Patents
Literature
257 results about "Statistical Confidence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
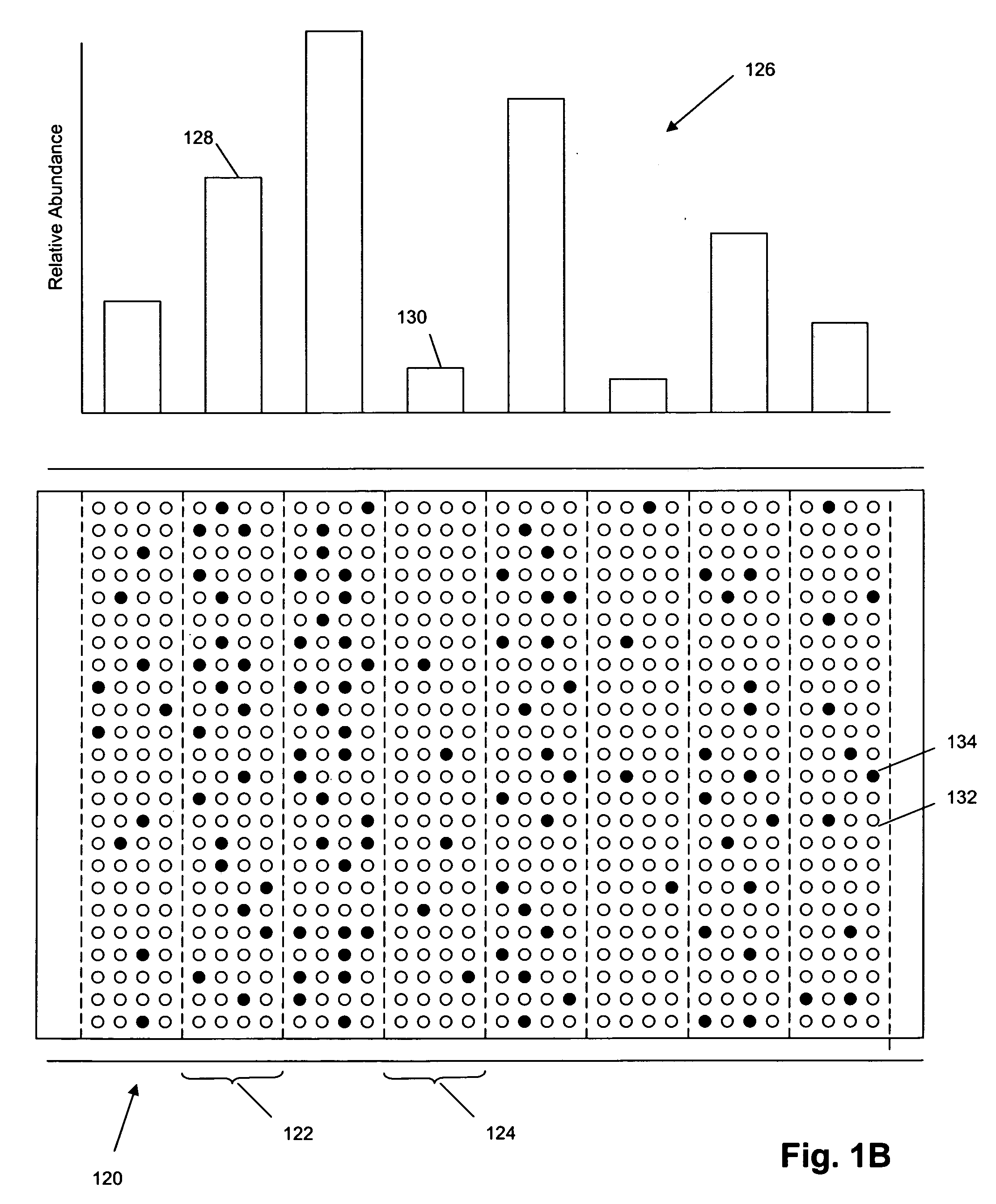
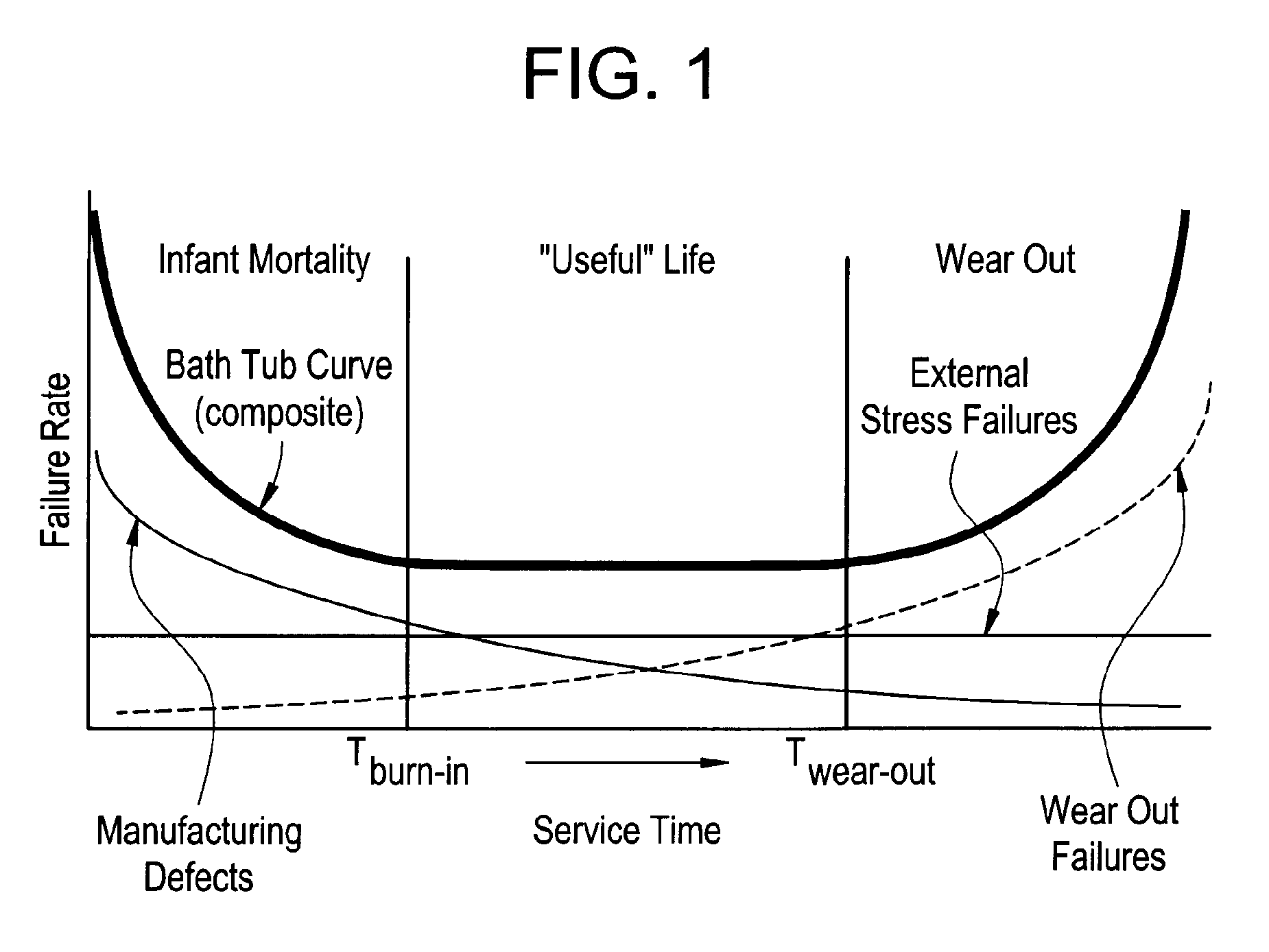
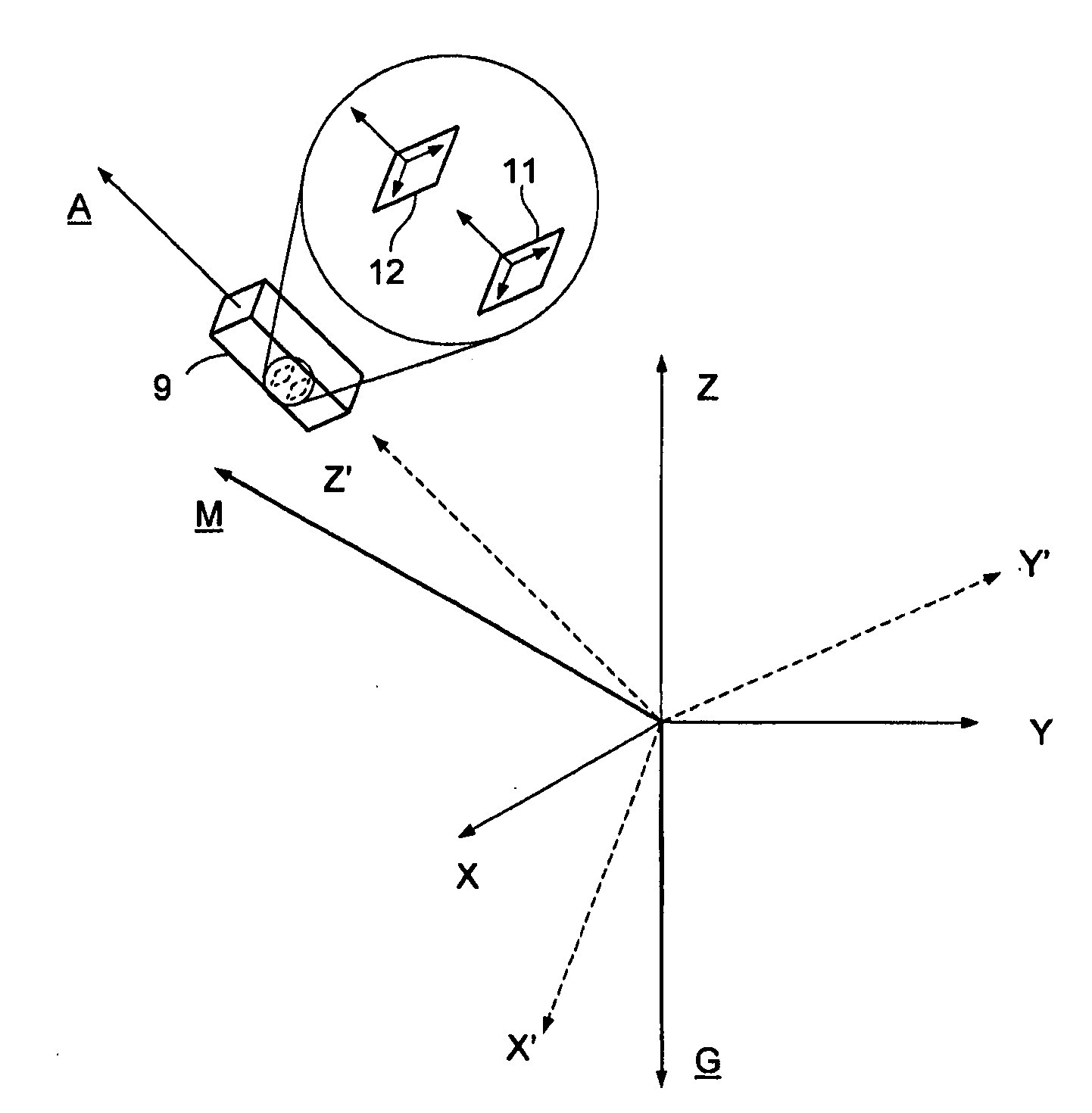
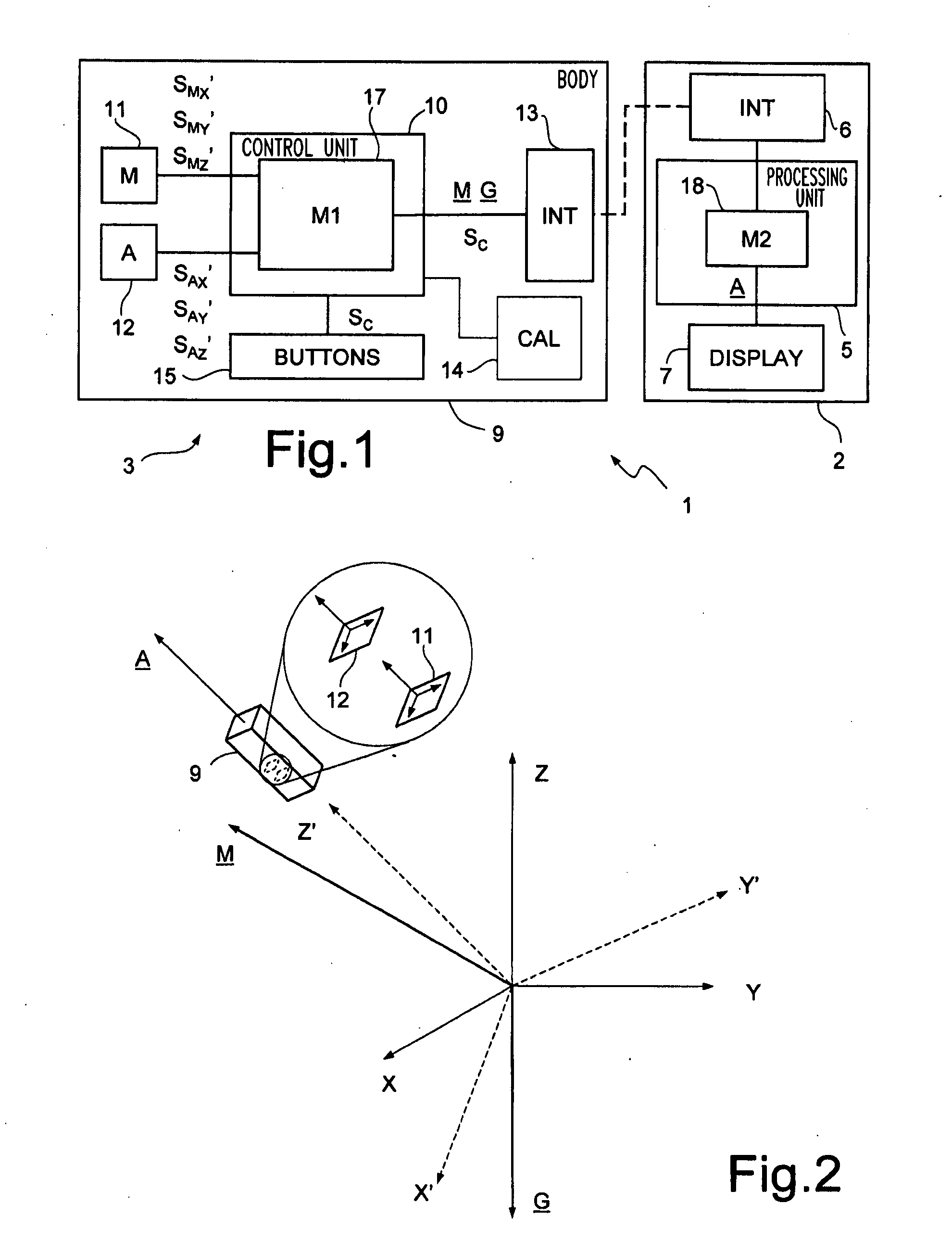
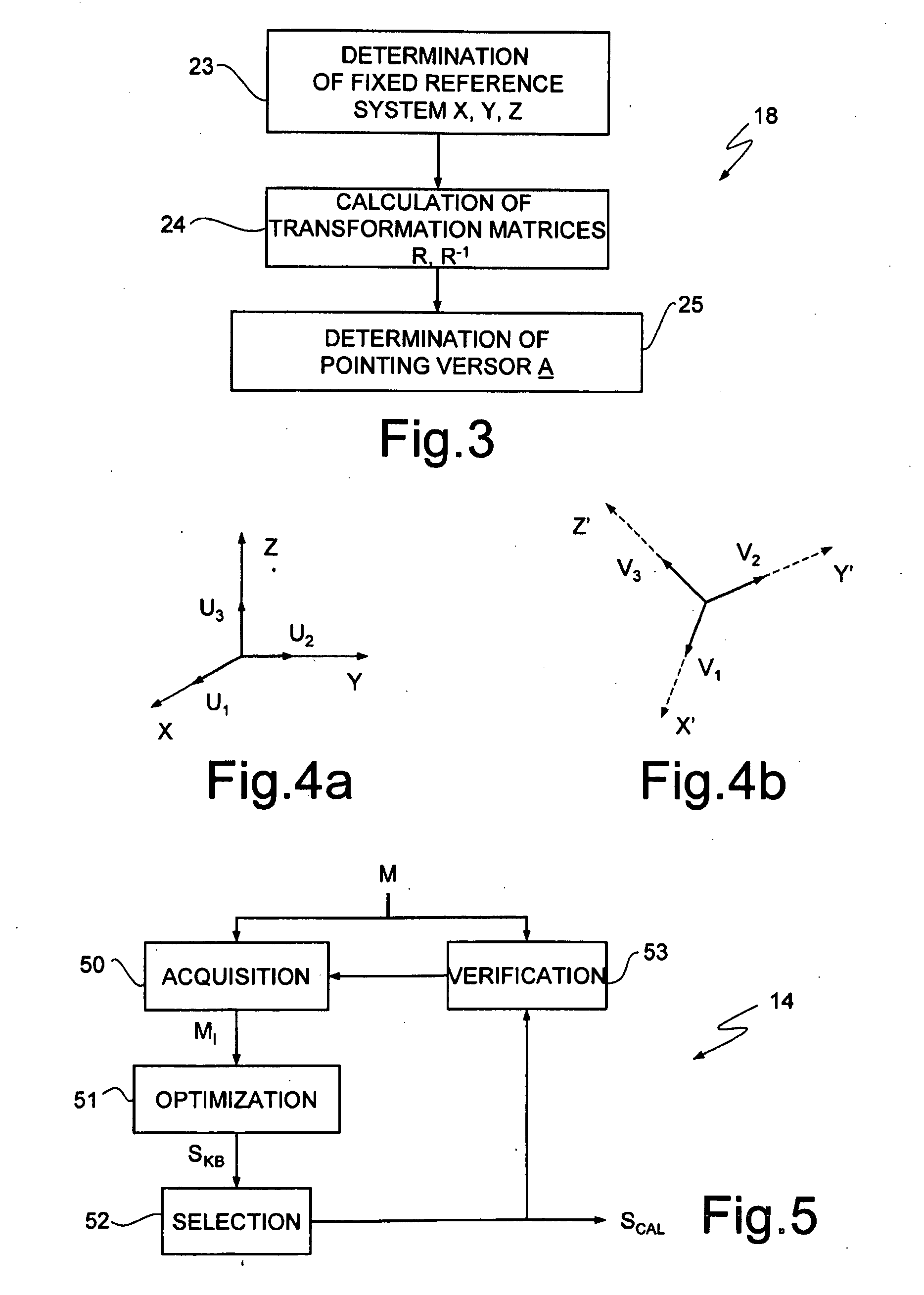
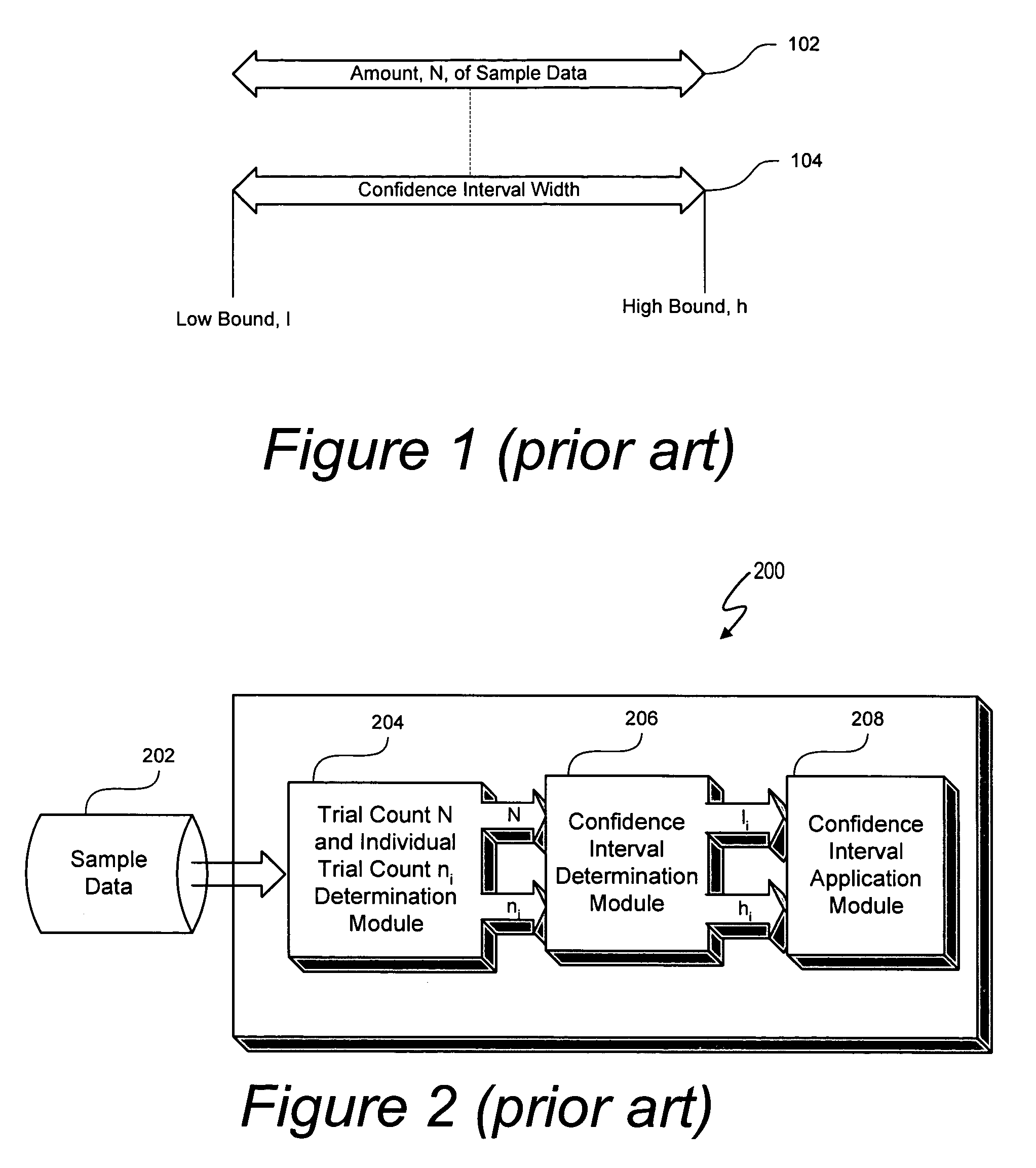
A confidence band is used in statistical analysis to represent the uncertainty in an estimate of a curve or function based on limited or noisy data. Similarly, a prediction band is used to represent the uncertainty about the value of a new data point on the curve, but subject to noise.
Method and apparatus for determining copy number variation using digital PCR
ActiveUS20090239308A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConfidence intervalStatistical Confidence
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
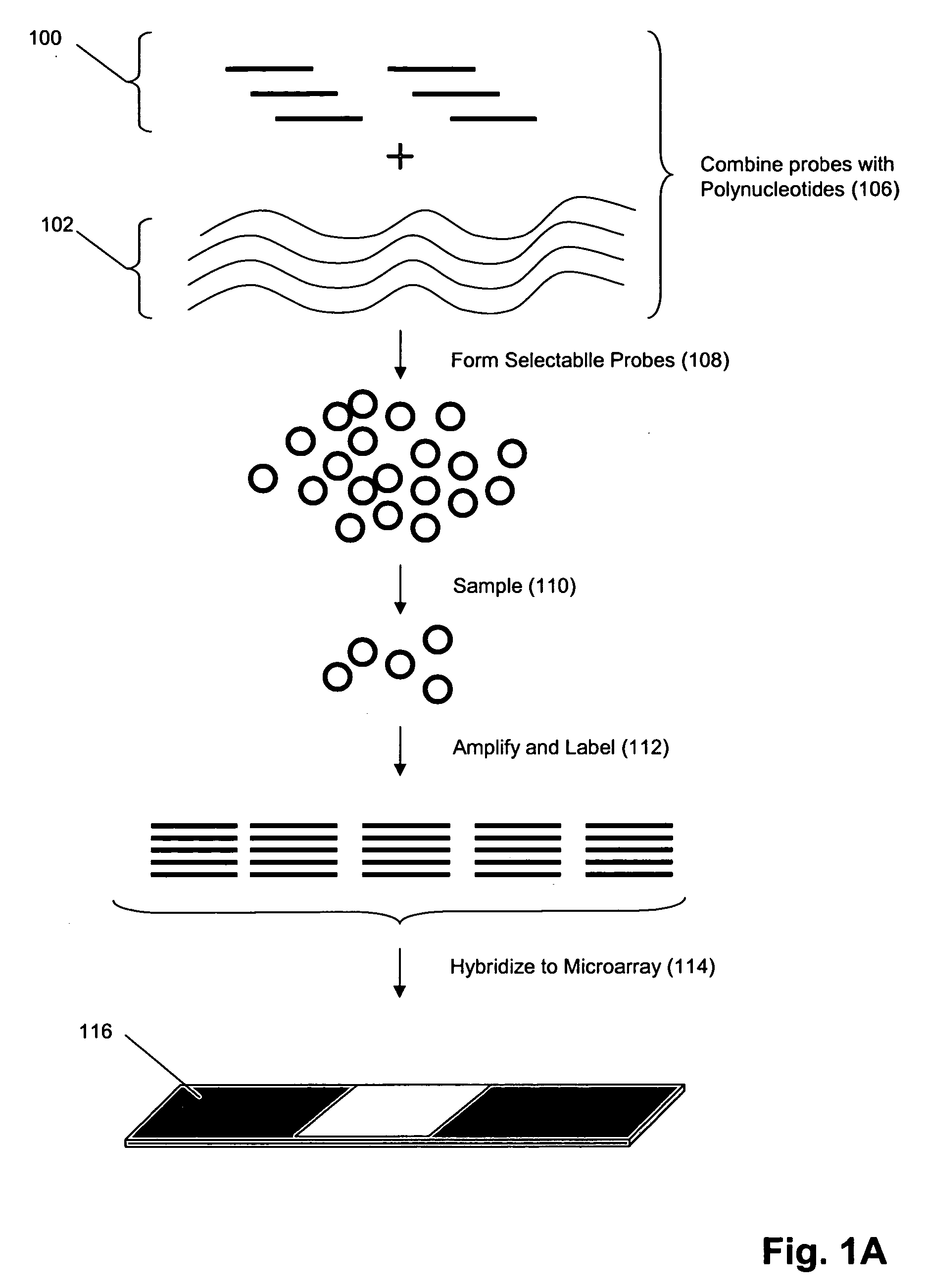
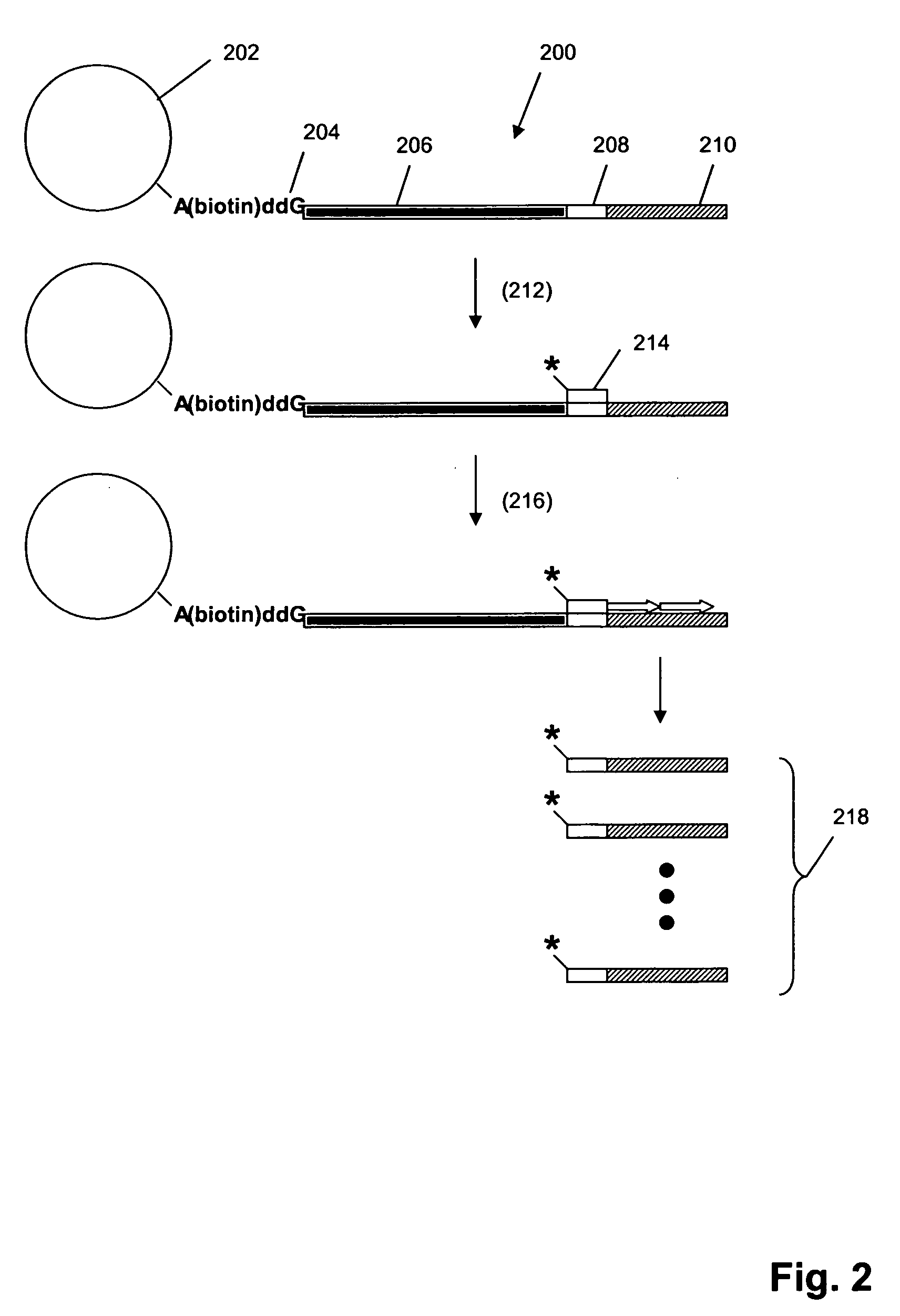
Digital profiling of polynucleotide populations
InactiveUS20050250147A1Improved statistical confidenceOvercome deficienciesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAssayHybridization probe
The invention provides methods and compositions for hybridization-based assays that employ oligonucleotide tags, wherein probes specific for the same target polynucleotide are labeled with a plurality of different oligonucleotide tags. When probes are used in conjunction with a microarray, or like, readout platform, containing hybridization sites of tag complements, assay of a target polynucleotide results in a signal being generated from any of a plurality hybridization sites with predetermined addresses and the number of such sites generating a signal is proportional to the relative amount of the target polynucleotide in a population, test sample, or reaction volume, as the case may be. The invention provides methods and compositions for measuring amounts of selected target polynucleotides in a sample and for providing a digital readout of such amounts. Statistical confidence in measurements made by the present invention may be increased as much as desired by increasing the size of the sample of successfully hybridized and selected probes from which signals are generated.
