Patents
Literature
199 results about "Voice traffic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
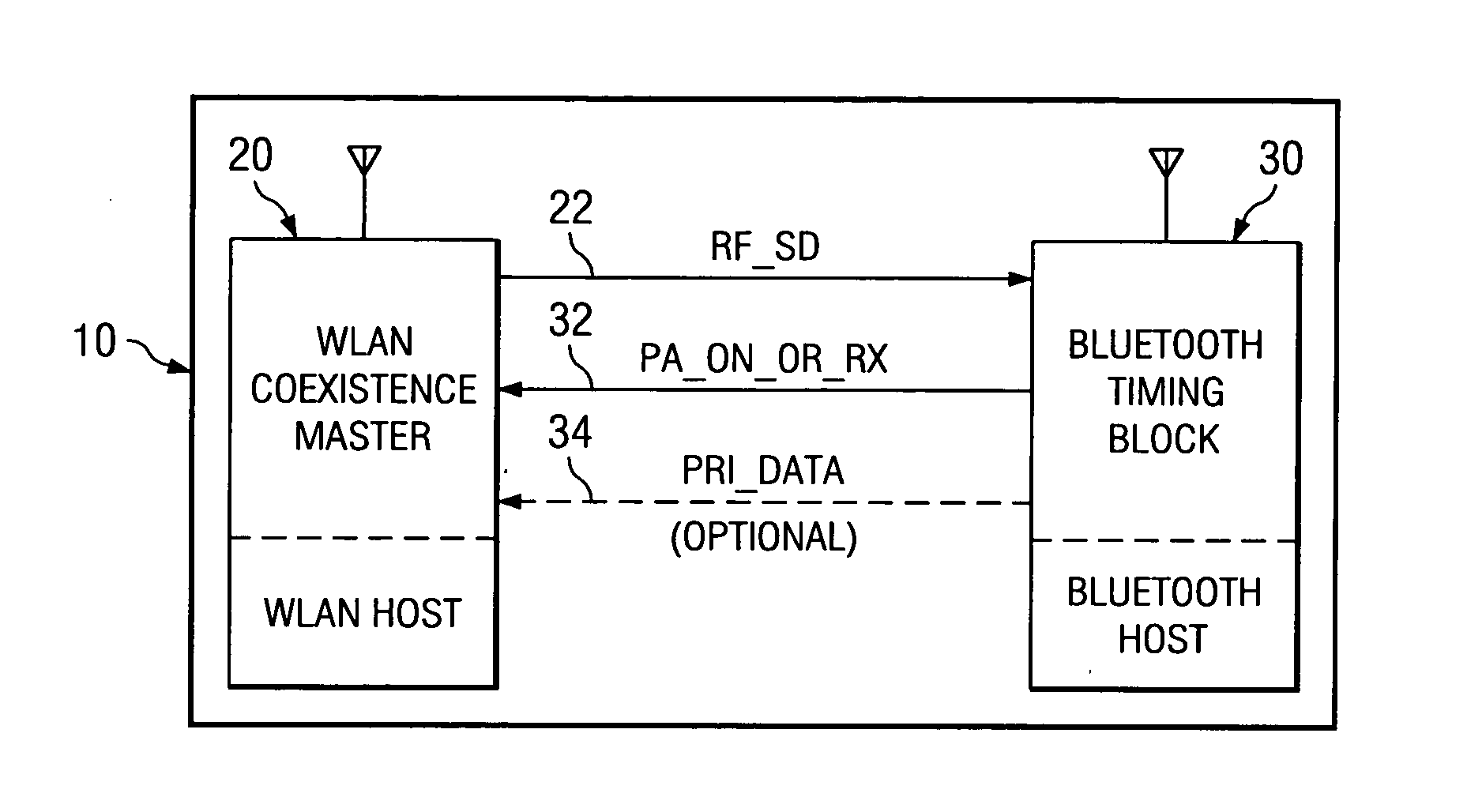
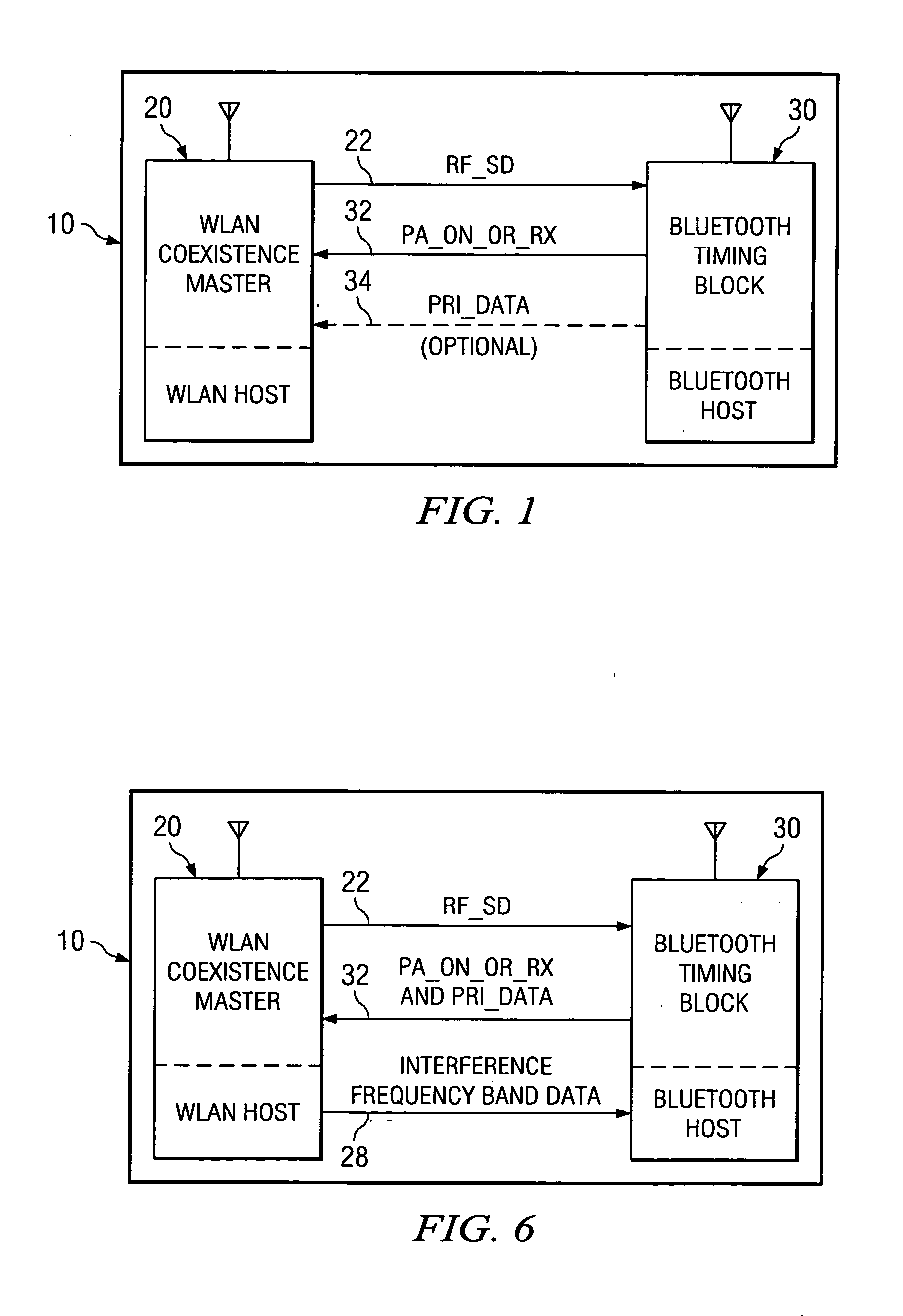
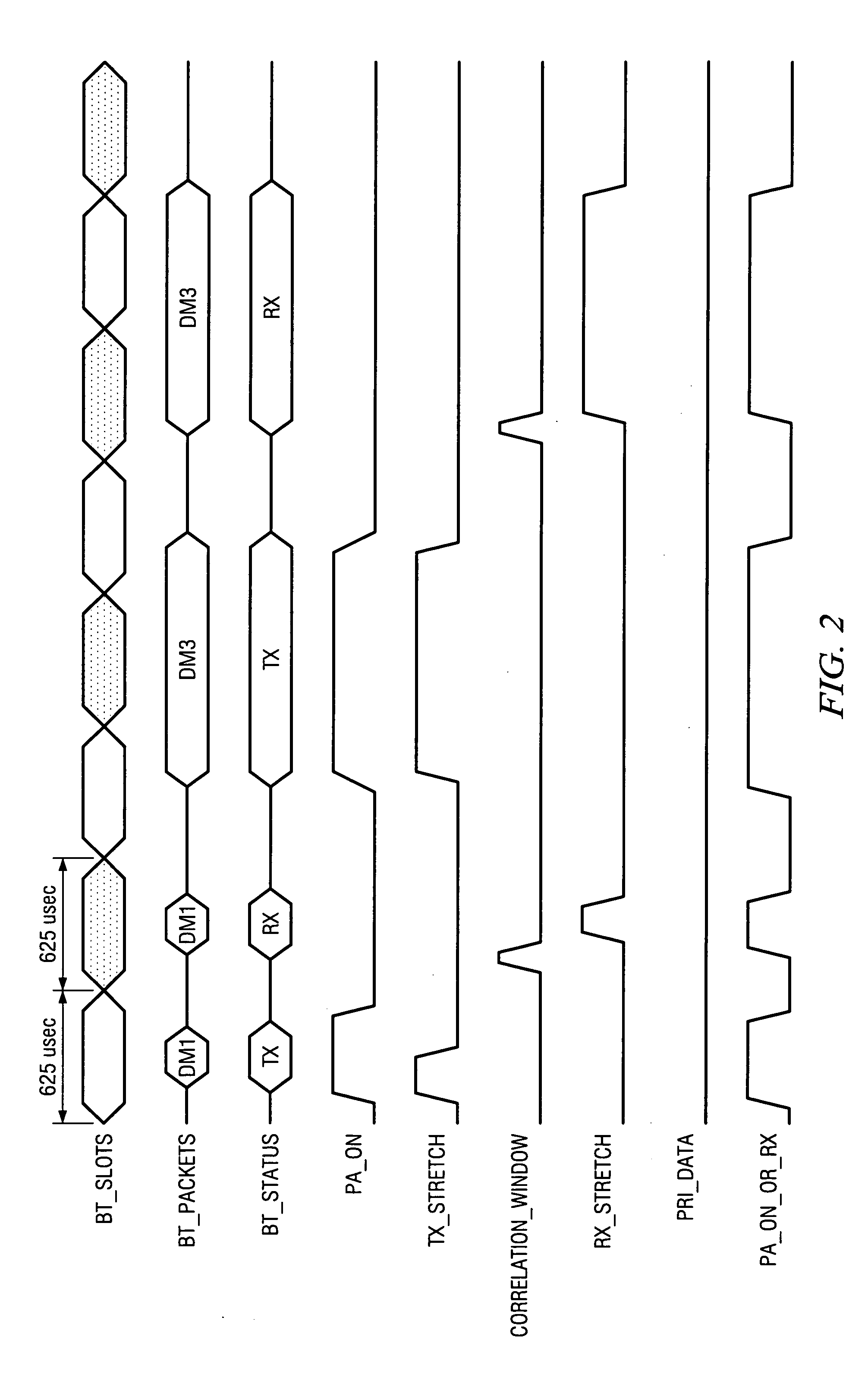
Coexistent bluetooth and wireless local area networks in a multimode terminal and method thereof
InactiveUS20060292986A1Devices with wireless LAN interfaceDevices with bluetooth interfacesTelecommunicationsVoice traffic
The present invention generally to a multimode terminal including a wireless local area network (WLAN) system and a Bluetooth system that avoids radio interference between the two systems by collaborative coexistence methods that include time-sharing, combined frequency and time-sharing, and forward looking combined frequency and time-sharing between the WLAN system and the Bluetooth system. The coexistent multimode terminal and the method of coexistence provide WLAN transmission / receptions that are not impacted when there is no Bluetooth traffic, Bluetooth transmissions / receptions that are not impacted when there is no WLAN traffic, Bluetooth and WLAN transmissions / receptions that are provided fair access to the medium when both Bluetooth and WLAN traffic are present, and high priority Bluetooth traffic, for example, voice traffic, that has priority over non-high WLAN traffic.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
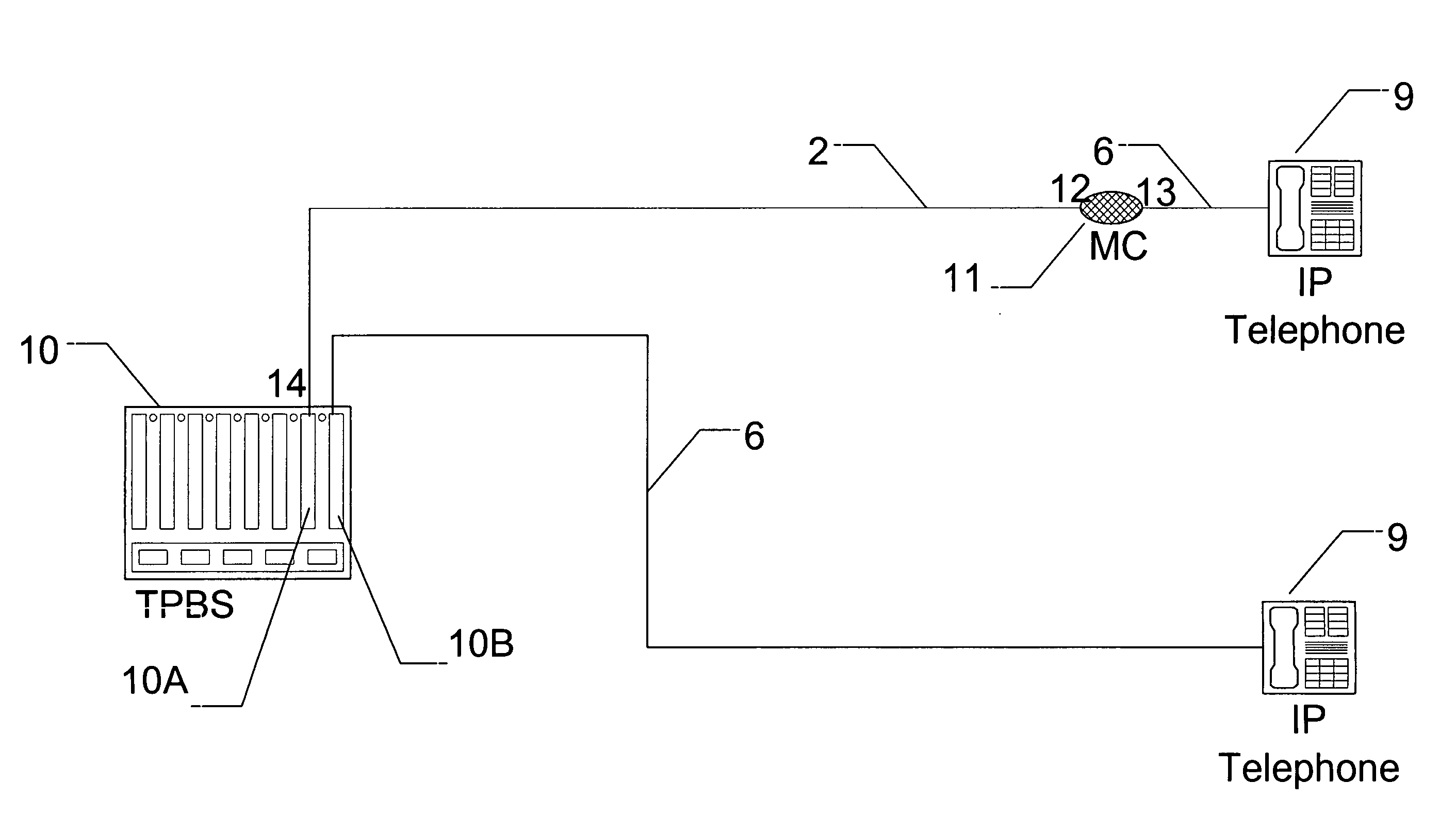
IP telephony transport
InactiveUS7408923B1Increase supplyEliminate needDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationElectric power transmissionEngineering
A system for simultaneously transporting internet protocol voice traffic and power to an internet protocol telephony transport using the existing twisted pair infrastructure of a traditional phone system. The system includes a twisted pair broadband switch. The twisted pair broadband switch connects on one end to an internet protocol telephone voice switch using Ethernet wiring and connects on another end to a media converter using a twisted pair wiring on the existing twisted pair infrastructure. The media converter condition the voice traffic between a twisted pair interface and an Ethernet interface to allow connection to an internet protocol telephone. Power is simultaneously transported with the voice traffic over the same twisted pair wiring of the existing twisted pair infrastructure.
Owner:KHAN MEHTAB +1
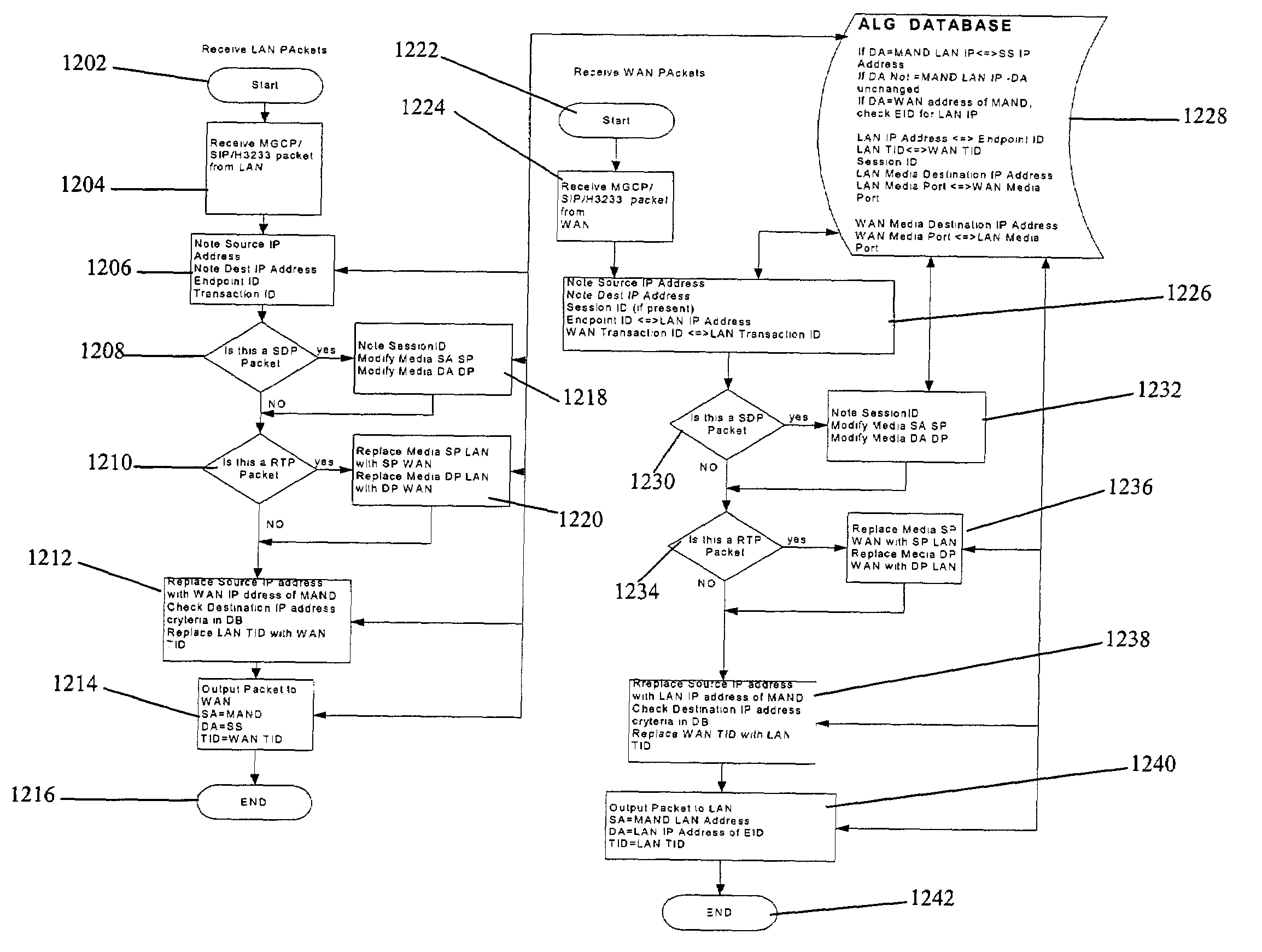
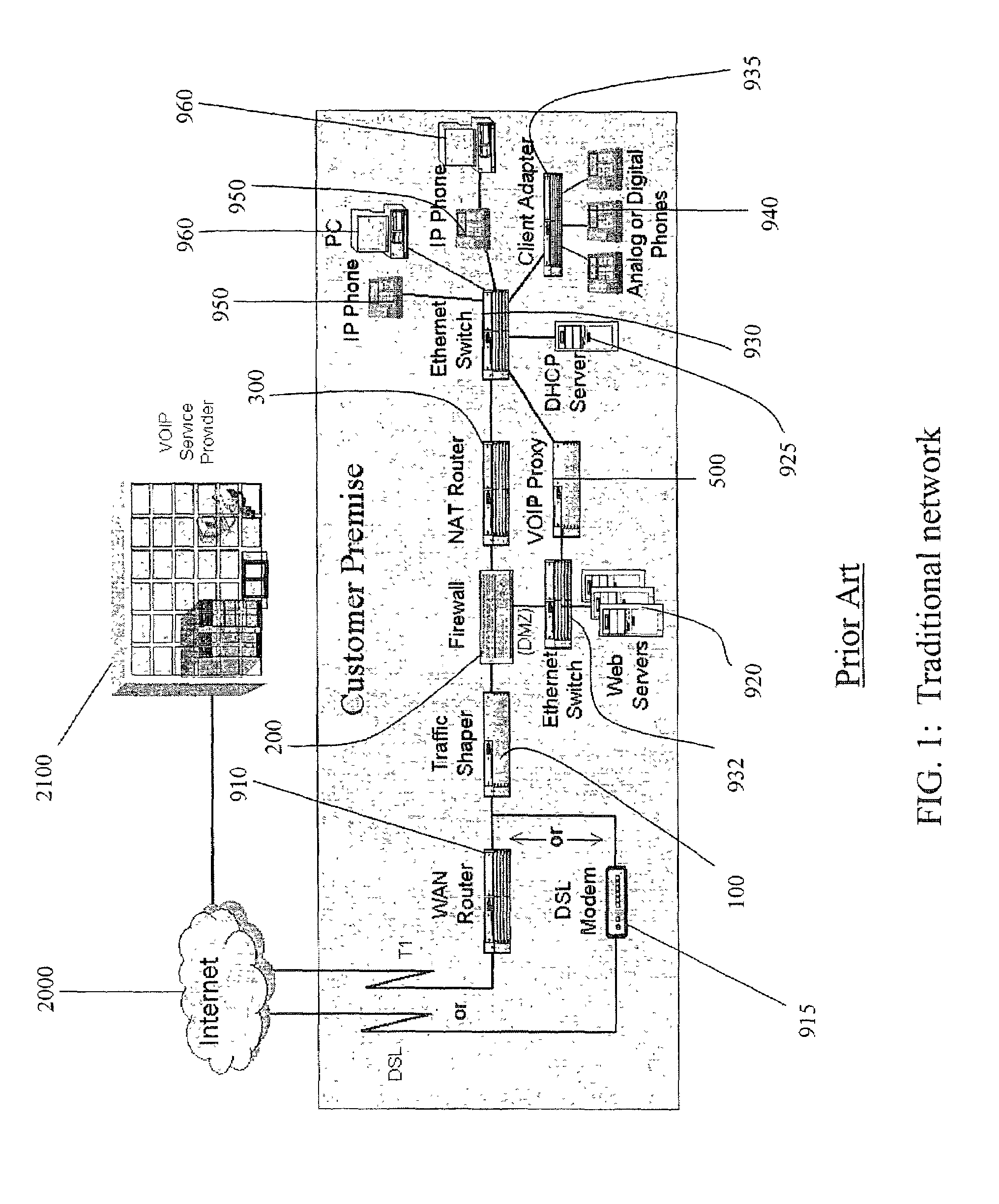
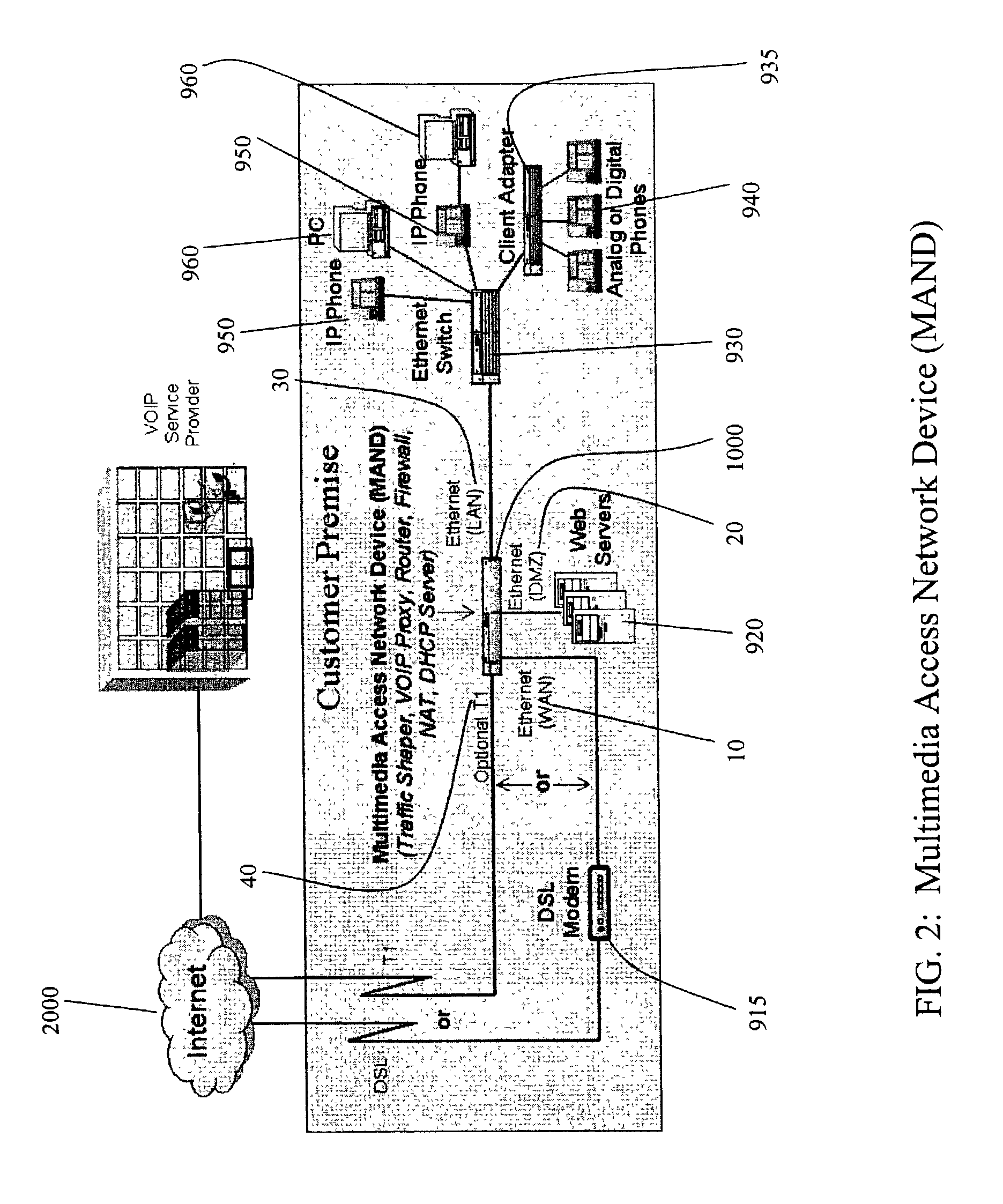
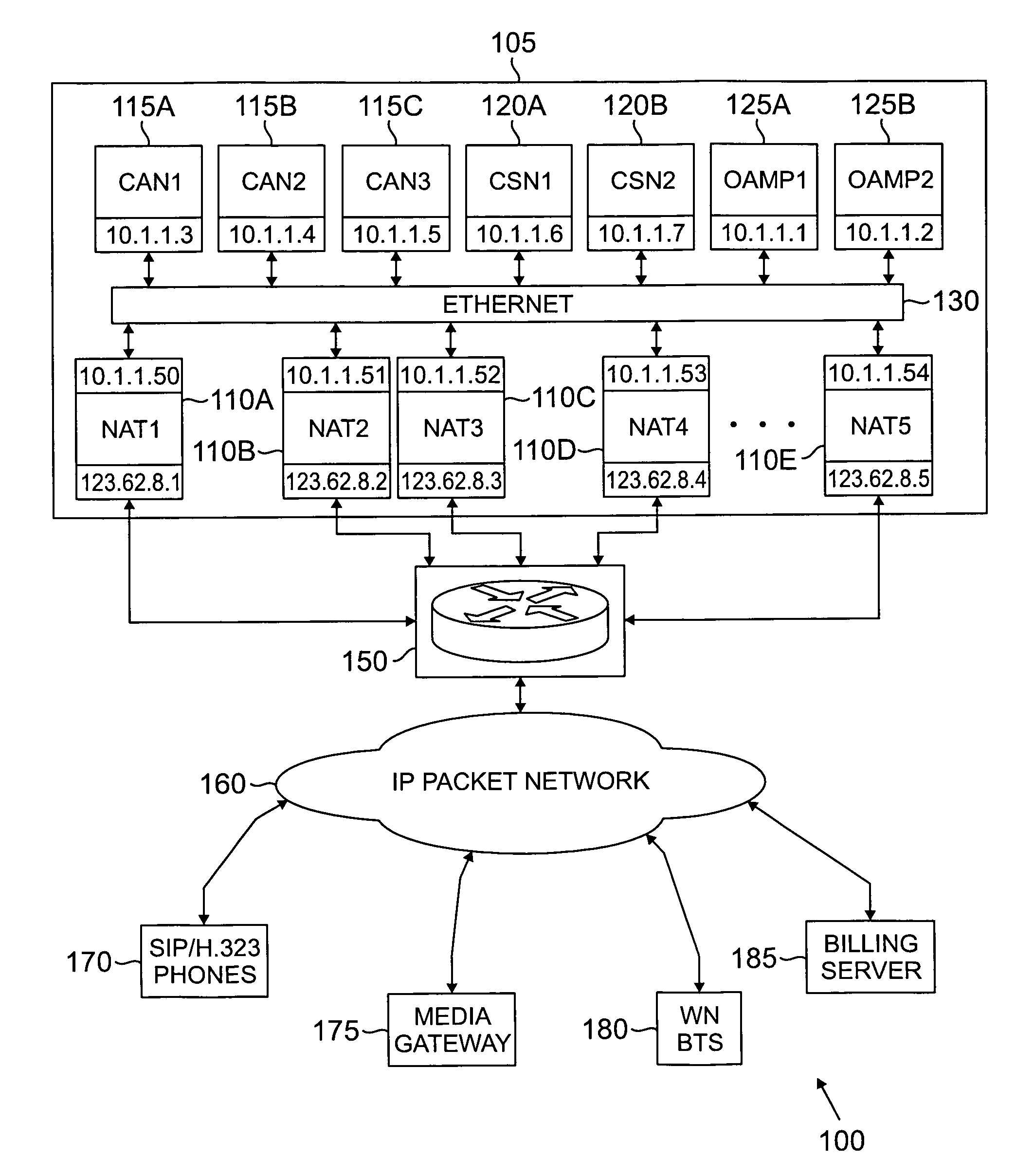
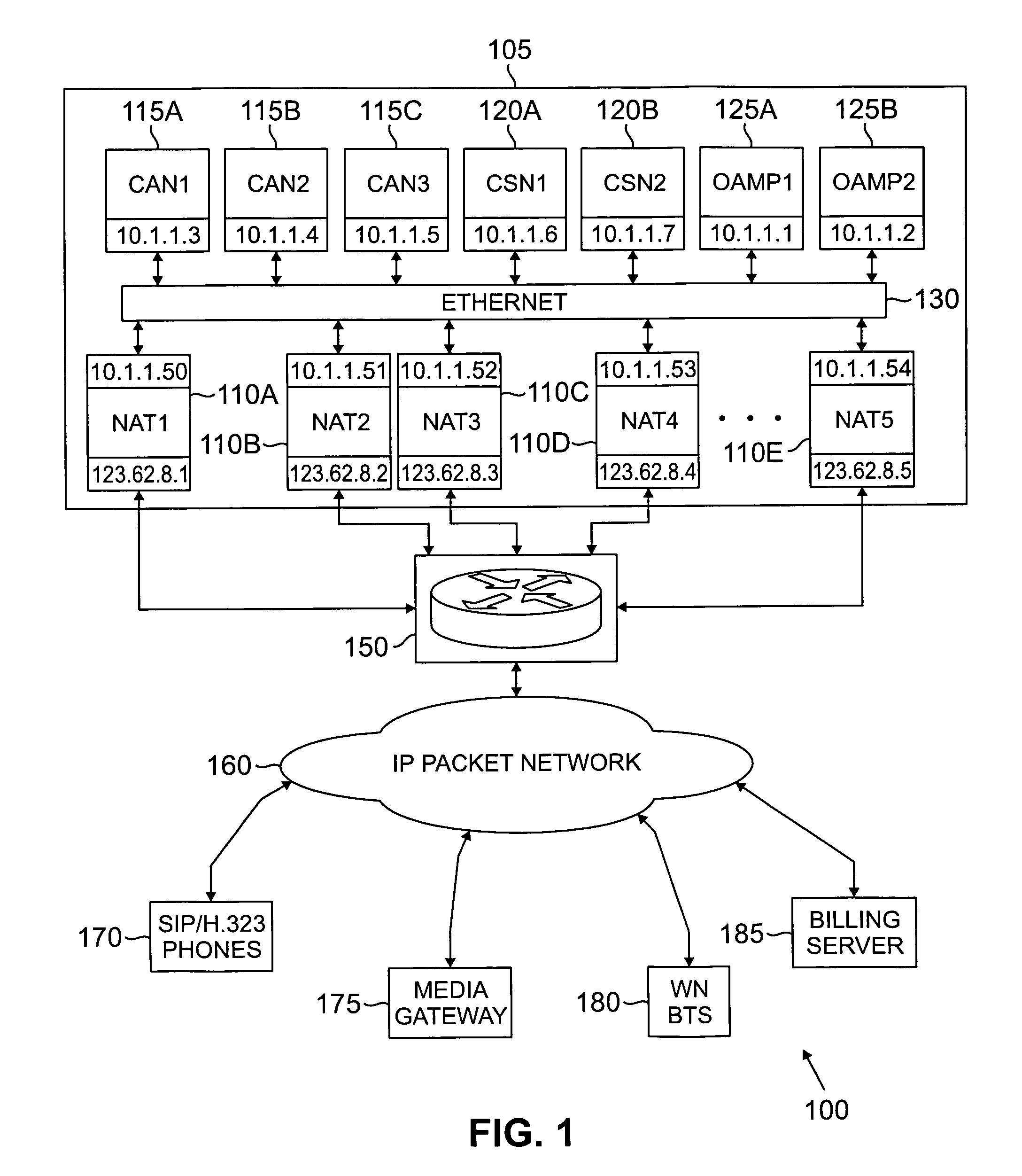
Method and system for implementing and managing a multimedia access network device
ActiveUS7274684B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationAuthentication
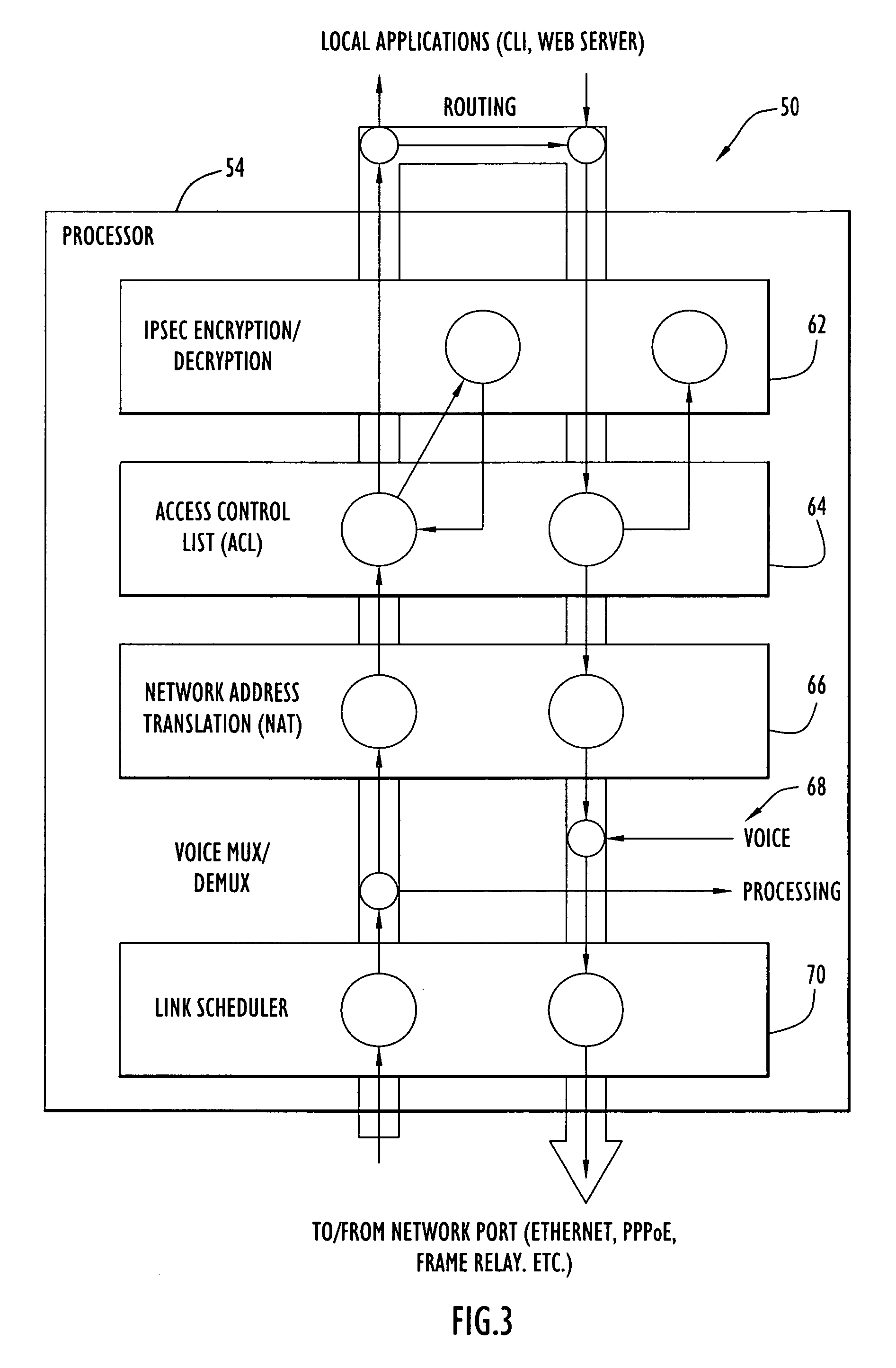
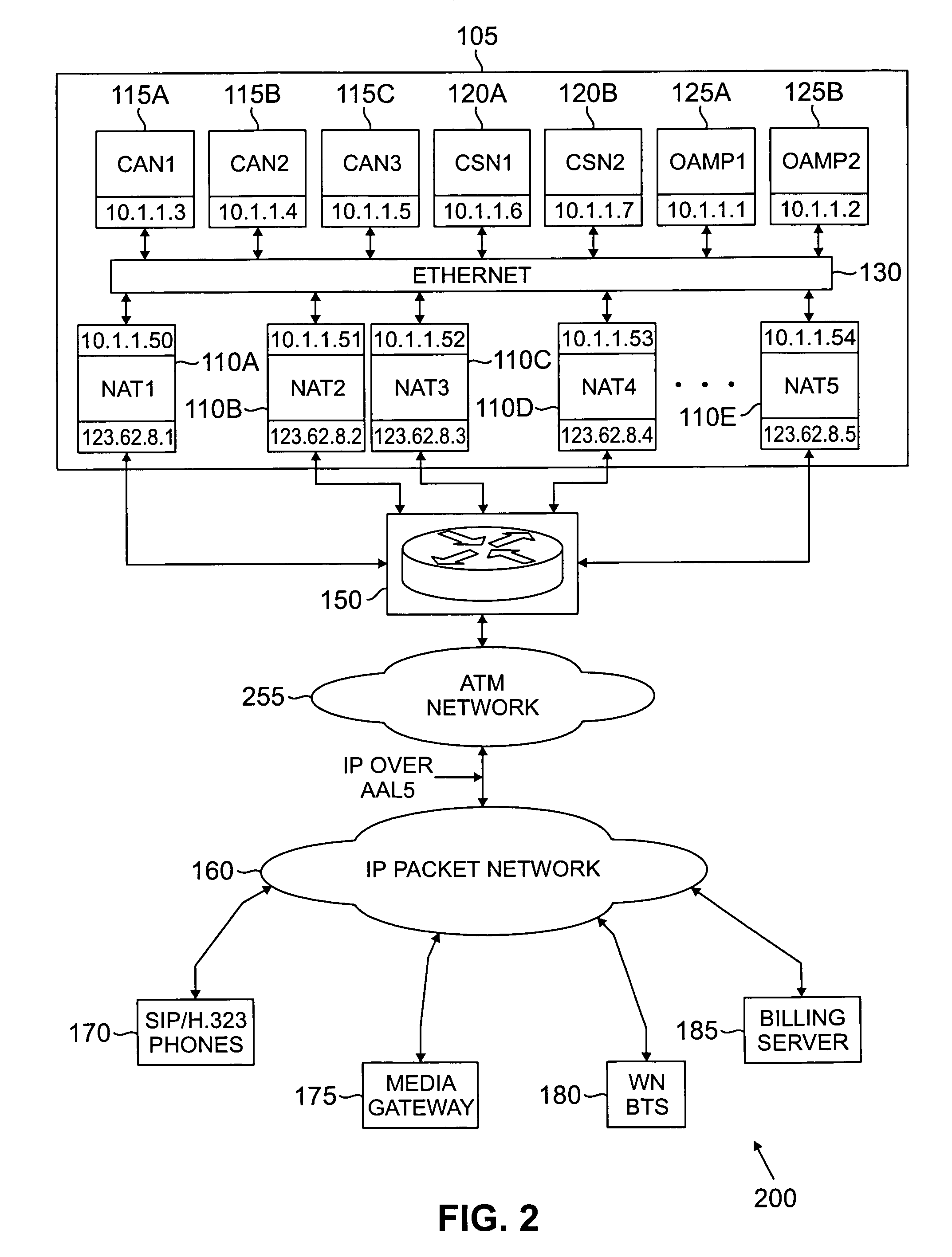
In a complete network-in-a-box system acting as an enterprise network demarcation point, packets such as voice, video and data packets, are routed over common network connections, such as LAN and WAN. The packets are mapped from a public address field (such as an IP address) and port number to a private address field and port number, the mapping process typically being handled by a NAT (Network Address Translation). The packets are also prioritized, by marking the packets for priority queuing and routing, and configuring the bandwidths of the WAN traffic and the voice traffic to predetermined quantities and configuring the address fields of the voice devices. Simultaneous transmission of the various packets can be limited to predetermined quantities, typically by utilizing a CAC (Client Access Control). Secure firewalls are also included as well as a performance test client application that provides a defined workload generated across the WAN interface for capacity planning measurements and allows remote monitoring of the QoS (Quality of Service) data, such as latency, jitter, lost packets and MOS scores. Optionally, a simple, common remote management interface is included, allowing service providers to configure, upgrade and manage the system. Additionally, address fields can be provided to voice, video or data devices attached to a LAN port. VPN authentication and encrypted sessions can be tunneled through the firewall for access to an internal network by using a VPN terminator. For power outages and other emergency purposes, additional ports that connect to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) analog telephone lines as well as other analog telephones or devices, can be provided. Another advantageous element is that most of the above components or features may be enabled or disabled.
