Patents
Literature
1151 results about "Primary Key" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
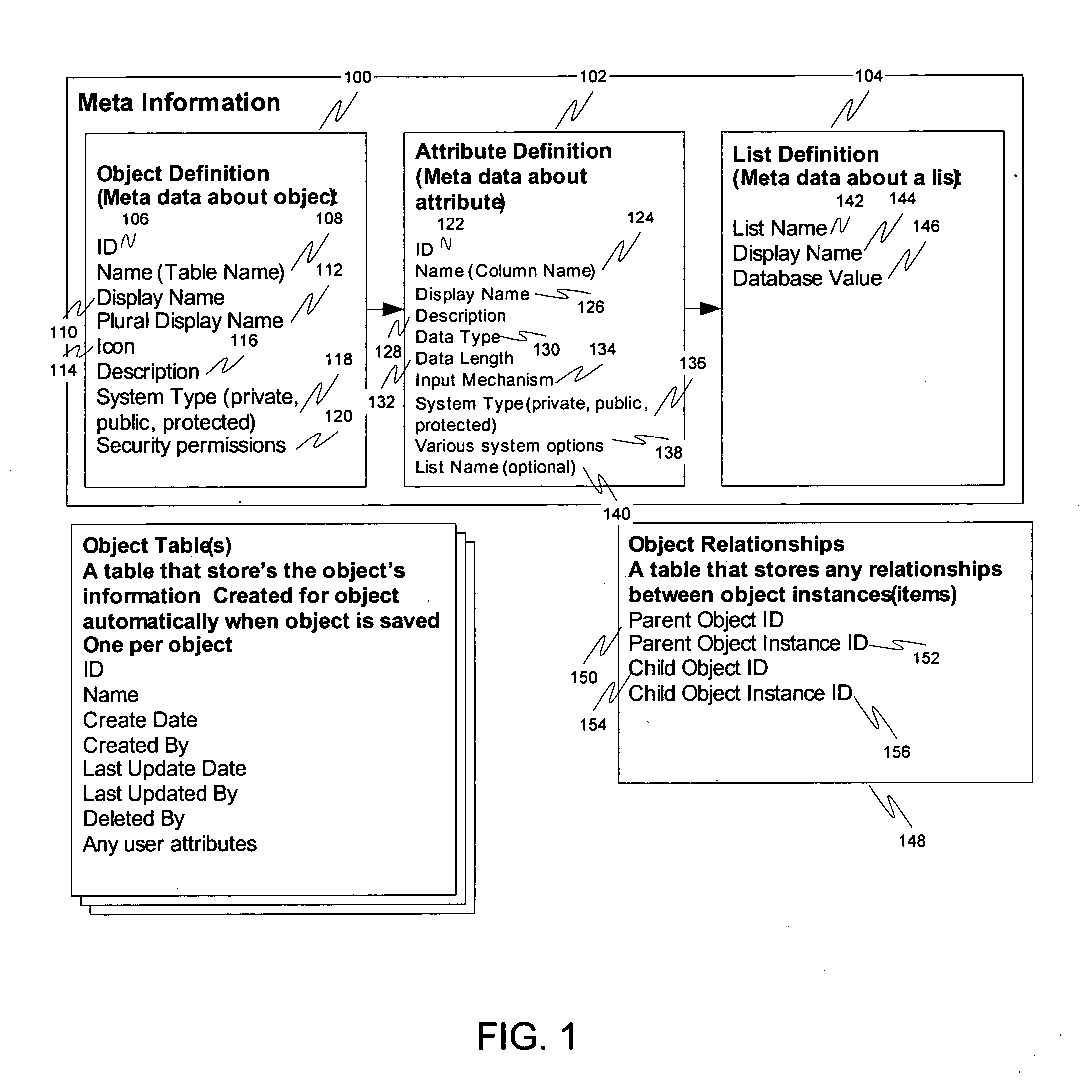
Custom entities and fields in a multi-tenant database system
Systems and methods for hosting variable schema data such as dynamic tables and columns in a fixed physical database schema. Standard objects, such as tables are provided for use by multiple tenants or organizations in a multi-tenant database system. Each organization may add or define custom fields for inclusion in a standard object. Custom fields for multiple tenants are stored in a single field within the object data structure, and this single field may contain different data types for each tenant. Indexing columns are also provided, wherein a tenant may designate a field for indexing. Data values for designated fields are copied to an index column, and each index column may include multiple data types. Each organization may also define custom objects including custom fields and indexing columns. Custom objects for multiple tenants are stored in a single custom object data structure. The primary key values for the single custom object table are globally unique, but also include an object-specific identifier which may be re-used among different entities.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
System and methods for mapping and searching objects in multidimensional space
ActiveUS20130138646A1Reduce in quantitySpeed up searchWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsData miningMultidimensional space
This invention relates to a system and methods for determining the placement of an object in a distributed key-value store by mapping the object to nodes in multidimensional hyperspace. A search function supports efficient object retrieval, even when the search query requests multiple objects and specifies them through non-primary keys. In response to a search query, the search is translated into hyperregions in the hyperspace to determine the set of nodes that hold the queried data object. The number of contacted nodes and the number of scanned objects are significantly reduced in comparison to prior art techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Associative database model for electronic-based informational assemblies
InactiveUS6112209AHigh degree of orderData processing applicationsRelational databasesData setData field
An indexing system and linking method for an assembly of electronic-based informational items stored in and ordered by a plurality of records uniquely identified over a plurality of relational data tables making up a data set wherein each table is assigned a unique domain of unique alphanumeric indicia for assignment and storage in the records. The records are ordered by the alphanumeric indicia whereby each data table acts as its own primary key. The records are bi-directionally linked to each other via a plurality of separate, central linking table indexes wherein each index record is structured with a plurality of linking fields defined to store sets of two or more alphanumeric indicia belonging to a plurality of records in the data set. Each record is further structured to include an internal set of unique indicum for each data field whereby the combination of the unique record indicum and the unique field indicum uniquely identify each record-field over the plurality of relational data tables making up the data set such that each record field may be linked to a plurality of other record-fields or records via the plurality of separate, central linking table indexes. Each central linking table indexes is further generalized to provide multiple arrays of linking indicia in a plurality of indexing fields such that a plurality of the records from a plurality of the data tables may be linked together as a data cluster. The linking values stored in the central linking table indexes may be predefined to automatically structure and link a plurality of unspecified data and changes in the data may alter the linking structure to provide further capabilities.
Owner:GUSACK MARK DAVID
Method and system for preventing identity theft in electronic communications
ActiveUS20050125686A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsThird partyElectronic communication
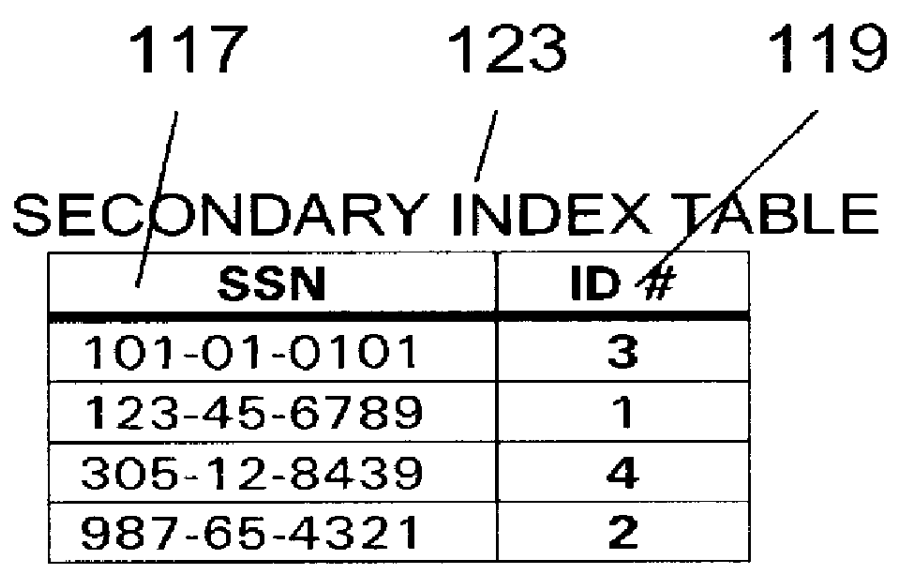
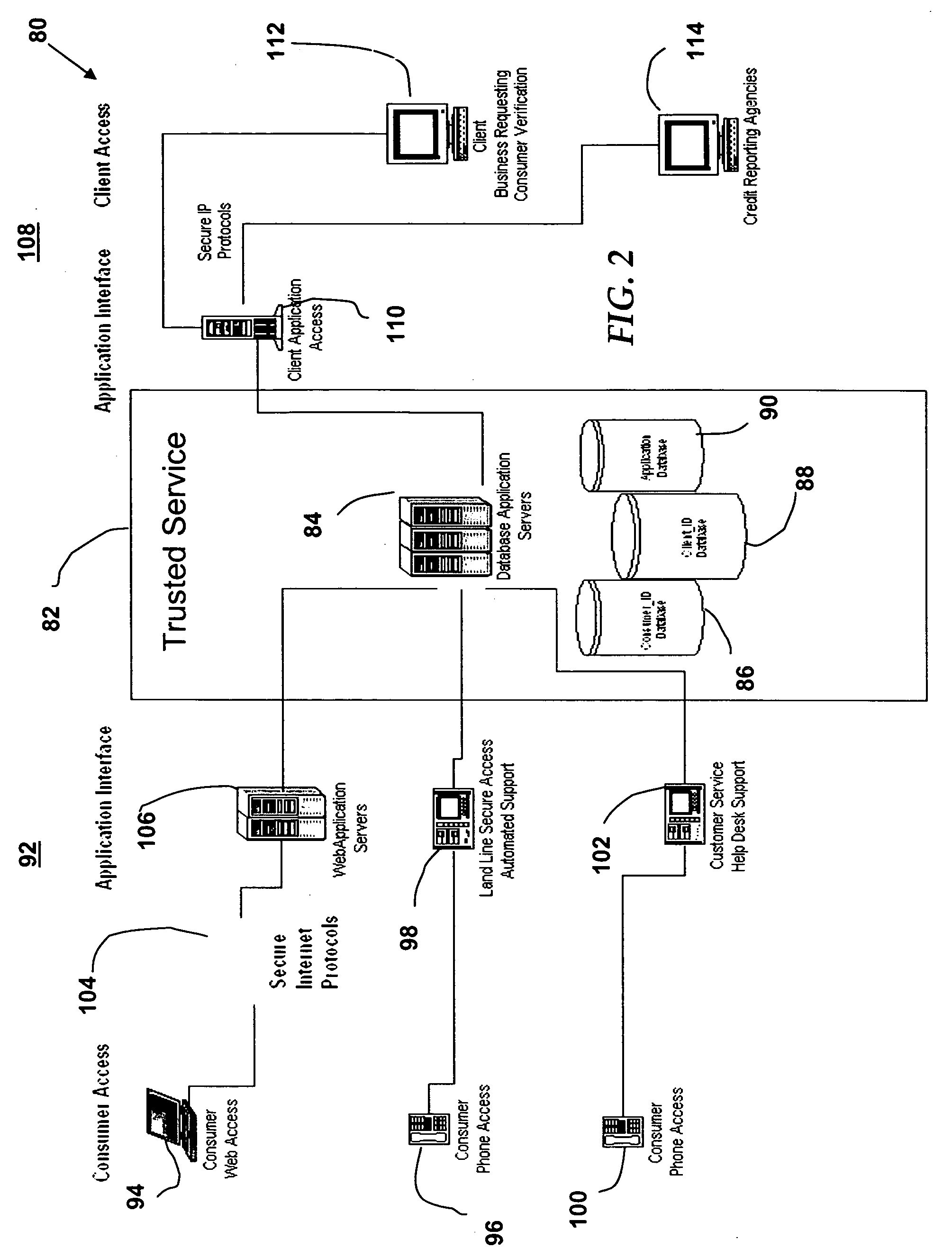
