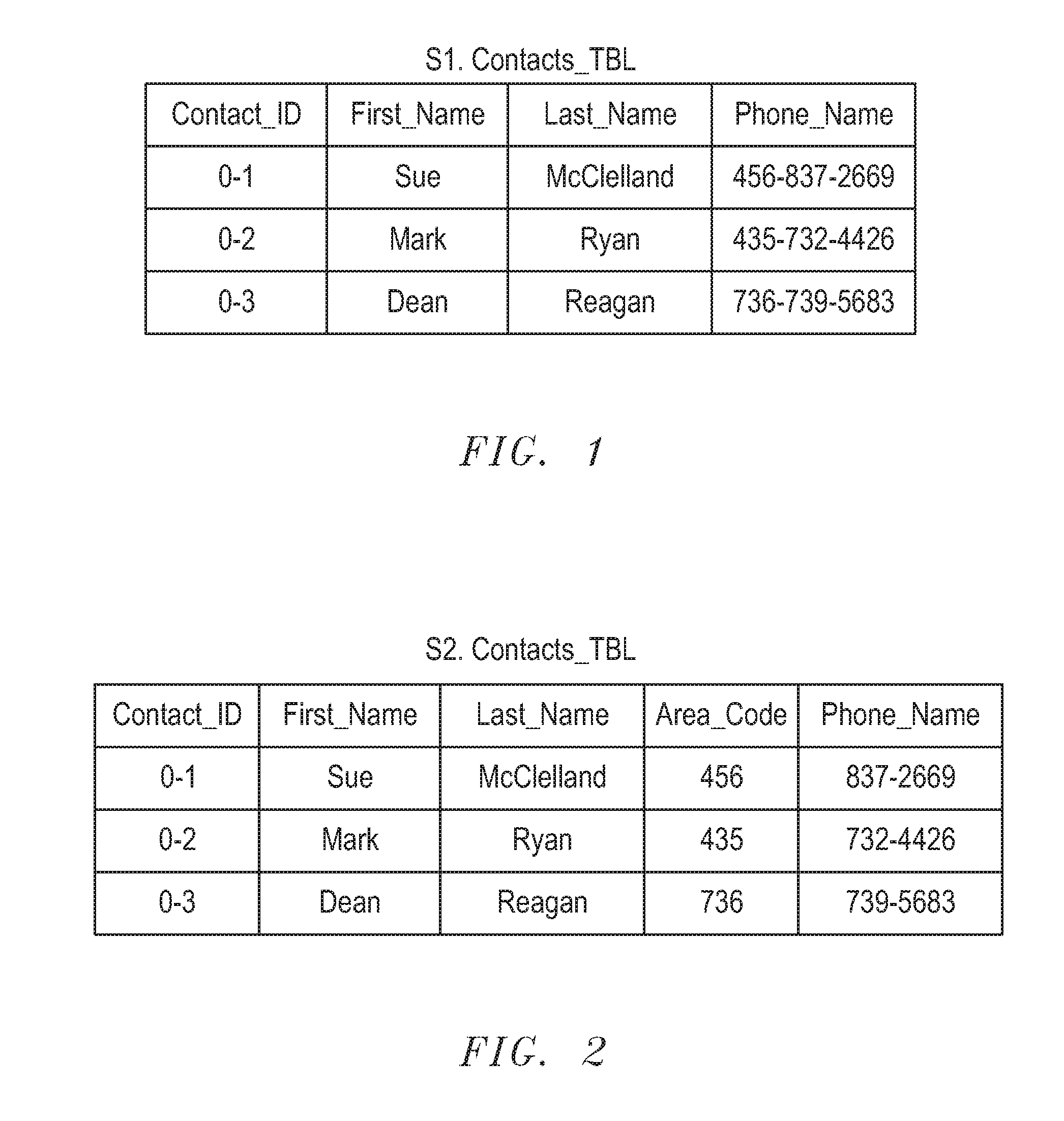
Systems and methods for tracking changes of address based on service disconnect/connect data
ActiveUS8175889B1Quick updateCustomer relationshipDigital data processing detailsEffective dateConfidence metric
A computer-implemented system for updating mailing address or other contact information using service disconnect and connect information, such as for telephone, utility, or other service, is described. Electronic information about service disconnect requests and service connection requests is received and compared to identify requests that are linked to the same individual, household, or other entity. A confidence assessment module may produce an indicator, such as a score, of a confidence level in a correct matching of a disconnect and a connect request, based at least in part on similarity of names or other account information, proximity of addresses, and proximity of effective dates associated with potentially matching service connect and disconnect requests. In some embodiments, service disconnect and connect records from a plurality of services are used.
Owner:EXPERIAN INFORMATION SOLUTIONS
Time controlled pre-paid delivery
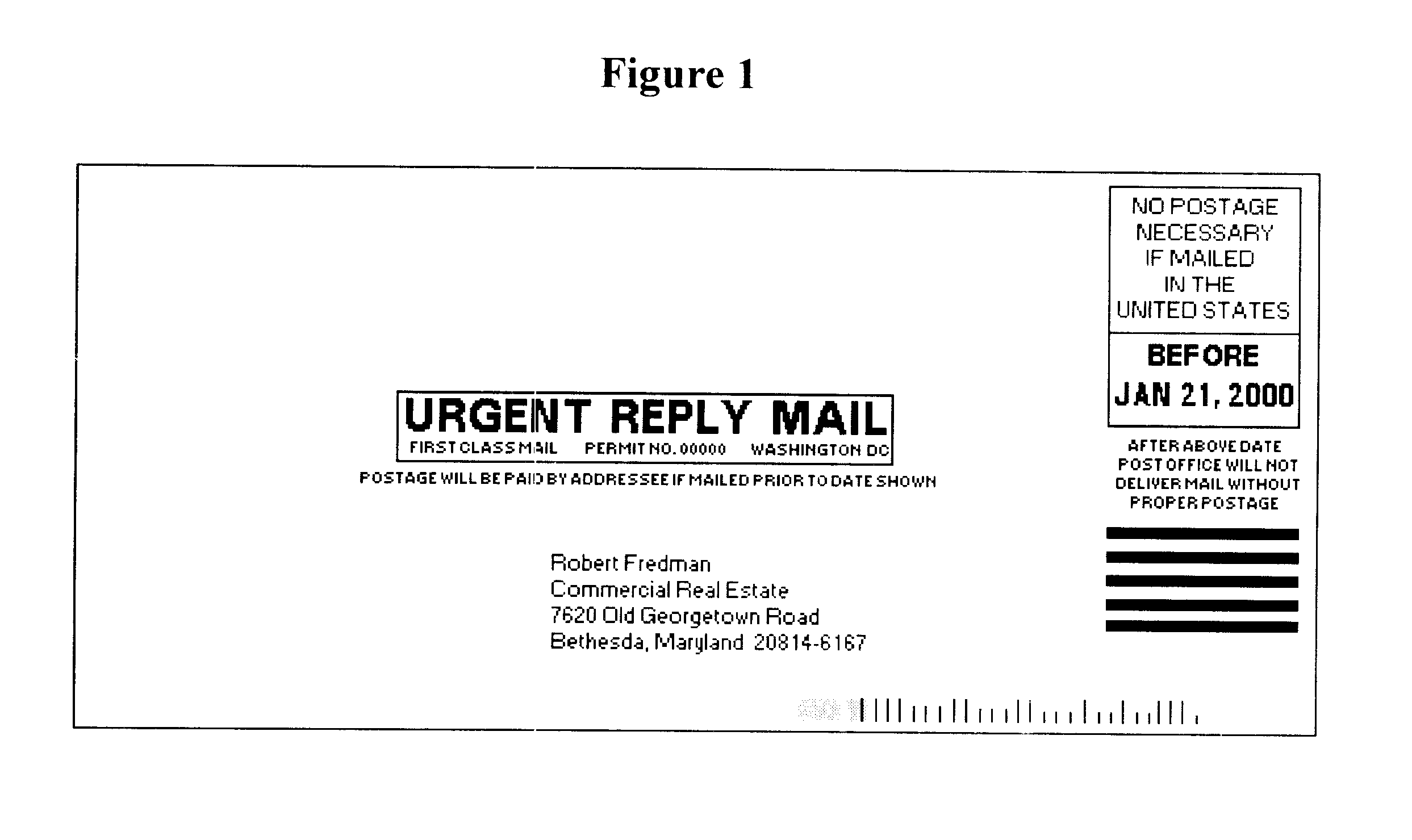
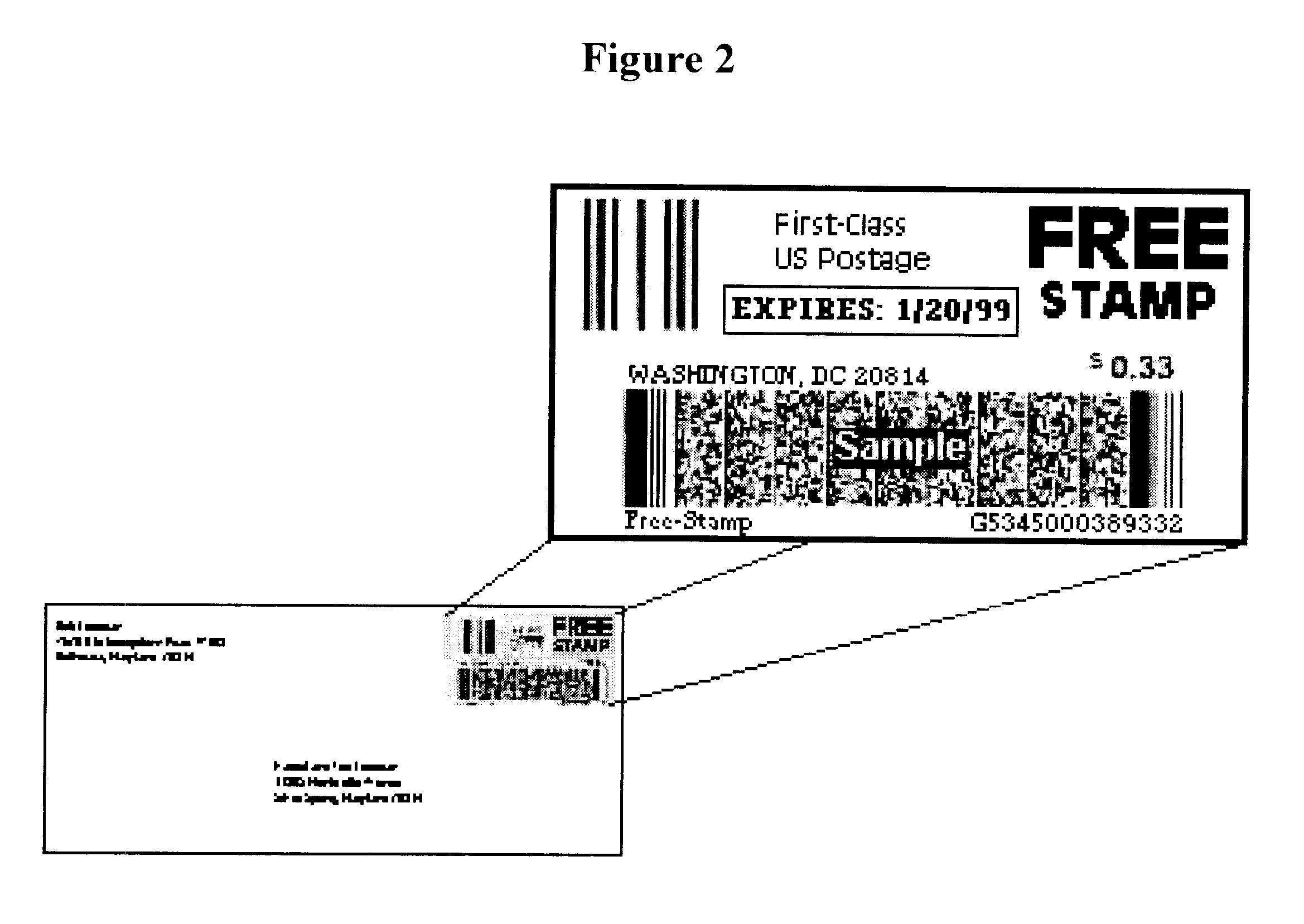
A method for generating, providing, and utilizing time controlled date sensitive pre-paid postage on an item to be delivered, including a desired delivery amount and personalized postage mark, with the intention of causing action prior to a chosen date. An Issuer would send prepaid postage to a Recipient with a chosen effective date and a chosen expiration date. Said effective date and expiration date would allow Issuer to encourage Recipients to initiate action within a predetermined time window. After effective expiration date, postage would expire requiring new postage / delivery fees to be added to the item for it to be mailed / delivered.
Owner:FREDMAN ROBERT ALAN
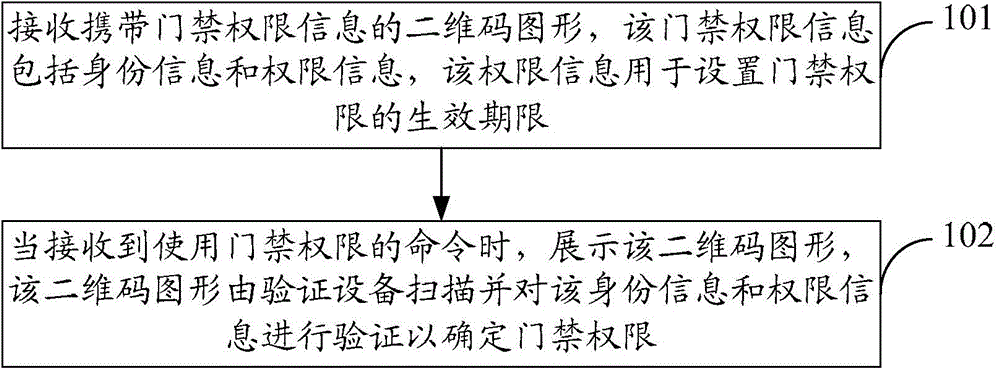
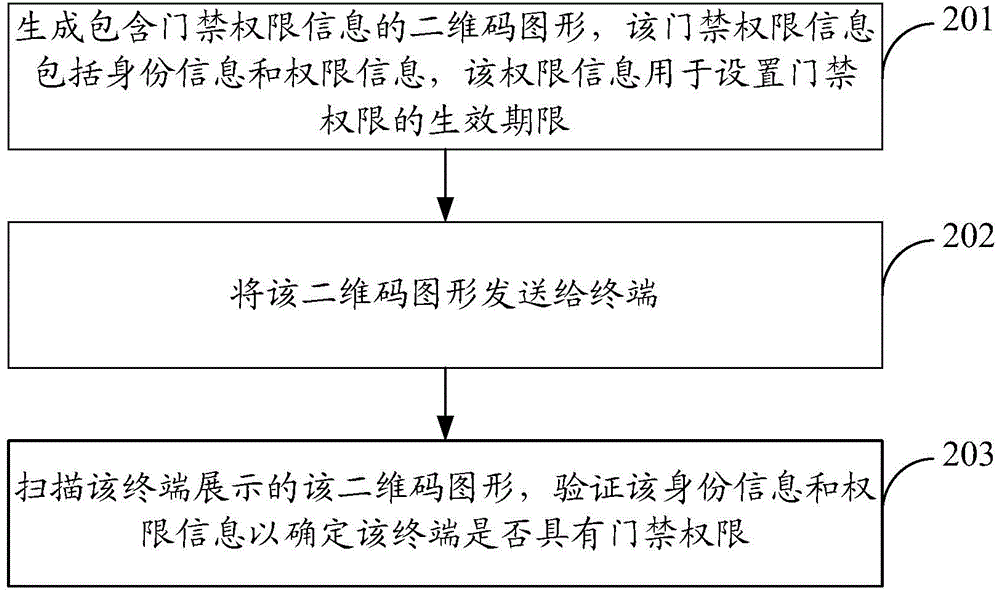
Method, equipment and system used for realization of intelligent entrance guard
The invention discloses a method, equipment and a system used for realization of intelligent entrance guard, and belongs to the field of entrance guard technology. The method comprises following steps: a 2-dimensional bar code graph carrying entrance guard authority information is received, wherein the entrance guard authority information comprises identity information and authority information, and the authority information is used for setting an effective date of entrance guard authority; when commands of using entrance guard authority are received, the 2-dimensional bar code graph is displayed, the 2-dimensional bar code graph is scanned by a verification device, and the identity information and the authority information are verified so as to confirm entrance guard authority. According to the method, the equipment and the system, the entrance guard authority information is transferred in a 2-dimensional bar code manner, and it does no need to prepare card for information storage, so that cost of intelligent entrance guard is reduced. In addition, the authority information contained by the entrance guard authority information can be used for setting the effective date of entrance guard authority, so that the method, the equipment and the system are suitable for long-term utilization of entrance guard, and temporary utilization of entrance guard, and application range is more extensive.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Deep blockage removal and injection increase method for water injection well of medium-and-high-permeability sandstone reservoir
InactiveCN104295275AImprove injection effectIncrease validity period of boosterCleaning apparatusFluid removalEffective dateSewage
The invention provides a deep blockage removal and injection increase method for a water injection well of a medium-and-high-permeability sandstone reservoir. The method mainly solves the problems of oil pollution, deep blockage removal of a ground layer and the like of a sewage injection well, which can not be solved in the existing conventional acidification method. In the method, the slug type injection technology of "washing-clearing-blockage removing-stabilizing" is adopted; and the injection increase effect can be improved and the injection increase effective date can be prolonged. The method comprises the following steps: during construction, firstly, the well is backwashed at high displacement, and impurities near a well bore and a bore hole are washed; secondly, organic blockages near an oil layer are washed; then, organic and inorganic blockages in the areas near the well and the deep part of the oil layer are removed in the mode of multistage injection and multiple acid liquid systems, so that the seepage capability is improved; and finally, stabilizing treatment is adopted for prolonging the injection increase effective date. Through the adoption of the slug type injection technology, blockage damage is removed in batches, and substrate treatment, scale prevention treatment and scale inhibition treatment are performed so that the injection increase effect is improved, the injection increase effective date is prolonged and a better blockage removal effect is achieved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
System and method for the display of versioned documents and amendments
InactiveUS20070057967A1Overcome limitationsEasy to viewCathode-ray tube indicatorsNatural language data processingEffective dateDisplay device
A system and method are disclosed for displaying on a computer display a periodically amended document, such as statutes, regulations, city ordinances, or other legal rules. The system enables a user to easily view the currently effective version of the document, prior versions of the document, future versions of the document containing amendments already passed by a legislative body, and the amending documents (or acts) that have altered or will alter the document, and the changes made by the amending documents. The displays of amendments and document text can be carried backward or forward to display multiple cycles of amendments and resulting text, resulting in a complete history of the document. Additionally, the invention informs the user of the precise dates upon which amendments took effect, or will take effect, along with the beginning and ending effective dates for each displayed version of the document.
