Patents
Literature
243 results about "Active message" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An Active message (in computing) is a messaging object capable of performing processing on its own. It is a lightweight messaging protocol used to optimize network communications with an emphasis on reducing latency by removing software overheads associated with buffering and providing applications with direct user-level access to the network hardware. This contrasts with traditional computer-based messaging systems in which messages are passive entities with no processing power.
Systems and methods for managing the transmission of electronic messages through active message date updating
InactiveUS6941348B2Easy accessFacilitate supplementing of the sourceData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsContent analyticsActive message
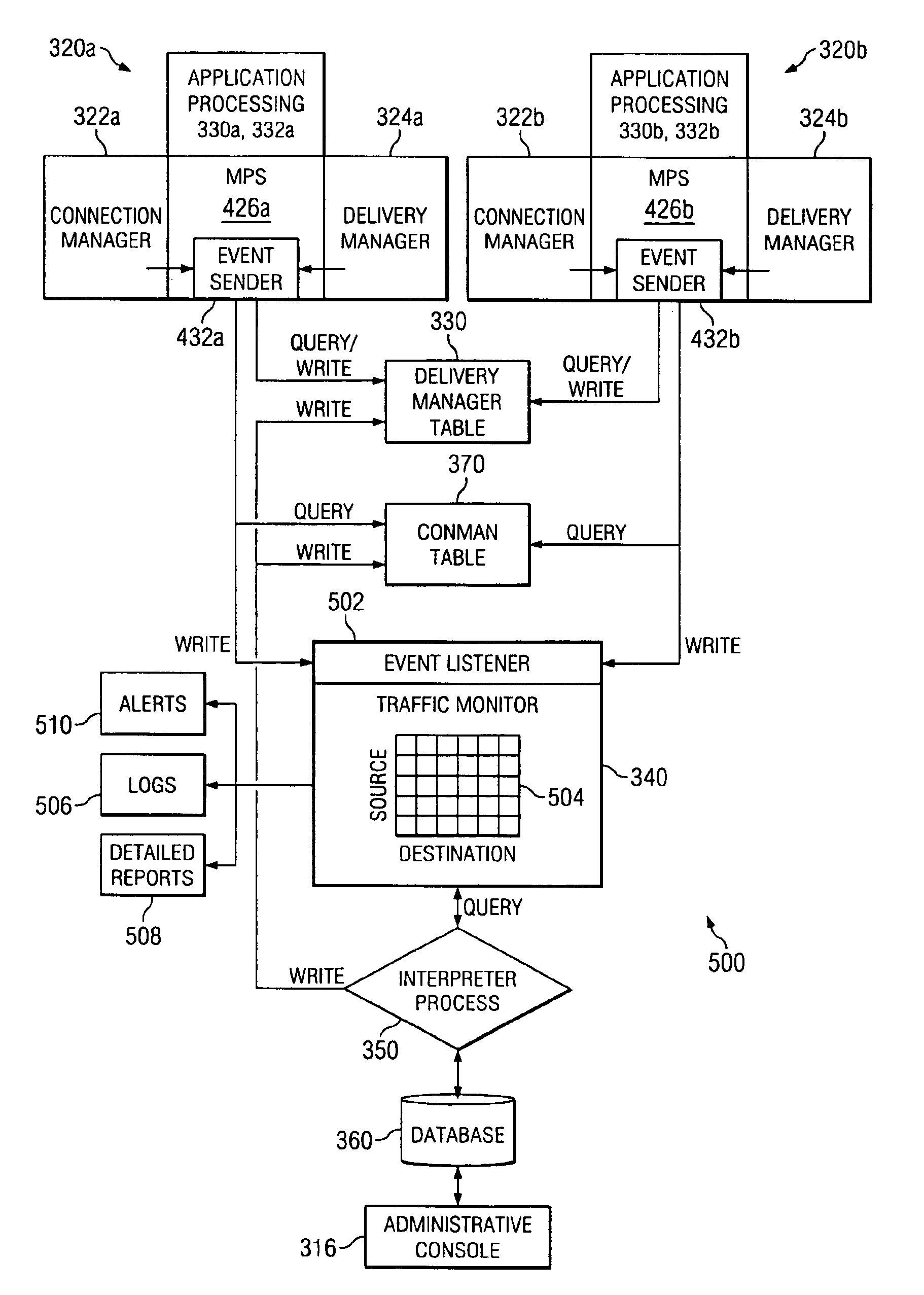
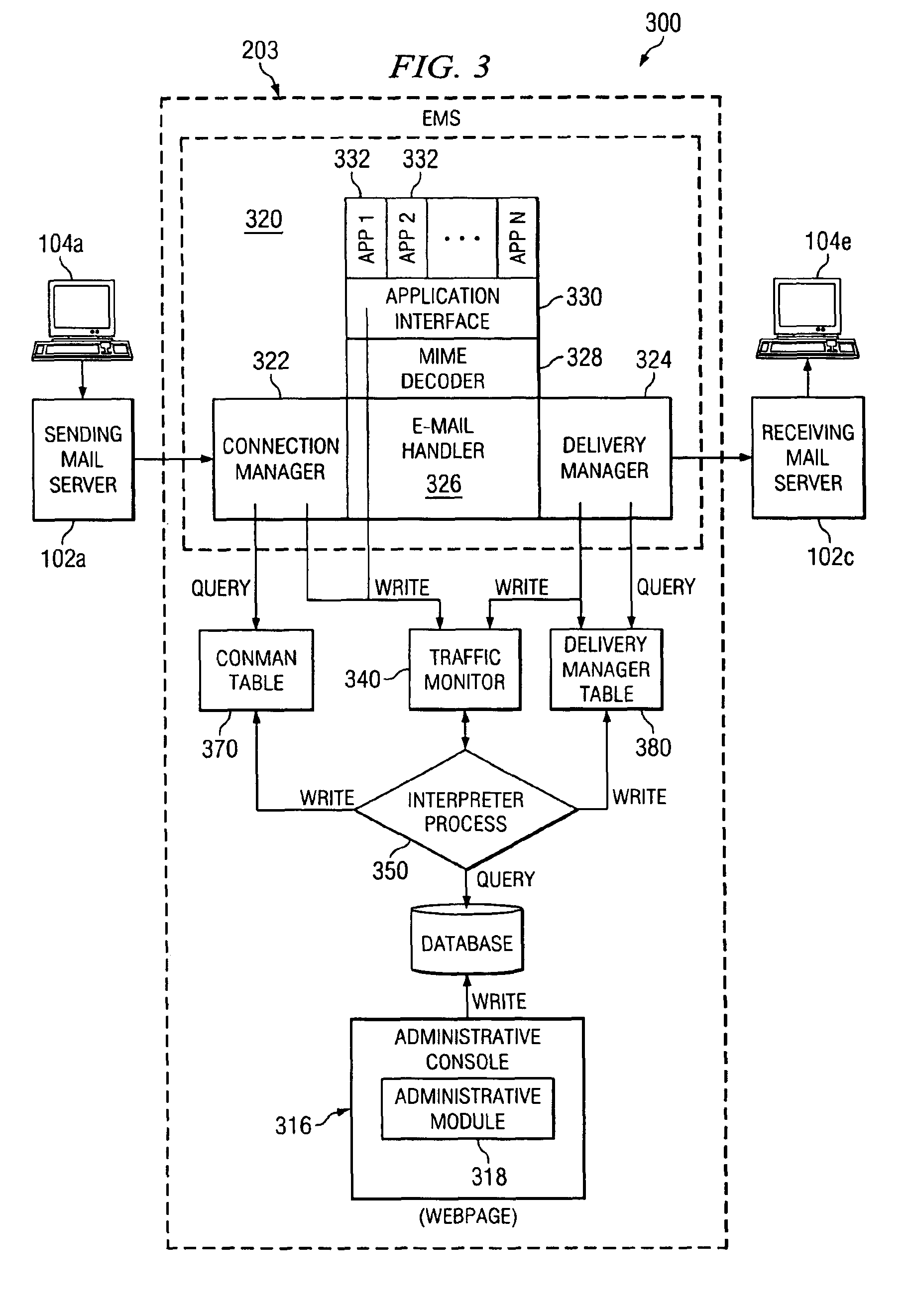
The present invention provides an electronic message management system (EMS) that includes a real-time feedback loop where data is collected from the electronic messages on incoming connection attempts, outgoing delivery attempts, and message content analysis, and written to a centralized data matrix. A separate process accesses the data matrix and analyzes trends in that data. The detected data patterns, trends or behavior is based on configuration parameters for the recipient. Based on these determinations, the process is able to instruct components in the EMS to accept, redirect, refuse, modify, defer, or otherwise dispose of the connection request, the delivery attempt, or the message. Associated methods for managing the transmission of electronic messages are also disclosed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
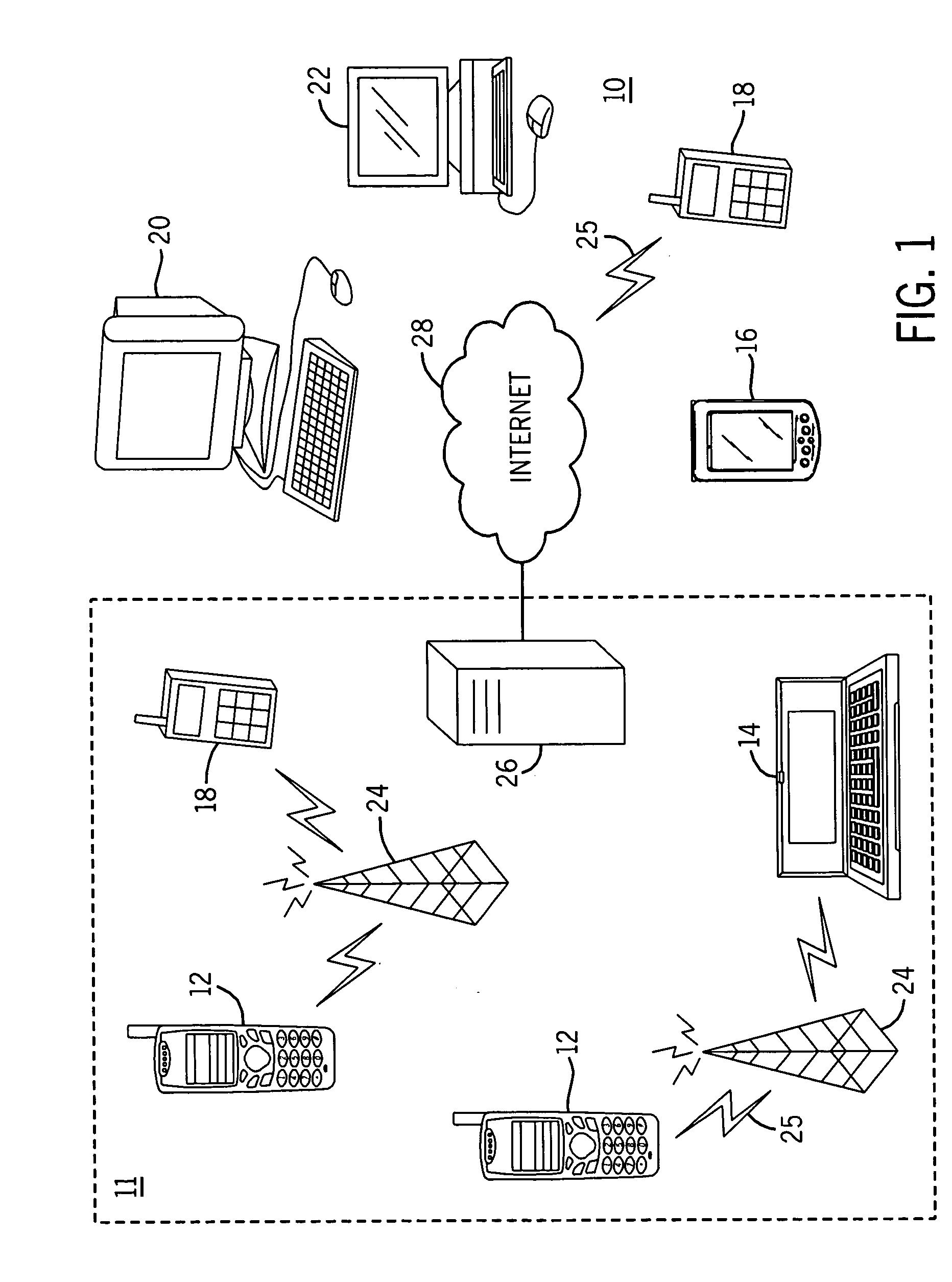
Mobile network optimized method for keeping an application IP connection always on
ActiveUS20080059582A1Reduce the burden onImprove device performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverApplication programming interface
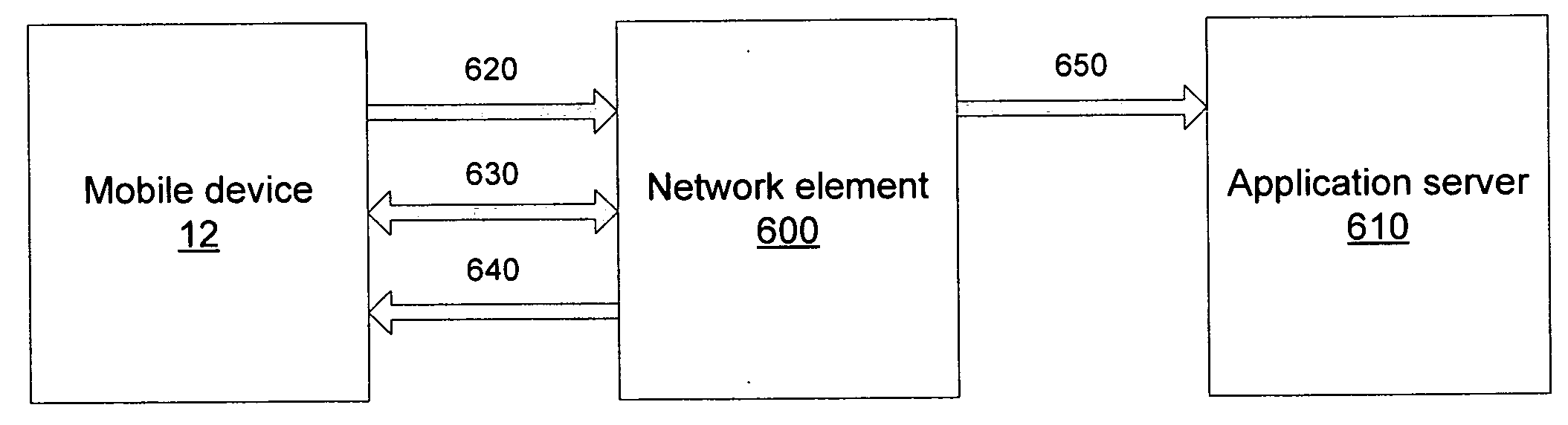
A system and method of maintaining an always-on application client communication is provided. An application programming interface implemented on a device hosting an always-on application client determines if network-based keep-alive functionality exists in a network where the device operates. If network-based keep-alive functionality exists, a network element is instructed to transmit keep-alive messages to the application server on behalf of the device. The network element can be implemented in or as a variety of existing network elements, e.g., as a GPRS gateway serving node or a standalone keep-alive network element. Alternatively, an application server communicatively connected to the always-on application client may query whether network-based keep-alive functionality exists. If network-based keep-alive functionality exists, the application server negotiates with the always-on application client to determine an application-specific mechanism for implementing the network-based keep-alive functionality. When an application server queries for network-based keep-alive functionality, an application programming interface need not be utilized.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Maintaining an IP connection in a mobile network
InactiveUS20070019610A1Time-division multiplexConnection managementStatistical ConfidenceMobile radio
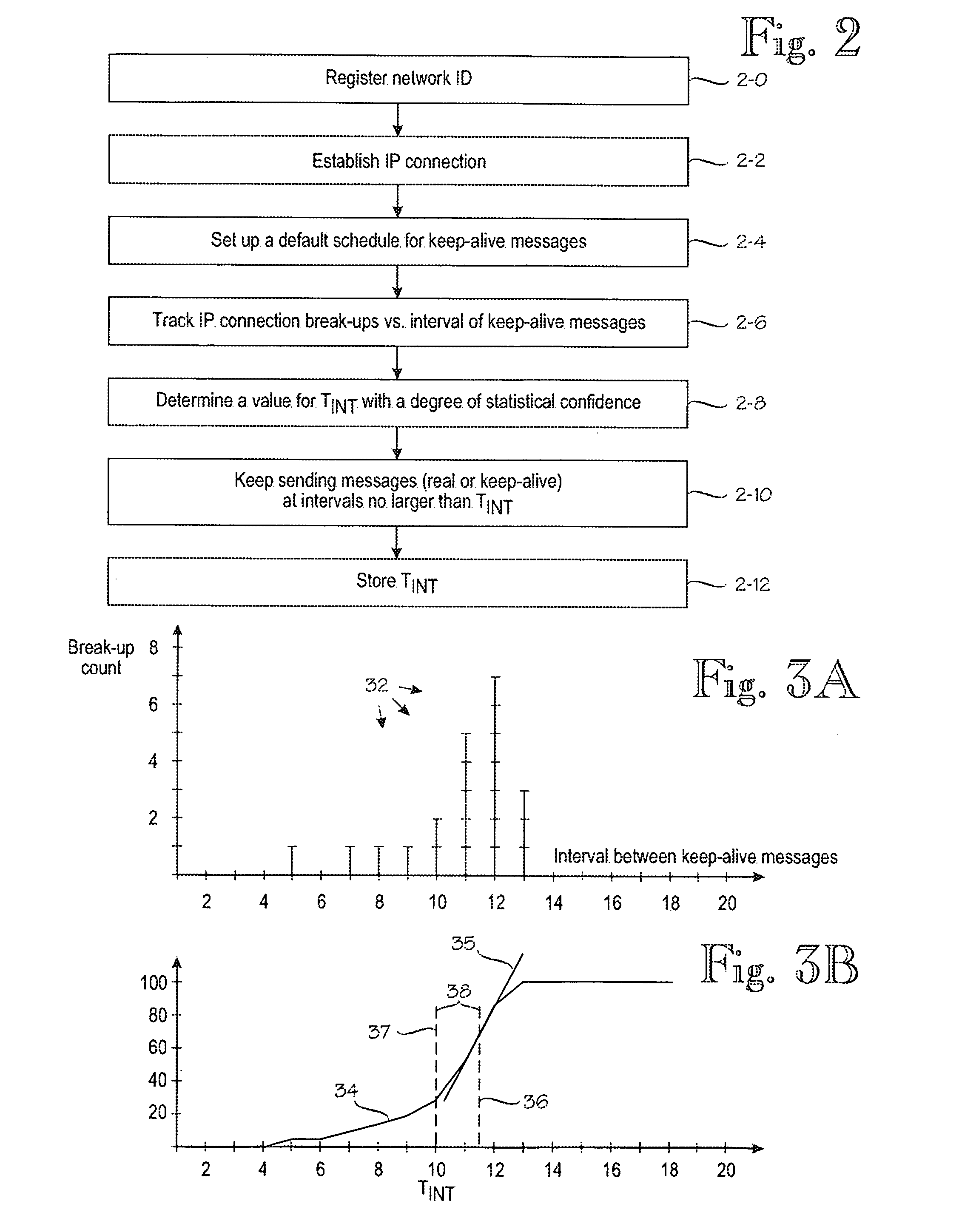
A method for IP [=Internet Protocol] communication between a mobile terminal and its correspondent node in a mobile radio network. The method comprises establishing (2-2) an IP connection between the mobile terminal and its correspondent node. After detecting a period of inactivity in the IP connection, (2-4) keep-alive messages are sent via the IP connection at predetermined intervals, which are varied. The method comprises monitoring (2-6) the lengths of several periods of inactivity at which the mobile radio network disconnects the IP connection. Based on the monitored lengths of periods of inactivity, a maximum interval (TINT) between keep-alive messages is determined (2-8) such that the maximum interval meets a predetermined criterion of statistical confidence, and the interval between keep-alive messages is set (2-10) to the maximum interval (TINT).
Owner:SEVEN NETWORKS INC
Systems and methods for deterring theft of electronic devices
InactiveUS20050073389A1Reduce stepsElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageNetwork onEngineering
Systems and methods for remotely shutting down or preventing operation of device via a wireless network infrastructure are provided. The device may be disabled using a defined command the device receives on a wide area network, such as a SPOT network or wireless carrier network. In various embodiments, the device responds to pre-defined command(s) and operation is disabled locally. Override codes may be used to locally re-enable the device. In a “keep alive” embodiment, the device operates as long as it continues to receive “keep alive” messages from the intended environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
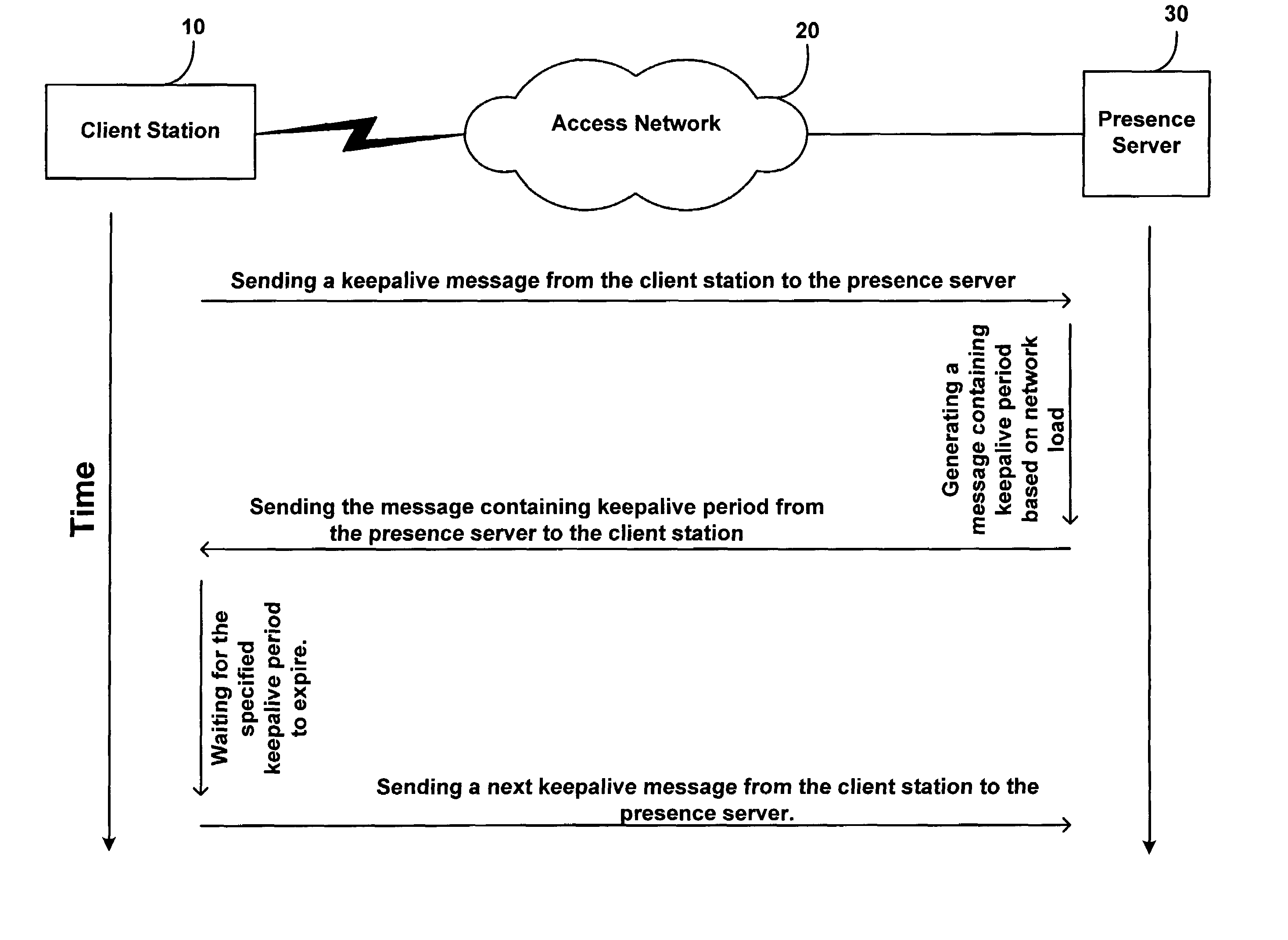
Method and system for updating network presence records at a rate dependent on network load
ActiveUS7634558B1Available bandwidthSimple methodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionActive messageRate dependent
A method is disclosed for determining how often a client station in a network should send keepalive messages. Based on a measure of network load, a presence server determines a keepalive period, which is a time interval in which a client station needs to send a keepalive message, and the presence server reports this keepalive period to the client station. The client station responsively sends a keepalive message to the presence server within the determined keepalive period.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Maintaining Connections Between Mobile Devices and Servers
ActiveUS20100281118A1Avoid connectionAssess restrictionConnection managementActive messageMobile device
A system, method, and computer-readable medium having computer-executable instructions for maintaining connections between a mobile device and a server are described herein. In an embodiment, the method operates by receiving a data request from the mobile device, the data request identifying at least a timeout interval. The method comprises sending the data request to a data server and then determining whether the timeout interval has passed. The method also comprises sending a keep alive message to the mobile device indicating that the request has timed out if it is determined that the timeout interval has passed. The method then receives a re post request from the mobile device, the re post request identifying a timeout interval. The method further comprises receiving a response from the data server, the response including at least data requested by the mobile device and then sends the response to the mobile device.
