Patents
Literature
34 results about "Entity Bean" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
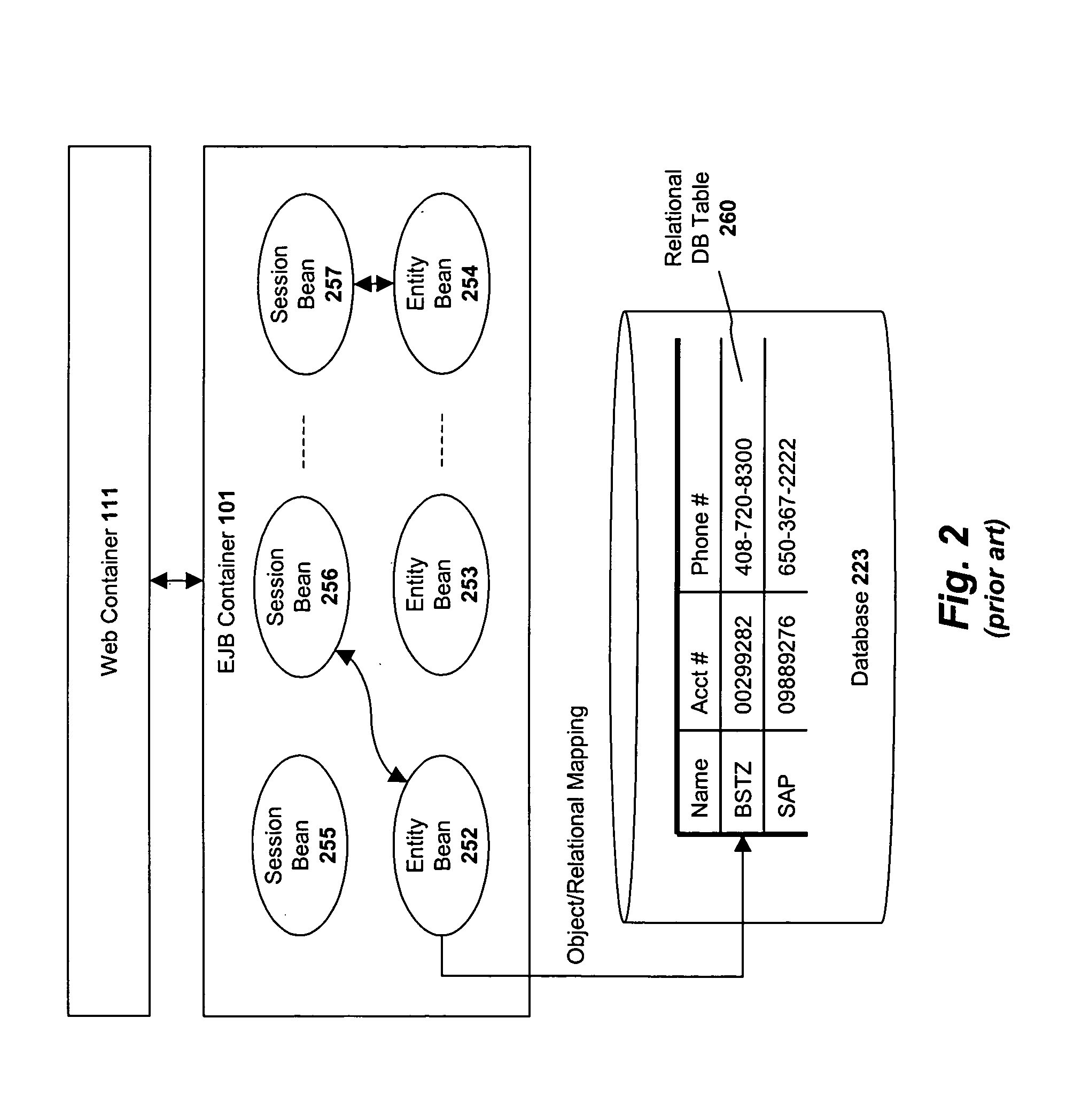
An "Entity Bean" is a type of Enterprise JavaBean, a server-side Java EE component, that represents persistent data maintained in a database. An entity bean can manage its own persistence (Bean managed persistence) or can delegate this function to its EJB Container (Container managed persistence). An entity bean is identified by a primary key. If the container in which an entity bean is hosted crashes, the entity bean, its primary key, and any remote references survive the crash.
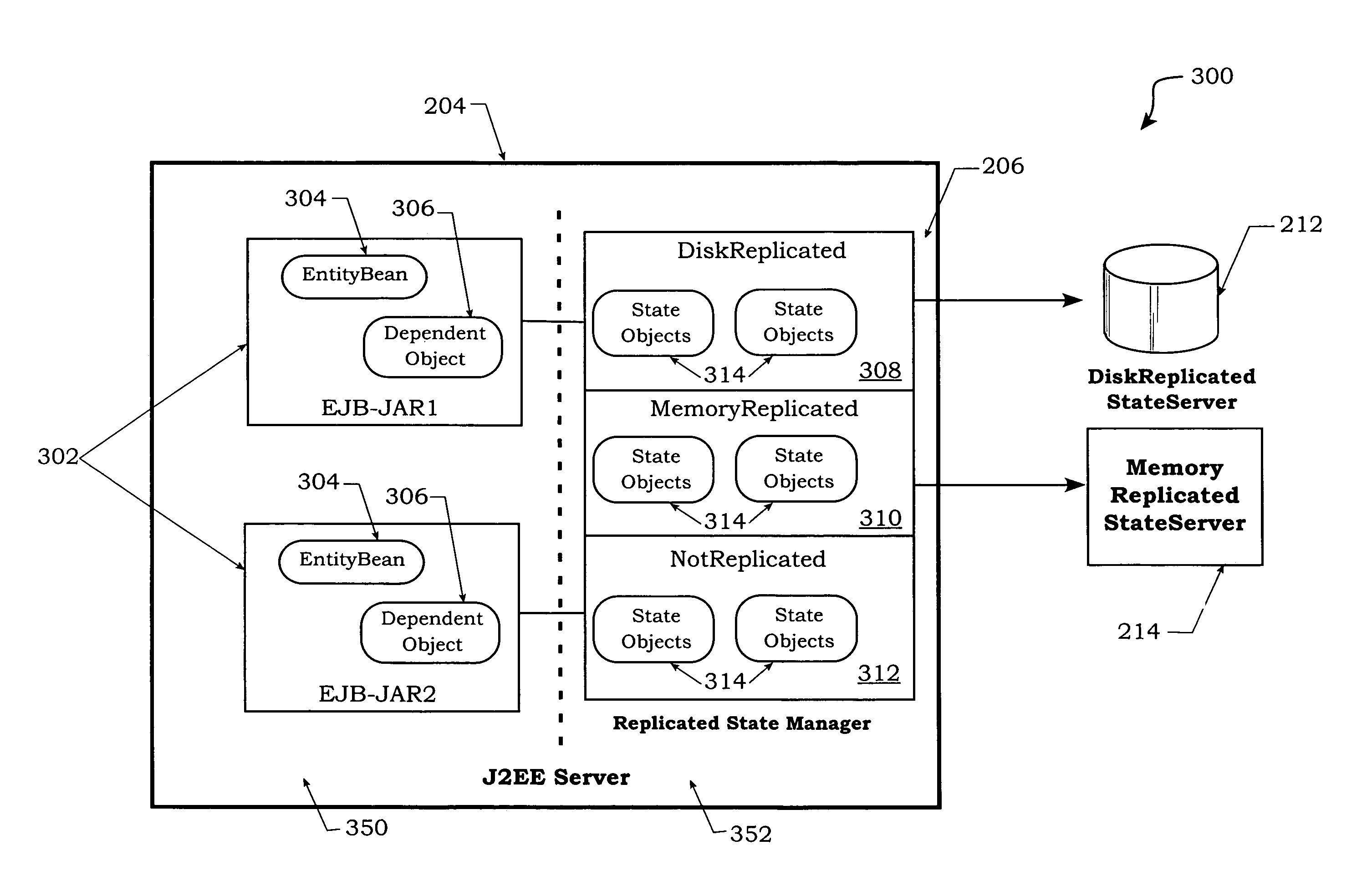
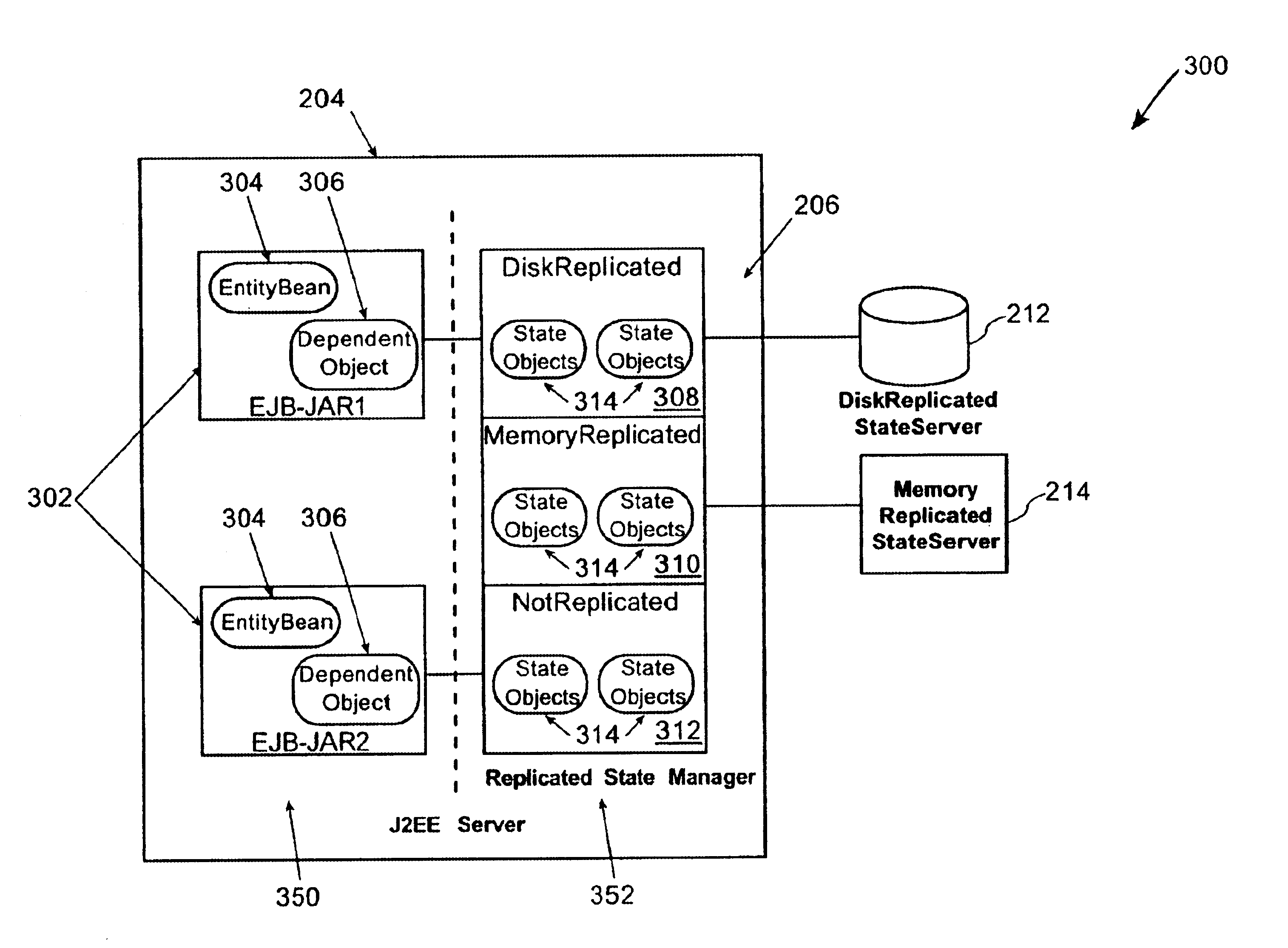
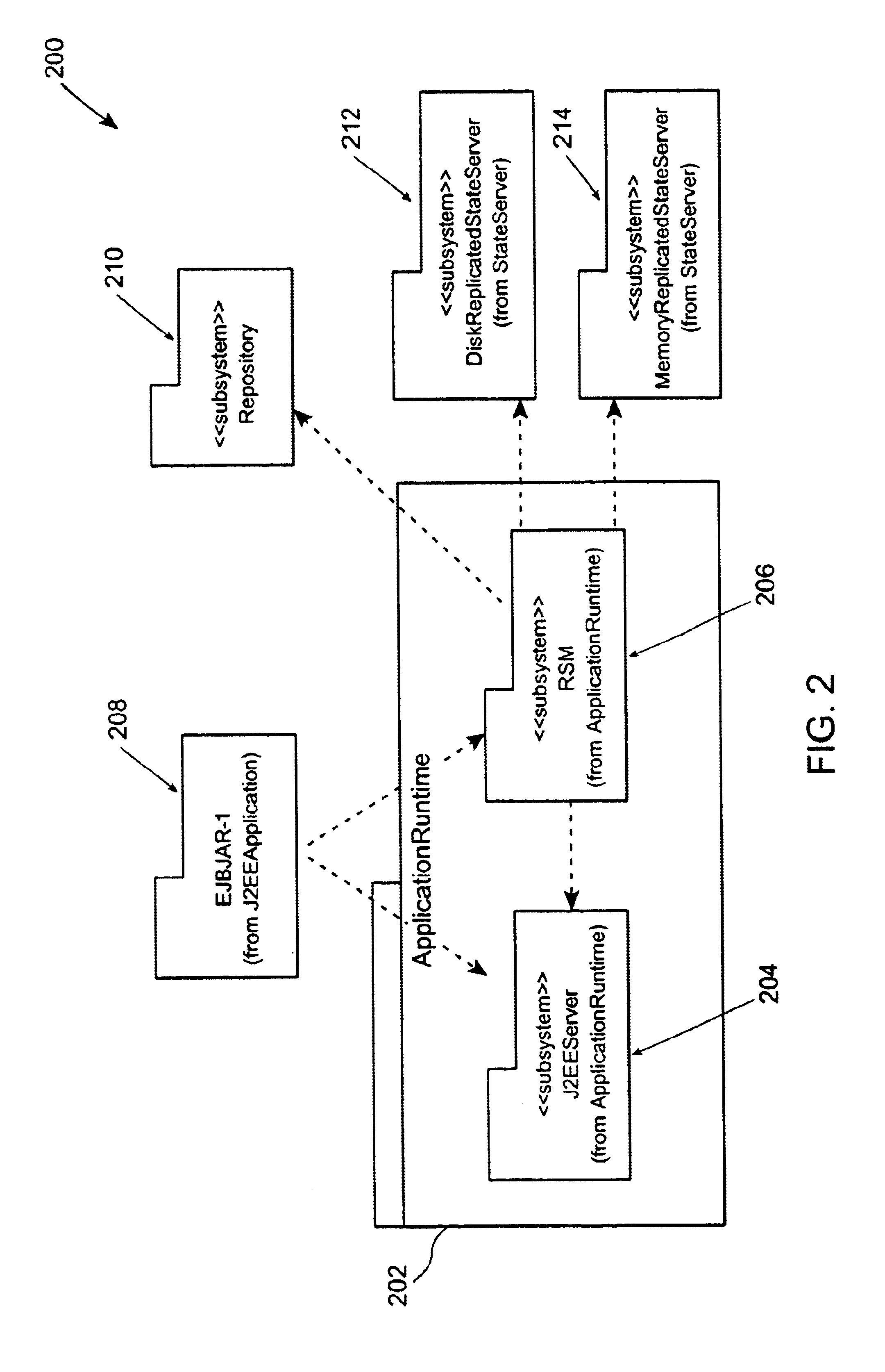
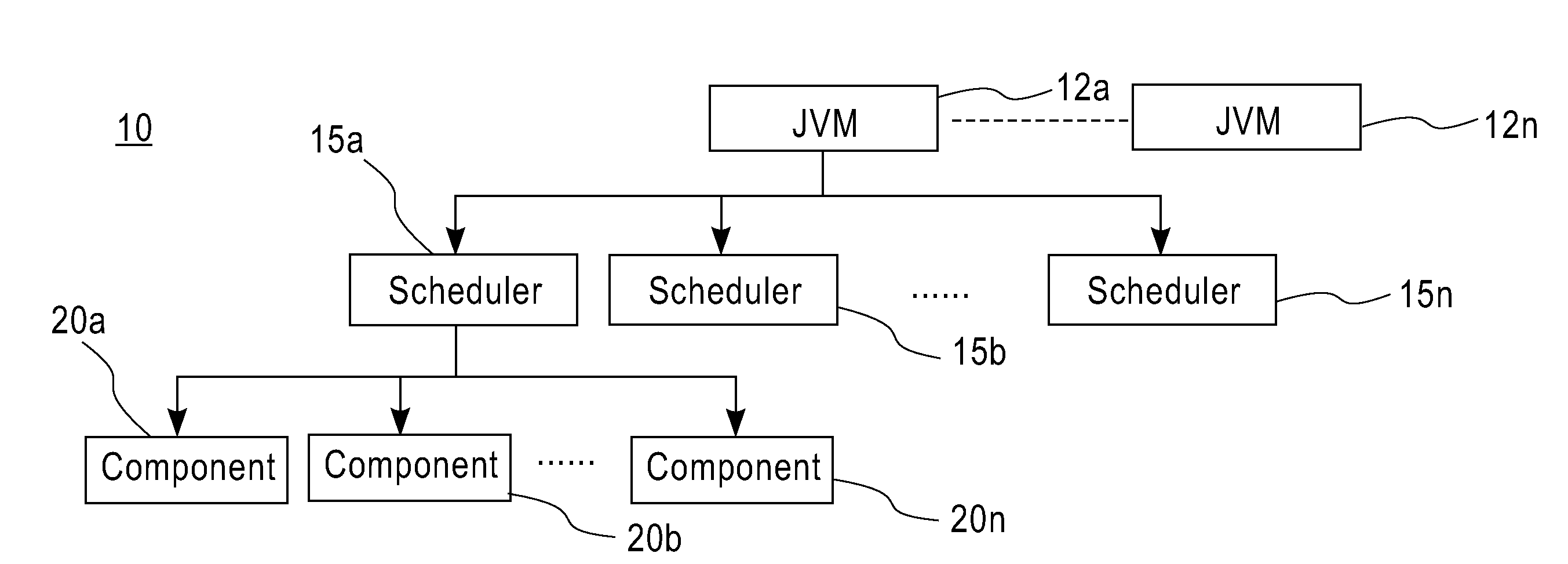
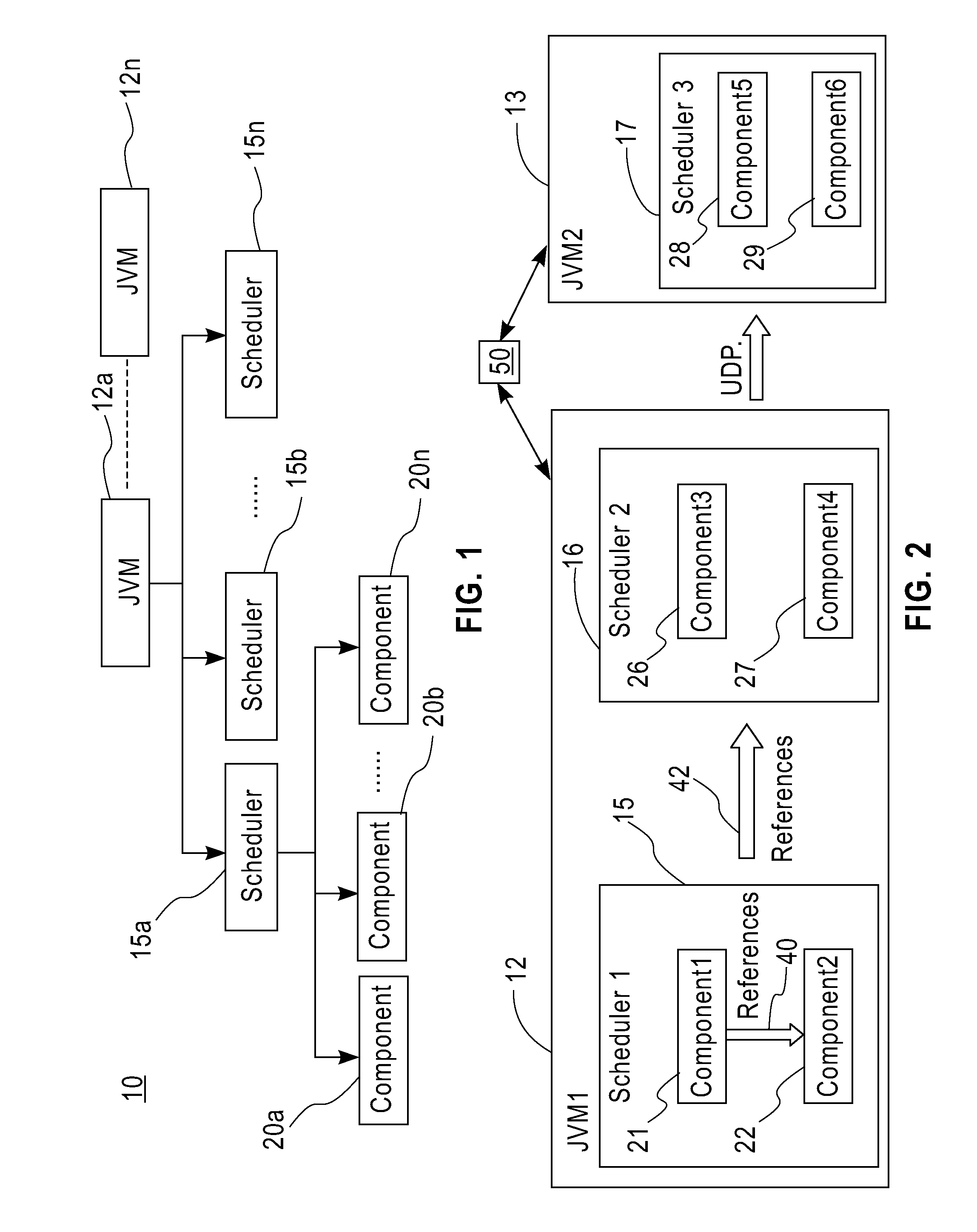
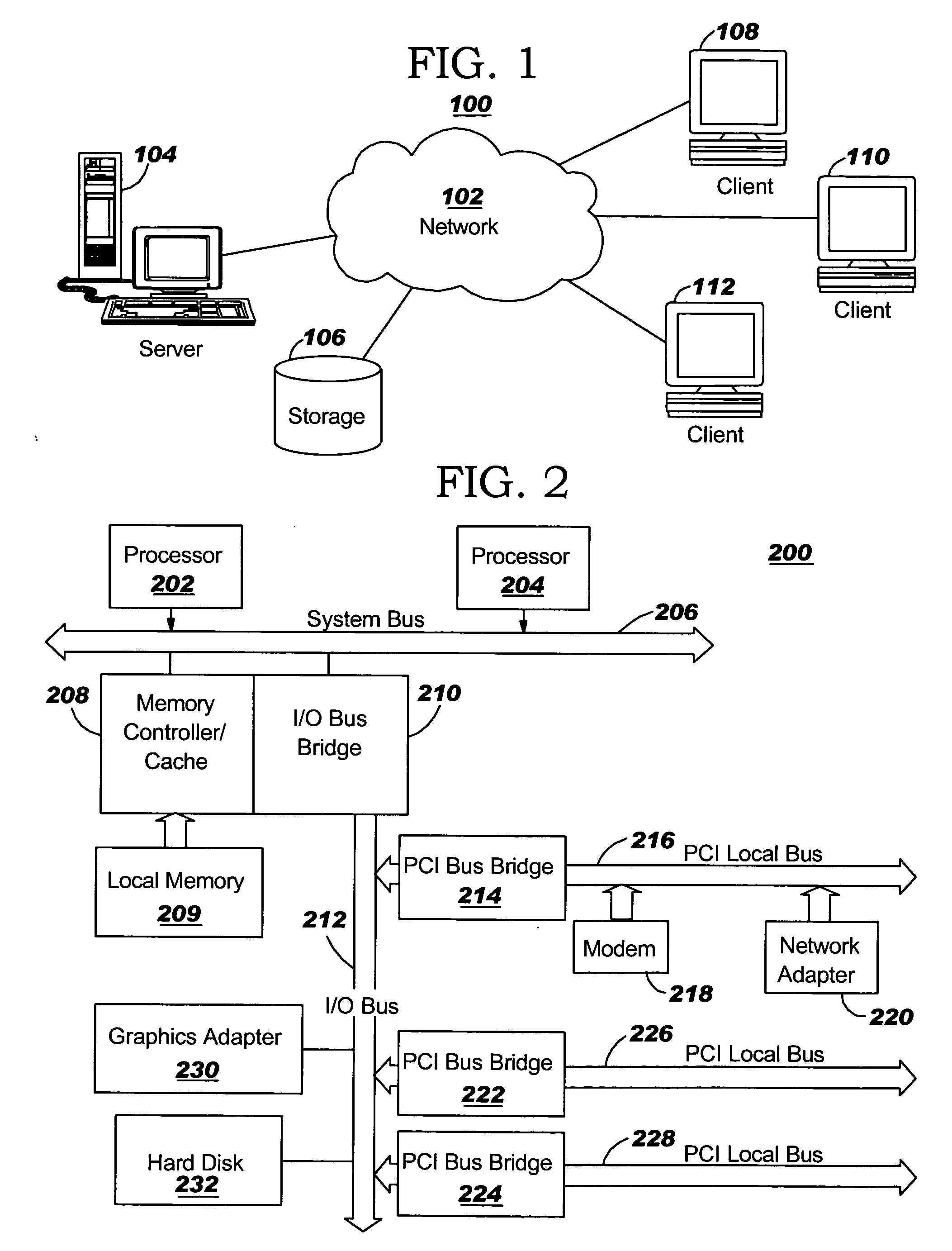
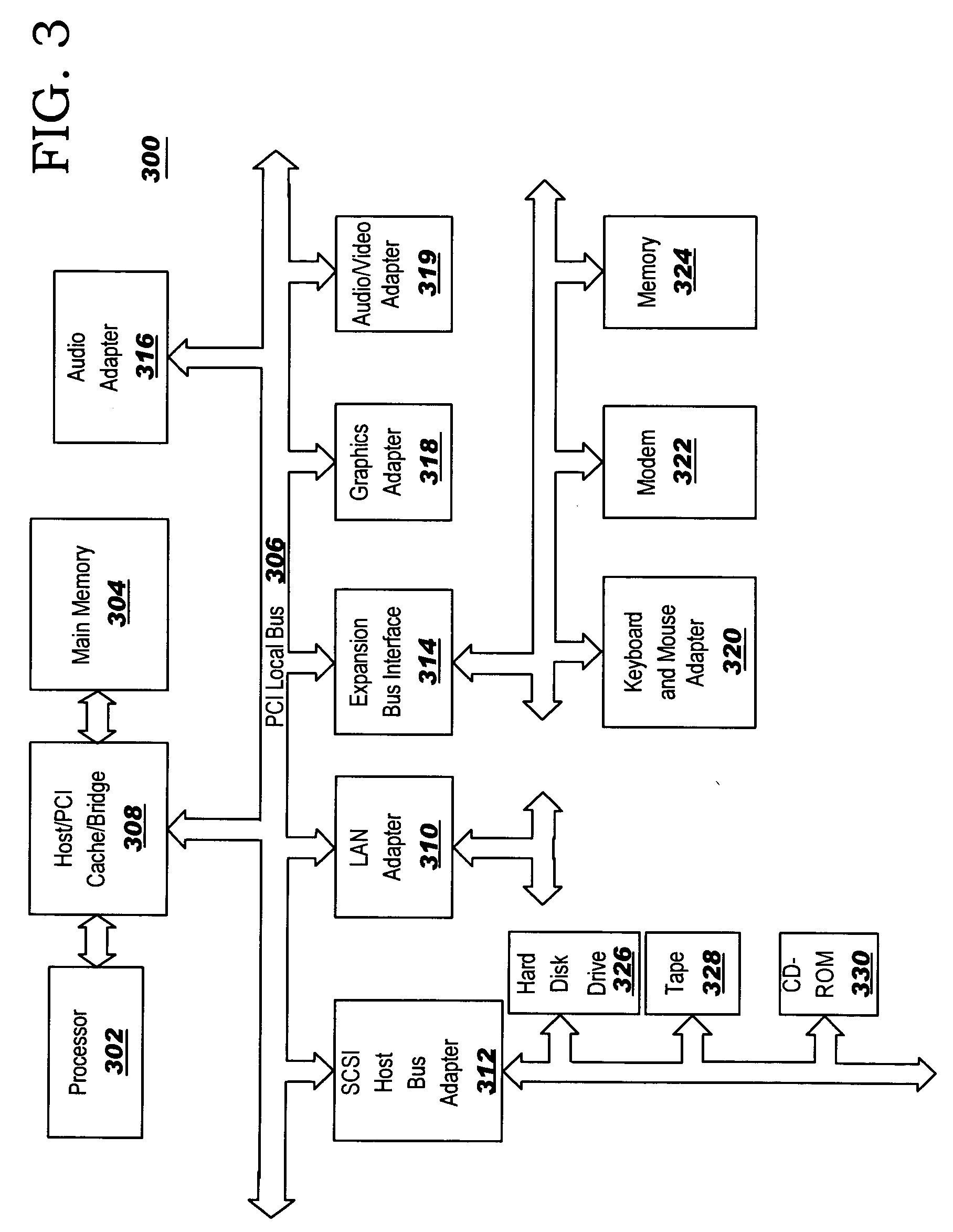
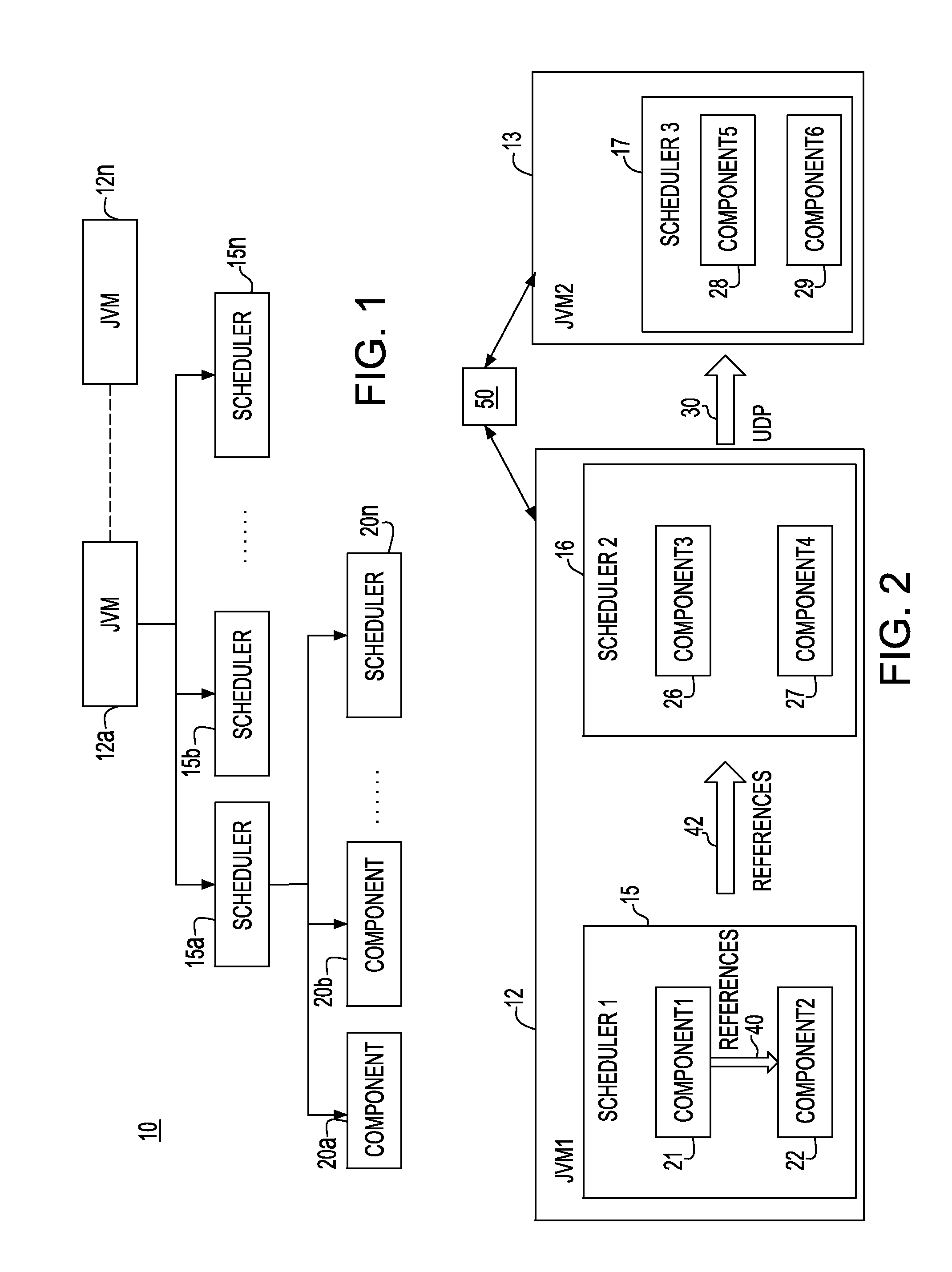
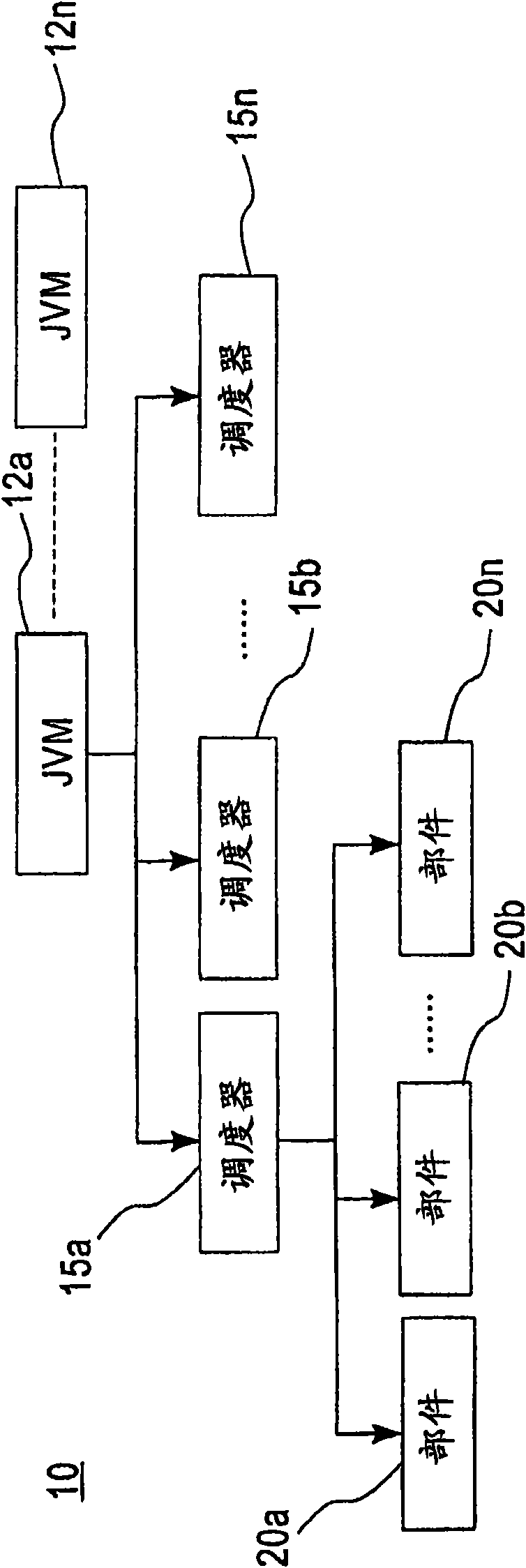
Method and apparatus for partitioning of managed state for a Java based application
InactiveUS7246345B1Easy to manageFacilitate state managementSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsMemory addressObject based
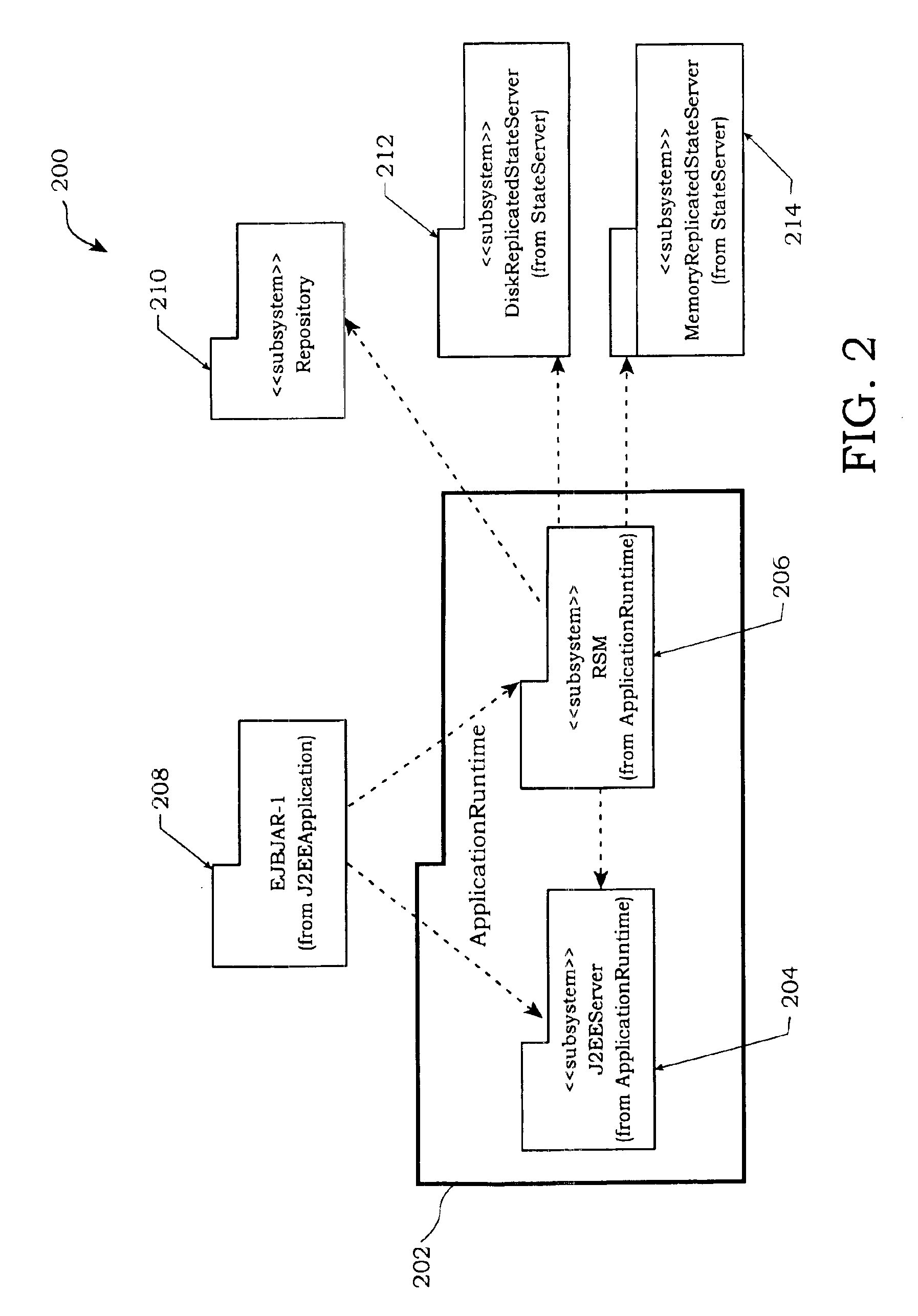
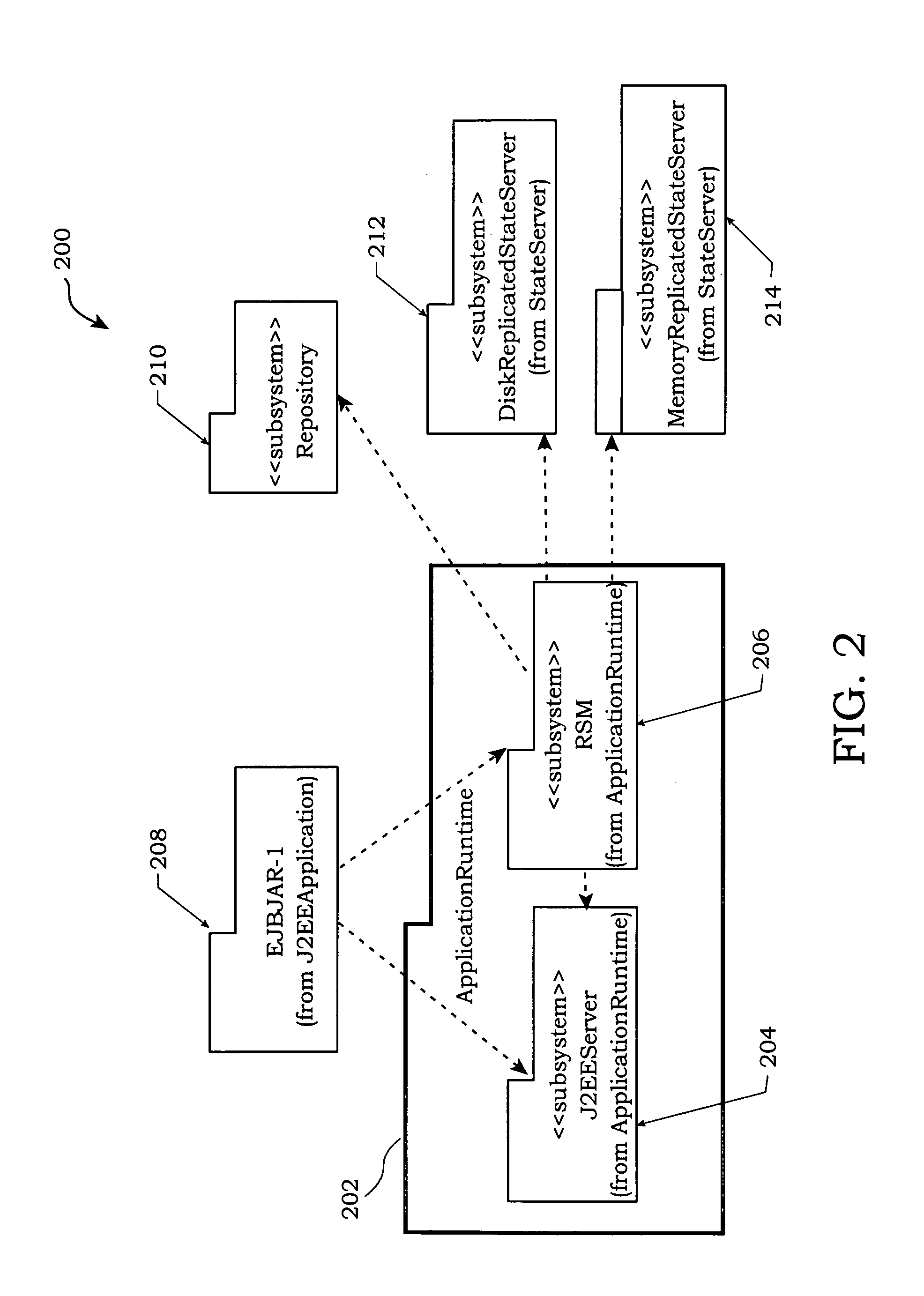
A method is disclosed for partitioning a managed state for a Java based application. The application developer is allowed to associate individual entity beans with a particular state management type. Then, during execution, a plurality of state objects are provided, where each state object stores a state of a corresponding entity bean object within the memory address space of a Java server process. Further, each state object is associated with the state management type of the corresponding entity bean object. In this manner, state management is provided for each entity bean object based on the associated state management type using a corresponding state object. The state management type can be a memory replicated state management type, a disk replicated state management type, a non-replicated state manage type.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
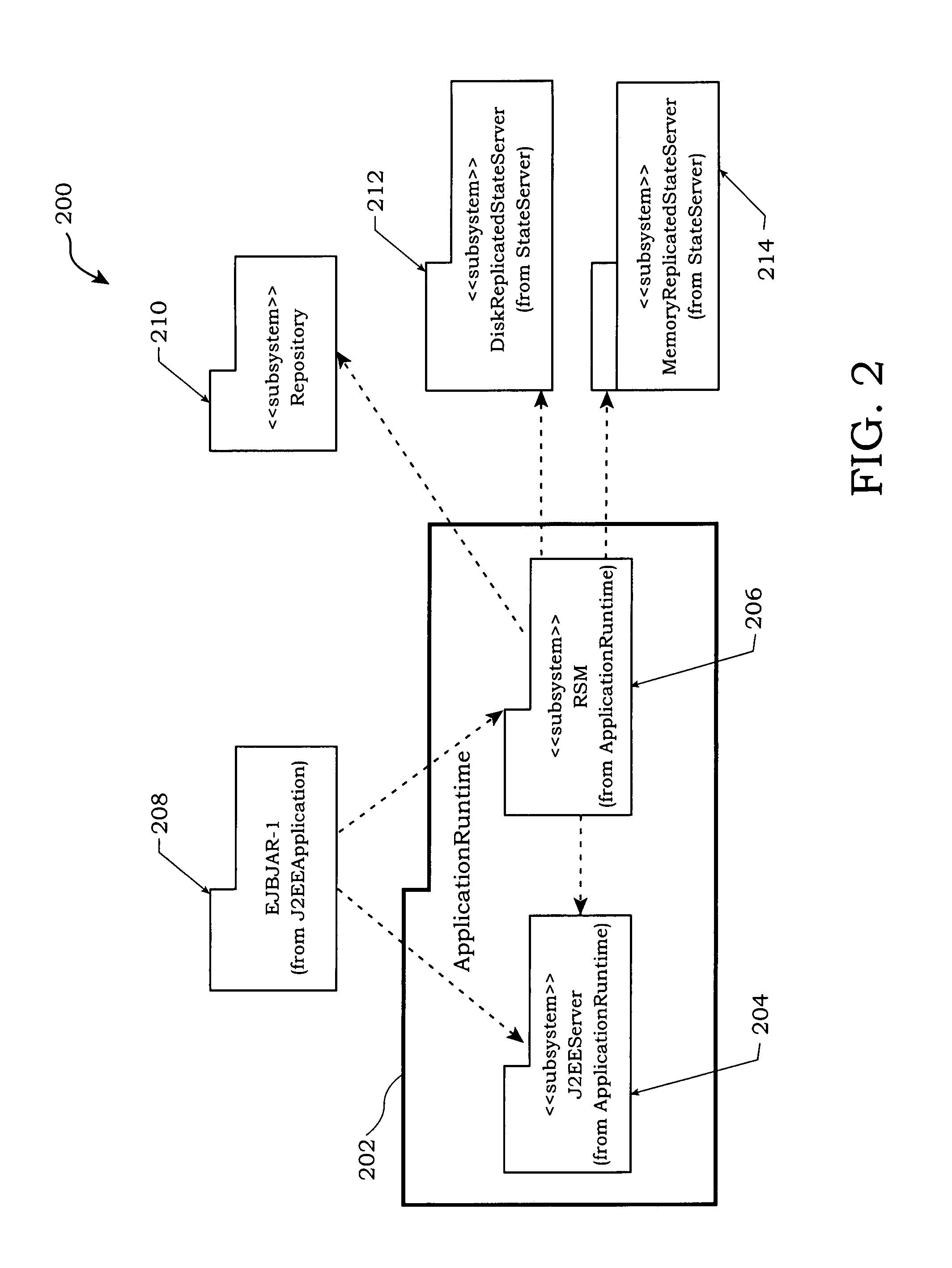
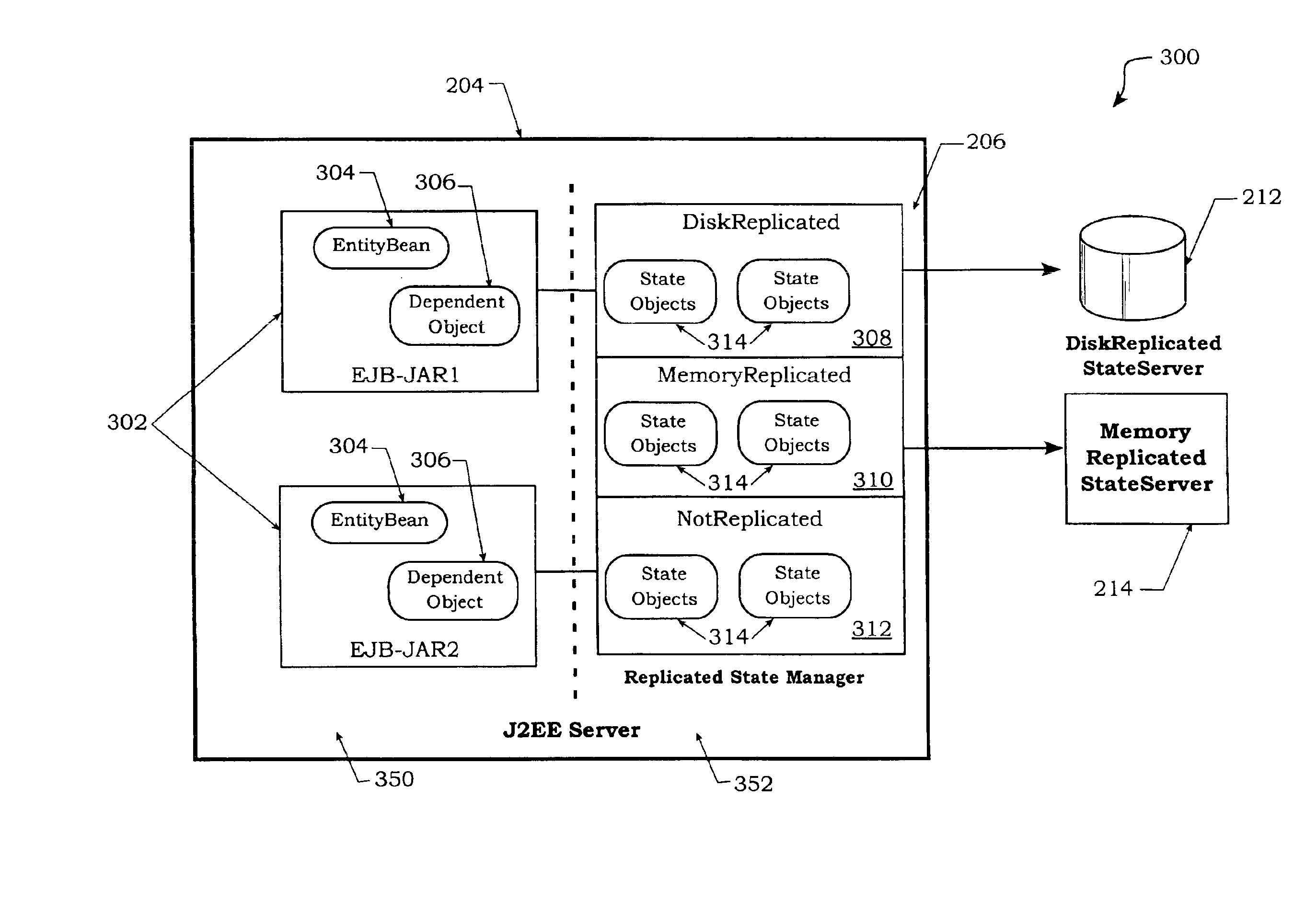
Method and apparatus for managing replicated and migration capable session state for a Java platform
InactiveUS6877111B2Facilitate application state managementError preventionResource allocationProgram instructionEnterprise Java Bean