Owner:GERONIMO DEV CORP
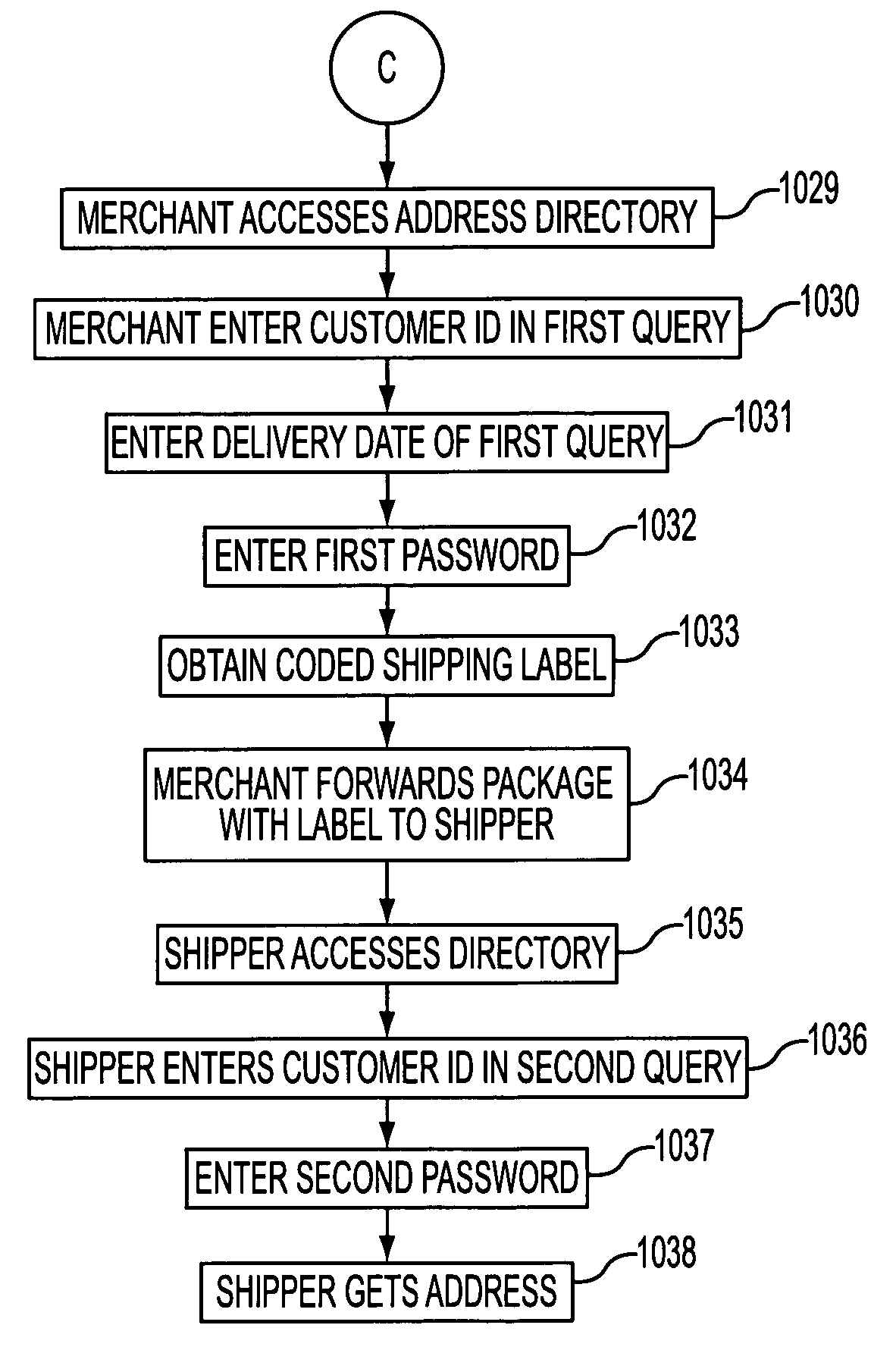
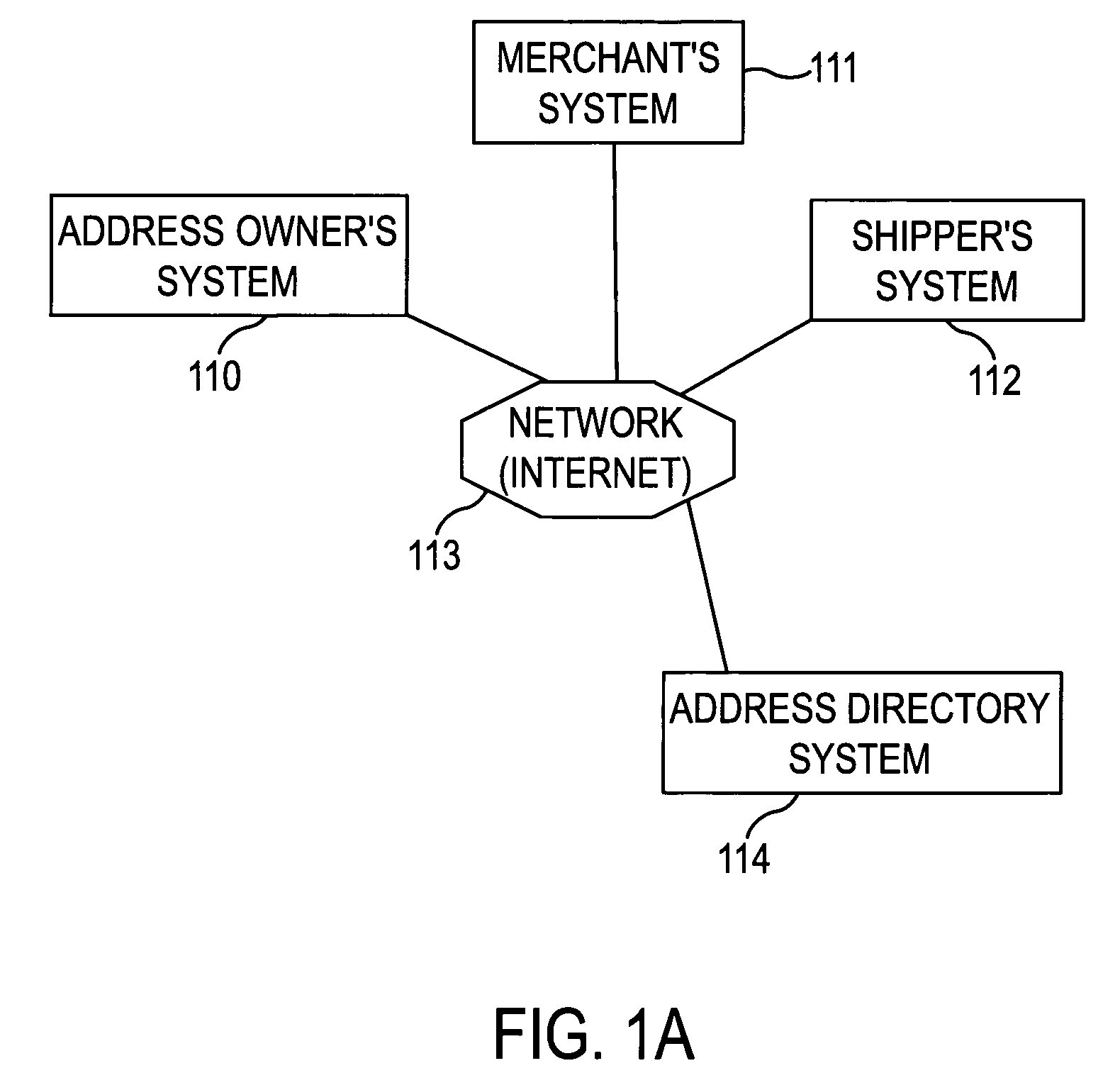
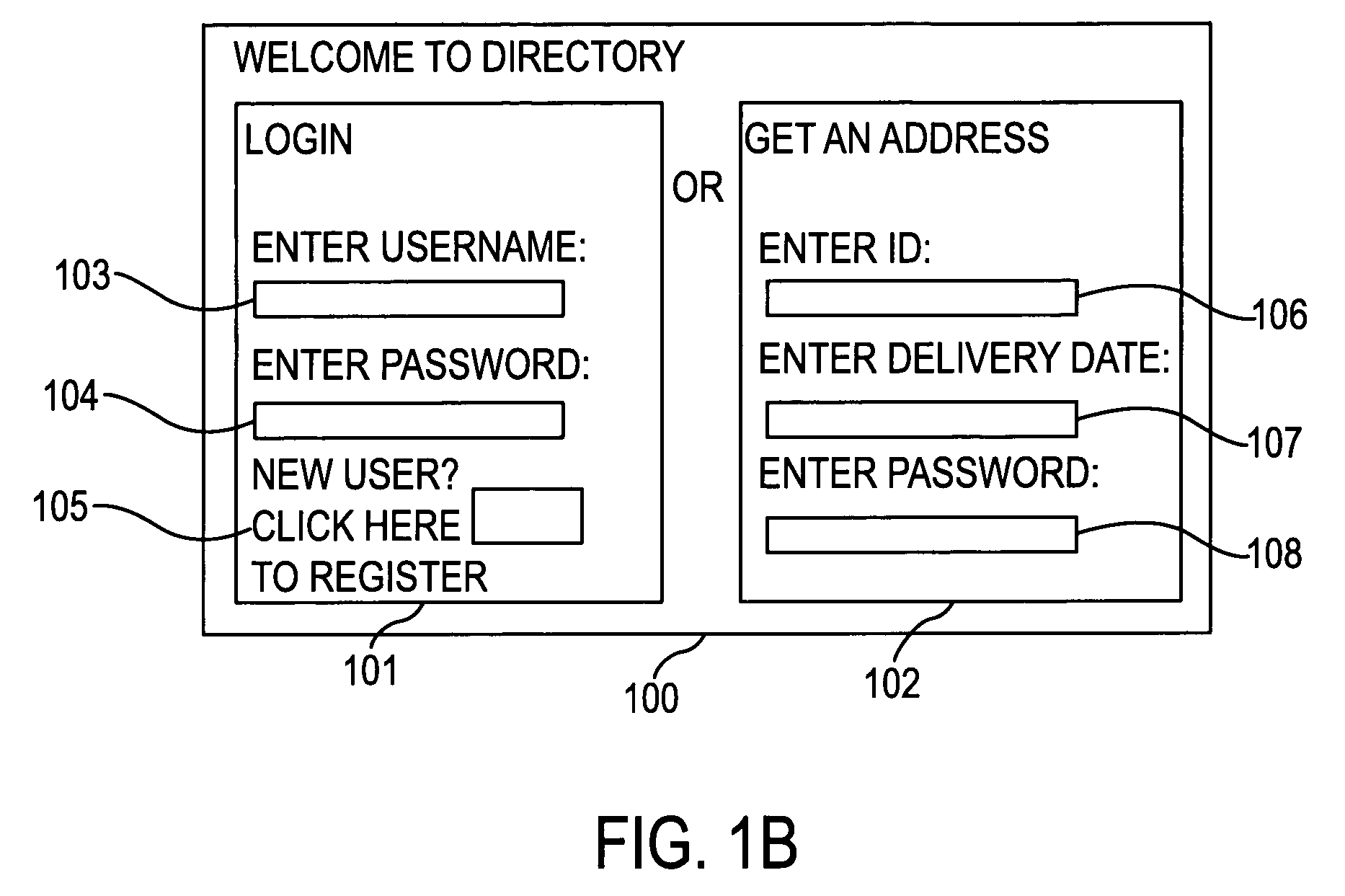
Real-time addresses for direct mail using online directories
InactiveUS7254549B1Quickly and easily updateAccurately reflectFinanceLogisticsEffective dateIp address
A system and a method are provided for an online address directory that may be updated by the address owner in real time, via the Internet, the telephone, wireless web, or otherwise. The address entry may contain an address for the address owner, together with beginning and ending effective dates for the address to ensure that the address information is current for any given date. The address owner may select a level of security for the address entry, to permit open or restricted access to the address entry, and may specify those persons who may view the entry. A person seeking address information for the address owner may obtain that information by entering an identifier correlating to the address owner, the dates of interest, and if required, a key, into a query in the directory, thereby obtaining accurate address information for the date of interest.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
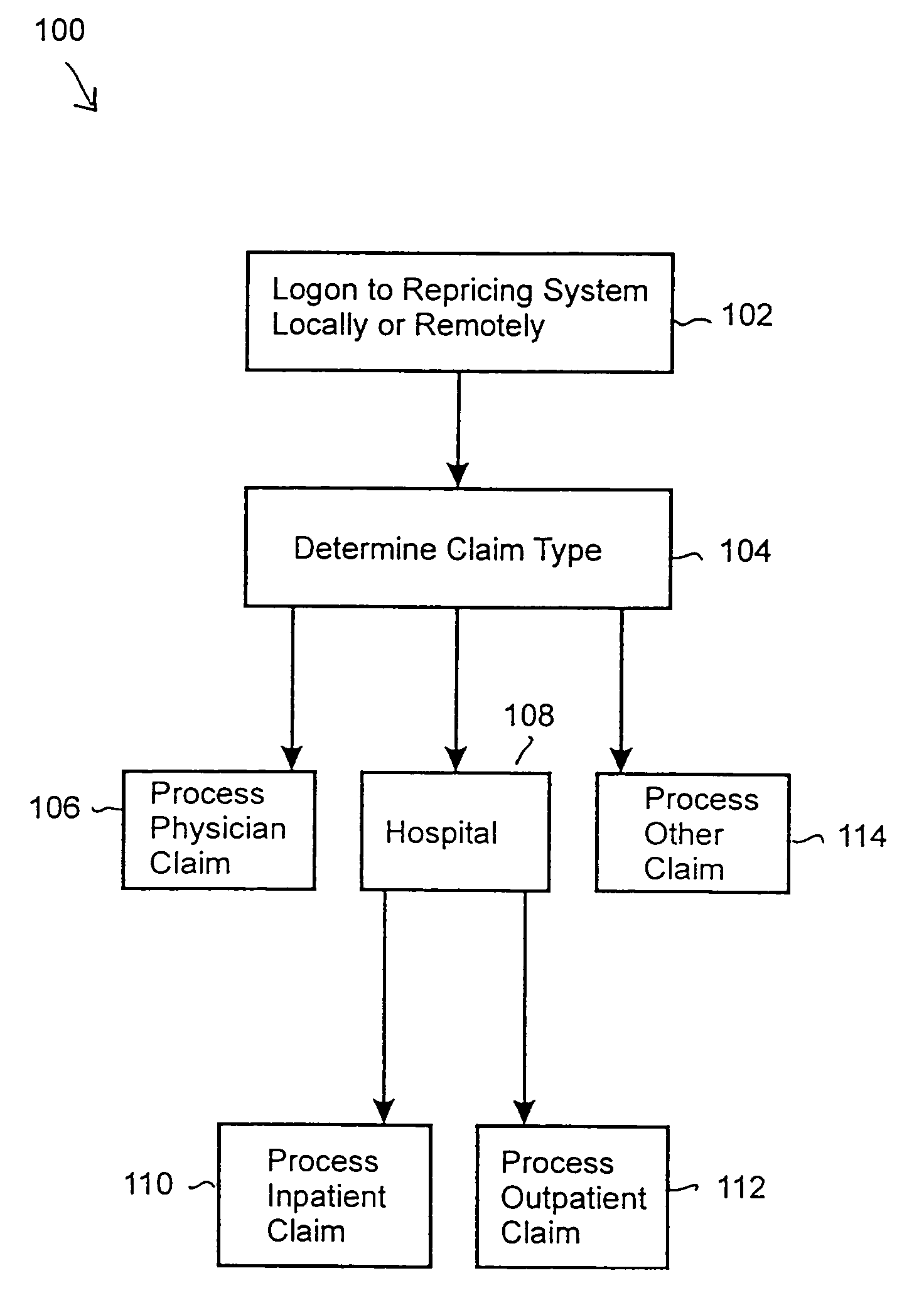
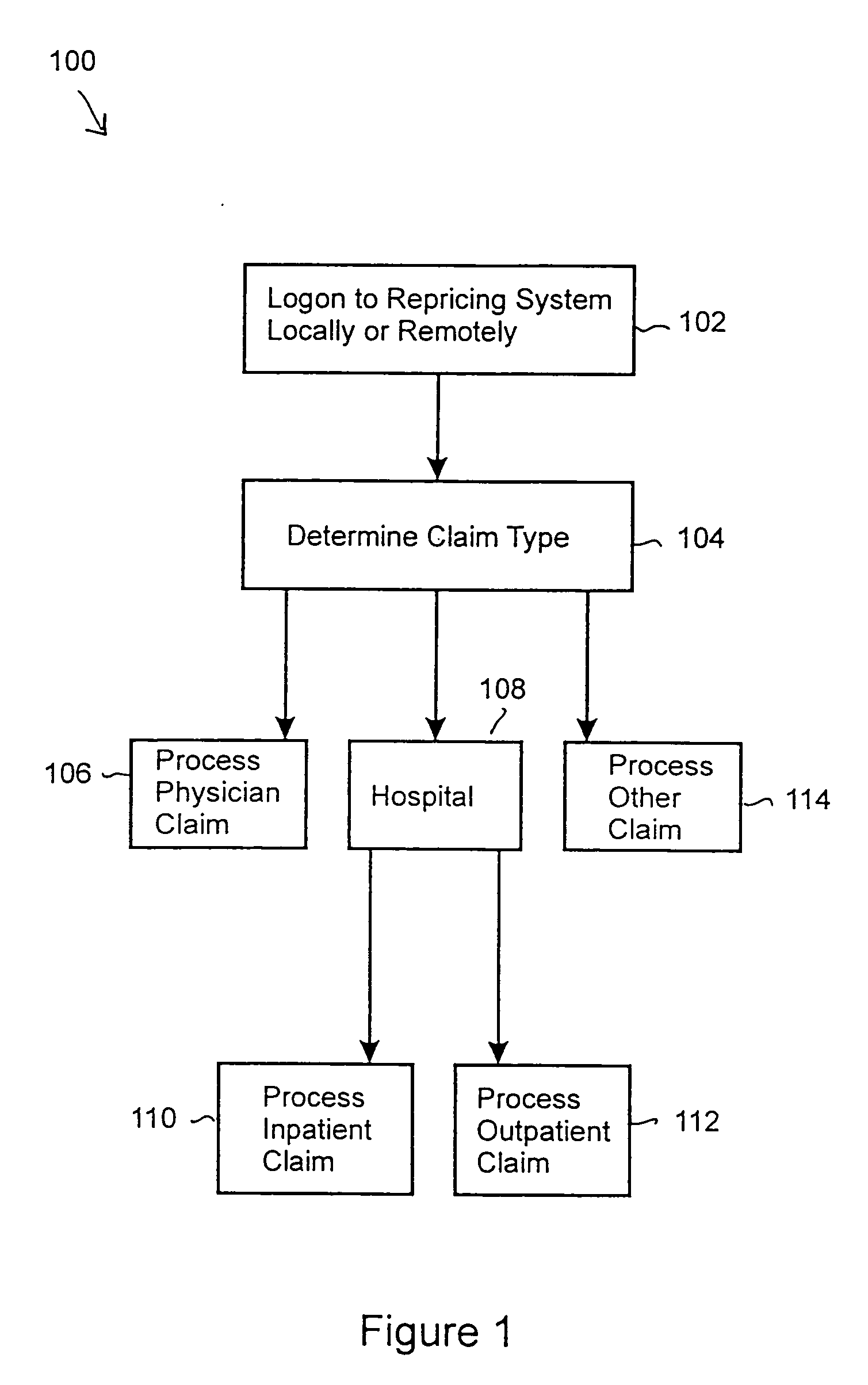
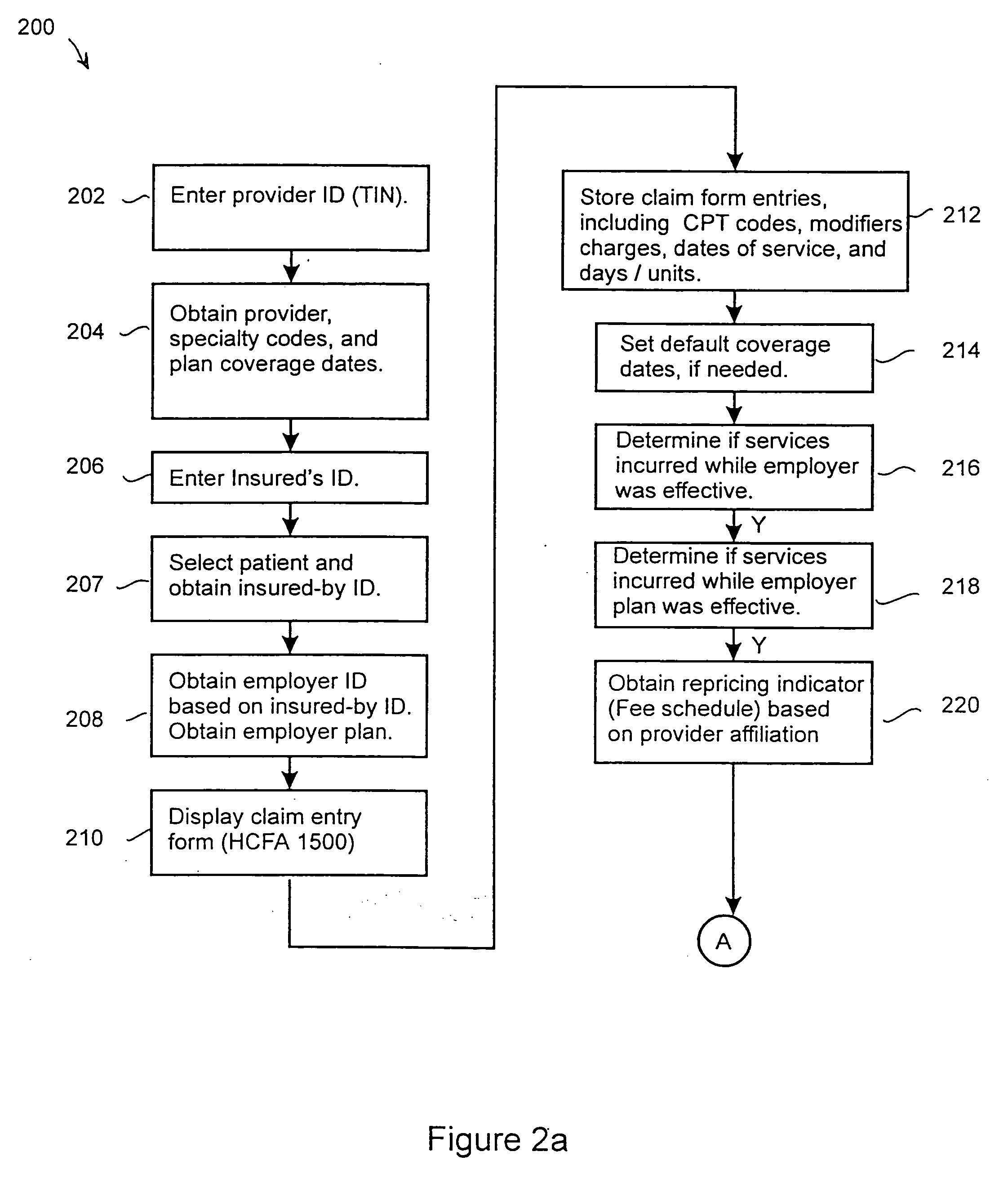
Automated claim repricing system
InactiveUS20050033612A1Quickly and accurately and reliable repriceQuick and efficientFinanceOffice automationEffective dateProgram instruction
The present claim repricing system generally includes a processor and a program and data memory coupled to the processor. The memory stores the requisite database tables, as well as program instructions for repricing several different types of claims, including physician, inpatient, and outpatient claims. The claim repricing system includes instructions for determining availability of insurance plan coverage to the patient based on an effective date of the employer insurance plan, as well as determining the availability of the physician or provider based on an effective provider date. The claim repricing system further handles specialty codes and exceptions. For example, the claim repricing system includes instructions for determining the presence of anesthesia specialty codes, and for determining the correct number of anesthesia units and an anesthesia repricing indicator. The anesthesia repricing indicator may be a percentage discount, for example, or a rate. Furthermore, the claim repricing system may operate in a batch processing mode to quickly, accurately, and reliable reprice large amounts of claims.