Preventing identity theft in electronic communications sequences (180) involves generating a consumer identifier (126) for an individual (92) from a trusted service (82), including a primary key (128), a unique identifier (130), and a consumer-defined sequence (132). The consumer-defined sequence (132) allows the individual (92) to control use of the consumer identifier (126) by third parties, such as business entities (112). The method and system further allows business entities (114) to verify use of the consumer identifier (126) by first initiating a verification process (196) via a secure connection (110). Verification includes comparing (200) the consumer identifier (126) with a pre-determined set of database records (86, 88, and 90). If the requesting business (108) has registered with the trusted service (82), the invention presents a positive or negative confirmation (208) to the requesting business (108) according to the inquiry (204). Then, the invention permits confirming (210) the requested information relating to the individual (92) via the secure connection (98, 102, 106), conditioned upon the requested information having previously been authorized by the individual for presenting to the requesting business (108).
Owner:MARQETA
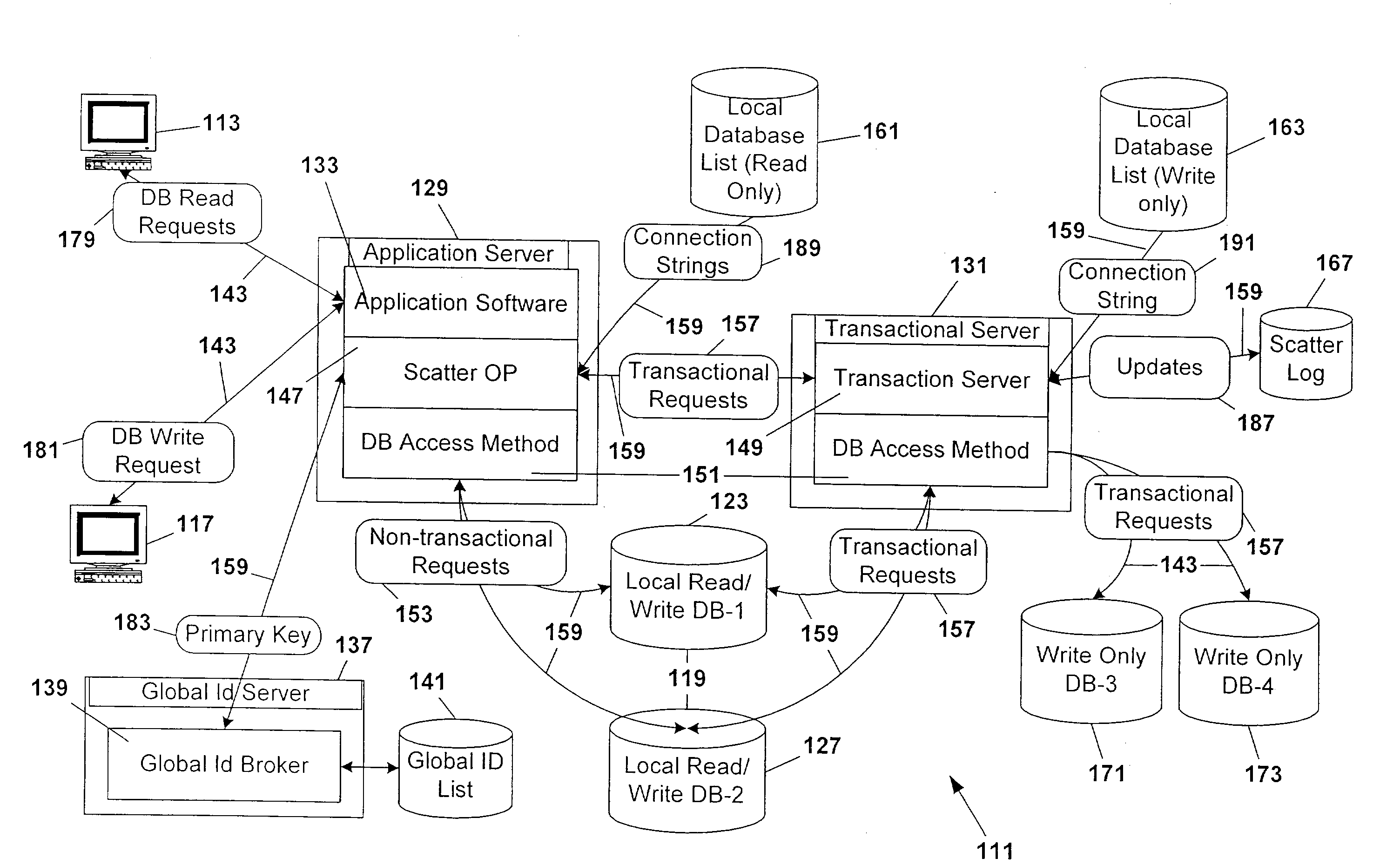
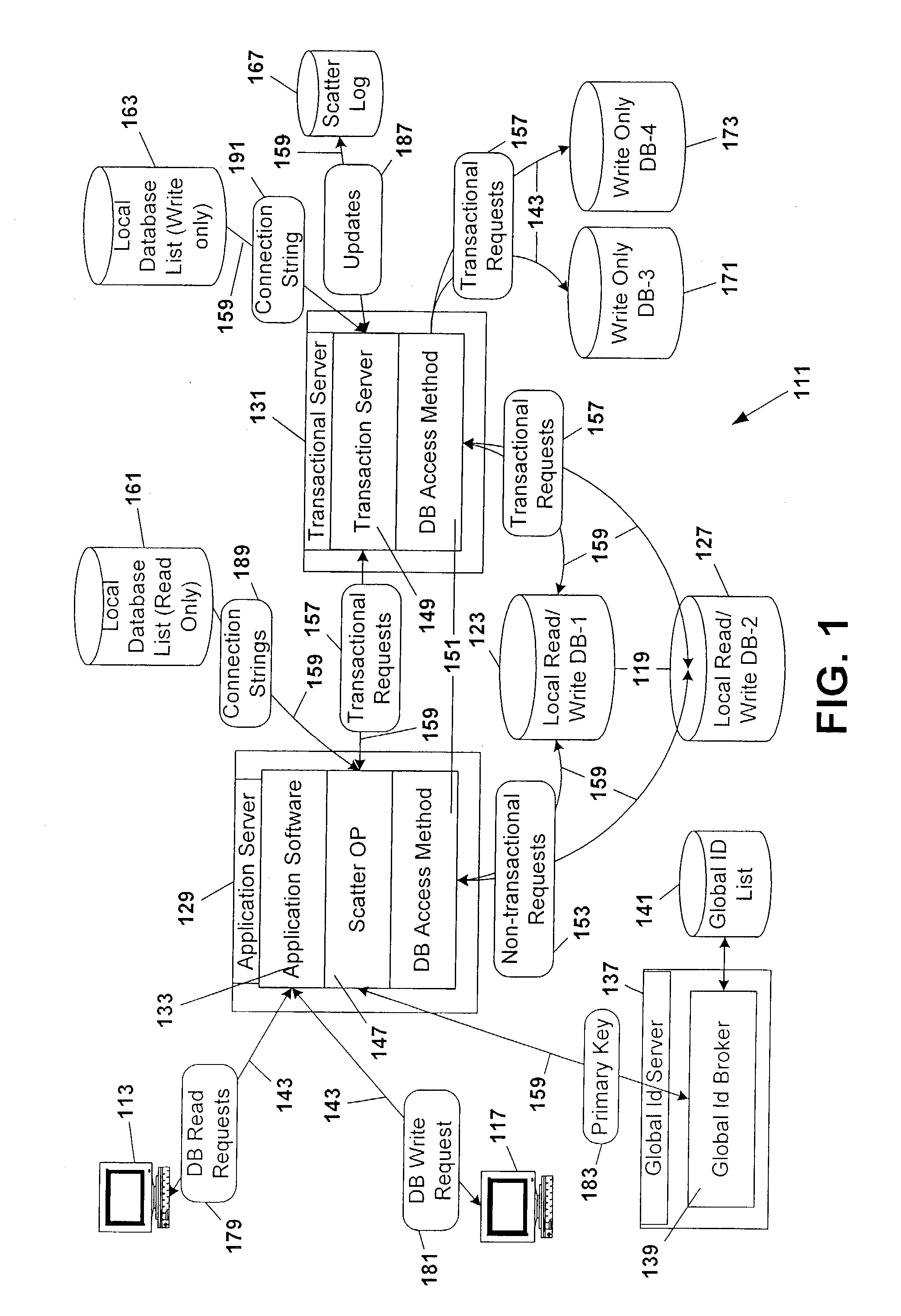
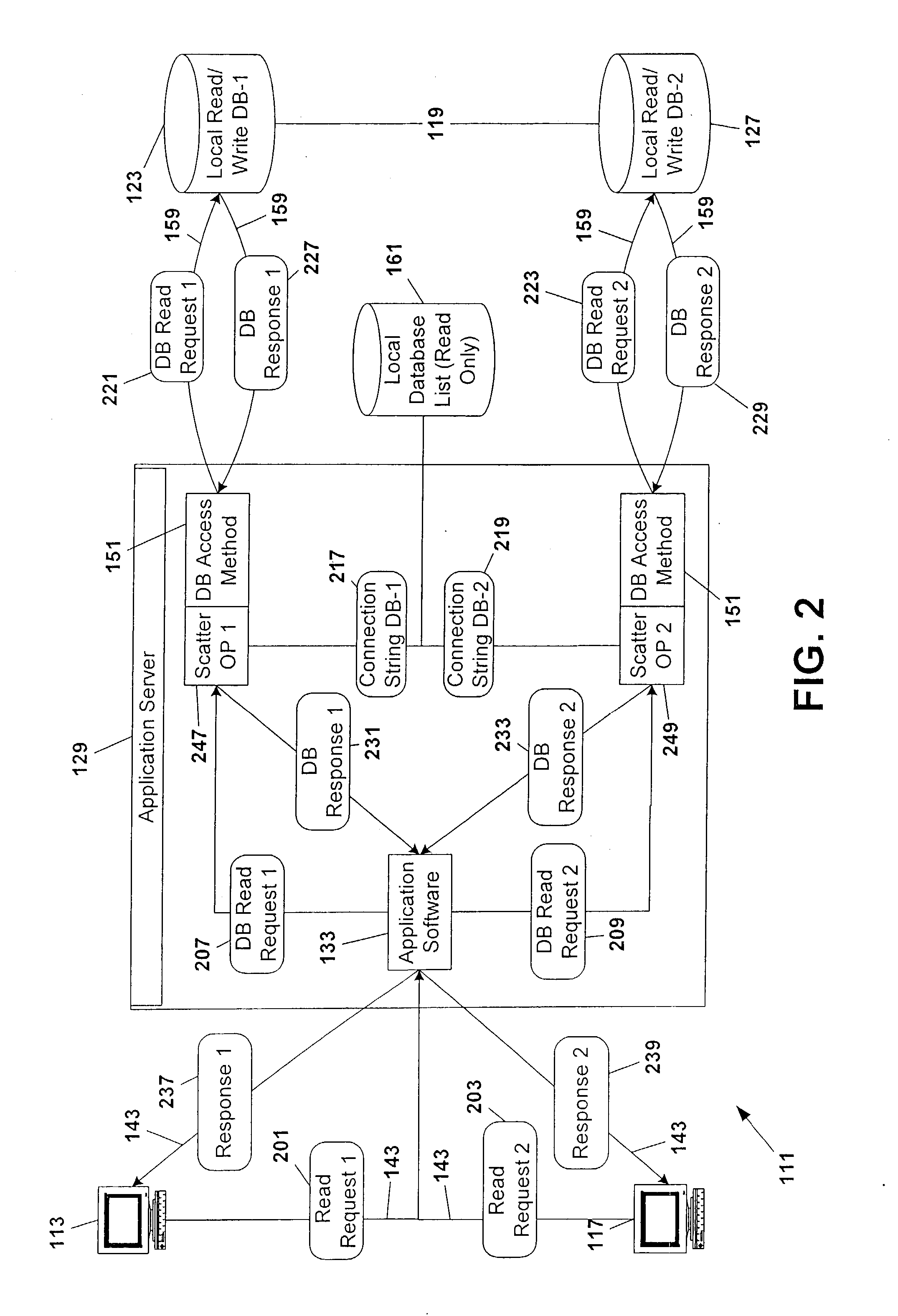
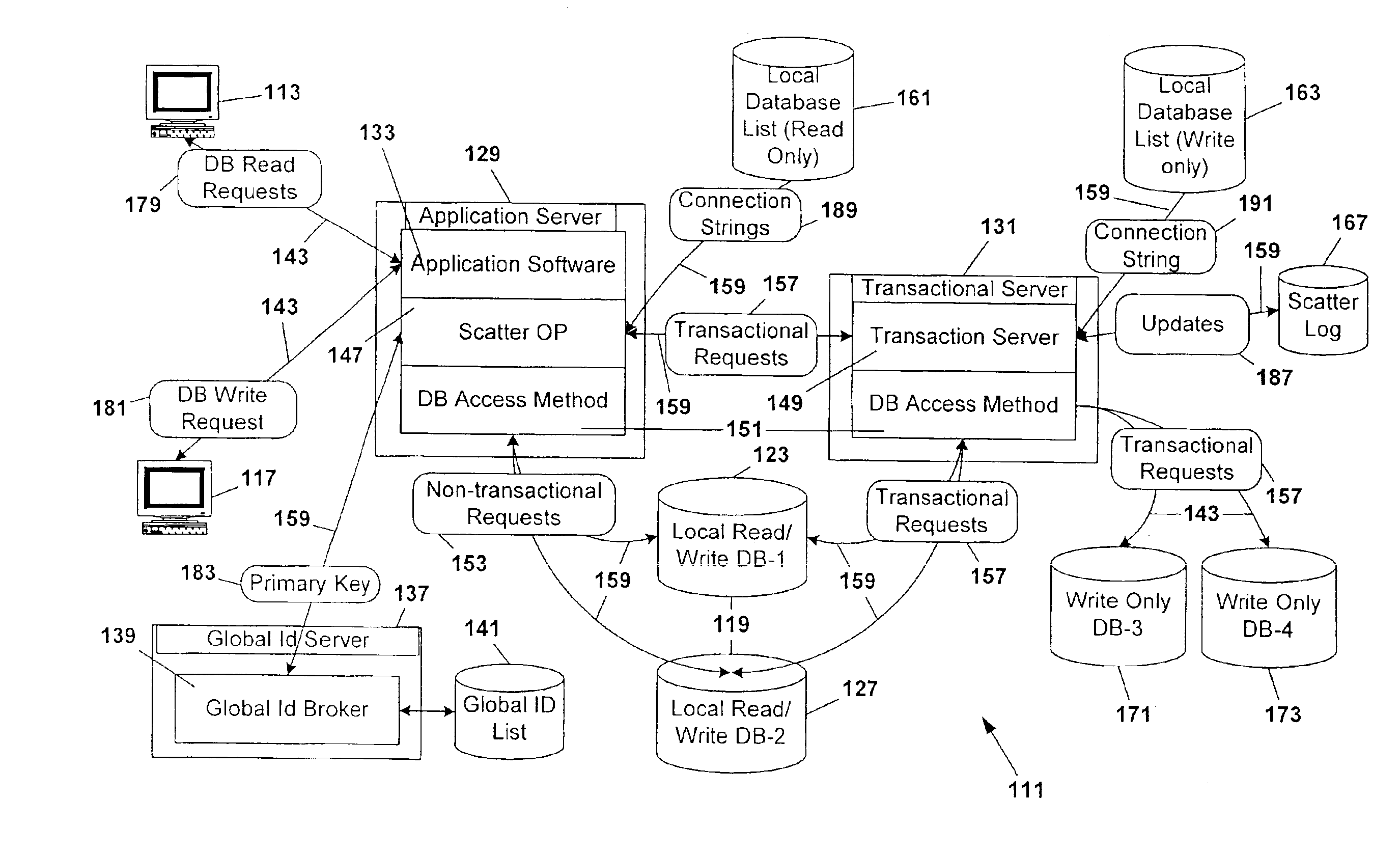
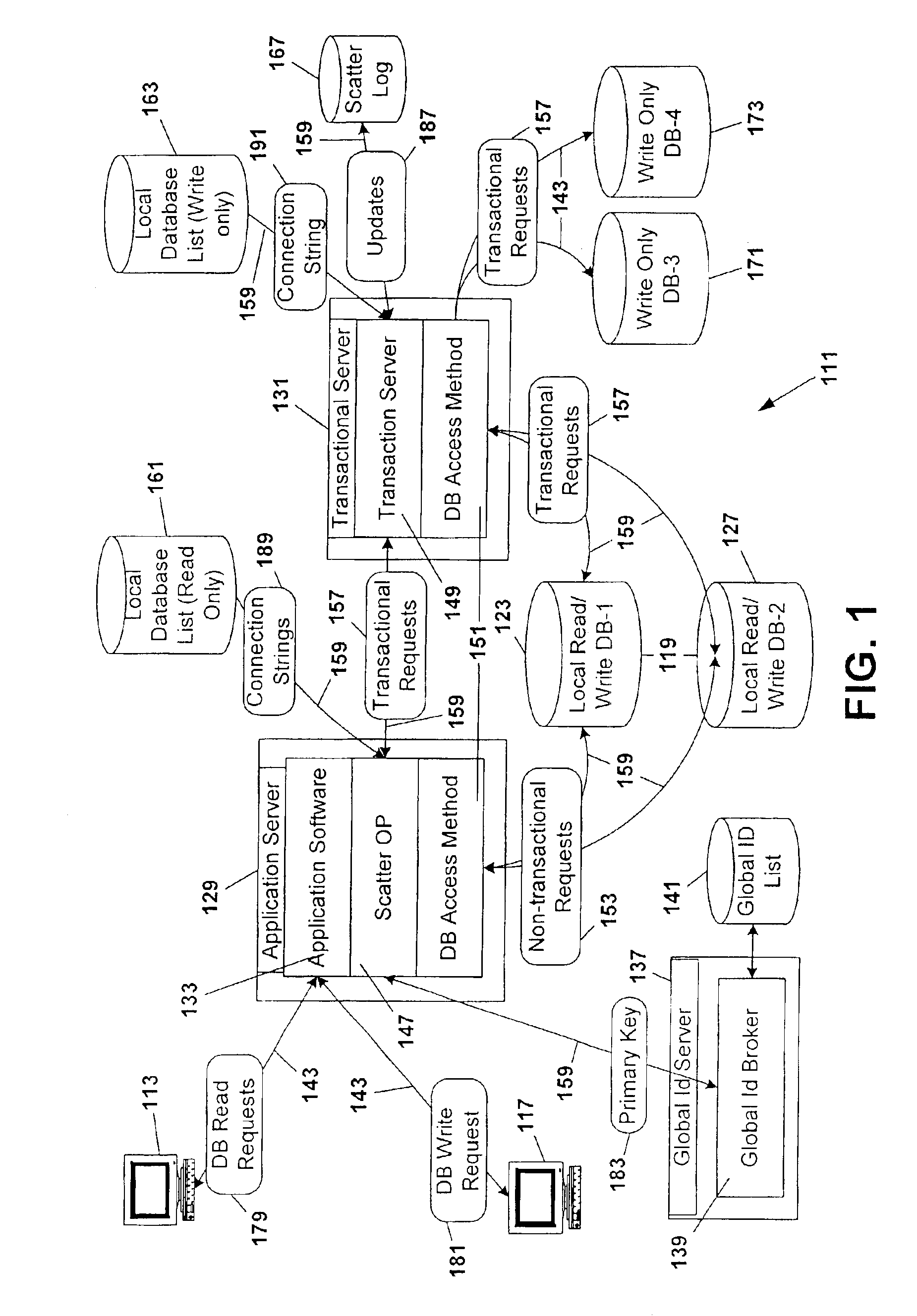
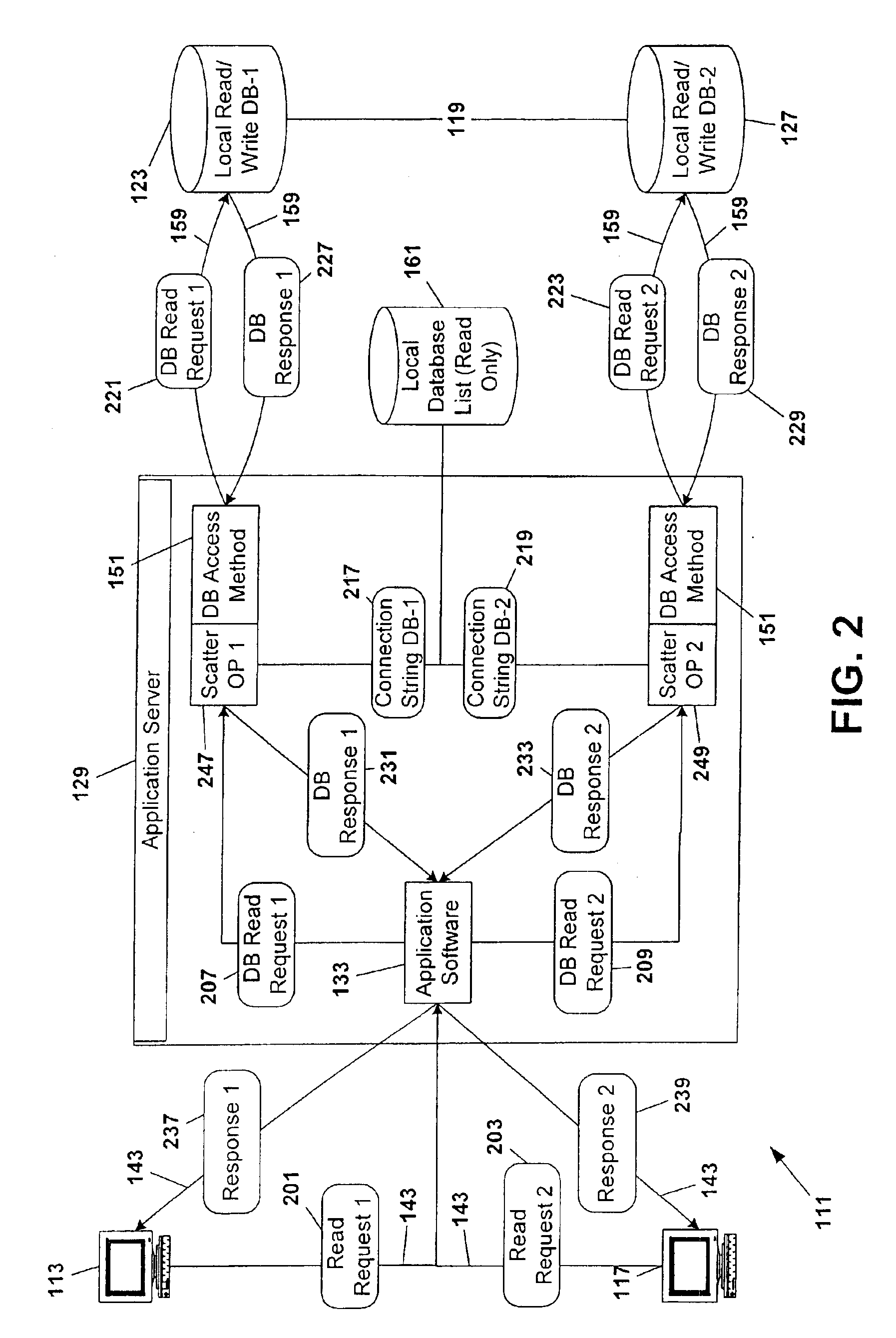
Database scattering system
InactiveUS20030212660A1Reduce needPermit scalabilityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalEngineeringNetwork data
A computer system for providing load balancing and scalable access to a network database system by providing multiple database instances with each instance being substantially identical in data content, database structure, and primary key system. Requests from users are received by the system, examined to determine their nature as transactional or non-transactional and, in the case of non-transactional queries, scattered among the multiple database instances. Such scattering of queries permits multiple instances of the database to be serving responses to multiple users at substantially the same time. In the case of transactional queries, the system automatically propagates the transactional query to all instances of the database to maintain homogeneity.
Owner:ENTERPRISEDB
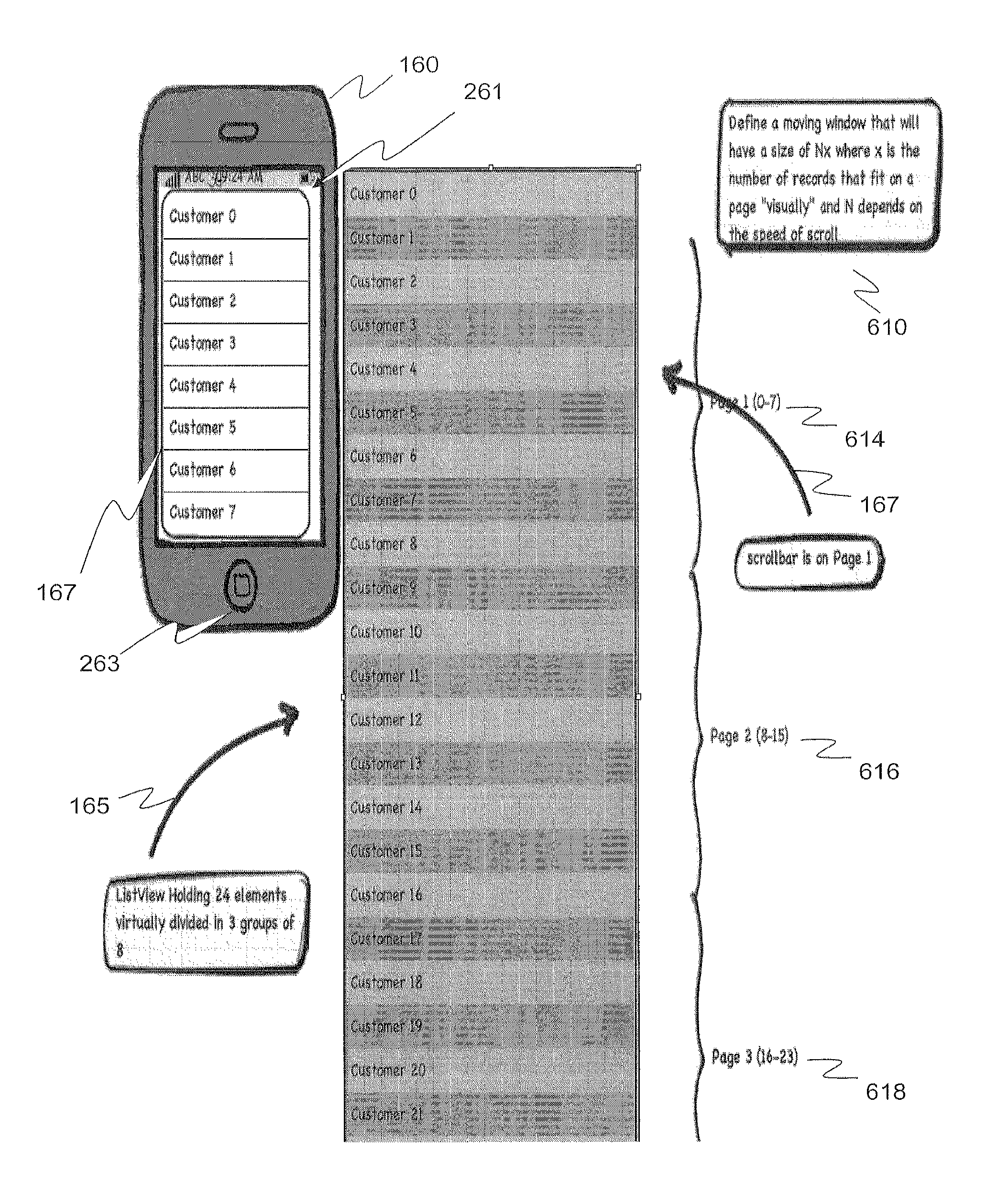
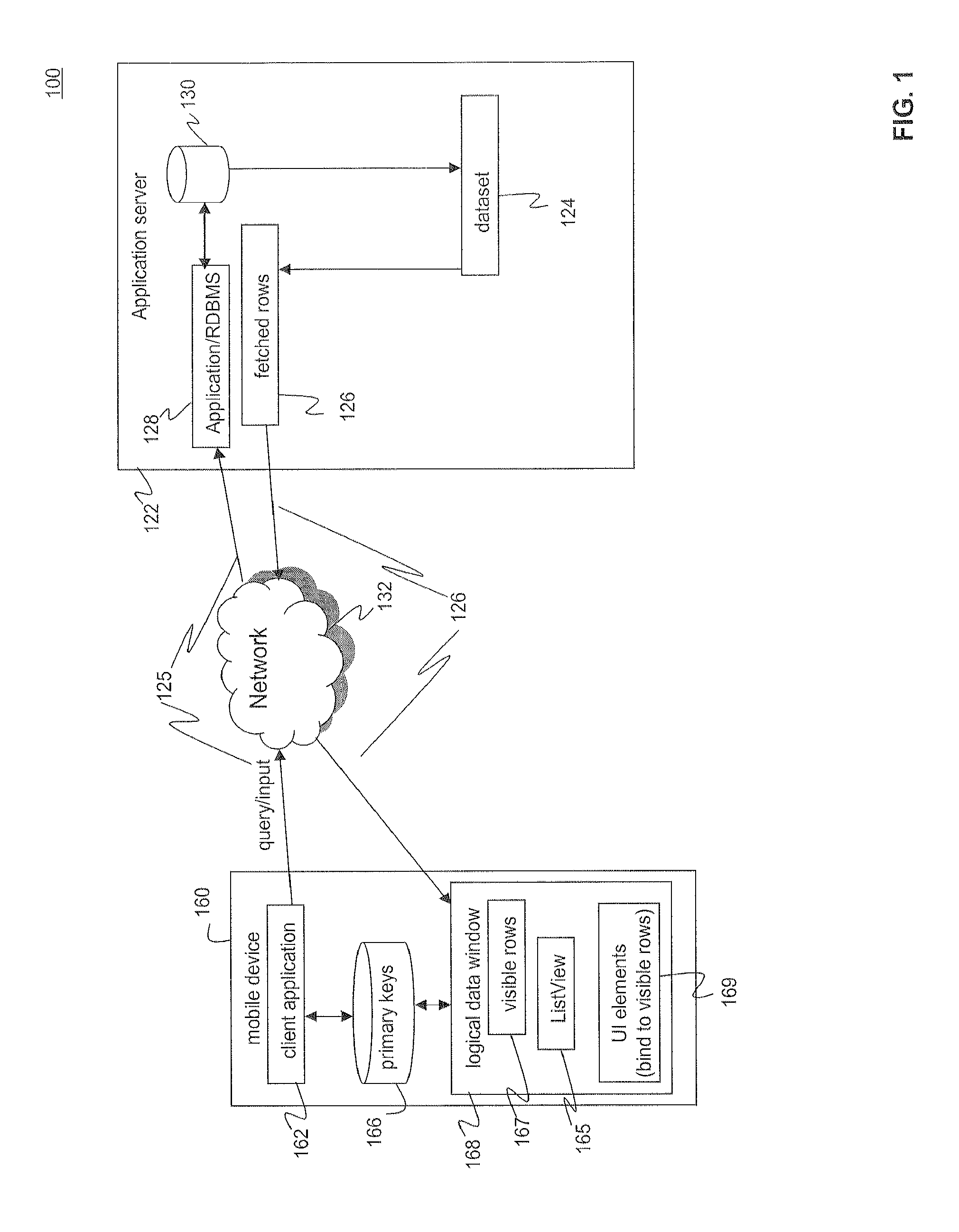
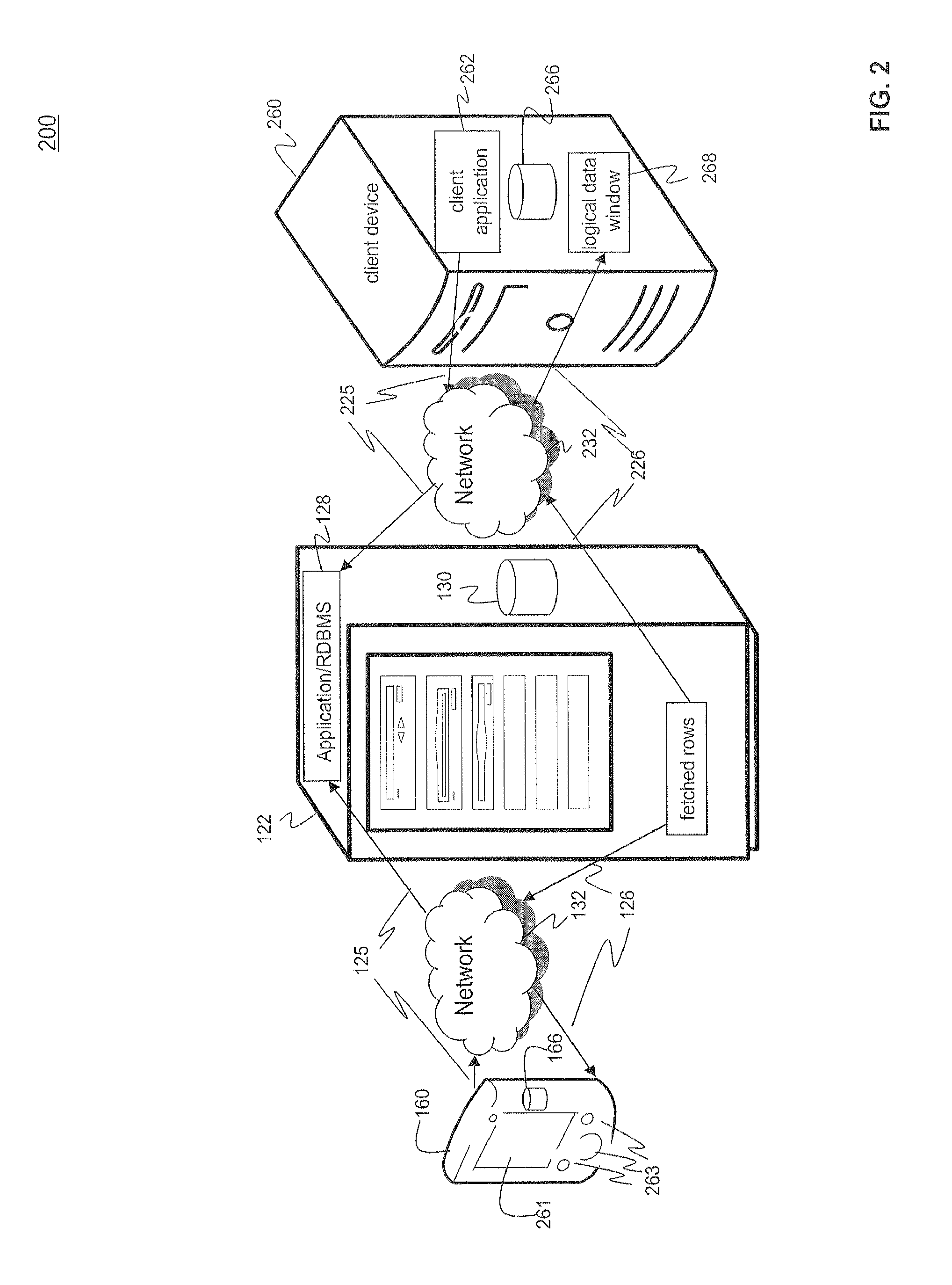
Efficiently Handling Large Data Sets on Mobile Devices
ActiveUS20120159393A1Efficient fetching of dataEfficiently fetch portionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemData set
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for efficiently fetching and displaying large datasets on mobile devices, such as devices running the iPhone™ operating system. The method fetches data for a mobile device from a server and displays a plurality of data rows in a ListView within a user interface on the mobile device. The method stores primary keys on the mobile device until their corresponding data rows are to be displayed. The method reacts to user inputs such as scrolling actions and touch screen gestures to efficiently fetch and display list view subsets of large datasets. The method facilitates quick response times when navigating through large lists of data on a mobile device by: fetching displayable or visible rows of data in a data list view, preloading the visible rows on the mobile device; and binding the visible rows to user interface elements on the mobile device.
Owner:SYBASE INC
Database scattering system
InactiveUS6898609B2Reduce needPermit scalabilityDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsComputerized systemData content
A computer system for providing load balancing and scalable access to a network database system by providing multiple database instances with each instance being substantially identical in data content, database structure, and primary key system. Requests from users are received by the system, examined to determine their nature as transactional or non-transactional and, in the case of non-transactional queries, scattered among the multiple database instances. Such scattering of queries permits multiple instances of the database to be serving responses to multiple users at substantially the same time. In the case of transactional queries, the system automatically propagates the transactional query to all instances of the database to maintain homogeneity.