Owner:EDGEWATER NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for signal interference processing
A system that incorporates the subject disclosure may perform, for example, a method for detecting signal interference in a first segment of a plurality of segments of a radio frequency spectrum of a wireless communication system, determining according to the signal interference a measure of quality of service of the first segment for transmitting voice traffic, comparing the measure of quality of service to a desired measure of quality of service measure for voice traffic, determining from the comparison that the first segment is not suitable for voice traffic, and notifying a system that the first segment is not suitable for voice traffic. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
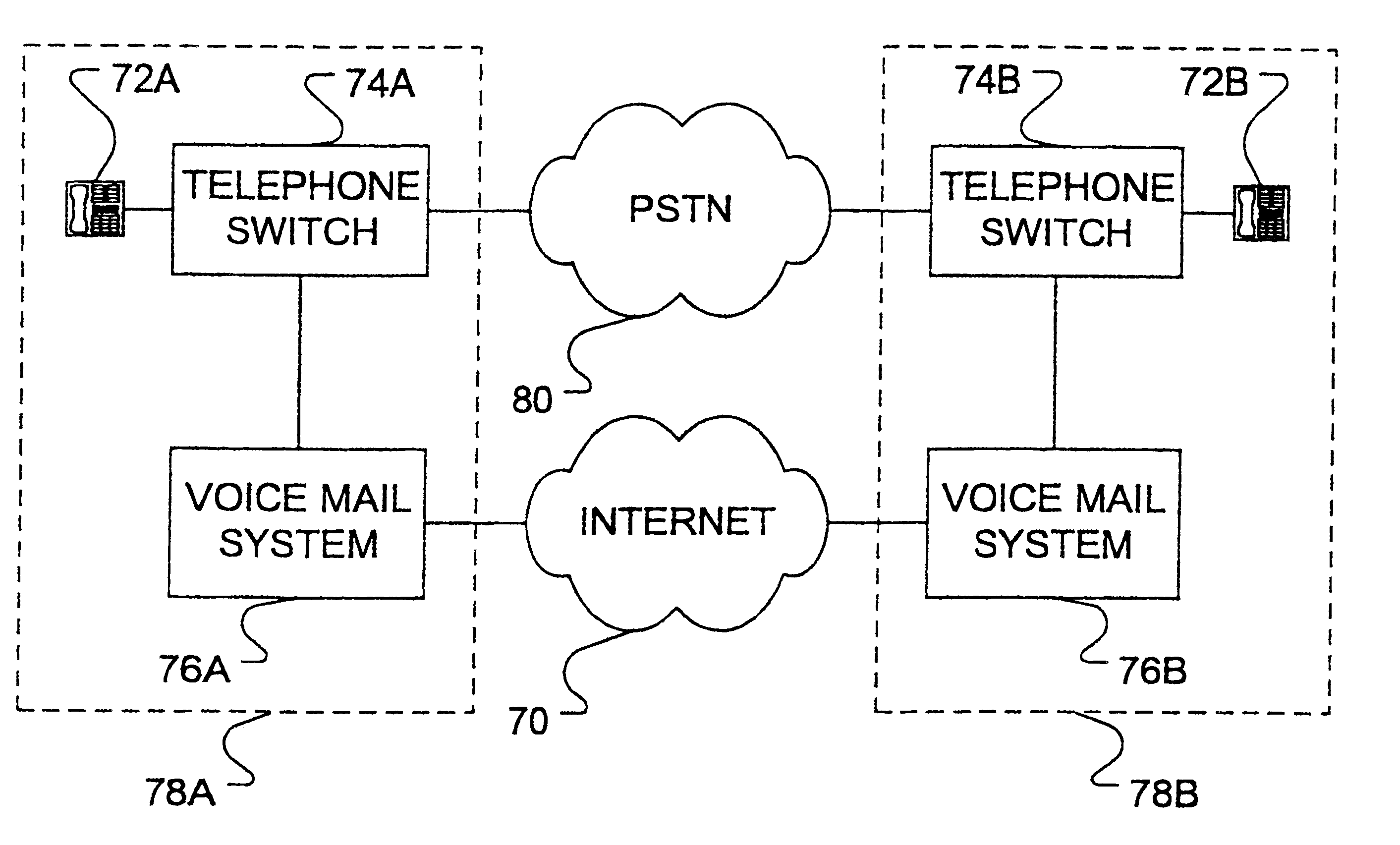
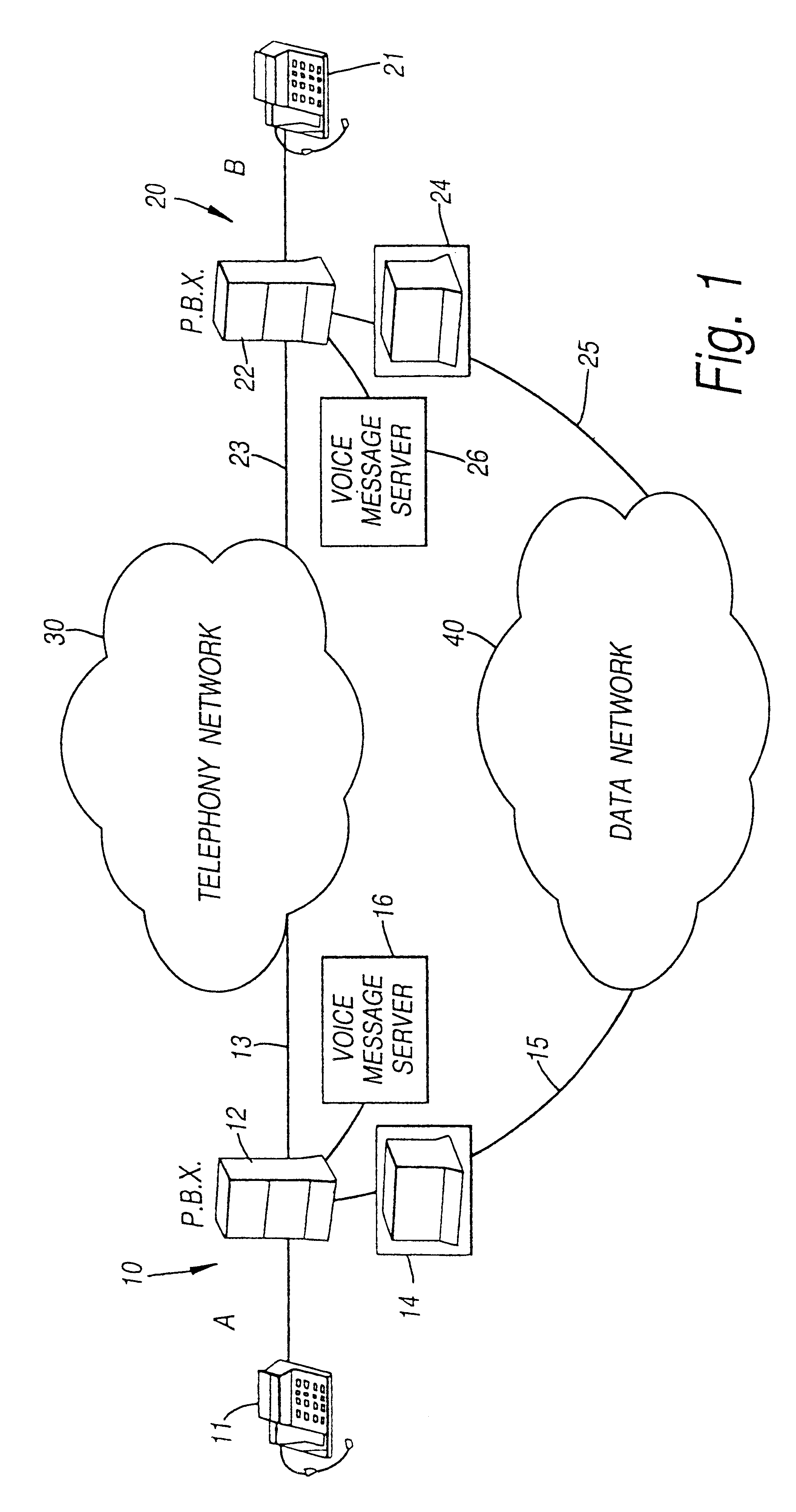
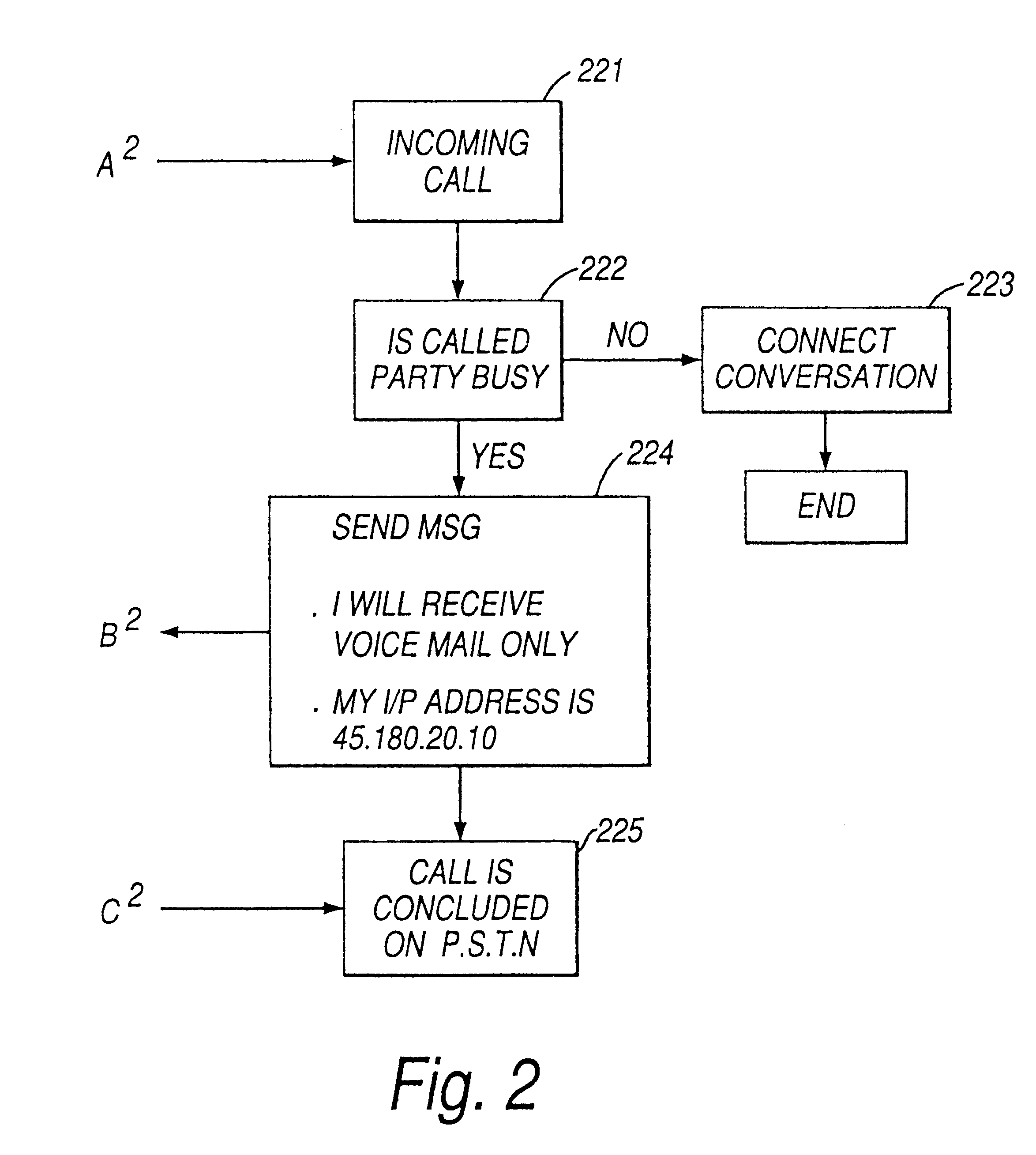
Message transfer system
InactiveUS6396908B1Minimize timeLow costTelephone data network interconnectionsSpecial service for subscribersVoice communicationTransfer system
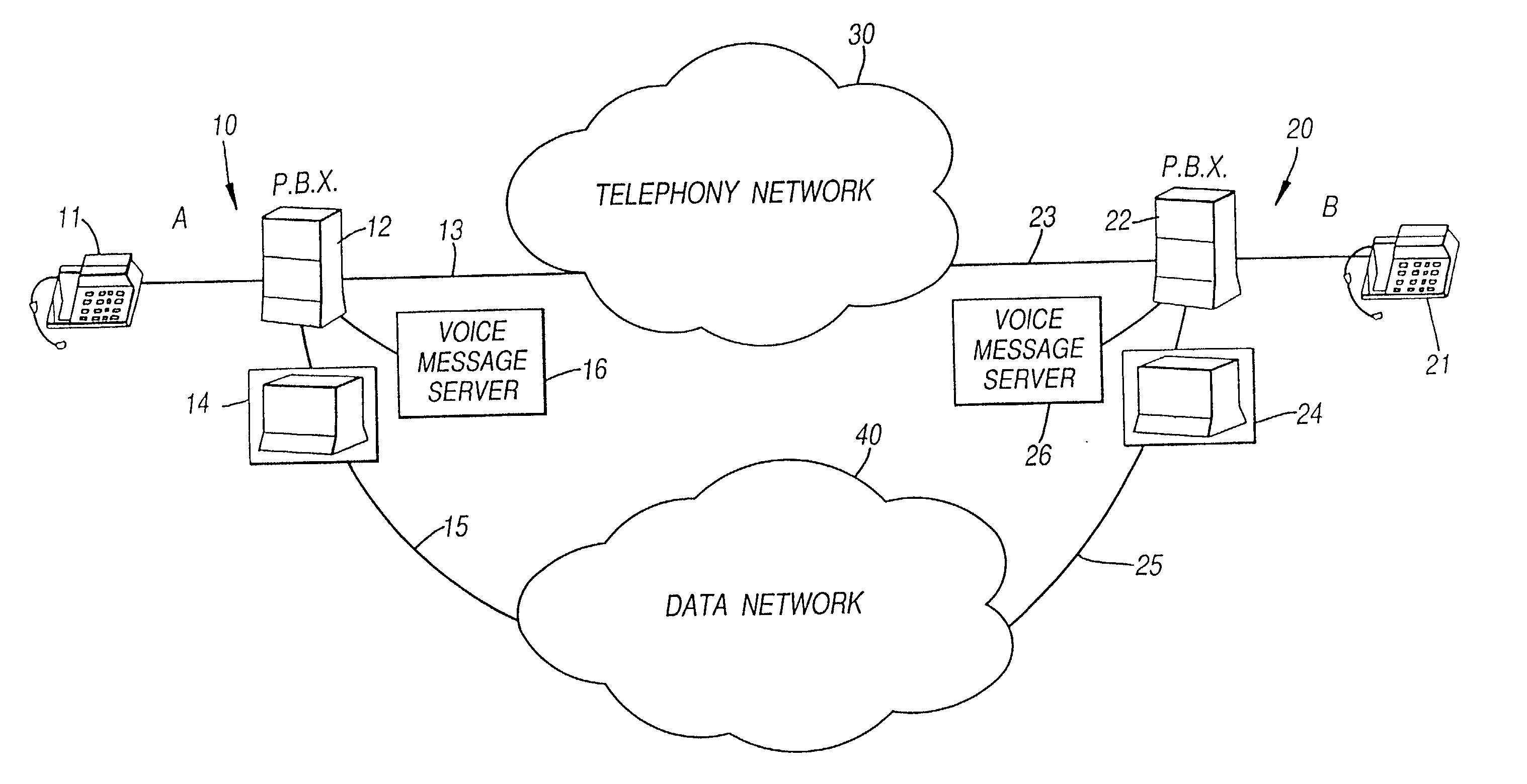
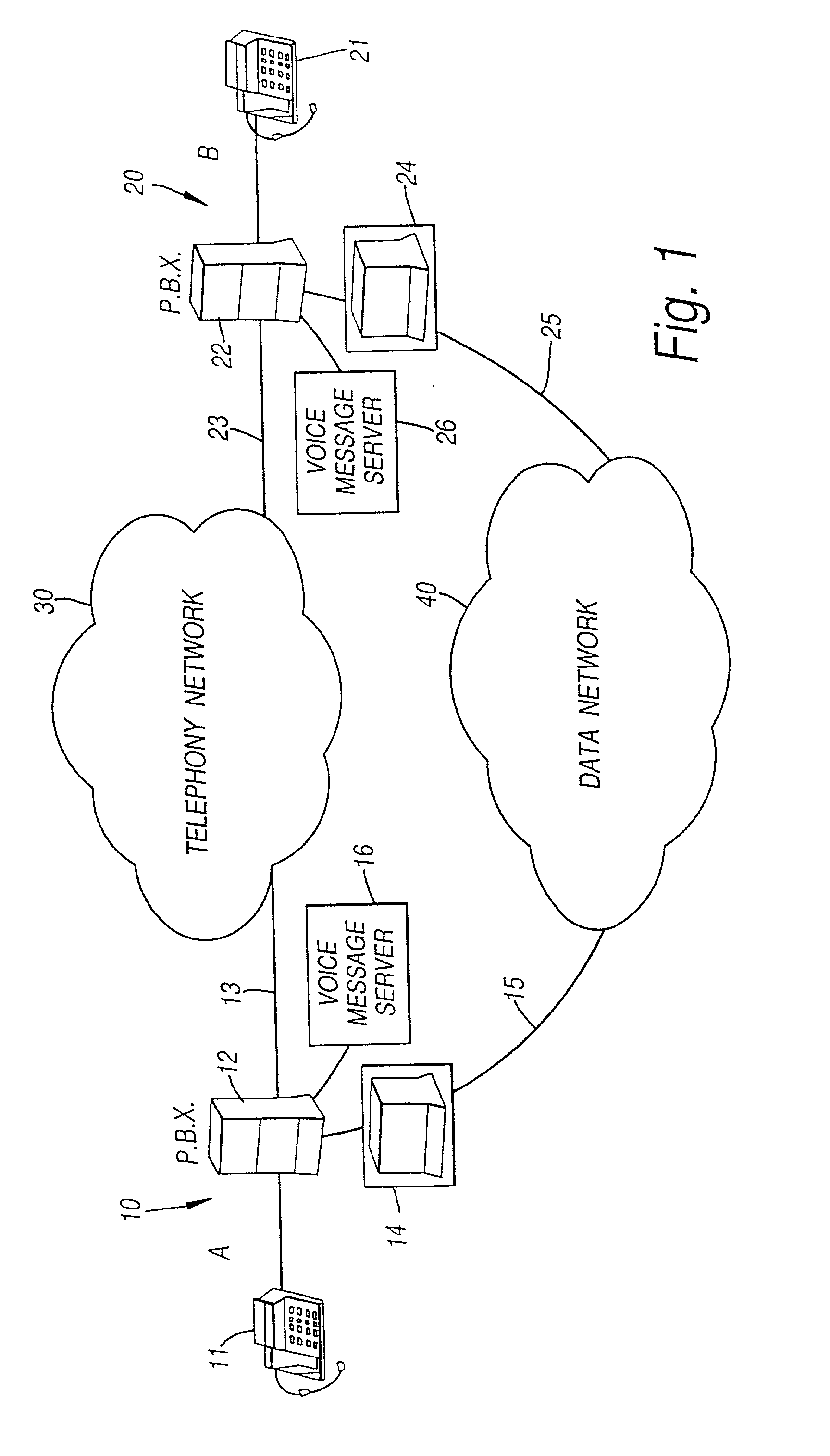
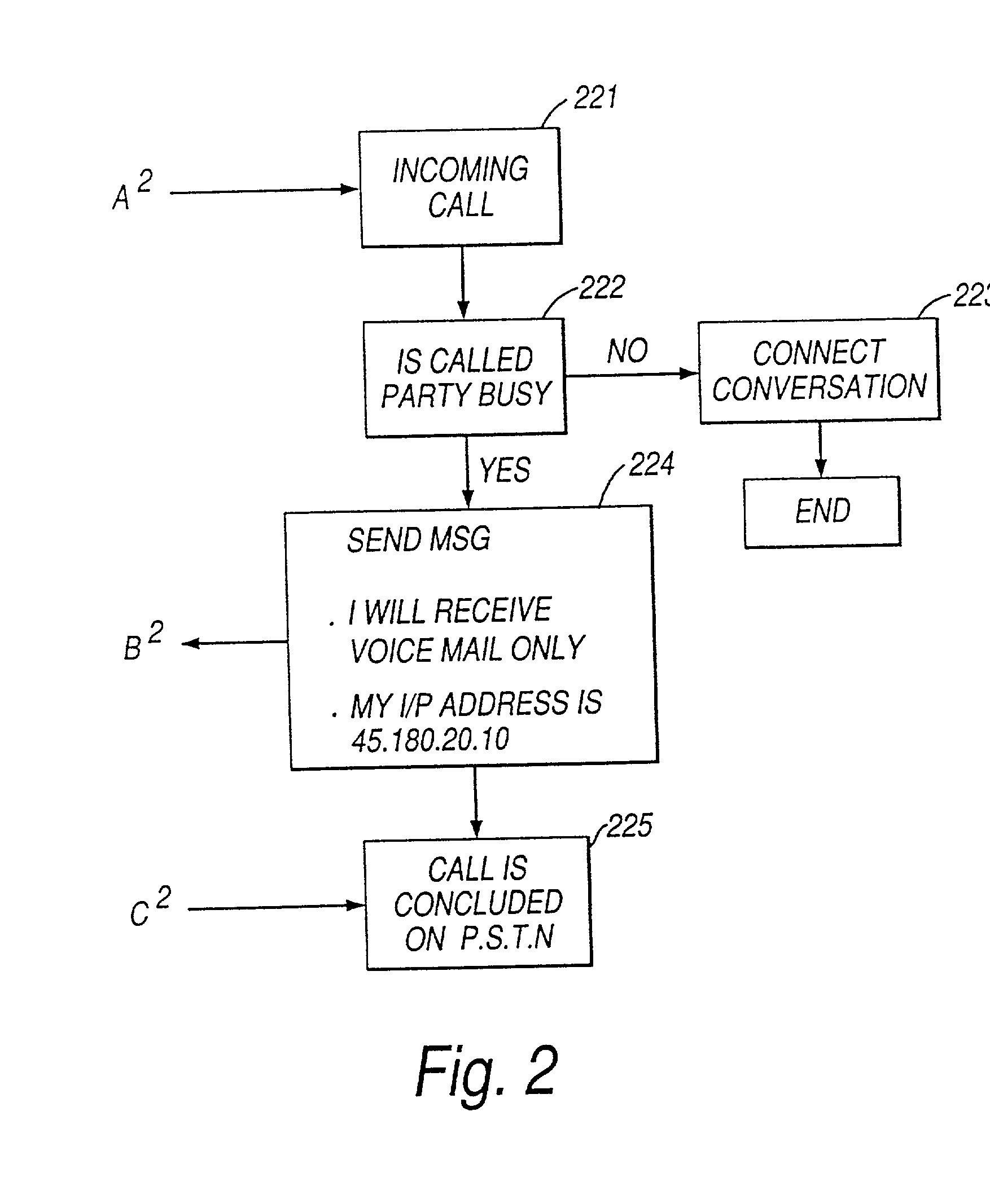
An apparatus and method for transferring a message from a calling party to an unavailable telephonically called party. The method comprises the steps of inititating a call to the called party over a communications channel, identifying that the called party is not available and instructing the calling entity to record the message at the calling entity and after recording to transmit the message to the called entity as a data message via a data channel for reception by the called entity. The system reduces the use of the voice / telephone communications networks by allowing a voice message to be transmitted through data channels, reducing the amount of voice traffic on the voice communication lines. The fact that the original voice message was actually stored with the calling entity after the telephone voice communication had been discontinued is transparent to both the calling party and the called party. Greetings for the called party can be stored at a messaging system of the calling entity.
