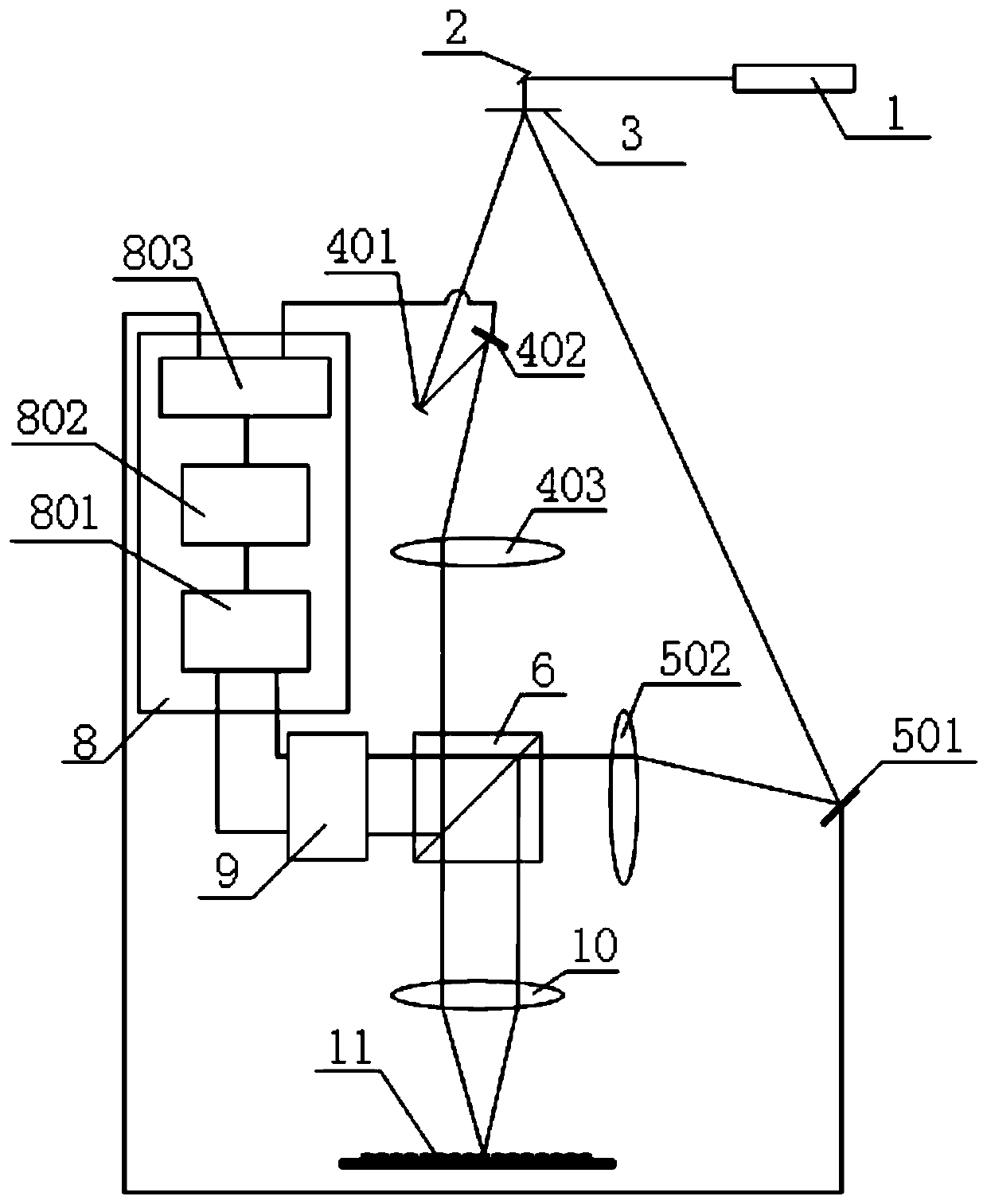
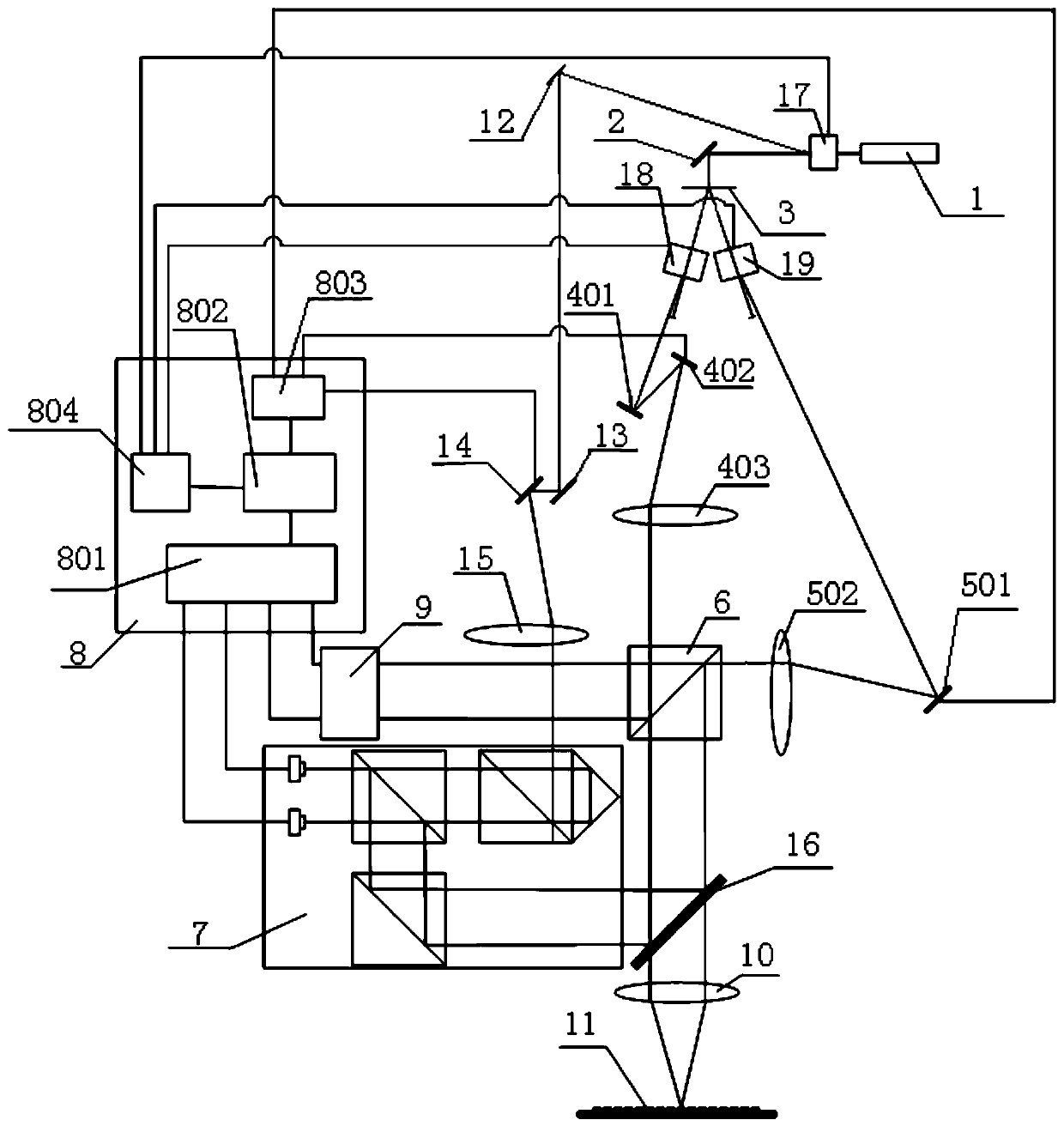
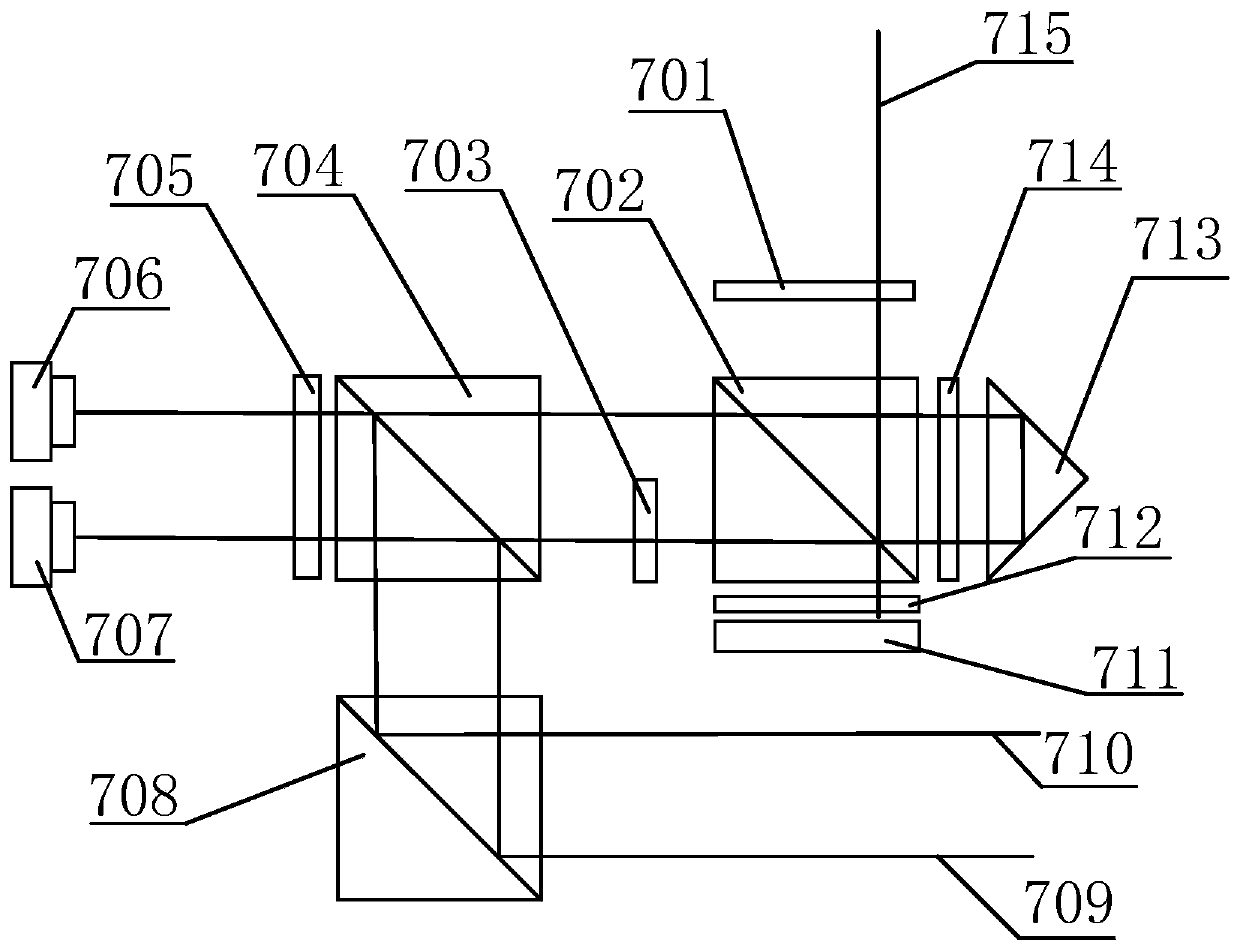
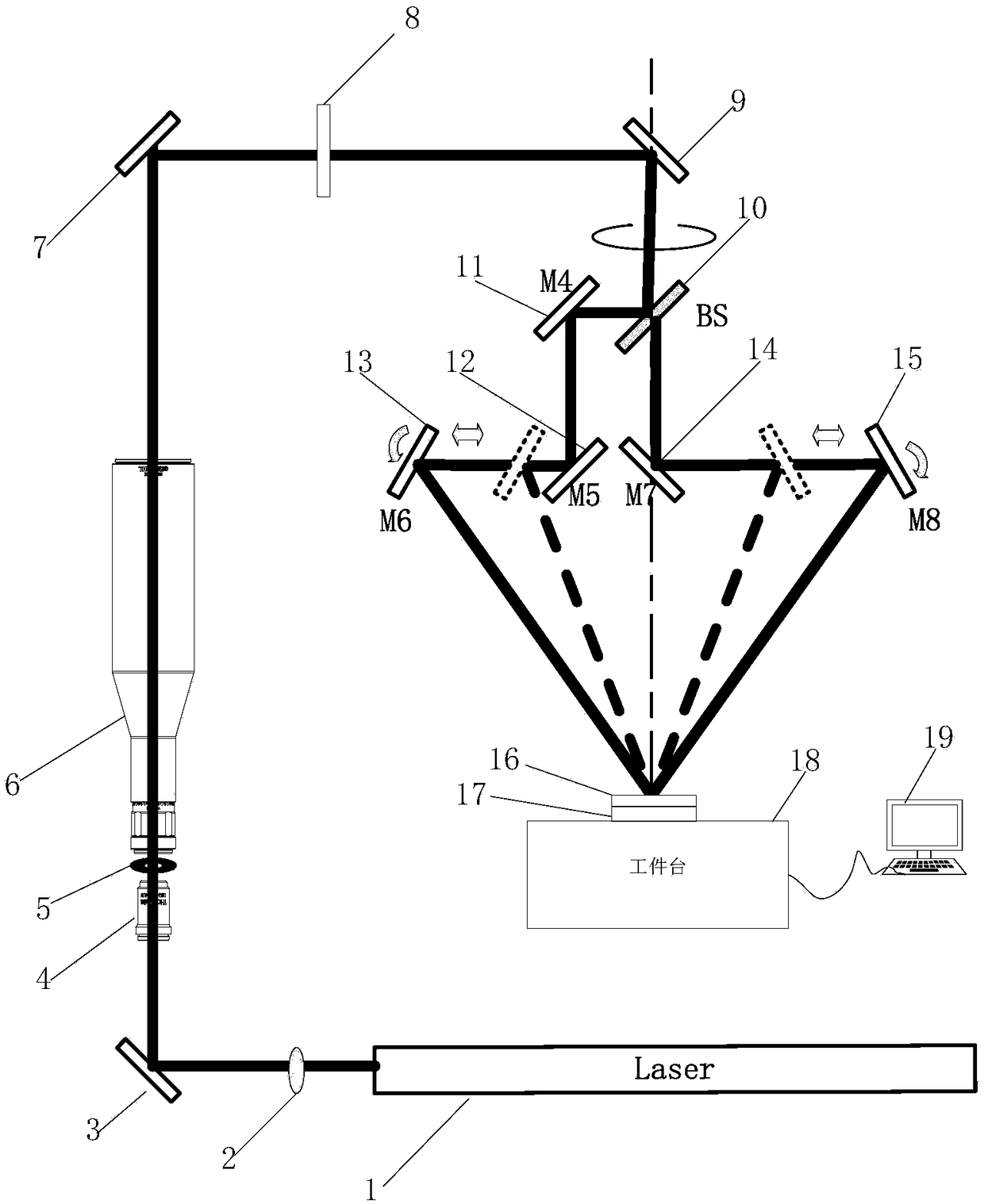
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Interference lithography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
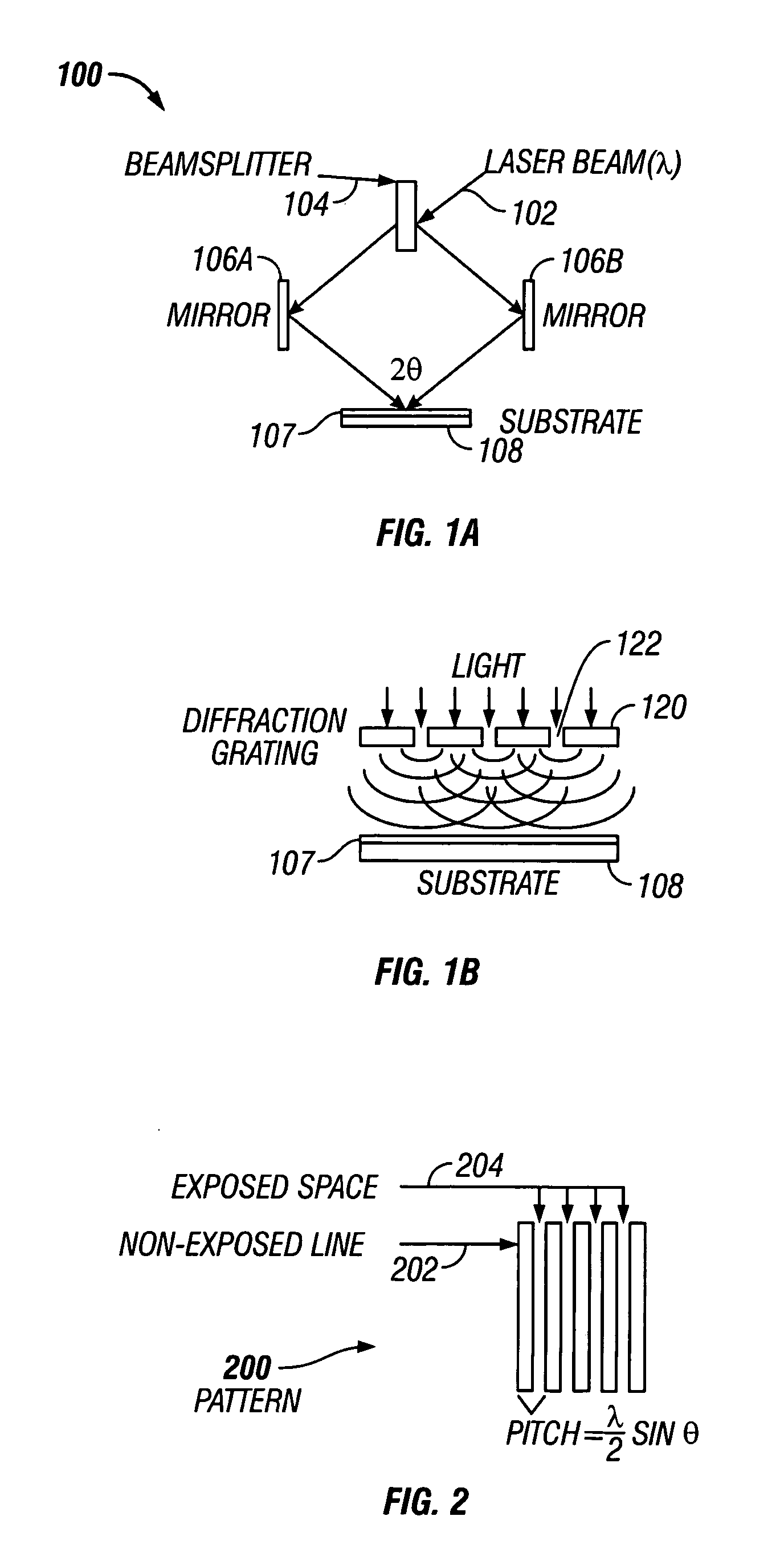
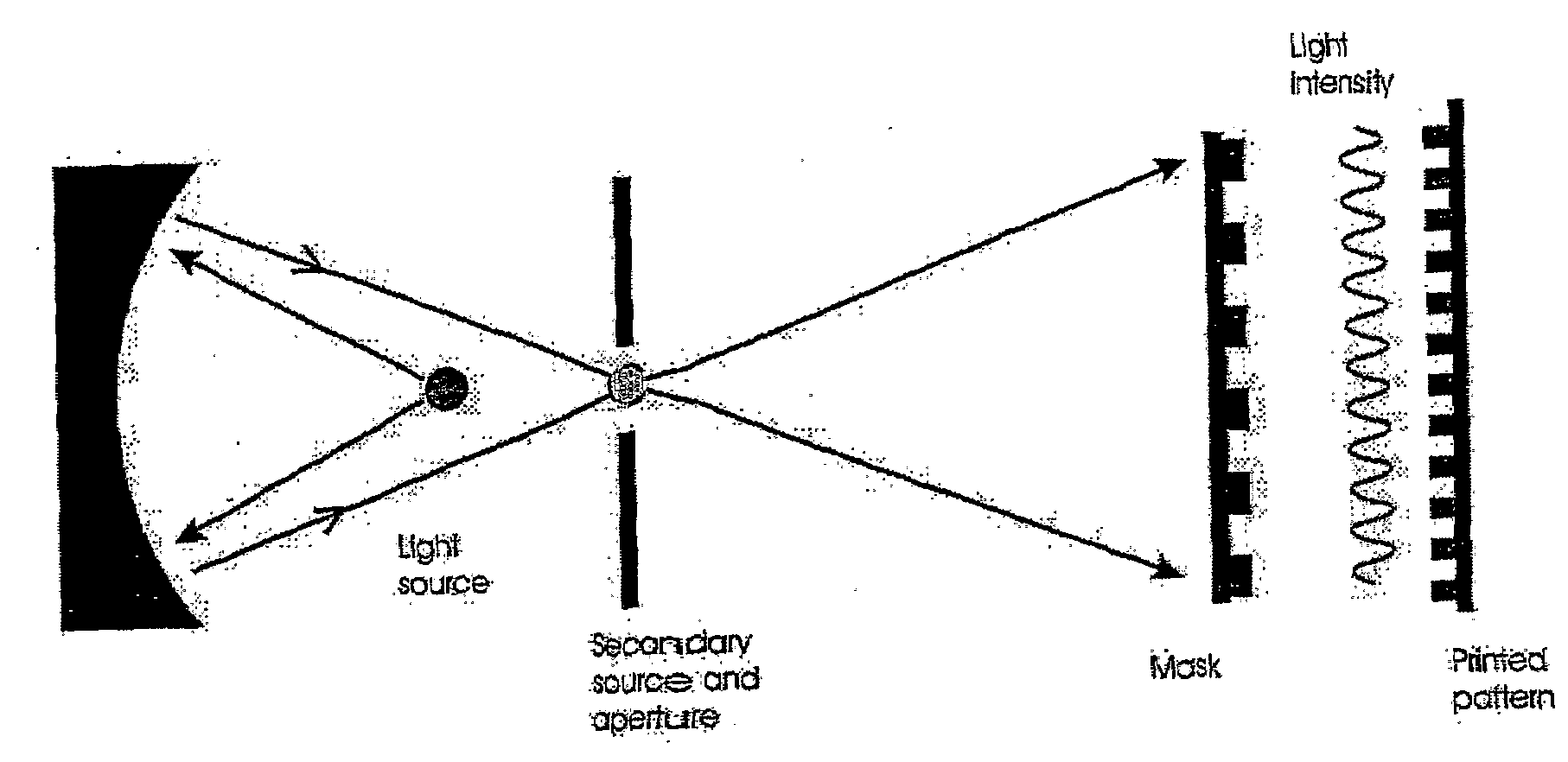
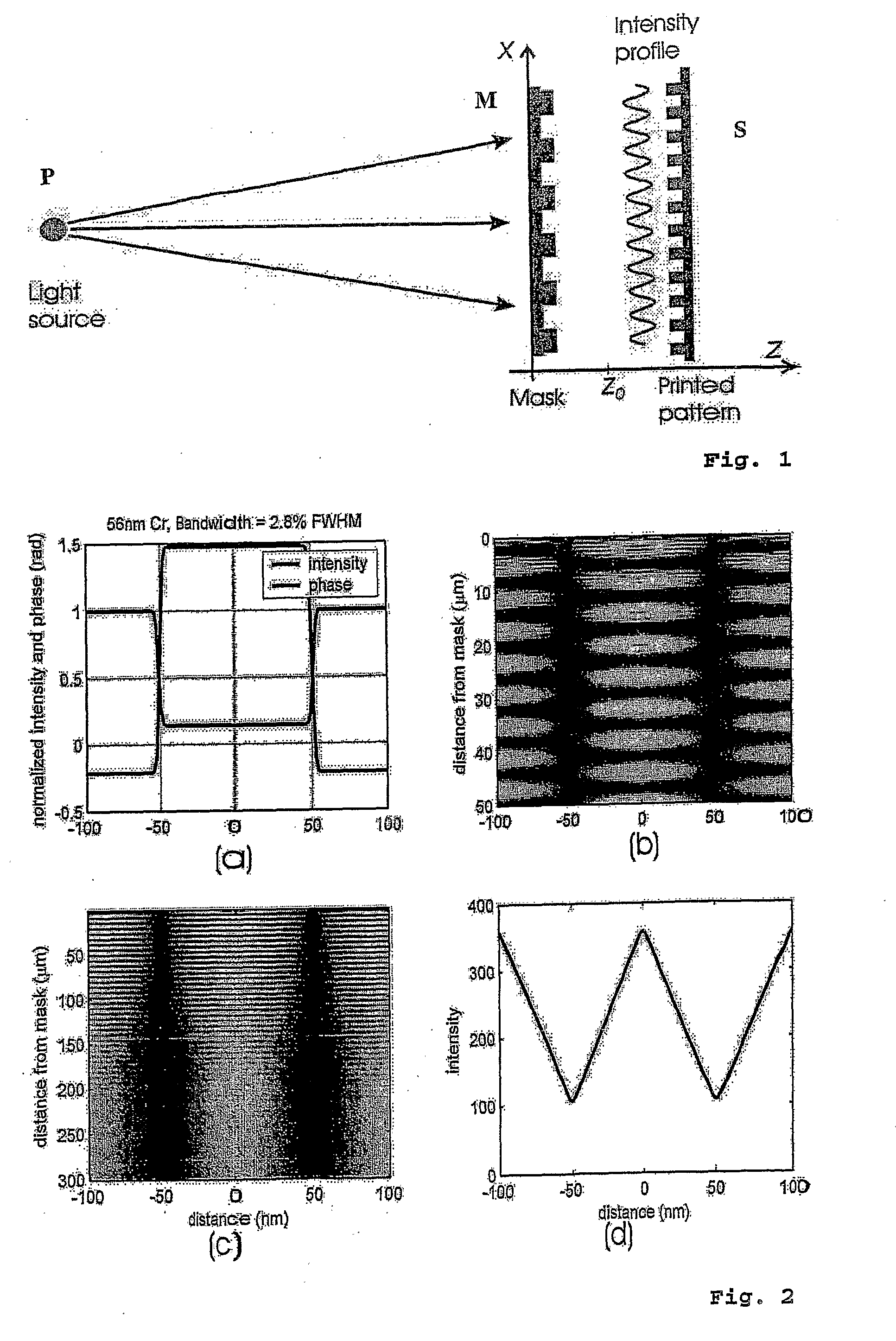
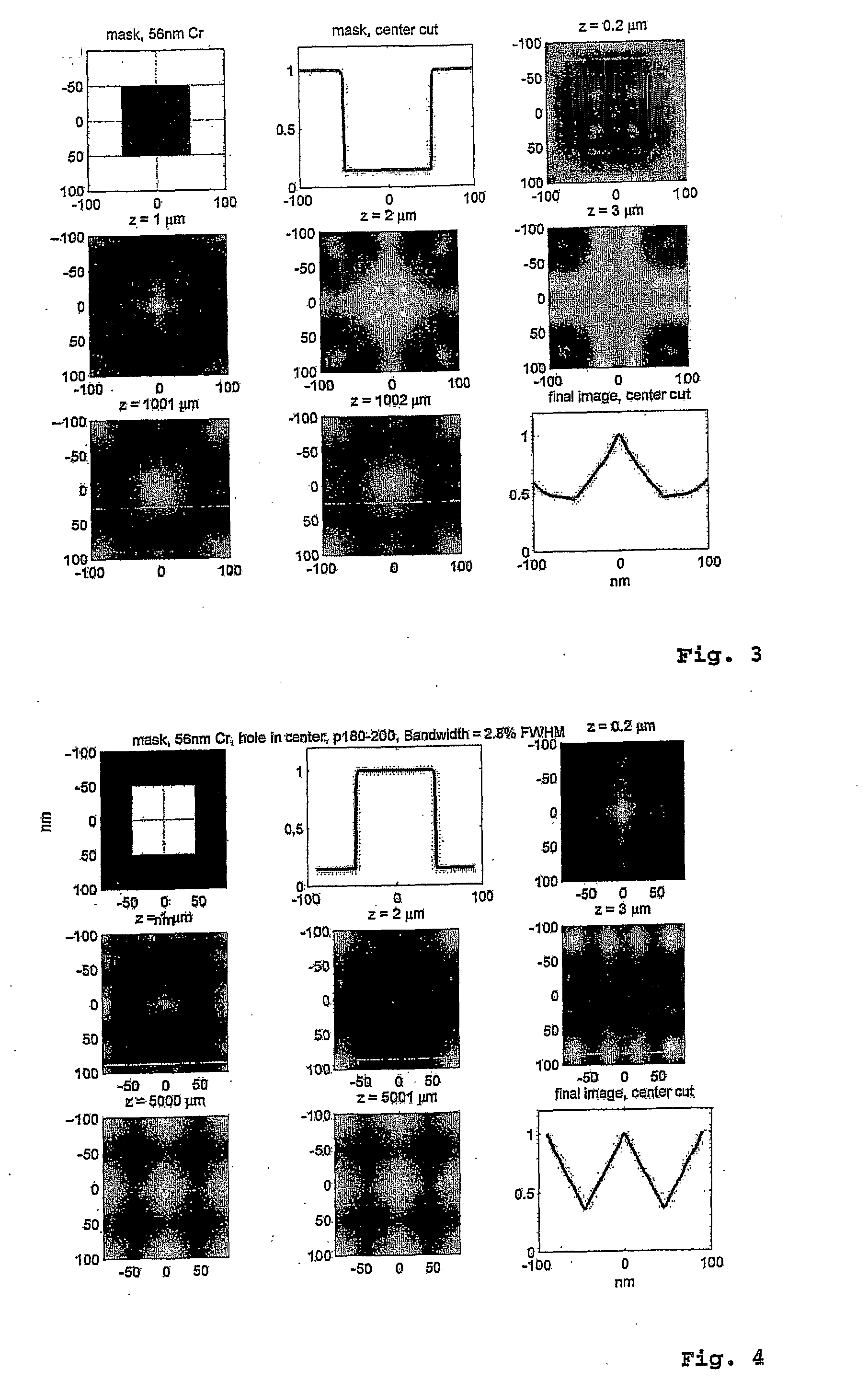
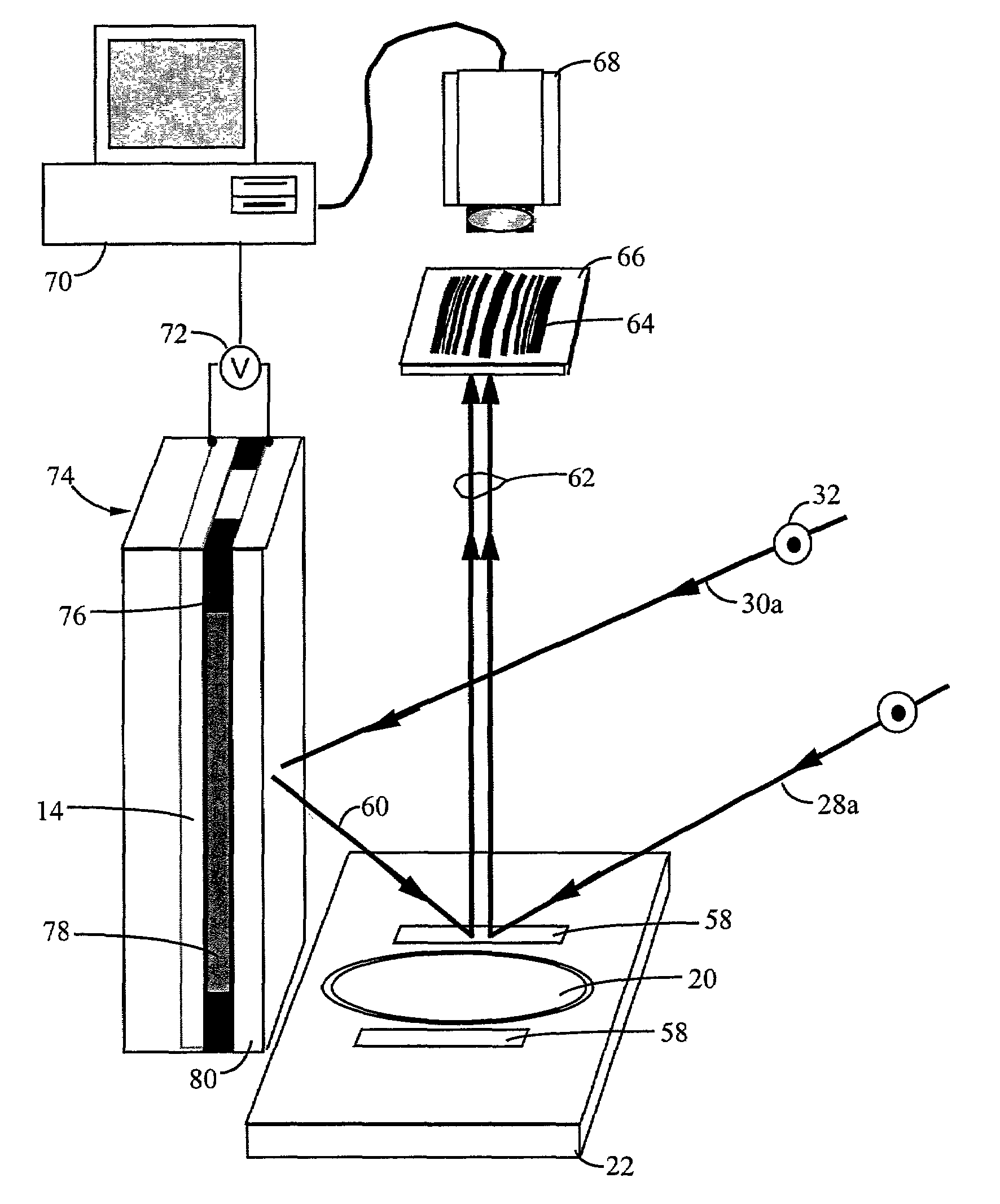
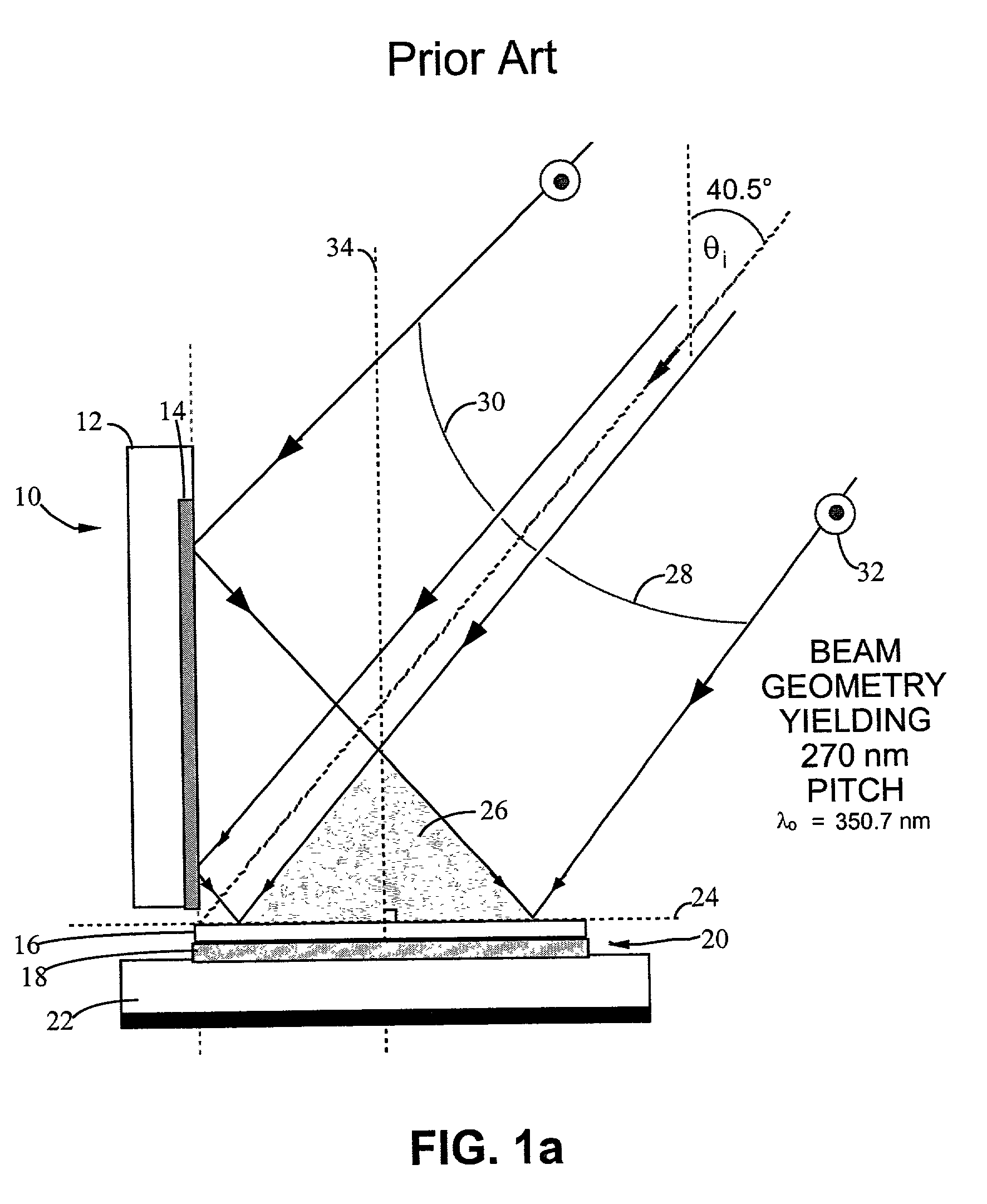
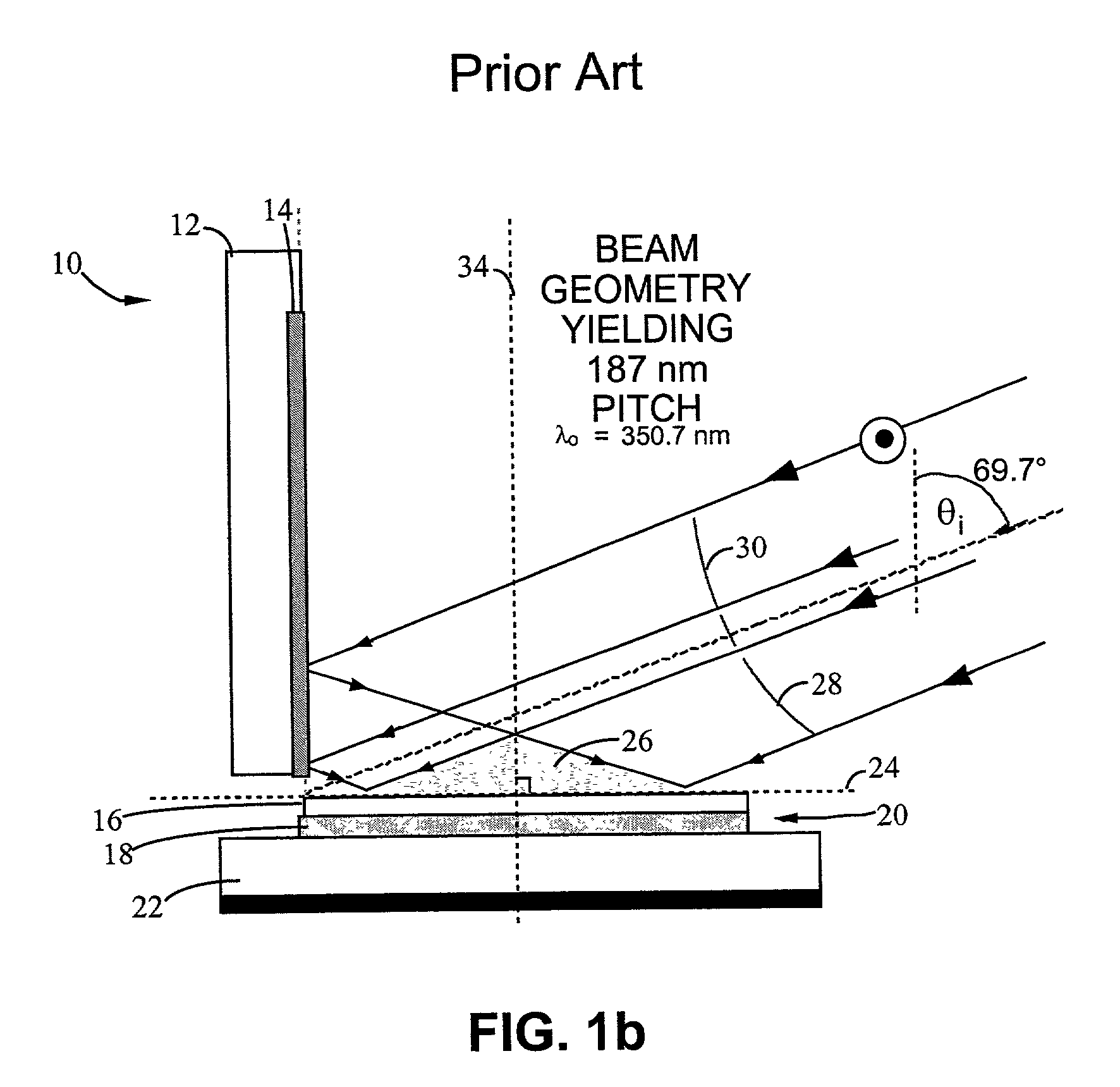
Interference lithography (or holographic lithography) is a technique for patterning regular arrays of fine features, without the use of complex optical systems or photomasks.
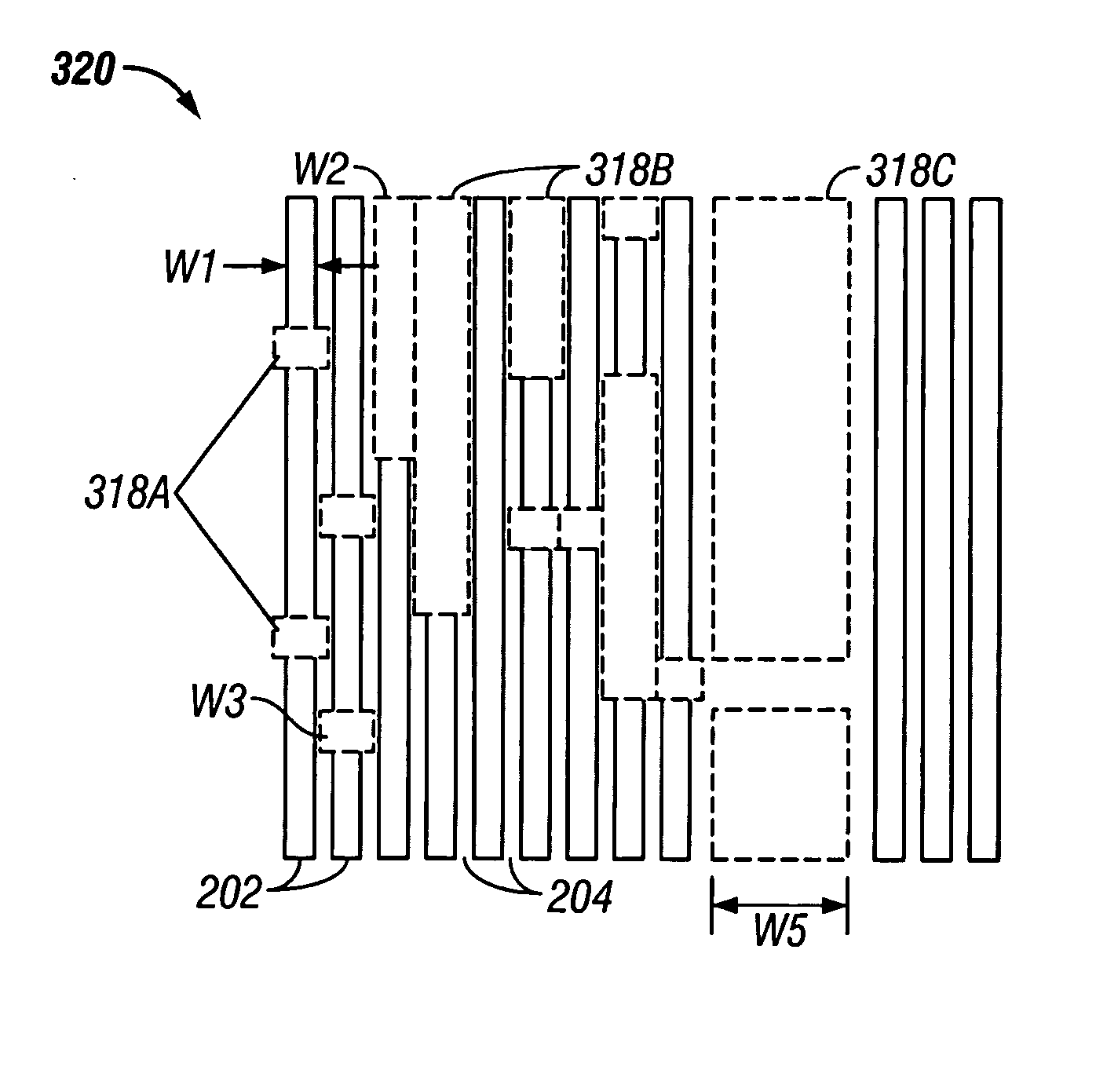
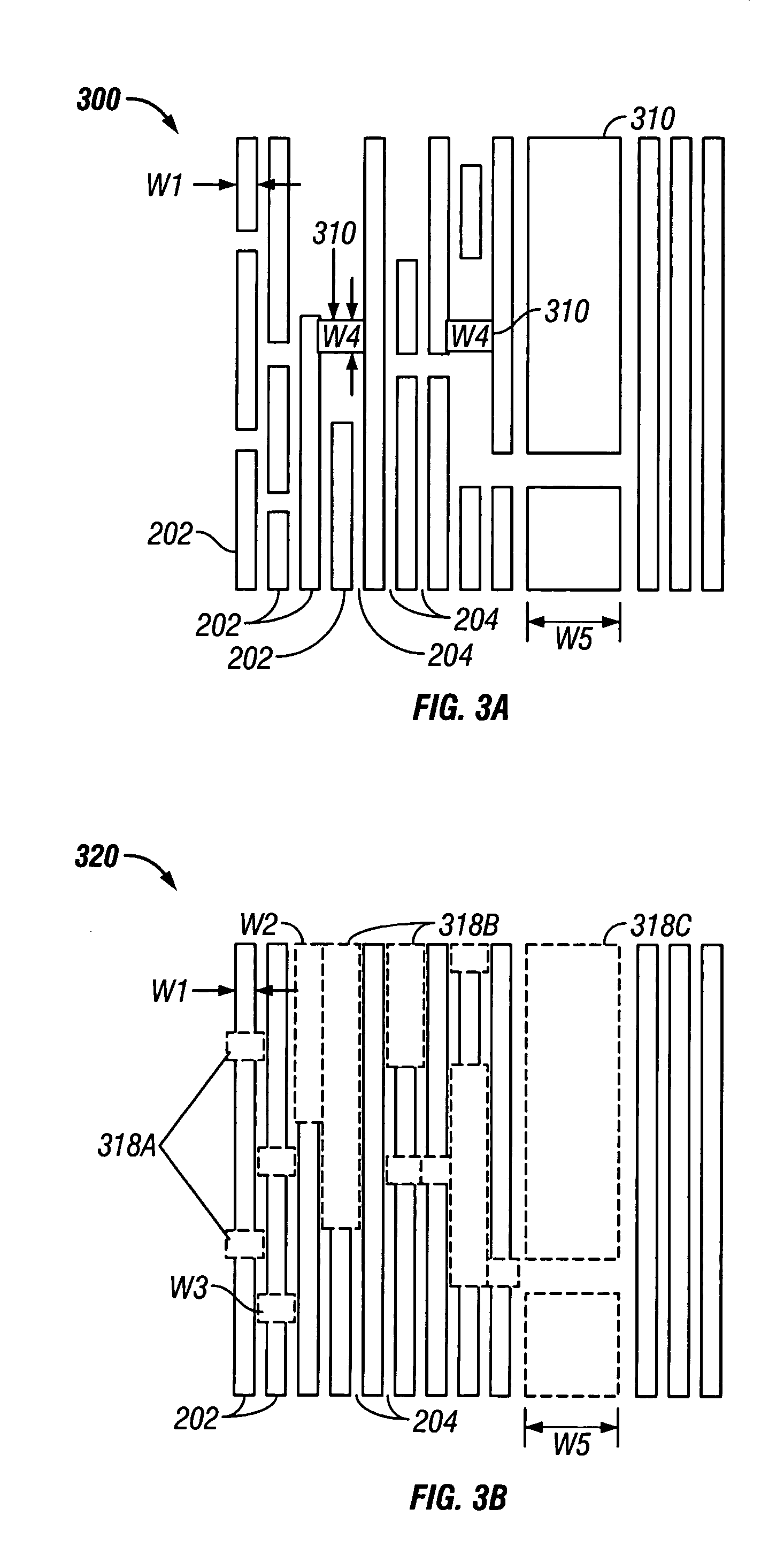
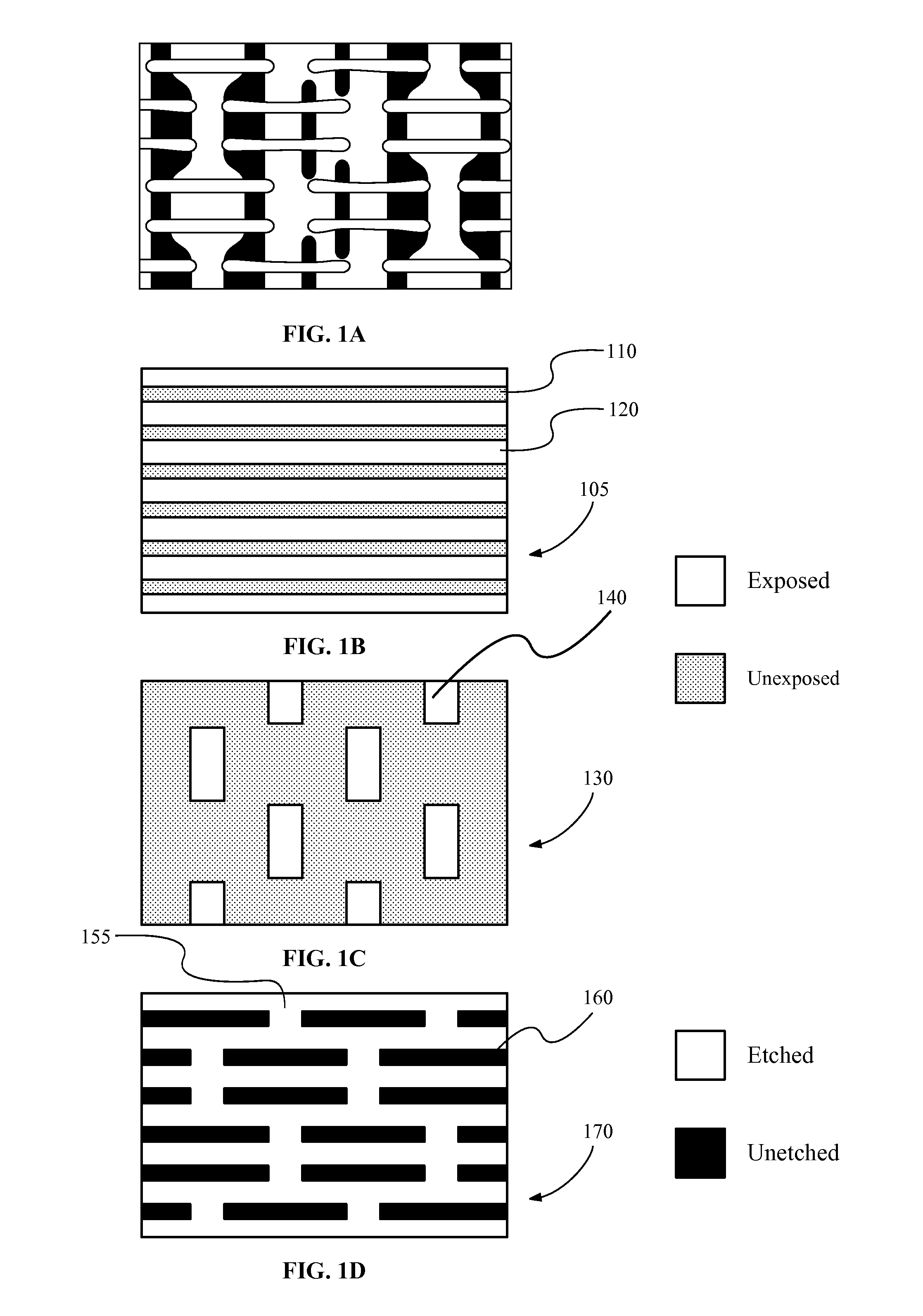
Composite optical lithography method for patterning lines of significantly different widths
InactiveUS20050074698A1Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processInterference lithography
A composite patterning technique may include three lithography processes. A first lithography process forms a periodic pattern of alternating continuous lines of substantially equal width and spaces on a first photoresist. A second lithography process uses a non-interference lithography technique to break continuity of the patterned lines and form portions of desired integrated circuit features. The first photoresist may be developed. A second photoresist is formed over the first photoresist. A third lithography process uses a non-interference lithography technique to expose a pattern on the second photoresist and form remaining desired features of an integrated circuit pattern.
Owner:INTEL CORP
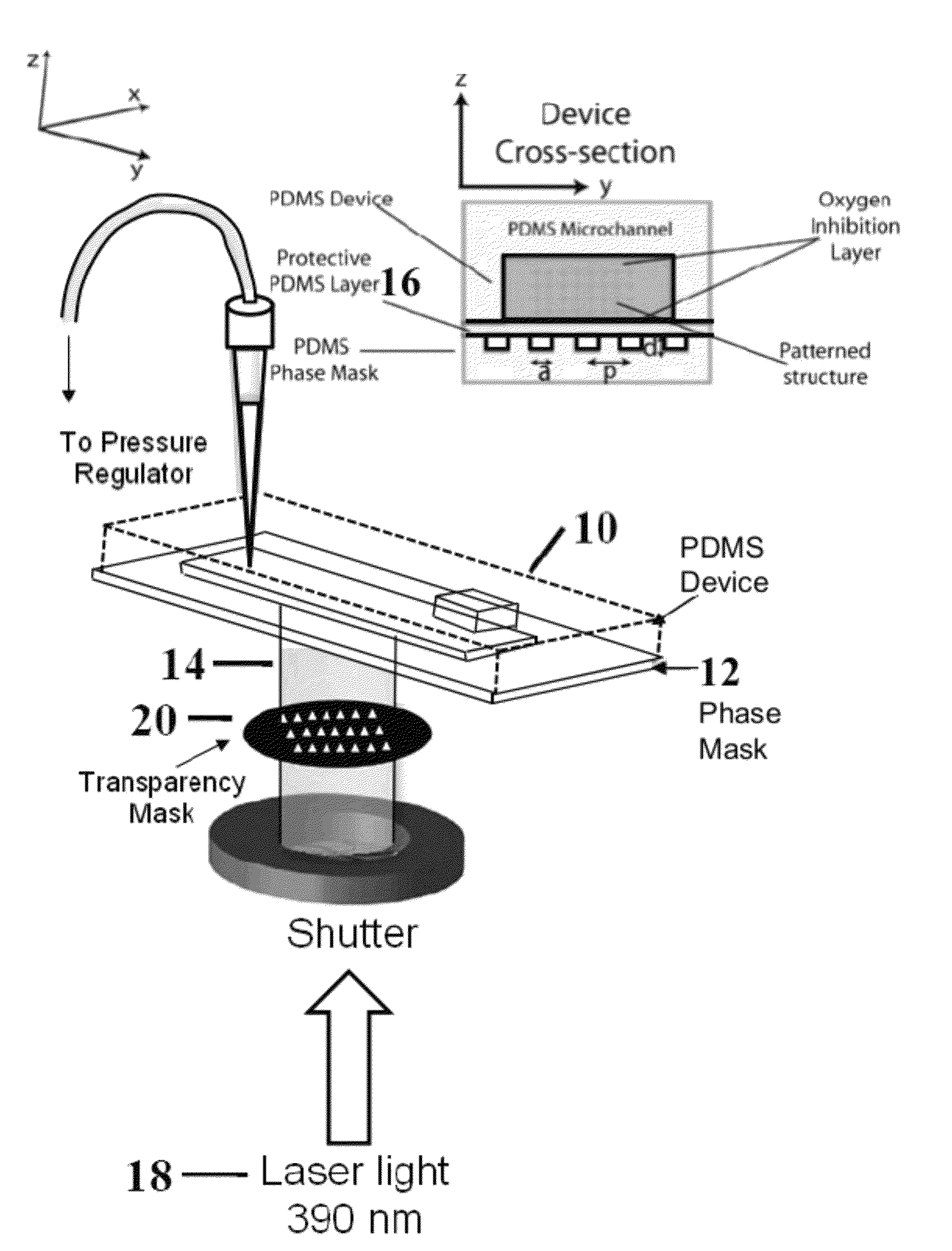
Stop flow interference lithography system
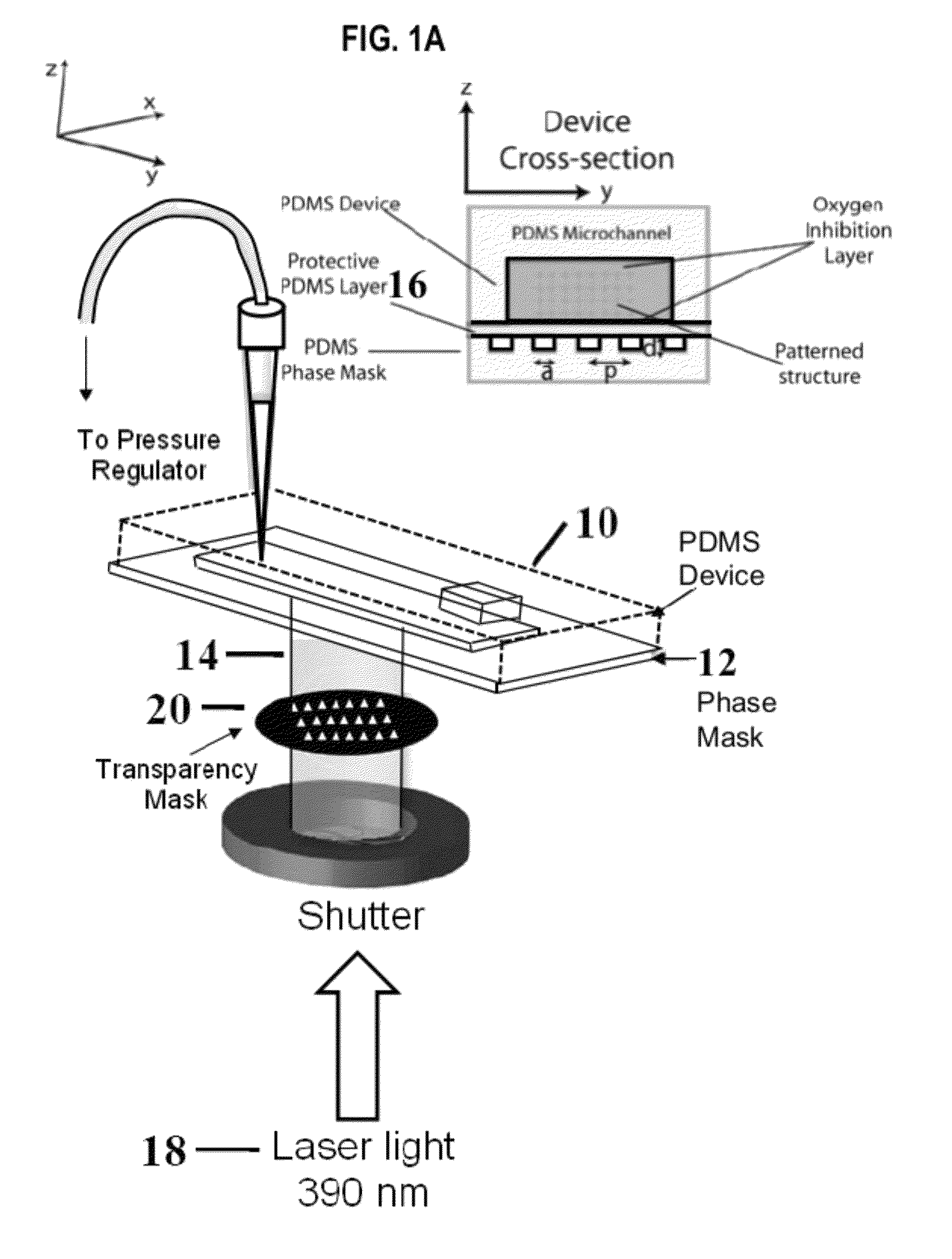
ActiveUS8252517B2Photo-taking processesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhase maskMicrofluidic channel
