Patents
Literature
33 results about "Interest rate swap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
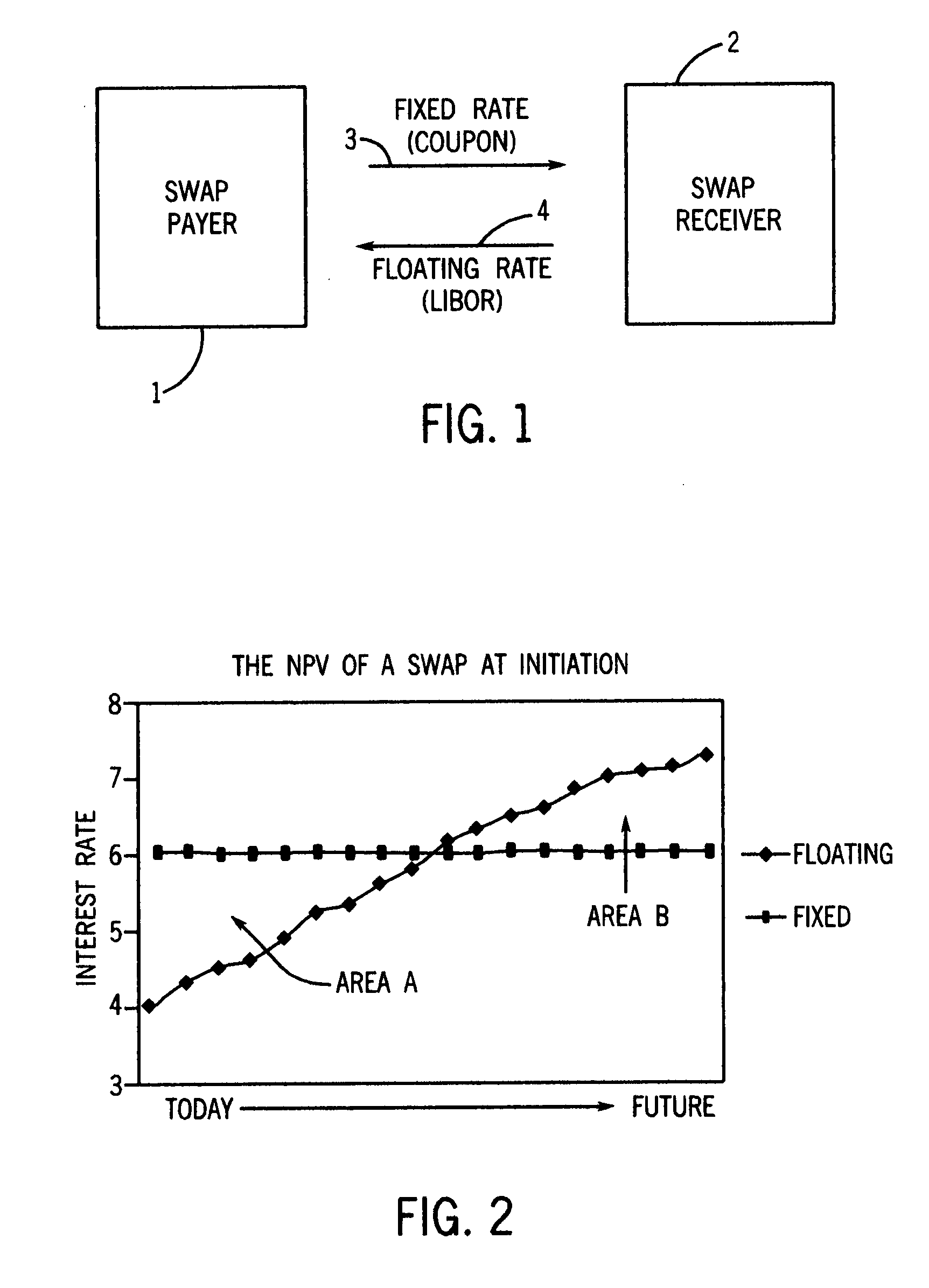
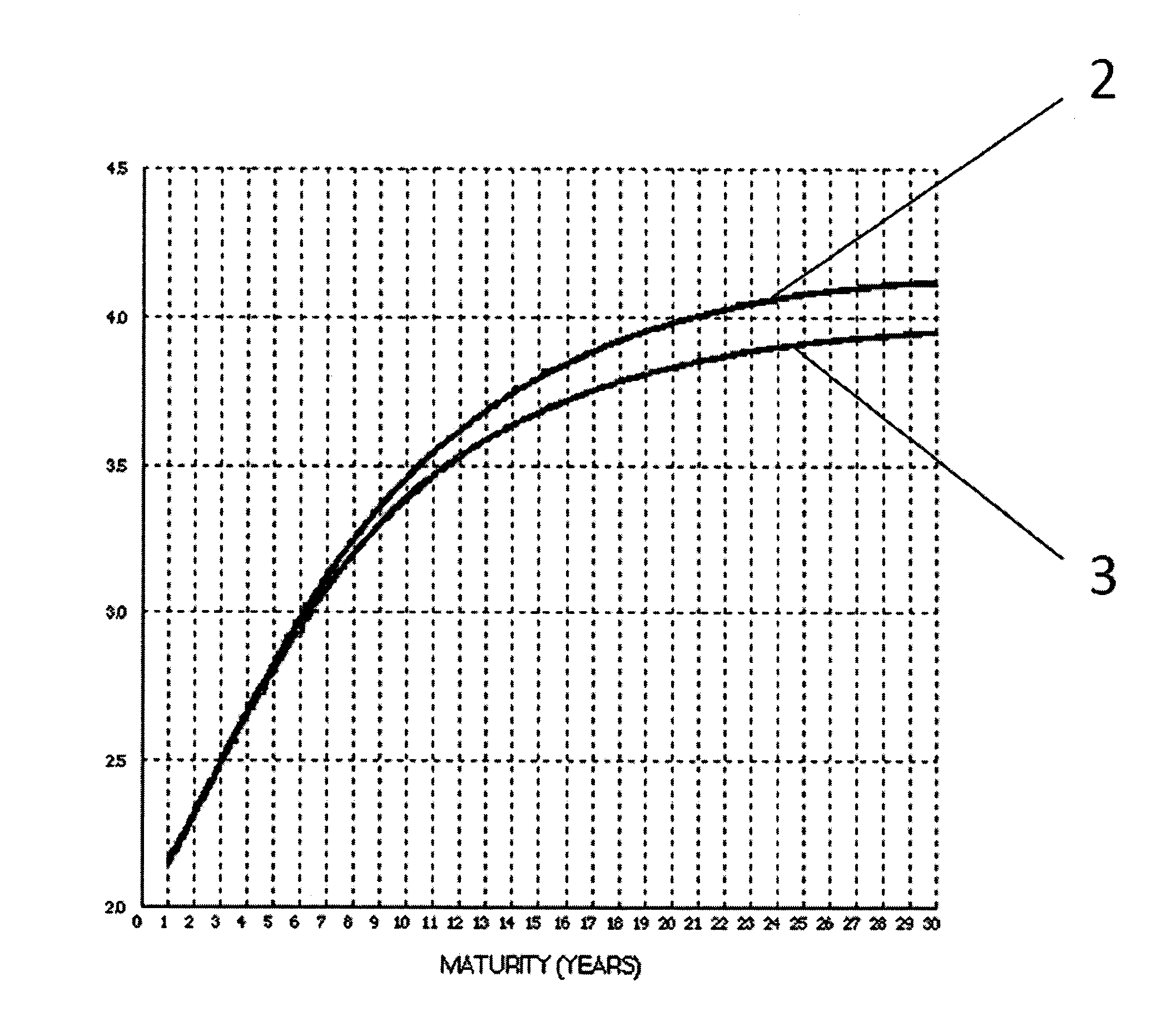
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a linear IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs).
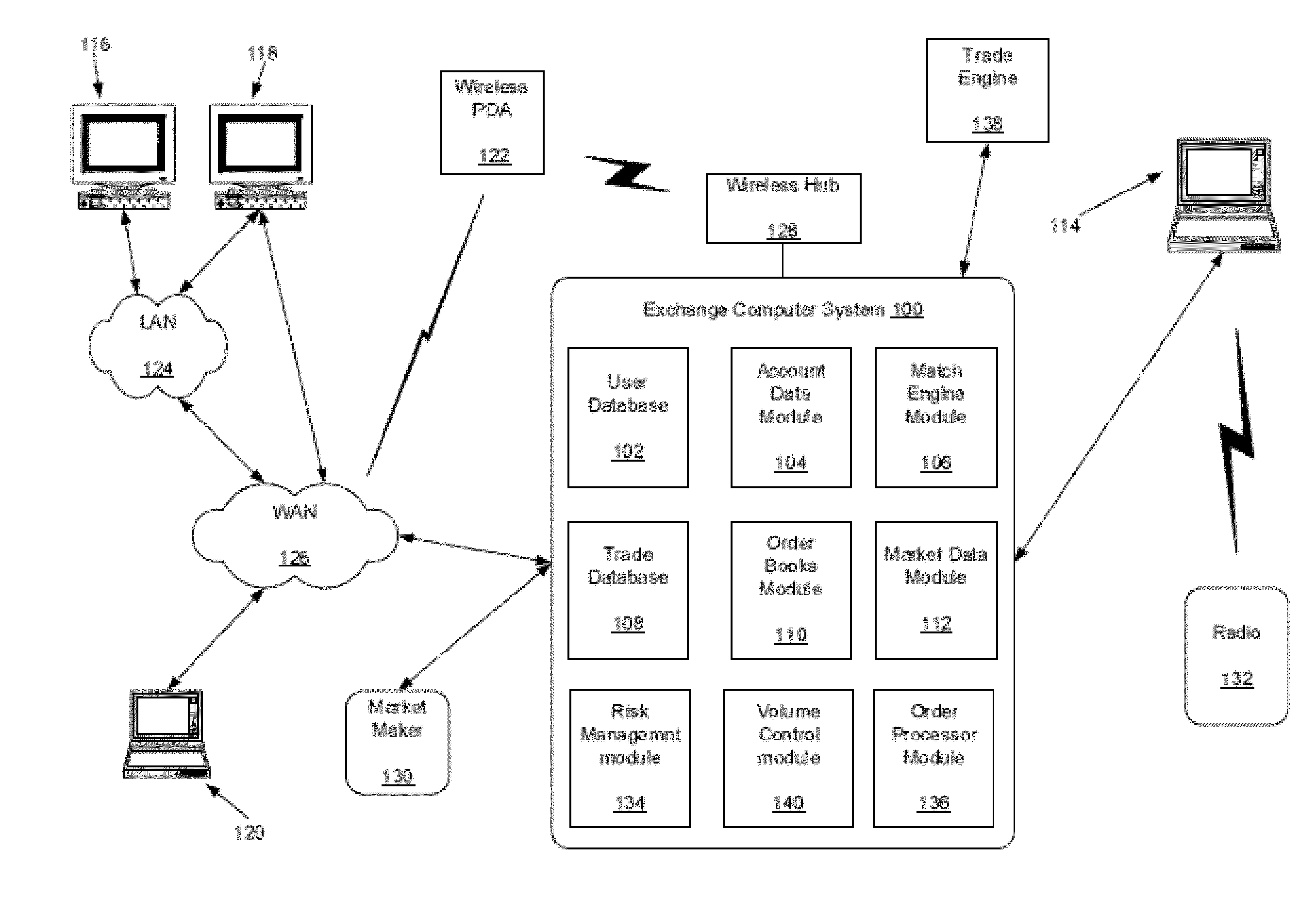
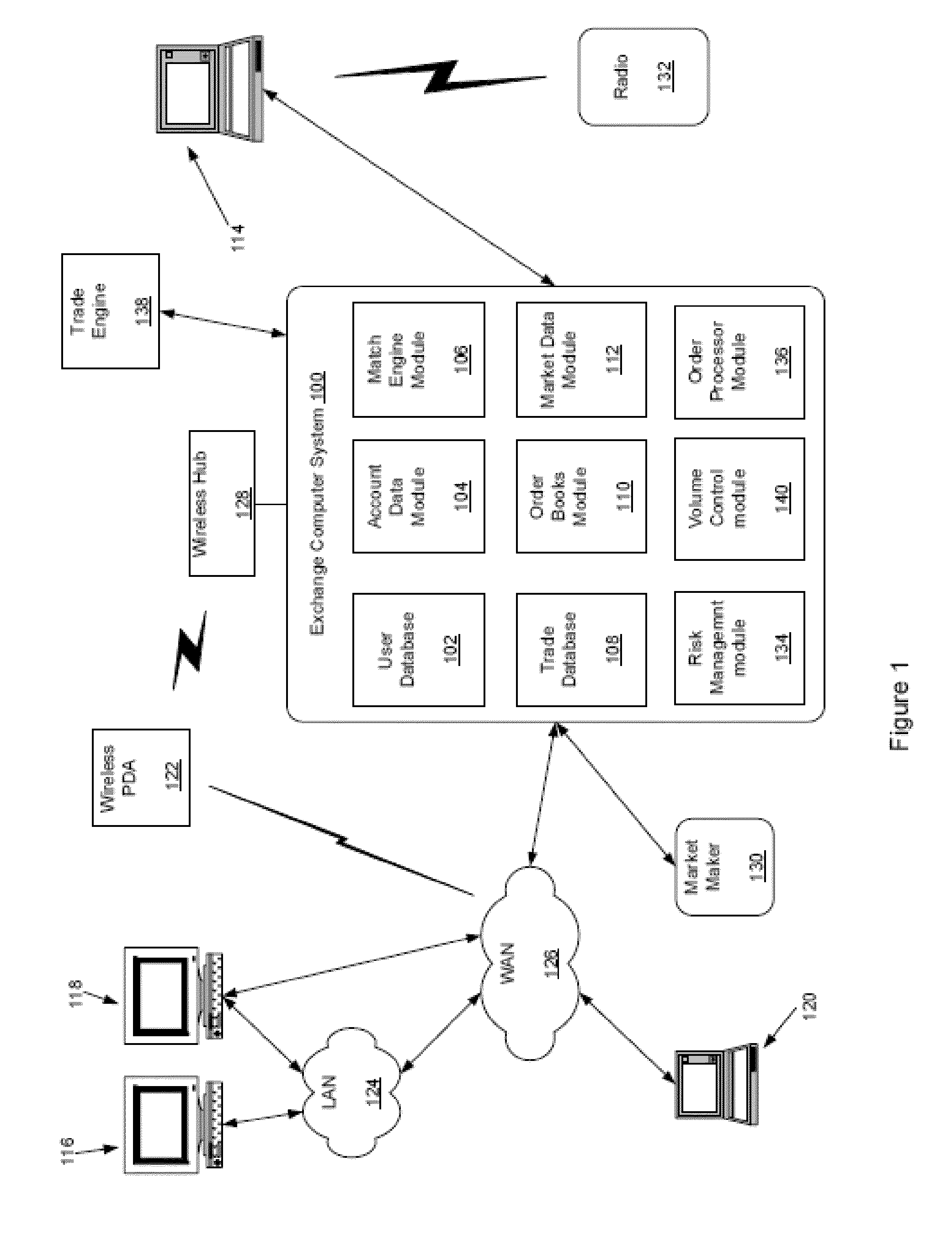
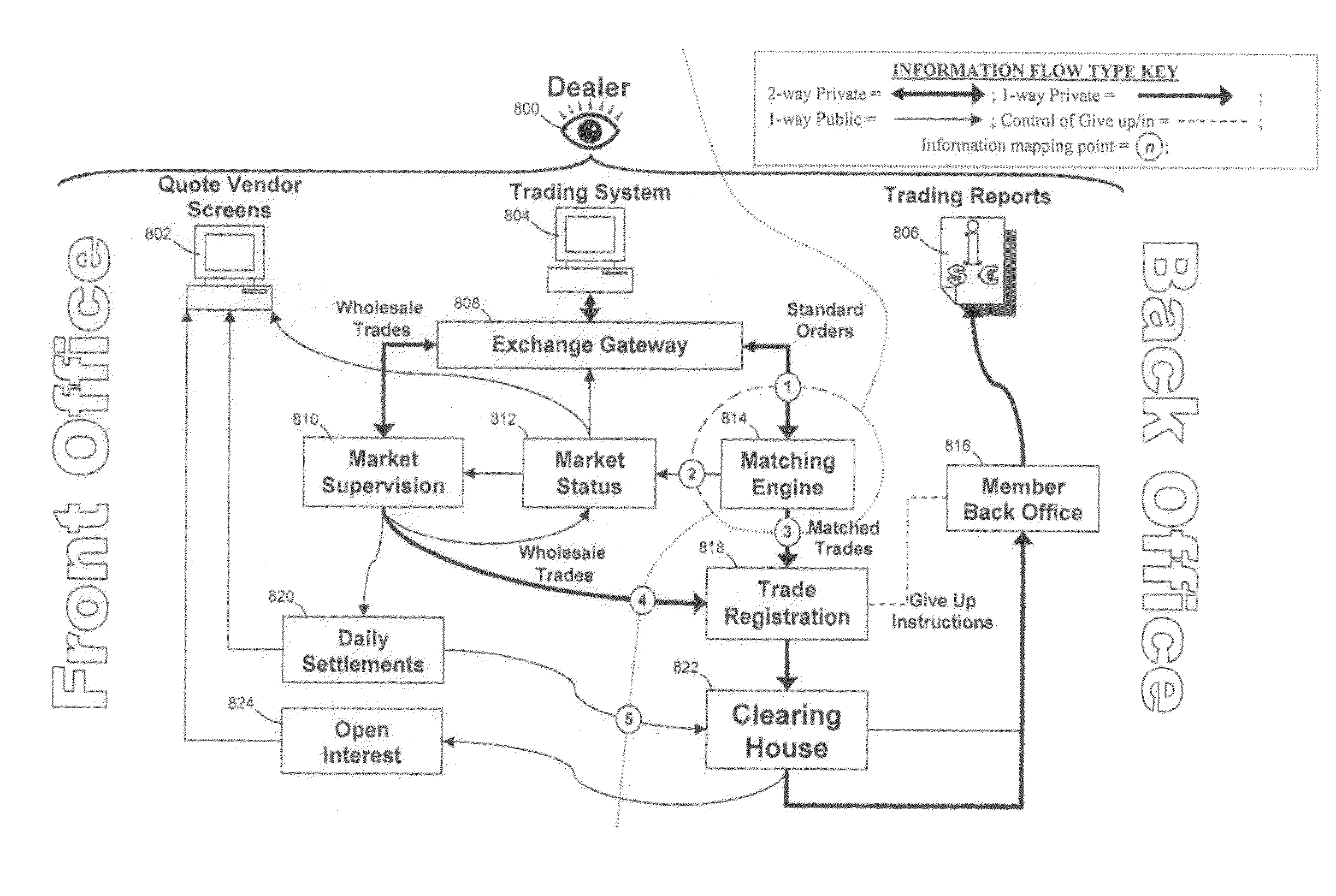
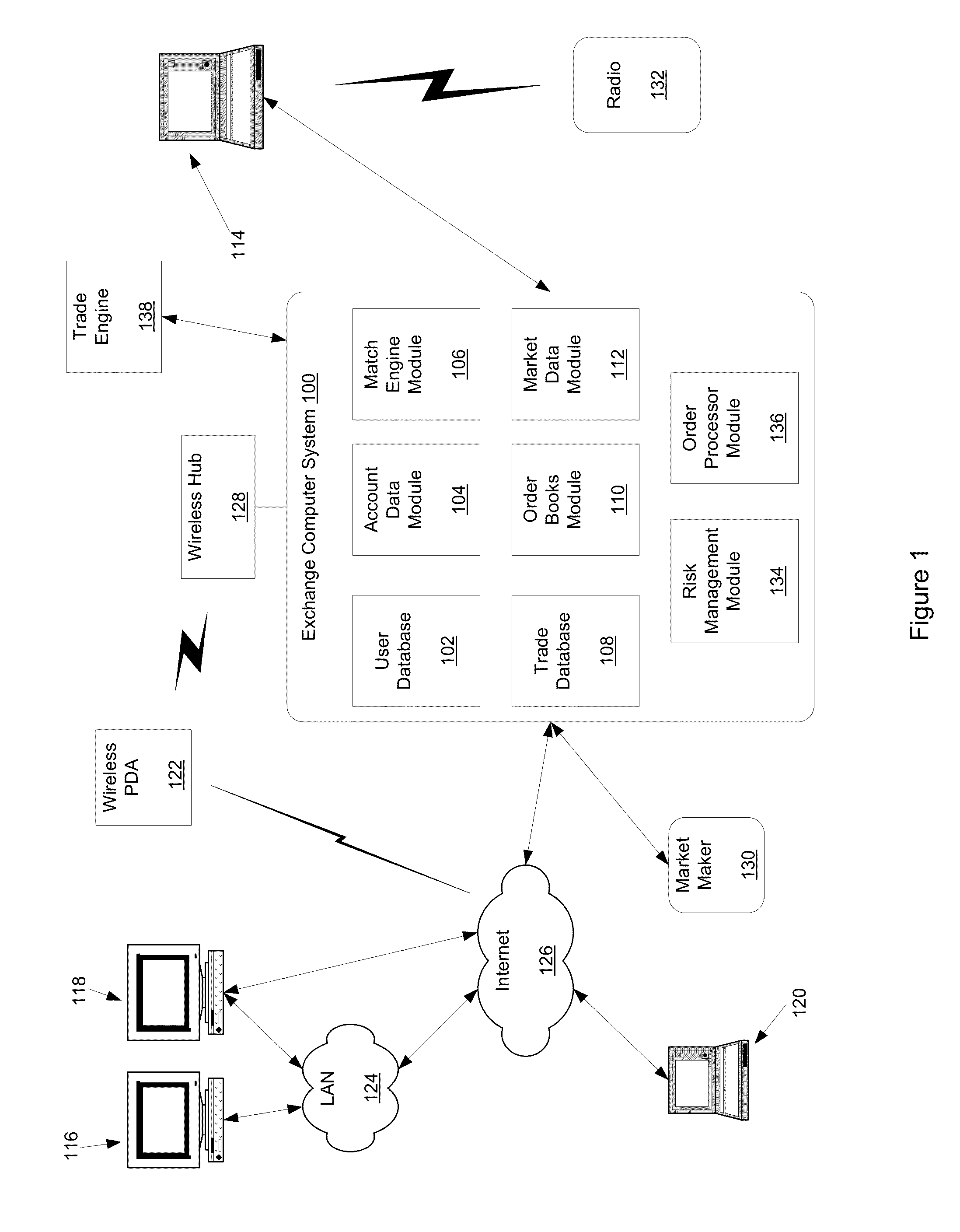
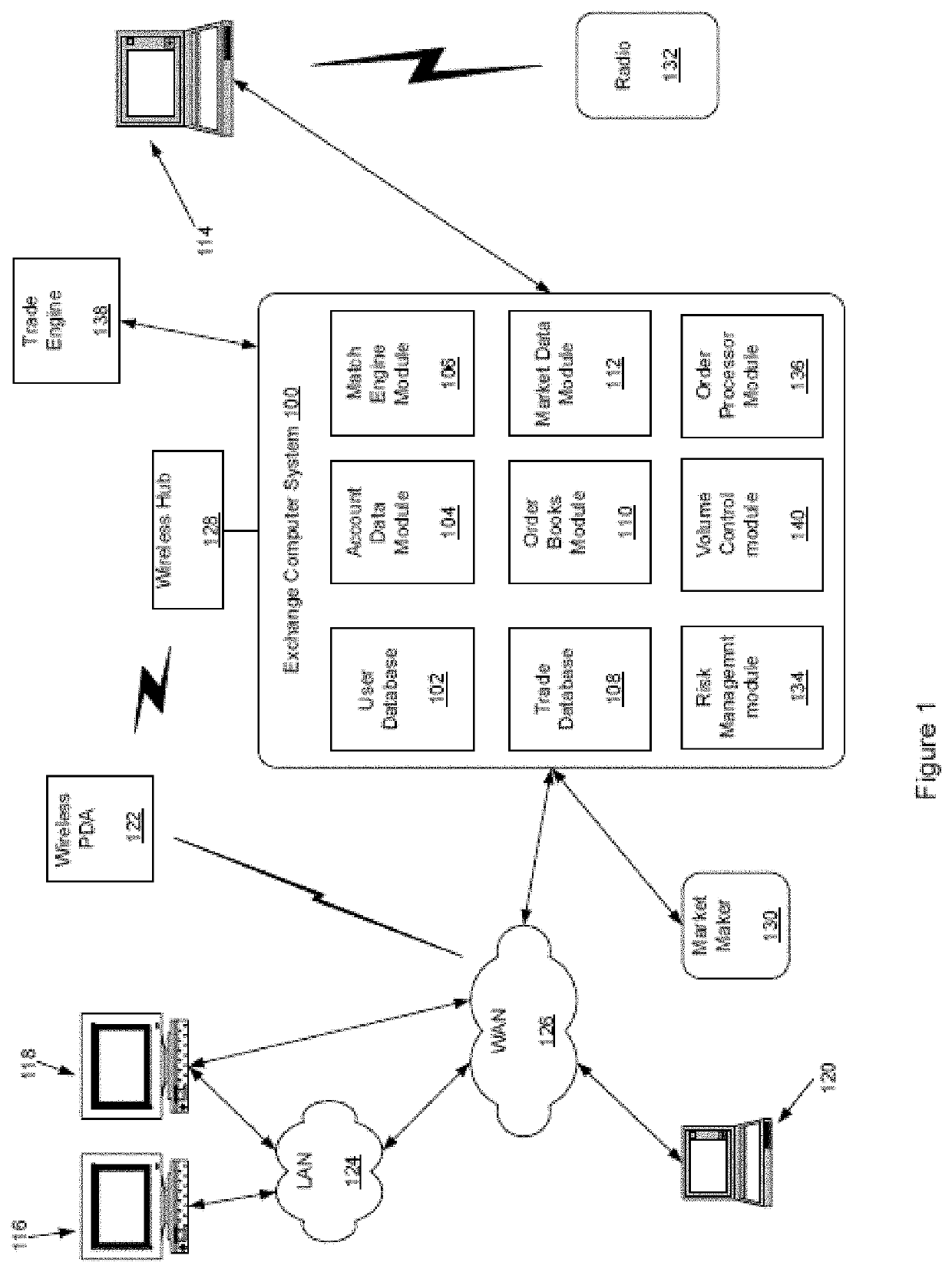
Method, system, and computer program product for trading interest rate swaps
InactiveUS20020010670A1Transparent pricingReduce management costsFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentEffective date
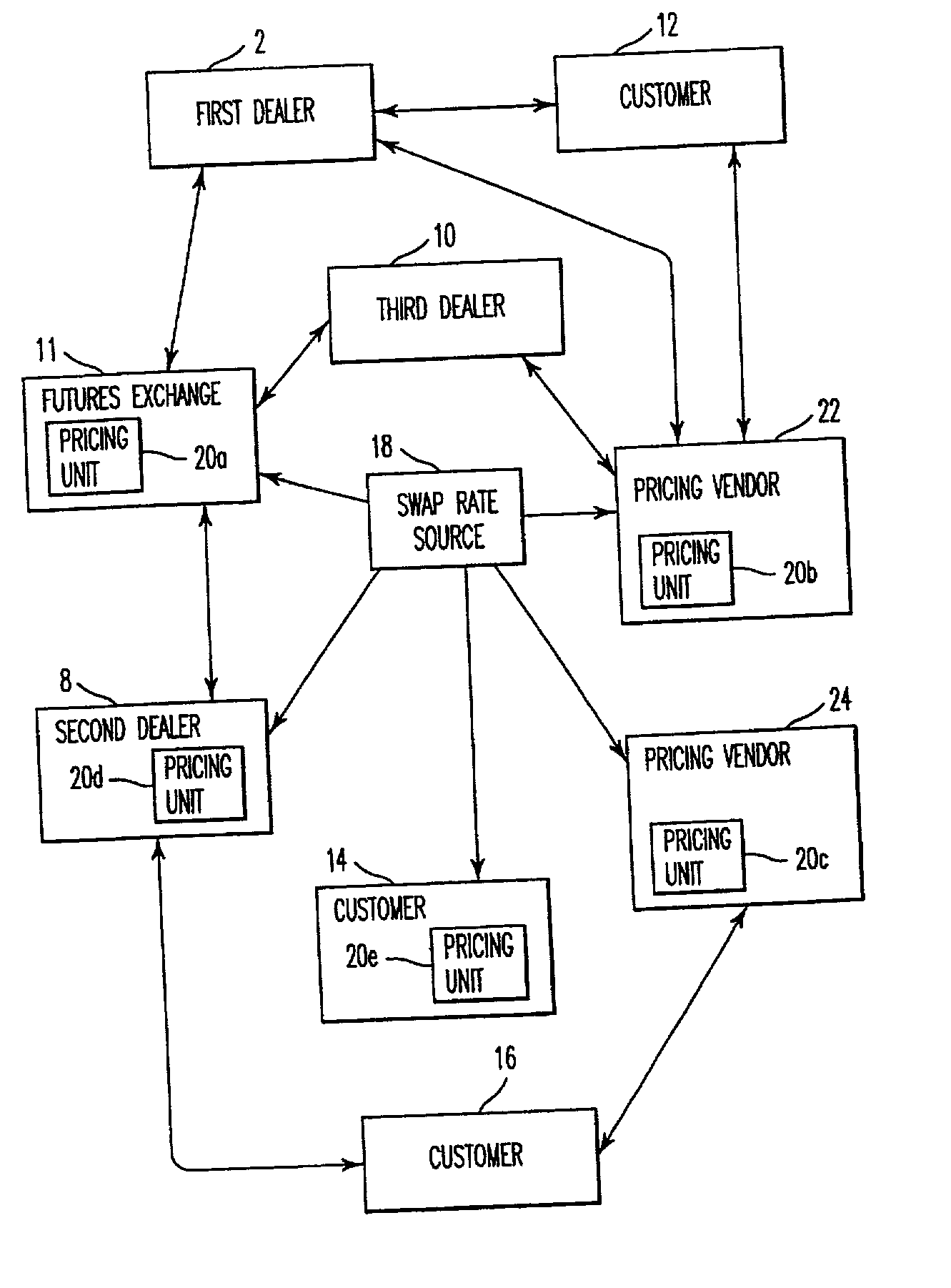
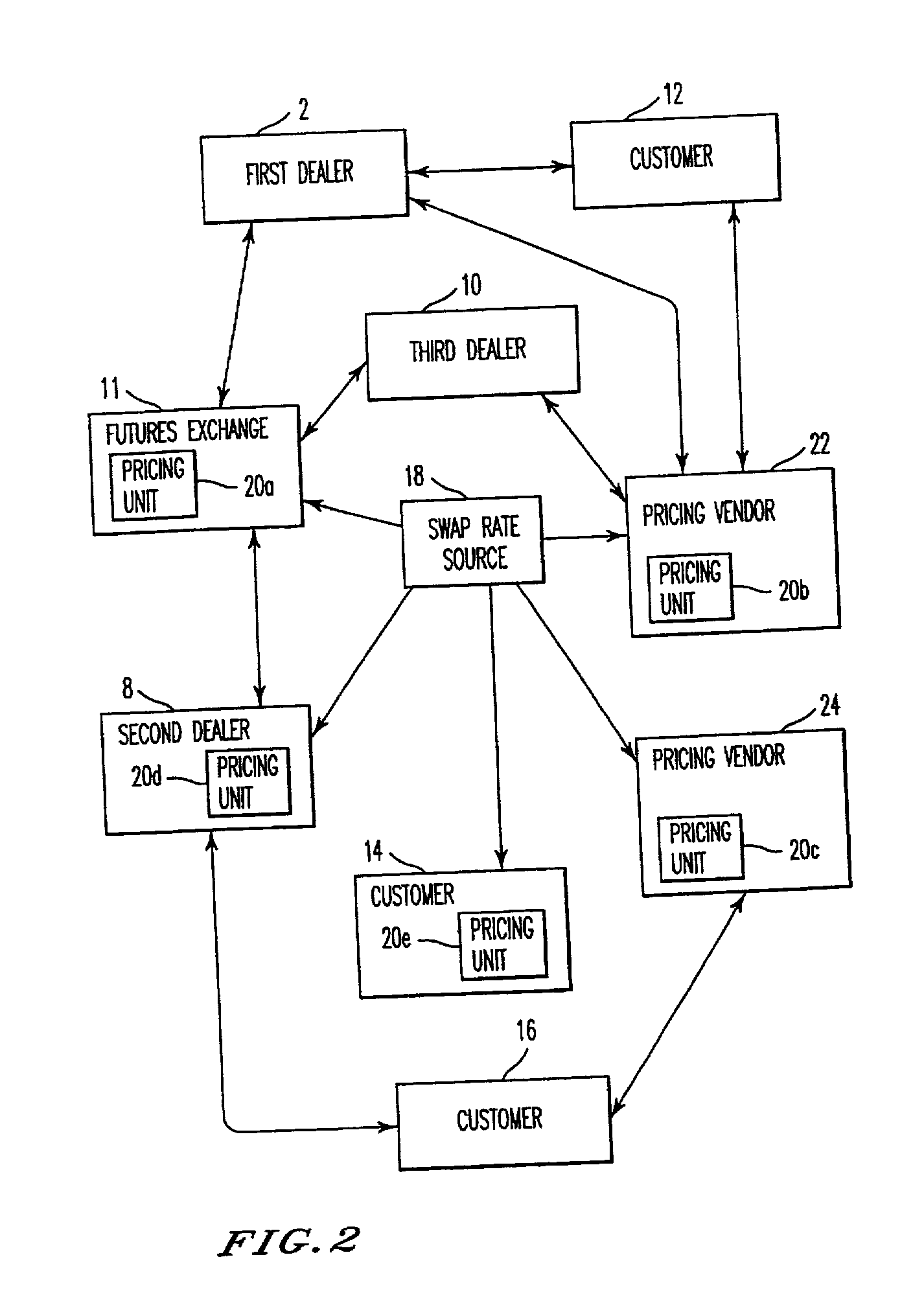
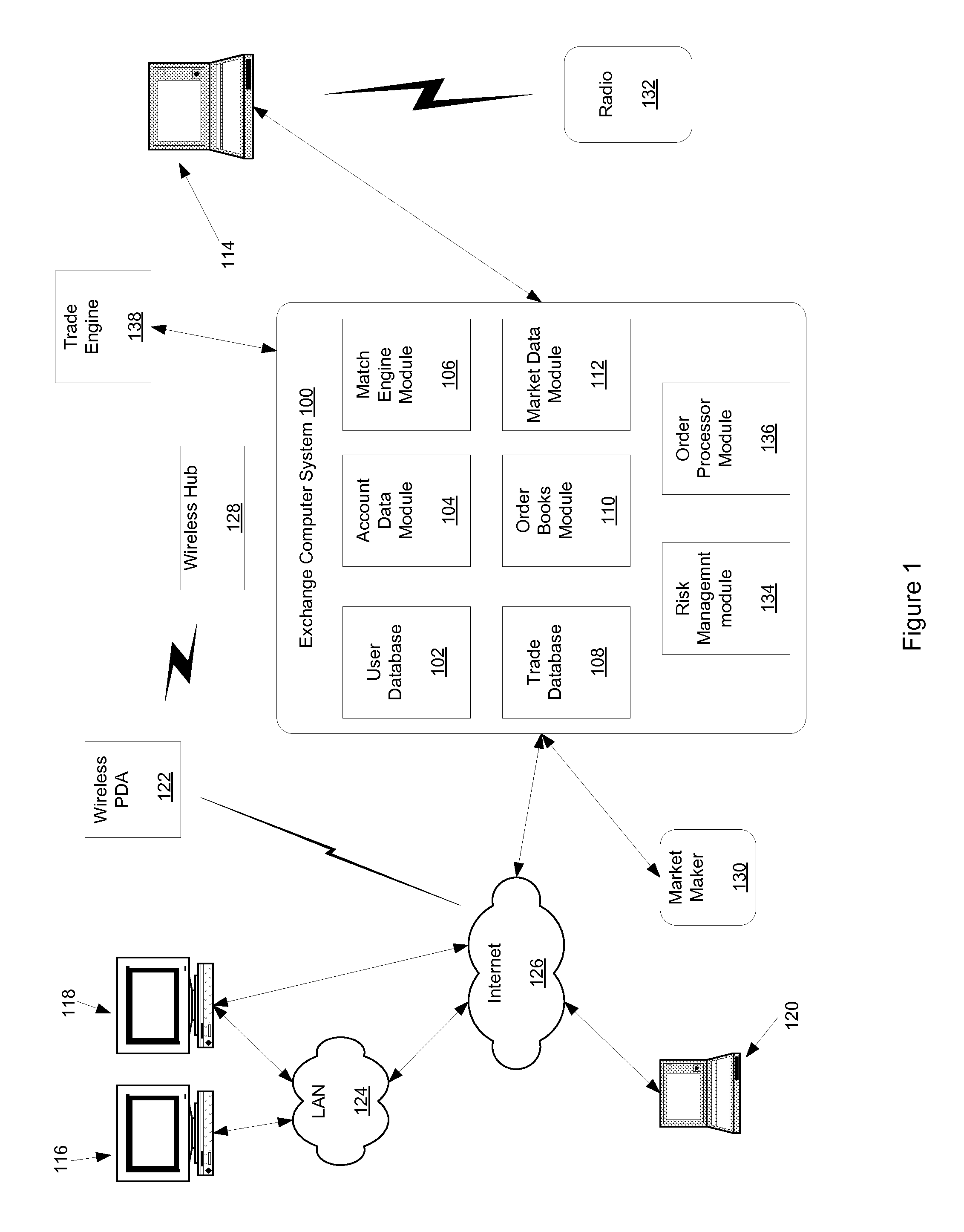
A method, system, computer program product, and data structure for trading in which a standardized contract is traded. The contract obligates a buyer and a seller to settle the contract based on a price of the contract at a first effective date. The contract is traded through an exchange that guarantees payment to the buyer of any amount owed to the buyer from the seller as a result of the contract and that guarantees payment to the seller of any amount owed to the seller from the buyer as a result of the contract. The price of the contract is determined based on preselected notional cash flows discounted by at least one point on an interest rate swap curve obtained from a preselected swap rate source.
Owner:MOSLER WARREN B +2
Method, system, and computer program for an electronically traded synthetic exchange traded coupon
InactiveUS20070288351A1Easy to trackReduce management costsFinanceInterest rate swapComputer science
In accordance with the principles of the present invention, a novel method, system, process, and computer program is provided that synthetically replicates a plain vanilla IR Swap through a future as well as to create a more fungible interest rate swap in the spot market. The forward start interest rate swaps of the present invention consist of a consecutive series of futures that value a forward start interest rate swap to start on a settlement date. The futures replicate the floating-rate payment terms for the interest rate swap that is being synthetically replicated. The spot interest rate swap is a standardized interest rate swap that is fungible.