Owner:ENTERPRISEDB
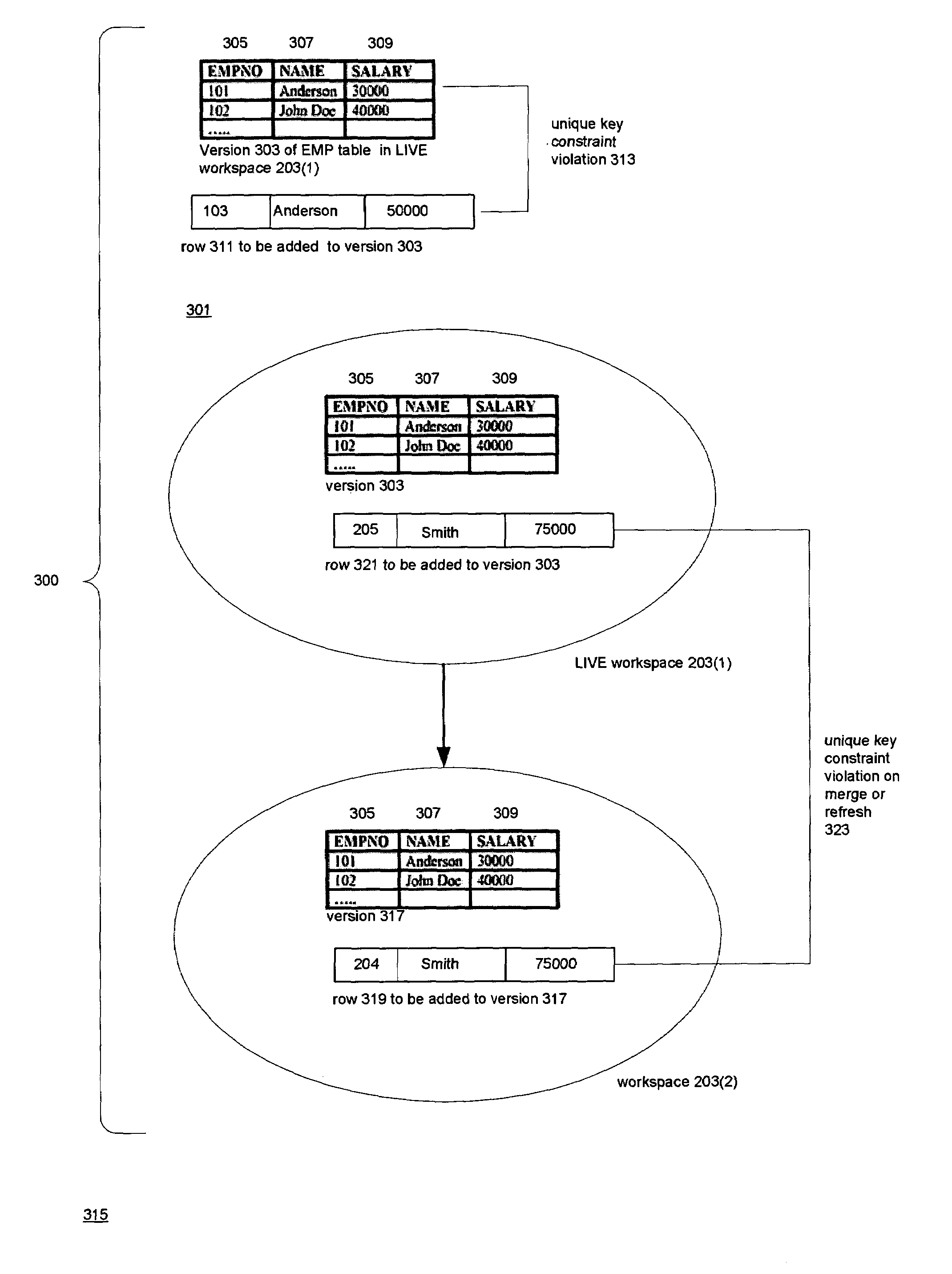
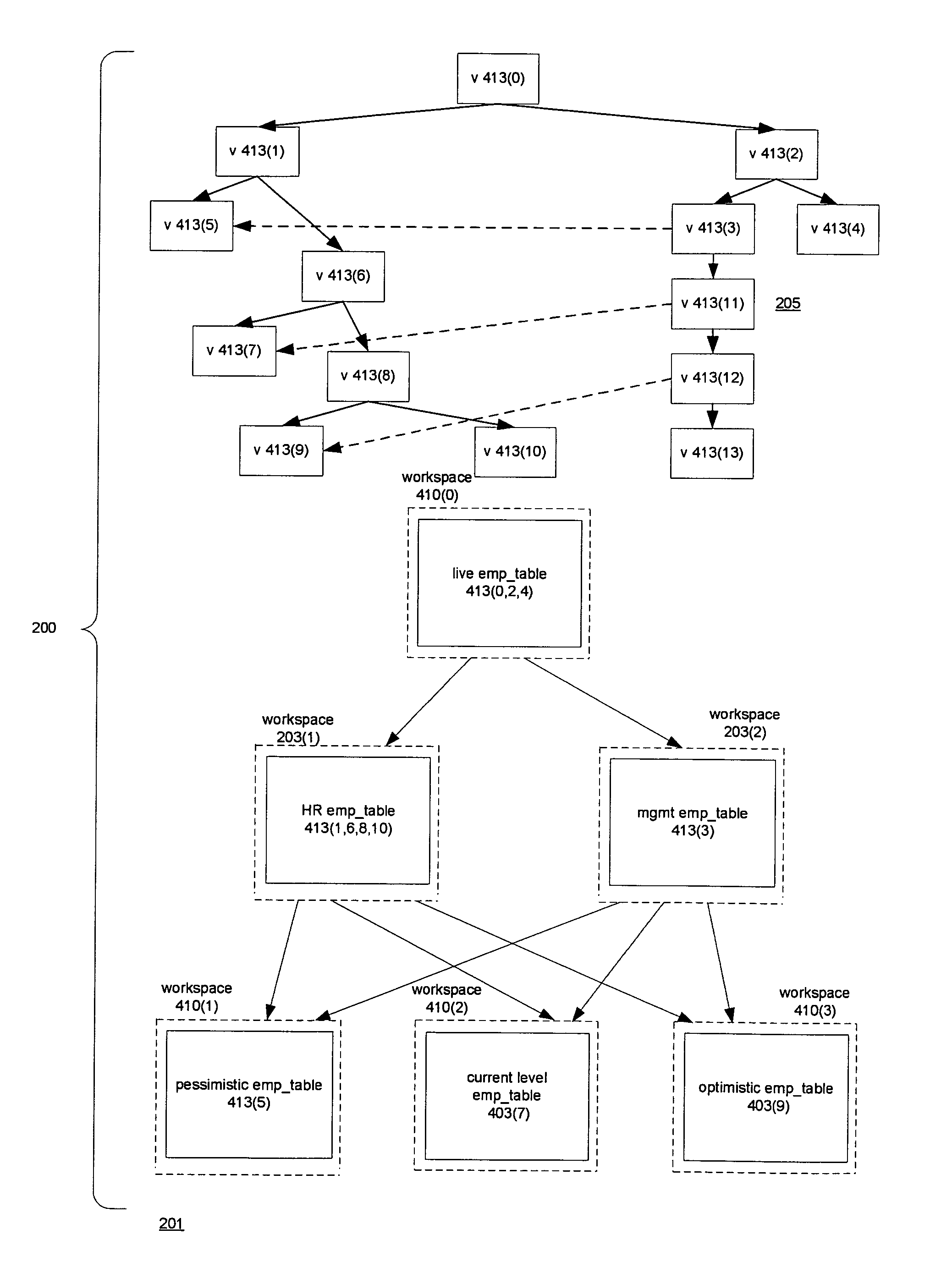
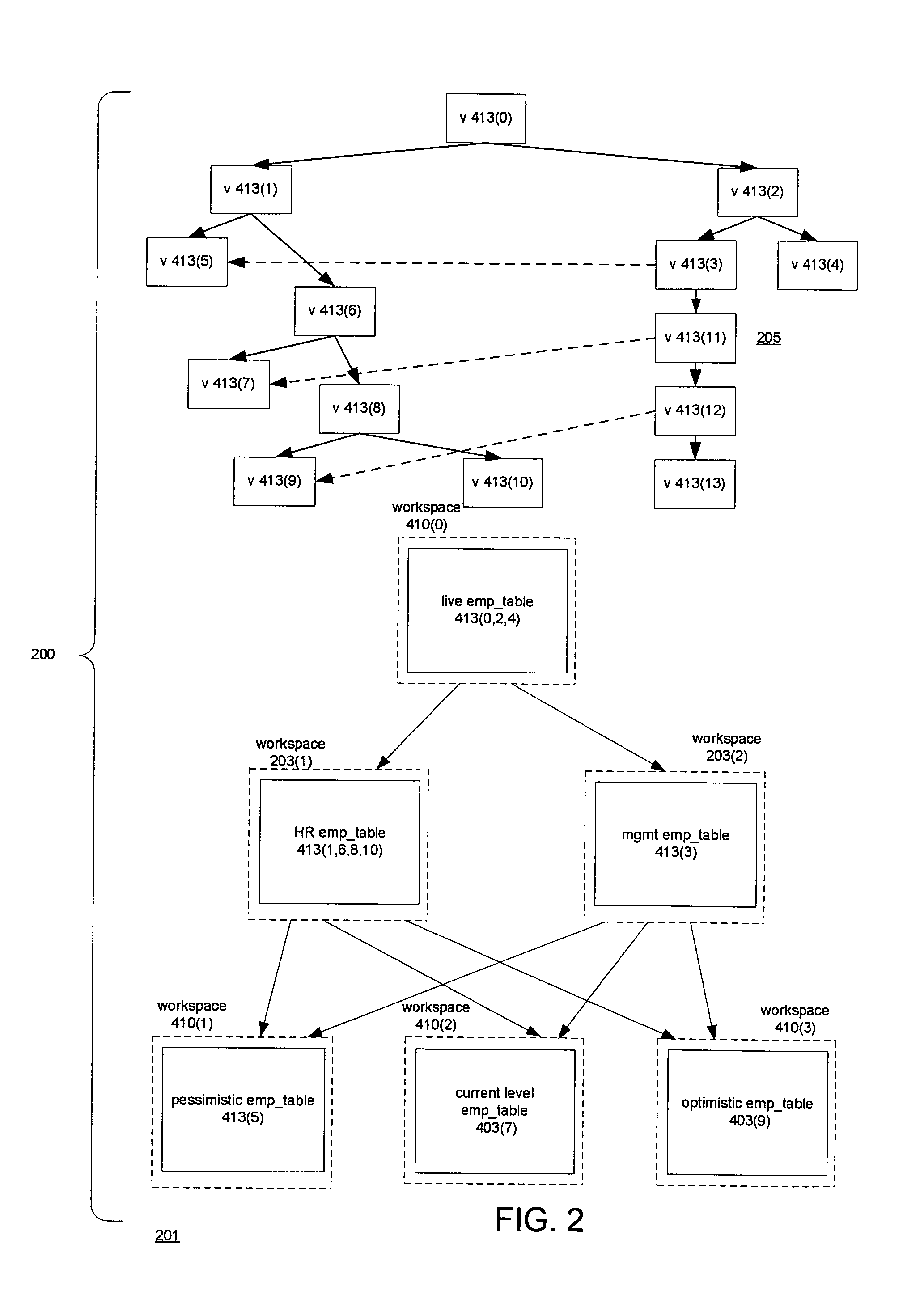
Versioned relational database system with an optimistic constraint model
InactiveUS7028057B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTheoretical computer scienceWorkspace
Techniques for doing optimistic constraint checking in a versioned relational database system. The techniques find a subset of the versions of a table that contain all of the rows that need be checked for violation of a constraint when a given version is modified. When the versions of a table are organized into a directed acyclic graph (DAG), the subset for a given version is the ancestry of the given version, that is, the given version plus the ancestors of the given version in the DAG. Within the ancestry, the set of rows that must be checked is termed the version view. A row that belongs to the set has a primary key that is the latest version of the primary key in the given version's ancestry. The technique may be used for constraints including the referential integrity constraint and the unique key constraint. The metadata used to compute the version view is disclosed, as well as the manner in which the constraint checking techniques interact with the workspaces that provide access to the versions. The workspaces may be organized as a DAG. The manner in which the workspaces are organized determines how changes are propagated in the versioned relational database and thus the versions whose ancestry has to be checked for constraint violations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data partitioning method for distributed parallel database system
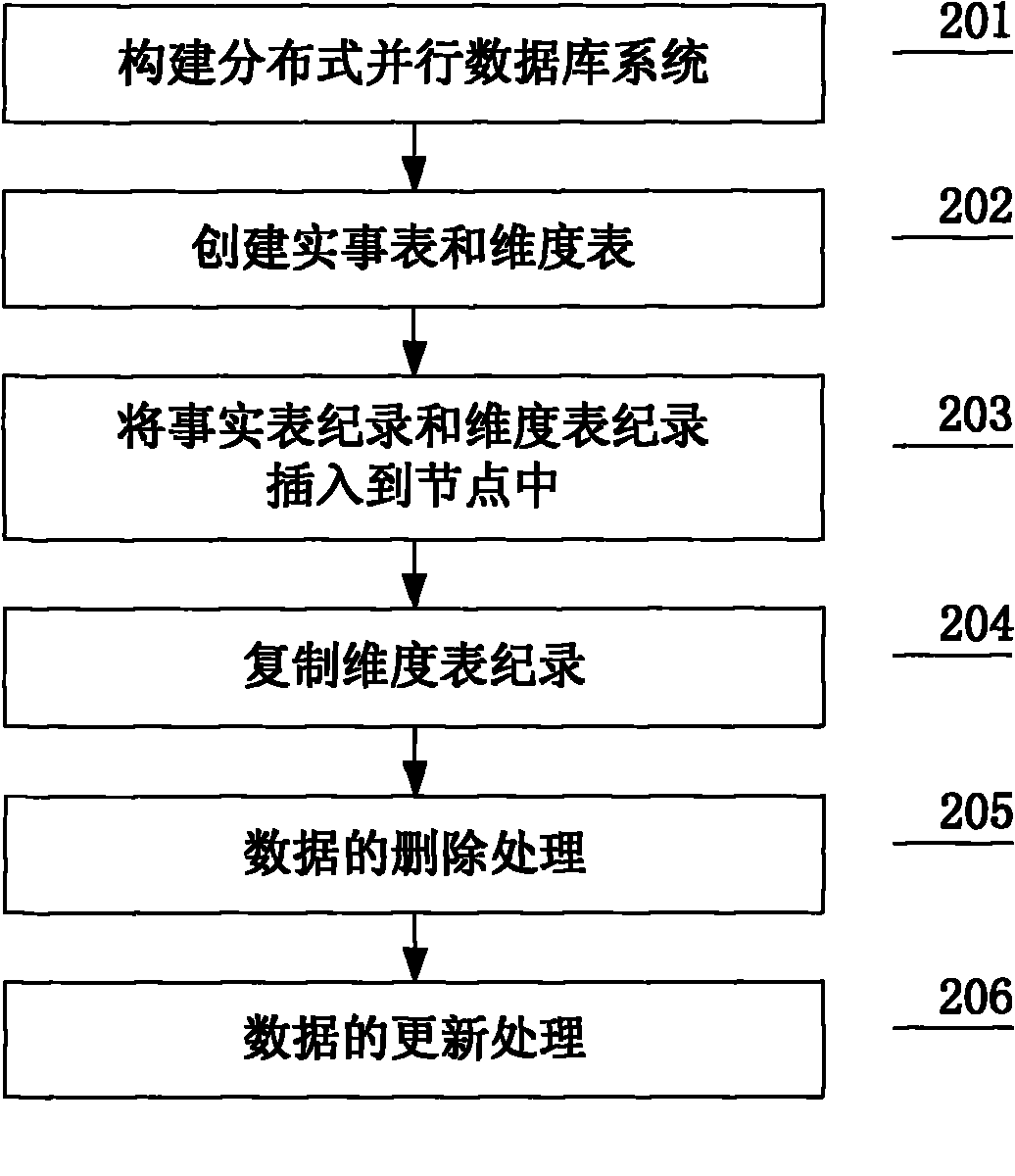
ActiveCN101916261APartially completeAvoid time-consuming network transmissionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setData stream
The invention discloses a data partitioning method for a distributed parallel database system. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a fact table and a dimension table according to the constructed distributed parallel database system; inserting records of the dimension table and the fact table on different nodes according to a partitioning rule; copying the records of the dimension table to the nodes of the fact table; and deleting and updating the data. When a data set or data stream is imported or inserted into the distributed database system in a partitioning way, the relation between tables defined by a database schema can be met on each node, particularly the primary key-foreign key restrictive condition, so the data on each node has local completeness of the data. For the query processing on the connection between the tables by using the primary key-foreign key restrictive condition, the data of each node has the local completeness on the query, so dynamic repartitioning of data between the nodes is not needed; and thus the method has the advantages of preventing time-consuming network transmission of the data, shortening the query response time and improving the query efficiency.
Owner:BORQS BEIJING +2
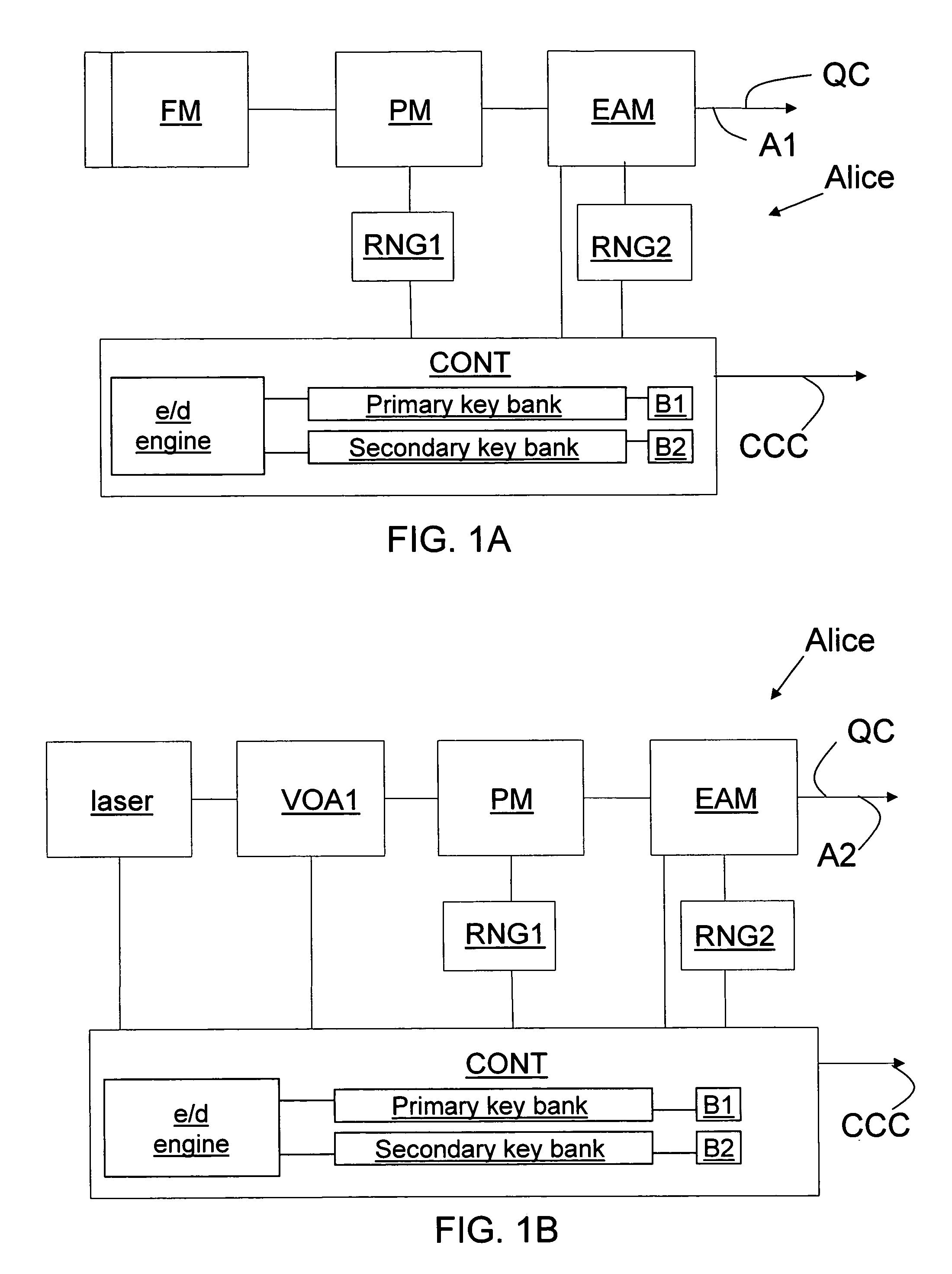
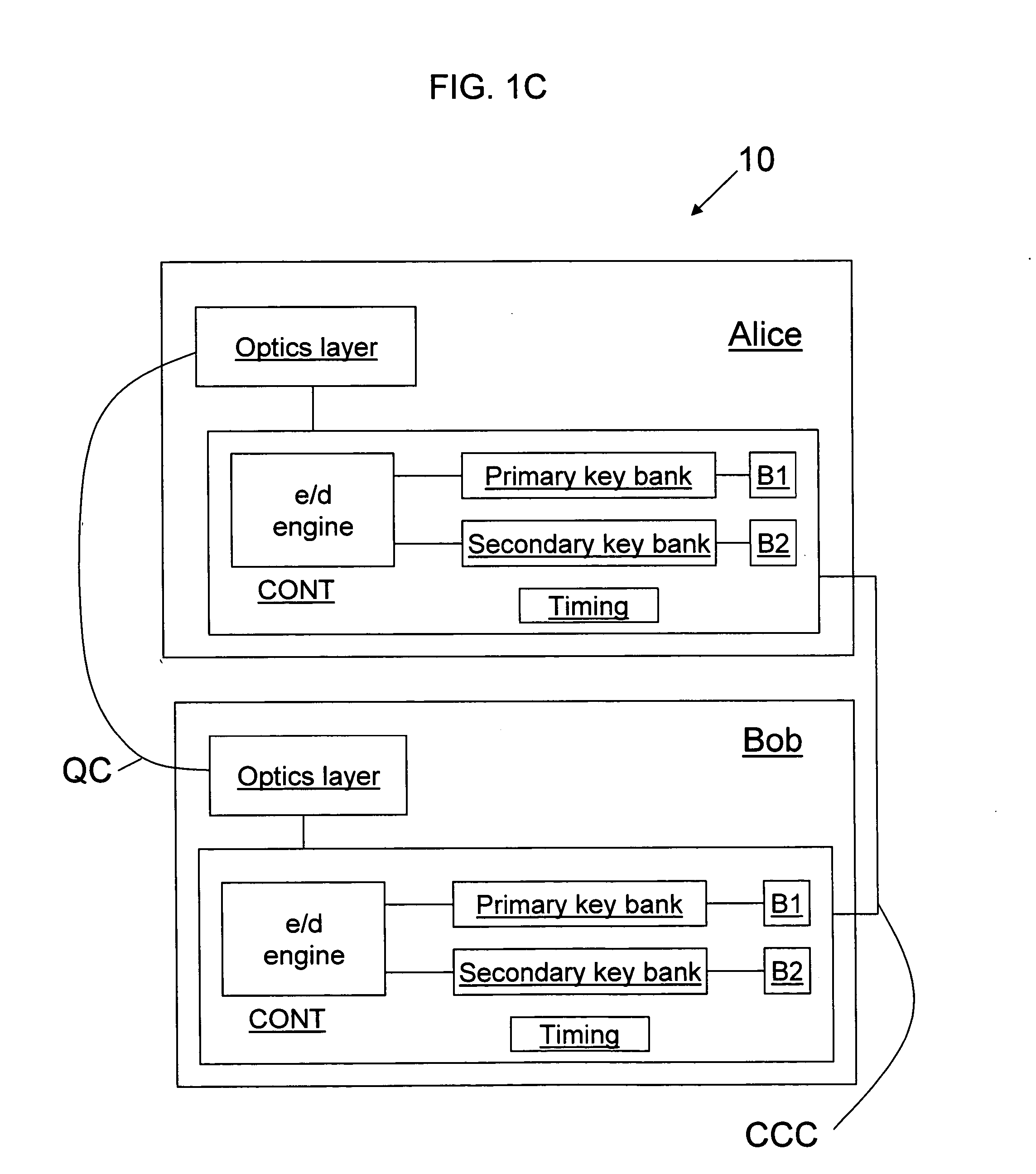
Key bank systems and methods for QKD
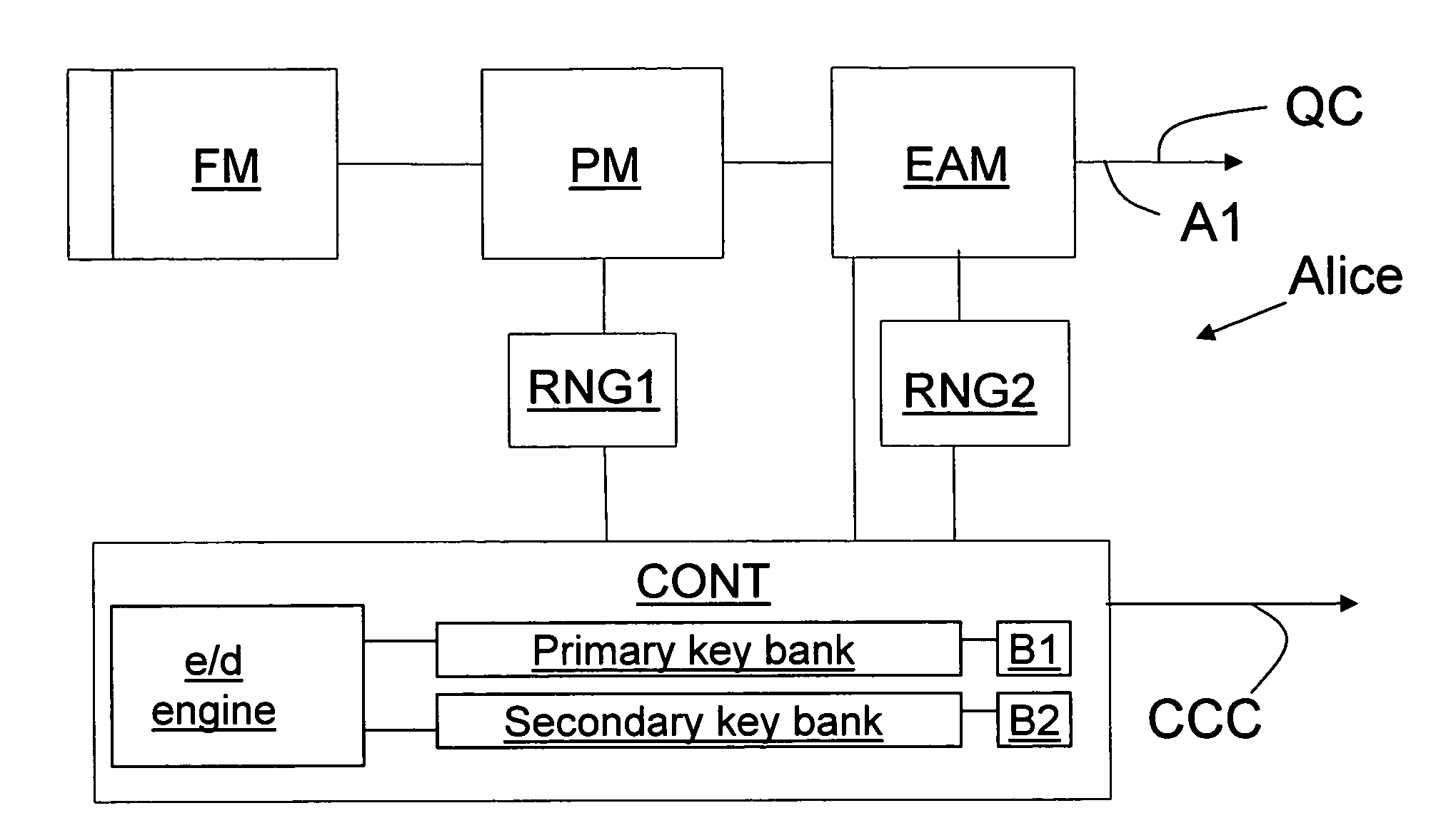
ActiveUS20050259825A1Increase distanceIncrease in key generation rateKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationAuthenticationQuantum key distribution