Stop flow interference lithography system for high throughput synthesis of 3-dimensionally patterned polymer particles. The system includes a microfluidic channel containing a stationary oligomer film and a phase mask located adjacent to the microfluidic channel. A source of collimated light is provided for passing the collimated light through the phase mask and into the microfluidic channel for interaction with the oligomer. The passage of the collimated light through the phase mask generates a 3-dimensional distribution of light intensity to induce crosslinking of the oligomer in high intensity regions thereby forming 3-dimensional structures.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Patterning resolution enhancement combining interference lithography and self-aligned double patterning techniques
InactiveUS20090246706A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistImage resolution
A method for providing regular line patterns using interference lithography and sidewall patterning techniques is provided according to one embodiment. The method comprising may include producing regularly spaced parallel lines on a template using interference lithography techniques and then depositing sidewalls on the longitudinal sides of the regularly spaced parallel lines using sidewall patterning techniques. Various deposition and etching steps may also be included. The embodiments of the invention may provide regular line patterns with a line density half the interference lithography line density. Various lithography techniques may also be used to crop rounded connecting resulting from the sidewall patterning and / or to alter portions of the line pattern.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
System and a Method for Generating Periodic and/or Quasi-Periodic Pattern on a Sample
ActiveUS20080186579A1Effective protectionPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsGratingInterference lithography
A system for generating periodic or quasi-periodic patterns on a sample by means of an interference lithography technique includes a photon source, a mask and a sample holder. The mask has a grating for generating a predetermined pattern, wherein the mask is positioned at a first distance from the photon source. The sample holder is disposed at a second distance from the mask on a side facing away from the photon source. The second distance is selected to be where an intensity distribution is substantially stationary and distance-invariant, or the second distance is varied to obtain a desired average intensity distribution on the sample surface.