Owner:HUNTLEY RUSSELL GUY
Trading and settling enhancements to the standard electronic futures exchange market model leading to novel derivatives including on exchange ISDA type interest rate derivatives and second generation bond like futures based in part or entirely on them
A set of linked methods allows accessing derivative products other than traditional futures and options within an adapted electronic futures exchange type market model, rules and legal environment. One embodiment comprises a linkage of such new methods which provides exchange members with access to exact OTC ISDA type interest rate swap and FRA related exposures. Another embodiment is a method comprising another specific linkage of the new methods which gives exchange members access to exact OTC ISDA type overnight index swap related exposures. An additional embodiment provides exchange members with convenient access to credit spread and\or interest rate swap embodiments via deliverable credit rate linked and swap rate linked bond like futures.
Owner:LIFFE ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT
Interest rate swap index
A set of indices is provided which allows accurate tracking of interest rate swap (IRS) markets. The indices are calculated using market data and synthetic purchasing and selling of synthetic interest rate swaps utilizing the present market data. The value of the synthetic interest rate swaps are the basis for the value of a particular index. The purchasing and selling of the synthetic interest rate swap occurs at a frequency to minimize effects of shortening terms on the index. One subset of the IRS indices reflects a plain-vanilla swap for a specific term of years. Another subset of the IRS indices reflects a spread between two specific terms of years. A third subset of the IRS indices reflect two spreads, sometimes referred to as a butterfly, between a middle term of years and a shorter term of years and the same middle term of years and a longer term of years.