Owner:PARALLELE BIOSCI
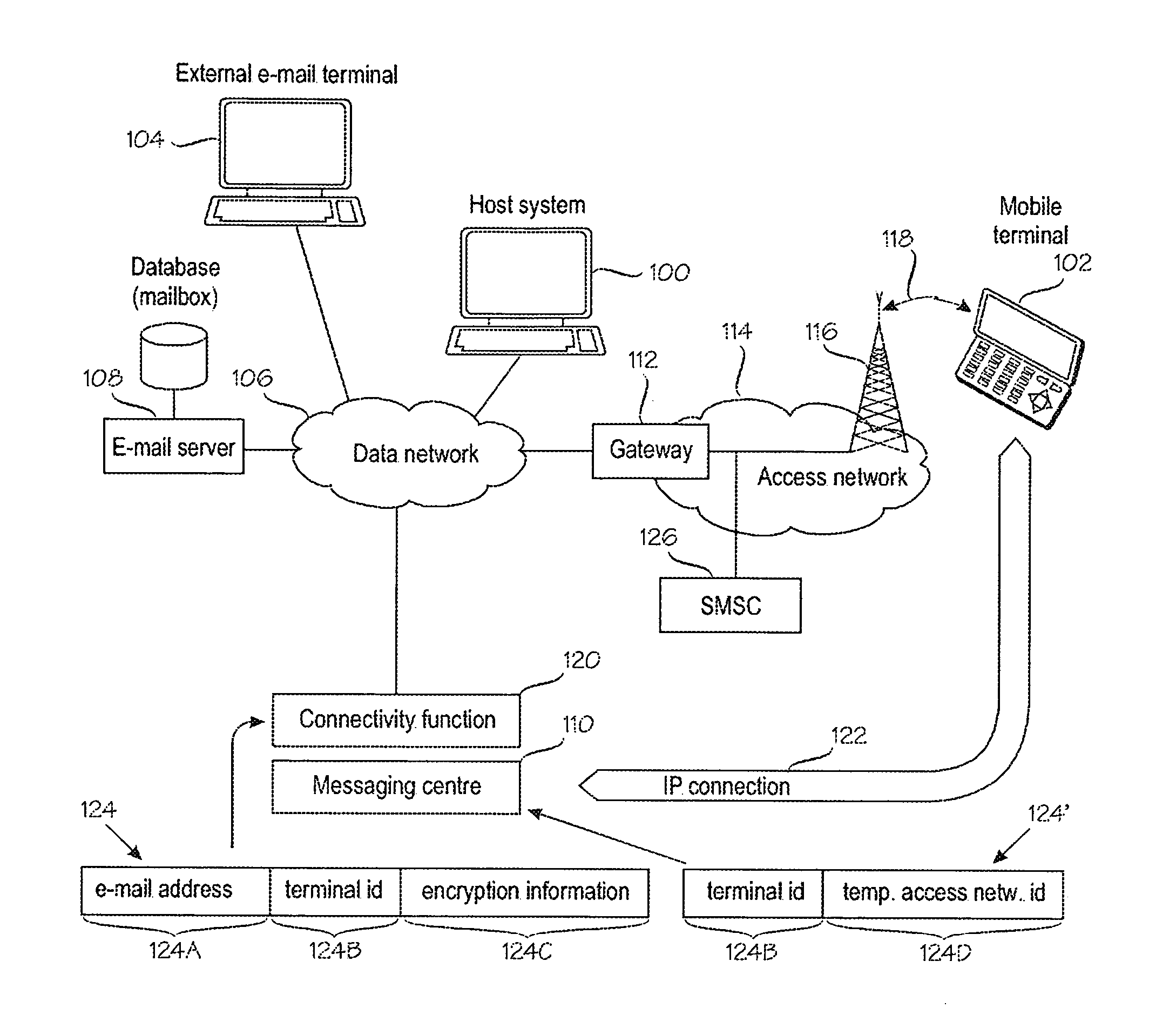
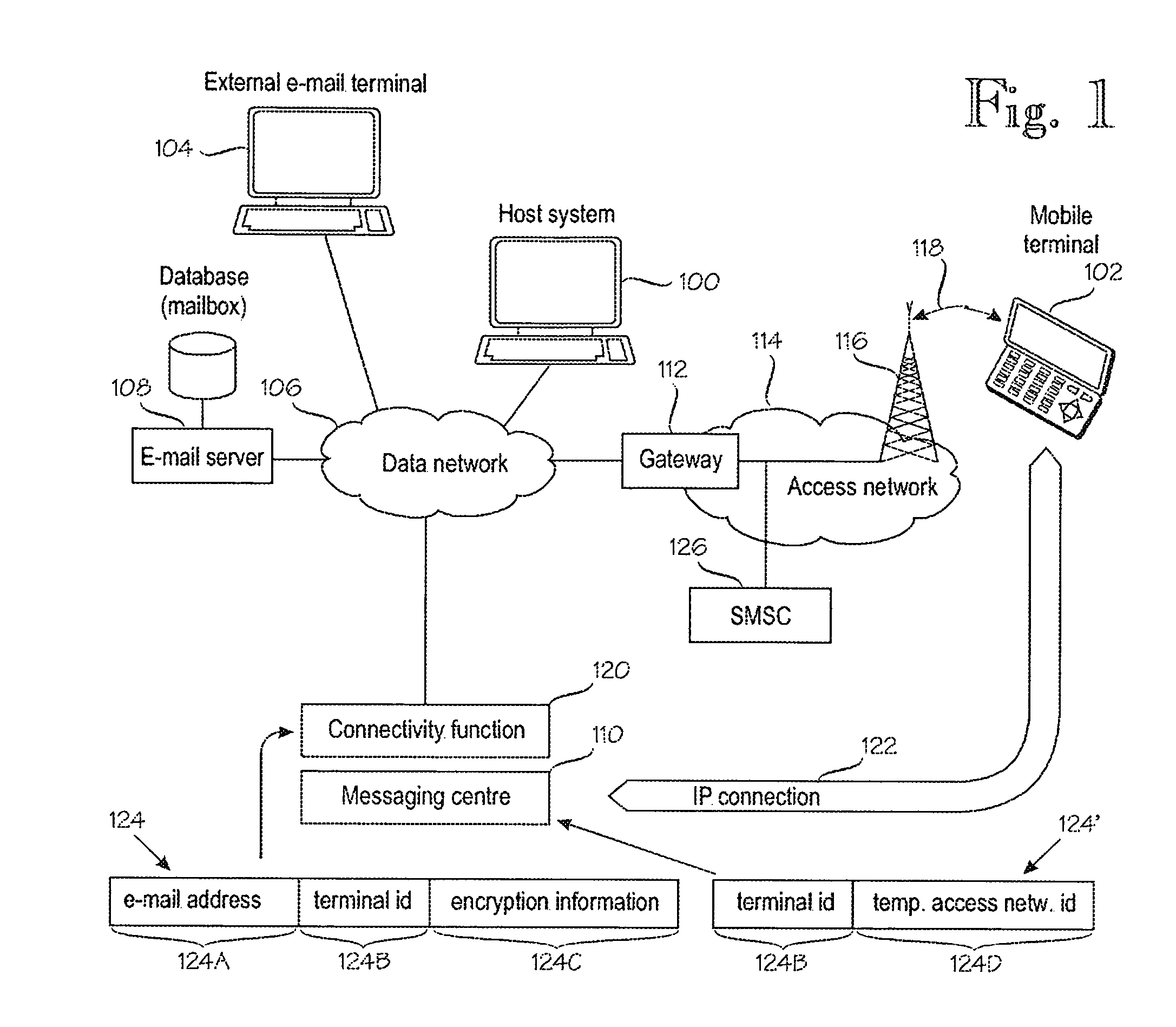
Maintaining an IP connection in a mobile network
InactiveUS20070019610A1Time-division multiplexConnection managementStatistical ConfidenceMobile radio
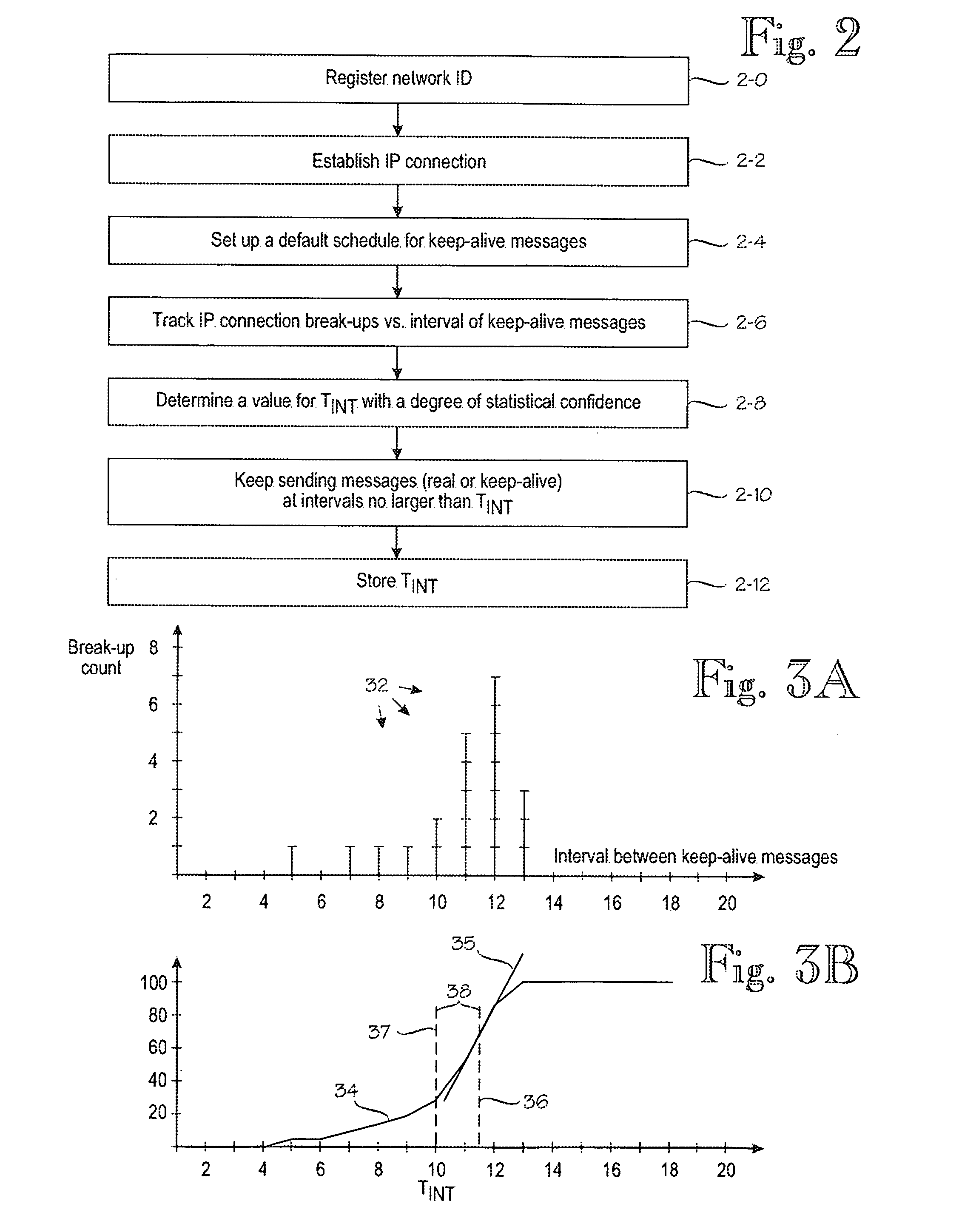
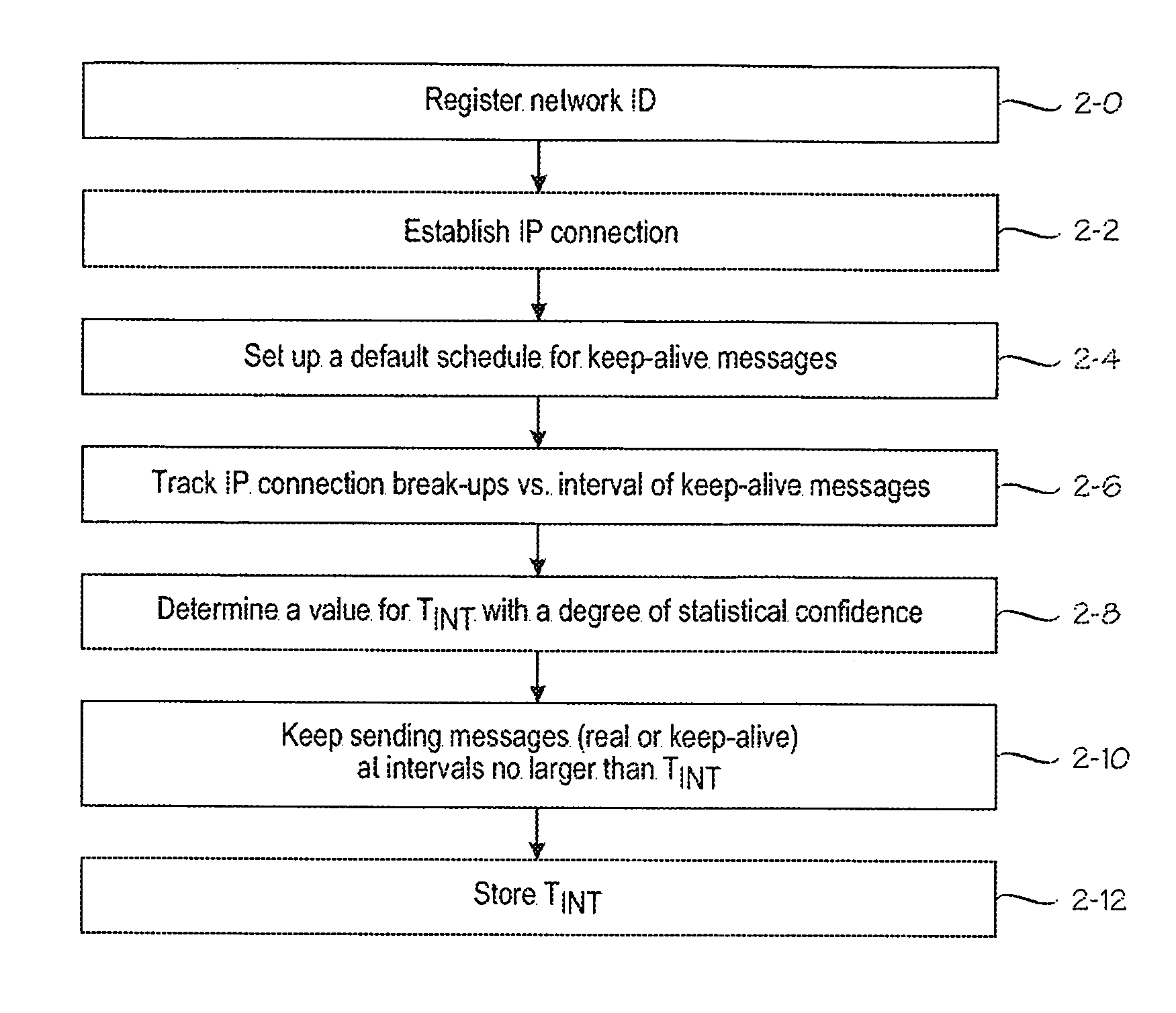
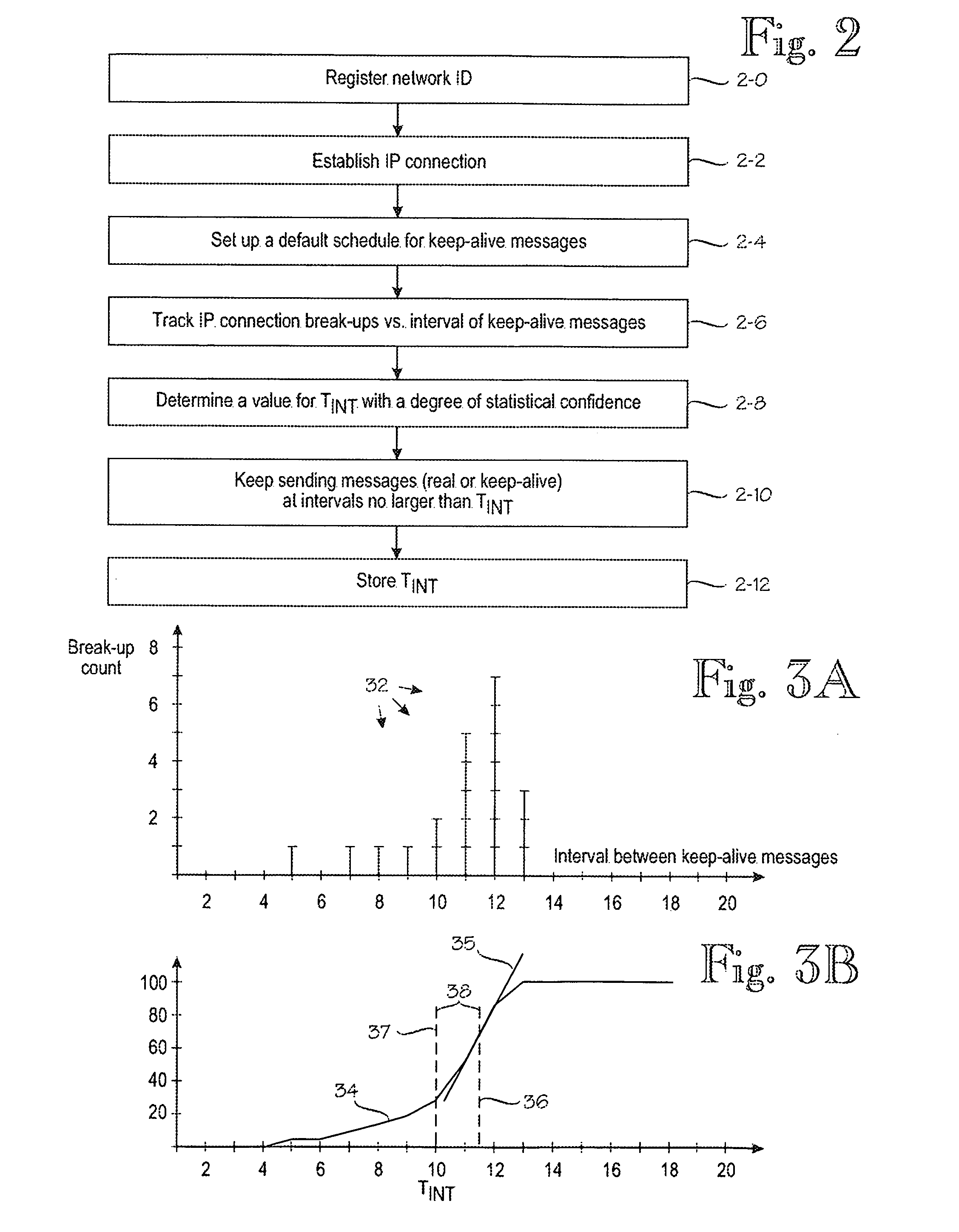
A method for IP [=Internet Protocol] communication between a mobile terminal and its correspondent node in a mobile radio network. The method comprises establishing (2-2) an IP connection between the mobile terminal and its correspondent node. After detecting a period of inactivity in the IP connection, (2-4) keep-alive messages are sent via the IP connection at predetermined intervals, which are varied. The method comprises monitoring (2-6) the lengths of several periods of inactivity at which the mobile radio network disconnects the IP connection. Based on the monitored lengths of periods of inactivity, a maximum interval (TINT) between keep-alive messages is determined (2-8) such that the maximum interval meets a predetermined criterion of statistical confidence, and the interval between keep-alive messages is set (2-10) to the maximum interval (TINT).
Owner:SEVEN NETWORKS INC
Method and system for estimating insurance loss reserves and confidence intervals using insurance policy and claim level detail predictive modeling
InactiveUS20060136273A1FinanceComputation using non-denominational number representationPredictive modellingConfidence interval
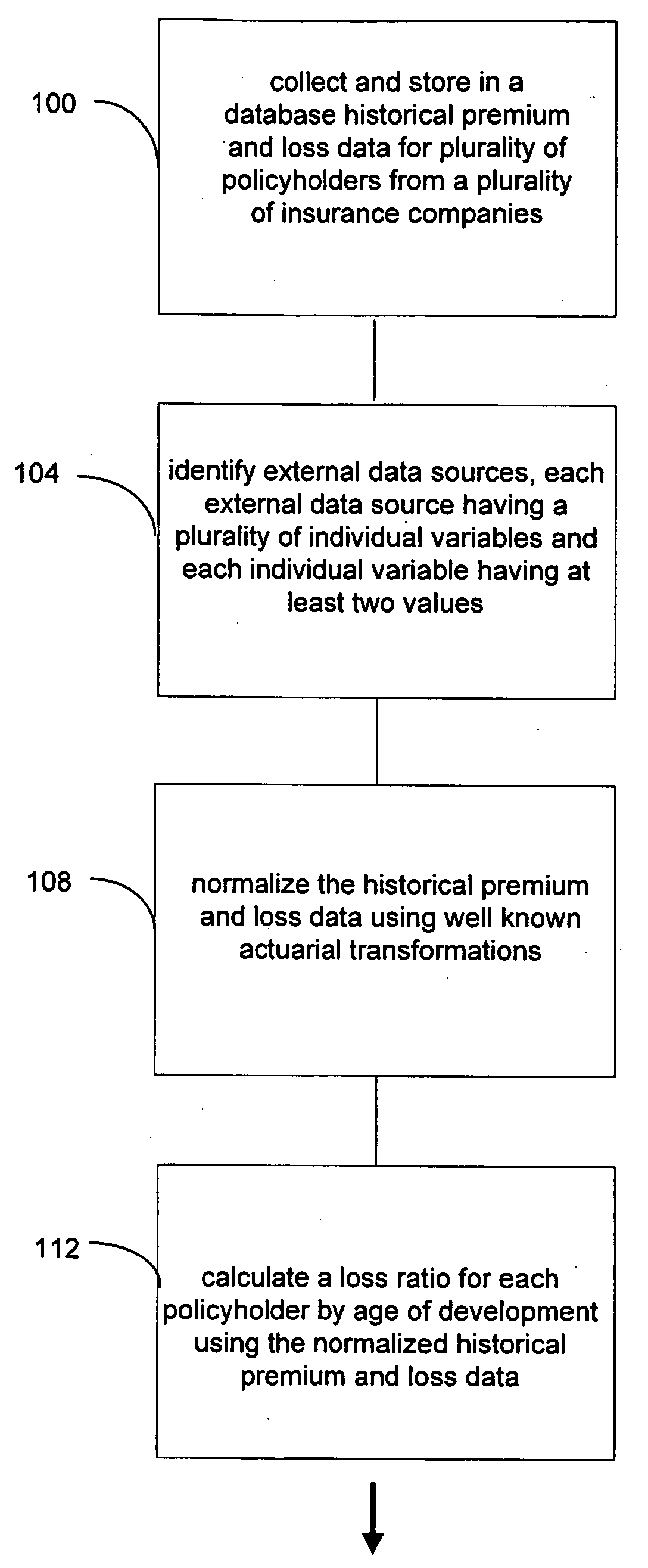
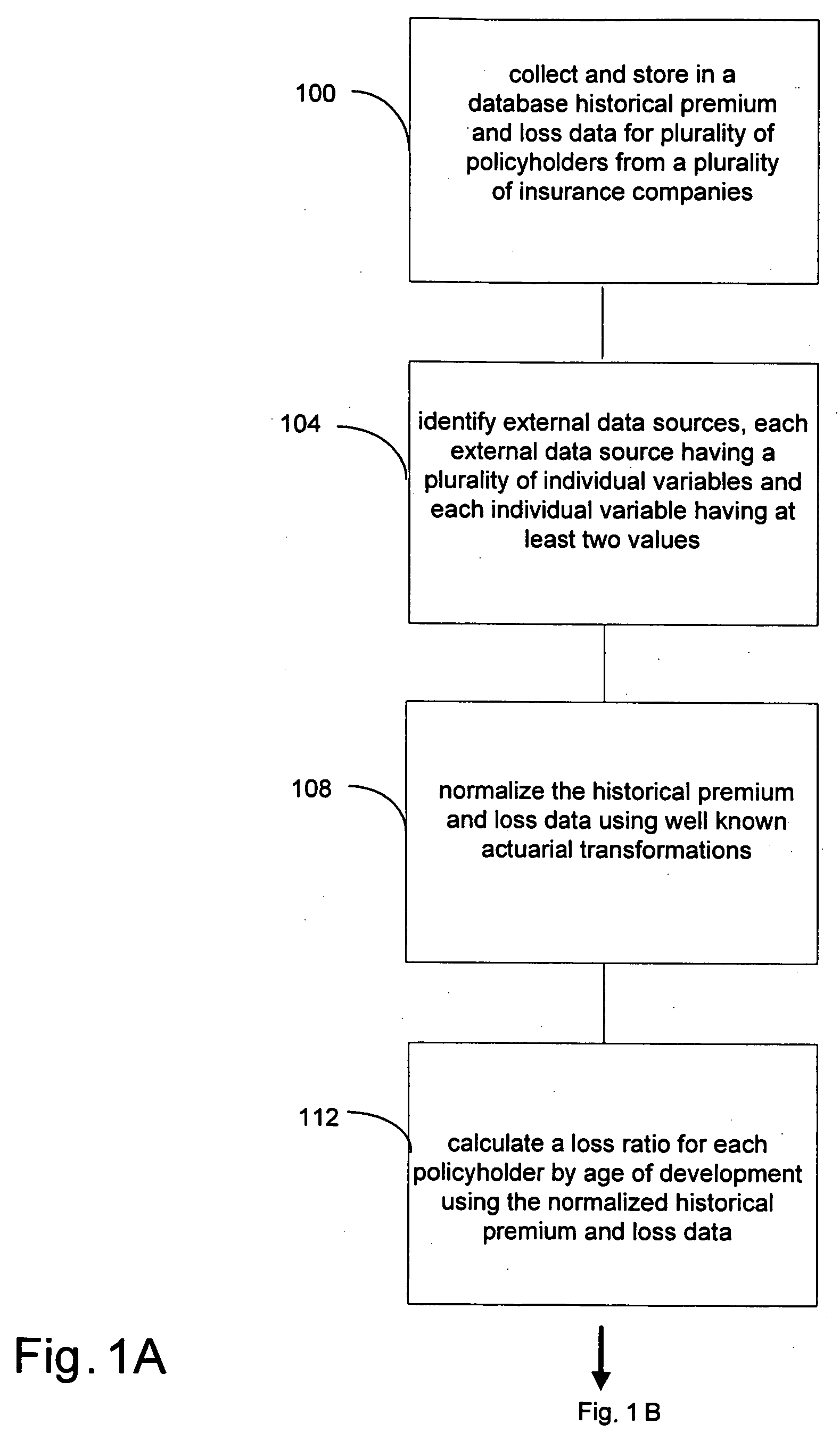
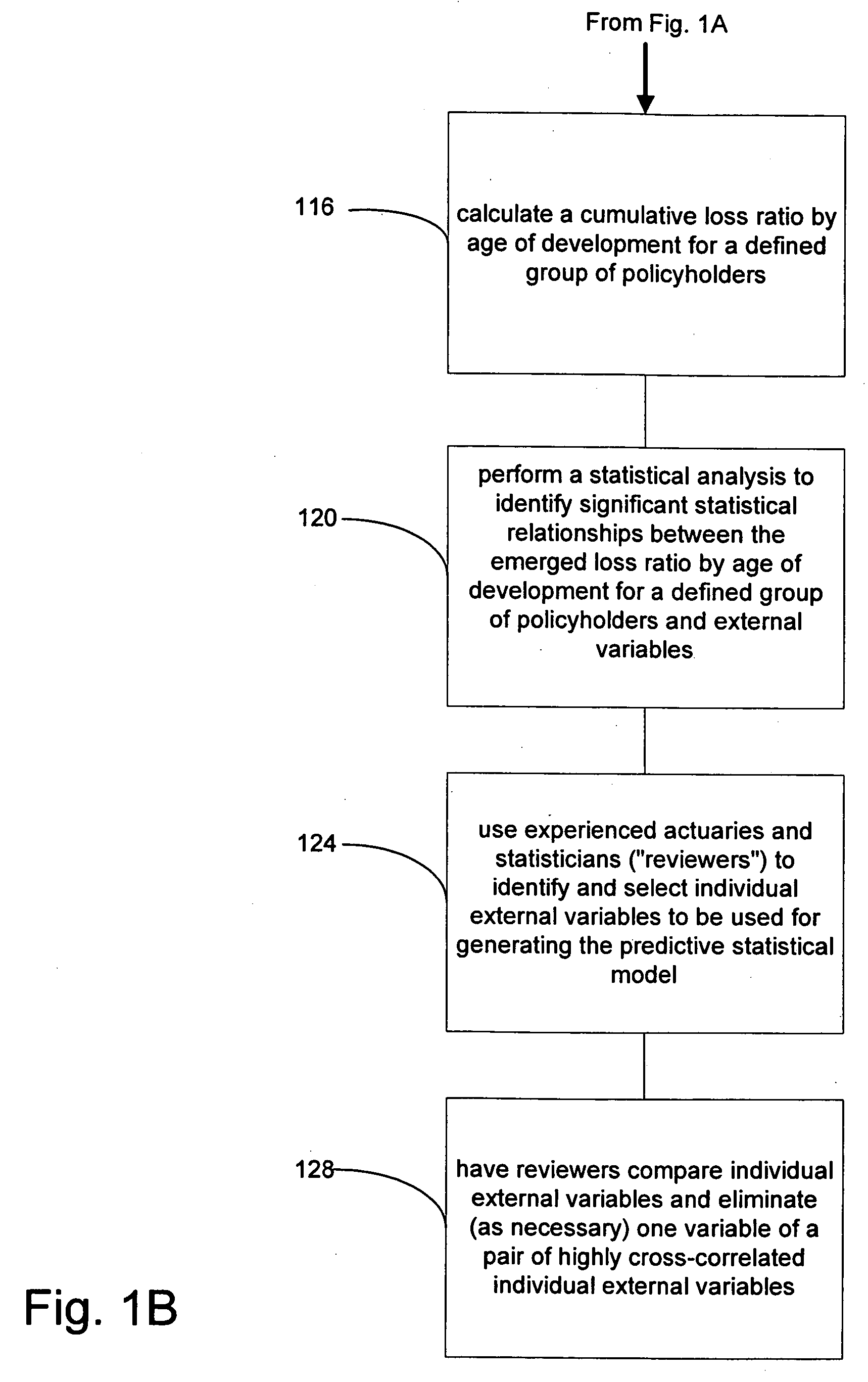
A computerized system and method for estimating insurance loss reserves and confidence intervals using insurance policy and claim level detail predictive modeling. Predictive models are applied to historical loss, premium and other insurer data, as well as external data, at the level of policy detail to predict ultimate losses and allocated loss adjustment expenses for a group of policies. From the aggregate of such ultimate losses, paid losses to date are subtracted to derive an estimate of loss reserves. Dynamic changes in a group of policies can be detected enabling evaluation of their impact on loss reserves. In addition, confidence intervals around the estimates can be estimated by sampling the policy-by-policy estimates of ultimate losses.