Owner:APPLE INC
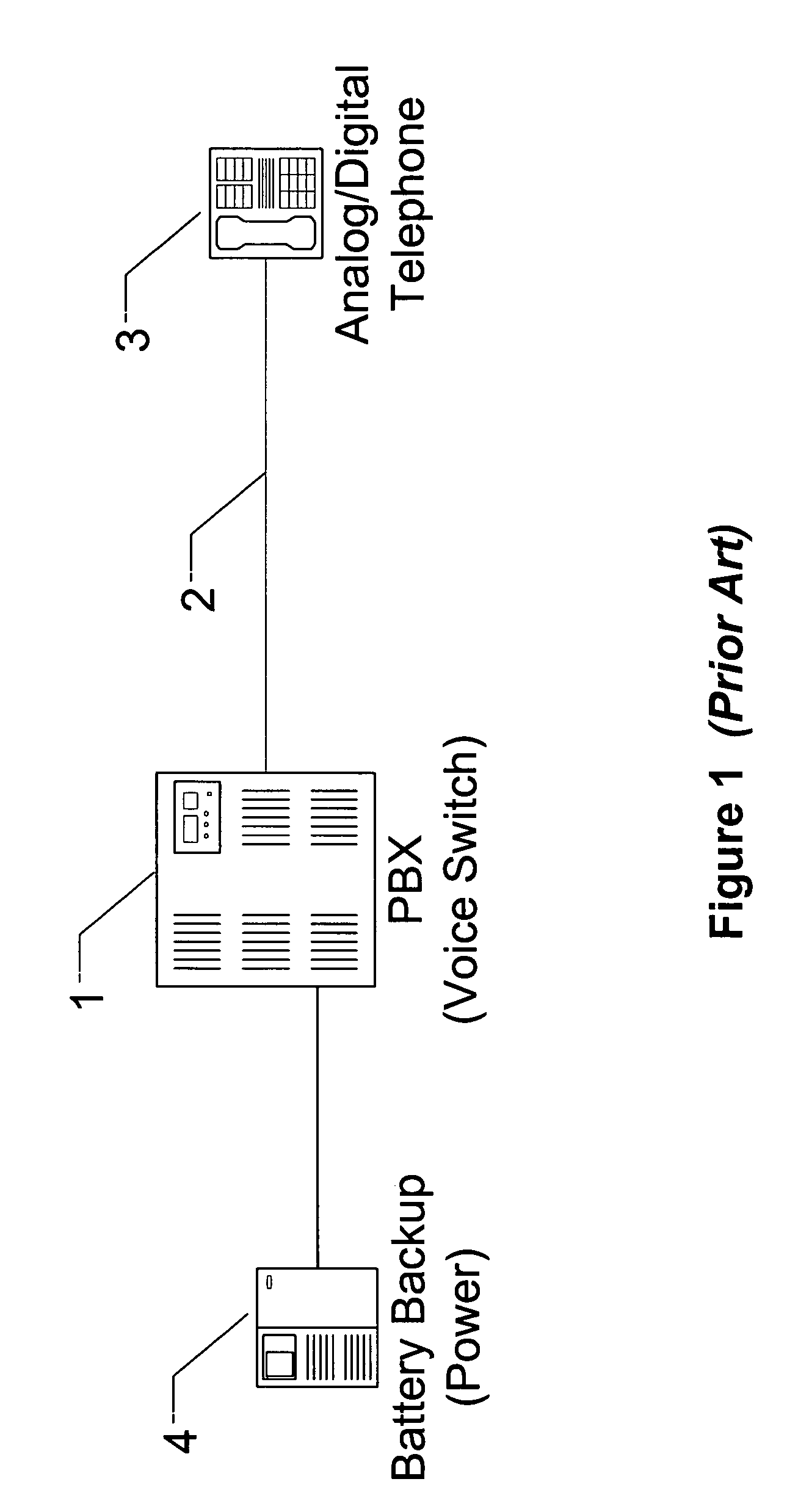
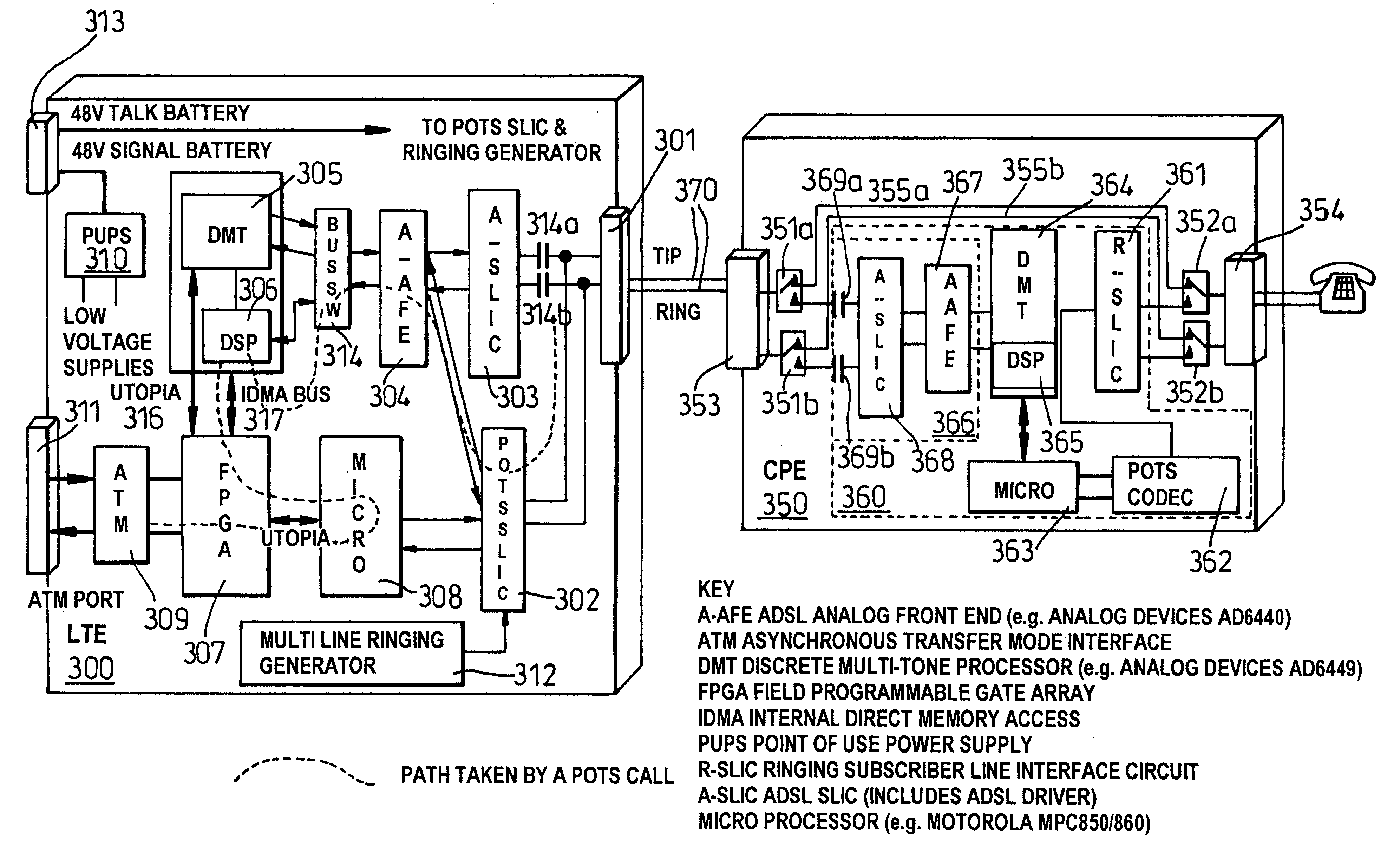
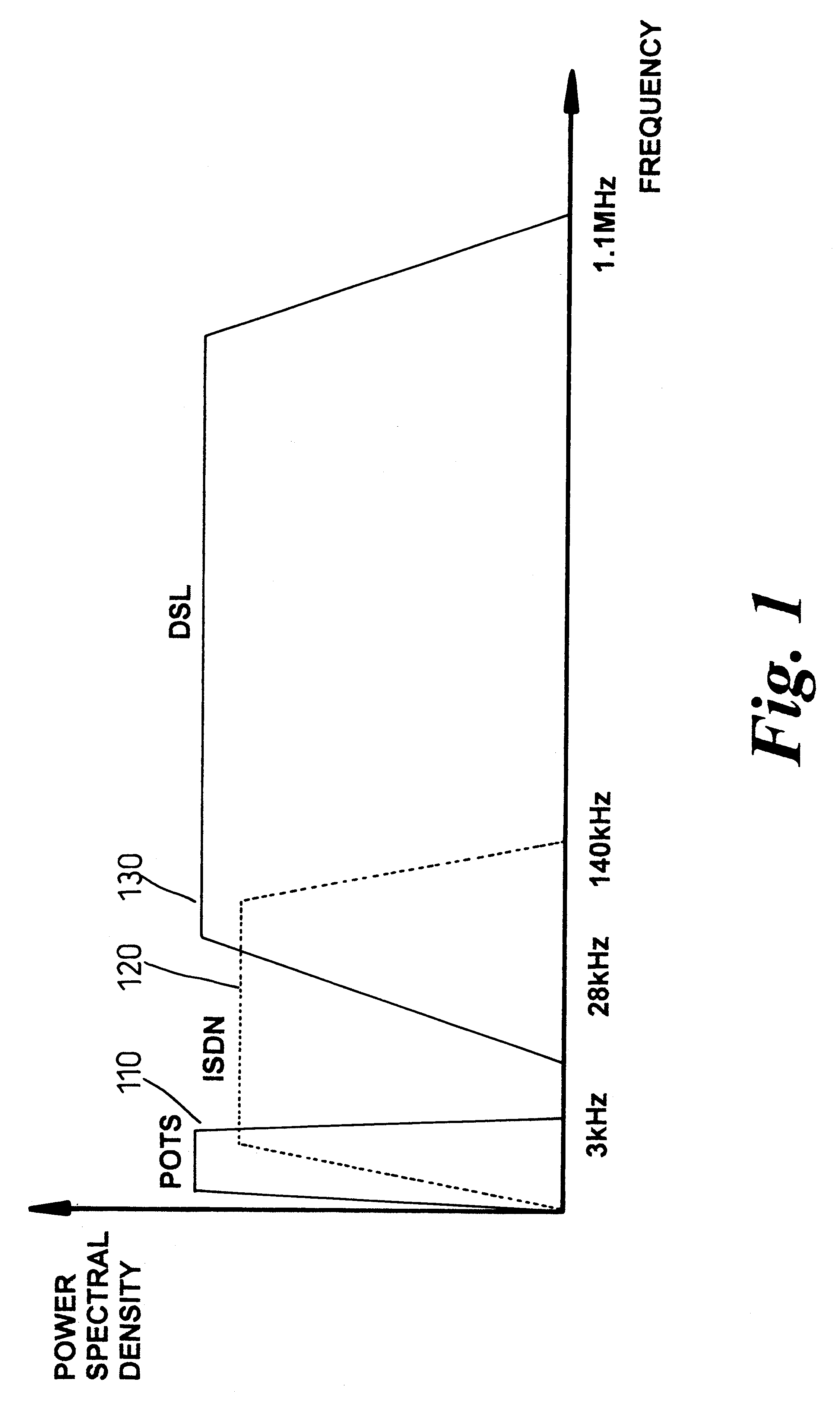
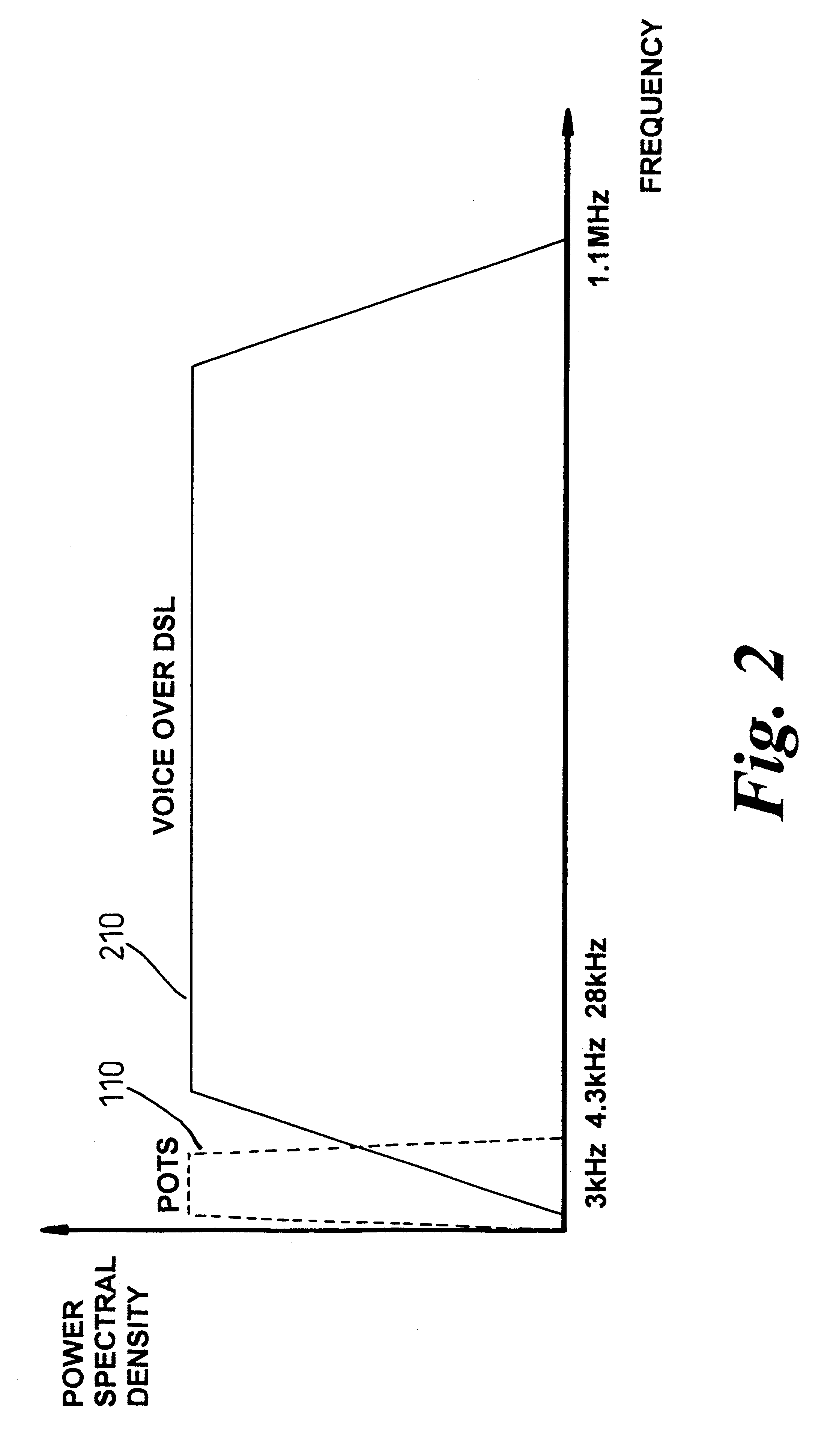
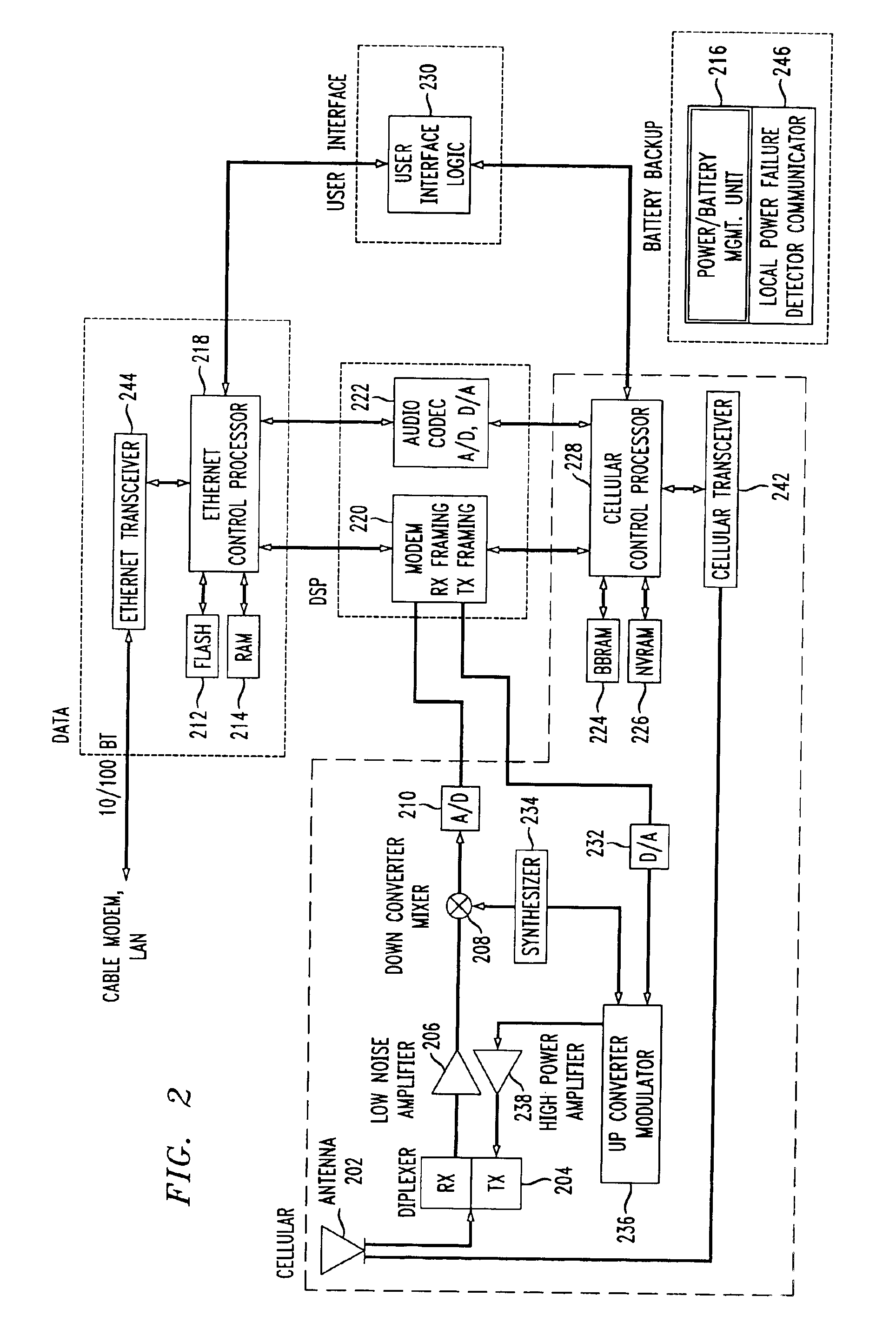
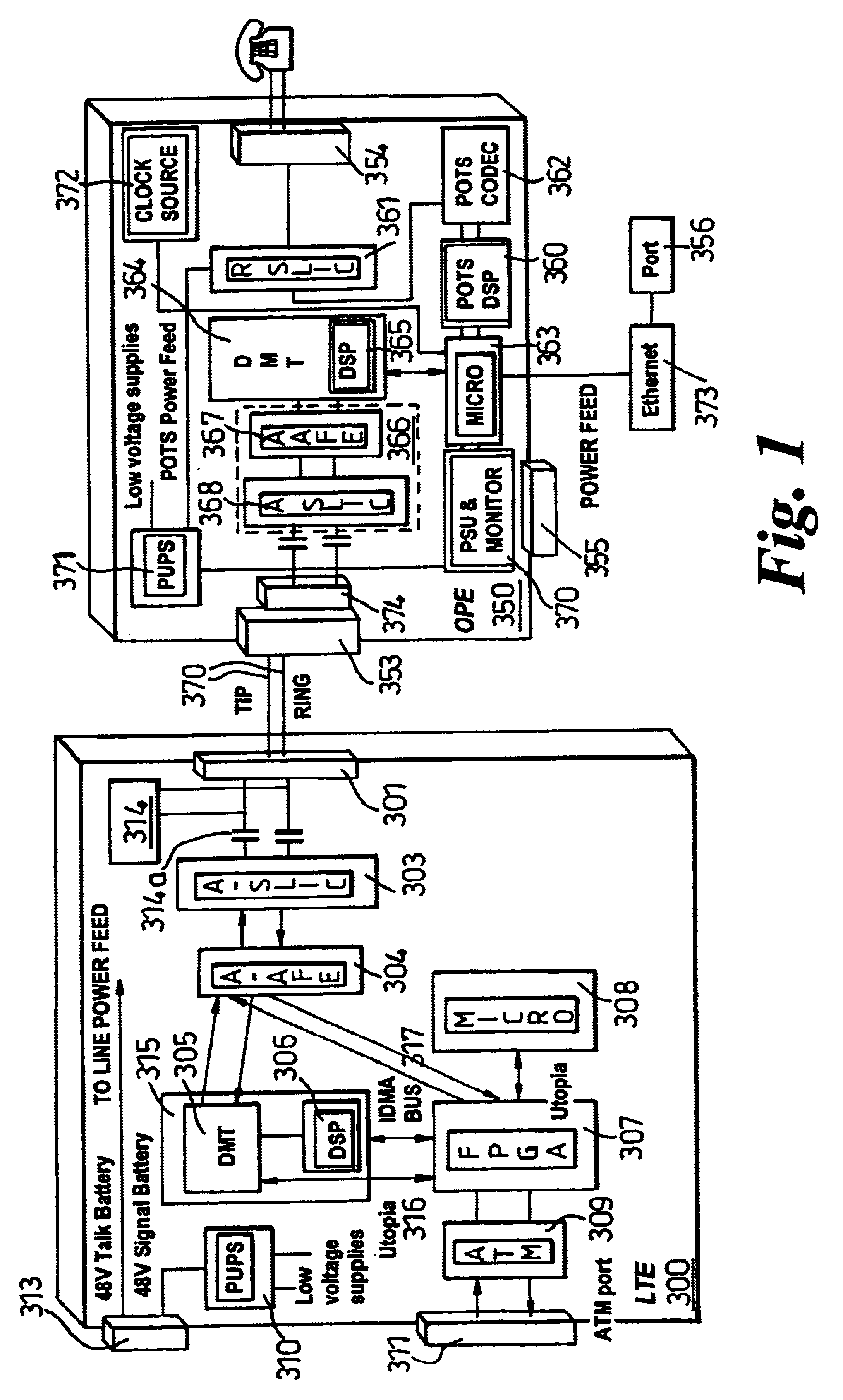
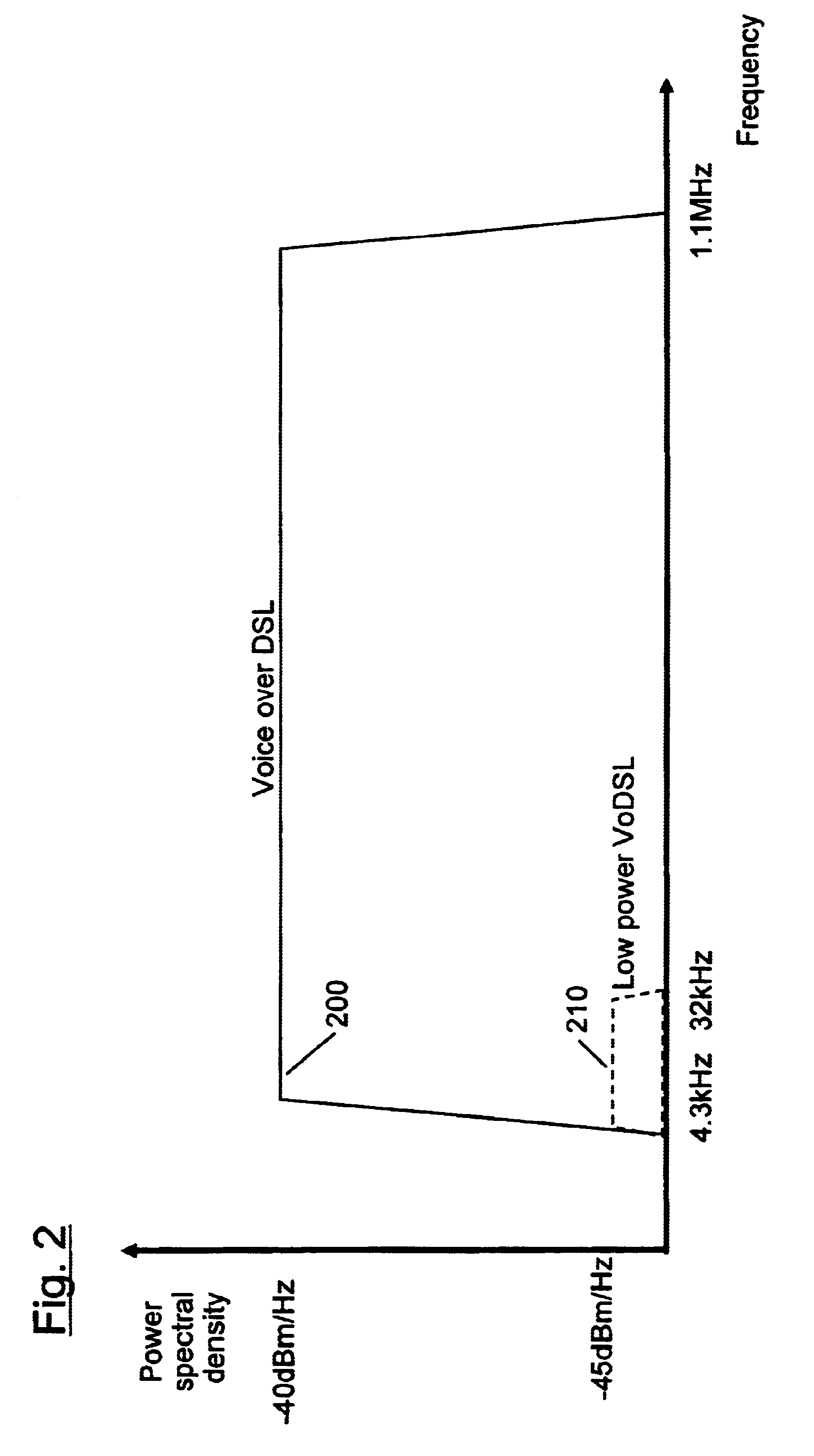
Lifeline telephony provision for voice over digital subscriber line
InactiveUS6272209B1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsHybrid transportVoice trafficCustomer-premises equipment
A method, apparatus, and software for providing lifeline service during power failure affecting Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) in a Digital Subscriber Loop (DSL) arranged to carry voice traffic in band rather than on a separate analogue POTS band. The arrangement provides a reduced service, capable of supporting at least one voice call, to operate during such power failure and, where a single call is in progress during power failure, that call may be maintained during the transition from DSL to analogue POTS lifeline service. Where a call is in progress upon power restoration, the lifeline POTS service may be maintained until completion of the call so as not to interrupt a potential lifeline call.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
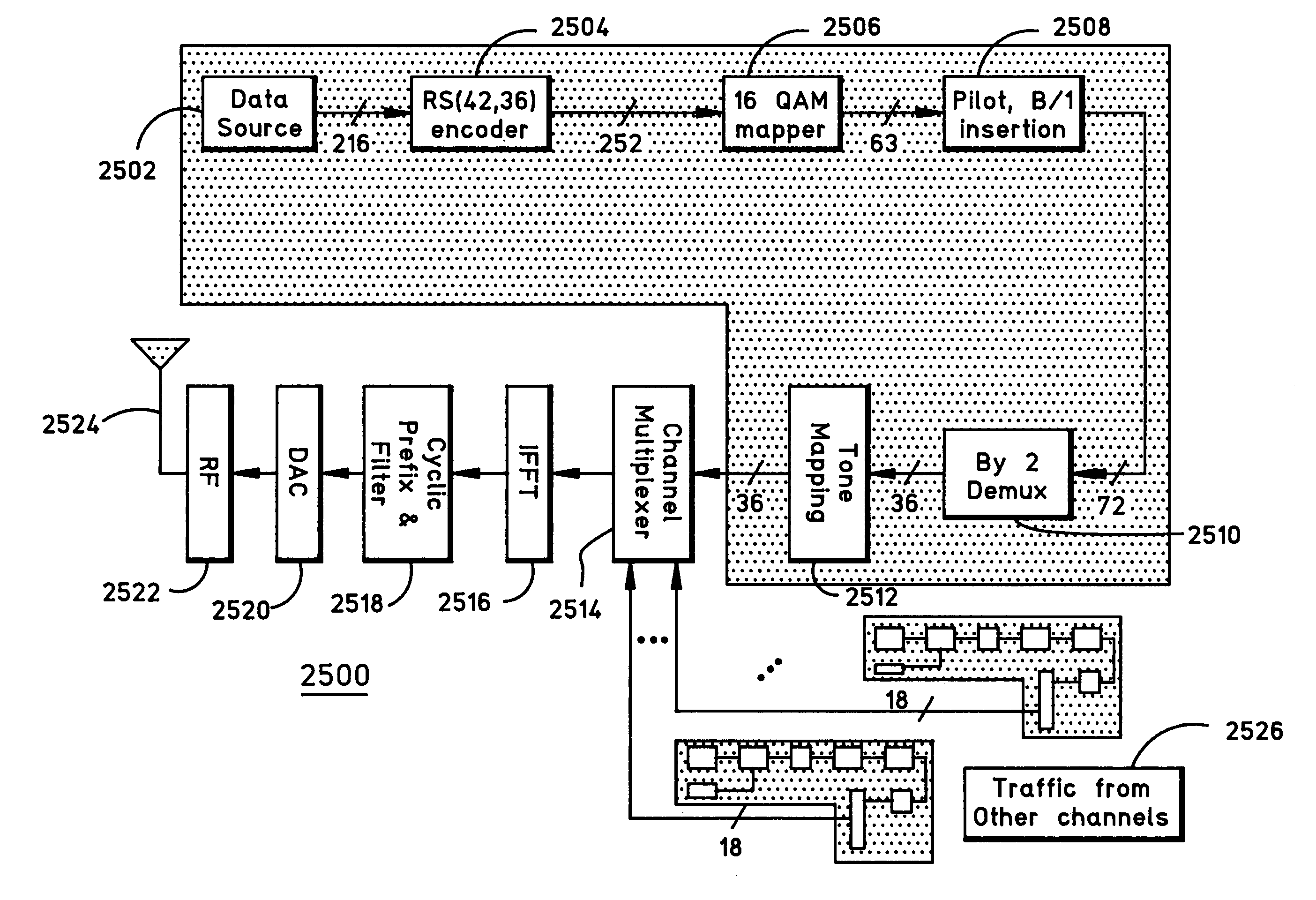
Methods and apparatus for use in communicating voice and high speed data in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS7095708B1Transmission path divisionOrthogonal multiplexFrequency spectrumVoice communication
A fixed wireless system (FWS) utilizing Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication techniques is spectrally efficient and responsive to communications involving both voice and high speed data, such as Internet data. The FWS includes a wireless base unit; a plurality of fixed wireless remote units; a plurality of wireless data traffic channels available between the wireless base unit and the plurality of fixed wireless remote units; and a plurality of wireless voice traffic channels available between the wireless base unit and the plurality of fixed wireless remote units. Each wireless traffic channel is identifiable by a unique combination of frequency and time slots. Each wireless data traffic channel is used for carrying high speed data in addressed data packets to and from the plurality of fixed wireless remote units. On the other hand, each wireless voice traffic channel can be assigned and dedicated to a particular voice communication call involving one of the plurality of fixed wireless remote units for carrying voice data of the call.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
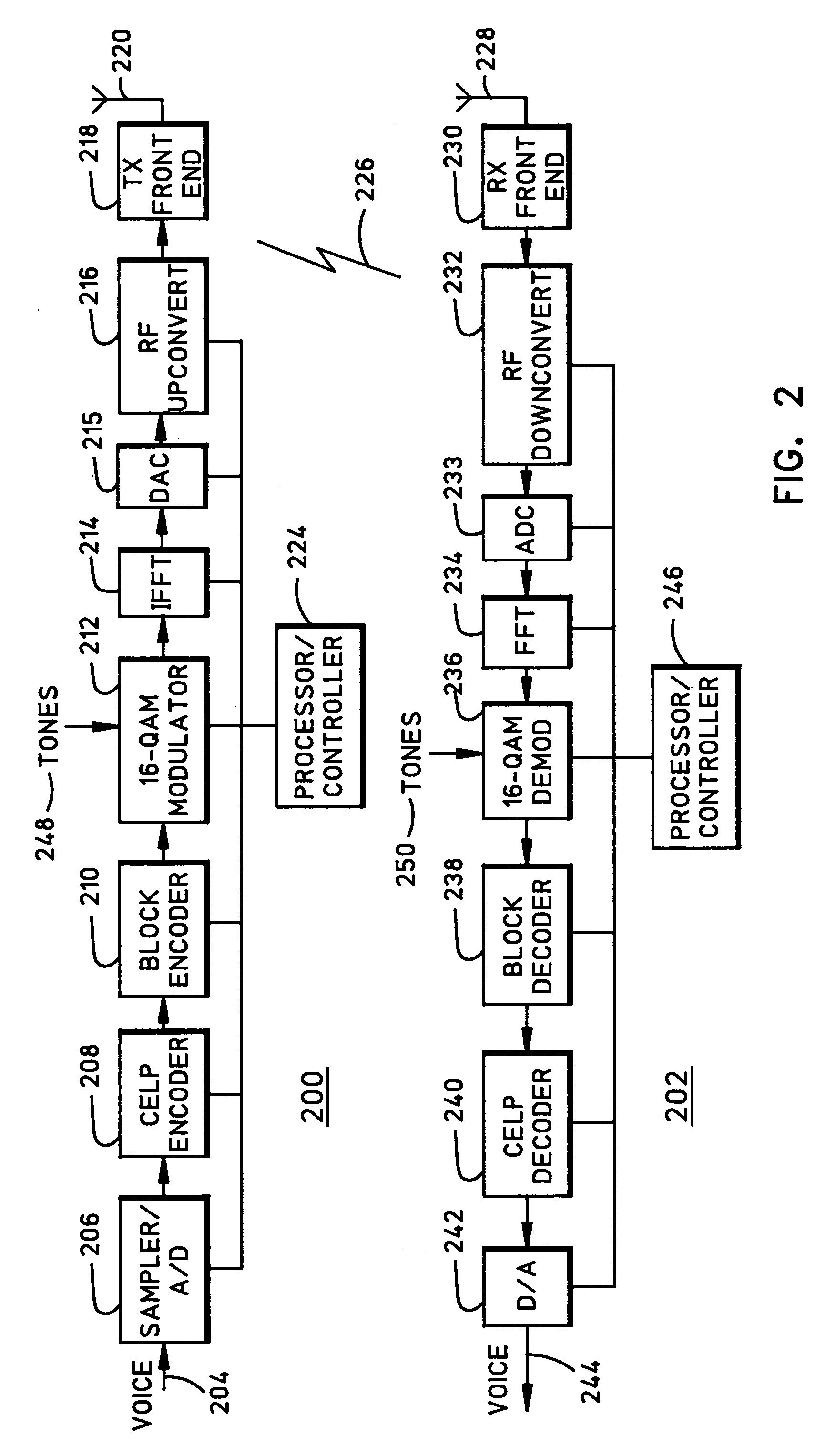
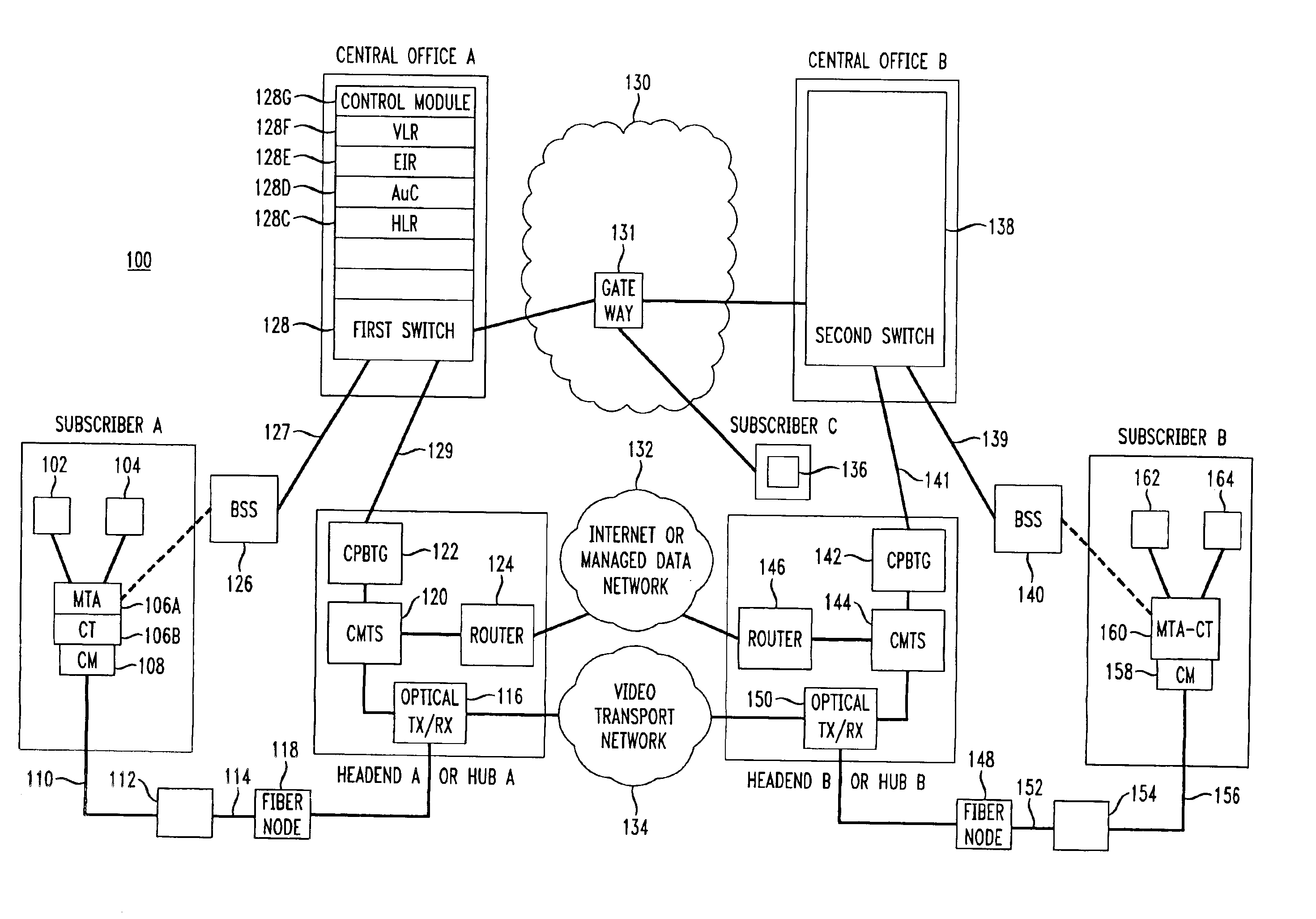
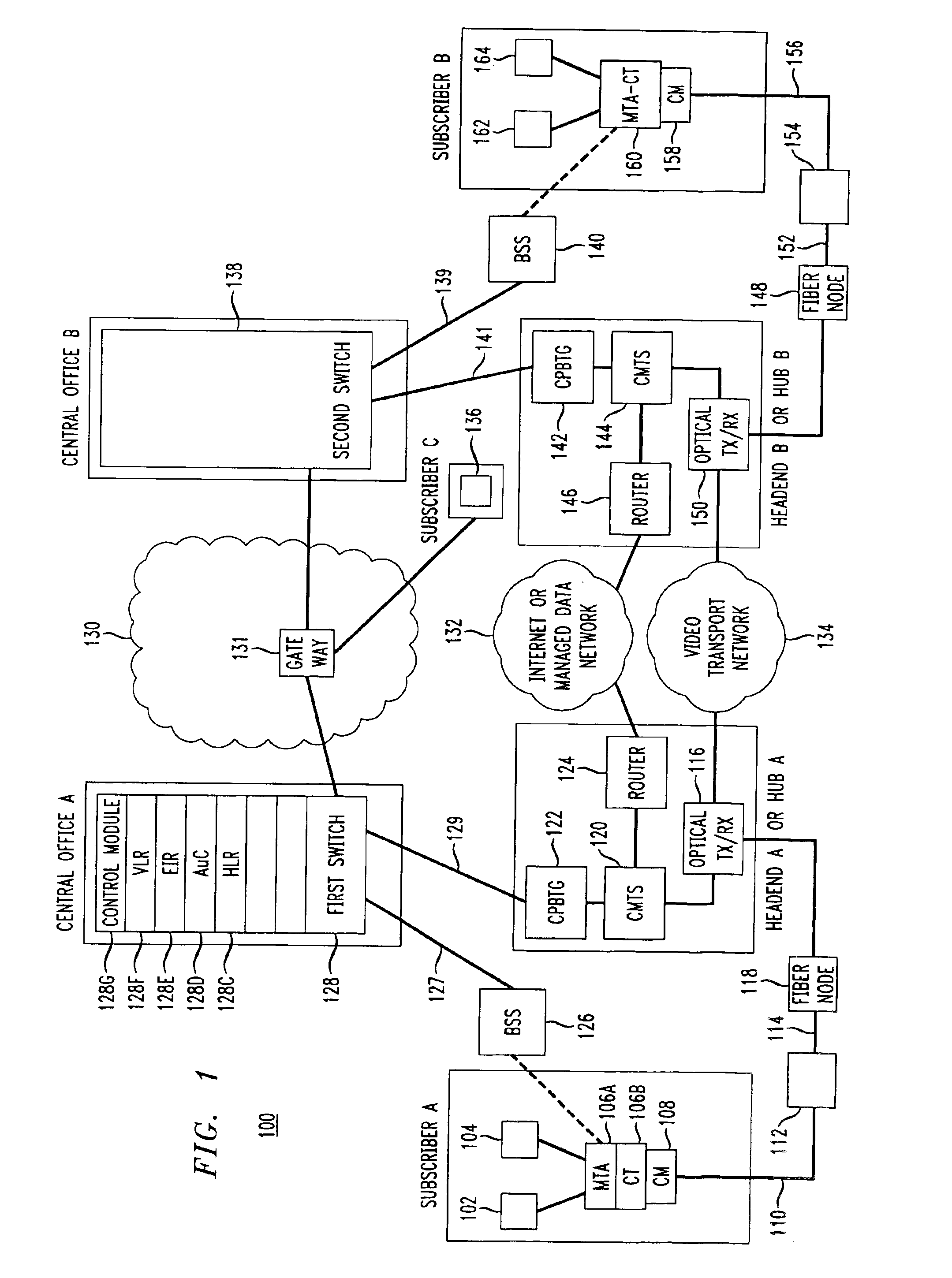
Media terminal adapter-cellular transceiver (MTA-CT)
InactiveUS6879582B1Efficient communicationReduce bottlenecksTime-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesTransceiverVoice traffic
An apparatus for providing bifurcated voice and signaling traffic over a cable telephony architecture by segregating signaling traffic and voice traffic and transmitting the respective traffic over two different mediums to a switch to establish a phone call.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
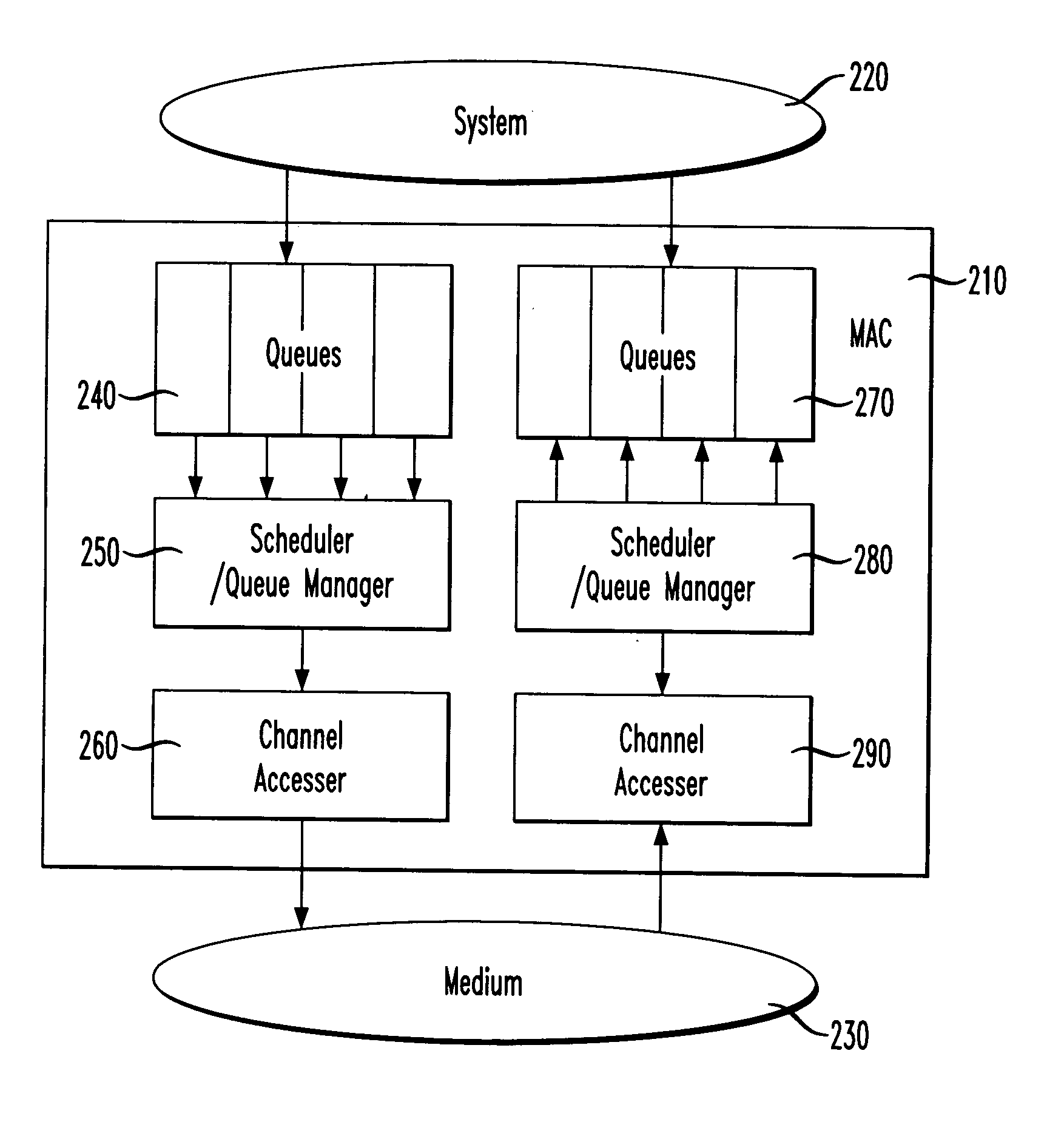
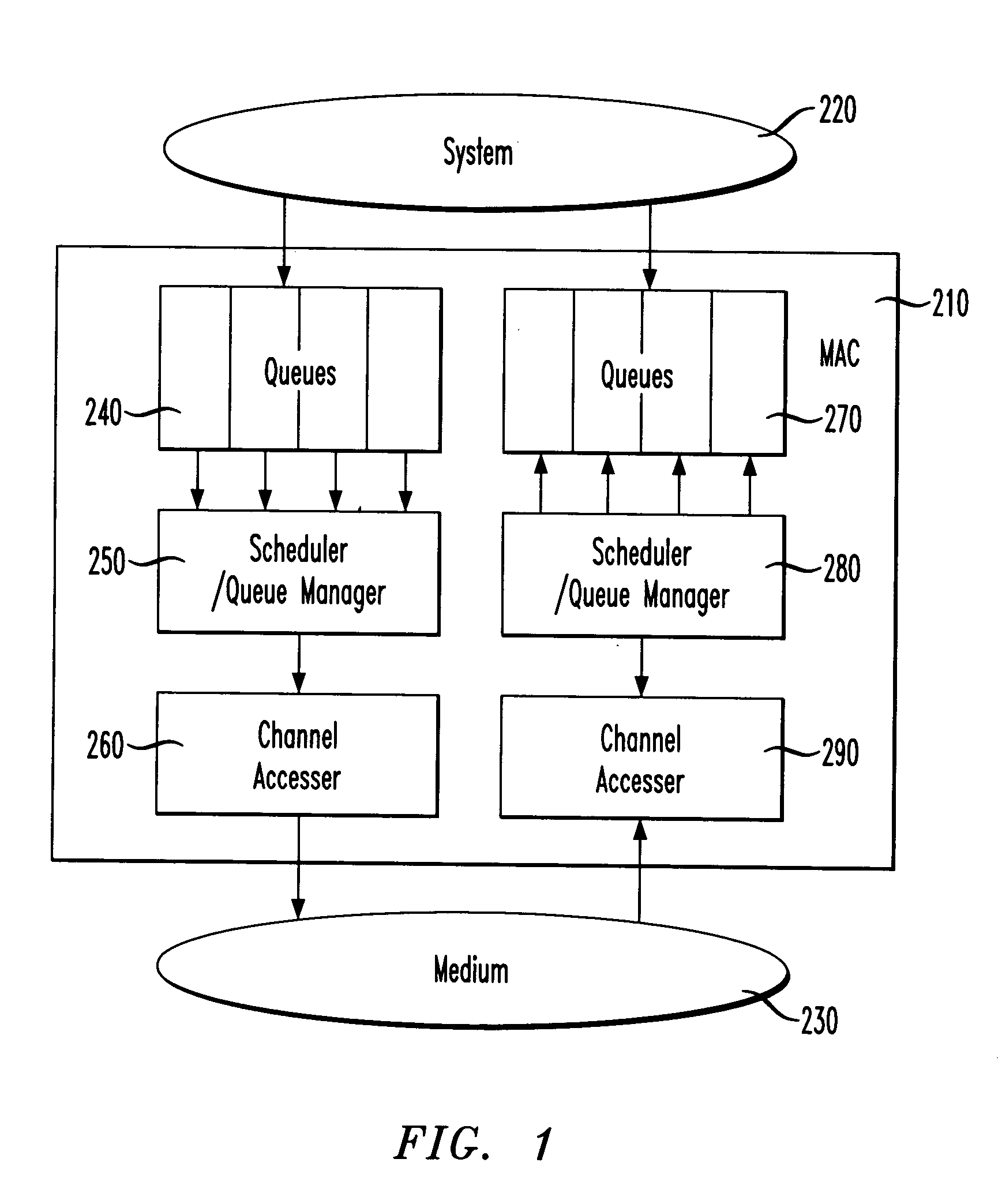
Managing priority queues and escalation in wireless communication systems
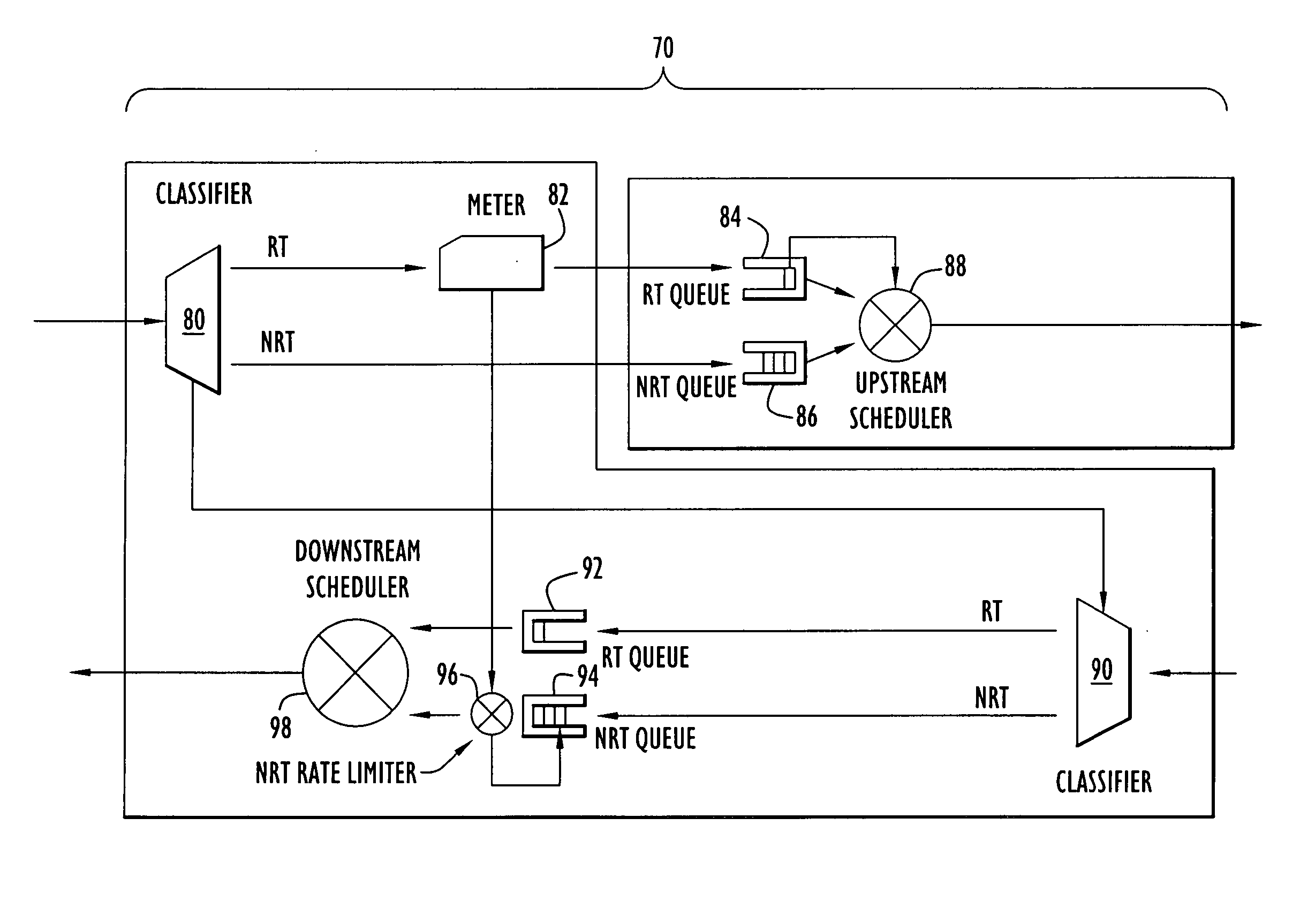
InactiveUS20040092278A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesStreaming dataLower priority