Owner:IANYWHERE SOLUTIONS
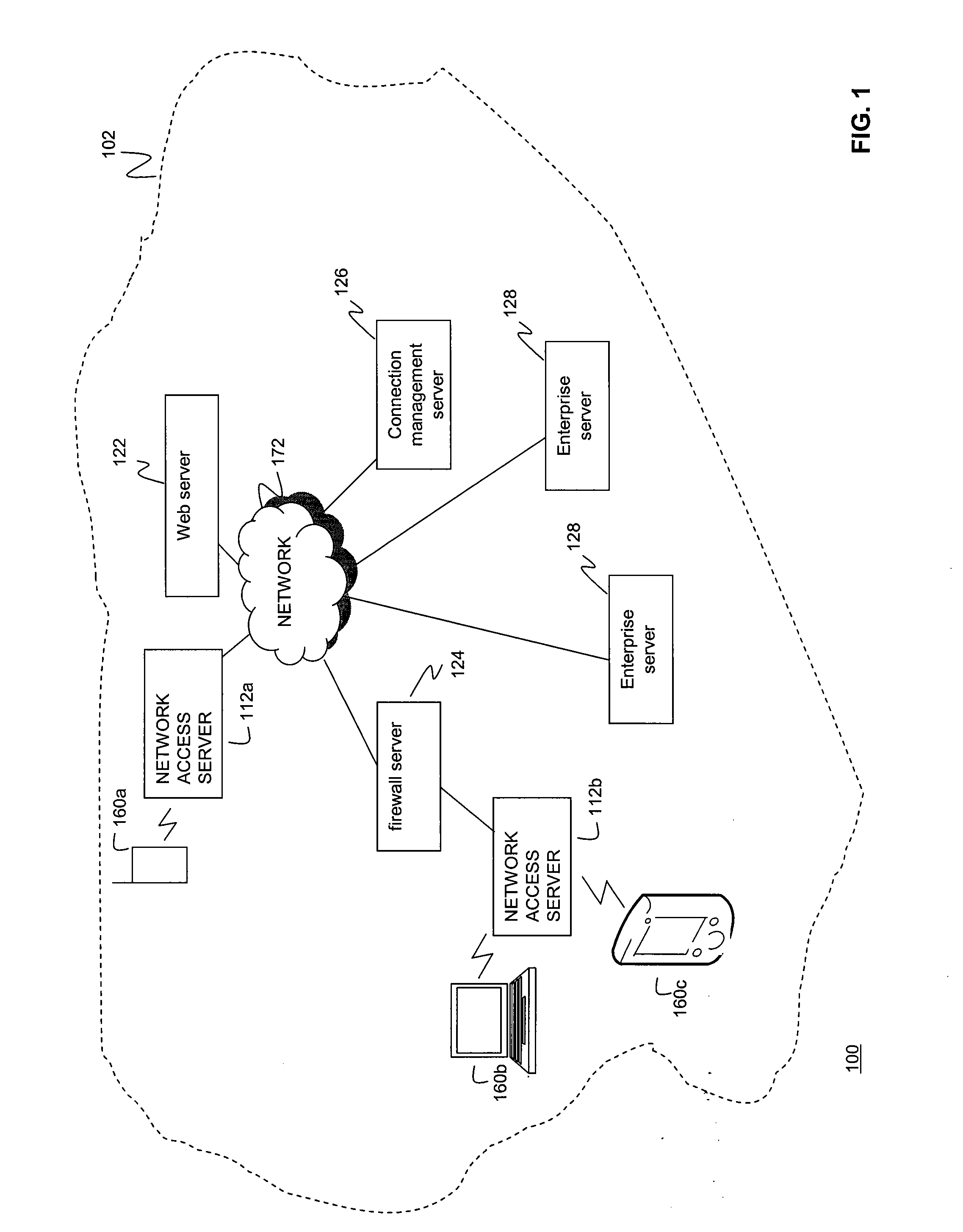
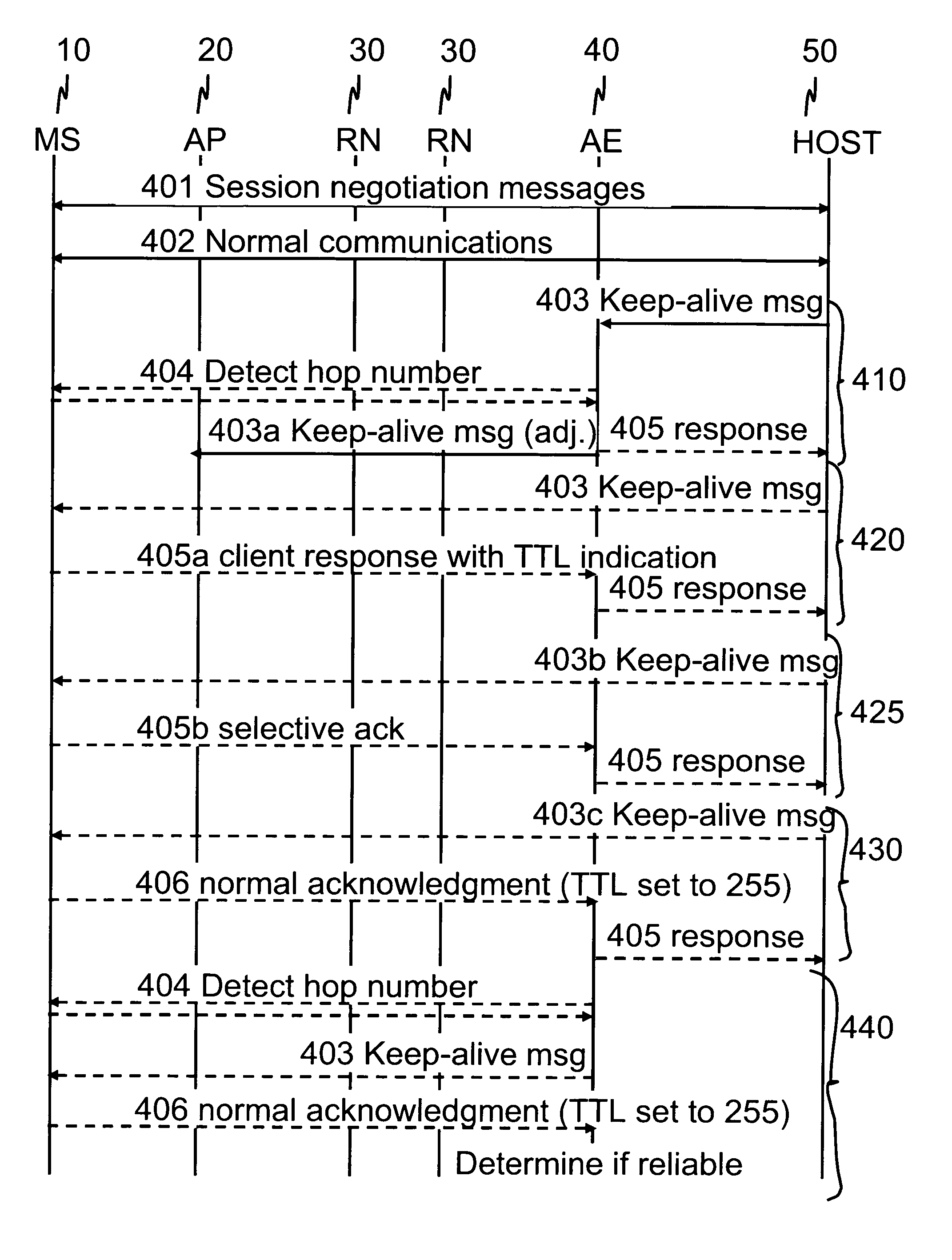
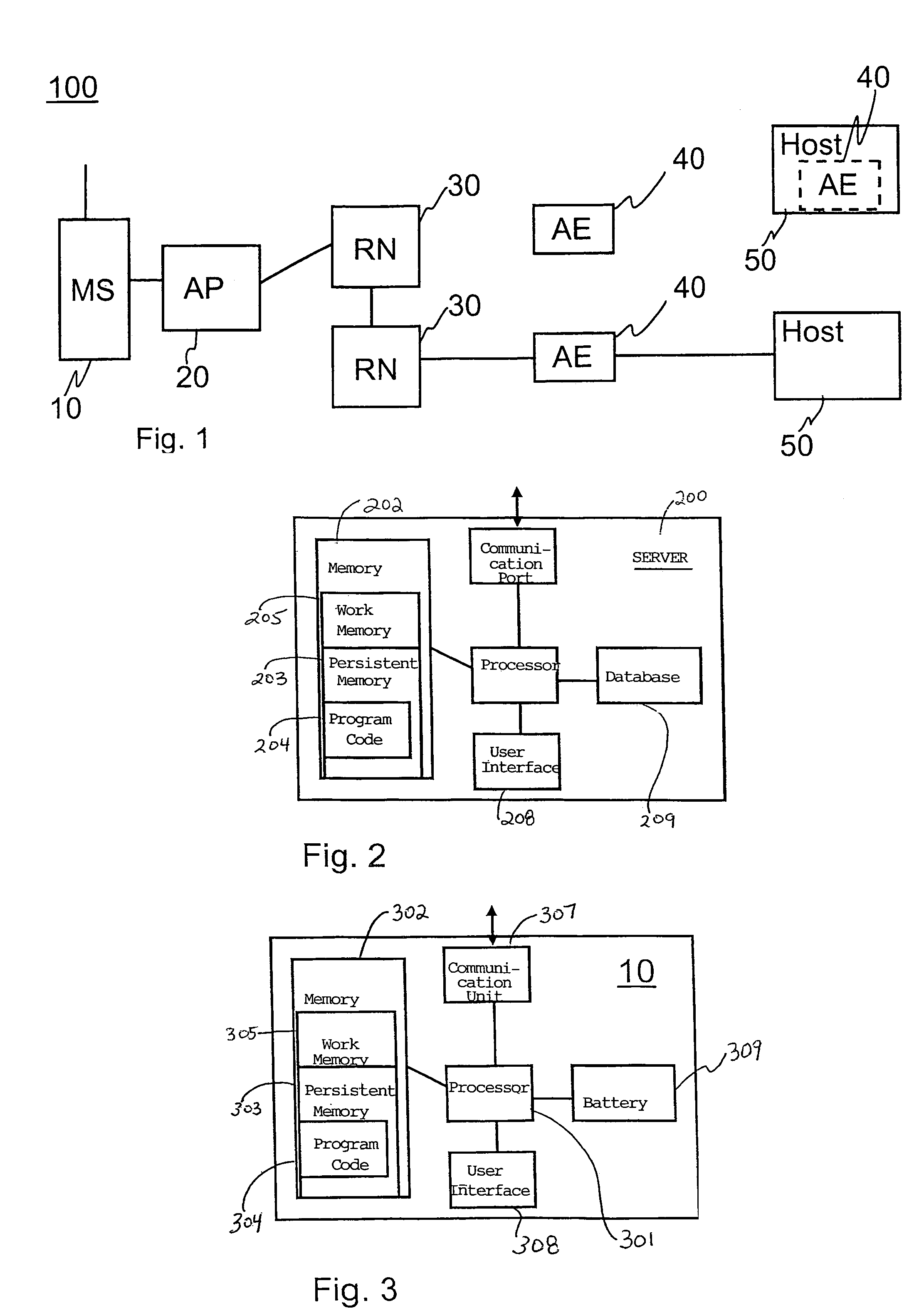
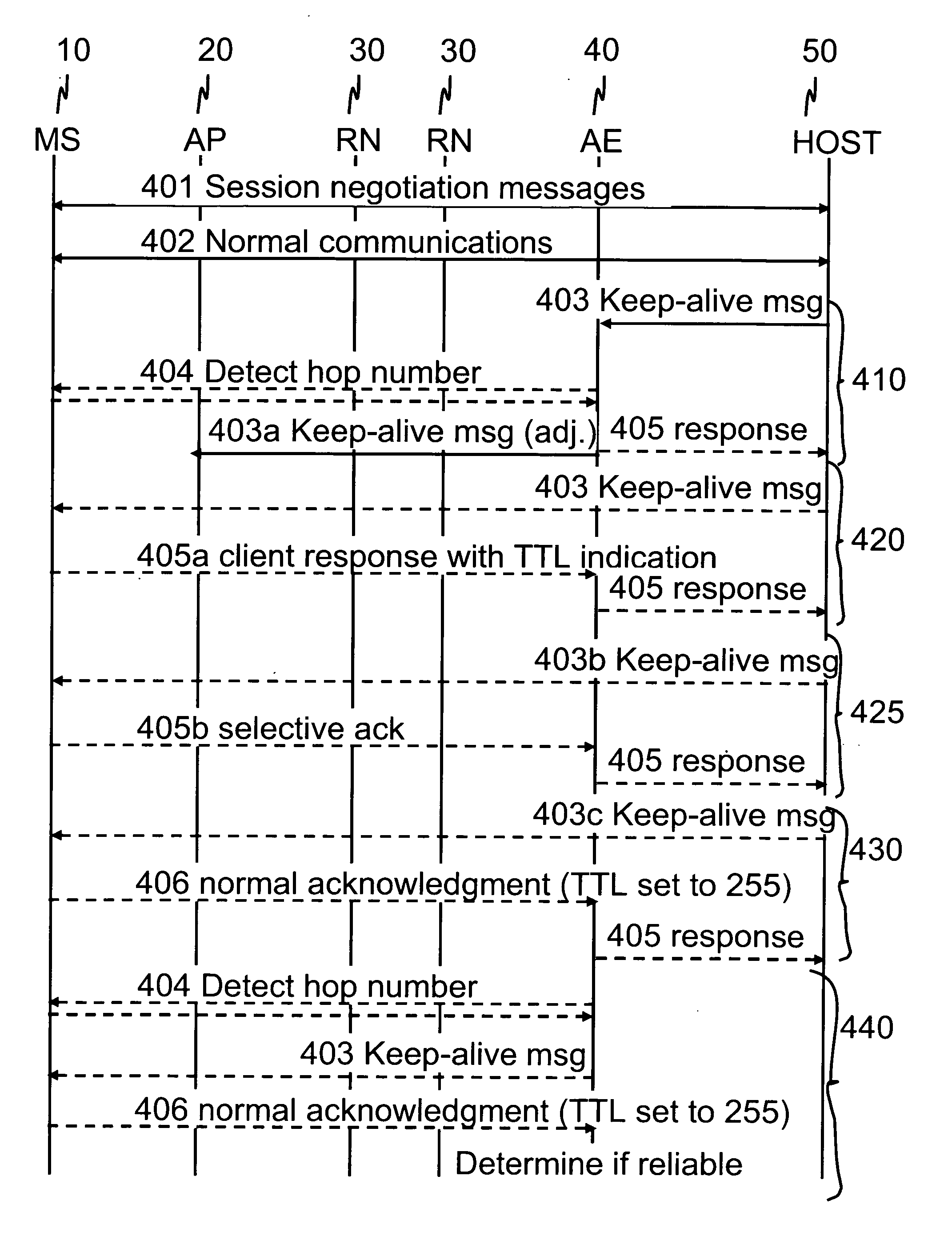
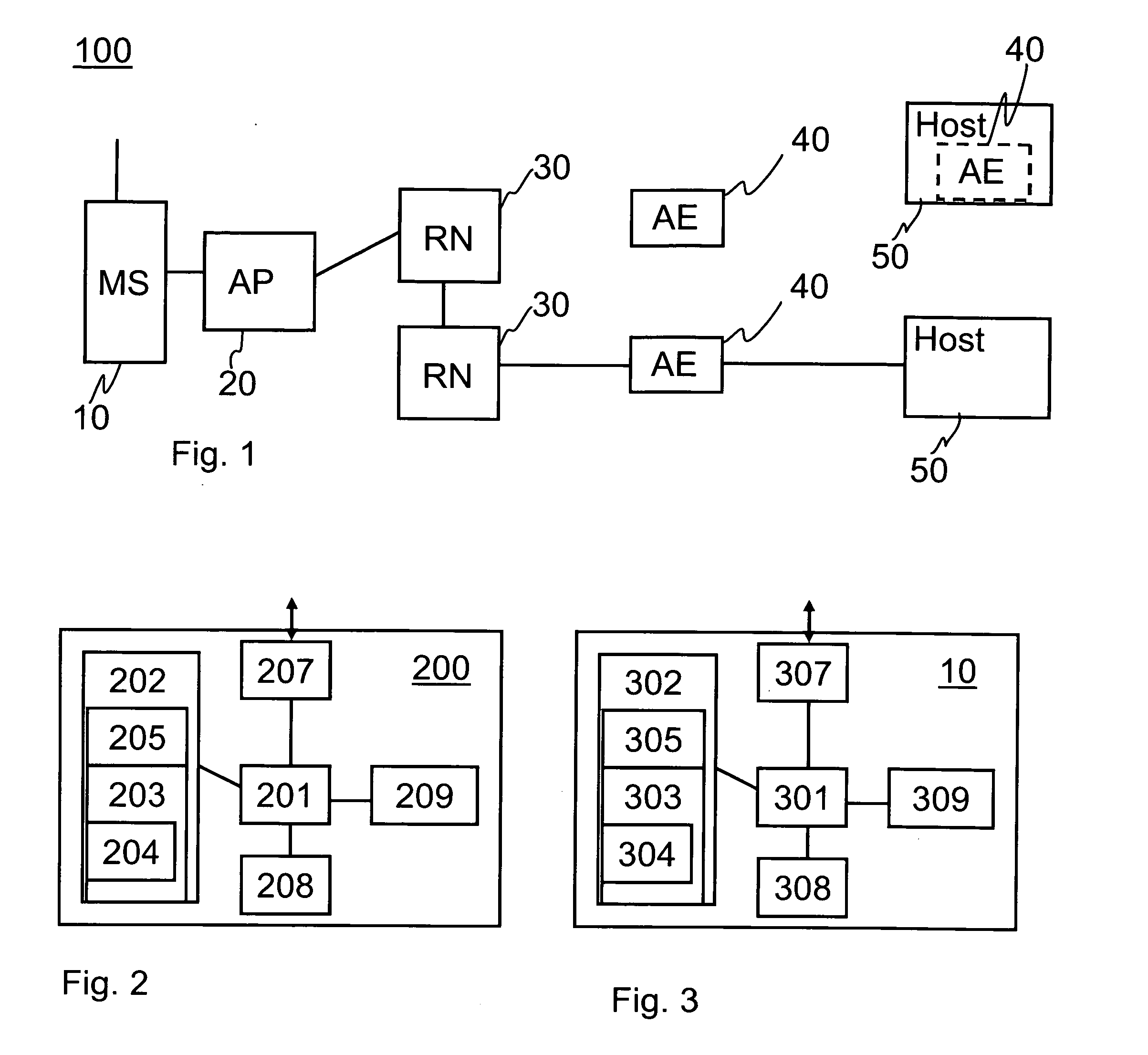
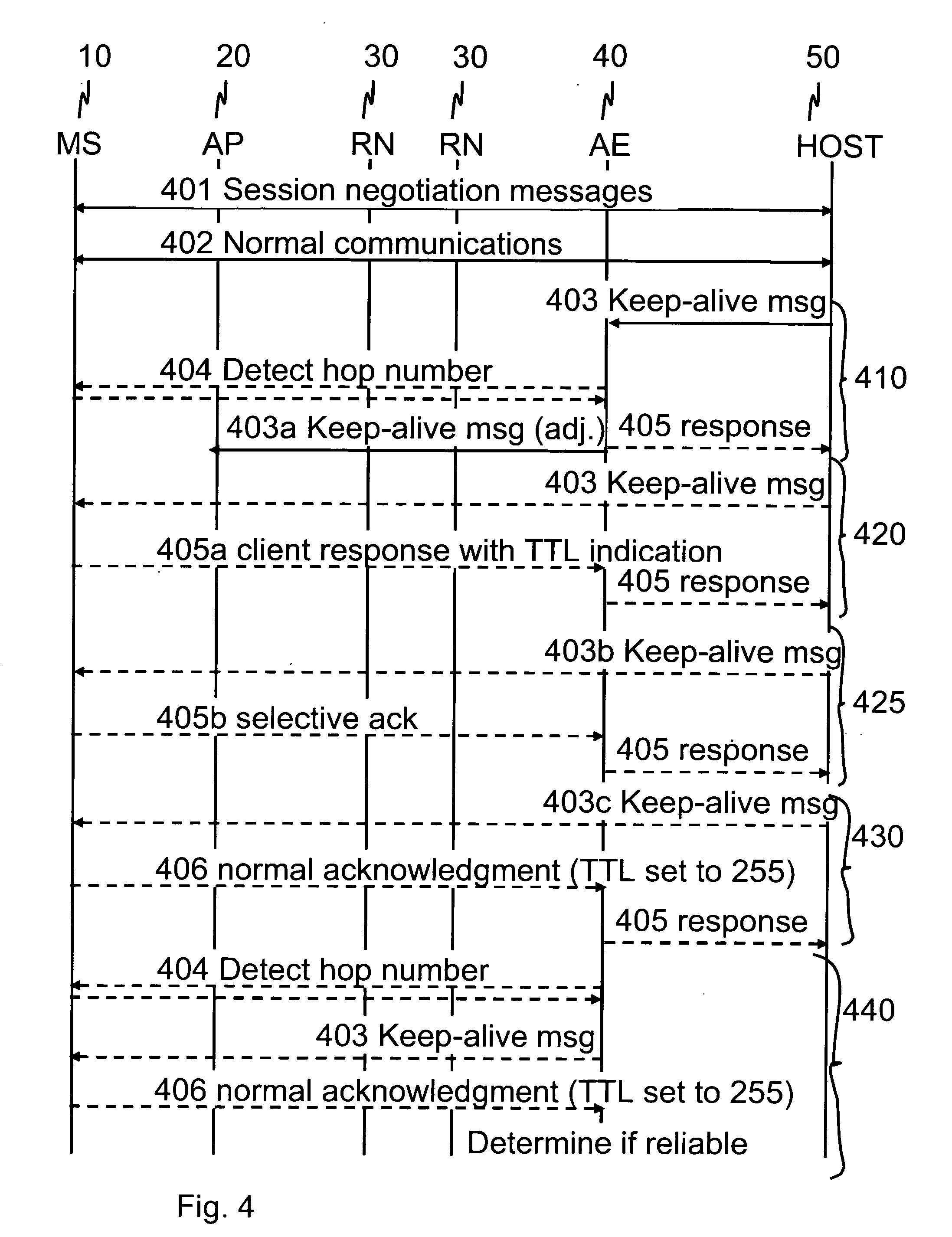
Communications control for extending the period over which a terminal is able to have an open connection with a host accessible via a packet data network
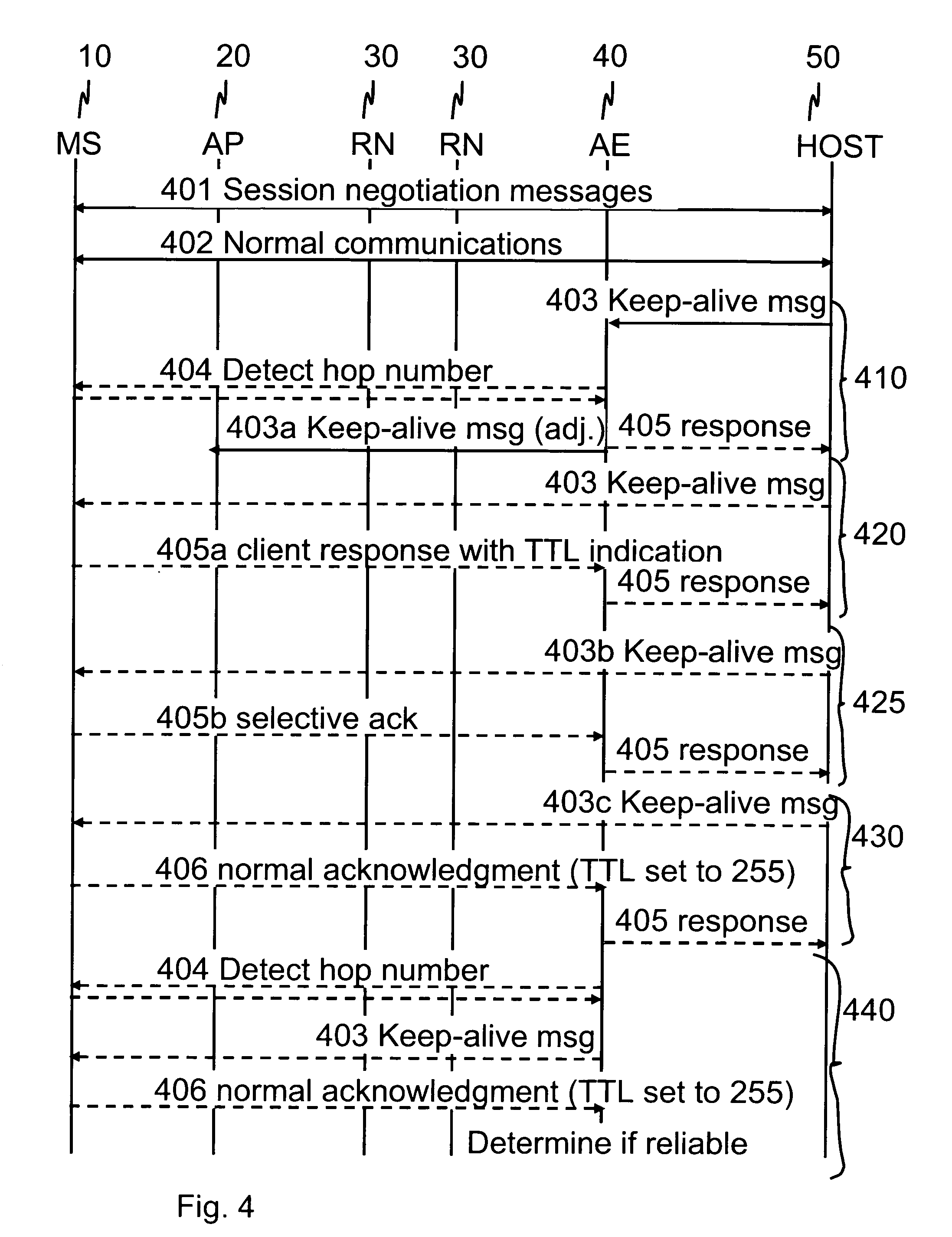
ActiveUS7684346B2Reduce power consumptionExtended maintenance periodError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityThe Internet
A client and a host communicate in a packet data network including a plurality of routing nodes such as routers and firewalls. The host is configured to provide the client with a session and to detect the accessibility of the client by repeatedly sending keep-alive messages to the client. In order to reduce the traffic actually arriving at the client, at least some of the keep-alive message are adjusted such that their routing towards the client will be stopped before the client by storing in a Time-To-Live field specified in the Internet Protocol a value of maximum routing hops defined to correspond with the last routing node before the client on a route from the host to the client. The adaptation of the keep-alive message can also be configured to allow some keep-alive message to reach the client to occasionally test the communication path between the client and server.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
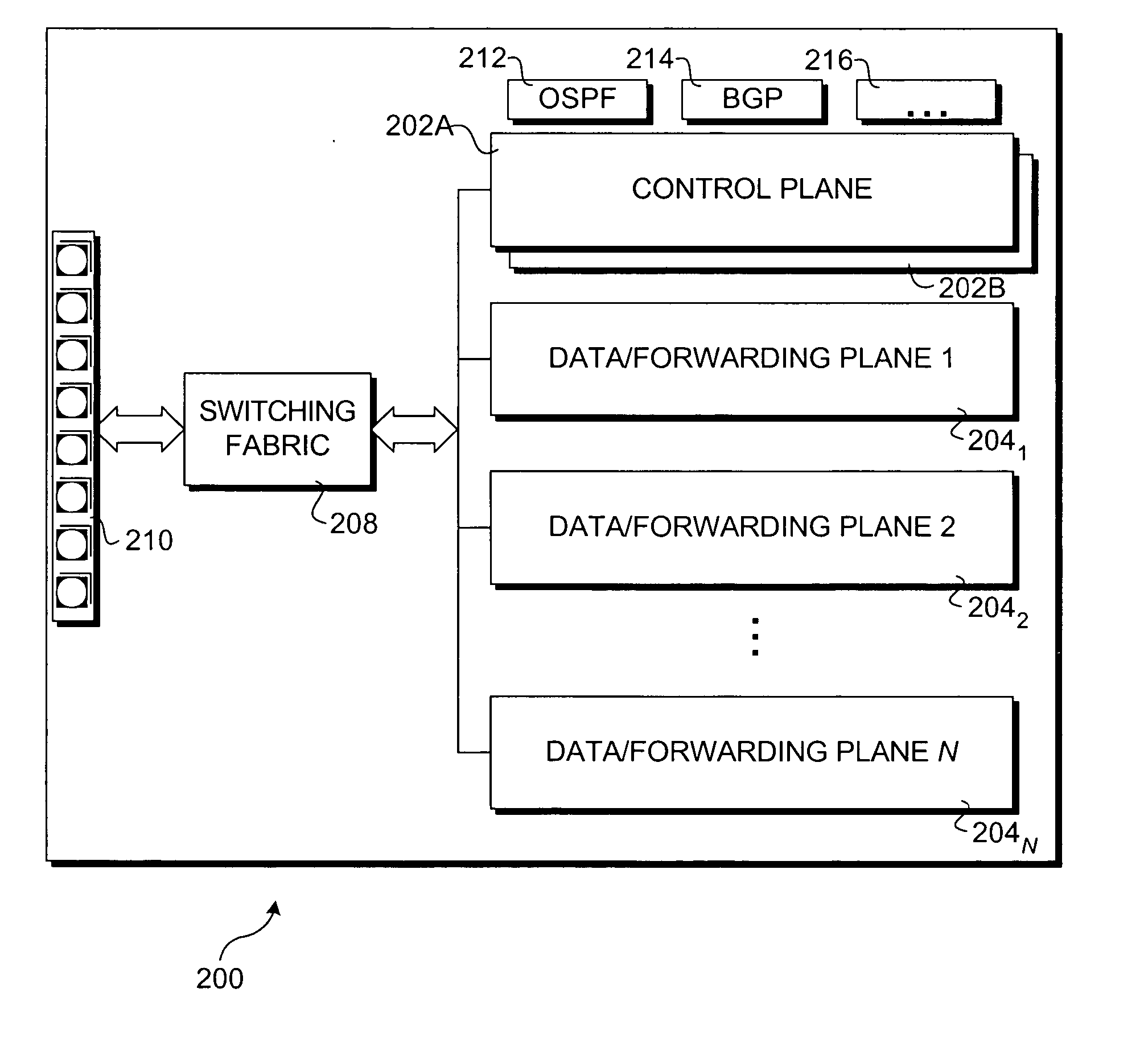
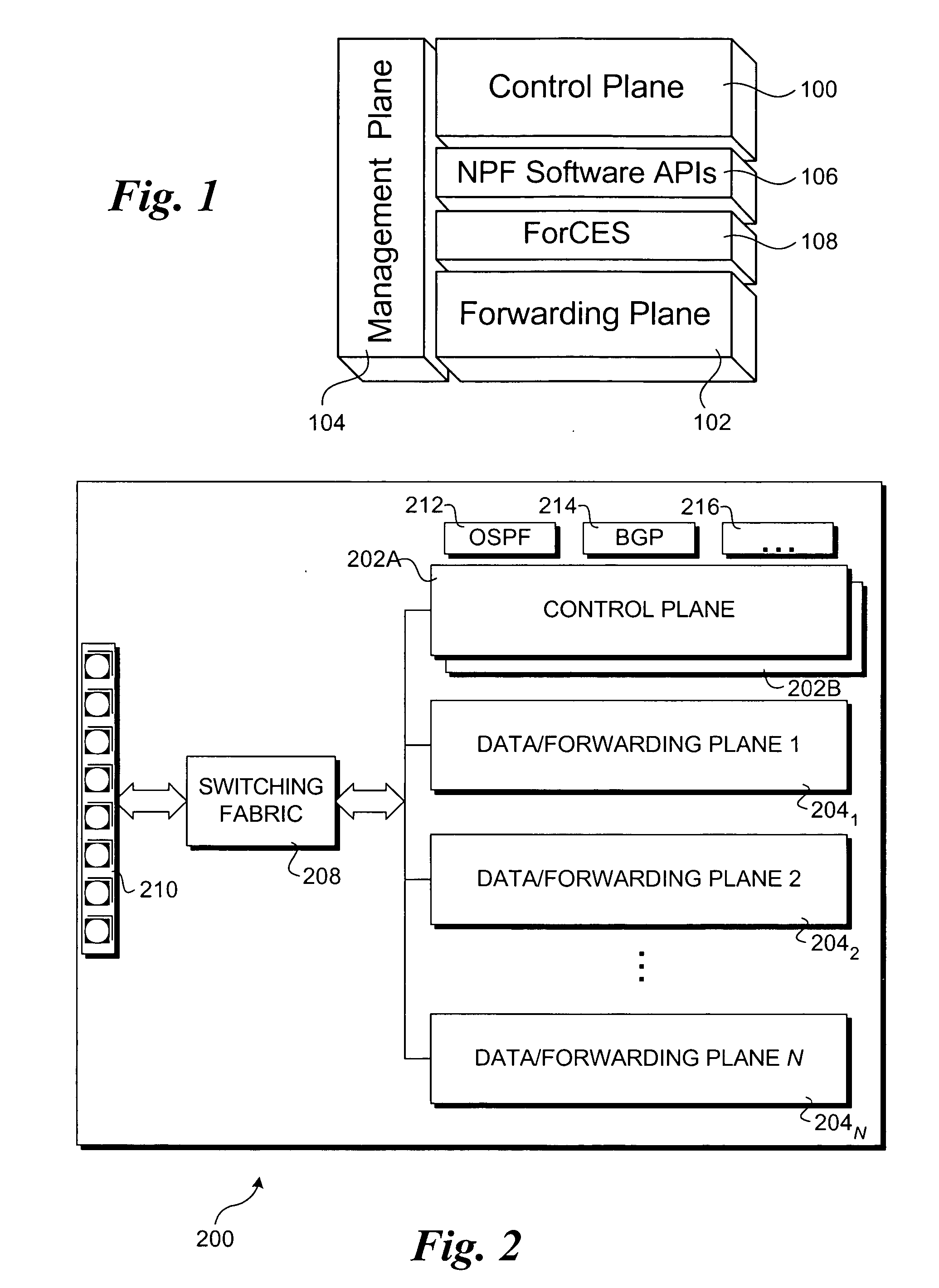
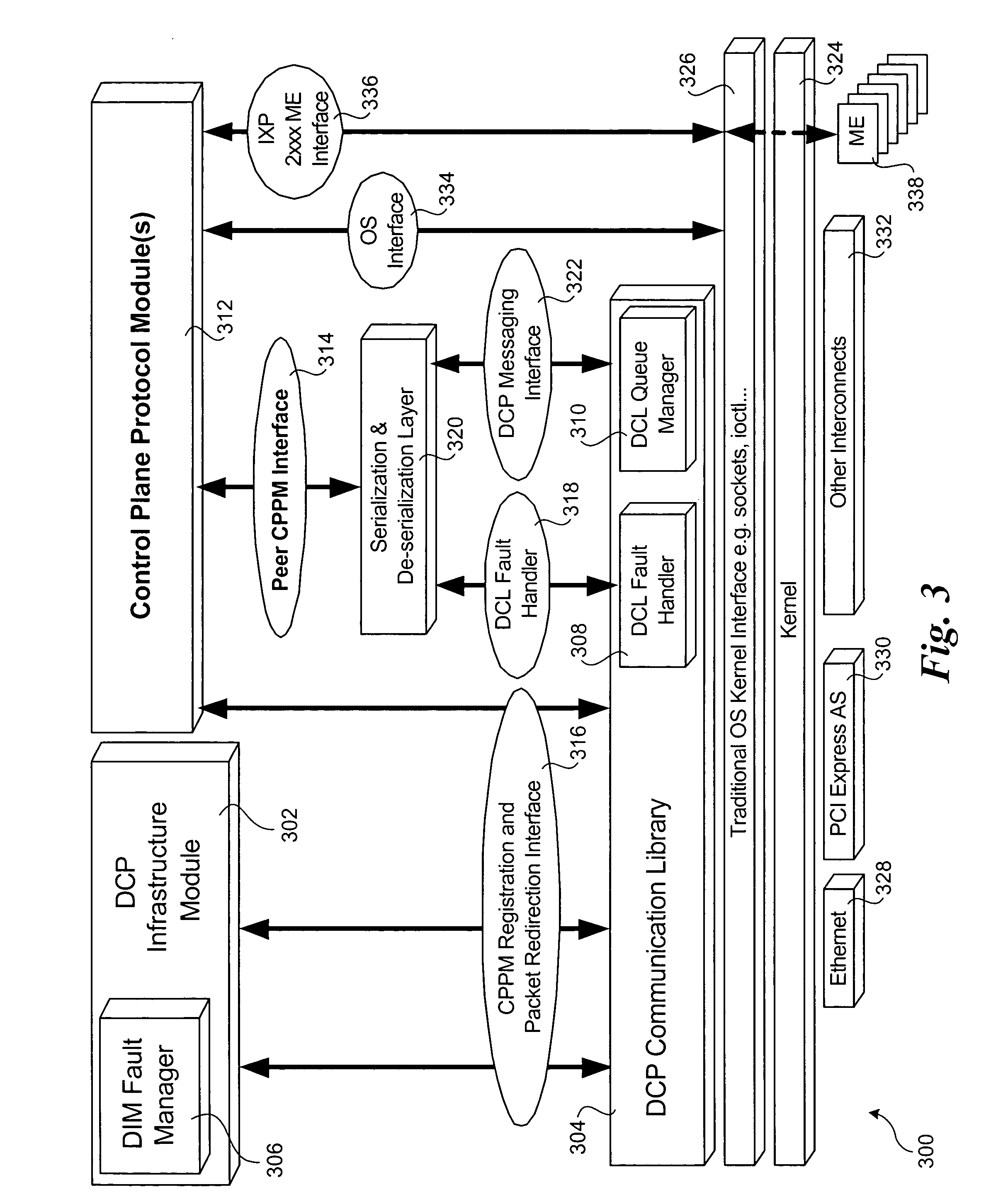
Method to provide high availability in network elements using distributed architectures
A method to provide high availability in network elements using distributed architectures. The method employs multiple software components that are distributed across data / forwarding plane and control plane elements in a network element. The software components in the data / forwarding plane include active and standby components. Components in the control plane are provided to communicate with the components in the data / forwarding plane. A keep-alive messaging mechanism is used to monitor operation of the various elements in the network element. Upon detection of a failure to a hardware or software component, the data / forwarding plane and / or control plane elements are reconfigured, as applicable, to replace a failed active component with a corresponding standby component. This enables the network element to be reconfigured in a manner that is transparent to other network elements, and provided high availability for the network element.
