Patents
Literature
547 results about "Virtual circuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
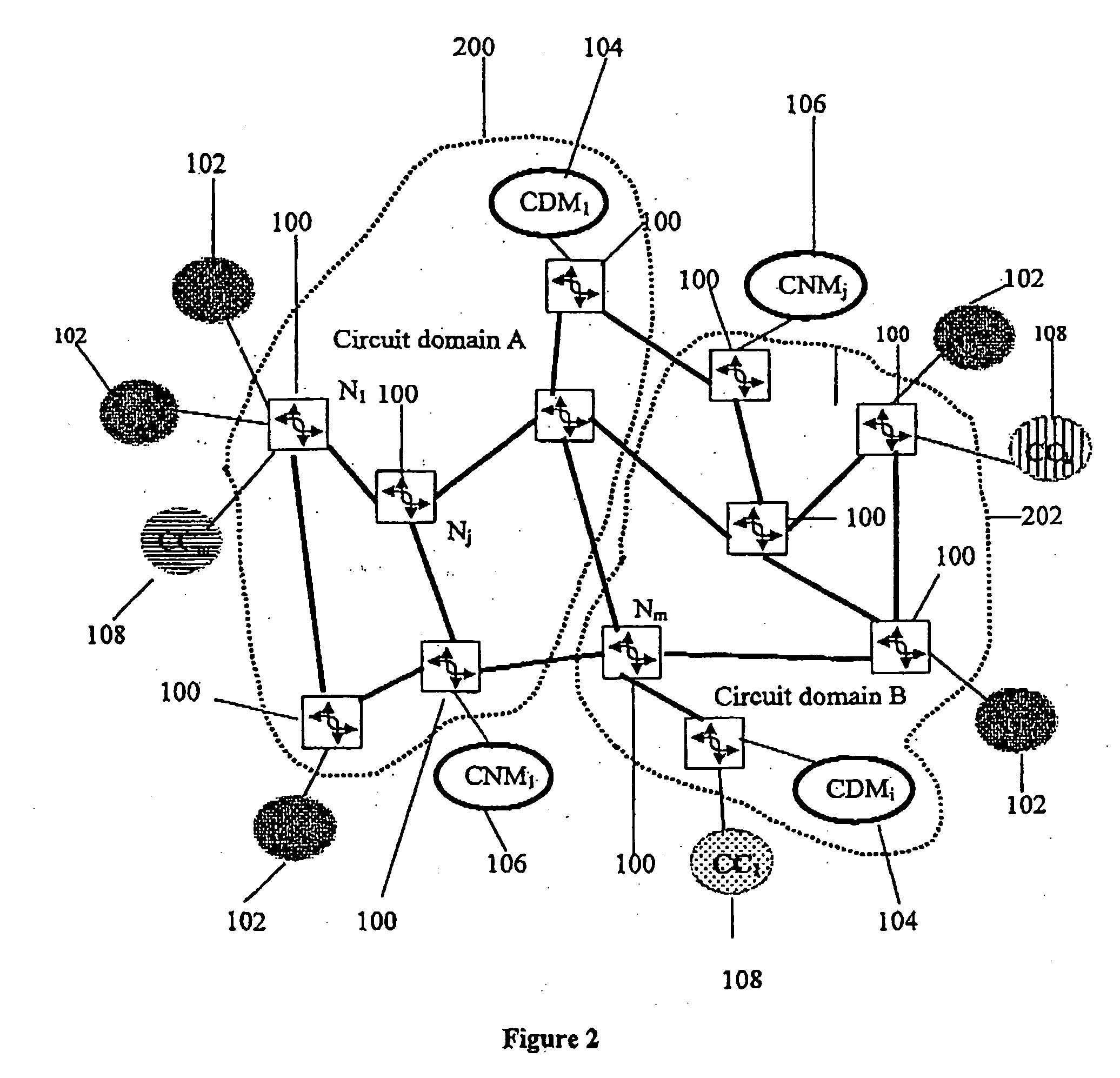
A virtual circuit (VC) is a means of transporting data over a packet switched computer network in such a way that it appears as though there is a dedicated physical layer link between the source and destination end systems of this data. The term virtual circuit is synonymous with virtual connection and virtual channel. Before a connection or virtual circuit may be used, it has to be established, between two or more nodes or software applications, by configuring the relevant parts of the interconnecting network. After that, a bit stream or byte stream may be delivered between the nodes; hence, a virtual circuit protocol allows higher level protocols to avoid dealing with the division of data into segments, packets, or frames.
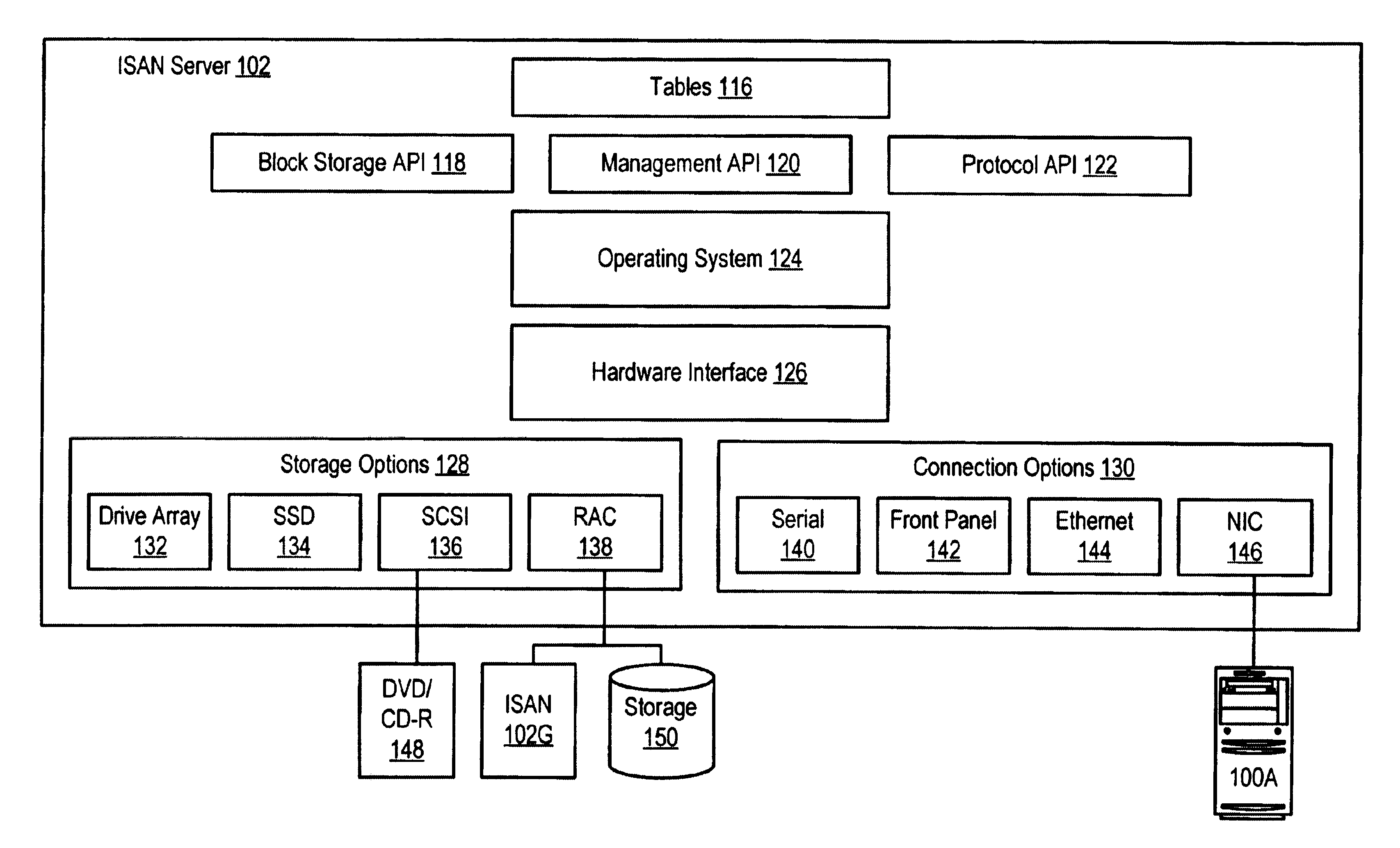
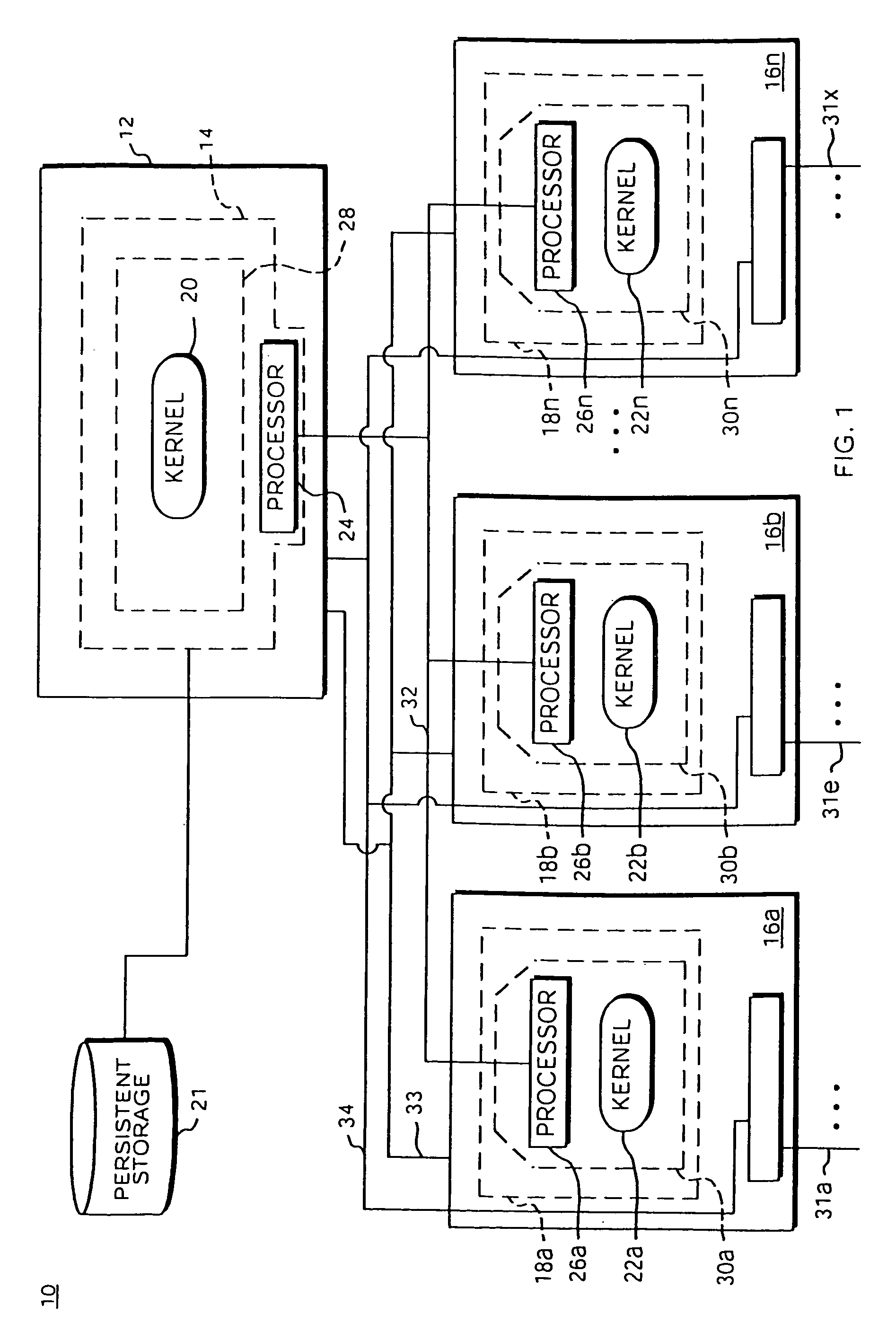
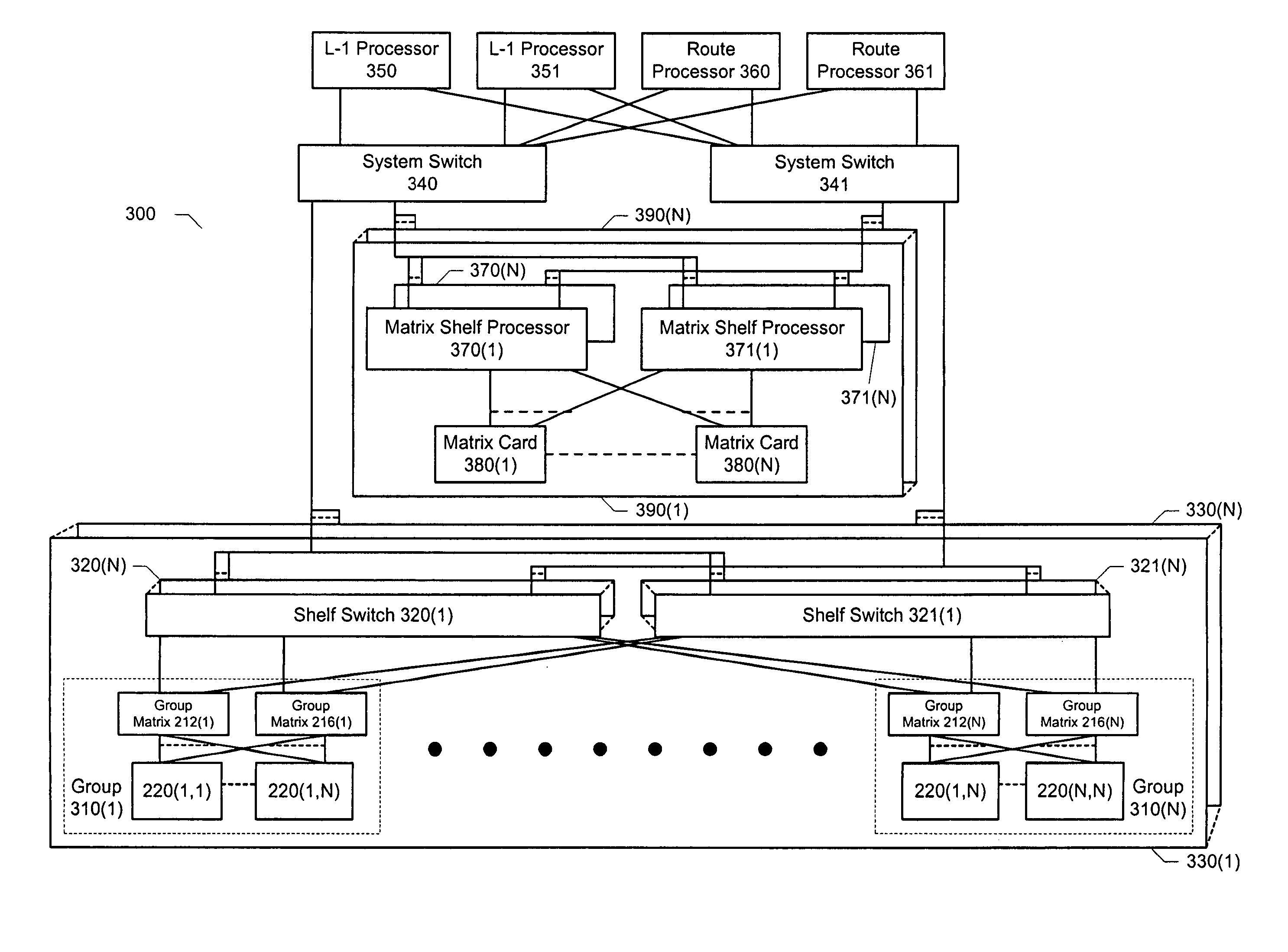
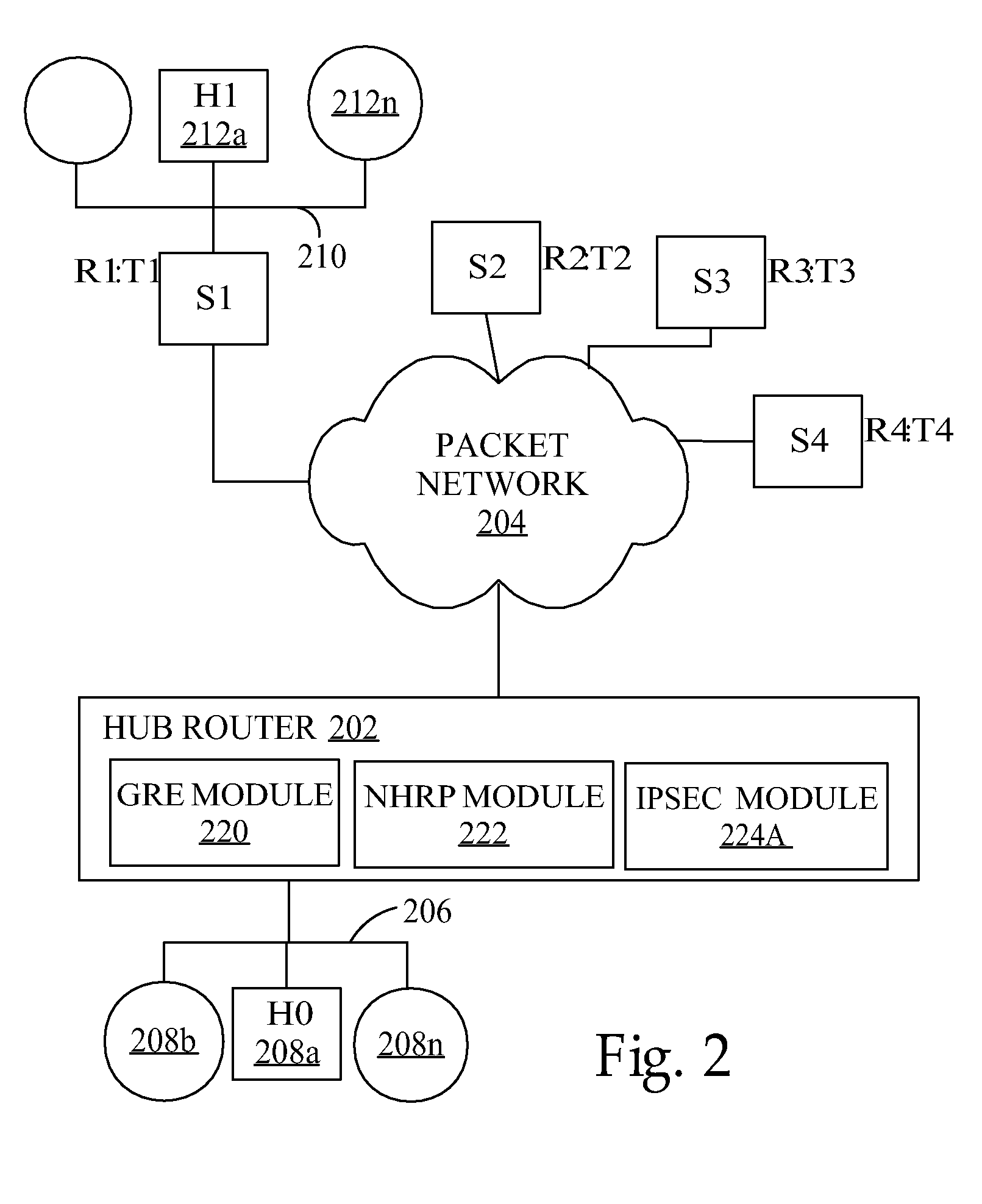
Method for configuration and management of storage resources in a storage network
InactiveUS6640278B1Improve performanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsCommunication interfaceStorage area network
A storage domain management system supports storage domains. The storage server includes a plurality of communication interfaces. A first set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to all kinds of users of data. A second set of communication interfaces in the plurality is adapted for connection to respective devices in a pool of storage devices for use in a storage domain. Data processing resources in the server are coupled to the plurality of communication interfaces for transferring data among the interfaces. The data processing resources comprise a plurality of driver modules and configurable logic linking driver modules into data paths. Each configured data path acts as a virtual circuit that includes a set of driver modules selected from the plurality of driver modules. A data storage transaction which is received at a communication interface is mapped to one of the configured data paths. A display and a user input device are included with data processing structures to manage images displayed on the display.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
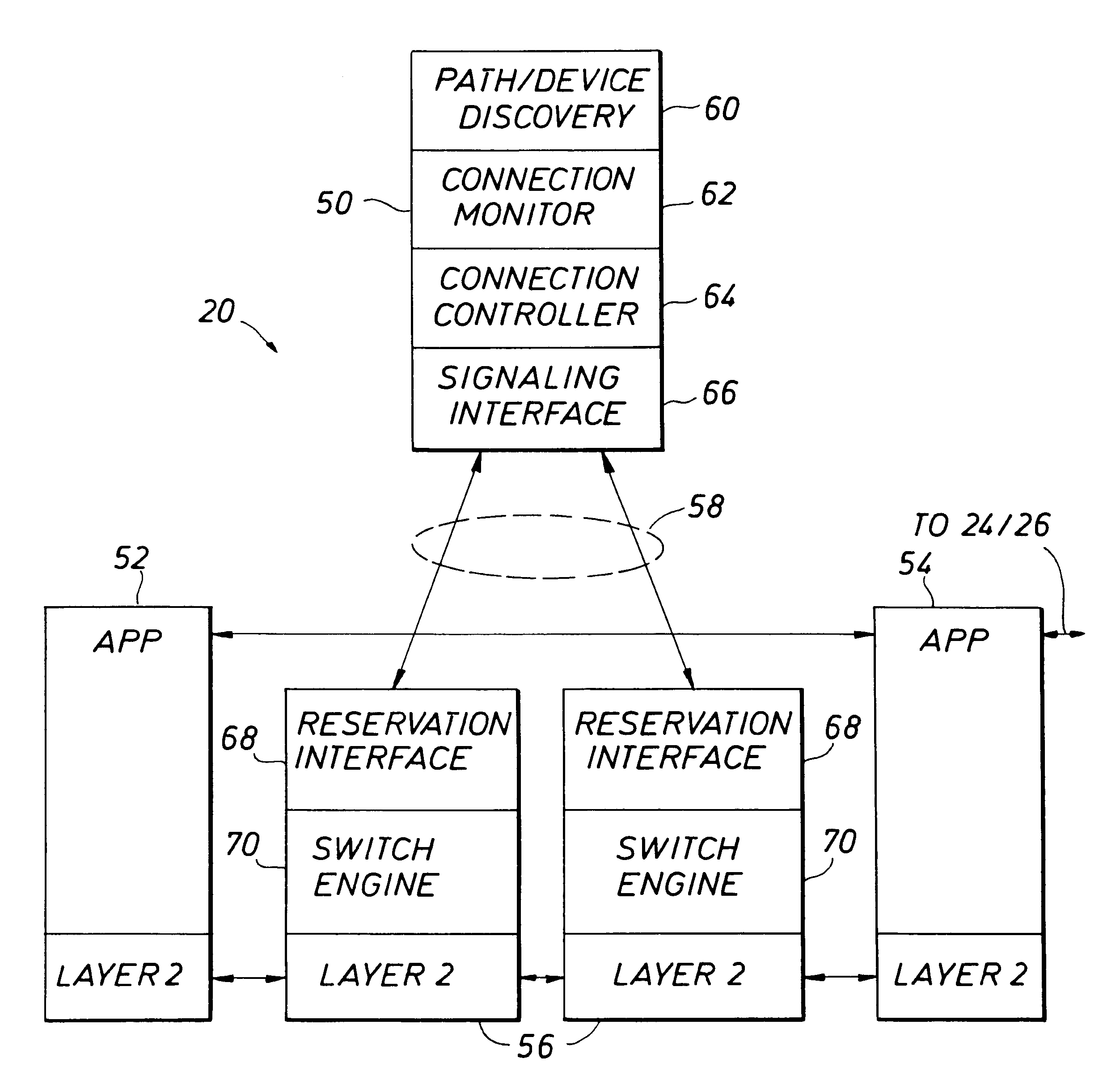
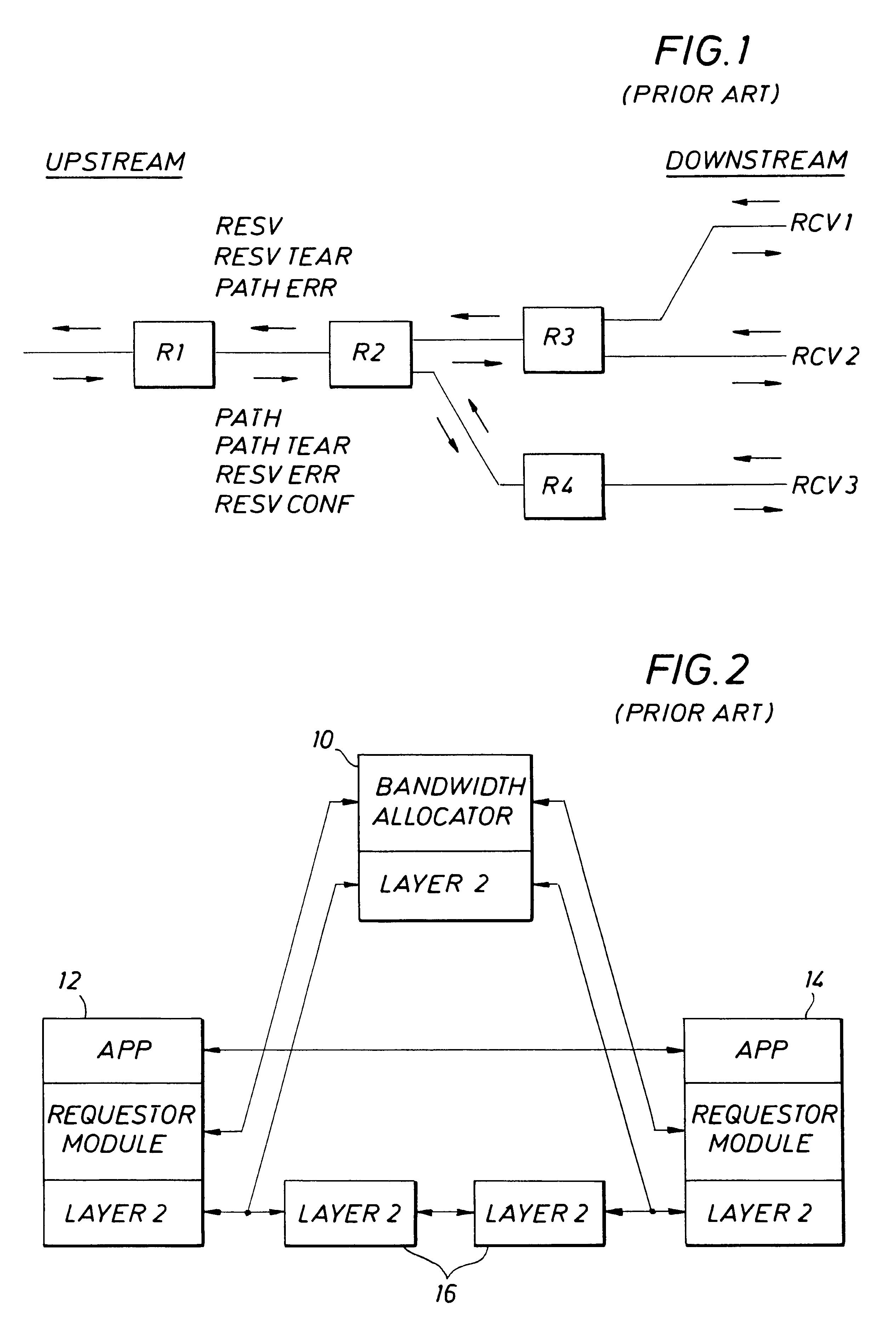
Method and apparatus for providing guaranteed quality/class of service within and across networks using existing reservation protocols and frame formats
InactiveUS6563793B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAssurance qualityClass of service
A method and apparatus provide reserved bandwidth and QOS / COS virtual circuit connections in a network using both conventional and novel reservation protocols and frame formats. An apparatus according to the invention includes an enterprise control point that communicates with switches via a reserved signaling channel. The switches have been upgraded or replaced to include enhanced functionality. The enhanced switches detect packets that include requests for reserved connections according to existing reservation protocols such as RSVP and IEEE 802.1P / Q. Such detected packets are forwarded to the enterprise control point for processing via a reserved signaling channel. The enterprise control point identifies a path within the network that can satisfy the requested QOS / COS and reserves the requested resources all along the path from beginning to end. A method according to the invention includes detecting packets that include requests for reserved connections according to existing reservation protocols such as RSVP and IEEE 802.1P / Q, forwarding detected packets to an enterprise control point for processing via a reserved signaling channel, identifying a path within the network that can satisfy the requested QOS / COS and reserving the requested resources all along the path from beginning to end.
