Patents
Literature
351 results about "CAC protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
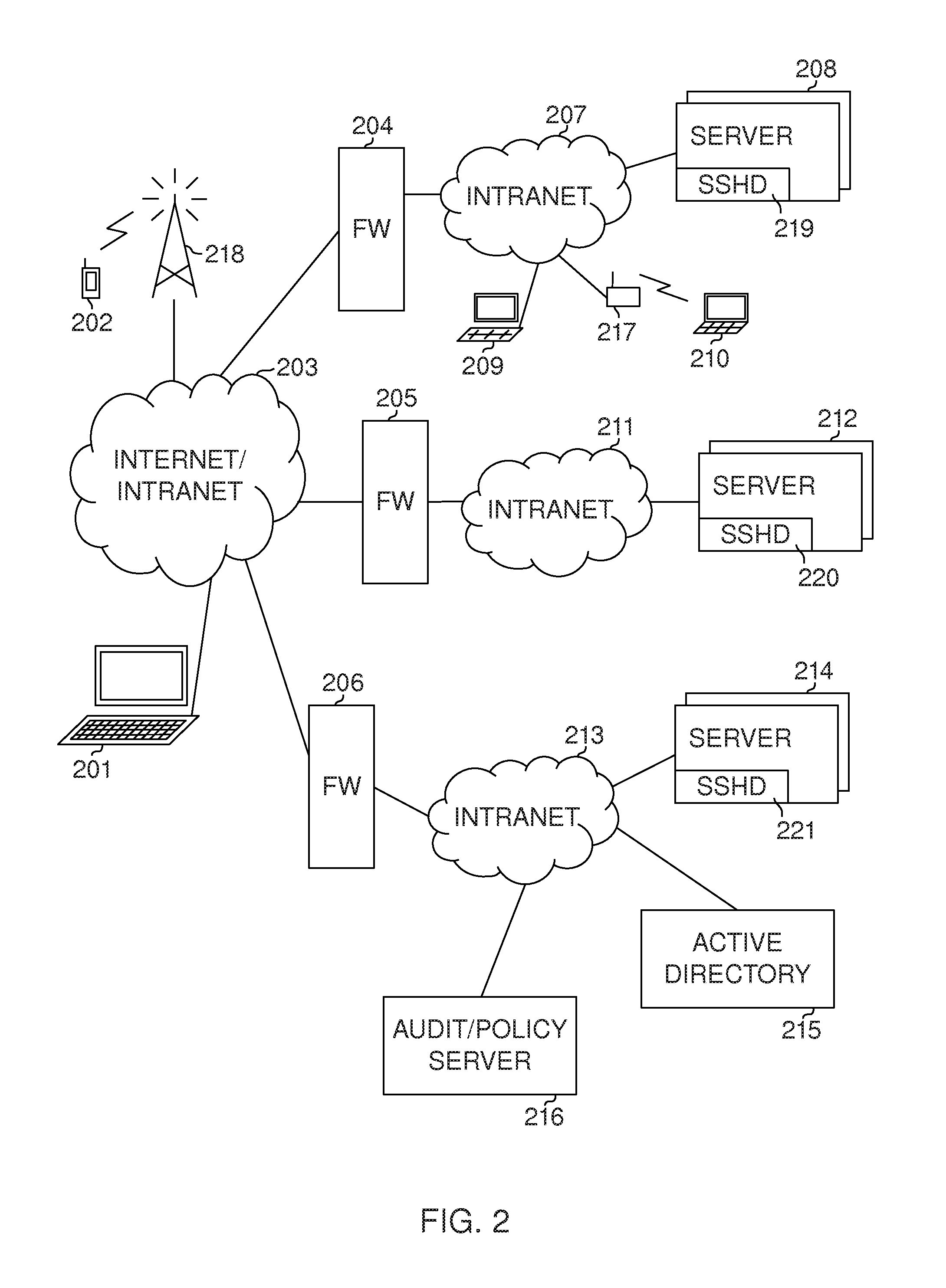
System and method for a specialized dynamic host configuration protocol proxy in a data-over-cable network
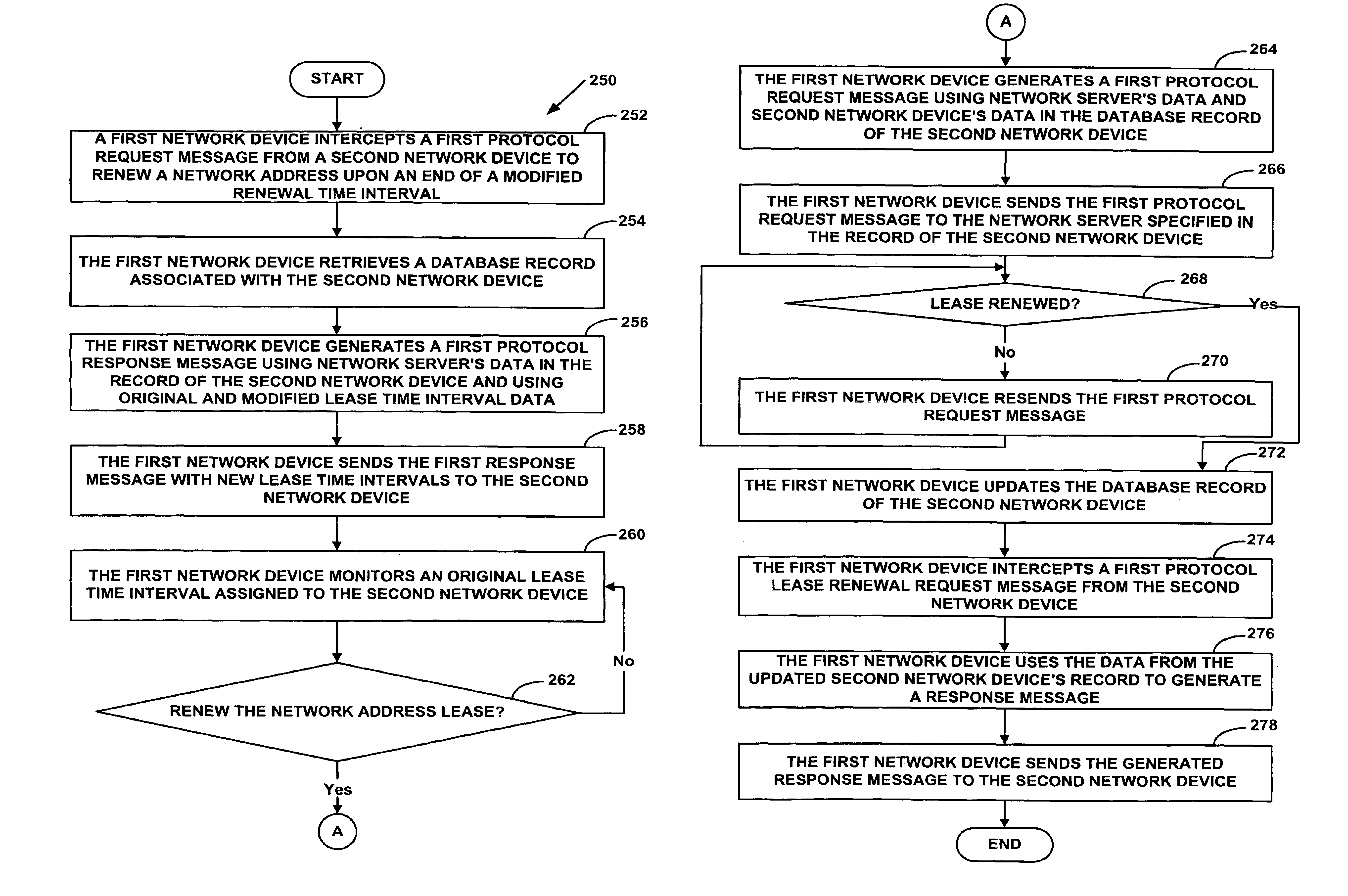
A system and method for proxying Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (“DHCP”) network services for a network device, such as, a customer premise equipment entity, on a network device, such as, a cable modem, include creating a specialized proxy task for the customer premise equipment entity on the cable modem. One method of the present invention includes intercepting DHCP message flow between a customer premise equipment having a specialized proxy task created on the cable modem and a DHCP server selected by the customer premise equipment entity. The methods further include modifying lease time intervals prior to providing a routable network address lease to a customer premise equipment entity and renewing an initial lease for the customer premise equipment entity by a cable modem prior to expiration of the lease time interval provided by a DHCP server. The methods include using known protocols, such as, for example, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
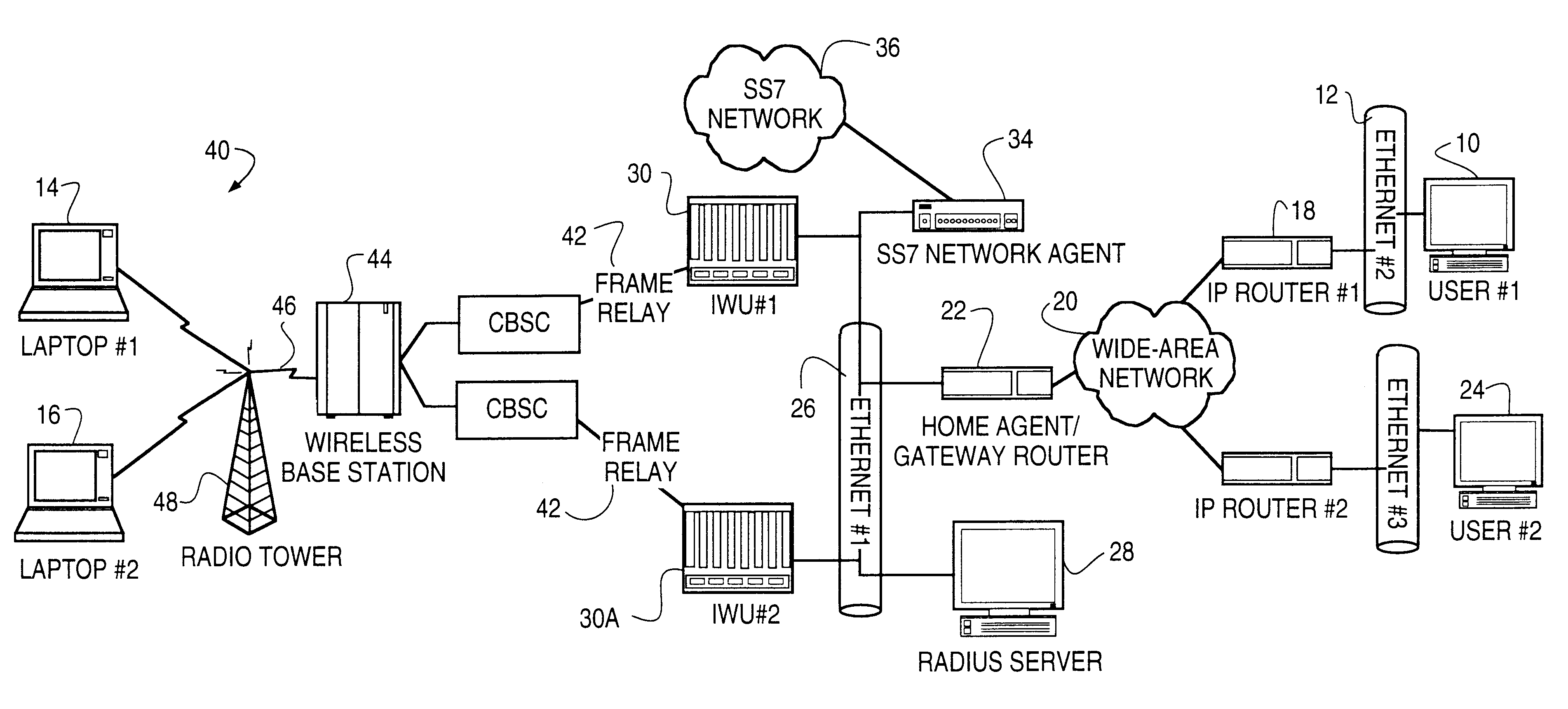
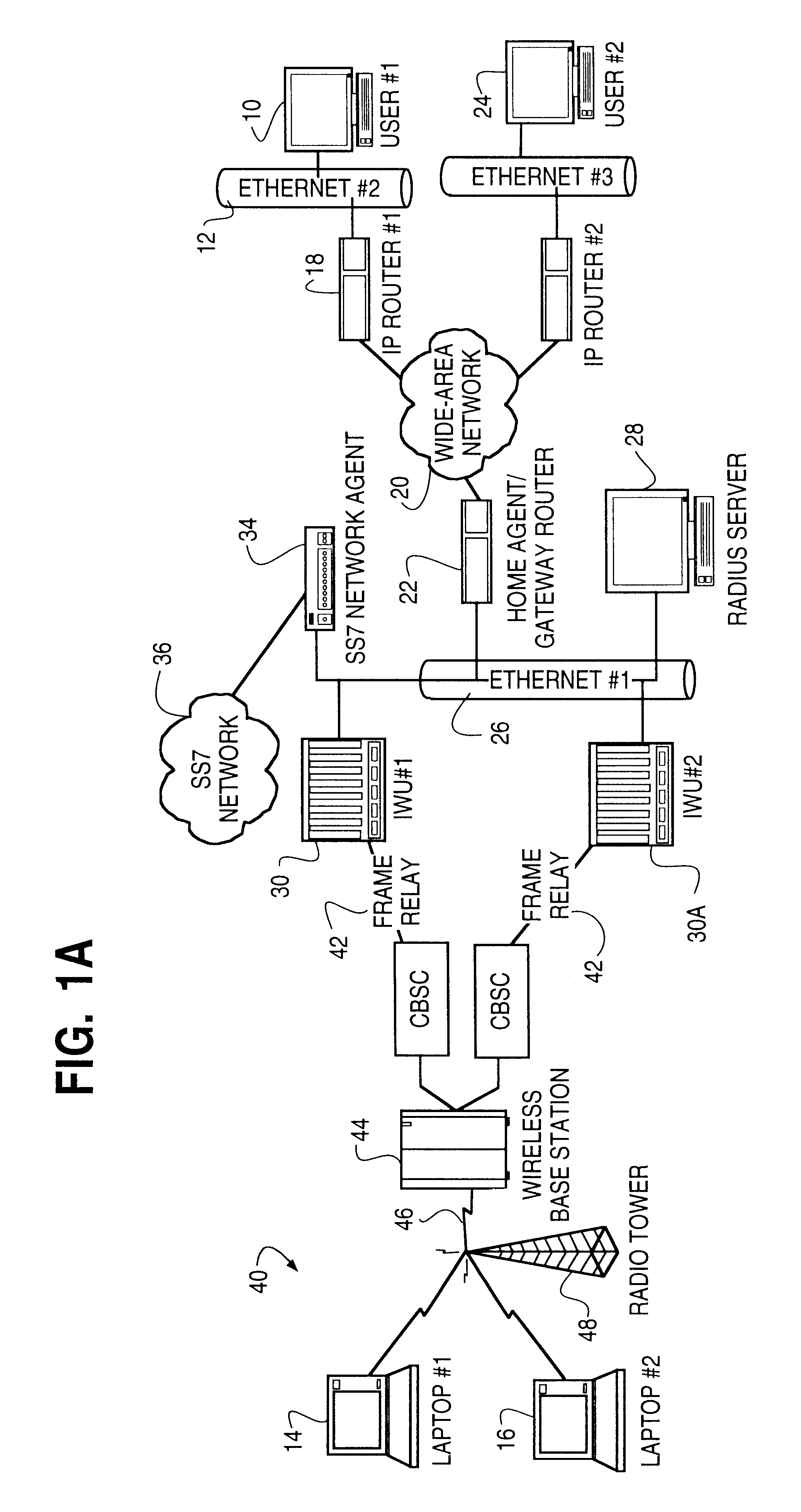
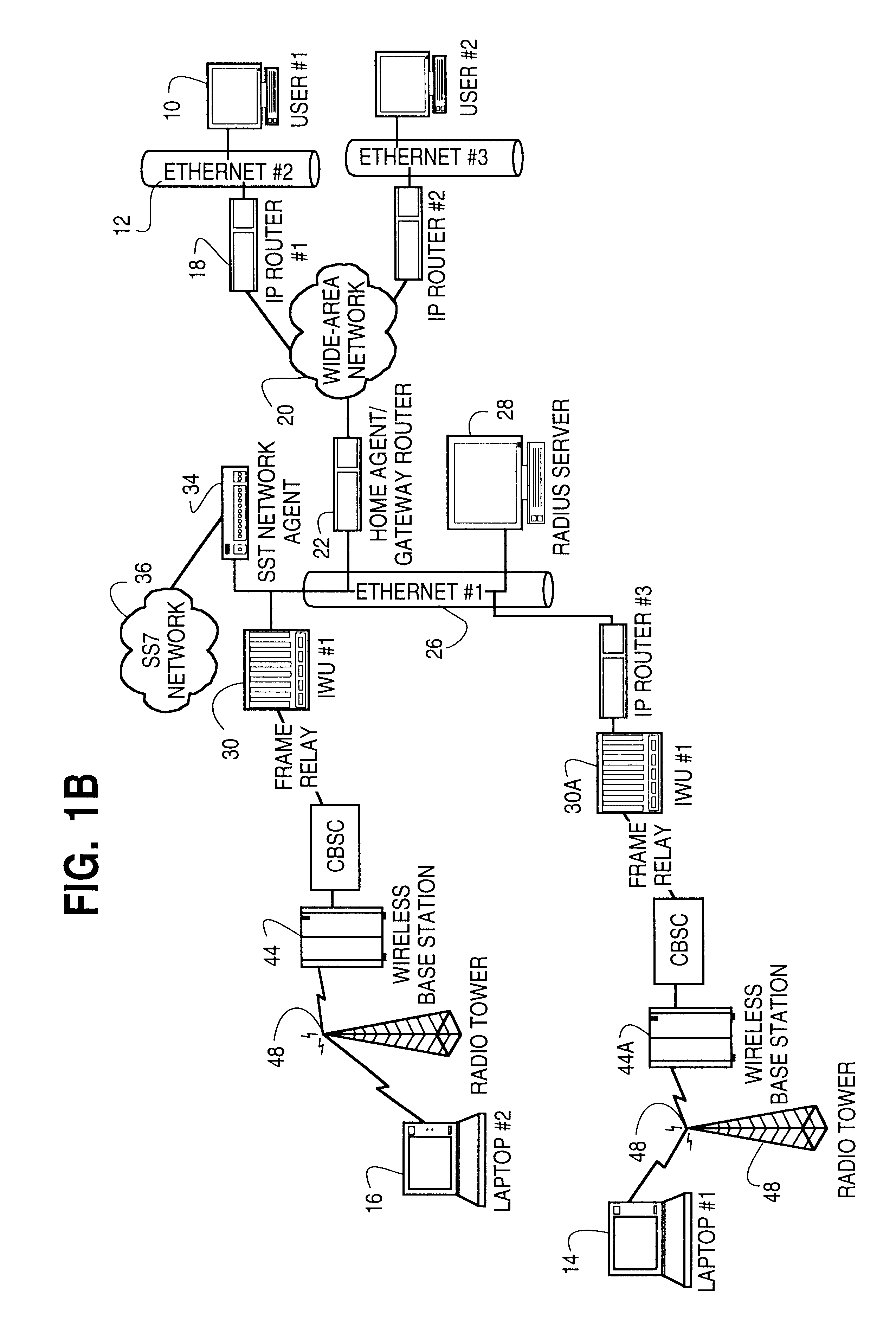
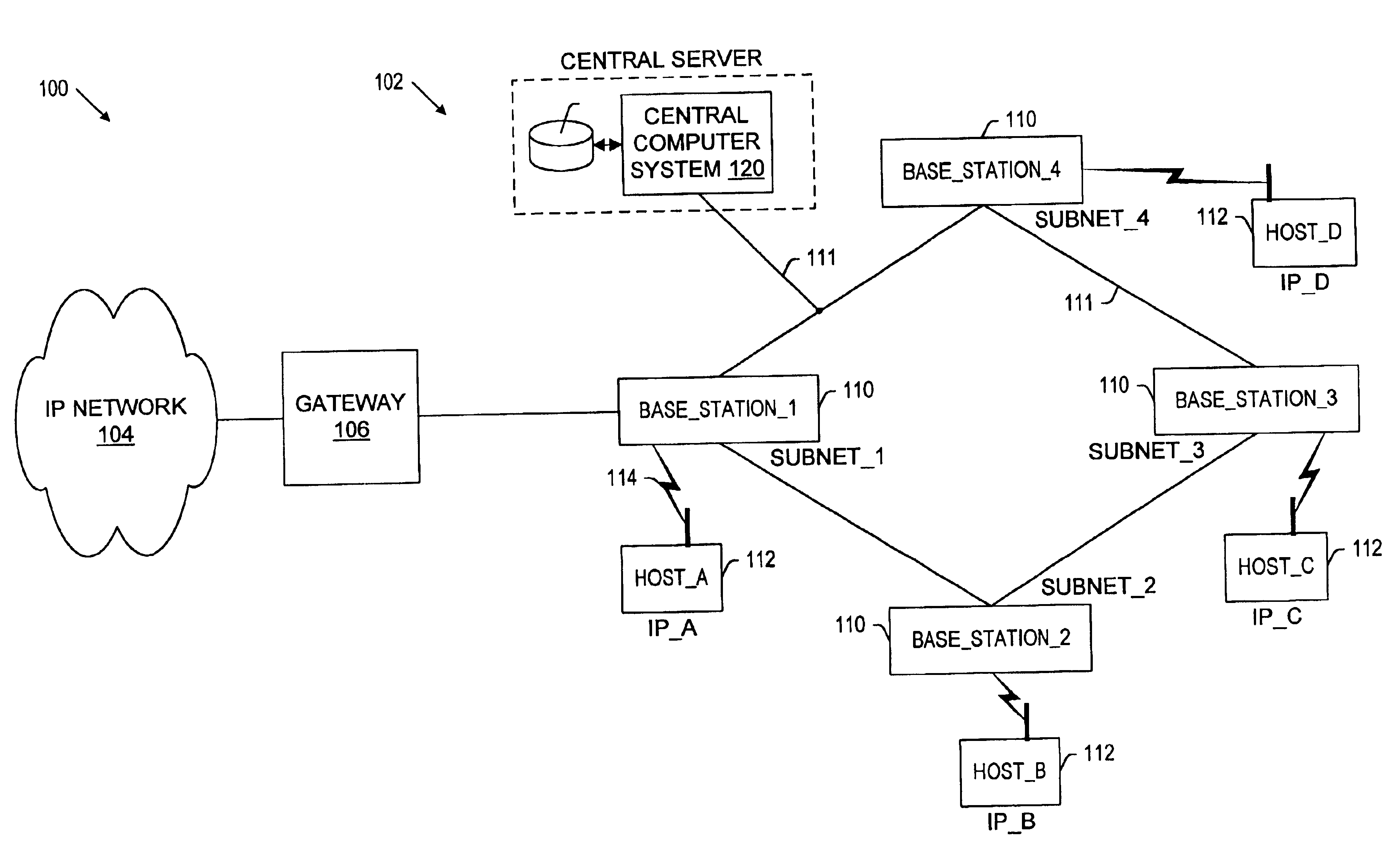
Dynamic allocation of wireless mobile nodes over an internet protocol (IP) network
InactiveUS6272129B1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsTTEthernetIp address
A method is described of automatically locating and connecting a mobile wireless communications device to a packet-switched network such as the Internet. An Internet Protocol (IP) packet from a terminal on the network, destined for receipt by the mobile device, is received at a home agent acting as a gateway or router linking the packet switched network to a second network, such as LAN, coupled to a wireless communications network. The home agent transmits an access-request message to an authentication server. The access-request message includes a destination IP address associated with the mobile device found in the IP packet. The authentication server responsively issues an access-accept message to the home agent if the mobile device is authorized to receive the IP packet. The access-accept message comprises (a) information uniquely identifying said device, such as the IMSI / ESN number for the device, and (b) information identifying a network to use to locate said device. The home agent issues a message containing the information uniquely identifying the device to a mobile node location server. The mobile node location server maintains a table mapping IP addresses for a plurality of mobile communication devices to information uniquely identifying the devices. In the event that the mobile node location server does not find an IP address for the device in the table, the device is paged via the wireless communications network. In response to the page, the mobile device dials into the wireless communications network and second network and initiates a connection to the packet switched network whereby the IP packet is transmitted to the device.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
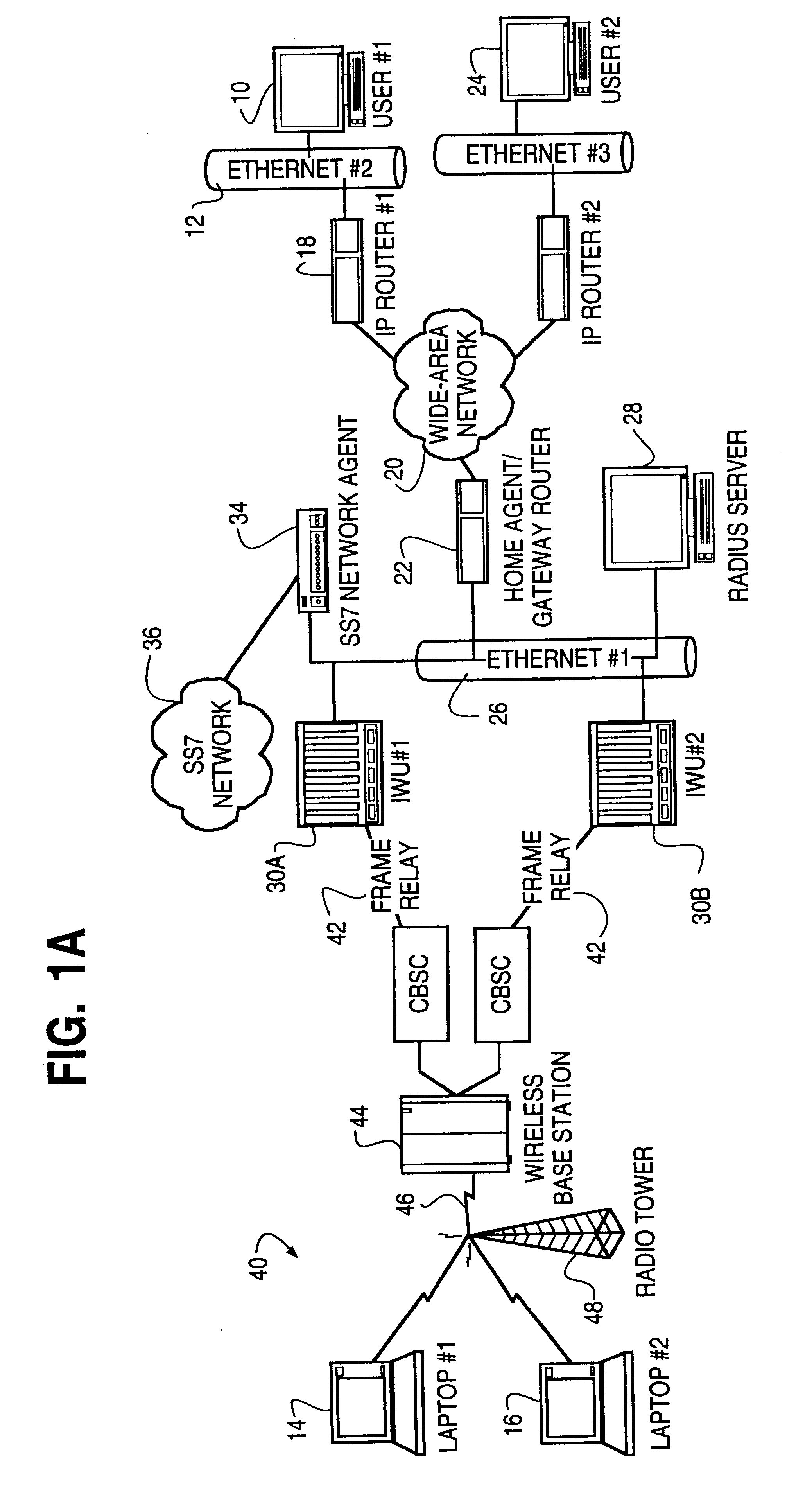
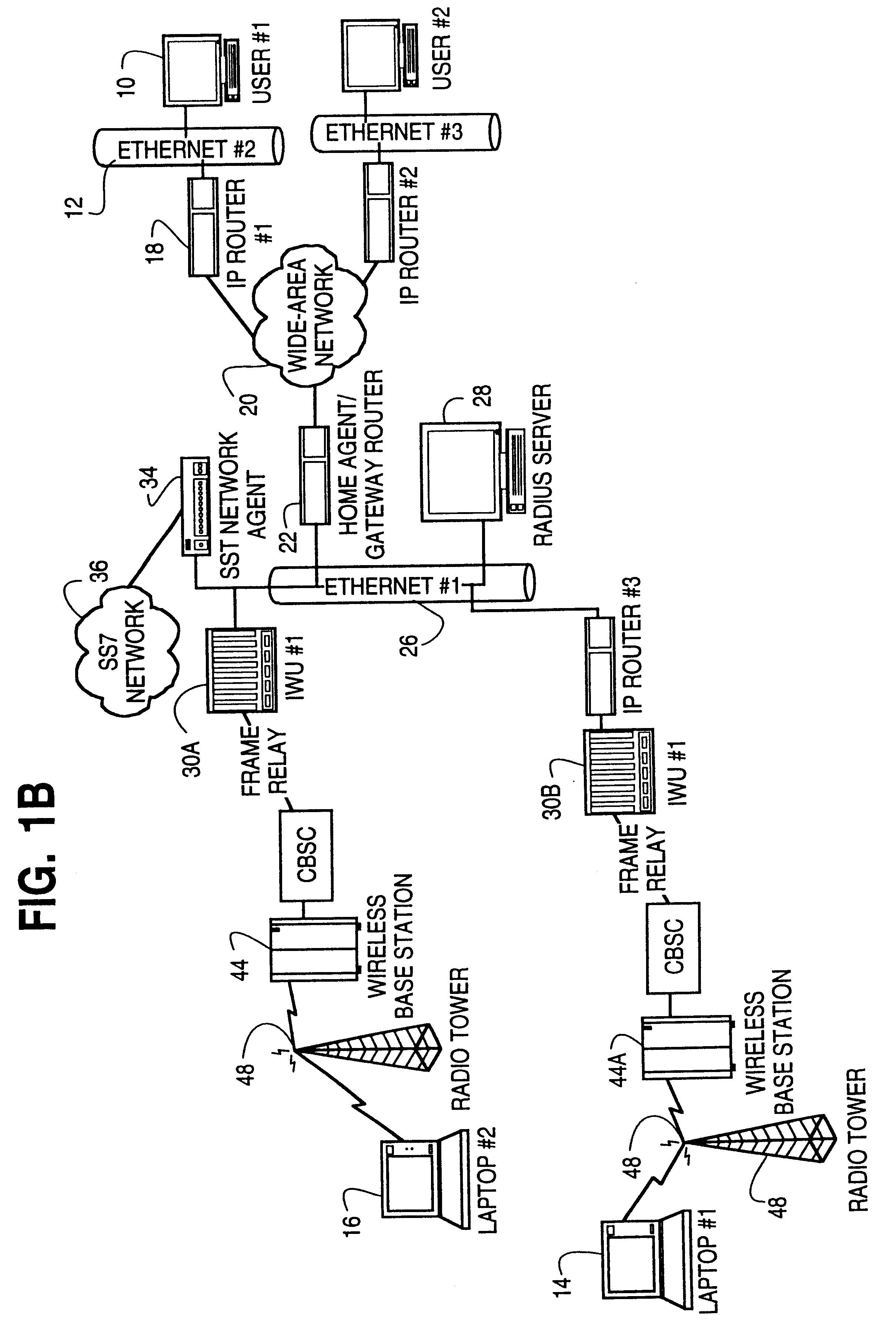
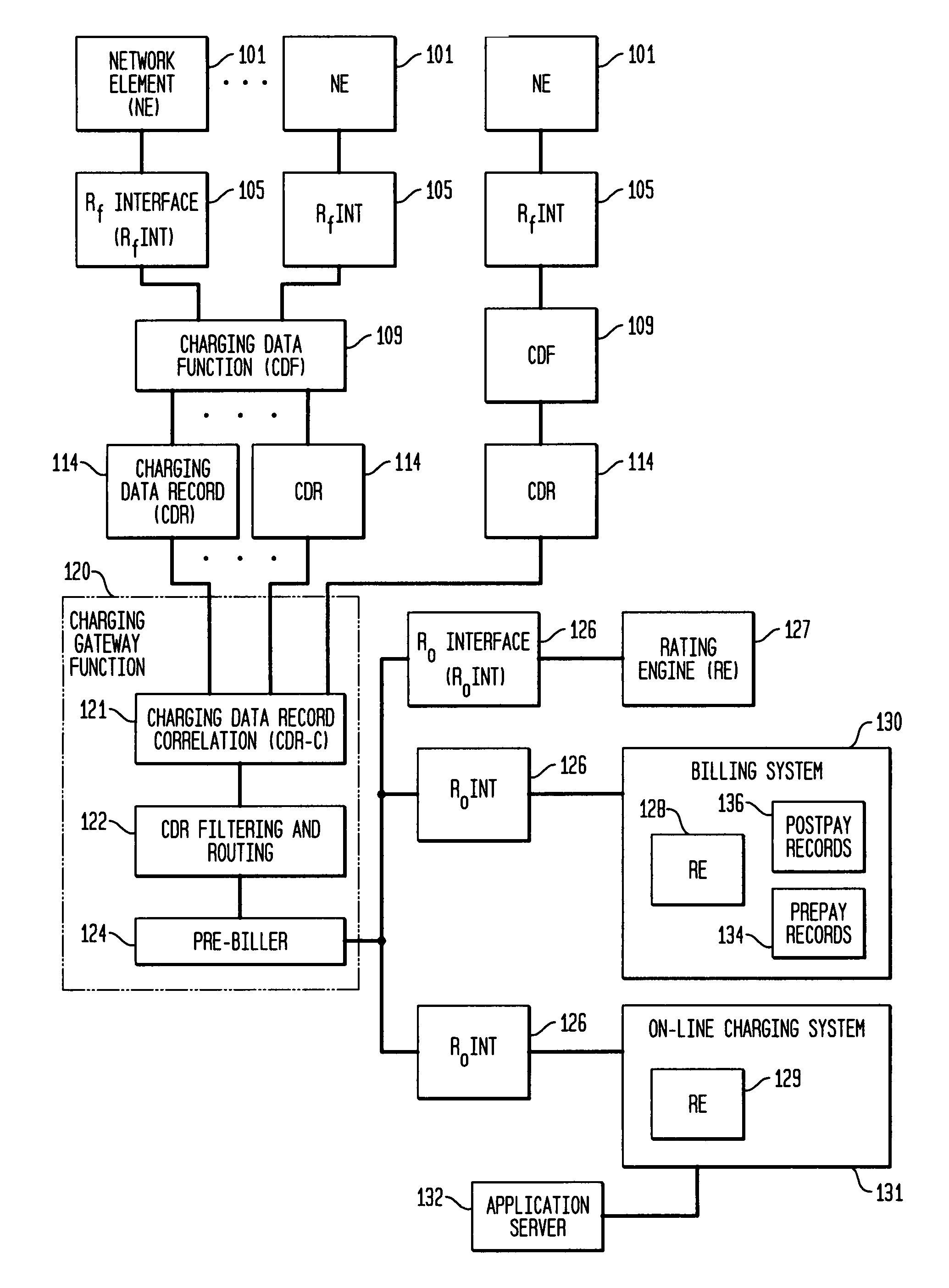
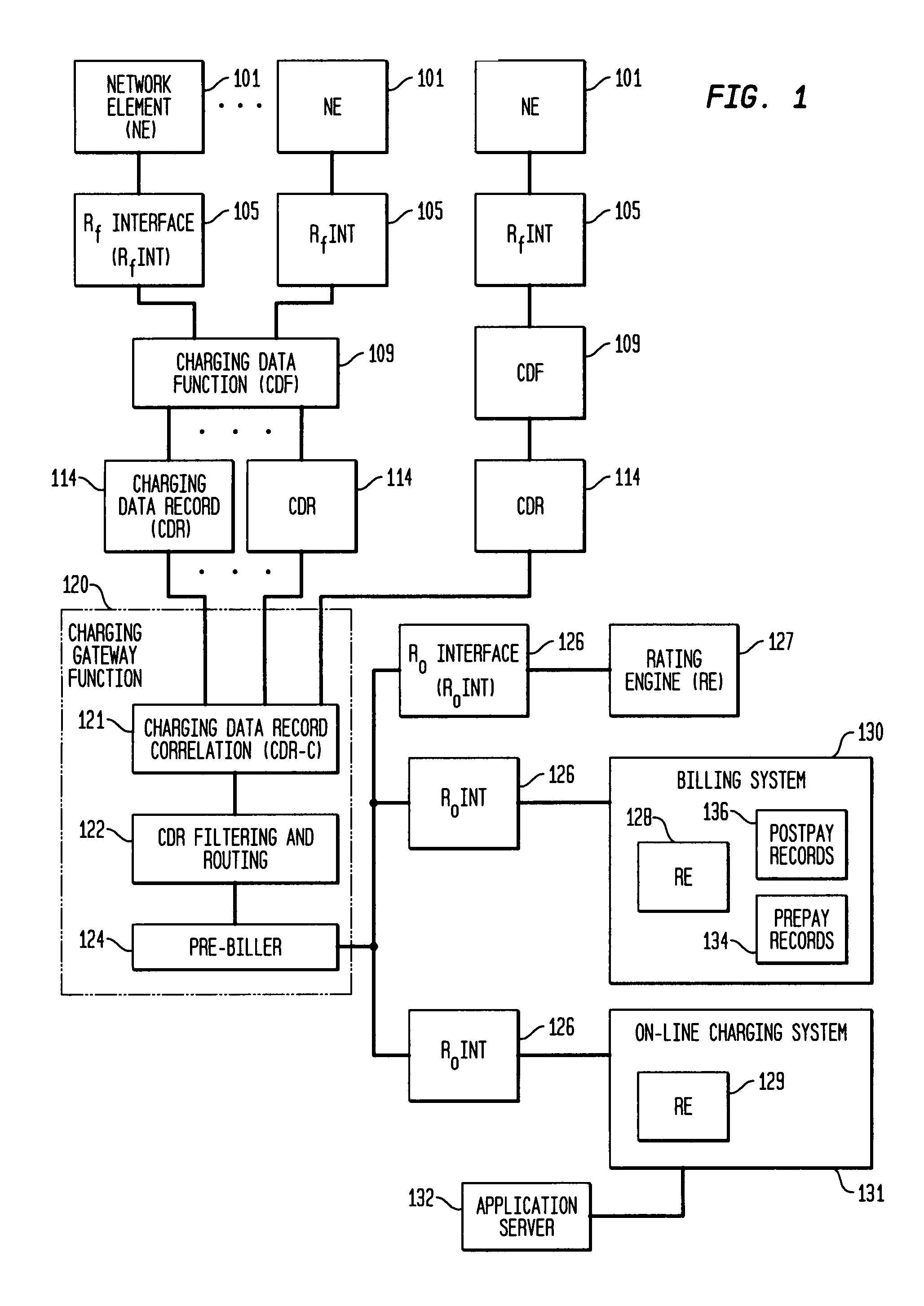
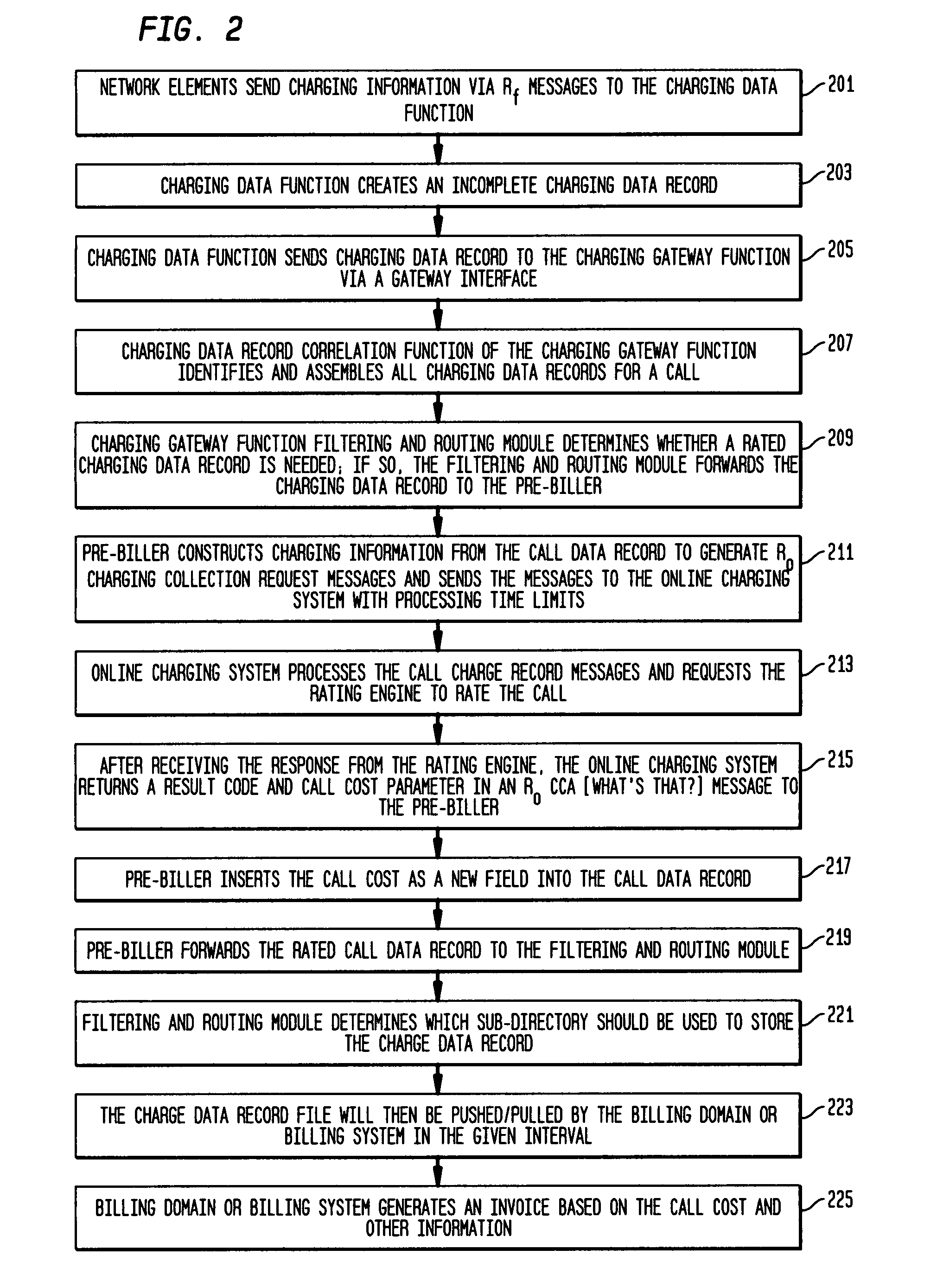
Pre-biller in internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS) charging gateway function (CGF)