Owner:INTEL CORP
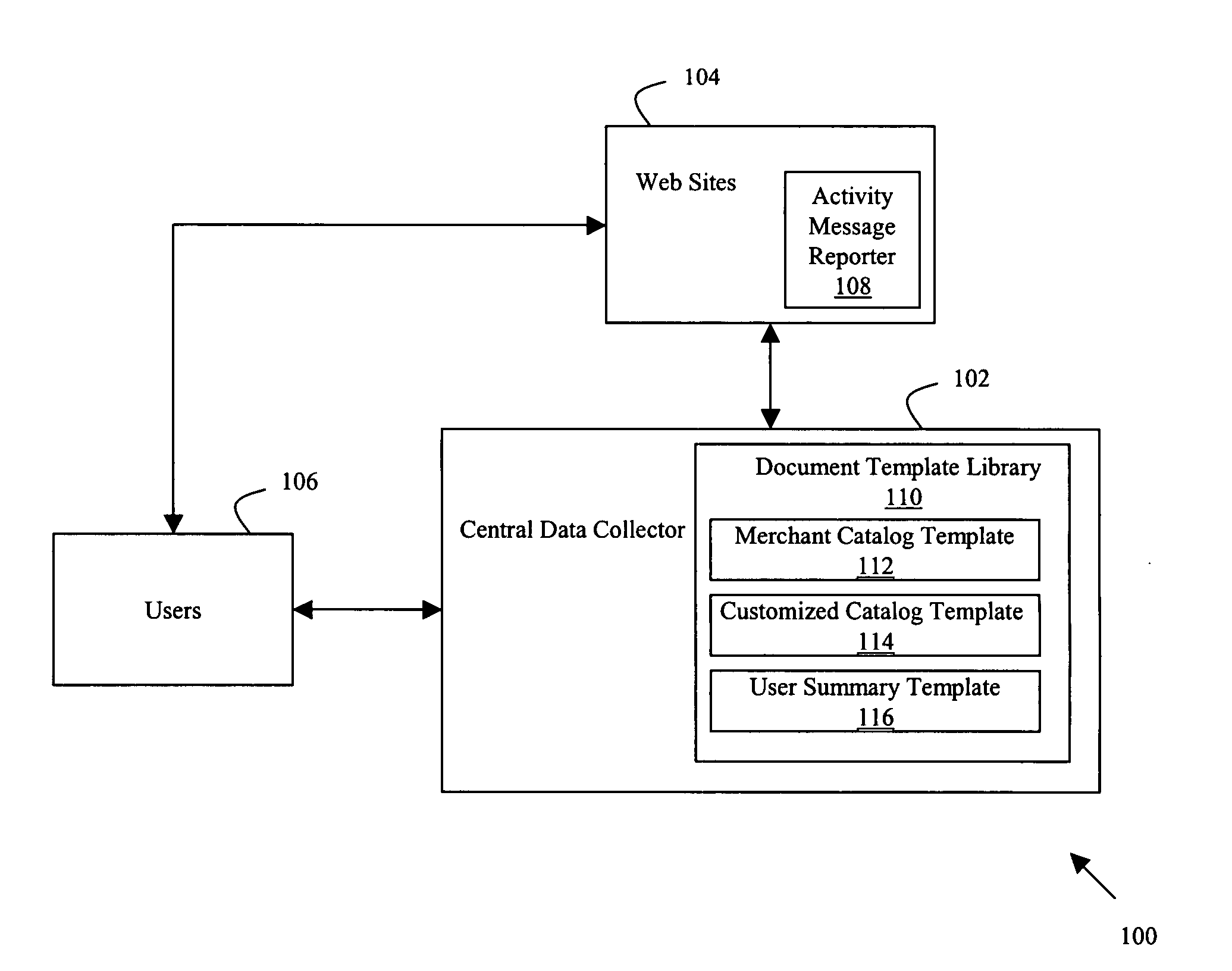
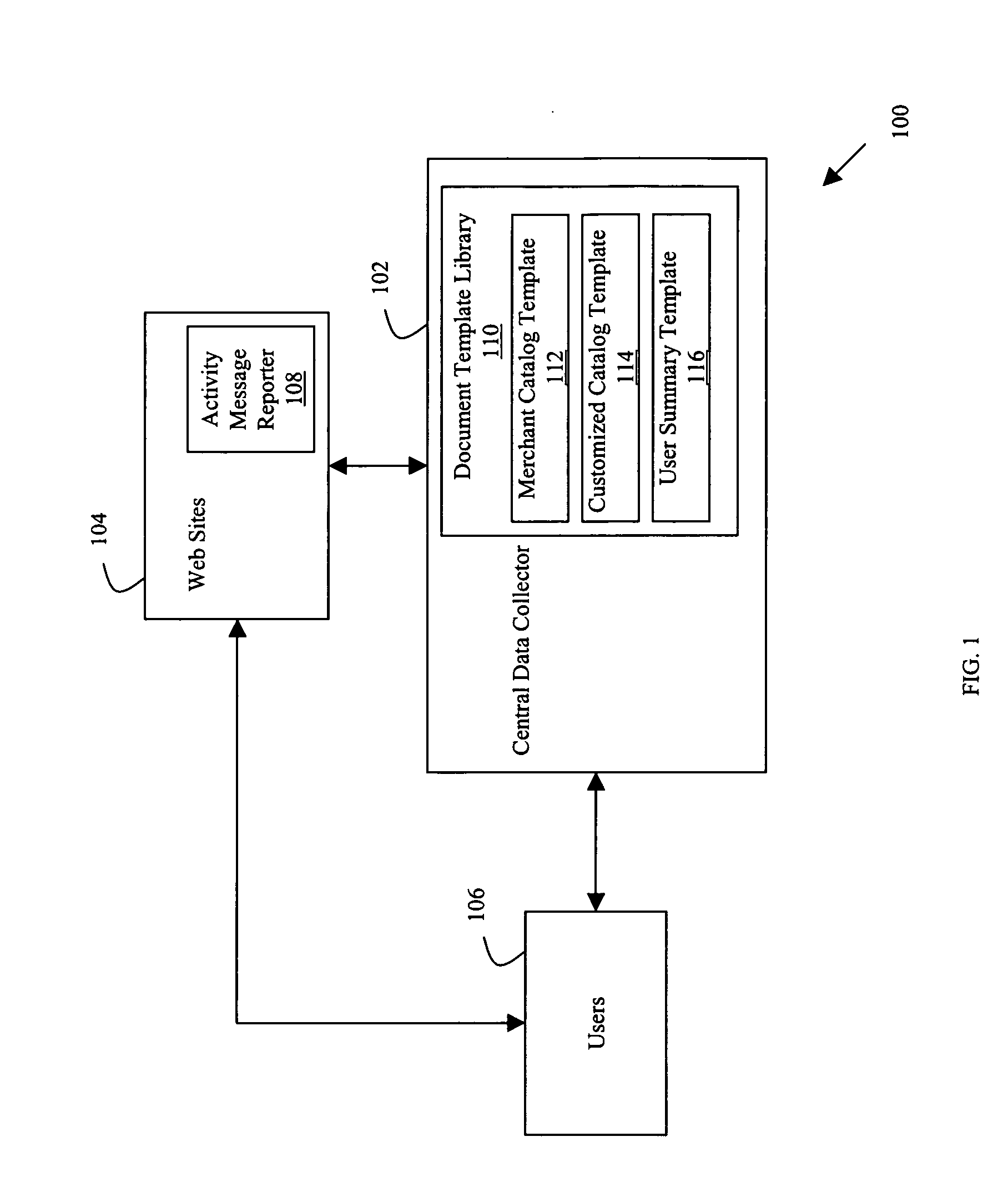
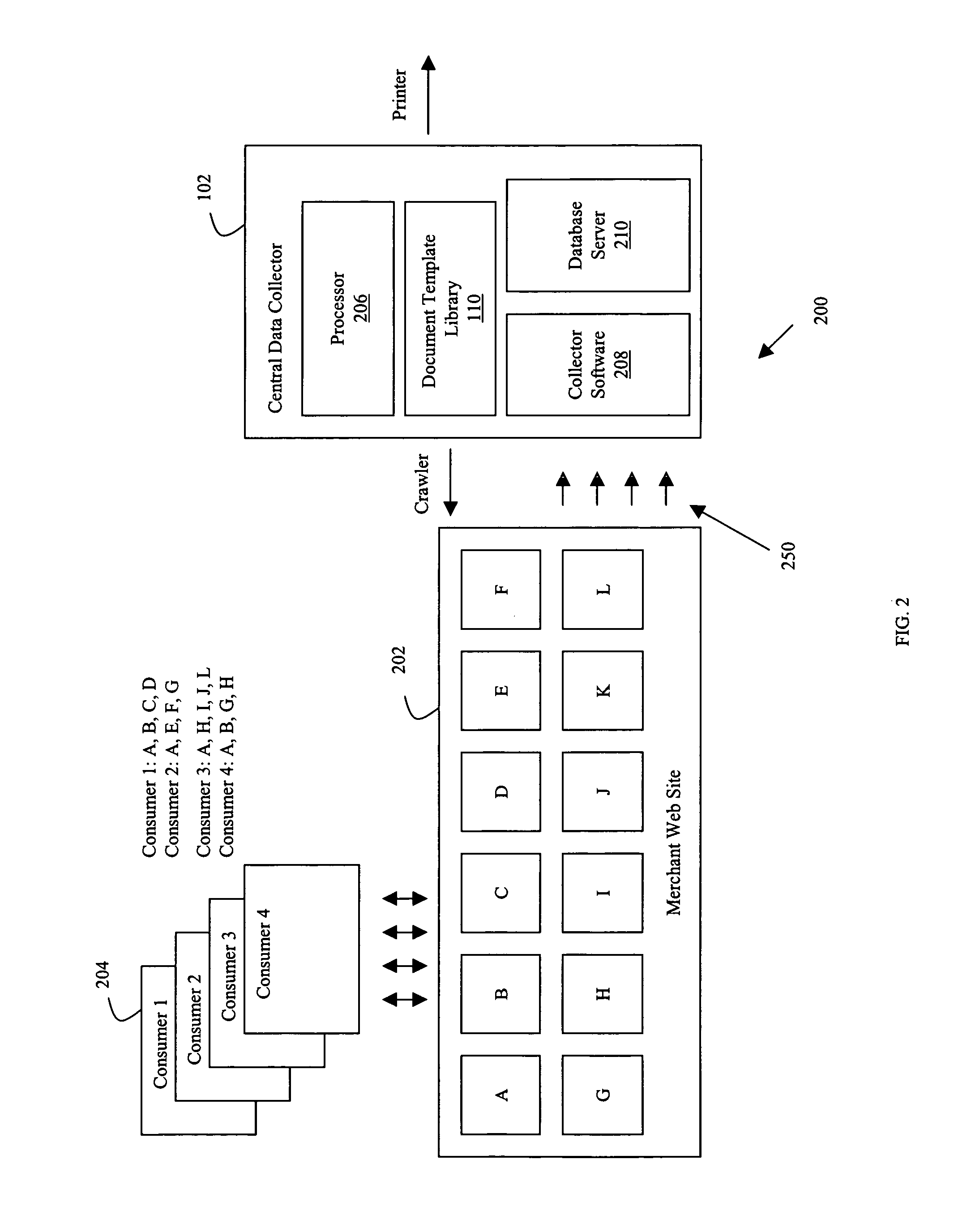
Method for dynamically building documents based on observed internet activity
A method of collecting data from pages viewed by a user of at least one web site, comprises receiving from at least one activity message reporter a plurality of access reports wherein an access report includes content from at least one web page of the at least one web site. Thereafter the method accumulates the received access reports, and formats content from the received access reports in accordance with a document template.
Owner:STB ENTERPRISES
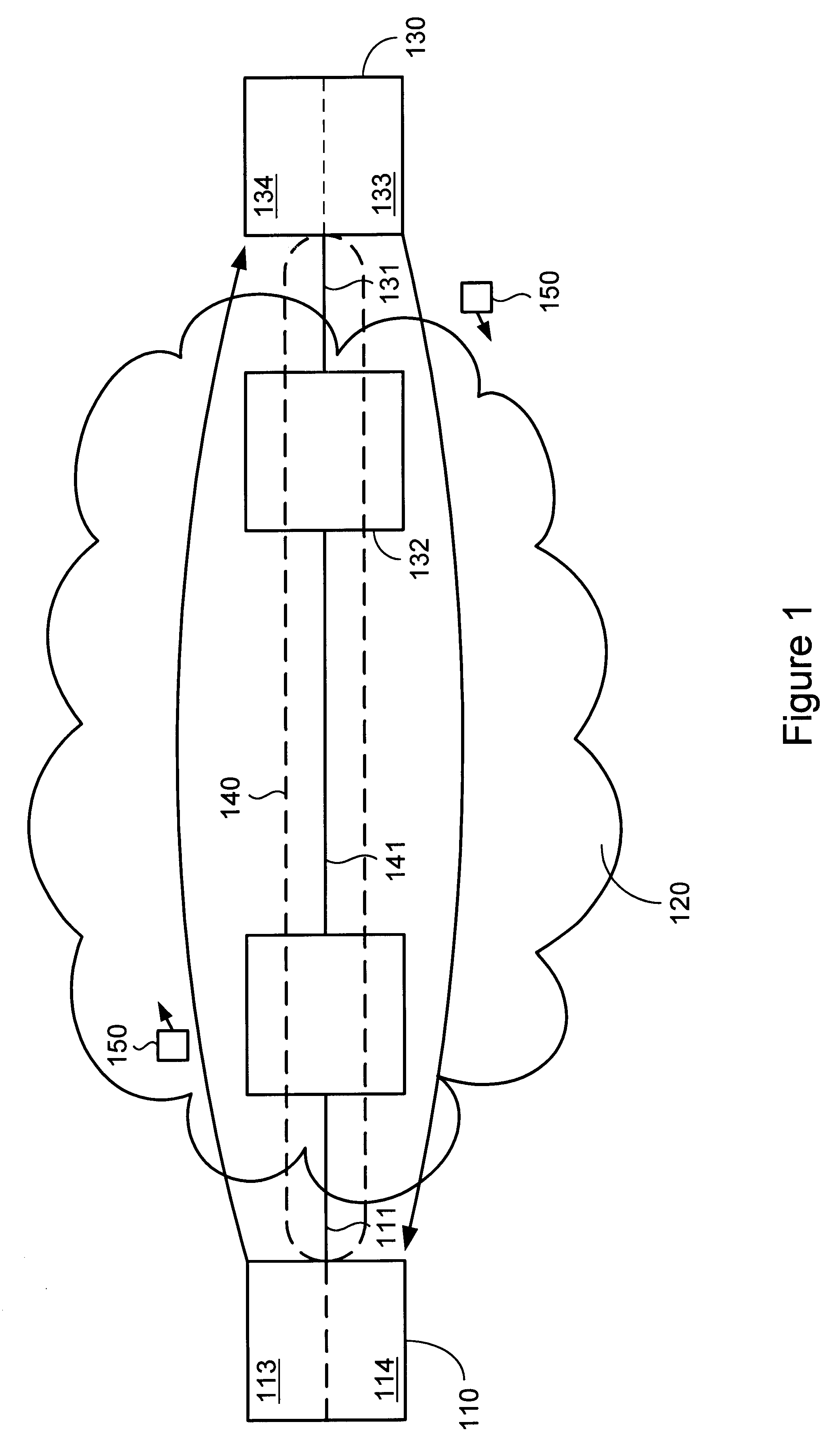
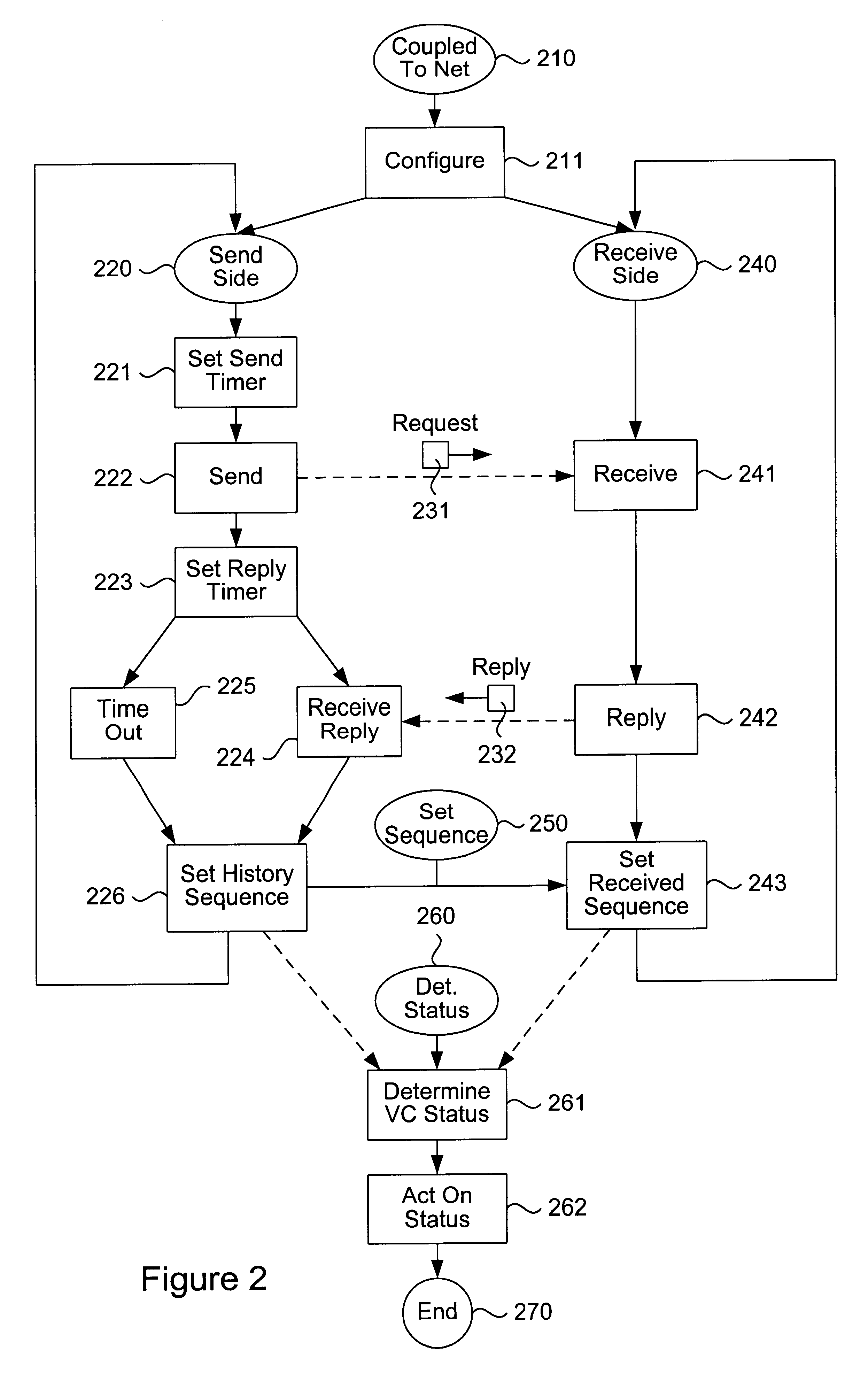
End-to-end bidirectional keep-alive using virtual circuits
The invention provides a method and system for sending and receiving end-to-end bidirectional keep-alive messages using virtual circuits. Nodes coupled to a network, such as a frame relay network, periodically exchange link-layer "keep-alive" messages which indicate information regarding configuration and status of the virtual circuit, as well as information regarding congestion at sending nodes. Nodes respond to received keep-alive messages, or to timed-out failure to receive keep-alive messages, with follow-on actions, such as attempting to reconnect when a virtual circuit fails. Keep-alive messages may be propagated across multiple networks of either similar or different architecture. Keep-alive messages include sent and received sequence numbers, thus providing receiving nodes with a technique for determining if any keep-alive messages have been lost. Keep-alive messages can also include information regarding configuration of the virtual circuit, status of the virtual circuit (including counts of recent keep-alive message failure or success), and congestion at the sending node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
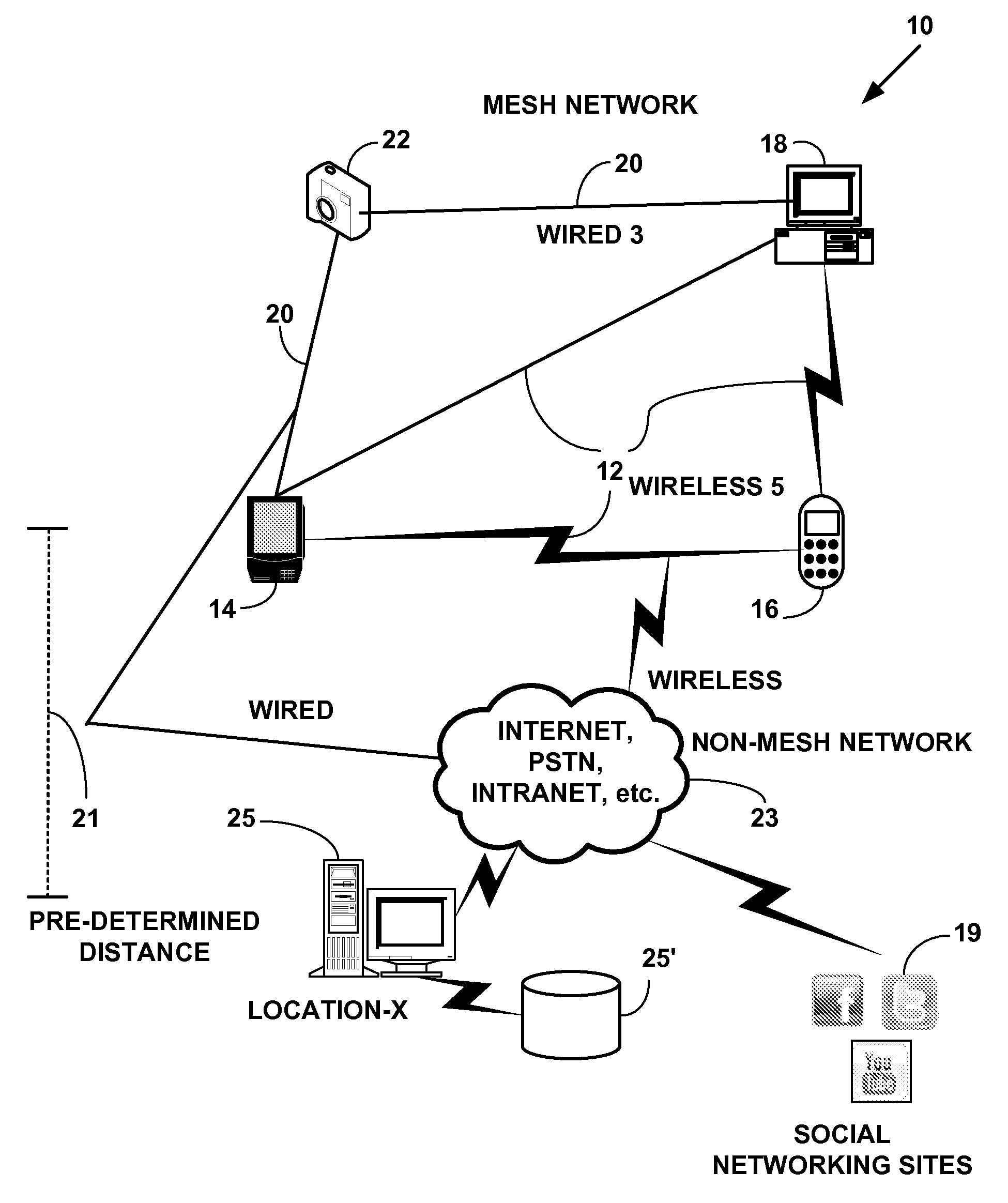
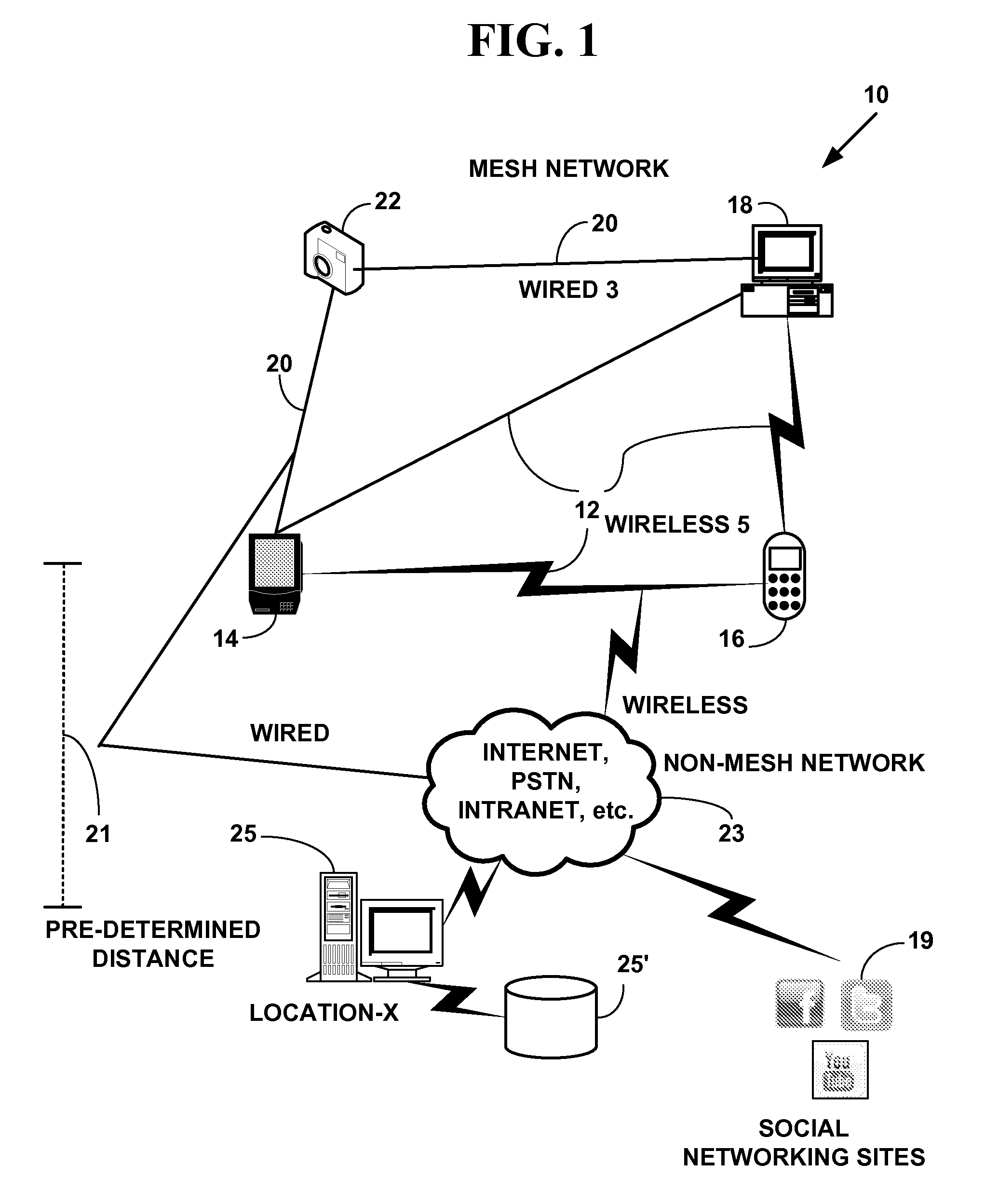
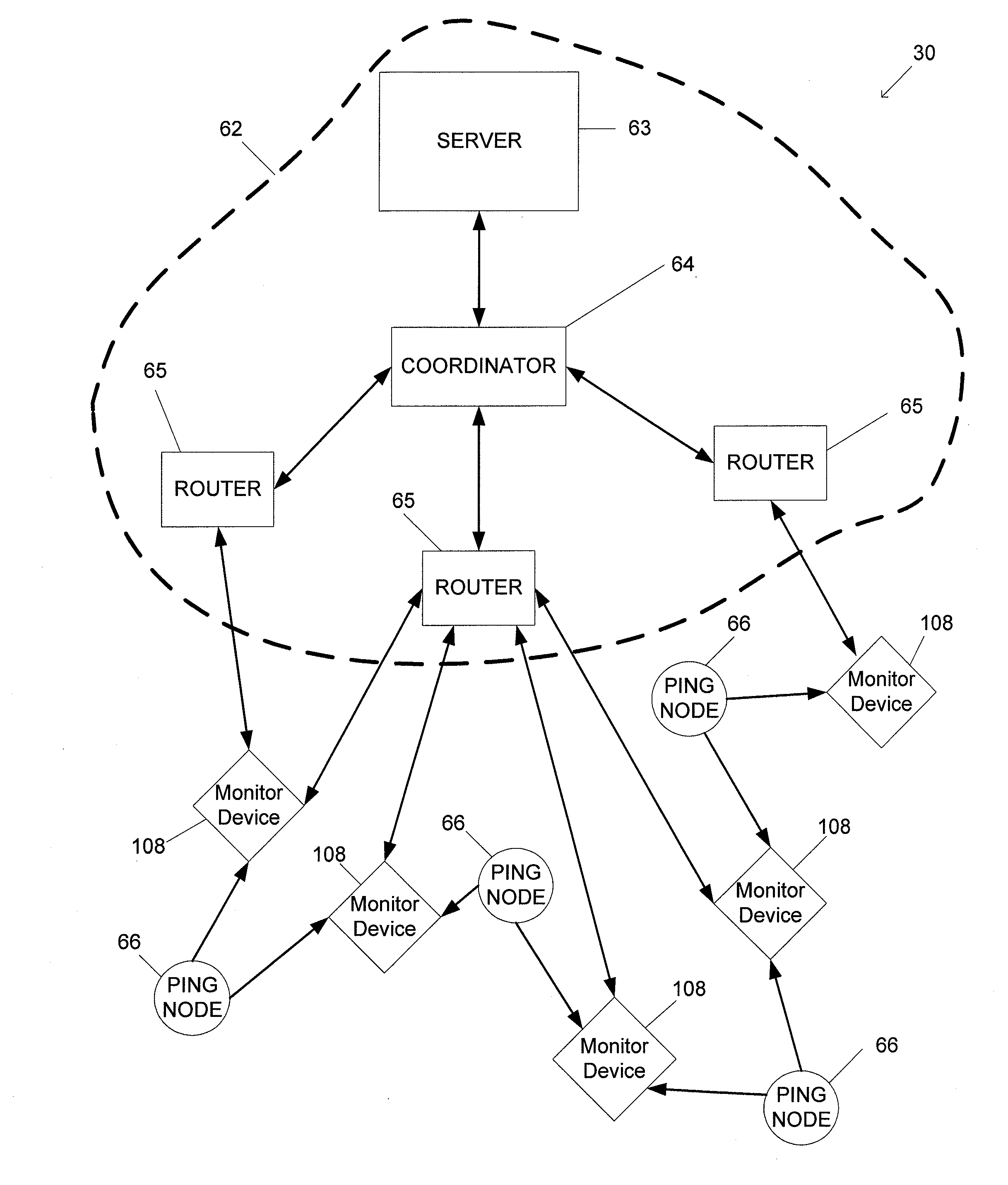
Method and system for dynamic information exchange on location aware mesh network devices
A method and system for dynamic information exchange on mesh network devices. The dynamic information exchange includes allowing a mesh network device to communicate location information with a network device at pre-determined physical location and invite social contacts of the mesh network device to come to the pre-determined physical location. The network device sends various types of electronic messages (e.g., text message, e-mail, etc.) on a mesh network and / or a non-mesh communications network (e.g., the Internet, etc.) and to social networking sites. The dynamic information exchange also includes exchanging plural activity messages including a security identification authorization message for allowing access to a secure area, a building management message for automatically and dynamically managing heating, ventilation and / or air conditioning (HVAC) and / or an emergency location message for providing three-dimensional (3D) emergency location information.
