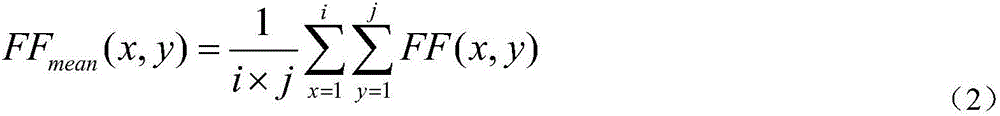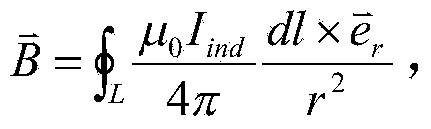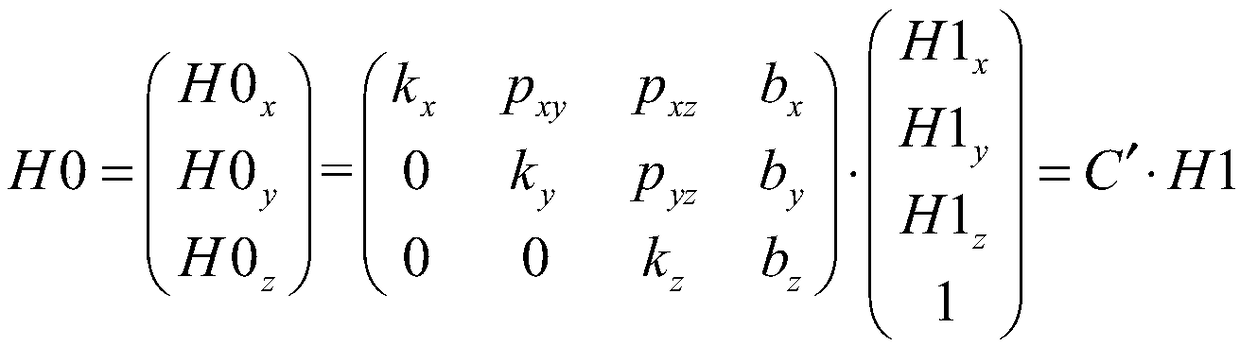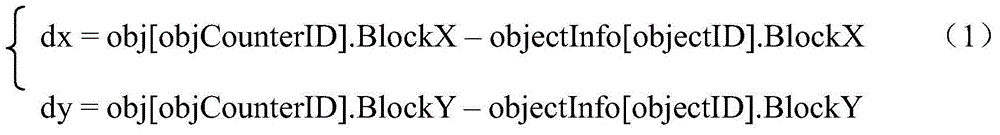Patents
Literature
79 results about "Field size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In American football the standard field dimensions are 120 yards long and 53 1/3 yards wide. The last 10 yards of length on either end of the field are considered "end zones" in which a player scores.
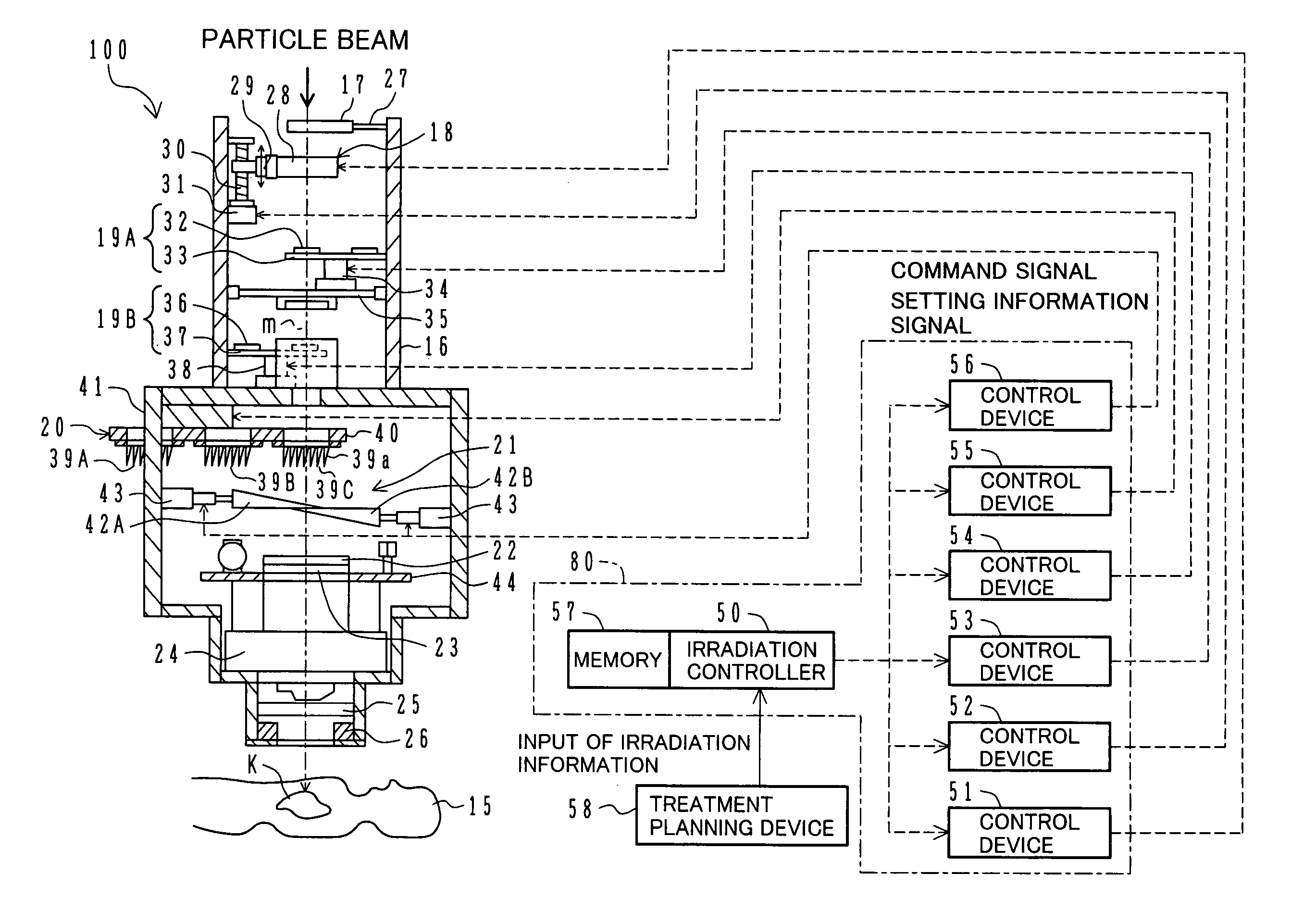
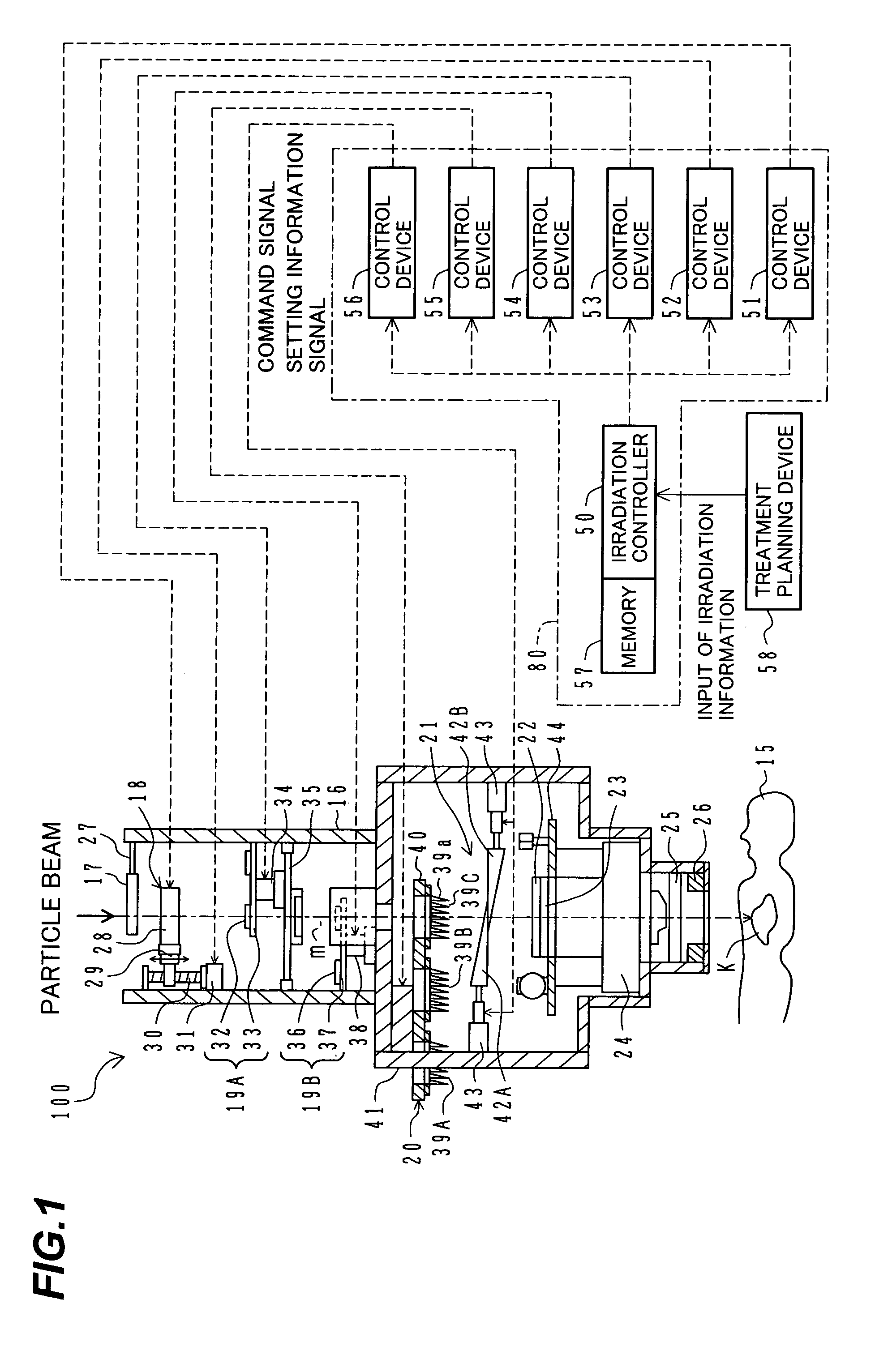
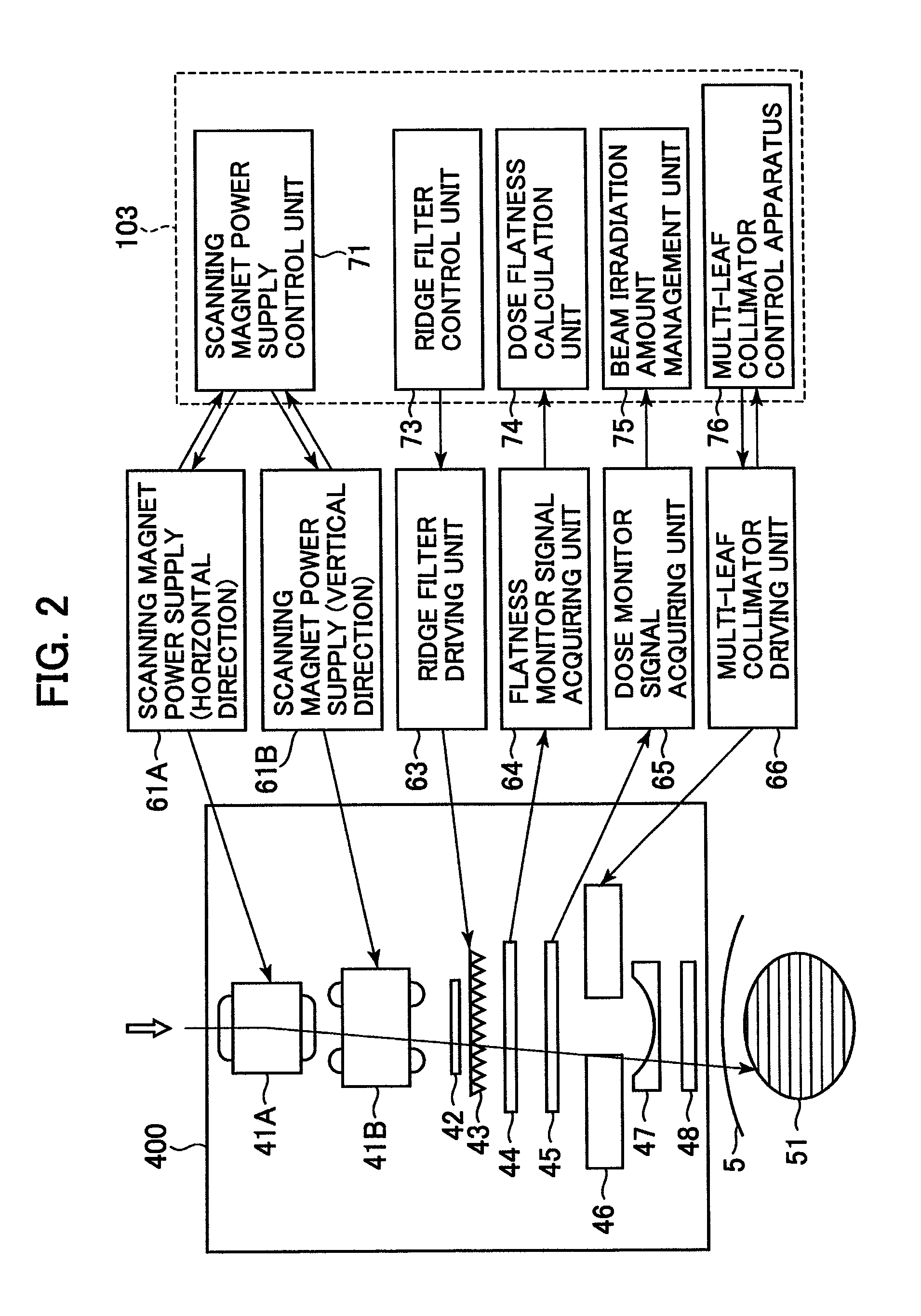
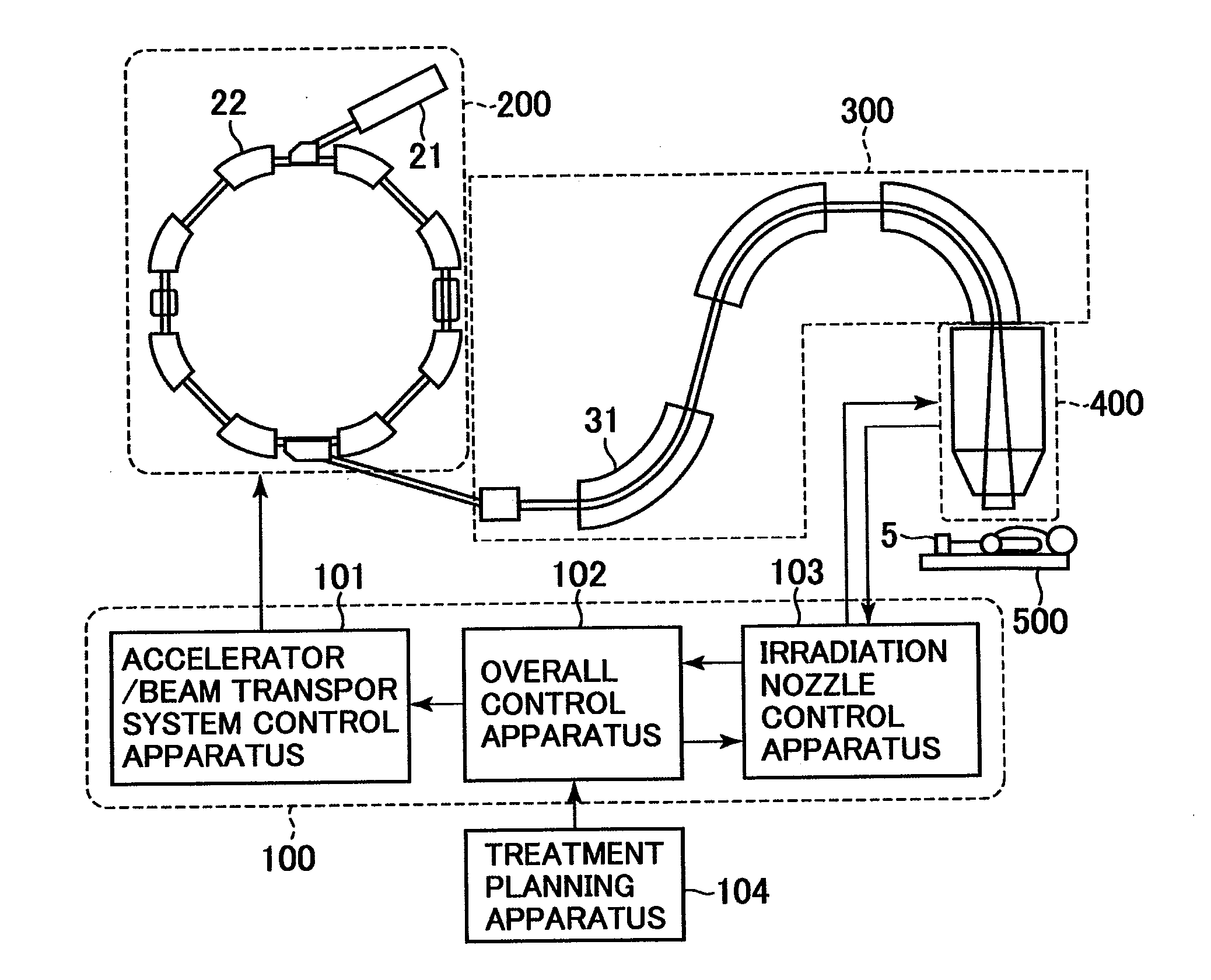
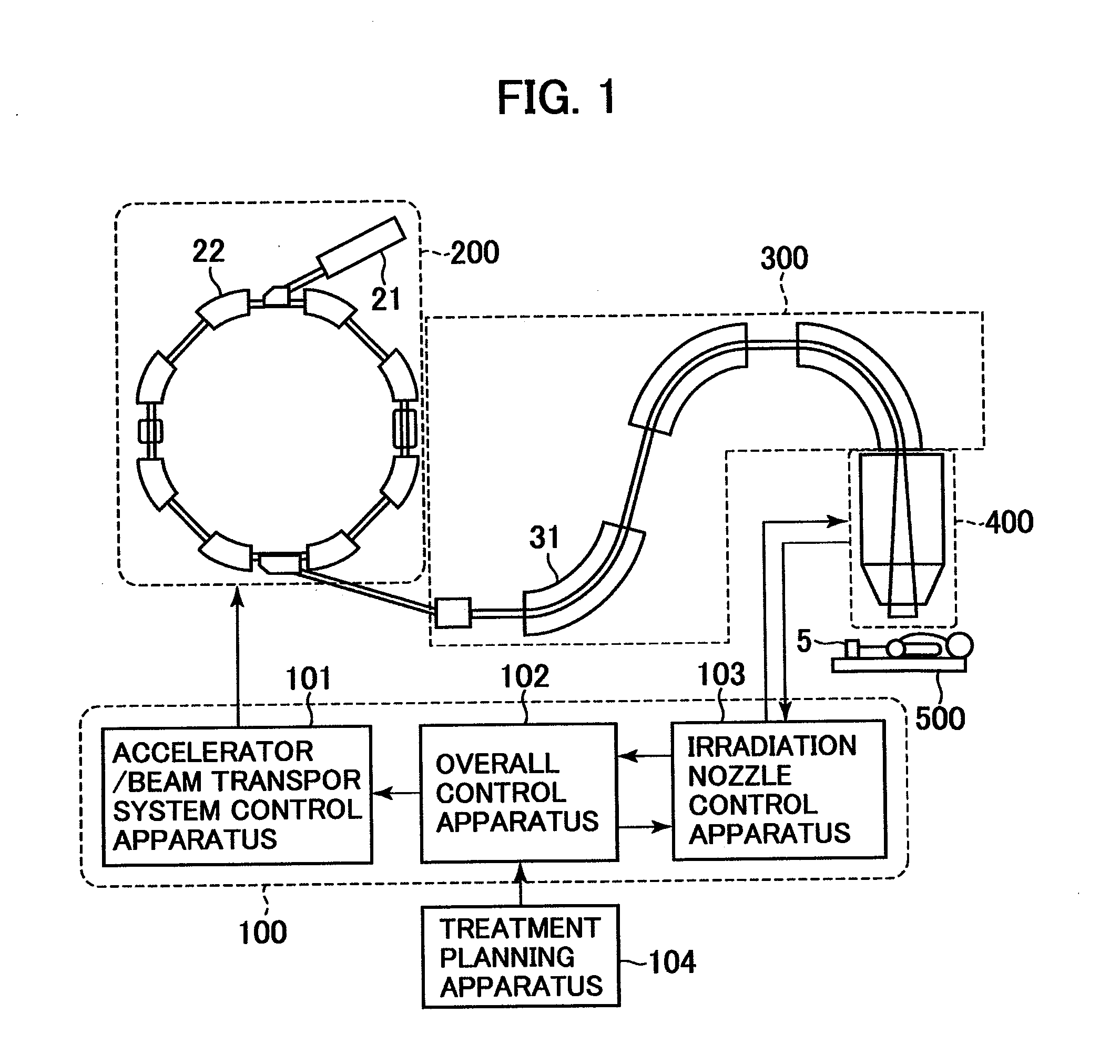
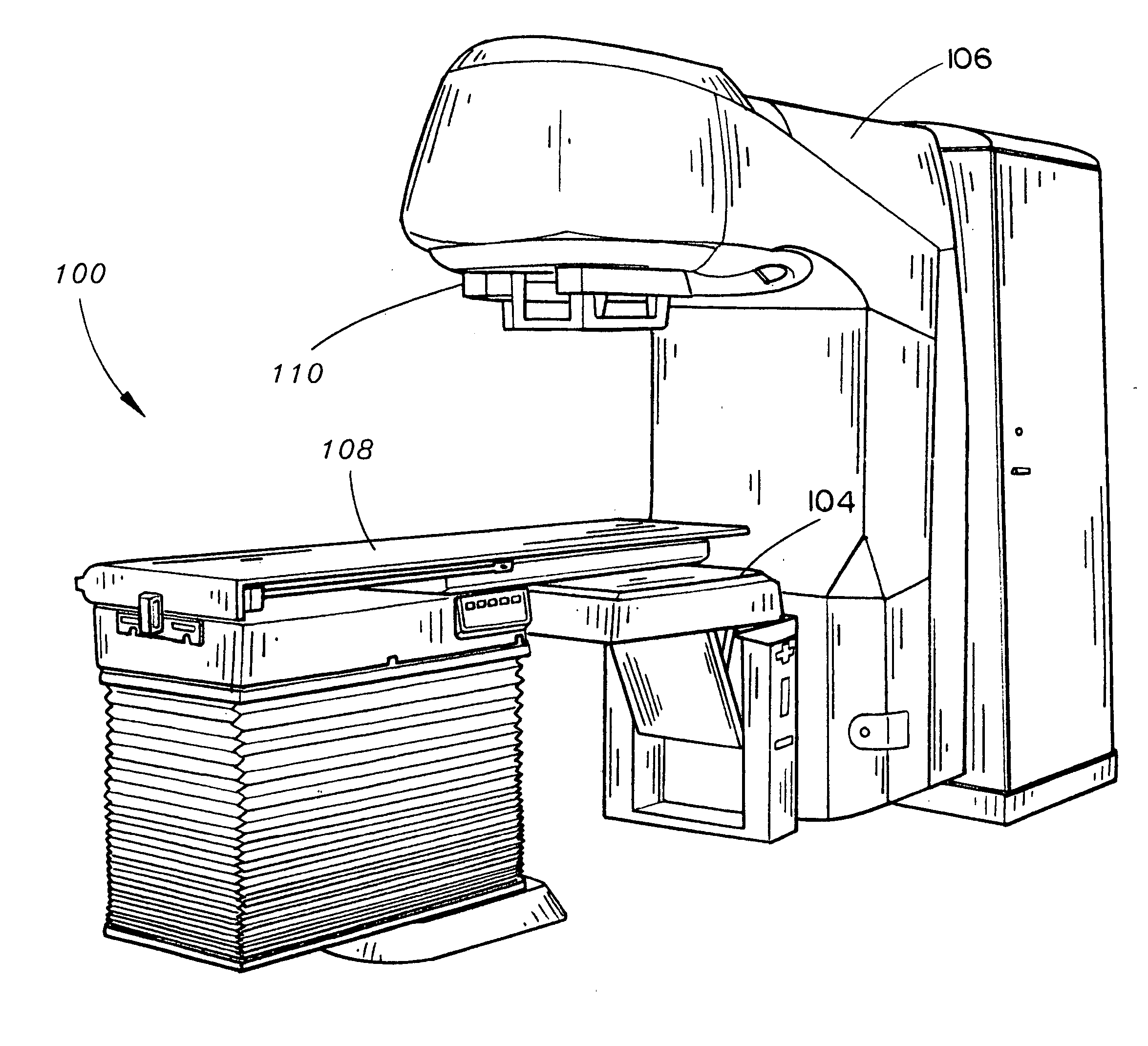
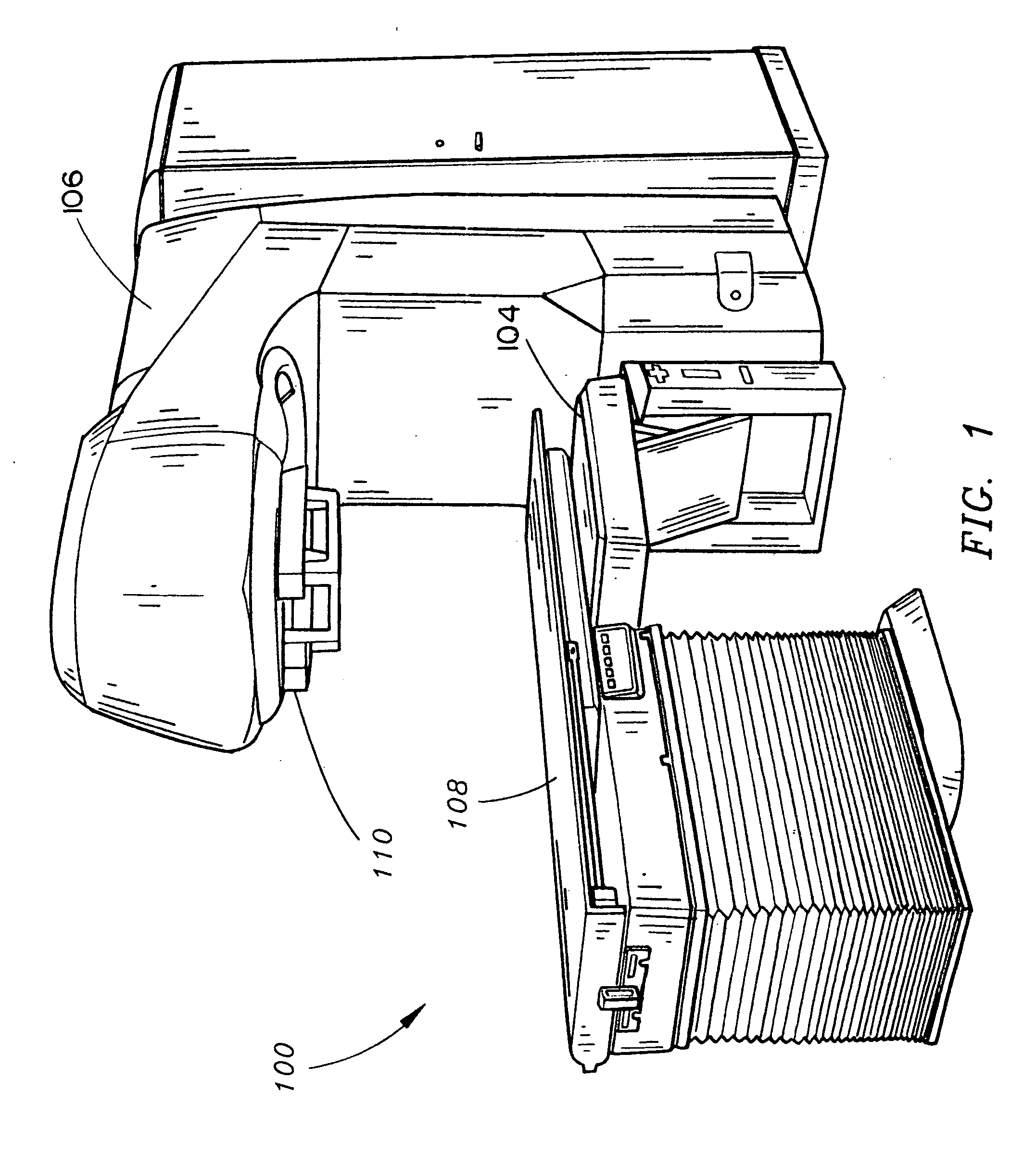
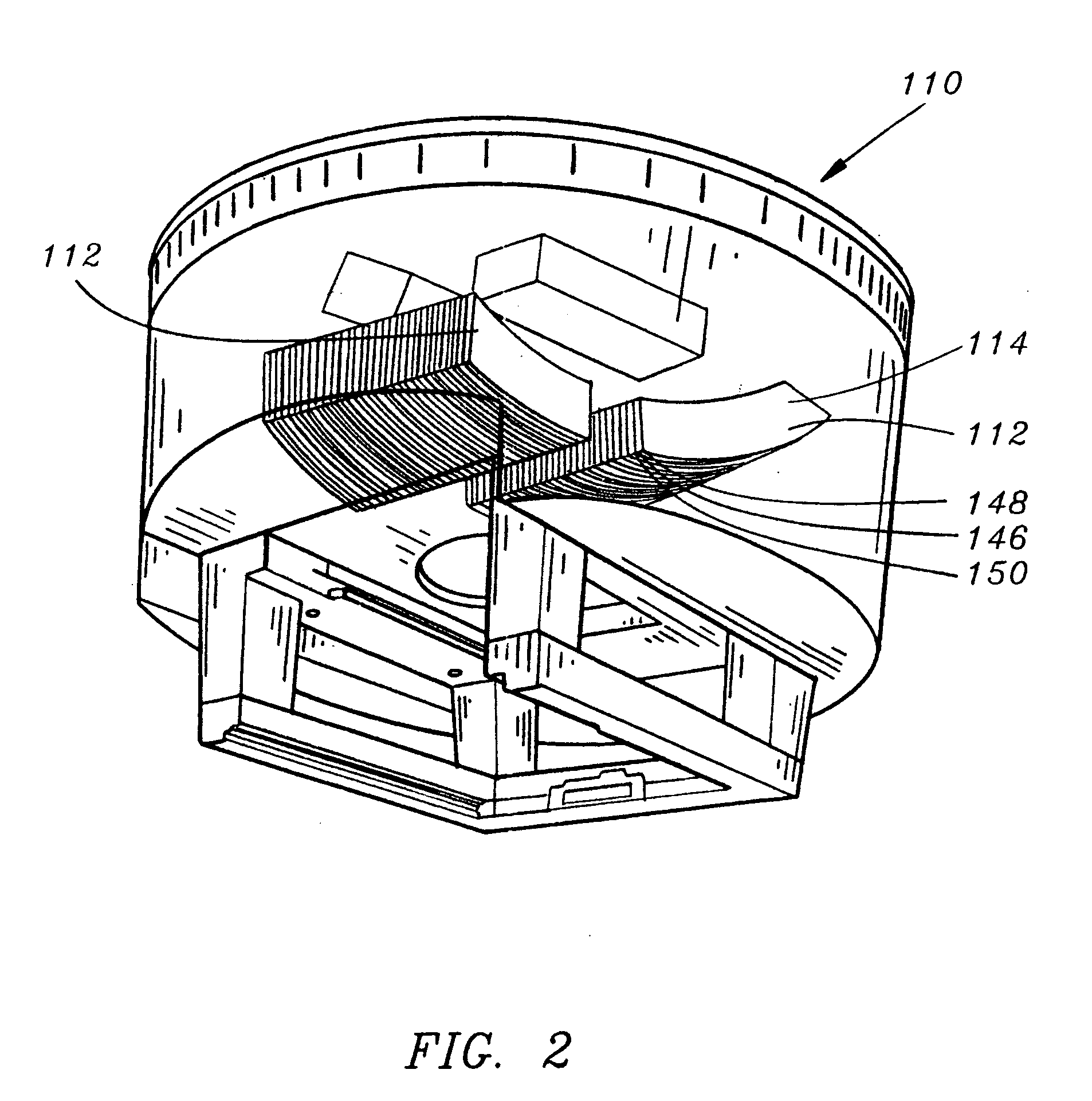
Particle beam irradiation equipment and particle beam irradiation method
ActiveUS7449701B2Improve dose uniformityLong rangeRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsField sizeParticle beam
Particle beam irradiation equipment and a method of adjusting irradiation nozzle, which can ensure a long range and high dose uniformity at any field size are provided. The particle beam irradiation equipment comprises charged particle beam generation equipment and an irradiation nozzle for irradiating a charged particle beam extracted from the charged particle beam generation equipment to an irradiation target. The irradiation nozzle comprises a first scatterer device including a first scatterer for spreading out the charged particle beam into a Gaussian-like distribution, and multiple stages of second scatterer devices including second scatterers for producing a uniform intensity distribution of the charged particle beam having been spread out into a Gaussian-like distribution by the first scatterer. For forming irradiation fields having sizes different from each other, the second scatterer devices are disposed downstream of the first scatterer device in the direction of travel of the charged particle beam at the spacing depending on the difference in the field size.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
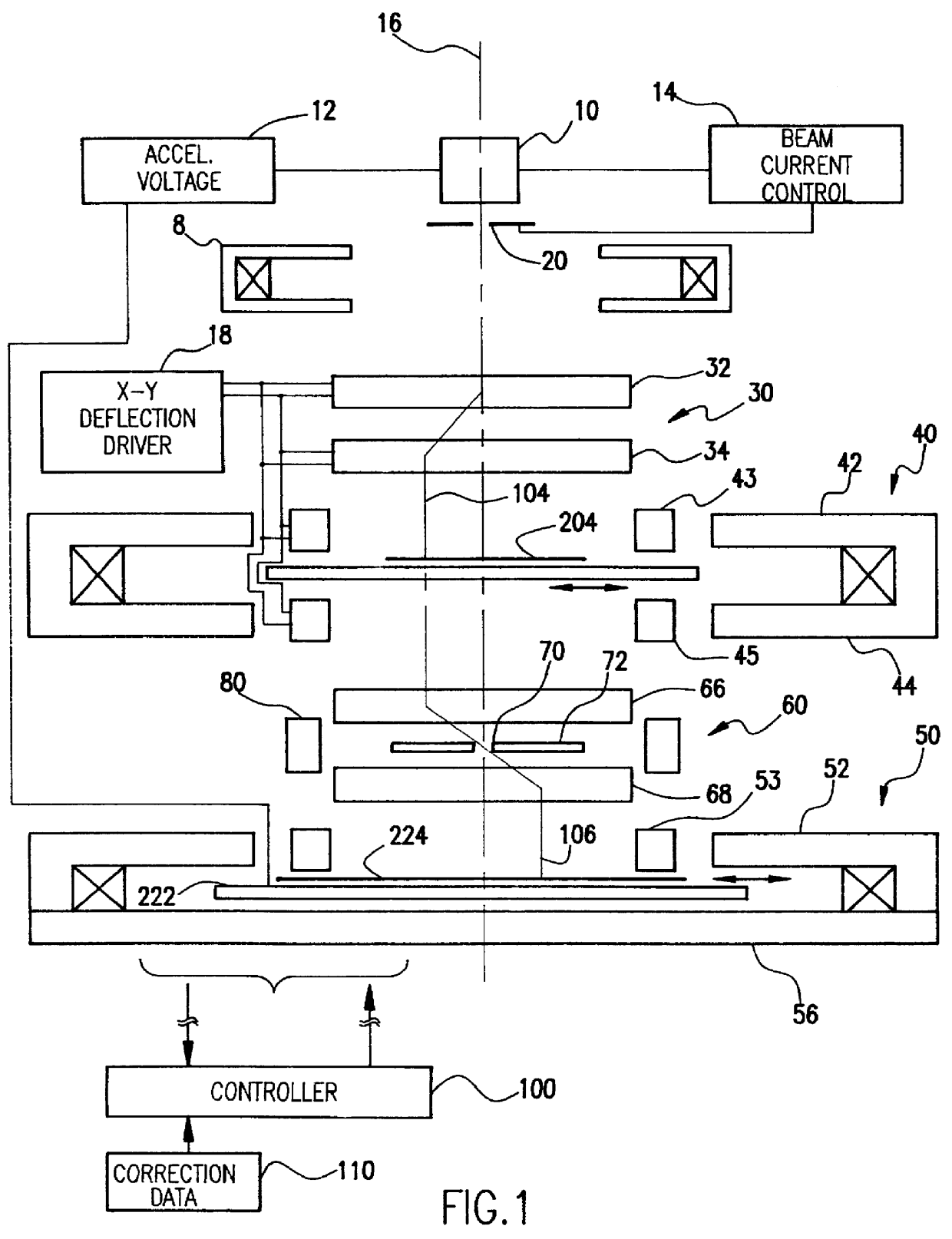
Electron beam projection lithography system (EBPS)
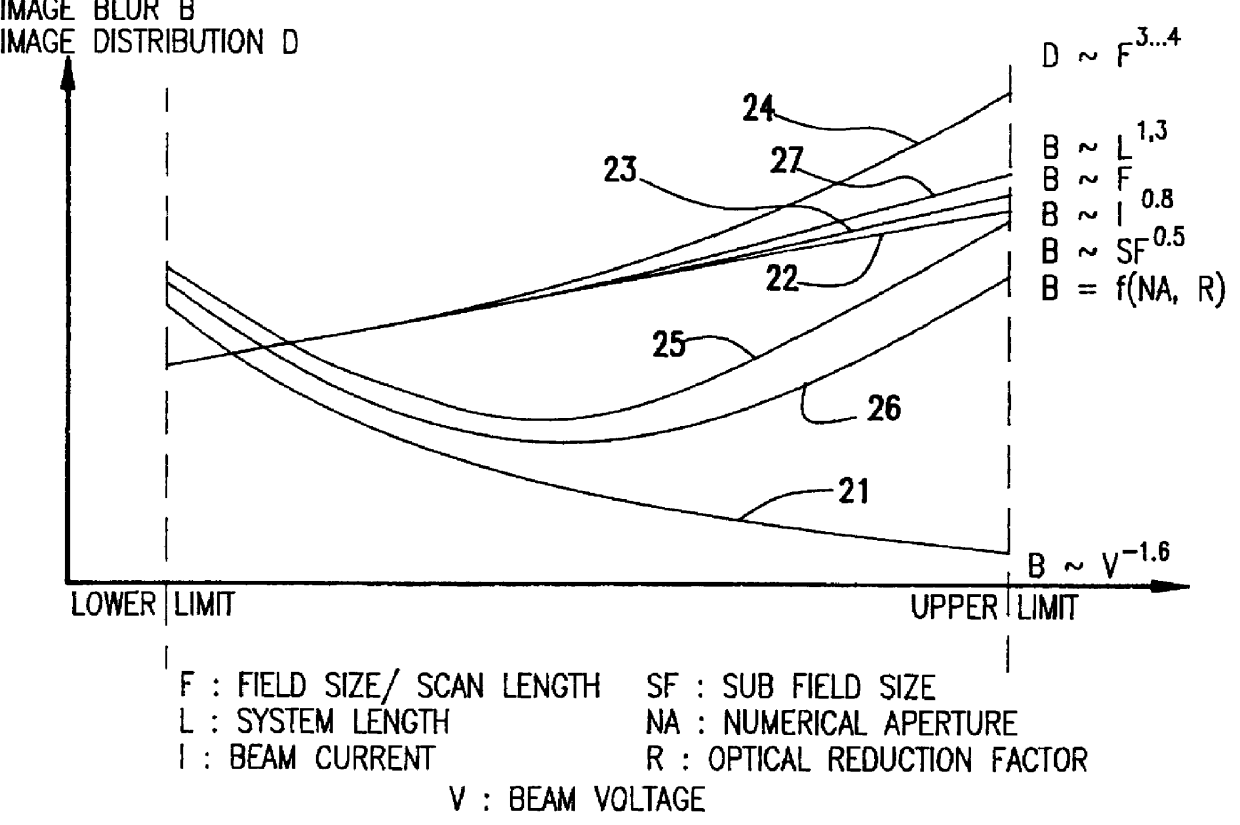
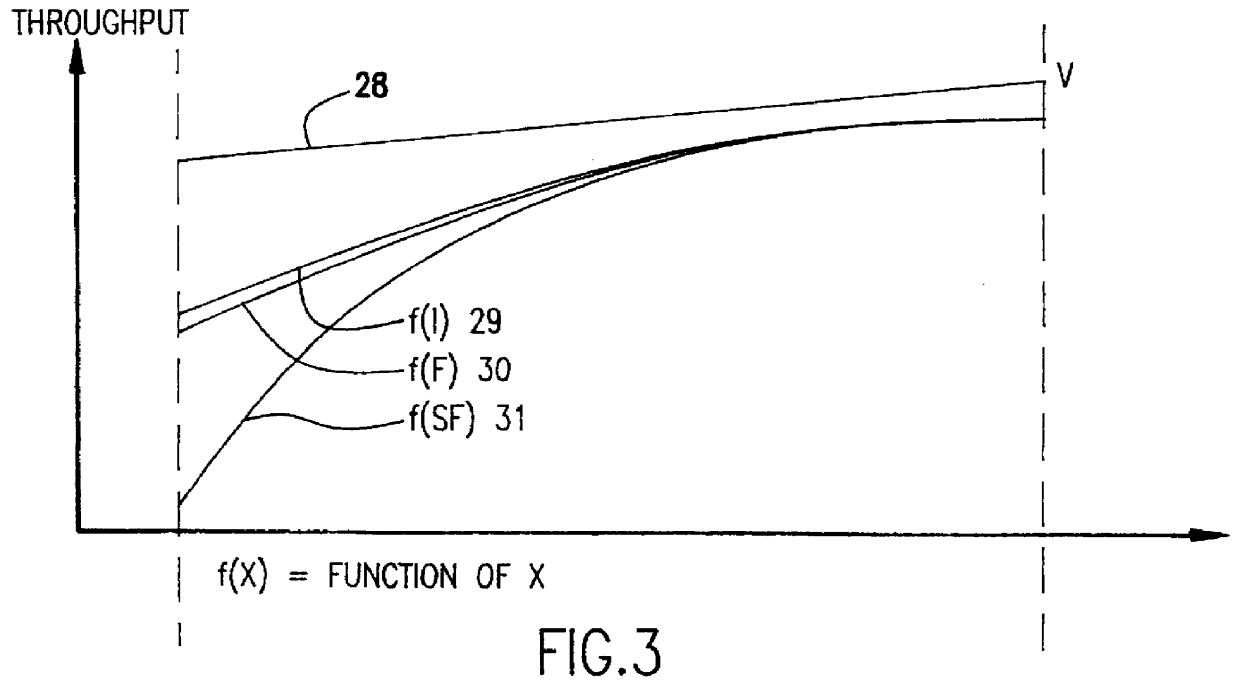
InactiveUS6069684AHigh resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsBeam energyBeam trajectory
Numerous largely unpredictable criticalities of operating parameters arise in electron beam projection lithography systems to maintain throughput comparable to optical projection lithography systems as minimum feature size is reduced below one-half micron and resolution requirements are increased. Using an electron beam projection lithography system having a high emittance electron source, variable axis lenses, curvilinear beam trajectory and constant reticle and / or target motion in a dual scanning mode wherein the target and / or wafer is constantly moved orthogonally to the direction of beam scan, high throughput is obtained consistent with 0.1 mu m feature size ground rules utilizing a column length of greater than 400 mm, a beam current of between about 4 and 35 mu A, a beam energy of between about 75 and 175 kV, a sub-field size between about 0.1 and 0.5 mm at the target at an optical reduction factor between about 3:1 and 5:1, a numerical aperture greater than 2 mrad and preferably between about 3 and 8 mrad and a scan length between about 20 mm and 55 mm. Reticle and target speed preferably differ by about the optical reduction factor.
Owner:IBM CORP
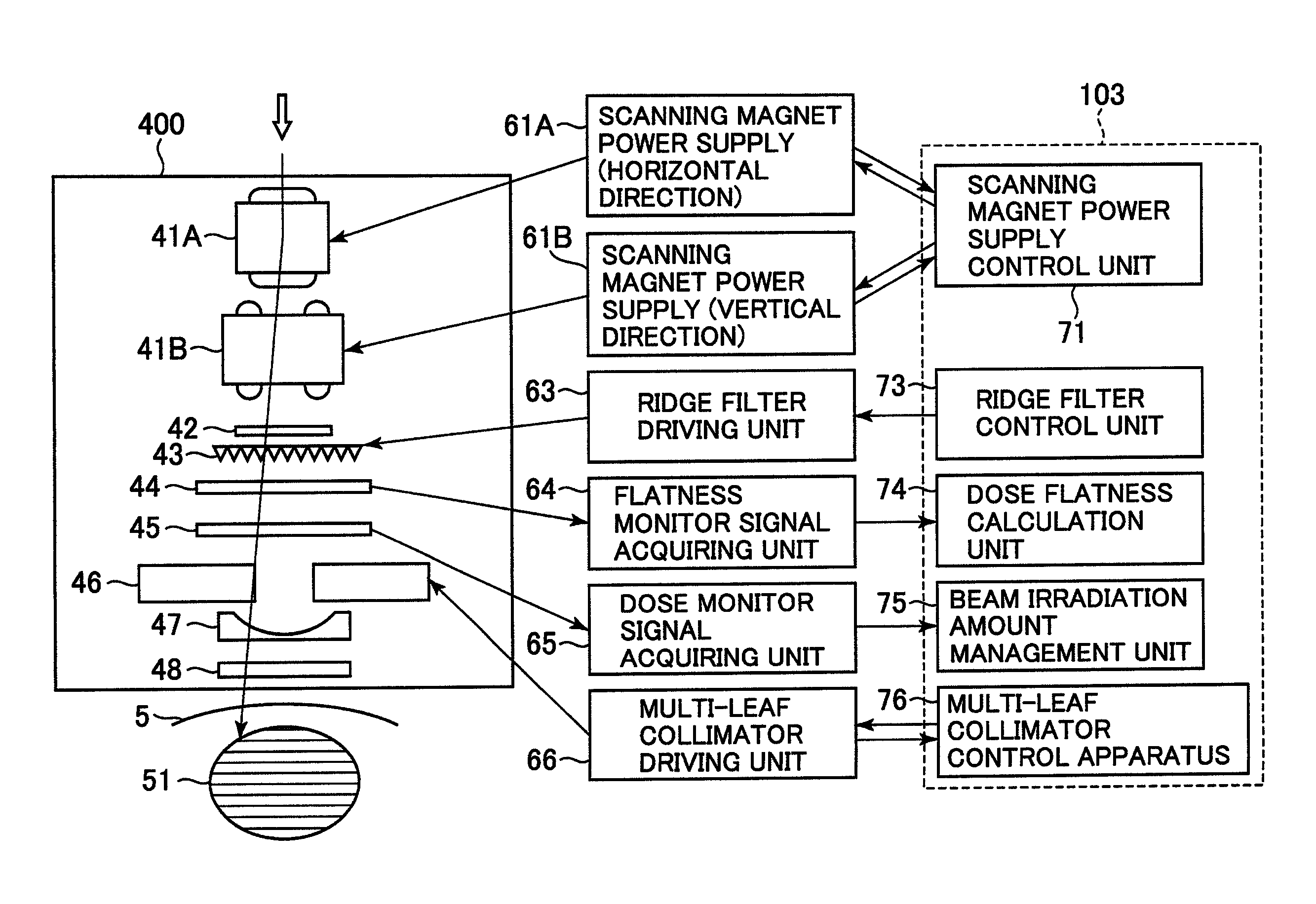
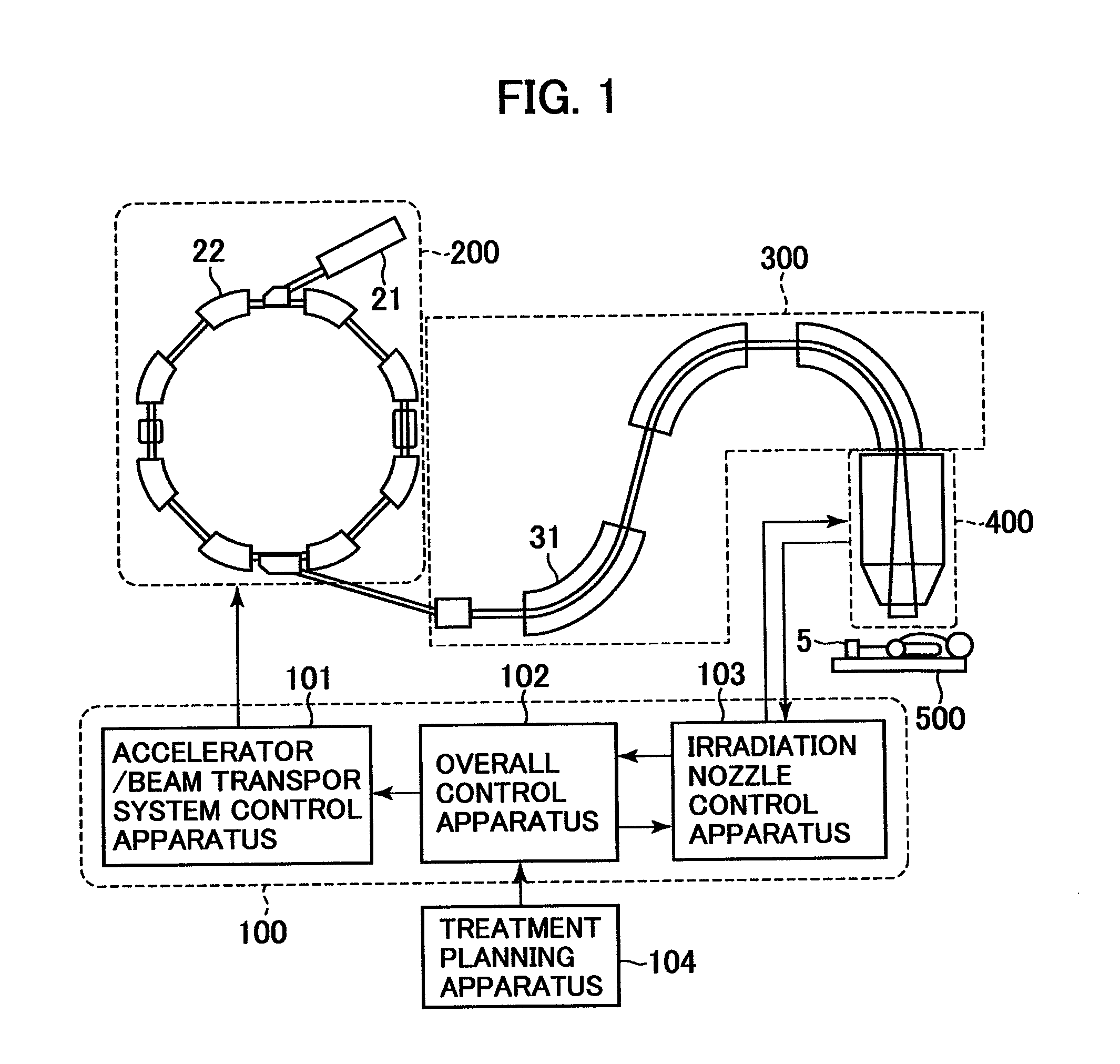
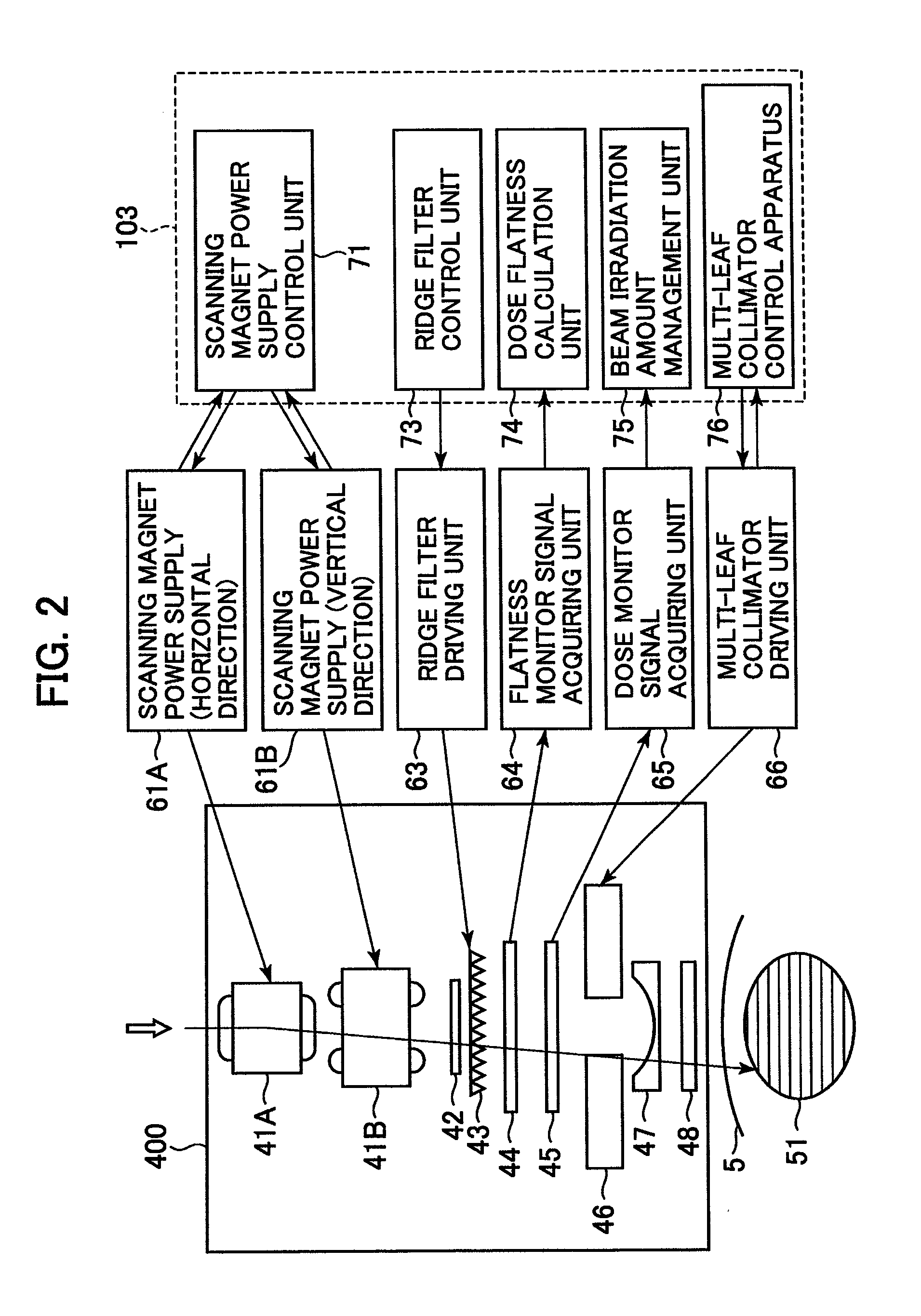
Treatment planning apparatus and particle therapy system