Owner:DELOITTE DEV
Method and system for continuous monitoring and diagnosis of body sounds
InactiveUS20060198533A1Reduce the impactQuality improvementStethoscopeTransmission noise suppressionContinuous measurementReal time analysis
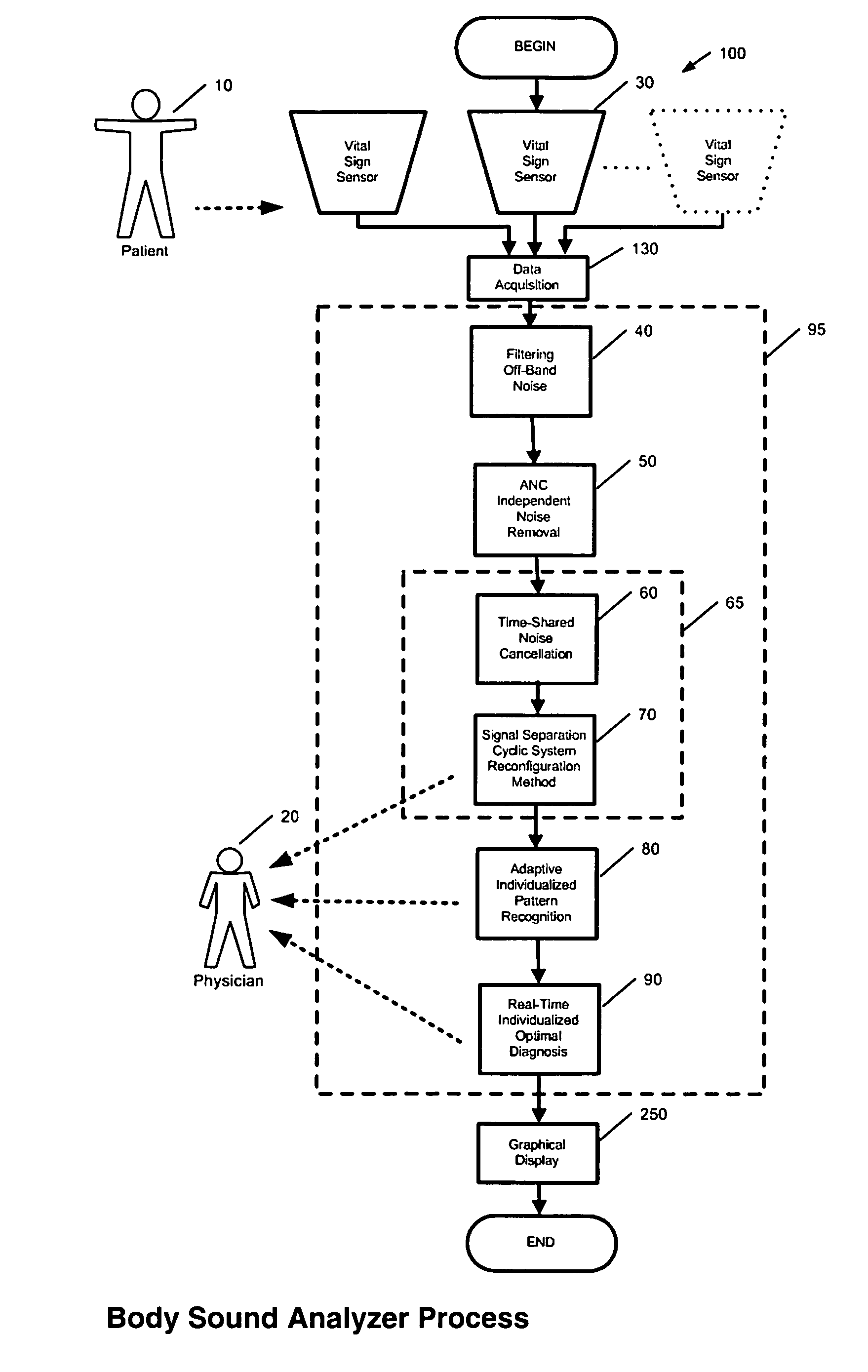
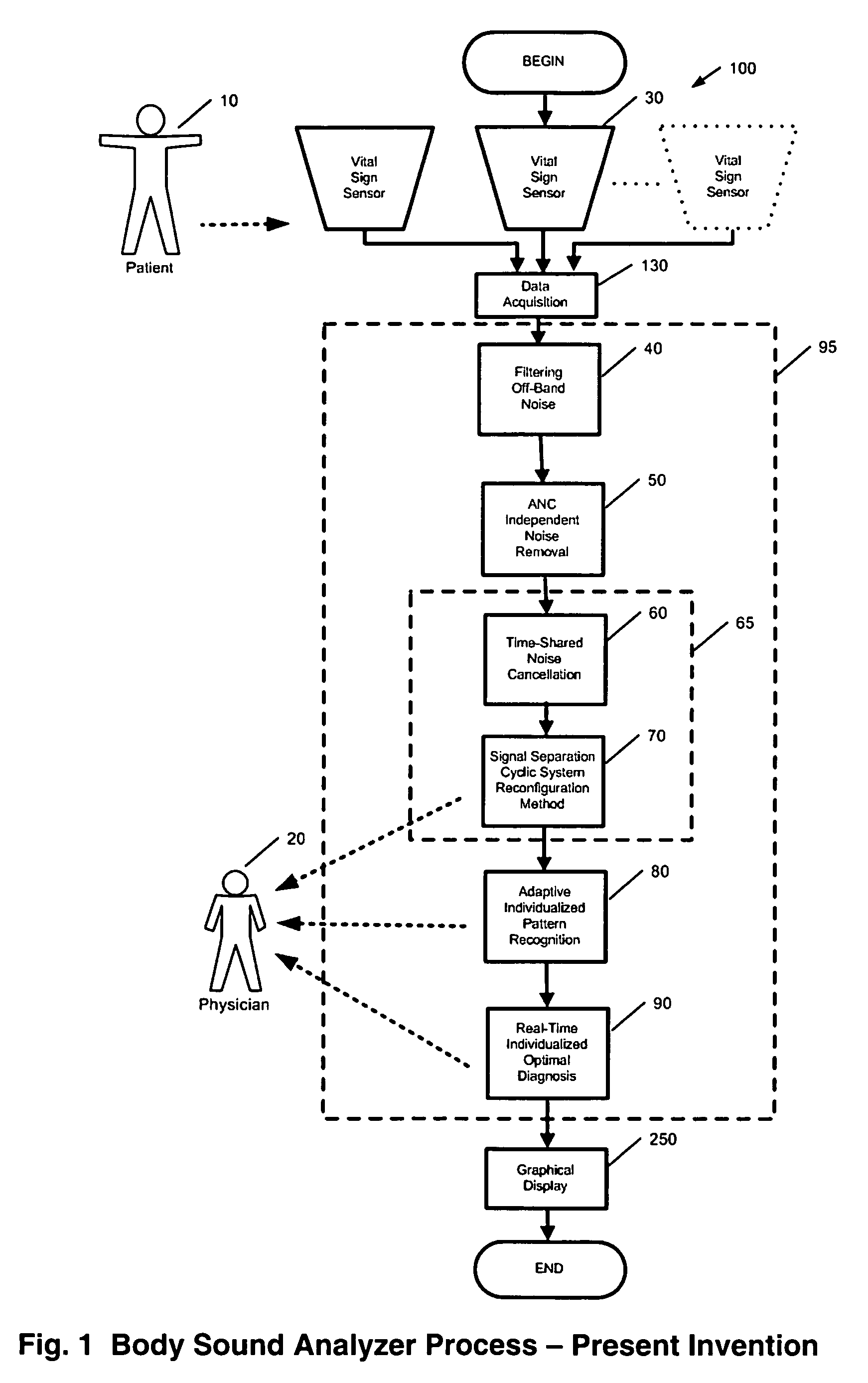
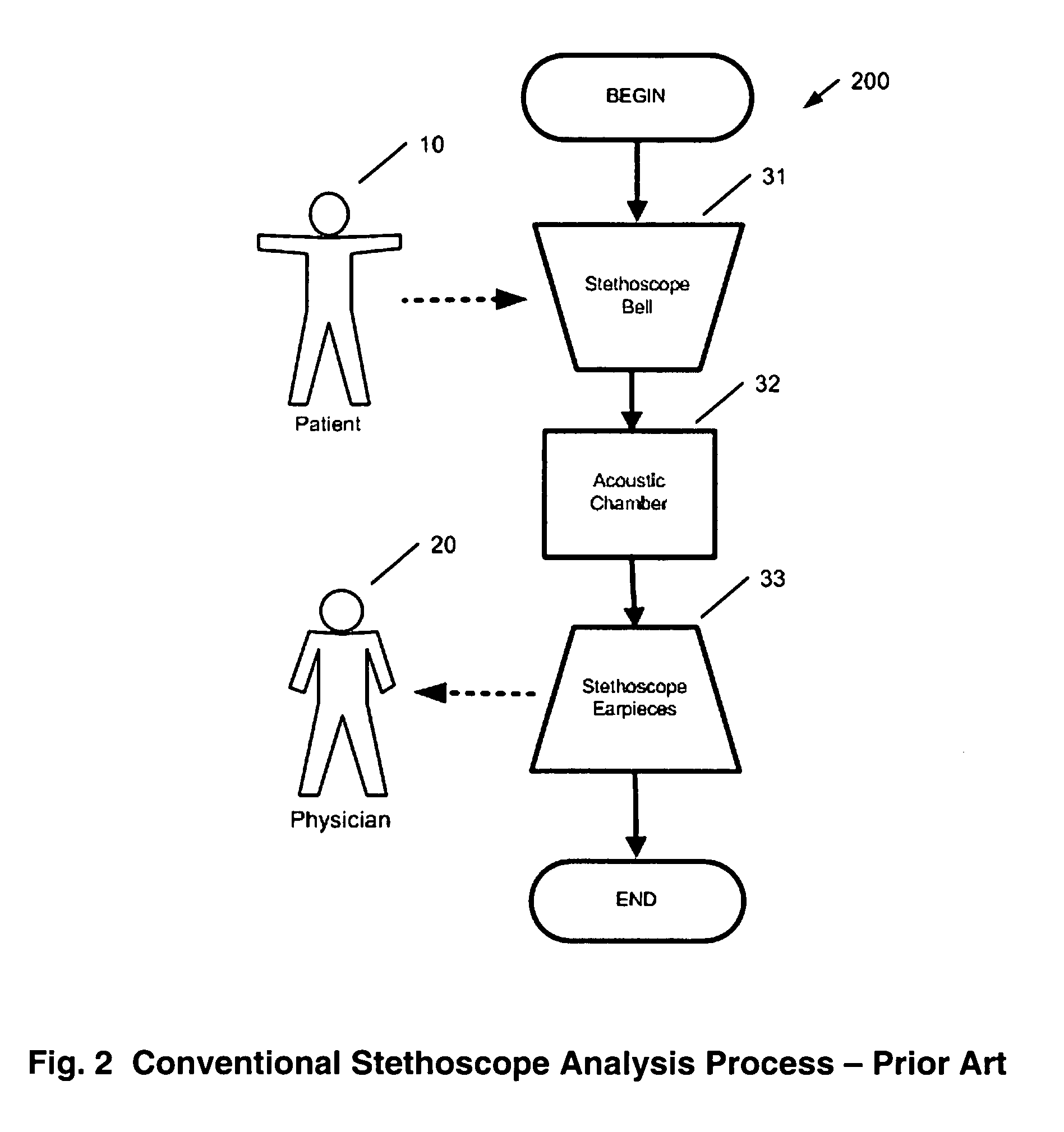
A method and system is invented for automated continuous monitoring and real-time analysis of body sounds. The system embodies a multi-sensor data acquisition system to measure body sounds continuously. The sound signal processing functions utilize a unique signal separation and noise removal methodology by which authentic body sounds can be extracted from cross-talk signals and in noisy environments, even when signals and noises may have similar frequency components or statistically dependent. This method and system combines traditional noise canceling methods with the unique advantages of rhythmic features in body sounds. By employing a multi-sensor system, the method and system perform cyclic system reconfiguration, time-shared blind identification and adaptive noise cancellation with recursion from cycle to cycle. Since no frequency separation or signal / noise independence is required, this invention can provide a robust and reliable capability of noise reduction, complementing the traditional methods. The invention further includes a novel method by which pattern recognition of groups of key parameters can be used to diagnosis physical conditions associated with body sounds, with confidence intervals on the diagnostic criterion to indicate accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:WANG LE YI +1
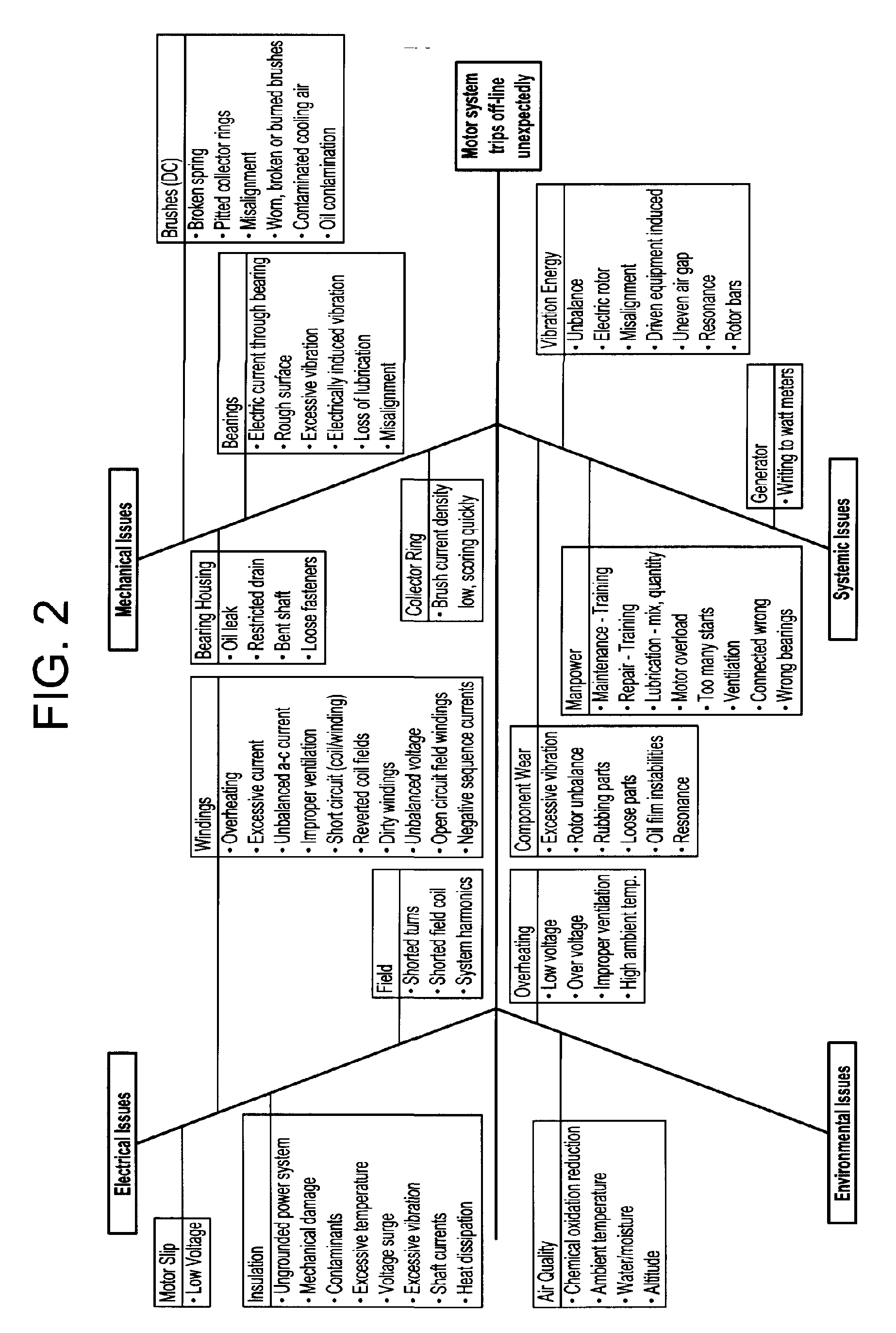
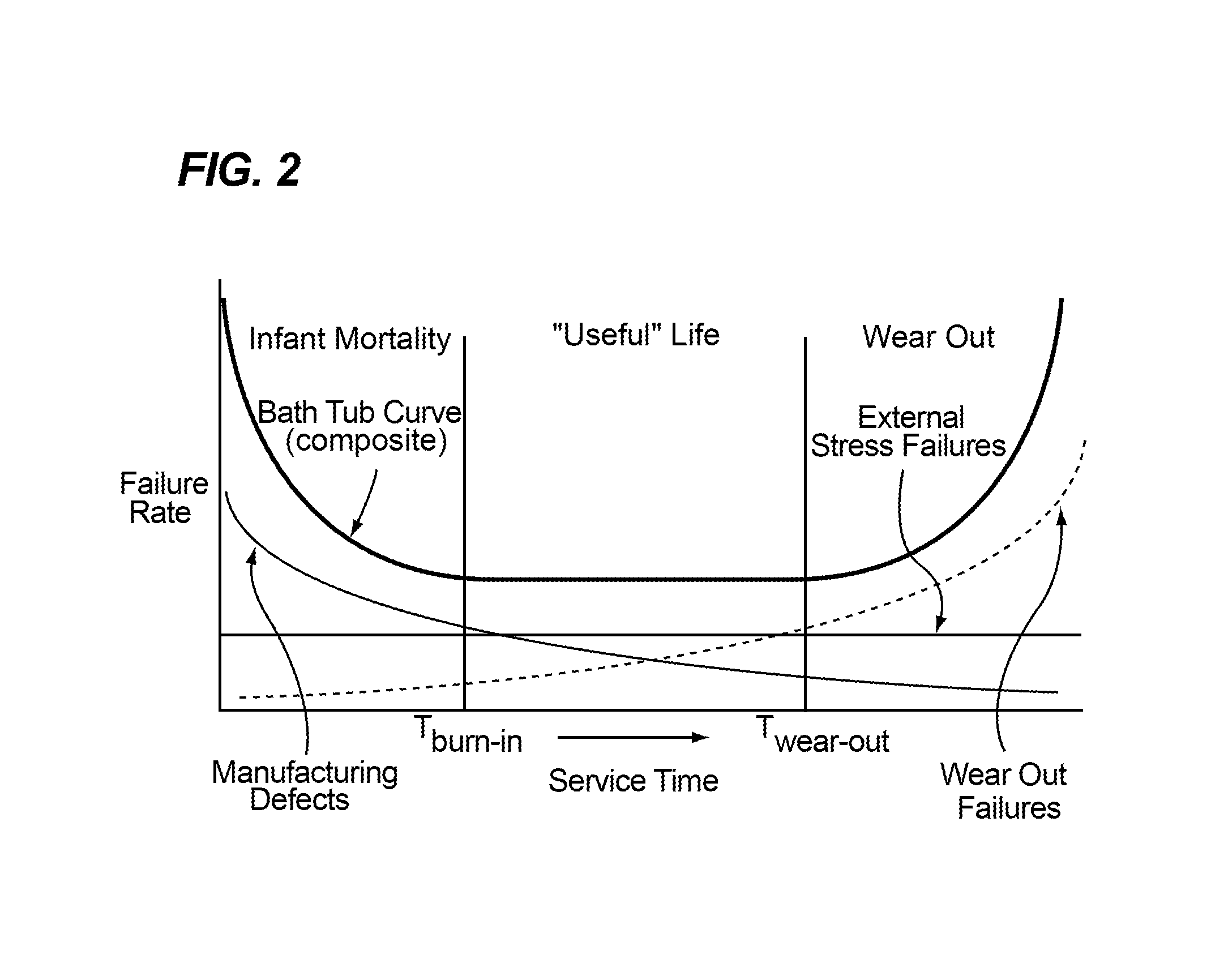
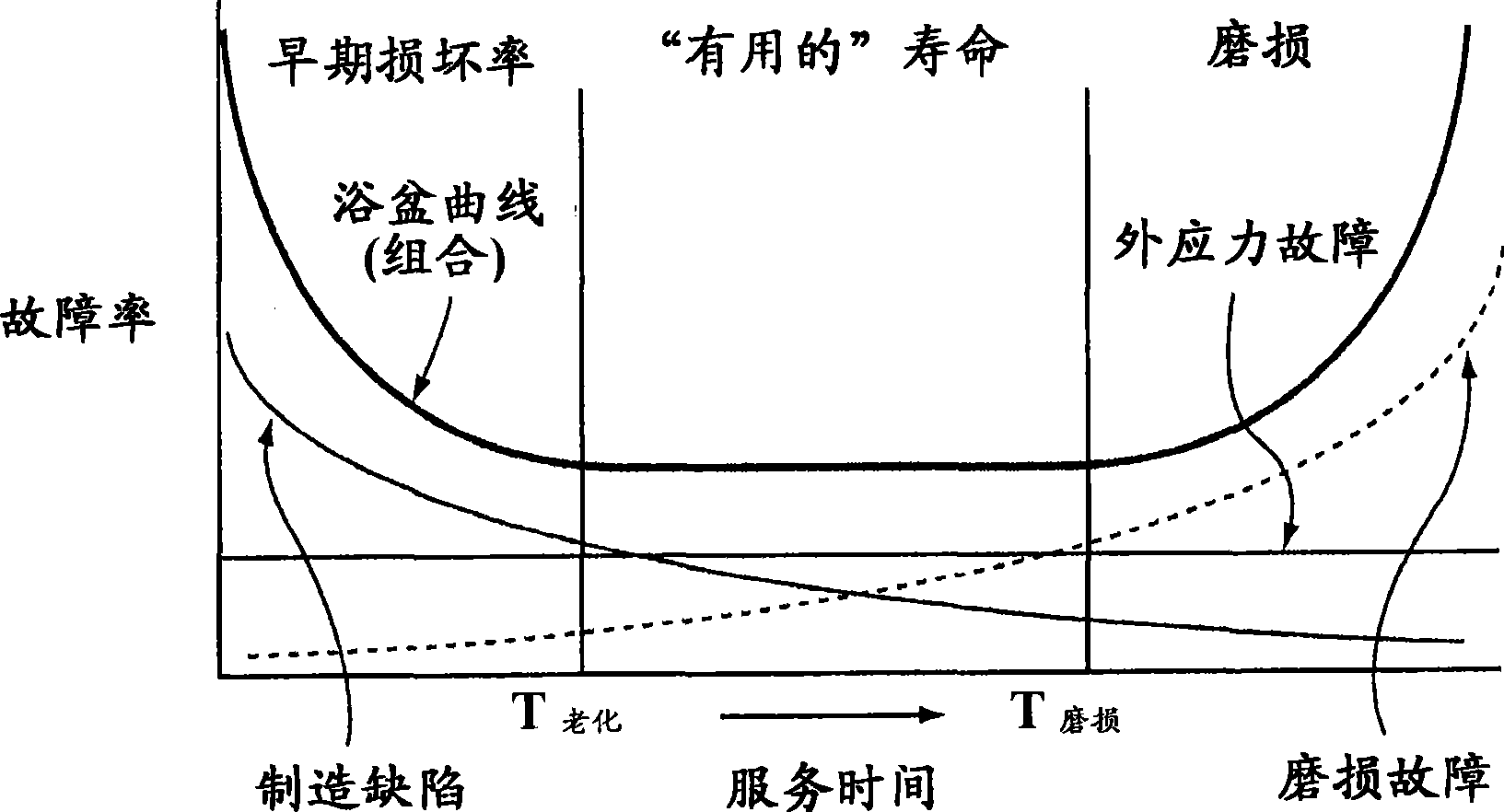
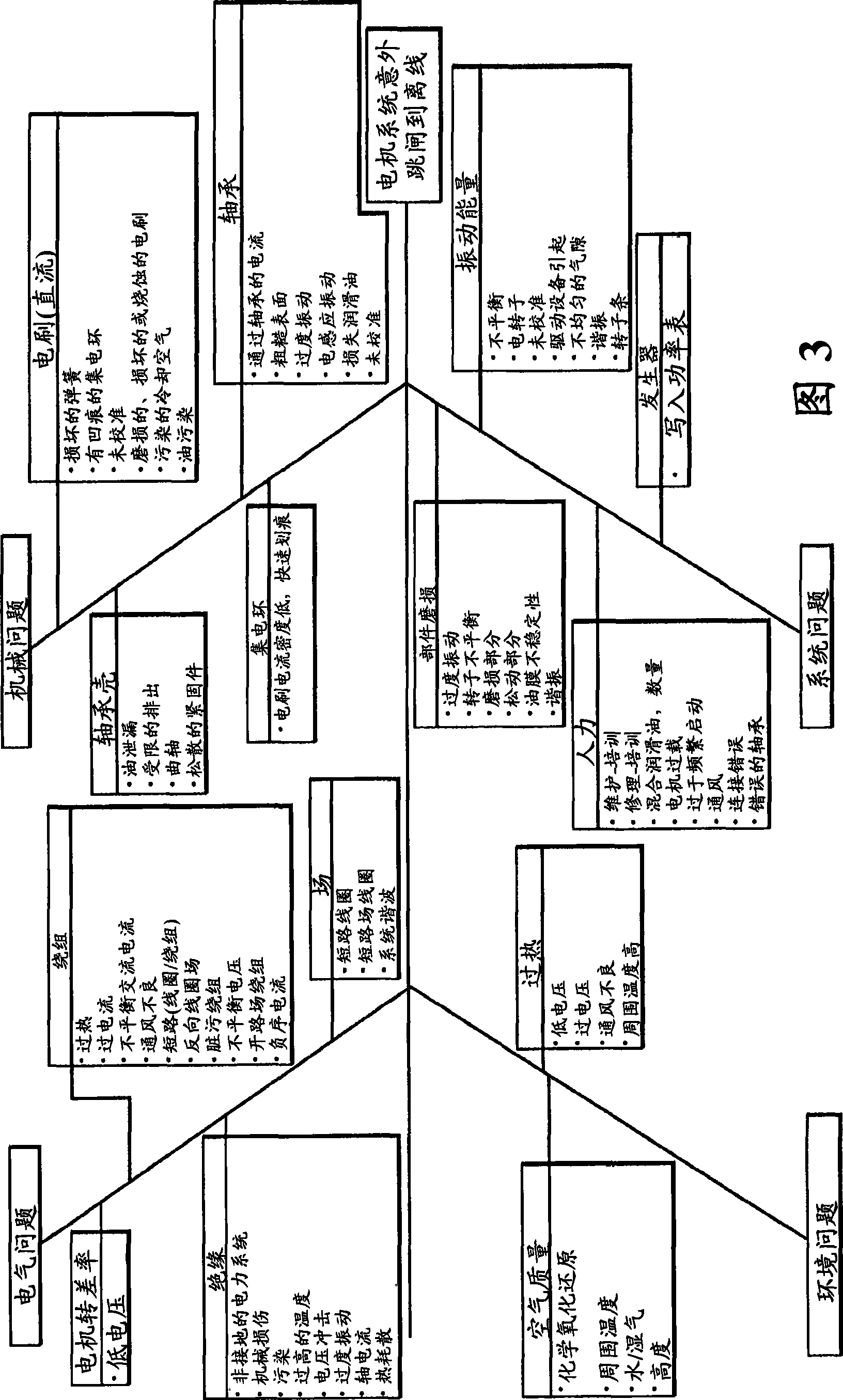
Method and system for predicting remaining life for motors featuring on-line insulation condition monitor
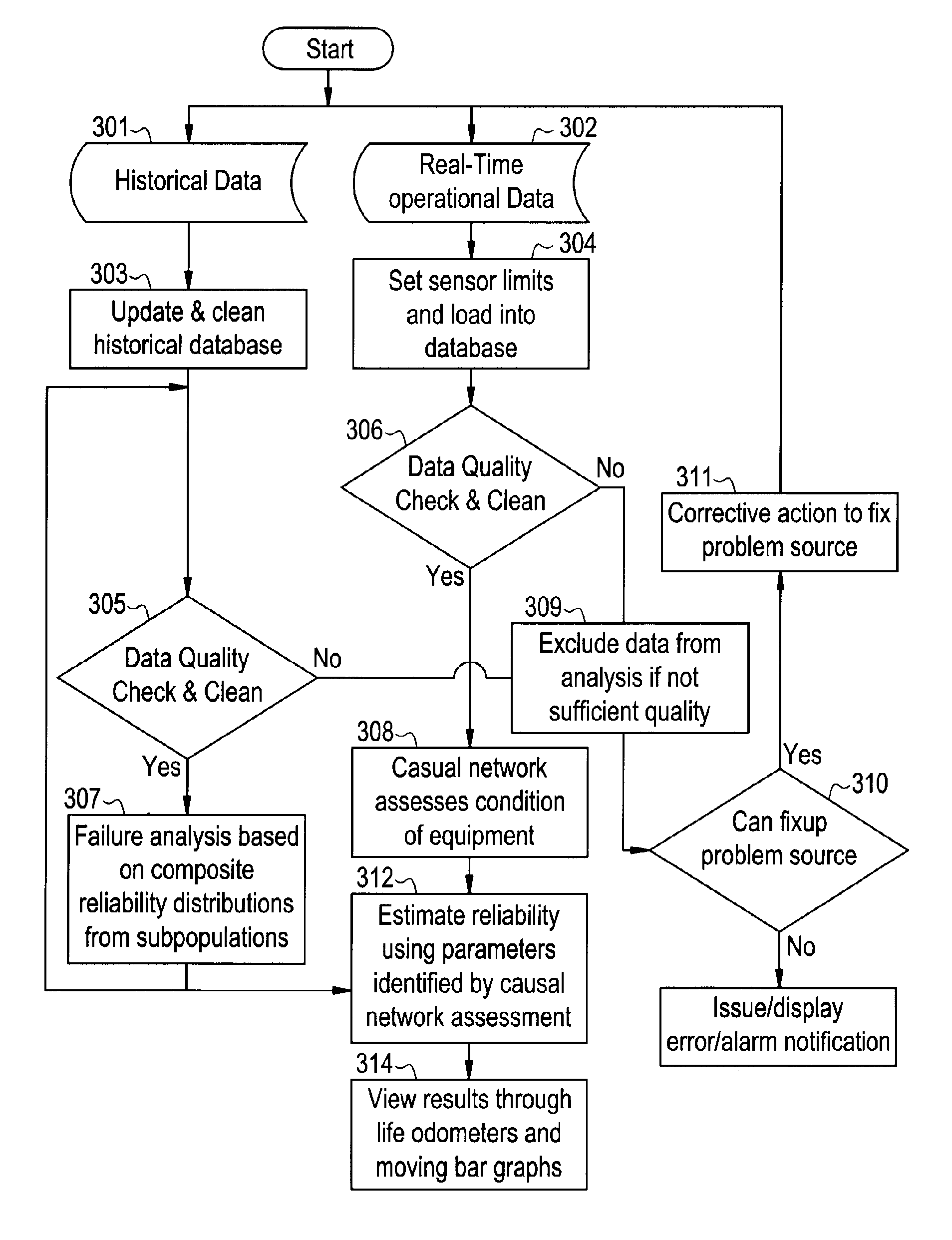
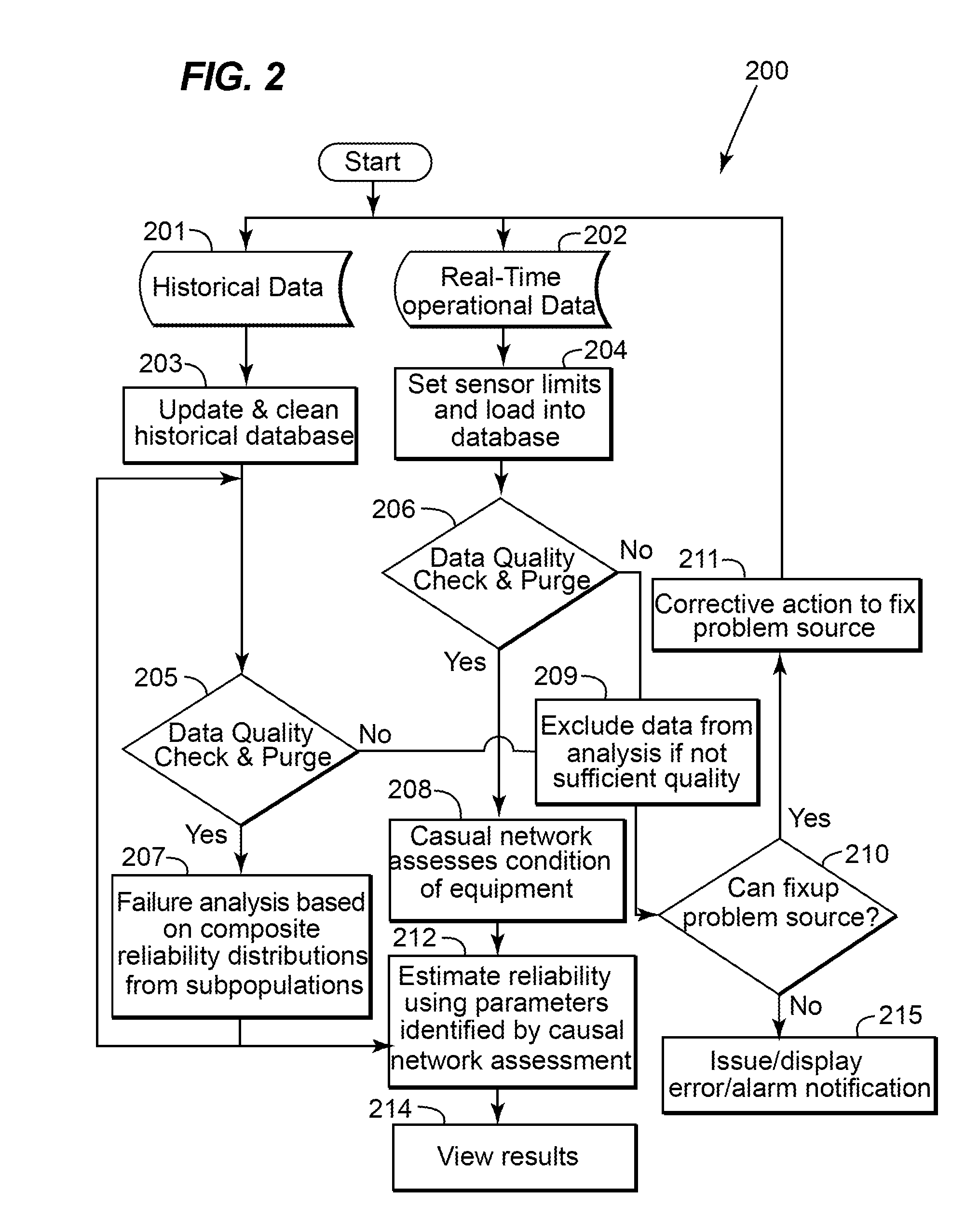
A method for determining reliability and a remaining time before failure with statistical confidence for a motor system includes acquiring historical motor data in a computer system, obtaining operational parameter data, uploading the operational parameter data to the computer system, performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the motor system. The historical motor data corresponds to the motor system. The operational parameter data is obtained from sensors at the motor system. The sensors include a tan delta sensor. The failure analysis is performed based on a composite of reliability probability distributions corresponding to predetermined sub-populations of historical motor system failure causes. The causal network is developed for modeling reliability of one or more motor system components and assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network. Results from the performing failure analysis are integrated with results from the assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network to compute a quantitative value for a time remaining before failure with an ascertained statistical confidence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
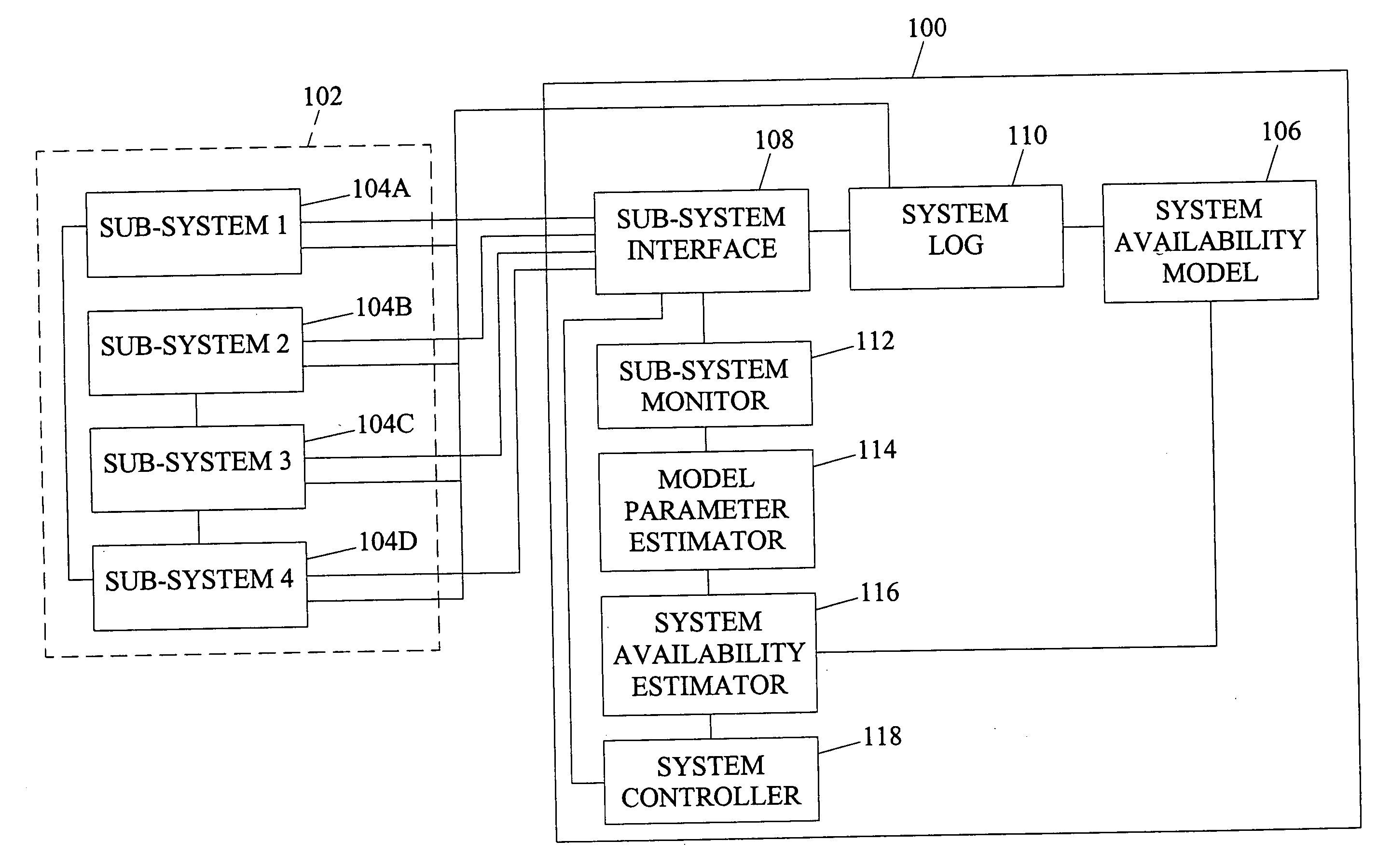
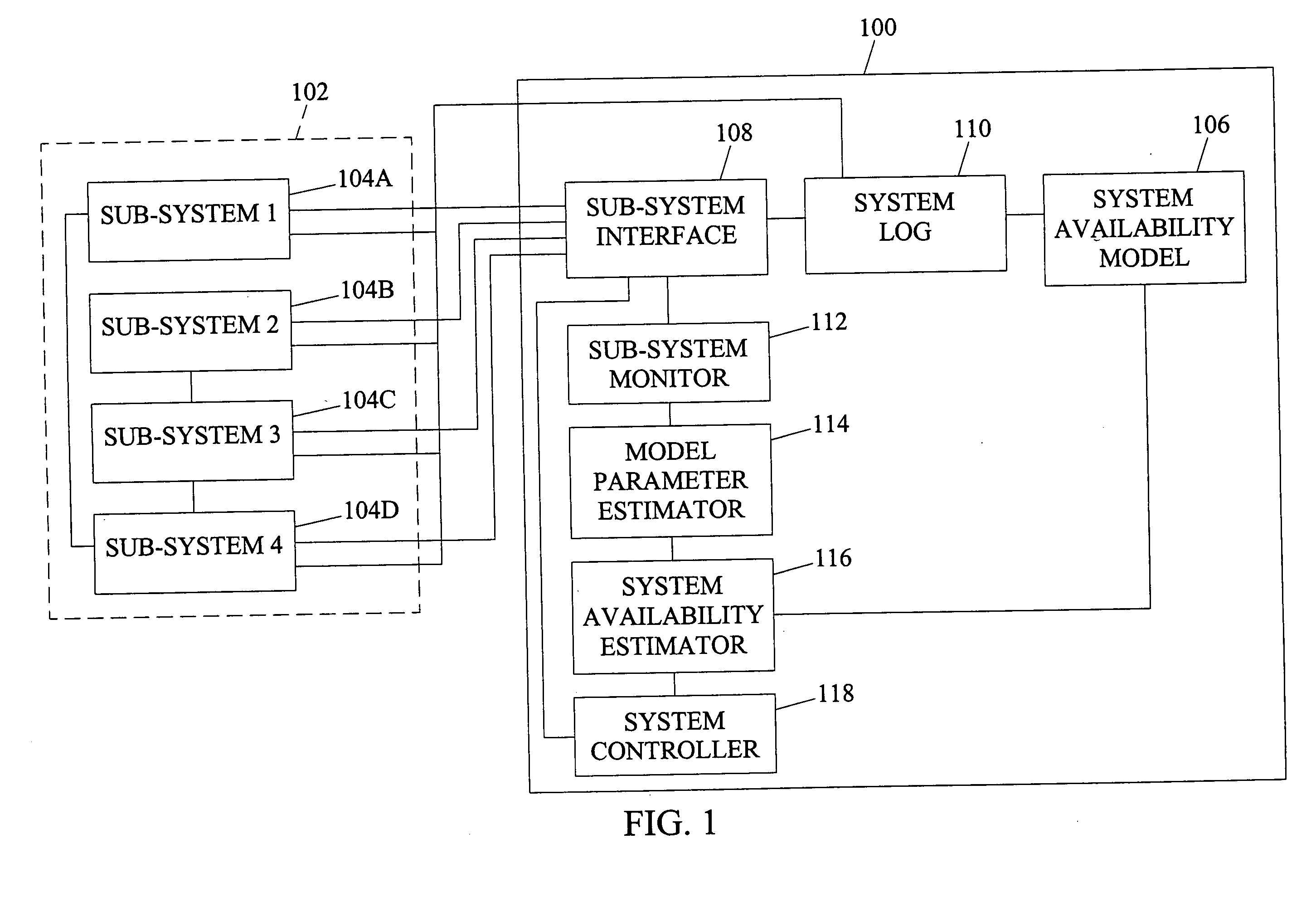
Systems, methods, and computer program products for system online availability estimation
InactiveUS20060129367A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusTransmissionConfidence intervalStatistical Confidence
Systems, methods, and computer program products for system online availability estimation. A method according to one embodiment can include a step for providing an availability model of a system. The method can also include a step for receiving behavior data of the system. In addition, the method can include estimating a plurality of parameters for the availability model based on the behavior data. The method can also include determining individual confidence intervals for each of the parameters. Further, the method can include determining an overall confidence interval for the system based on the individual distributions of the estimated parameters. The method can also include determining control actions based on the estimated overall availability or inferred parameter values.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