Owner:EULITHA
Method and device for producing a coupling grating for a waveguide
InactiveUS20040042724A1Reduce contrastAdequate averagingCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction effectEffective solution
The invention relates to a method and a device for producing a coupling grating (5) for a waveguide. The method relies on the technique of interference lithography, whereby an interference pattern on a light-sensitive layer (2) is exposed by superimposing two coherent light beams (3, 4) on said light-sensitive layer (2). Said pattern is then transferred onto the surface of the substrate (1) that lies underneath by subsequent developing and an etching process. The method is characterized in that it uses a shadow mask (6) that is mounted at minimum clearance relative to the surface of the light-sensitive layer (2). By observing said minimum clearance, the Fresnel diffraction images of both light beams (3, 4) are separated on the edge(7). The thickness of the light-sensitive layer (2) is selected in such a way that the superimposition of the Fresnel diffraction pattern of one light beam with the other undisturbed light beam suffices to uncover areas of the substrate (1) during subsequent developing of the layer (2). The method makes it possible to avoid transfer of unwanted diffraction effects on the edge of the shadow mask to the substrate. The method provides a cost-effective solution for the production of large-surface coupling grating matrices.
Owner:GOMBERT ANDREAS +2
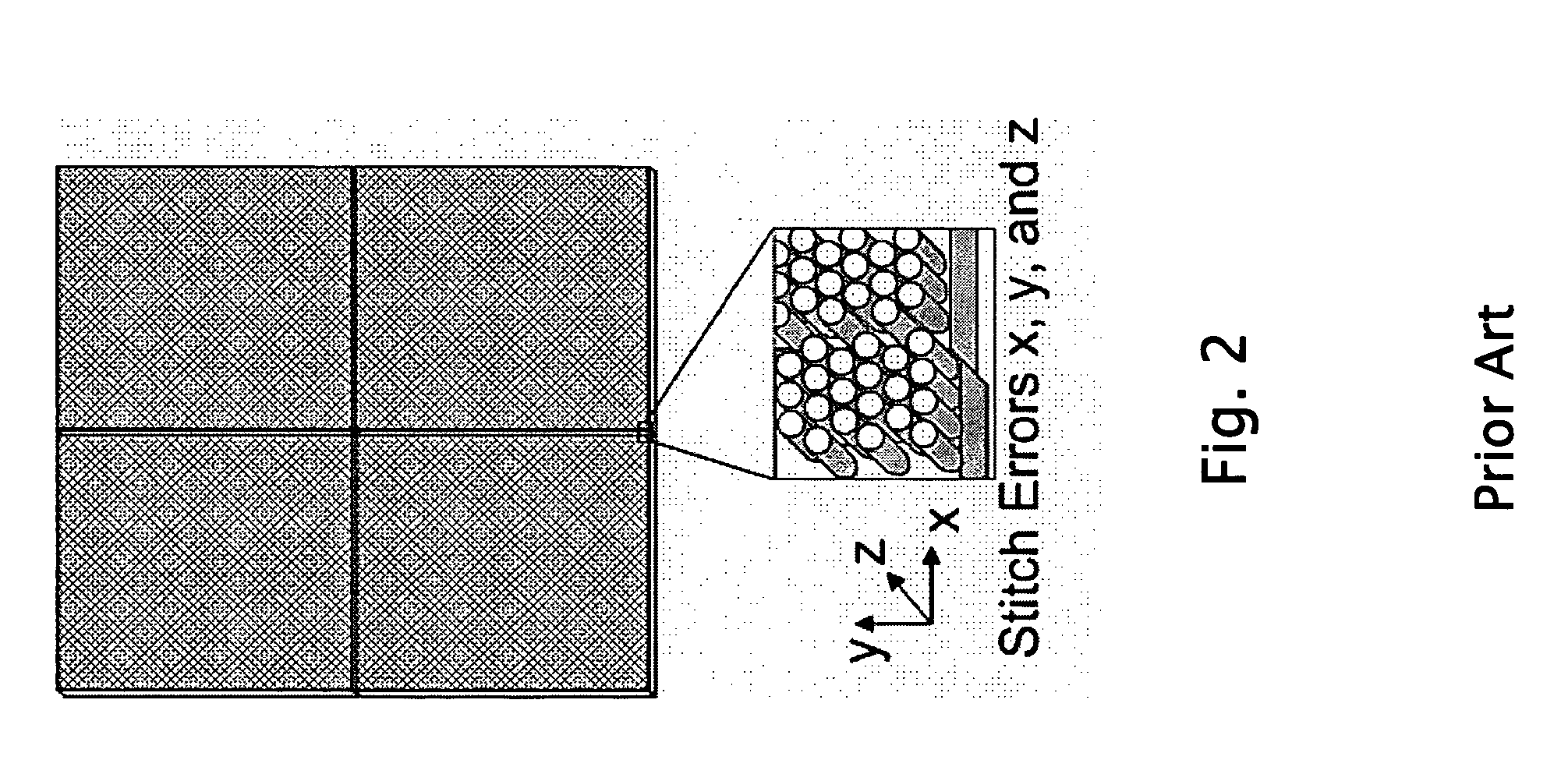
Seamless stitching of patterns formed by interference lithography
ActiveUS20070023692A1High optical modulationPhotomechanical apparatusRadiation therapyLarge screenExposure level
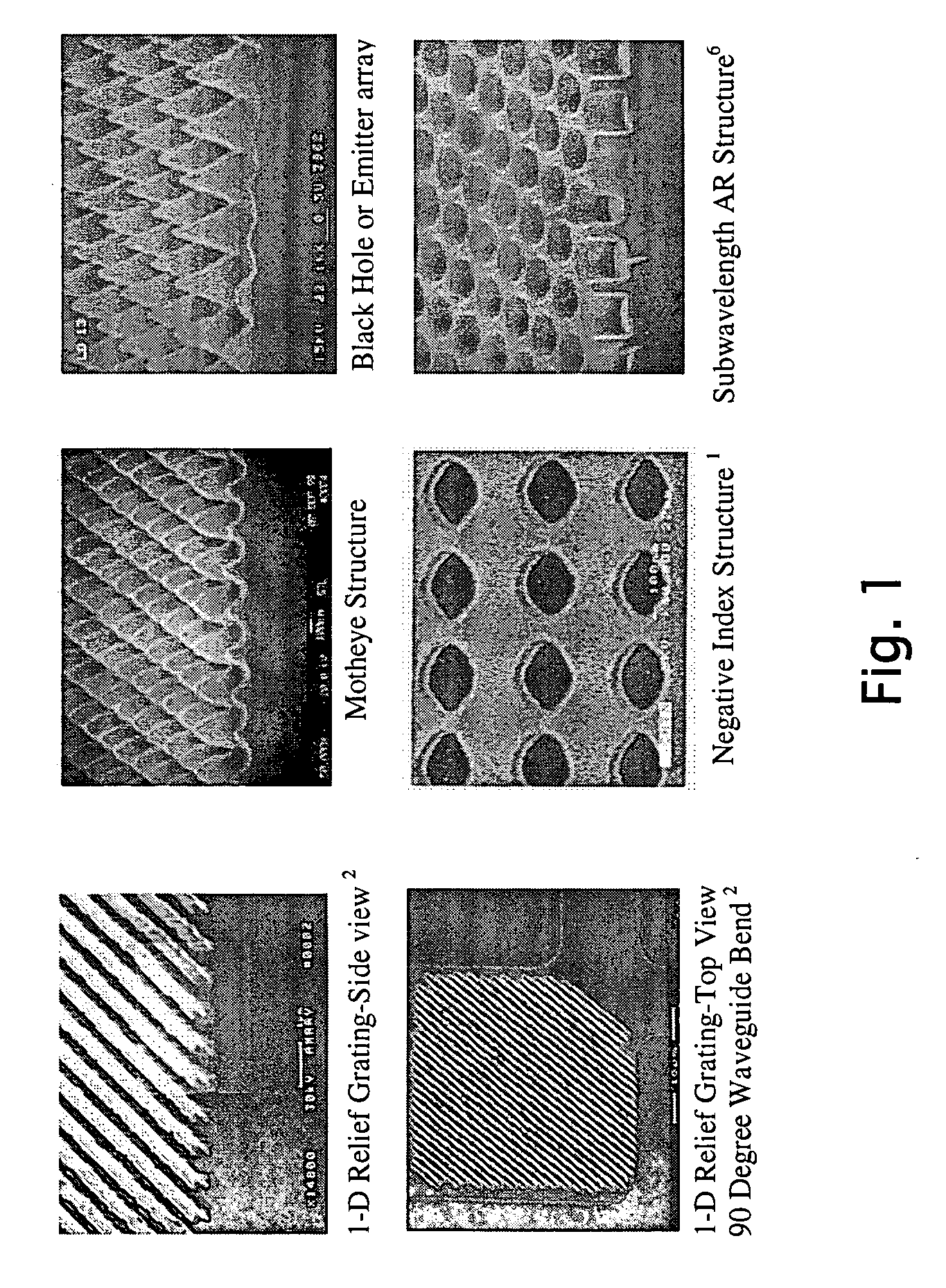
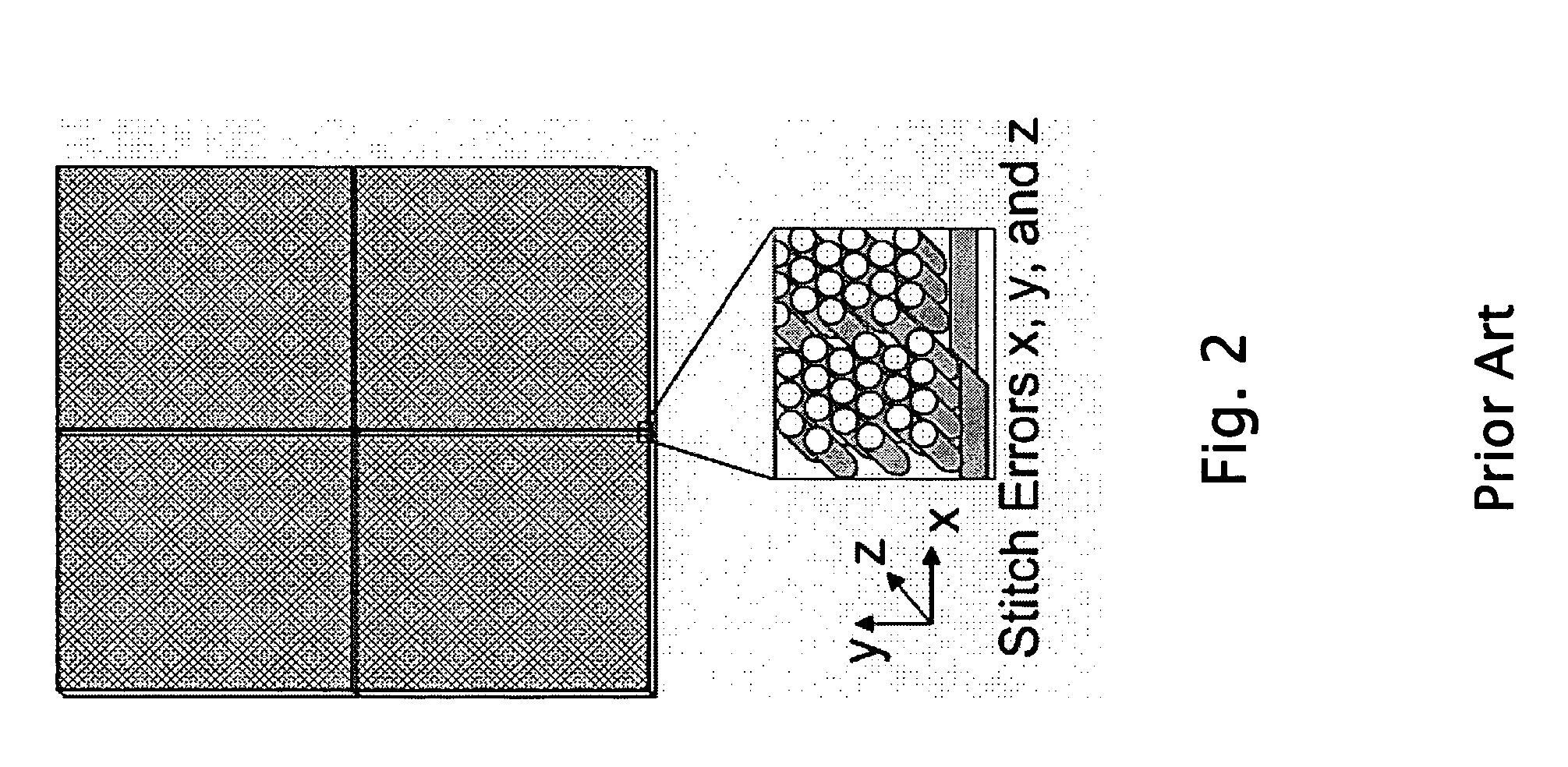
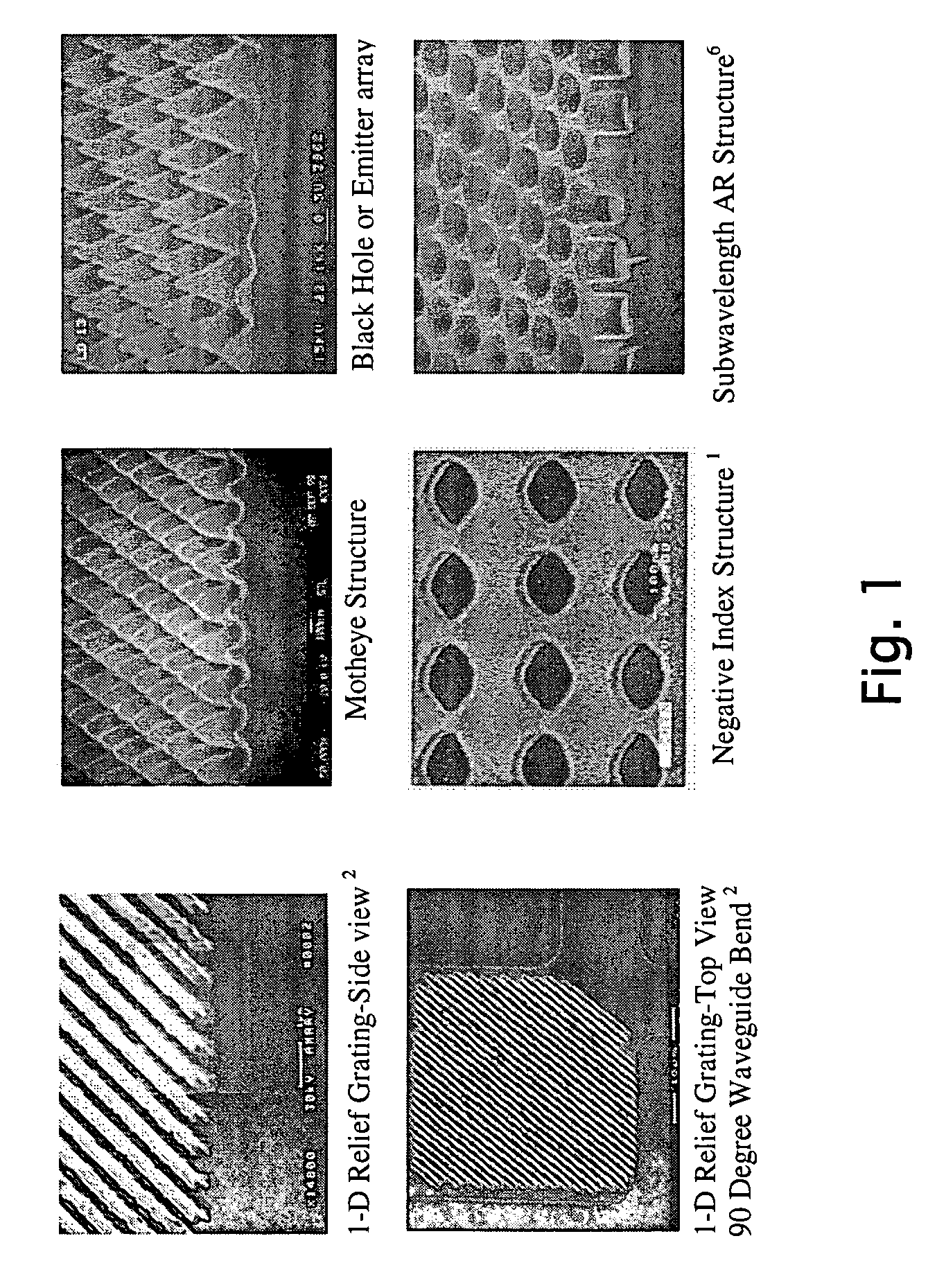
This invention addresses the scalability problem of periodic “nanostructured” surface treatments such as those formed by interference lithography. A novel but simple method is described that achieves seamless stitching of nanostructure surface textures at the pattern exposure level. The described tiling approach will enable scaling up of coherent nanostructured surfaces to arbitrary area sizes. Such a large form factor nanotechnology will be essential for fabricating large aperture, coherent diffractive elements. Other applications include high performance, antiglare / antireflection and smudge resistant Motheye treatments for display products such as PDA's, laptop computers, large screen TV's, cockpit canopies, instrument panels, missile and targeting domes, and, more recently, “negative-index” surfaces. Although ideal for seamless stitching of nanometer scale patterns, the technology is broadly applicable to any situation where an arbitrarily large area needs to be seamlessly tiled with a smaller base pattern that has periodic overlap able boundaries.