An invention is disclosed managing the replicated and migration capable state for an enterprise Java bean (EJB) application. The invention includes executing a Java application on a server that includes an entity bean. In addition, a replicated state manager is executed that includes program instructions for managing an in-memory state of the Java application, and program instructions for replicating the in-memory state of the Java application to a replicated state server. The replicated state server can be a memory replicated state server, or a disk replicated state server. To facilitate application state management, embodiments of the present invention store states of the entity beans objects using state objects, which are updated in response to changes in the state of the application. Hence, the embodiments of the present invention define a logical separation between the application and the state objects.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
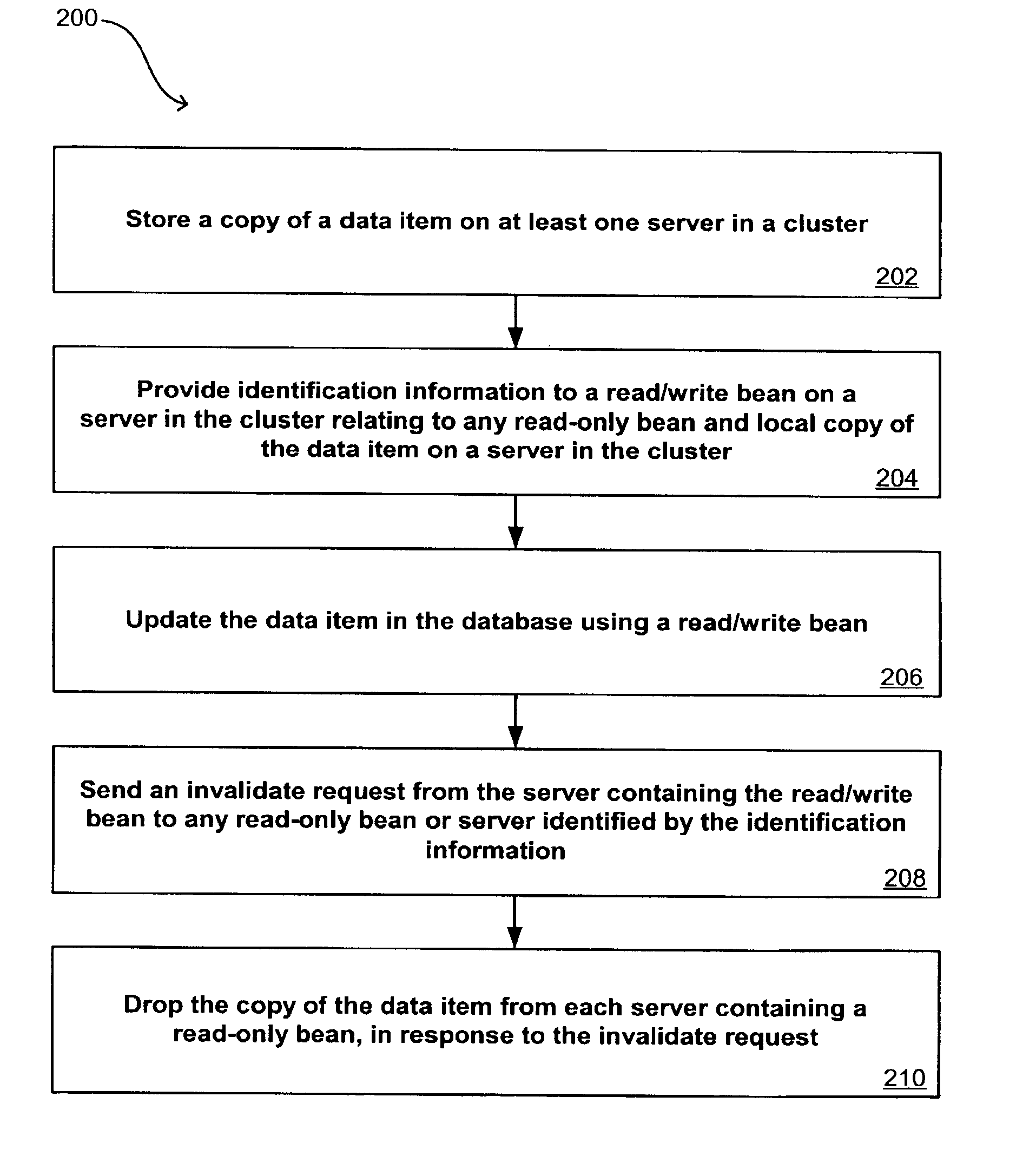
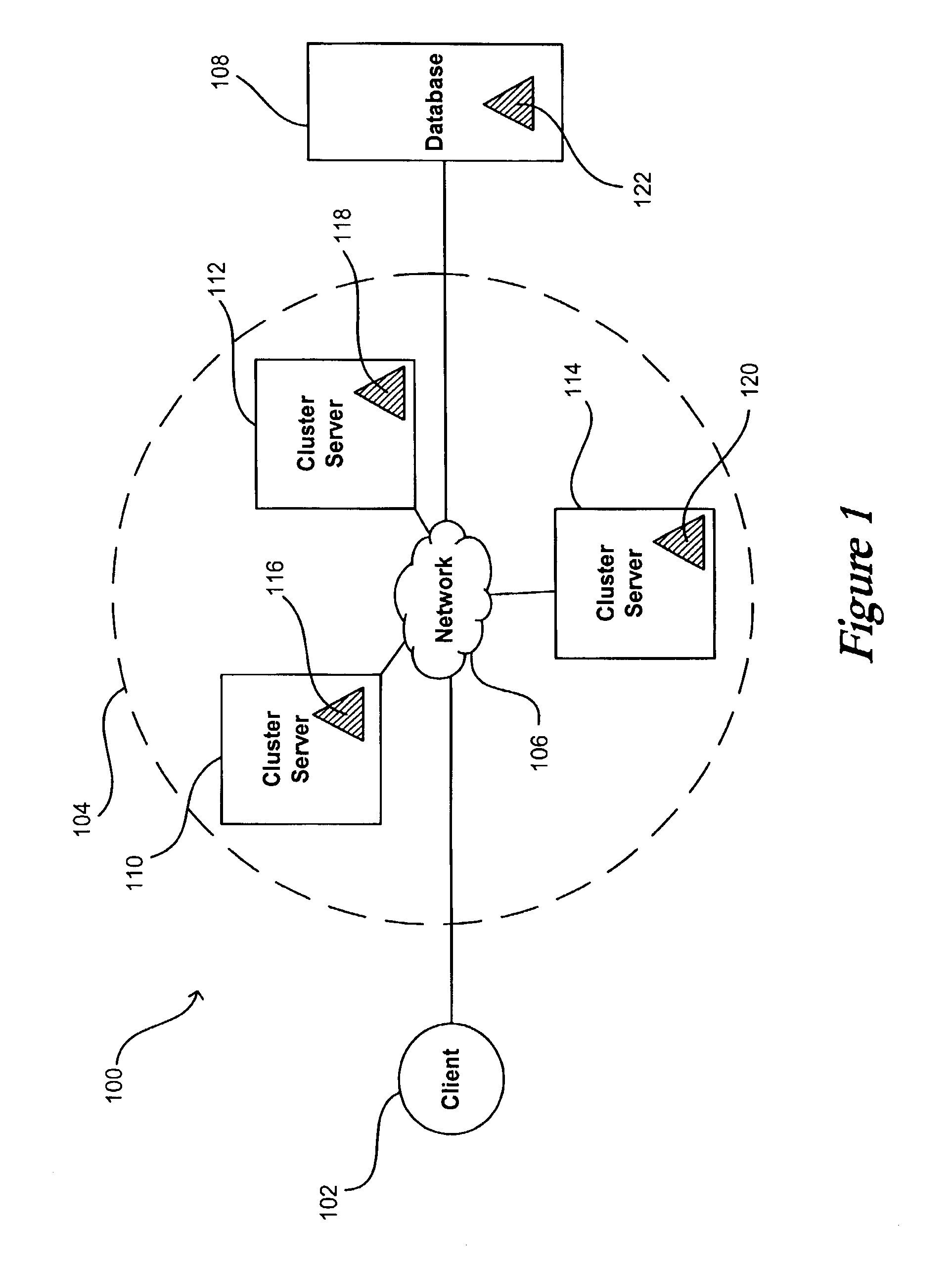
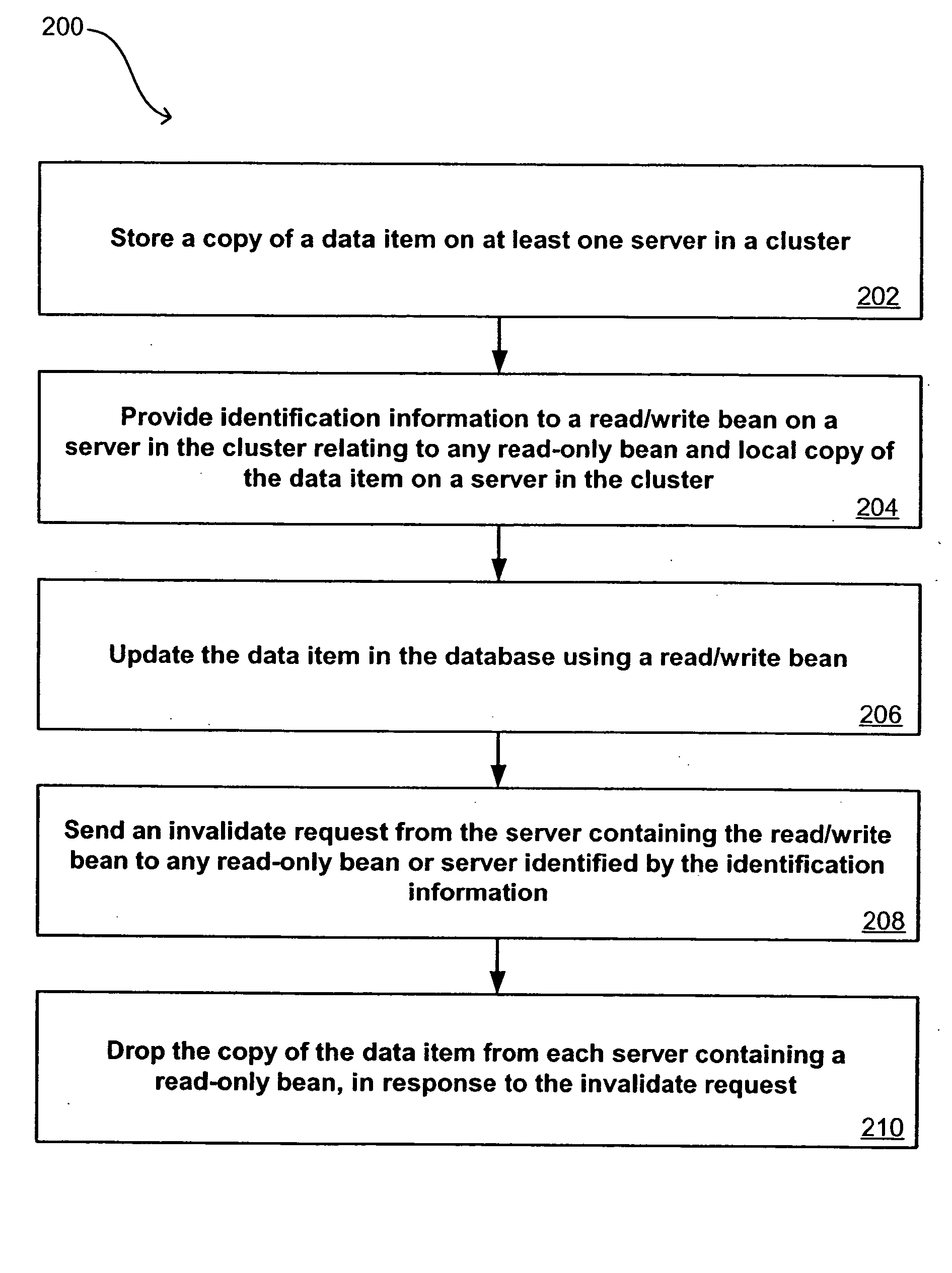
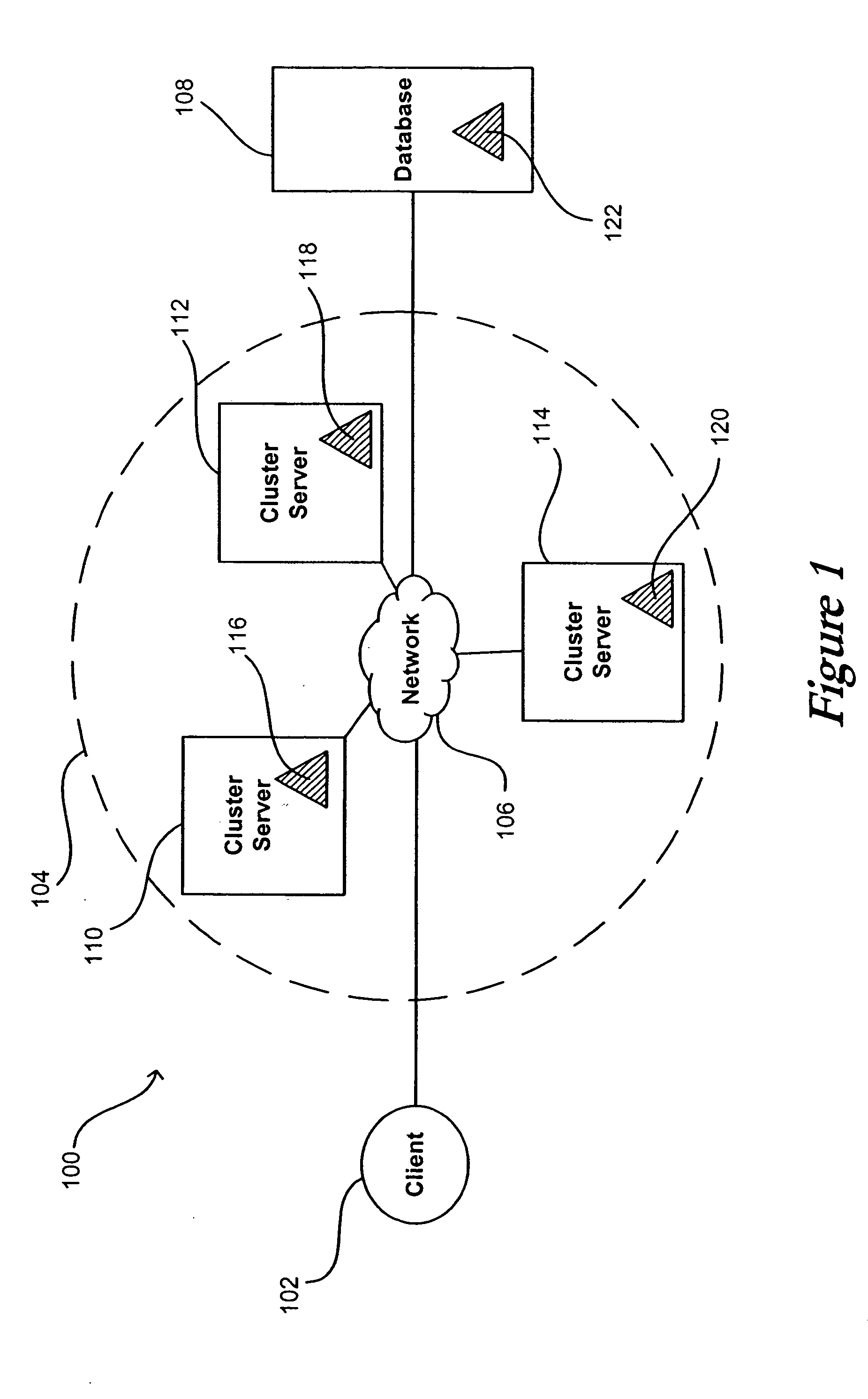
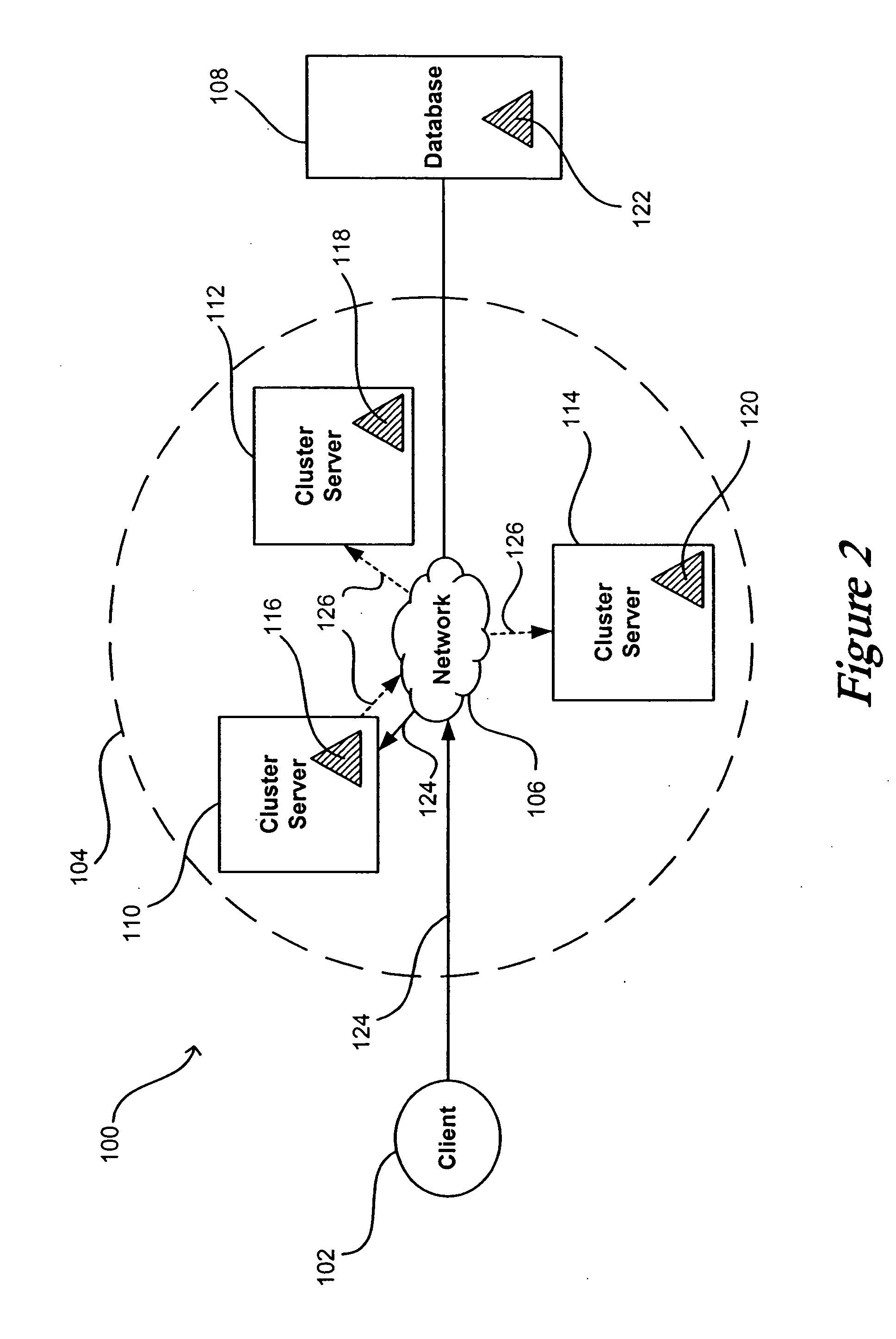
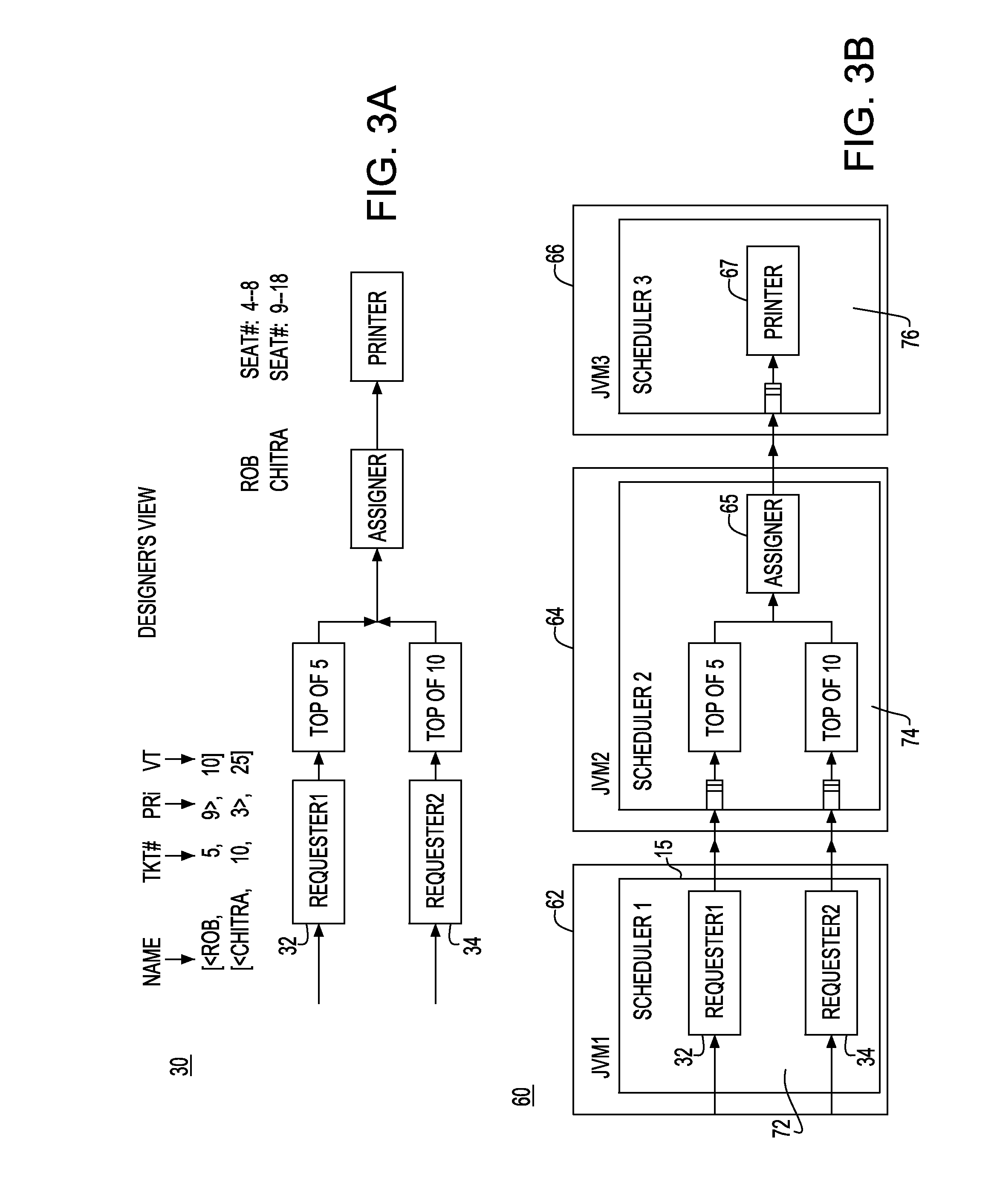
System and method for flushing bean cache
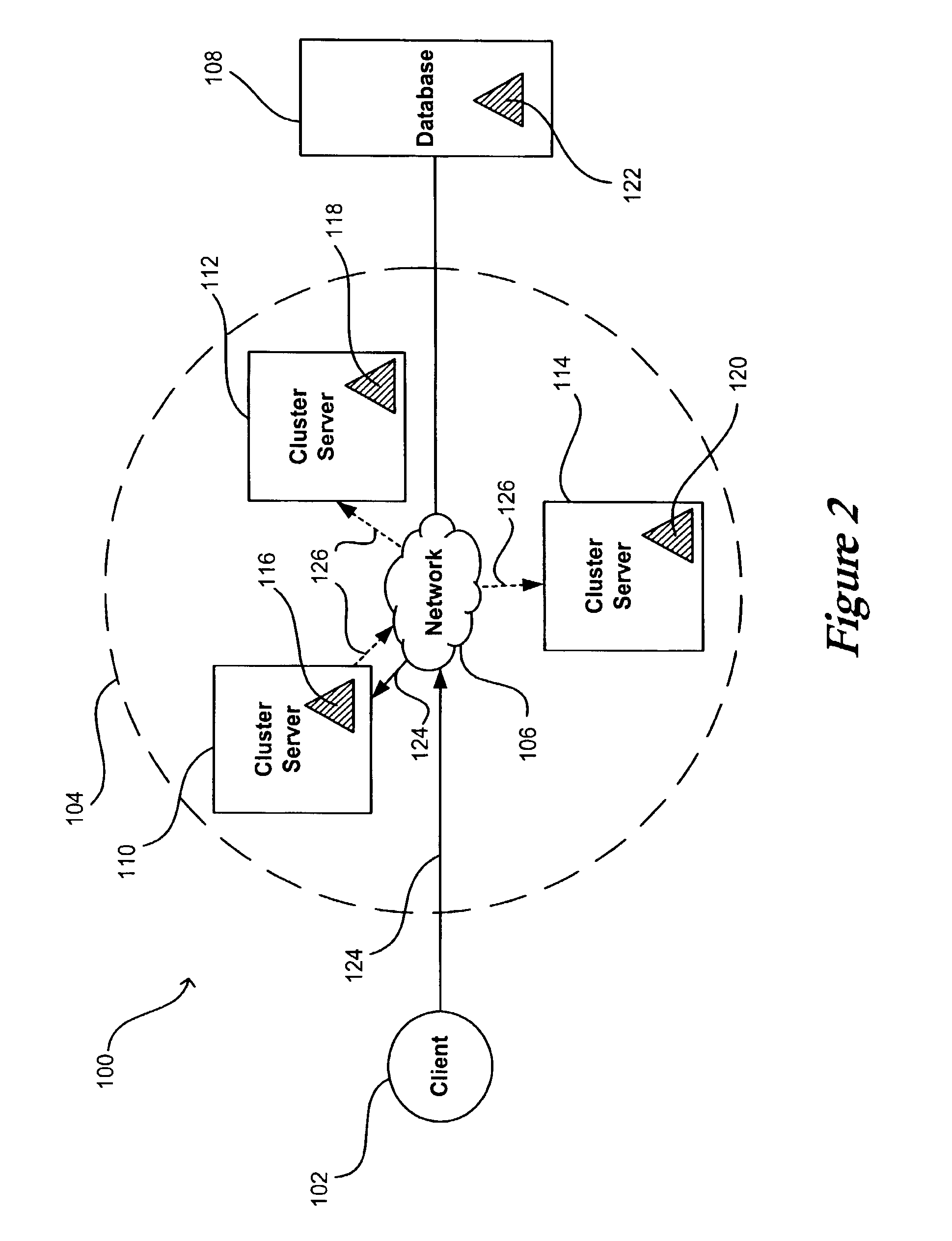
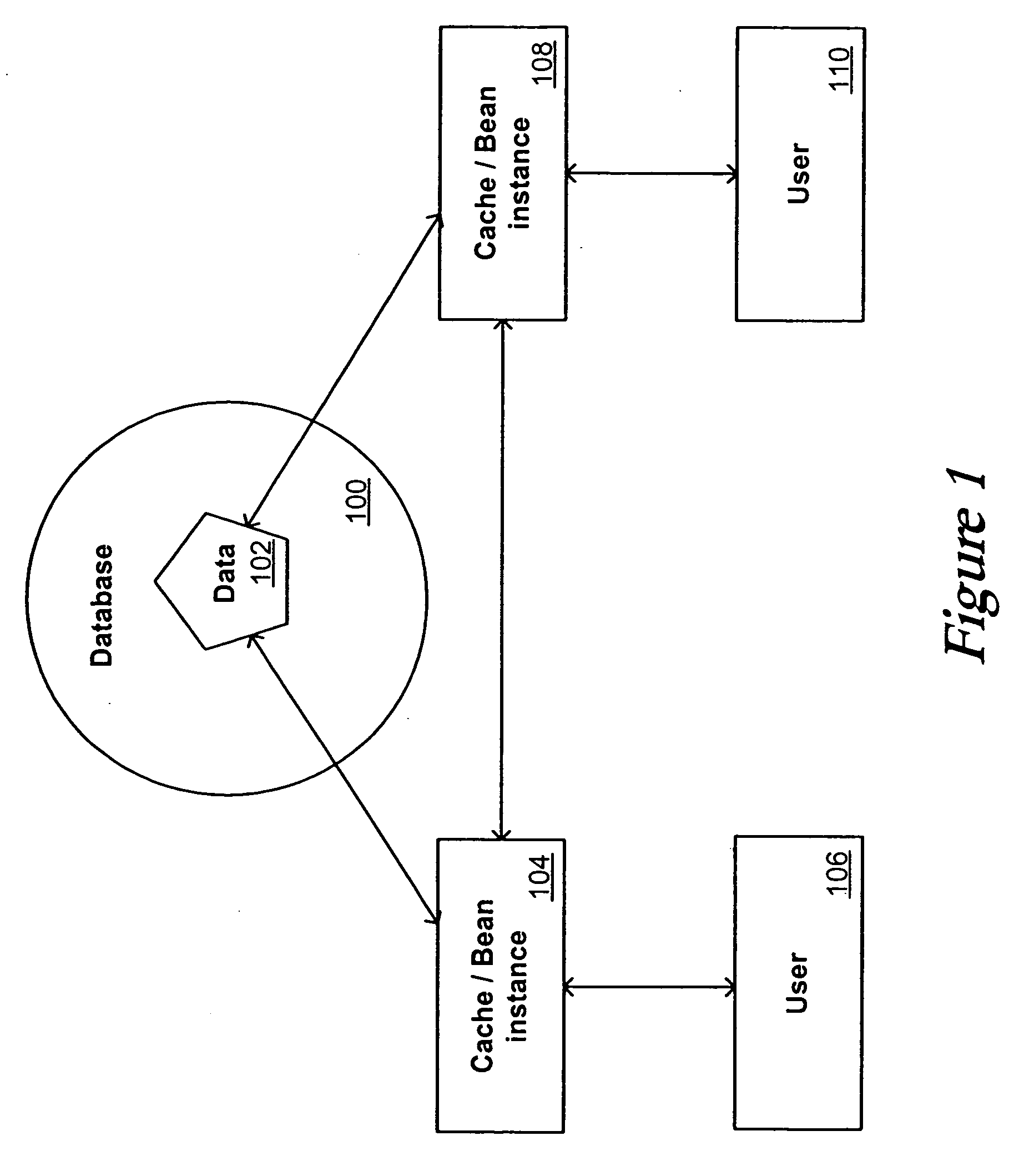
Servers in a network cluster can each store a copy of a data item in local cache, providing read access to these copies through read-only entity beans. The original data item in the database can be updated through a read / write entity bean one of the cluster servers. That cluster server has access to an invalidation target, which contains identification information relating to copies of the data item stored on servers in the cluster. Once the read / write bean updates the data item in the database, an invalidate request can be sent or multicast to all cluster members, or to any read-only bean or server contained in the invalidation target. Each server or read-only bean receiving the request knows to drop any copy of the data item in local cache, and can request a current copy of the data item from the database.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Distributed, fault-tolerant and highly available computing system
InactiveUS20080270838A1Improve usabilityProgram control using stored programsFault responseTimestampHigh availability