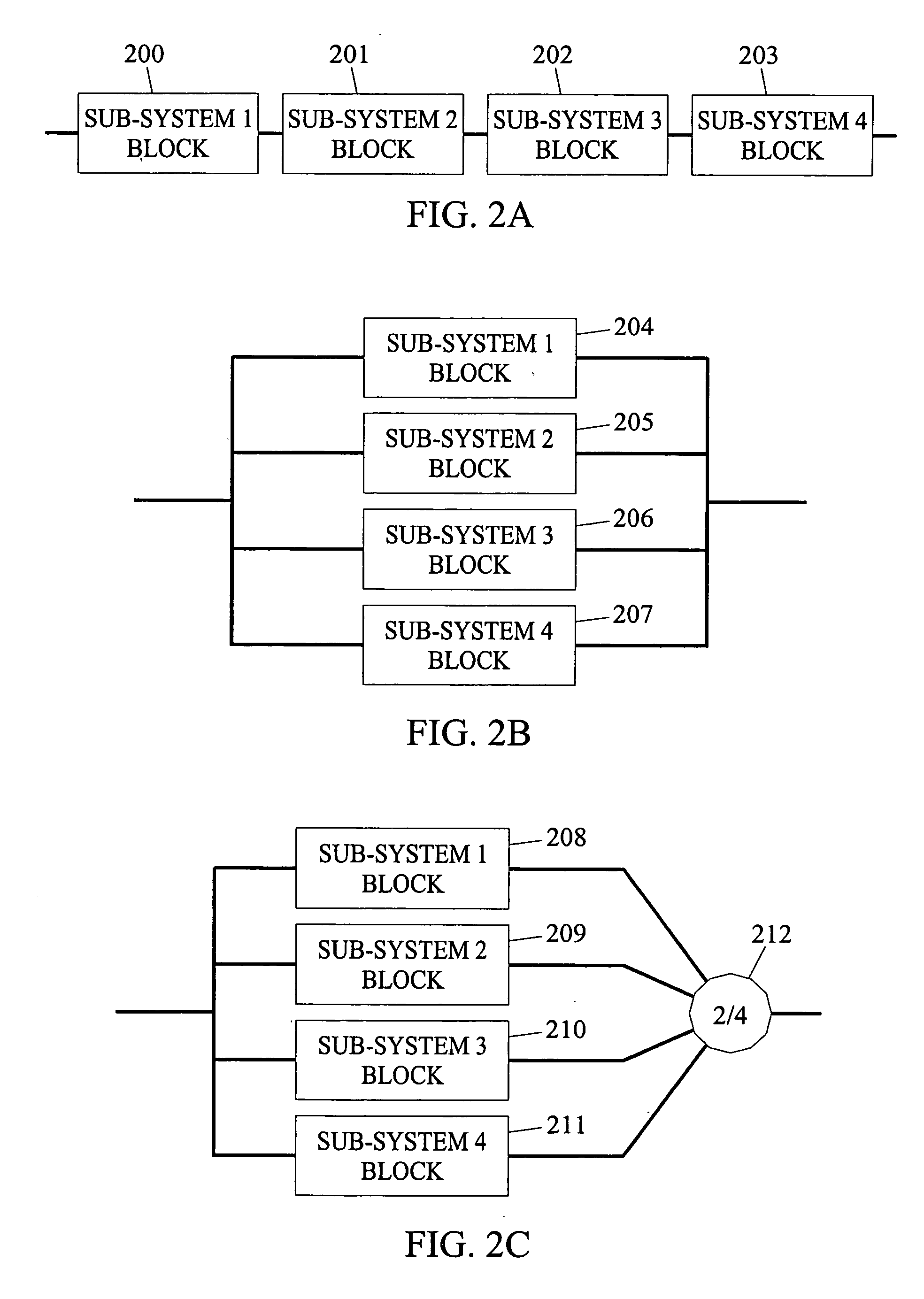
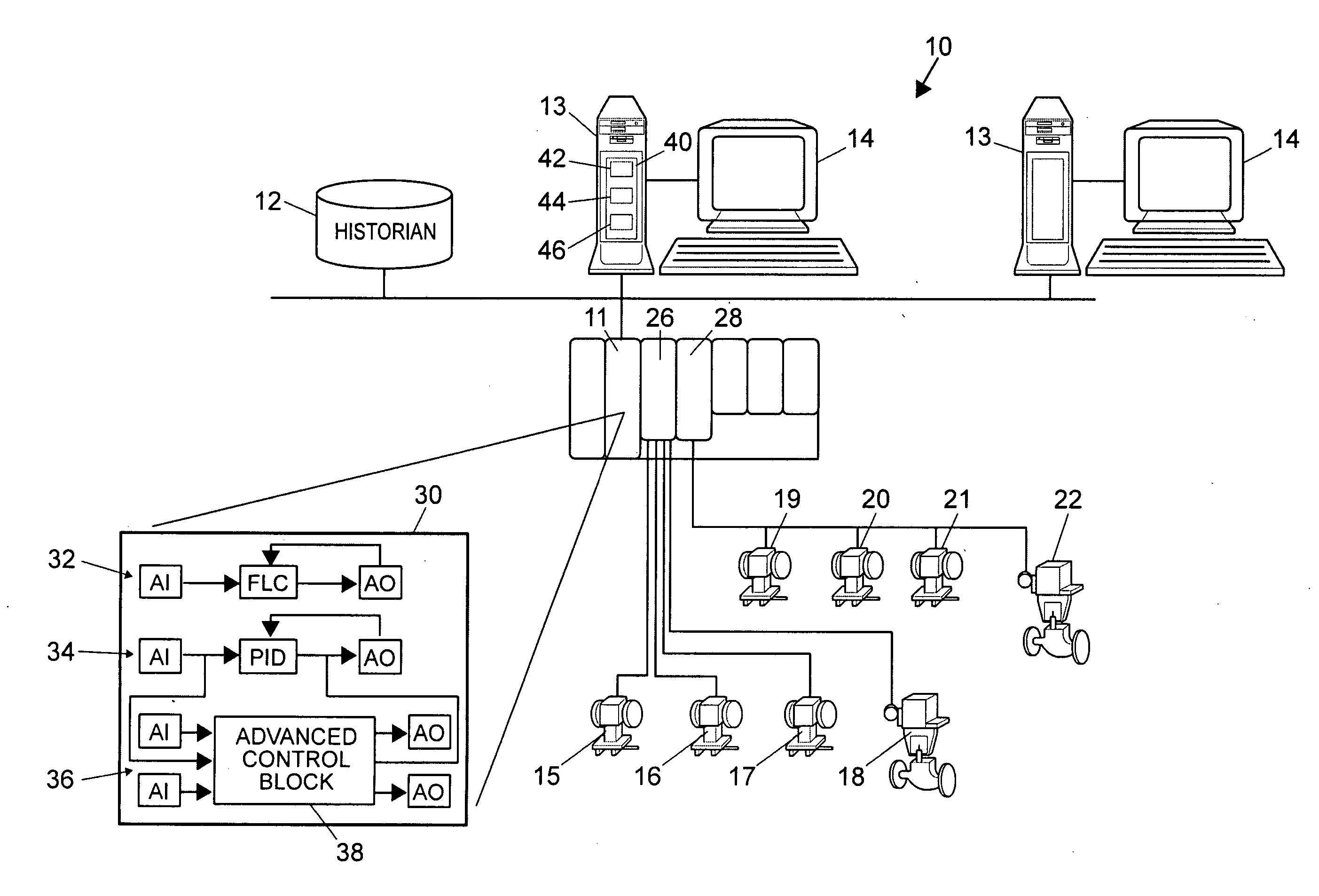
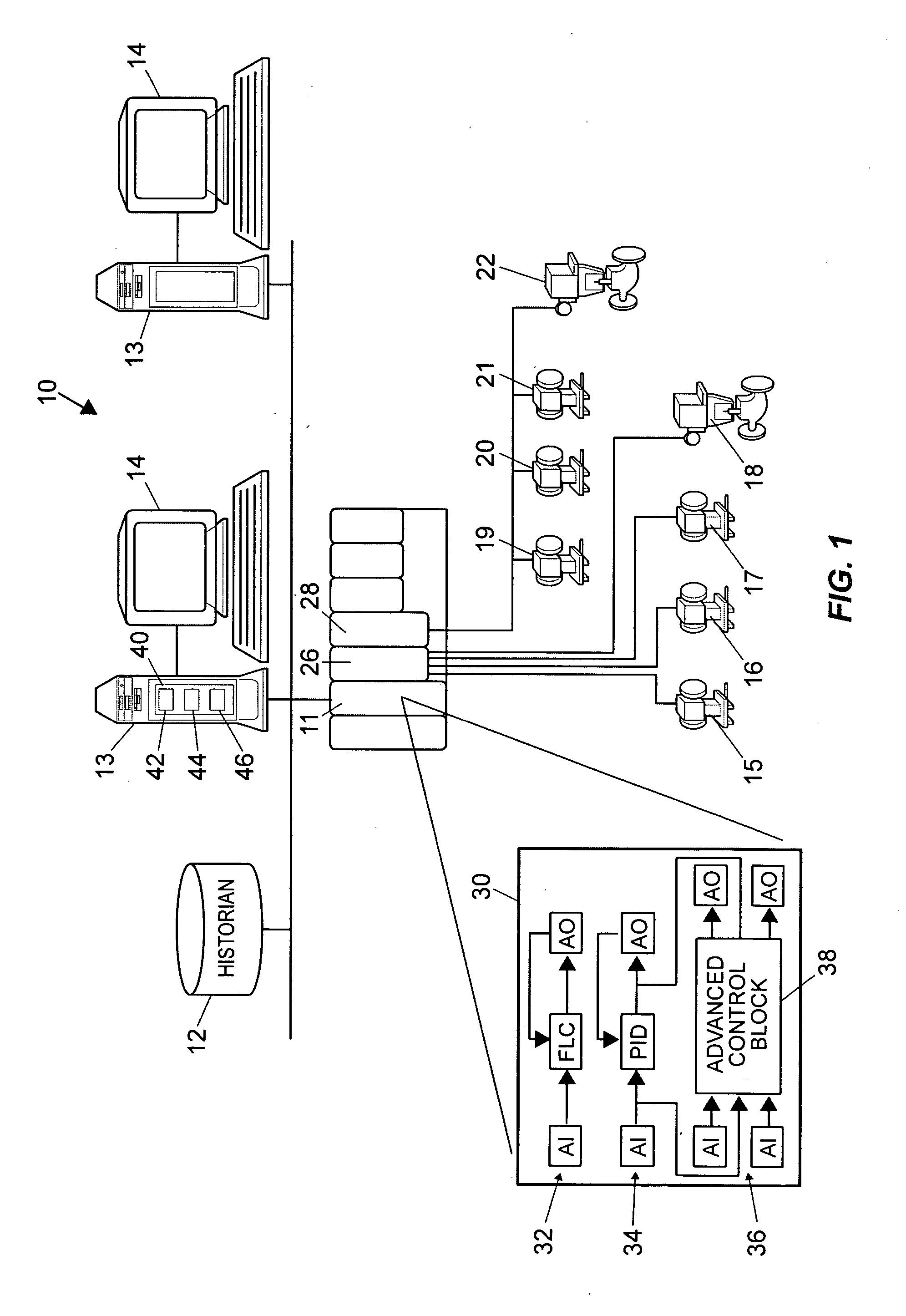
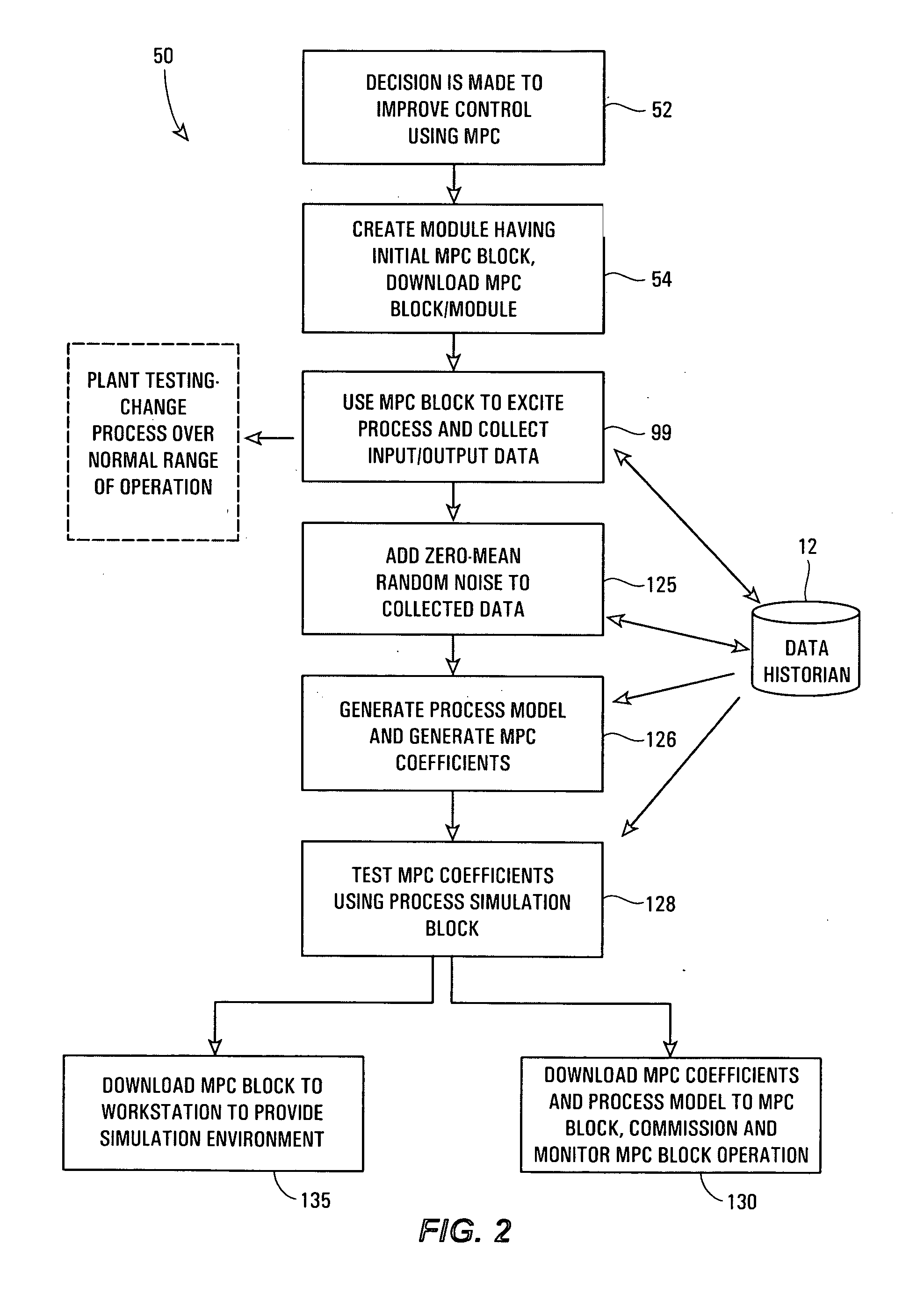
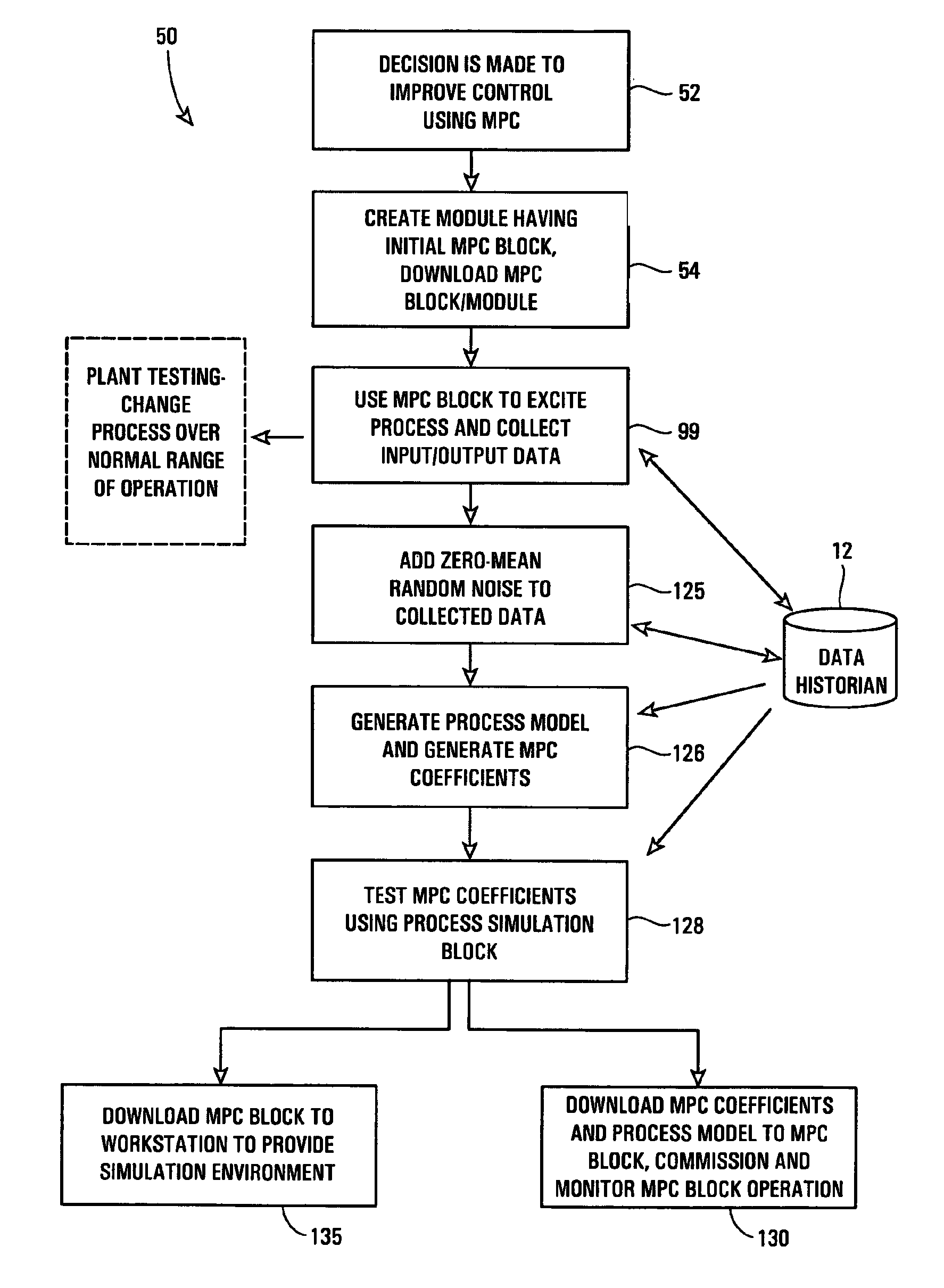
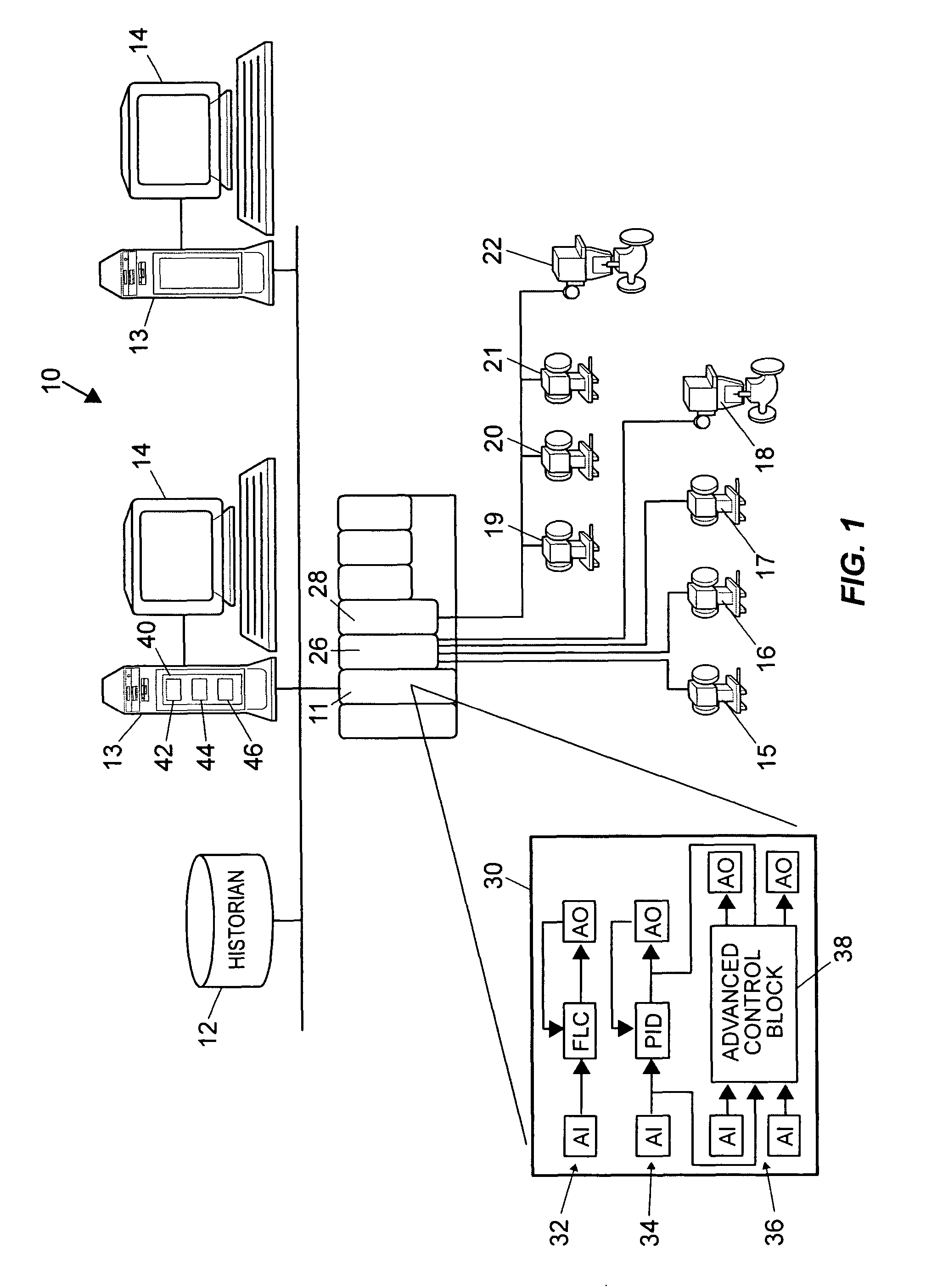
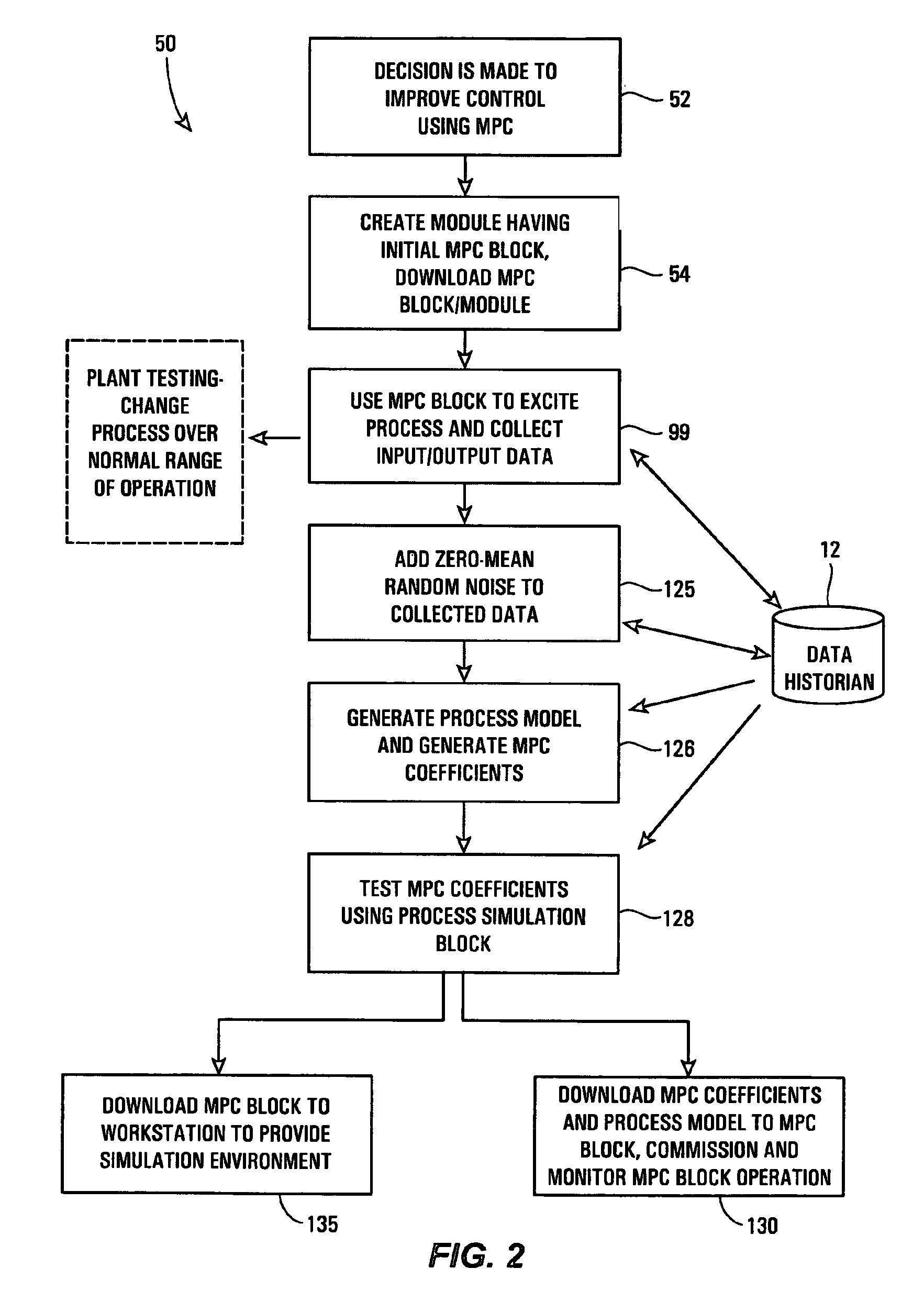
ActiveUS20070244575A1Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Lithium ion power battery self-discharge consistency evaluation method
InactiveCN107607881AImprove self-discharge rateReduce shelf lifeElectrical testingCapacitanceElectrical battery
A lithium ion power battery self-discharge consistency evaluation method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a plurality of batteries with good capacitance and internal resistance consistencyfrom lithium iron phosphate batteries of the same production batch, the same specification model and the same material system; using a constant current constant voltage charging system and a constantcurrent discharge system to charge and discharge the batteries for many times in cycle under the room temperature; 2, adjusting the batteries to an empty charge state under the room temperature; 3, screening batteries with the self discharging rate bigger than 3%; 4, adjusting the battery SOC to 10%SOC to 30% SOC charge state; 5, measuring the open-circuit voltage after battery high temperature laying, and calculating the battery voltage drop [delta]V or voltage drop K in a unit time; 6, calculating the average value X of all battery [delta]V or K values and the standard deviation [sigma], andselecting the batteries in the confidence interval of [X-2[sigma], X+2[sigma]]. The method can improve the battery self discharging rate, can shorten the laid-up period, and can reduce the productioncost.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
System and method for generating conversion-related estimates utilizing adaptive sample size
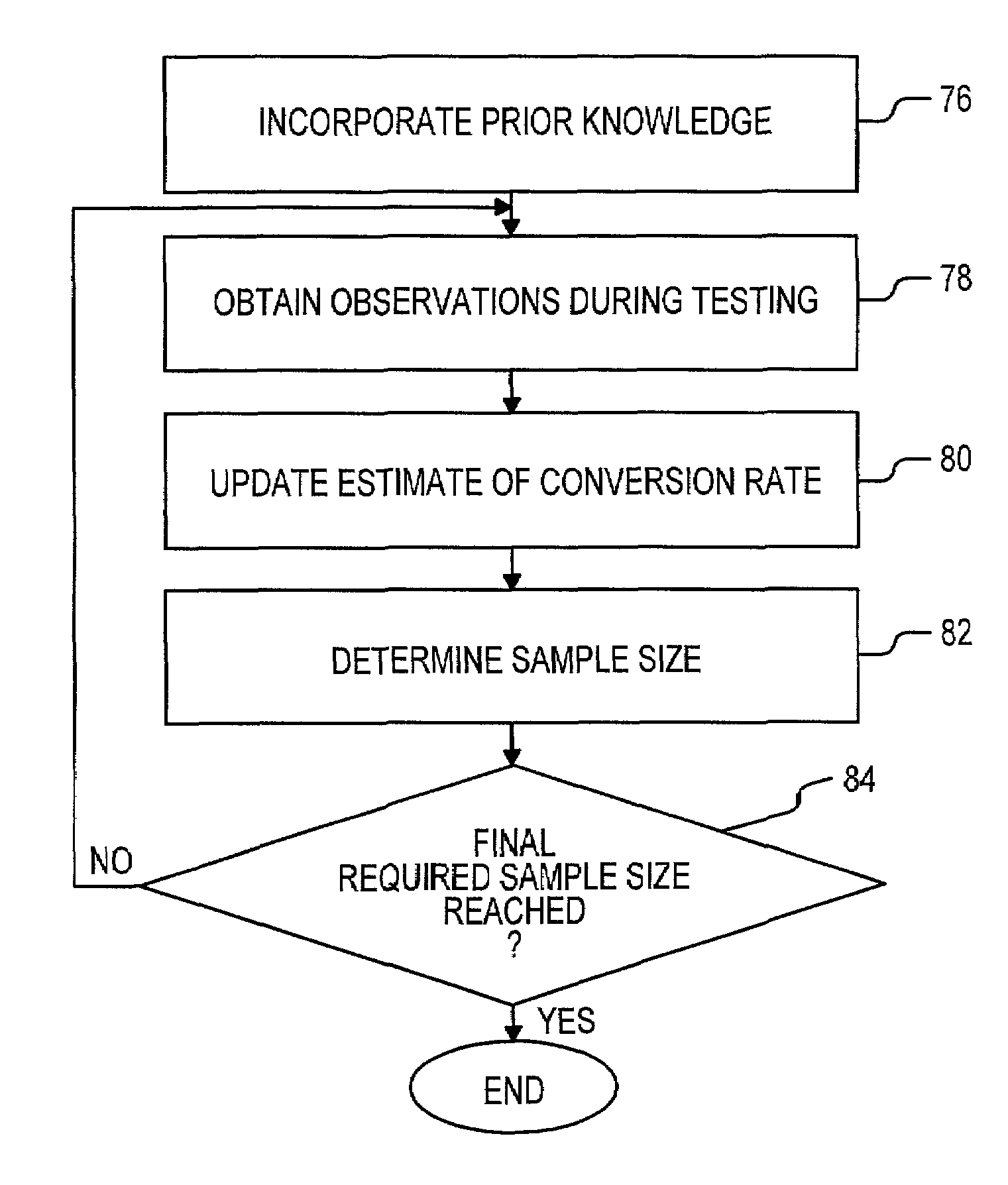
InactiveUS7058590B2Operational agilityMaintaining confidenceCash registersMarket data gatheringTest sampleStatistical Confidence
A method and system for processing test data relevant to specific behavior of visitors of a network accessible site, such as a website, includes a number of components. A first component is configured to determine an initial estimate of visitor behavior on the basis of pre-testing information. Such information may be entered by a manager of the site. A second component is configured to generate updates of the estimate in response to monitored behavior. Bayesian estimation may be employed in this component. The third and fourth components cooperate to dynamically adjust a measure of the required test sample size of the visitors so as to maintain a target statistical confidence level. The third component utilizes systematic sampling, while the fourth component uses negative binomial sampling.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS7840287B2Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
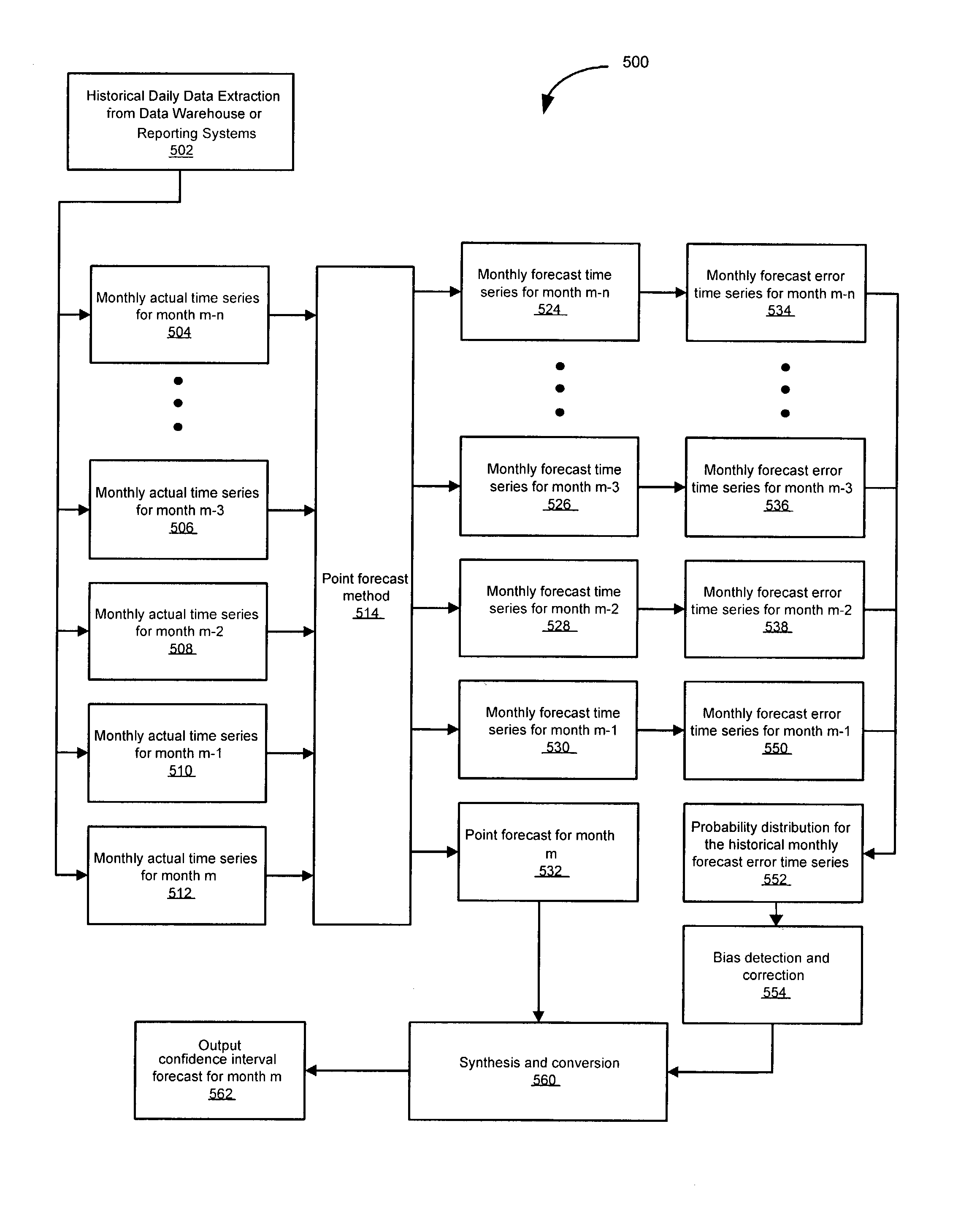
Method and system for constructing prediction interval based on historical forecast errors
A method and system is used to construct a forecast error confidence interval. The predication interval provides a range of error for a current forecast value to any desired confidence level. The method and system involve running a forecast method on a set of historical data. For each historical period, a forecast is obtained at each time point in the period. The forecasts are compared to the target value of interest in each period. The comparison of target values to forecast values is used to build an error series for each historical period. The error values within each error series are pooled to form an error distribution series. The error distribution series can be used to provide a confidence interval for the current forecast.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
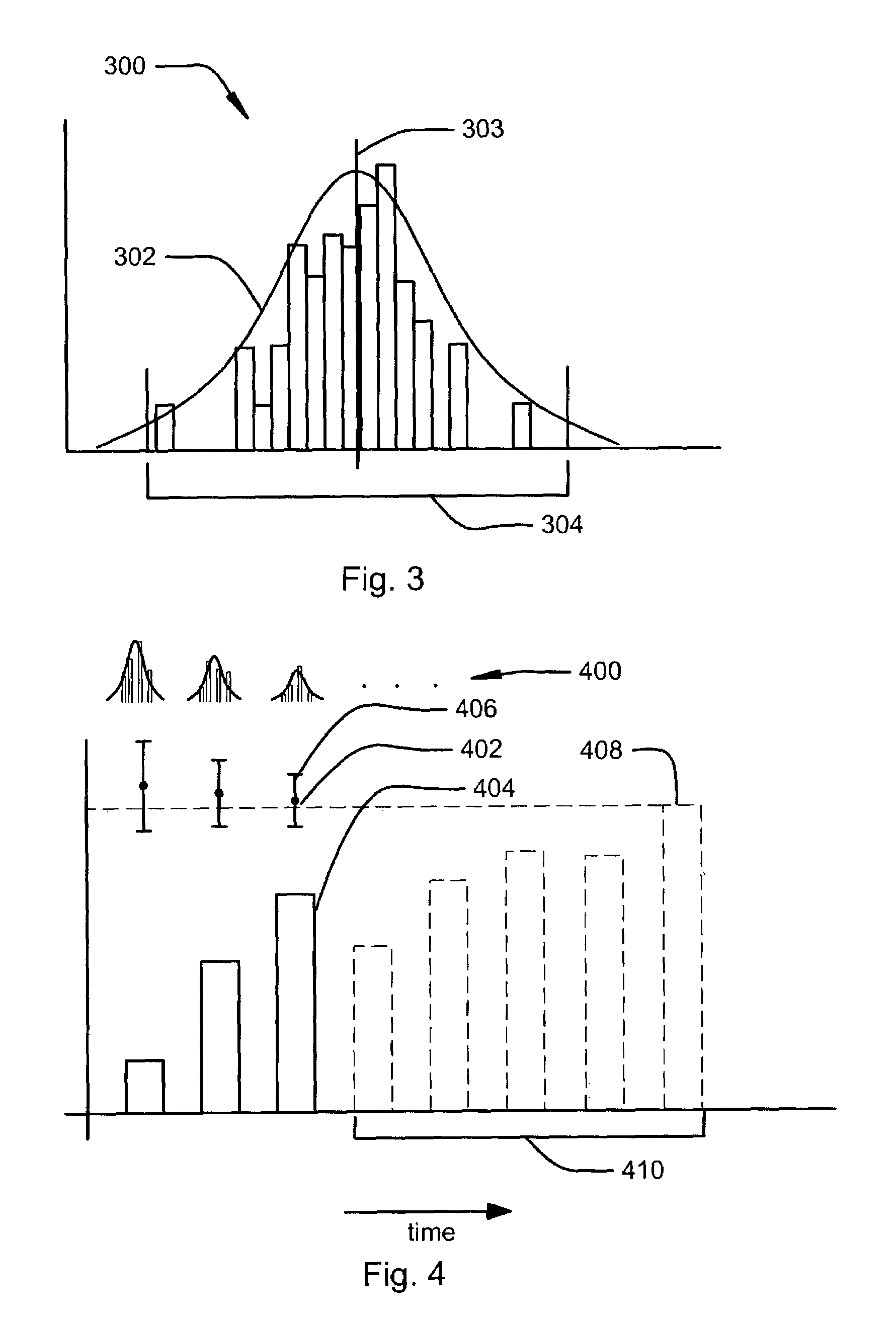
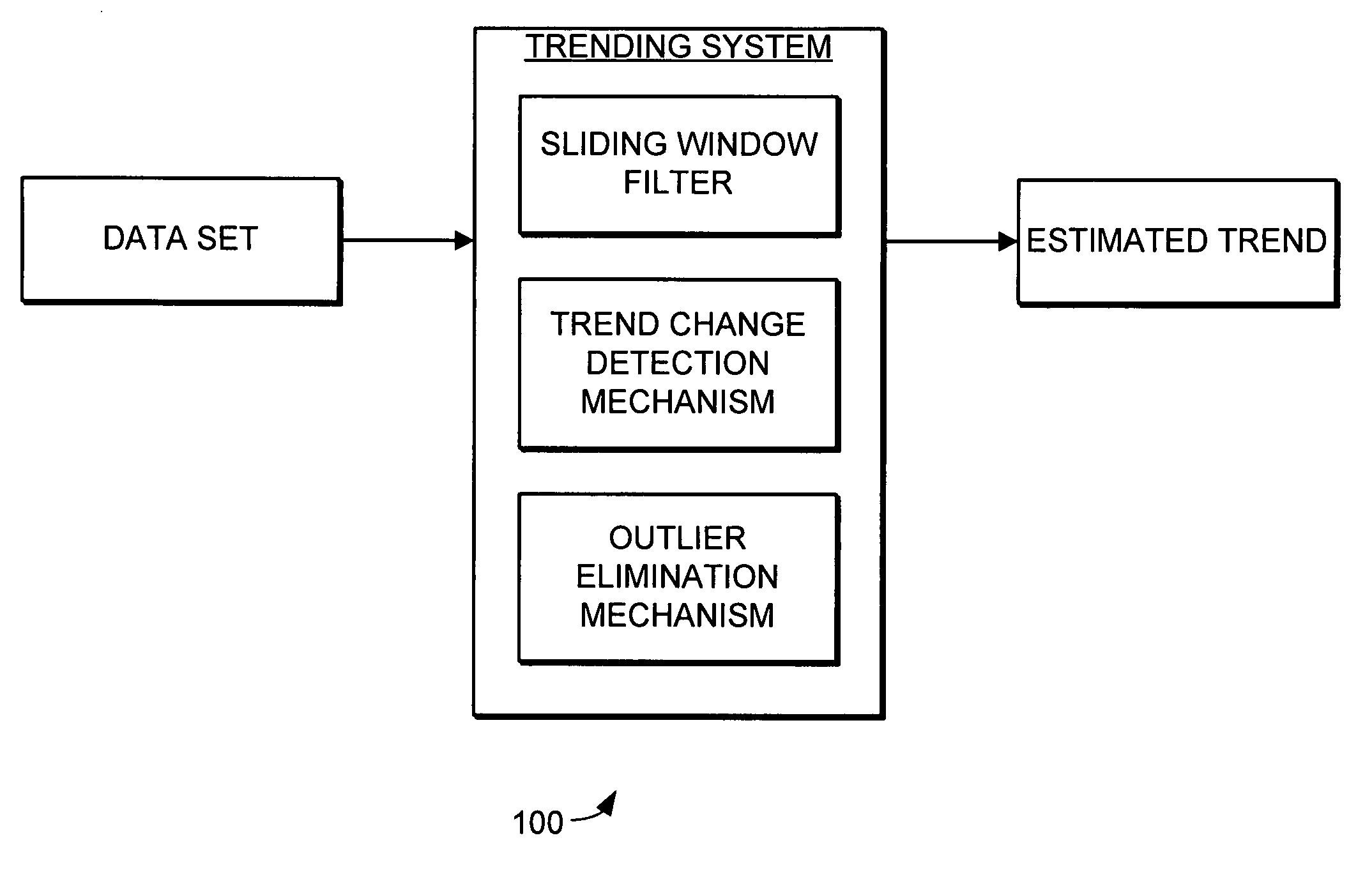
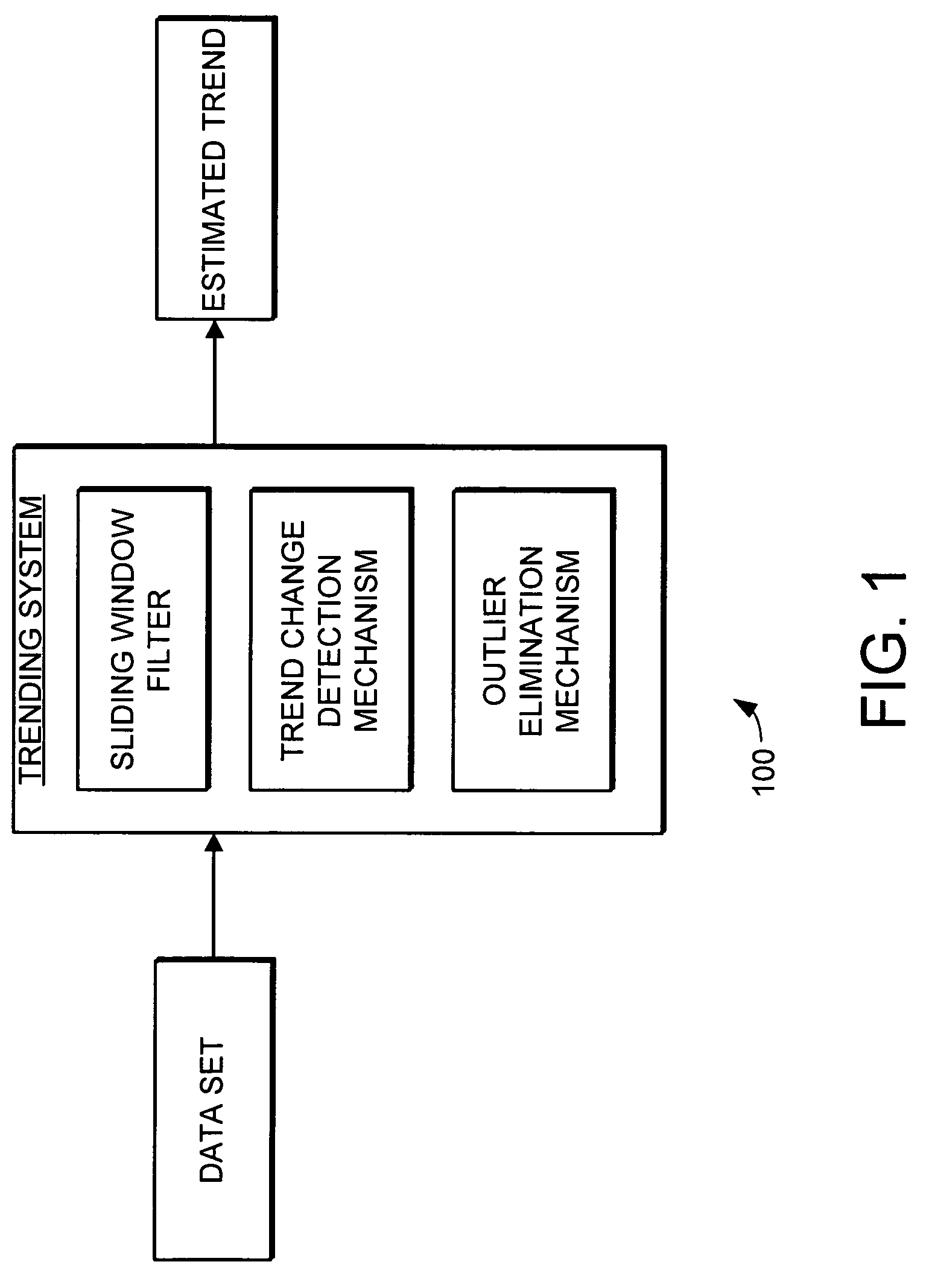
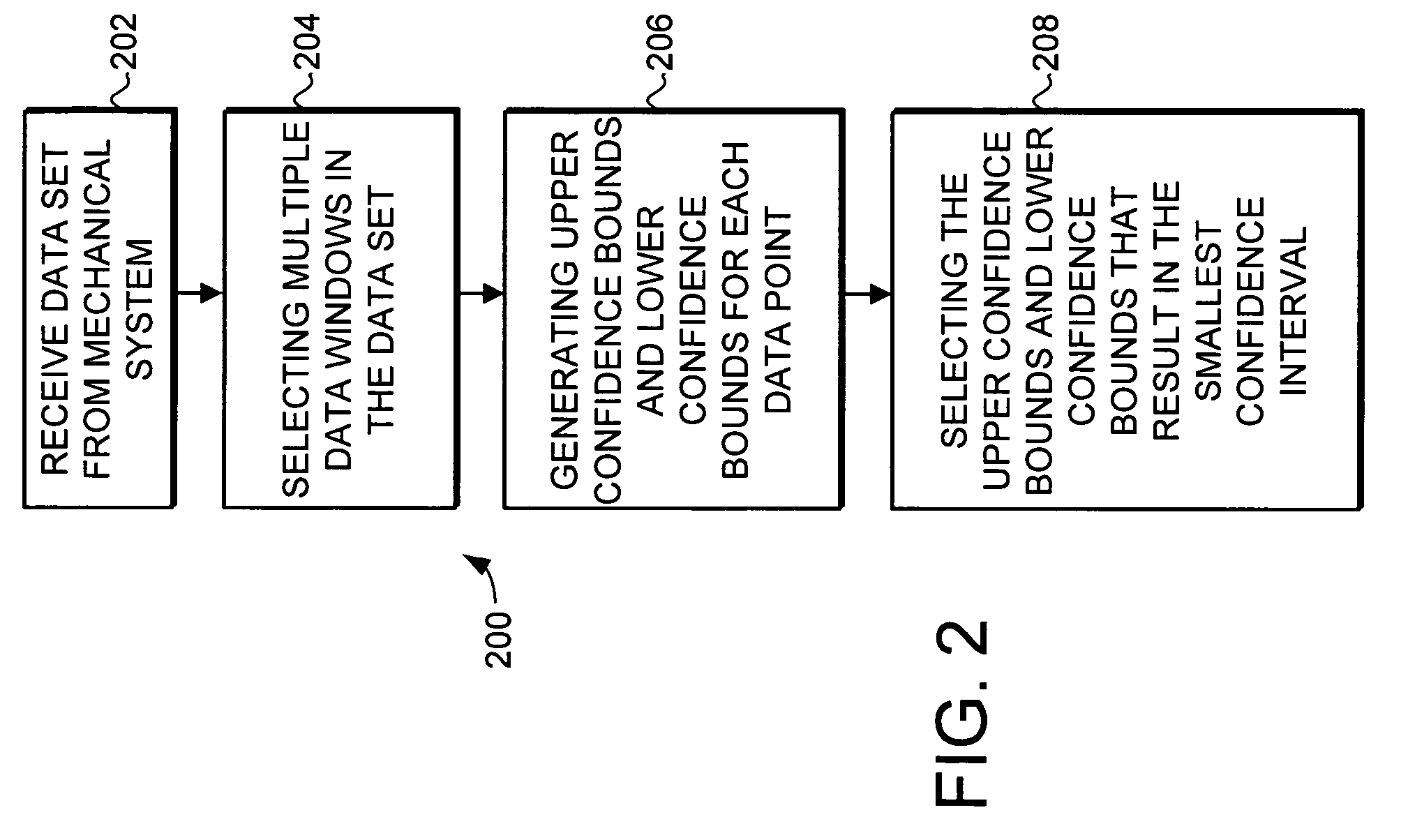
