Patents
Literature
95 results about "Application-level gateway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
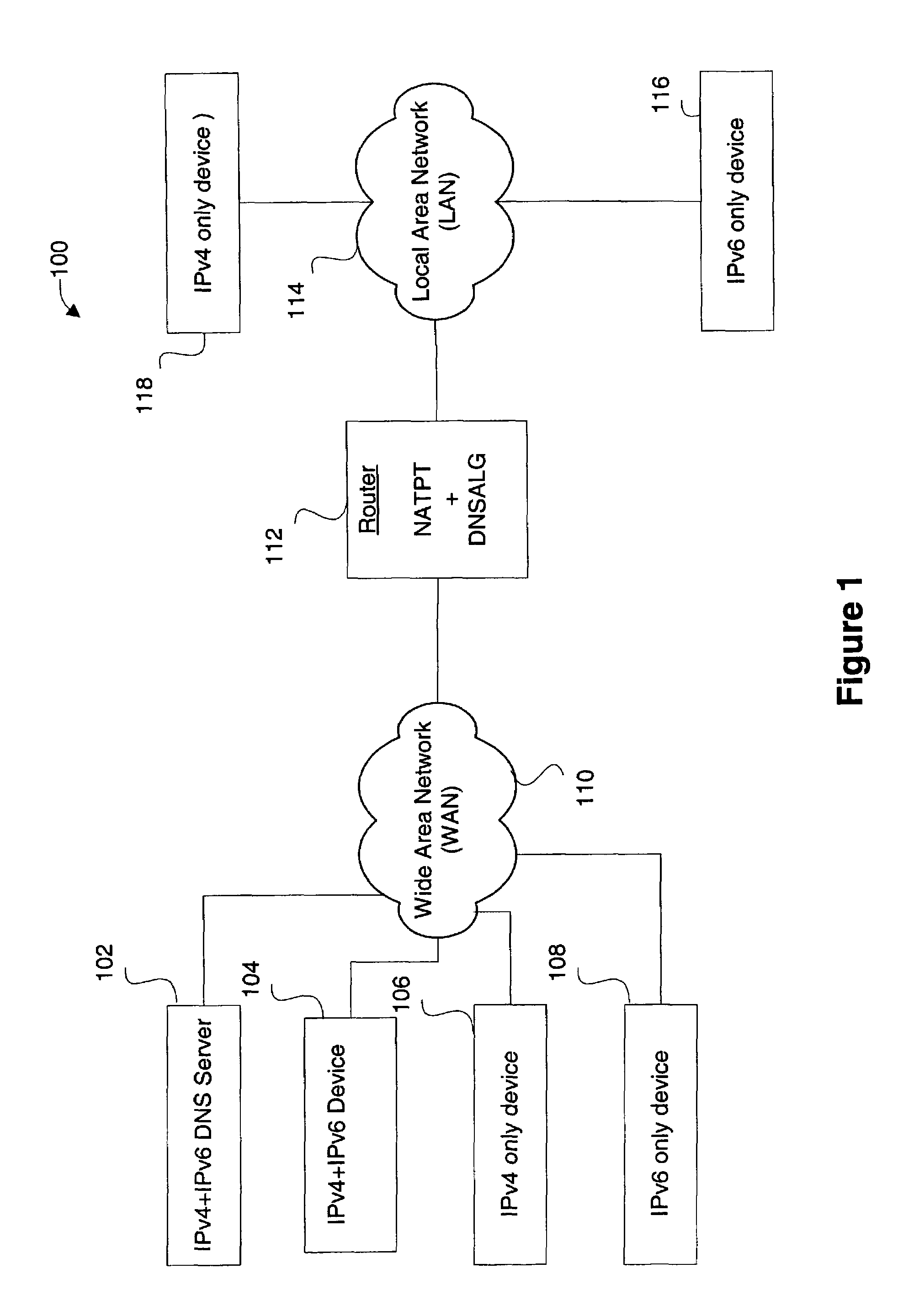
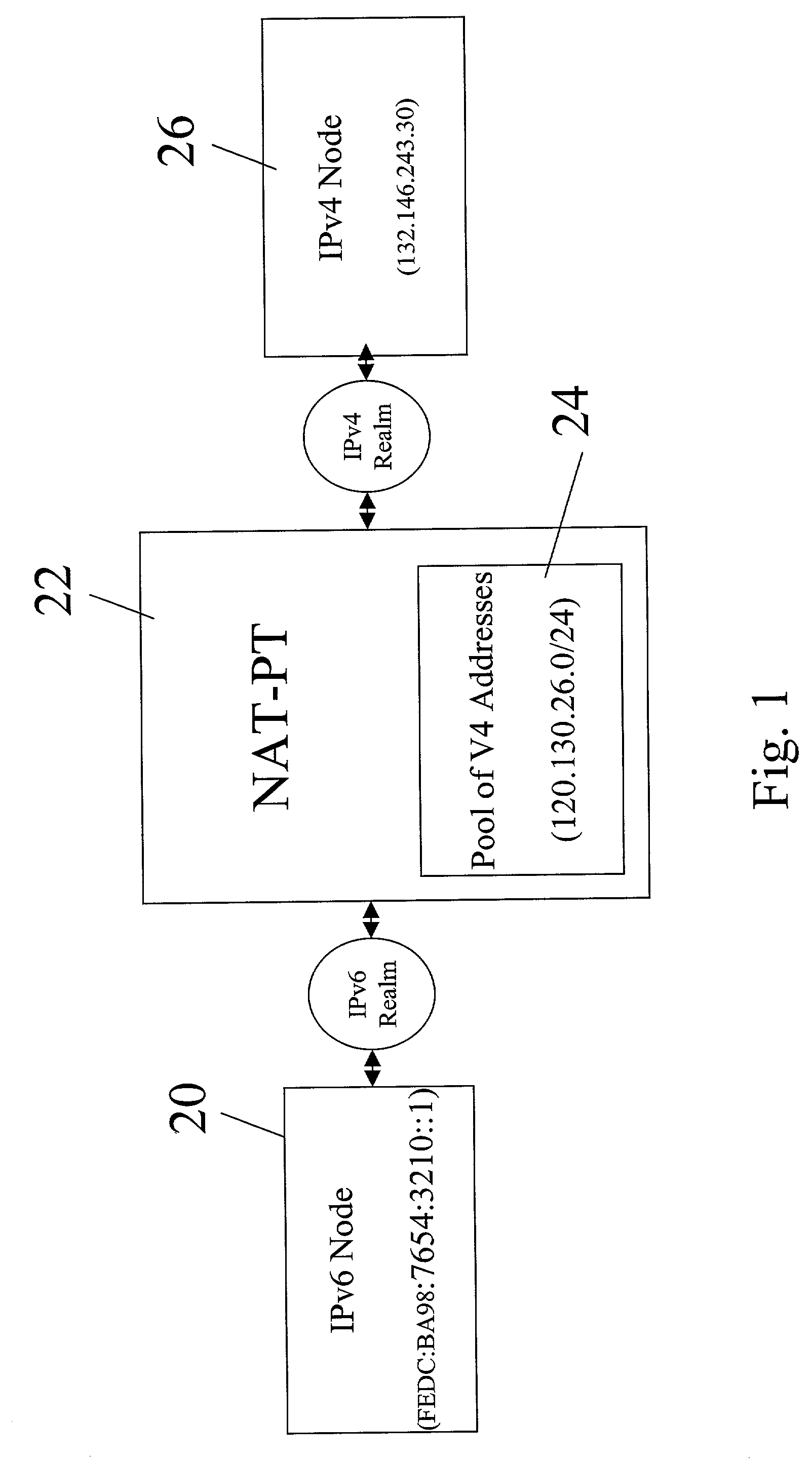
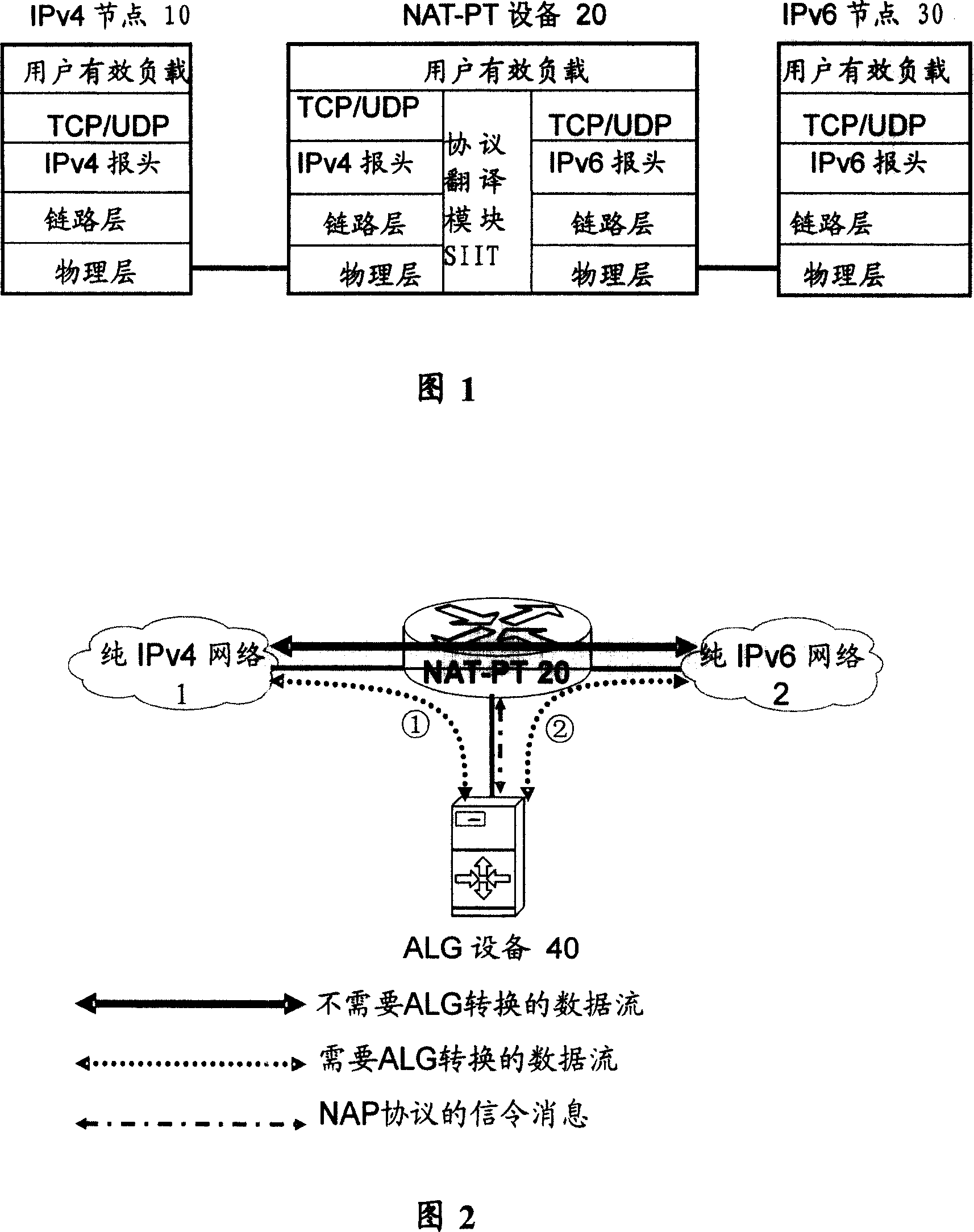
In the context of computer networking, an application-level gateway (also known as ALG, application layer gateway, application gateway, application proxy, or application-level proxy) consists of a security component that augments a firewall or NAT employed in a computer network. It allows customized NAT traversal filters to be plugged into the gateway to support address and port translation for certain application layer "control/data" protocols such as FTP, BitTorrent, SIP, RTSP, file transfer in IM applications, etc. In order for these protocols to work through NAT or a firewall, either the application has to know about an address/port number combination that allows incoming packets, or the NAT has to monitor the control traffic and open up port mappings (firewall pinhole) dynamically as required. Legitimate application data can thus be passed through the security checks of the firewall or NAT that would have otherwise restricted the traffic for not meeting its limited filter criteria.
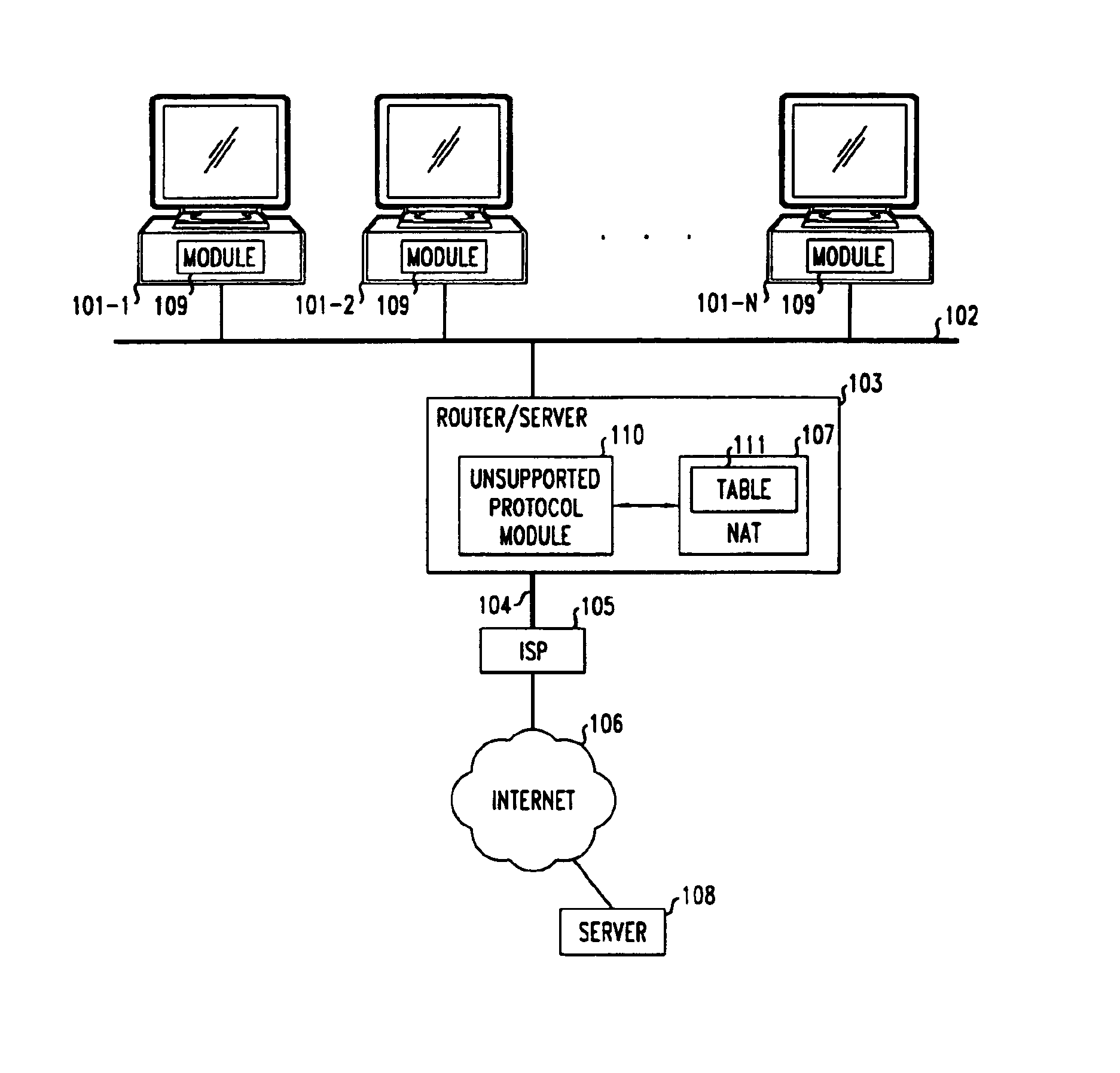
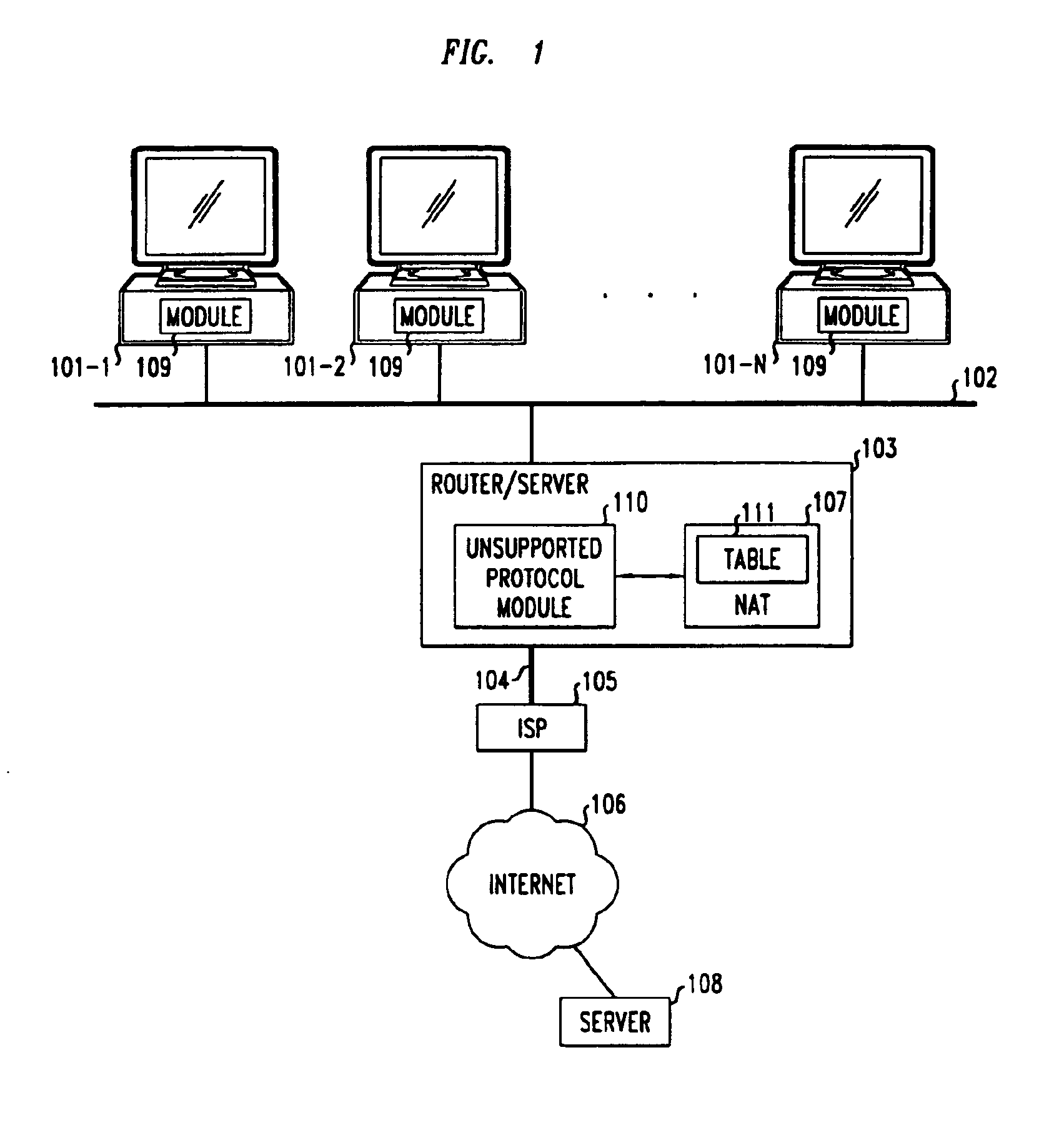
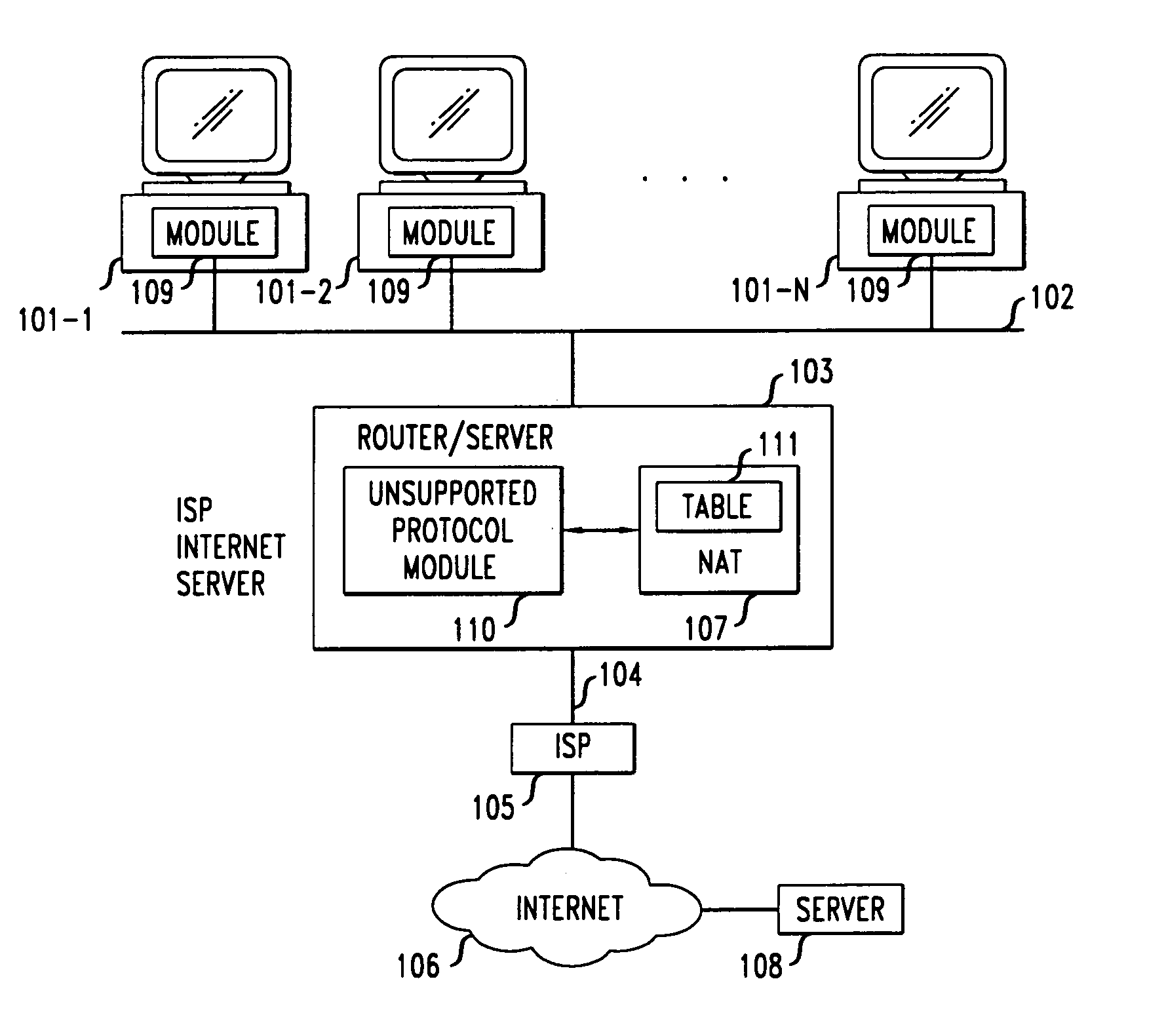
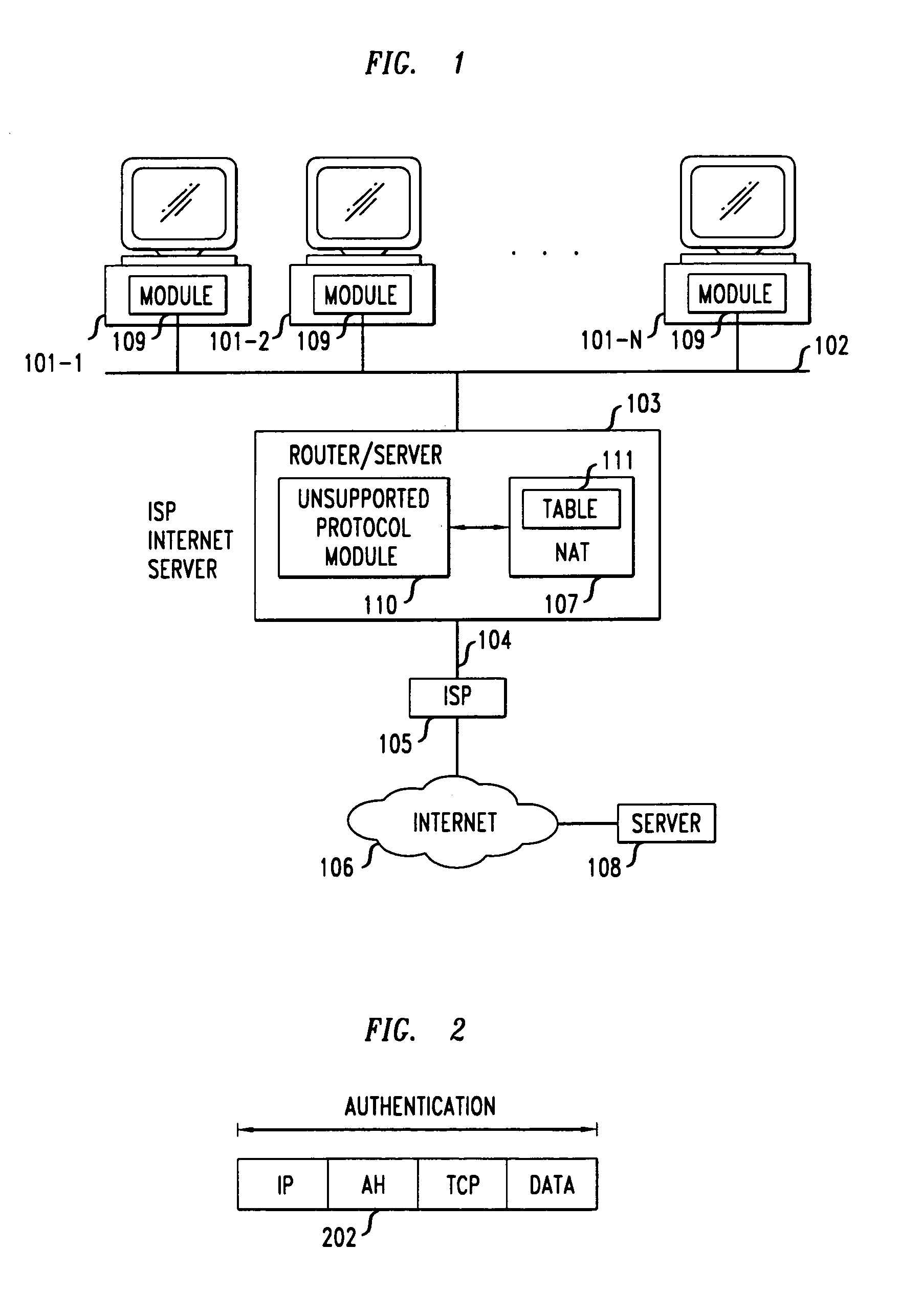
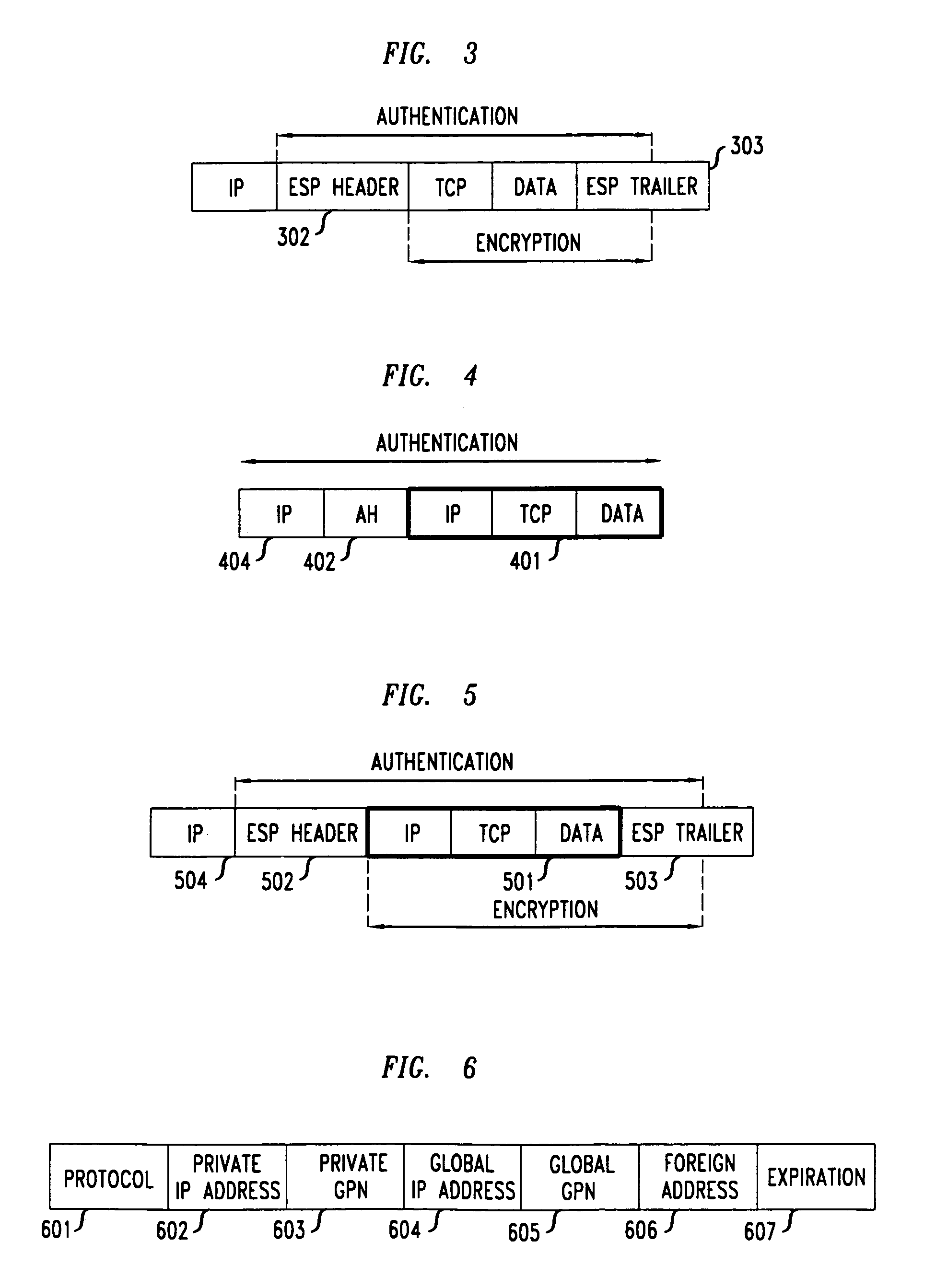
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
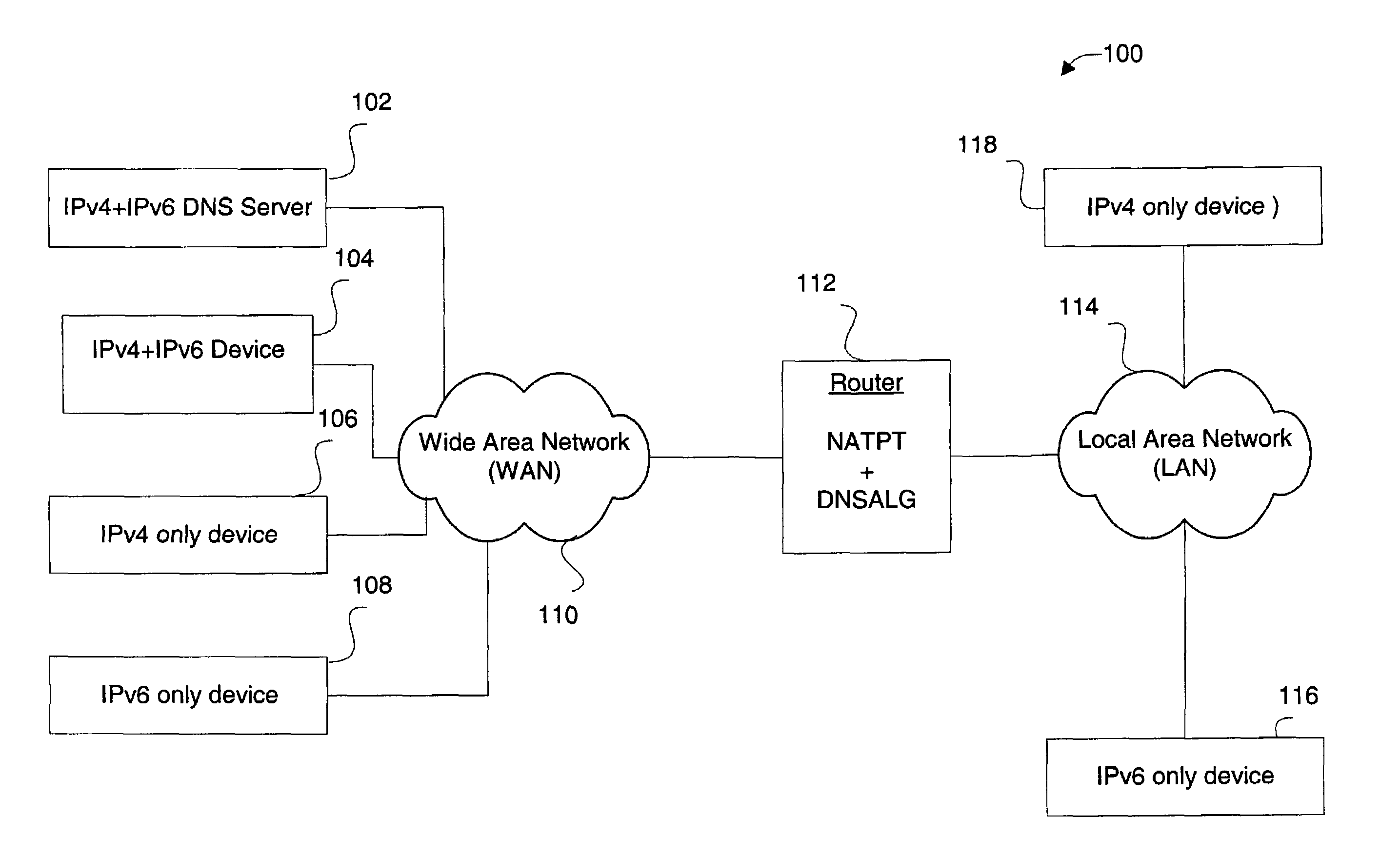
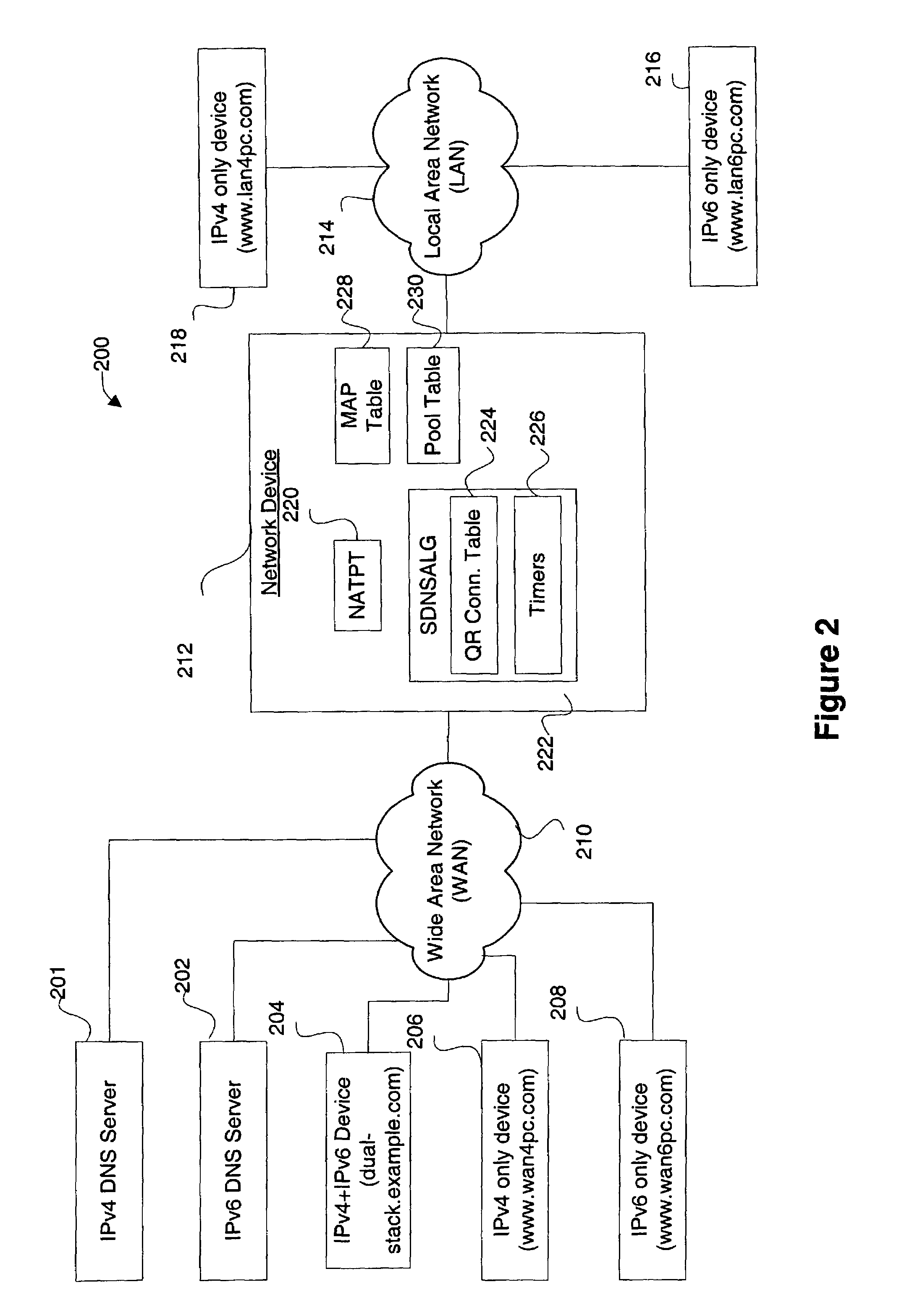
Stateful IPv4-IPv6 DNS application level gateway for handling topologies with coexisting IPv4-only, Ipv6-only and dual-stack devices
ActiveUS7526562B1Efficient and reliable processingTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain nameClient-side
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for efficiently and reliably handling DNS (domain name service) queries and responses. In general terms, mechanisms are provided for forwarding only one DNS response to a DNS client when two DNS responses having different protocols (IPv4 or IPv6) may be received, e.g., within a DNS handling device for a particular DNS query. The DNS handling device determines whether to forward or hold a first received DNS response based on a number of criteria. The DNS handling device also determines whether to forward a first or second received response to the DNS client when a first and second response for a particular query is received. In certain cases, a first received DNS response for a particular DNS query may be held until a second better response is received or a timer expires.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
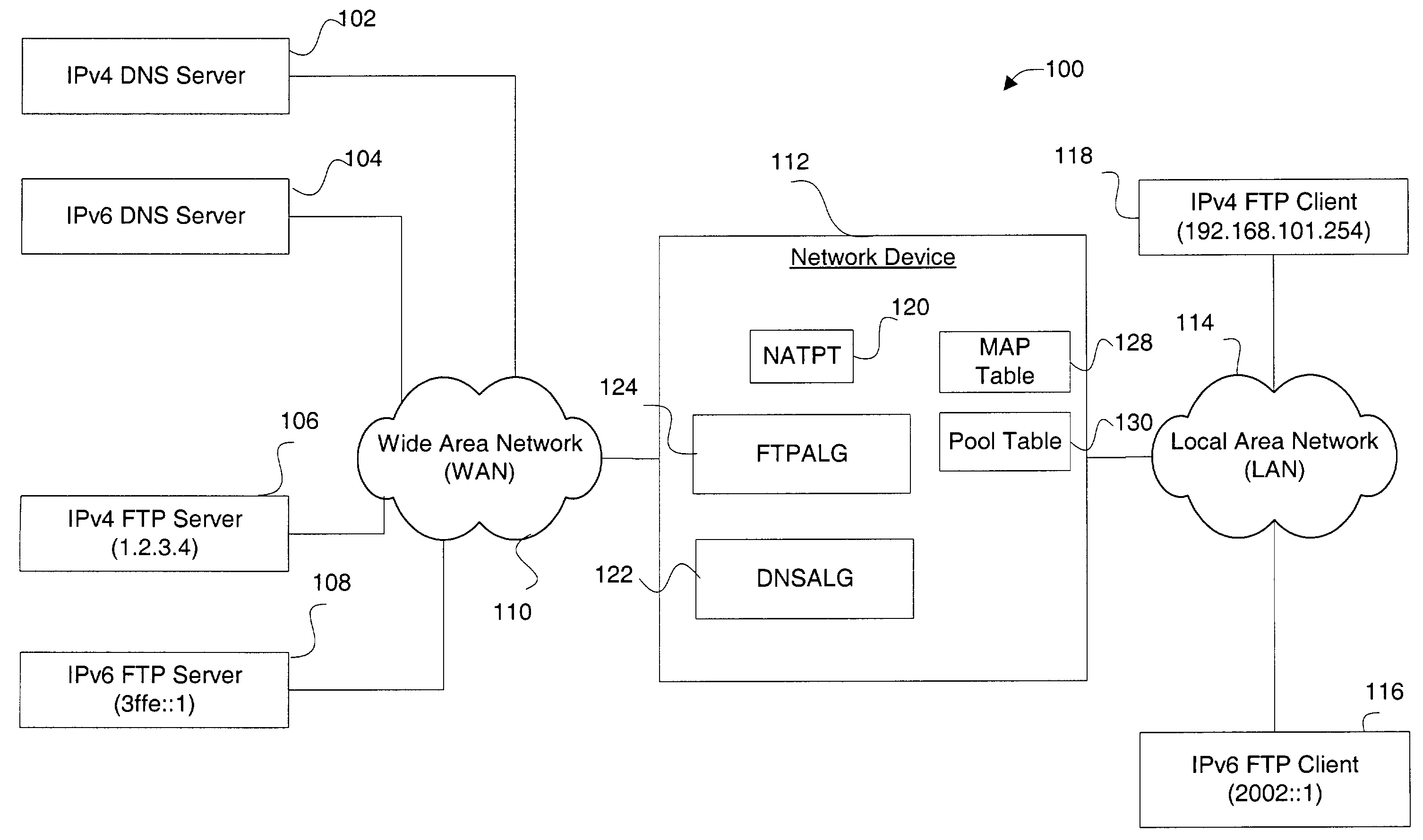
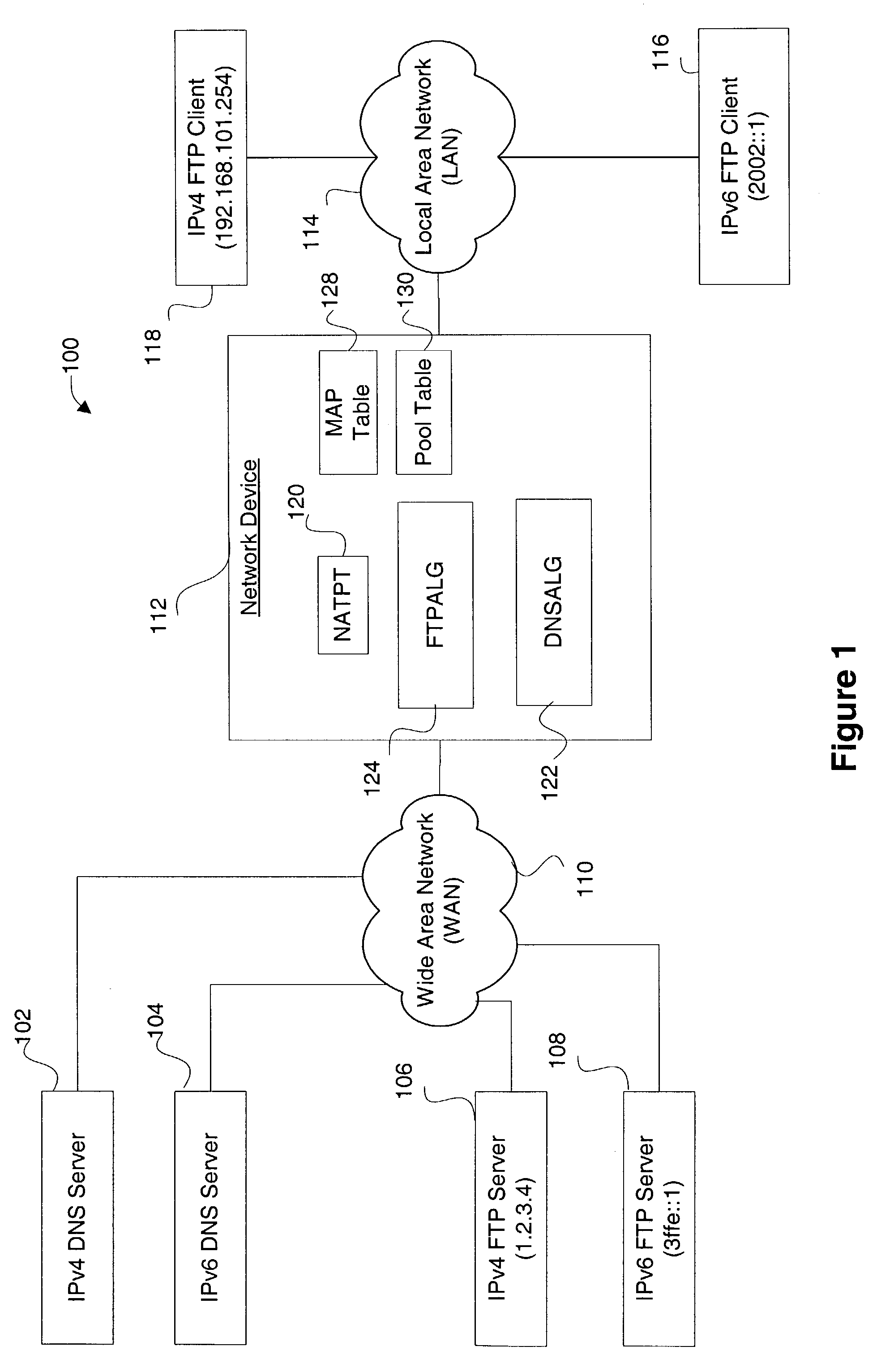
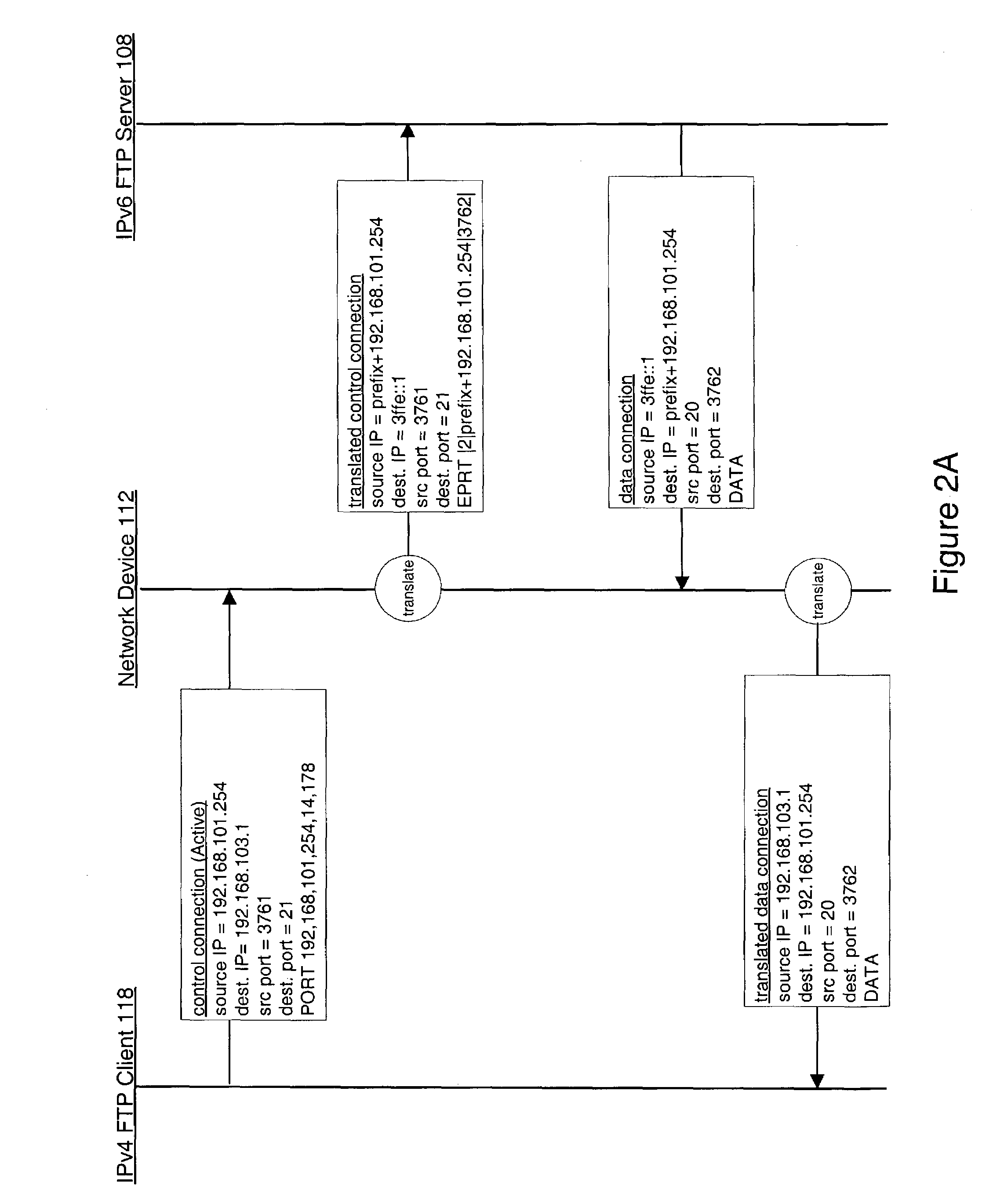
