Patents
Literature
120 results about "System reconfiguration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
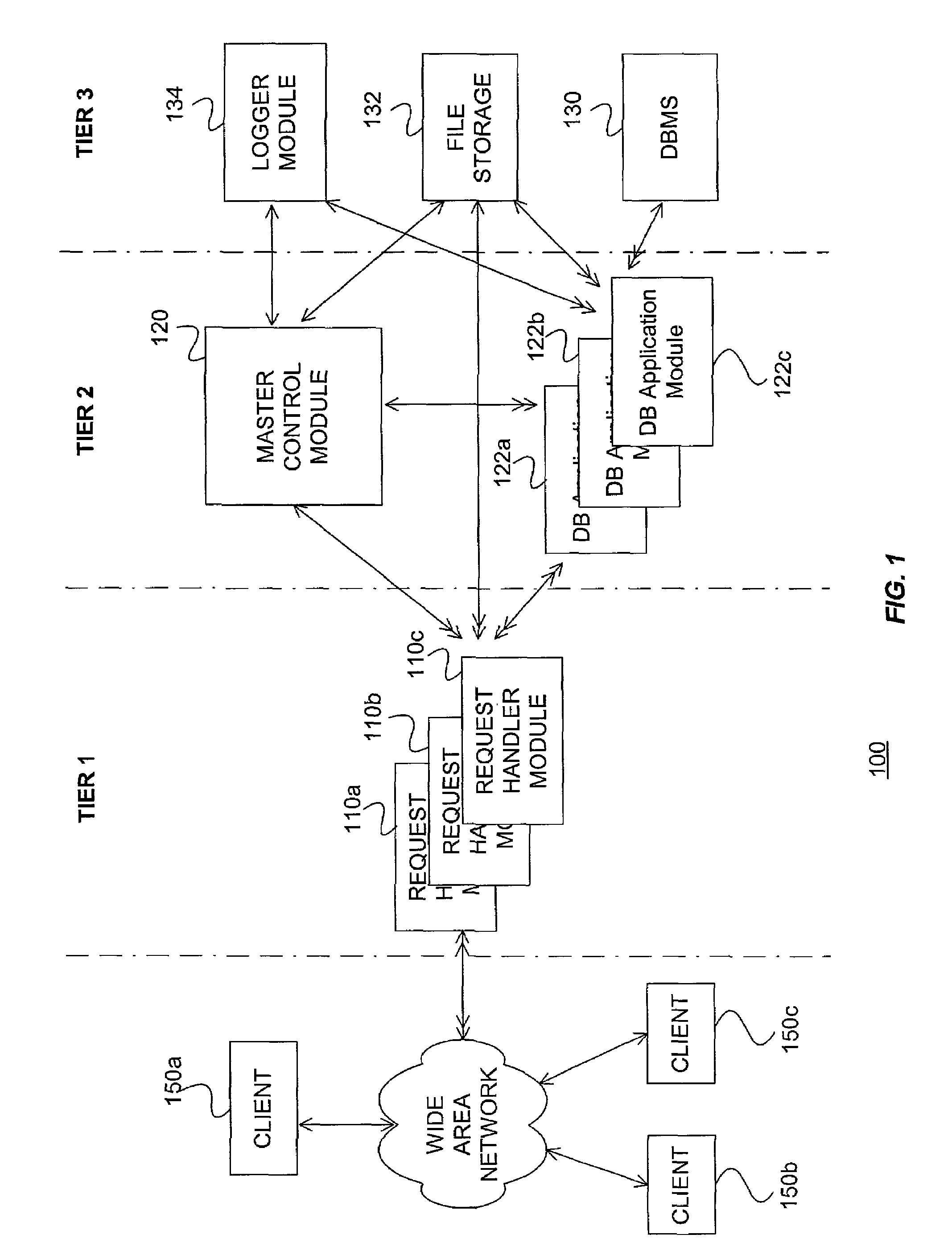
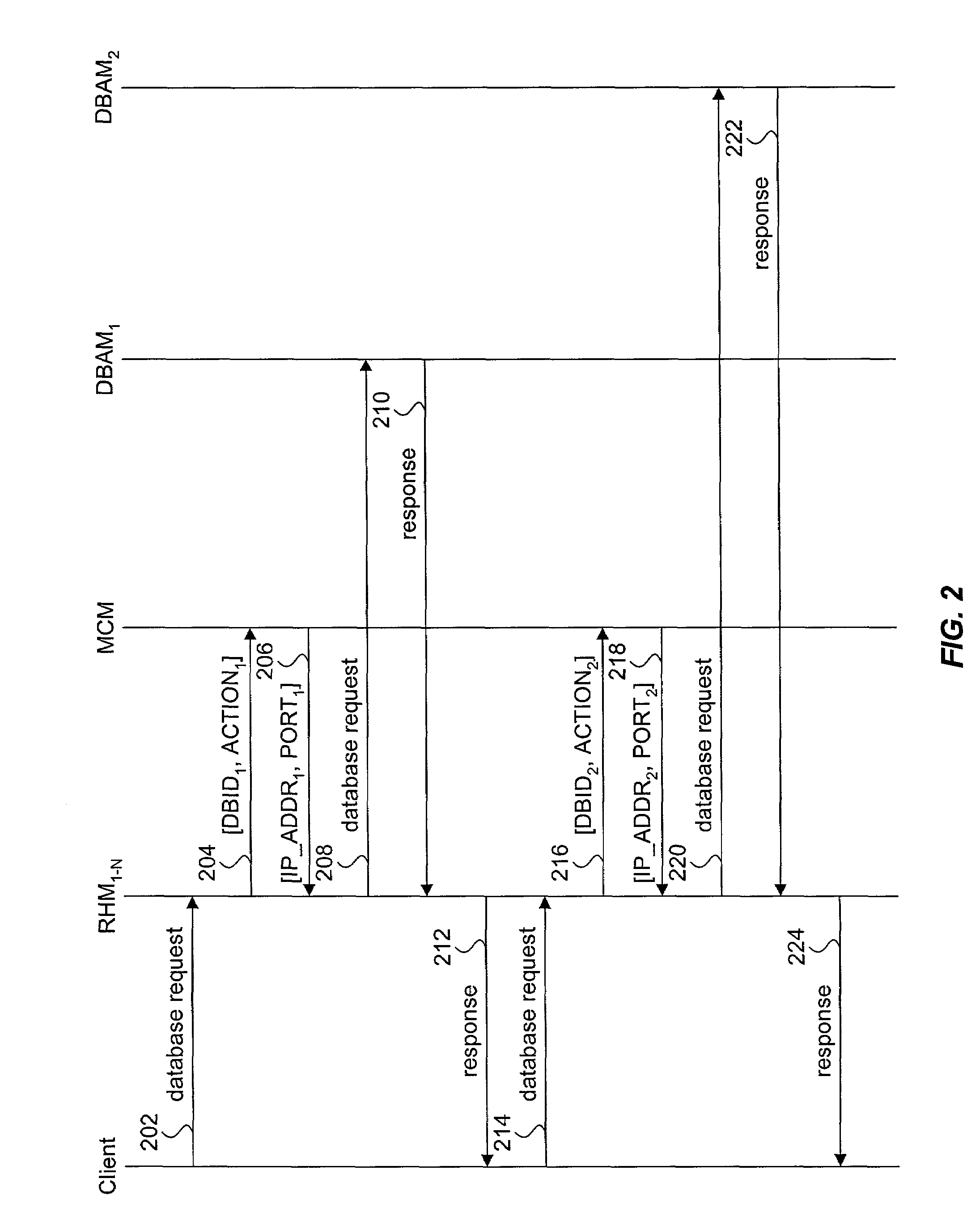
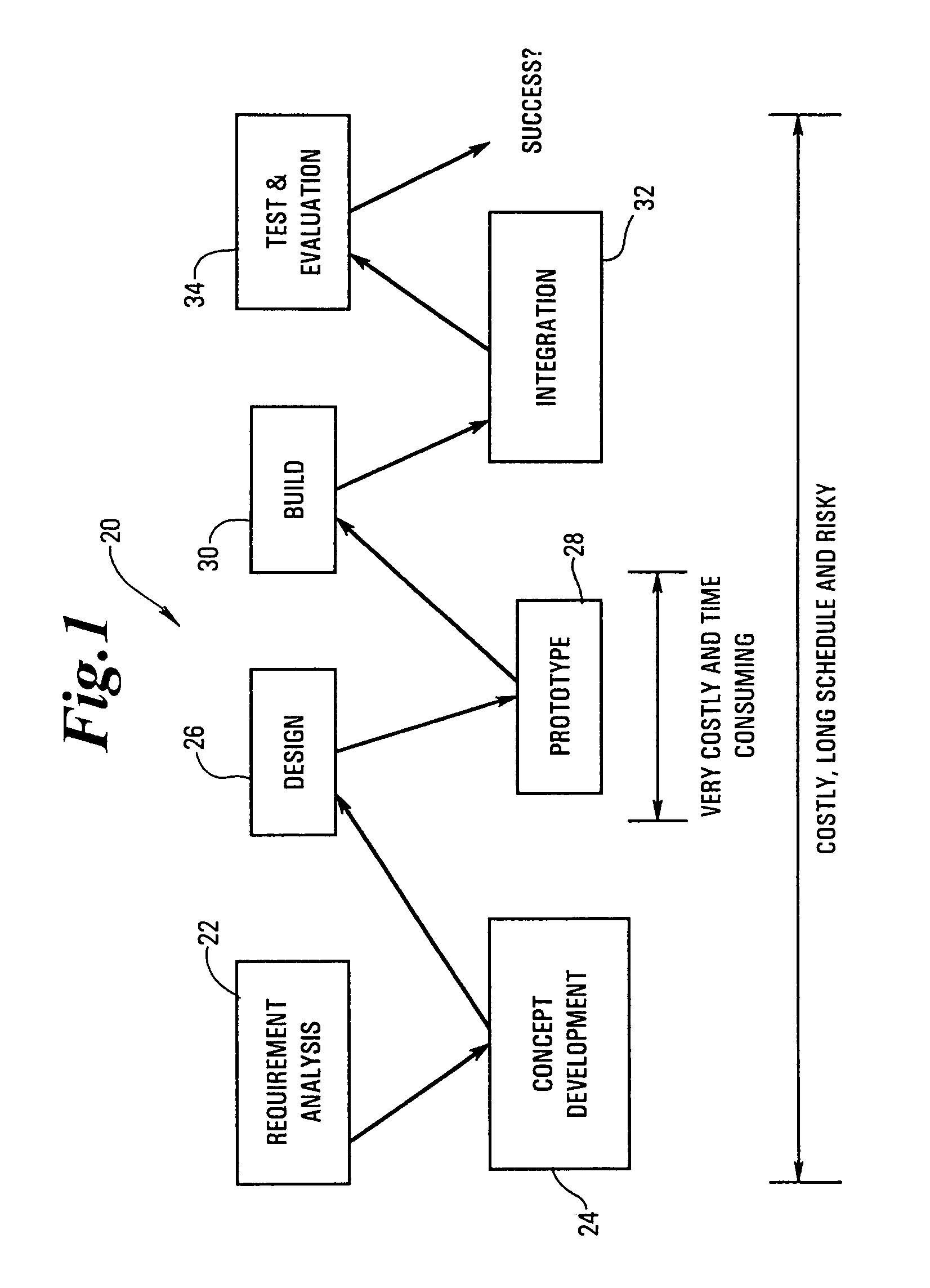
System Reconfiguration. Reconfiguration is the process of adding hardware units to, or removing hardware units from, a configuration. Units can be either: Online: Units in use by a system are called online. When both physically and logically online, a unit is available to be used by the system.
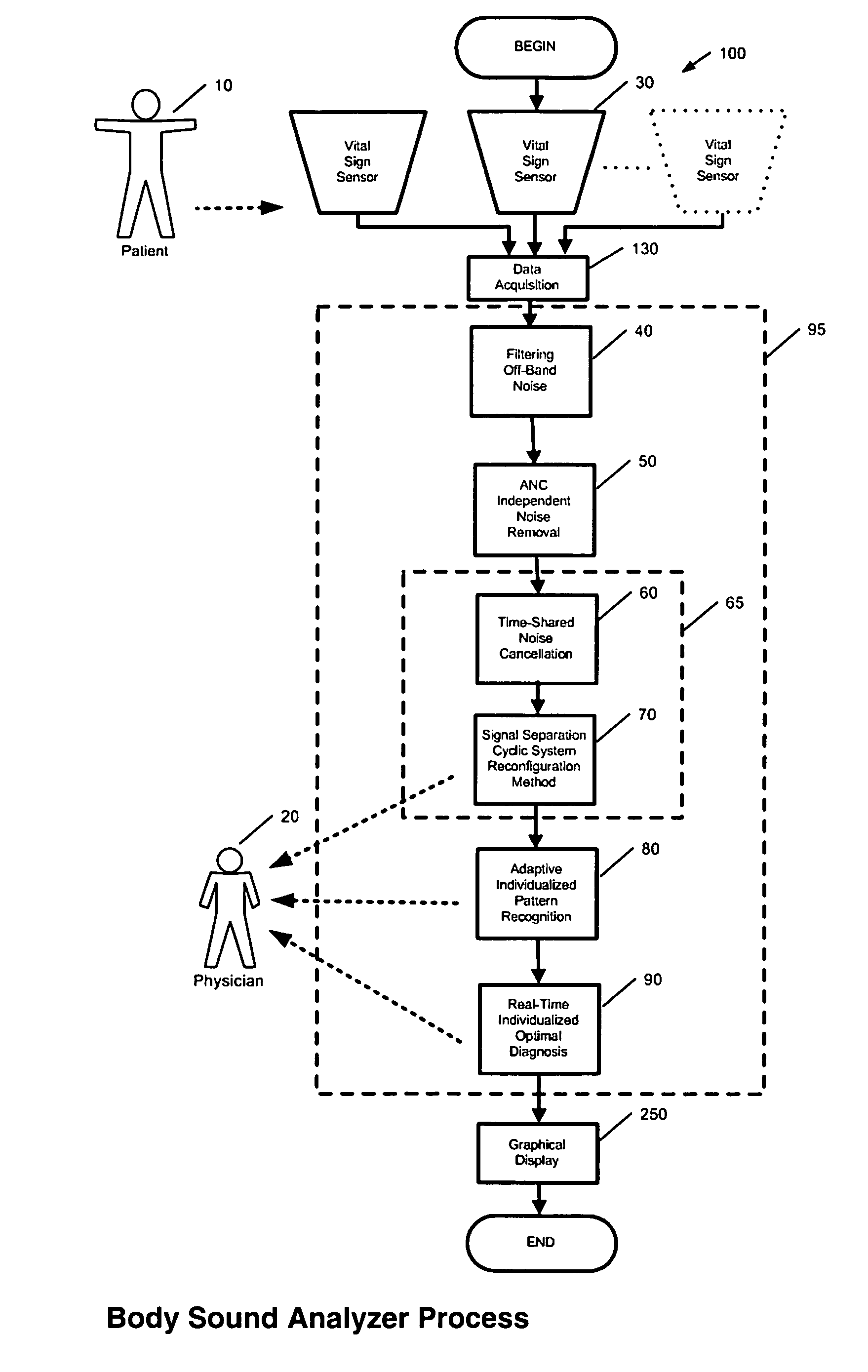
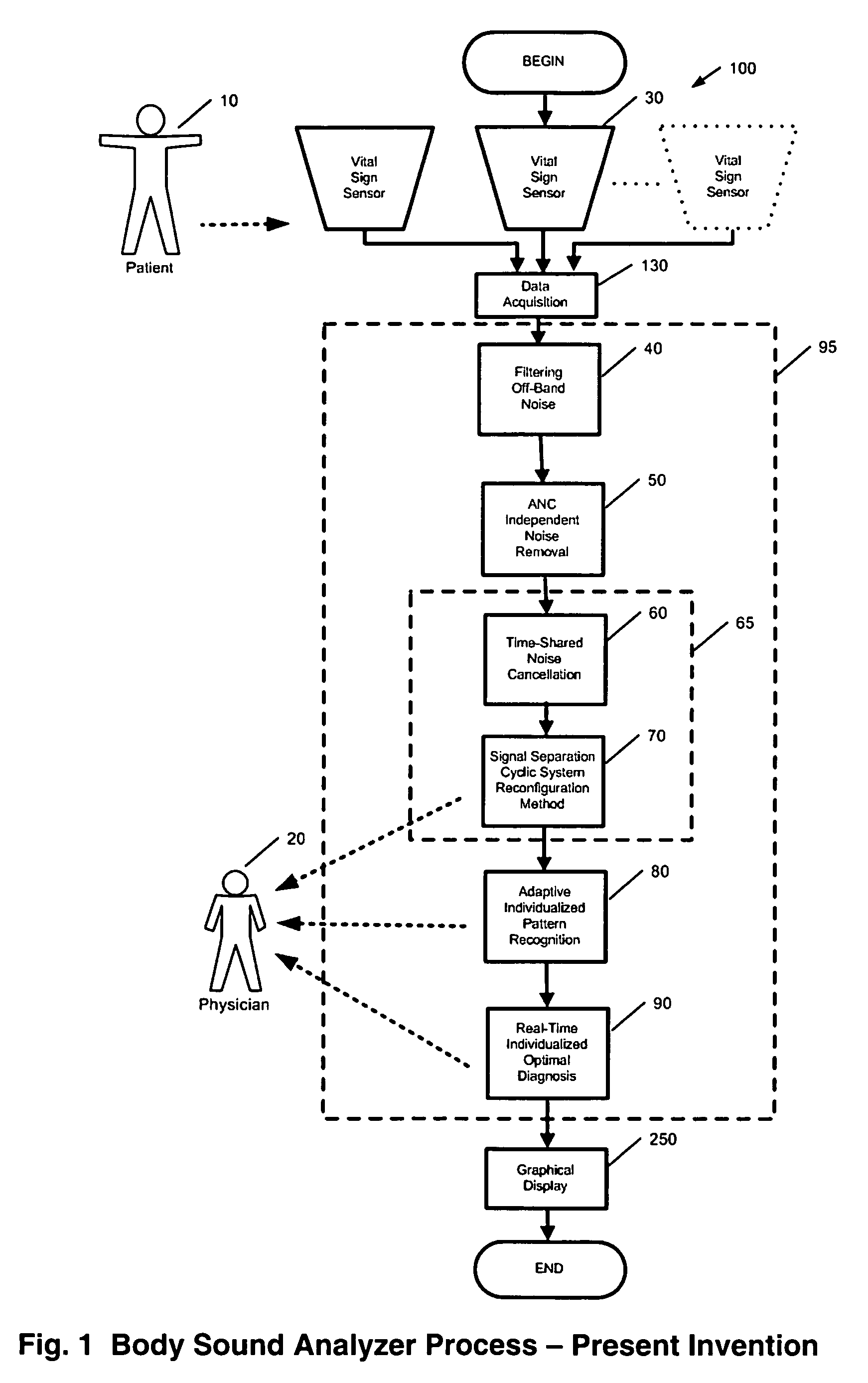
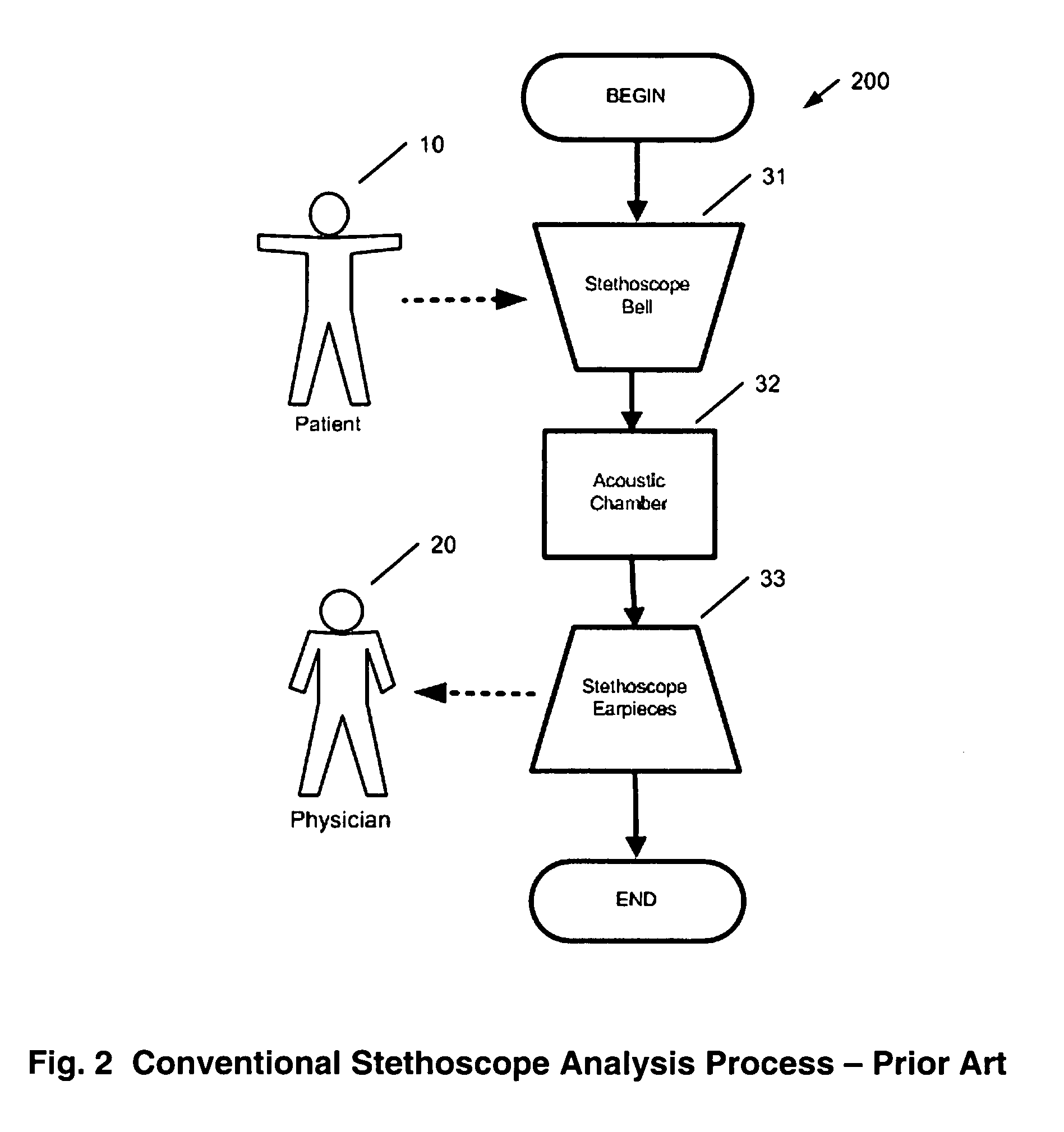
Method and system for continuous monitoring and diagnosis of body sounds
InactiveUS20060198533A1Reduce the impactQuality improvementStethoscopeTransmission noise suppressionContinuous measurementReal time analysis
A method and system is invented for automated continuous monitoring and real-time analysis of body sounds. The system embodies a multi-sensor data acquisition system to measure body sounds continuously. The sound signal processing functions utilize a unique signal separation and noise removal methodology by which authentic body sounds can be extracted from cross-talk signals and in noisy environments, even when signals and noises may have similar frequency components or statistically dependent. This method and system combines traditional noise canceling methods with the unique advantages of rhythmic features in body sounds. By employing a multi-sensor system, the method and system perform cyclic system reconfiguration, time-shared blind identification and adaptive noise cancellation with recursion from cycle to cycle. Since no frequency separation or signal / noise independence is required, this invention can provide a robust and reliable capability of noise reduction, complementing the traditional methods. The invention further includes a novel method by which pattern recognition of groups of key parameters can be used to diagnosis physical conditions associated with body sounds, with confidence intervals on the diagnostic criterion to indicate accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:WANG LE YI +1
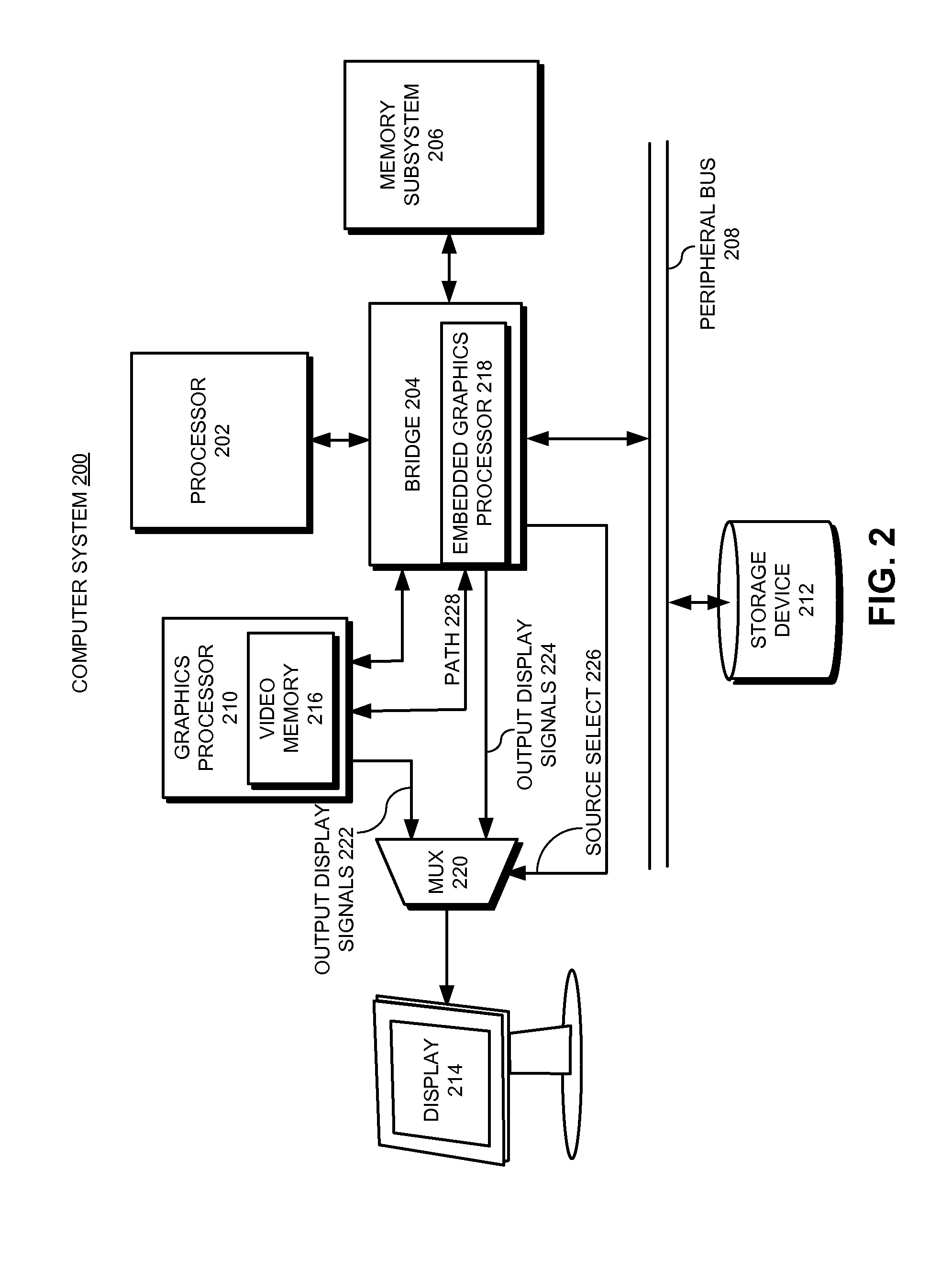
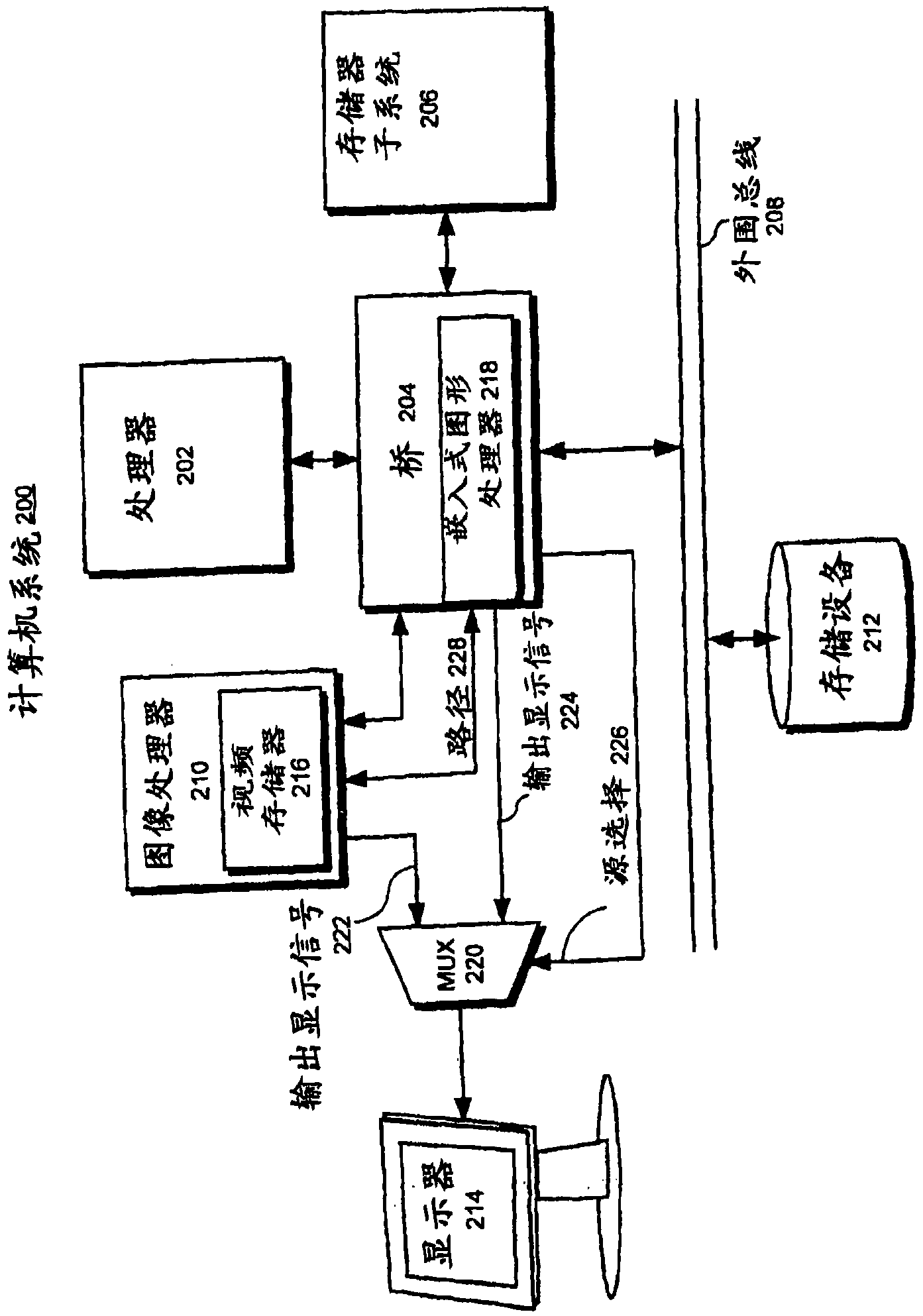
Switching between graphics sources to facilitate power management and/or security
InactiveUS20090079746A1Digital data processing detailsDigital data protectionGraphicsSystem reconfiguration
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that switches between frame buffers which are used to refresh a display. During operation, the system refreshes the display from a first frame buffer which is located in a first memory. Upon receiving a request to switch frame buffers for the display, the system reconfigures data transfers to the display so that the display is refreshed from a second frame buffer which is located in a second memory.