InactiveUS8126123B2Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesNetworking protocolCAC protocol
This invention relates to apparatus and a method for assembling and coordinating call data records from a plurality of network elements of an Internet Protocol Multimedia System call to generate charging information. A pre-biller stores an integrated charging record and accesses a rating engine to obtain the charging information to complete a charging data record. Advantageously, the information from a plurality of network elements is integrated into a combined charging data record.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Radius-based mobile internet protocol (IP) address-to-mobile identification number mapping for wireless communication
InactiveUS6466571B1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsIp addressCommunication device
A method of finding a mobile wireless communications device when an Internet Protocol (IP) packet from a remote user is sent to the device over an IP network. The mobile device does not have to register with the IP network in order to receive the IP. The method comprises the steps of receiving the IP packet at a home agent associated with a wireless communications network. The IP packet includes an IP address assigned to the device. If there is no current mobility binding record for the mobile device, instead of dropping the packet the home agent sends an access-request packet, containing the IP address, to an authentication server. The authentication server, e.g., a RADIUS server, maintains a table mapping the IP address for the device to an identification number uniquely associated with the device, such as the device's International Mobile Subscriber Identity number. The authentication server sends an access-accept packet to the home agent in the event that the device is authorized to receive the IP packet, in which case the access-accept packet includes the identification information. The home agent uses the identification number to locate, page and automatically connect the wireless device to the IP network via an InterWorking Unit (IWU) configured as a IP network access server.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
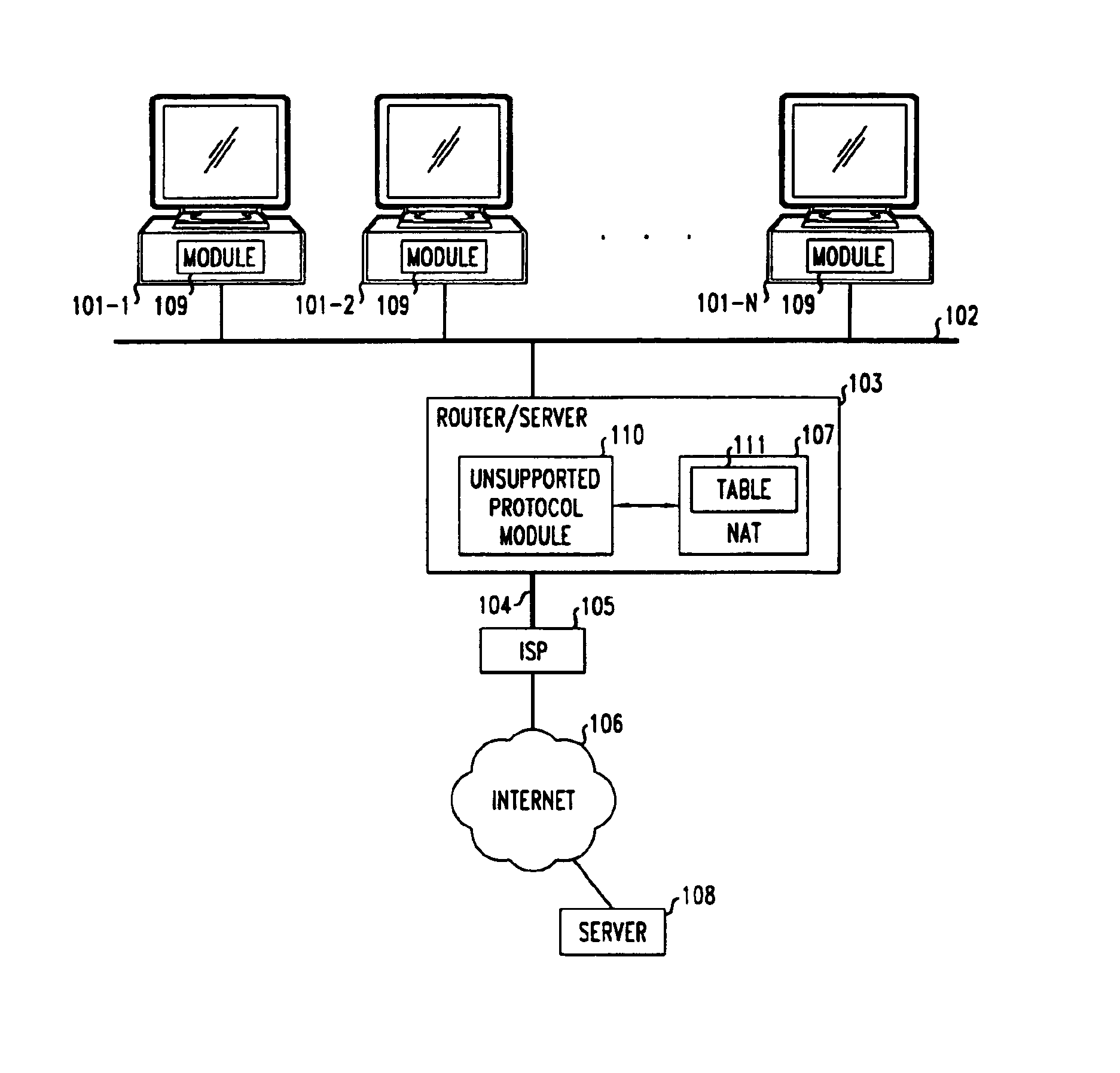
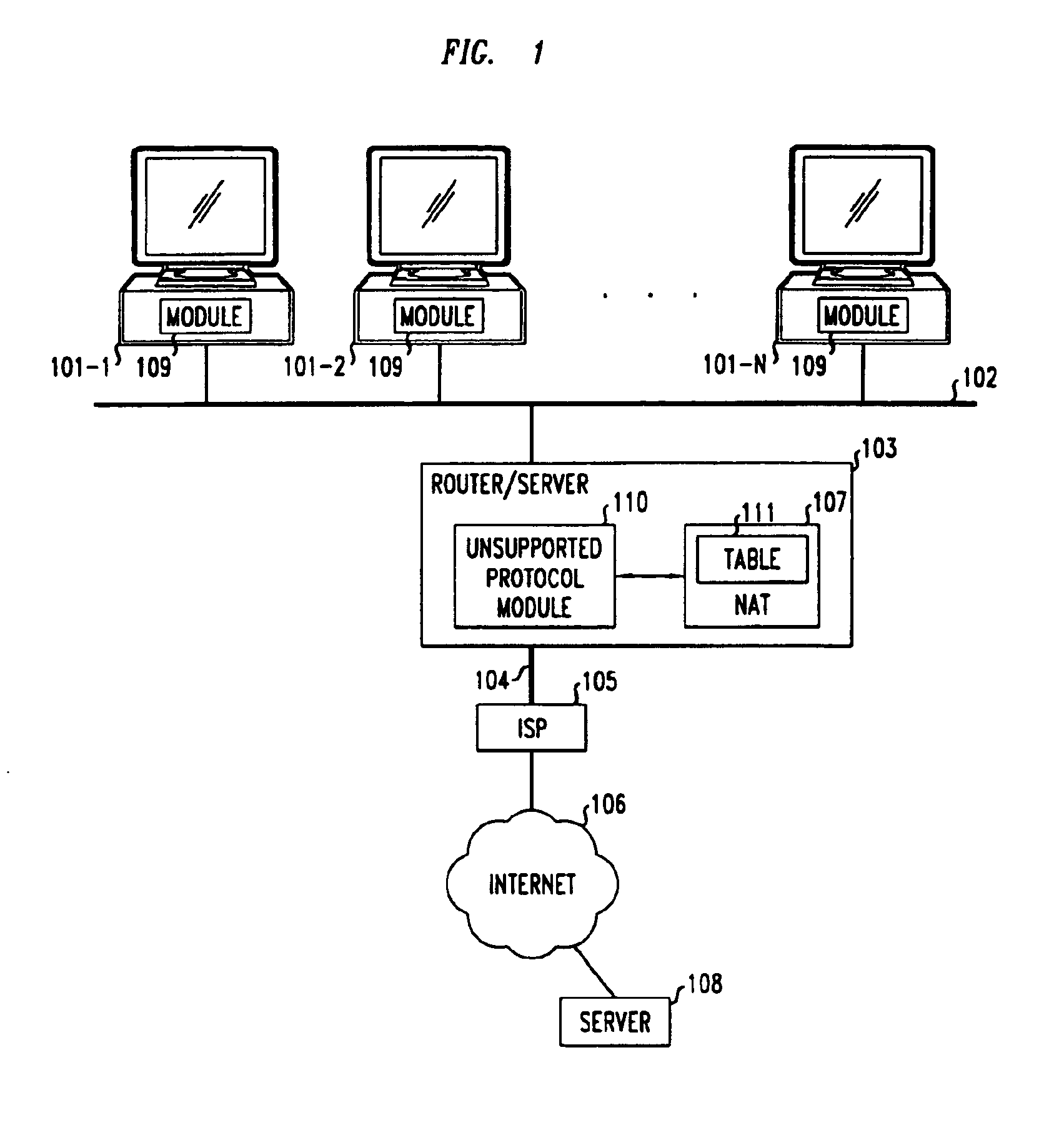
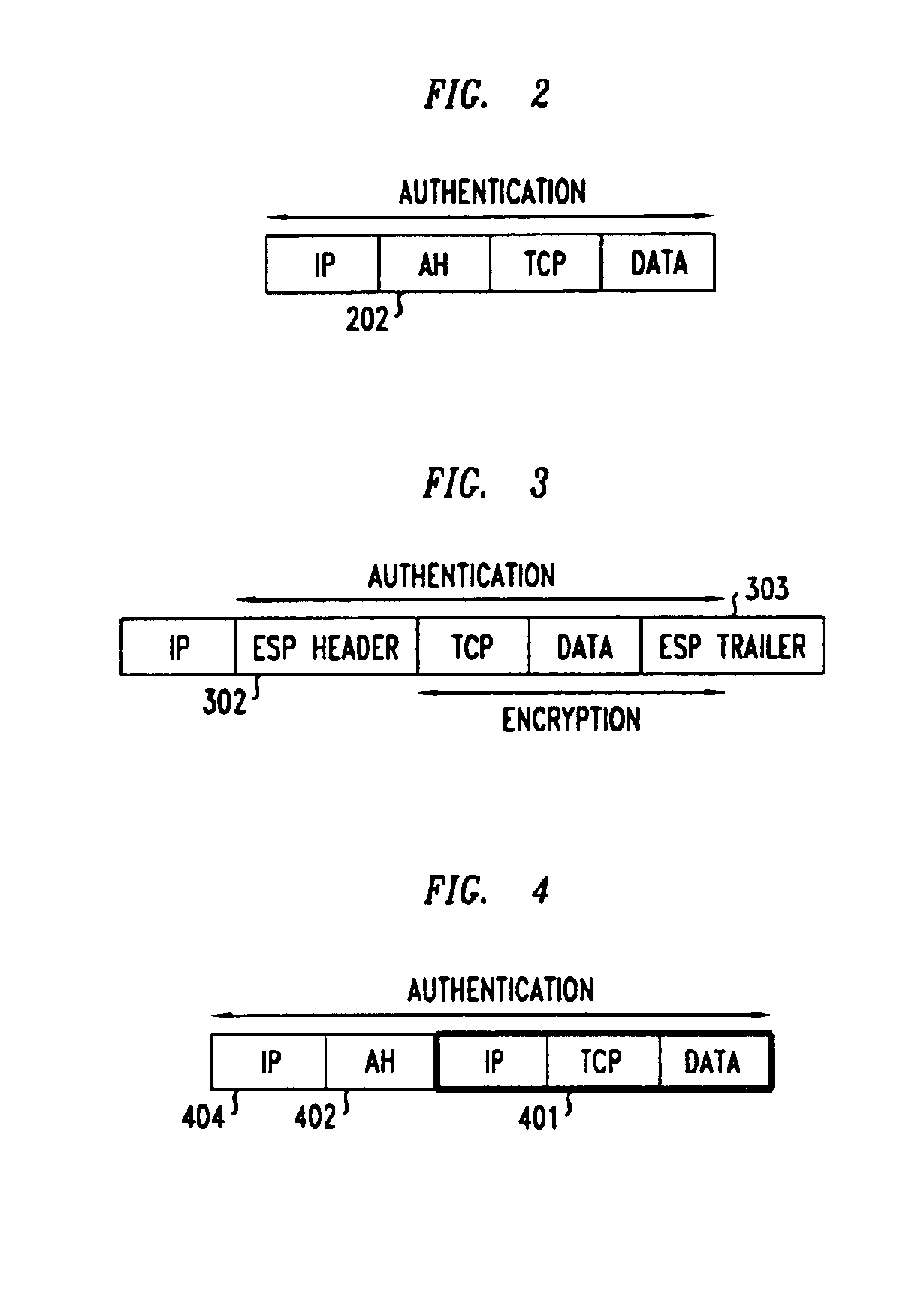
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
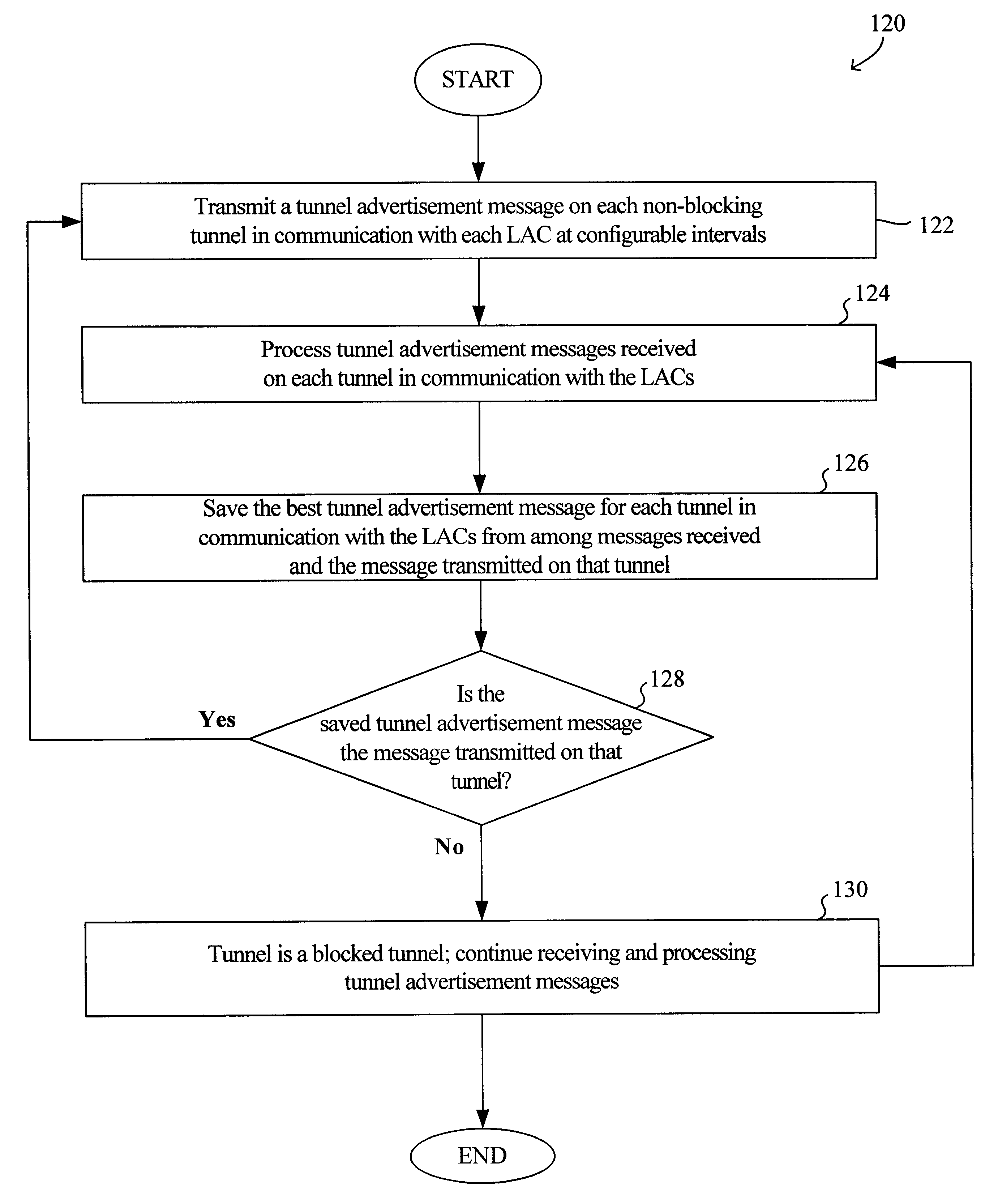
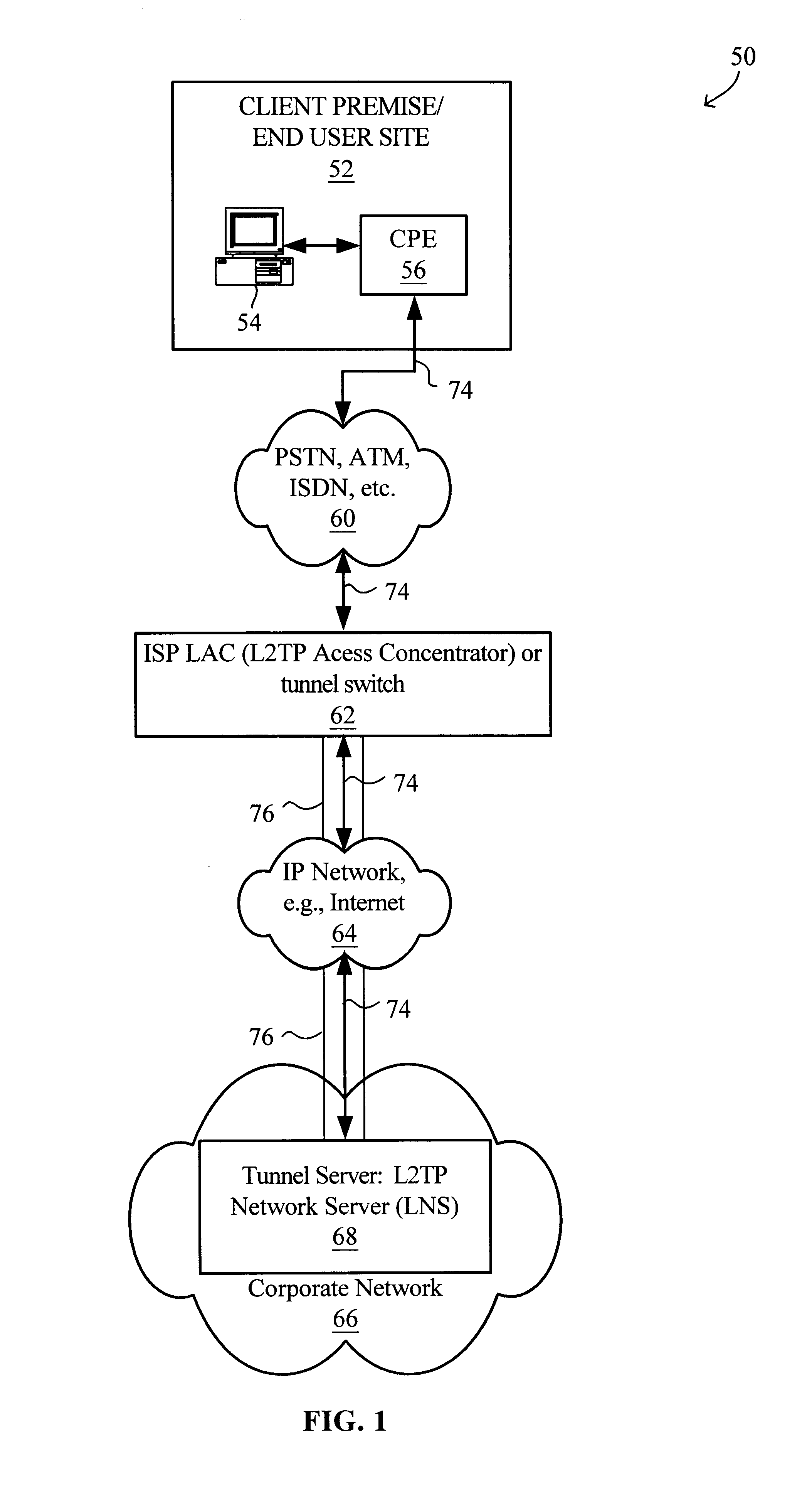
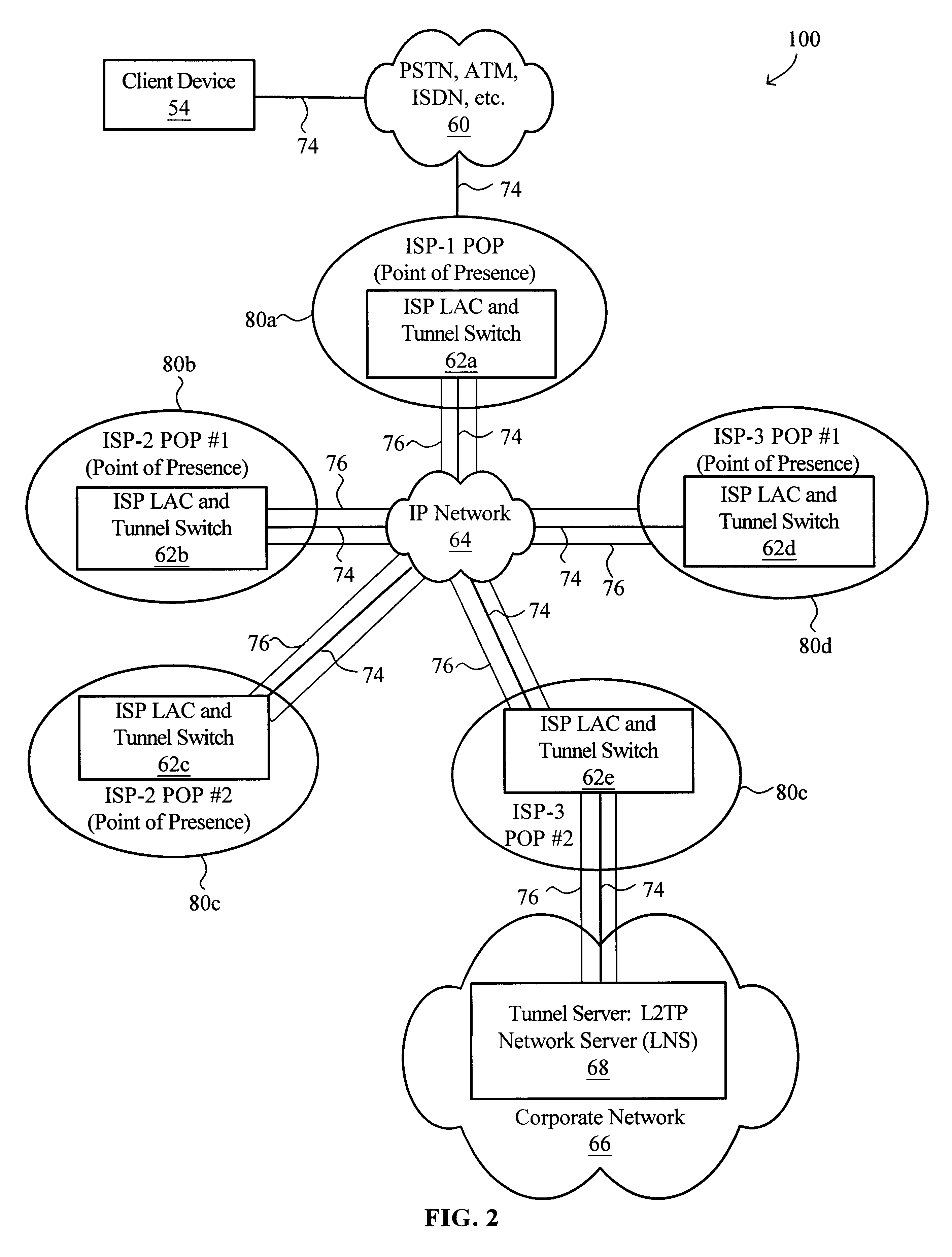
Virtual L2TP/VPN tunnel network and spanning tree-based method for discovery of L2TP/VPN tunnels and other layer-2 services
A virtual L2TP / VPN tunnel network as well as a system and method for automatic discovery of VPN tunnels, such as L2TP tunnels, and other layer-2 services using a method such as one based on the spanning tree protocol are disclosed. The method for automatic discovery of layer-2 services across a network of layer-2 devices generally comprises transmitting an advertisement message on each tunnel of each layer-2 device, the advertisement message containing information for generating a spanning tree based on spanning tree algorithm, receiving advertisement message on the tunnels of each layer-2 device, and processing the received advertisement messages to generate a spanning tree topology of the network of layer-2 devices whereby each layer-2 device in the network automatically discovers layer-2 services of other layer-2 devices on the network. The transmitting is preferably repeated at predetermined configurable intervals.