Owner:WARPSPEED COMM
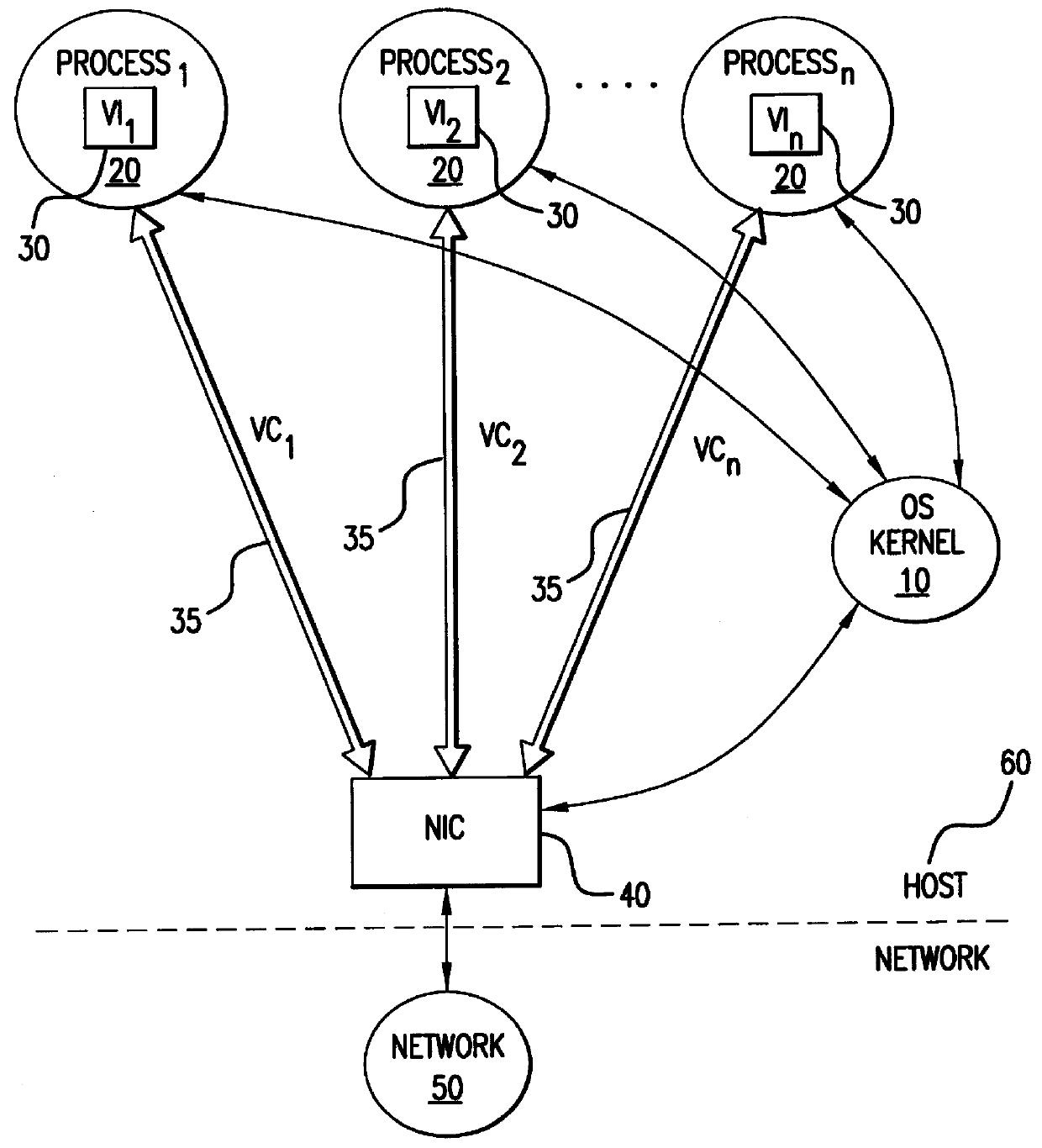
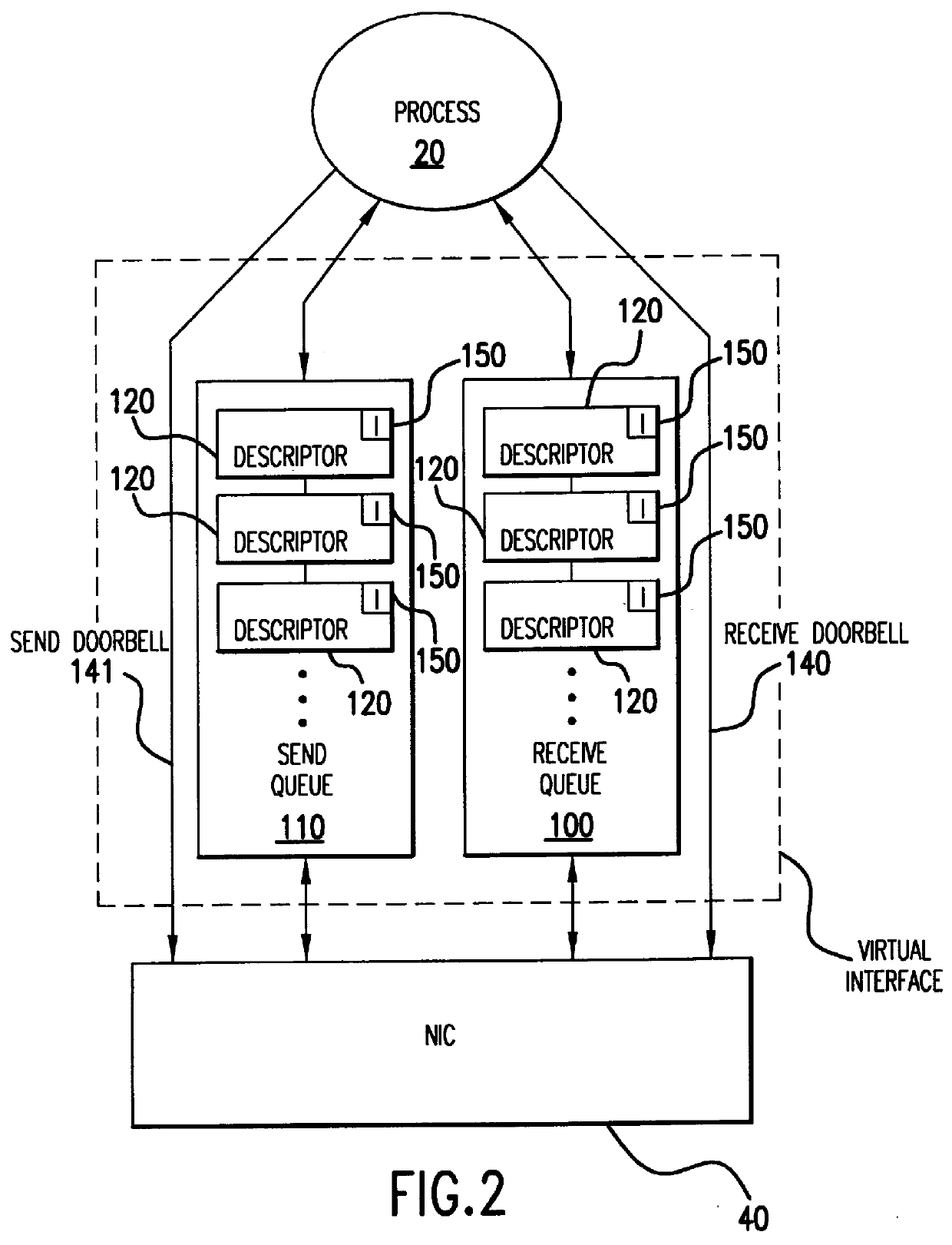
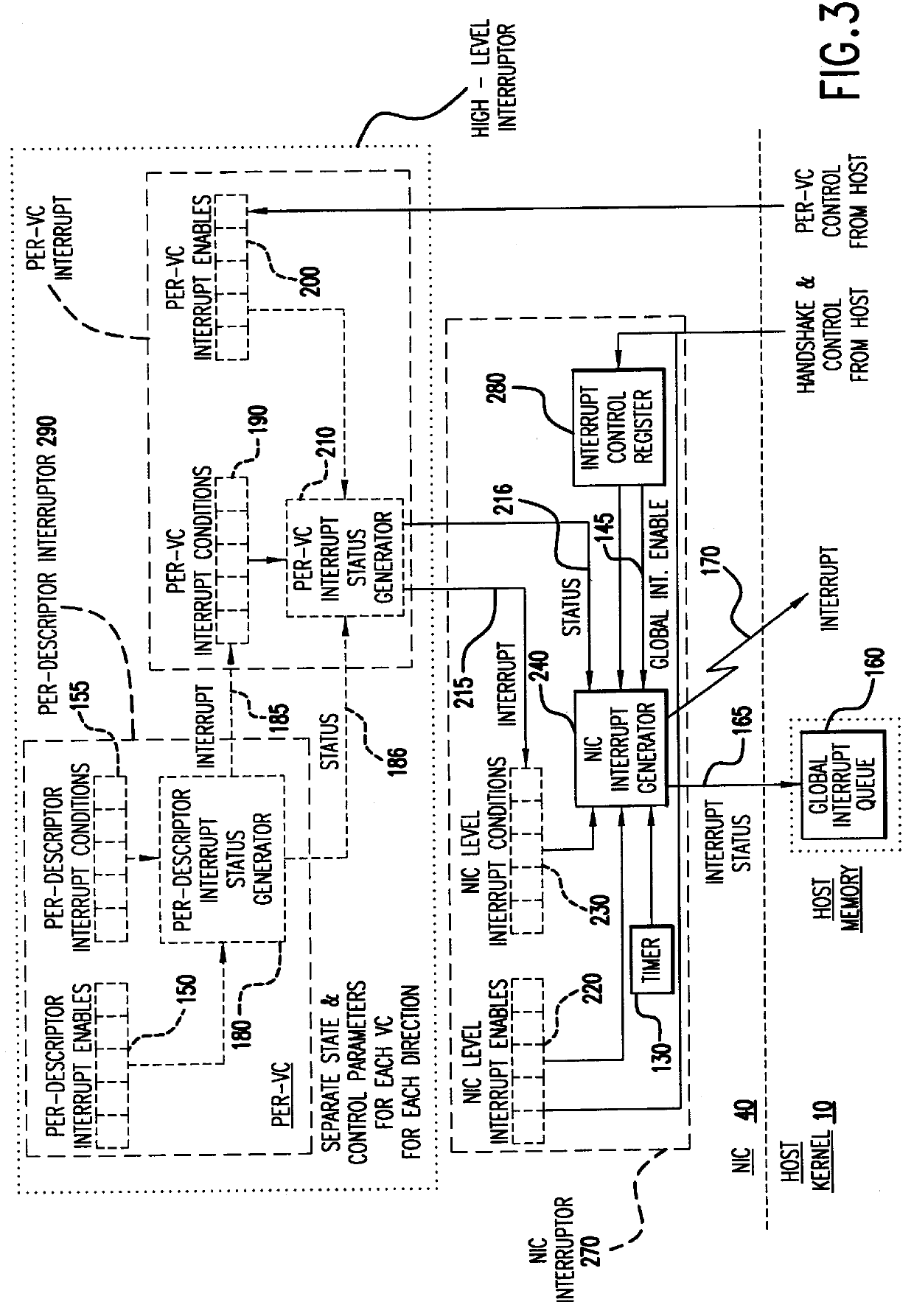
Hierarchical interrupt structure for event notification on multi-virtual circuit network interface controller
Methods and apparatus process a plurality of interrupt status words from a network interface controller (NIC) to a plurality of processes. A first per-virtual circuit interrupt status word and a second per-virtual circuit interrupt status word can be sent by a per-virtual circuit interrupter having a per-virtual circuit interrupt output. A NIC interrupter can be in communication with the per-virtual circuit interrupt output and have a NIC interrupt output to send a first NIC interrupt status word and a second NIC interrupt status word to a global interrupt queue of a host system. The NIC interrupter can generate an interrupt signal to the host system, and a proxy interrupt handler of the host system can be in communication with the NIC interrupter. The proxy interrupt handler can awaken at least in part in response to the interrupt signal, and read the first NIC interrupt status word and the second NIC interrupt status word from the global interrupt queue, wake the first process and the second process, and send the first NIC interrupt status word to the first process and the second NIC interrupt status word to the second process.
Owner:INTEL CORP
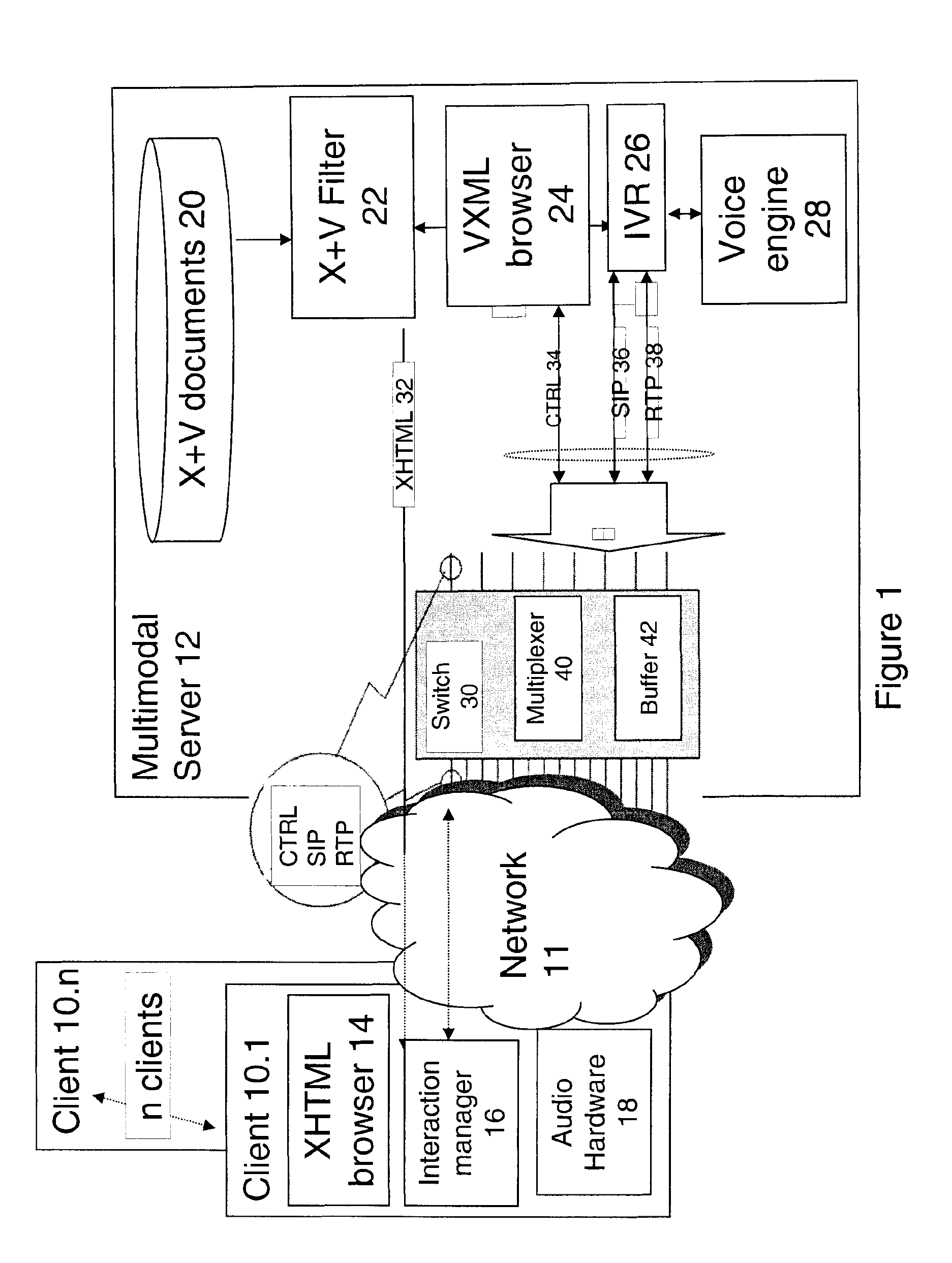
Method and Apparatus For Multimodal Voice and Web Services
InactiveUS20090144428A1No setup overheadReduce latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexerWeb service
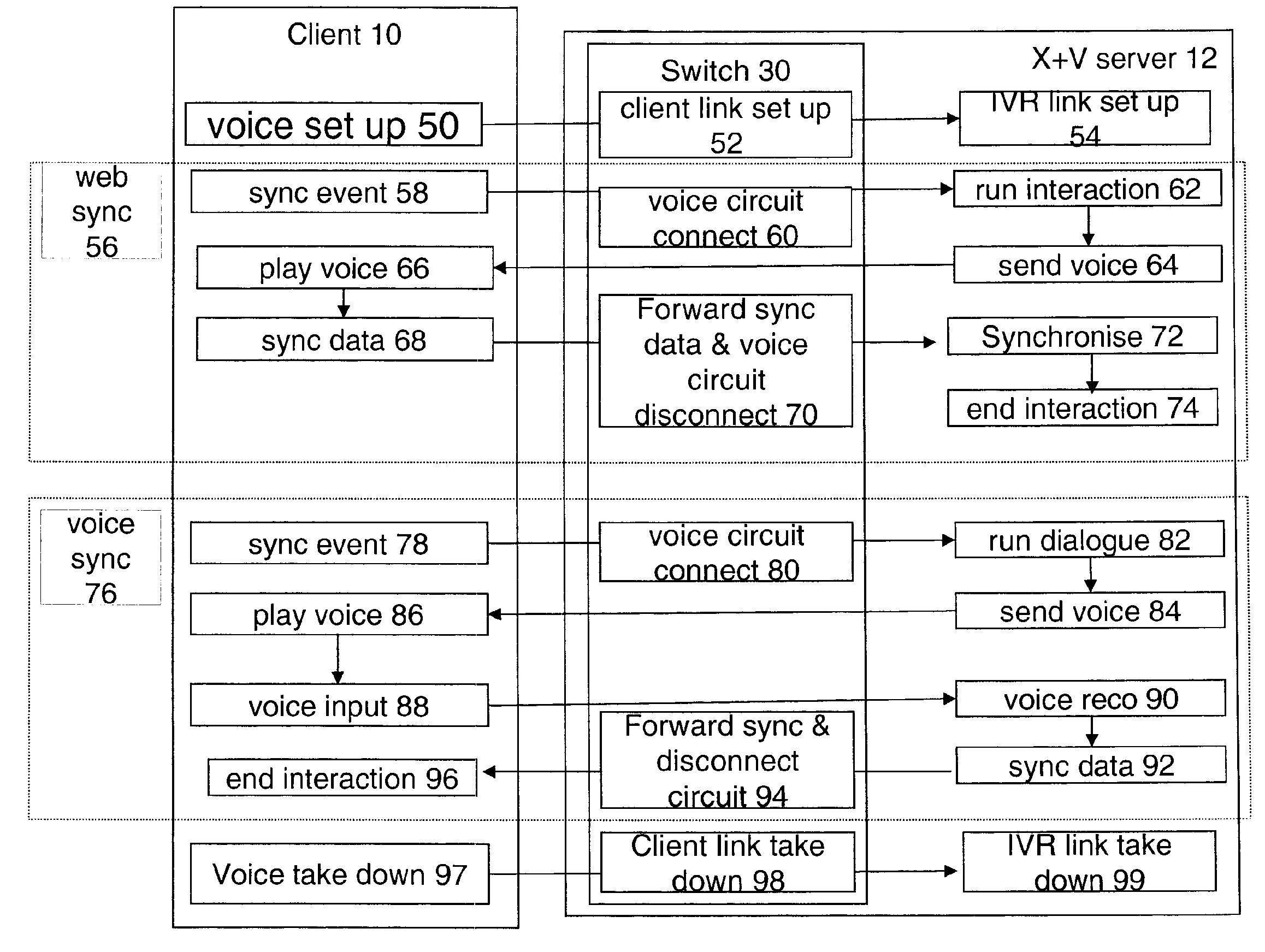
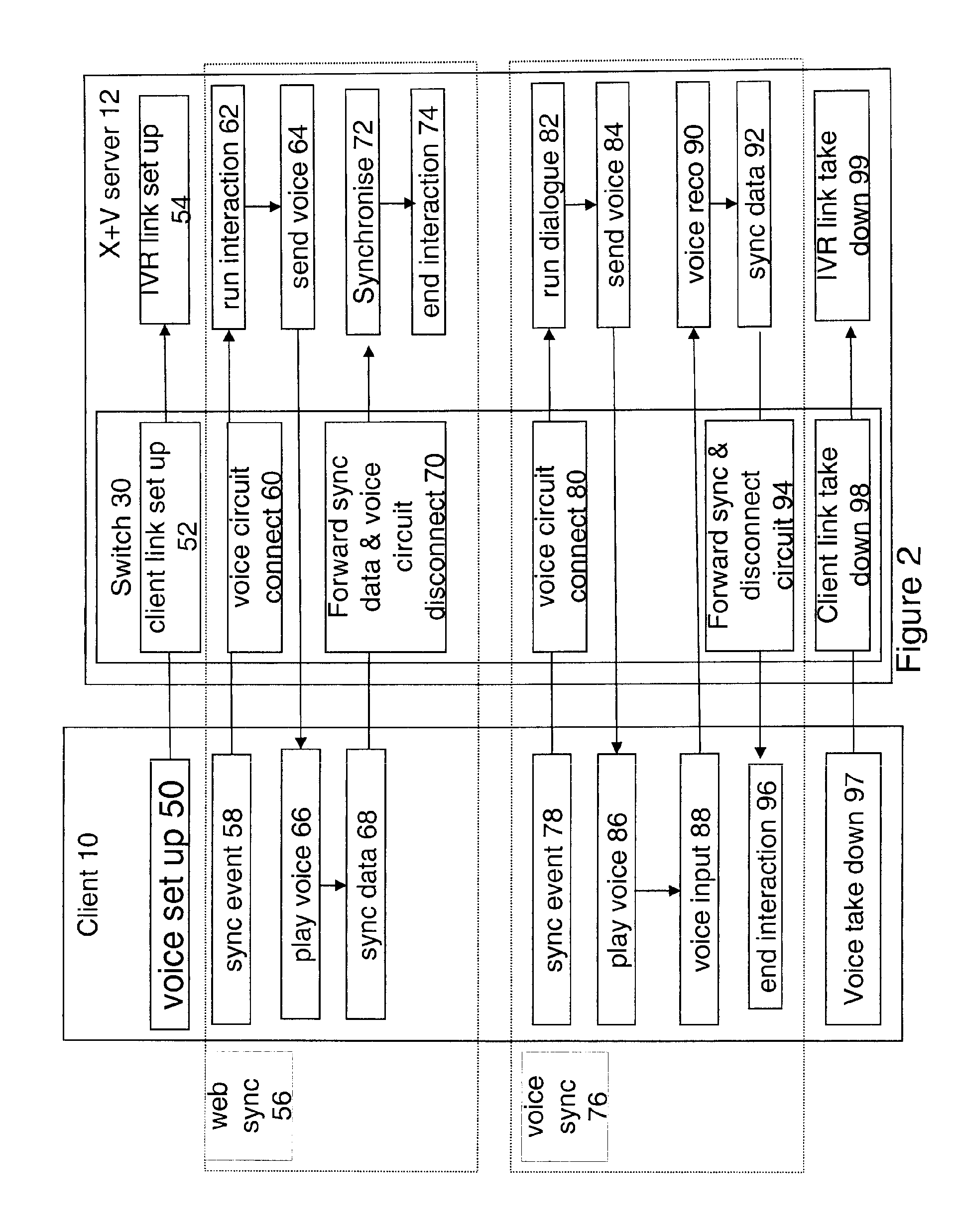
This invention is based on being able to locate a voice server, temporarily allocate it, send it the audio of you saying “When is flight 683 due to arrive?”, getting the results of what you said back in the browser, and deallocating the voice server for use by the next person talking into their browser. Voice channels and IVR ports are initially set up by a switch and the IVR using conventional audio protocols. The Voice channels are not initially connected to the client. The switch handles the allocation and deallocation of IVR voice channels without having to communication further with the IVR. A user indicates (usually by pressing a PTT button) to the client device that he wishes to initiate a voice interaction during an X+V session. This translates to a request on the CTRL channel to synchronise the XHTML and VXML forms which the embodiment uses as a trigger for the VXML browser to execute a conversational turn. The multiplexer intercepts this control command and connects the virtual voice circuit between the device and an existing open but unattached voice port. The virtual circuit is connected without having to set up an RTP channel. The CTRL signal is then forwarded to the interaction manager so that the conversation can take place. At the end of the conversation the virtual circuit is disconnected.
Owner:IBM CORP
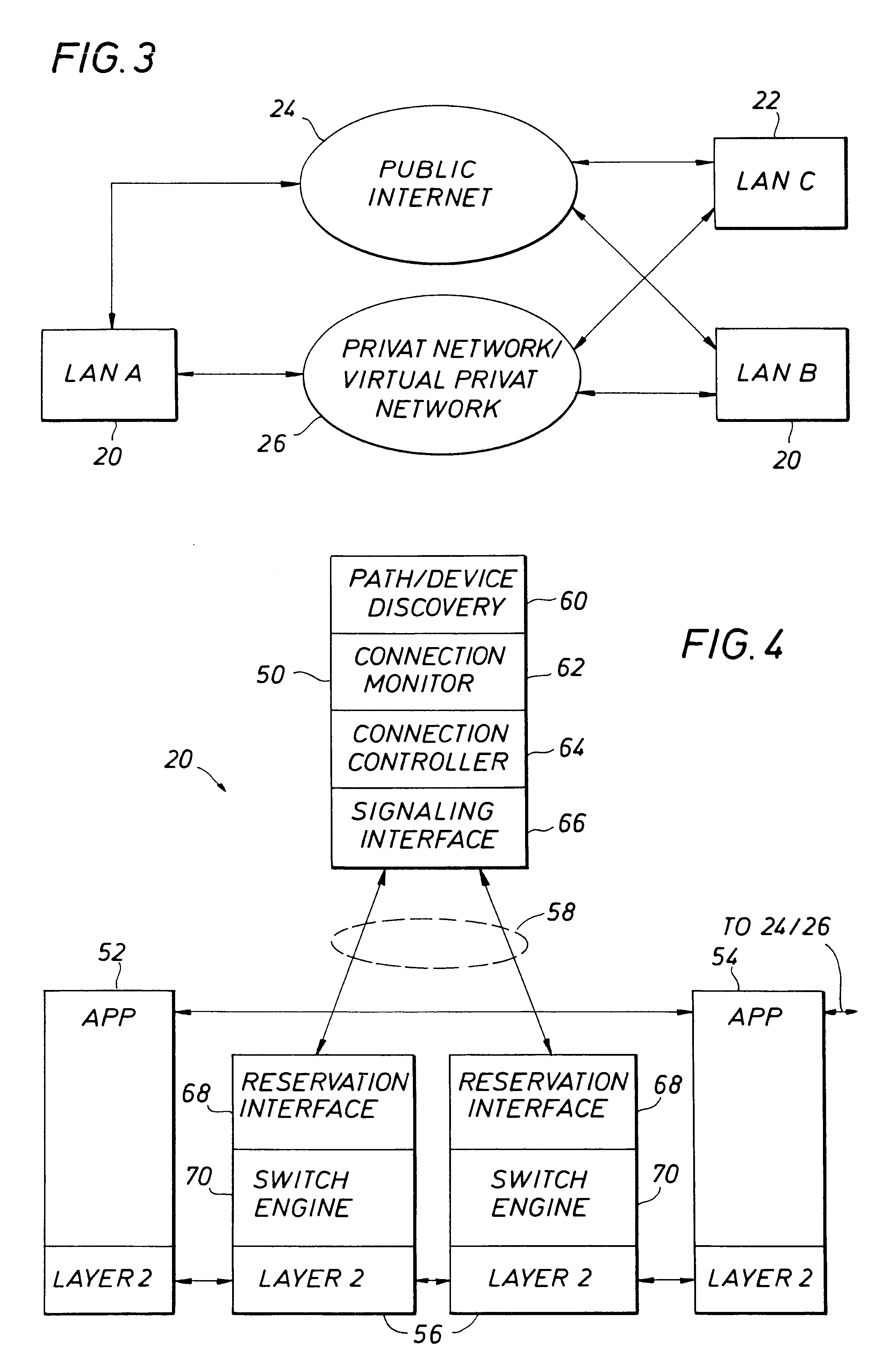
Method of providing network services
InactiveUS6912221B1Overcome limitationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionQuality of serviceNetwork service
A method of providing network services is described. The network includes a number of nodes, each one of which is coupled to at least one other of the nodes by at least one of a number of optical links. The network is preferably capable of supporting a number of virtual circuits. The method begins with the receiving of a request for a virtual circuit between a first node and a second node of the network. Preferably, the request specifies a quality of service of the virtual circuit. Next, the availability of network resources for supporting a virtual circuit at the requested quality of service is determined. Assuming sufficient network resources are available for support of the virtual circuit, the request is then serviced by provisioning (and maintaining) the requested virtual circuit. Servicing the request preferably includes actions such as provisioning, maintaining, and restoring the virtual circuit, using the requested parameters.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Policy based provisioning of network device resources
InactiveUS7062642B1Reduce administrative workloadProgram control using wired connectionsData resettingQuality of serviceData transmission
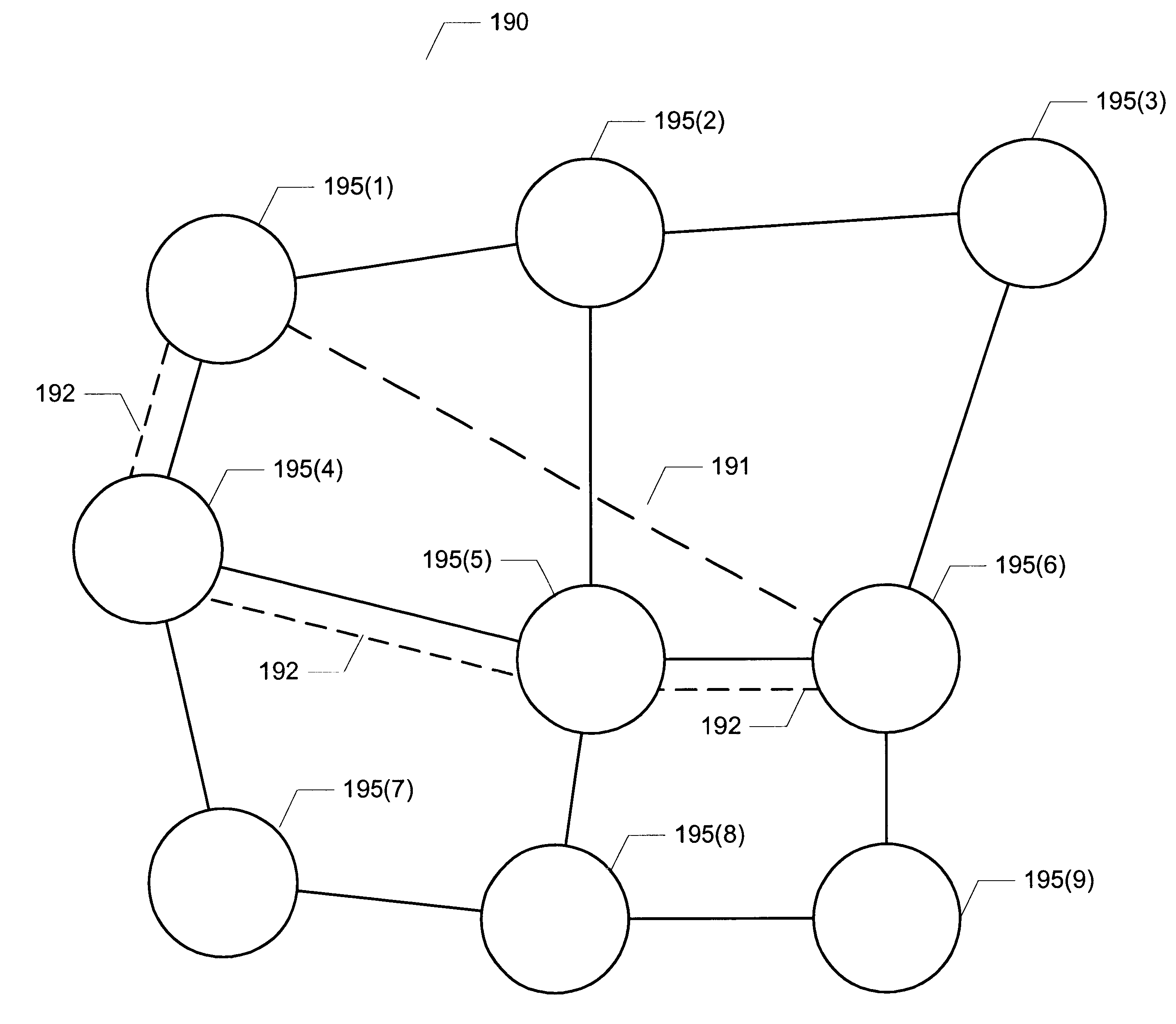
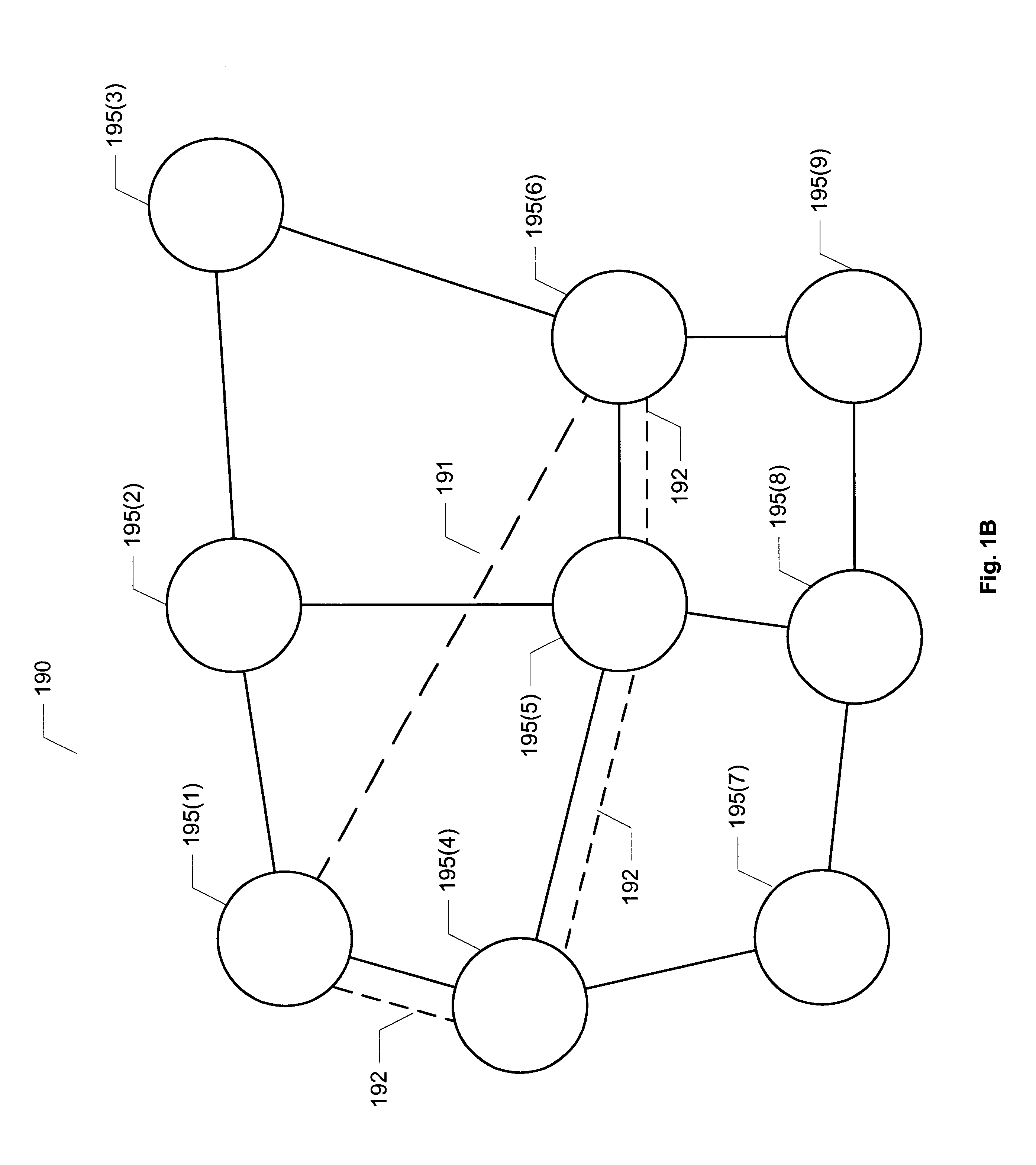
Methods are disclosed for establishing a path for data transmissions in a system having a plurality of possible paths by creating a configuration database and establishing internal connection paths based upon a configuration policy and the configuration database. The configuration policy can be based on available system resources and needs at a given time. In one embodiment, one or more tables are initiated in the configuration database to provide connection information to the system. For example, a path table and a service endpoint table can be employed to establishing a partial record in the configuration database whenever a user connects to a particular port on a universal port card in the system. The method can further include periodically polling records in the path table and transmitting data from the partial records to a policy provisioning manager (PPM). The PPM then implements a connection policy by comparing one or more of the new path characteristics, to the available forwarding card resources in the quadrant containing the universal port card port and path. The path characteristics can include the protocol, the desired number of time slots, the desired number of virtual circuits, and any virtual circuit scheduling restrictions. The PPM can also take other factors into consideration, including quality of service, for example, redundancy requirements or dedicated resource requirements, and balancing resource usage (i.e., load balancing) evenly within a quadrant.