Trending system and method using window filtering
ActiveUS20050165519A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital data processing detailsLower limitData set
A trending system and method for trending data in a mechanical system is provided. The trending system includes a sliding window filter. The sliding window filter receives a data set of data points generated by the mechanical system. The sliding window filter partitions the data set into a plurality of data windows, and uses the data windows to calculate upper and lower confidence bounds for the data set. Specifically, the sliding window filter calculates an upper confidence bounds and lower confidence bounds for each data point using each of the multiple data windows that includes the data point. The sliding window filter then selects the upper confidence bounds and the lower confidence bounds that results in the smallest mean prediction confidence interval for that data point. This results in a smoothed estimated trend for the data set that can be used for prognostication and fault detection.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
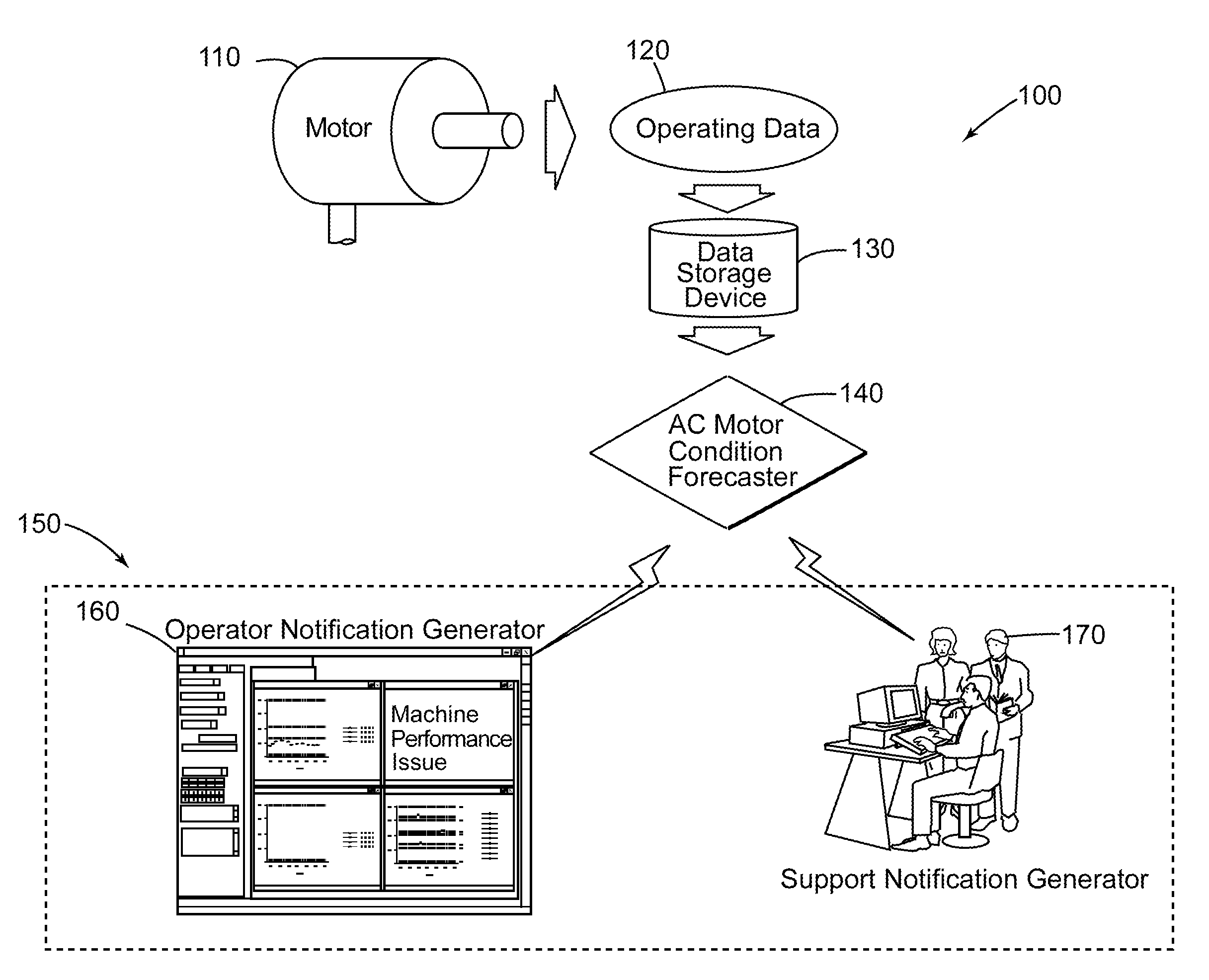
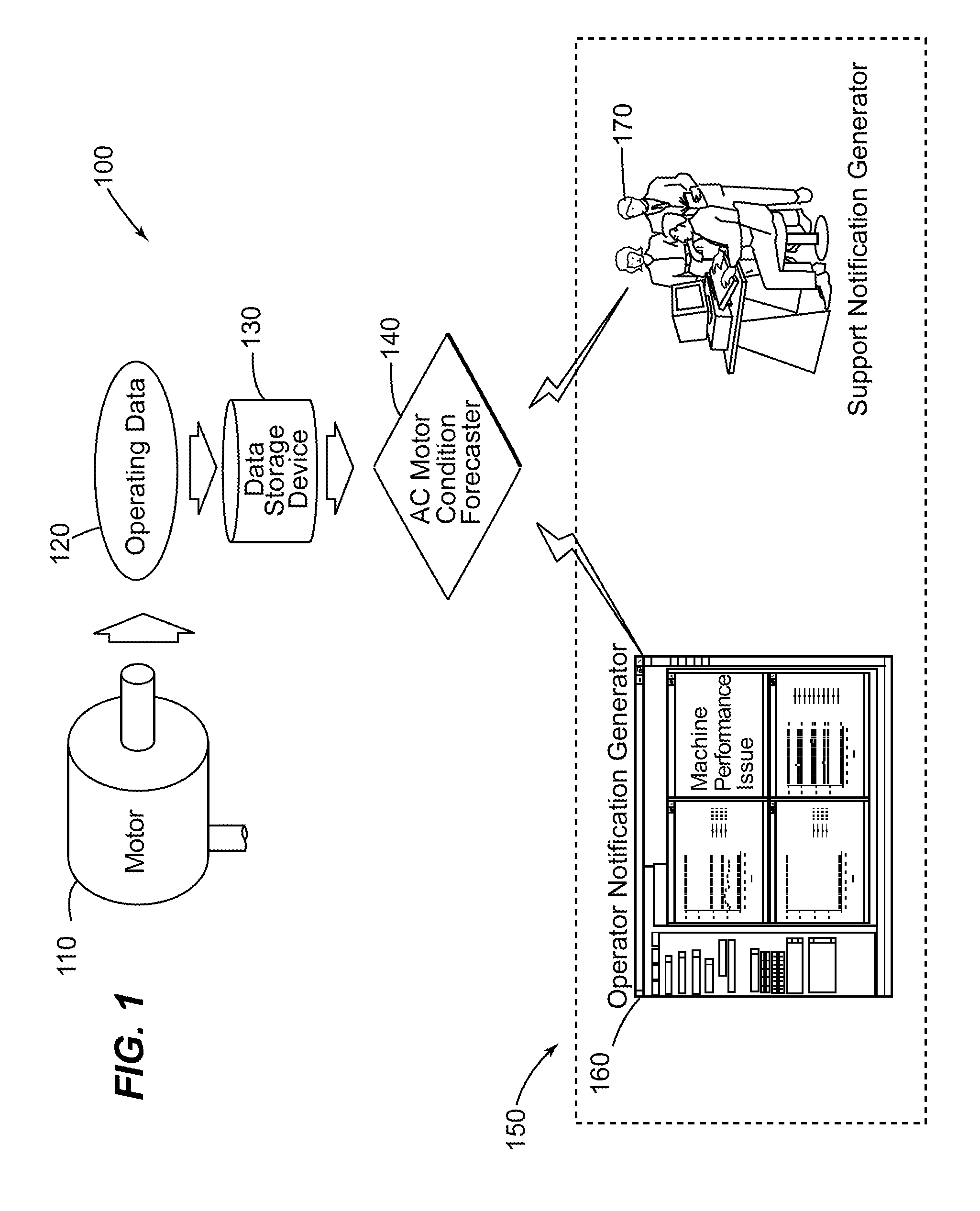
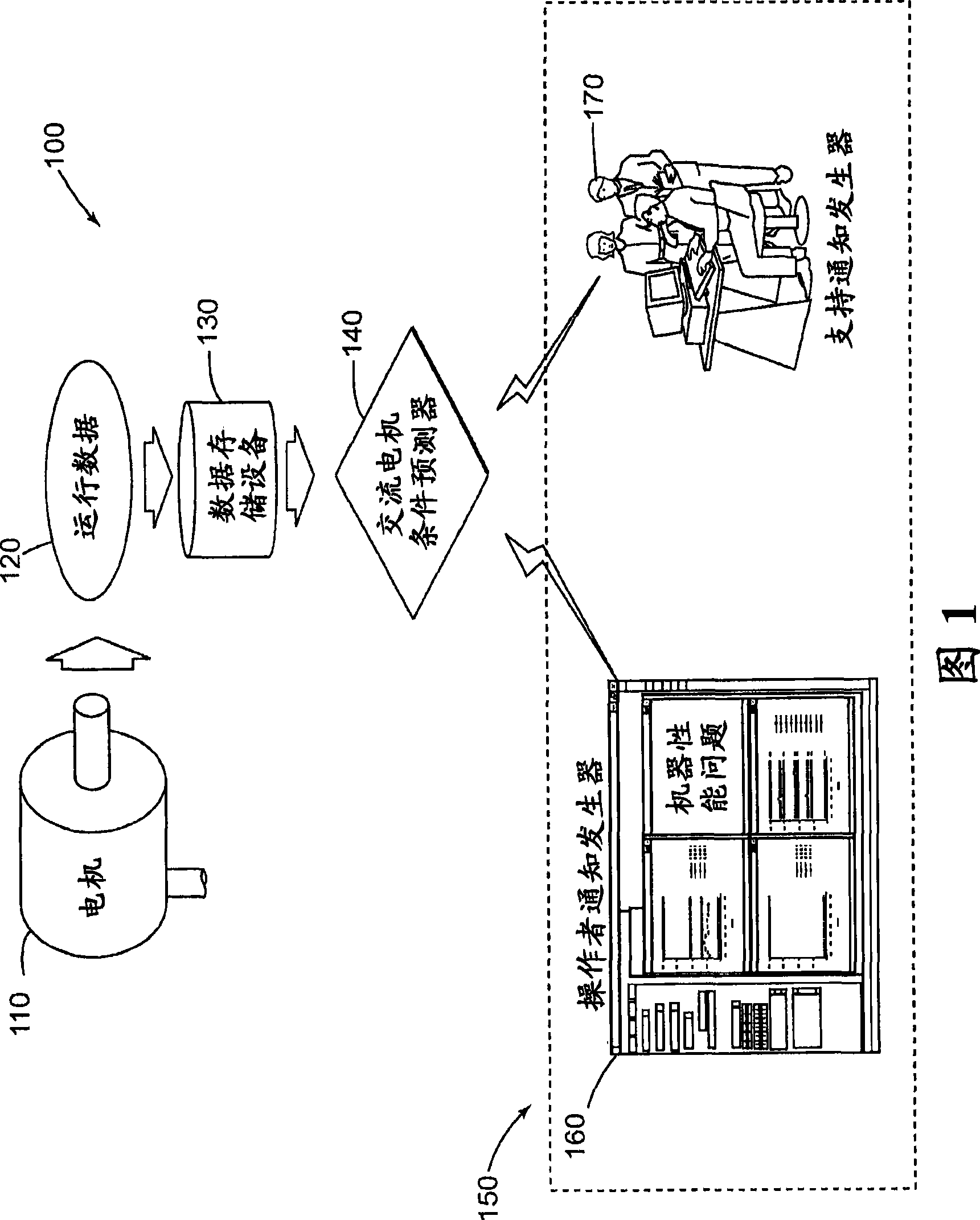
Method and system for remotely predicting the remaining life of an ac motor system
A method and system for remotely predicting the reliability and the remaining time before failure for an AC motor system is provided. The method and system may remotely determine the reliability and a remaining time before failure with a statistical confidence utilizing an AC motor condition forecaster. The method and system may include acquiring historical motor data, obtaining operational data, performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the AC motor system. The method and system may provide at least one notification of an issue with the AC motor system or at least one component of the AC motor system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
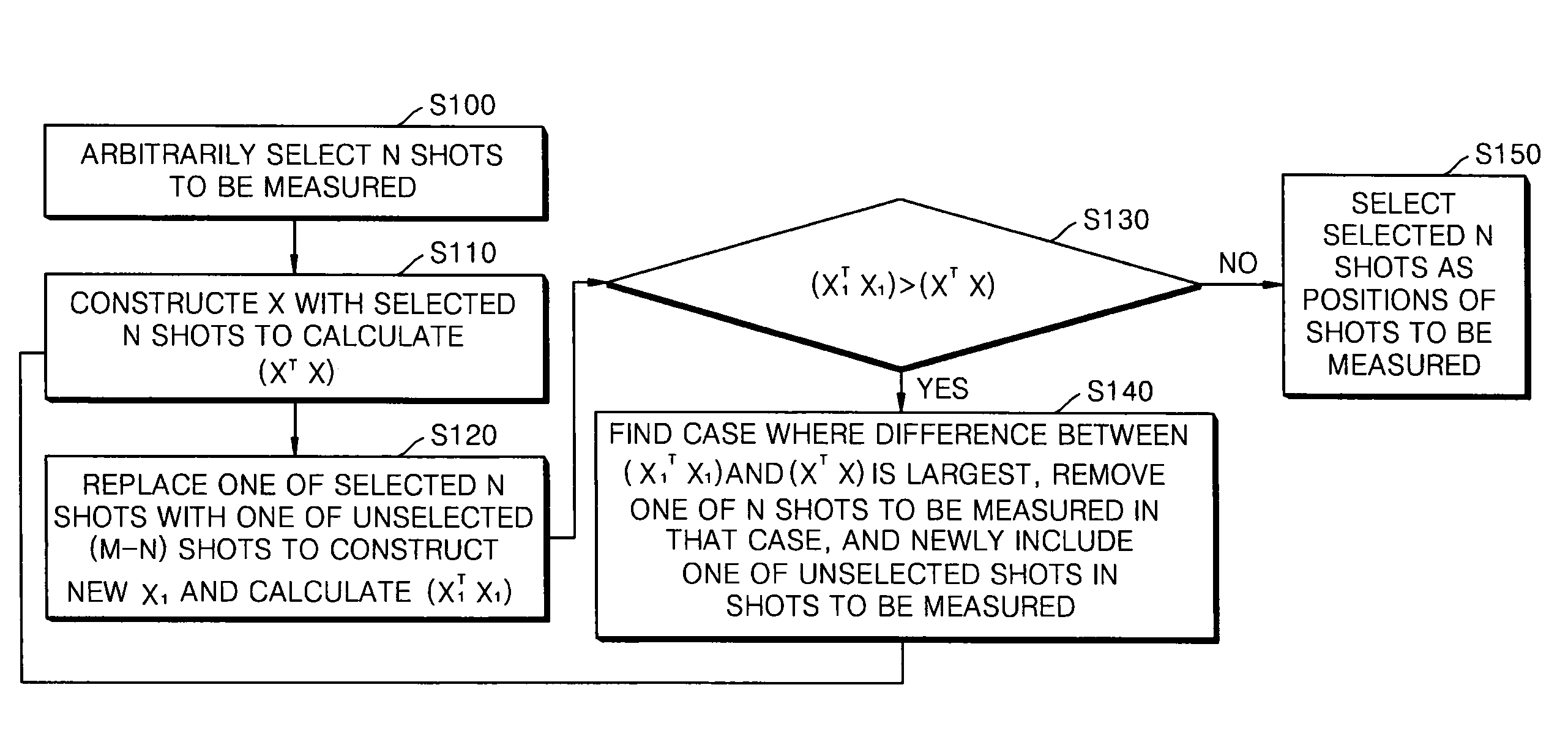
Measurement system for correcting overlay measurement error
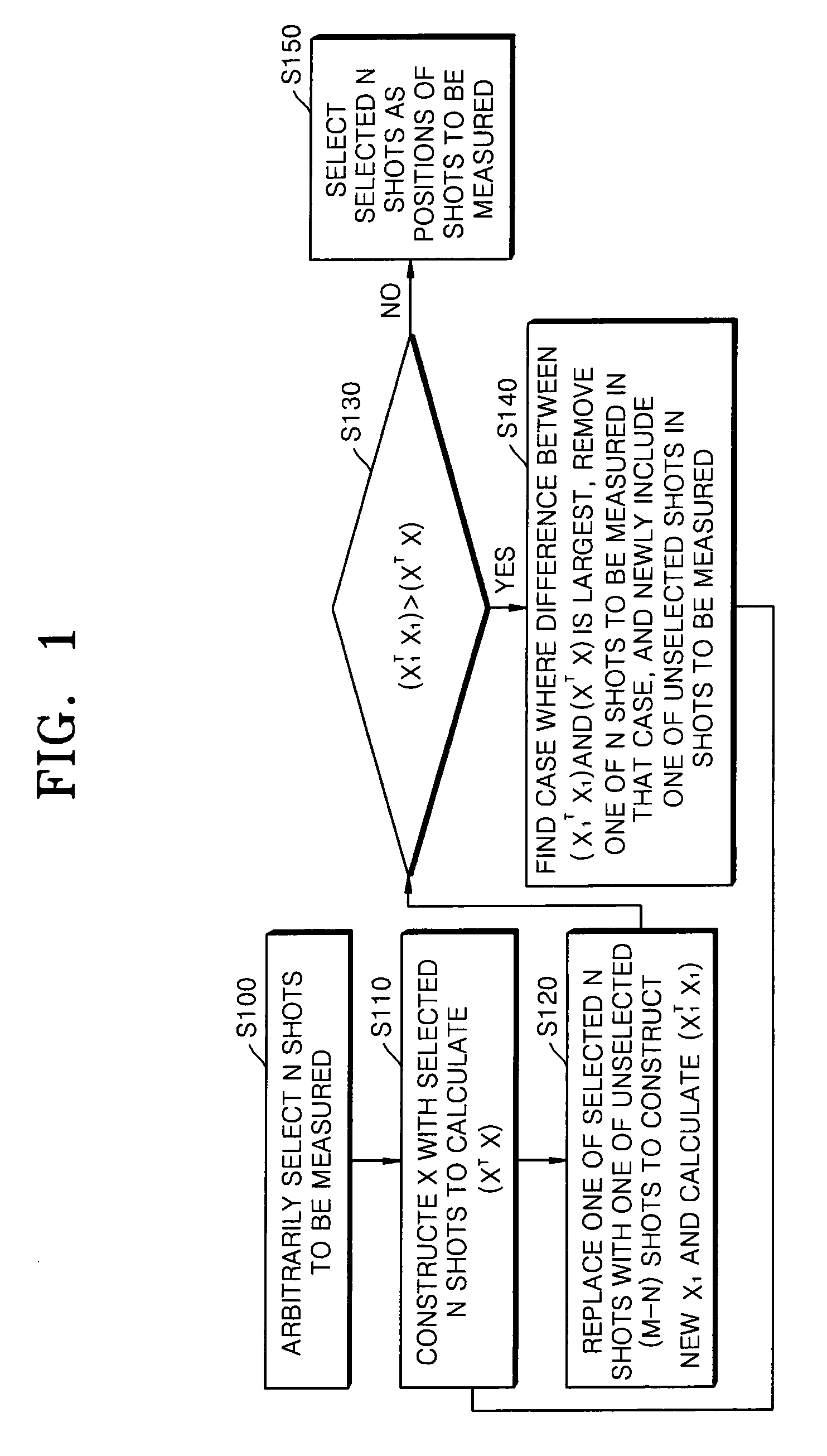
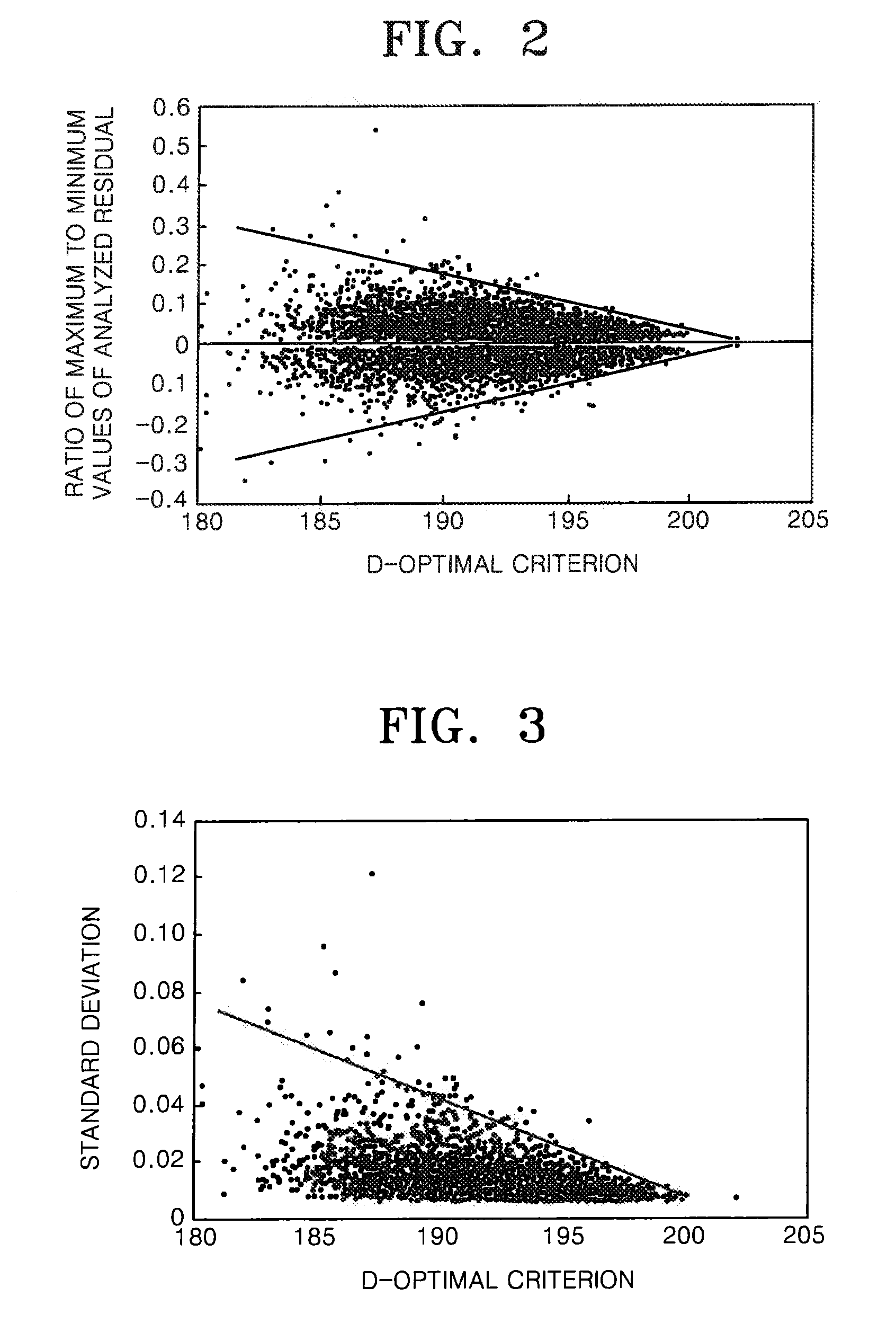
ActiveUS20080228435A1Minimized in sizeError detection/correctionPhotomechanical apparatusMissing dataConfidence interval
A measurement system and a measurement method, which can obtain a measurement value close to a true value considering an overlay measurement error according to a higher order regression analysis model. The measurement system and the measurement method provide a technique for determining optimal positions of shots to be measured using an optimal experimental design. When the regression analysis model and the number of shots to be measured are determined in advance, a method is used for determining an optimal number of shots to be measured according to the regression analysis model and process dispersion using a confidence interval estimating method. A dynamic sampling method is used for dynamically changing the number and positions of shots to be measured according to a change in process features by combining the above two methods. And, when erroneous data is detected, or when measured data is missing, a robust regression analysis method and a technique for filtering the erroneous data and the missing data are used.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
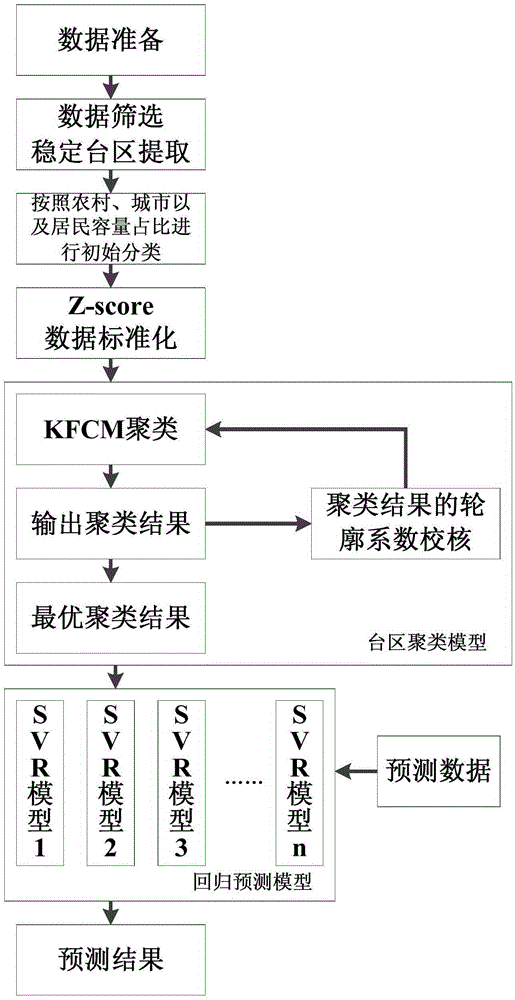
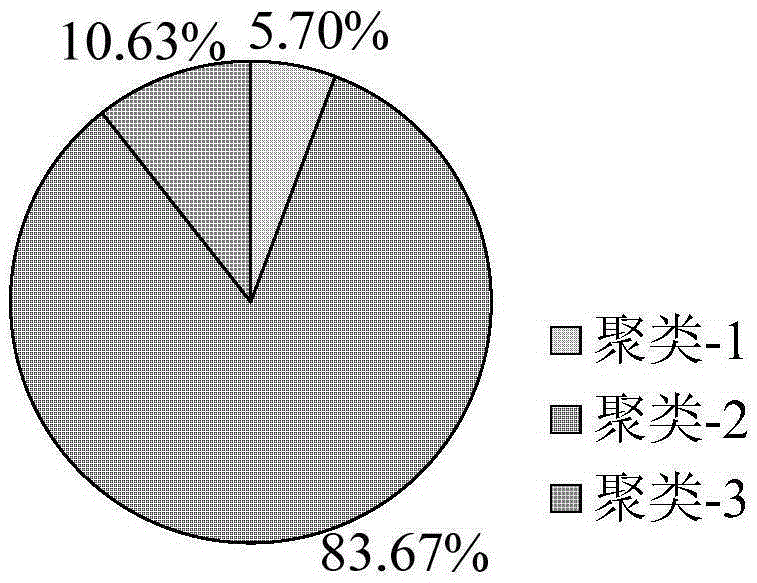
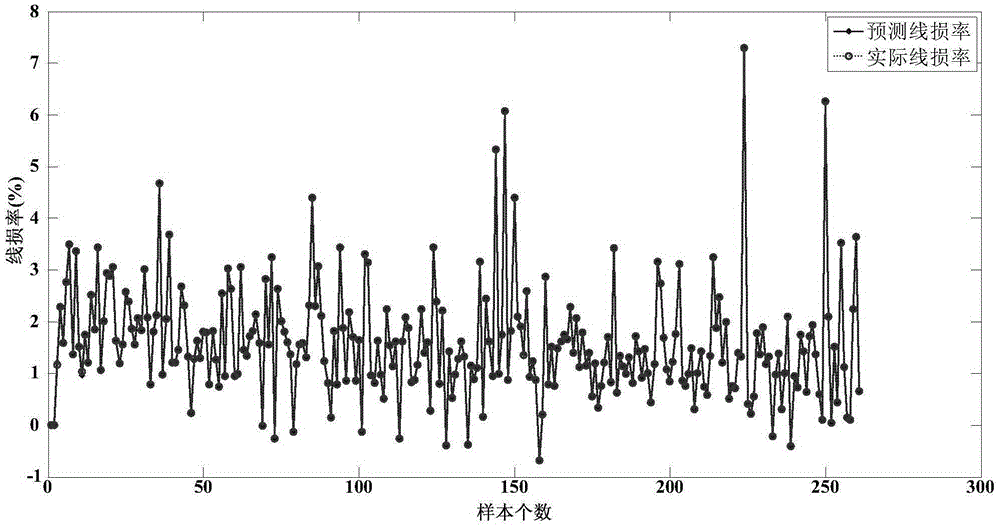
Low-voltage area KFCM-SVR reasonable line loss prediction method
InactiveCN105389636AMeet the requirements of the power systemReasonableForecastingConfidence intervalAlgorithm