A method and system for servicing data traffic in wireless local area networks (such as IEEE 802.11 networks) in multiple queues having different levels of priority. These queues include at least a low priority queue for 'best effort' traffic, a medium priority queue for streaming data such as video pictures, and a high priority queue for voice traffic, and are serviced in order of decreasing priority. To prevent the 'best effort' traffic in the low priority queue from being 'starved', a bit is set to indicate when such a condition is likely to occur, and the low priority queue is served first when that bit has been set. Alternatively, low and medium priority traffic is handled on a weighted round-robin basis, and high priority traffic is given strict priority over both. Transmit and receive queues are handled on a rotating priority basis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
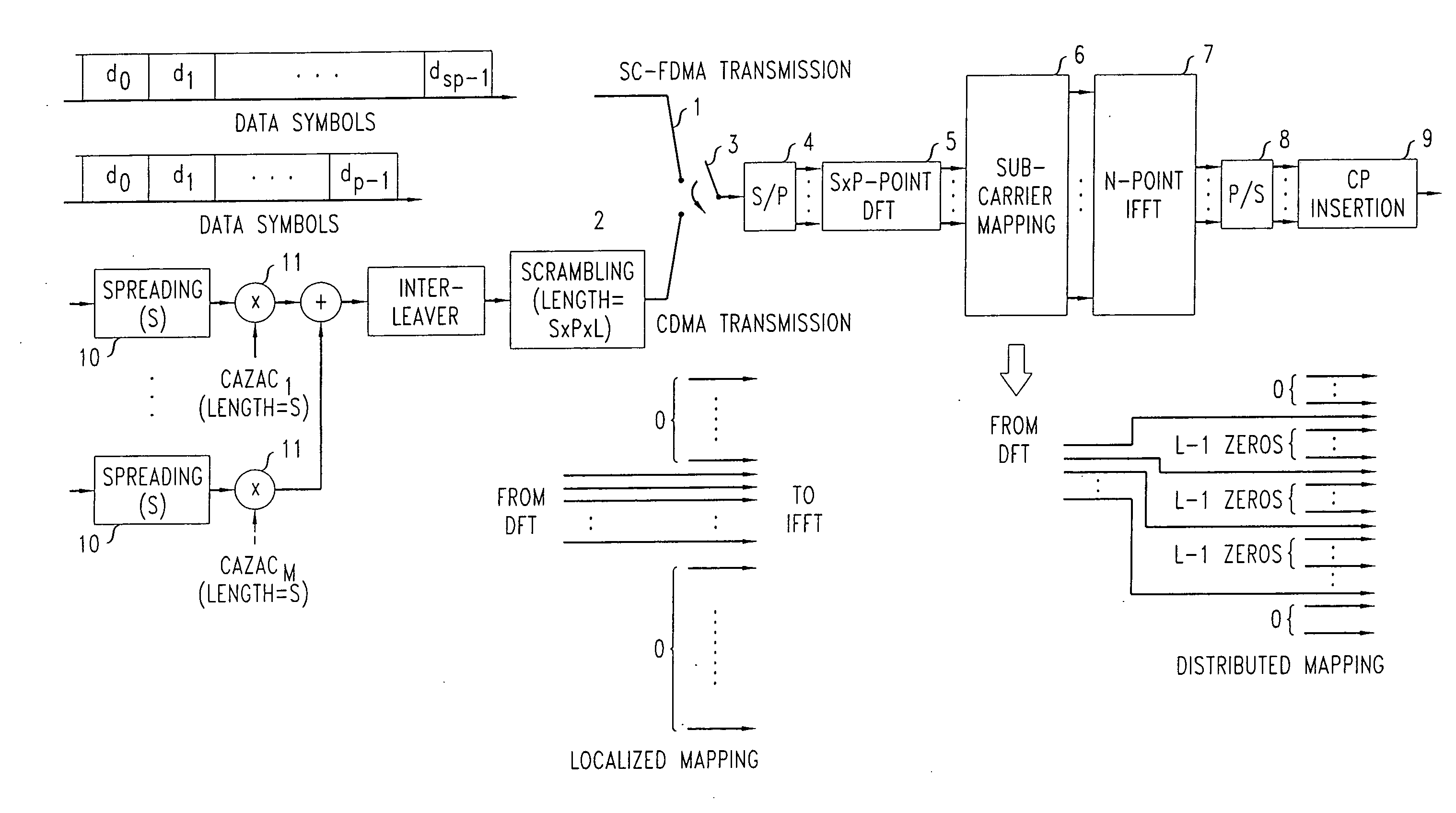
Method and apparatus for packet wireless telecommunications
ActiveUS20080267157A1Lower latencySimple processError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio transmissionTelecommunications networkCode division multiple access
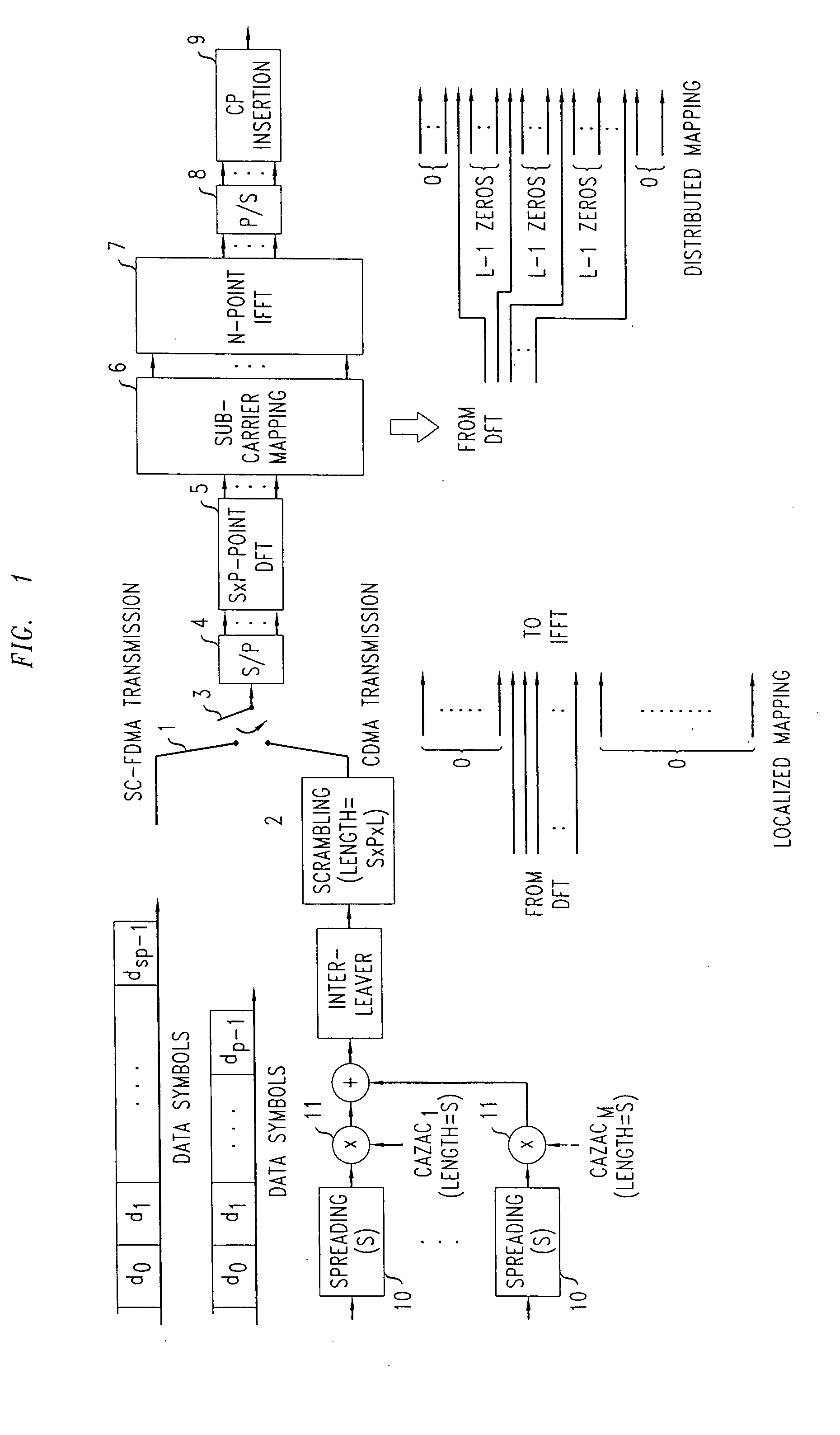
In a wireless telecommunications network, a Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) scheme is applied to data to encode it. The encoded data transmitted in the uplink using an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) frame structure including a cyclic prefix (CP). The CDMA encoded data may be time multiplexed with Single Carrier-Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) transmissions. The CDMA transmissions may be used for relatively small payloads, such as those associated with voice traffic and control signals, and the SC-FDMA transmissions used for higher date rate transmissions. This enables autonomous transmission, without scheduling, for smaller payloads. A transmitter includes a selector 3 for performing time multiplexing in the uplink, the required mode being indicated by the Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) ID. A first branch 1 carries SC-FDMA data and a second branch 2 carries data to be transmitted as a CDMA scheme. A CAZAC code may be used in encoding the CDMA data.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Communication device and method of prioritizing transference of time-critical data
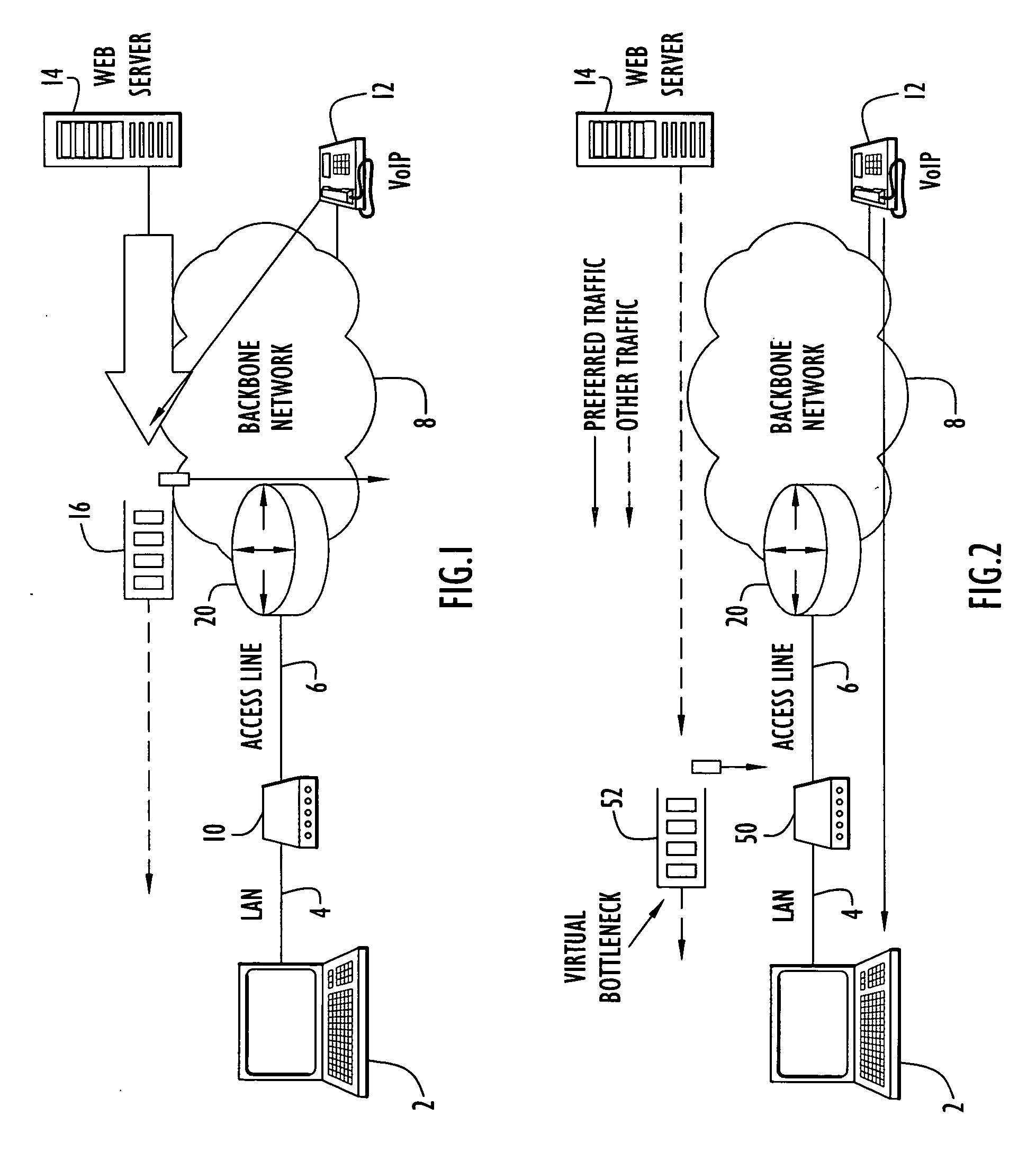
InactiveUS20060187836A1Raise transfer toSolve insufficient bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsData packTime critical
A communication device according to the present invention enhances transfer of time-critical data between one or more LANs and a device (e.g., edge router, etc.) coupled to a backbone network. A virtual bottleneck in the form of a queue is introduced by the communication device at the customer premises or customer end of a backbone network access line where the network congestion or bottleneck resides. The virtual bottleneck delays and / or discards time insensitive traffic prior to time-critical or voice traffic being delayed in the edge router. This is accomplished by the virtual bottleneck queue including a storage capacity or length less than that of a queue utilized by the edge router. A traffic manager or scheduler controlling the virtual bottleneck dynamically adjusts the virtual bottleneck based on the bandwidth required for time-critical packets to ensure sufficient bandwidth is available for those packets.
Owner:PATTON ELECTRONICS
Message interworking gateway
InactiveUS20070110076A1Data switching by path configurationMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsMessage routingVoice traffic
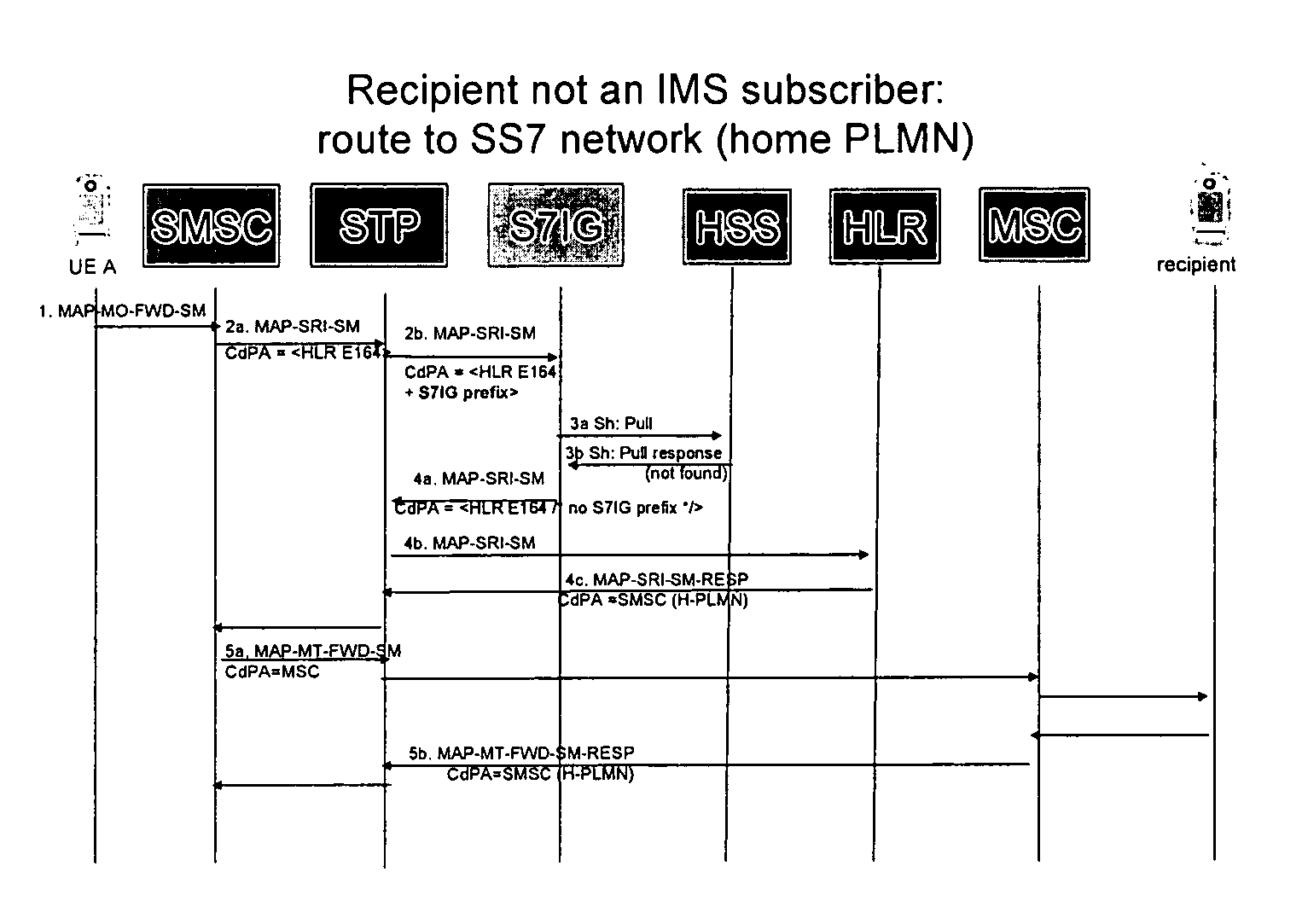
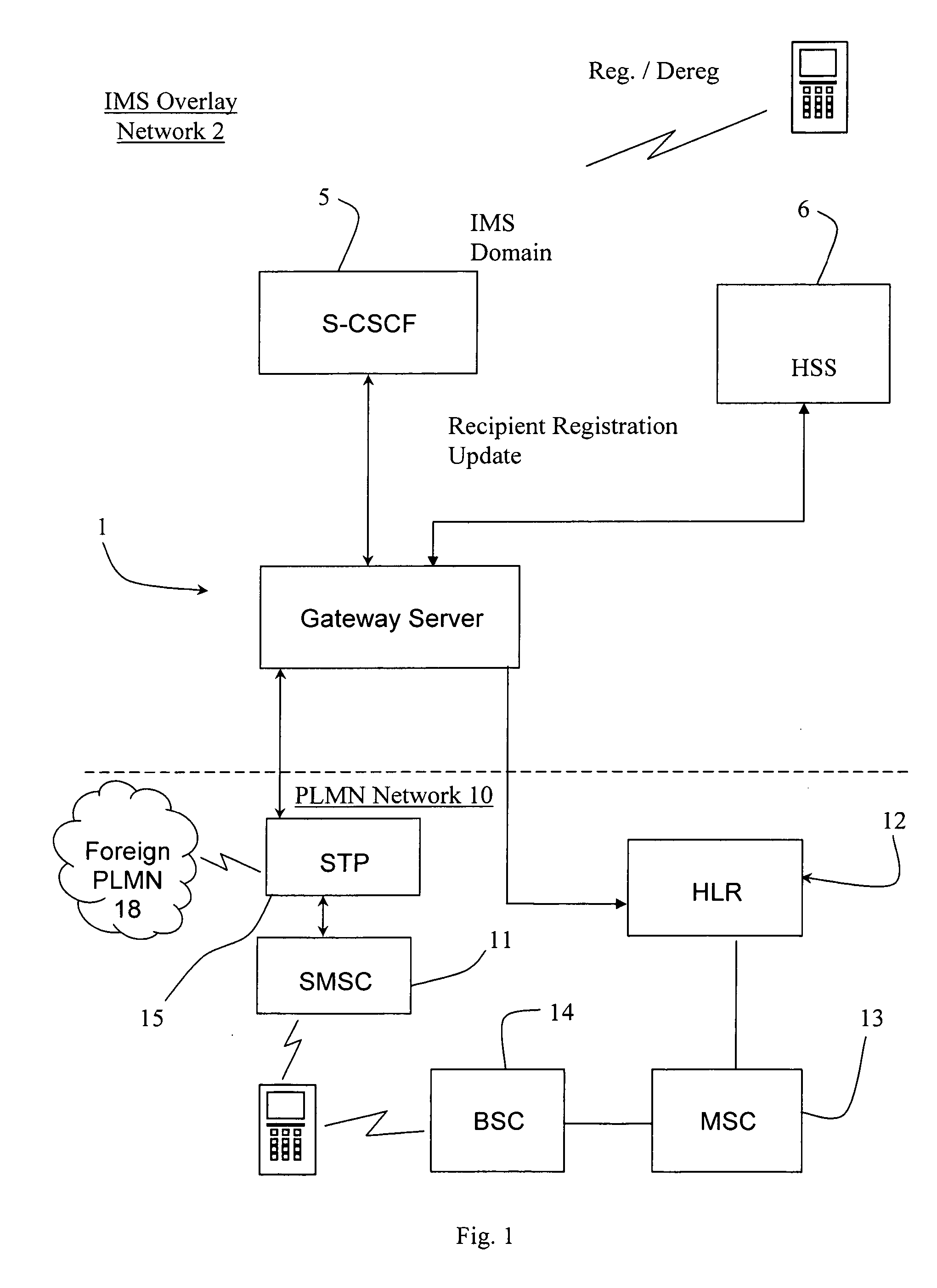
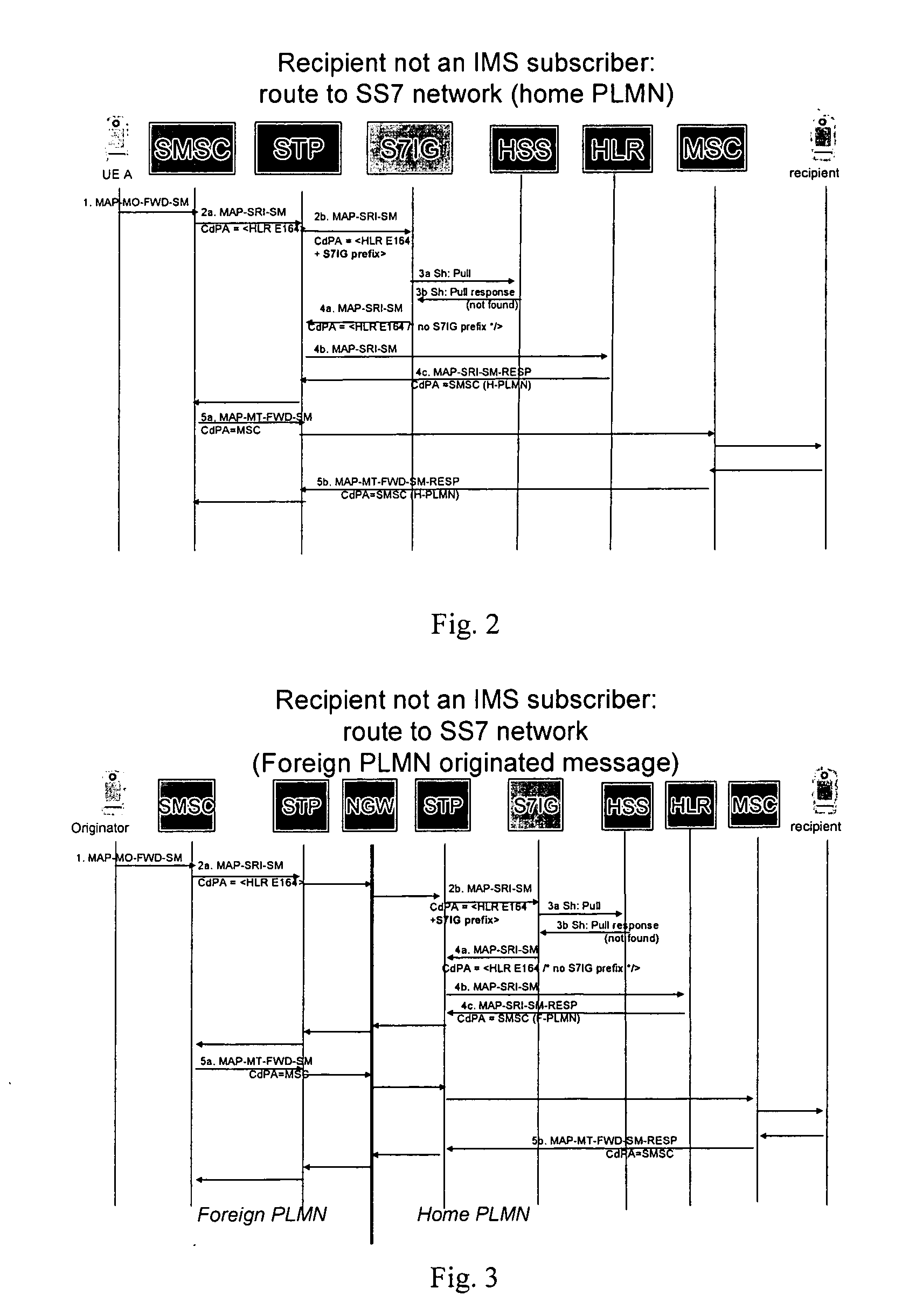
A message interworking gateway (1) resides in an overlay IMS network (2) associated with a home SS7 network (10). The gateway (1) intercepts requests for routing information (MAP-SRIs) from either the home SMSC (11) or a foreign SMSC. If the message recipient is available on the IMS overlay network (2) the gateway (1) performs protocol translation AND routes the translated message to the recipient. If not, the gateway returns the SRI to the home (10) network. The gateway operates without updating the home HLR (12) with user presence data and hence voice traffic can be kept on circuit switched technology without being routed to the IMS overlay network (2).