ActiveUS8847179B2Reduce lossesLow costComputer controlSimulator controlField sizeMulti leaf collimator
A charged particle beam reduces treatment time in the uniform scanning or in the conformal layer stacking irradiation. In the uniform scanning, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a collimator aperture area is calculated. In the conformal layer stacking irradiation, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer for each of the layers obtained by partitioning the target volume is calculated. Alternatively, a minimum irradiation field size that covers the multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer is calculated, and a scan path corresponding to the irradiation field size, prestored in a memory of a particle therapy control apparatus, is selected. The charged particle beam scan path is optimally changed in the lateral directions in conformity with the collimator aperture area in the uniform scanning or in each layer in the conformal layer stacking irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
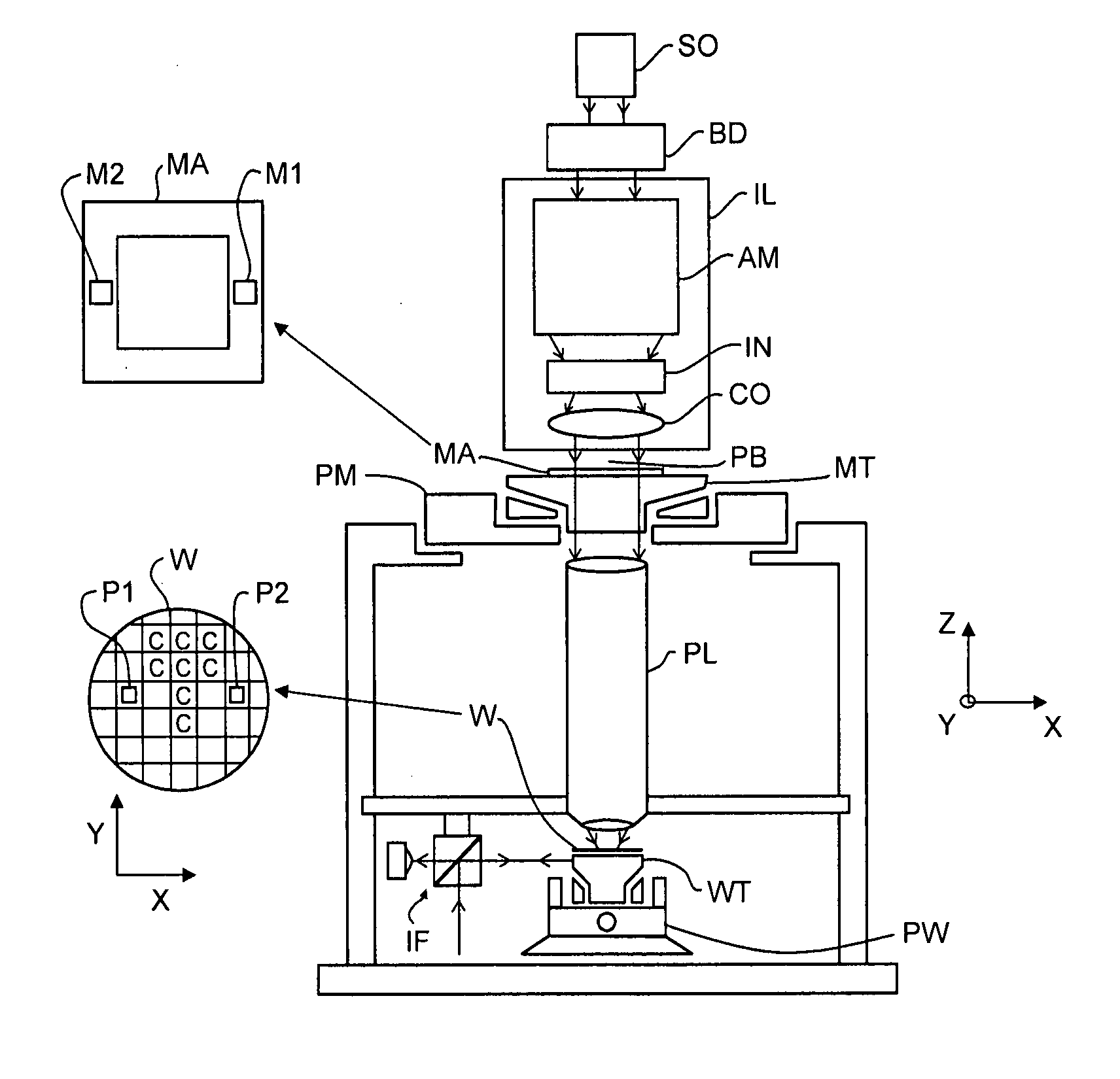
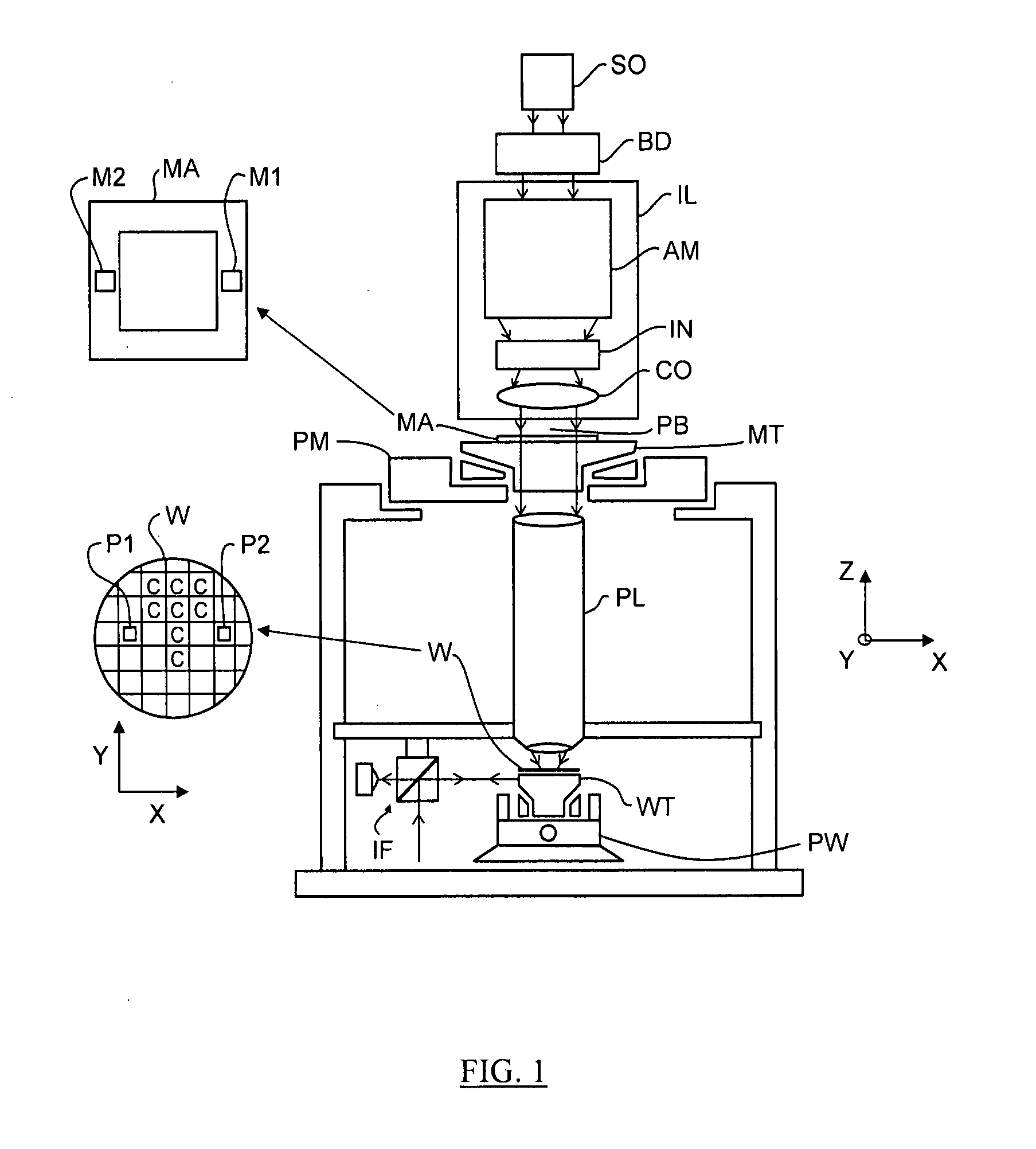
Lithographic apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080259304A1Affect propertyPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingField sizeSpatial light modulator
A lithographic apparatus includes an illumination system to provide a beam of radiation; a support structure to support a patterning device, the patterning device serving to impart the radiation beam with a pattern in its cross-section; a substrate table to hold a substrate; and a projection system to project the patterned radiation beam onto a target portion of the substrate. The illumination system includes a first spatial light modulator including a first array of individually controllable elements controllable to control the field size of the radiation beam, the field position of the radiation beam or the uniformity of the radiation beam, and a second spatial light modulator arranged to apply a desired angular distribution to the radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
System and method for three-dimensional dose verification in radiosurgery
InactiveCN105854191AVerify accuracyImprove Dose Verification AccuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryDose verification
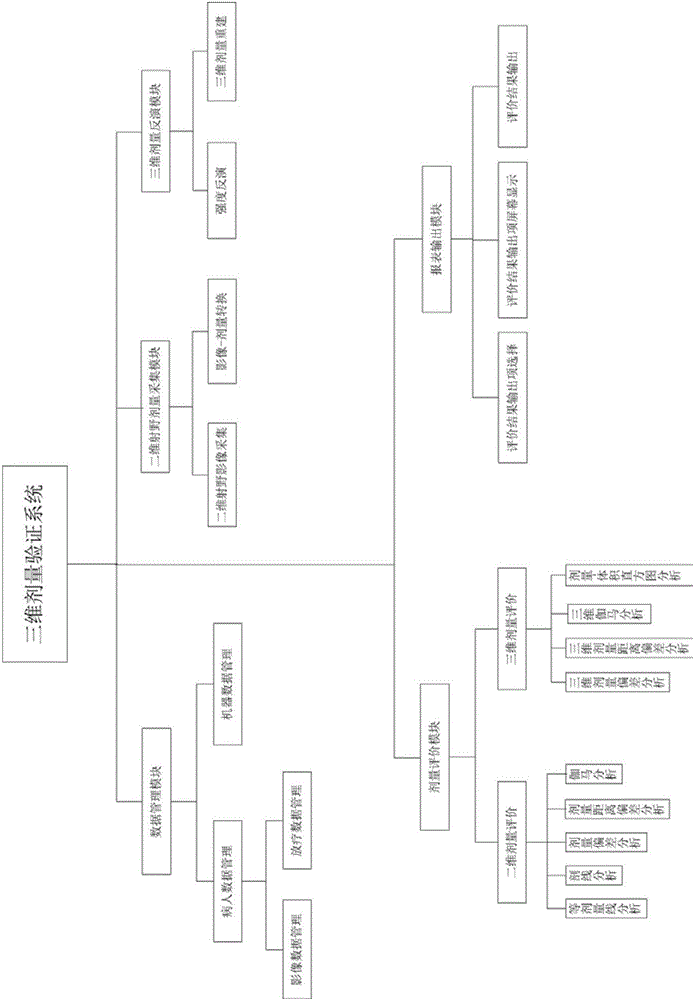
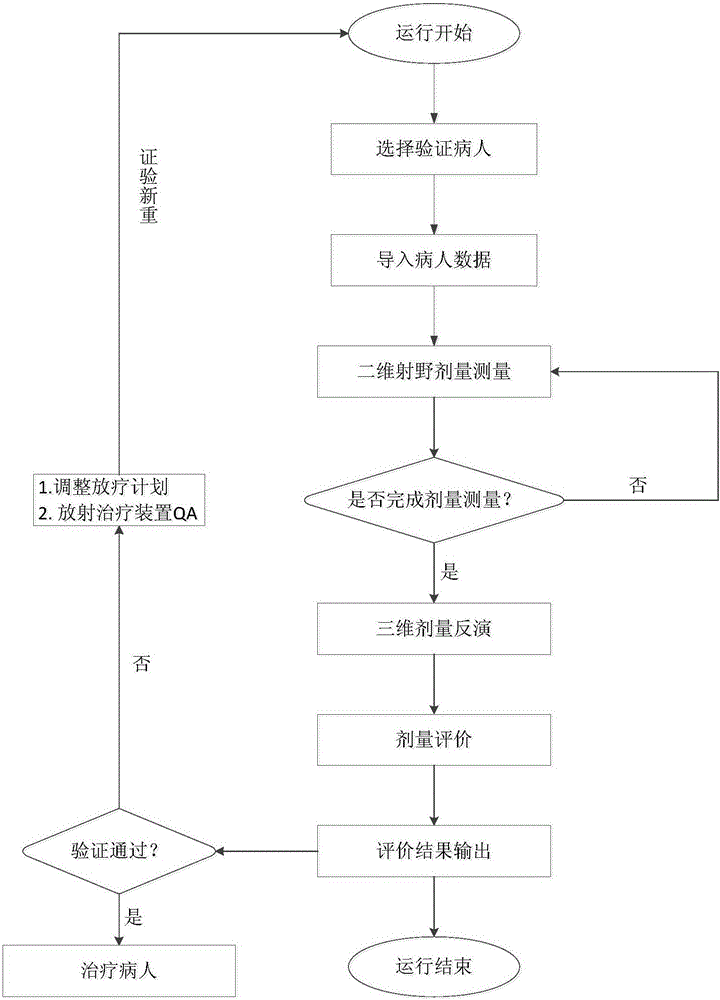
The invention provides a system and method for three-dimensional dose verification in radiosurgery. First a patient's image data and radiotherapy planning data are led in through a data management module, a patient's actual illuminated three-dimensional dose field distribution during the treatment is quickly reconstructed by utilization of a two-dimensional field size dosage collecting module and a three-dimensional dose inversion module; three-dimensional evaluation analysis is performed on a irradiation dose and a planning dose through a dose evaluation module; whether an error is in a permissible range is judged; if the error is in the permissible range, the patient is treated according to a radiotherapy plan, or else the radiotherapy plan is adjusted or a radiosurgery accelerator is subjected to quality control detection, irradiation is not performed on the patient until the dose verification passes, and the consistency between the irradiation dose and the planning dose is guaranteed finally. According to the system and method for three-dimensional dose verification in radiosurgery, the shortcoming of two-dimensional plane dose verification of using water instead of a person prior to existing treatment is overcome, and precise dose verification of three-dimensional space dose field distribution in the patient prior to fractionated treatment and during the fractionated treatment can be implemented.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treatment planning apparatus and particle therapy system