A method and system for achieving highly available, fault-tolerant execution of components in a distributed computing system, without requiring the writer of these components to explicitly write code (such as entity beans or database transactions) to make component state persistent. It is achieved by converting the intrinsically non-deterministic behavior of the distributed system to a deterministic behavior, thus enabling state recovery to be achieved by advantageously efficient checkpoint-replay techniques. The method comprises: adapting the execution environment for enabling message communication amongst and between the components; automatically associating a deterministic timestamp in conjunction with a message to be communicated from a sender component to a receiver component during program execution, the timestamp representative of estimated time of arrival of the message at a receiver component. At a component, tracking state of that component during program execution, and periodically checkpointing the state in a local storage device. Upon failure of a component, the component state is restored by recovering a recent stored checkpoint and re-executing the events occurring since the last checkpoint. The system is deterministic by repeating the execution of the receiving component by processing the messages in the same order as their associated timestamp.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
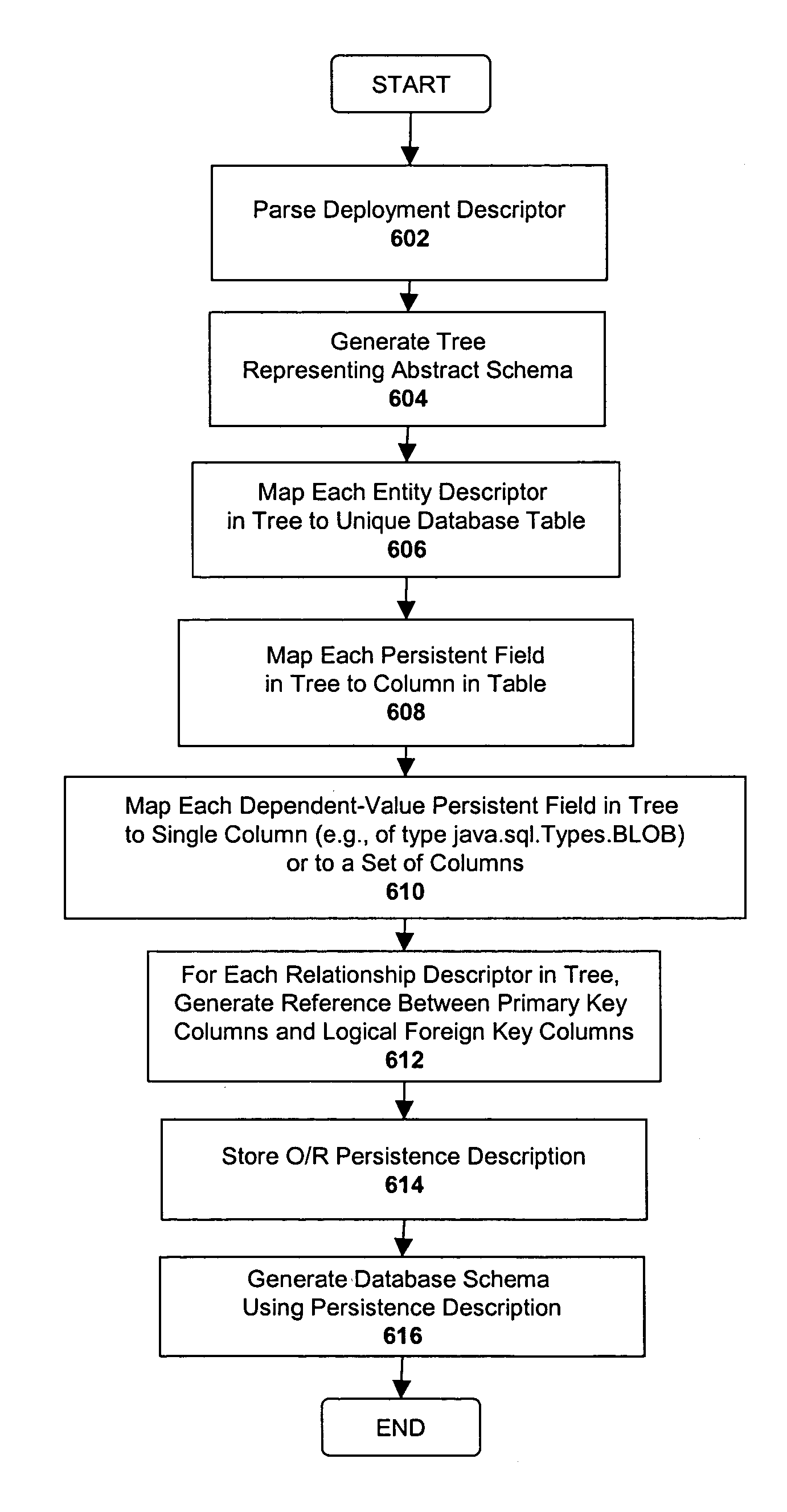
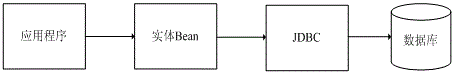
System and method for mapping object-oriented program code to a database layer
One embodiment of the invention employs techniques for providing a default object-relational mapping between persistent data objects (i.e., the objects that represent persistent data from a database) and a relational database. In a Java environment, for example, each entity bean is mapped to a particular database table, and each of the persistent fields within the entity bean are mapped to columns of the database table. Relationships between entity beans are expressed as mappings between primary keys and foreign keys within the database schema. Dependent-value persistent fields may be mapped to multiple columns or to a single column of a special Java type (java.sql.Types. BLOB). In addition, one embodiment of the invention generates a default database schema using the default O / R mapping by executing a series of SQL commands generating the tables and columns.