Owner:MARKPORT LTD
Method and system for providing remote telephone service via a wireless local area network
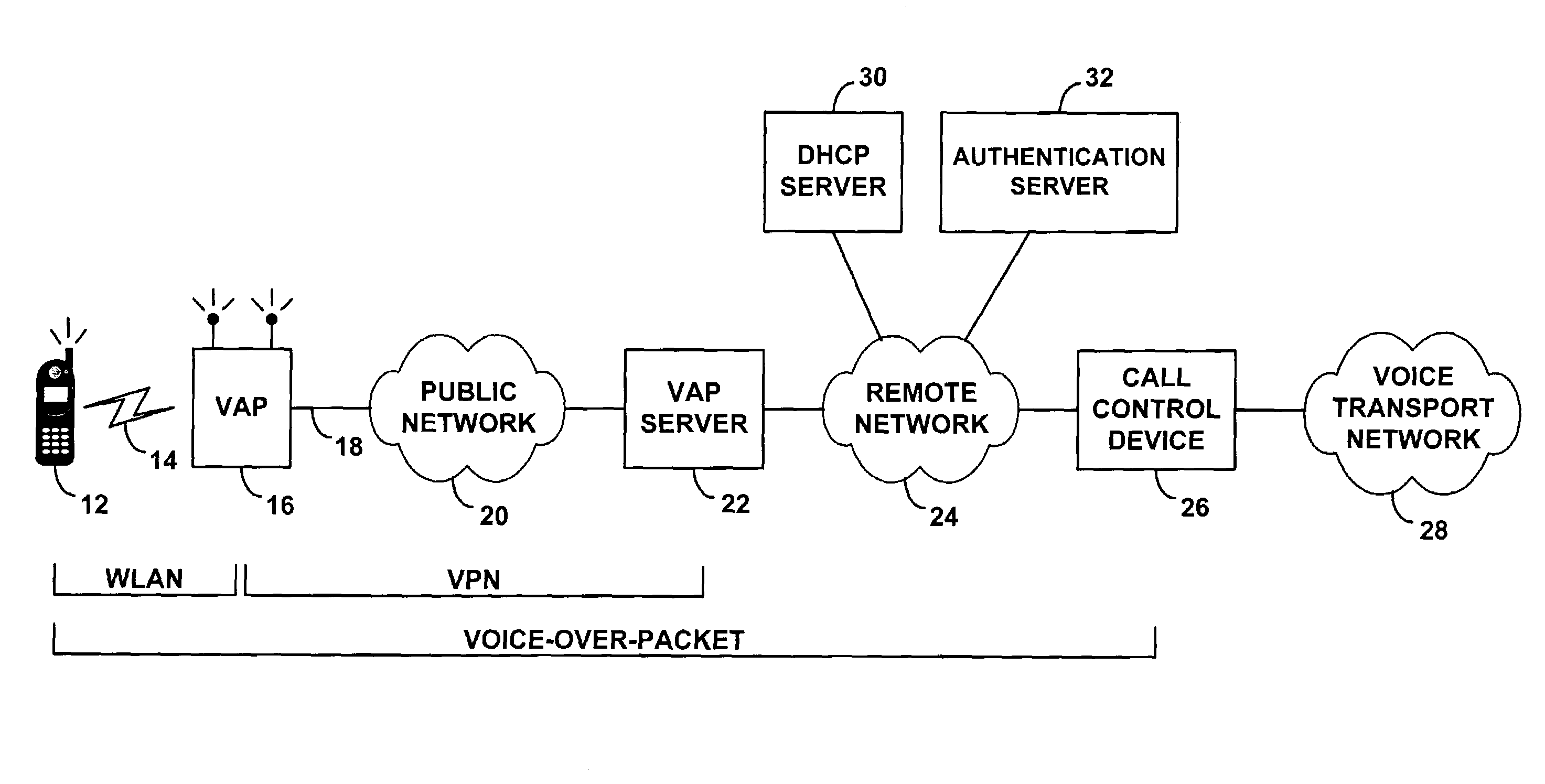
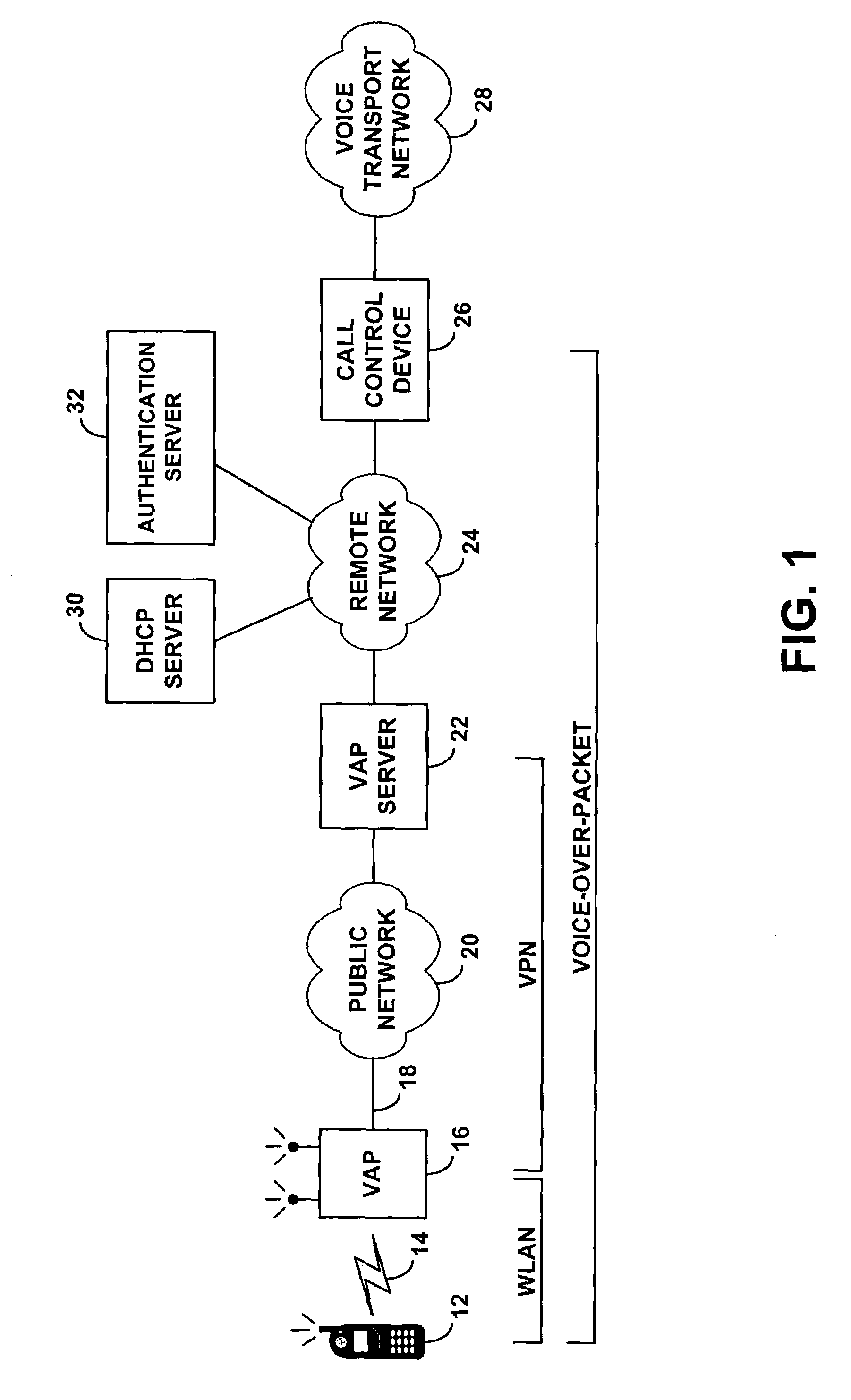
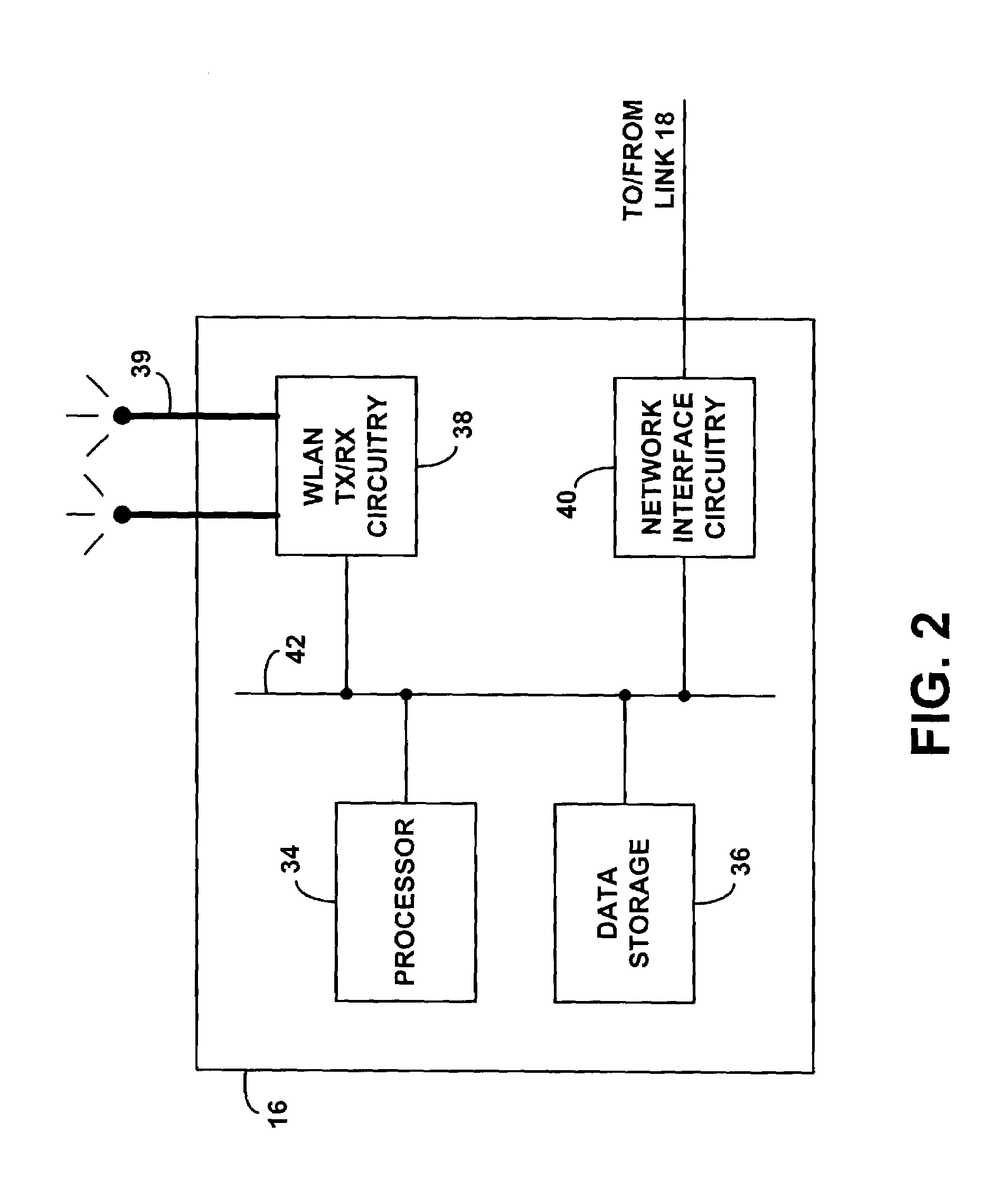
ActiveUS7298702B1Communication securityReadily engage in voice over packet (VoP) communicationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityVoice communication
A method and system for providing remote voice communication service via a wireless local area network (WLAN). A WLAN access point is arranged with predefined security settings to establish a VPN tunnel over a packet network with a VPN terminator on a remote network. The access point then wirelessly receives voice traffic from a wireless terminal operating in the WLAN and sends the voice traffic over the VPN tunnel to the remote network, for transmission to a call control device, which provides connectivity with a voice transport network. And the access point similarly receives voice traffic via the VPN tunnel from the remote network and sends the voice traffic wirelessly to the wireless terminal. Advantageously, multiple wireless terminals operating on the WLAN can engage in voice calls concurrently via the access point.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Continuity of voice carried over DSL during power failure
InactiveUS6647117B1Easy to transportInterconnection arrangementsCurrent supply arrangementsDigital subscriber lineTraffic capacity
A digital subscriber loop modem arrangement is arranged to respond to a fault condition so as to provide at least a voice lifeline service over DSL service on a digital subscriber line in which data and voice traffic are transported on a plurality of carriers. On detection of a power loss at the subscriber end of the line, the number of carriers is reduced so as to maintaining transmission only of those carriers transporting the voice traffic. This reduces the power demand which can now be met from the remote end of the line. A method of operating a digital subscriber loop modem arrangement under a fault condition so as to provide at least a voice over DSL service on a digital subscriber line in which data and voice traffic are transported on a plurality of carriers, the method comprising the steps of: replacing the data with random data, disabling those data carriers on which the random data is transported, and maintaining transmission of those carriers transporting the voice traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Soft switch using distributed firewalls for load sharing voice-over-IP traffic in an IP network
InactiveUS7072332B2Interconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationVoice trafficVoice over IP
A switch capable of handling voice-over-IP (VoIP) traffic between calling devices and called devices. The switch comprises: 1) call application nodes for executing call process server applications, wherein a first call process server application and a similar second call process server application form a first load sharing group server application; and 2) network address translation nodes for executing firewall server applications. A first firewall server application executed on a first network address translation node is associated with a similar second firewall server application executed on a second network address translation nodes separate from the first network address translation node. The first and second firewall server applications form a second load sharing group server application. The second load sharing group server application receives VoIP traffic and selects one of the first and second firewall server applications to verify that the VoIP traffic is authorized to access at least one of the call process server applications in the call application nodes according to a load distribution algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
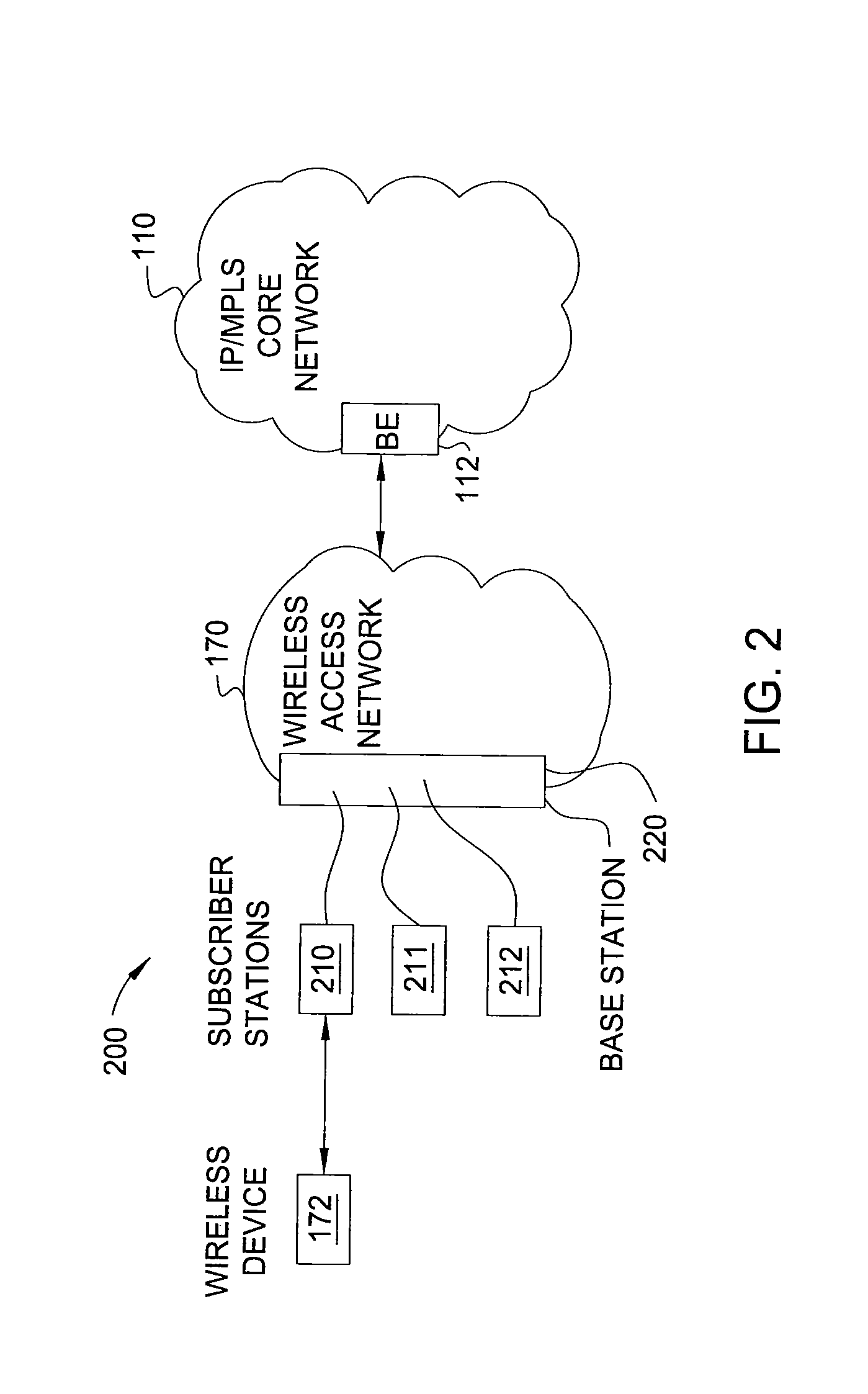
Method and apparatus for allocating bandwidth for a network
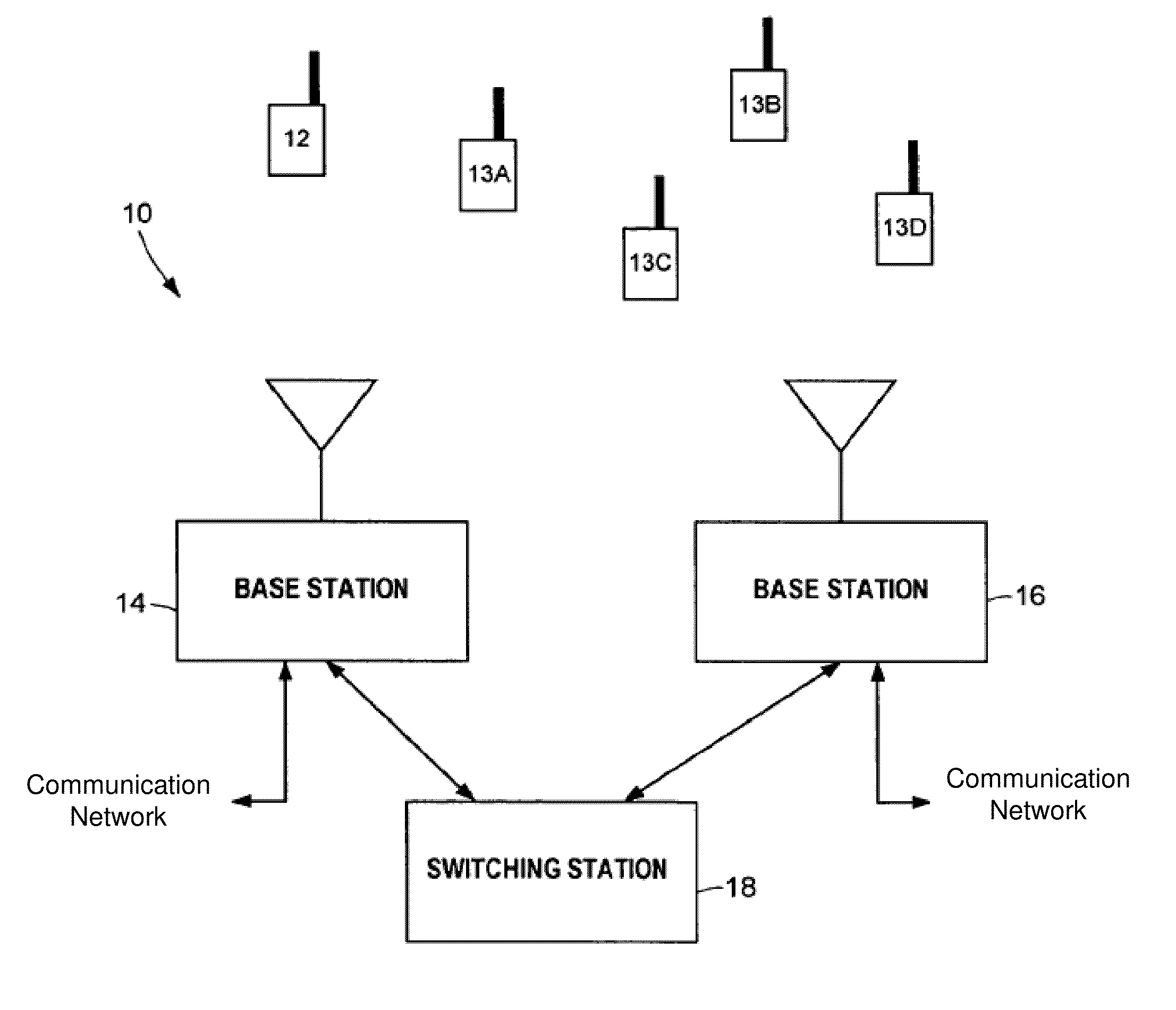
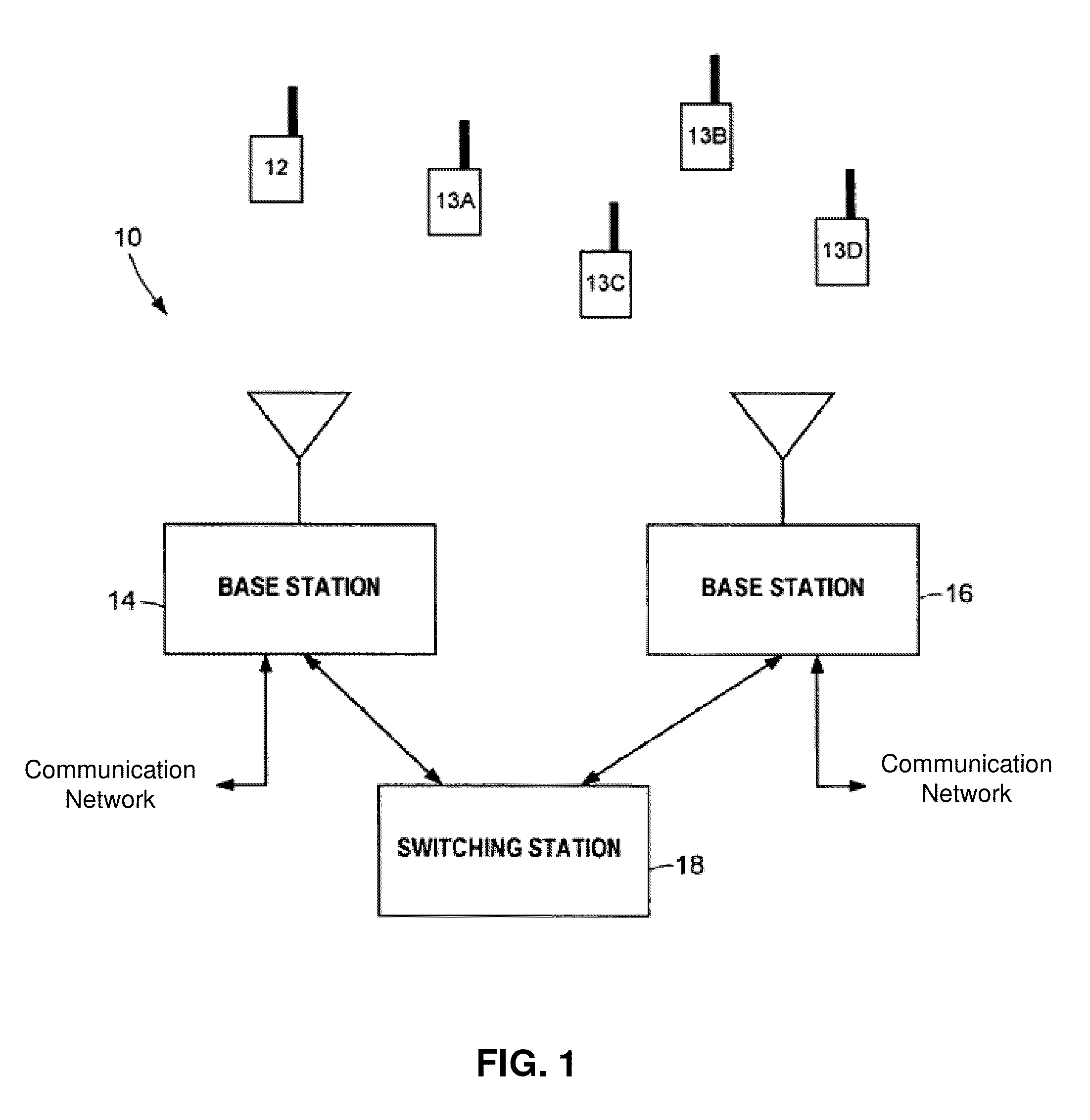
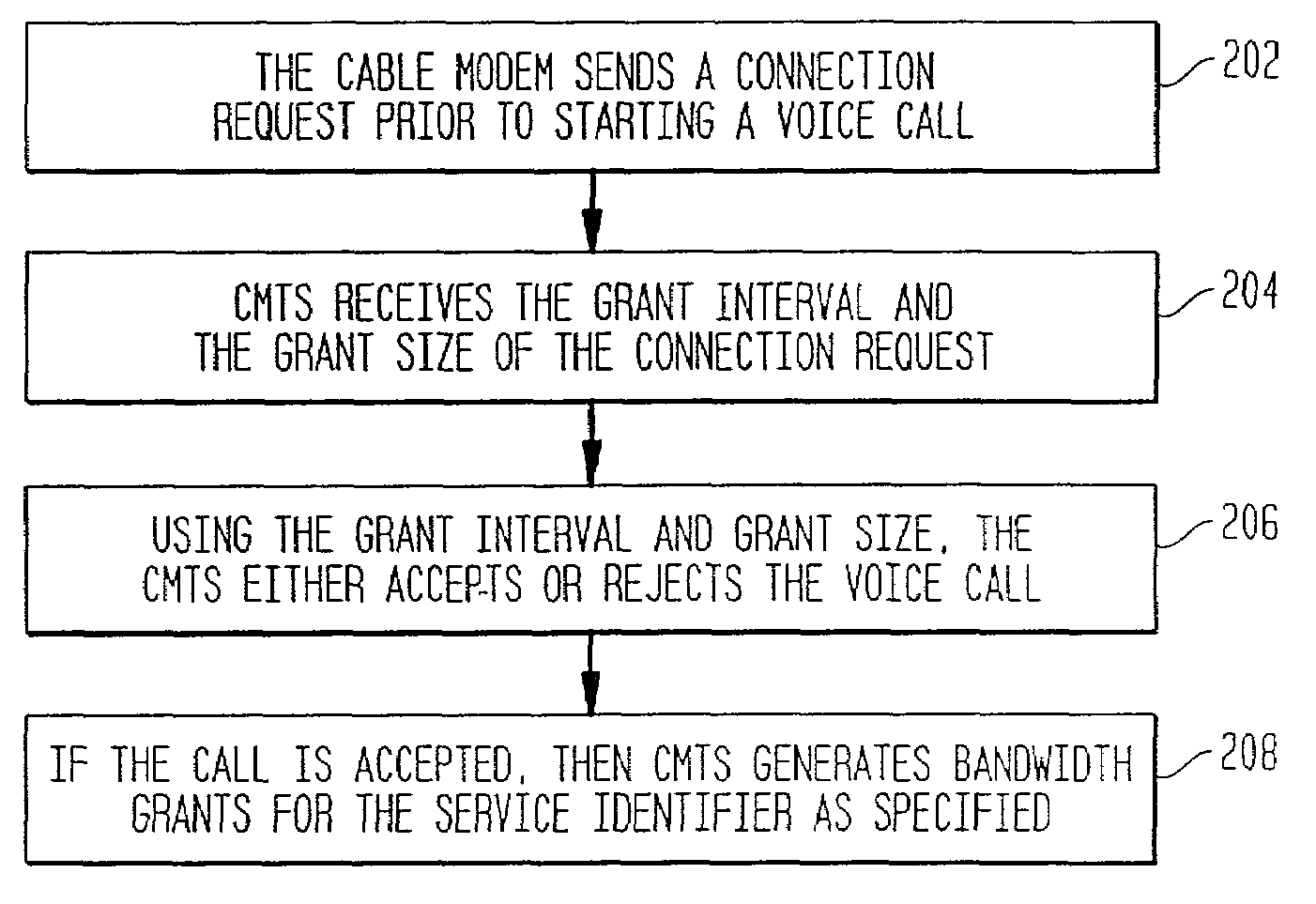