ActiveUS20120264998A1Uniform dose distributionReduce radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyField sizeMulti leaf collimator
A charged particle beam reduces treatment time in the uniform scanning or in the conformal layer stacking irradiation. In the uniform scanning, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a collimator aperture area is calculated. In the conformal layer stacking irradiation, an optimum charged particle beam scan path for uniformly irradiating a multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer for each of the layers obtained by partitioning the target volume is calculated. Alternatively, a minimum irradiation field size that covers the multi-leaf collimator aperture area of each layer is calculated, and a scan path corresponding to the irradiation field size, prestored in a memory of a particle therapy control apparatus, is selected. The charged particle beam scan path is optimally changed in the lateral directions in conformity with the collimator aperture area in the uniform scanning or in each layer in the conformal layer stacking irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
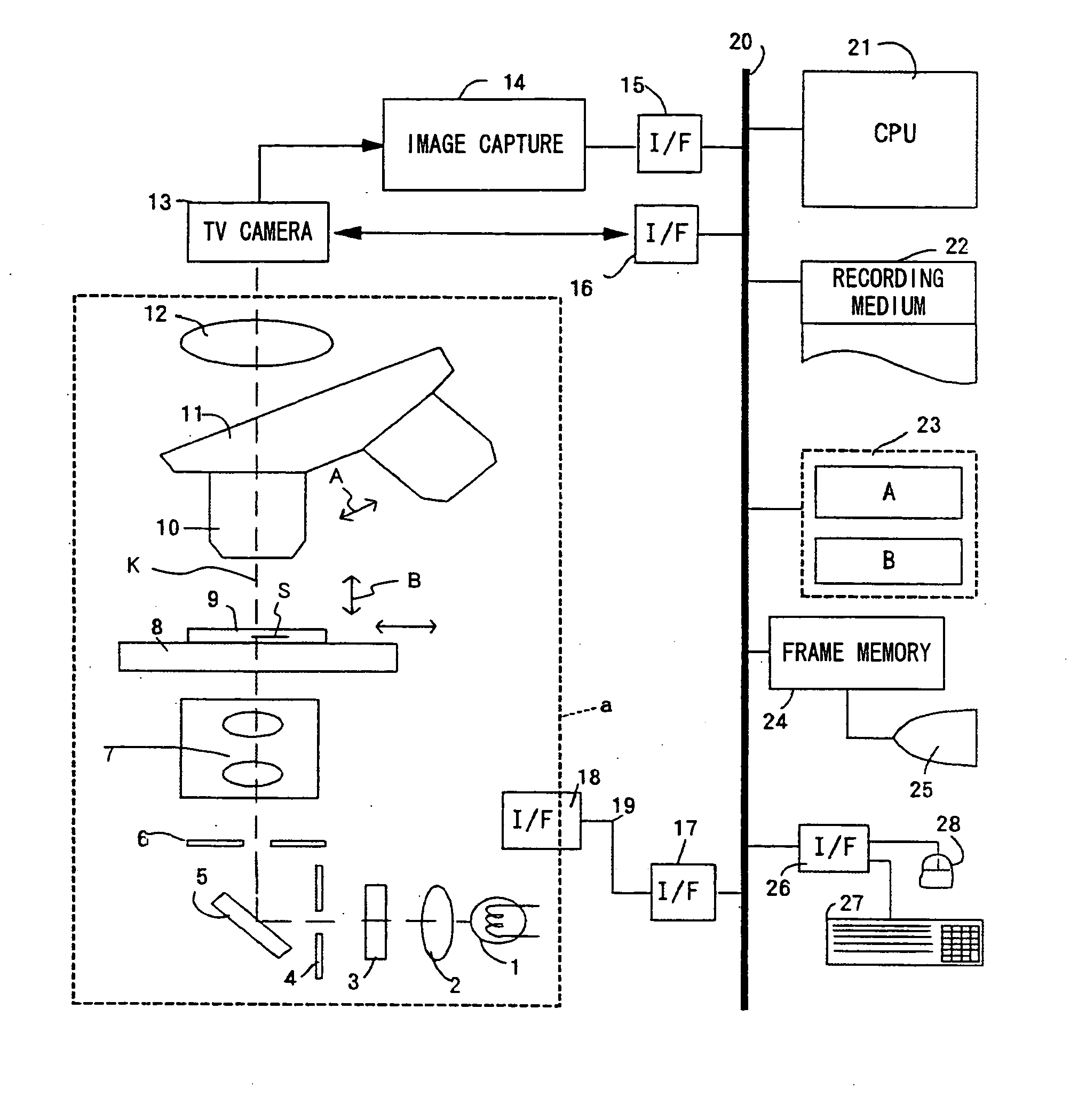
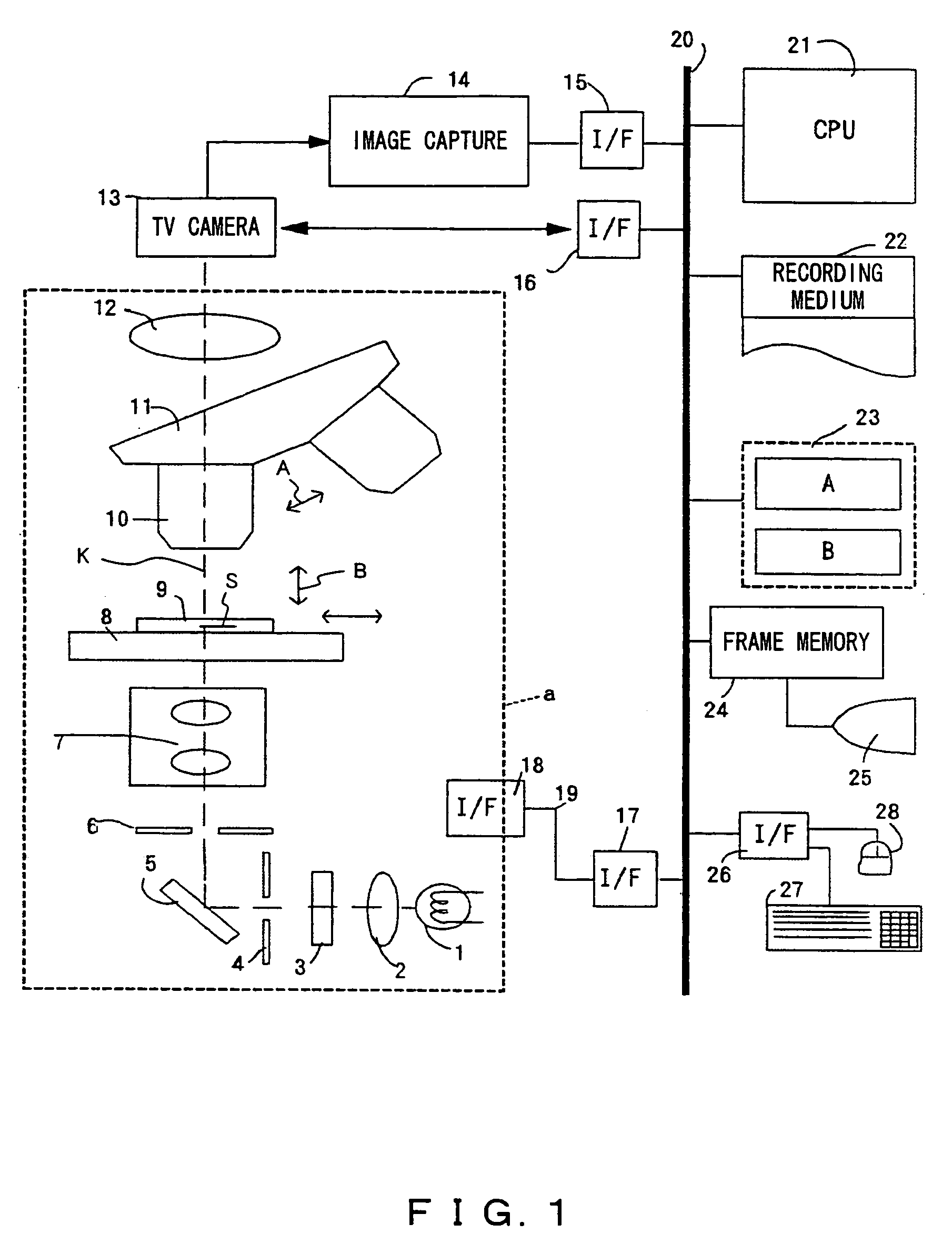
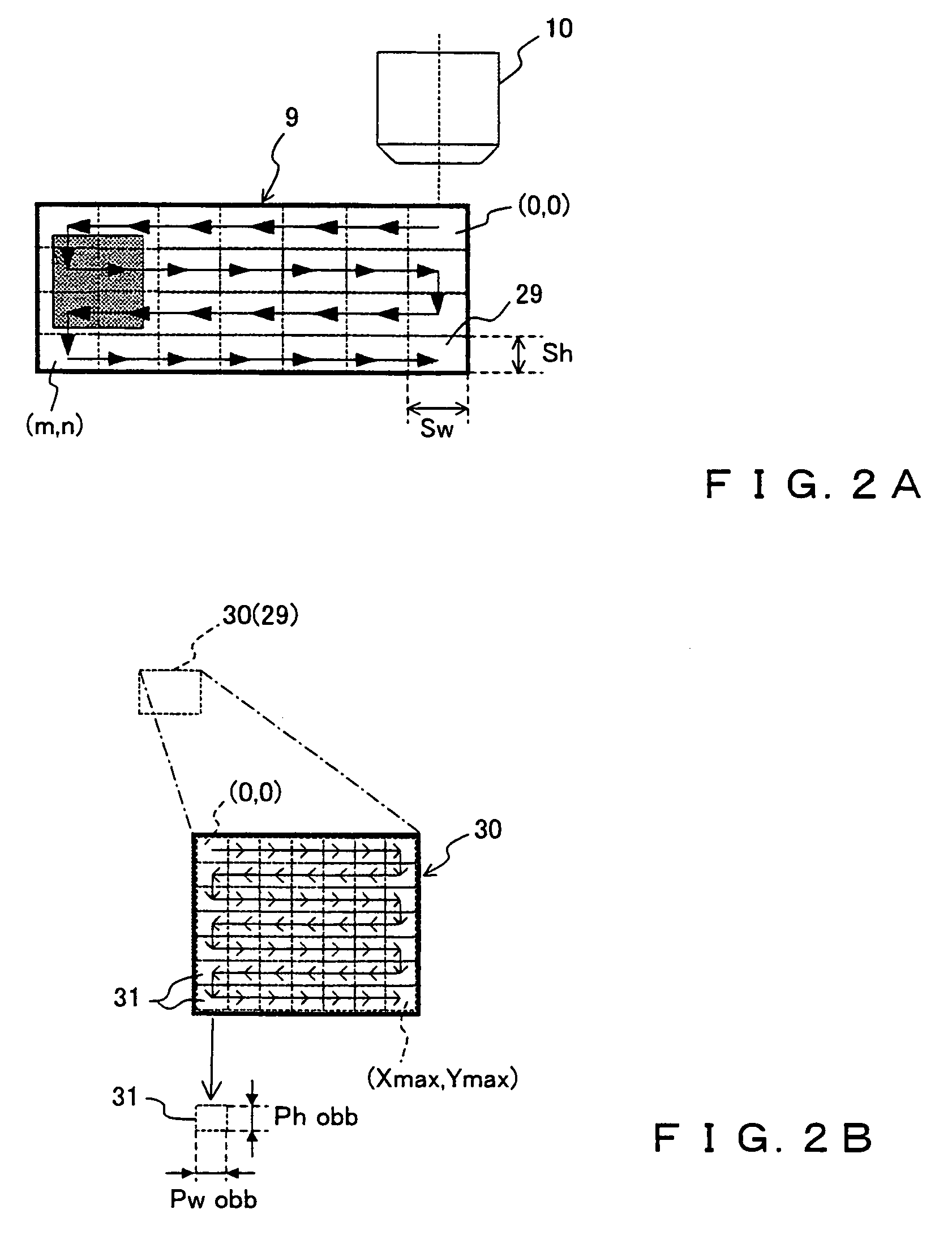
Microscopic image capture apparatus and microscopic image capturing method
ActiveUS20050190437A1High precision imagingLong is wastedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageField size
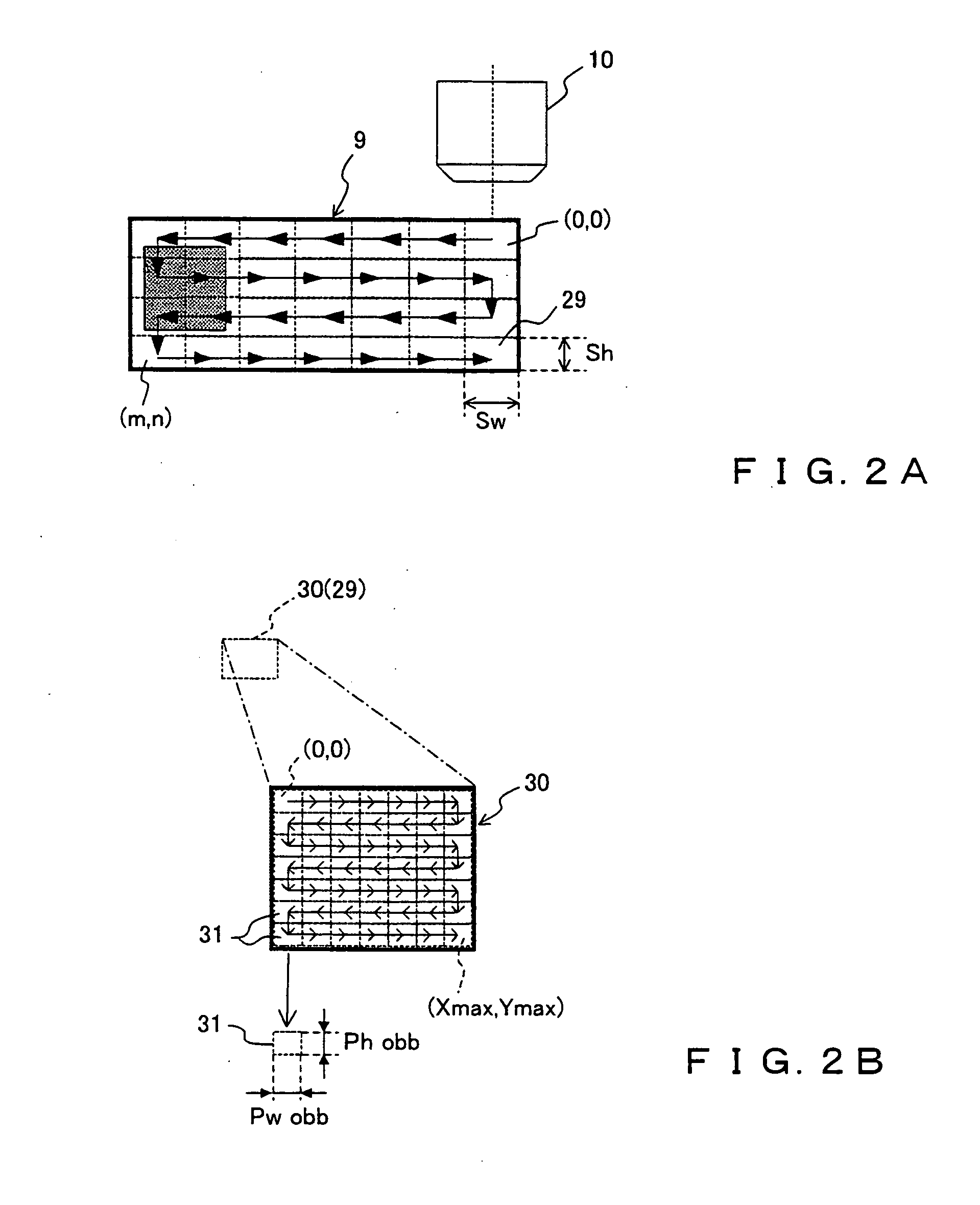
A microscopic image capture apparatus and a microscopic image capturing method allow a wide-angle field and high-precision microscope digital image to be efficiently captured. First, the entire area of a slide glass on a stage is divided into field size sections (low-magnification sections) of a low-powered objective lens, the stage is sequentially transferred perpendicular to an optical axis, image information is obtained for each low-magnification section of the entire area, each low-magnification section is divided into high-magnification size sections (high-magnification sections), a high-magnification image is captured using a high-powered objective lens only on a high-magnification section including simultaneously in the high-magnification sections, a high-magnification image is generated by correctly maintaining the relative position between the obtained image information and the area of a high-magnification section which is not captured, and a high-magnification composite image information about a sample on the slide glass is generated.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Systems and methods for patterning using a laser
InactiveUS20150298253A1Increase the areaSufficient fine resolutionLaser beam fibre treatmentDyeing processField sizeLaser scanning
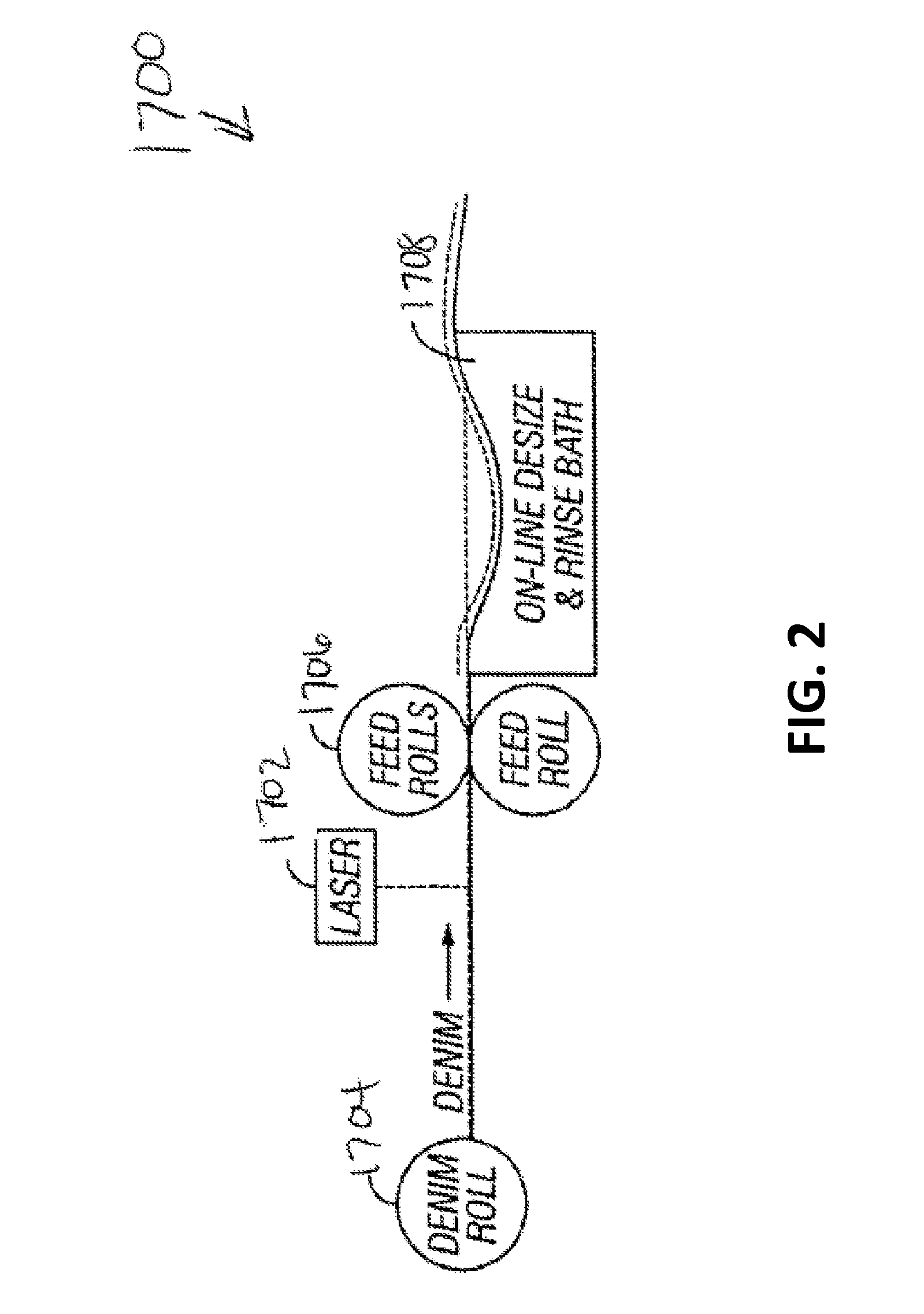
The present invention generally relates to a surface treatment of fabric with a laser and, more specifically, to a system and method for generating a pattern used to process a surface of a fabric through laser irradiation and the fabric resulting from such treatment. The present invention provides small laser spot sizes while operating a laser at large field size by 1) using a laser system with post-objective scanning architecture; 2) using multiple lasers across the width of a fabric roll; and / or 3) increasing the size and weight of the laser scanning mirrors. The spot size normally associated with a smaller laser field size (e.g. 500 mm) may be achieved with a laser having a larger field size (e.g. 950 mm or greater) by practicing the teachings of this invention.