The present invention discloses a low-voltage area KFCM-SVR reasonable line loss prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) presorting data samples twice after data screening; 2) clustering six types of data by using fuzzy kernel clustering to obtain a plurality of small types; 3 ) establishing a regression fitting model by virtue of a least squares support vector machine (LS-SVR); 4 ) calculating a residual error confidence interval limit value; 5) classifying to-be-predicted data into each small types according to a Euclidean distance principle; 6) after classification, inputting the to-be-predicted data into each respective corresponding LS-SVR model, and calculating to obtain a prediction residual error; and 7) comparing the prediction residual error with the residual error confidence interval limit value to provide a conclusion. In the low-voltage area KFCM-SVR reasonable line loss prediction method disclosed by the present invention, an algorithm has certain reasonableness under a big data condition, and a computed result of the algorithm can provide relatively reliable guidance for area line loss management of an electric power department, and provide a new idea for reasonable utilization and mining of big data in the current smart power network.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
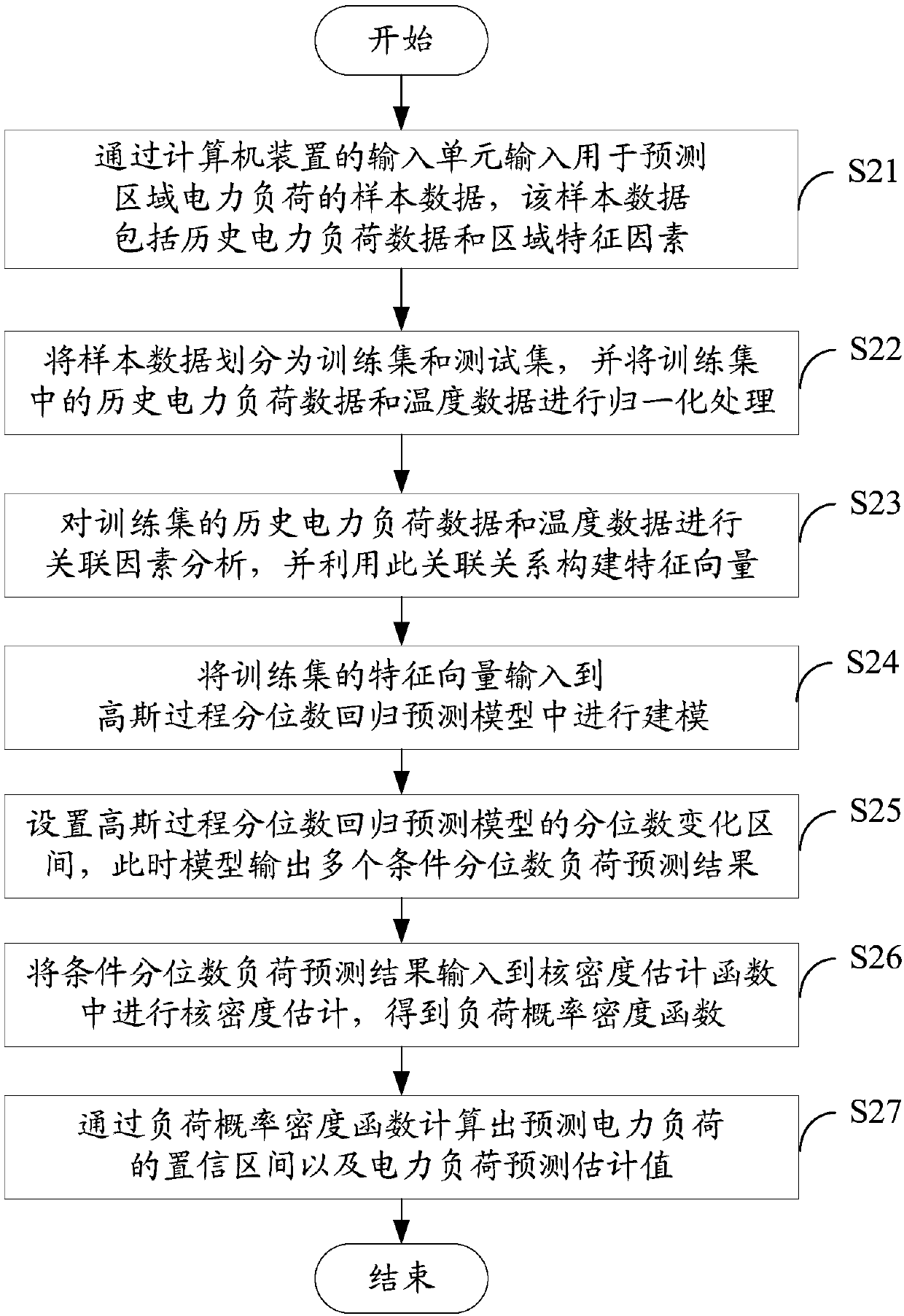
Probabilistic load prediction system and method based on Gaussian process quantile regression model
The invention discloses a probabilistic load prediction system and method based on a Gaussian process quantile regression model. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a sample data set through an input unit; dividing the sample data set into a training set and a test set, and performing normalization processing on historical power load data and temperature data of the training set; performing correlation factor analysis on the historical power load data and the temperature data of the training set to construct a feature vector; inputting the feature vectors into a Gaussian process quantile regression prediction model; setting a quantile change interval of the model, wherein the model outputs a plurality of conditional quantile load prediction results; inputting the conditional quantile load prediction result into a kernel density estimation function for kernel density estimation to obtain a load probability density function; and calculating a load confidence interval anda load prediction estimation value through a load probability density function. According to the method, the confidence interval and probability density of power load prediction can be effectively constructed, and the accuracy of power load prediction is improved.
Owner:X TRIP INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
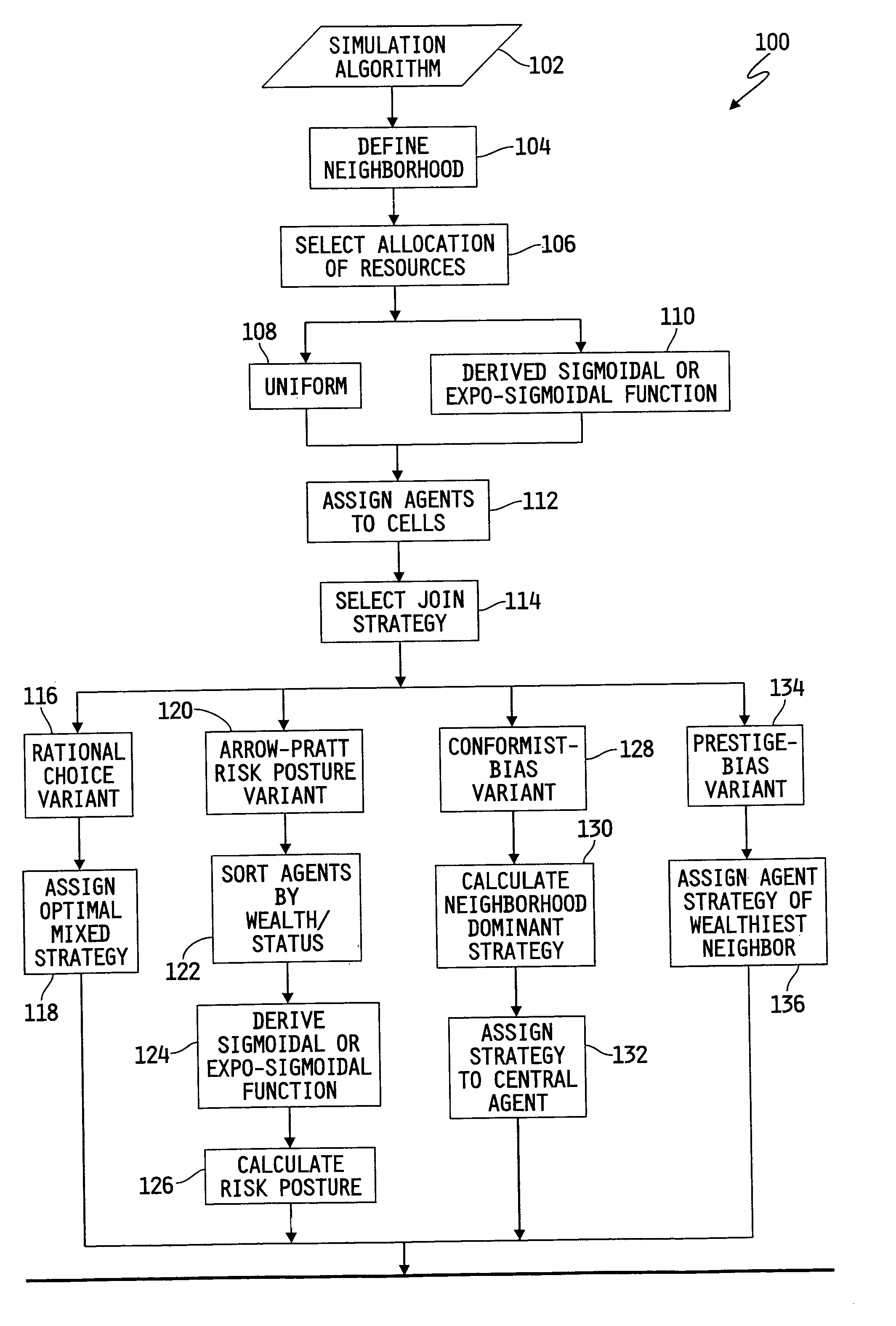
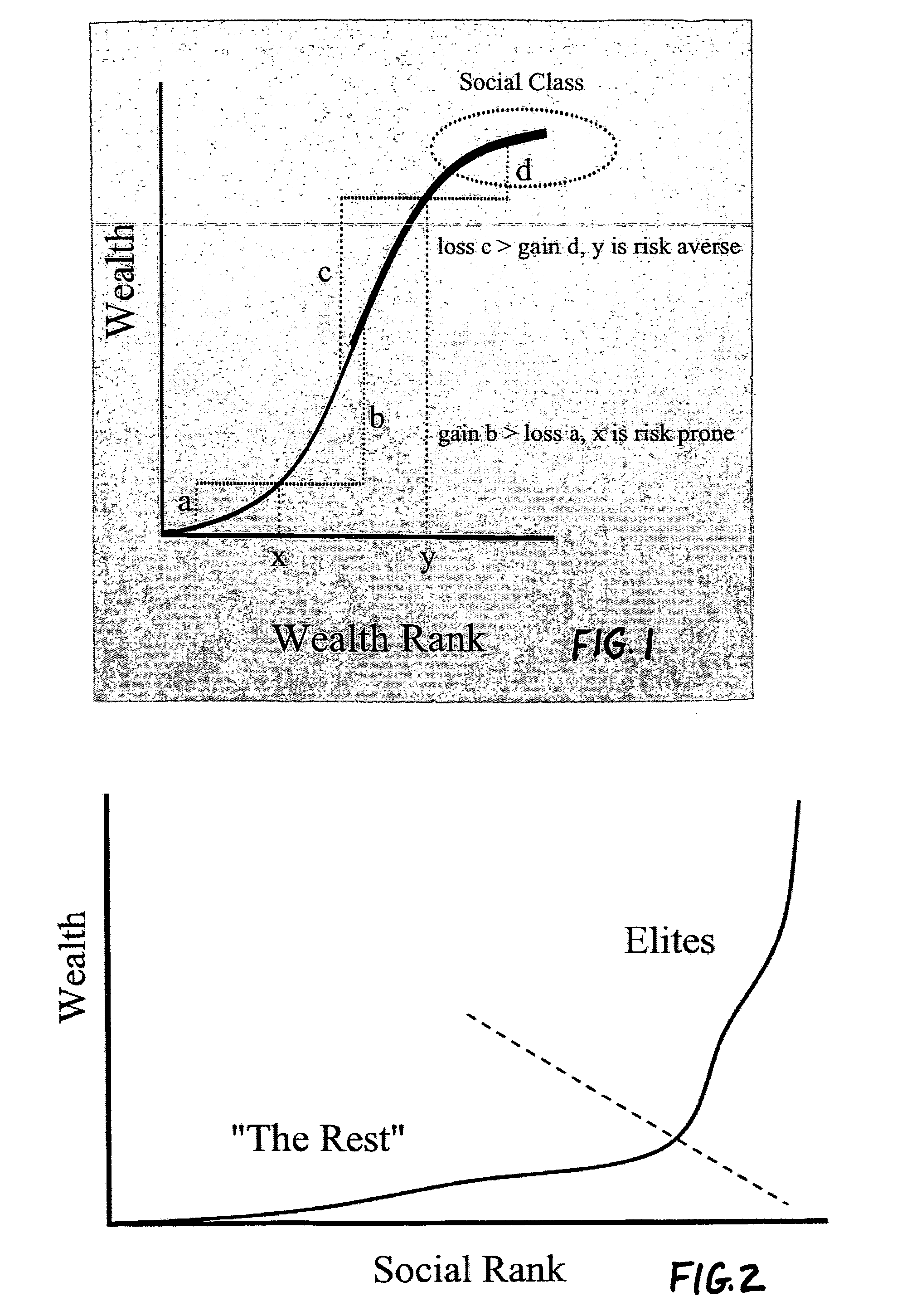
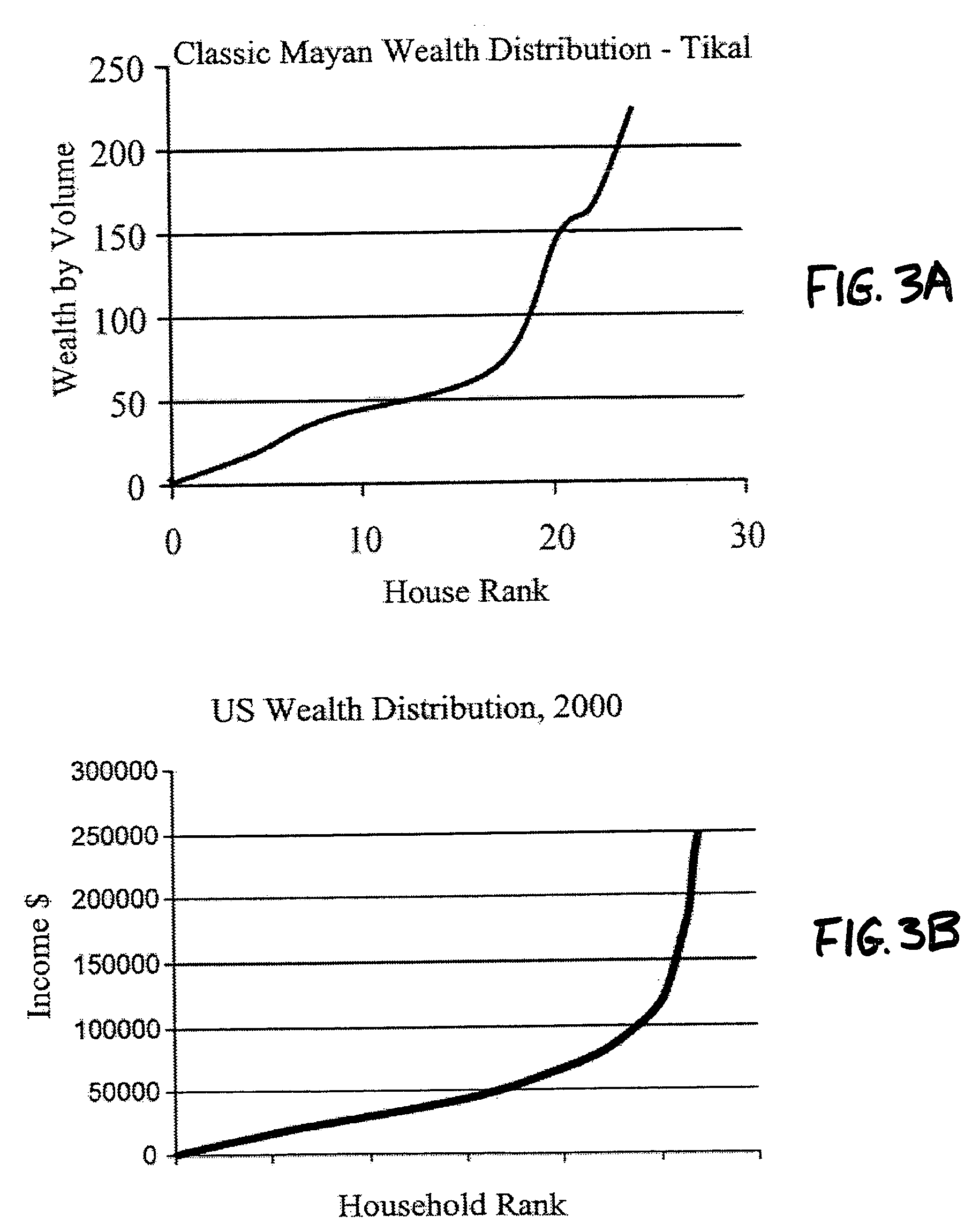
Agent based modeling of risk sensitivity and decision making on coalitions
An agent based model system provides simulation of the influence of environmental variables and tendencies in individual and social decision making relating to the formation of coalitions and ethnic groups. The system is based on improved understandings of human decision making under risk, and incorporates recent theoretical developments and computational tools. The system gives analysts the ability to predict the development of coalitions and ethnic groups, as well as the ability to manage the behavior of individuals in such groups. The model results provide confidence intervals for various possible scenarios in a mix of agents' decision rules and distribution of environmental resources. Applications include management of ethnic groups and violent conditions in unstable nations, the tracking of terrorist organizations, development of coalitions and oligopolies in business, and the modeling and interdiction of criminal organizations.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for analyzing measurements
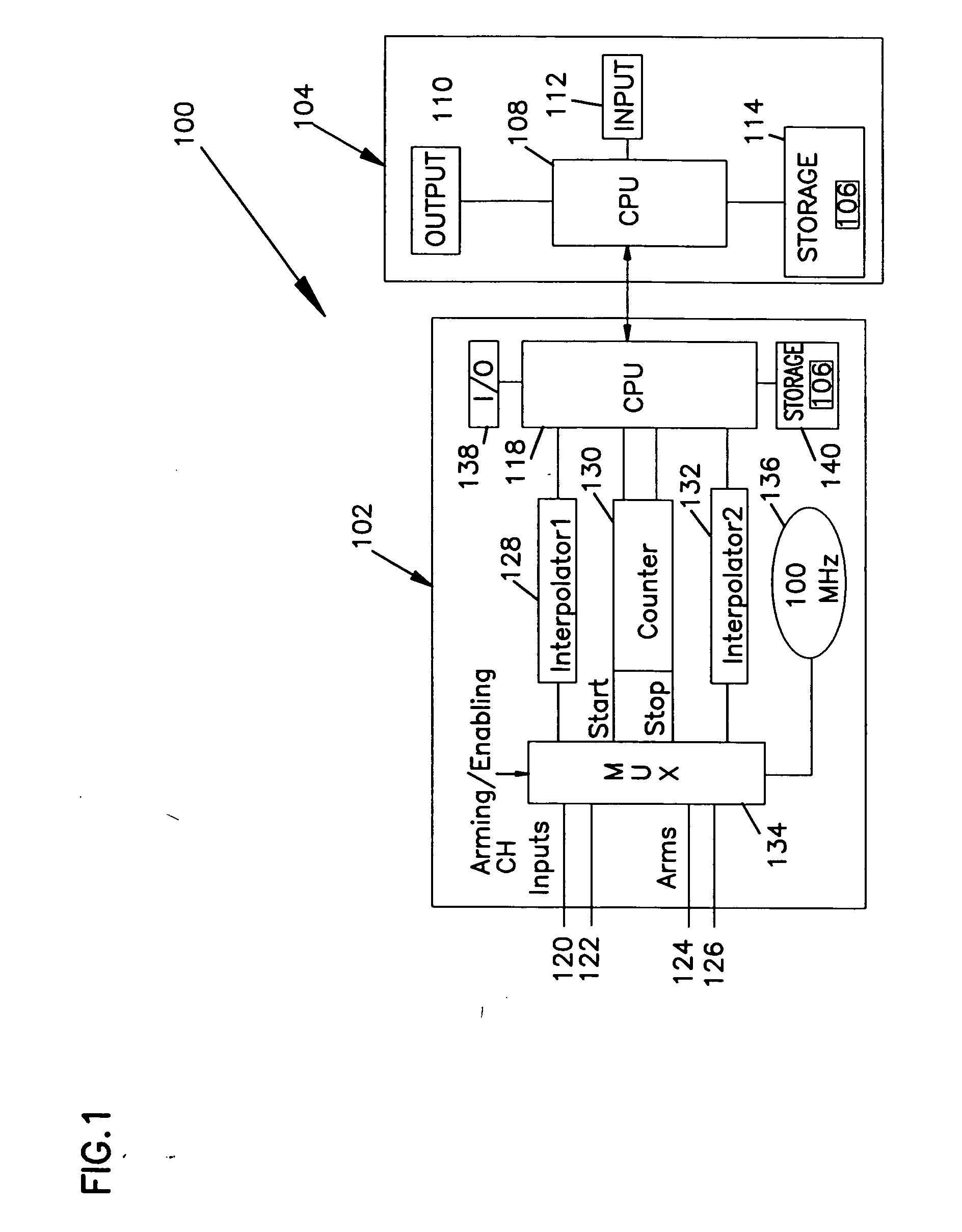
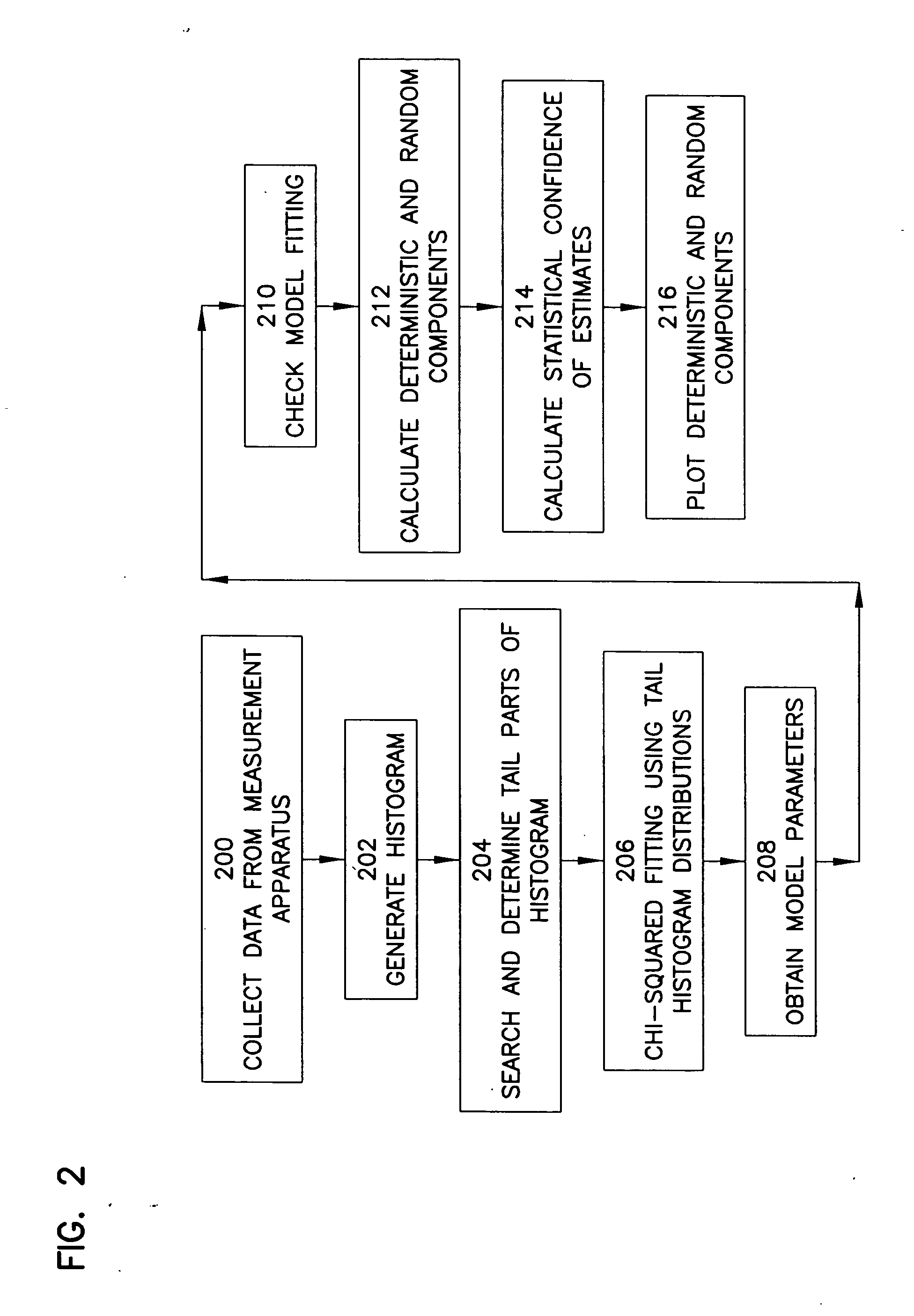
InactiveUS20050027477A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement deviceStatistical Confidence
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for analyzing measurements. The invention provides a method for separating and analyzing the components of a distribution, such as deterministic and random components. The method performs the steps of collecting data from a measurement apparatus, constructing a histogram based on the data such that the histogram defines a distribution, fitting tails regions wherein deterministic and random components and associated statistical confidence levels are estimated.