Owner:PIPELINE CAPITAL
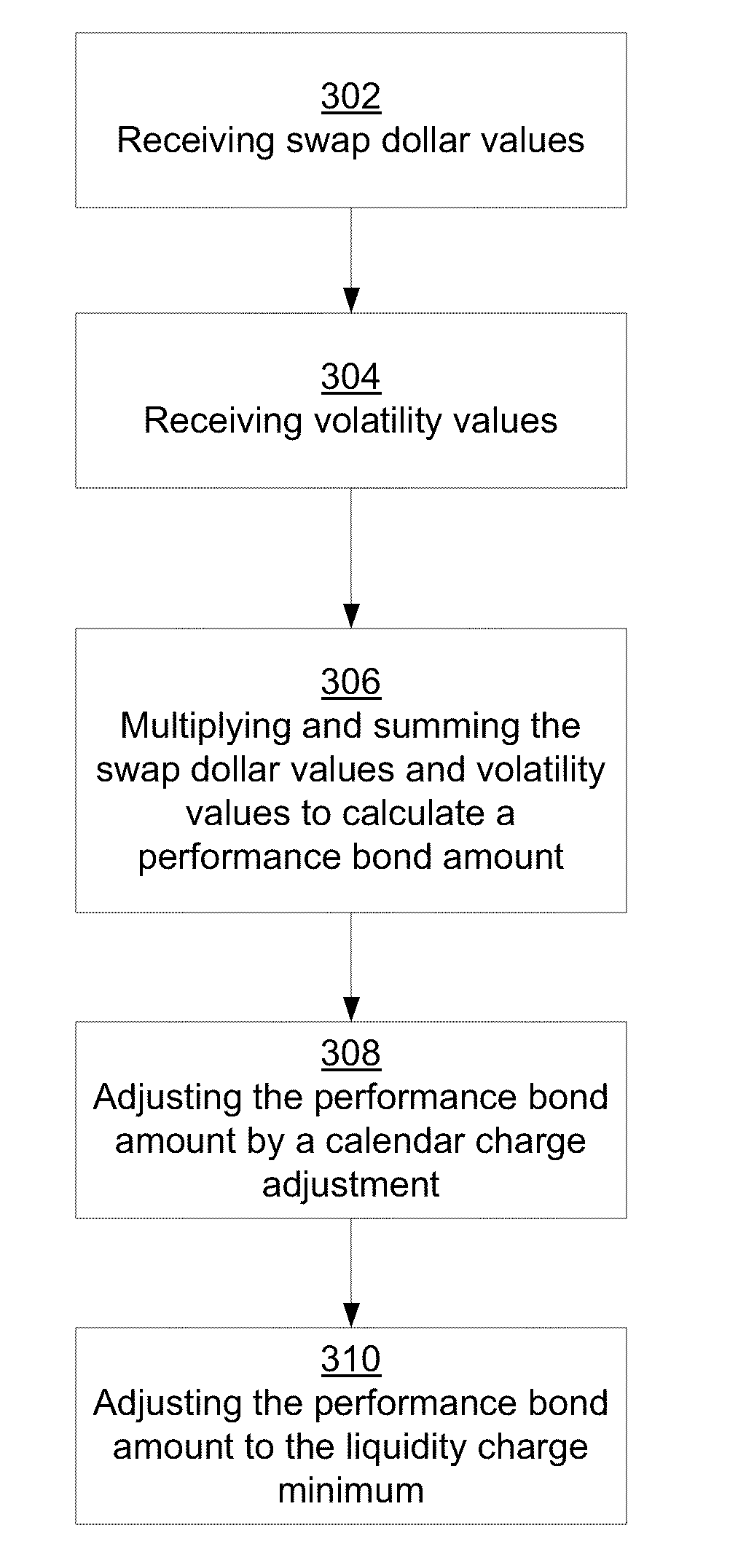
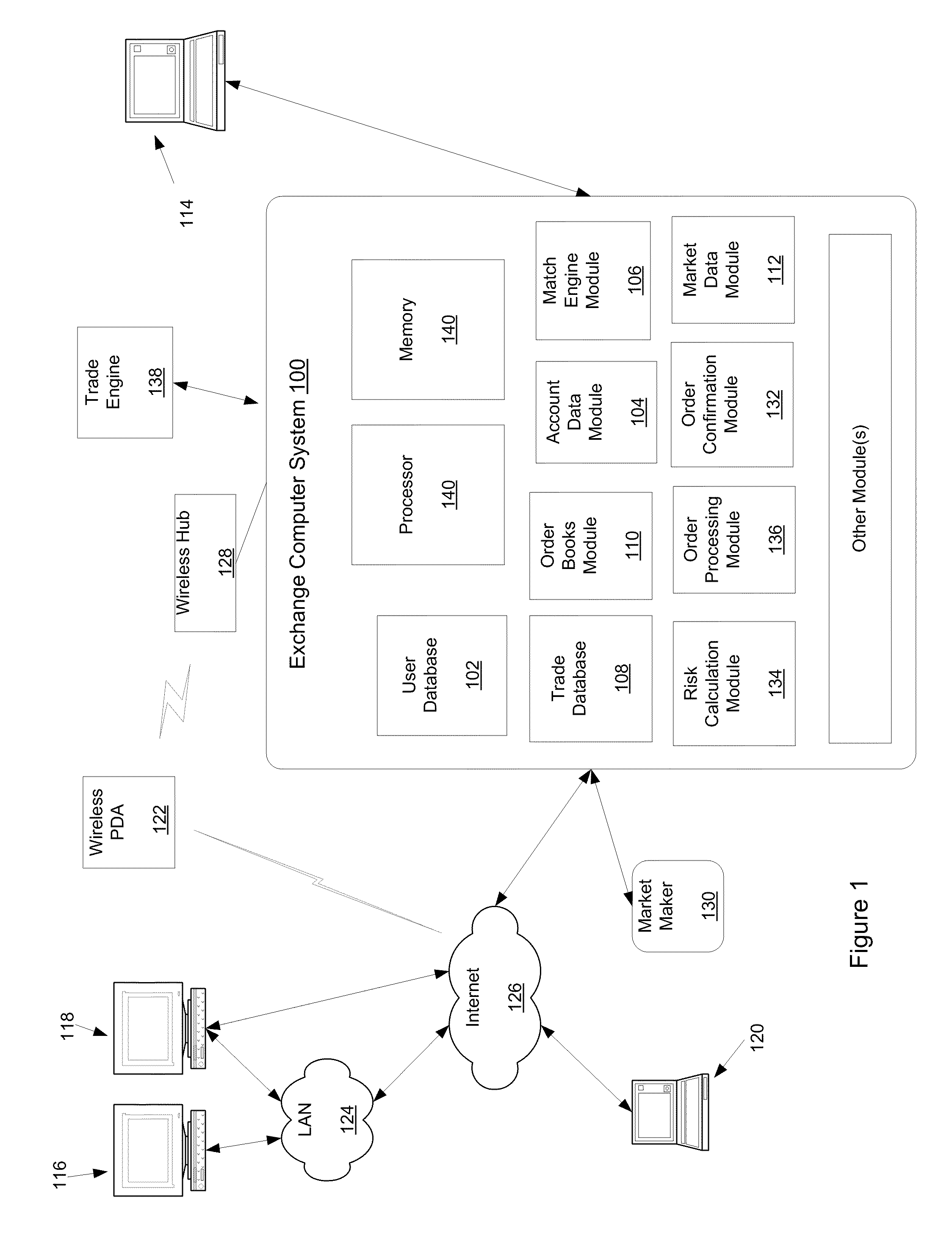
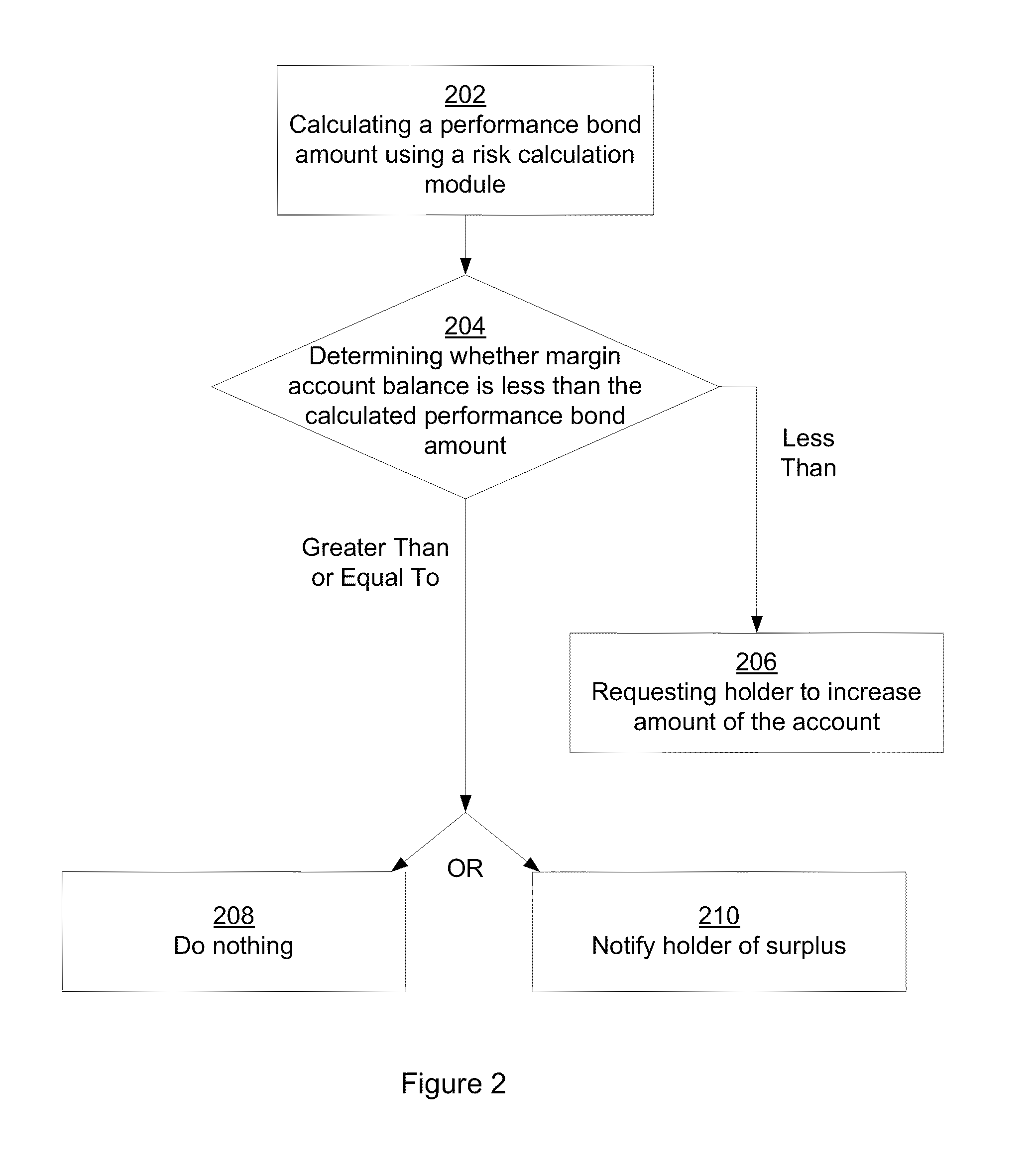
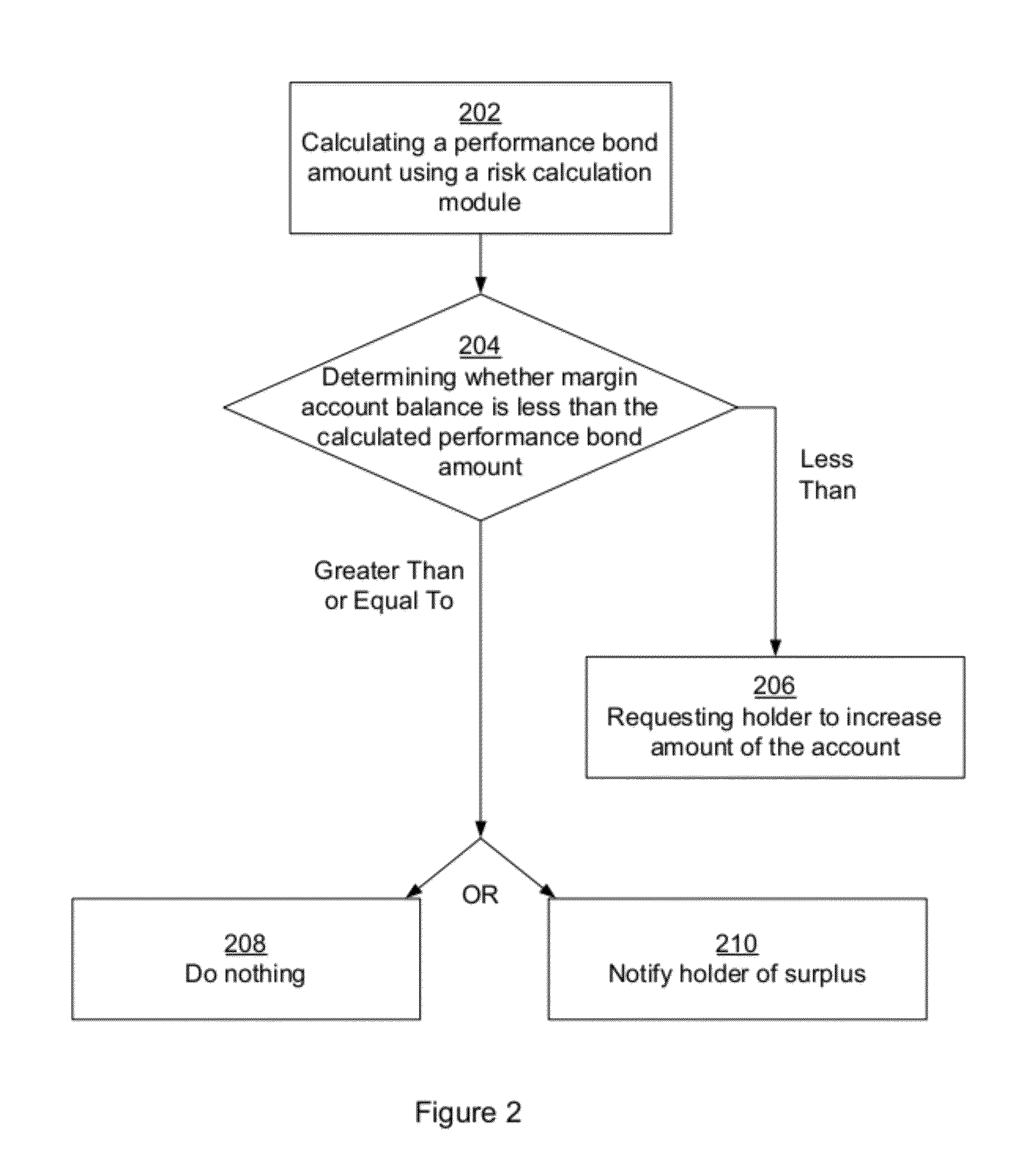
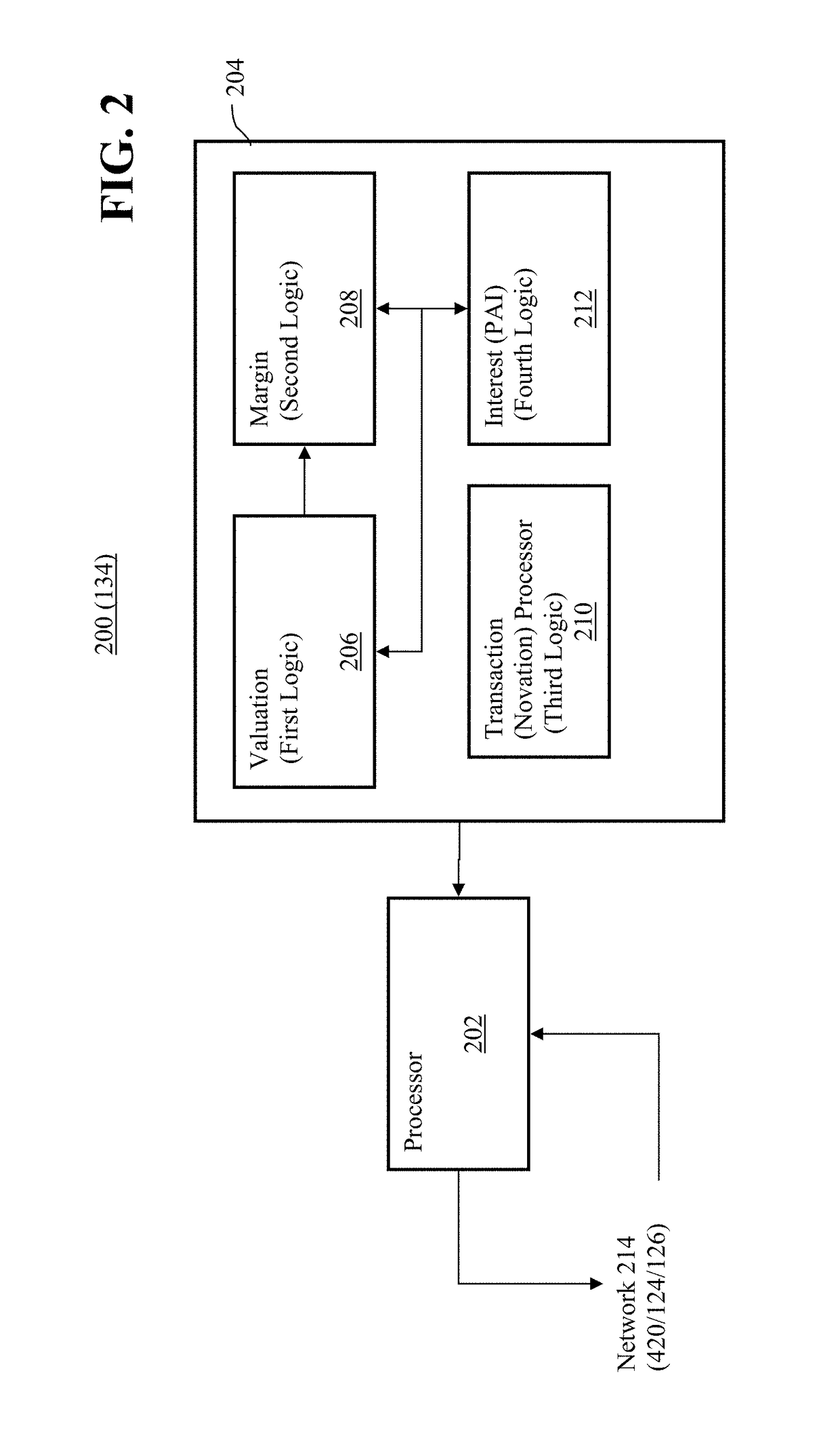
Clearing System That Determines Margin Requirements for Financial Portfolios
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
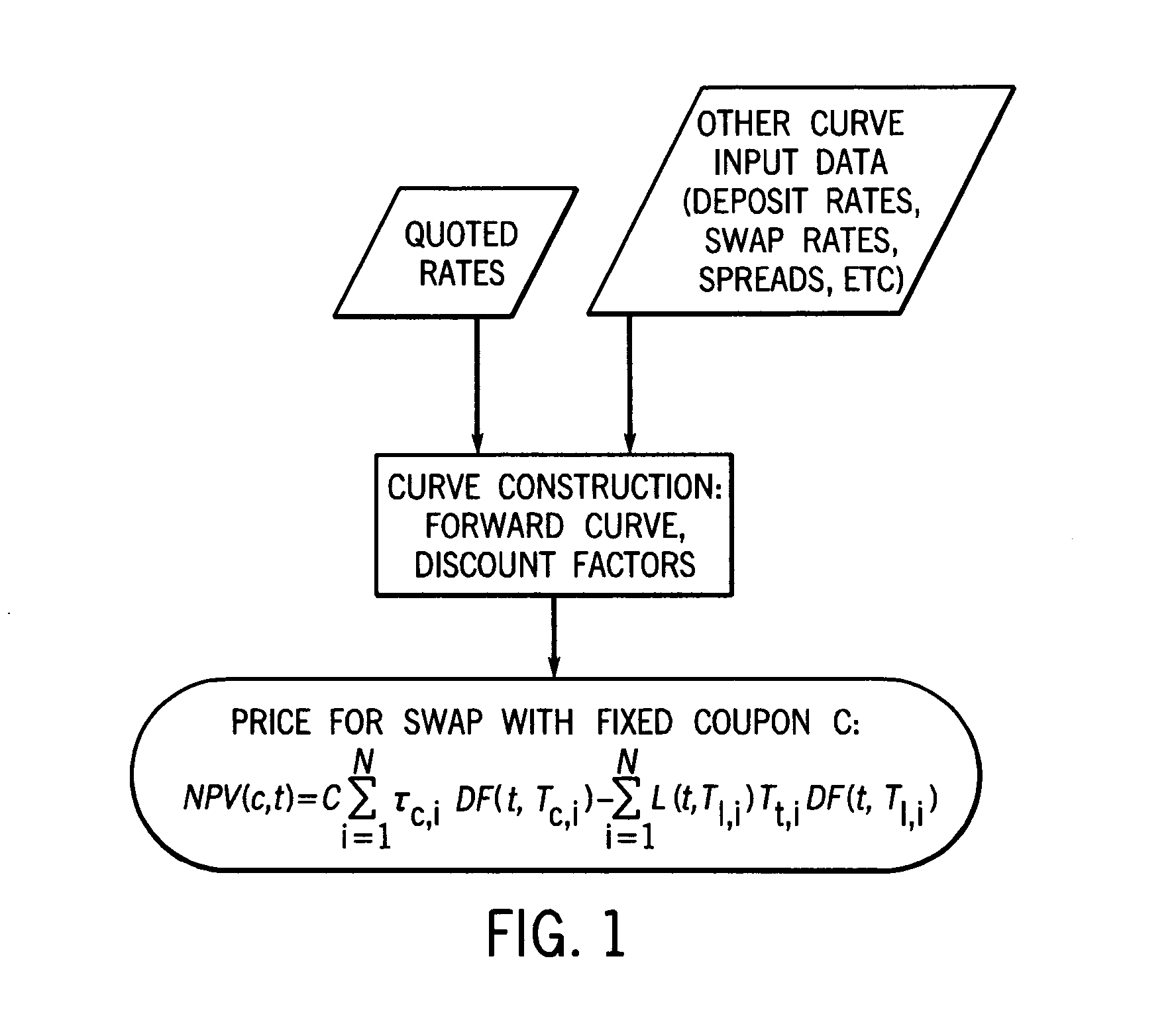
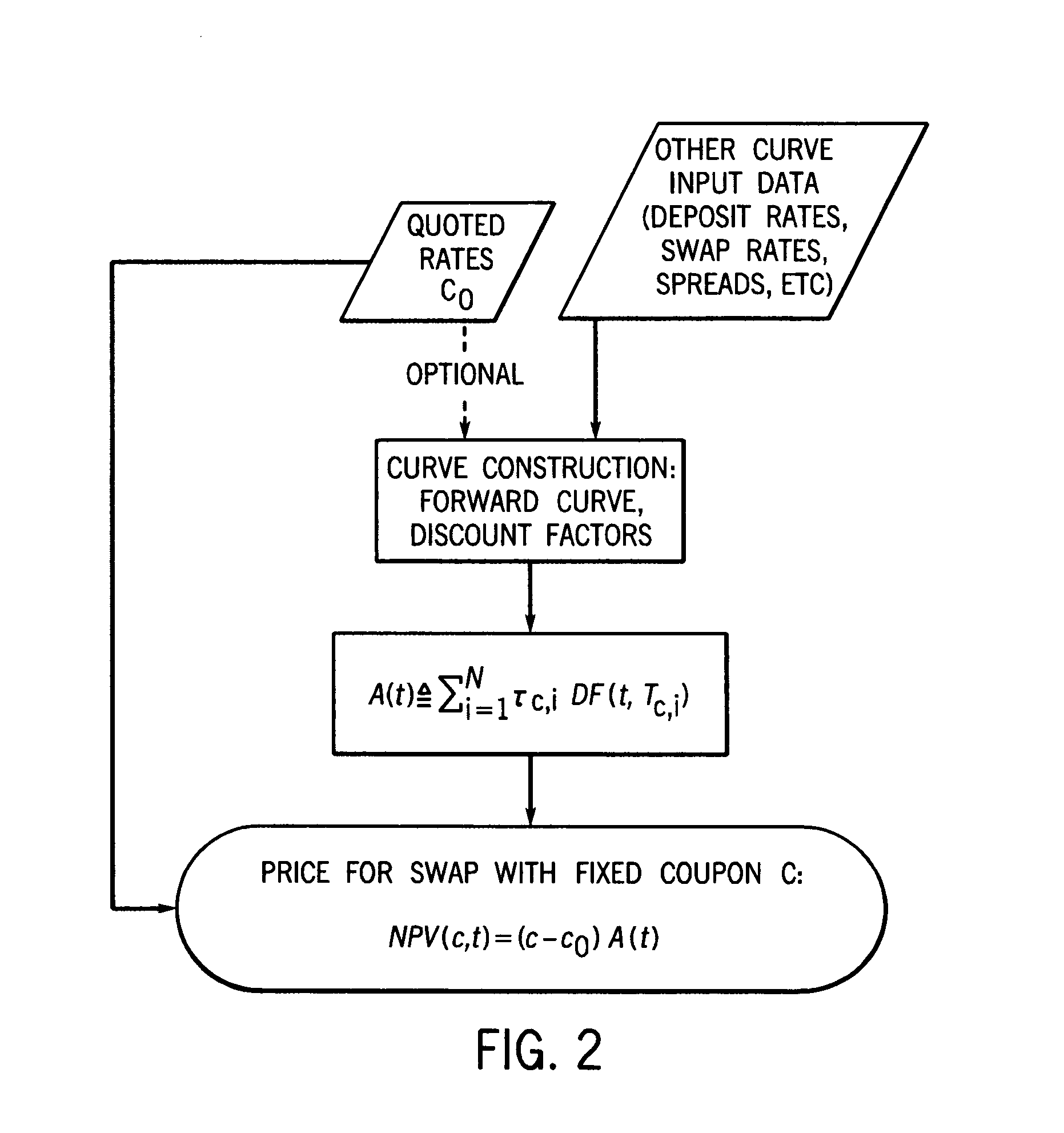
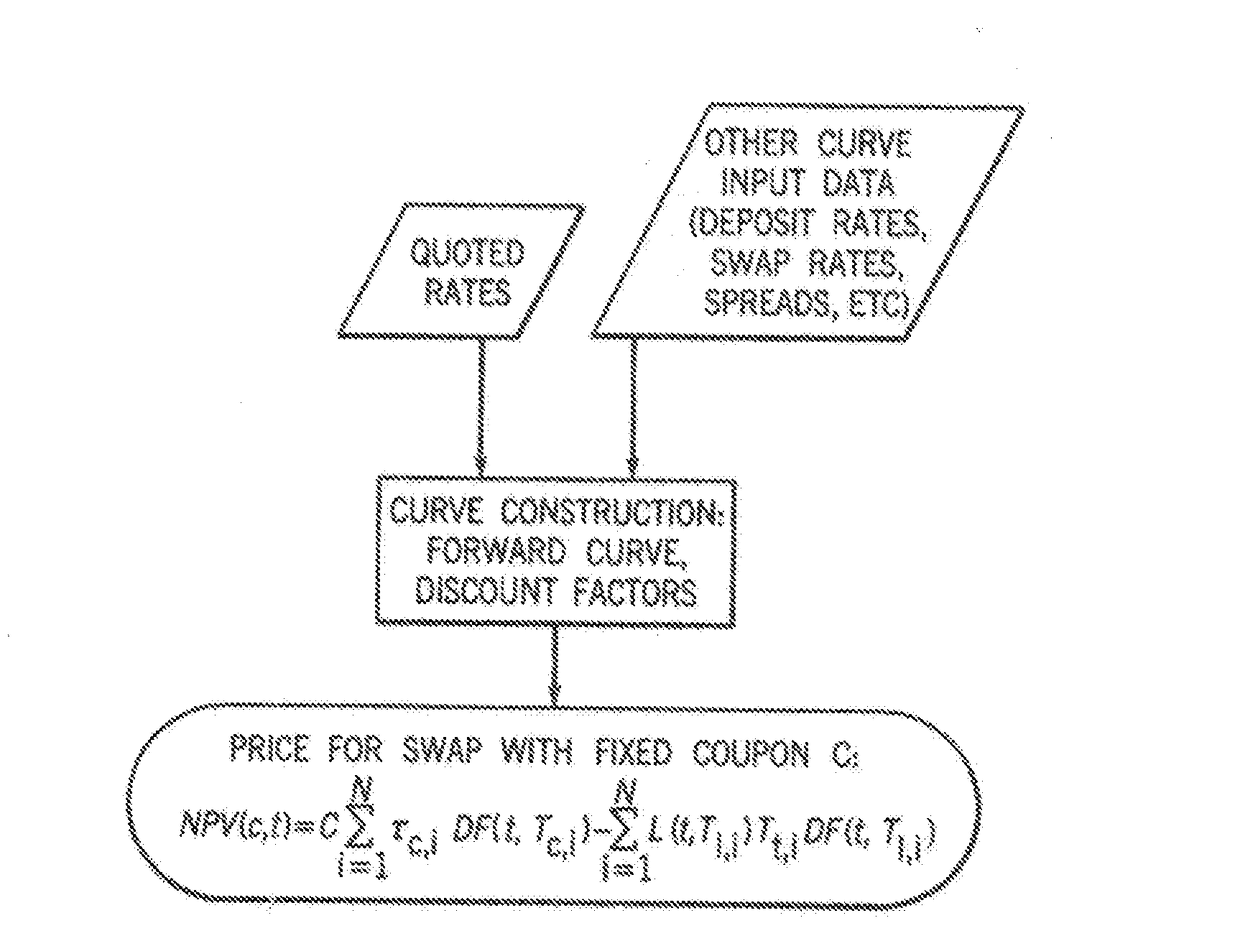
Rate-negotiated, standardized-coupon financial instrument and method of trading
InactiveUS20120296793A1Mitigates granularization issueMitigates the granularization issueFinanceInterest rate swapStandardization
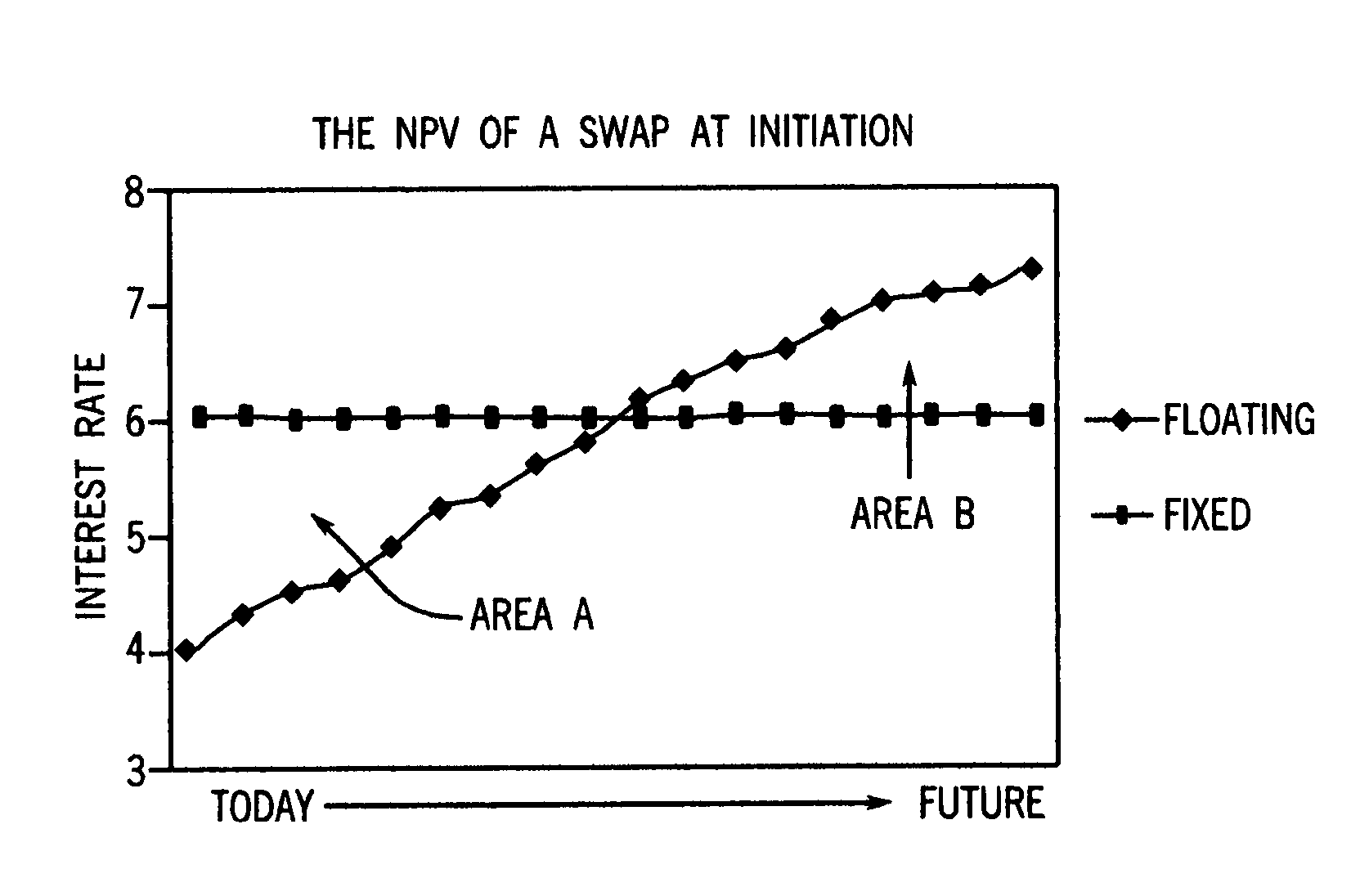
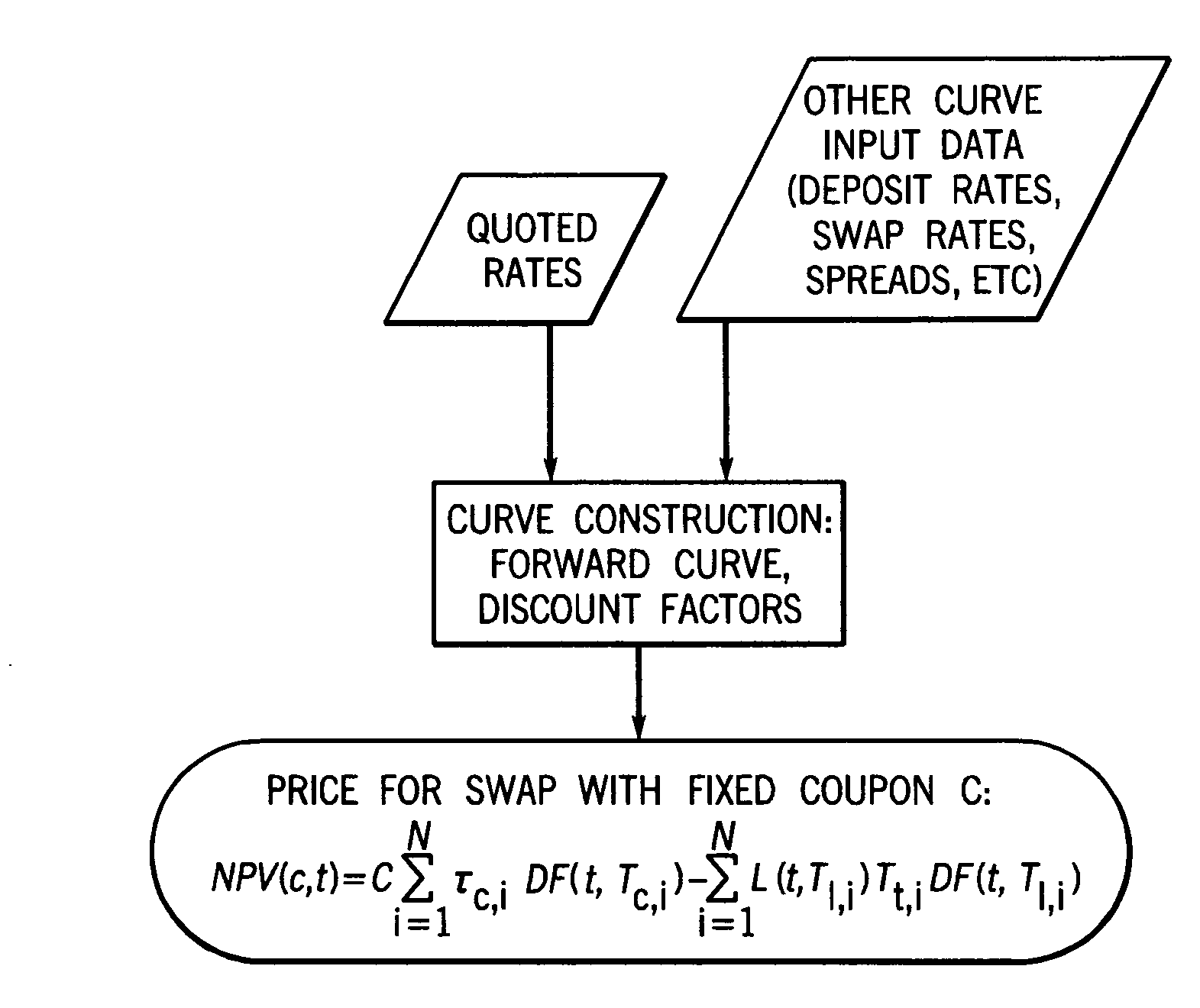
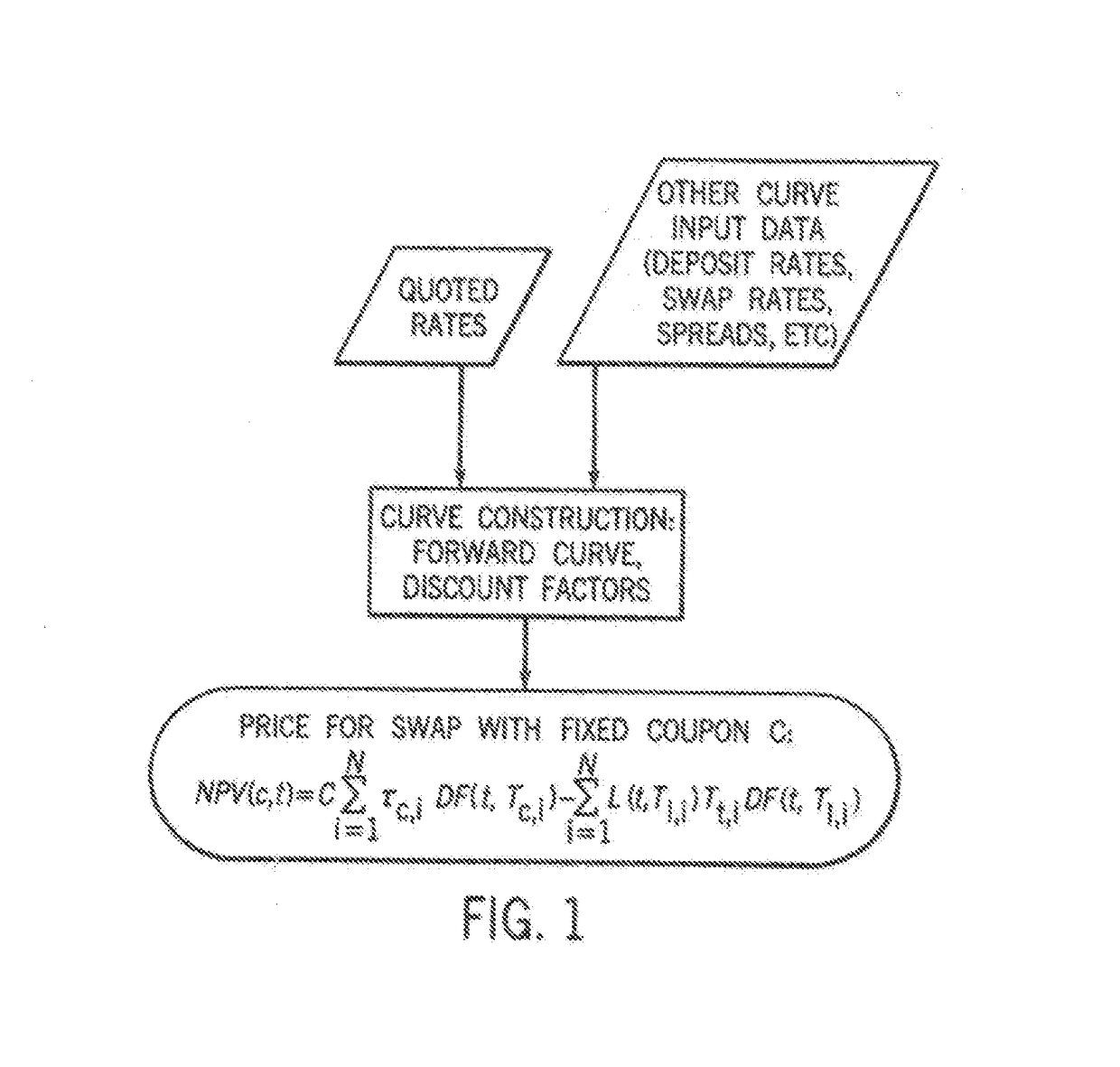
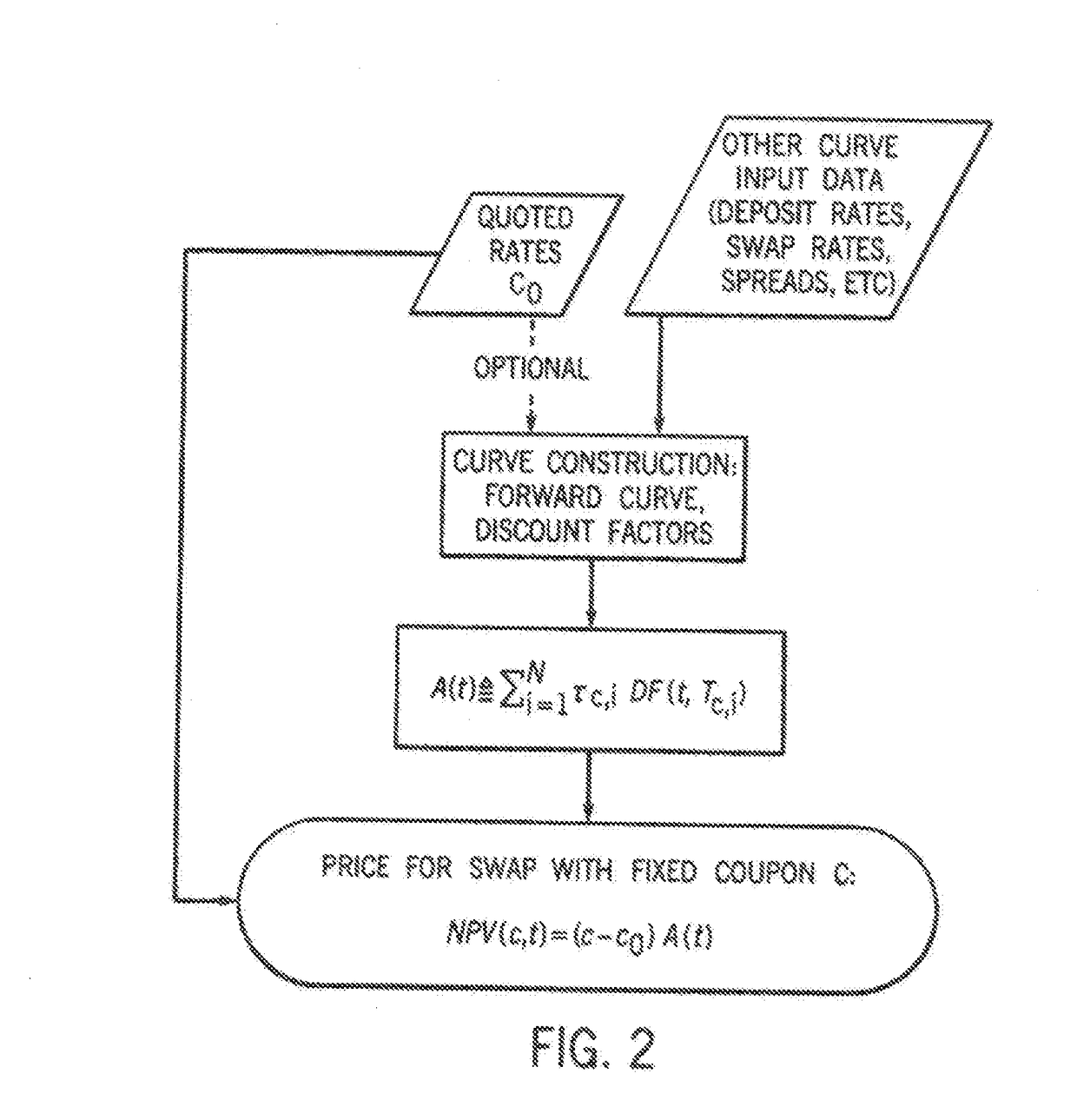
In accordance with the principles of the present invention, a rate-negotiated, standardized-coupon financial instrument and method of trading are provided. A coupon is negotiated between two parties. At least one forward curve and a discount curve are implied or approximated to be consistent with the negotiated coupon. A consistent value for a swap with a different coupon is determined. The consistent value can comprise the net present value (NPV) of the interest rate swap written as the difference between the present values of two interest payment legs. In the case of a vanilla swap the two legs correspond to fixed coupon payments and floating coupon payments. In the case of a basis swap, one leg is the floating coupon payments with a reference rate plus a fixed coupon, and the other leg is floating coupon payments with a different reference rate. The rate-negotiated, standardized-coupon financial instrument of the present invention provides for a financial instrument negotiated in rate terms to be substituted with an equivalent position in an instrument with a different coupon rate, at an adjusted price.