A method and apparatus for performing traffic engineering, e.g., allocating bandwidth, on a wireless access network are disclosed. For example, the method determines a number of subscriber stations (SSs) that a Base Station (BS) is capable of supporting in accordance with at least one performance objective for voice traffic, wherein the at least one performance objective for voice traffic comprises a type of codec. The method then allocates bandwidth by the base station in accordance with the number of subscriber stations that the base station is capable of supporting.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
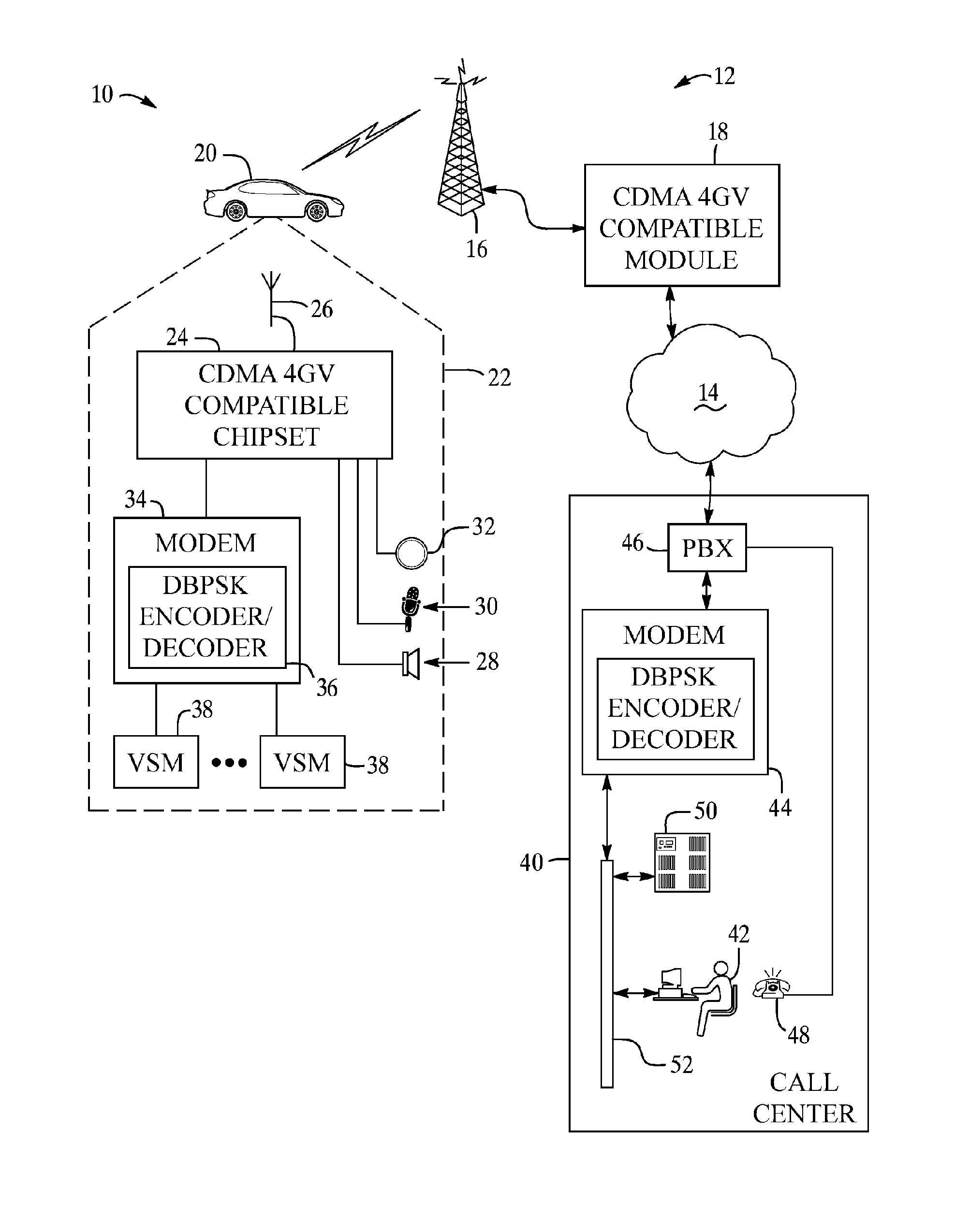
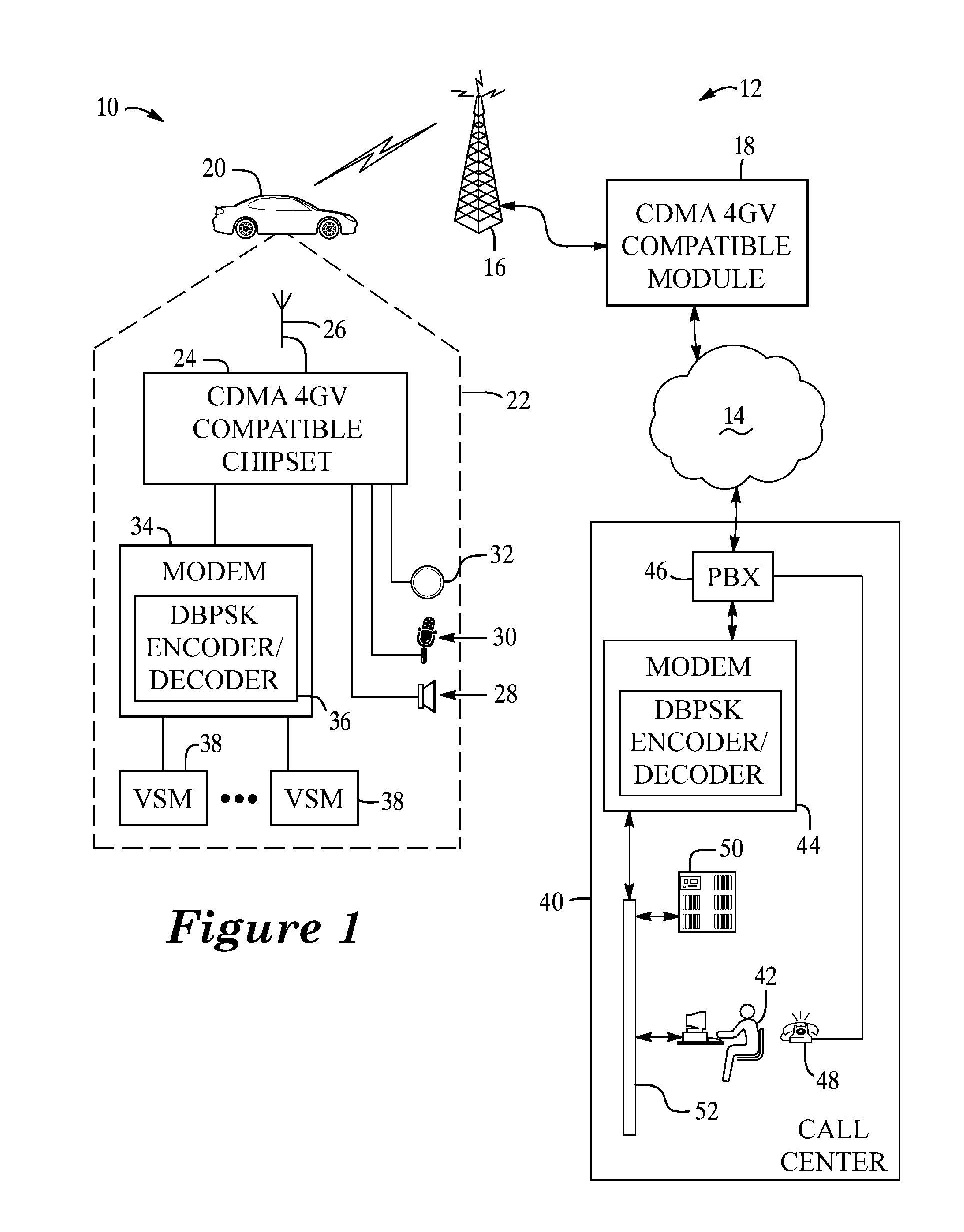
Method for data communication via a voice channel of a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20070258398A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataCarrier signal
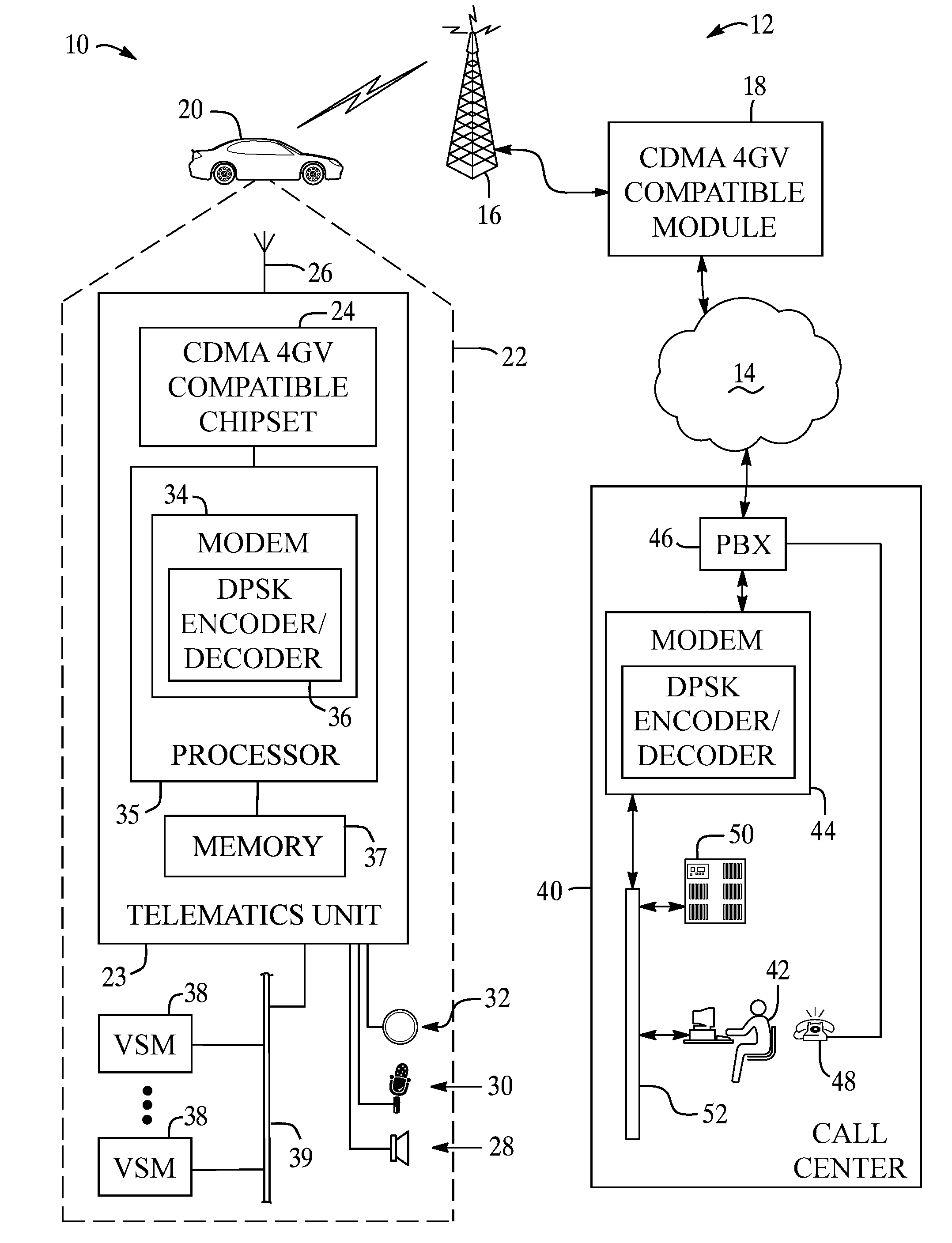
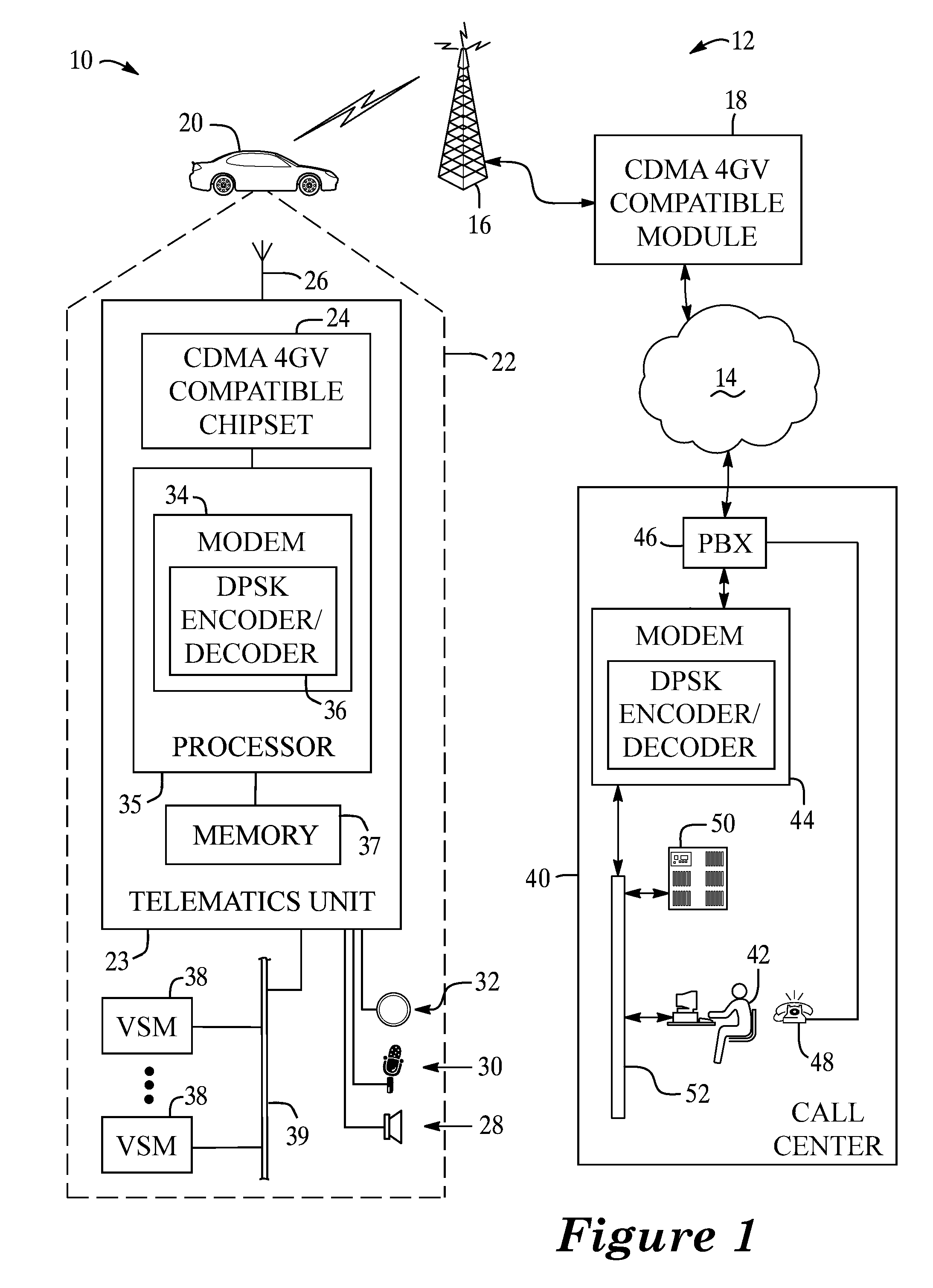
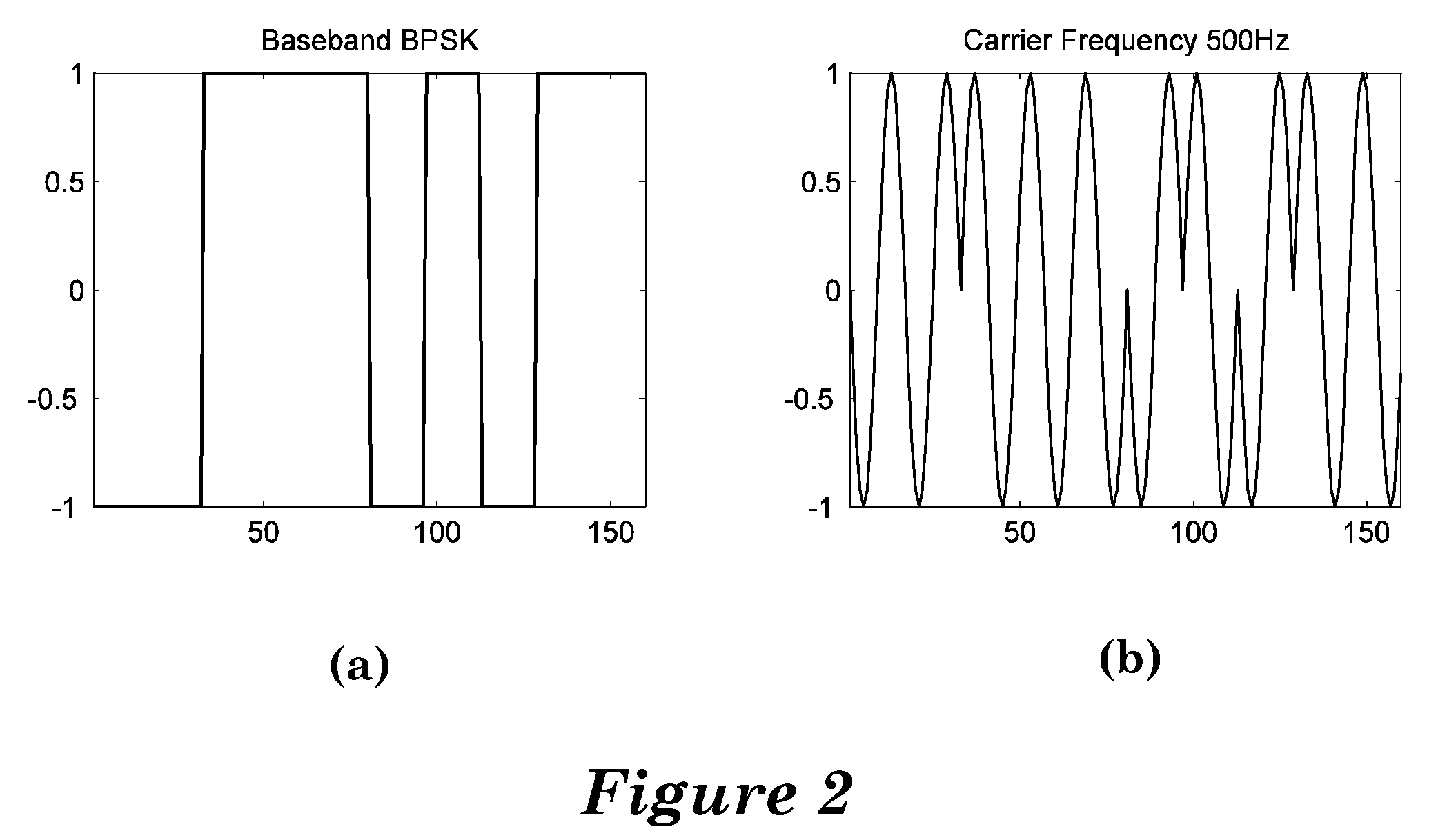
A system and method for data communication over a cellular communications network that allows the transmission of digital data over a voice channel using a vocoder that operates in different modes depending upon characteristics of the inputted signal it receives. To prepare the digital data for transmission, one or more carrier signals are encoded with the digital data using one of a number of modulation schemes that utilize differential phase shift keying to give the modulated carrier signal certain periodicity and energy characteristics that allow it to be transmitted by the vocoder at full rate. The modulation schemes include DPSK using either a single or multiple frequency carriers, combined FSK-DPSK modulation, combined ASK-DPSK, as well as PSK with a phase tracker in the demodulator. These modulation schemes permit data communication via a CDMA, GSM, or other type of voice traffic channel at a low bit error rate.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
Remote location VOIP roaming behind firewalls
InactiveUS7664096B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate IPTraffic capacity
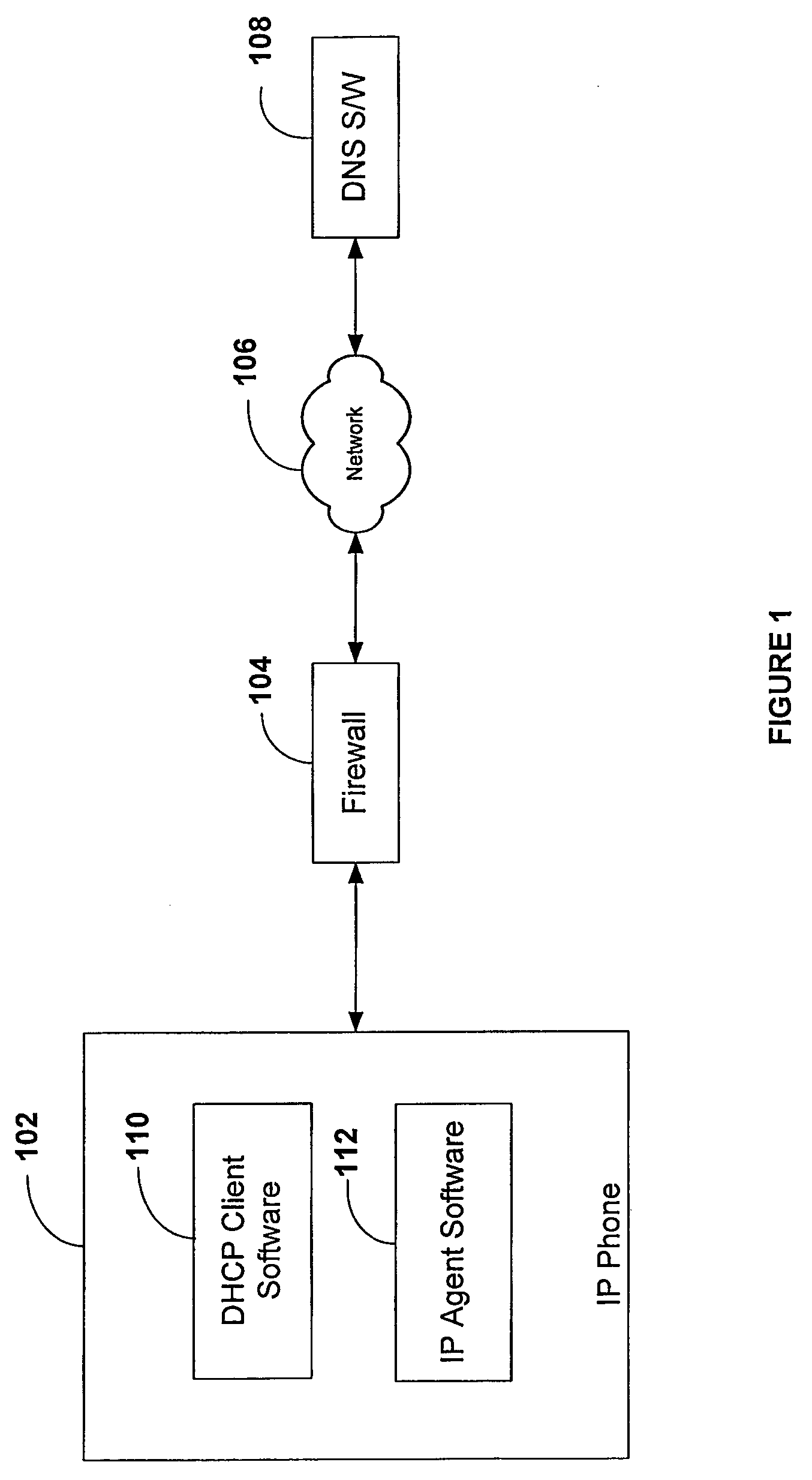
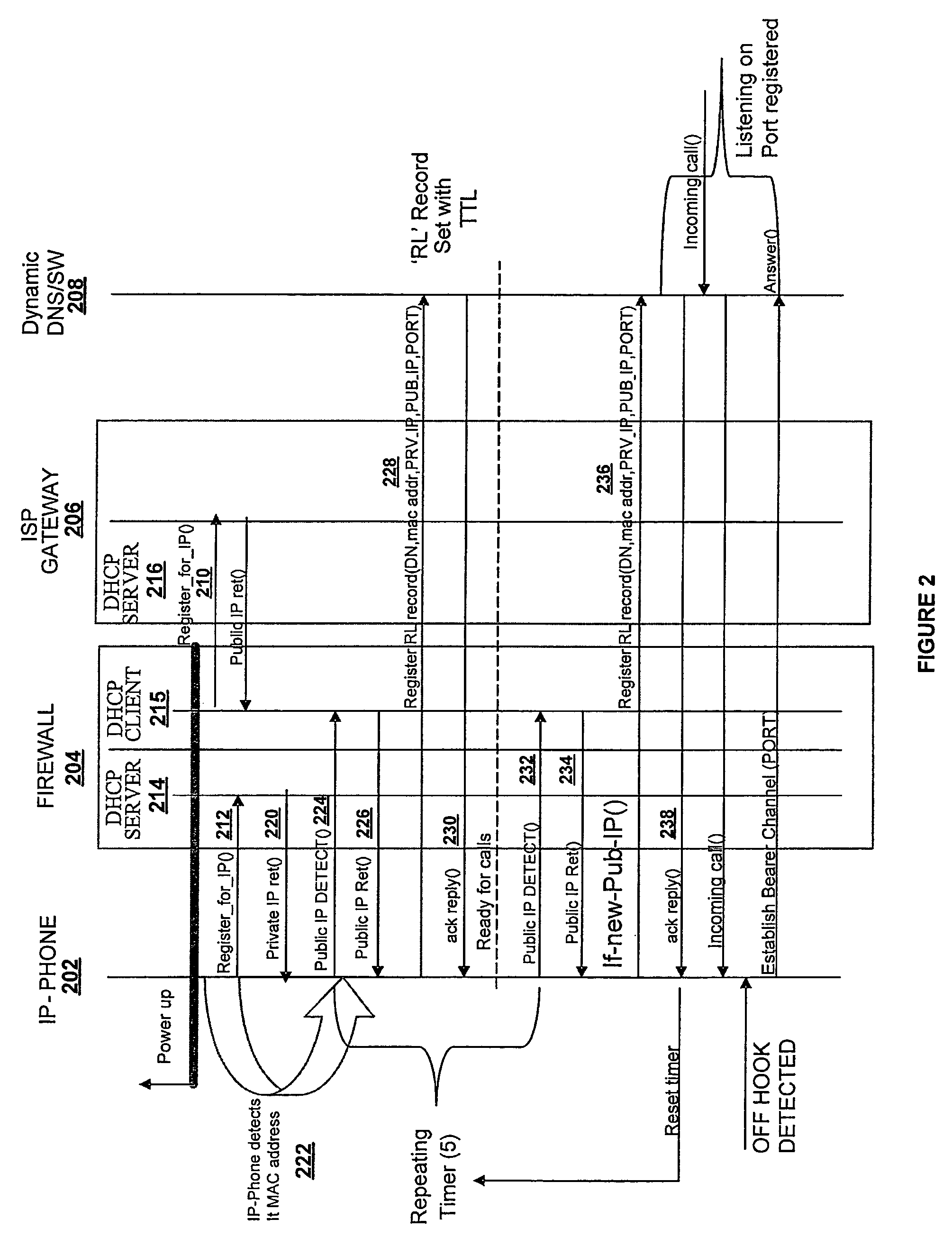
A connection between an external host and a host internal to a network (e.g., VPN or LAN) and located behind a firewall and / or NAT-enabled device is established and maintained. A dynamic DNS server is updated with the remote location (RL) information associated with the internal host. This information includes the dialed number (i.e. the number assigned to the internal host), the physical address of the internal host, the private IP address corresponding to the internal host, the public IP address corresponding to the firewall, and the port on which voice data is to be communicated. Each time the internal host's location changes, a new and updated record is sent to the dynamic DNS server. The call placed by an external host reaches its final destination based on the record information in the DNS server table. Once the connection between the external host and the internal host is established, voice traffic is “cut-through” the firewall on this channel associate with the port designated by the RL record.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
System and method for suppressing silence in voice traffic over an asynchronous communication medium
InactiveUS6993007B2Improve efficiencySignificant bandwidth savingBroadband local area networksNetwork traffic/resource managementComfort noiseAsynchronous communication
A method and system for increasing the efficiency of providing bandwidth for voice traffic to a data provider via asynchronous communication mediums is provided. This is generally accomplished by not transmitting any data during the silence periods and playing out background noise (i.e., comfort noise) at the other end, to obtain significant bandwidth savings.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for providing voice communications through a packet network
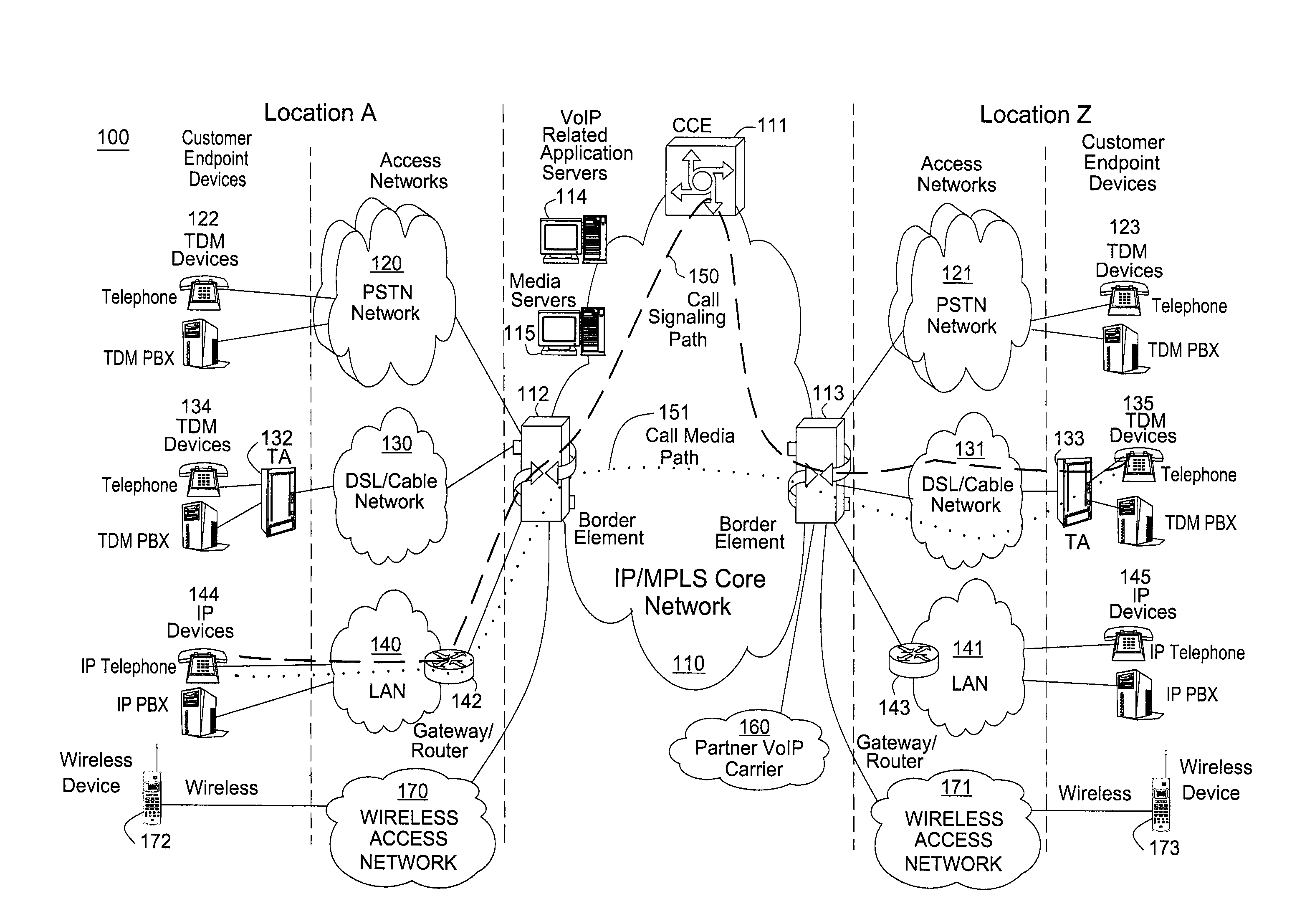
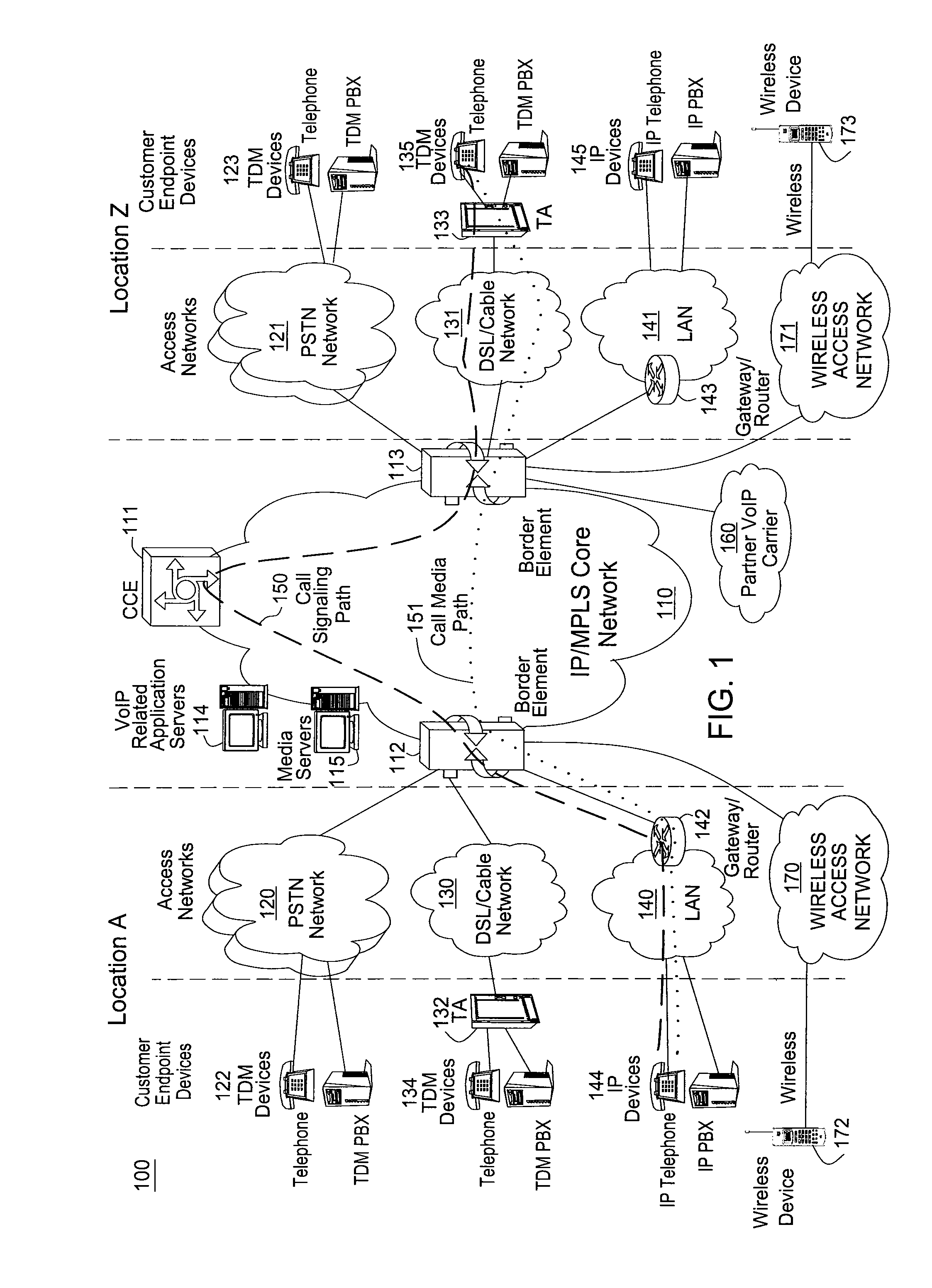
InactiveUS7170887B2Improve efficiencyImprove abilitiesInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVoice communicationThe Internet
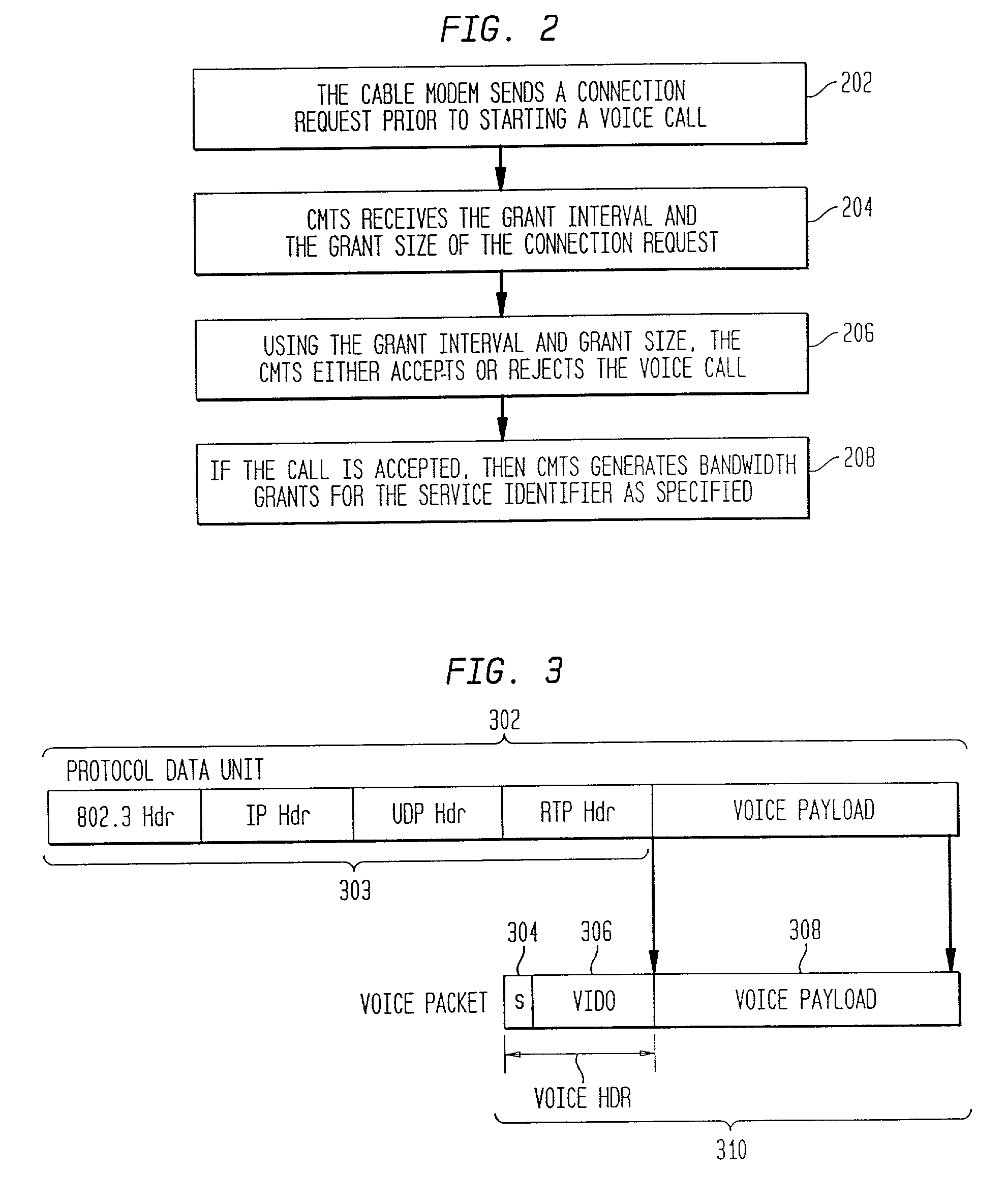
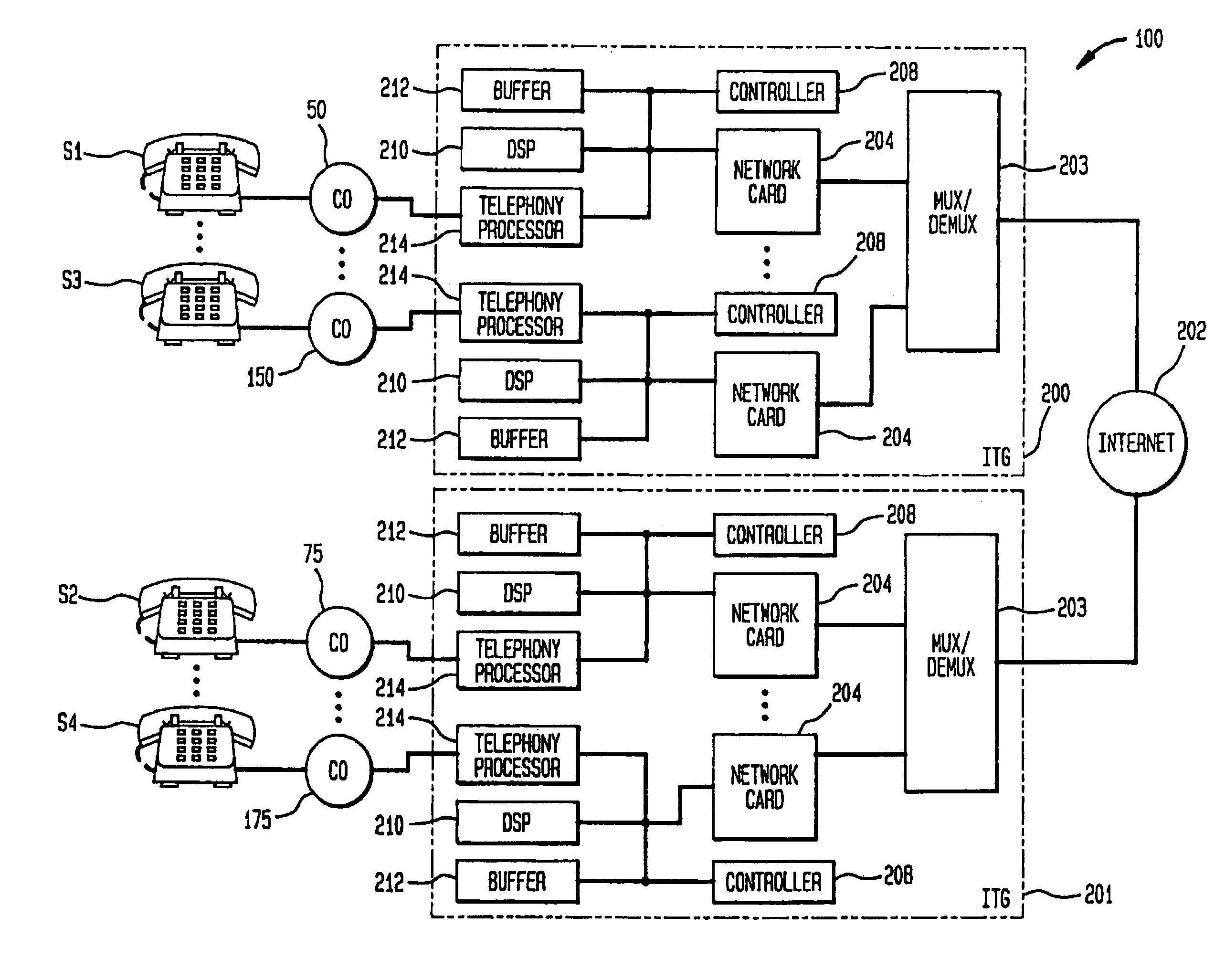
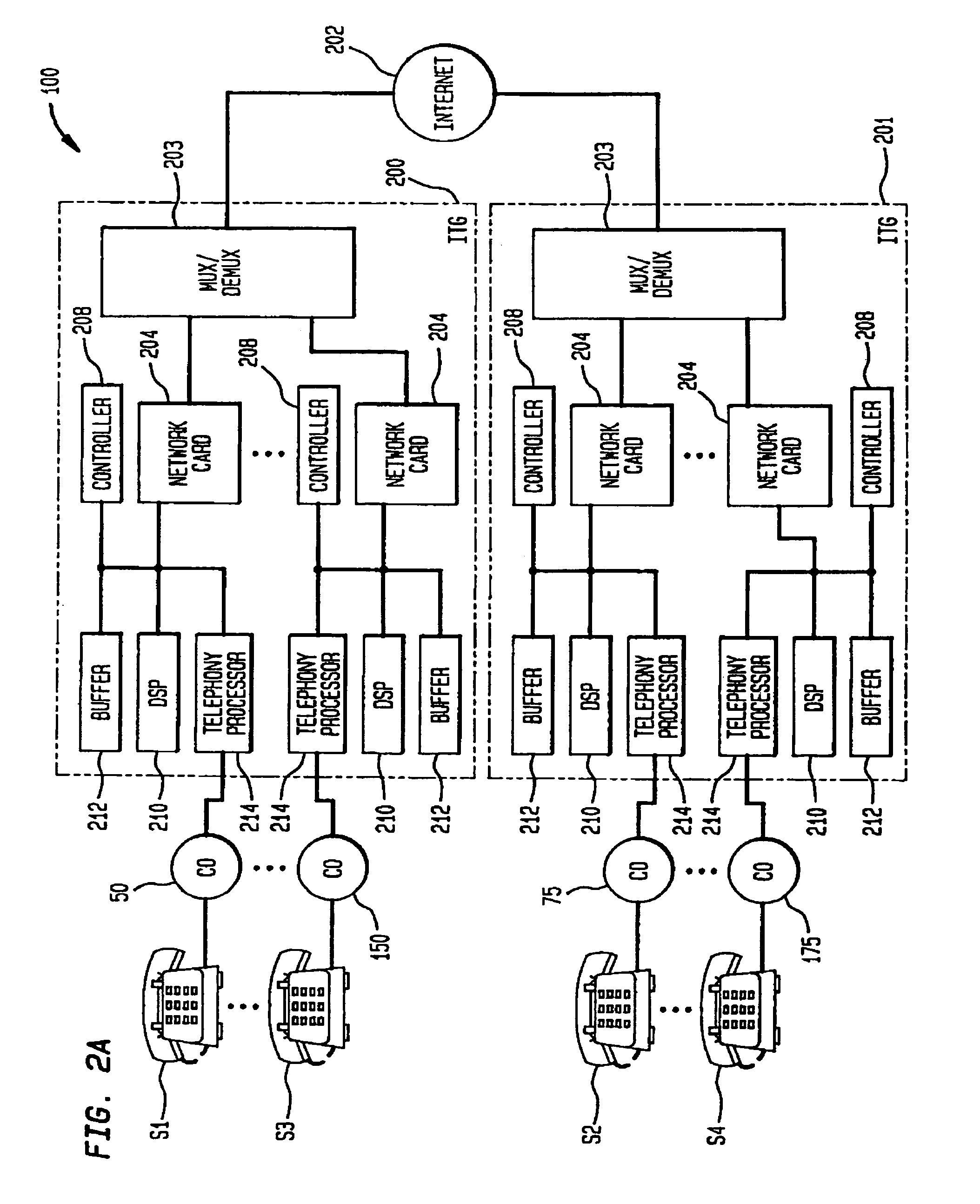