Owner:WAVECREST
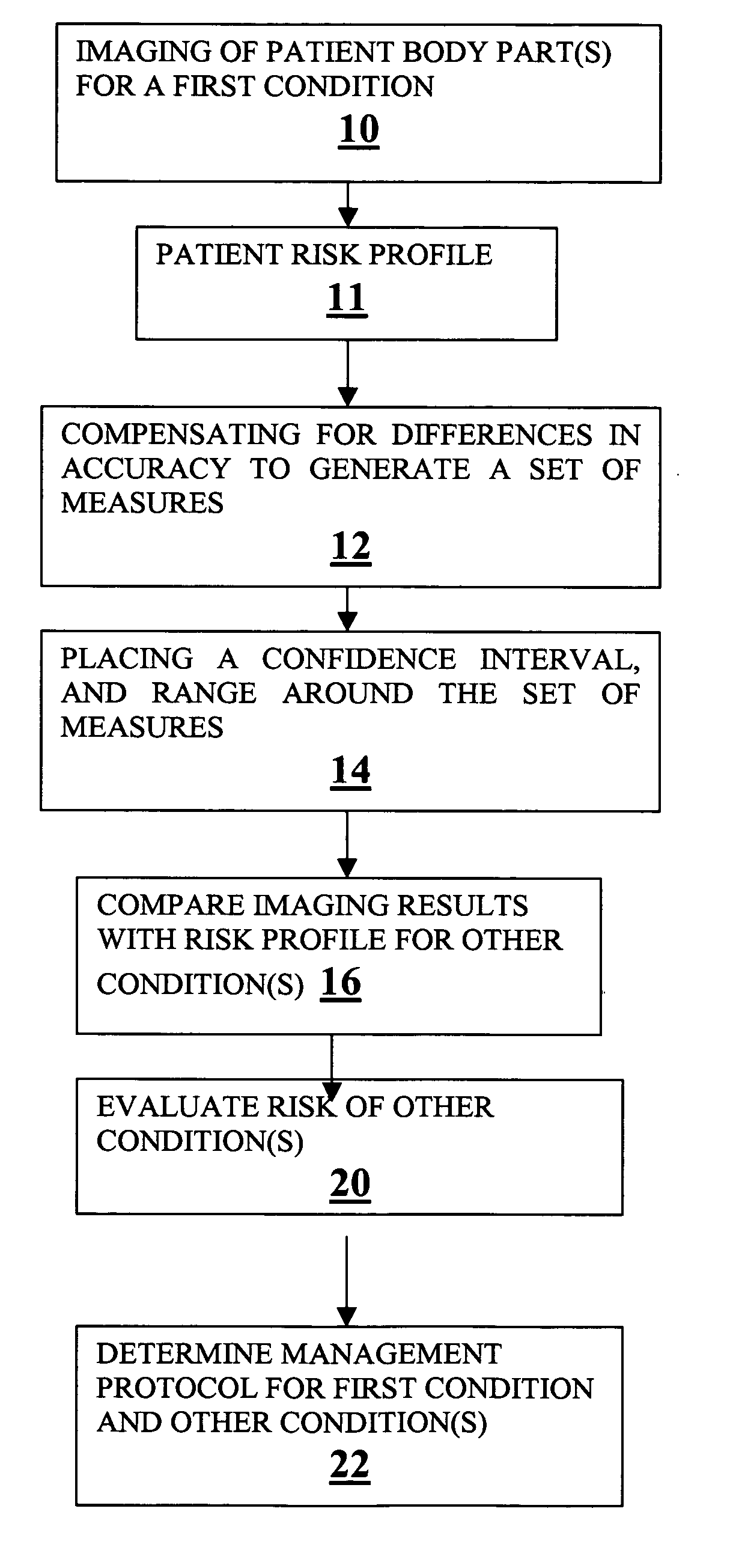
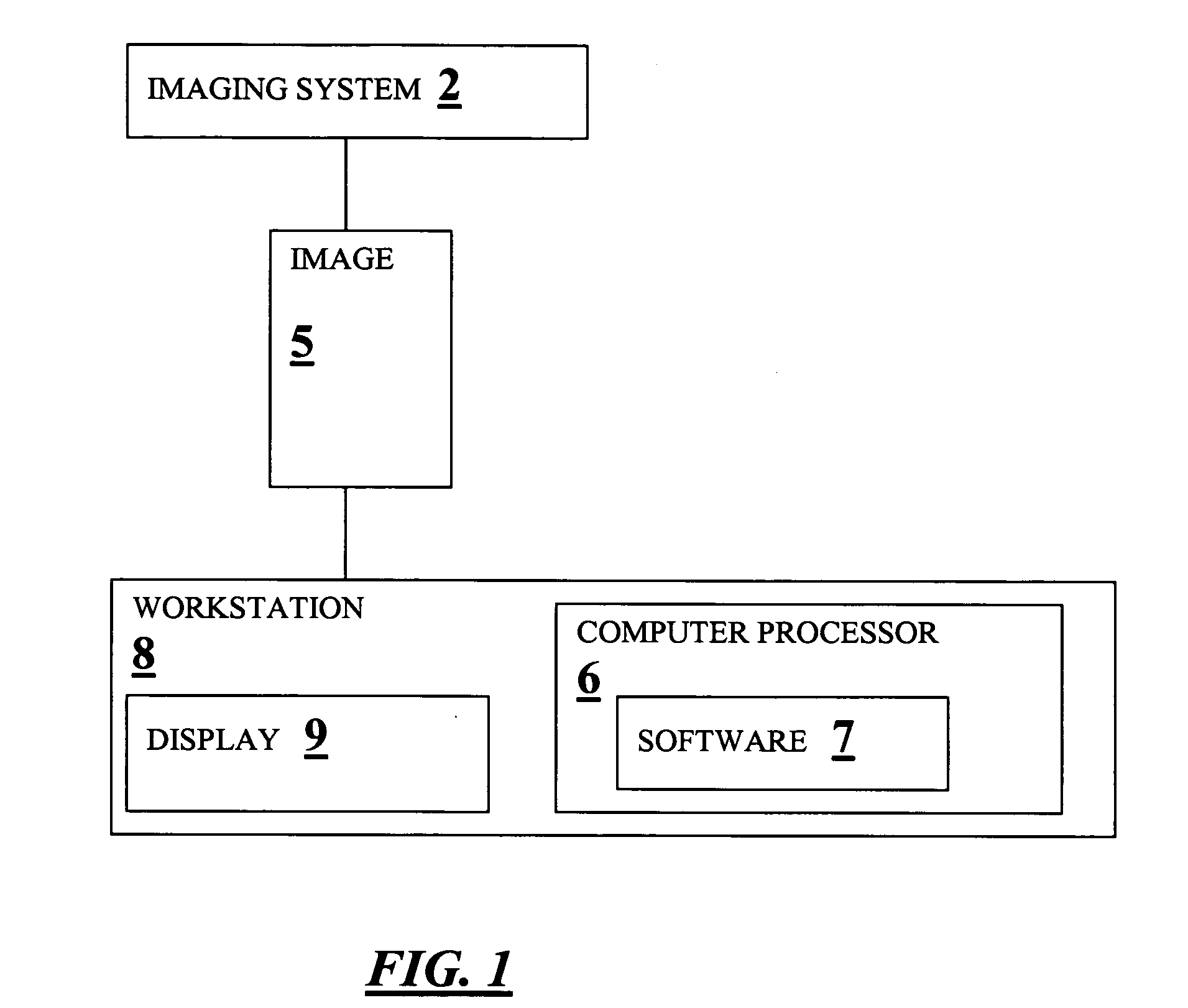
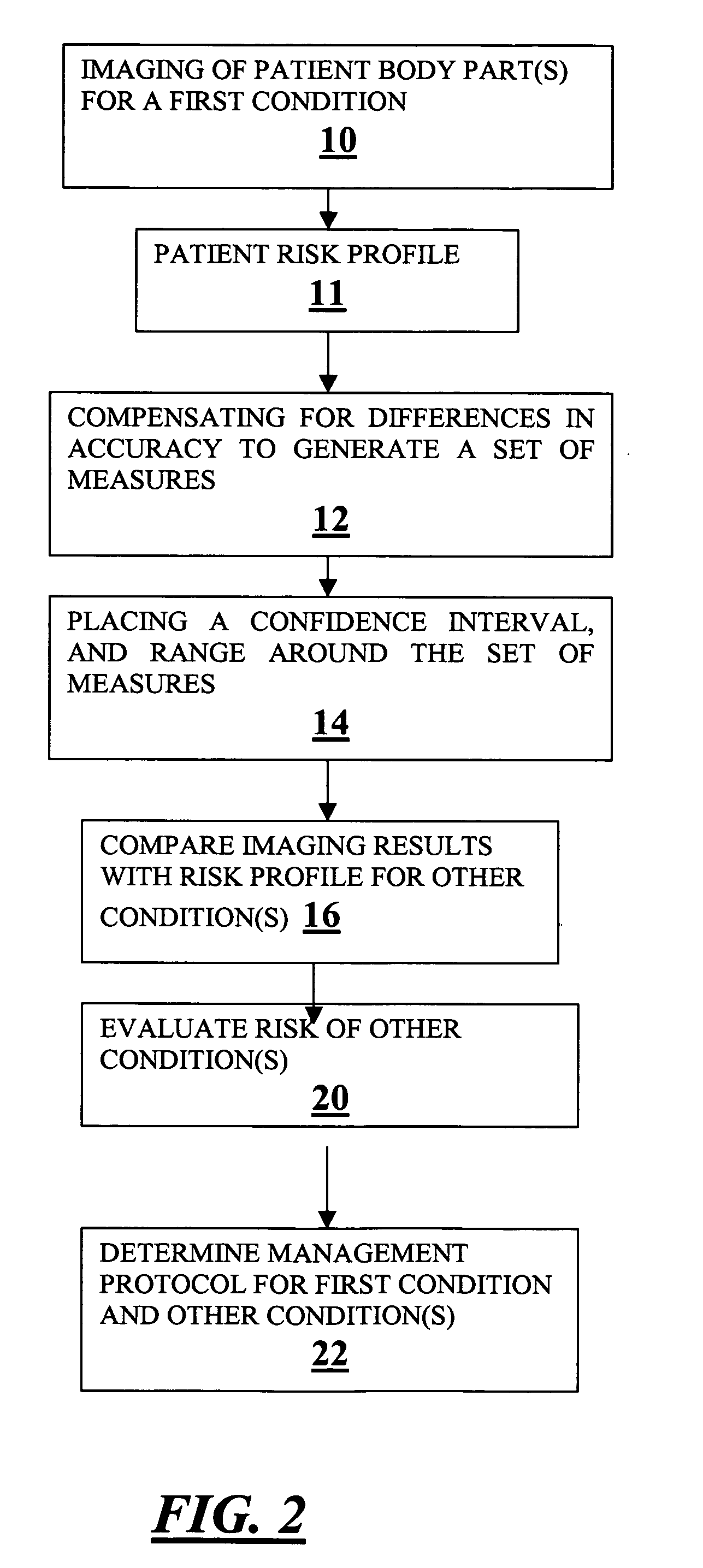
Method for expanding the domain of imaging software in a diagnostic work-up
A method for expanding the domain of imaging software in a diagnostic work-up includes the steps of: imaging a patient's body parts for a first condition using a first imaging technique directed to a first condition; acquiring known patient risk factors indicating a second condition; compensating for differences in accuracy between a first imaging technique directed to a first condition, and a second imaging technique directed to testing for the second condition to generate a set of measures; placing a range and confidence interval around the set of measures; and evaluating for a second condition using the set of measures and known patient risk factors.
Owner:YANKELEVITZ DAVID DR +1
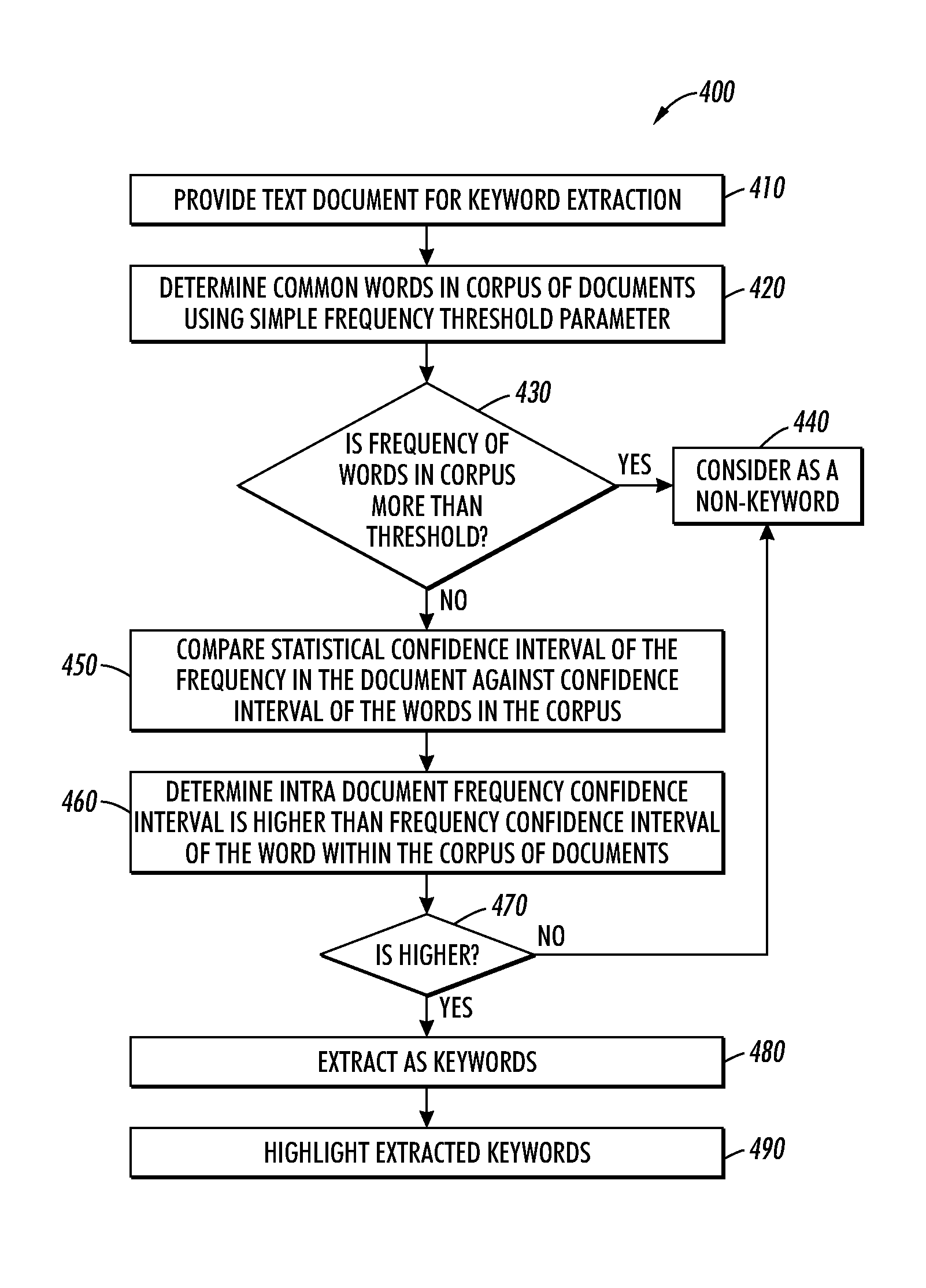
Frequency based keyword extraction method and system using a statistical measure
InactiveUS20100005083A1Avoid frequency quantization problemAvoid problemsDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHypothesisConfidence interval
Frequency based keyword extraction method and system utilizing a statistical measure is disclosed which generates keywords within a page and / or document that can distinguish the document from an average document. A simple frequency threshold parameter can be utilized to determine a number of common stop words if a word in the document possesses a frequency in a corpus that is more than the threshold parameter. A statistical confidence interval of the frequency in the document can be compared against a frequency confidence interval of the word in the corpus. The extracted keyword possesses a greater intra-document frequency confidence interval than the frequency confidence interval of the word within the corpus. A statistical hypothesis test can also be utilized to determine the keyword by calculating a test statistic and testing whether the test statistic is greater than some threshold.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for monitoring the operation of a wind energy plant and wind energy plant
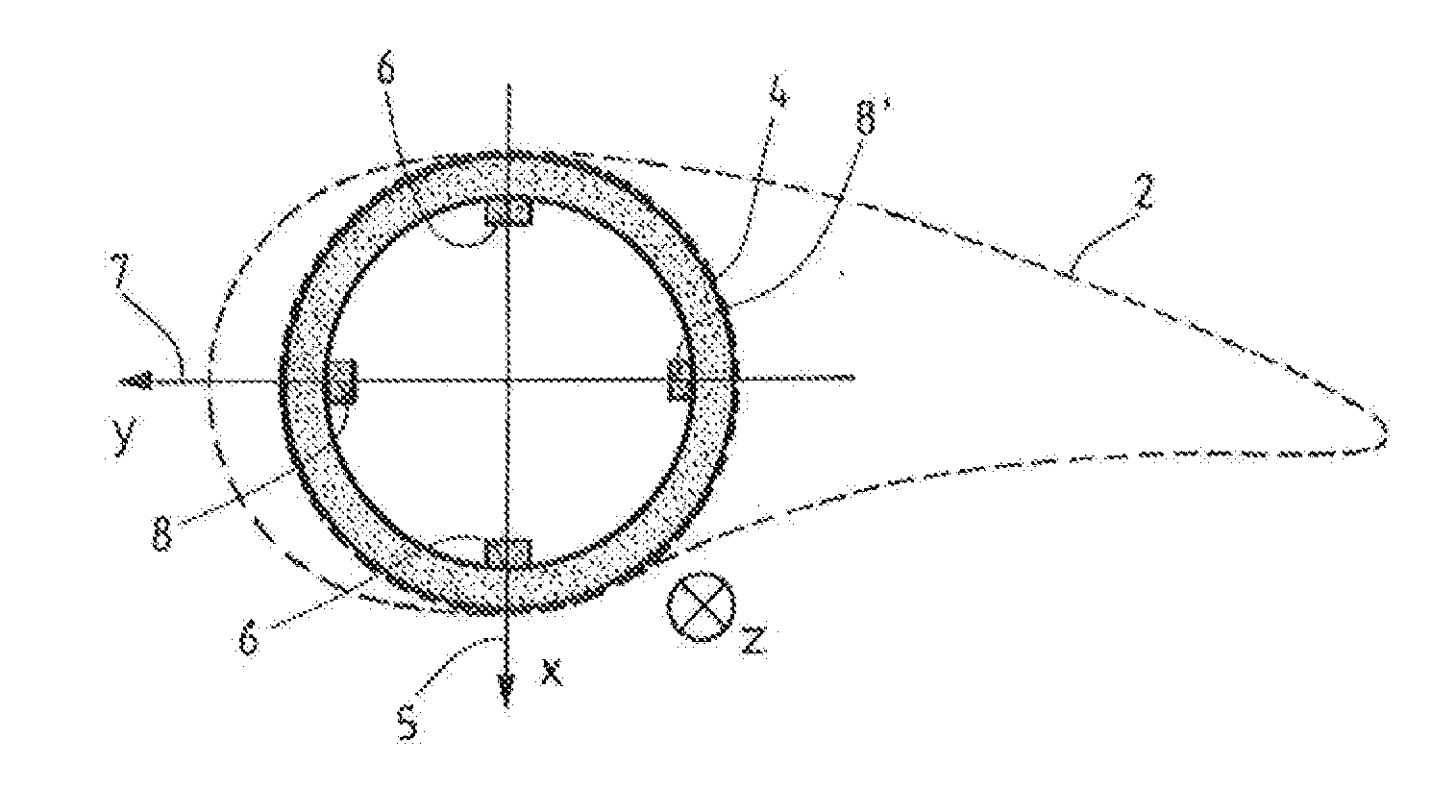
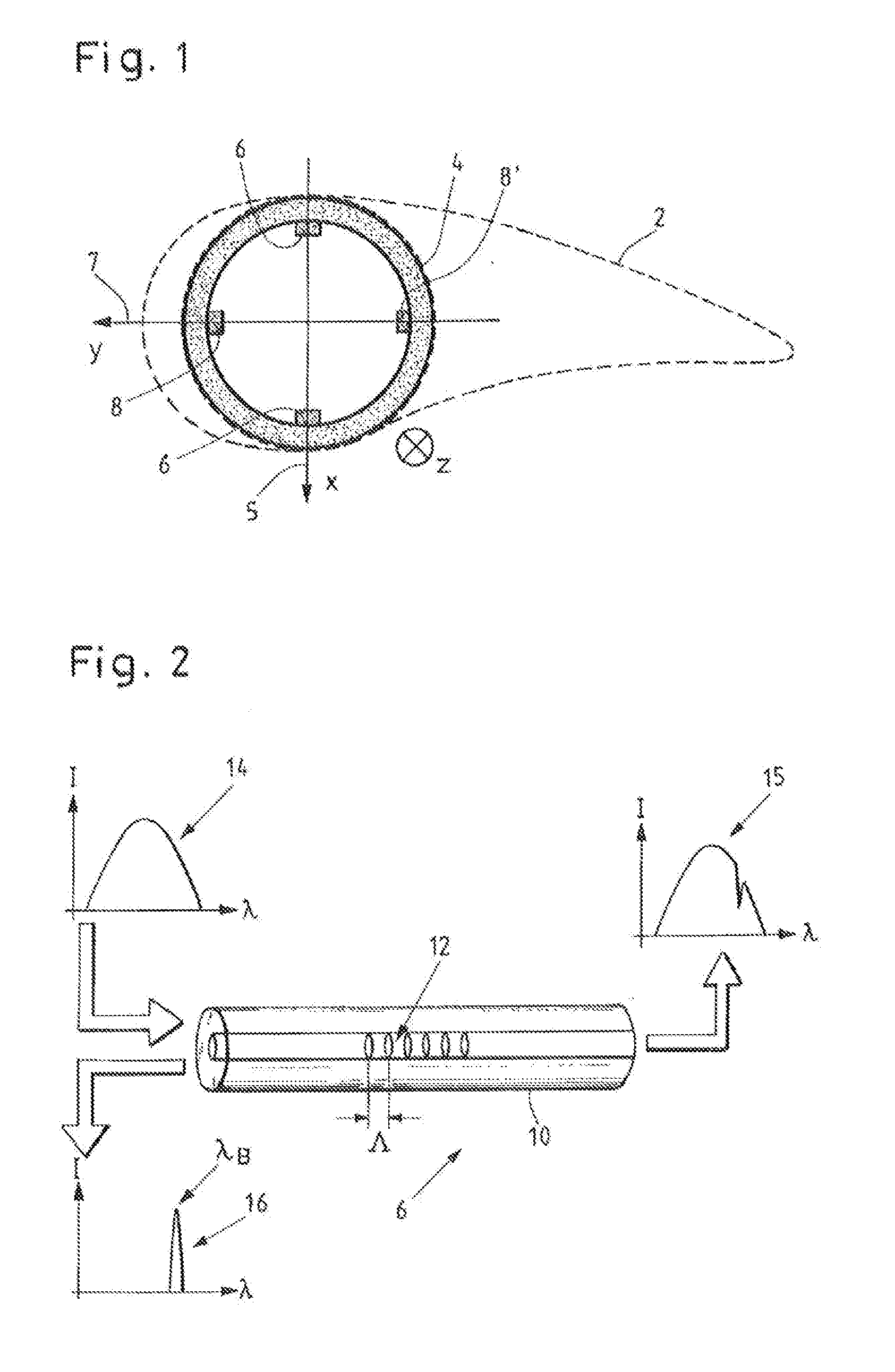
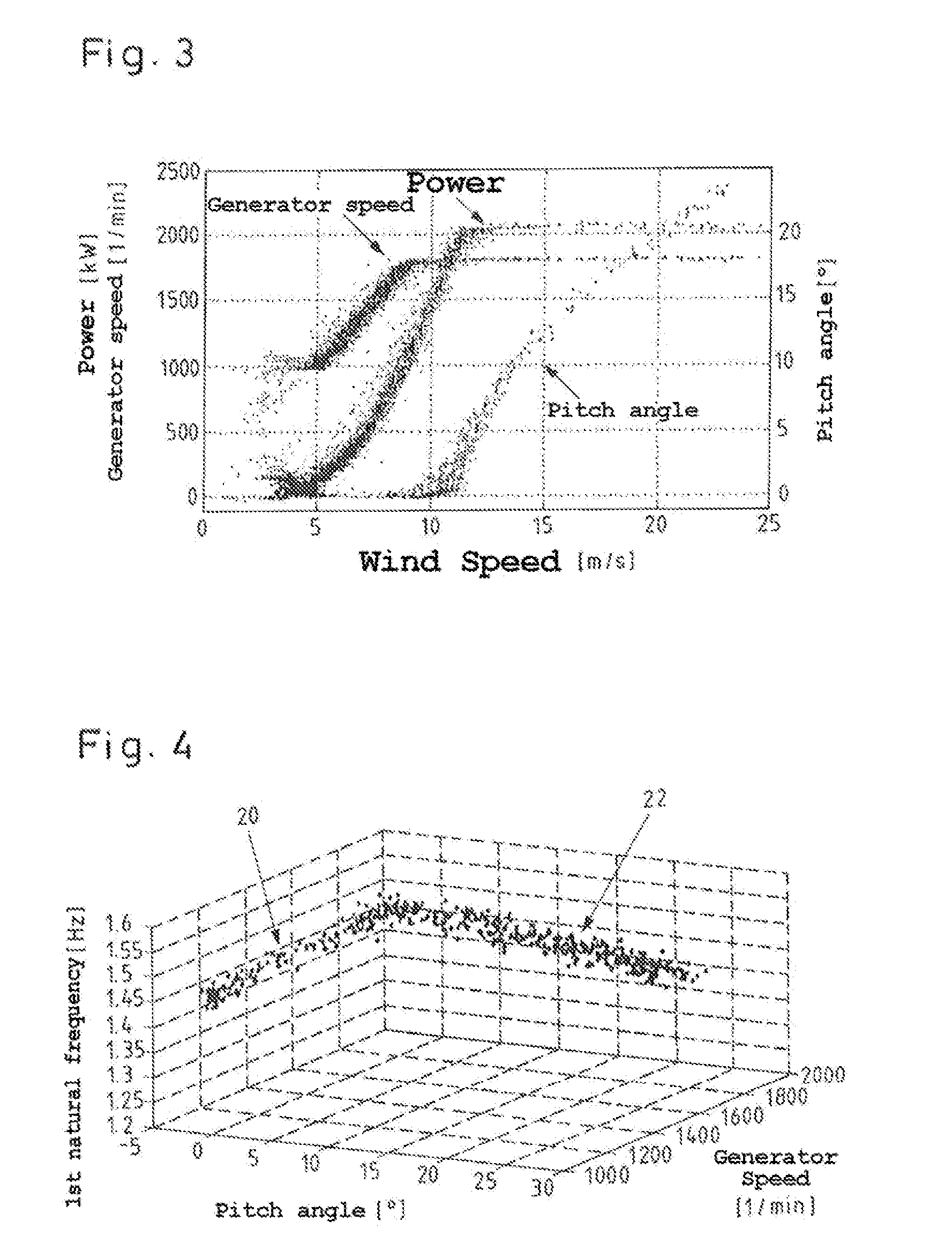
ActiveUS20150345467A1Function increaseConvenient statisticsWind motor controlEngine fuctionsEngineeringStatistical Confidence
A method for monitoring the operation of a wind energy plant having at least one blade angle adjustable rotor blade. Rotor blade vibrations are registered during operation by at least one measuring device, and at least one current natural frequency is established from the registered vibrations. At least one environmental parameter and / or at least one operational parameter, which influence the natural frequency of the rotor blade, is or are additionally registered. At least one natural frequency expected value dependent on the additionally registered parameter(s) and at least one confidence interval are calculated for the at least one established current natural frequency of the rotor blade, and whether the established current natural frequency lies within, or outside of, the confidence interval around the natural frequency expected value is monitored. Also disclosed is an operational control apparatus of a wind energy plant and a corresponding wind energy plant.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
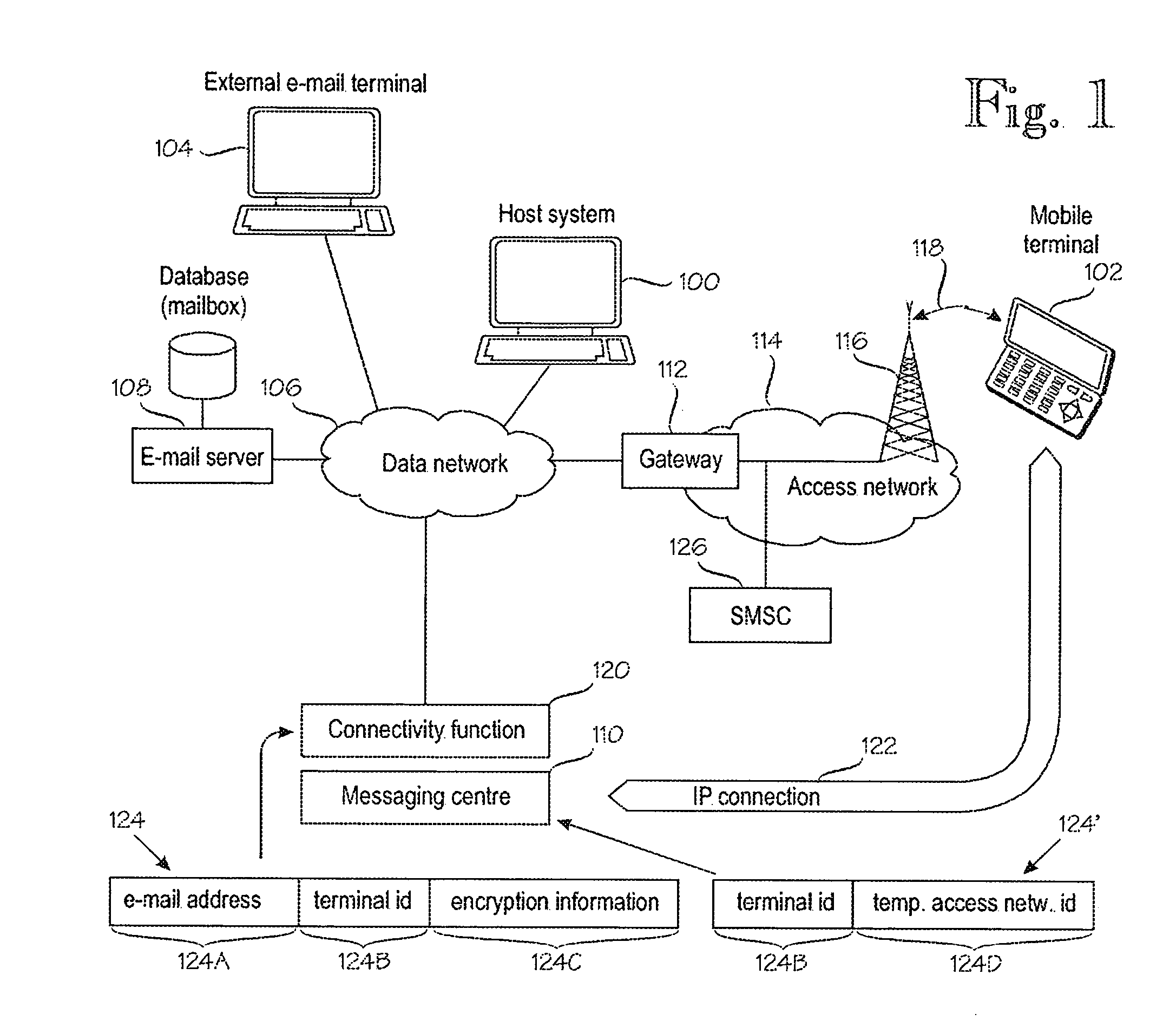
Maintaining an IP connection in a mobile network
InactiveUS7774007B2Transmission control/equalisingConnection managementStatistical ConfidenceMobile radio
A method for IP [=Internet Protocol] communication between a mobile terminal and its correspondent node in a mobile radio network. The method comprises establishing (2-2) an IP connection between the mobile terminal and its correspondent node. After detecting a period of inactivity in the IP connection, (2-4) keep-alive messages are sent via the IP connection at predetermined intervals, which are varied. The method comprises monitoring (2-6) the lengths of several periods of inactivity at which the mobile radio network disconnects the IP connection. Based on the monitored lengths of periods of inactivity, a maximum interval (TINT) between keep-alive messages is determined (2-8) such that the maximum interval meets a predetermined criterion of statistical confidence, and the interval between keep-alive messages is set (2-10) to the maximum interval (TINT).