Owner:CIENA
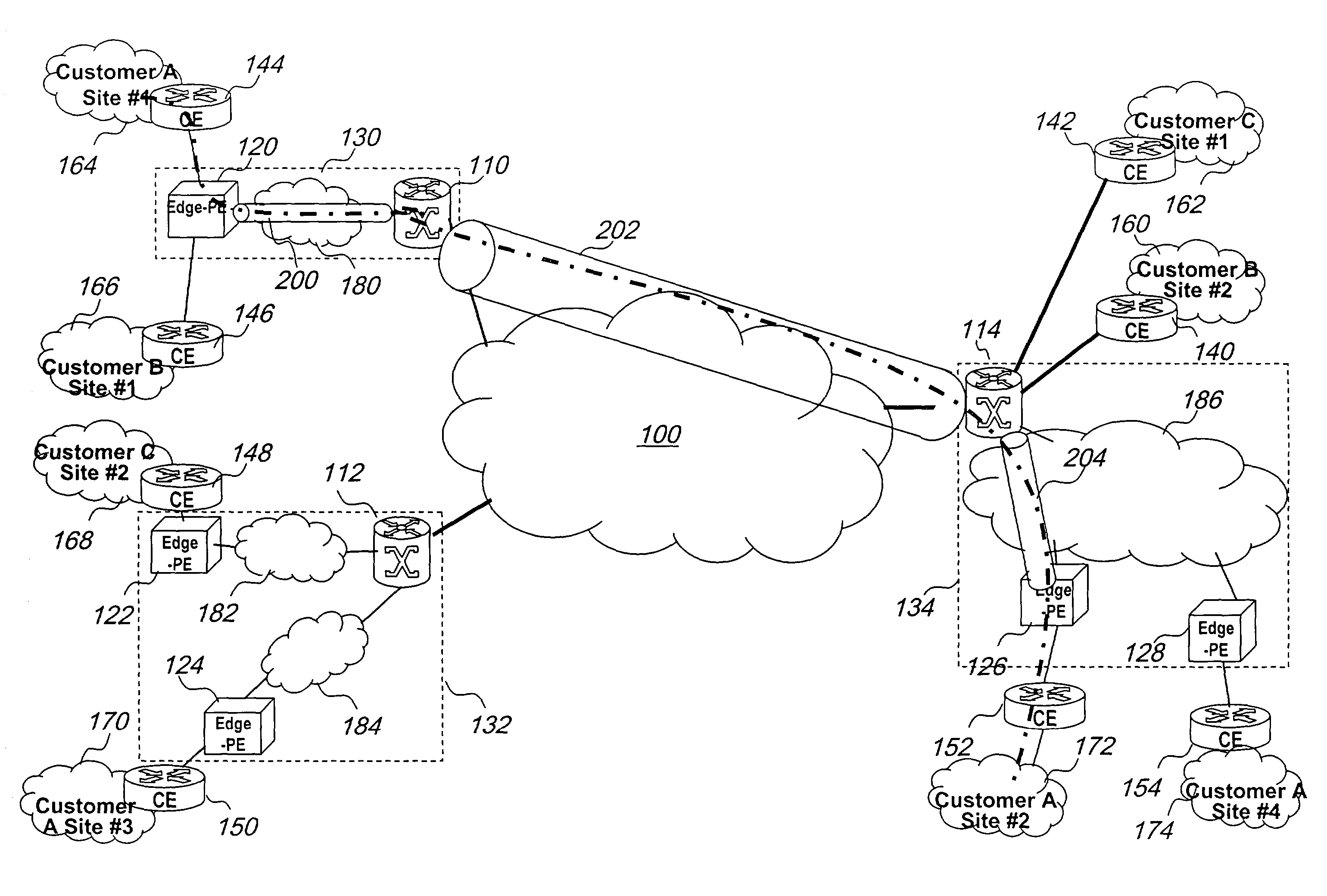
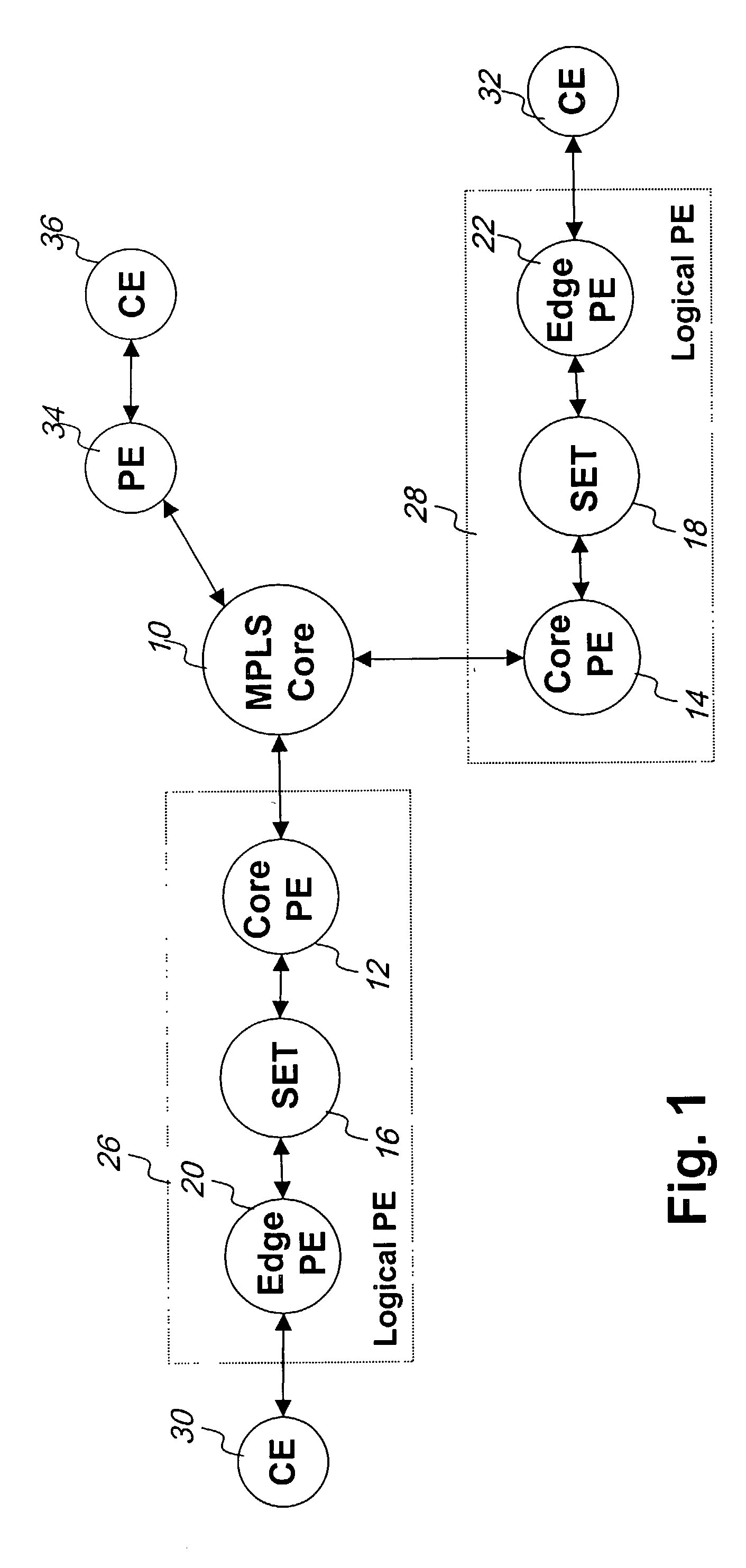
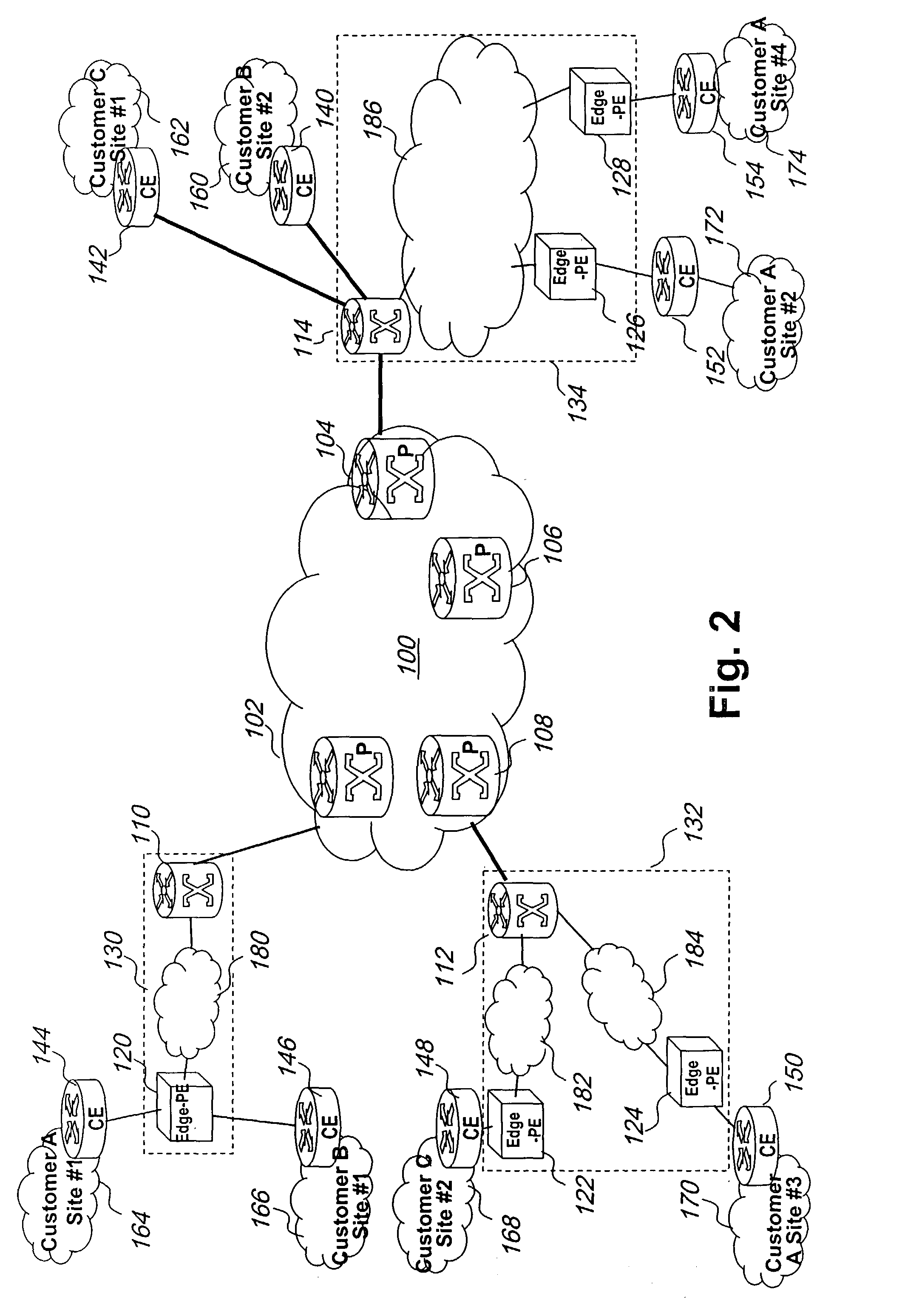
Label control method and apparatus for virtual private LAN segment networks
InactiveUS7260097B2Improved label control methodNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityDistributed computing
A network can be organized for providing virtual private LAN segment (VPLS) services to customers into a network core and an associated number of logical provider edges. Each logical provider edge is partitioned into a plurality of Edge-PEs and a Core-PE. Customers connect to the Edge-PE. The Edge-PE maintains a context (a virtual bridge) for each customer VPLS it serves, VPLS service is realized by a full mesh of so called virtual circuit (VC) tunnels between virtual bridge ports. Each VC tunnel is identified by 3 VC labels in each direction, the first label is used in the encapsulation of customer traffic from the ingress Edge-PE to the ingress Core-PE, the second from ingress Core-PE to egress Core-PE and the third from egress Core-PE to Egress Edge-PE. The mechanisms for the allocation of the label values to and how the label values are used provide a realization of VPLS service that is scalable and easy to administer.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for medium access control in powerline communication network systems
InactiveUS6854059B2Backward compatibilityKey distribution for secure communicationPower distribution line transmissionNetworked systemMedia access control
An inventive Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol for powerline networking systems is described. The inventive MAC protocol controls access to and use of a physical medium (power lines) in a powerline networking system. The MAC protocol method and apparatus includes a method of providing “blanking intervals” in which devices using newer versions of the protocol “clear out” earlier version devices. The use of blanking intervals greatly eases backward compatibility of the network when the protocol is upgraded with new versions. The method of using blanking intervals is closely coupled to a technique of using “beacons.” The beacons are used to propagate blanking interval information throughout the network. The beacons also include a mechanism for informing devices of the expiration of blanking information. The MAC also includes a method of establishing and maintaining “virtual circuit” connections between selected devices on the network. The virtual circuits can be established in powerline networking systems not having a central controller. A method of assigning unique Logical Network Identifiers (LNIs) to logical networks in the powerline networking system is also described. The LNIs uniquely identify each of the logical networks in the network. A means for creating, managing and distributing network encryption keys is also described. The encryption keys are used by the devices in the powerline networking system to prevent data from being shared with unauthorized users.
Owner:CONEXANT SYST INC
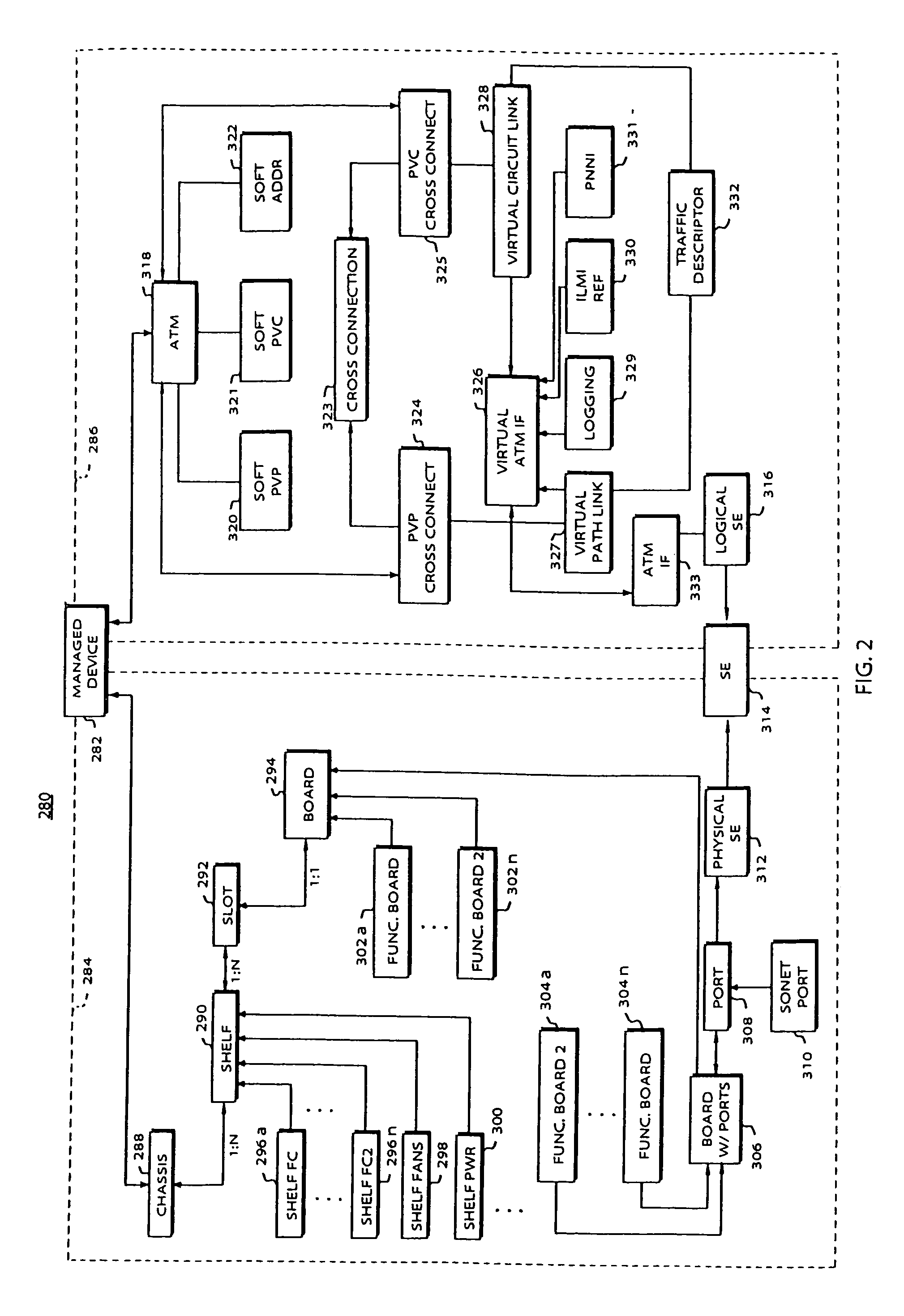
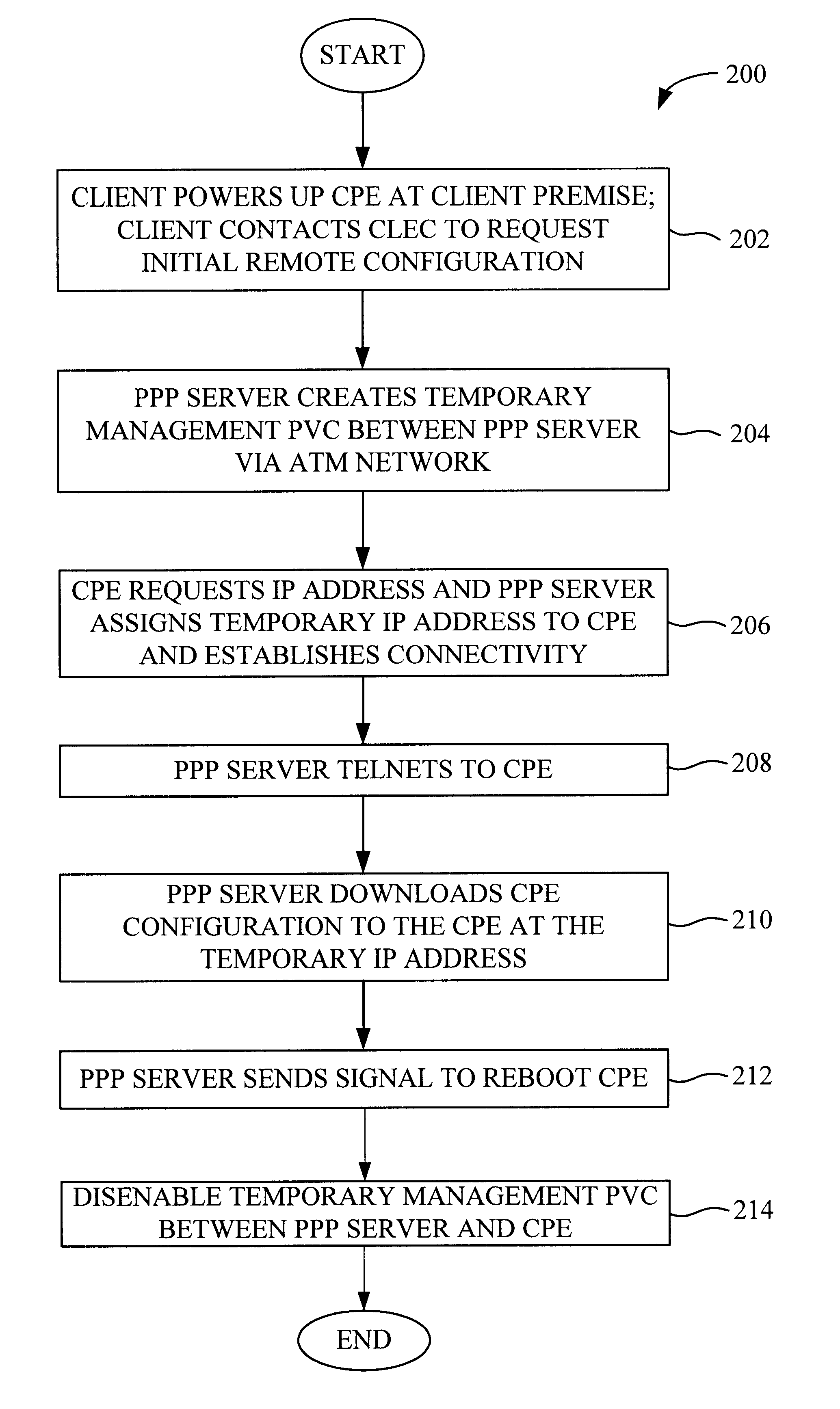
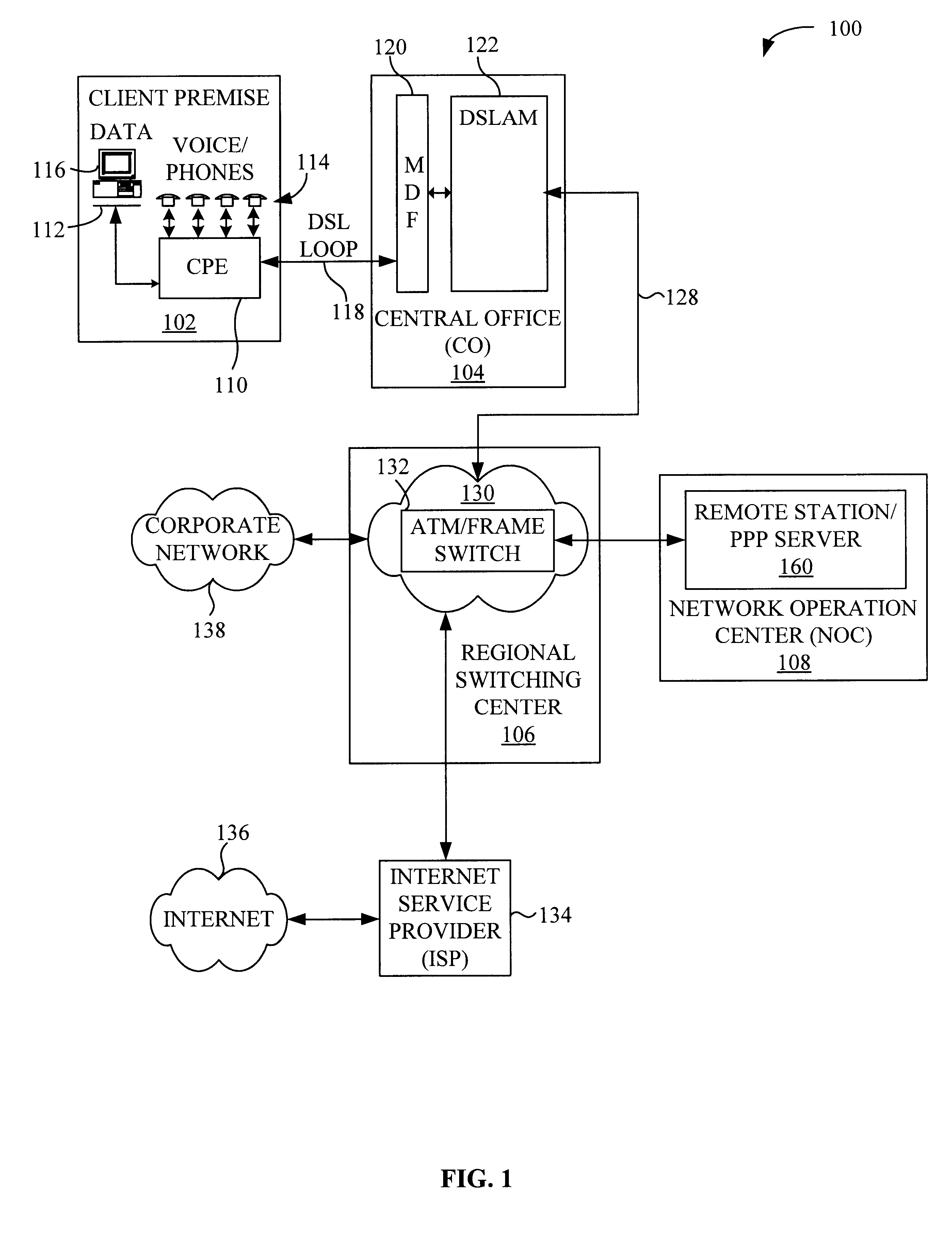
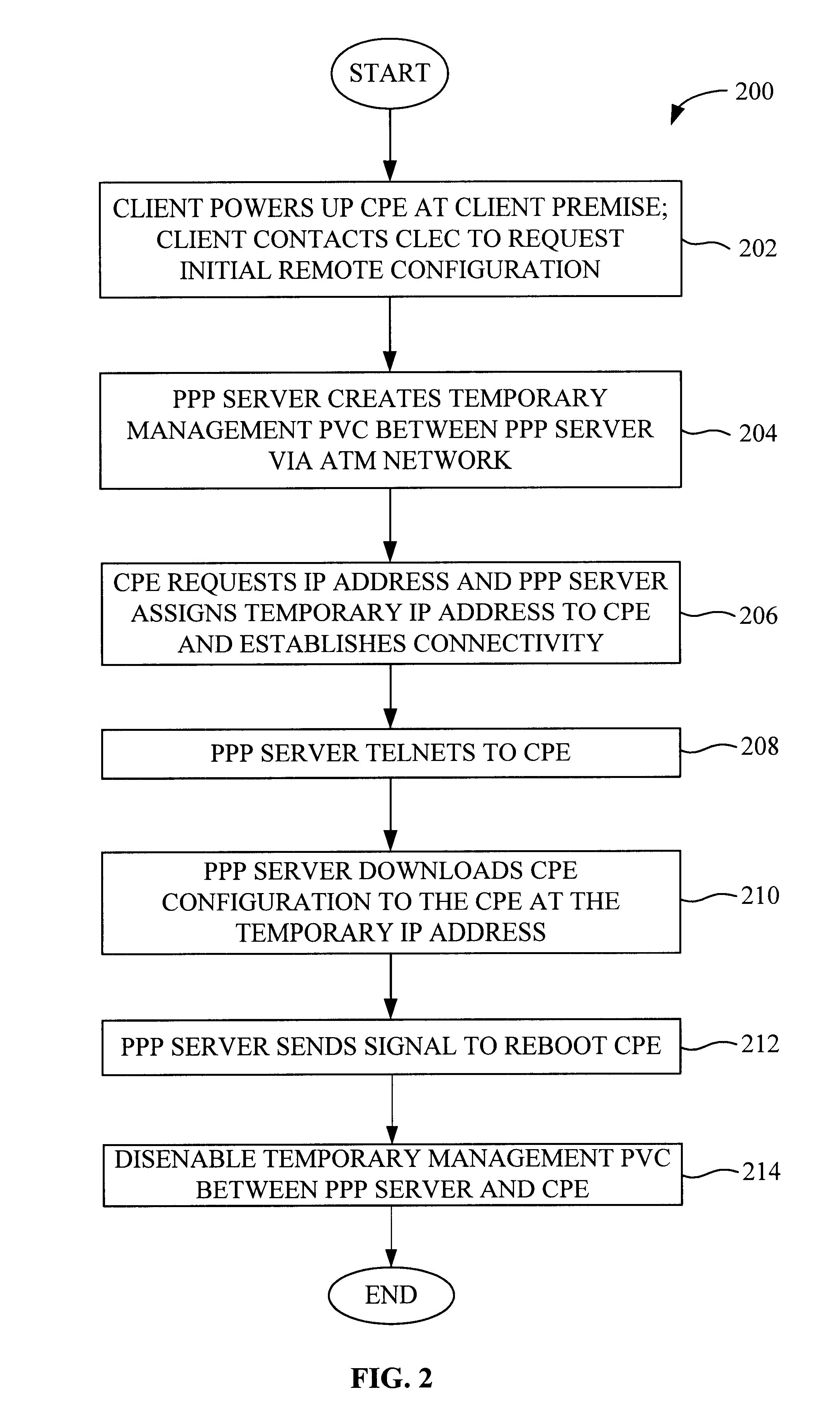
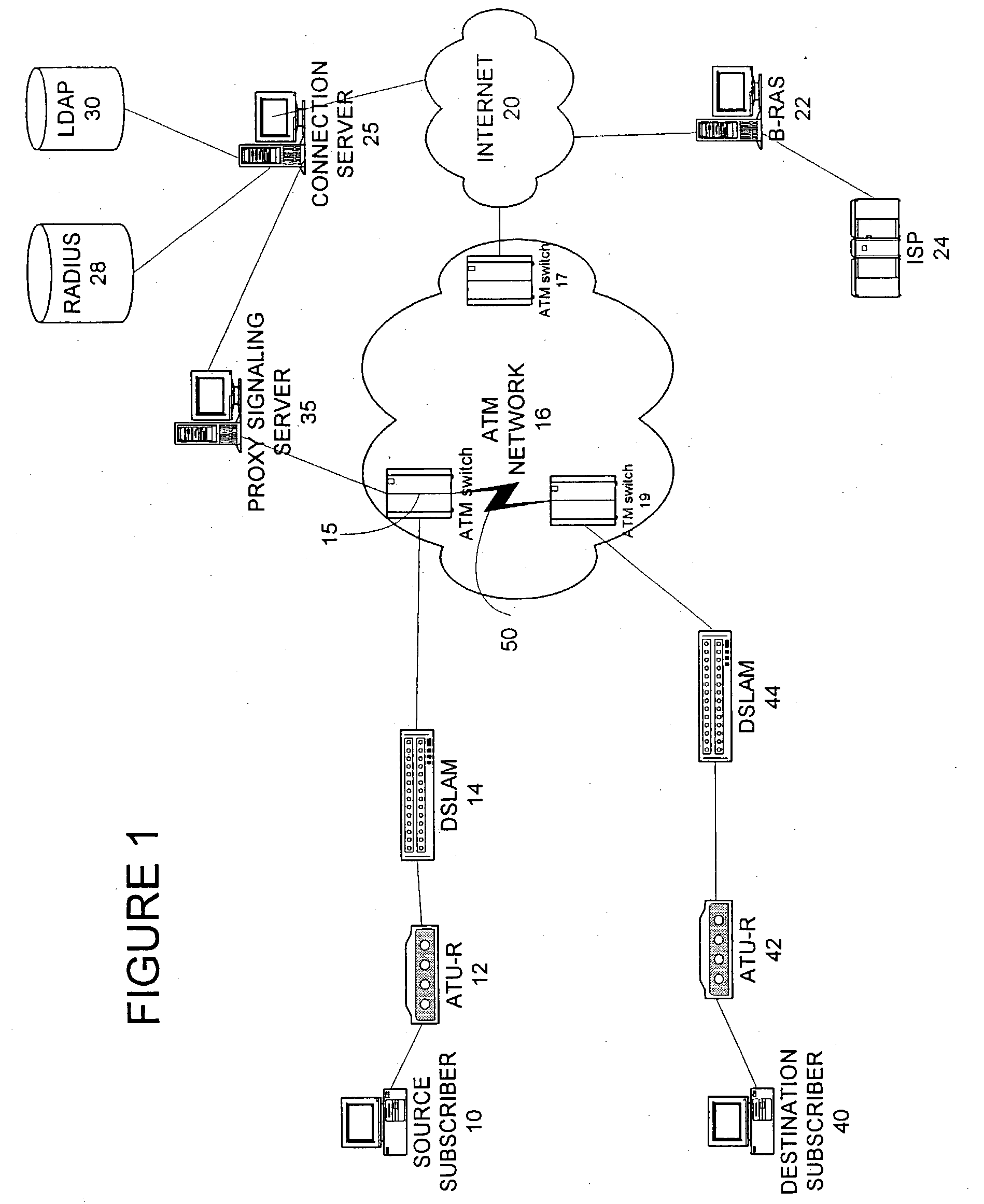
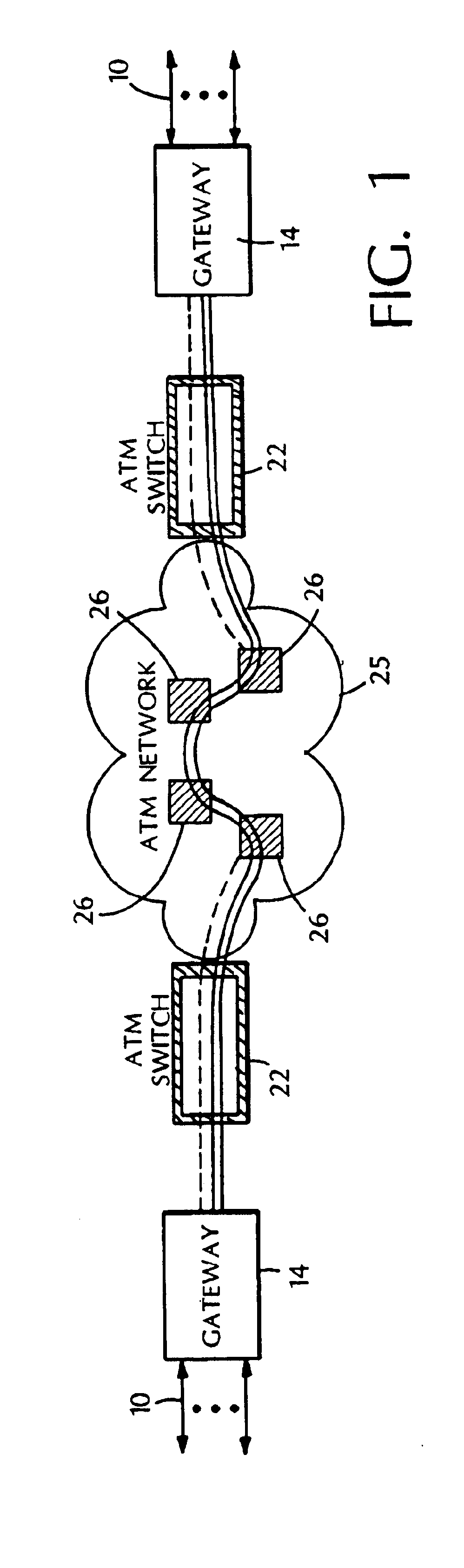
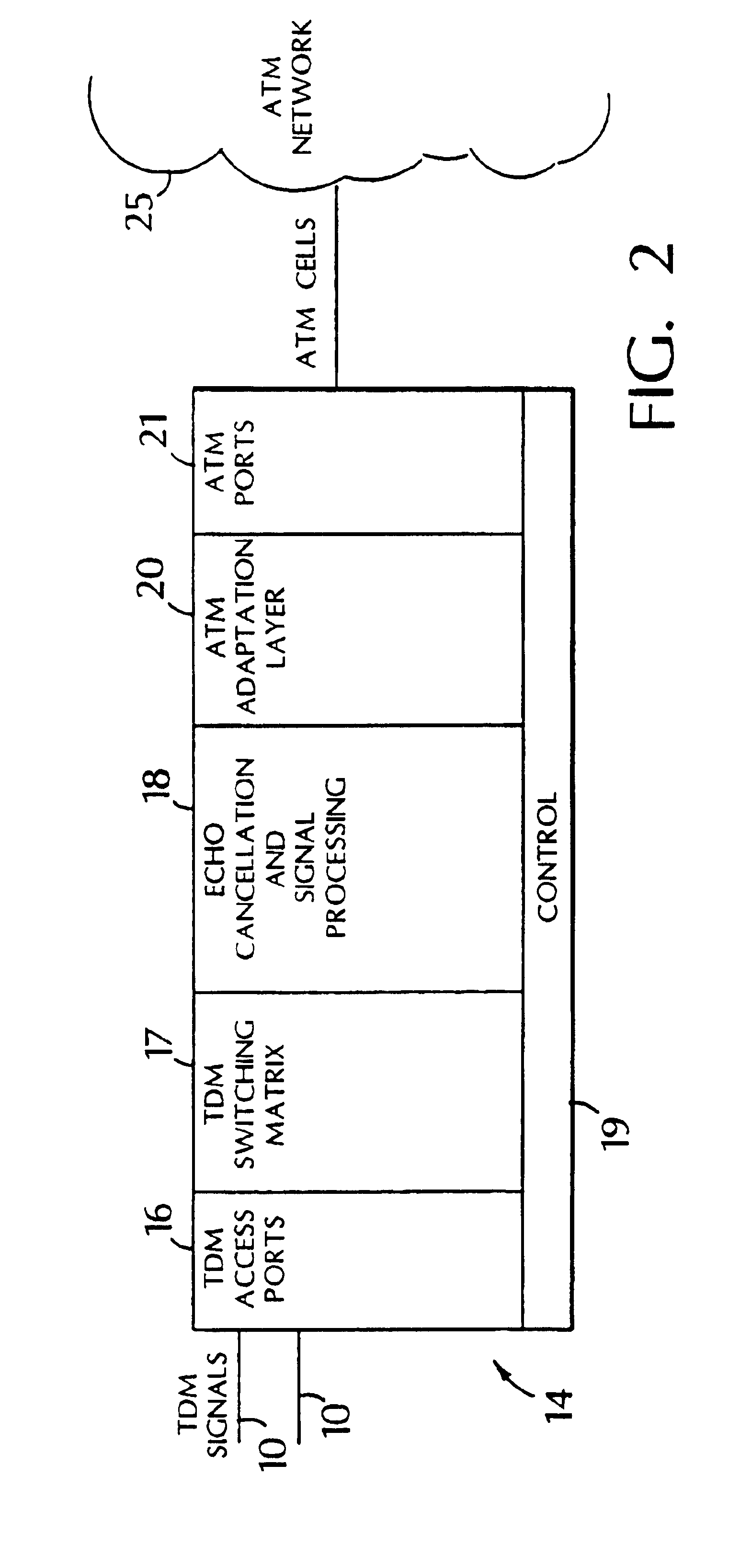
System and method for remote configuration and management of customer premise equipment over ATM
InactiveUS6584074B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPoint-to-Point ProtocolTTEthernet
Systems and methods for providing remote configuration and on-demand management of a CPE over DSL are disclosed. The method generally comprises creating a temporary management ATM virtual circuit between a remote Point-to-Point Protocol ("PPP") server and the CPE via an ATM network, assigning a temporary Internet Protocol ("IP") address to the CPE using PPP over ATM, telneting from the PPP server to the temporary IP address of the CPE, and downloading CPE configuration from the PPP server to the CPE. The creating, assigning, telneting, and downloading may be performed between the remote PPP server and a management port of the CPE. The system generally comprises a remote PPP server, a CPE including a management port adapted to send requests for connection to the PPP server and to receive data downloaded from the PPP server, and a temporary management ATM virtual circuit between the PPP server and the management port of the CPE.
