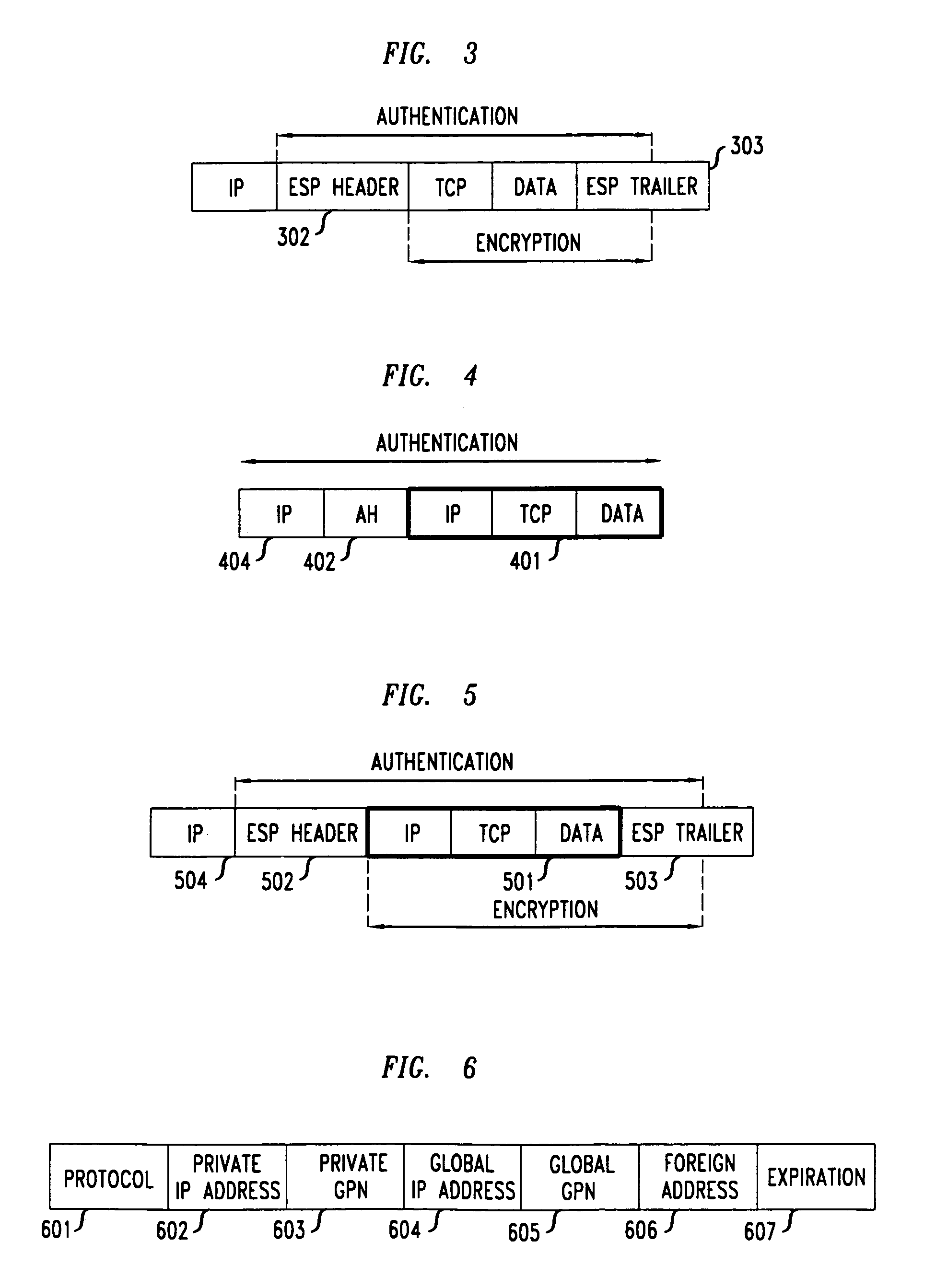
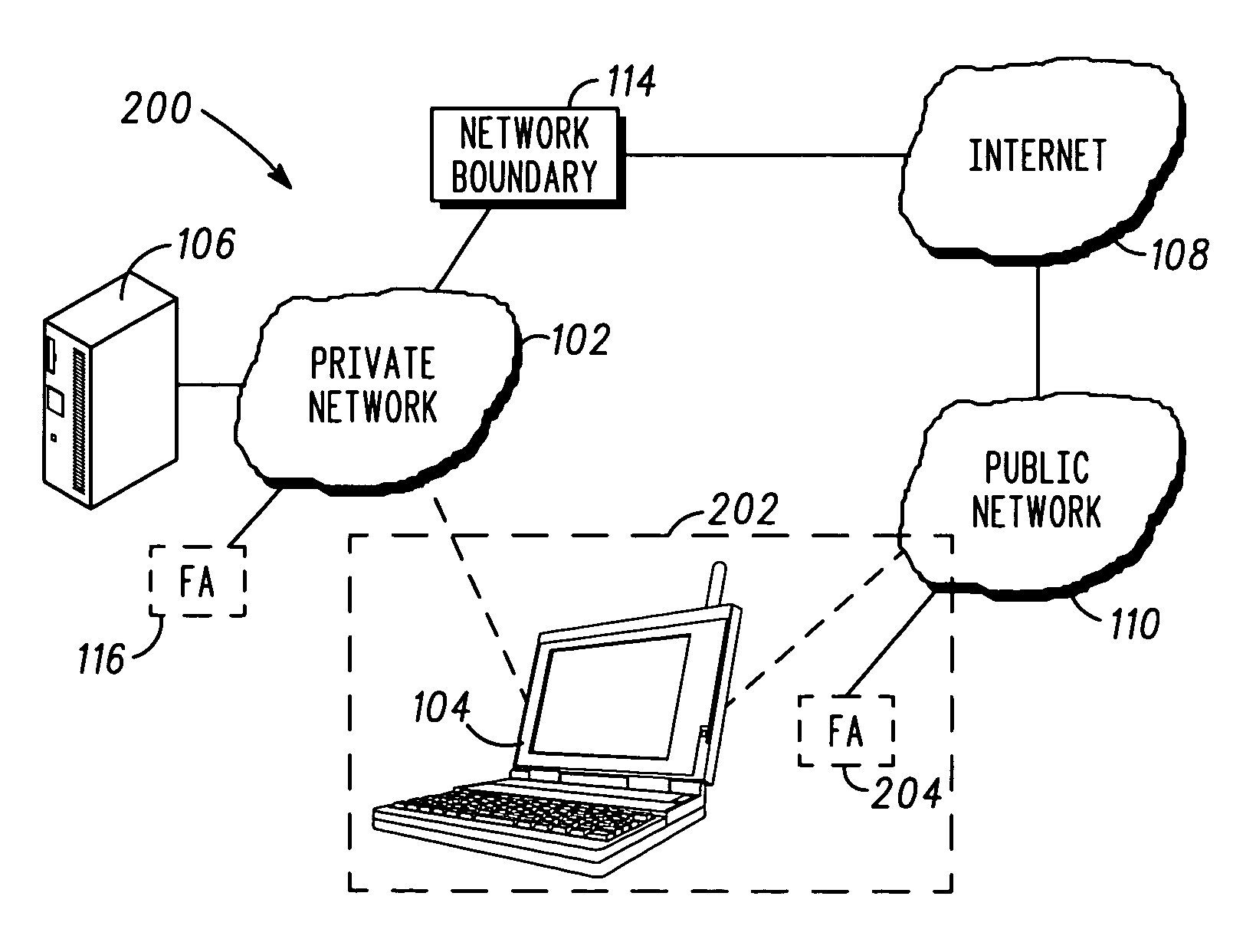
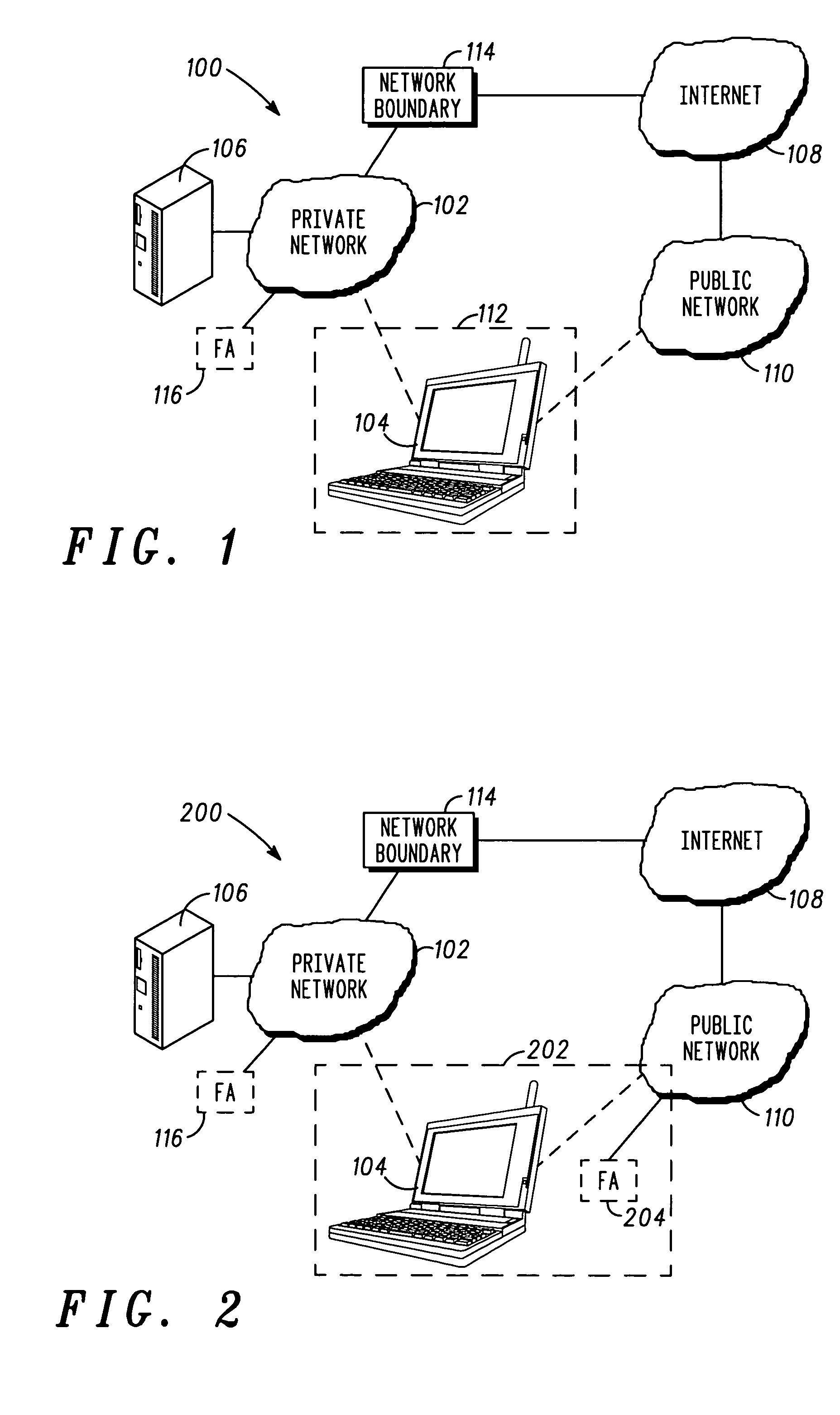
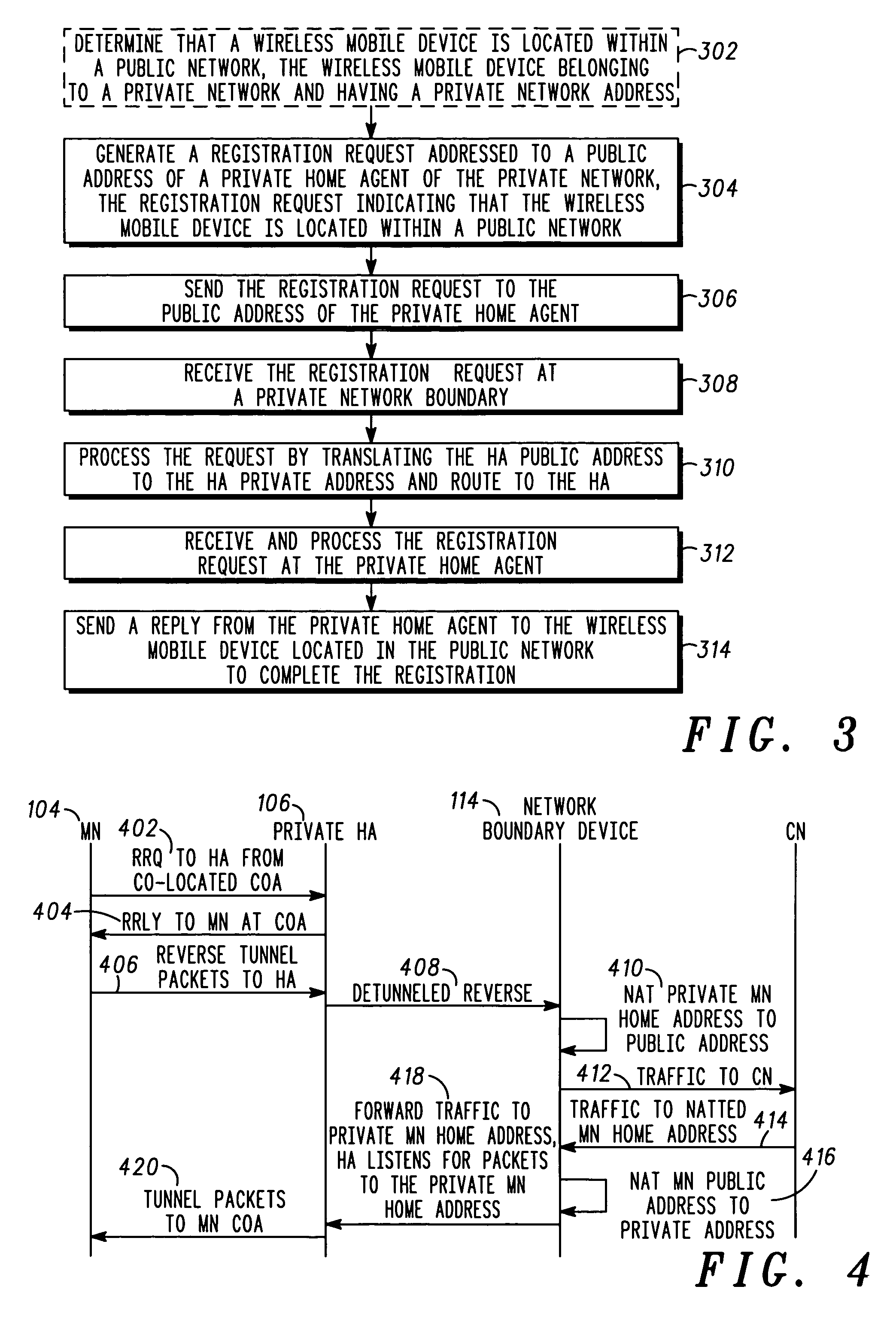
Patents
Literature
259 results about "Private address" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A private IP address is a non-Internet facing IP address on an internal network. Private IP addresses are provided by network devices, such as routers, using network address translation (NAT).
Managed peer-to-peer applications, systems and methods for distributed data access and storage
InactiveUS20050114711A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPrivate communicationDisplay device
Applications, systems and methods for securely and remotely operating a remote computer from a local computer over a network while providing seamless, firewall-compliant connectivity. Secure and remote operation includes authenticating at least one remote computer for connection to at least one computer over the network and / or at least one local computer for connection to at least one remote computer over the network; establishing a secure connection between the at least one local computer and the at least one remote computer over the network; and integrating a desktop of at least one remote computer on a display of at least one local computer. The connections may be made over a public network, as well as through multiple firewalls without loss of functionality. A method of accessing and using at least one remote computer from a local computer over a public network may include centrally authenticating, at a location having a public address, a first computer having a first, firewall protected private address; creating a first firewall compliant connection between a publicly addressed connection server and the first computer upon authentication of the first computer; establishing a second firewall compliant connection between the publicly addressed connection server and a second computer having a second firewall protected private address; establishing a private-to-public-to-private communications tunnel, wherein the connection server routes communications from the first computer through the first firewall compliant connection and the second firewall compliant connection to the second computer, and from the second computer through the second firewall compliant connection and the first firewall compliant connection to the first computer; and performing at least one further step selected from the group consisting of: integrating a file structure of accessible files accessed at the second or first computer, into a file structure contained at the first or second computer, respectively; at least one of integrating a desktop of the second computer on a display of the first computer and integrating a desktop of the first computer on a display of the second computer; and directly operating the second computer from the first computer or the first computer from the second computer, wherein the computer that is directly operated is selected from the group consisting of: home appliances, video equipment, audio equipment, printers, fax machines, office equipment, medical devices, vehicles, cameras, RFID equipment, laboratory equipment, manufacturing machinery, GPS equipment, and devices having one or more embedded microprocessors.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
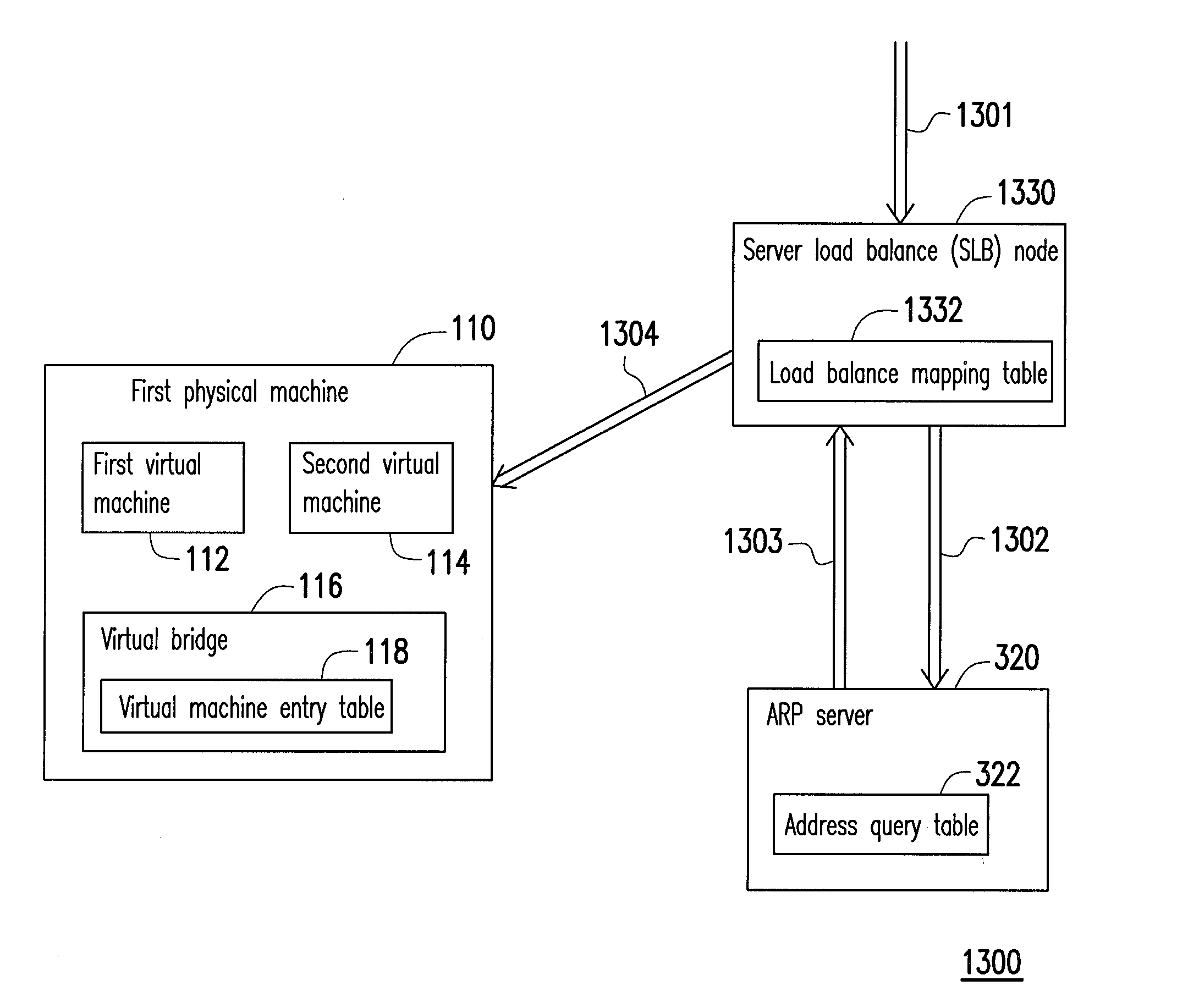
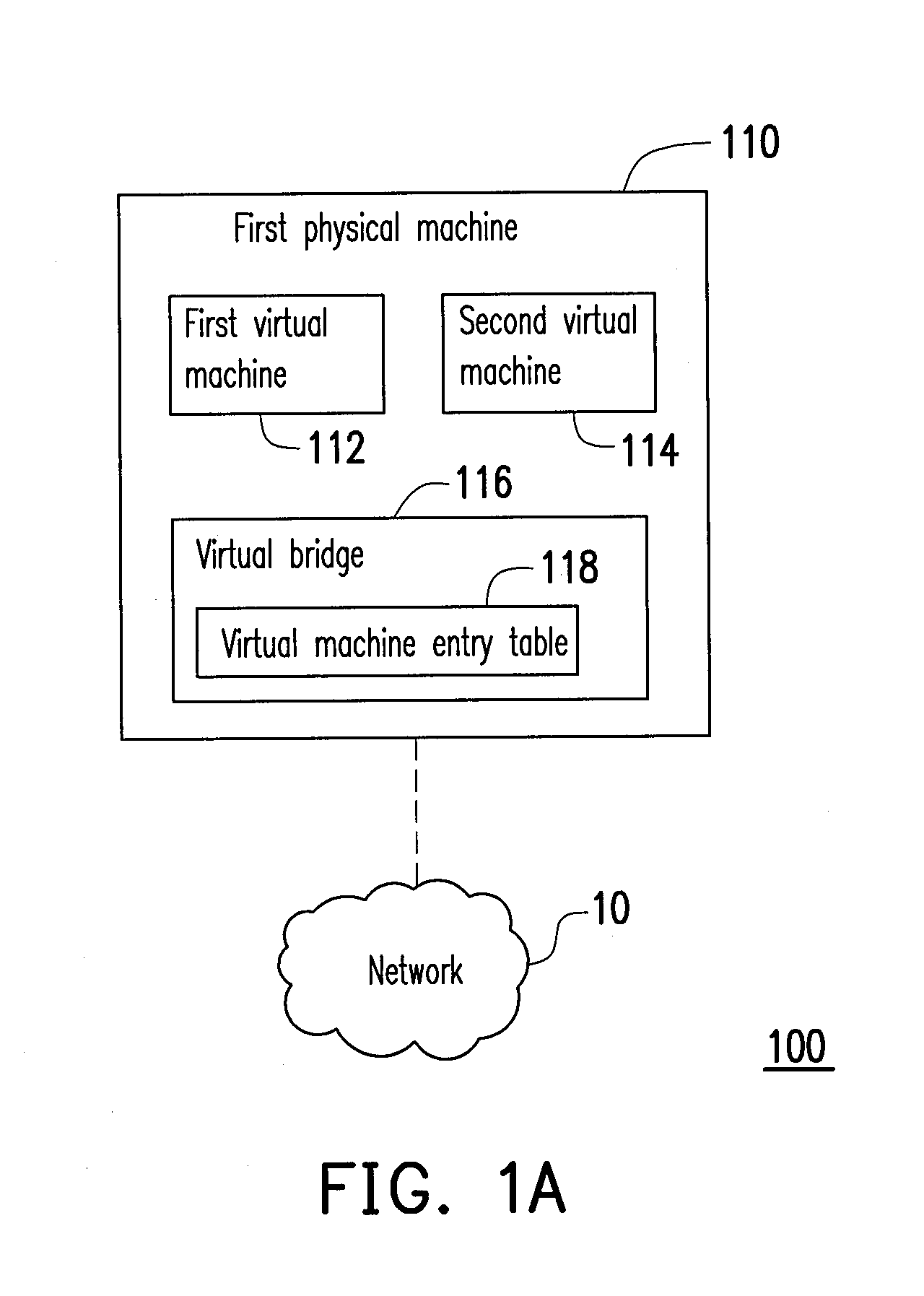
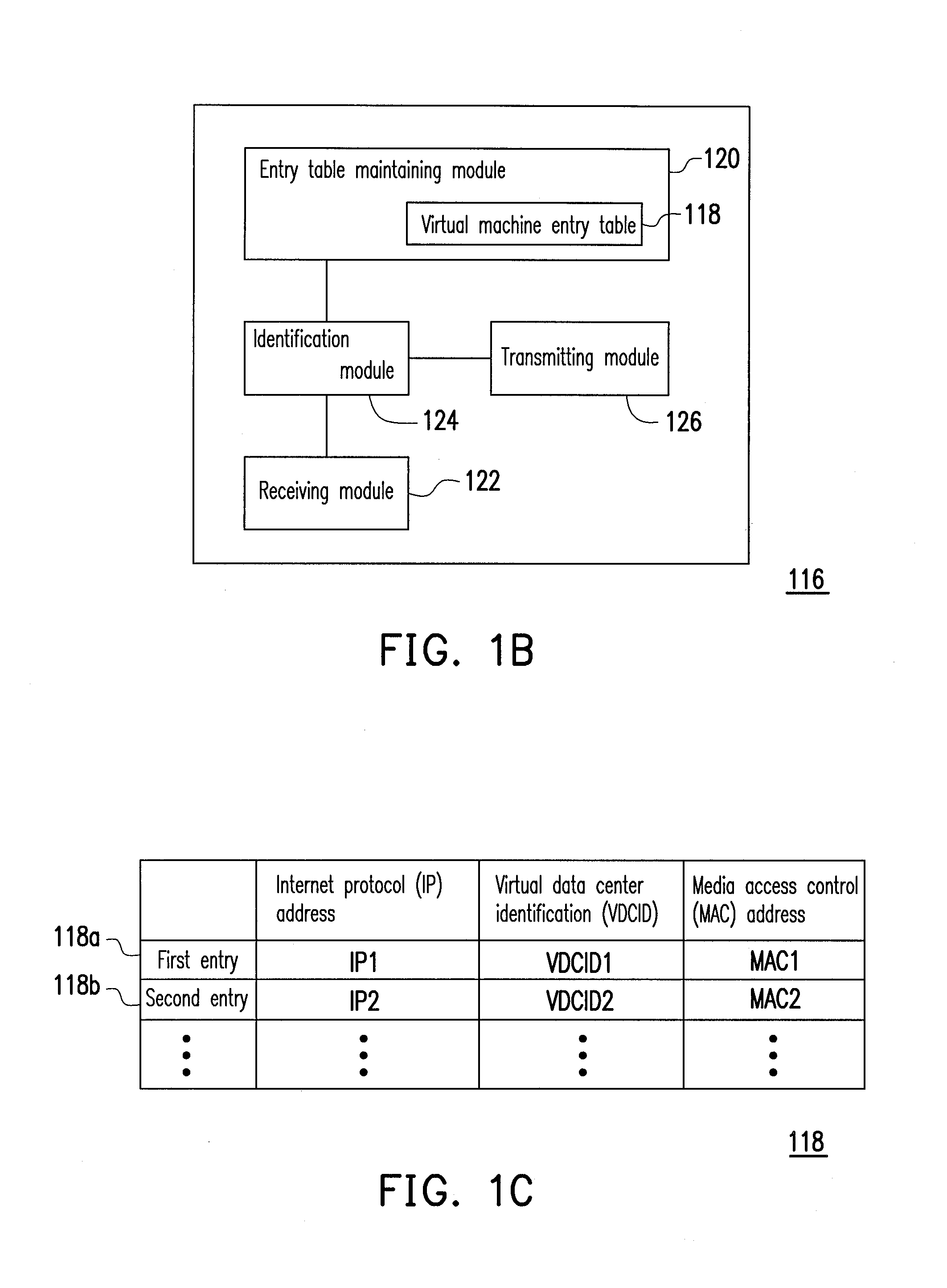
Data center network system and packet forwarding method thereof
ActiveUS20130136126A1Efficient solutionData switching by path configurationProgram controlPrivate IPAddress Resolution Protocol
A data center network system and a packet forwarding method thereof are provided. The data center network system includes a virtual bridge and an address resolution protocol (ARP) server. The virtual bridge intercepts an ARP request having an identification field and a destination IP address field and adds a corresponding virtual data center identification to the identification field of the ARP request and redirecting the ARP request to the ARP server. Additionally, the ARP server queries a corresponding MAC address according to an IP address recorded in the destination IP address field of the ARP request and the corresponding VDCID recorded in the identification field of the ARP request, and transmits the corresponding MAC address in response to the ARP request. Accordingly, the same private IP address can be reused in the data center network system.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for IP network interfacing