IPv4-IPv6 FTP application level gateway
ActiveUS7391768B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideComputer science
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for handling FTP (file transfer protocol) control packets. In general terms, mechanisms are provided for facilitating FTP sessions between devices utilizing different protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6. For example, FTP control packets from an IPv6 client to an IPv4 server are handled to facilitate such communication. Likewise, FTP control packets from an IPv4 client to an IPv6 server are handled to facilitate such communication. Communication is also facilitated when either or both of the client or server is in the form of a dual-stack device. To facilitate FTP session between devices having different protocols, FTP control packets between two different protocol devices are translated from one protocol to another protocol when required, e.g., from an IPv6 to an IPv4 format or visa versa.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
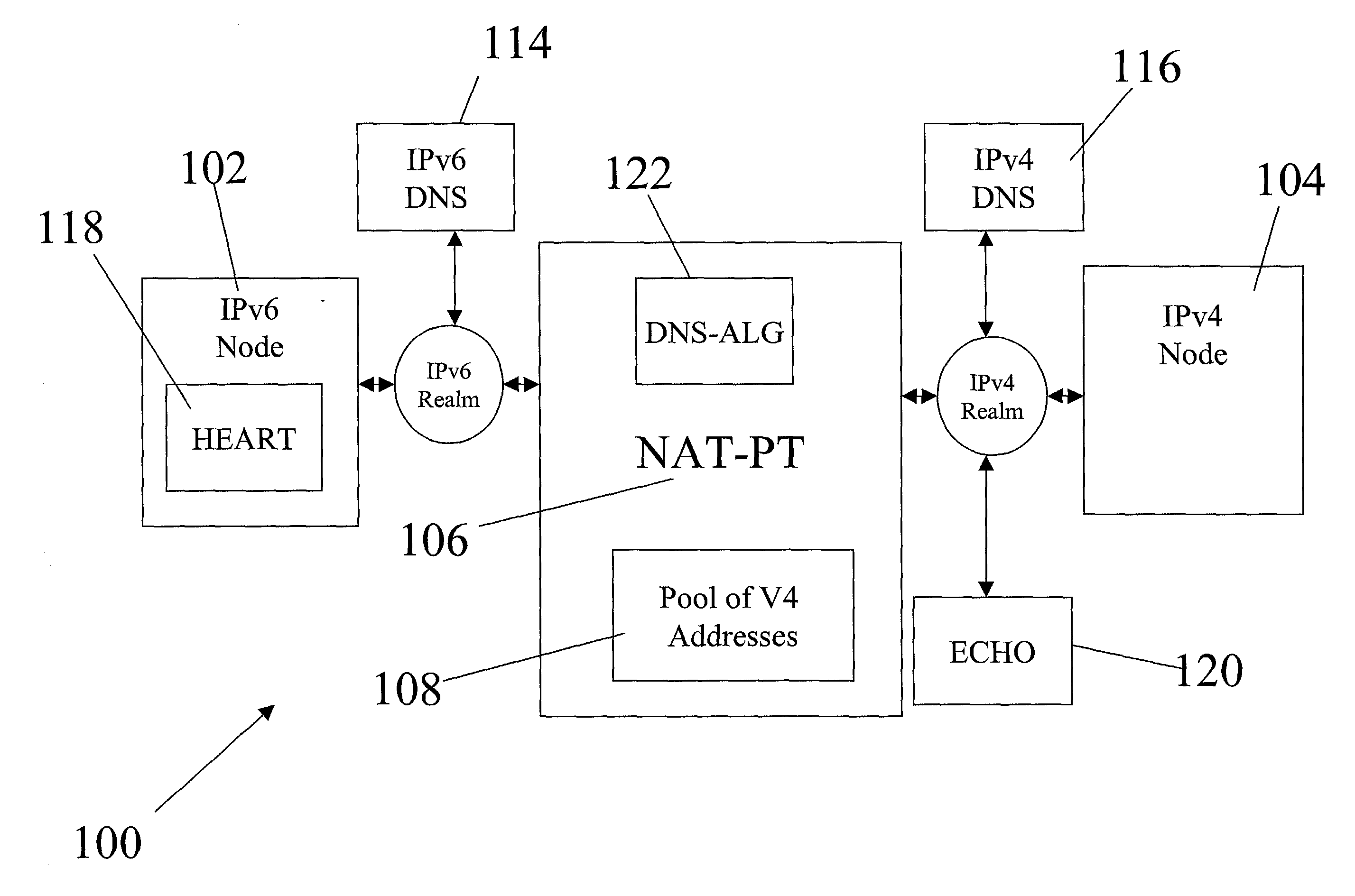
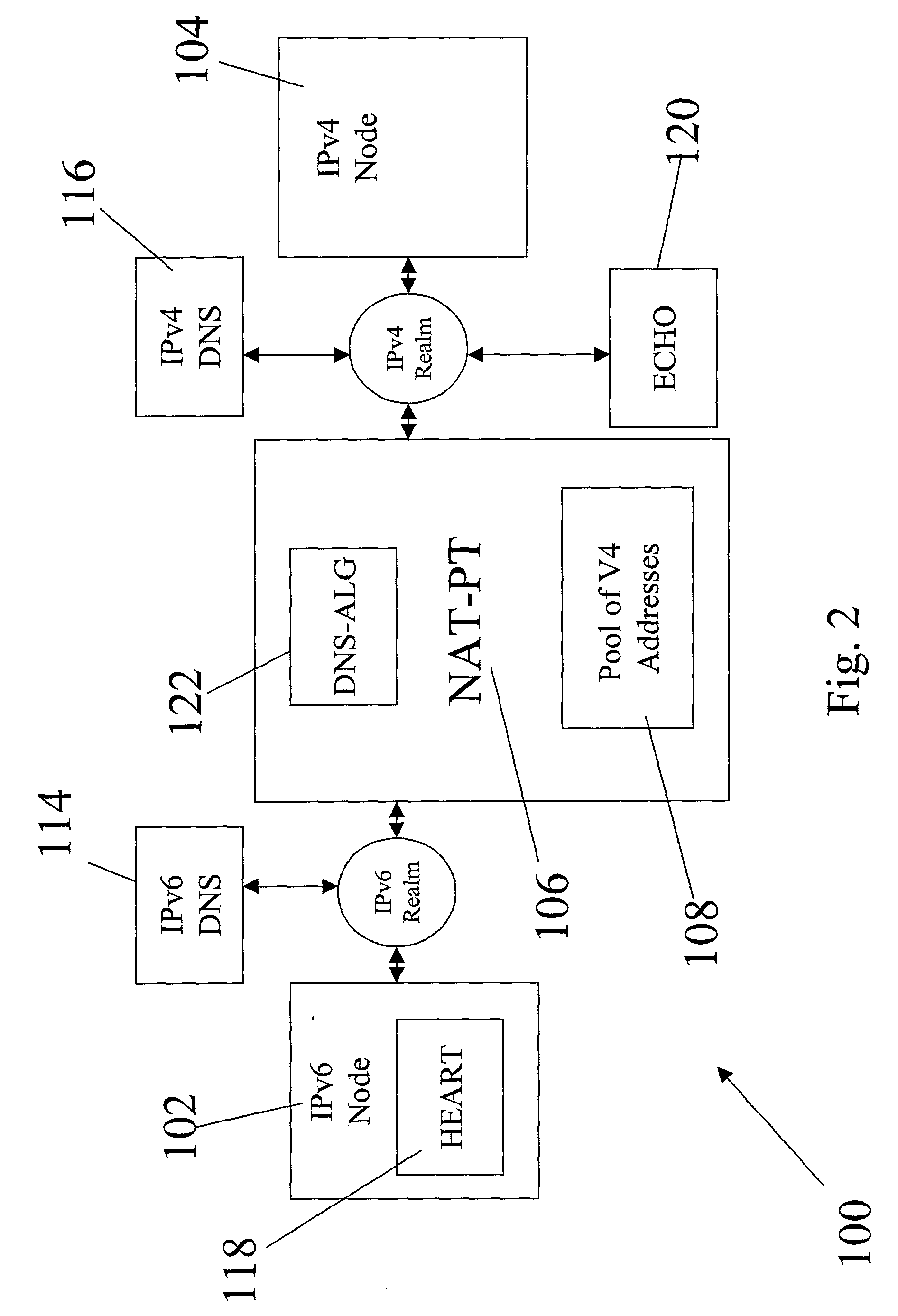
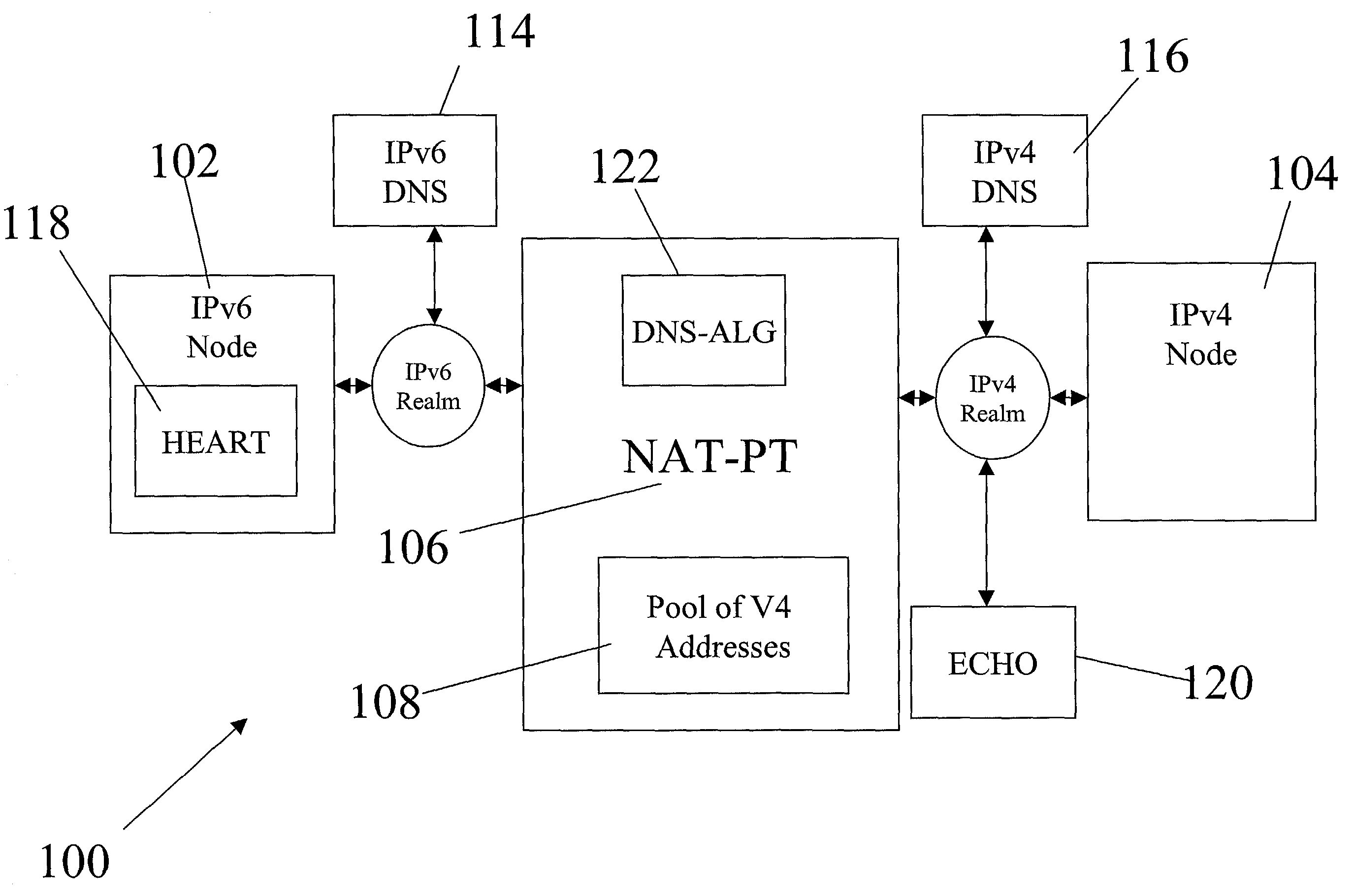
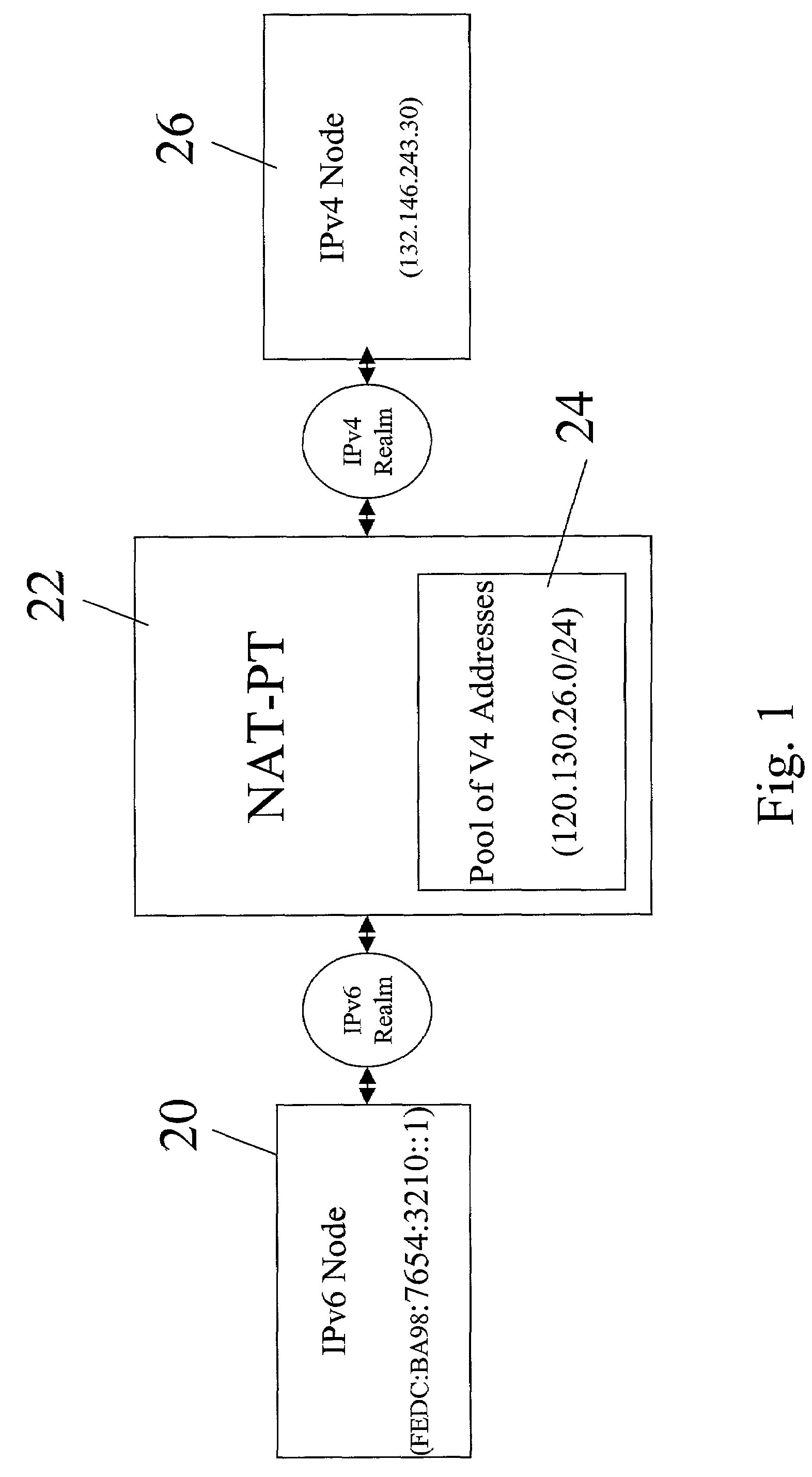
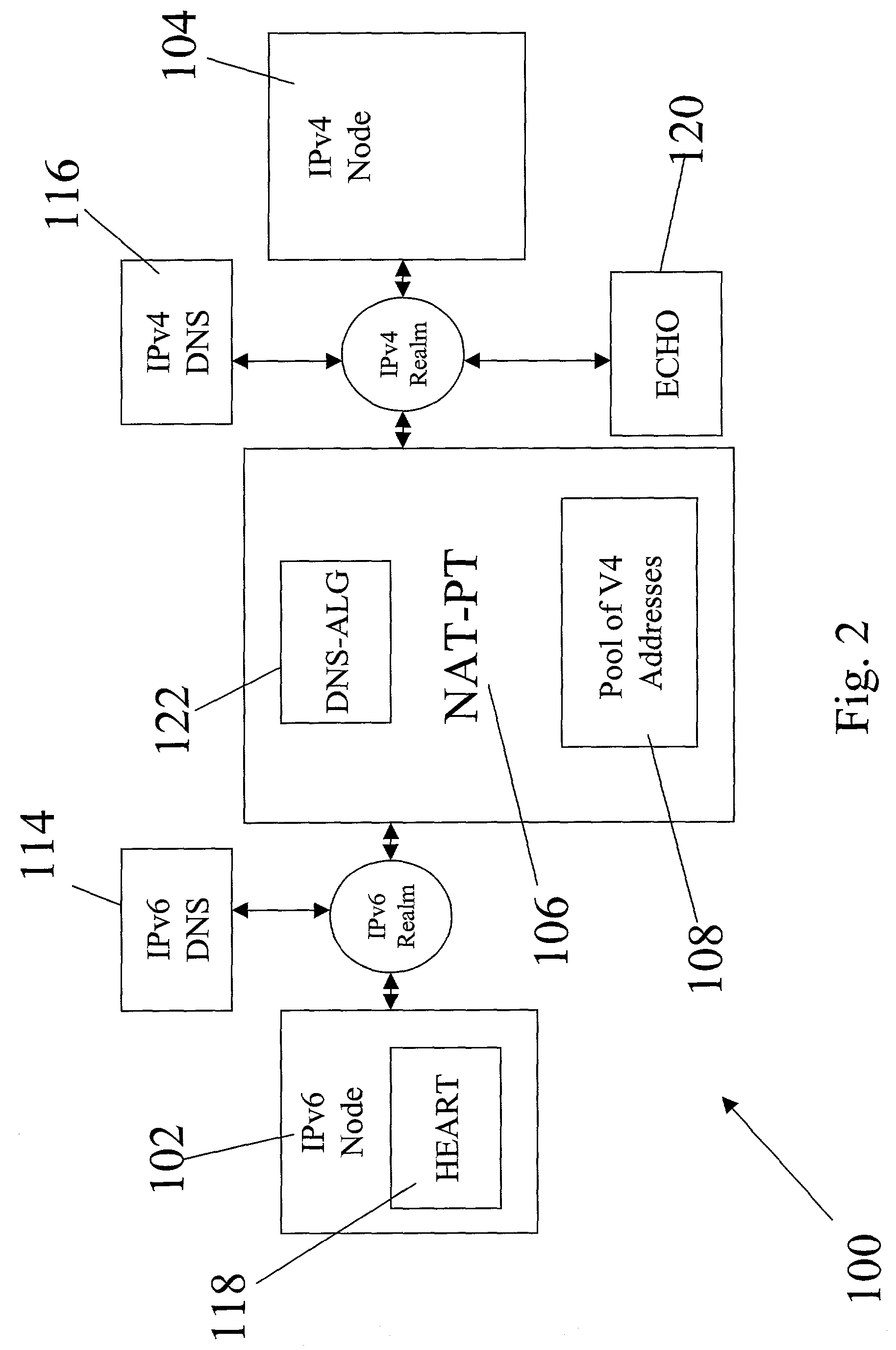
Non-ALG approach for application layer session traversal of IPv6/IPv4 NAT-PT gateway
InactiveUS20040001509A1Time outSimple and efficient techniqueTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingNetwork address
A structure for coupling together addressably disparate nodes, such as IPv4 nodes and IPv6 nodes, without the use of an application level gateway. Instead, the system includes two executable applications, HEART and ECHO, that avoid the necessity of an application level gateway. In general, HEART and ECHO cooperate with each other through a network address translator-protocol translator (NAT-PT) to cause the NAT-PT to temporarily assign an IPv4 address to a control session between the IPv4 and IPv6 nodes and also prevent the control session from timing out due to lack of timely communications between the IPv4 and IPv6 nodes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Setting up a name resolution system for home-to-home communications
InactiveUS20050066041A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionPrivate addressA domain
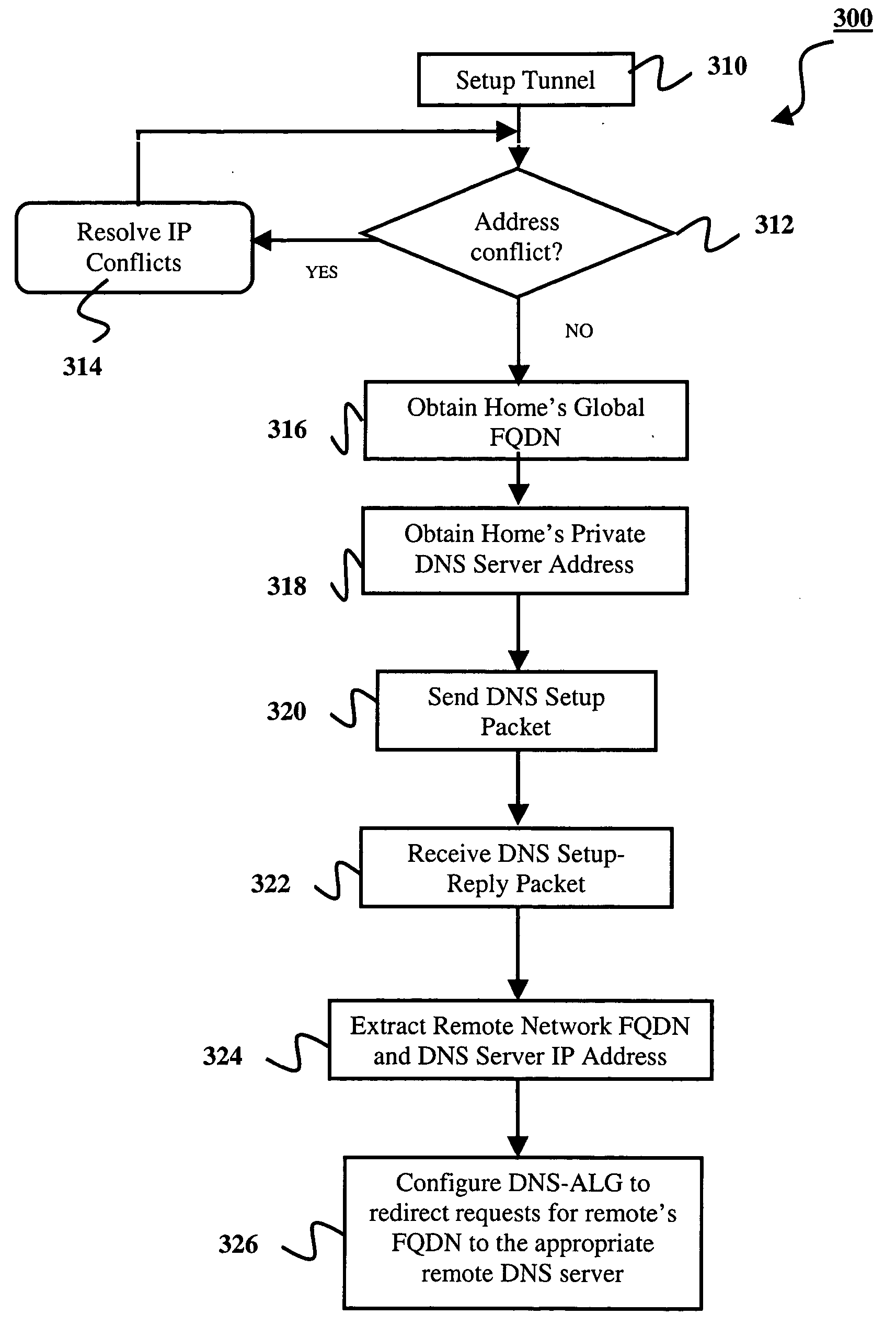
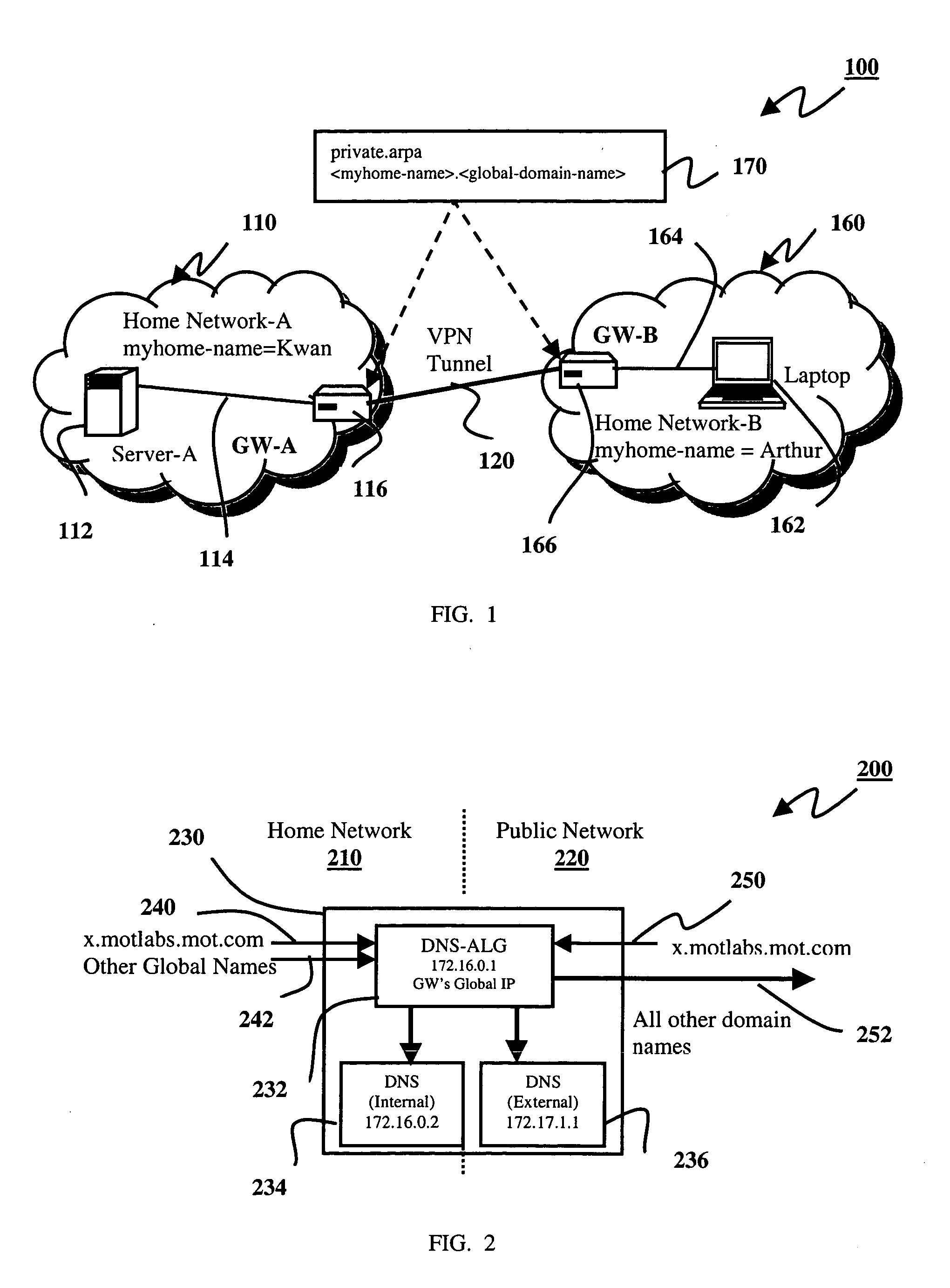
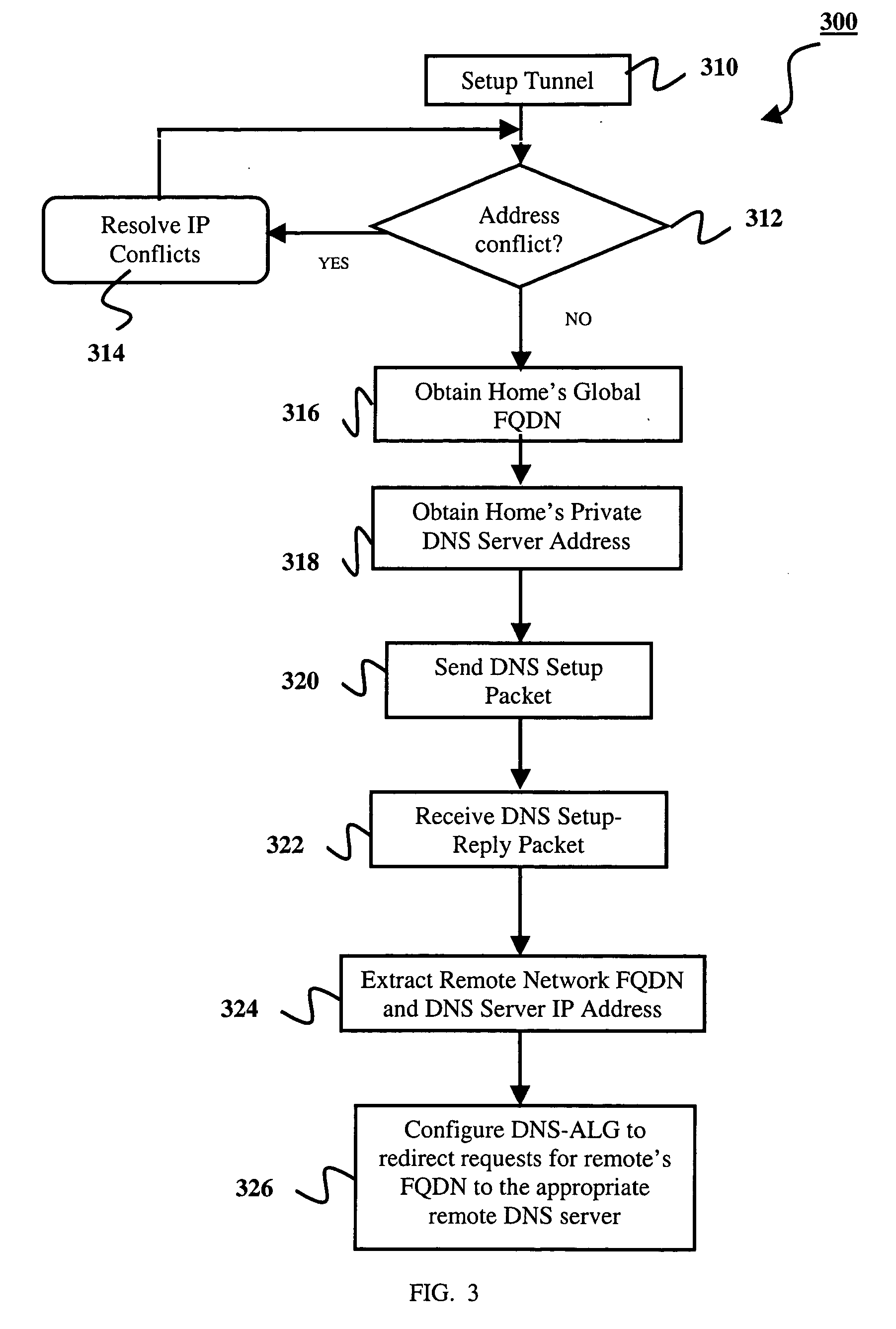