Owner:SAP AG
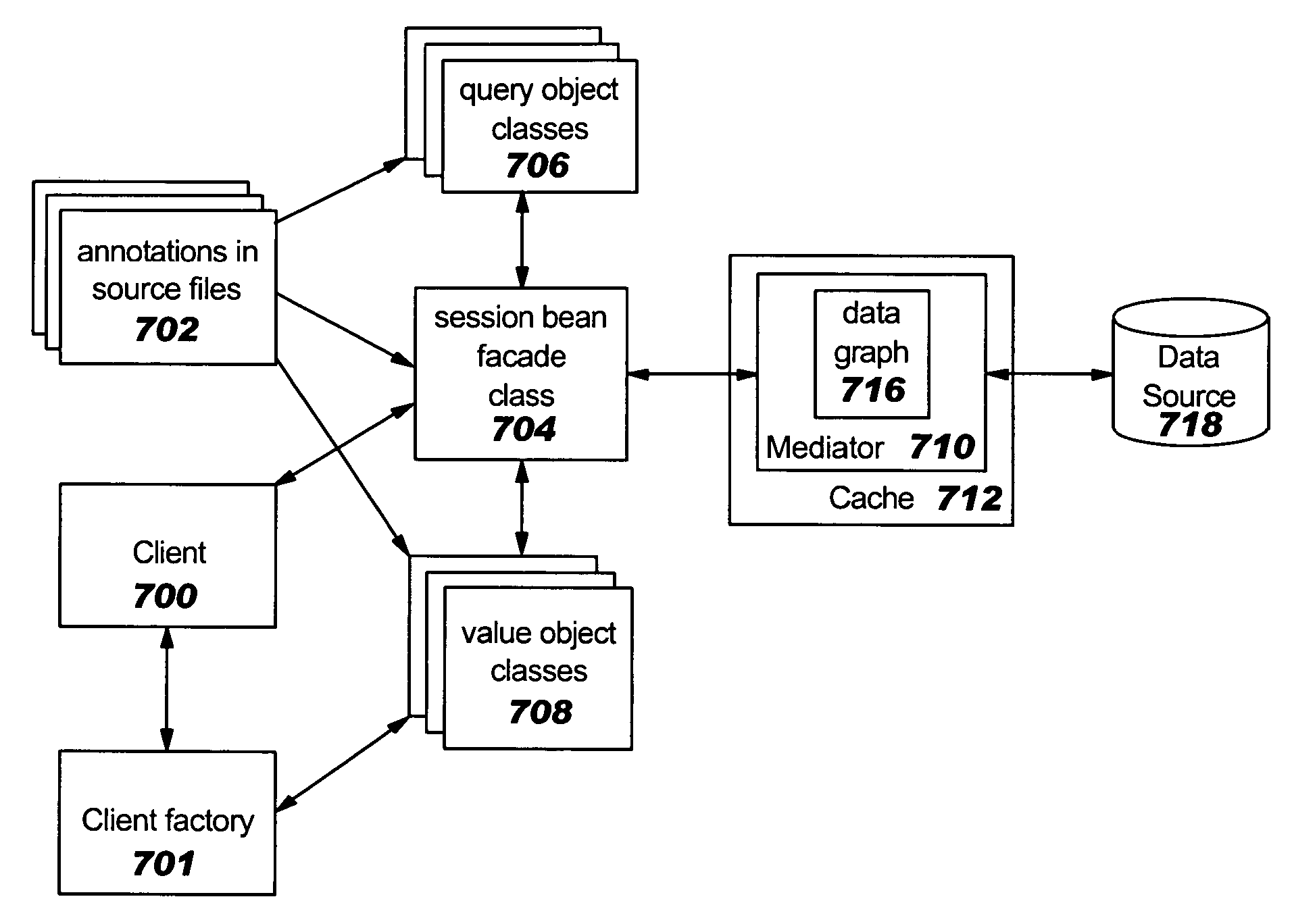
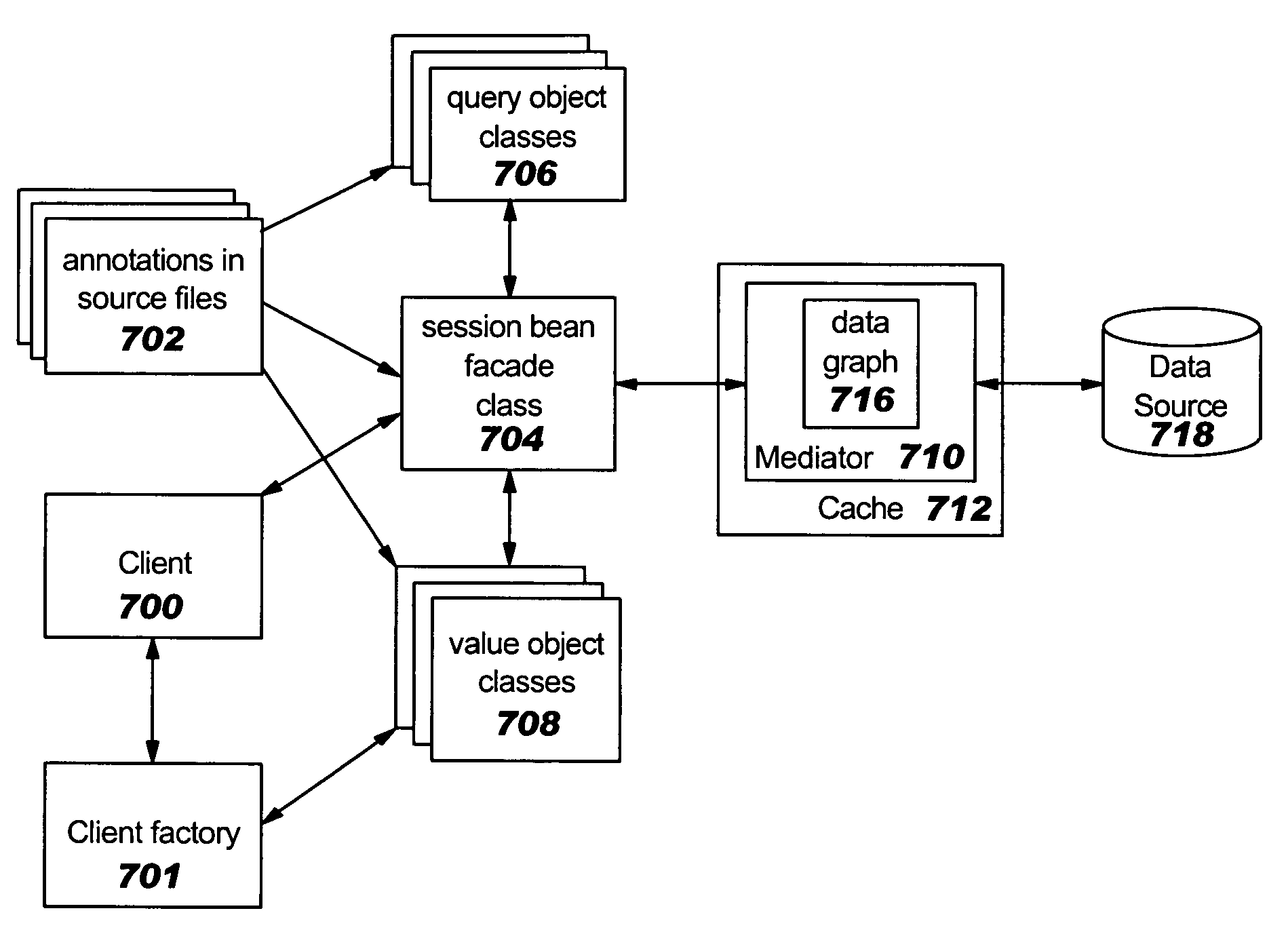
Method and apparatus for generating a service data object based service pattern for an enterprise java beans model
InactiveUS20060122971A1Digital data processing detailsProgram controlProgramming languageEnterprise Java Bean
A method and apparatus for generating a service data object based service pattern for an EJB model is provided. Definitions of session bean façade, SDOs, and queries are defined in entity beans. When the definitions are processed, SDOs, related SDOs, and queries for SDOs are added to the session bean façade. At run time, a client may manipulate the SDOs and apply changes to the SDOs via a mediator obtained from a mediator cache. The mediator persists the SDOs to a data graph without interfering the entity bean.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Method and apparatus for migration of managed application state for a Java based application
InactiveUS6912569B1Serious impact performanceResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsFistObject store
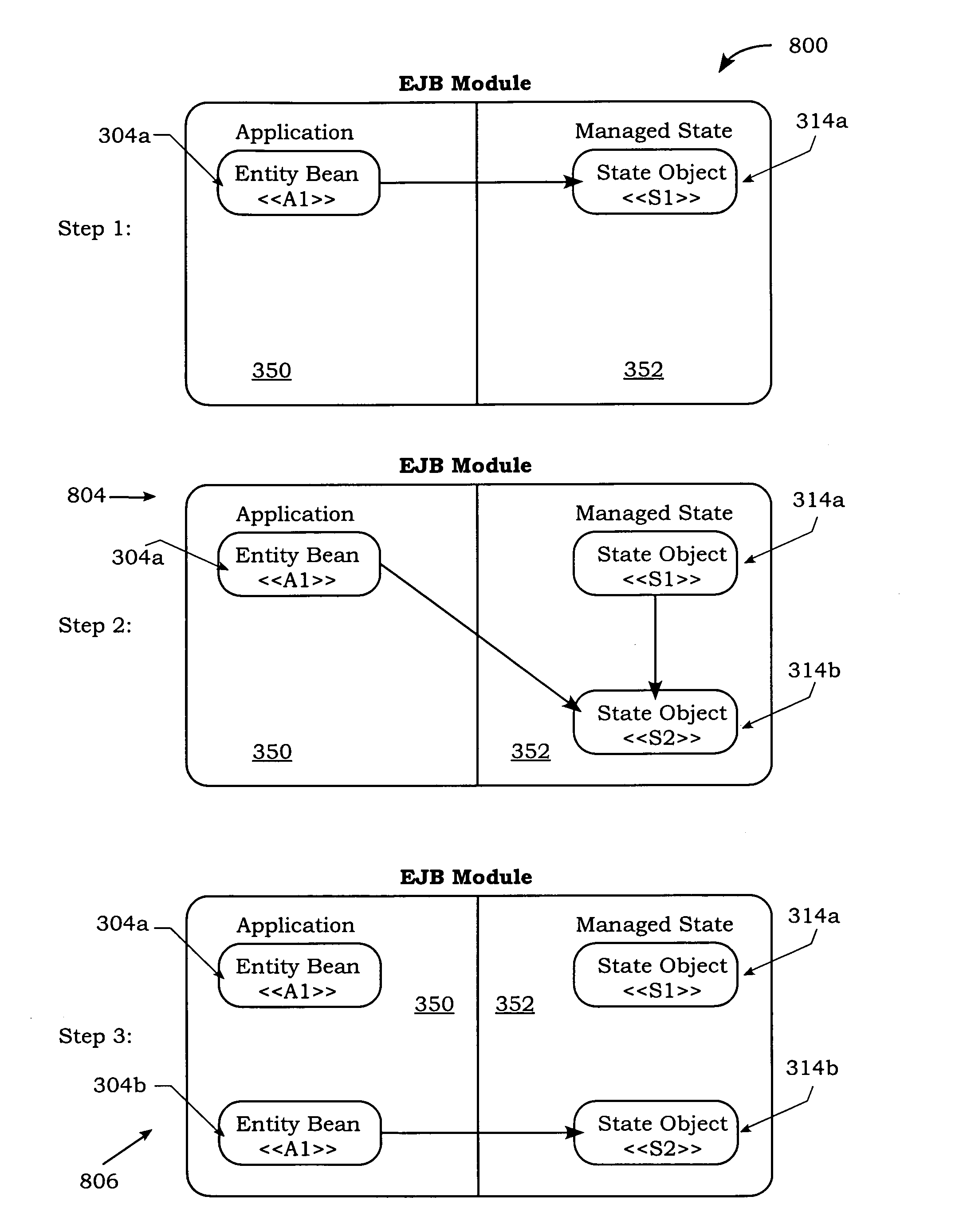
An invention for migrating managed application state for a Java based application is disclosed. A first Java module is executed on a first server. The first Java module includes a first entity bean and a first state object in communication with the first entity bean. The first state object stores a state of the first entity bean. The first state object is replicated to a state server or stored in-memory and made capable of migration by replicated state manager. Then, a second Java module is started on a second server as part of the module migration by a control module. The second Java module includes a second state object that is populated with state by either recovering from replica of fist state object stored on the state server or by getting transferred state of an in-memory copy of first state object managed on first server.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for upgrading managed application state for a java based application
InactiveUS7266816B1Functionality is not disruptedSoftware engineeringProgram loading/initiatingPrimitive stateObject store
An invention is disclosed for performing online upgrades of applications, including the managed application state, without disrupting the functionality of the application during the upgrade process. A Java module is executed on a server, where the Java module includes at least one original entity bean and at least one original state object in communication with the original entity bean. The original state object stores a state of the original entity bean. Then, an upgraded state object is generated and the state stored in the original state object is transferred to the upgraded state object. In this manner, state management for the original entity bean can be provided using the upgraded state object.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for raising reliability of software system based on strucural member
InactiveCN1710865ASolve centralized problemsData switching networksApplication serverSoftware system
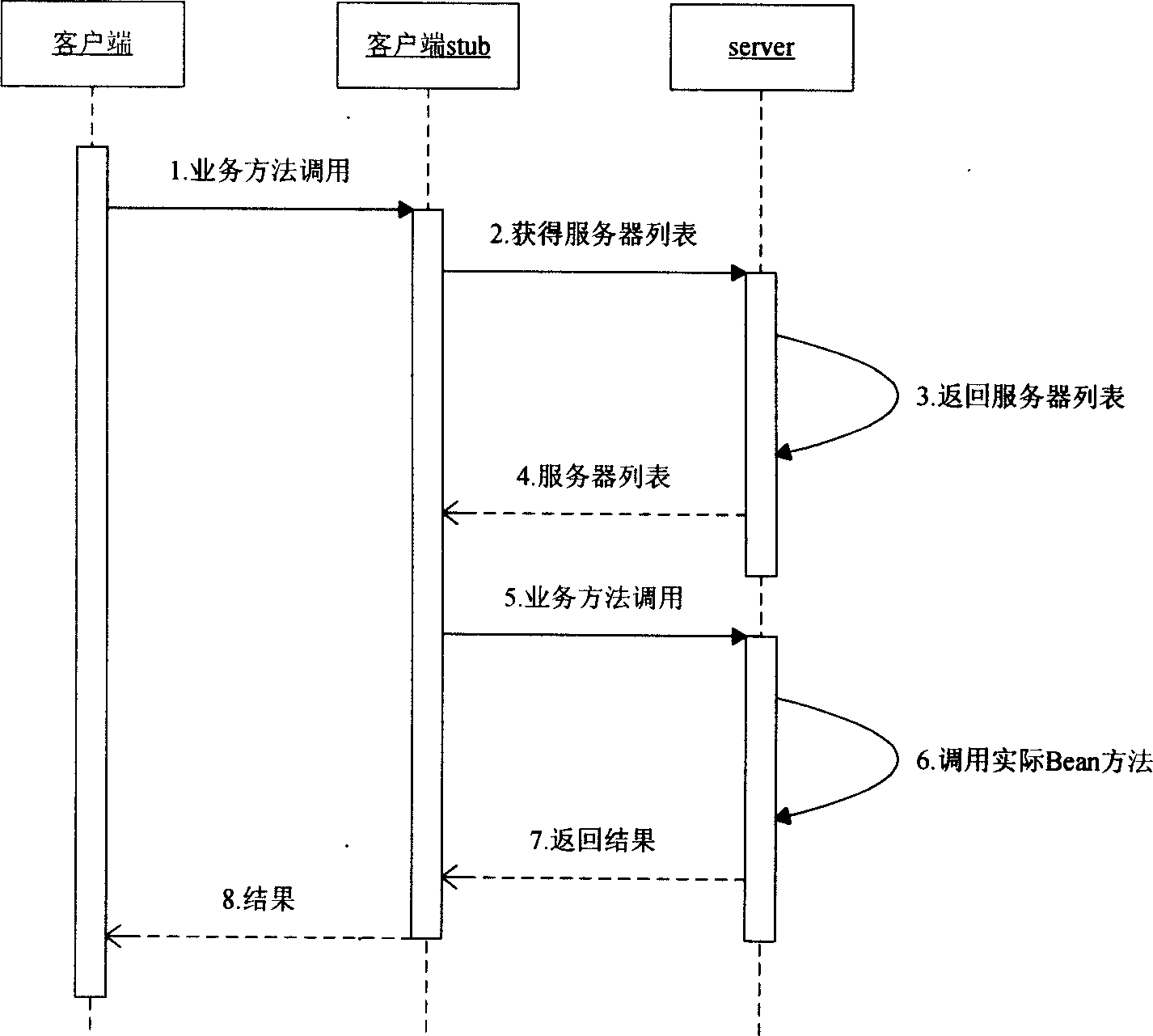
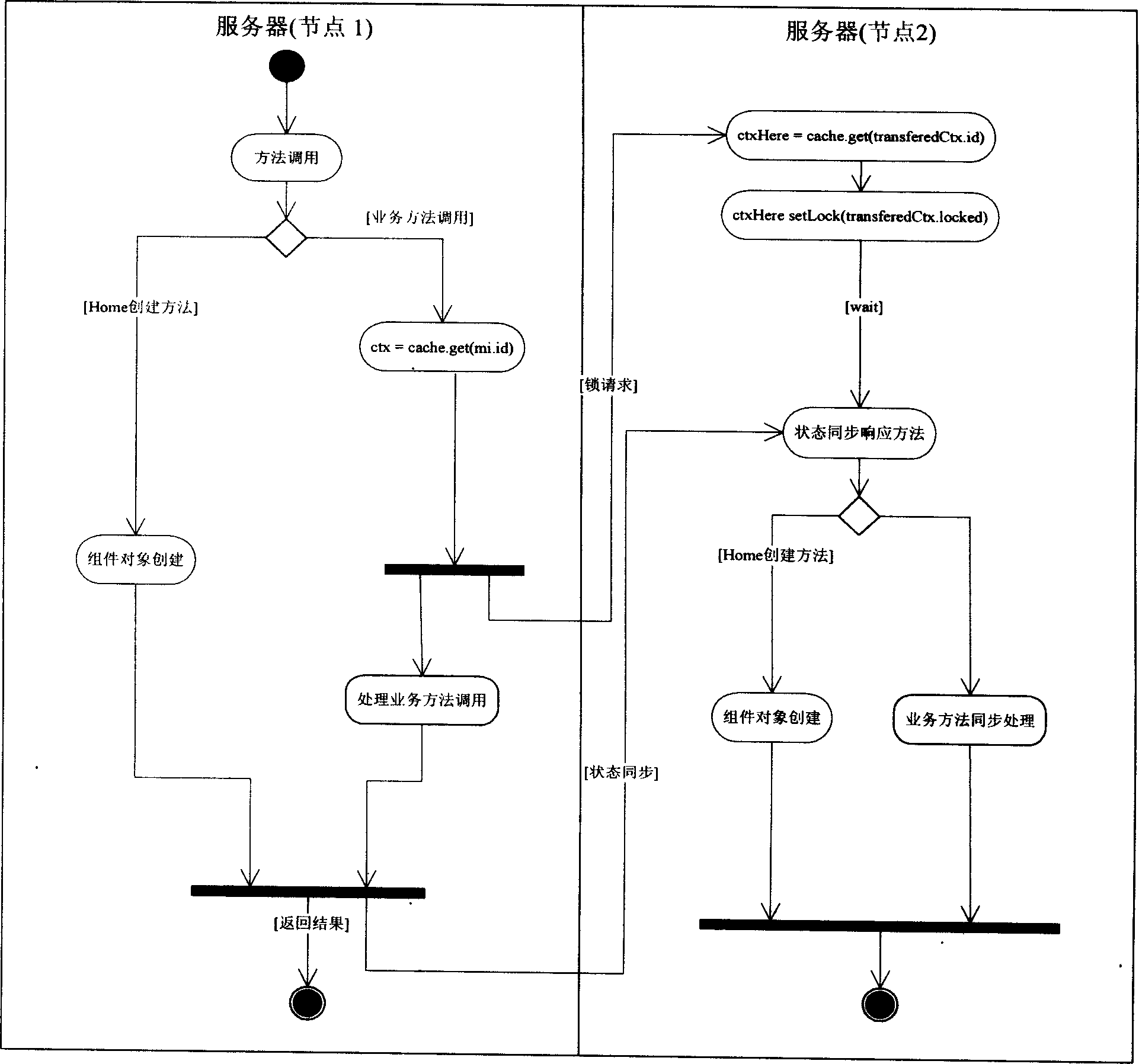
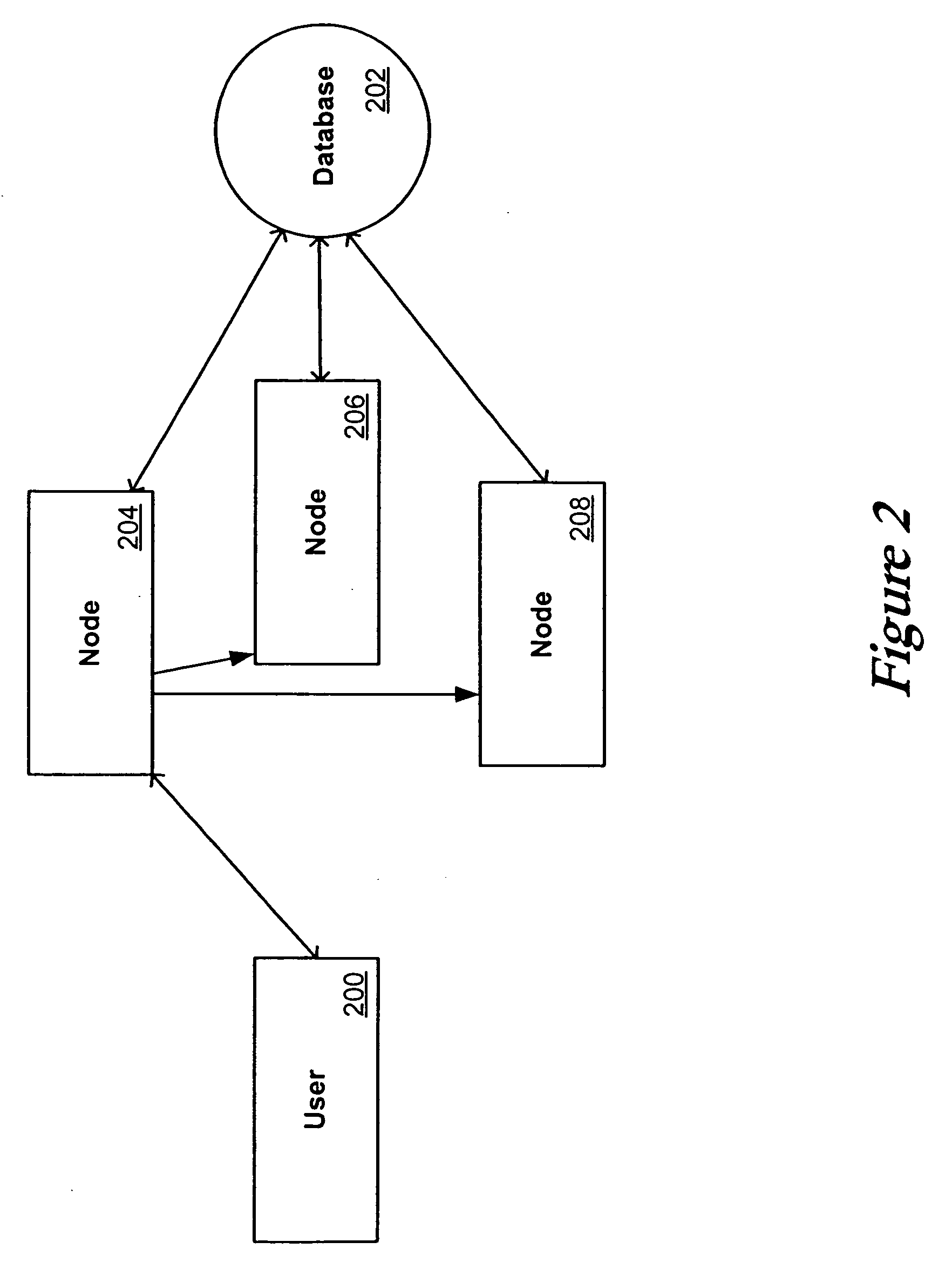
Under condition that JToneFrame application server cluster with multiple nodes does not stop service, using strategy of distributed load allocation, the disclosed method can realize following functions: loading and deleting node in cluster dynamically; supporting horizontal and vertical segmentation; balancing EJB container loads in object level and method level; cluster of supporting non state conversation Bean, state conversation Bean and entity Bean. In the invention, there is no possibility of single nonserviceable point; load divider is not self-existent, and load divider is as a module of each node. Thus, the invention solves issue of centeralization, and allocates requests to each node dispersedly.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for flushing bean cache
InactiveUS20050177550A1Digital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationCache serverOriginal data
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a service data object based service pattern for an enterprise Java beans model
InactiveUS7769747B2Digital data processing detailsProgram controlProgramming languageEnterprise Java Bean
A method and apparatus for generating a service data object based service pattern for an EJB model is provided. Definitions of session bean façade, SDOs, and queries are defined in entity beans. When the definitions are processed, SDOs, related SDOs, and queries for SDOs are added to the session bean façade. At run time, a client may manipulate the SDOs and apply changes to the SDOs via a mediator obtained from a mediator cache. The mediator persists the SDOs to a data graph without interfering the entity bean.