Owner:DONOVAN EDWARD JOSEPH +2
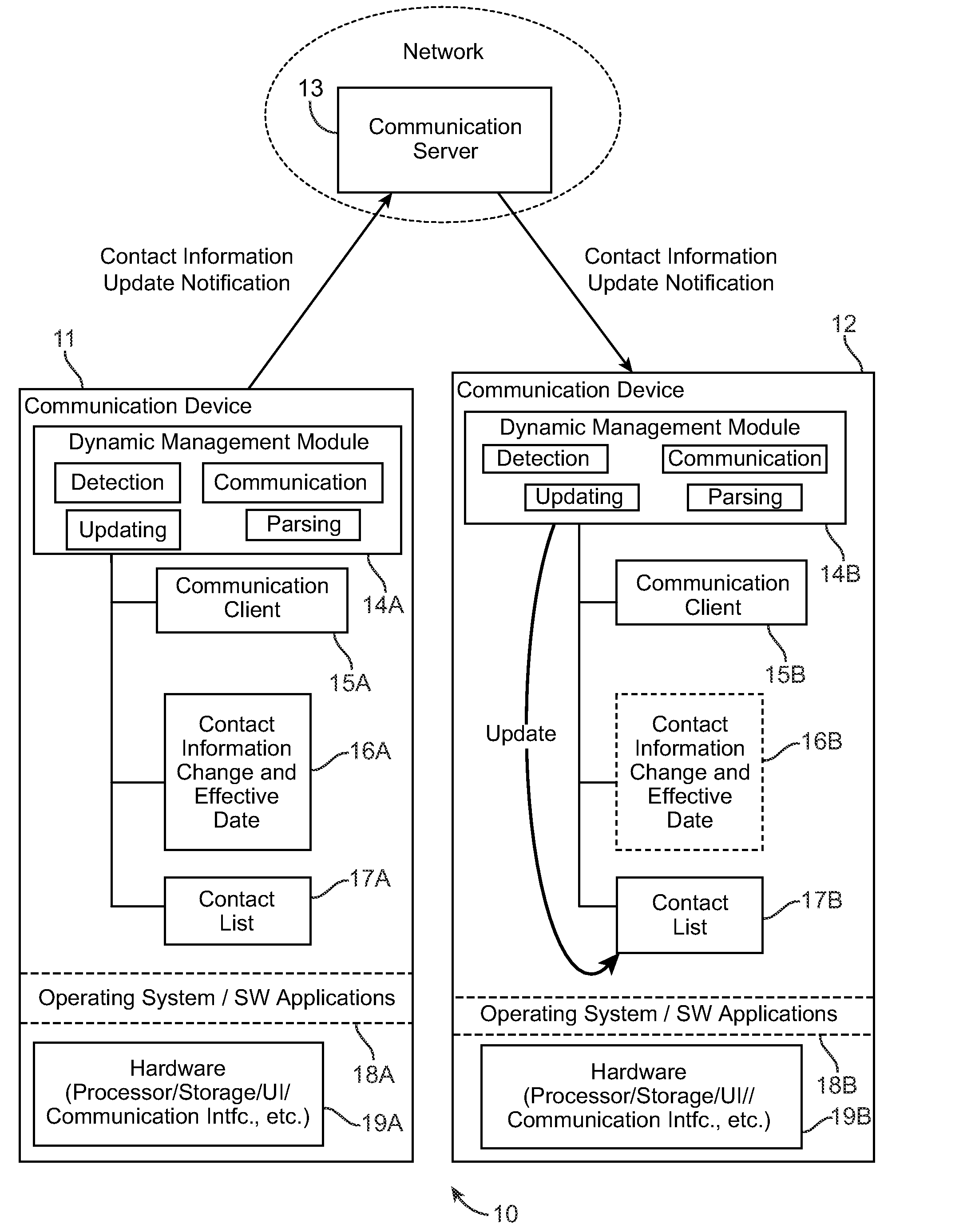
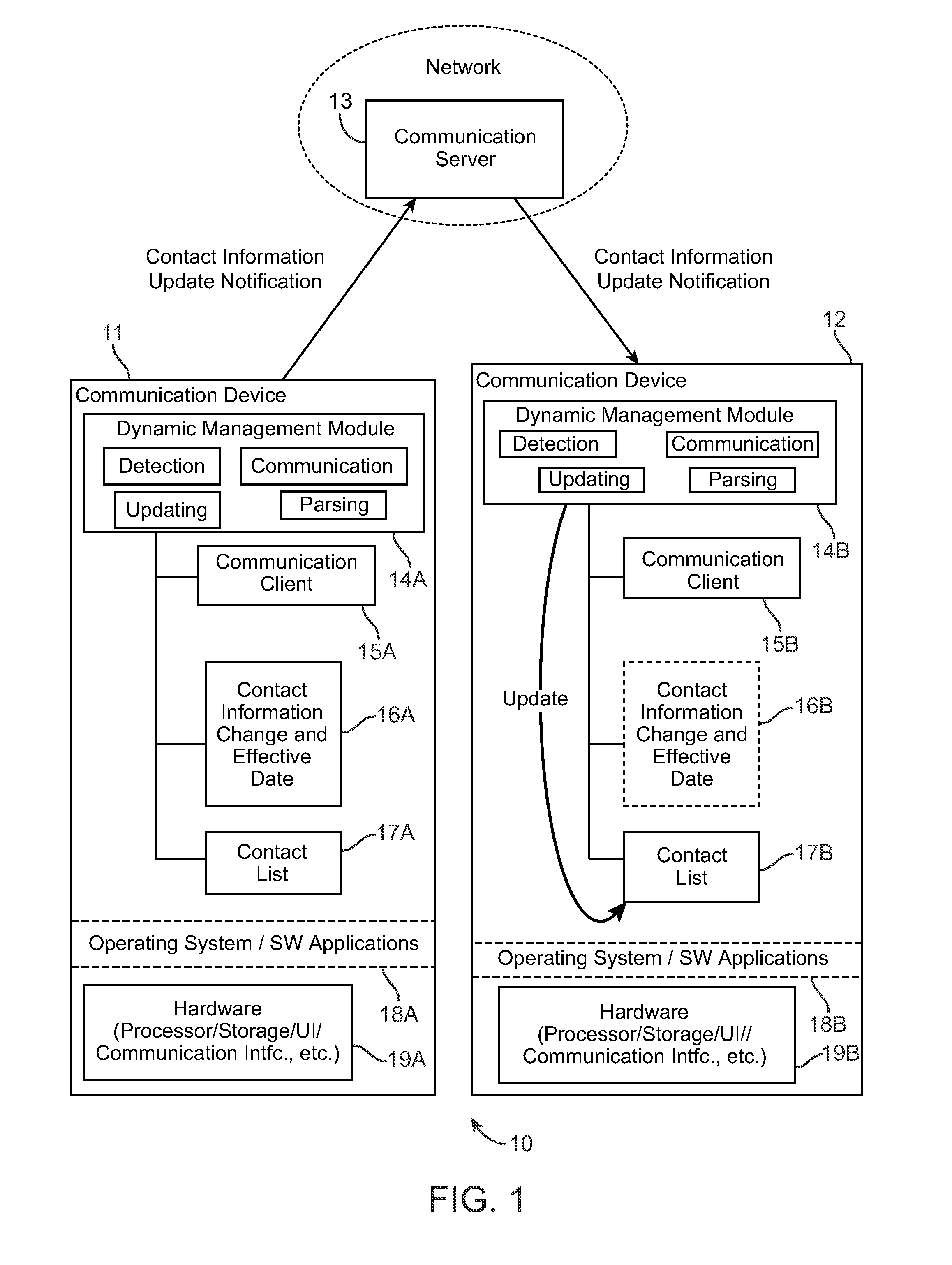
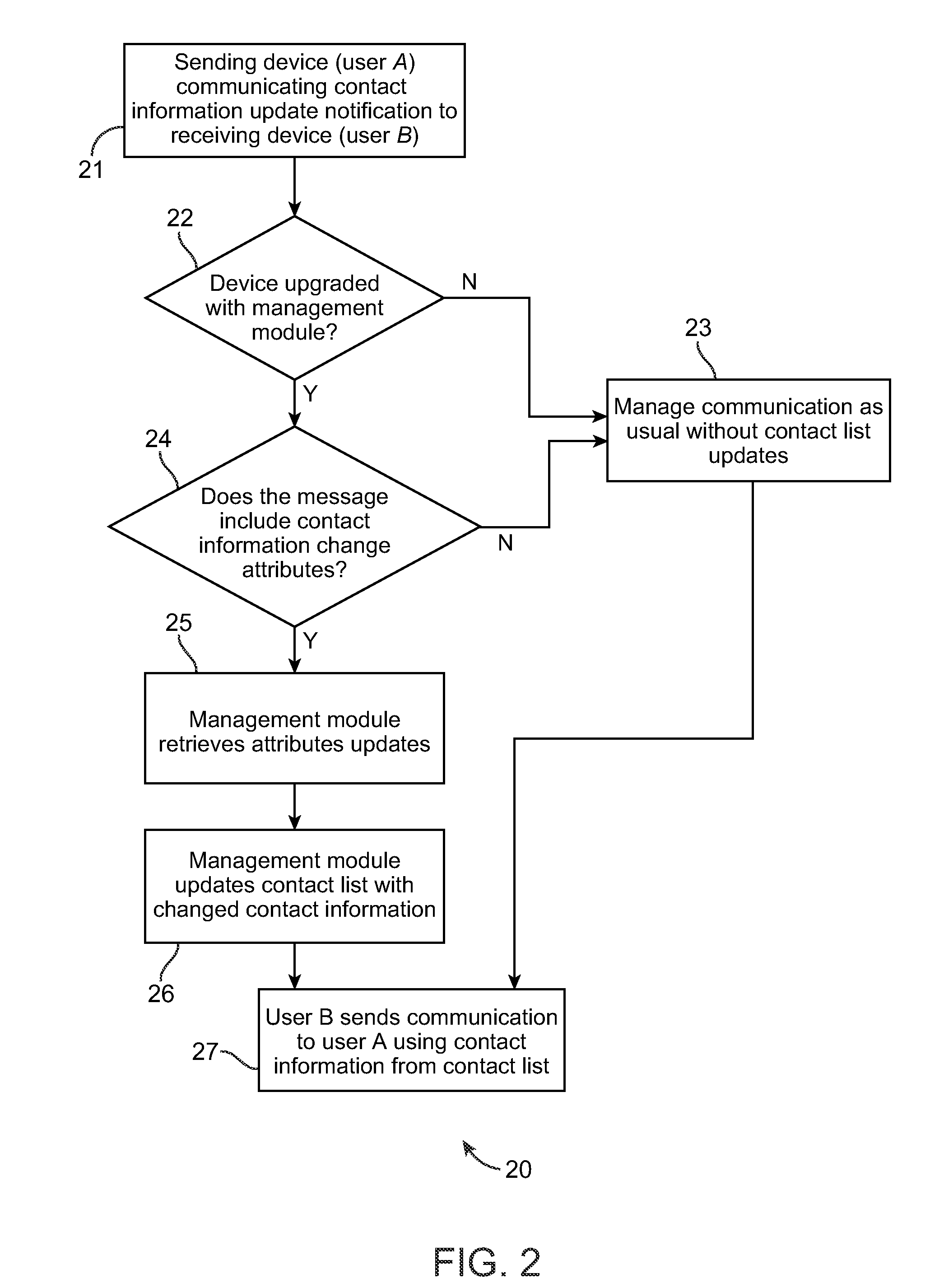
Method and system for dynamic contact information management in electronic communication devices
InactiveUS20100076926A1Digital data processing detailsSubstation equipmentEffective dateElectronic communication
A method and system for user contact information in electronic devices is provided. One implementation involves detecting a change in a user contact information at a first electronic device, determining effective date of the change in the contact information, storing the contact information change and effective date in a memory store, automatically communicating the contact information change and effective date to a second electronic device, and applying the received contact information change to a contact information list in a memory store of the second device, on or after the effective date.