Methods, systems, and gateways are disclosed for automatically setting up a redirector of domain name system (DNS) name requests. A DNS setup packet is transmitted to a remote gateway via a tunnel of a virtual private network (VPN). The setup packet comprises a global name of a home network and a private address of a DNS server in the home network. A DNS setup reply packet is received from the remote gateway via the tunnel. The reply packet comprises a global name of another home network and a private address of a DNS server in the other home network. An application level gateway of the DNS server (DNS-ALG) in the home network is configured dependent upon the DNS setup reply packet to redirect DNS name requests for the global name of the other network to the DNS server in the other network. Methods, systems, and gateways are also disclosed for resolving a domain name request in a DNS.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for application-independent end-to-end security in shared-link access networks
InactiveUS6963982B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeEnd to end security
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
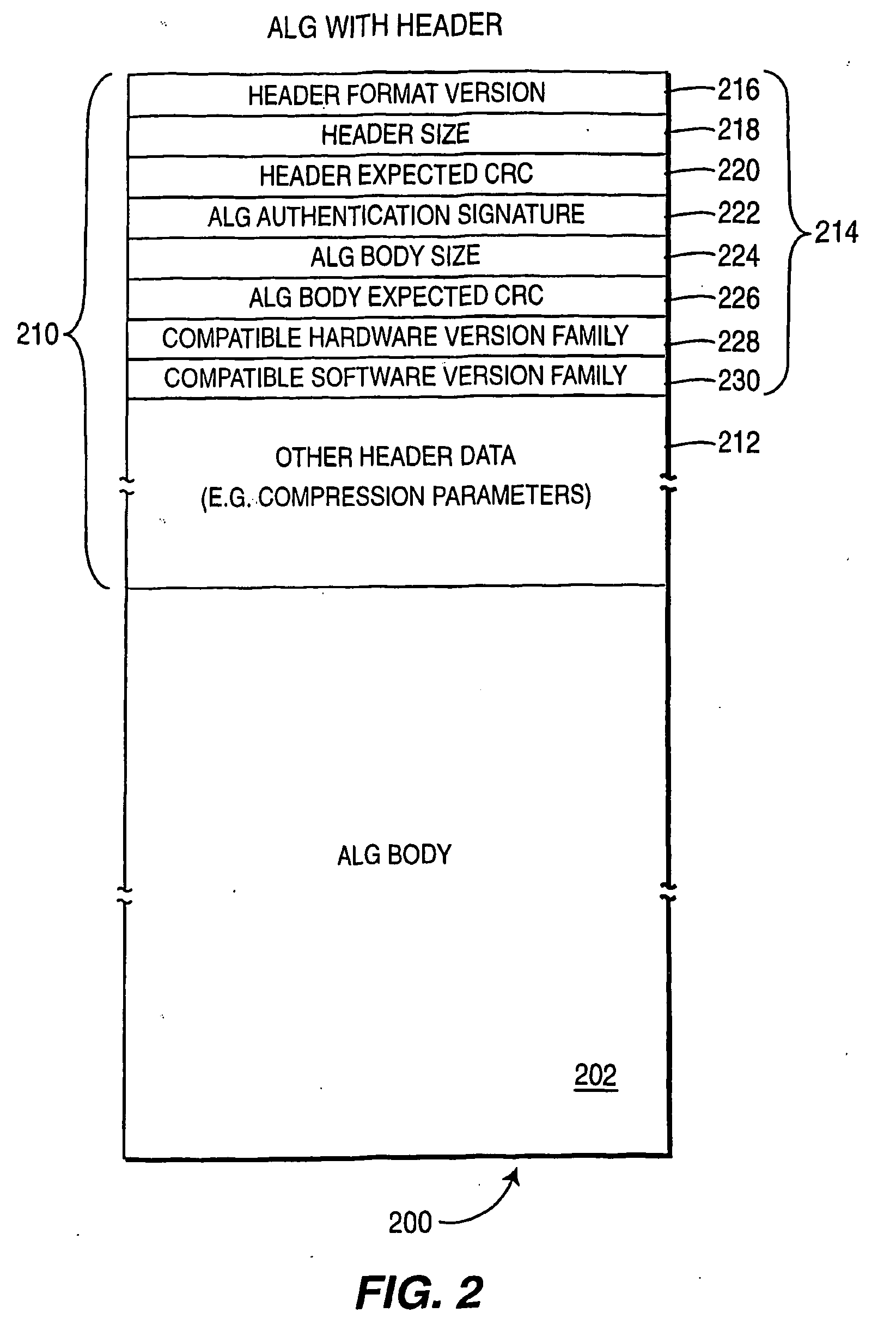
Application level gateway and firewall rule set download validation
InactiveUS20050220126A1Broadband local area networksProgram loading/initiatingValidation methodsComputer compatibility
Method ( 300 ) and apparatus for validating application level gateway files or firewall rulsets. The method and apparatus include receiving at a bidirectional communications device, an application level gateway file, and comparing at least one compatibility parameter of said ALG file with features of said bi-directional communications device. In an instance where all of the compatibility parameters compare favorably, the ALG file is stored at the bidirectional communications device.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
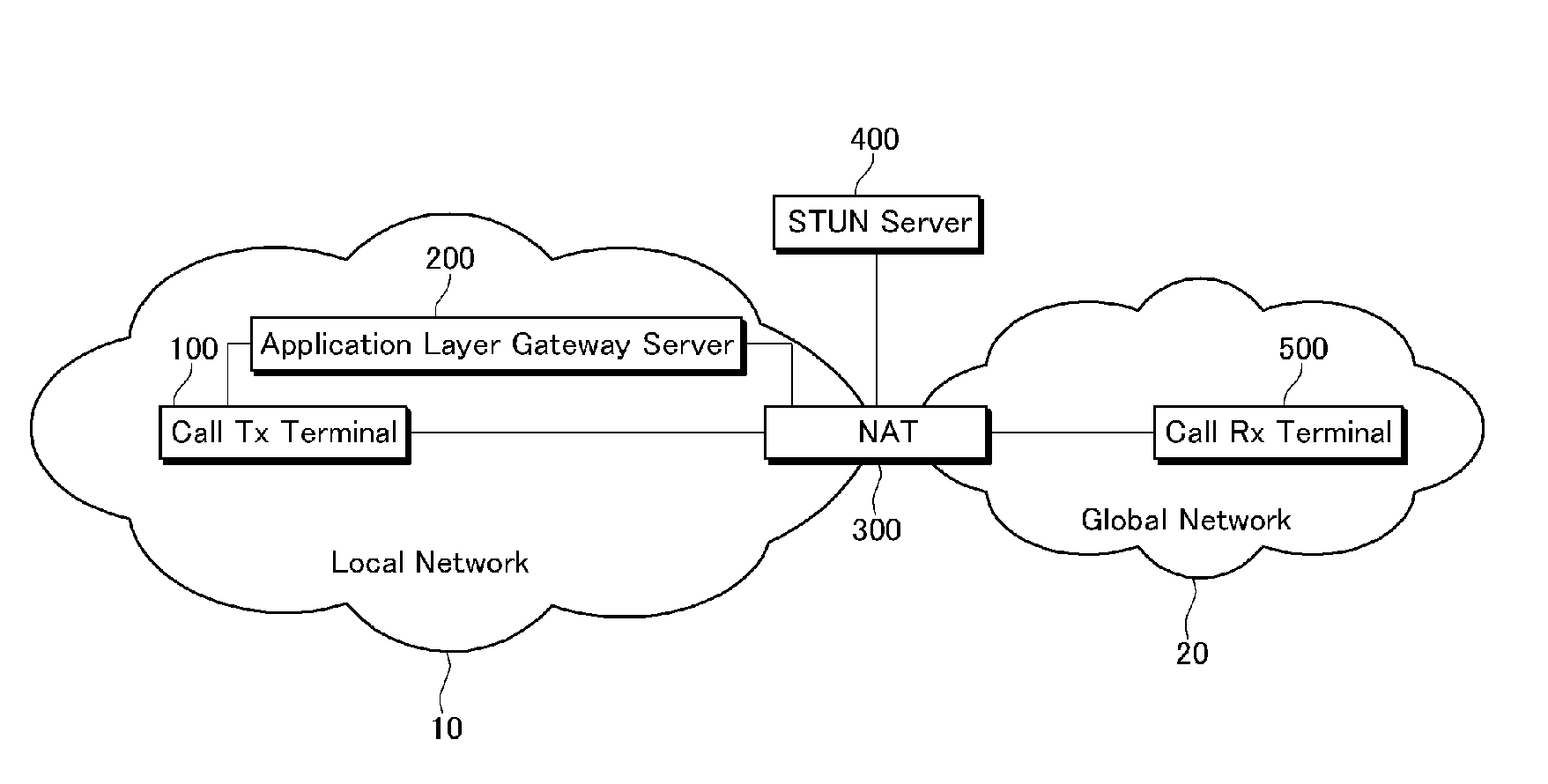
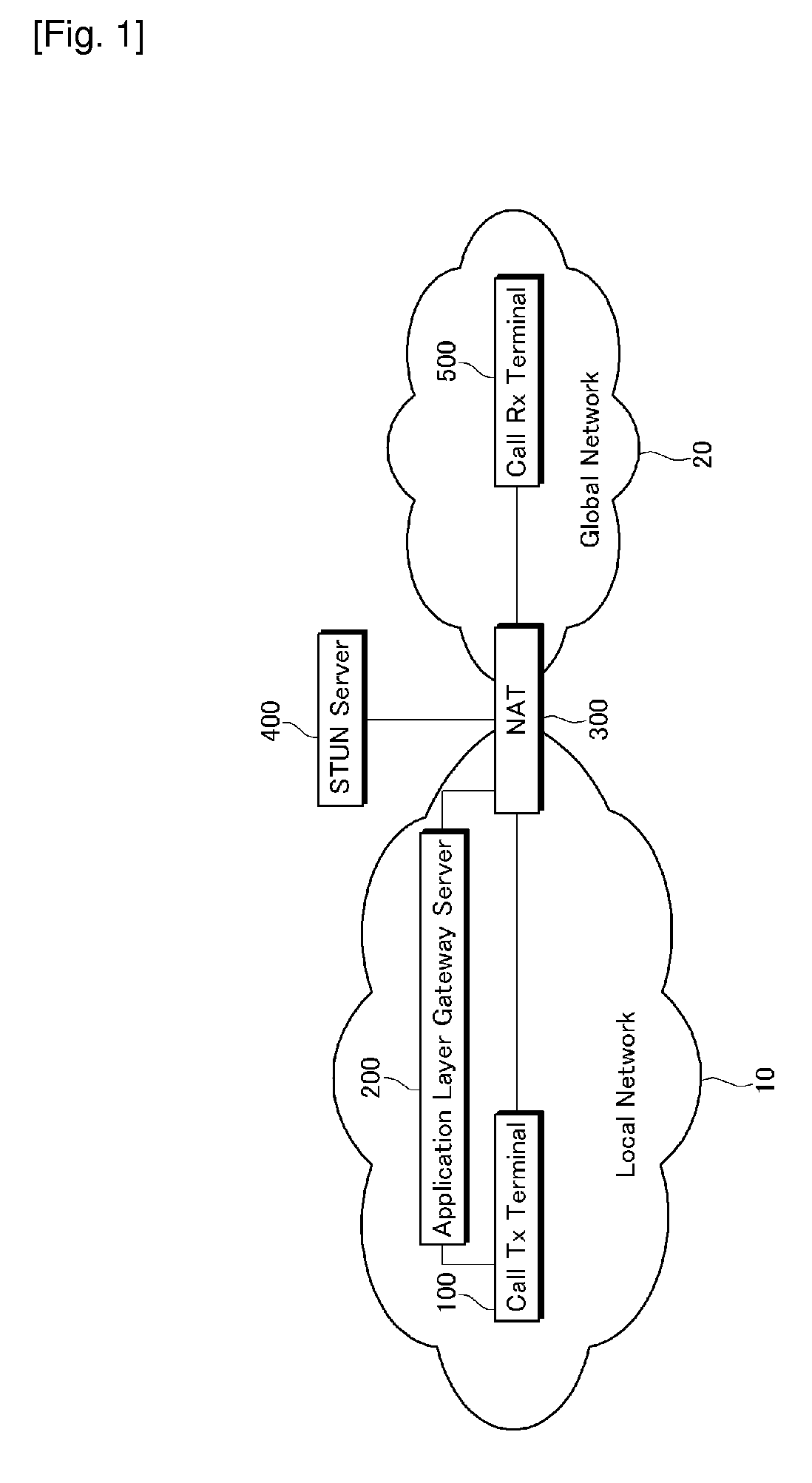
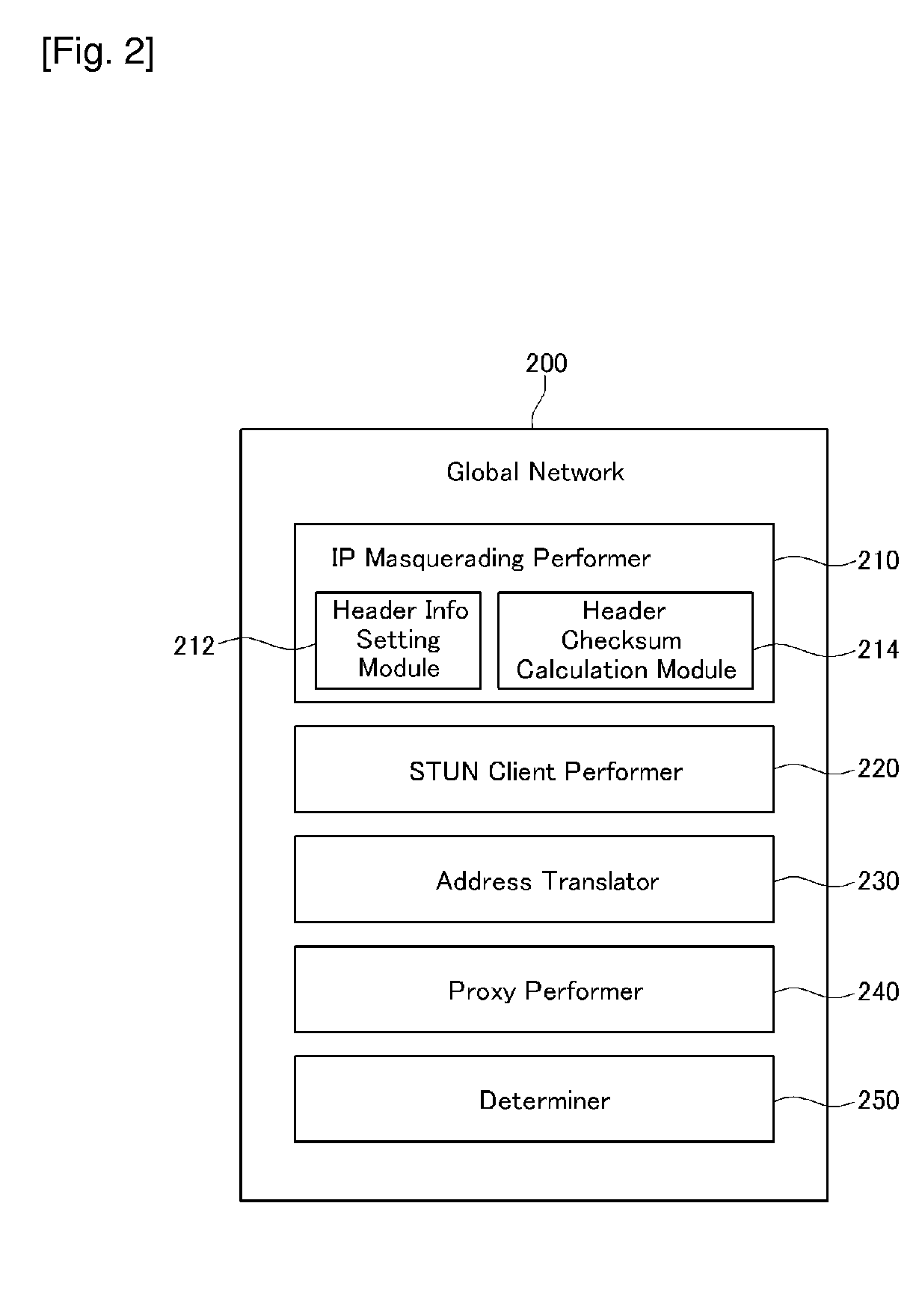
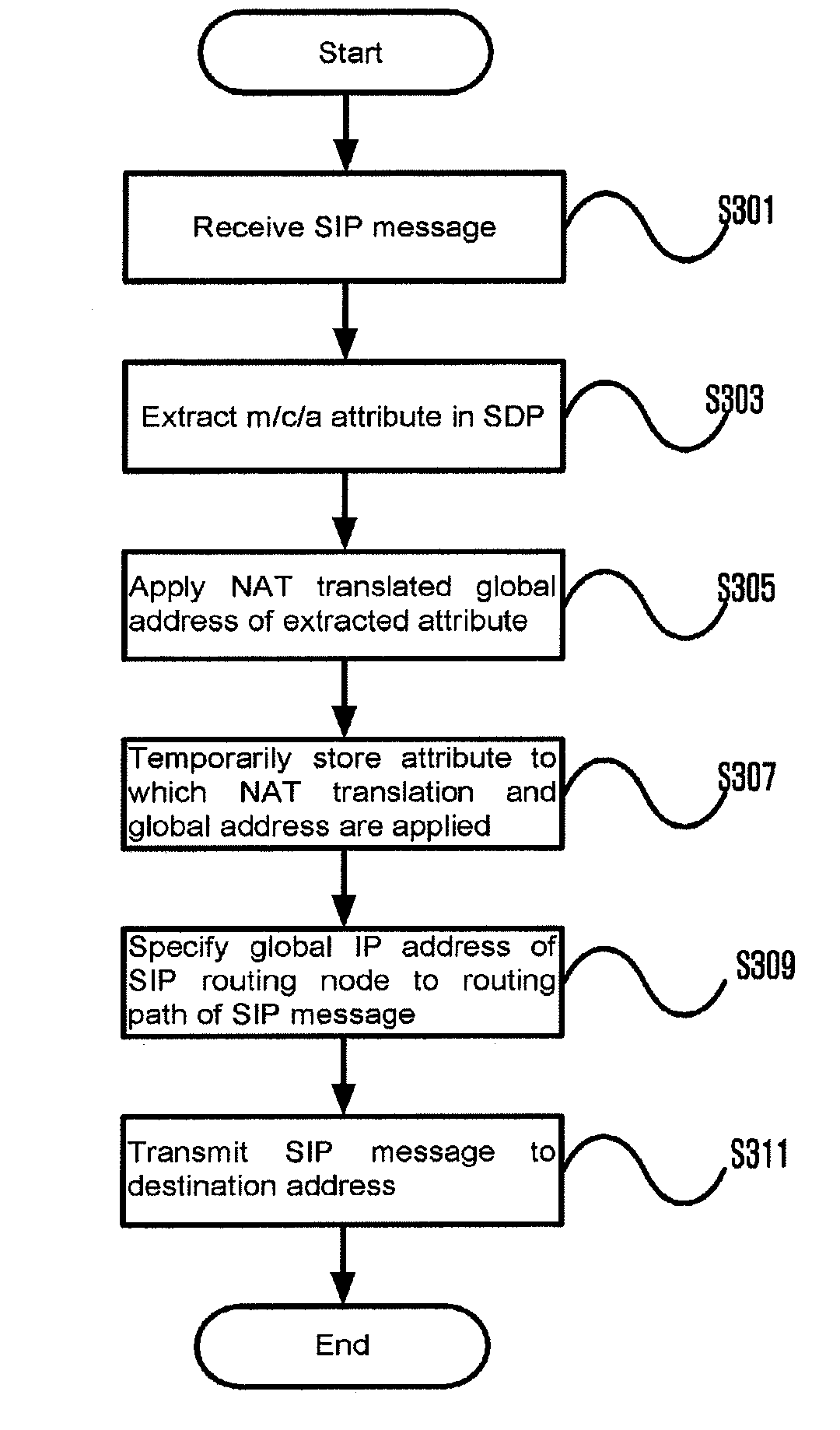
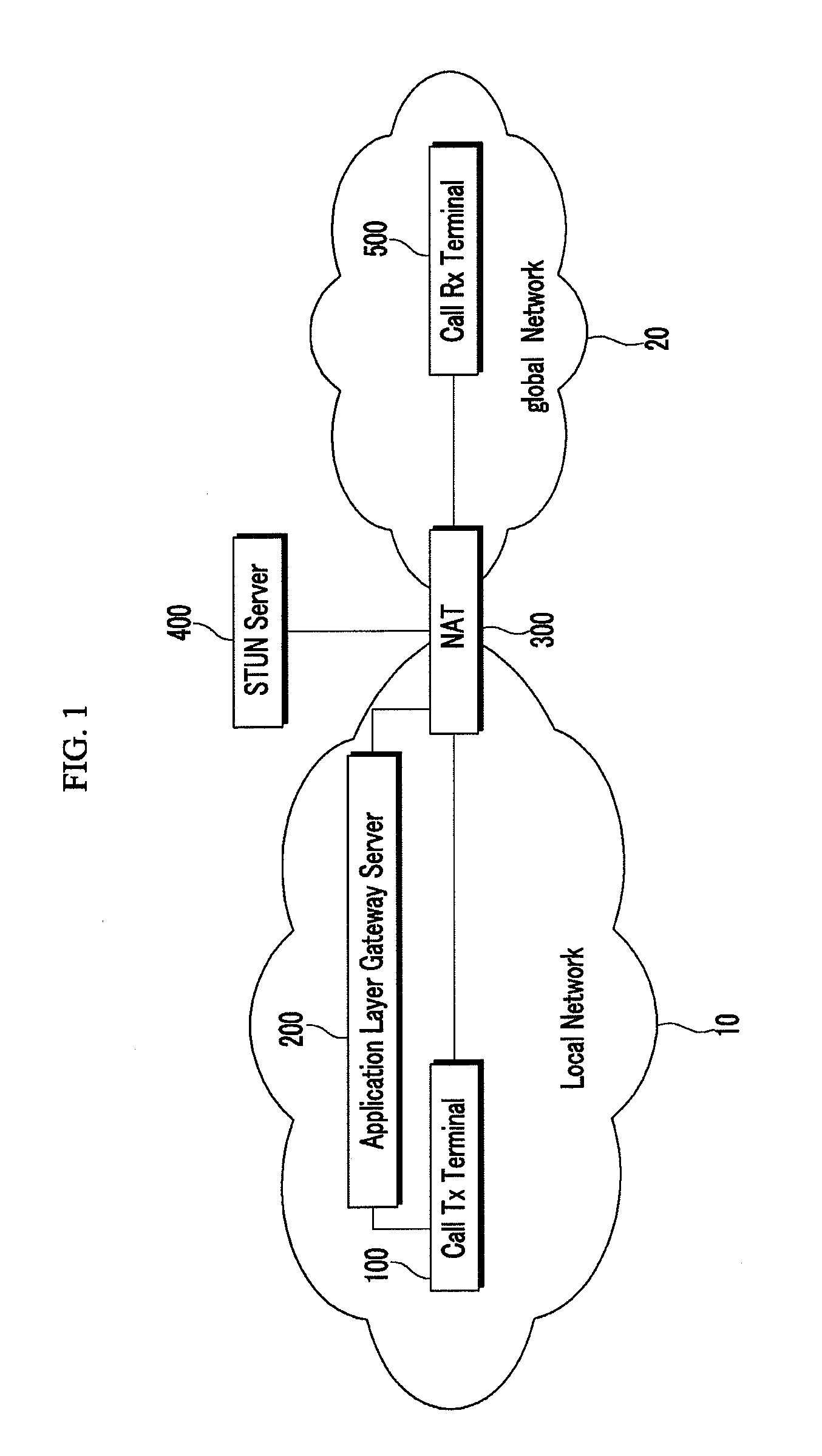
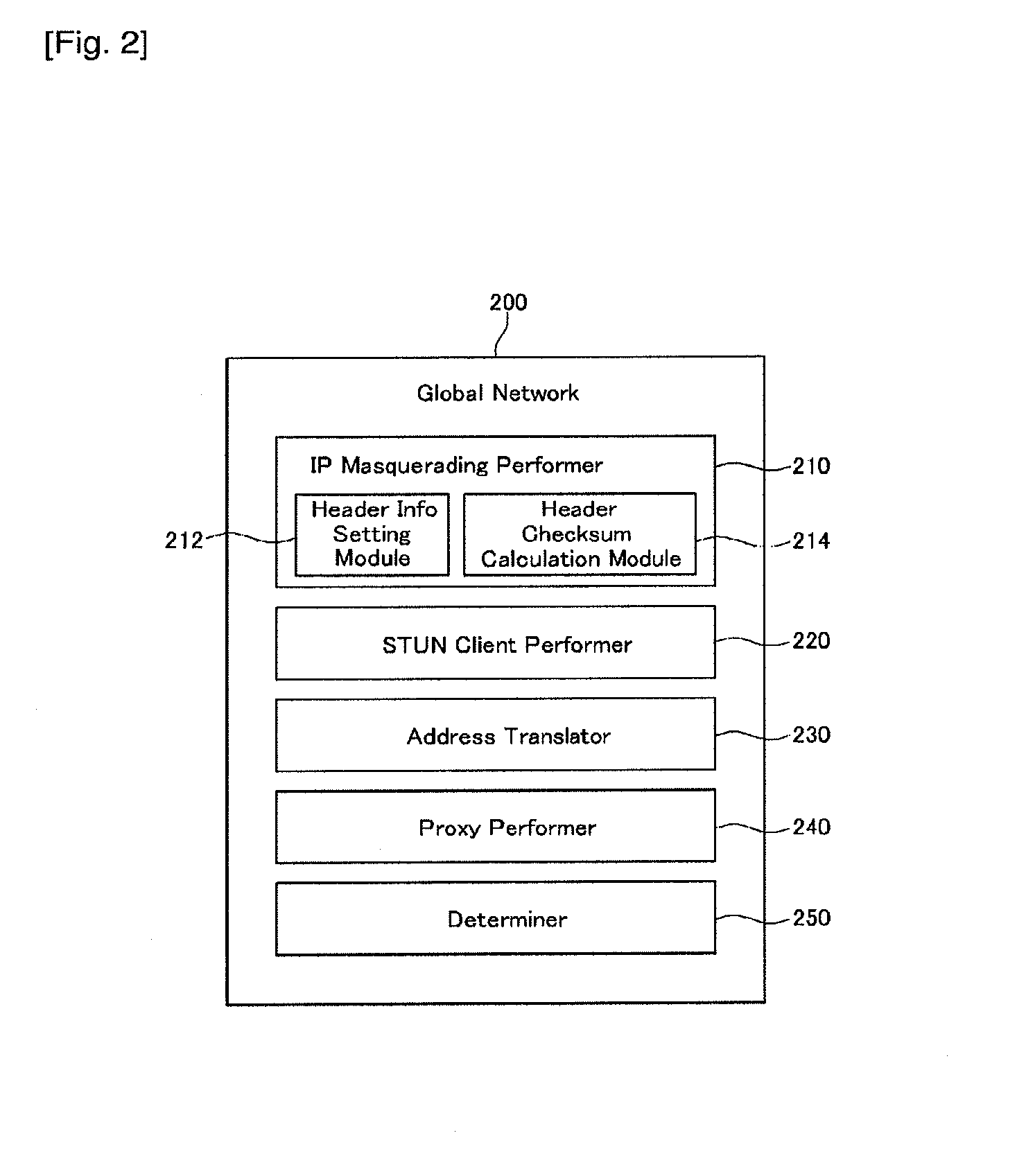
Inter working system between IP networks using different IP address format, application layer gateway (ALG) server, stun server, network address translator, interworking method thereof, and sIP message routing method thereof
ActiveUS20090180476A1Load minimizationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionPrivate IPSTUN
Disclosed are an interworking system between IP networks using different IP address format, an application layer gateway (ALG) server, a network address translator, an interworking method, and a SIP message routing method. The interworking system between a local network using a private IP and a public network using a public IP includes a STUN server and an application layer gateway (ALG) server. The STUN server provides binding information of header information of a public IP binding request. The application layer gateway (ALG) server performs a public IP binding request with header information changed by IP masquerading, and performs routing by applying the received binding information to media receiving address information of a SIP message.