Owner:REVOLAZE LLC
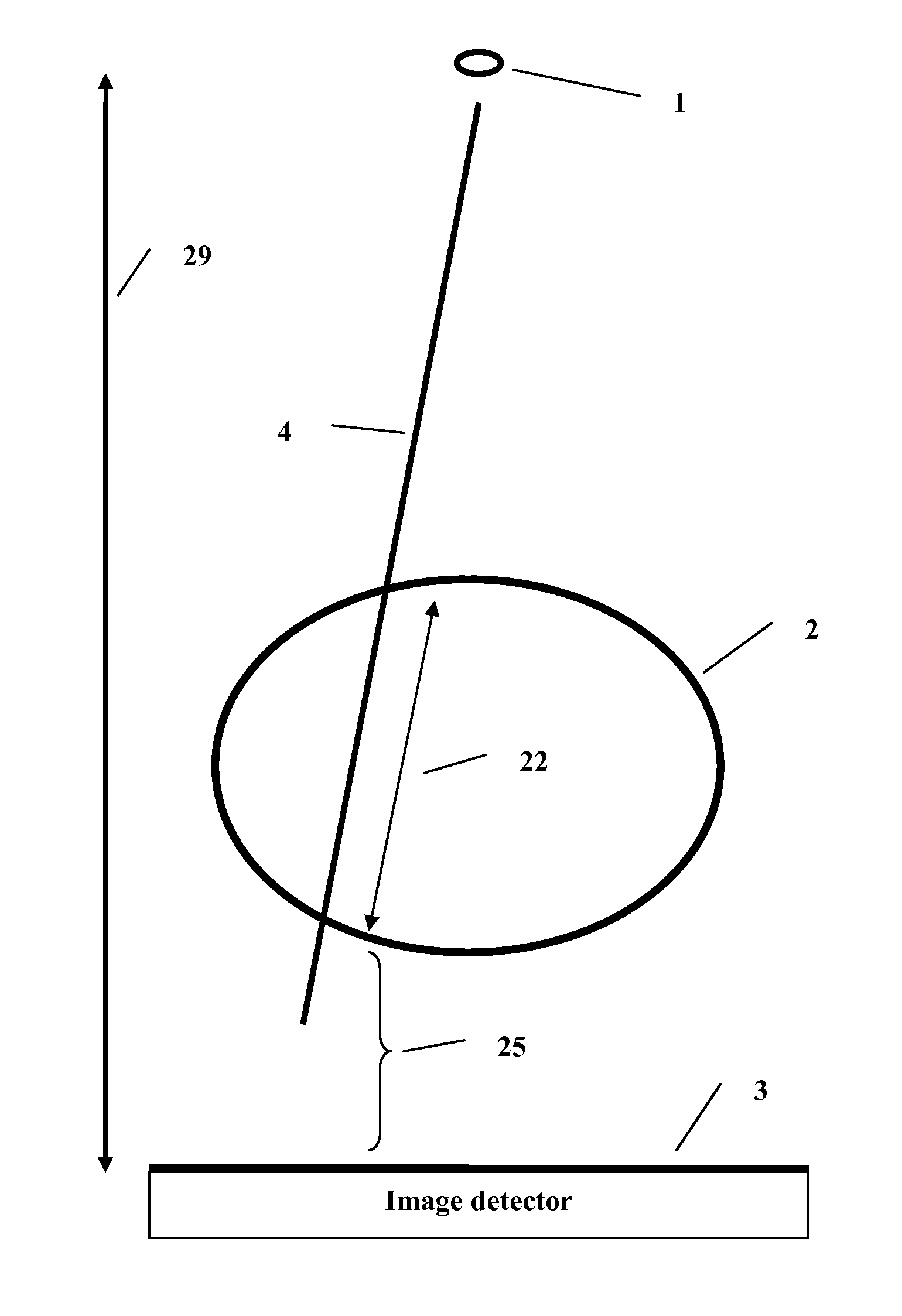
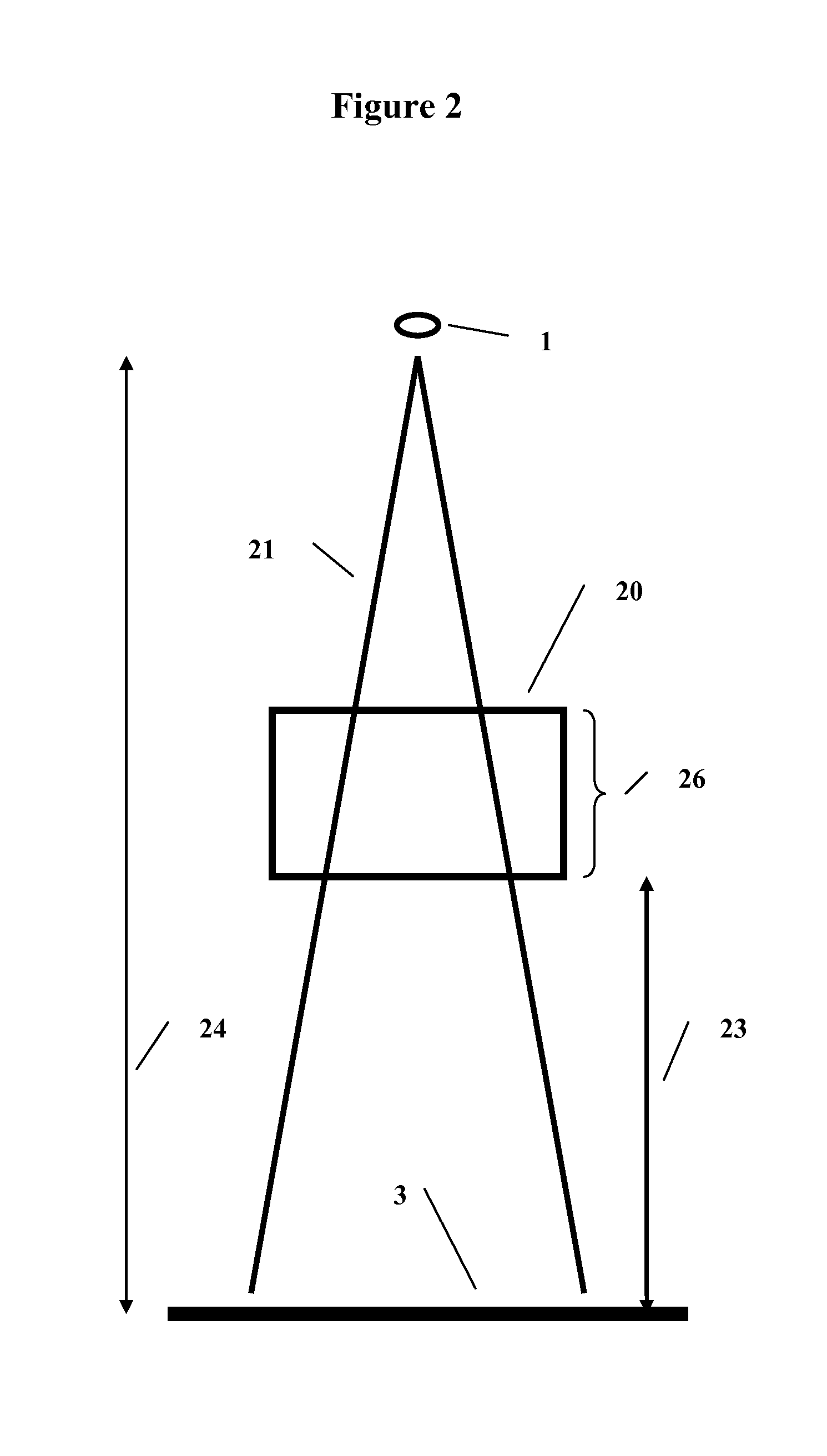
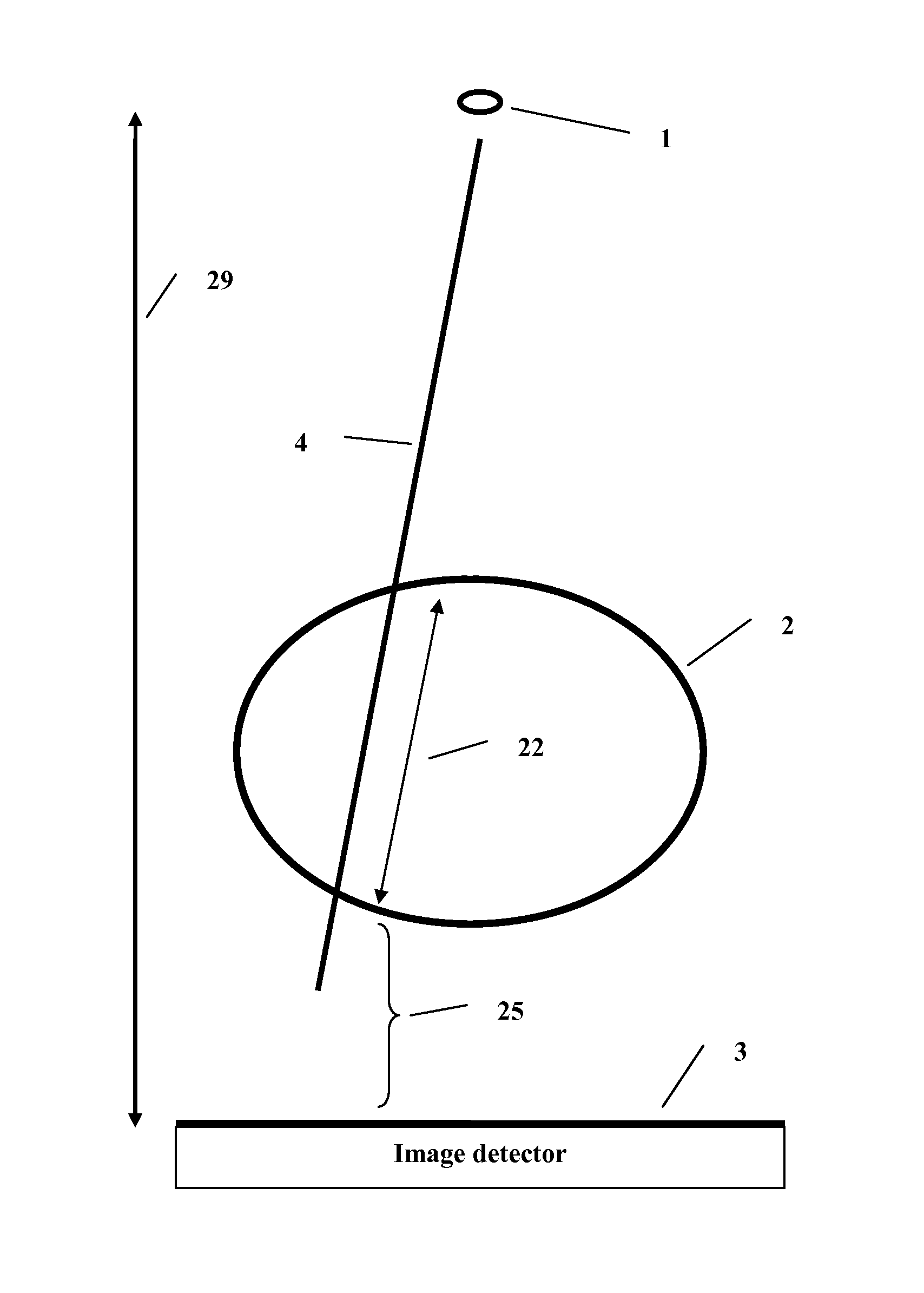
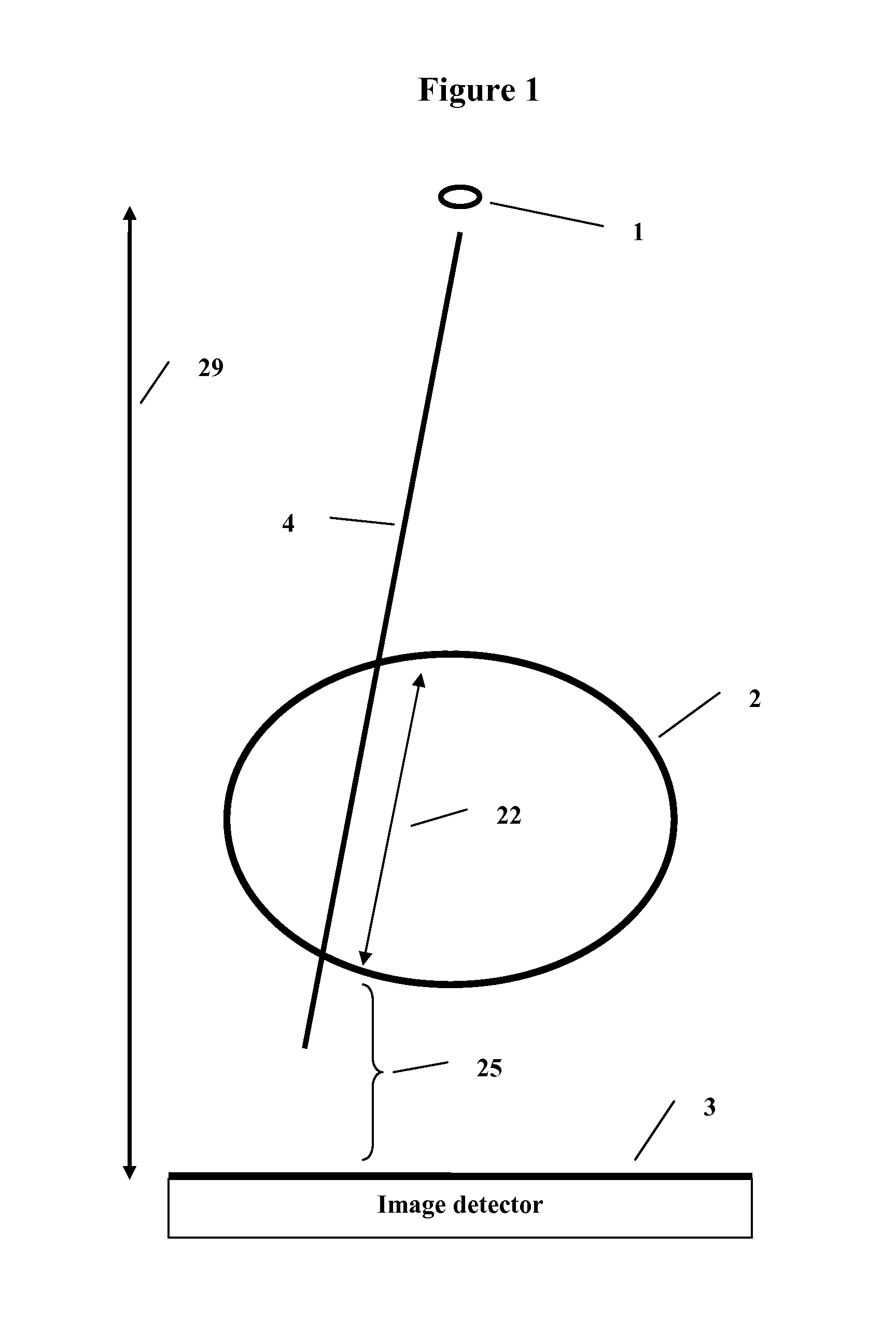
Method and system to reconstruct treatment dose to a patient from integrated exit-transit images of radiation fields taken during treatment
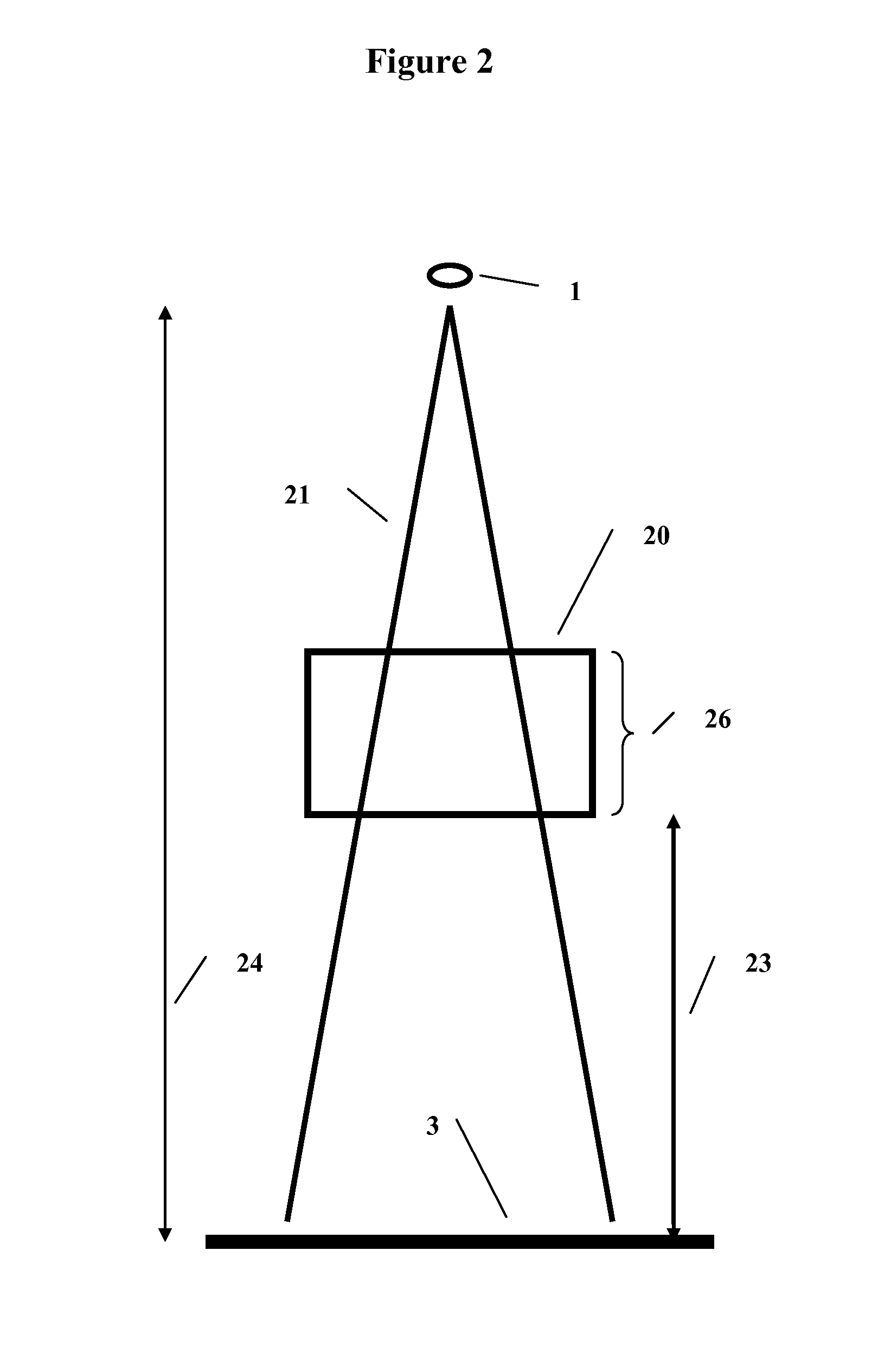
A method and system to compute the dose to a patient (2) given a captured integrated exit-transit image (5) of the radiation rays (4) traveling from the source of x-rays (1) through the patient (2) to the imaging device (3) to product the exit-transit image (5). Each radiation field image (5) is transformed (6,8,10,12) to multiple images (7,9,11,13) for each phantom thickness (26) that was measured with the imaging device (3) for a range of field sizes (21). Given the water equivalent path (22) through the patient for a ray (4) reaching a pixel (15, 16), the final pixel value (19) is interpolated from the images (9, 11) that bracket the water equivalent path through the patient (22).