Owner:ERIS INNOVATIONS
Interest Rate Swap Compression Match Engine
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system for trading using a central counterparty which allows market participants to minimize risk and / or transactional fees associated with a portfolio of bilateral positions without substantially altering a risk profile thereof. In particular, the disclosed embodiments allow a market participant holding a portfolio of heterogeneous bilateral positions, such as positions in interest rate swap (“IRS”) contracts, to net together similar but not identical positions within their portfolio, thereby reducing margin requirements and / or transaction fees, according to criteria specified by the market participant, and which may be different from criteria specified by other market participants, wherein the overall risk exposure desired by the market participant in entering into the positions remains substantially unchanged as does the desired overall risk exposure of the counterparty market participants to those positions.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE INC
Interest rate swap compression match engine
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system for trading using a central counterparty which allows market participants to minimize risk and / or transactional fees associated with a portfolio of bilateral positions without substantially altering a risk profile thereof. In particular, the disclosed embodiments allow a market participant holding a portfolio of heterogeneous bilateral positions, such as positions in interest rate swap (“IRS”) contracts, to net together similar but not identical positions within their portfolio, thereby reducing margin requirements and / or transaction fees, according to criteria specified by the market participant, and which may be different from criteria specified by other market participants, wherein the overall risk exposure desired by the market participant in entering into the positions remains substantially unchanged as does the desired overall risk exposure of the counterparty market participants to those positions.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
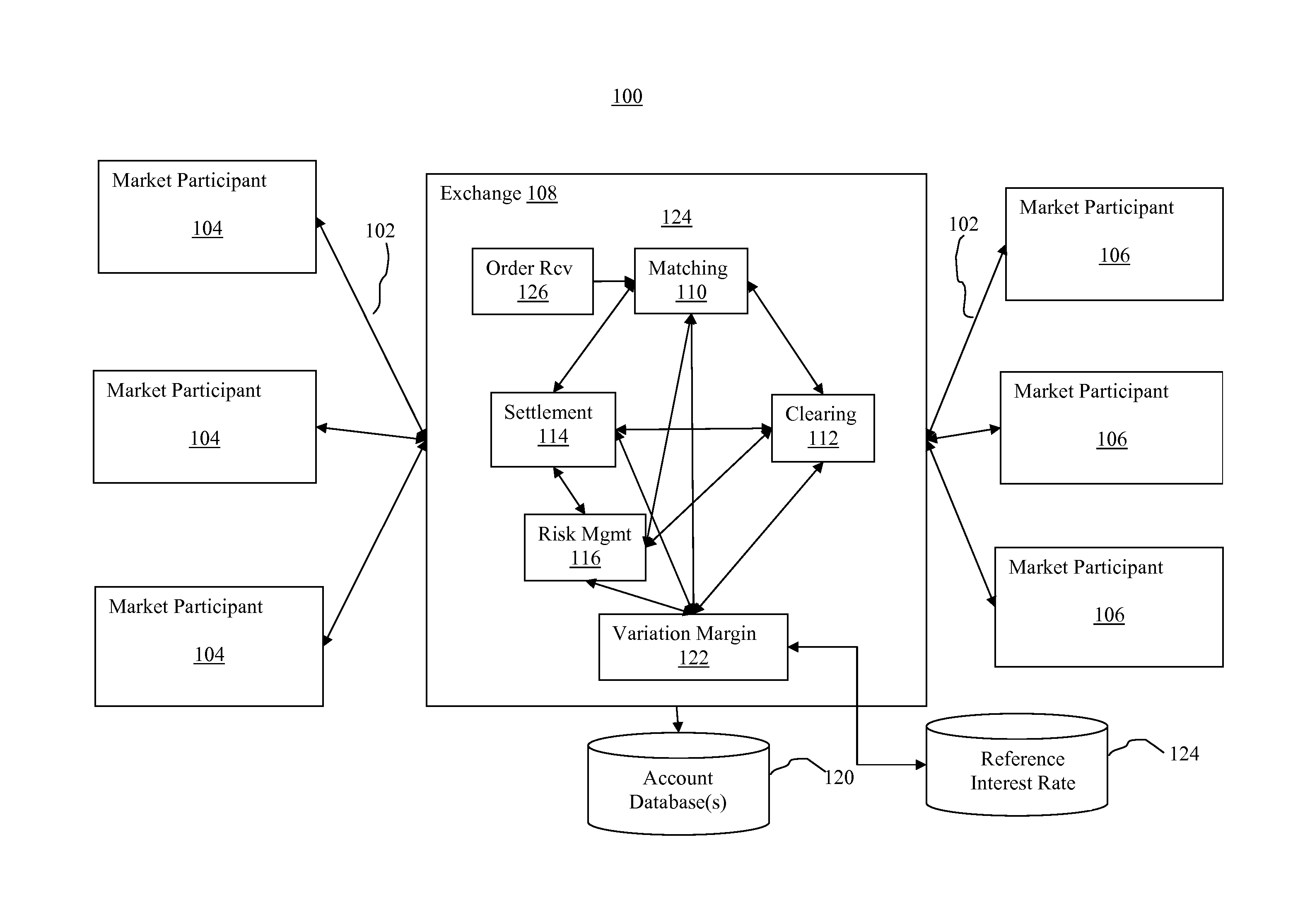
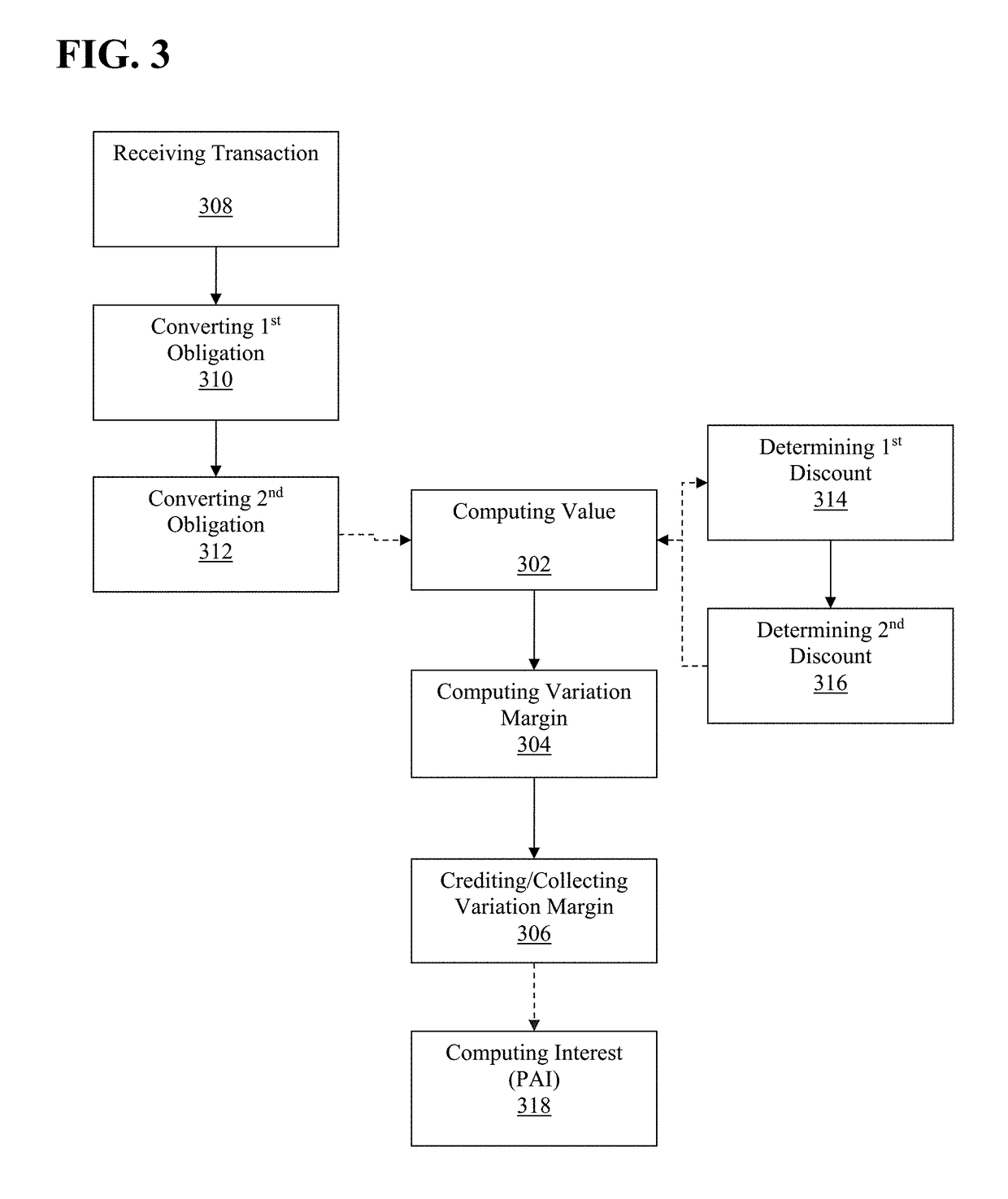
Compound overnight bank rate accrual futures contract and computation of variation margin therefore
The disclosed embodiments relate to an exchange-traded futures contract, guaranteed by a clearing house, and characterized by an embedded price dynamic comprising a compound accrual of a periodic interest rate up to a date on which trading therein is terminated, as specified in the futures contract terms and conditions. A trader may be allowed and / or enabled to take a position in a futures contract with respect to an interest bearing underlier with a variable interest rate and, thereby, minimize the number of transactions and attendant costs with respect to monitoring and correcting for divergences between the futures position and the notional interest rate swap exposure for which the futures position is intended to serve as a proxy. Variation margin for the position is computed based on an underlying reference interest rate as opposed to being computed solely on the basis of the end-of-business day price of the futures contract.