Owner:VINCENT E STENGER
Method for preparing surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrate and substrate prepared by using method
InactiveCN104634772AGood repeatabilityNo reunionDecorative surface effectsRaman scatteringSputteringGas phase
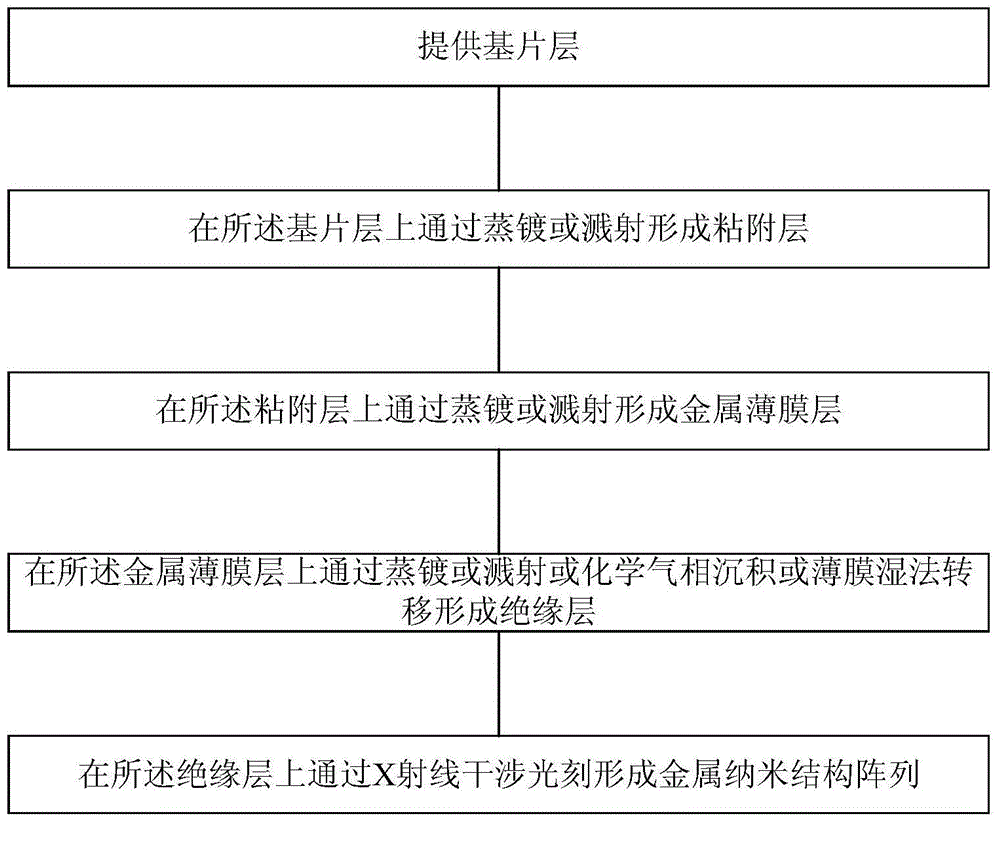
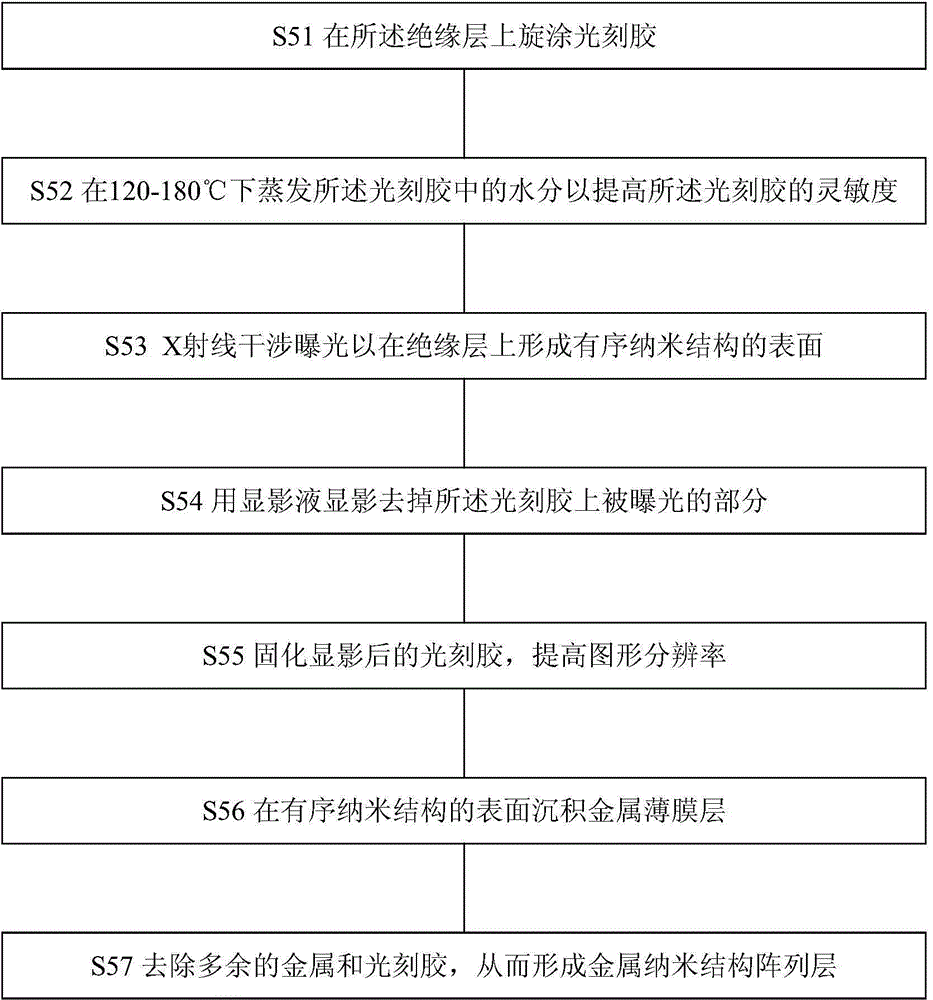
The invention provides a method for preparing a surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrate. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a substrate layer; forming an adhesion layer on the substrate layer by virtue of evaporation plating or sputtering; forming a metal thin film layer on the adhesion layer by virtue of evaporation plating or sputtering; forming an insulating layer on the metal thin film layer by virtue of evaporation plating or sputtering or chemical vapor deposition or thin film wet-process transfer; forming a metal nano-structure array layer on the insulating layer by virtue of X-ray interference lithography, wherein the X-ray interference lithography comprises photoresist spin-coating; evaporating moisture in a photoresist at 120-180 DEG C; performing X-ray interference exposure; performing development by using a developing solution; curing the developed photoresist; depositing the metal thin film layer on the surface of an ordered nanostructure; and removing excess metals and photoresists. The invention also relates to a surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrate comprising the substrate layer, the adhesion layer, the metal thin film layer, the insulating layer and the metal nano-structure array layer. The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum substrate prepared by using the method disclosed by the invention has both good sensitivity and stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
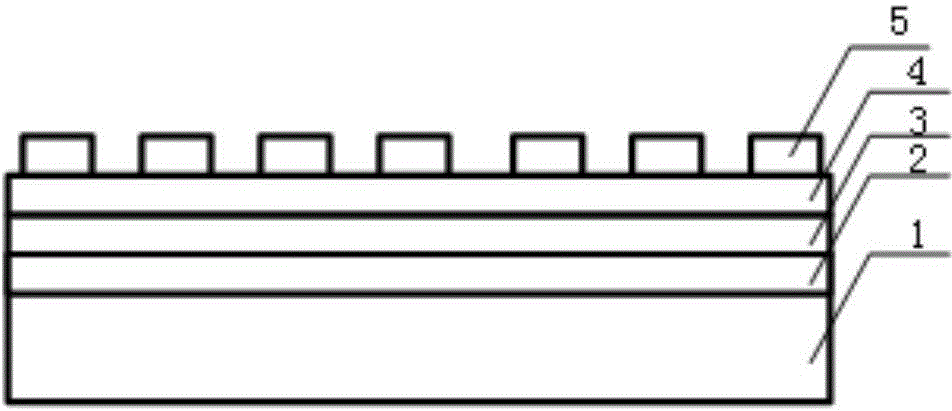
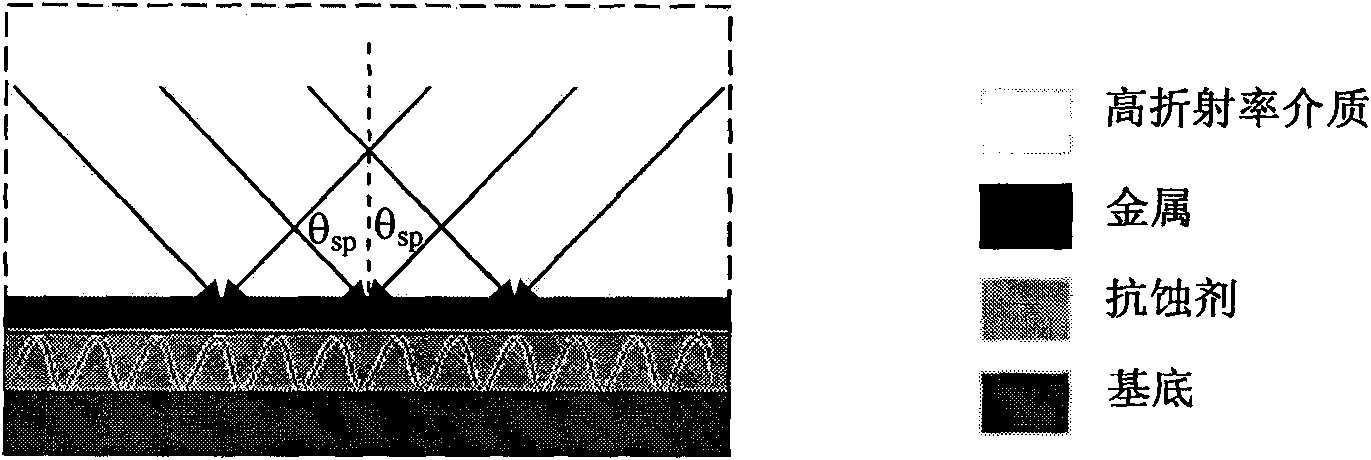
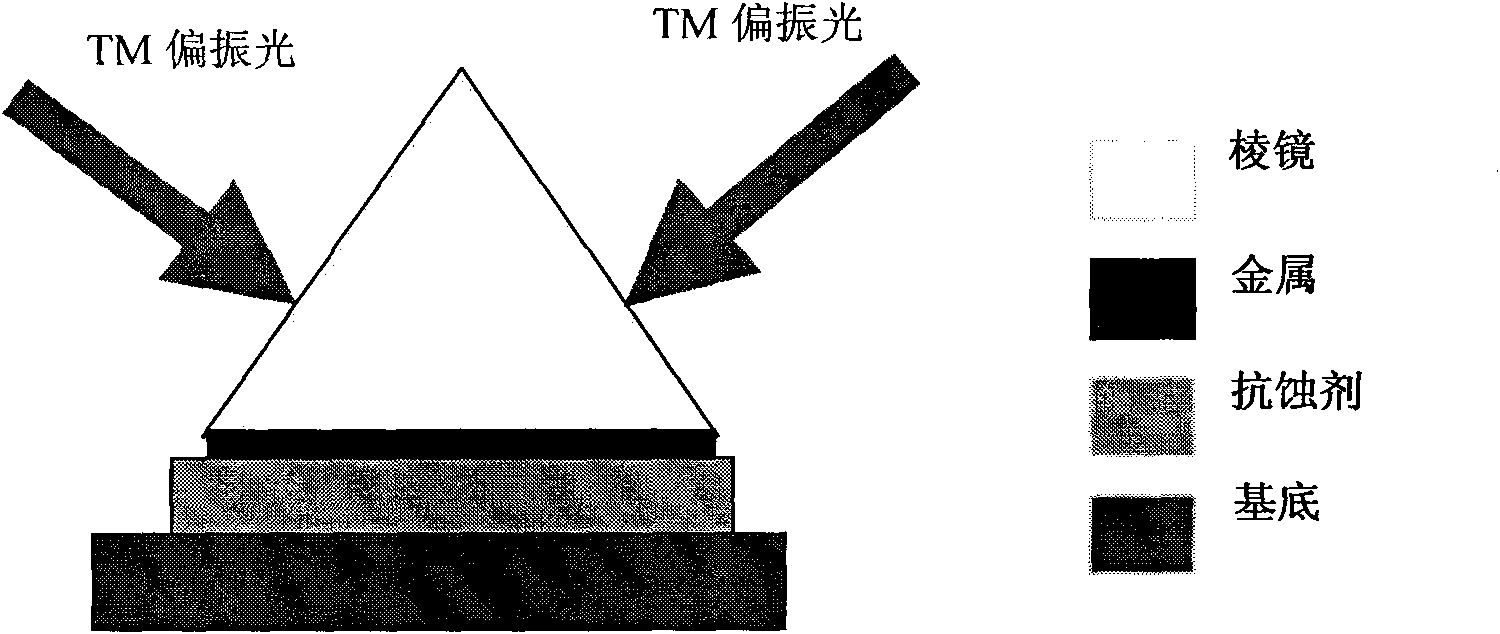
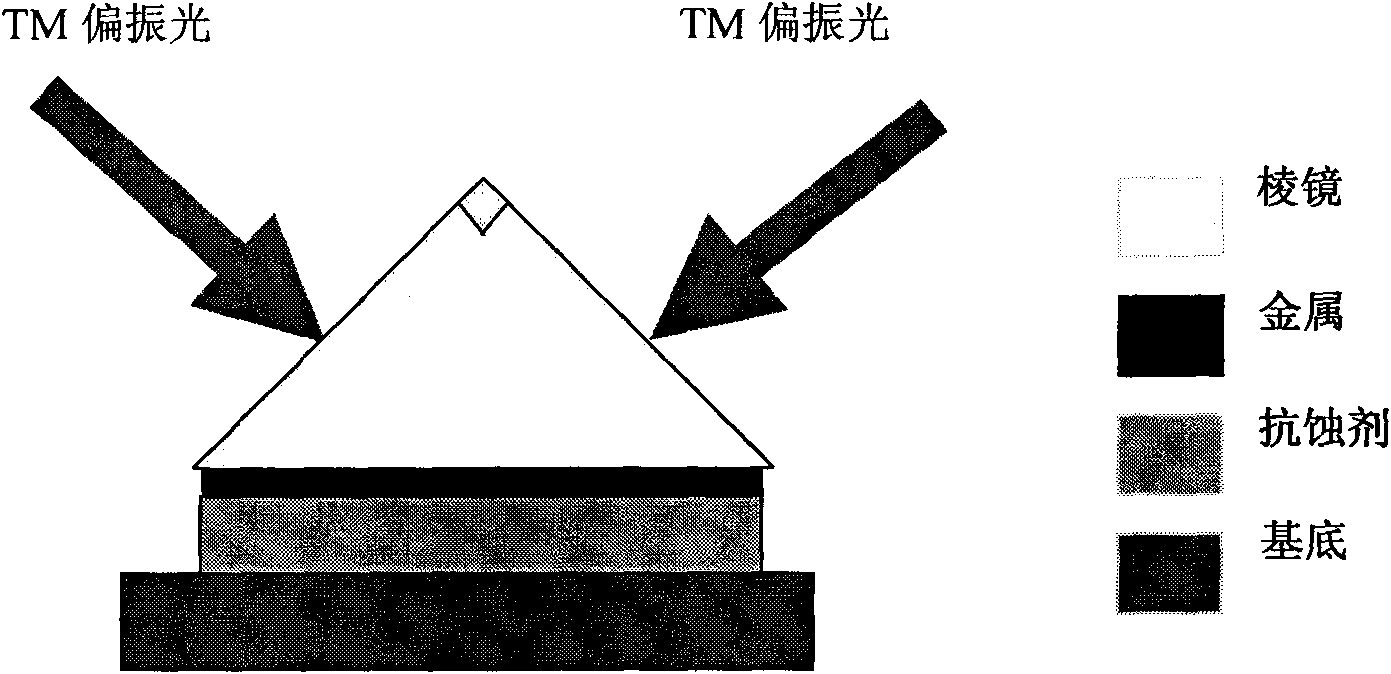
Surface plasmon (SPP)-based large-area interference lithography technology
InactiveCN101963761AChange structurePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNanolithographyResist
The invention provides surface plasmon (SPP)-based large-area interference lithography technology. In the technology, a dielectric layer with high refractive index is irradiated by two broad-beam light sources, the SPP on the surface of metal is excited in an attenuated total internal reflection coupled mode, and mutual interference exists among the SPP, so that a large-area periodic nanometer graph is formed in a resist; the SPP has the function of reinforcing a near field, so the graph has high contrast; meanwhile, the SPP has the characteristic of short wavelength, so high spatial resolution can be obtained and nanowires exceeding diffraction limit can be realized. Compared with the conventional nanometer lithography technology, the technology has the advantages of low lithography cost, large area exposure, no need of a complex and expensive optical imaging system with high numerical aperture, and wide application prospect in the manufacturing of large-scale integrated circuits and novel optical and electronic nanostructure devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manufacture system of anti-reflection structure on surface of solar cell and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN101924166ALithographic feature size adjustablePromote absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesFine structureEngineering
The invention relates to a manufacture system of an anti-reflection structure on the surface of a solar cell and a manufacture method thereof, which is characterized in that a plurality of coherent laser beams are combined by a laser interference lithography system to modulate the light intensity distribution in an interference field; the material surface of a photovoltaic cell device is ablated with redistributed laser energy after modulation; and micro or nano-stage dense hole and column relief structures are generated in a large-area range so as to reduce the reflectivity, enhance the light absorption and improve the photovoltaic conversion efficiency. Lacking of external materials, the anti-reflection fine structure generated on the substrate surface by using the method is more stableand durable, and the cycle and the size of the structure can be adjusted by adjusting the incidence angle of the interference lithography system so that the received wavelength has better pertinence and has the advantage of good working band controllability.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
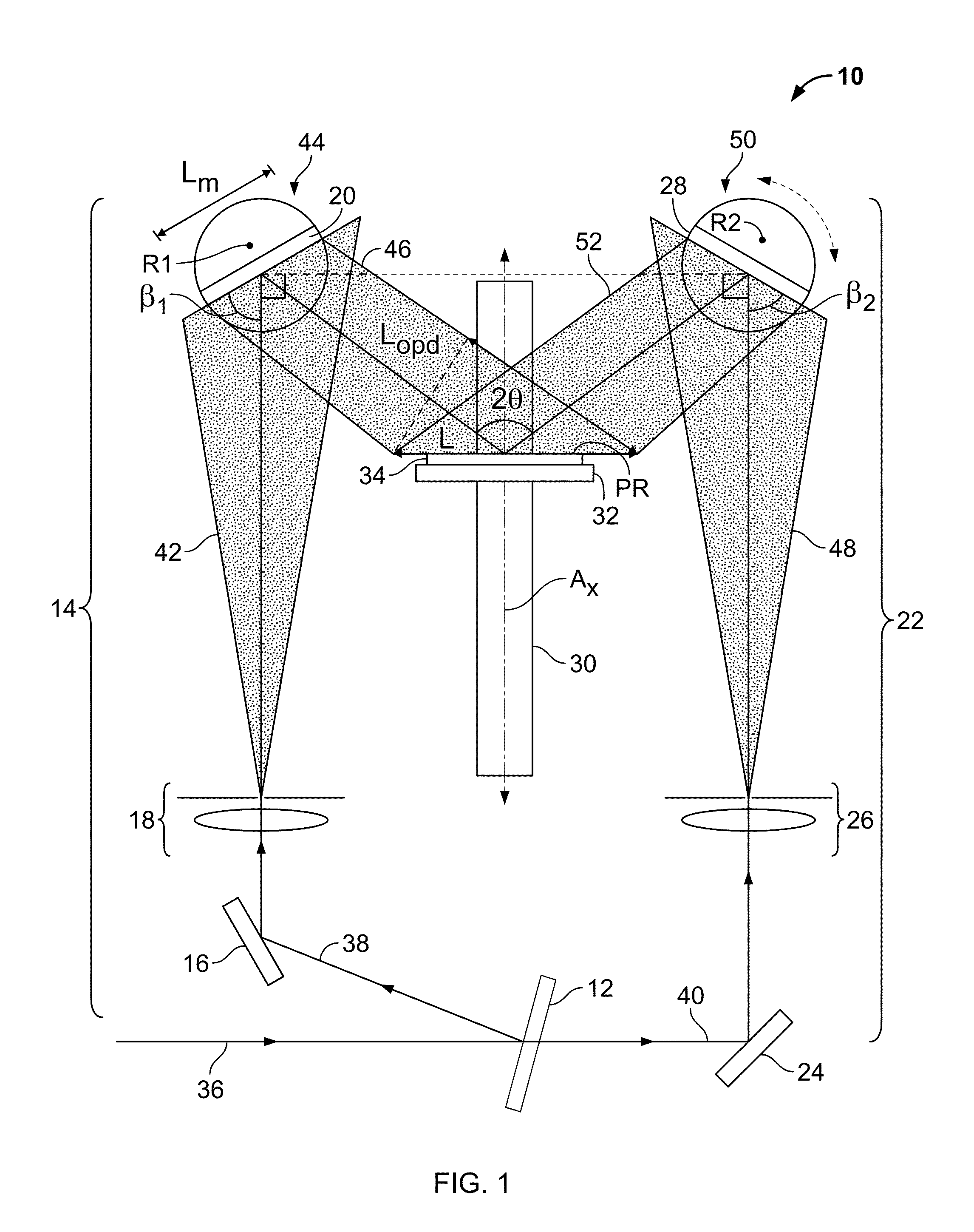
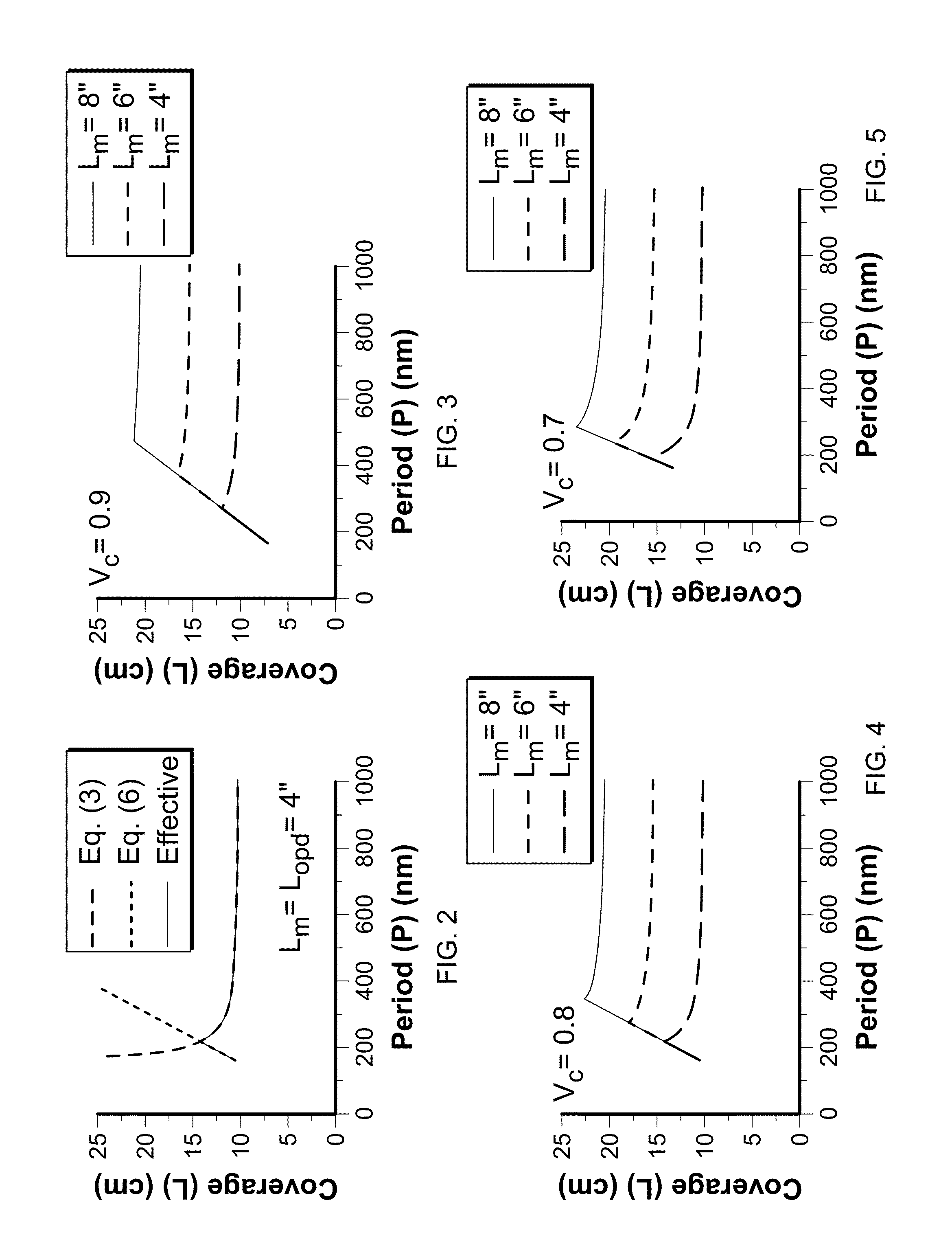
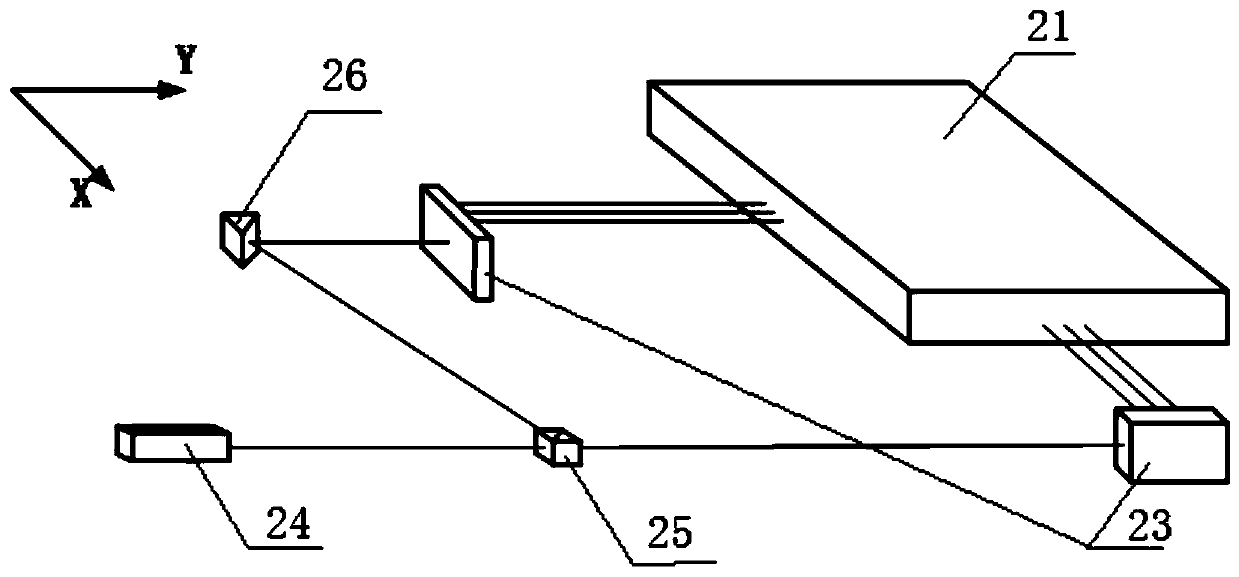
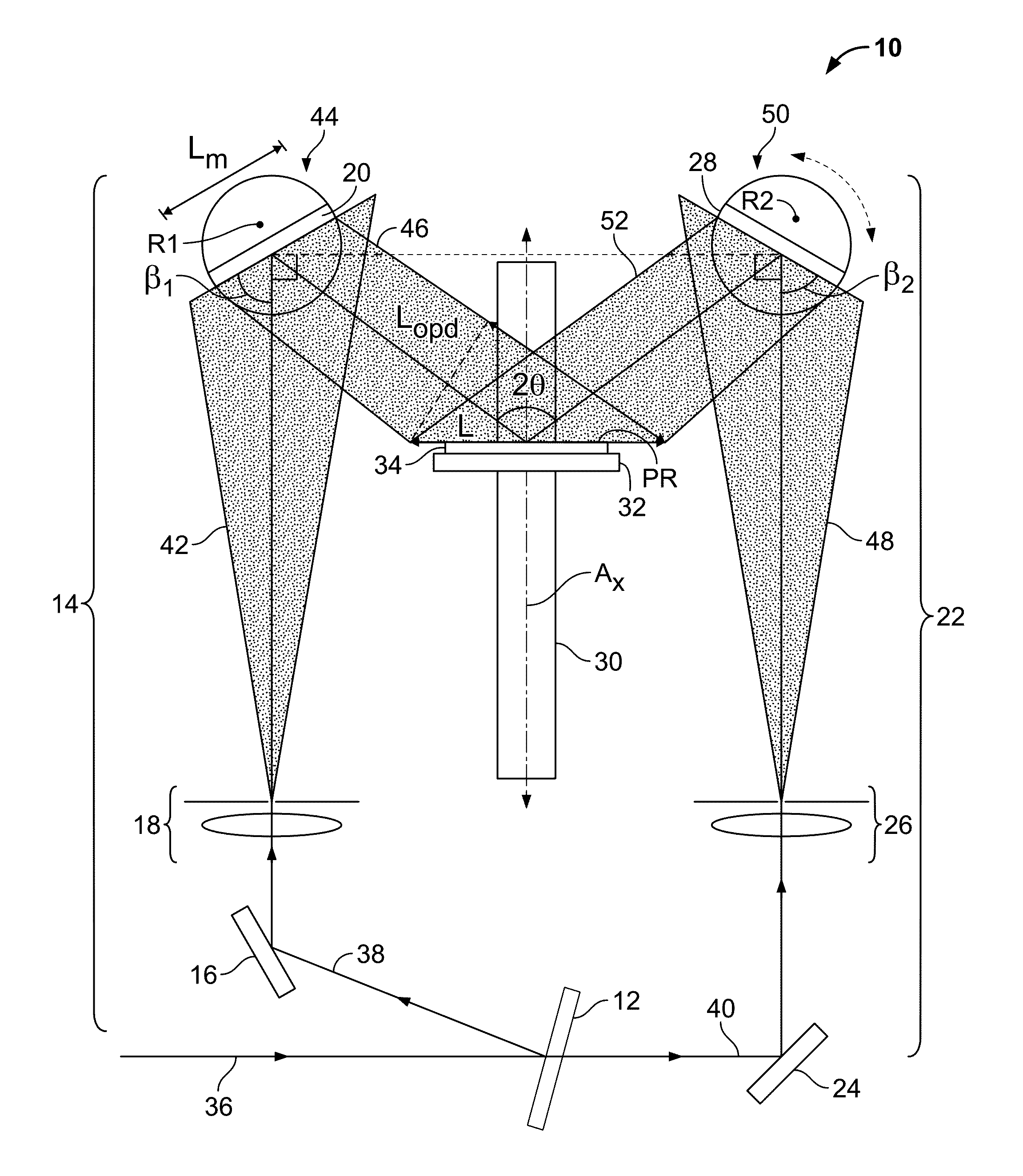
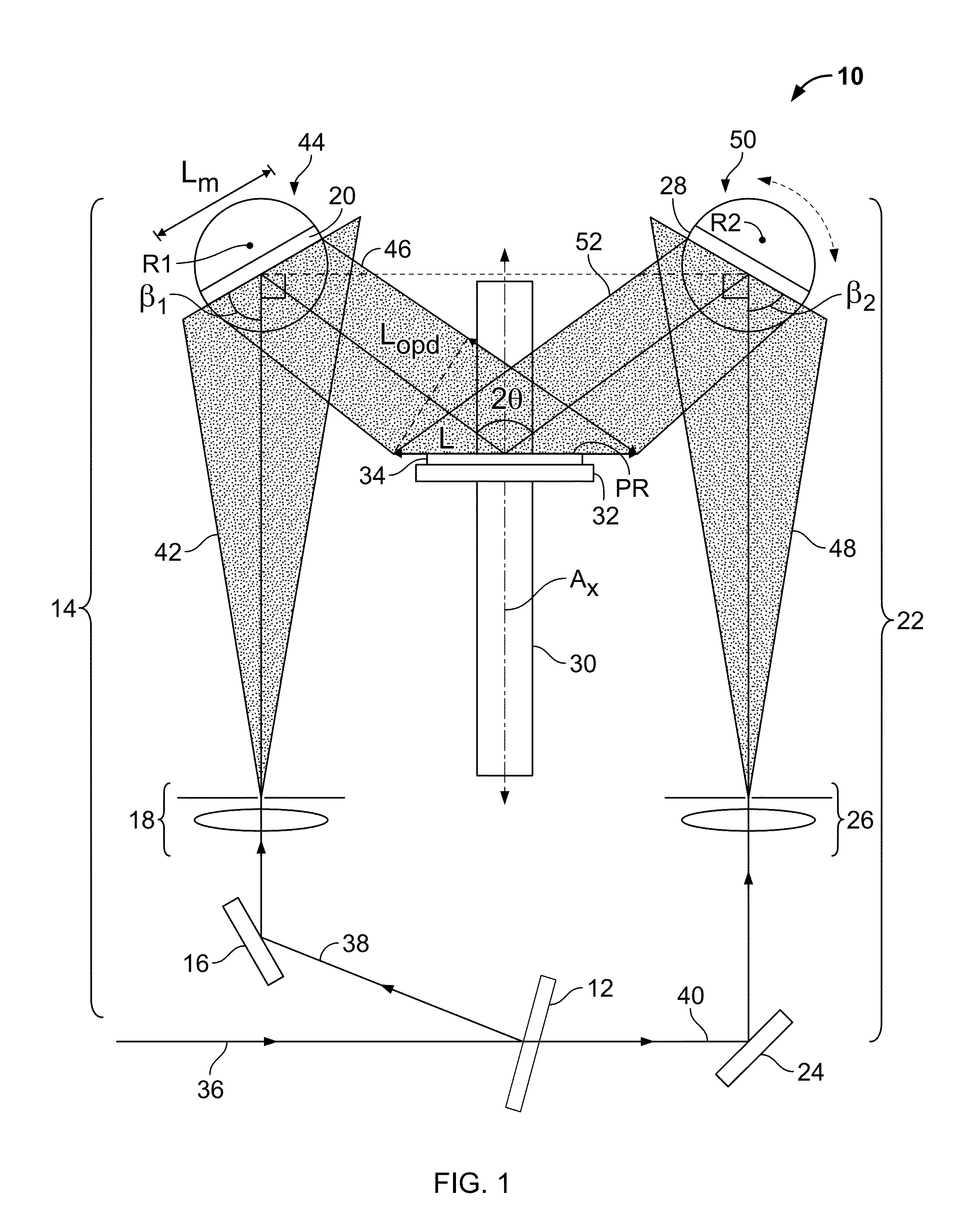
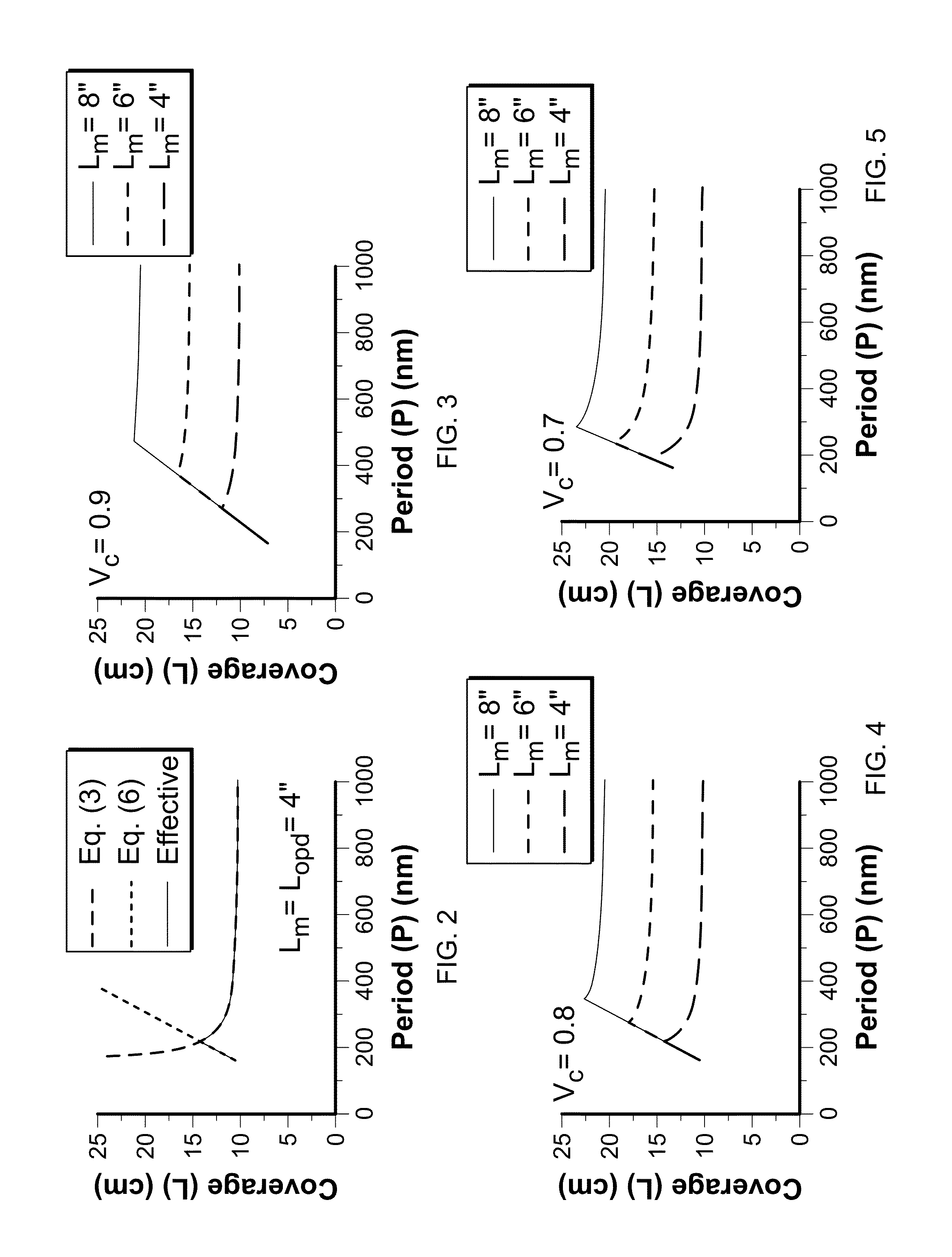
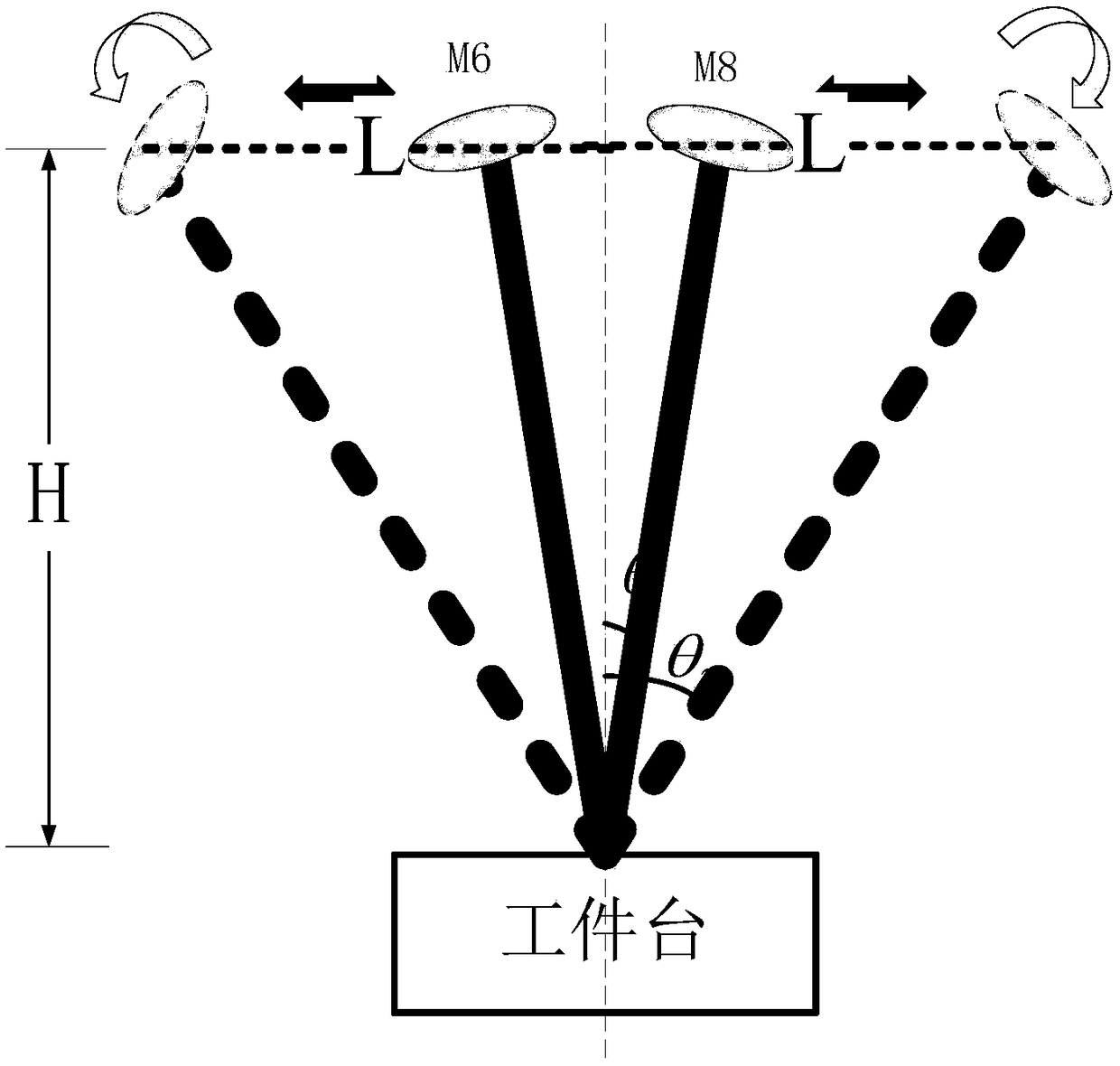
Tunable two-mirror interference lithography system
InactiveUS20130017498A1TunabilityEasy to supervisePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistLight beam
A two-beam interference lithography system offers large-area nanopatterning with tunability of pattern periodicities. The tunable feature is achieved by placing two rotatable mirrors in the two expanded beam paths which can conveniently be regulated for the designed pattern periodicities. While the effective interference pattern coverage is mainly determined by the optical coherence length and mirror size, the minimum pattern coverage area is as large as the effective coherence length of the laser and the selected mirror size over a wide range of periodicities.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for fabrication of large area 3D photonic crystals with embedded waveguides
In accordance with some aspects of the present disclosure, a maskless interferomeric lithography system for fabricating a three-dimensional (3D) photonic crystal using a multiple two-beam-exposures is disclosed. The system can comprise an illumination system comprising an optical arrangement operable to receive radiation from a radiation source and provide three or more tilted two-beam interference pattern exposures to be combined into a three-dimensional pattern; and a substrate operable to be supported by a substrate table, wherein the substrate comprises a photoresist formed on a top surface of the substrate and operable to receive the three-dimensional pattern and wherein means are provided to adjust the position of the substrate in all six mechanical degrees of freedom.