Owner:LIFELINE SOFTWARE INC
Focussed radiotherapy apparatus and radiation therapy device
ActiveCN106456991AWill not complicate the structureRich combination numberTomographyRadiation diagnosticsField sizeRadiation therapy
Owner:CYBERMED TECH XIAN
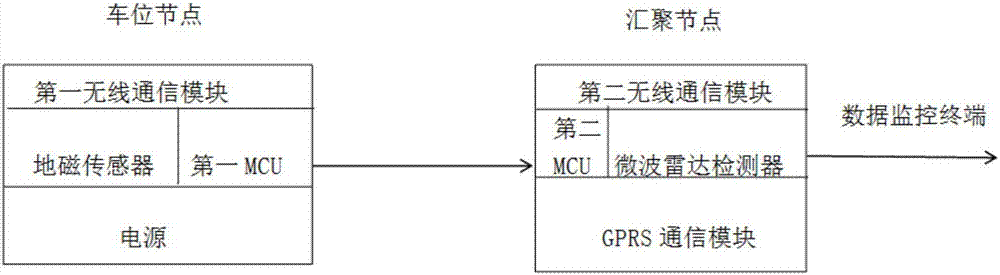
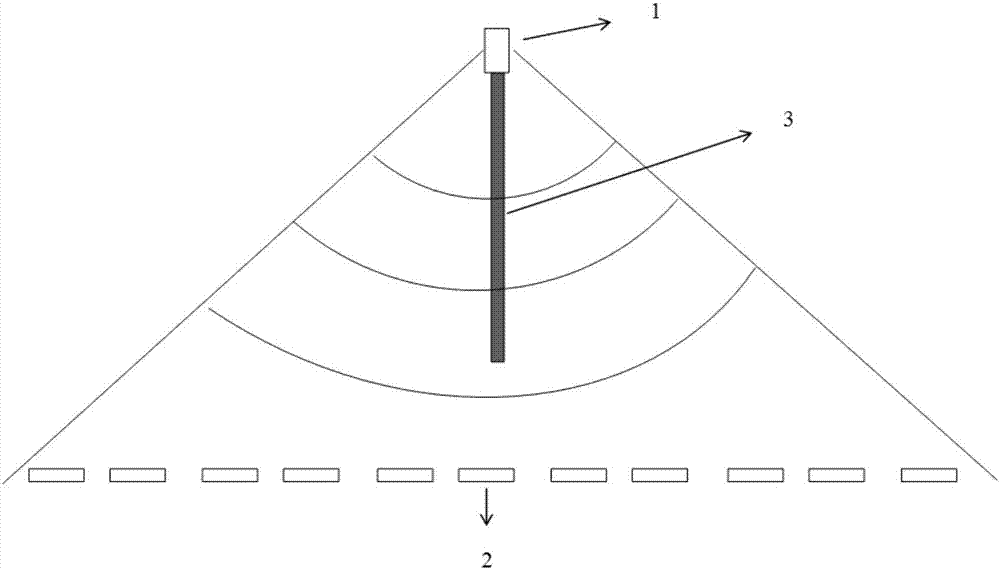
Multi-sensor low power consumption vehicle detection system and method based on adaptive environment
ActiveCN106875733AReduce volumeEasy to installIndication of parksing free spacesEngineeringVehicle detection
The invention relates to a multi-sensor low power consumption vehicle detection system and method based on an adaptive environment. A parking space node is installed in each parking space, when a vehicle enters or leaves the parking space, the geomagnetic field size of the parking space is changed obviously, a parking space node in a dormant state is woken, a parking space number and a parking space state are sent to a sink node, the sink node receives related data and read a Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) value, at the same time a microwave radar detector on the sink node of the area is started, the parking space which is calibrated in advance subjected to distance measurement again, and the state of the parking space at that time is determined when the vehicle enters or leaves. When the parking space information can not be detected by the RSSI value due to external factors such as a parking lot parking space environment or weather, a geomagnetic sensor is started as an auxiliary detection mode, and the reliability and accuracy of the method are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
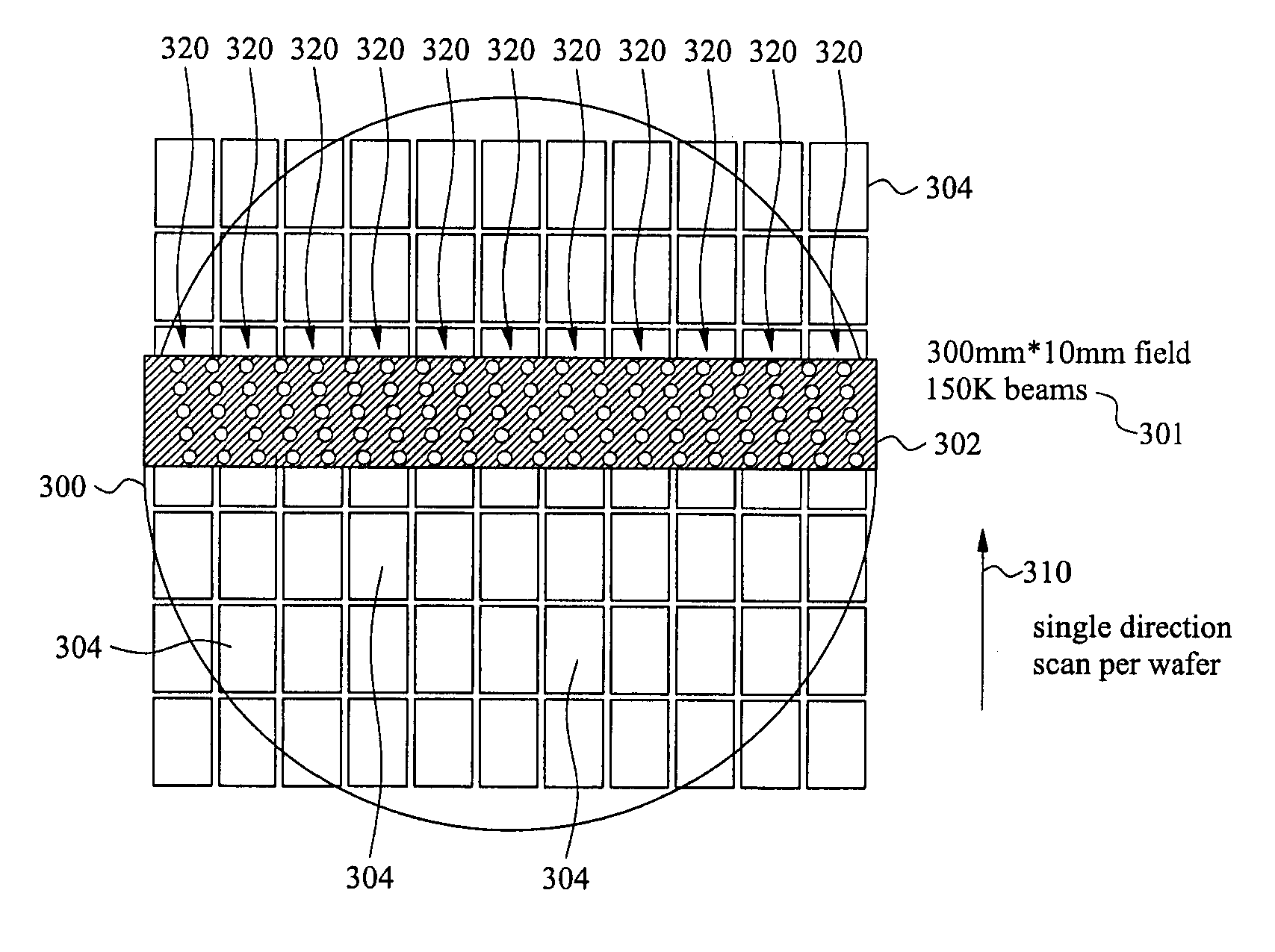
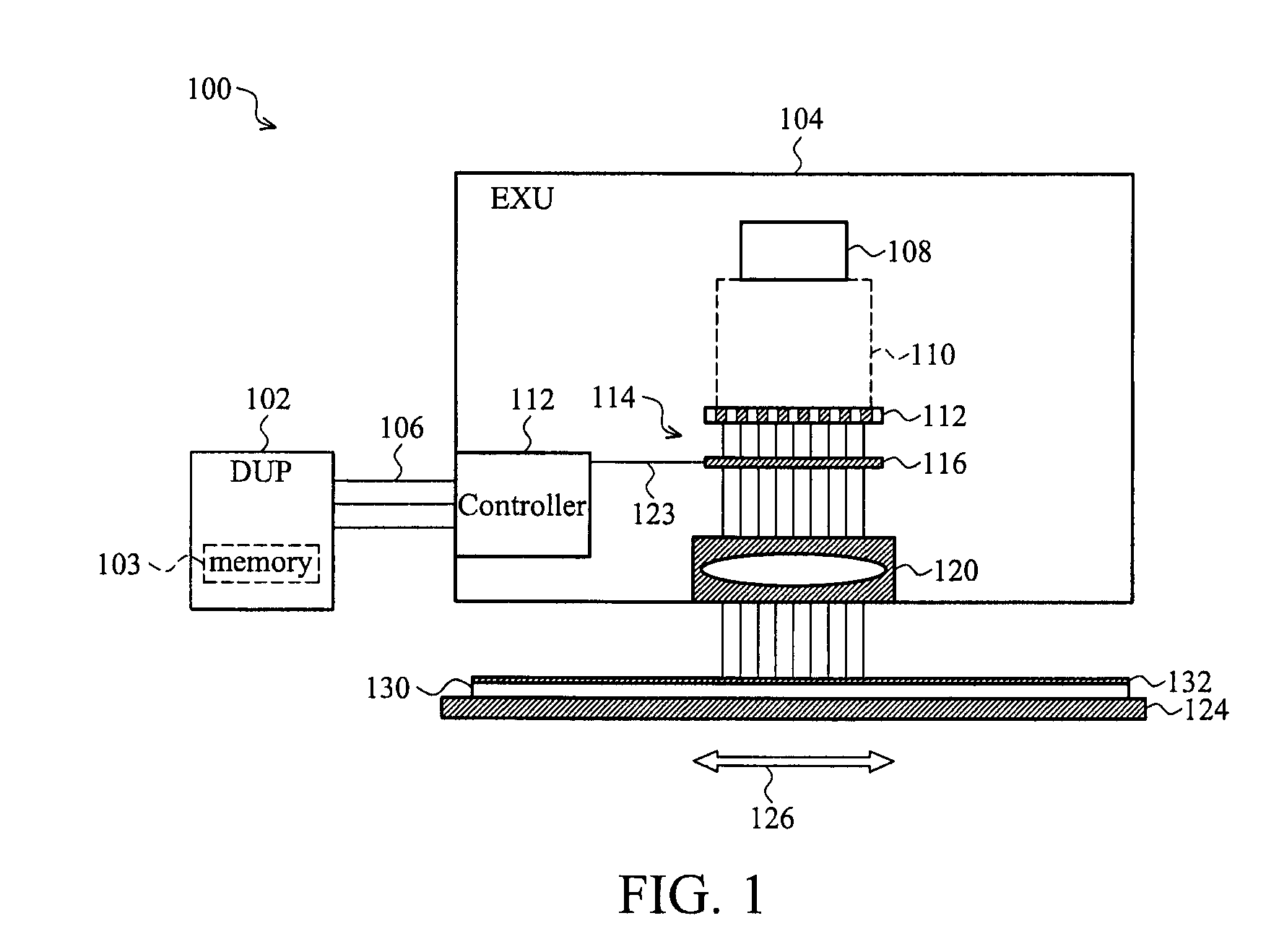
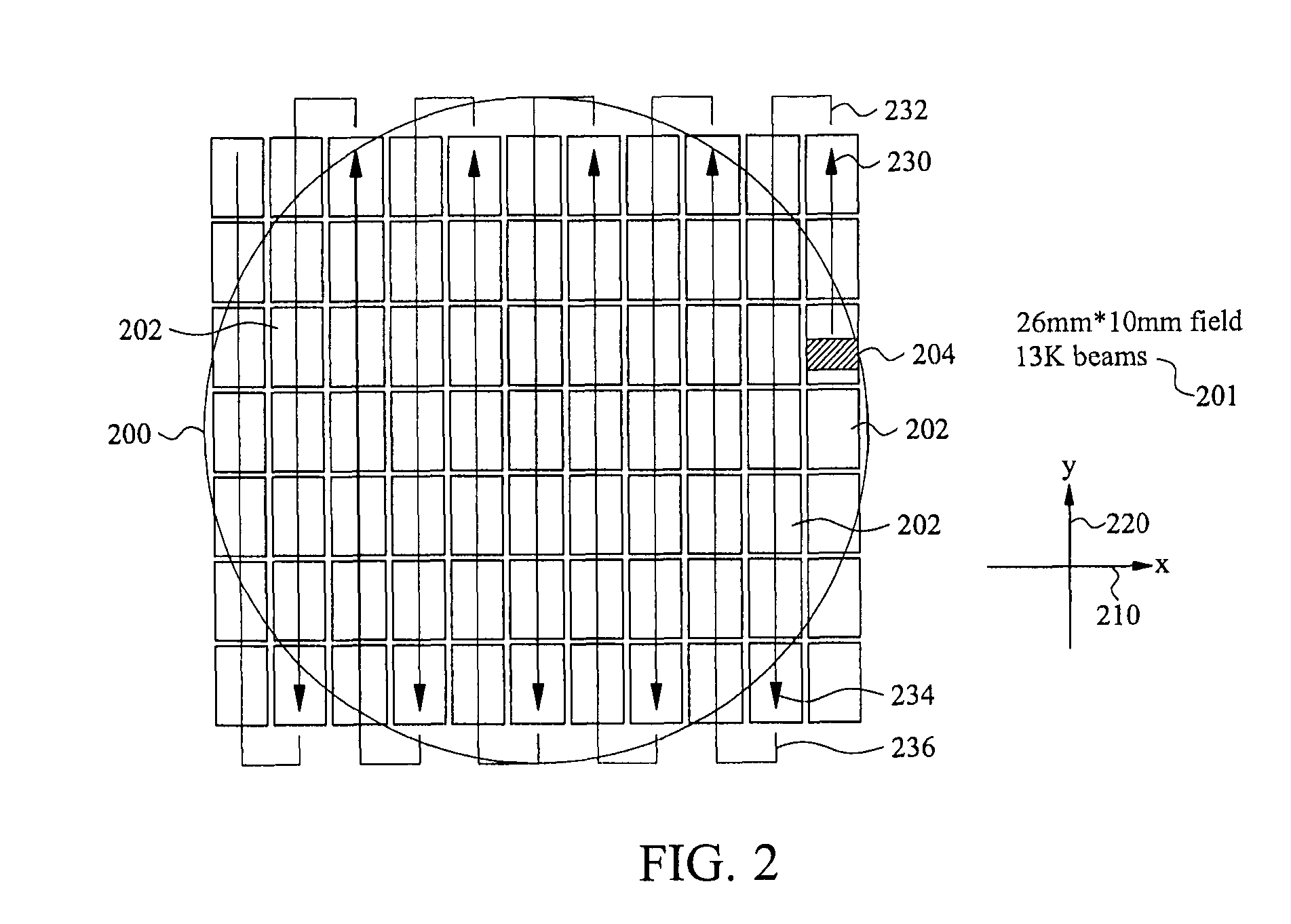
System and Method for Direct Writing to a Wafer
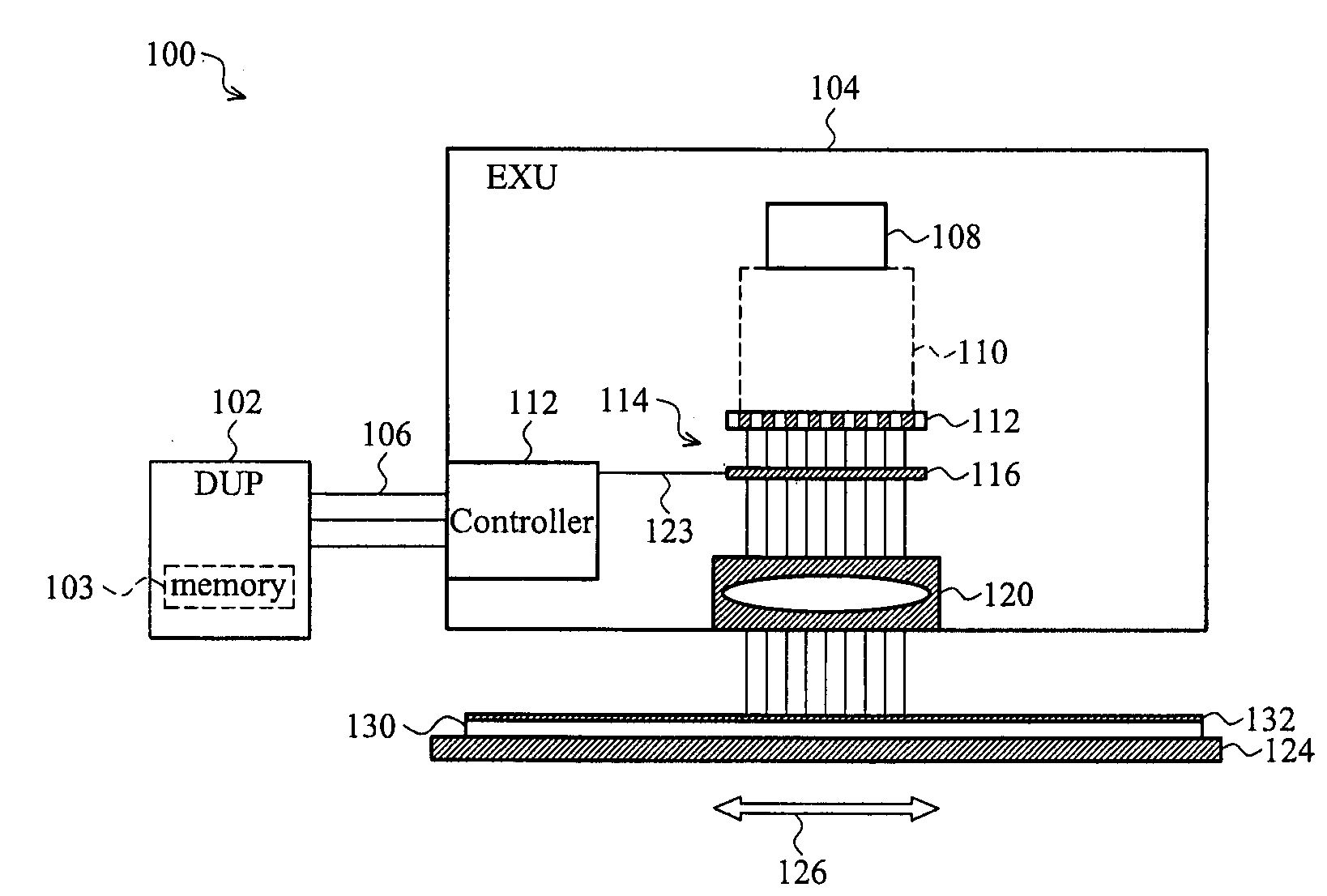
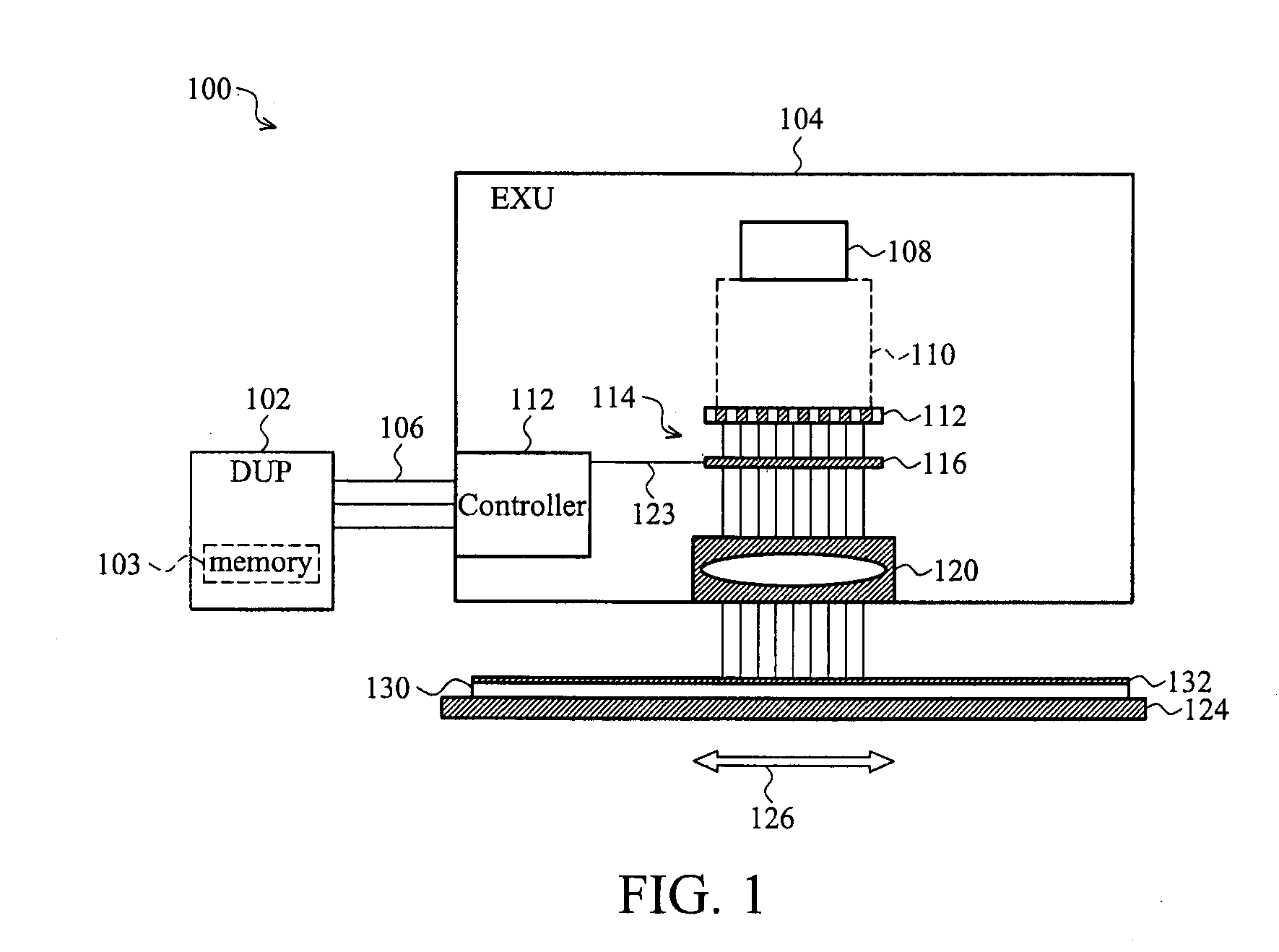
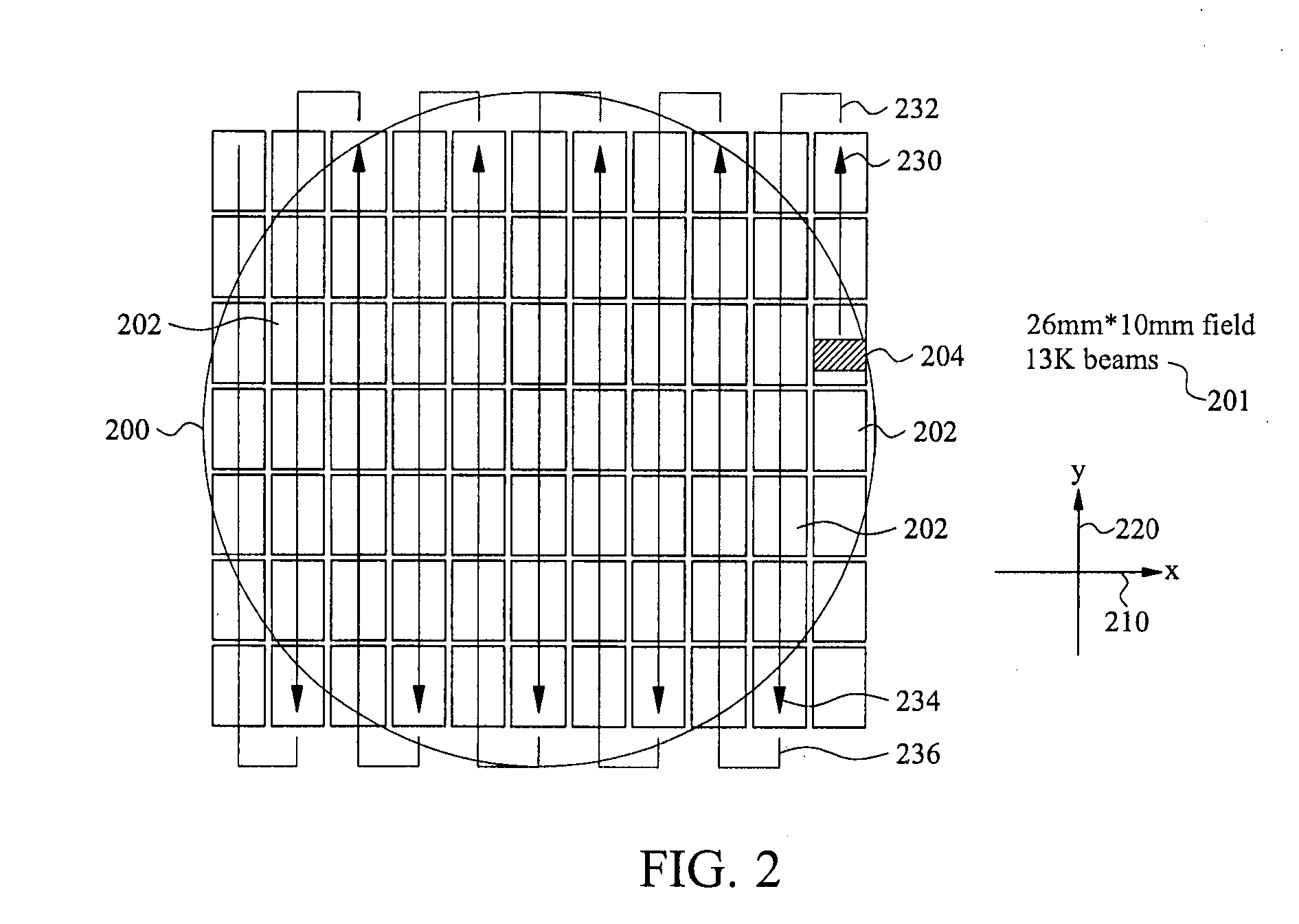
ActiveUS20090268184A1Expensive to ownExpensive to operateElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsField sizeComputer module
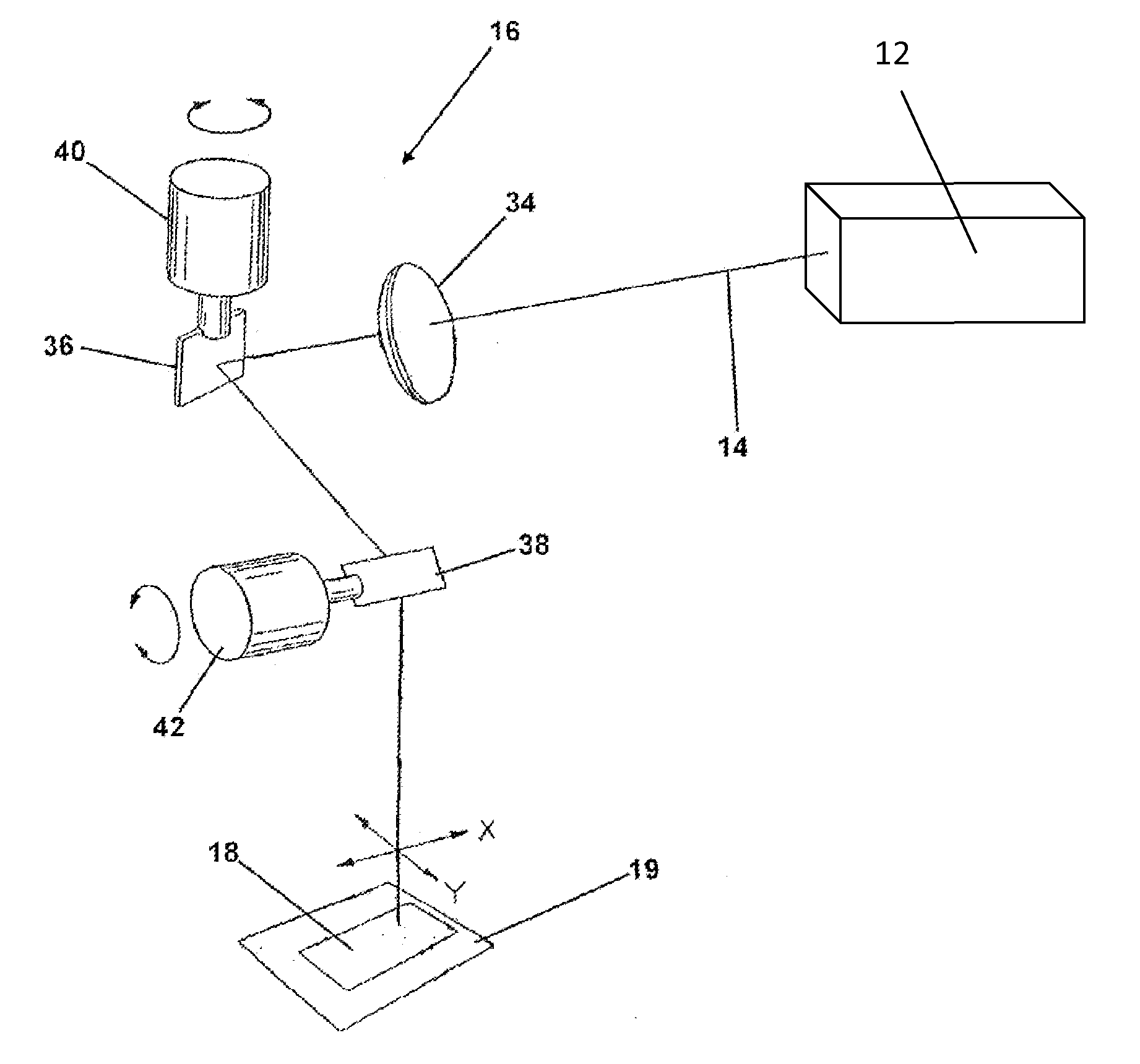
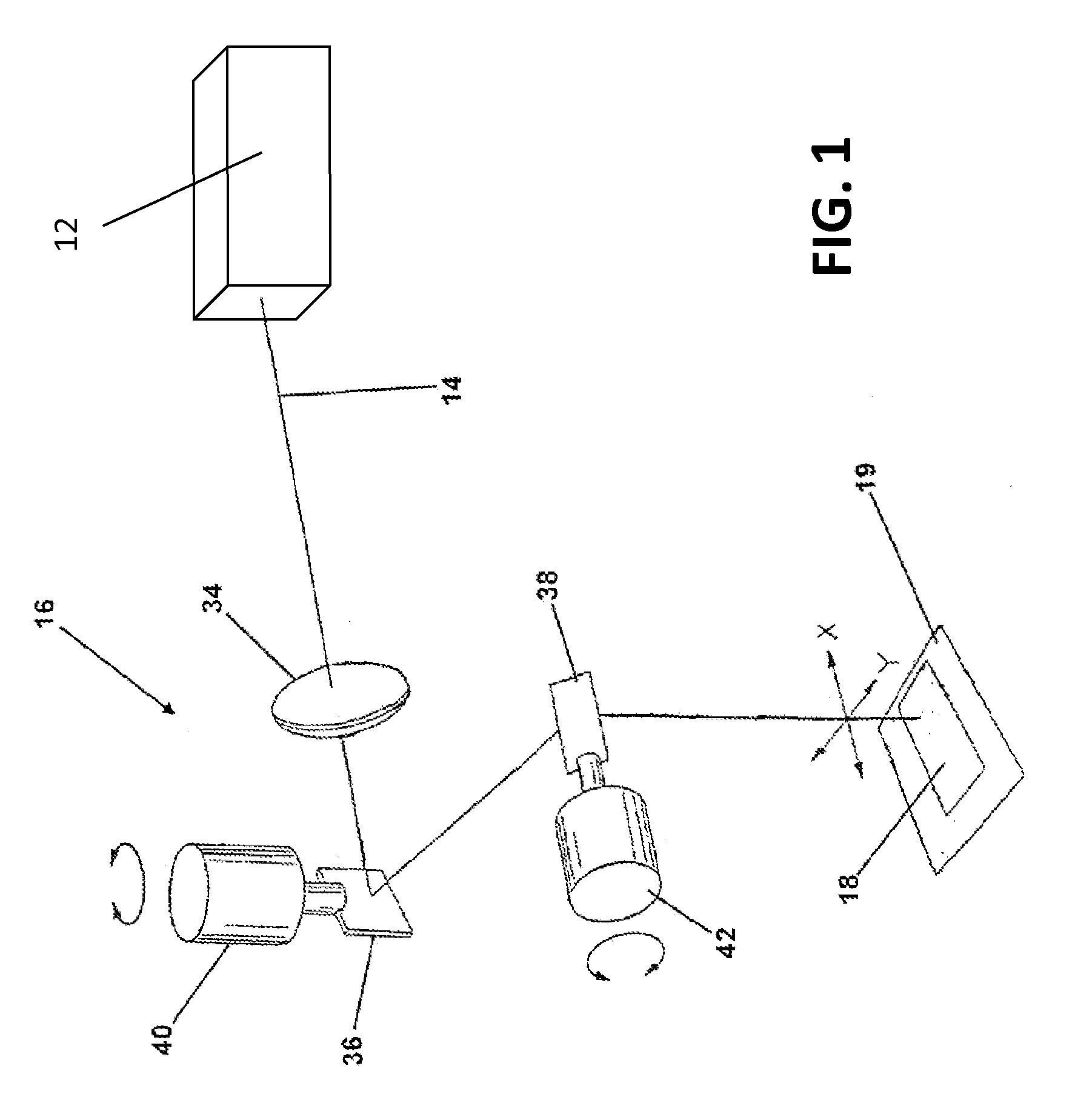
A direct-write (DW) exposure system is provided which includes a stage for holding a substrate and configured to scan the substrate along an axis during exposure, a data processing module for processing pattering data and generating instructions associated with the patterning data, and an exposure module that includes a plurality of beams that are focused onto the substrate such that the beams cover a width that is larger than a width of a field size and a beam controller that controls the plurality of beams in accordance with the instructions as the substrate is scanned along the axis. The widths are in a direction different from the axis.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
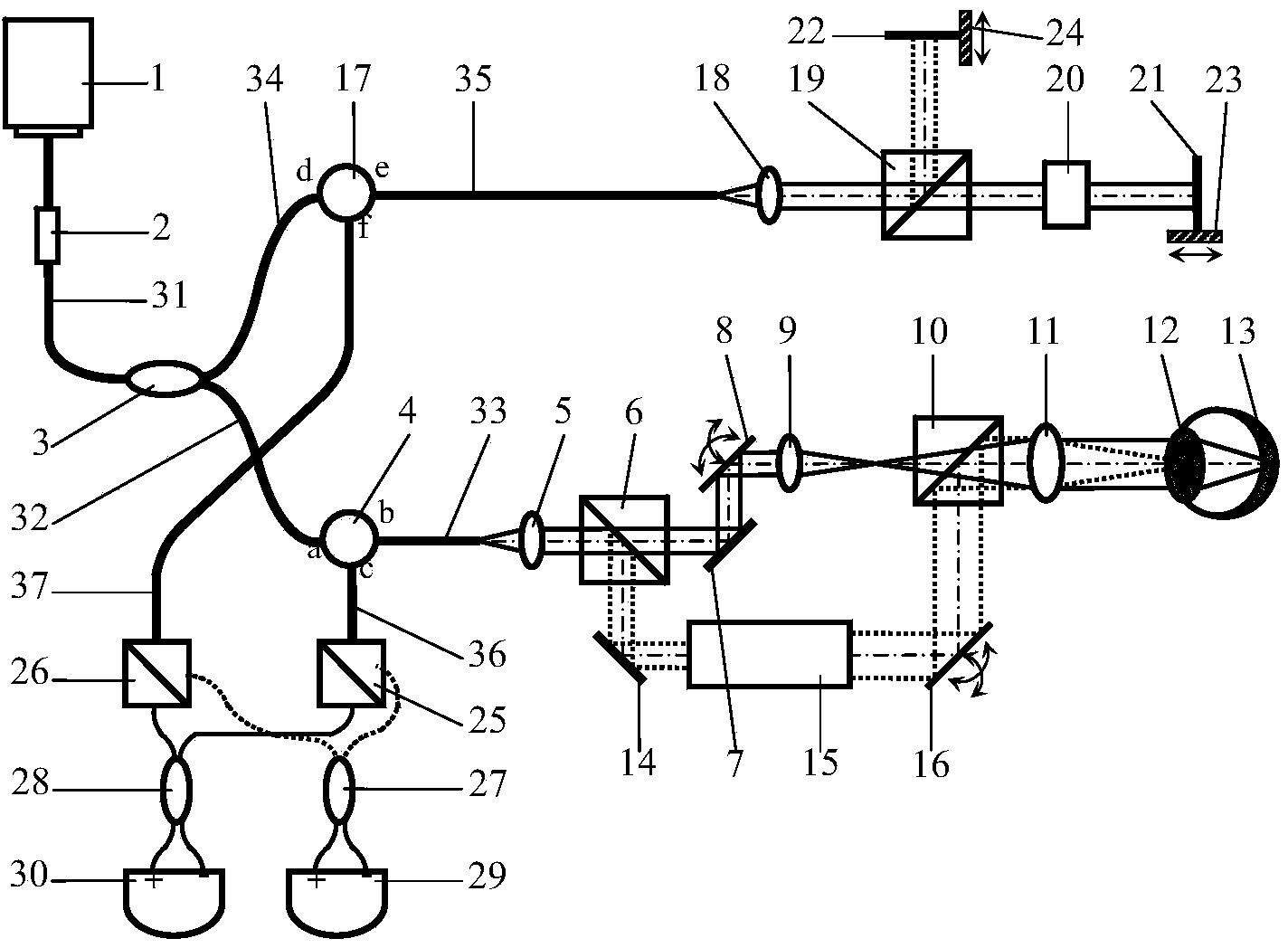
Full-eye optical coherence tomography imager
ActiveCN103815868ARealize 3D high-resolution imagingHigh sweep rateOthalmoscopesImaging qualityData acquisition
A full-eye optical coherence tomography imager comprises a frequency sweeping light source, an optical fiber polarizer, a first optical circulator, a second optical circulator, a first broadband polarization splitting prism, a second broadband polarization splitting prism, an ocular anterior segment scanning imaging light path, an eye ground scanning imaging light path, a third broadband polarization splitting prism, two reference mirrors, a fourth broadband polarization splitting prism, a fifth broadband polarization splitting prism, a second polarized light protecting coupler, a third polarized light protecting coupler, a first balance detector, a second balance detector, a function generation card, a data acquisition card, a computer and the like, wherein the first broadband polarization splitting prism, the second broadband polarization splitting prism, the ocular anterior segment scanning imaging light path and the eye ground scanning imaging light path are arranged in a sample arm; the third broadband polarization splitting prism and the two reference mirrors are arranged in a reference arm; the fourth broadband polarization splitting prism, the fifth broadband polarization splitting prism, the second polarized light protecting coupler, the third polarized light protecting coupler, the first balance detector and the second balance detector are arranged at a detecting end. The imager is based on a frequency sweeping optical coherence tomography technology, a component p and a component s of a polarized beam are used for conducting imaging on an eye ground and an ocular anterior segment respectively, and thus three-dimensional high resolution real-time imaging can be conducted on an full eye structure at the same time on the same system without any device for conversion. By means of the full-eye optical coherence tomography imager, optical path length and dispersion matching and scan setting can respectively be carried out on ocular anterior segment imaging and eye ground imaging, and thus the optimal imaging quality and the view field size of ocular anterior segment imaging and eye ground imaging can be obtained at the same time.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
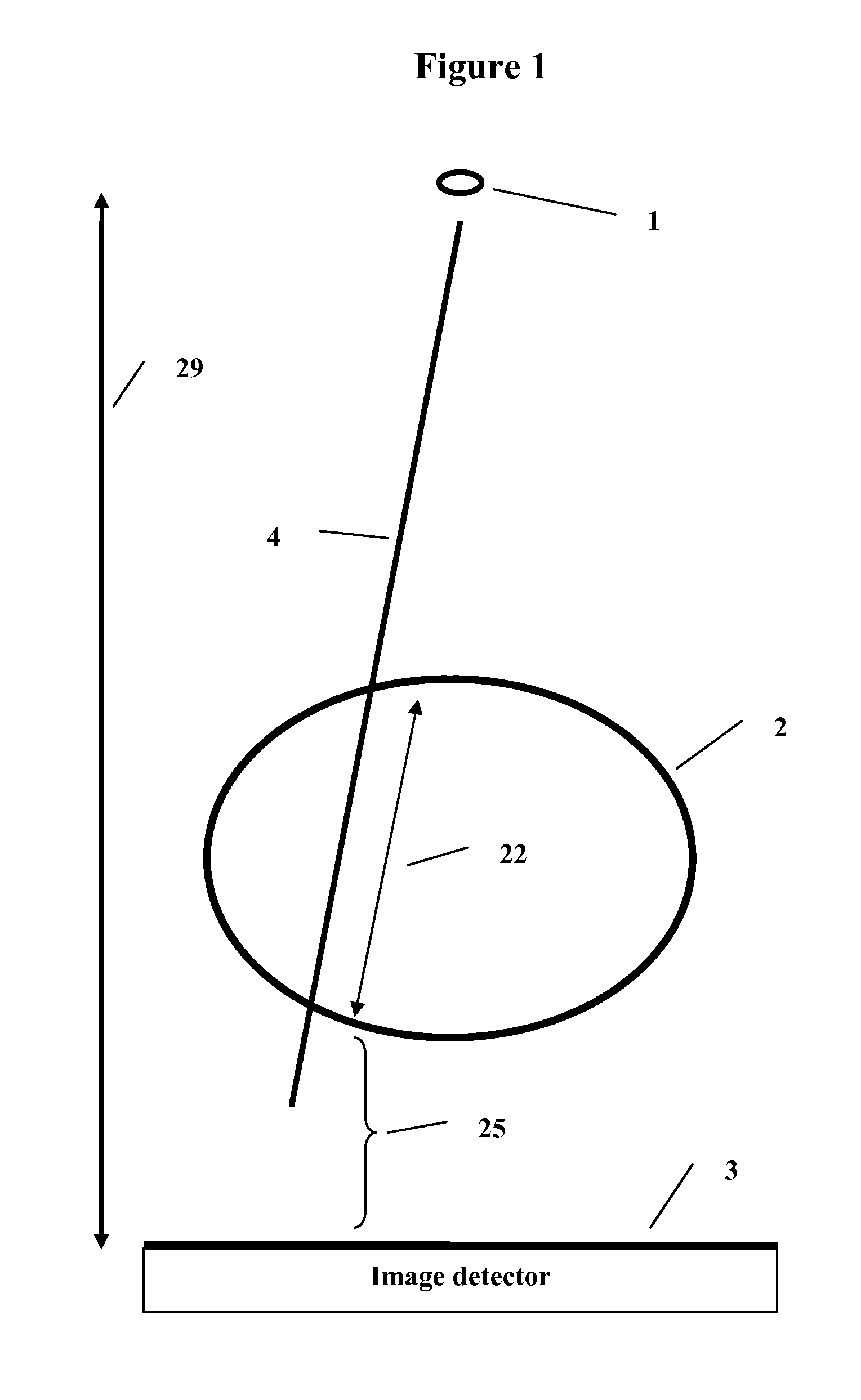
Method and system to reconstruct treatment dose to a patient from integrated exit-transit images of radiation fields taken during treatment
A method and system to compute the dose to a patient (2) given a captured integrated exit-transit image (5) of the radiation rays (4) traveling from the source of x-rays (1) through the patient (2) to the imaging device (3) to product the exit-transit image (5). Each radiation field image (5) is transformed (6,8,10,12) to multiple images (7,9,11,13) for each phantom thickness (26) that was measured with the imaging device (3) for a range of field sizes (21). Given the water equivalent path (22) through the patient for a ray (4) reaching a pixel (15, 16), the final pixel value (19) is interpolated from the images (9, 11) that bracket the water equivalent path through the patient (22).