Owner:GC PIVOTAL LLC
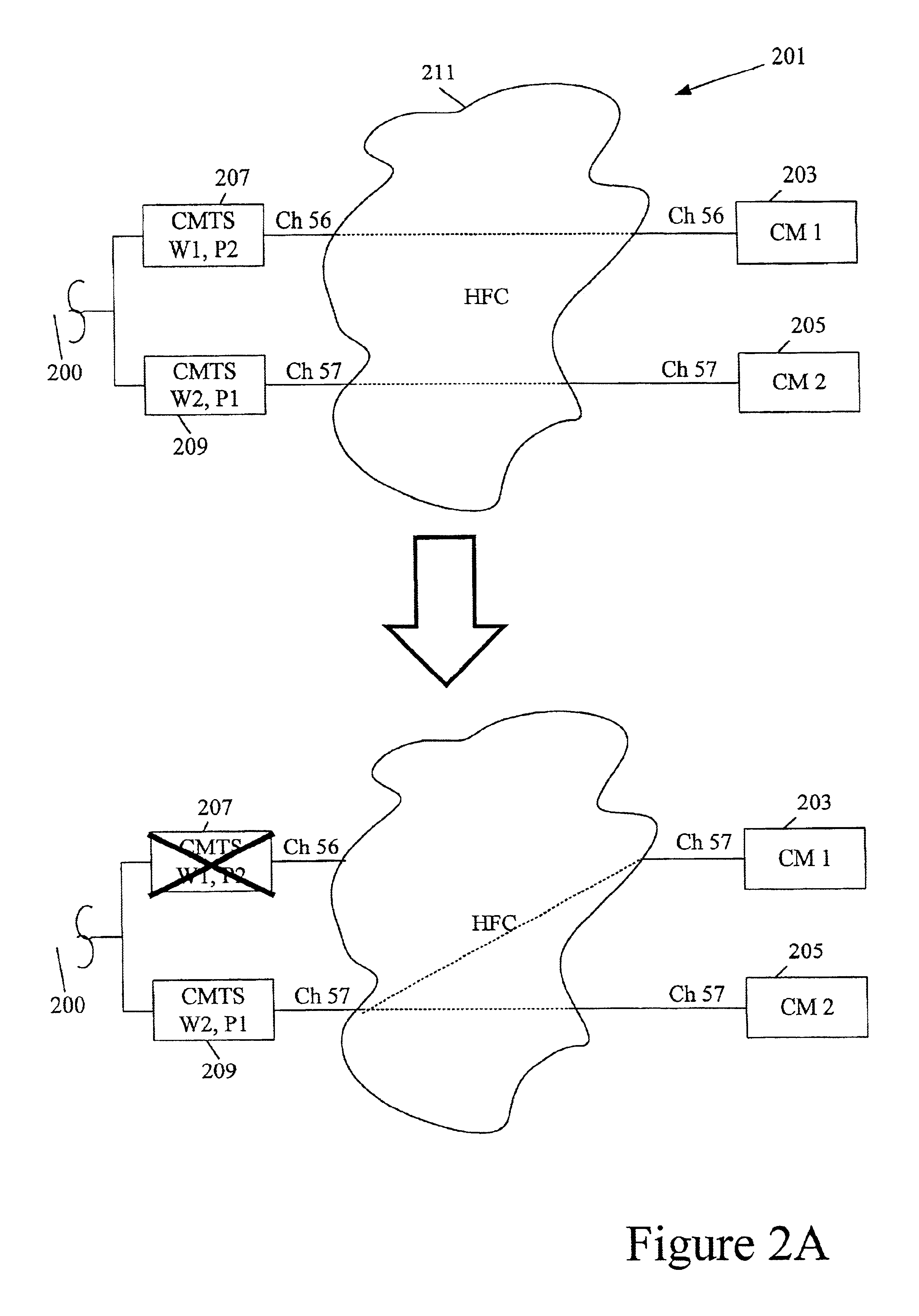
Routing protocol based redundancy design for shared-access networks
InactiveUS6839829B1Reduce delaysFew significant disruptionError preventionBroadband local area networksAccess networkModem device
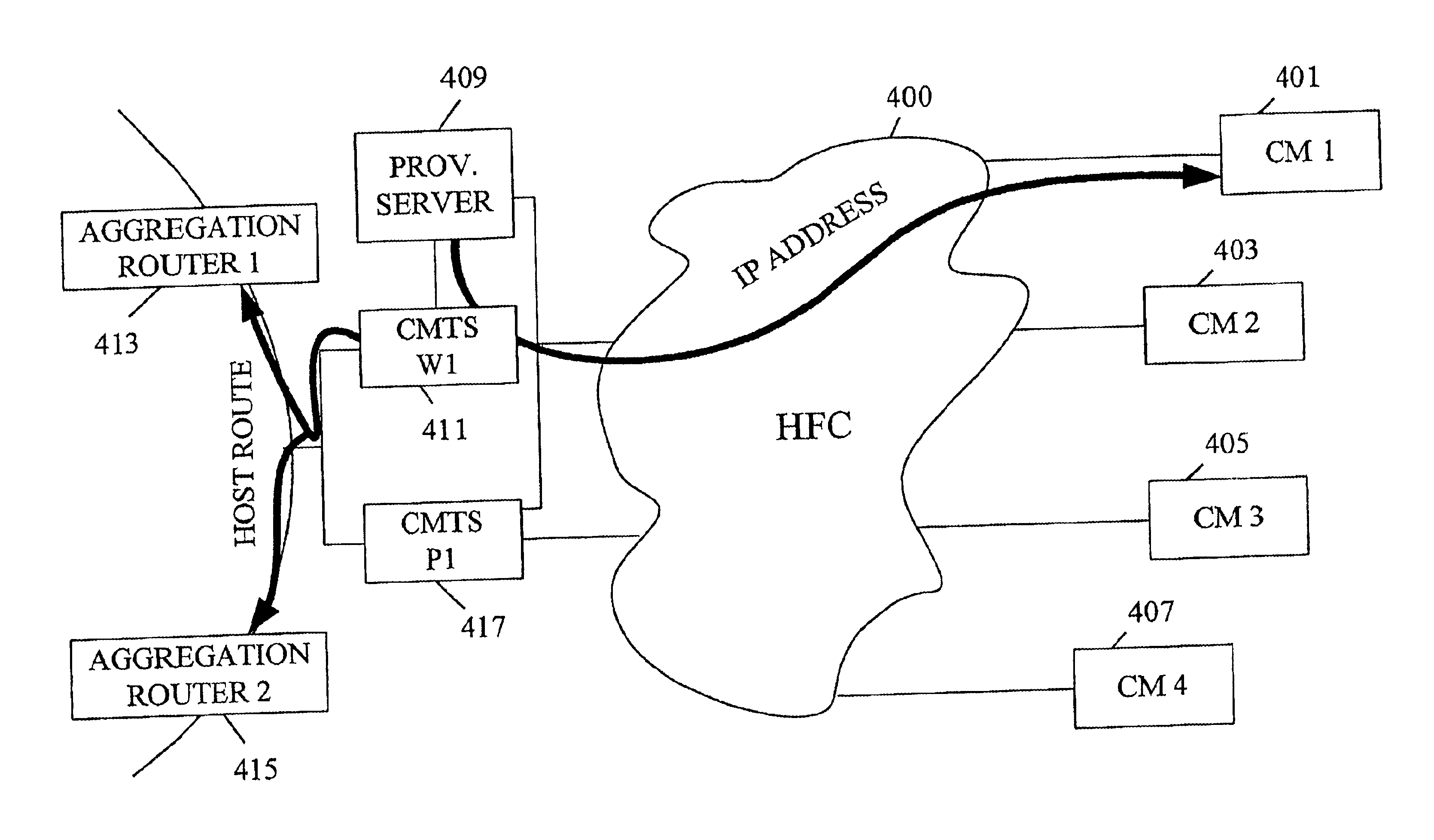
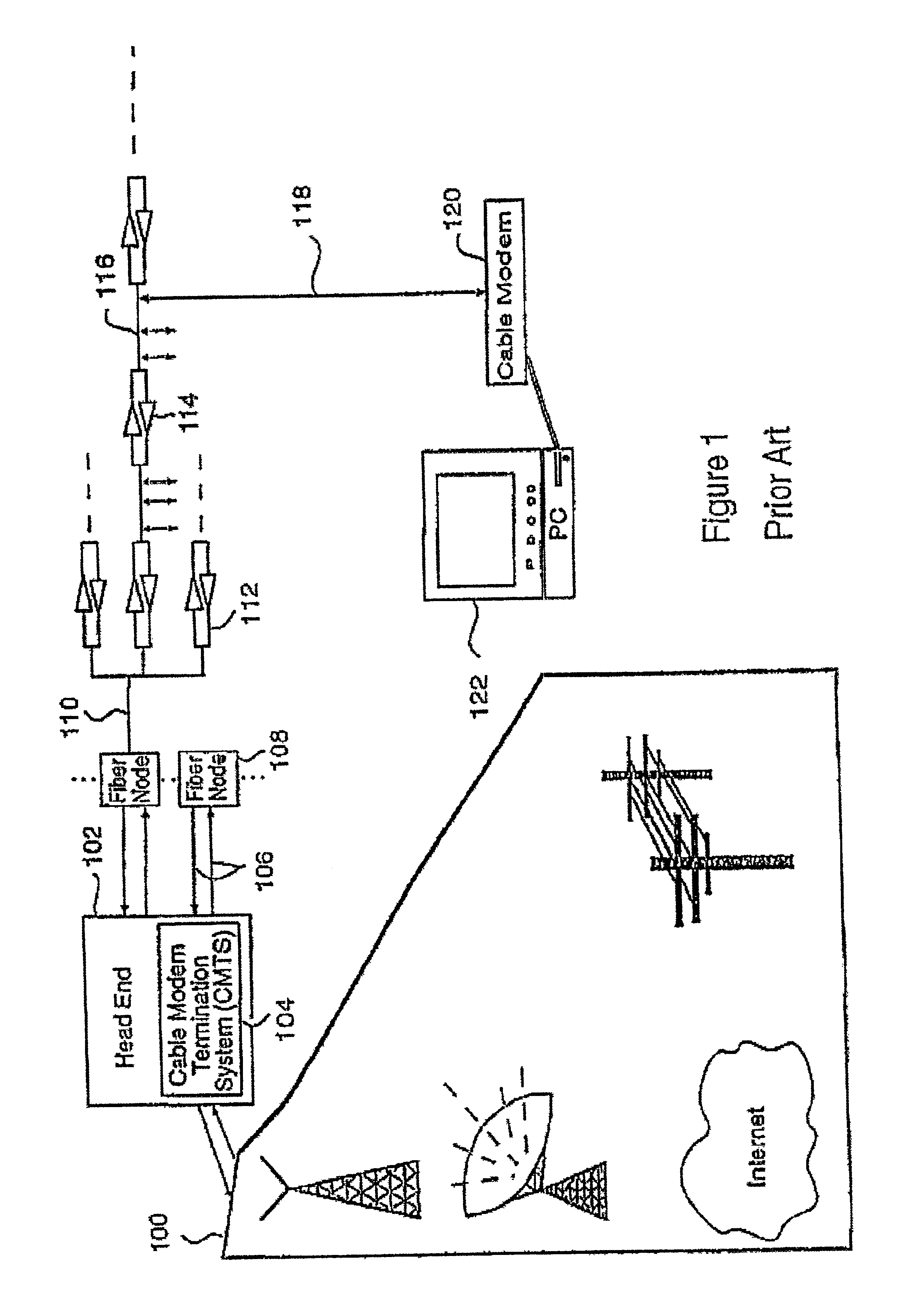
A protection CMTS is available to immediately service a cable modem should that modem's service from a working CMTS fail for any reason. To speed the service transfer (cutover) from the working CMTS to the protection CMTS, the cable modem may preregister with the protection CMTS well before the cutover becomes necessary. The cable modem's registration with both the working CMTS and the protection CMTS preferably employs a single IP address, so that the cable modem need not obtain a new IP address during cutover. While the cable modem may register with both the working CMTS and the protection CMTS, the devices are designed or configured so that only the working CMTS injects a host route for the cable modem into the appropriate routing protocol. Only after cutover to the protection CMTS does the protection CMTS inject its host route.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
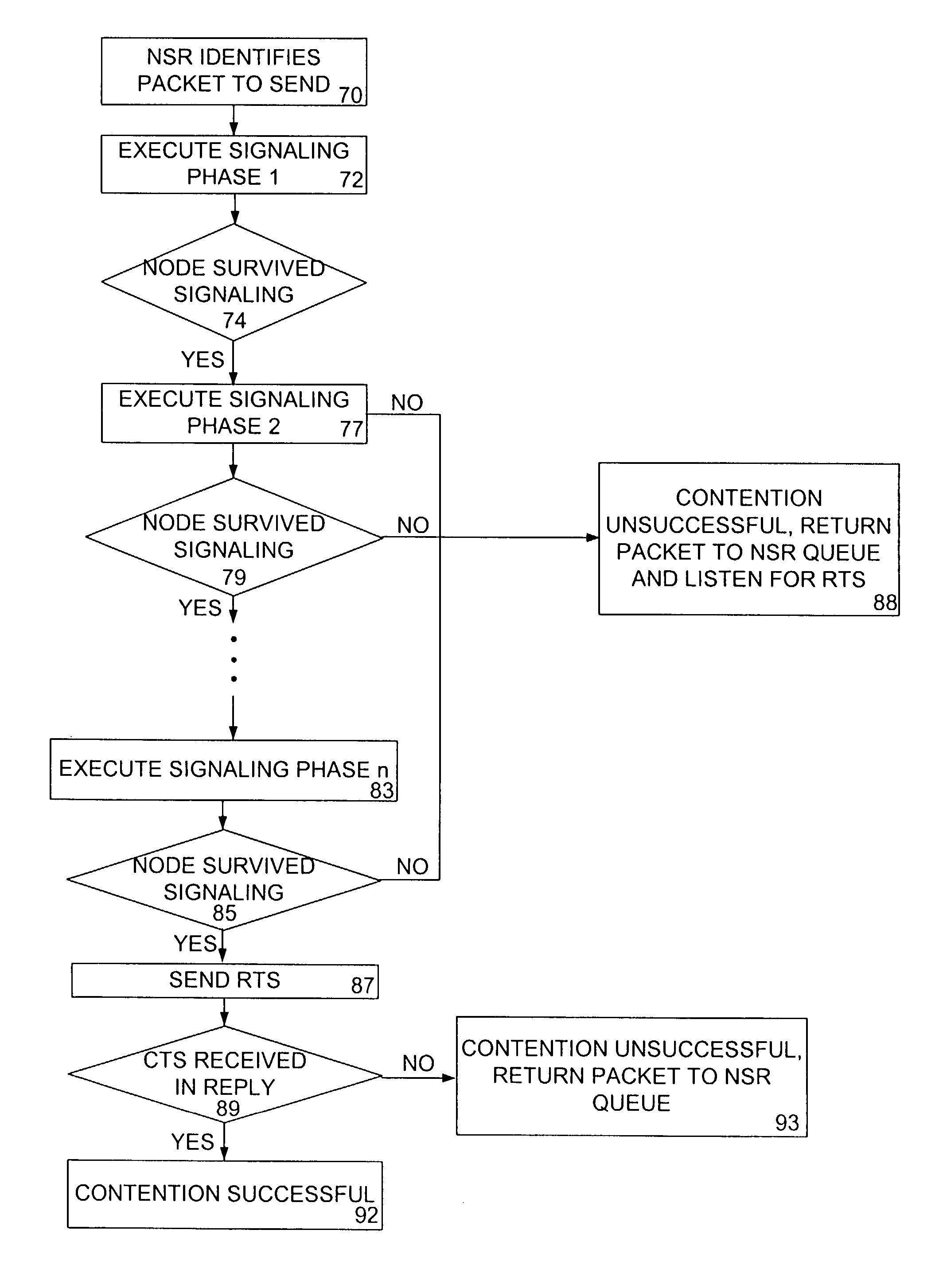
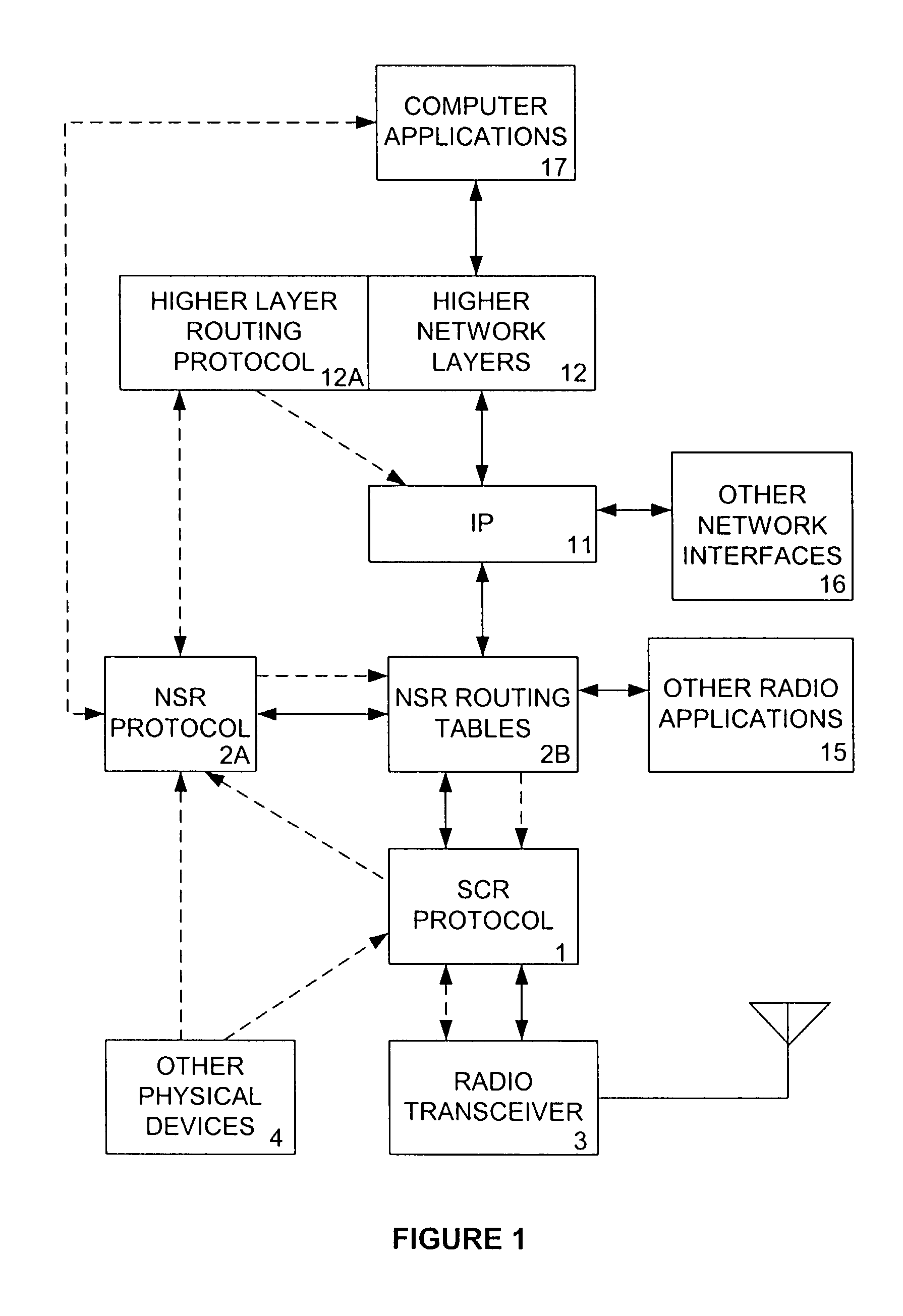
Access and routing protocol for ad hoc network using synchronous collision resolution and node state dissemination
ActiveUS7266085B2Without sacrificing performanceImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTError preventionQuality of serviceSelf-organizing network
An ad hoc network organizes itself to provide communications without need for an a priori designated central control mechanism or base stations. Such self-organization is challenging in a multihop ad hoc network having member nodes that are highly mobile and widely distributed. A Synchronous Collision Resolution (SCR) protocol and a Node State Routing (NSR) protocol are well suited to provide efficient ad hoc network organization. SCR is an access protocol that achieves high capacity collision free access using a signaling approach that creates a random cellular-like network after each signaling period. NSR is a routing protocol that uses the dissemination of node states to predict link availability and to assign metrics to those links for the creation of optimized routes. In use, the present invention provides quality of service and supports energy conservation for the mobile nodes.
Owner:SCR NETWORKS LLC
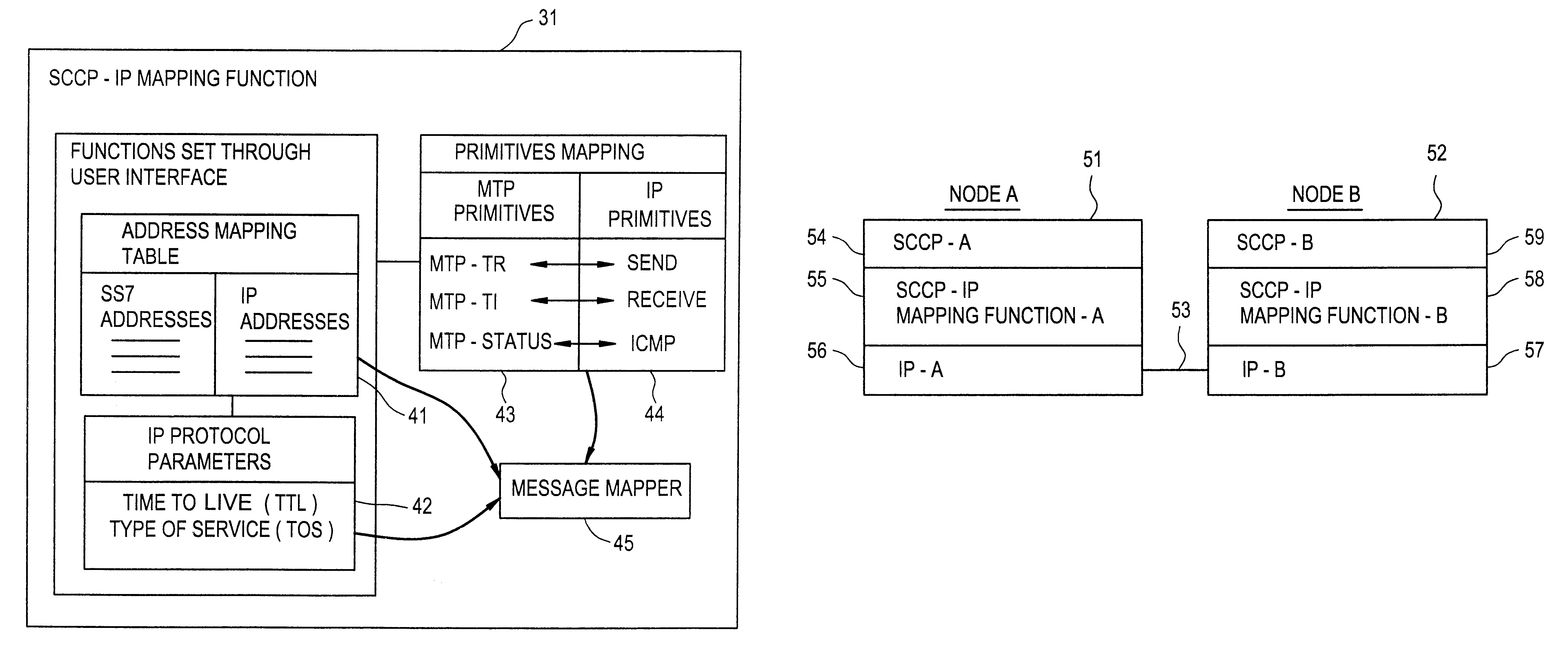
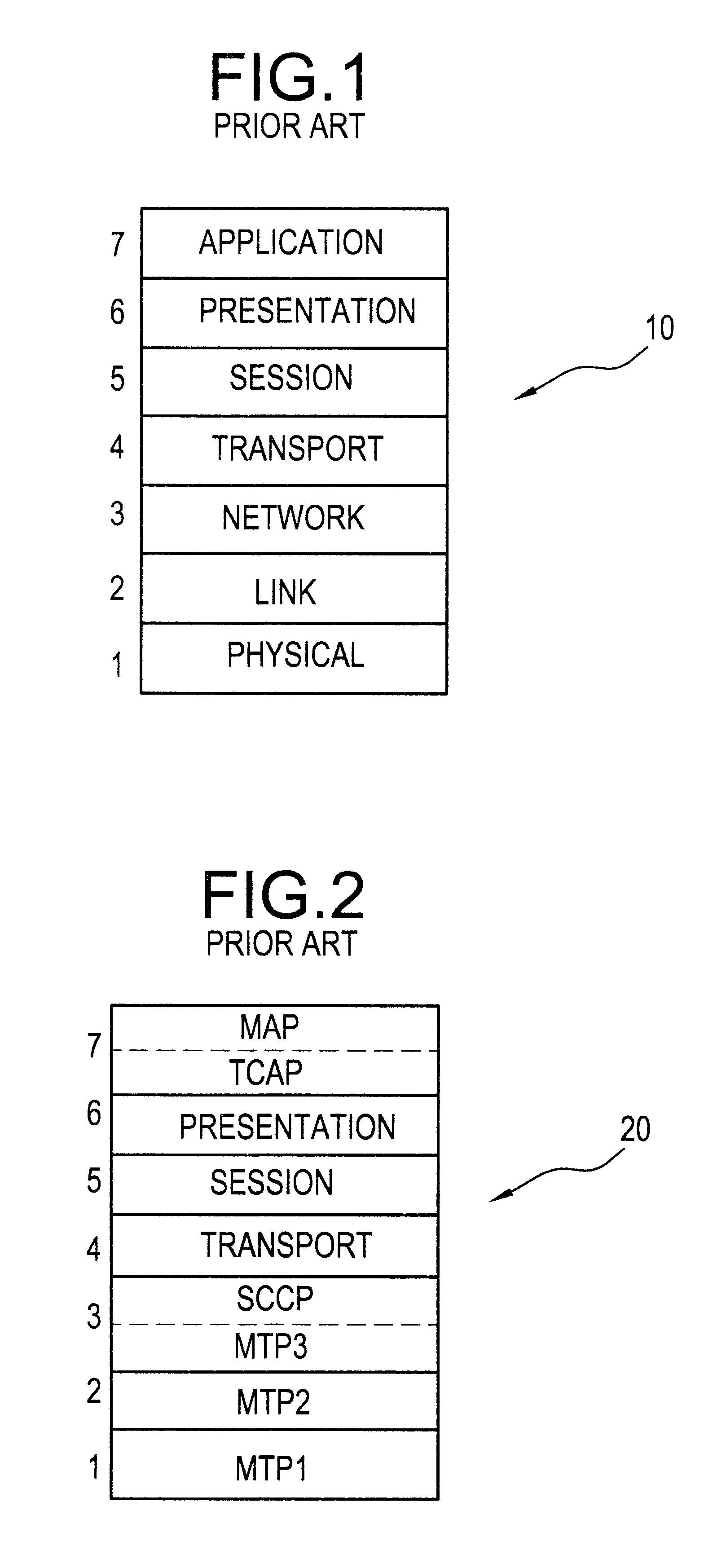
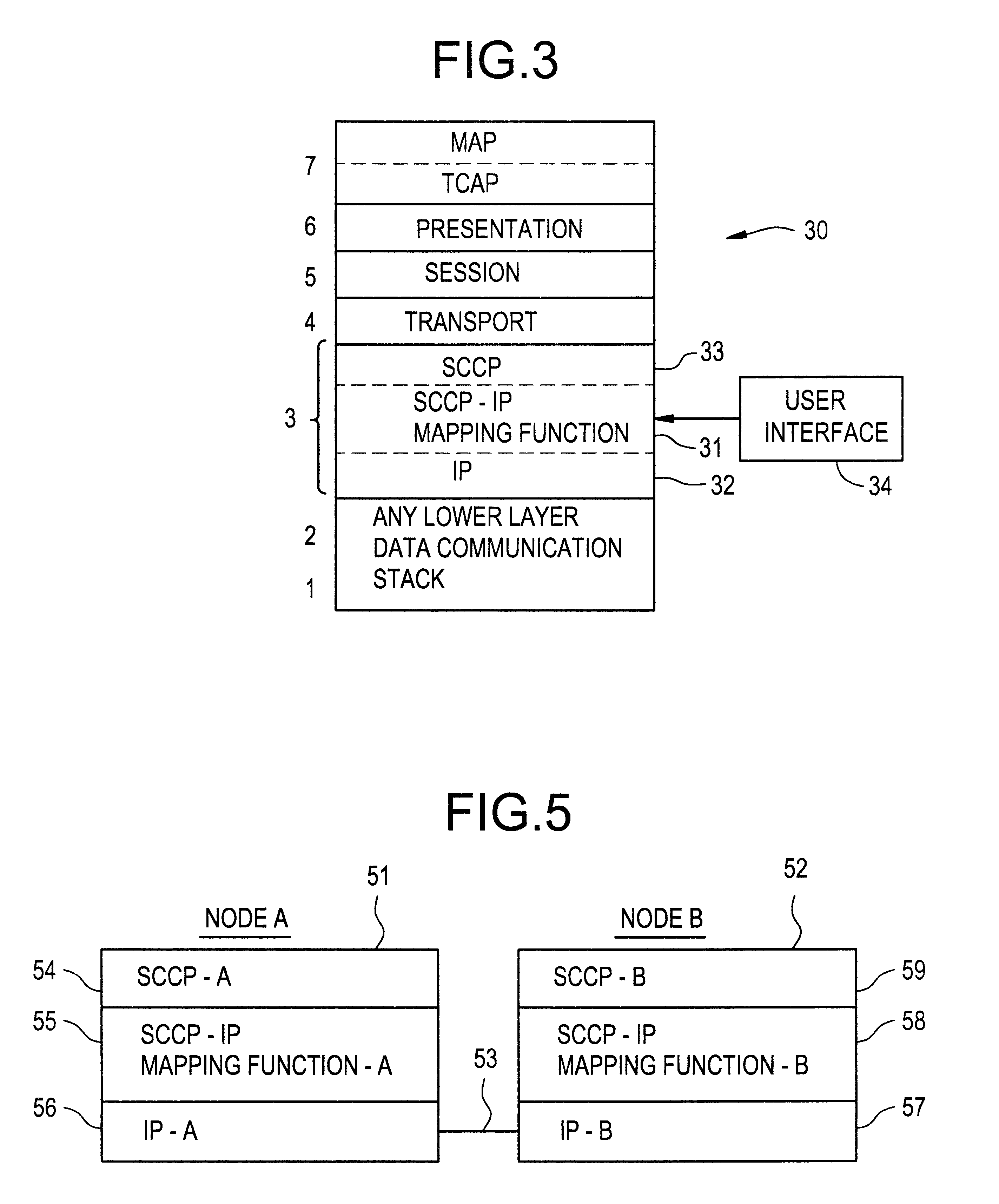
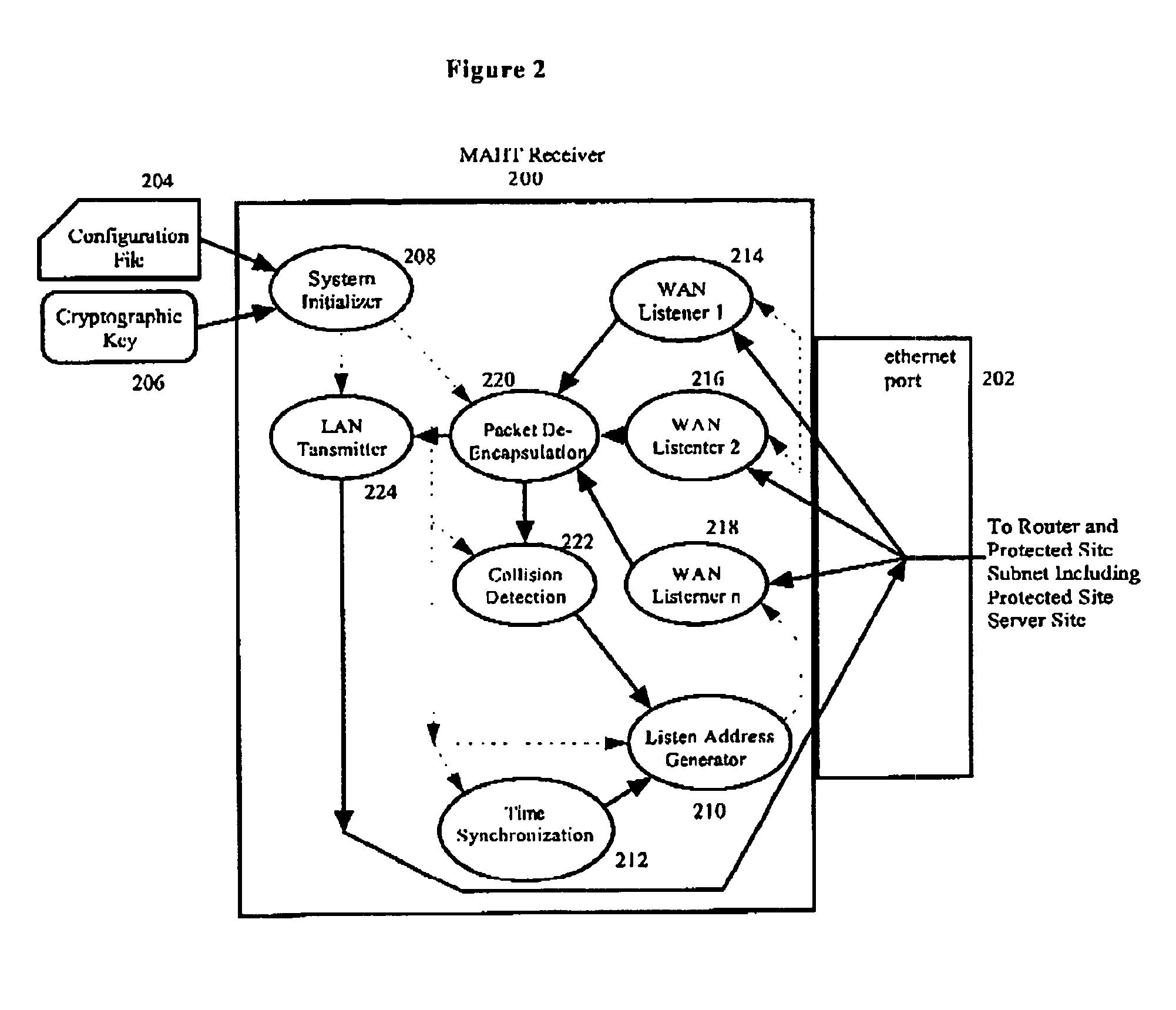
Mapping function and method of transmitting signaling system 7(SS7) telecommunications messages over data networks