Key banking methods and systems for quantum key distribution (QKD) are disclosed. A method of the invention includes establishing a primary key bank that stores perfectly secure keys associated with exchanging true quantum pulses between two QKD stations Bob and Alice. The method also includes establishing a secondary key bank that stores less-than-perfectly secure keys associated with exchanging relatively strong quantum pulses between Bob and Alice. The primary keys are used for select applications such as authentication that are deemed to require the highest security, while the secondary keys are used for applications, such as encrypted bit sifting, that are deemed to require less-than-perfect security. A benefit of the two-key-bank architecture is that exchanging primary and secondary keys actually allows for an increase in the distance over which the primary keys can be securely distributed
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
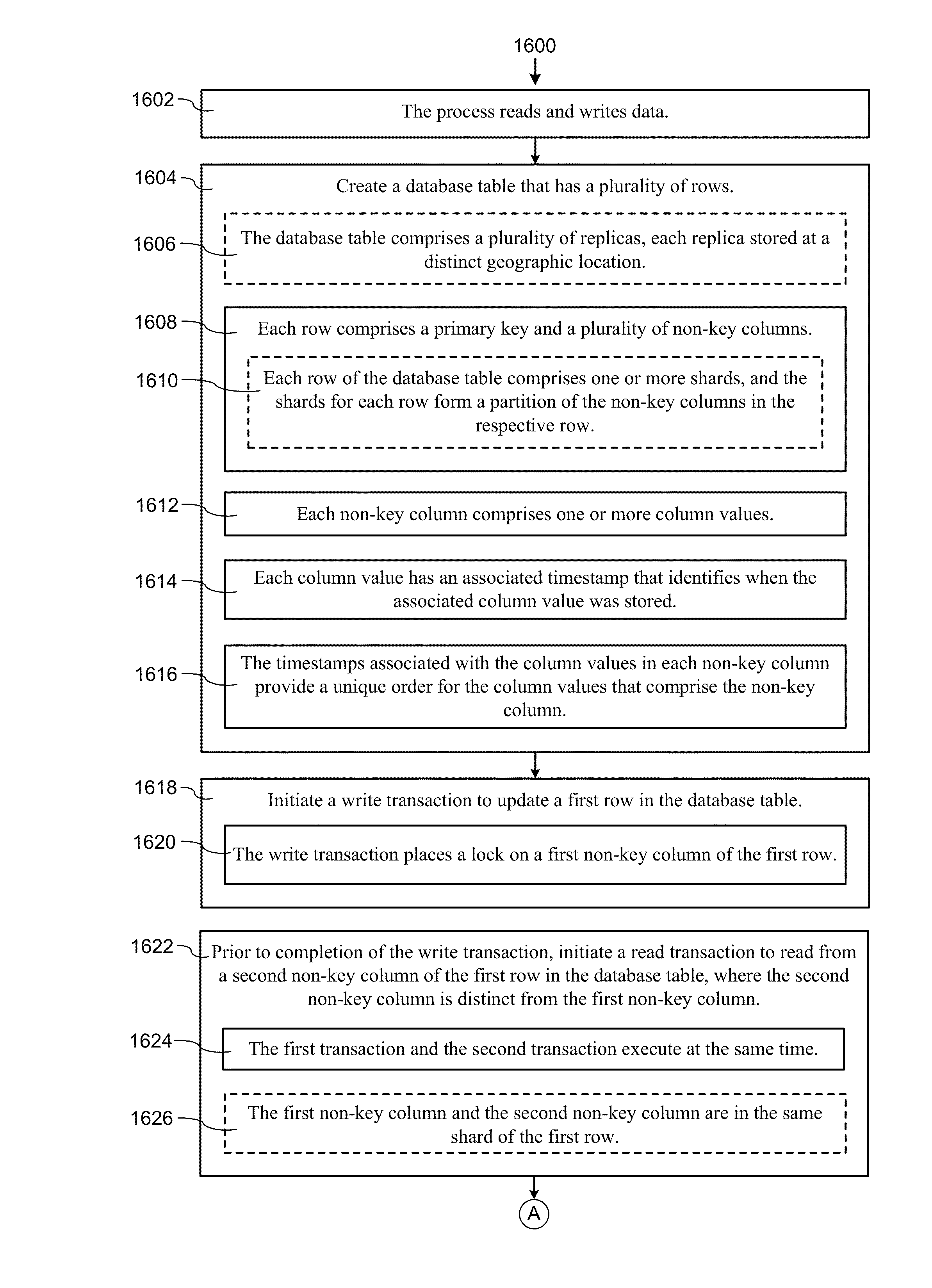
Systems and Methods of Increasing Database Access Concurrency Using Granular Timestamps
ActiveUS20140006458A1Improve parallelismMore dataDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTimestampDatabase access
A method reads and writes data from a database table. Each row in the table has a primary key and multiple non-key columns. Each non-key column has one or more column values, and each column value has an associated timestamp that identifies when the column value was stored. The timestamps associated with the column values in each non-key column provide a unique order for the column values. A read transaction is initiated to read from a first non-key column of a first row. A write transaction is in progress that is updating a second non-key column of the first row, where the second non-key column is distinct from the first non-key column. The write transaction holds a lock on the second non-key column of the first row. The method concurrently reads the data from the first non-key column and writes a new column value to the second non-key column.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Reporting and summarizing metrics in sparse relationships on an oltp database
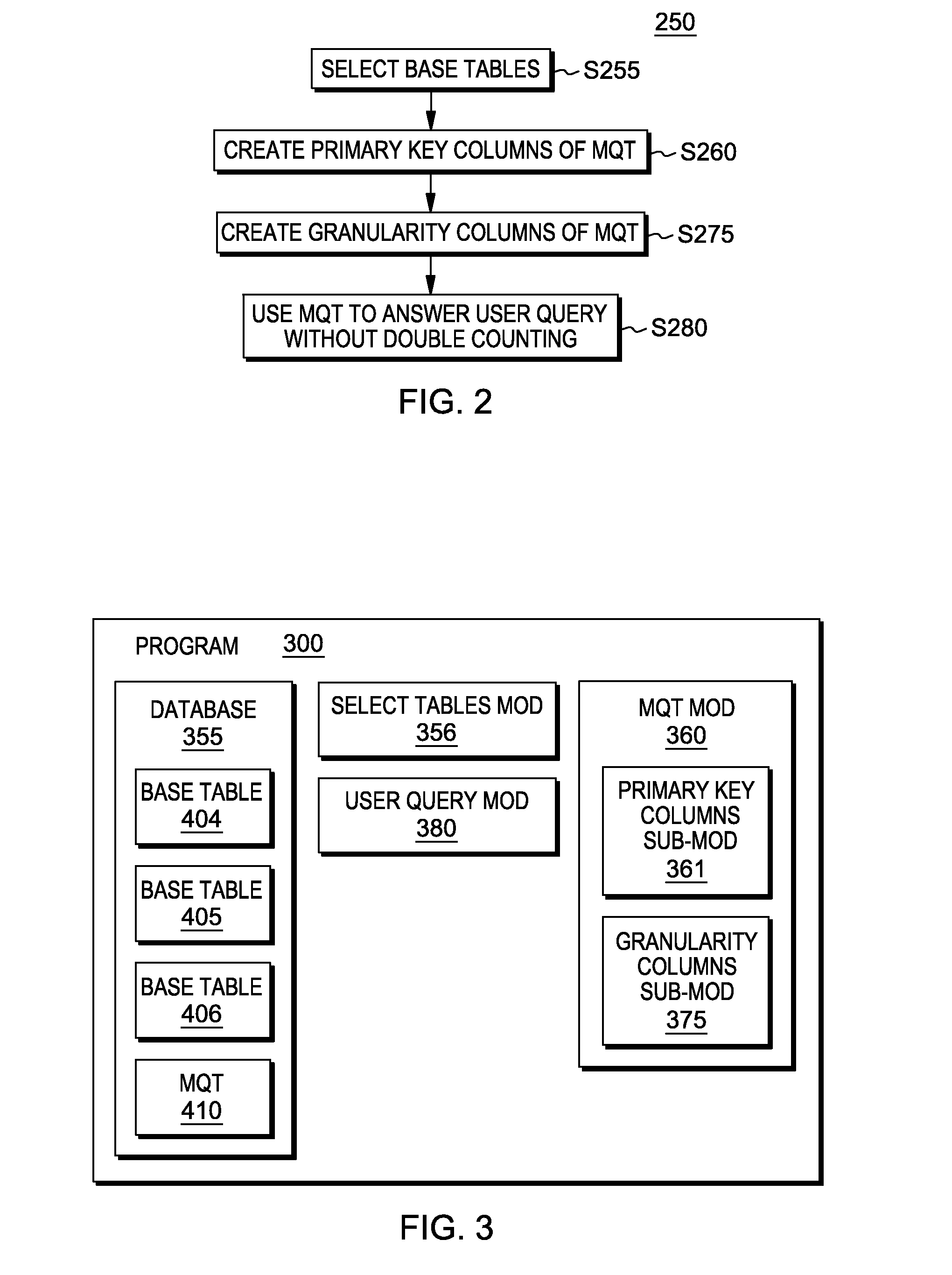
InactiveUS20150134599A1Database management systemsDigital data processing detailsPrimary KeyComputer science
Storing and / or accessing data in a transactional database, with use of the following technique: (i) selecting a set of base tables in a transactional database; and (ii) creating a factless materialized query table, having maximum sparsity, for the set of base tables. The set of base tables includes at least two base tables. The set of base tables includes a set of keys including at least two distinct primary keys. The factless materialized query table includes one record associated with each record in the set of base tables. Each record in the materialized query table includes a value for every primary key in the set of base tables.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
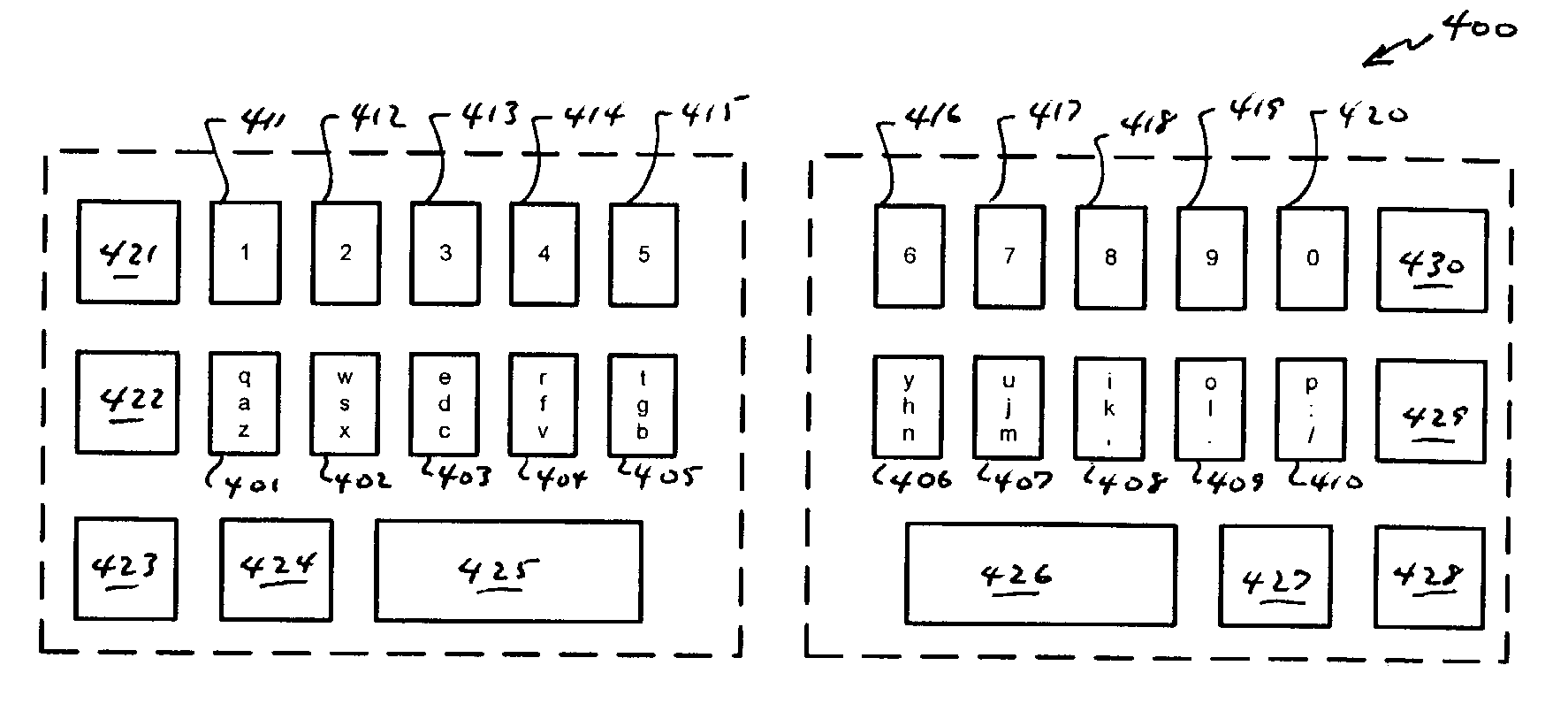
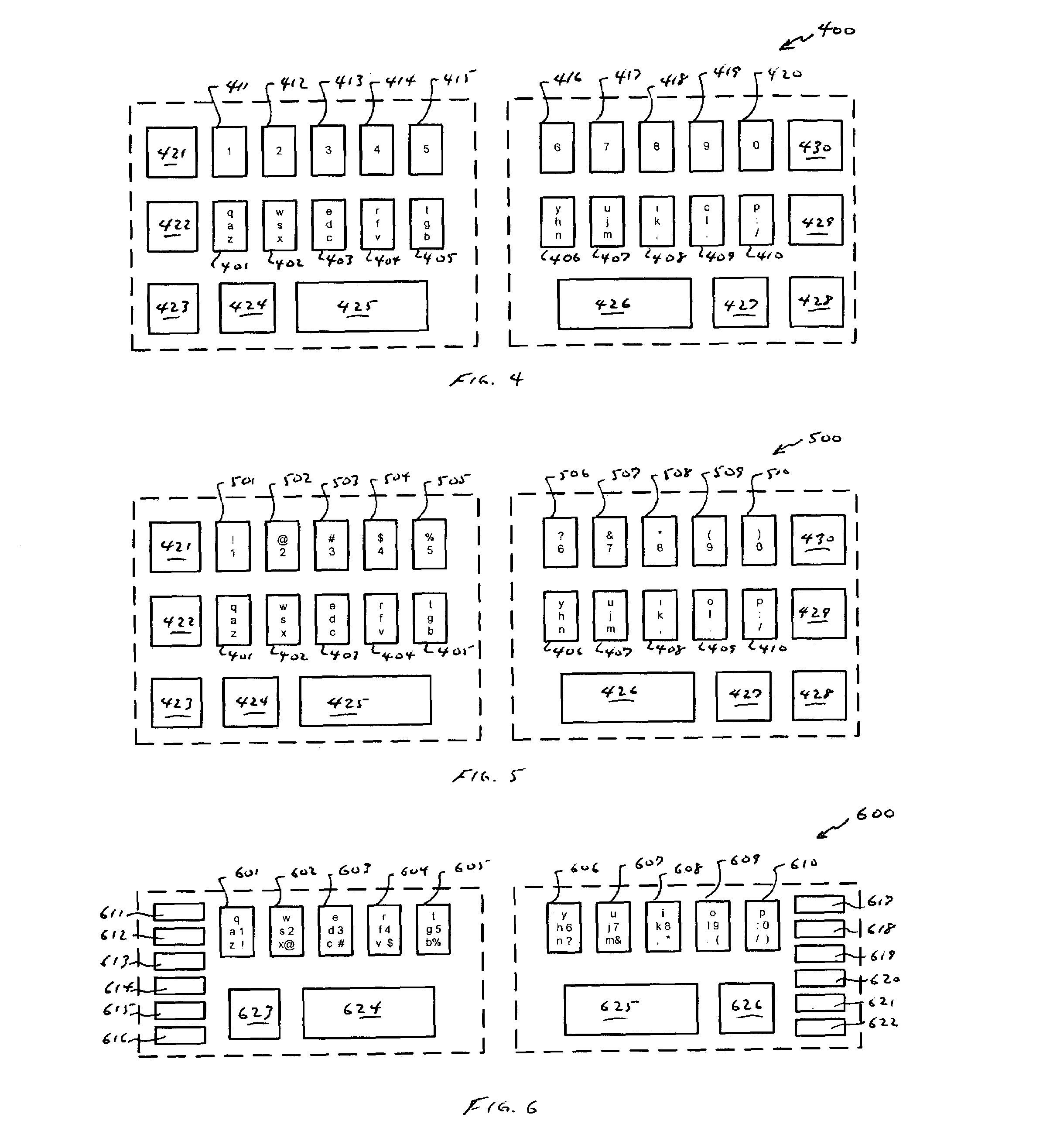
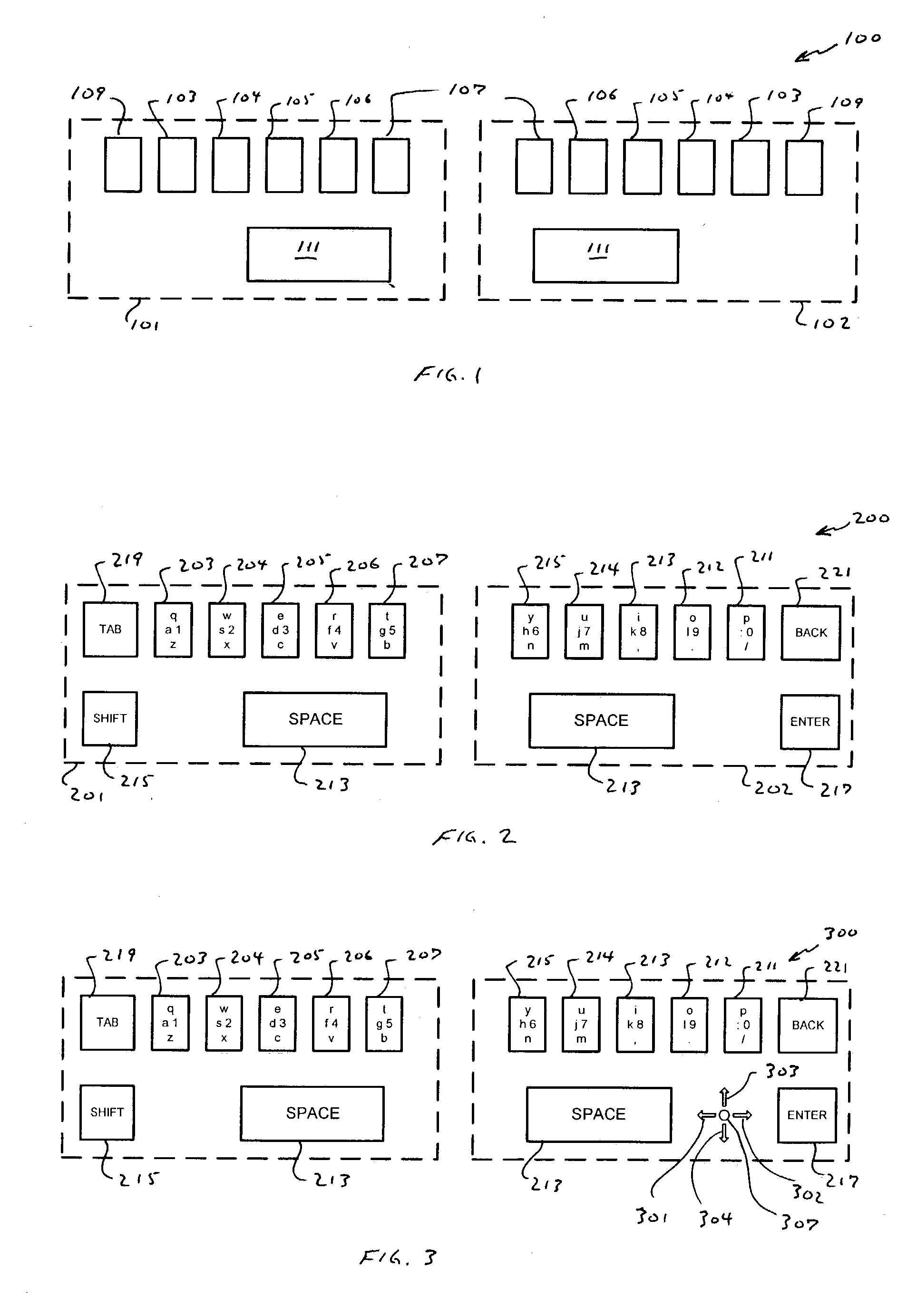
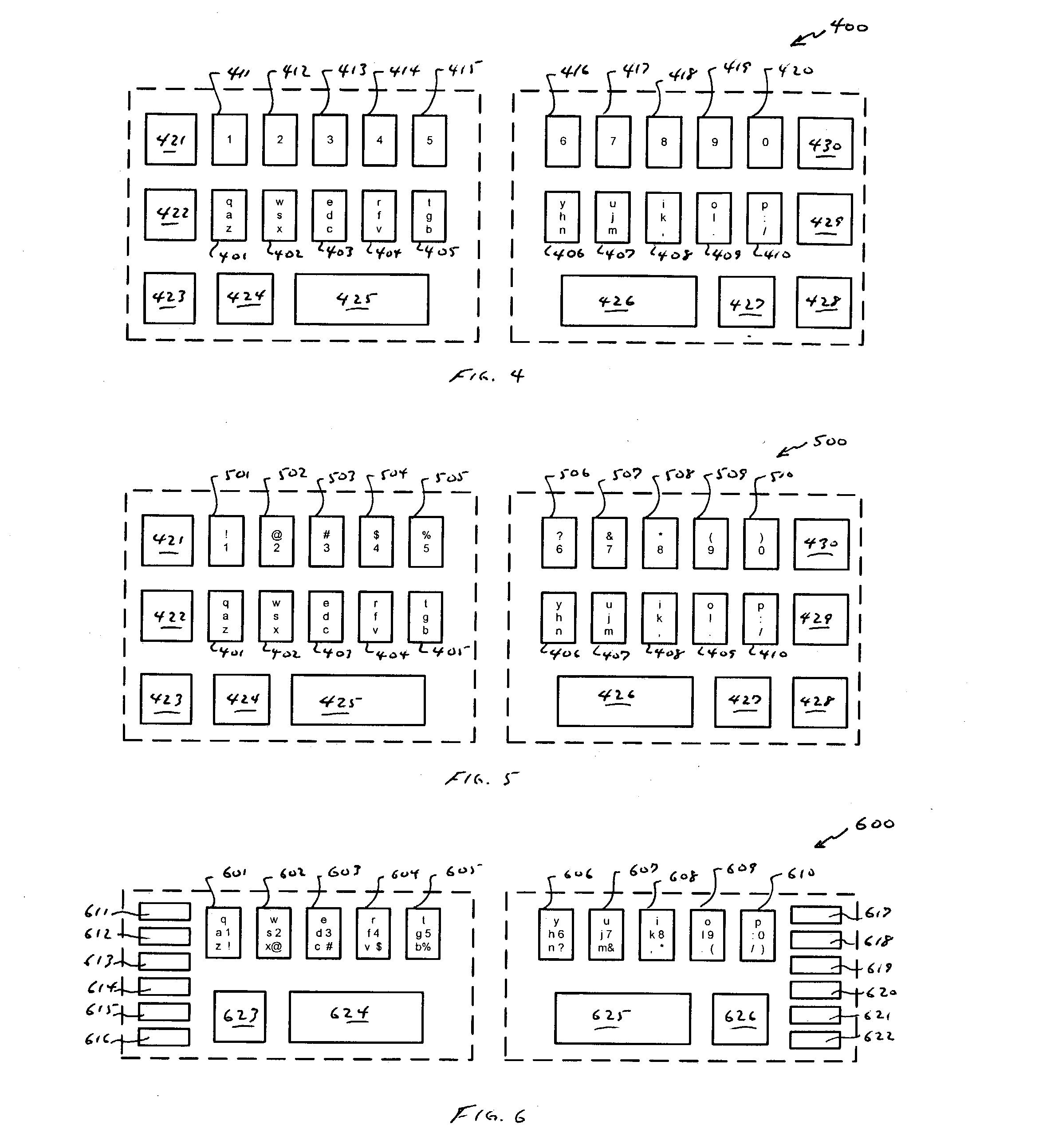
Compressed standardized keyboard
InactiveUS7081837B2Reduce size requirementsSmall sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsReduced sizeComputer science
A keyboard of reduced size is provided in which multiple characters are assigned to each of the primary keys. The selection of the characters to be assigned to each specific primary key is based on the touch typing rules associated with a specific standardized keyboard, preferably allowing at least three rows of keys to be reduced to a single row of keys. A disambiguating system is used to interpret which of the characters and / or symbols assigned to a particular key is intended, typically by applying a set of disambiguating rules to generated input sequences.