InactiveUS20080101357A1Facilitates multi-homingData switching by path configurationPrivate IPPrivate address
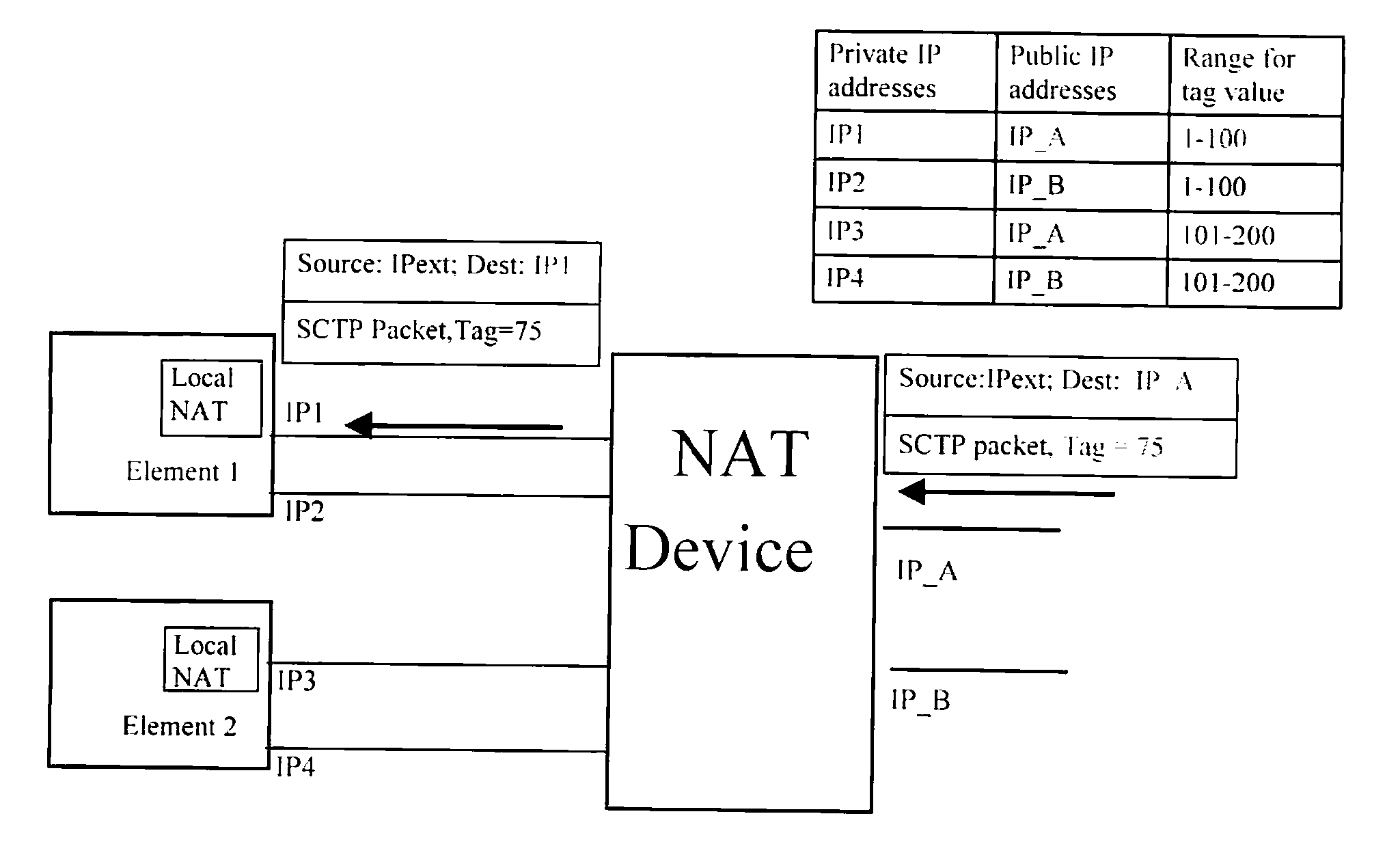
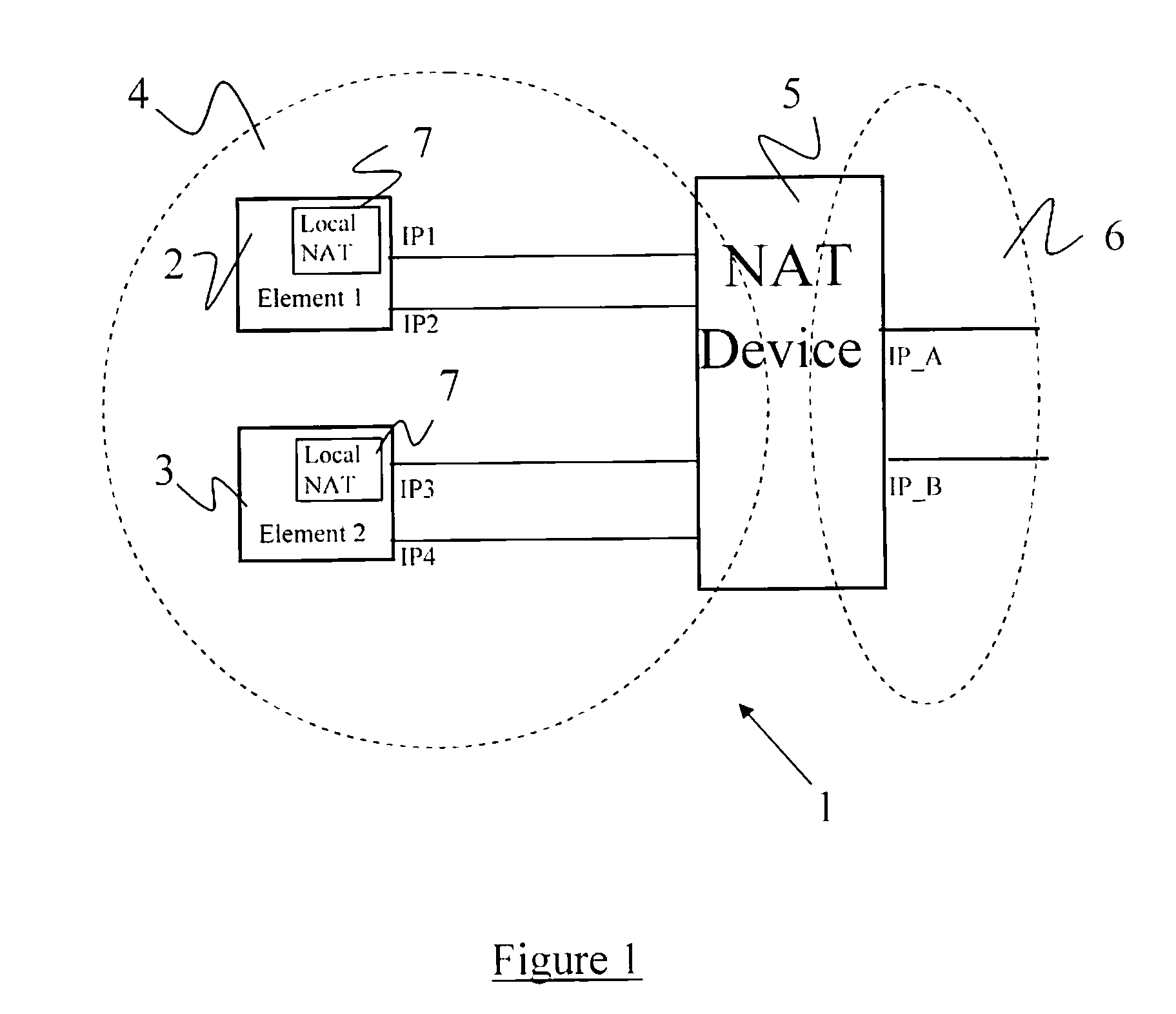
A method of operating a node of a telecommunications system, the node comprising a plurality of entities each arranged to send and receive IP packets to peer entities, via a Network Address Translation function, using a layer 4 control protocol which facilitates multi-homing by allowing an entity to include more than one IP address in a layer 4 packet chunk. The method comprises maintaining at each of said plurality of entities a table mapping one or more private addresses of the entity to one or more public addresses of the Network Address Translation function, and, for each association initiation message generated by an entity, including in said layer 4 packet chunk of the message the public IP address(es) of the Network Address Translation function obtained from said table for the corresponding private IP address(es).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
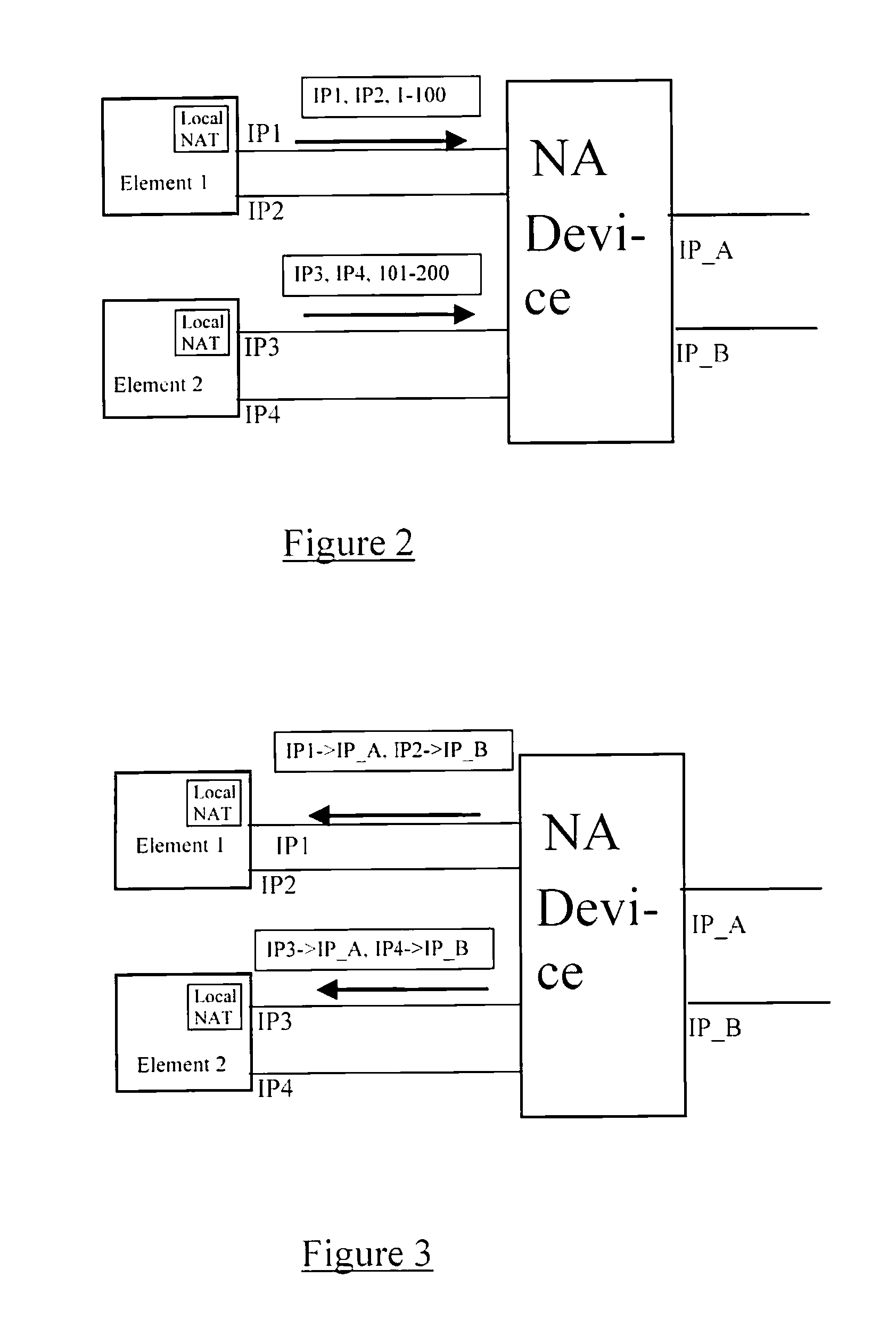
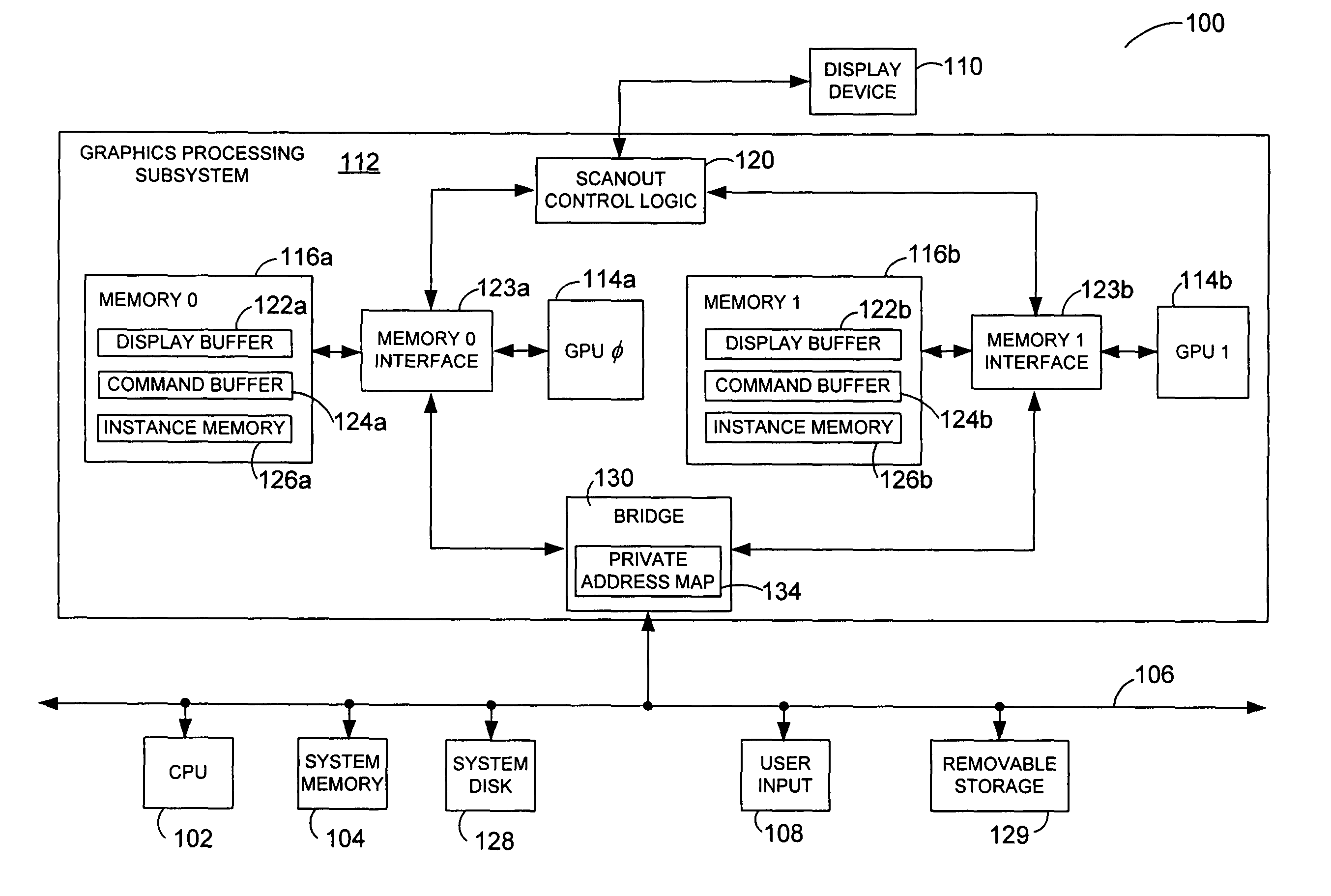
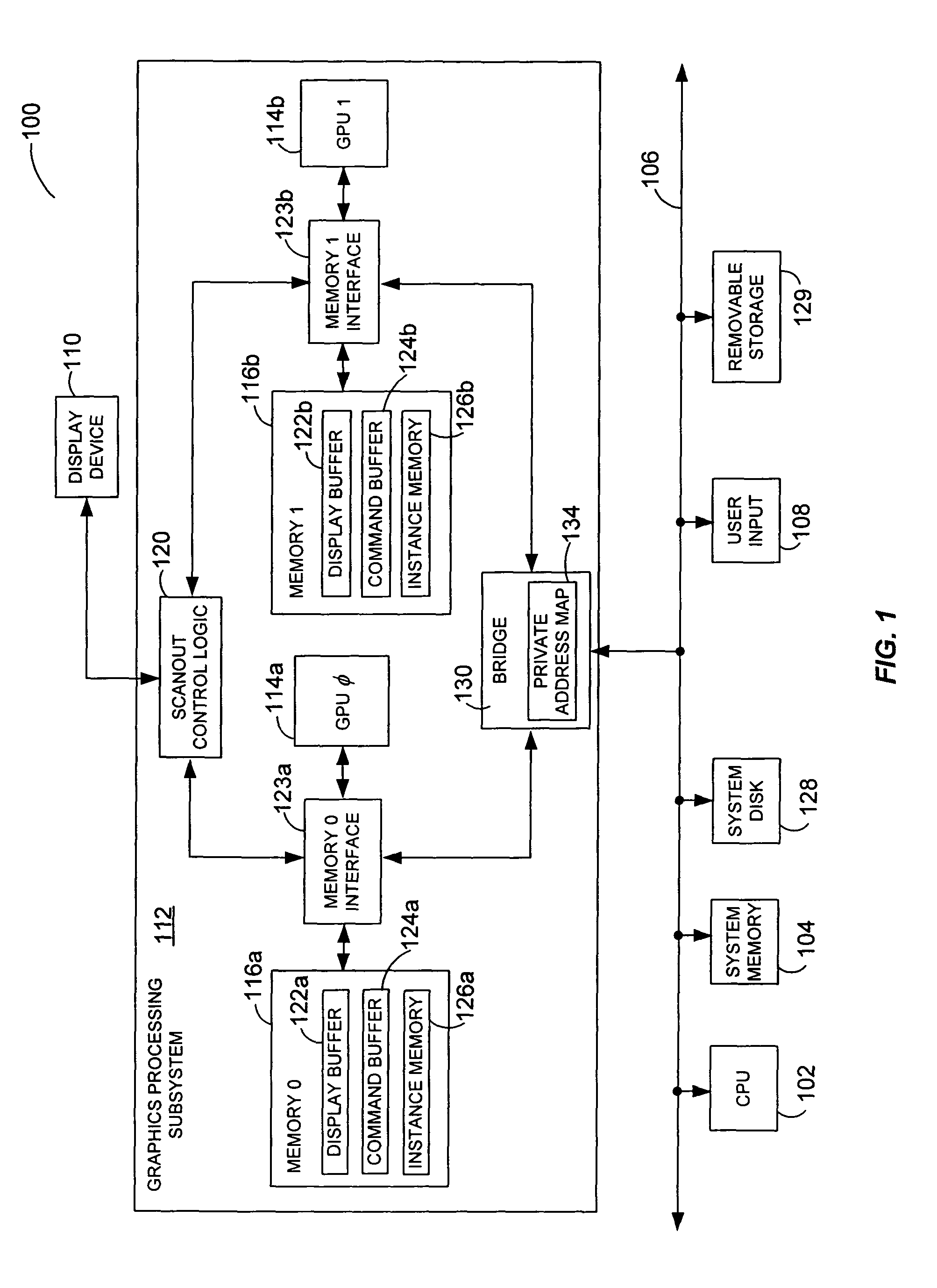
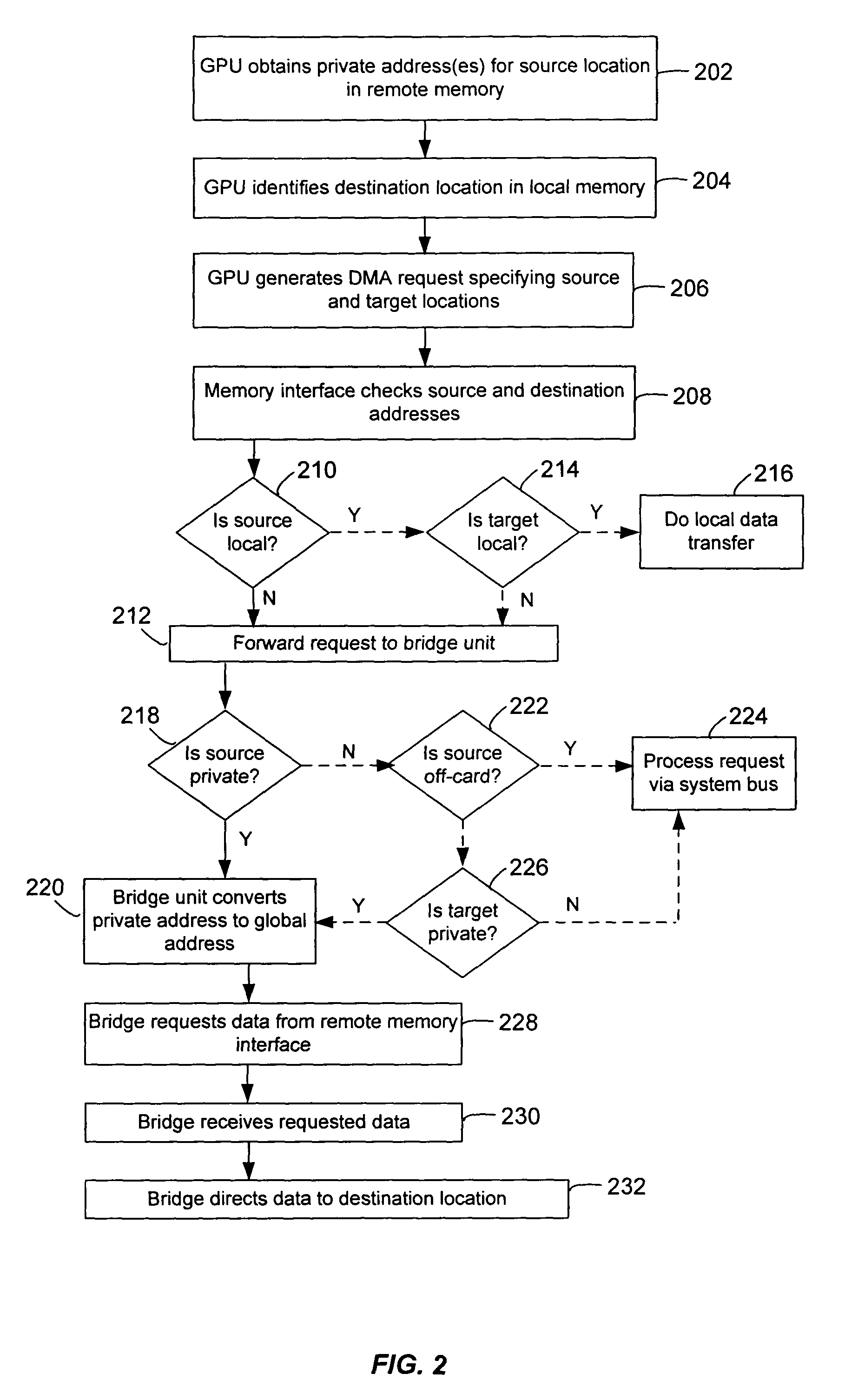
Private addressing in a multi-processor graphics processing system
ActiveUS6956579B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsMulti processor
Systems and methods for private addressing in a multi-processor graphics processing subsystem having a number of memories and a number of graphics processors. Each of the memories includes a number of addressable storage locations, and storage locations in different memories may share a common global address. Storage locations are uniquely identifiable by private addresses internal to the graphics processing subsystem. One of the graphics processors is able to access a location in a particular memory by referencing its private address.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
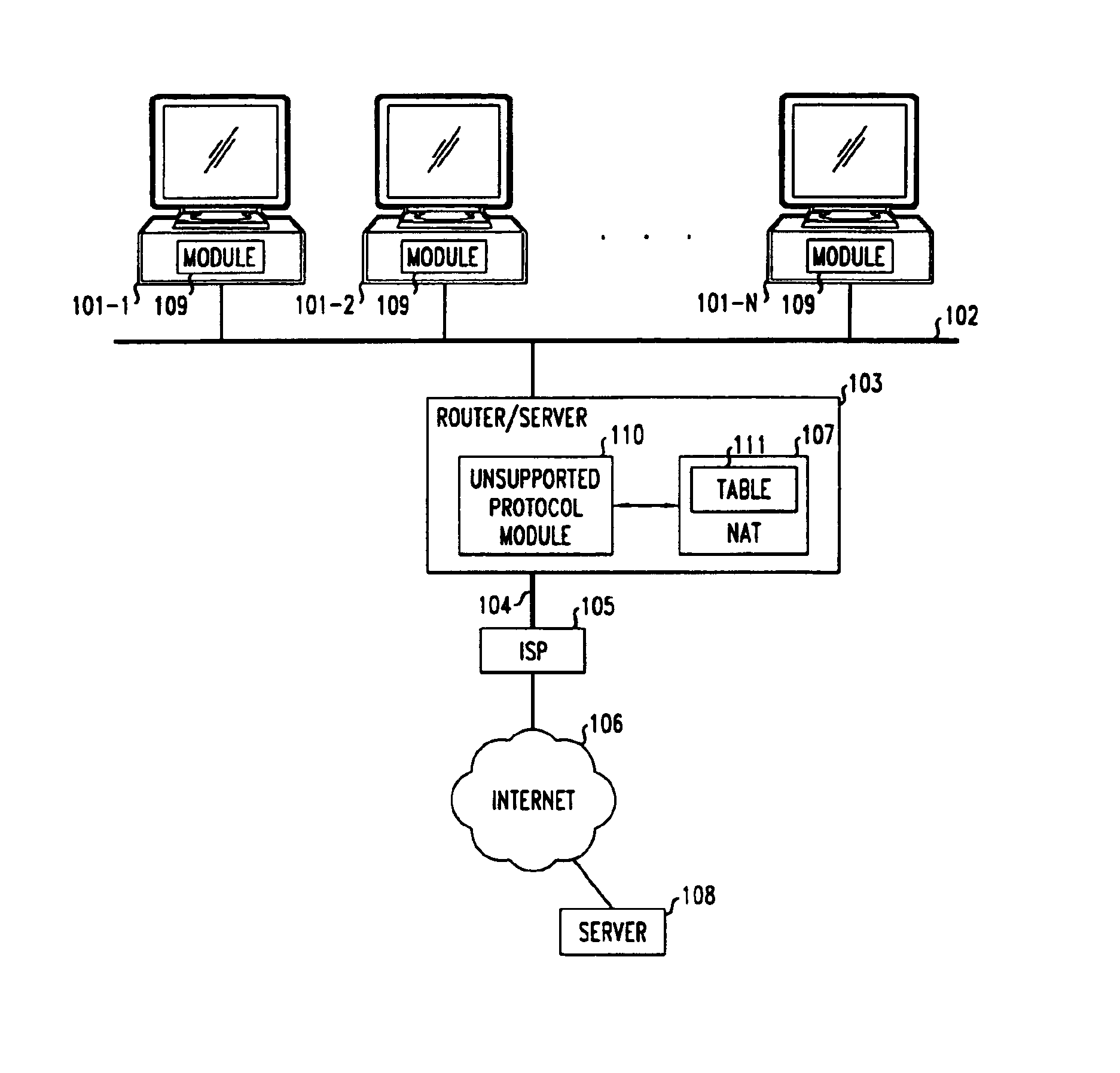
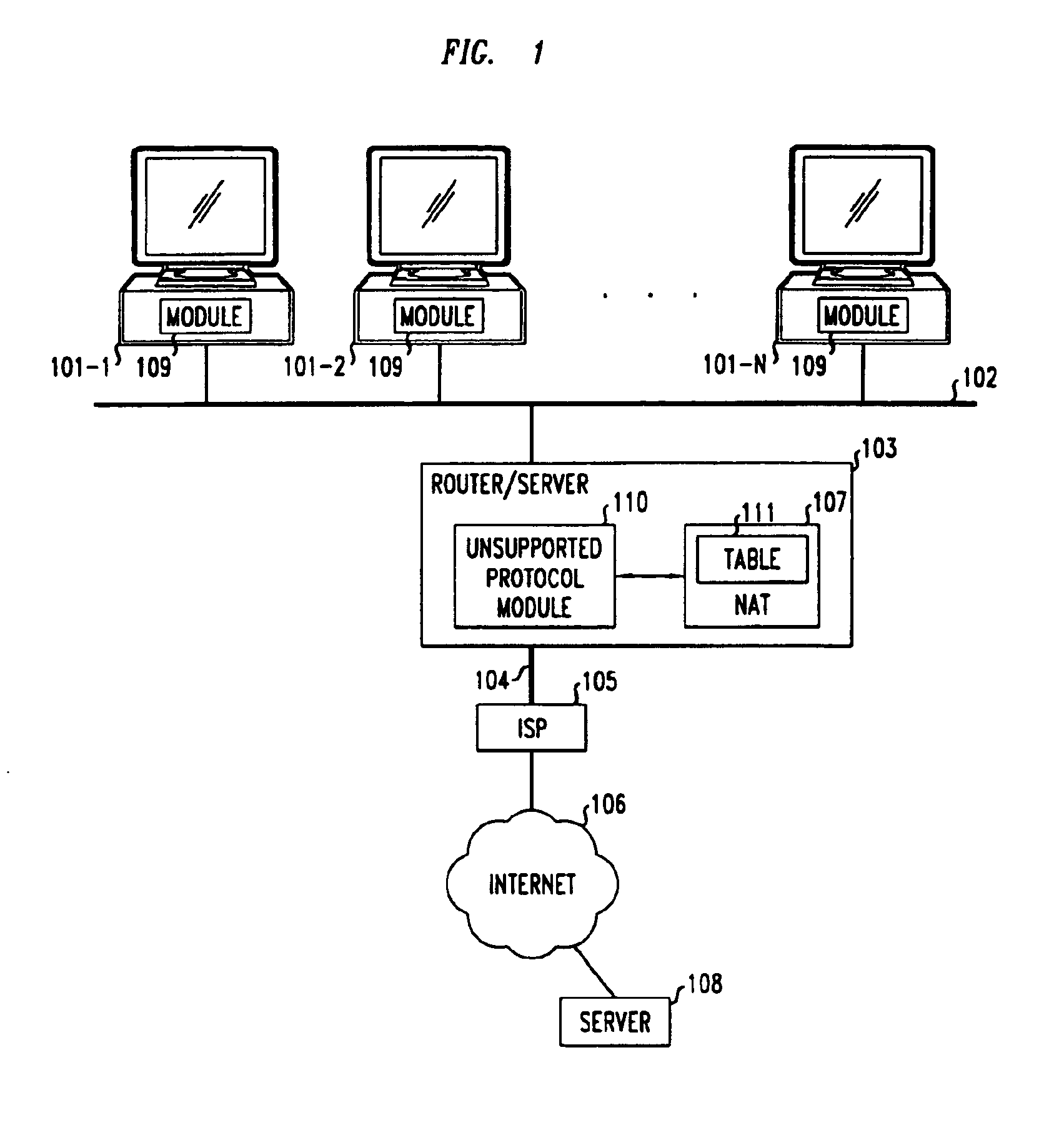
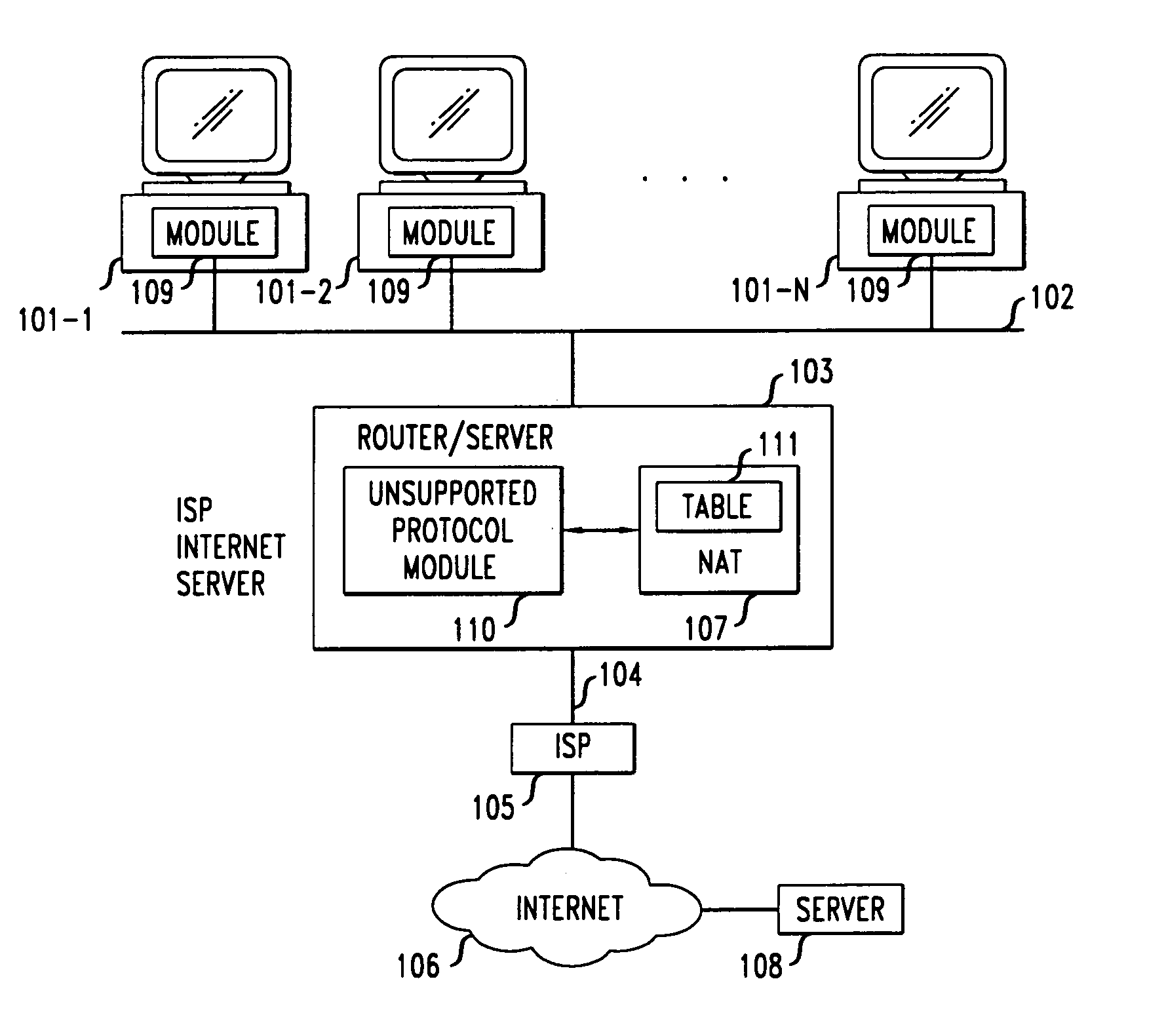
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
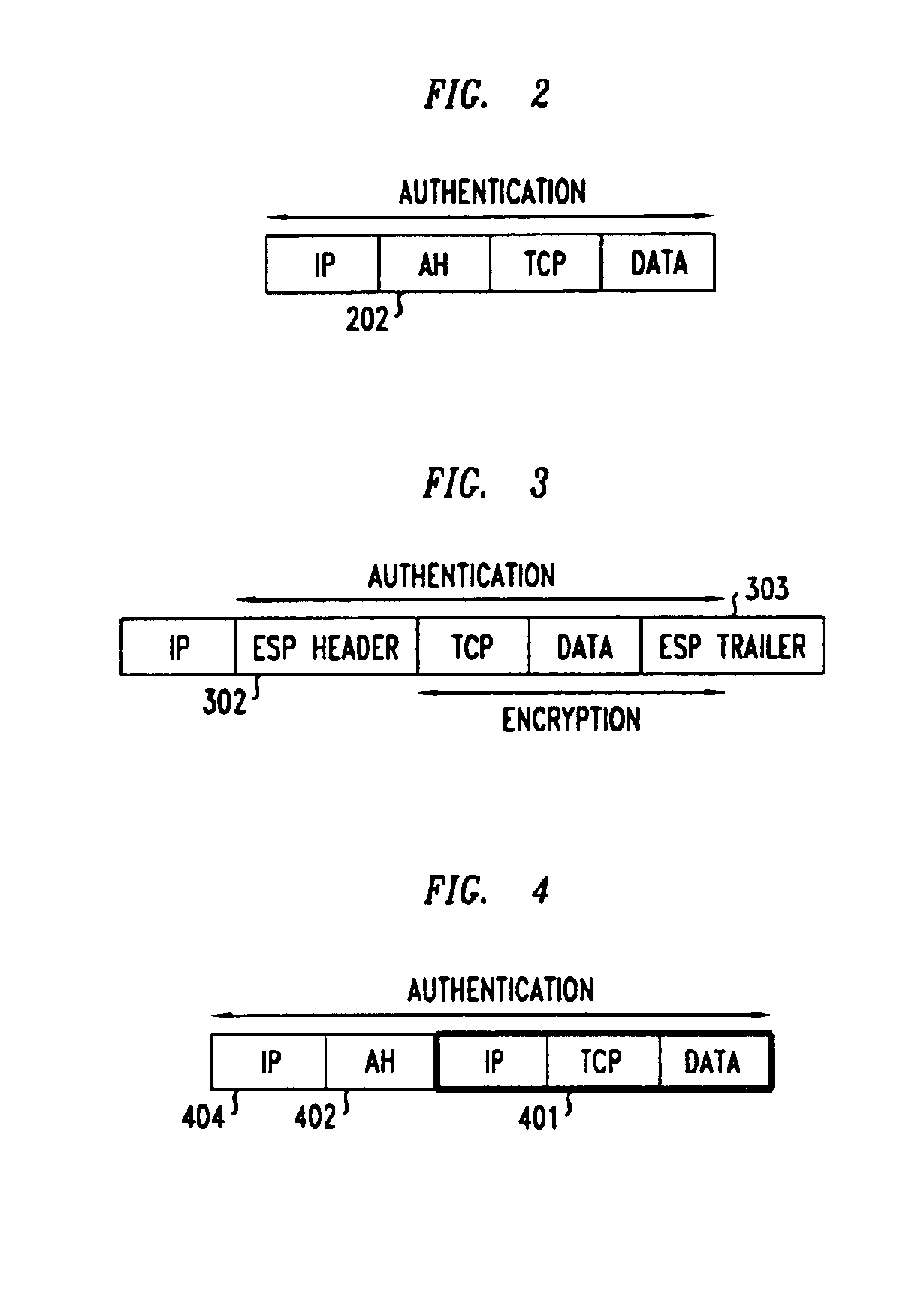
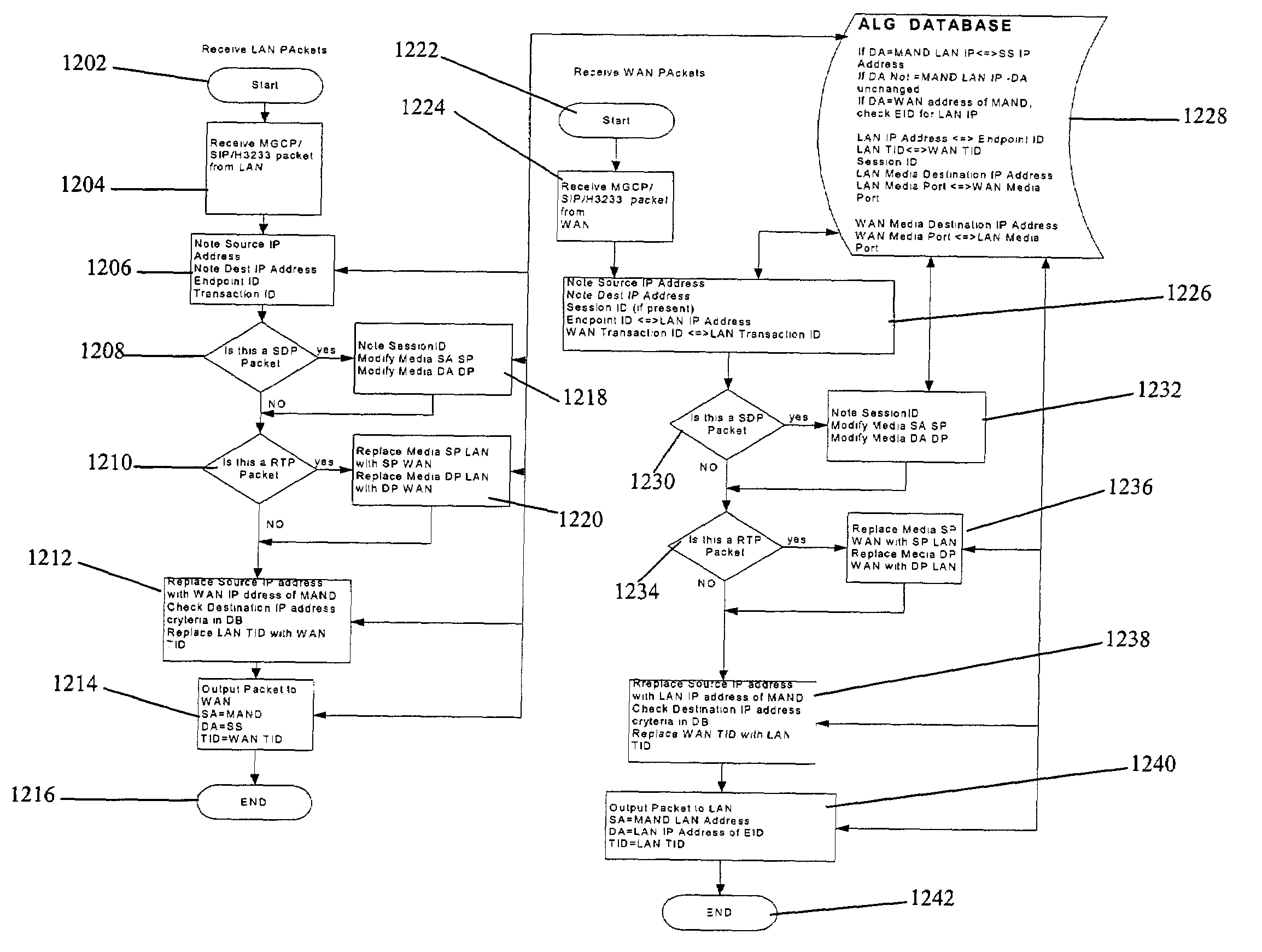
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
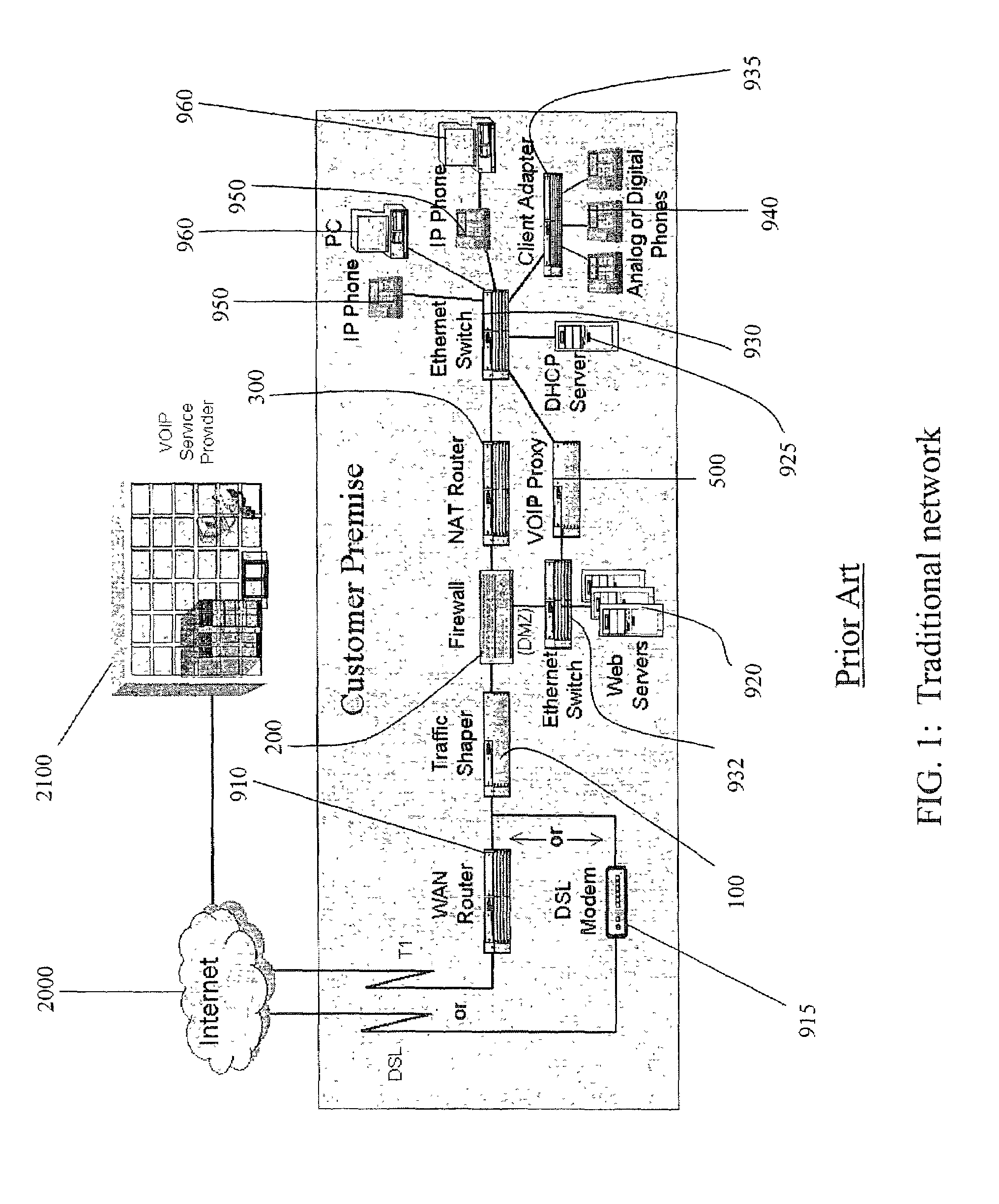
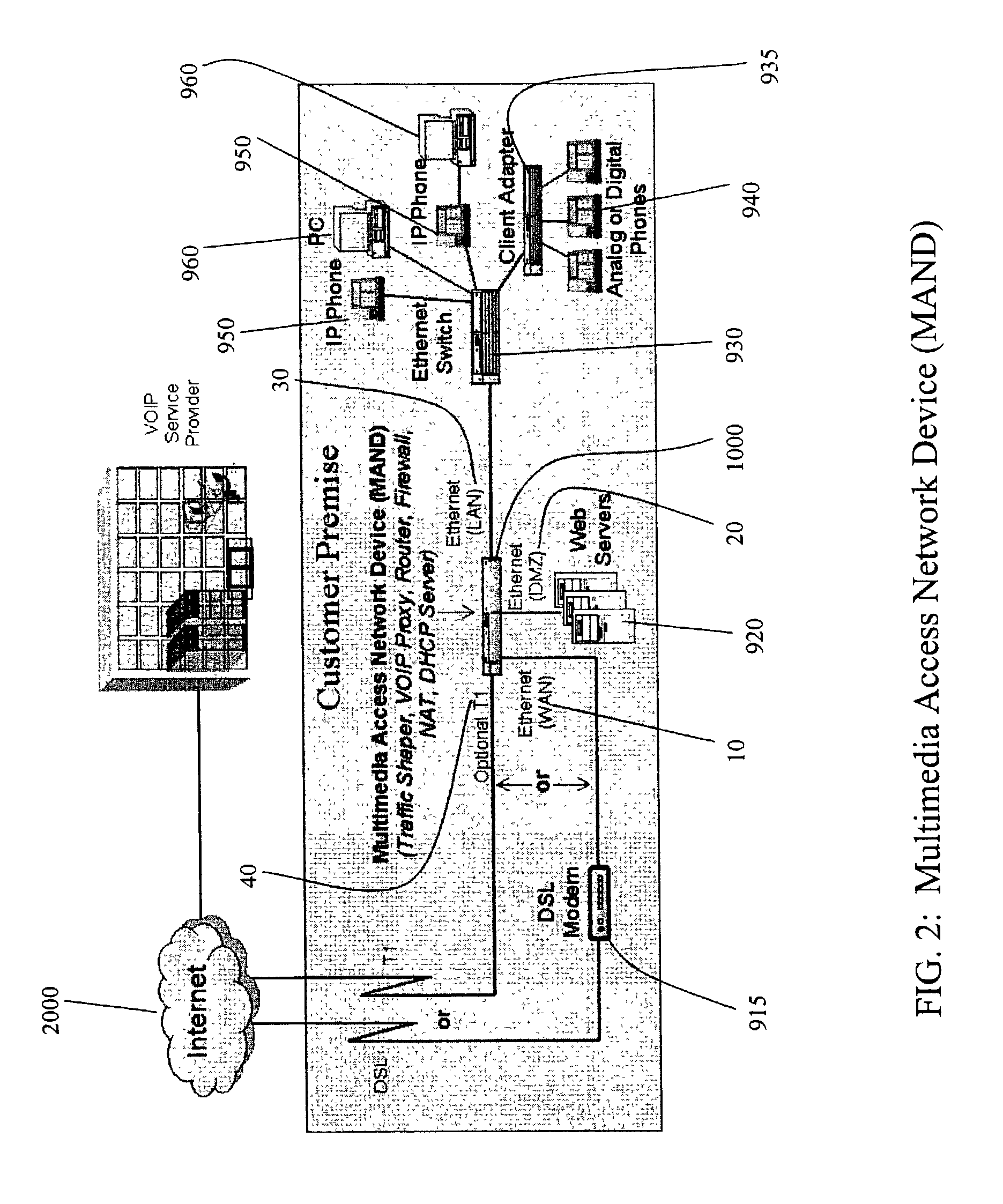
Method and system for implementing and managing a multimedia access network device
ActiveUS7274684B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationAuthentication
In a complete network-in-a-box system acting as an enterprise network demarcation point, packets such as voice, video and data packets, are routed over common network connections, such as LAN and WAN. The packets are mapped from a public address field (such as an IP address) and port number to a private address field and port number, the mapping process typically being handled by a NAT (Network Address Translation). The packets are also prioritized, by marking the packets for priority queuing and routing, and configuring the bandwidths of the WAN traffic and the voice traffic to predetermined quantities and configuring the address fields of the voice devices. Simultaneous transmission of the various packets can be limited to predetermined quantities, typically by utilizing a CAC (Client Access Control). Secure firewalls are also included as well as a performance test client application that provides a defined workload generated across the WAN interface for capacity planning measurements and allows remote monitoring of the QoS (Quality of Service) data, such as latency, jitter, lost packets and MOS scores. Optionally, a simple, common remote management interface is included, allowing service providers to configure, upgrade and manage the system. Additionally, address fields can be provided to voice, video or data devices attached to a LAN port. VPN authentication and encrypted sessions can be tunneled through the firewall for access to an internal network by using a VPN terminator. For power outages and other emergency purposes, additional ports that connect to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) analog telephone lines as well as other analog telephones or devices, can be provided. Another advantageous element is that most of the above components or features may be enabled or disabled.