Owner:BARKER PETER +5
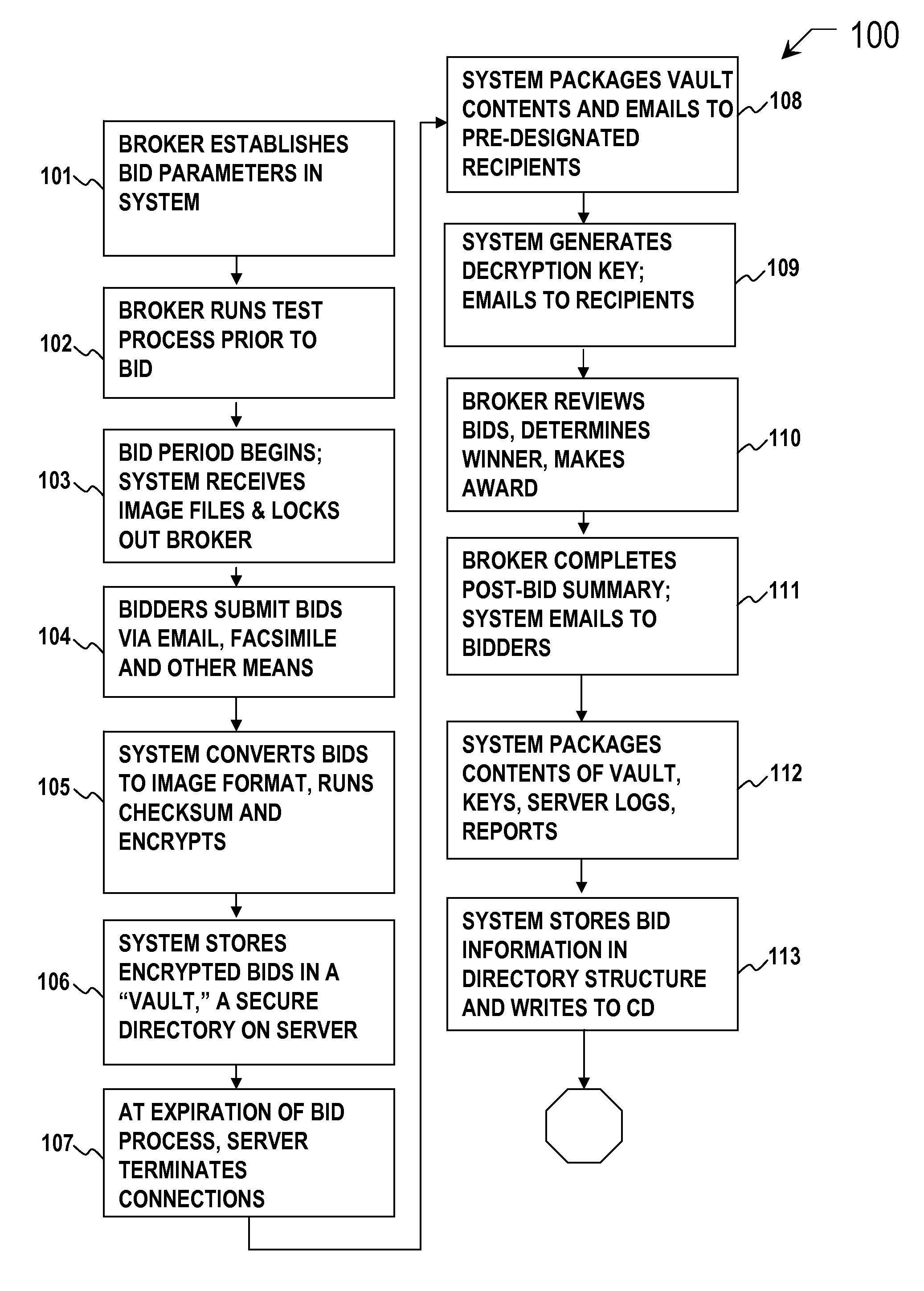
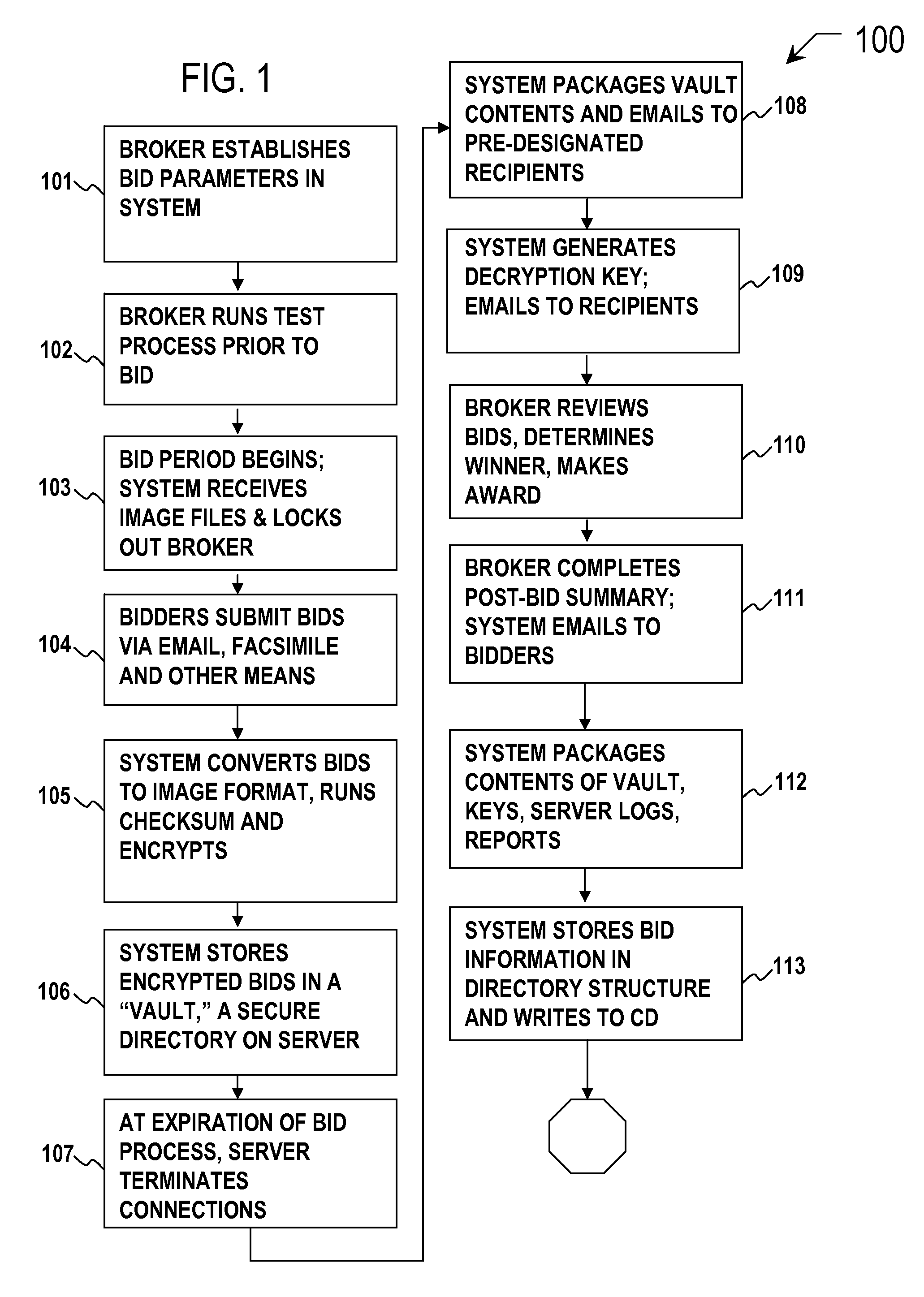
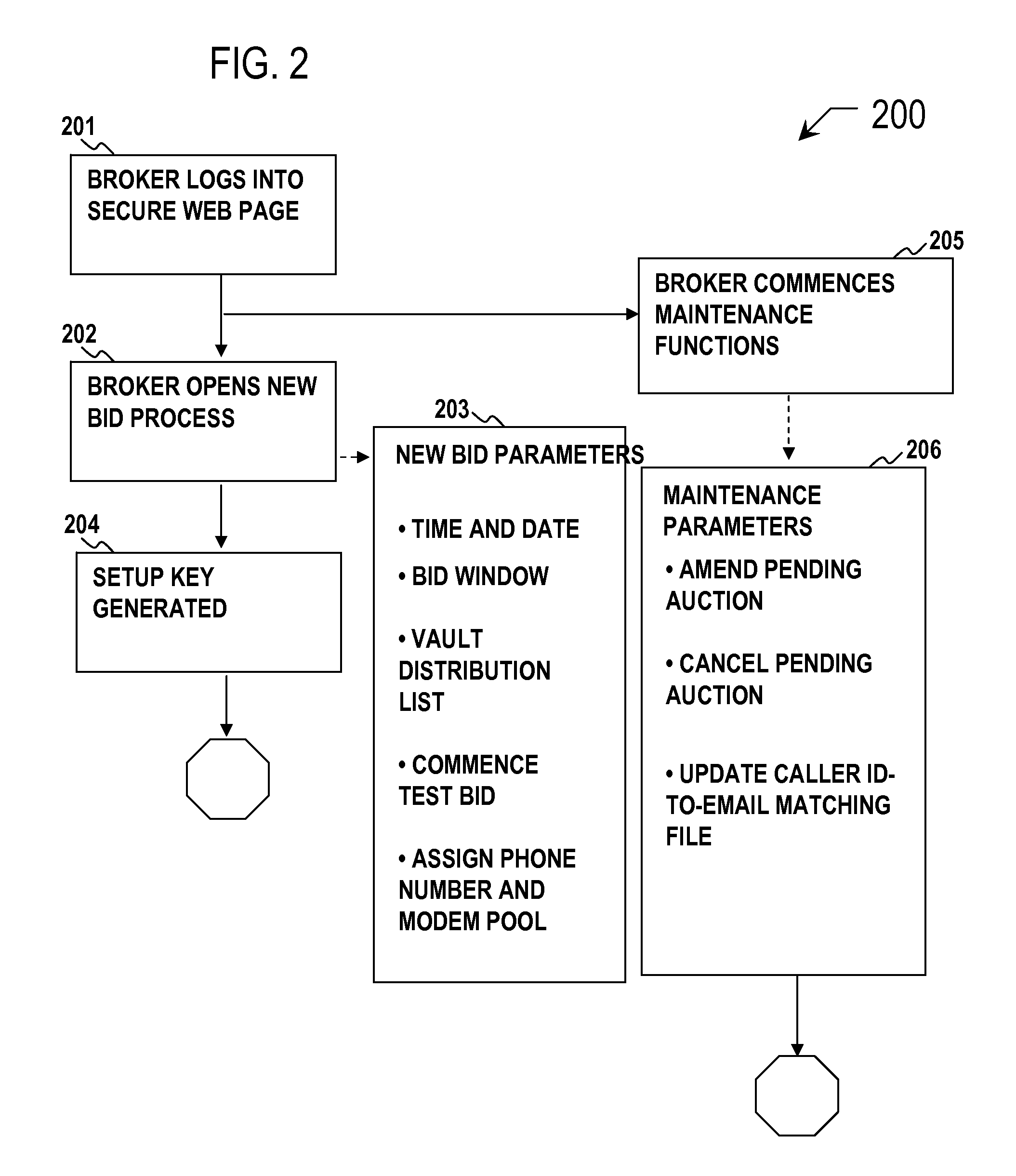
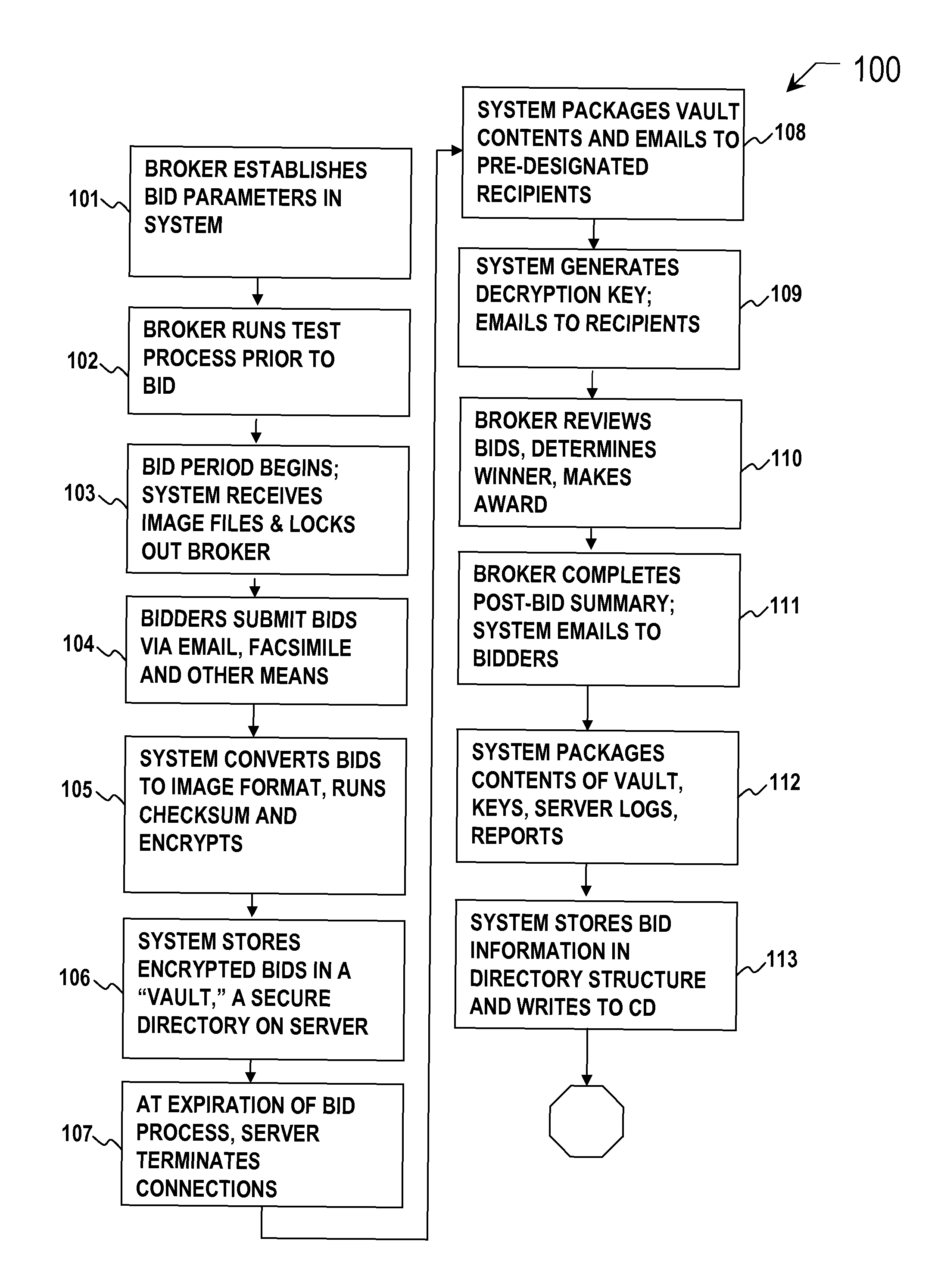
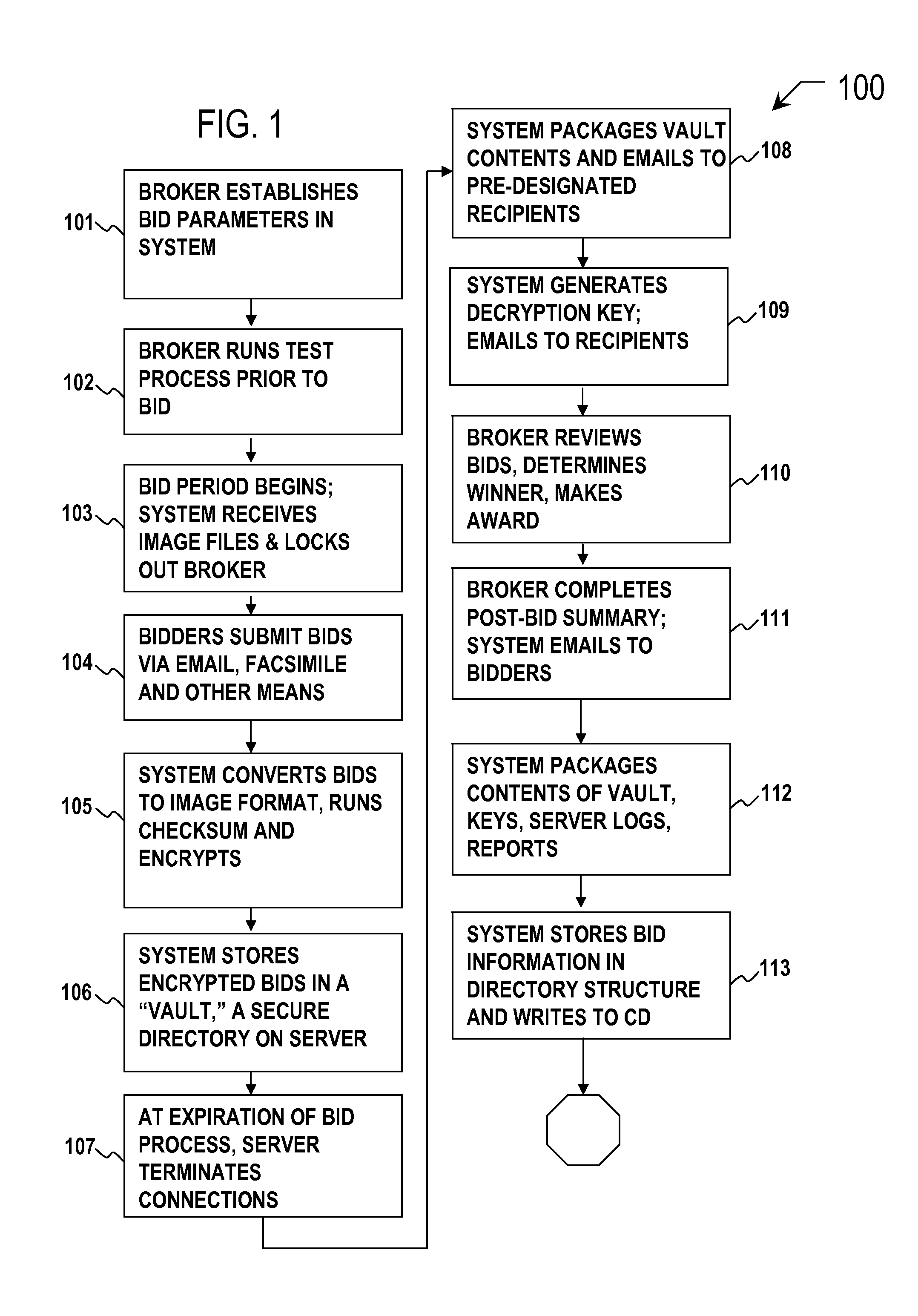
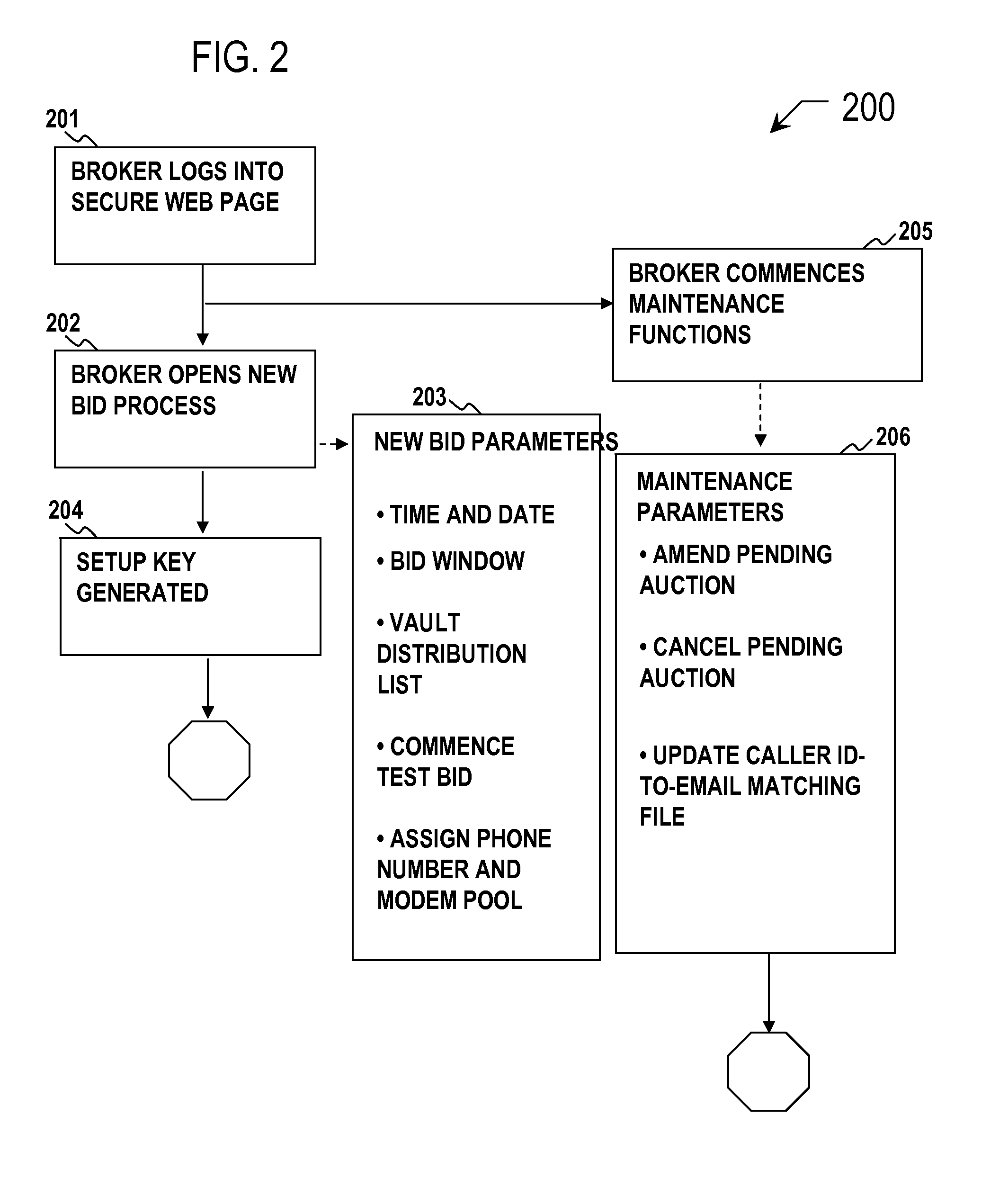
Secure image bidding system
Secure image bidding system process for financial transactions, including structured investment products, escrows and interest rate swaps. Some embodiments provide a secure image bidding system and process for image-based bid transmissions where each of a plurality of bids received by the system is encrypted and held in a digital “Vault” until the specified end of the bid period, at which time a package containing the encrypted bids, a log of server activity, and a digital checksum of the original bid file is sent via electronic mail to the bid broker and other participants. A second electronic mail message is sent to the bid broker and other participants containing the decryption key. During the bid process, no party has access to the bid information and there is no human interaction in the receipt, conversion to image, encryption, storage or conveyance of compiled information.
Owner:COLUMBIA CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
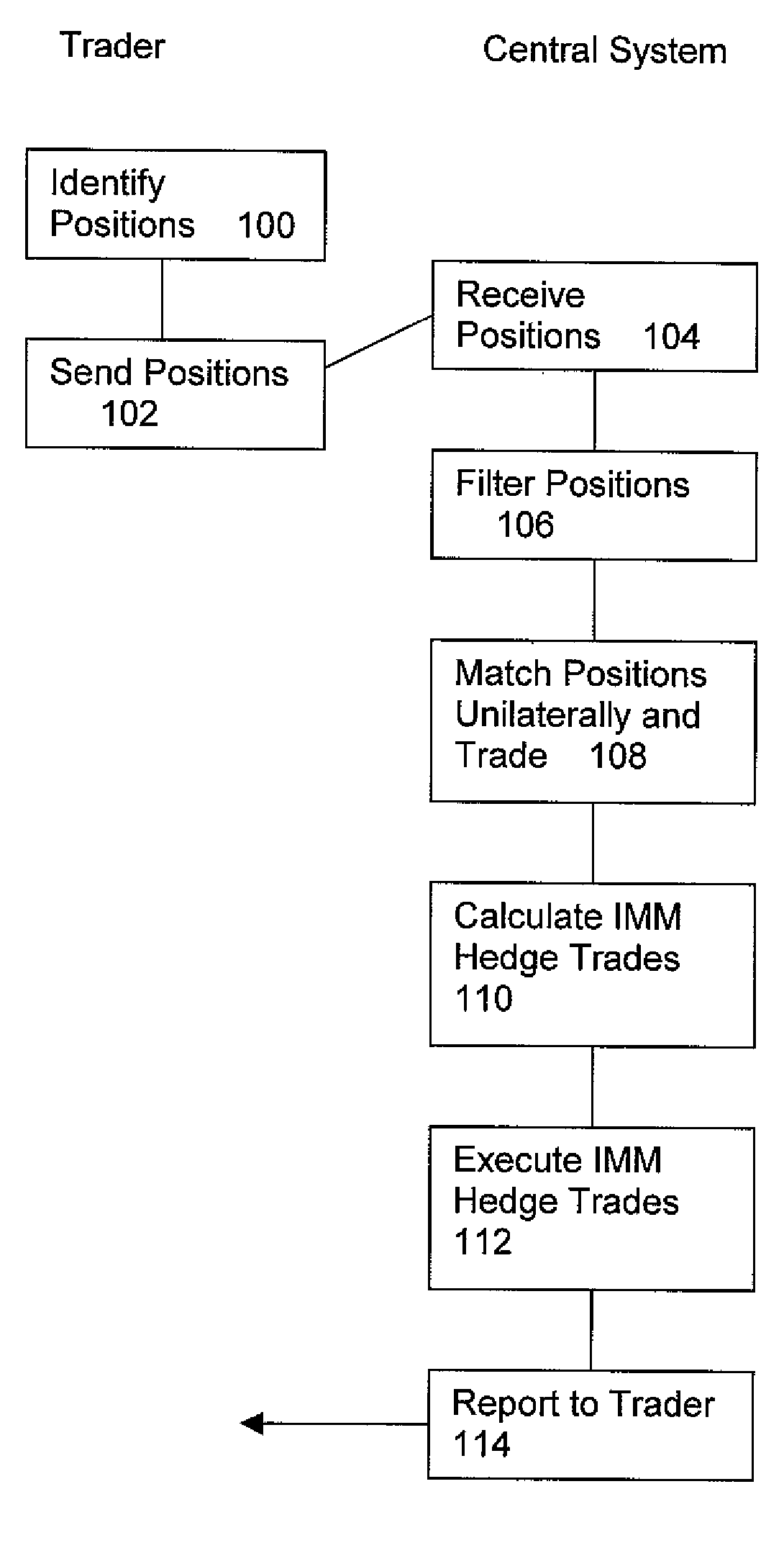
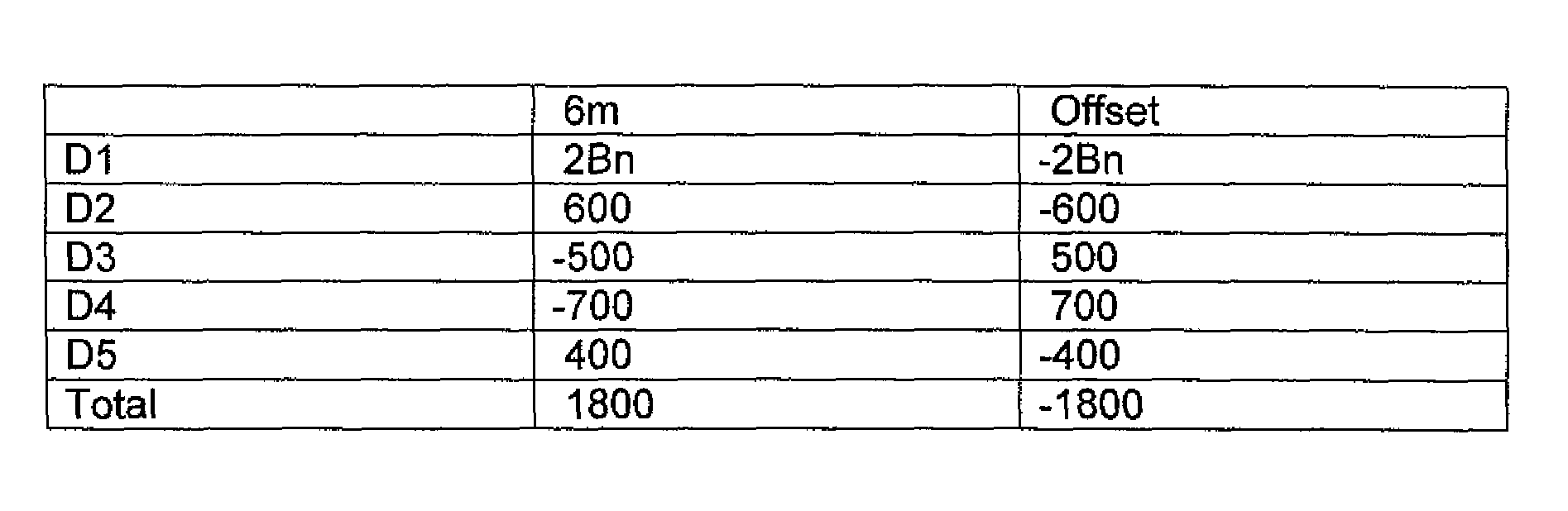
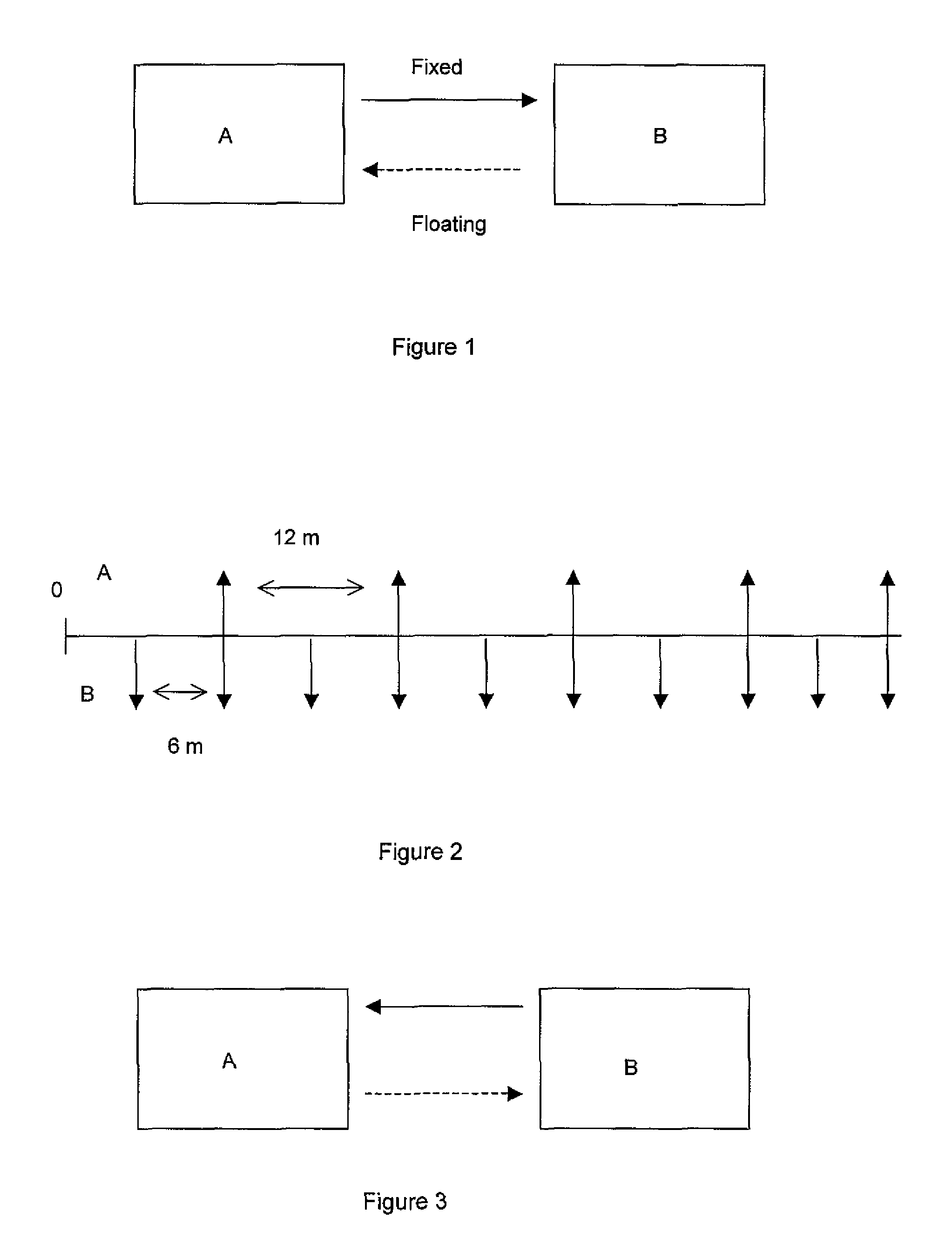
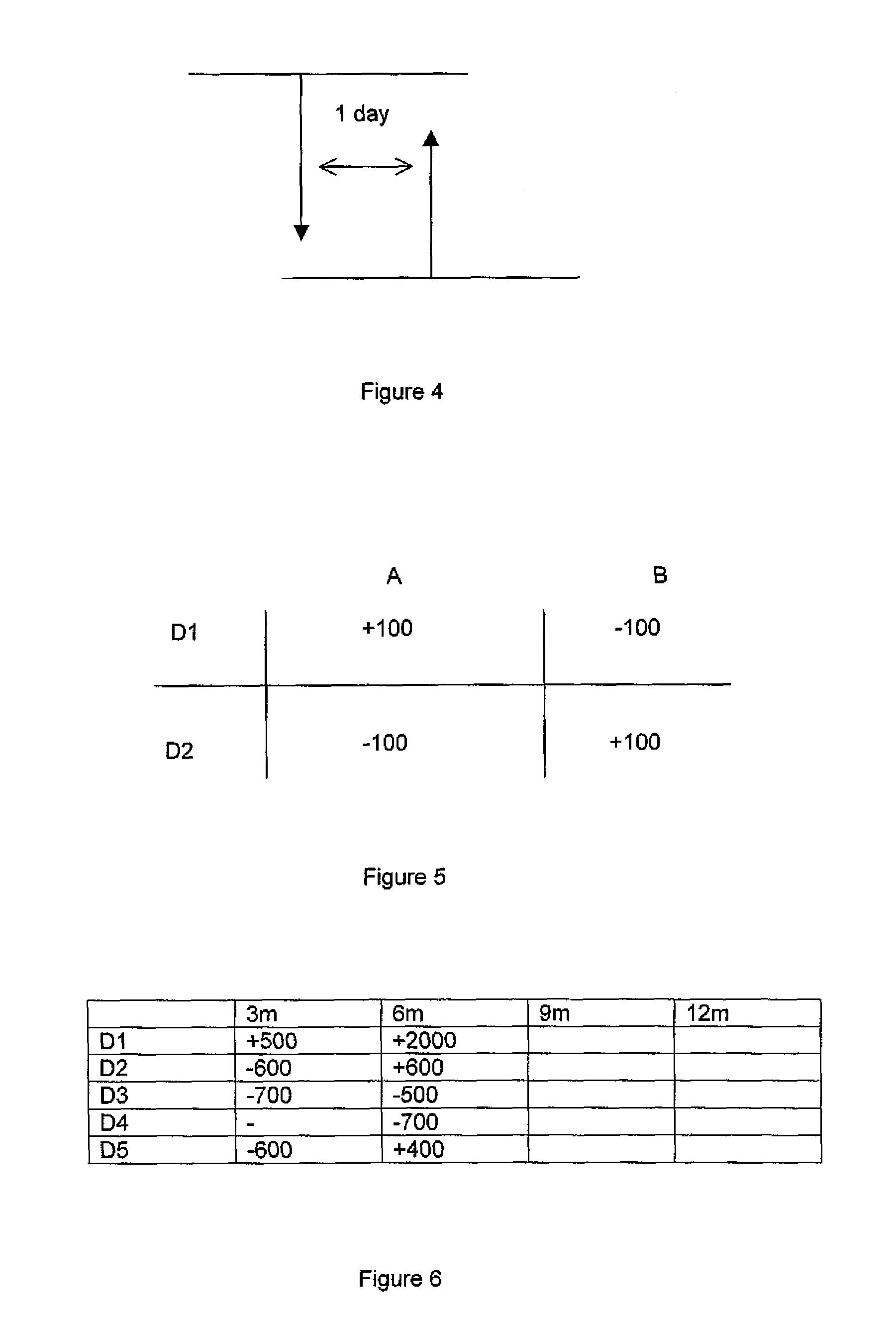
Method and System for Offset Matching
The trading of interest rate swaps or other interest rate derivatives gives rise to mismatch exposure. This can be offset by a series of FRA trades. Rather than conducting a series of exposure neutral trades, FRAs can be bought or sold for the entire amount of a trader's reset exposure. To hedge the offset trades, a series of IMM FRA trades are conducted. The relative size of the IMM contracts will be determined by the distance in time from the IMM quarterly contract settlement date. A system is disclosed for performing offset trades and IMM hedges. The embodiments allow for non-neutral trading and subsequent heging brings trading back to a neutral position.
Owner:INTERCAPITAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES NO 2 LTD +1
Interest rate swap index
A set of indices is provided which allows accurate tracking of interest rate swap (IRS) markets. The indices are calculated using market data and synthetic purchasing and selling of synthetic interest rate swaps utilizing the present market data. The value of the synthetic interest rate swaps are the basis for the value of a particular index. The purchasing and selling of the synthetic interest rate swap occurs at a frequency to minimize effects of shortening terms on the index. One subset of the IRS indices reflects a plain-vanilla swap for a specific term of years. Another subset of the IRS indices reflects a spread between two specific terms of years. A third subset of the IRS indices reflect two spreads, sometimes referred to as a butterfly, between a middle term of years and a shorter term of years and the same middle term of years and a longer term of years.