Owner:BOLLMAN TAYLOR
Custom entities and fields in a multi-tenant database system
ActiveUS20100205227A1Digital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesDatabase schemaData value
Systems and methods for hosting variable schema data such as dynamic tables and columns in a fixed physical database schema. Standard objects, such as tables are provided for use by multiple tenants or organizations in a multi-tenant database system. Each organization may add or define custom fields for inclusion in a standard object. Custom fields for multiple tenants are stored in a single field within the object data structure, and this single field may contain different data types for each tenant. Indexing columns are also provided, wherein a tenant may designate a field for indexing. Data values for designated fields are copied to an index column, and each index column may include multiple data types. Each organization may also define custom objects including custom fields and indexing columns. Custom objects for multiple tenants are stored in a single custom object data structure. The primary key values for the single custom object table are globally unique, but also include an object-specific identifier which may be re-used among different entities.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Secondary index search
InactiveUS6266660B1Reduce in quantityAddressing slow performanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsRelational databaseSelection criterion
A secondary index search in a relational database system compares primary key selection criteria against a primary key value stored in a secondary index record that satisfies secondary key selection criteria instead of searching a primary index for a primary key value that satisfies the primary key selection criteria.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Database re-organizing system and database
InactiveUS20060143238A1Reduce storage efficiencyRemove debrisData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData retrievalData store
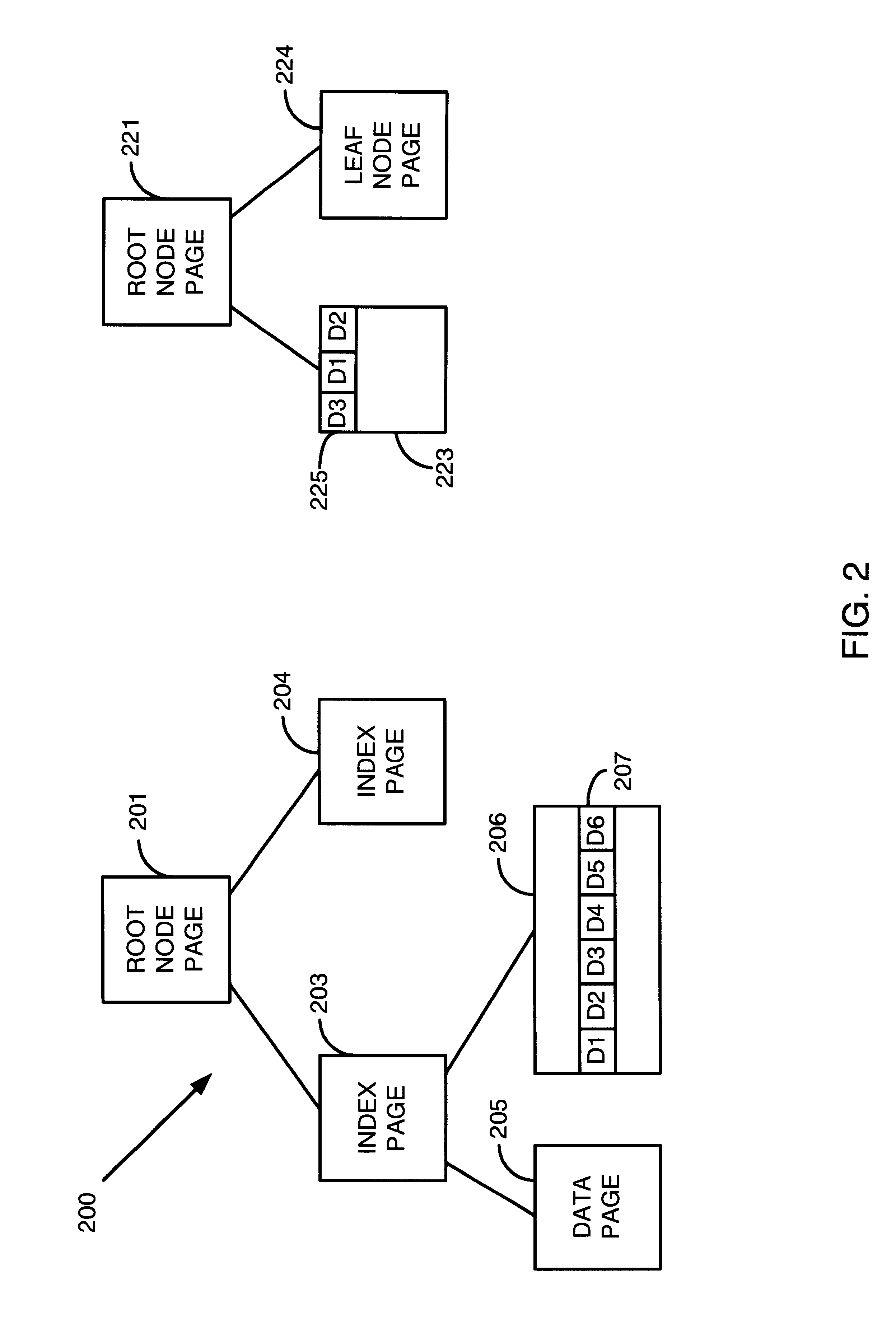
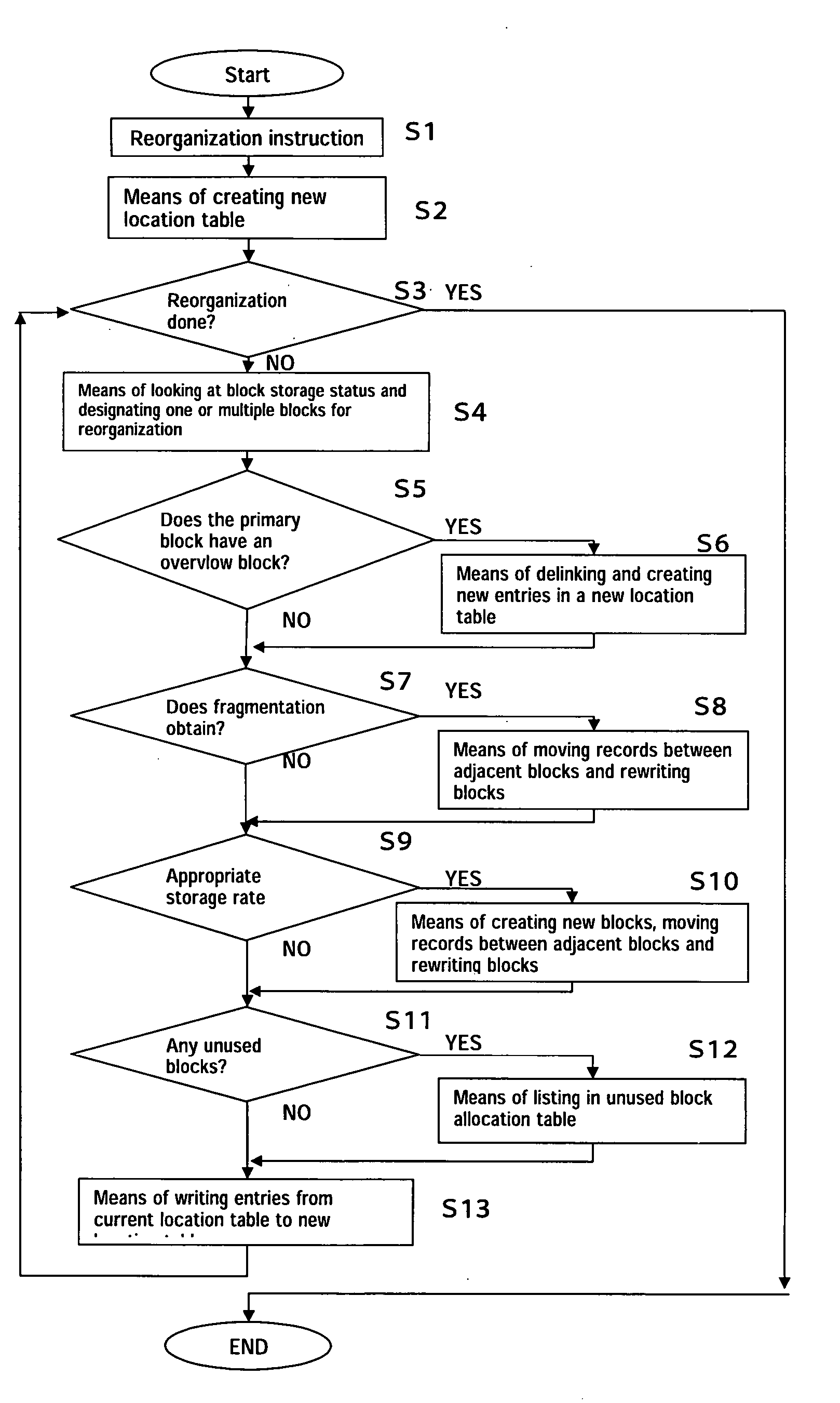
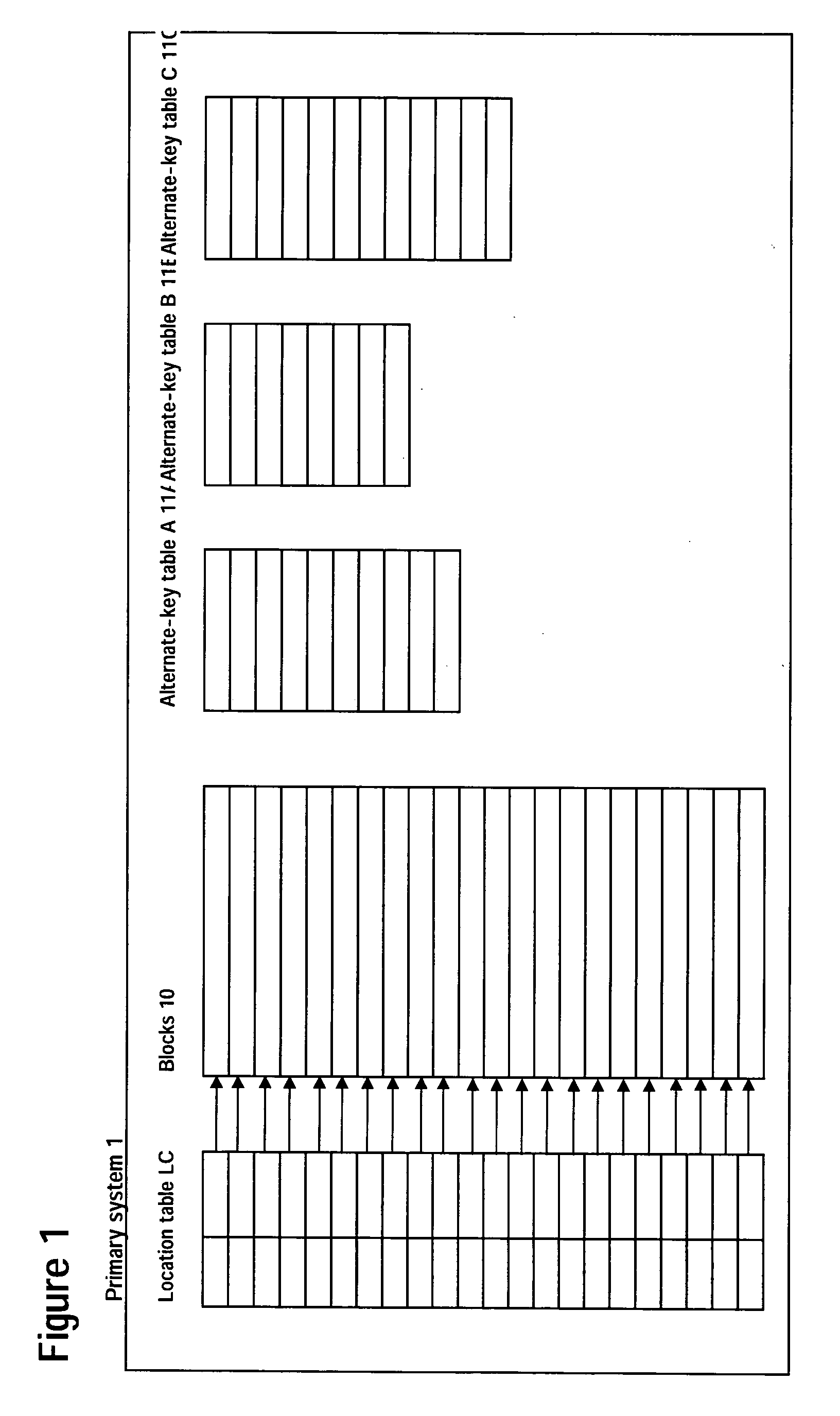
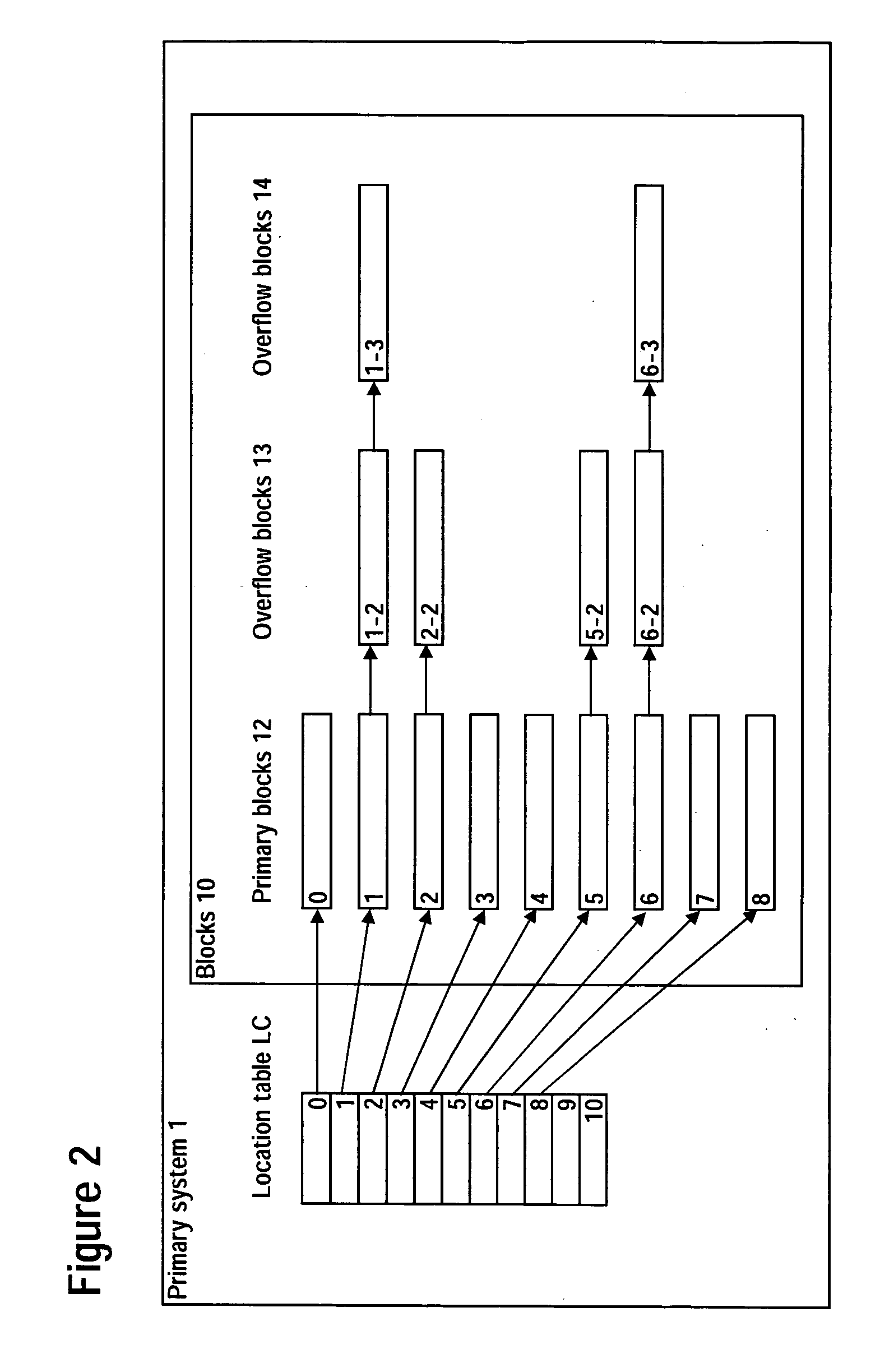
A reorganization system permitting reorganization in an operating implementation of the data storage and retrieval system invention disclosed in Japanese Patent Hei11-310096 Japanese Patent 3345628. The invention permits the reorganization of primary keys and blocks storing records by means of the provision of current location tables LC and new location tables LN and writing location table entries from LC to LN for one or multiple blocks in a given reorganization pass. Alternate-key indices may also be reorganized in the same fashion. Reorganization is performed continuously. The use of reorganization pointers to indicate during reorganization how far reorganization has advanced permits reorganization of a database without suspending the database while executing data retrieval, addition, updating and deletion by means of primary keys and alternate keys.
Owner:ANNEX SYST
Systems, methods, and articles of manufacture for performing product availability check
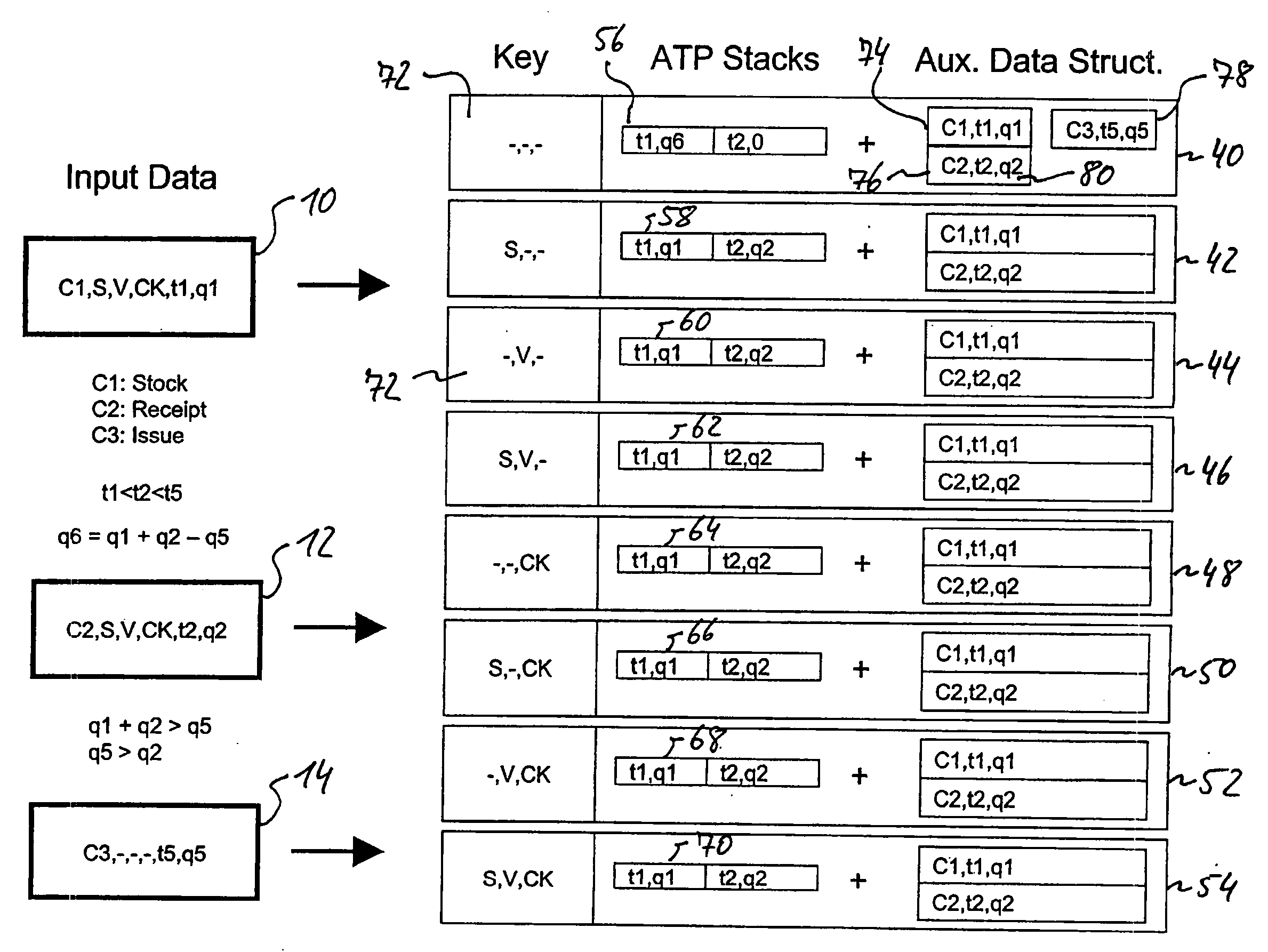
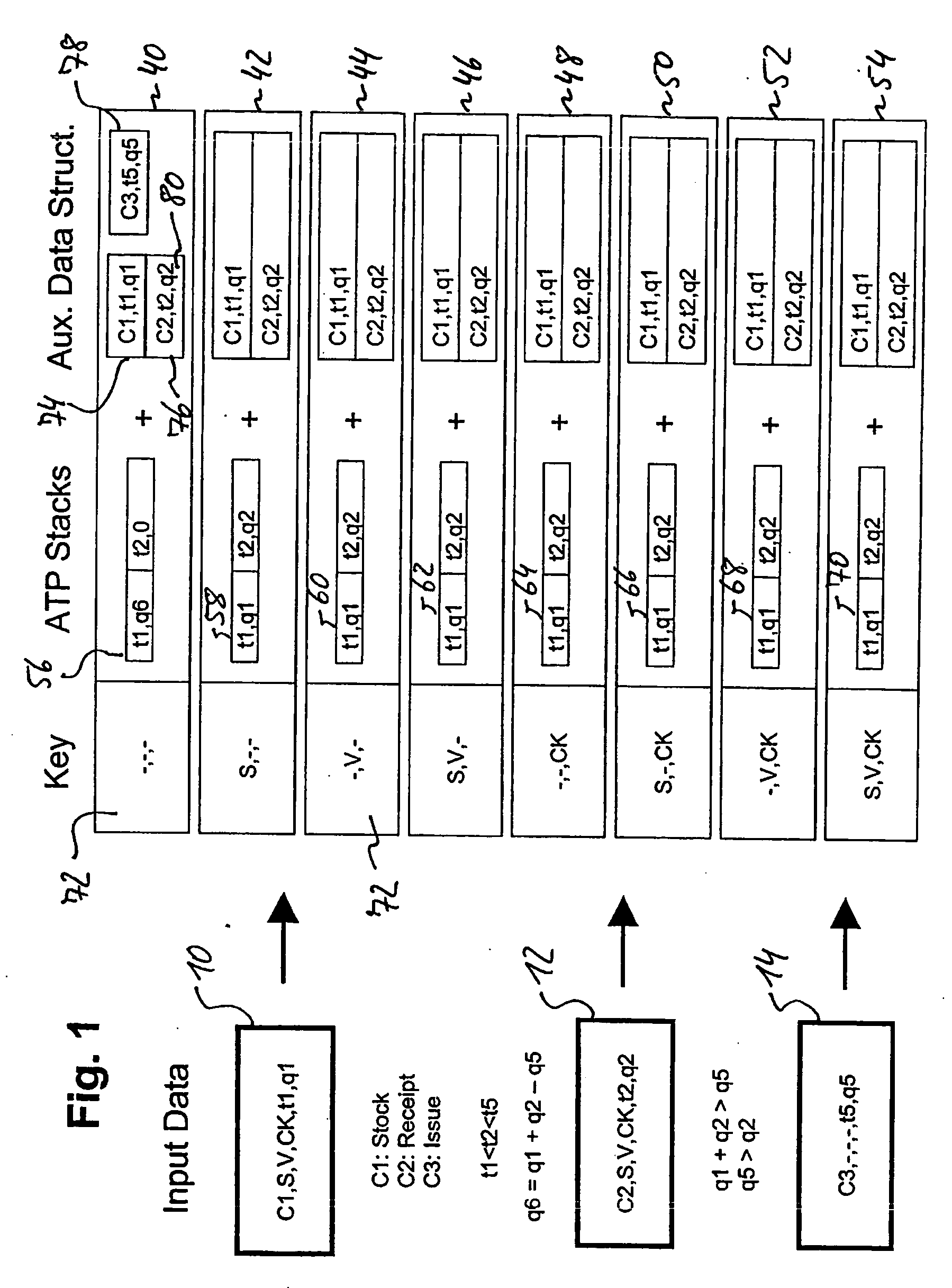
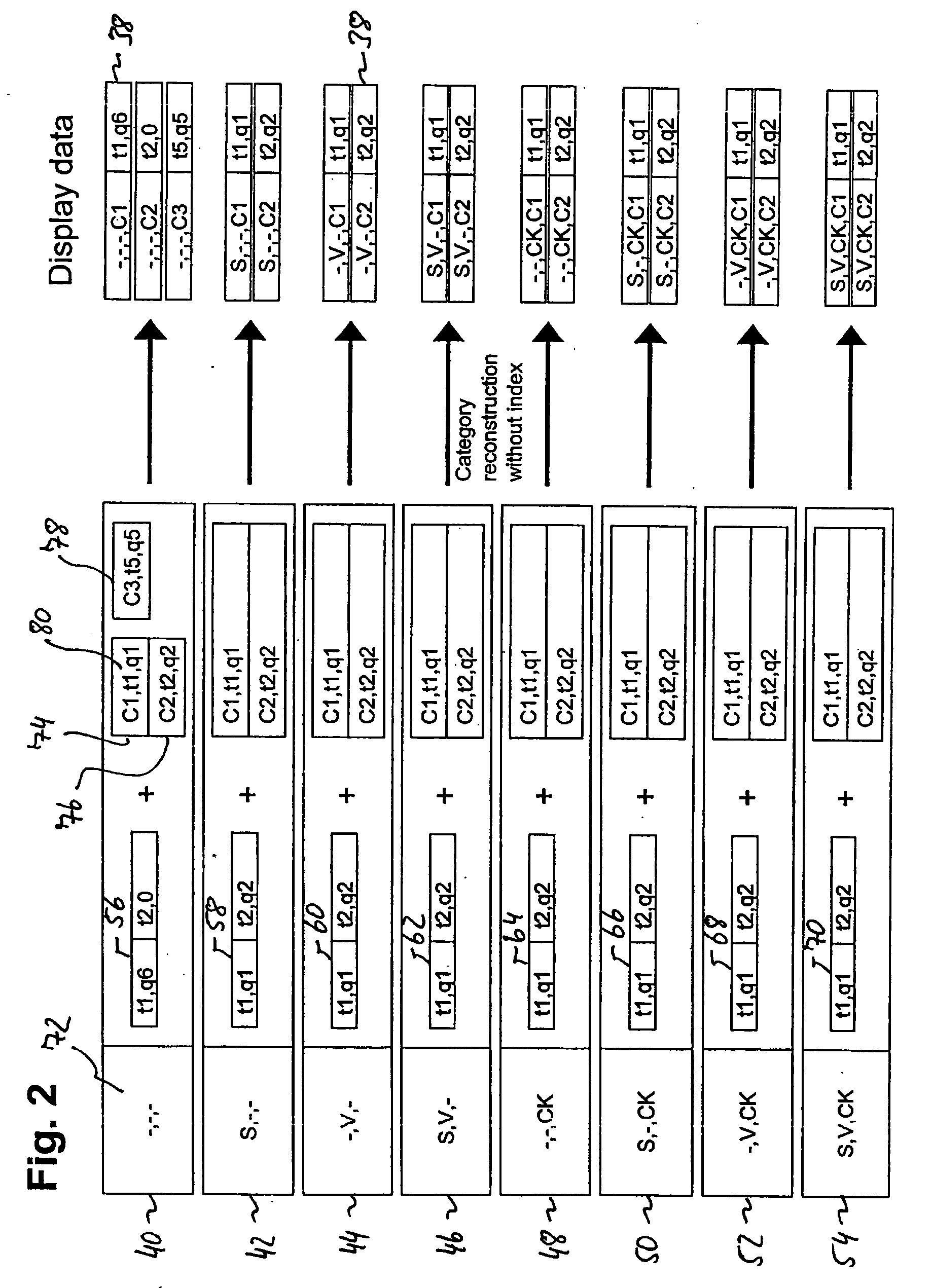
ActiveUS20060036516A1Overcome excessive storage spaceSave storage spaceHand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsData setData element
A computer-implemented method of performing a product availability check comprises the step of receiving information on a plurality of first electronic data sets, each of which includes a first key and a product quantity in relation to a single point of time or time period. The first key includes a primary key element and a plurality of secondary key elements representative of product-related conditions each. The method further comprises the step of deriving, based on the information on the first data sets, information on one or more second electronic data sets, each of which includes a second key and product quantities in relation to a series of points of time or time periods. The second key is formed exclusively of the secondary key elements. Based on the information on the one or more second data sets, result information on the availability of one or more products in dependence of time and the primary and secondary key elements is then derived. According to the invention, the information on the one or more second data sets is generated to further include in each second data set one or more auxiliary data structures, each auxiliary data structure including one or more auxiliary data elements, each auxiliary data element including the primary key element, product quantity and point of time or time period as included in a respective first data set that contributes to the time-dependent product quantities in the corresponding second data set.
Owner:SAP AG
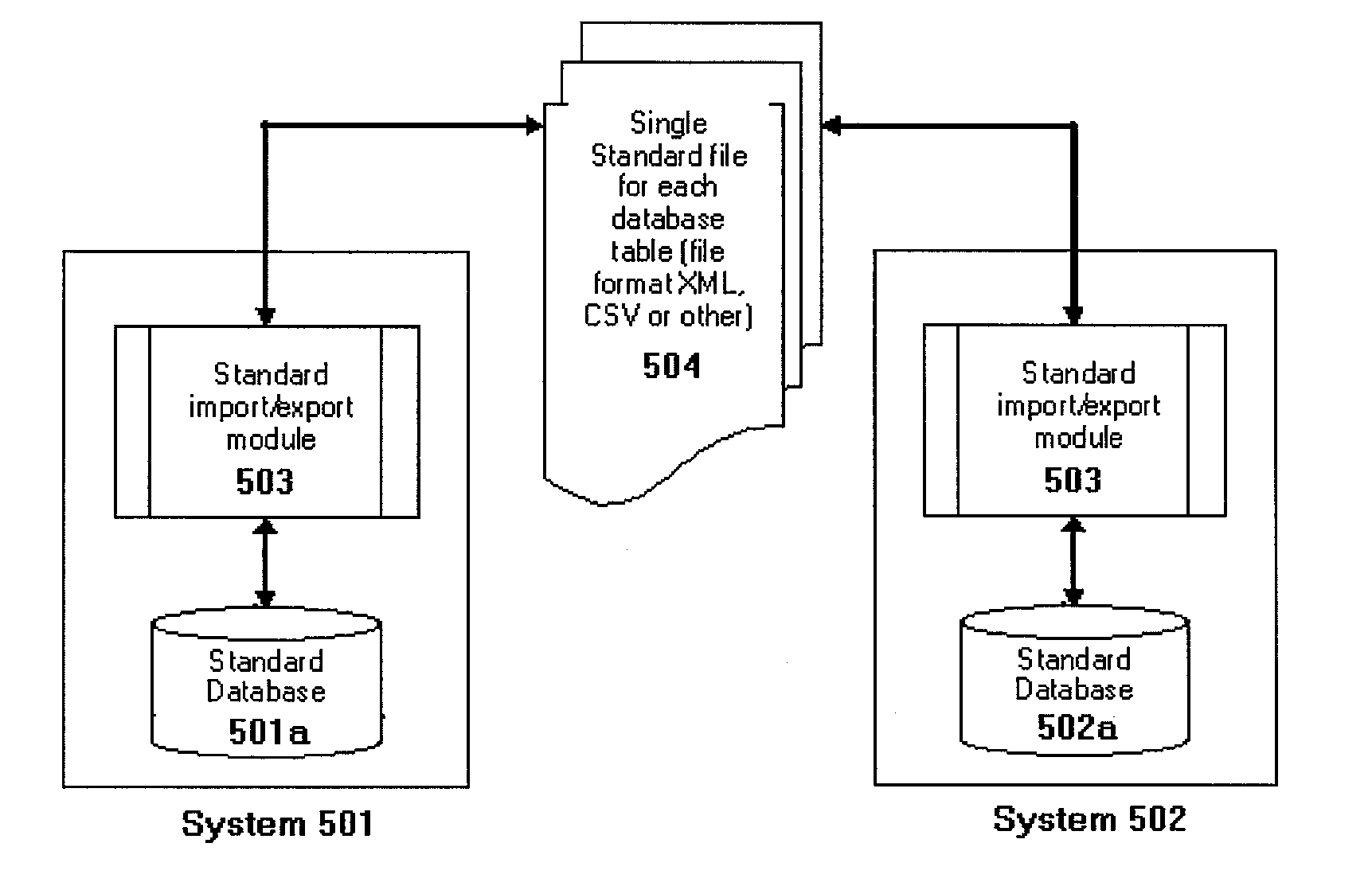
Global Information Management System and Method
ActiveUS20110320400A1Avoid repetitionDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationRelational databaseGlobal information
A global information management system (GIMS) includes a collection of standards and methods that allow information management on a global scale. A GIMS computer network includes a central registration database (CRD) and one or more GIMS computer systems connected over a network. Each GIMS computer system includes a relational database having a set of standardized tables. The CRD may provide a GIMS network-unique system ID to each GIMS computer system. Each GIMS computer system uses the GIMS network-unique system ID as part of a primary key for each record generated by and stored in the set of standardized tables of the GIMS database. The GIMS enables global database normalization through the globally unique identification of database records.