Owner:APPLE INC
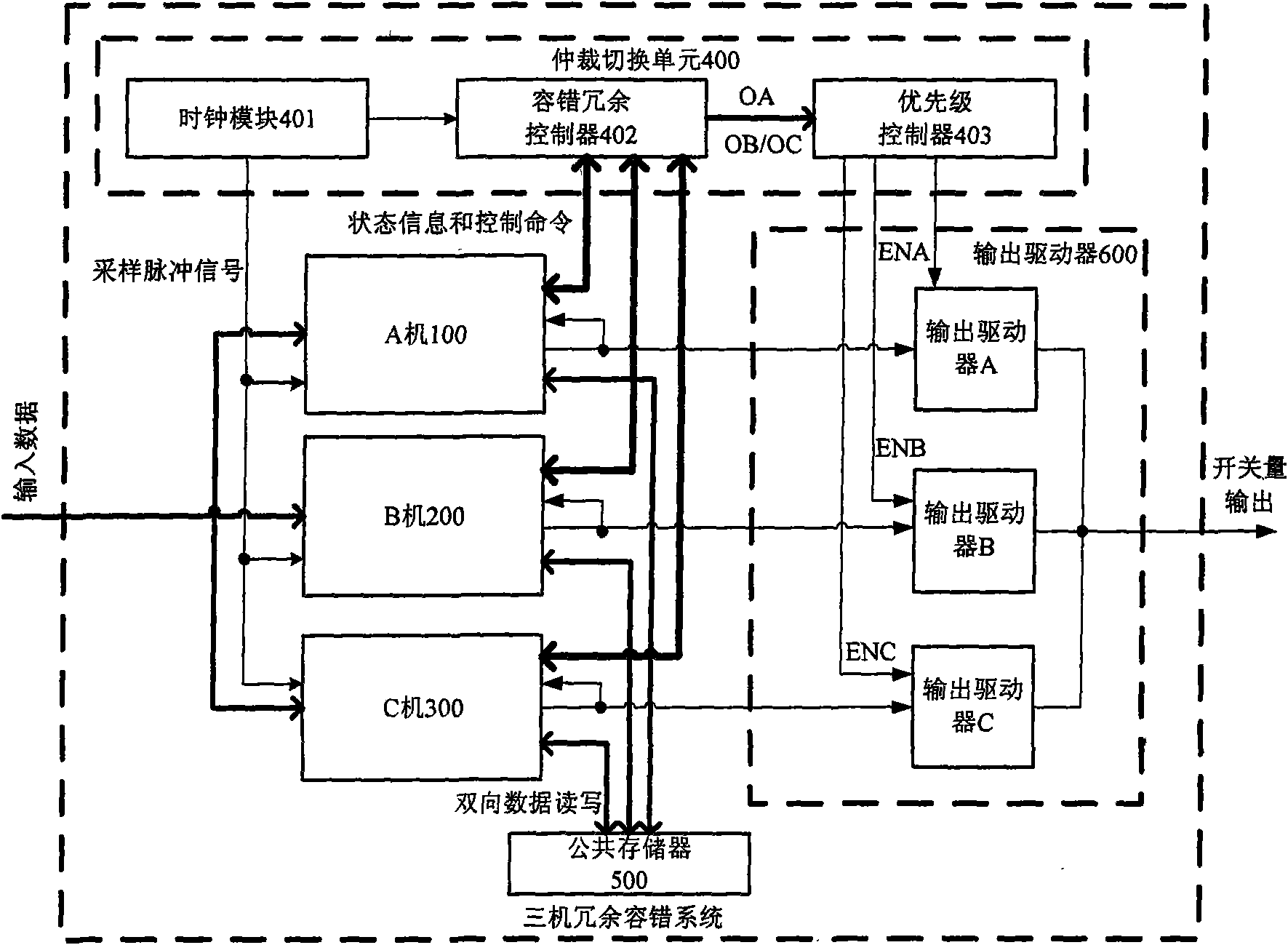
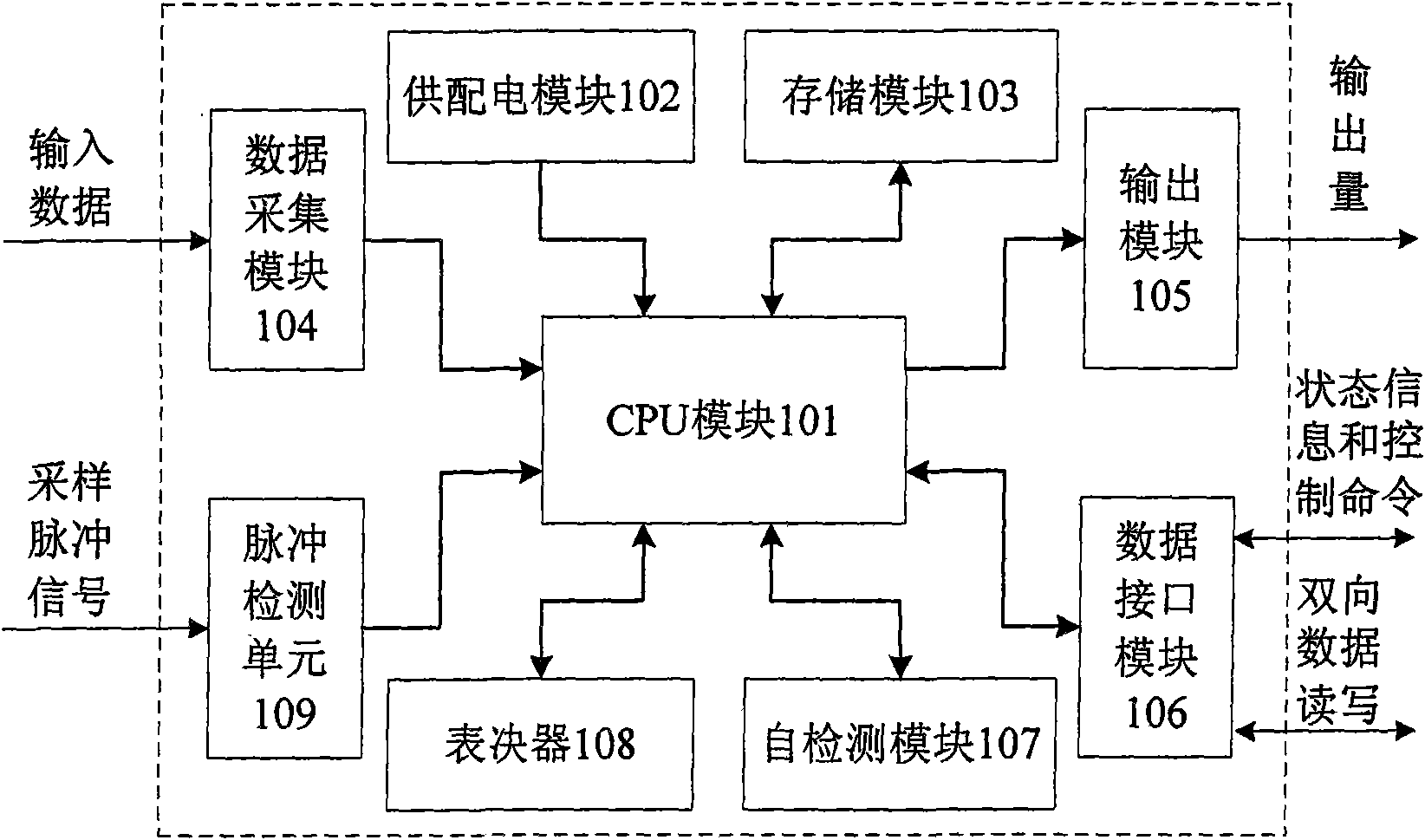
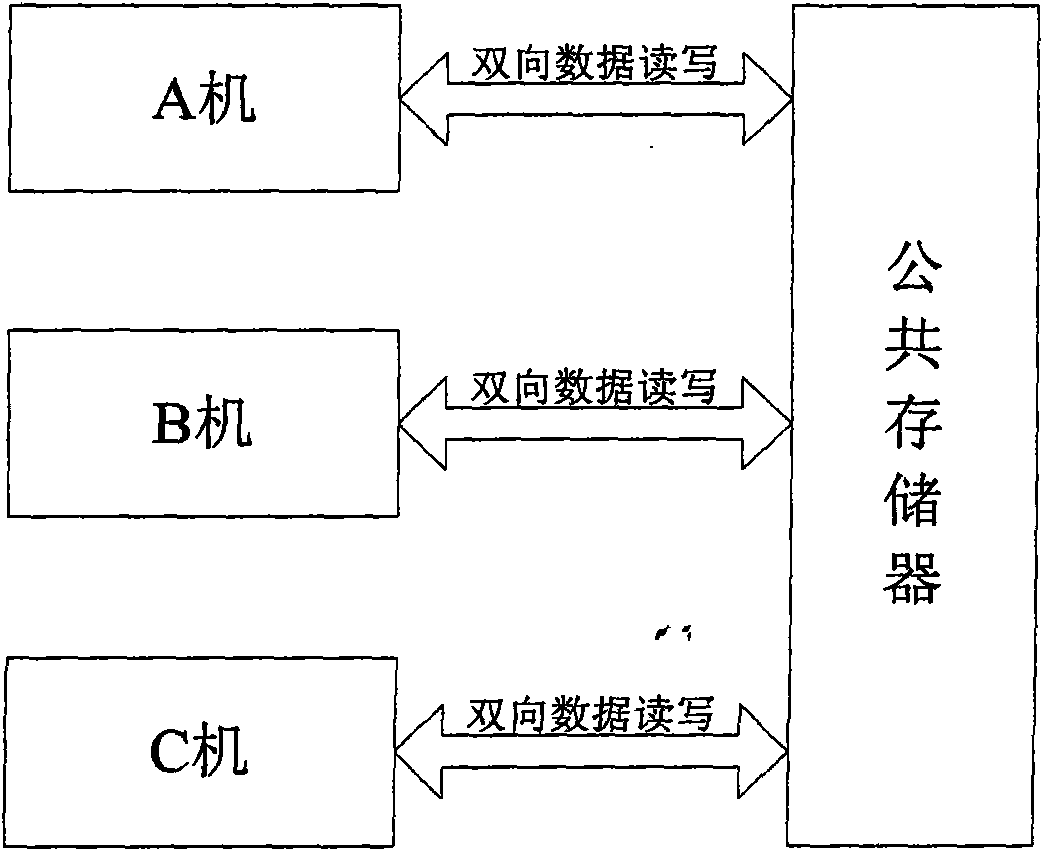
Degradable three-machine redundancy fault-tolerant system
InactiveCN101576836AAvoid single point of failureImprove reliabilityRedundant hardware error correctionSystem reconfigurationTreatment results
A degradable three-machine redundancy fault-tolerant system consists of three single machines such as a machine A, a machine B, a machine C which have the same structure, a public memory, an arbitration switching unit, and the output drivers of the three machines; the machine A, the machine B and the machine C achieve the exchange of treatment results among the three machines by reading and writing the output results of the single machines in the public memory so as to conduct three-machine voting; in addition, the machine A, the machine B and the machine C can also achieve three-machine or dual-machine synchronization by reading and writing the process information in the public memory; the machine A, the machine B and the machine C are connected with each other so that any one machine can read the status information whether another party is in normal work currently; the machine A, the machine B and the machine C are also connected with the arbitration switching unit and provide self-status information for the arbitration switching unit, and the arbitration switching unit can conduct the redundancy degrading of three-machine work / dual-machine work / single-machine work and the redundancy system reconfiguration of three-machine work / dual-machine work / single-machine work, in addition, the arbitration switching unit is also connected with the output drivers of the three machines and decides the use right of the machine A, the machine B and the machine C to the output line; and as for the three machines in normal work, the output is provided with a priority order, namely the machine A-the machine B-the machine C in sequence. The invention has the advantages of high reliability and long service life.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
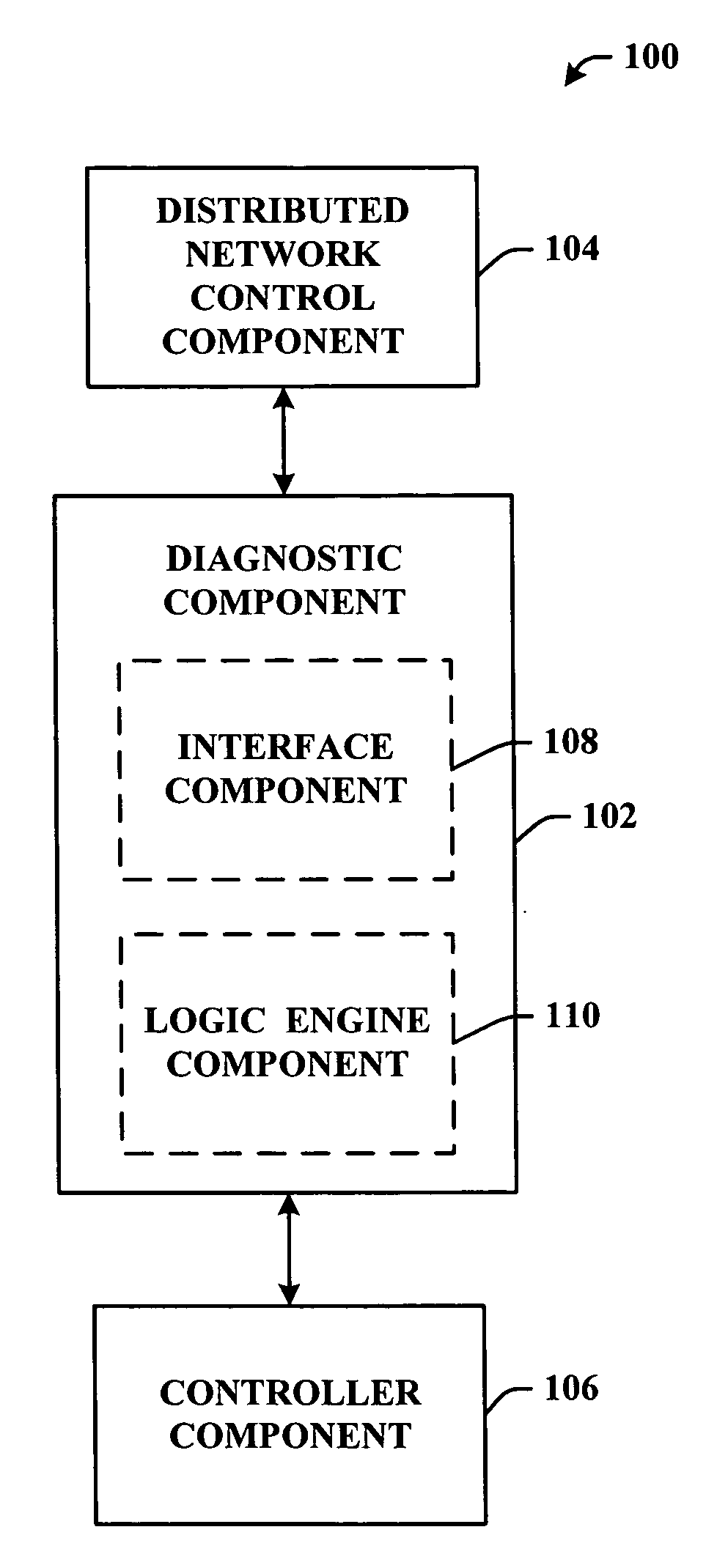
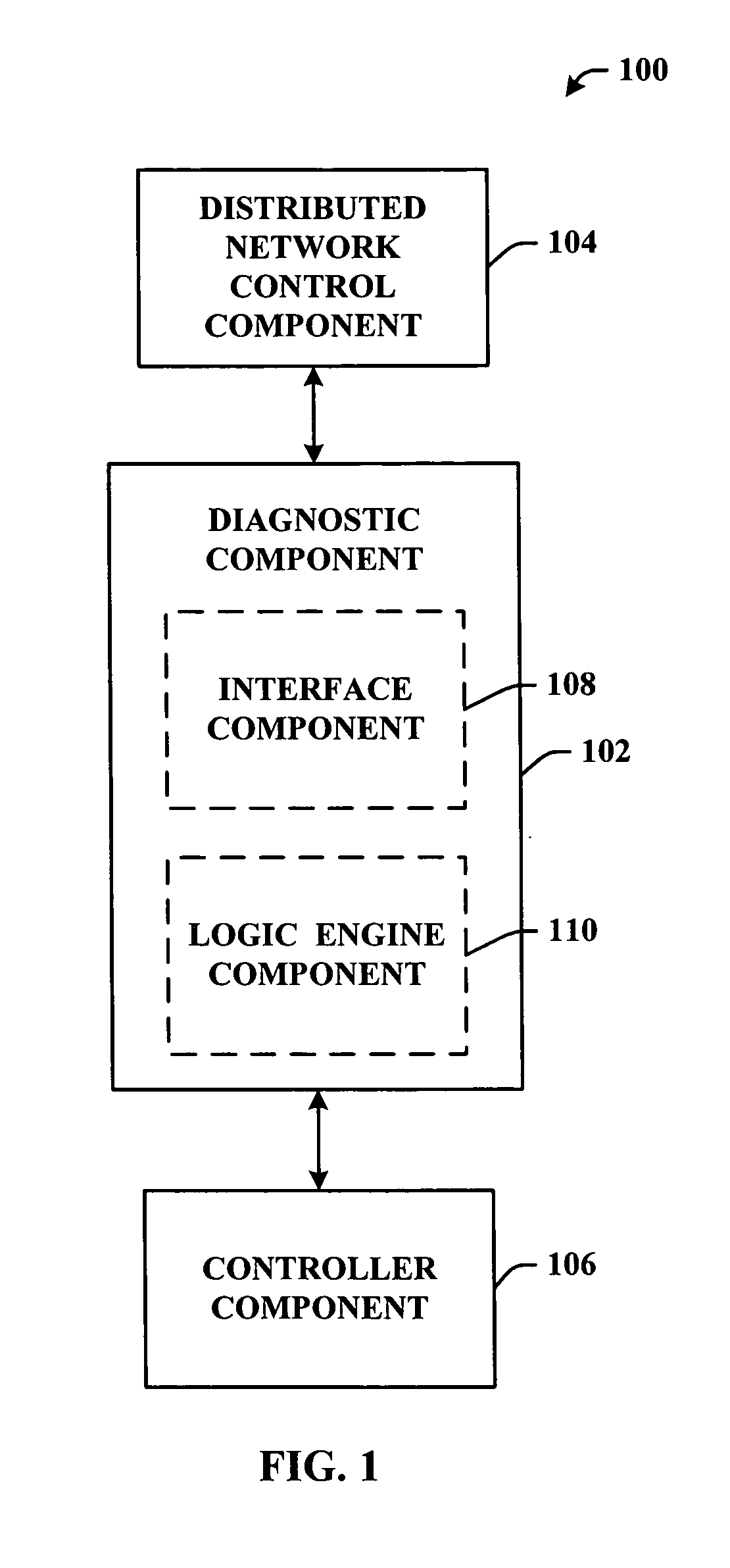
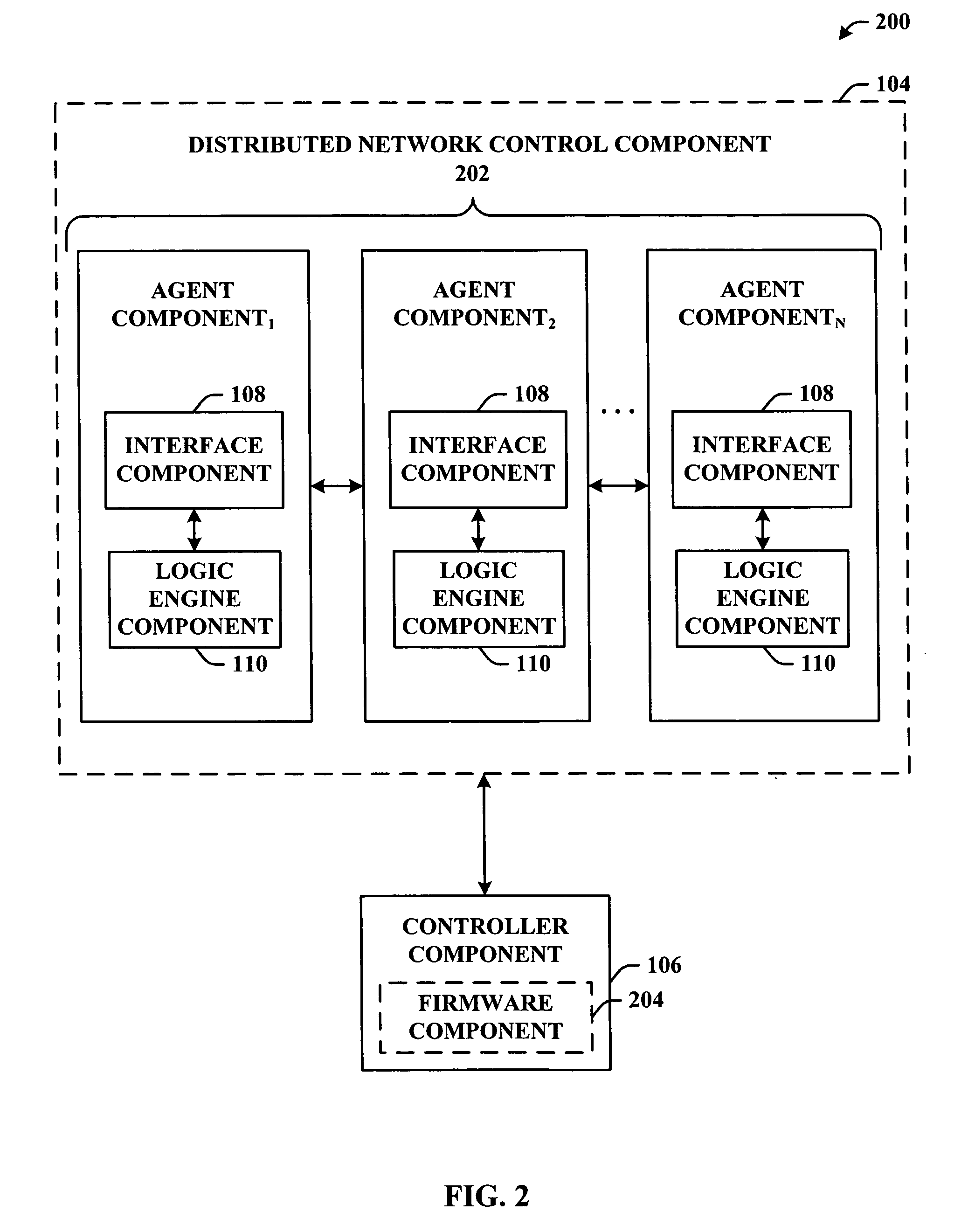
Distributed intelligent diagnostic scheme
InactiveUS20060168195A1Facilitates logic reasoning and decision makingImprove abilitiesMultiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingDistributed intelligenceSystem reconfiguration
A system and methodology that employs an agent technology logic layer operating in connection with or integral to a controller is provided. The logic layer can be a functional extension of the controller's firmware that facilitates logical reasoning and decision-making with regard a network as a function of individual agent(s) state and / or status. The components of the subject invention can facilitate combining high level reasoning and / or decision making capabilities with conventional control programs to effect agent-based system diagnosis and / or system reconfiguration.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for wireless network management
ActiveUS20130288735A1Improve understandingEfficient use of resourcesService provisioningAssess restrictionRelevant informationSystem reconfiguration
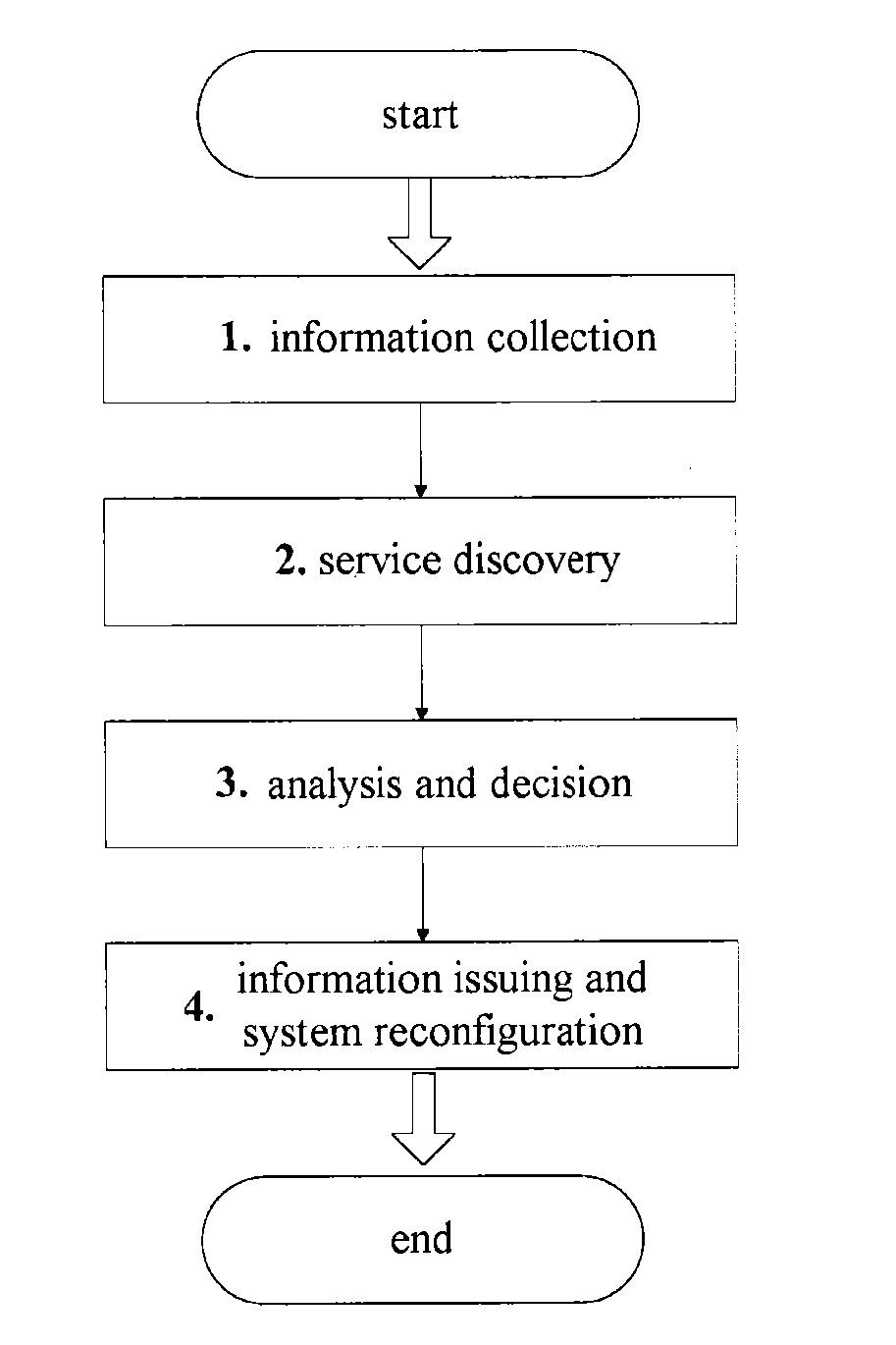
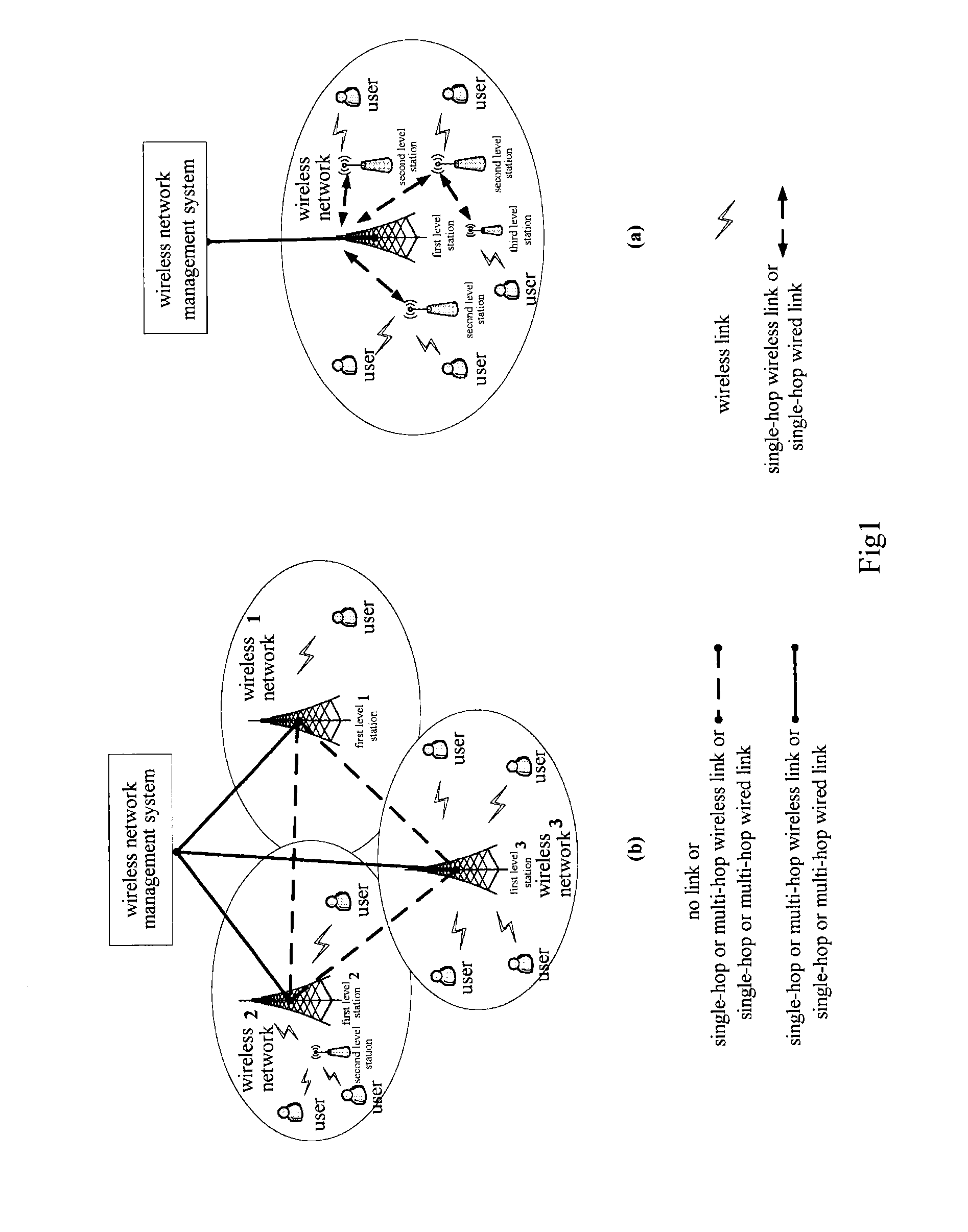
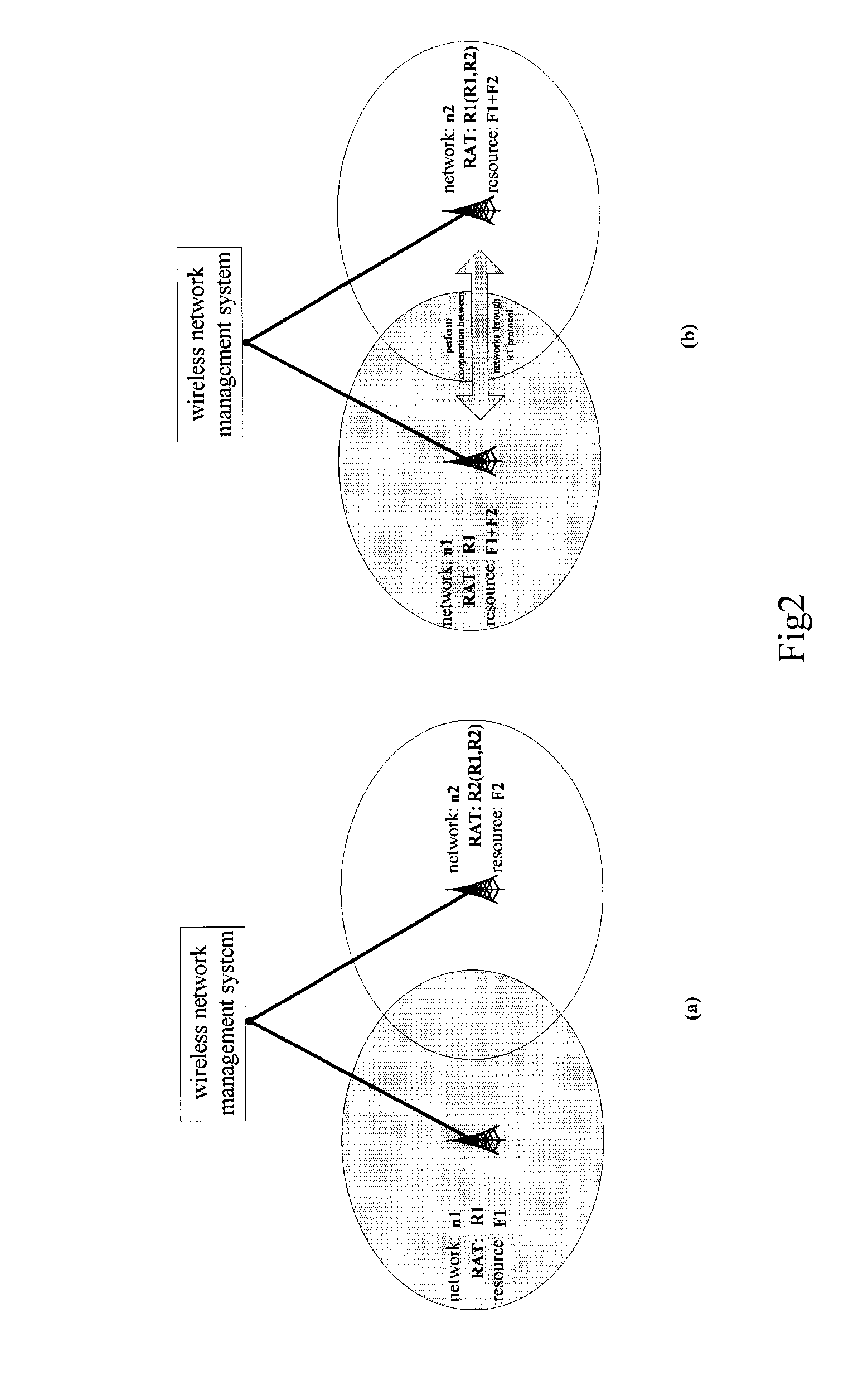
A system and method for wireless network management, for managing wireless access technology and available resources of plural wireless networks. The wireless network management system includes: an information interaction module for collecting wireless network relevant information; a service discovery module for discovering service demands of the wireless networks to generate a set of service demand networks; and an analysis and decision module for determining a new wireless network configuration by merging networks and / or partitioning a network group, wherein the information interaction module is also used for distributing the new wireless network configuration to the wireless networks to allow these to carry out system reconfiguration. With the system and method, cooperative and competitive relationships between wireless networks can be adjusted to enable the networks to adapt to dynamic change of user distribution and resource demands thereof more flexibly and quickly, thereby achieving effective utilization of resources.