Owner:III HLDG 2
Method and System for Filtering Electronic Messages
ActiveUS20080256187A1Minimum delayMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksThird partyAnalysis data
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with filtering emails having data therein identifying a link to a remote processing system, which, when activated, causes the recipient to retrieve data from the remote processing system.Embodiments of the invention provide a method of modifying an electronic message during transmission through a communications network, said electronic message having a source address and a recipient address, the method comprising:interrupting transmission of the electronic message;identifying a link specified within the electronic message;analyzing the electronic message on the basis of at least an attribute intrinsic to the received electronic message so as to classify the received message as either a first type of message or a second, different, type of message;if the received message is classified as the first type of message, modifying the received electronic message so as to replace the link with an alternative network location, said alternative network location corresponding to a remote processing system different to that corresponding to the link; andtransmitting the modified electronic message.In comparison to known methods, which either modify the links blindly or which perform analysis of the data to which the link is connected, embodiments of the invention selectively modify the link on the basis of various tests relating to attributes intrinsic to the email. This means that only those emails that present some sort of risk to the recipient are modified, and, because the criteria for performing the modification relate to attributes intrinsic to the emails instead of the content associated with the link, the delivery of emails is not significantly delayed by processes involved in retrieval and analysis of data from third party sites.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
Resource management protocol for a configurable network router
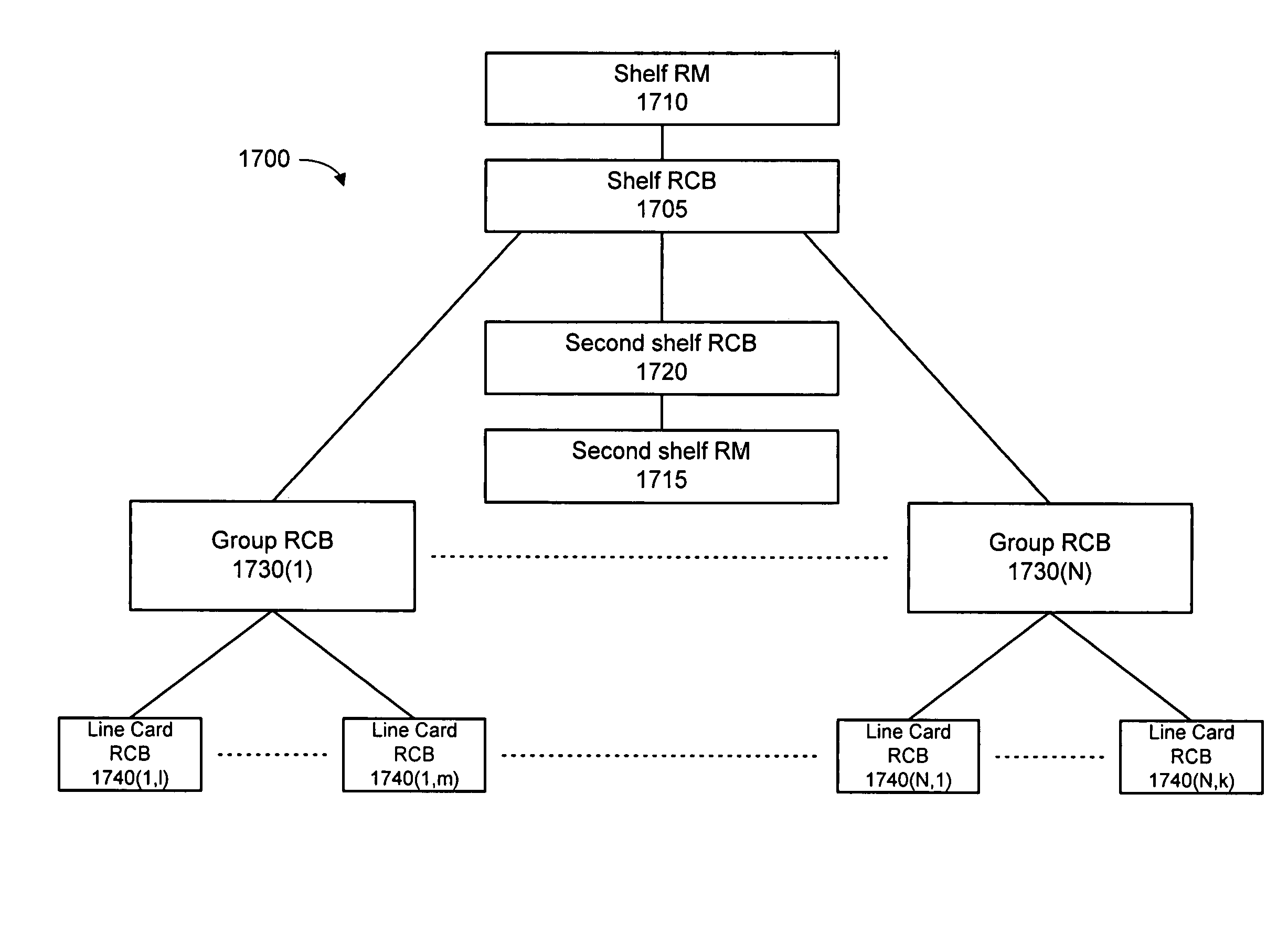
InactiveUS7293090B1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsCommunications systemResource management
A method of managing a communications system is disclosed. The method begins with the creation of a resource control block corresponding to a resource of the communications system. The communications system includes, for example, a processor and a resource coupled to the processor. The resource control block maintains information regarding the resource. The method also provides for the maintenance of the resource control block. The processor is configured to maintain the resource control block, and the resource control block is maintained by the processor in response to communications (e.g., a keep-alive message) between the processor and the resource. This embodiment can also include the creation of a processor resource control block corresponding to the processor that is created by the controller in response to a power-up message from the resource. The resource can be, for example, a hardware component of the communications system.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
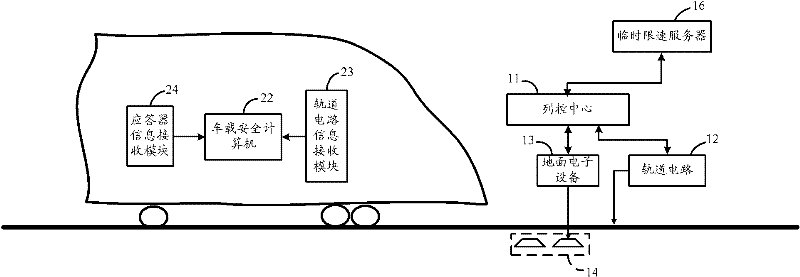
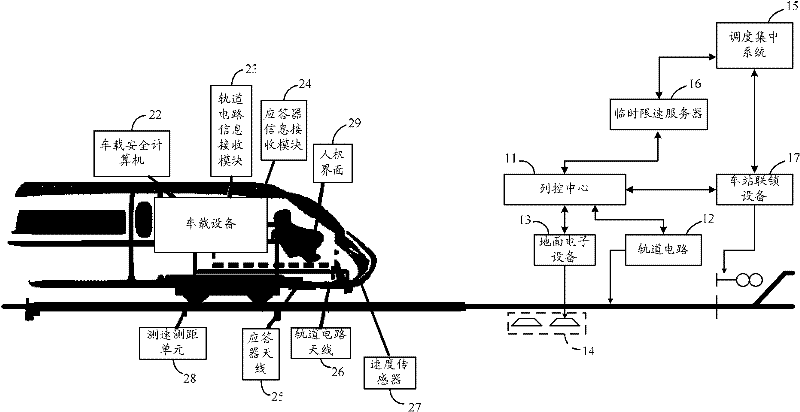
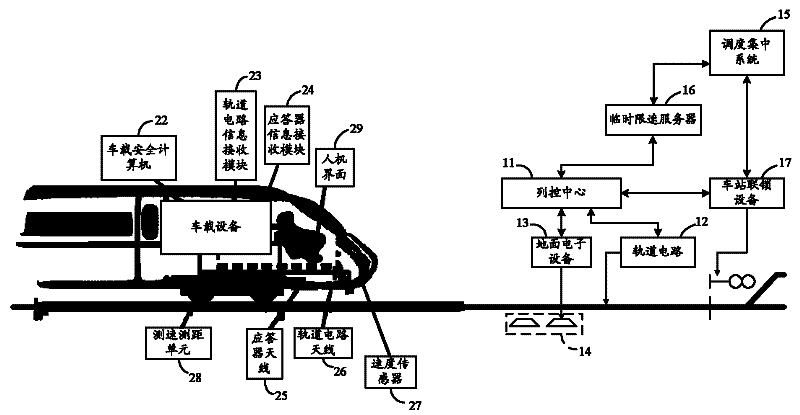
CTCS (China Train Control System)-2 train operation control system