Owner:NAMINI BORSU ASISI
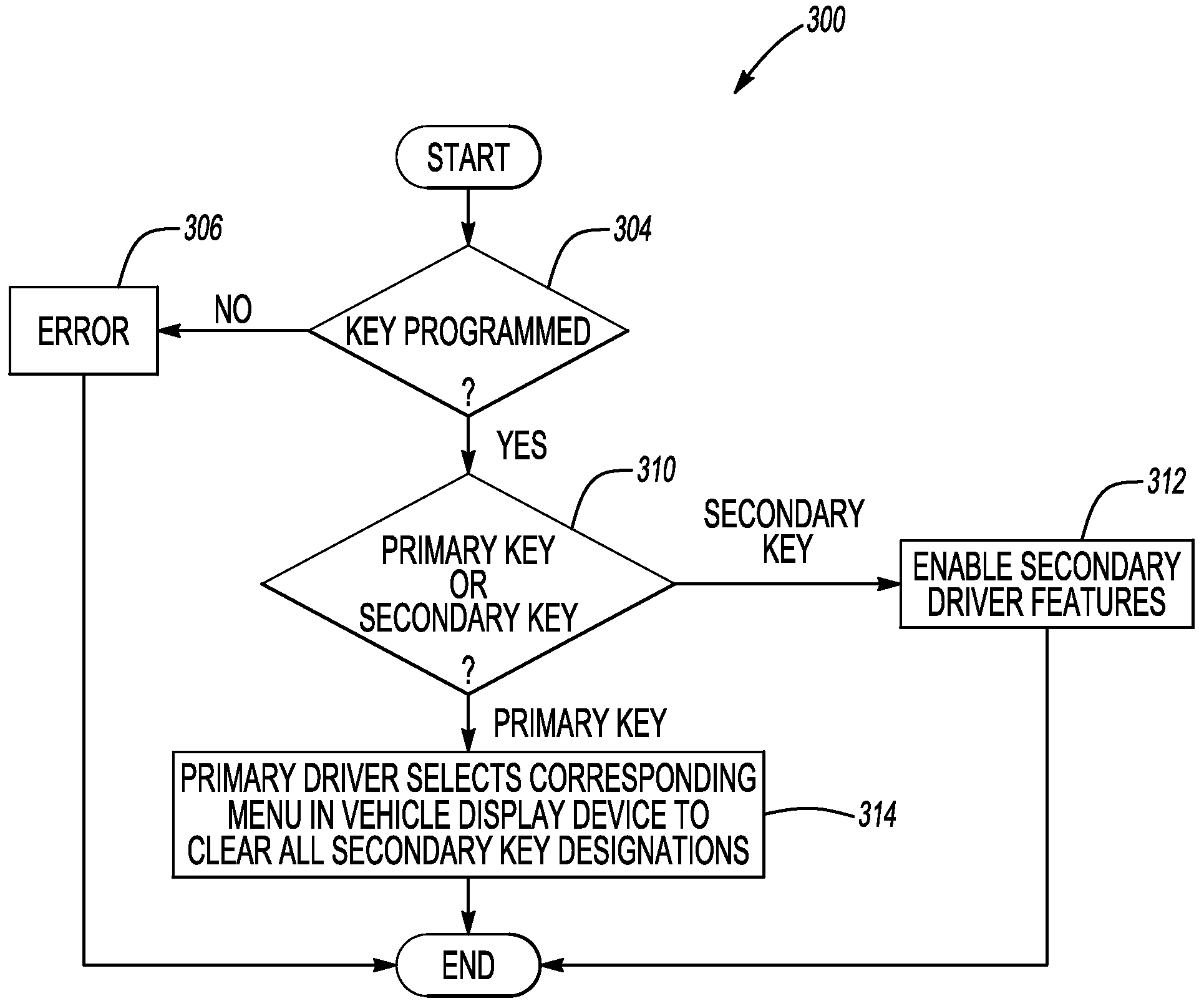
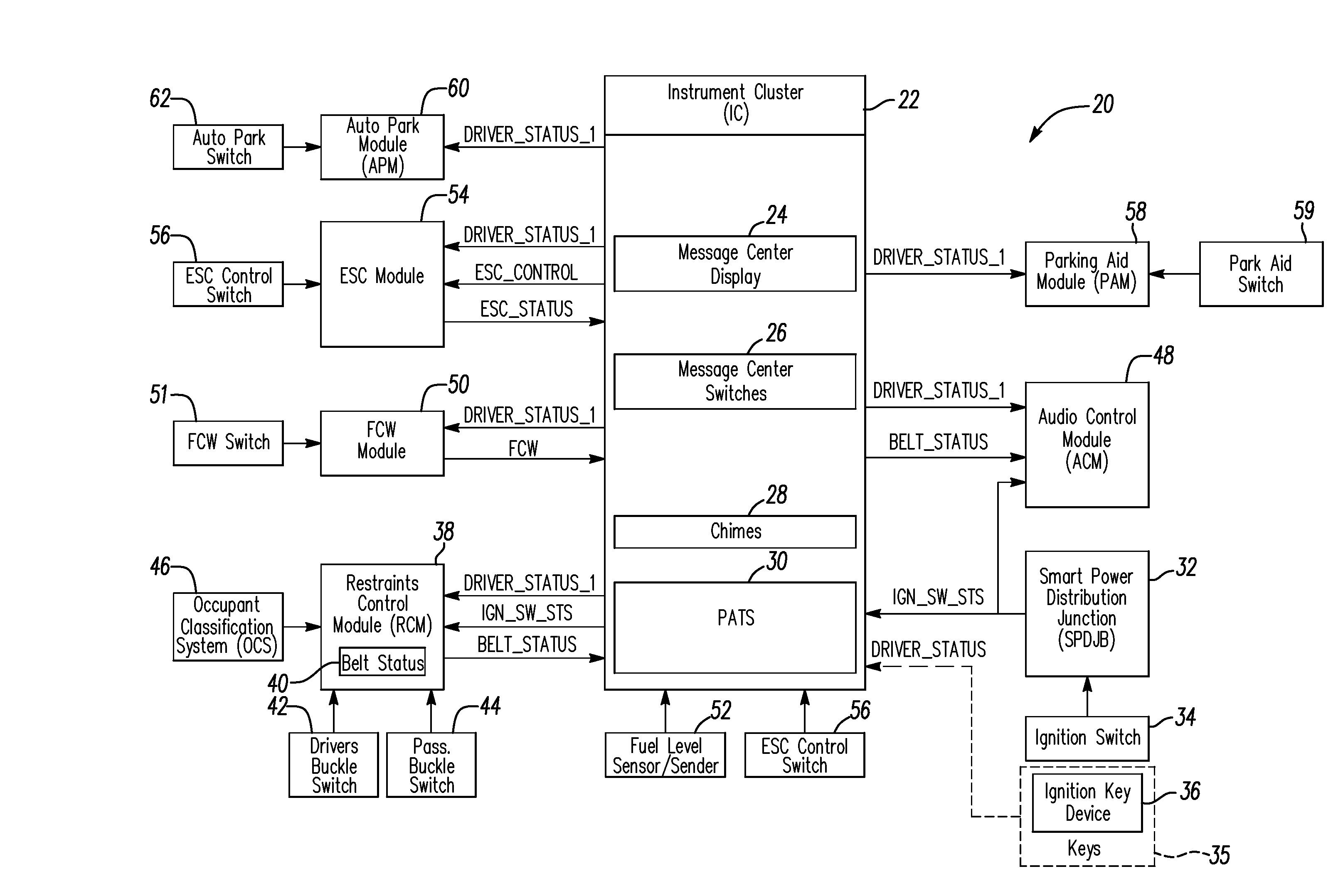
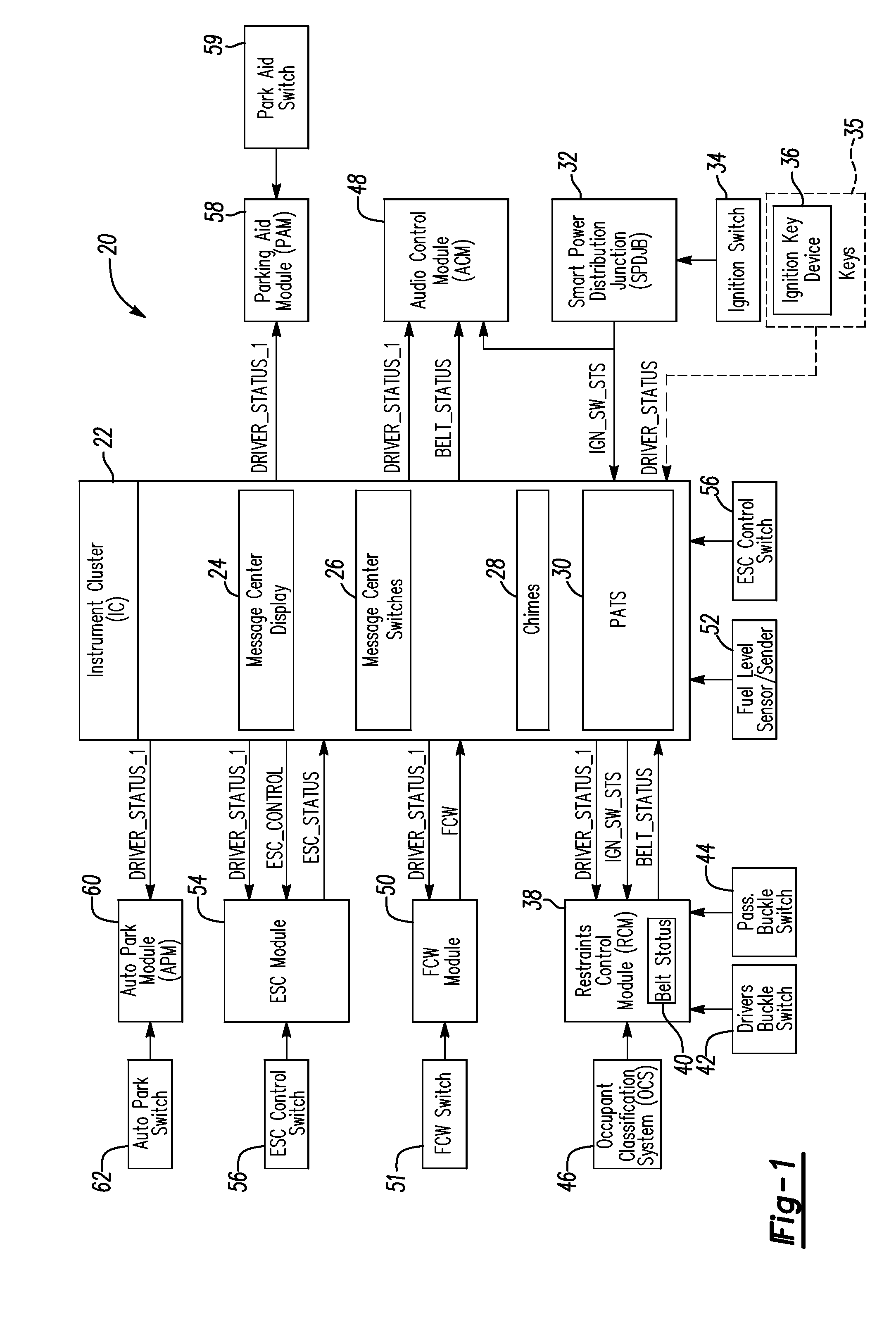
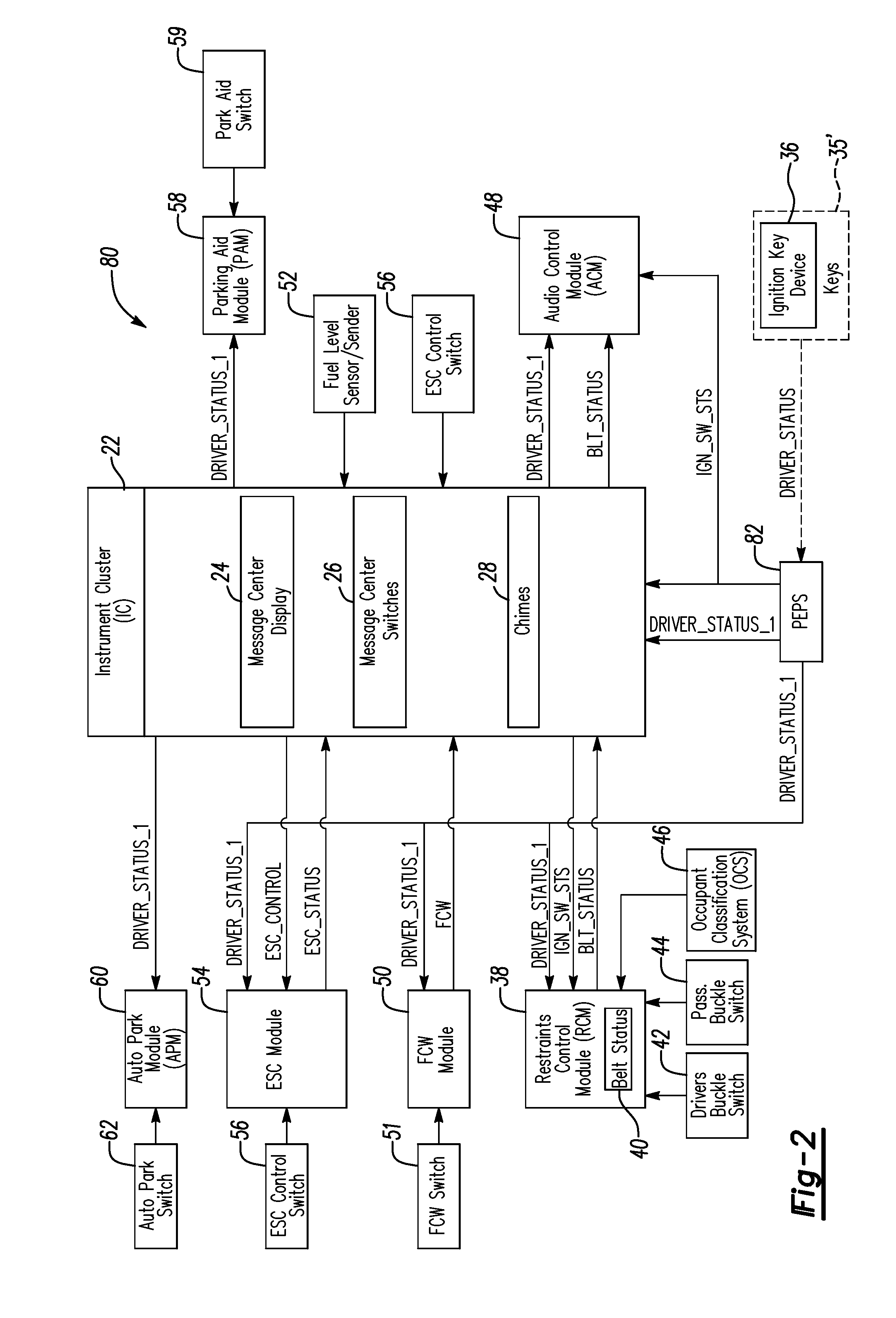
System and method for programming keys to vehicle to establish primary and secondary drivers
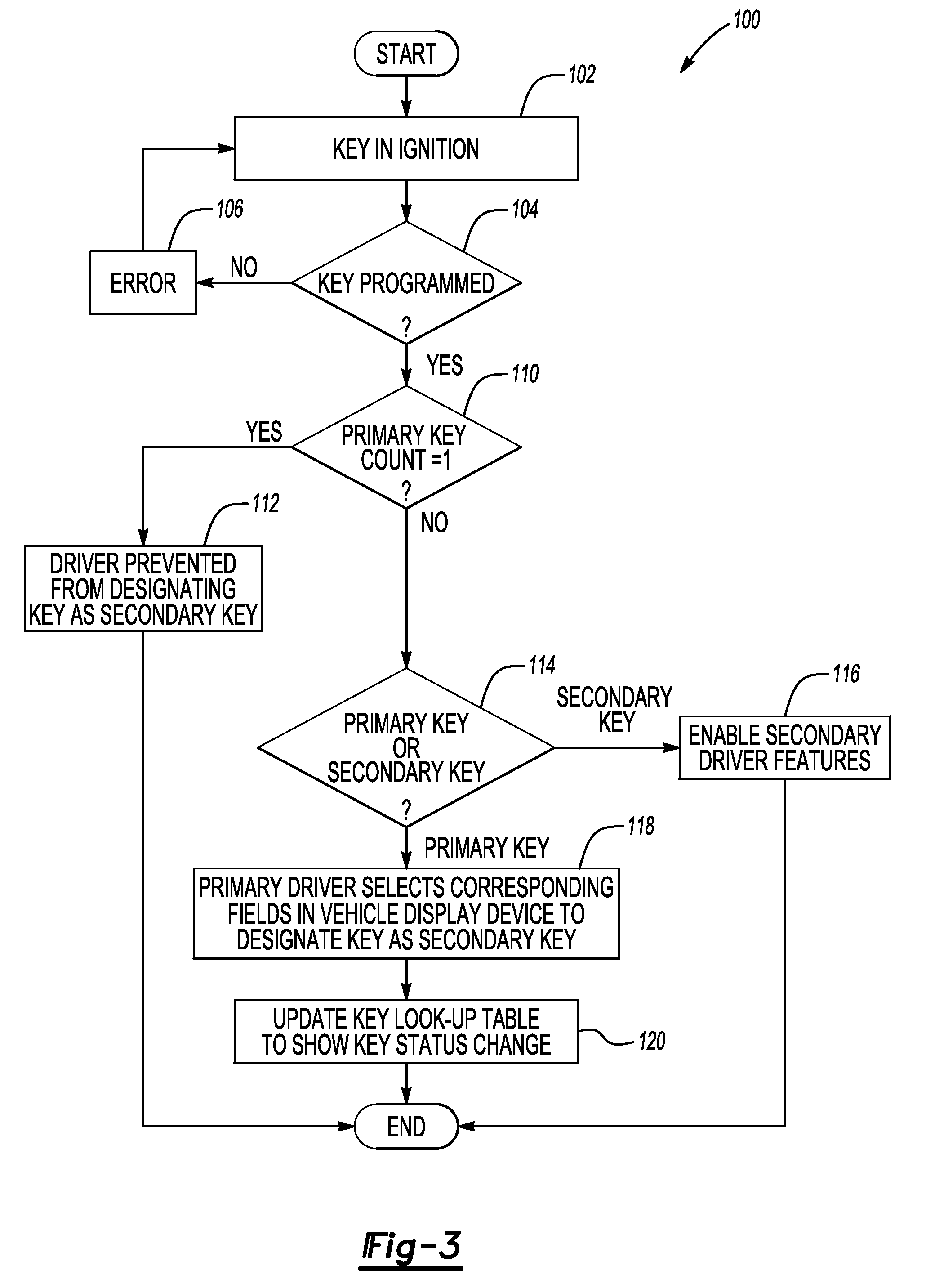
ActiveUS20090309697A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageDriver/operatorDisplay device
In at least one embodiment, a method for programming keys to a vehicle to establish primary keys and secondary keys to control vehicle functionality is disclosed. The method comprises receiving a key identification signal from a first key. The method further comprises generating a key status signal indicative of whether the first key is one of a primary key and a secondary key in response to the key identification signal. The method further comprises transmitting the key status signal to a vehicle interface display. The method further comprises allowing a user to change a status of at least one of the first key and an additional key with the vehicle interface display in response to determining that the key status signal corresponds to the primary key.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Object graph editing context and methods of use
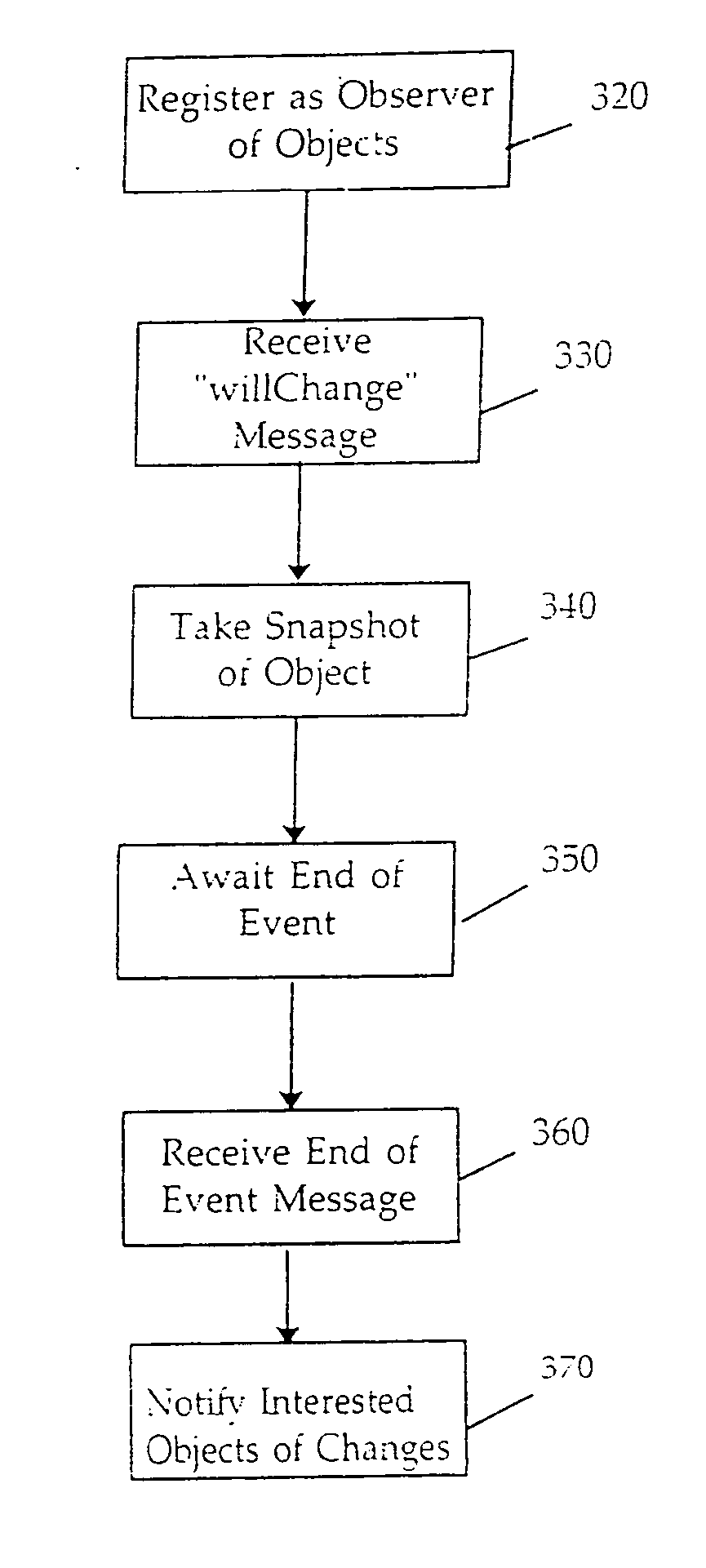
InactiveUS20060271586A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsManaging change
The present invention comprises a novel system for managing changes to a graph of data bearing objects. In one embodiment, an object graph manager object referred to as an editing context is used to identify changes made to data bearing enterprise objects and to notify other interested objects when changes occur. As a result, data bearing objects need not themselves contain code necessary for monitoring changes. In another embodiment of the invention, the editing context is used to provide event-based “undo” capabilities. In another embodiment of the invention, each enterprise object has a primary key that is used to maintain the identification between an enterprise object instance and a corresponding database row. In another embodiment of the invention, multiple levels of editing contexts are used to provide multiple isolated object graphs, each of which allows independent manipulation of the underlying data bearing objects.