Owner:STC UNM
Method for accomplishing sub-wavelength interference photolithography utilizing multiple layer metal dielectric-coating structure
InactiveCN101261454AWith uniformitySolve the problem that sub-wavelength pattern lithography cannot be realizedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistPhotolithography
A method for utilizing multilayer metal dielectric film structure to realize the sub-wavelength interference lithography is characterized by the following steps of selecting a substrate material; coating an anticorrosion agent on the surface of the substrate; carrying out the alternate vapor deposition of a metal material film and a dielectric material film on the surface of the anticorrosion agent to form a metal layer and a dielectric layer which are arranged alternately; designing and arranging a periodic structure pattern mask on the surface of the structure which is obtained by the above step; carrying out the exposure of the obtained structure; removing the mask structure after the finish of the exposure; further removing the material of the metal layer and the material of the dielectric layer; arranging the obtained structure in a developing liquid which is matched with the anticorrosion agent for carrying out the development; carrying out the dry etching of the structure after the development and transferring the structure on the substrate; removing the residual anticorrosion agent on the surface of the structure and obtaining a final sub-wavelength periodic structure pattern; the utilization of the method of the invention can realize the periodic structure pattern with a large area, evenness and the period of which is below the wavelength.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
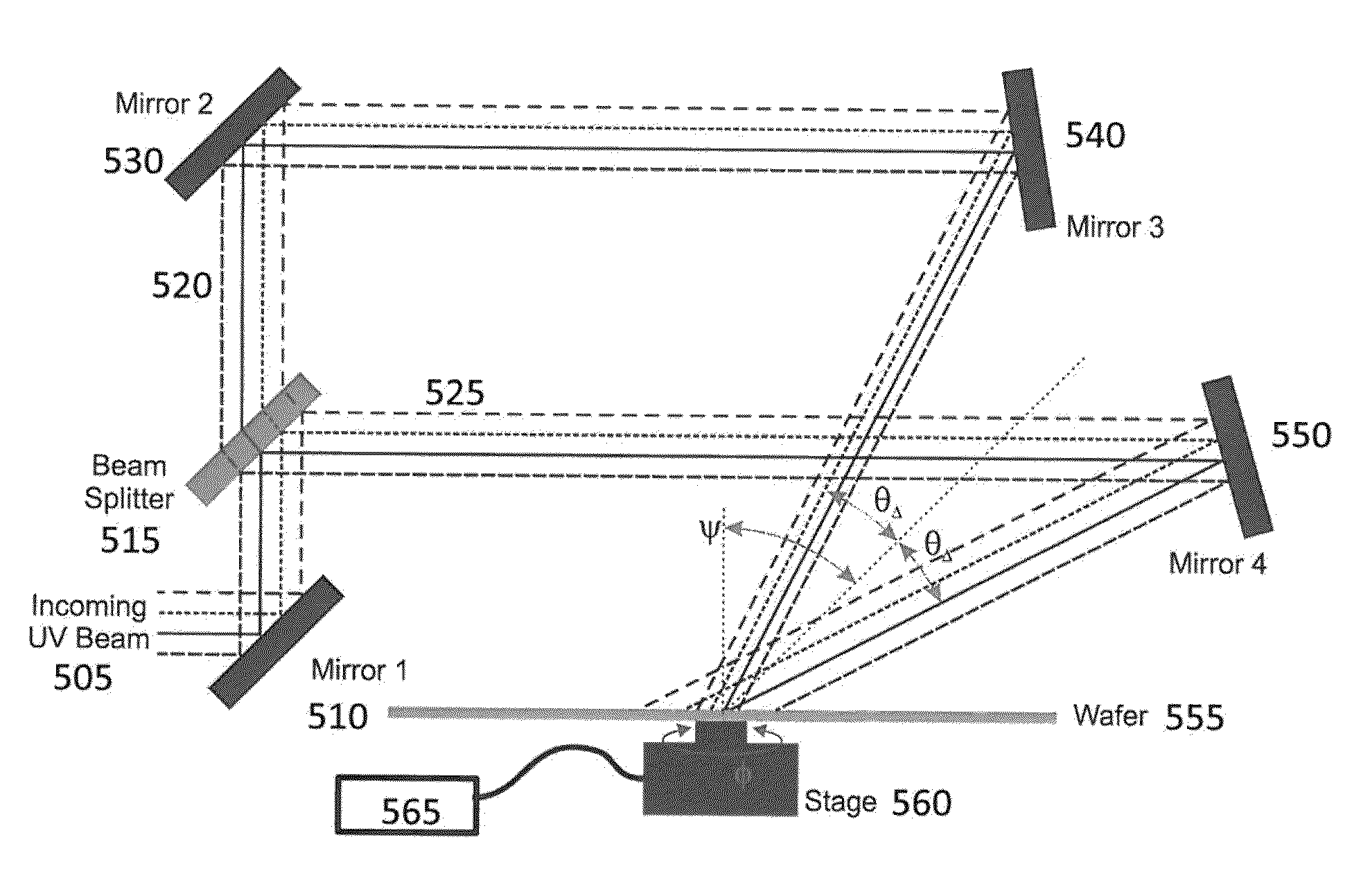
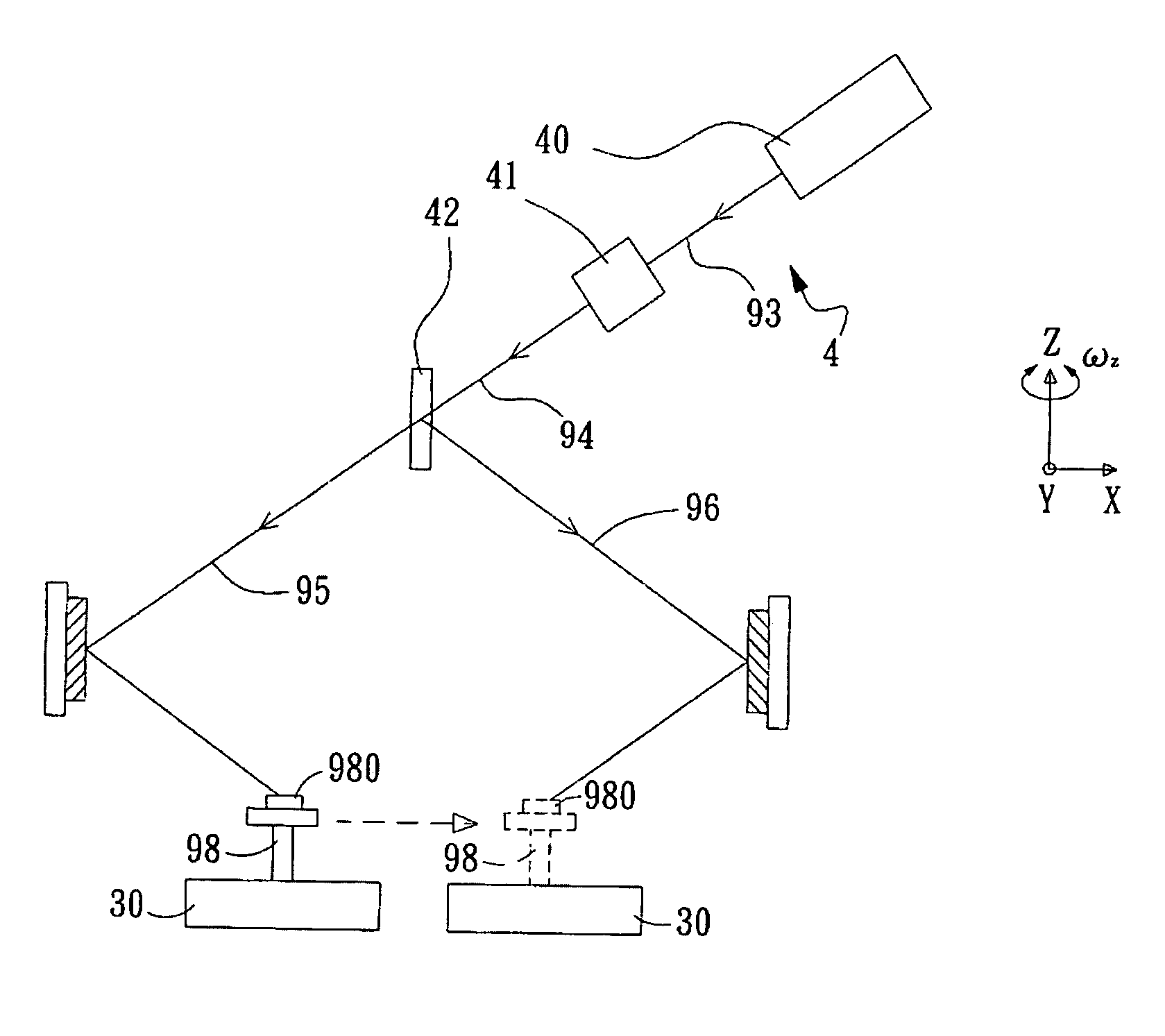
Scanning interference photoetching system
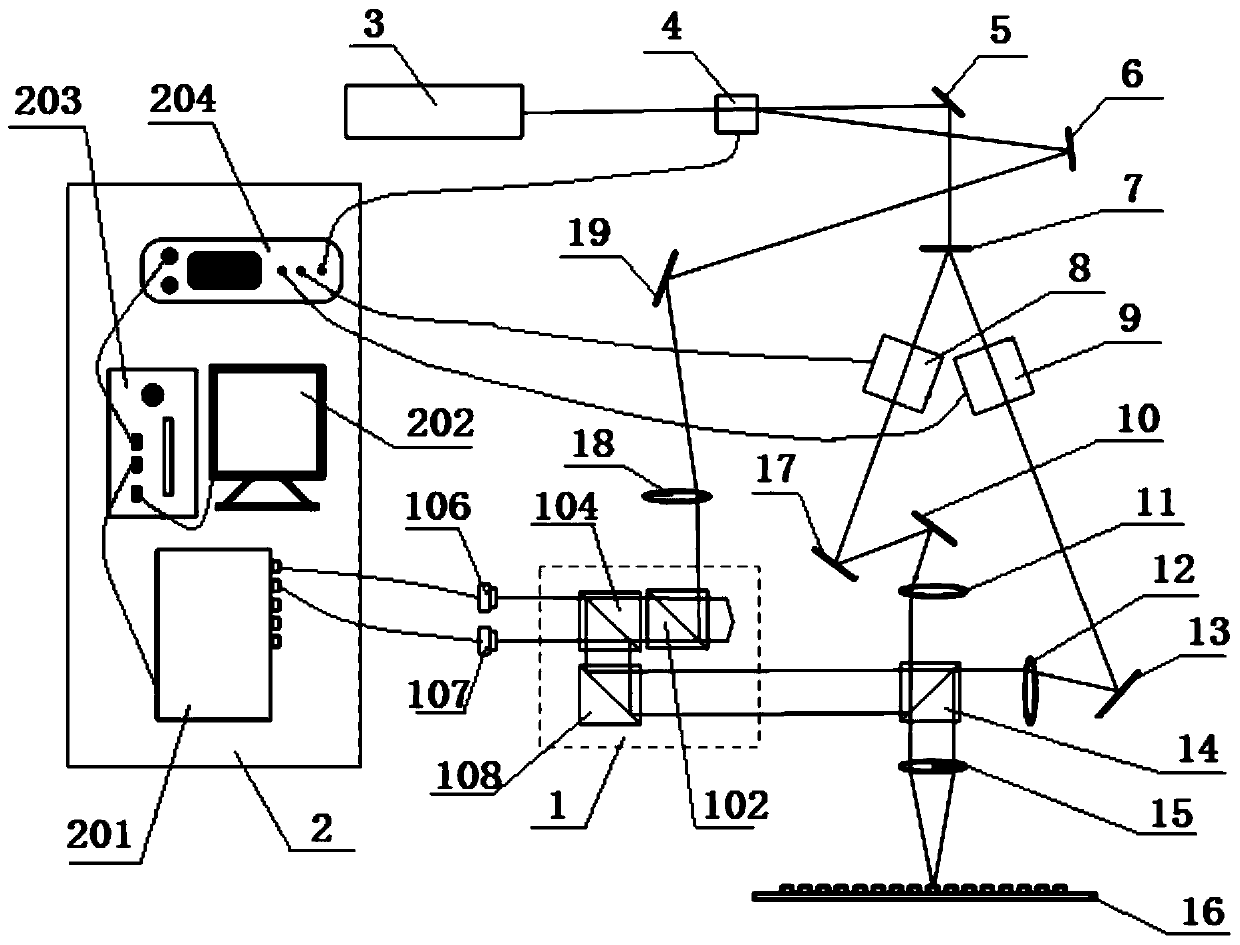
ActiveCN110837214AHigh locking precisionImprove laser utilizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFirst lightExposure control
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical instruments and meters, and provides a scanning interference photoetching system, which comprises a heterodyne light path, a first interferencelight path, a second interference light path, a motion platform and a control subsystem, wherein the motion platform is used for bearing a substrate, the displacement of the motion platform is measured by a displacement measuring interferometer, and the first beam of light and the second beam of light are focused, interfered and exposed on the substrate; the control subsystem generates an instruction according to various measurement information, adjusts the angle of a corresponding device or the phase of a light beam, and completes locking of the phase drift of the interference exposure fringes of the first light beam and the second light beam. The scanning interference photoetching system disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high fringe pattern locking precision, high laser utilization rate and the like; a heterodyne phase meter is used for measuring the phase of an exposure light beam, a displacement measuring interferometer is used for measuring the motion error of a motion platform, the control subsystem is used for compensating and controlling exposure interference fringes, and the system can be used for manufacturing large-area high-precision dense grid line gradient periodic gratings.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
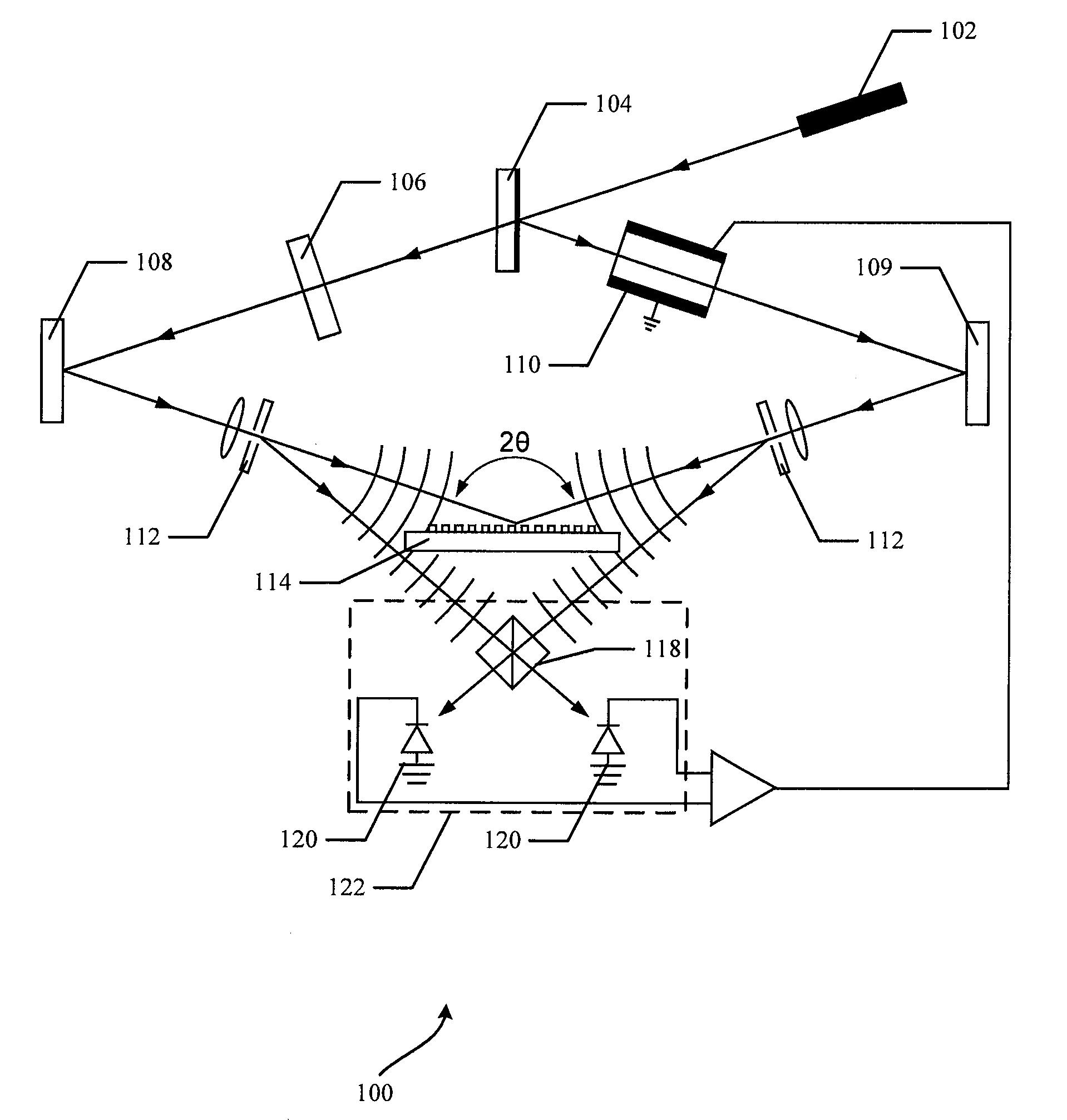
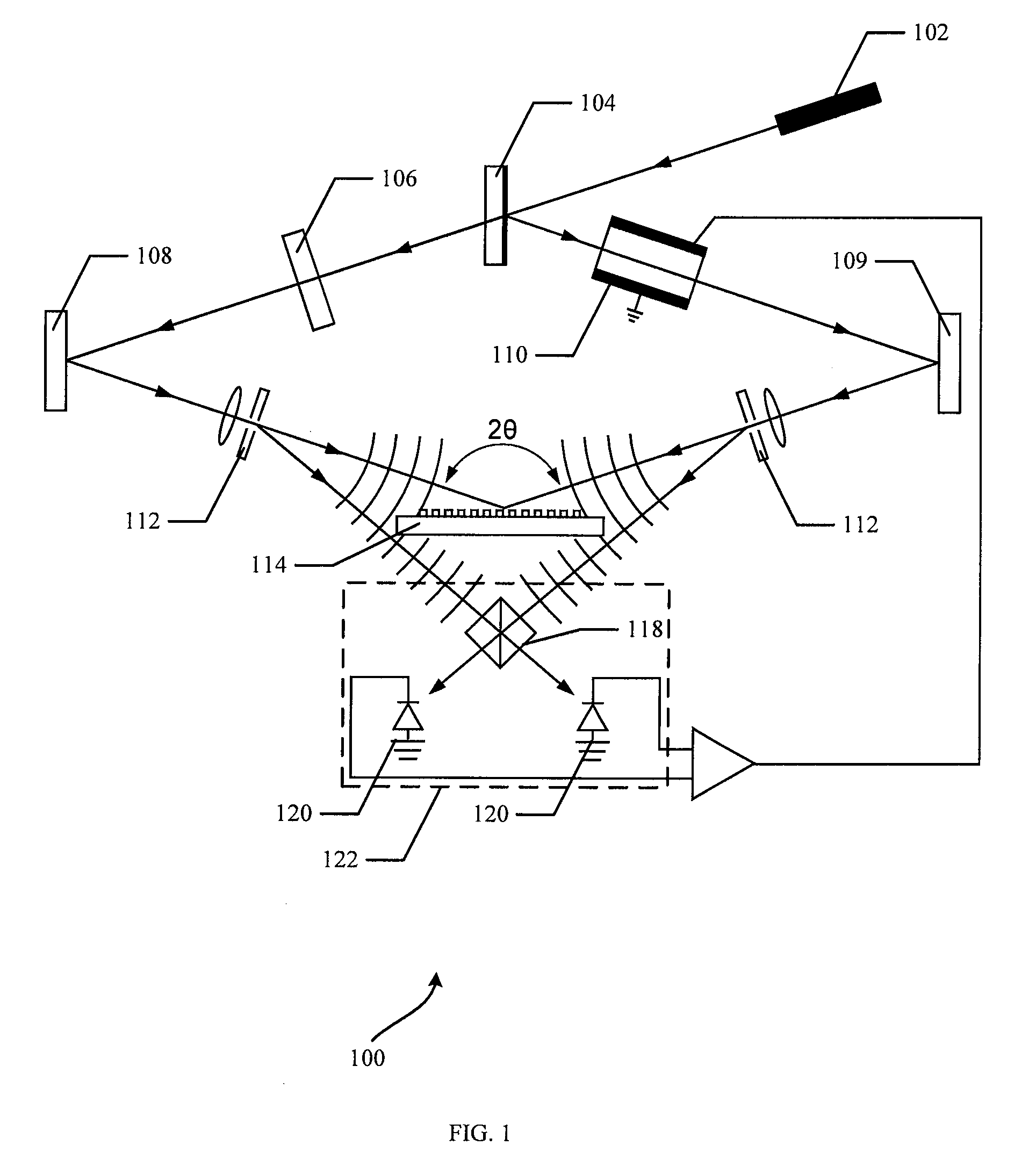
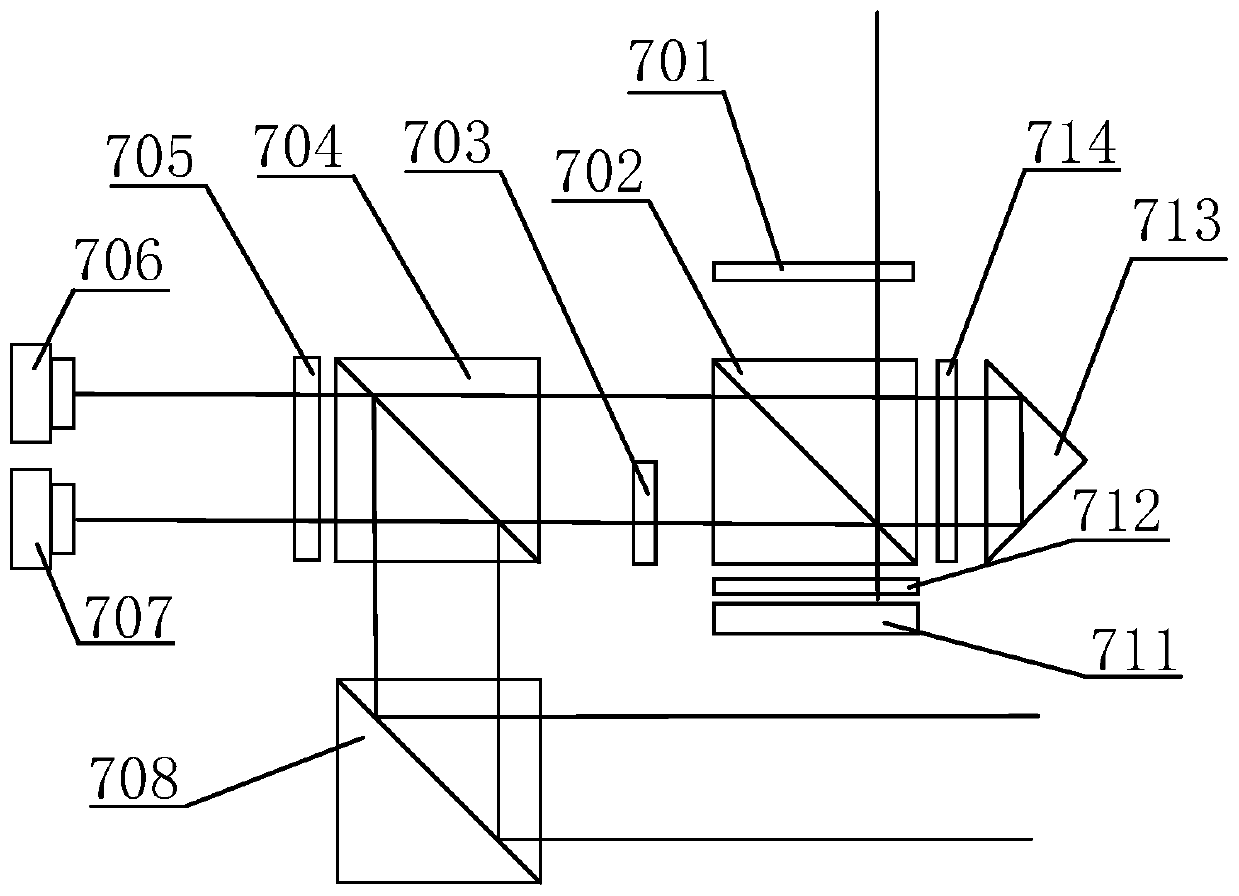
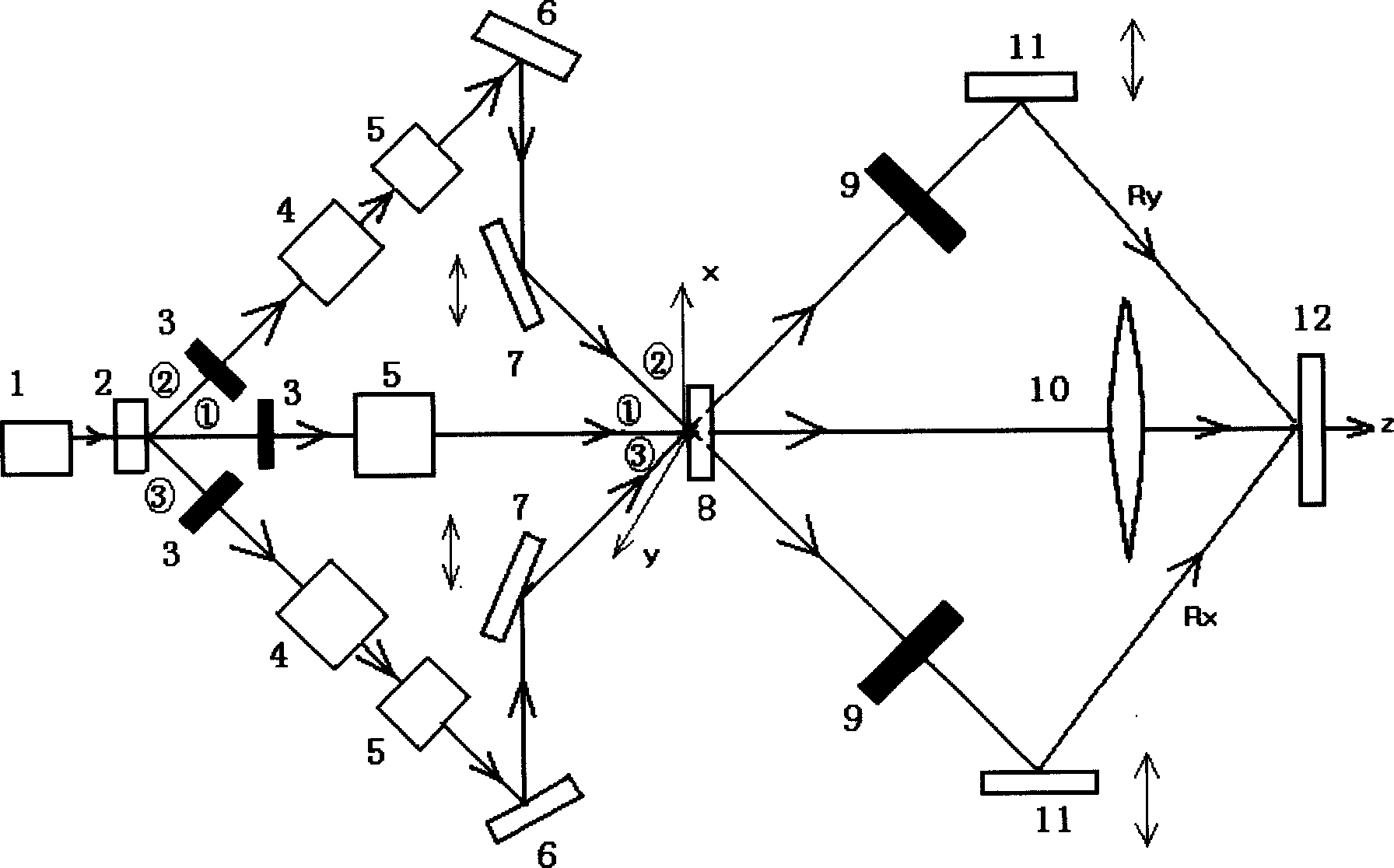
Actively stabilized, single input beam, interference lithography system and method
InactiveUS7304775B2OptimizationActively stabilizedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringPhotolithography
An interference lithography system is described that is capable of exposing high resolution patterns in photosensitive media and employing yield increasing active stabilization techniques needed in production environments. The inventive device utilizes a division-of-wavefront interference lithography configuration which divides a single large field size optical beam using one or more mirrors, and is actively stabilized with a subsystem employing; a phase modulator operating on each divided wavefront section; a novel feedback apparatus for observing the relative phase shifts between interfering wavefront sections; and a control system for holding the relative phase shifts constant. The present invention also includes; a method for shaping the illumination beam's intensity distribution for more efficient power utilization and greater feature size uniformity; a horizontal substrate loading configuration compatible with robotic handling; an automated pattern pitch calibration for simple, flexible system reconfiguration; a compact clean-room compatible superstructure for increased passive stability in high vibration manufacturing environments; and a method for optimizing the polarization state of the interfering beam sections in a multiple mirror system.