Owner:KT CORP
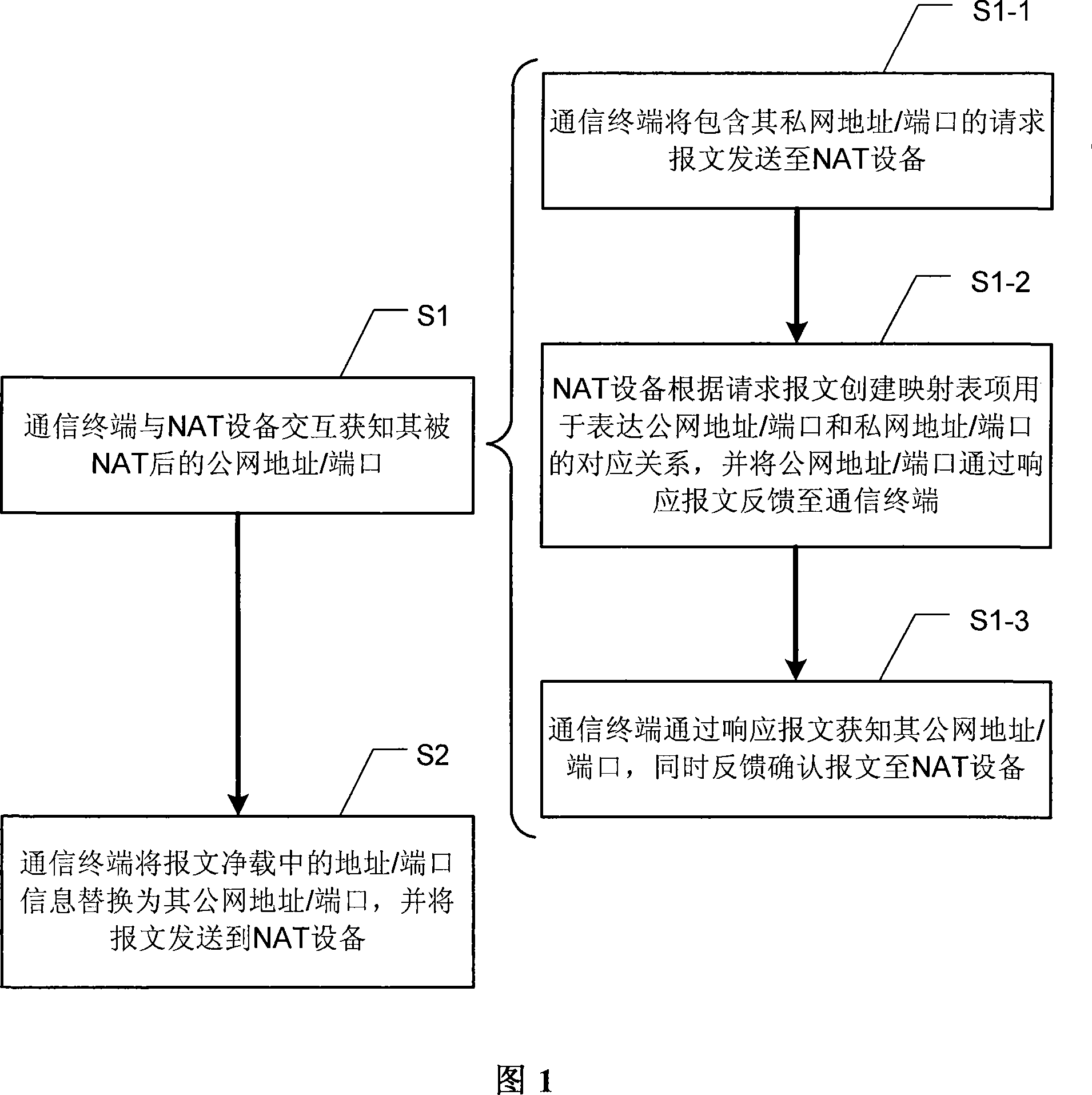
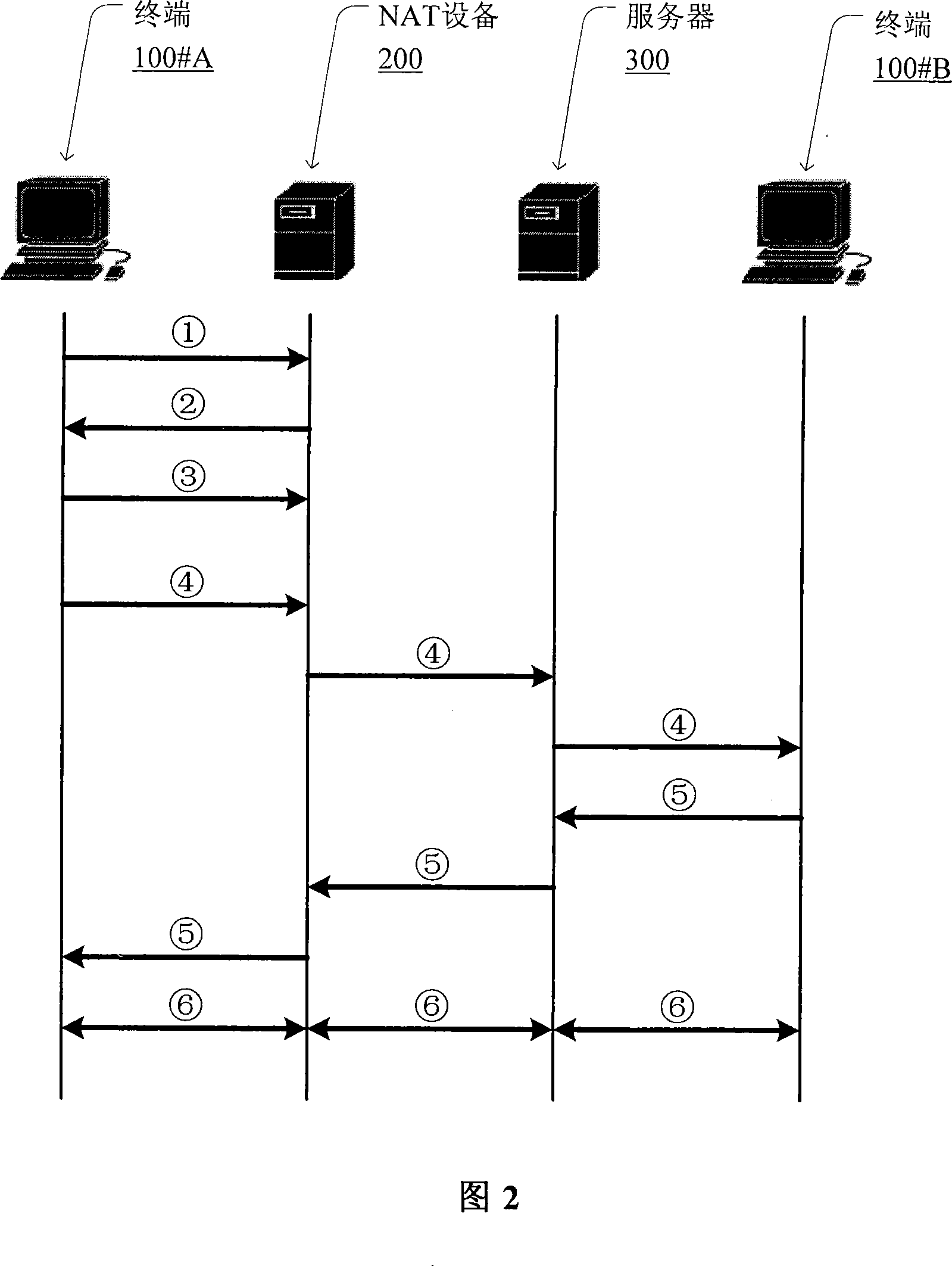
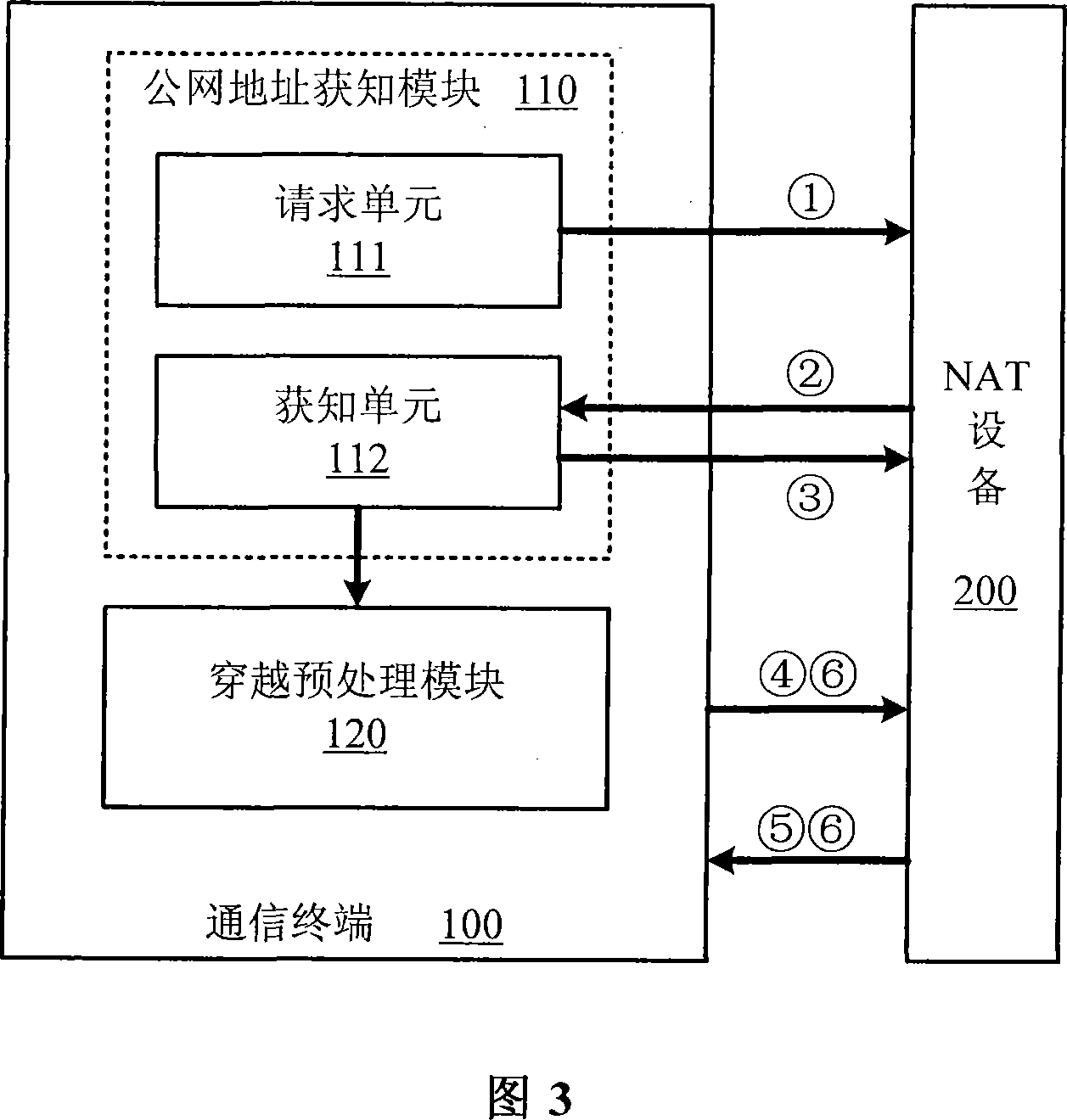
Method for penetrating the NAT and corresponding communication terminal and NAT device
The invention relates to a network communication area and discloses a method for penetrating the NAT. The method mainly includes: step S1: the communication terminal after the NAT device interacts with the NAT device to get the public network address and / or port behind the NAT from the NAT; step S2: the communication terminal fills the private network address and / or port information of the packet net payload as the public network address and / or port, and send the packets to the NAT device. The invention discloses the corresponding communication terminal and NAT device to support the implementation of the above method. Compared with the existing technology, the invention does not require NAT device to support the ALG (application layer gateway) and need not realize the STUN (UDP simple penetration mode of NAT) protocol, so it eliminates the limit of the static manual configuration.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
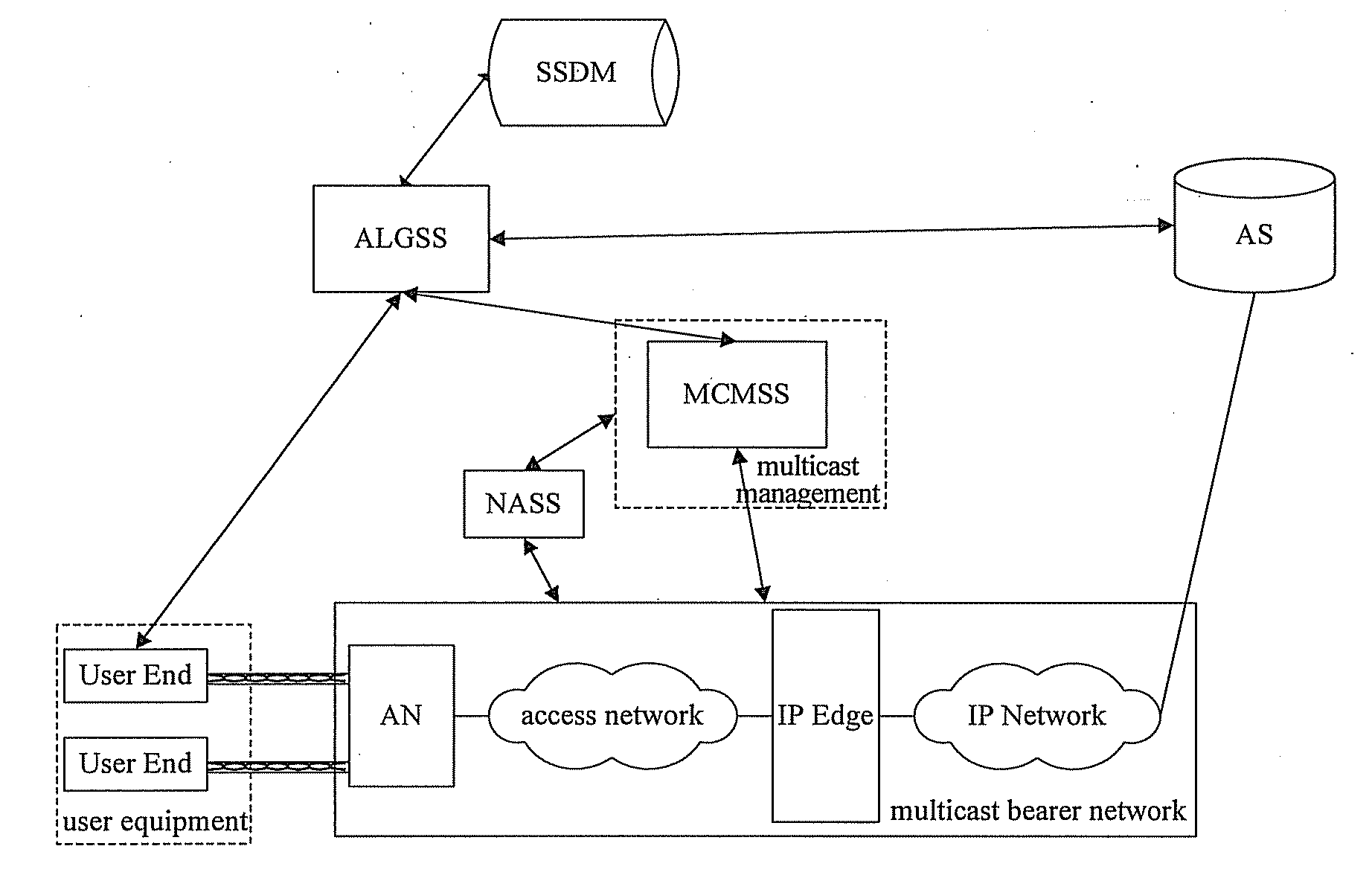
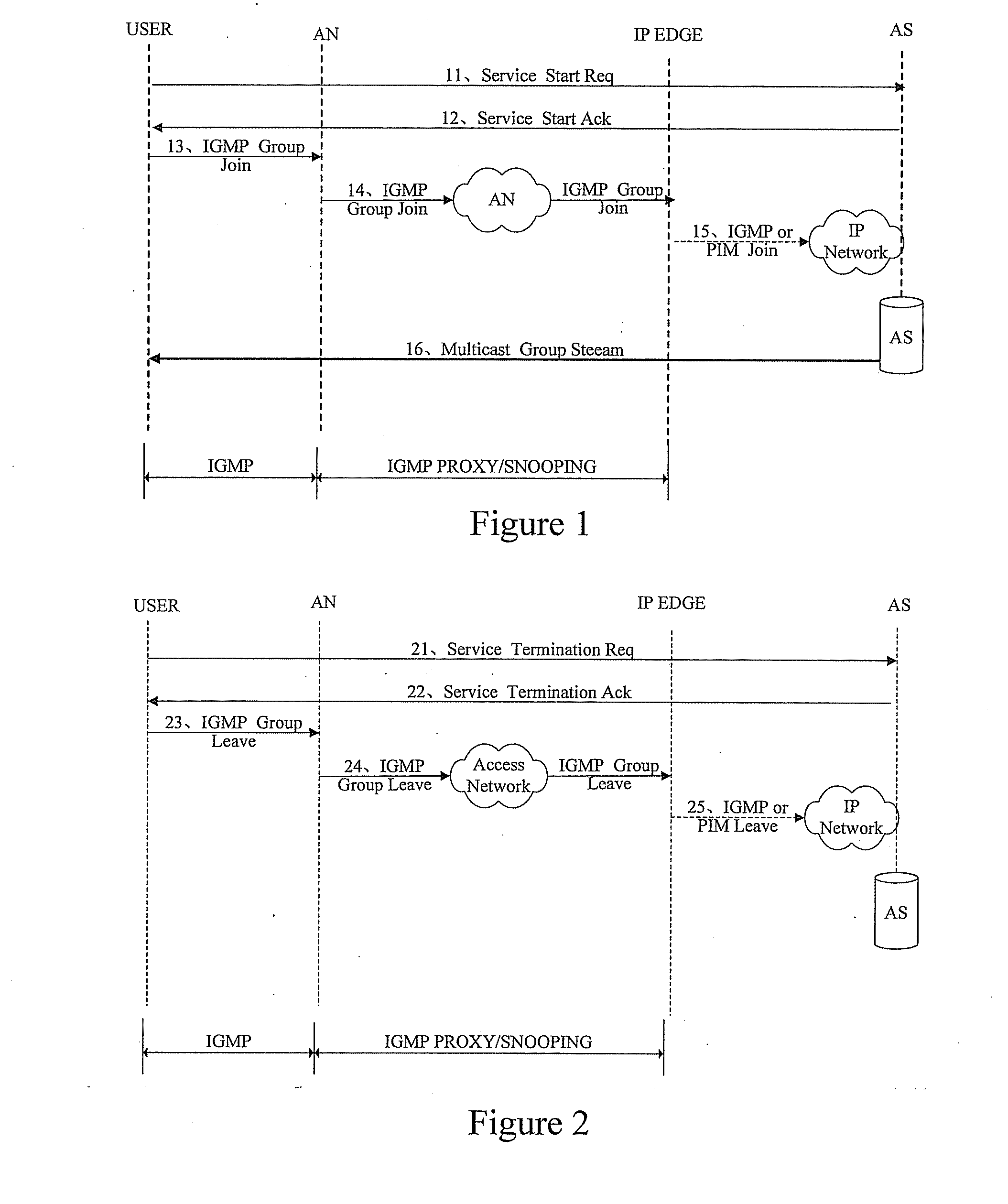
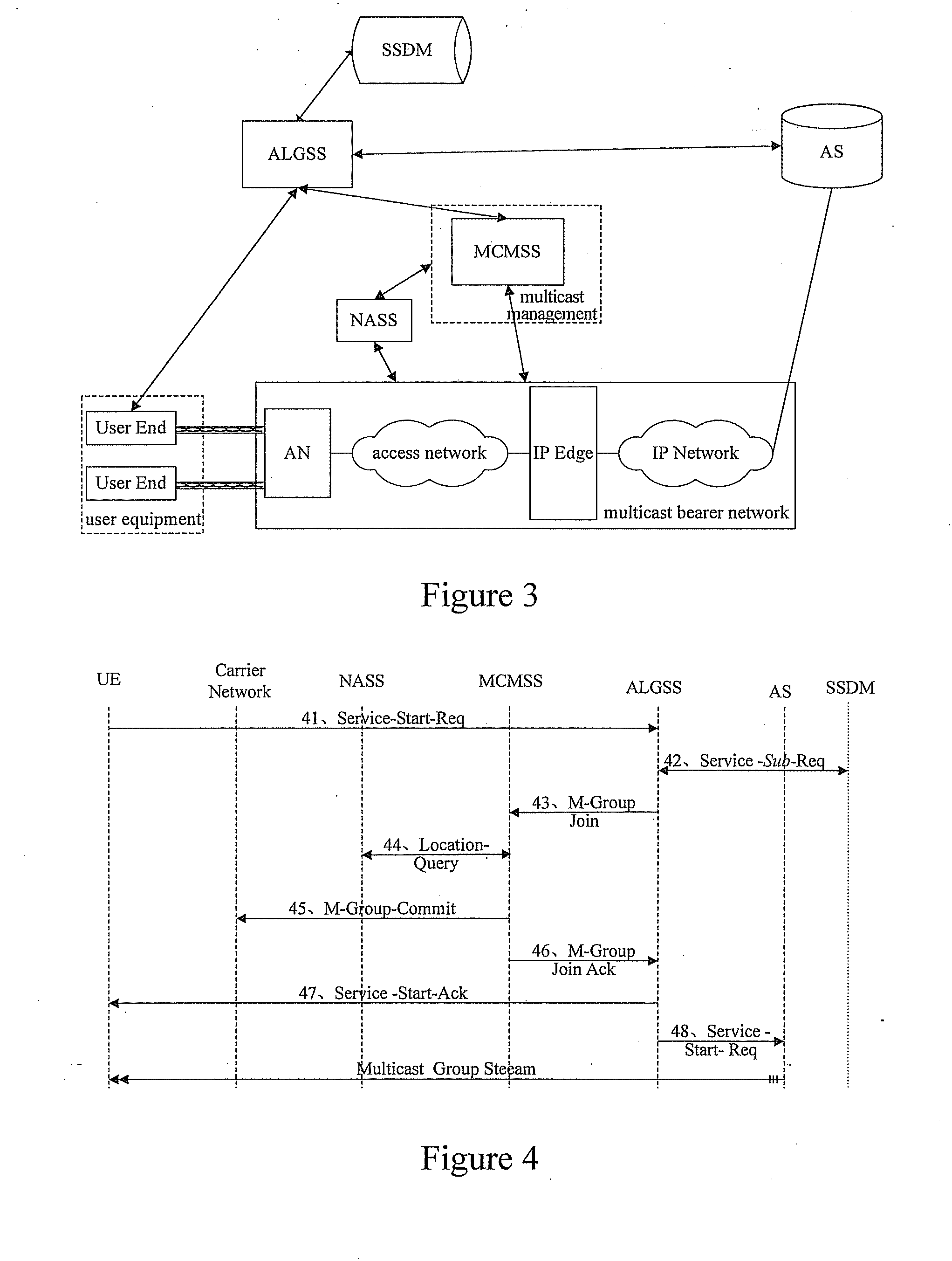
System and method for providing multicast service
InactiveUS20070280236A1Improve securityManage the multicast service flexiblyTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMulticast networkProtocol Application
A system and a method for performing a multicast service are disclosed. In accordance with embodiments of the present invention, an Application Layer Gateway Subsystem set in the network side handles application layer protocol messages communicated between the network side and a UE, and triggers, according to a handling result of the application layer protocol messages, a Multicast Carrier Management Subsystem set in the network side to configure and manage multicast paths in the bearer network, including establishing and deleting the multicast paths. In accordance with the embodiments of the present invention, because the application layer protocol and the multicast management protocol are combined with each other effectively, it is convenient to manage a multicast network, provide an operator with flexible operation management through the application layer protocol, and the security of the multicast service may be guaranteed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Non-ALG approach for application layer session traversal of IPv6/IPv4 NAT-PT gateway
InactiveUS7272148B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingNetwork address
A structure for coupling together addressably disparate nodes, such as IPv4 nodes and IPv6 nodes, without the use of an application level gateway. Instead, the system includes two executable applications, HEART and ECHO, that avoid the necessity of an application level gateway. In general, HEART and ECHO cooperate with each other through a network address translator-protocol translator (NAT-PT) to cause the NAT-PT to temporarily assign an IPv4 address to a control session between the IPv4 and IPv6 nodes and also prevent the control session from timing out due to lack of timely communications between the IPv4 and IPv6 nodes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
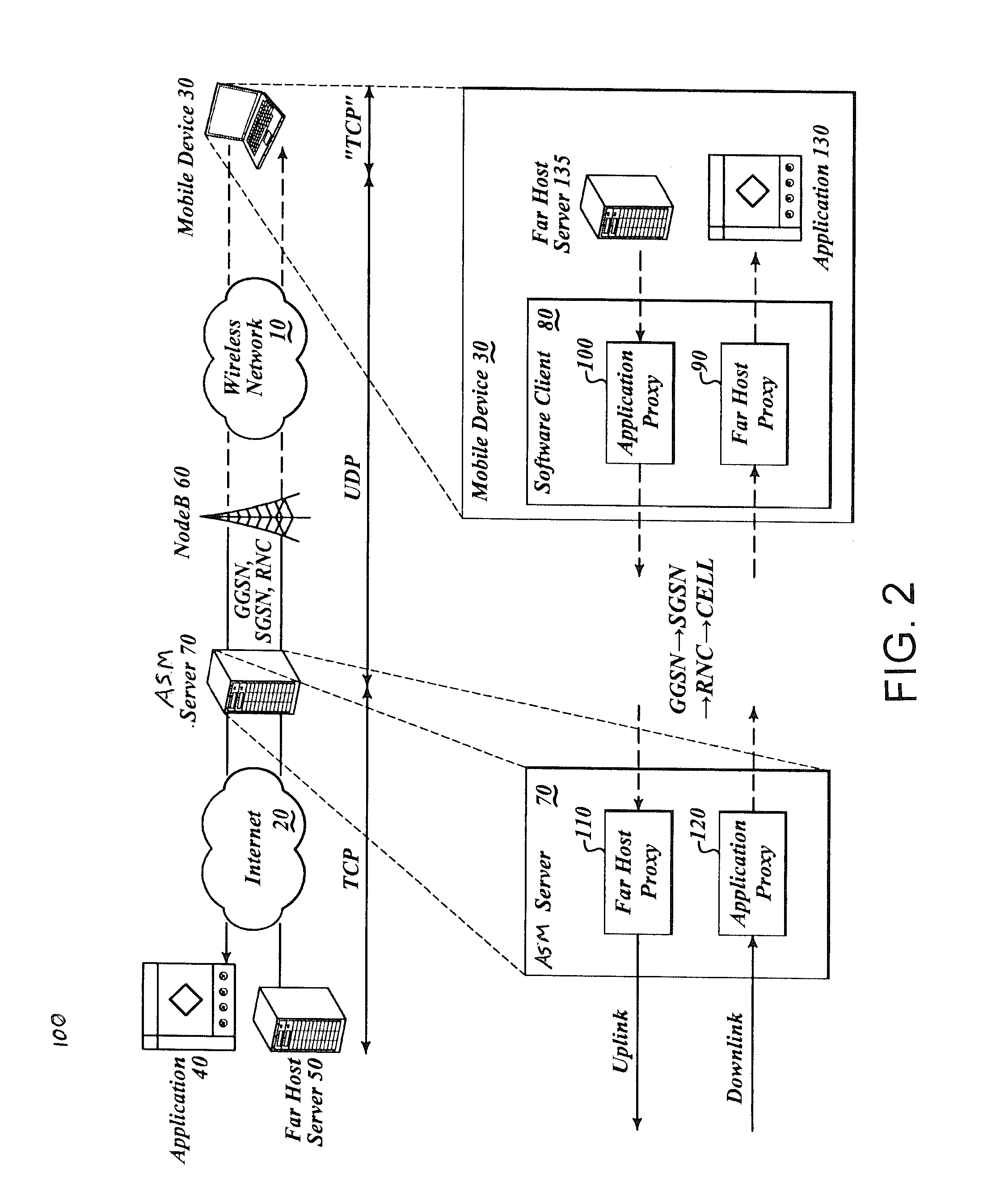
Method and system for client assisted stateful handling of packets in a communications network
InactiveUS20110219113A1Unduly burdensomeAvoiding indeterminismMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork packetClient-side
A method and system for stateful handling of packets in a network are described. In a client-server network environment, the stateful inspection of incoming protocols is offloaded from the server and distributed to the client device. The stateful inspection, as well as the provisioning of the client with the necessary functions required by the handlers, is referred to as Client Assisted Application Level Gateway (ALG). This version of ALG, in which the client performs or assists the server by performing at least some of the inspection and provisioning tasks, allows for a marked performance gain to the network gateway by reducing its packet inspection load.
Owner:MOBIDIA TECH
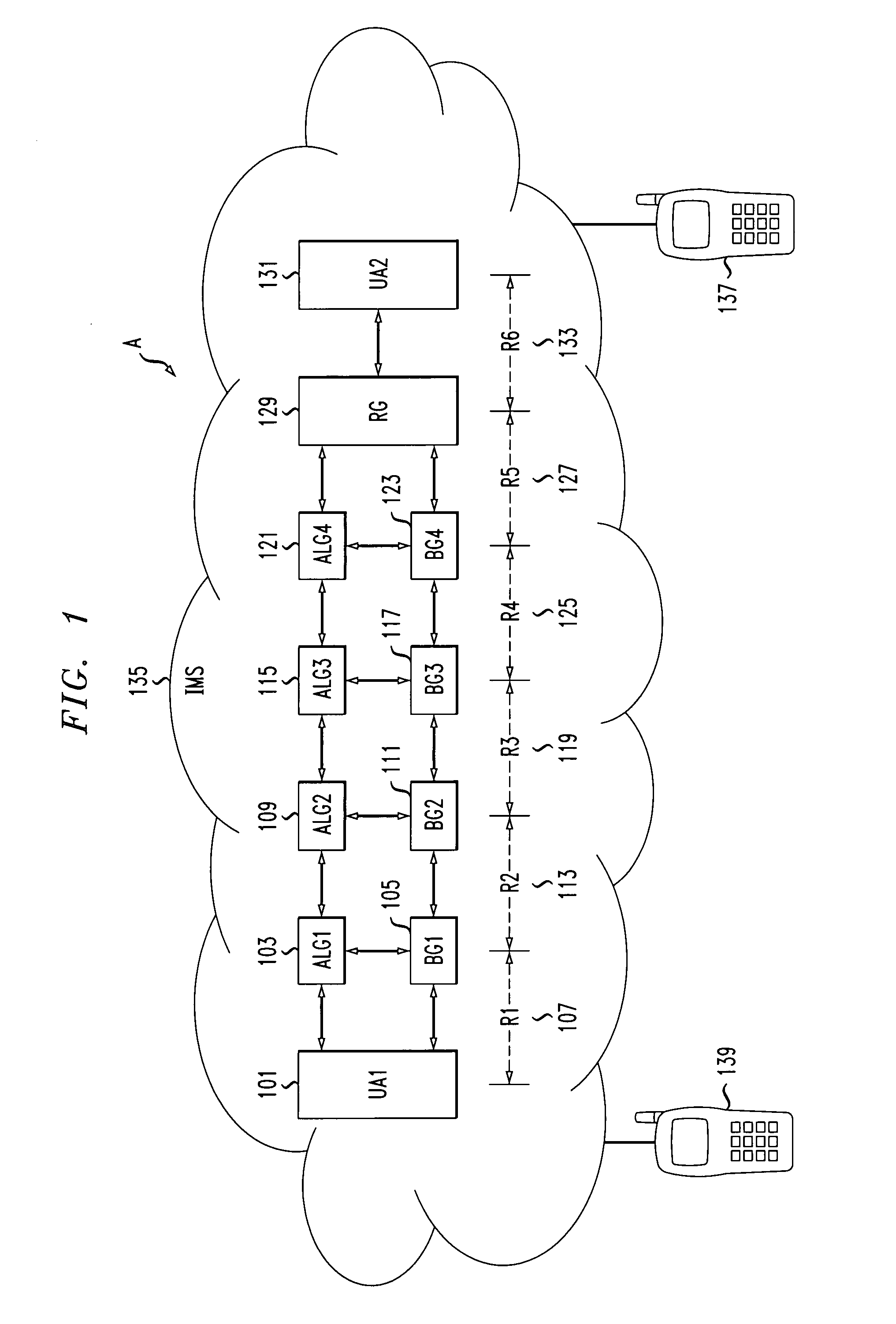
Method and apparatus for internet protocol multimedia bearer path optimization through a succession of border gateways
InactiveUS20090010270A1Precise constructionData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsTTEthernetComputer network
A method for identifying alternate end-to-end media paths through internet protocol realms using substitute session description protocol parameters is disclosed. The method includes receiving an session description protocol offer, including a list of previously traversed through internet protocol realms. The method continues with determining the next internet protocol realm for a media path based on unspecified signaling criteria. Finally, the method includes that if the next internet protocol realm to be traversed through is on the list of previously traversed through internet protocol realms, bypassing at least one border gateway associated with the current and previously traversed through internet protocol realms. The system implementing a method for identifying optimal end-to-end media paths and internet protocol multimedia subsystems include a list of internet protocol realm instances, an application level gateway configured to receive a session description protocol offer having connection information and port information, and a procedure to determine that if the next internet protocol realm that the media path may traverse through is on the list of instances, the media path connection information and port information is substituted to facilitate border gateway bypassing.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