InactiveUS6178181B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexSignalling Connection Control PartSignaling system
A mapping function and method for mapping a Signaling System 7 (SS7) telecommunication signaling message from a Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) protocol layer to an Internet Protocol (IP) protocol layer in order to transmit the SS7 signaling message over a data network from an origination node to a destination node. The mapping function receives the SS7 signaling message from the SCCP protocol layer by sending and receiving Message Transfer Protocol (MTP) primitives from the mapping function to the SCCP protocol layer. The mapping function then maps the received SS7 signaling message into an IP message by mapping MTP primitives into IP primitives, mapping the SS7 message address into an IP message address, and utilizing a user interface to set IP protocol parameters that cannot be transferred by the SCCP protocol layer. The mapping function then sends the mapped IP message to the IP protocol layer by sending and receiving IP primitives from the mapping function to the IP protocol layer.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
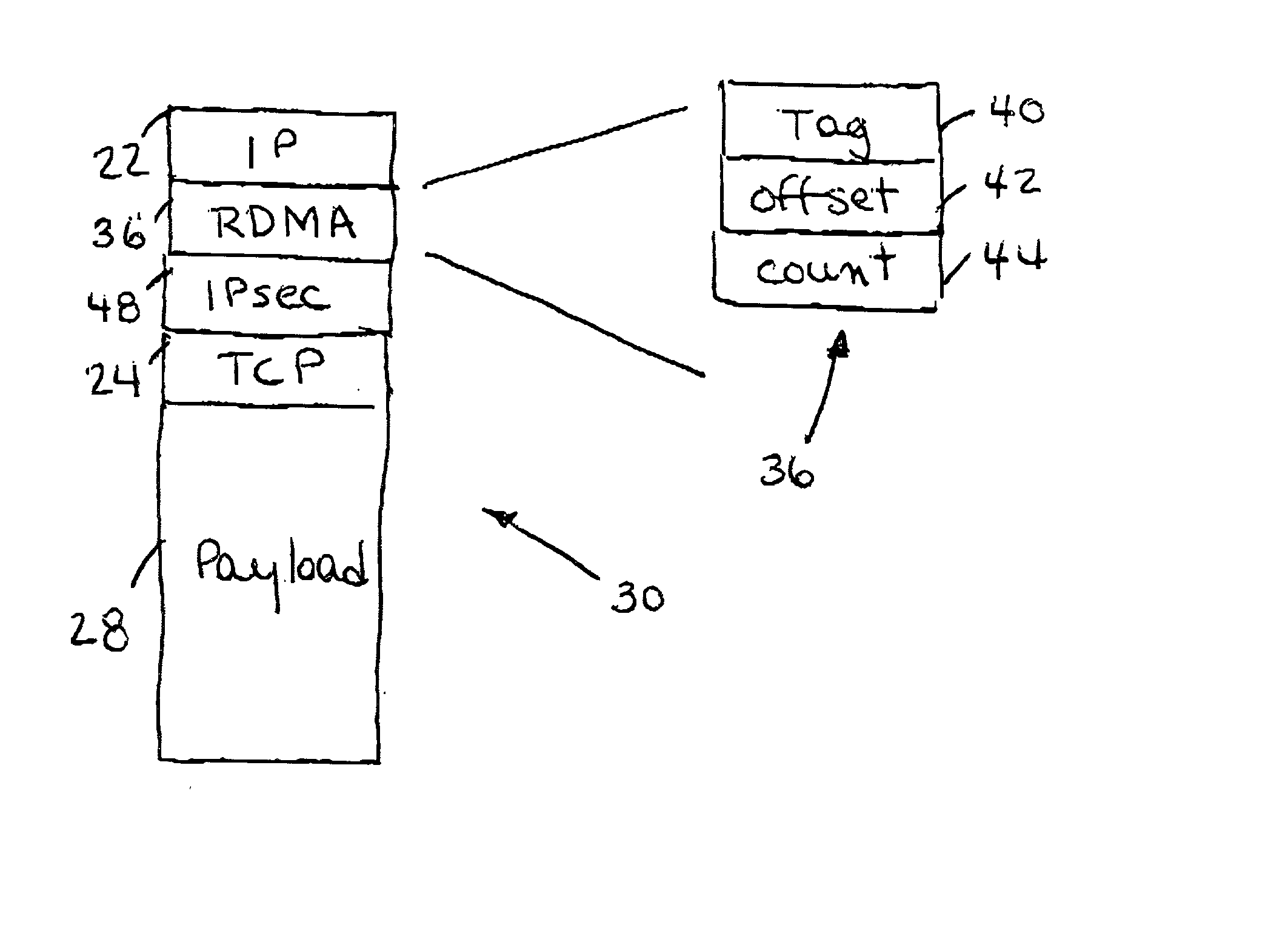
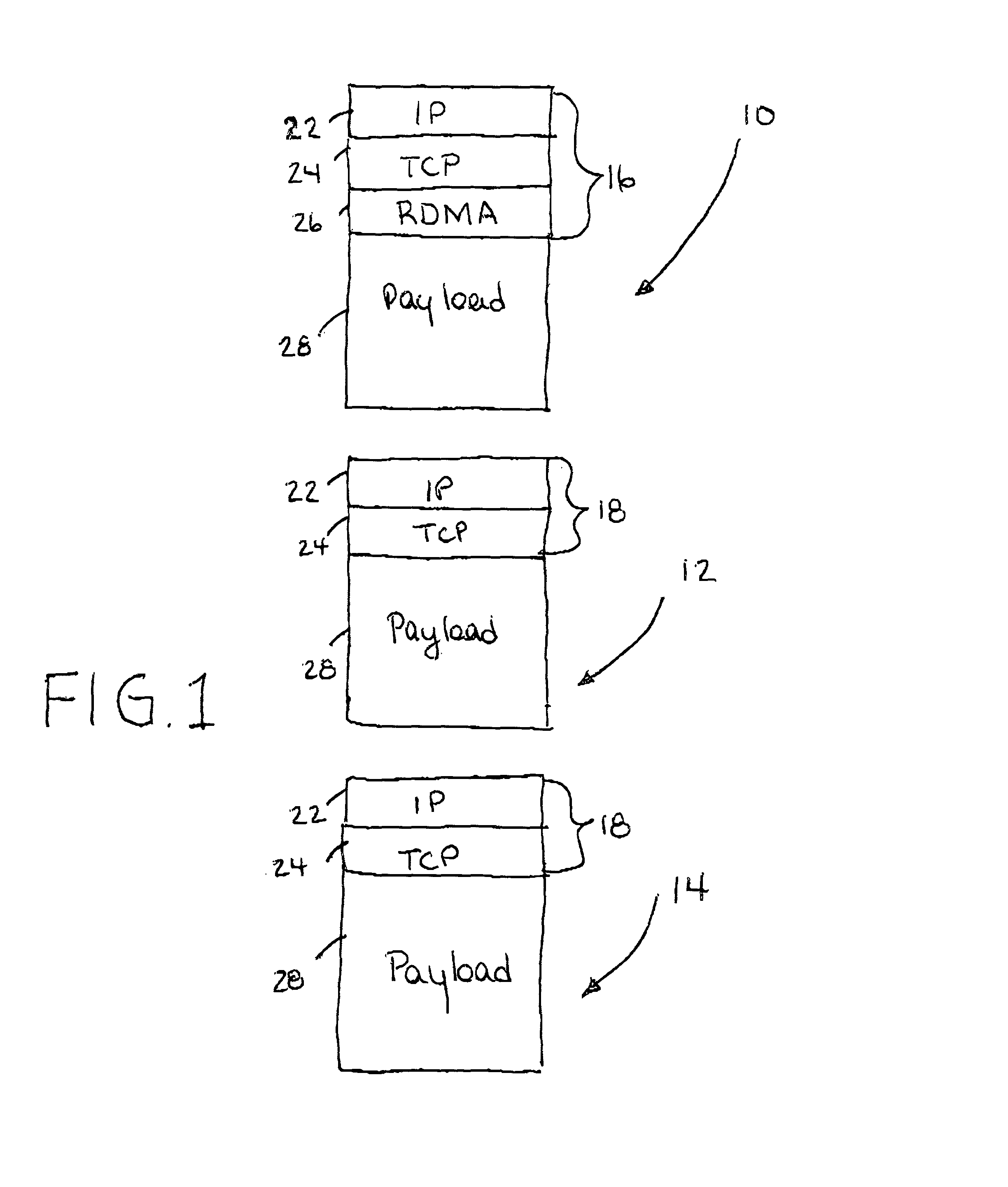
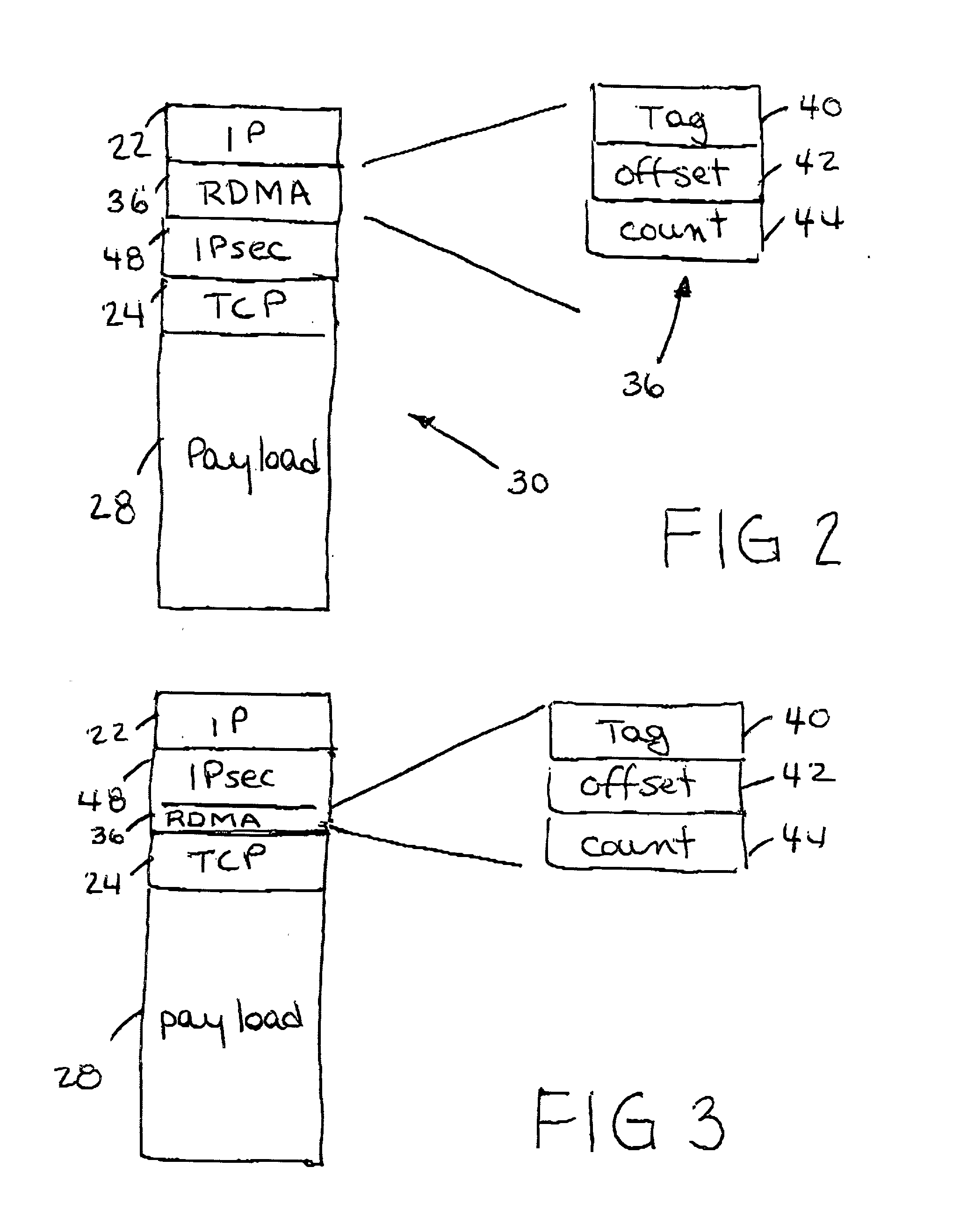
IP headers for remote direct memory access and upper level protocol framing
InactiveUS20020085562A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDirect memory accessRemote direct memory access
A data packet header including an internet protocol (IP) header, a remote direct memory access (RDMA) header, and a transmission control protocol (TCP) header, wherein the RDMA header is between the IP header and the TCP header.
Owner:IBM CORP
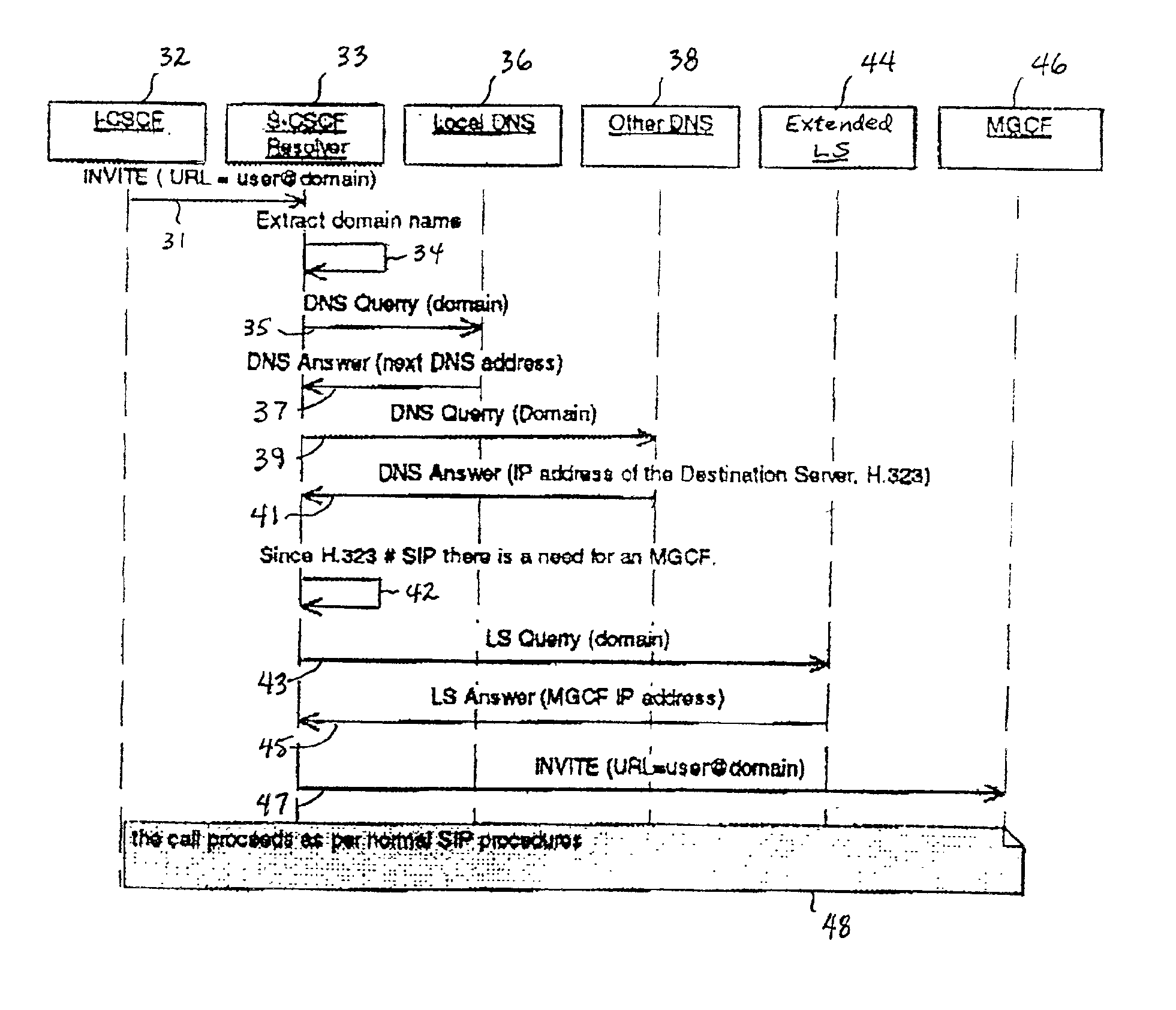
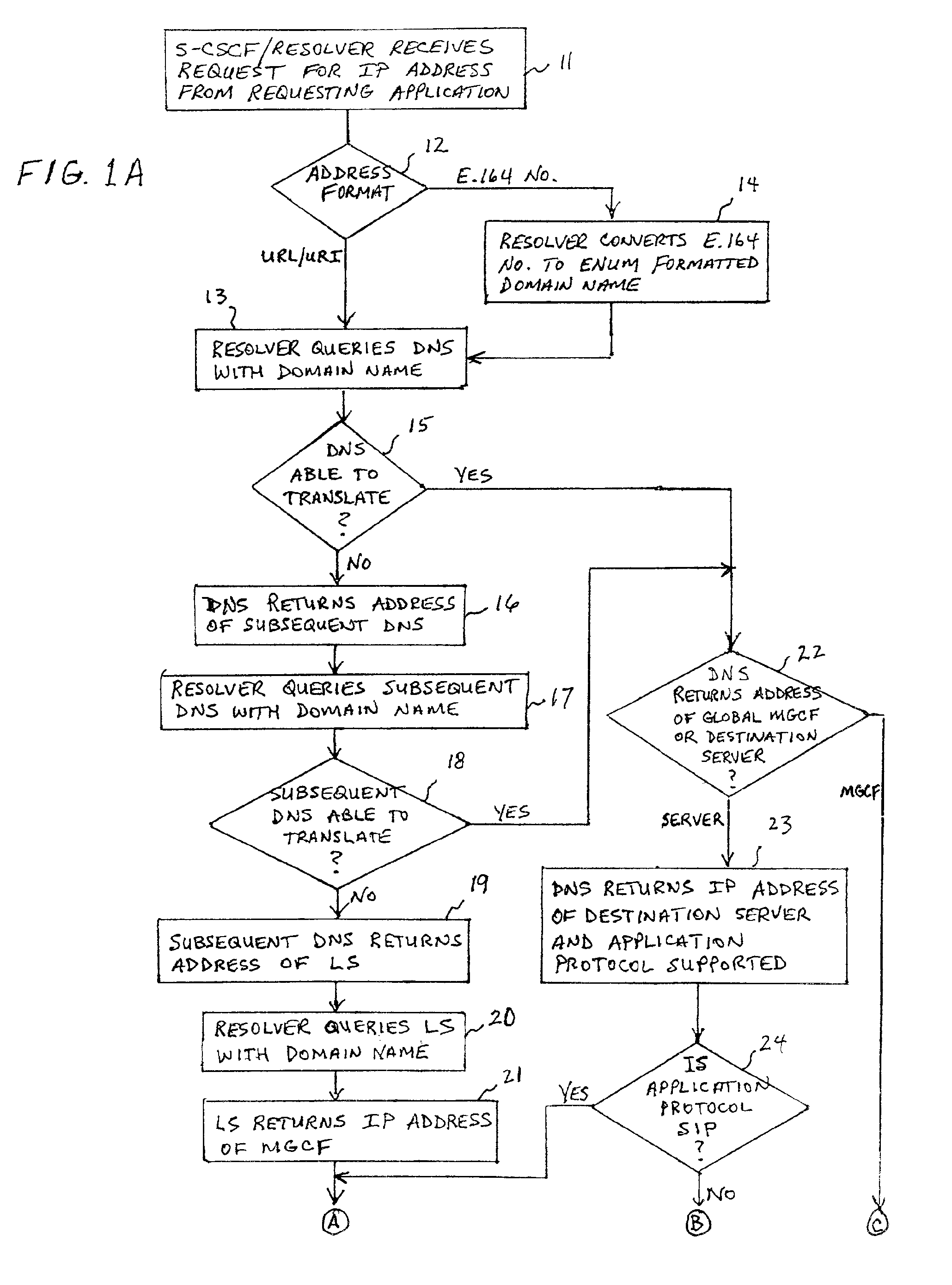
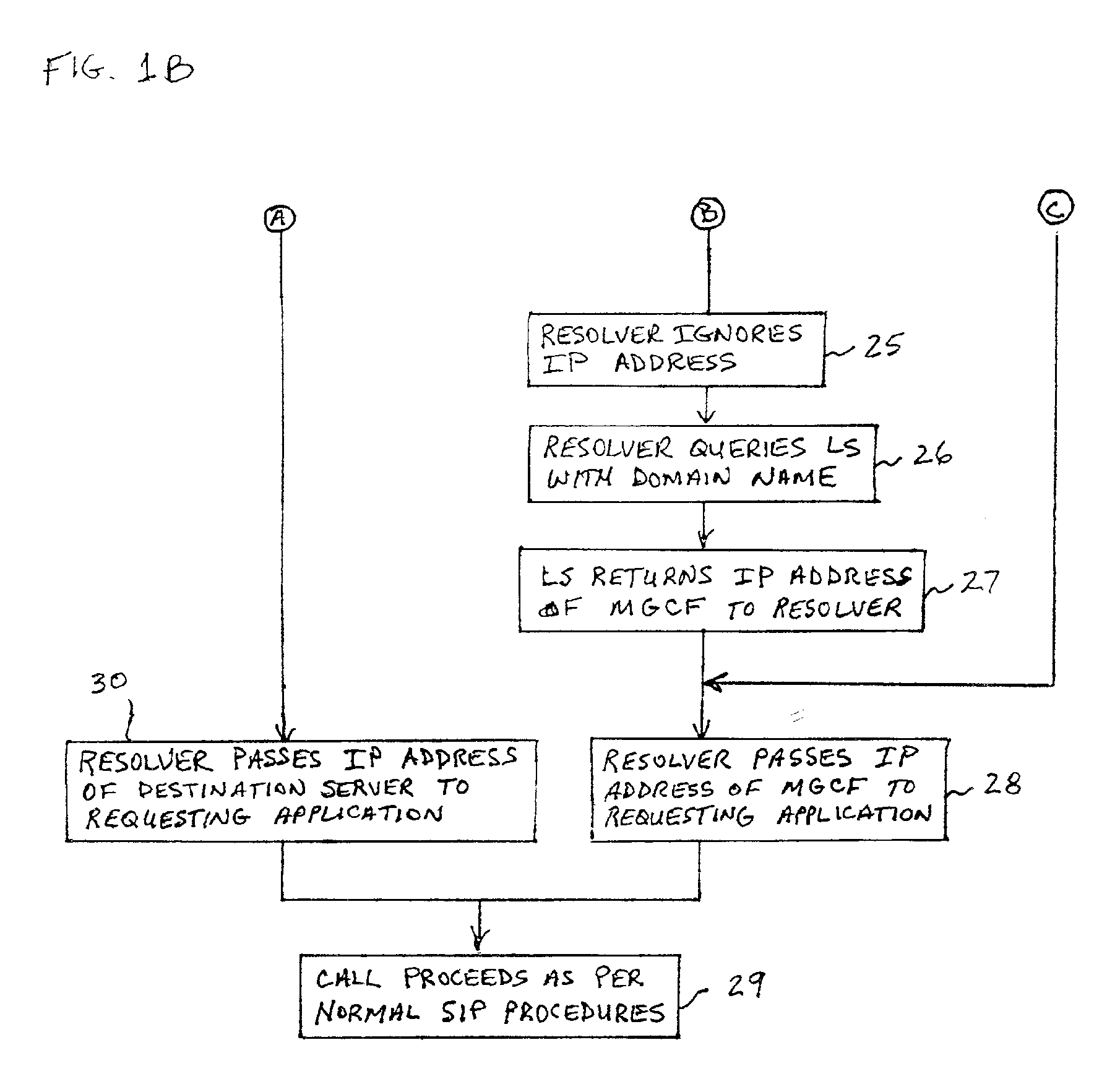
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP) -based networks
ActiveUS20020027915A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
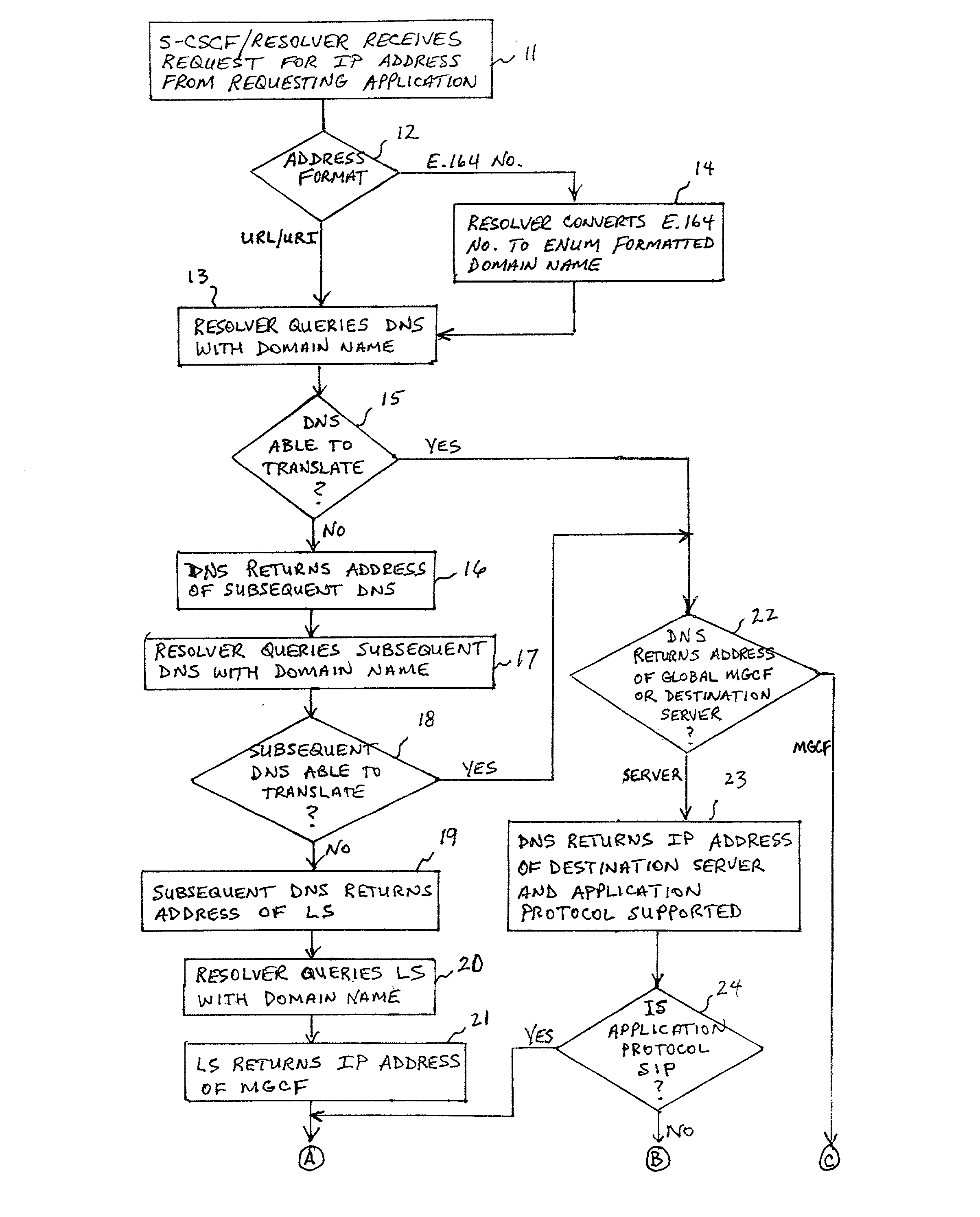
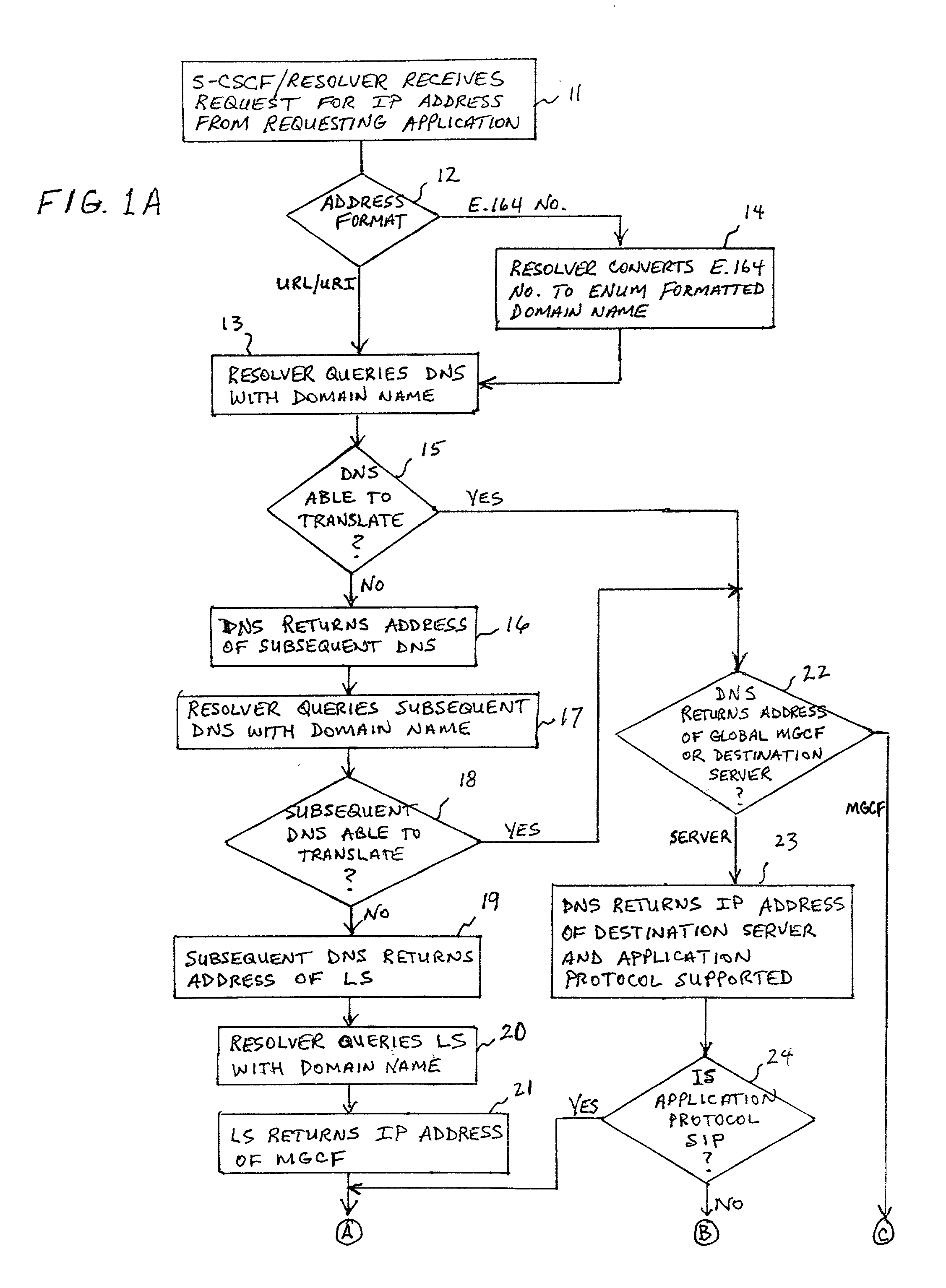
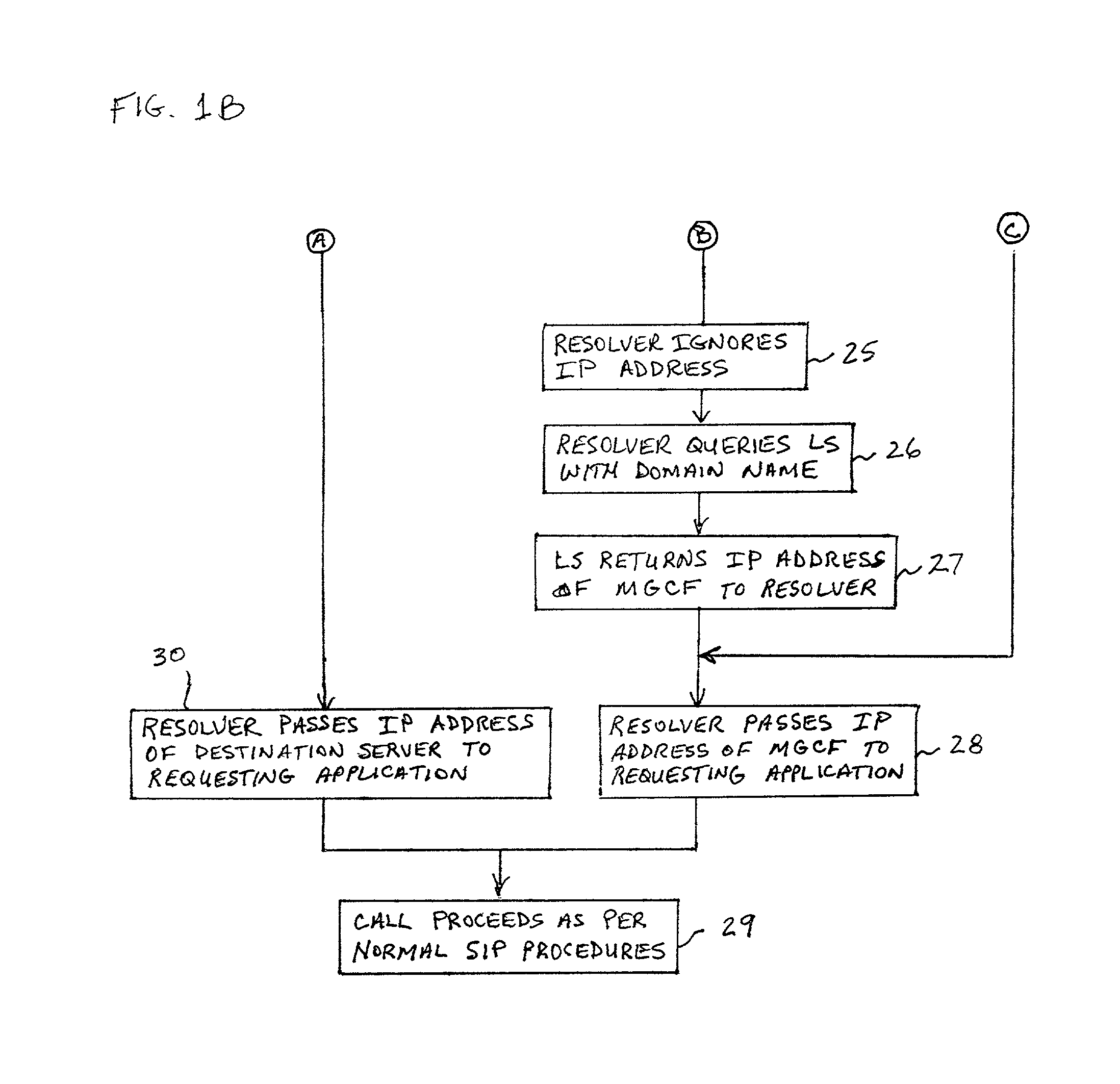
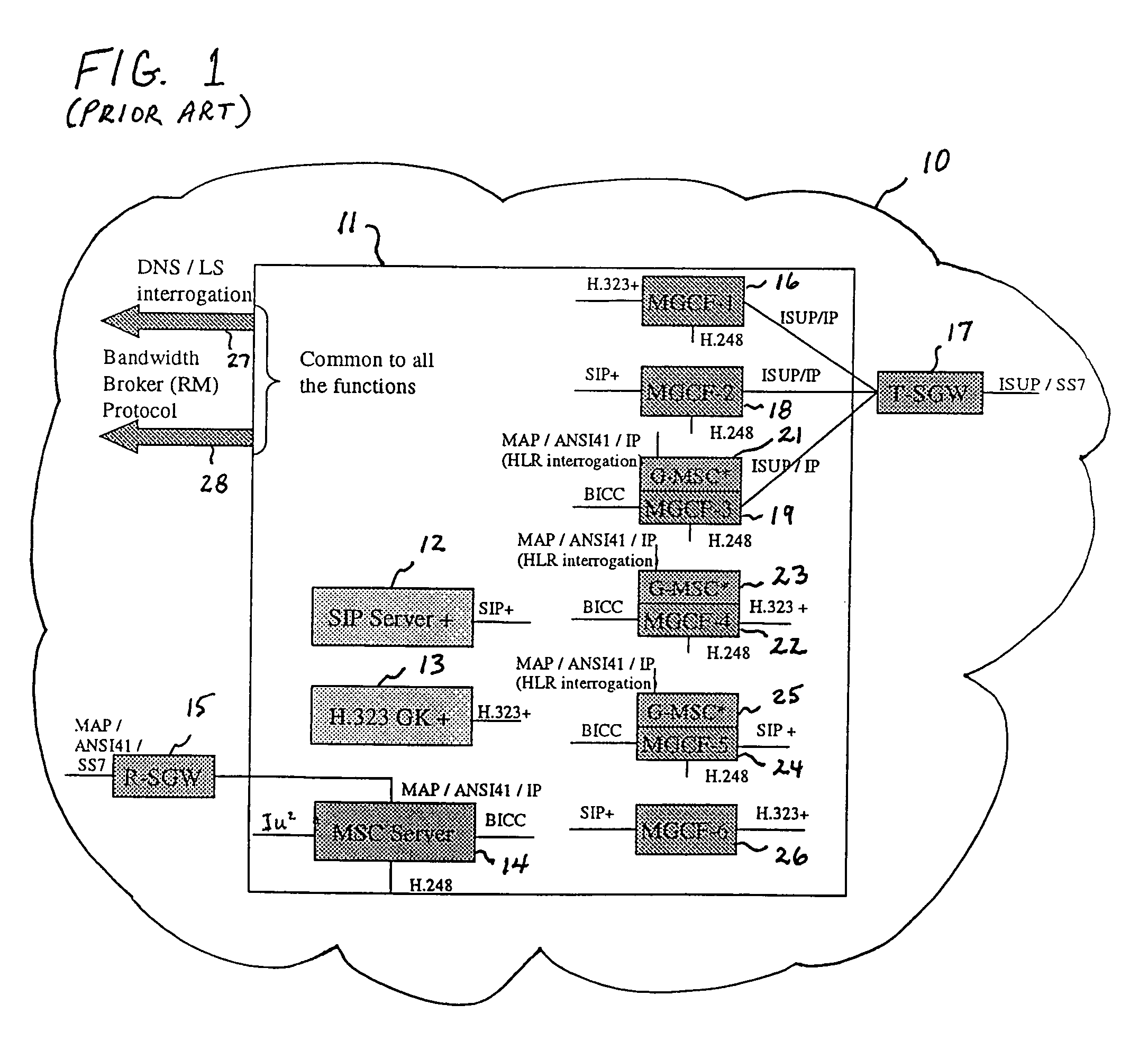
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and apparatus for protecting against IP address assignments based on a false MAC address
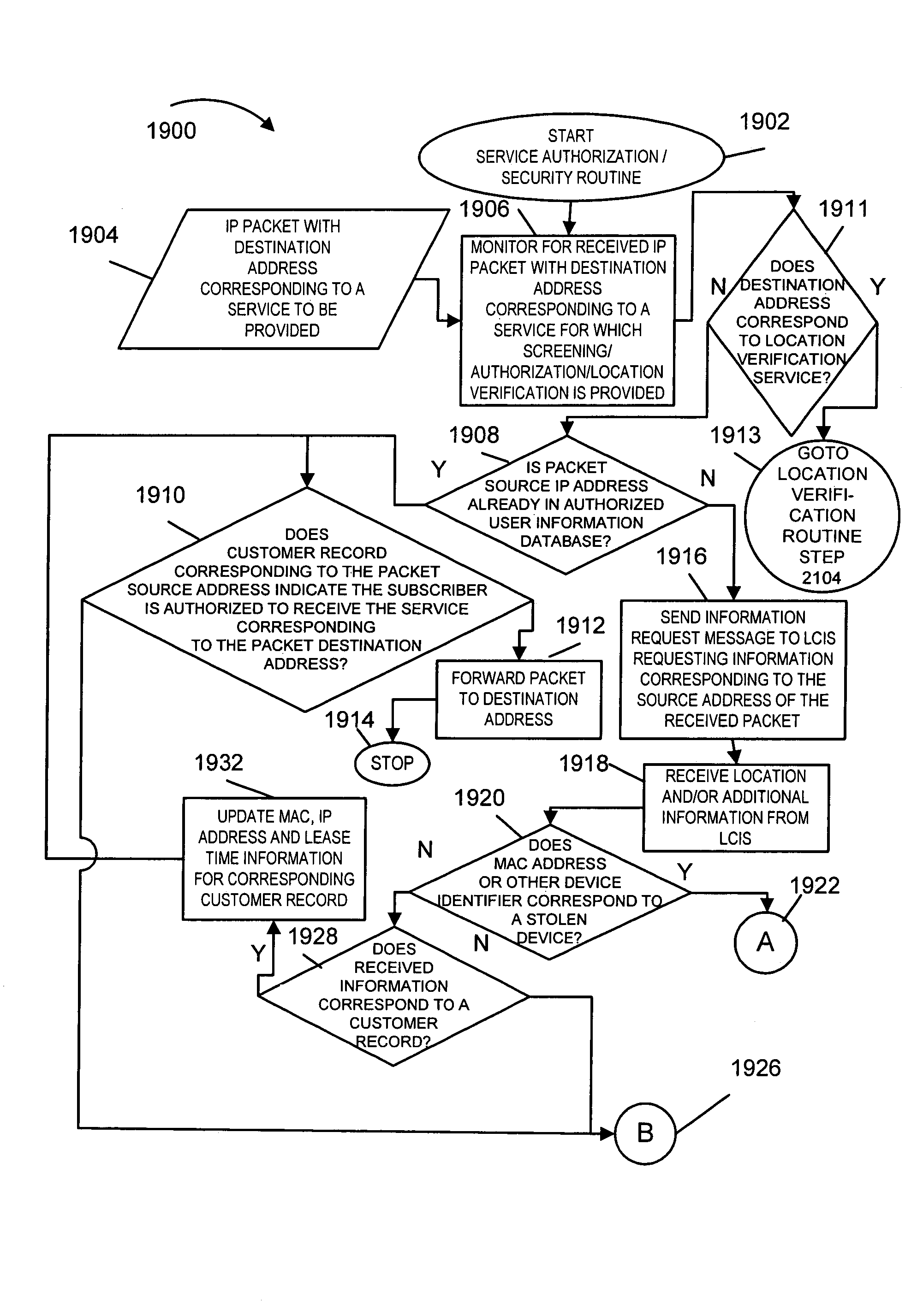
ActiveUS7320070B2Remove the burdenCollect revenueTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressCAC protocol