Owner:AZTEC SYST
Method and apparatus for generating periodic patterns by step-and-align interference lithography
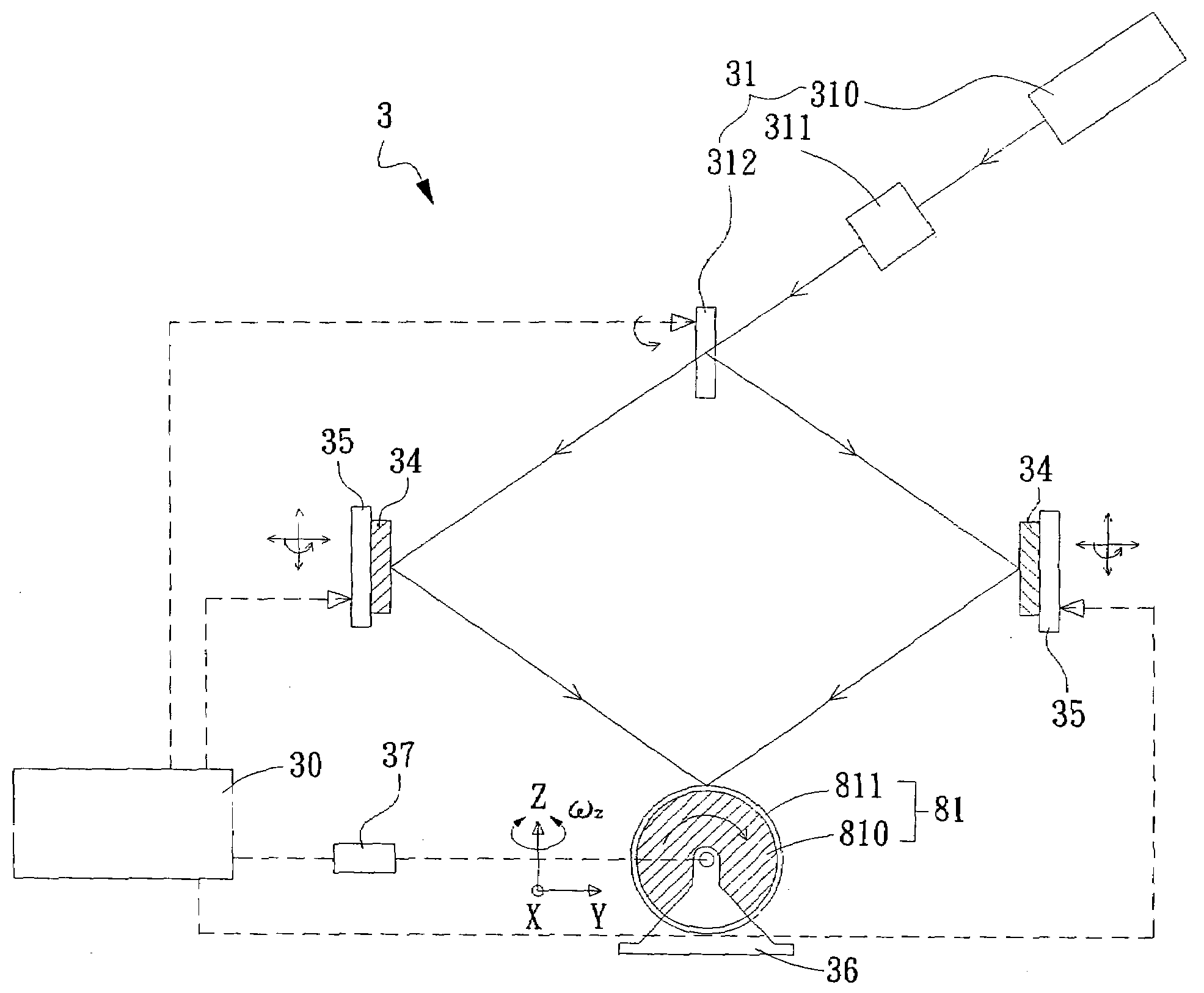
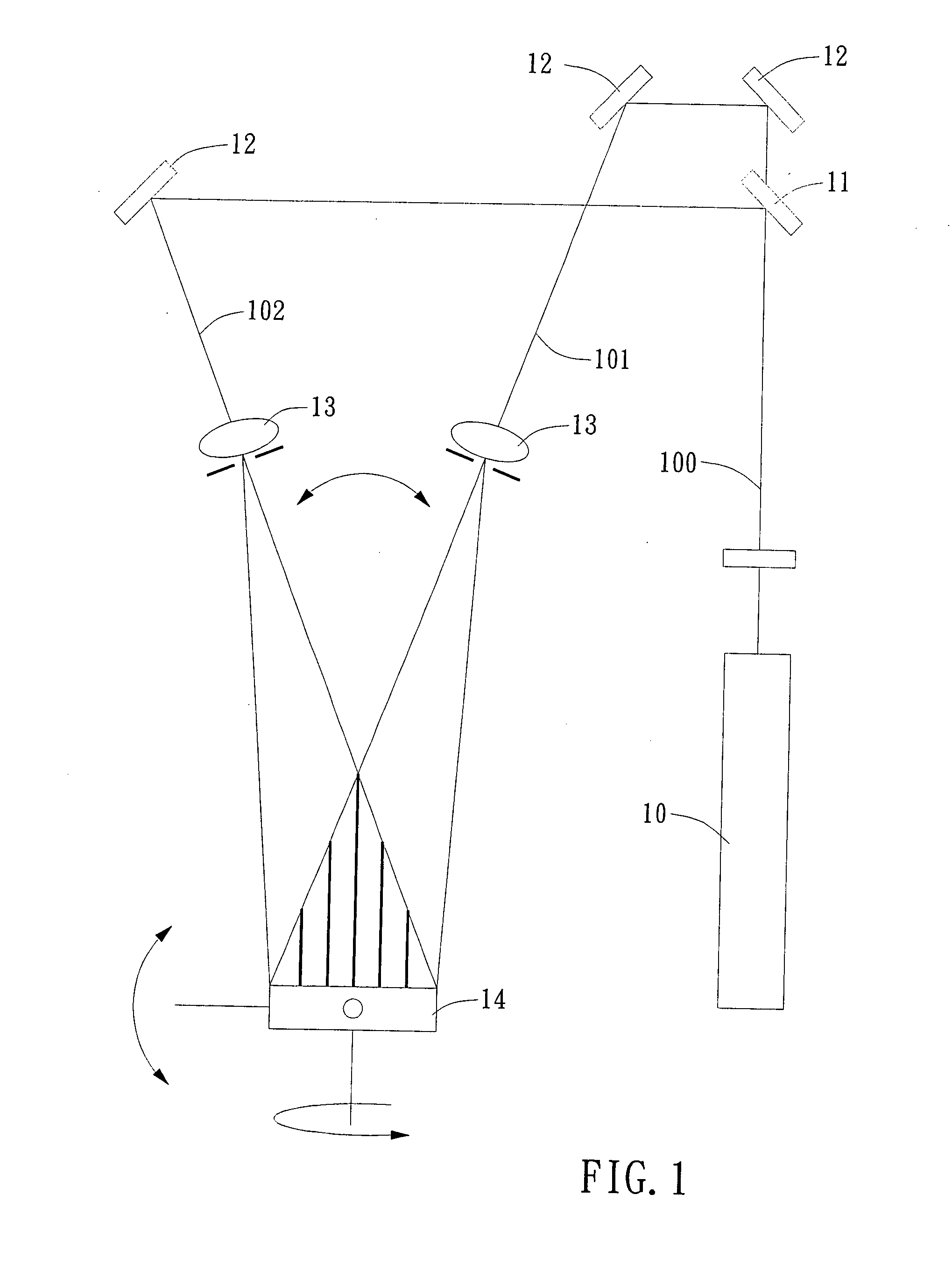
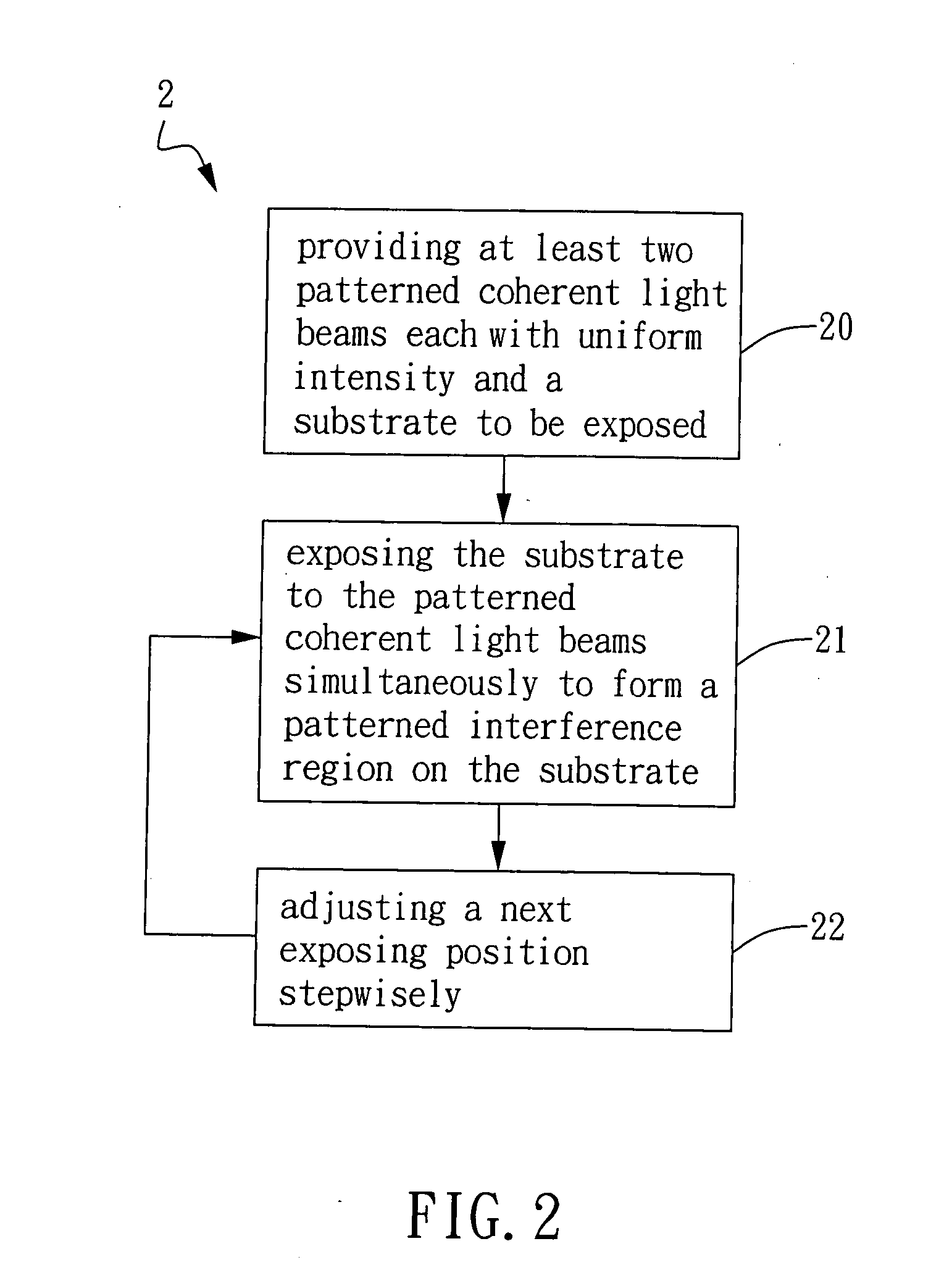
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for generating periodic patterns by step-and-align interference lithography, wherein at least two coherent light beams with a pattern are controlled to project onto a substrate to be exposed to form an interference-patterned region on the substrate. Thereafter, by means of moving the substrate or the light beams stepwisely, a patterned region with a large area can be formed on the substrate. According to the present invention, the optical path and exposure time may be shortened to reduce defect formation during lithographic processing and to improve the yield.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
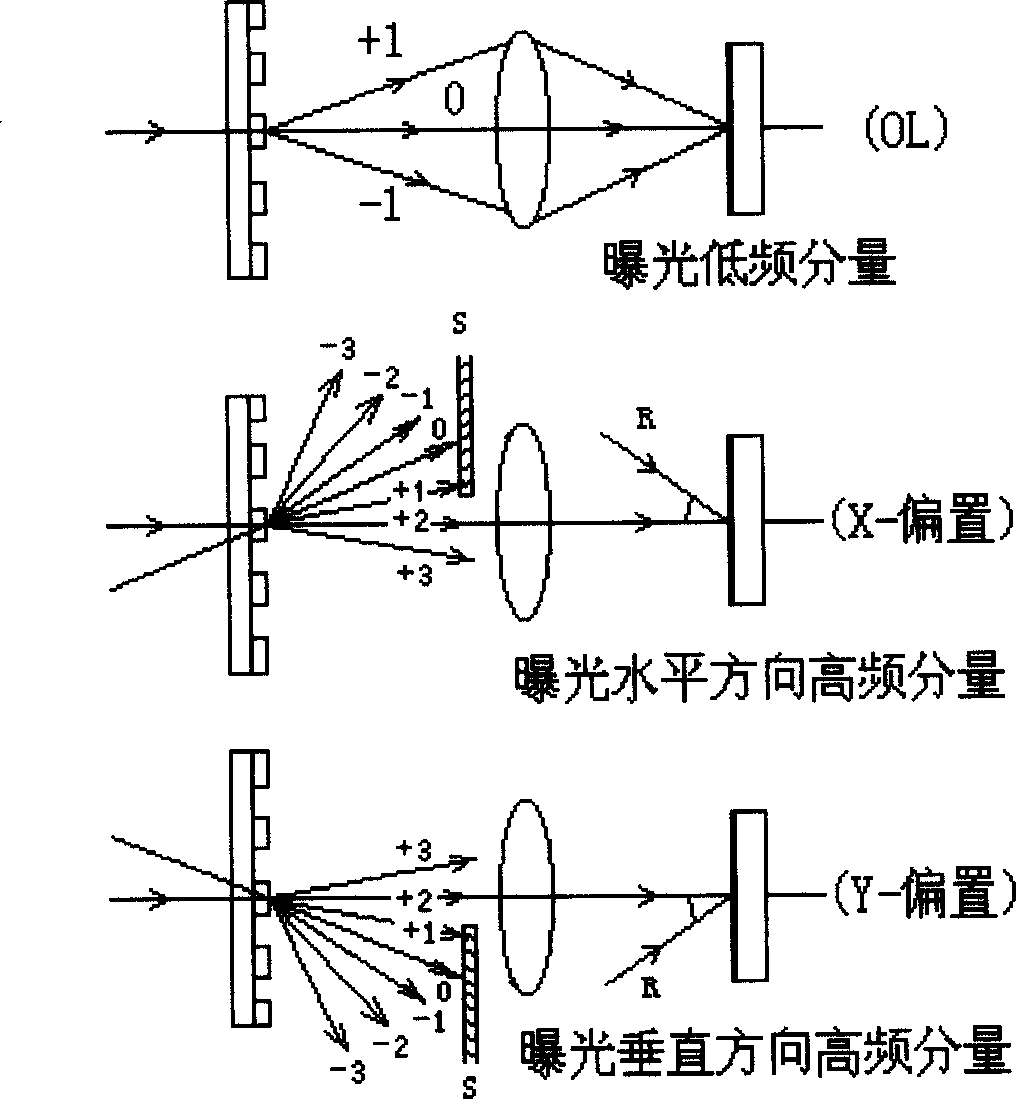
Acoustooptic frequency modulation single exposure imaging interference photo-etching method and system thereof
InactiveCN1607463AReduce exposureImprove exposure efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOff-axis illuminationAcousto-optics
A method and system for acousto-optic FM one-shot exposing imaging interference photo-etching characterizes in using two acousto-optic frequency modulators to move the laser frequency with lambda wave length emitted from a laser to form beams of laser for off-axis illumination light mask on X direction, to form an other beam of laser used in off-axis illuminating the same light mask and using the laser of lambda wavelength to vertically illuminate the light mask. Since three beams of light are incoherent interference beams, images generated by them are laminated incoherently to form a final mask picture, which does not use three laser in different wavelength to expose three times, only needs one shot exposing to finish the imaging photo-etching exposure.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
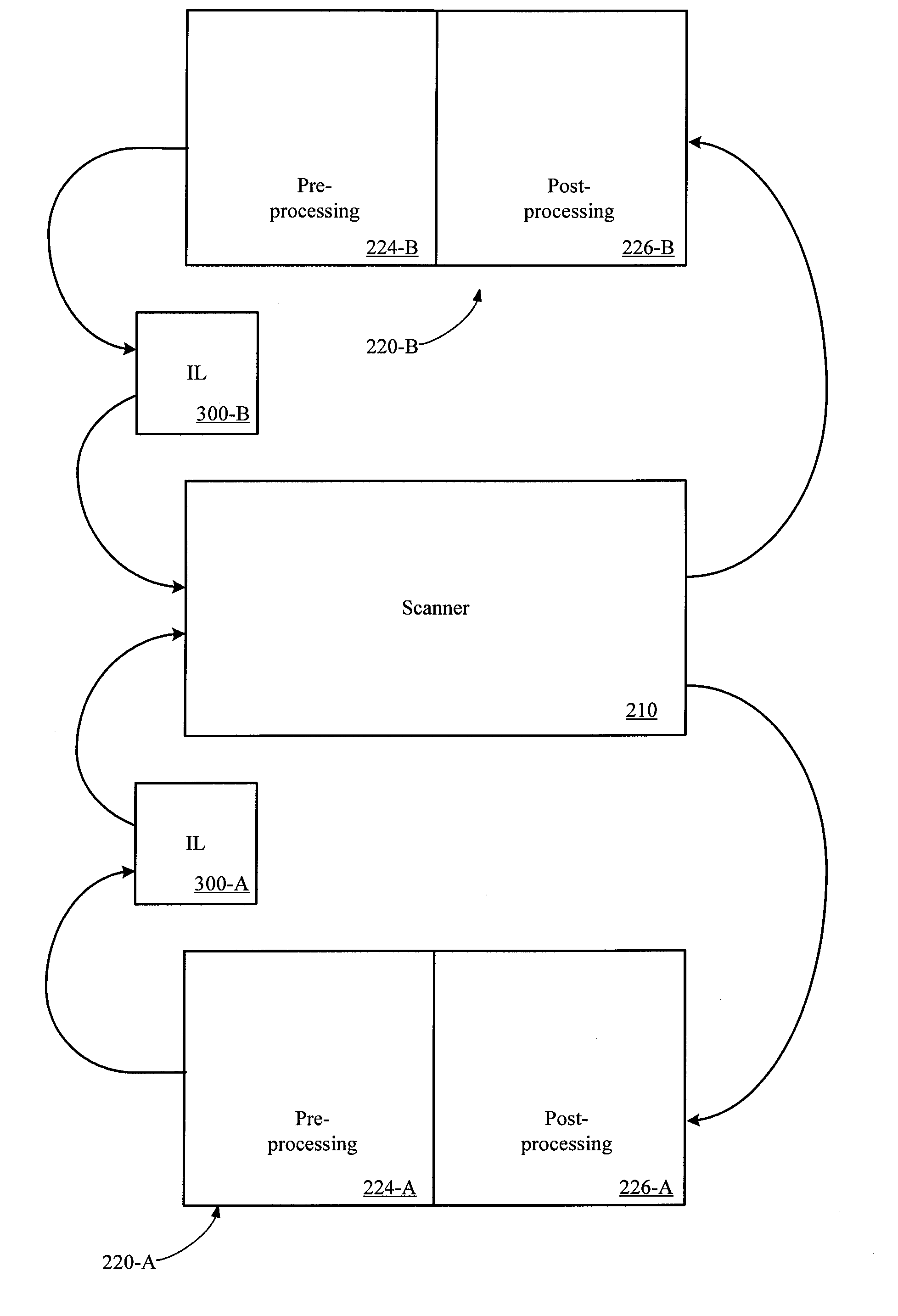
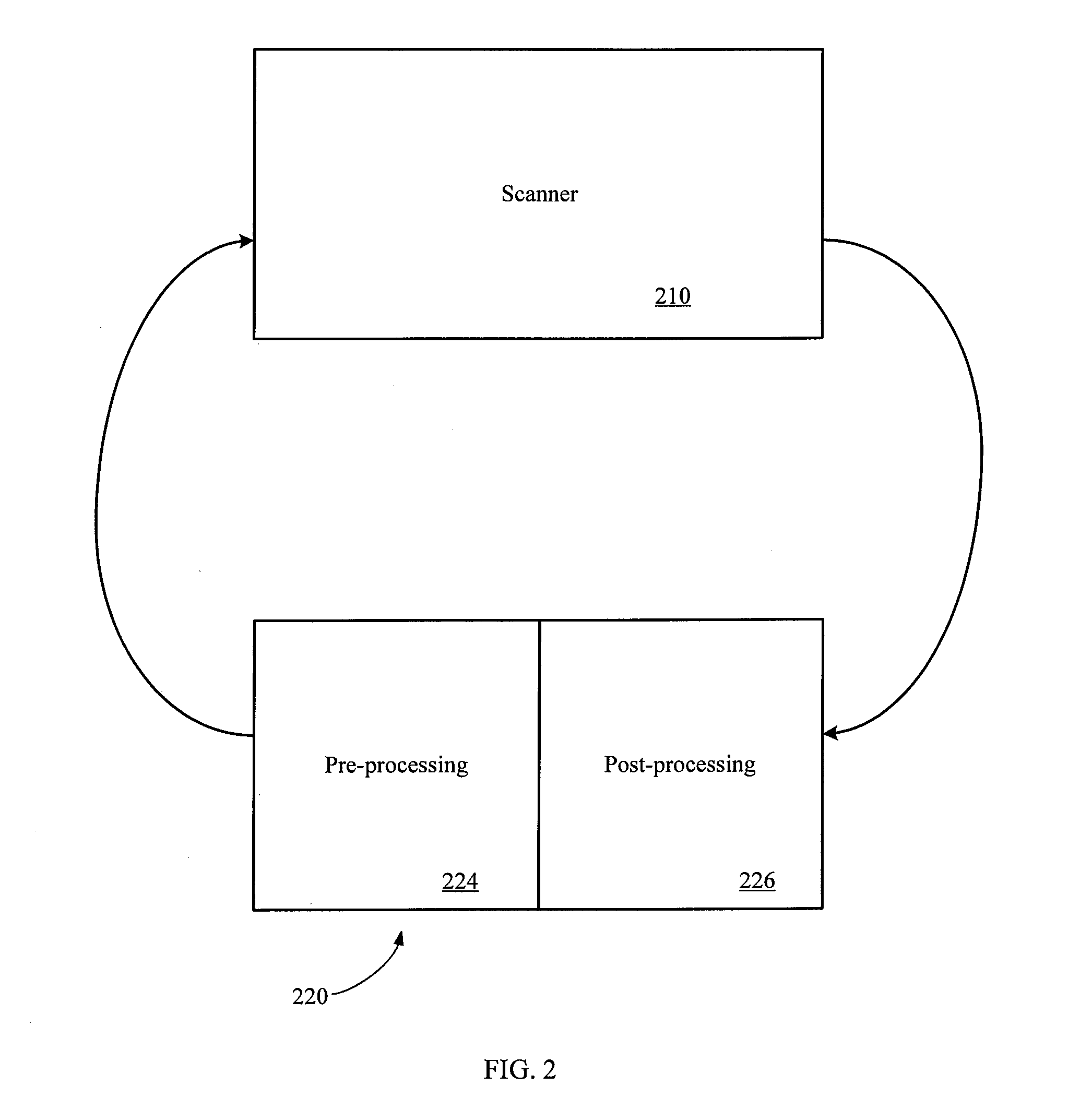
Integrated interference-assisted lithography
InactiveUS20100002210A1Photomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLithographic artistPre and post
A lithography scanner and track system is provided that includes an interference lithography system according to one embodiment. The scanner provides a first optical exposure of a wafer. The track system provides pre and post-processing functions on a wafer. The interference lithography system may be included within the scanner and may expose a wafer either before or after the first optical exposure. The interference lithography system may also be included within the track system as part of the pre or post processing. The first optical exposure may include optical photolithography.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
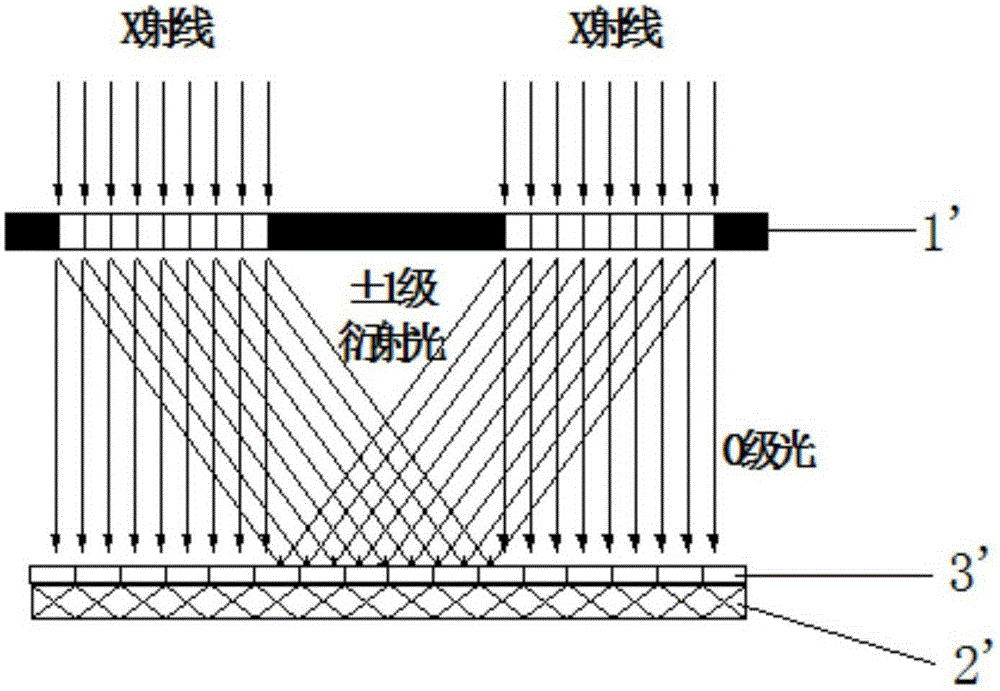
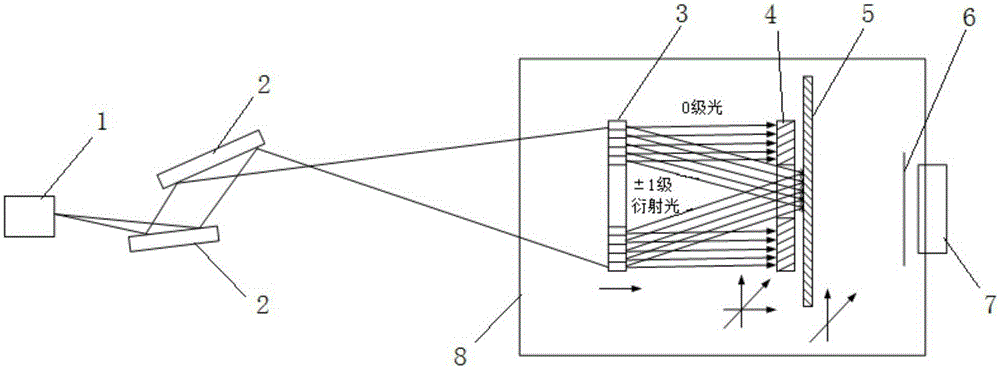
Synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system
ActiveCN105182701AAvoid exposureGuaranteed Alignment AccuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingBeam splitting
The invention relates to a synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system. The synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system comprises an undulator light source, multiple reflected focusing mirrors, a mask grating, a grading diaphragm with a diaphragm hole, a sample table with an observation hole, an aluminum film and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector which are arranged in sequence. According to the synchrotron radiation X-ray large-area interference lithography system disclosed by the invention, position alignment between the mask grating and the grading diaphragm is ensured by additionally arranging the grading diaphragm between the mask grating and a sample and by means of the CCD detector, so that the grading diaphragm has the capability of reliably sheltering 0-grade light generated by beam splitting passing the mask grating to prevent the 0-grade light from irradiating the sample, and therefore no 0-grade light region exists around a + / -1 grade diffracted light coherent region generated on the sample; accordingly, large-area splicing of an effective exposure area on the sample can be realized by moving the sample table. Meanwhile, X-ray is filtered by adopting the reflected focusing mirrors and the aluminum film, so that a relative position of the mask grating and the grading diaphragm can be observed clearly by using the CCD detector, and therefore the alignment precision therebetween can be ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable two-mirror interference lithography system
InactiveUS8681315B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistLight beam
A two-beam interference lithography system offers large-area nanopatterning with tunability of pattern periodicities. The tunable feature is achieved by placing two rotatable mirrors in the two expanded beam paths which can conveniently be regulated for the designed pattern periodicities. While the effective interference pattern coverage is mainly determined by the optical coherence length and mirror size, the minimum pattern coverage area is as large as the effective coherence length of the laser and the selected mirror size over a wide range of periodicities.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Seamless stitching of patterns formed by interference lithography
This invention addresses the scalability problem of periodic “nanostructured” surface treatments such as those formed by interference lithography. A novel but simple method is described that achieves seamless stitching of nanostructure surface textures at the pattern exposure level. The described tiling approach will enable scaling up of coherent nanostructured surfaces to arbitrary area sizes. Such a large form factor nanotechnology will be essential for fabricating large aperture, coherent diffractive elements. Other applications include high performance, antiglare / antireflection and smudge resistant Motheye treatments for display products such as PDA's, laptop computers, large screen TV's, cockpit canopies, instrument panels, missile and targeting domes, and, more recently, “negative-index” surfaces. Although ideal for seamless stitching of nanometer scale patterns, the technology is broadly applicable to any situation where an arbitrarily large area needs to be seamlessly tiled with a smaller base pattern that has periodic overlap able boundaries.