Owner:GC PIVOTAL LLC
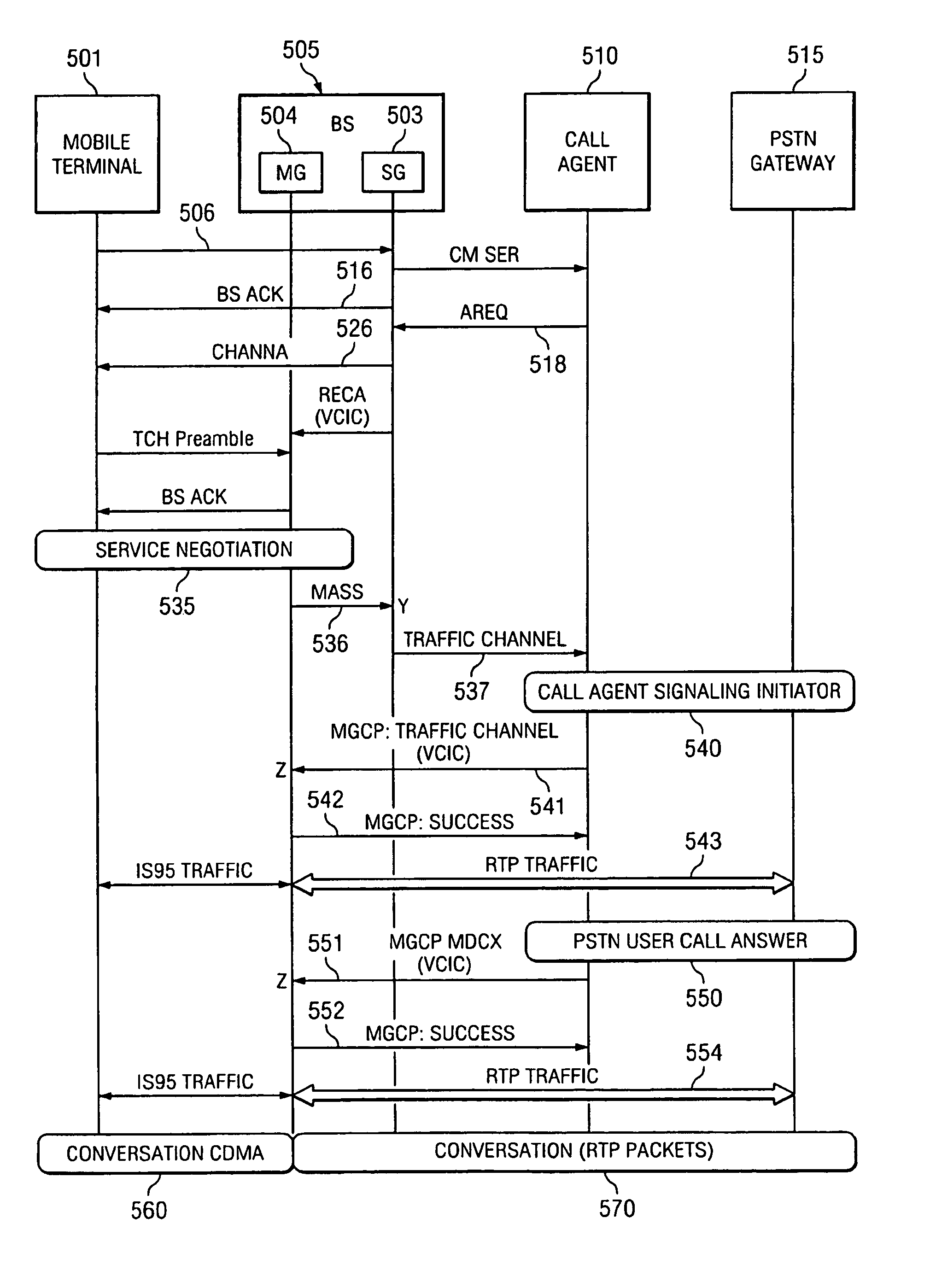
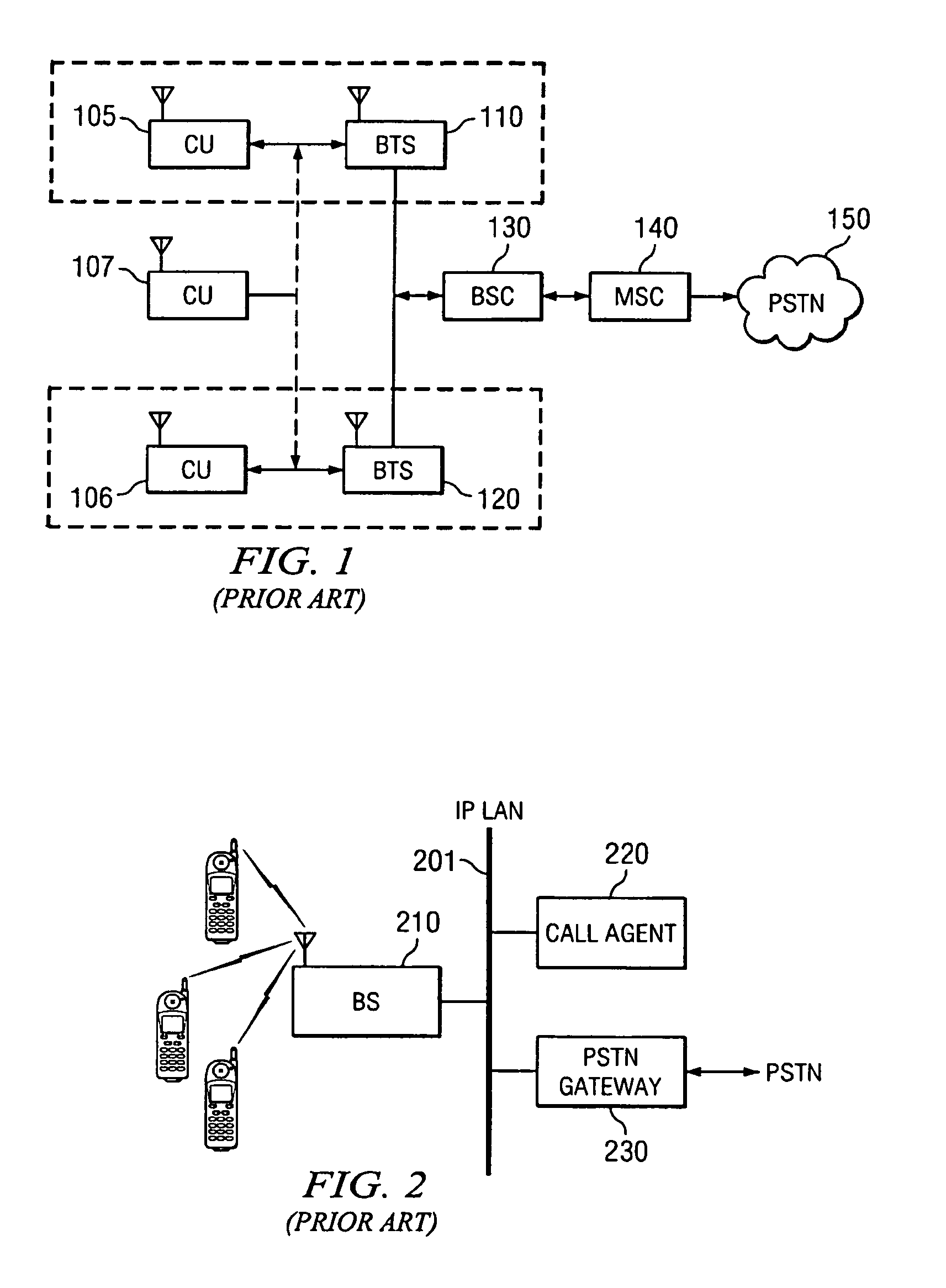
System and method of linking a wireless signaling protocol with a media gateway control protocol in a packet-based network
InactiveUS7120133B1Shorten the timeReduce data lossNetwork topologiesConnection managementCommunication unitCommunications system
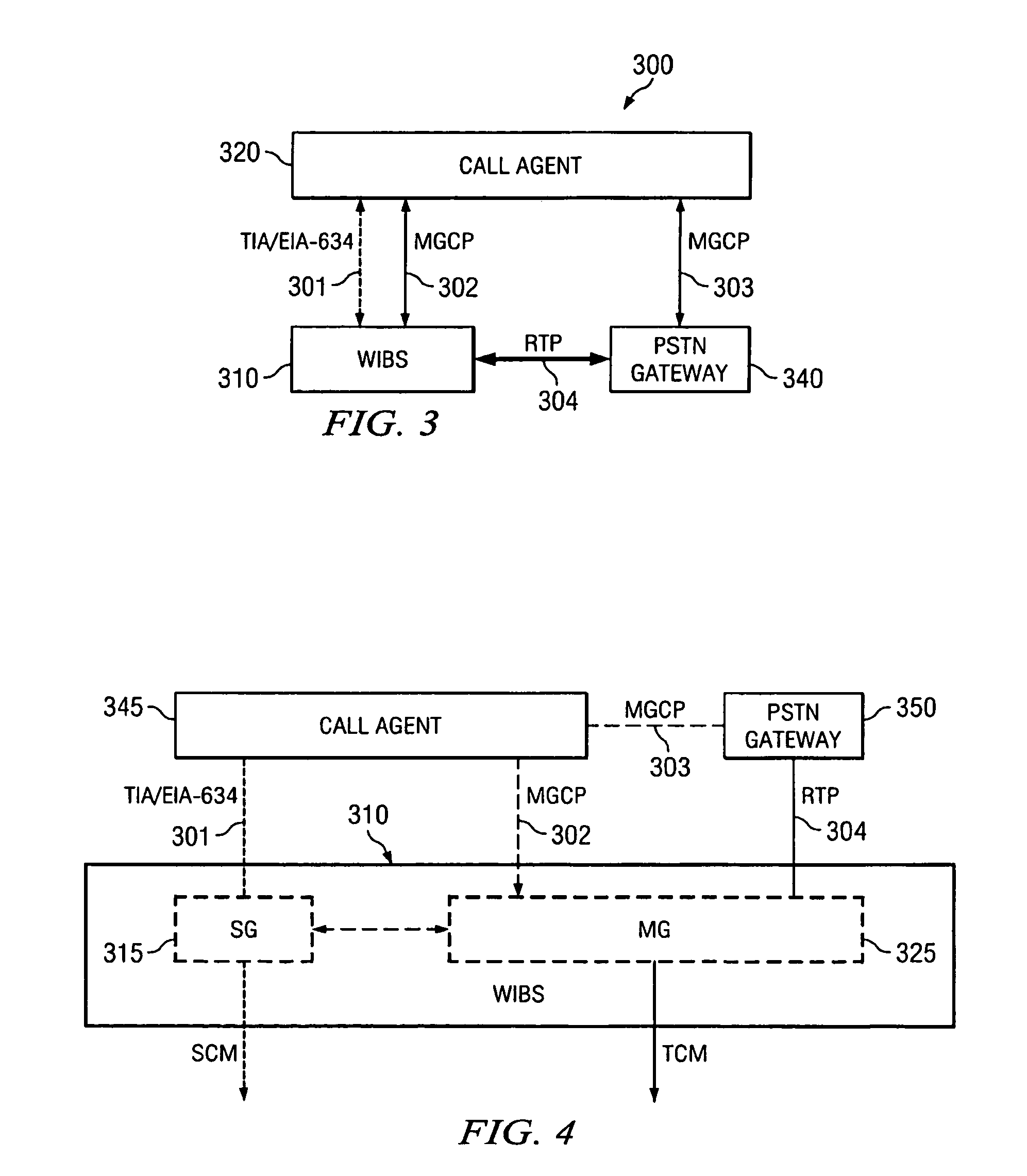
A wireless office communication system including a multi-protocol wireless internet base station (WIBS) encompassing a base station controller (BSC), a mobile switch controller (MSC) and an ethernet interface module for coupling the WIBS to an existing internet protocol (IP) based network. The interface module provides for coupling the WIBS to an ethernet back-bone, a mobile communication unit and a public switch telephone network (PSTN). In one embodiment the wireless communication system includes wireless signaling logic and media gateway logic to enable the wireless office communication system to handle signal transmission between a mobile terminal and a media gateway. A virtual circuit identity code (VCIC) enables the base station to provide a virtual traffic path (VTP) to link communications between TIA / EIA-634 wireless signaling and media gateway control protocol (MGCP).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Transferring data such as files
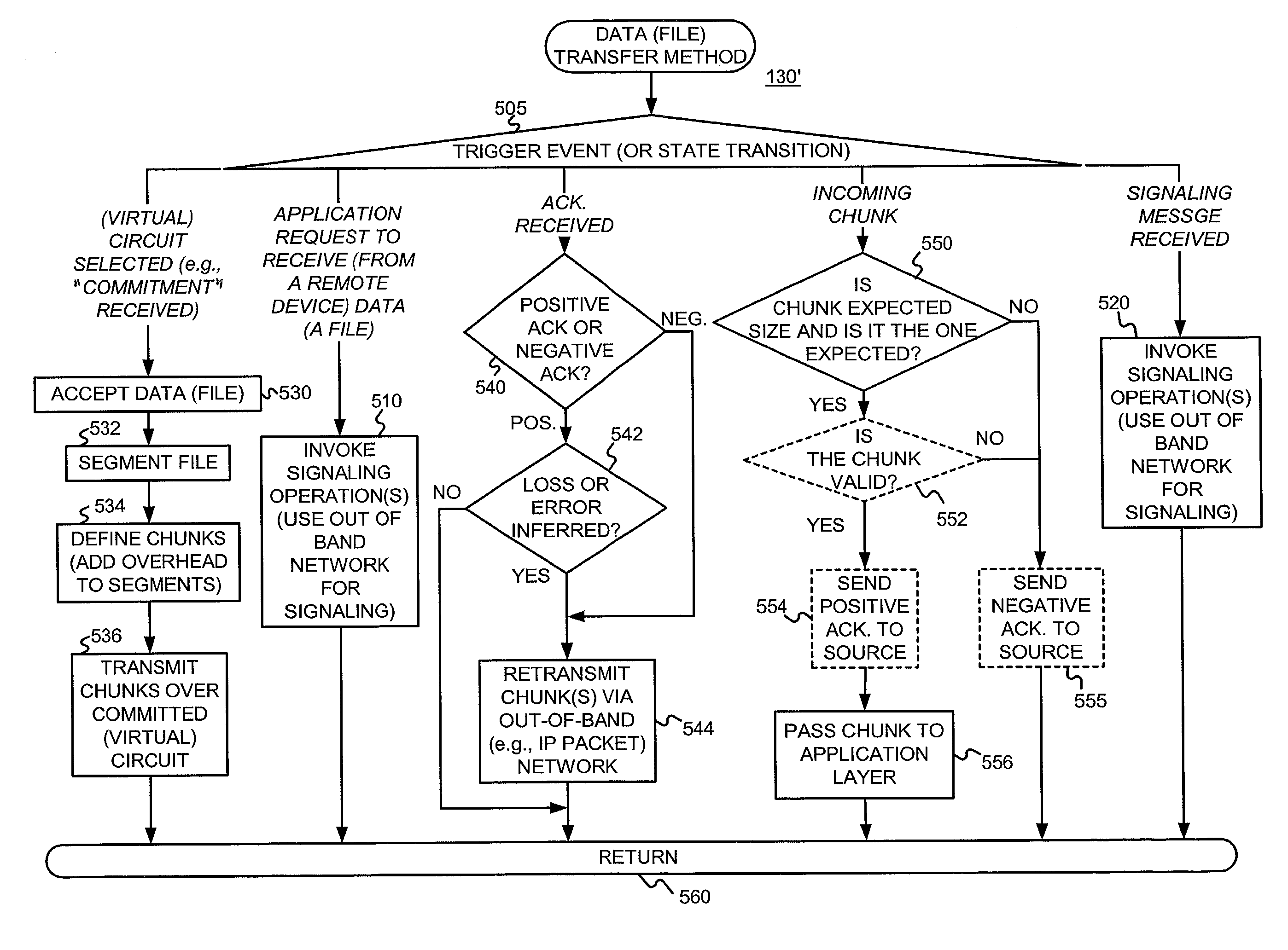
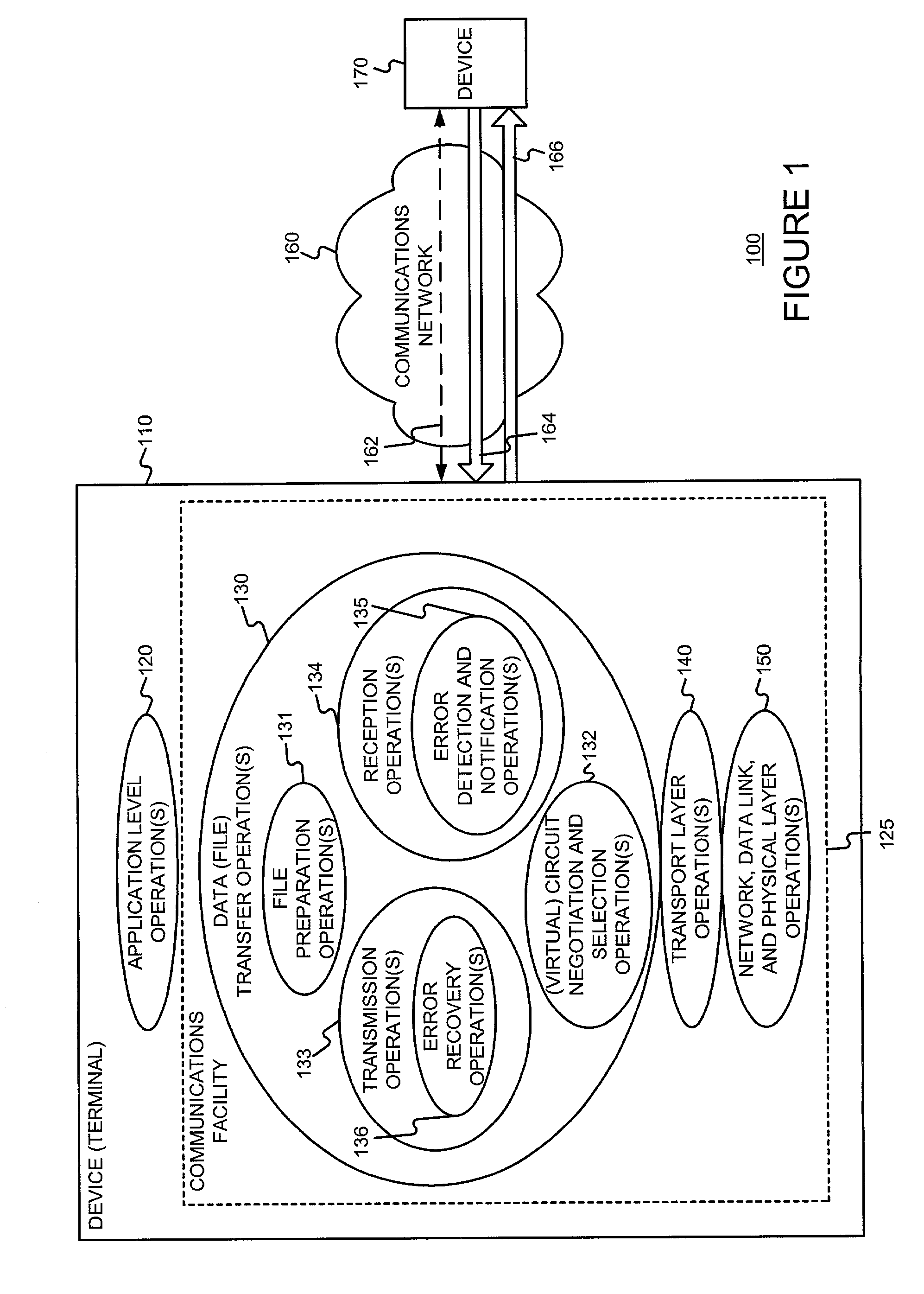
ActiveUS20030053475A1Easy to useAvoid complex processError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareNetwork connection
Transferring data (such as files) on an end-to-end, high-speed packet-switched network connection (a "virtual circuit") or on a circuit. An out-of-band path is used for signaling and status messages (control). The same, or a separate, out-of-band path may be used to retransmit chunks of data that were received with errors or that were not received at all. By simplifying the data being sent over the high-speed (virtual) circuit, the resources of the (virtual) circuit are used efficiently since less overhead is required. Further, since the size of the file to be transferred can be predetermined, and since any retransmissions can be made over a path other than the (virtual) circuit, the (virtual) circuit that best meets the needs of the data transfer can be selected, thereby further increasing the efficiency with which the (virtual) circuit is used.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Method of providing network services
InactiveUS20050185654A1Overcome limitationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceNetwork service
A method of providing network services is described. The network includes a number of nodes, each one of which is coupled to at least one other of the nodes by at least one of a number of optical links. The network is preferably capable of supporting a number of virtual circuits. The method begins with the receiving of a request for a virtual circuit between a first node and a second node of the network. Preferably, the request specifies a quality of service of the virtual circuit. Next, the availability of network resources for supporting a virtual circuit at the requested quality of service is determined. Assuming sufficient network resources are available for support of the virtual circuit, the request is then serviced by provisioning (and maintaining) the requested virtual circuit. Servicing the request preferably includes actions such as provisioning, maintaining, and restoring the virtual circuit, using the requested parameters.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
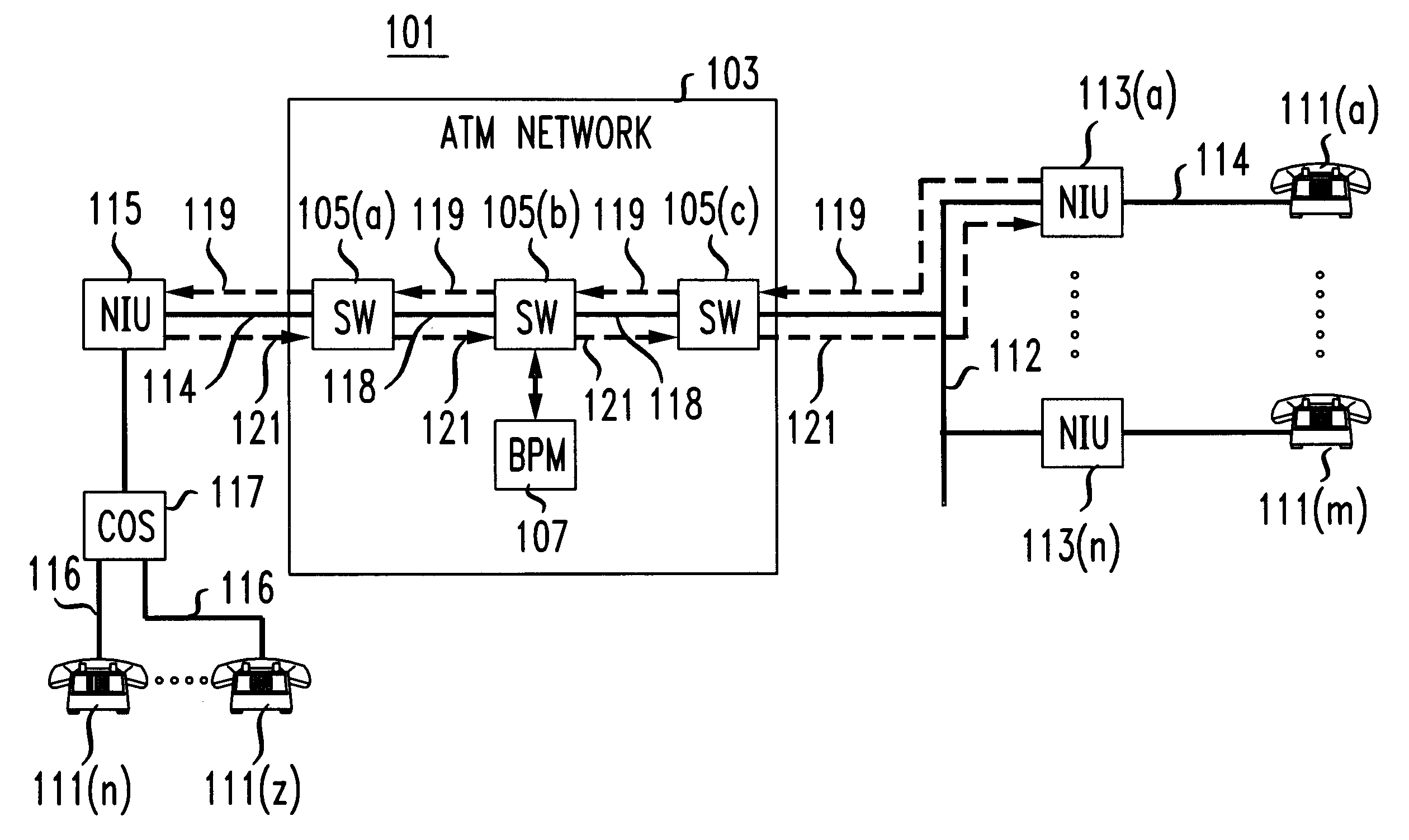
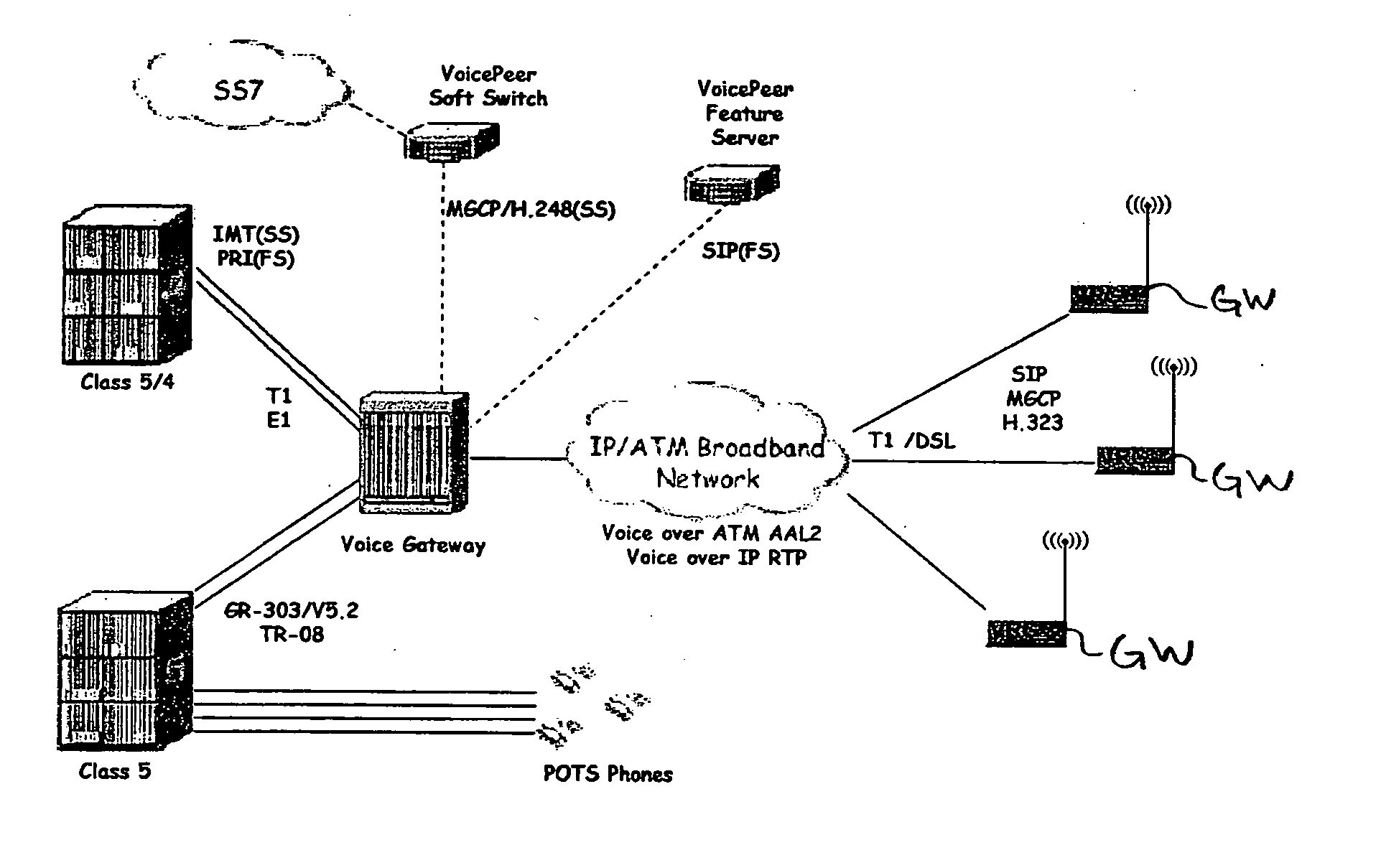
Packet telephone system
InactiveUS6487200B1Simple designReduce the amount requiredInterconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsData connectionBounded delay
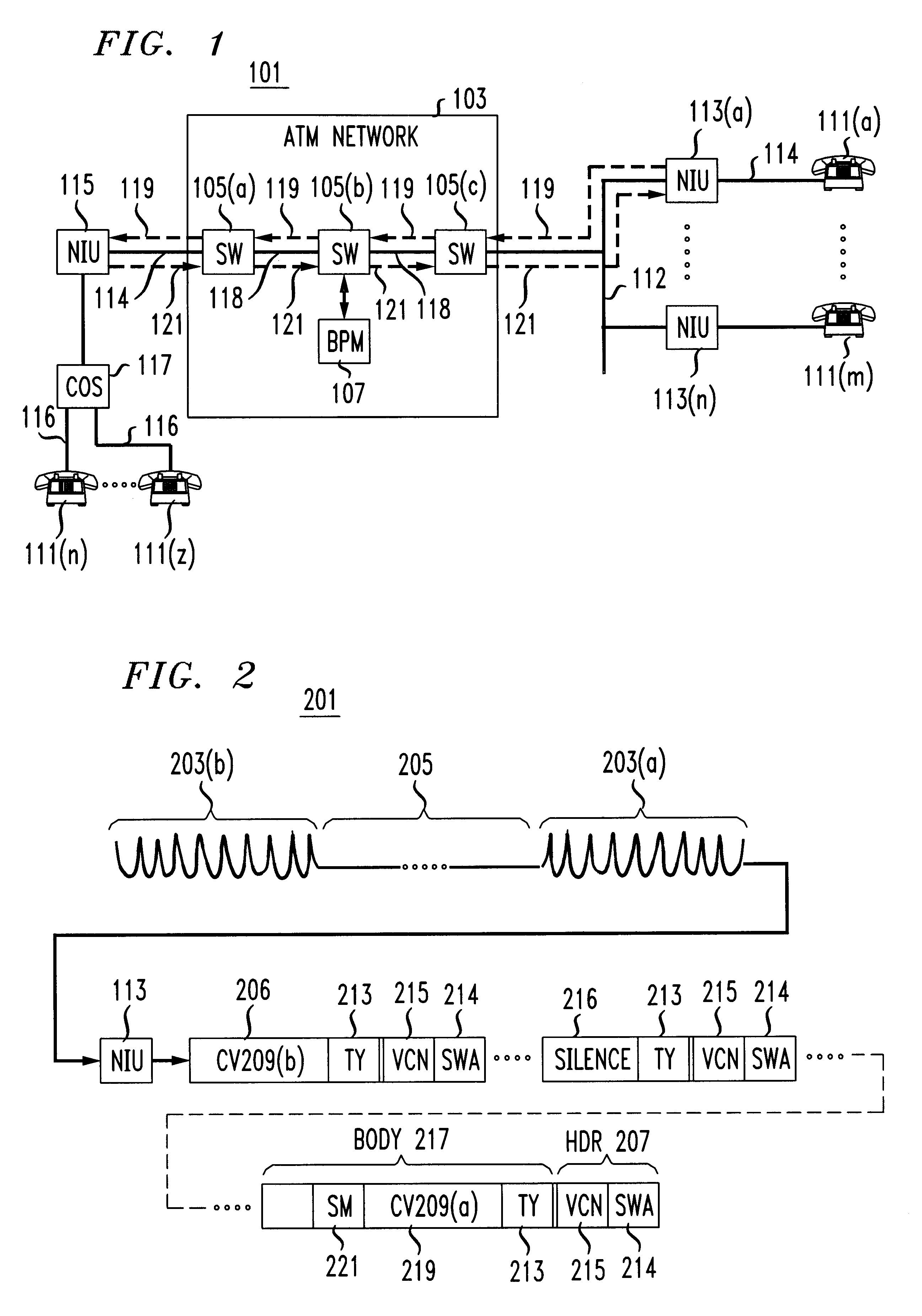
A packet telephone system which employs a packet network that provides virtual circuits. The packet telephone system employs short packets containing compressed speech. The use of the short packets makes possible compression and decompression times and bounded delays in the virtual circuits which are together short enough to permit toll-quality telephone service. The packet telephone system employs an intelligent network interface unit to interface between the packet network and standard telephone devices. The network interface unit does the speech compression and decompression and also responds to control packets from the packet network. Consequently, many telephone system features can be implemented in the network interface unit instead of in the switches. The network interface unit may also be used to provide data connections to devices attached to it. The combination of virtual circuits, with bounded delays, short packets, rapid compression and decompression, and intelligent network interface units makes it possible to build a telephone system with fewer and cheaper switches and fewer links for a given volume of traffic than heretofore possible and also permits substantial savings in provisioning and maintaining the system.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