A communications system multiplexes voice communications signals onto one or more transport level connections established through a packetized network, such as the Internet. The invention supports the use of variable-length packets and accommodates variable jitter. The system conforms to real time protocol (RTP) and employs internet telephone gateways (ITGs) to bind users to channel identifiers, to indicate payload type and length, to provide channel identification and time stamps, and to indicate cessation and resumption of voice traffic from a particular user through use of, for example, marker bits.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
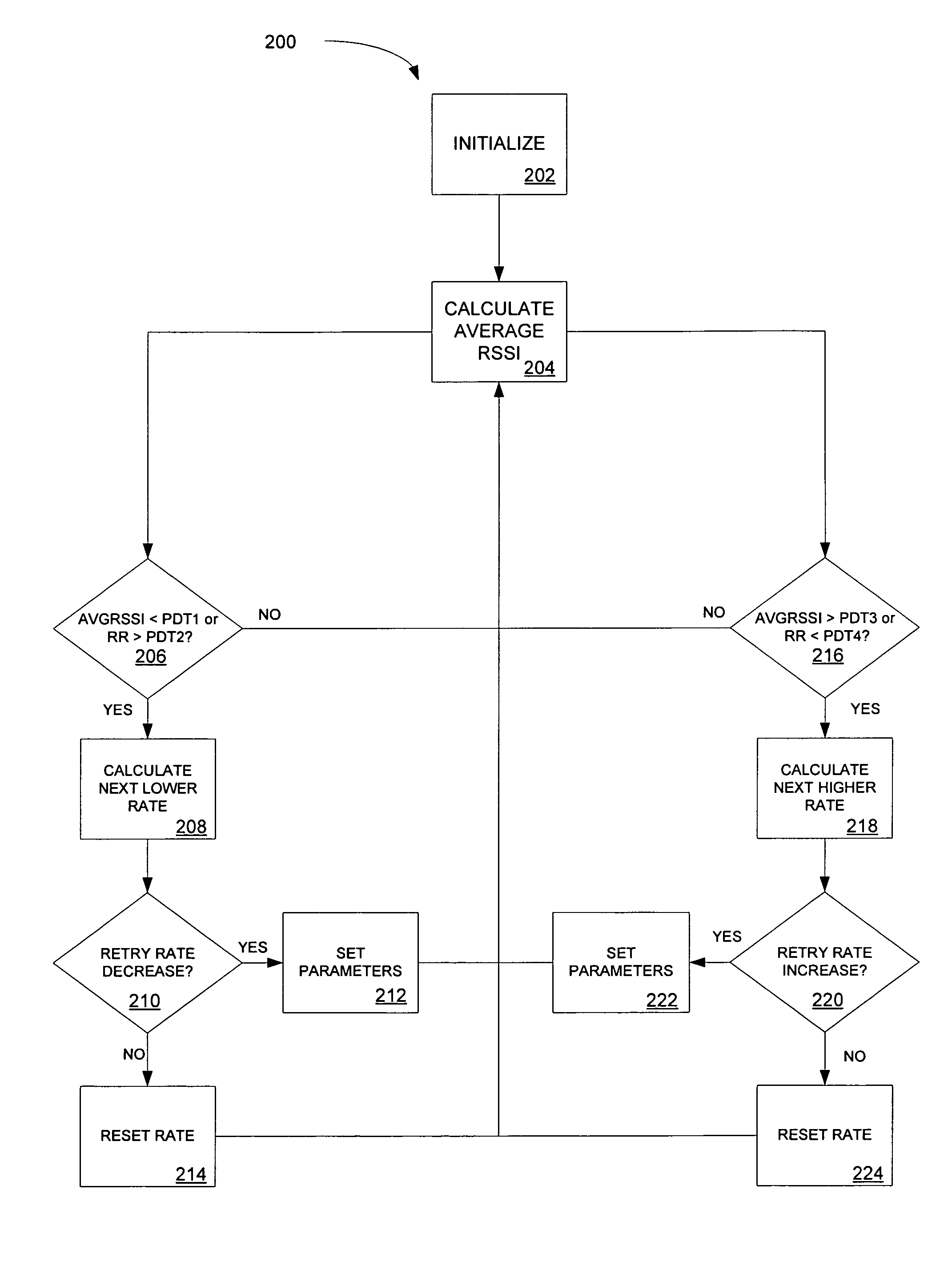
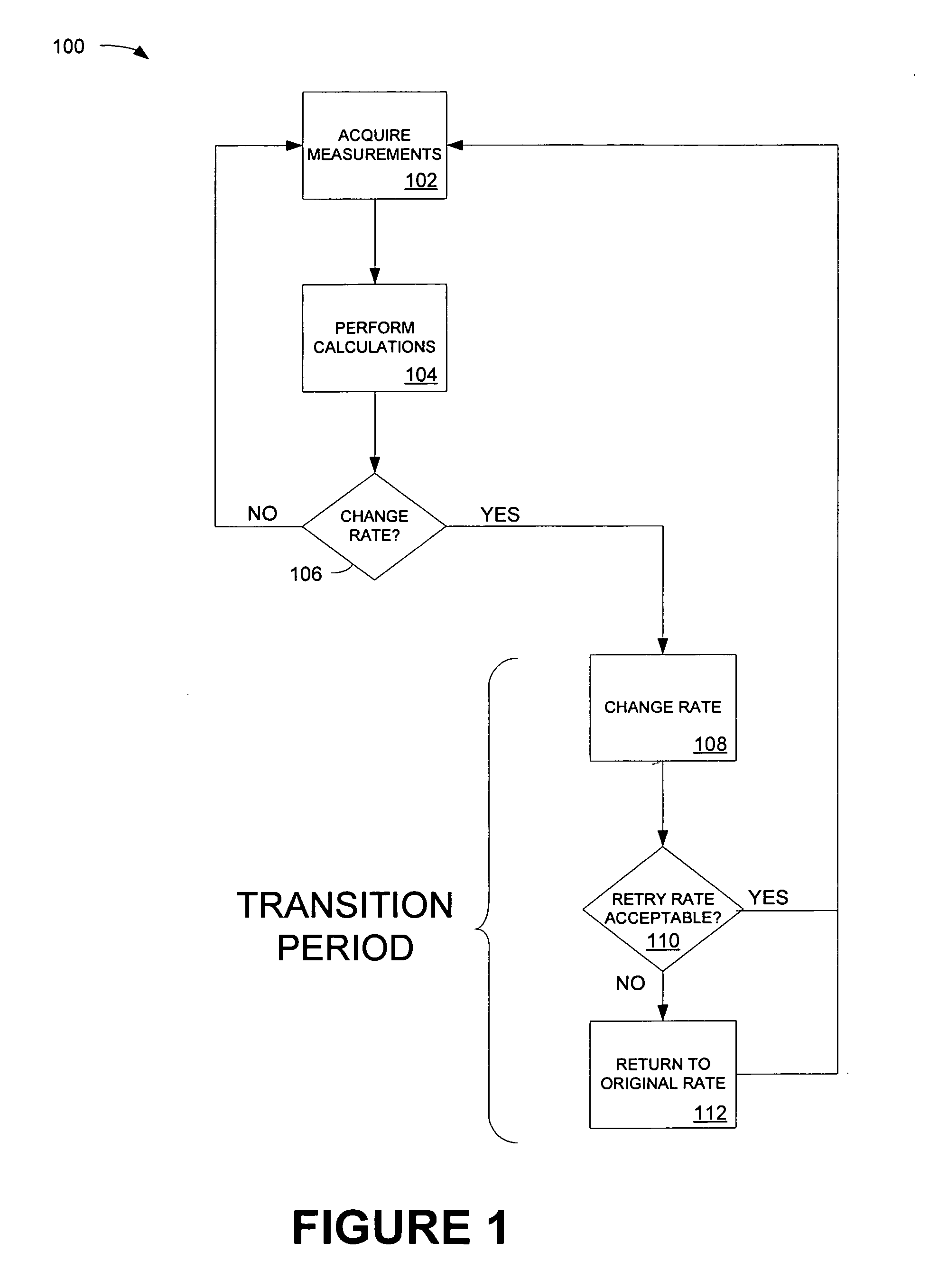
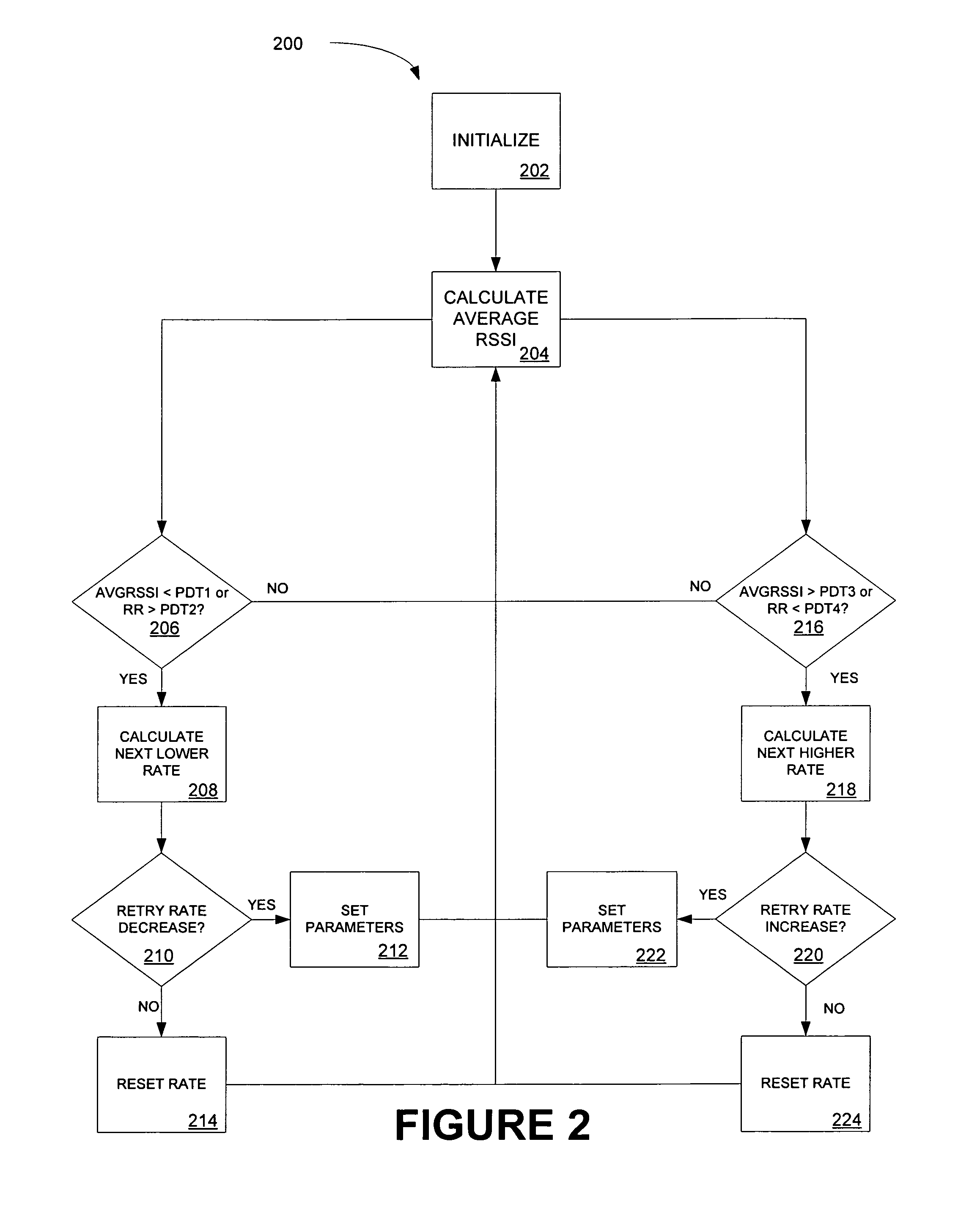
System and method for rate shifting for wireless VoIP
ActiveUS20070189225A1Low rate of false shiftingLow false rateError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsInternet traffic
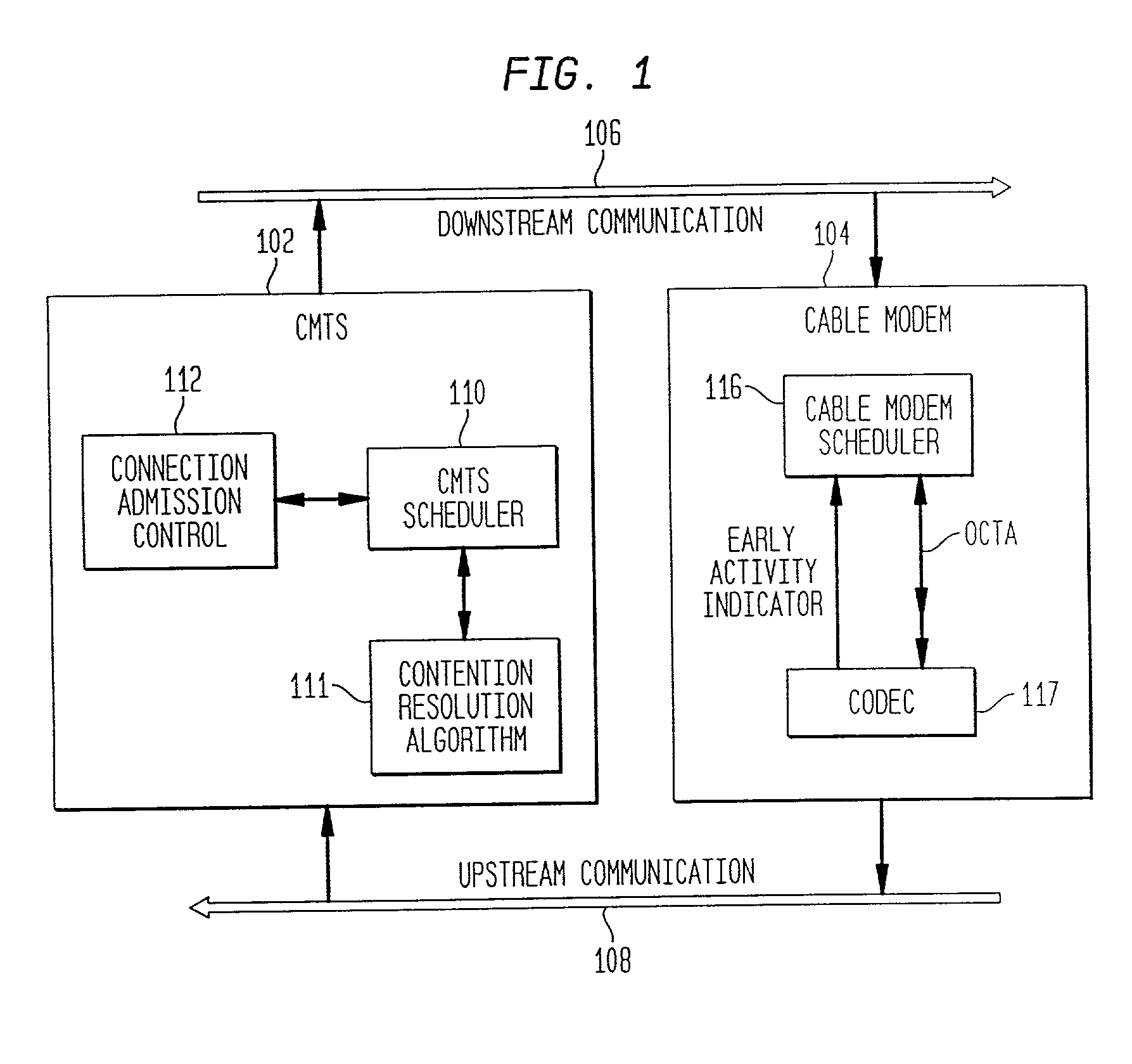
A method of rate shifting specially suited for the voice traffic, which differentiates poor channel conditions from a heavily loaded channel of a WLAN and adapts to the network traffic condition and channel condition promptly with low rate of false shifting. Determining when to rate shift is based on a combination of the received signal strength indication and the retry rate.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
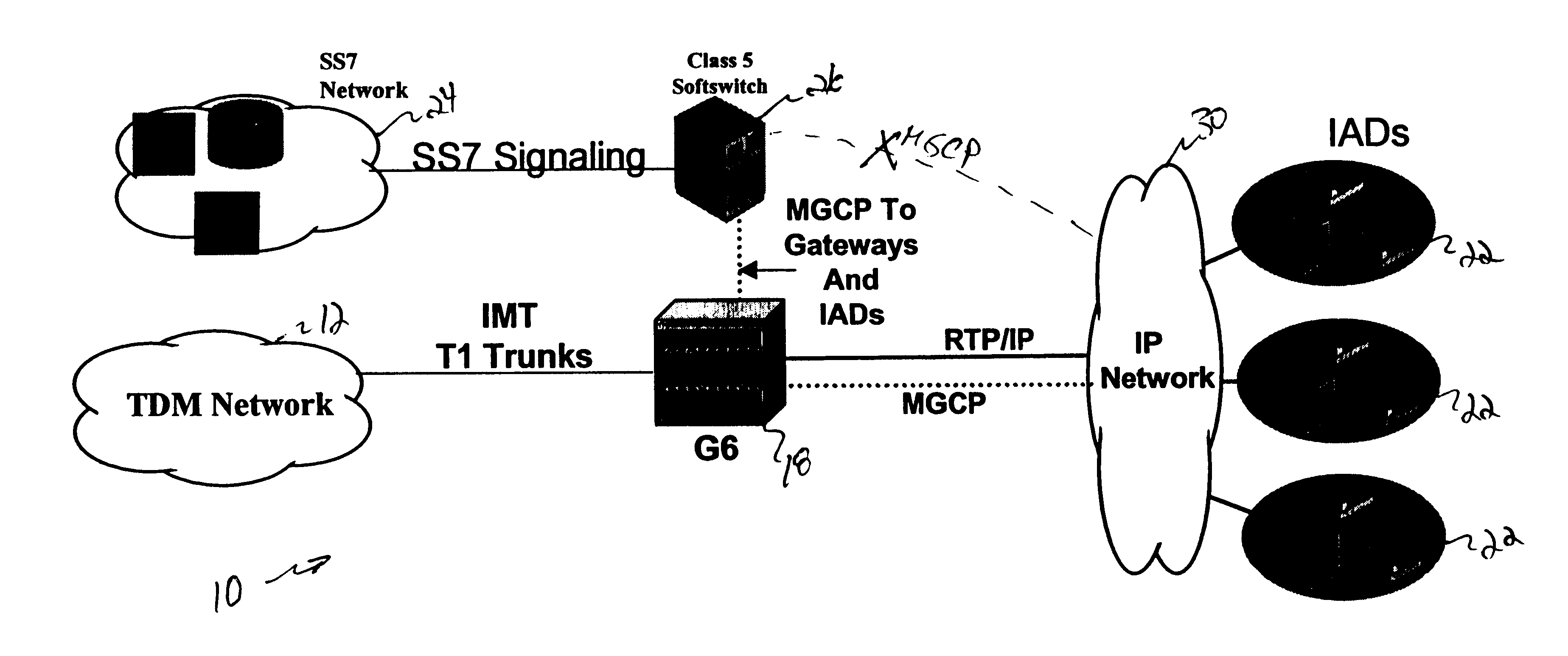
System and method for interfacing signaling information and voice traffic
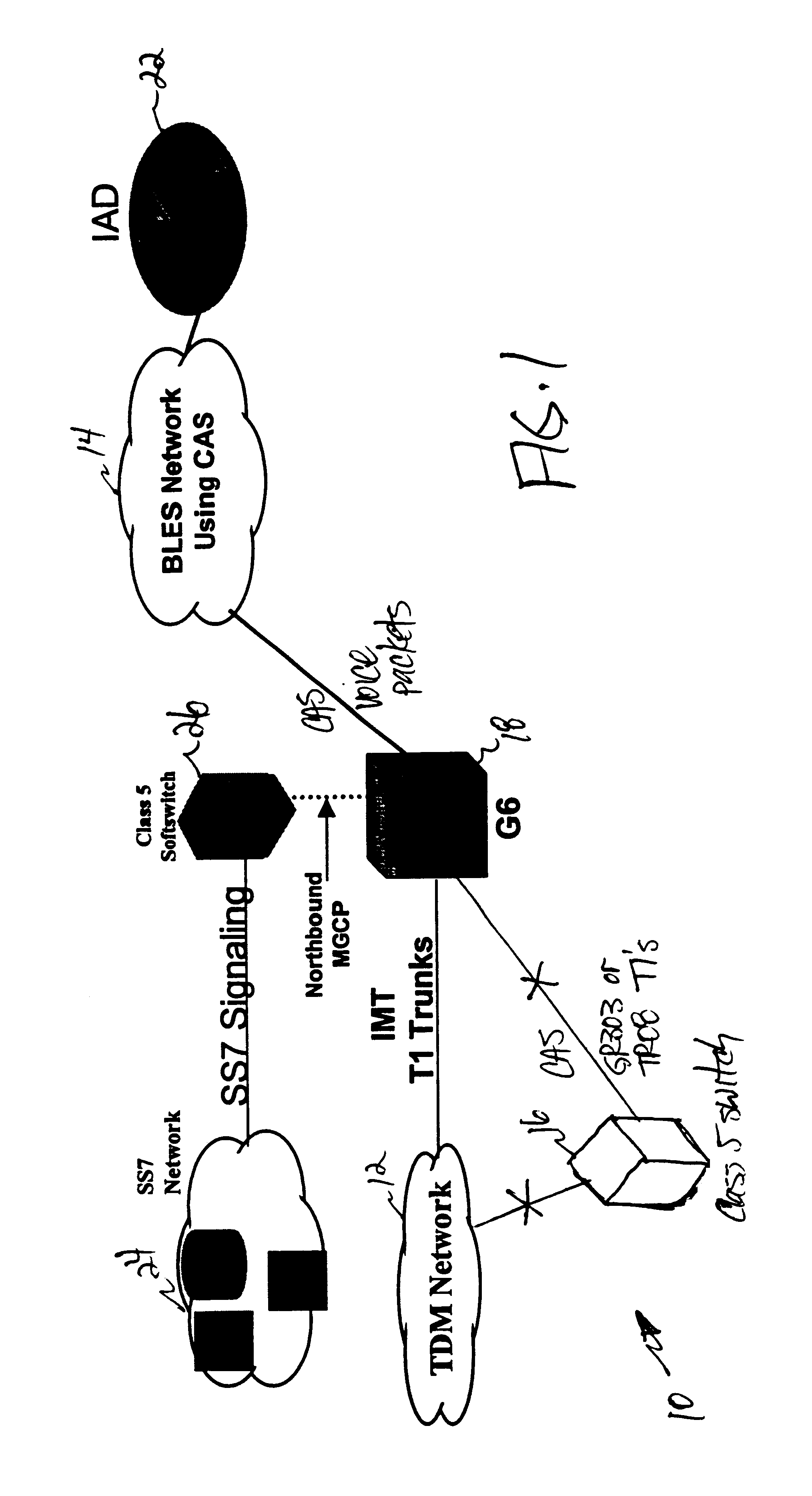
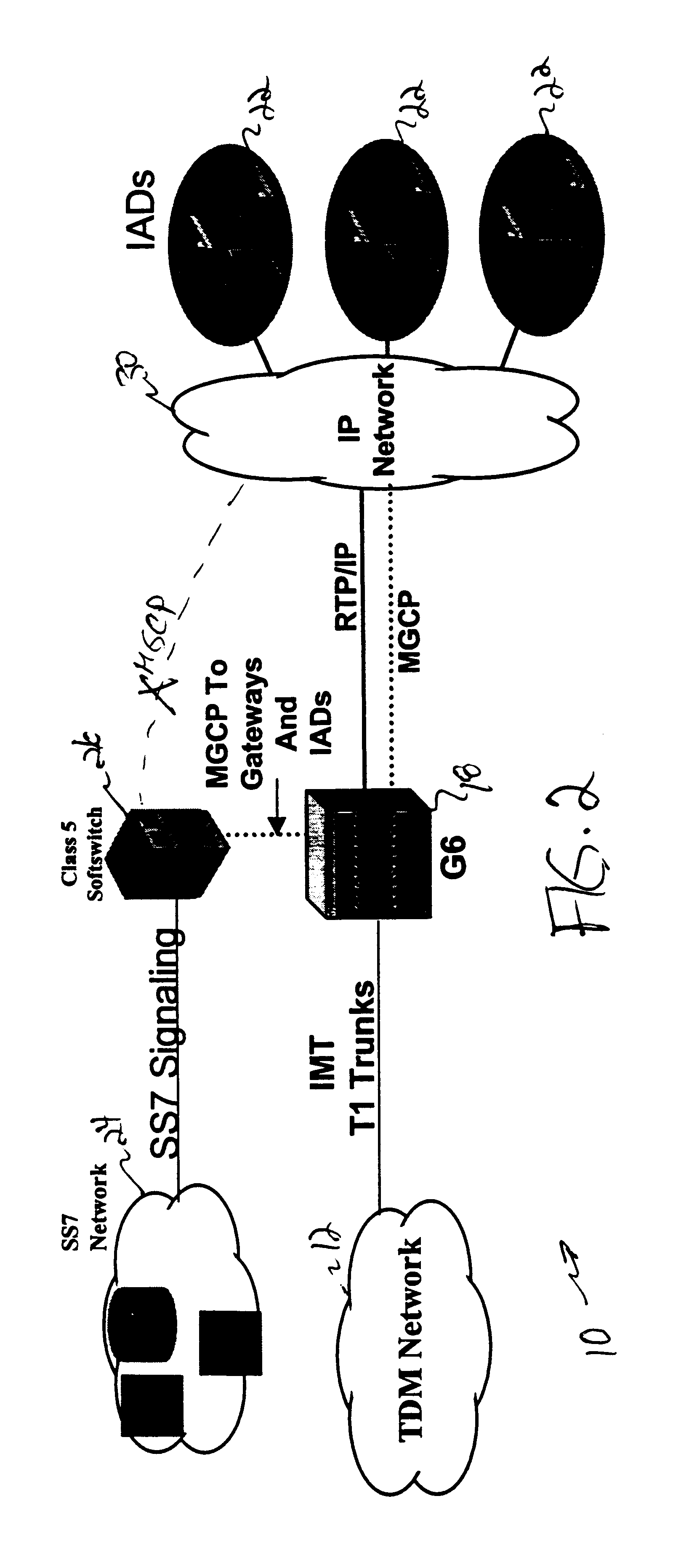
InactiveUS6839342B1Eliminate and greatly reduce disadvantageEliminate and greatly reduce and problemMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsSoftswitchTelecom network
A telecommunications network (10) includes a gateway (18) that receives signaling information in a message based signaling format from a Class 5 softswitch (26). The gateway (18) also receives voice traffic over an inter-machine trunk from a public switched telephone network (12). The gateway (18) places the voice traffic into data packets. The gateway (18) transfers the data packets and the signaling information to an Internet Protocol network (30). The data packets and the signaling information may be transferred over a common physical link and over separate logical links.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
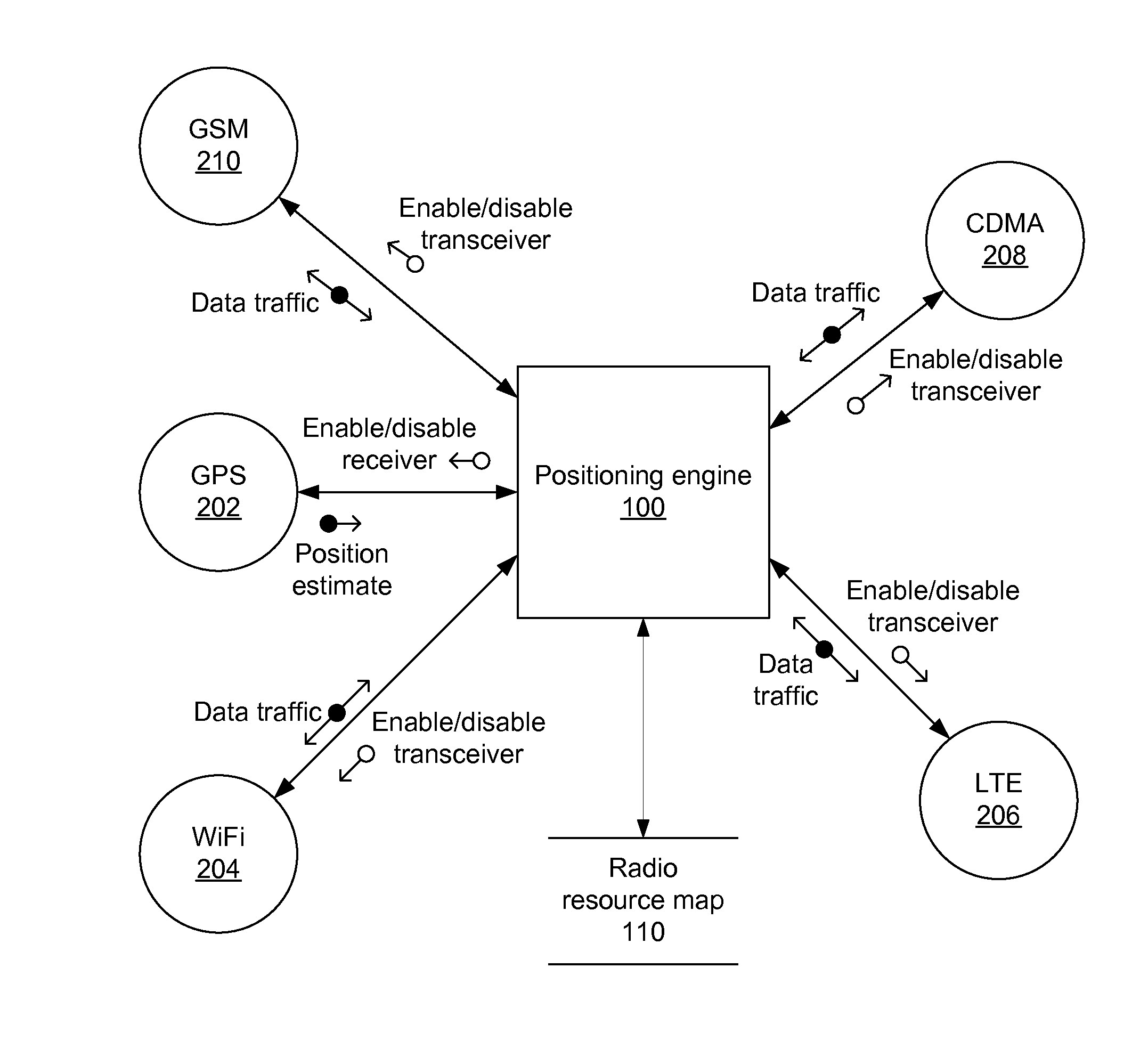
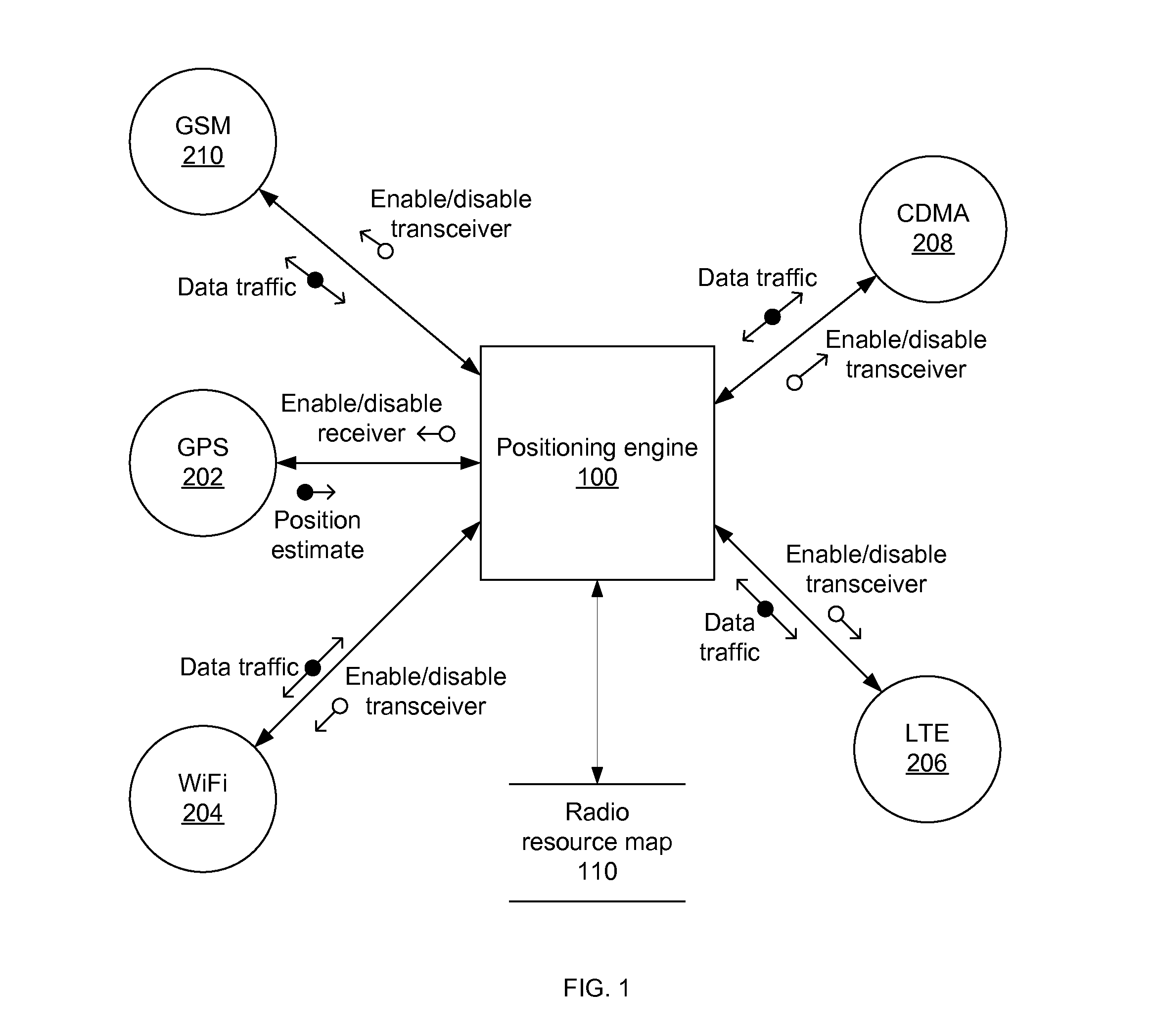
Location-aware network selection
Systems, apparatus and methods in a mobile device for saving power by powering down all transceivers not carry traffic are presented. The traffic may be voice and / or data traffic. A mobile device may select single transceiver to carry voice traffic and the same or different transceiver to carry data traffic. A mobile device first determines its position (e.g., a coarse position estimate) then consults a database or map to determine which networks are theoretically available. The mobile device executes a rule against the theoretically available networks to select the single network, then enables the transceiver for the one network to determine if the network is actually available for use. If the database inaccurately states a network is available from a current position but the transceiver shows that the network is actually not actually available, a next network from the database or map and corresponding transceiver are selected.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
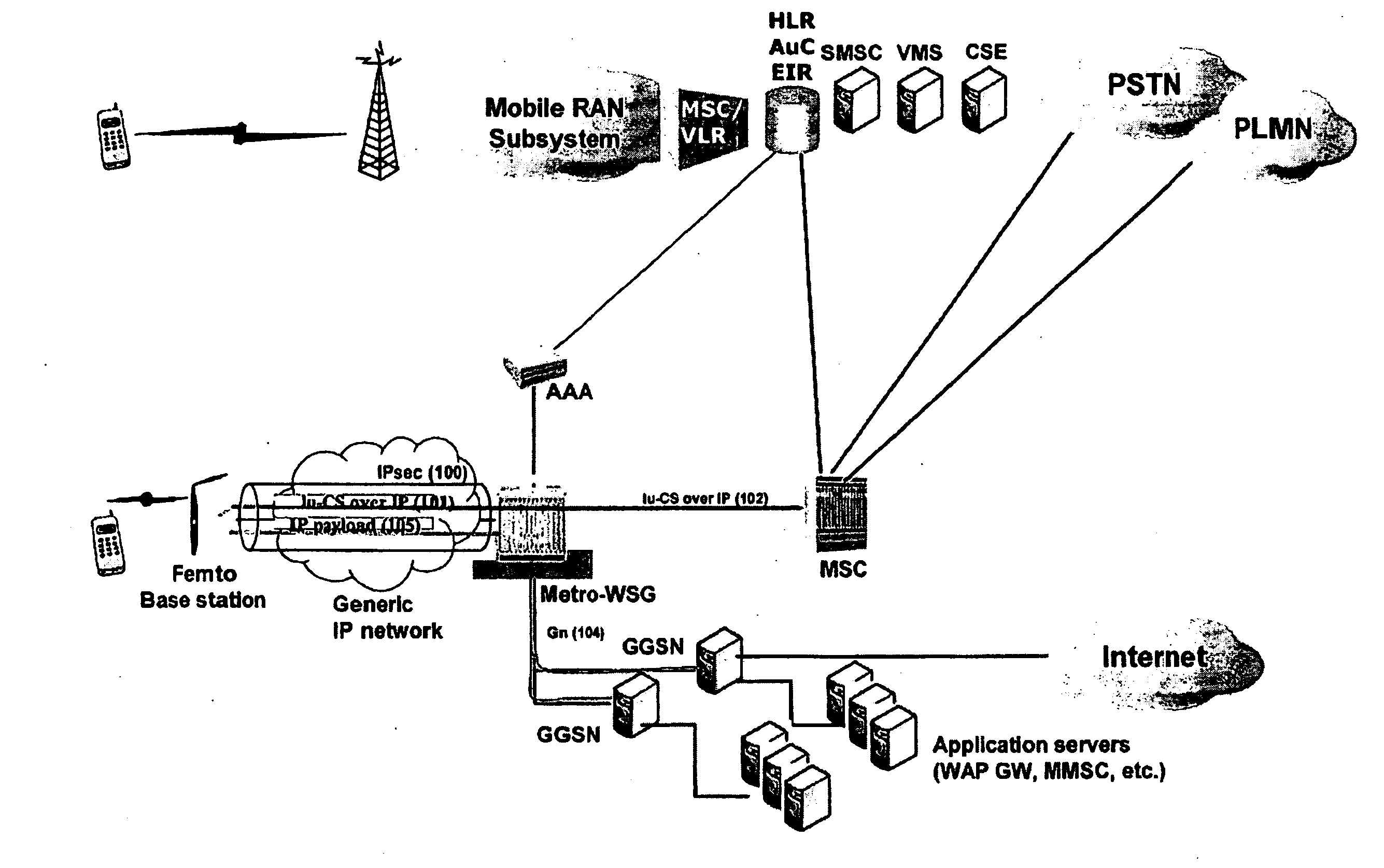
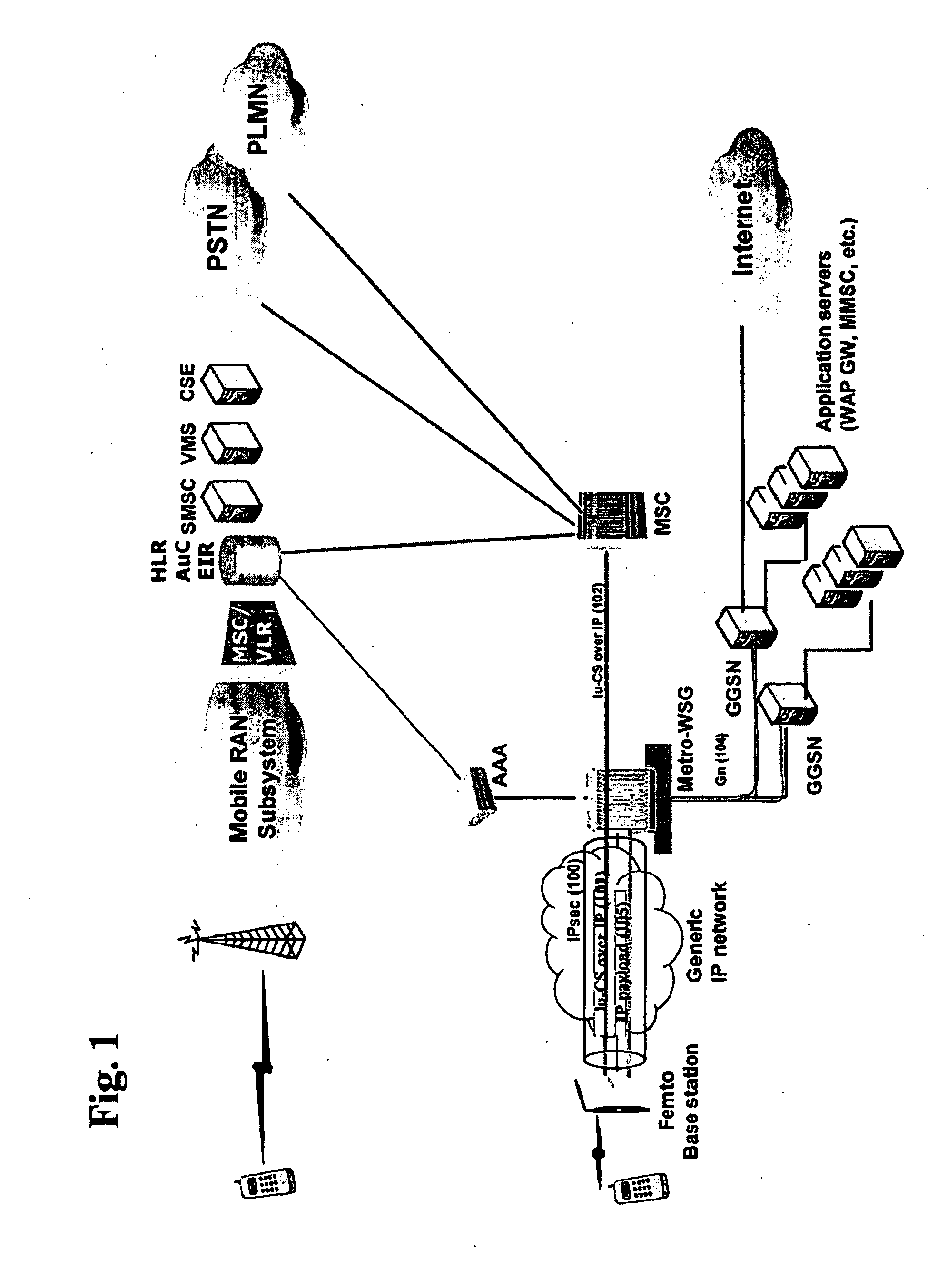
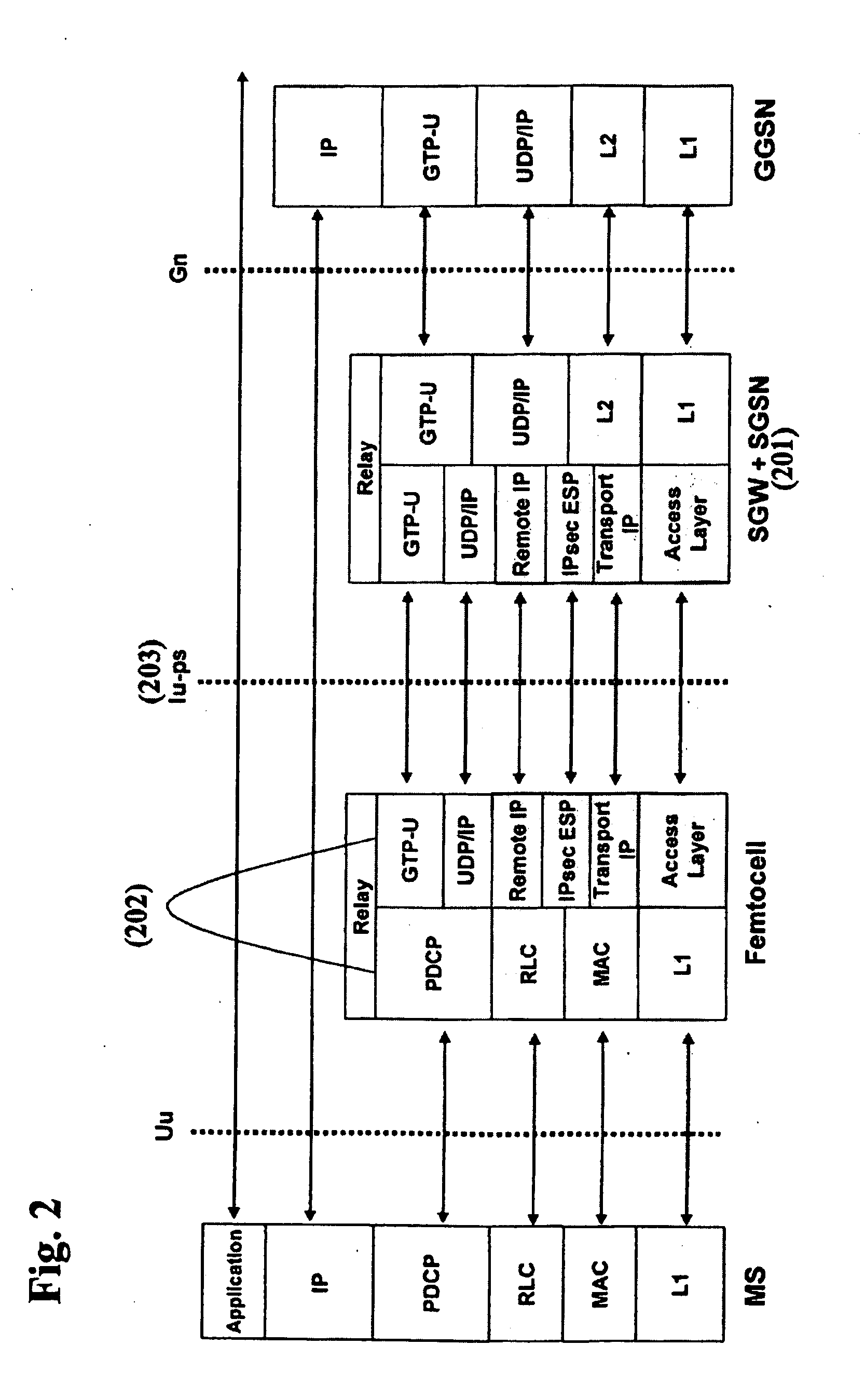
Femtocell architecture in support of voice and data communications
ActiveUS20090135795A1Significant overheadEasy to handleNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesThird generationVoice traffic
Methods and systems for providing voice and date services in a femtocell wireless network. The proposed approach integrates IWLAN architecture into femtocell architecture by introducing a gateway to serve both IWLAN and femtocell users. The proposed approach handles the voice and data in a different way so that it enhances the data handling efficiency while re-using existing MSC investment. The proposed approach carries the data traffic from a femtocell base station to the gateway in native IP packet, instead of encapsulating them in 3G data, thus enhancing the efficiency and performance for the data traffic. The data traffic can then be sent to GGSN or directly to packet data network. The approach tunnels voice traffic to MSC through the gateway as in conventional Iu-CS approach.