Owner:SONY CORP
Scalable database management system
InactiveUS7065526B2Promote migrationIncrease capacityDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsSystem reconfigurationDatabase server
Owner:QUICKBASE INC
Method and system for multiple mobile network operators to share broadcast television white space
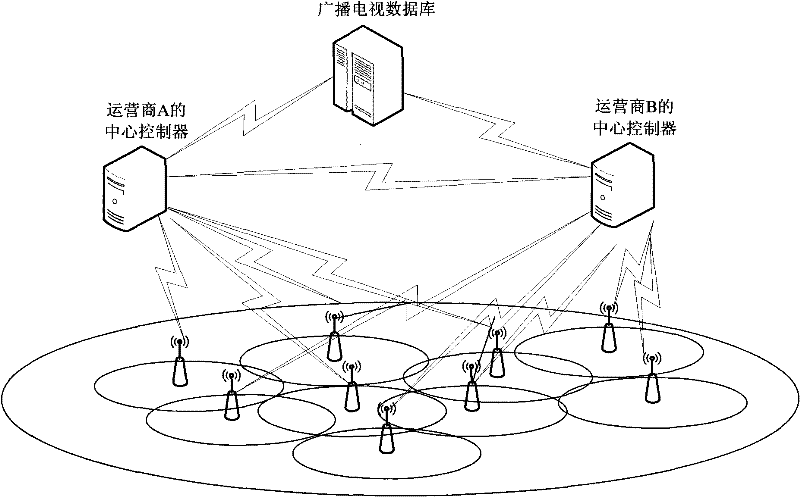
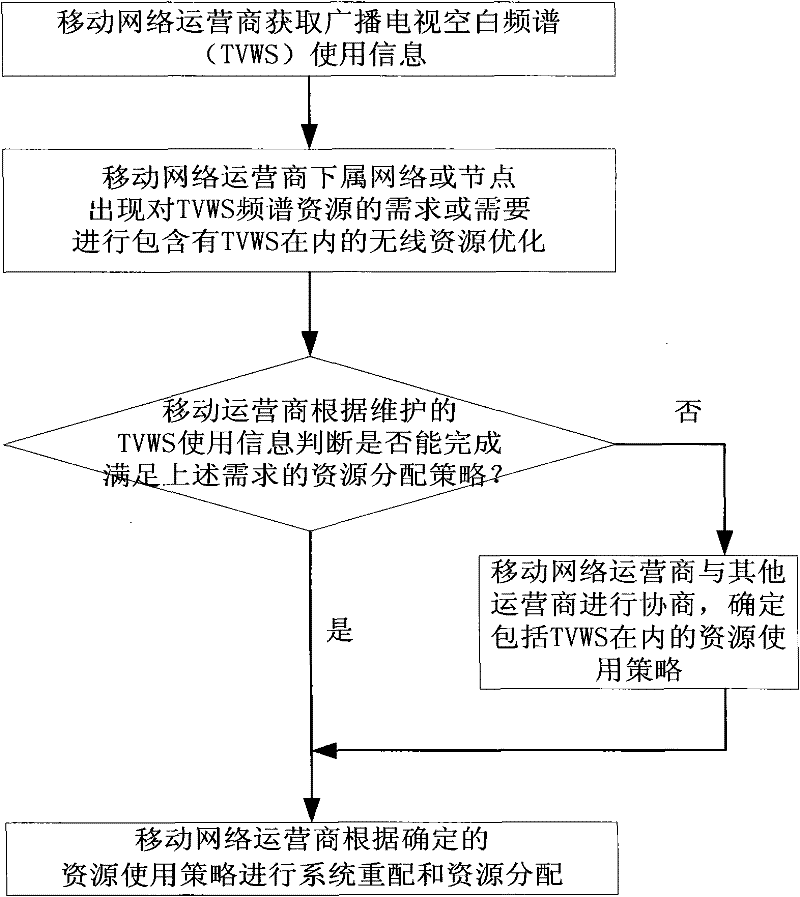
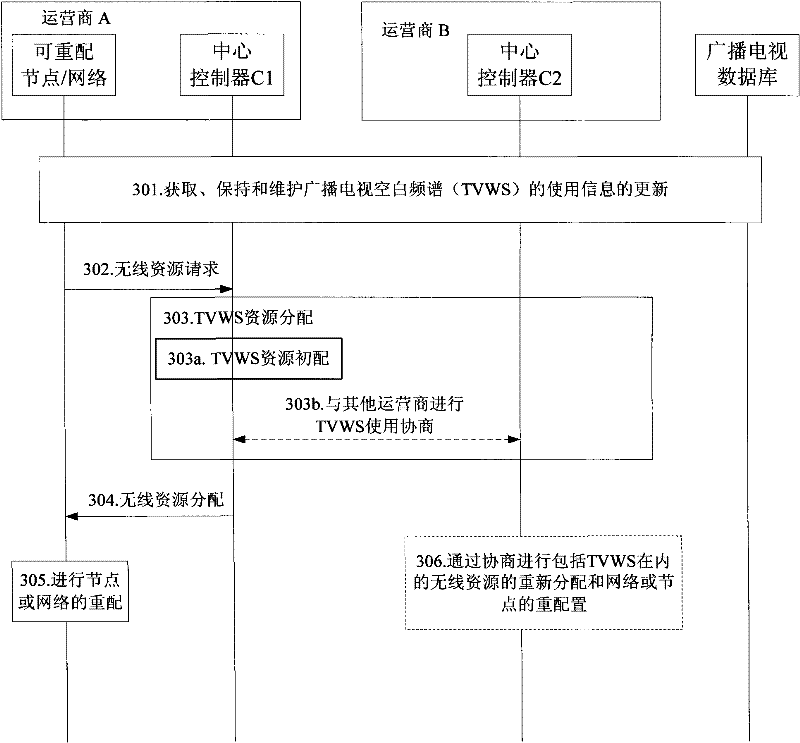
InactiveCN102412919AEasy to useSolve the problem of non-interference and efficient coexistenceResource management arrangementsNetwork planningResource poolSystem reconfiguration
The invention discloses a method and system for multiple mobile network operators to share the broadcast television white space. In the method, use information of the white space is obtained through a central controller of one mobile network operator; when subordinate networks or nodes of the mobile network operator have a new requirement for the white space or need to optimize the white space in use, a white space use strategy is determined based on the use information of the current white space of the central controller or by negotiating with the central controllers of other mobile network operators; and the central controller of the mobile network operator executes system reconfiguration or resource allocation according to the white space use strategy. Through the method and system disclosed by the invention, multiple mobile network operators can share the TVWS (Television Broadcast White Space) effectively in the same broadcast television white space resource pool, and can coexist fairly and efficiently without interference to each other.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Automatic airplane seat location mapping
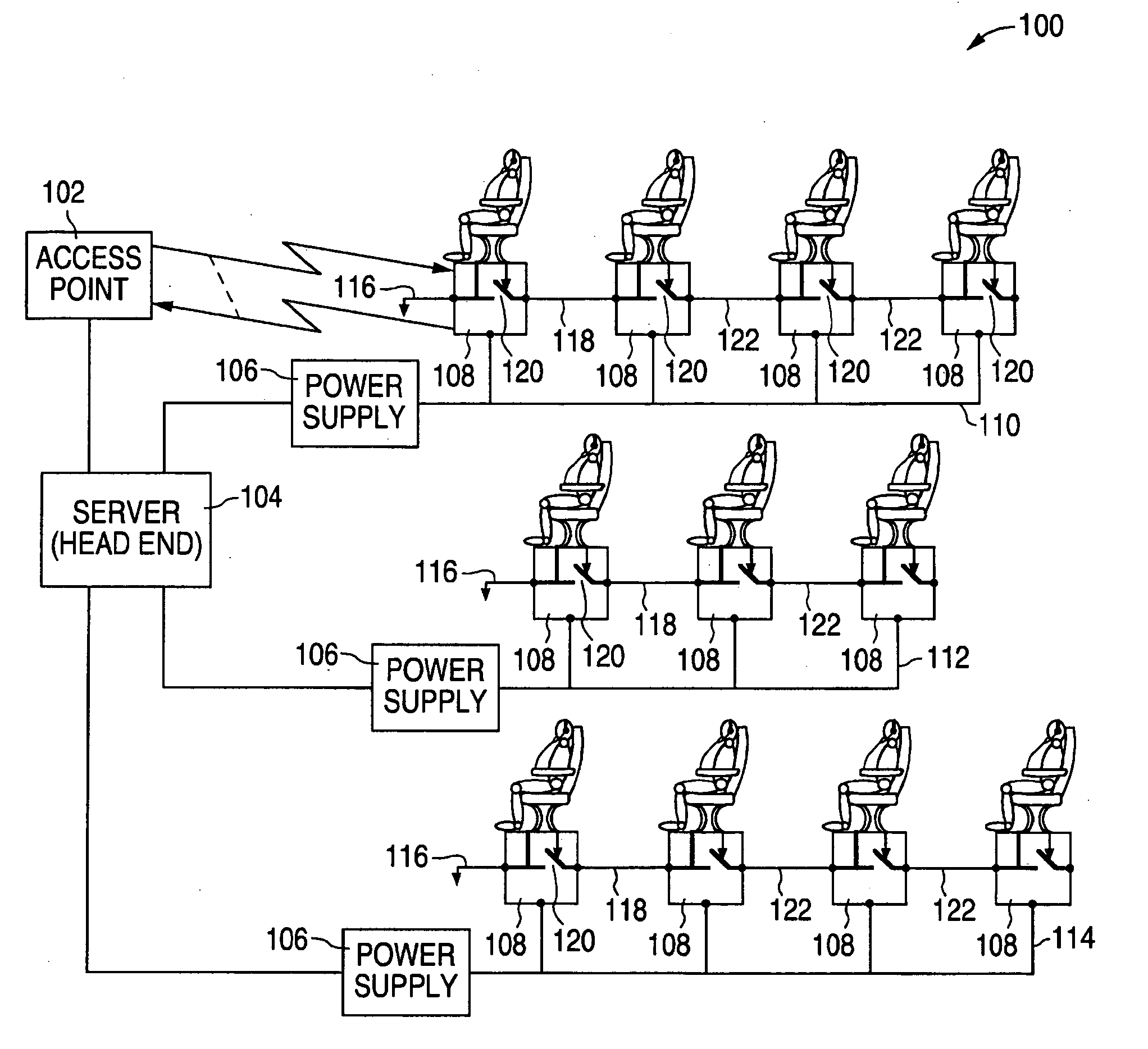
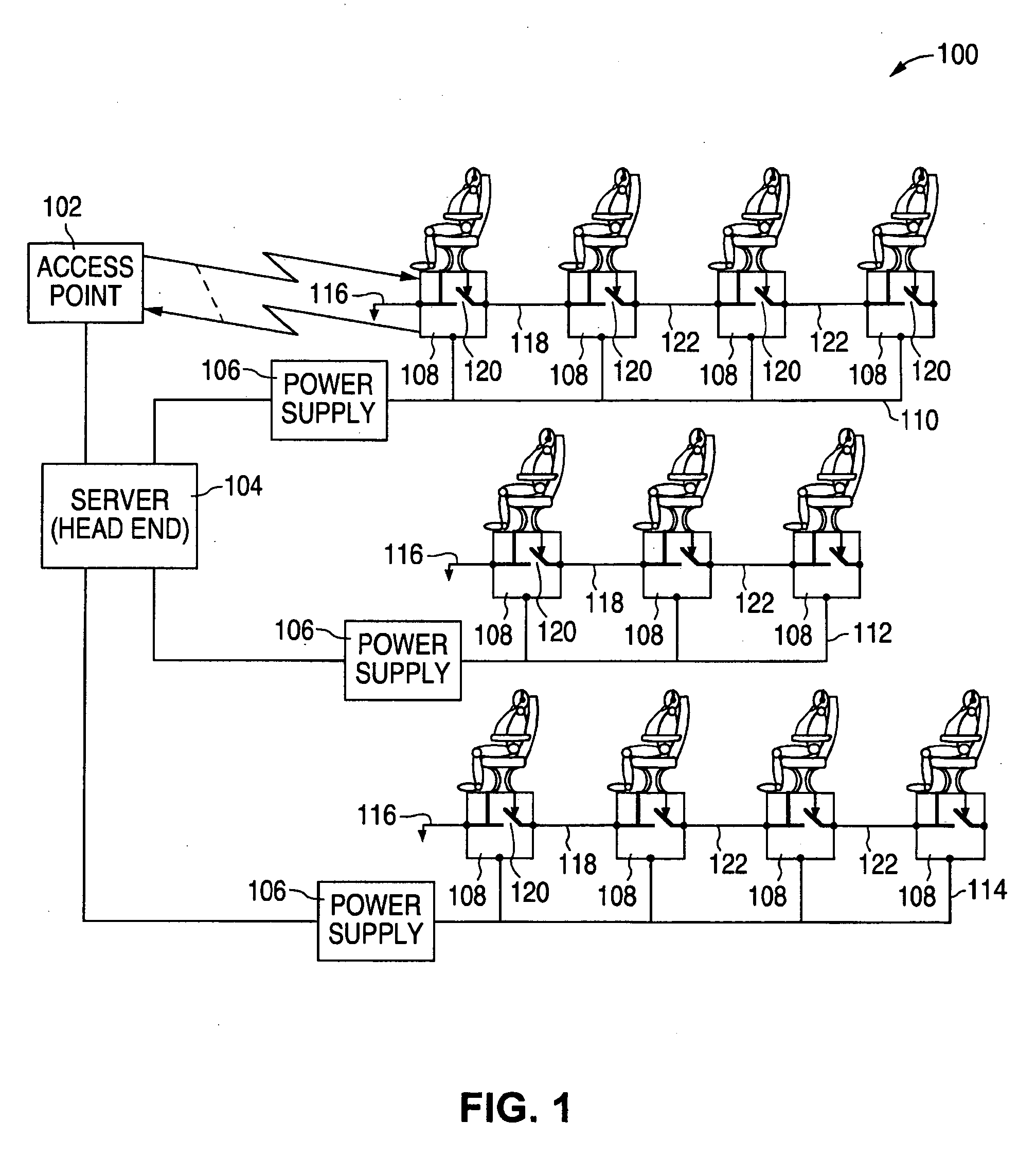
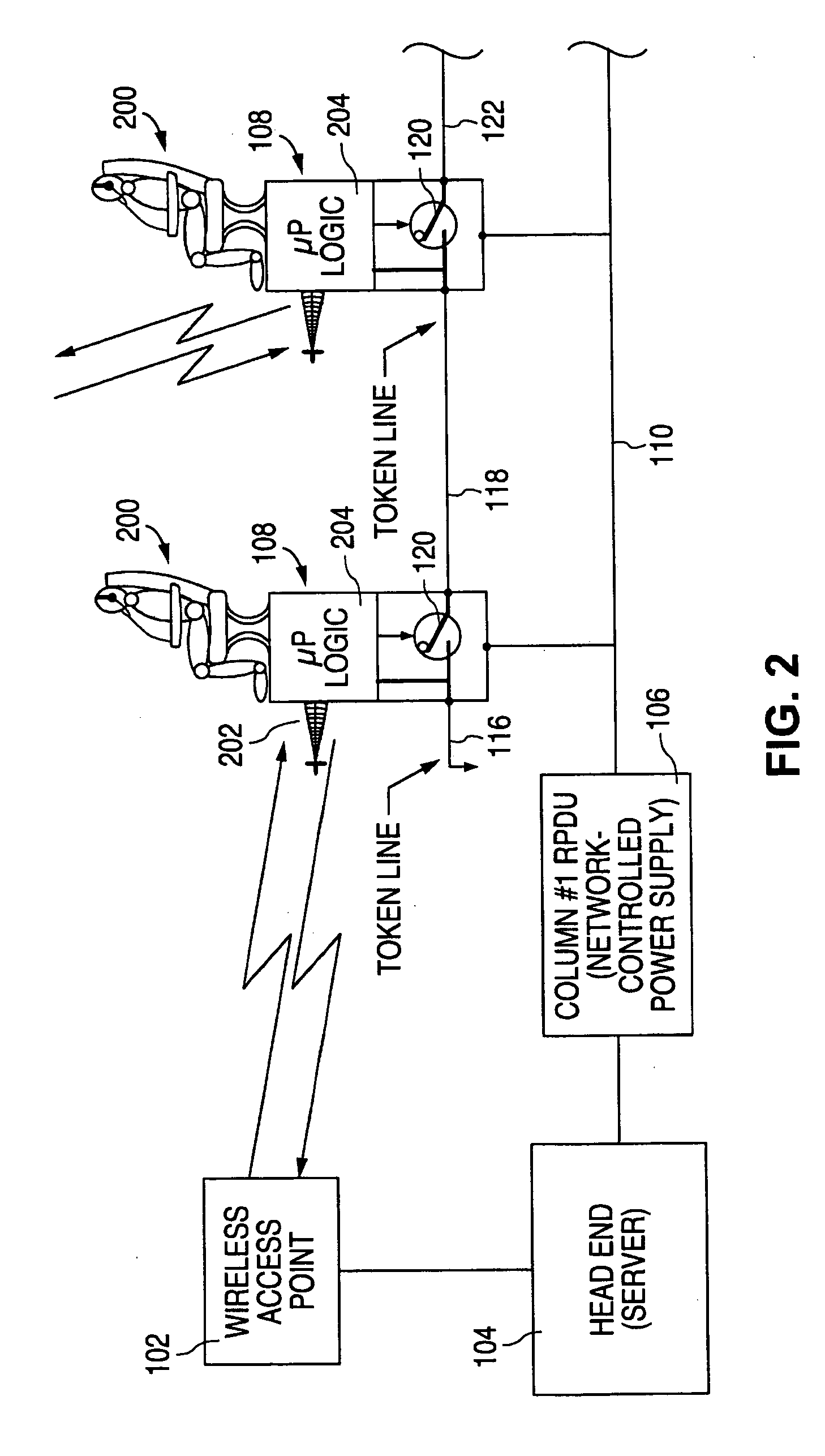
ActiveUS20060246892A1Less complexityLess costNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSystem reconfigurationEngineering
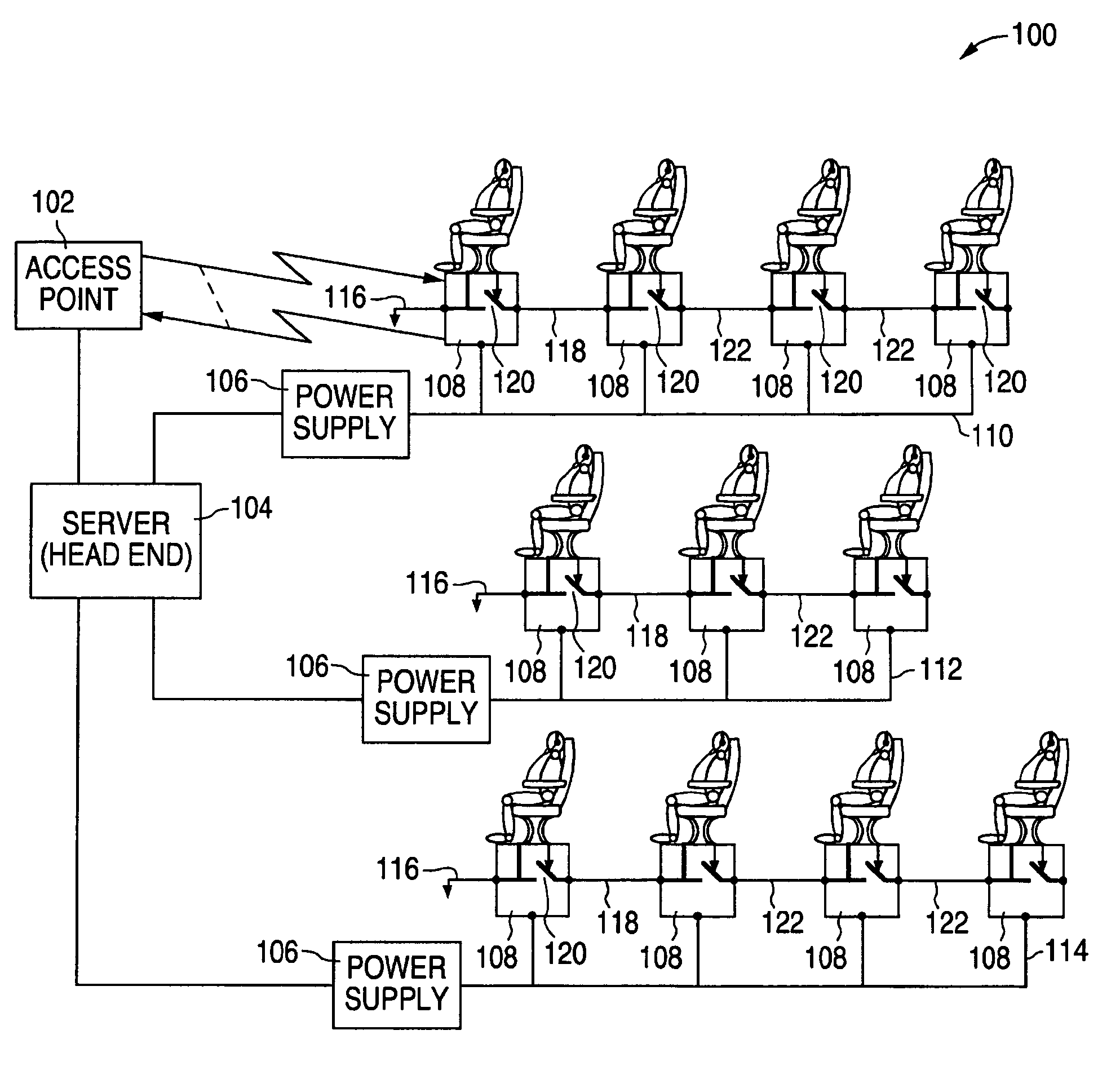
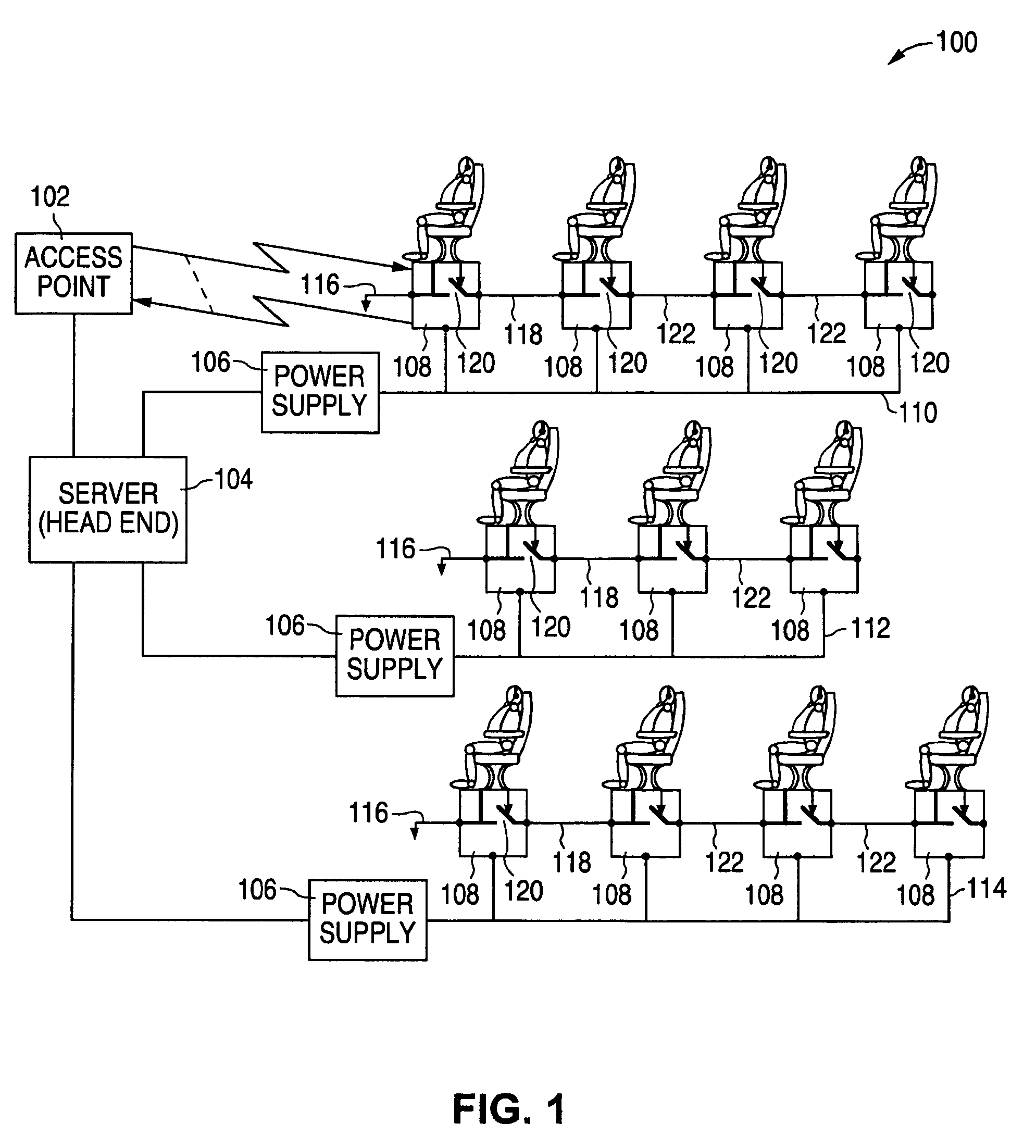
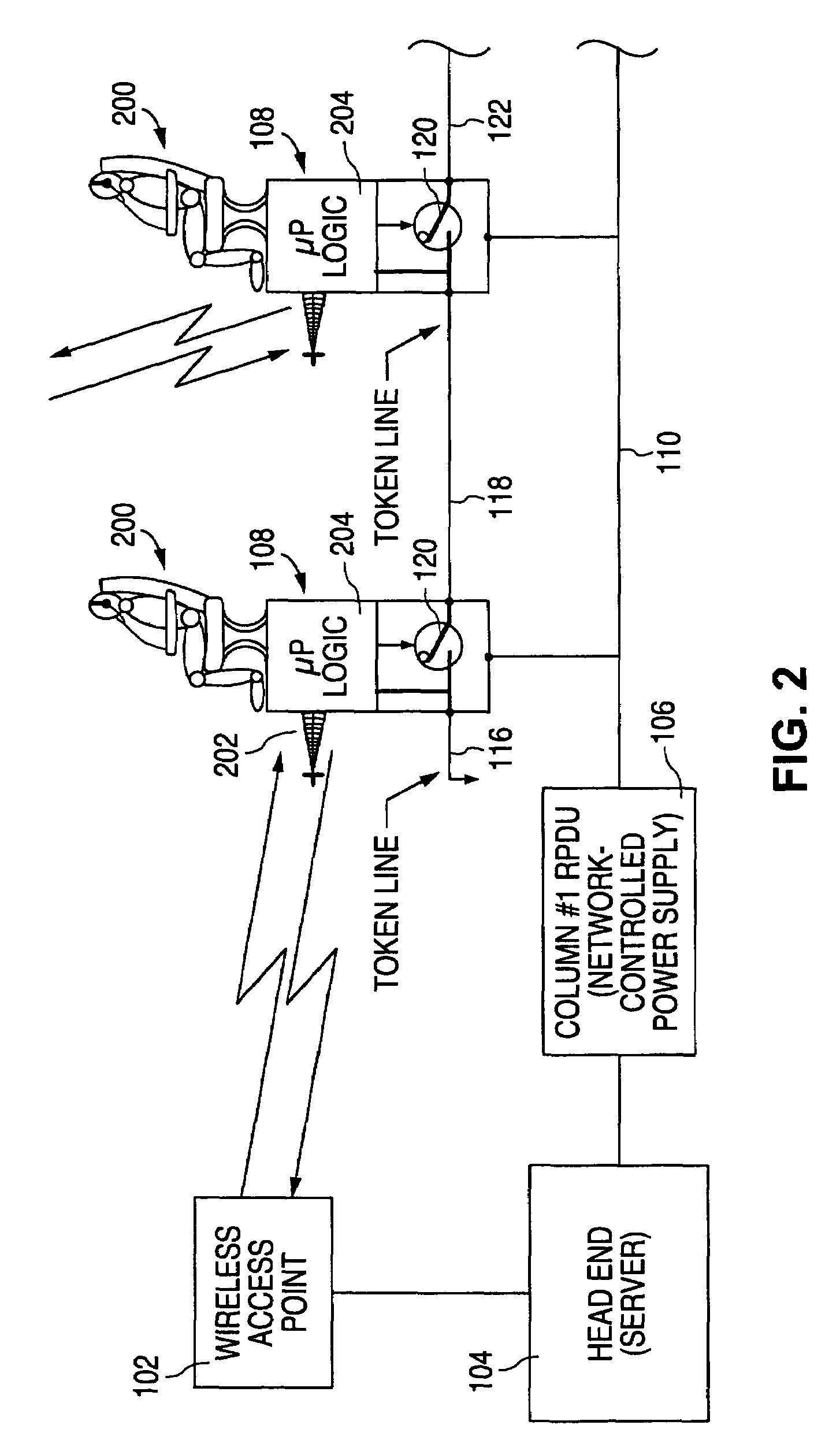
During a system reconfiguration, a selected column or column of wireless units, such as associated with airplane seats, are powered up. The first unit in the column detects a ground and begins a wireless identification process with an access point which allows the system to determine a corresponding physical location for each node's logical address. The first unit then closes a switch, which connects the ground to the next unit. As the next unit detects the ground on the line, such as a token line, the second unit communicates with the AP. This process continues sequentially down the column until the last unit is assigned a physical location / address. The next column of units can then be powered up and identified.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Fault-tolerant combined method of strapdown inertial integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles
InactiveCN102221363AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed fault toleranceNavigation instrumentsFault toleranceTerrain
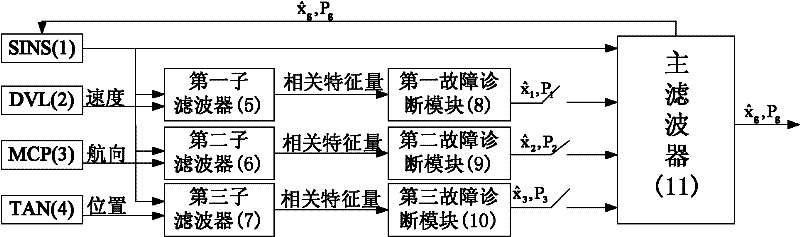
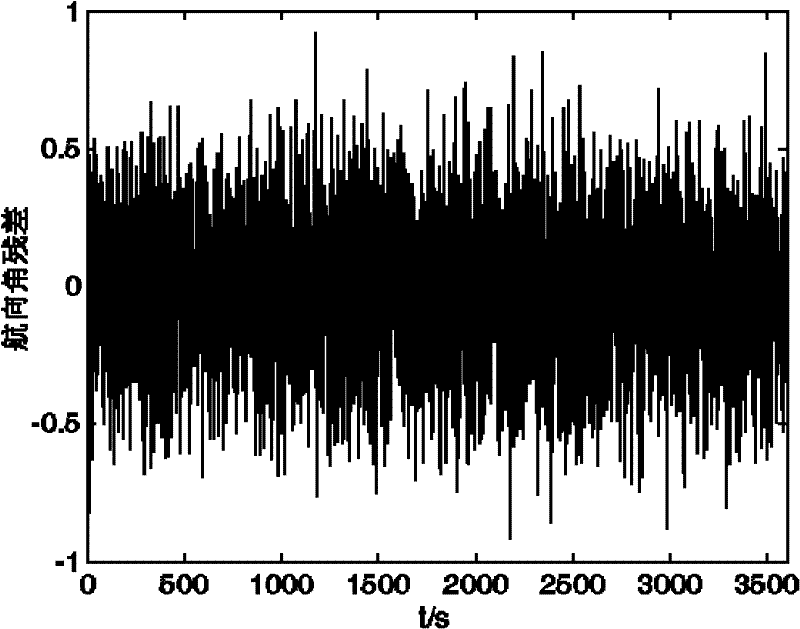
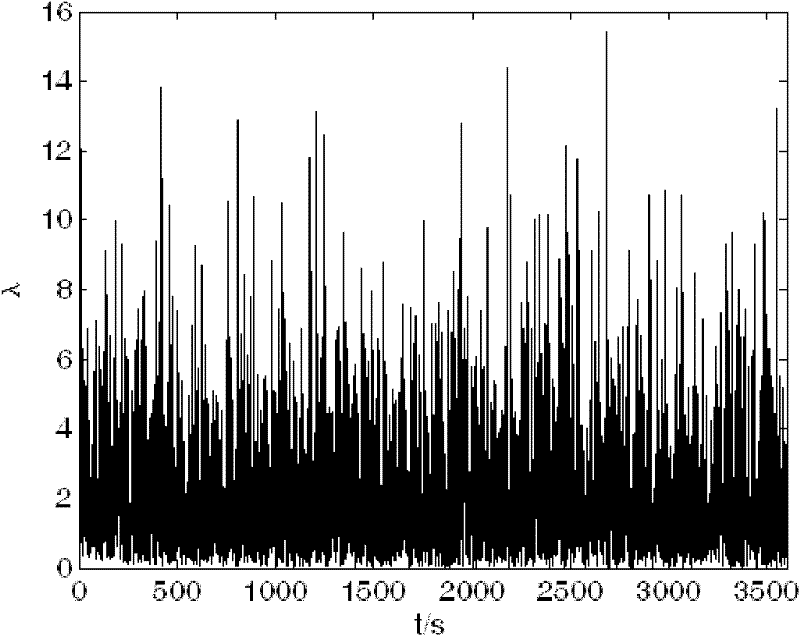
The invention provides a fault-tolerant combined method of a strapdown inertia integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles. The method is composed of a strapdown inertial navigation system SINS, a terrain aided navigation system TAN, a Doppler velocity log DVL and a magnetic compass pilot MCP, and realizing an integrated navigation process through a decentralized filter structure and an intelligent fault-tolerance method. The method comprises the following steps of constructing sub-filters respectively with the SINS as a reference navigation system and the TAN, the SINS and the DVL, and the SINS and the