Owner:EDGEWATER NETWORKS
Intelligent network address translator and methods for network address translation
ActiveUS7752334B2Effective IP address reusability factorImprove reusabilityData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsIntelligent NetworkIp address
An intelligent network address translation system and methods for intelligent network address translation. The invention analyzes all data packets being communicated between the private address realm and the public address realm and performs a predefined mode of network address translation based on the packet type. By analyzing every packet that the network encounters and adjusting the network address translation mode based on the packet type, the system and method of the present invention is able to adjust the mode of network address translation dynamically during a network user's ongoing network session. Additionally, by basing which mode of translation will be employed based on packet type the translation method of the present invention insures that IP addresses are distributed efficiently and distribution of the amount of addresses is minimized.
Owner:NOMADIX INC
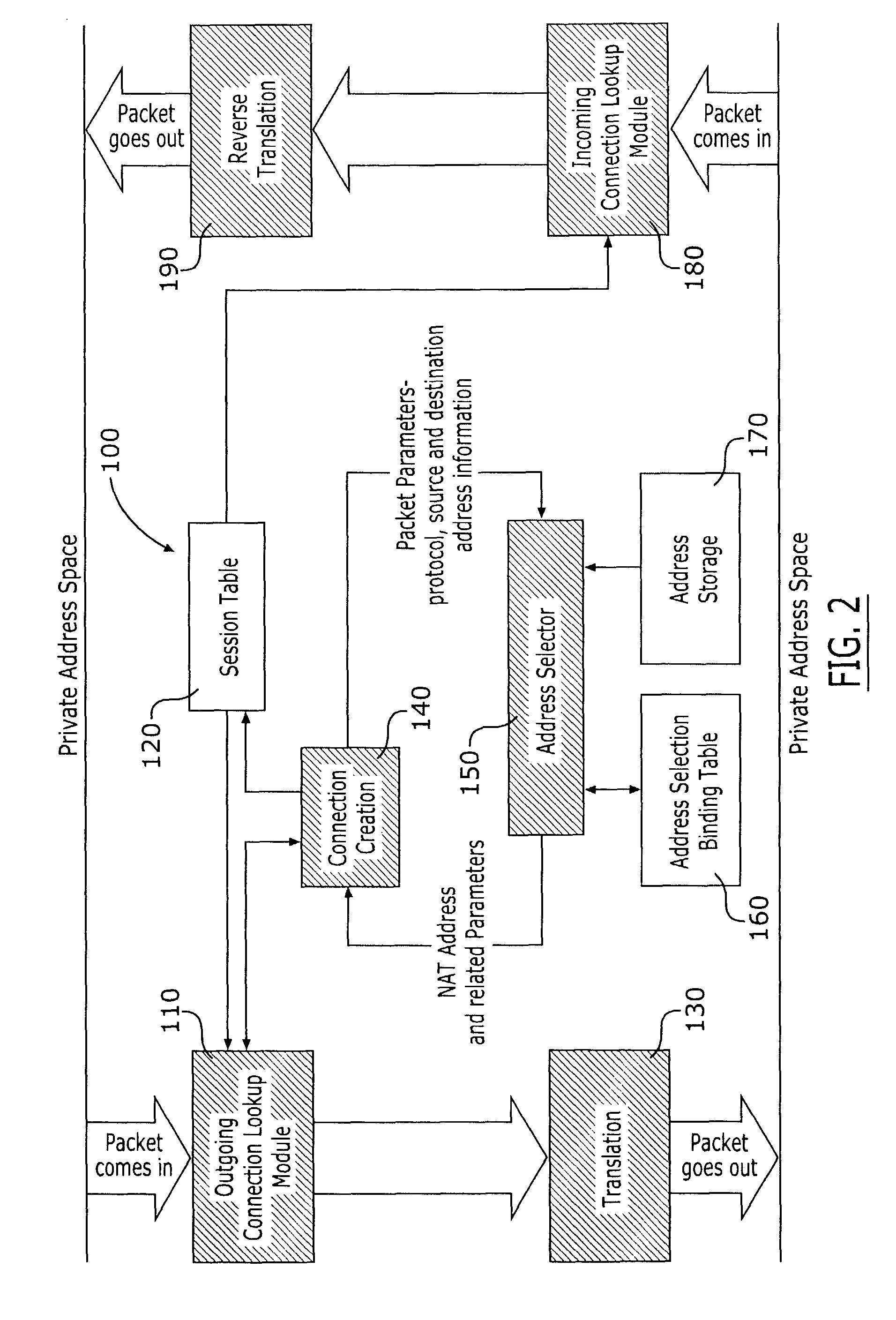
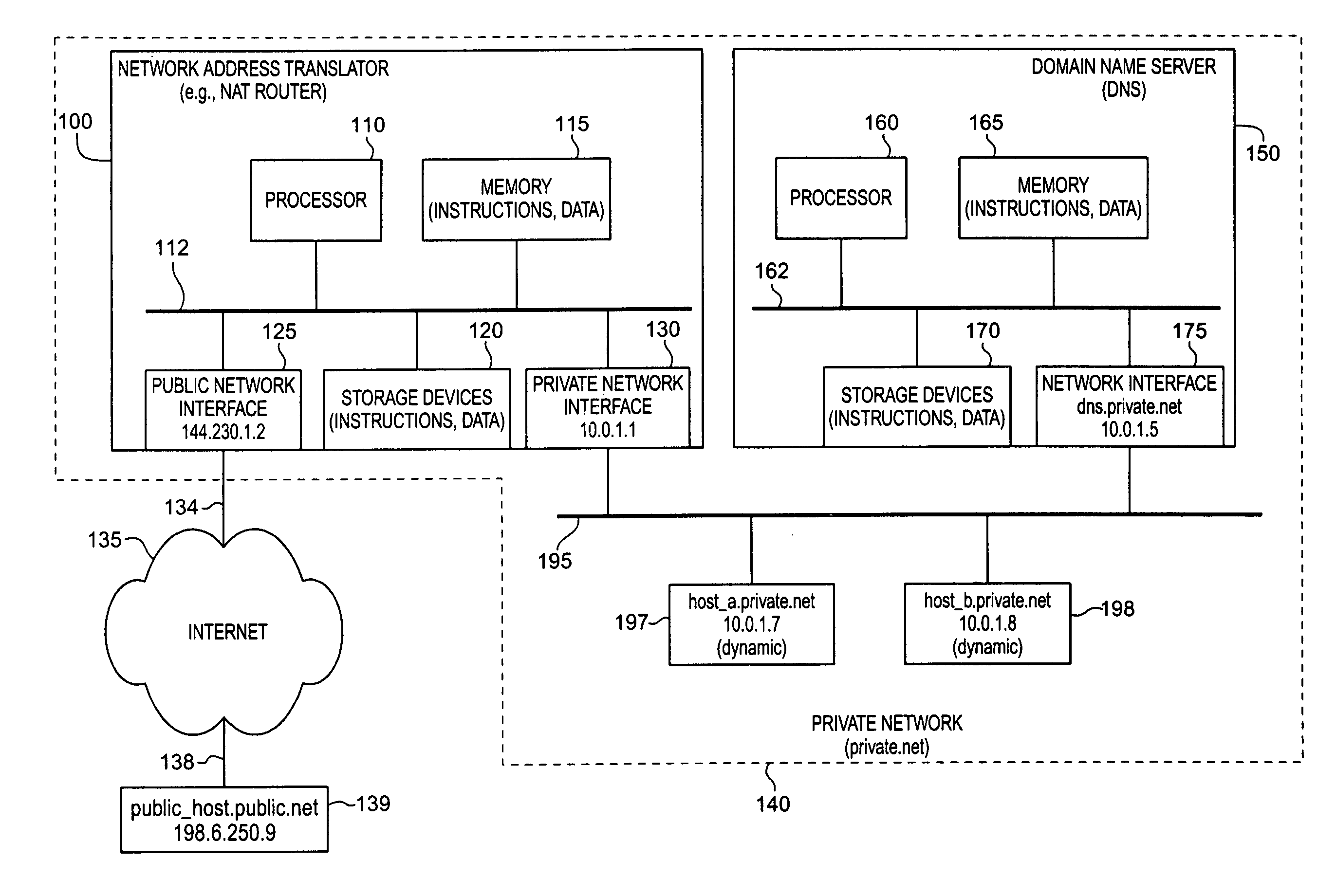
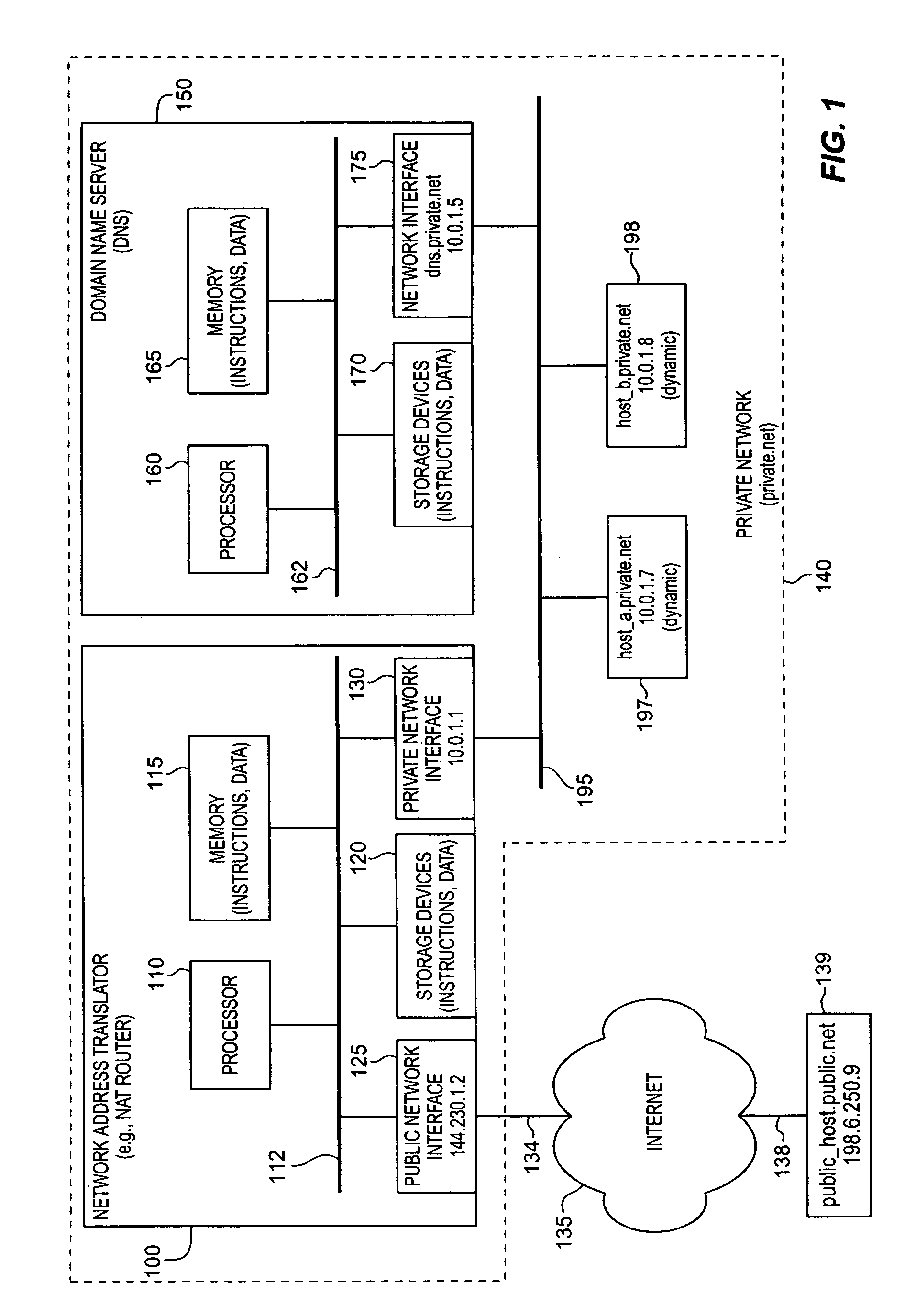
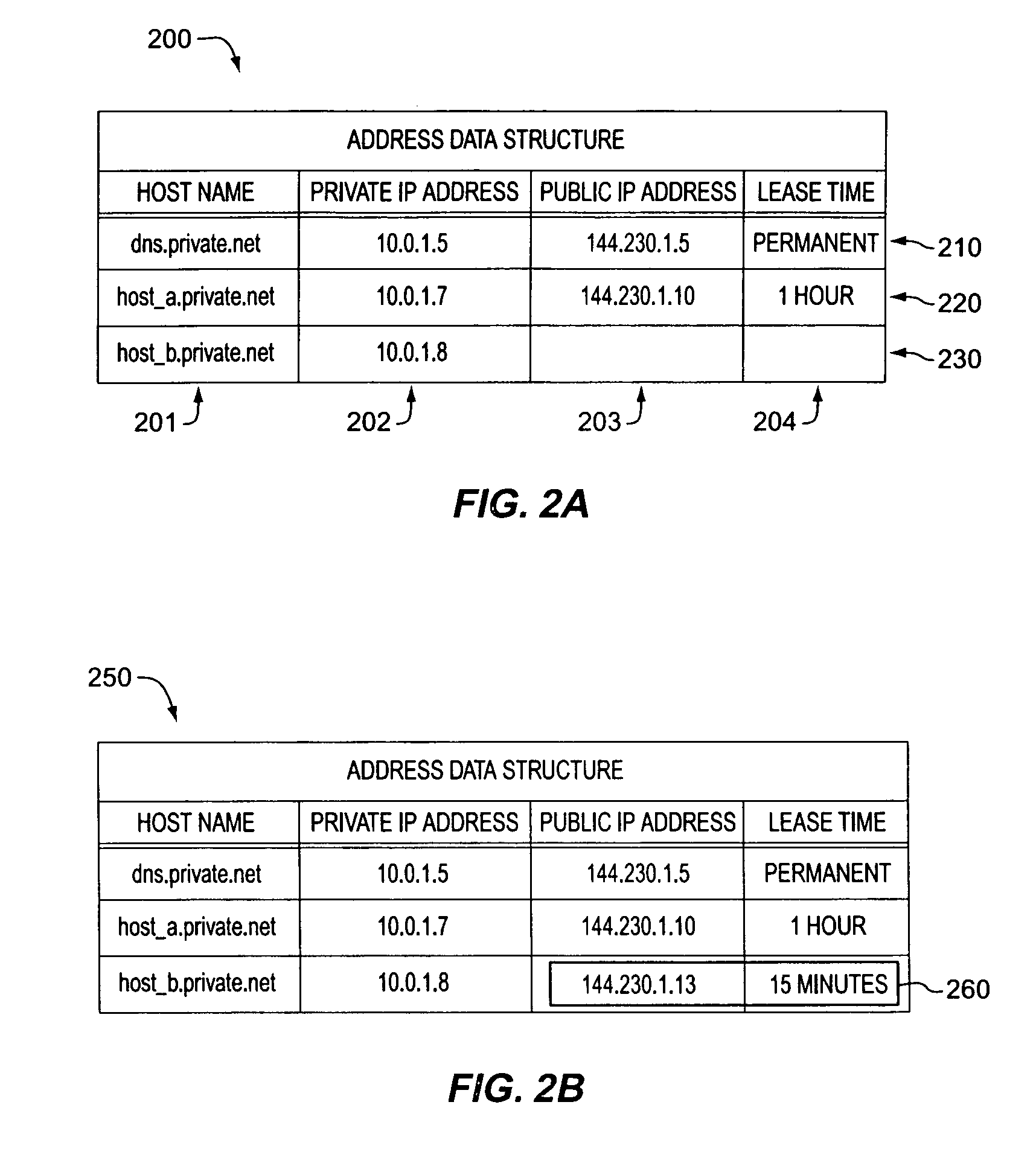
Method and apparatus for dynamic allocation of private address space based upon domain name service queries
InactiveUS6944167B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameName server
According to the invention, a method and apparatus are disclosed for dynamically assigning a public network address for a private network host in response to a request generated external to the private network. A requesting host desiring access to a host with the private network queries a domain name server for the public network address of the private network host. Then, the domain name sever queries a network address translator of the private network, and receives a reply indicating a dynamically allocated public network address for the specified private network host. The requesting host can then use this returned public network address for communicating with the private network host. In this manner, a set of public addresses can be shared, with a public network address being dynamically allocated to a private network host in response to a request for access by a host external to the private network. Moreover, a public network address is assigned to a private network host for a limited period of time. This time period can be specified as a period of network inactivity related to the public network address, or a specified time duration (e.g., for one hour, from 3:00 PM to 5:00 PM). The aging of these assigned public addresses is processed by the domain name server itself, or by the network address translator which sends a message to the domain name server when an assigned public address is no longer valid for a particular private network host.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
Address translation change identification
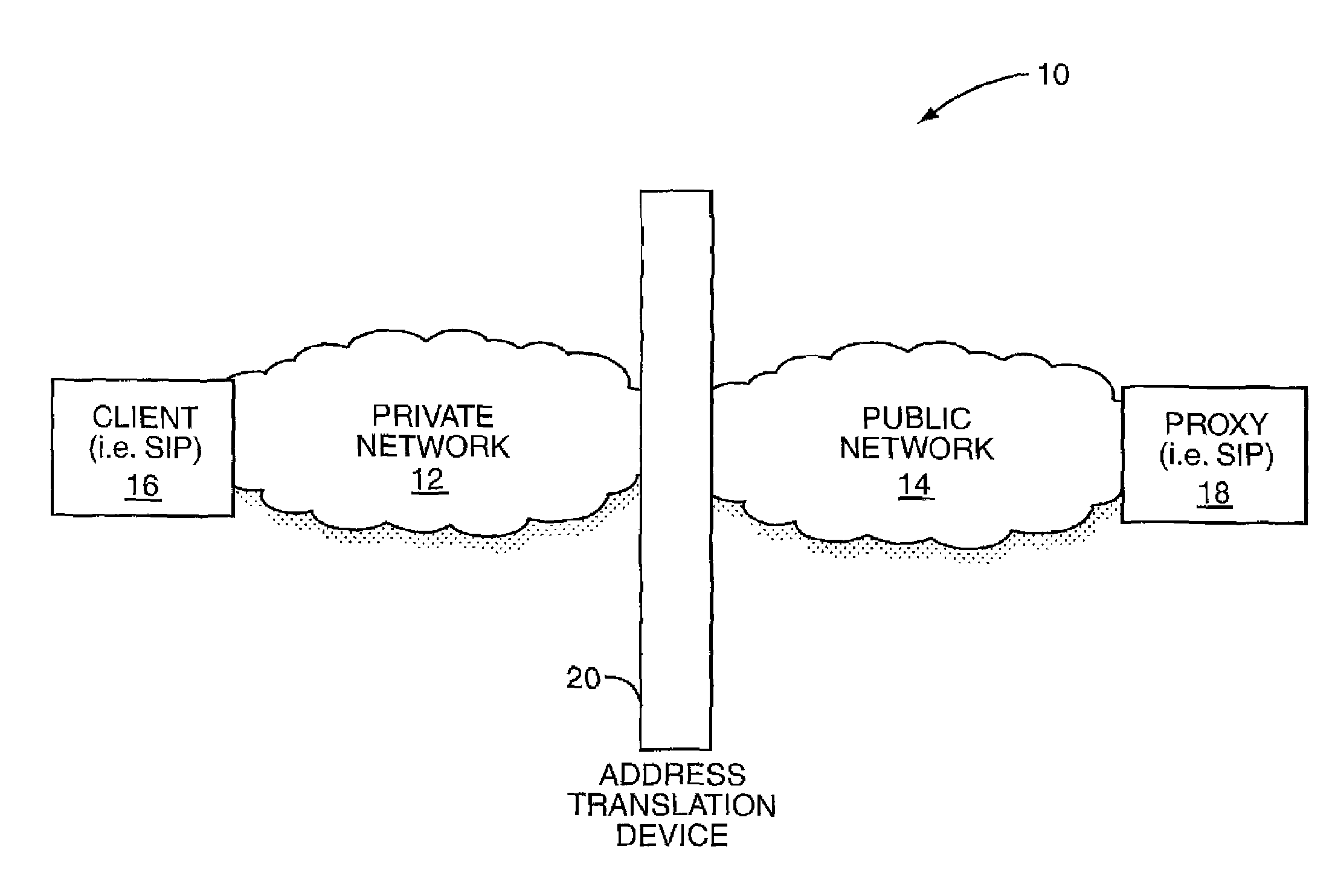
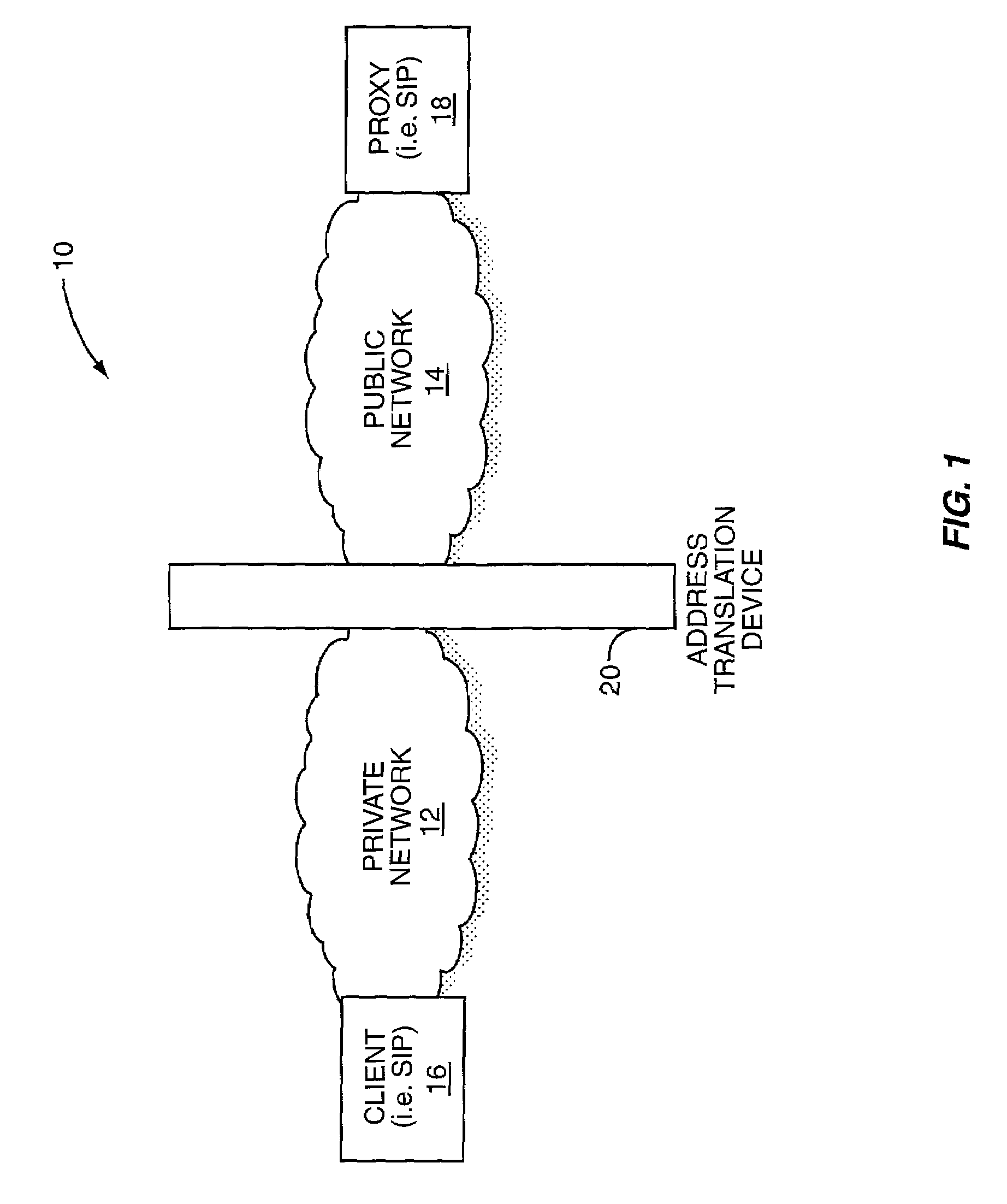
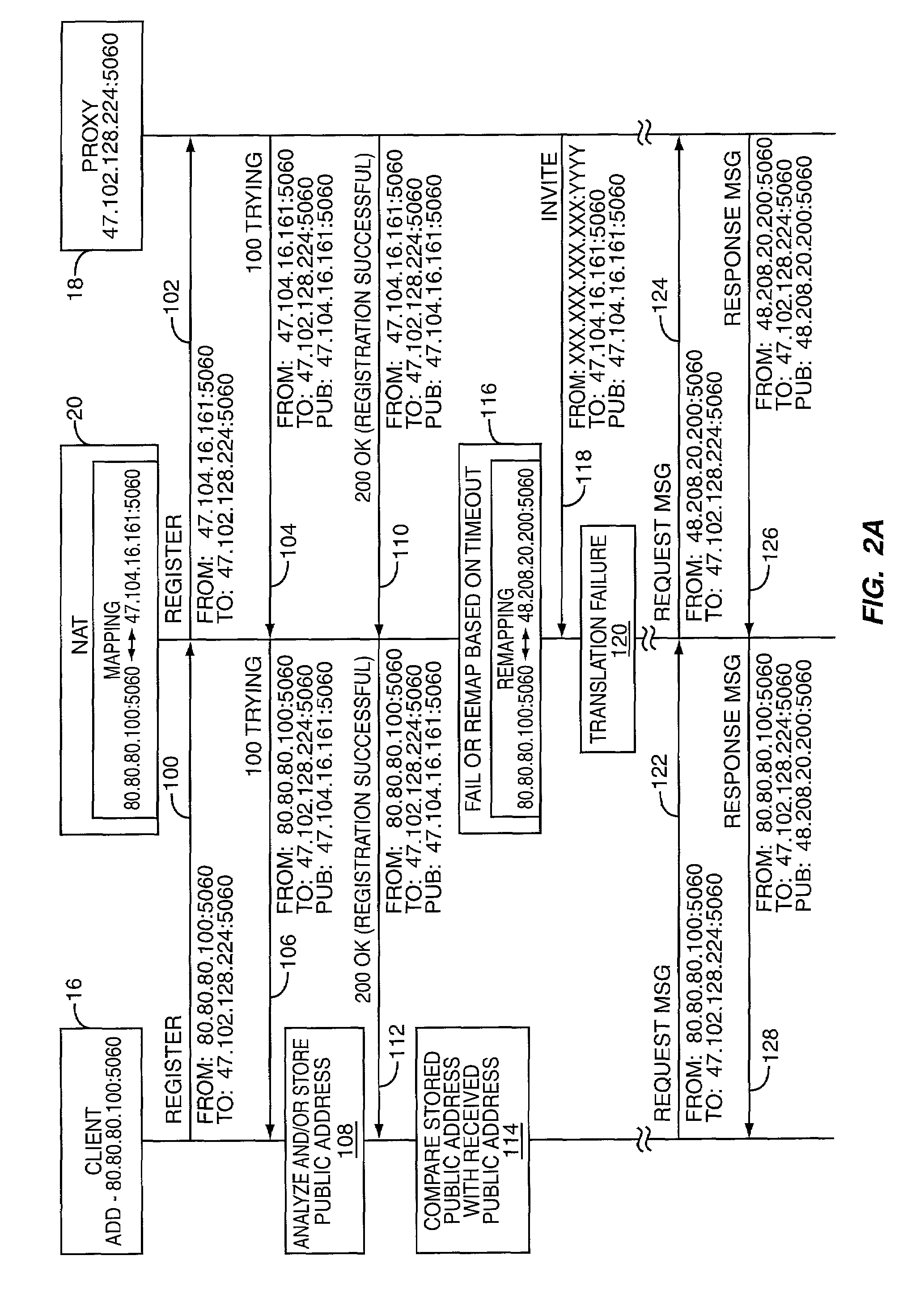
ActiveUS6993595B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate addressPublic network
The present invention allows a client on a private network to determine changes in a public address, which is provided by an address translation device and used for communications on a public network. The client will receive messages over the private network from the public network via the address translation device. In the message, a copy of the public address is placed in a portion of the message. When the address translation device modifies the message such that the client's private address is used for delivery of the message to the client, the copy of the public address remains in the message. Upon receipt, the client will analyze the message to identify the public address and compare the public address with a previously known public address. If the public address provided in the message is different from the stored public address, the client can recognize that it has changed.