Owner:LIFELINE SOFTWARE INC
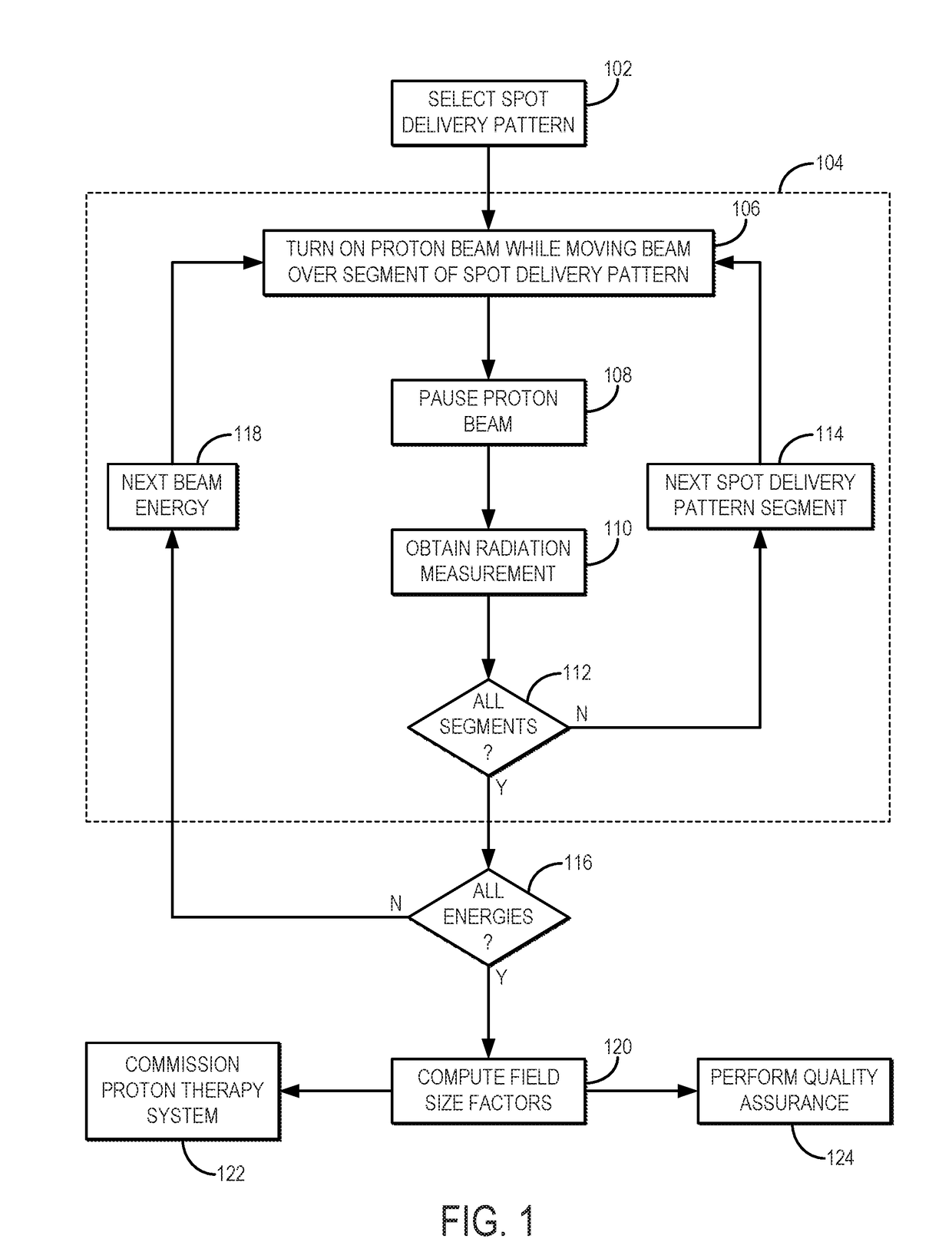
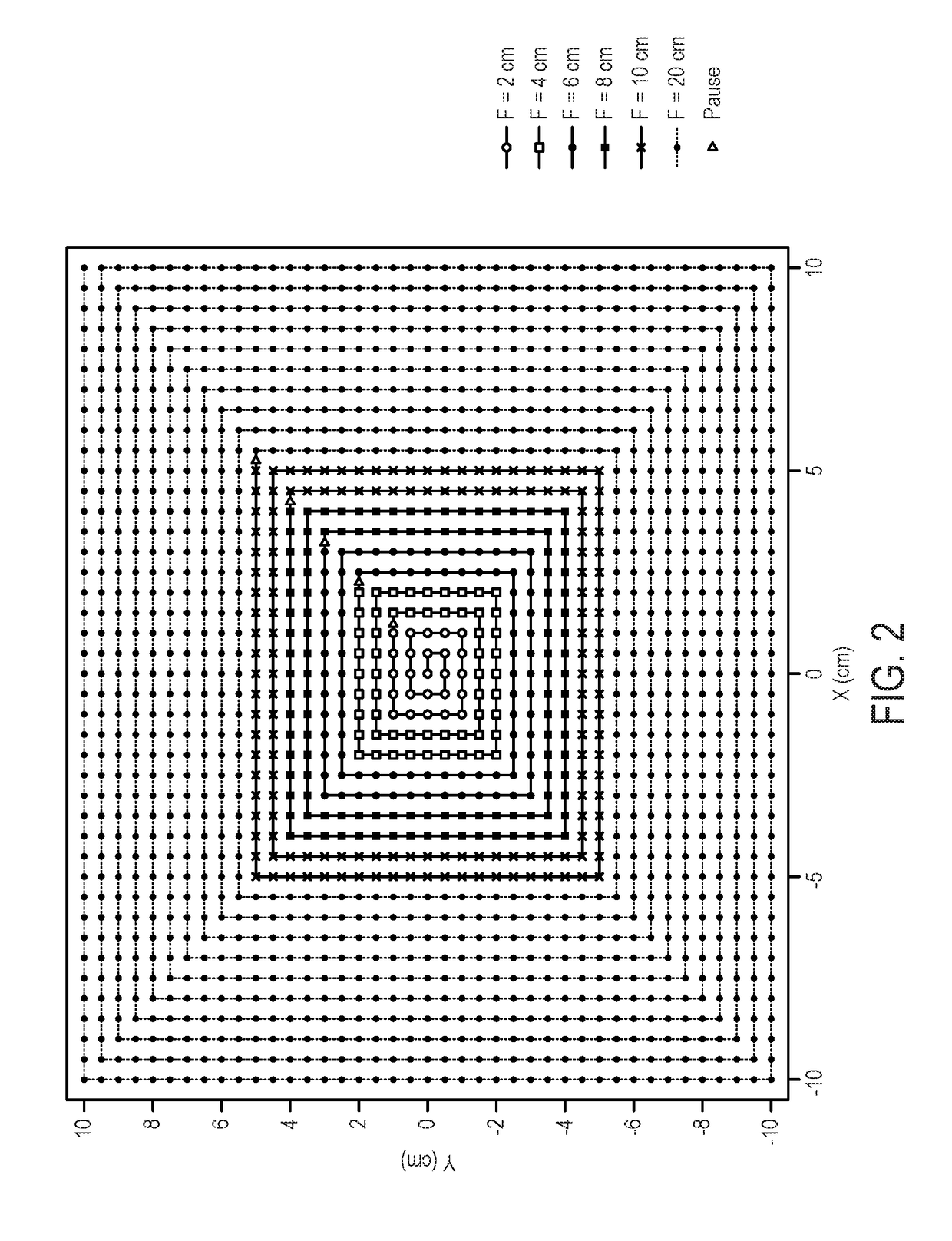
Method for measuring field size factor for radiation treatment planning using proton pencil beam scanning
Systems and methods for radiation treatment planning in proton therapy using pencil beam scanning (“PBS”) are described. More particularly, the systems and methods described in the present disclosure related to quantifying the output from a proton therapy system implementing PBS. The systems and methods described in the present disclosure can therefore be implemented when commissioning a new proton therapy system, or when performing quality assurance (“QA”) on a proton therapy system. A spot delivery pattern that includes a spiral out pattern is used for beam delivery. A number of control points along the spot delivery pattern define a beam pause time during which delivery of the proton beam is paused. Radiation measurements are obtained at the control points and at the end of the spot delivery pattern, and these radiation measurements are used to compute field size factors for field sized associated with the segments of the spot delivery pattern.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
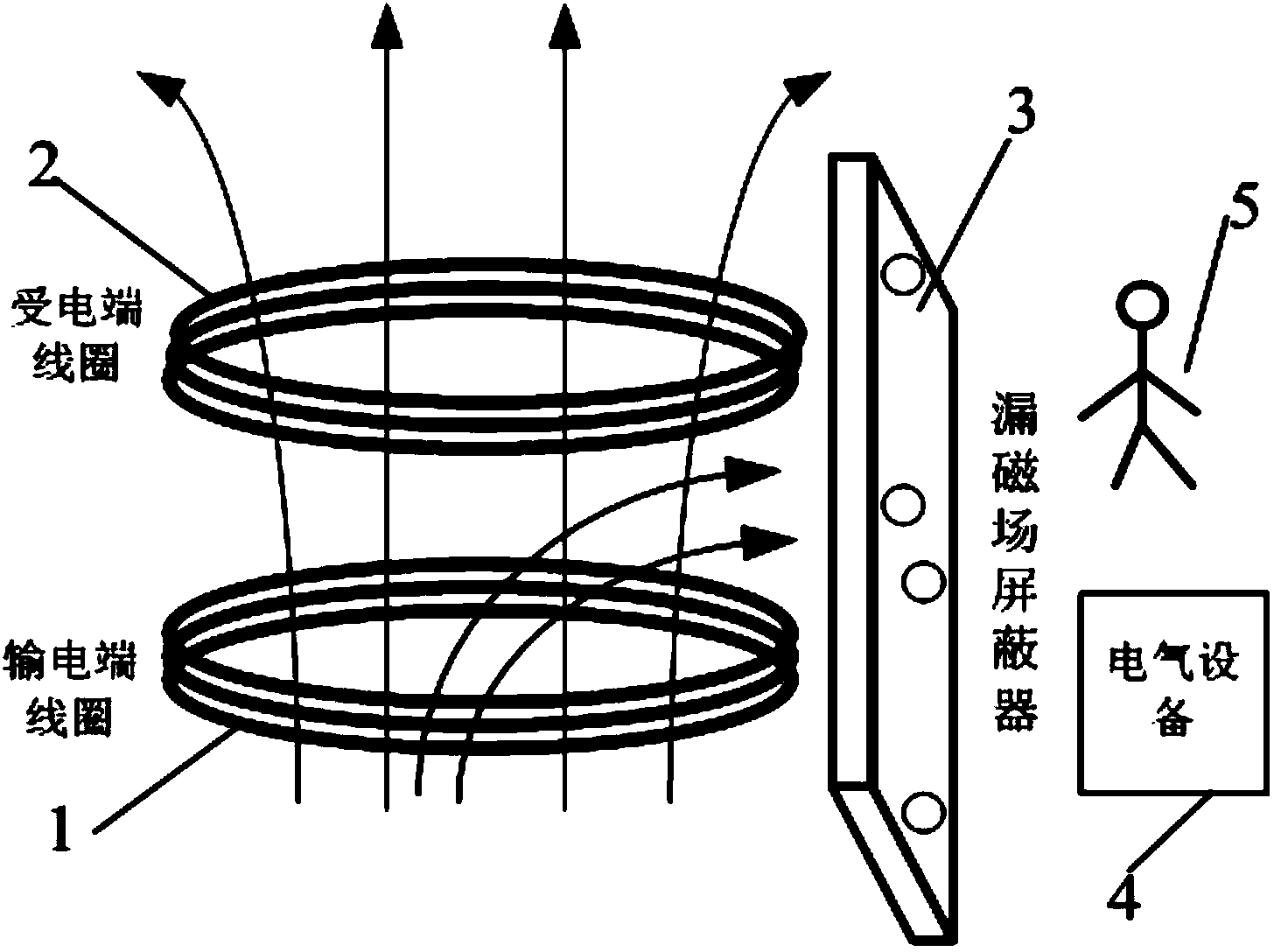
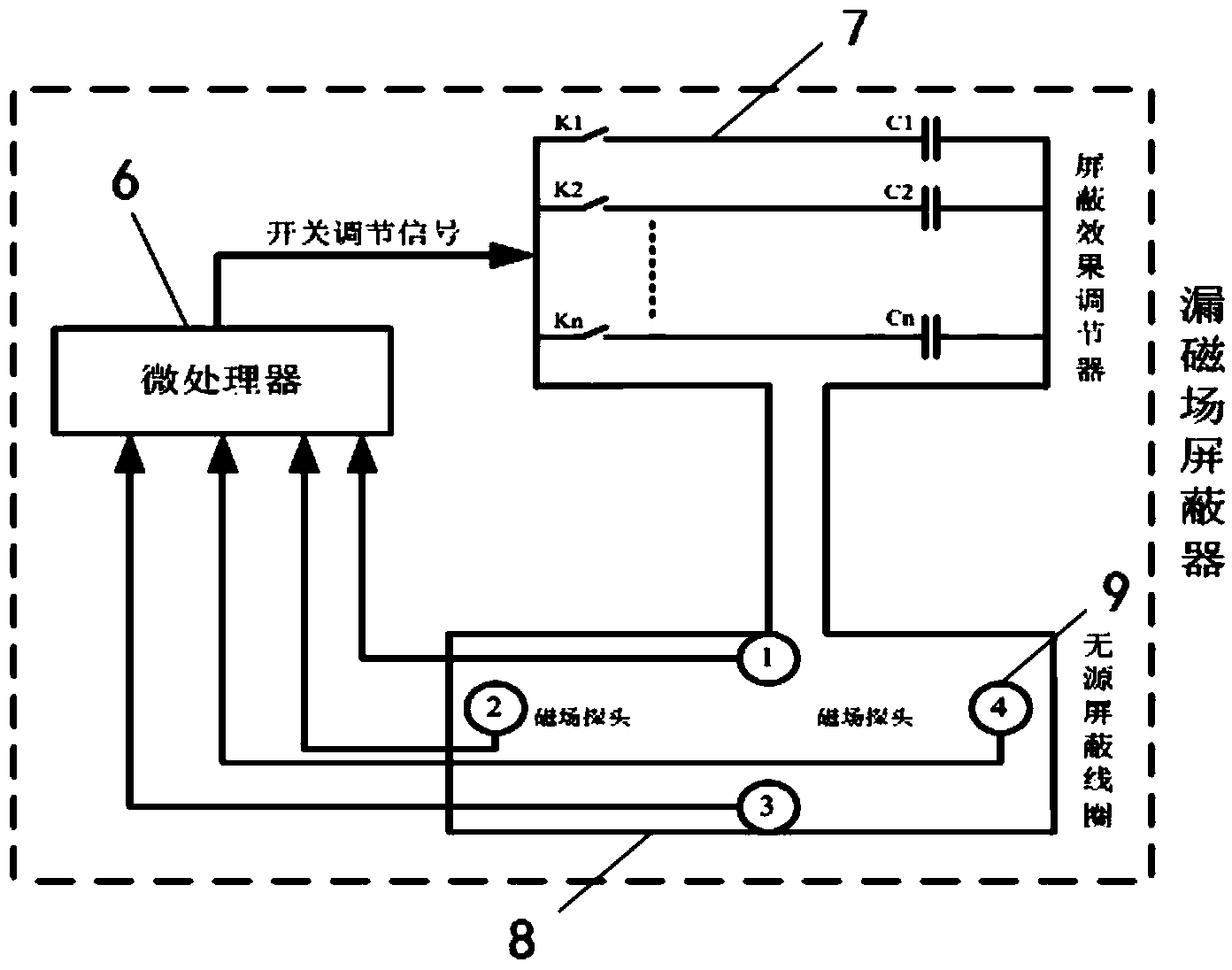
Magnetic leakage field shield method of wireless electric energy transmission system
ActiveCN104023512ASolve the shielding effectReduce adverse effectsElectromagnetic wave systemMagnetic/electric field screeningElectrical devicesClosed loop
The invention discloses a magnetic leakage field shield method of a wireless electric energy transmission system. The method employs a magnetic leakage field shield apparatus of the wireless electric energy transmission system. The apparatus comprises a power transmission end coil and a power receiving end coil which are in parallel arrangement. A magnetic leakage field shield device is vertically arranged at one side of the power transmission end coil and the power receiving end coil, an electrical device and people are respectively arranged at the other side of the magnetic leakage field shield device. The method provided by the invention solves the problems of unadjustable shield capability and poor shield tracking performance of a passive shield device in a passive shield method, and solves the problems of quite large loss power and incapability of forming a closed loop self-adjusting shield effect in an active shield method. The magnetic leakage field size of the wireless electric energy transmission system is detected by use of a single-chip microcomputer, according to a magnetic leakage field value, the input size of the parallel capacitor combination of a passive coil is given through calculating, and a magnetic leakage field shield function is realized in a dynamic closed loop mode, such that the unfavorable influences caused by an electromagnetic field to surrounding human bodies and electrical devices are effectively reduced.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
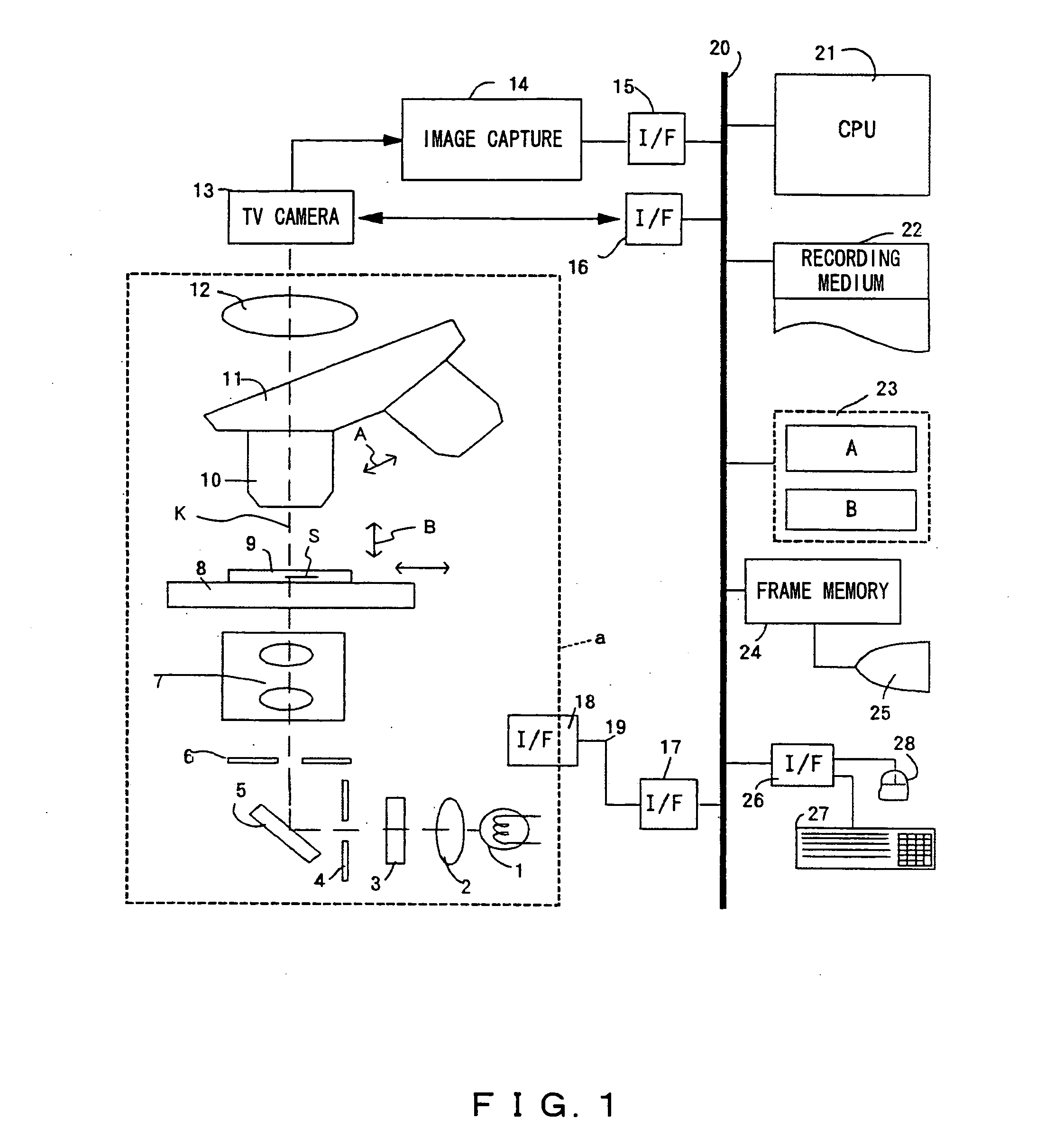
Microscopic image capture apparatus and microscopic image capturing method
InactiveUS7248403B2Keep for a long timeEfficient captureGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionField sizeMicroscopic image
A microscopic image capturing apparatus and method are provided. First, the entire area of a slide glass on a stage is divided into field size sections (low-magnification sections) of a low-powered objective lens. The stage is transferred perpendicular to an optical axis, and image information is sequentially obtained for each low-magnification section. Each low-magnification section is divided into high-magnification size sections (high-magnification sections), and a high-magnification image is captured using a high-powered objective lens only in high-magnification sections corresponding to a sample. A high-magnification image is generated by correctly maintaining the relative position between the obtained image information and an area corresponding to high-magnification sections which are not captured, and high-magnification composite image information of the sample is generated.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
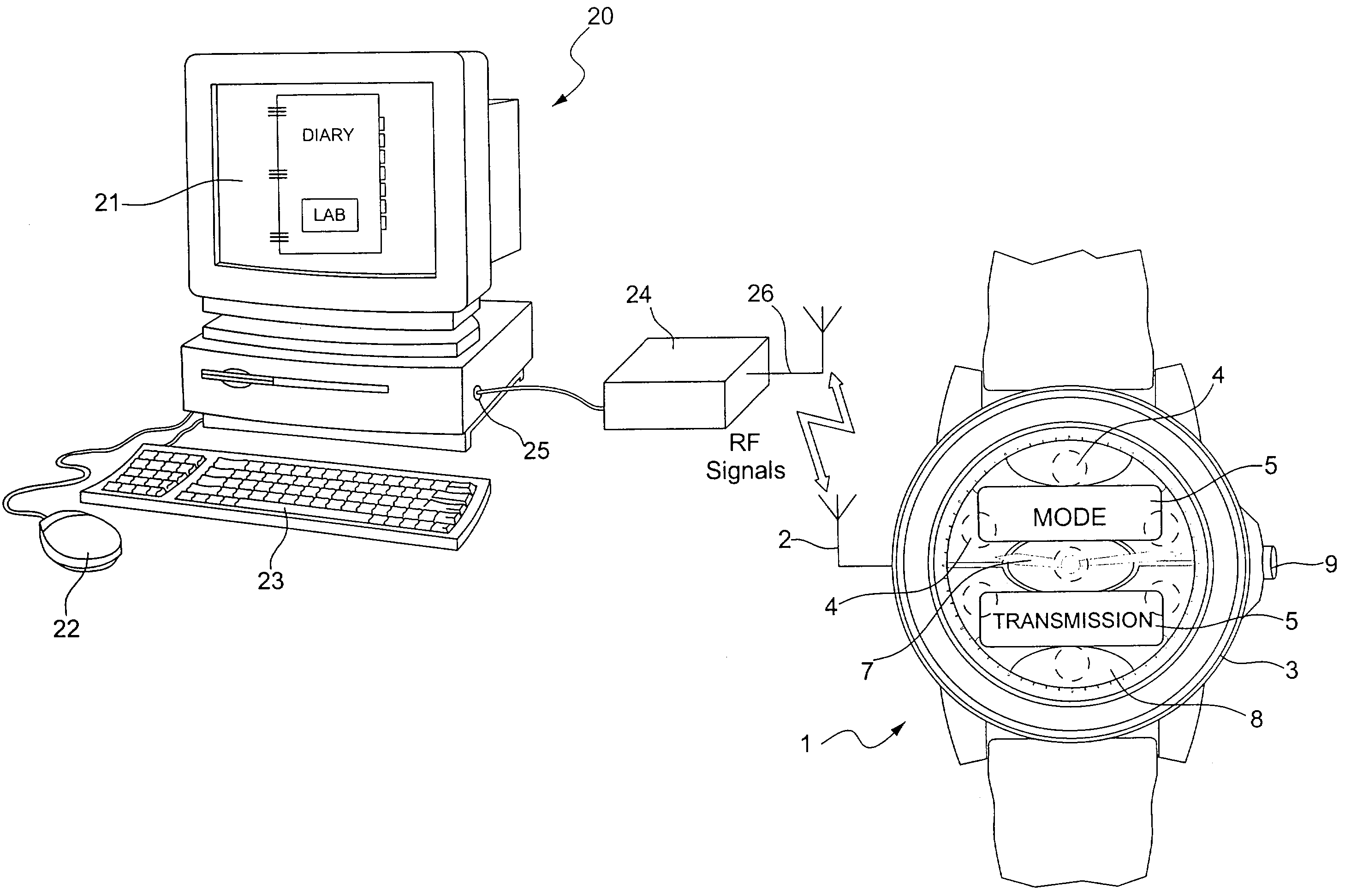
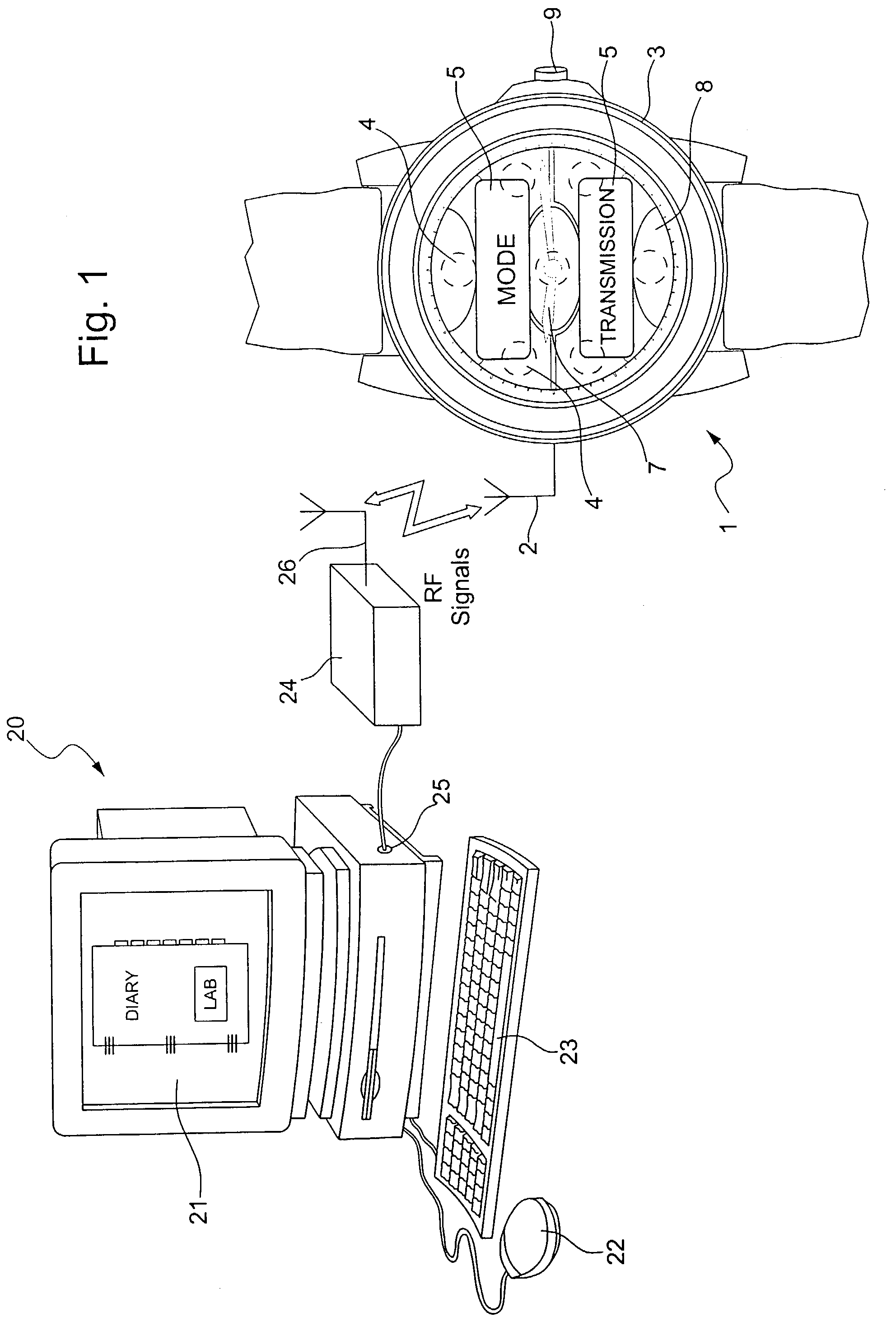
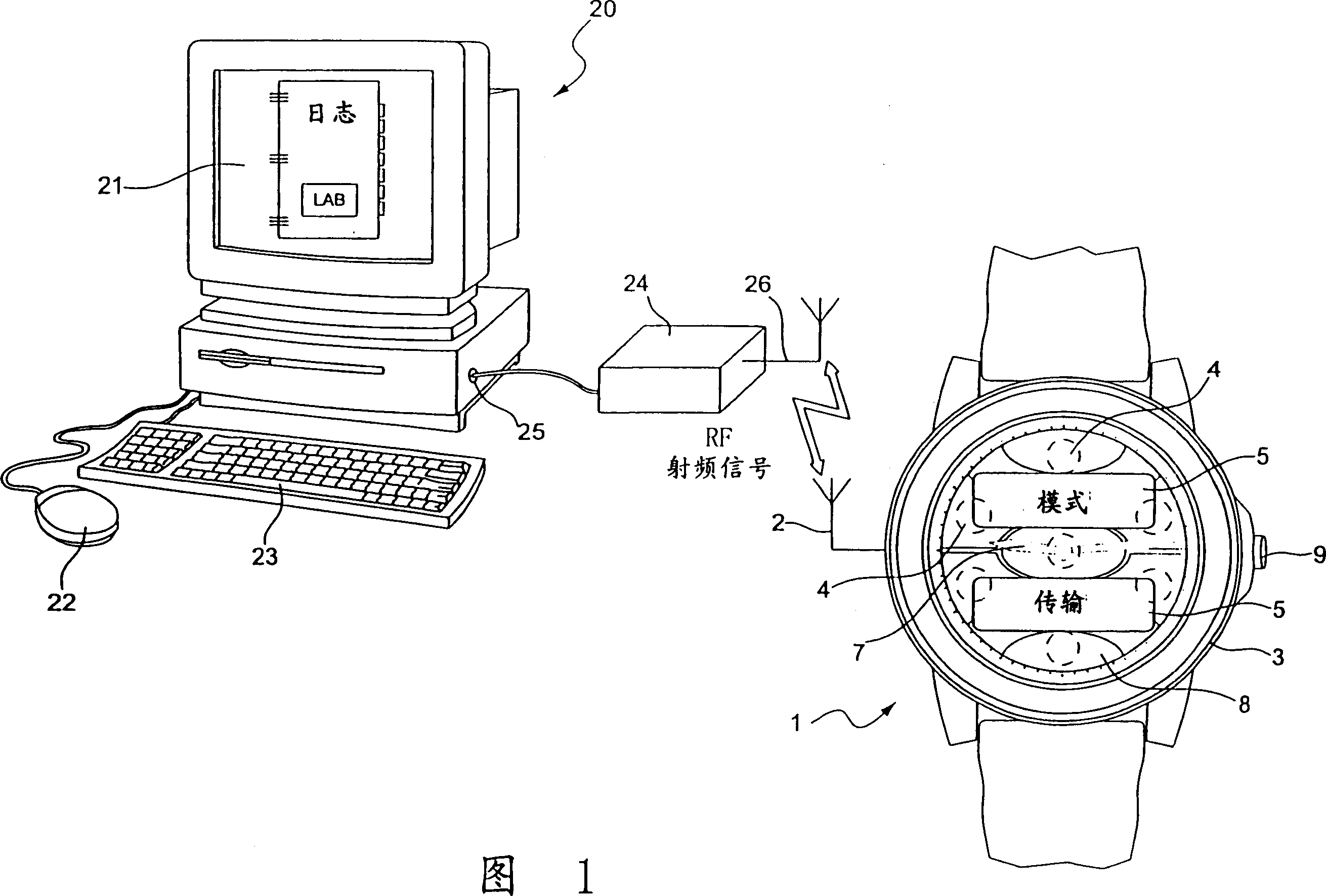
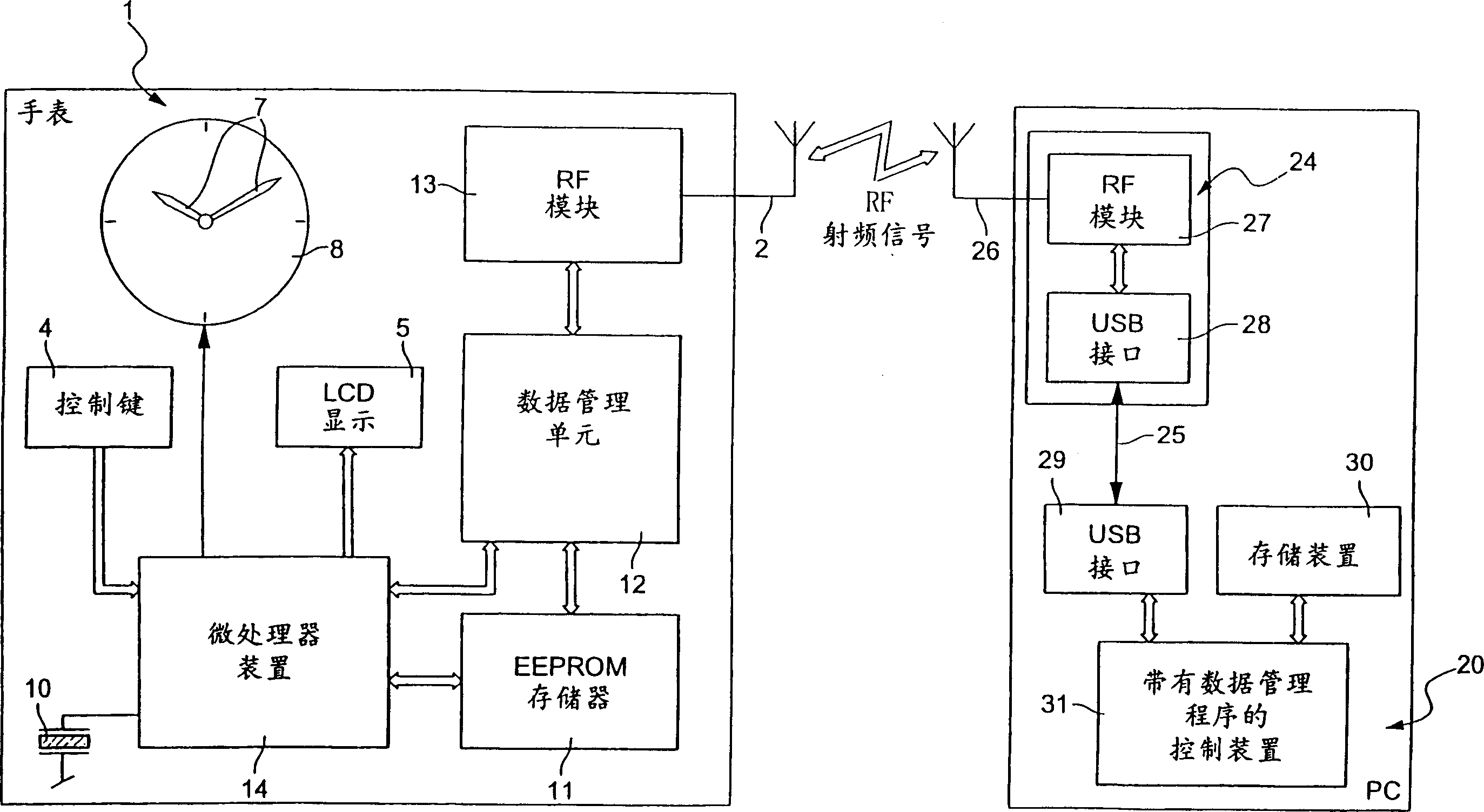
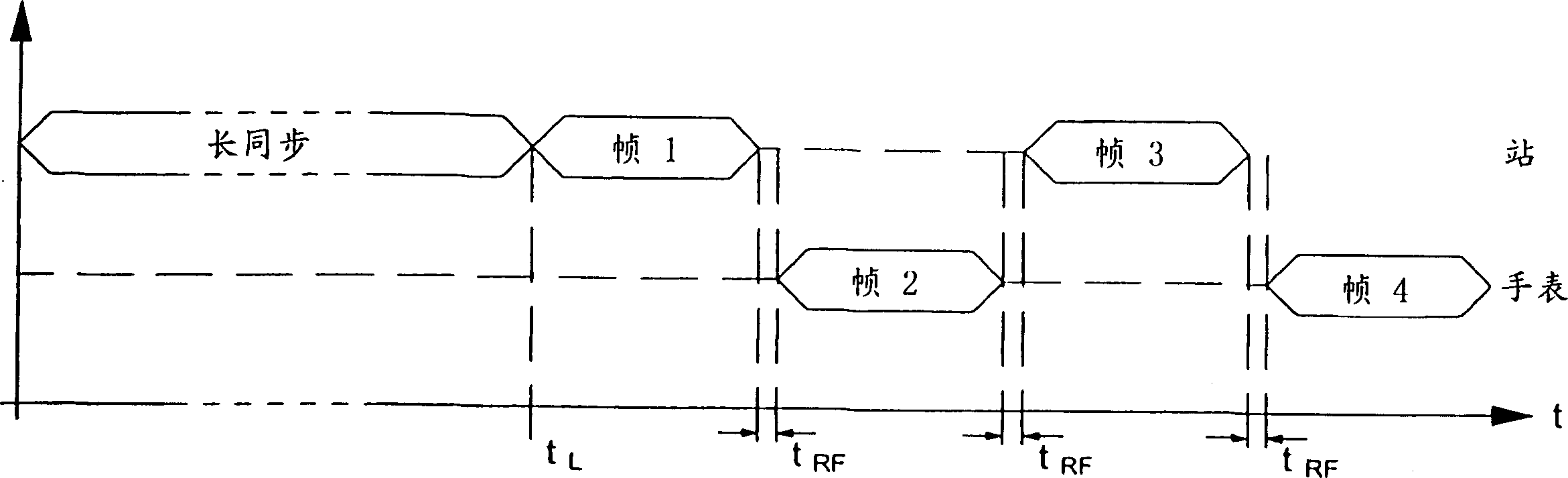
Method of transmitting information between two units each provided with means for sending and/or receiving signals