Owner:VINCENT E STENGER
A method for preparing a transferable bonded PDMS-based nanostructure
InactiveCN109116684AIncrease success rateGuaranteed flatnessNanotechnologyPhotomechanical coating apparatusMicro nanoOrganic solvent
A method for preparing a transferable bonded PDMS-based nanostructure, which includes the following steps: spin coating a sacrificial layer on a rigid substrate which can be dissolved by an organic solvent such as acetone; then, spin coating a layer of PDMS on the surface of the sacrificial layer, and after curing, fabricating periodic nano-patterns on the PDMS by interference photolithography; then etching the fabricated patterns to obtain the patterned PDMS; putting the etched PDMS into an organic solvent such as acetone, dissolving the sacrificial layer, and finally obtaining the transferable bonded PDMS film with nanor-patterns. The invention uses the interference photolithography method to prepare the periodic nanometer patterns, which greatly improves the efficiency. Compared with several existing methods for preparing flexible material micro-nano structures, interference lithography has the advantages of high speed, low cost, large area, and easy period and duty cycle adjustment. The operation difficulty of film release in the fabrication process is greatly lowered, and the success rate of film fabrication is improved, and the social and economic benefits are very remarkable.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Reflection type beam splitting raster and interference photolithographic system
InactiveCN103424795AHigh diffraction efficiencyImprove uniformityDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGratingHigh energy
The invention discloses a reflection type beam splitting raster and an interference photolithographic system. The reflection type beam splitting raster comprises a raster groove-shaped area located on a reflection face and a light blocking area located on the periphery of the raster groove-shaped area. The raster groove-shaped area comprises raster structures which are distributed periodically. Each raster structure comprises a groove-shaped reflection face and a non-reflection face. An inclined angle is formed between the groove-shaped reflection face and a raster base face. The reflection type beam splitting raster can realize largest modulation on +-1-level light, and enables reflected beam splitting light to have a highest energy utilization rate. An interference pattern obtained through the reflection type beam splitting raster has good boundary quality, is capable of finishing precise spliced patterns, and enables the large-width interference photolithographic technology to be improved remarkably.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Laser interference photoetching system
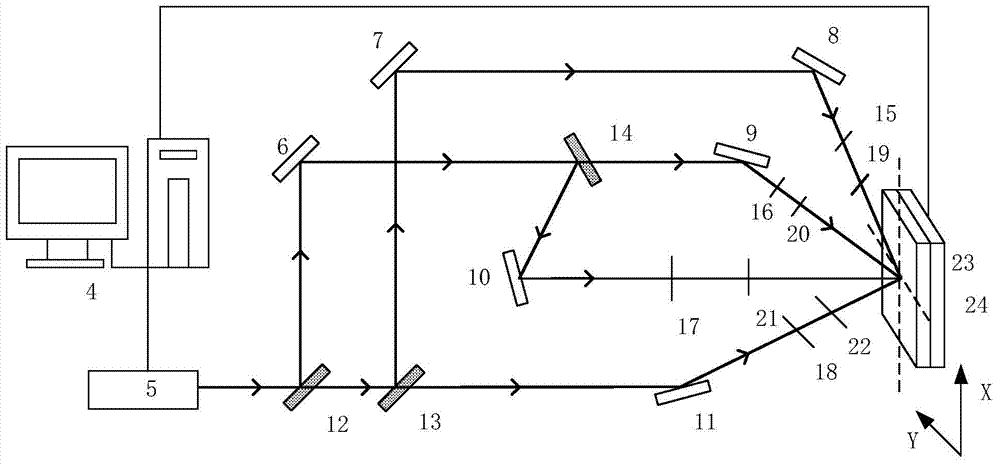
ActiveCN110806680ASmall sizePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam splitterGrating
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical instruments and meters, and discloses a laser interference photoetching system, which comprises a laser, a first reflector, a grating beam splitter, a second reflector, a first universal reflector, a first lens, a second universal reflector, a second lens, a beam splitter prism, a control module, an angle measurement module, a third lens anda substrate, wherein the control module comprises a signal processing end, a controller and a driver; the signal processing end is connected with the angle measuring module; the controller is connected with the signal processing end and the driver; and the driver is connected with the first universal reflector and the second universal reflector. A light source emitted by the laser is divided intotwo beams of light through the system and focused on the substrate for exposure; and by adjusting the exposure angle, the manufacturing of the large-area grating with the gradient period is realized.The size of the grating manufactured in a scanning interference photoetching mode is not limited by the size of an exposure light spot, and a large-size gradient period grating can be manufactured.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
An interferometric lithography system with controllable period and direction
InactiveCN108983560ALow costFast preparationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusComputer control systemGrating
The invention discloses an interference lithography system with controllable period and direction, wherein the light of the light source is reflected by a first mirror and collimated into parallel beams through a beam expansion filter module, the beams are reflected twice by a second mirror and a third mirror and propagated vertically downward, and then are divided into two coherent beams with equal amplitude by a beam splitter mirror. The reflected beam is reflected three times by the fourth, fifth and sixth mirrors, and the transmitted beam is reflected twice by the seventh and eighth mirrors, and finally converges and interferes on the substrate. A mask plate locate above that substrate is closely attached to the substrate, and the substrate is place on the workpiece table. By moving the positions of the sixth and eighth mirrors laterally and adjusting the angles of the sixth and eighth mirrors, interference of different angles is achieved without changing the height of the substrate in the z direction. The computer control system realizes the horizontal movement and rotation of the sixth and eighth mirrors as well as the precise control of the worktable. The pixel-level array polarization grating with different periods can be prepared by the invention.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
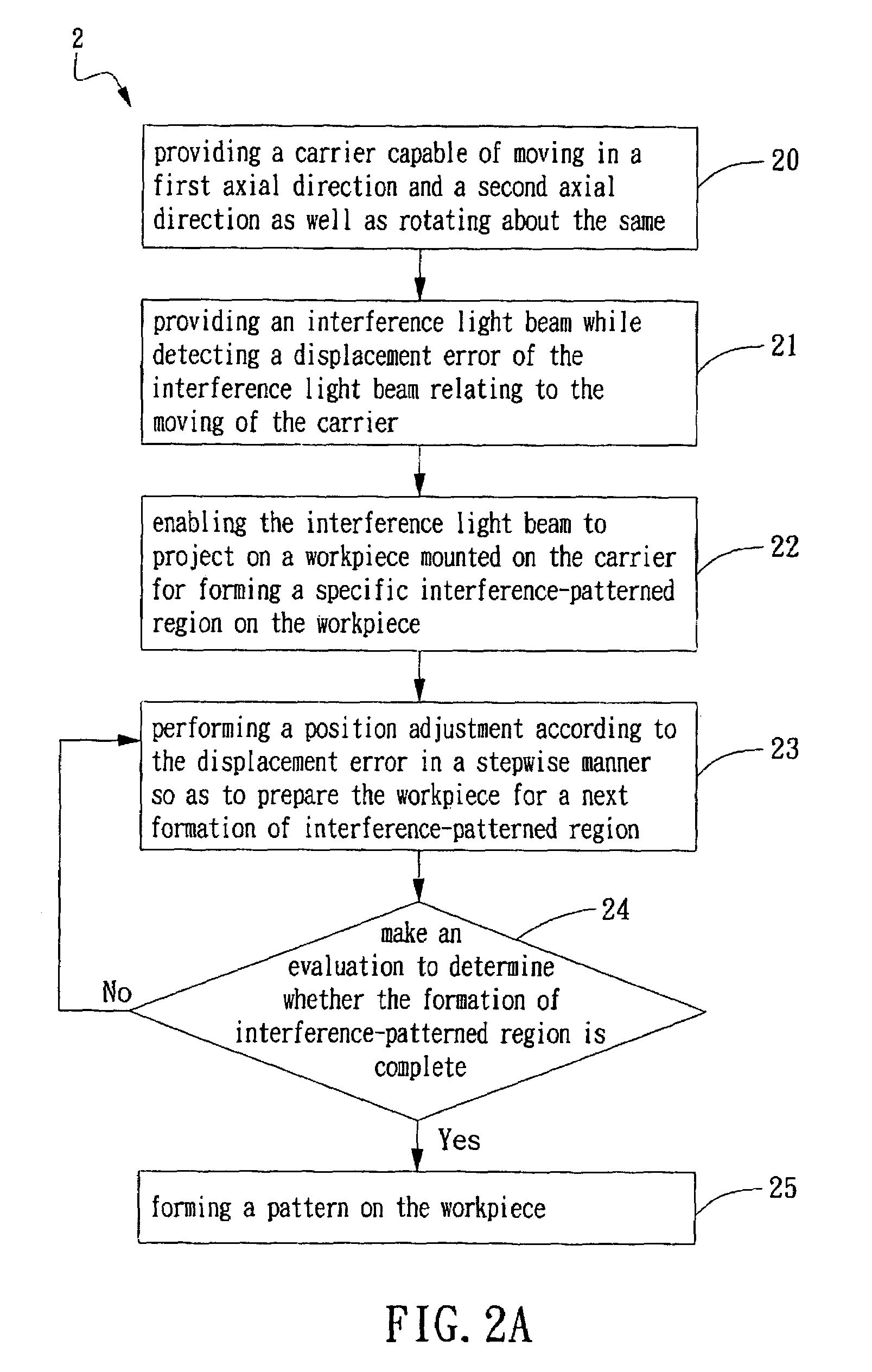
Method and system for step-and-align interference lithography
InactiveUS7969580B2Precise alignmentImprove accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansLight beamDisplacement error
A method for step-and-align interference lithography is provided in the present invention, by which a displacement error relating to the moving of an interference light beam as the source of the interference light beam is being carried to move by a carrier is measured before interference lithography, and then the displacement error is used as a reference to compensate a positioning error between adjacent interference patterns during step-and-align interference lithography. Besides, the present invention further provides a system for step-and-align interference lithography, which is capable of compensating the positioning error caused by a stepping movement control used for moving a substrate or the light beams in a stepwise manner to form interference-patterned regions by interference lithography and thus the so-generated interference-patterned regions are accurate aligned with one another on a two-dimensional plane for preparing the same to be stitched together to form a two-dimensional large-area periodic structure.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
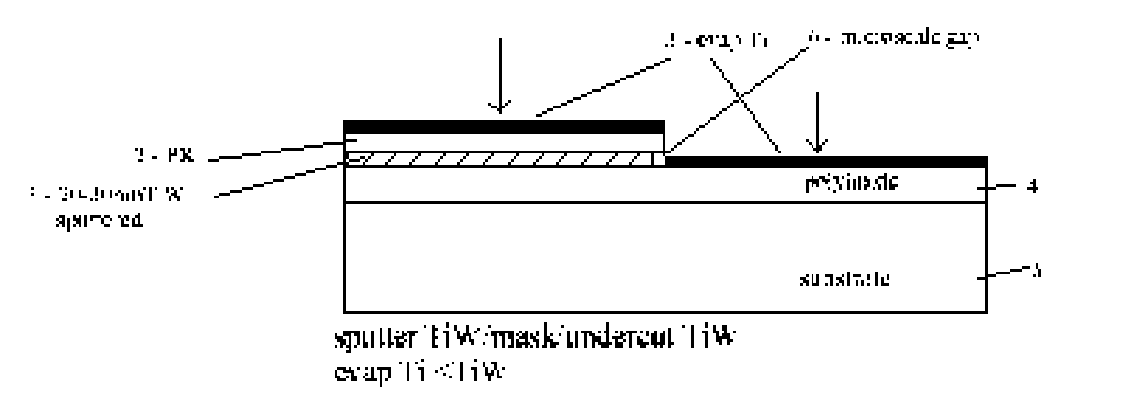
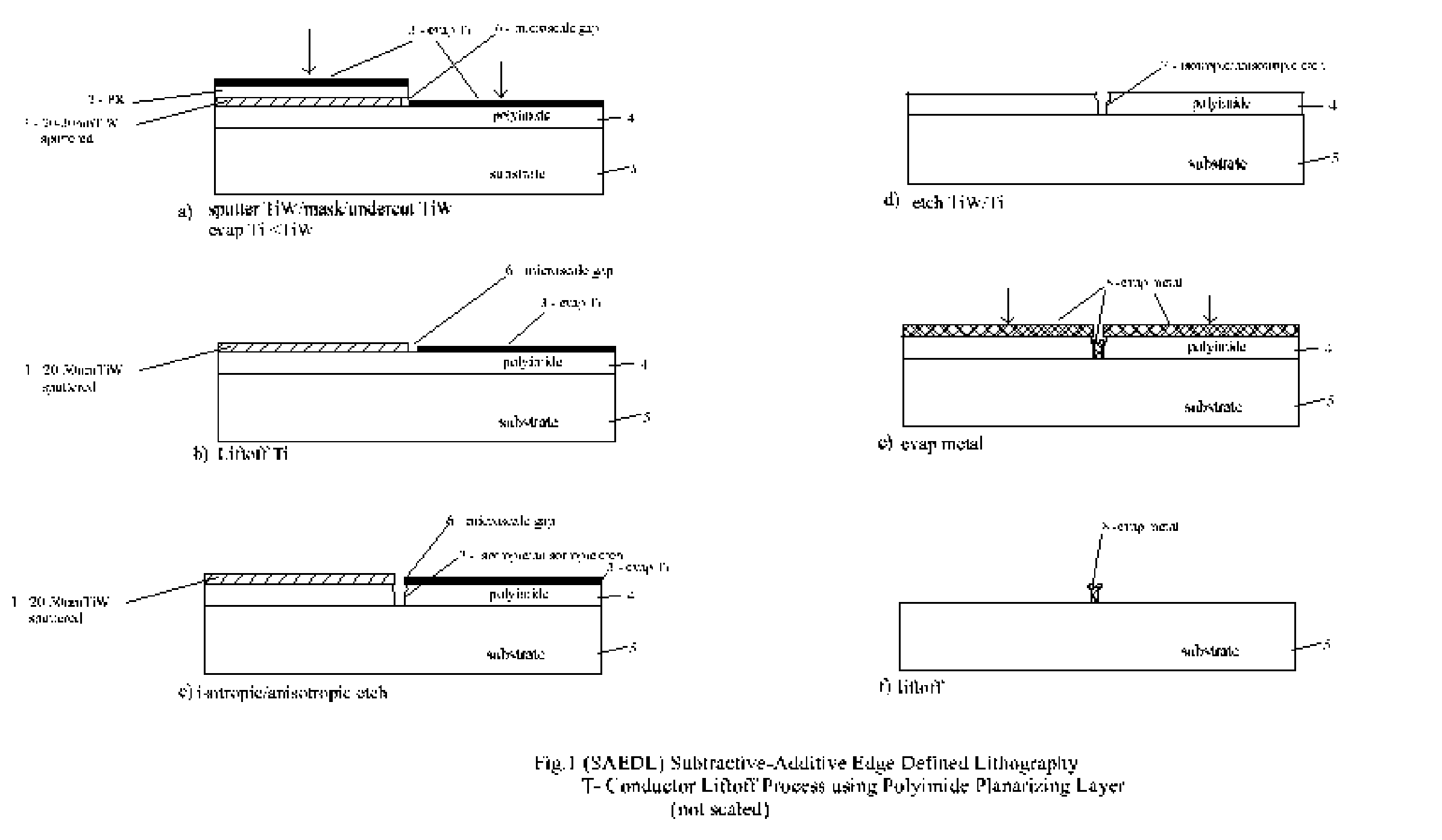
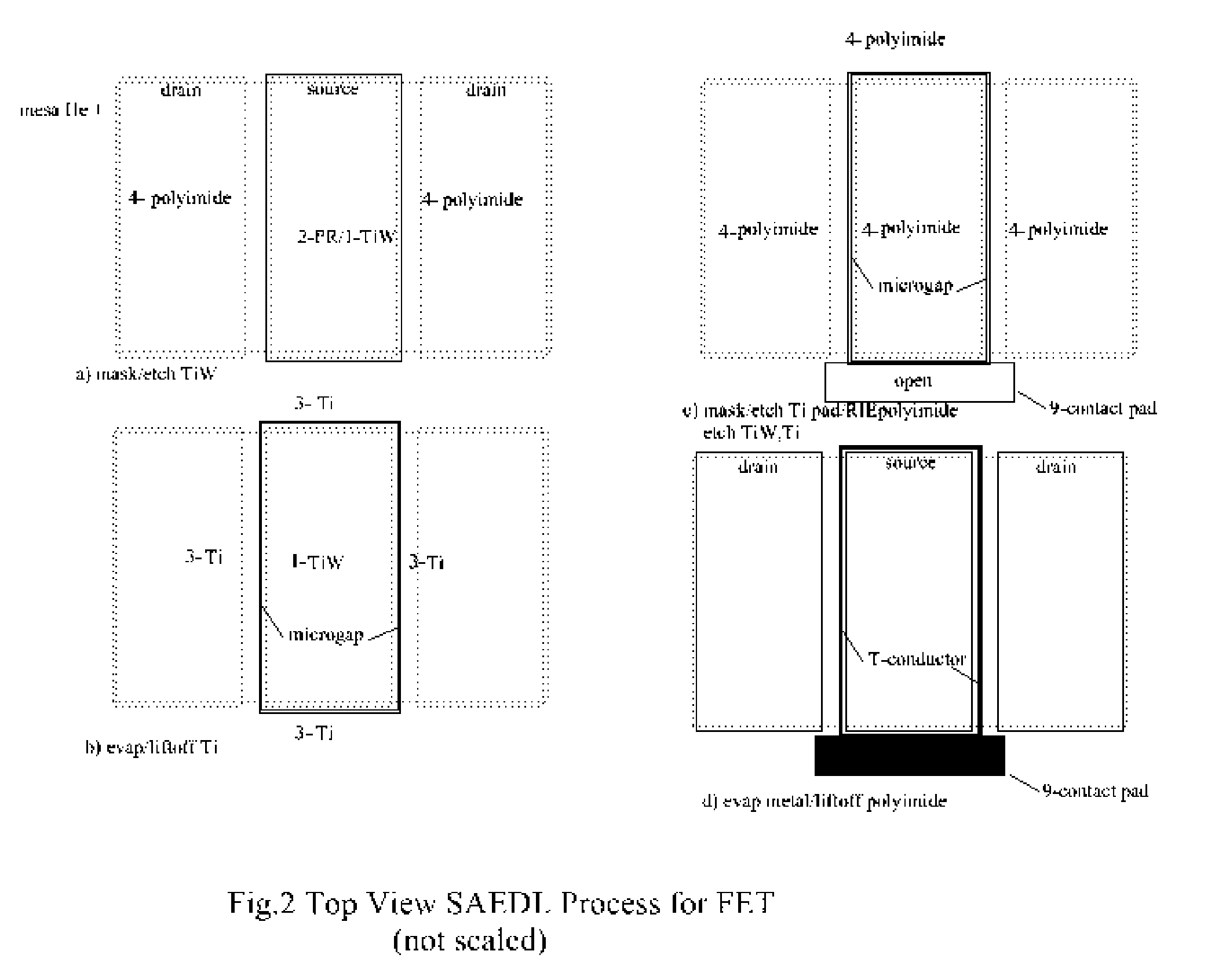
Subtractive-Additive Edge Defined Lithography
InactiveUS20060166518A1High selectivityAccurate patternPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingRC time constant
A subtractive-additive, differential lithography technique capable of generating sub-half micron geometries using a larger feature parent mask is described. The basic technique is defect tolerant with respect to electrical shorting, can fabricate T-shaped conductors of optimum geometry to minimize electrical RC time constant, and can be extended to very small, dense geometries by utilizing interference lithography or nano-imprint parent masks. Demonstration fabrication examples include a Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) transducer, Field Effect Transistor (FET), and grating interconnection method.
Owner:DUNNROWICZ CLARENCE JOHN
Three-beam interference lithography method and system
InactiveCN102736451AImprove processing efficiencyLow costPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusComplex amplitudeLevel structure
The invention discloses a three-beam interference lithography method and a system. The method comprises that: a laser beam is divided into three beams by phase grating and then N times of interference exposure are realized on surface of a workpiece; a dislocation value of two adjacent exposure positions is dI / N, wherein N is an odd number greater than or equal to 3, and dI is a light intensity distribution cycle after the exposure; and the three beams are respectively a first beam, a second beam and a 0 beam with the same complex amplitude. With the three-beam interference lithography method of the invention, a large-size precision multi-level structure can be directly prepared in photoresist with high processing energy efficiency and the components used are easily obtained and have low cost. In addition, by adopting the three-beam interference exposure, the grating and the system have no zero elimination requirement and are easy to prepare.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Exposure beam phase measurement method in laser interference lithography and lithography system
ActiveCN110716397AReal-time measurementRealize real-time controlDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusGratingInterference lithography
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical instruments and meters, and discloses an exposure beam phase measurement method in laser interference lithography. The method comprises the steps: separating measuring light from an exposure light beam of laser interference lithography and inputting the measuring light into a laser phase measuring interferometer to carry out phase measurementon the exposure light beam of laser interference lithography; and introducing a reference light beam homologous with the laser interference lithography exposure light beam, inputting the reference light beam into the laser phase measuring interferometer, processing the reference light beam by the laser phase measuring interferometer to form an interference measurement light signal, and performingresolving to obtain the phase of the laser interference lithography exposure light beam. The invention discloses a laser interference lithography system. The system comprises the laser phase measurement interferometer, a controller and a phase modulator; the system adopts the exposure light beam phase measurement method in laser interference lithography, and the laser phase measurement interferometer is used for measuring whether the phase of the exposure light beam drifts or not; the controller controls the phase modulator to carry out phase modulation, the locking of exposure fringe phase drift is completed, and the manufacturing of a high-precision variable-period grating is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Manufacturing method for increasing effective photosensitive area of photoelectric material
ActiveCN104708196AAchieve preparationIncrease contact areaFinal product manufacturePhotomechanical exposure apparatusHost materialInterference lithography
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for increasing the effective photosensitive area of a photoelectric material. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that three laser beams with modulation performance are utilized for carrying out interfering and photoetching on the surface of a host material or the photosensitive material, multi-periodicity micro-nano composite structures in different shapes and of different structures are obtained and manufactured through the mode of multi-angle overlapping exposure or movable distance overlapping exposure, multiple laser beams with the modulation performance can be utilized for carrying out interfering and photoetching on the surfaces of the materials, the multi-periodicity micro-nano composite structures can be directly manufactured, and the three-dimensional effective photosensitive area is increased in a two-dimensional unit plane .