Owner:PIPELINE CAPITAL
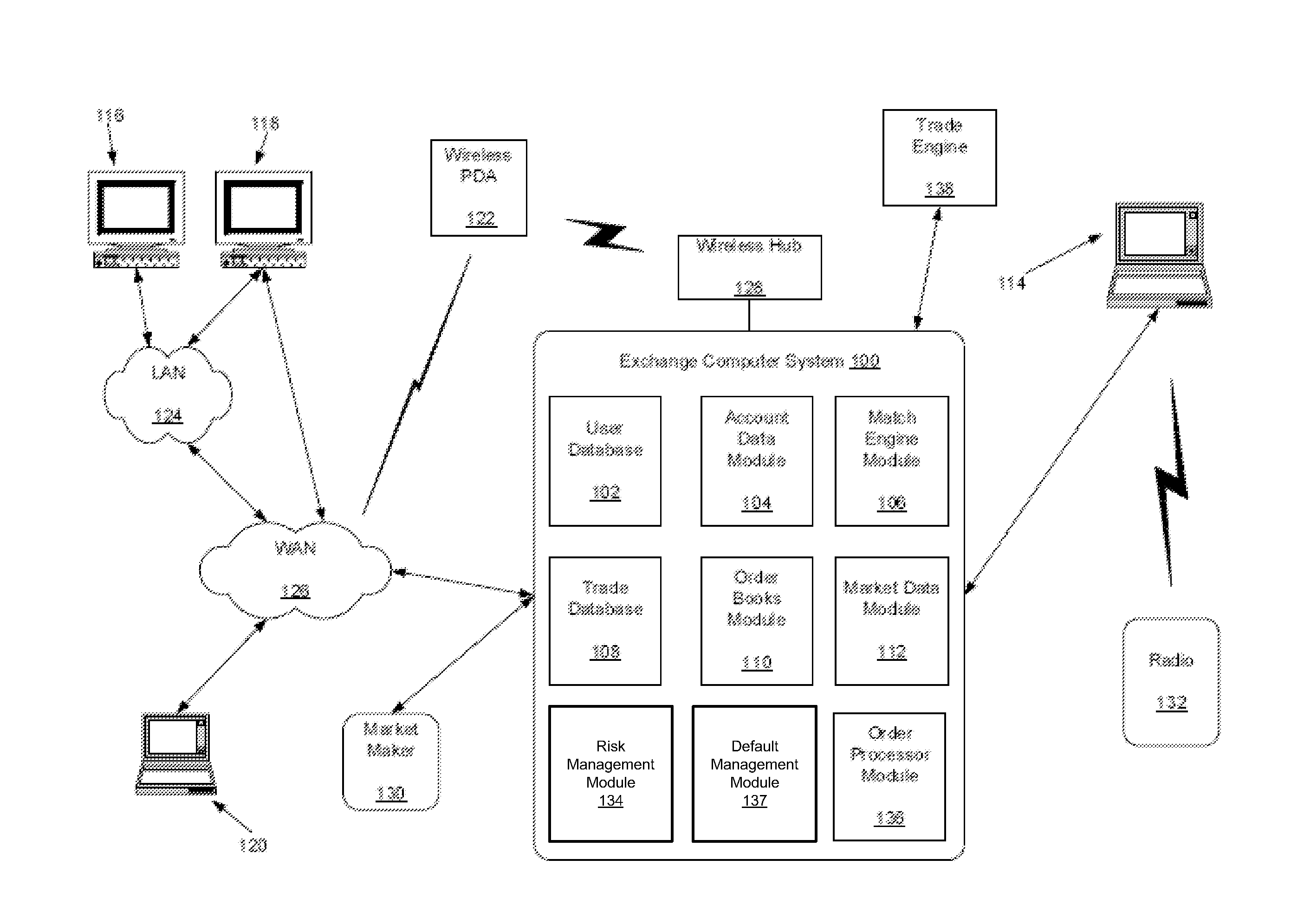
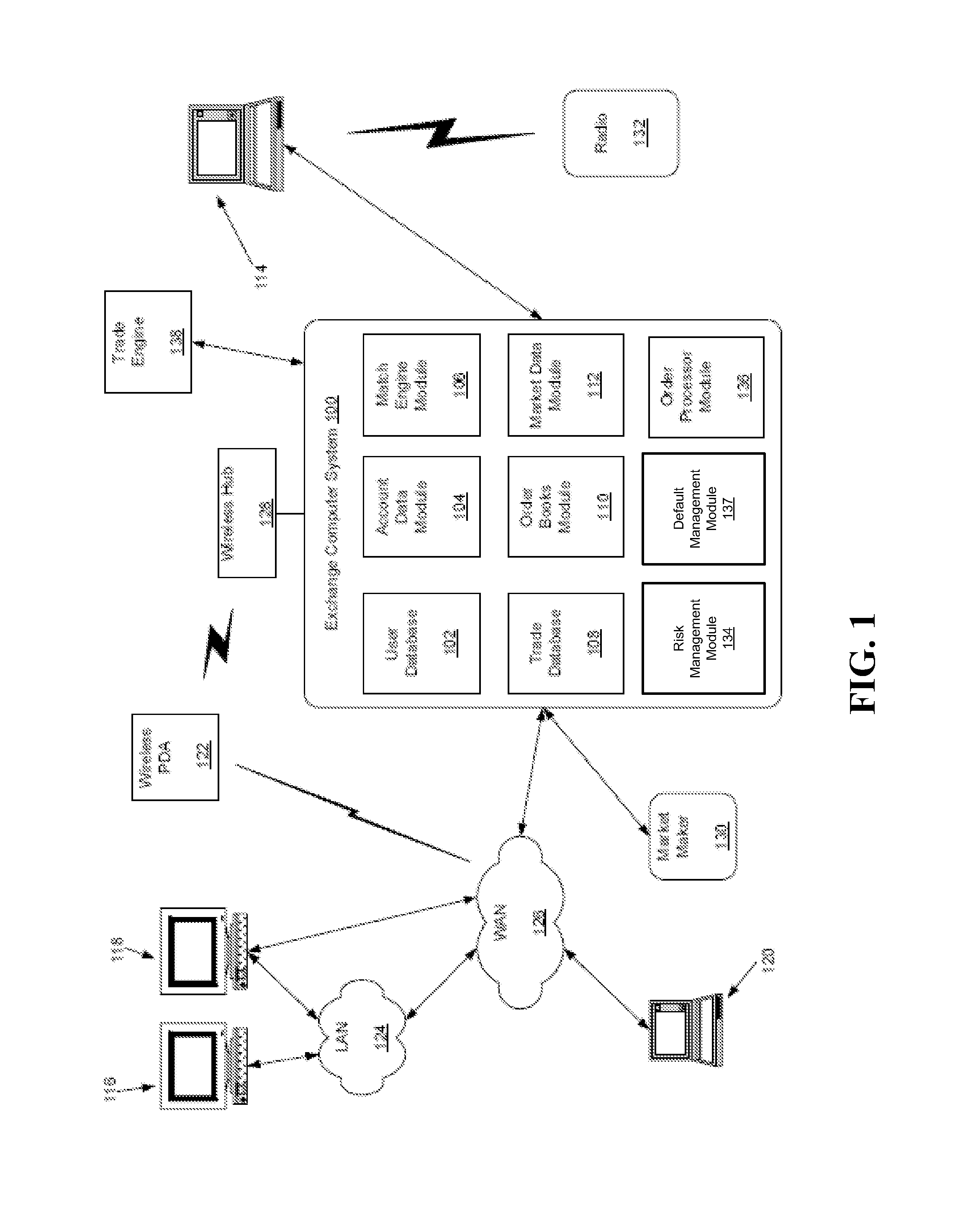
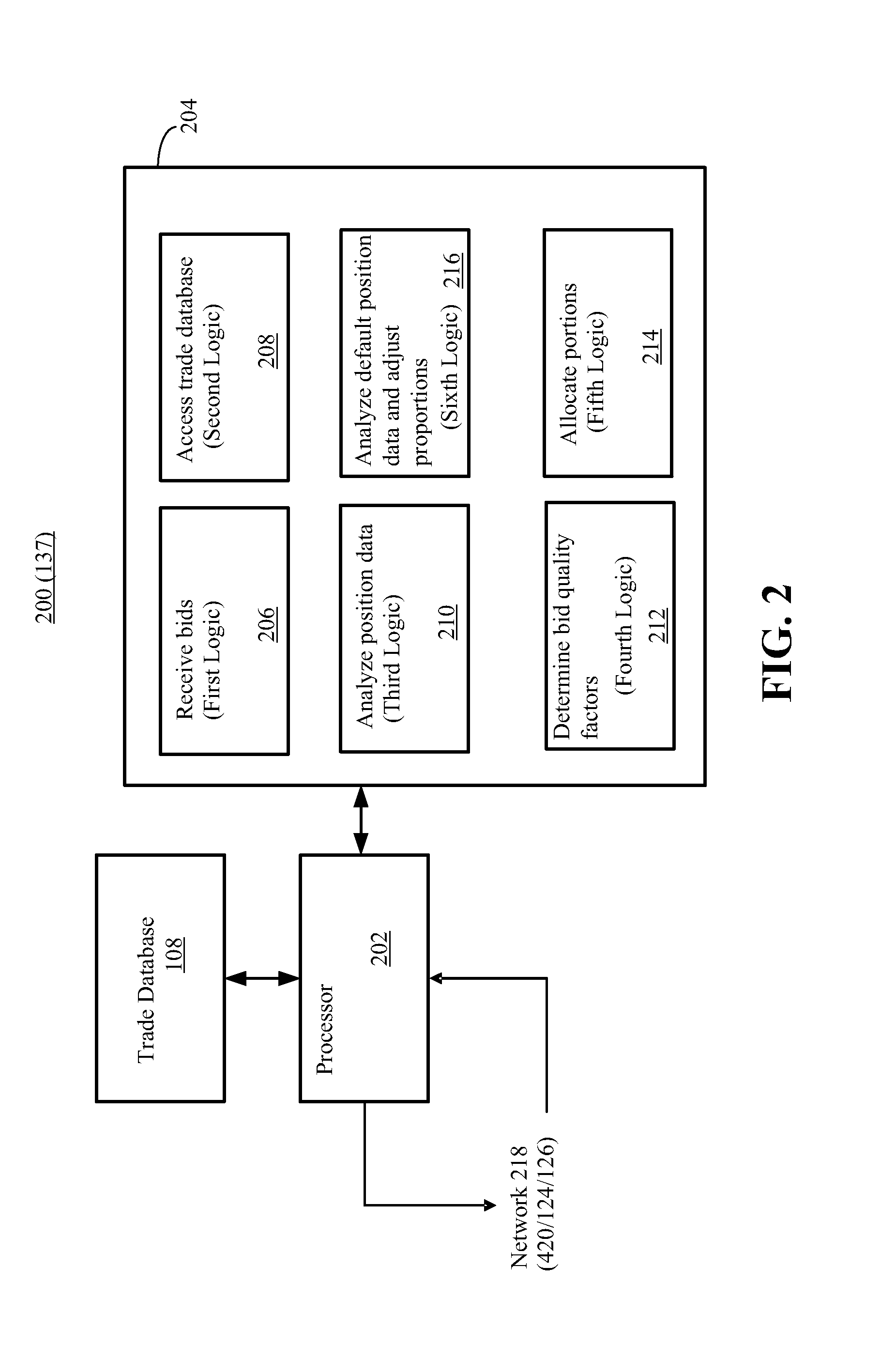
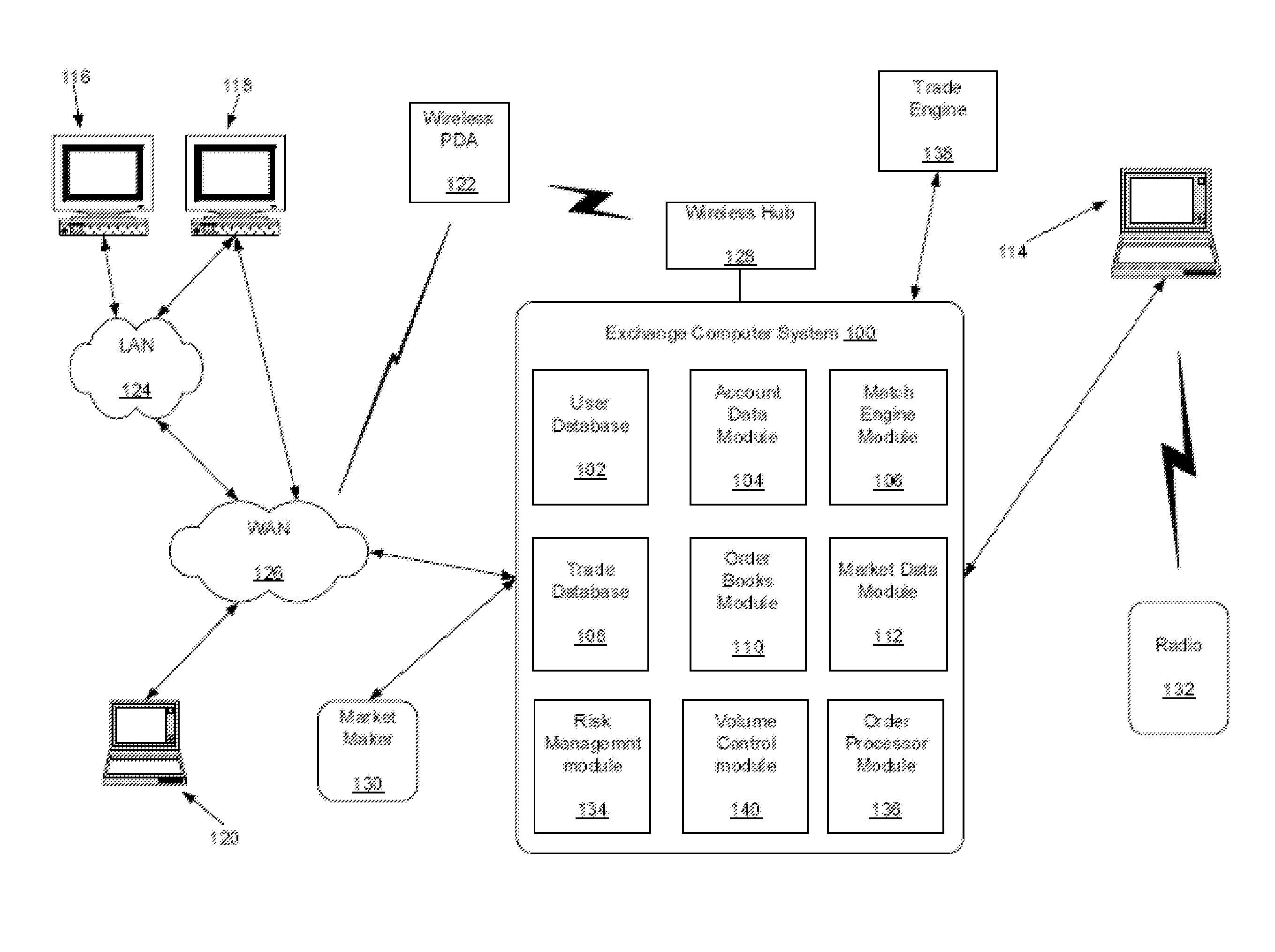
Guaranty Fund Apportionment in Default Auctions
A method apportions guaranty fund contributions into tranches in connection with an auction directed to transferring open positions in a set of markets, such as positions in interest rate swap contracts. Bids for the open positions from non-default market participants are received, and position data indicative of respective positions of non-default market participants is analyzed to determine a risk assessment proportion for each market of the non-default market participant. A quality factor is determined for each bid based on an offset between the bid and a winning bid in the auction for each open position. For each market and for each non-default market participant, a portion of the guaranty fund contribution of the non-default market participant is allocated to one of the tranches based on the quality factor for the market, the portion being defined in accordance with the risk assessment proportion for the market.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
Interest Rate Swap Risk Compression
The disclosed embodiments relate to minimization of risk of loss, and thereby minimization of margin and / or guarantee fund requirements, for a portfolio of interest rate swap (“IRS”) positions held by a market participant. The disclosed embodiments identify proposed trades across portfolios wherein execution of the proposed trade would result in a reduction of the risk of loss of the portfolio and the other portfolio, by iteratively testing each of a set of candidate trades between substantially equivalent positions in the portfolio and other portfolio for an effect on the risk of loss of the portfolio, the identified proposed trade comprising a candidate trade which results in a reduction in risk of loss of the portfolio in excess of a threshold. The disclosed embodiments then provide each of the identified proposed trades to at least the market participant who holds the subject portfolio for acceptance thereby.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
Clearing system that determines margin requirements for financial portfolios
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE INC
Methods and systems for creating an interest rate swap volatility index and trading derivative products based thereon
Systems and methods for creating and disseminating an interest rate swap volatility index based on an underlying interest rate swaption, and for creating and trading derivative investment products based on the interest rate swap volatility index, are disclosed. In one aspect, an interest rate swap volatility index based on an underlying interest rate swaption is calculated. The interest rate swap volatility index may be accessed by a processor of a trading platform and a standardized, exchange traded derivative may be created based on the calculated interest rate swap volatility index. Information associated with the interest rate swap volatility index derivative may then be transmitted for display.
Owner:CBOE EXCHANGE INC
Method of accessing exact OTC ISDA type overnight indexed swap exposures within an electronic futures exchange environment
A set of linked methods allows one to access derivative products (other than traditional futures and options) within an electronic futures exchange. In an embodiment of the invention, exchange members are given access to exact OTC ISDA type interest rate swap and FRA related exposures. Another In another embodiment, exchange members are given access to exact OTC ISDA type overnight index swap related exposures. In a further embodiment, exchange members are given convenient access to credit spread and\or interest rate swap embodiments via deliverable credit rate linked and swap rate linked bond-like futures.
Owner:LIFFE ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT
Automated, computerized electronic trading system for cleared rate-negotiated, standardized-coupon financial instruments
InactiveUS20180068390A1Mitigates the granularization issueFinancePaymentPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A system for electronically trading a rate-negotiated, standardized-coupon financial instrument said system including a memory receiving a coupon negotiated between two parties. At least one forward curve and a discount curve are implied or approximated by at least one processor in communication with the memory to be economically equivalent to the negotiated coupon. An economically equivalent value for a swap with a different coupon is determined by at least one processor. The economically equivalent value can comprise the net present value (NPV) of the interest rate swap written as the difference between the present values of two interest payment legs. In the case of a vanilla swap the two legs correspond to fixed coupon payments and floating coupon payments in the case of a basis swap, one leg is the floating coupon payments with a reference rate plus a fixed coupon, and the other leg is floating coupon payments with a different reference rate.
Owner:ERIS INNOVATIONS
Interest rate swap and swaption liquidation system and method
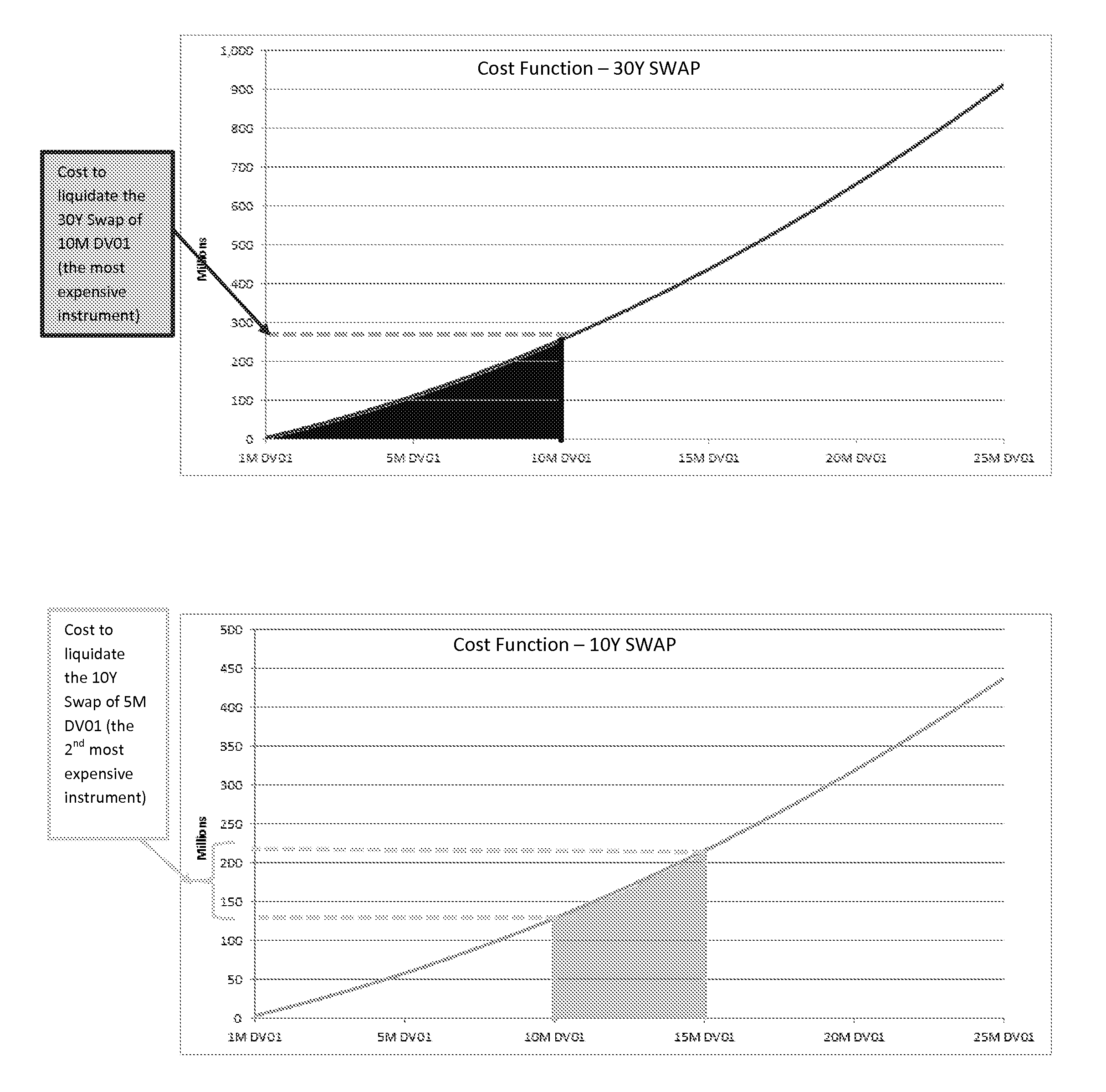
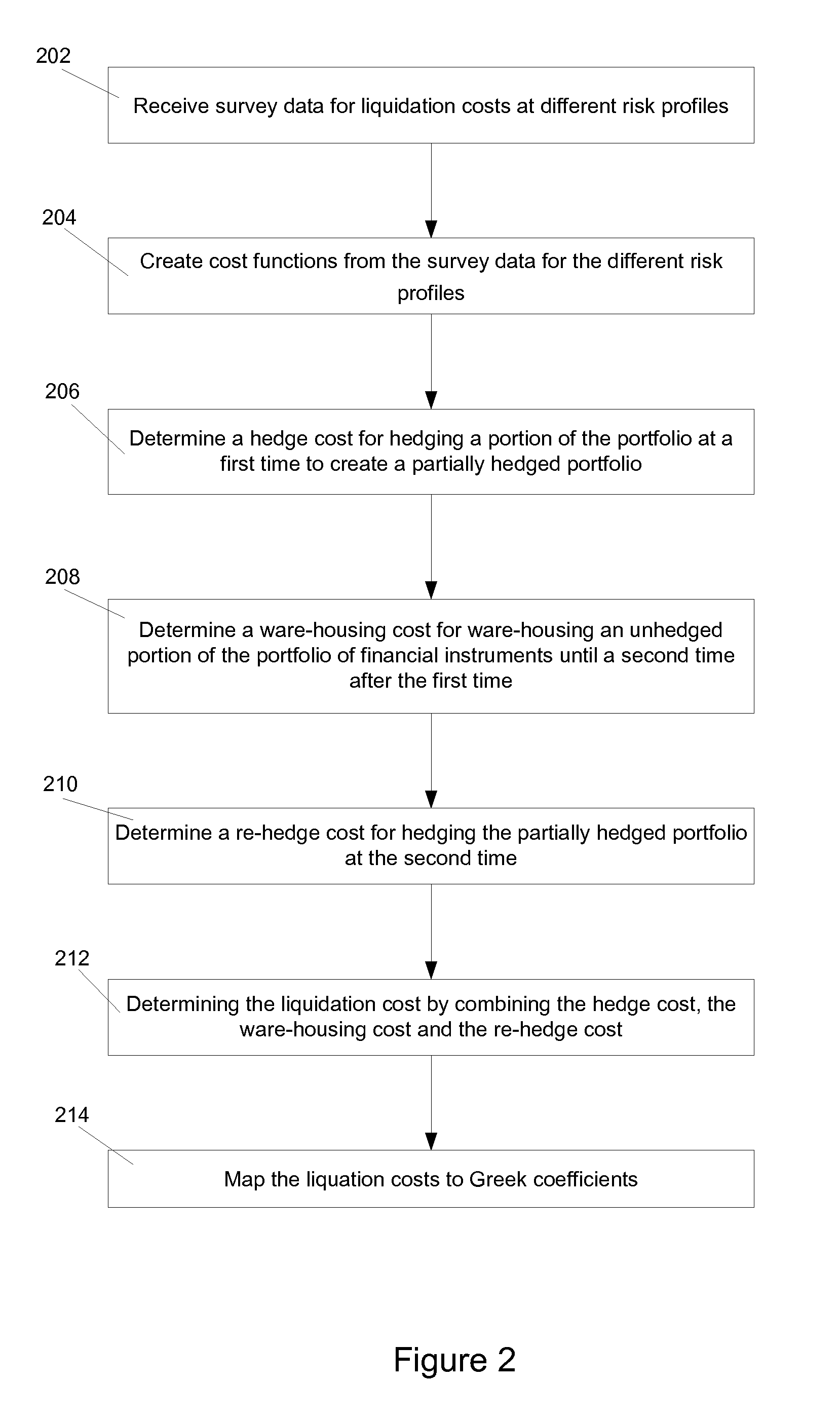
Systems and methods are provided for determining liquidations costs for portfolios of financial instruments. Survey data for liquidation costs at different risk profiles is received from market participants. An initial attempt is made to hedge part of the portfolio. Some hedges may not be available during market stress conditions. A warehousing cost for warehousing the unhedged portion of the portfolio is determined and a re-hedge cost for hedging the partially hedged portfolio when hedges are available is determined. A liquidation cost is a combination of the hedge cost, the warehousing cost and the re-hedge cost. Weighting for Greek ladder may be created by mapping liquidation costs to Greek ladders. Lookup tables may be created from liquidity cost. The lookup tables may be used to look up for liquidity cost using aggregated Greek generated by weighted sum of Greek ladder and provide a simplified mechanism for determining liquidation costs.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