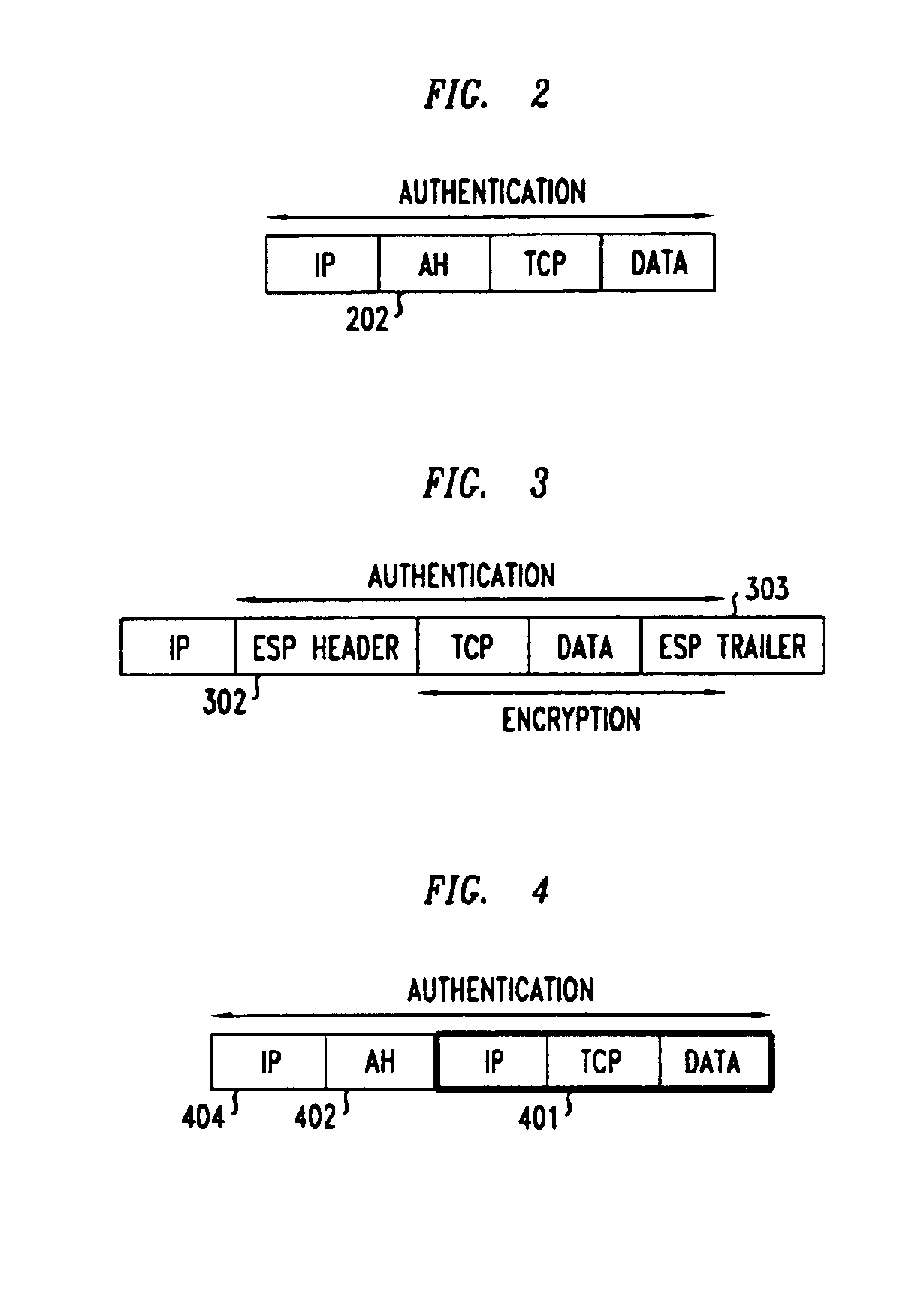
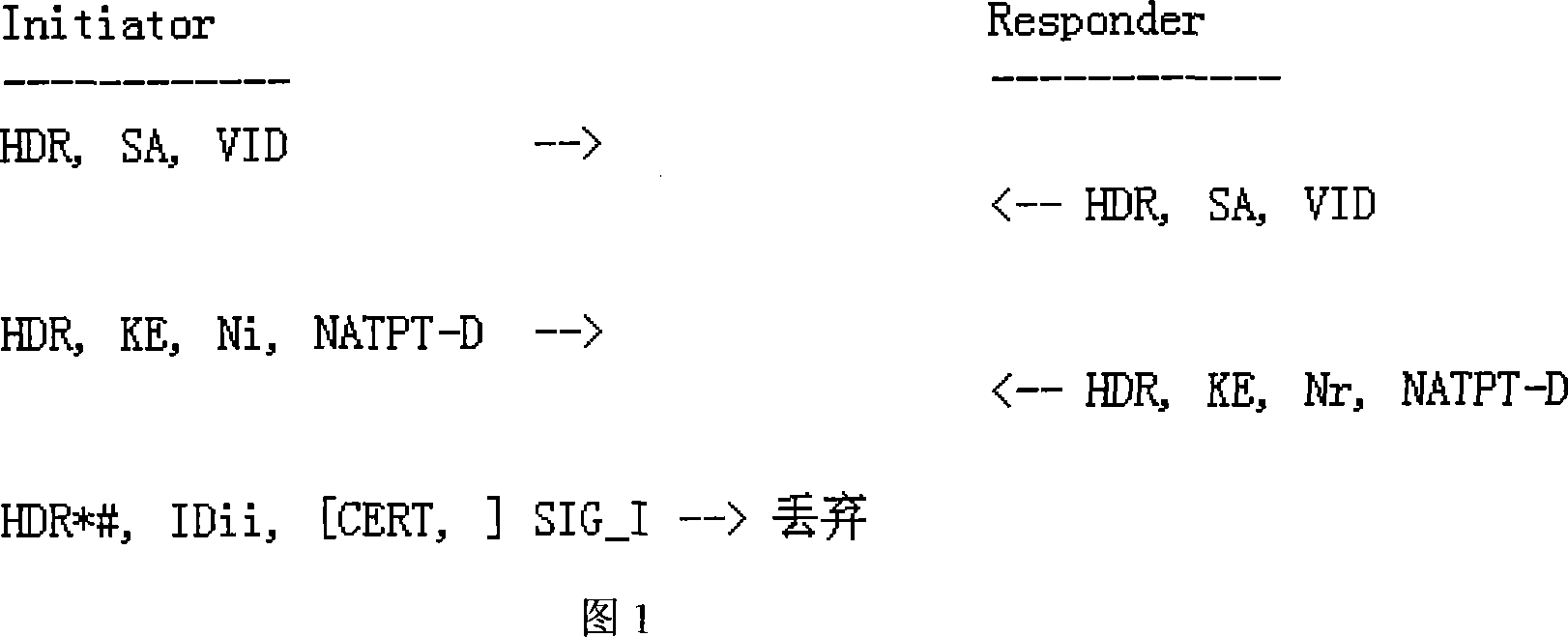
Method for crossing NAT-PT by IPSec
InactiveCN101030935AResolve incompatibilitiesReduce processing burdenNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsIPsecApplication-level gateway
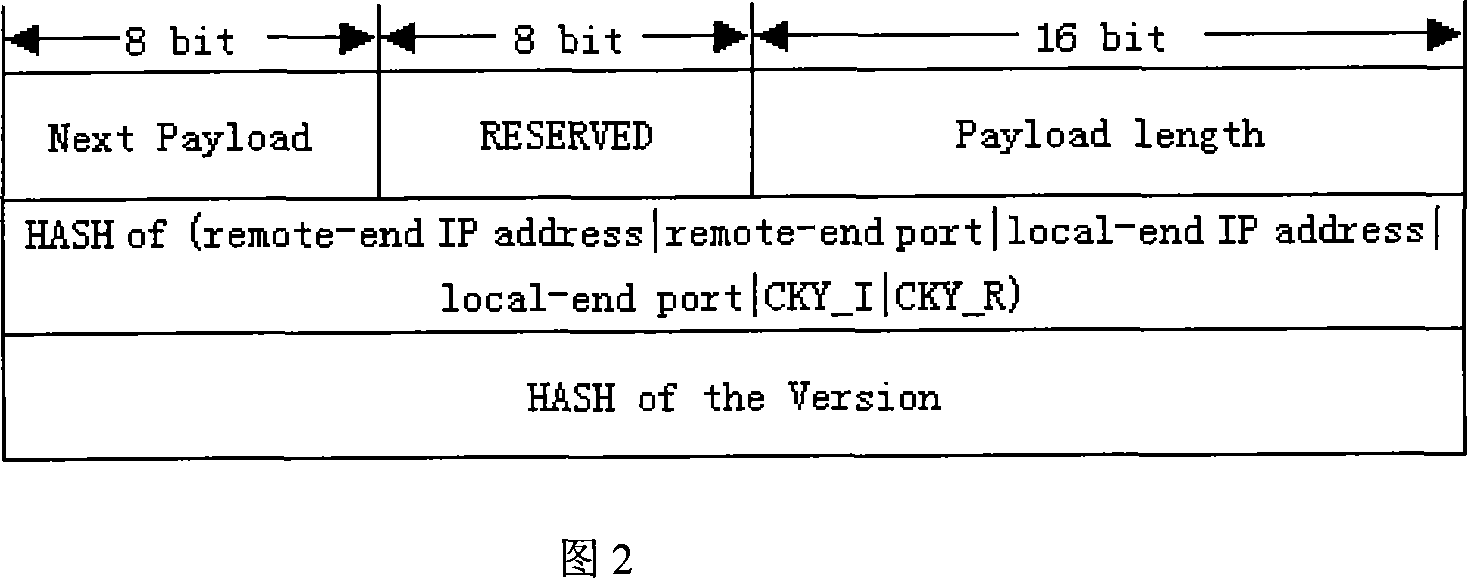
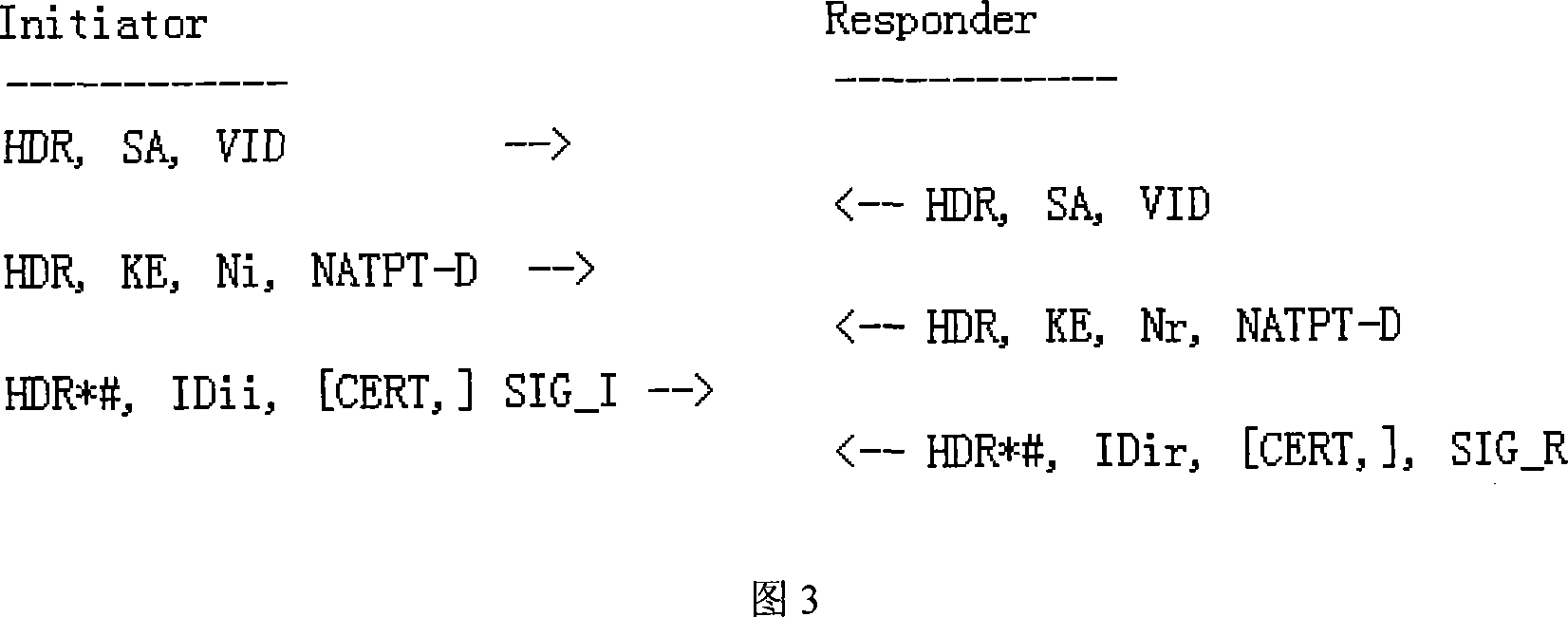
The method comprises: in main mode stage of IKE negotiation, newly adding the NATPT-D load used to realize the mechanism of finding 'NAT-PT'; in the communication stage under IPSec protection, after detecting the NAT-PT gateway, when calculating the Authentication Data of AH, using a 'pseudo IP header' to replace the original IP header to solve the incompatibility problem between AH and NAT-PT. By the invention, IPSec can cross over the NAT-PT gateway under the AH transmission mode, AH tunnel mode, ESP transmission mode and ESP tunnel mode.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Network address and protocol translating equipment and application layer gateway equipment
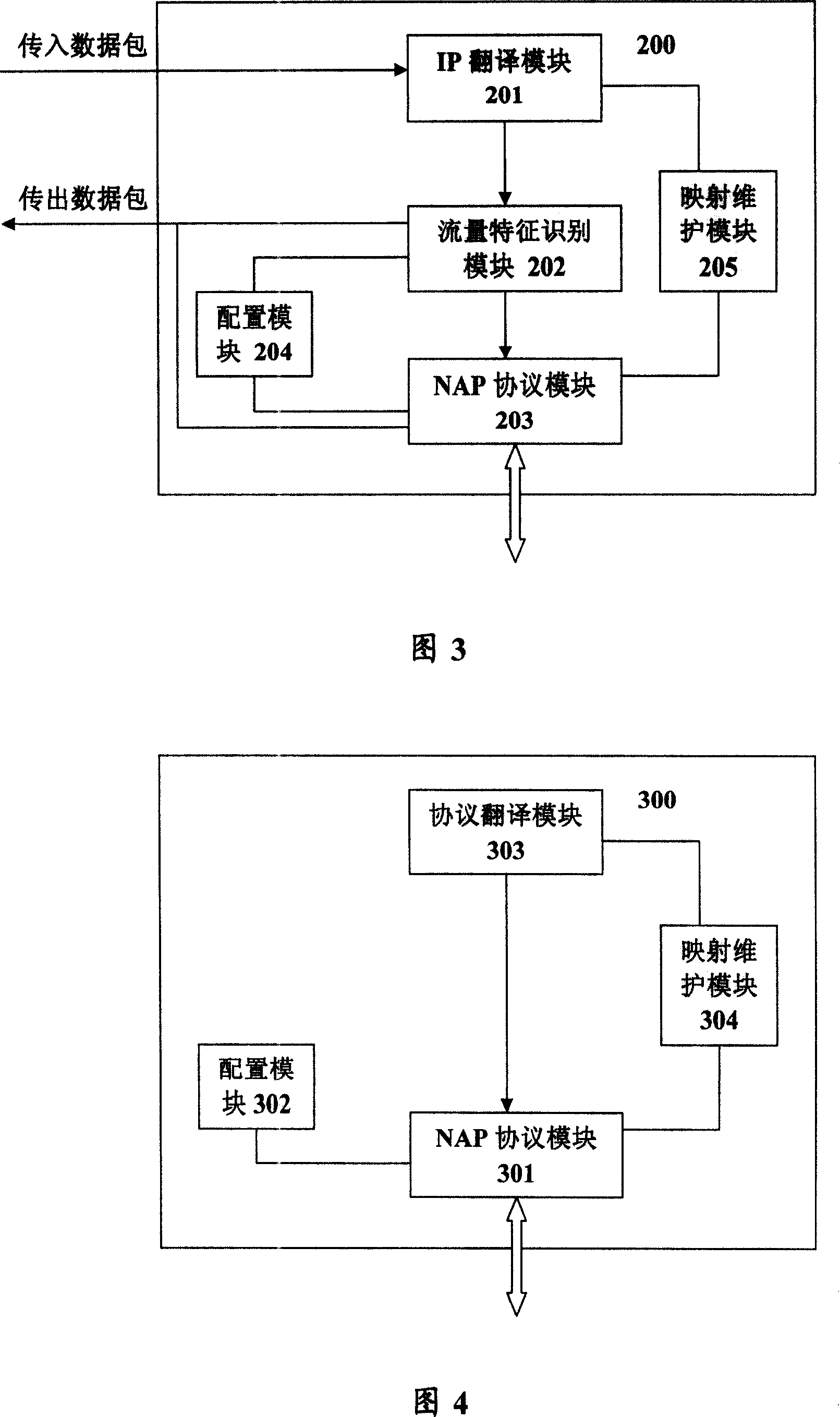
Being able to communicate with one or more application layer gateway (ALG), the network address (Add) and protocol translation (NAT-PT) equipment includes devices: aiming at each dialog process, mapping maintenance device (MMD) is in use for buffering IPv4 Add and port numbers of source and destination (APNSD) associated to dialog ID as well as corresponding (Corr) IPv6 APNSD; based on IPv4 / IPv6 Add mapping info of dialog ID of the dialog belonging to Corr input data packet (DP) buffered by MMD, the IP translation device is in use for translating IP head of input DP; NAP protocol device (NAPD) is in use for communicating with ALG device; flow feature recognition device is in use for checking whether the translated DP is matched to flow feature related to one of ALG devices; if not, sending the DP normally; if yes, then NAPD forwards the DP to the matched ALG device. Responding to request of ALG device, NAPD can provide mapping info of IPv4 / IPv6 Add Corr to dialog ID.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Dynamic network security system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20070180527A1Good choiceReduce system loadFrom solar energyMemory loss protectionNetwork packetSpeech applications
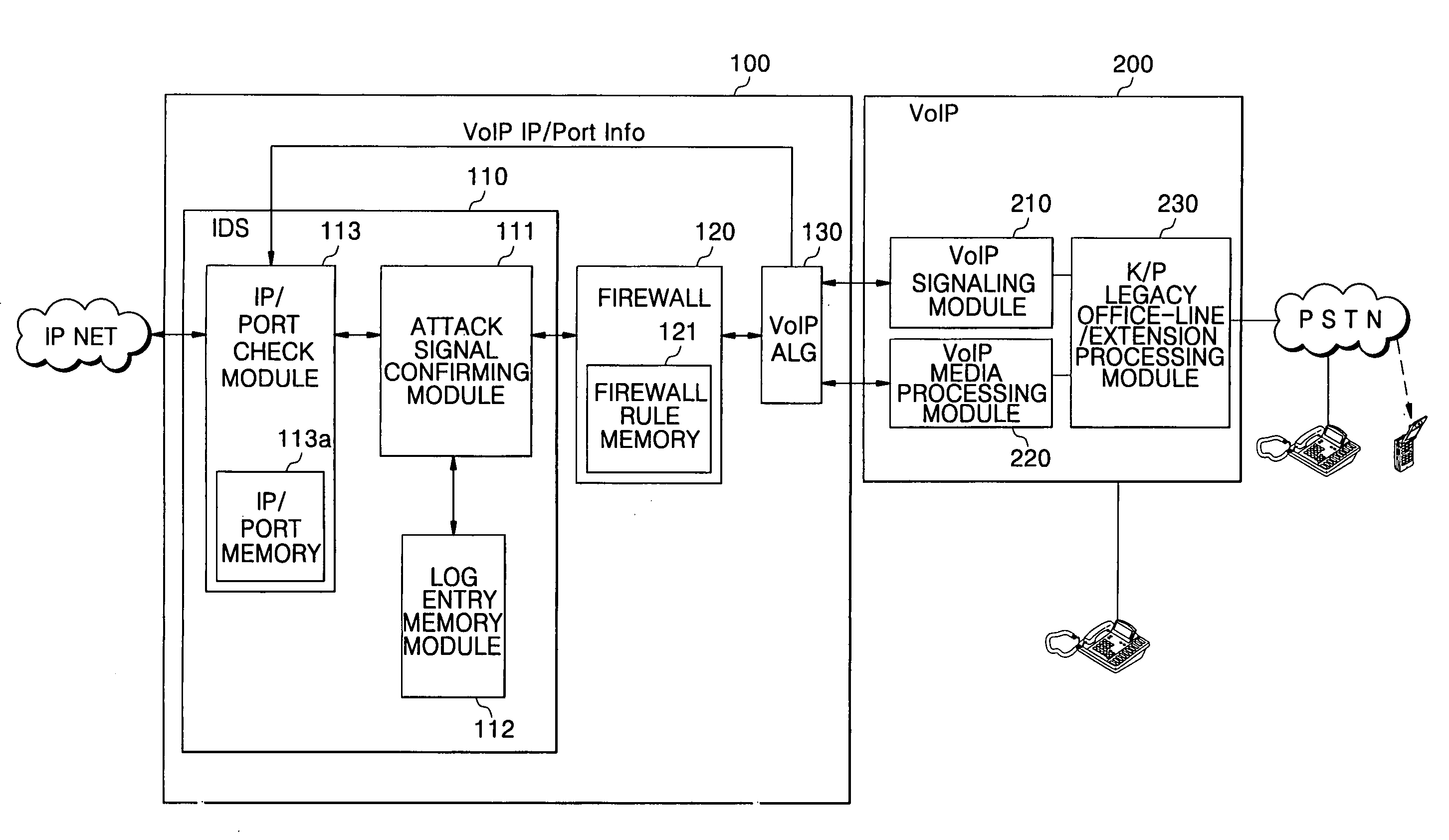
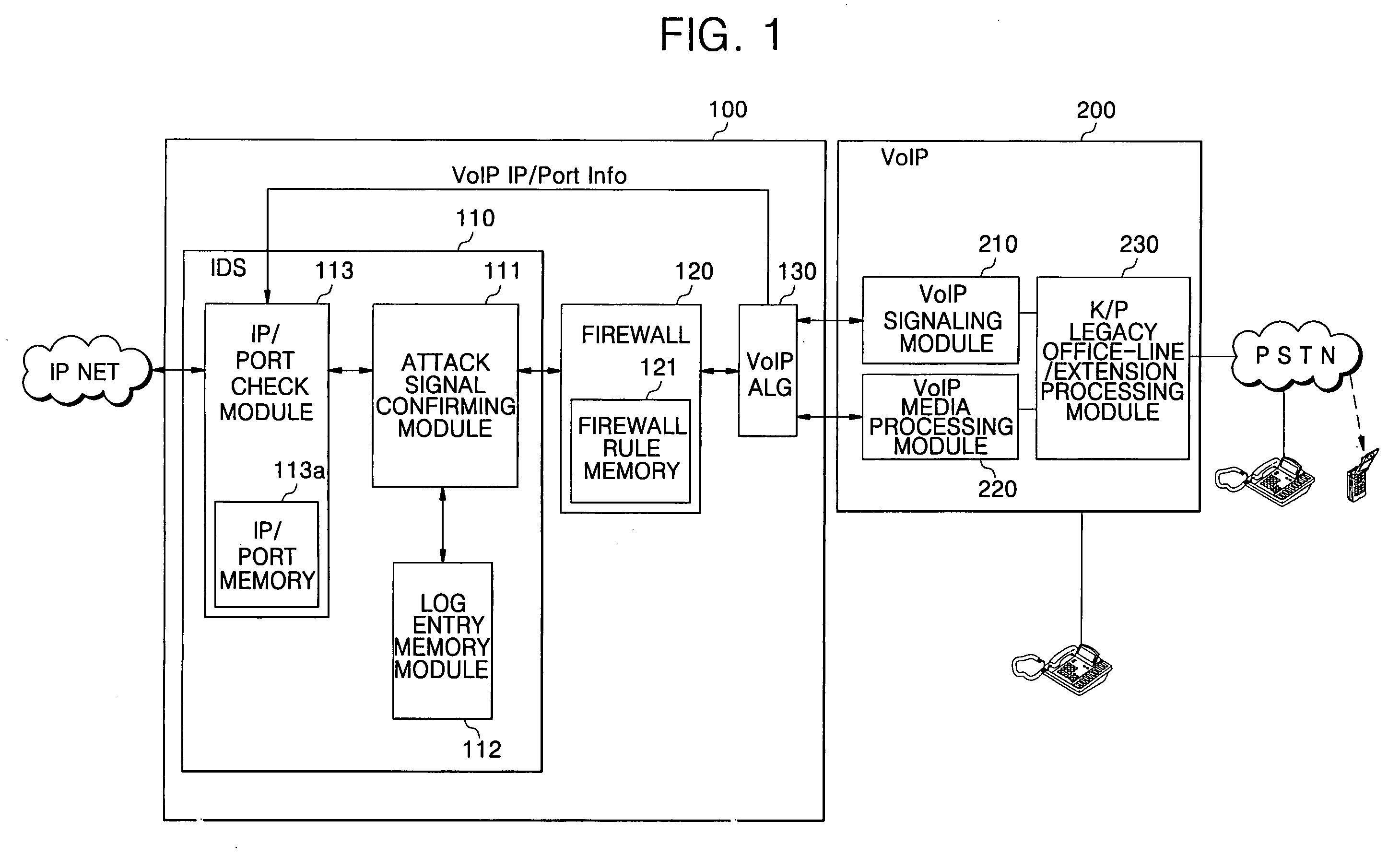
A dynamic network security system and a control method thereof in a router where an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and a Voice over Internet Protocol Application Level Gateway (VoIP ALG) are integrated, system including: a VoIP ALG module for acquiring VoIP IP / port information of a counterpart unit in use for determining whether or not to perform intrusion detection on a packet received via VoIP signaling with the counterpart unit; an intrusion detection module for comparing the received packet with a preset intrusion detection log entry to perform intrusion detection on the received packet, and based on a result of the intrusion detection, determining whether or not to allow passage of the received packet; and an IP / port check module for checking VoIP IP / port information of the received packet according to the VoIP IP / port information of the counterpart unit provided from the VoIP ALG module to determine whether or not to perform the intrusion detection, and providing result information on the determination whether or not to perform the intrusion detection to the intrusion detection module.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for managing dynamic network sessions
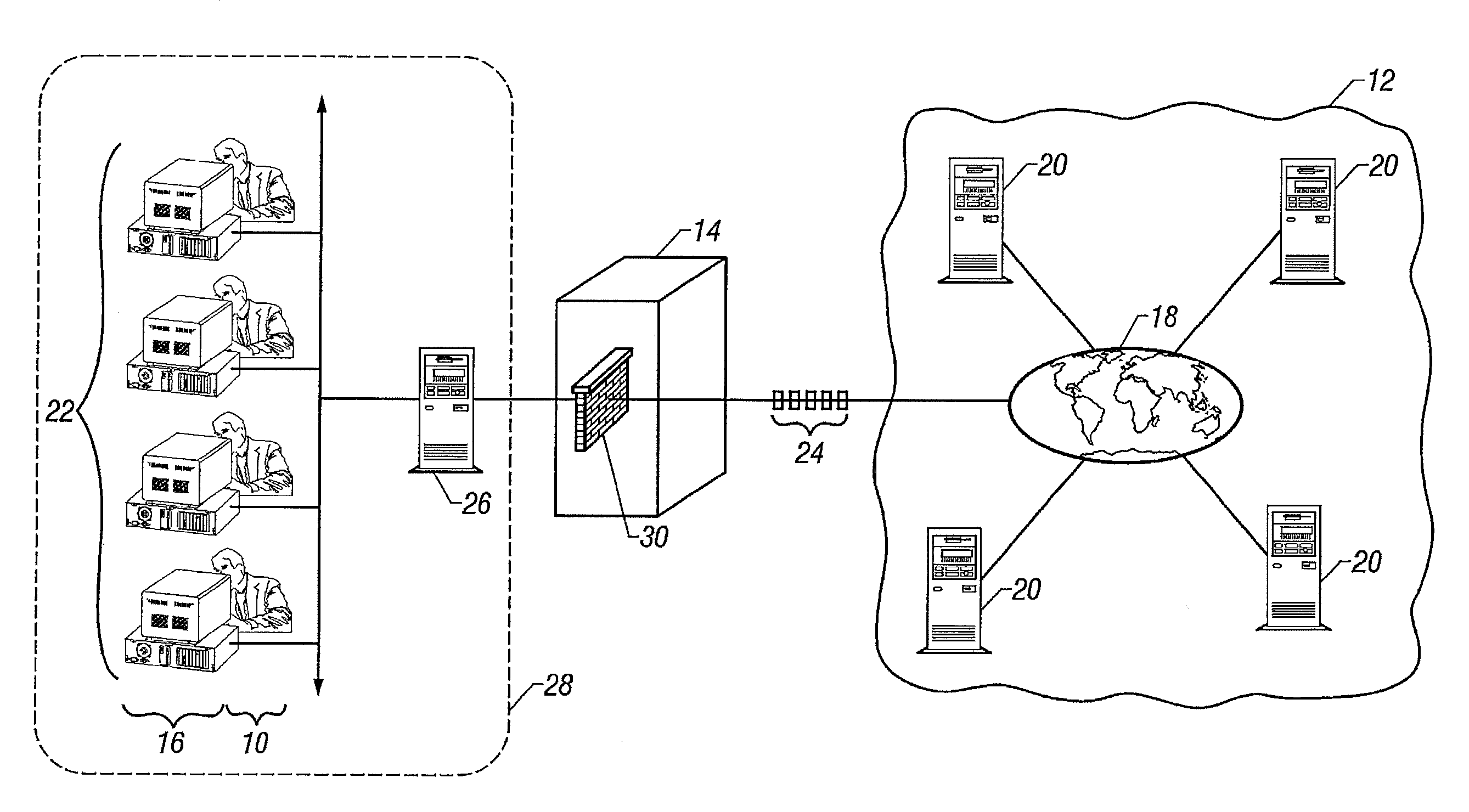
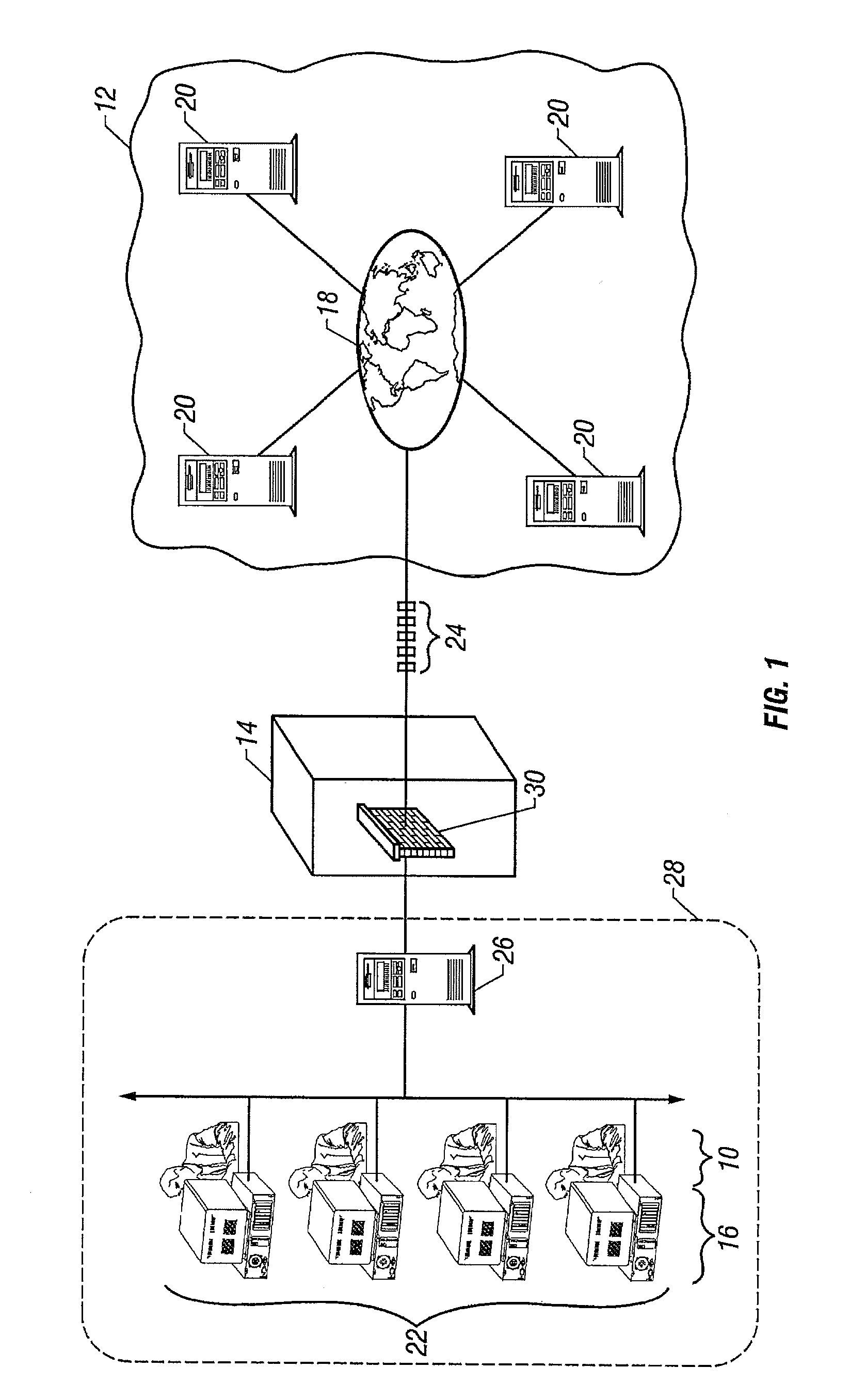
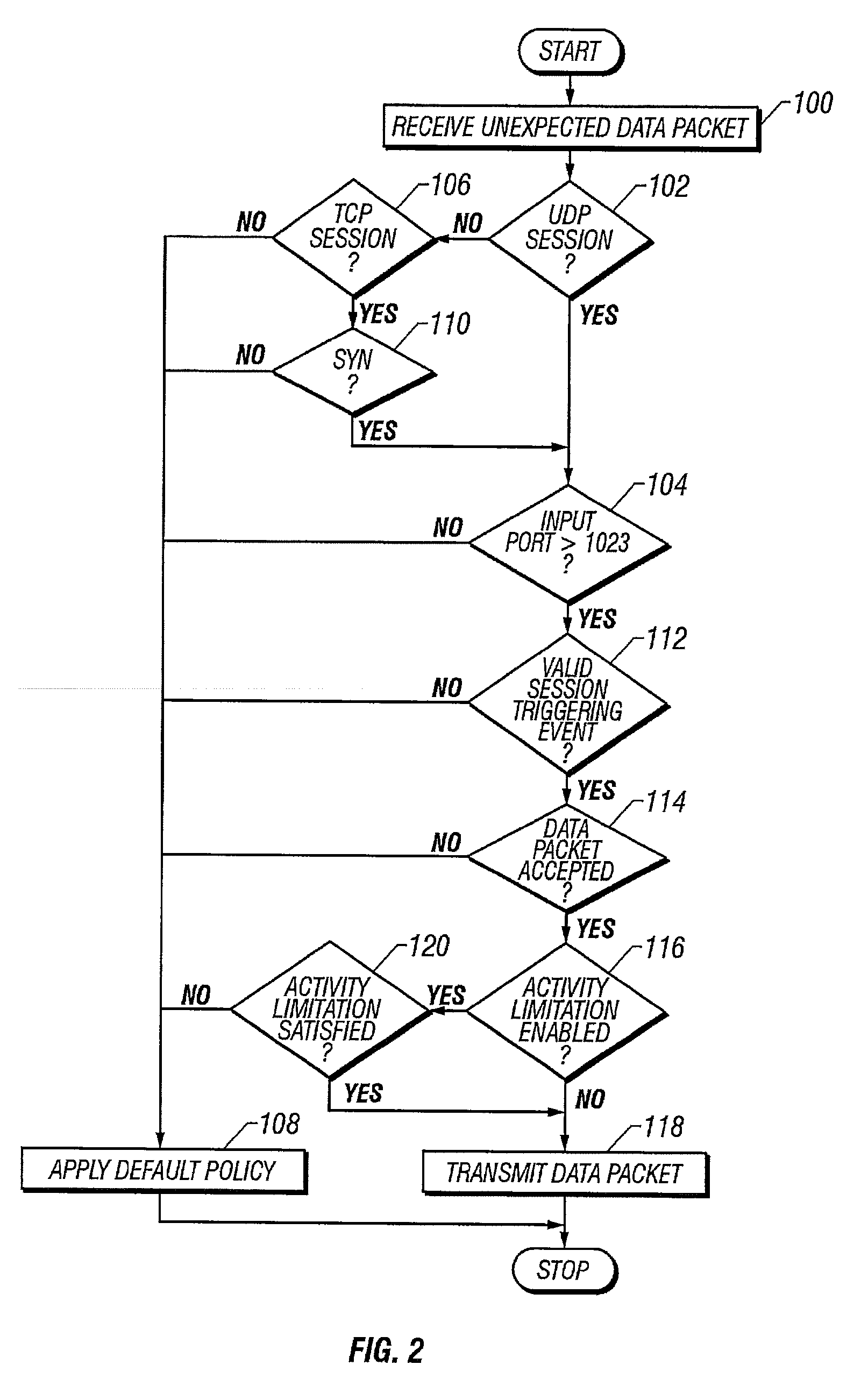
InactiveUS20080267201A1Improve throughputLess costData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsArea networkInternet access
For an Internet Access Gateway operative between an area network and a public network, managing dynamic network sessions therebetween whereby a primary server on the public network in a primary session with a client of the area network initiates an additional session with an additional server on the public network, for which an unexpected data packet received at the gateway from the additional server is associated with the primary session, and accordingly allowed access to the area network through the gateway, provided the gateway received the data packet at an input port exceeding 1023, the additional session comprises a pre-defined Session Triggering Event, and at least one internal network component of the area network indicates willingness to receive the data packet. Wherefore, a preferred Application Level Gateway is thereby provided for firewall and NAT implementations to enhance network security.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
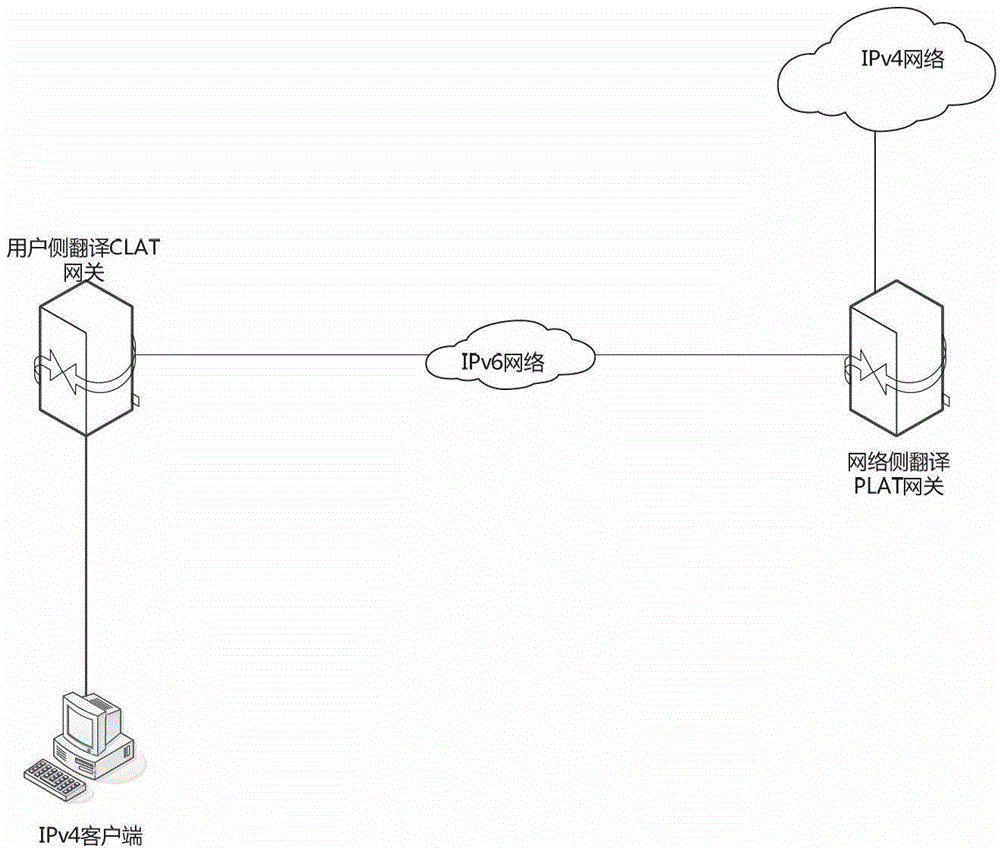
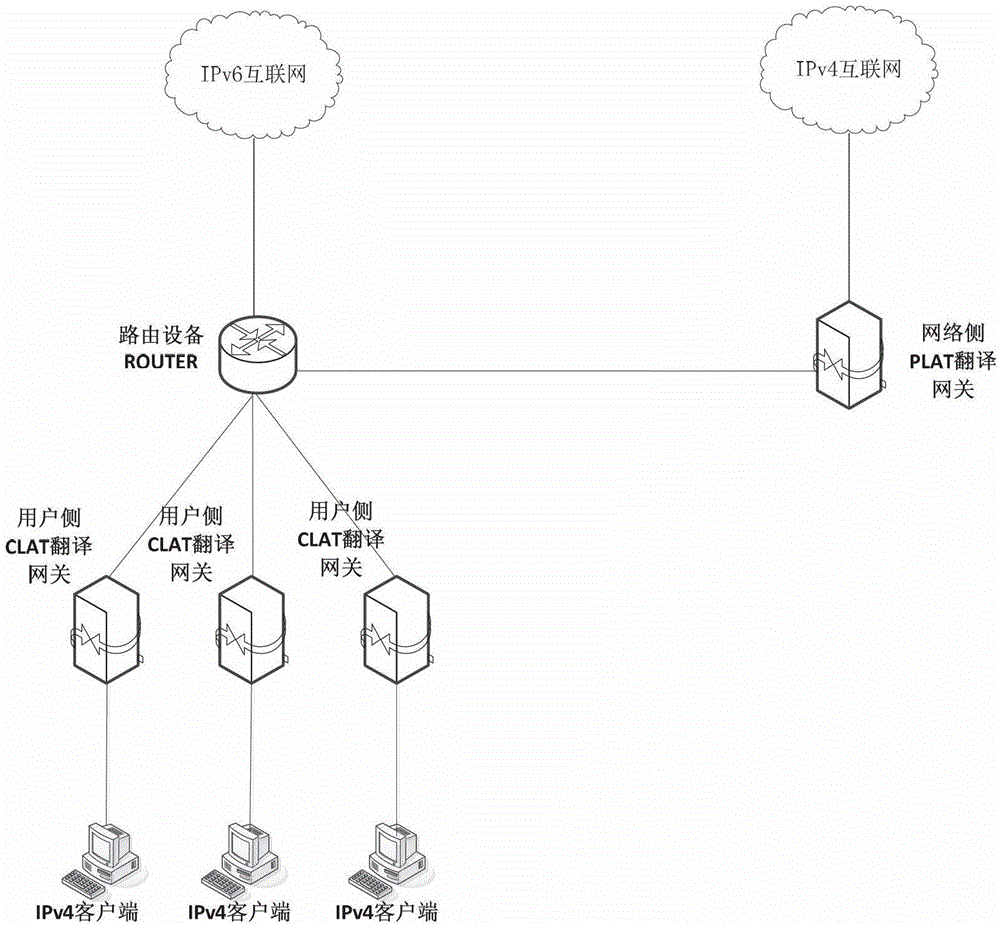
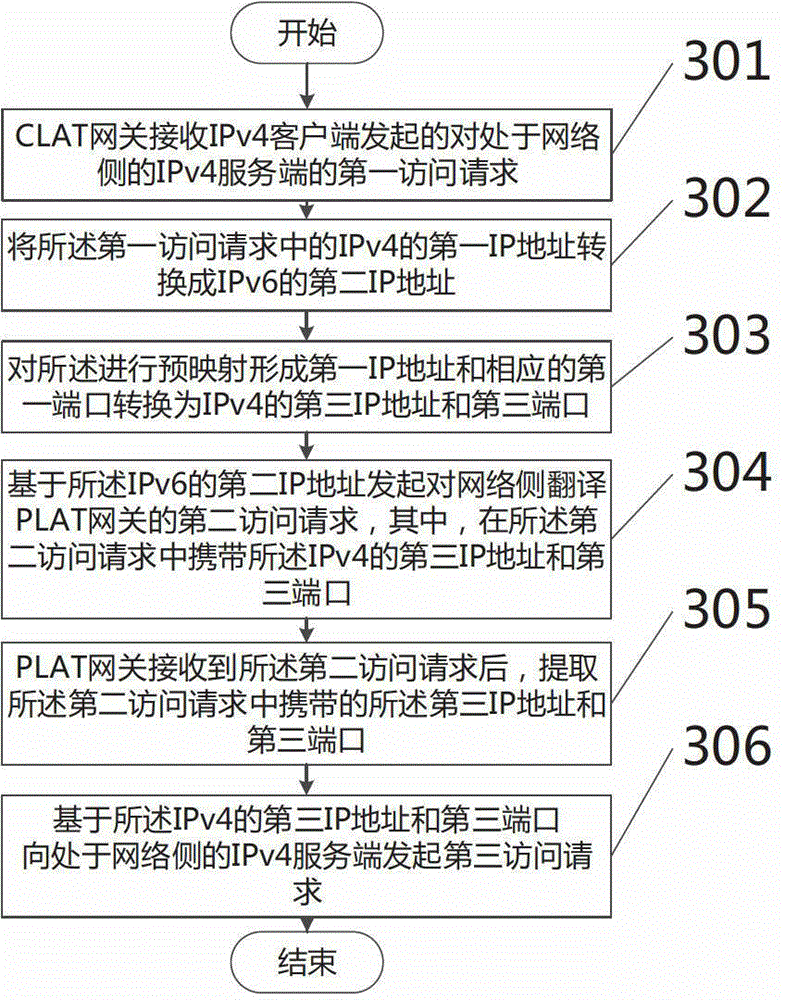
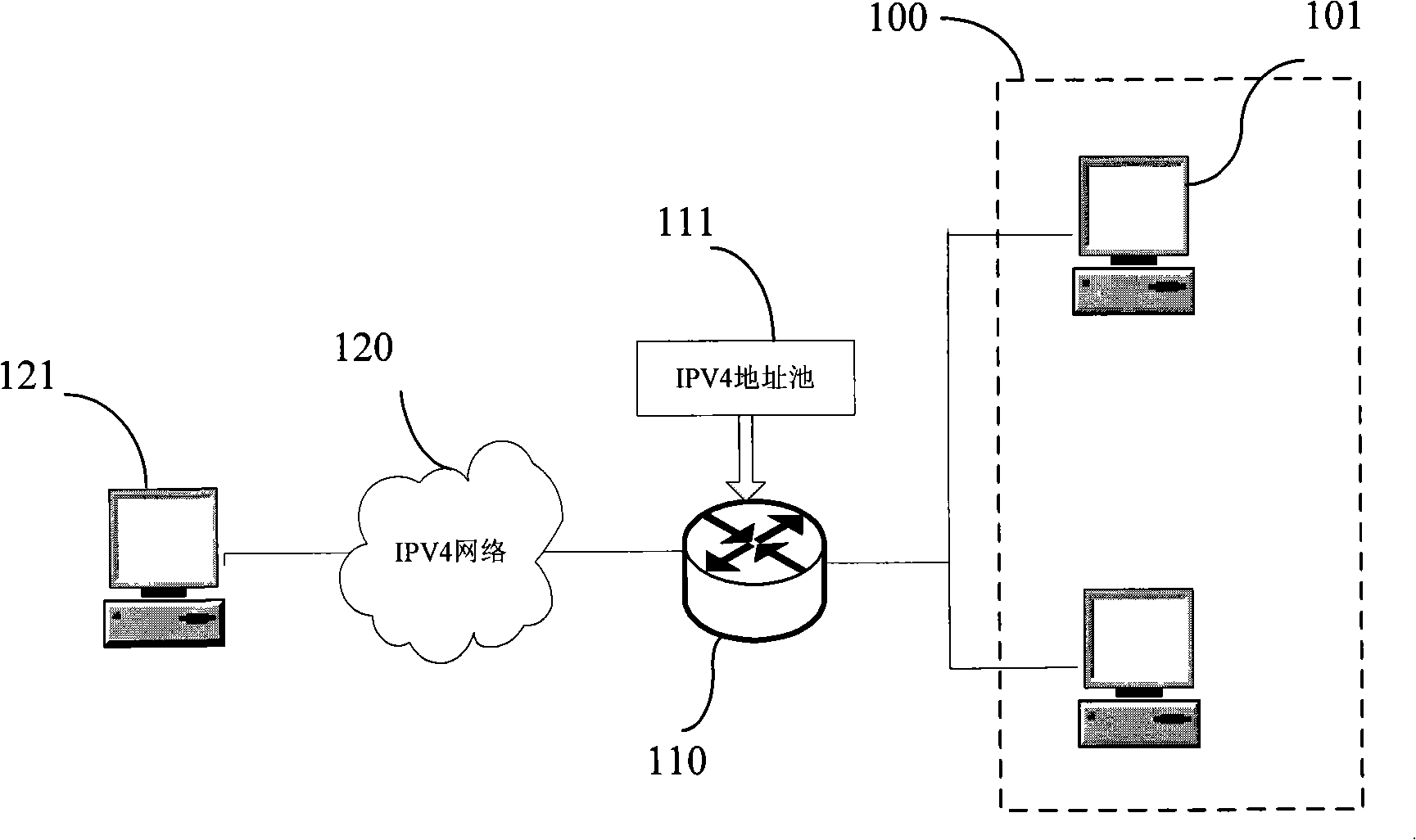
Distributed gateway system in 4-6-4 hybrid protocol network and access method