Owner:LINKEDIN
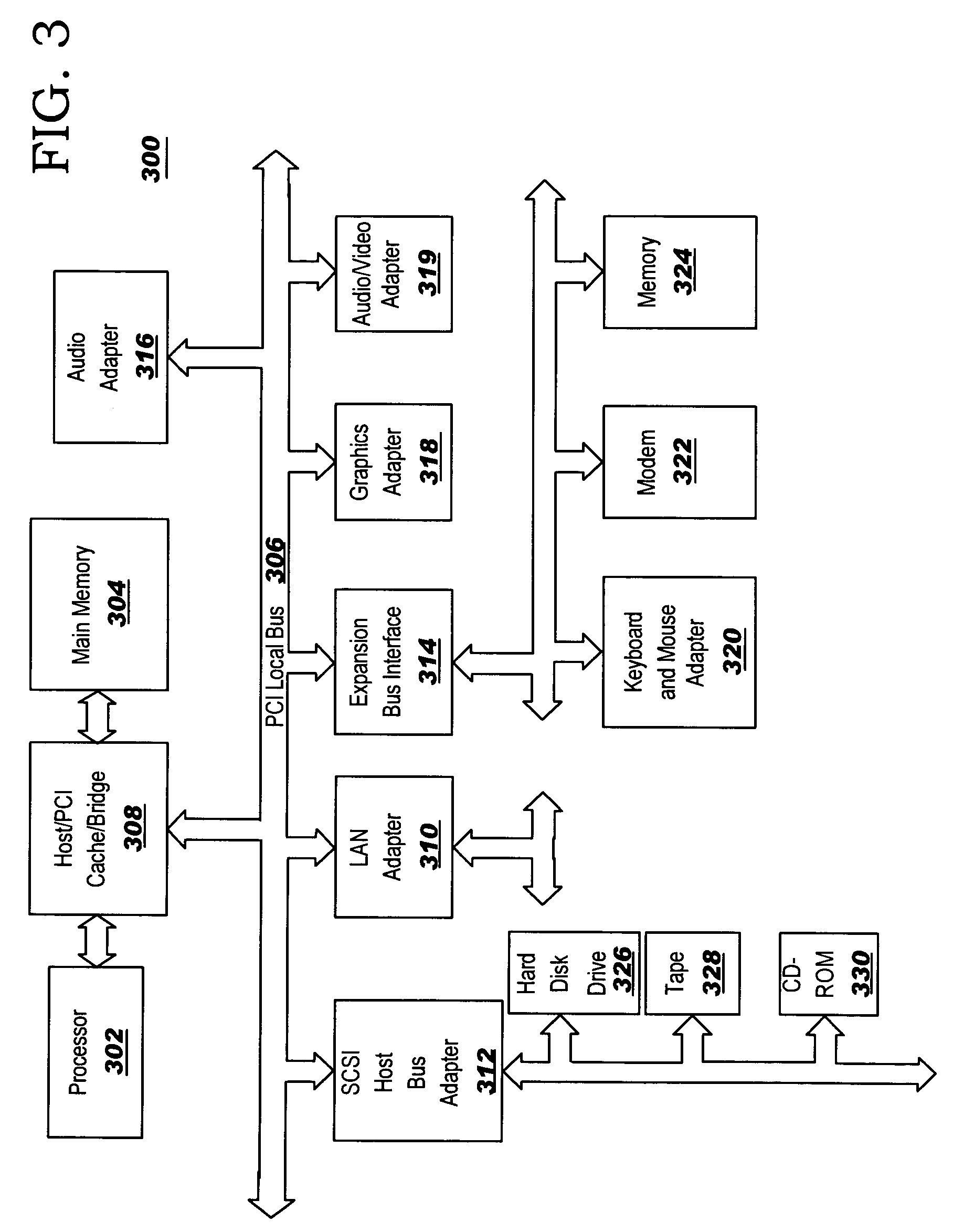
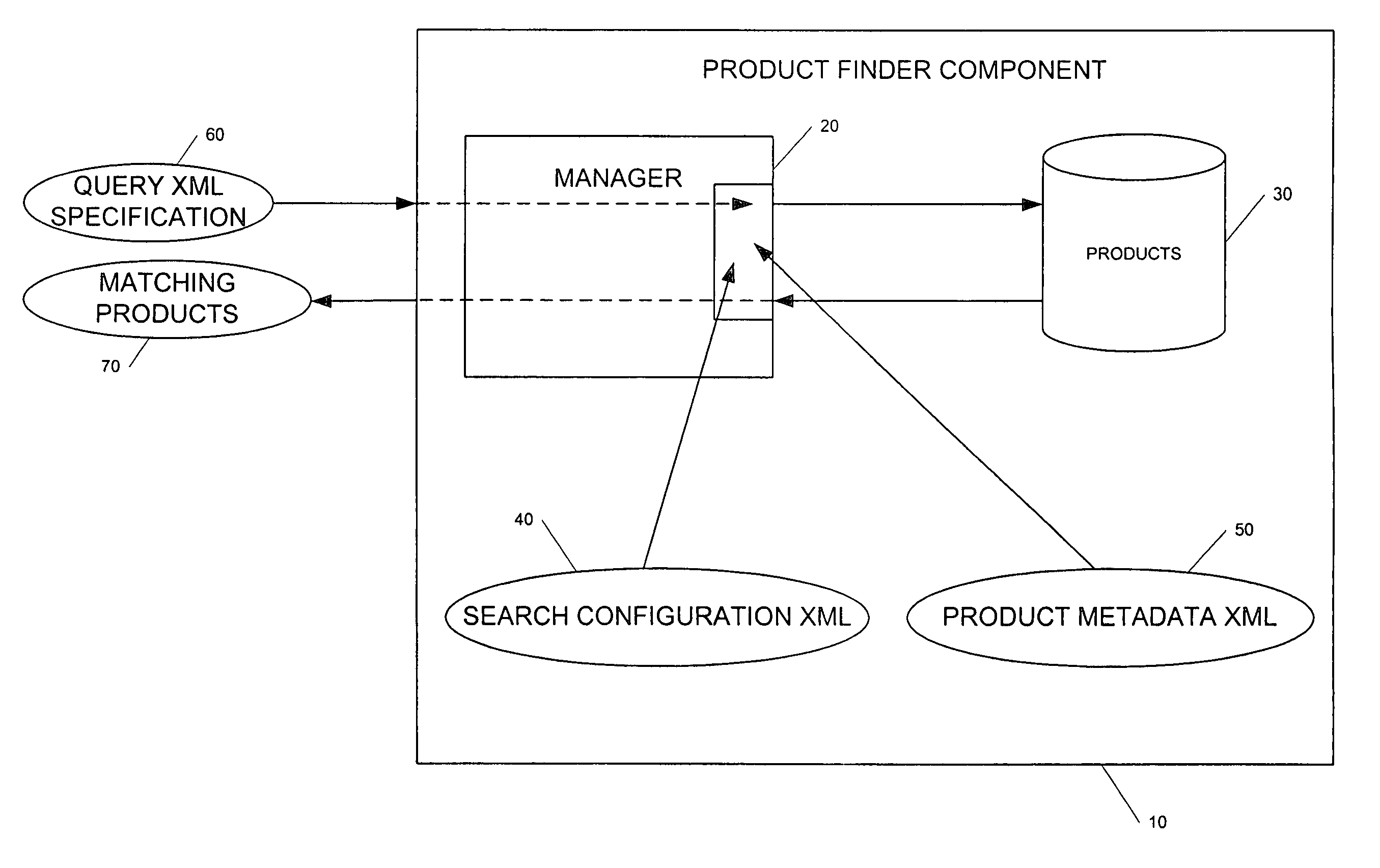
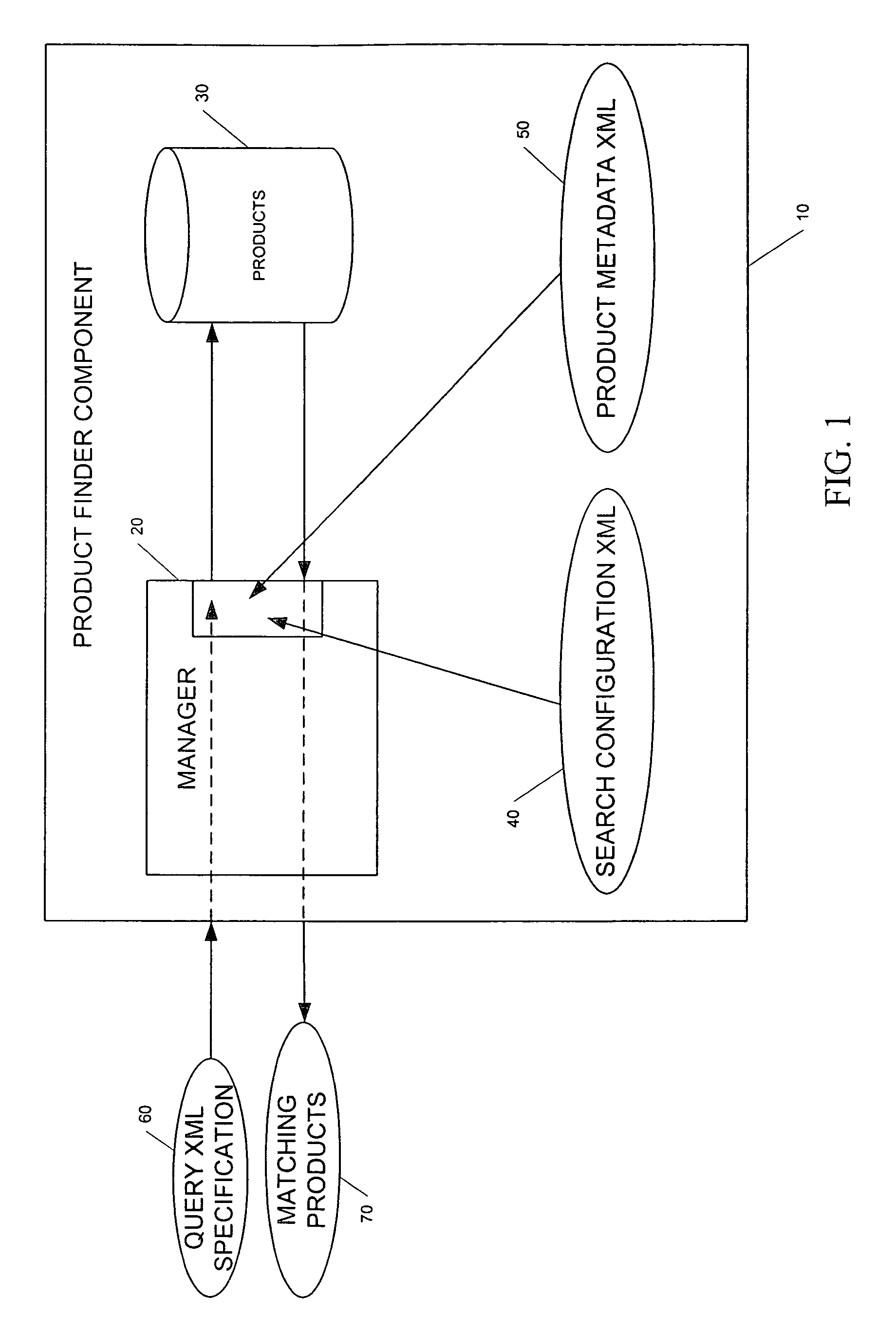
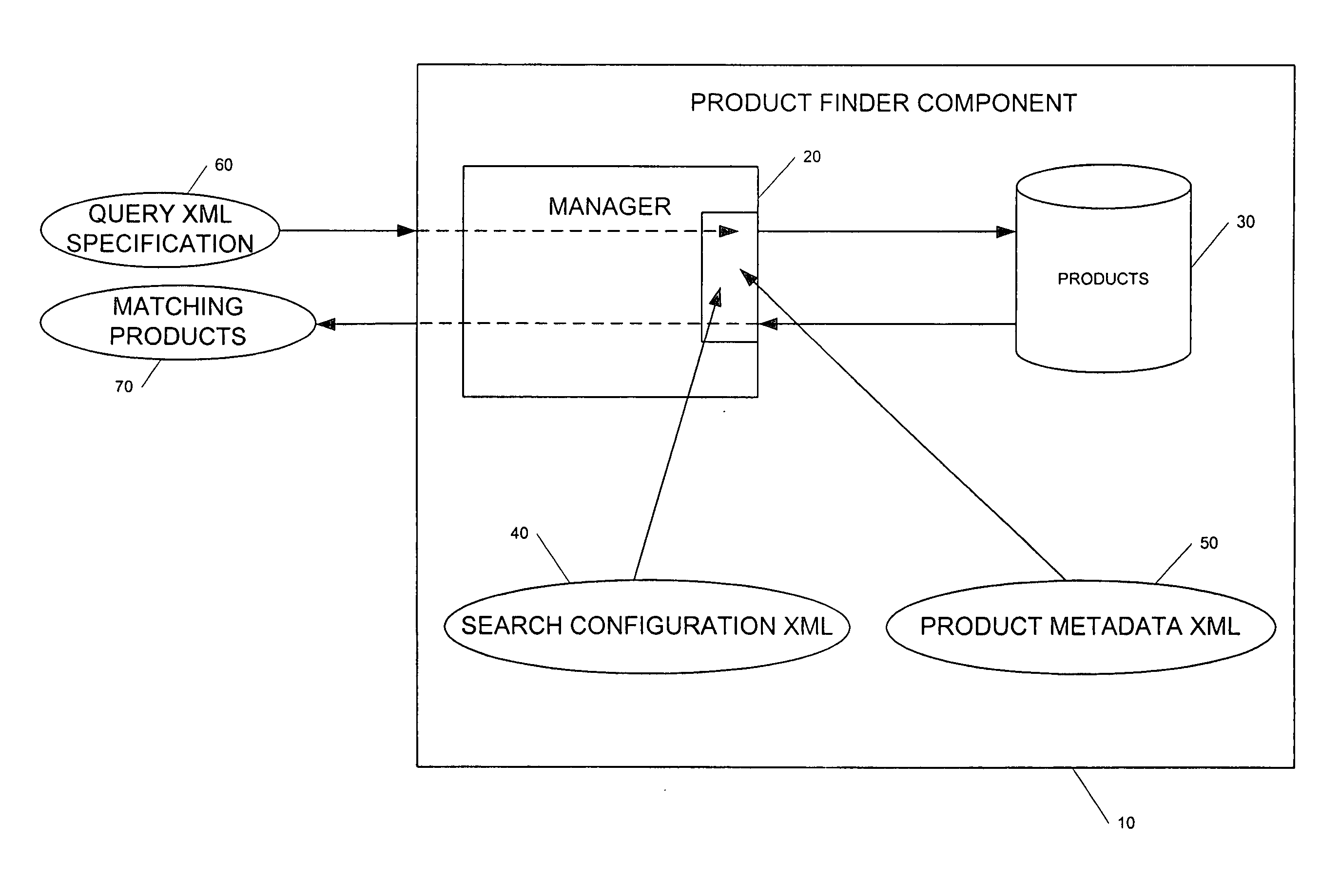
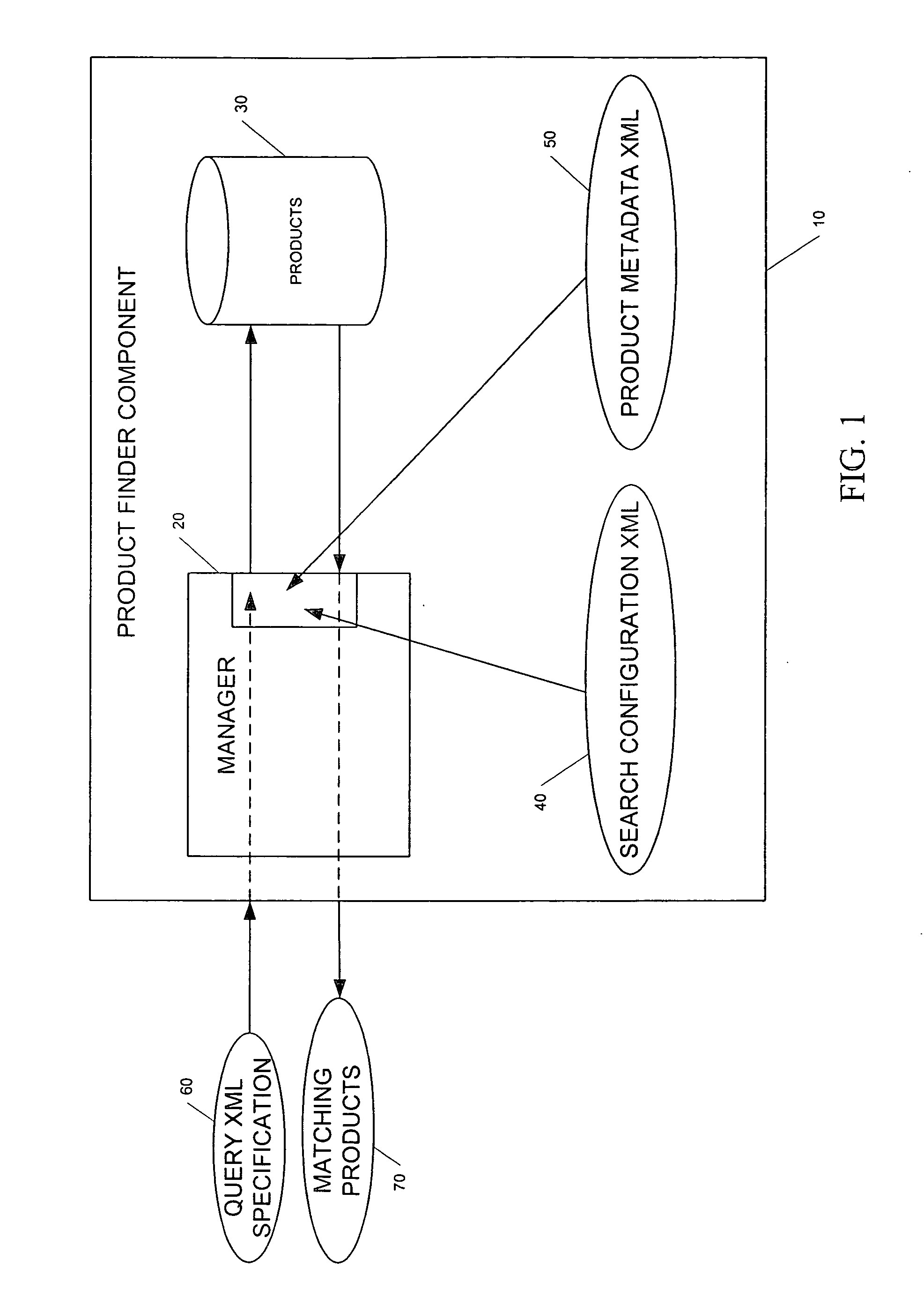
Generic product finder system and method
A generic product finder system that provides the capability of managing and performing searches on configurable products in a J2EE application. The generic product finder system includes a manager component for performing searches in response to a search query; a product component for persisting a plurality of product information and interacting with the manger component in conducting searches of the product information; a product metadata component that interacts with the manager component for defining a product; and a search configuration component that interacts with the manager component for constructing a set of search rules in a product search configuration. Internally, the product finder system represents products with a specification divided into parameters representing characteristics and optional attributes. This specification exists in a generic state by the use of Java objects. Multiple product specifications may co-exist and their information is persisted by the use of entity beans. The generic product also contains a session bean that acts as manager and single point-of-entry to the product information. Since the products are maintained in a generic form, search rules can be constructed and applied to the product set to perform complex queries.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
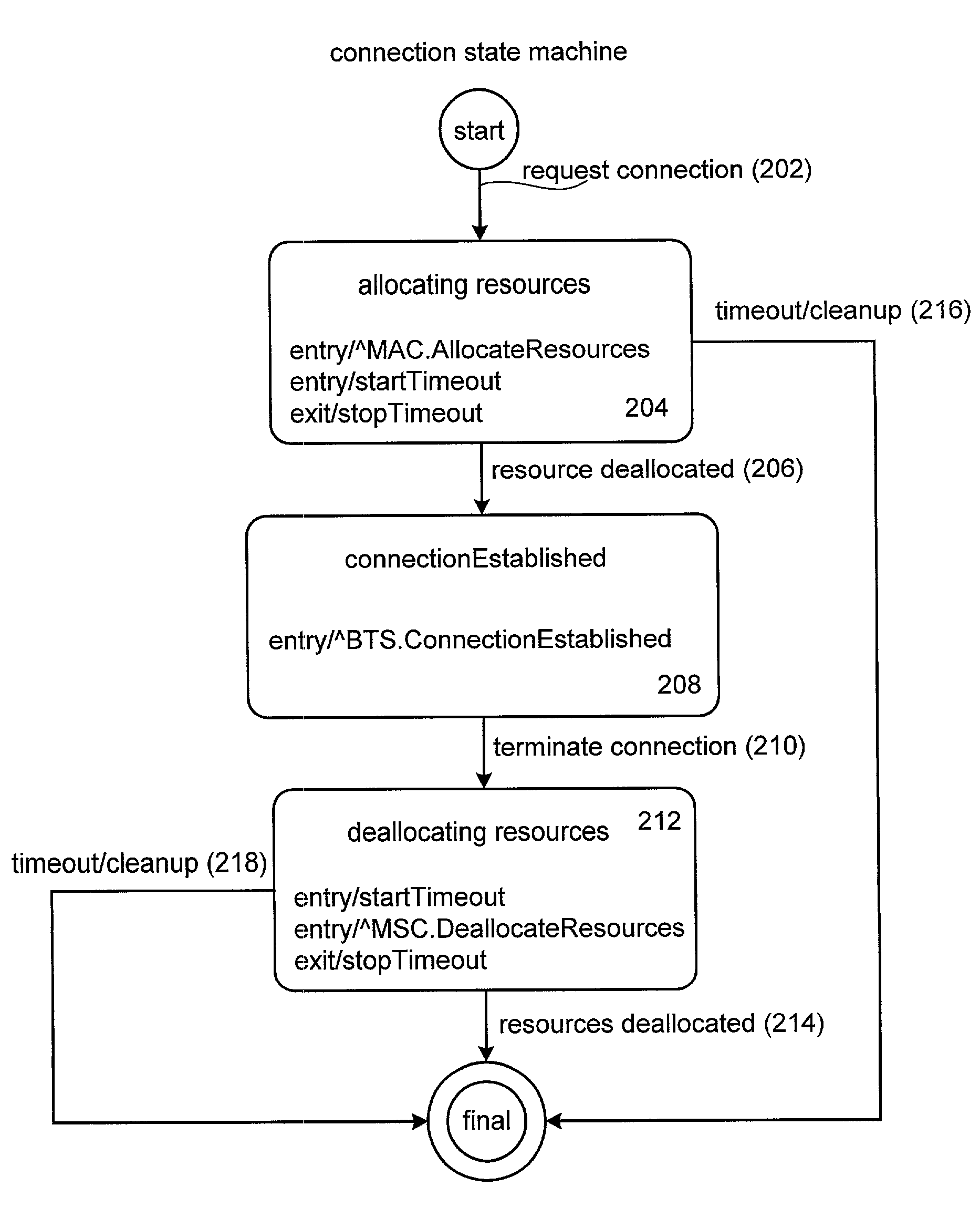
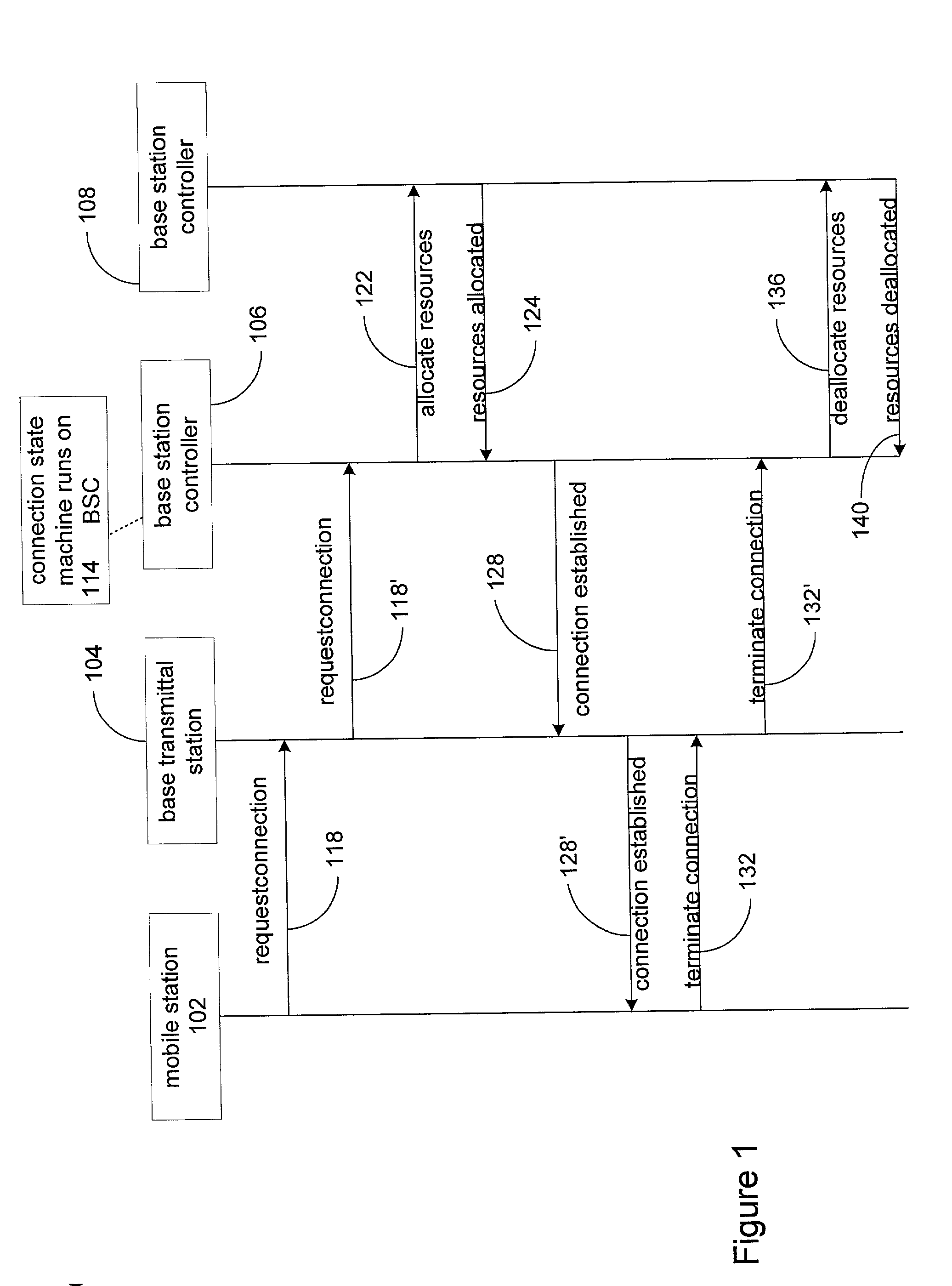
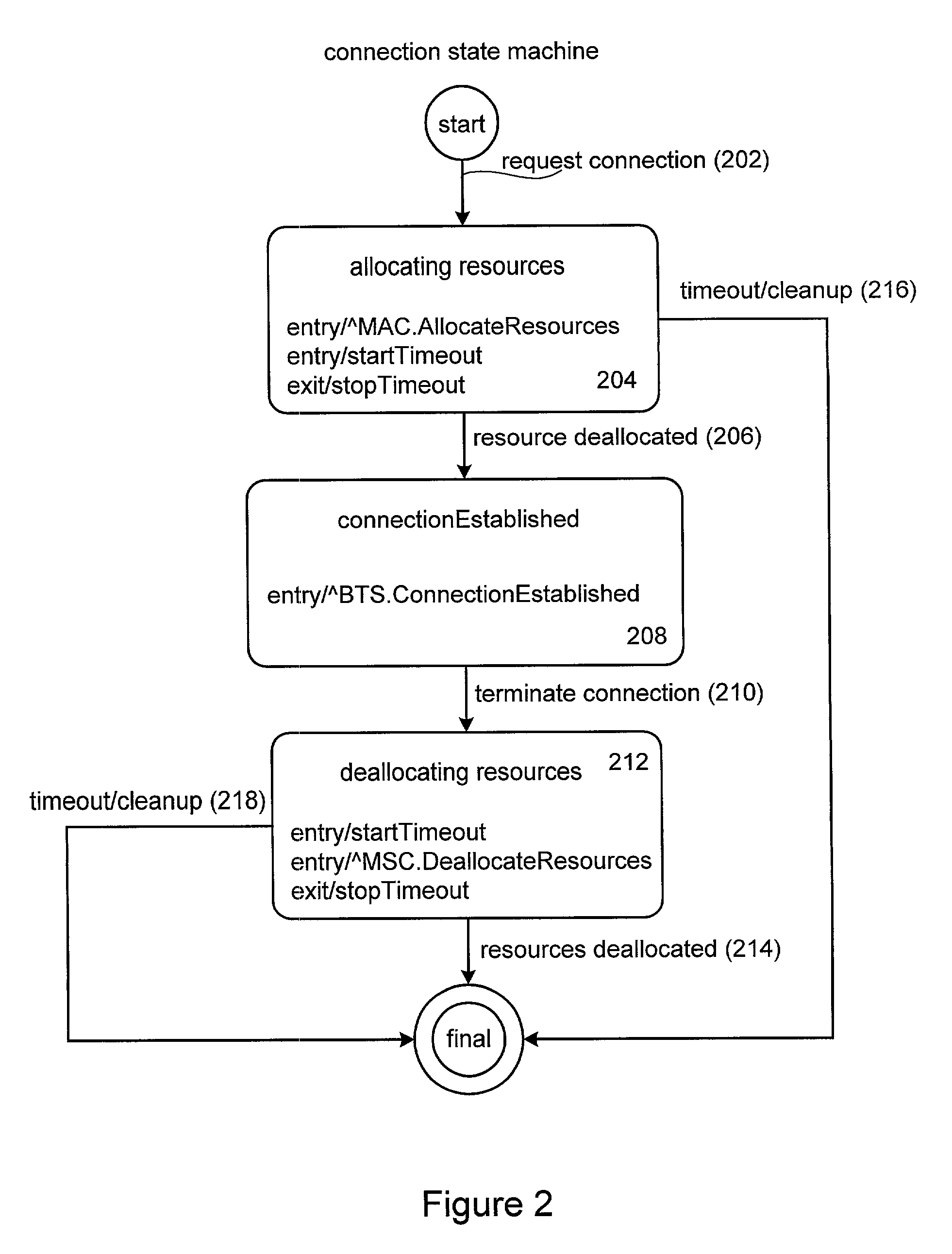
Method and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise javabean components
InactiveUS20020040409A1Interprogram communicationSpecific program execution arrangementsDatabaseEntity Bean
Methods and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise beans on an enterprise platform are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a state machine which is arranged to be used within a computing system that supports an enterprise platform includes an entity bean class, a home interface associated with the entity bean class, and a remote interface that is also associated with the entity bean class. The home interface is arranged to create, find, and remove entity objects, while the remote interface being arranged to drive the state machine. In one embodiment, the entity bean class is associated with an entity object. In such an embodiment, the entity object, the home interface, and the remote interface are included in an entity bean which may be an Enterprise JavaBean.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
System and method for time-aware run-time to guarantee time
InactiveUS8424005B2Improve usabilityError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsTimestampRunning time
A method and system for achieving time-awareness in the highly available, fault-tolerant execution of components in a distributed computing system, without requiring the writer of these components to explicitly write code (such as entity beans or database transactions) to make component state persistent. It is achieved by converting the intrinsically non-deterministic behavior of the distributed system to a deterministic behavior, thus enabling state recovery to be achieved by advantageously efficient checkpoint-replay techniques. The system is deterministic by repeating the execution of the receiving component by processing the messages in the same order as their associated timestamps and time-aware by allowing adjustment of message execution based on time.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
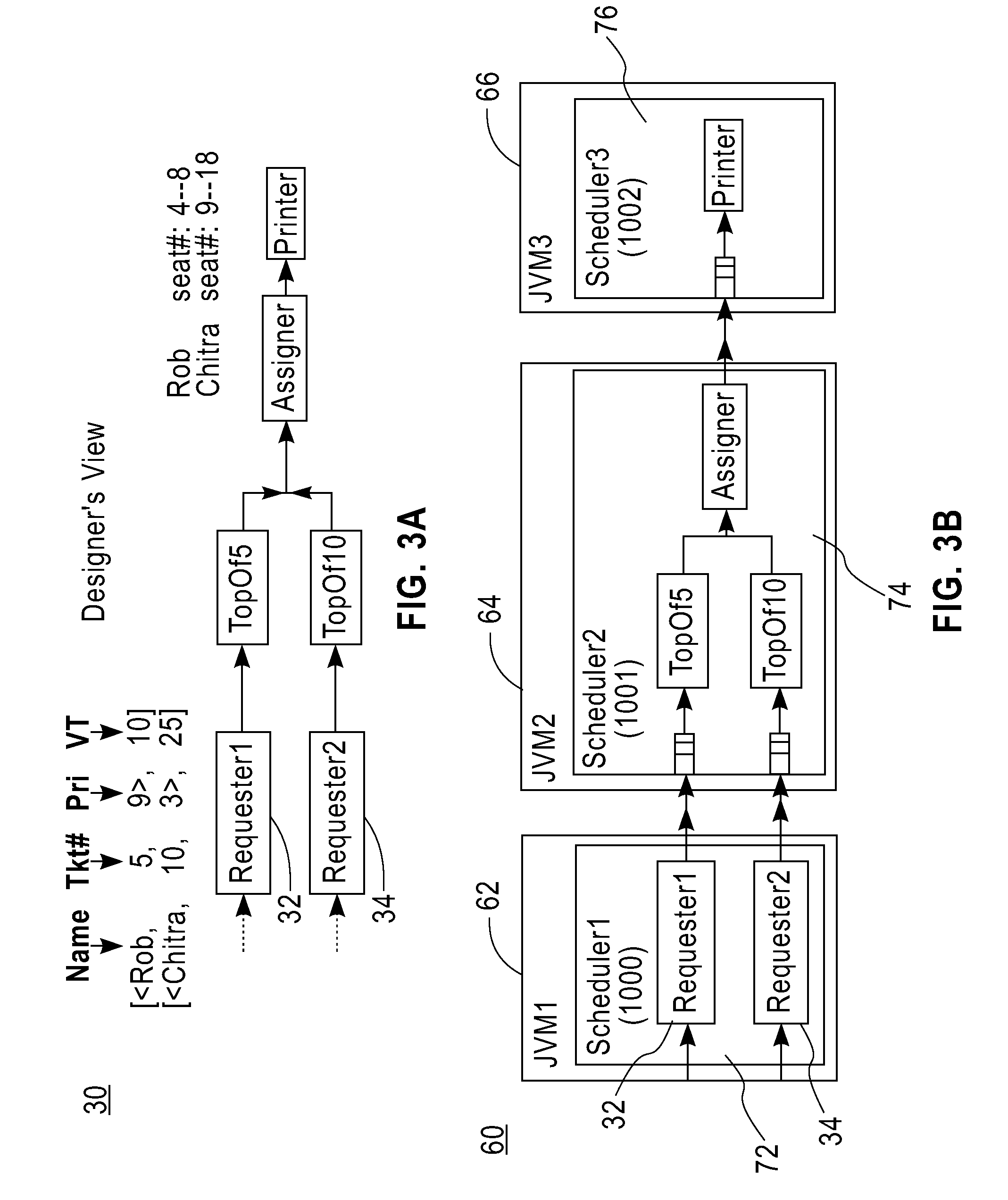
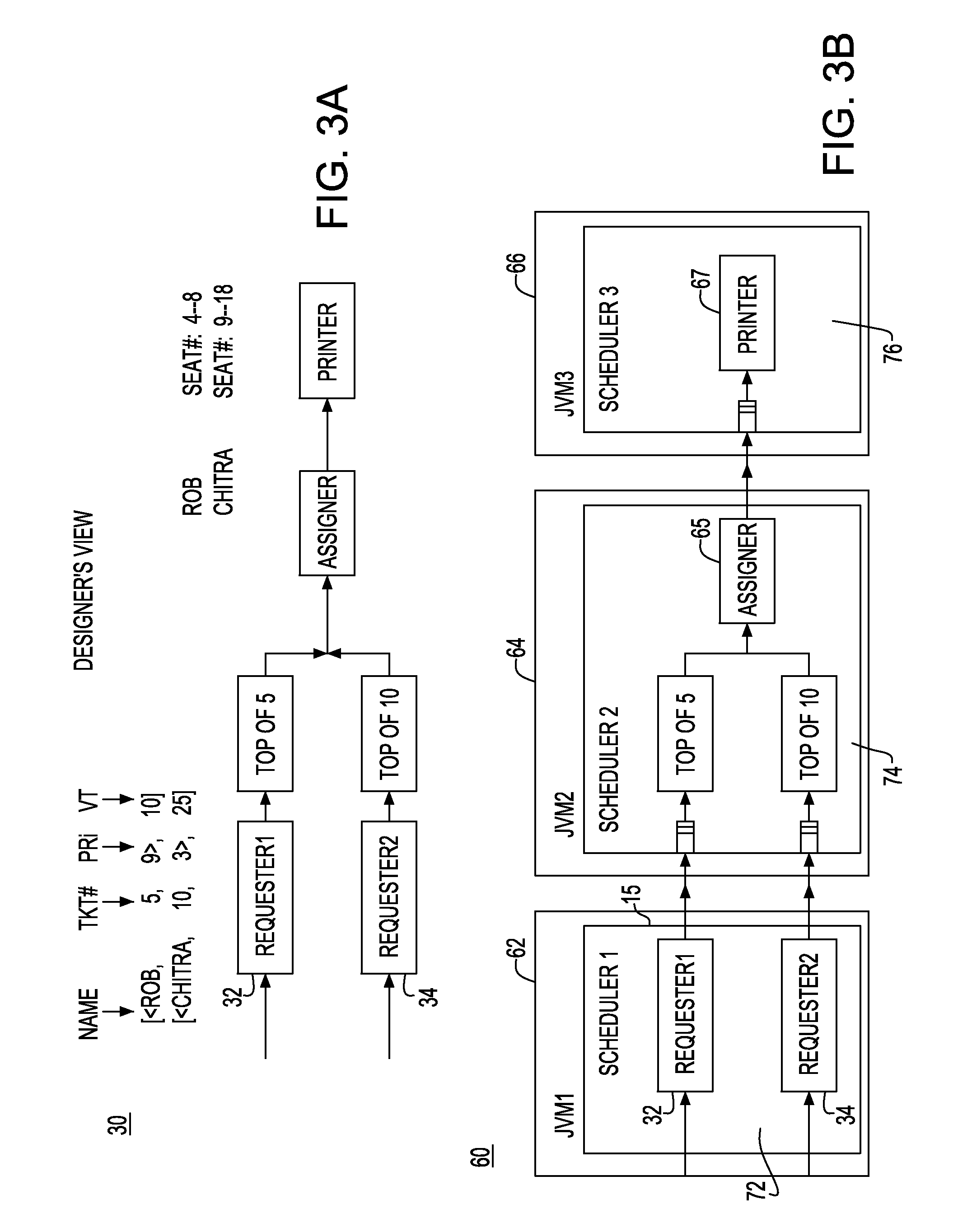
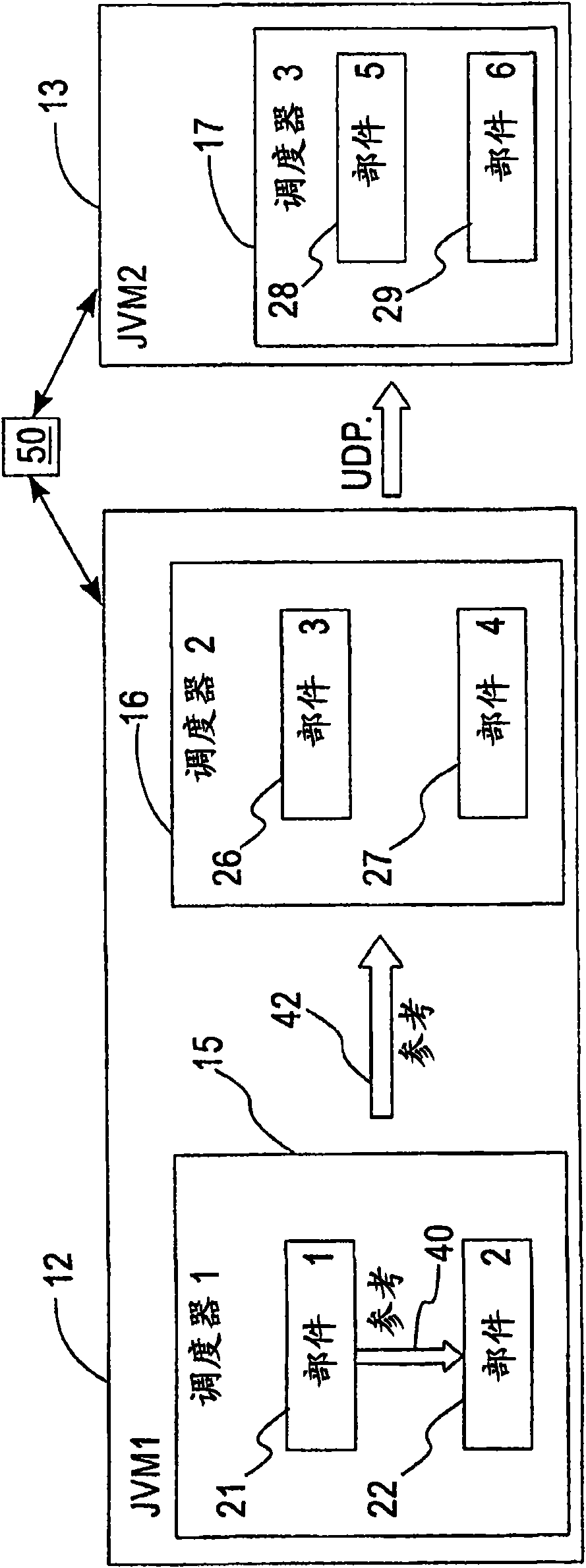
Graphical user interface and background search methodology for creating references between software components
ActiveUS7360170B1Software designSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