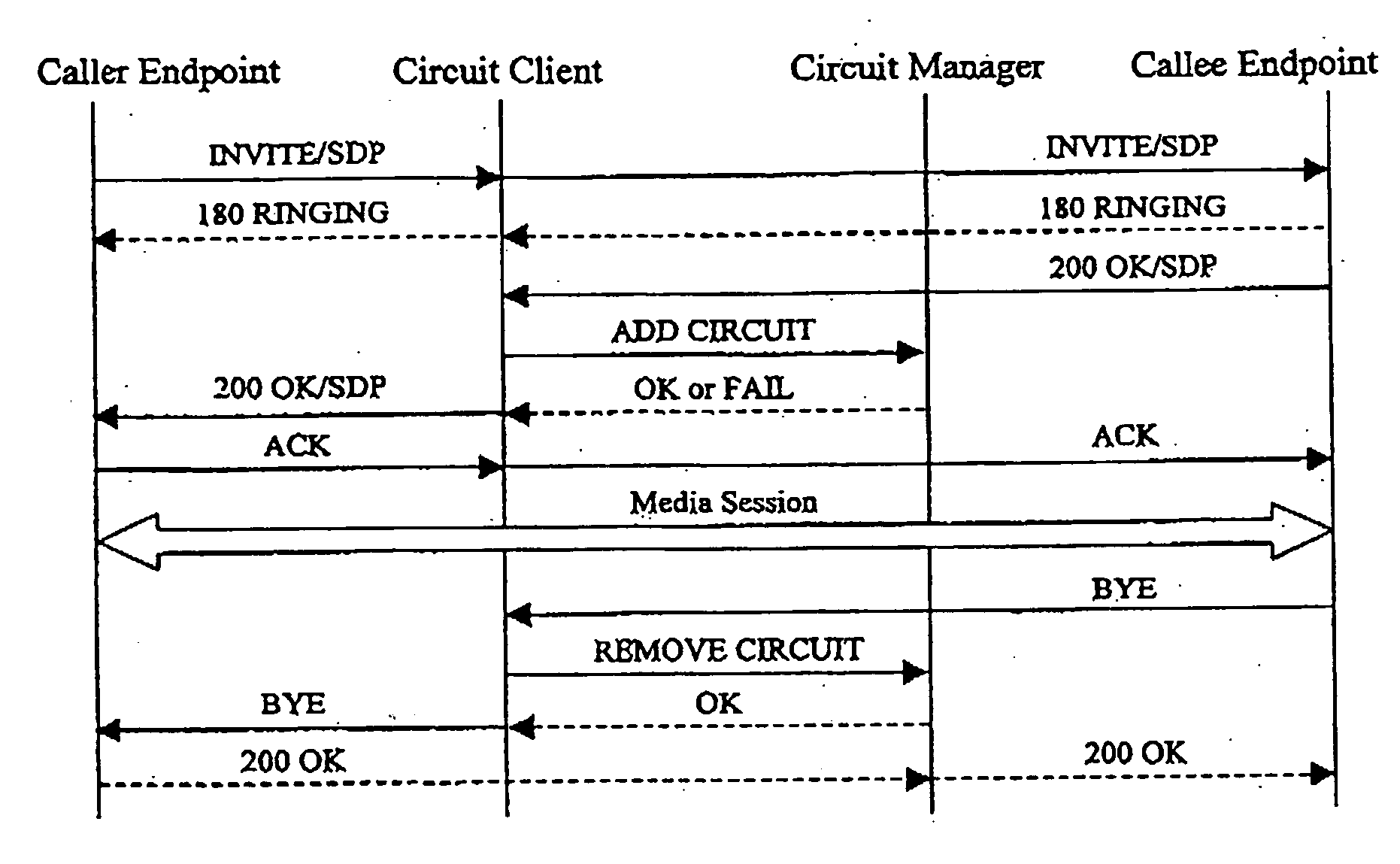
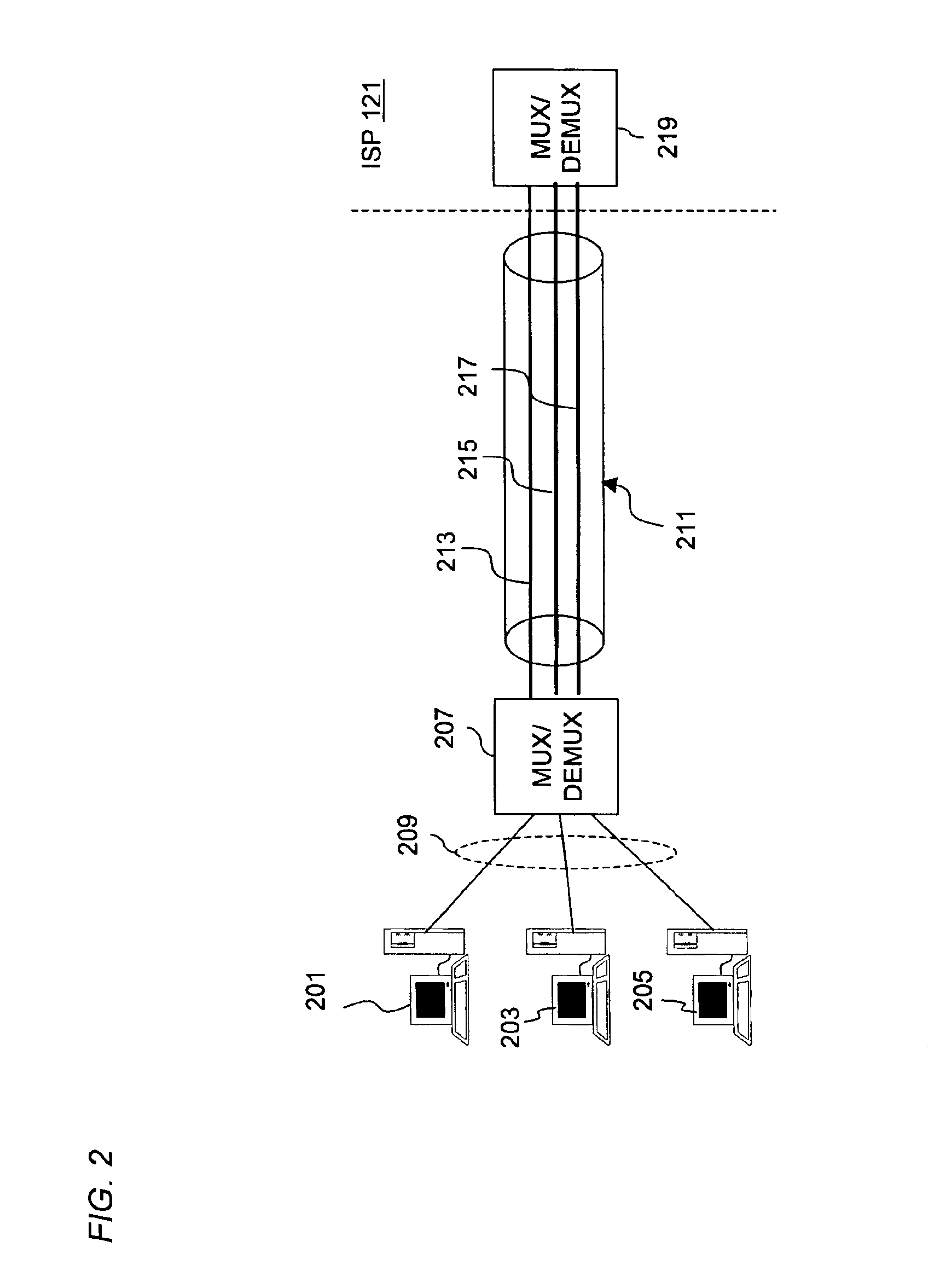
Virtual circuits in packet networks
InactiveUS20060291447A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationQuality of serviceThe Internet
Systems and methods for provisioning a virtual circuit having a predetermined Quality of Service (QoS) in packet networks such as the Internet. A system for provisioning a virtual circuit having a predetermined QoS is provided for a packet network, consisting of (1) a circuit client (108) connected to the network and able to generate a request for a packet flow between two nodes at a predetermined QoS; and (2) a circuit manager (CM) able to receive the circuit client's (108) request and process such request in order to provide a route between the two nodes, such route having the predetermined QoS.
Owner:XELOR SOFTWARE
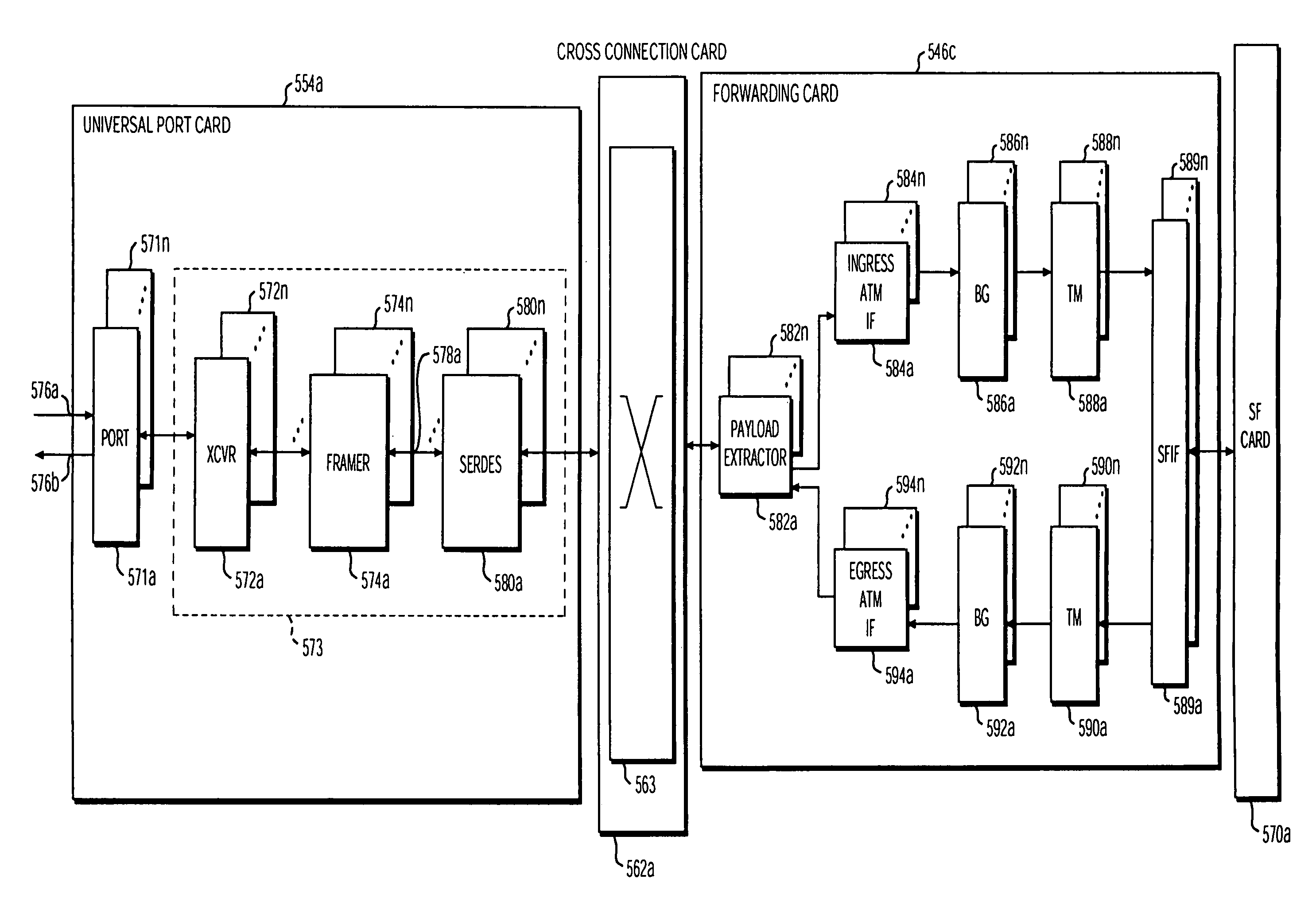
Ethernet to ATM interworking with multiple quality of service levels
A method of supporting multiple quality of service (QoS) levels for data being transmitted between two networking devices, such as customer equipment (CE), that use Ethernet and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The method supports multiple QoS services in a network where a first CE is connected to a first edge device (interworking unit) using the Ethernet protocol and a second CE is connected to a second edge device using the ATM protocol. The edge devices may be directly connected together or they may be connected through a network backbone using any generally accepted network protocol. The first CE may be connected to the first edge device using a single Ethernet port, multiple Ethernet ports, a single virtual local area network (VLAN), or multiple VLAN's. The second CE is connected to an edge device using a single virtual circuit connection (VCC), a single virtual path connection (VPC), or multiple VCC's. The method ensures QoS for data transmitted between the first and the second CE via the Ethernet protocol to the ATM protocol and vice versa.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
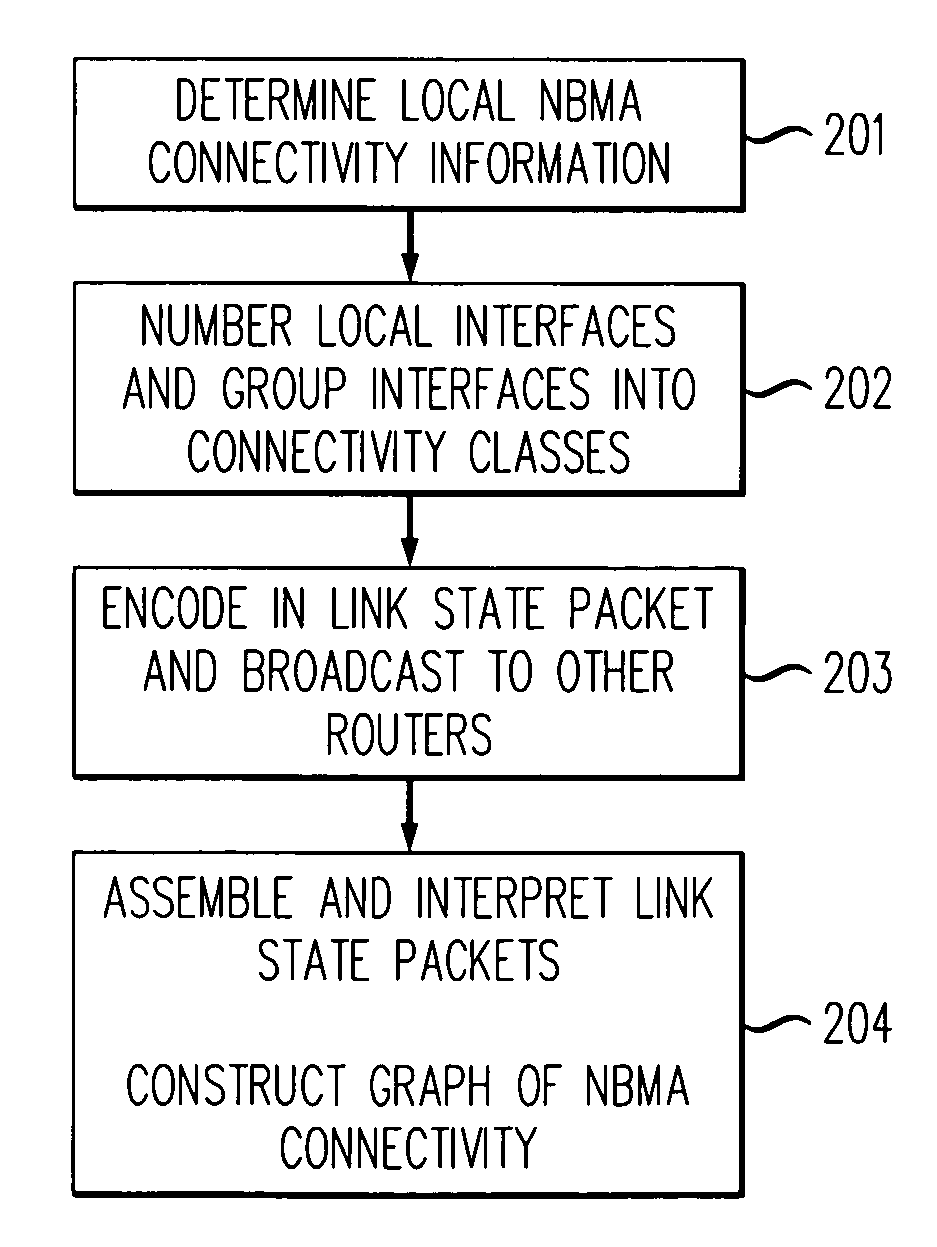
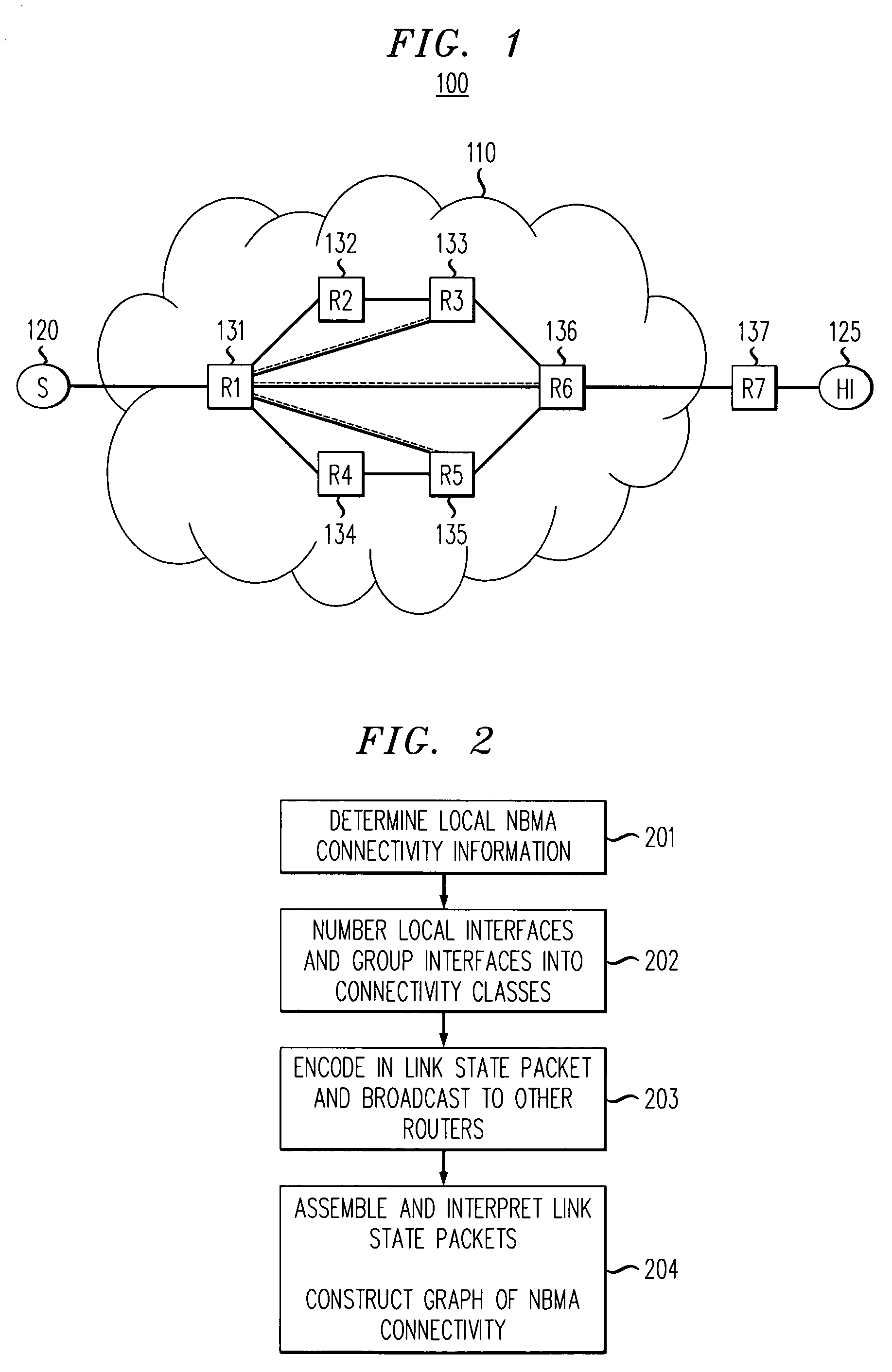
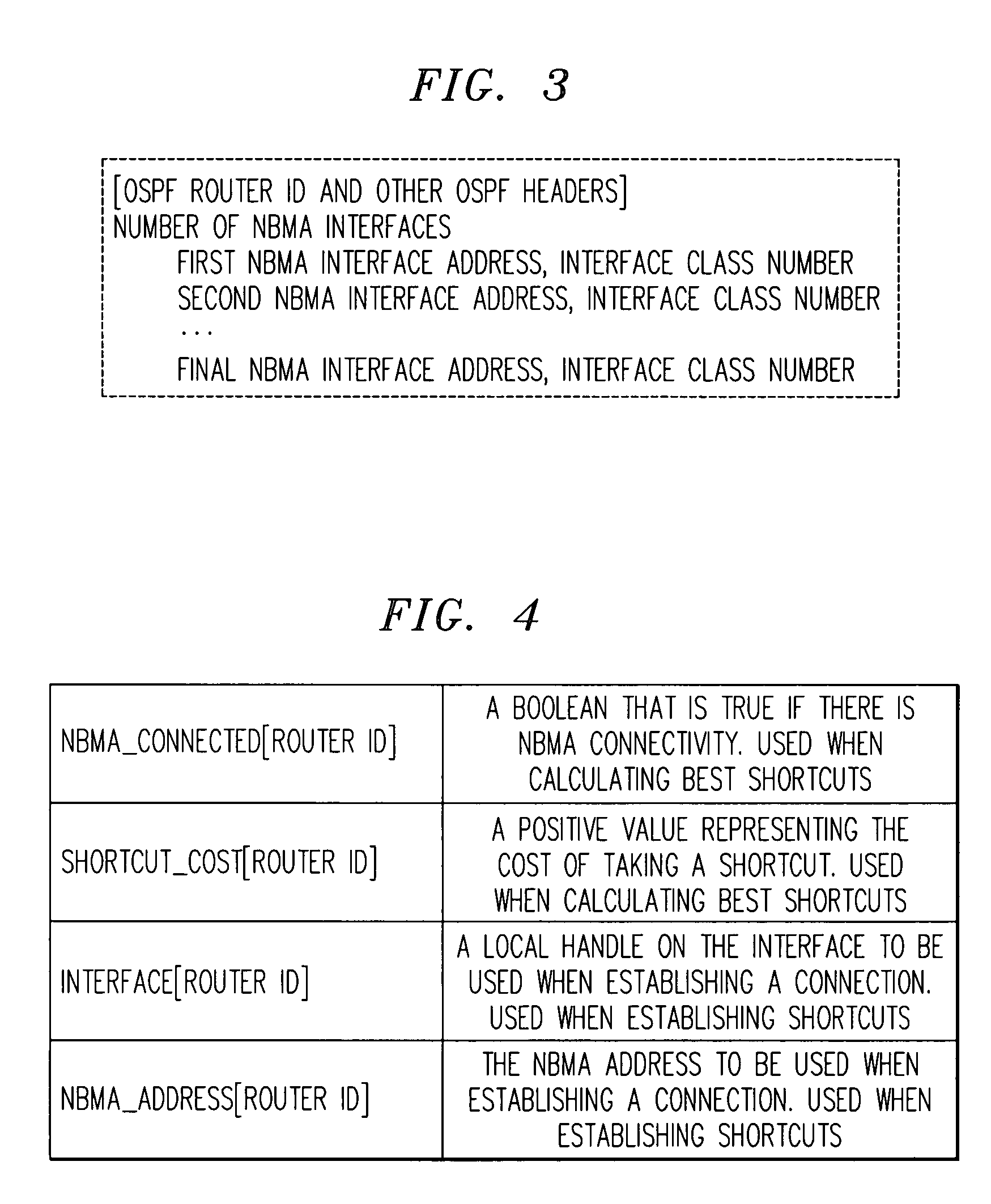
Method for determining non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) connectivity for routers having multiple local NBMA interfaces
InactiveUS7808968B1Avoid overheadIntroduce latencyData switching by path configurationTier 2 networkLink state packet
The present invention discloses an efficient architecture for routing in a very large autonomous system where many of the layer 3 routers are attached to a common connection-oriented layer 2 subnetwork, such as an ATM network. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, a permanent topology of routers coupled to the subnetwork is connected by permanent virtual circuits. The routers can further take advantage of both intra-area and inter-area shortcuts through the layer 2 network to improve network performance. The routers pre-calculate shortcuts using information from link state packets broadcast by other routers and store the shortcuts to a given destination in a forwarding table, along with corresponding entries for a next hop along the permanent topology. The present invention allows the network to continue to operate correctly if layer 2 resource limitations preclude the setup of additional shortcuts.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Extended virtual user-to-network interface with ATM network
An SVC is established via an ATM switch port, which includes multiple virtual paths (VPs), by associating multiple virtual user-to-network interfaces (UNIs) to each of the VPs. Each of the VPs includes multiple virtual circuit (VC) ranges, each of which corresponds to a different virtual UNI. Each VC range includes at least one VC for control and at least one VC for data transfer. Associating the virtual UNIs to each of the VPs includes mapping each virtual UNI to a corresponding VC range within a VP based on a virtual path index (VPI) / virtual channel index (VCI) of the virtual UNI initially received by the ATM switch port.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
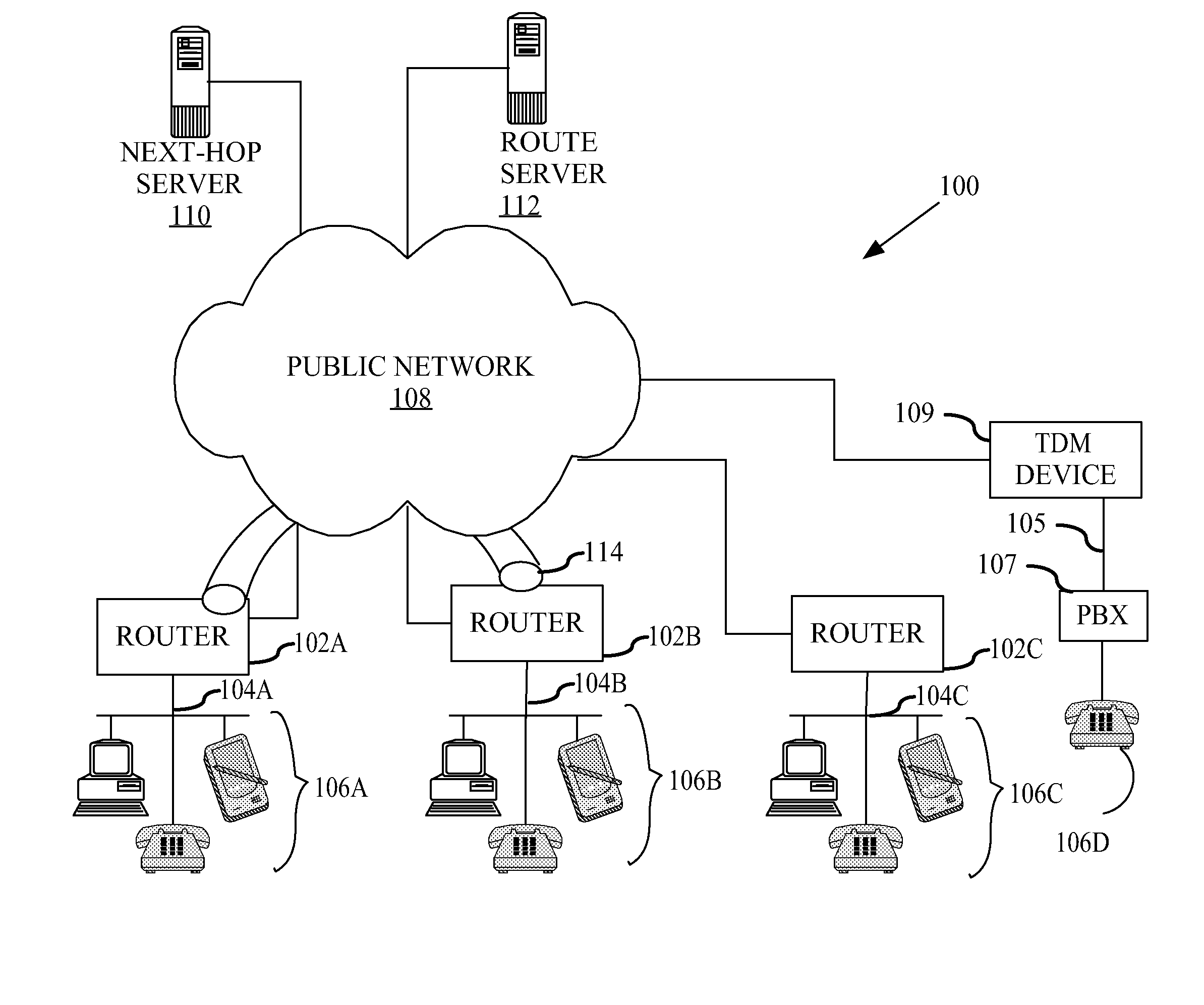
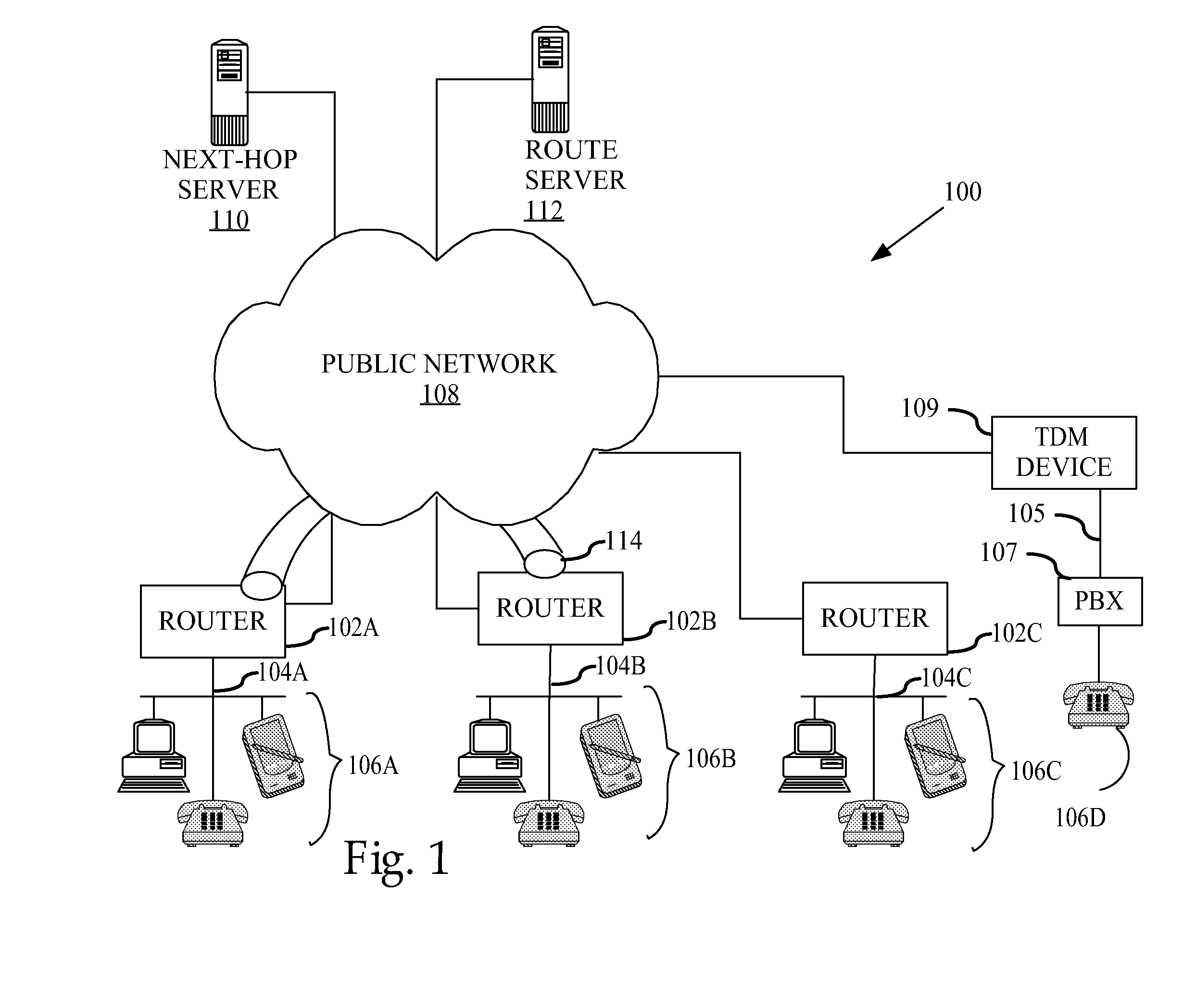
Method and apparatus for dynamically securing voice and other delay-sensitive network traffic
InactiveUS20080229095A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityPrivate network