Owner:IBM CORP
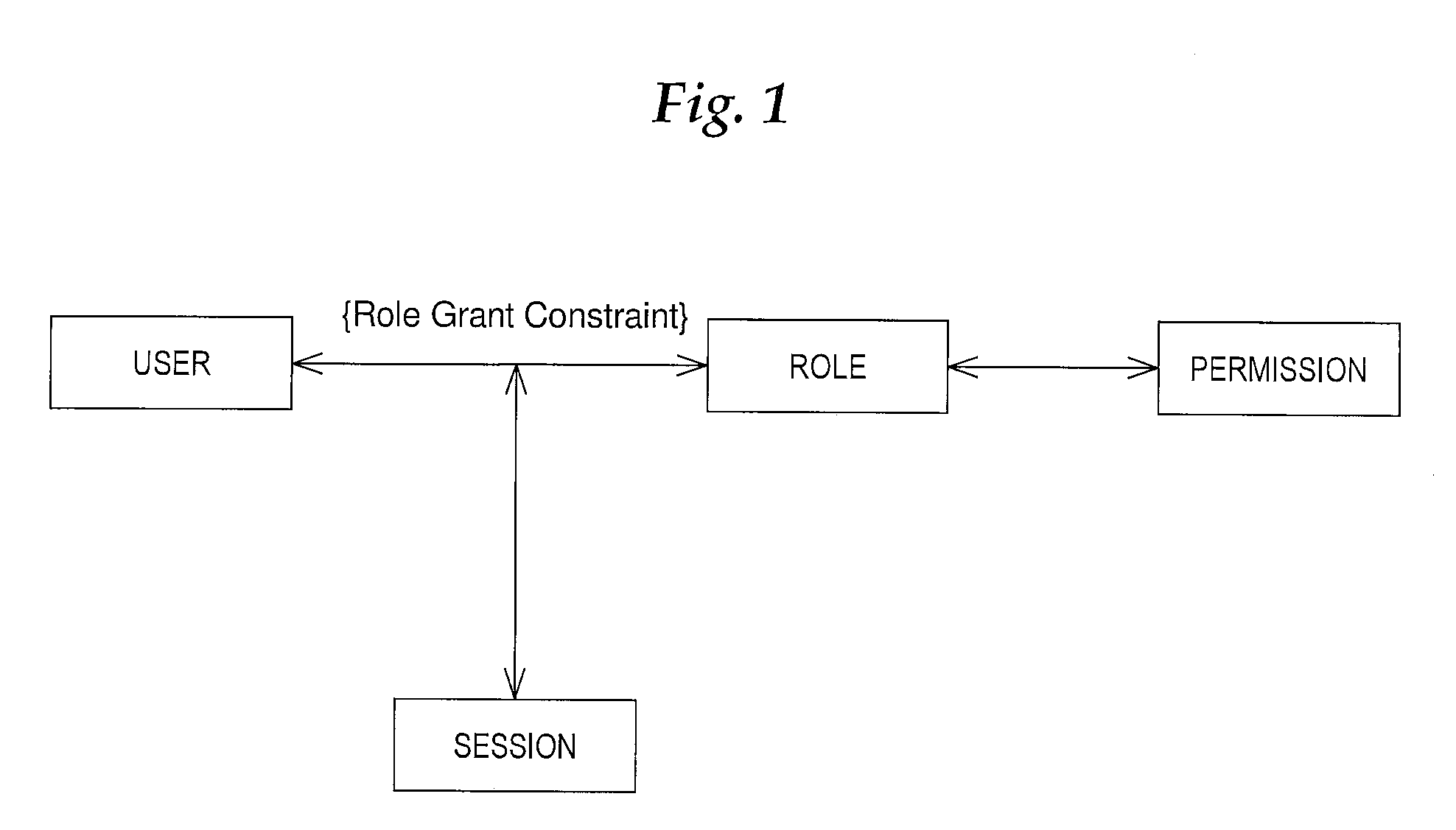
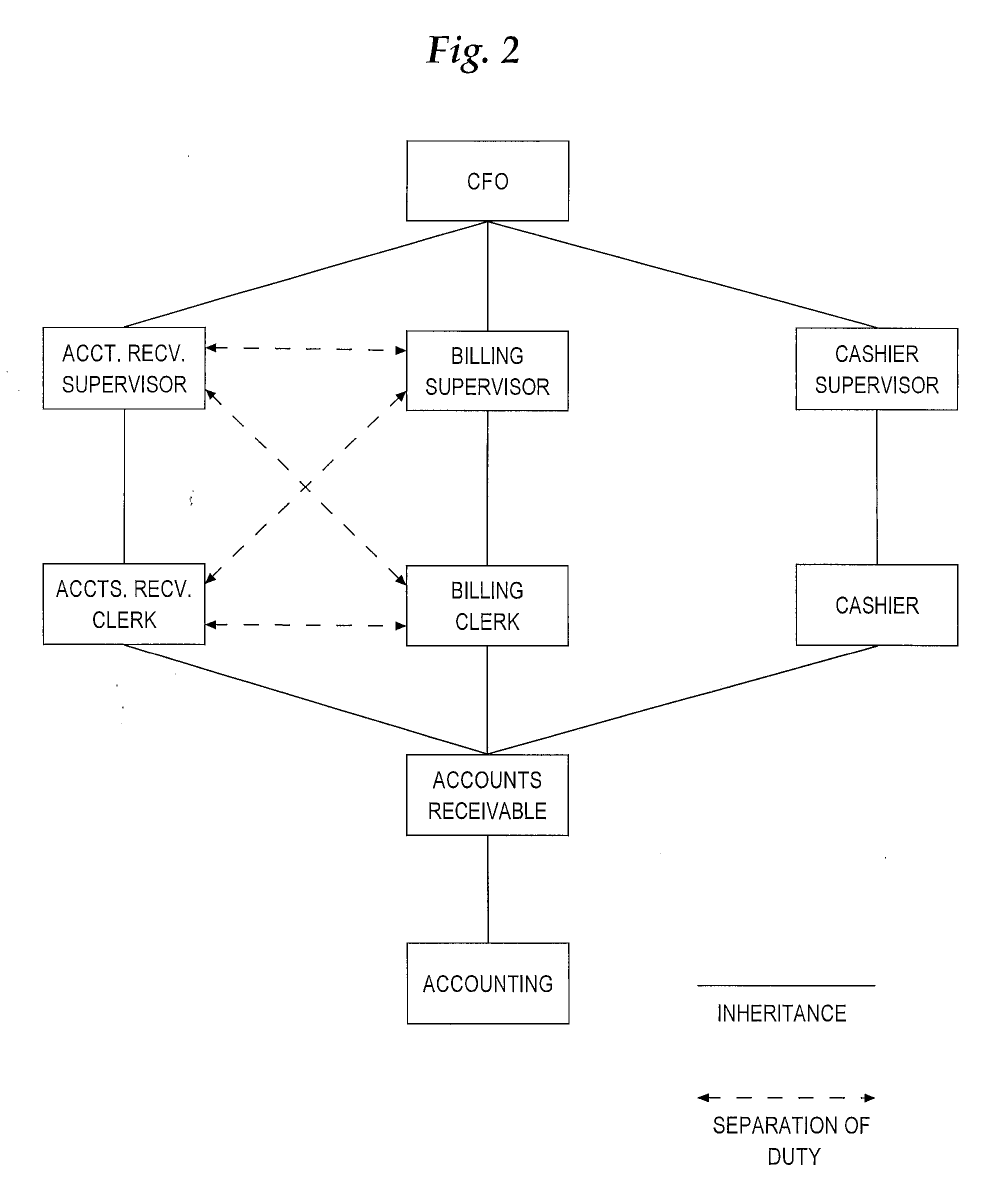
System and method for implementing effective date constraints in a role hierarchy
ActiveUS20100306268A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsEffective dateData store
A system providing a method for implementing effective date constraints in a role hierarchy is described. In one embodiment, for example, the method comprises the steps of: storing data that represents a first effective date constraint on a role of a role hierarchy, the first effective date constraint having a start date and an end date; storing data in a database that represents a second effective date constraint on a grant of the role to a grantee, the second effective date constraint having a start date and an end date; storing data in a database that represents a third effective date constraint on the grantee, the third effective date constraint having a start date and an end date; and computing a net effective date constraint for the role by computing the intersection of the first effective date constraint, the second effective date constraint, and the third effective date constraint.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
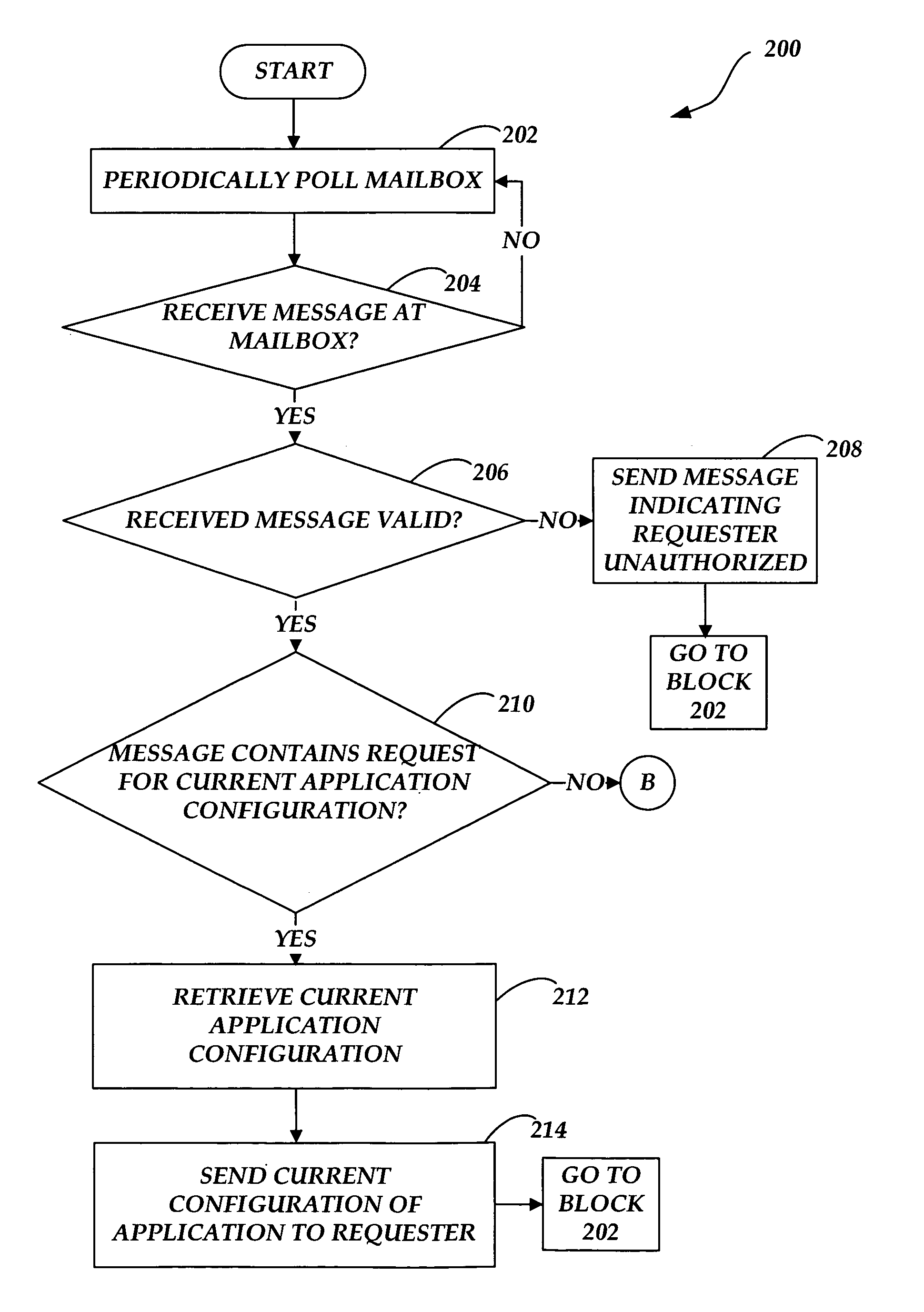
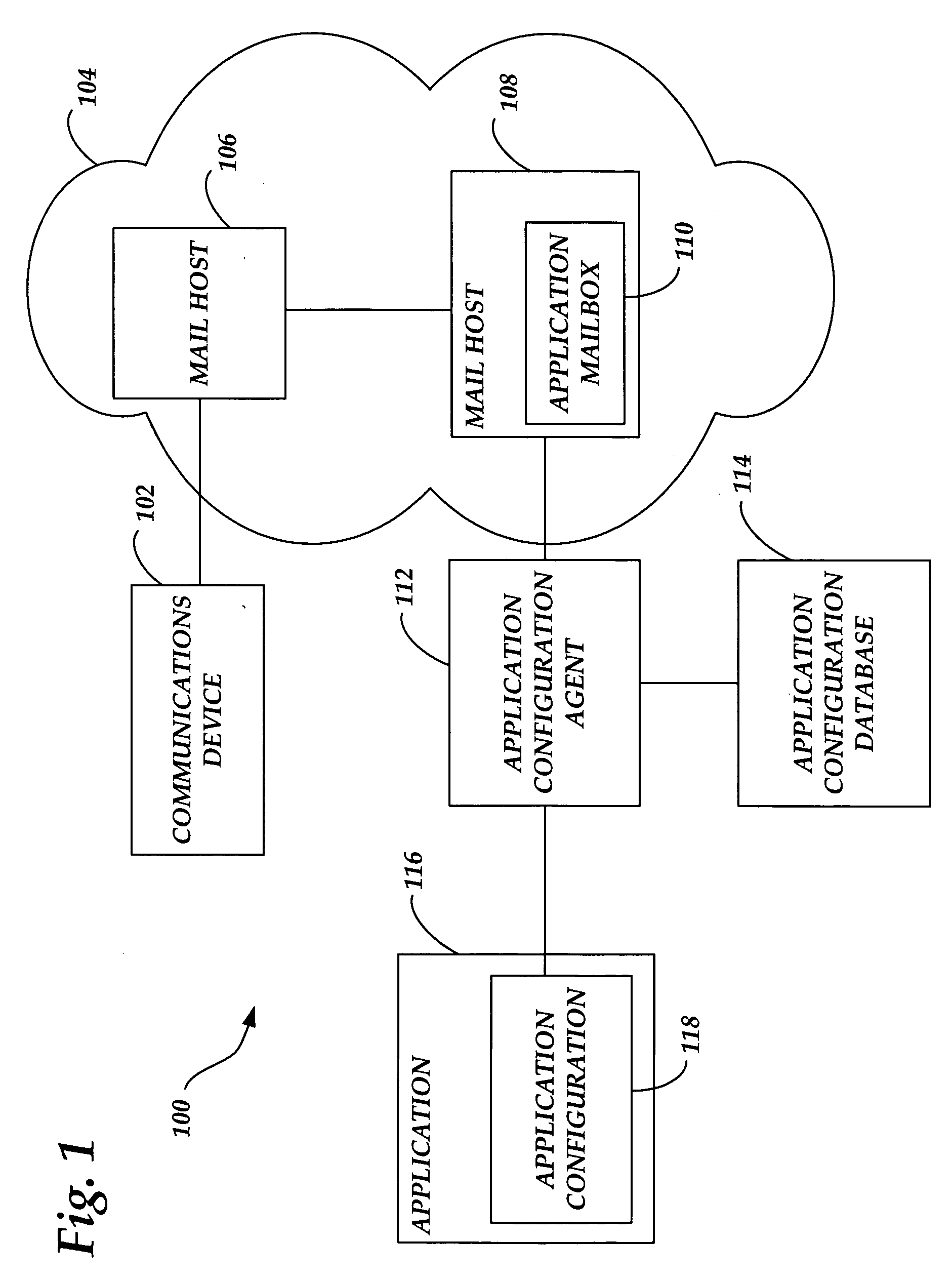
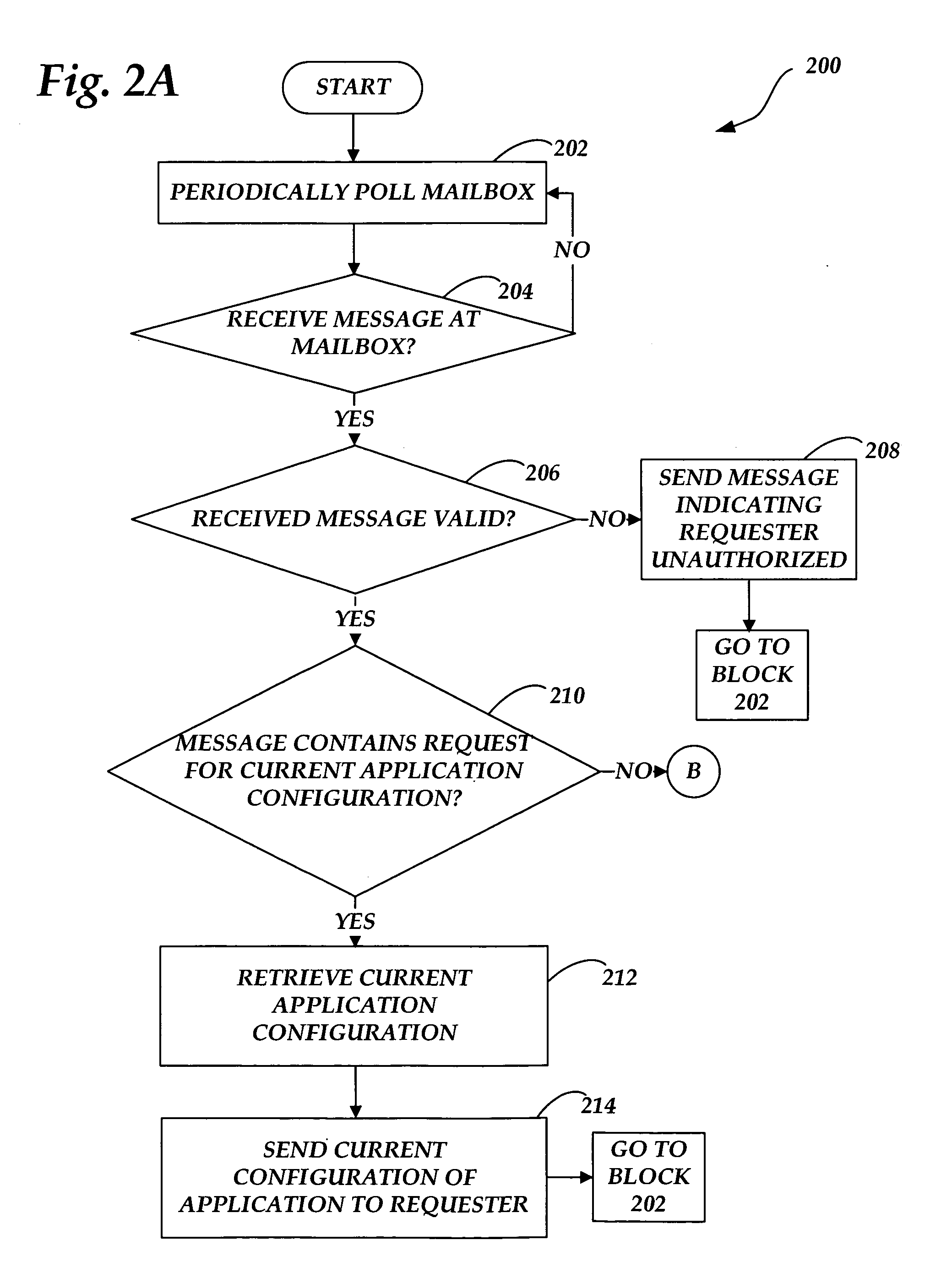
Systems and methods for managing application configuration
ActiveUS20060242637A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsEffective dateMessage passing
Systems and methods are provided for managing an application configuration using messaging over a communications network. A configuration message including configuration changes to the application and a corresponding effective date when the configuration changes are to be applied to the application is received. Following the receipt of the configuration message, the message is stored. When the effective date occurs, the configuration changes from the received configuration message are applied to the current configuration of the application.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
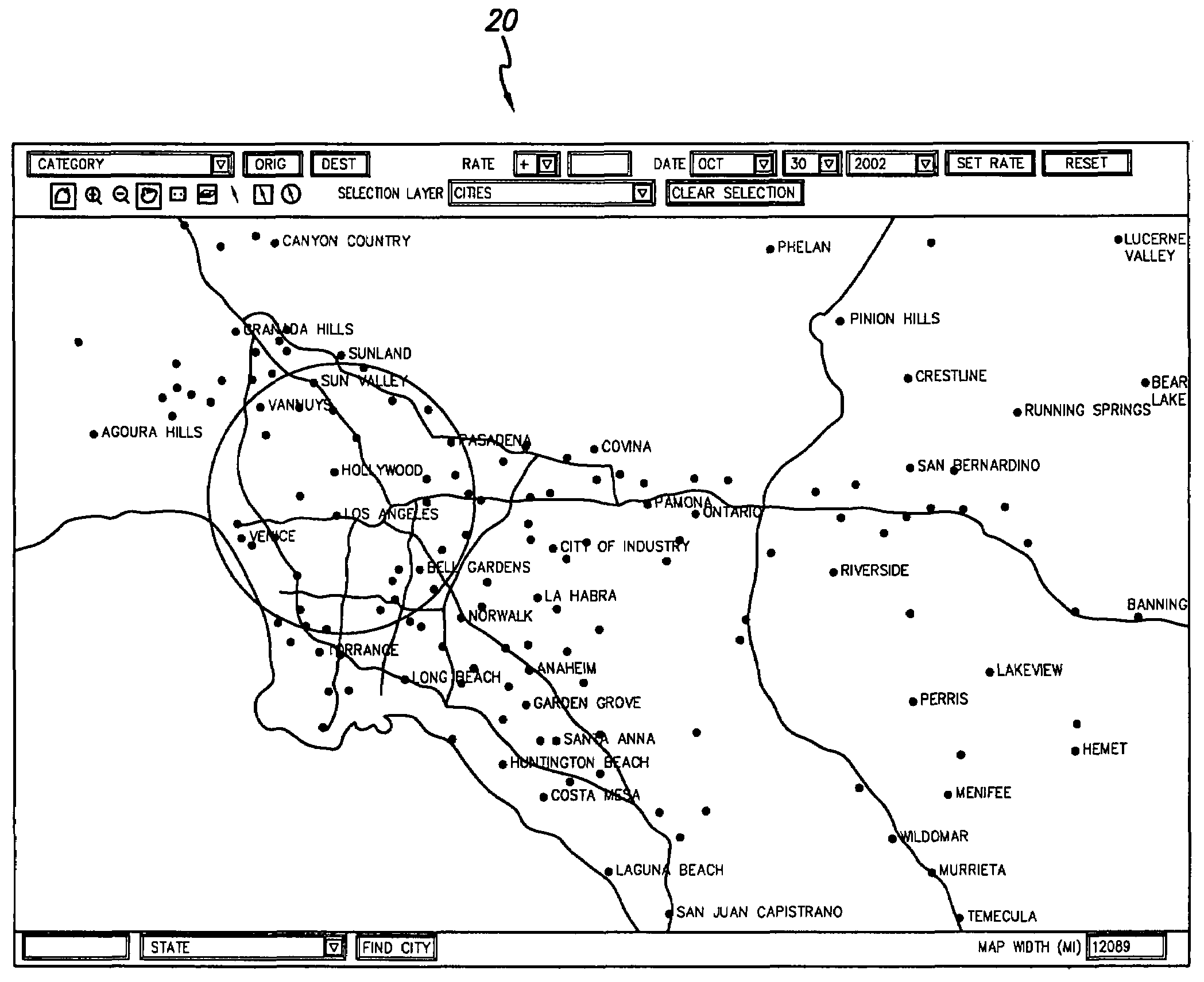
Rate and distribution system
ActiveUS7676376B2Accurately and quickly generateReservationsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsGraphicsEffective date
The rate and distribution system of the present invention enables an user to more accurately and quickly generate specific rental rates employing a browser-based system. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the rate and distribution system includes an interactive graphical mapping interface depicting the geographic location of the entities of an equipment rental business. The mapping interface preferably comprises a touchscreen and is configured to allow an user to define a region by selecting it on the map. Upon defining a region, the system enables the user to set a rental rate for the defined region. In a more preferred embodiment of the invention, the system enables the user to identify the equipment category to which the rate applies and select a future effective date for the rate.