According to one aspect of the invention a graphical user interface is provided. The graphical user interface includes a window displaying a first item and a menu listing a second item. Selection of the first item within the window and the second item in the menu helps to define a reference created between the first item and a target software component. The first item may be a source software component, a page, or a servlet. The second item may be the target software component or an interface to the target software component. The graphical user interface may also include a second menu listing the interface to the target software component. The source and target software components may be session or entity beans. The interface may be a remote, remote home, local, or local home interface.
Owner:SAP AG
Web services database cluster structure and method thereof
InactiveCN101042767AData switching detailsDatabase distribution/replicationWeb serviceData virtualization
There is disclosed configuring of clustered web services nodes accessing a common database, including implementing a data virtualization layer at each node to abstract an instance of the database from a web service application. In one embodiment, at each node is performed creating a first, data virtualization entity bean having all read and write operations of an application-developed (master) entity bean, creating a second entity bean that carries only the read operations of the master entity bean and addresses the replica instance, receiving an operation request at the first entity bean, and routing a request to either the master entity bean or the second entity bean depending upon the requested operation to access the respective database instance. In another embodiment, at each node is performed implementing an empty database instance having a schema matching the common database, identifying a relevant partitioning in a query utilizing the empty database, and routing the query to a respective partitioned database instance.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for time-aware run-time to guarantee time
InactiveUS20110023050A1Improve usabilityError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsTimestampRunning time
A method and system for achieving time-awareness in the highly available, fault-tolerant execution of components in a distributed computing system, without requiring the writer of these components to explicitly write code (such as entity beans or database transactions) to make component state persistent. It is achieved by converting the intrinsically non-deterministic behavior of the distributed system to a deterministic behavior, thus enabling state recovery to be achieved by advantageously efficient checkpoint-replay techniques. The system is deterministic by repeating the execution of the receiving component by processing the messages in the same order as their associated timestamps and time-aware by allowing adjustment of message execution based on time.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method to implement container managed streams in J2EE environments
InactiveUS20060155745A1Automatic generatedSimple methodRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsData streamBatch processing
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for implementing container managed streams in an enterprise JavaBean™ environment. Uses, ownership, reference relationships between entity beans and sessions are specified in a deployment descriptor file. When an input data stream is received for a batch job, the file is processed and a method is generated on the entity beans, wherein the method allows for creating a container managed ownership entity representing a stream object for the input data stream, associates an entity bean with the stream, and returns the last unprocessed object in the stream to the user. A method may also be generated on the entity beans for creating a stream object for an output data stream, associating an entity bean with the stream, rerouting an object to the stream object, and appending the stream object to the end of the batch job queue.