A method comprises receiving a request for secure network traffic from a device having a private network address at a source node, obtaining the private network address of a requested destination device at a destination node from a route server based on signaling information associated with the request, obtaining the public network address of the destination node associated with the private network address, creating in response to the request a virtual circuit between the source node and the destination node based on the public network address of the destination node, and encrypting network traffic for transporting at least from the source node to the destination node through the virtual circuit. The process is dynamic in that the virtual circuit is created in response to the request. Hence, the process operates as if a fully meshed network exists but requires less provisioning and maintenance than a fully meshed network architecture. Furthermore, the process is readily scalable as if a hub and spoke network exists but is more suitable for delay-sensitive traffic, such as voice and video, than a hub and spoke network architecture.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
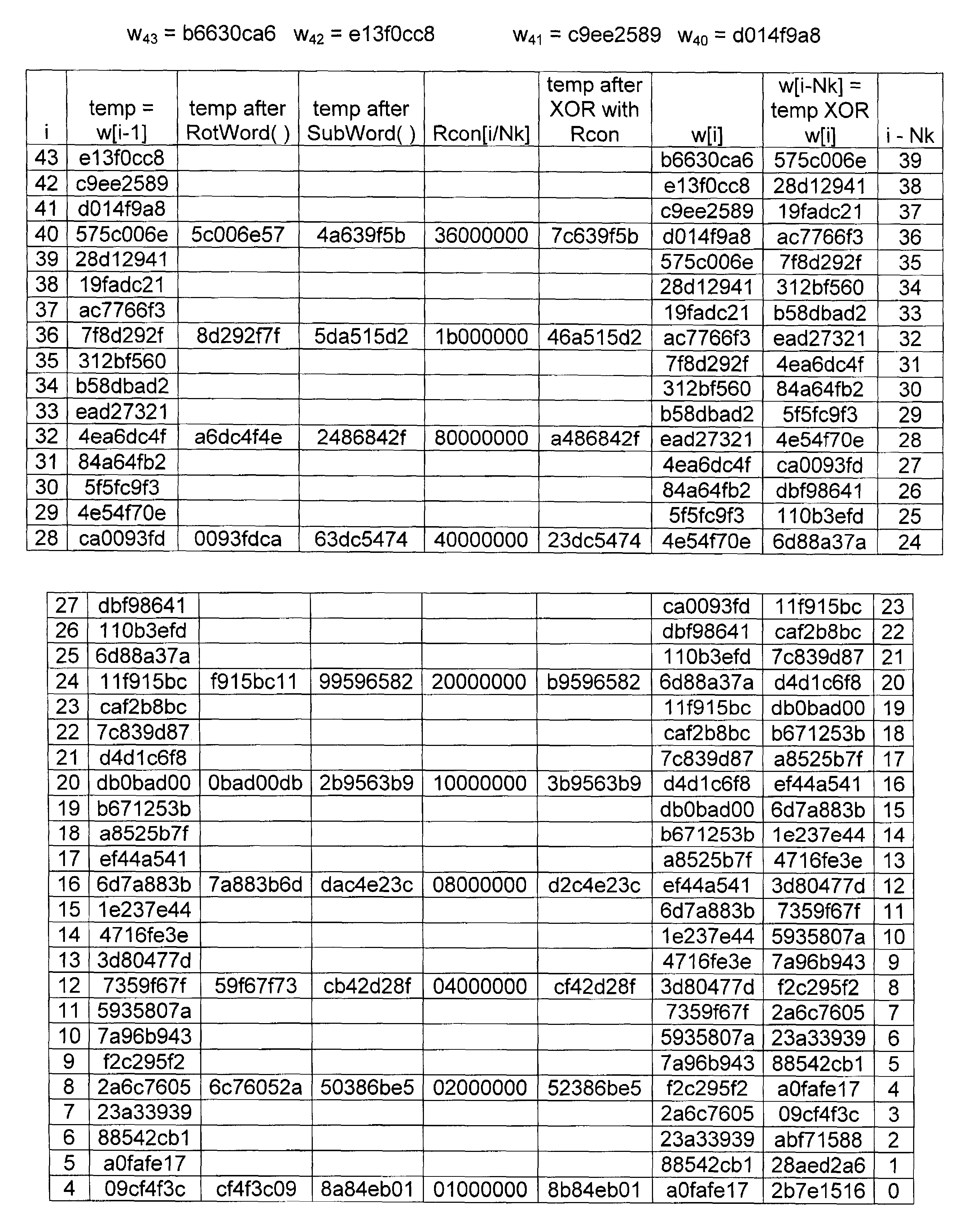
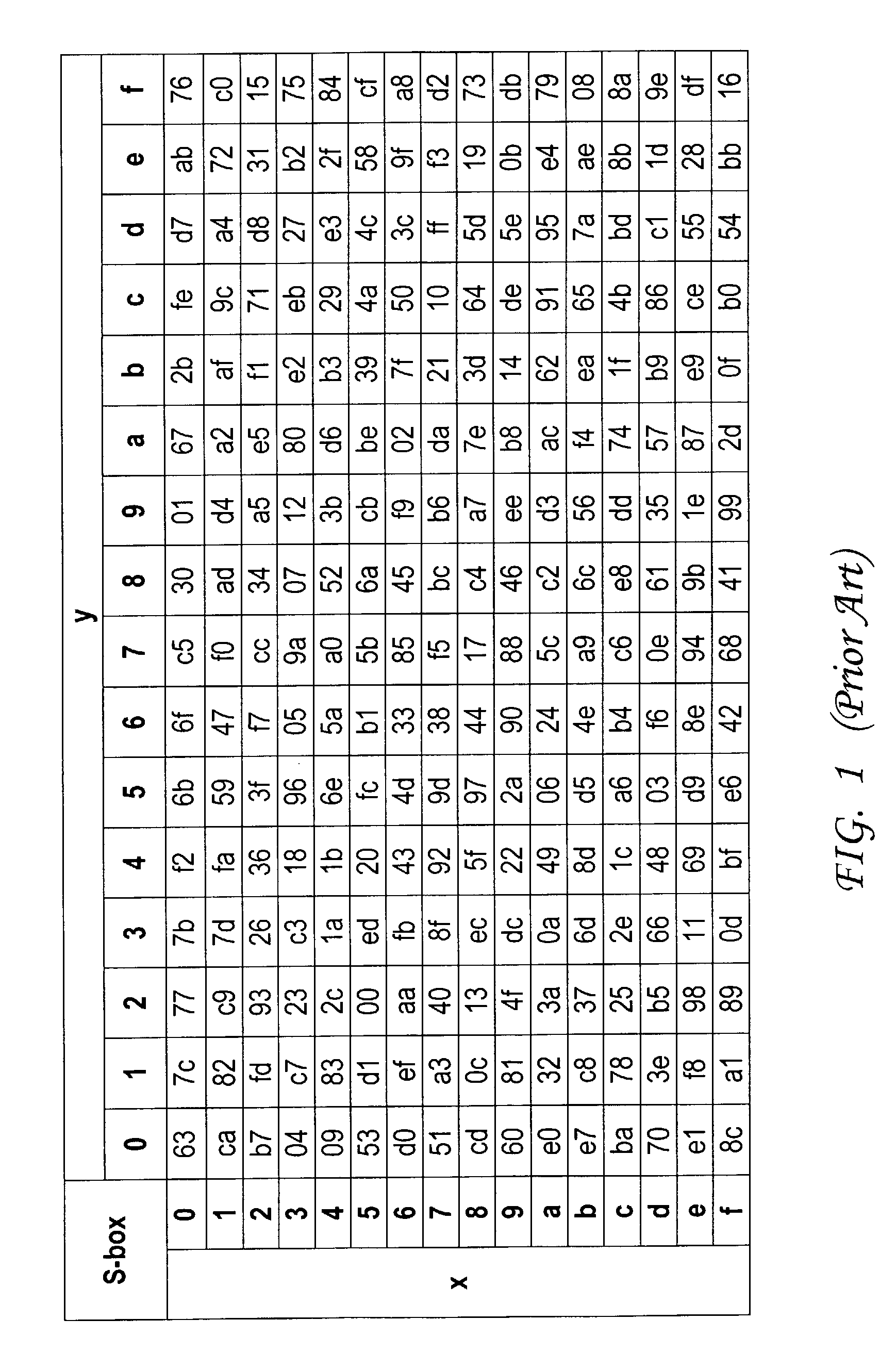
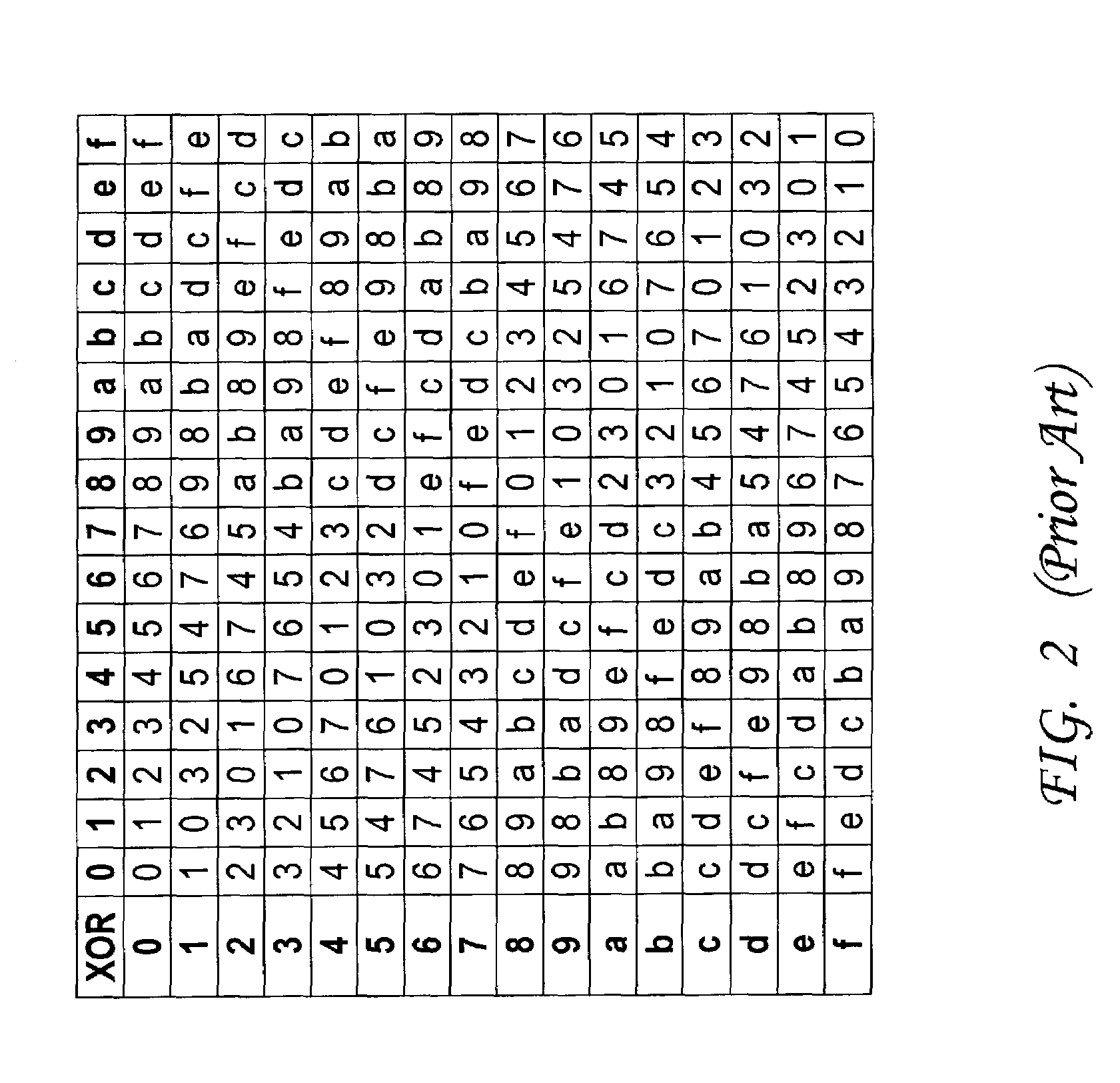
Advanced encryption standard (AES) hardware cryptographic engine
ActiveUS7295671B2Reduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageS-boxAdvanced Encryption Standard
A cryptographic method and related implements the Rijndael—AES encryption standard. In one improvement, the decryption round keys are generated on a round by round basis from the final Nk round keys saved from a previous encryption key scheduling operation. Latency and memory requirements are thereby minimized. S-boxes for the AES key generation and cipher operation itself, may be implemented multiple times in different ways with different power signatures, with a pseudo-random selection of the pathway for the different bytes to be substituted. The premix operation occurs simultaneously with the generation of first round keys, and a dummy circuit with substantially identical timing as the real premix circuitry adds power consumption noise to the premix.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
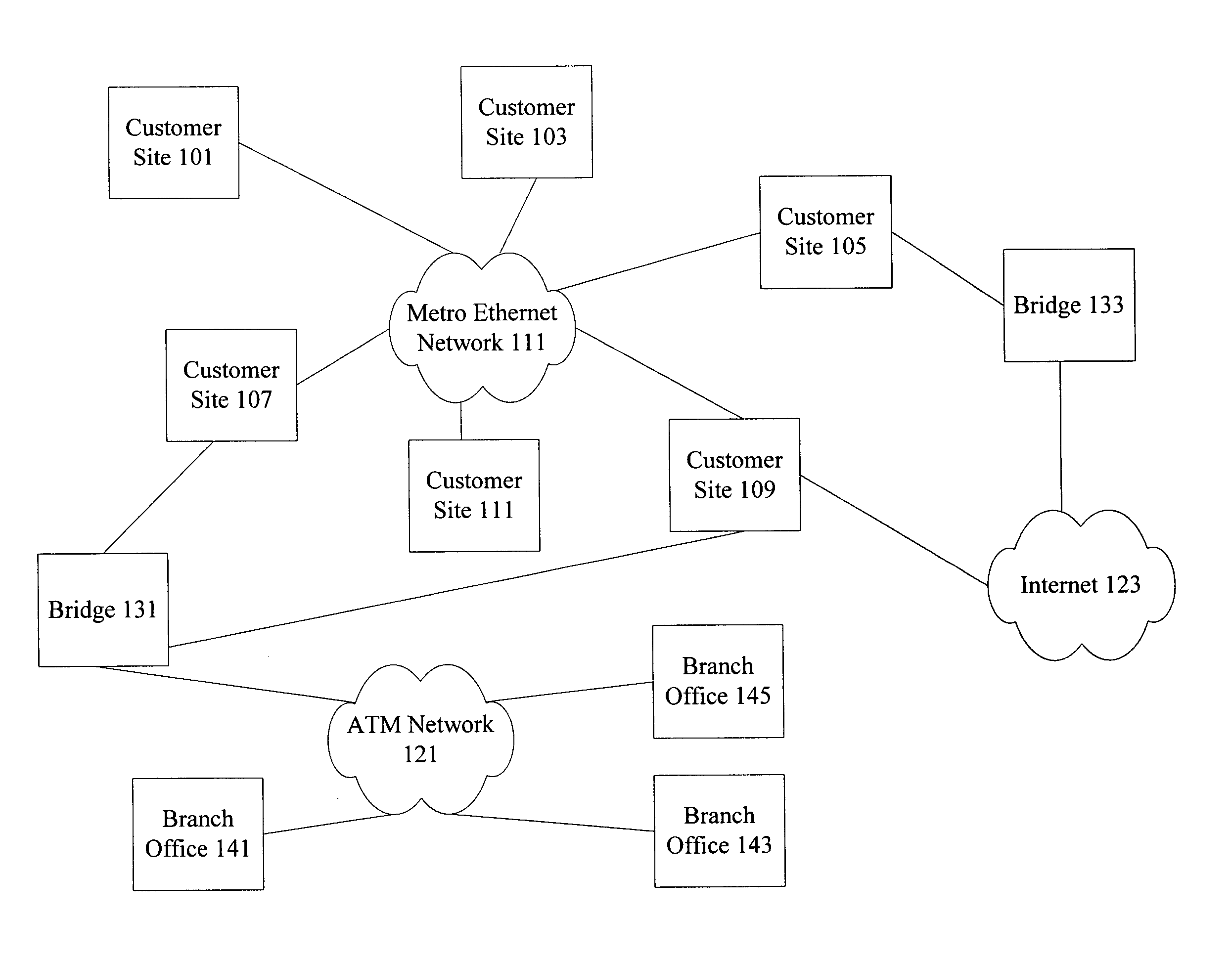
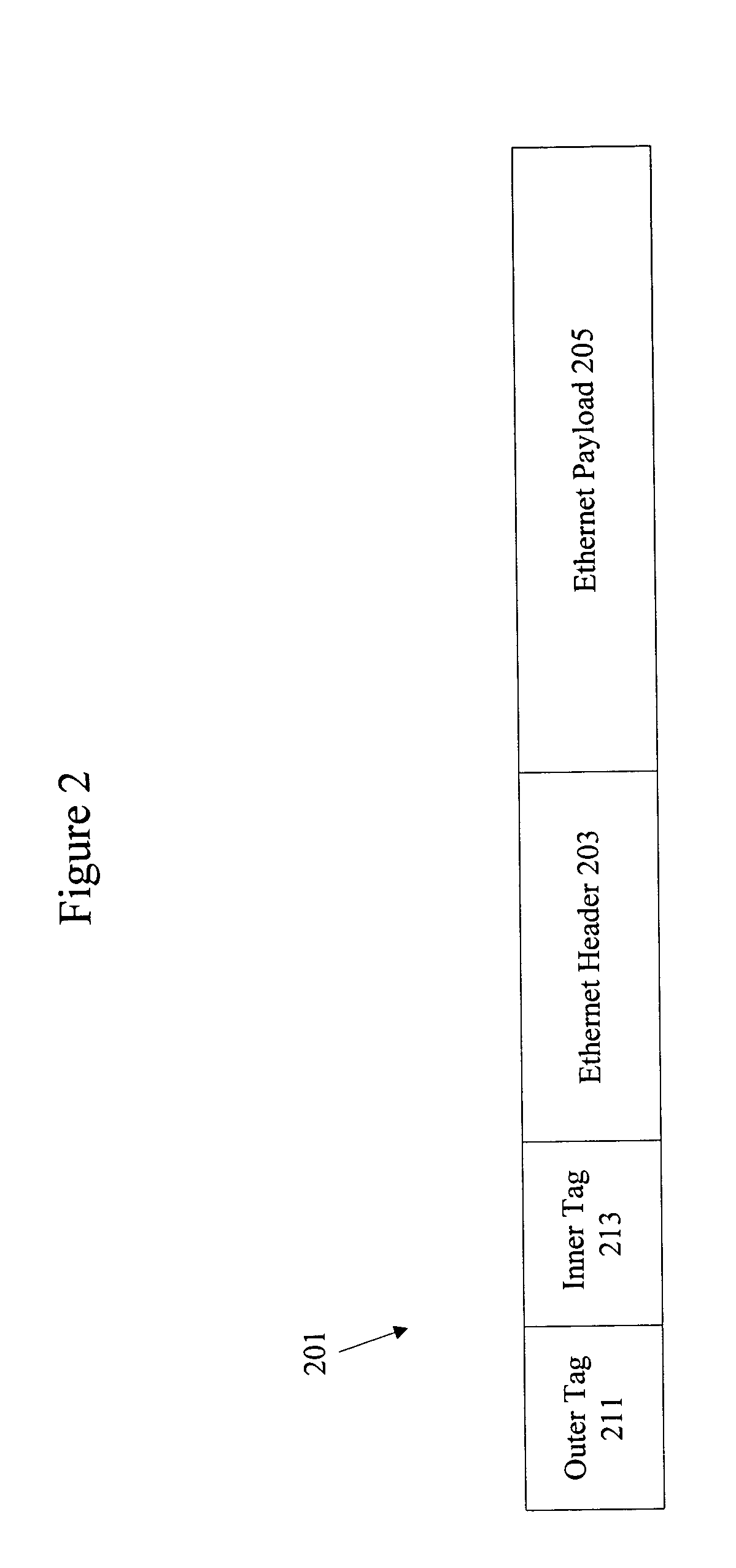
Methods and apparatus for switching between Metro Ethernet networks and external networks
InactiveUS20050063397A1Efficient switchingNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsVirtual LANMetro Ethernet
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided to allow efficient switching of frames for transmission between a Layer 2 Virtual Local Area Network such as a Metro Ethernet Network and an external network. Reserved inner tags are used to identify particular services. In one example, inner tags allow mapping of frames associated with a particular subnetwork onto a particular virtual circuit associated with an ATM network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Establishing sessions with defined quality of service
ActiveUS20070002832A1Facilitate communicationFacilitate multimedia serviceNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementComputer hardwareQuality of service
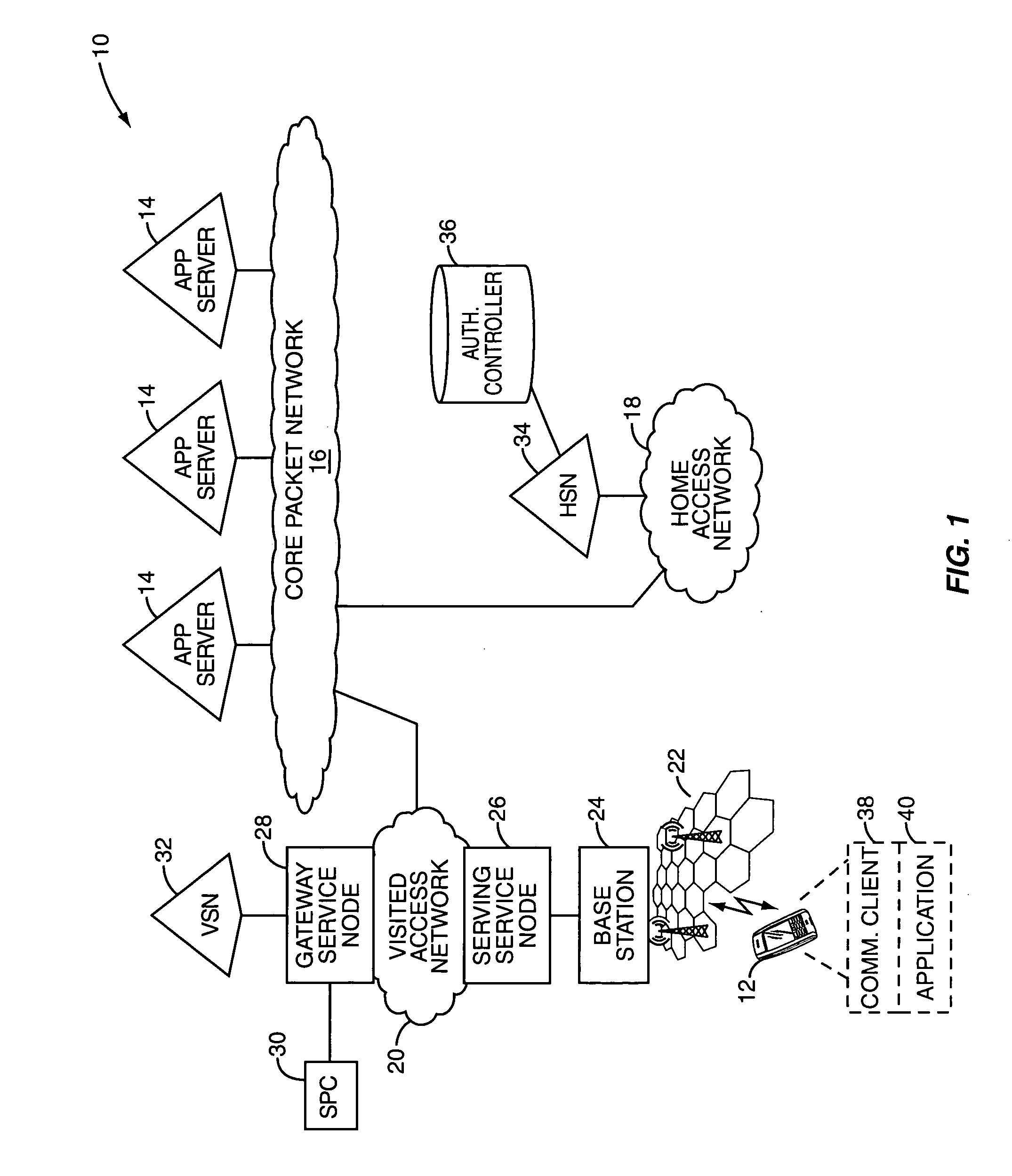
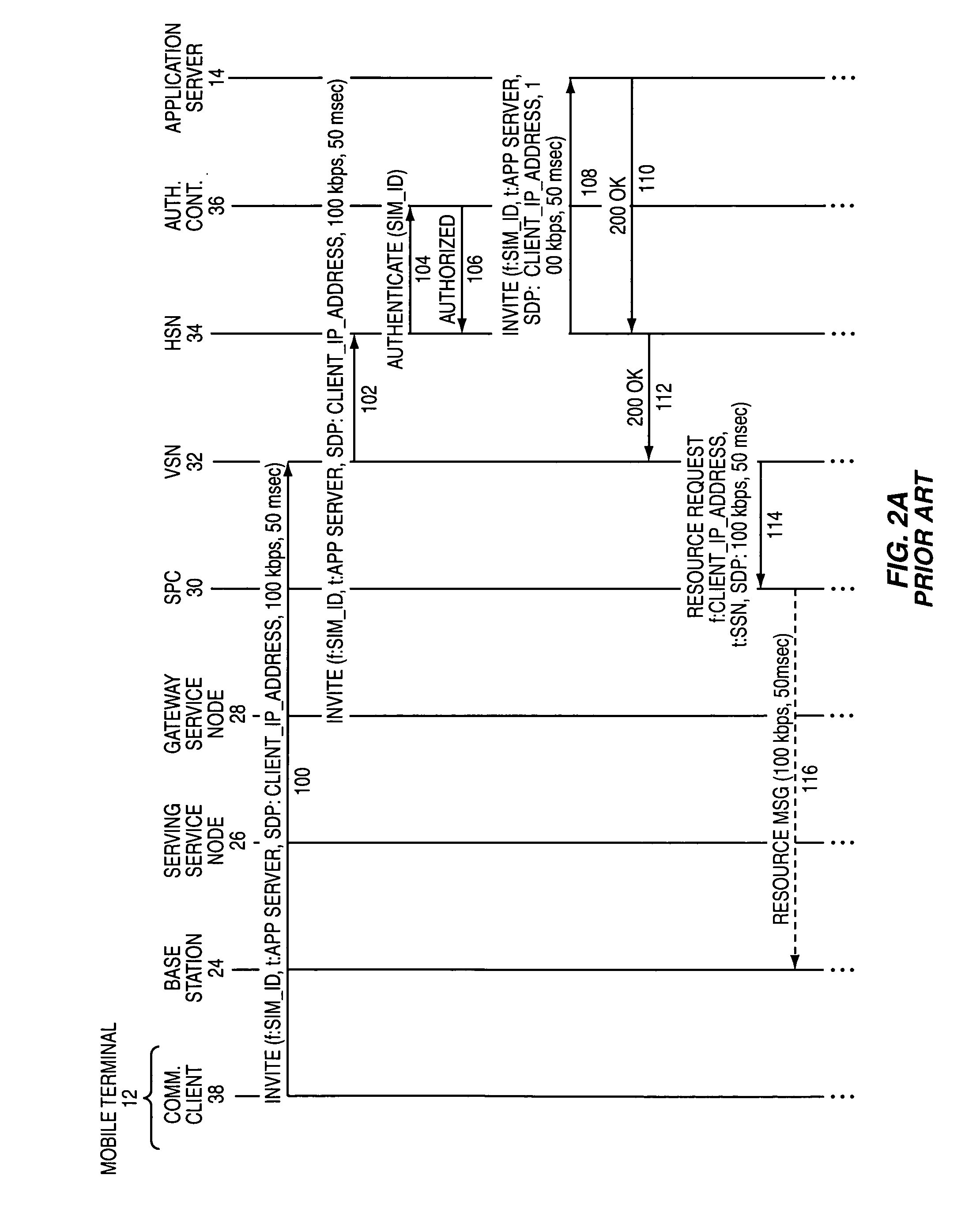
The present invention allows different types of communication applications to cooperate with an associated communication client to facilitate communications having a defined quality of service. The communication client may establish an authorized virtual circuit having a defined quality of service through a network using a first session establishment protocol on behalf of the communication application. Once the authorized virtual circuit is established, the communication application may establish one or more communication sessions, which may support different types of multimedia services, through the virtual connection. In one embodiment, the virtual connection extends through the local access network, which may be supported by an IP multimedia subsystem (IMS). The communication client may use the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) as the first session establishment protocol to establish the virtual circuit through the local access network.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
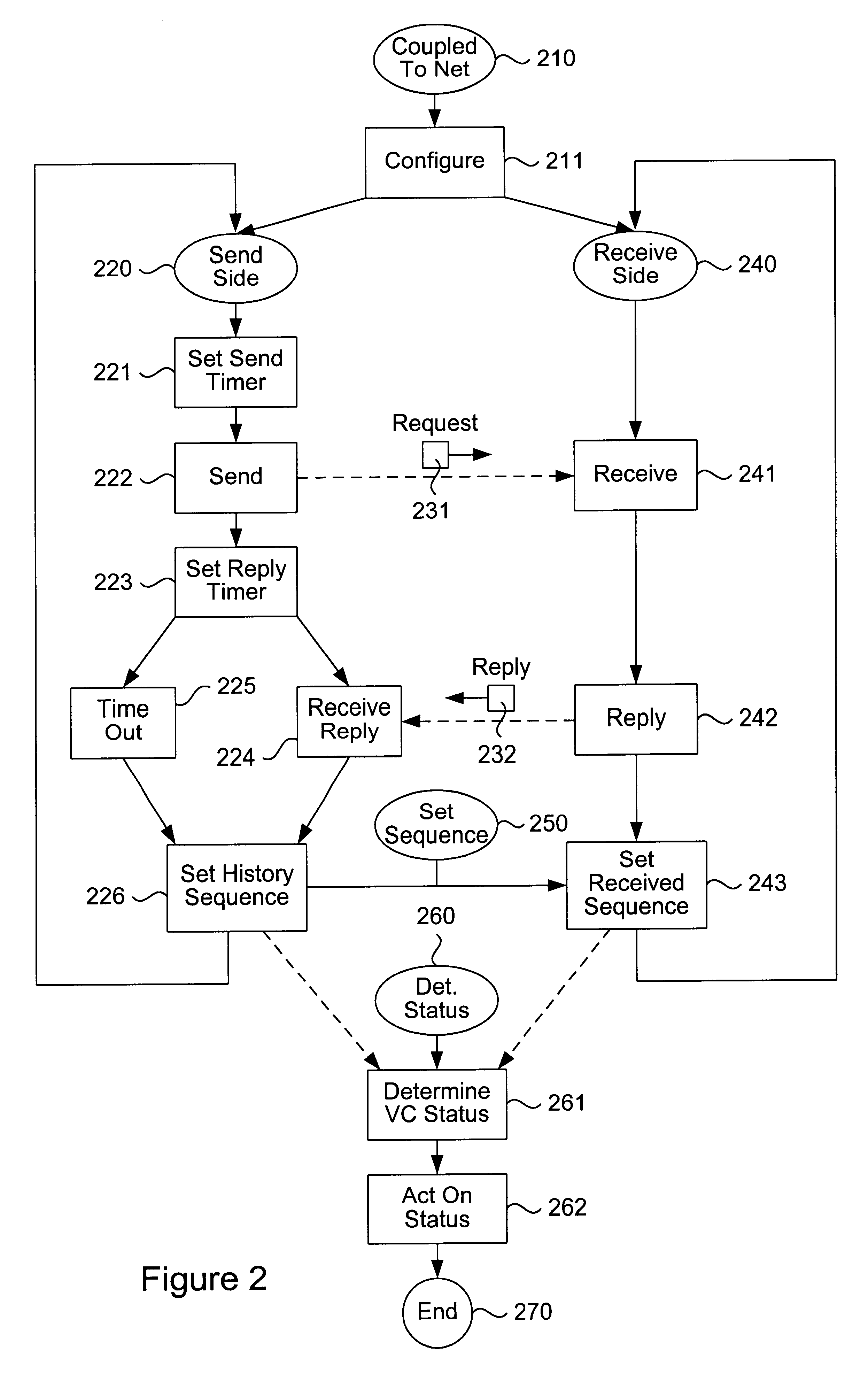
End-to-end bidirectional keep-alive using virtual circuits
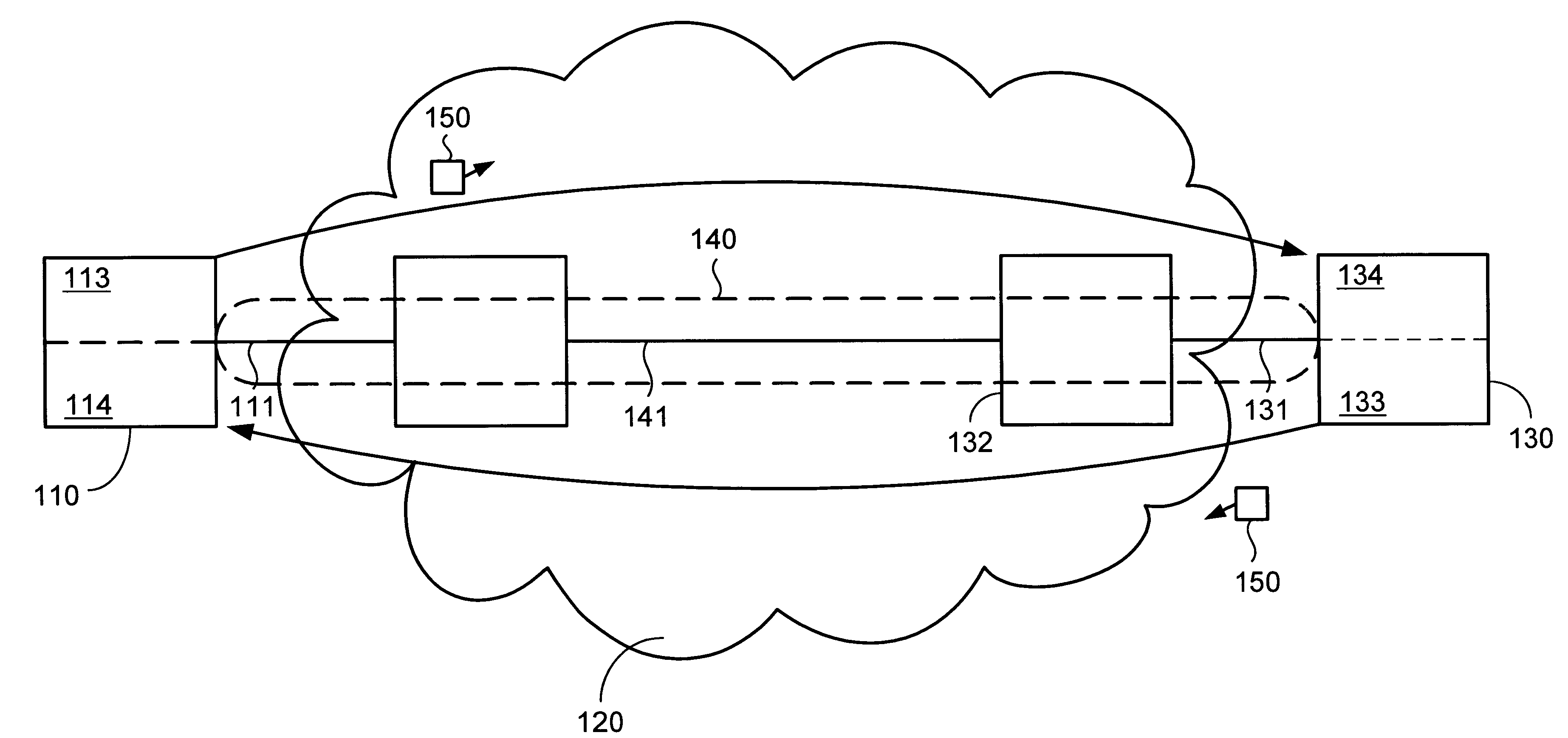
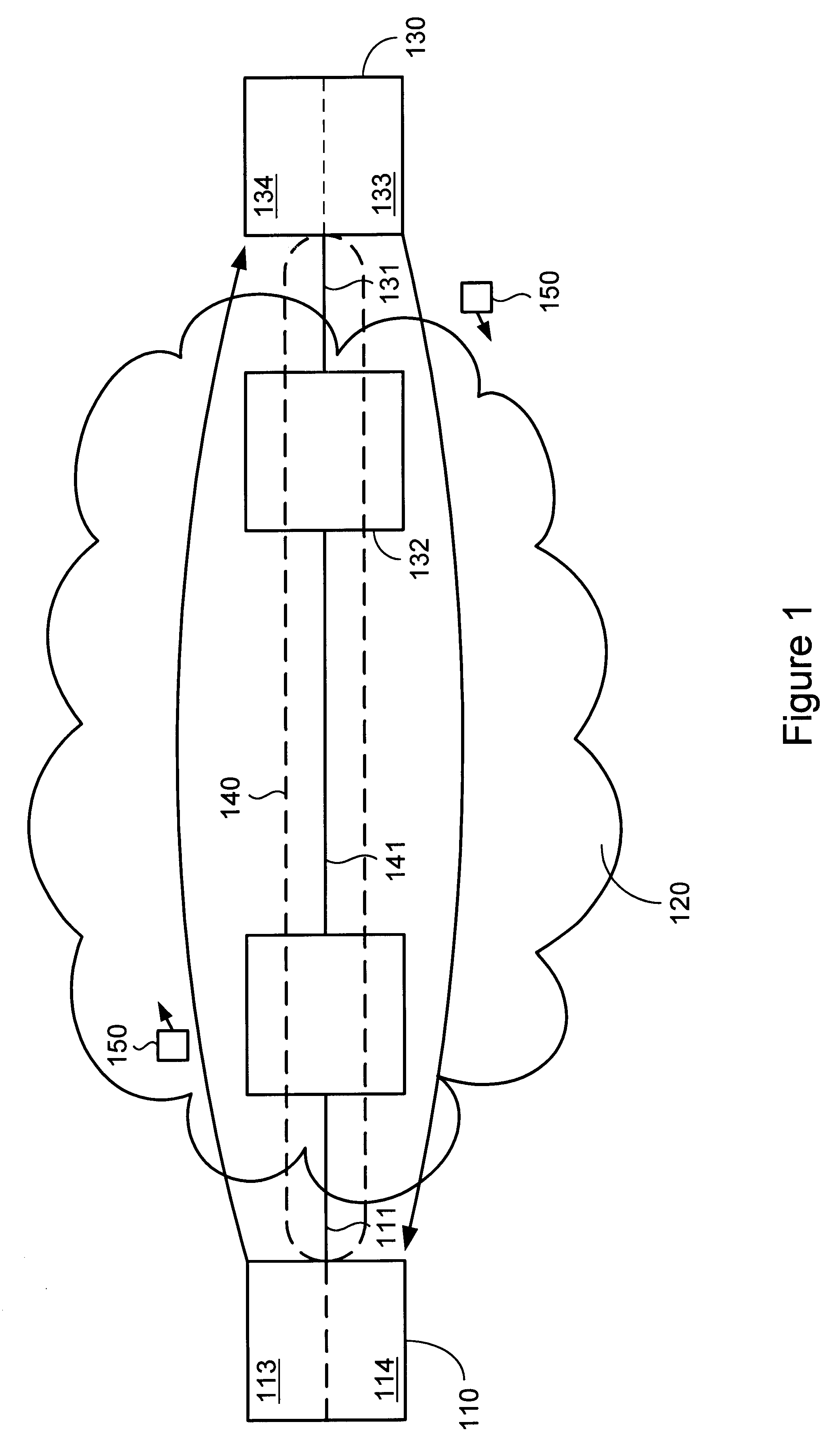