Owner:SEVEN NETWORKS INC
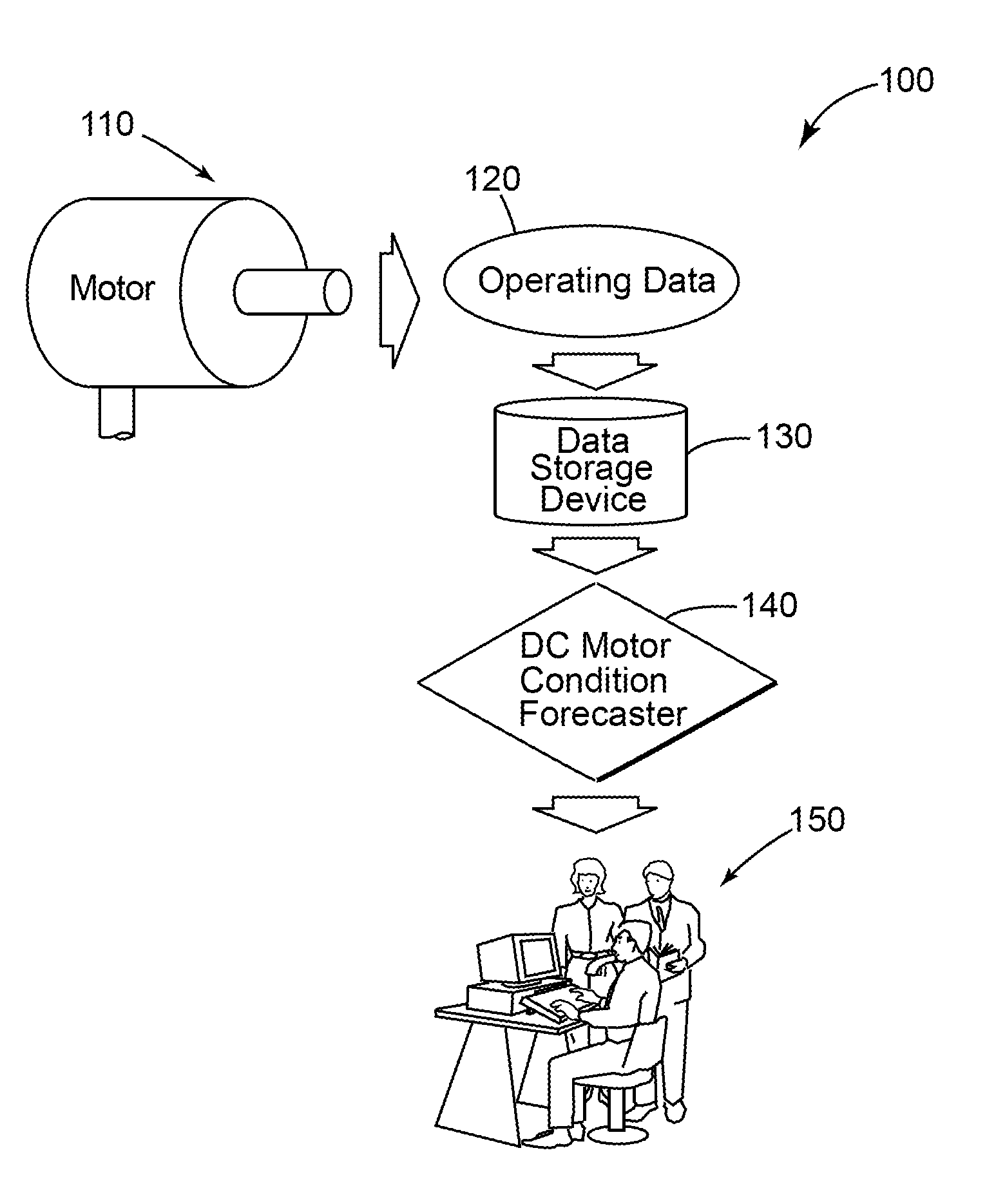
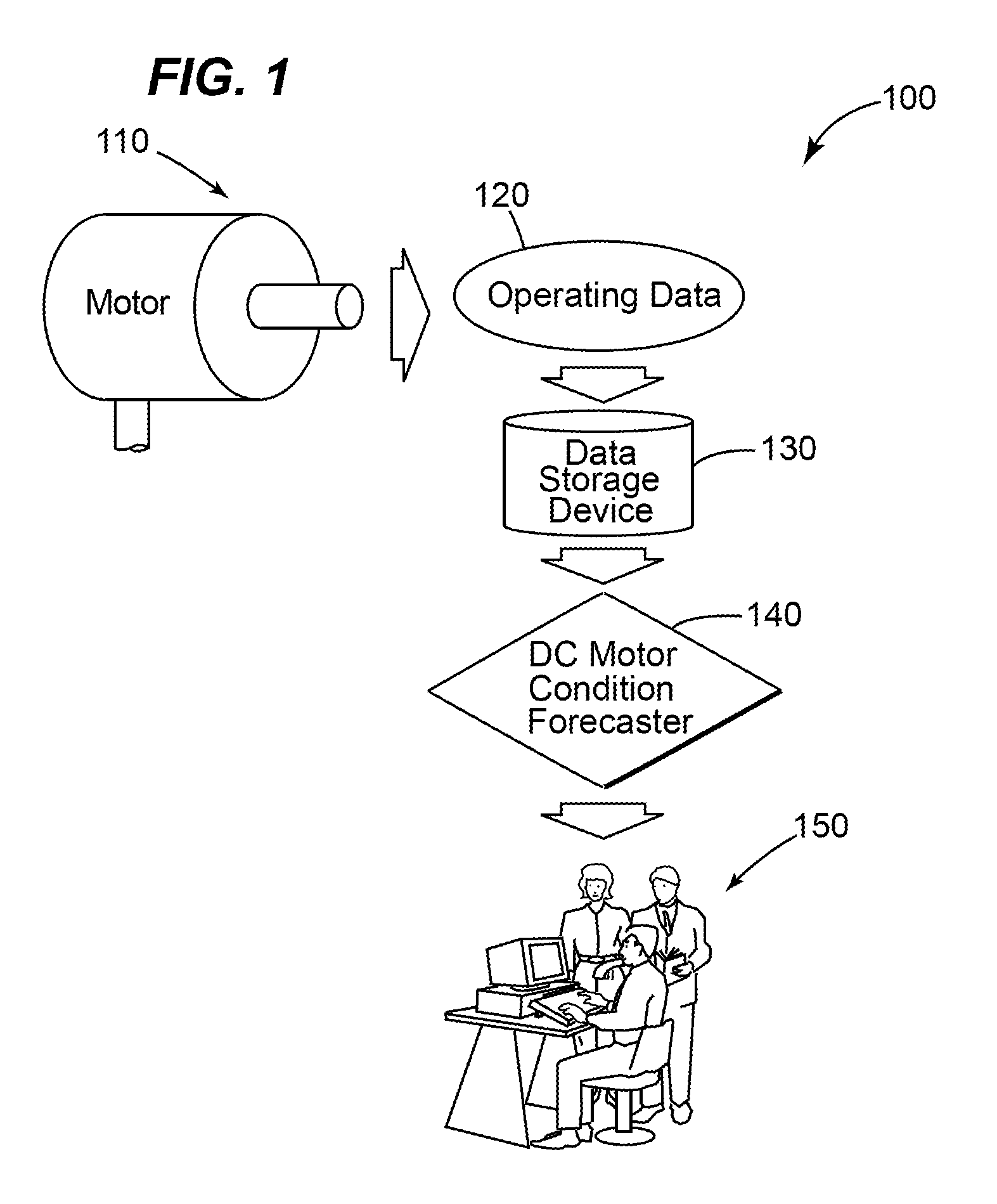
Method and system for determining the reliability of a DC motor system
InactiveUS20090096406A1Safety arrangmentsDigital computer detailsStatistical ConfidenceFailure analysis
A method and system for determining the reliability and a remaining time before failure for a DC motor system is provided. The method and system may determine the reliability and a remaining time before failure with a statistical confidence. The method and system may includes acquiring historical motor data, obtaining operational data, performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the DC motor system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Spectral clustering method for automatically determining number of clusters based on neighboring point method
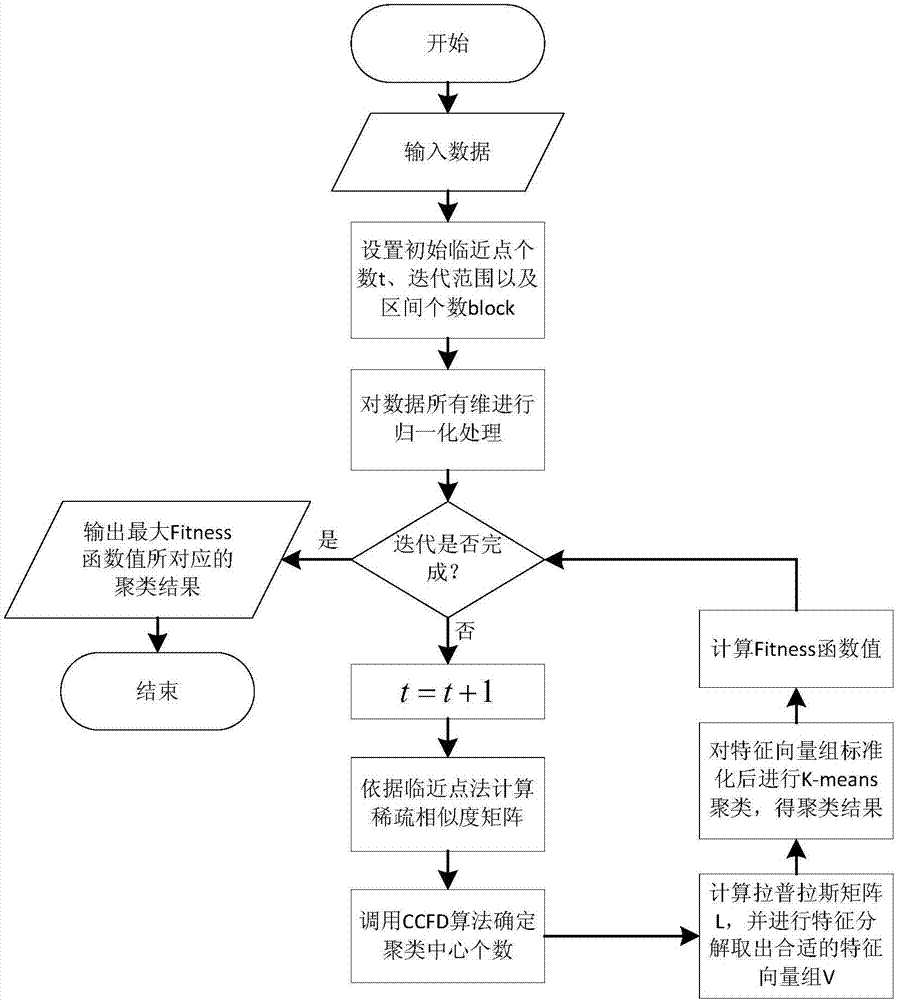
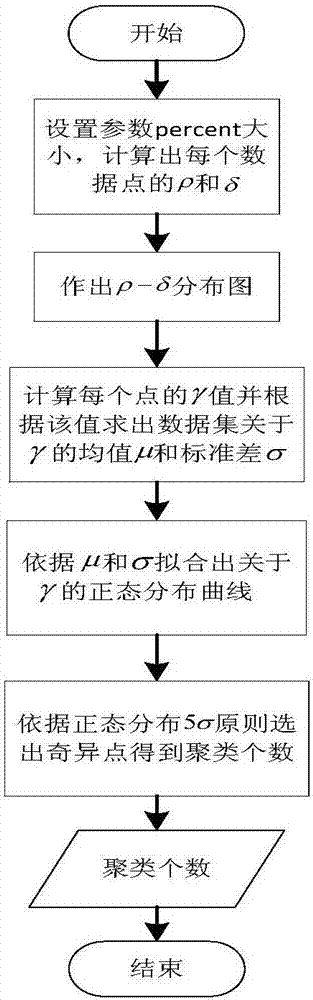
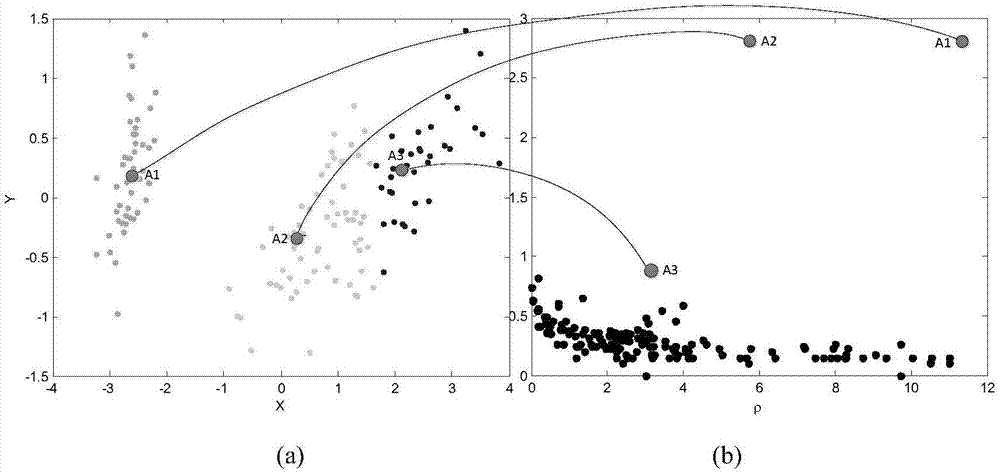
InactiveCN106991430AAchieve adaptiveQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setLocal scale
A spectral clustering method for automatically determining the number of clusters based on a neighboring point method comprises the steps of 1) normalizing all dimensions of a data set; 2) calculating an interval sparse distance matrix by a neighboring point method and defining the matrix as local scale parameters of distance mean values of the neighboring points to obtain a whole sparse similarity matrix; 3) determining the local density of each data point and the minimum distance to other points with a higher local density by calling a CCFD method, and obtaining the number of singular points generated by the fitting outside a confidence interval; 4) calculating a degree matrix D and a Laplacian matrix L according to a formula and extracting an eigenvector group by eigen decomposition of L; 5) outputting clustering results; and 6) selecting and outputting the clustering result with the optimal number of neighboring points corresponding to the maximum Fitness function value. According to the invention, the local scale parameter of each data point can be estimated according to data distribution, the number of clustering centers is automatically determined, and the parameter adaptation of the number of neighboring points is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for calibrating a magnetic sensor
InactiveUS20090070056A1Overcome limitationsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsConfidence intervalPartial solution
Measurements are acquired from a magnetic sensor during a non-pre-ordered movement, and a plurality of sets of solutions are determined for respective expected values of intensity of the Earth's magnetic field. The solutions are defined by a plurality of parameters, including at least one gain value for each detection axis of the magnetic sensor. For each solution, a figure of merit is determined, correlated to a calibration error, and a partial solution is selected in each set of solutions, based on the figure of merit. Once a gain confidence interval has been defined, a calibration solution is selected based on the figure of merit, from among the partial solutions having respective gain values all falling within the gain confidence interval.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
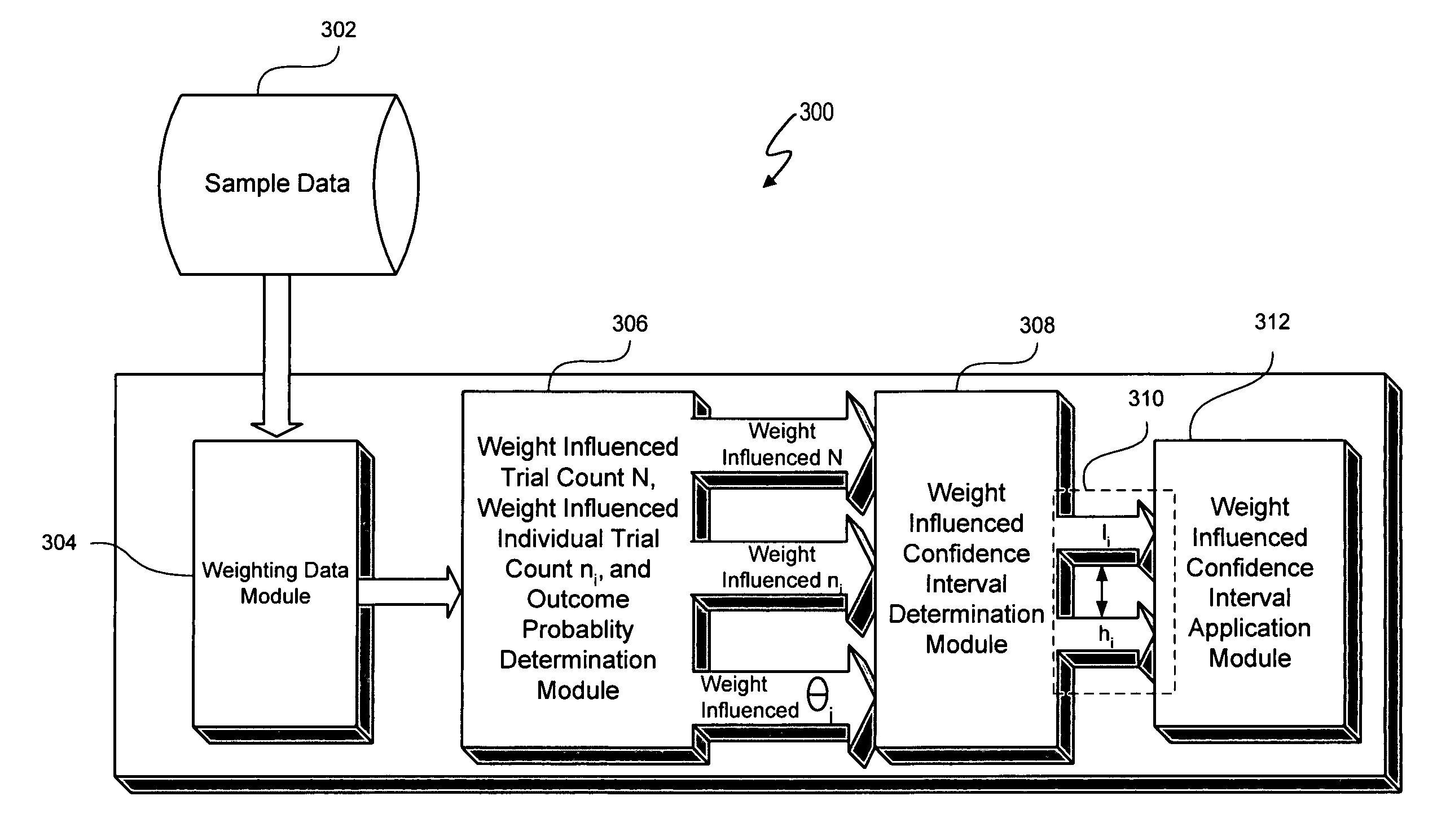
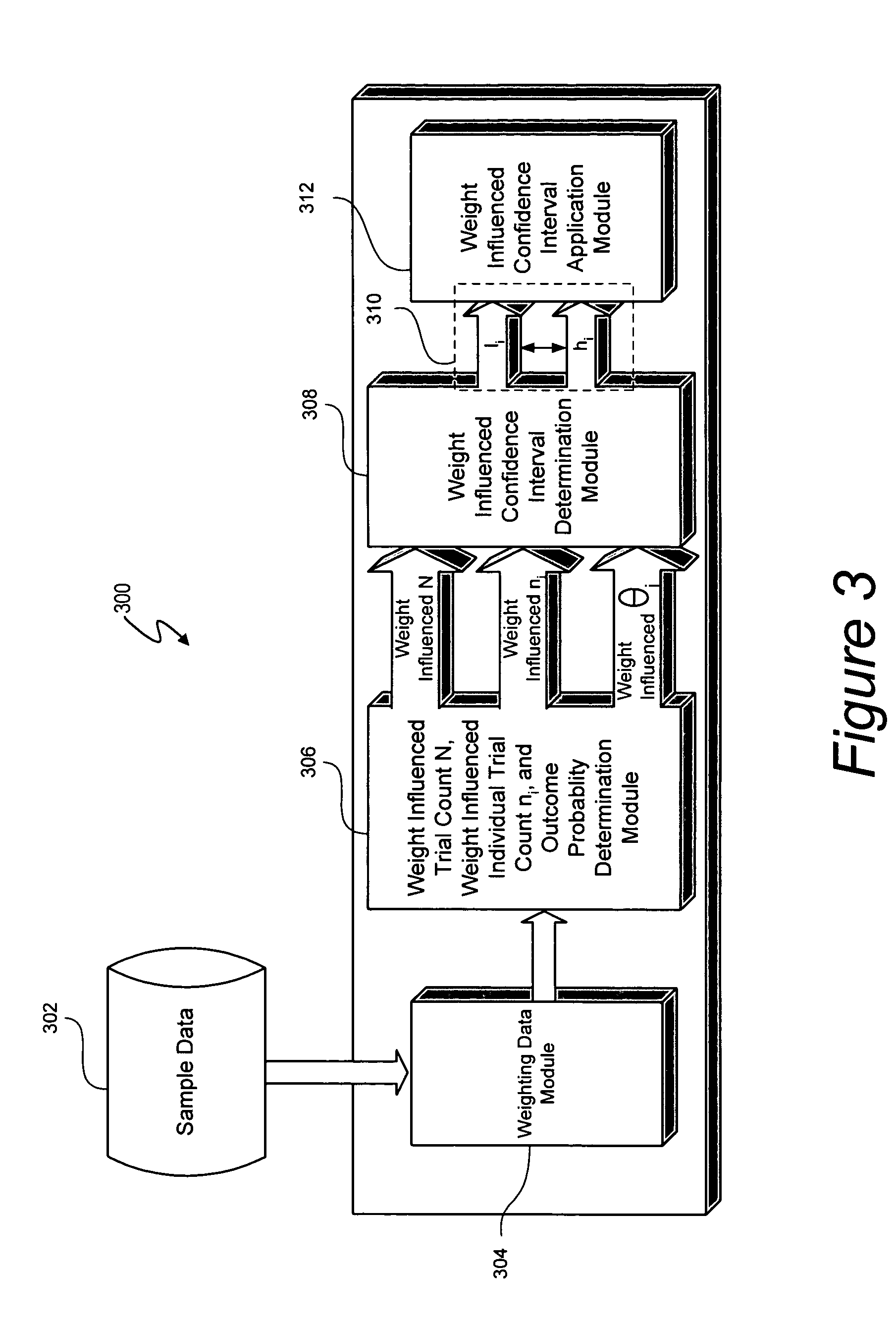
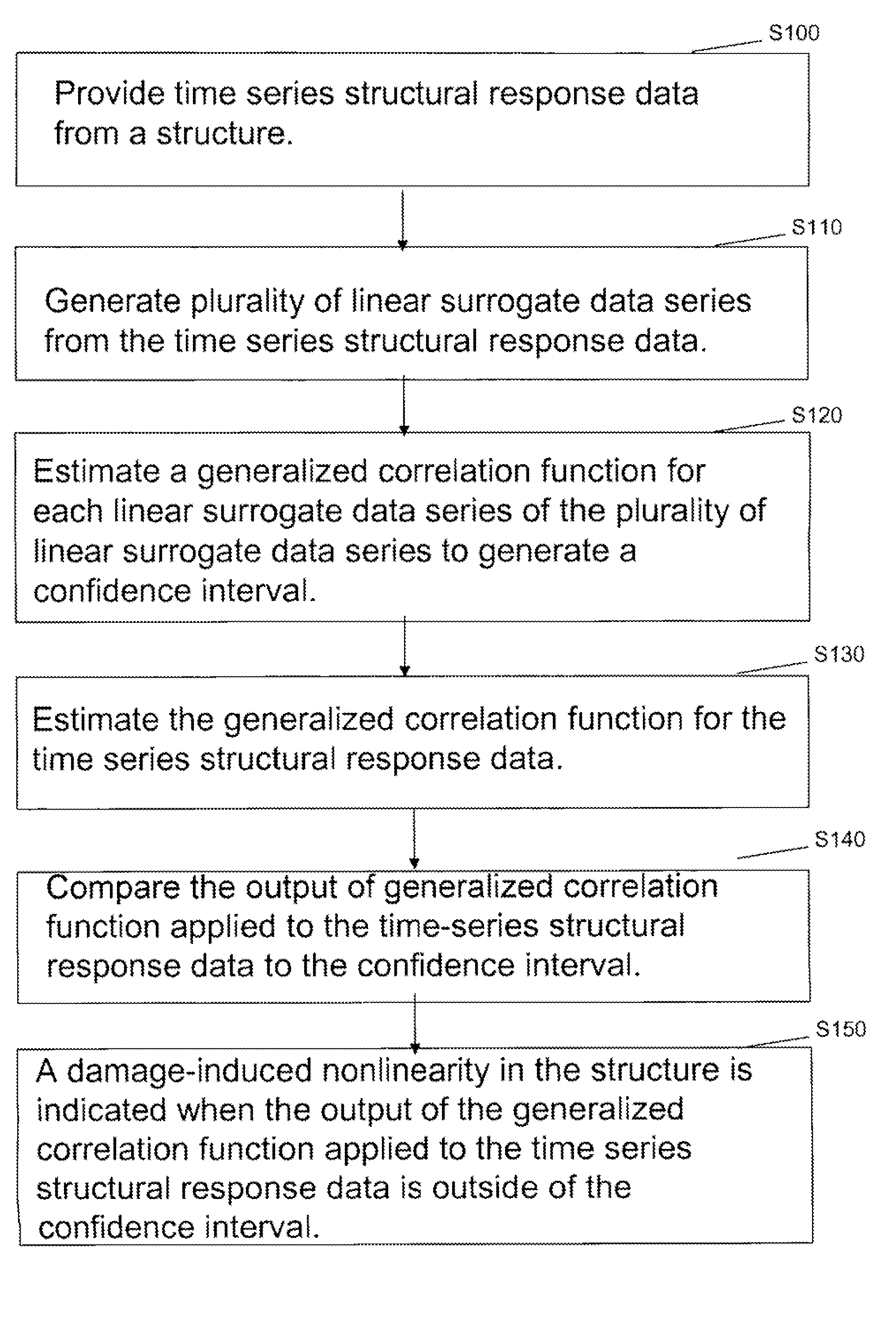
Determining confidence intervals for weighted trial data
ActiveUS7092844B1Reduce overestimationTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksStatistical ConfidenceAccurate estimation
Collected trial data is weighted to, for example, reflect the relevance of the data. A weighted confidence interval determination and application process described herein determines a confidence interval used to interpret the data. The confidence interval is derived by adjusting the sample size N to account for the impact of weighting when determining confidence intervals. The sample size N is adjusted in a downward trend to avoid overestimating the confidence interval. Lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval are determined using weight influenced variables. Thus, interpretation of weighted trial data, such as product demand data, can be achieved and acted upon with an accurate estimation of risk.
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
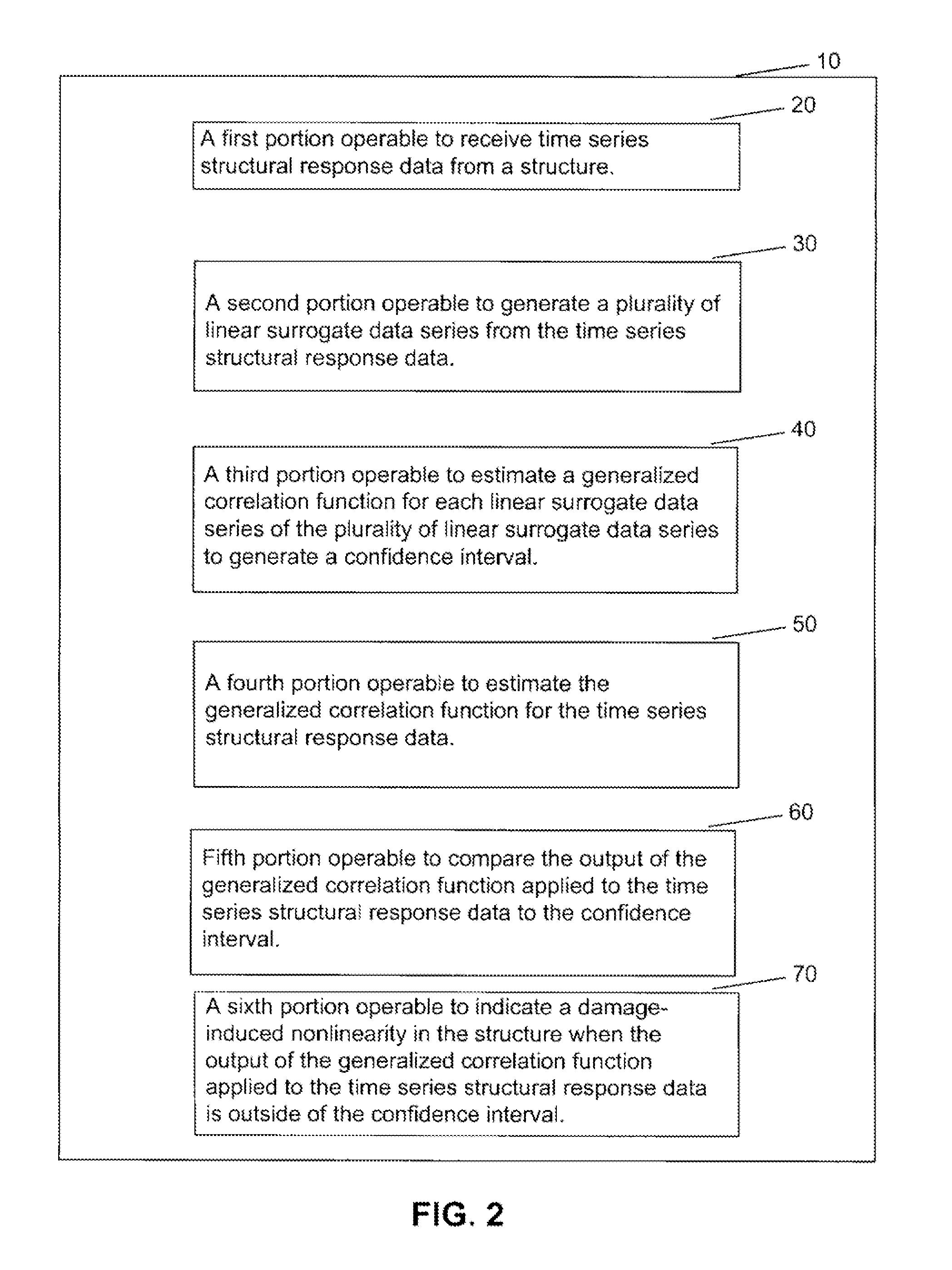
Method and apparatus for detecting damage in structures
InactiveUS20070168341A1Low variabilityDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsConfidence intervalCorrelation function
A method including providing time series structural response data from a structure. A plurality of linear surrogate data series is generated from the time series structural response data. A first generalized correlation function is estimated for each linear surrogate data series of the plurality of linear surrogate data series to generate a confidence interval. The same correlation function is estimated for the time series structural response data. The output of the generalized correlation function applied to the structural response data is compared to the confidence interval. A damage-induced nonlinearity in the structure is indicated when the output of the generalized correlation function applied to the structural response data is outside of the confidence interval.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
Method and system for remotely predicting the remaining life of an AC motor system
A method and a system for remotely predicting the reliability and the remaining time before failure for an AC motor system (110) are provided. The method and the system may remotely determine the reliability and a remaining time before failure with a statistical confidence utilizing an AC motor condition forecaster. The method and the system may include acquiring historical motor data, obtaining operational data (120), performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the AC motor system. The method and system may provide at least one notification of an issue with the AC motor system (110) or at least one component of the AC motor system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
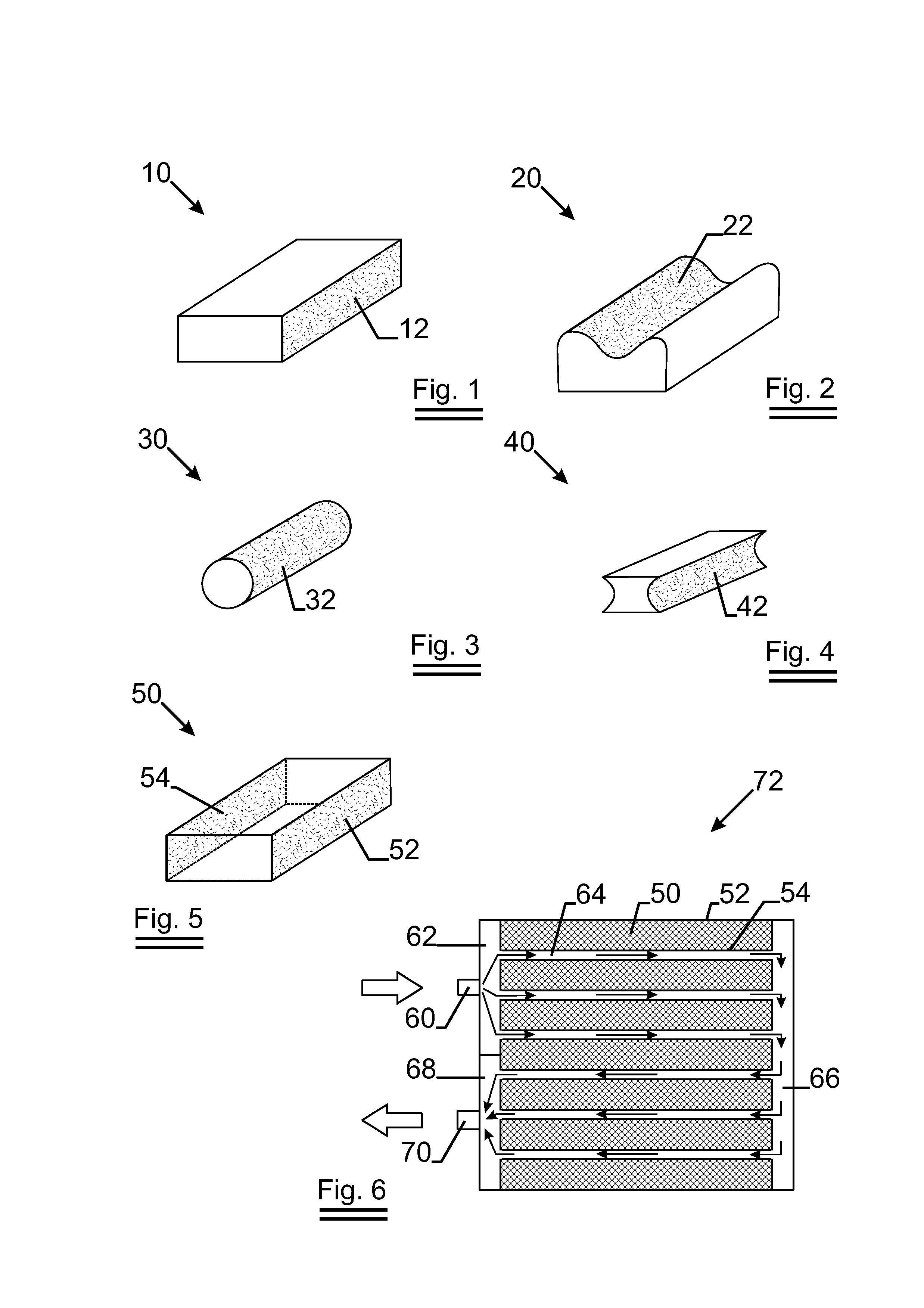
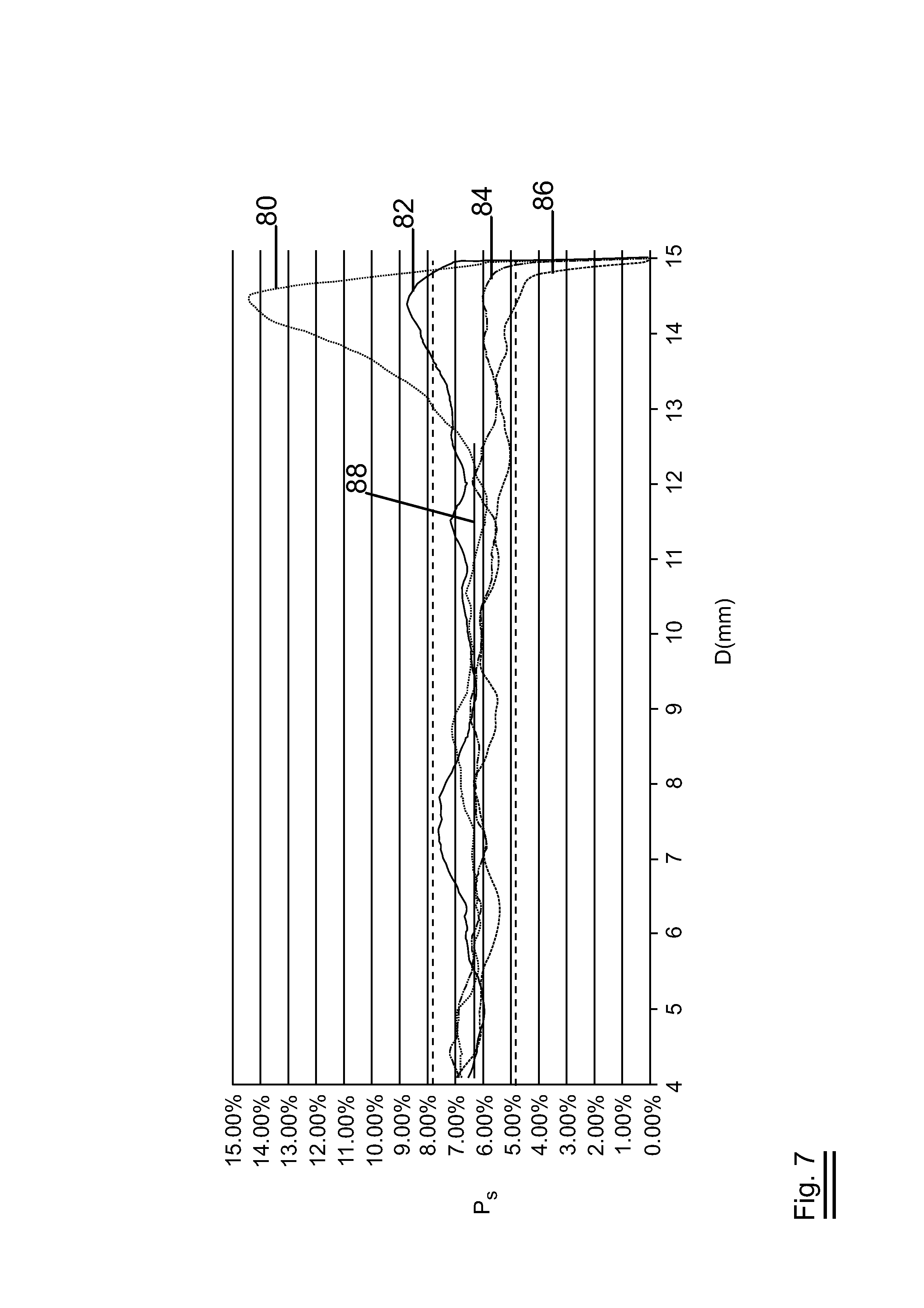
3D porous material comprising machined side
InactiveUS20130168071A1Improve heat transfer performanceIncrease surface areaMetal sawing devicesLayered productsConfidence intervalStatistical Confidence
3D porous material comprises at least one machined side. The machined side has a solid percentage Ps being (1−Po), said Po is the porosity of the bulk of said 3D porous material and said Ps is within the 99.5% confidence interval. The present invention provides the method of manufacturing such 3D porous material. Preferably, the 3D porous material is open cell metal foam. The present invention also provides use of such open cell metal foam in a heat exchanger. The present invention further provides a heat exchanger comprising open cell metal foam.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com