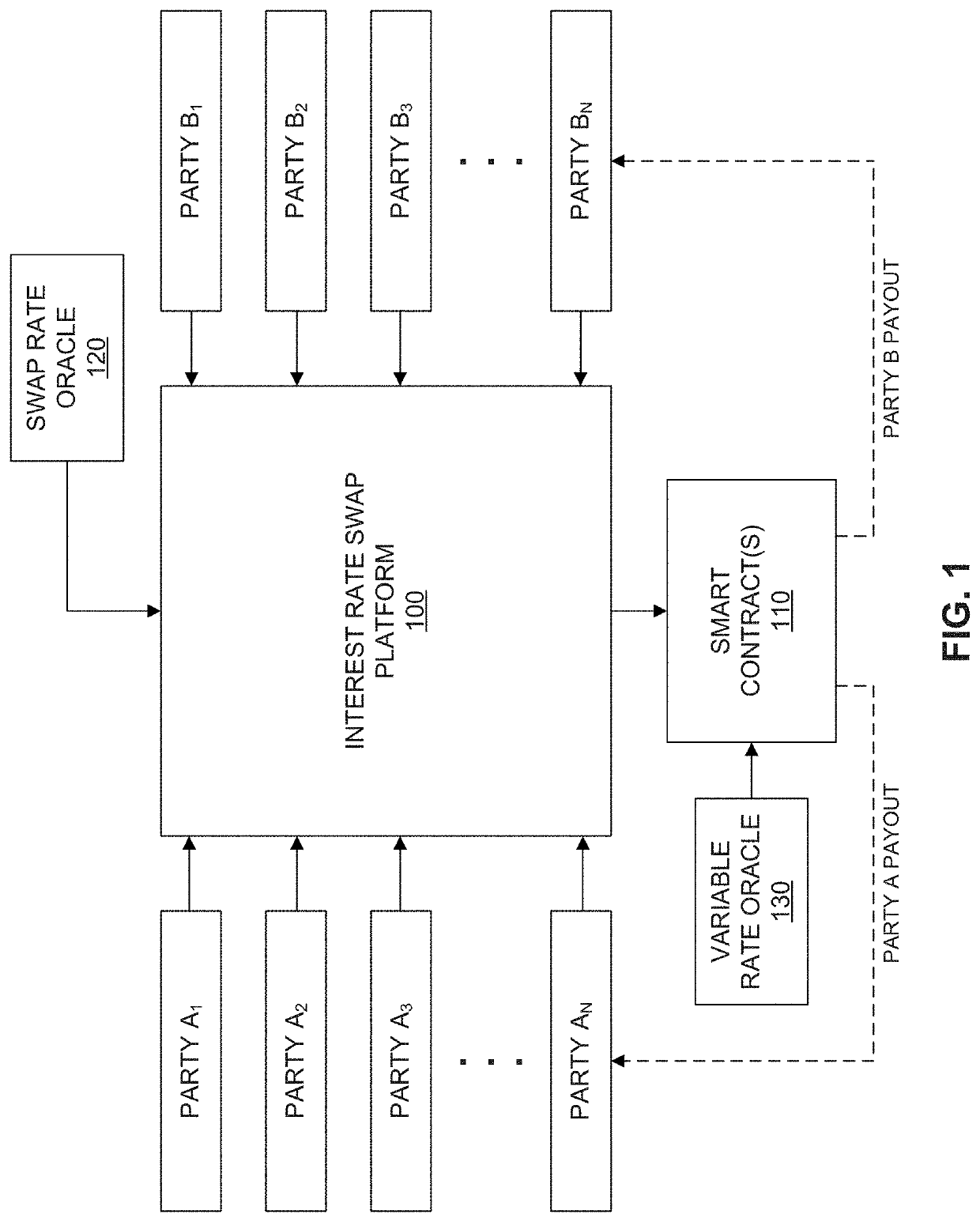
Fractionalized interest rate swaps
ActiveUS20200258148A1Improve securityEliminate needFinanceCryptography processingInterest rate swapSmart contract
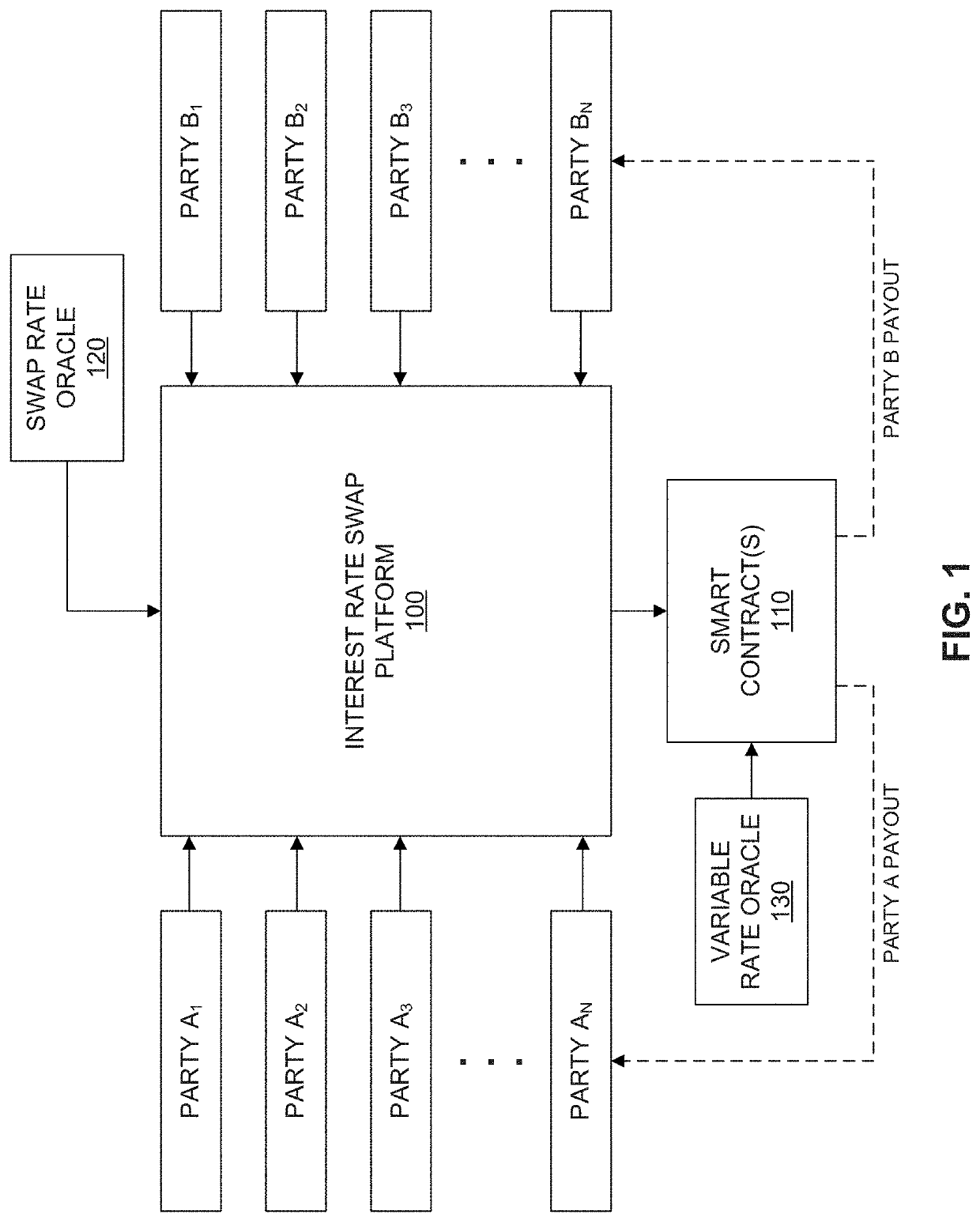
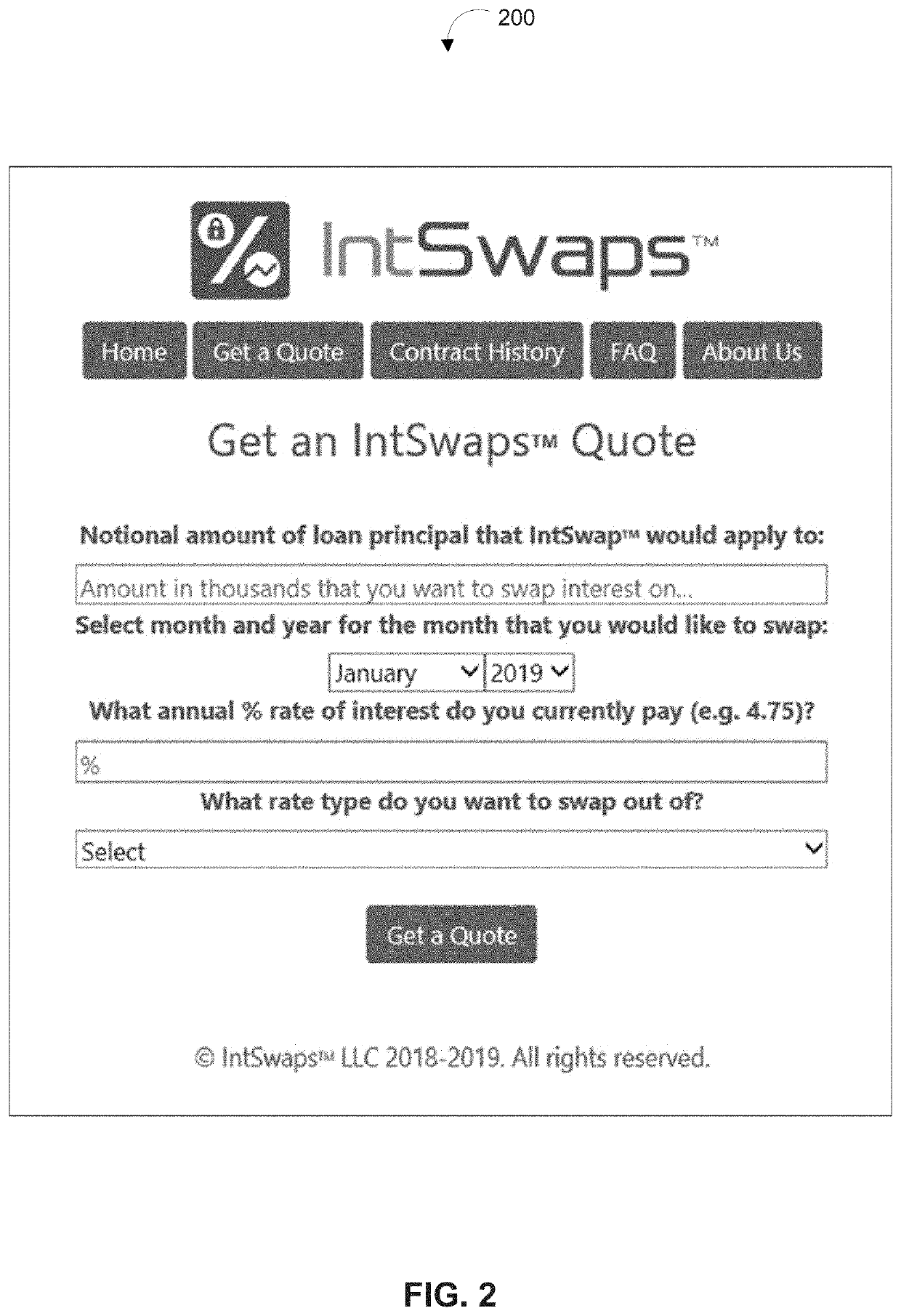
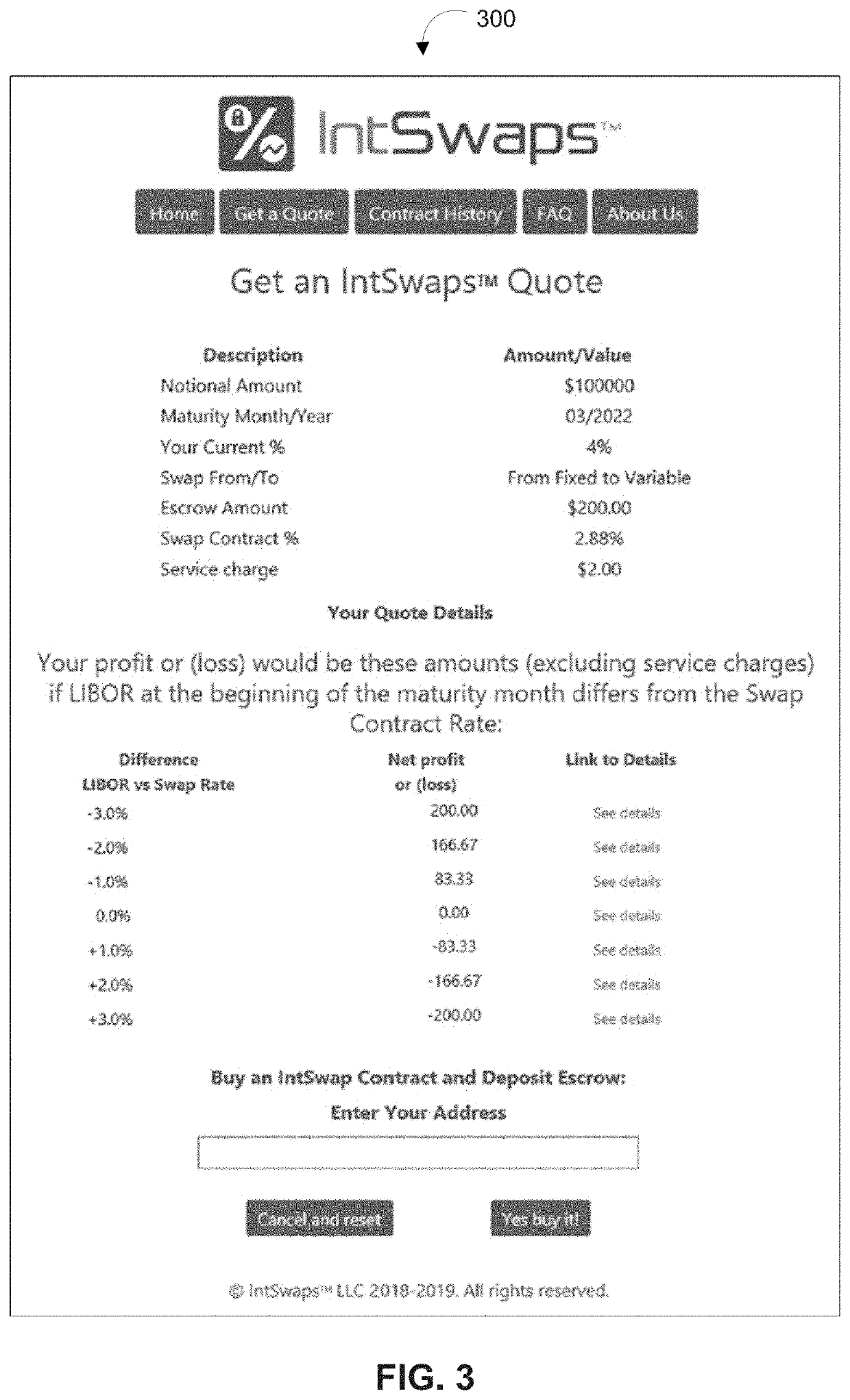
Systems and methods for implementing and managing one-to-many fractionalized interest rate swaps between a borrower and one or more investors via a distributed ledger-based platform are described herein. The distributed ledger-based platform may be configured to generate and provide user interfaces through which a user may provide a set of input variables for a fractionalized interest rate swap. Based on the set of input variables, the platform may automatically configure a customizable smart contract configured to initialize the fractionalized interest rate swap between at least one borrower and one investor. At the maturity date of the fractionalized interest rate swap, the smart contract may be configured to calculate amounts to be allocated to the borrower and investor, automatically release the amounts from the escrow account associated with the smart contract, and settle the contract by transferring the corresponding amounts to accounts of the borrower and investor.
Owner:HUMMER MELANIE SUSAN
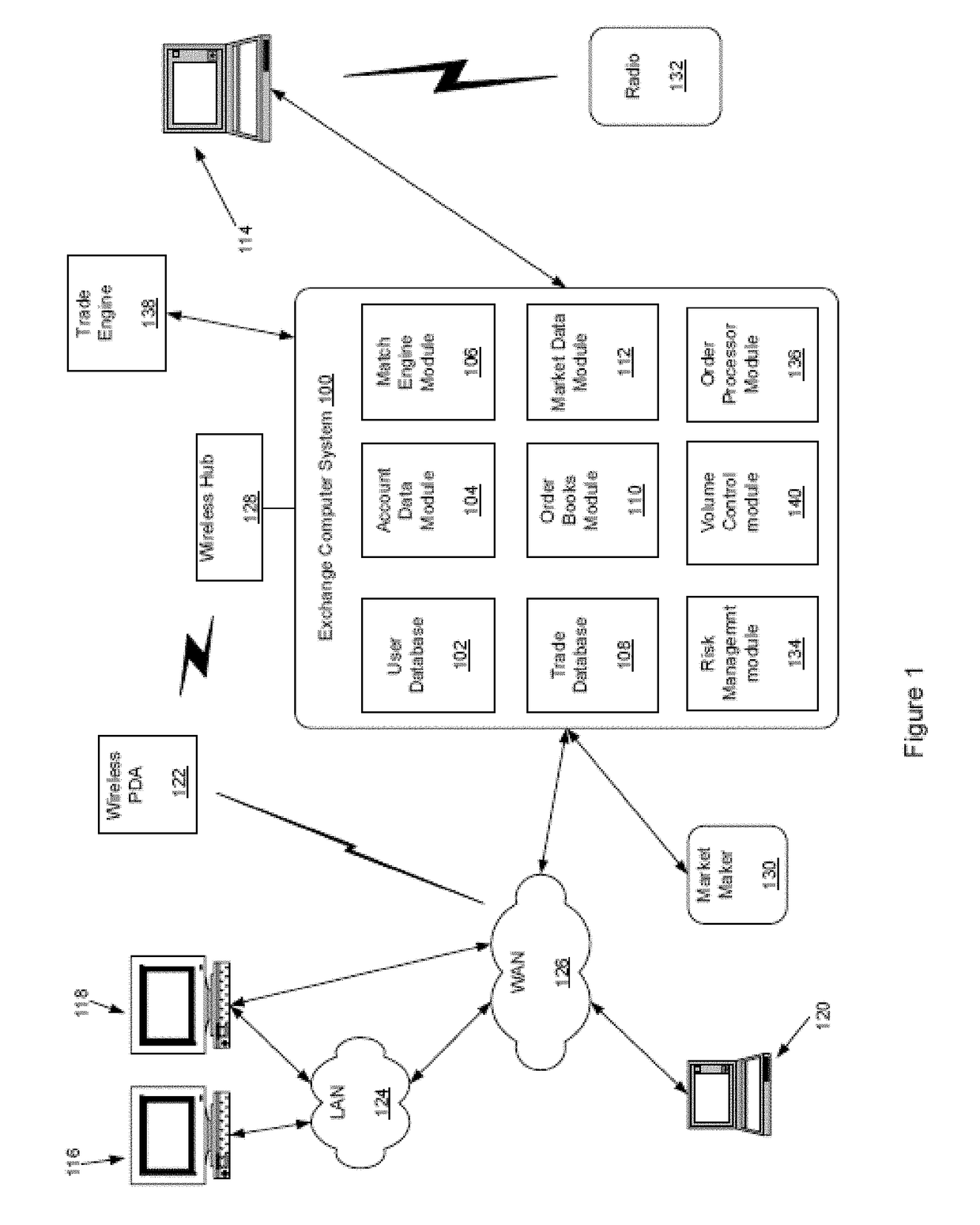
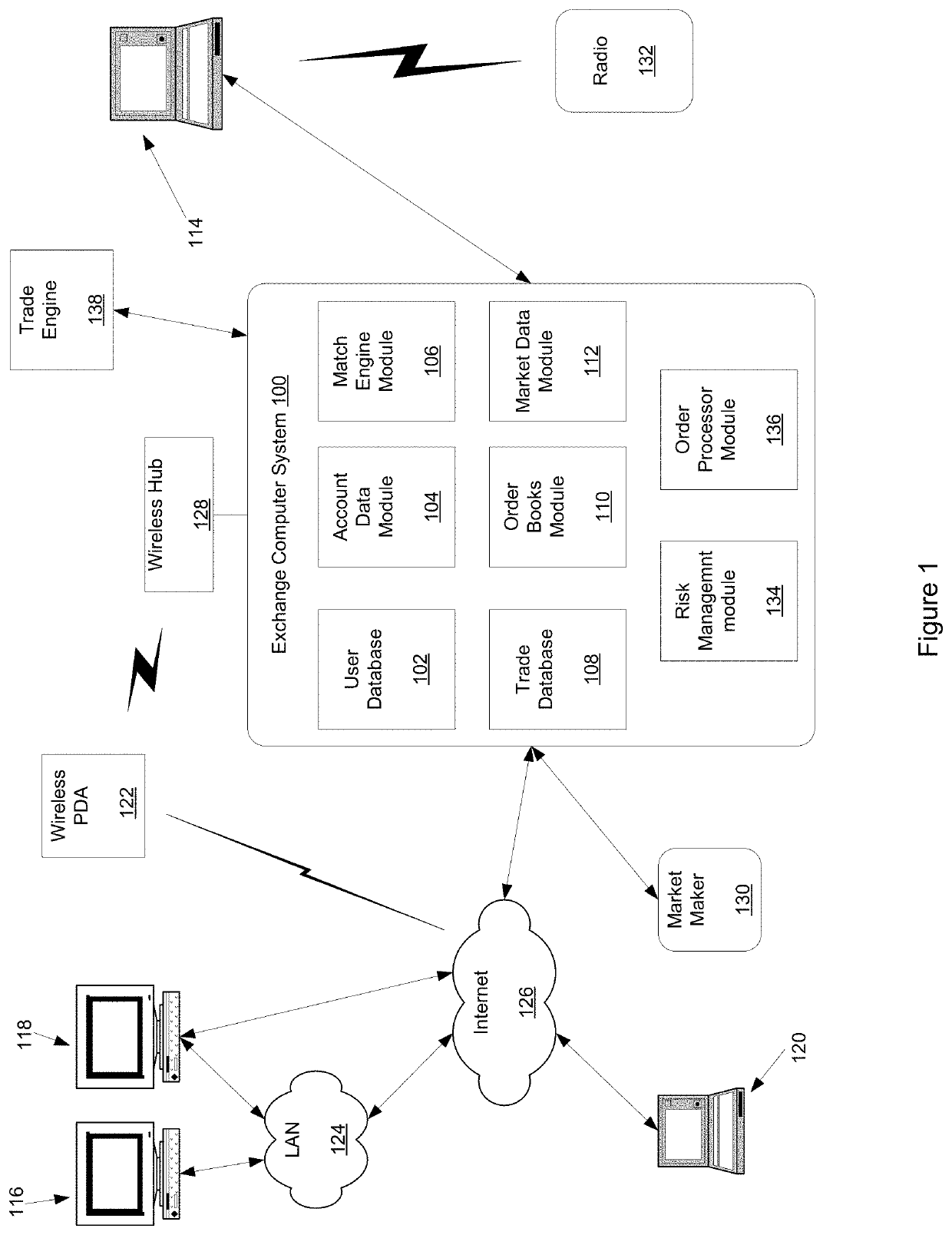
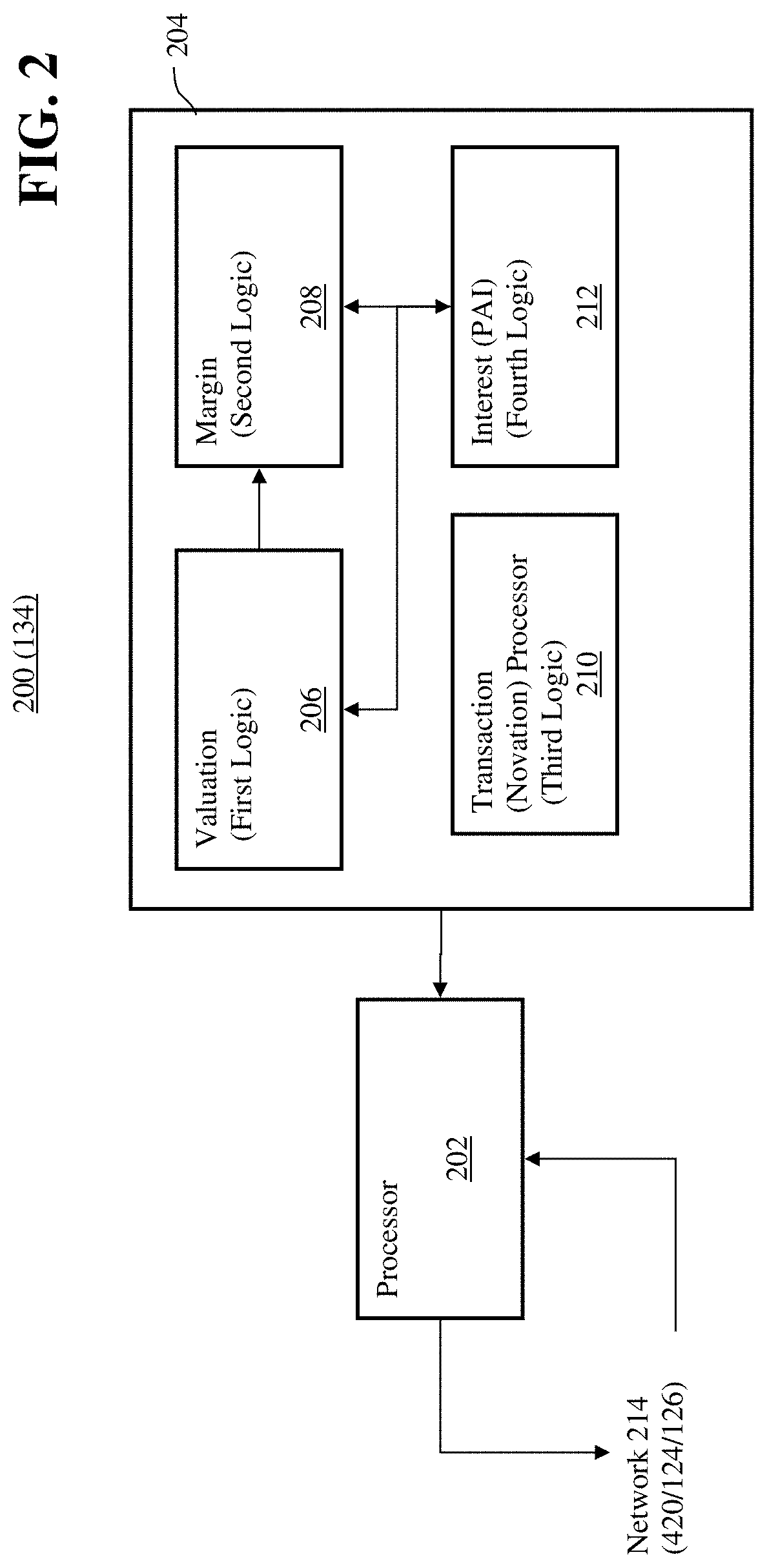
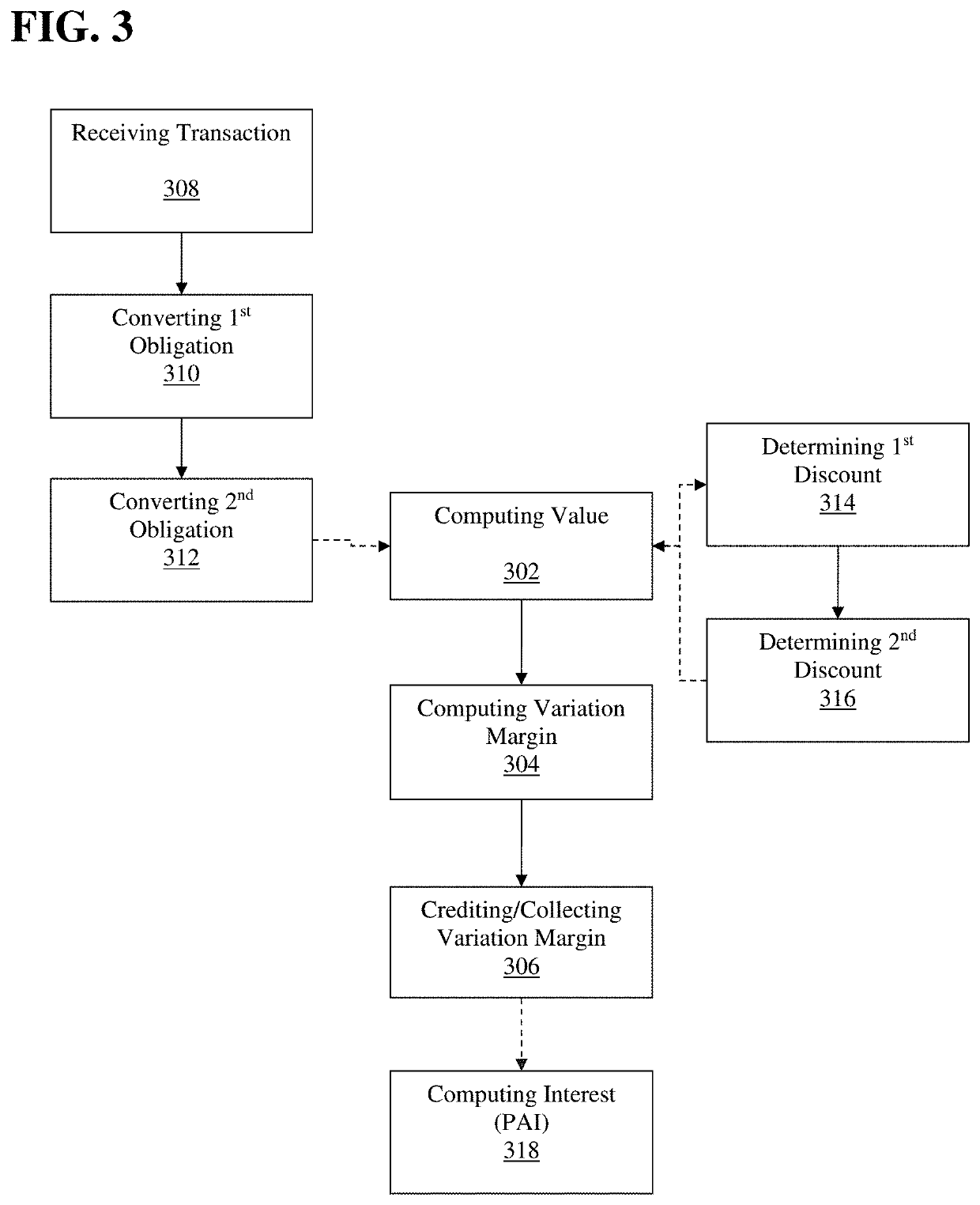
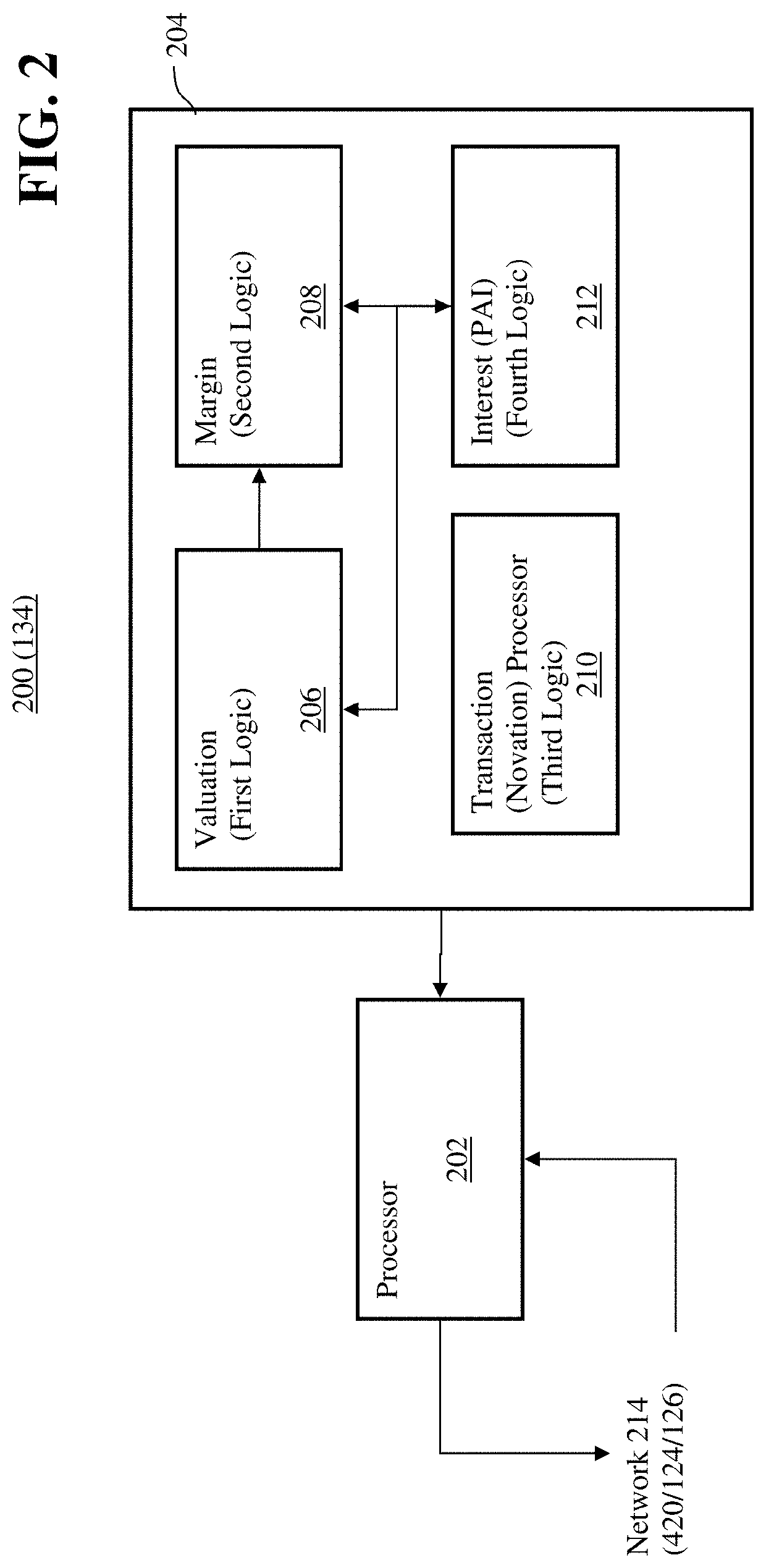
Transaction processor for clearing interest rate swaps with improved efficiency
The disclosed embodiments relate to improving the efficiency of an electronic trading system for interest rate swaps (“IRS”) by allowing for IRS contracts to be funded in a base currency while the cash flows, e.g. coupon payments, price alignment interest, variation margin, are denominated in a local currency different from the base currency. Thereby cash flows may be netted and offset minimizing the magnitude of funds needed to be moved and reducing the number of transactions processed by the electronic trading system as well as the consumption of computational resources thereby. Furthermore, the disclosed embodiments facilitate entering into IRS transactions is a currency different from the currency of cash flows while eliminating Herstatt risk due to volatility of foreign exchange rates, which allows for increased off shore participation and thereby increased transaction volume.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
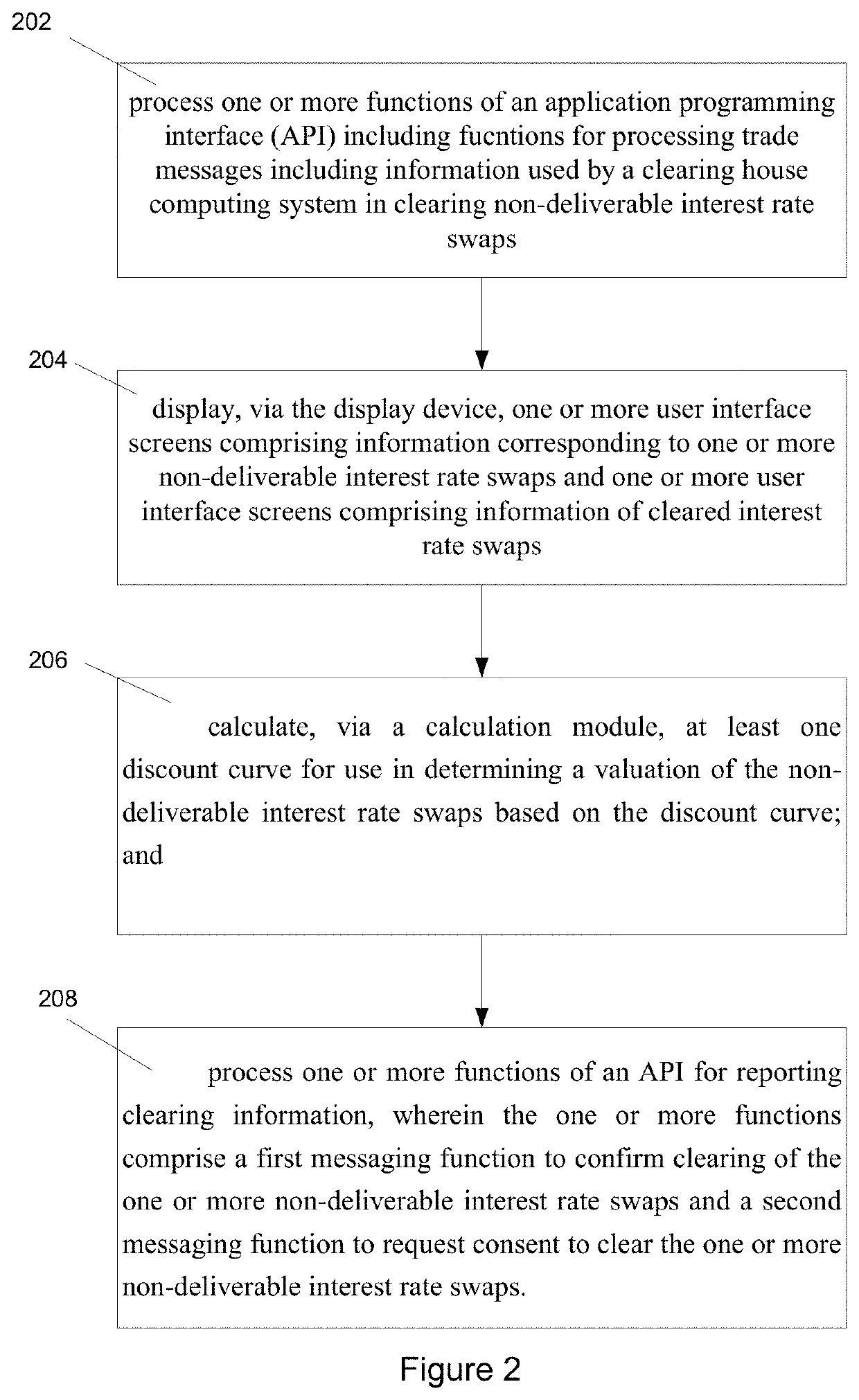
Api framework for clearing non-deliverable interest rate swaps
ActiveUS20200065904A1FinancePayments involving neutral partyApplication programming interfaceMessage delivery
Systems and methods are provided for a clearing framework for clearing a non-deliverable interest rate swap. The clearing framework includes an application programming interface (API) including functions for processing trade messages including information used by a clearing house computing system in clearing non-deliverable interest rate swaps; one or more user interface screens comprising information corresponding to one or more non-deliverable interest rate swaps and one or more user interface screens comprising information of cleared interest rate swaps, one an API for reporting clearing information, wherein the one or more functions comprise a first messaging function to confirm clearing of the one or more non-deliverable interest rate swaps and a second messaging function to request consent to clear the one or more non-deliverable interest rate swaps.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE INC
Secure bidding system and method
Secure image bidding system process for financial transactions, including structured investment products, escrows and interest rate swaps. Some embodiments provide a secure image bidding system and process for image-based bid transmissions where each of a plurality of bids received by the system is encrypted and held in a digital “Vault” until the specified end of the bid period, at which time a package containing the encrypted bids, a log of server activity, and a digital checksum of the original bid file is sent via electronic mail to the bid broker and other participants. A second electronic mail message is sent to the bid broker and other participants containing the decryption key. During the bid process, no party has access to the bid information and there is no human interaction in the receipt, conversion to image, encryption, storage or conveyance of compiled information.
Owner:COLUMBIA CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Swap index
A set of indices is provided which allows accurate tracking of interest rate swap (IRS) markets. The indices are calculated using market data and synthetic purchasing and selling of synthetic interest rate swaps utilizing the present market data. The value of the synthetic interest rate swaps are the basis for the value of a particular index. The purchasing and selling of the synthetic interest rate swap occurs at a frequency to minimize effects of shortening terms on the index. One subset of the IRS indices reflects a plain-vanilla swap for a specific term of years. Another subset of the IRS indices reflects a spread between two specific terms of years. A third subset of the IRS indices reflect two spreads, sometimes referred to as a butterfly, between a middle term of years and a shorter term of years and the same middle term of years and a longer term of years.
Owner:PIPELINE CAPITAL
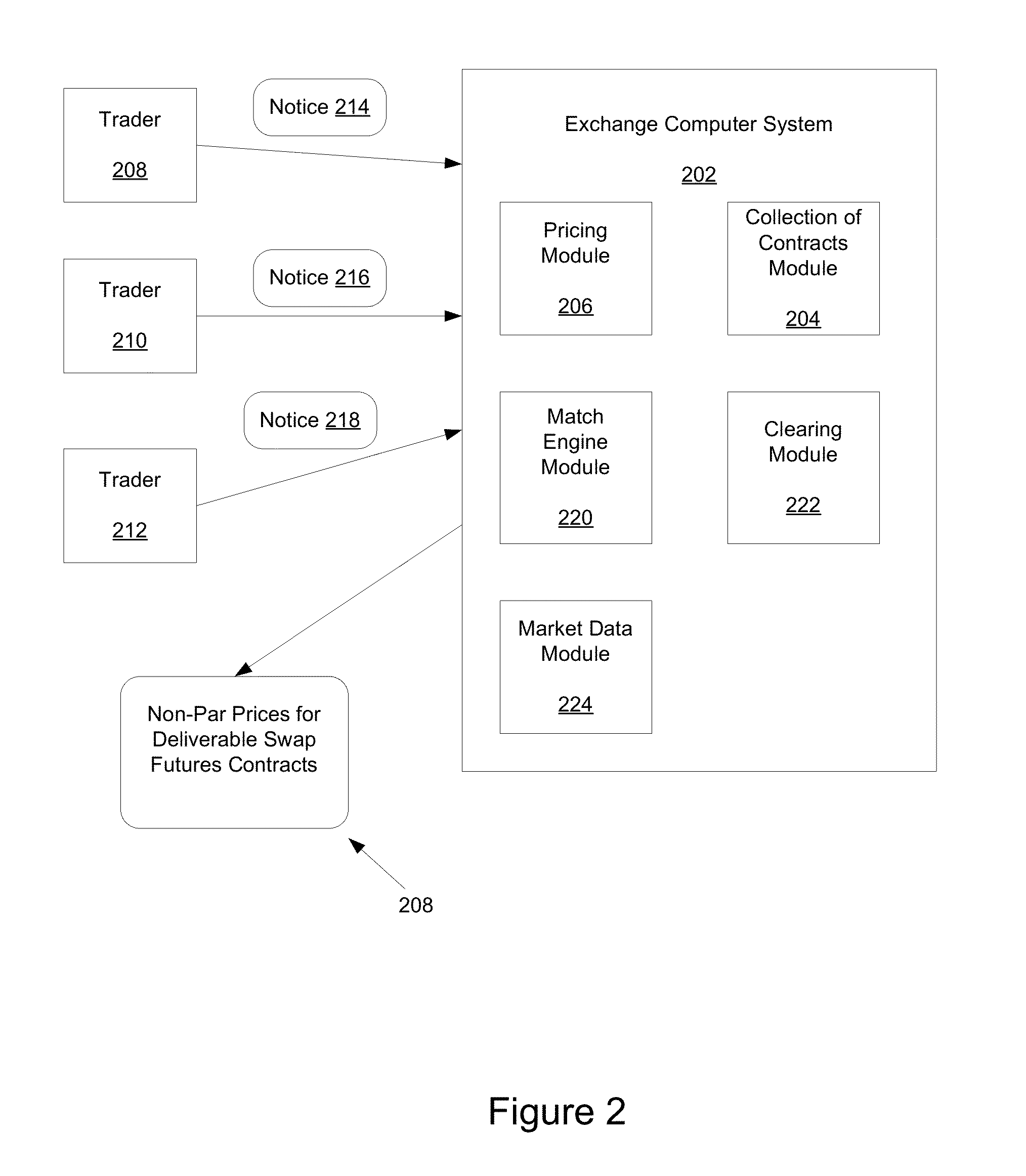
Automated Book-Entry Exchange of Futures for Interest Rate Swap (EFS) at Implied Current Coupon