Owner:IBM CORP
Generic product finder system and method
A generic product finder system that provides the capability of managing and performing searches on configurable products in a J2EE application. The generic product finder system includes a manager component for performing searches in response to a search query; a product component for persisting a plurality of product information and interacting with the manger component in conducting searches of the product information; a product metadata component that interacts with the manager component for defining a product; and a search configuration component that interacts with the manager component for constructing a set of search rules in a product search configuration. Internally, the product finder system represents products with a specification divided into parameters representing characteristics and optional attributes. This specification exists in a generic state by the use of Java objects. Multiple product specifications may co-exist and their information is persisted by the use of entity beans. The generic product also contains a session bean that acts as manager and single point-of-entry to the product information. Since the products are maintained in a generic form, search rules can be constructed and applied to the product set to perform complex queries.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
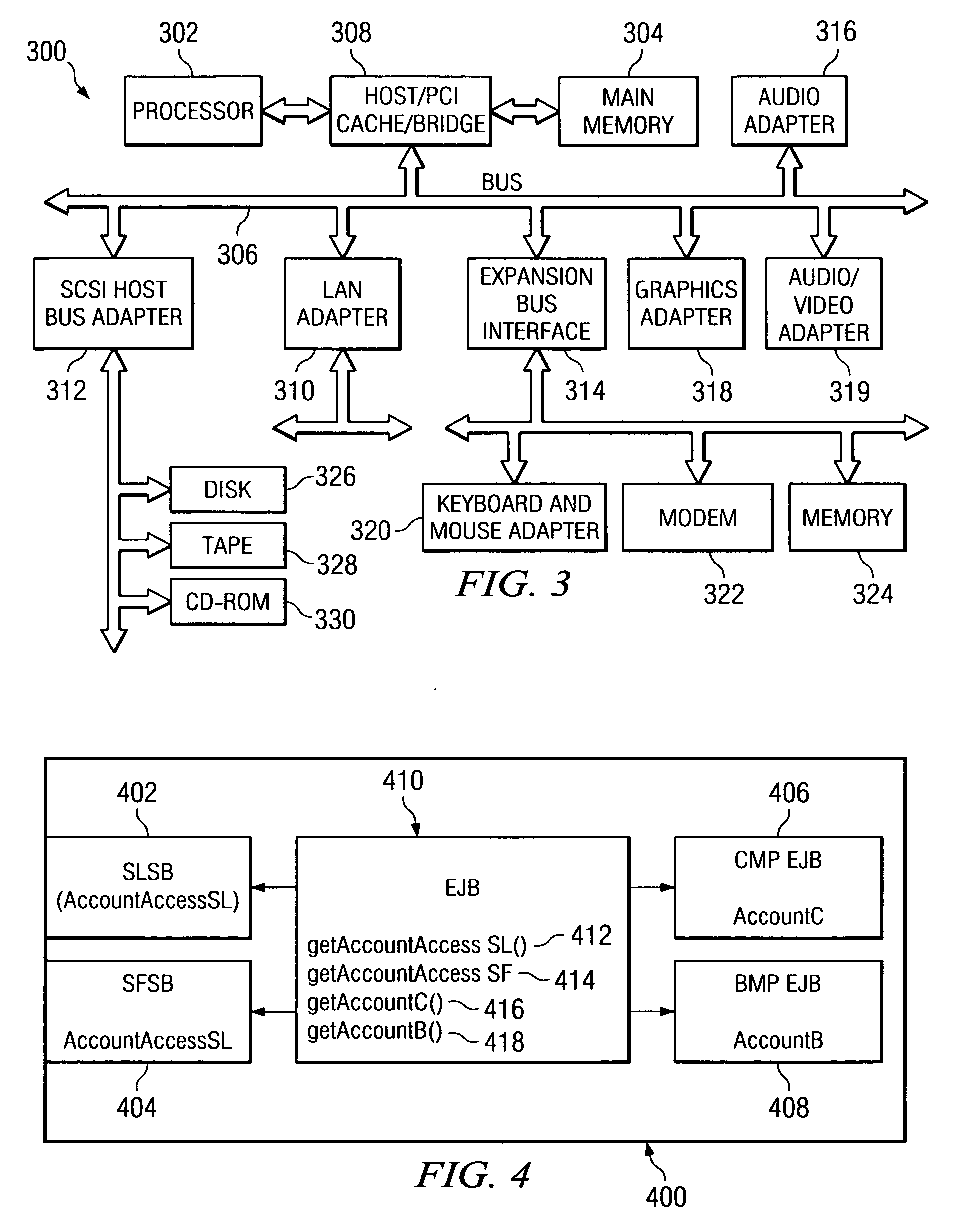
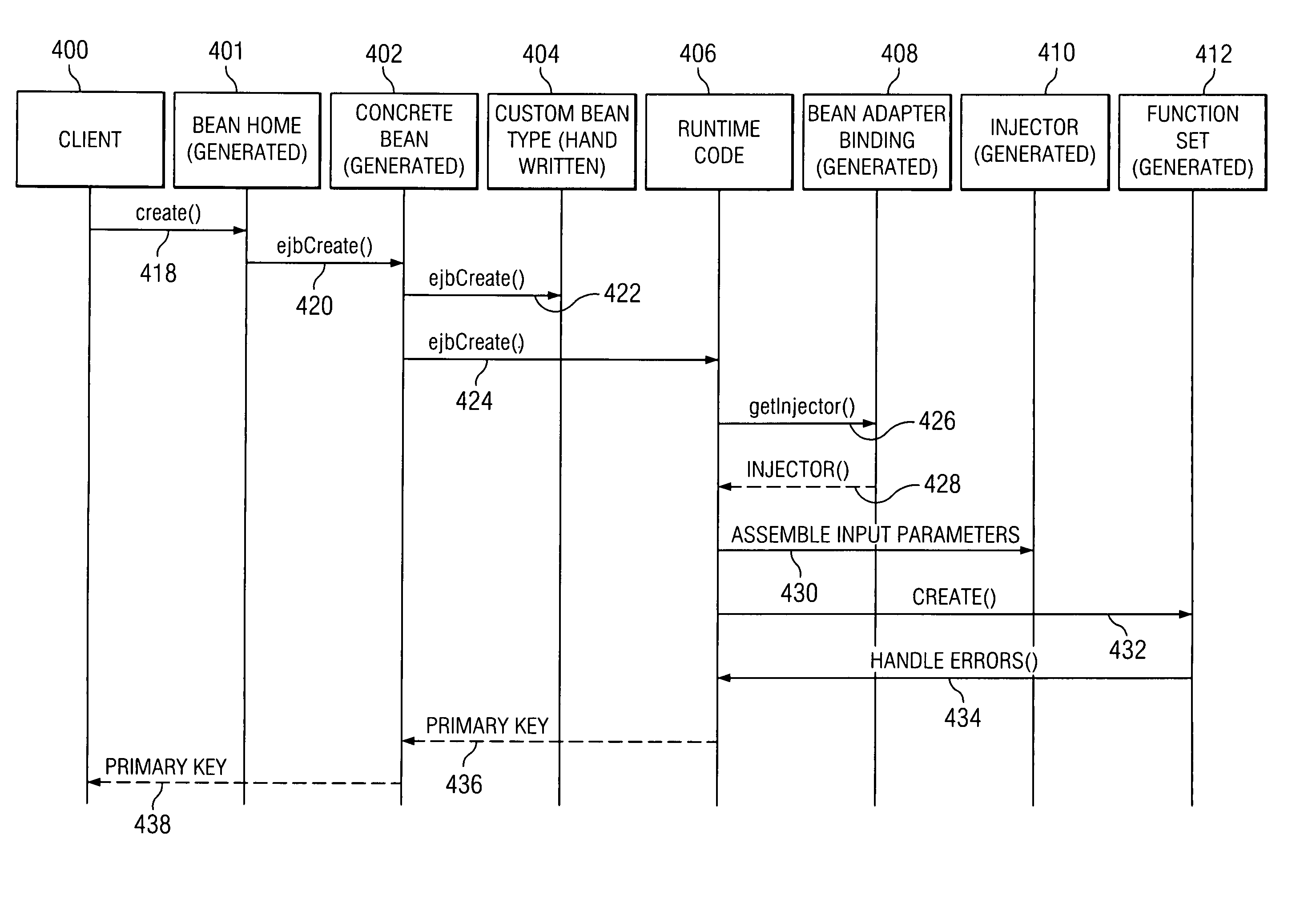
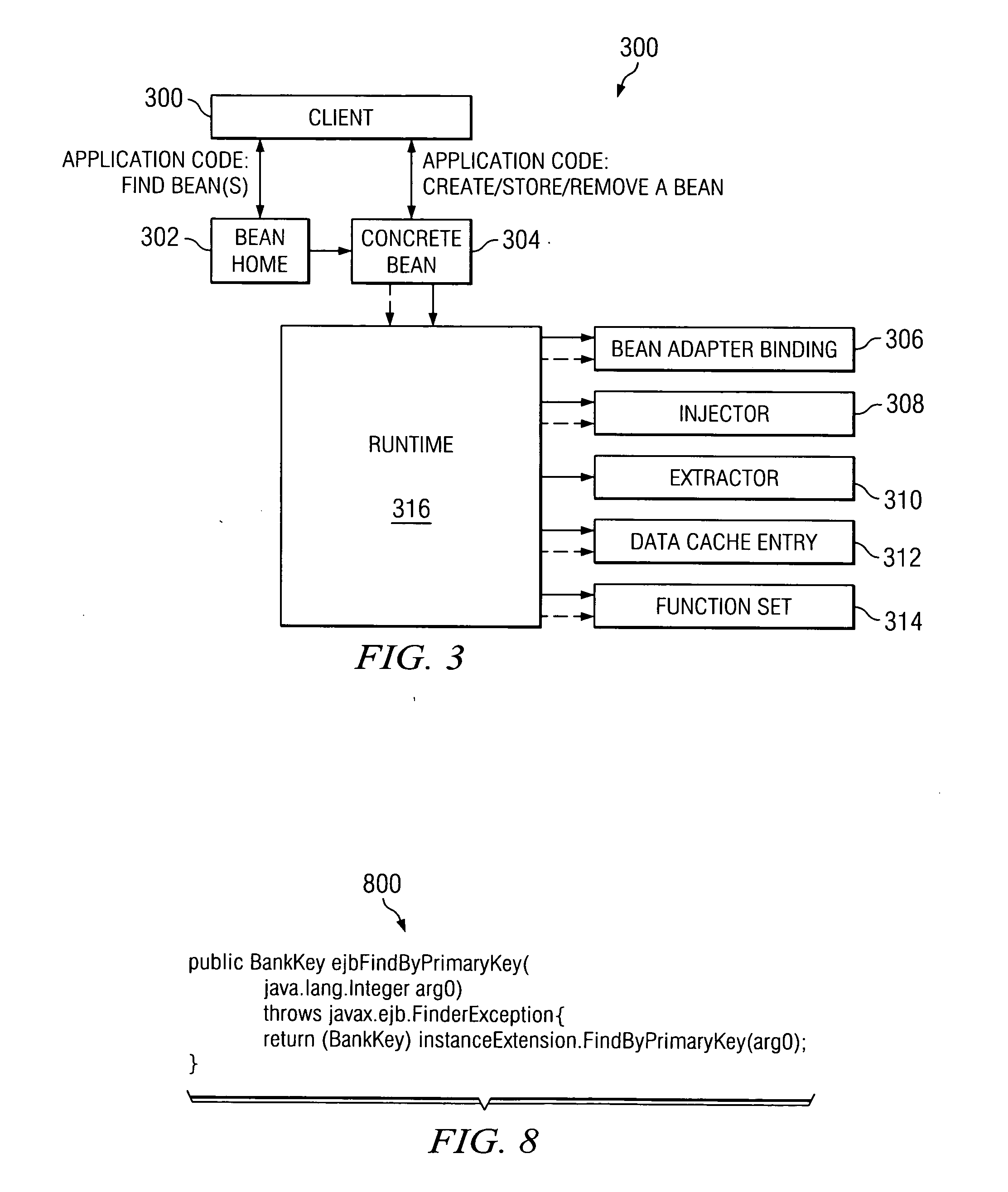
Method and apparatus for a container managed persistent entity bean support architecture
InactiveUS20050114835A1Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsProgramming languageCombined use
The present invention provides methods, apparatus and computer instructions for a container managed persistent support architecture that meets the Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) Specification. The support architecture provides application programmers a model for balancing generated components with runtime code to better optimize flexibility and efficiency of applications. Six generated components: concrete bean, bean adaptor binding, injector, extractor, data cache entry and function set, are used in combination with runtime code to perform typical operations of CMP entity beans.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for time-aware run-time to guarantee timeliness in component-oriented distributed systems
InactiveUS20130212592A1Improve usabilityProgram initiation/switchingError detection/correctionHigh availabilityEngineering
A method and system for achieving time-awareness in the highly available, fault-tolerant execution of components in a distributed computing system, without requiring the writer of these components to explicitly write code (such as entity beans or database transactions) to make component state persistent. It is achieved by converting the intrinsically non-deterministic behavior of the distributed system to a deterministic behavior, thus enabling state recovery to be achieved by advantageously efficient checkpoint-replay techniques. The system is deterministic by repeating the execution of the receiving component by processing the messages in the same order as their associated timestamps and time-aware by allowing adjustment of message execution based on time.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
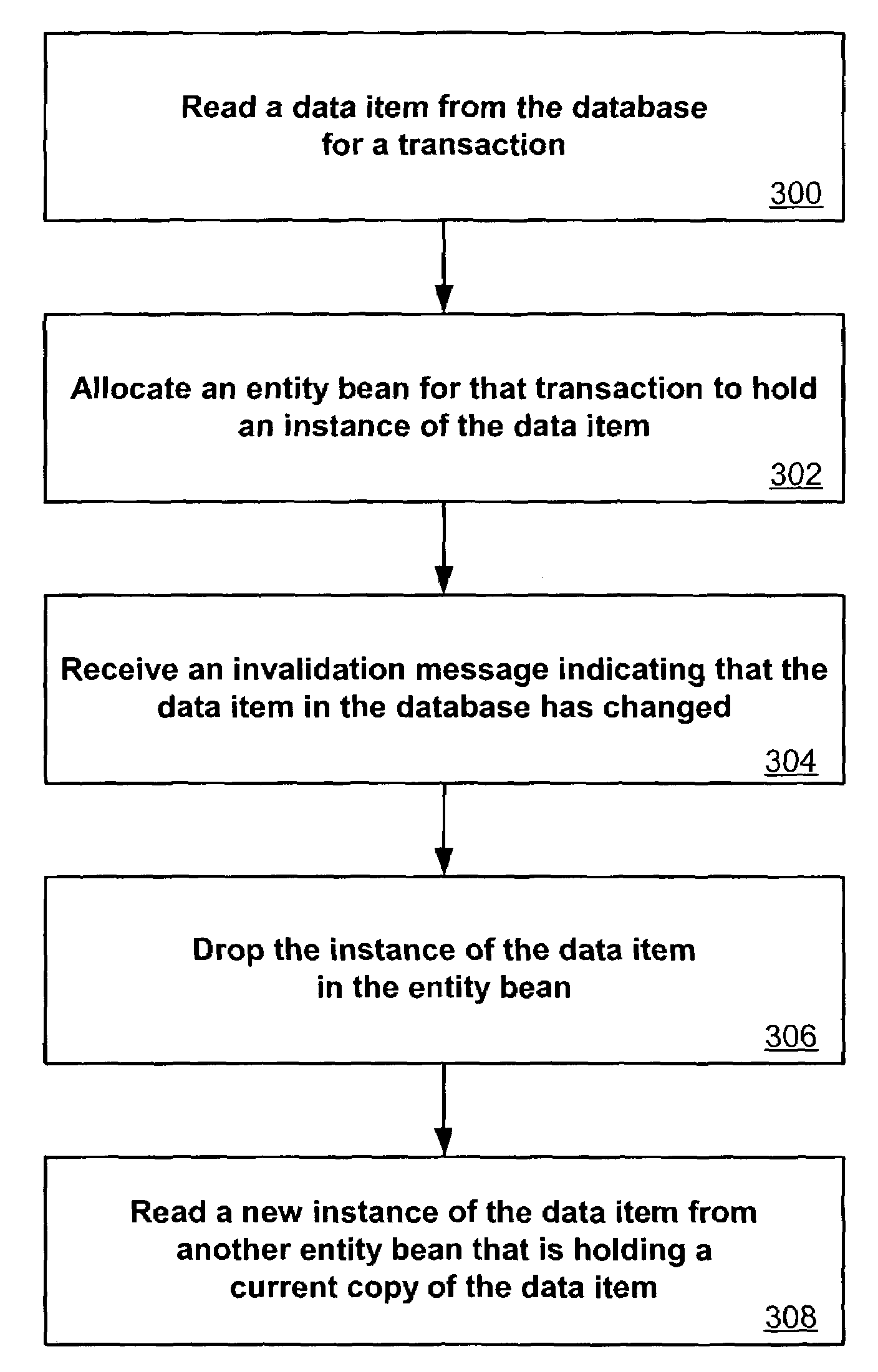
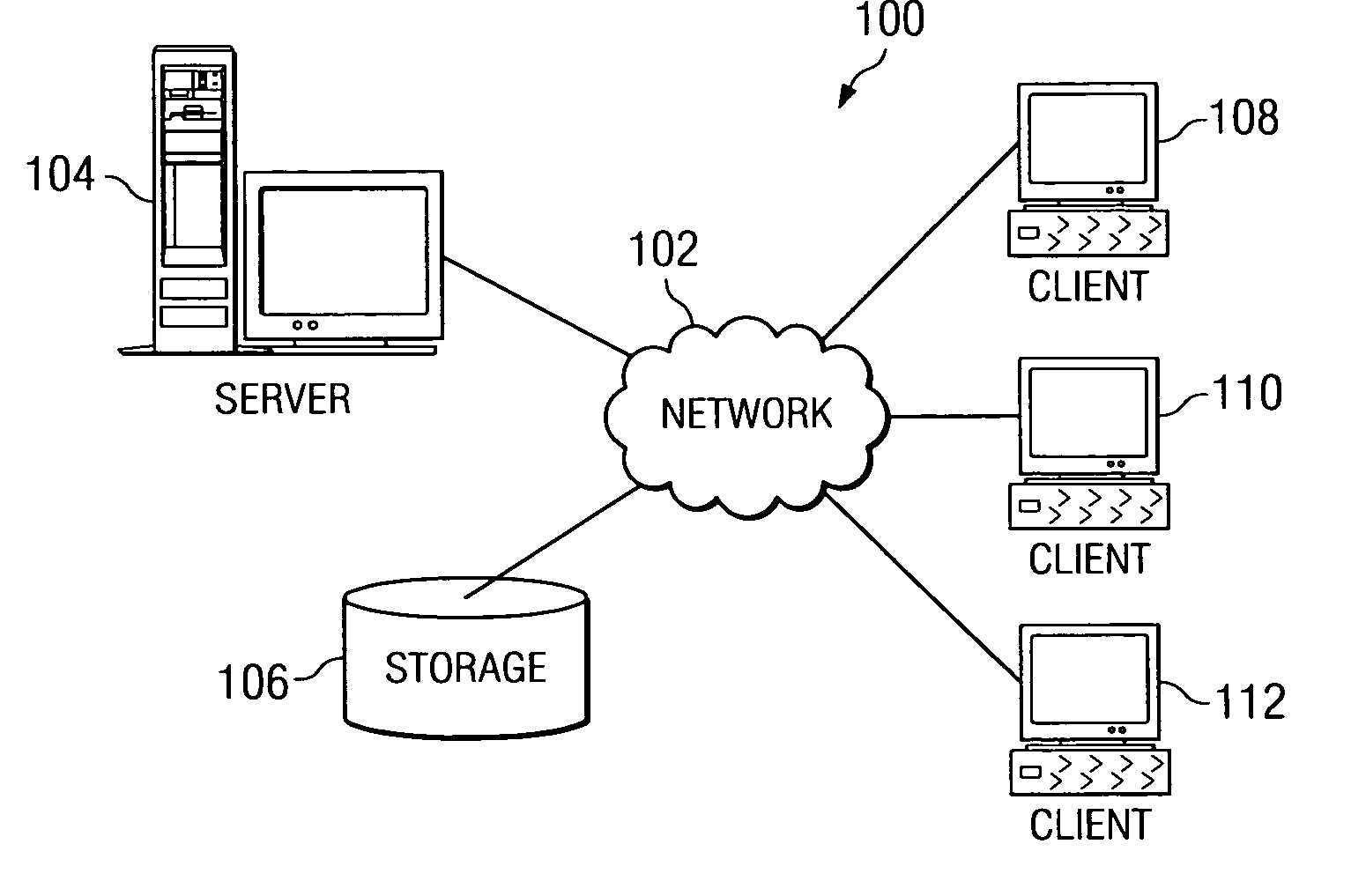
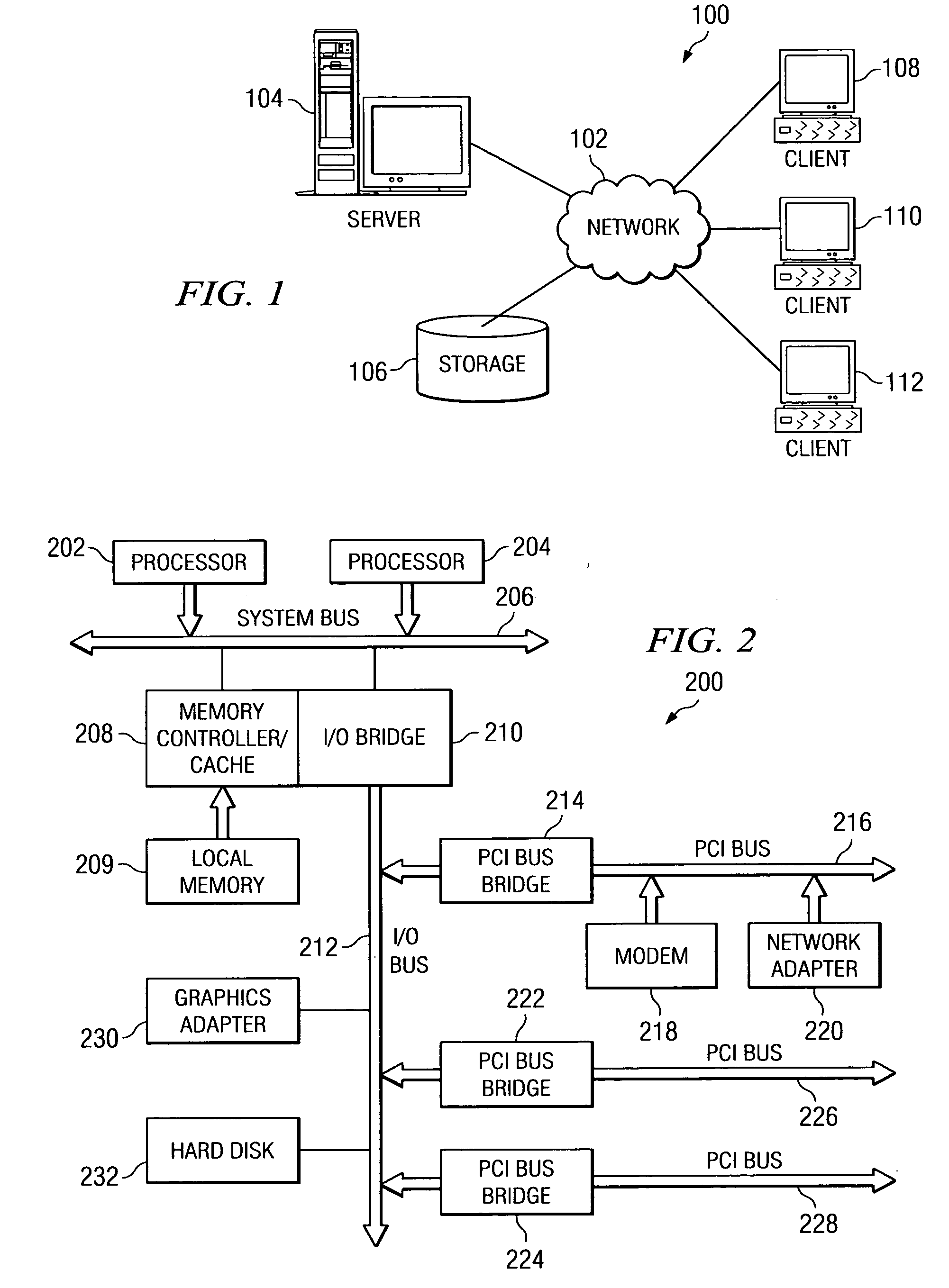
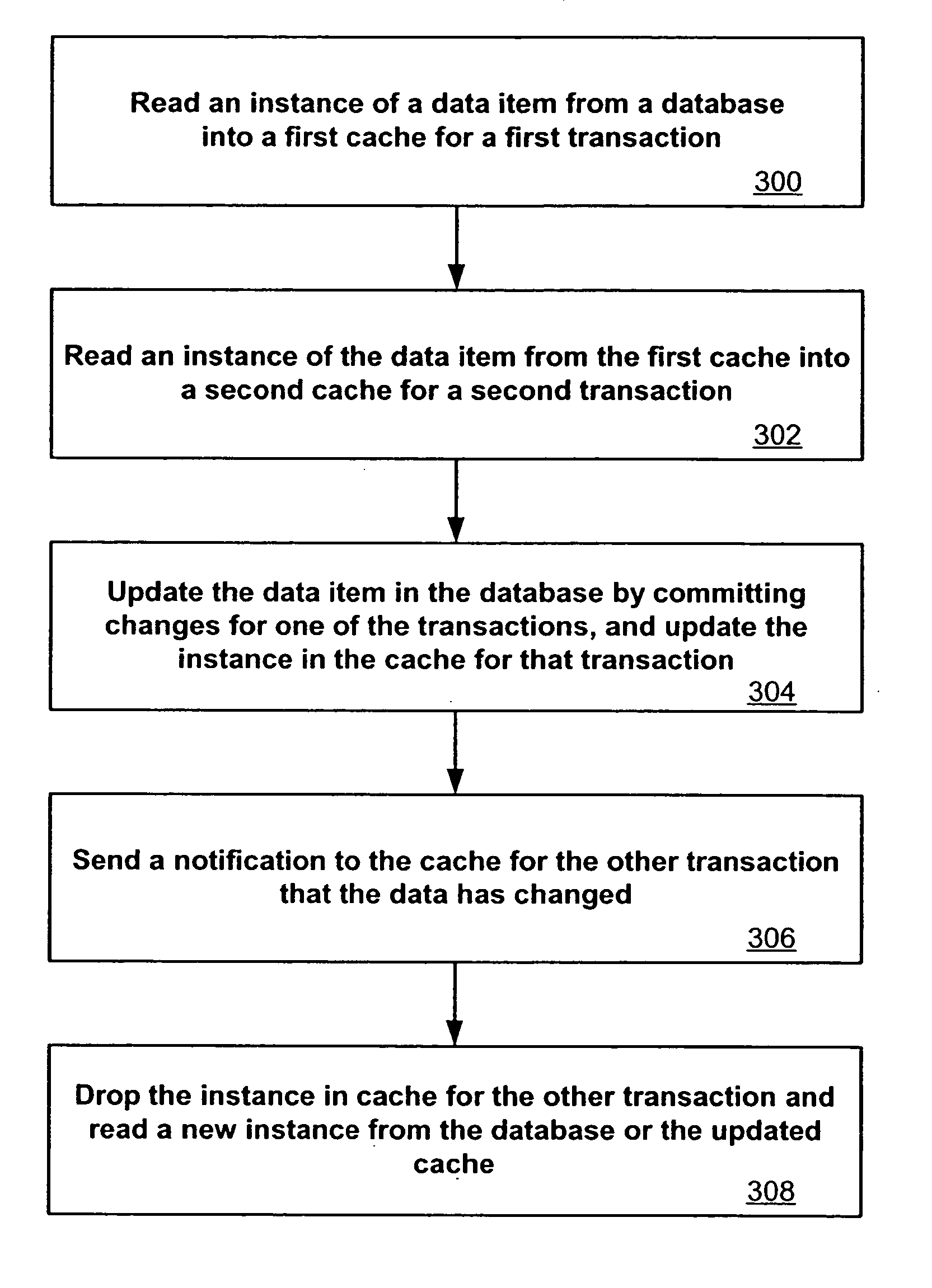
System and method for read-only entity bean caching
ActiveUS7136879B2Improved data cachingDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDatabaseEntity Bean
Separate instances of a data item can be allocated for each transaction in a system. Each instance can be held by an entity bean capable of updating by either reading a copy of the data item from the database or by reading a copy from another entity bean. When the data item in the database is changed, the system can notify each entity bean that it should read an updated copy of the data item before the next transaction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing container managed uses, ownerships, and references in an enterprise JavaBean environment
InactiveUS20060155744A1Automatic generatedSimple methodData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabaseEntity Bean
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for optimistic caching
InactiveUS20060123199A1Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent algorithmSoftware engineering
Transactions are granted concurrent access to a data item through the use of an optimistic concurrency algorithm. Each transaction gets its own instance of the data item, such as in a cache or in an entity bean, such that it is not necessary to lock the data. The instances can come from the data or from other instances. When a transaction updates the data item, the optimistic concurrency algorithm ensures that the other instances are notified that the data item has been changed and that it is necessary to read a new instance, from the database or from an updated instance. This description is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention. Other features, aspects, and objects of the invention can be obtained from a review of the specification, the figures, and the claims.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing container managed uses, ownerships, and references in an enterprise JavaBean environment
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
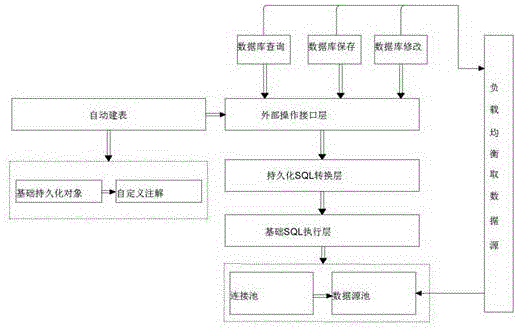
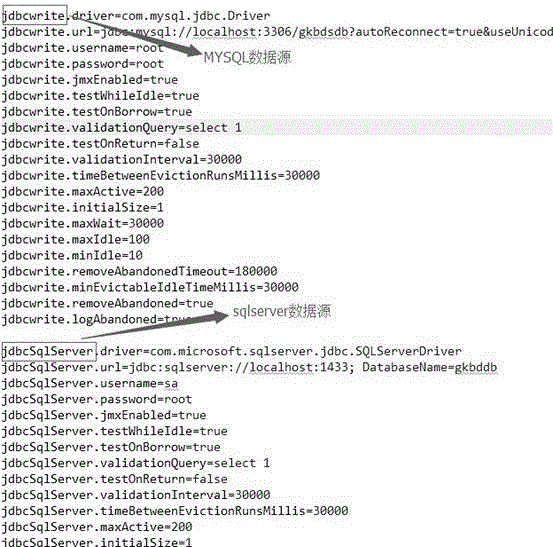
Database engine
InactiveCN106446182AHigh SQL execution efficiencyImprove execution efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData connectionConnection pool
The invention discloses a database engine. The database engine comprises a load balancing data fetching device and a database entity bean, and is characterized in that multiple data source pools which can be connected with databases of different types are established through data source configuration files, data source names are used to obtain data connection from the data source pools, the data connection is put in a thread data connection pool, and the data source pools and the data connection pool are successively connected with a basic sql execution layer, a persistent object sql conversion layer and an external operation interface layer. By adopting the database engine, the higher SQL execution efficiency can be reached, and unnecessary repeated database connection and related operations of jdbc processing can be reduced to gain time and efficiency for developers.