ActiveCN102233886ARealize automatic controlMeet operational requirementsRailway traffic control systemsRoute devices for controlling vehiclesAutomatic controlControl system
The invention provides a CTCS (China Train Control System)-2 train operation control system comprising ground facilities and a vehicle-mounted apparatus, wherein the ground facilities include a temporary speed limit server, a train control centre, a railway circuit, a ground electric unit and a transponder group; the temporary speed limit server generates a temporary speed limit command; the train control centre generates carrier frequency and low frequency coded messages and active messages according to rail zone state messages and the temporary speed limiting command; the rail circuit generates a modulation signal according to the coded message, sends the modulation signal, generates and sends a rail zone state message; the ground electric unit sends the active transponder messages to a transponder group; the transponder group sends a fixed transponder message and an active transponder message; and the vehicle-mounted apparatus includes a vehicle-mounted safety computer, a railway circuit message receiving module and a transponder message receiving module. The CTCS-2 train operation control system provided by the invention realizes automatic control of train operation based on train operation permission messages transmitted by the rail circuit and the transponder group.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +1
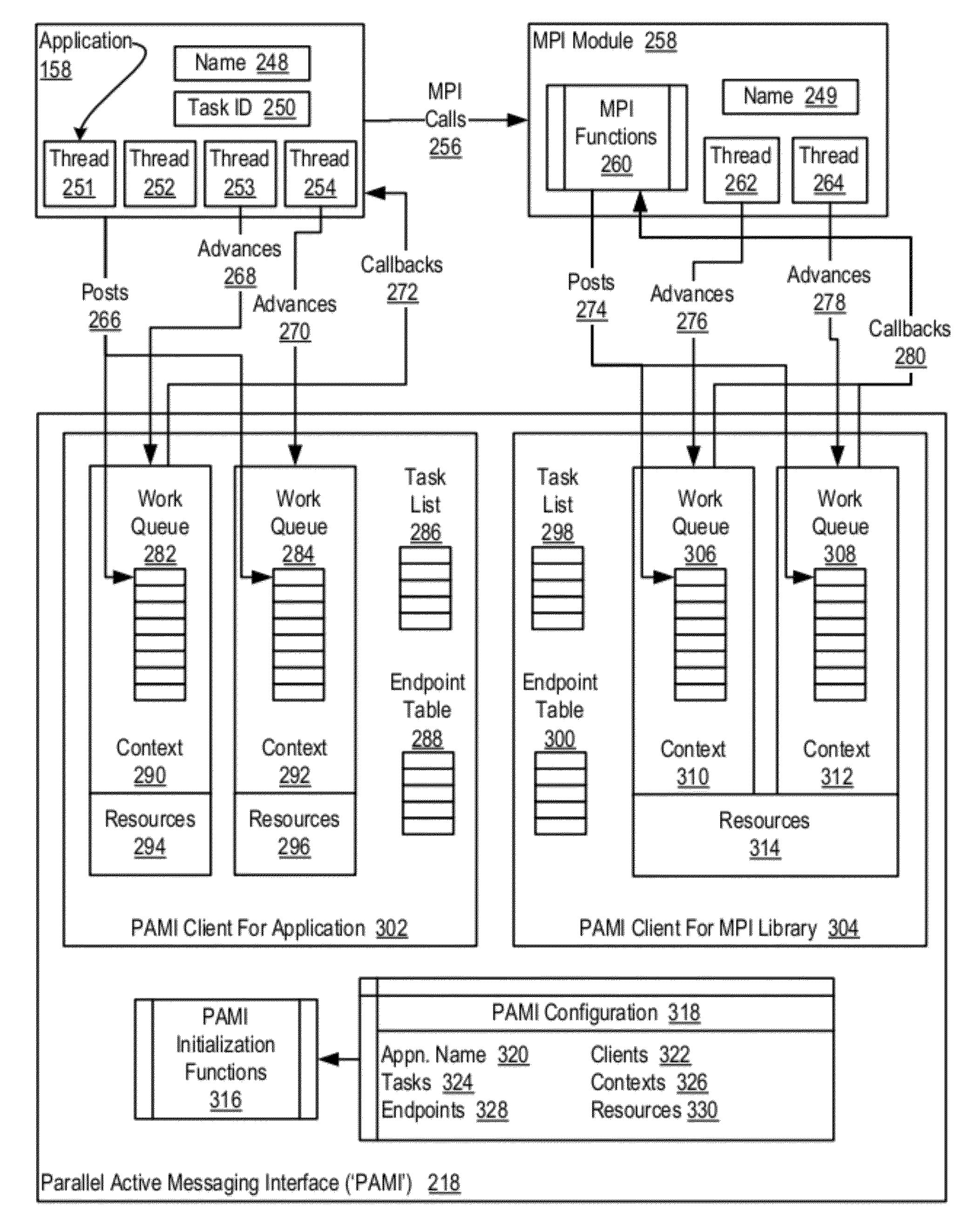
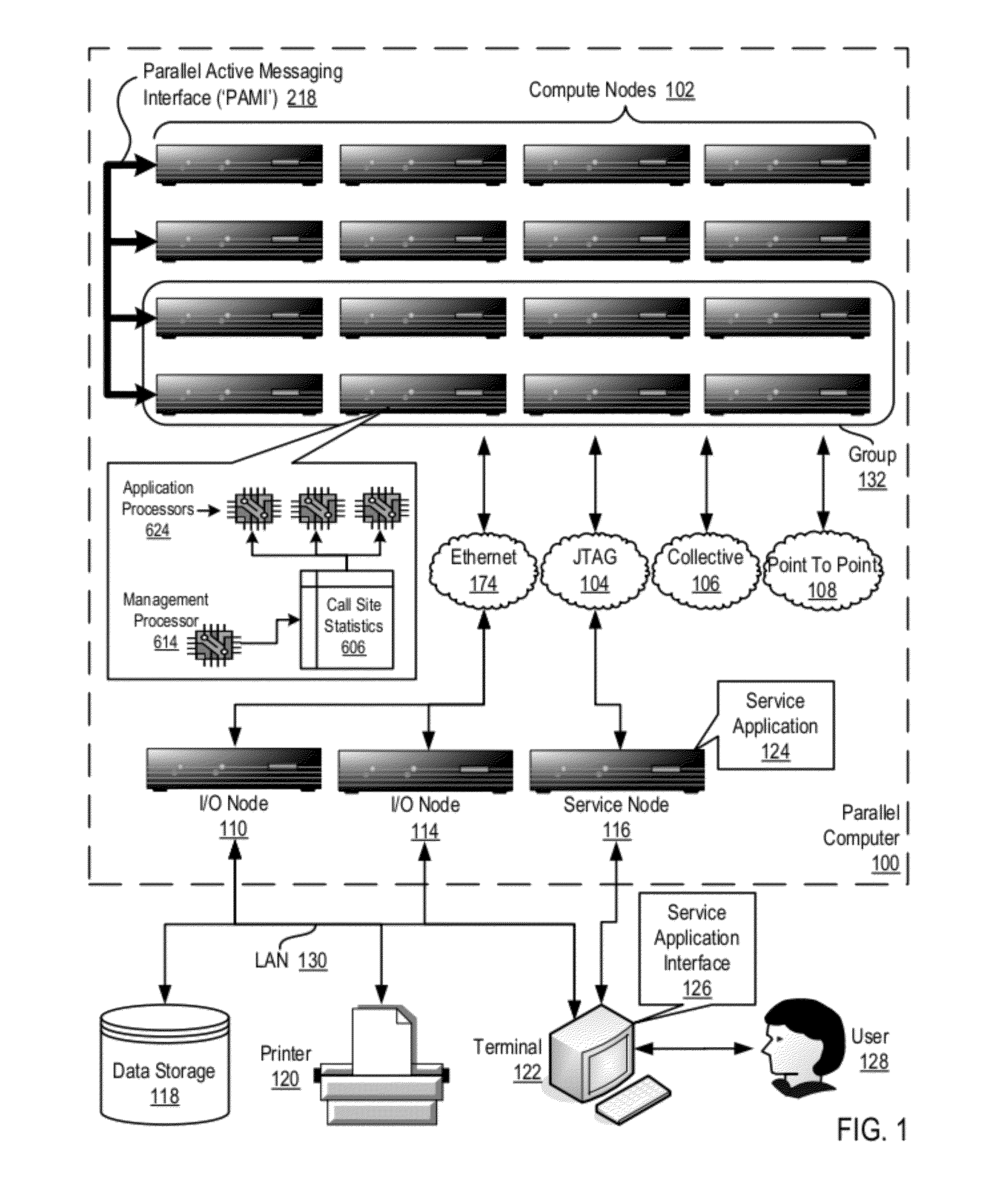
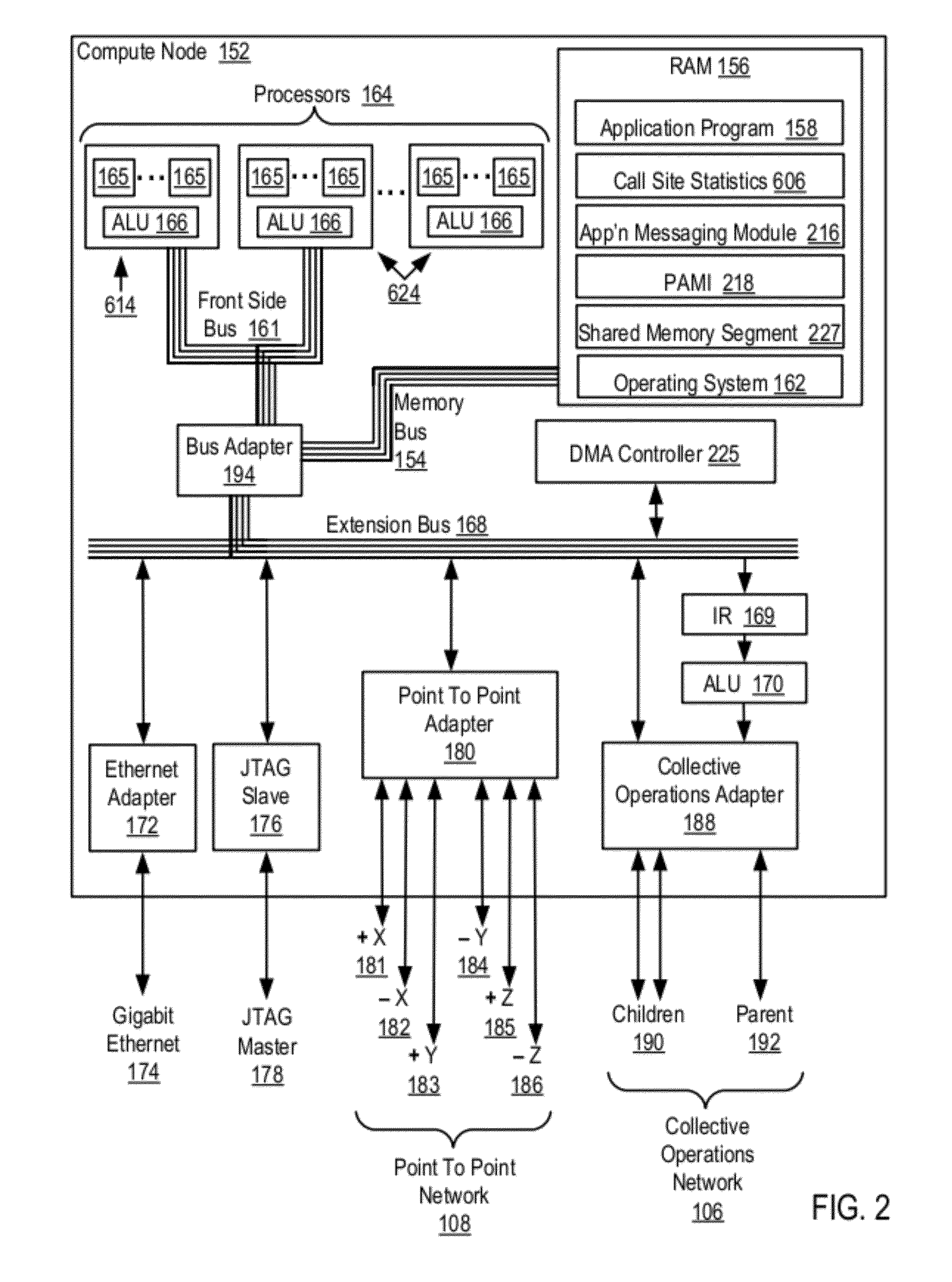
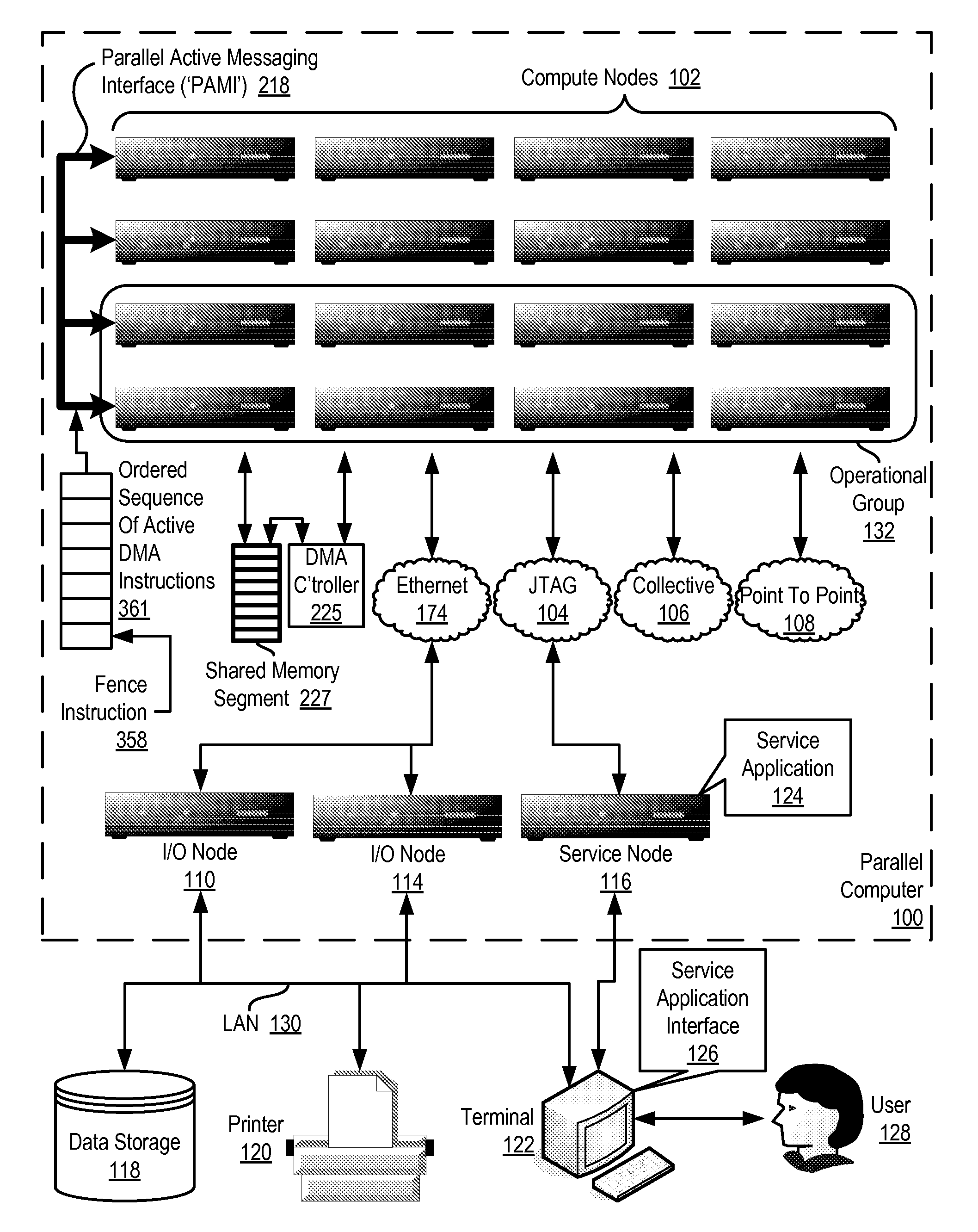
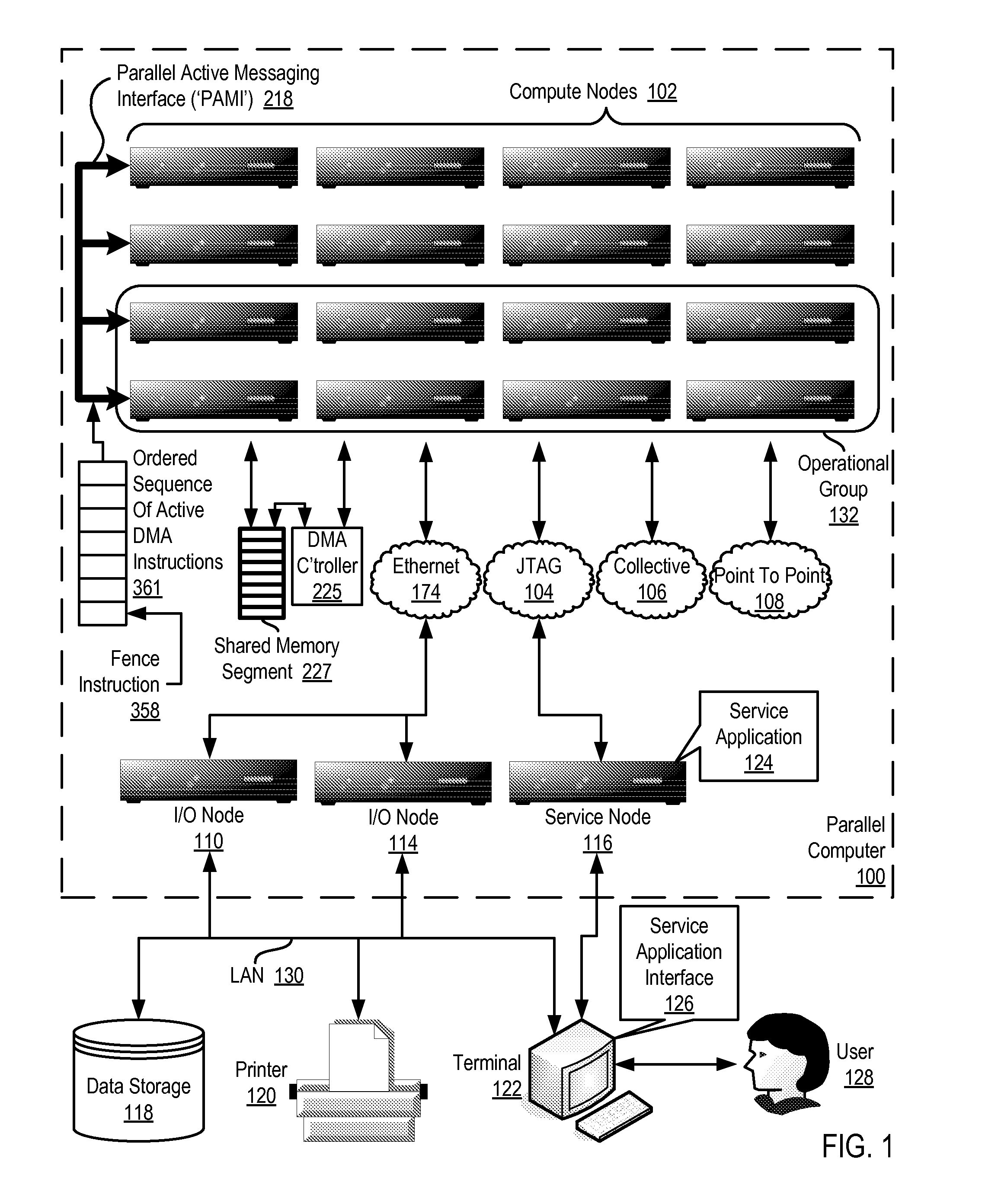
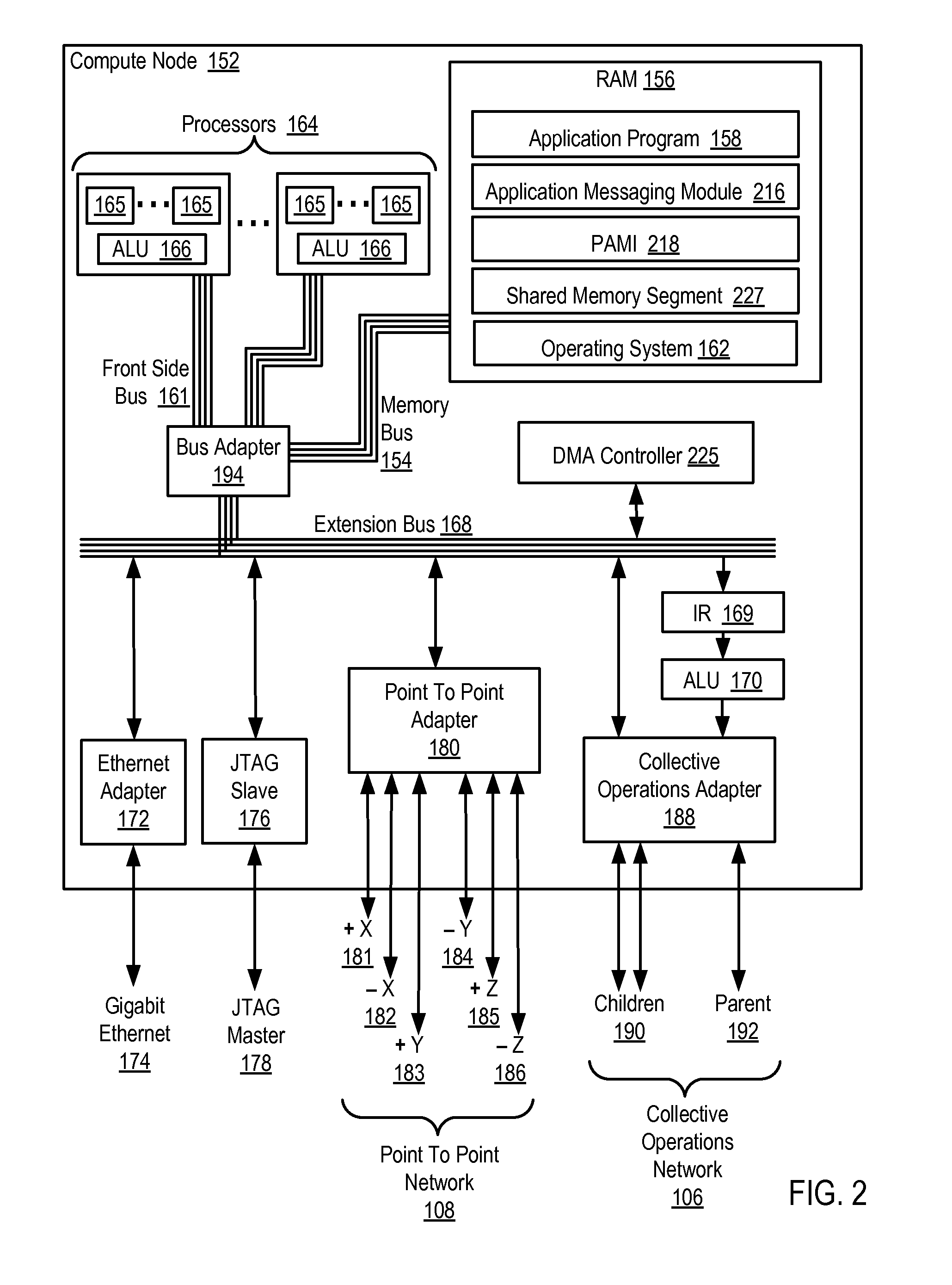
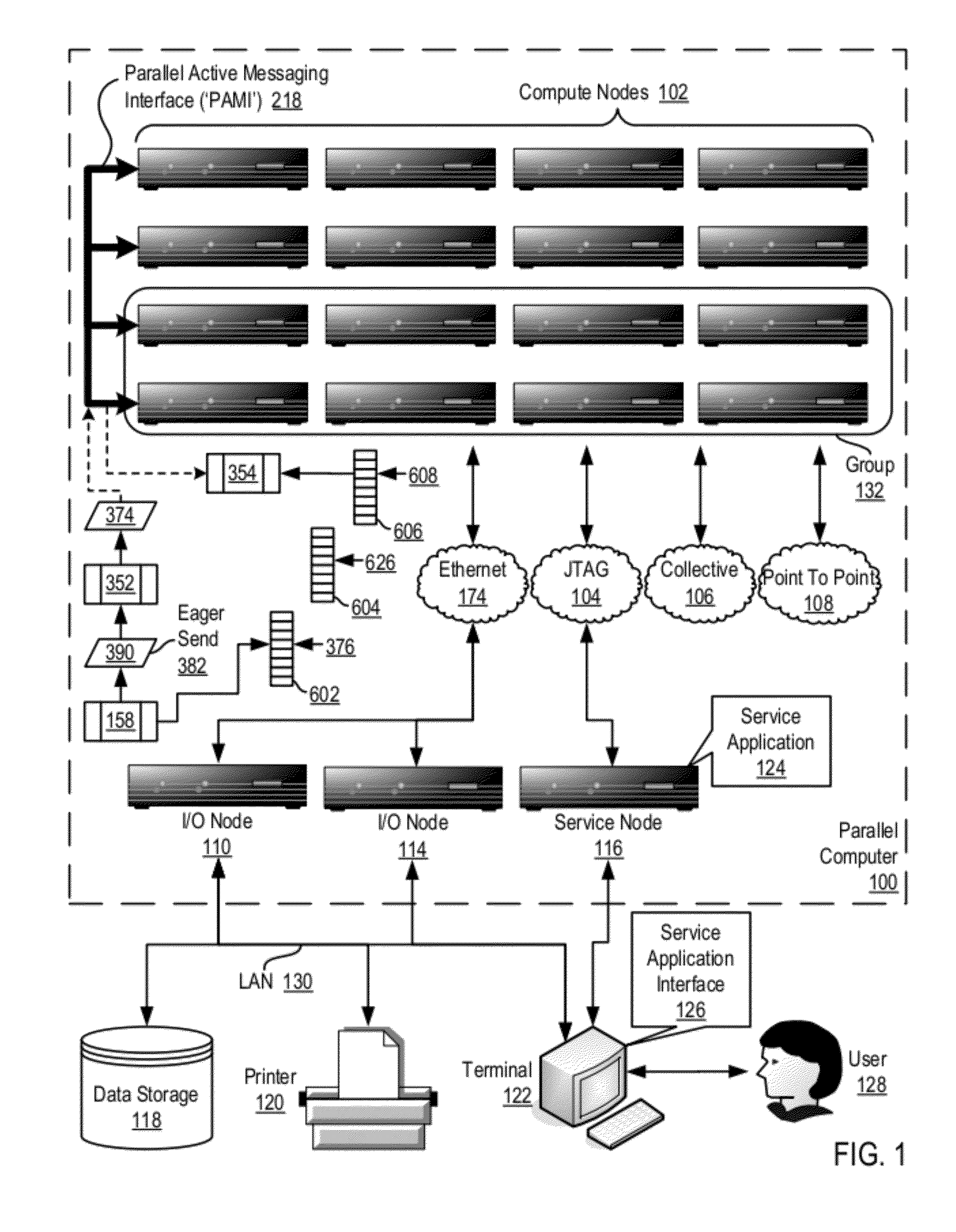
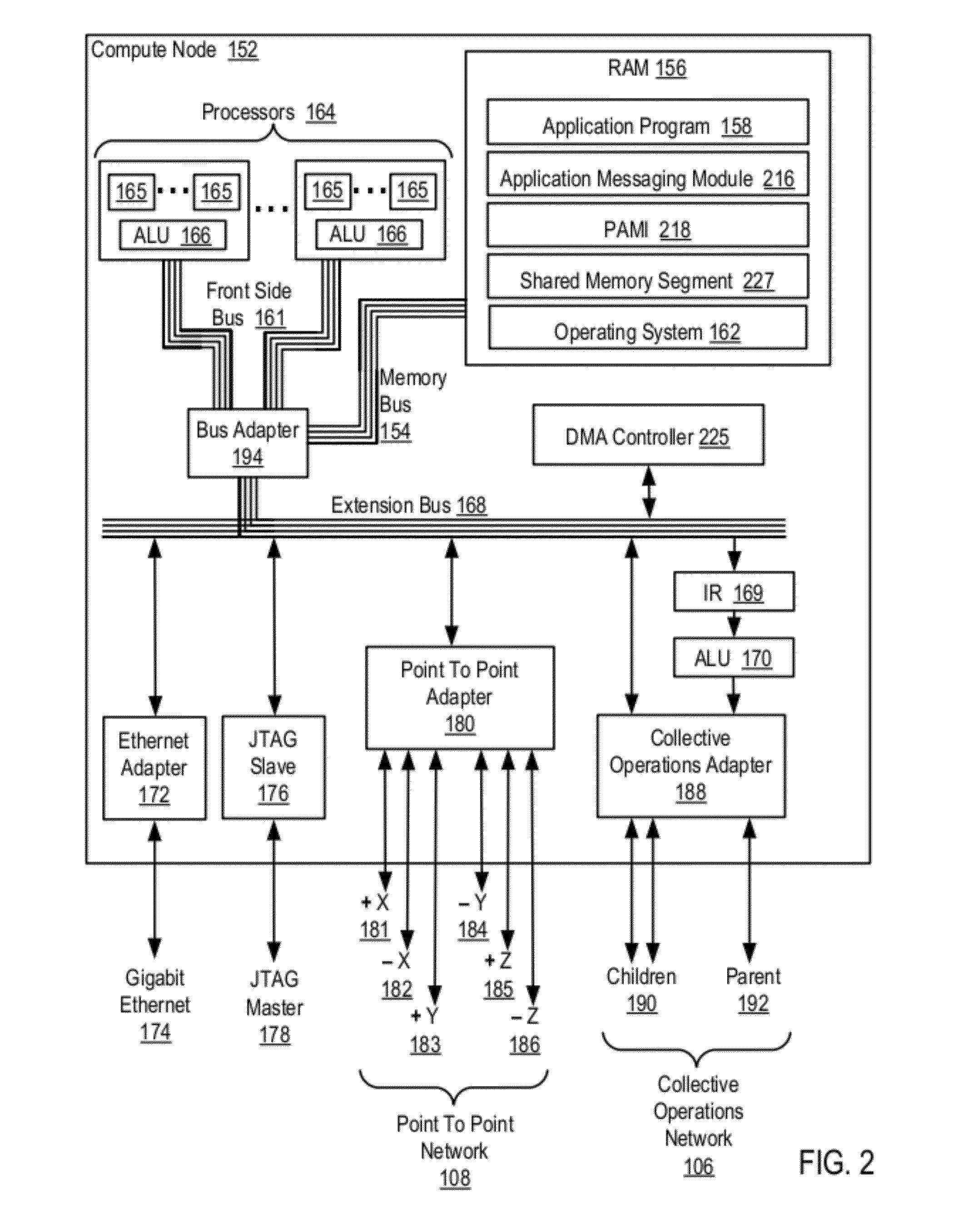
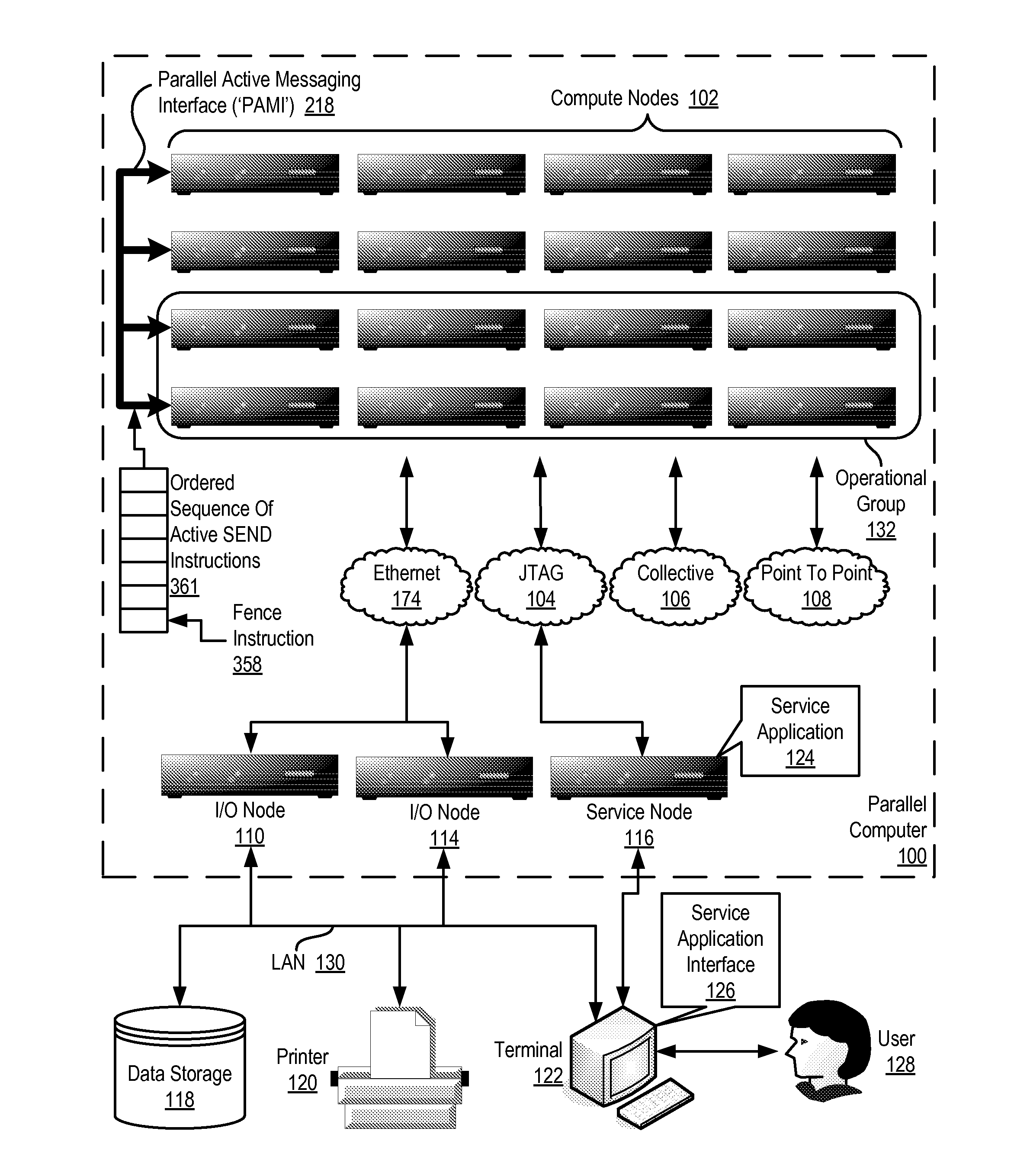
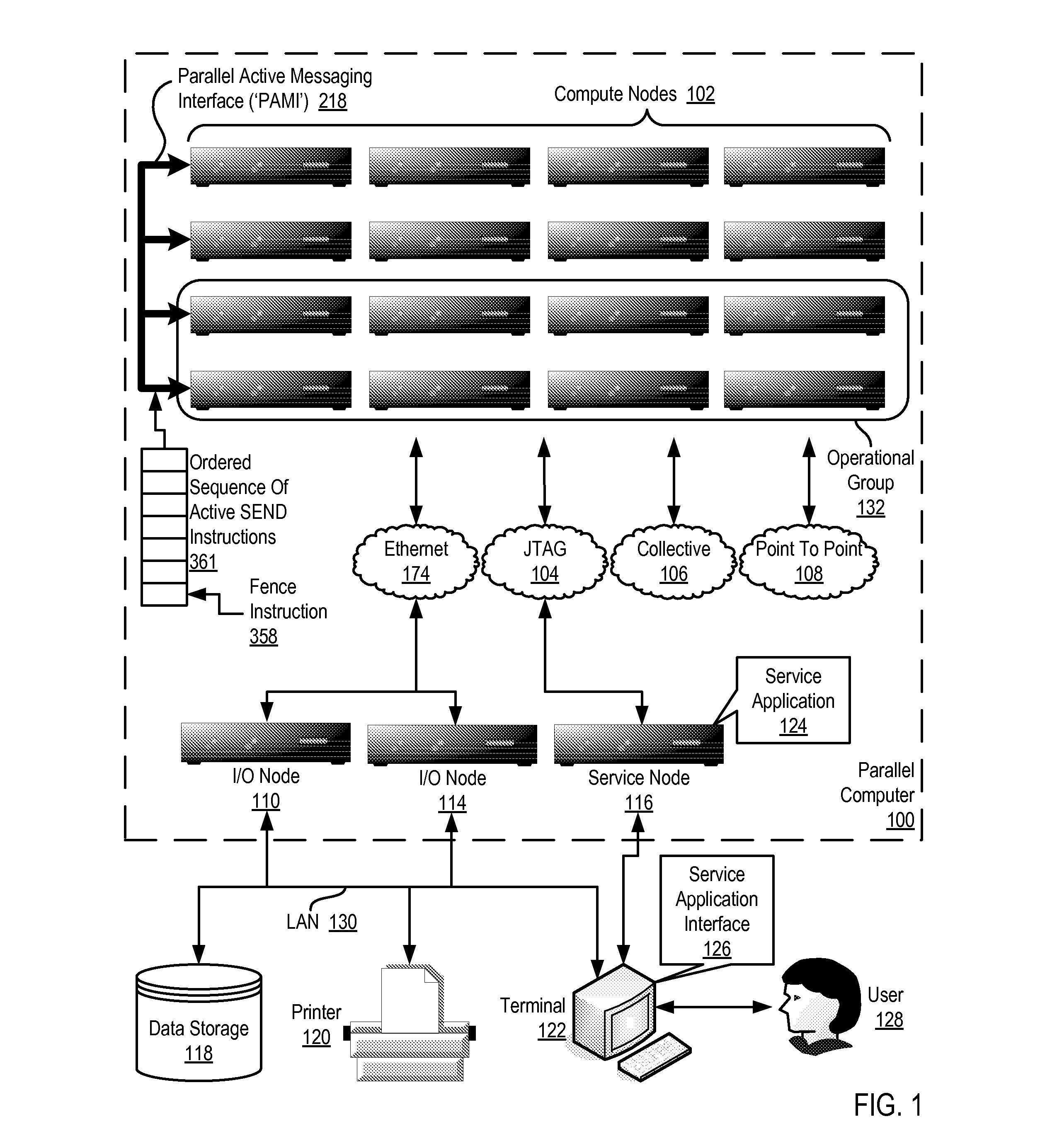
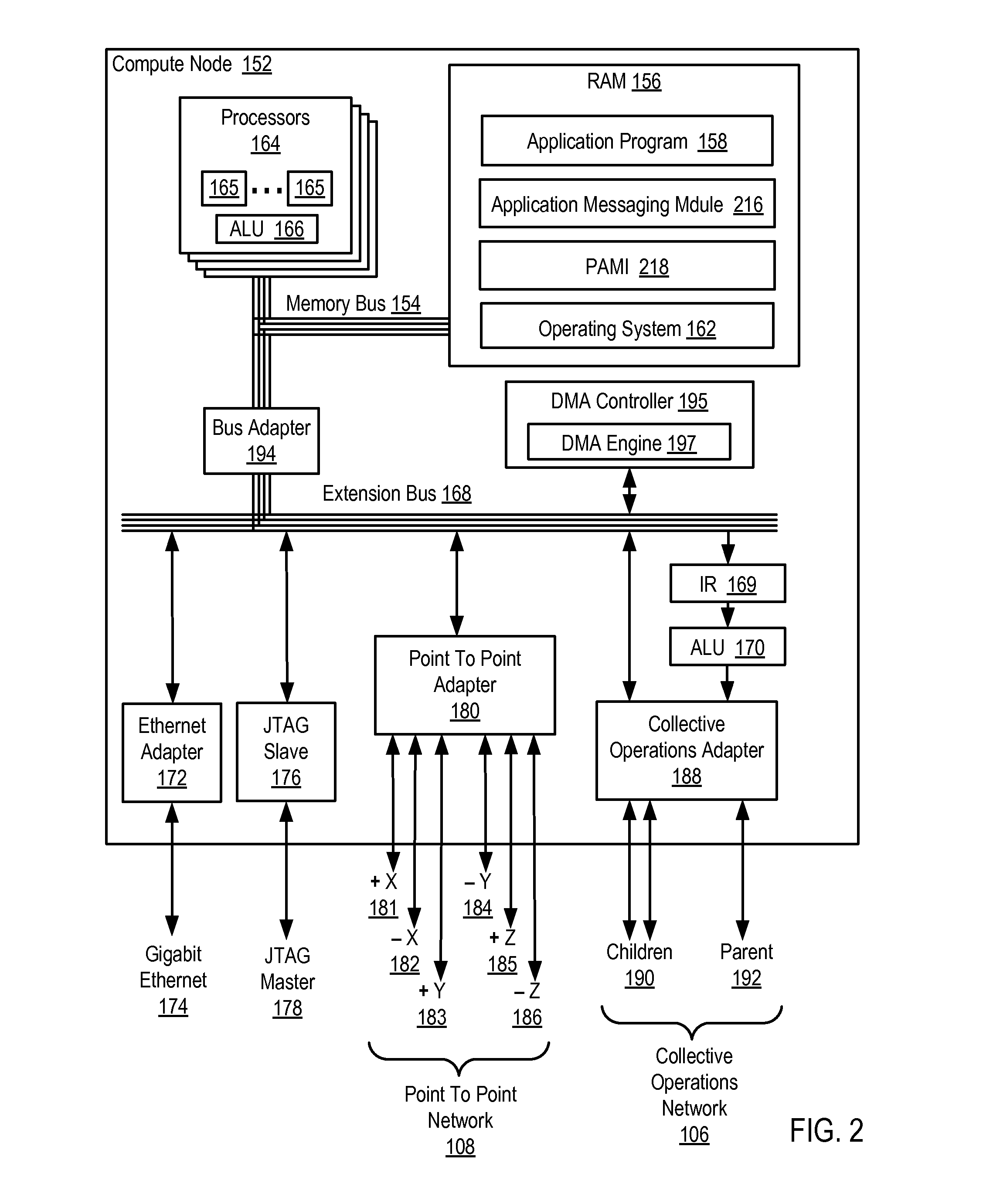
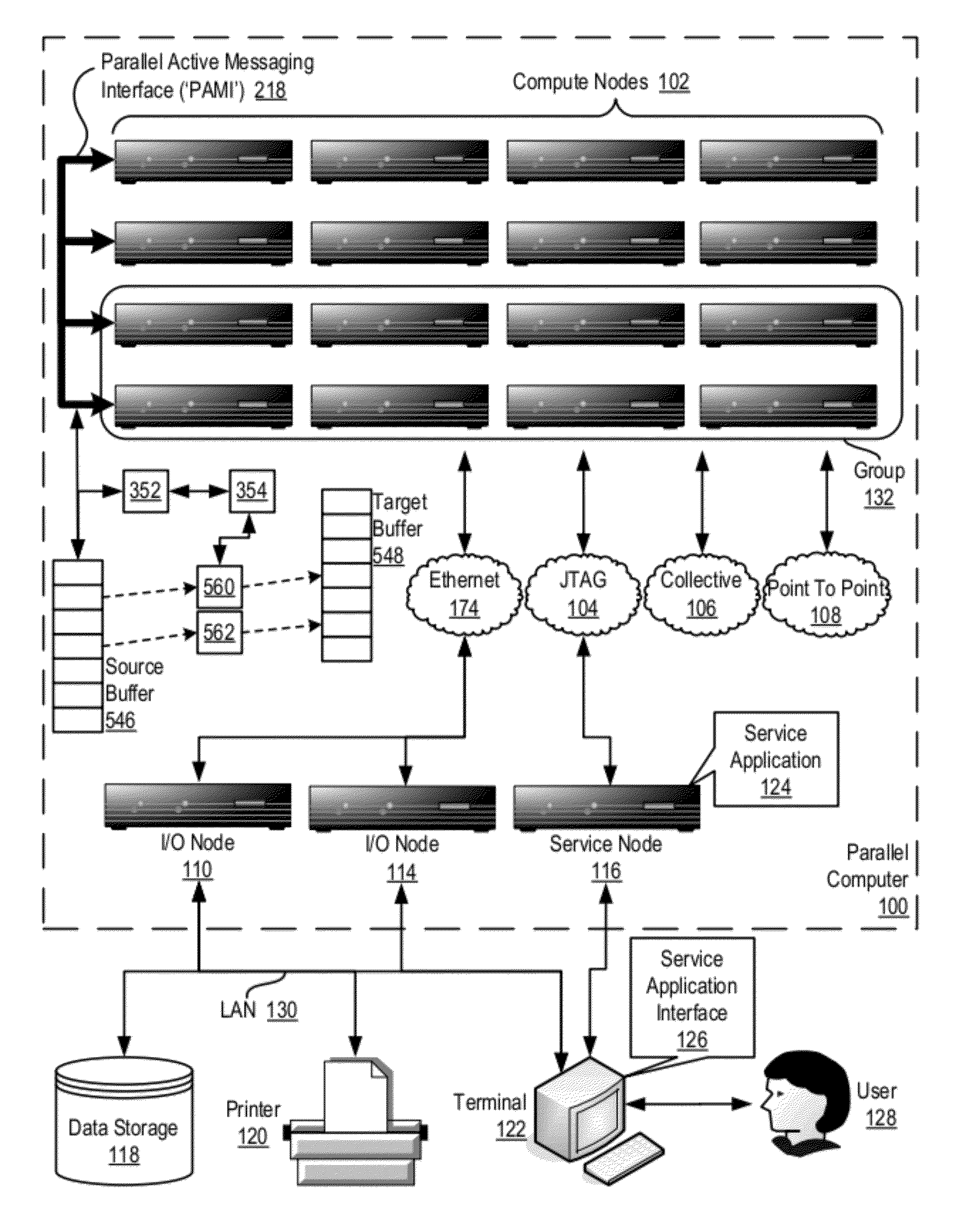
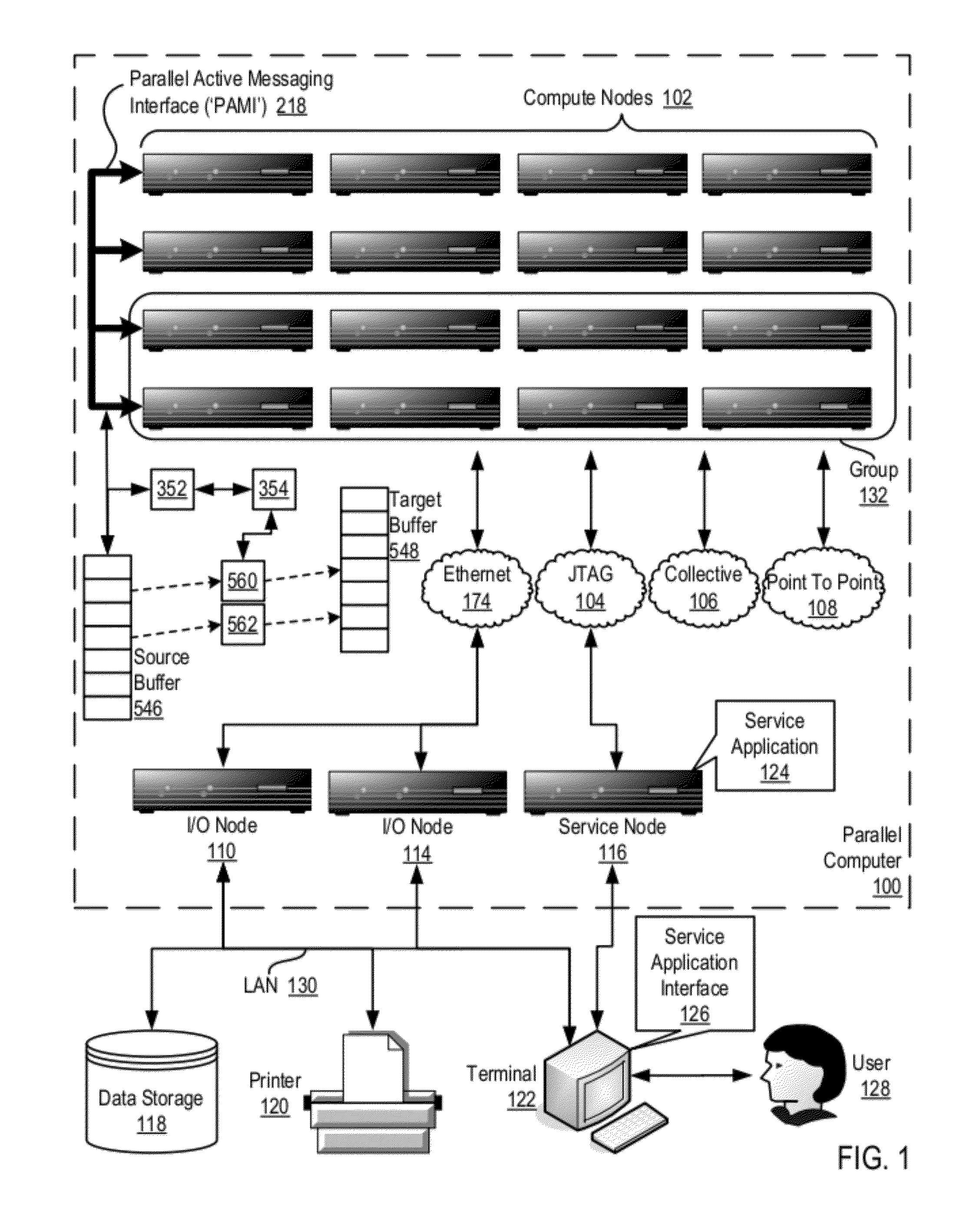
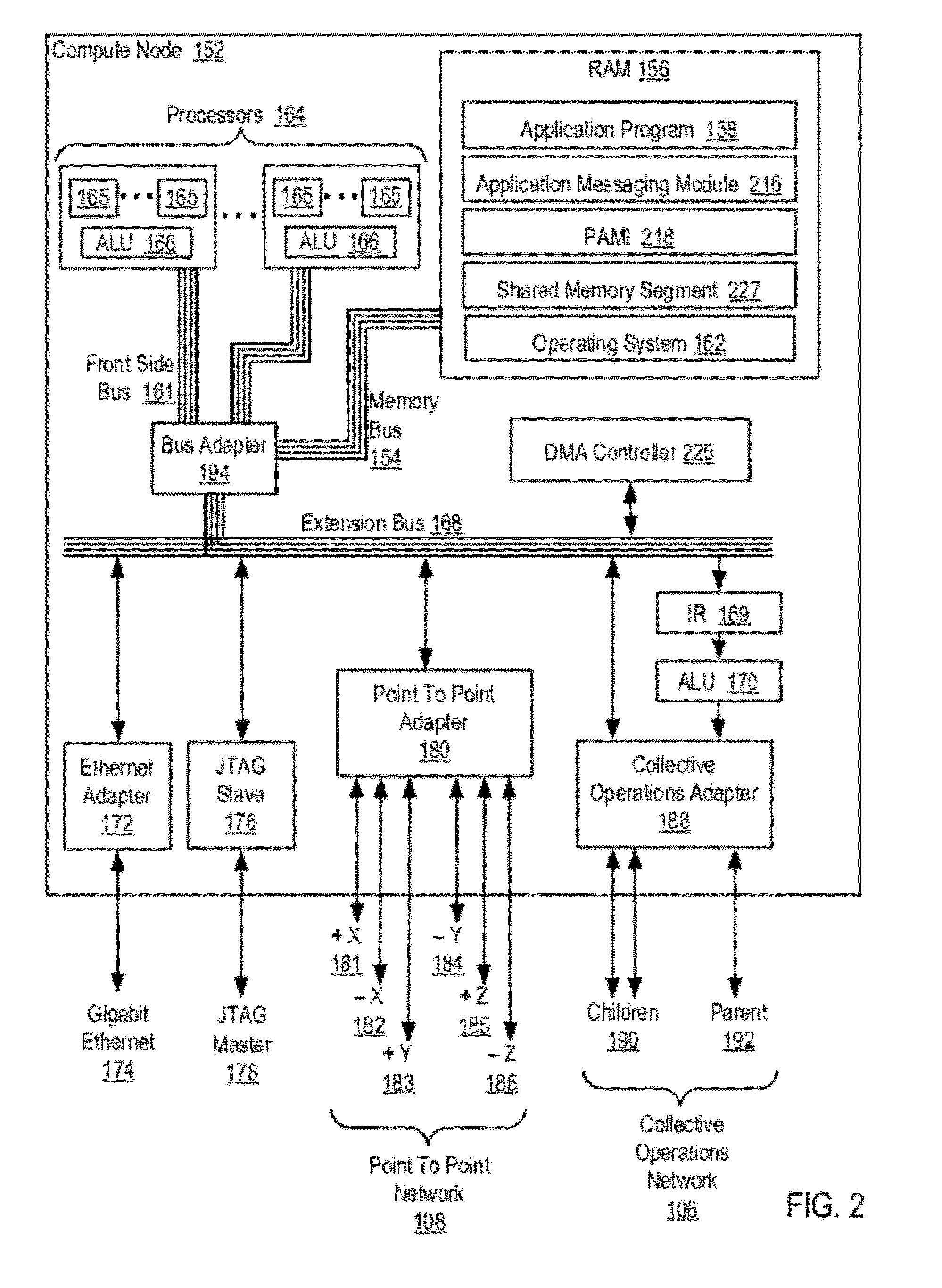
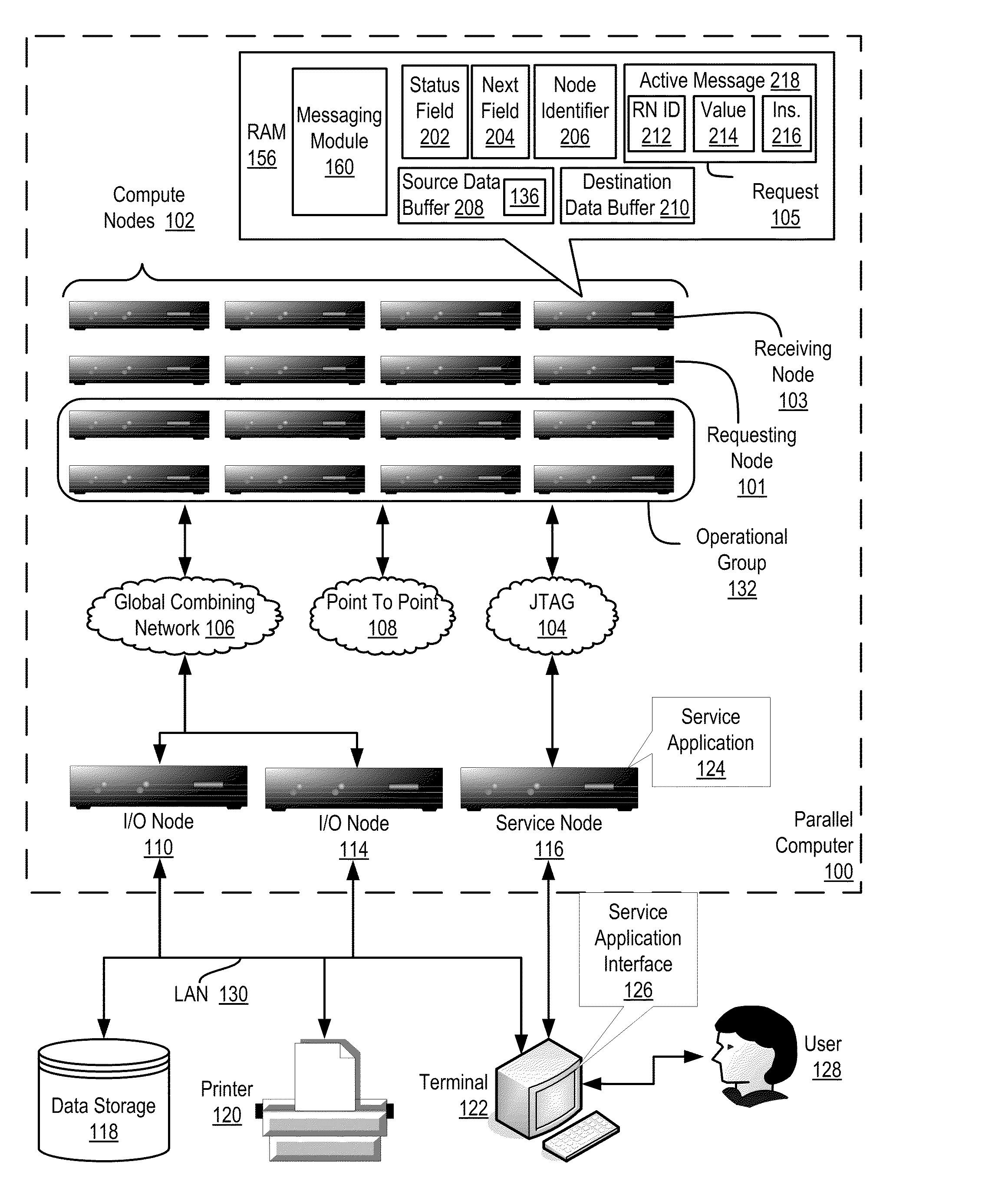
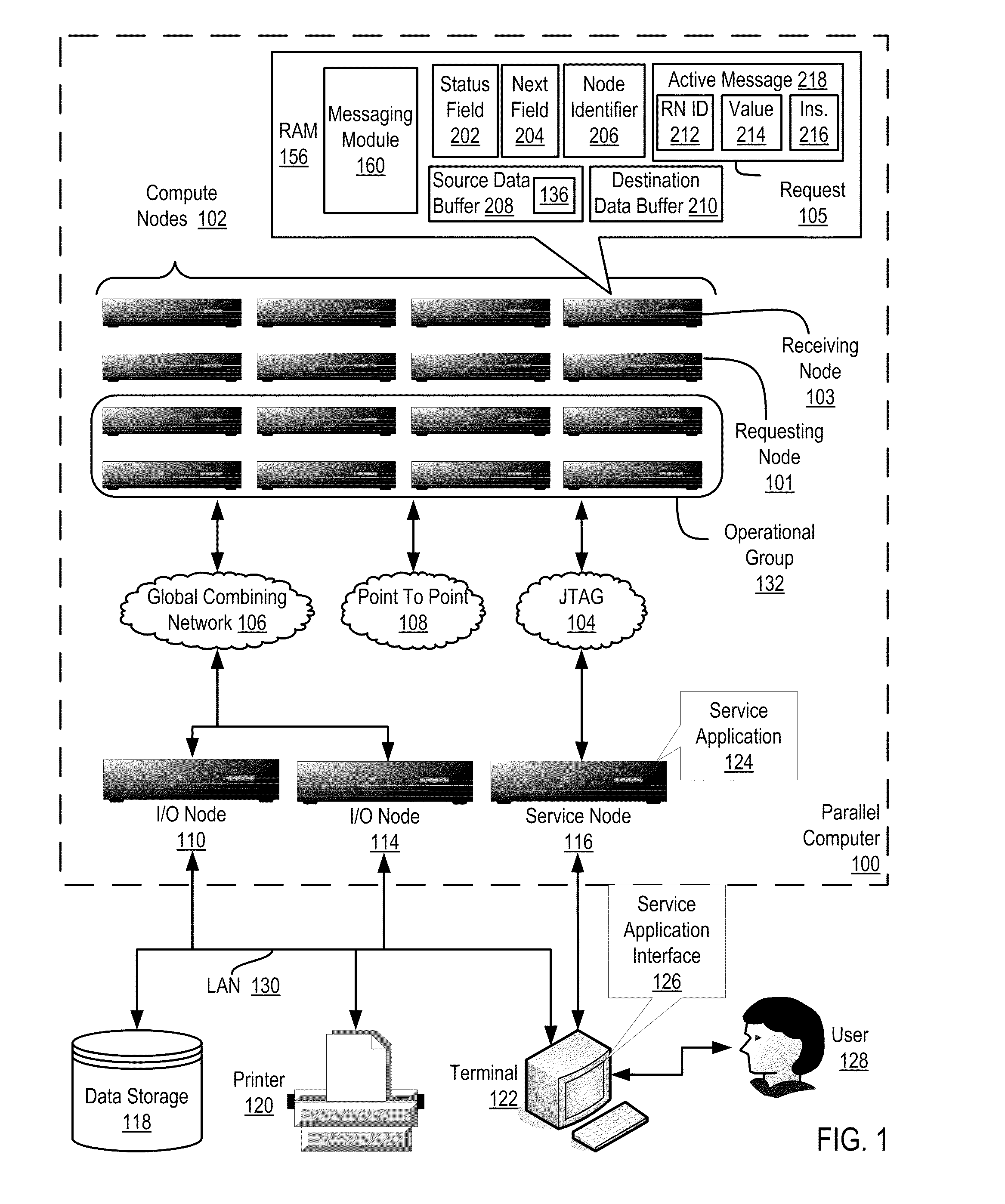
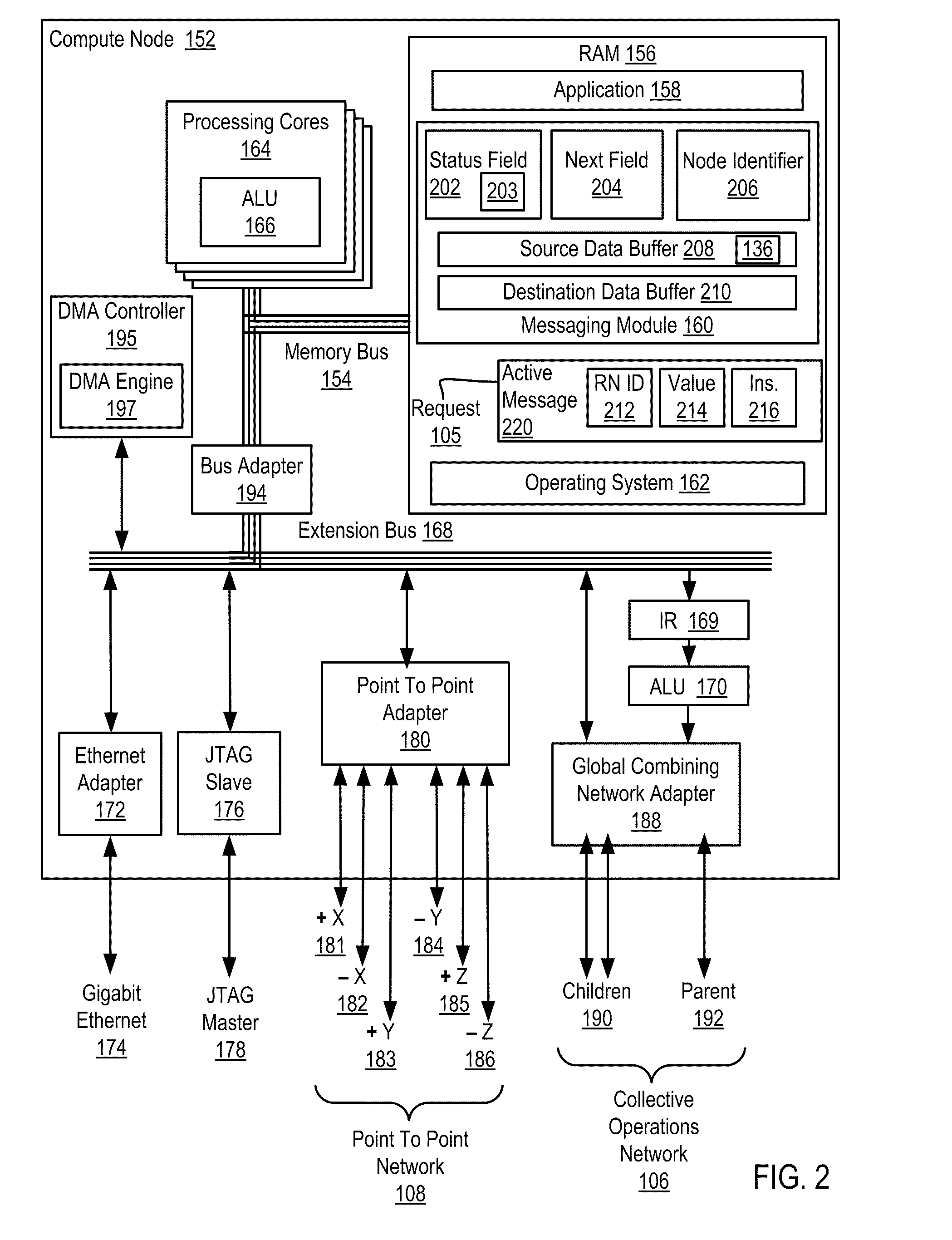
Data Communications In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20120185873A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsCommunication endpointParallel computing
Data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer composed of compute nodes that execute a parallel application, each compute node including application processors that execute the parallel application and at least one management processor dedicated to gathering information regarding data communications. The PAMI is composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint composed of a specification of data communications parameters for a thread of execution on a compute node, including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, the compute nodes and the endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI and through data communications resources. Embodiments function by gathering call site statistics describing data communications resulting from execution of data communications instructions and identifying in dependence upon the call cite statistics a data communications algorithm for use in executing a data communications instruction at a call site in the parallel application.