Owner:GENBAND US LLC
Temporary unique private address
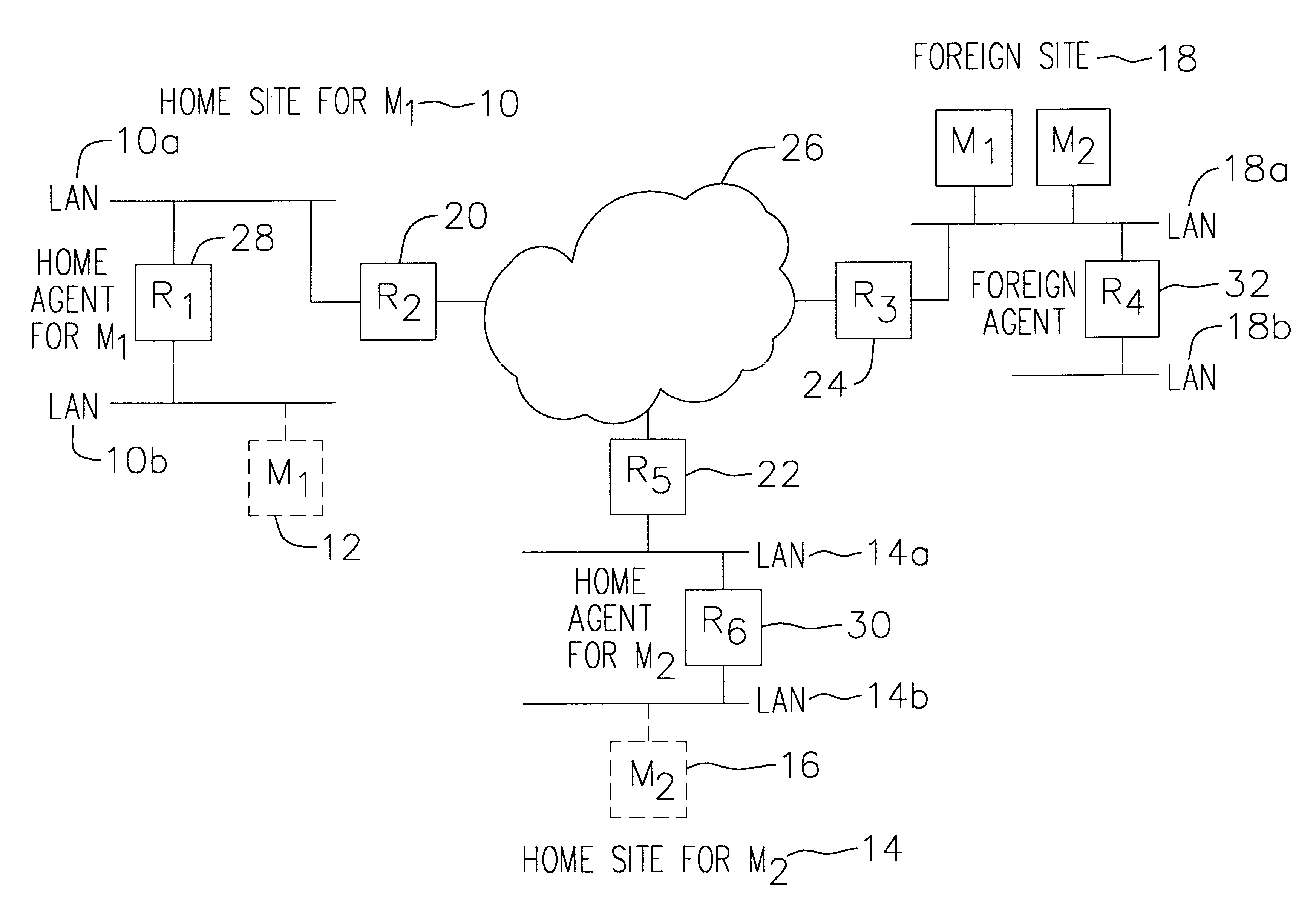
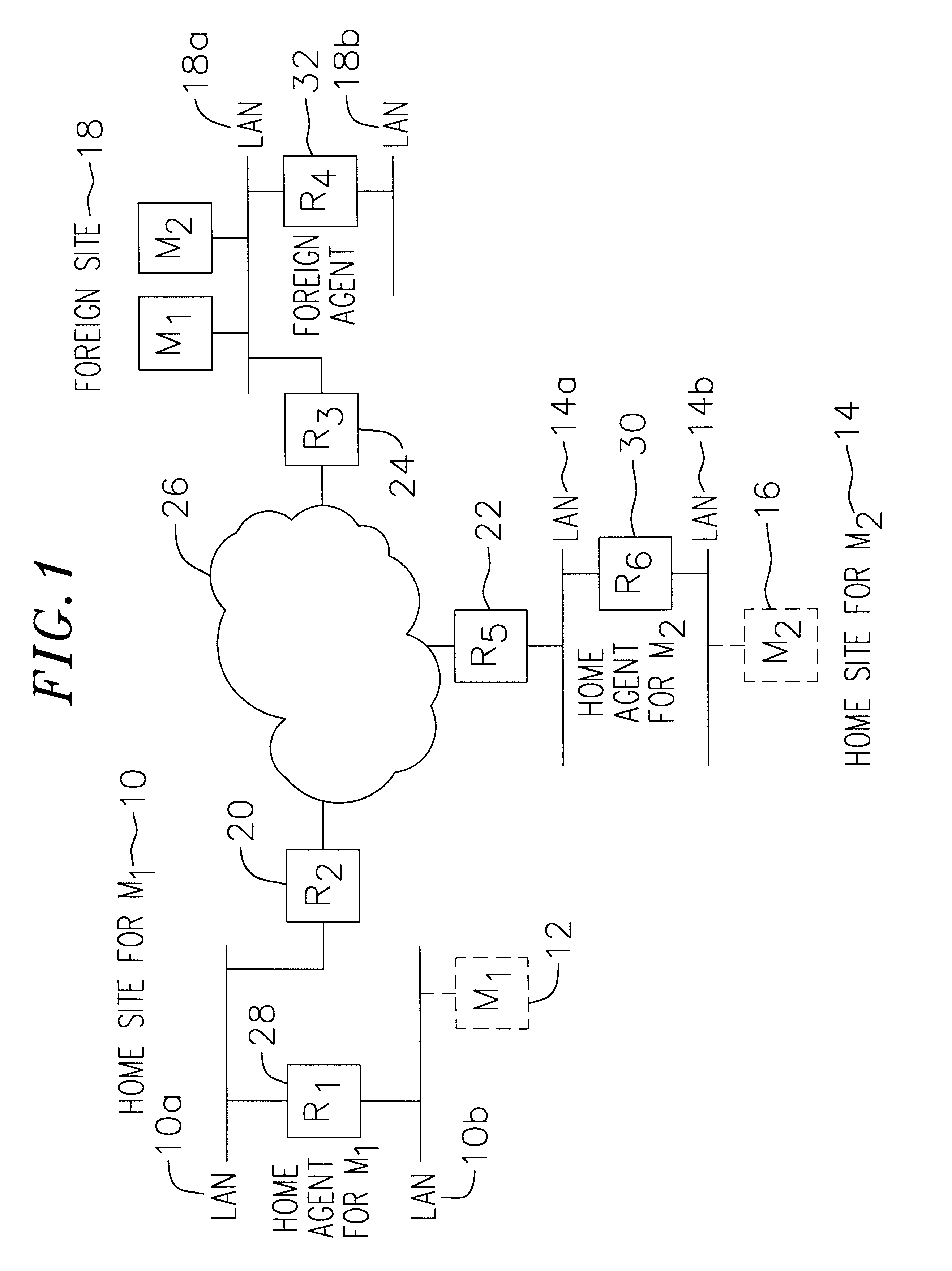
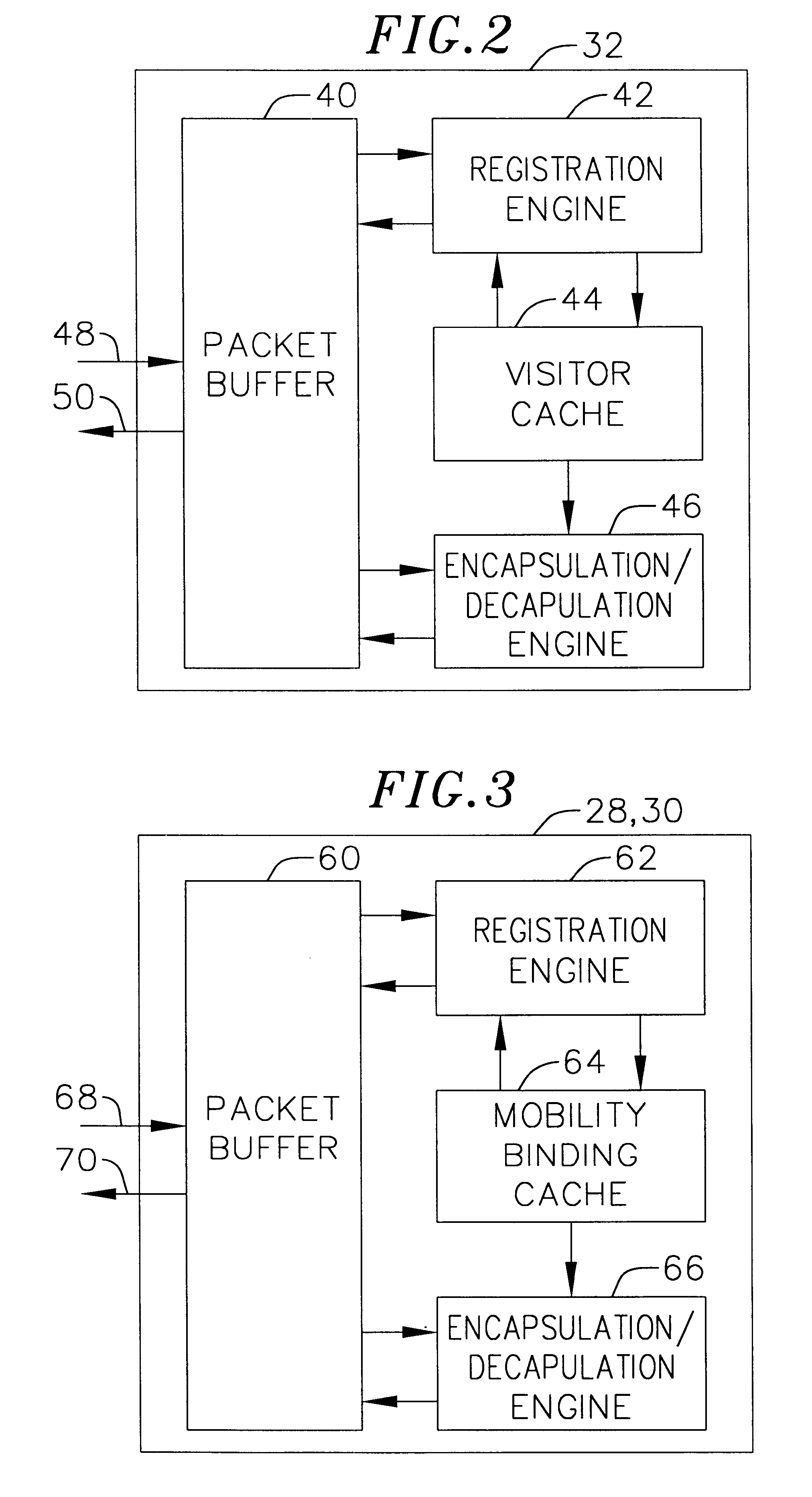
InactiveUS6856624B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPrivate IPTelecommunications
A communication network providing mobile IP services to mobile nodes sharing the same private IP address. A mobile node visits a foreign network from its home network and transmits a registration request including its private IP address to a foreign agent on the foreign network. If the foreign agent determines that another mobile node with a valid registration shares the same private IP address, the foreign agent requests the mobile node to use a temporary address. The temporary address is sent along with the registration request to the registering mobile node's home agent. When the home agent receives a packet addressed to its mobile node, it creates two tunnels. An outer tunnel is created using a care-of address associated with the foreign agent. An inner tunnel is created using the temporary address assigned to mobile node. The packet is then forwarded via the two tunnels. Upon receipt of the tunneled packet by the foreign agent, it de-tunnels the outer tunnel to uncover the inner tunnel, and forwards the inner tunnel to the mobile node. The mobile node de-tunnels the inner tunnel to recover the original packet.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
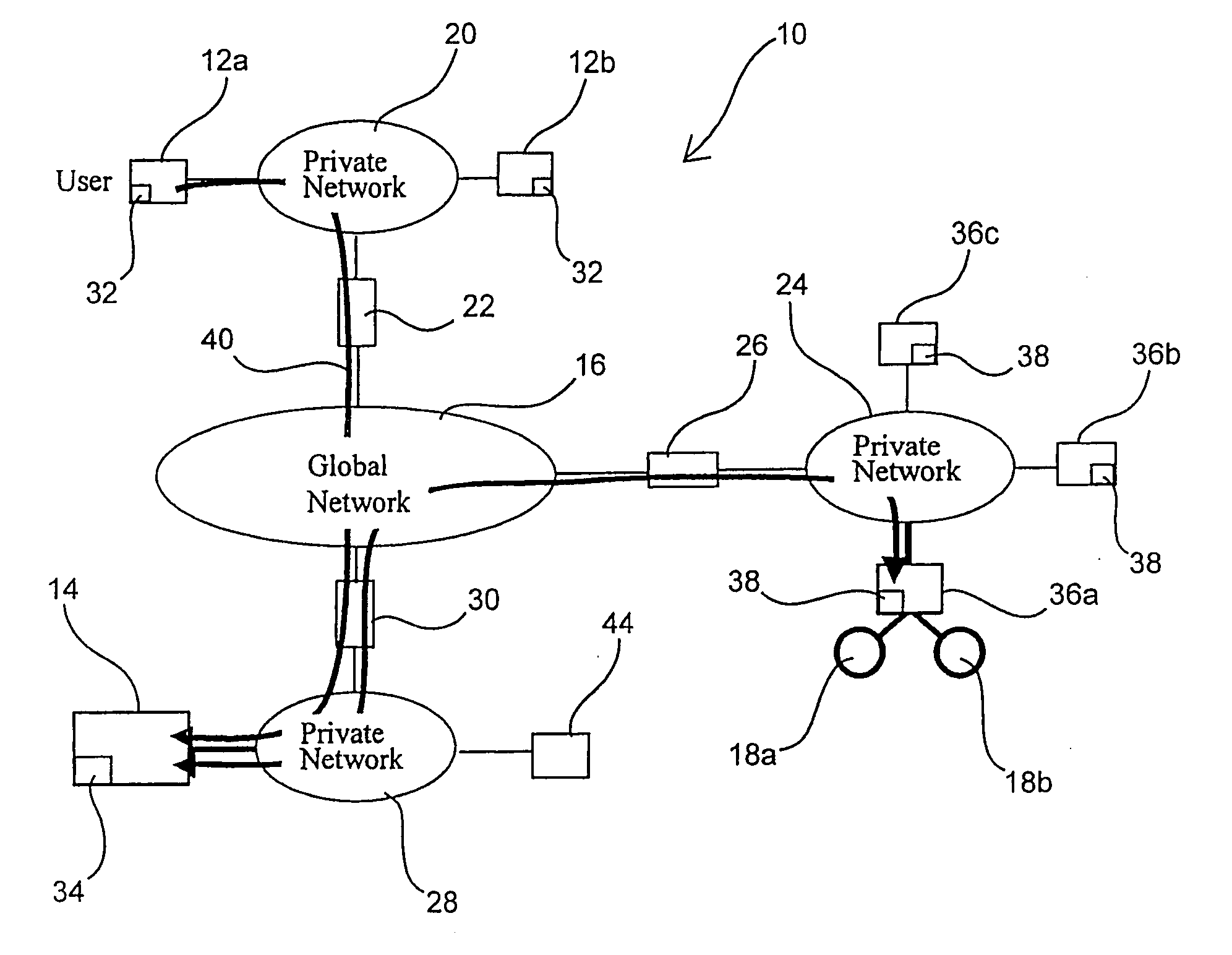
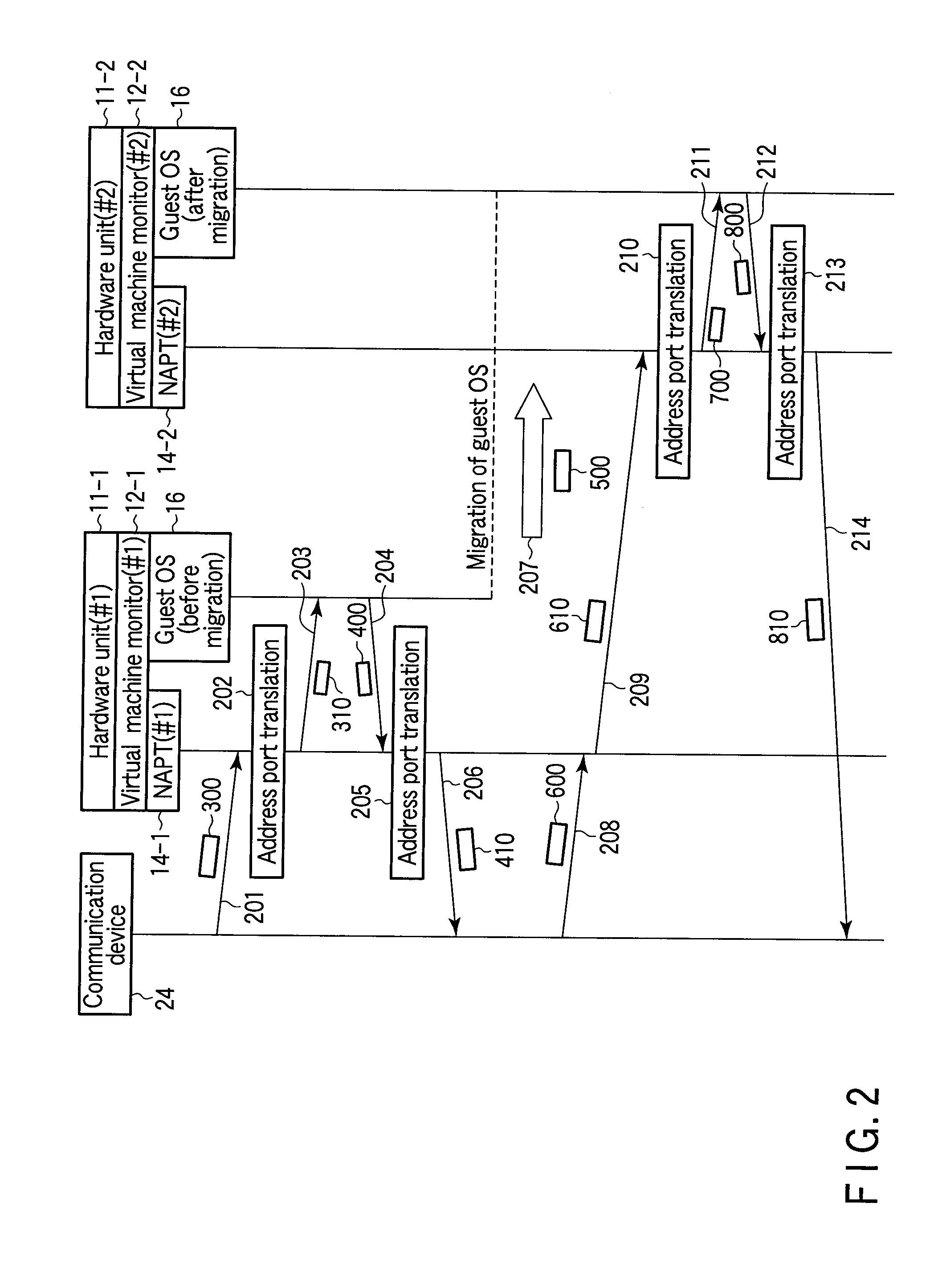
Method of controlling the communication between a machine using private addresses and a communication device connected to a global network
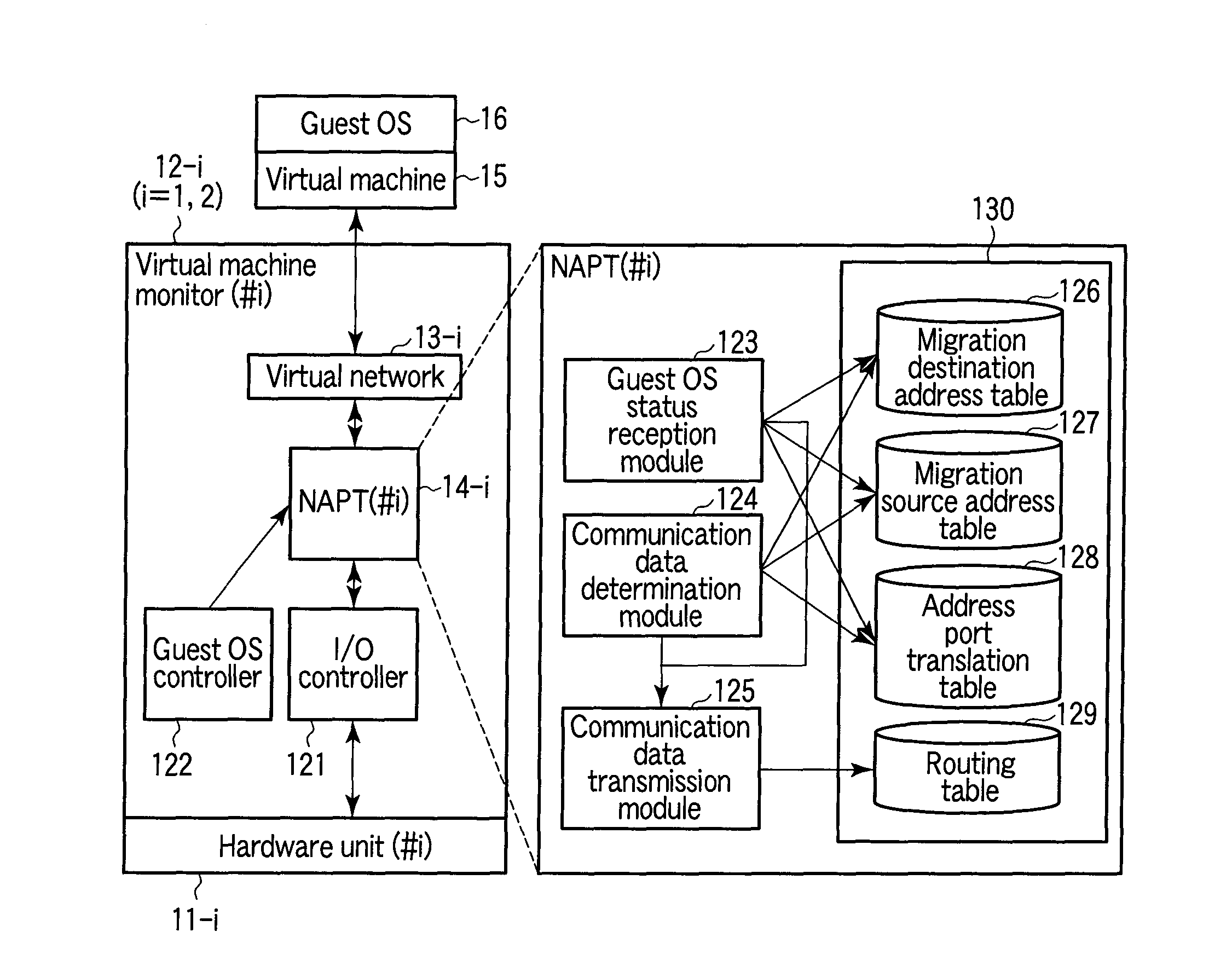
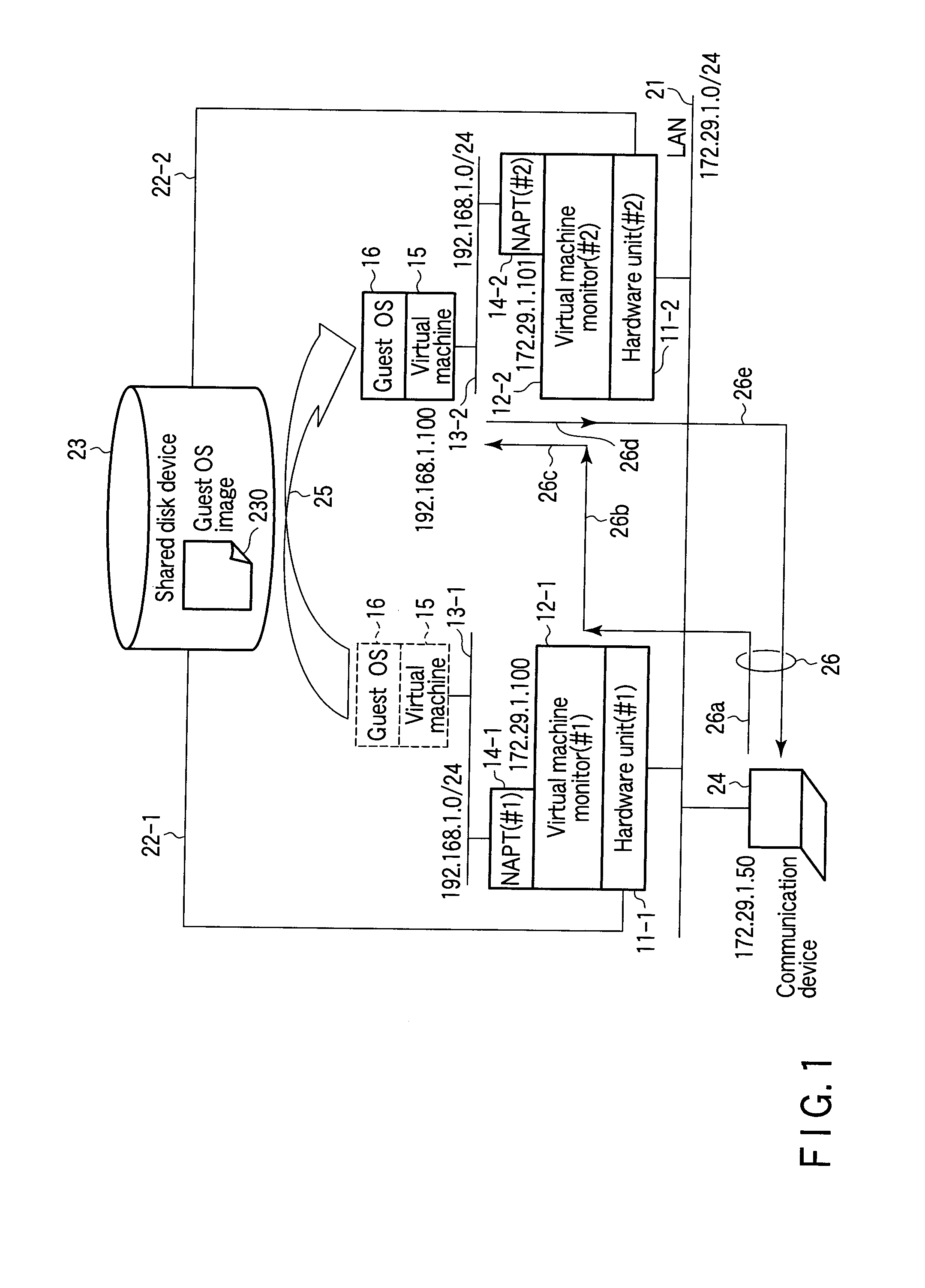
InactiveUS20100115080A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address port translationPrivate address
According to one embodiment, when having received first communication data addressed to a machine migrated to a second network address port translation module, a first network address port translation module translates a destination network address in the first communication data into a global address of the second network address port translation module. The first network address port translation module transfers the translated first communication data as second communication data to the second network address port translation module. When having received the second communication data transferred by the first network address port translation module, the second network address port translation module transmits third communication data addressed to the machine corresponding to the second communication data to the machine.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
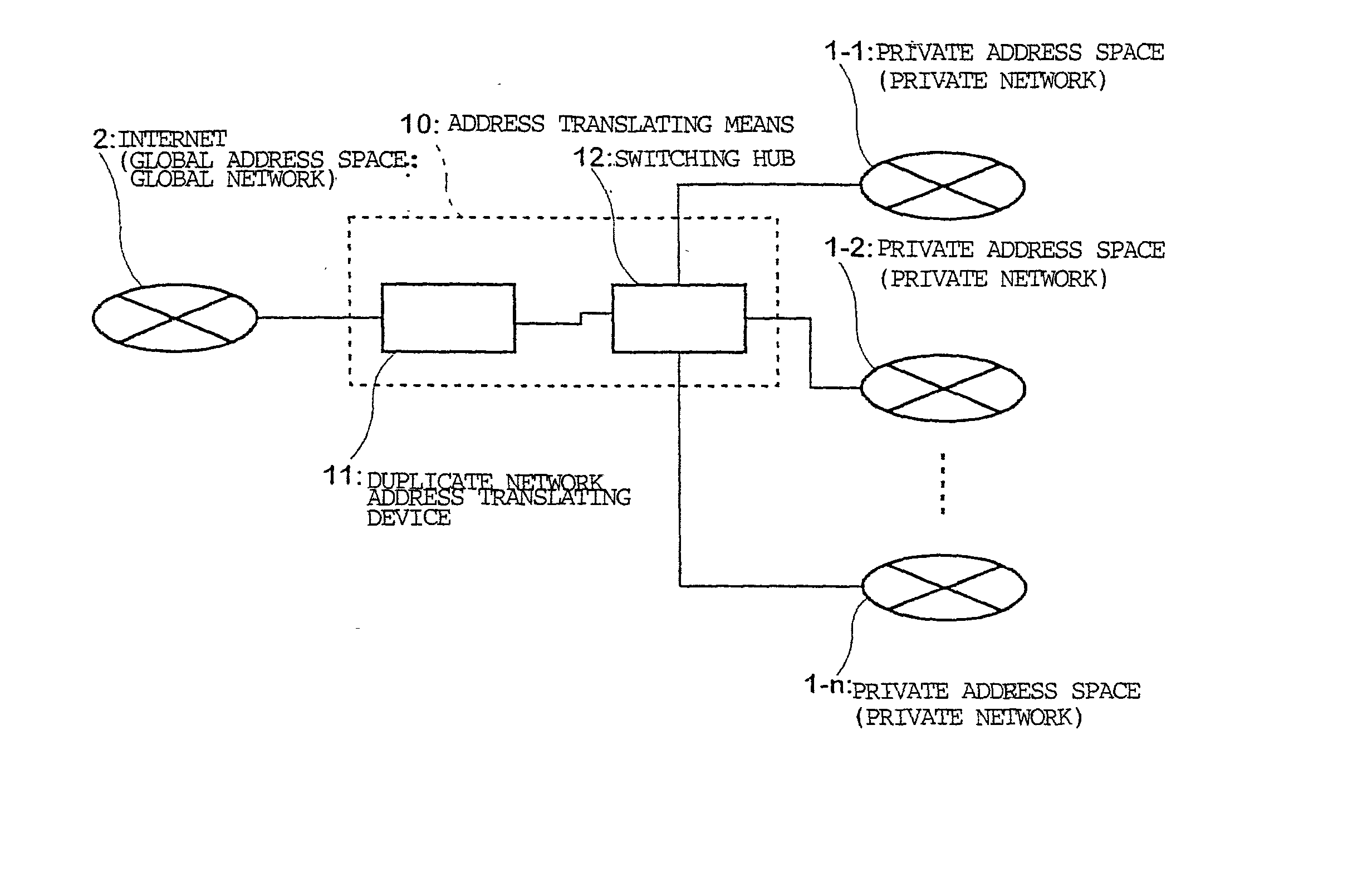
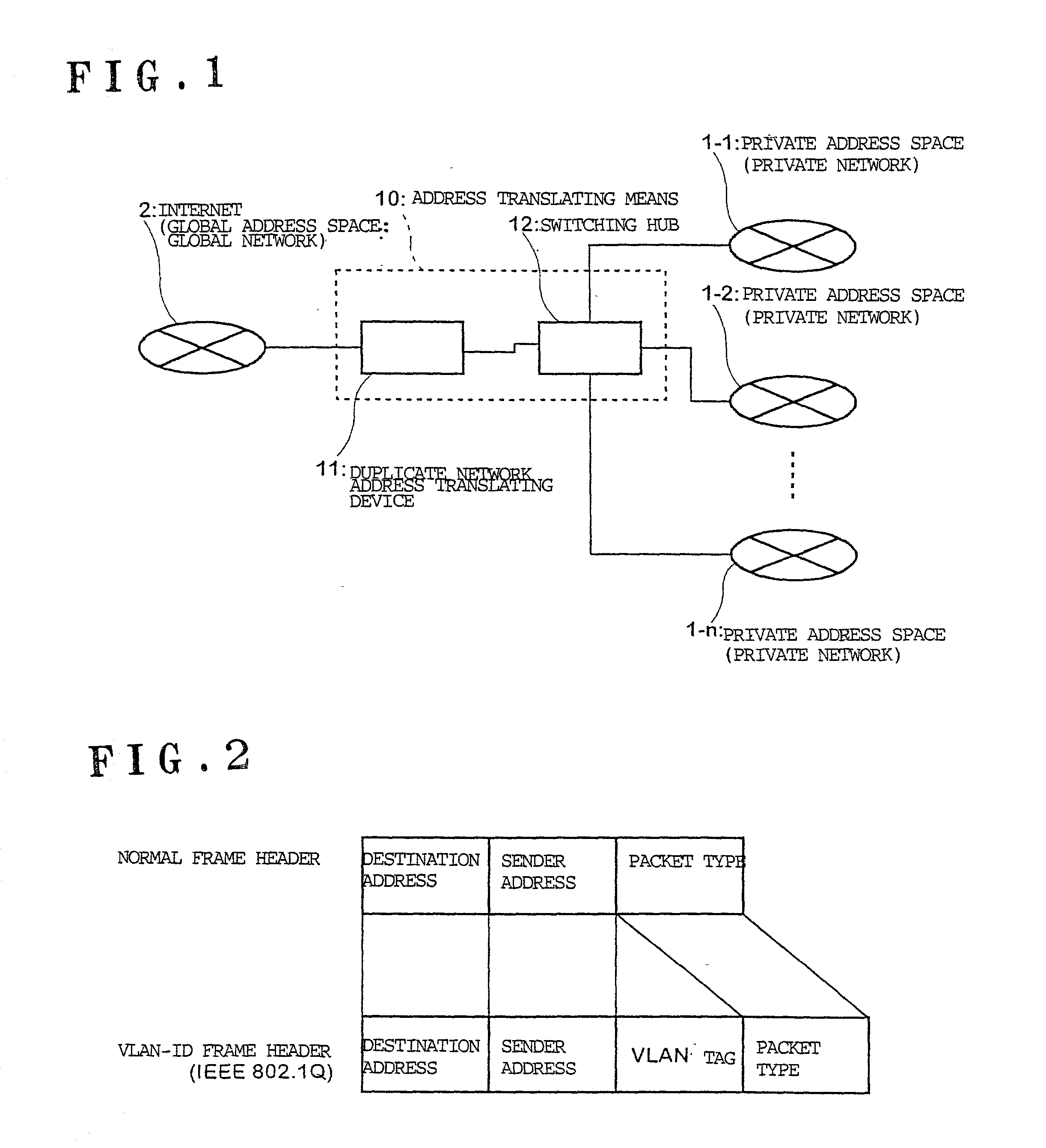
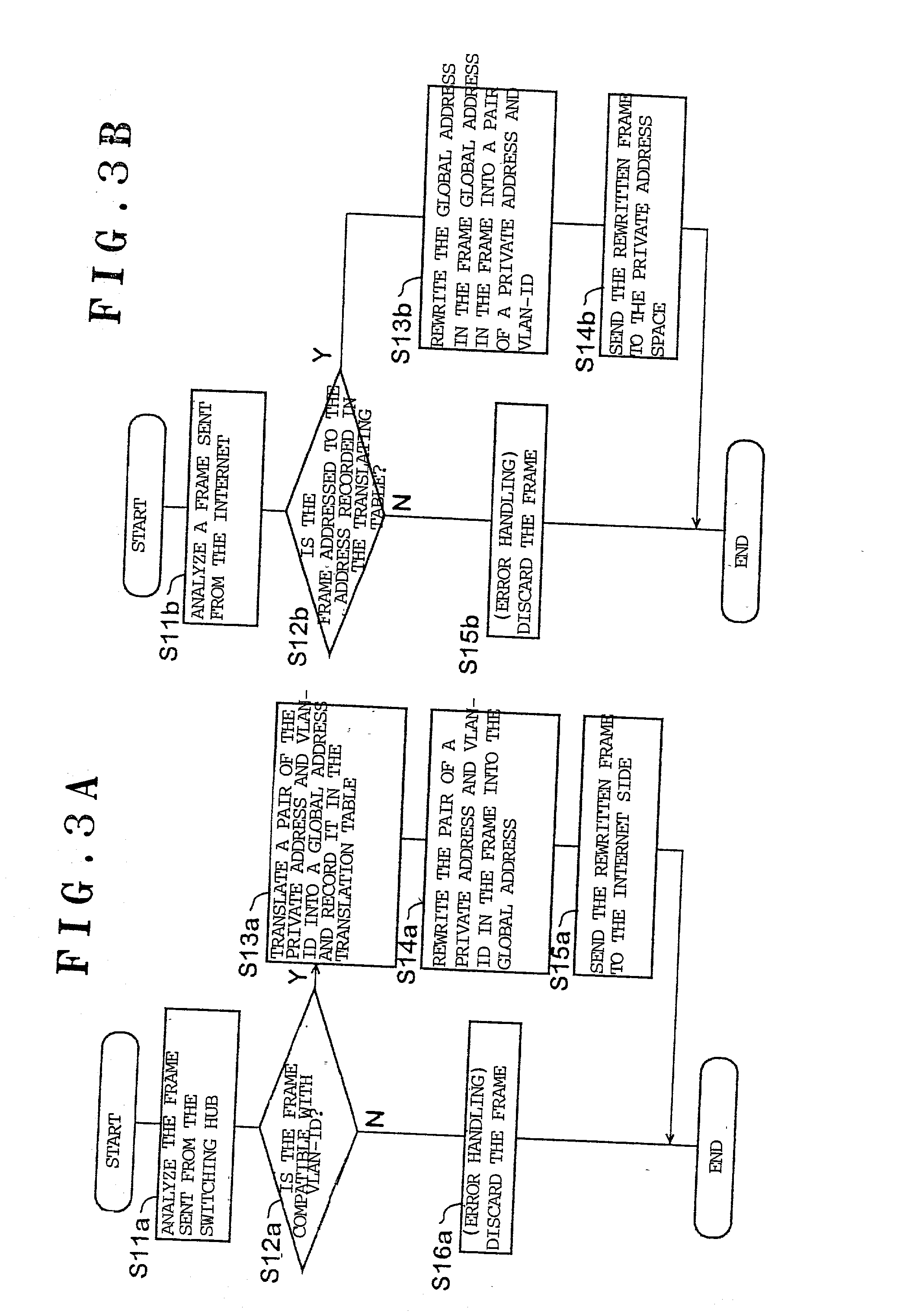
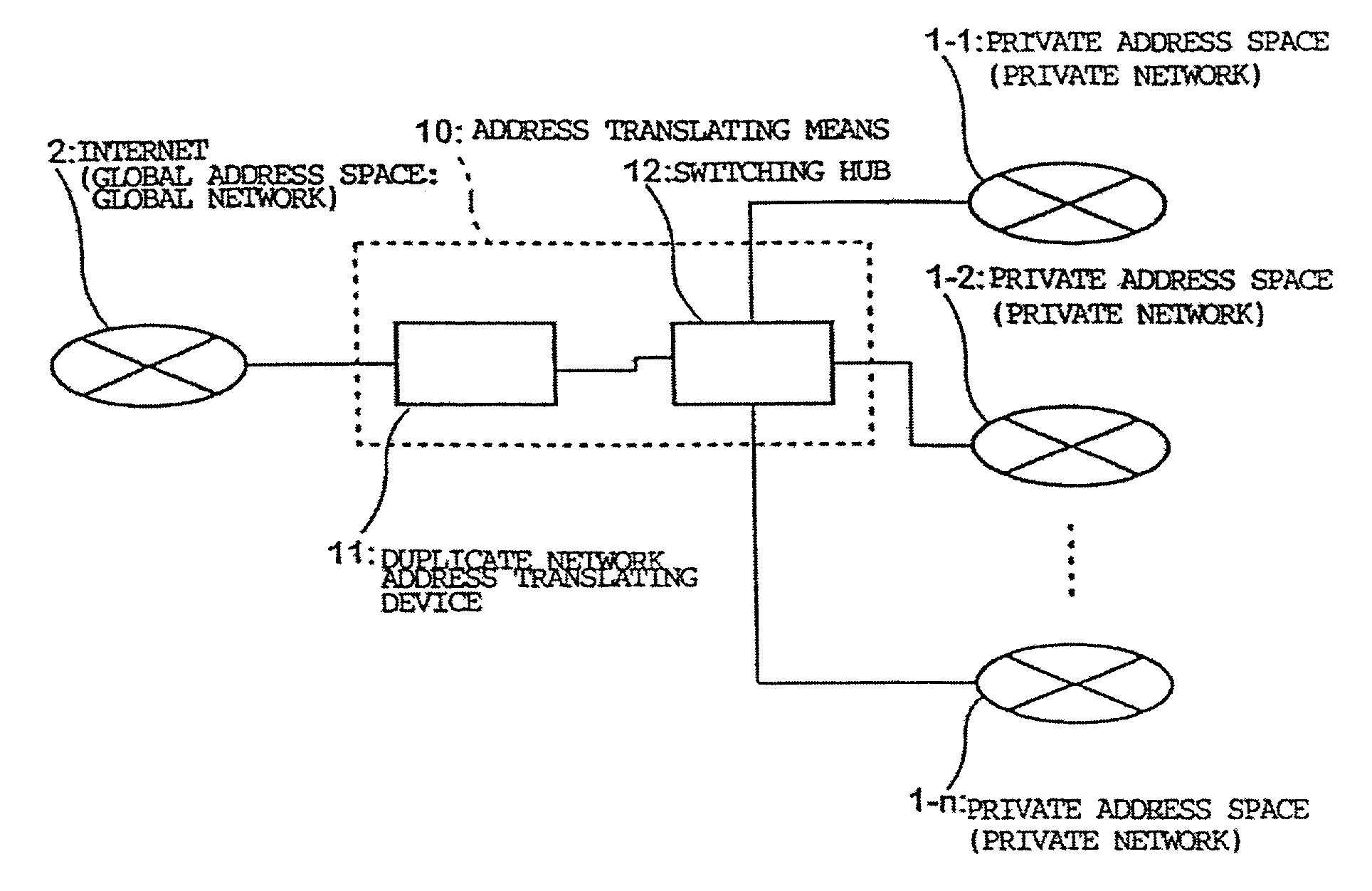
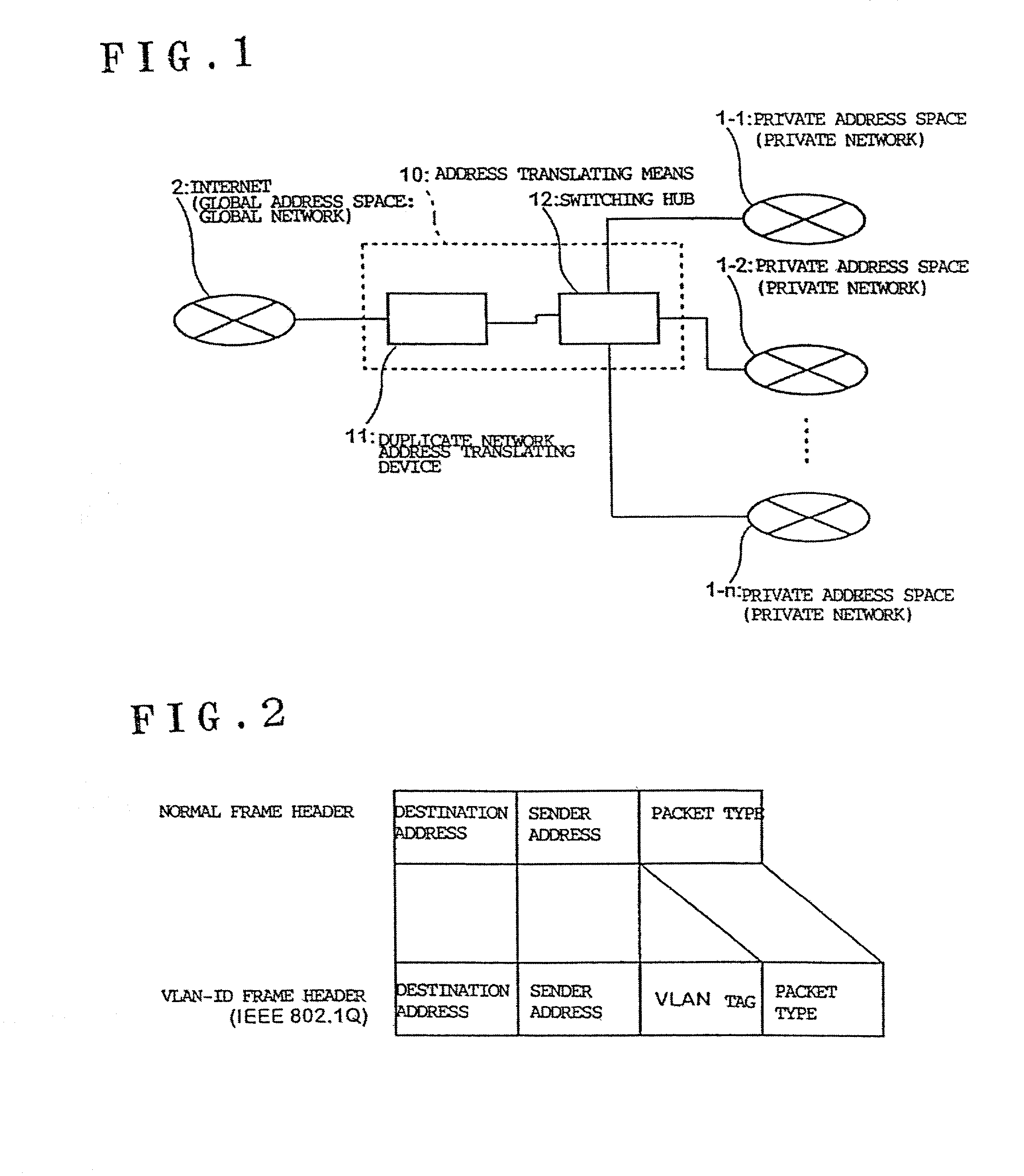
Duplicate private address translating system and duplicate address network system
ActiveUS20020087721A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationGlobal address spaceRouting table
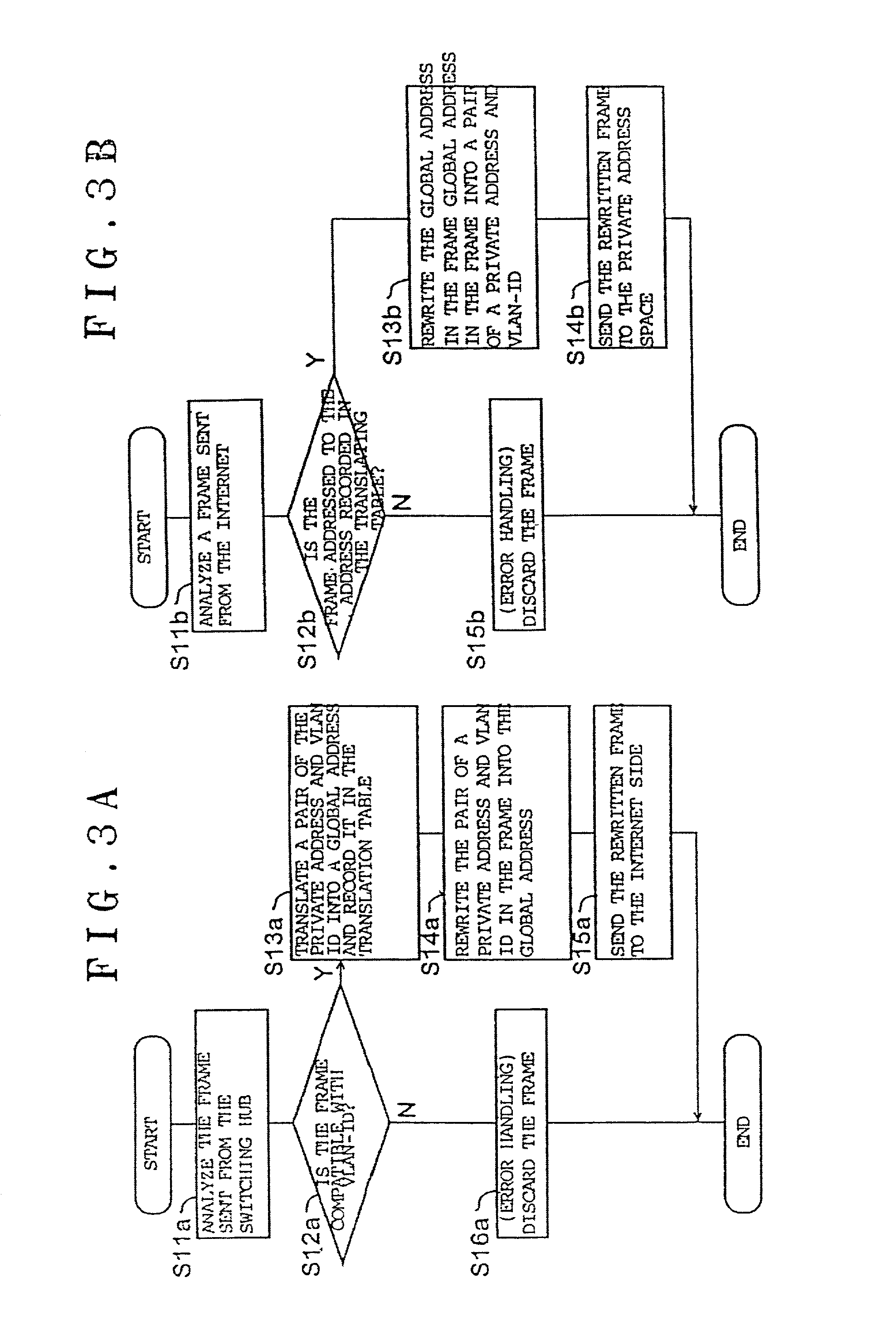
A plurality of private address spaces where private addresses may possibly overlap are connected with a global address space. Respective private address spaces possess VLAN-IDs as identification information for VLANs. When connecting the respective private address spaces with the Internet, a duplicate network address translating device performs, with VLAN-ID and the private address of the respective private address spaces in pairs, mutual translation between the private address and global address of the Internet. According to another aspect of the invention, a duplicate addresses-handling server is provided with a routing table which shows the relationship between virtual interfaces corresponding to VLAN-IDs and addresses of the respective private address spaces. A server portion of the duplicate addresses-handling server records, if a request is made from apparatuses of a private address space, the request and VLAN-ID, refers to, if making a response thereto, the routing table, selects a virtual interface which corresponds to the address of the response receiver, and makes a response. A virtual interface processing portion gives an applicable VLAN-ID and carries out an output to a switching hub.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
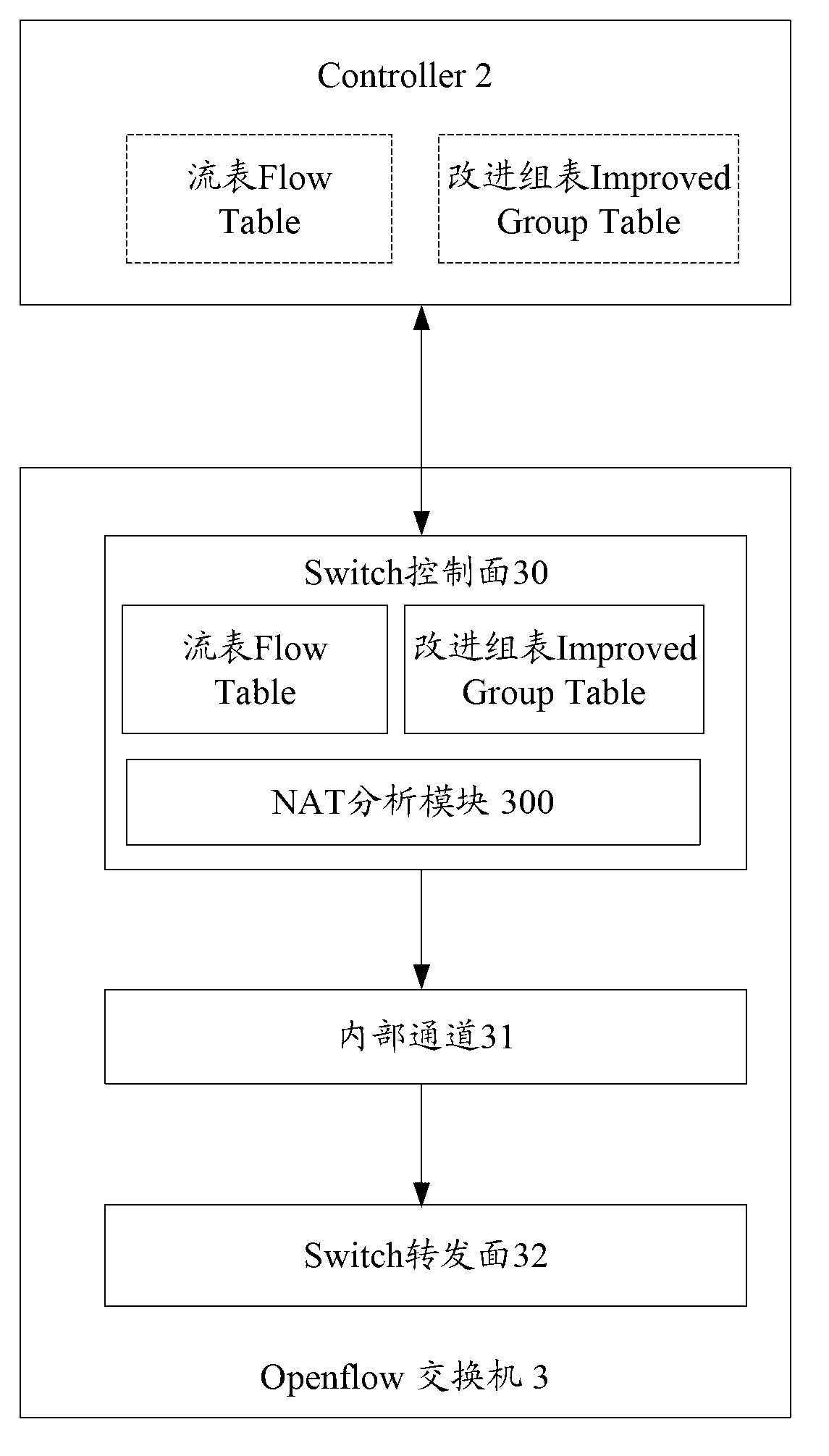
Network address translation (NAT) implementing system, method and openflow switch
ActiveCN103067534AReduce forwarding delayImprove transmission efficiencyHybrid transportNetwork address port translationOpenFlow