MCP, extracting related characteristic quantities from the sub-filters to transmit them into fault diagnosis modules composed of a supporting vector machine, determining if faultsexist in the TAN, the DVL or the MCP, if the faults exist, information of the TAN, the DVL or the MCP with the faults is screened, then carrying out a system reconfiguration process, and then feedingback errors outputted from a main filter to the SINS for correction. The method can guarantee a good reliability and a high fault tolerance of a strapdown inertial integrated navigation system for underwater vehicles, especially make a support vector machine trained in small samples have a strong popularization capability, and provide a novel method for a fault diagnosis.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Control system architecture for a multi-component armament system
InactiveUS7092867B2Improve robustnessStrong system scalabilityDigital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSystem reconfigurationApplication software
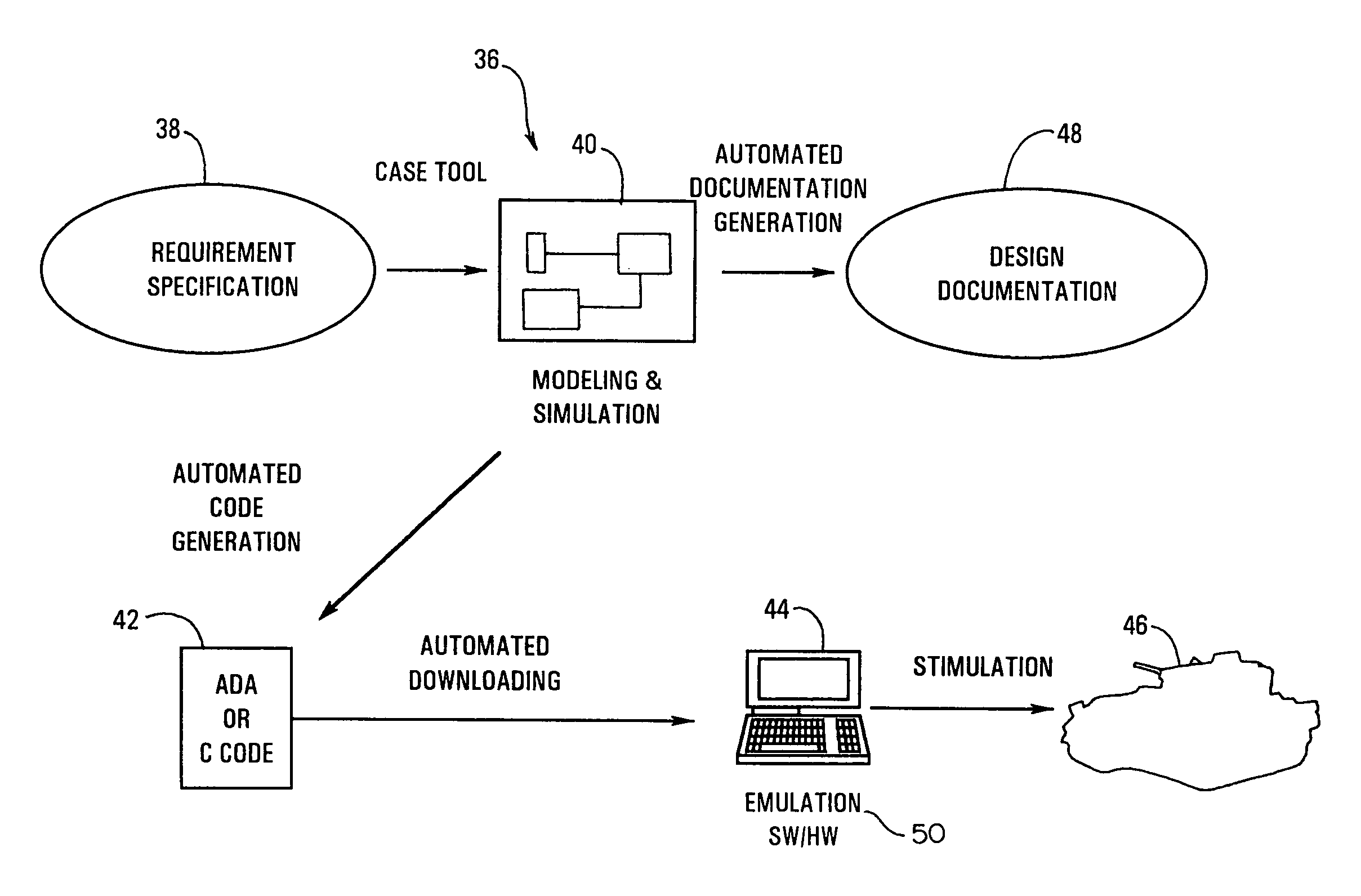
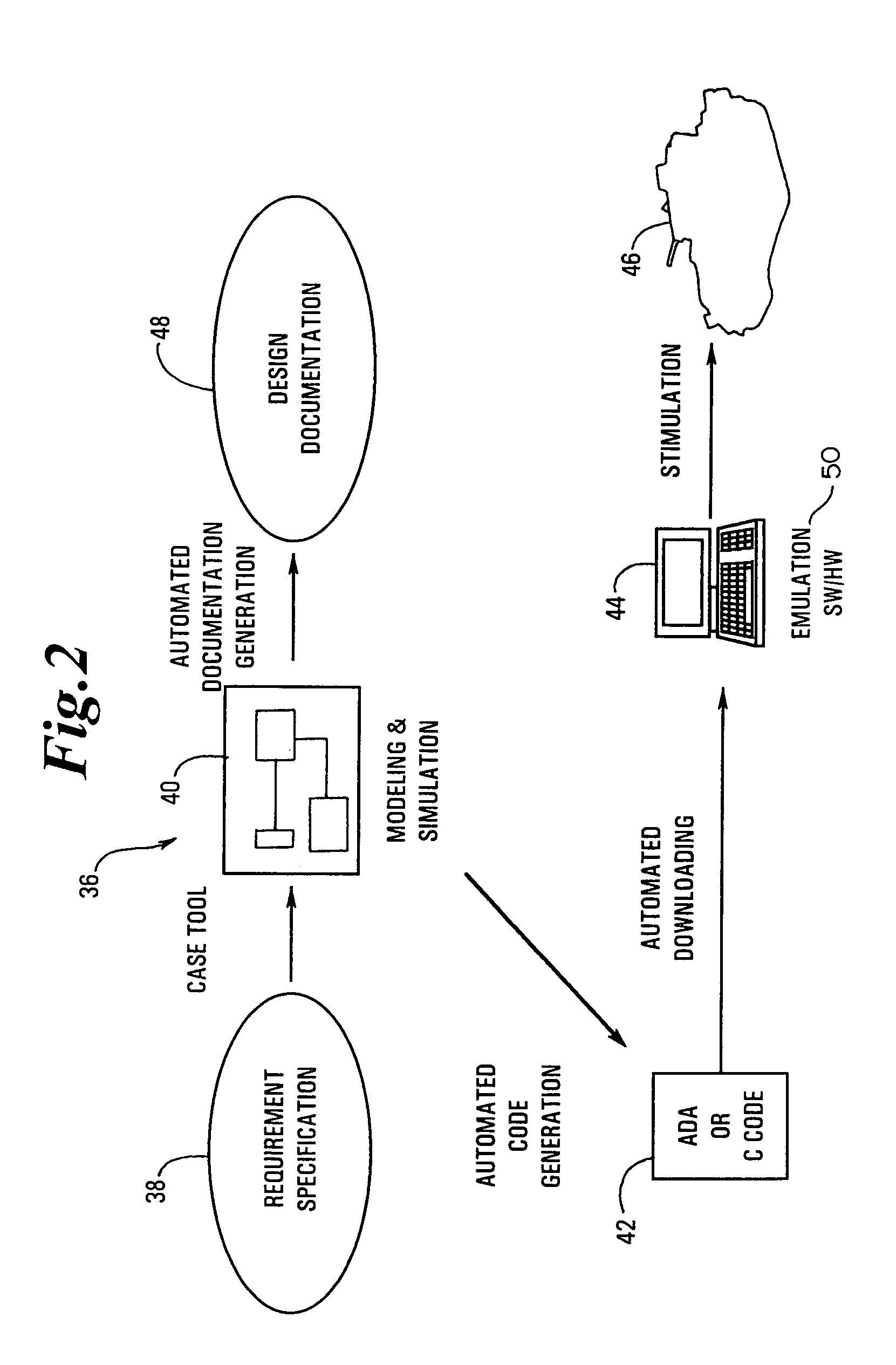
The present invention is a Control System Architecture (CSA) for a multi-component armament system. The CSA provides dynamic reconfiguration of multiple nodes (e.g. a component, a subsystem, or a virtual simulation) in a Simulation-Emulation-Stimulation (SES) environment utilizing redundant client-server bus configuration of the nodes in a hierarchical model. The CSA provides for ease of configuration of nodes for any specific application, automated system reconfiguration capabilities to detect and bypass failed nodes or re-group available remaining nodes in the event of degraded mode operation, and expansion and / or downsizing of nodes without requiring a modification to the overall system architecture.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS LAND & ARMAMENTS LP
Management method and apparatus for storage apparatus
InactiveUS7512888B2Avoid problemsConfirm appropriatenessInput/output to record carriersDigital computer detailsSystem reconfigurationEmbedded system
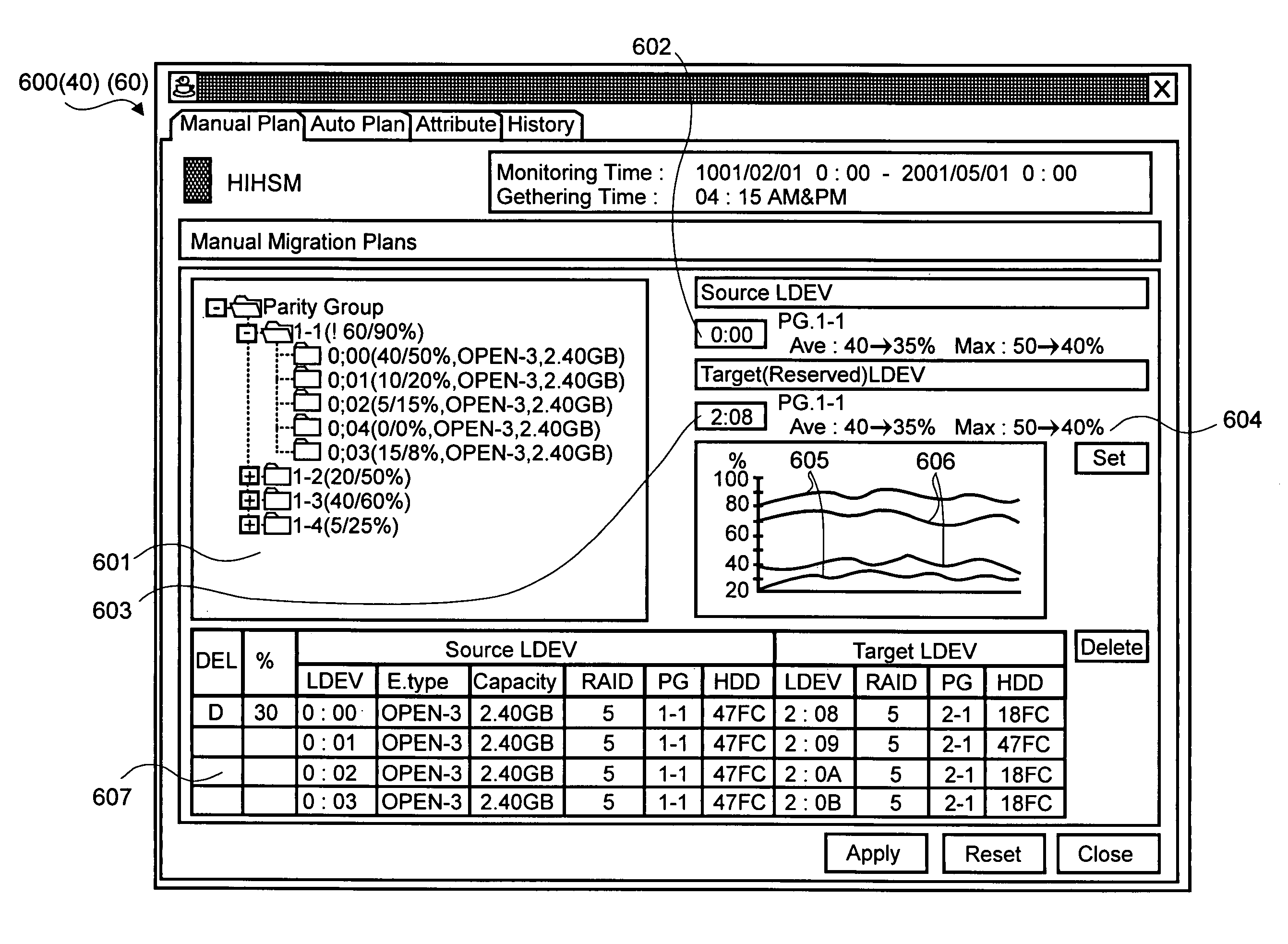
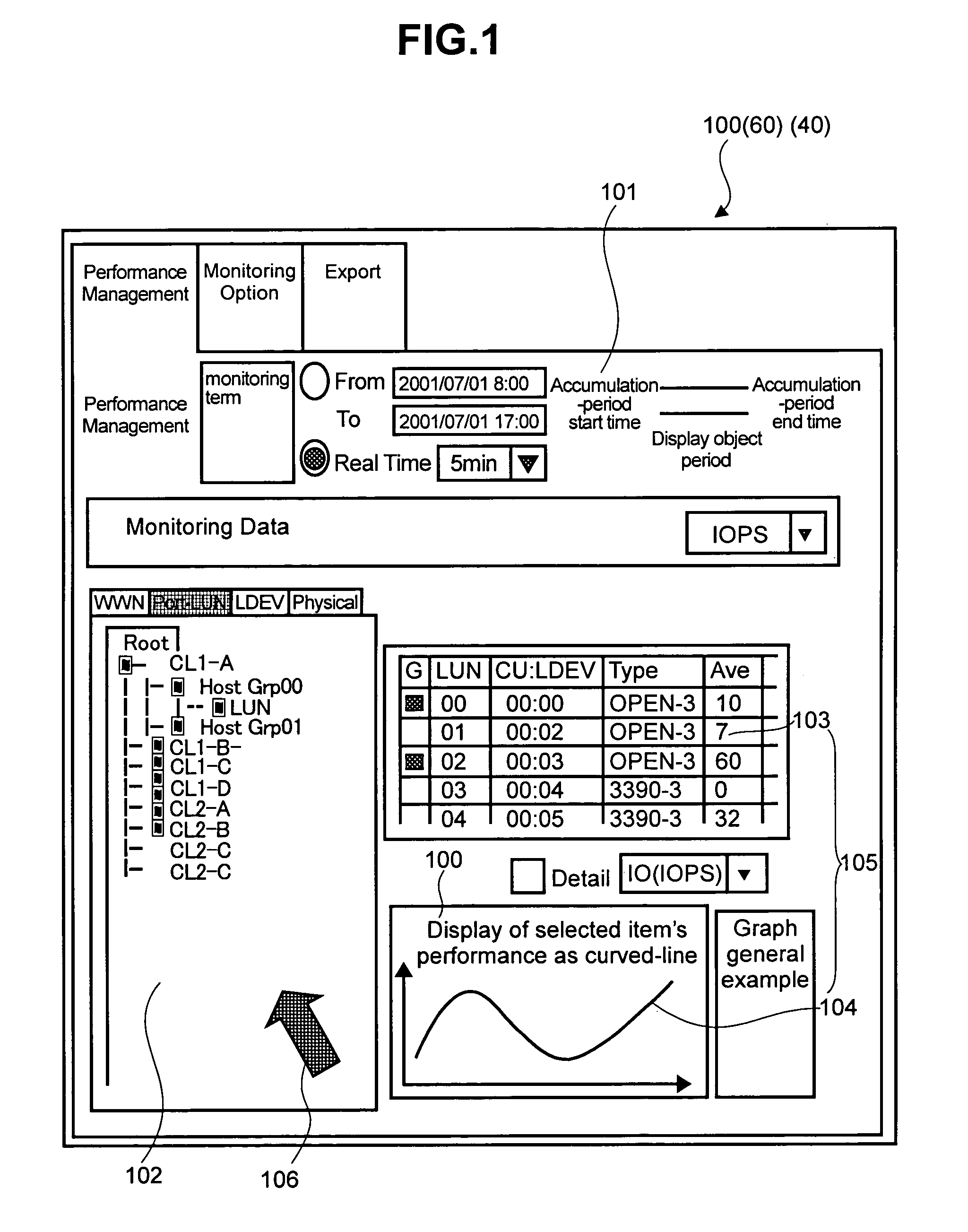
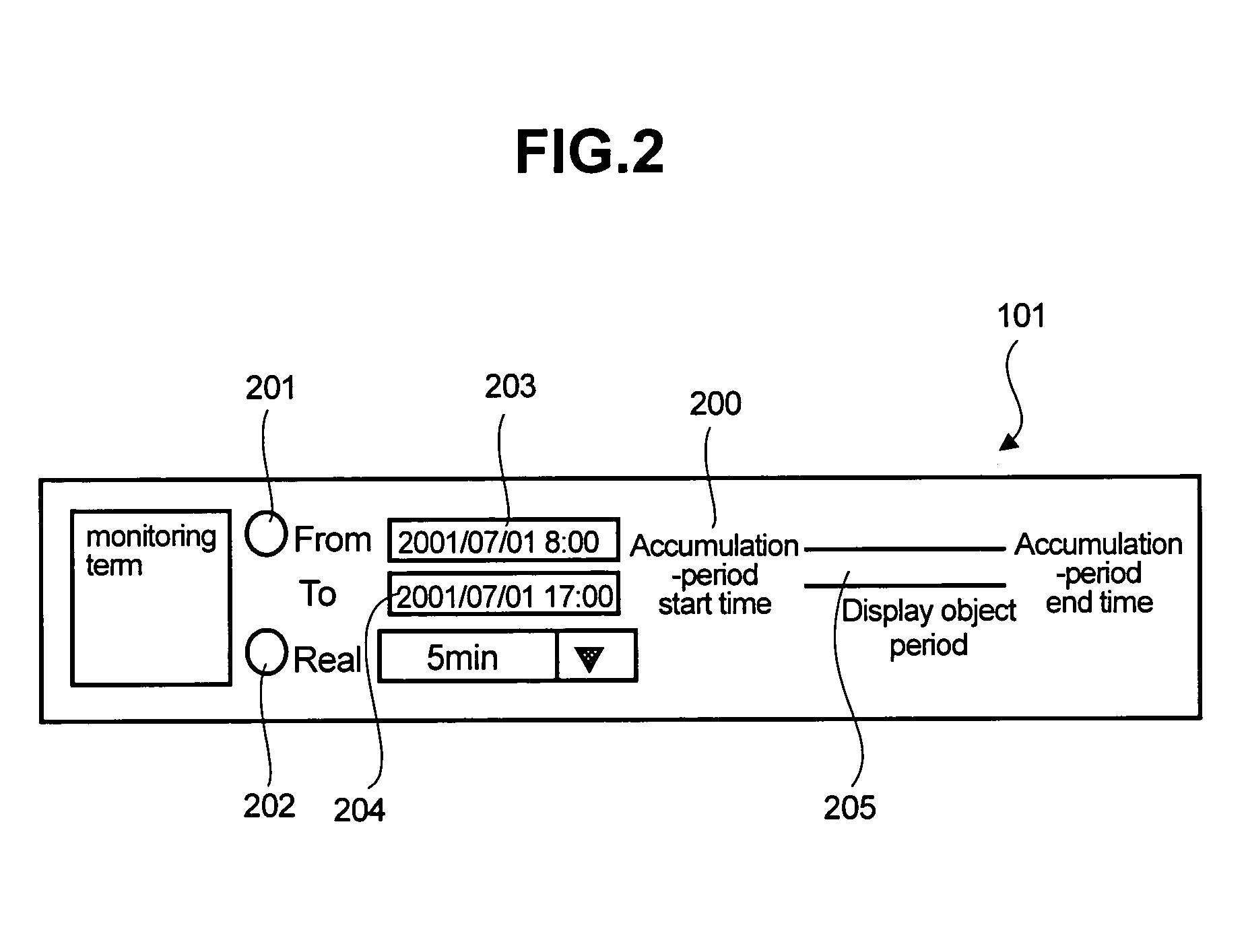
A method for performing a system reconfiguration of a storage system includes displaying a configuration window visually showing a configuration of a plurality of components in the storage system within an operation screen. An input area is displayed within the operation screen, the input area being provided for entering one or more components to be reconfigured. A performance window is displayed within the operation screen, the preference window providing bandwidth utilization information of one or more of the components in the storage system. The configuration window, performance window, and the input area are all viewable at the same time without activating another operation screen.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fault detection method for Hall position sensors
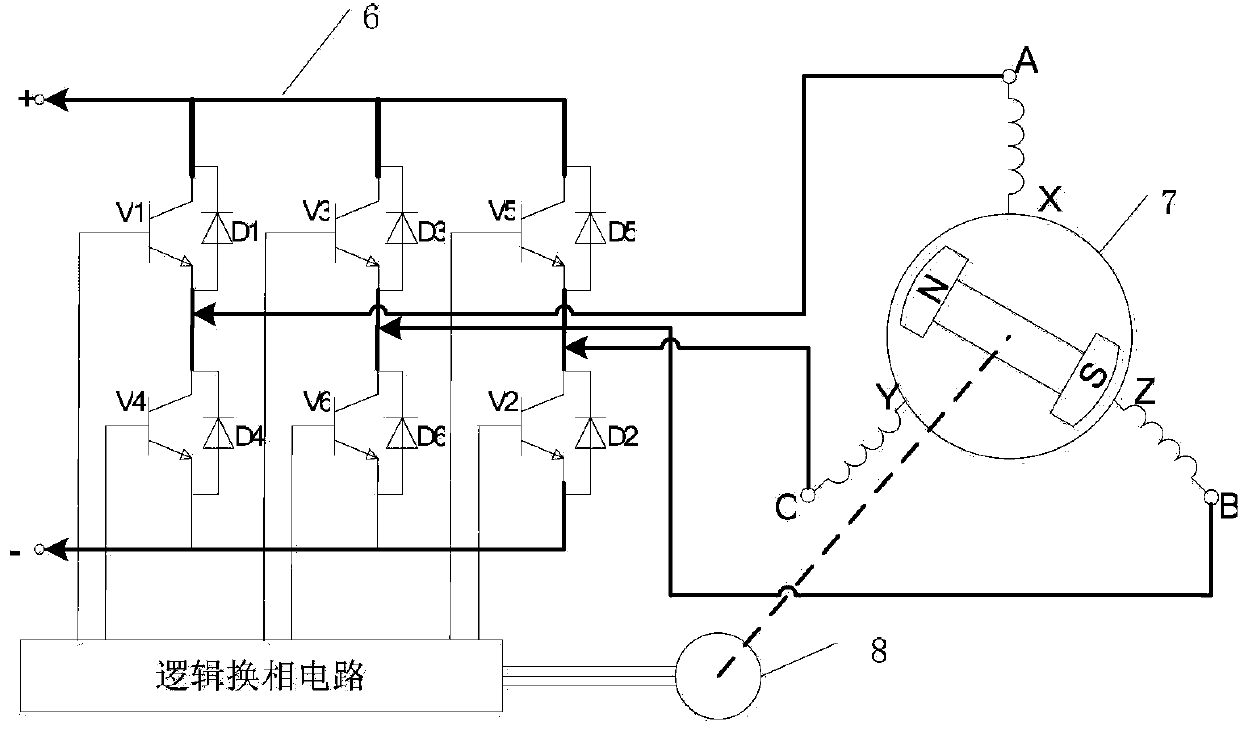
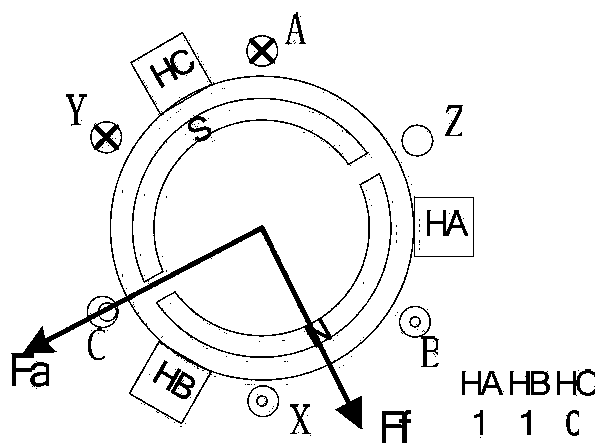
ActiveCN103424651AAccurate detectionAccurate replacementElectrical testingMotor driveArray data structure
The invention discloses a fault detection method for Hall position sensors. The method is available for comprehensively and accurately detecting Hall sensor faults and accurately locating faults of motor Hall position sensors; a user can replace the failed Hall sensor timely and accurately according to fault information. The method includes initializing variables, giving PSWM wave with proper duty ratio, controlling a motor drive module to allow a driver to operate, observing a value of an array when a motor stops rotating, comprehensively judging Hall state, and accurately detecting the fault of the Hall sensor so as to provide forcible support for fault identification and system reconfiguration. Compared with the traditional methods of detecting only whether the Hall sensors are all in high level or low level or not, the method has the advantages that the method is simple and practical, false alarm rate is low, modification on hardware circuits is avoided, the effect can be good just after software is optimized, and optimization cost is low.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