Systems and methods are provided for liquidating existing deliverable swap futures contracts, such as deliverable interest rate swap futures contracts. An exchange determines non-par prices for existing deliverable swap futures contracts using estimates for future floating interest rate as selected by the exchange. The prices are listed and traders may submit notices of intention to liquidate existing deliverable swap futures contracts. The exchange matches notices and clears matched notices.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
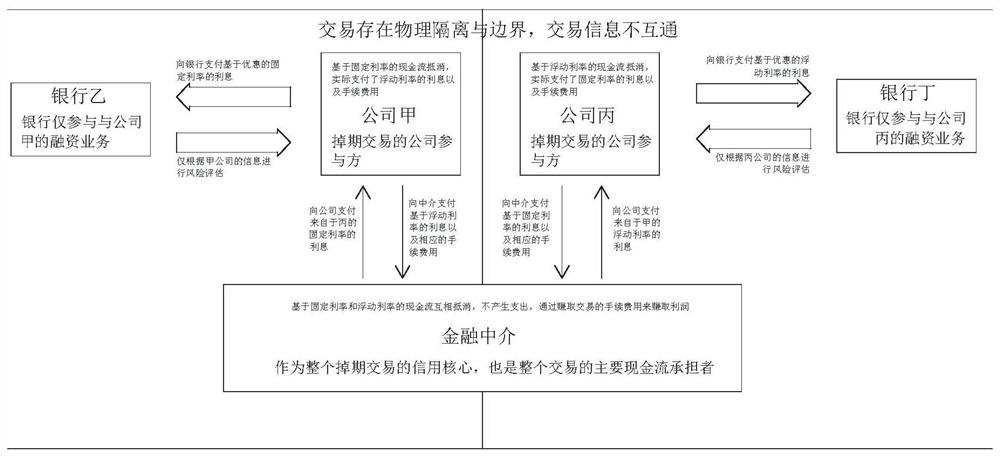
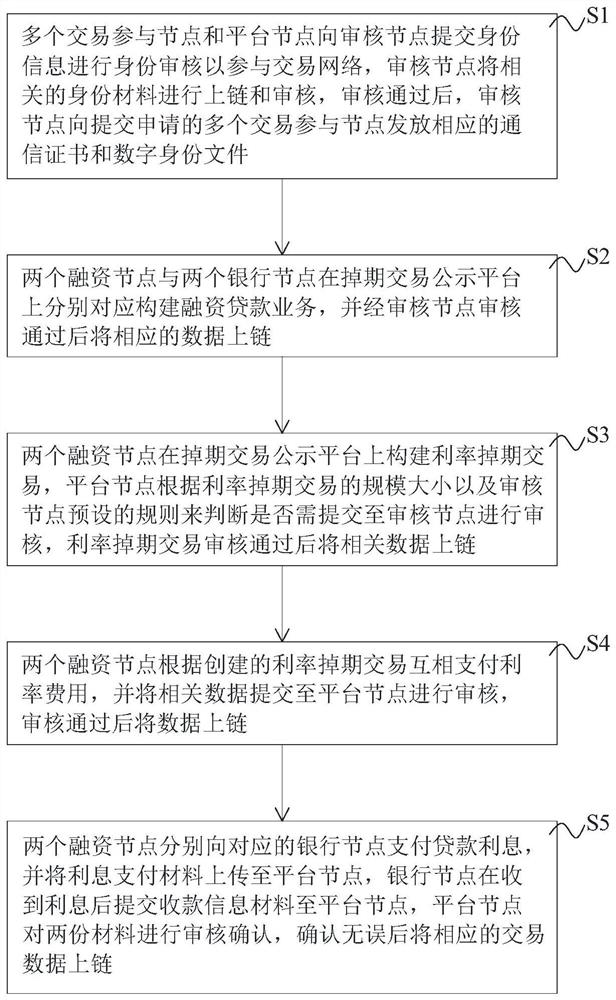
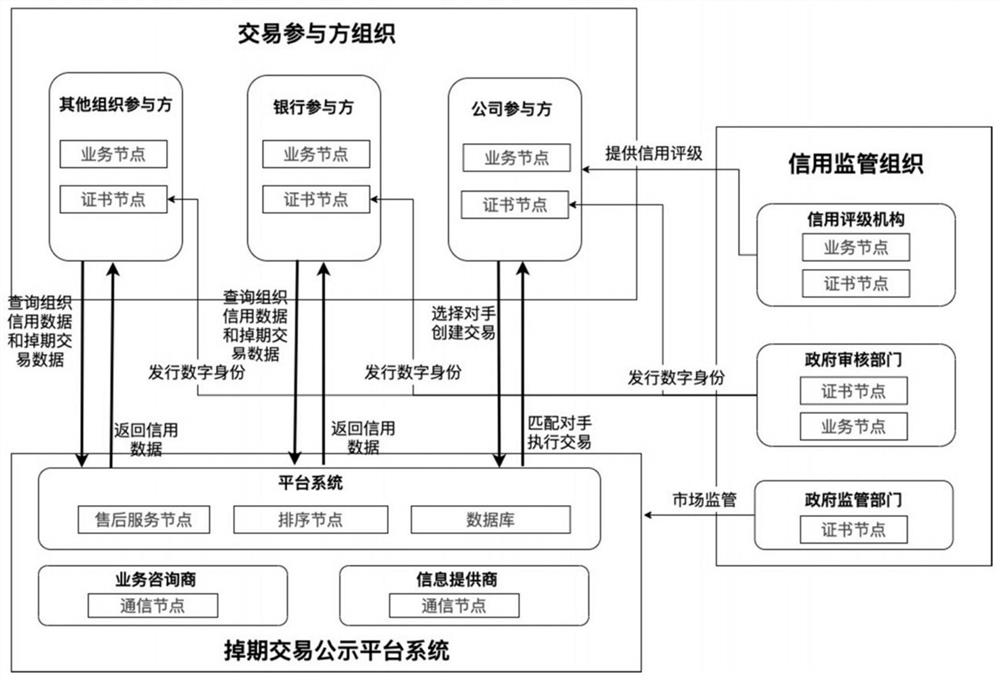
Interest rate out-of-date transaction method and system based on block chain, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112862595AIncrease authenticity and transparencyRemove asymmetryFinanceDatabase distribution/replicationThird partyFinancing cost
The invention discloses an interest rate out-of-date transaction method and system based on a block chain, equipment and a storage medium. According to the method, a technical scheme of combining a block chain with identity authentication and an intelligent contract is utilized, a third-party organization participated in a traditional interest rate off-period transaction is removed, an intermediate process is simplified, direct docking of a transaction enterprise is realized, real financing cost reduction is realized, a convenient financing interest rate is really returned to the enterprise, and the achievement of transactions and the development of the industry are promoted. Moreover, the supervision of the financial market is improved, the credit transparency and information publication of the whole interest rate out-of-date market are realized, the risks of banks and participants are reduced, the interest rate out-of-date transaction matching and transaction realization are optimized, and the open transaction market which is safer, more convenient and more consistent with supervision is created and realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Transaction processor for clearing interest rate swaps with improved efficiency
The disclosed embodiments relate to improving the efficiency of an electronic trading system for interest rate swaps (“IRS”) by allowing for IRS contracts to be funded in a base currency while the cash flows, e.g. coupon payments, price alignment interest, variation margin, are denominated in a local currency different from the base currency. Thereby cash flows may be netted and offset minimizing the magnitude of funds needed to be moved and reducing the number of transactions processed by the electronic trading system as well as the consumption of computational resources thereby. Furthermore, the disclosed embodiments facilitate entering into IRS transactions is a currency different from the currency of cash flows while eliminating Herstatt risk due to volatility of foreign exchange rates, which allows for increased off shore participation and thereby increased transaction volume.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE INC
Method and system for offset matching
The trading of interest rate swaps or other interest rate derivatives gives rise to mismatch exposure. This can be offset by a series of FRA trades. Rather than conducting a series of exposure neutral trades, FRAs can be bought or sold for the entire amount of a trader's reset exposure. To hedge the offset trades, a series of IMM FRA trades are conducted. The relative size of the IMM contracts will be determined by the distance in time from the IMM quarterly contract settlement date. A system is disclosed for performing offset trades and IMM hedges. The embodiments allow for non-neutral trading and subsequent hedging brings trading back to a neutral position.
Owner:INTERCAPITAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES NO 2 LTD +1
Transaction processor for clearing interest rate swaps with improved efficiency
The disclosed embodiments relate to improving the efficiency of an electronic trading system for interest rate swaps (“IRS”) by allowing for IRS contracts to be funded in a base currency while the cash flows, e.g. coupon payments, price alignment interest, variation margin, are denominated in a local currency different from the base currency. Thereby cash flows may be netted and offset minimizing the magnitude of funds needed to be moved and reducing the number of transactions processed by the electronic trading system as well as the consumption of computational resources thereby. Furthermore, the disclosed embodiments facilitate entering into IRS transactions is a currency different from the currency of cash flows while eliminating Herstatt risk due to volatility of foreign exchange rates, which allows for increased off shore participation and thereby increased transaction volume.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE INC
Fractionalized interest rate swaps
ActiveUS10817936B2Low costGreat investment returnFinanceCryptography processingInterest rate swapSmart contract
Systems and methods for implementing and managing one-to-many fractionalized interest rate swaps between a borrower and one or more investors via a distributed ledger-based platform are described herein. The distributed ledger-based platform may be configured to generate and provide user interfaces through which a user may provide a set of input variables for a fractionalized interest rate swap. Based on the set of input variables, the platform may automatically configure a customizable smart contract configured to initialize the fractionalized interest rate swap between at least one borrower and one investor. At the maturity date of the fractionalized interest rate swap, the smart contract may be configured to calculate amounts to be allocated to the borrower and investor, automatically release the amounts from the escrow account associated with the smart contract, and settle the contract by transferring the corresponding amounts to accounts of the borrower and investor.
Owner:HUMMER MELANIE SUSAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com