Owner:IBM CORP
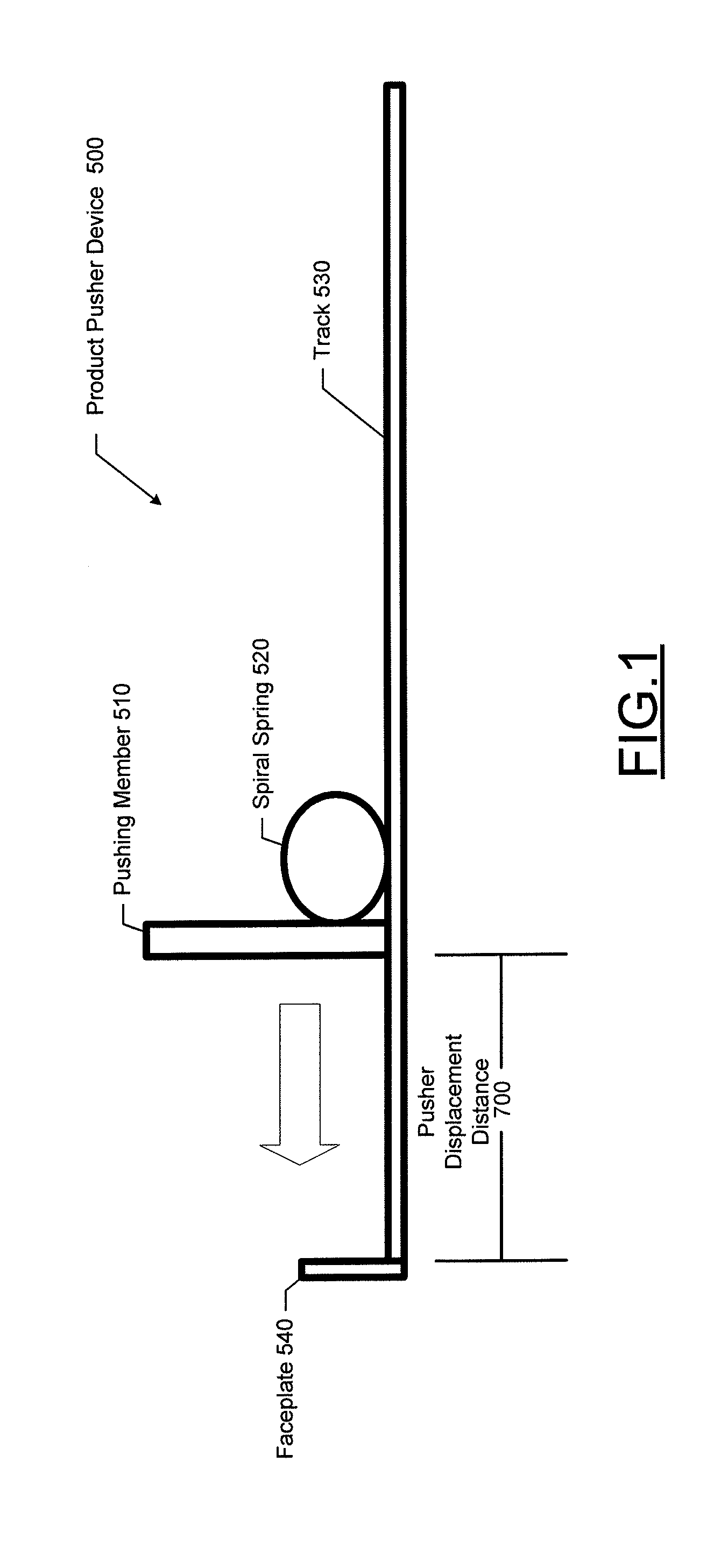
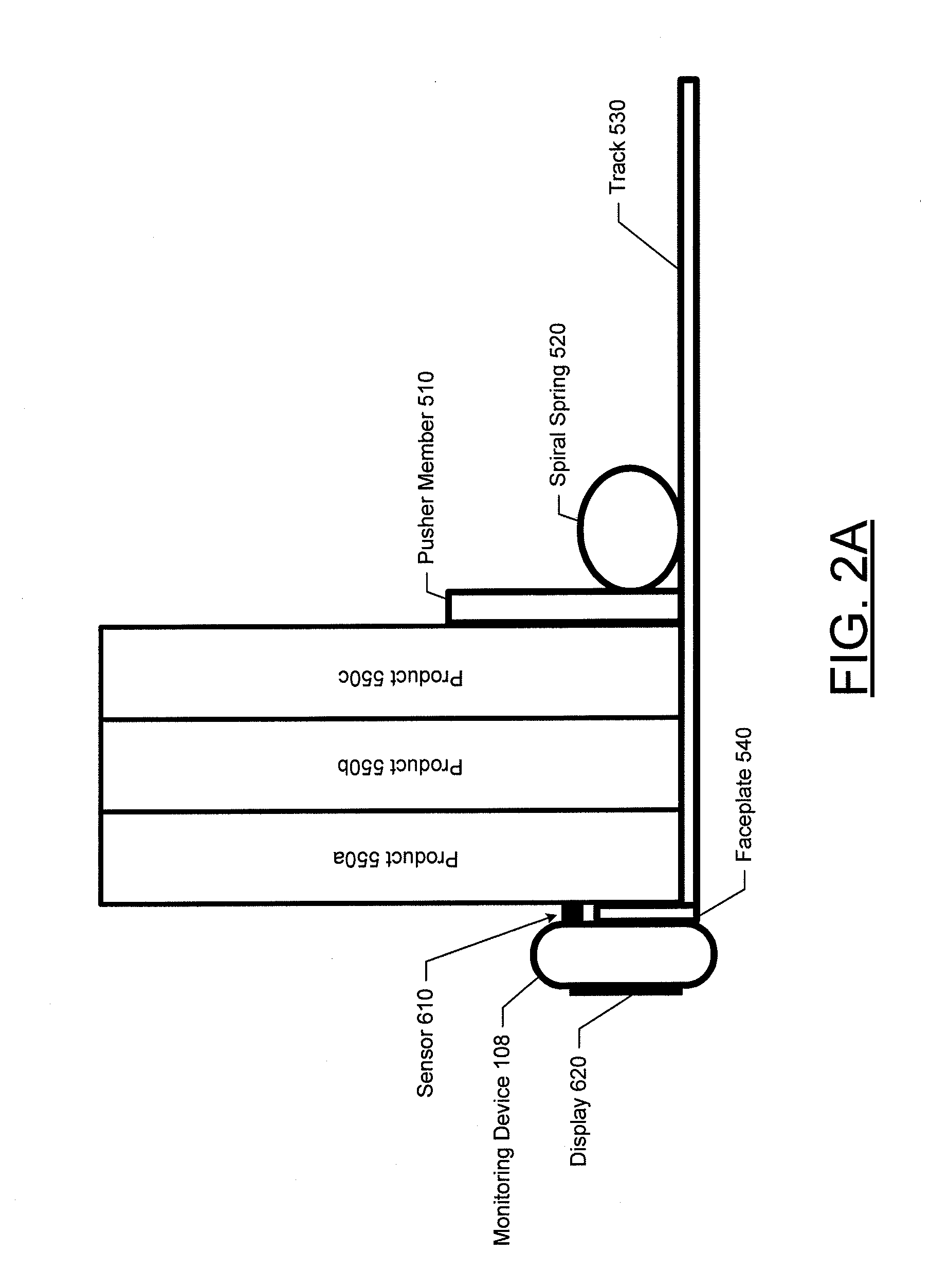
Wireless shelf pusher activity detection system and associated methods
InactiveUS20130002422A1Burglar alarm by openingElectric signalling detailsCommunication interfaceMovement activity
According to some example embodiments, systems, apparatus, methods, computer readable media, and computer program products are provided for implementing a wireless shelf pusher activity detection system. One example apparatus is a monitoring device for monitoring theft or sales activity associated with a product pusher device. The monitoring device may include a sensor configured to detect movement of a pusher member of the product pusher device, a wireless communications interface, and a processor. The processor may be configured to receive at least one sensor signal from the sensor indicating movement of the pusher member, determine a product movement activity type based on characteristics of the at least one sensor signal, and generate, for transmission via the wireless communications interface, a pusher activity message indicating the product movement activity type.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
Fencing Direct Memory Access Data Transfers In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
Fencing direct memory access (‘DMA’) data transfers in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI including data communications endpoints, each endpoint including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, the endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI and through DMA controllers operatively coupled to segments of shared random access memory through which the DMA controllers deliver data communications deterministically, including initiating execution through the PAMI of an ordered sequence of active DMA instructions for DMA data transfers between two endpoints, effecting deterministic DMA data transfers through a DMA controller and a segment of shared memory; and executing through the PAMI, with no FENCE accounting for DMA data transfers, an active FENCE instruction, the FENCE instruction completing execution only after completion of all DMA instructions initiated prior to execution of the FENCE instruction for DMA data transfers between the two endpoints.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data Communications In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
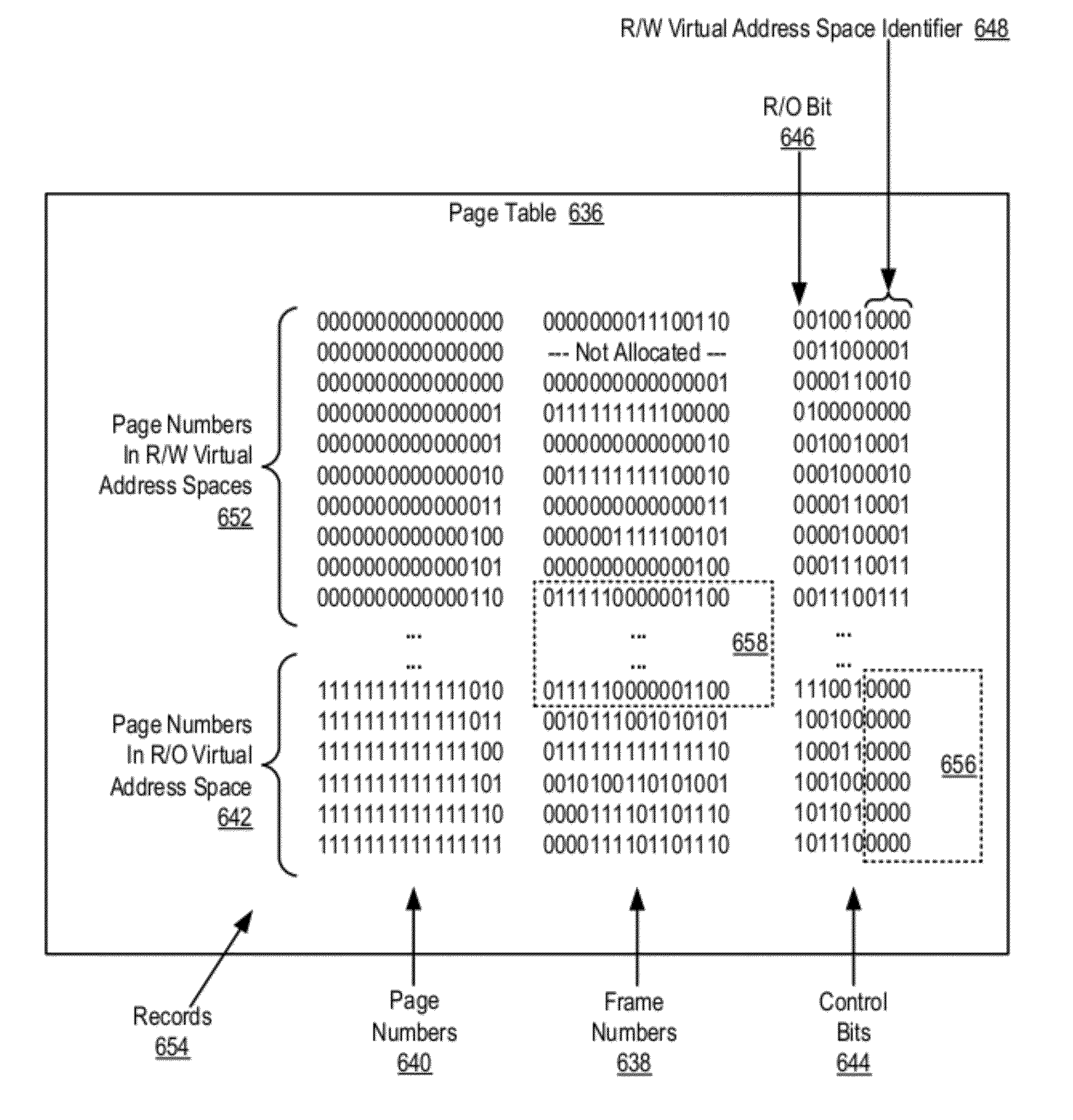
InactiveUS20120210094A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsVirtual memoryMemory address
Eager send data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (PAMI) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints that specify a client, a context, and a task, including receiving an eager send data communications instruction with transfer data disposed in a send buffer characterized by a read / write send buffer memory address in a read / write virtual address space of the origin endpoint; determining for the send buffer a read-only send buffer memory address in a read-only virtual address space, the read-only virtual address space shared by both the origin endpoint and the target endpoint, with all frames of physical memory mapped to pages of virtual memory in the read-only virtual address space; and communicating by the origin endpoint to the target endpoint an eager send message header that includes the read-only send buffer memory address.
Owner:IBM CORP
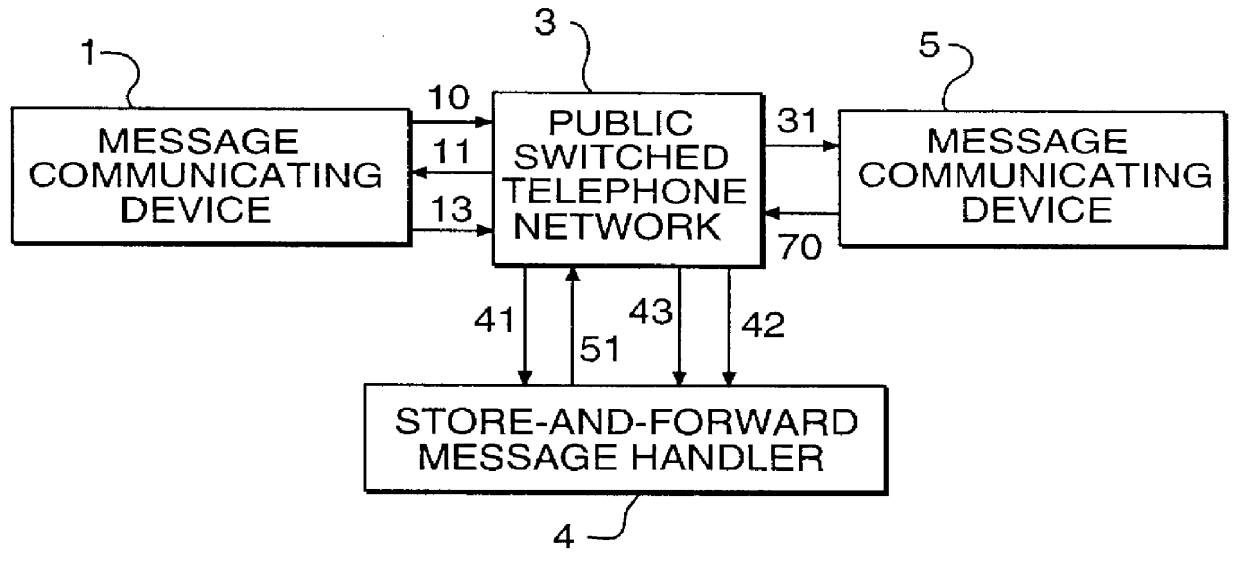
Pro-active message delivery system and method
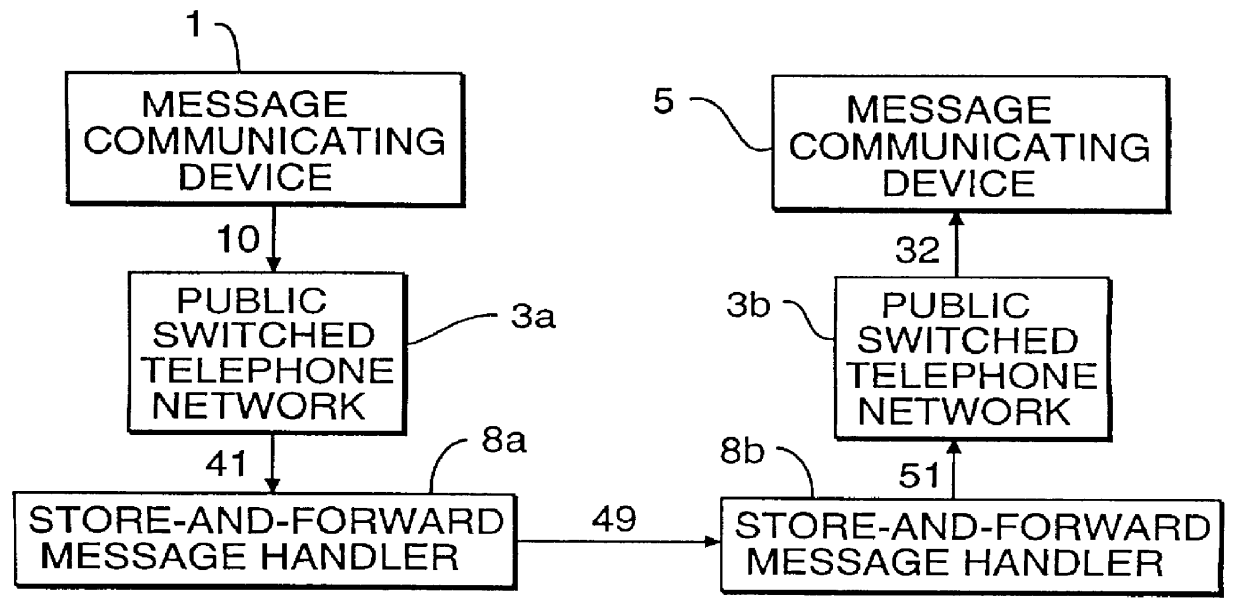
A pro-active message delivery system which routes digitally-encoded messages via public-switched telephone networks and wide area networks to most cost-effectively deliver the messages, subject to security, privacy, and availability considerations. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, digitally encoded messages entered into a wide area network, either directly or via a public-switched telephone network, are sent to their destination using the most cost-effective route, by calculating the cost of sending the message via the available routes, and selecting the lowest cost route. Generally, the lowest cost route might use the node on the wide area network closest to the recipient of the message, or might use or node located in an area which charges off-peak rates at the time of transmission.
Owner:NET2PHONE
Fencing Data Transfers In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20120117211A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlCommunication endpointParallel computing
Fencing data transfers in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI including data communications endpoints, each endpoint comprising a specification of data communications parameters for a thread of execution on a compute node, including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, the compute nodes coupled for data communications through the PAMI and through data communications resources including a deterministic data communications network, including initiating execution through the PAMI of an ordered sequence of active SEND instructions for SEND data transfers between two endpoints, effecting deterministic SEND data transfers; and executing through the PAMI, with no FENCE accounting for SEND data transfers, an active FENCE instruction, the FENCE instruction completing execution only after completion of all SEND instructions initiated prior to execution of the FENCE instruction for SEND data transfers between the two endpoints.