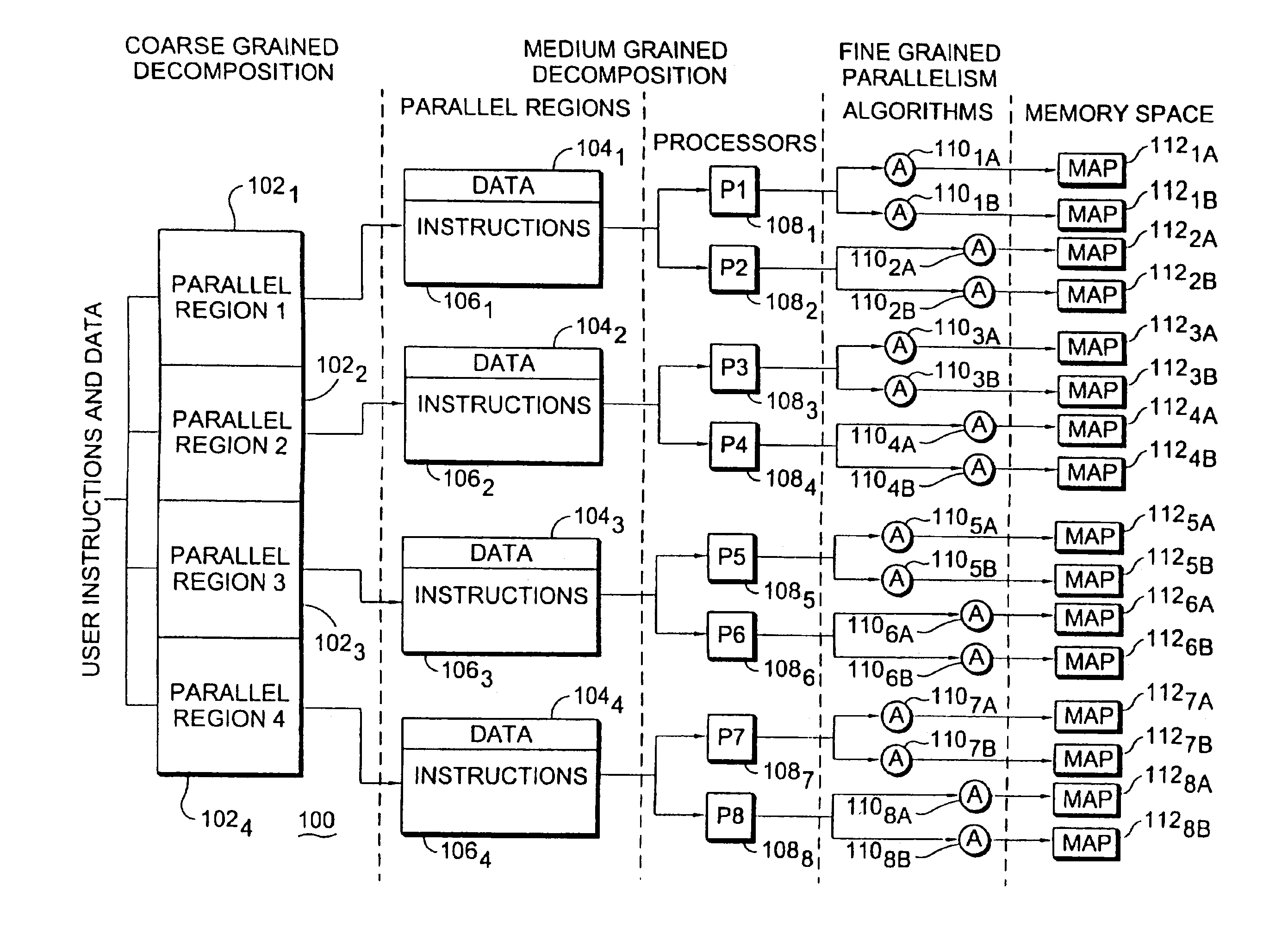
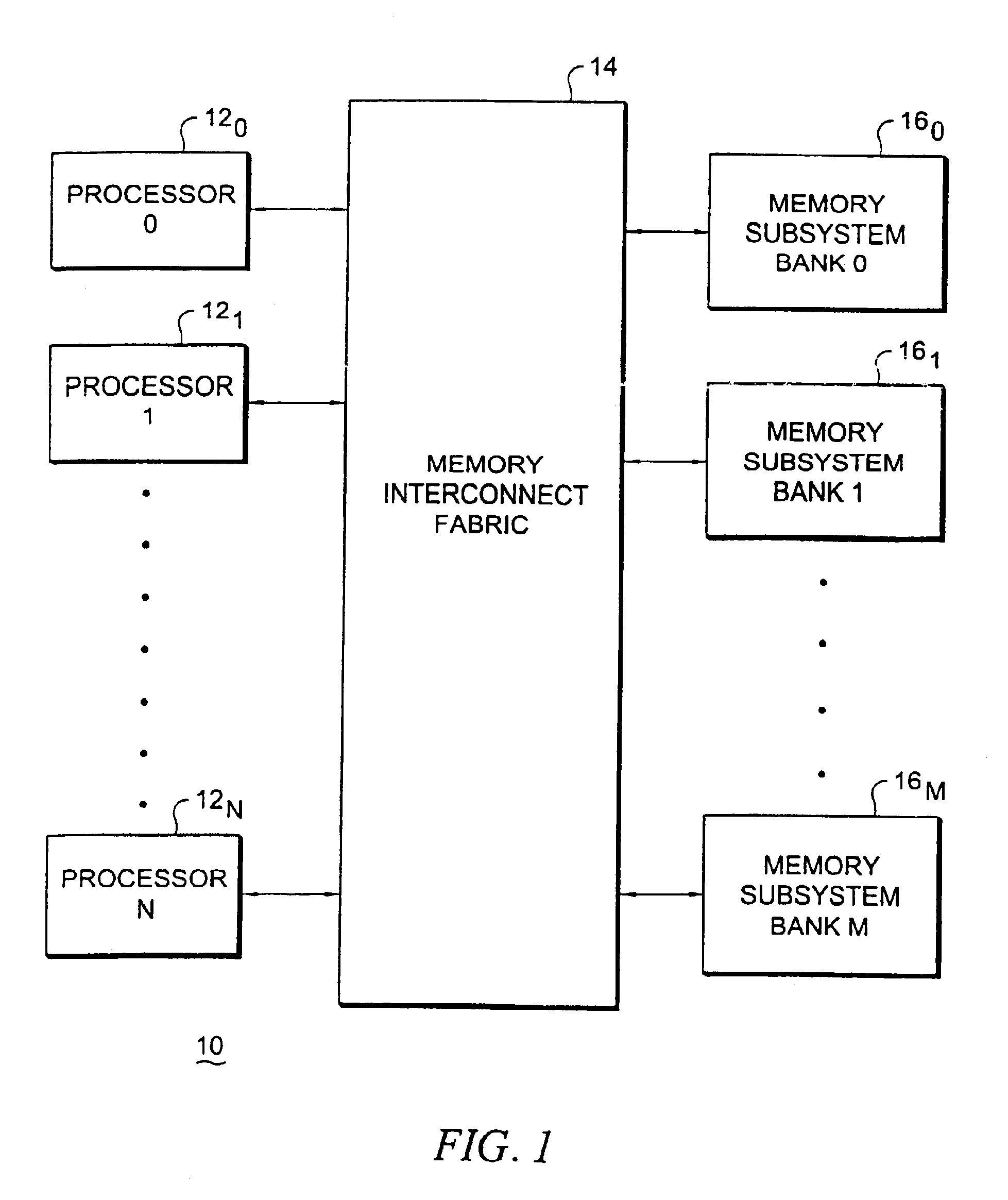
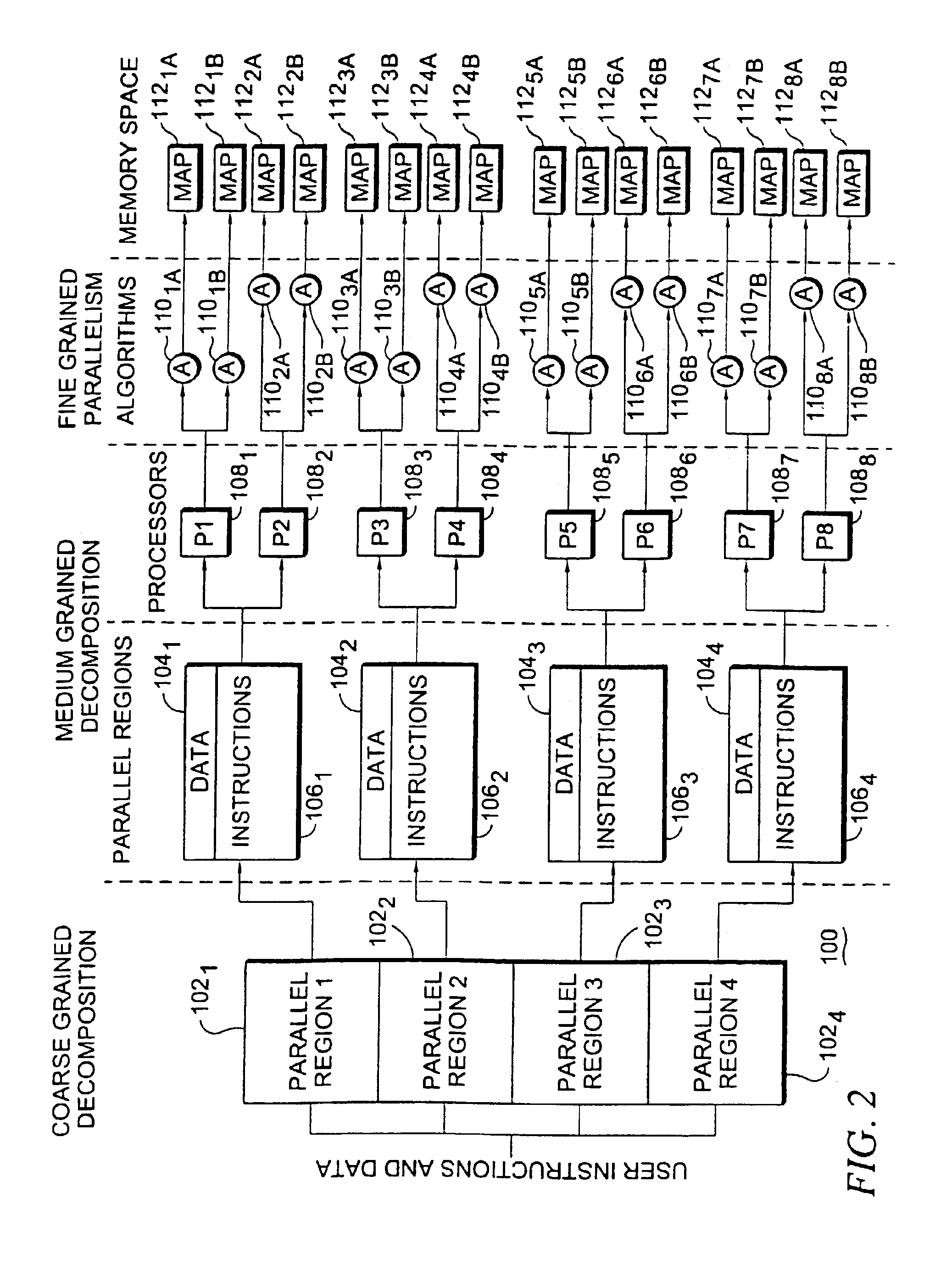
Multiprocessor computer architecture incorporating a plurality of memory algorithm processors in the memory subsystem
InactiveUS6961841B2Improve performanceLow costComputer controlSimulator controlDirect memory accessSystem reconfiguration
A multiprocessor computer architecture incorporating a plurality of programmable hardware memory algorithm processors (“MAP”) in the memory subsystem. The MAP may comprise one or more field programmable gate arrays (“FPGAs”) which function to perform identified algorithms in conjunction with, and tightly coupled to, a microprocessor and each MAP is globally accessible by all of the system processors for the purpose of executing user definable algorithms. A circuit within the MAP signals when the last operand has completed its flow thereby allowing a given process to be interrupted and thereafter restarted. Through the use of read only memory (“ROM”) located adjacent the FPGA, a user program may use a single command to select one of several possible pre-loaded algorithms thereby decreasing system reconfiguration time. A computer system memory structure MAP disclosed herein may function in normal or direct memory access (“DMA”) modes of operation and, in the latter mode, one device may feed results directly to another thereby allowing pipelining or parallelizing execution of a user defined algorithm. The system of the present invention also provides a user programmable performance monitoring capability and utilizes parallelizer software to automatically detect parallel regions of user applications containing algorithms that can be executed in the programmable hardware.
Owner:SRC COMP
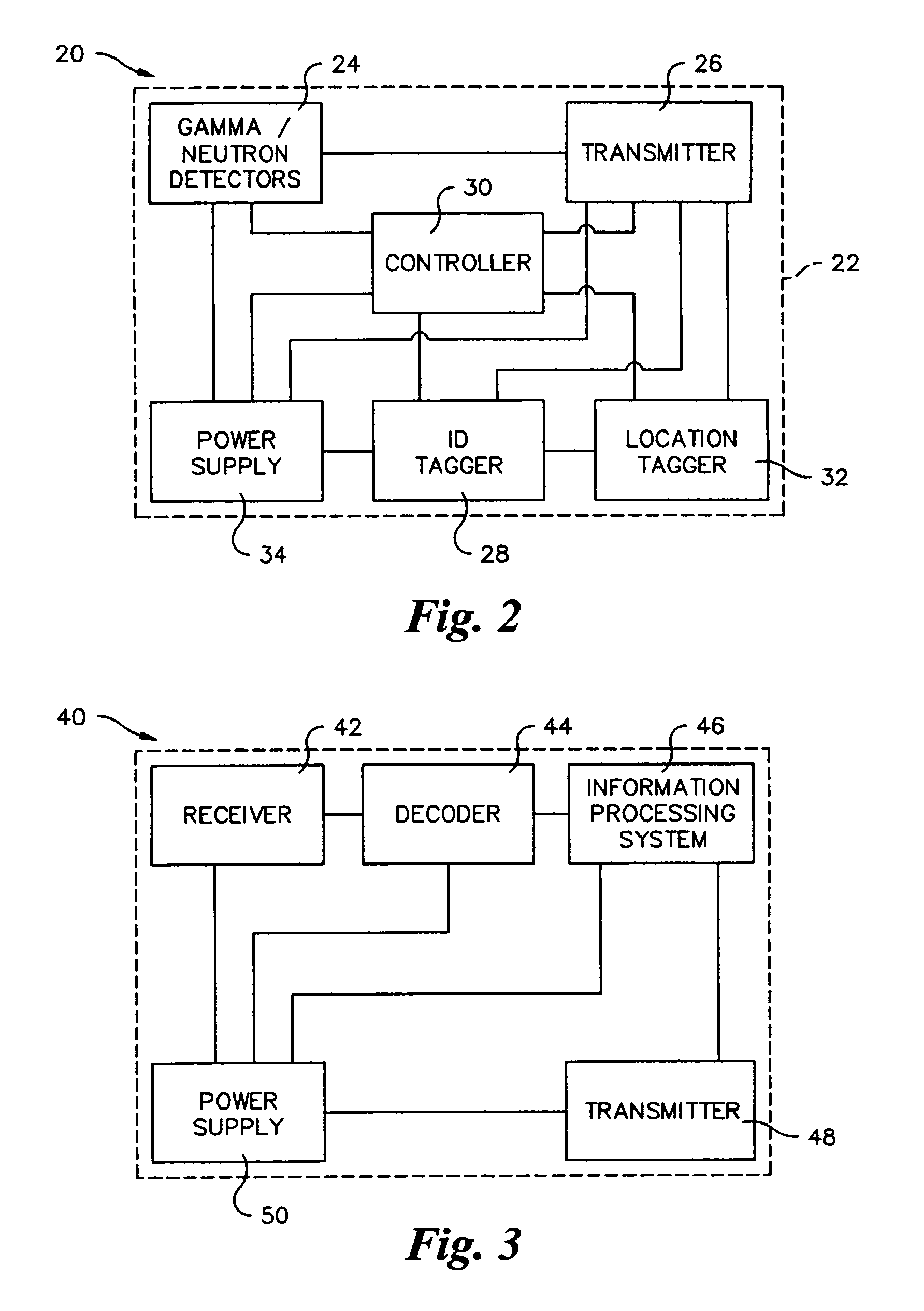
Method and apparatus for detection of radioactive material
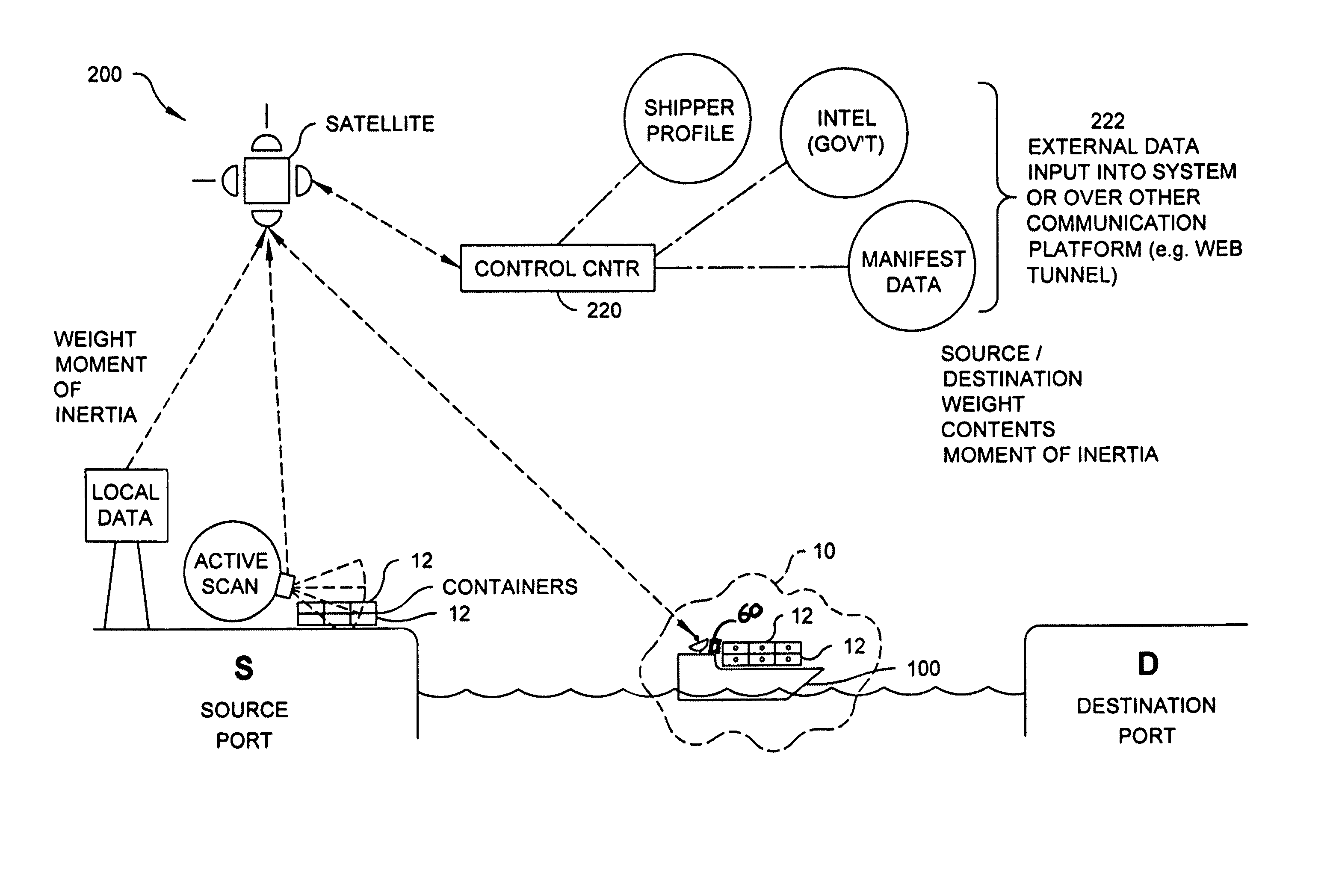
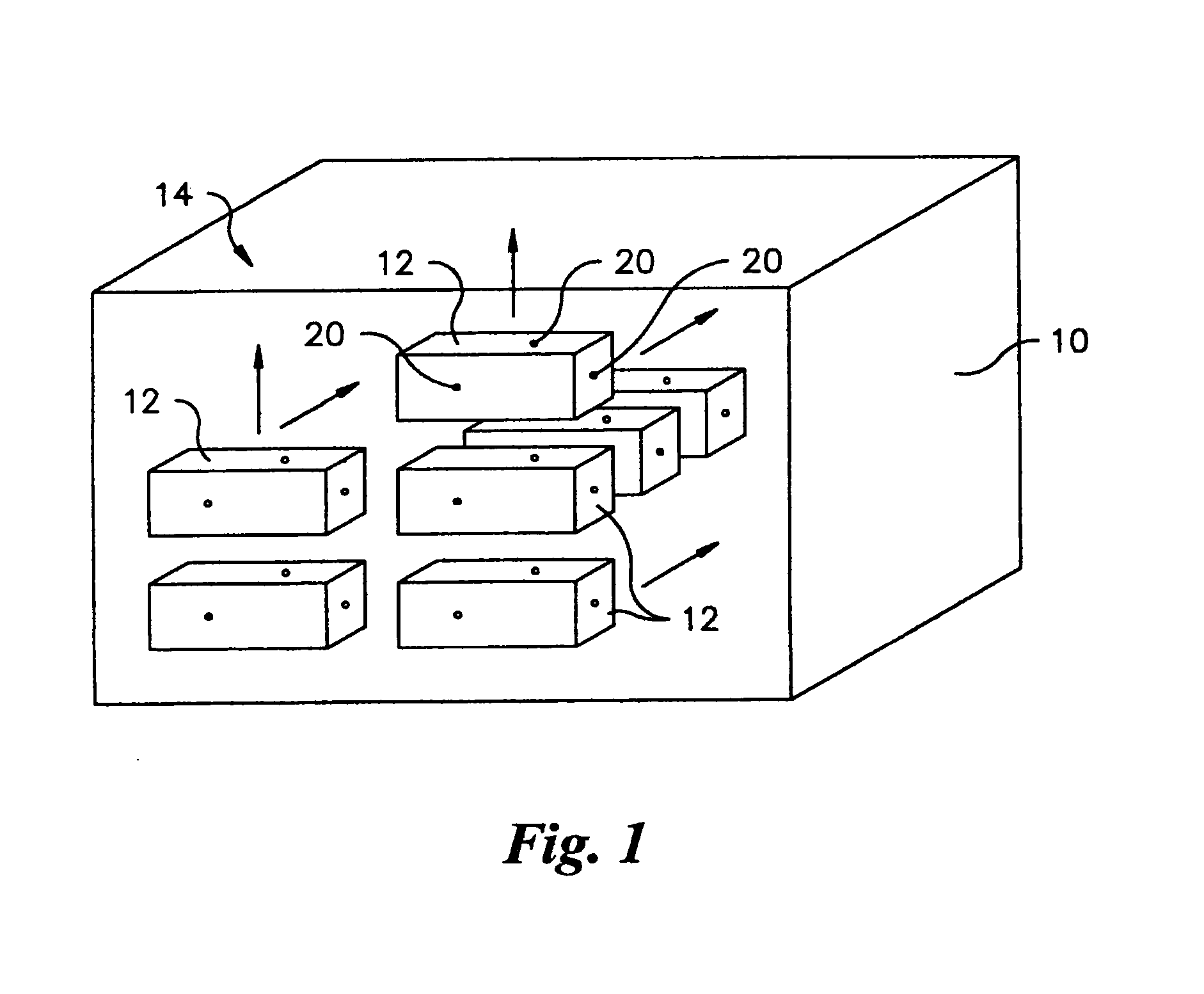
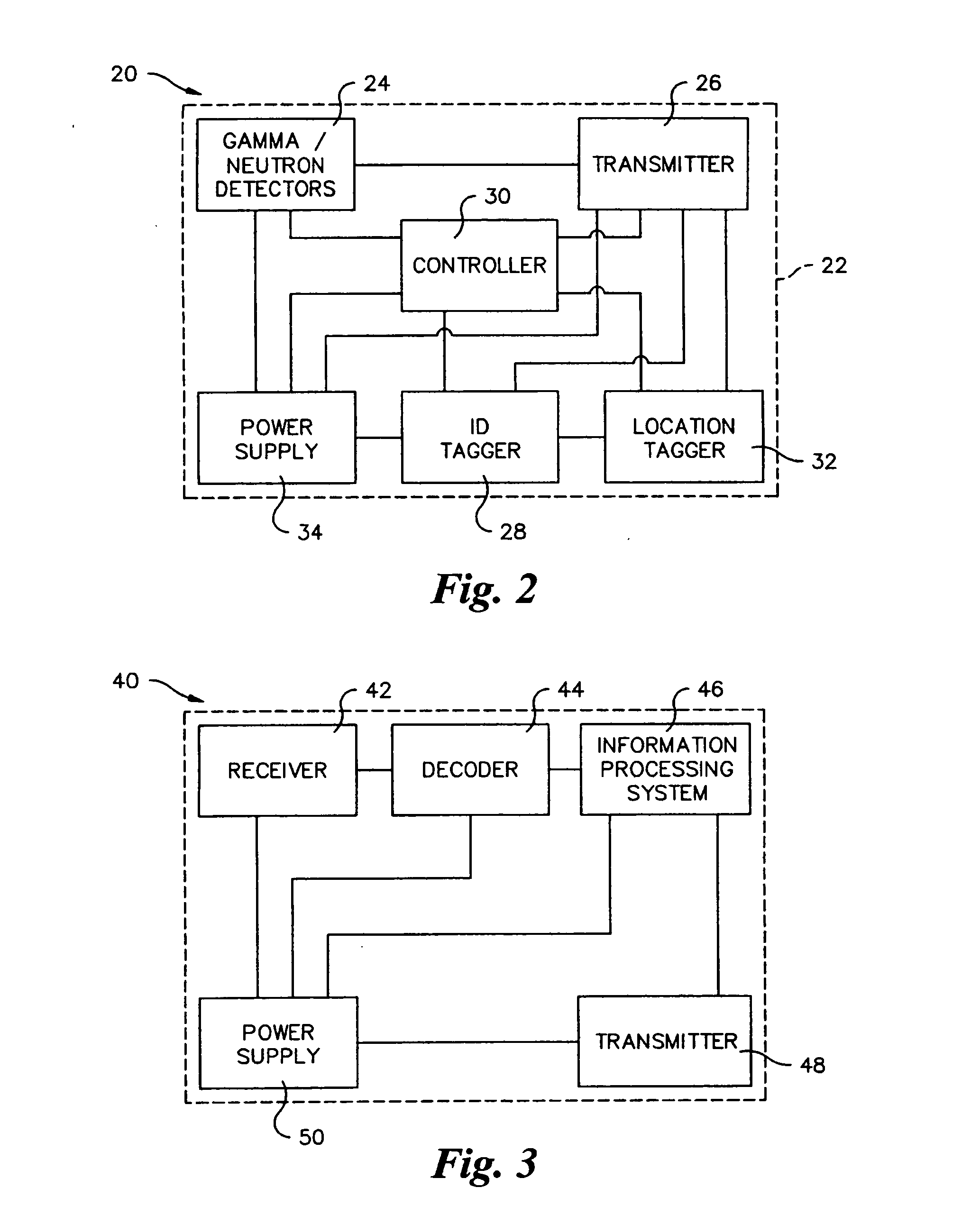
InactiveUS20070096037A1Easy to identifyMaterial analysis by optical meansMachines/enginesSystem reconfigurationRadioactive agent
A radioactive material detection system includes a plurality of radioactive material detection apparatuses and a command center. Each apparatus is disposed in or on a cargo receptacle. Each apparatus includes a wireless transmitter, a radiation sensor, a detection controller and an identification tag. The radiation sensor is configured to detect radiation over a predetermined or commanded period of time. The command center is configured to receive the wirelessly transmitted information directly or indirectly from each of the wireless transmitters of the plurality of radioactive material detection apparatuses. The system is configured to detect fissile or nuclear material that emits radiation. The system is reconfigurable from a passive sensing system to an at least partially active sensing system in the event that the system detects a nuclear anomaly within a cargo receptacle.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
Lubrication work center
InactiveUS20110278324A1Reduce confusionReduce mistakesOpening closed containersBottle/container closureSystem reconfigurationModularity
Systems and methods for storing, dispensing, and working with fluids are disclosed. Embodiments include modular systems designed to facilitate pre-assembled shipping and system reconfiguration. Embodiments further include color-coding and shape-coding of various items and labels to reduce confusion and mistakes.