Owner:U HAUL INT
Mobile file, indentification and security system device
InactiveUS20080055050A1Save livesStrengthen security controlAnti-theft devicesSubscribers indirect connectionDriver/operatorCheck point
A mobile file, identification and security system device is disclosed with a particular architecture for allowing a card swiper / reader, vehicle computer, signal processor, signal receiver / transmitter, and receiver with display screen and speaker to transmit status / data-information i.e. a person name, vehicle tag and registration numbers, vehicle insurance effective dates, vehicle driver-owner-occupant name, vehicle make-model-color and associated business-commercial name and address affiliation, etc to any home, medical office, security gate check point, law enforcement / security vehicle, or remote location for verification, convenience, and identification and also for allowing a law enforcement / security officer portable handheld vehicle anti-theft device to jam / disable a vehicle engine-electronics system while in motion (being pursued) or parked. Intended user is the military and law enforcement, and any home, medical office, security gate checkpoint, or vehicle. The present systems key advantages provides a standoff identification-security system and a highway safety offensive-defensive weapon system tool / device for the military, law enforcement, and general public, and an assistive mobile / portable medical file / record and tool for emergency situations. The present systems key objectives are to support, improve and reinforce the Department of Homeland Security Highway Safety Initiatives and the War on Terror.
Owner:BROWN ROBERT
Systems and methods of managing assignments
Disclosed are systems and methods of making assignments, particularly of sales leads. The assignments are considered either committed or uncommitted responsive to an effective date associated with one or more assignment rule used to make the assignments. Uncommitted assignments may be used to review the effects of changes in assignment rules. Examples are provided including the use of uncommitted assignments to review the effects of changes in a hierarchical territory structure.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dynamic legal database providing historical and current versions of bodies of law
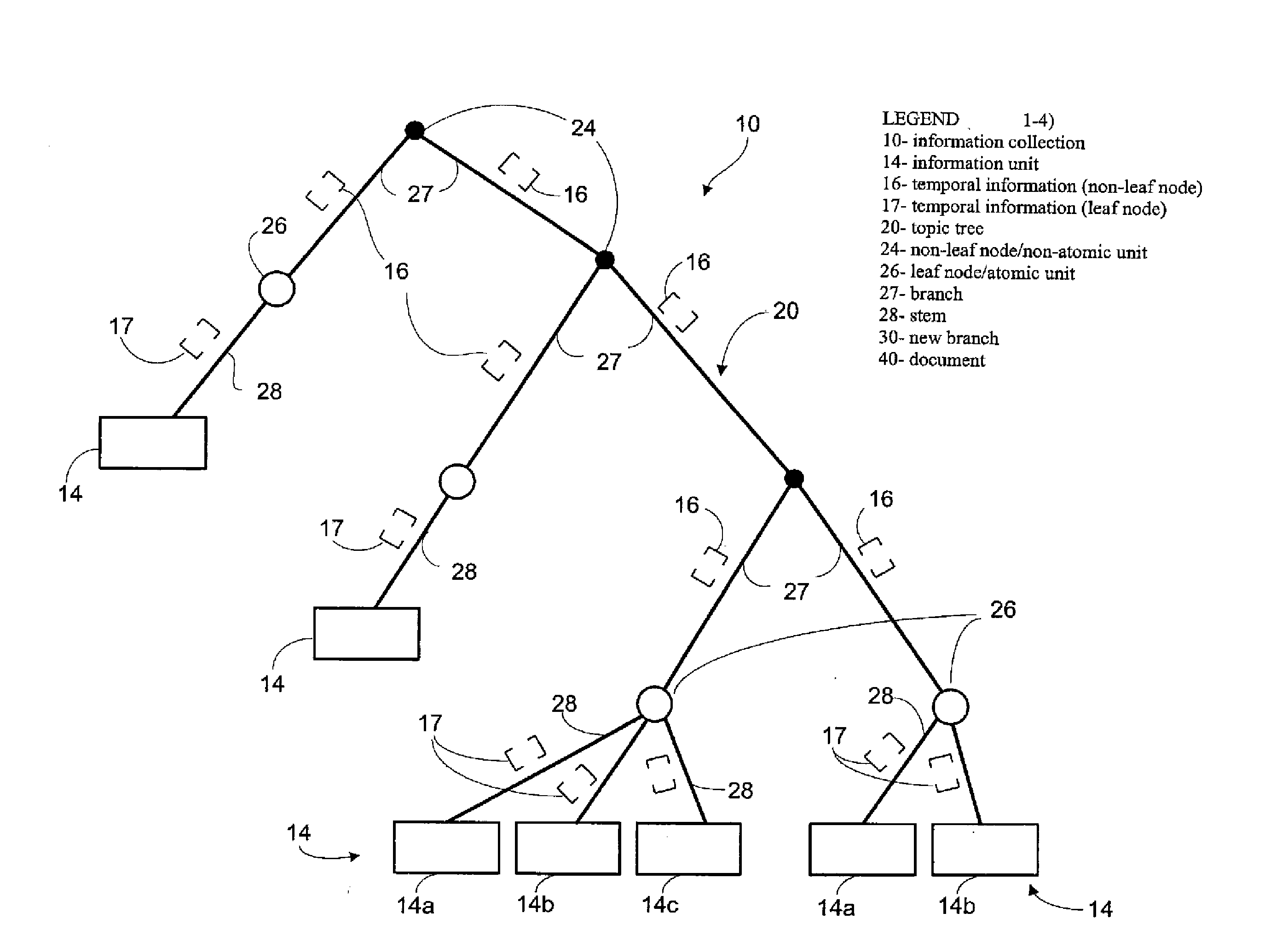
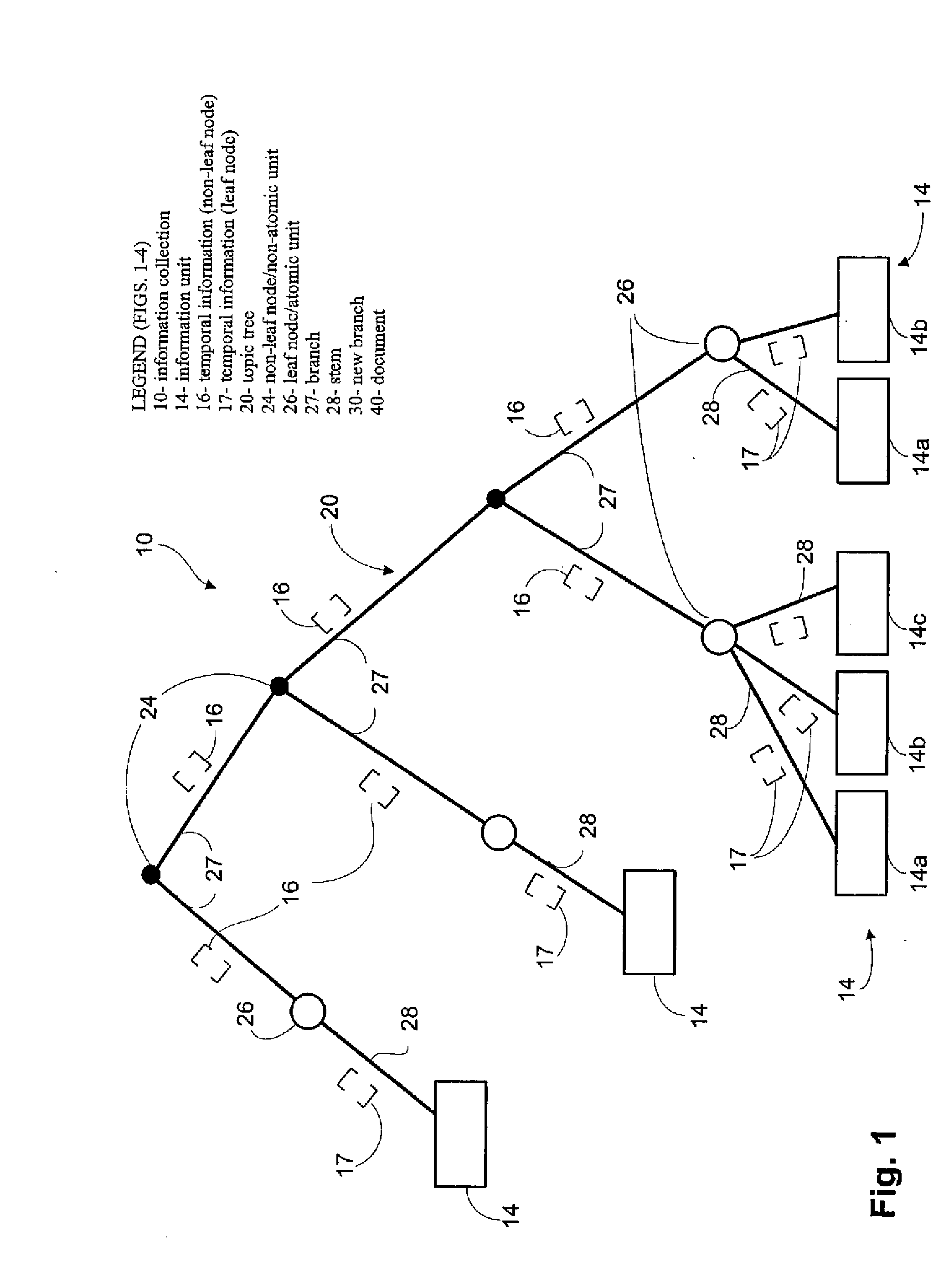
InactiveUS7412463B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsTemporal informationEffective date
Information collections defining a common subject such as a codified or uncodified body of law are stored on a computer readable medium in association with temporal information indicating the state or status with respect to time of parts of the information collection, including different versions of the same part. Parts of an information collection that are different versions of each other have different temporal information associated therewith and can be accessed based on the temporal information. Thus, the temporal information may be used to control access to and display of parts of the subject in a computer system based on time as search or request parameter. In a preferred embodiment, the subject is a statutory body of law such as the United States Code. Sections of the Code are stored in association with temporal information such as date of enactment, effective date and termination date. A researcher can access a version of any part of the Code in effect at any particular time.
Owner:BLOOMBERG GP FINANCE +2
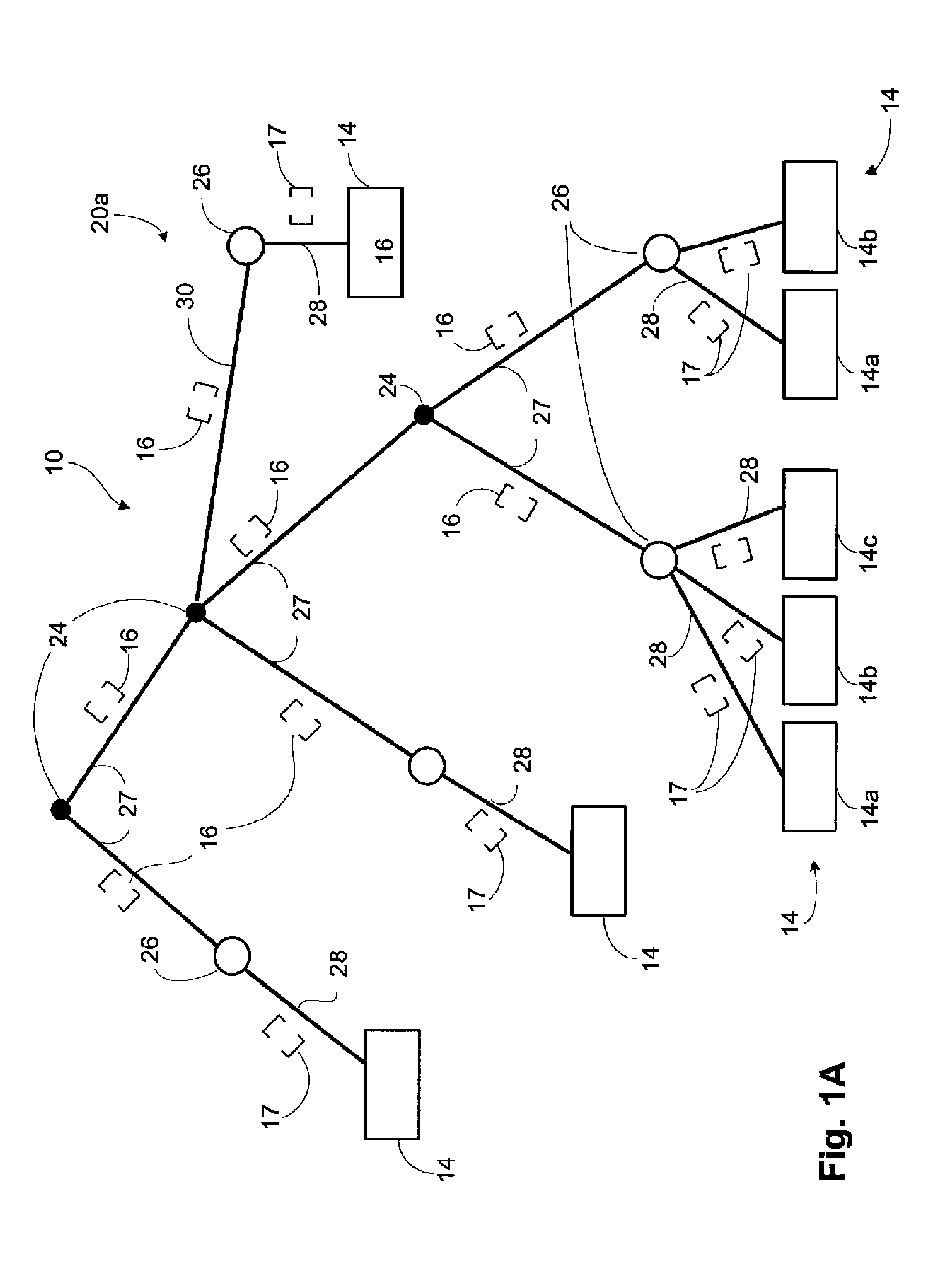
Effective dating for table or relationship modifications
InactiveUS20120036166A1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationEffective dateSQL
A method of application phased upgrade and phased user migration. In one embodiment, in one embodiment a first version of an application generates a first SQL insert statement, wherein the first SQL insert statement comprises a first table name, a first field name, and a first value. A second version of an application generates a second SQL insert statement, wherein the second SQL insert statement comprises the first table name, the first field name, and a second value. A database system inserts a first record into a first table in response to the database system receiving the first SQL insert statement. The database system inserts a second record into the first table via a view in response to the database system receiving the second SQL insert statement. The first record comprises distinct first and second fields corresponding to the first name and a second field name, respectively. The first field stores the first value. The second record comprises distinct first and second fields corresponding to the first and second field names, respectively. The second field of the second record stores the second value.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