Methods and apparatus detecting attempts to obtain IP addresses by faking a MAC address in a data portion of an IP address request message are described. In accordance with the present invention, rather than use standard address allocation protocols, e.g., ARP, the DNS DCHP contacts the requesting edge router via a private secure network. The MAC address received in the address request is compared to the MAC addresses stored in the edge routers port / MAC address resolution table. If the MAC address received in the request message cannot be found in the edge router's table which was created from the MAC address included in the message's header, a fraudulent attempt to obtain a MAC address is declared. The fraudulent attempt to obtain an IP address can be reported and steps taken to identify the perpetrator of the fraud.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
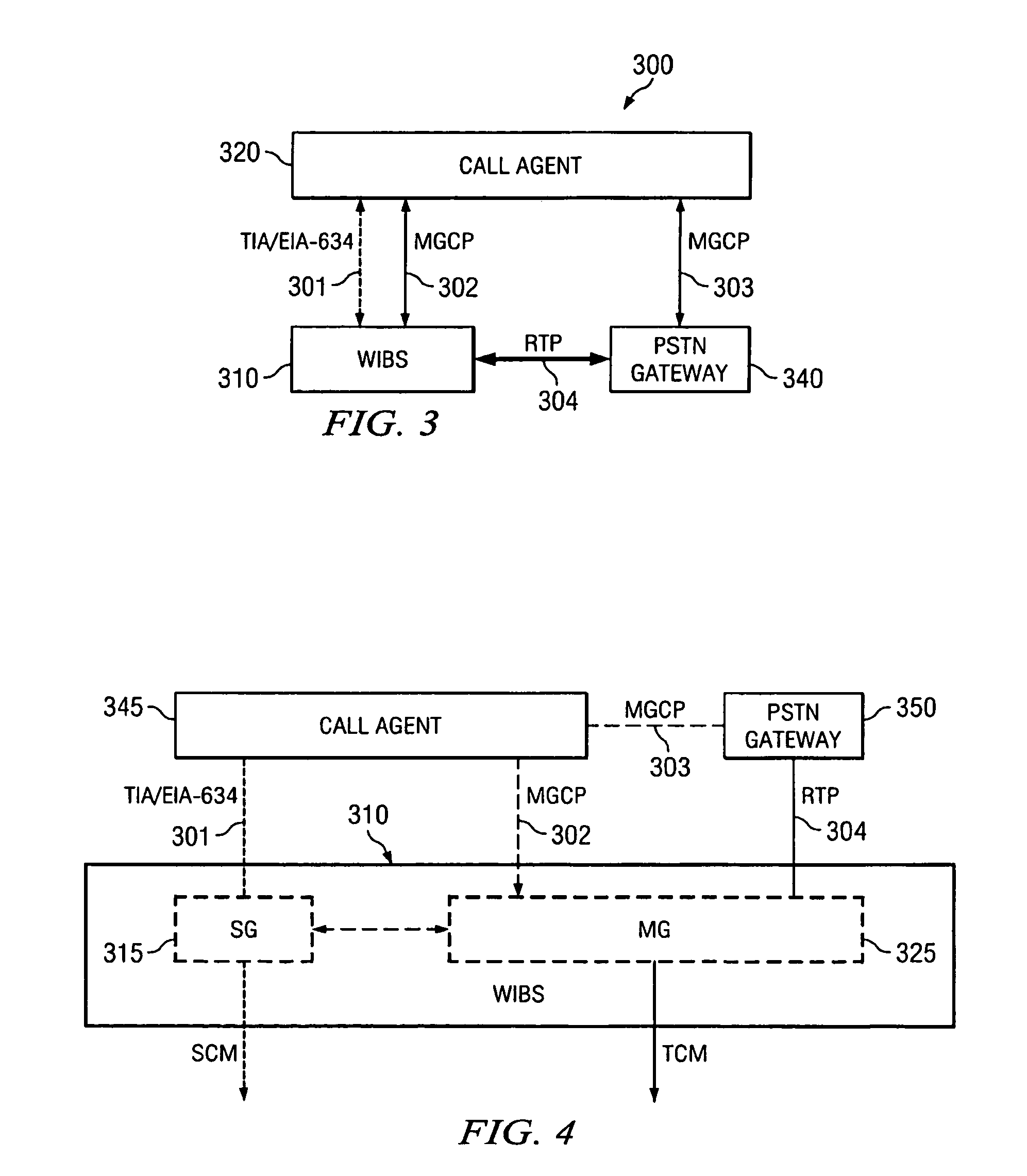
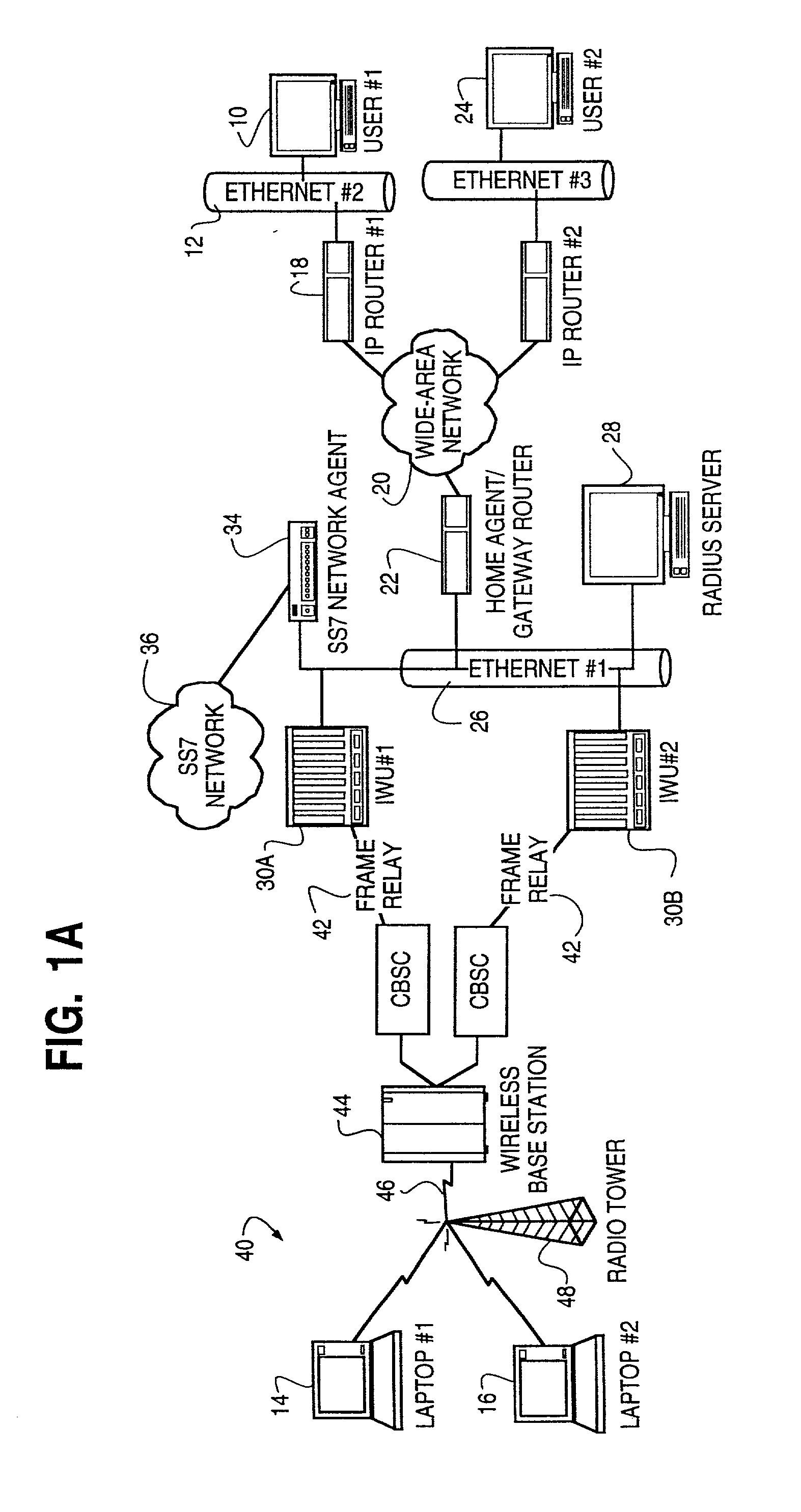
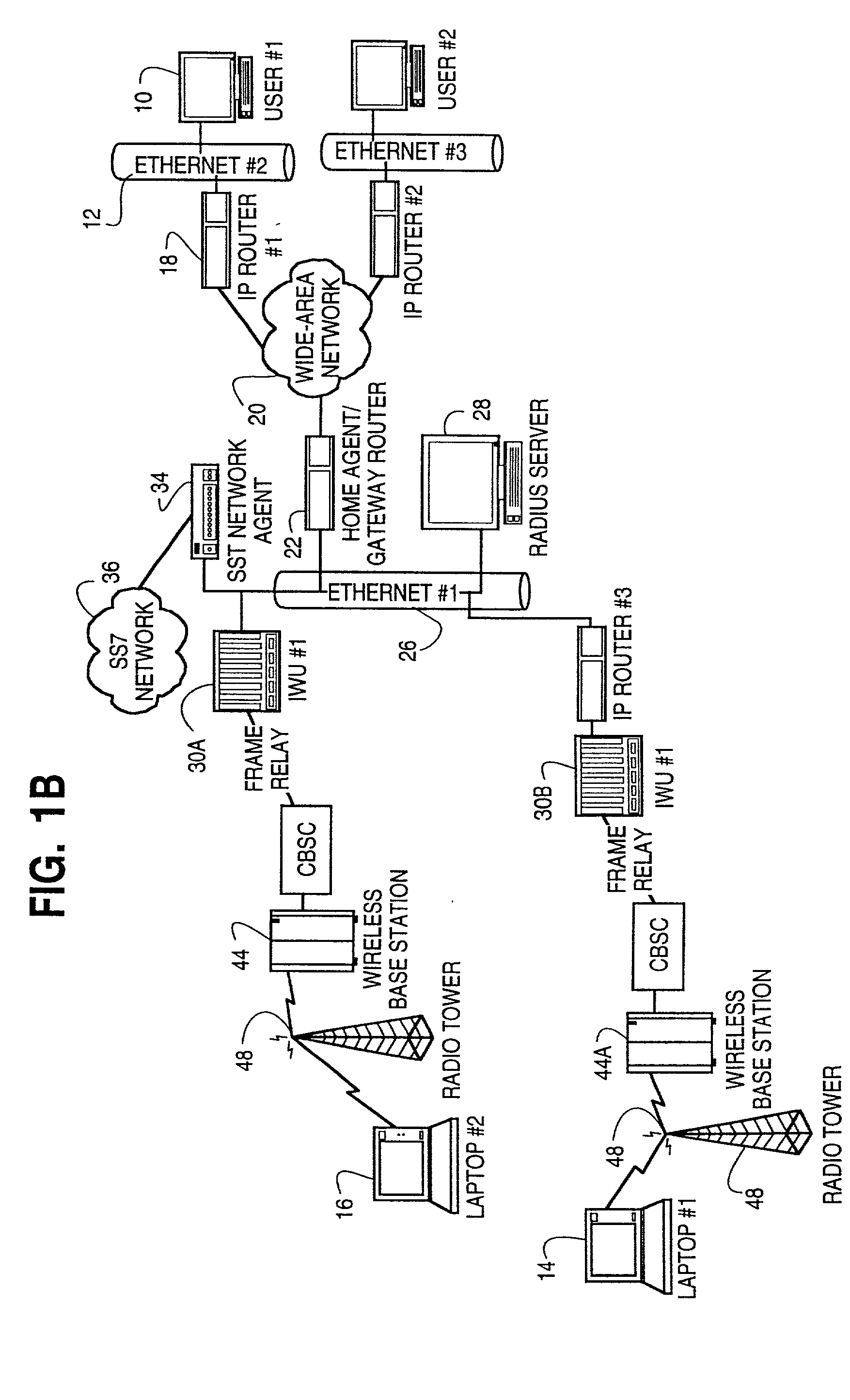
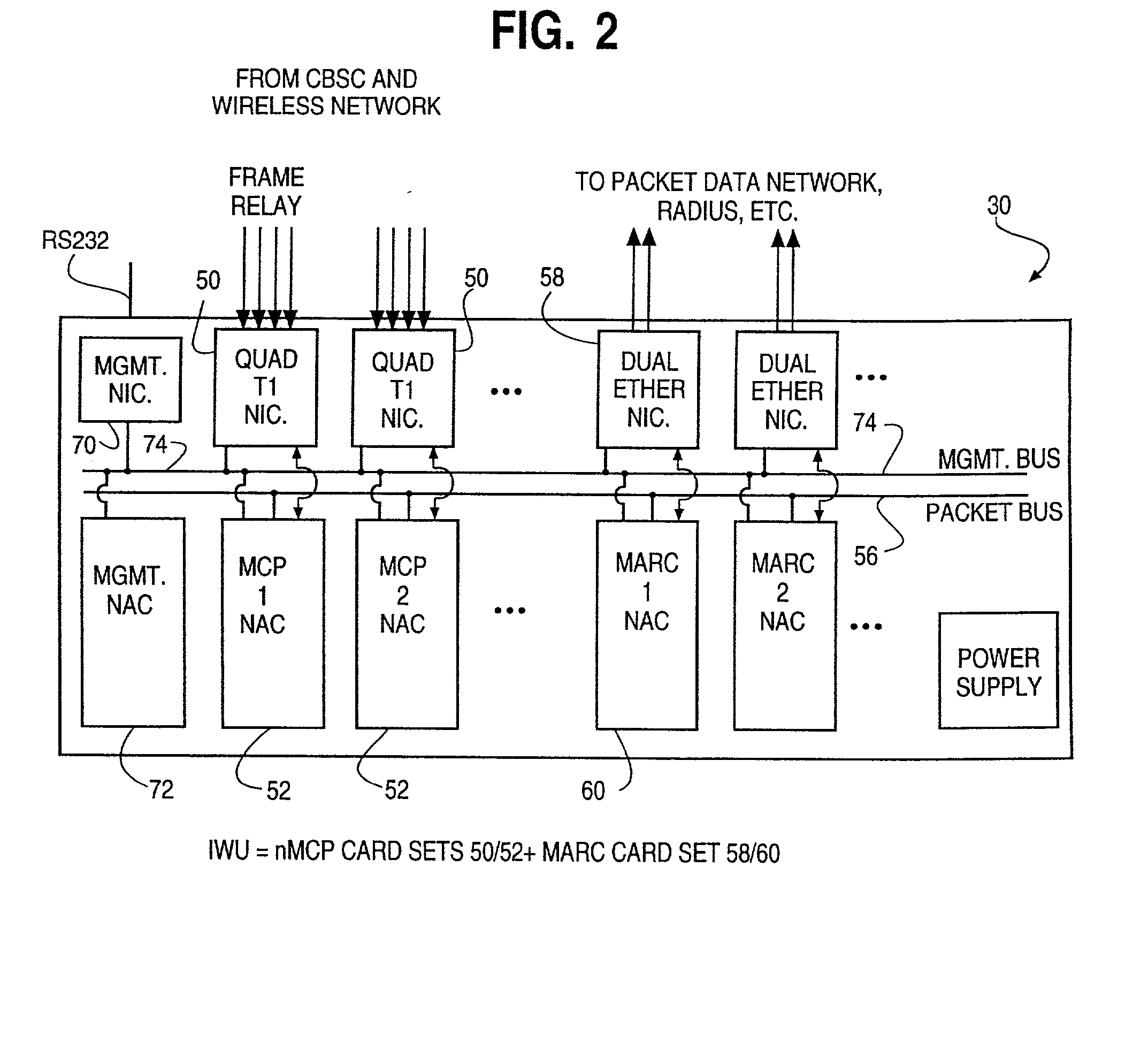
System and method of linking a wireless signaling protocol with a media gateway control protocol in a packet-based network
InactiveUS7120133B1Shorten the timeReduce data lossNetwork topologiesConnection managementCommunication unitCommunications system
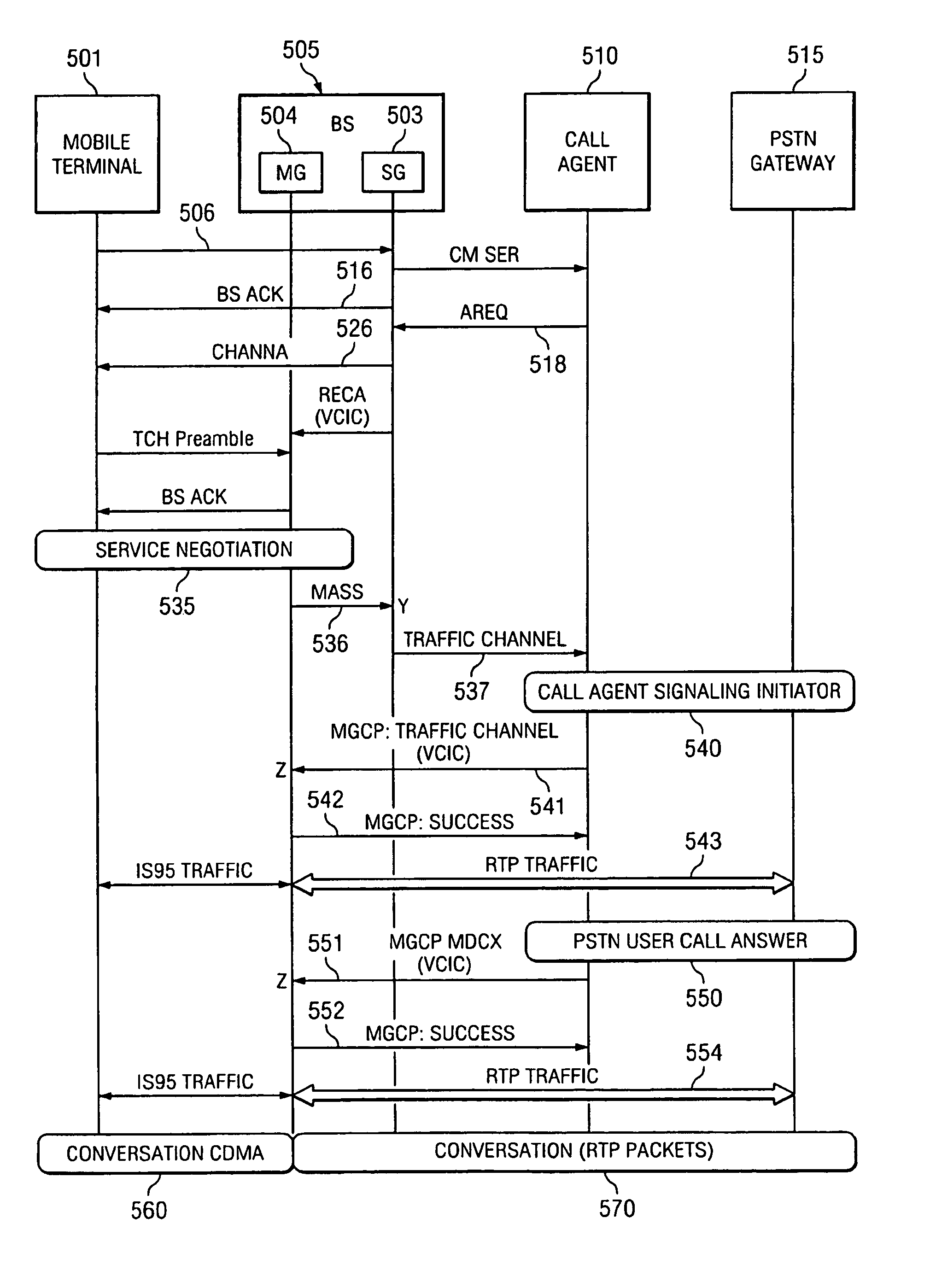
A wireless office communication system including a multi-protocol wireless internet base station (WIBS) encompassing a base station controller (BSC), a mobile switch controller (MSC) and an ethernet interface module for coupling the WIBS to an existing internet protocol (IP) based network. The interface module provides for coupling the WIBS to an ethernet back-bone, a mobile communication unit and a public switch telephone network (PSTN). In one embodiment the wireless communication system includes wireless signaling logic and media gateway logic to enable the wireless office communication system to handle signal transmission between a mobile terminal and a media gateway. A virtual circuit identity code (VCIC) enables the base station to provide a virtual traffic path (VTP) to link communications between TIA / EIA-634 wireless signaling and media gateway control protocol (MGCP).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP)-based networks
ActiveUS6917612B2Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and systems for providing message translation, accounting and routing service in a multi-protocol communications network environment
InactiveUS6967956B1Easy to routeFacilitates accountingTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransmission protocolMessage routing
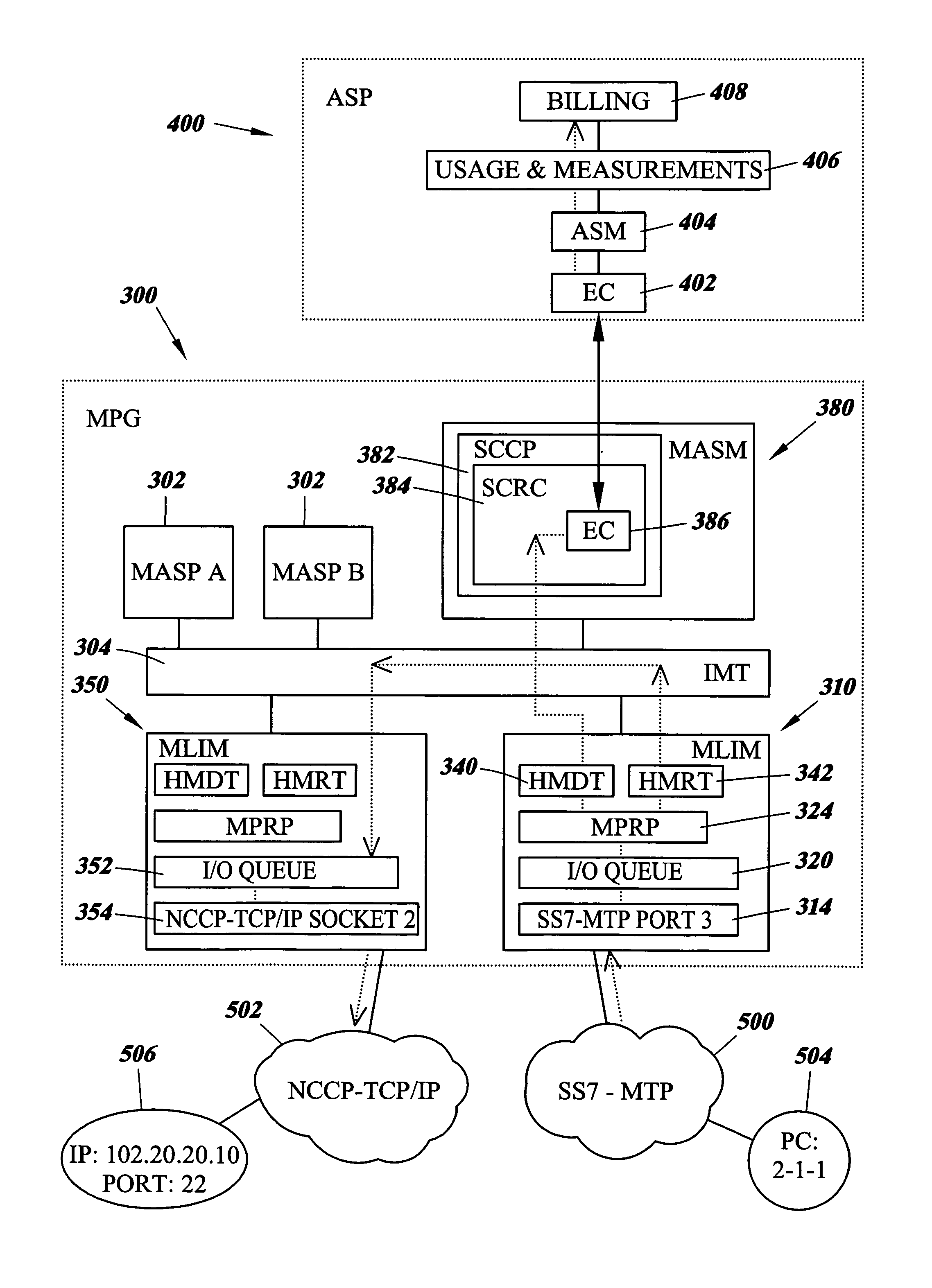
A network element that is capable facilitating the routing and accounting of messages between a plurality of network elements that do not share a common signaling application protocol nor a common transport protocol suite. In one embodiment of the present invention, a Multi-Protocol Gateway (MPG) is adapted to receive a signaling message and subsequently translate both the signaling and transport protocol suite prior to message routing. The MPG node is also configured to create and maintain usage and measurements data that may subsequently be used to produce billing records.