The invention discloses a network address translation (NAT) implementing system which comprises a controller and an openflow switch, wherein the controller issues a flow table and an improved group table, the openflow switch receives the flow table and the improved group table, a data package which needs to conduct address translation is matched according to a matching rule of the address translation recorded by the flow table, translation between a private address and a public internet protocol (IP) address is conducted according to a rule of address translation recorded by the improved group table, and the data package is transmitted out through an address which is translated. The invention further discloses an NAT implementing method and the openflow switch. According to the NAT implementing system, only the flow table and the improved group table are transmitted to the openflow switch once, frequent intersection between the openflow switch and the controller is not required, time delay of transmission of the data package is shortened, and transmission efficiency of a network is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Technique for enabling multiple virtual filers on a single filer to participate in multiple address spaces with overlapping network addresses
InactiveUS6895429B2Improve performanceDigital computer detailsSecuring communicationOperational systemRouting table
A technique enables a server, such as a filer, configured with a plurality of virtual servers, such as virtual filers (vfilers), to participate in a plurality of private network address spaces having potentially overlapping network addresses. The technique also enables selection of an appropriate vfiler to service requests within a private address space in a manner that is secure and distinct from other private address spaces supported by the filer. An IPspace refers to each distinct address space in which the filer and its storage operating system participate. An IPspace identifier is applied to translation procedures that enable the selection of a correct vfiler for processing an incoming request and an appropriate routing table for processing an outgoing request.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
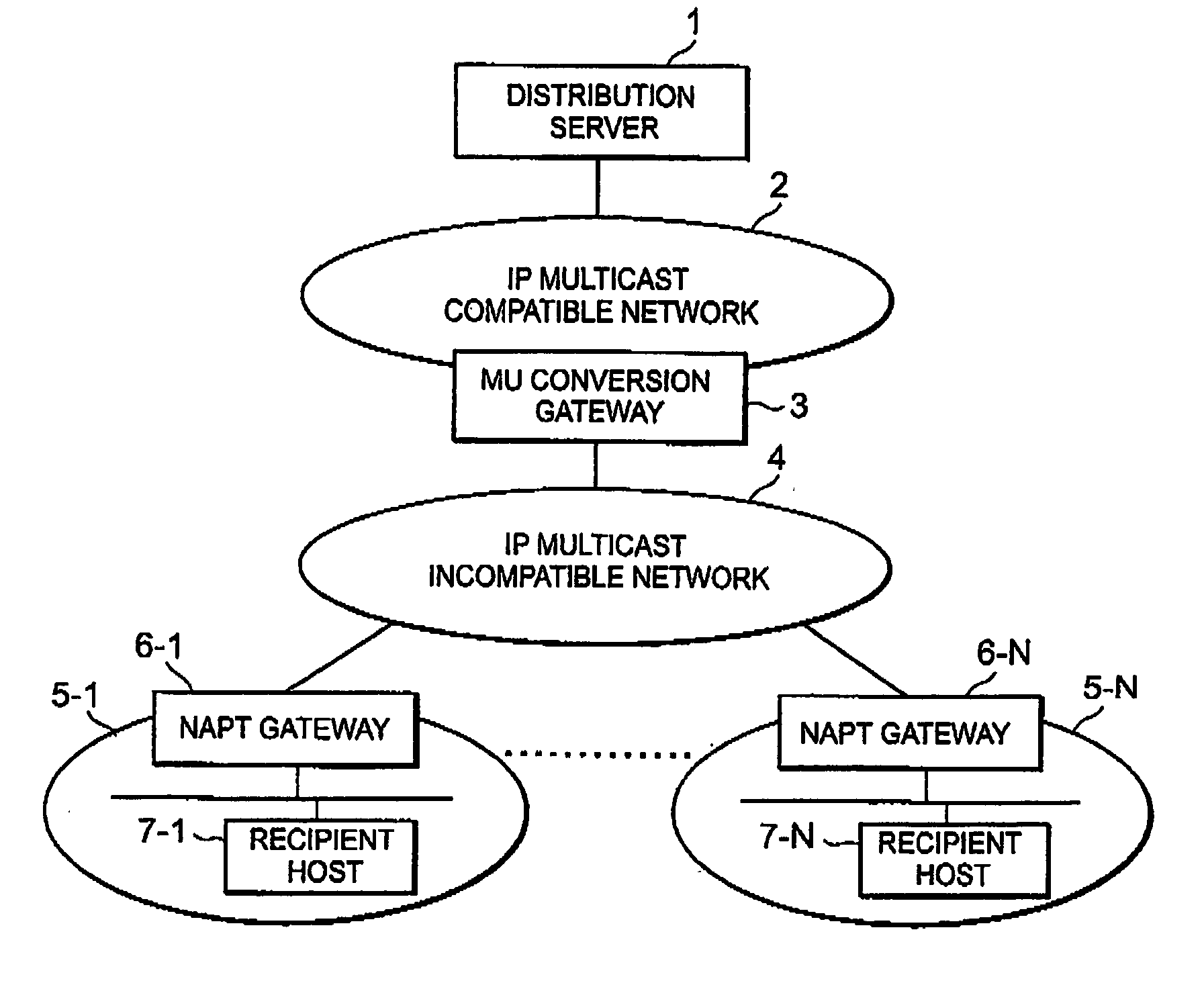
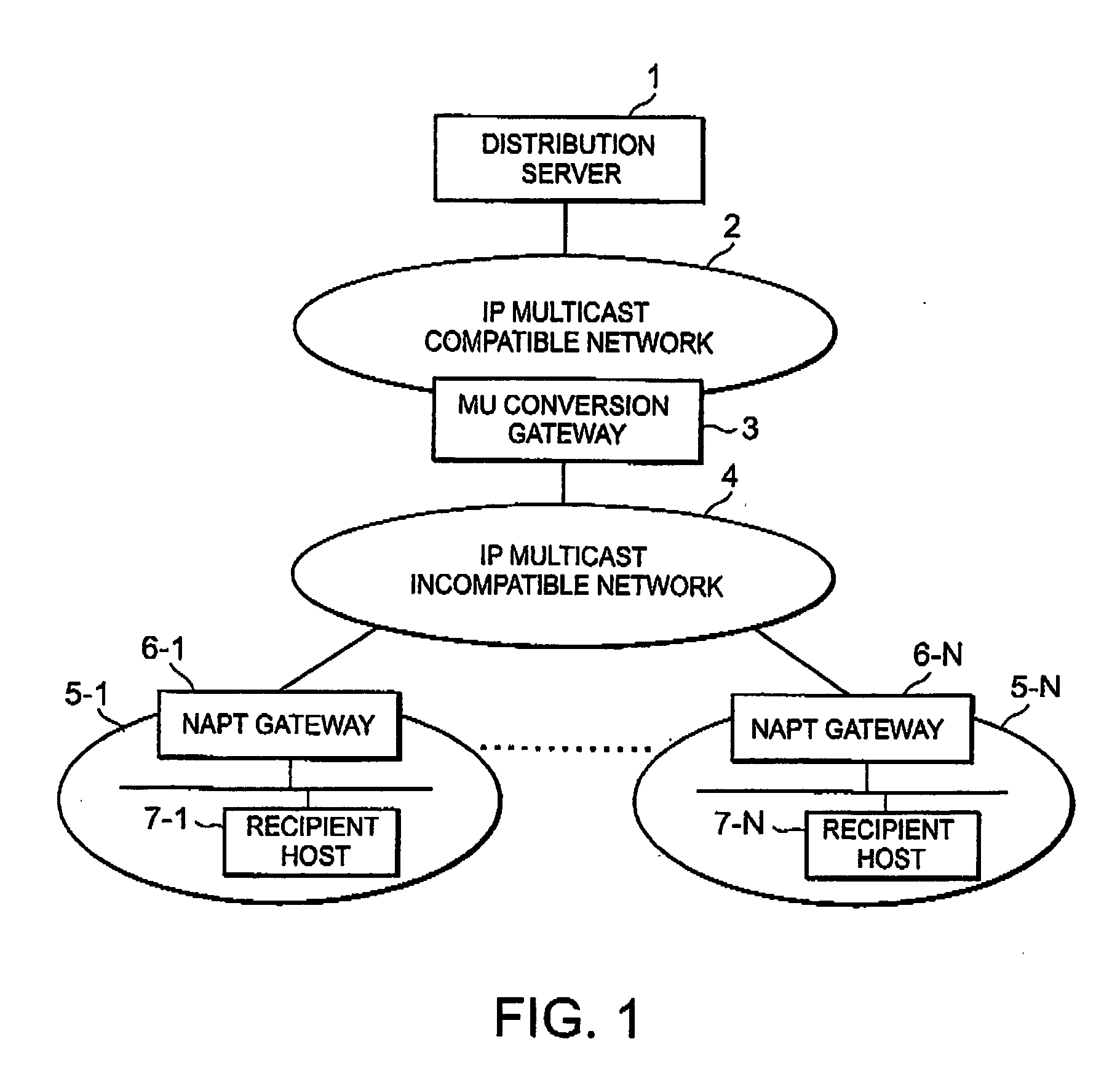
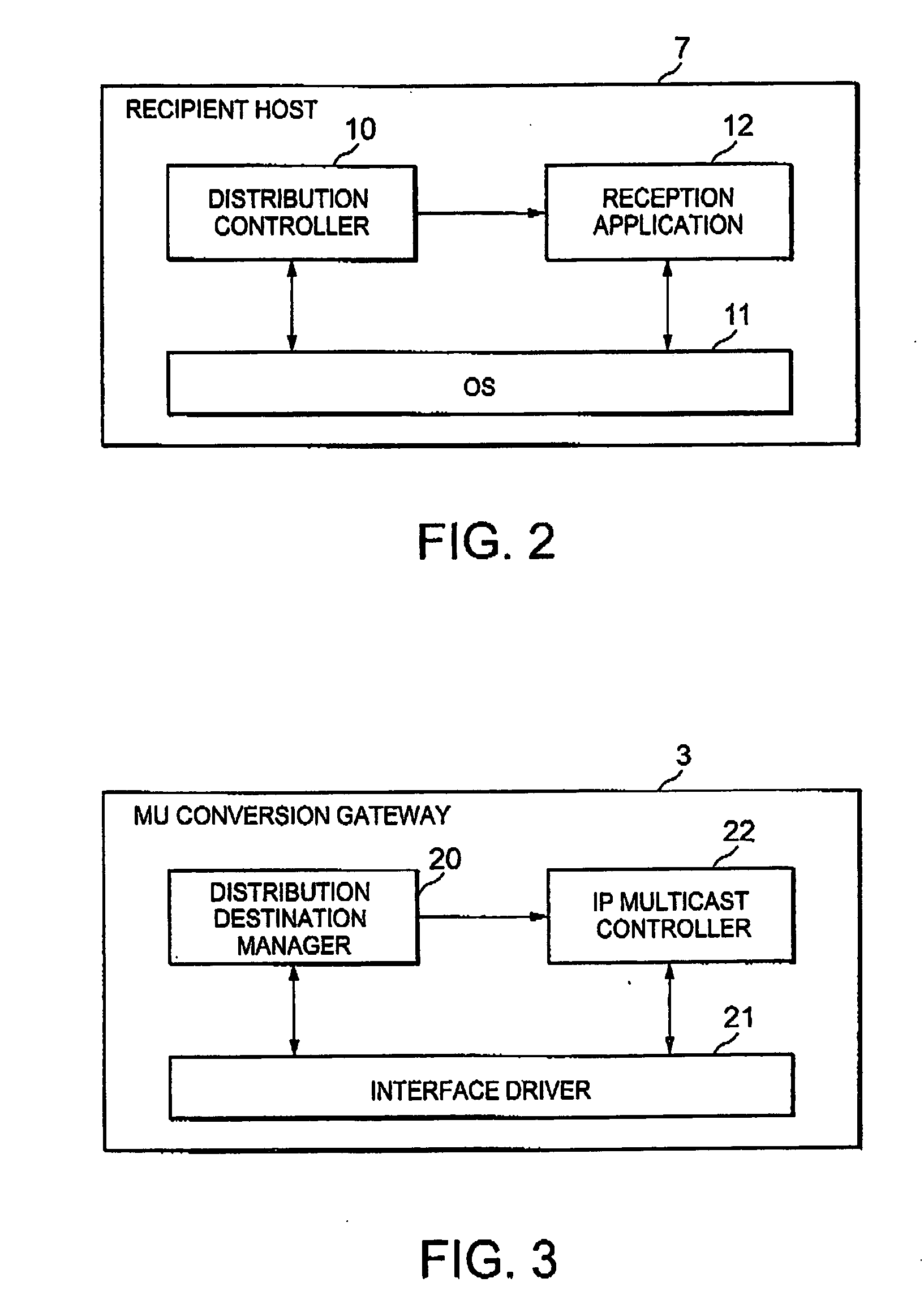
IP multicast distribution system, streaming data distribution system and program therefor
InactiveUS20050002395A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexStreaming dataData pack
Disclosed is an IP multicast distribution system that can convert IP multicast data into packets for individual unicast addresses and can transmit the data to a recipient host in a private address space. According to the present invention, before accepting streaming distribution from the distribution server, a recipient host transmits, to an NAPT gateway, a distribution request for which the IP address of an MU conversion gateway is designated as a destination address, a source port number is designated a port number, determined in advance by the distribution server, in order to enable the reception of data by a reception application provided for the recipient host, and a destination port number is designated as an acceptance port number for the MU conversion gateway. Upon receiving the distribution request, the NAPT gateway designates a source IP address as the global IP address for the NAPT gateway and the source port number as the predetermined port number, and transfers data to the MU conversion gateway.
Owner:NEC CORP
Network system, virtual private connection forming method, static NAT forming device, reverse proxy server and virtual connection control device
InactiveUS20120185563A1Multiple digital computer combinationsAutomatic exchangesElectrical conductorReverse proxy
To provide a new network system, a new network connection device and a new reverse proxy device enabling to solve the problems of the conventional VPN and achieve strong security and flexible operability by adding extremely light software and hardware.After a static NAT forming device has performed authentication with a conductor through a control session, if a terminal makes a connection request to a server in a network existing before a reverse proxy server, the static NAT forming device and a stepping node will set a static NAT, and the reverse proxy server will set a reverse proxy, so that a data session will be formed between the terminal and the server. By configuring a network system in such a manner, it is possible to pass through the firewall to achieve a connection from the terminal to the server in a virtual connection state without causing private address collision.