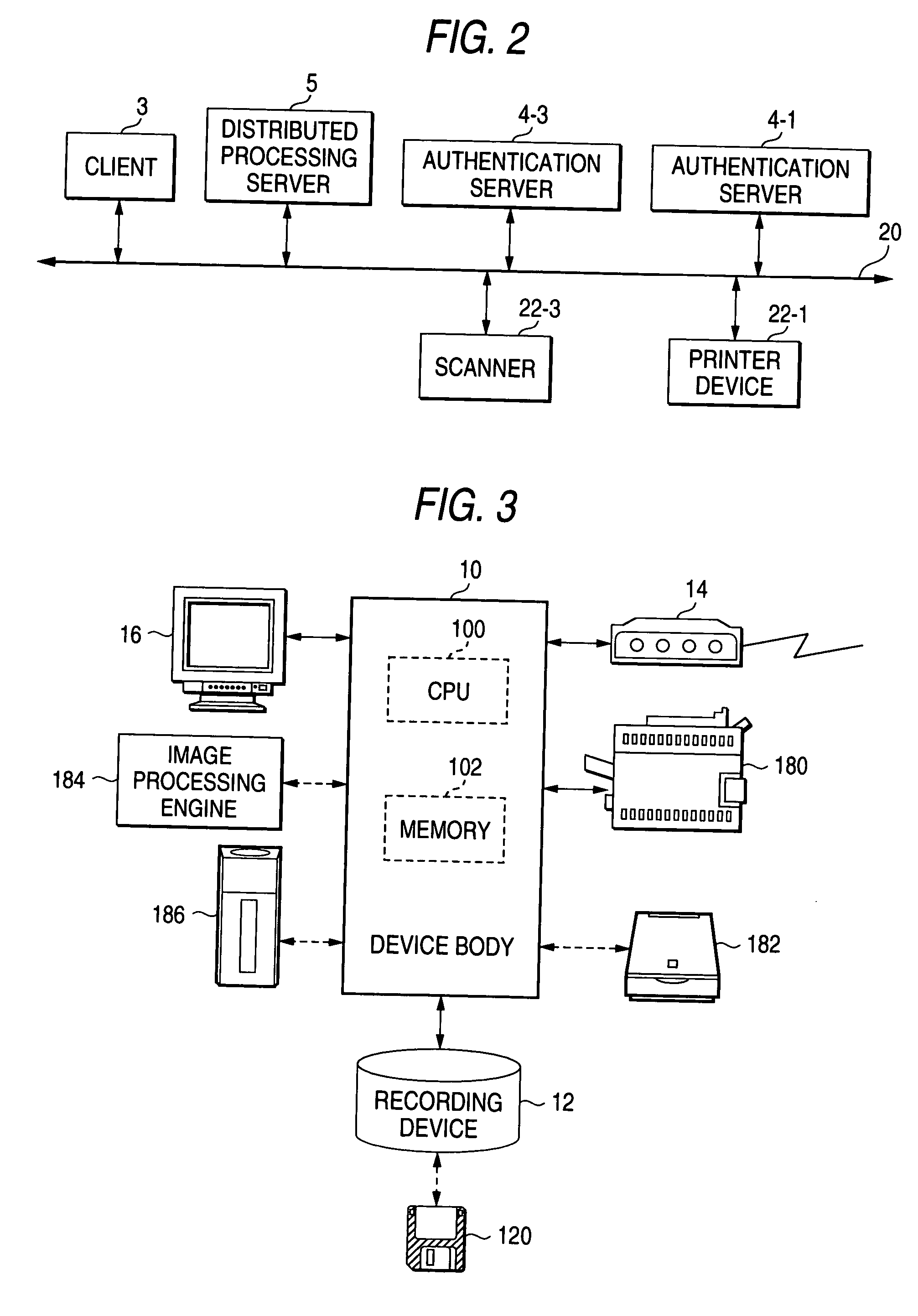
Client server system and devices thereof
ActiveUS20040025020A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsEffective dateClient server systems
A client server system and devices thereof, which perform a distributed processing while performing access control. when a client device demands a job of the server device, the server device outputs an authentication demand message to an authentication server via a network. The authentication device performs authentication of a user taking account of an effective range of authentication information and effective dates and returns results of authentication to the server device via the network. The server device implements the demanded job in accordance with the results of authentication.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
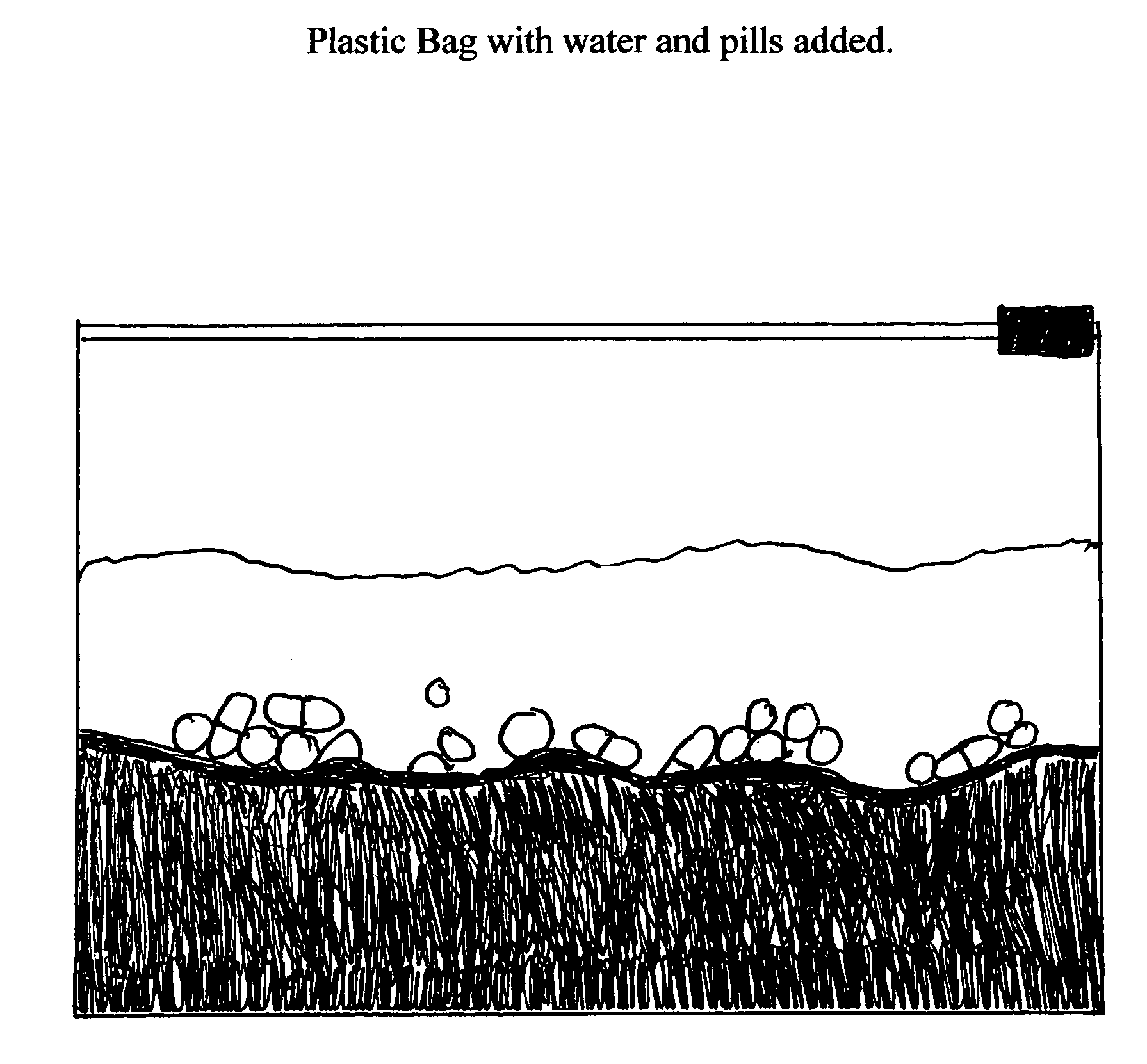
Pill catcher
InactiveUS7918777B2Eliminate riskLow cost safe treatmentSludge treatmentGlass furnace apparatusSlurryCvd risk
A method for the exclusive and singular treatment of all pharmaceuticals and drugs in any form that have passed their effective date, or are no longer of use to the individual, by mixing the pharmaceuticals and drugs with a granular solidification agent and water to form a non hazardous slurry which will solidify the liquefied pharmaceuticals and drugs into a non hazardous, environmentally friendly mixture safe for disposal into normal solid trash receptacles and landfills, and no longer a potential legal risk from ingestion after depositing into trash system. In this treatment the additional potential health risk and legal liability is eliminated from drugs and pharmaceuticals going into toilets and drains to sanitary sewers or septic tanks, and becoming liquid and untreatable at municipal wastewater treatment plants or septic fields, thereby returning to fresh water resources causing a risk to the general public health.
Owner:THE FRANCES I PARROTT LIVING TRUST
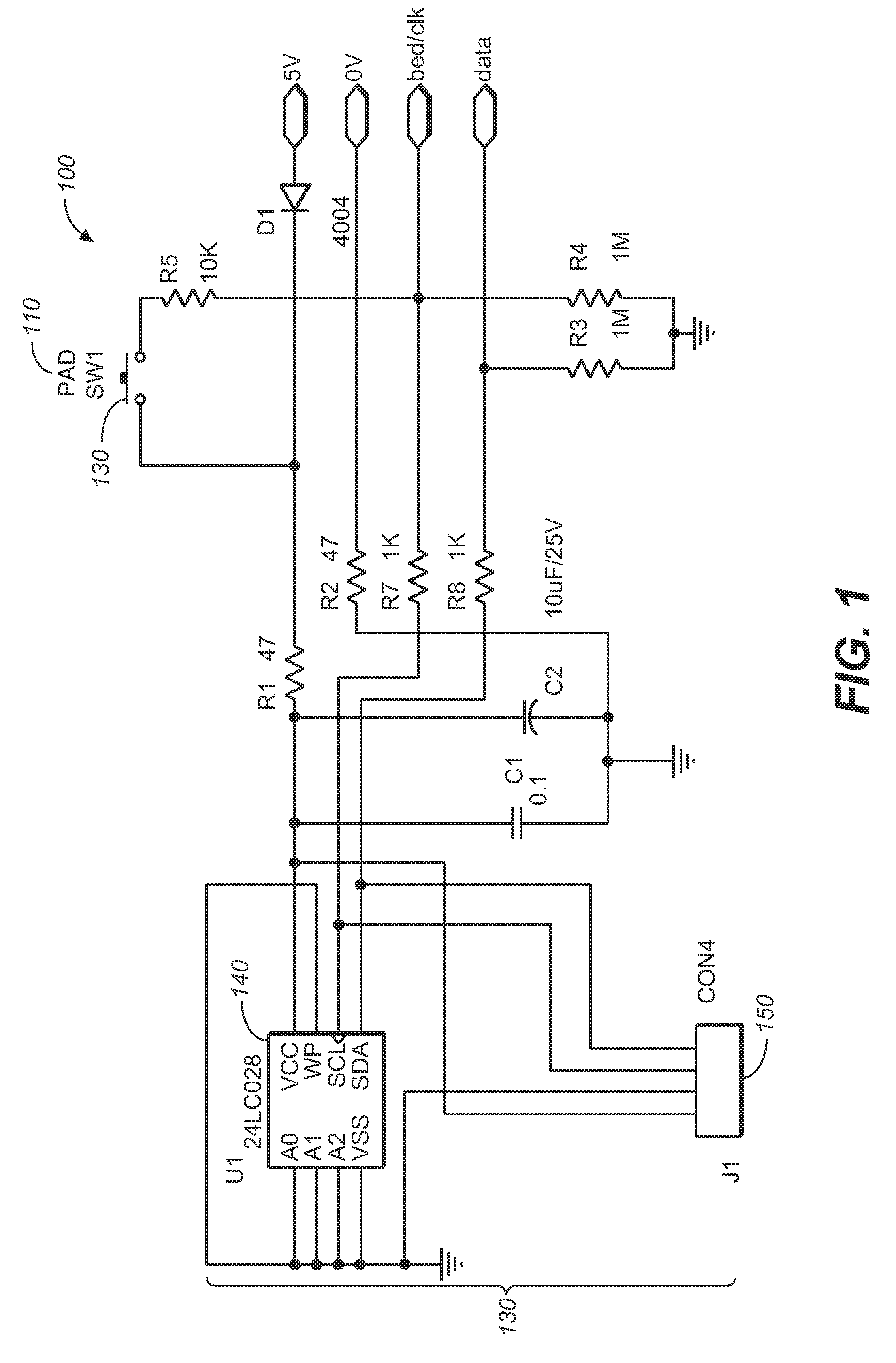
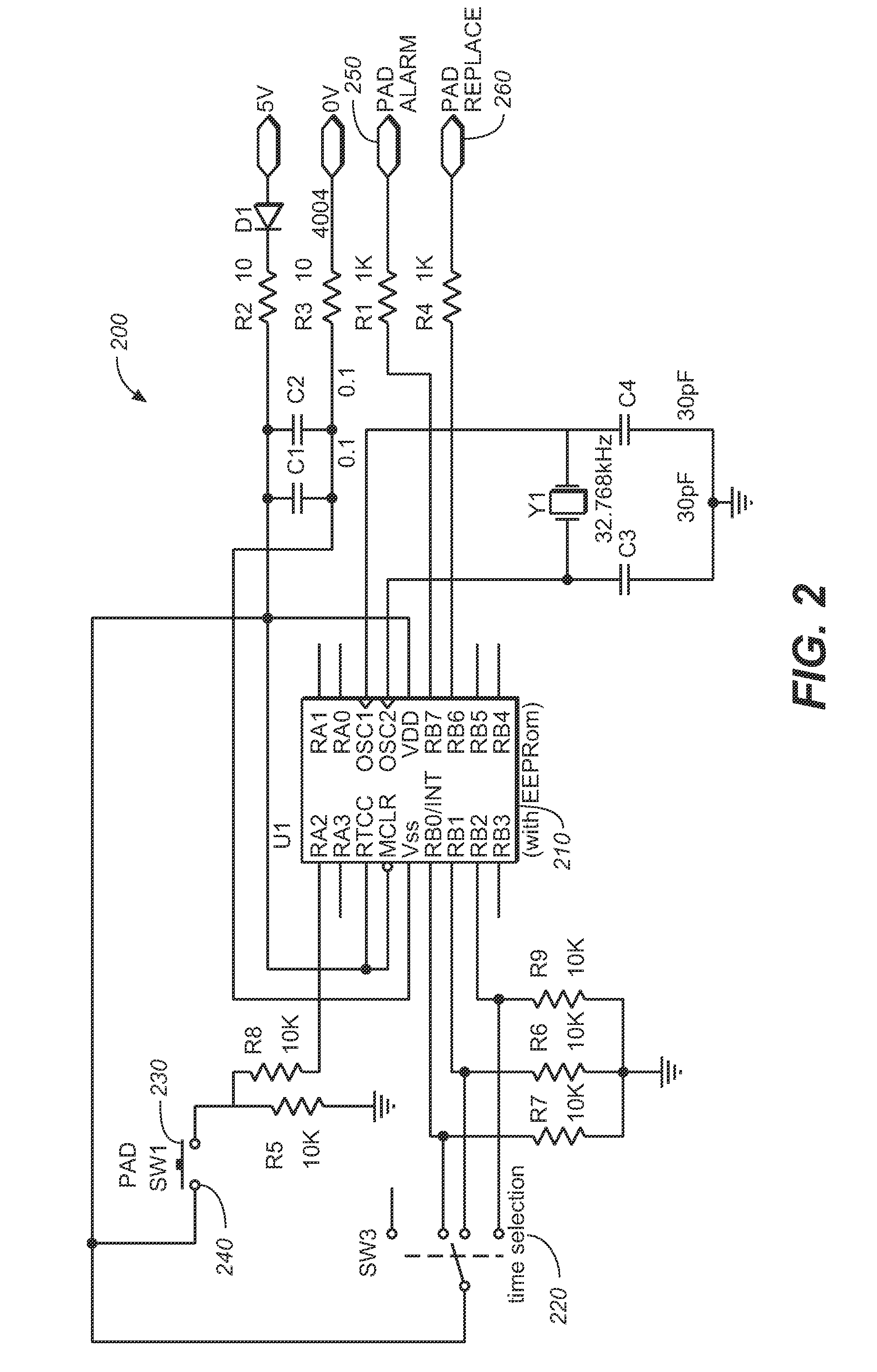
Patient monitor pressure pad with effective date warning alarm
ActiveUS7557719B1Reduce usagePrevent needless accidents causedSignalling system detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringEffective dateEngineering
A patient monitor pressure pad having a time sensor and alarm circuit that produces an audible or visible alarm output to alert facility care staff that the effective life of the pressure pad is nearing its end.
Owner:RONDISH
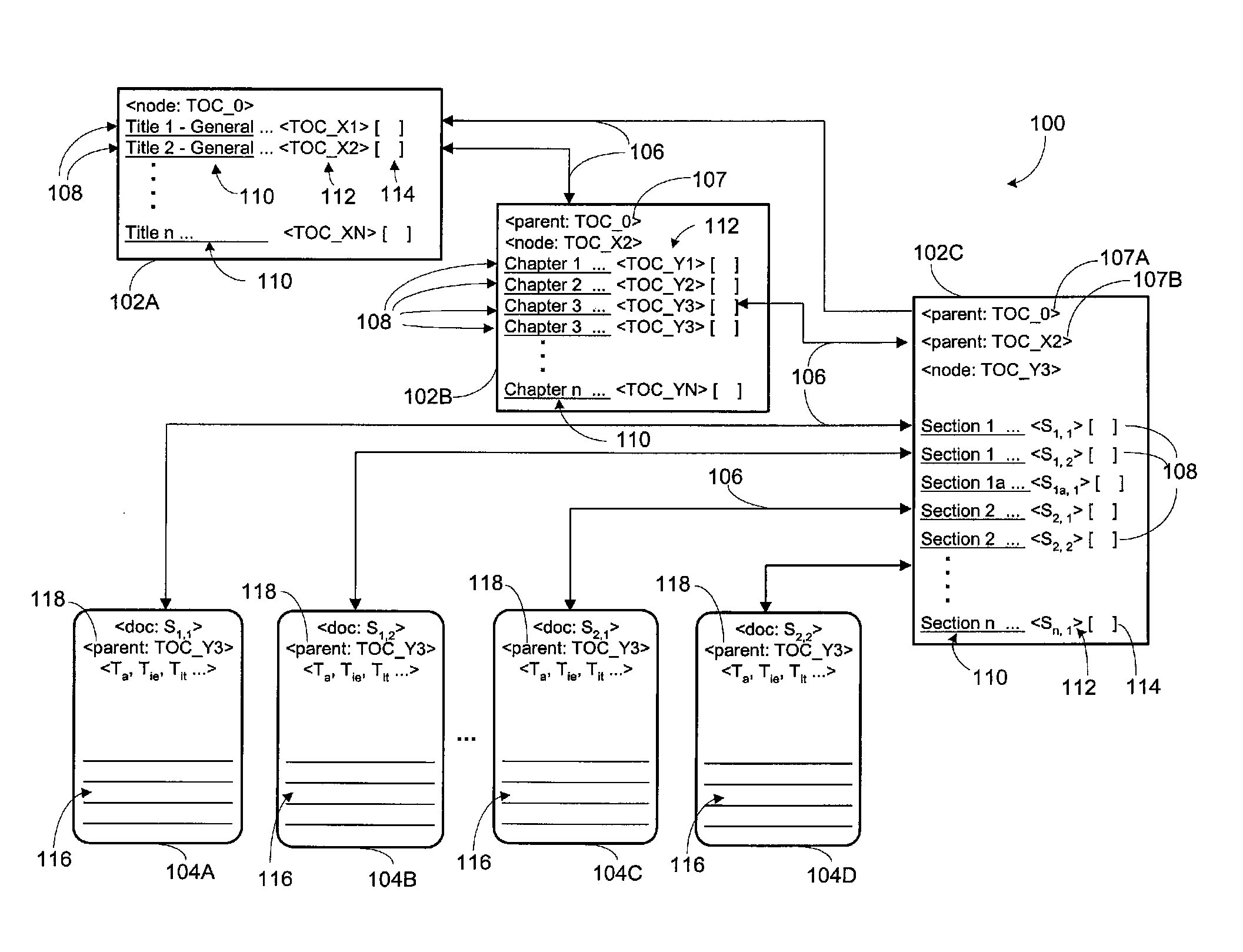
Dynamic legal database providing historical and current versions of bodies of law
InactiveUS20090043827A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalHyperlinkTemporal information
Information collections defining a common subject such as a codified or uncodified body of law are stored on a computer readable medium in association with temporal information indicating the state or status with respect to time of parts of the information collection, including different versions of the same part. Parts that are different versions of each other have different temporal information associated therewith and can be accessed based on the temporal information. Thus, the temporal information may be used to control access to and display of parts of the subject in a computer system based on time as a search or request parameter. Parts of the common subject may be organized and stored according to various schemes, including hierarchical schemes such as topic trees, a relational database, a file system or a structured document system (e.g., using XML). Parts of the common subject and temporal and other information may be associated in various ways, including linking (e.g., hyperlinking), with pointers, or by including them in the same file, record or document. A hierarchical arrangement of hyperlinked, structured documents collectively provide a table of contents (TOC) to the subject. In the preferred embodiment, the subject is a statutory body of law such as the United States Code. Sections of the Code are stored in associated with temporal information such as date of enactment, effective date and termination date. A researcher can then access the version of the code in effect at any particular time. For example, historical and current versions of a section of the United States Code can be viewed, as accessed hierarchically or directly by identification of the section and a date. Other information, stored in association with a part of a body of law may include historical information, commentary, annotations, descriptive information, legislative history, references, and / or links to laws, judicial decisions and other information.