The invention discloses a distributed gateway system in a 4-6-4 hybrid protocol network and an access method. The method comprises the steps that one or more distributed CLAT (Customer Side Translator) gateways receive a first access request to an IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4) server located on a network address translation PLAT (provider side translator) gateway side initiated by an IPv4 client; a first IP (Internet Protocol) address of IPv4 in the first access request is converted to a second IP address of IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) according to an address conversion rule in the CLAT gateways; and a second access request to the PLAT gateway is initiated based on the second IP address of the IPv6; the second access request also carries a third IP address of the IPv4 and a third port; and the third IP address and the third port conduct pre-mapping formation on the first IP address of the IPv4 and a first port corresponding to the first IP address according to a preset address mapping rule via the CLAT gateways. The problems of gateway server pressure and network delay caused during an application-level gateway processing course are solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
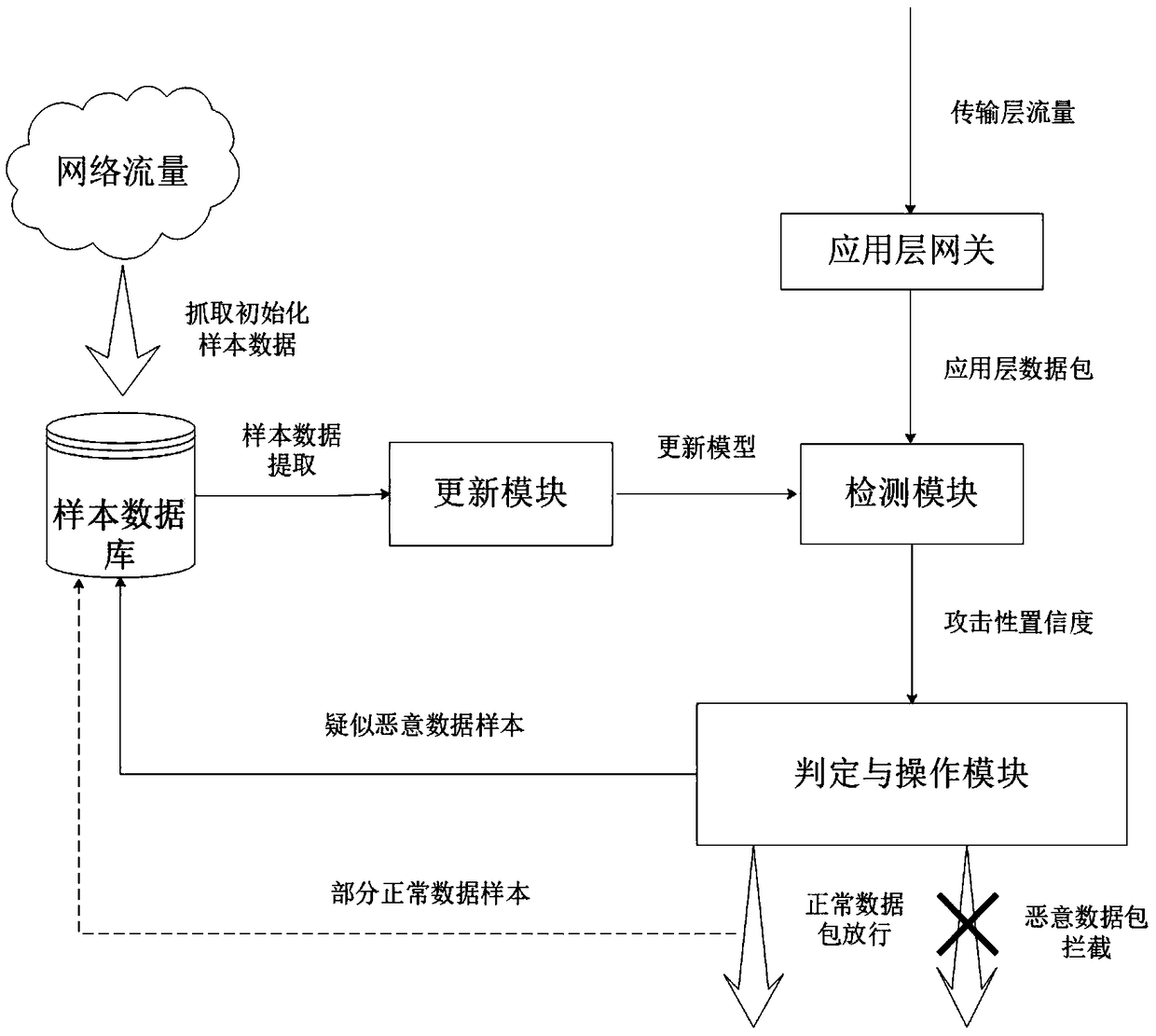
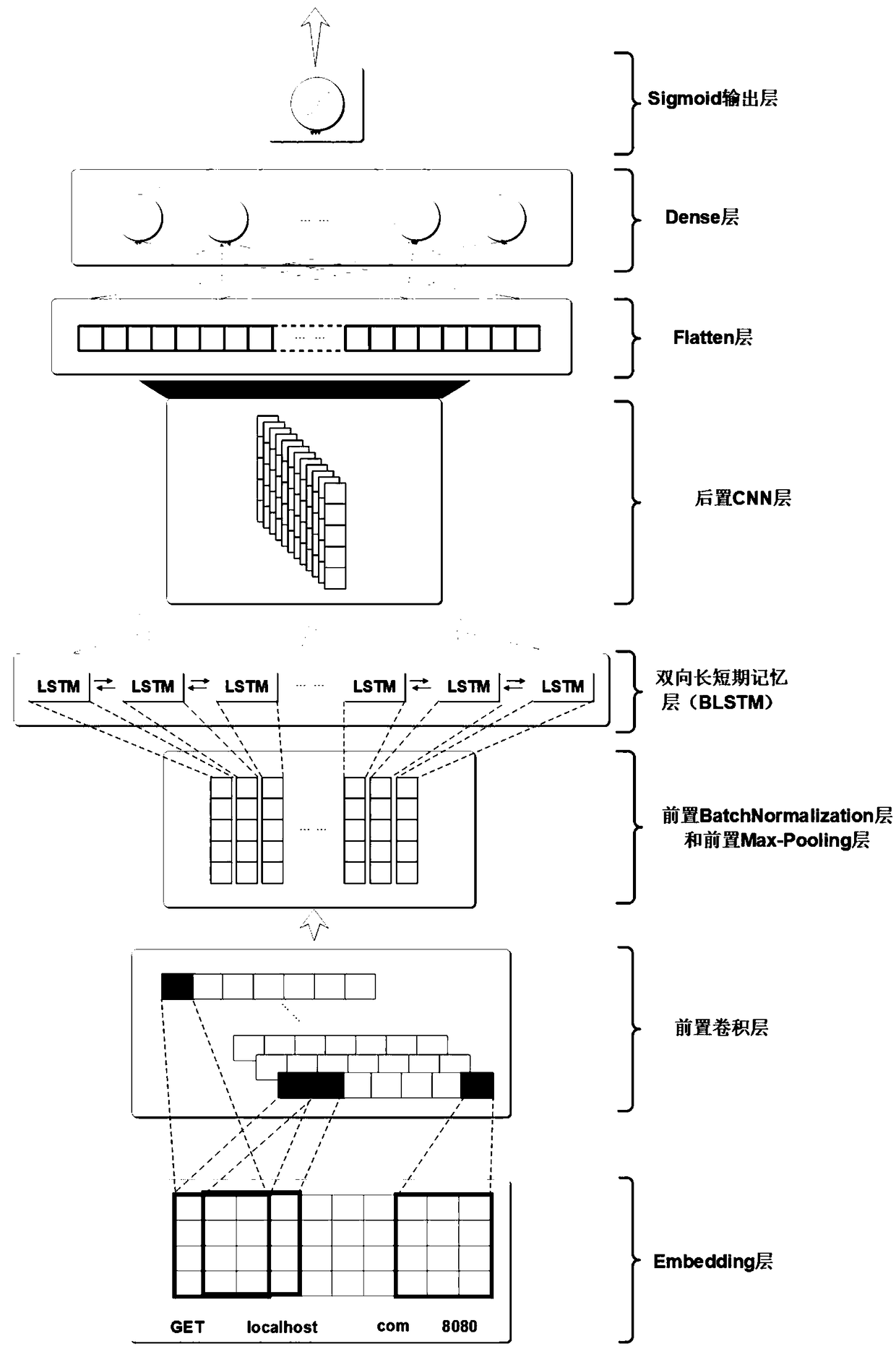
Application layer dynamic intrusion detection system and detection method based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN108898015AImprove detection accuracyFast convergencePlatform integrity maintainanceNeural architecturesApplications of artificial intelligenceShort-term memory
The invention discloses an application layer dynamic intrusion detection system and detection method based on artificial intelligence, wherein the detection system comprises an application layer gateway, a detection module, a judgment and operation module, a sample database and an updating module, the detection module comprises a detection model mixed with a convolutional neural network and a bidirectional long and short term memory neural network. The detection module after initialization is used for making an attack judgment on an application layer data packet, filtering the data packet above the threshold value and putting the data packet into a malicious sample database, and meanwhile, the data packet under the threshold value is not processed. The updating module is used for traininga new model by using the malicious samples and normal samples with a certain proportion in the sample database and updating the detection model in the detection module in real time. According to the invention, a universal detection method is used for the attack method of the application layer, the method has the advantages of high detection rate and low misjudgment rate. Meanwhile, the intrusion detection system has the advantage of dynamic updating model, and has good filtering effect on unknown zero-day attack.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
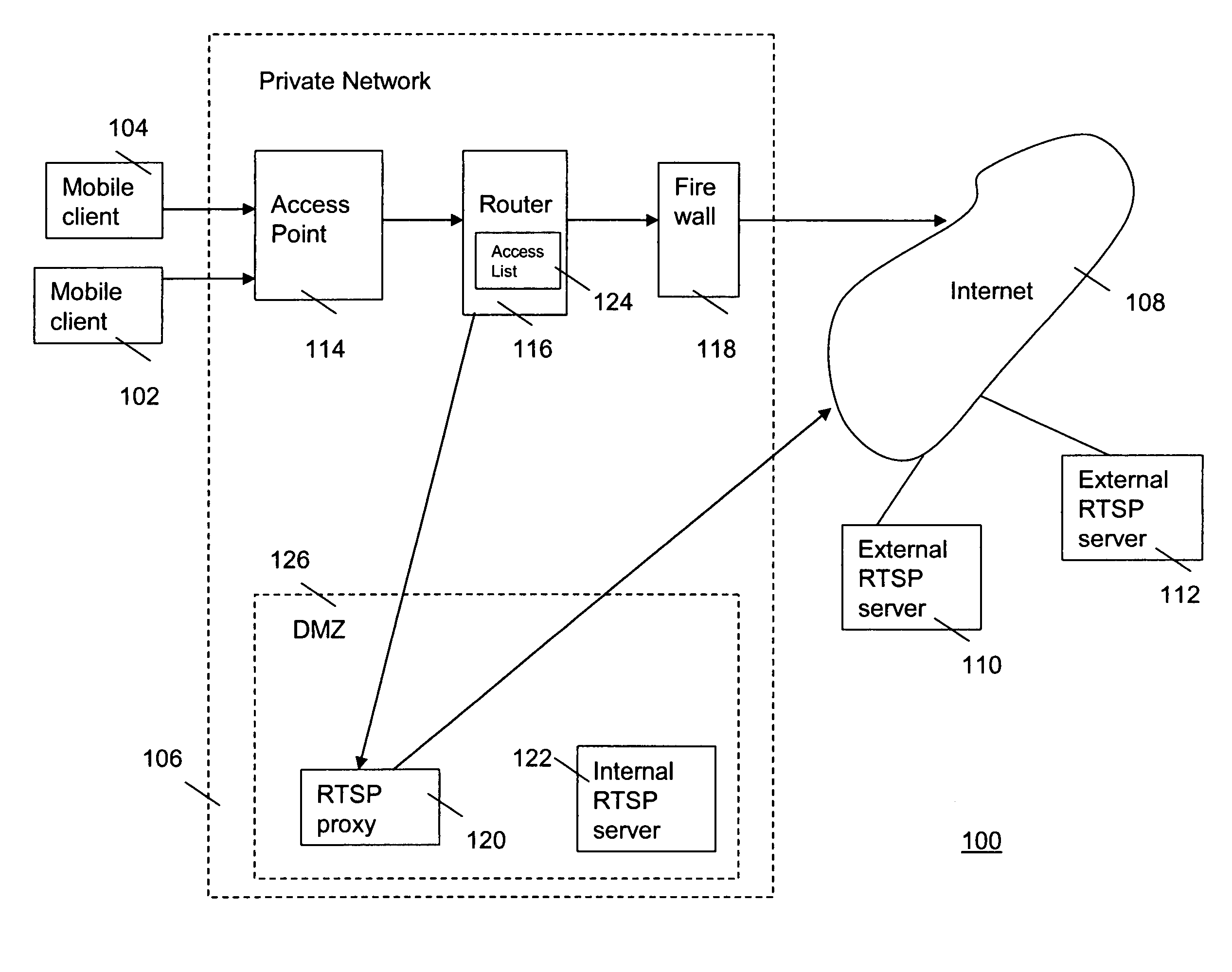
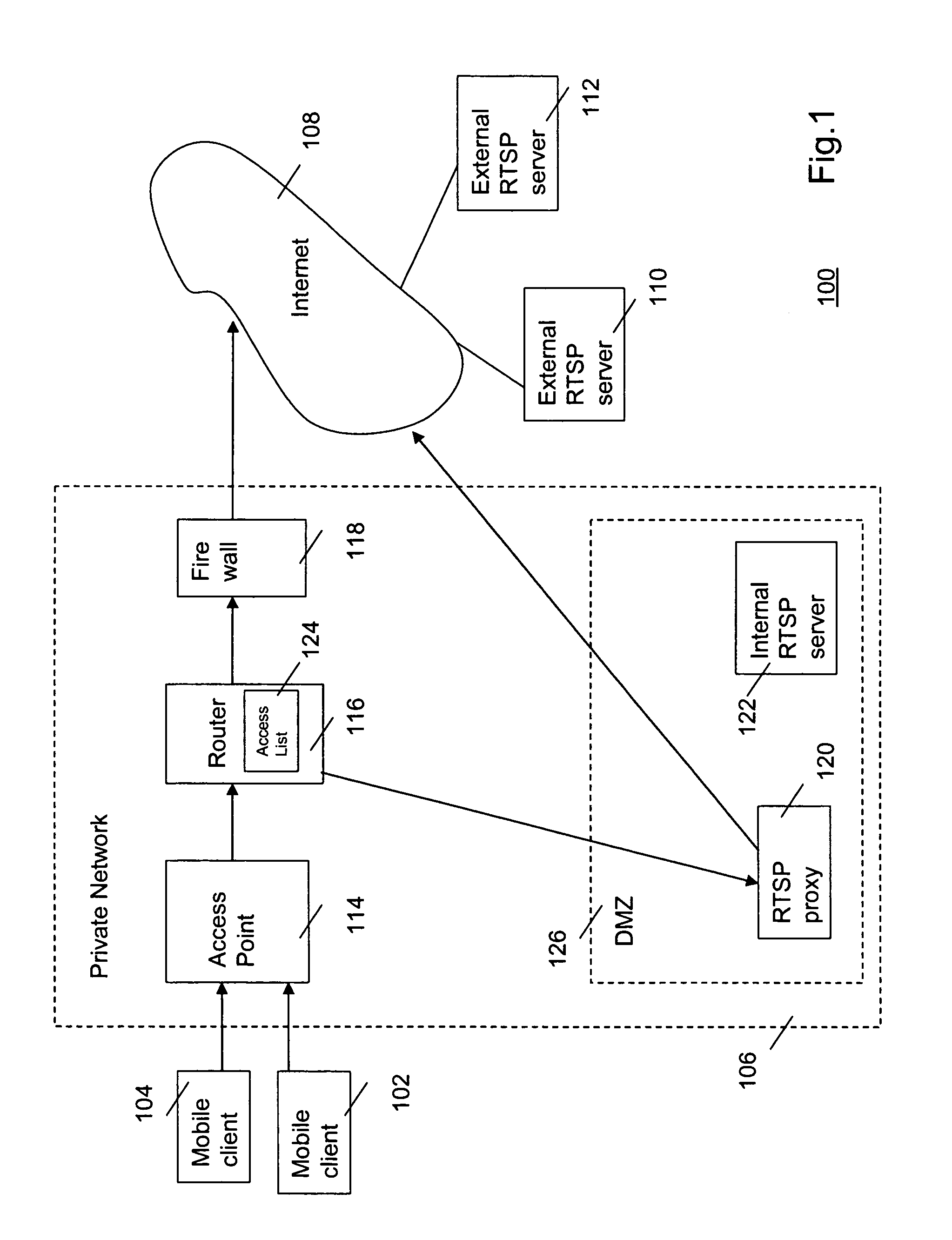
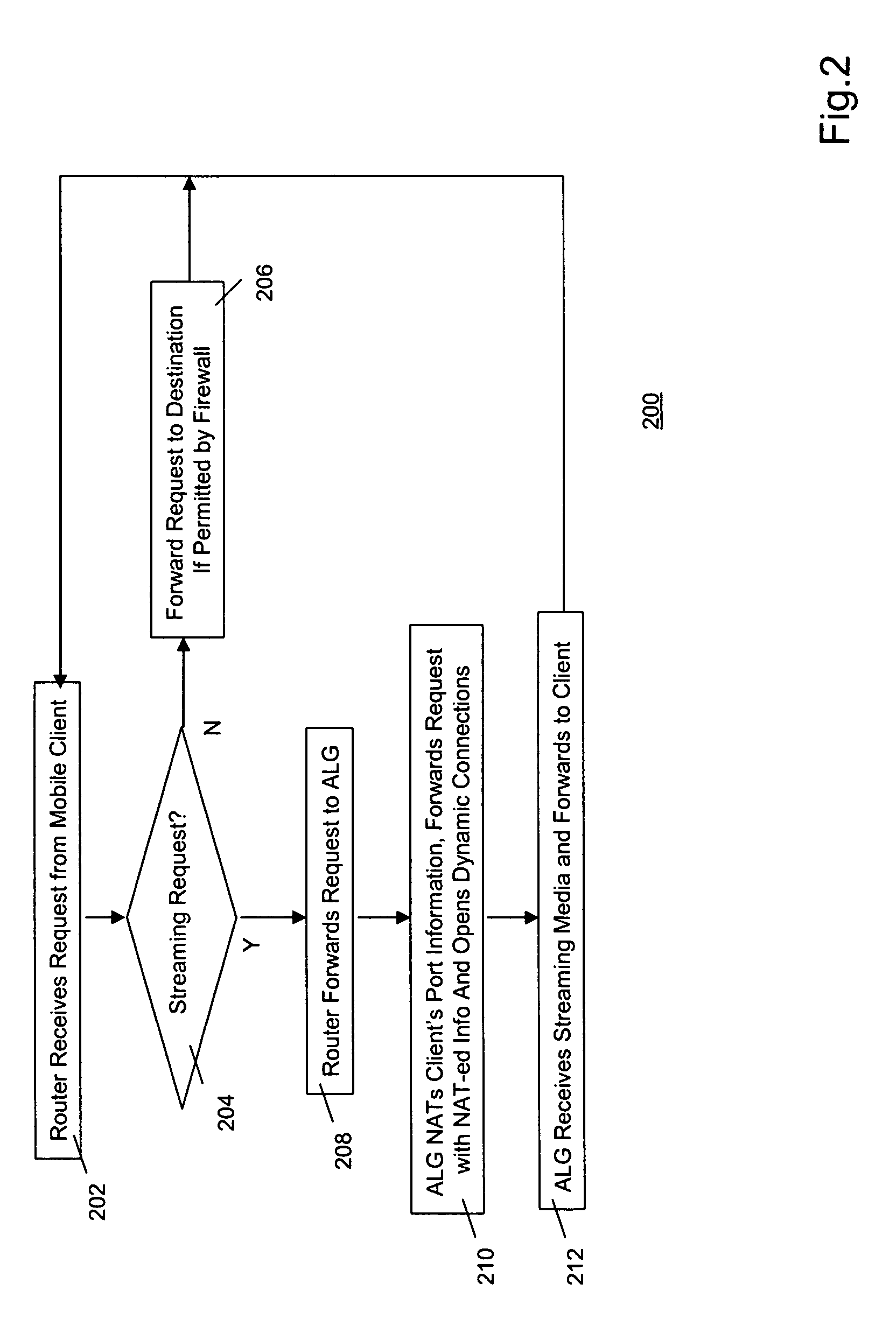
Streaming Media Service For Mobile Telephones
InactiveUS20100031339A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkThe Internet
A mobile client (104) on a private network (106) sends a request for receiving streamed media from a server (110,112) on a public network such as the Internet (108). The private network has a firewall (118). The private network has a router (116) that routes requests for streaming media to an application layer gateway (120) on the private network. The application layer gateway takes care of the NAT and security issues. Owing to this configuration, the mobile clients need not be re-configured when used for receiving streaming media.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Method of using SIP communicati protocal frame as mobile VPN
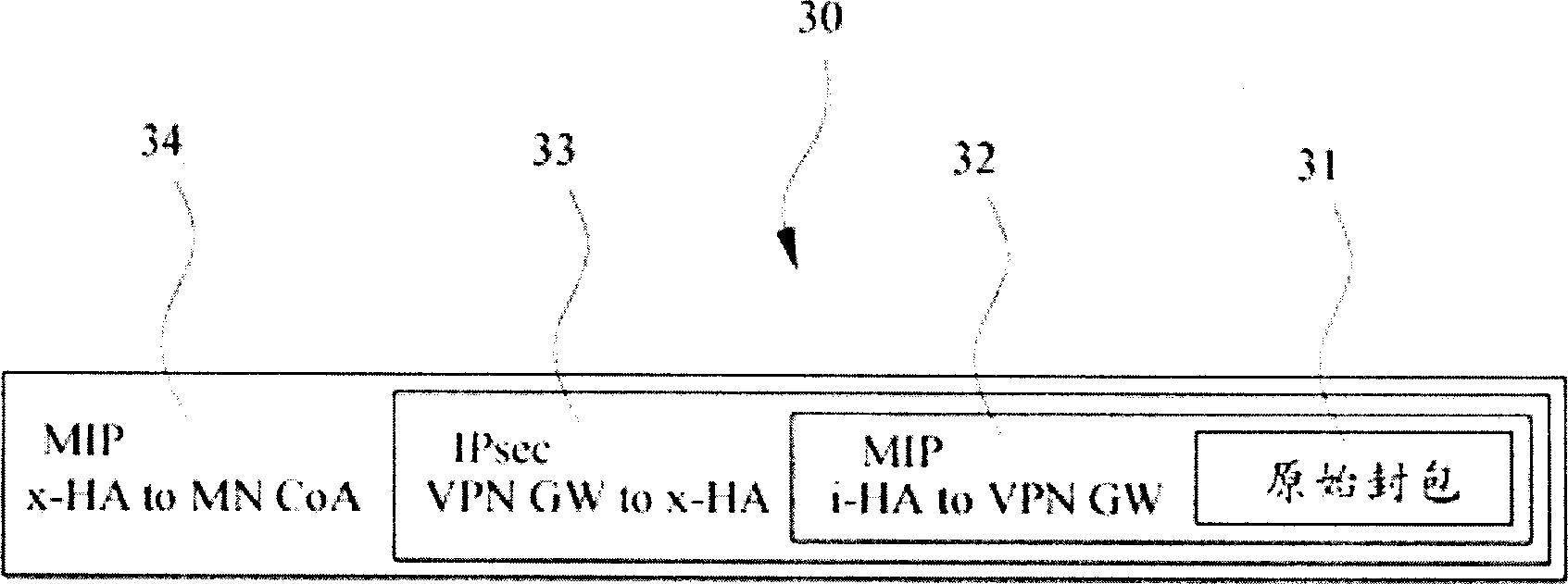
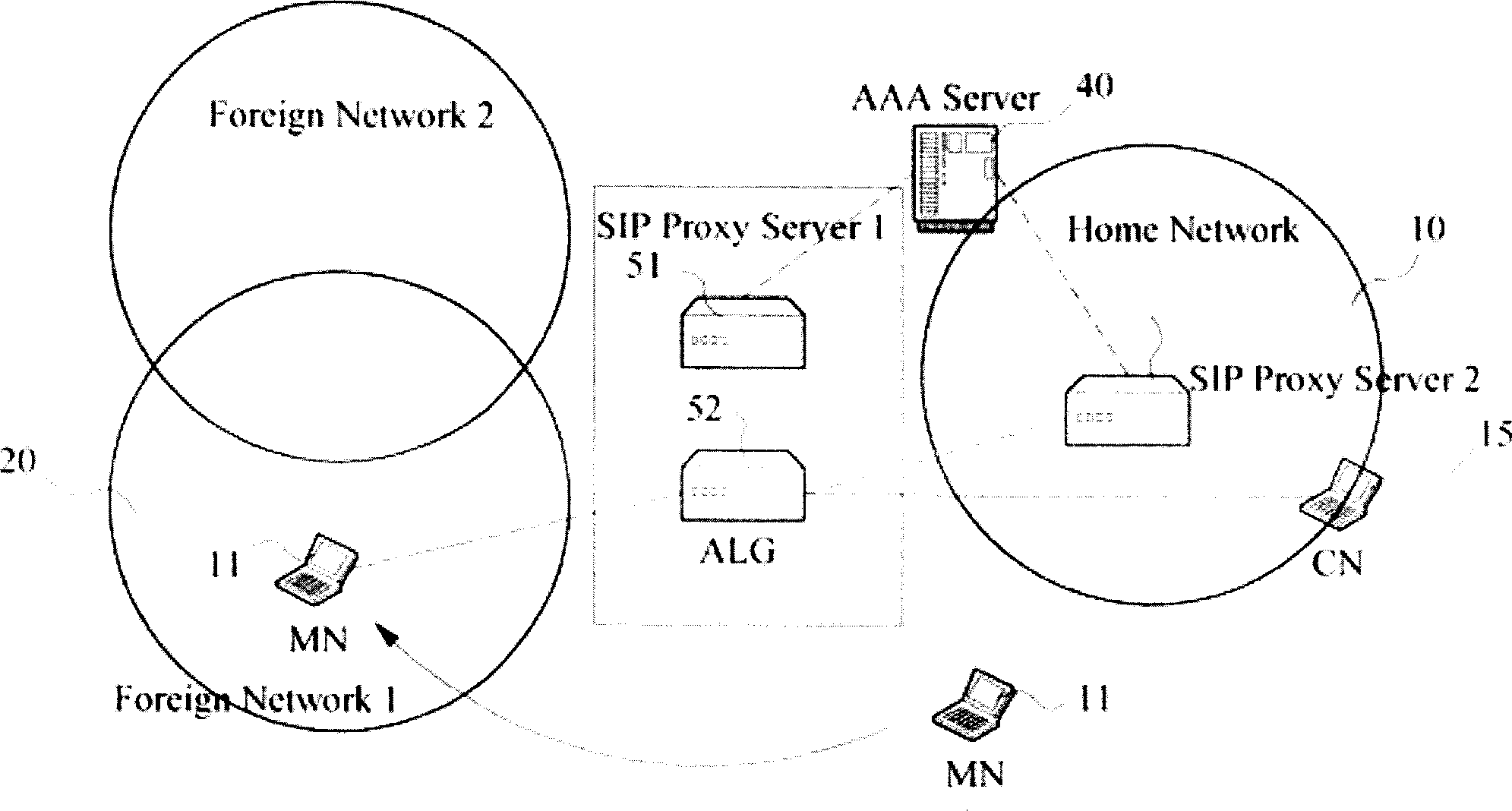
InactiveCN1835480AConvenient time creationReduce consumptionNetwork connectionsProxy serverProtocol Application
The method for use in making a mobile node roaming at external network capable of safely communicating with the communication nodes in internal network comprises: setting a first SIP proxy server, an application layer gateway, a second SIP proxy server and an AAA server between the internal network and the external network; when the second SIP proxy server detects the mobile node is closing to the internal network, it modifies the data transmission direction of the communication node information packet, and transmits it to the application layer; the first SIP proxy server authenticates and authorizes the mobile node through the AAA server, and generates a negotiation key that is transmitted to the application gateway; finally the application gateway takes over the transmission between the mobile node and the communication node.
Owner:ZYXEL
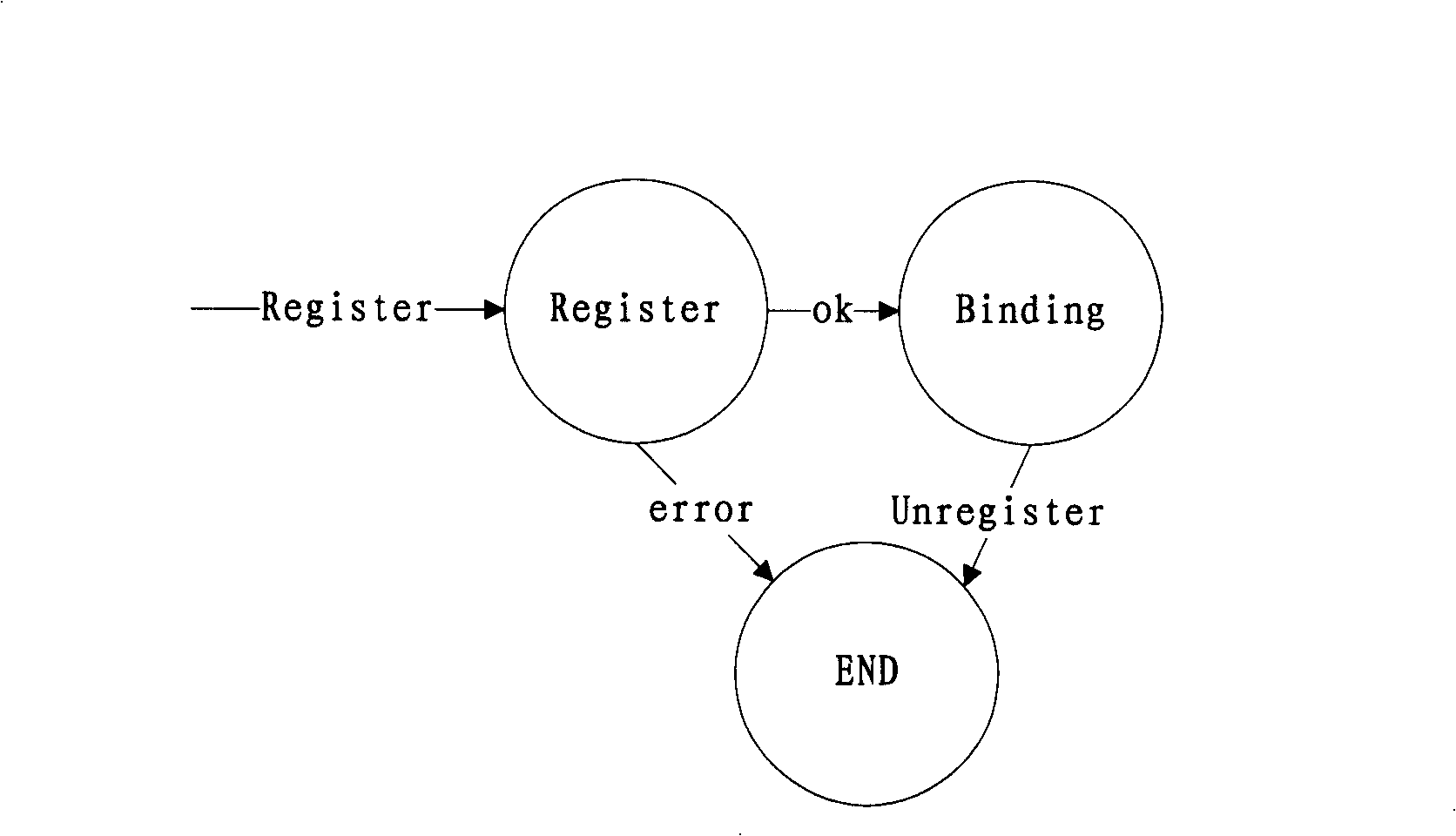
Implementing method of SIP application-level gateways based on NAT-PT
InactiveCN101257435AImprove interoperabilityRealize distributionData switching networksResponse processWorld Wide Web
Disclosed is a method for applying a NAT-PT-based SIP onto the gateway to convert SIP message between an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network, comprising: obtaining the identification number and length of the SIP message; analyzing the first line of the message head to judge whether the type of the SIP message is a request or a response; if the answer is request, executing the request process; if the answer is response, executing the response process. The invention can record the conversion of the IP address and the port via a conversion information table, manage the conversion state of the message by a state machine, and carry out the conversion from the IPv4 address to IPv6 address (or visa versa) based on an address prefixing and an address pool, accordingly, the conversion between the IPv4 network and IPv6 network is achieved.