Owner:NEXT
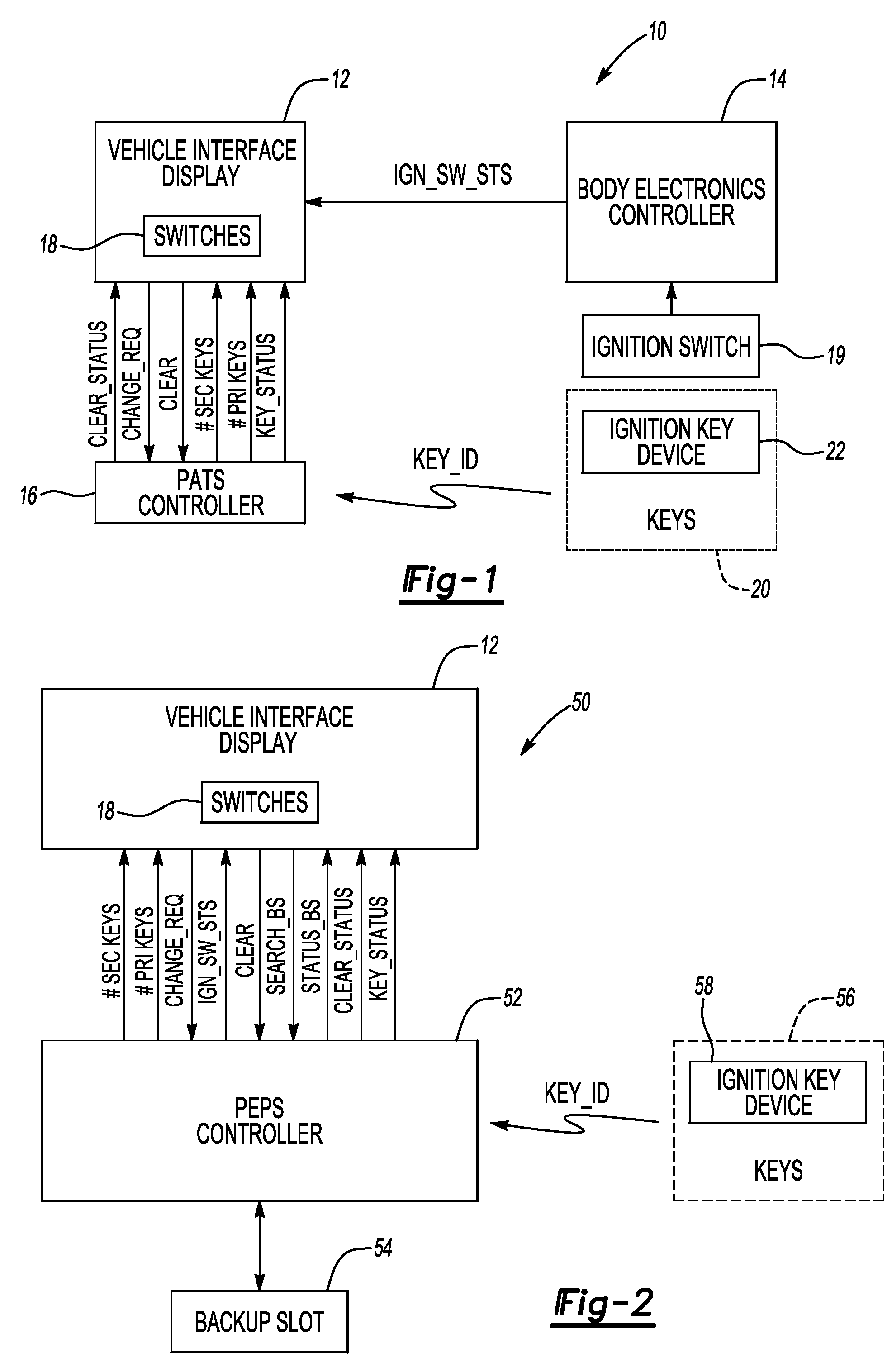
System and method for controlling a safety restraint status based on driver status
ActiveUS20090195376A1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAnti-theft devicesEmbedded systemMajor and minor
A system and method for notifying primary and second drivers about a status of a safety restraint in a vehicle is provided. A primary and secondary keys are adapted to be associated to the primary and secondary drivers. A key ignition device is positioned on each of the primary key and secondary keys. The key ignition device is adapted to generate driver status signals indicative of whether the driver the primary driver or the secondary driver. A controller is adapted to determine whether the driver of the vehicle is the primary driver or the secondary driver based on the driver status signals. The controller is further adapted to generate restraint status signals indicative of the status of the safety restraint. The controller is further adapted to selectively control the operation of generating the restraint signals based on whether the driver of the vehicle is the primary or secondary driver.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
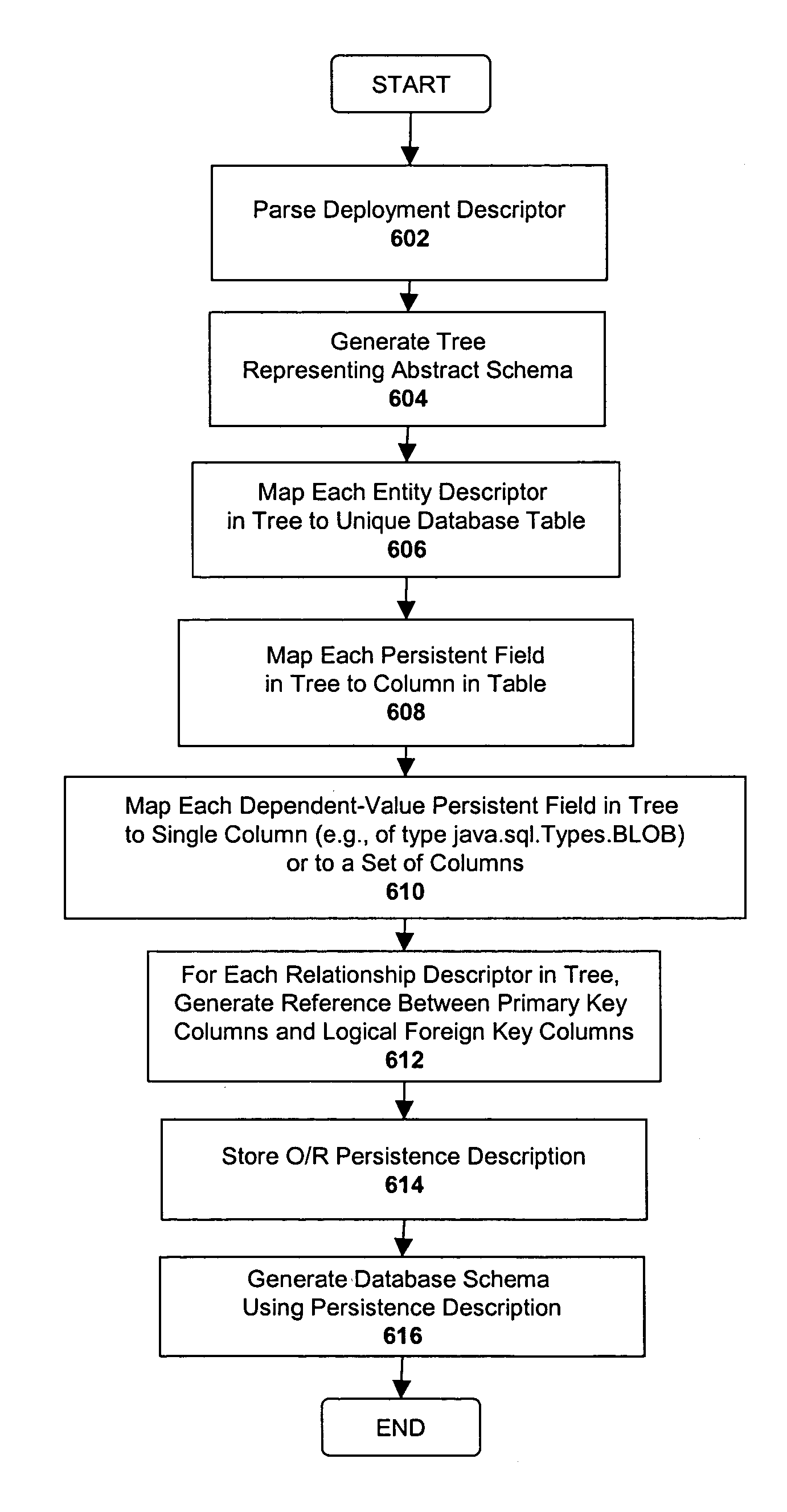
System and method for mapping object-oriented program code to a database layer
One embodiment of the invention employs techniques for providing a default object-relational mapping between persistent data objects (i.e., the objects that represent persistent data from a database) and a relational database. In a Java environment, for example, each entity bean is mapped to a particular database table, and each of the persistent fields within the entity bean are mapped to columns of the database table. Relationships between entity beans are expressed as mappings between primary keys and foreign keys within the database schema. Dependent-value persistent fields may be mapped to multiple columns or to a single column of a special Java type (java.sql.Types. BLOB). In addition, one embodiment of the invention generates a default database schema using the default O / R mapping by executing a series of SQL commands generating the tables and columns.
Owner:SAP AG
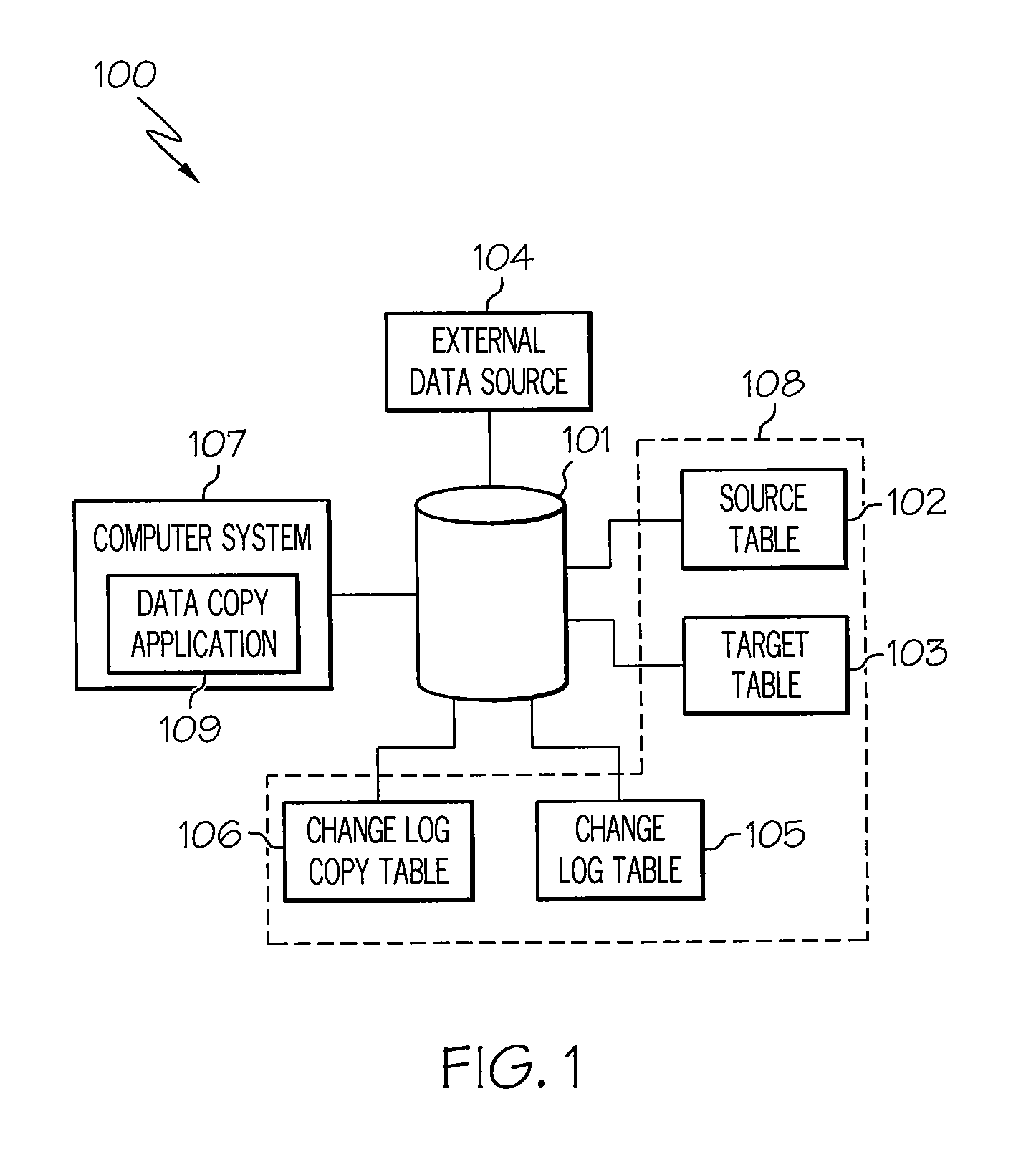
Ensuring that the archival data deleted in relational source table is already stored in relational target table
ActiveUS20090083341A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsExternal dataData source
A method, system and computer program product for ensuring that archival data deleted in a source table is already stored in a target table. An external data source sets a flag in the first table to identify the row in the source table to be deleted. An application sets a flag in a second table for each row of the source table that is marked to be deleted according to the first table. The application performs uncommitted read operations on the source table for each row corresponding to the distinct primary key values stored in the first table. The application inserts the data read into the corresponding rows of the target table. The application deletes the rows in the source table indicated to be deleted by the second table. In this manner, the archival data deleted from the source table is ensured to already be stored in the target table.
Owner:IBM CORP
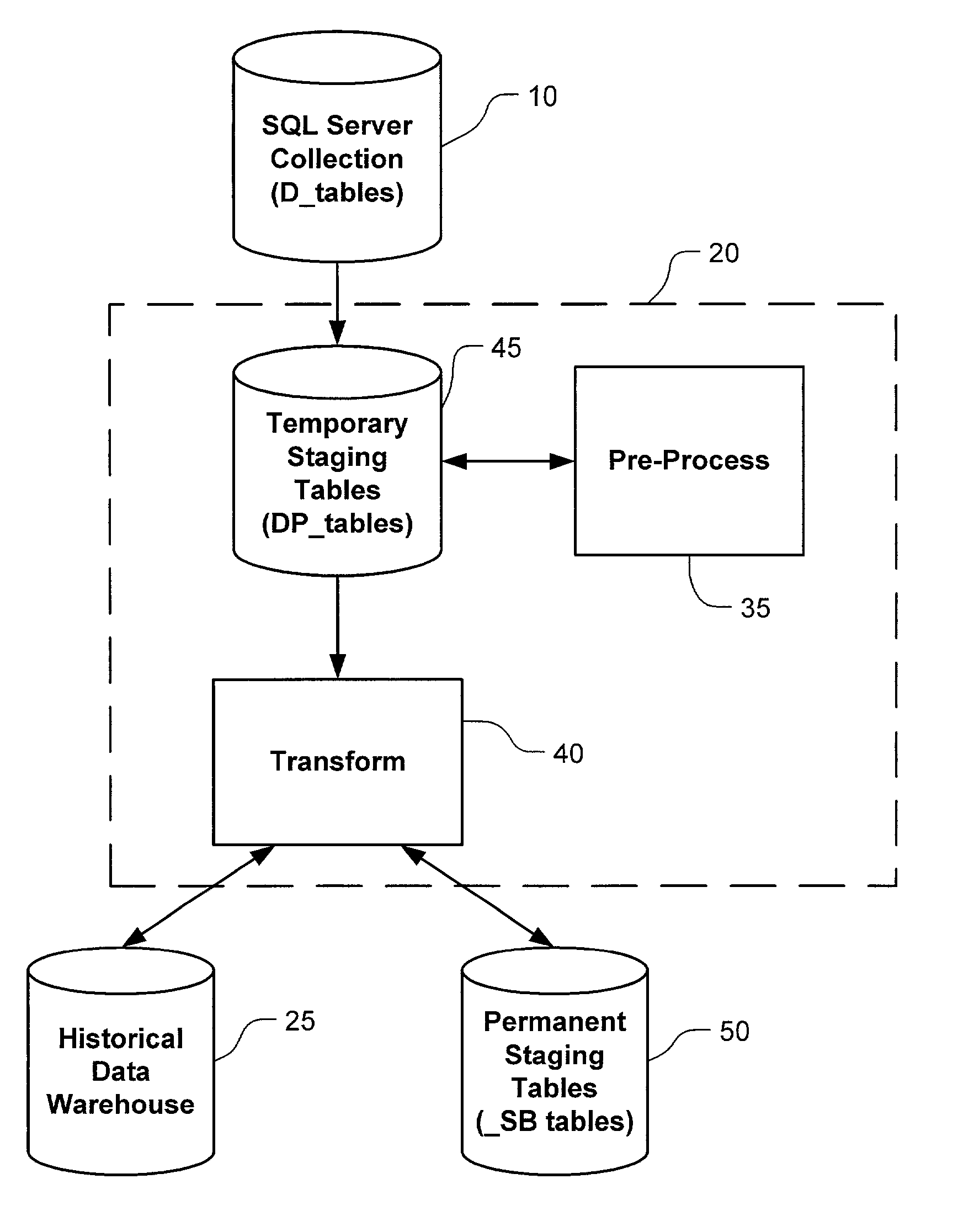
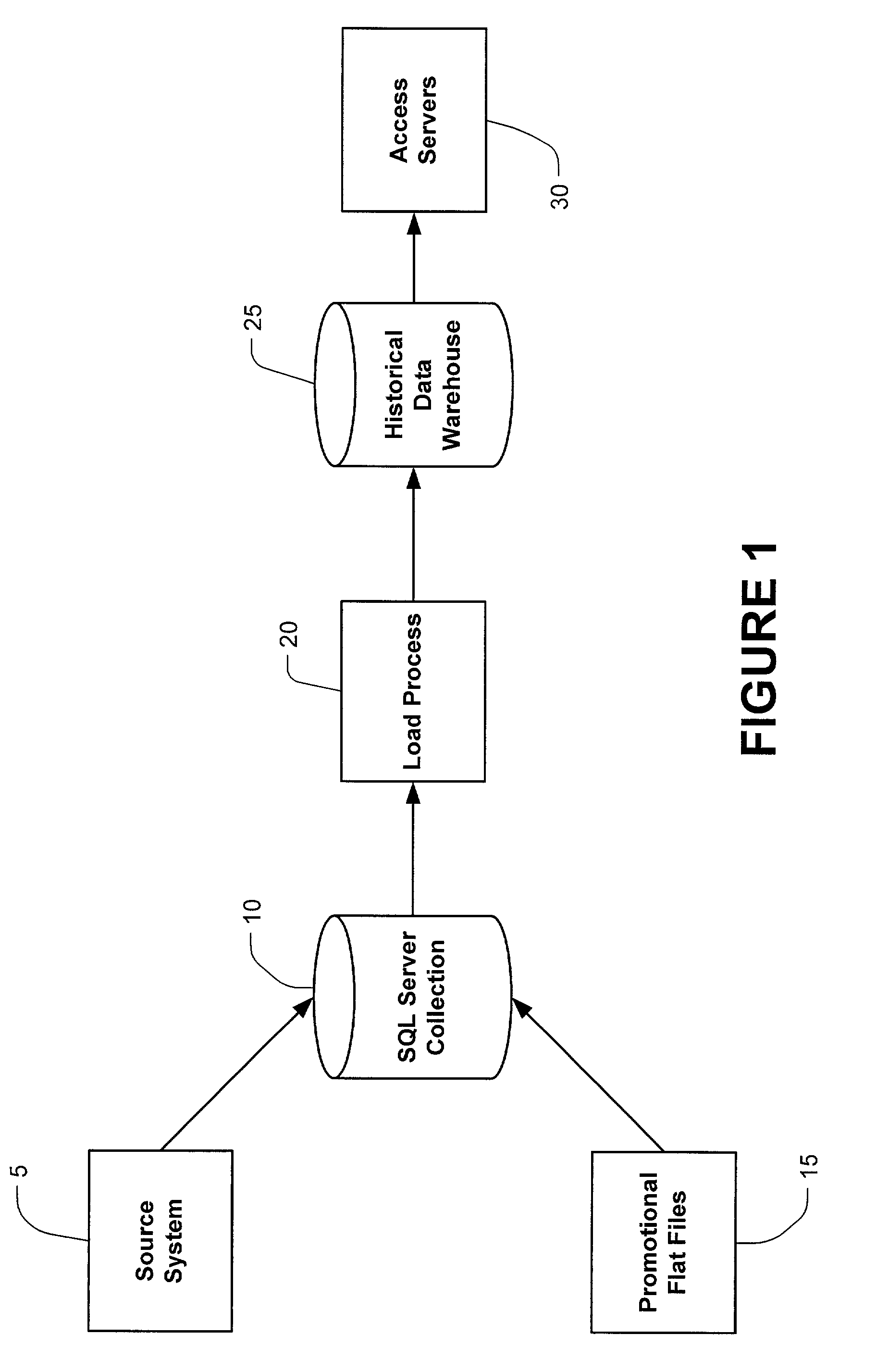
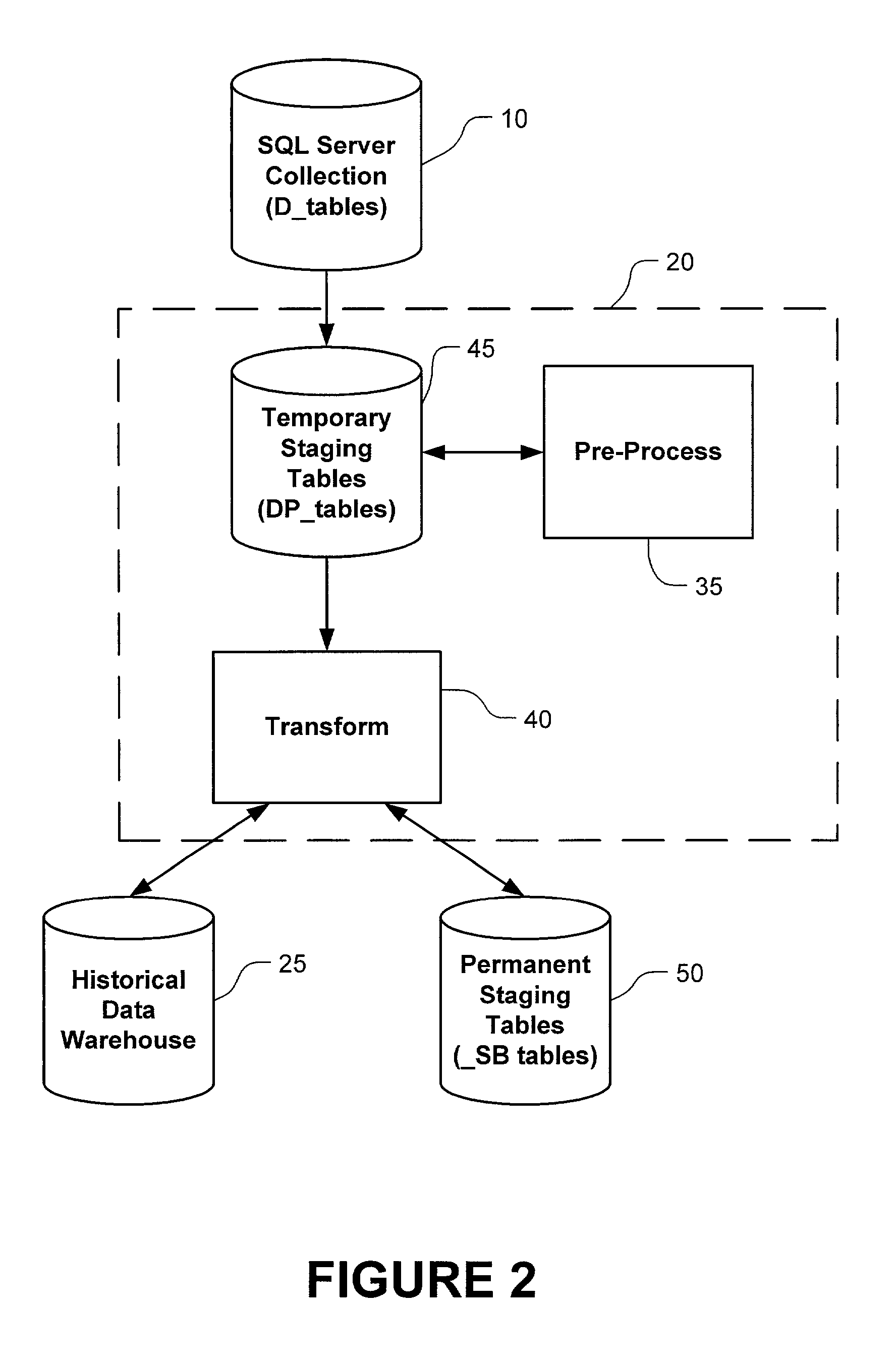
Historical data warehousing system
Utilizing change data capture methodology, a computer facilitated historical data warehousing system accepts transactional / operational data having no directly tied dates from a legacy source system and processes that data into a subject-oriented format that is optimized for analytical and query reports via a two step process comprised of pre-processing and transforming. The pre-processing step entails a serial modification of data with only the last modification being recorded. The transforming step involves linking related data by utilizing reusable primary keys and dates obtained from an RDBMS in an operation system of the legacy source system that supplied the transactional / operational data.