Owner:SPRINGSOFT
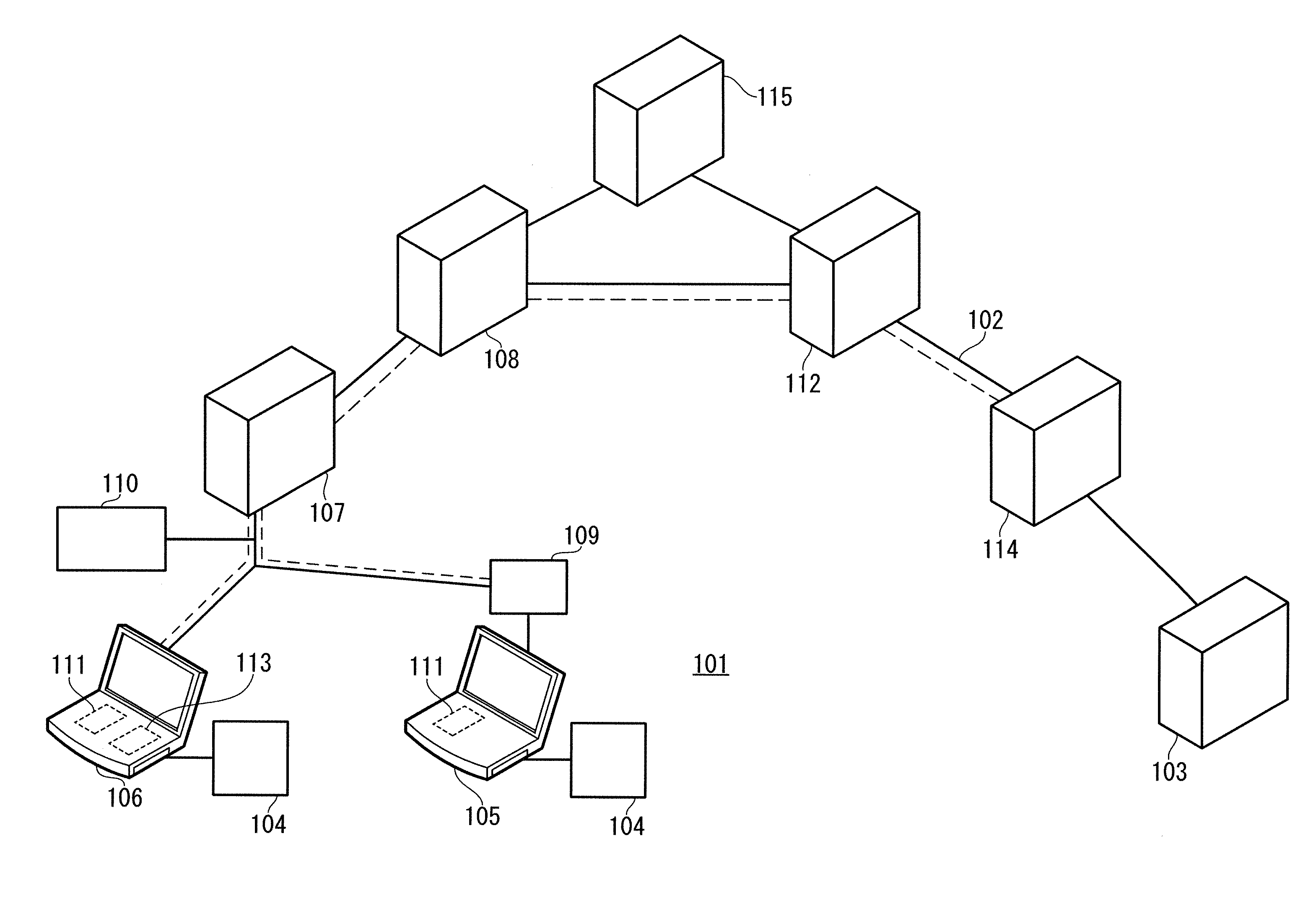
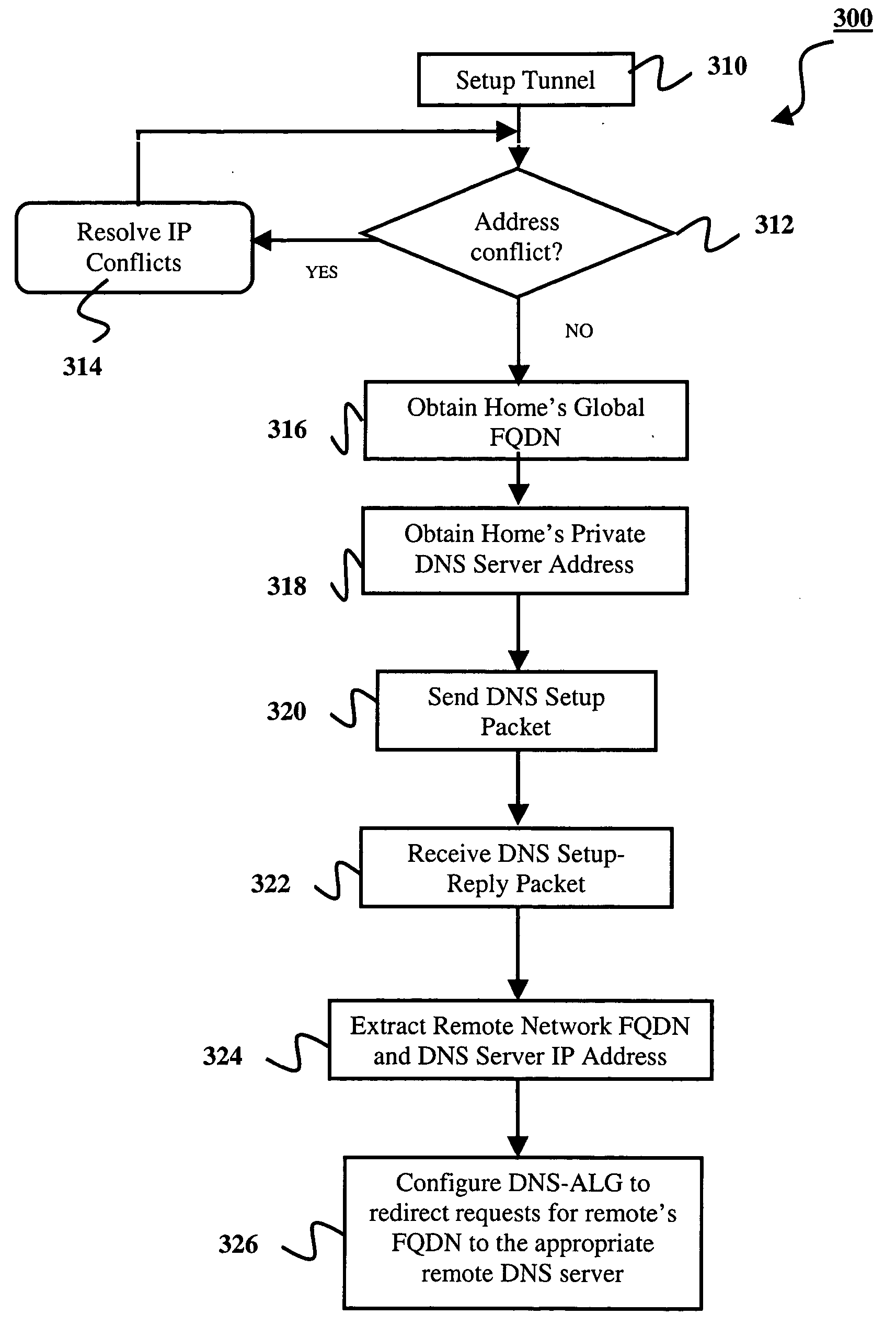
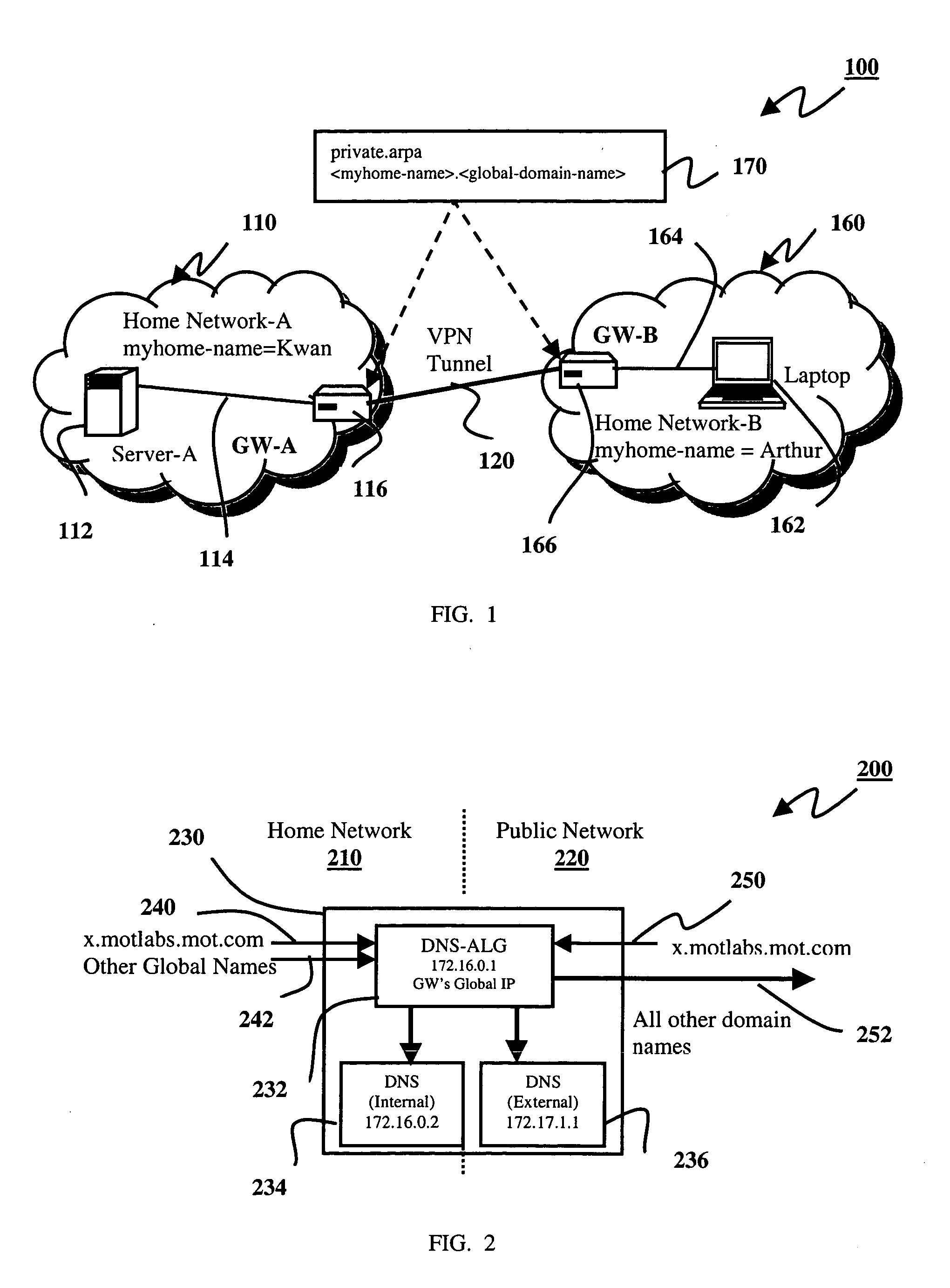
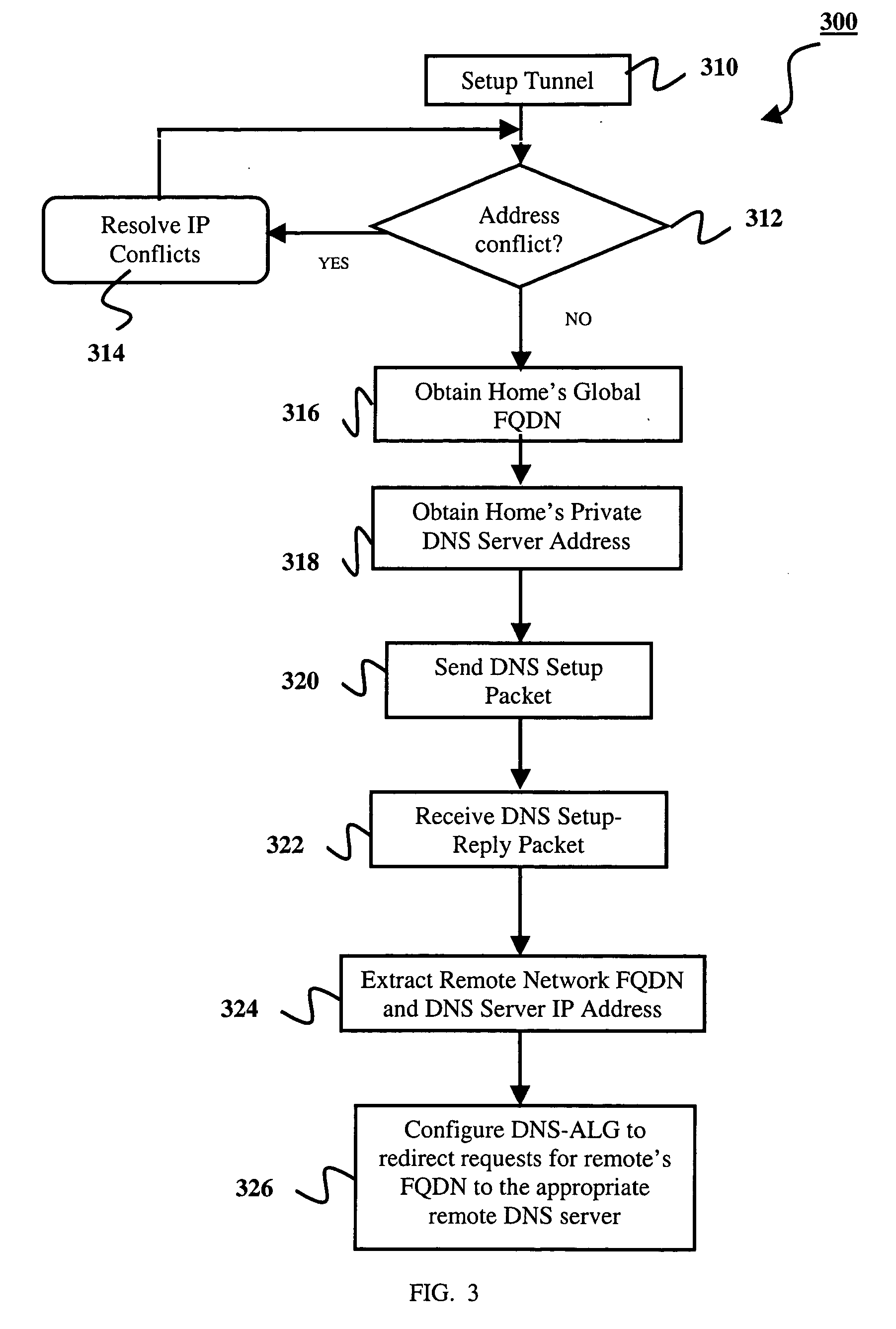
Setting up a name resolution system for home-to-home communications
InactiveUS20050066041A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionPrivate addressA domain
Methods, systems, and gateways are disclosed for automatically setting up a redirector of domain name system (DNS) name requests. A DNS setup packet is transmitted to a remote gateway via a tunnel of a virtual private network (VPN). The setup packet comprises a global name of a home network and a private address of a DNS server in the home network. A DNS setup reply packet is received from the remote gateway via the tunnel. The reply packet comprises a global name of another home network and a private address of a DNS server in the other home network. An application level gateway of the DNS server (DNS-ALG) in the home network is configured dependent upon the DNS setup reply packet to redirect DNS name requests for the global name of the other network to the DNS server in the other network. Methods, systems, and gateways are also disclosed for resolving a domain name request in a DNS.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for application-independent end-to-end security in shared-link access networks
InactiveUS6963982B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeEnd to end security
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for a mobile device to address a private home agent having a public address and a private address
InactiveUS6978317B2Substation remote connection/disconnectionData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsPrivate address
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
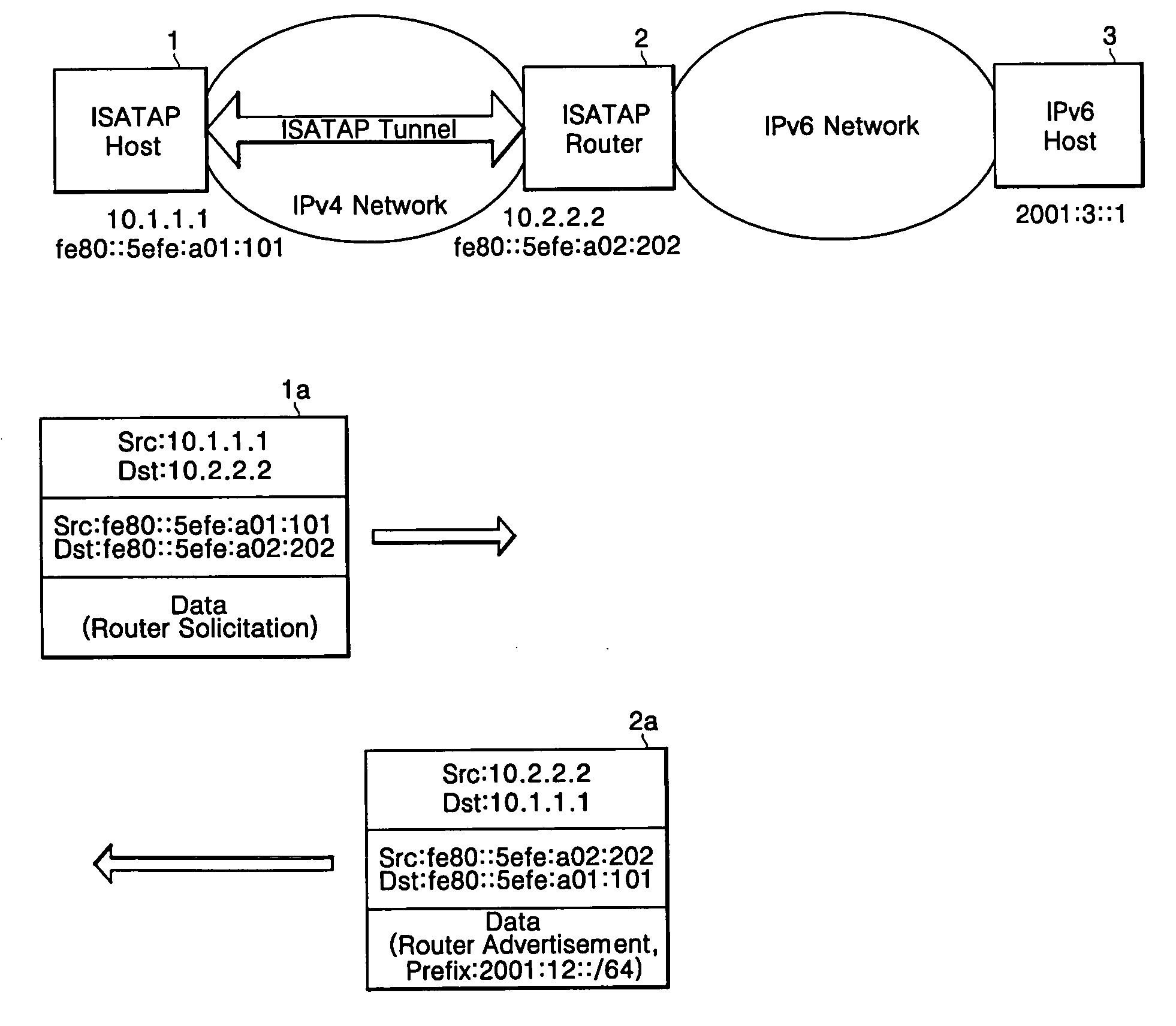
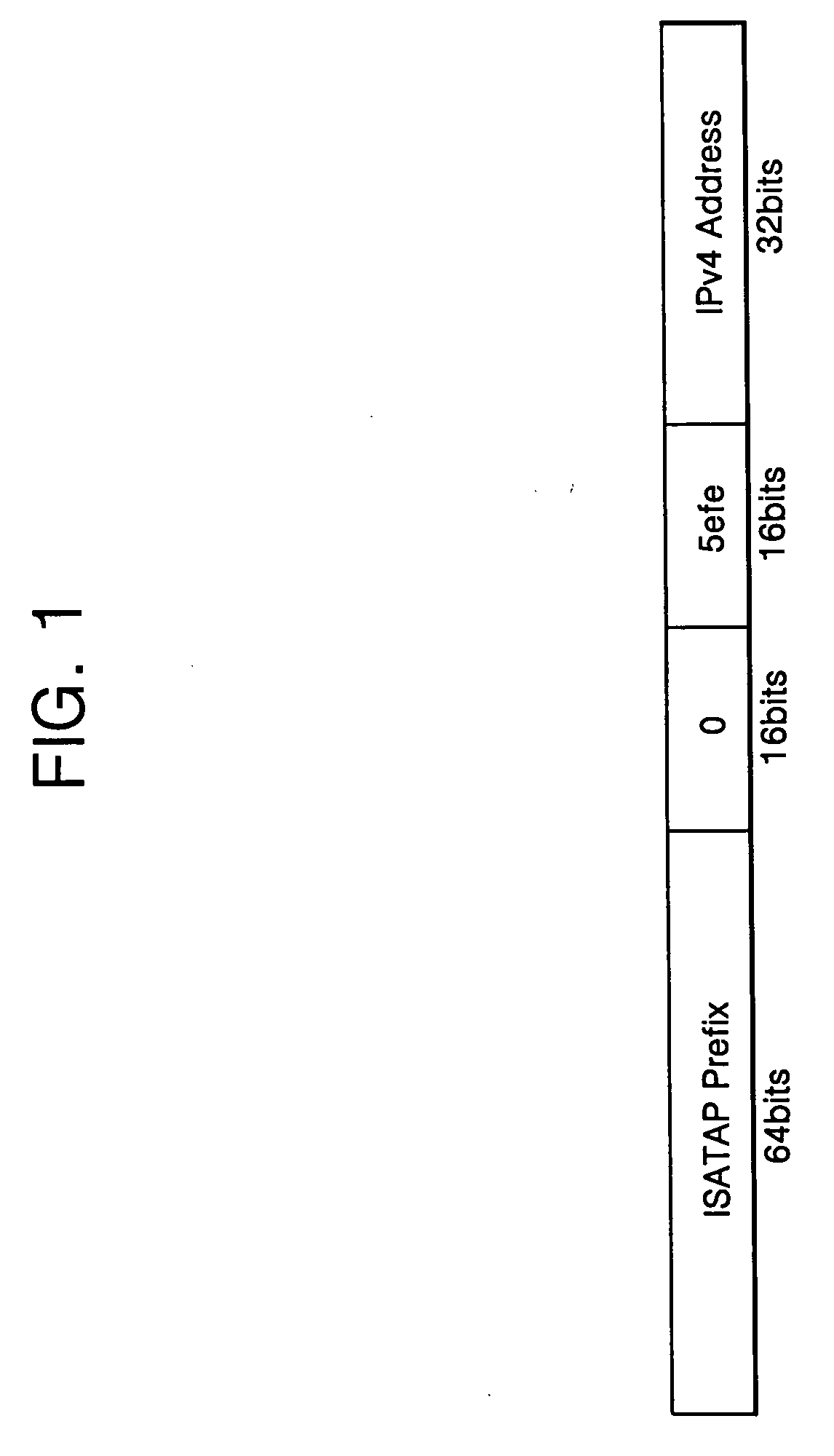
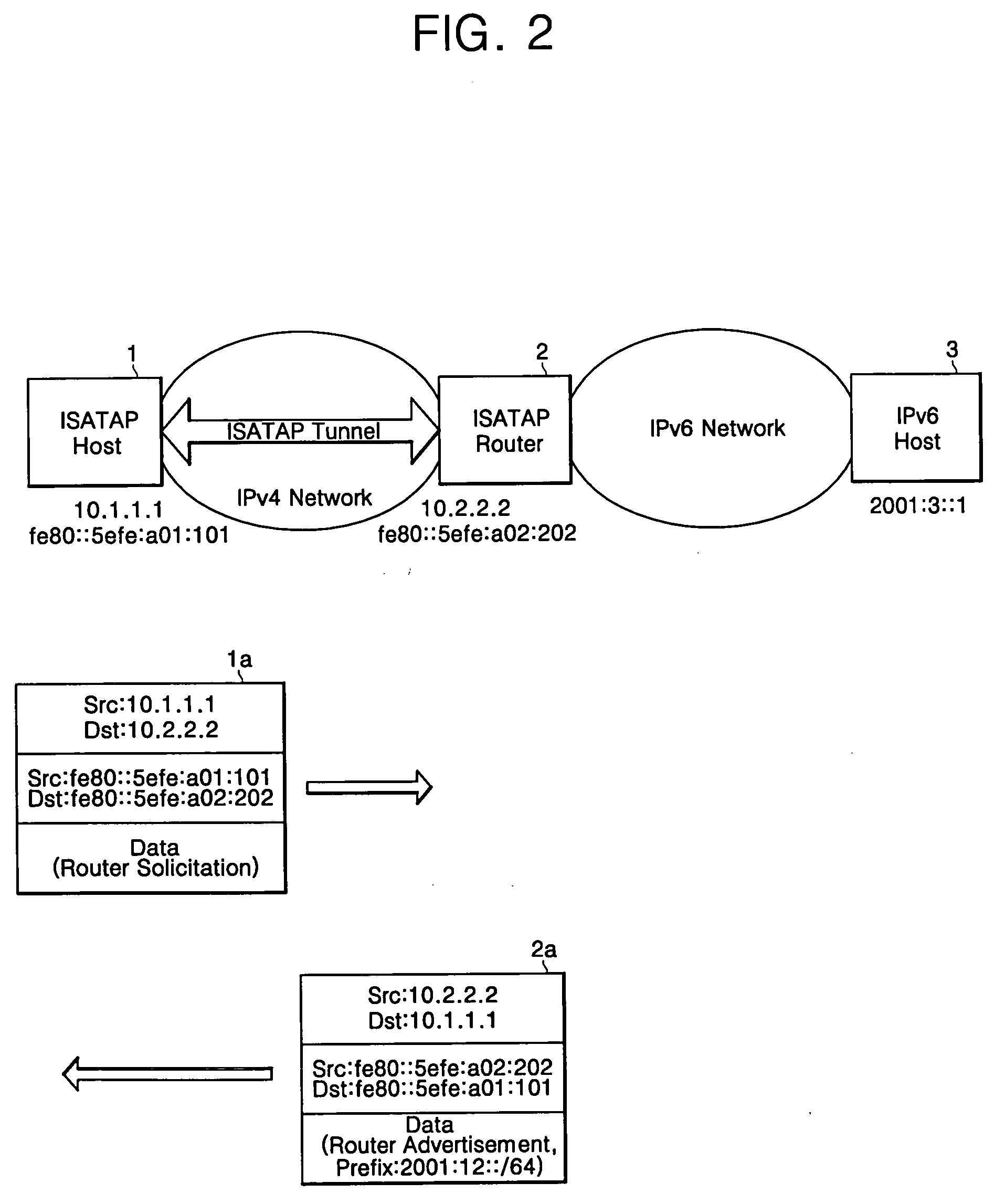
ISATAP tunneling system and method between IPv4 network and IPv6 network
InactiveUS20060215657A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsTime-division multiplexPrivate addressNetwork address translation
In an Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) tunneling system and method, an ISATAP tunnel which is a type of an IPv6 transition tunnel is used, even through a network address translation (NAT) region. The tunneling system for tunneling data having address formats different from one another includes: a host for encapsulating a message of a first address format in a message of a second address format; an address translator for receiving the encapsulated message of the second address format from the host, and for translating a source address of a private address format into a global address format; and a router responsive to reception of the encapsulated message of the global address format from the address translator for assigning the source address translated into the global address format as a destination address, and for transmitting to the host the message of the second address format having the assigned destination address included in prefix information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Addressing scheme
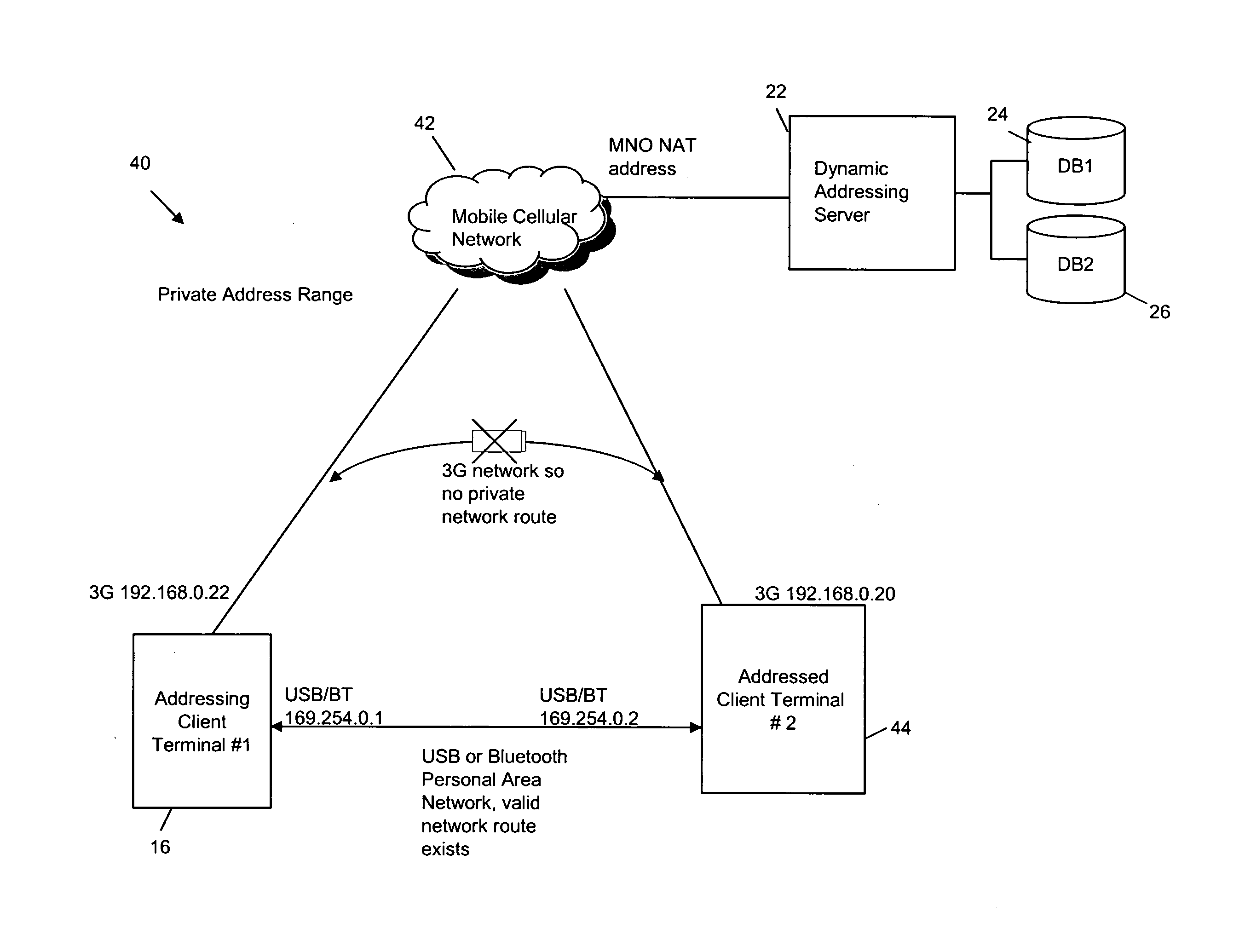
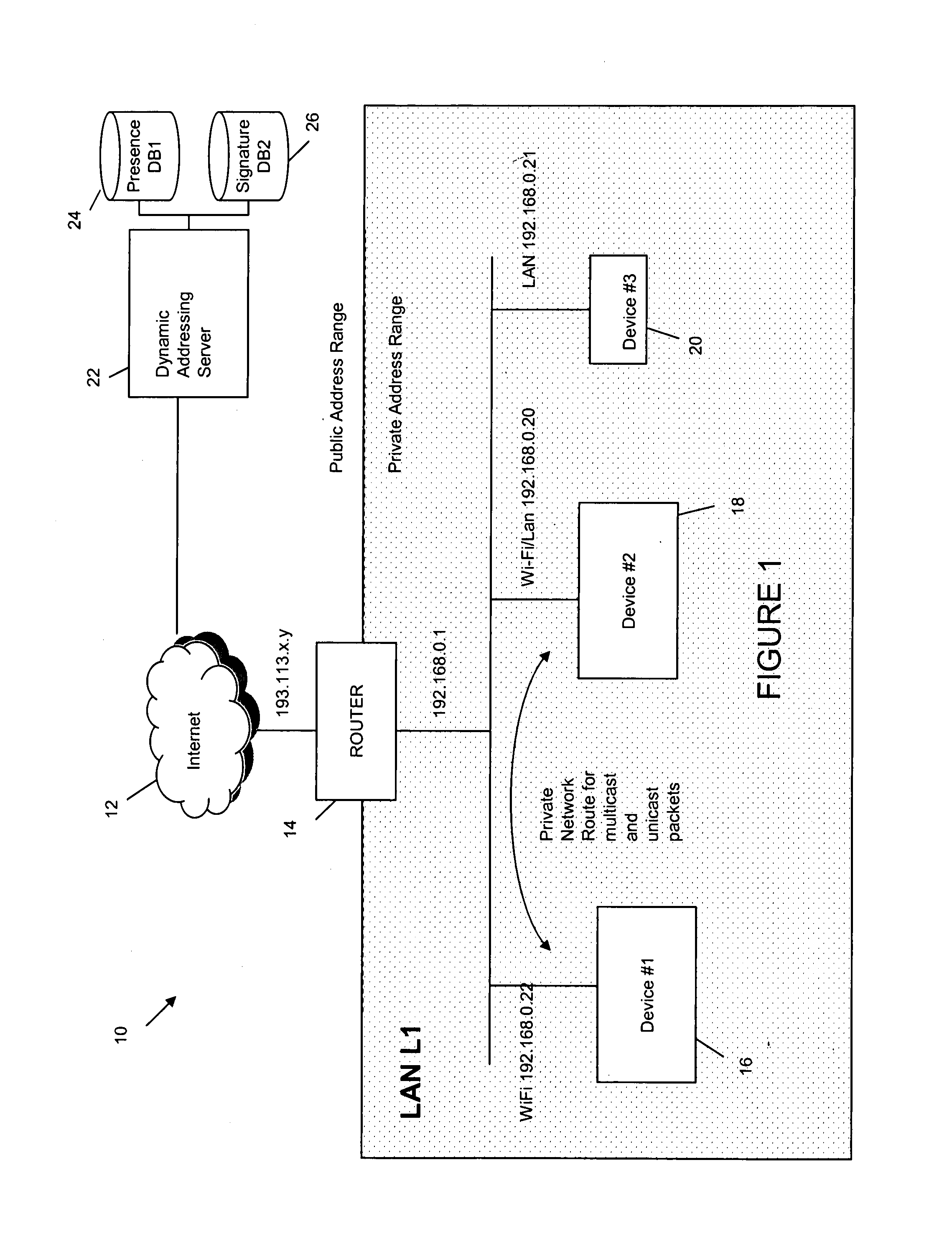
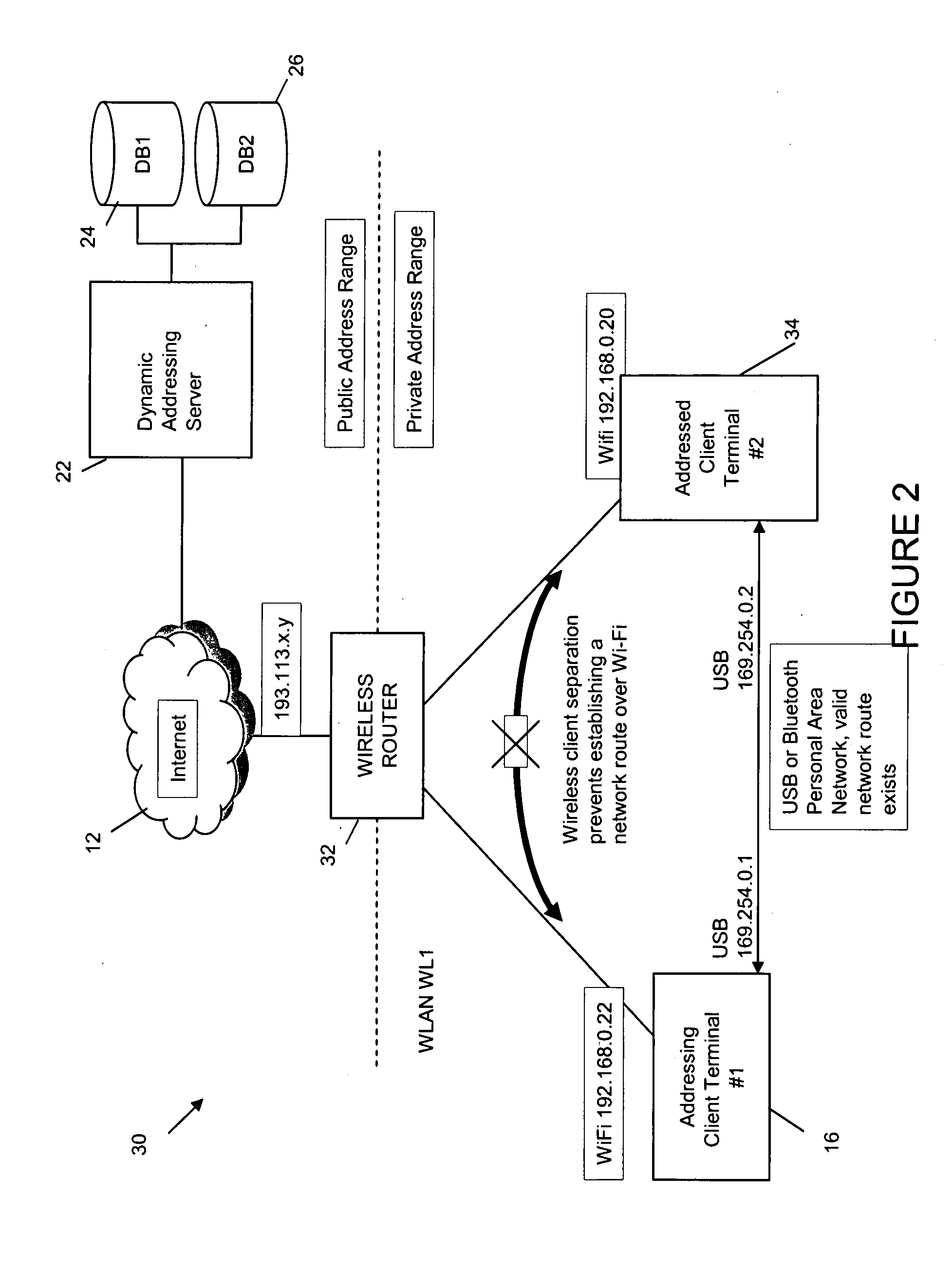
An addressing scheme enables mobile web-service providing devices located within private address domains to be contacted by other devices located on the same LAN segment regardless of whether or not the two devices are located in the same private IP address domain, providing a working network path can be identified directly or indirectly between the two devices. In this way, if a device-label (such as a telephone number which is associable with an addressed device) is provided by an addressing device to an addressing server, the server is able to resolve the device-label to a private address via which the addressing device can contacted. The private address is utilized by the web-browser application to seamlessly and transparently obtain a requested web-service from the addressed device using any suitable communications channel, e.g. WiFI, Bluetooth, etc, that provides a working path between the two devices.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
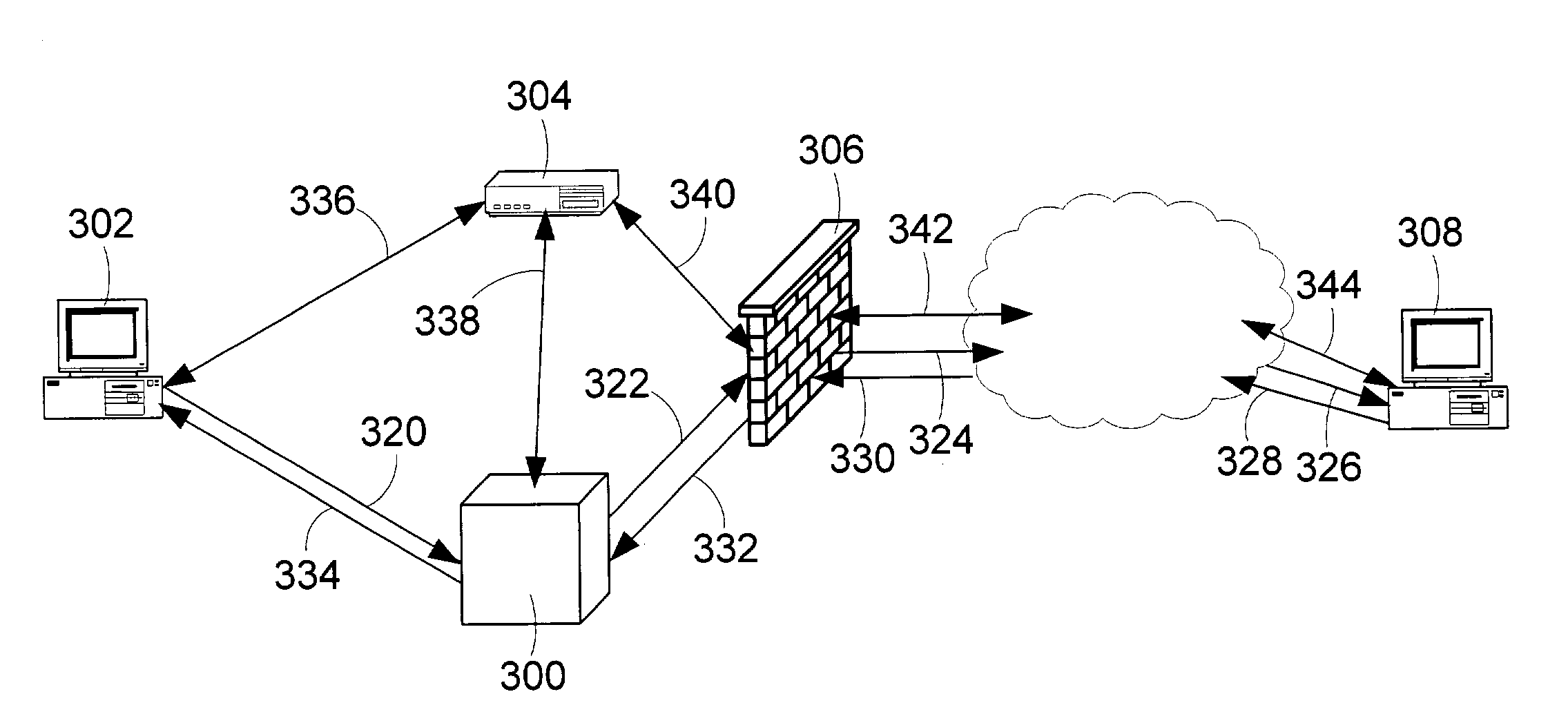
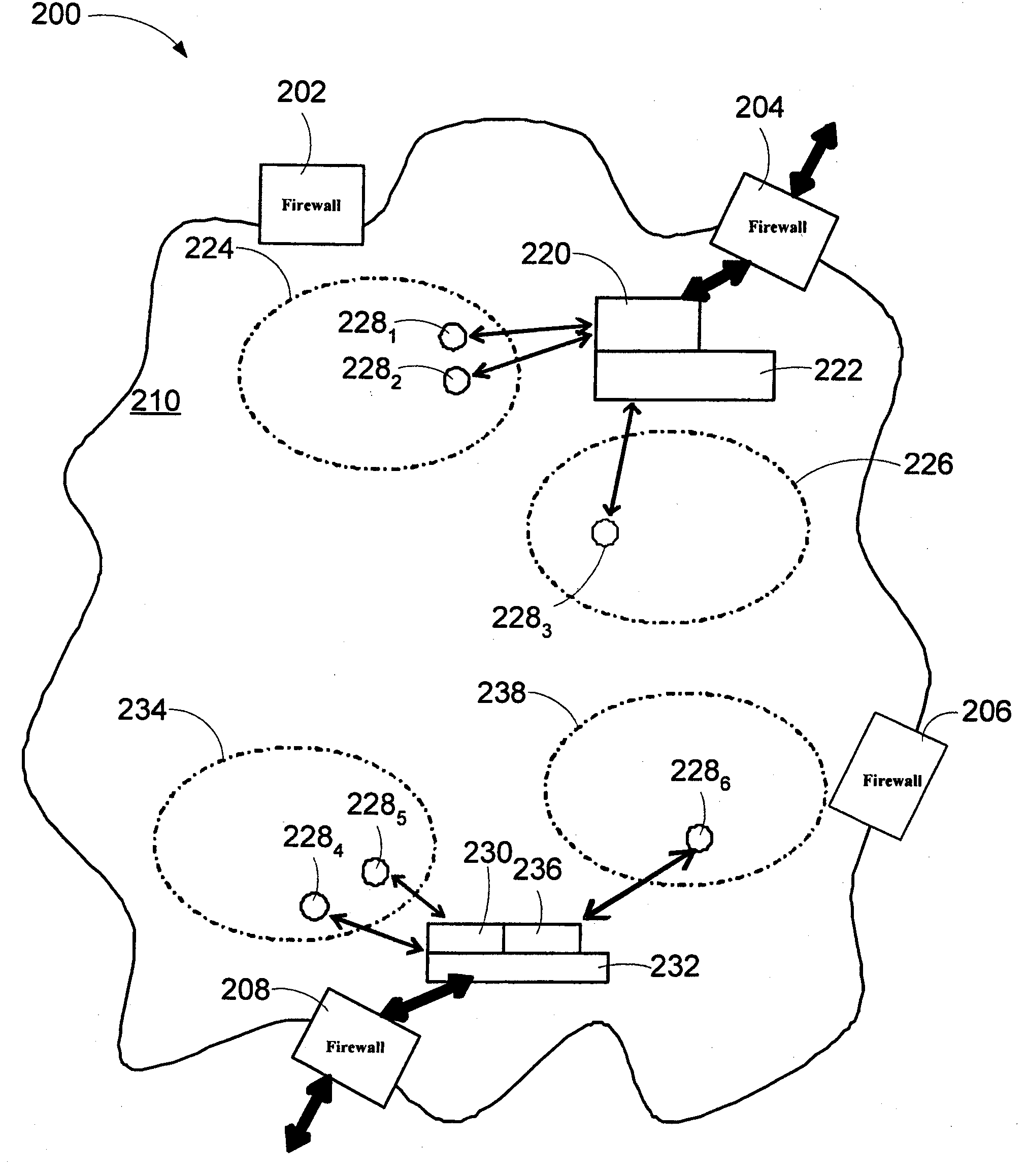