Owner:TEKELEC
Method for source-spoofed IP packet traceback
Method for source-spoofed internet protocol packet traceback. This is an IP packet traceback technique for locating the origin of a malicious packet, even if the packet's IP source address is incorrect (spoofed). This is done by having routers lookup the source address in their routing tables, and mark the relevant entry.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method and system for protection of internet sites against denial of service attacks through use of an IP multicast address hopping technique
InactiveUS6880090B1Traffic analysisTimely controlSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsIp addressIP multicast
The present invention relates to a method and system for Internet Protocol network communications and a use thereof for protecting Internet sites against denial of service attacks on insecure public networks such as the Internet. The method utilizes a multicast address hopping technique which selectively varies the chosen multicast IP address from a set of available multicast addresses according to a predetermined scheme known to the communicating end stations but not to unauthorized end stations. The packets associated with the multicast stream are then communicated on the chosen multicast address. The set of available multicast IP addresses may also be selectively varied according to a secret predetermined scheme known to the transmitter and subscriber end stations, particularly by adding to and dropping from the set of multicast IP addresses in a seemingly random fashion. Using the method of the present invention, potential attackers are prevented from knowing which address to disrupt or monitor for traffic between end stations.
Owner:SHAWCROSS CHARLES BYRON ALEXANDER
Dynamic allocation of wireless mobile nodes over an internet protocol (IP) network
A method is described of automatically locating and connecting a mobile wireless communications device to a packet-switched network such as the Internet. An Internet Protocol (IP) packet from a terminal on the network, destined for receipt by the mobile device, is received at a home agent acting as a gateway or router linking the packet switched network to a second network, such as LAN, coupled to a wireless communications network. The home agent transmits an access-request message to an authentication server. The access-request message includes a destination IP address associated with the mobile device found in the IP packet. The authentication server responsively issues an access-accept message to the home agent if the mobile device is authorized to receive the IP packet. The access-accept message comprises (a) information uniquely identifying said device, such as the IMSI / ESN number for the device, and (b) information identifying a network to use to locate said device. The home agent issues a message containing the information uniquely identifying the device to a mobile node location server. The mobile node location server maintains a table mapping IP addresses for a plurality of mobile communication devices to information uniquely identifying the devices. In the event that the mobile node location server does not find an IP address for the device in the table, the device is paged via the wireless communications network. In response to the page, the mobile device dials into the wireless communications network and second network and initiates a connection to the packet switched network whereby the IP packet is transmitted to the device.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
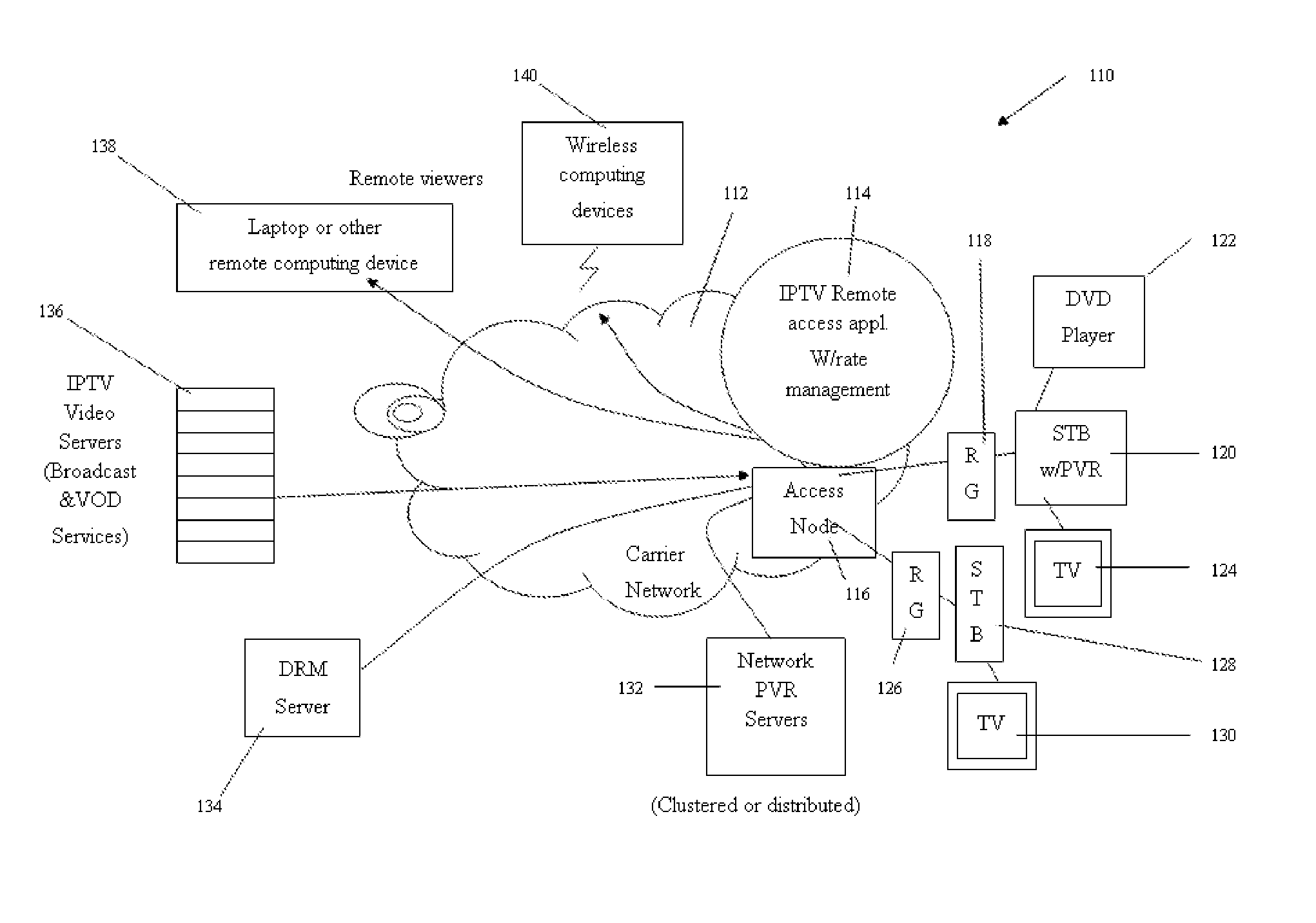
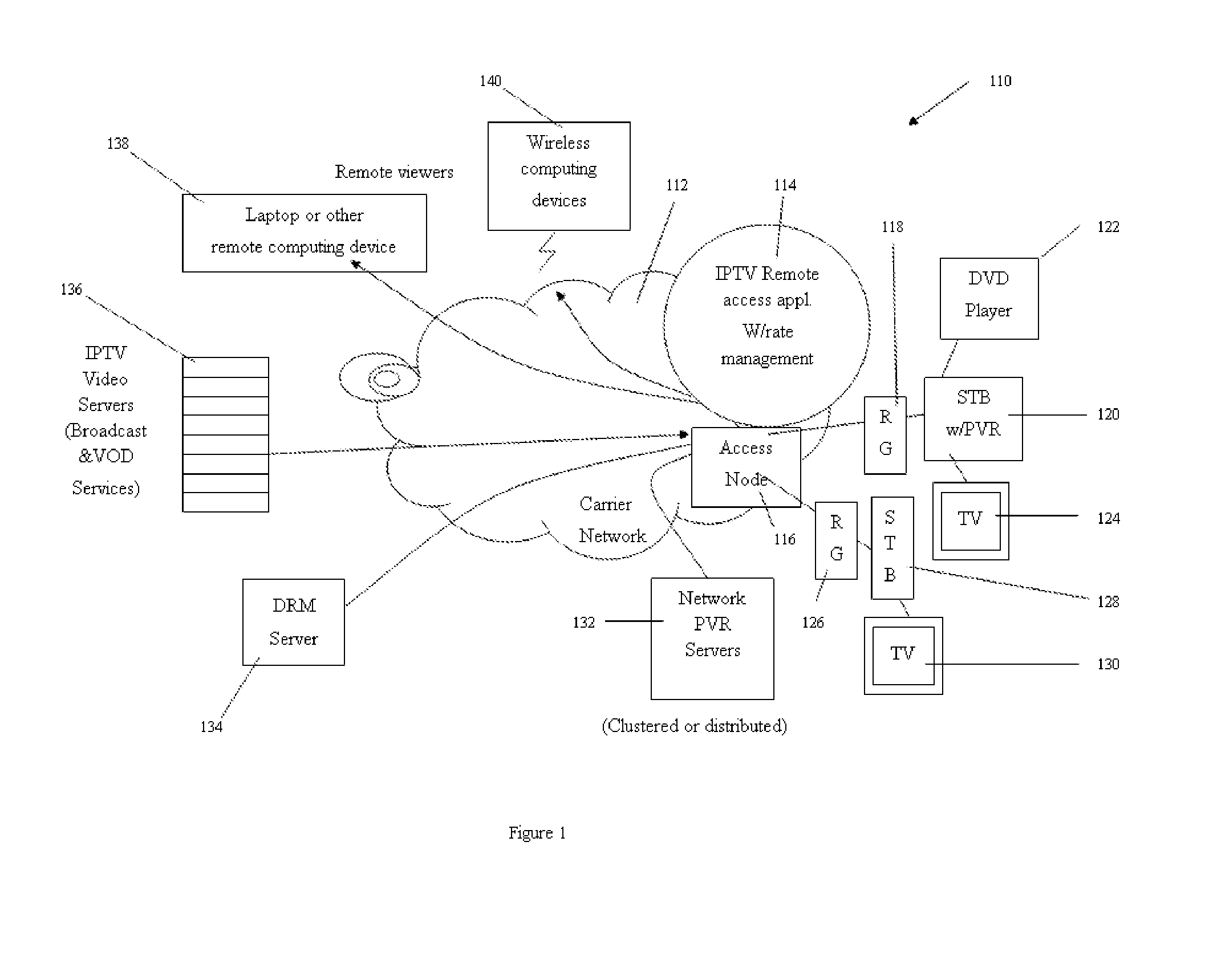
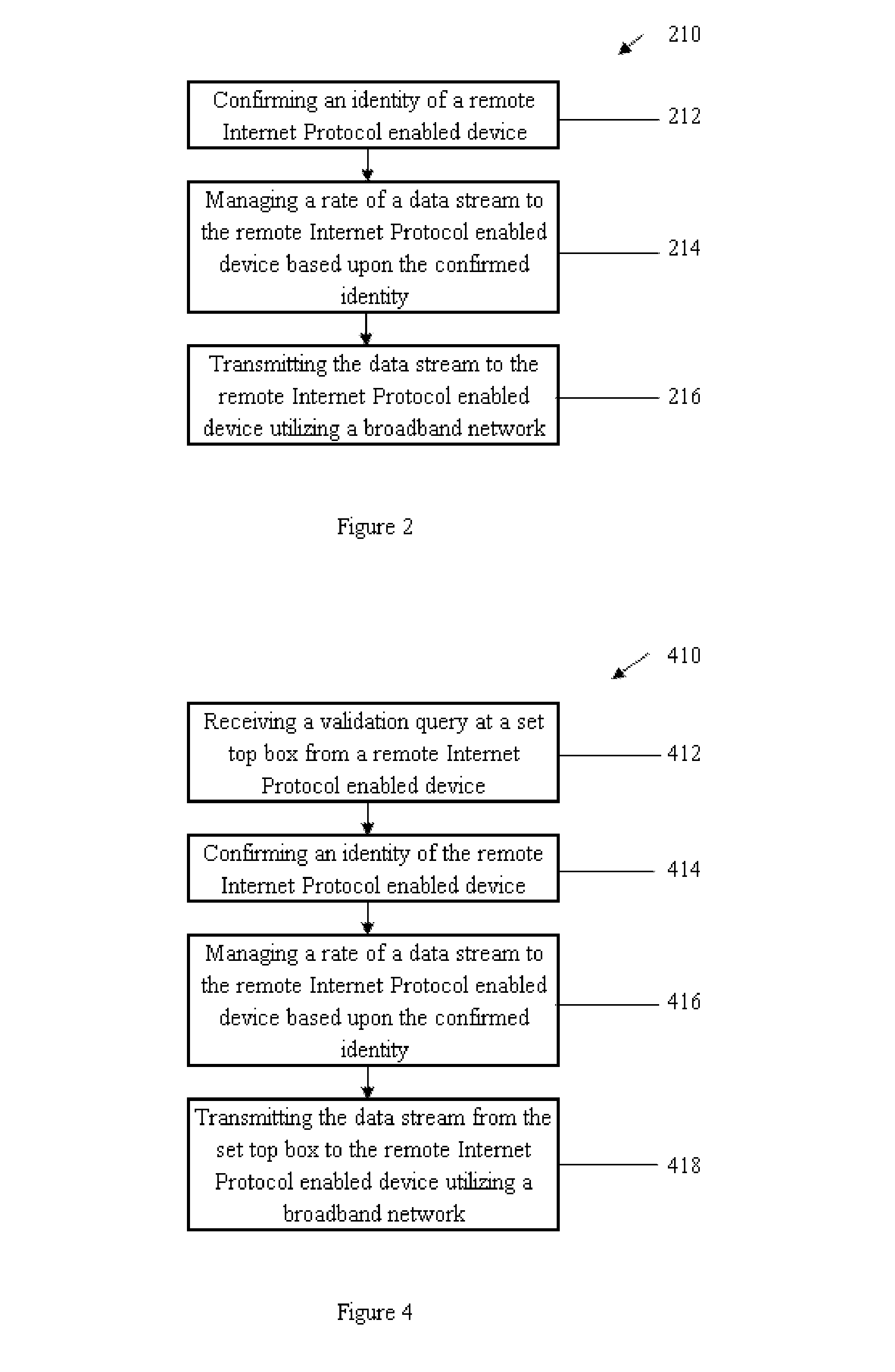
Remote Access to Internet Protocol Television by Enabling Place Shifting Utilizing a Telephone Company Network
InactiveUS20080134267A1Less susceptible to transmission problemShort response timeData switching by path configurationTwo-way working systemsData streamTelephone network
A system, method, and computer readable medium for remote access to Internet Protocol television by enabling place shifting utilizing a telephone company network, that comprises, confirming an identity of a remote Internet Protocol enabled device, managing a rate of a data stream to the remote Internet Protocol enabled device based upon the confirmed identity, and transmitting the data stream to the remote Internet Protocol enabled device utilizing a broadband network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
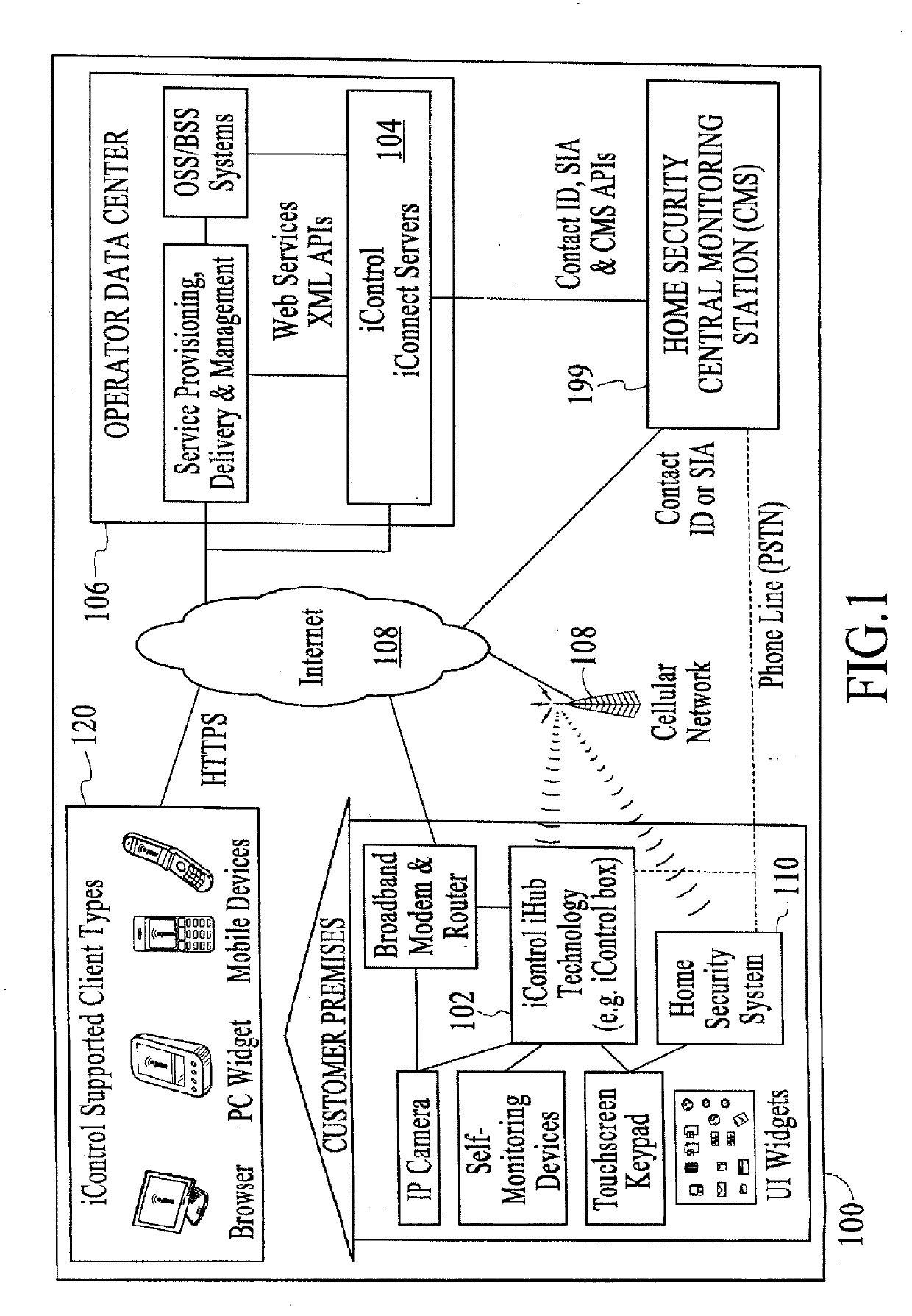
Communication protocols over internet protocol (IP) networks
ActiveUS20190379766A1Closed circuit television systemsIndividual entry/exit registersInternet protocol suiteThe Internet
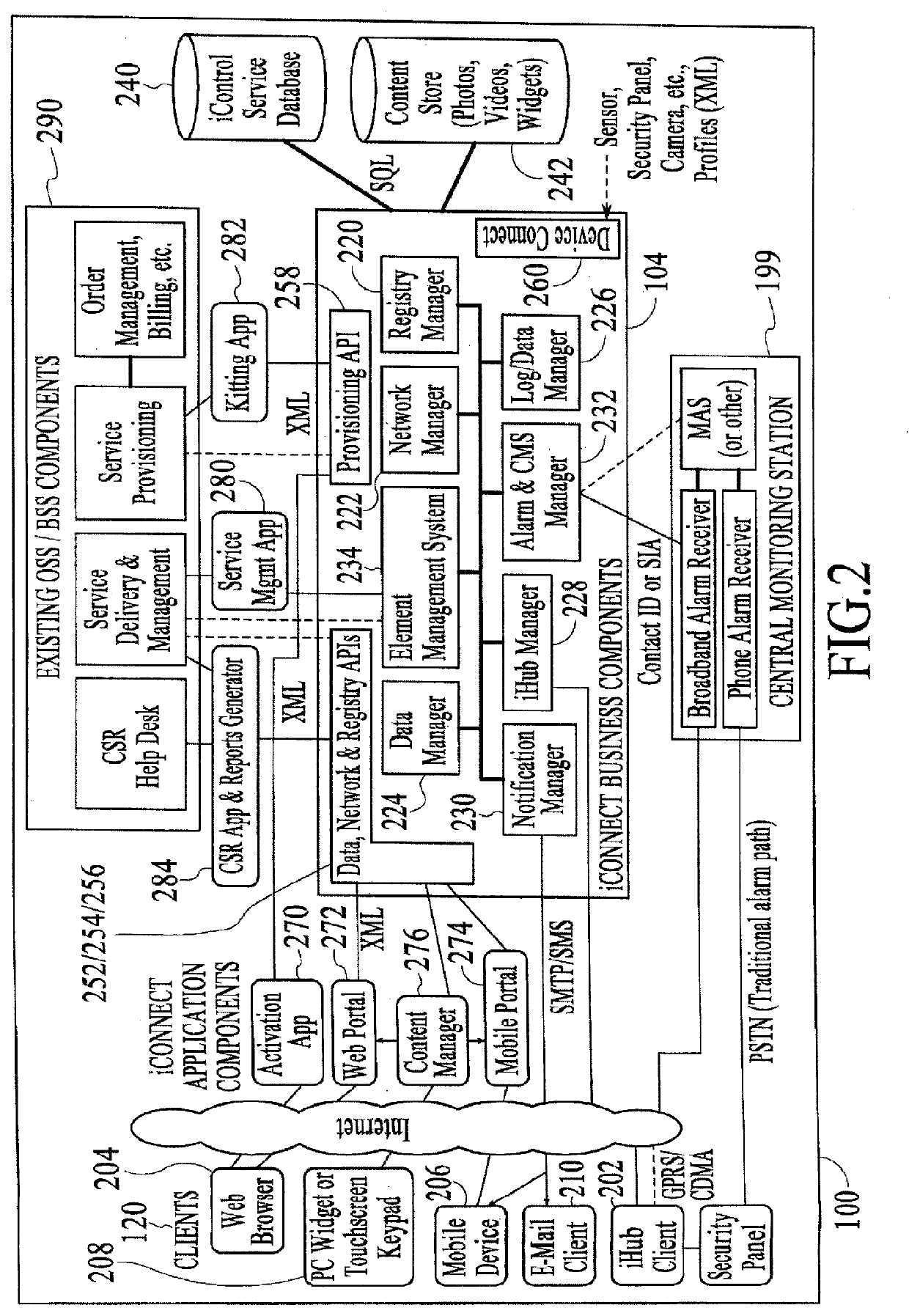
A system and methods comprise a touchscreen at a premises. The touchscreen includes a processor coupled to a security system at the premises. User interfaces are presented via the touchscreen. The user interfaces include a security interface that provides control of functions of the security system and access to data collected by the security system, and a network interface that provides access to network devices. A camera at the premises is coupled to the touchscreen via a plurality of interfaces. A security server at a remote location is coupled to the touchscreen. The security server comprises a client interface through which remote client devices exchange data with the touchscreen and the security system.