Owner:IBM CORP
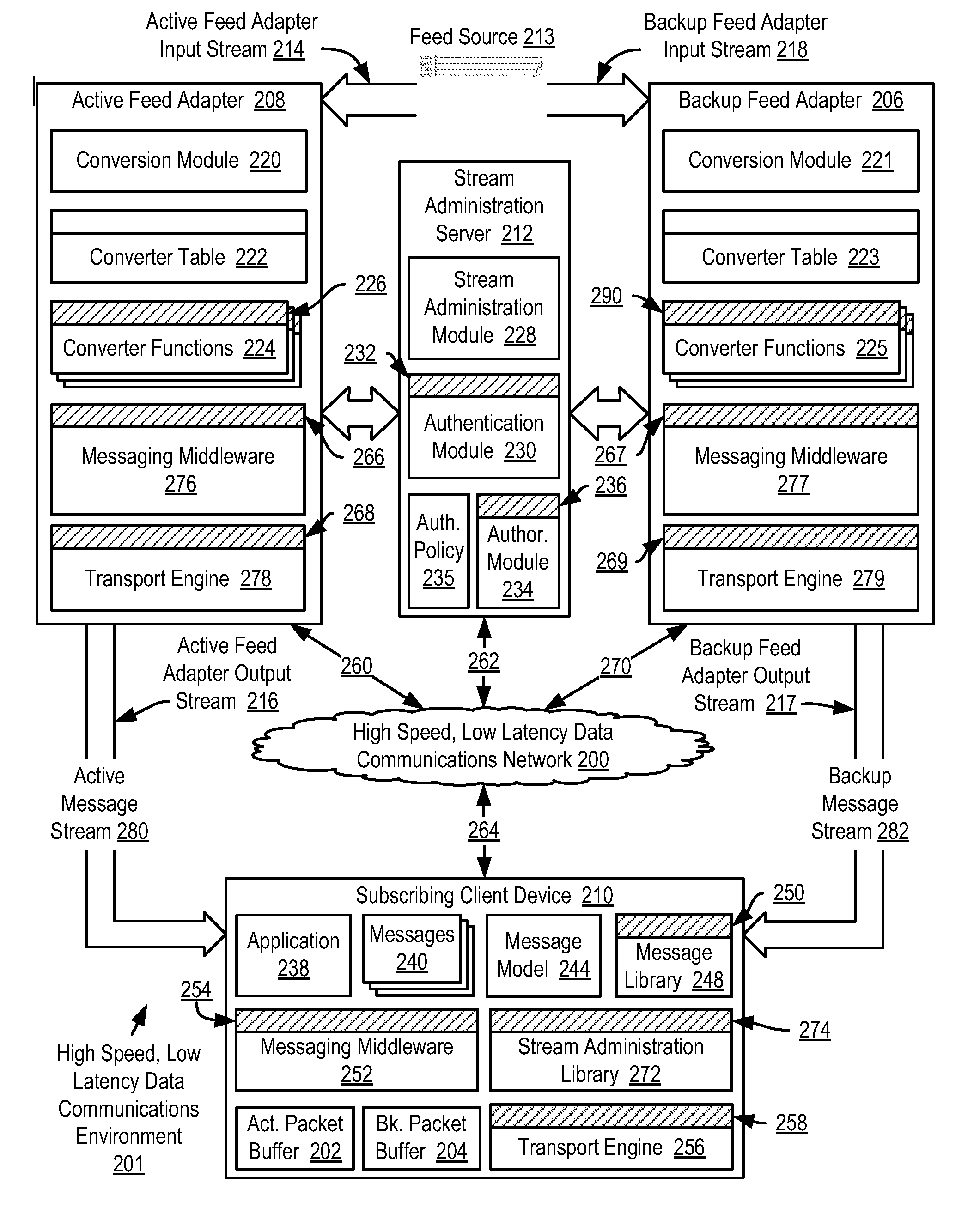
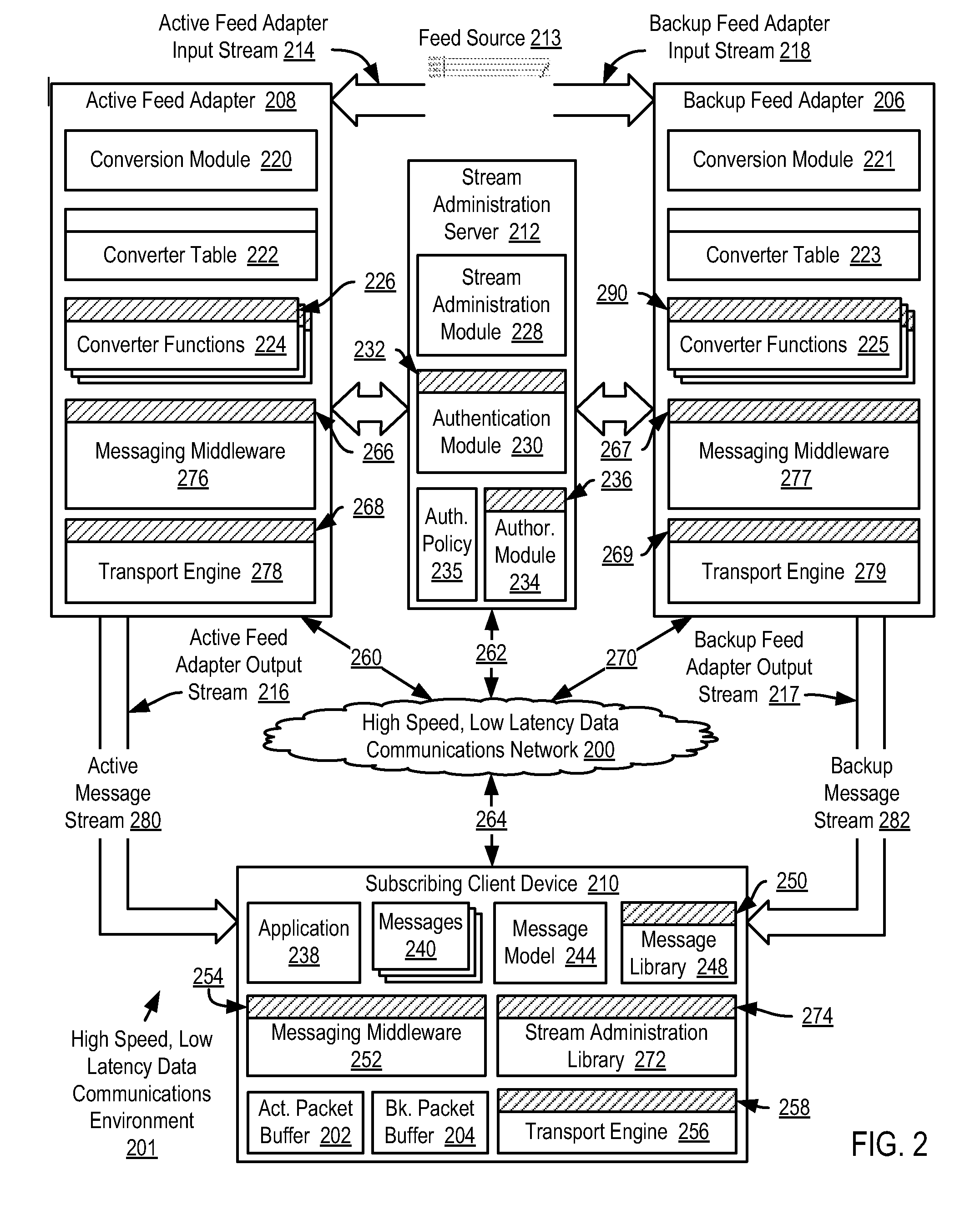
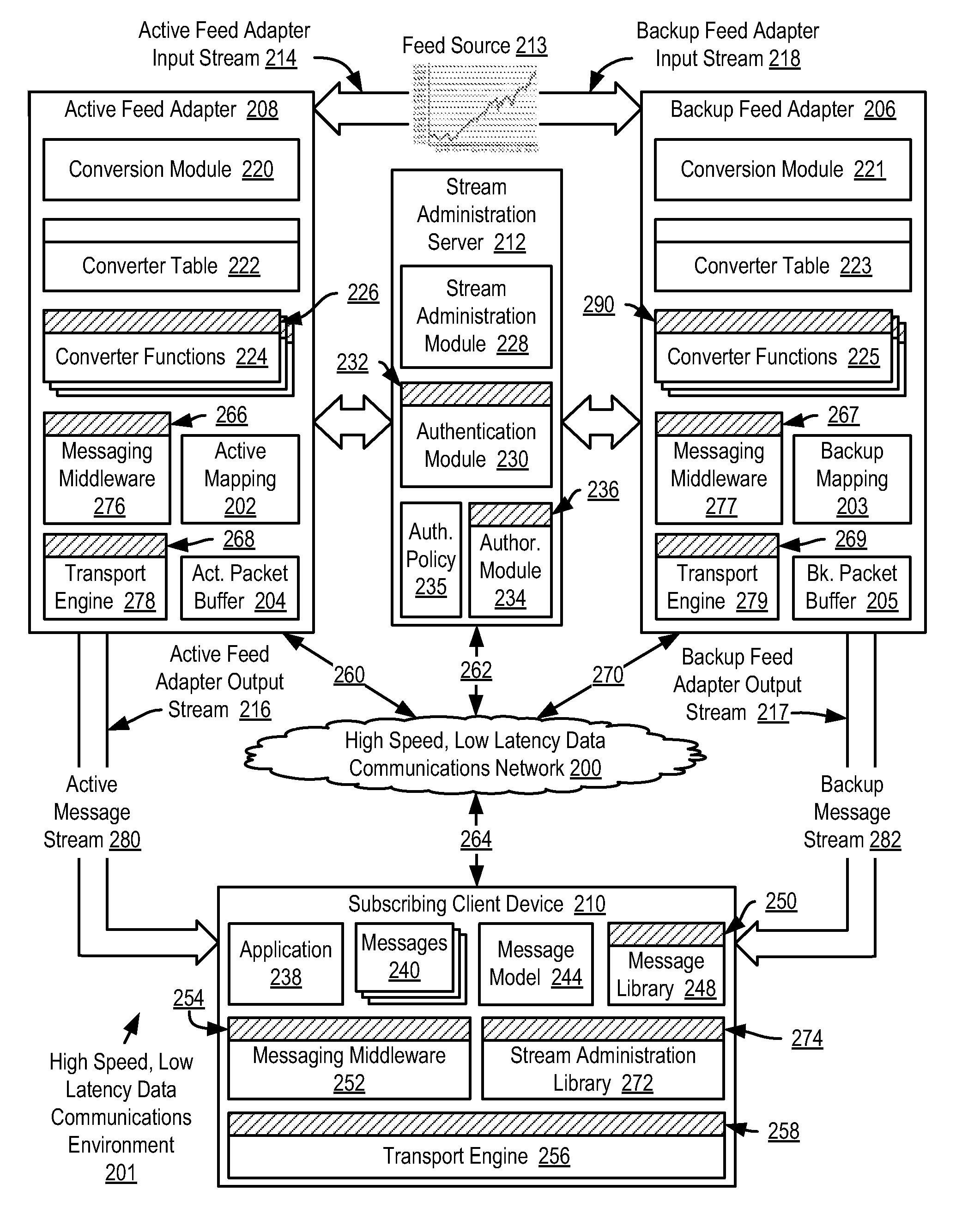
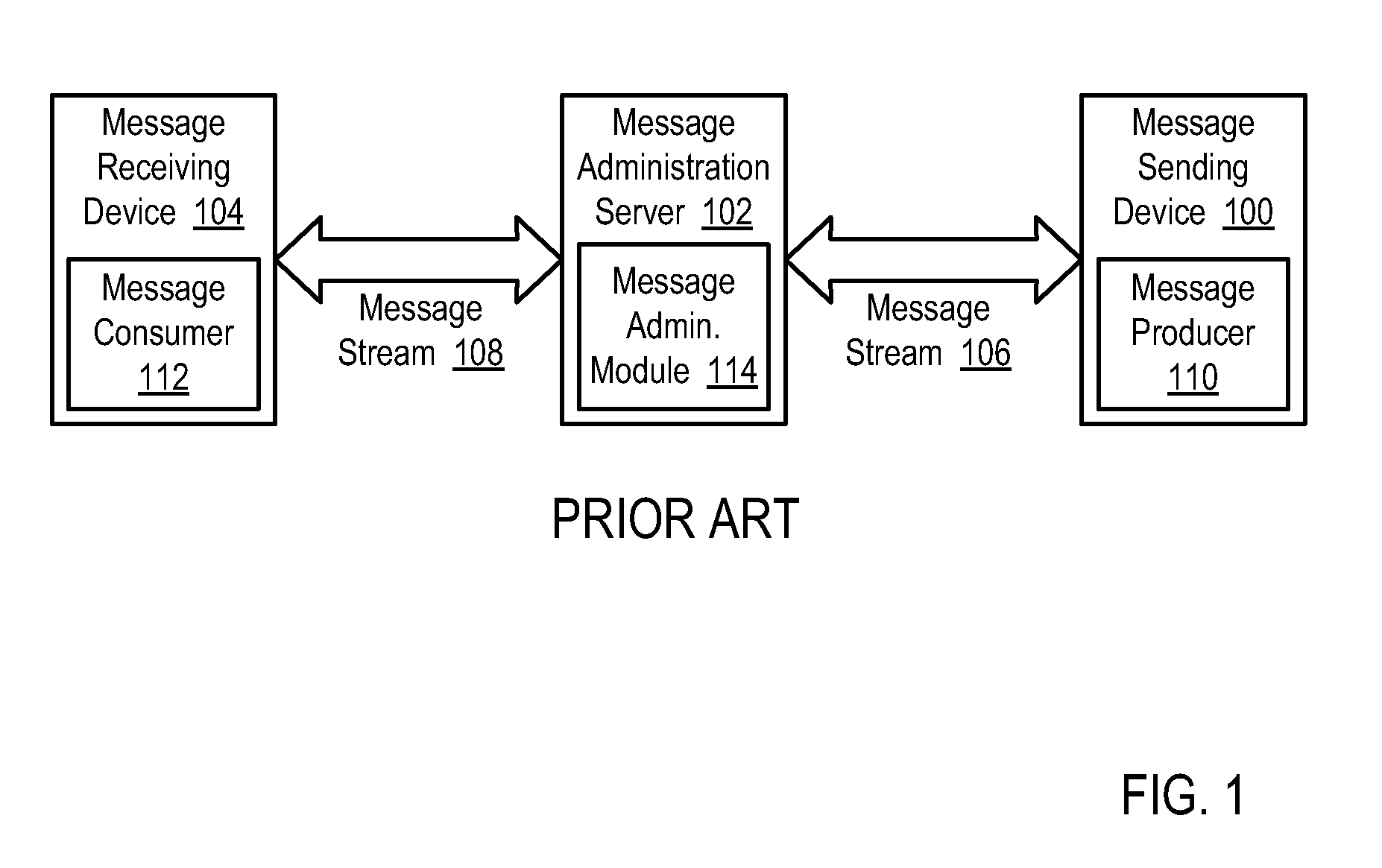
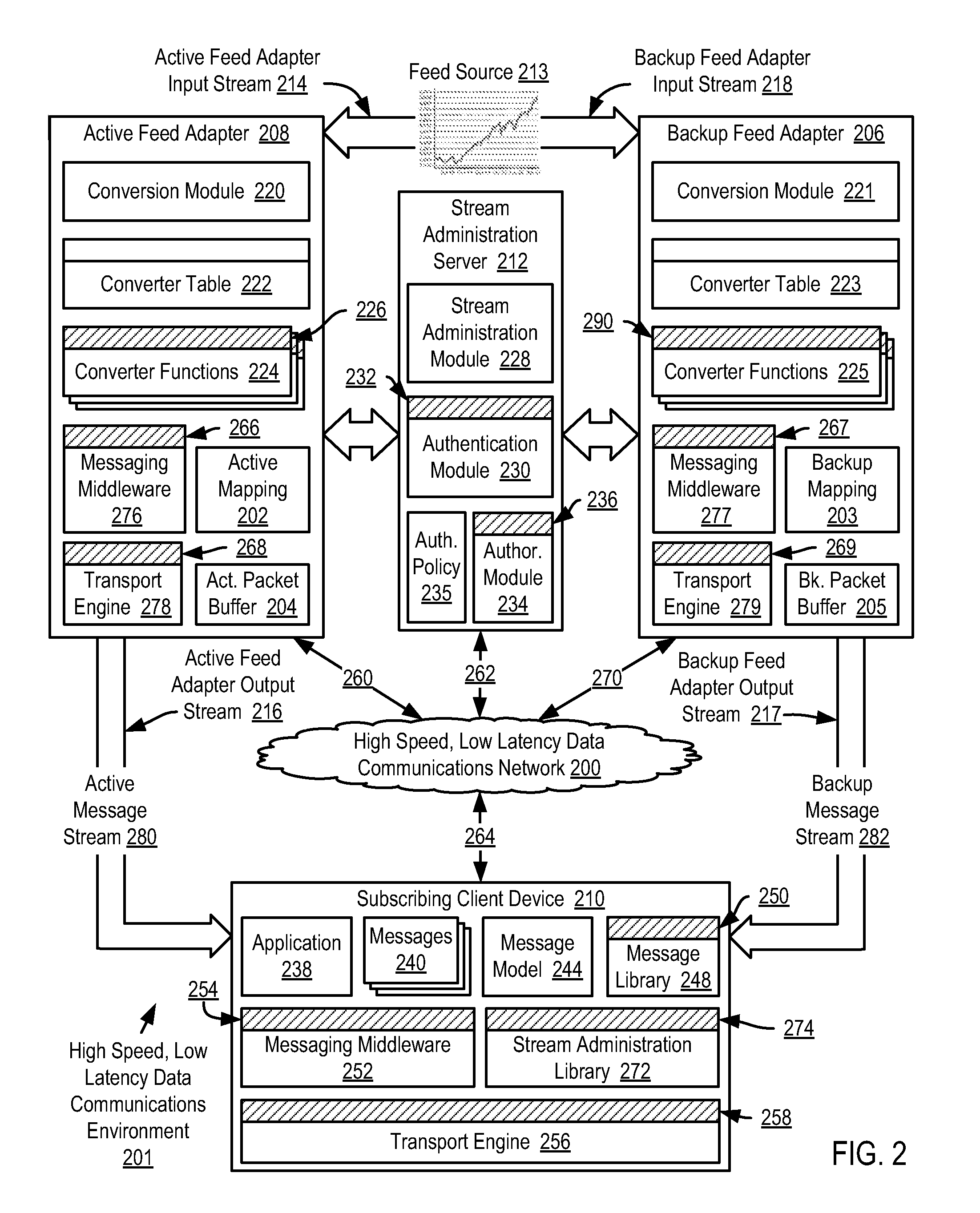
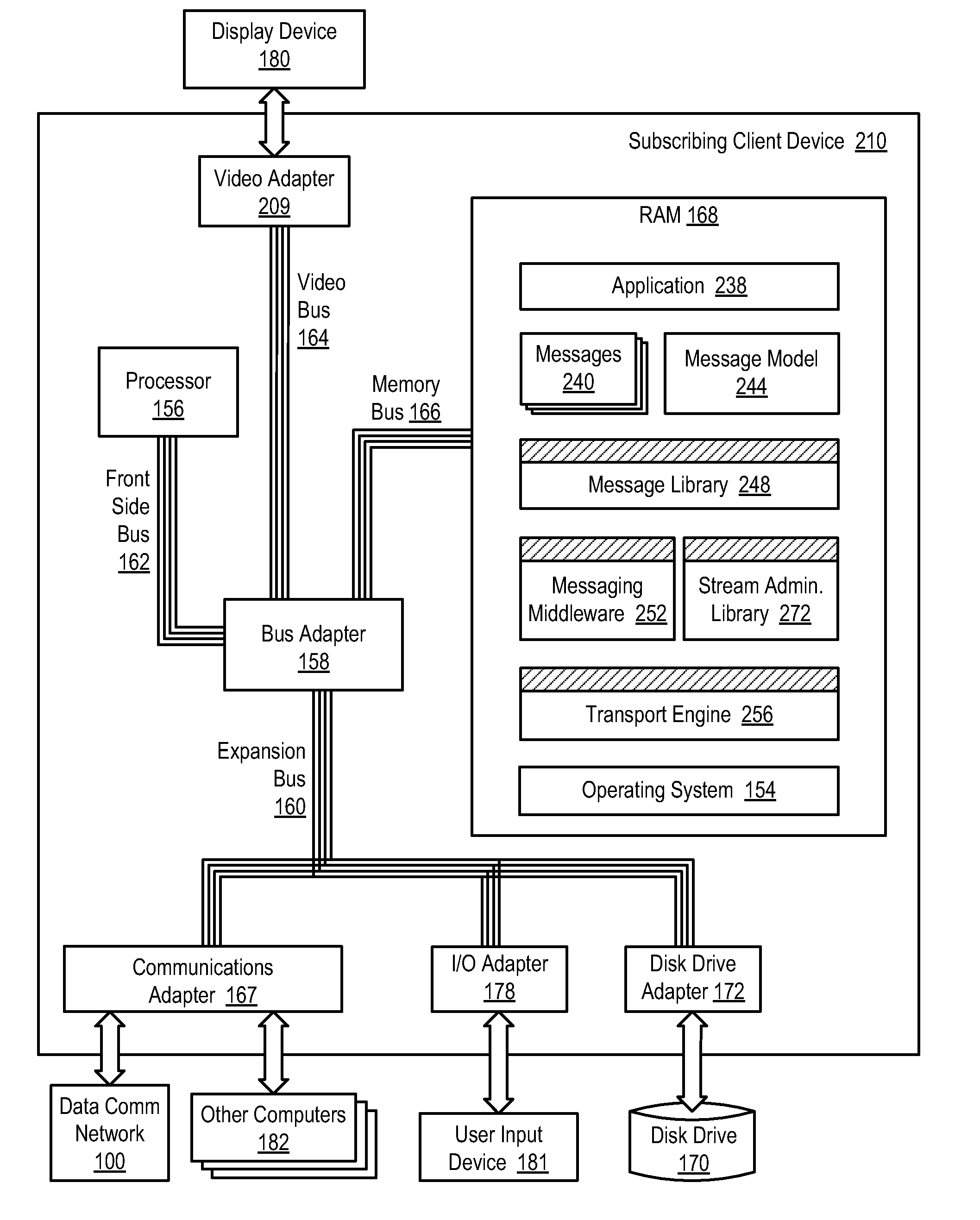
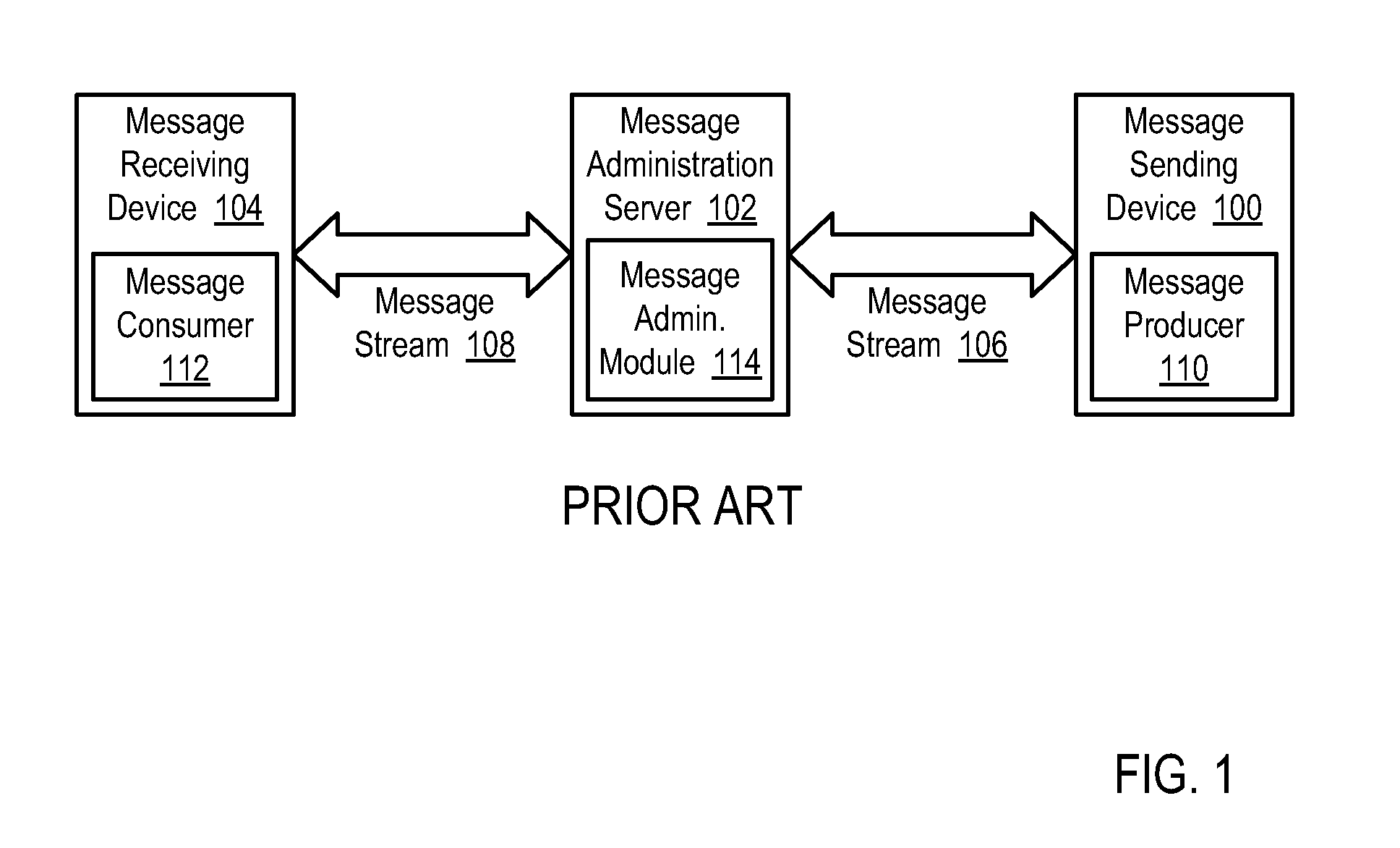
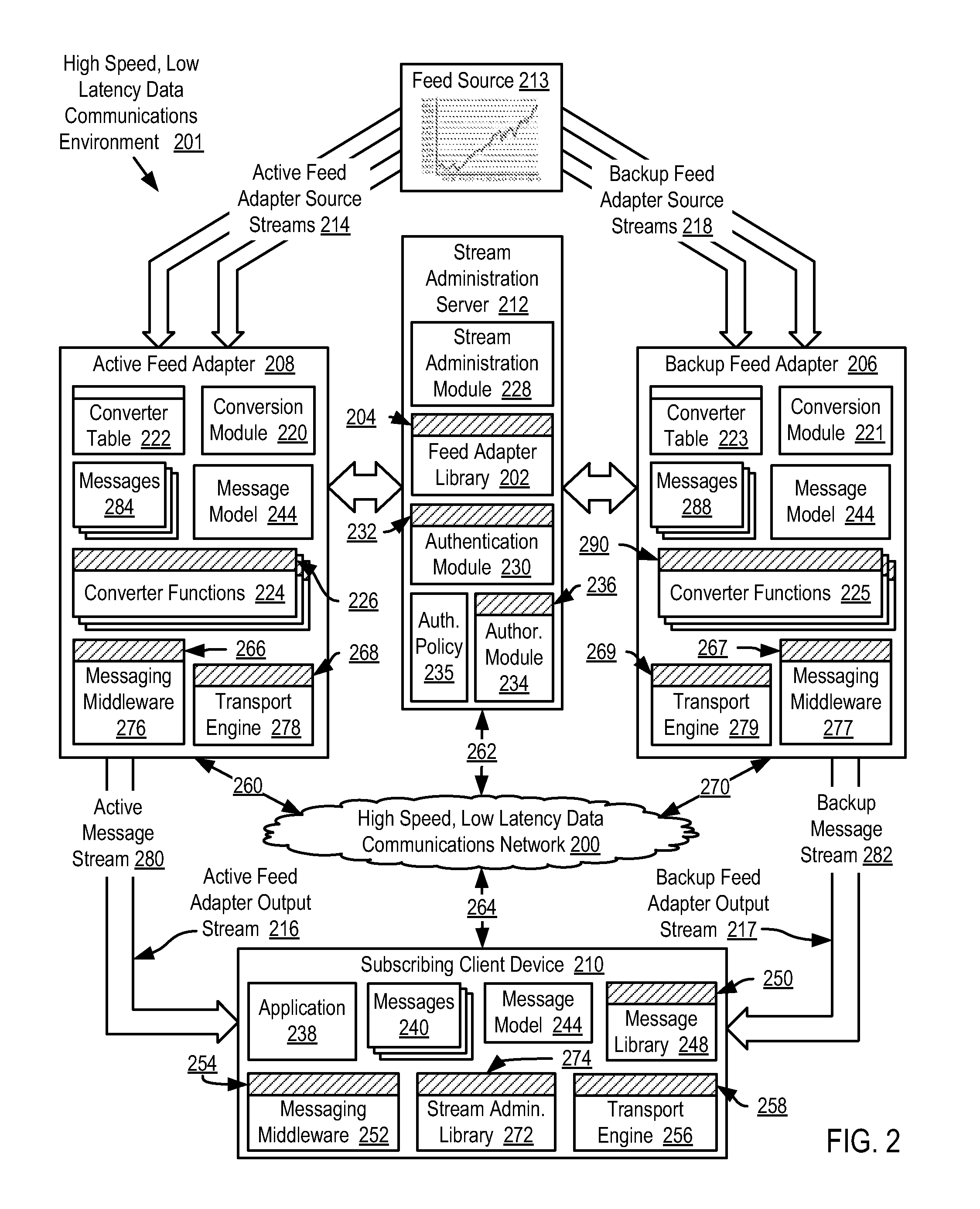
Selecting application messages from an active feed adapter and a backup feed adapter for application-level data processing in a high speed, low latency data communications environment
InactiveUS20070300234A1Increase speedLower latencyMultiprogramming arrangementsData switching networksMessage flowLatency (engineering)
Selecting application messages from redundant feed adapters for application-level data processing in a high speed, low latency data communications environment, including brokering establishment of an active message stream to a subscribing client device from an active feed adapter; brokering establishment of a backup message stream to the subscribing client device from a backup feed adapter; receiving active transport packets in a transport engine of the subscribing client device from the active feed adapter; receiving and buffering backup transport packets; identifying a missing active transport packet; determining whether a corresponding backup transport packet for the missing active transport packet has been received from the backup transport adapter; and replacing the missing active transport packet with the corresponding backup transport packet for further data processing if the corresponding backup transport packet for the missing active transport packet has been received.
Owner:IBM CORP
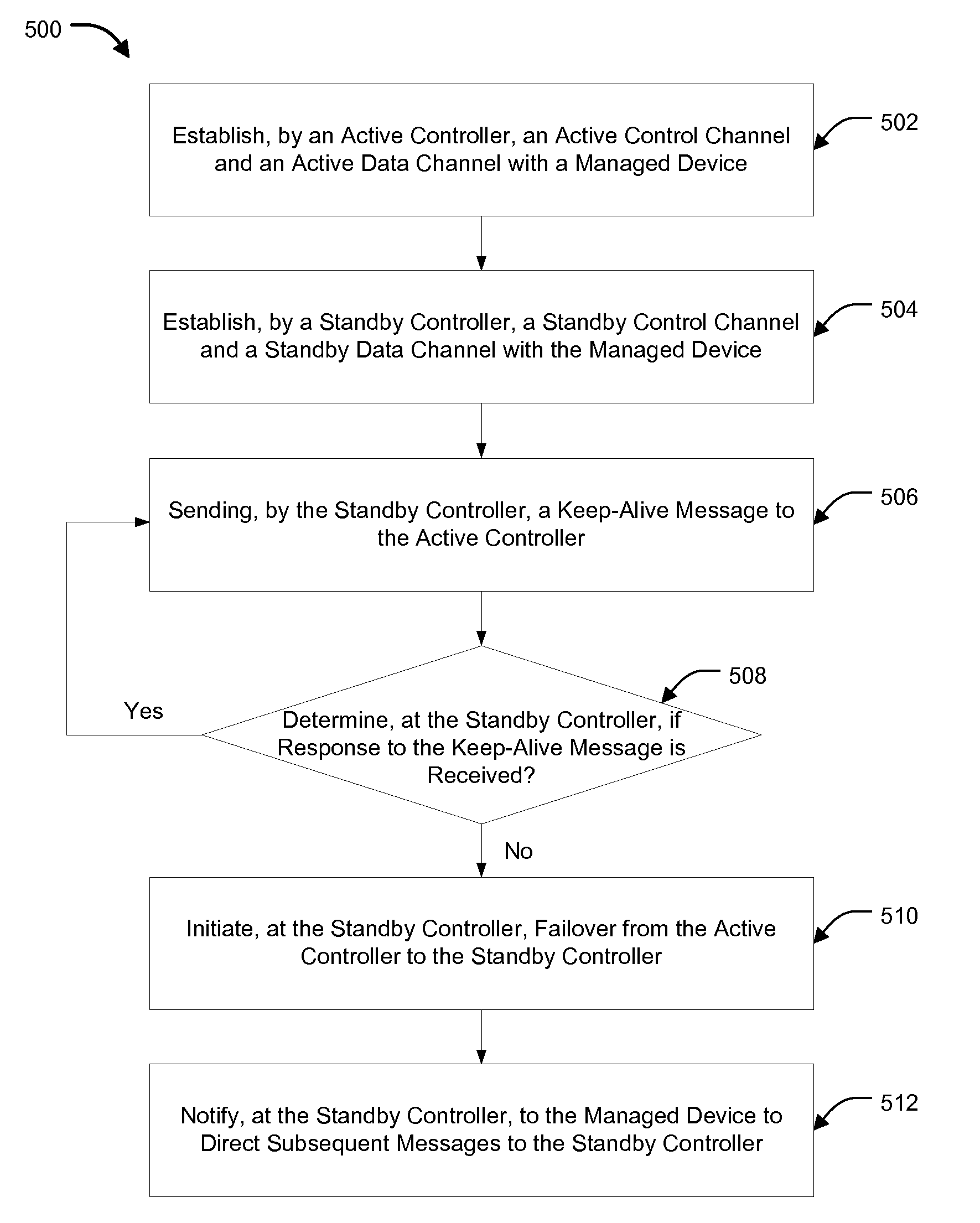
Stand-by controller assisted failover
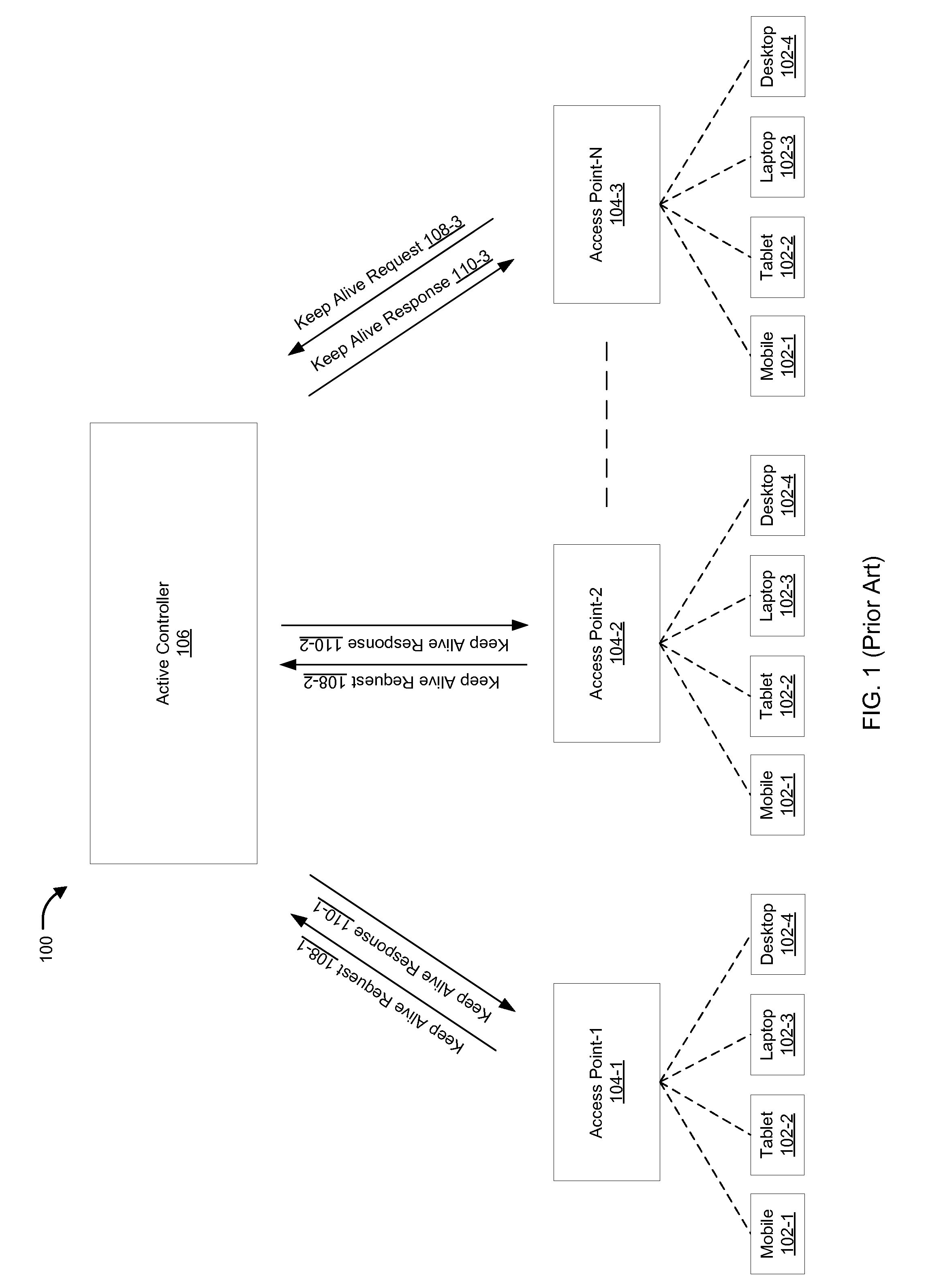
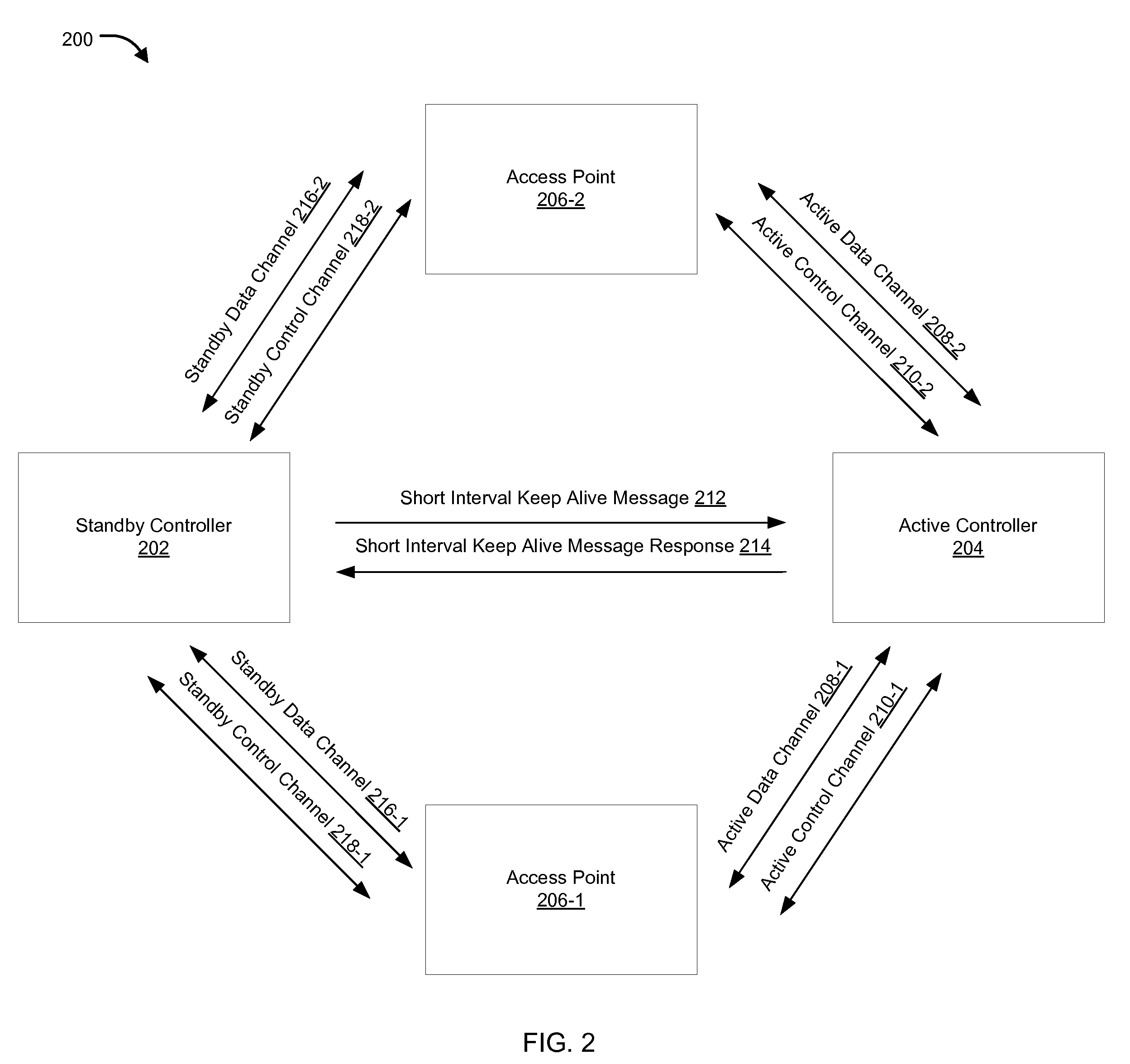
Methods and systems for standby controller aided failover are provided. According to one embodiment, an active control channel and an active data channel are established by an active controller with a managed device via a management protocol. A standby control channel and a standby data channel are established by a standby controller with the managed device via the management protocol. A keep-alive message is periodically sent by the standby controller to the active controller. When a response to the keep-alive message is not received by the standby controller within a predefined time, failover from the active controller to the standby controller is initiated by: (i) taking over for the active controller; and (ii) notifying the managed device to direct subsequent management protocol messages to the standby controller via the standby control channel.