Owner:WHITMORE MFG LLC
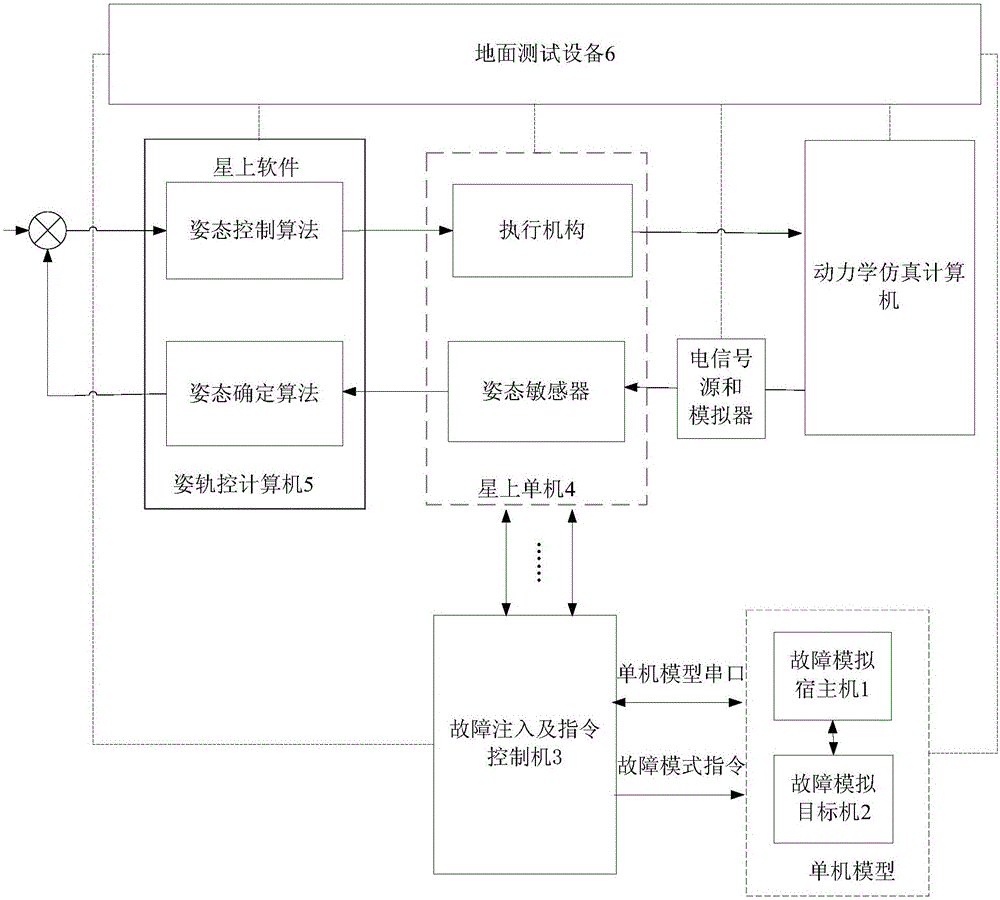
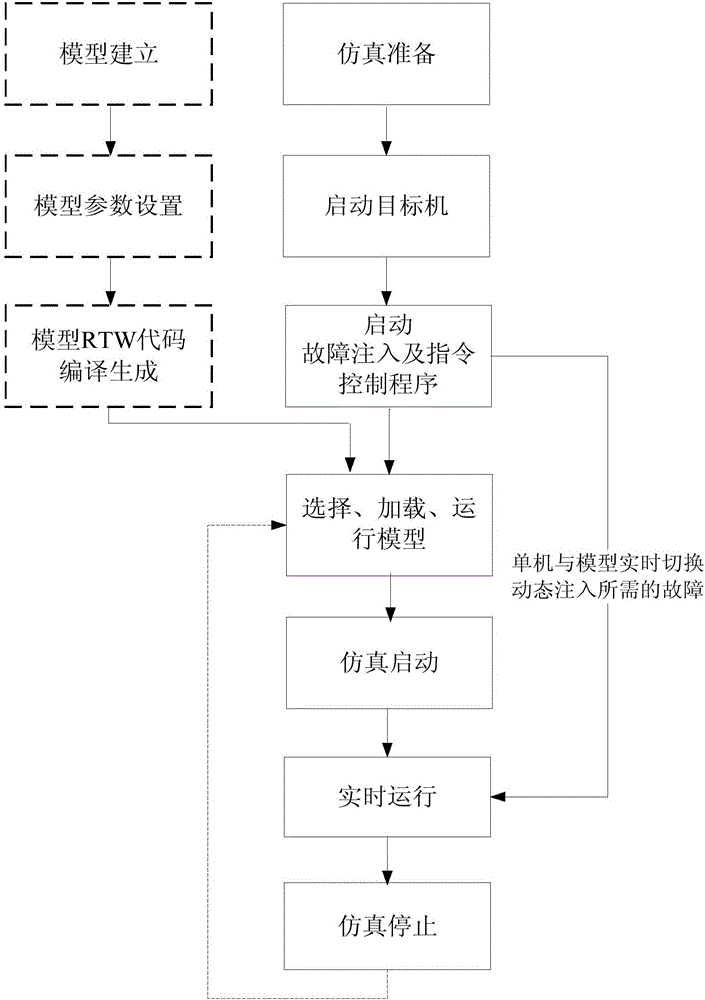
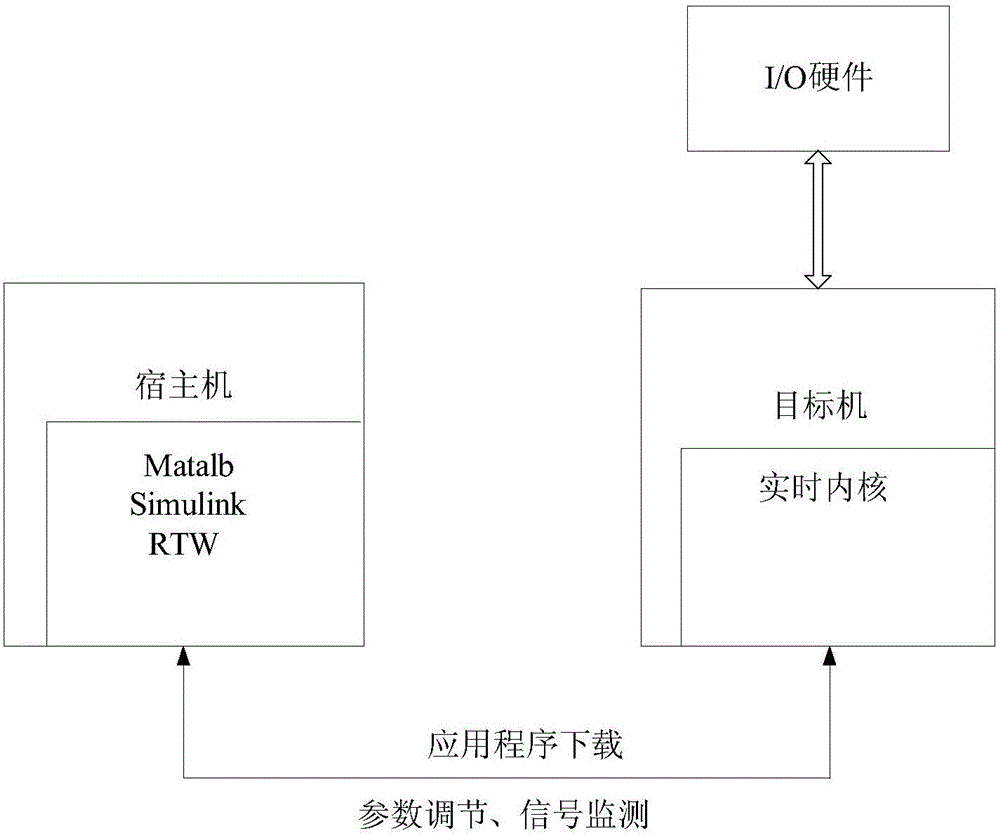
Embedded VxWorks based satellite attitude and orbit control system fault simulation system and method
The invention relates to an embedded VxWorks based satellite attitude and orbit control system fault simulation system and method, which adopts a host computer and a target machine technology to realize a single machine model and a failure mode. The method comprises the following steps. A fault simulation host computer runs the Matlab modeling software, establishes a fault model based on Simulink, and generates a target application under the VxWorks real-time operating system under. A fault simulation target machine, connected with the fault simulation host computer through a network, runs the VxWorks real-time operating system and the target application for fault simulation. A fault injection and instruction control machine, connected with the fault simulation target machine and a satellite mounted single-mode machine respectively for transmitting the failure mode instruction of the single-mode machine to realize the switching between the single-mode simulation serial port of the fault simulation target machine and the real single-mode serial port of the satellite mounted single-mode machine. The system and the method of the invention can carry out fault diagnosis and system reconfiguration tests to improve the fault-tolerant ability of the single-machine hardware and the attitude track working in the failure mode of the satellite attitude control system so as to ensure the safety of the satellite.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Satellite Redundancy for Critical Applications
InactiveUS20090209277A1Reduce operating costsIncrease spacingRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionSystem reconfigurationEngineering
A system includes a method for automatically reconfiguring a satellite network with a high accuracy in order to enable system reconfiguration very quickly and at a low cost. The system employs a single axis steering mechanism.
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
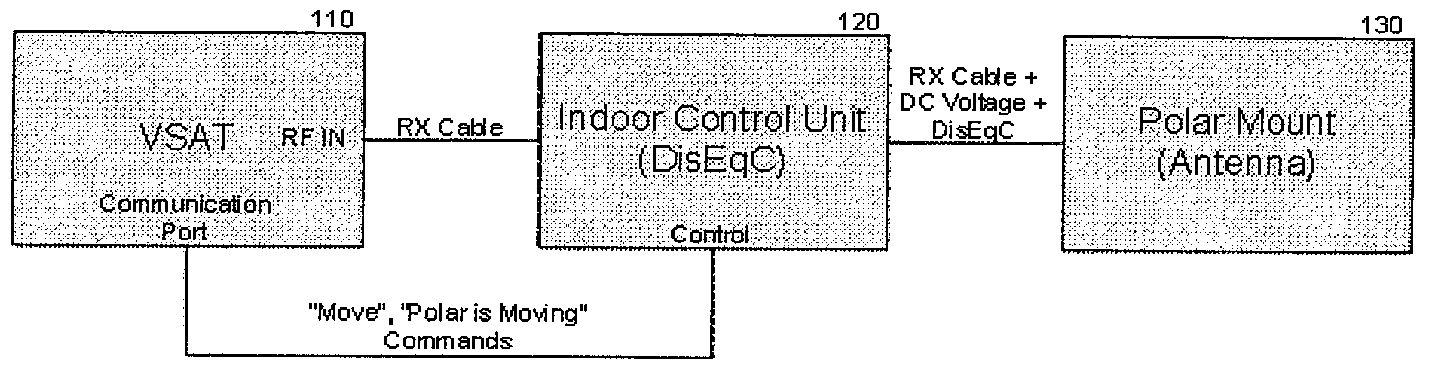
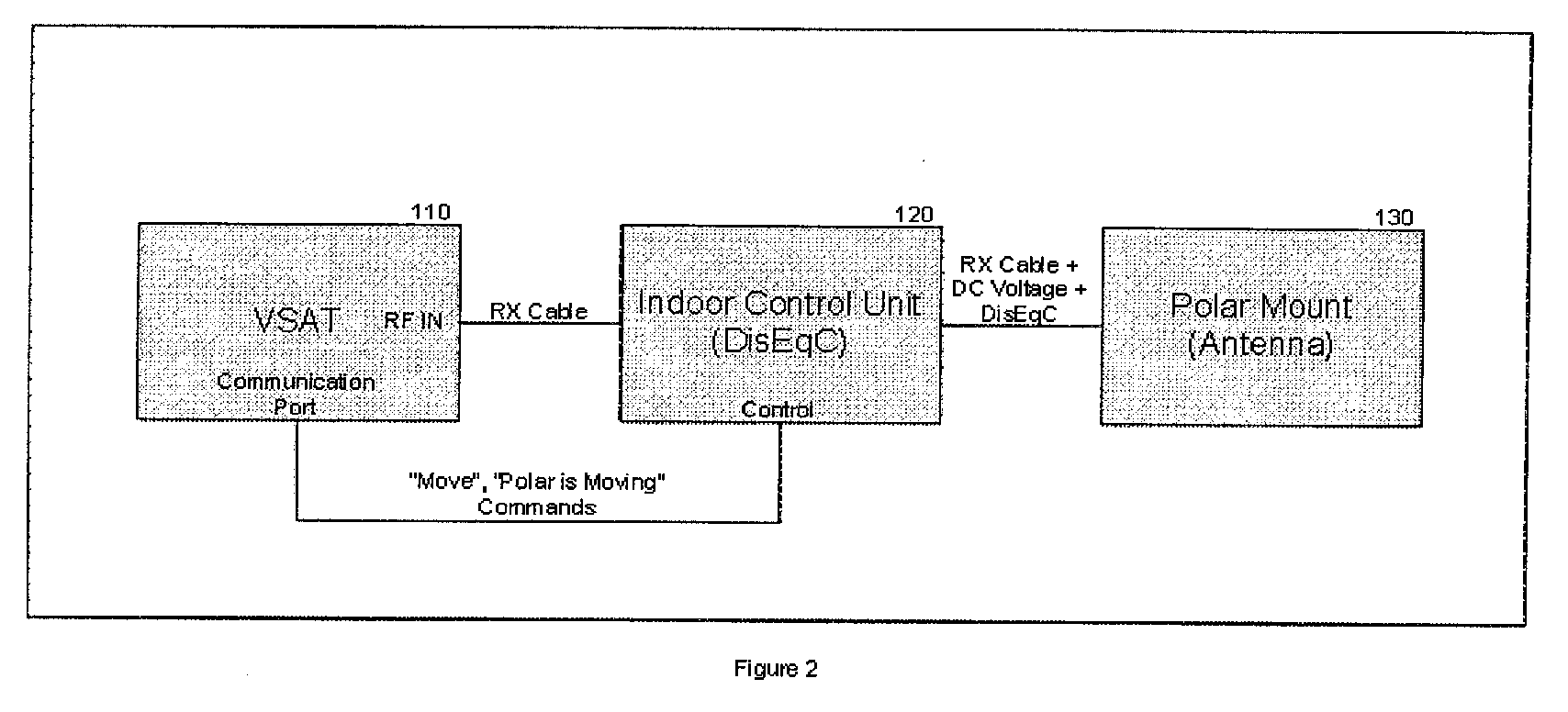
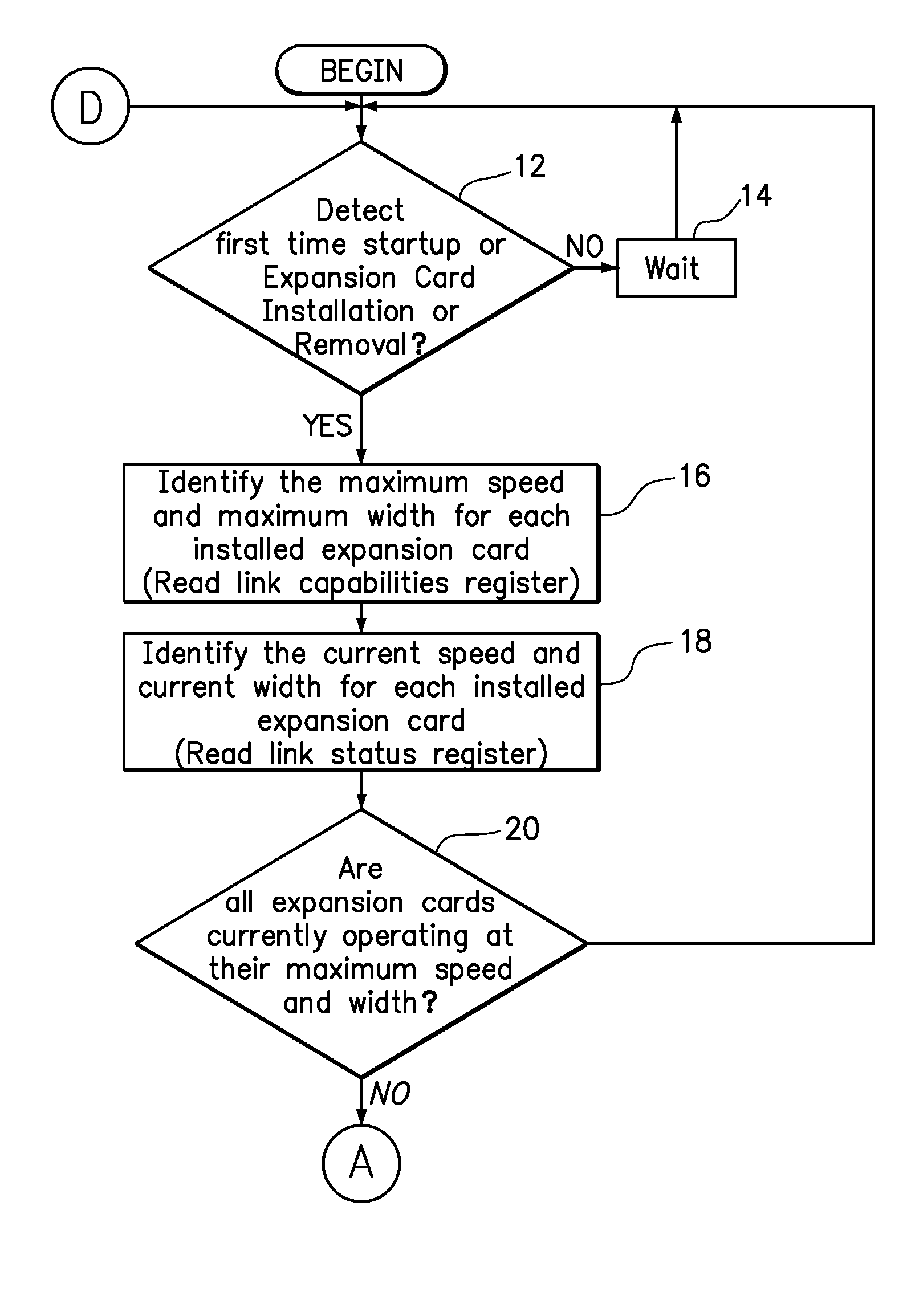
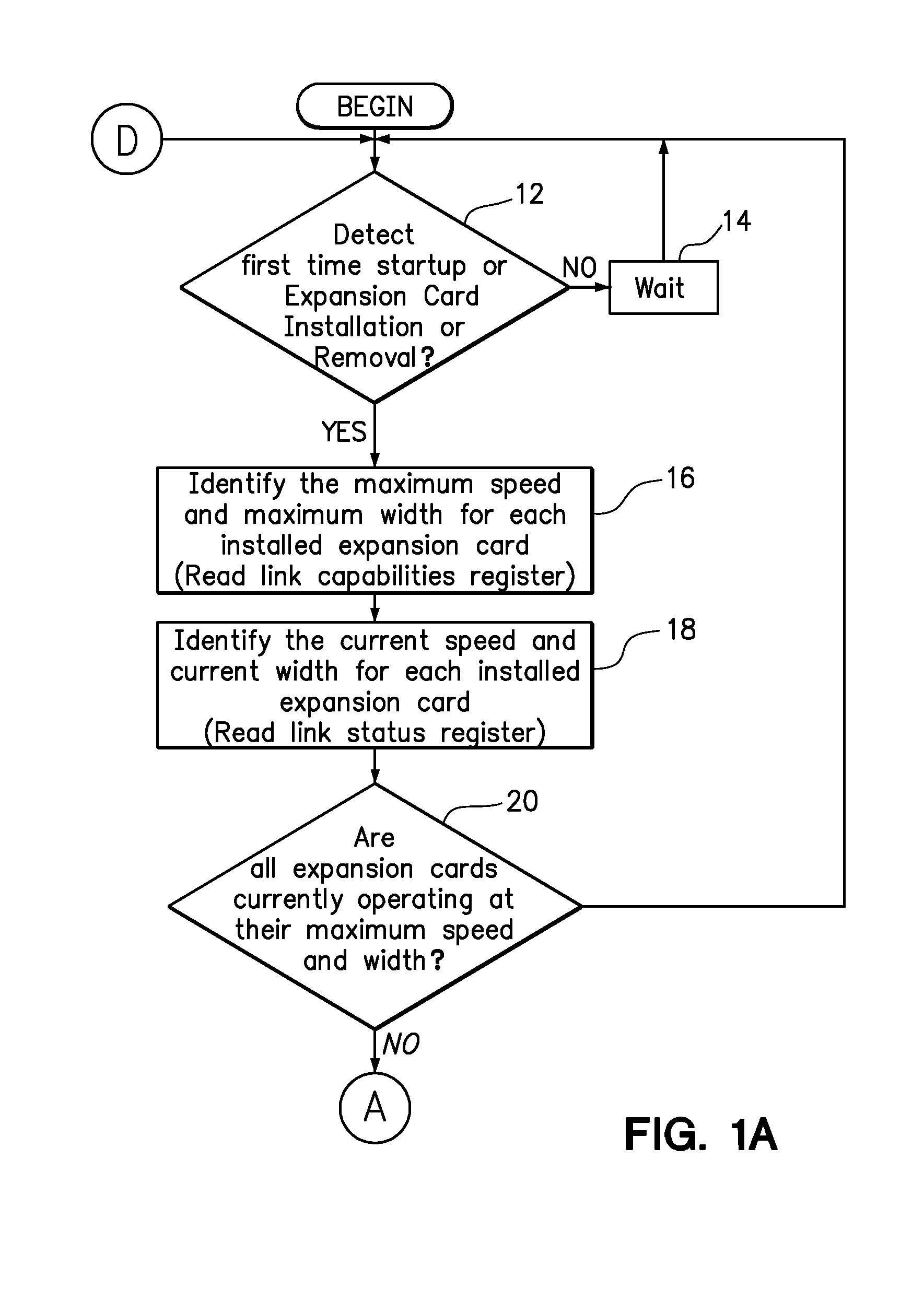
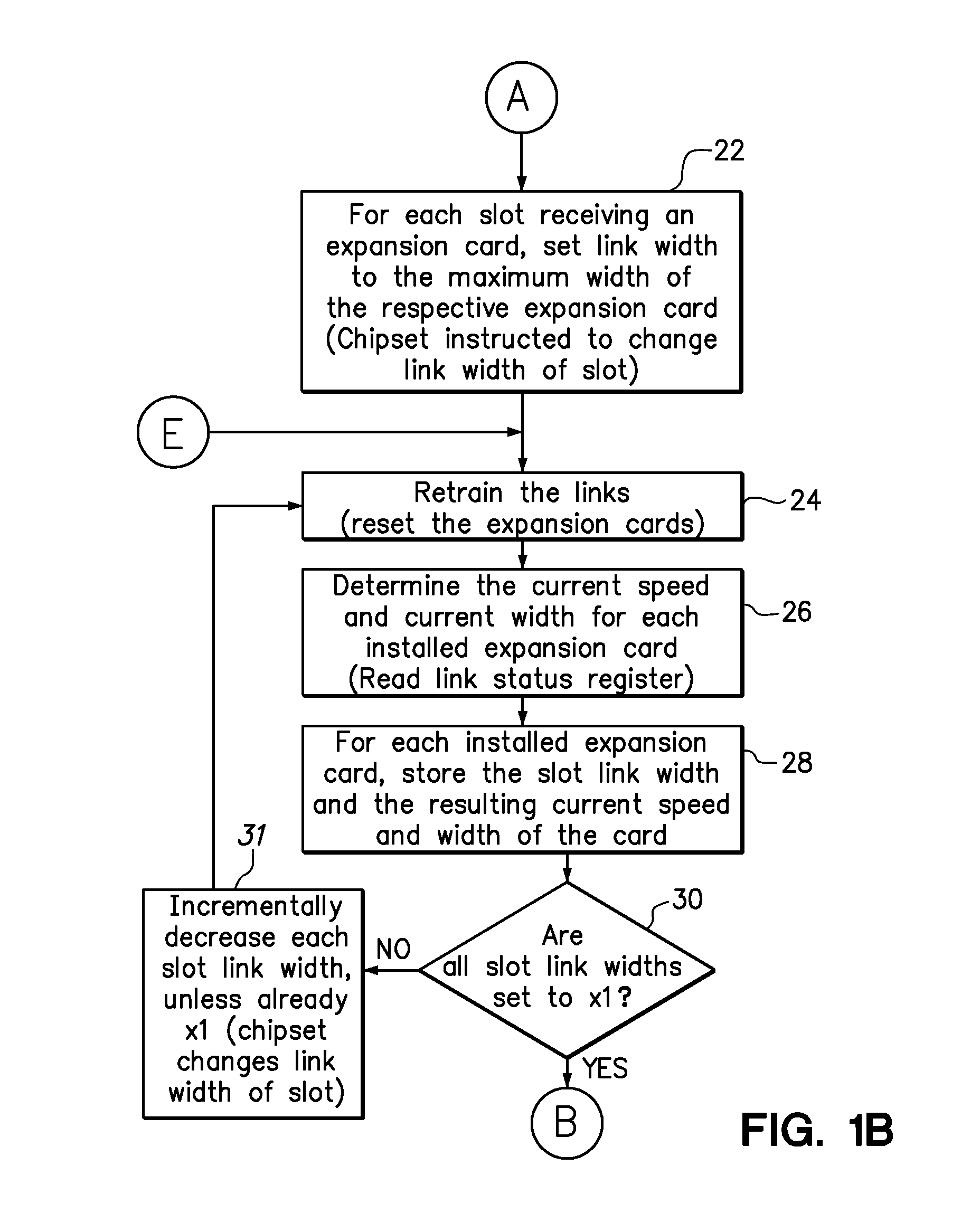
System reconfiguration of expansion cards
ActiveUS20110040916A1Component plug-in assemblagesElectric digital data processingExpansion cardSystem reconfiguration
A method and computer program product for improving or optimizing the configuration of expansion cards and expansion card slots in a computer system. The slot width of each slot is serially set to two or more link widths supported by the expansion card that is connect in each slot and each of the plurality of expansion cards is retrained at each of the set slot widths. The current link speed and a current link width for each of the plurality of expansion cards may be identified at each of the set slot widths to enable a determination of a configuration of the plurality of expansion cards within the plurality of expansion card slots that will improve collective throughput of the expansion cards. Optionally, the throughput of one expansion card may be prioritized over the throughput of another expansion card, such as those expansion cards or functionalities specified by user preferences or identified by system monitoring of loads placed on the expansion cards.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Method and apparatus for detection of radioactive material
InactiveUS7220967B1Easy to identifyMaterial analysis by optical meansMachines/enginesRadioactive agentRadioactive waste
A radioactive material detection system includes a plurality of radioactive material detection apparatuses and a command center. Each apparatus is disposed in or on a cargo receptacle. Each apparatus includes a wireless transmitter, a radiation sensor, a detection controller and an identification tag. The radiation sensor is configured to detect radiation over a predetermined or commanded period of time. The command center is configured to receive the wirelessly transmitted information directly or indirectly from each of the wireless transmitters of the plurality of radioactive material detection apparatuses. The system is configured to detect fissile or nuclear material that emits radiation. The system is reconfigurable from a passive sensing system to an at least partially active sensing system in the event that the system detects a nuclear anomaly within a cargo receptacle.
Owner:QUINTELL OF OHIO
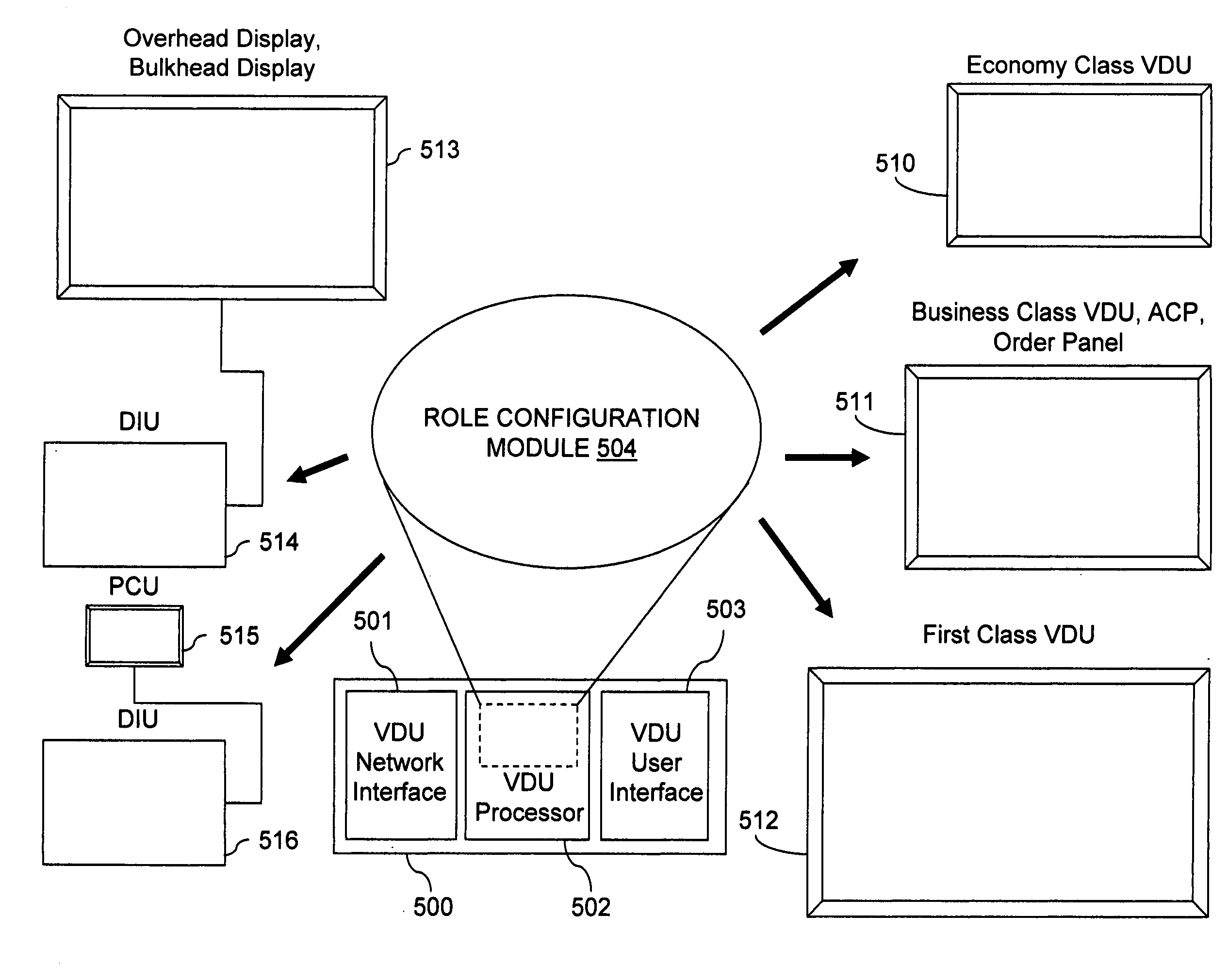
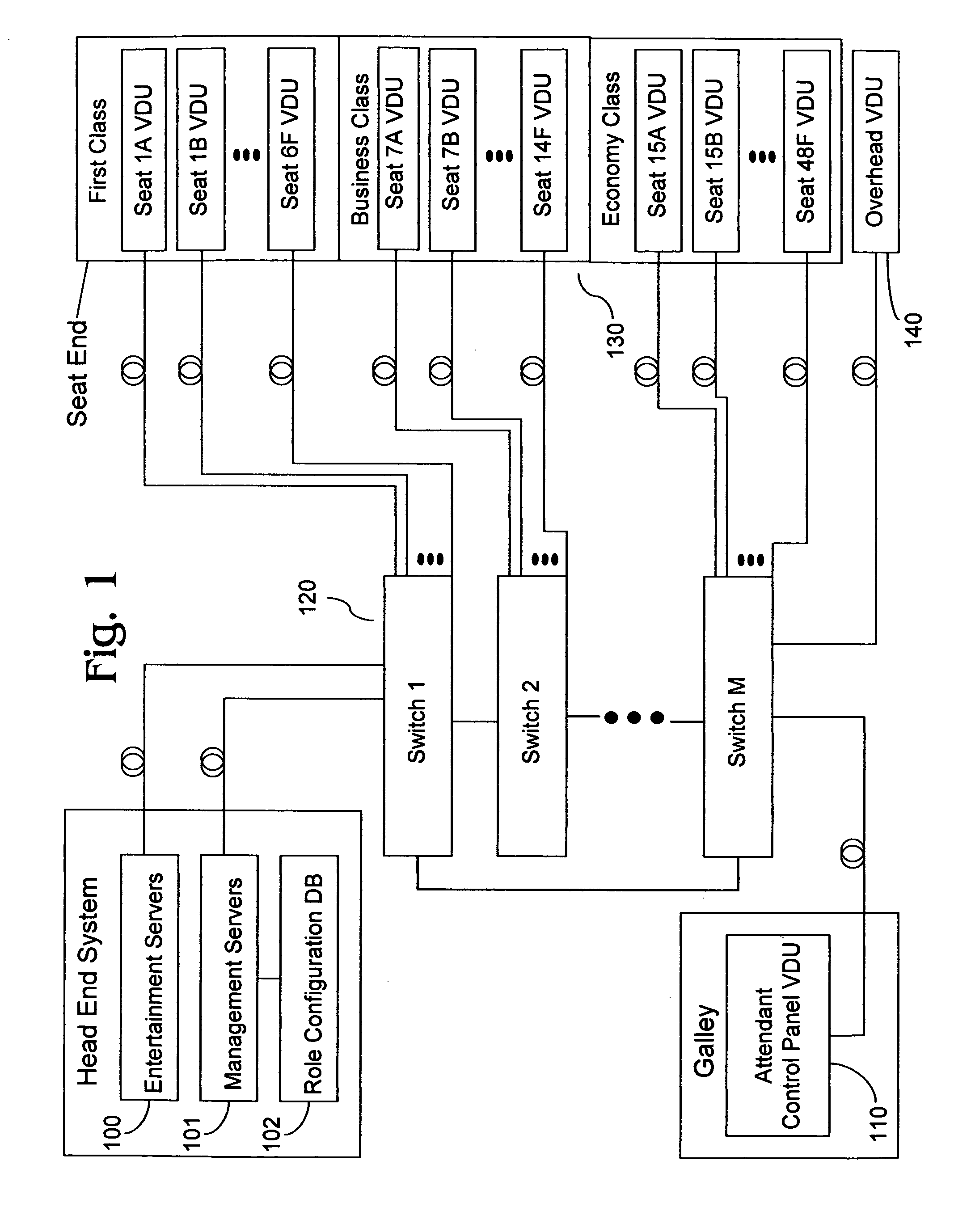
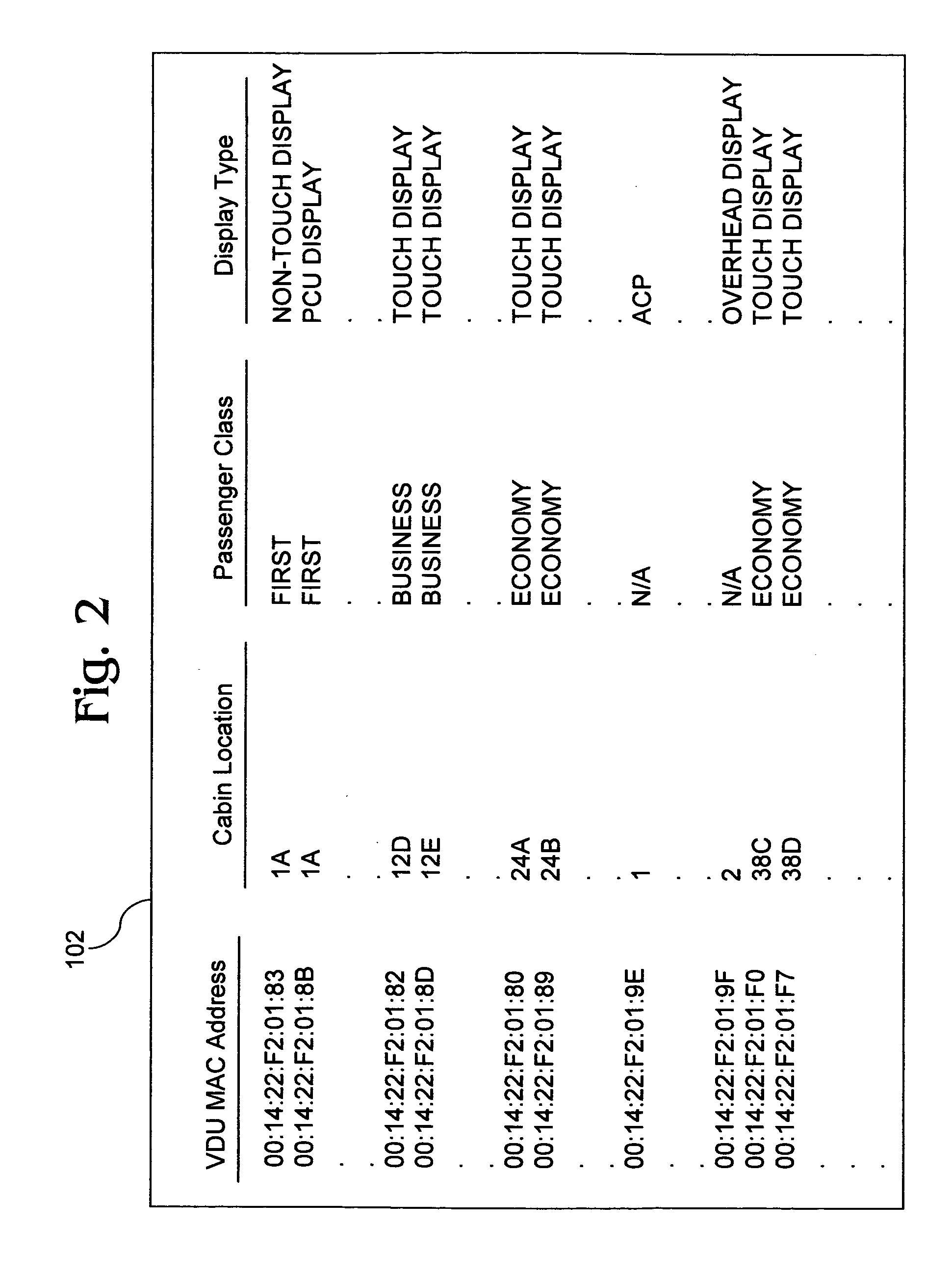
Inflight entertainment system with screen configurable video display unit roles
InactiveUS20110126242A1Reduce in quantityReducing hardwareCathode-ray tube indicatorsClosed circuit television systemsSystem reconfigurationEnd system
An inflight entertainment (IFE) system provides screen configurable video display unit (VDU) roles. Screen configurable VDU roles allow a role for each VDU in the system to be specified in the field through user inputs on the VDU and advertised to the head end system to create awareness of the specified role. Screen configurable VDU roles can reduce the number of discrete VDU line replaceable unit (LRU) types deployed on a single aircraft and across a fleet of aircraft, reducing hardware and software upgrade and sparing costs, while adding substantial flexibility to the system by removing cabin positioning restrictions on certain VDU types and facilitating system reconfiguration.