Owner:THE BUREAU OF NAT AFFAIRS +2
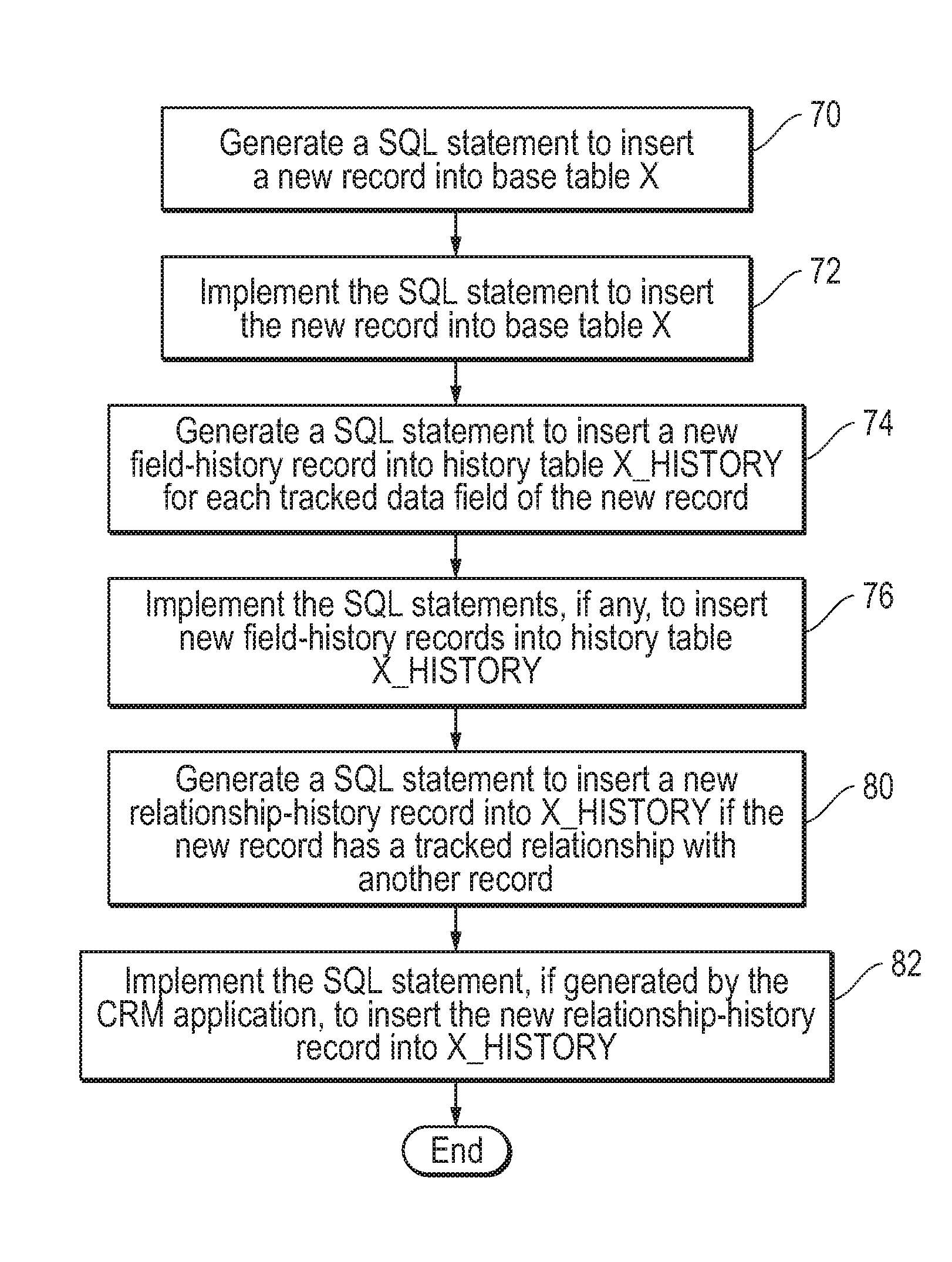
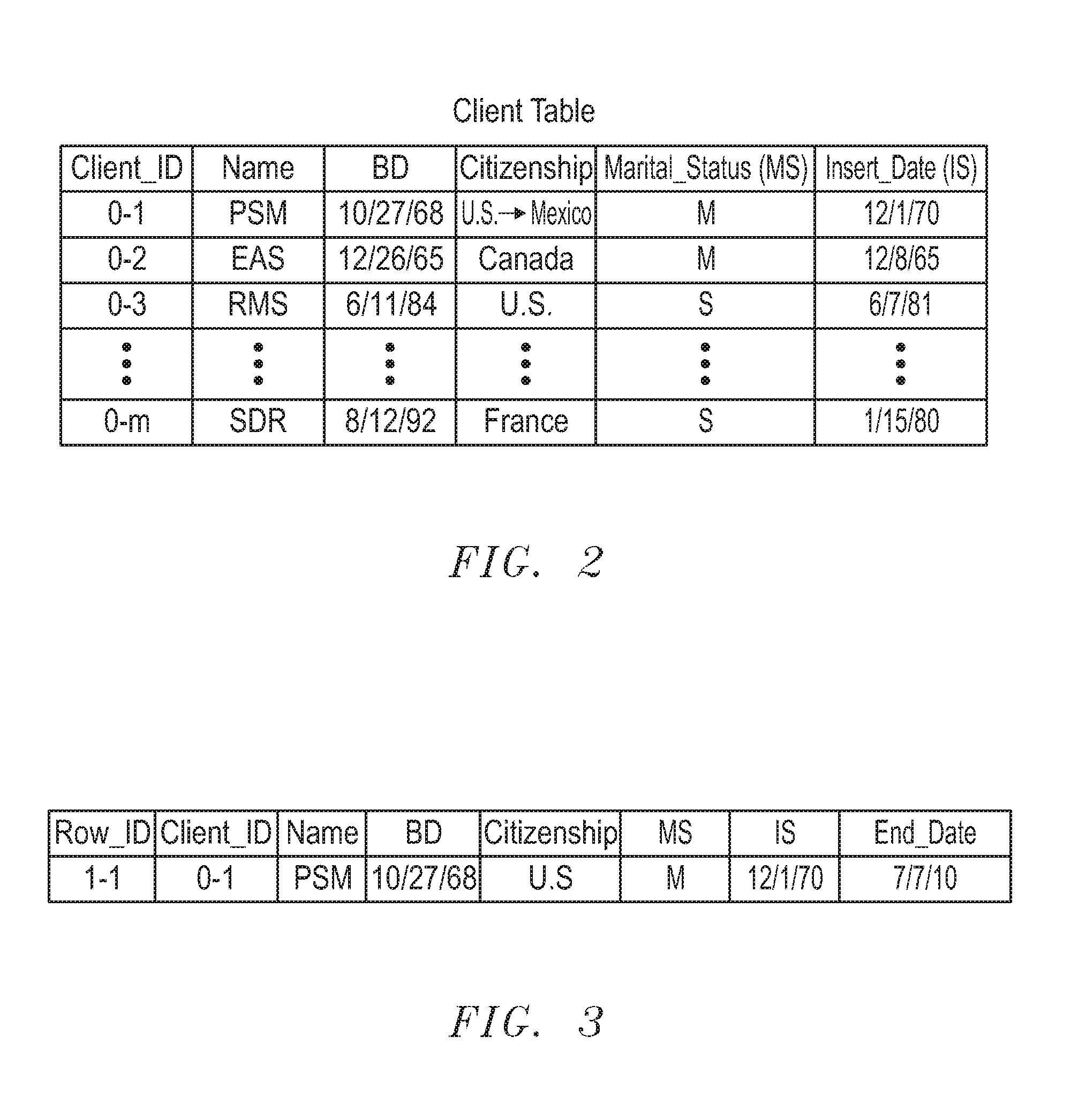
Effective Dating for Entity Attributes and Relationships
ActiveUS20120030258A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsEffective dateCustomer relationship management
A method for tracking modifications to tables or relationships. In one embodiment, the method includes updating a first value stored in a first field of a record in a table in response to a database system receiving a first structured query language (SQL) statement from a customer relationship management (CRM) application. A first record is inserted into a history table in response to the first SQL statement, wherein the first record comprises a foreign key field that stores a copy of the primary key of the record, a field that stores a copy of the first value after it is updated, a field that stores a name of the first field, and a first date field. The first date field stores either the date when the first SQL statement was received by the database system, the date of the day that immediately follows the date when the first SQL statement was received by the database system, or a date that was entered into a field of a user interface.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Docetaxel lyophilization dry emulsion for injections and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN101095660ALow toxicityImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryEffective dateEmulsion
The invention relates to pharmacology field, which in detail provides a frozen died emulsion that contains docetaxel and findings, with the weight proportion being 1-50 and 3-1000, respectively. The invention also relates to the preparation method. Said method comprises following steps: (1)mixing docetaxel, emulsifier and solvent top prepare dispersed docetaxel emulsion; (2)adding frozen dried protecting agent into dispersed emulsion; (3)removing water through freeze drying and preparing dried docetaxel emulsion. The invention is characterized by low-toxic frozen dried emulsion, increased medicine safety and body durability, improved medicine treatment index and stability for storage and transportation, prolonged medicine effective date and increased medicine quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aqueous long-acting anticorrosion paint and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a water long-acting anti-rot paint and the preparing method, which solves the problem how to provide the long effective date, sunlight-resistant, ultra-violet resistance water long-acting anti-rot paint. The method comprises the following steps: preparing high-modulus potassium lithium silicate solution with the mature electrodialysis technique; modifying with monomethyl triethoxysilicane and water epoxide modified propylene silicon resin; acquiring the organic silicon modified composite silicate inorganic resin; dispersing the powder material and adjuvant in the composite film material with dispersing coupling technique; forming composite phase solubility steady uniform painting system. The paint is provided with the high adhesive force, the high strength, ageing resistance, radio resistant and preservation, which is fit for the outdoor anticorrosion paint.
Owner:GUANGDONG DEKANG CHEM IND
Pill catcher
InactiveUS20100076244A1Low cost safe treatmentEliminate riskSludge treatmentGlass furnace apparatusFresh water organismSlurry
A method for the exclusive and singular treatment of all pharmaceuticals and drugs in any form that have passed their effective date, or are no longer of use to the individual, by mixing the pharmaceuticals and drugs with a granular solidification agent and water to form a non hazardous slurry which will solidify the liquefied pharmaceuticals and drugs into a non hazardous, environmentally friendly mixture safe for disposal into normal solid trash receptacles and landfills, and no longer a potential legal risk from ingestion after depositing into trash system. In this treatment the additional potential health risk and legal liability is eliminated from drugs and pharmaceuticals going into toilets and drains to sanitary sewers or septic tanks, and becoming liquid and untreatable at municipal wastewater treatment plants or septic fields, thereby returning to fresh water resources causing a risk to the general public health.
Owner:THE FRANCES I PARROTT LIVING TRUST
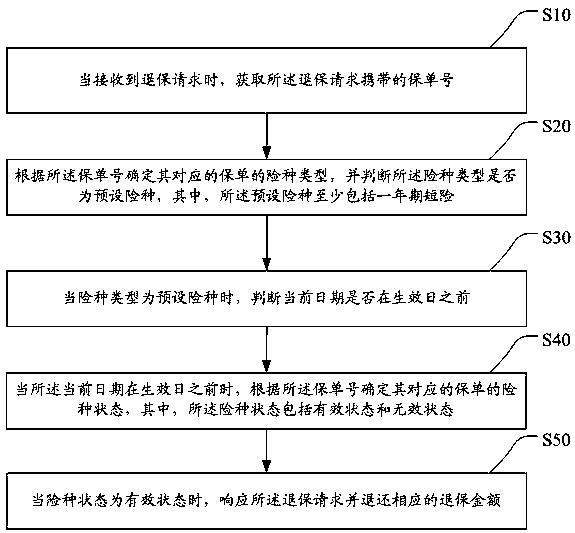
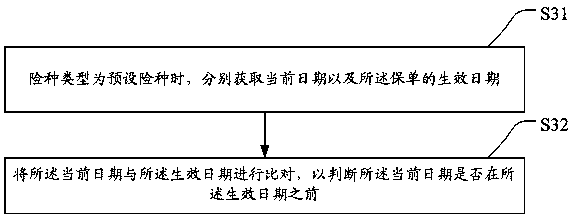
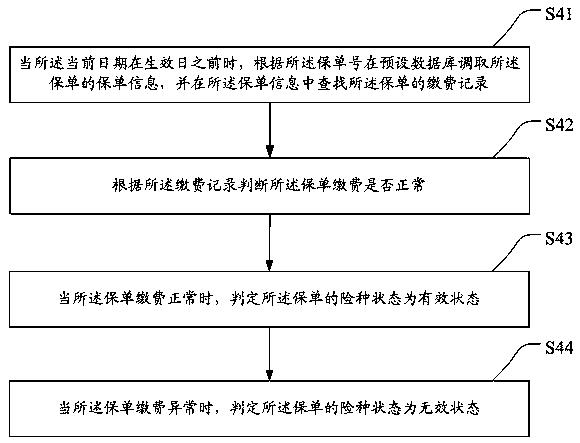
Insurance cancellation method, terminal device and storage medium
The invention discloses an insurance cancellation method, a terminal device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of calling corresponding insurance policy information to determine whether an insurance type of an insurance policy corresponding to the insurance policy information is a preset insurance type or not when an insurance cancellation request is received, wherein the presetinsurance type at least comprises a one-year short-term insurance; when the insurance type is the preset insurance type, further verifying whether an insurance cancellation date is before an effectivedate or not; if the insurance cancellation date is before the effective date, obtaining an insurance type state of the insurance policy; and when the insurance type state is an effective state, judging that an insurance cancellation condition is met, making a response to the insurance cancellation request, and returning a corresponding insurance cancellation amount. Whether the insurance cancellation request is executed or not is determined after the insurance cancellation request is subjected to conventional check, and when the insurance cancellation request of the insurance type being the one-year short-term insurance is received, the insurance cancellation request can be checked, so that the application range of the one-year short-term insurance is expanded and the insurance cancellation flexibility is improved.