Owner:上海亿人通信终端有限公司
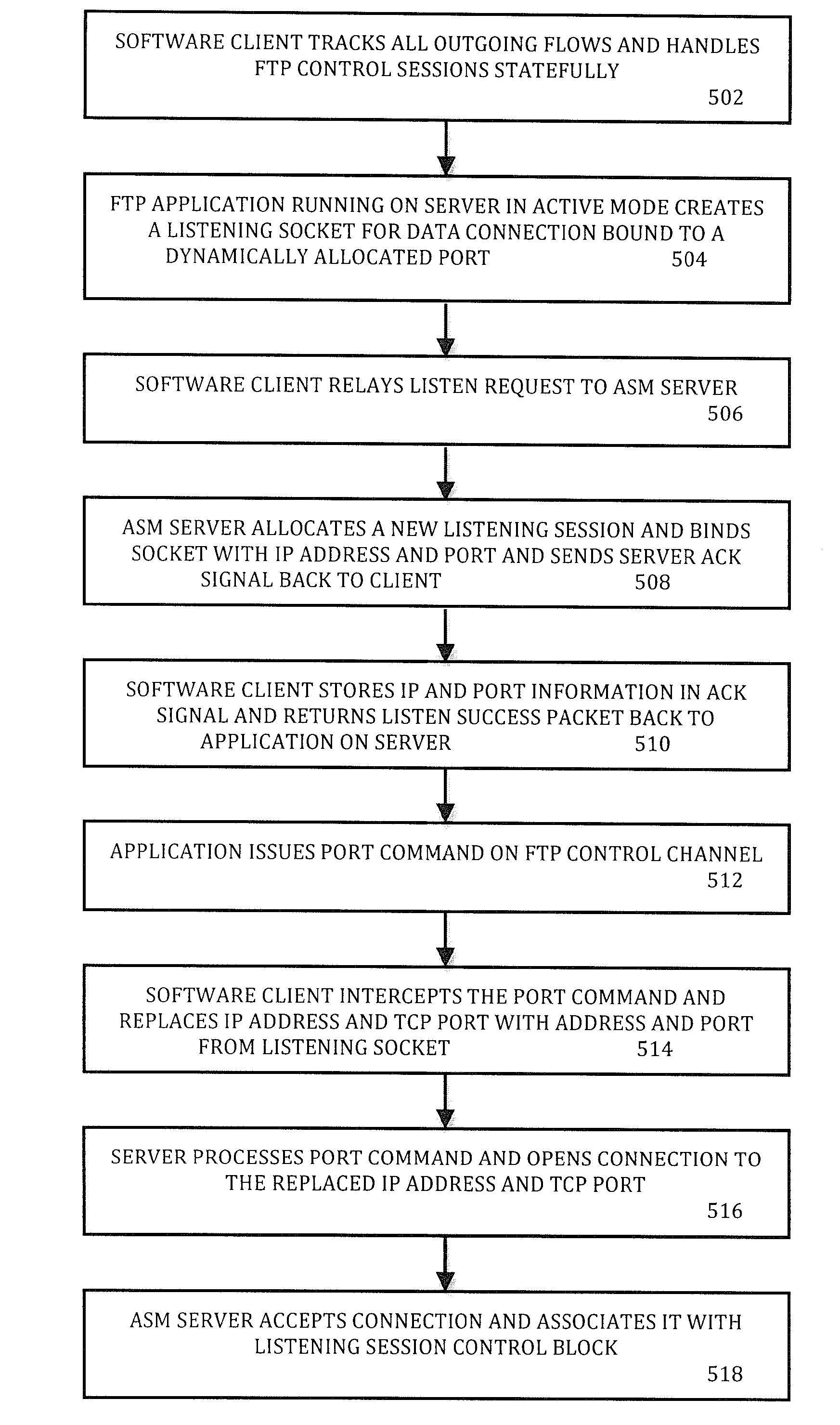
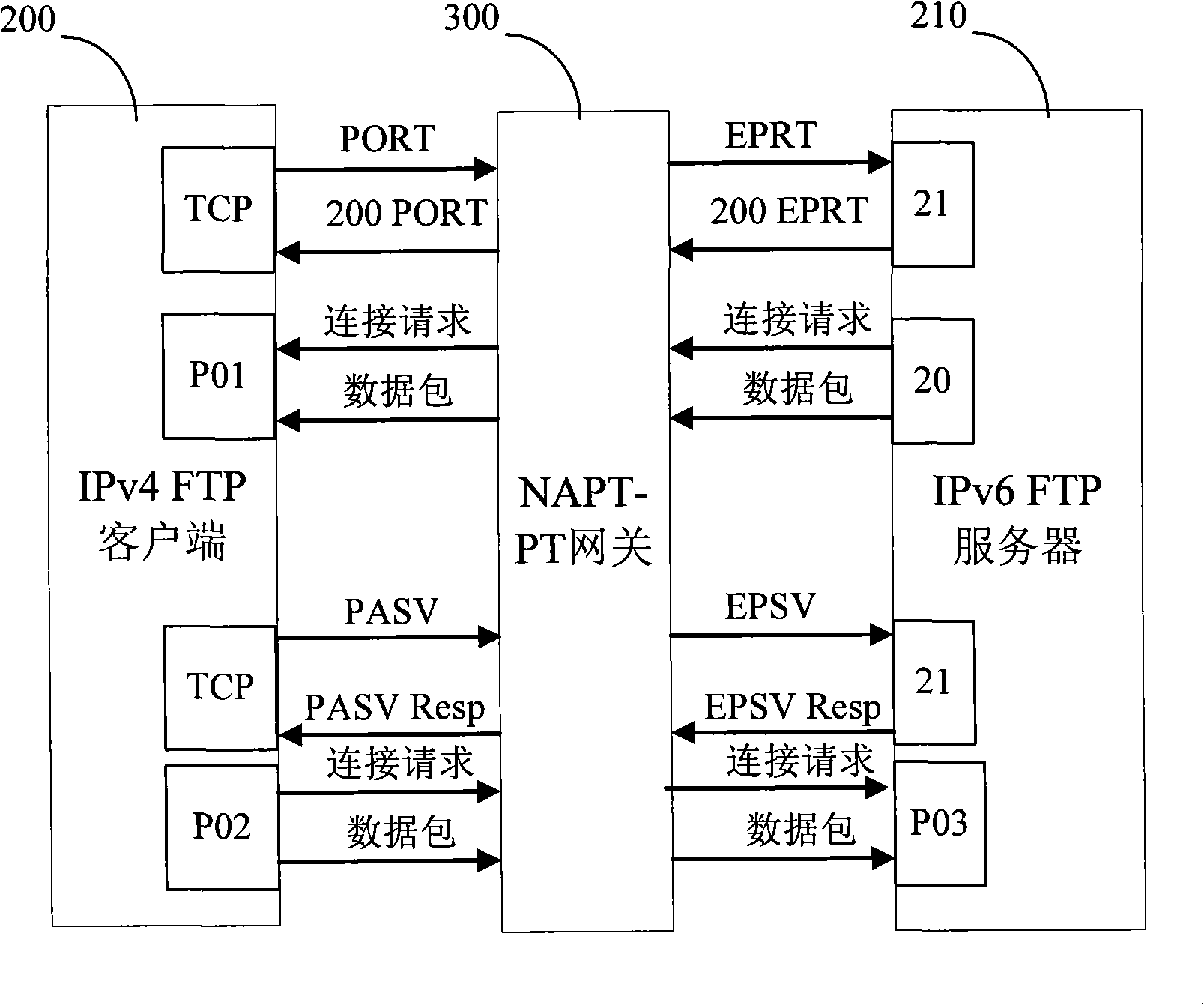
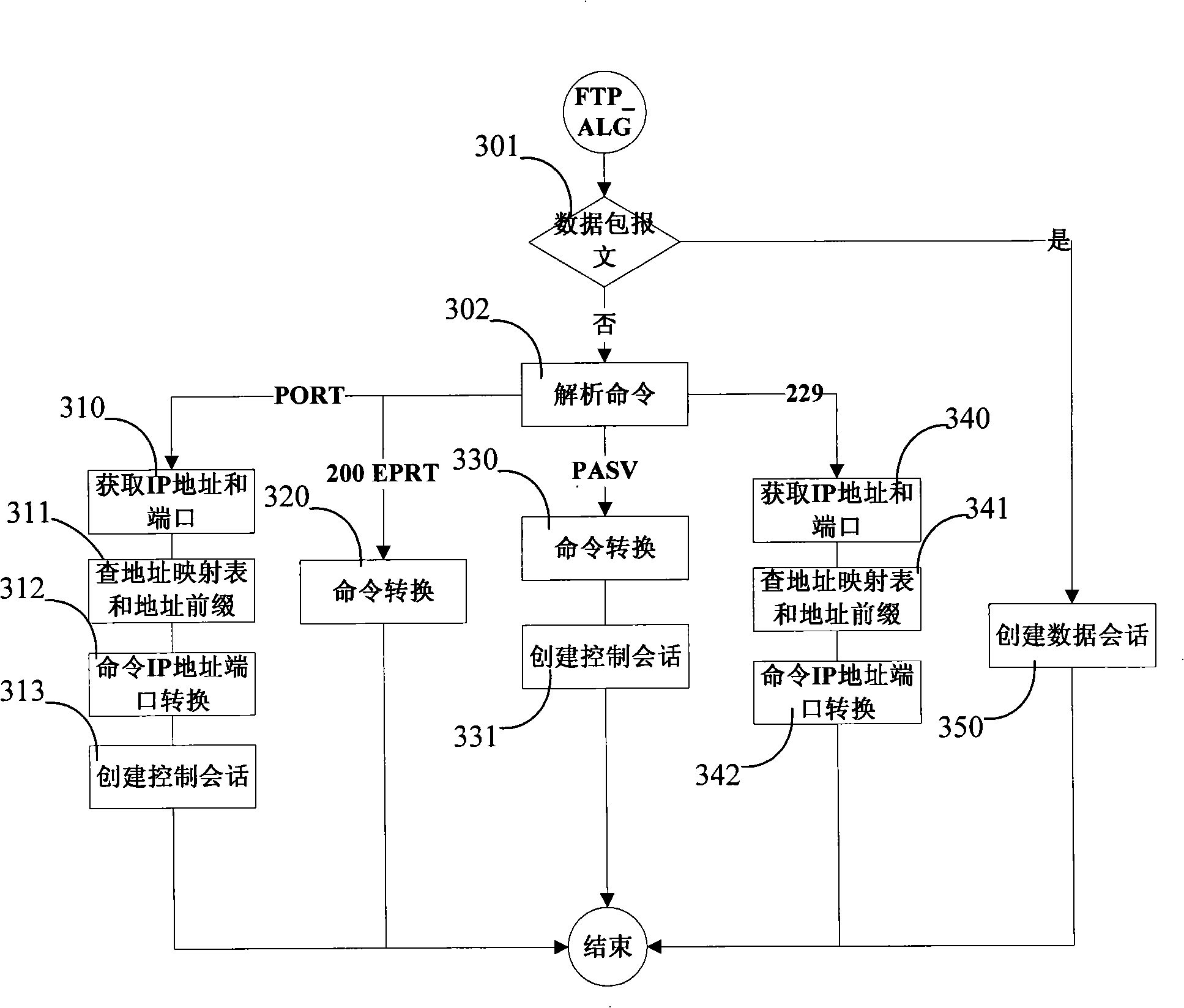
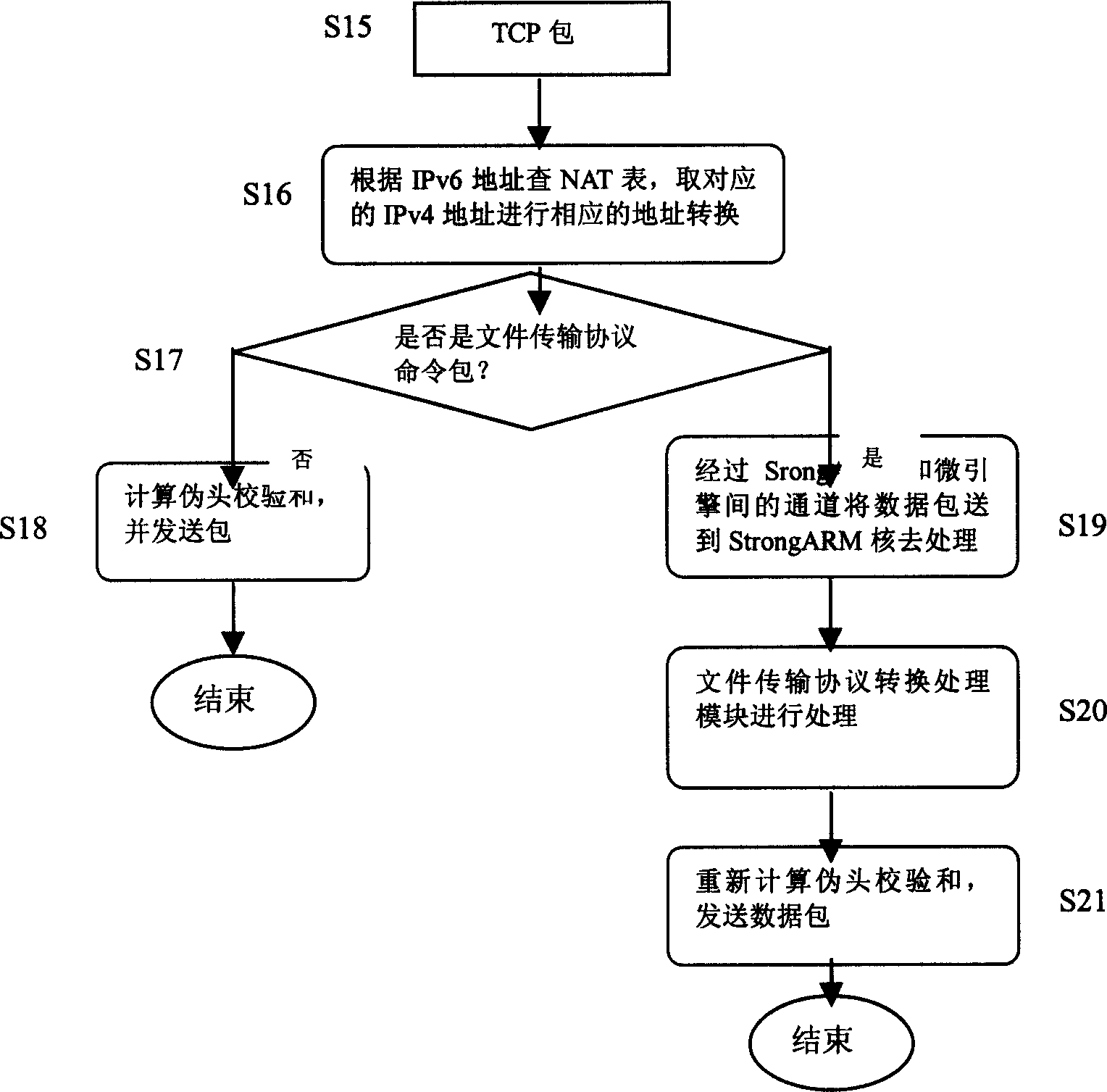
Method for implementing FTP application-layer gateway based on NAT-PT
The invention discloses an implementing method for FTP application-level gateways based on NAT-PT, for conversion of FTP protocol between IPv4 network and IPv6 network, including the following steps: a. receiving an FTP message, judging whether the FTP packet is a data packet message, if so, establishing a data conversation; otherwise, executing the following steps; b. resolving the FTP command for knowing the command types; c. converting the FTP command, simultaneously converting IP address and / or terminal port when the command includes IP address and / or terminal port; d. establishing a control conversation when the FTP command is PORT command, EPRT command, PASV command or EPSV command; and e. establishing a data conversation simultaneously when establishing a control conversation, when the FTP command is the EPRT command; and establishing a data temporary conversation simultaneously when establishing a control conversation, when the command is the EPSV command.
Owner:上海亿人通信终端有限公司
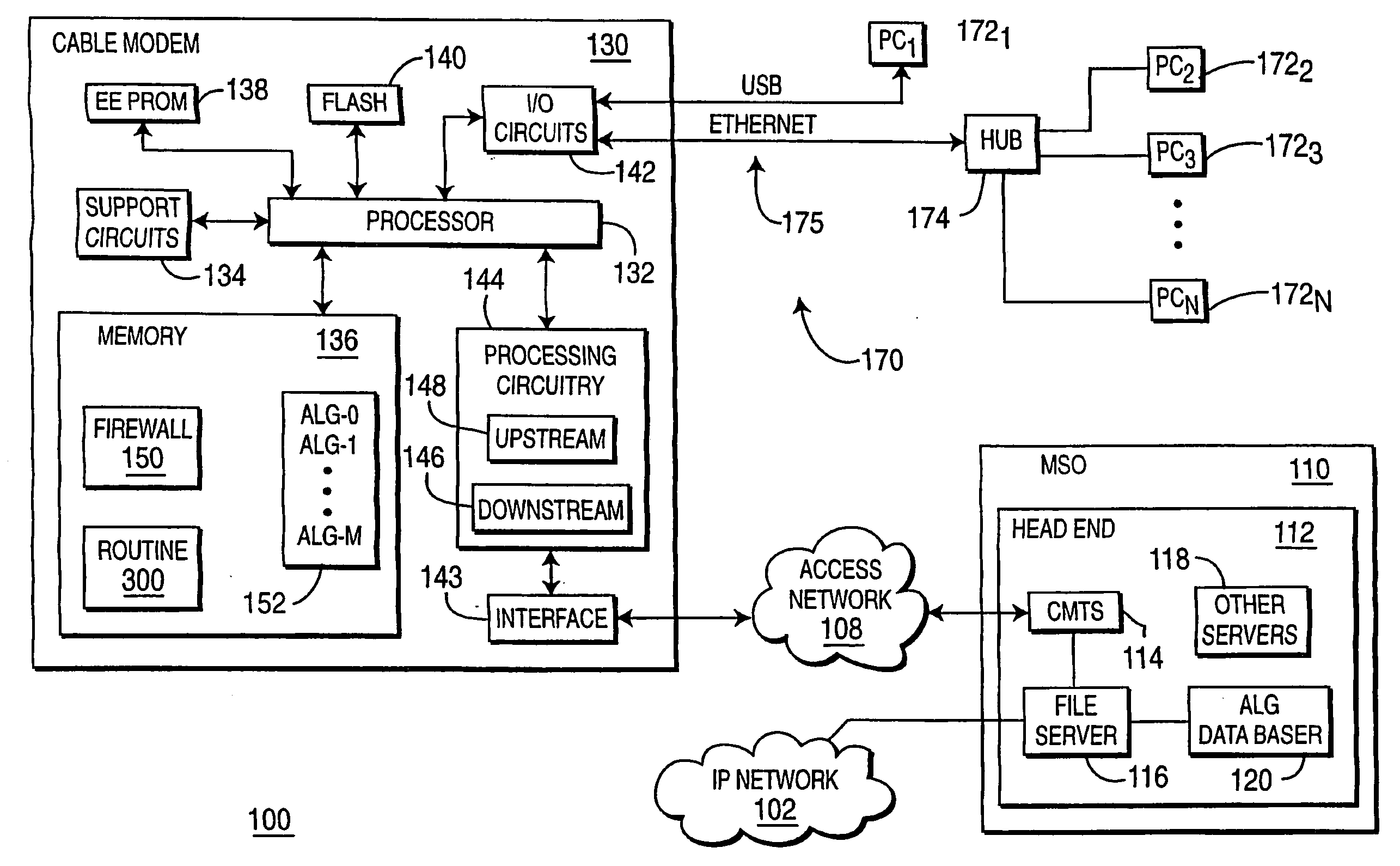
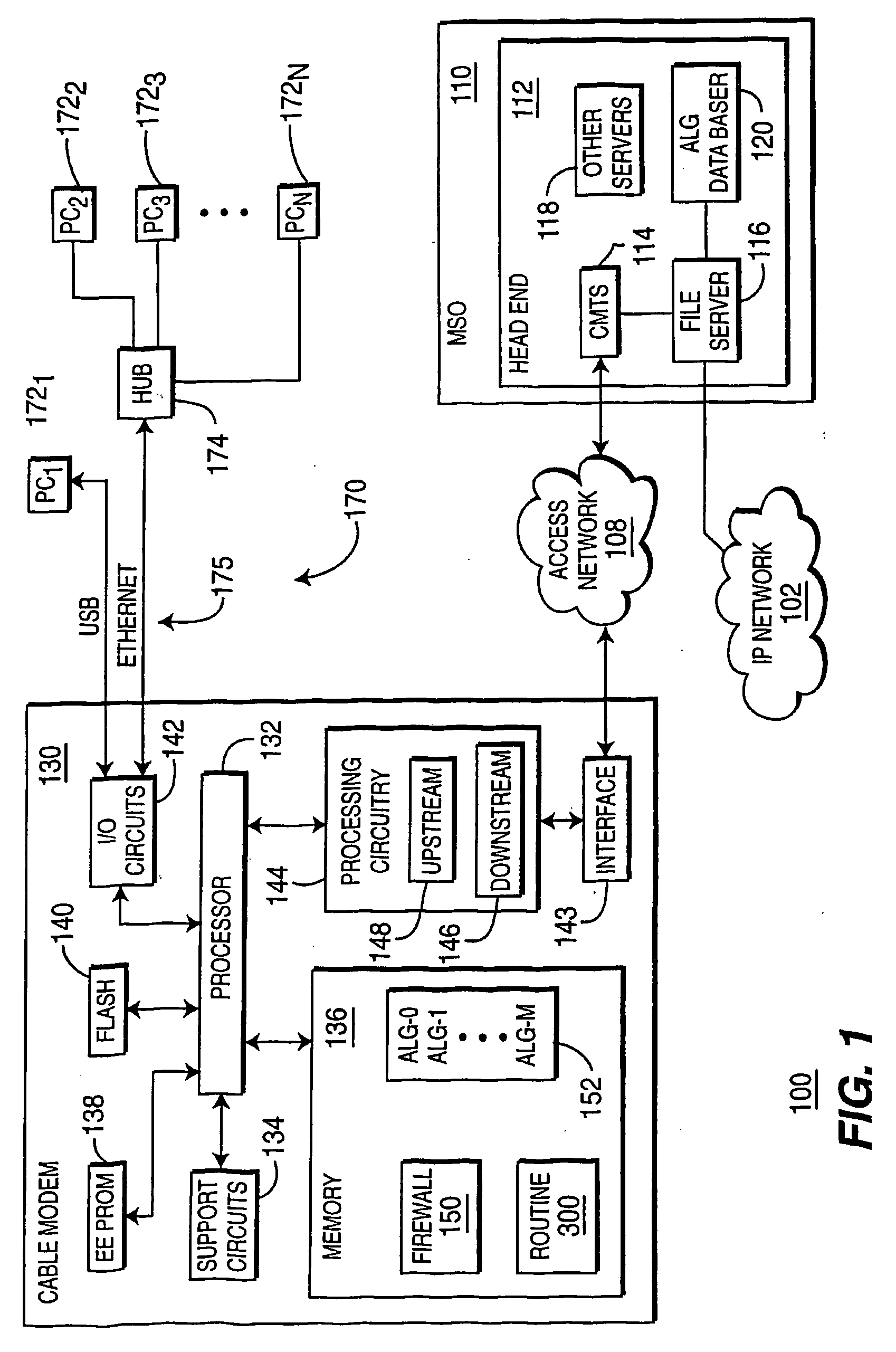
Apparatus and methods for providing an application level gateway for use in networks
ActiveUS7788407B1Overcome problemsMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionThe InternetNetwork addressing
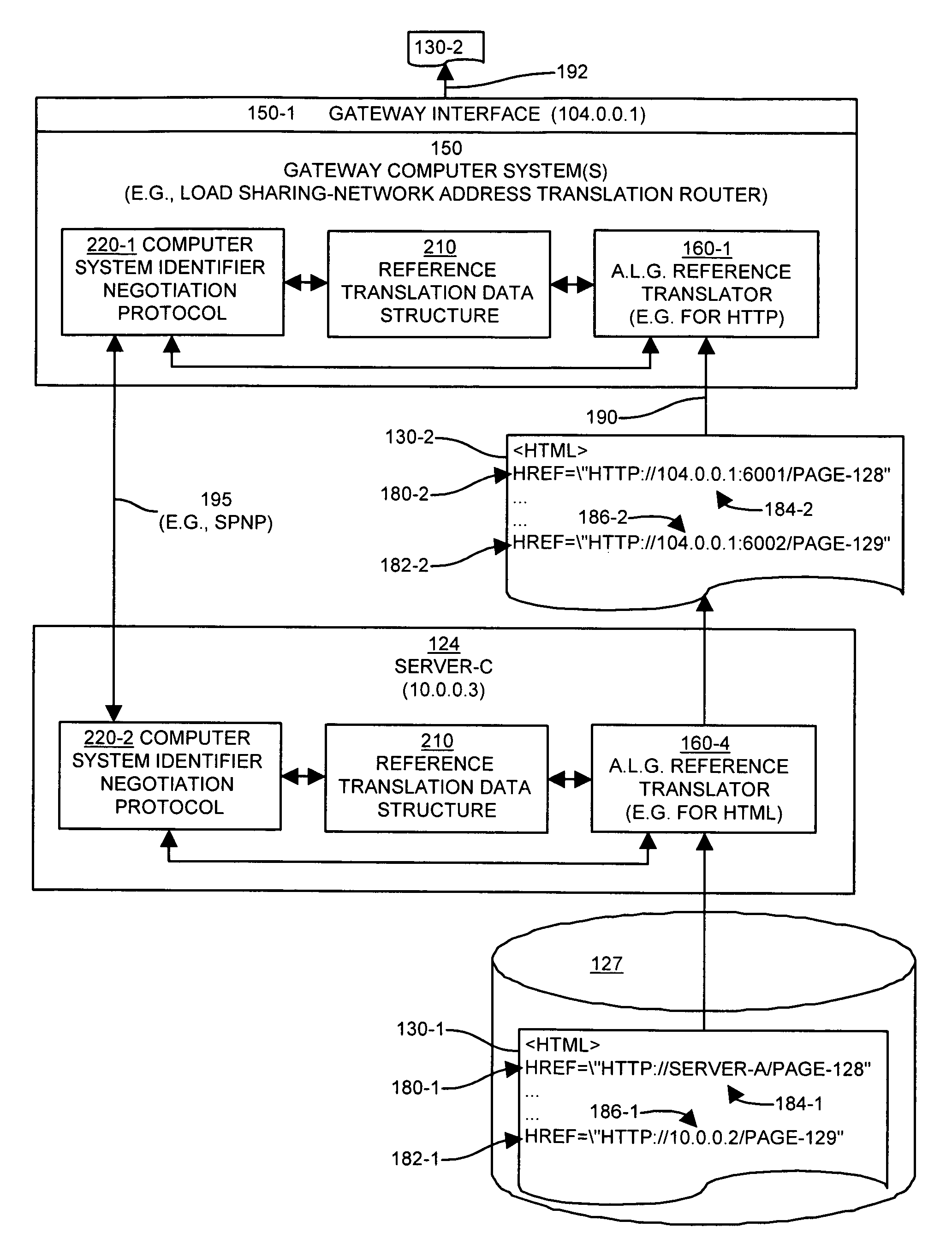
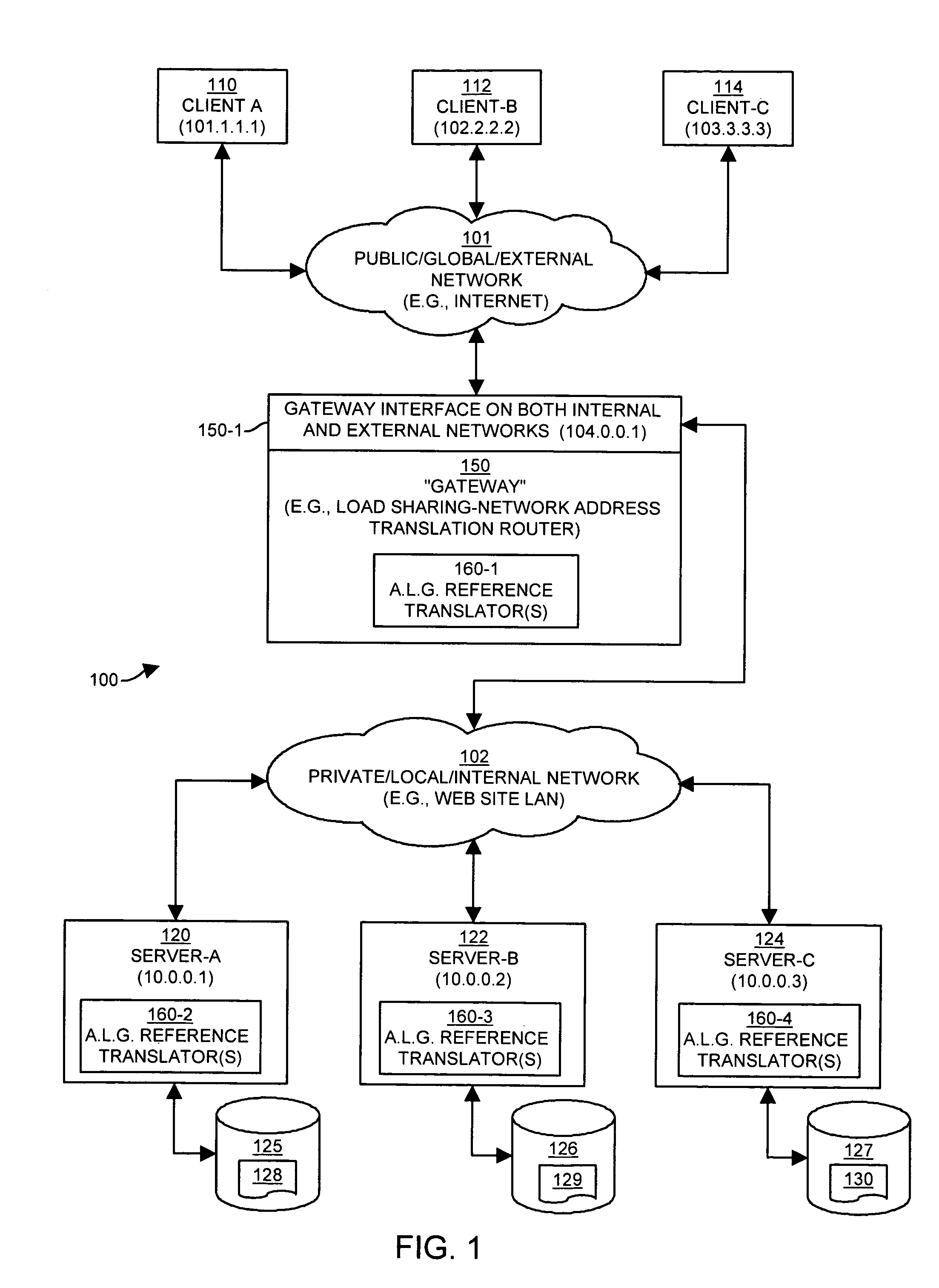
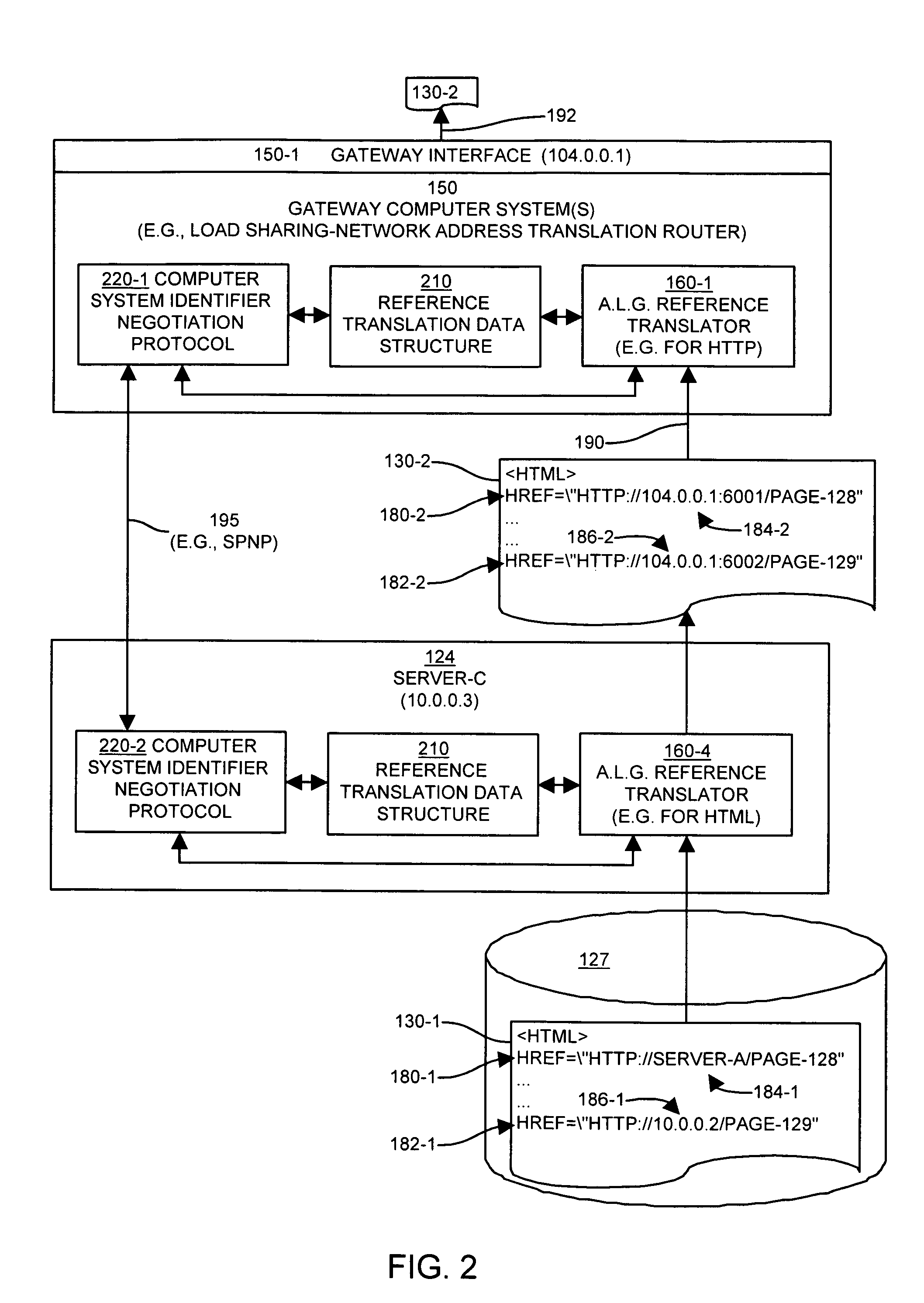
An application level gateway allows computers on a local area or “internal” network to serve data (e.g., web pages, files or other constructs) to computer systems on an external or public network such as the Internet, even though references such as hostnames and / or network addresses within the internal network that are contained within the data (e.g., URLs in web pages) might not be compatible (e.g., DNS resolvable or routable) with the external network. The system detects, in a portion of data (e.g., a web page), a local reference to a computer system on the internal network, determines whether a computer system identifier is mapped to the computer system specified in the local reference, and replaces the local reference with a translated reference obtained from the mapping. The translated reference contains the computer system identifier and a reference to a gateway computer system coupled to the internal network, such that subsequent referrals to the translated reference are directed to the gateway computer system. When a request for the data is subsequently received, the gateway performs a reverse mapping to determine the identity of the computer system on the internal network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
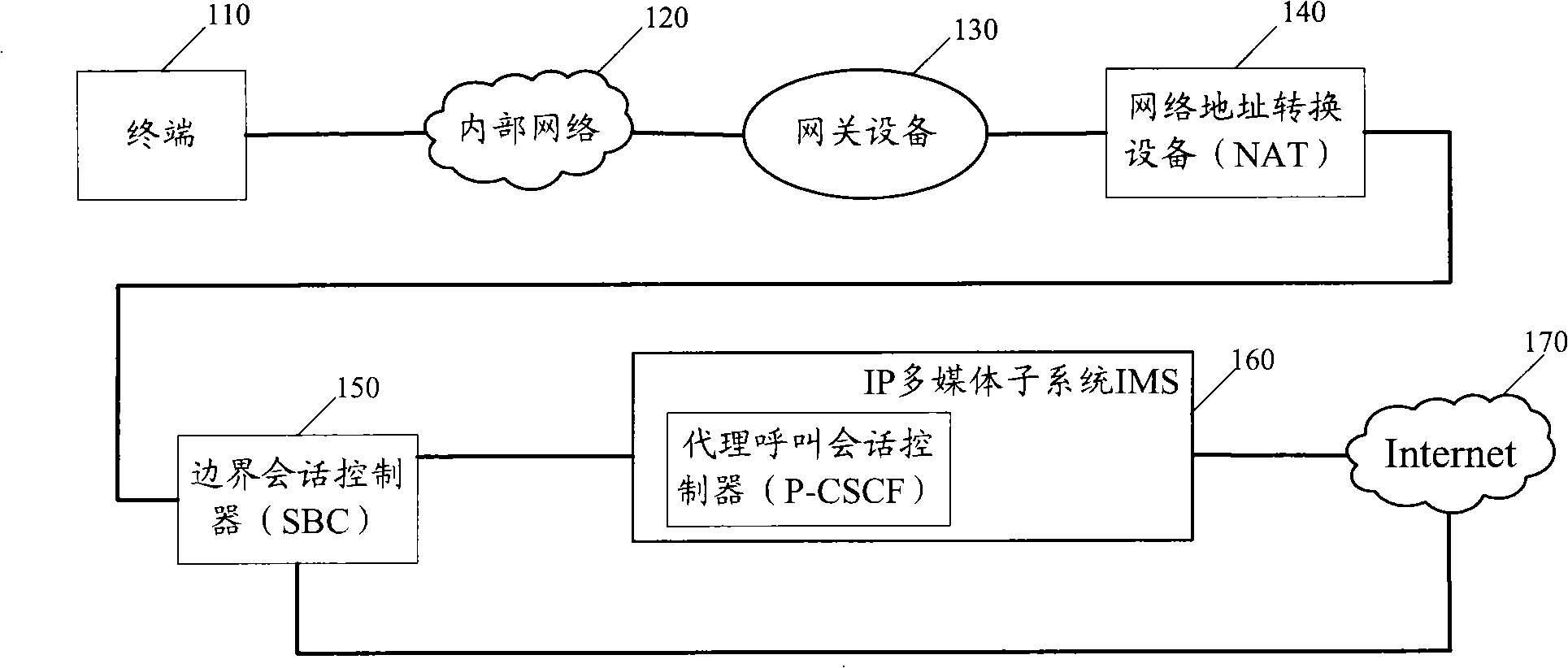
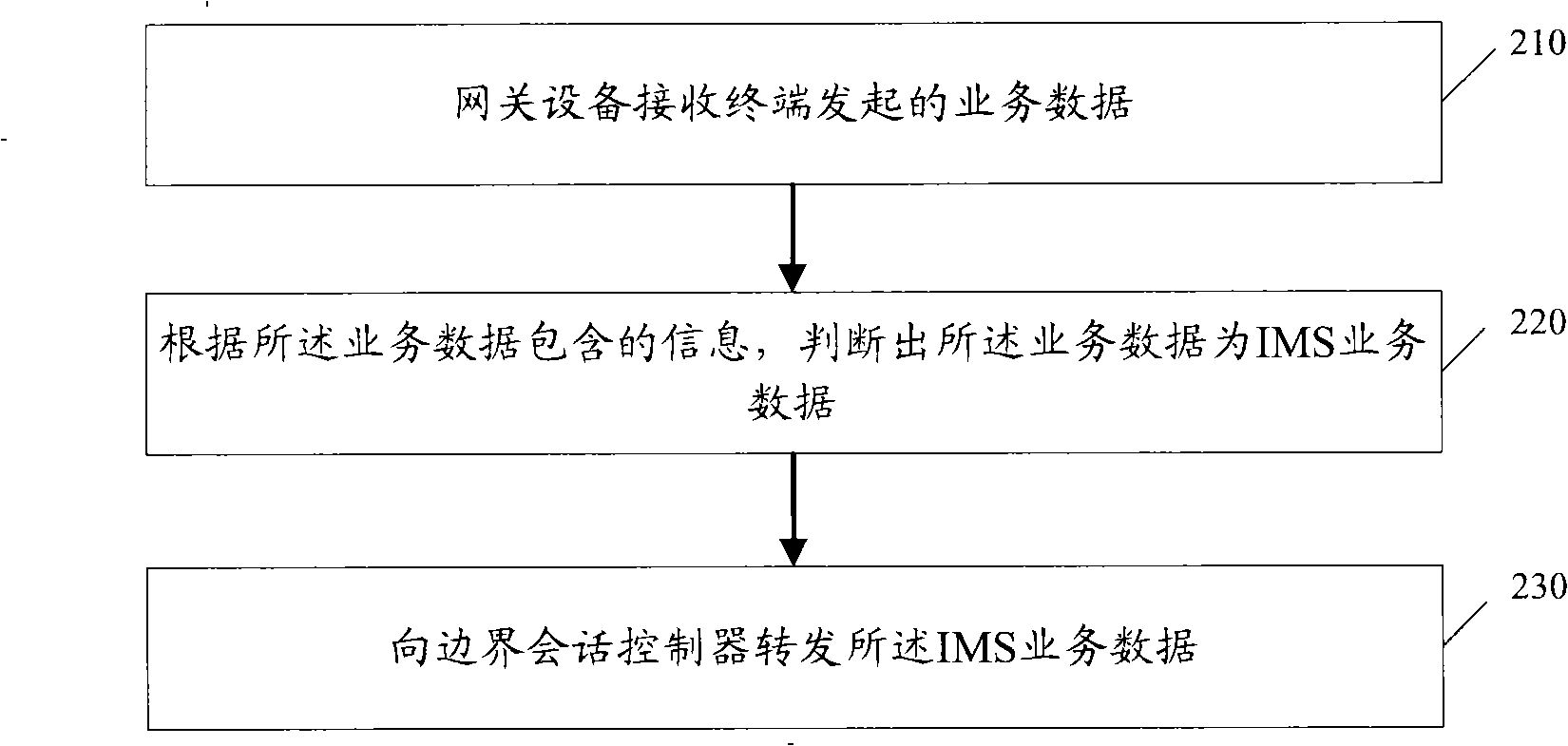
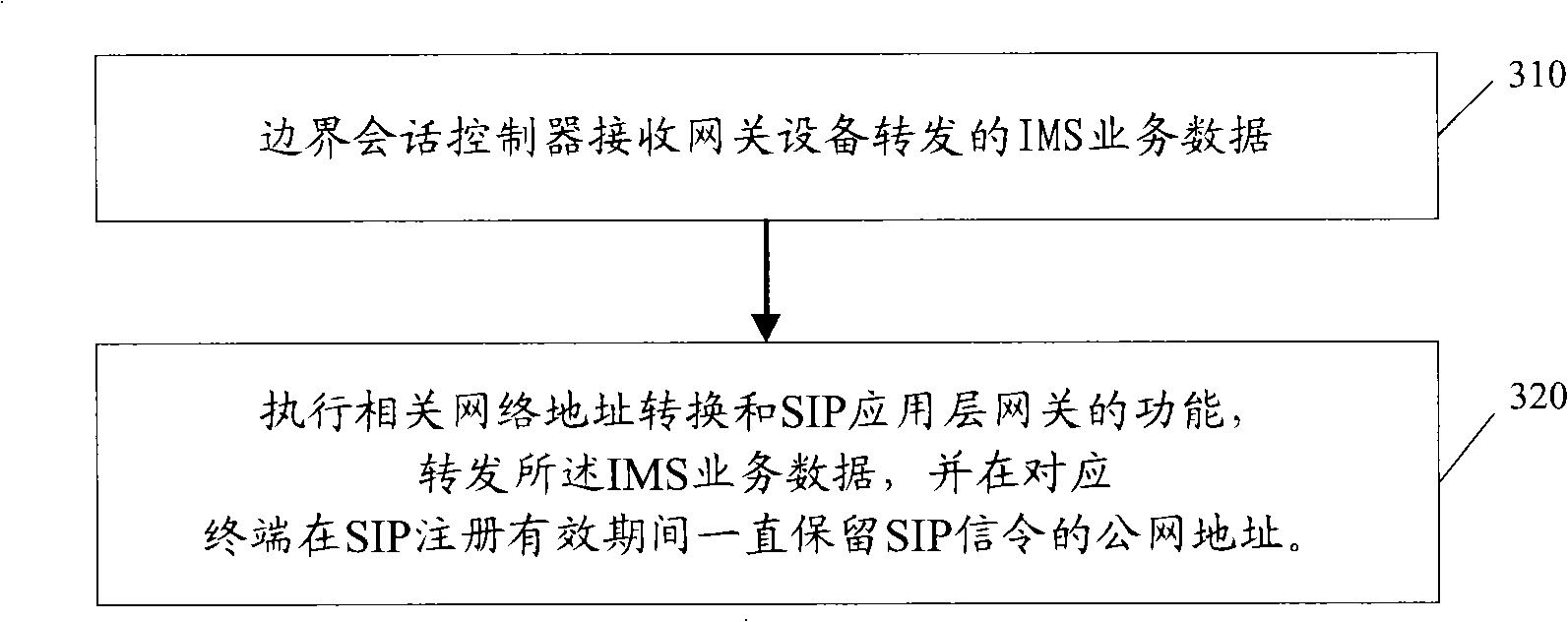
Route processing method, IMS service processing method and related equipment
Embodiments of the invention disclose a route processing method, an IMS service processing method and related equipment. The IMS service processing method comprises: a border session controller receives IMS service data forwarded by a gateway device; executes the network address conversion and functions of application-level gateways of initiation session protocol SIP, and forwards the IMS service data; and a public net address of SIP signaling is reserved all the time in the valid period of registration of SIP at the corresponding terminal. In the technical proposal of the embodiments, the border session controller reserves the corresponding public net address in the valid period of registration of SIP for the terminal, the processing method is simple, and the invalid information interaction between the related equipment and data processing burden can also be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Network data pipelining type analysis process method
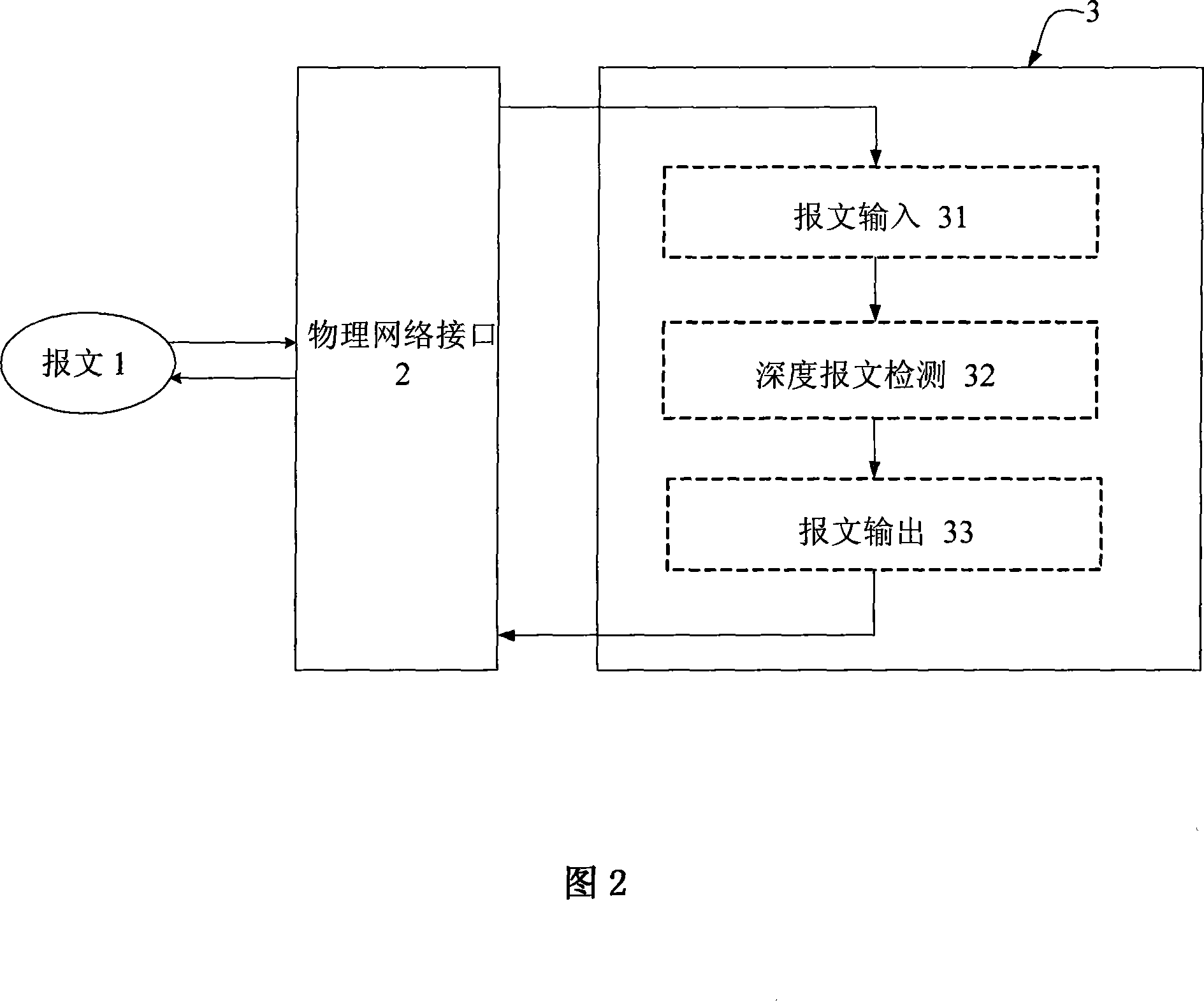
InactiveCN101141458AImprove processing efficiencyReduce latencyData switching networksQuality of serviceNetworked system
The present invention provides an analysis and treatment method of a network data pipeline type, firstly, the message enters a network system through a physical network entrance, the operation of an IP banding recombination, a TCP message reordering, a service quality and a bandwidth management is executed; and then a detection from a first floor to a sixth floor is performed to the message, a detection content comprises a classification and treatment based on a state, a firewall treatment, an antivirus filtering, a counterespionage software detection, an intrusion detection / intrusion defense, a content filtering, an application level gateway and a VPN treatment; a detection result reflects a treatment decision to the message, a part of message is dropped, the other message enters a normal message output treatment; a further treatment is performed again, the operation of a route, a streaming ordering, a bandwidth management and a service quality is executed, subsequently, the message is sent out through a physical network gateway. The efficiency of the network data treatment is greatly improved, and the network delay and the network cost are obviously reduced.