Owner:ICONTROL NETWORKS
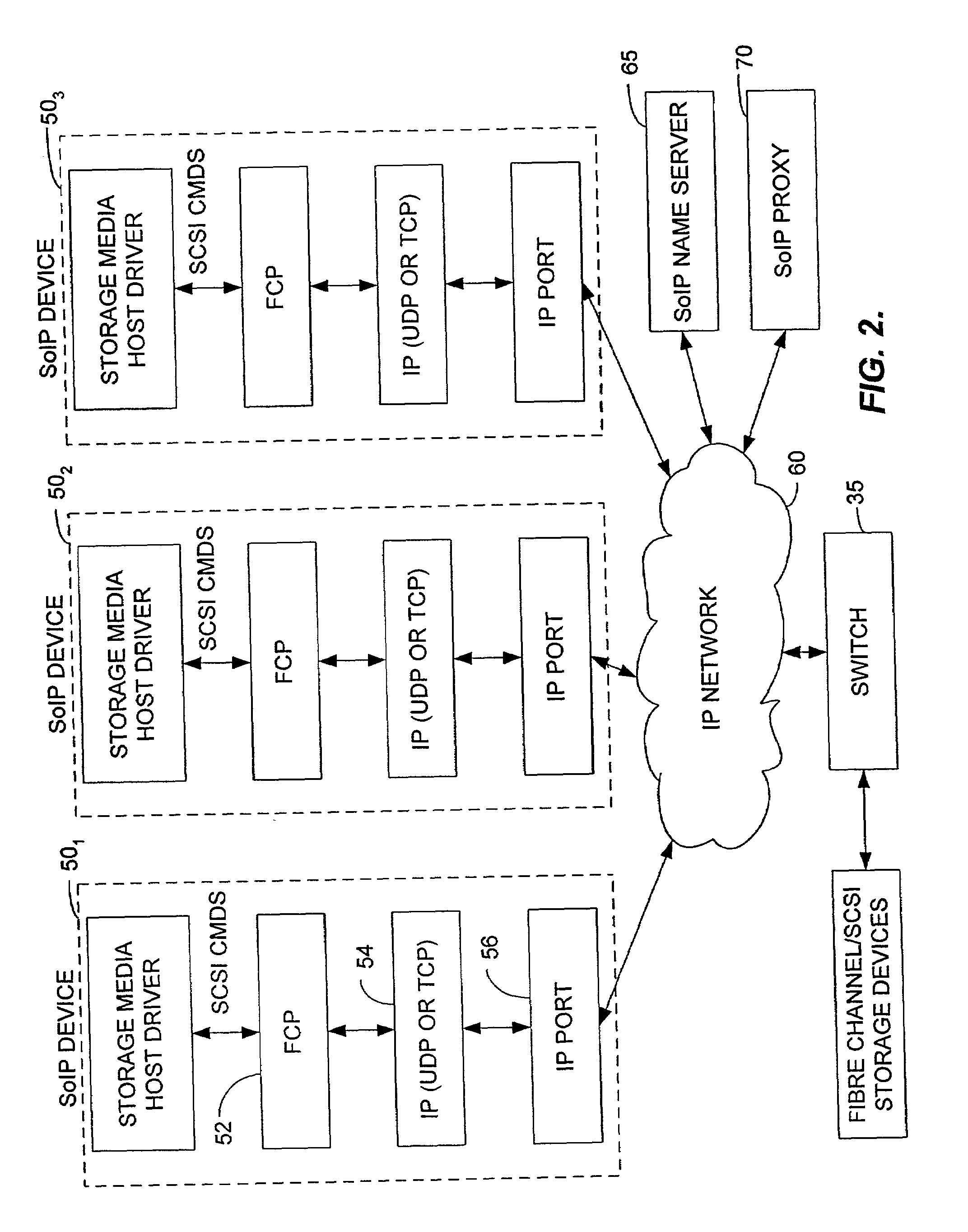
Method and apparatus for transferring data between IP network devices and SCSI and fibre channel devices over an IP network
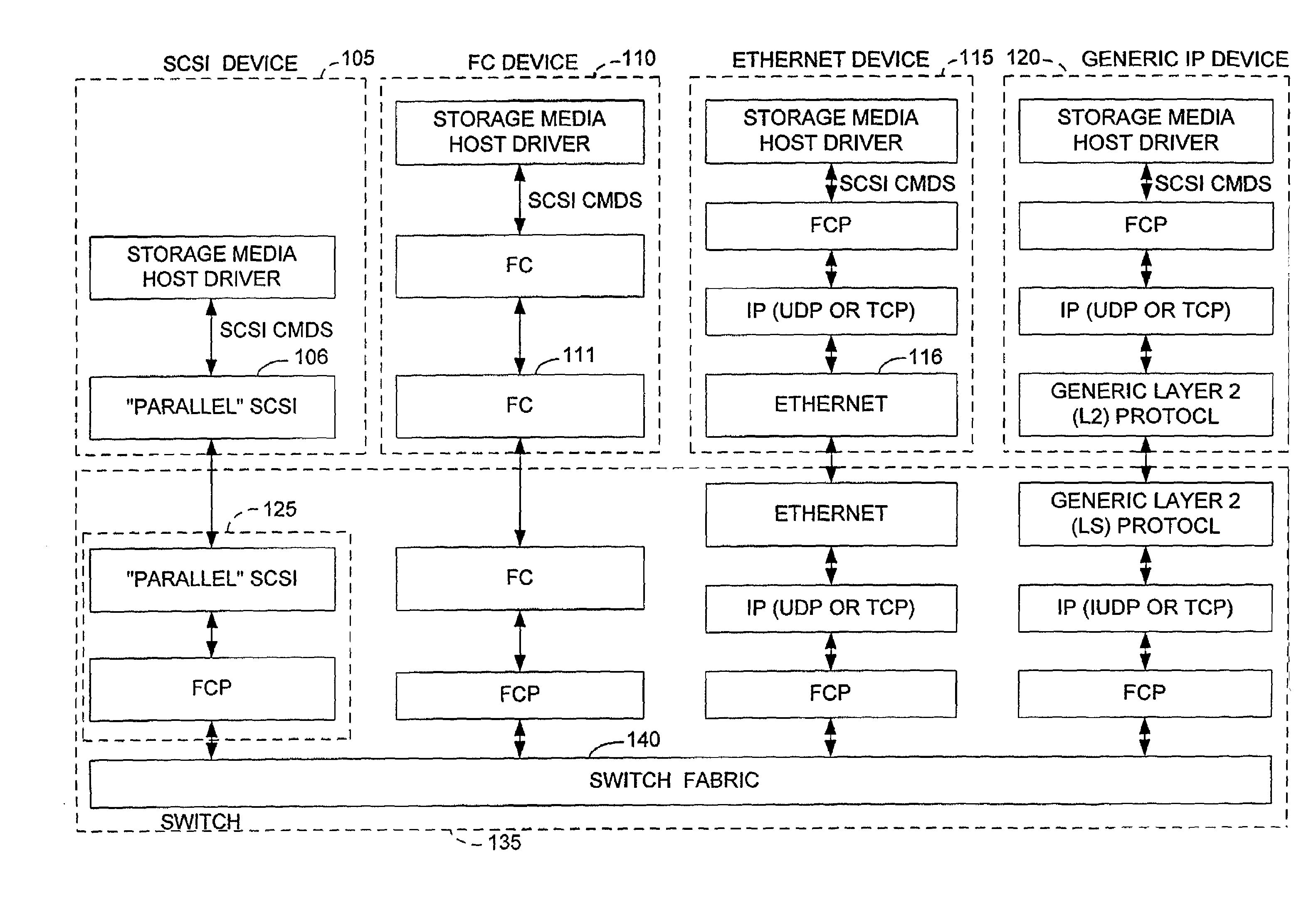
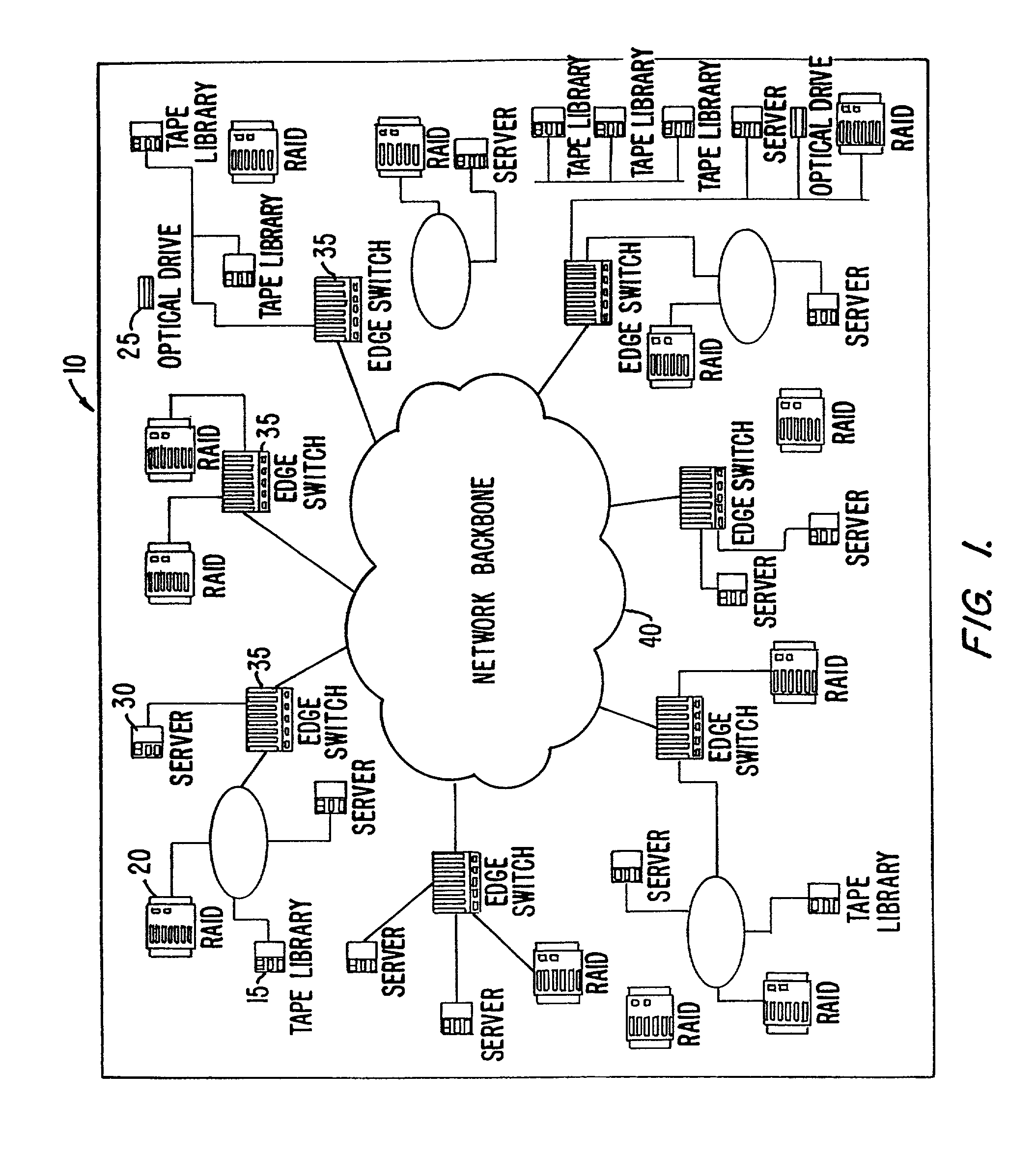
InactiveUS7197047B2Good conditionFast transferAnswer-back mechanismsTime-division multiplexSCSIFibre Channel
A method and apparatus for transferring data between IP devices (including, but not limited to, Gigabit Ethernet devices) and SCSI or Fibre Channel devices. The device interfaces may be either SCSI, Fibre Channel or IP interfaces such as Gigabit Ethernet. Data is switched between SCSI and IP, Fibre Channel and IP, or between SCSI and Fibre Channel. Data can also be switched from SCSI to SCSI, IP to IP and FC to FC. The port interfaces provide the conversion from the input frame format to an internal frame format, which can be routed within the apparatus. The amount of processing performed by each port interface is dependent on the interface type. The processing capabilities of the present invention permit rapid transfer of information packets between multiple interfaces at latency levels meeting the stringent requirements for storage protocols. The configuration control can be applied to each port on a switch and, in turn, each switch on the network, via an SNMP or Web-based interface, providing a flexible, programmable control for the apparatus.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
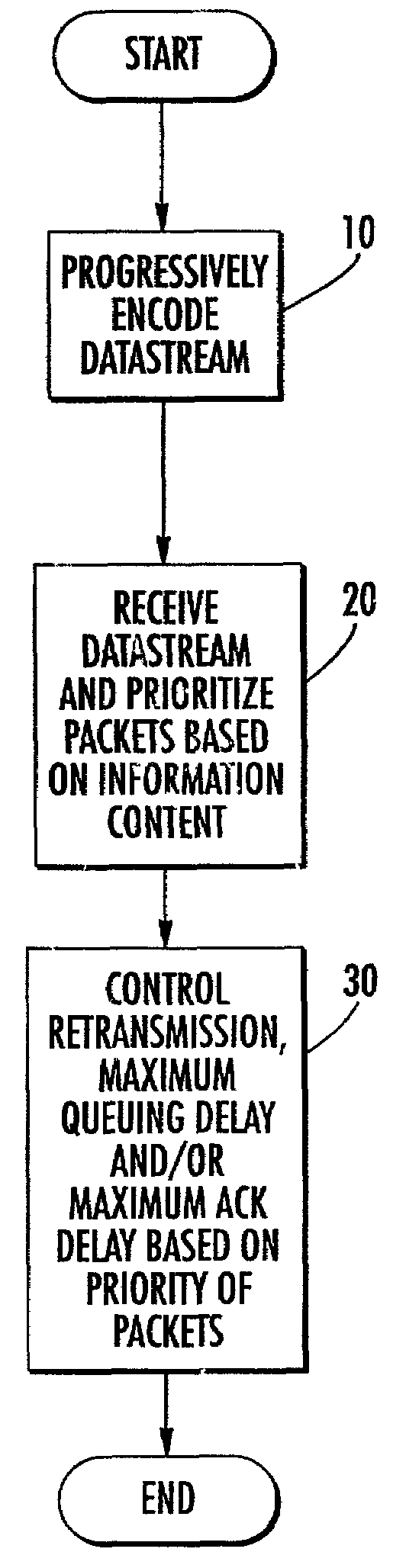
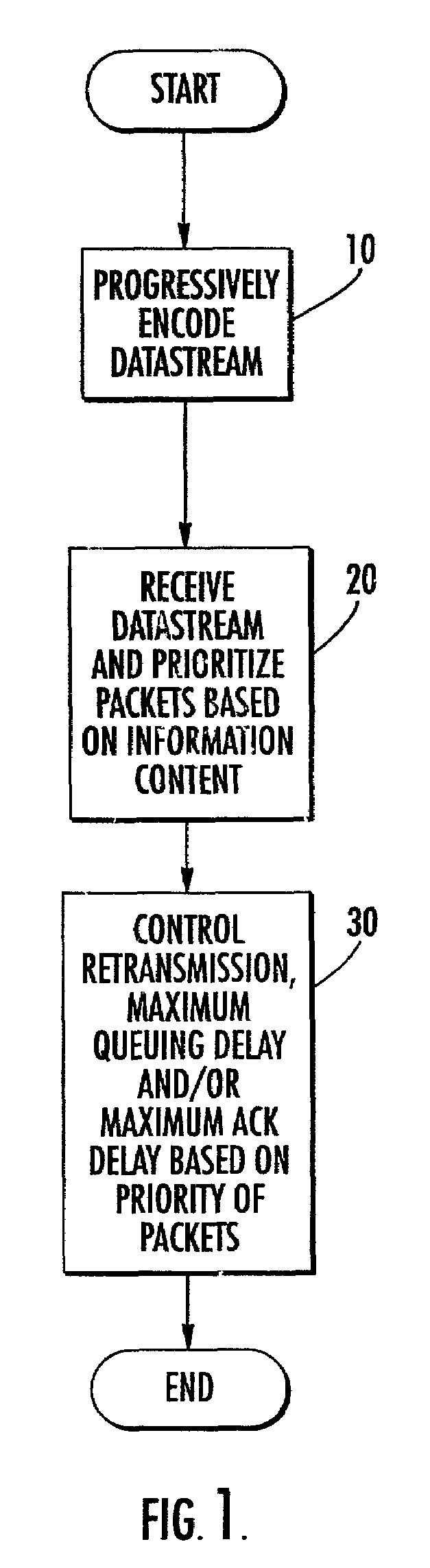
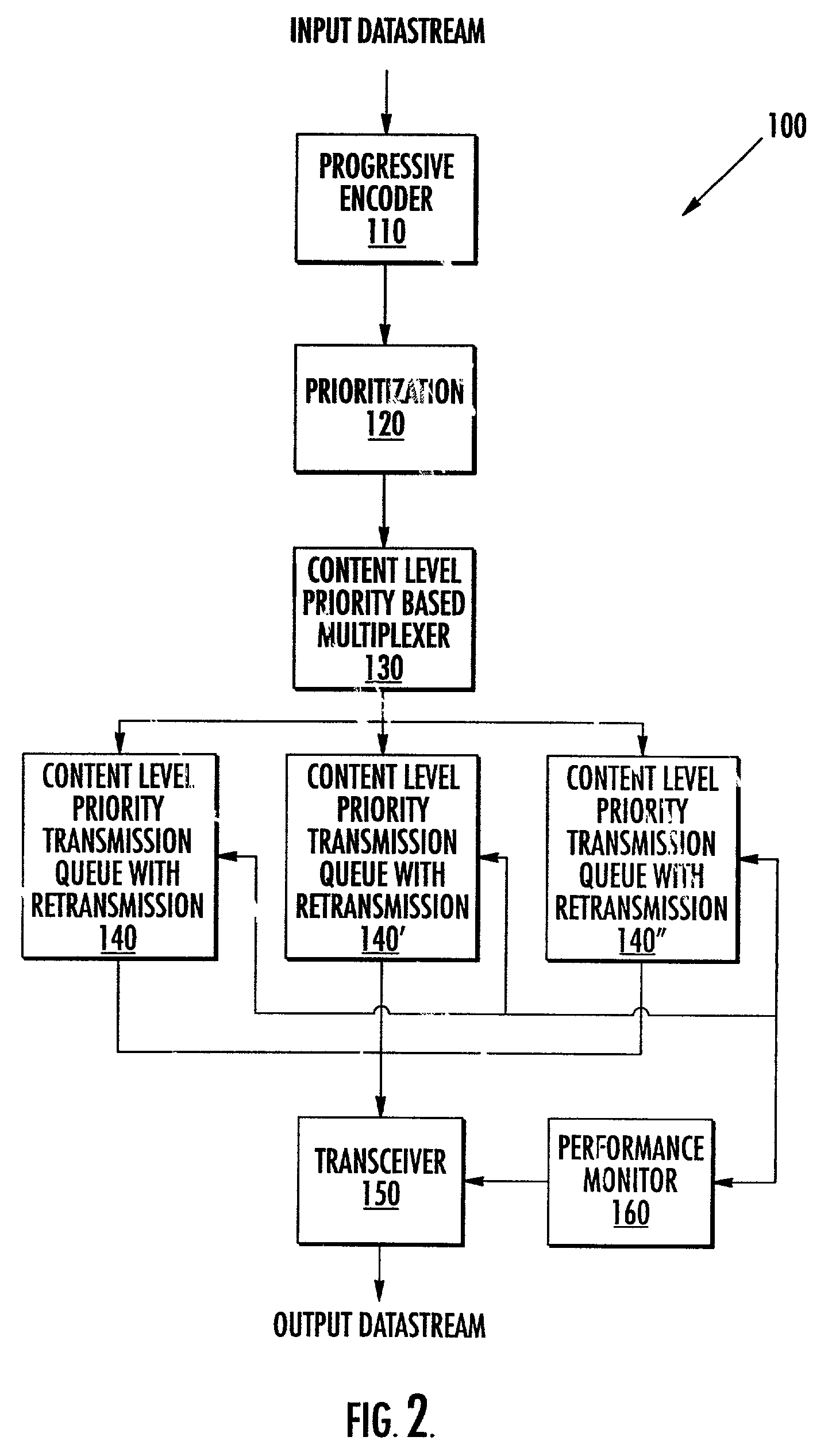
Methods and systems for provision of streaming data services in an internet protocol network
InactiveUS7194000B2Color television with pulse code modulationNetwork traffic/resource managementData processing systemStreaming data
Control of the transmission of streaming data between a first data processing system and a second data processing system in a packet network is provided. Priorities are assigned to packets of the streaming data based on characteristics of the packets of streaming data. Performance of transmission of the packets from the first data processing system to the second data processing system is monitored and retransmission of selected ones of the packets from the first data processing system to the second data processing system is terminated based on the assigned priority of the selected ones of the packets and the monitored performance of transmission. The streaming data may be progressively encoded. Furthermore, the priorities assigned to the packets of streaming data may be based on the level of progressive coding associated with a packet of data.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
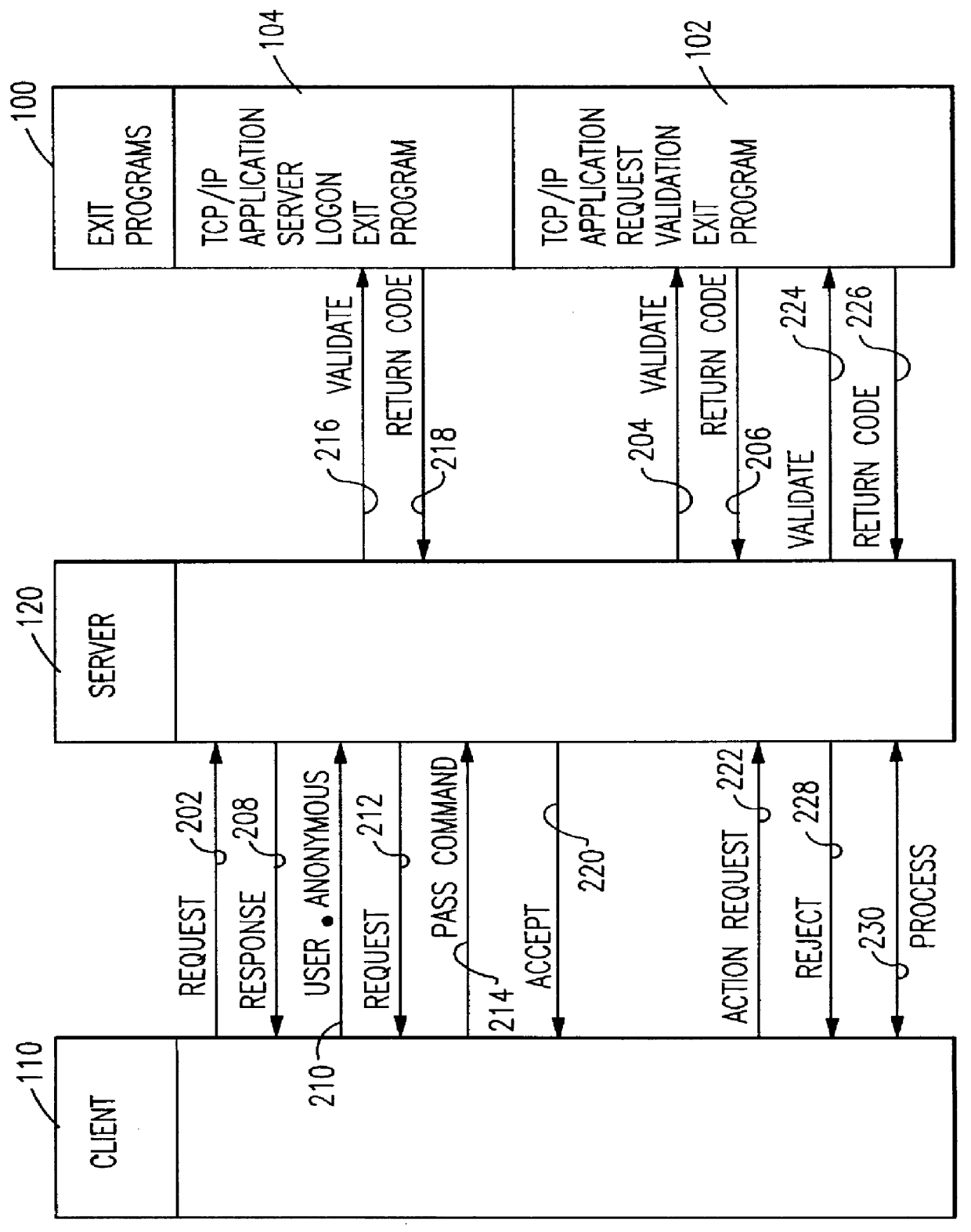
System and method for enabling and controlling anonymous file transfer protocol communications
InactiveUS6092198ADigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmission protocolNetwork addressing
Control of anonymous file transfer protocol server using exit programs: FTP and anonymous FTP communications are enabled and controlled by operating a server logon exit program to deny or authorize a logon request based on any combination of a user authentication string and / or client network address; and operating a request validation exit program to deny or authorize an action request based on any combination of type of request, user, client network address, and specific data requested.
Owner:IBM CORP
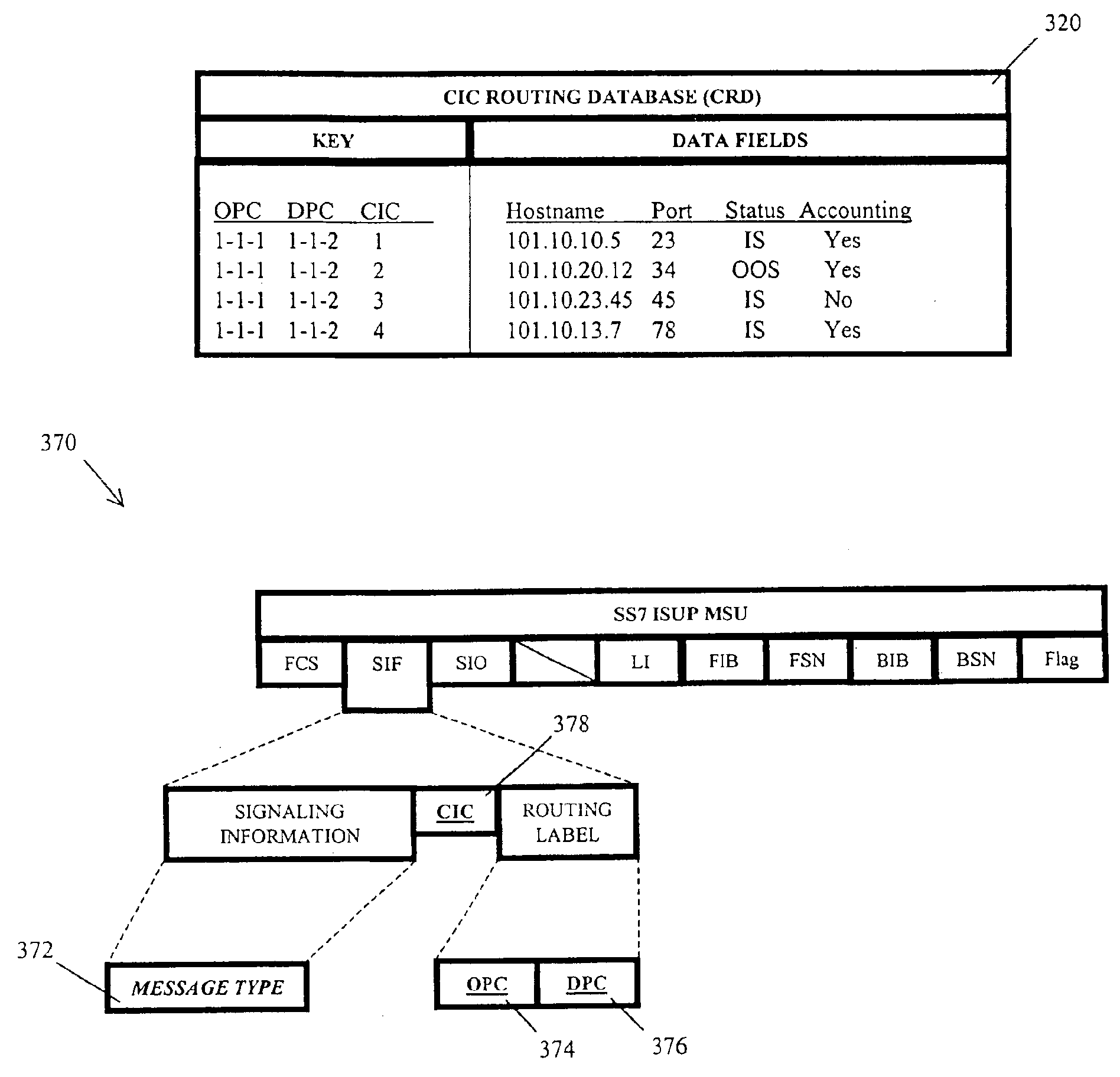
Methods and systems for routing signaling messages in a communications network using circuit identification code (CIC) information
InactiveUS6987781B1Easy to routeFacilitates setting up and tearing downInterconnection arrangementsError preventionCircuit identification codeCommunication link
A routing node for receiving, processing, and subsequently transmitting Signaling System 7 (SS7) signaling messages destined for a Media Gateway Controller (MGC) type network element is disclosed. A Circuit Identification Code (CIC) routing node is adapted to receive an ISUP message from an associated SS7 network and determine the routing destination of the message based, at least in part, on a CIC parameter value contained within the message. The ISUP message is subsequently encapsulated in an Internet Protocol (IP) envelope and transmitted to a destination node via an IP communication link. Such a CIC routing node also provides network service providers with a method of generally eliminating the need for the assignment of unique SS7 network point codes to each MGC node in a network. That is, a CIC routing node allows multiple MGC nodes to effectively correspond to a single SS7 network point code.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Network address translation based internet protocol mobility
InactiveUS6845094B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationInternet protocol suiteIp address