Owner:FORTINET
Monitoring Operating Parameters In A Distributed Computing System With Active Messages
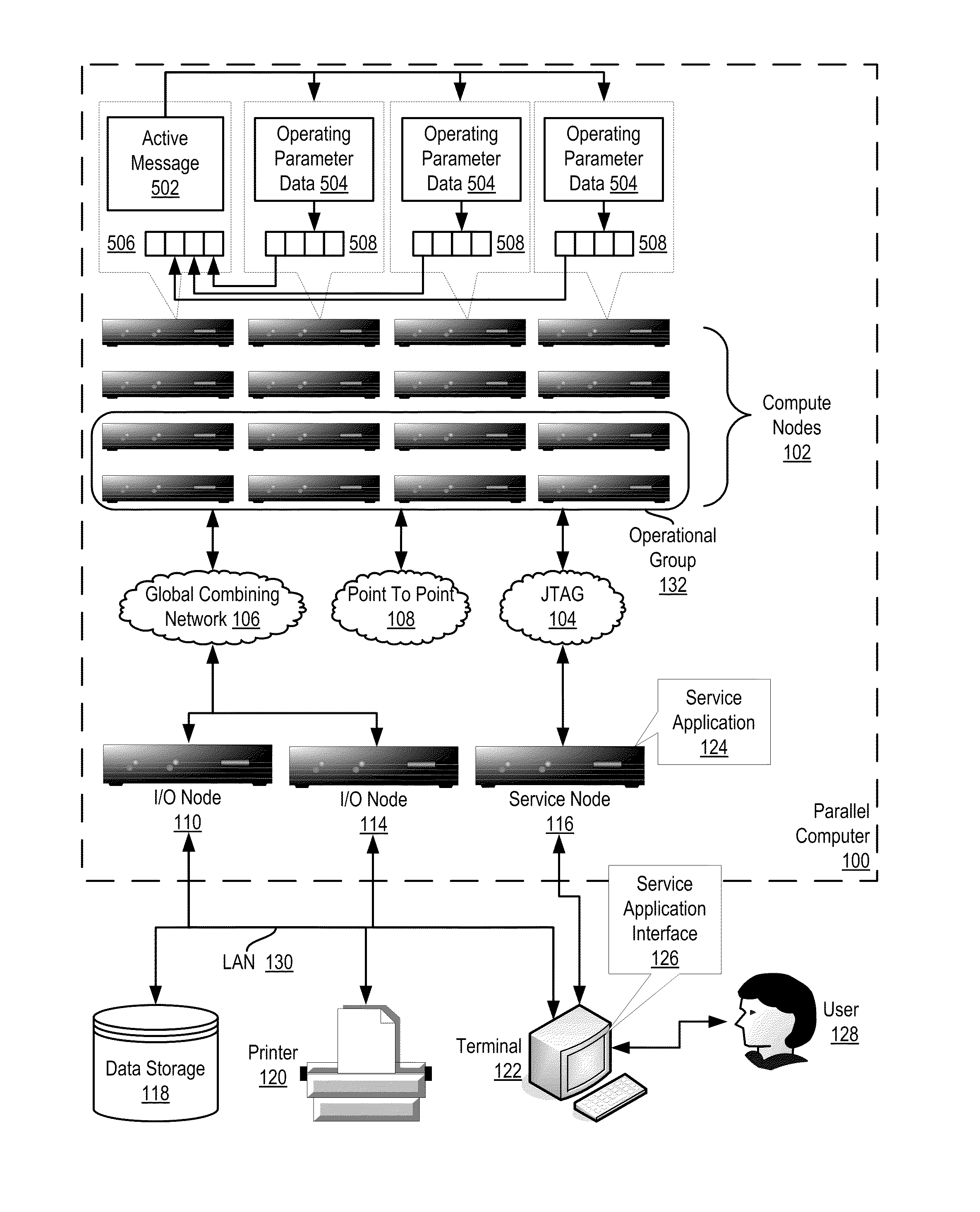
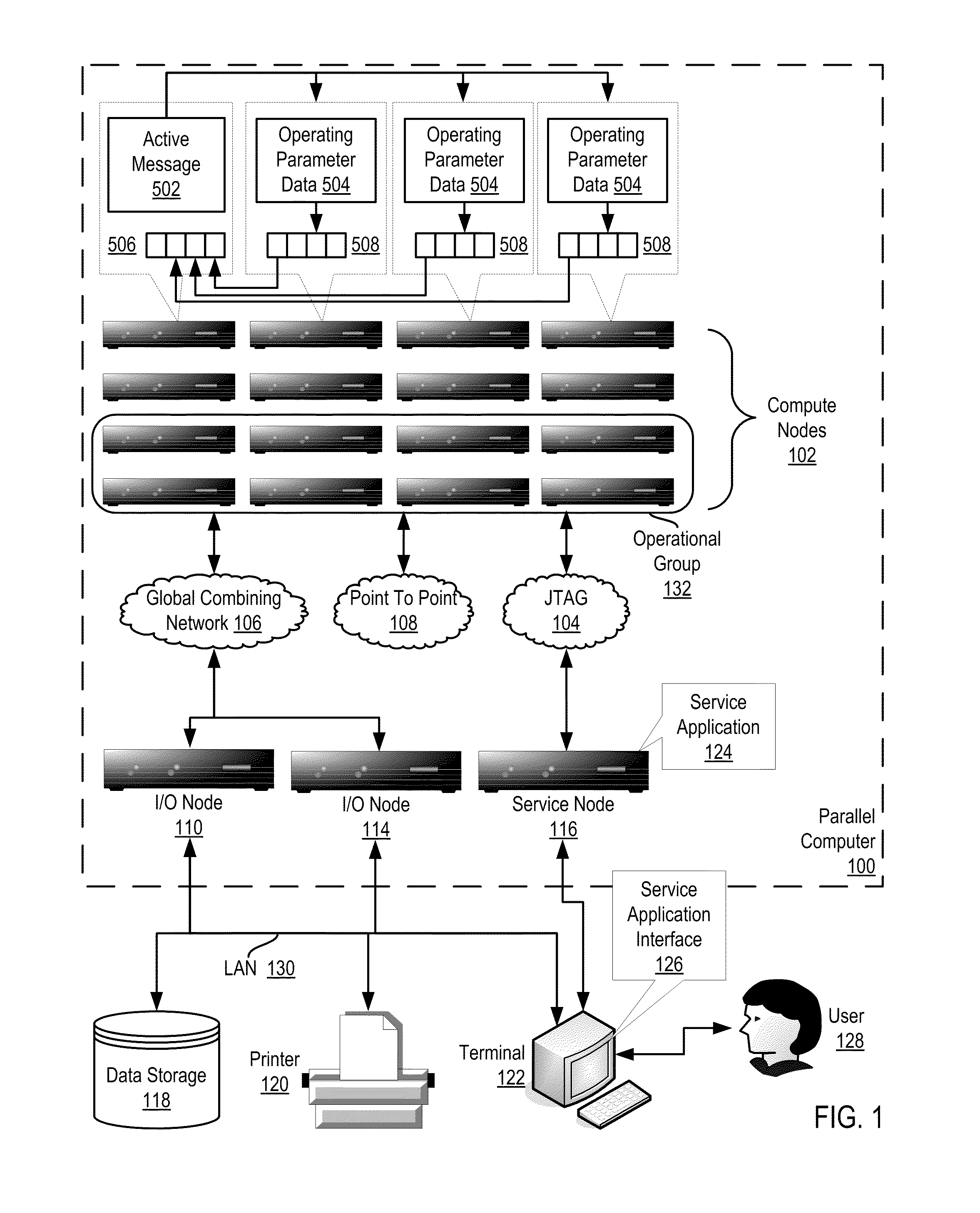
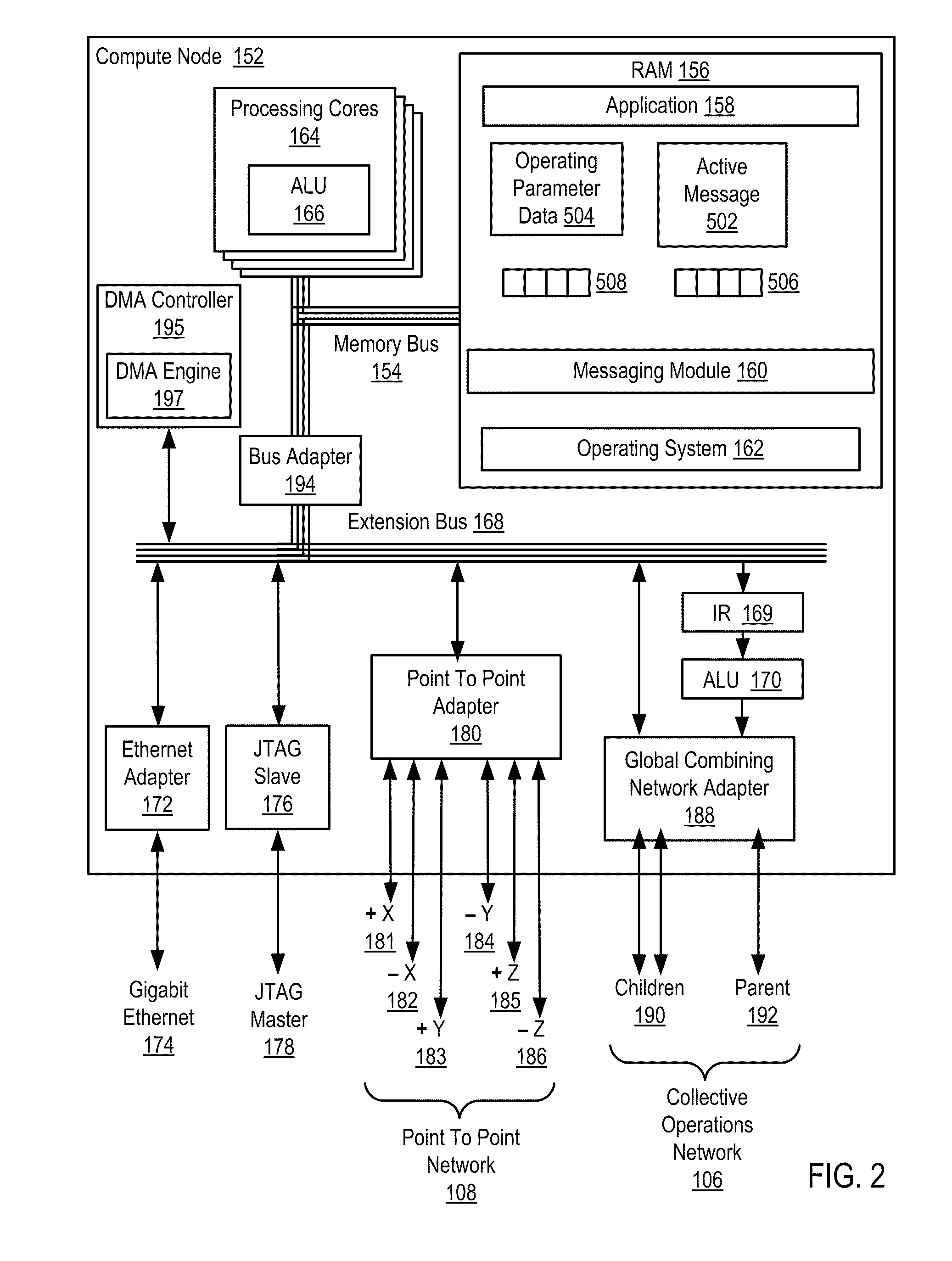
InactiveUS20110267197A1Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsActive messageCollective operation
In a distributed computing system including a nodes organized for collective operations: initiating, by a root node through an active message to all other nodes, a collective operation, the active message including an instruction to each node to store operating parameter data in each node's send buffer; and, responsive to the active message: storing, by each node, the node's operating parameter data in the node's send buffer and returning, by the node, the operating parameter data as a result of the collective operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data Communications In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20120137294A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsCommunication endpointParallel computing
Data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint including a specification of data communications parameters for a thread of execution on a compute node, including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI and through data communications resources, including receiving in an origin endpoint of the PAMI a SEND instruction, the SEND instruction specifying a transmission of transfer data from the origin endpoint to a first target endpoint; transmitting from the origin endpoint to the first target endpoint a Request-To-Send (‘RTS’) message advising the first target endpoint of the location and size of the transfer data; assigning by the first target endpoint to each of a plurality of target endpoints separate portions of the transfer data; and receiving by the plurality of target endpoints the transfer data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Controlling Access To A Resource In A Distributed Computing System With A Distributed Access Request Queue
InactiveUS20110225297A1Reduce stepsMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlActive messageSource data
Controlling access to a resource in a distributed computing system that includes nodes having a status field, a next field, a source data buffer, and that are characterized by a unique node identifier, where controlling access includes receiving a request for access to the resource implemented as an active message that includes the requesting node's unique node identifier, the value stored in the requesting node's source data buffer, and an instruction to perform a reduction operation with the value stored in the requesting node's source data buffer and the value stored in the receiving node's source data buffer; returning the requesting node's unique node identifier as a result of the reduction operation; and updating the status and next fields to identify the requesting node as a next node to have sole access to the resource.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reliable messaging using a message stream in a high speed, low latency data communications environment
InactiveUS20070300235A1Increase speedLower latencyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationReliable messagingMessage flow
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for reliable messaging using a message stream in a high speed, low latency data communications environment that include brokering, by a stream administration server, establishment of an active message stream to a subscribing client device from an active feed adapter; receiving, in a transport engine of the subscribing client device from the active feed adapter on an active message stream, active application messages encapsulated in active transport packets; receiving, by the transport engine from the active feed adapter, an active transport packet containing an active mapping; identifying, by the transport engine in dependence upon active sequence numbers, a missing active transport packet; identifying, by the transport engine, missing active application messages of the missing active transport packet in dependence upon the active mapping; and requesting, by the transport engine, transmission of the missing active application messages from the active feed adapter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Synchronizing an active feed adapter and a backup feed adapter in a high speed, low latency data communications environment
InactiveUS20080010487A1Increase speedLower latencyError detection/correctionData switching networksServer agentMessage flow
Owner:IBM CORP
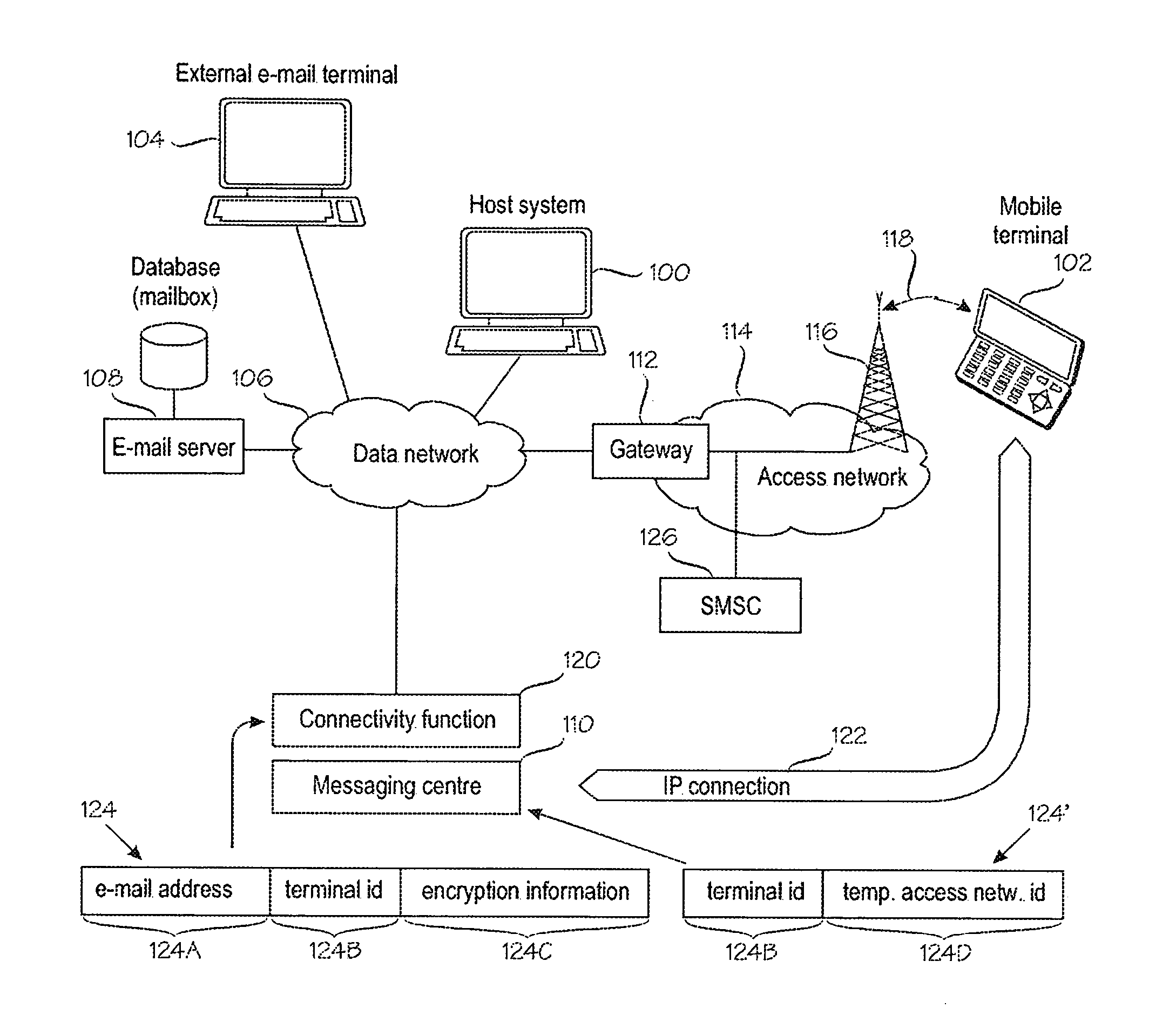
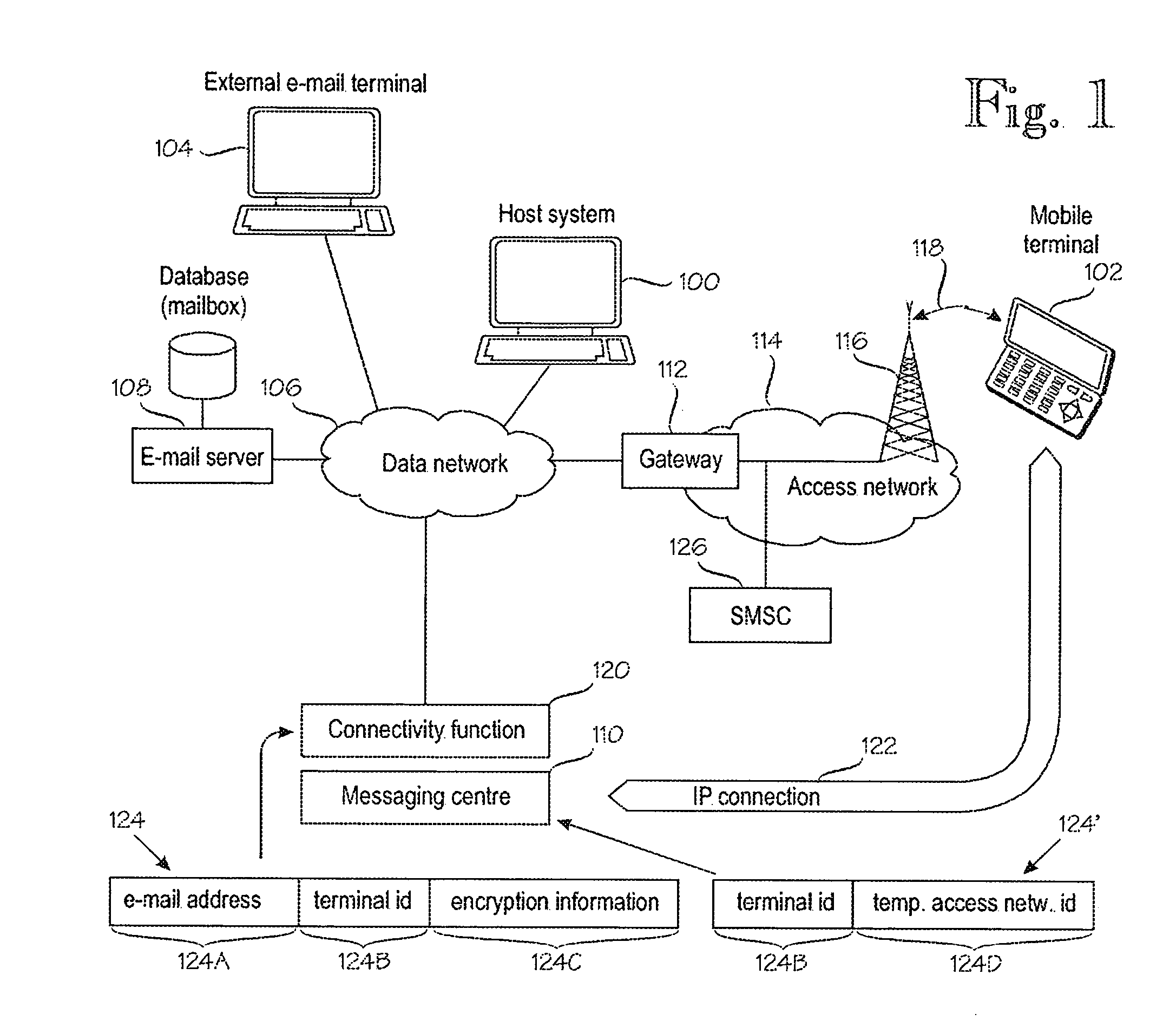
Mobile messaging system
InactiveUS20080261635A1Facilitate initiationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsActivity IdentifierActive message
A mobile messaging campaign is established to process bidirectional mobile campaign messages associated with each of a plurality of mobile numbers using a single short code. A mobile message associated with the mobile messaging campaign is received. The received mobile message is parsed to extract a campaign identifier and the received mobile message is processed based upon the campaign identifier.
Owner:IVISIONMOBILE
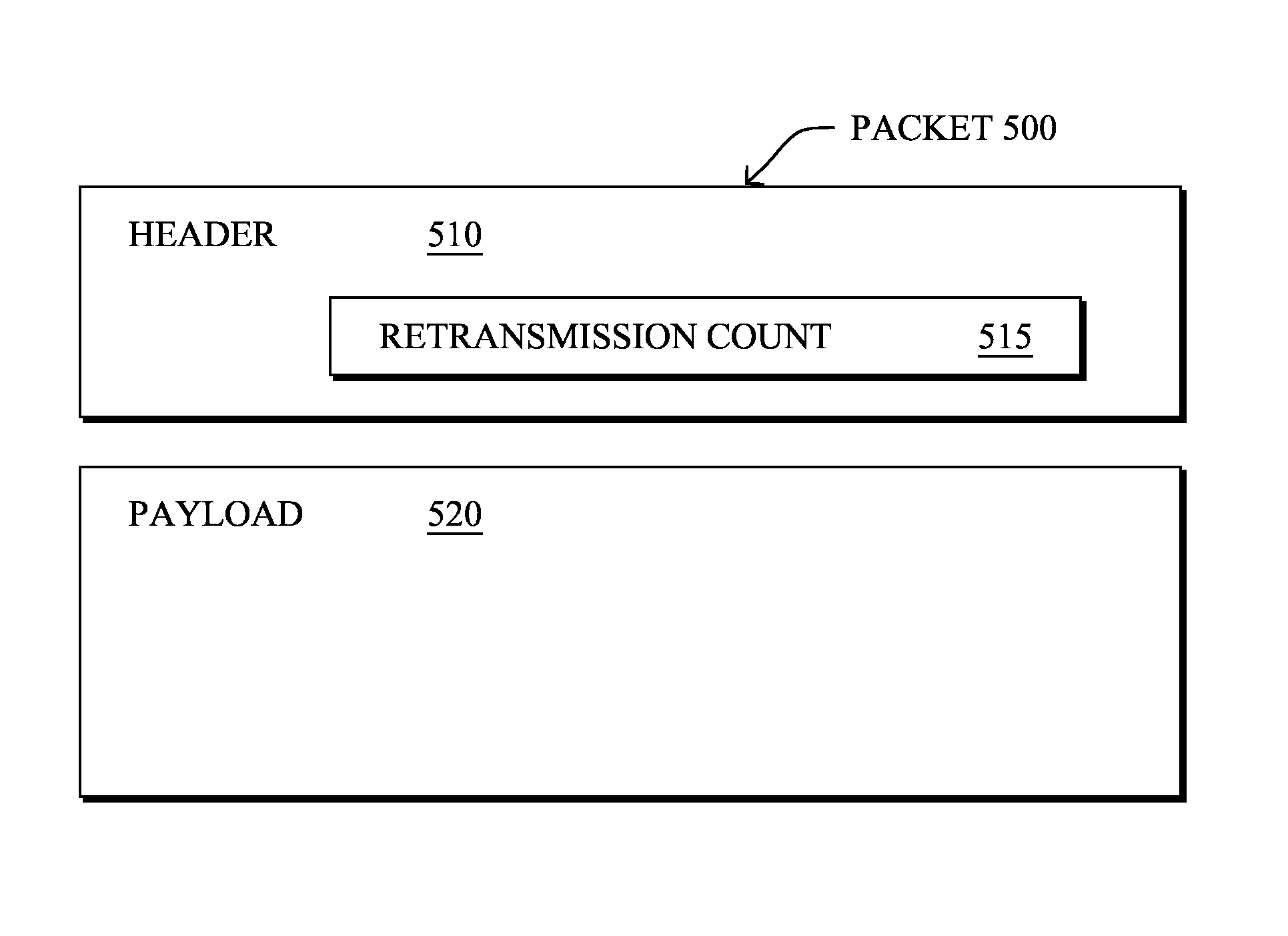
Dynamic keepalive parameters for reverse path validation in computer networks
In one embodiment, a network device determines a path from itself to a source device in a computer network, where the source device utilizes the path in reverse to reach the network device. Based on determining a reliability of the path in reverse, the network device may dynamically adjust one or more keepalive parameters for keepalive messages sent on the path. Accordingly, the network device may then send keepalive messages on the path based on the dynamically adjusted keepalive parameters.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communications control
ActiveUS20080159163A1Reduce power consumptionExtended maintenance periodError preventionTransmission systemsThe InternetCommunication control
A client and a host communicate in a packet data network including a plurality of routing nodes such as routers and firewalls. The host is configured to provide the client with a session and to detect the accessibility of the client by repeatedly sending keep-alive messages to the client. In order to reduce the traffic actually arriving at the client, at least some of the keep-alive message are adjusted such that their routing towards the client will be stopped before the client by storing in a Time-To-Live field specified in the Internet Protocol a value of maximum routing hops defined to correspond with the last routing node before the client on a route from the host to the client. The adaptation of the keep-alive message can also be configured to allow some keep-alive message to reach the client to occasionally test the communication path between the client and server.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com