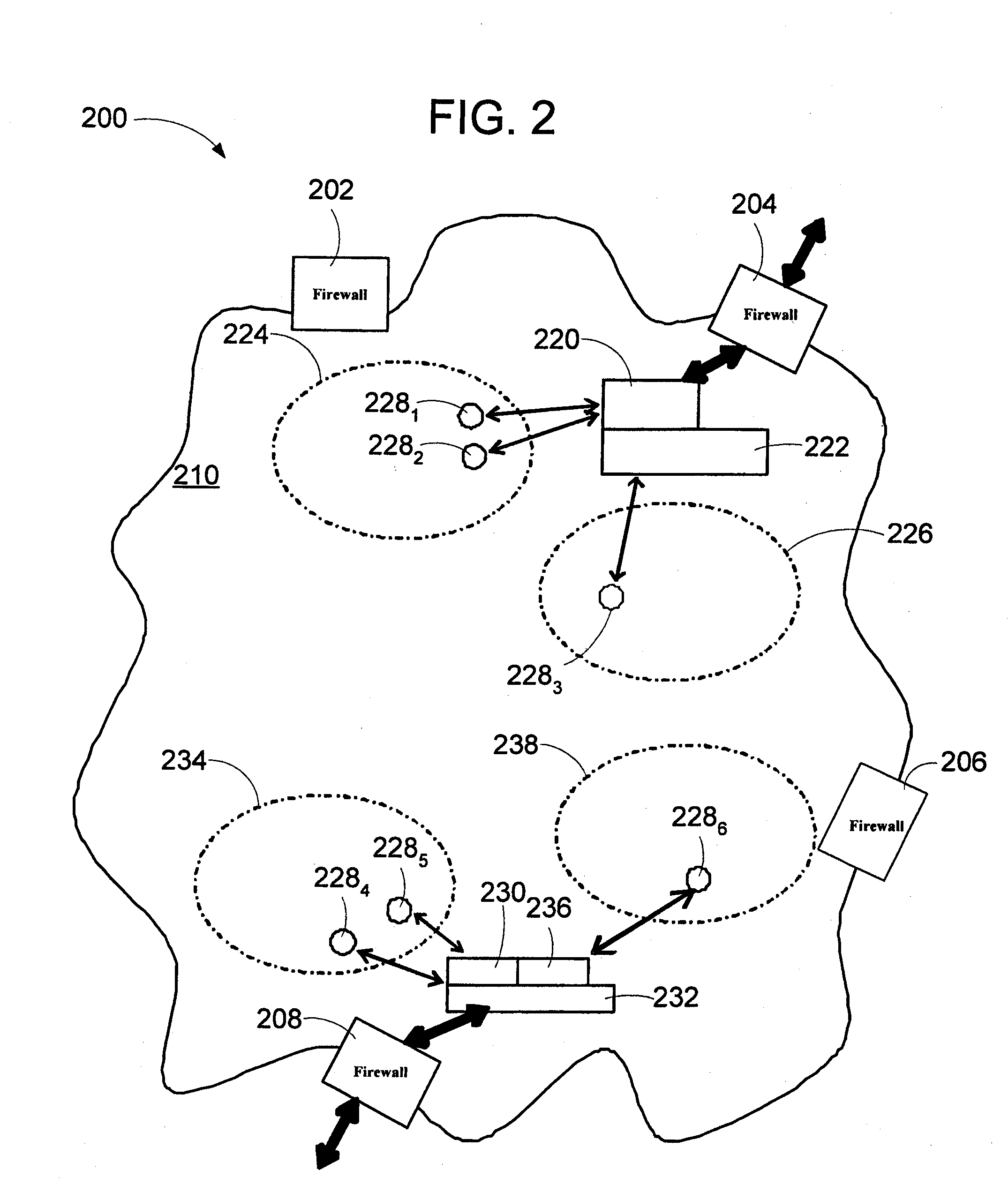
Controlled relay of media streams across network perimeters
The invention provides an apparatus and method to establish media sessions for media streams crossing a network boundary. The system includes a media relay controlled by a media configurator control module. The media relay reserves media paths (that include ports in the network boundary), opens the media paths, closes the media paths, and provides information about the media paths. A media configurator is adapted to communicate with the media configurator control module and the media relay. The control module has an event handler handling multimedia session events, a local address resolver that determines if an address identifier of the media session belongs to a private address space and a control element used to establish the media path. The control element manages resources for the media relay. A state-refresh timer is used to maintain state consistency between all media relays controlled by a proxy engine and control elements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and methods for performing network address translation (NAT) in a fully connected mesh with NAT virtual interface (NVI)
InactiveUS7334049B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityPrivate address
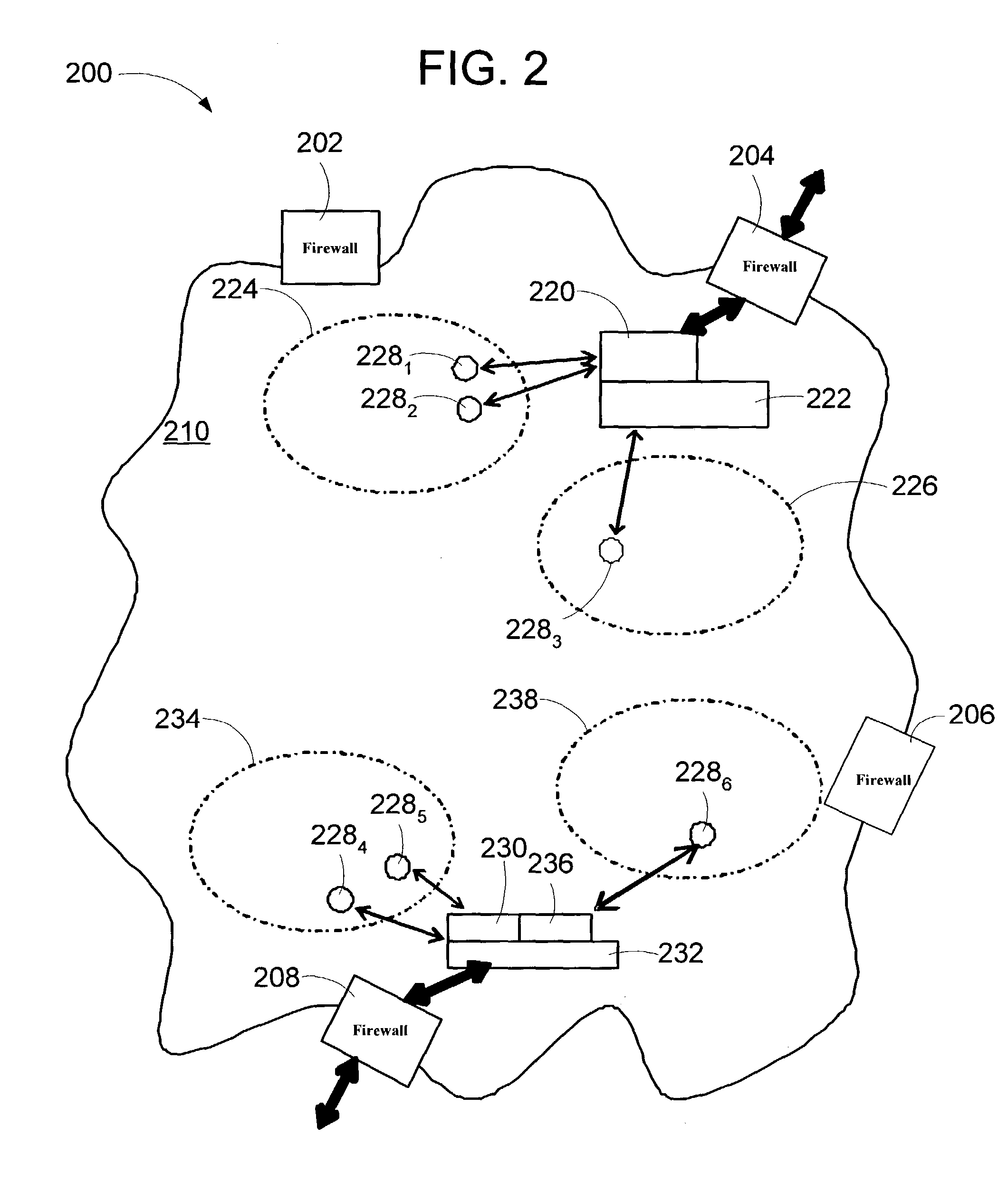
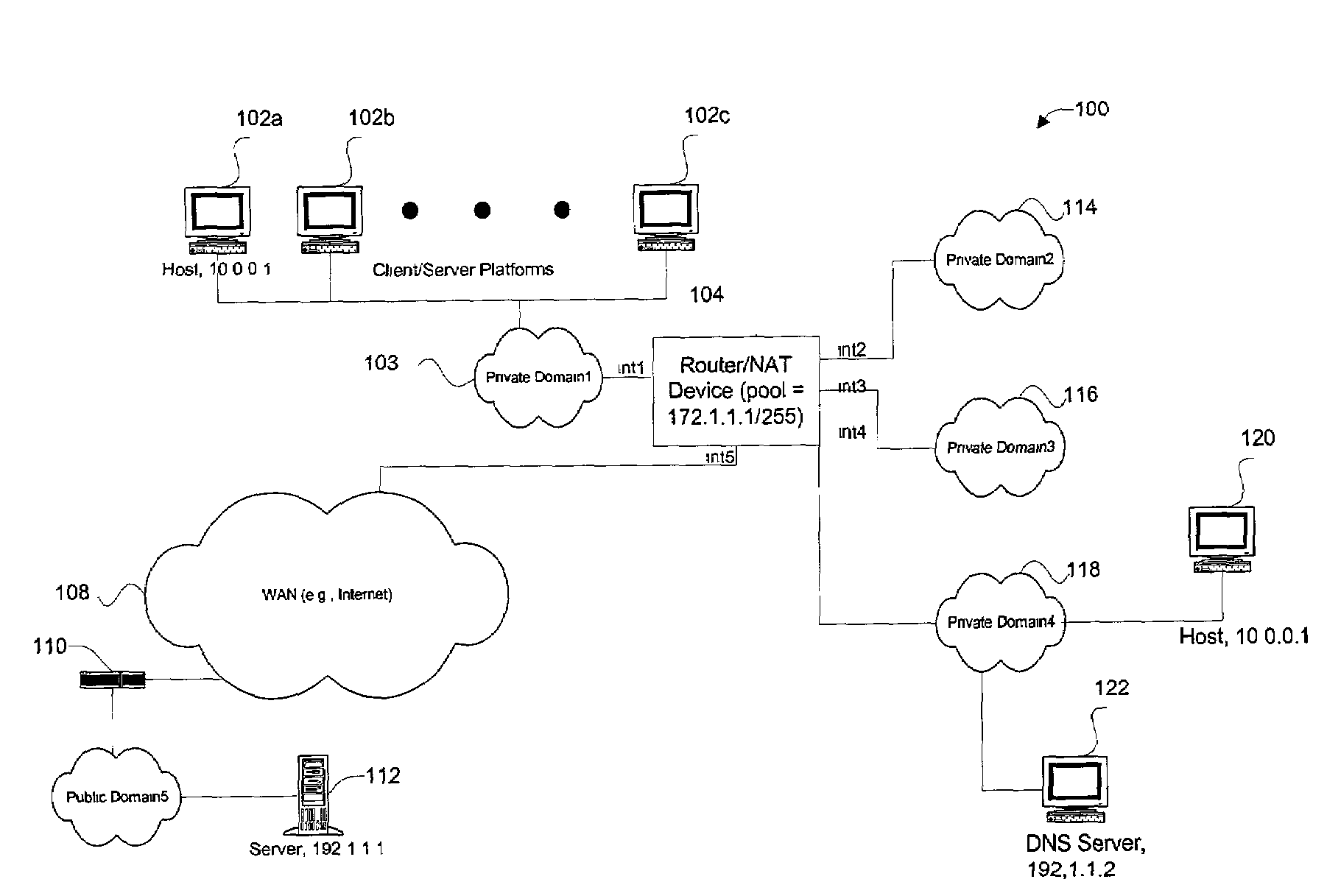
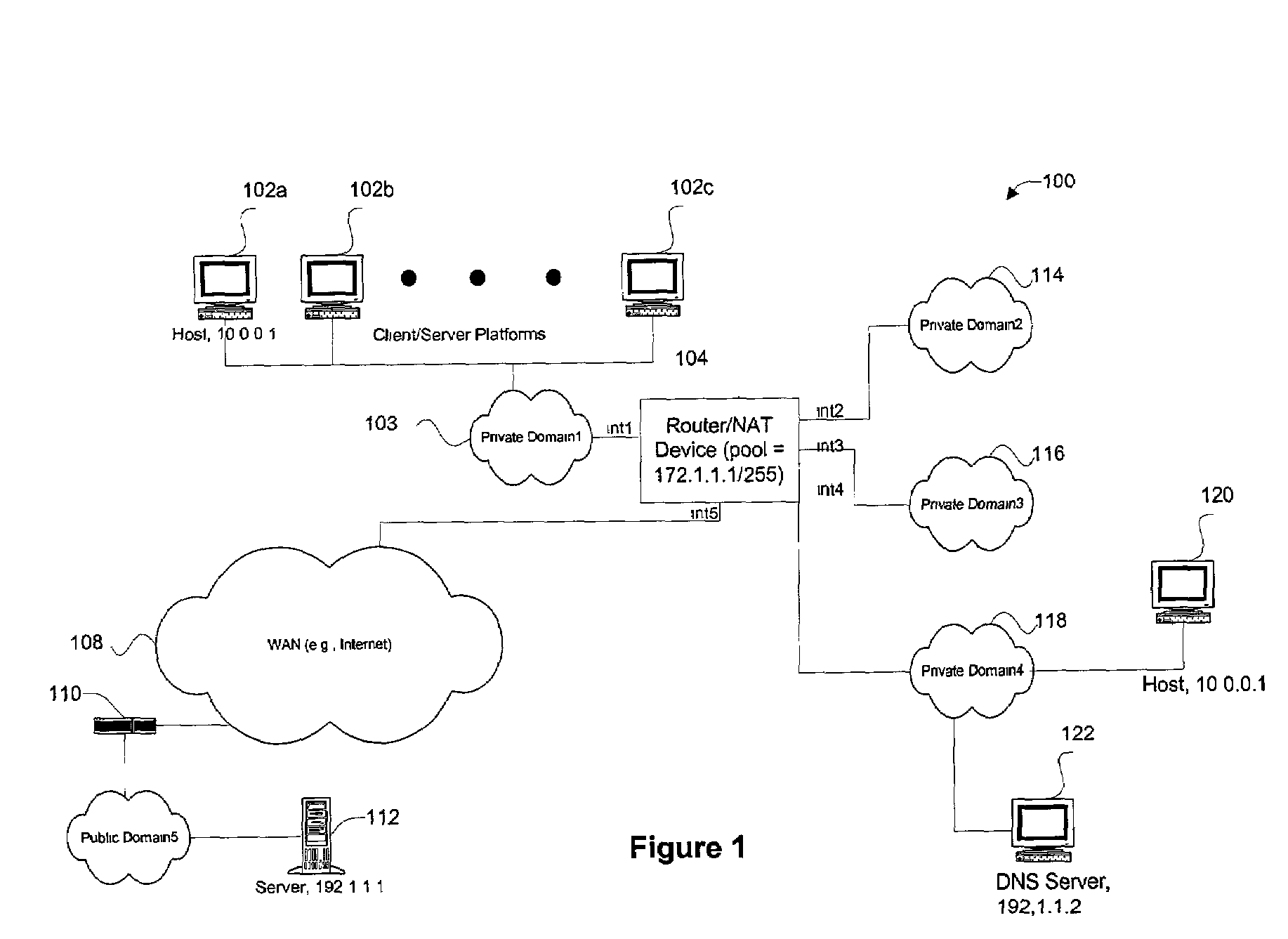
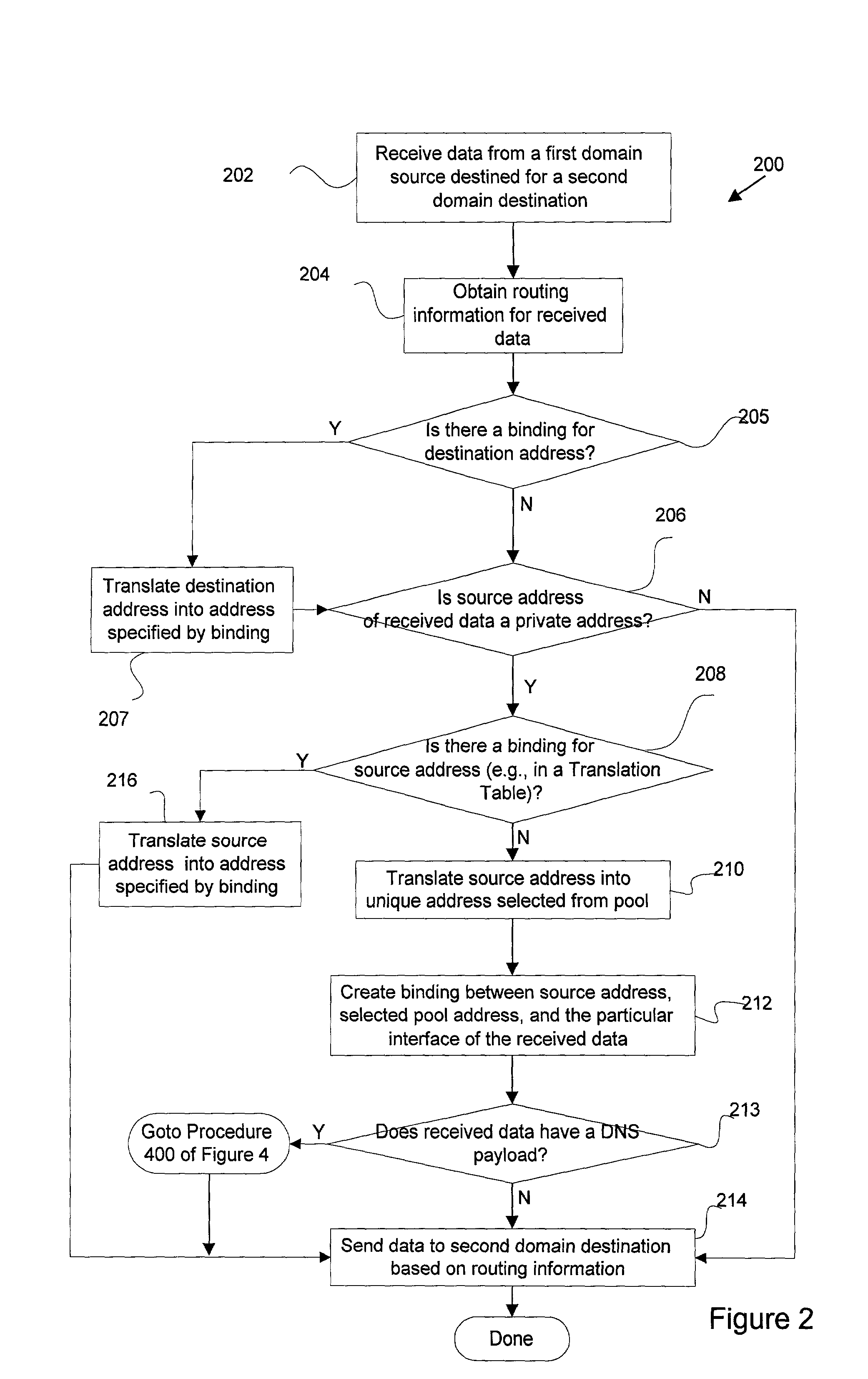
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for performing network address translation (NAT) in a fully connected mesh with NAT virtual interface (NVI). In general terms, mechanisms (e.g., within a combination router / NAT device) are provided for translating network addresses of traffic going between two private domains or realms. These mechanisms may also be used to translate traffic going between a private and public domain. When a particular private address is translated into a public address, a binding is formed between the pre-translation address, the post-translation address, and the interface associated with the private or public address (e.g., an interface of the router / NAT device). Since bindings of different interfaces are tracked, a private address and its associated particular interface may be associated with a particular public address. Accordingly, the translation mechanisms of the present invention may be applied to two duplicate private addresses from two different private domains because the two identical private addresses are distinguished based on their different interfaces.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
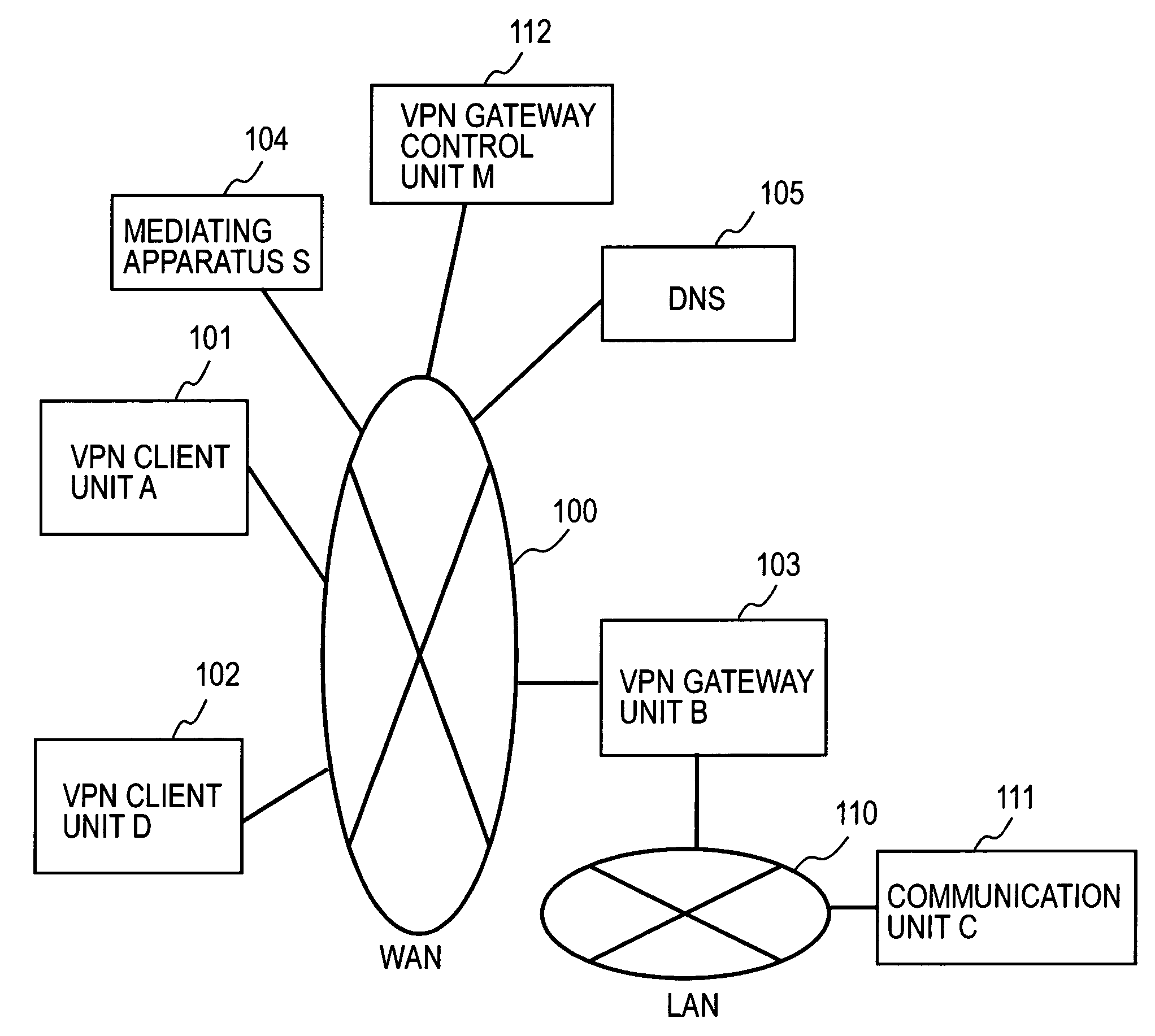
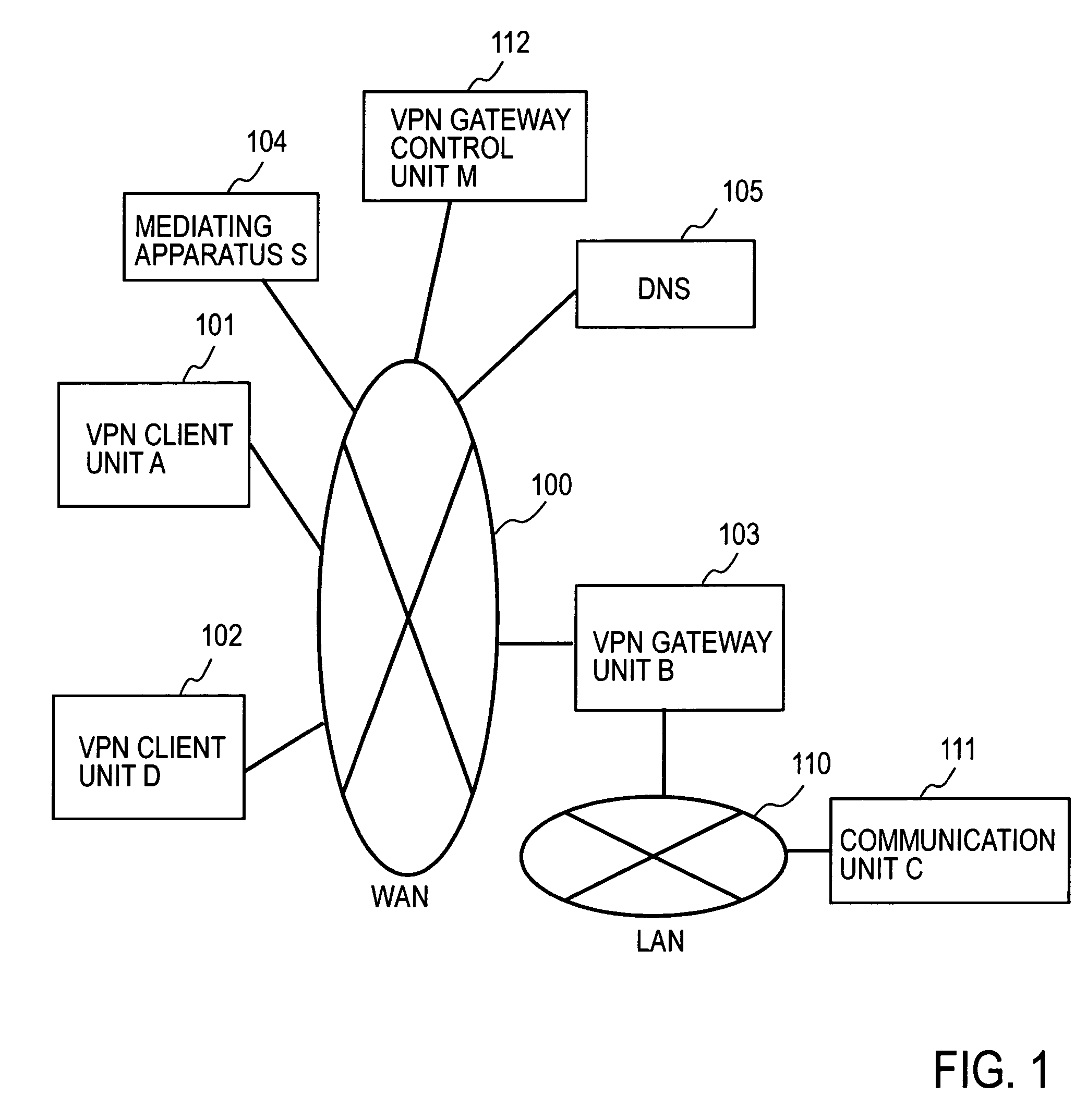
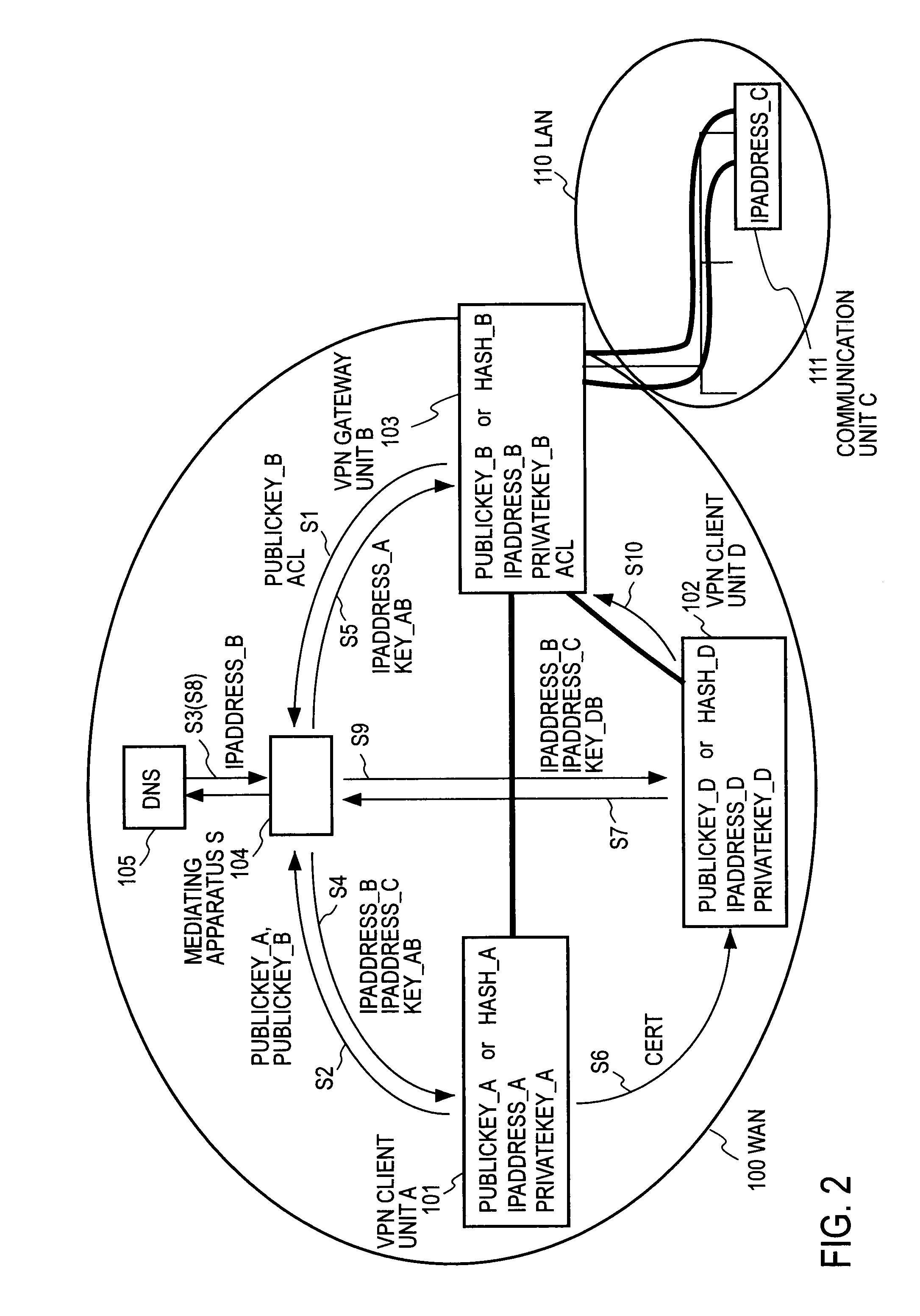
Remote access VPN mediation method and mediation device
InactiveUS7665132B2Secure distributionKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPrivate IPCommunication unit
A mediating apparatus is provided on an IP network, and stores an access control list (ACL) retained in a VPN gateway unit. The mediating apparatus: receives a retrieval request from a VPN client unit; acquires a private IP address of a communication unit by reference to ACL; searches DNS to acquire therefrom an IP address of the VPN gateway unit; generates a common key that is used for authentication between the VPN client unit and the VPN gateway unit and for encrypted communication therebetween; sends the IP address of the VPN gateway unit, the private IP address of the communication unit, and the common key to the VPN client unit; and sends the IP address of the VPN client unit and the common key to the VPN gateway unit.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
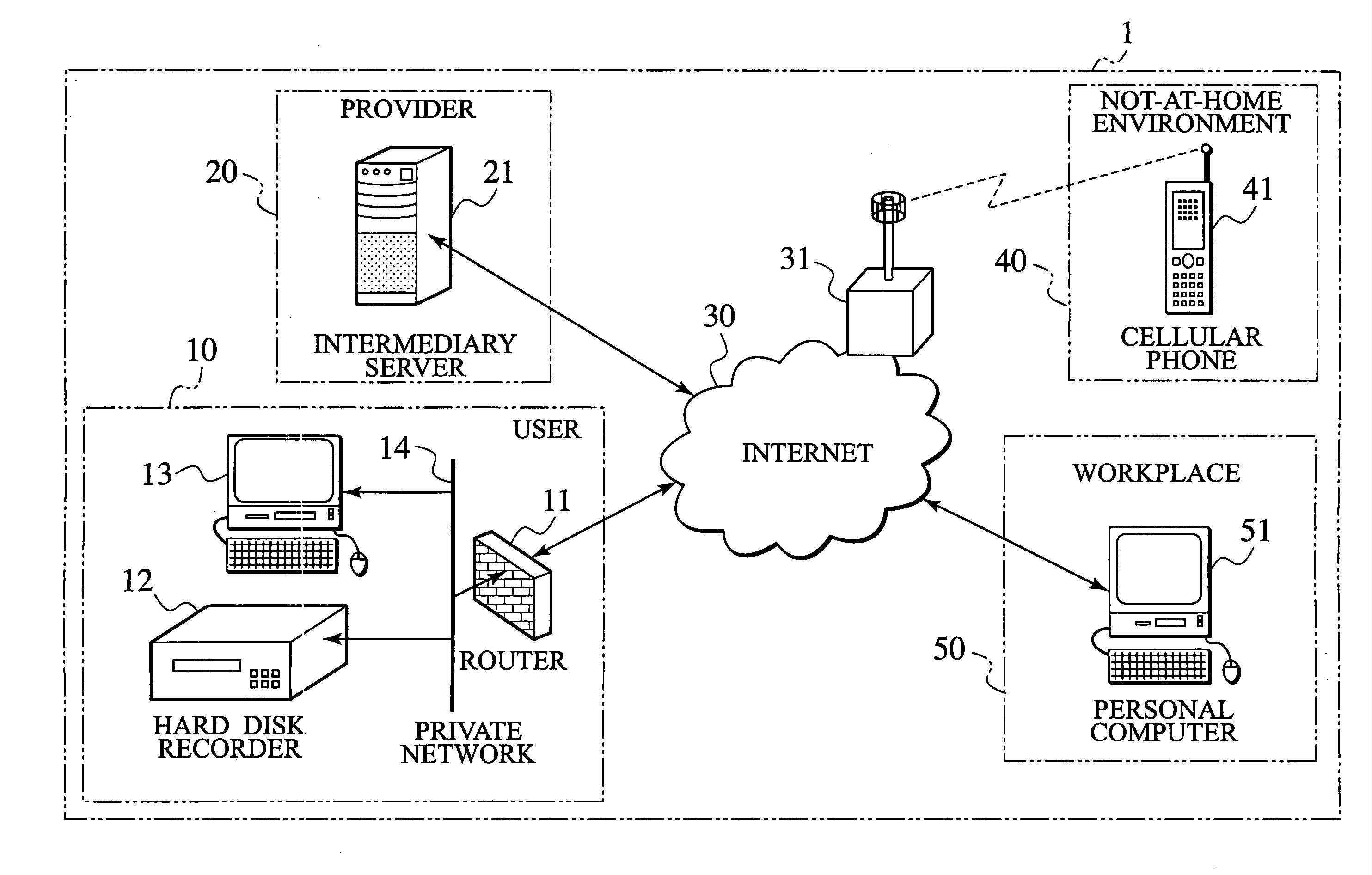
Control information transmission method, relay server, and controllable device
ActiveUS20060161639A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationComputer hardwareInformation transmission
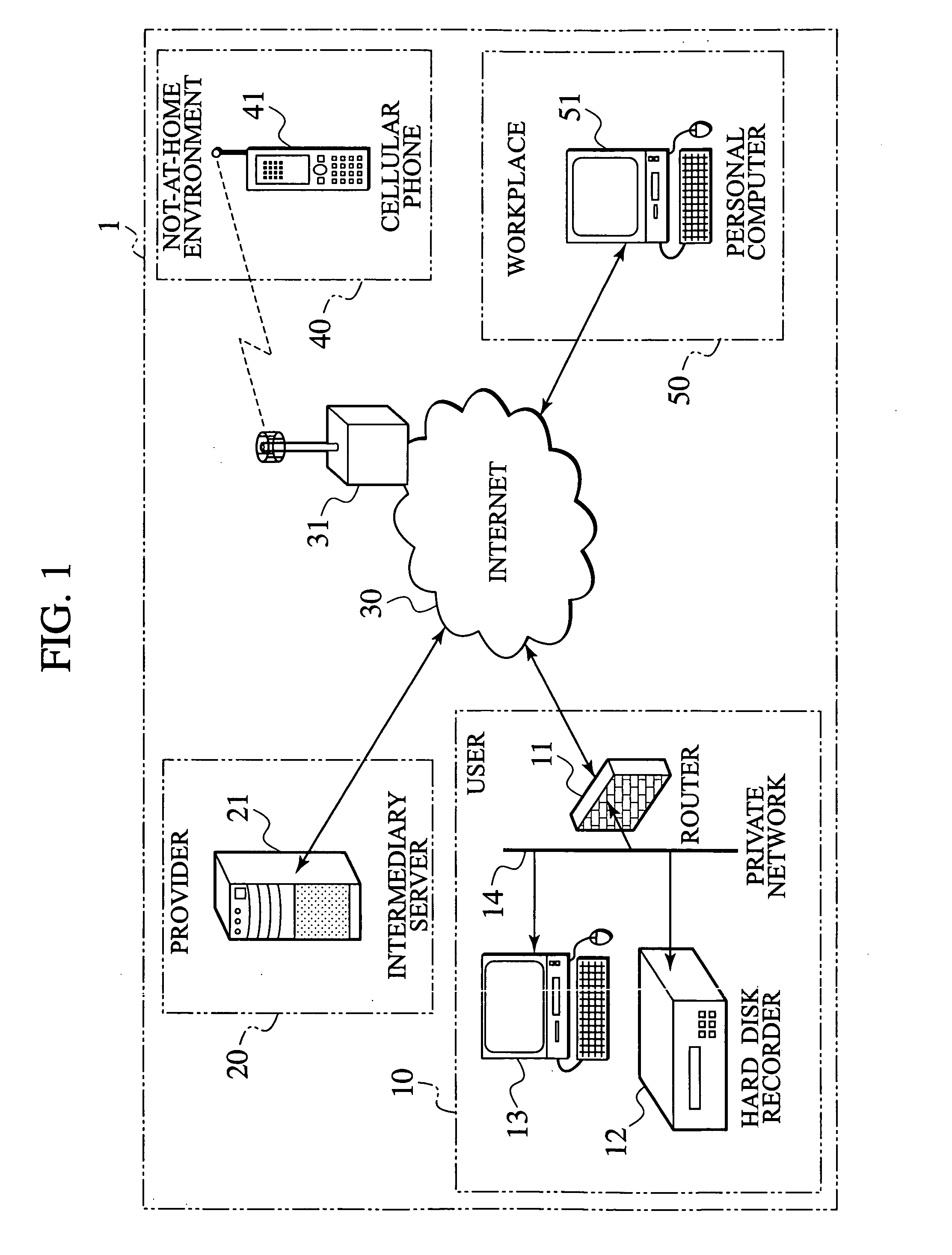
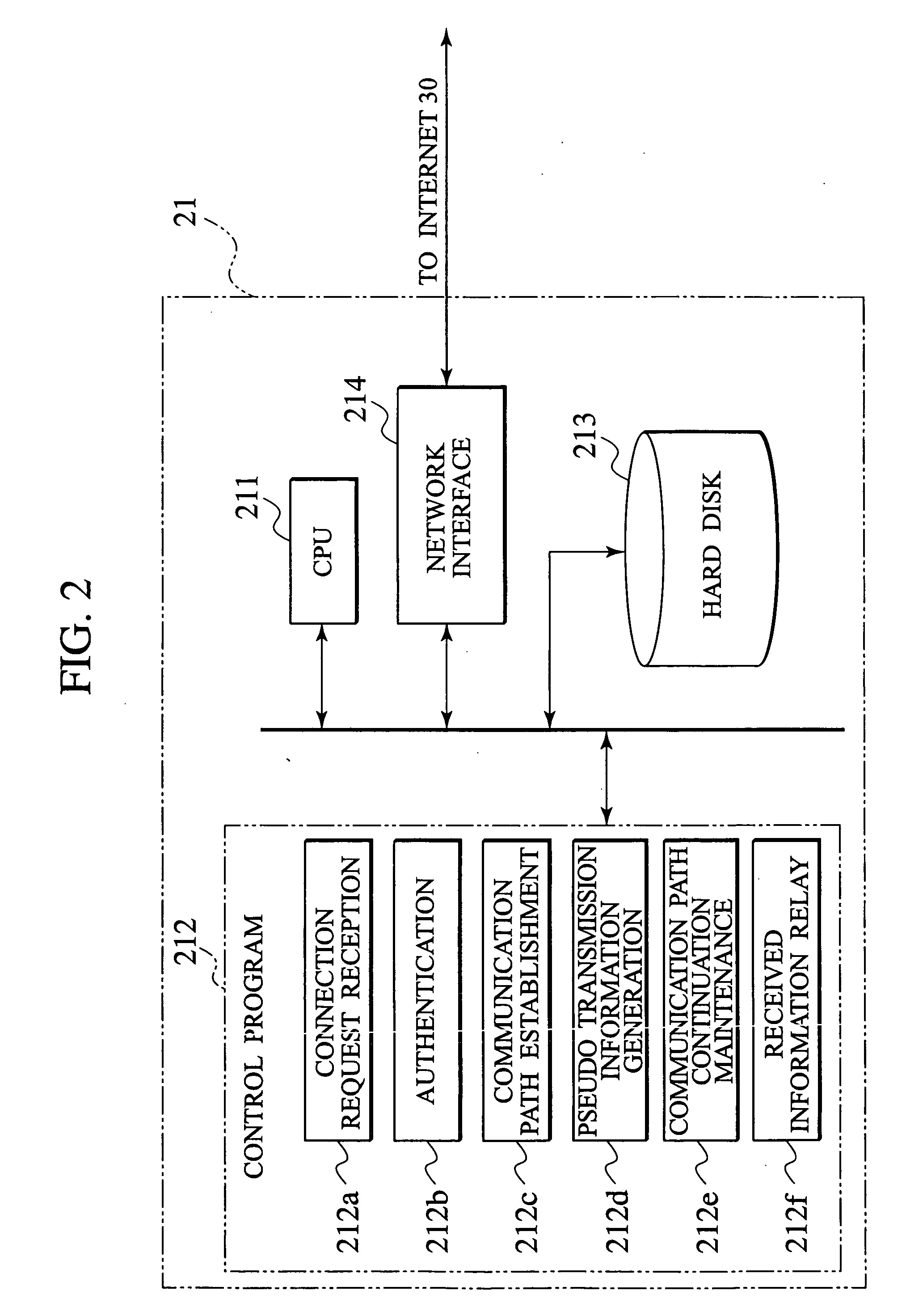