Owner:贵州云众知乐教育科技有限公司
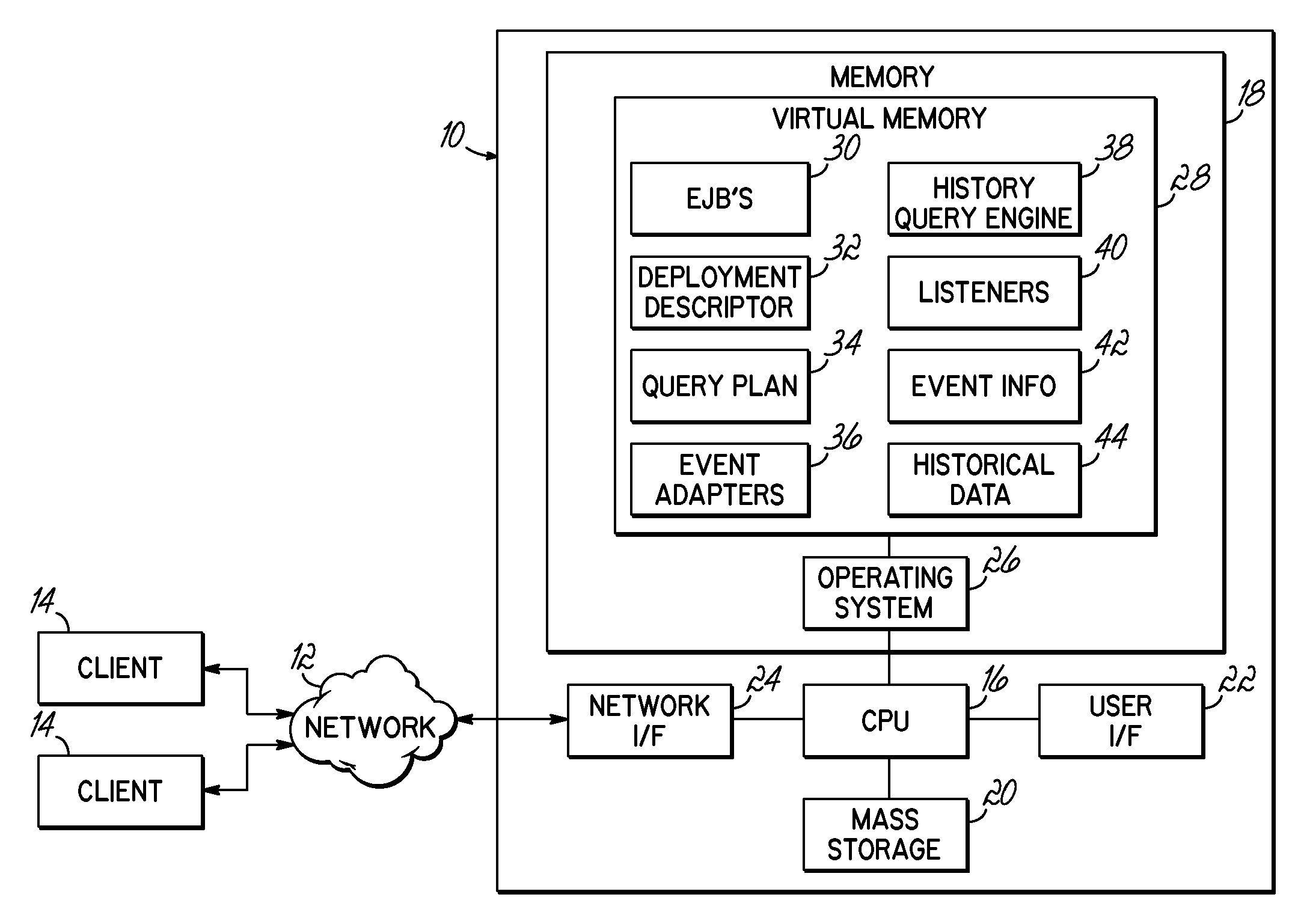
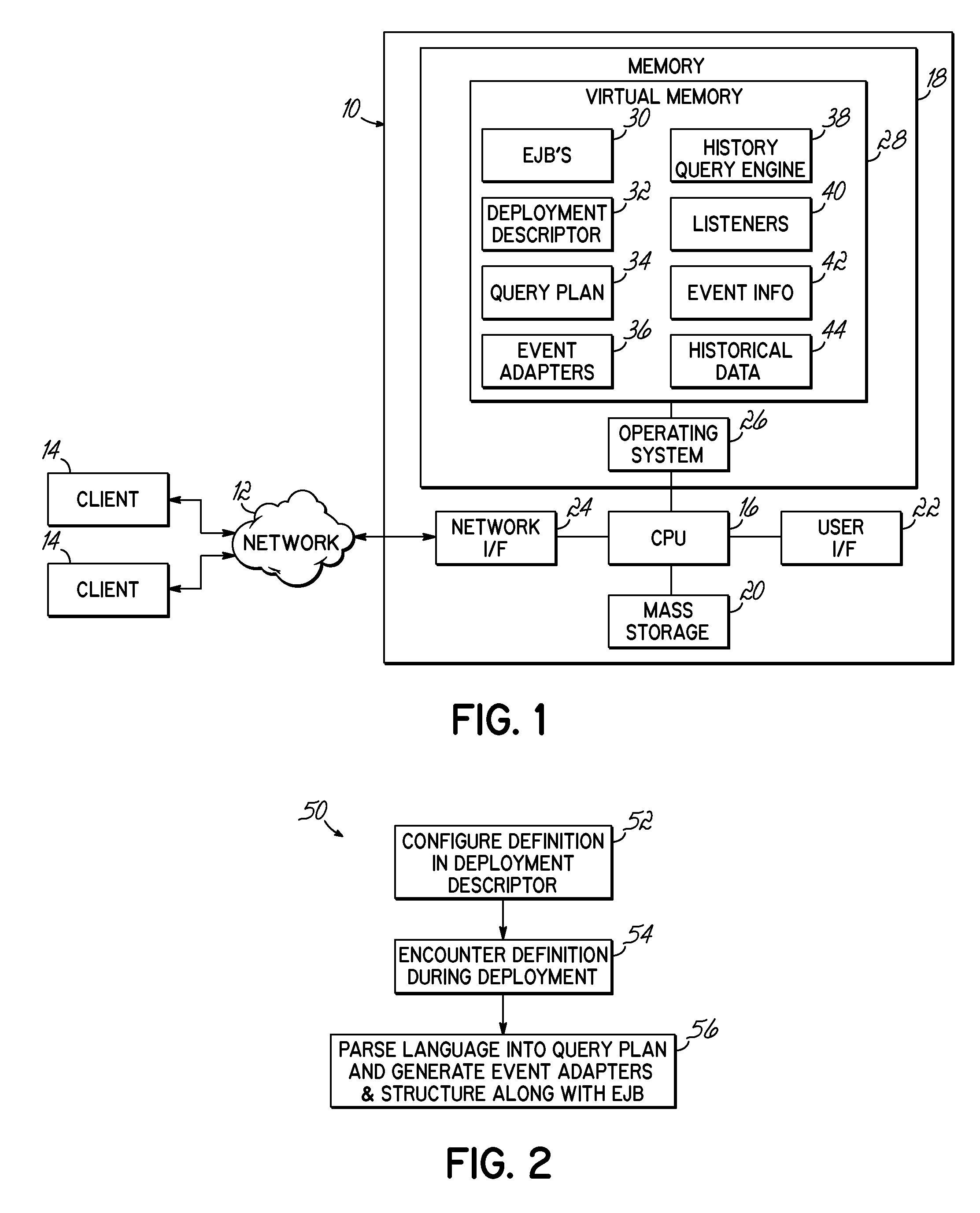
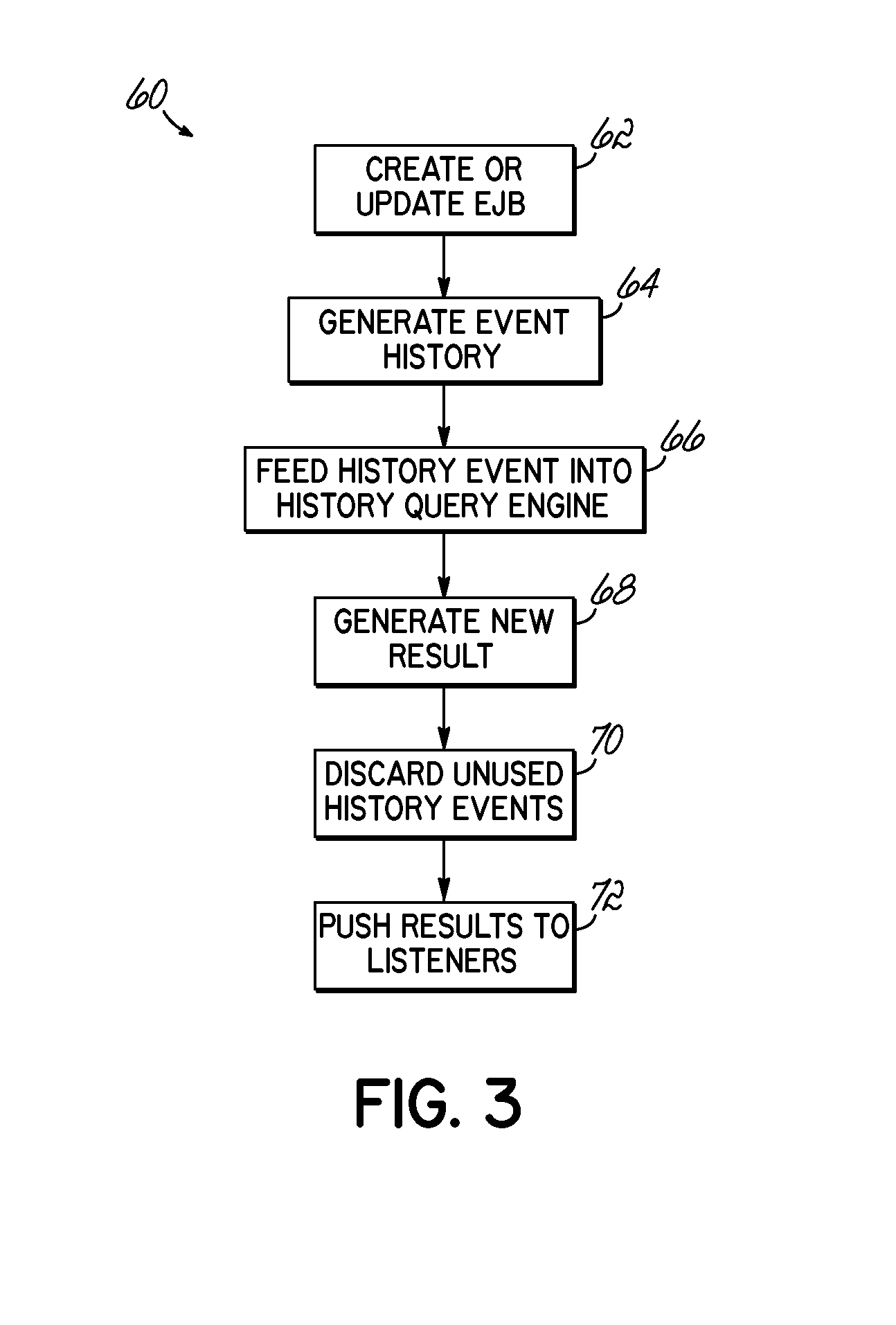
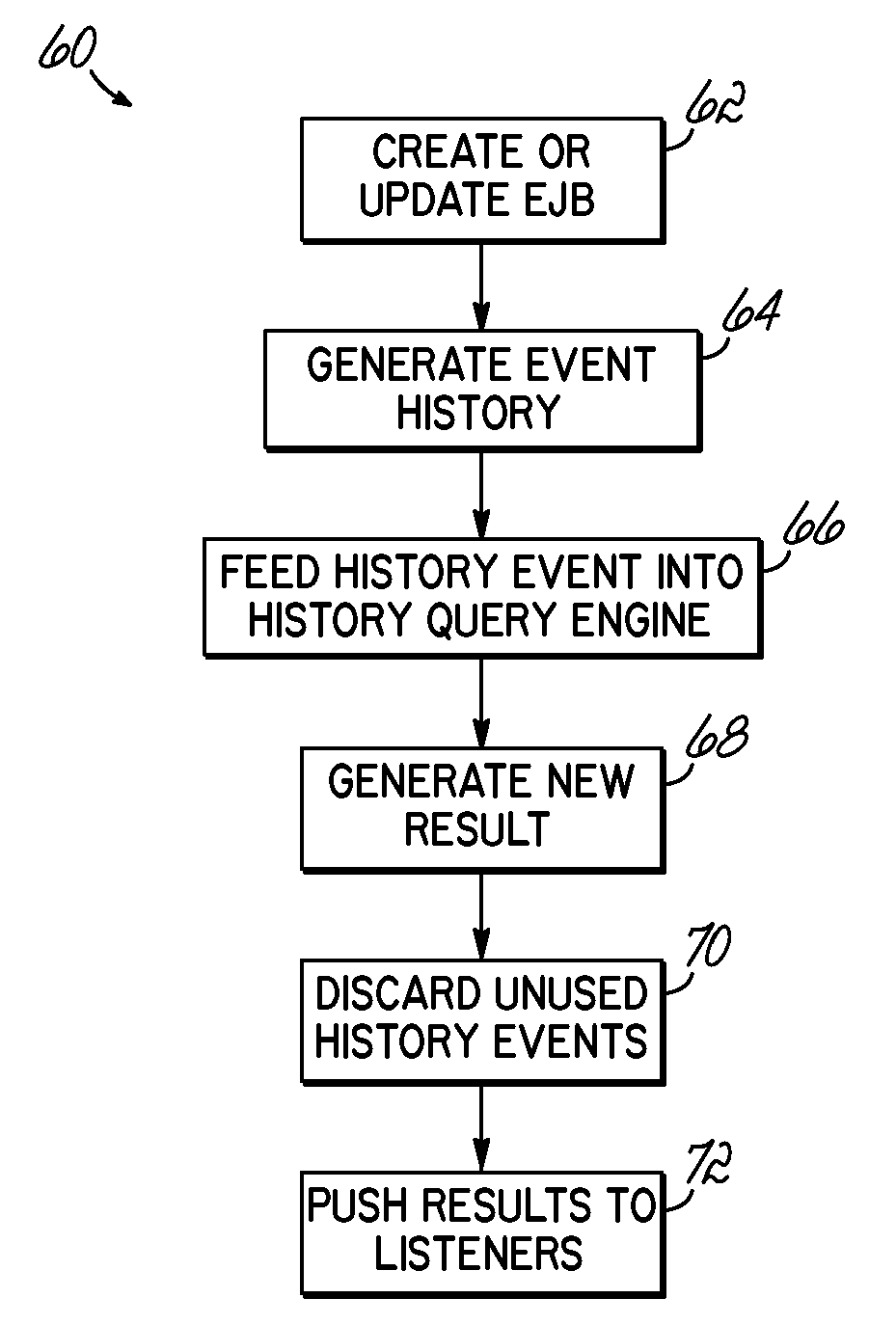
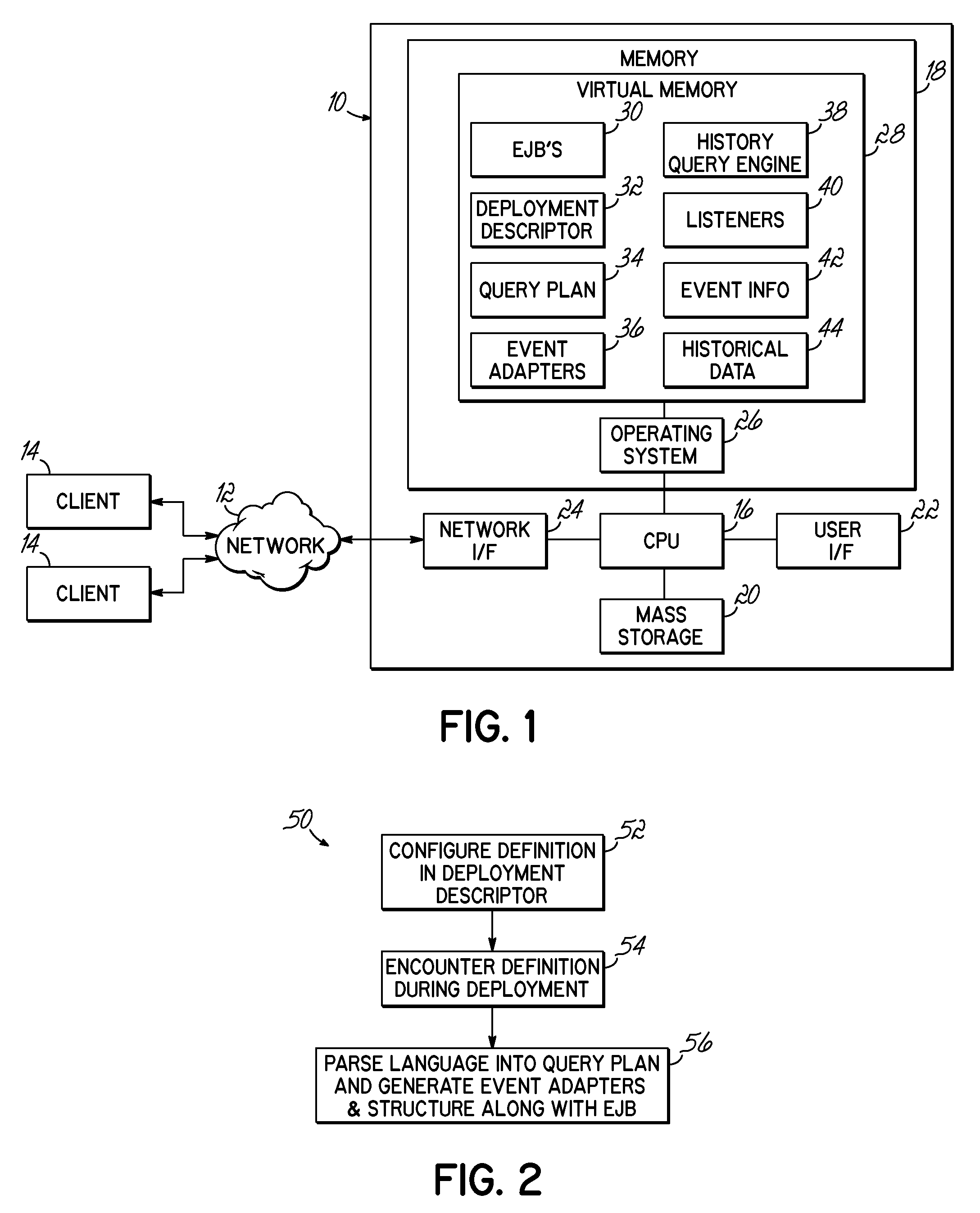
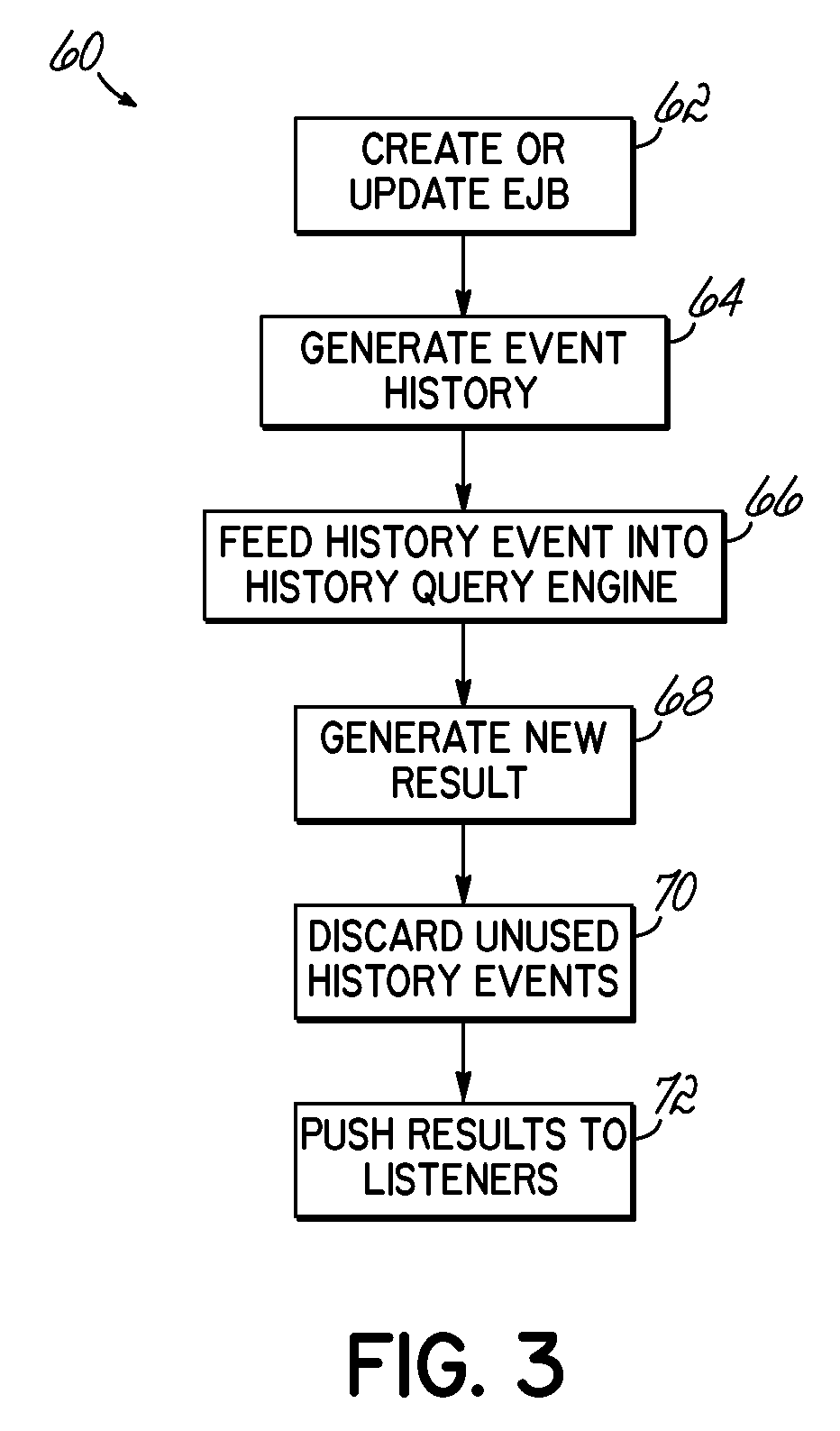
System and Method for Querying Historical Bean Data
InactiveUS20090144323A1Digital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesStatistical analysisUser input
A computer implemented method, apparatus and program product receives user input requesting historical data associated with an entity bean, and generates event information according to the user input. The event information is stored and used to determine the historical bean data. Where so desired, the determination may involve automatically performing statistical analysis relating to the bean.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for querying historical bean data
InactiveUS8341647B2Digital data processing detailsObject oriented databasesStatistical analysisUser input
A computer implemented method, apparatus and program product receives user input requesting historical data associated with an entity bean, and generates event information according to the user input. The event information is stored and used to determine the historical bean data. Where so desired, the determination may involve automatically performing statistical analysis relating to the bean.
Owner:IBM CORP
Database connection structure based on json format
InactiveCN105468777AReduce workloadReduce professional requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsEncapsulated dataWorkload
The invention discloses a database connection structure based on a json format. A middleware based on the json format is arranged between an application program and a database; JDBC and SQL statements are packaged; when operation and access are carried out to the database, the method provided by the middleware based on the json format is directly invoked, and operation to the database is finished. The structure is advantaged by that with respect to different data table structures, the data are unnecessarily packaged by respectively developed corresponding entity Bean; the workload of a developer is greatly reduced; the professional requirement to a programmer is reduced; and data exchange is more general.
Owner:JIANGSU DINGFENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Distributed, fault-tolerant and highly available computing system
InactiveCN101663660AProgram control using stored programsFault responseParallel computingHigh availability
A method and system for achieving highly available, fault-tolerant execution of components in a distributed computing system, without requiring the writer of these components to explicitly write code(such as entity beans or database transactions) to make component state persistent. It is achieved by converting the intrinsically non-deterministic behavior of the distributed system to a deterministic behavior, thus enabling state recovery to be achieved by advantageously efficient checkpoint-replay techniques. The method comprises: adapting the execution environment for enabling message communication amongst and between the components; automatically associating a deterministic timestamp in conjunction with a message to be communicated from a sender component to a receiver component during program execution, the timestamp representative of estimated time of arrival of the message at a receiver component. At a component, tracking state of that component during program execution, and periodically checkpointing the state in a local storage device. Upon failure of a component, the component state is restored by recovering a recent stored checkpoint and re-executing the events occurring since the last checkpoint. The system is deterministic by repeating the execution of the receiving component by processing the messages in the same order as their associated timestamps.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com