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for reducing inbound traffic congestion in a voice frame network
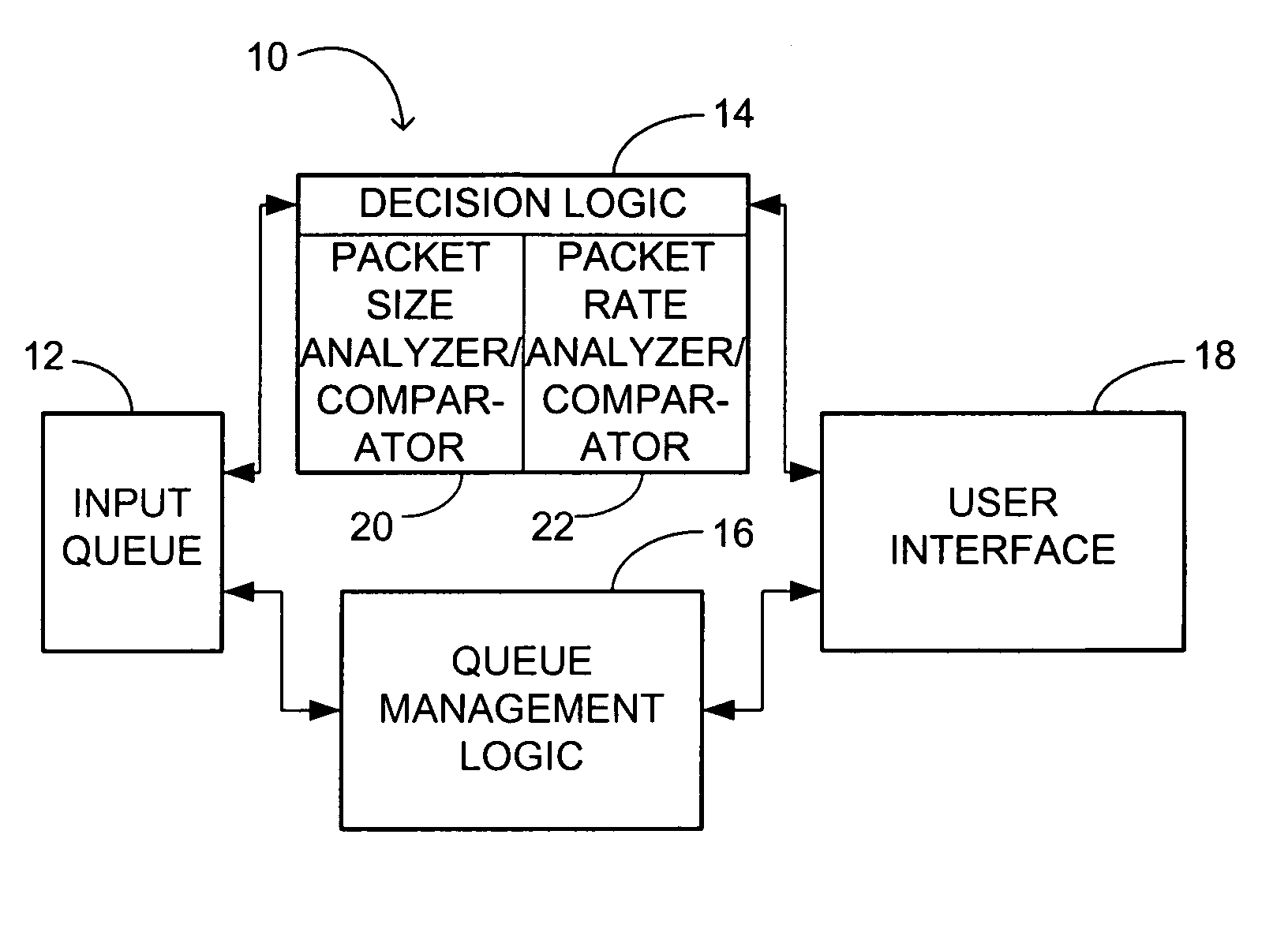
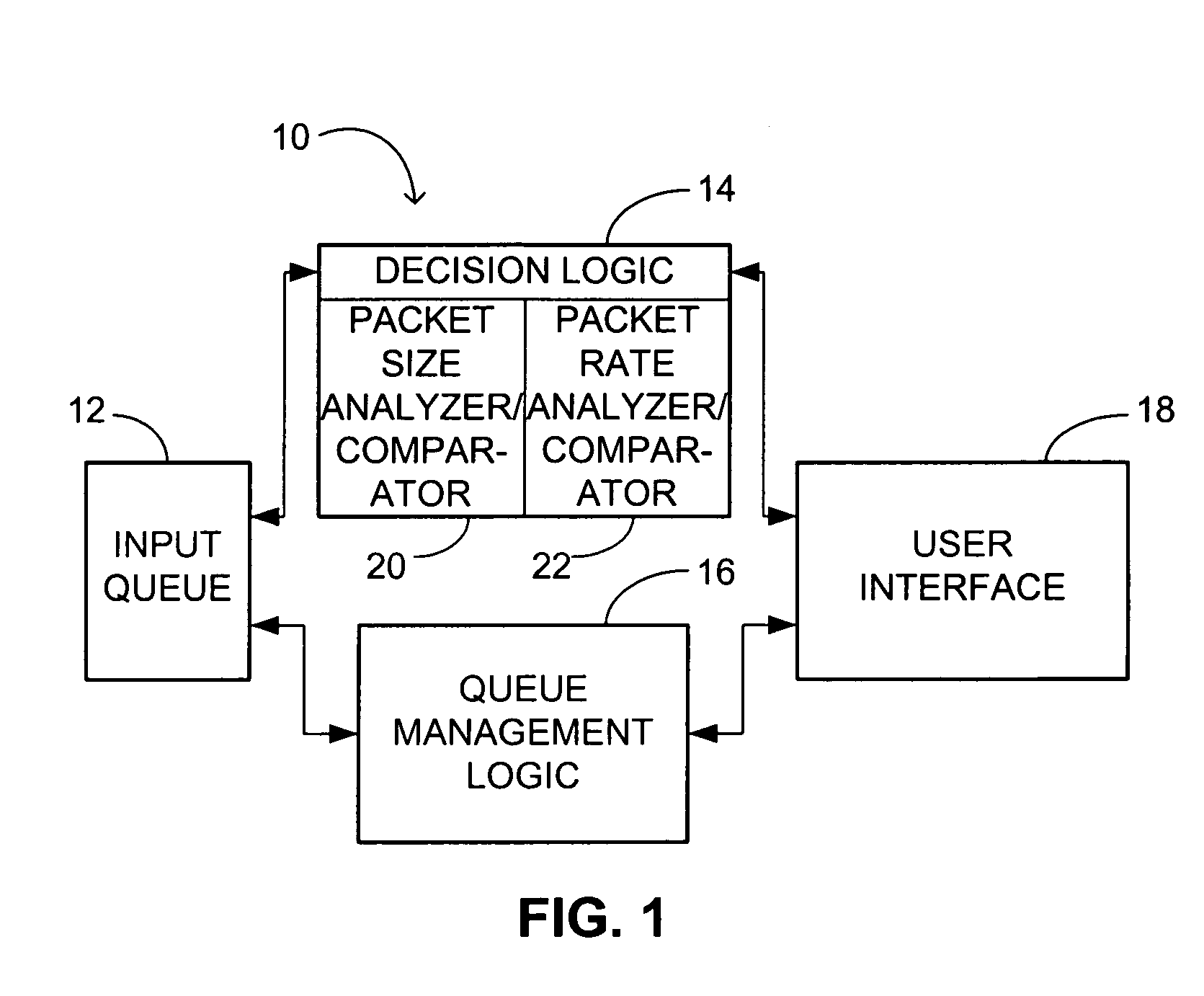
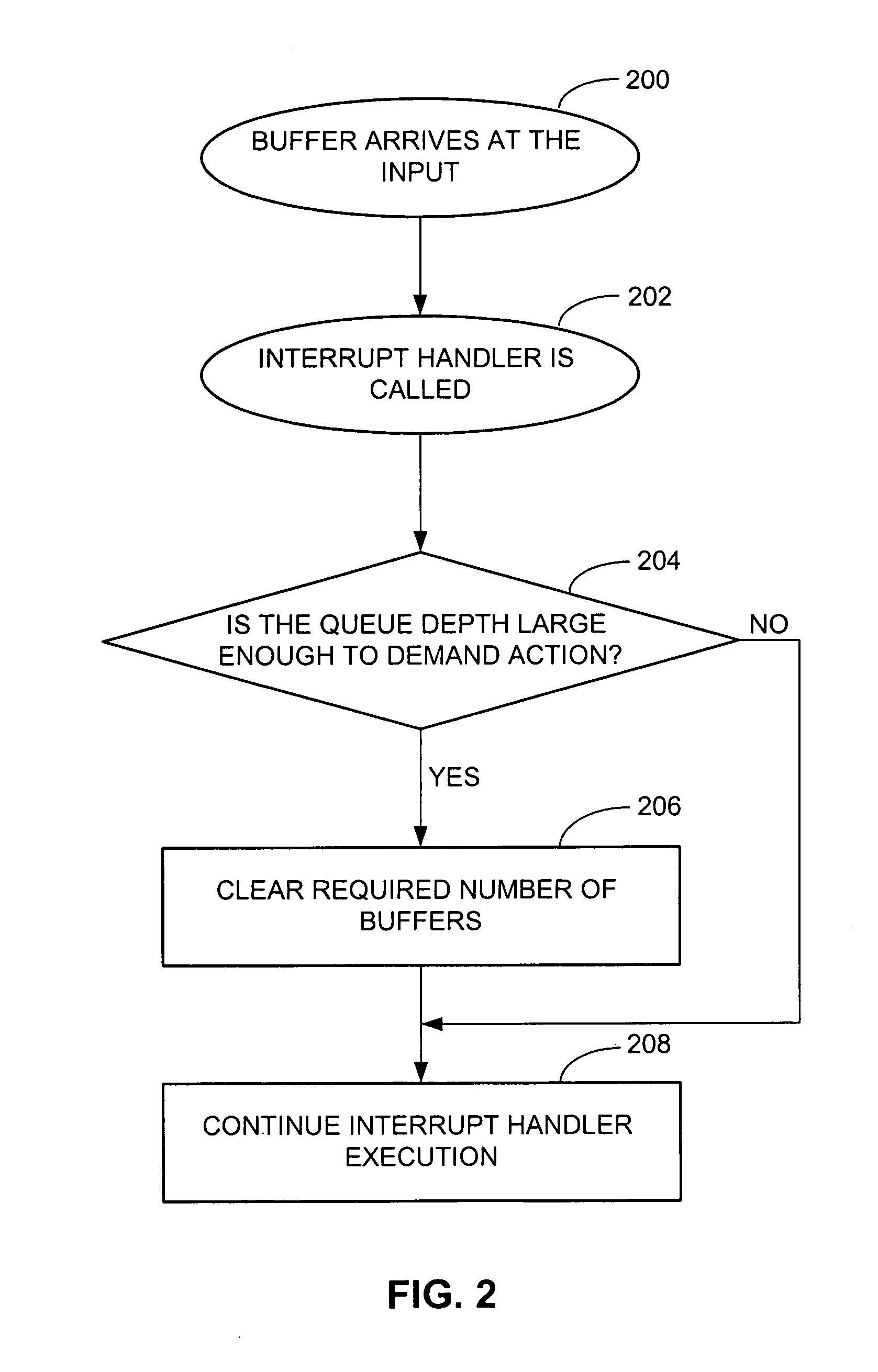
The invented method of reducing voice frame network inbound traffic congestion first determines whether a first defined threshold level of inbound voice and data traffic is reached. If so, then the method discriminates between inbound voice and data traffic within an input queue. Discrimination is by analyzing the size of each packet and comparing it to predefined packet size criteria and / or by analyzing the rate at which packets of inbound voice and data traffic arrive in the input queue and comparing it to predefined arrival rate criteria. Finally, the method frees space within the input queue for use by inbound voice traffic until the first defined threshold level of inbound traffic no longer is reached. The freeing of space includes selectively discarding data, which discarding preferably continues until a second defined threshold level of inbound traffic is reached, the second defined threshold level being less than the first defined threshold level. The invented apparatus includes decision logic for making such a determination and queue management logic responsive thereto for such discrimination and freeing of space. A user interface preferably is provided that permits a user to define the first and second defined threshold levels, which are implementation- and application-dependent.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
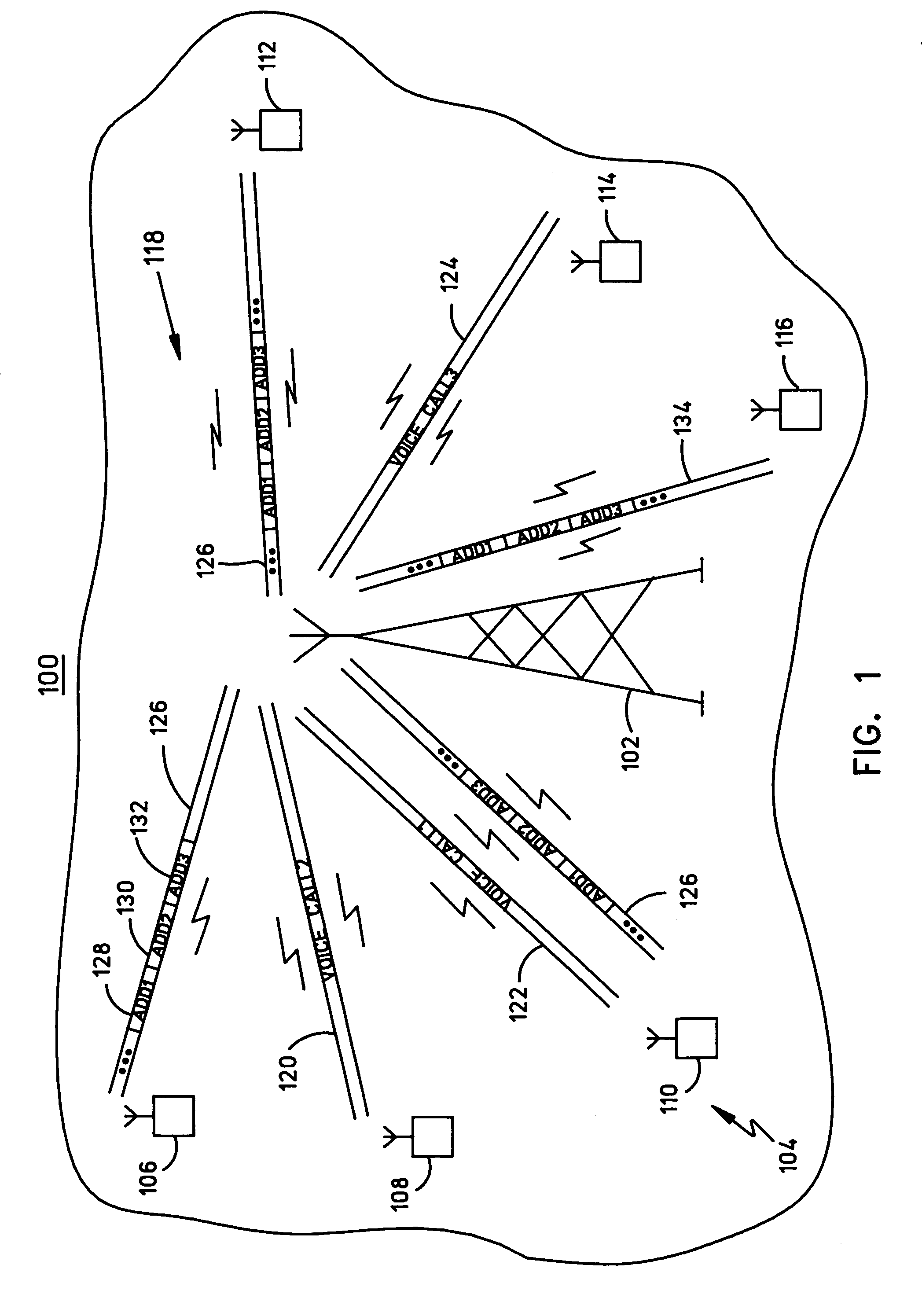
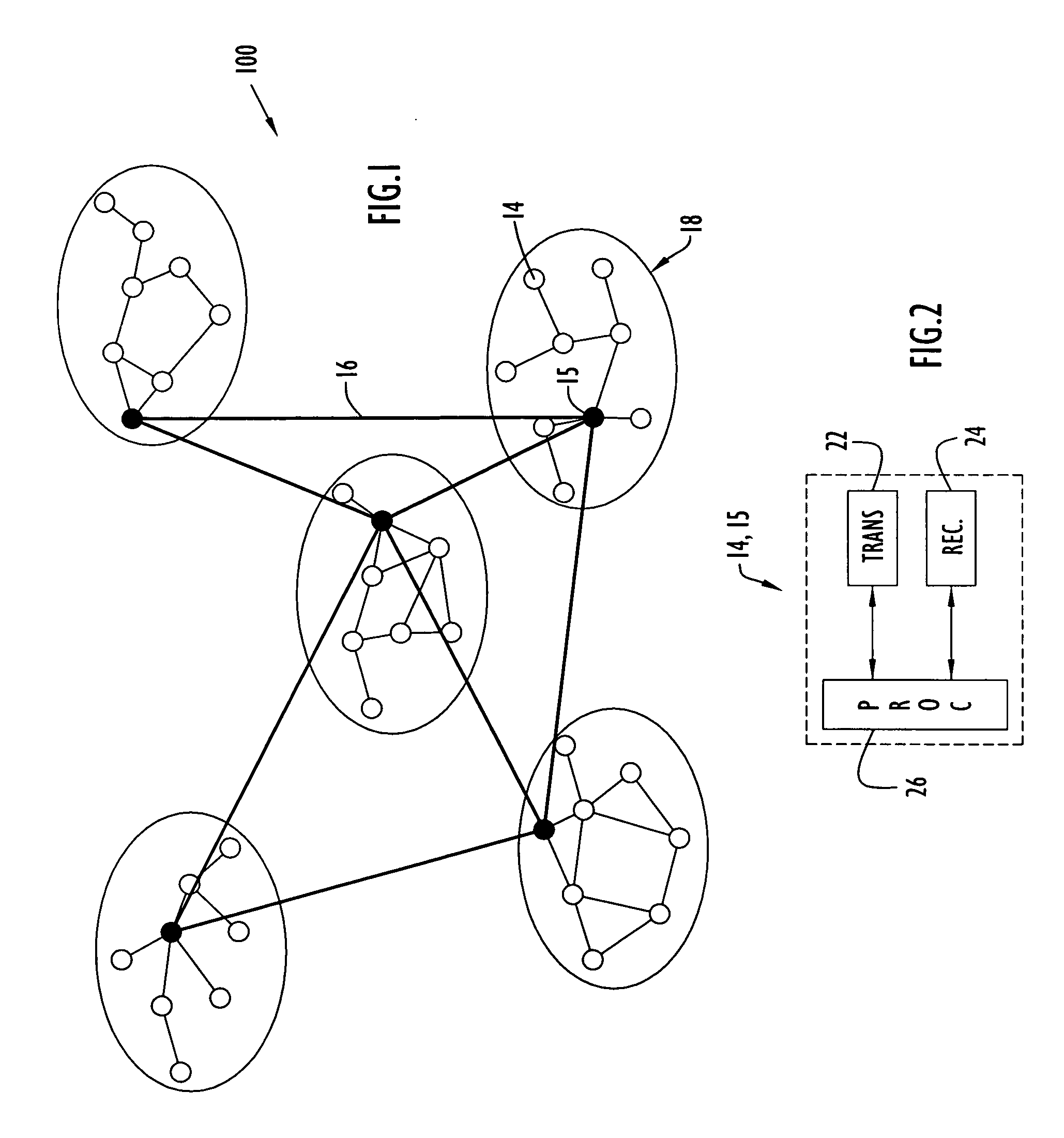
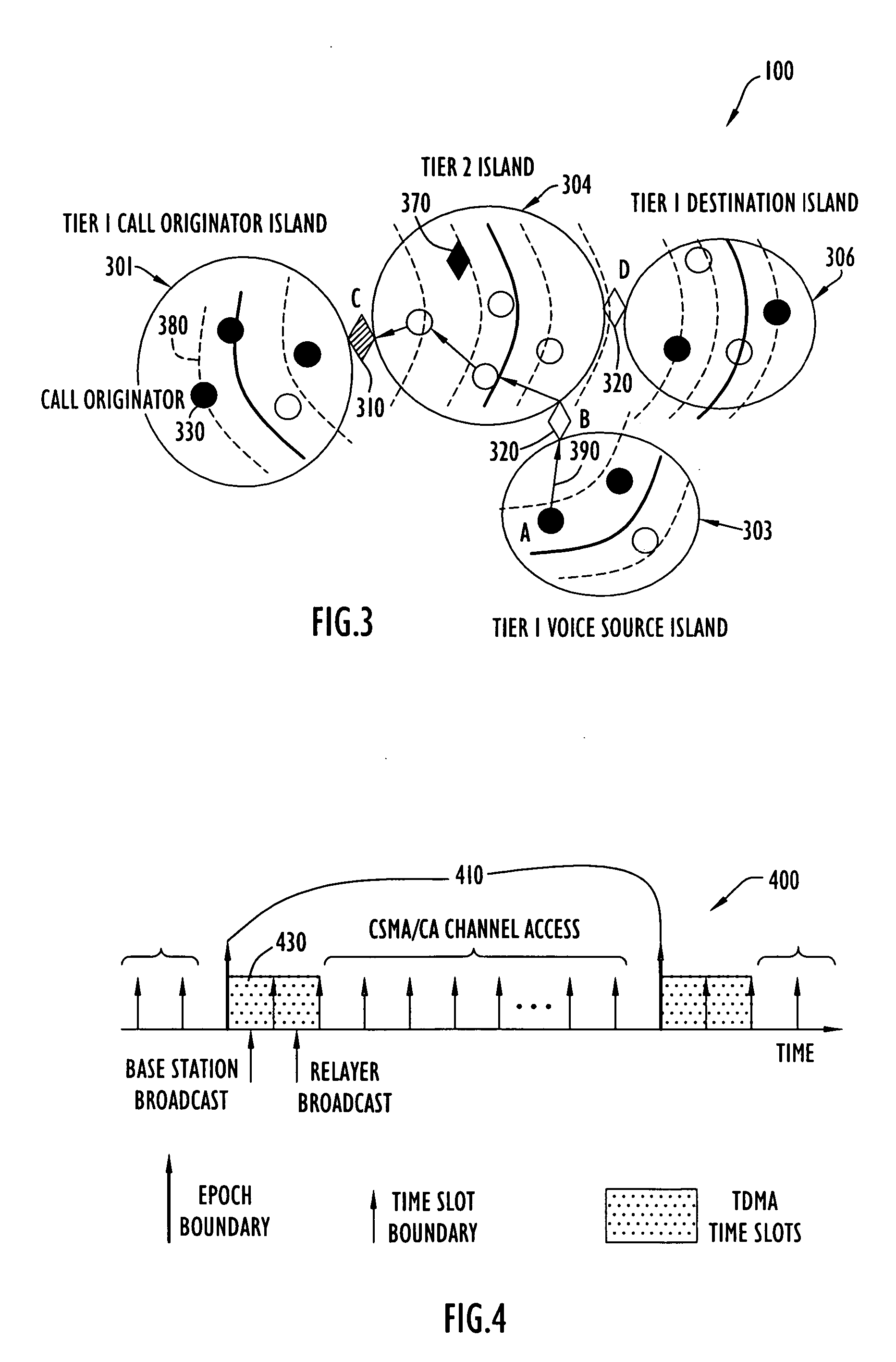
Method and apparatus for multipoint voice operation in a wireless, AD-HOC environment
ActiveUS20060198324A1High strengthExtend signal rangeSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsVoice trafficConference call
The present invention protocol offers guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS) for concurrent calls in a highly dynamic, scalable network. The invention employs a TDMA reservation technique to transmit voice traffic to multiple destinations and a CSMA / CA contention scheme to support data traffic. The present invention operates over a link-state based routing protocol that reliably floods routing and resource reservation information to network nodes. The present invention is suitable for general networking applications that require QoS for multimedia traffic in a mobile, Ad-Hoc network and enables conference calls to be established and operated in that type of network under various conditions. Moreover, the present invention capitalizes on certain properties of a radio, such as a RAKE type receiver, that sums up multiple, identical transmissions from multiple sources. In addition, the present invention enables roaming between and / or within a group or island of network nodes during the lifetime of a call.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
Method for data communication via a voice channel of a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20070092024A1Frequency-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataVoice traffic
A system and method for data communication over a cellular communications network that allows the transmission of digital data over a voice channel of the communications network. Digital data is encoded into DBPSK data using differential binary phase shift keying encoding. The DBPSK data is then sent across the cellular network using a vocoder having a linear predictive or other speech compression codec. At the receiving end, the DBPSK data is demodulated back into the original digital data. This approach permits data communication via a CDMA, GSM, or other type of voice traffic channel at a low bit error rate.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
Method and system for providing private voice call service to mobile subscriber and wireless soft switch apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20060159039A1Easy to provideError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemNetwork addressing
A method and system for providing a private voice call service to a mobile subscriber are provided. A soft switch in a mobile communication system, upon receipt of an origination message including a private voice request information from a calling MS, transmits to a VPN server a private circuit service request message including a service ID for the private voice call service and the network address information of a caller and called. The VPN server establishes a communication path for edge routers connected to calling and called gateways according to network address information. Thus, voice traffic is transmitted between the calling MS and called MS though the communication path of the VPN.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Message transfer system
InactiveUS20020039407A1Low costShorten the timeTelephone data network interconnectionsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTransfer systemVoice communication
An apparatus and method for transferring a message from a calling party to an unavailable telephonically called party. The method comprises the steps of inititating a call to the called party over a communications channel, identifying that the called party is not available and instructing the calling entity to record the message at the calling entity and after recording to transmit the message to the called entity as a data message via a data channel for reception by the called entity. The system reduces the use of the voice / telephone communications networks by allowing a voice message to be transmitted through data channels, reducing the amount of voice traffic on the voice communication lines. The fact that the original voice message was actually stored with the calling entity after the telephone voice communication had been discontinued is transparent to both the calling party and the called party. Greetings for the called party can be stored at a messaging system of the calling entity.
Owner:APPLE INC
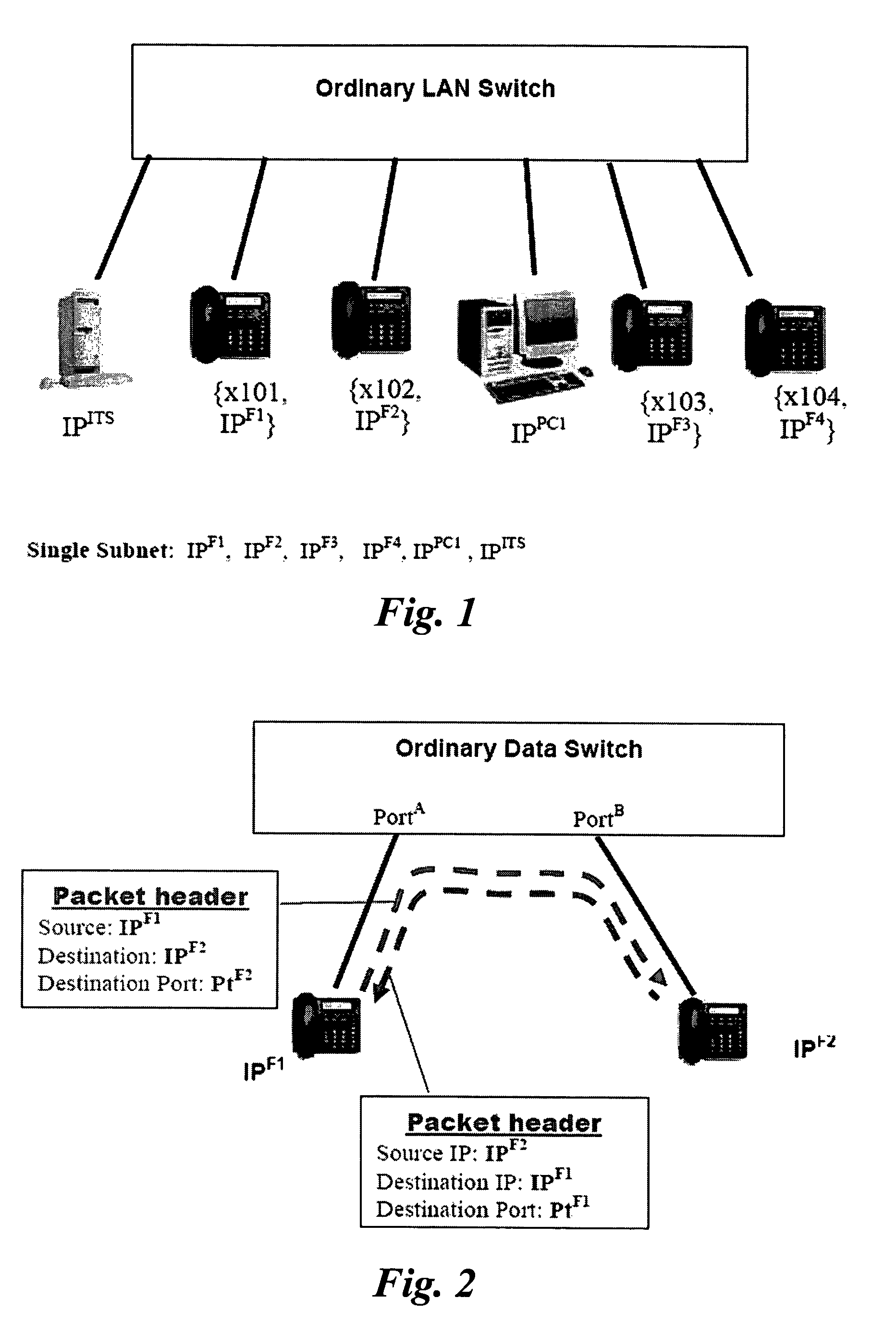
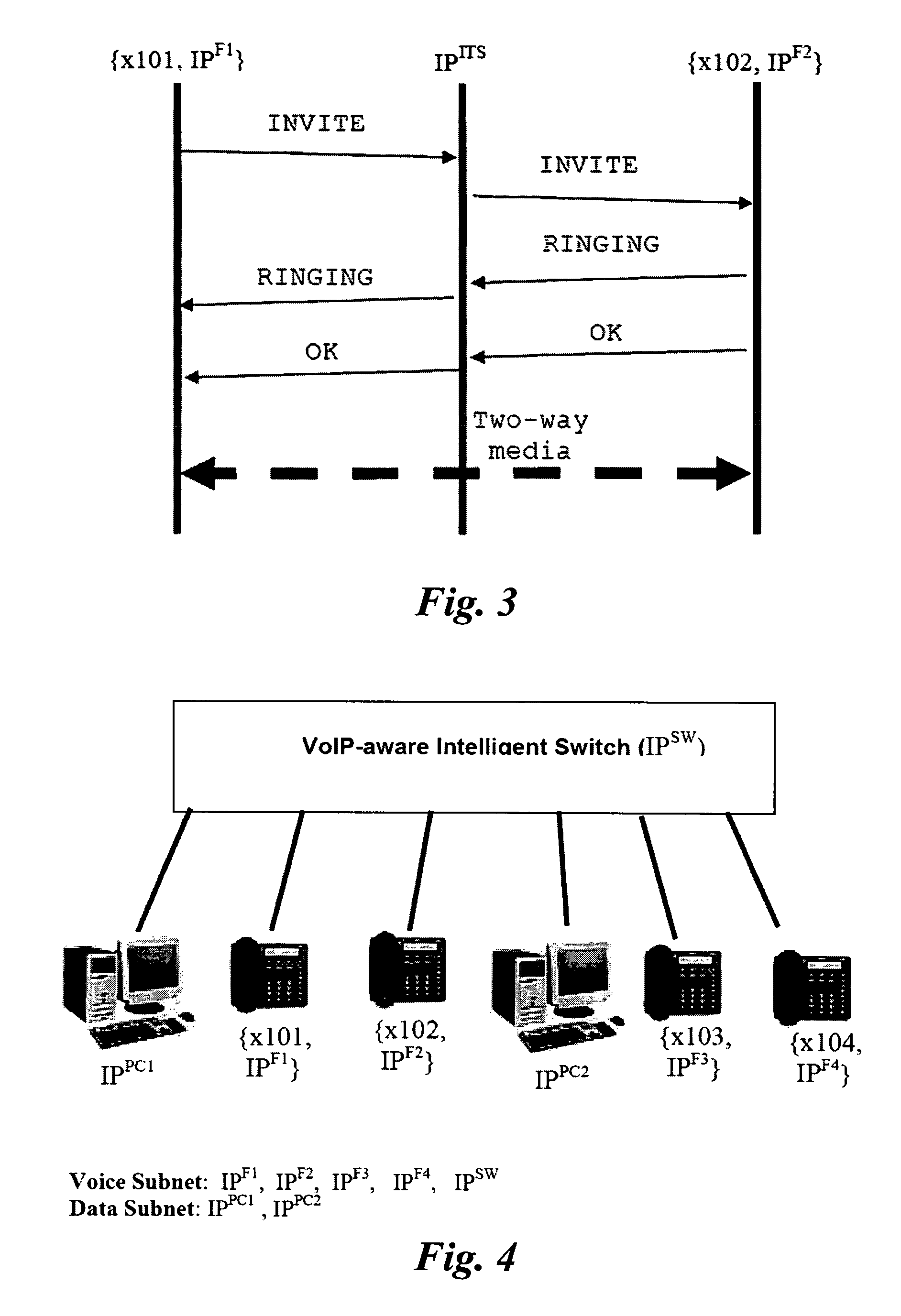
Intelligent switching for secure and reliable voice-over-IP PBX service
ActiveUS7920548B2Improve securityAutomatic exchangesNetwork connectionsIntelligent lightingVoice traffic
A switching apparatus for switching packetized voice traffic between a plurality of communication devices, the switching apparatus comprises a multi-layer switch, a plurality of communication ports, control means and ingress processing means, said packetized voice traffic comprises call control packets and medium packets which are exchanged between the communication devices via said communication ports, wherein medium packet traffic from a first communication device to a second communication device is split into a first call segment and a second call segment, the first call segment originates from said first communication devices and terminates at said switching apparatus, the second call segment originates from said switching apparatus and terminates at said second communication device, each medium packet from said first communication device is processed by said ingress processing means of said switching apparatus before onward transmission to said second communication device.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com