Owner:AMDOCS SOFTWARE SYST +1
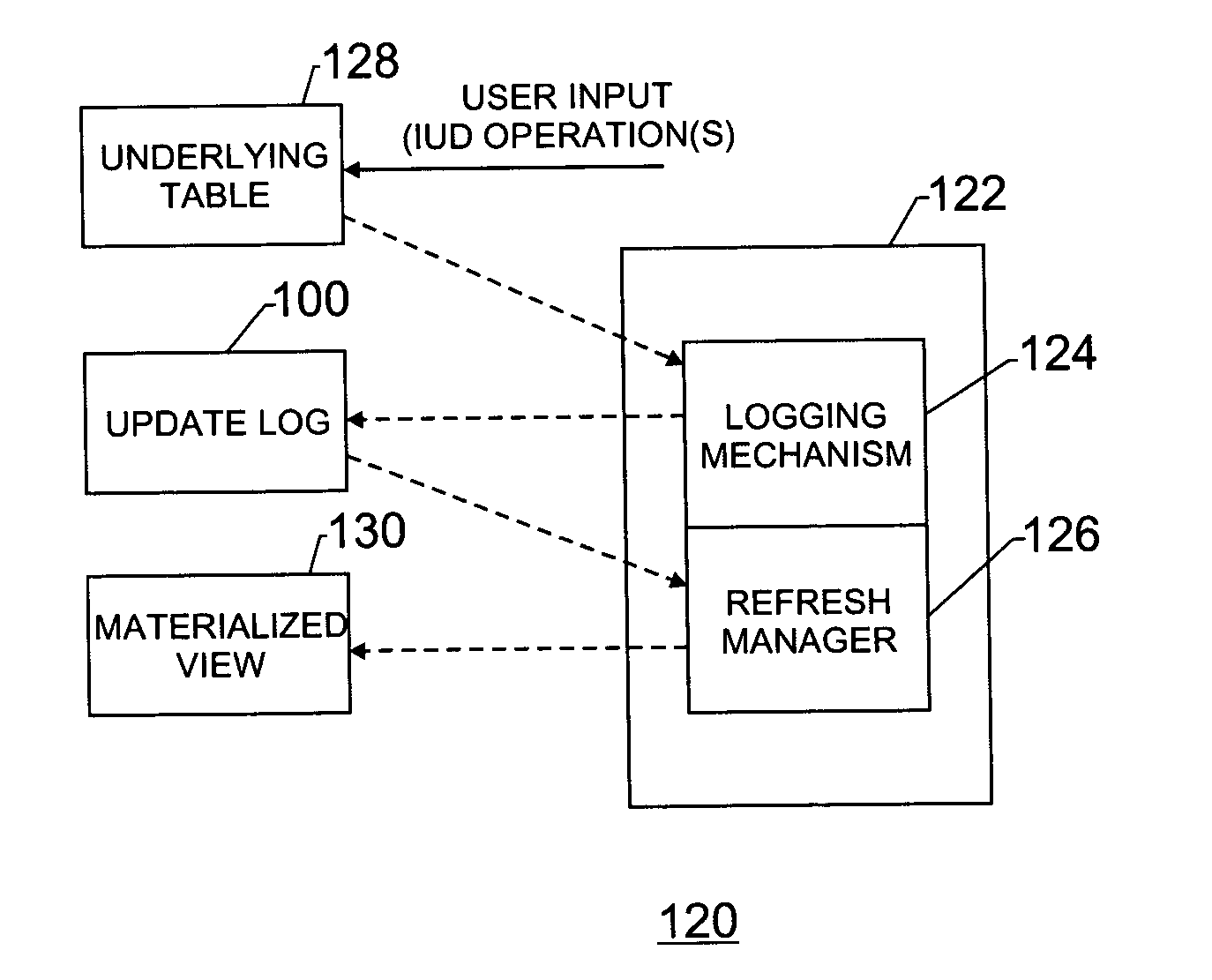
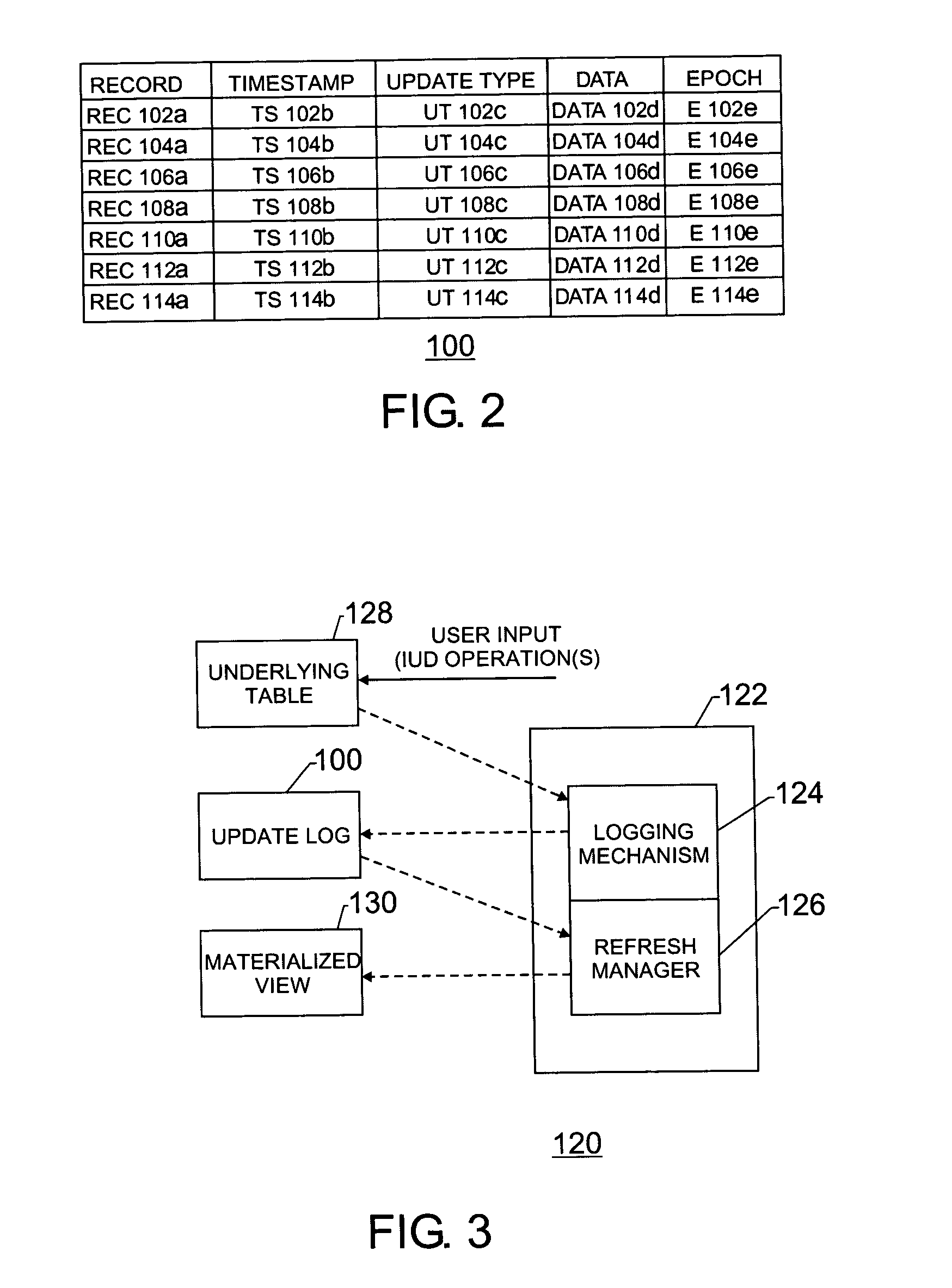
Method and apparatus for refreshing materialized views
InactiveUS20050091180A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceMaterialized view
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system and method for refreshing a materialized view that is at least in part derived from a table. The system may be adapted to provide availability of the table and the materialized view while the materialized view is being refreshed. The system may include a refresh log that contains a plurality of entries, each of the plurality of entries corresponding to a change in the table, each of the plurality of entries comprising an epoch identifier. The system may also include a refresh manager that performs a refresh operation on the materialized view in multiple steps by (a) successively reading a first subset of the plurality of entries indicated by a specific epoch identifier from the refresh log, (b) identifying a second subset of the plurality of entries from within the first subset of the plurality of entries, the second subset of the plurality of entries falling within a primary key value boundary and (c) applying the second subset of the plurality of entries to the materialized view.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Compressed standardized keyboard
InactiveUS20040239533A1Small sizeRealized benefitsInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsReduced sizeComputer science
A keyboard of reduced size is provided in which multiple characters are assigned to each of the primary keys. The selection of the characters to be assigned to each specific primary key is based on the touch typing rules associated with a specific standardized keyboard, preferably allowing at least three rows of keys to be reduced to a single row of keys. A disambiguating system is used to interpret which of the characters and / or symbols assigned to a particular key is intended, typically by applying a set of disambiguating rules to generated input sequences.
Owner:BOLLMAN TAYLOR
Multidimensional interval querying method and system thereof
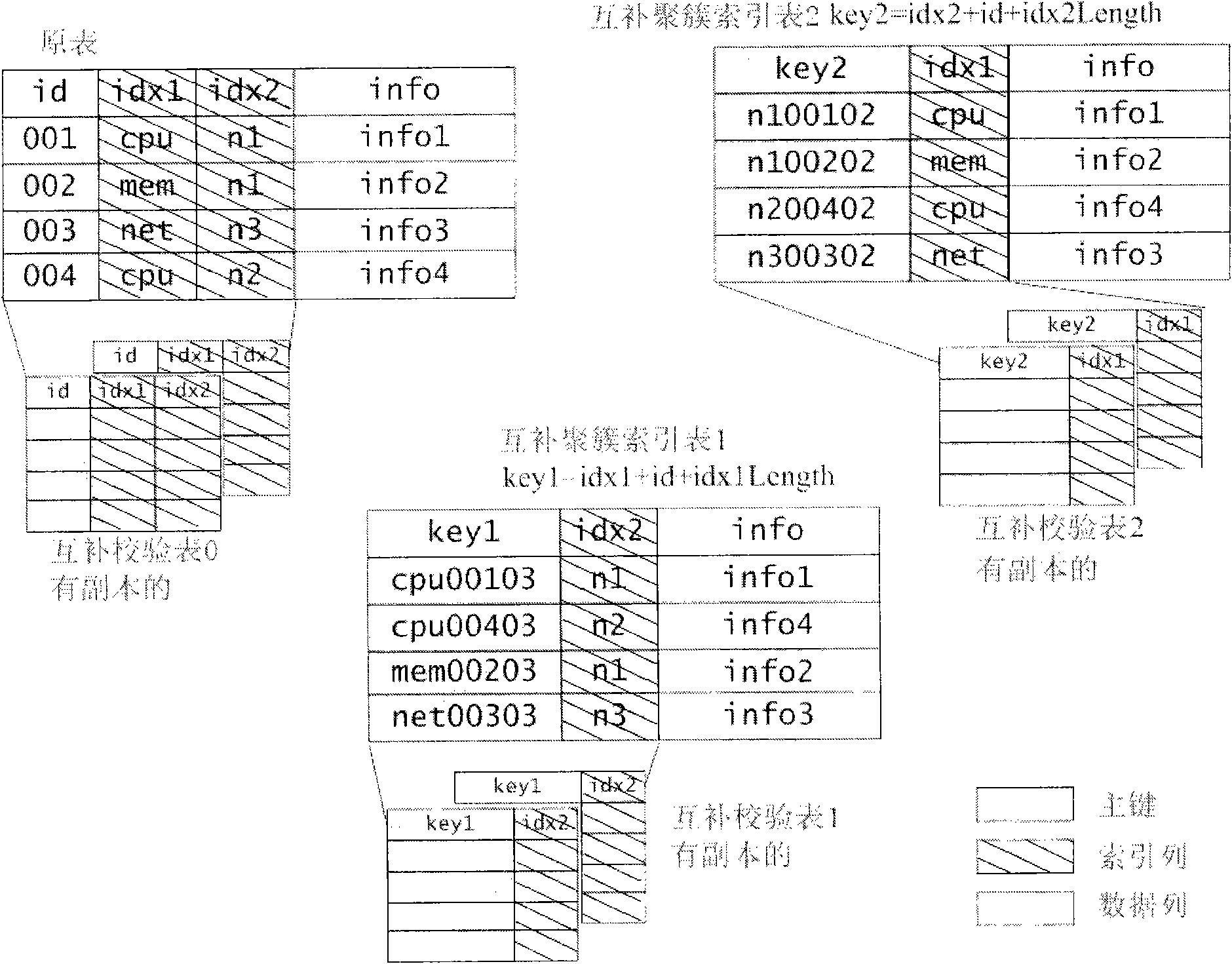
ActiveCN101866358AResilience remains the sameFast executionSpecial data processing applicationsQuery stringQuery optimization
The invention relates to a multidimensional interval querying method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: 1. organizing a transcript for copying data to be a plurality of complementary cluster index tables which are mutually compensated and verified, wherein each complementary cluster index table builds a sequence table which takes the length of a column value, an original line primary key and a column value as a primary key by means of each index column, completely stores the data of the other columns in the original line, and is used for continuously scanning when querying; and 2. converting a query string into a query plane tree, and performing query optimization to complete the query. The invention can simultaneously meet the requirements of high performance, low storage cost and high reliability.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
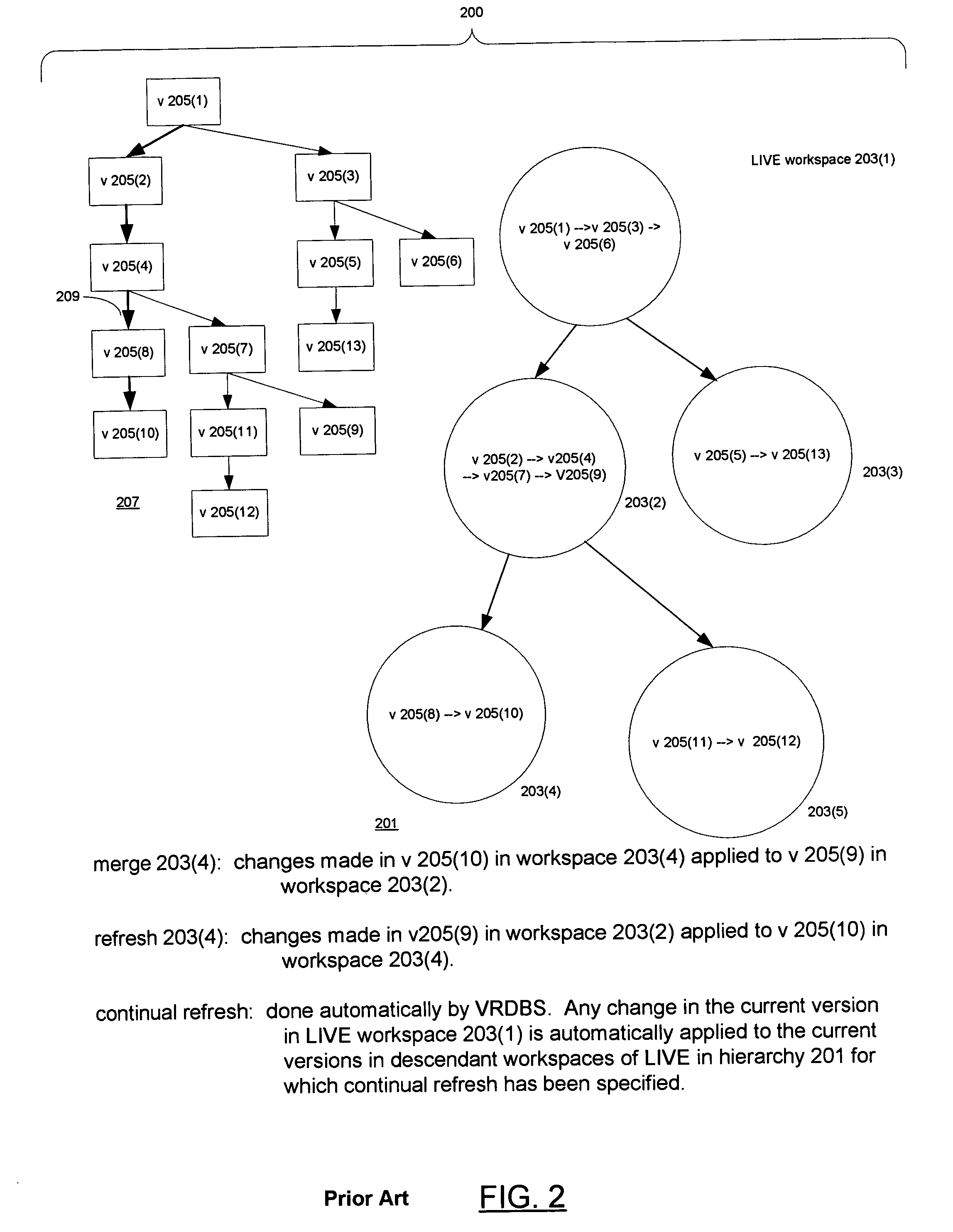
Versioned database system with multi-parent versions
InactiveUS7836028B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsWorkspaceMetadata
A versioned relational database system (VRDBS) in which versions of data contained in a relational database system are accessed by means of workspaces. Metadata in the VRDBS permits a workspace to have multiple parents. The multi-parented VRDBS performs operations including specifying that a workspace be made an additional parent of another workspace or that an additional parent be removed as a parent of the other workspace. The fact that a workspace may have multiple parents affects the manner in which merge and refresh operations are performed and the manner in which system-enforced constraints such as primary key constraints, unique key constraints, and referential integrity constraints are handled. The metadata for the VRDBMS includes a multi-parent graph for each workspace that has multiple parents. The multi-parent graph is used in the performance of the merge and refresh operations and in determining constraint violations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method of data movement between a data source and a destination
ActiveUS20080140692A1Stay flexibleImprove usabilityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData sourceApplication software
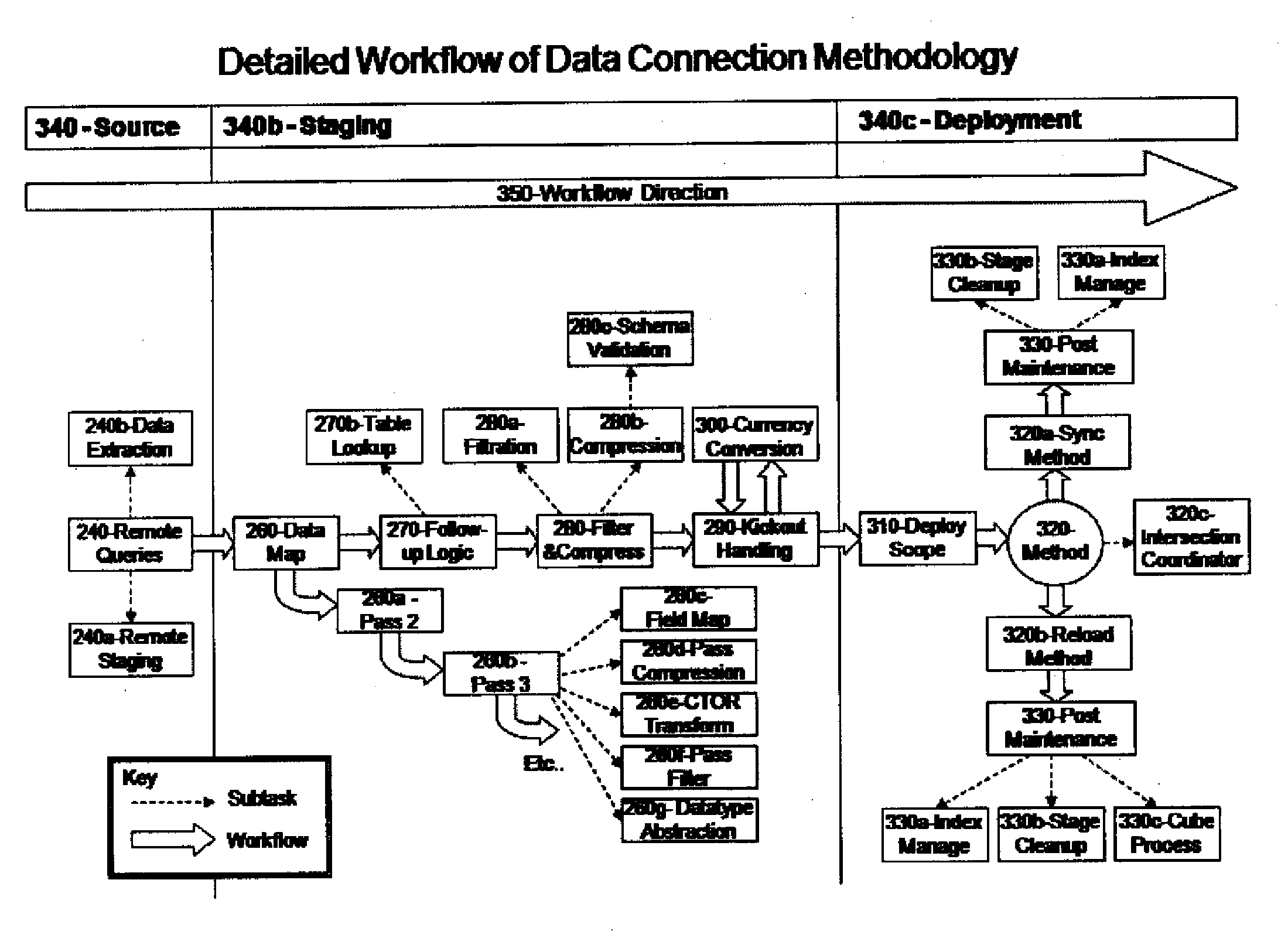
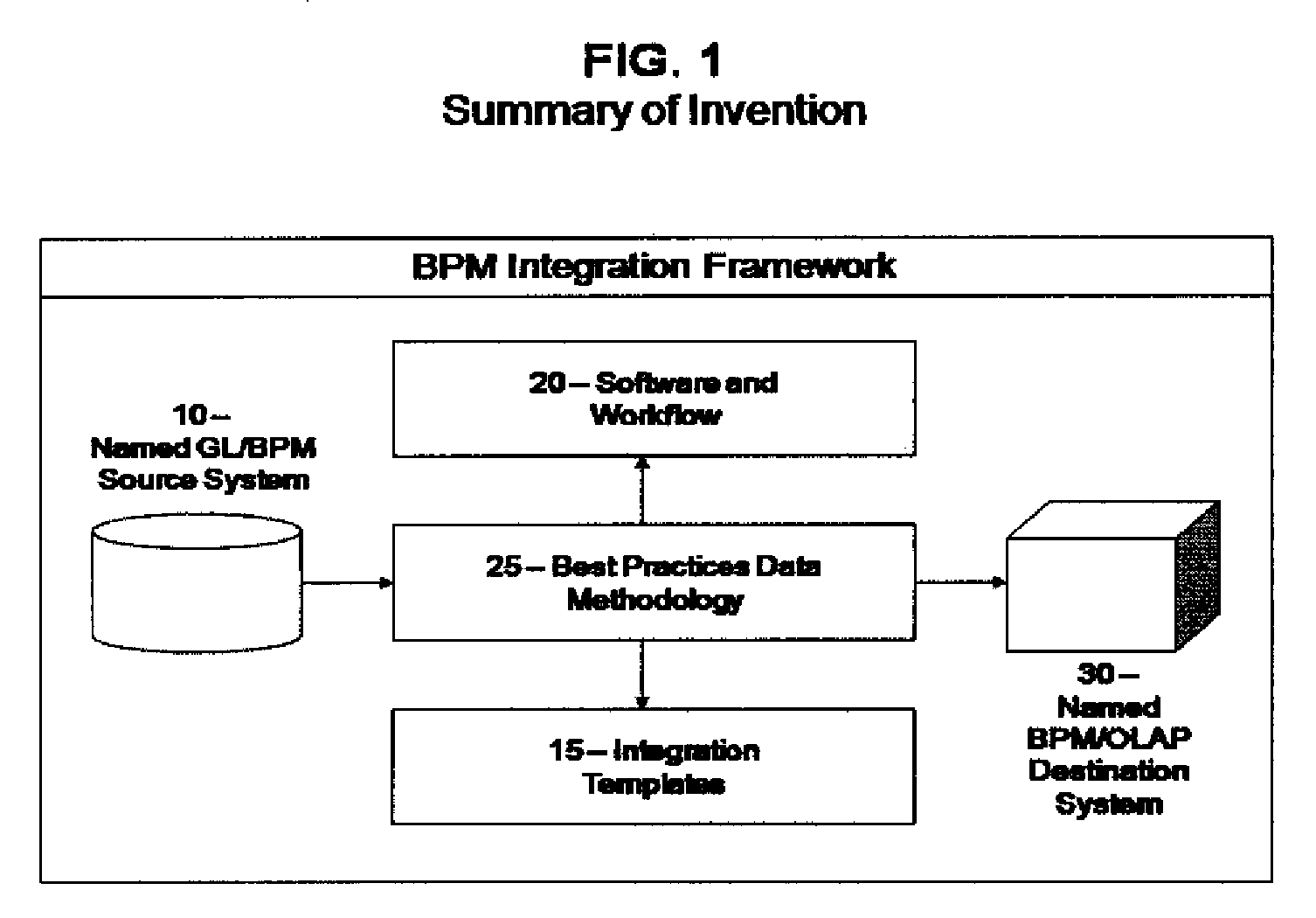
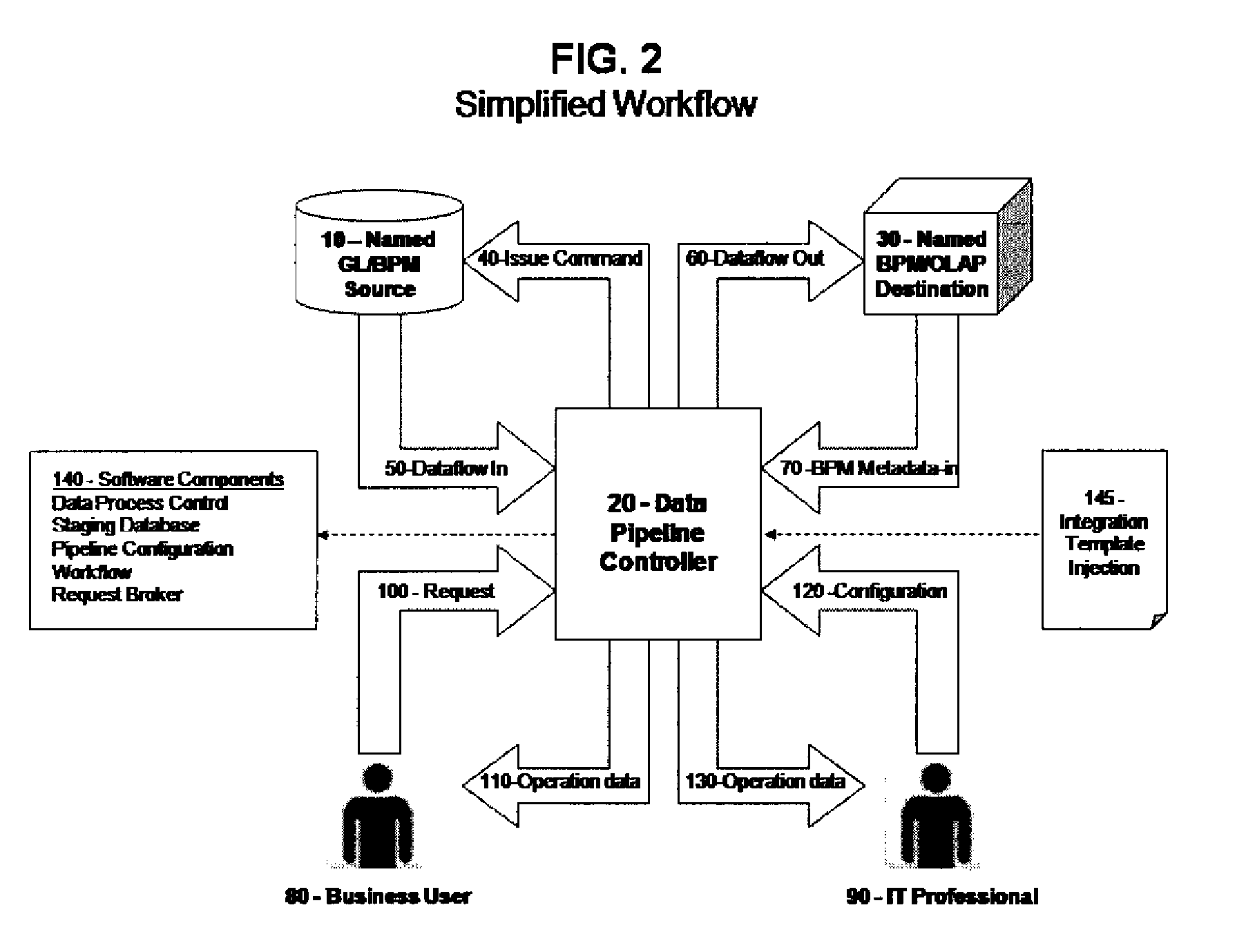
A reusable business performance management integration framework provides high performance and maximum efficiency for data transfer of general ledger data. The system issues commands to extract data from a named data source and then processes, tracks, prepares and delivers the data to a named system designation. The system identifies unique data intersections and synchronizes and / or reloads data against data intersection patterns without the use of primary keys. Integration templates may be applied to the basic framework. Each template contains the map for data transmission between a given general ledger system and the destination application type.
Owner:BREAKAWAY TECH
Smart database
ActiveUS20050182785A1Eliminates traditional heavy-weight dependenceEfficient and robust structureDigital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesHeavy weightIntelligent database
A solution is provided wherein only primary keys are used as meta-data to construct many-to-many relationships between table, resulting in amore robust, efficient database structure. Once tables of user-specific data are bound to the database as meta-data using their primary keys, the system may automatically ensure the handling of the records as related units. This eliminates the traditional heavy-weight dependence on foreign key relationships.
Owner:MOBILEFRAME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com