In an end to end fully internet protocol (IP) enabled network, a dynamic IP address space is used to address mobile hosts in order to facilitate mobility management. The network includes a wireless mobile network having a plurality of base stations each being associated with a portion of the dynamic IP address space. The base stations are operative to allocate dynamic IP addresses from the associated portion of the dynamic IP address space for each authenticated mobile host. Each of the base stations provides translation between the dynamic IP address space and a permanent IP address space so that the dynamic IP address space is transparent from the point of view of the mobile hosts. A gateway provides communicative coupling between the backbone of the wireless mobile network and a wire lined IP network. The gateway also provides translation between the dynamic IP address space and the permanent IP address space.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
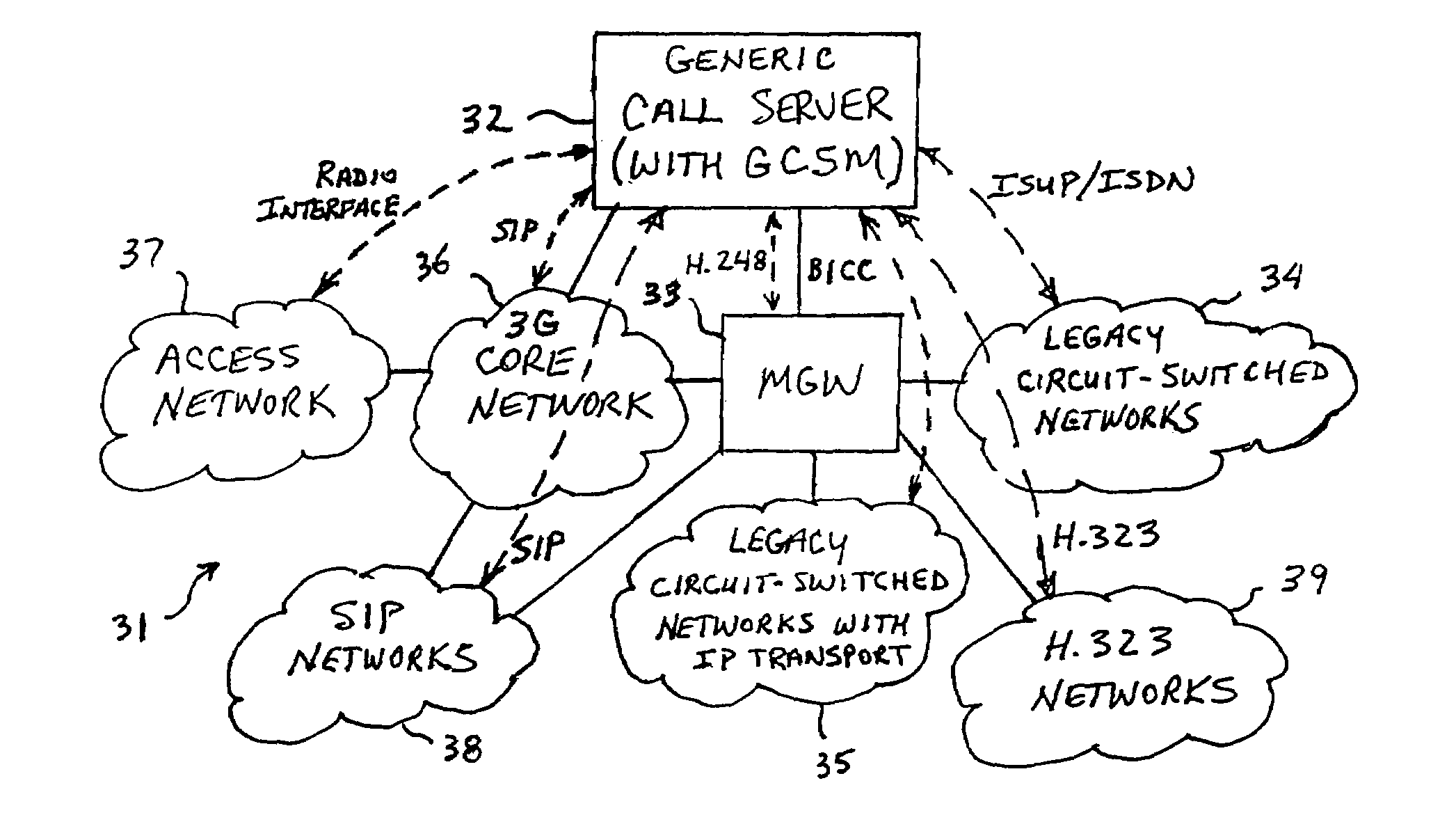
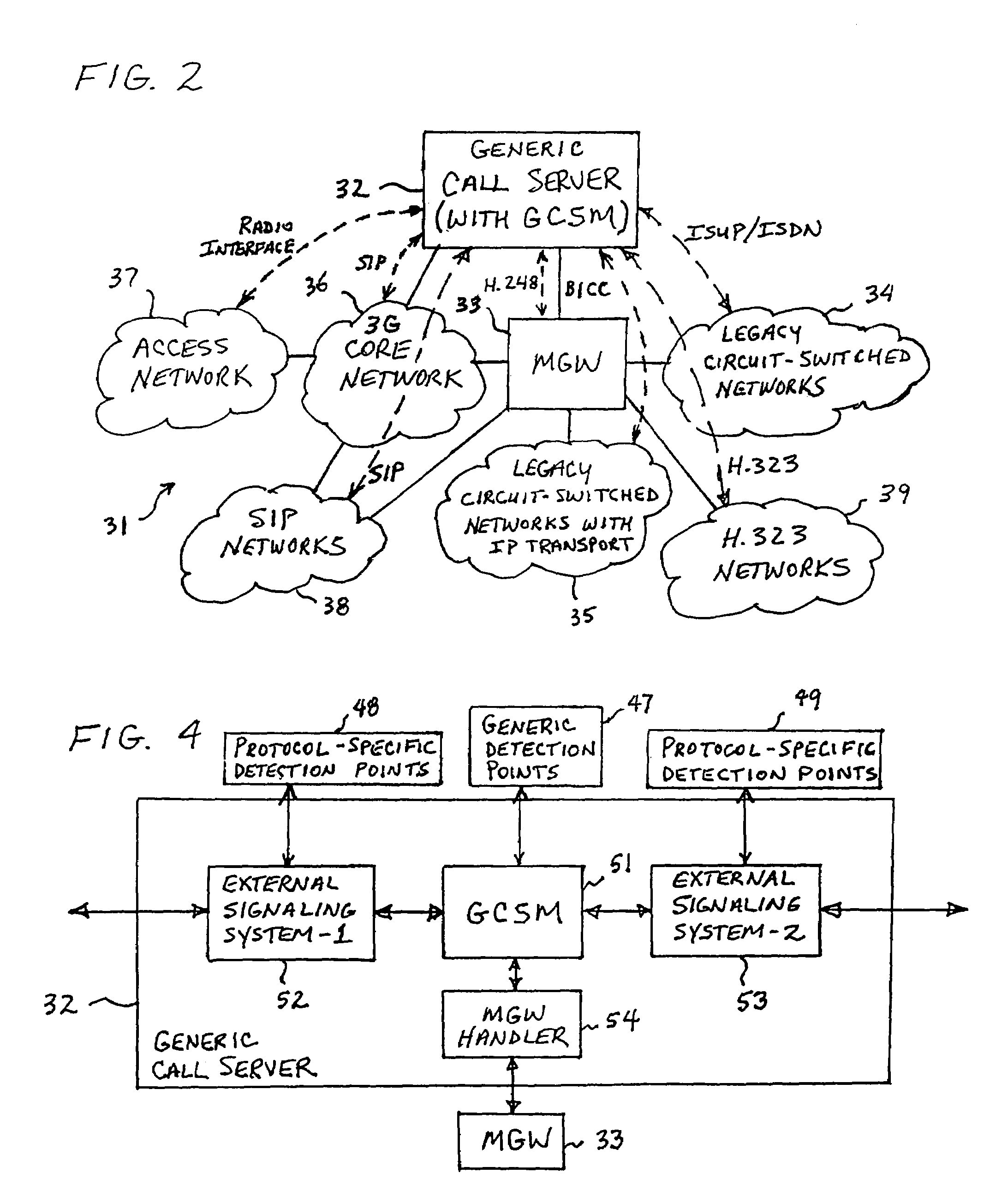
Generic call server and method of converting signaling protocols
InactiveUS6963583B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunications networkThird generation
A generic call server in a hybrid 2G / 3G telecommunications network having a plurality of network components that utilize a plurality of different signaling protocols. The call server performs call-control functions and interfaces between any two network components selected from the plurality of components. A Generic Call-control State Machine (GCSM) performs call-control functions that are common to all of the protocols. A plurality of external signaling systems interface between the GCSM and the network components and perform call-control functions that are specific to each protocol. The generic call server may also include a Media Gateway (MGW) Handler that acts as a media signaling protocol handling server and interfaces between the GCSM and a media gateway.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
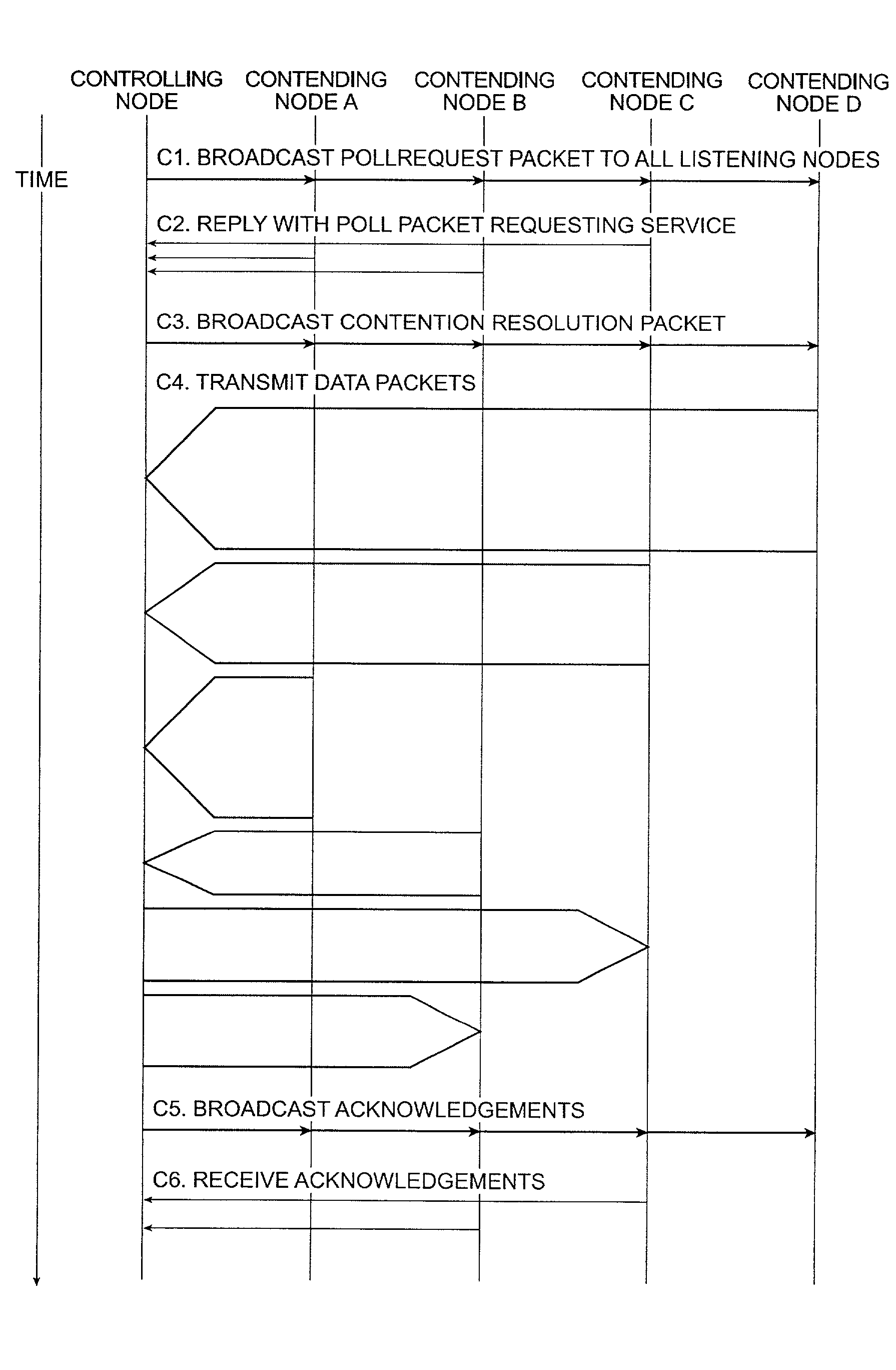
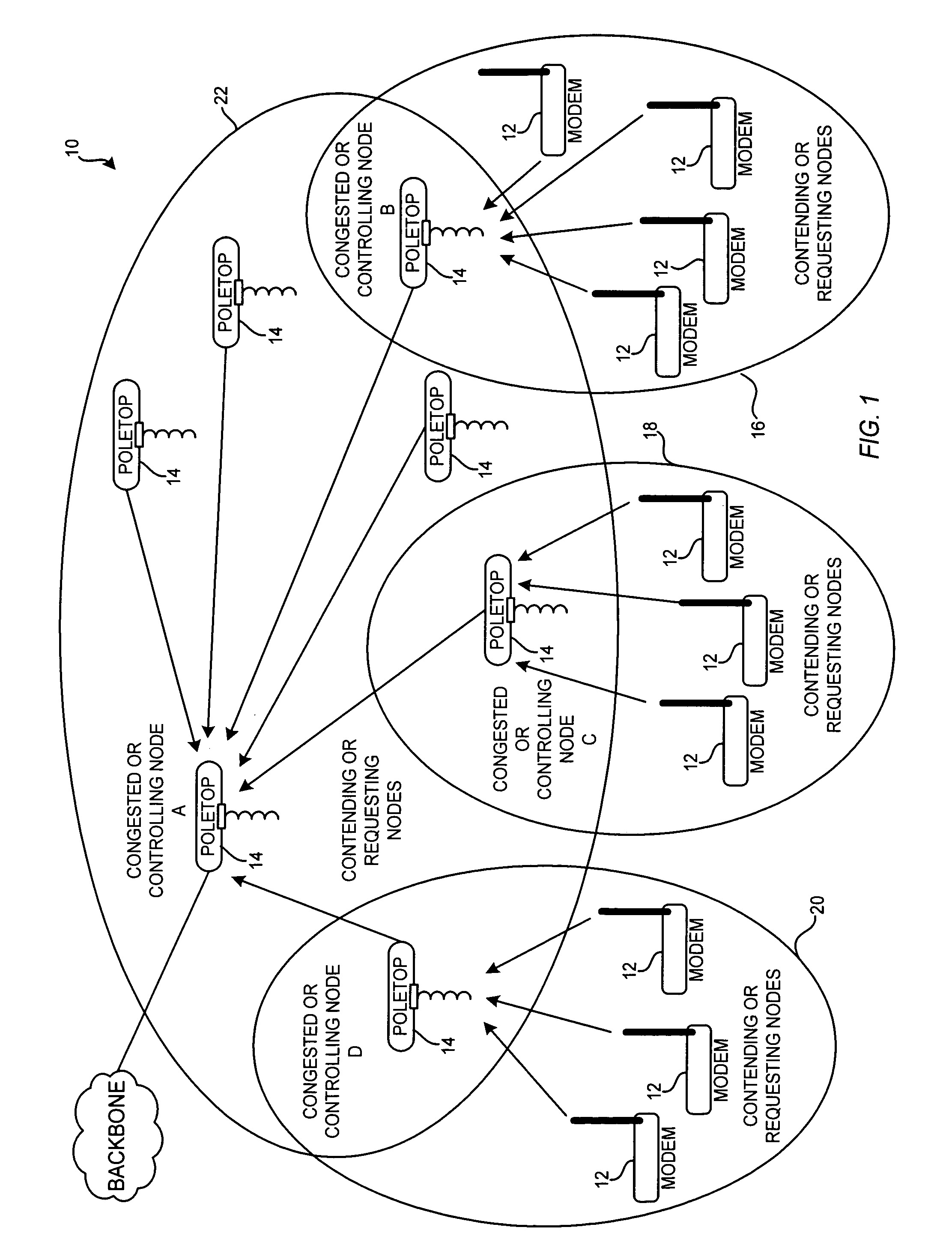
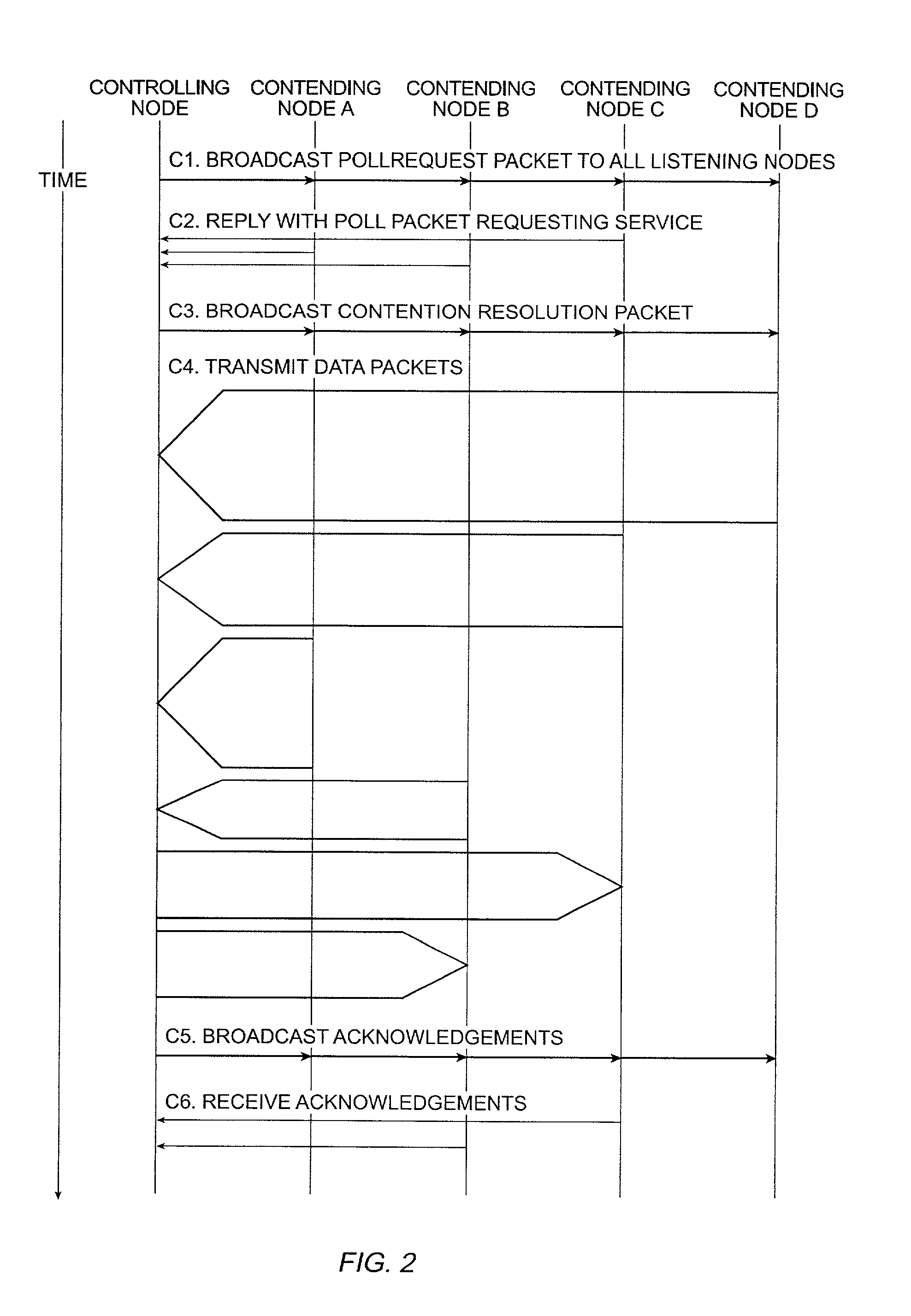
Method and apparatus for contention management in a radio-based packet network
ActiveUS6999441B2Efficiency advantageEfficiency fairnessError preventionTransmission systemsBroadcastingDistributed computing
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Residential gateway for ethernet based metro networks and a global hierarchical ethernet addressing system
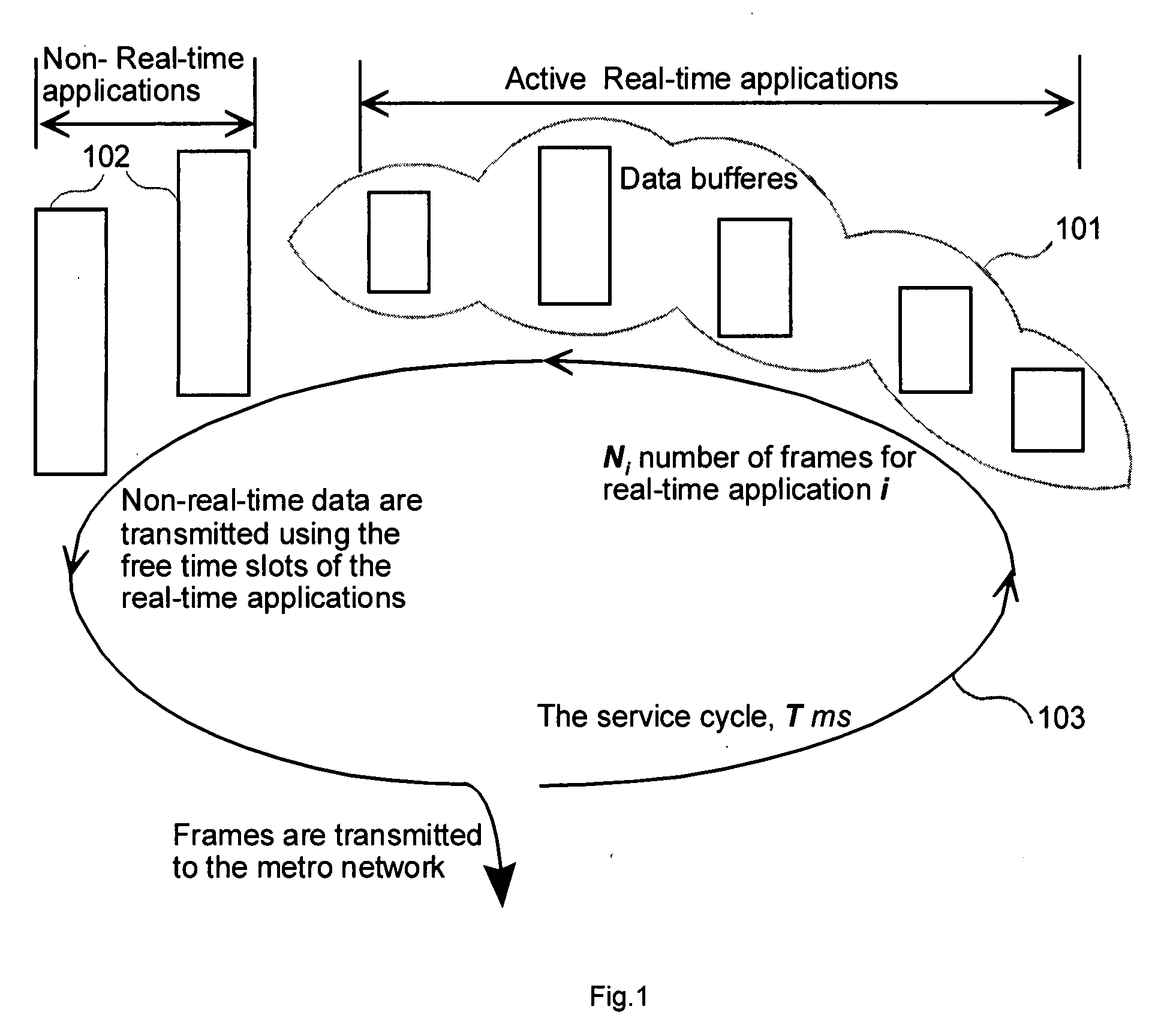
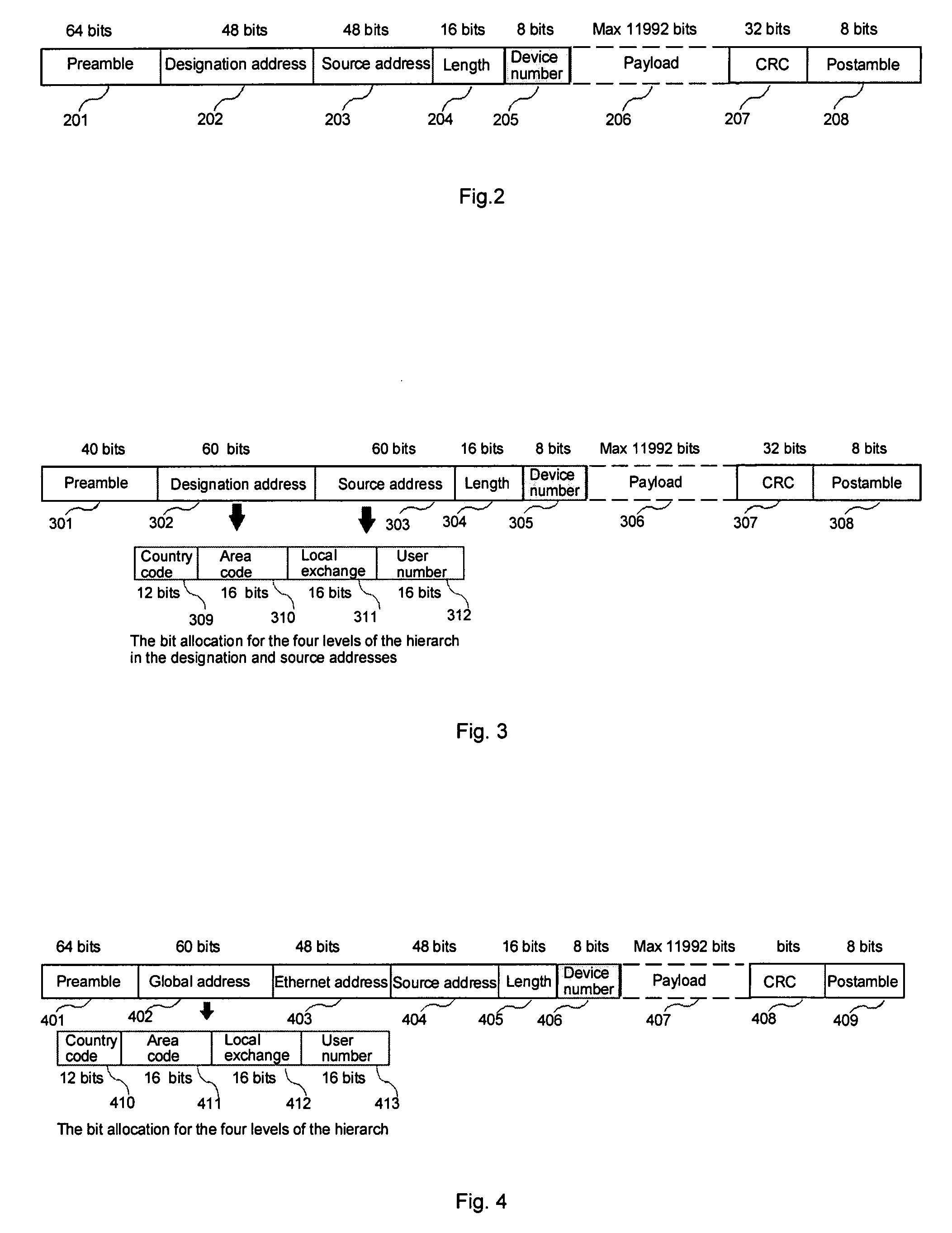
InactiveUS20080144642A1Eliminate requirementsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFiberAccess network
A residential gateway (RG) for distributing multimedia services to residential and business premises is disclosed. The RG connects multiple communication devices, such as TVs, telephones, computers, security cameras, and utility billing devices, to an Ethernet based metro / access network through either an optic fiber or a coaxial cable. The RG multiplexes upstream data from various communication devices into Ethernet frames according to the said Fixed-bandwidth Multimedia to Ethernet (FibME) protocol, and transmit the Ethernet frames through the link between the RG and the metro network. The RG also distributes the downstream data from the metro network to their corresponding destination devices in real time, also according to the said FibME protocol. The default bandwidth between the residential premise and the metro network is 100 Mbps full duplex. One Gbps or ten Gbps can be implemented based on the same FibME protocol for business applications. A Global Ethernet Addressing System (Global-HEAS) which will simplify the switch for the Ethernet systems is also disclosed.
Owner:SONG SHAOWEN
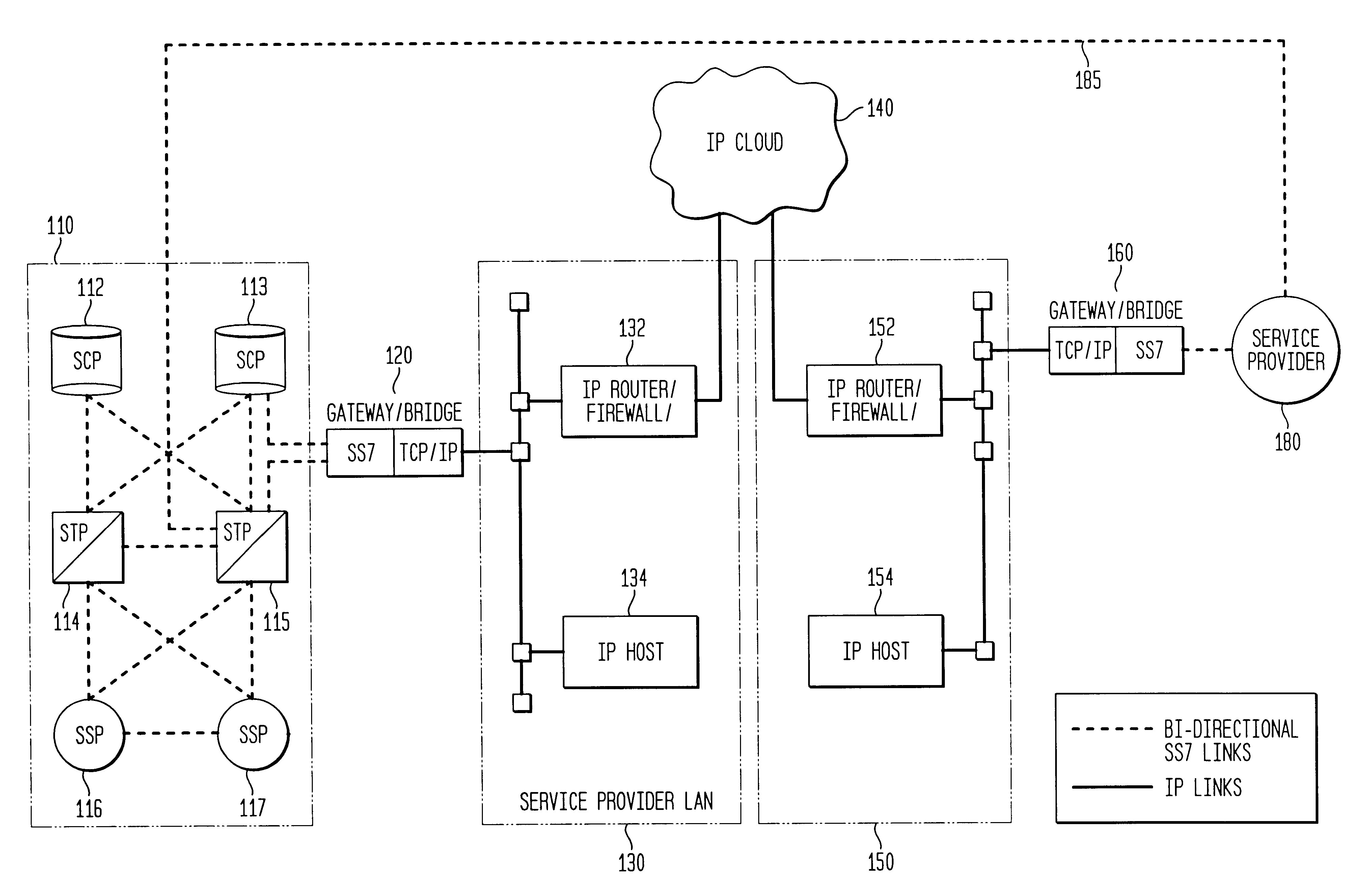
Intelligent network signaling using an open system protocol
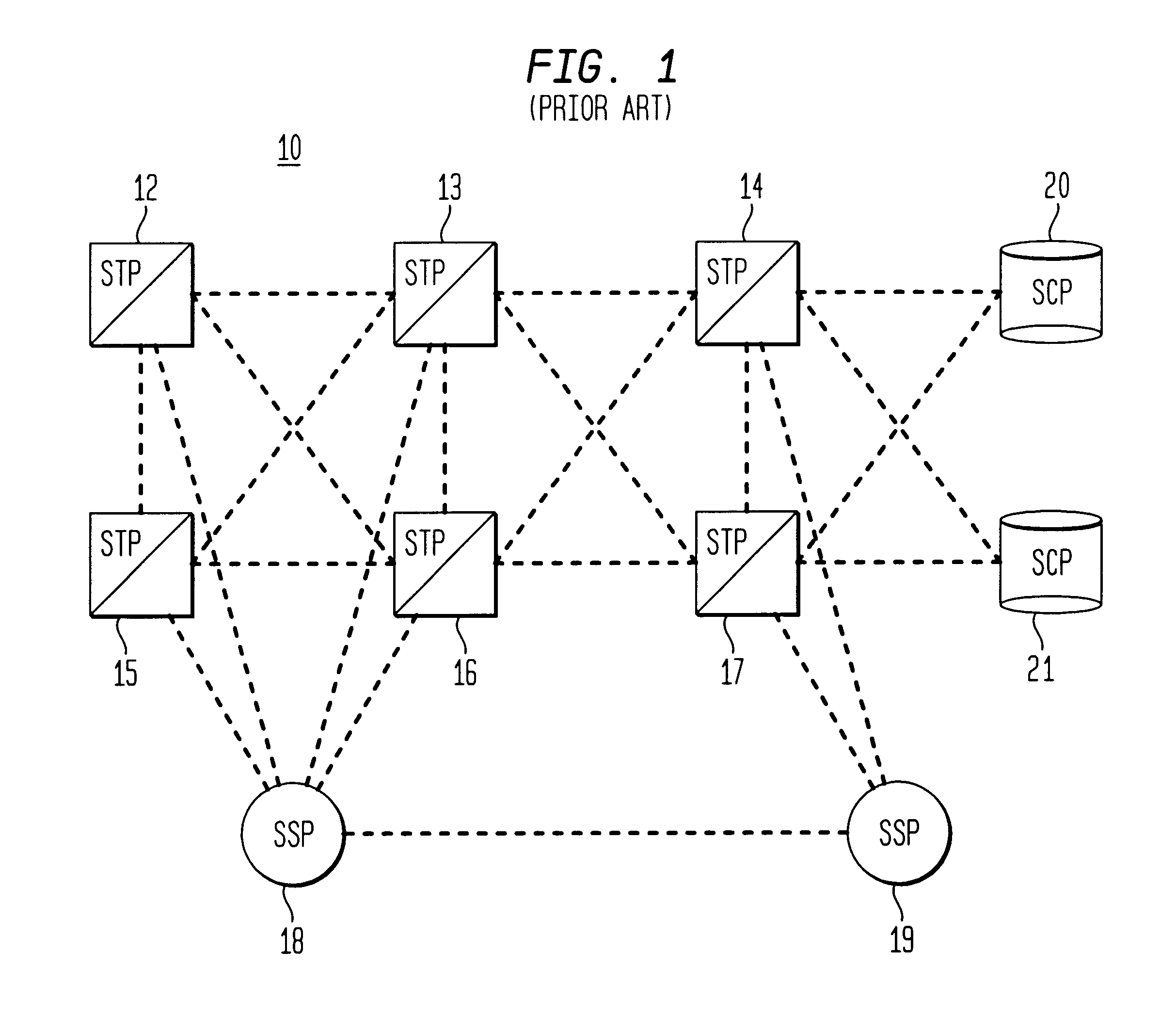
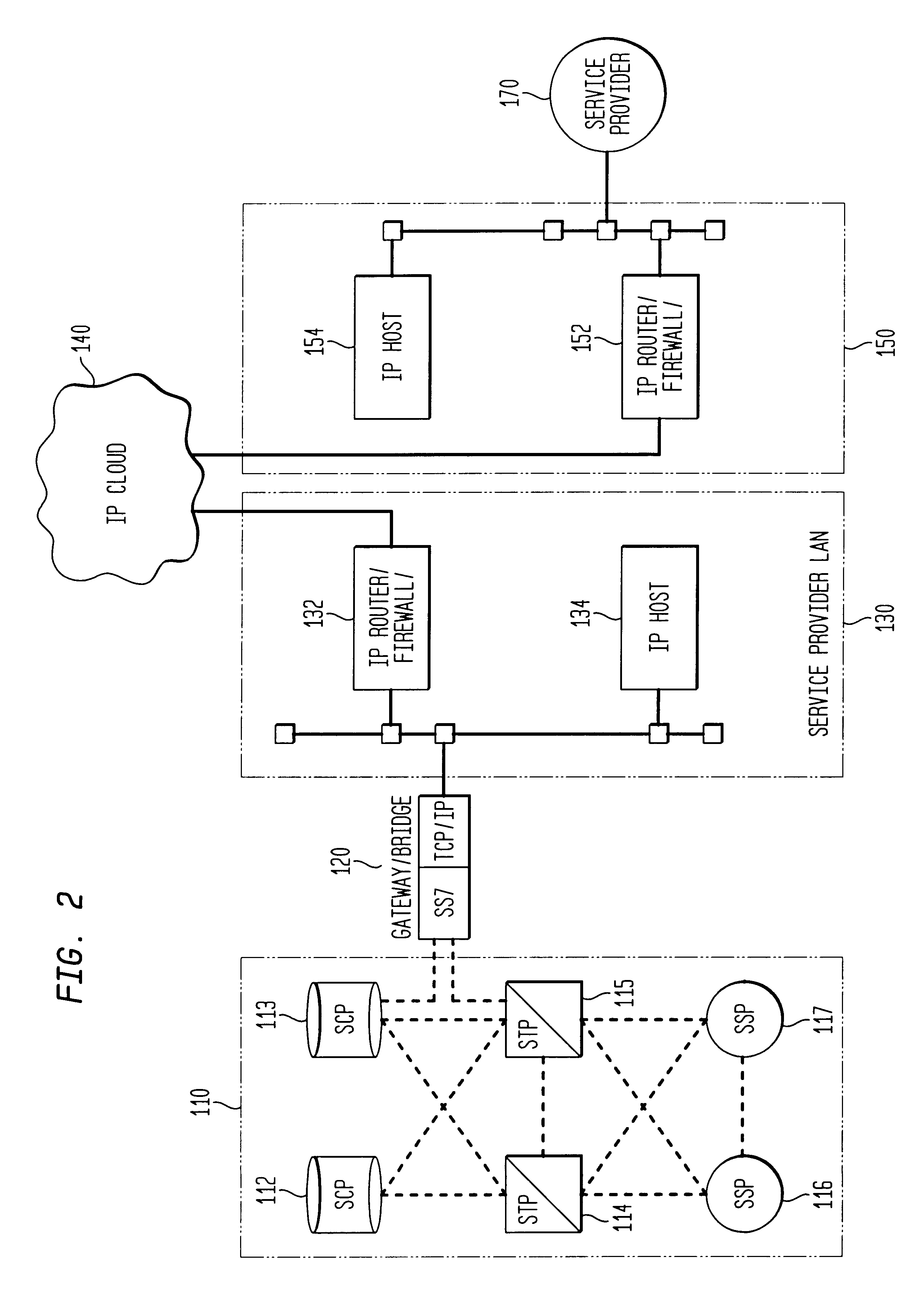
InactiveUS6782004B1Time-division multiplexNetwork connectionsIntelligent NetworkCommunications system
A communication system utilizes an open system network protocol, such as the Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP / IP), to transport Intelligent Network signaling messages from an SS7 network to a service provider which is not directly linked to the SS7 network. A gateway / bridge is provided between the SS7 network and a network which operates in accordance with an Internet protocol to transform Internet protocol messages, such as TCP / IP format messages, into SS7 format, and vice versa. In this way, an Internet protocol network may be used to transport Intelligent Network signaling messages between an SS7 network and a non-SS7 network service provider.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com