Owner:GLOBAL EAGLE ENTERTAINMENT
Method for creating a 3-d object
ActiveUS20040148040A1Constant speedIncrease speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsSystem reconfigurationData shipping
A system that executes a process, the system including a plurality of subsystems, each of which performs a stage of the process, each of the subsystems configured to perform one of a first subset of N1 of the stages, where N1 is greater than 1 and to change the stage of the subset being performed on receipt of a change instruction; wherein, in the event that one of the subsystems fails, at least one of the remaining subsystems synchronously changes to performing the respective stage of the failed subsystem without requiring transfer of data relating the respective stage to the said at least one remaining subsystems, and when a subsystem changes to performing a different stage, the system reconfigures the subsystem to be capable of performing a second subset N2 of the stages where N1 and N2 have the same number of stages.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Switching between graphics sources to facilitate power management and/or security
ActiveCN101802774ADigital data processing detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsSystem reconfiguration
The invention relates to a method, a device and a system for selective switching between frame buffers. One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that switches between frame buffers which are used to refresh a display. During operation, the system refreshes the display from a first frame buffer which is located in a first memory. Upon receiving a request to switch frame buffers for the display, the system reconfigures data transfers to the display so that the display is refreshed from a second frame buffer which is located in a second memory.
Owner:APPLE INC
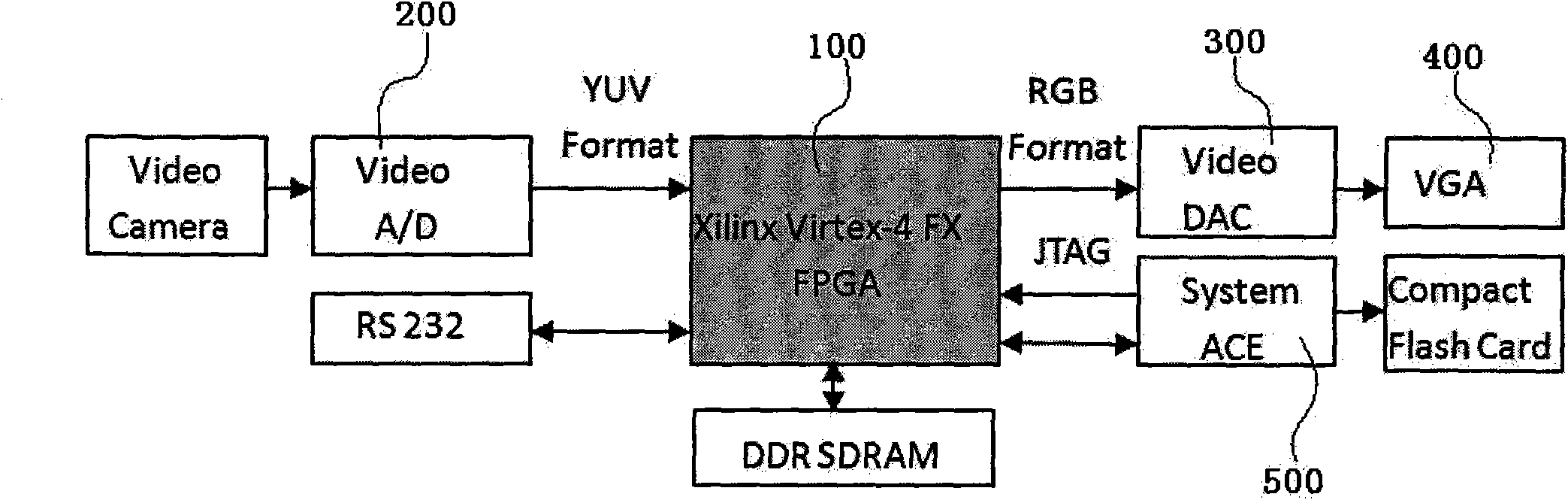
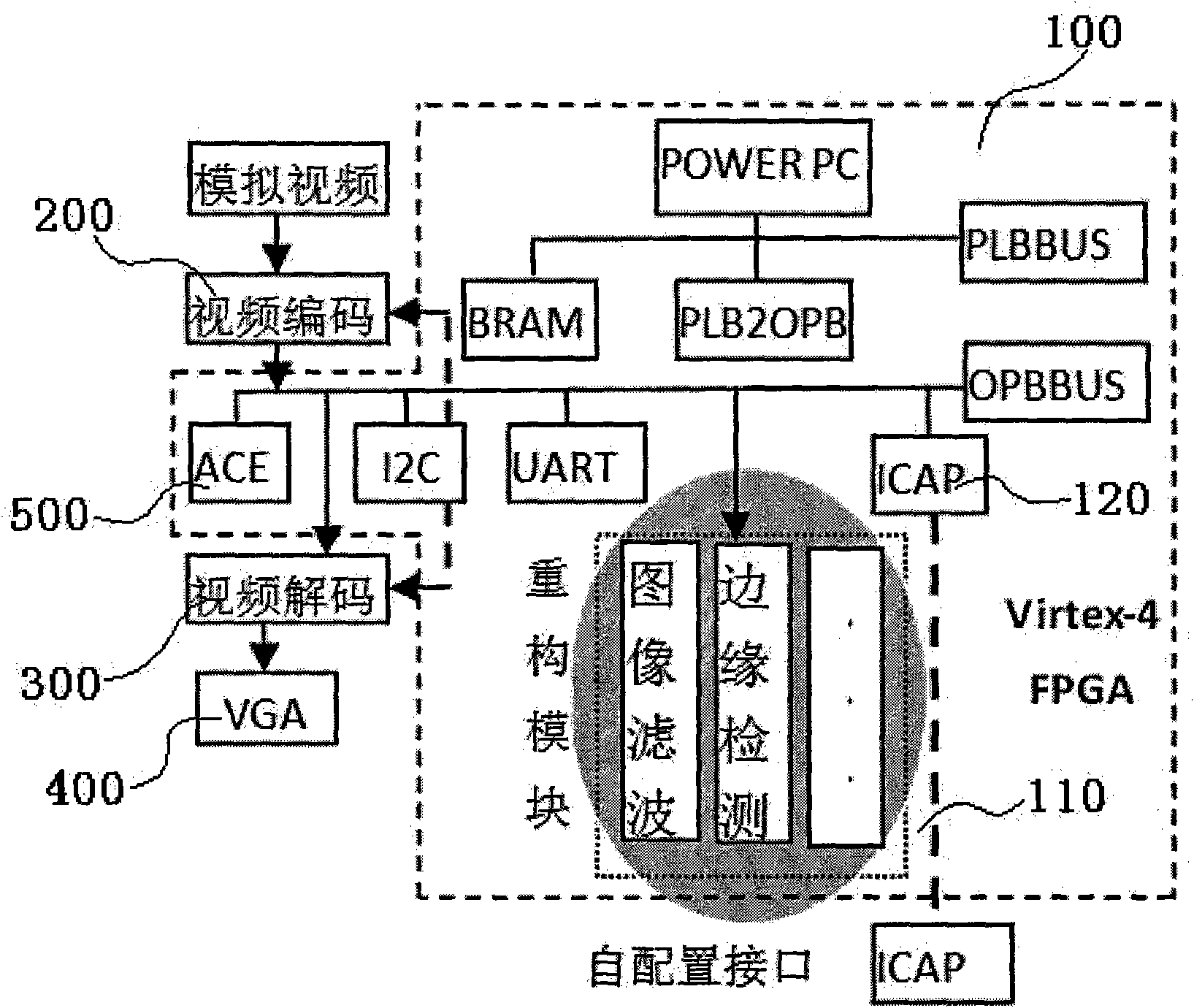
Dynamic reconfiguration technology-based universal image processing platform and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN101976431AImprove general performanceIncrease flexibilityImage data processing detailsSystem reconfigurationImaging processing
The invention aims to disclose a dynamic reconfiguration technology-based universal image processing platform and an implementation method thereof. By the dynamic reconfiguration technology, a reconfigurable module is provided. On the one hand, as the reconfigurable module can perform corresponding algorithm configuration on a system according to different computation tasks, the reconfigurable module has high universality and flexibility; and on the other hand, when reconfiguration is performed, a non-reconfigurable part still runs, the contents of a related register cannot be lost, and the contents of the register does not need to be stored in a memory outside a field programmable gate array (FPGA) when the reconfiguration is performed, so that the expense of system reconfiguration is reduced, the operational efficiency of the system is improved, the system has high universality, and the aim of the invention is fulfilled.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Automatic airplane seat location mapping
ActiveUS7319854B2Less cost and complexityNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionJet aeroplaneSystem reconfiguration
During a system reconfiguration, a selected column or column of wireless units, such as associated with airplane seats, are powered up. The first unit in the column detects a ground and begins a wireless identification process with an access point which allows the system to determine a corresponding physical location for each node's logical address. The first unit then closes a switch, which connects the ground to the next unit. As the next unit detects the ground on the line, such as a token line, the second unit communicates with the AP. This process continues sequentially down the column until the last unit is assigned a physical location / address. The next column of units can then be powered up and identified.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
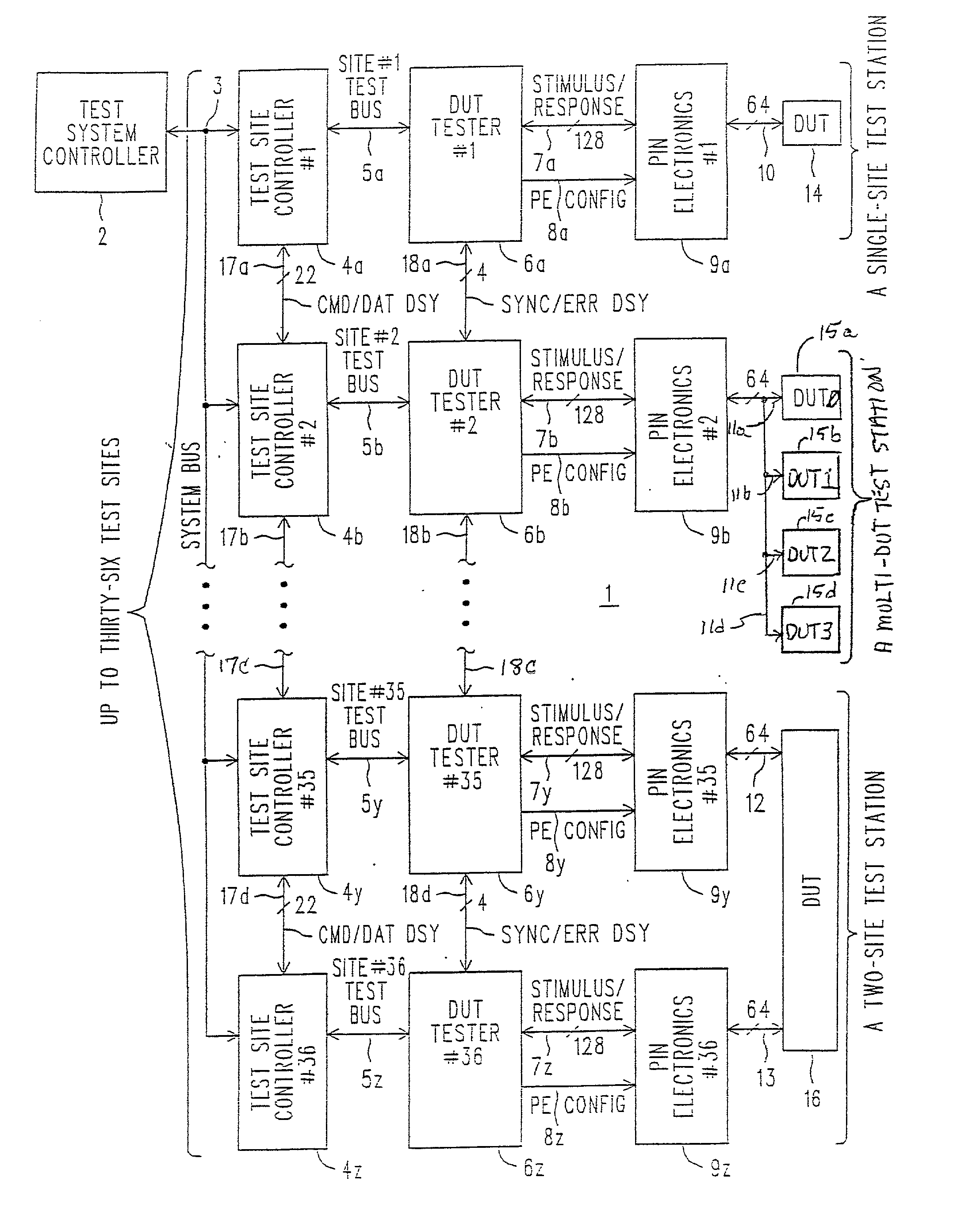
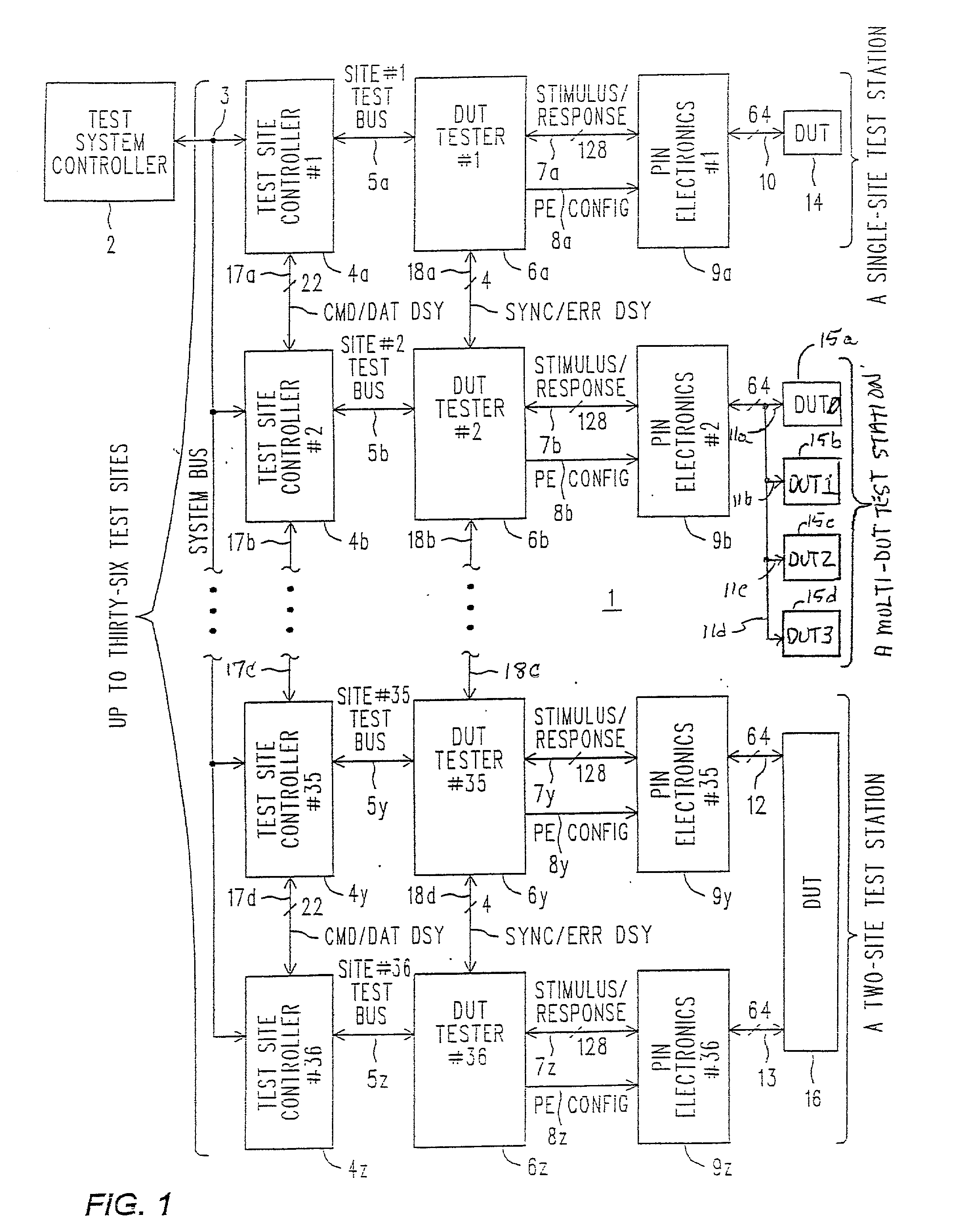
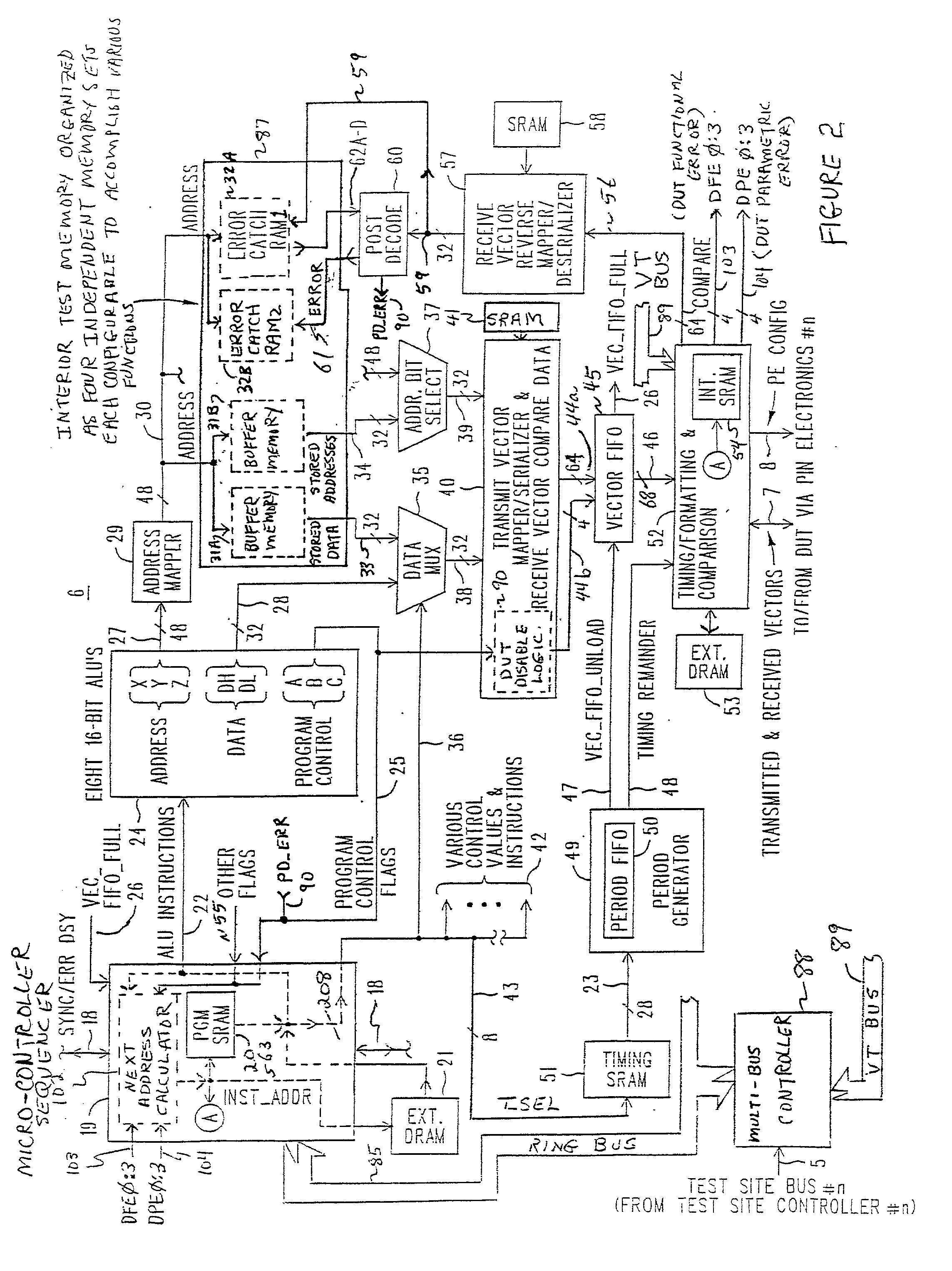
Algorithmically programmable memory tester with history FIFO's that aid in ERROR analysis and recovery
The problem is to branch back to an appropriate location within a memory tester test program, and also restore its state of algorithmic control, when an error associated therewith occurs later in time at the DUT. Owing to delays in pipelines connecting the program execution environment to the DUT and back again. These delays allow the program to arbitrarily advance beyond where the stimulus was given. The arbitrary advance makes it difficult to determine the exact circumstances that were associated with the error. A branch based on the error signal can restart a section of the test program, but it is likely only a template needing further test algorithm control information that varies dynamically as the test program executes. The solution is to equip the memory tester with History FIFO's whose depths are adjusted to account for the sum of the delays of the pipelines, relative to the location of that History FIFO. When the error flag is generated the desired program location and state information is present at the bottom of an appropriate History FIFO. This is also readily applicable when the test program uses an ALU to generate its own DUT stimuli, as well as to the case when the test program / ALU addresses an intermediate Buffer Memory whose contents are central to the nature of the testing the DUT is to undergo. The first is an ALU History FIFO, while the second is a Buffer Memory History FIFO. There can also be ECR History FIFO's. There is a mechanism to track system re-configuration as it occurs and adjust the depths of the various History FIFO's according to resulting pipeline depth. There is a mechanism to freeze the contents of a History FIFO upon the generation of an error. A History FIFO can be extended to allow a branching instruction in the test program to not prematurely respond to an error flag sooner than the pipeline delay needed for that error flag's value to be determined by a cause located within the test program.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
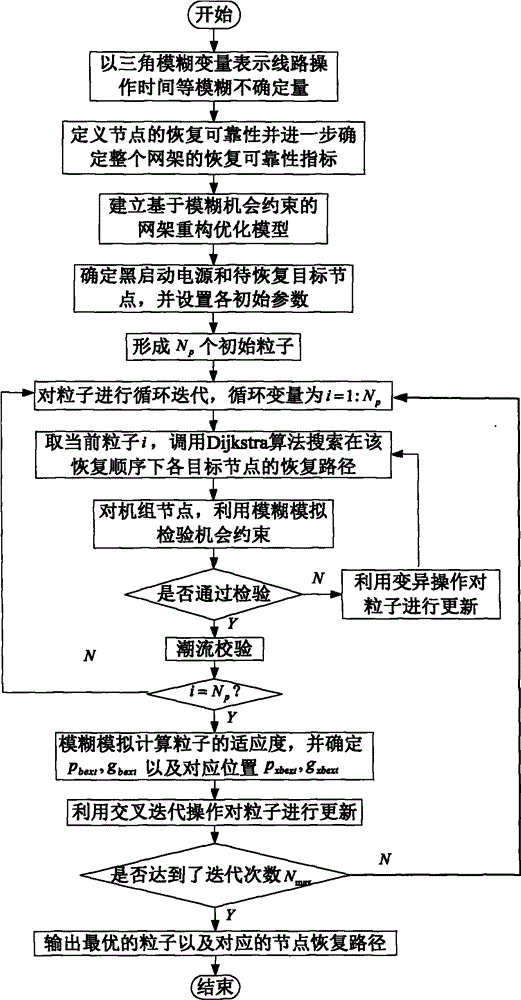
Power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method based on fuzzy chance constraint
The invention relates to a power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method based on fuzzy chance constraints, which belongs to the field of power system security defense and restoration control. The power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method comprises a grid structure reconfiguration and optimization model establishing module and a grid structure reconfiguration and optimization algorithm module. The power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method adopts triangular fuzzy variables for representing line operation time and restoration reliability, defines an restoration reliability index for evaluating performance of a target grid structure, considers unit start-up time limit, establishes a grid structure reconfiguration and optimization model based on fuzzy chance constraints under the framework of the fuzzy chance constraints, adopts a solution method of combining fuzzy simulation, a crossed particle swarm optimization algorithm and a Dijkstra algorithm, optimizes and determines unit start-up sequence, and reconfigures a restoration grid structure with shortest reconfiguration time and highest reliability. According to the power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method based on fuzzy chance constraints, the fuzziness of operation time and restoration reliability when the line is put into operation at the grid structure reconfiguration stage is reasonably considered, the optimized and determined optimal grid structure reconfiguration scheme takes both system reconfiguration speed and safety requirements into account, and the power system grid structure reconfiguration and optimization method has more practical significance.