InactiveUS7295526B2Increased and reduced in sizeIncrease the number ofPower managementError preventionField sizeWireless transmission
The method is one of wireless transmission of information between two units consisting primarily of a portable object, such as a personalized watch (1), and a computer station (20). Each unit includes signal transmitting and / or receiving means (2, 24, 26) switched alternately to a transmitting mode and into a receiving mode. Information is transmitted by transmitting a plurality of information frames alternately between the two units. Each information frame comprises a synchronization field, which includes a particular number of synchronization bytes, an information packet and filler bytes. On receiving a frame, the receiving unit counts the synchronization bytes. The receiving unit transmits, in a heading of the information packet, a synchronization indication which is a function of the number of synchronization bytes received. The synchronization indication is used to correct the size of the synchronization field of the next frame received by the receiving unit. These synchronization field size correction operations are effected in a similar manner in both units.
Owner:ASULAB SA
Multi-leaf collimator based field size clipping for automatic adaptation to allowed image area
InactiveUS20070195936A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationField sizeMulti leaf collimator
A system and method for capturing a portal image using a linear accelerator having a multi-leaf collimator (MLC) and an imager allows the portal image field to be automatically clipped using the multi-leaf collimator so that the projection of the portal image field onto the imager falls within the allowed image area of the imager. In this manner, portal images may be obtained in instances where the projection of the portal image field onto the flat-panel imager is larger than an allowed image area of the imager, or where the projection of the portal image field onto the imager is not centered and would extend beyond the allowed image area, so that radiation sensitive electronics outside of the allowed image area are protected from undesirable exposure to radiation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and device for coding video levels in a plasma display panel
ActiveUS20100053200A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionField size
The invention relates to a method and a device for coding video levels of pixels of a colour component of a picture to be displayed on a display device into code words. The invention is more particularly applicable to Plasma Display Panels (PDP) to improve the picture quality (grayscale enhancement, dynamic false contour reduction). The main idea of the invention is to automatically change the floor and ceiling levels used classically for dithering each pixel value depending on the neighboring pixels of the same color component. The size of the window determining the neighboring pixels is dependent on the definition of the wanted flat field size.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
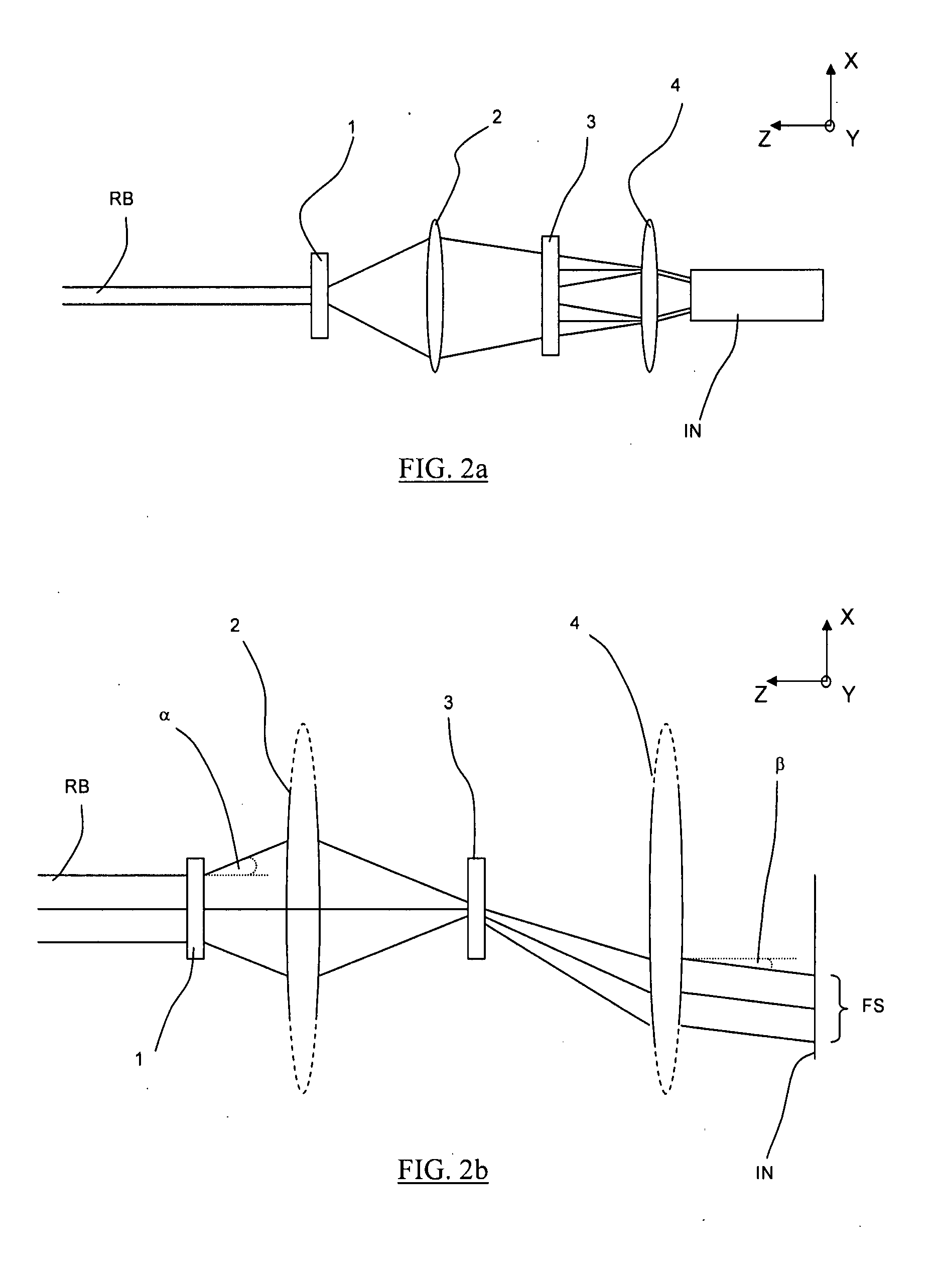
Actively stabilized, single input beam, interference lithography system and method
InactiveUS7304775B2OptimizationActively stabilizedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringPhotolithography
An interference lithography system is described that is capable of exposing high resolution patterns in photosensitive media and employing yield increasing active stabilization techniques needed in production environments. The inventive device utilizes a division-of-wavefront interference lithography configuration which divides a single large field size optical beam using one or more mirrors, and is actively stabilized with a subsystem employing; a phase modulator operating on each divided wavefront section; a novel feedback apparatus for observing the relative phase shifts between interfering wavefront sections; and a control system for holding the relative phase shifts constant. The present invention also includes; a method for shaping the illumination beam's intensity distribution for more efficient power utilization and greater feature size uniformity; a horizontal substrate loading configuration compatible with robotic handling; an automated pattern pitch calibration for simple, flexible system reconfiguration; a compact clean-room compatible superstructure for increased passive stability in high vibration manufacturing environments; and a method for optimizing the polarization state of the interfering beam sections in a multiple mirror system.