Owner:网经科技(苏州)有限公司
System and method for interworking between IPv4 (internet protocol version 4) and IPv6 (internet protocol version 6) based on DHT (distributed hash table)
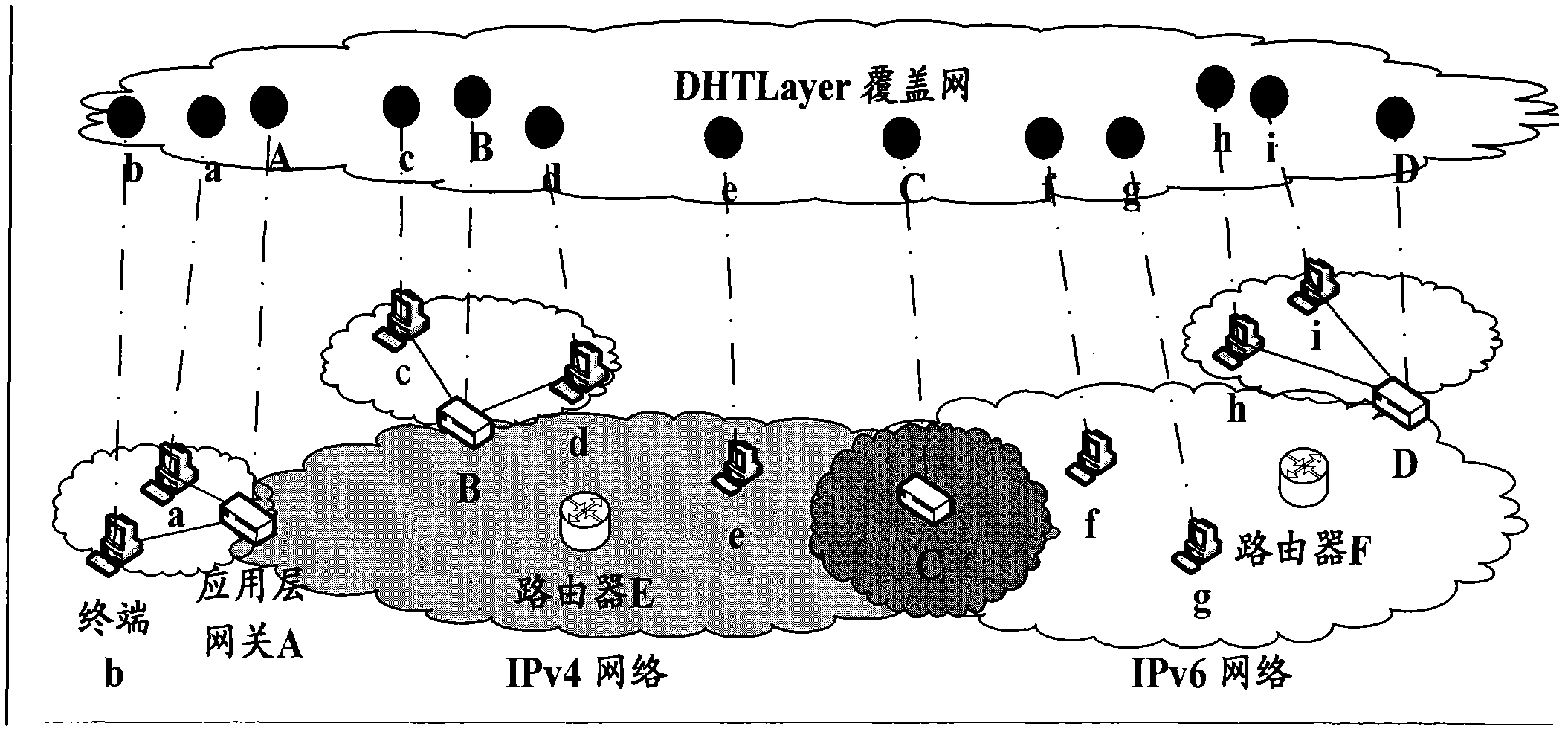
InactiveCN102098353ASuitable for dynamic deploymentLoad balancingData switching networksExtensibilityIp address
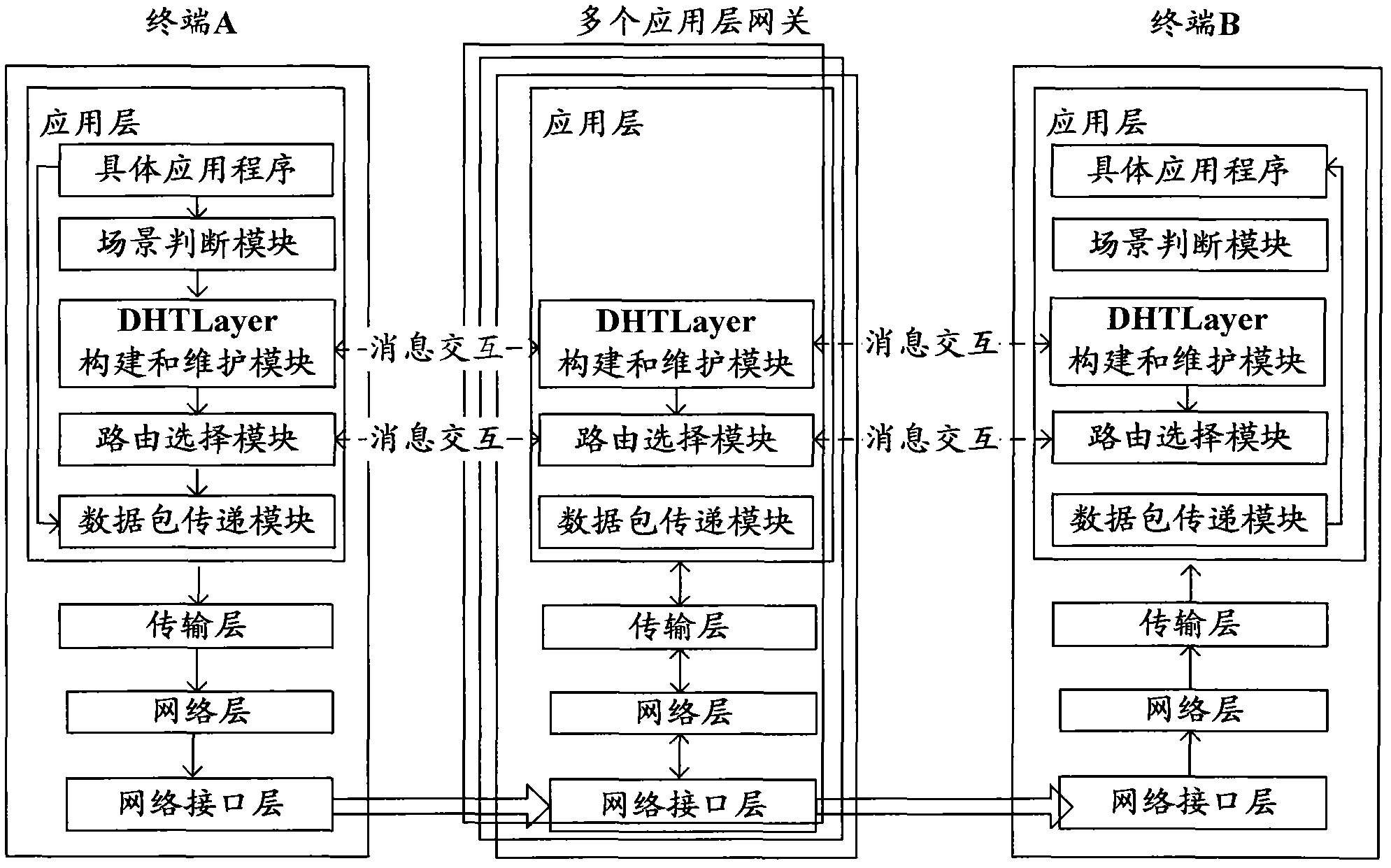
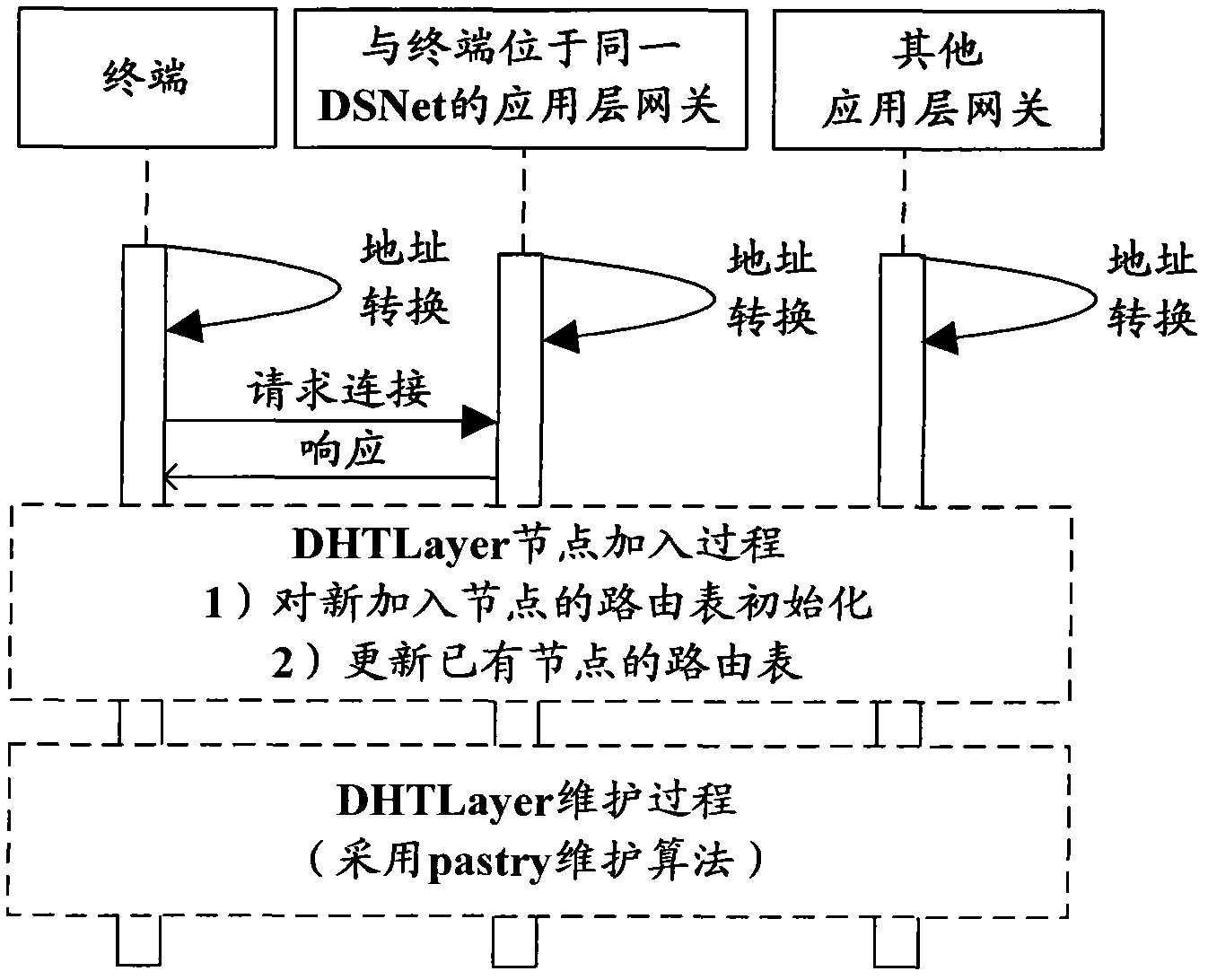
The invention provides a system and method for interworking between the IPv4 (internet protocol version 4) and the IPv6 (internet protocol version 6) based on a DHT (distributed hash table). The system only improves a terminal and takes a new double stack gateway which is arranged at the network perimeter between the IPv4 and the IPv6 as an application layer gateway rather than changing the othernetwork element equipment arranged in the original IPv4 or IPv6 network. The common point of the terminal and the application layer gateway is that an application later is additionally provided with five sequence connection modules, namely an address conversion module, a DHT layer building and maintaining module, a route path querying module, a shortest route path computing module and a data packet transmitting module; and on the basis of the added modules, each application layer gateway is logically mapped to form a DHT converge network. In order to realize the interconnection and the intercommunication of the IPv4 node and the IPv6 node, the terminal is further additionally provided with a scene judging module. The invention is used for realizing the interconnection and the intercommunication of the IPv4 and the IPv6 on the basis that the existing IPv4 protocol and IPv6 protocol are minimally changed. In the invention, the address difference of the original IPv4 network node and IPv6 network node is eliminated, and the data communication is completed by two different host machines according to an IP (internet protocol) address sequence with a set rule. By adopting the DHT technology, the invention is good in expandability and scalability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for realizing distributed application tier conversion gate-link in network processor
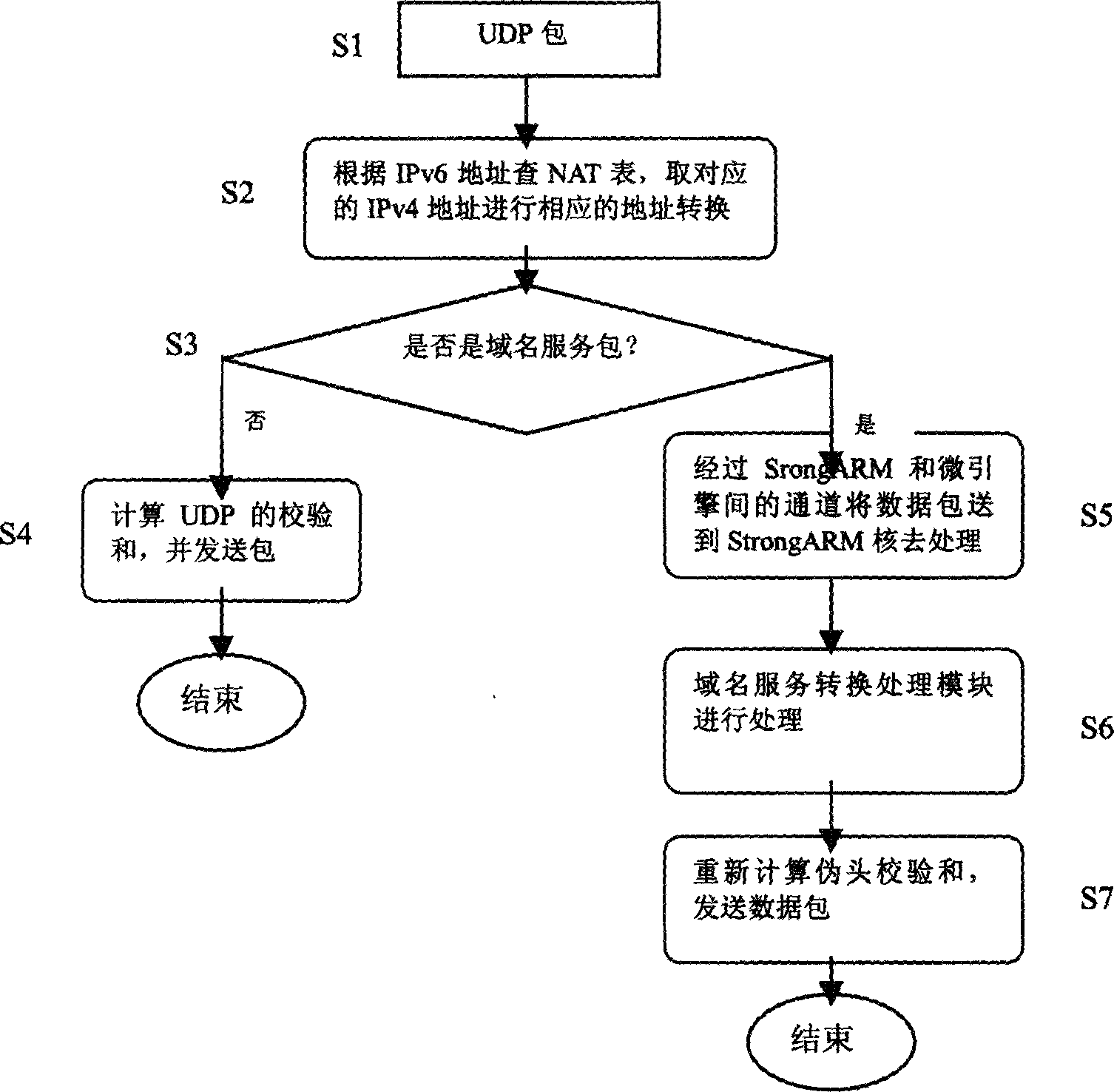
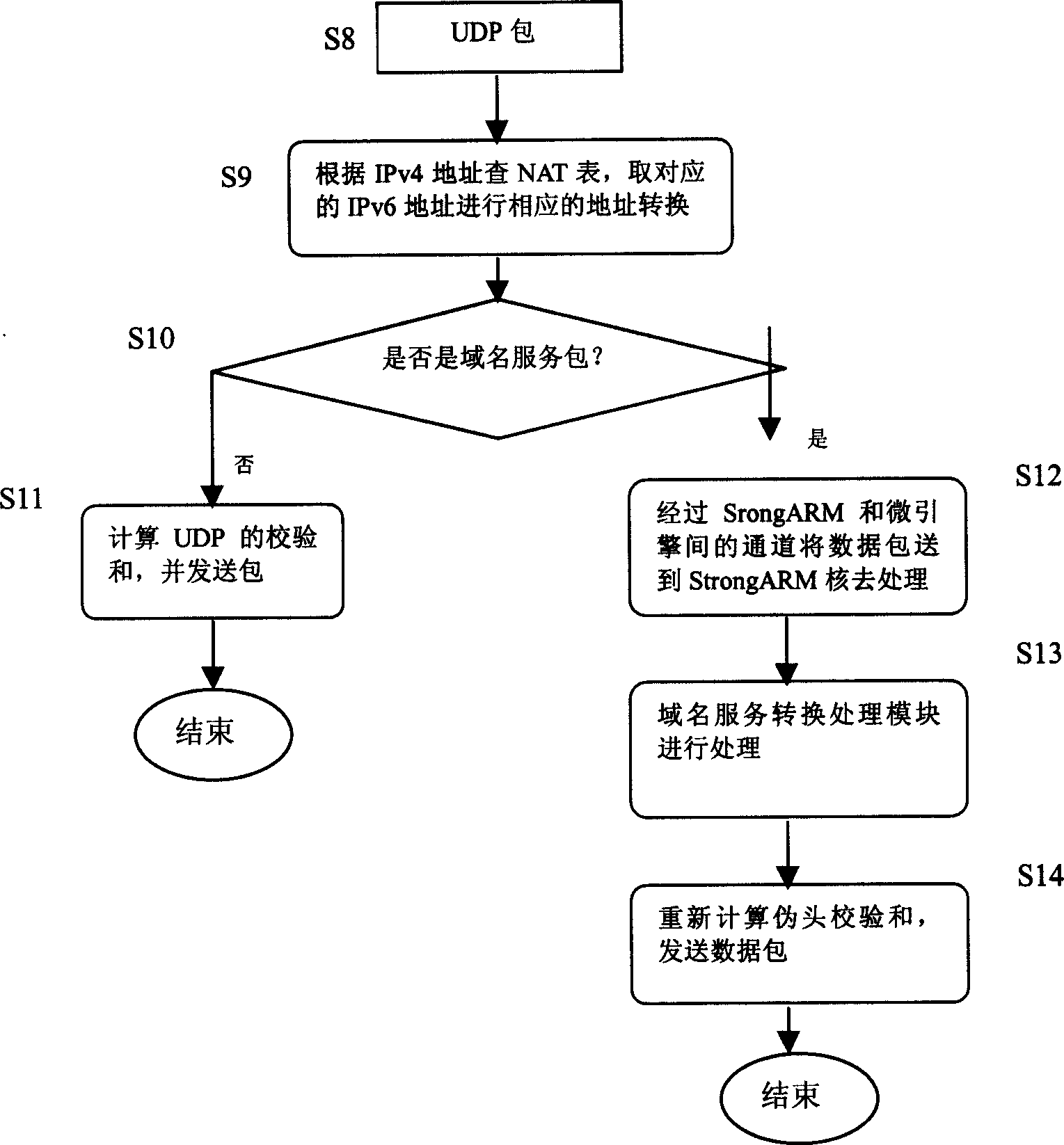
InactiveCN1529481AGuaranteed the speed of finding NAT table entriesImprove performanceNetwork connectionsDomain nameNetwork processor
The invention relates to method of domain name service (DNS) conversion gateway as well as file transfer protocol (FTP) conversion gateway in network processor platform. Steps of the method are as following: (1) receiving port receives data packet; (2) converting address and protocol for received data packets by micro engine; (3) checking port number of protocol, structuring data packet for DNS packet or FTP command packet found by using 'taking along' technique; (4) SltongARM calls module of DNS conversion gateway to process DNS packet, and calls module of FTP conversion gateway to process FTP command packet; (5) data packet processed by conversion module of application layer gateway is sent to transmission queue to be transmitted. Practical testing verifies that NAT-PT realized by the invented method is capable of processing accesses between IPv4 network and IPv6 in real time.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interworking system between IP networks using different IP address format, application layer gateway (ALG) server, stun server, network address translator, interworking method thereof, and sIP message routing method thereof
ActiveUS20110191493A1Load minimizationDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionPrivate IPSTUN
Disclosed are an interworking system between IP networks using different IP address format, an application layer gateway (ALG) server, a network address translator, an interworking method, and a SIP message routing method. The interworking system between a local network using a private IP and a public network using a public IP includes a STUN server and an application layer gateway (ALG) server. The STUN server provides binding information of header information of a public IP binding request. The application layer gateway (ALG) server performs a public IP binding request with header information changed by IP masquerading, and performs routing by applying the received binding information to media receiving address information of a SIP message.
Owner:KT CORP
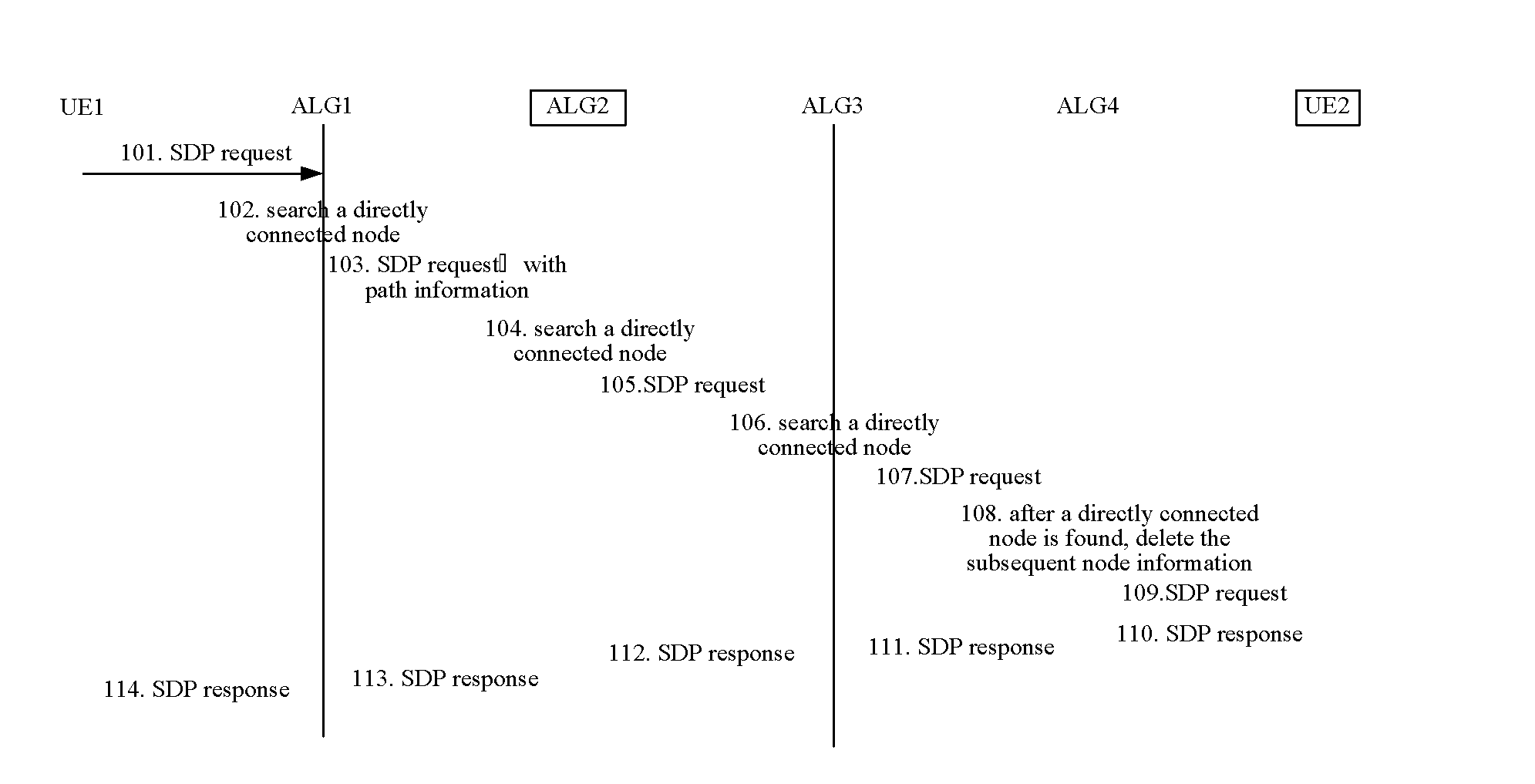
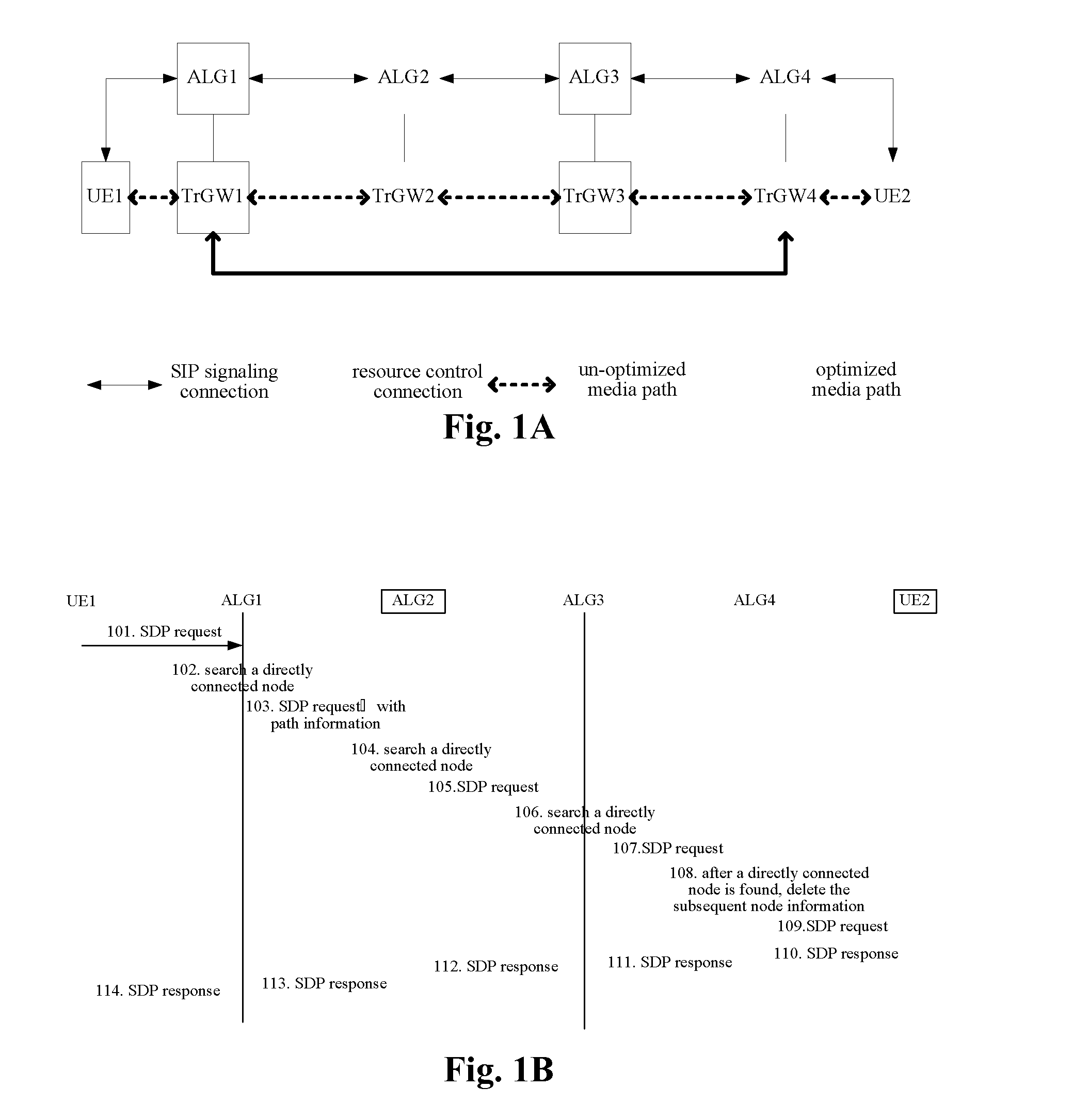
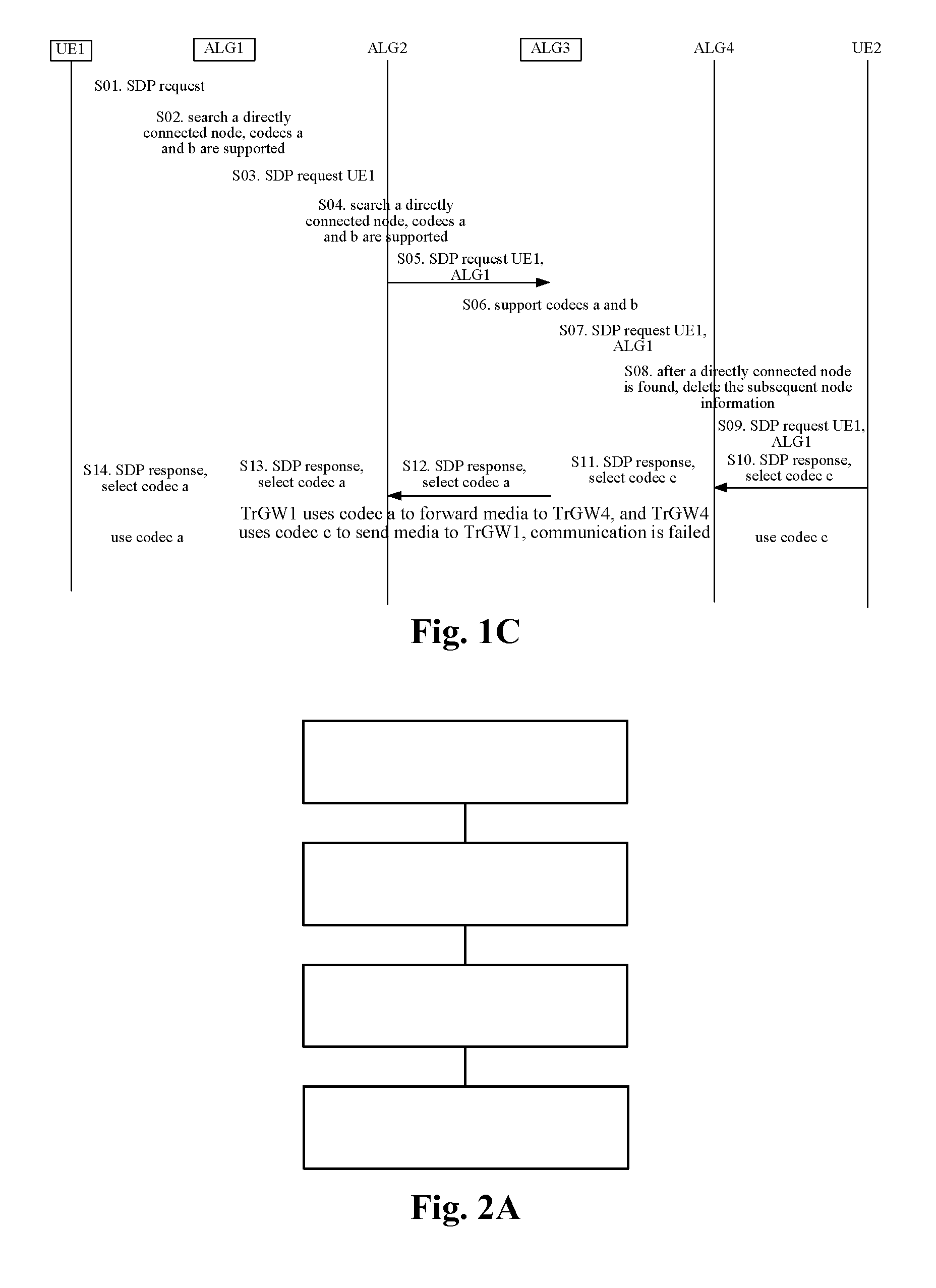
Method and device configured for processing an sdp request in a media path optimization process
ActiveUS20120303825A1Ensure normal communicationThe implementation process is simpleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionProtocol ApplicationDistributed computing
The present invention provides a method and device configured for processing an SDP request in a media path optimization process. In this case, the method comprises: an application layer gateway (ALG) receiving a session description protocol (SDP) request; the ALG determining that media connection information used by the SDP request is different from media connection information in last accessible domain information in node information of the SDP request; and the ALG sequentially adding its forward accessible domain information and its backward accessible domain information to an end of a queue of the node information of the SDP request, and then sending the SDP request. By virtue of the present invention, an optimized media path and normal communication can be ensured.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com