Owner:YUNNAN ELECTRIC POWER DISPATCH CONTROL CENT +1
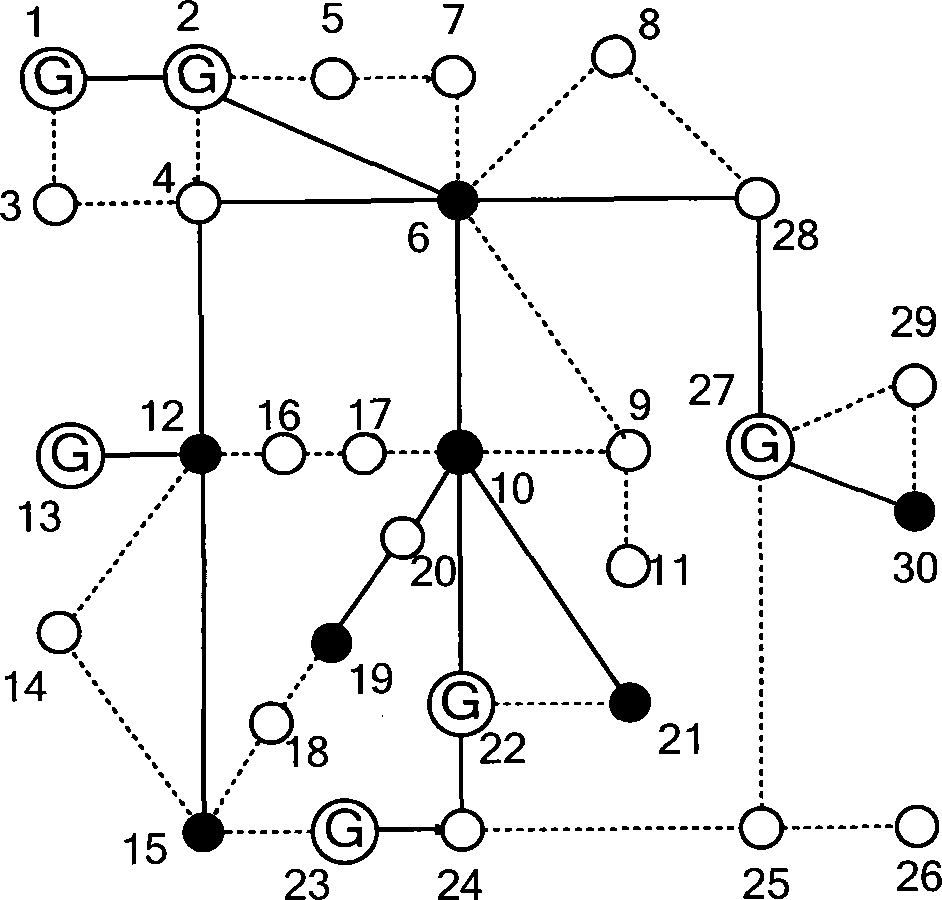
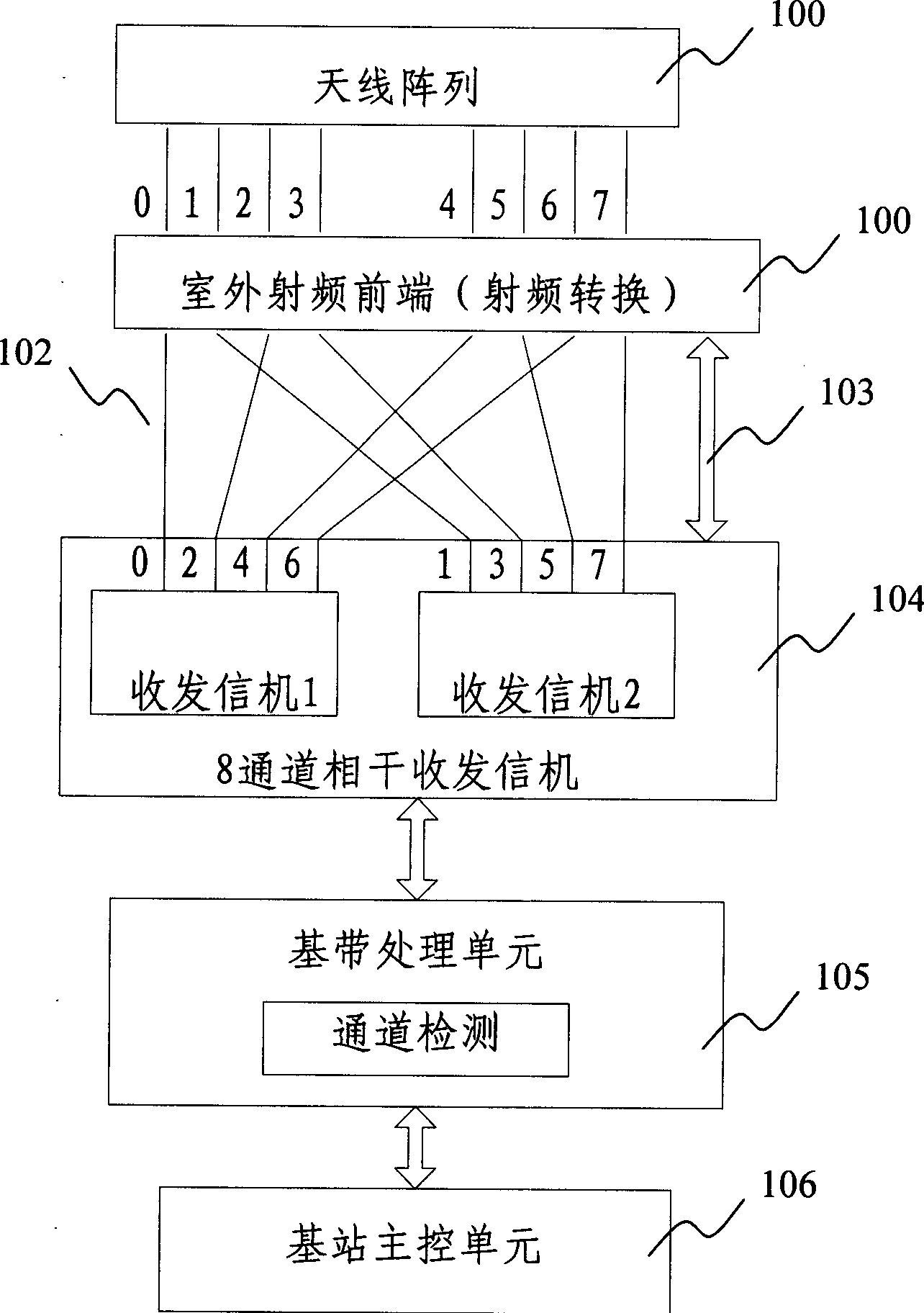
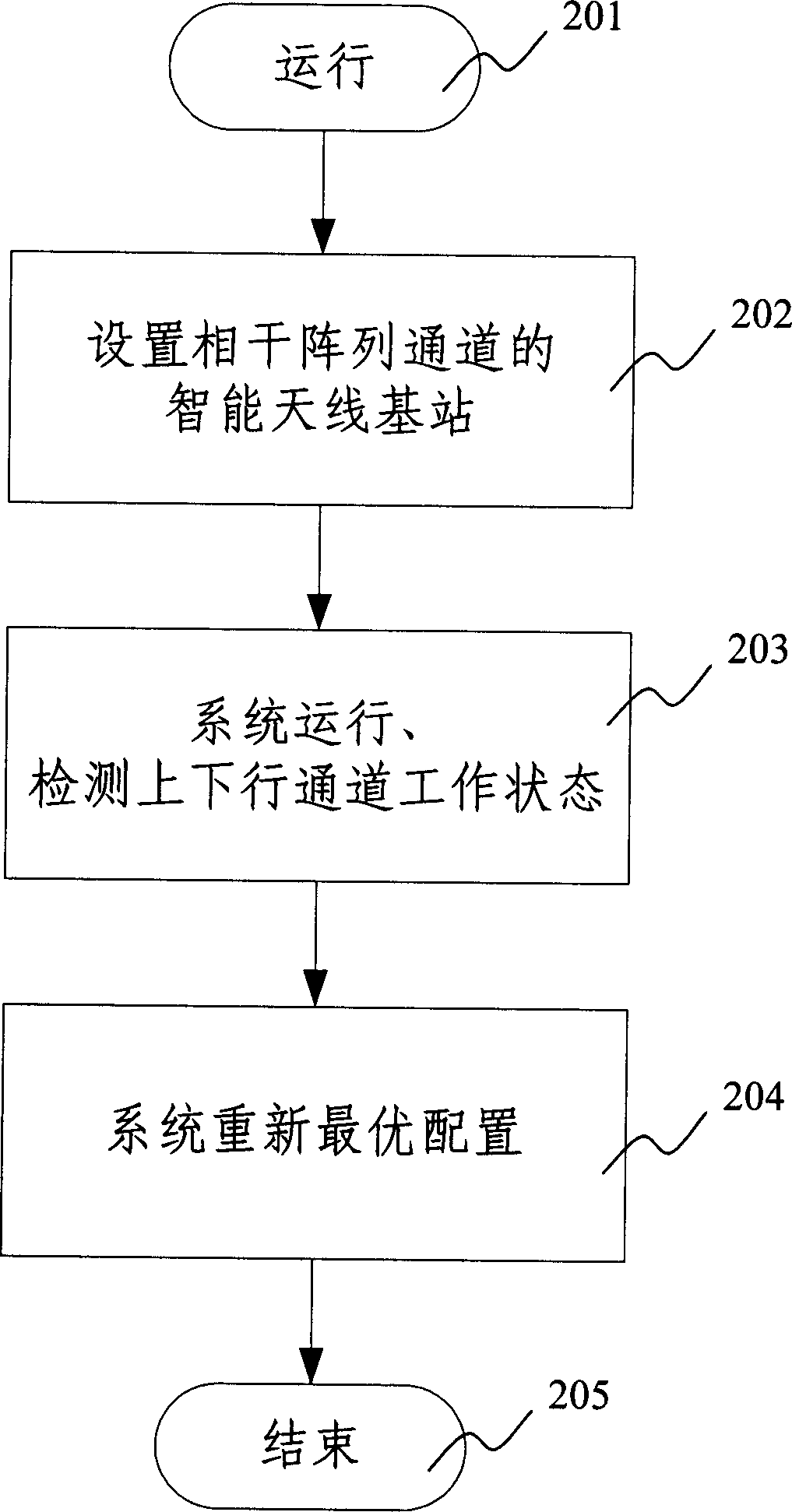
Method of optimal system reconfiguration after intelligent antenna array element failure
InactiveCN1722871AImprove performanceGuaranteed communication functionSpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSystem reconfigurationSmart antenna
This invention relates to an optimal reconfiguring method after the intelligent aerial losing, which comprises the following steps: a) setting intelligent aerial base station which makes up the coherent array channel; b) the base station will operate and check the working condition of the transmitting-receiving channel in the array channel, including generating the ascending and descending channel checking signal and measuring the channel response signal; c) checking the loss ascending and descending channel signals; d)allocating the system again according to the present condition, making the property optimal. By said method, when the array element loss, the system can check working condition if the hardware bug not sweep to the whole resource.
Owner:ZTE CORP
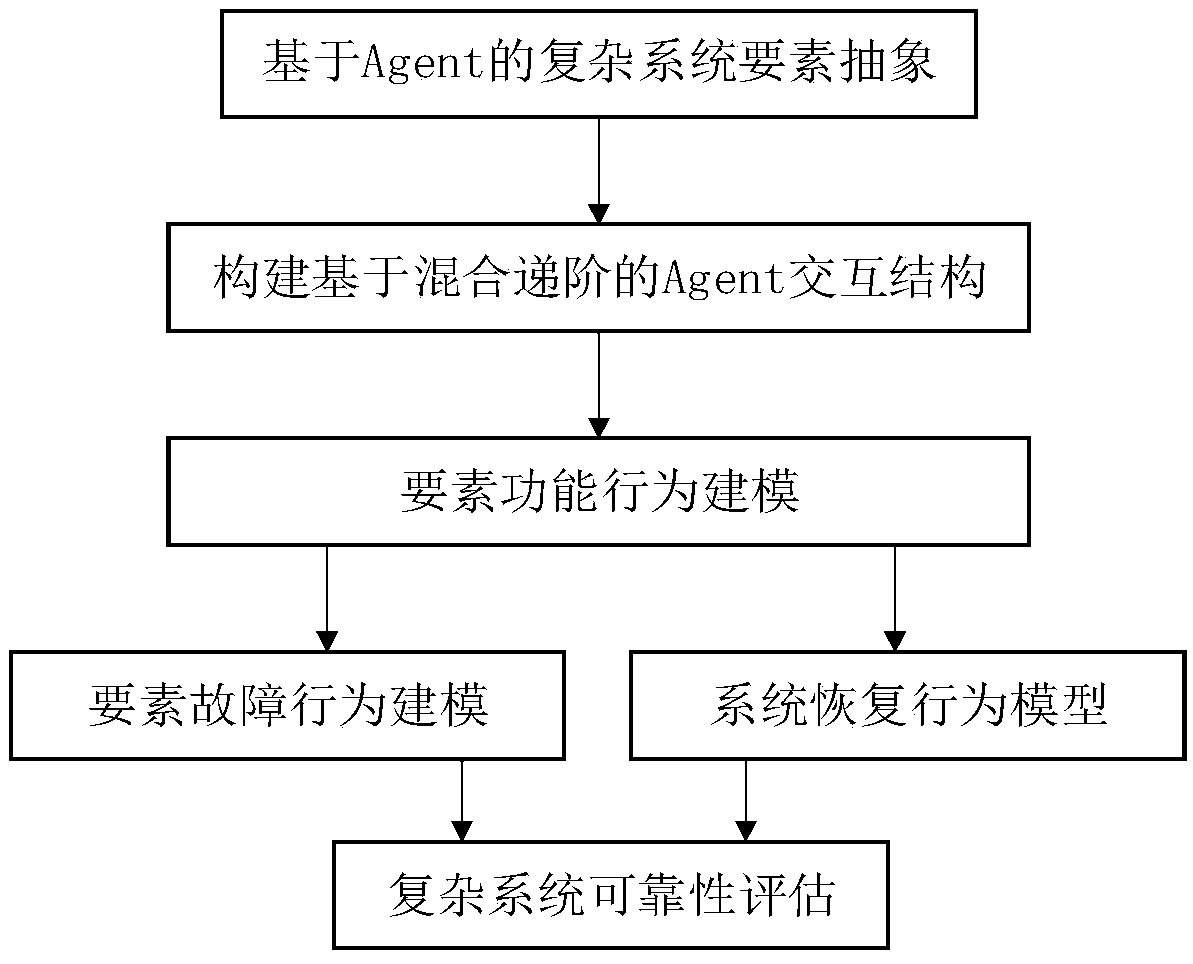
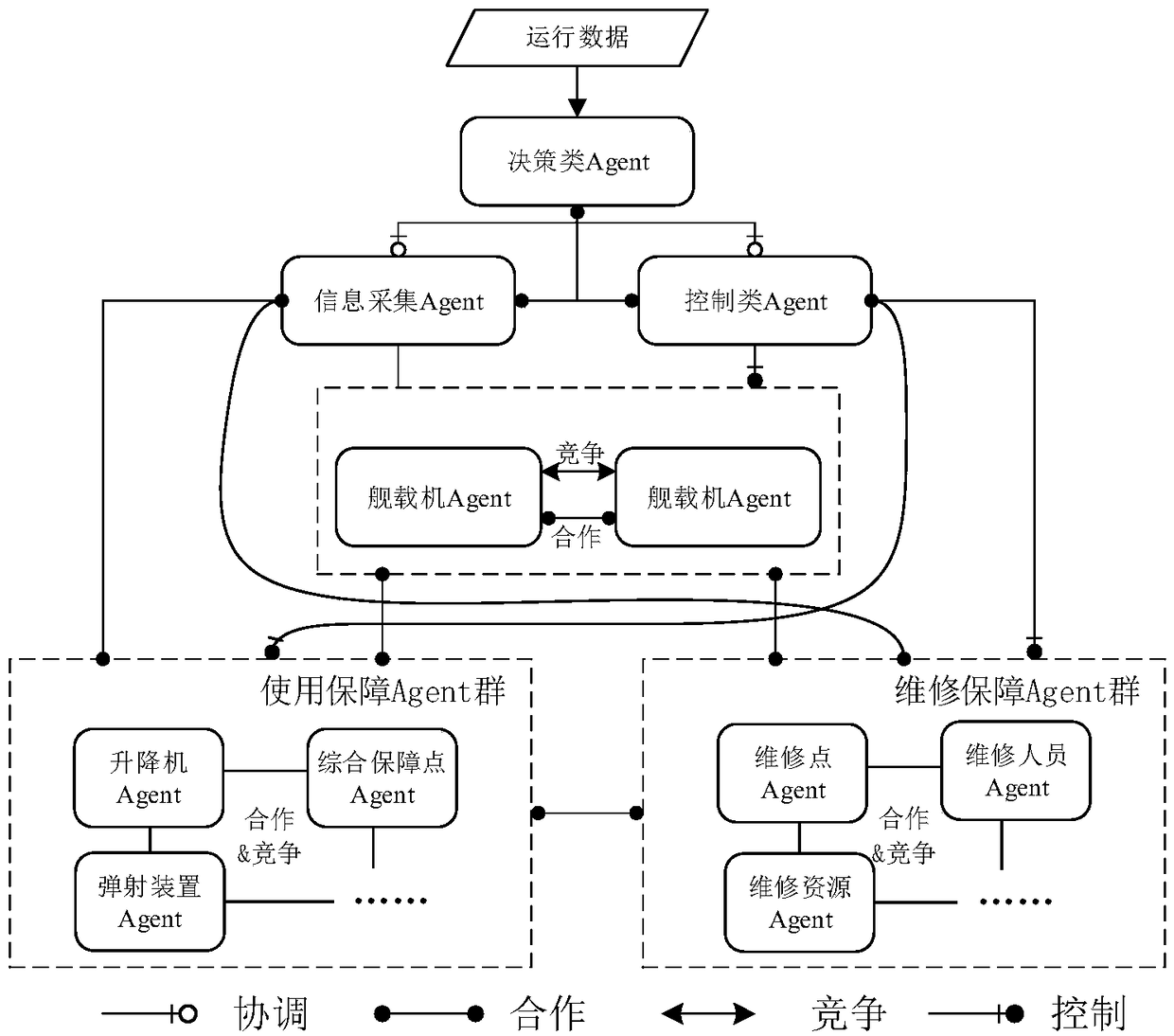
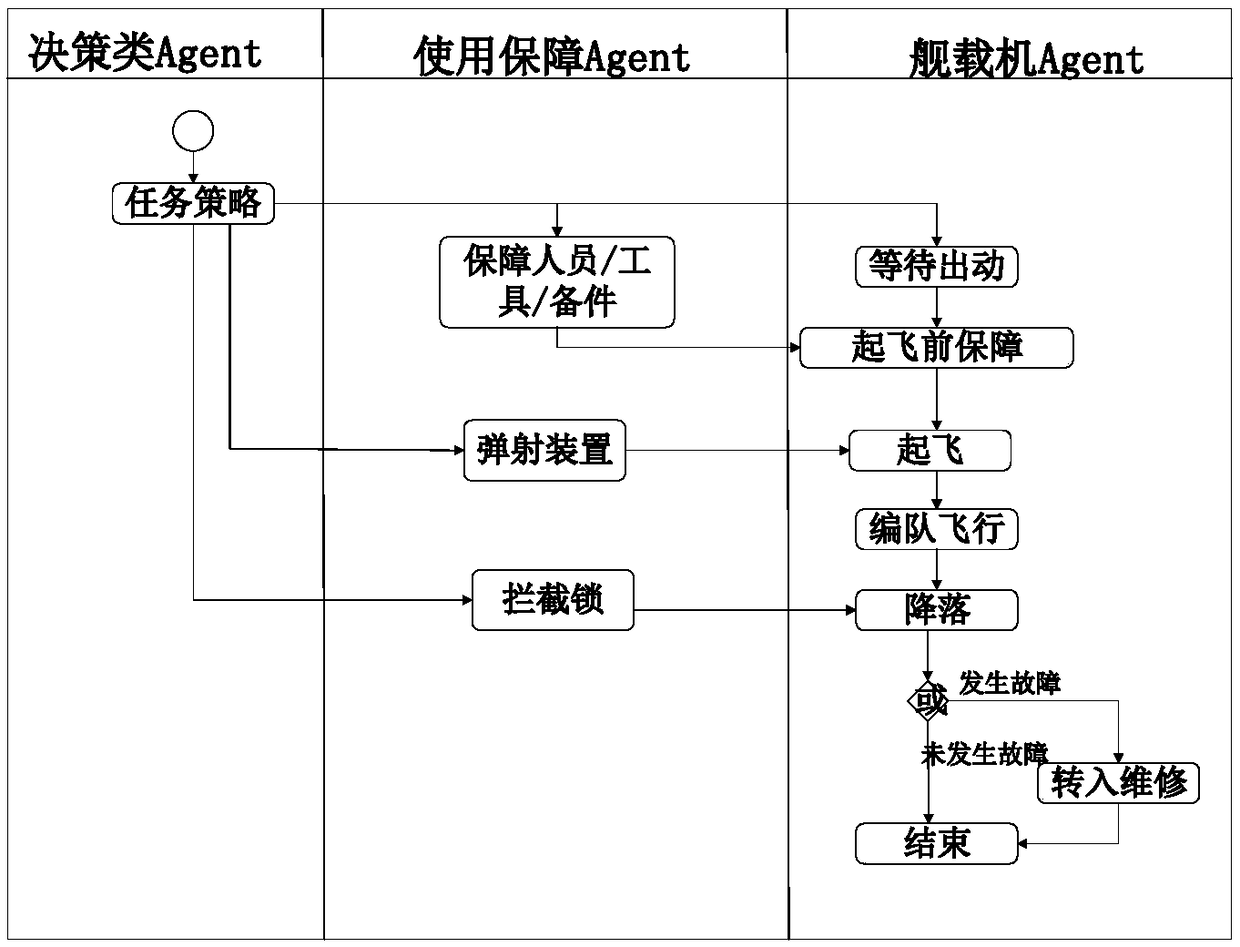
Complex system reliability evaluation method based on multiple agents
ActiveCN108983747AAccurate and reliableProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringSystem reconfigurationSystem recovery
The invention discloses a complex system reliability evaluation method based on multiple agents. The method comprises the following steps: 1, elements of the Agent-based complex system are abstracted,and according to the composition of the complex system, the elements are abstracted to three kinds of Agents: a management kind, a system kind and a guarantee kind; 2, a hybrid hierarchy-based Agentinteraction structure is built, the hybrid hierarchy structure is adopted, and the interaction structure with centralized main control coordination and distributed local coordination is built; 3, element function behaviors are modeled, and according to functions of the Agents and an interaction rule, a life state diagram of the Agents is built; 4, element fault behaviors are modeled, a unit-levelRBD model for the Agents is built, and the fault time for unit random sampling is used as fault clock stock; 5, a system recovery behavior is modeled, system reconfiguration and maintenance are carried out according to a damage degree, a maintenance success rate is set, and the maintenance time is acquired through sampling; and 6, a complex system reliability evaluation mechanism is built, Monte Carlo simulation based on a complex system Agent model is carried out, and the complex system reliability is solved according to Rs=ns / n.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Actively stabilized, single input beam, interference lithography system and method
InactiveUS7304775B2OptimizationActively stabilizedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringPhotolithography
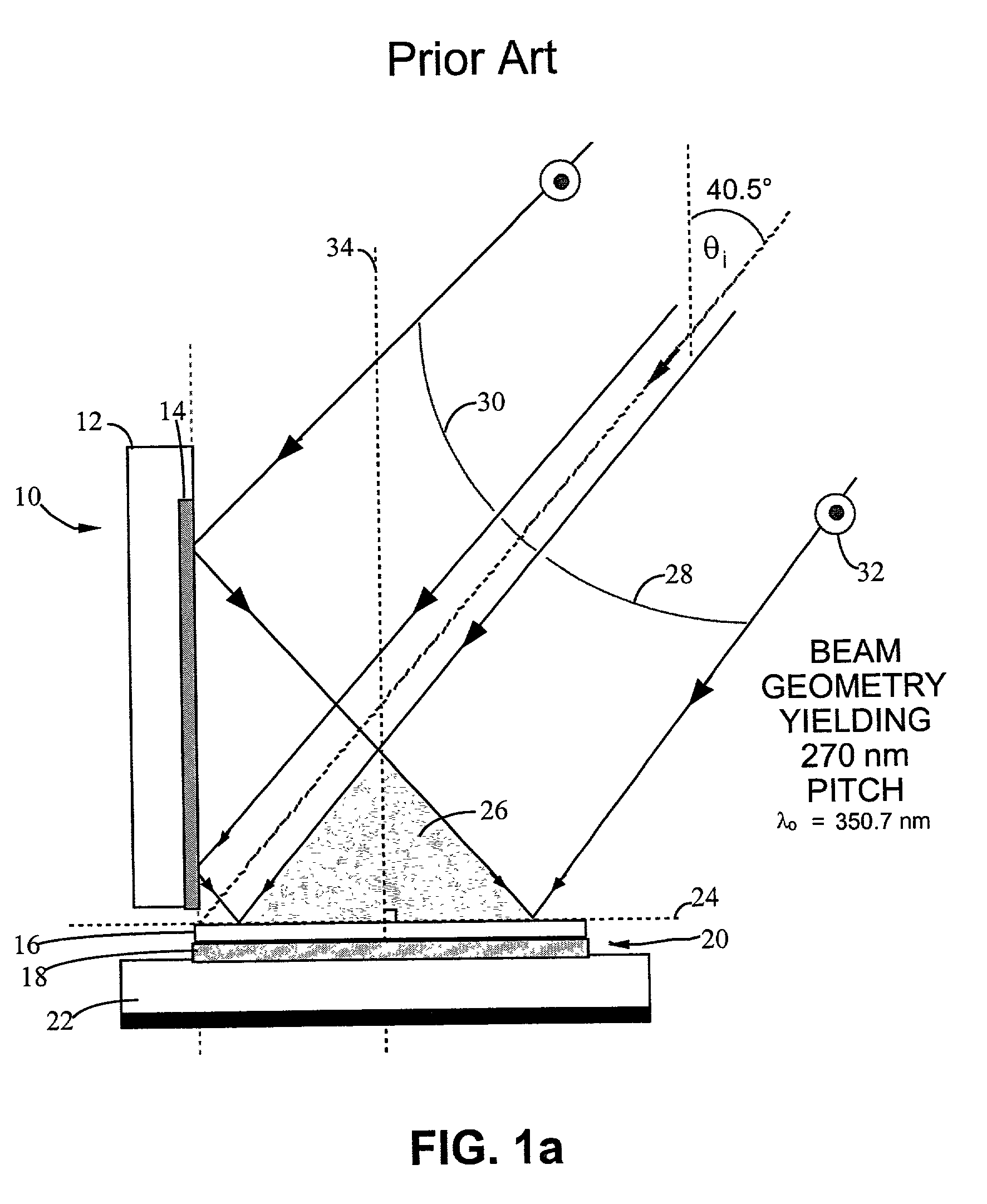
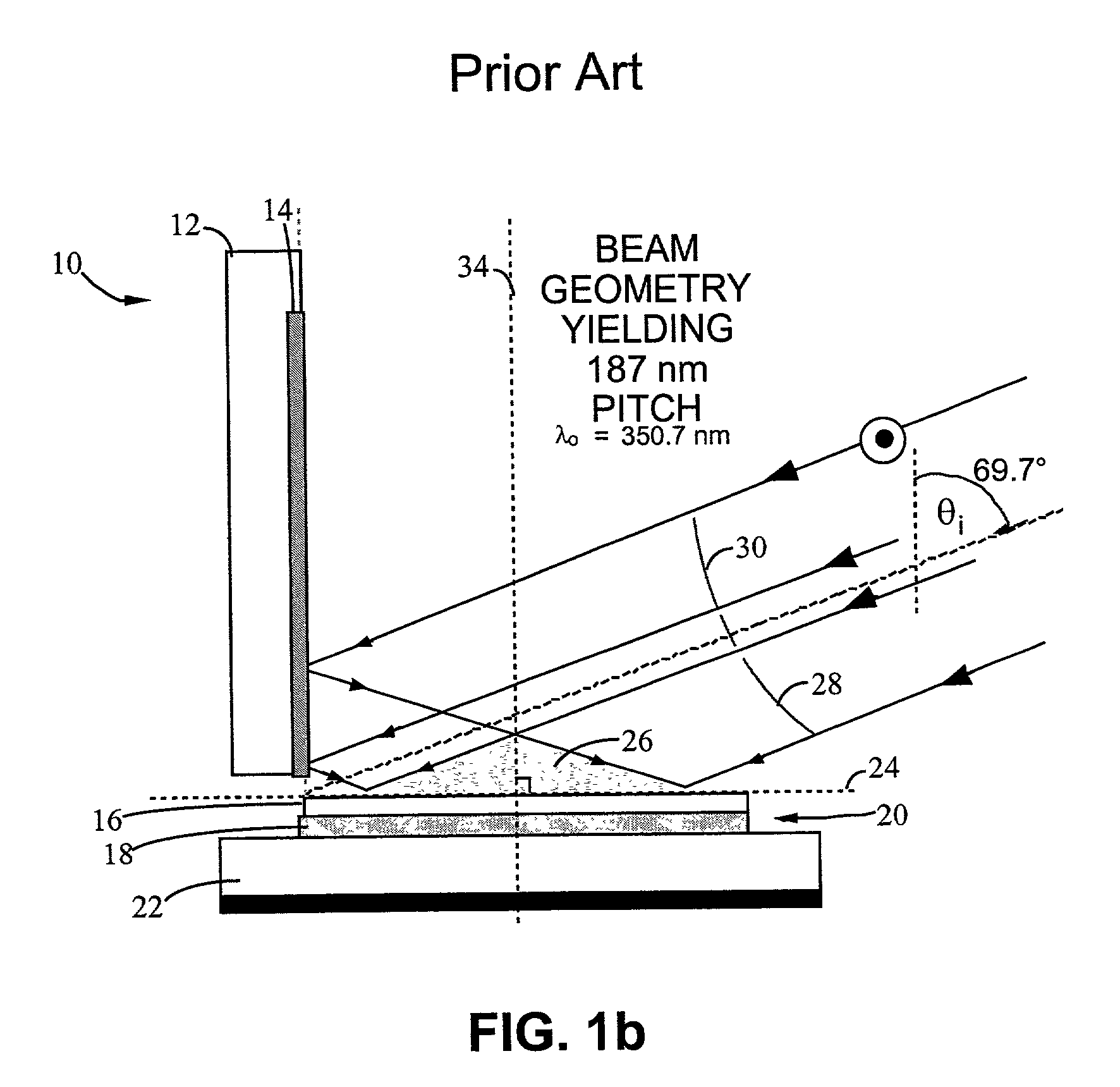
An interference lithography system is described that is capable of exposing high resolution patterns in photosensitive media and employing yield increasing active stabilization techniques needed in production environments. The inventive device utilizes a division-of-wavefront interference lithography configuration which divides a single large field size optical beam using one or more mirrors, and is actively stabilized with a subsystem employing; a phase modulator operating on each divided wavefront section; a novel feedback apparatus for observing the relative phase shifts between interfering wavefront sections; and a control system for holding the relative phase shifts constant. The present invention also includes; a method for shaping the illumination beam's intensity distribution for more efficient power utilization and greater feature size uniformity; a horizontal substrate loading configuration compatible with robotic handling; an automated pattern pitch calibration for simple, flexible system reconfiguration; a compact clean-room compatible superstructure for increased passive stability in high vibration manufacturing environments; and a method for optimizing the polarization state of the interfering beam sections in a multiple mirror system.
Owner:AZTEC SYST
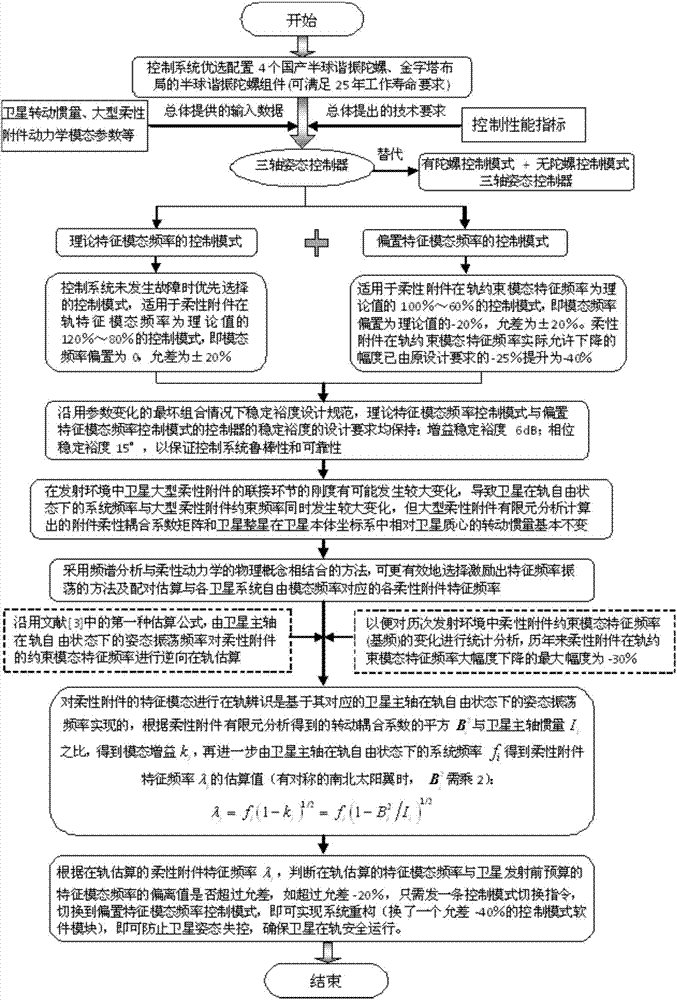
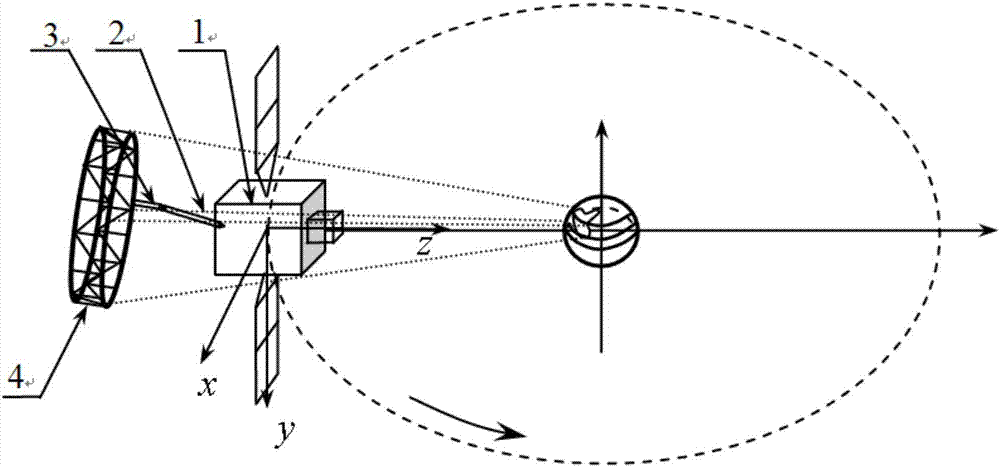
On-orbit fault countermeasure method based on multi-flexible appendage satellite dynamics optimization control mode
ActiveCN107089348AGuaranteed safe operationAvoid getting out of controlArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSmall probabilityCountermeasure
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com