The invention provides a method and system for sending and receiving end-to-end bidirectional keep-alive messages using virtual circuits. Nodes coupled to a network, such as a frame relay network, periodically exchange link-layer "keep-alive" messages which indicate information regarding configuration and status of the virtual circuit, as well as information regarding congestion at sending nodes. Nodes respond to received keep-alive messages, or to timed-out failure to receive keep-alive messages, with follow-on actions, such as attempting to reconnect when a virtual circuit fails. Keep-alive messages may be propagated across multiple networks of either similar or different architecture. Keep-alive messages include sent and received sequence numbers, thus providing receiving nodes with a technique for determining if any keep-alive messages have been lost. Keep-alive messages can also include information regarding configuration of the virtual circuit, status of the virtual circuit (including counts of recent keep-alive message failure or success), and congestion at the sending node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Authentication for use of high speed network resources
A method and system for associating a switched virtual circuit (SVC) connection request from an access port in an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network to a subscriber and optionally registering an address of the access port in relation to the subscriber. The method and system include receiving a signaling protocol message requesting the SVC connection from the access port, determining whether the signaling protocol message contains subscriber authentication data and, when authenticated, establishing the SVC connection. Furthermore, the SVC connection may be established only if service policies corresponding to the subscriber retrieved from a database indicate that the subscriber is entitled to make SVC connections. The method and system further include registering an address of the access port in the ATM network by substituting the address of the access port for an original subscriber address.
Owner:AT&T LABS
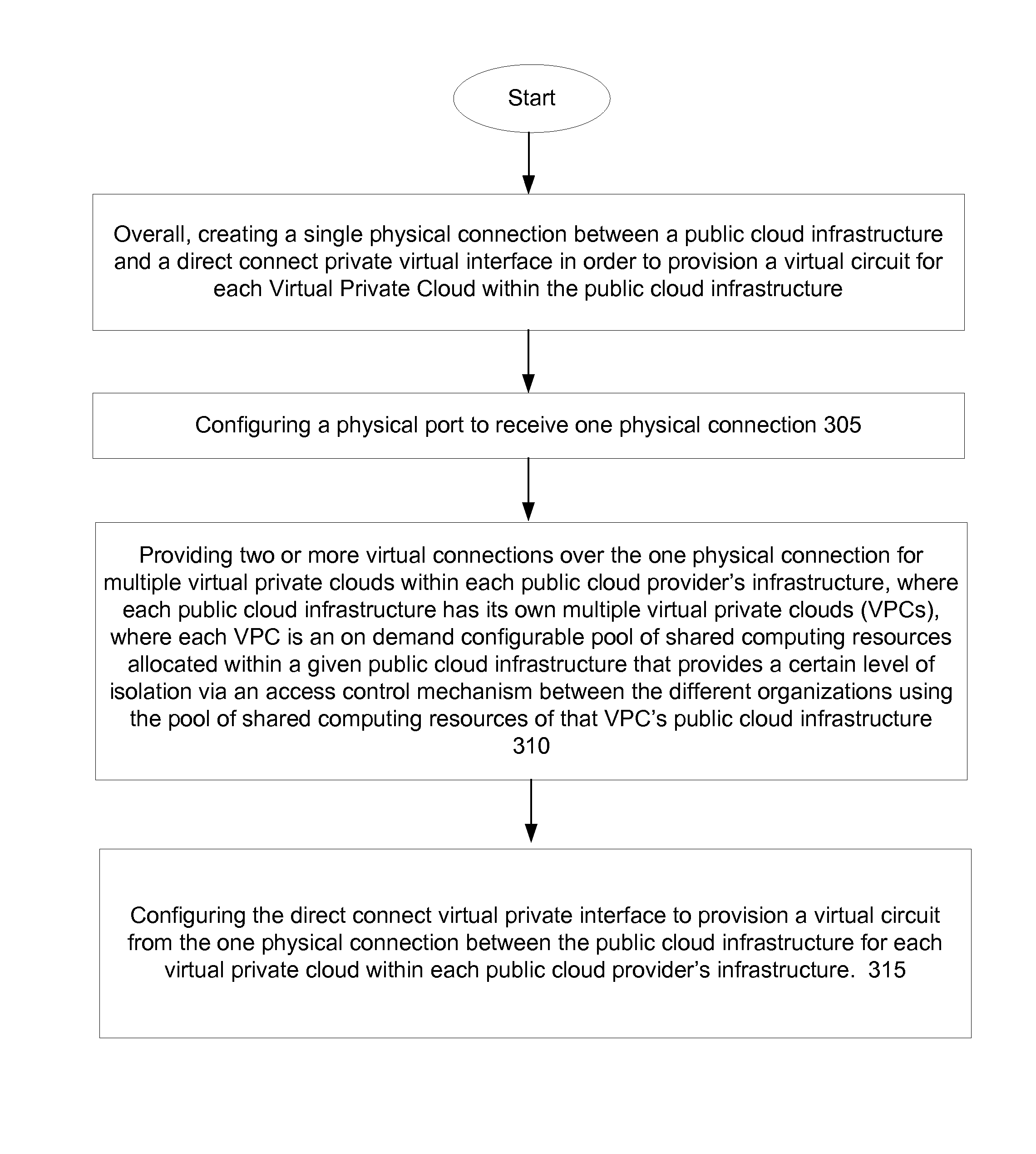
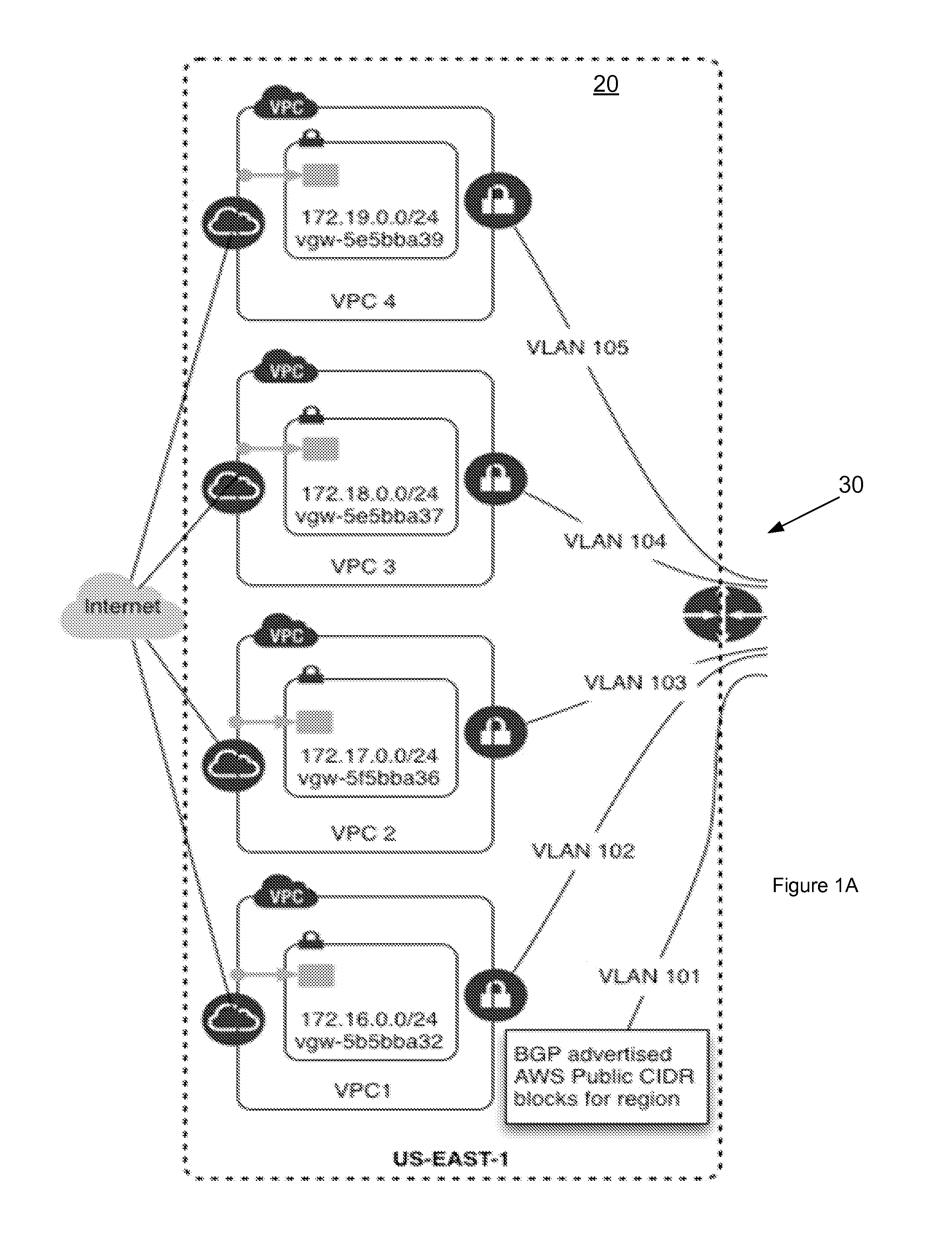
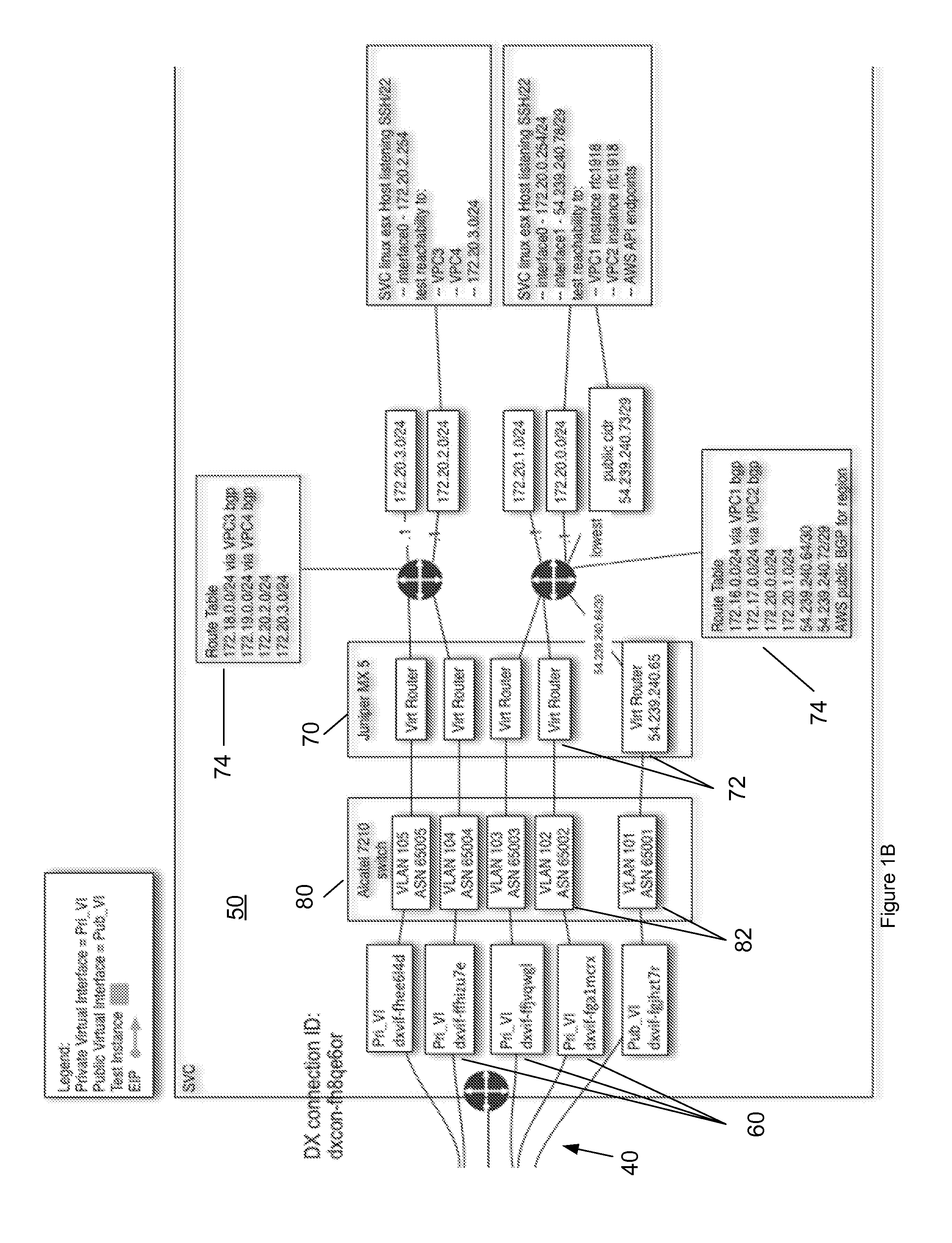
Direct Connect Virtual Private Interface for a One to Many Connection with Multiple Virtual Private Clouds
ActiveUS20140334495A1Good serviceData switching by path configurationProgram controlResource poolCloud provider
Systems and methods include a direct connect virtual private interface includes a physical port configured to receive one physical connection in order to provide two or more virtual connections for multiple virtual private clouds (VPCs) within a public cloud provider's infrastructure. Each public cloud infrastructure has its own multiple VPCs. Each VPC is an on demand configurable pool of shared computing resources allocated within each public cloud provider's infrastructure that provides a certain level of isolation via an access control mechanism between different organizations using the pool of shared computing resources of that VPC's public cloud infrastructure. The direct connect virtual private interface is configured to provision a virtual circuit from the one physical connection between the public cloud infrastructure for each VPC within each public cloud provider's infrastructure.
Owner:EQUINIX
Multi-hop peer-to-peer wireless local loop phone system and method
InactiveUS20050036470A1Lower latencyLarge installationEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmitted powerCo-channel interference
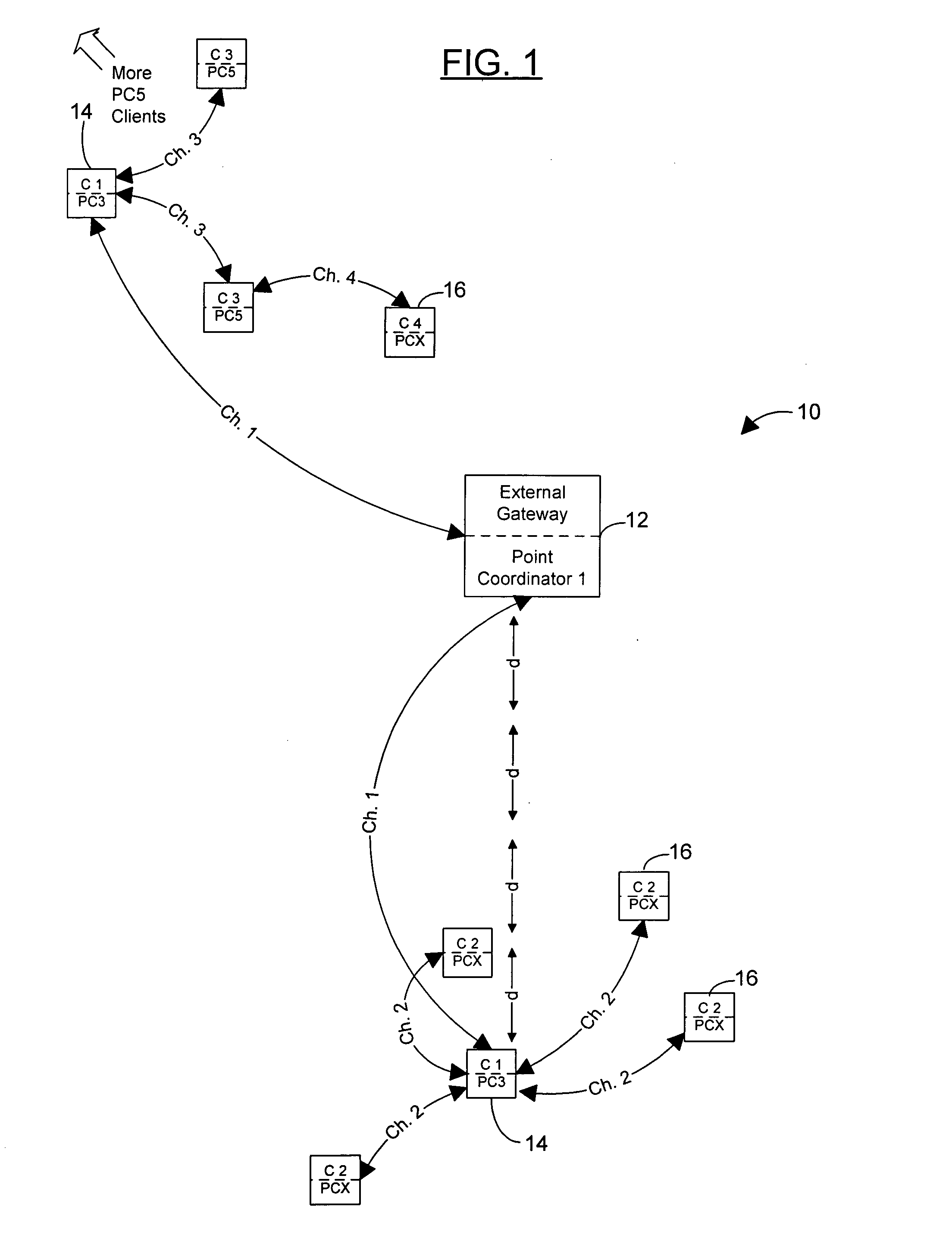
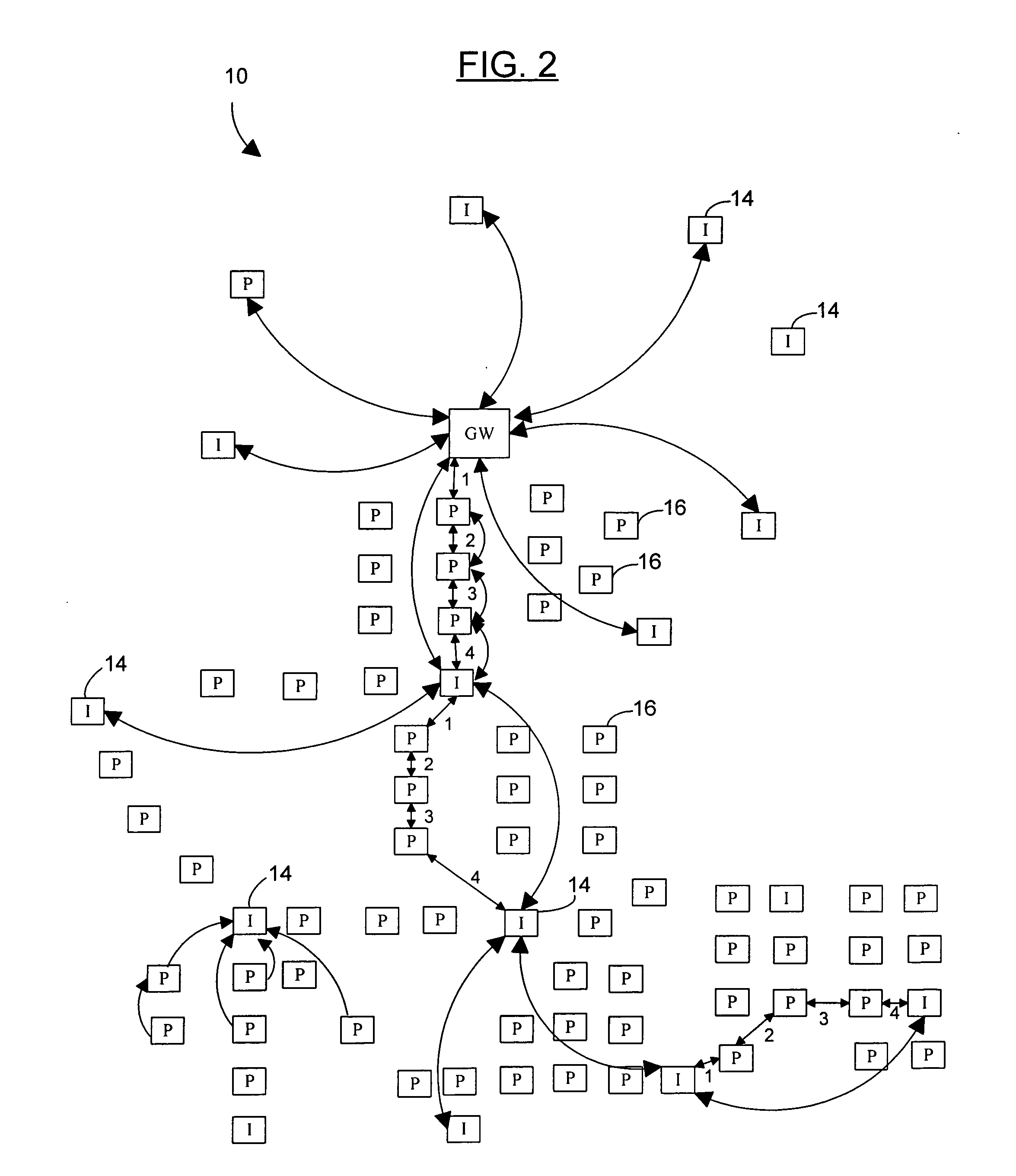
A peer-to-peer wireless phone system with peer-to-peer units and network configuration algorithms by which a virtual circuit data path is established by minimizing the latency added at each hop starting with the external network gateway or the most loaded hop and choosing closest time slots for each next hop until a the virtual circuit is completed. Also, certain embodiments of the present invention include network configuration algorithms by which traffic around any external network gateway(s) is optimized to maximize throughput around the gateway by allocating certain of many available channels to a group of P2P units around the gateway, these units acting as an “infrastructure” through which other units route virtual circuits through the gateway. The network topology is also configured to let these units transmit at higher power levels and ranges than other P2P units in the network, and thereby help minimize the number of hops needed to reach the external network gateway. Further, other sets of units can be configured with similar larger transmit ranges (around 4 of the standard P2P hop ranges), positioned at such a range on the opposite side of from the gateway to also act as “infrastructure units”, both to pass calls forward to the group of units in the gateway's Point Coordinator group, and to also route circuits that are internal to the network around the Point Coordinator group on the gateway, thereby maximizing efficient use of the gateway capacity. Such rings or layers of infrastructure can be repeated as necessary to minimize hops as the network grows larger, making the tradeoff between minimizing hops (which maximizes transmit power and increases co-channel interference) and minimizing power (which maximizes the number of hops and produces poor latency).