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Self-organized pin-type nanostructures, and production thereof on silicon
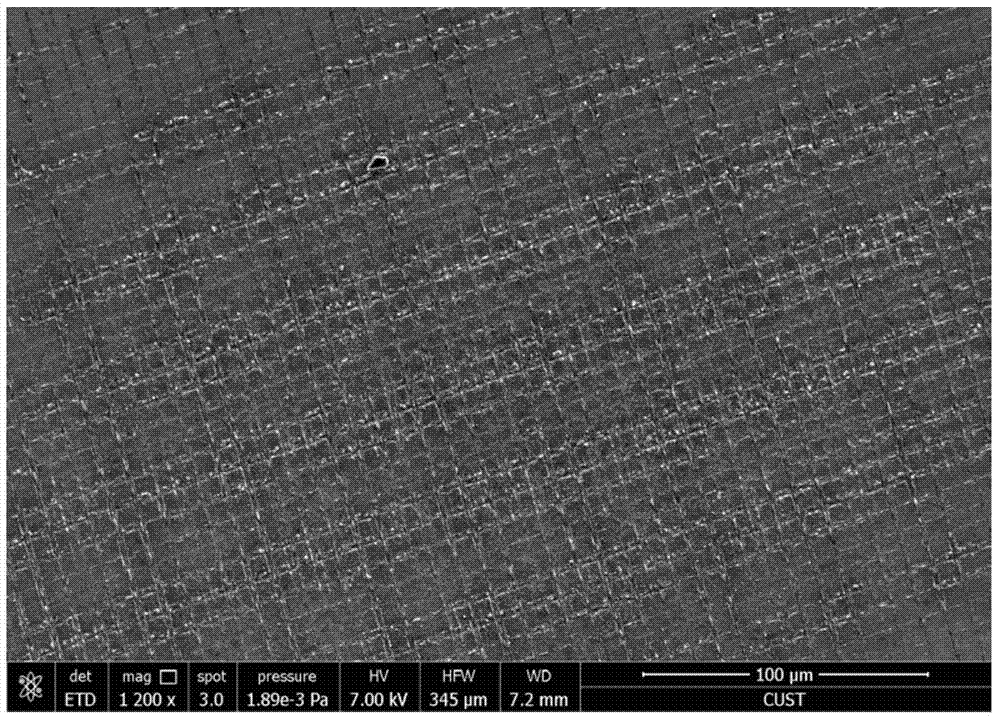
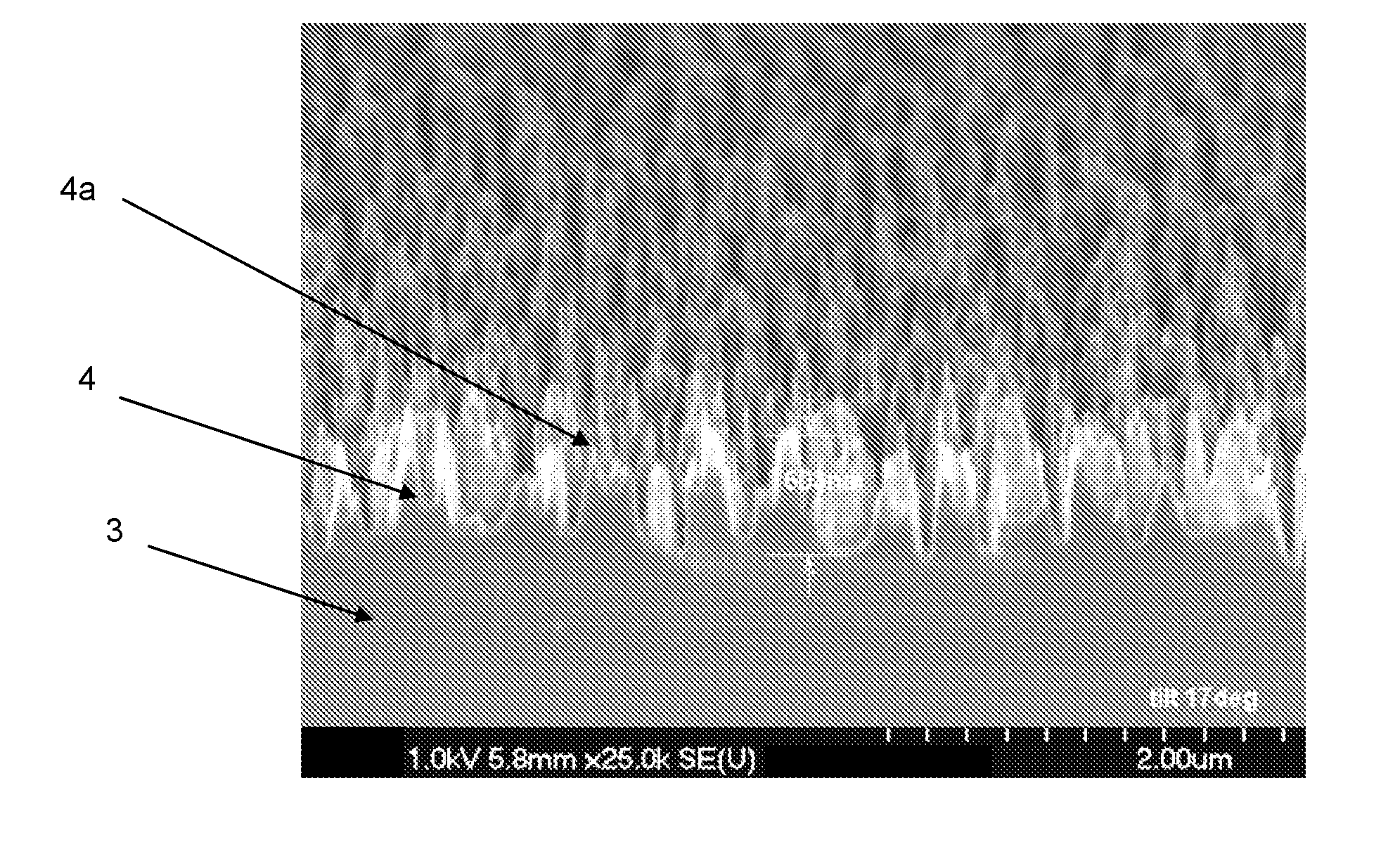
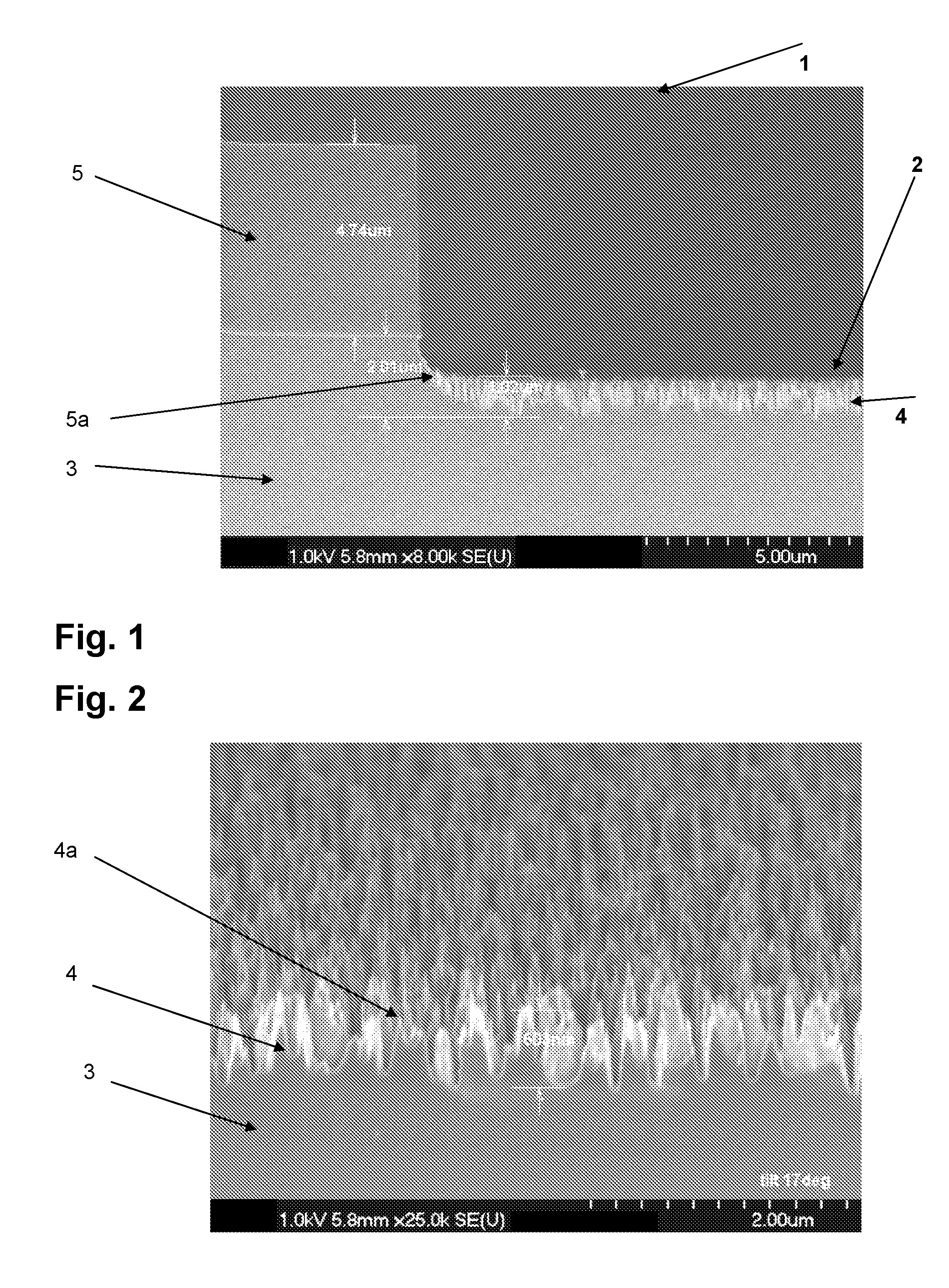
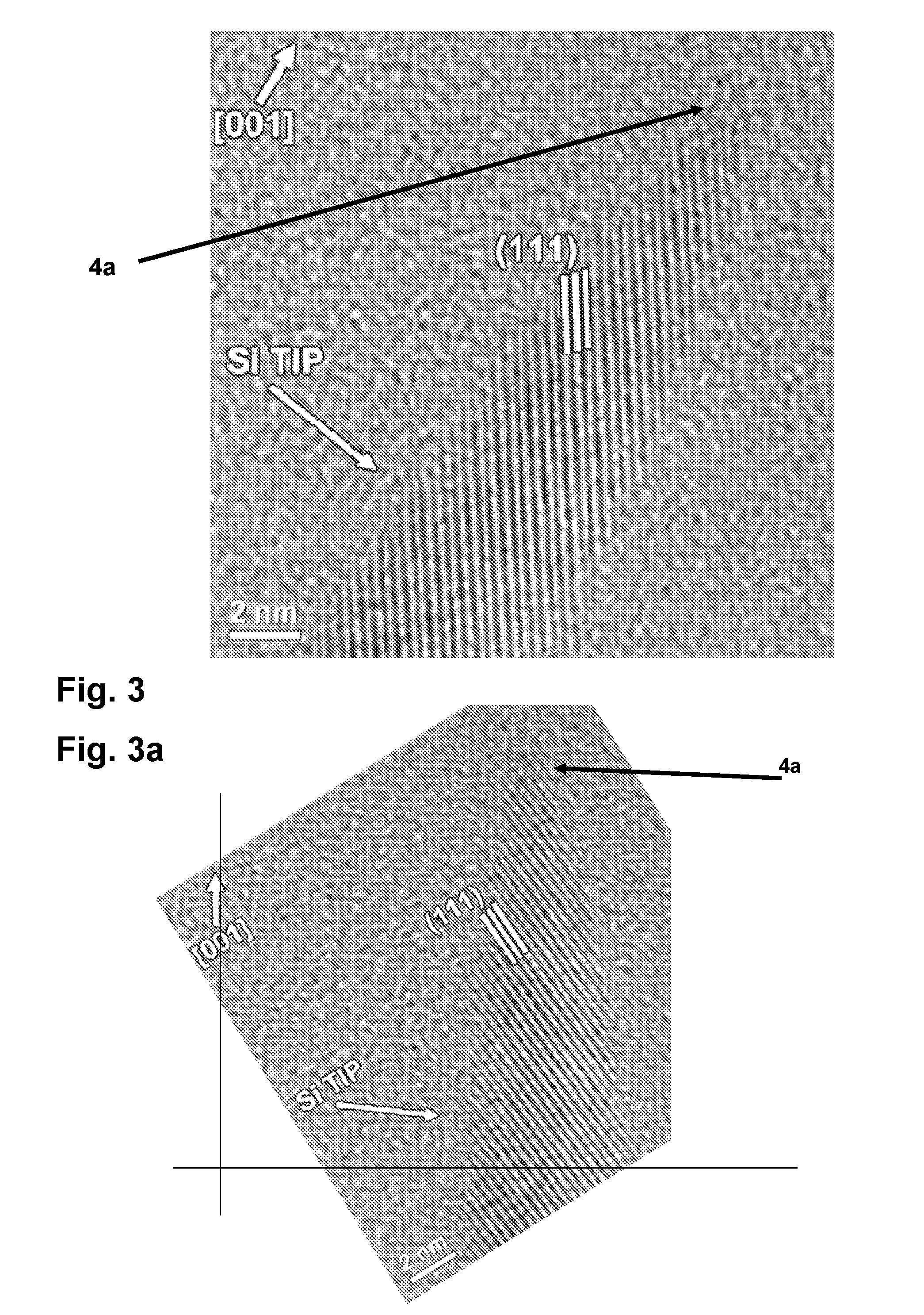
ActiveUS20110127641A1High aspect ratioHigh dimensionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterference lithographyBroadband
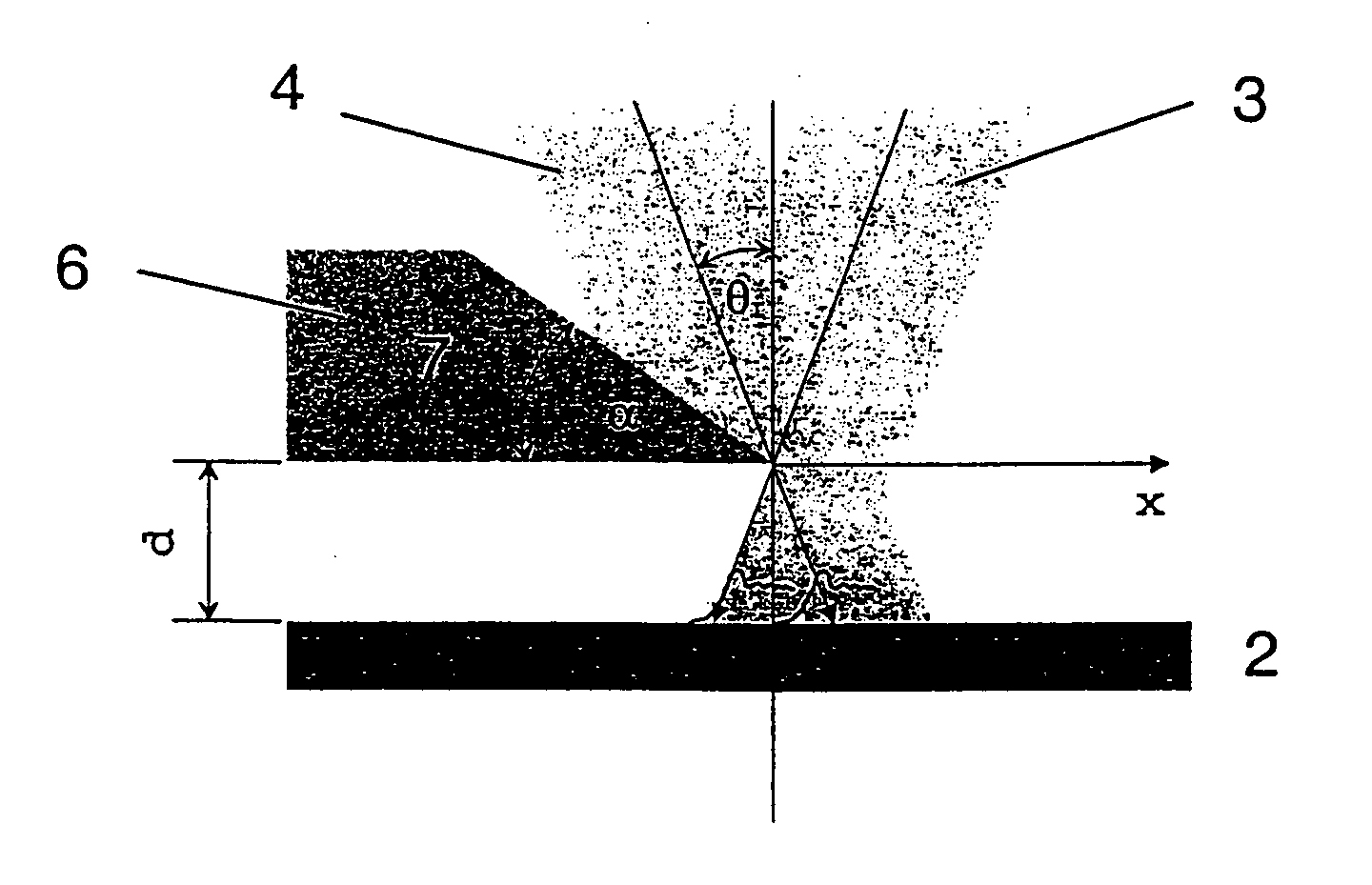
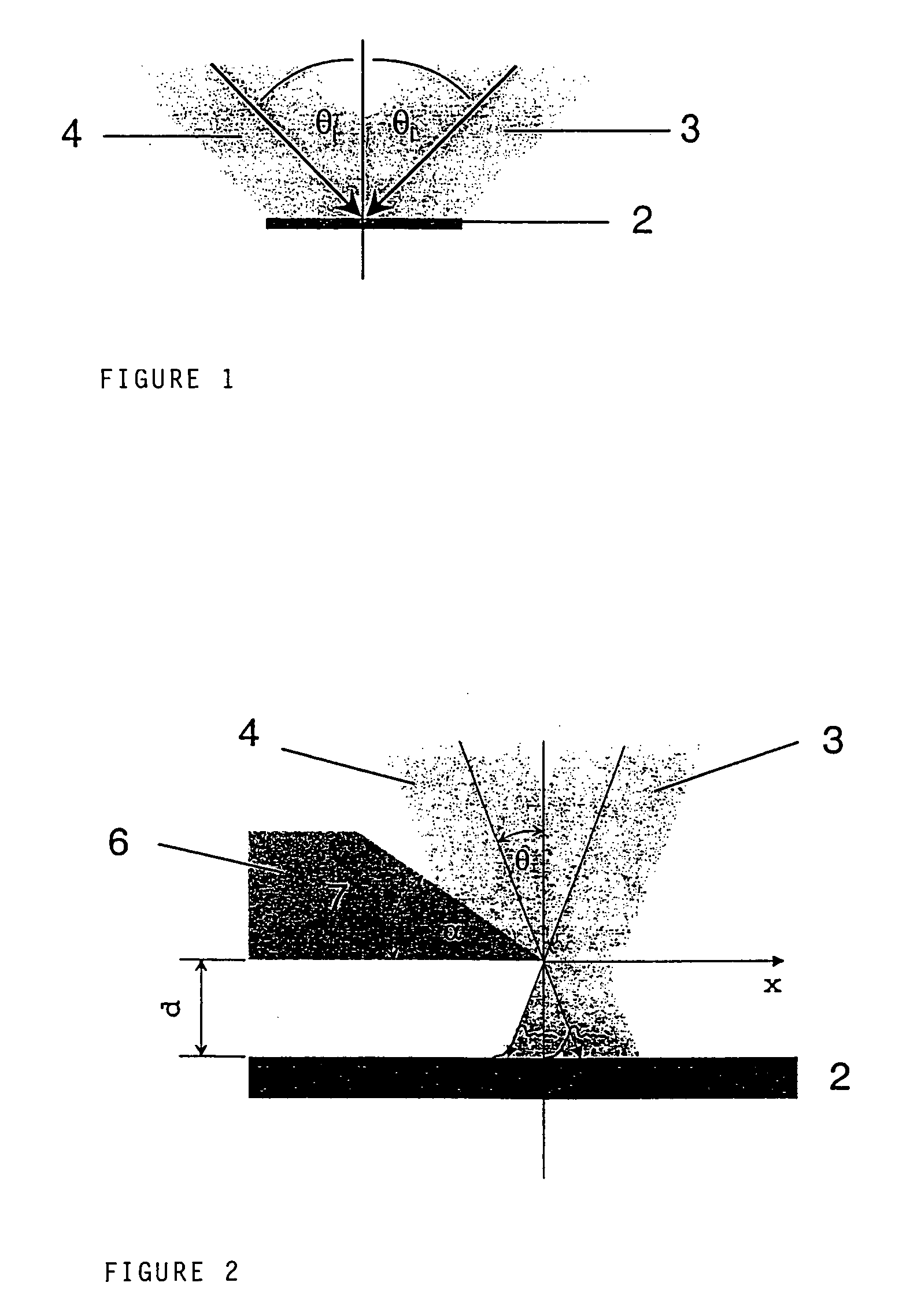
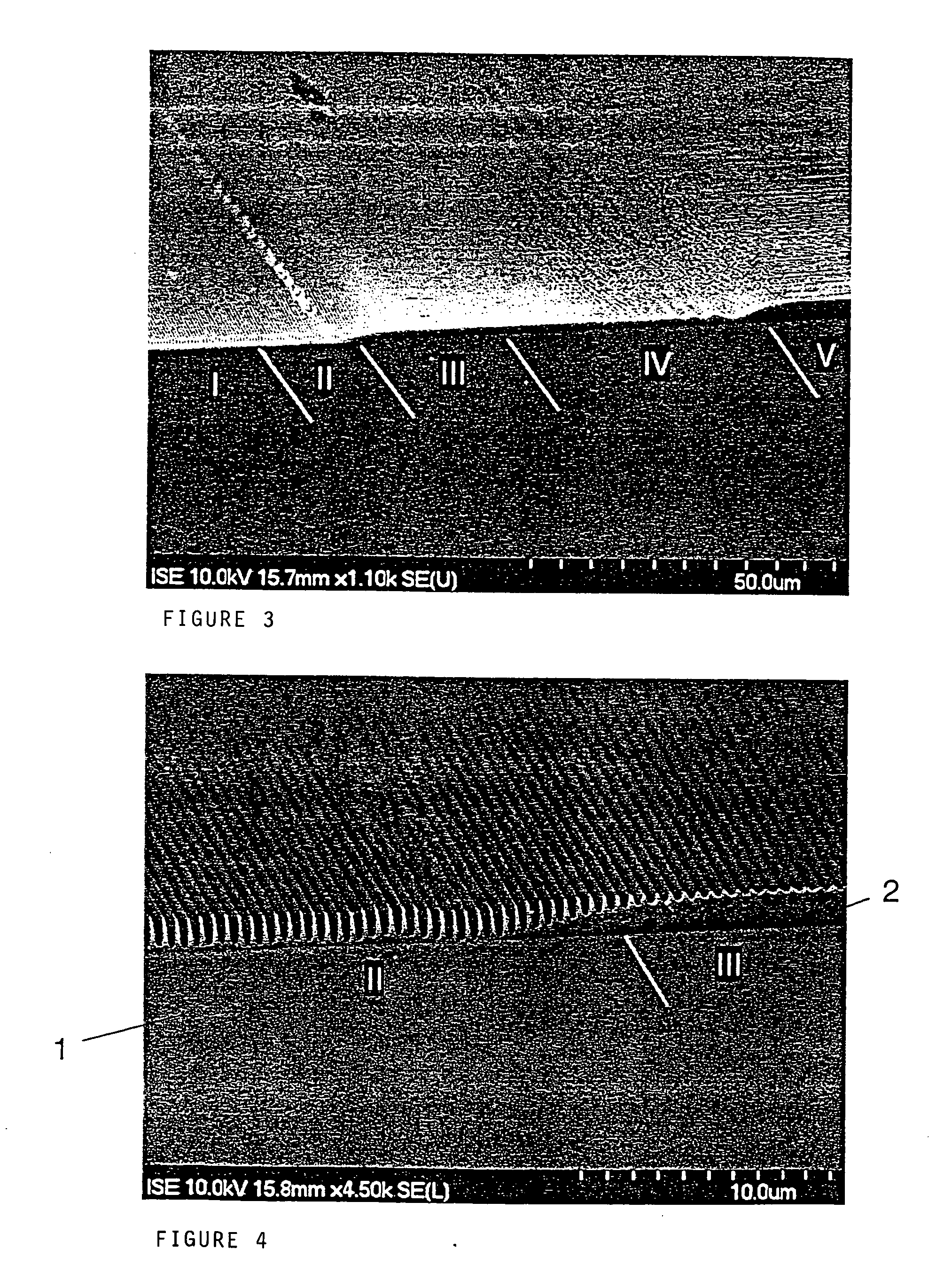
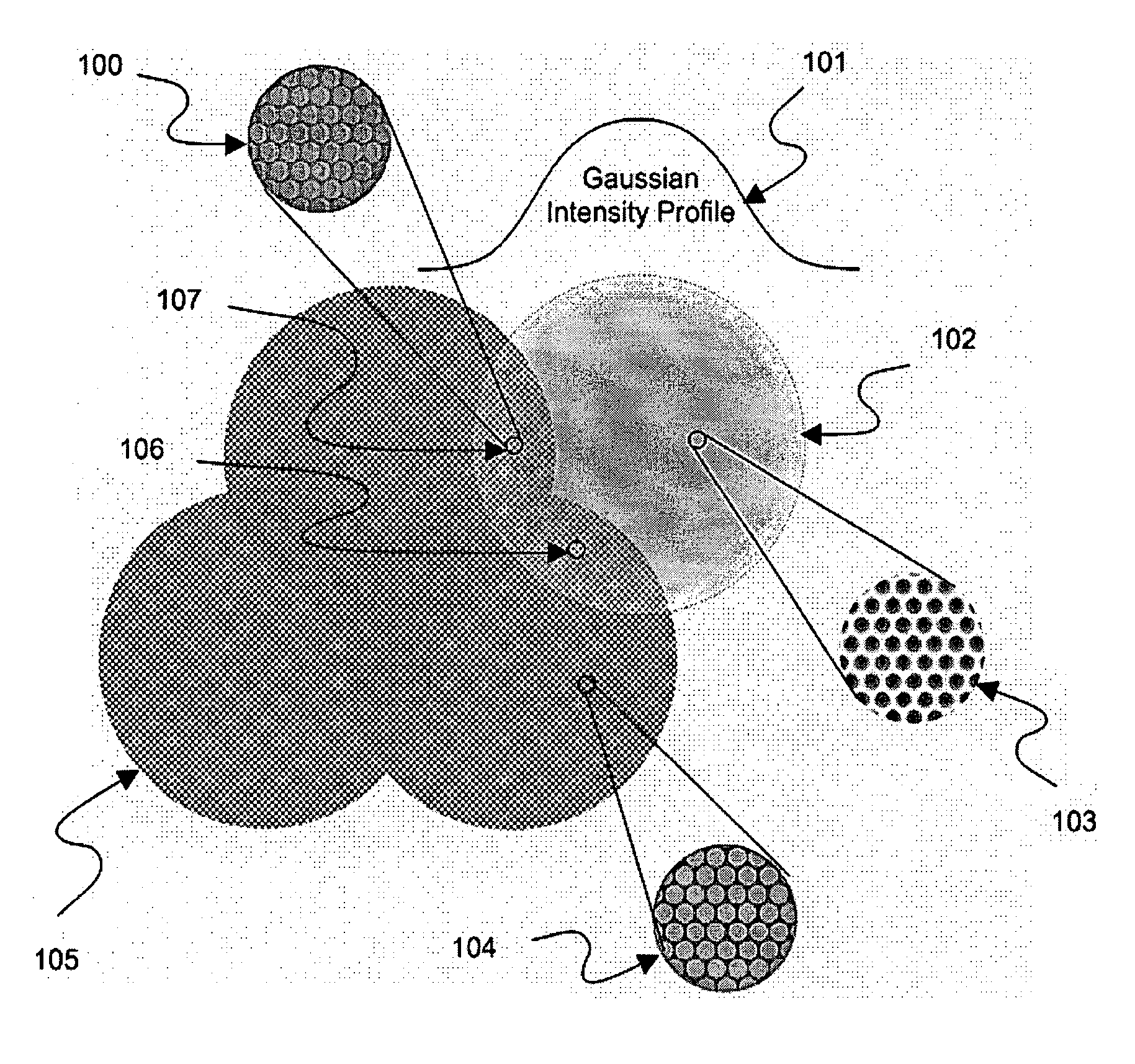
By means of an RIE etch process for silicon (3), a pin-type structure (4,4a) without crystal defects is formed with high aspect ratio and with nano dimensions on the surface of silicon wafers without any additional patterning measures (e-beam, interference lithography, and the like) by selecting the gas components of the etch plasma in self-organization wherein, among others, a broadband antireflective behaviour is obtained that may be applicable in many fields.
Owner:X FAB SEMICON FOUNDRIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com