A controlled device (12) sends a signal to a intermediary server (21) at a predetermined time interval, and the intermediary server (21) receives the signal from the controlled device (12) with a private address allocated by a router (11) and changes an operation mode from a passive mode to an active mode. The operation of the controlled device (12) is changed to the passive mode. The intermediary server (21) continuously establishes a communication path with the controlled device (12). The intermediary server (21), which receives control information from a control terminal (41), relays data transmitted via two communication paths, that is, a communication path established with the control terminal (41) and a communication path established with the controlled device (12), to allow the control terminal (41) to control the controlled device (12) operating in the passive mode.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Duplicate private address translating system and duplicate address network system
ActiveUS7047314B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationGlobal address spaceRouting table
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Controlled relay of media streams across network perimeters
InactiveUS20090028146A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate addressTimer
The invention provides an apparatus and method to establish media sessions for media streams crossing a network boundary. The system includes a media relay controlled by a media configurator control module. The media relay reserves media paths (that include ports in the network boundary), opens the media paths, closes the media paths, and provides information about the media paths. A media configurator is adapted to communicate with the media configurator control module and the media relay. The control module has an event handler handling multimedia session events, a local address resolver that determines if an address identifier of the media session belongs to a private address space and a control element used to establish the media path. The control element manages resources for the media relay. A state-refresh timer is used to maintain state consistency between all media relays controlled by a proxy engine and control elements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method, system, and program for managing memory options for devices
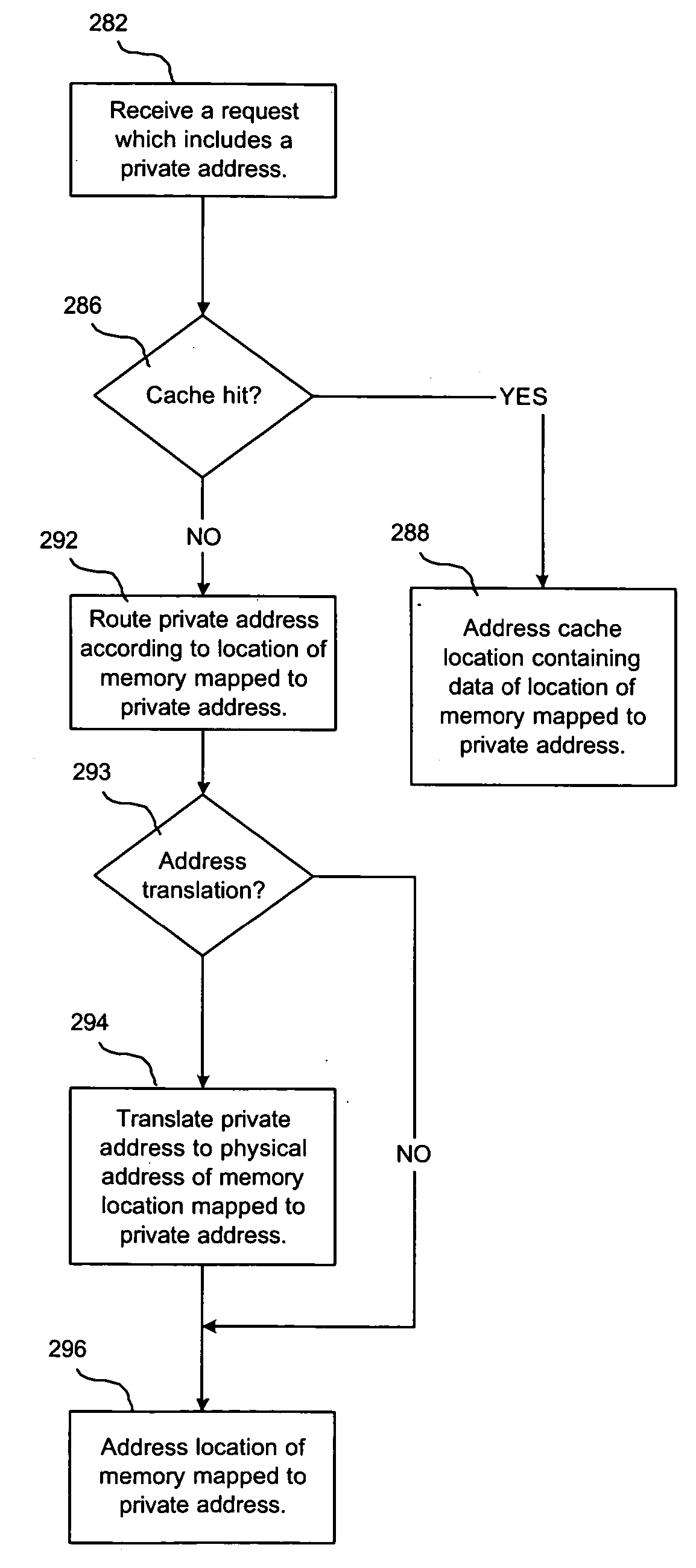
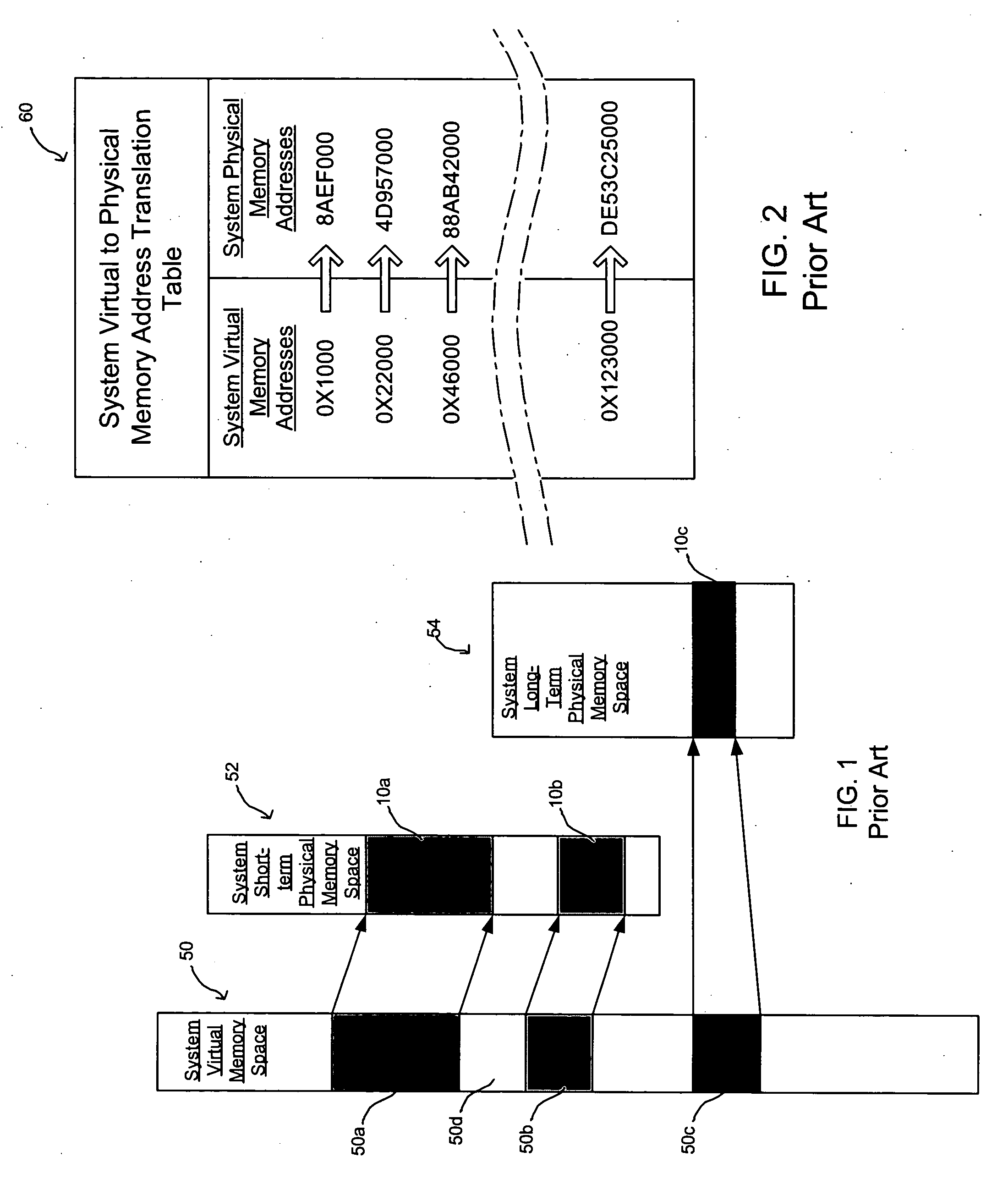
InactiveUS20060004983A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationExternal storagePrivate address
Provided are a method, system, and program for managing memory options for a device such as an I / O device. Private addresses provided by logic blocks within the device may be transparently routed to either an optional external memory or to system memory, depending upon which of the optional memories the private address has been mapped.
Owner:INTEL CORP
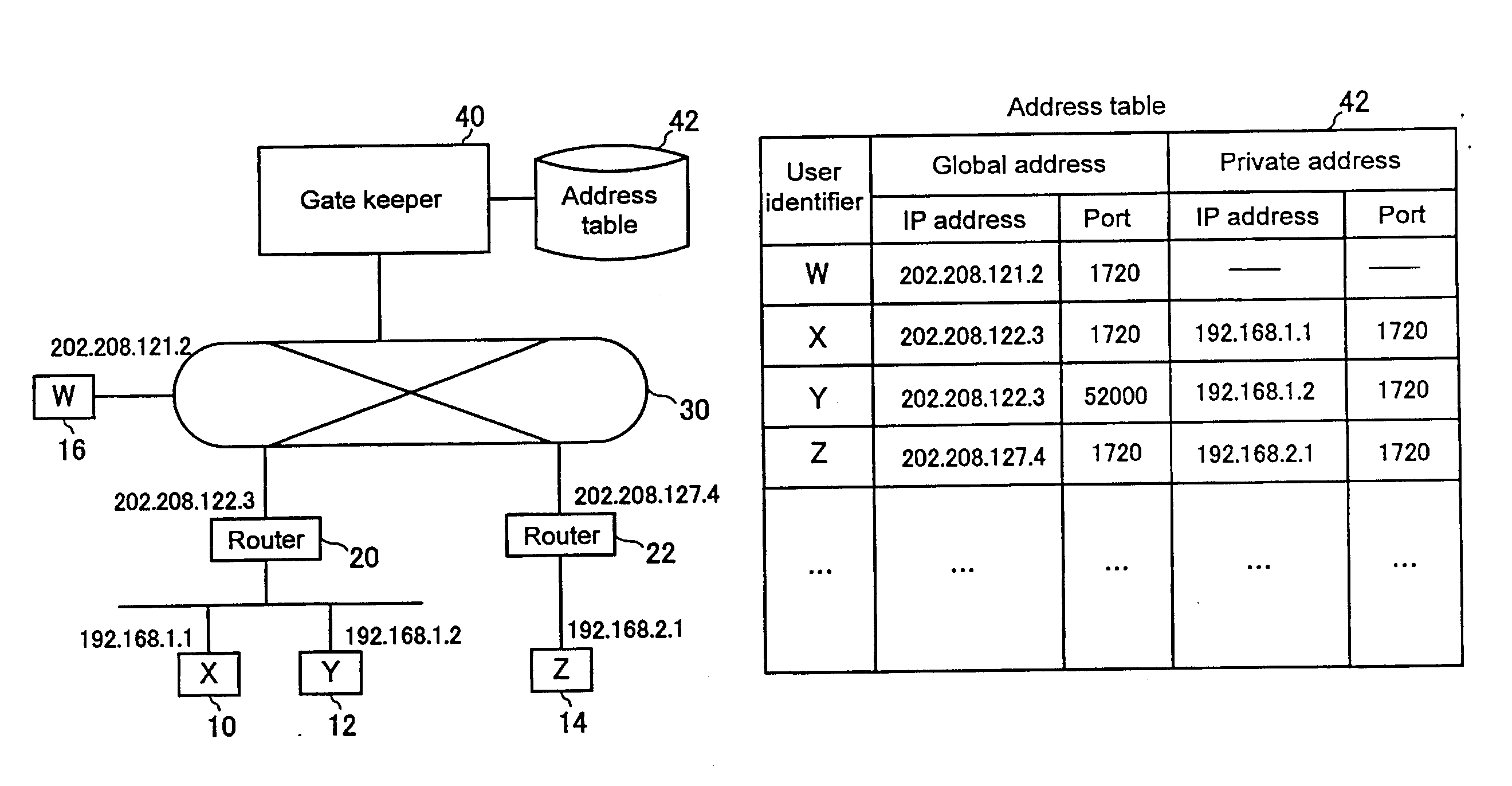
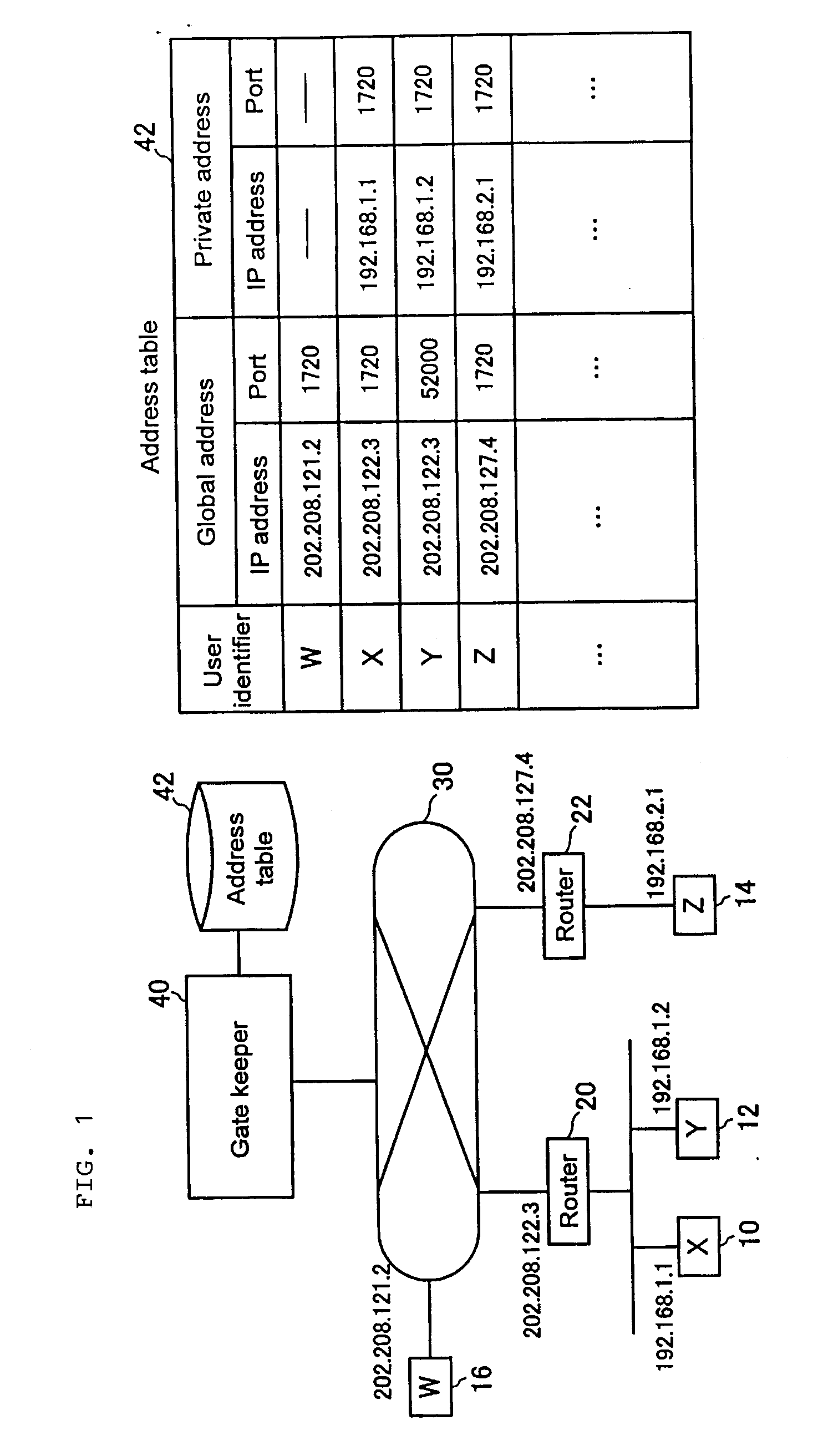
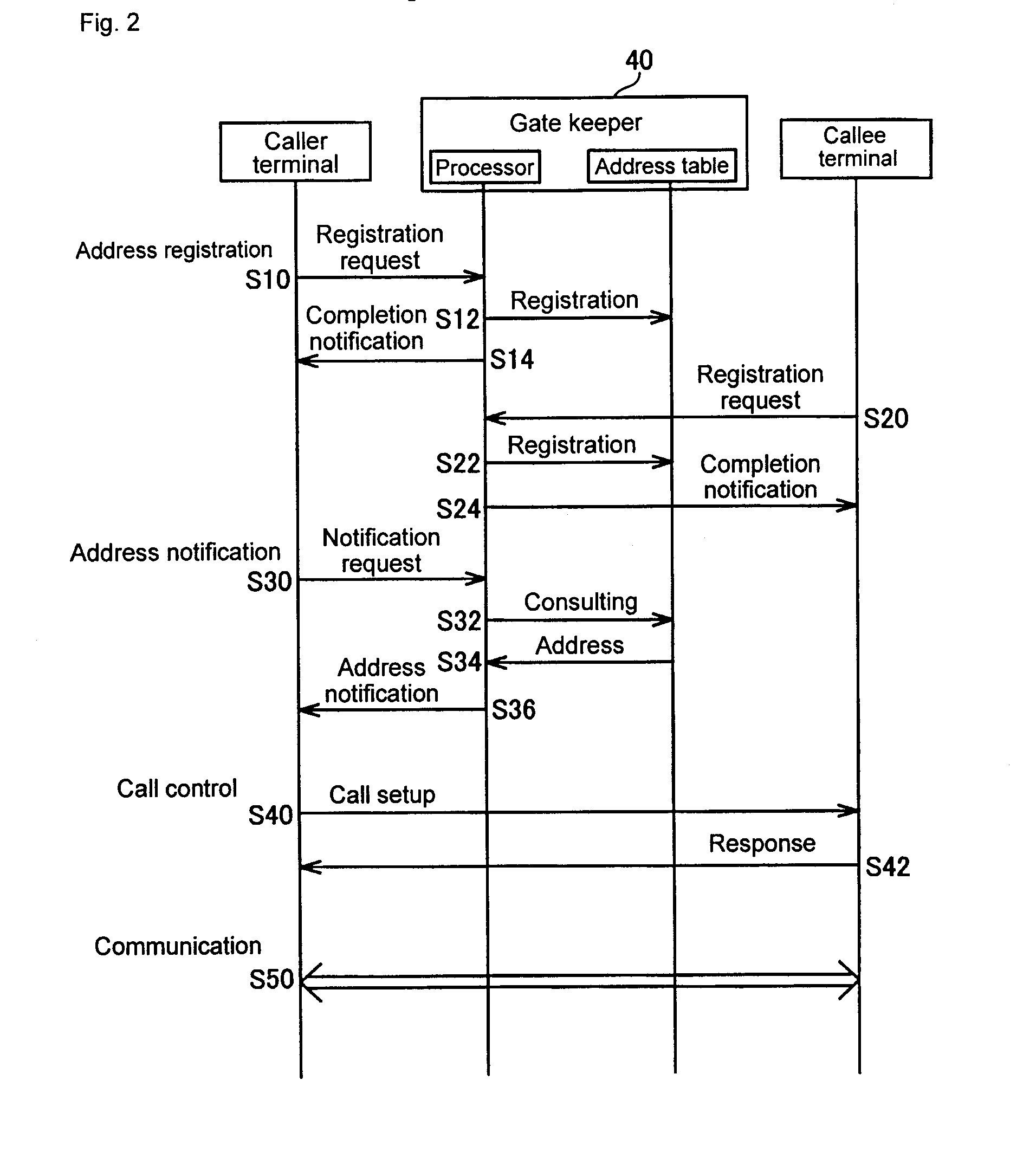
Address Resolution Device, Address Resolution Method, And Communication System Including The Same
An address resolution device includes a gate keeper having an address table with which global addresses, private addresses, and grouping IDs can be registered. During address registration, the gate keeper registers the address of a communication packet into the global addresses, the address assigned to the terminal into the private addresses, and if available, a Grouping ID into grouping IDs. During address notification, the gate keeper consults the address table to notify the caller terminal of the callee terminal private address when the callee terminal and the caller terminal have the same Grouping ID or when they have the same global address. Otherwise, the gate keeper notifies the caller terminal of the callee terminal global address.
Owner:GINGANET CORP
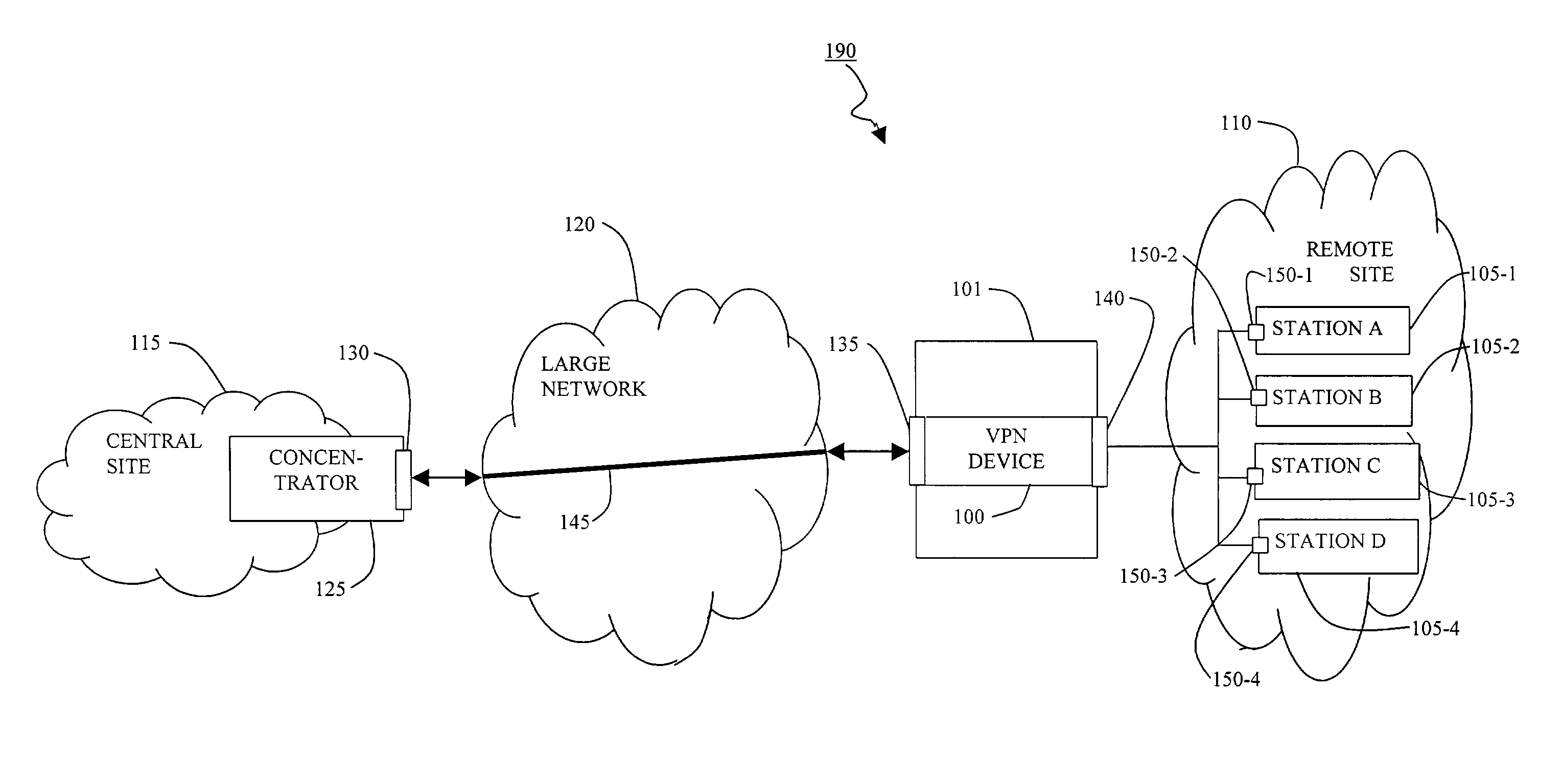
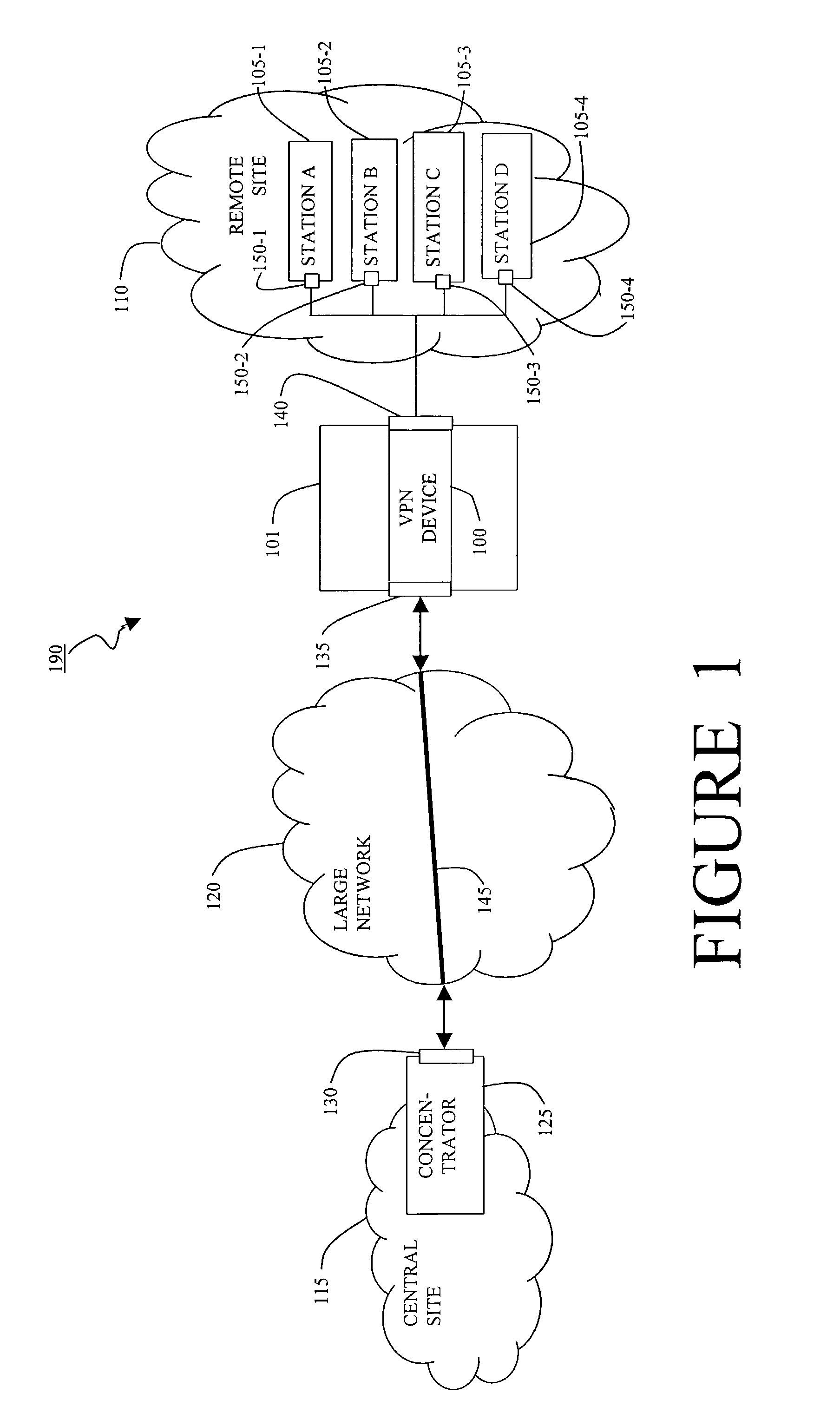
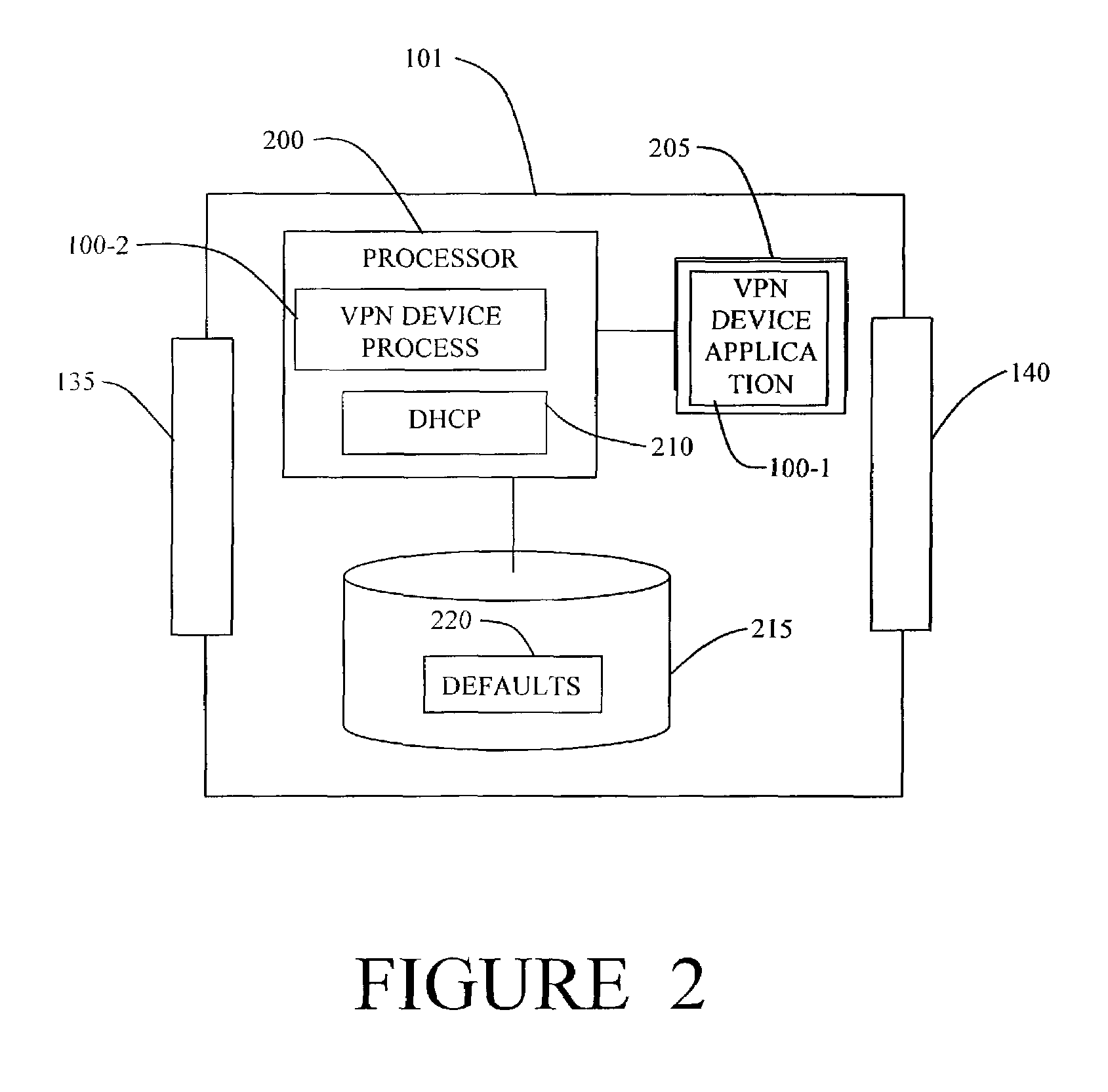
Method and apparatus providing virtual private network access
ActiveUS7444415B1Easy to deployImprove securityMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPrivate addressDistributed computing
A virtual private network device enables individual machines at a remote subnet to be visible and addressable from a central site by establishing a private address range for the remote machines, forming a virtual private network tunnel from the virtual private network device to the central site, and communicating the private address range to the central site to enable connections from the central site to individual machines on the remote subnet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com