Owner:CALVERT NATHAN HUNTER
Method and system of providing multi-user access to a packet switched network
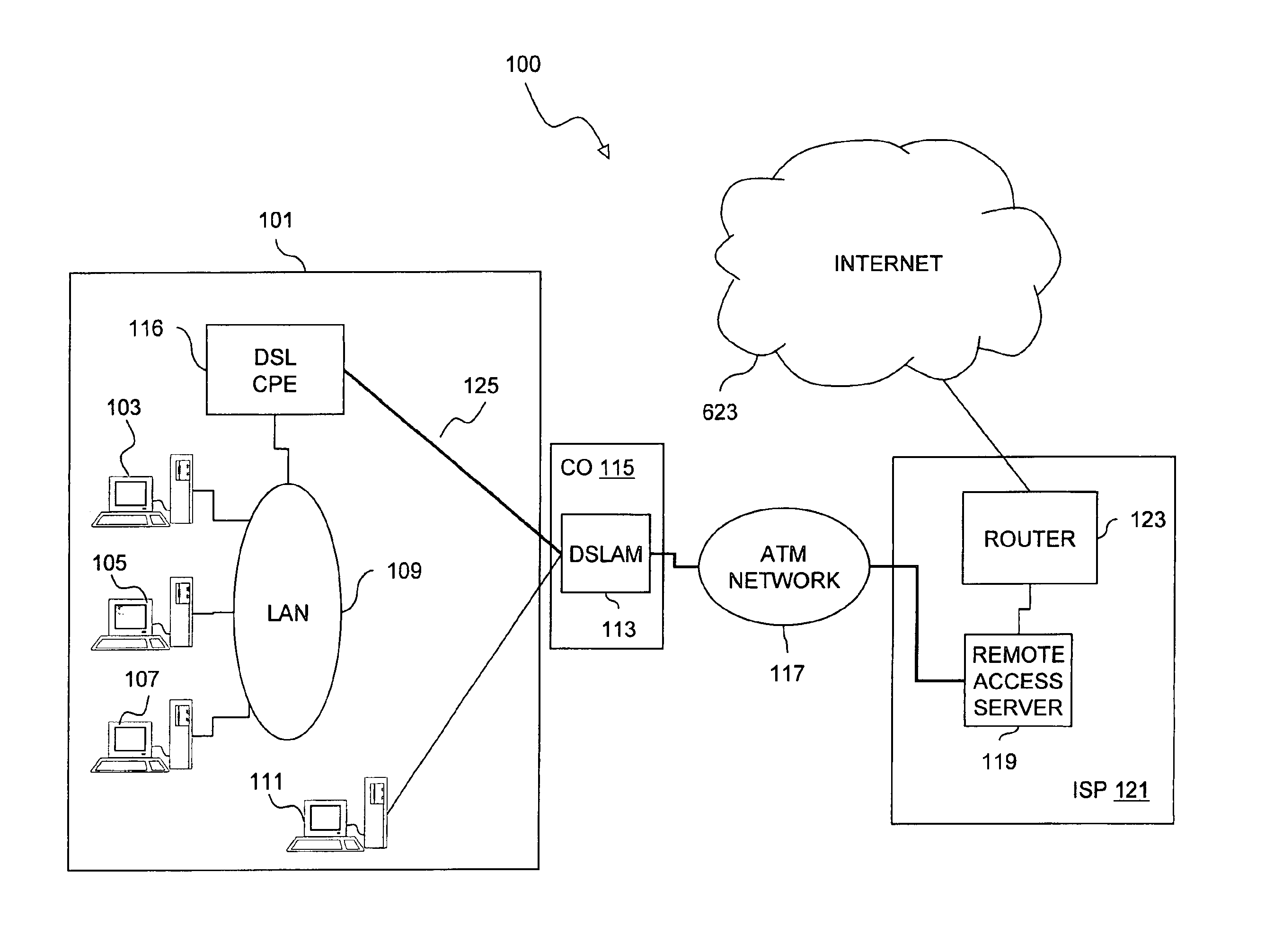
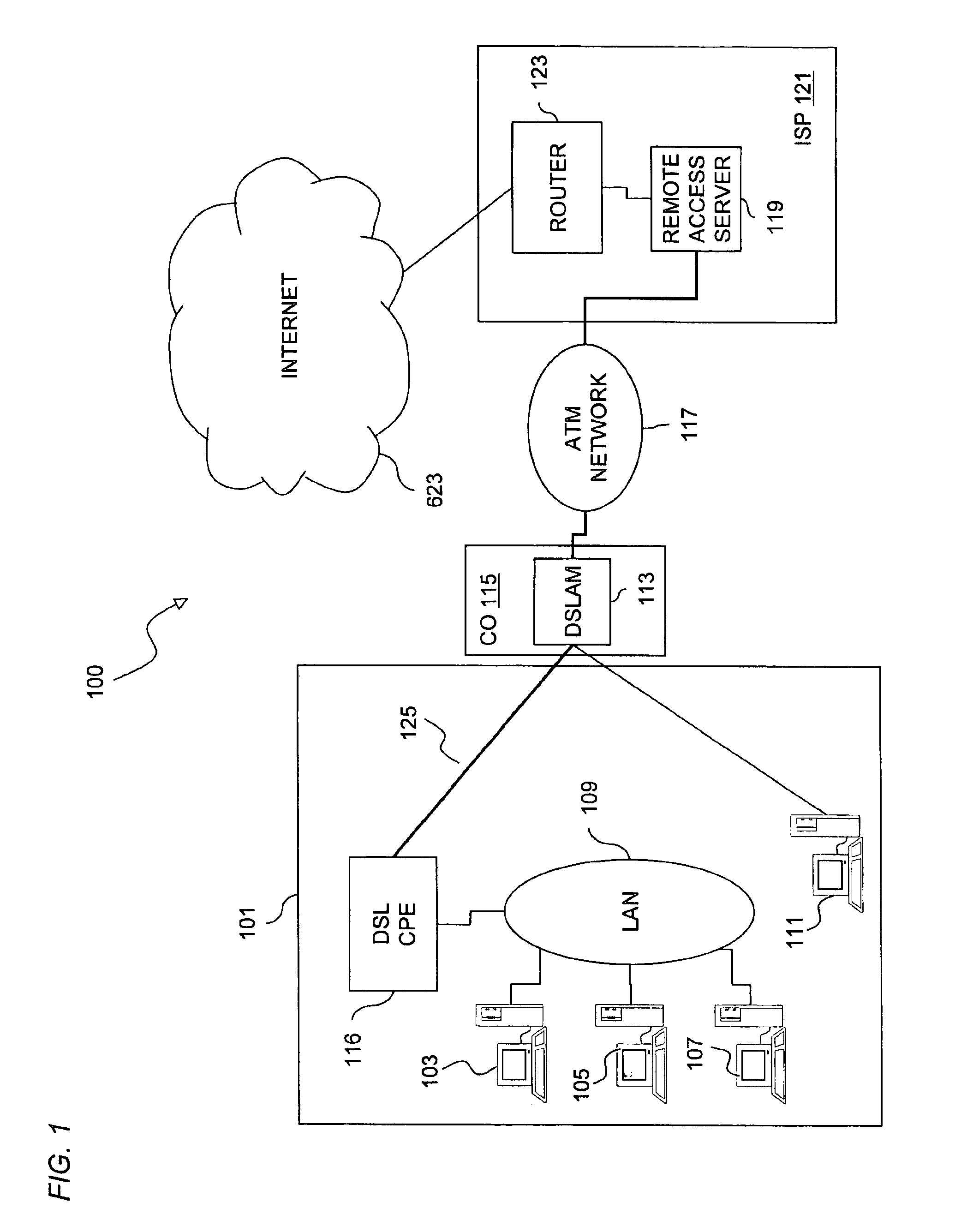
InactiveUS6891825B1Low costSimple configurationTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexCommunications softwareNetwork Communication Protocols
An approach for providing multi-user access to a packet switched network via a shared Ethernet-based local area network (LAN) is disclosed. Multiple end user stations are connected to the LAN, in which each of end user stations executes a communication software. The communication software is based upon a communication protocol (e.g., Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)) that establishes a point-to-point communication session. The end user stations generate packets based upon the communication protocol. In addition, each of the end user stations selectively encapsulates the communication protocol packets using the Ethernet-based LAN protocol. Further, attached to the LAN is a customer premise equipment (CPE), which transmits the encapsulated packets to a line terminating equipment, which according to one embodiment is a digital subscriber line (DSL) access multiplexer that is located in a central office. The line terminating equipment transports the multiple PPP sessions to a multiplexer / demultiplexer, which is located within a regional carrier's network. In one embodiment, the multiplexer / demultiplexer is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switch, which simultaneously transports the multiple PPP sessions over a single permanent virtual circuit (PVC); VPI / VCIs (Virtual Path Identifier / Virtual Connection Identifier) are mapped to the multiple PPP sessions. The multiple PPP sessions are terminated at a remote access server, which recovers and forwards the packets to a backbone router. Thereafter, the backbone router forwards the packets to the packet switched network.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
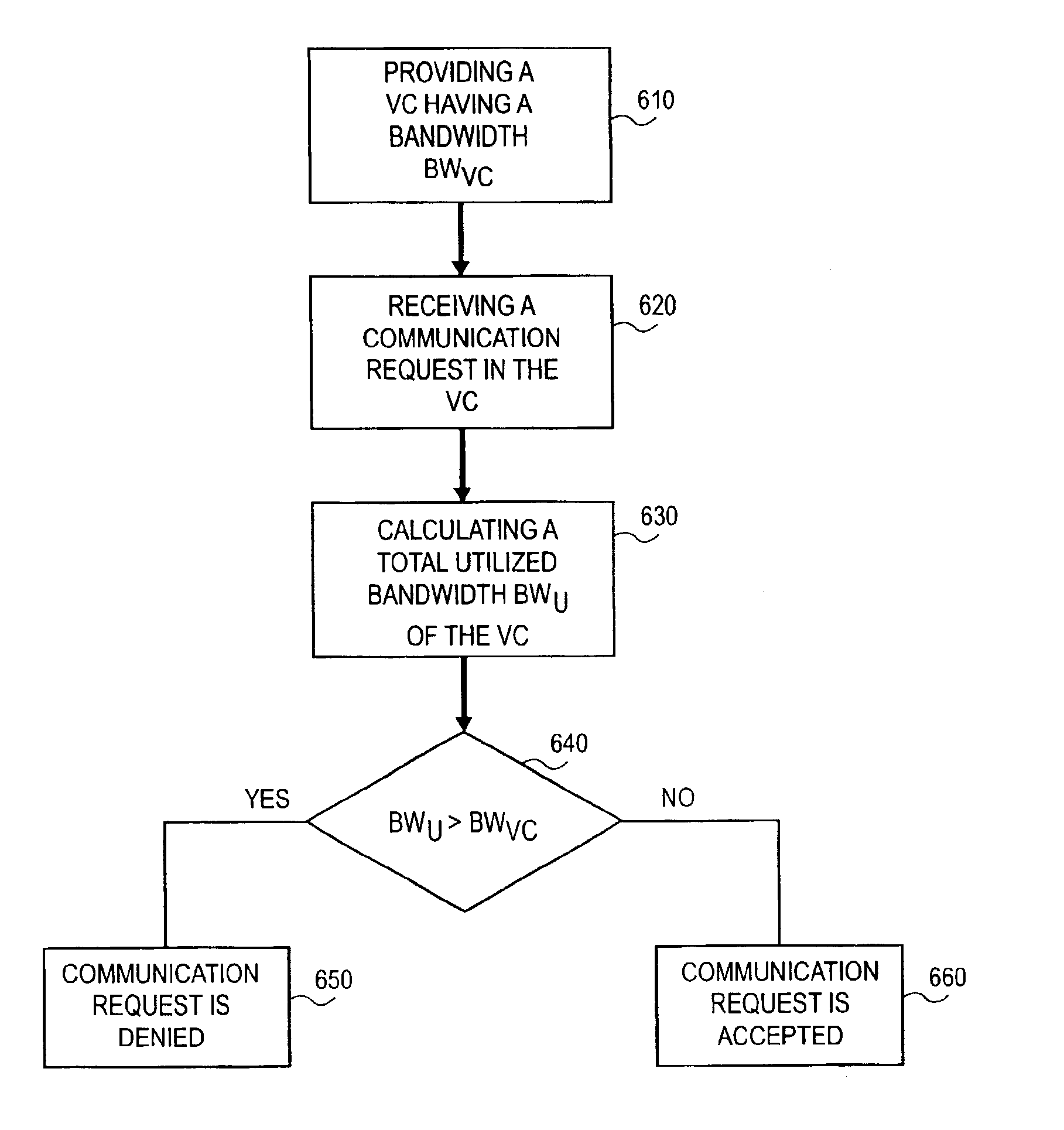
System and method for controlling admission of voice communications in a packet network
InactiveUS6865150B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsVoice communicationCommunication bandwidth
A system and method for controlling admission of a communication in a network are disclosed. In the network, a virtual circuit having a predetermined bandwidth is provided. A request is received for a communication having a communication bandwidth, and a total utilized bandwidth of the virtual circuit is calculated, including the communication bandwidth. If the total utilized bandwidth is less than the predetermined bandwidth of the virtual circuit, then admission in the network is granted to the communication.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Scaling private virtual local area networks (VLANs) across large metropolitan area networks (MANs).
InactiveUS7606939B1Multiple digital computer combinationsMetropolitian area networksVirtual LANPrivate VLAN
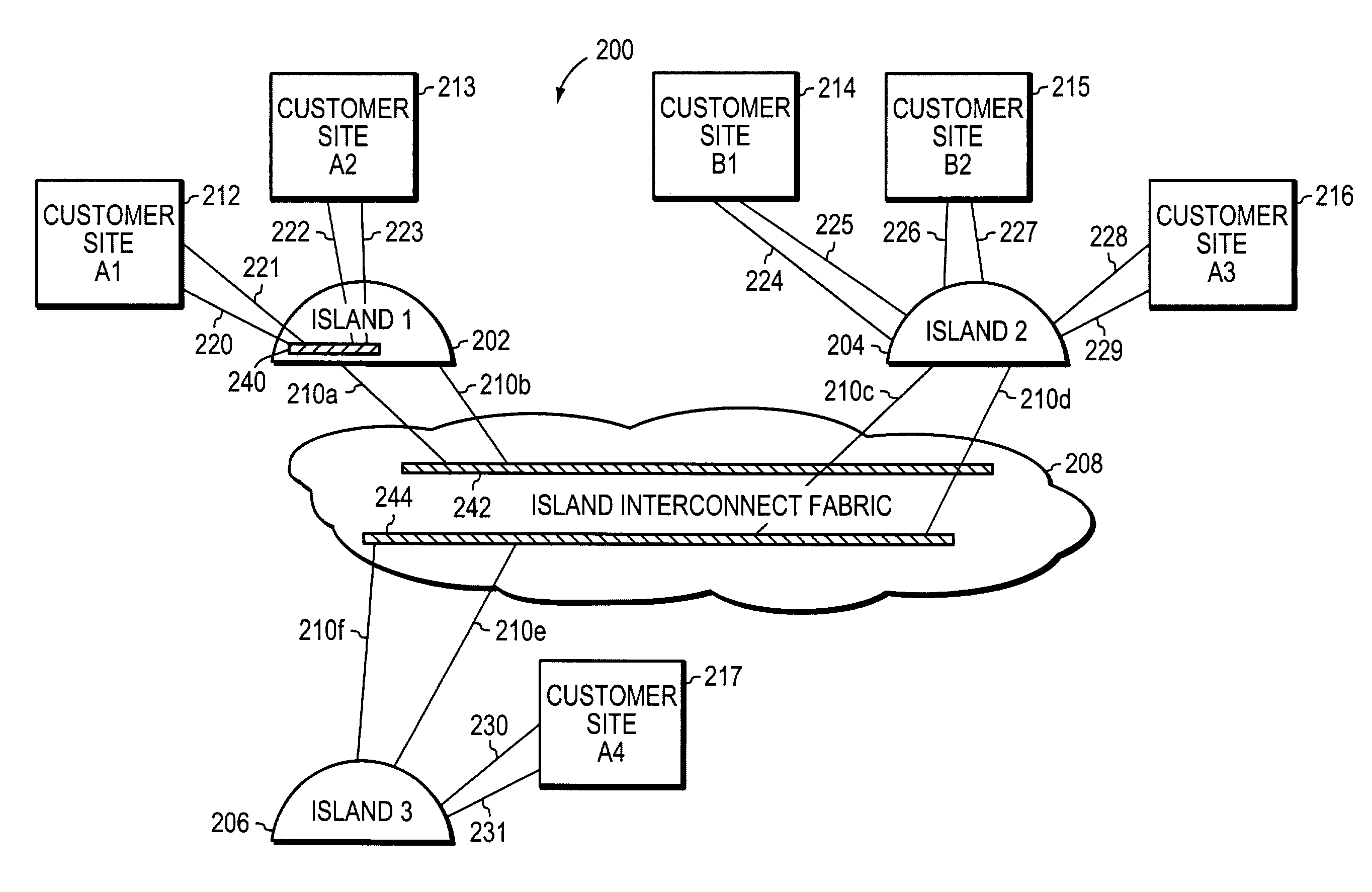
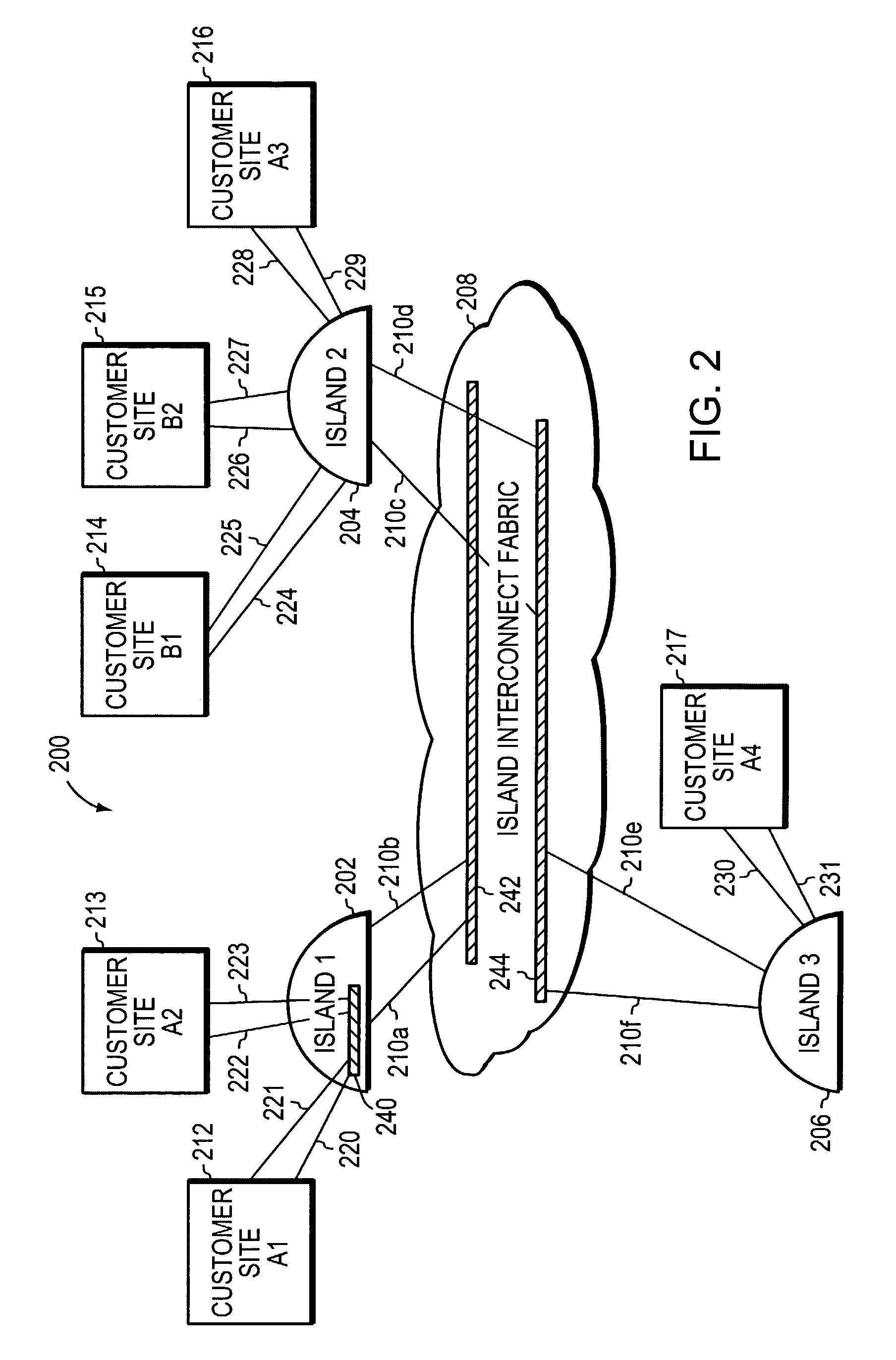
A system and method scales private Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) to a large computer network, such as a very large Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), so that the VLAN designations can be re-used across the network. In the illustrative embodiment, the MAN includes different groups of Layer 2 (L2) switches that are logically organized into Islands interconnected by an interconnect fabric. Within each Island, Customer-Equipment VLAN Identifiers (CE-VLAN IDs) are mapped to MAN Provider-Equipment VLAN IDs (PE-VLAN IDs). The PE-VLAN IDs defined within the MAN support the creation of Private VLANs. Each Private VLAN includes one Primary VLAN, one Isolated VLAN and may include one or more Community VLANs. Different PE-VLAN IDs may be used as the Primary, Isolated and Community VLANs in different Islands. Nonetheless, the Primary, Isolated and Community VLANs from all of the Islands are assigned the same Virtual Circuit IDs, which are loaded into encapsulated frames traversing the interconnect fabric, thereby maintaining the message's association with the Primary, Isolated and Community VLANs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Private lines traversing a packet network and re-arrangement of channels among packet network connections
InactiveUS6882652B1Easy to adaptReduce needTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionPacket generatorNetwork connection
Techniques for providing communication services include provisioning a packet network connection that has packet channels, each of which is independently capable of carrying narrowband signals so as to emulate a private line circuit. A narrowband private line that traverses the packet network connection using a particular one of the packet channels is established. Delays that might otherwise be introduced as a result of packetizing the narrowband signals can be reduced. Private lines that traverse the packet network connection using other packet channels can be added or removed without adversely affecting the existing lines. Additionally, a narrowband communication line that traverses a channel in a first virtual circuit connection in a packet network can be rolled over to a channel in a second virtual circuit connection in the packet network. The latter technique can improve the use of available bandwidth and can be applied to non-private line applications as well.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
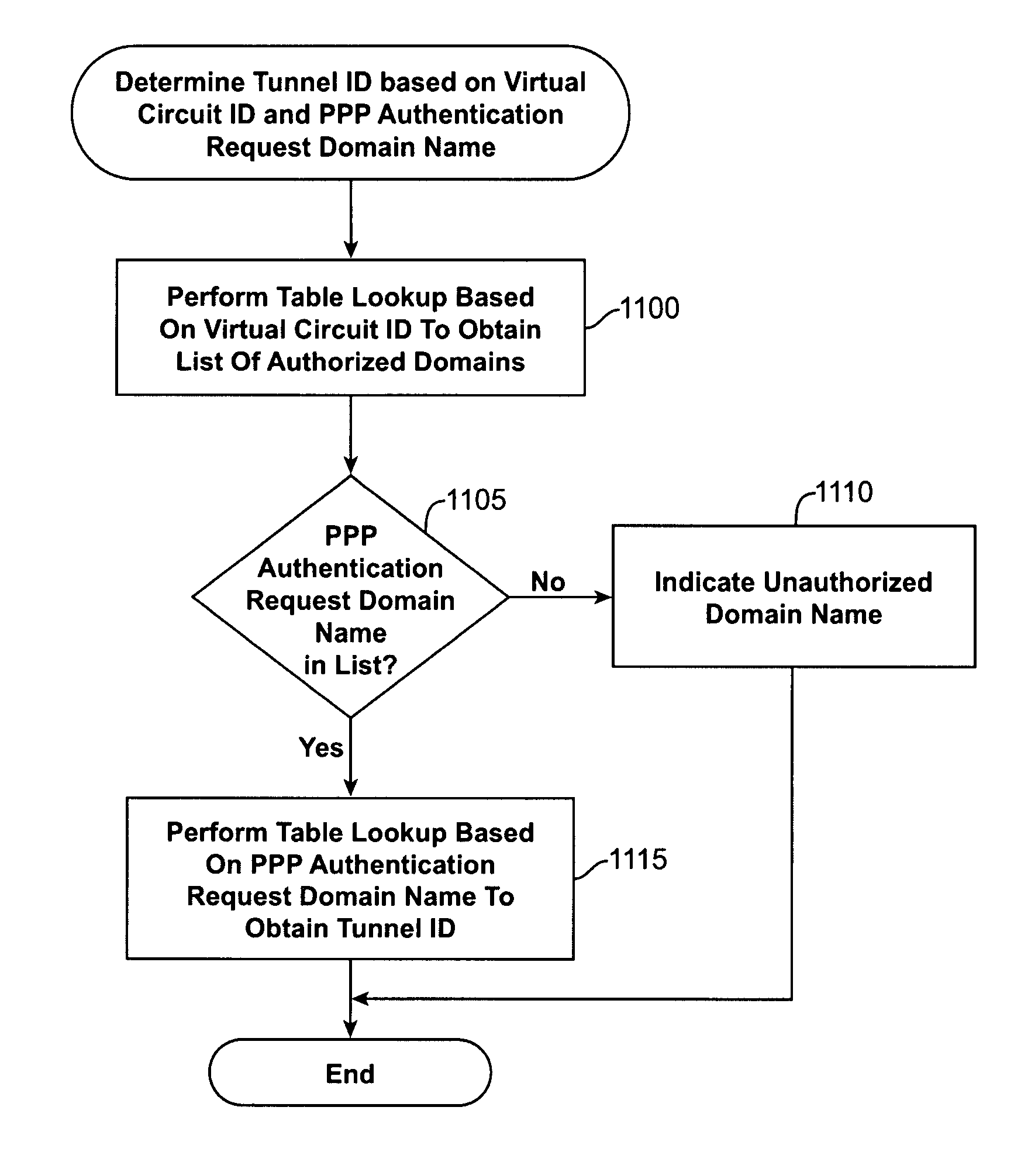
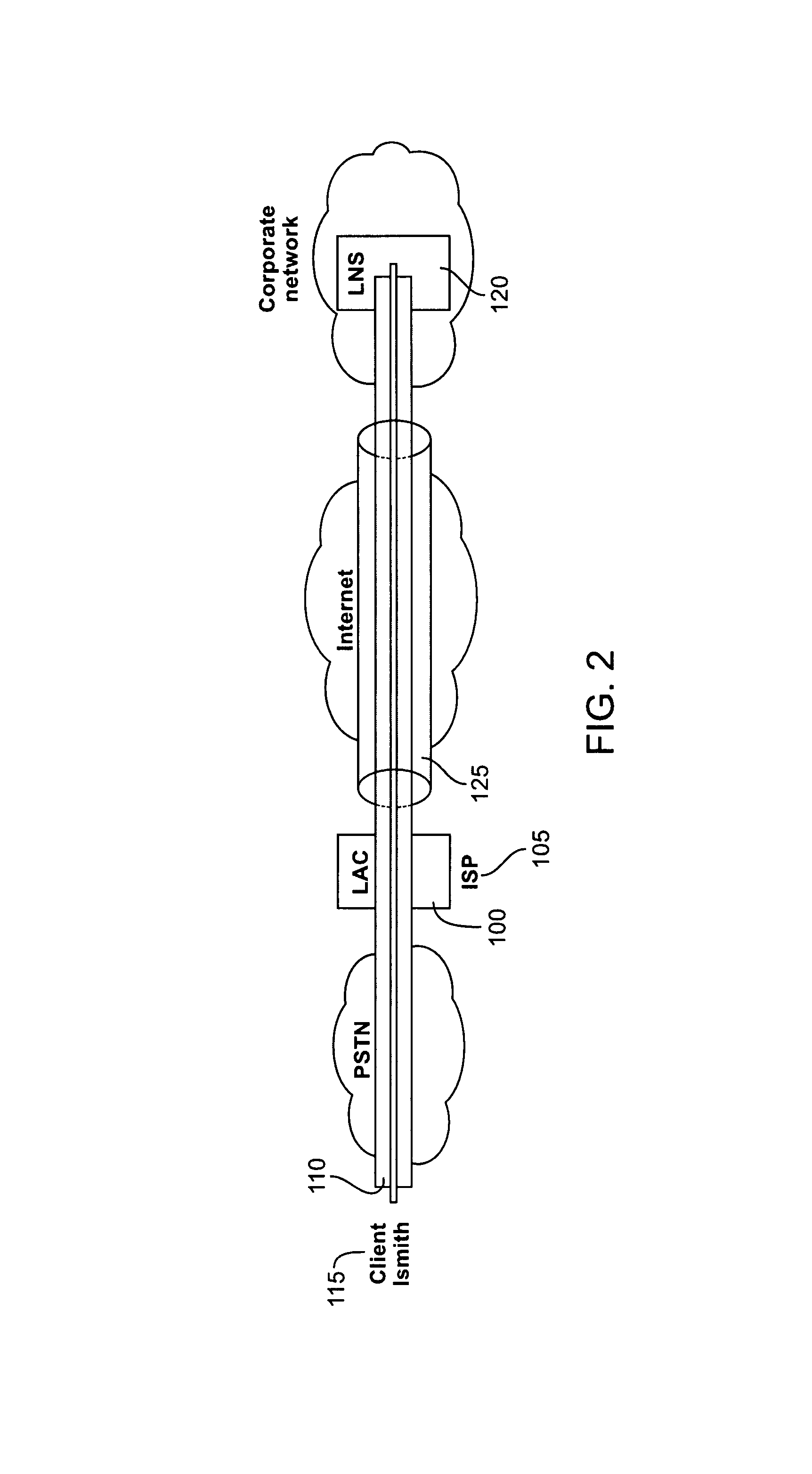
Method and system for controlling subscriber access in a network capable of establishing connections with a plurality of domain sites
InactiveUS7325058B1Control moreMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTelecommunicationsA domain
A method for controlling subscriber access in a network capable of establishing connections with a plurality of domains includes receiving a communication from a subscriber using a first communication network coupled to at least one other communication network, the communication optionally including a domain identifier associated with a domain on the at least one other communication network, determining whether the subscriber is authorized to access the domain based upon the domain identifier and a list of authorized domains for a virtual circuit used to receive the communication and authorizing subscriber access to the domain when the domain identifier is included in the list. An access server includes a tunnel ID request generator and an authorizer. The tunnel ID request generator generates a tunnel ID request that includes a virtual circuit identifier associated with a virtual circuit used to accept a PPP authentication request. The authorizer grants subscribers domain access based upon a list of authorized domains for the virtual circuit.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com