Owner:CHINA PING AN LIFE INSURANCE CO LTD
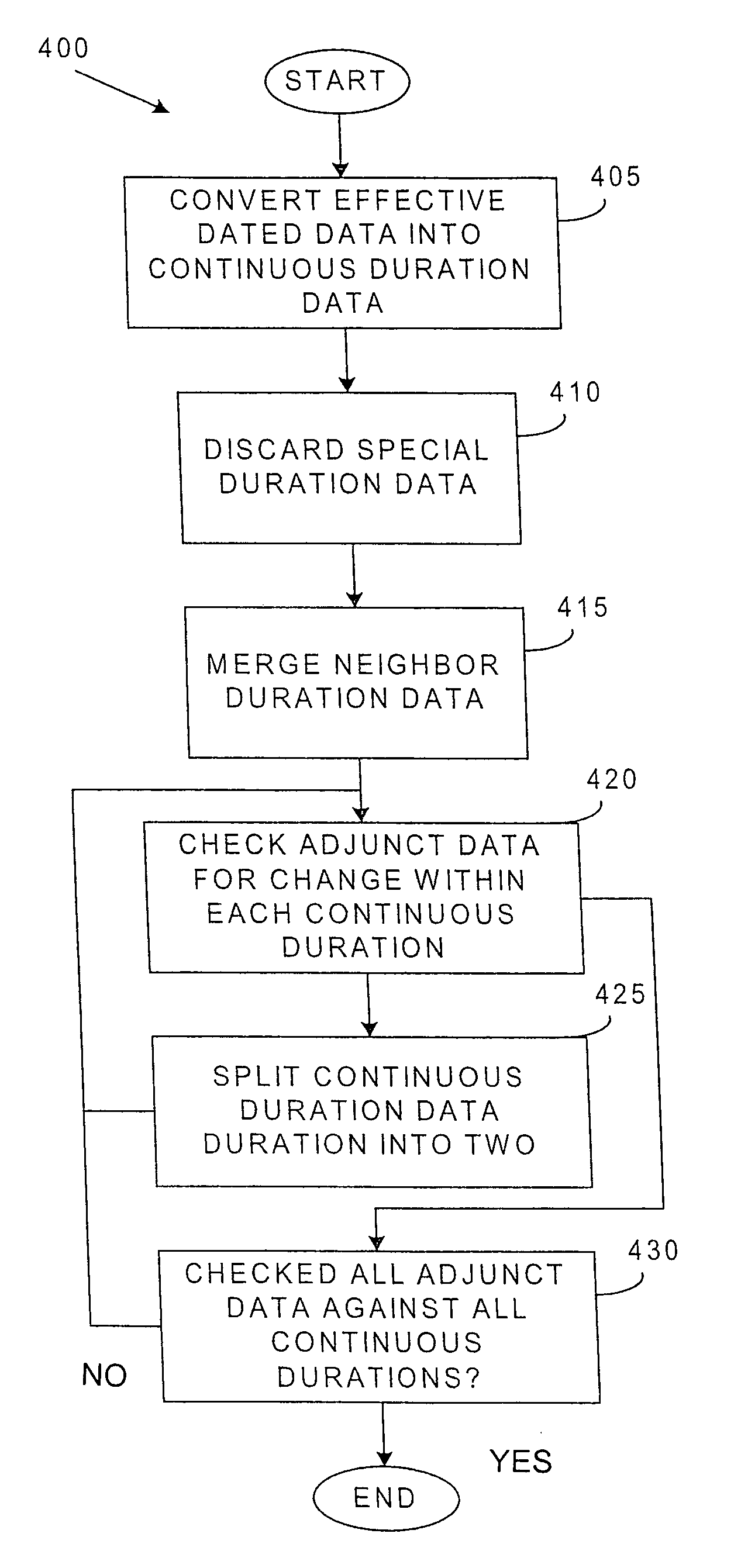
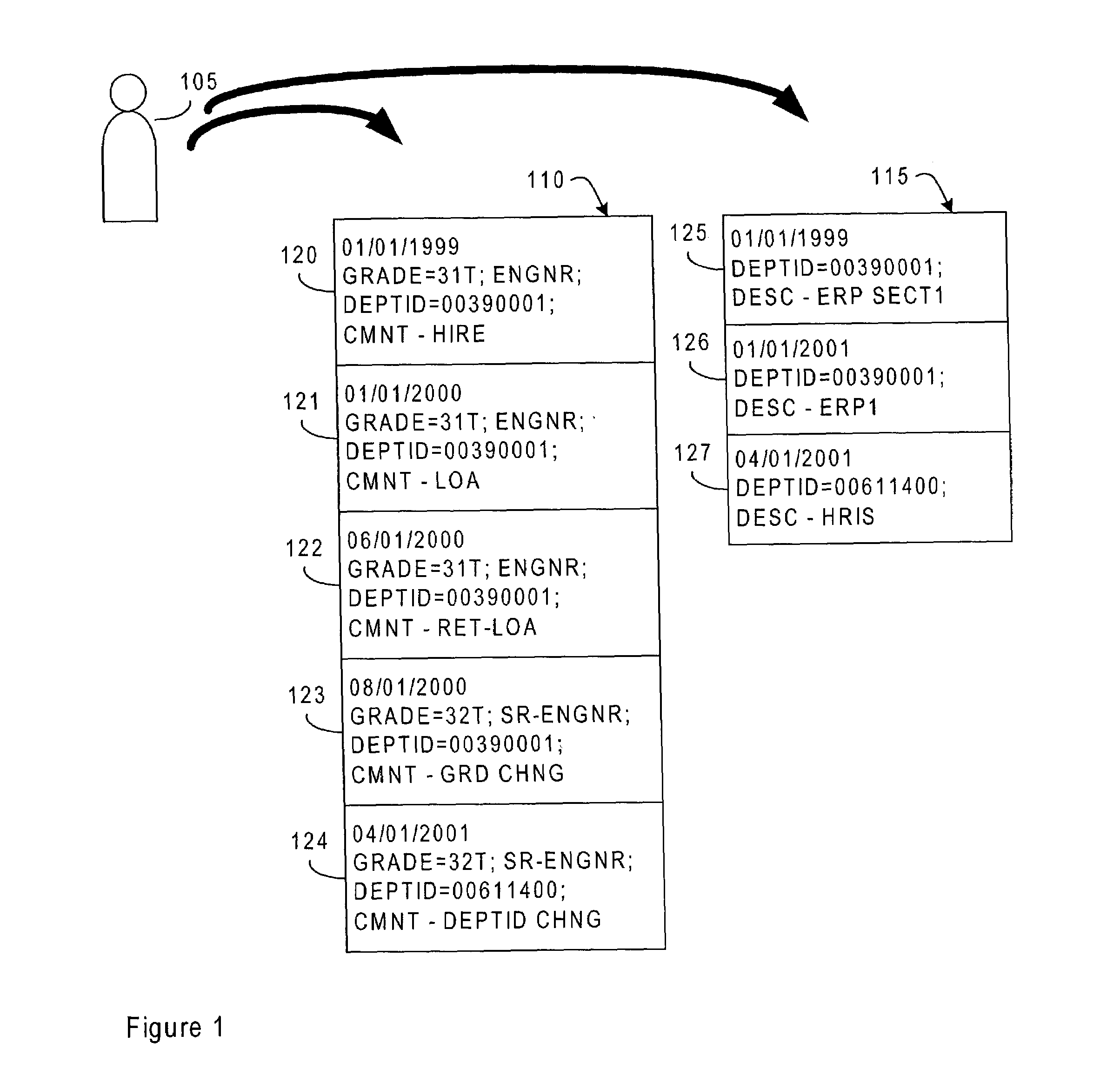
Method for merging information from effective dated base tables
InactiveUS7165072B2Easily excludedData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalEffective dateData mining
Method for merging data entries from a plurality of effective-dated tables. A preferred embodiment comprises converting the data entries from an effective-dated table into a continuous duration data table (for example, algorithm block 405) and then merging continuous neighbors that contain repetitive data (for example, algorithm block 415). Finally, data from other effective-dated tables are used to split the continuous duration data into parts (for example, algorithm block 425) so that associations between the continuous duration data and the data from the other effective-dated tables are made clear.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Systems and methods of managing assignments
Disclosed are systems and methods of making assignments, particularly of sales leads. The assignments are considered either committed or uncommitted responsive to an effective date associated with one or more assignment rule used to make the assignments. Uncommitted assignments may be used to review the effects of changes in assignment rules. Examples are provided including the use of uncommitted assignments to review the effects of changes in a hierarchical territory structure.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
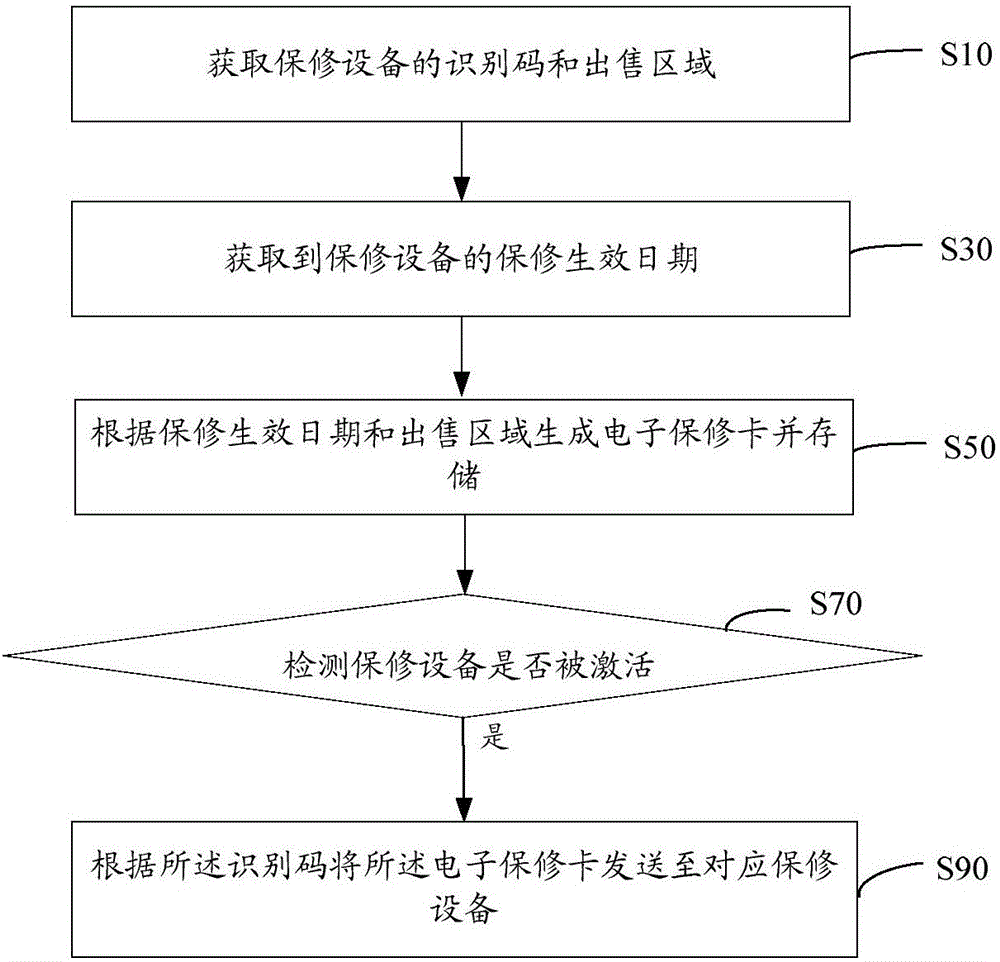
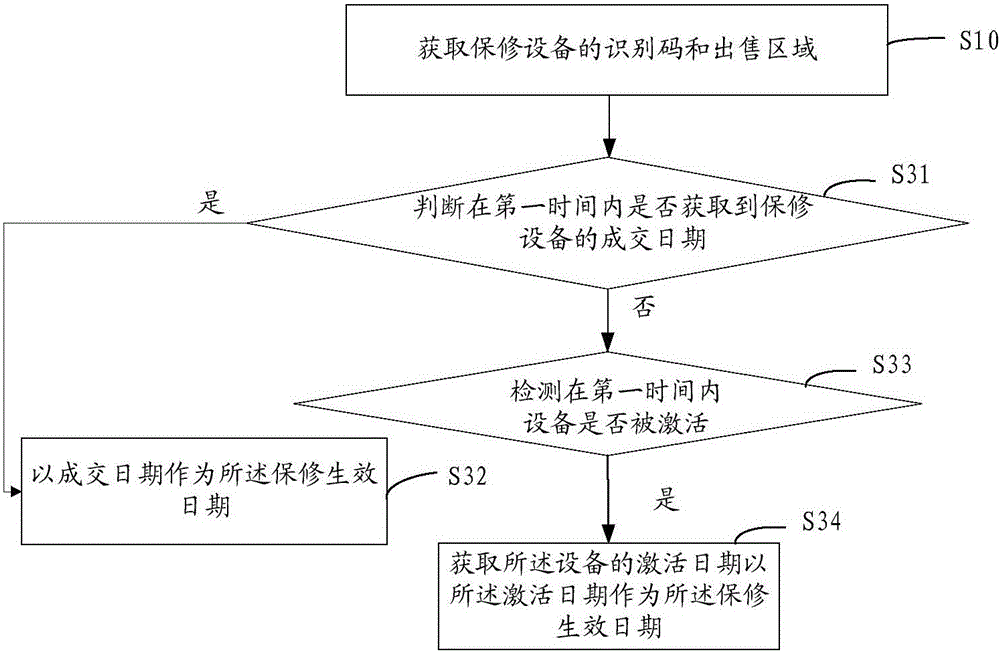
Electronic warranty card generating method, server, query method and device
InactiveCN105956865AImprove experienceCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsEffective dateComputer hardware
The invention relates to an electronic warranty card generating method, server, query method and device. The electronic warranty card generating method comprises obtaining the identification code and sale area of a maintenance facility; obtaining the warranty effective date of the maintenance facility; generating and storing an electronic warranty card according to the warranty effective date and the sale area; detecting whether the maintenance facility is activated; and when the maintenance facility is detected to be activated, sending the electronic warranty card to a corresponding maintenance facility according to the identification code. The electronic warranty card is easy to store; when a facility needs maintaining in a warranty period, the electronic warranty card is shown to after-sales personnel so as to obtain after-sales service, and other fields do not need to be carried, thereby providing convenience for users, and improving user experience.
Owner:ONEPLUS TECH SHENZHEN
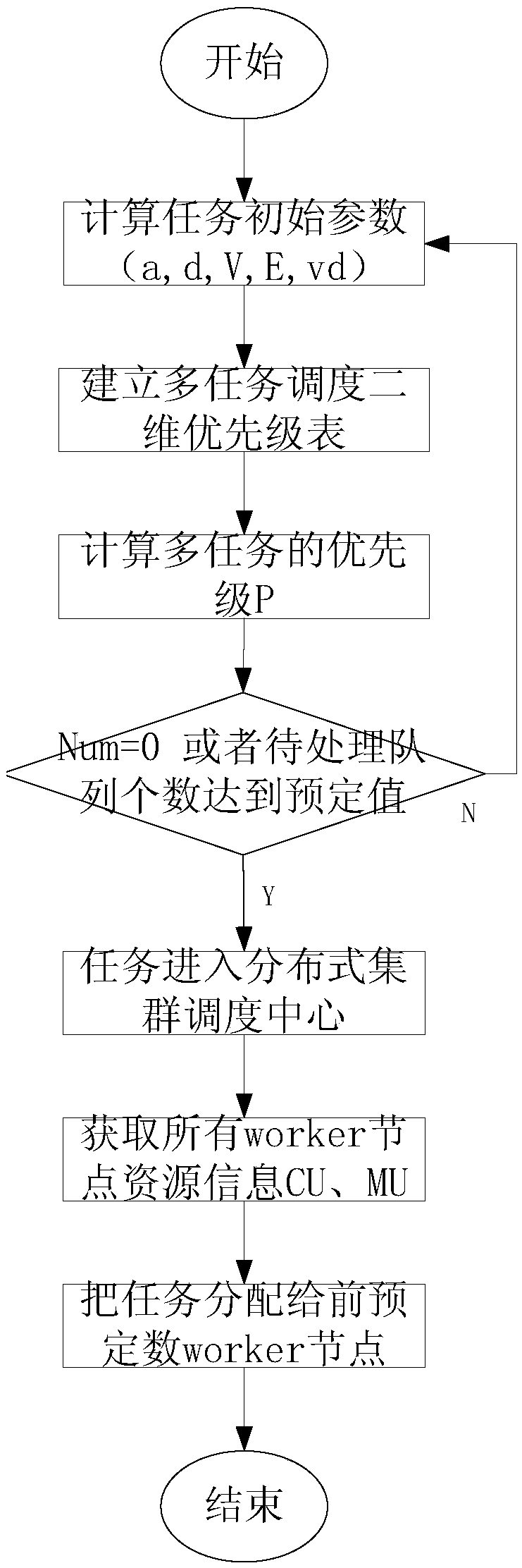
Multi-task real-time scheduling method for energy integrated collection system
InactiveCN108711007AEfficient managementImplement automatic downgradeResourcesEffective dateCollection system
The invention discloses a multi-task real-time scheduling method for an energy integrated collection system. The method comprises the steps that initial parameters of tasks are calculated; according to effective dates and value densities of the tasks, priorities of all the tasks in a two-dimensional priority table calculation queue for multi-task scheduling are established; when the priorities ofthe tasks are identical, the task arriving first is added into to-be-processed task queues of a front communication module first; when the number of the to-be-processed task queues of the front communication module reaches a predetermined value, a SPARK cluster Master node scheduling center is entered, and otherwise the steps continue to be circulated; a self-adaptive task scheduling strategy is adopted to regularly and dynamically adjust node weights; and the tasks newly added into the SPARK cluster Master node scheduling center are allocated to selected Worker nodes, and the tasks enter thecorresponding nodes for execution. Through the method, task processing performance is improved, and efficient management of a multi-task processing system is realized.
Owner:NARI NANJING CONTROL SYST +5
Access control permission management method and access control permission system for automobiles
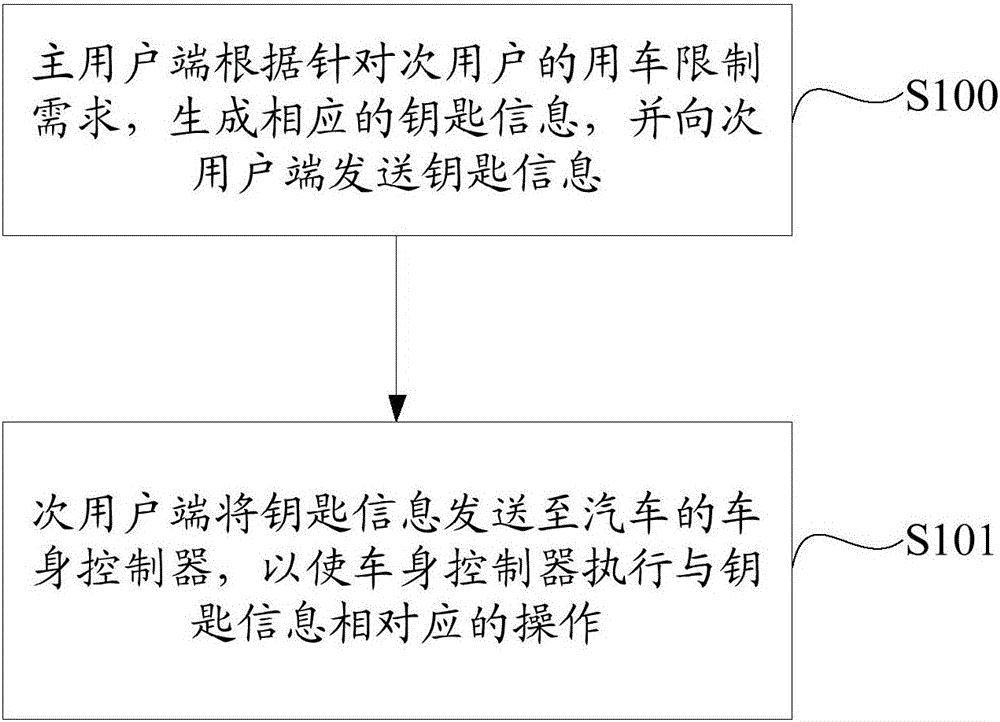
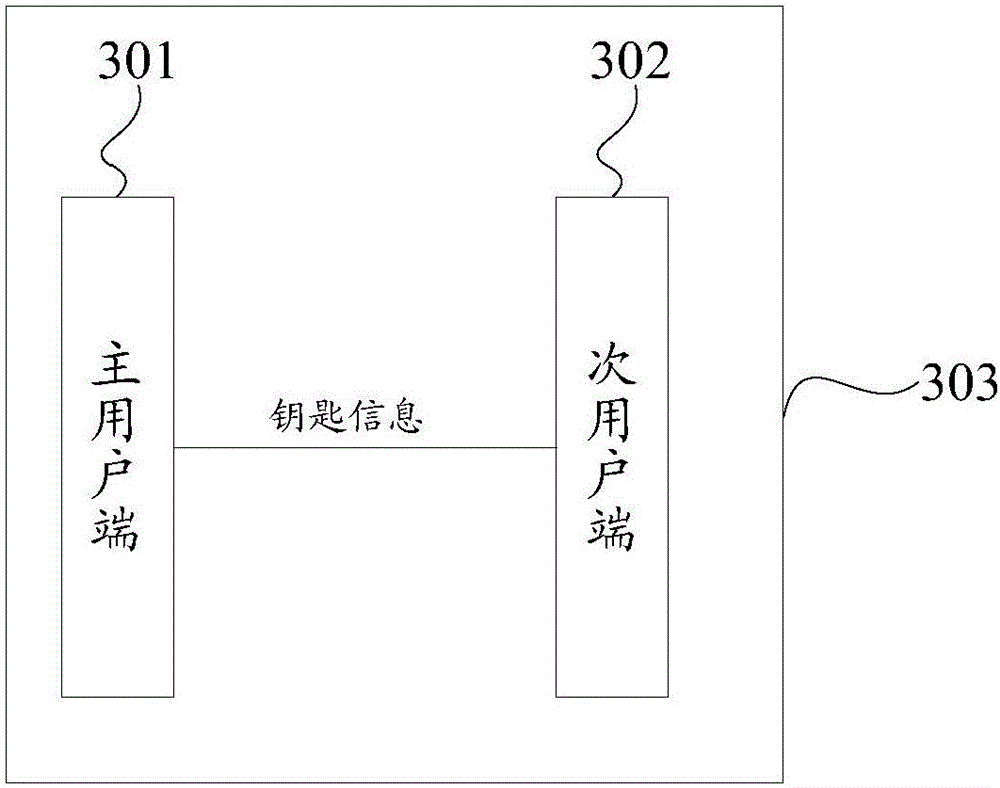
InactiveCN105976472AEasy to manageFlexible managementIndividual entry/exit registersTransmissionEffective datePermission system
The invention discloses an access control permission management method and an access control permission system for automobiles. The method comprises the following steps that: a main user terminal generates corresponding key information according to vehicle utilization limit requirements of a secondary user and sends the key information to a secondary user terminal, wherein the key information include access right contents, valid number of times and effective date; and the secondary user terminal sends the key information to a vehicle body controller of an automobile to drive the vehicle body controller to carry out operations corresponding to the key information. According to the access control permission management method of the technical scheme, the purposes of conveniently, rapidly and flexibly managing the access control permission of the automobile when the main user shares the access control permission of the automobile with the secondary user can be achieved.
Owner:KOSTAL SHANGHAI MANAGEMENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com