Owner:AZTEC SYST
Dose profile measurement system for clinical proton fields
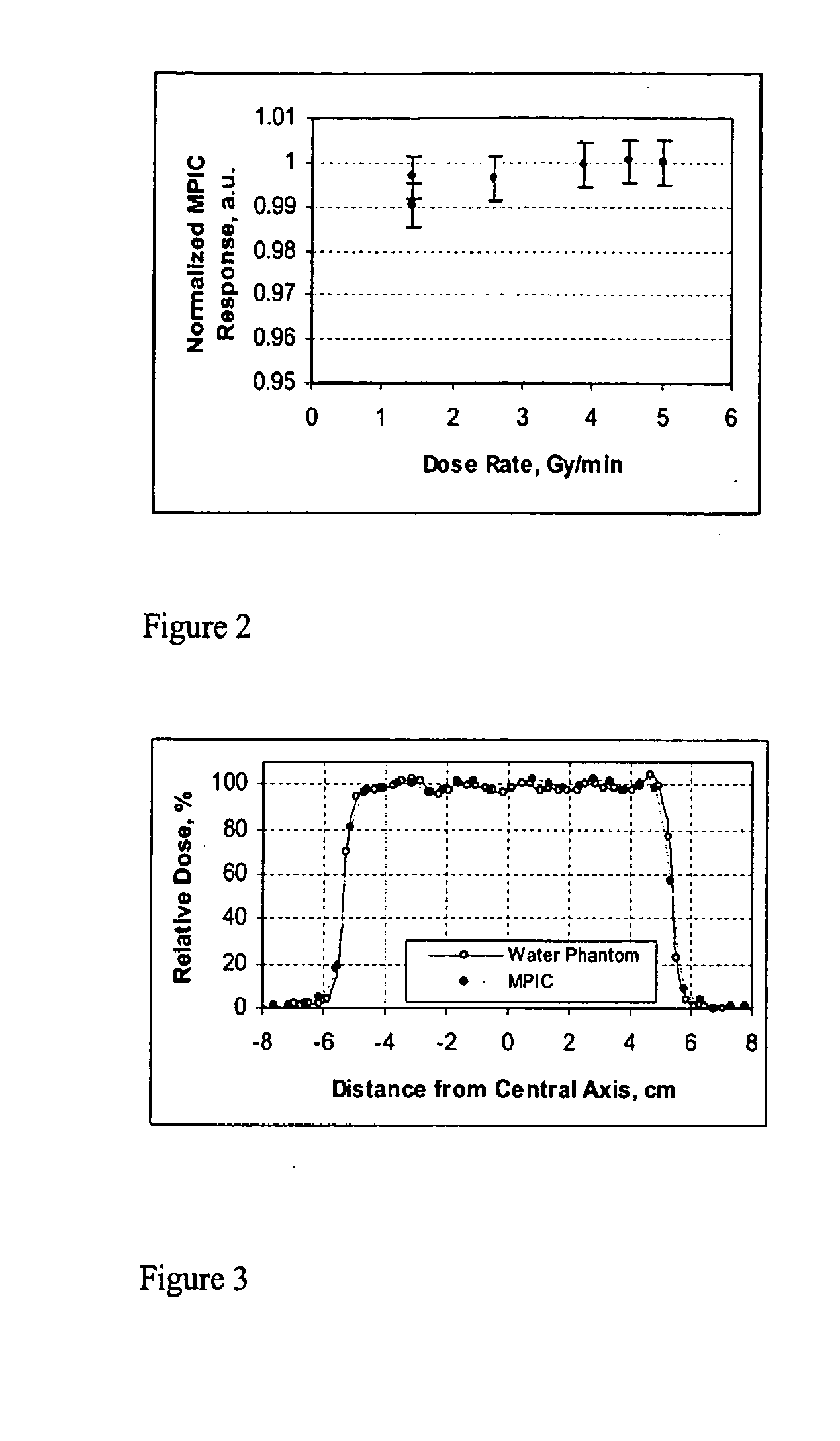
InactiveUS20100171504A1Sufficient precisionMinimize the numberMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDose profileData acquisition
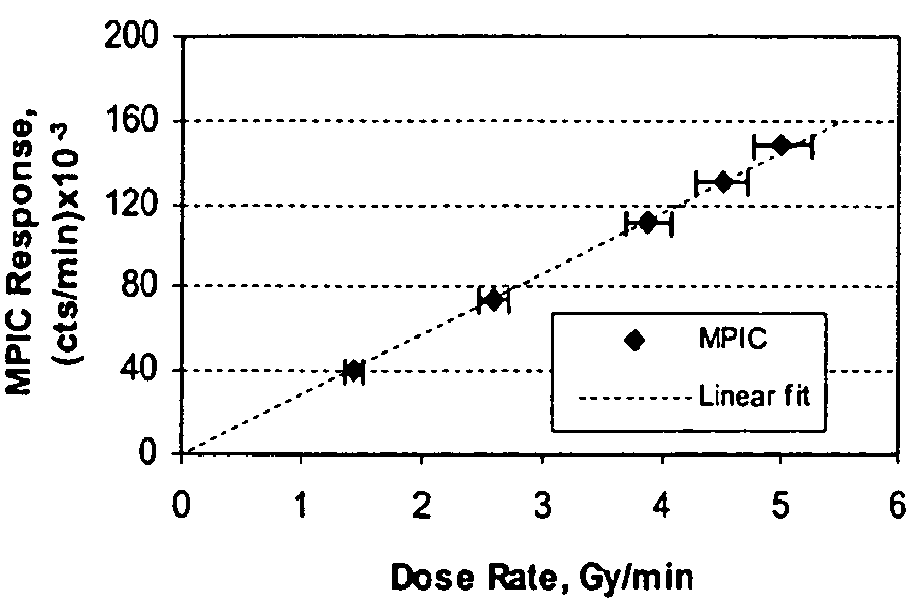
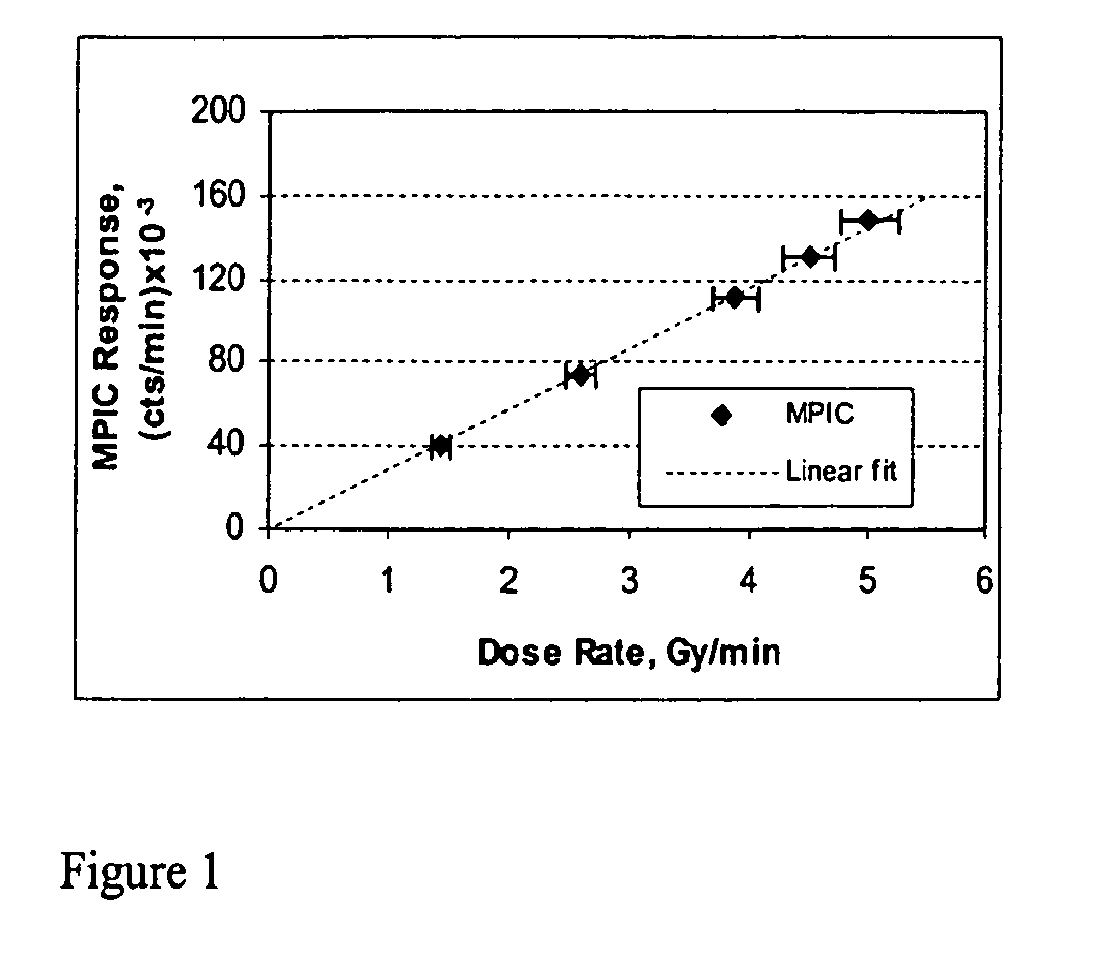
A beam profile measurement detector is a tool to efficiently verify dose distributions created with active methods of a clinical proton beam delivery. A Multi-Pad Ionization Chamber (MPIC) has 128 ionization chambers arranged in one plane and measure lateral profiles in fields up to 38 cm in diameter. The MPIC pads have a 5 mm pitch for fields up to 20 cm in diameter and a 7 mm pitch for larger fields, providing an accuracy of field size determination of about 0.5 mm. The Multi-Layer Ionization Chamber (MLIC) detector contains 122 small-volume ionization chambers stacked at a 1.82 mm step (water-equivalent) for depth-dose profile measurements. The MLIC detector can measure profiles up to 20 cm in depth, and determine the 80% distal dose fall-off with about 0.1 mm precision. Both detectors can be connected to the same set of electronics modules, which form the detectors' data acquisition system. The detectors operate in proton fields produced with active methods of beam delivery such as uniform scanning and energy stacking. The MPIC and MLIC detectors can be used for dosimetric characterization of clinical proton fields.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
System and method for direct writing to a wafer
ActiveUS7851774B2Expensive to ownExpensive to operateStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsField sizeLight beam
A direct-write (DW) exposure system is provided which includes a stage for holding a substrate and configured to scan the substrate along an axis during exposure, a data processing module for processing pattering data and generating instructions associated with the patterning data, and an exposure module that includes a plurality of beams that are focused onto the substrate such that the beams cover a width that is larger than a width of a field size and a beam controller that controls the plurality of beams in accordance with the instructions as the substrate is scanned along the axis. The widths are in a direction different from the axis.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
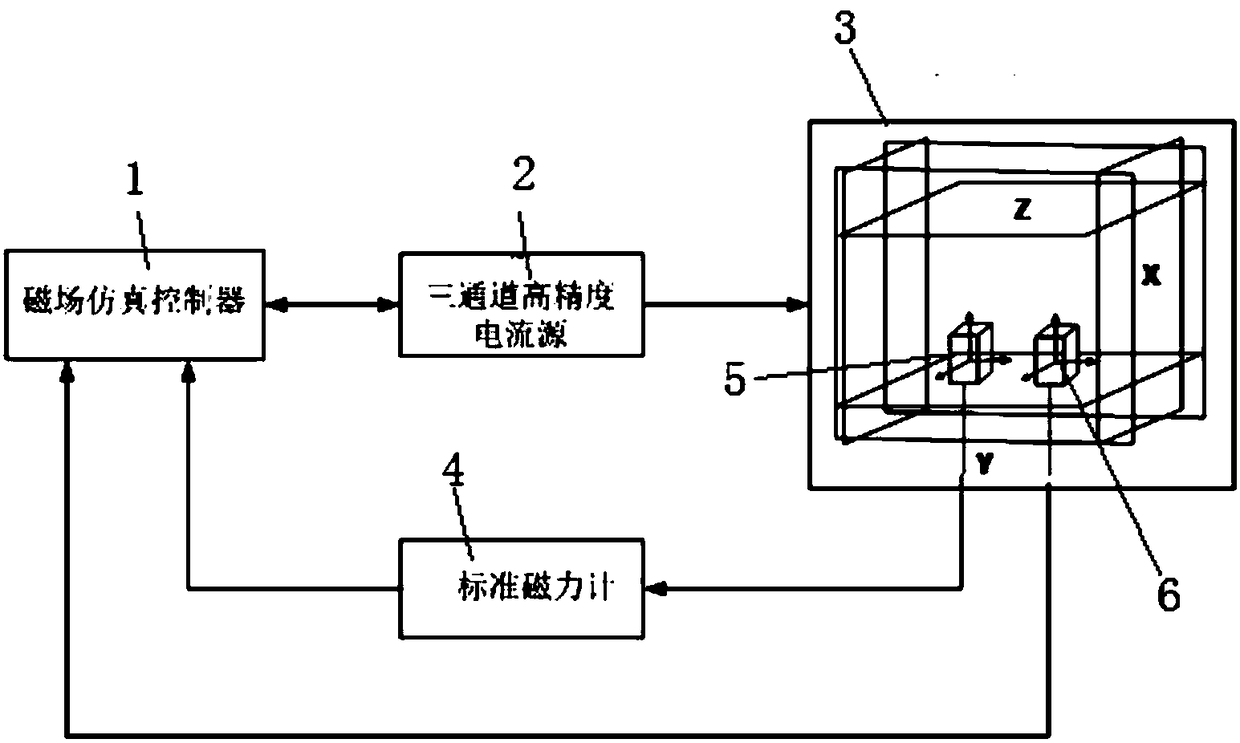
Calibration device and method for orthogonality and gain consistency of three-axis magnetic sensor
ActiveCN109298365AImprove calibration accuracyImprove performanceElectrical measurementsField sizeArray data structure
The invention relates to a calibration device and a calibration method for the orthogonality and the gain consistency of a three-axis magnetic sensor. The device is composed of a magnetic field simulation controller, a three-channel high-precision current source, a three-dimensional coil, and a high-precision standard magnetometer. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling the magnitude and the direction of the energized current in the three-dimensional coil by the magnetic field simulation controller using the three-channel high-precision current source, actually measuring themagnetic field size H0 generated by the three-dimensional coil in a uniform region by the standard magnetometer, and transmitting the magnetic field size to the magnetic field simulation controller bythe standard magnetometer in a communication mode; measuring a three-axis magnetic field H1 by a three-axis magnetic sensor to be calibrated, recording the three-axis magnetic field H1 by the magnetic field simulation controller; repeating the second step n times, recording the magnetic field size H0 and the three-axis magnetic field H1 for each change; calculating the calibration parameter C' ofthe orthogonality and the gain consistency of the three-axis magnetic sensor by the magnetic field simulation controller using the arrays H0<n> and H1<n>; and calibrating the output magnetic field H1of the three-axis magnetic sensor using the parameter C' to obtain a calibrated magnetic field H0.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARINE EQUIP RES INST
Method of transmitting information between two units each provided with means for sending and/or receiving signals
InactiveCN1449125ATransmission moreShorten the timePower managementError preventionField sizeWireless transmission
Owner:ASULAB SA
Orthogonal linear scanning CL imaging system and analysis method
ActiveCN107764846AImprove resolutionIncrease flexibilityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationField sizeFlat panel detector
The invention relates to an orthogonal linear scanning CL imaging system and an analysis method, and belongs to the field of scanning imaging. An X-ray source is positioned at the bottommost end, andhas two degrees of freedom, i.e., the X-ray source moves left and right and up and down and emits a cone beam X-ray upwards; a carrying stage is positioned above the X-ray source, and can implement plane translational motion and rotating motion; a flat panel detector is positioned above the carrying stage, and has two degrees of freedom, i.e., the flat panel detector moves left and right and up and down and synchronously receives the attenuated X-ray. The method comprises the steps that: in a first step, an object is fixed, the flat panel detector and the ray source take relatively parallel motion along sliding rails and acquire one group of projection data; in a second step, after the object rotates by 90 degrees in a plane of the carrying stage, the flat panel detector and the ray sourcealso take relatively parallel motion and acquire a second group of projection data. According to the orthogonal linear scanning CL imaging system and the analysis method, an amplification ratio and view field size can be regulated according to detection demands so as to adapt to different detection demands. By adopting orthogonal linear CL scanning, CL resolving power in two directions can be obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for aligning electron beam projection lithography tool
InactiveUS20020175295A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesField sizeLithographic artist
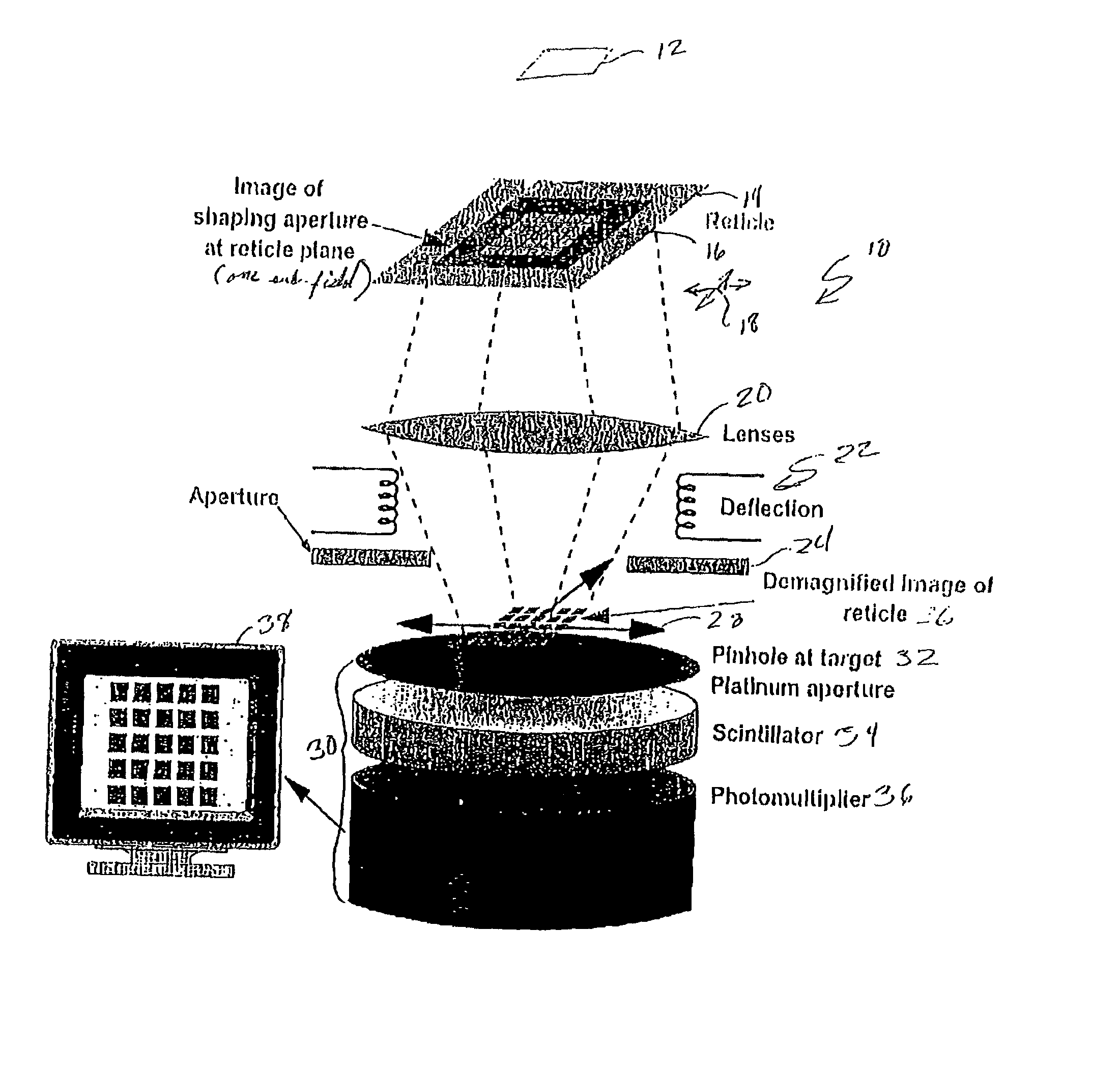
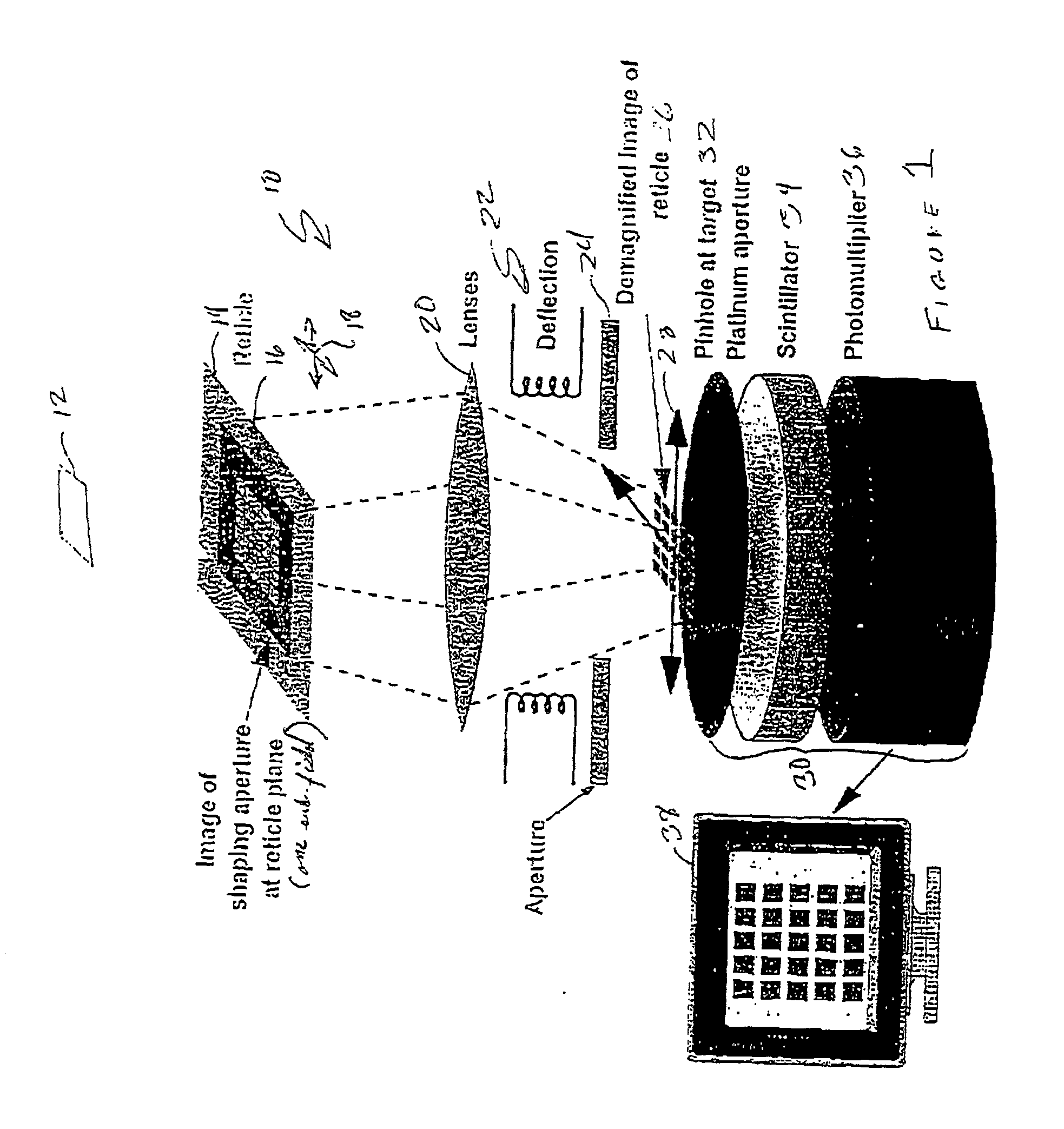
A method of aligning elements of an electron beam beam tool such as an electron beam projection lithography tool utilizes a detector such as a pinhole and scintillator over which an image is rastered to provide a real-time display of a projected image at a target plane. A shaping aperture is projected and the detector centered thereon. A reticle sub-field image is then centered on and aligned with the image of the shaping aperture and the compound image thus formed is rotated using deflectors. The compound image is then aligned with movement of a translation device at the target plane using lenses and compound image orientation is corrected by electrical or mechanical rotation of the deflectors. Sub-field size can then be adjusted and any observed further rotation of the compound image may be corrected by reiteration of rotation adjustment with lenses and deflectors, in sequence.
Owner:NIKON CORP
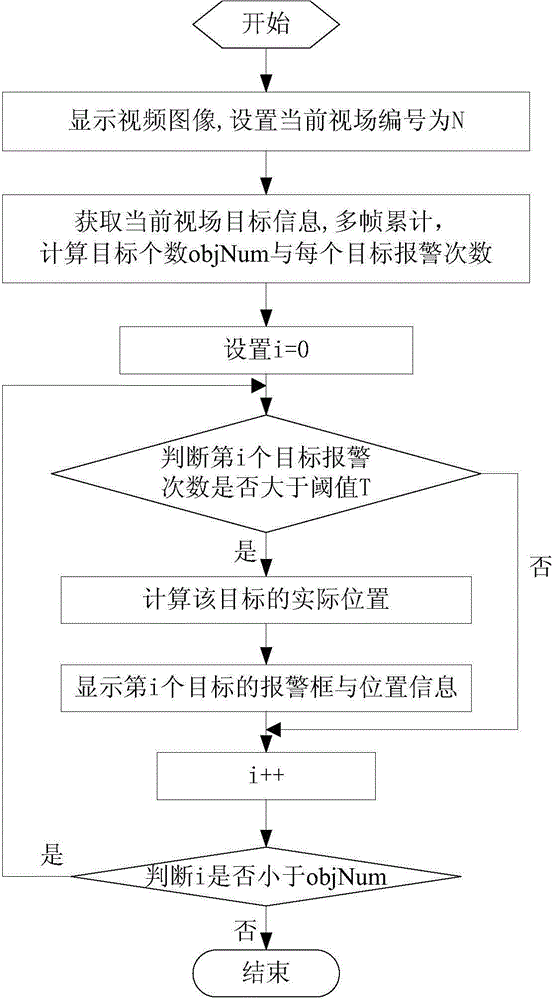
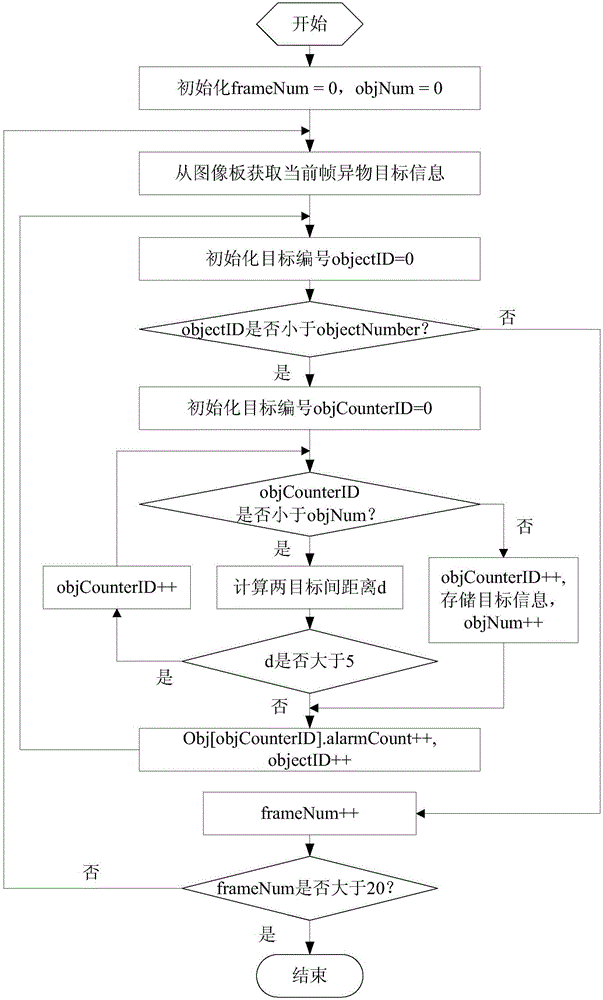
Airfield runway foreign body detecting and rapid positioning method
ActiveCN104463901AHumanized operationRapid positioningImage enhancementImage analysisField sizeMultiple frame
The invention belongs to the technical field of optoelectronic product application, and particularly relates to an airfield runway foreign body detecting and rapid positioning method. By the adoption of a multi-frame accumulation algorithm, foreign body alarming position information and the number of alarming times are counted; targets of which the number of alarming times is greater than a threshold T are calculated by the adoption of the method of combining a simulation runway with actual position information, and actual positions of the targets are obtained according to the current view field serial number, actually measured view field size and target position information; finally, alarming frames of the targets and actual position information are displayed on an stimulation airfield runway image, and therefore rapid positioning for airfield runway foreign body detecting is achieved. By application of the technical scheme, operation of an airfield runway foreign body detecting system is more humanized, and foreign body position information is more accurate. Meanwhile, the actual positions of foreign bodies are displayed in a visual mode, the foreign bodies are positioned more rapidly, and convenience is brought to later clear-up work of the foreign bodies.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Radiotherapy dosage rapid quantitative method
InactiveCN105288873AEasy to operateFast resultsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyField sizeNuclear medicine
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dosage rapid quantitative method, comprising the steps of: step 1, storing accelerator data in a database according to energy grades; step 2, setting the field size m and depth dose n of radiotherapy dosage to be calculated; step 3, looking up two data points m1 and m2 adjacent to the field size m, and two data points n1 and n2 adjacent to the depth dose n in step 2 in the database to obtain corresponding PDD data; and step 4, utilizing the PDD data obtained in step3, and employing a linear interpolation algorithm to calculate PDD (m,n) set in step 2. Compared with a hand computation method, the method of the invention has an input time less than one minute, and can rapidly obtain an accurate dosage result through a computer; a user can rapidly obtain a result by only inputting parameters to be calculated, thereby greatly facilitating doctor operation, and realizing higher precision than hand computation.
Owner:金乔 +3
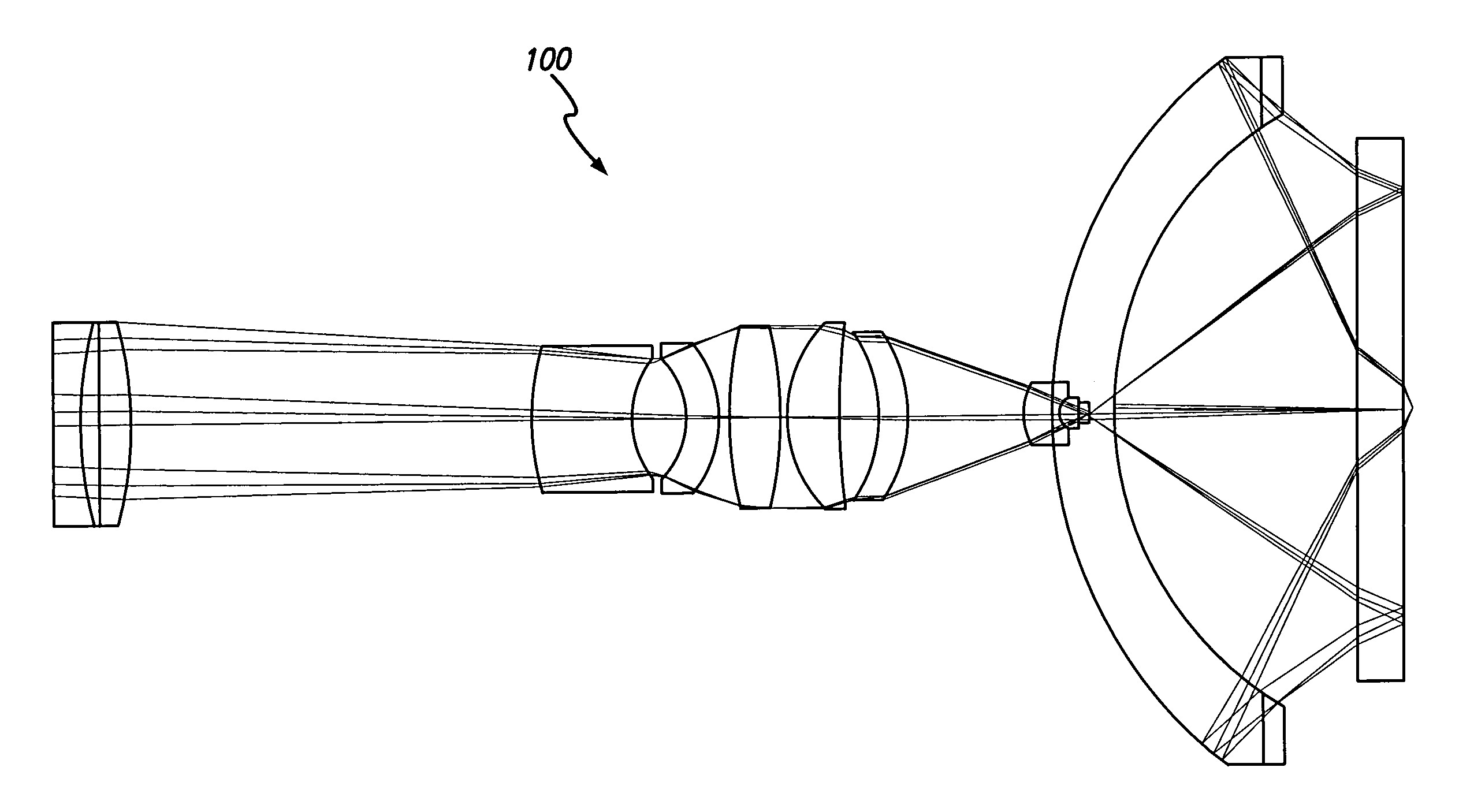
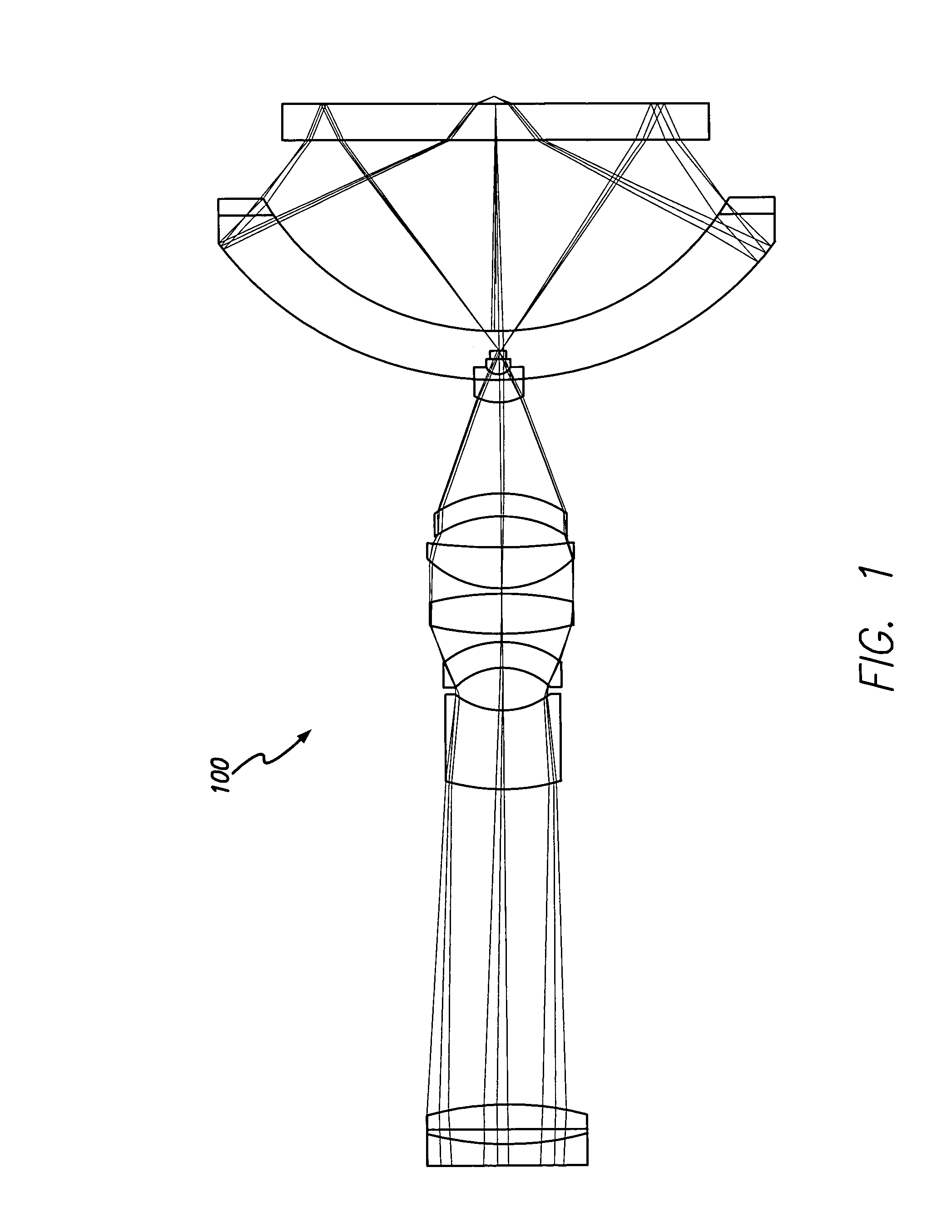
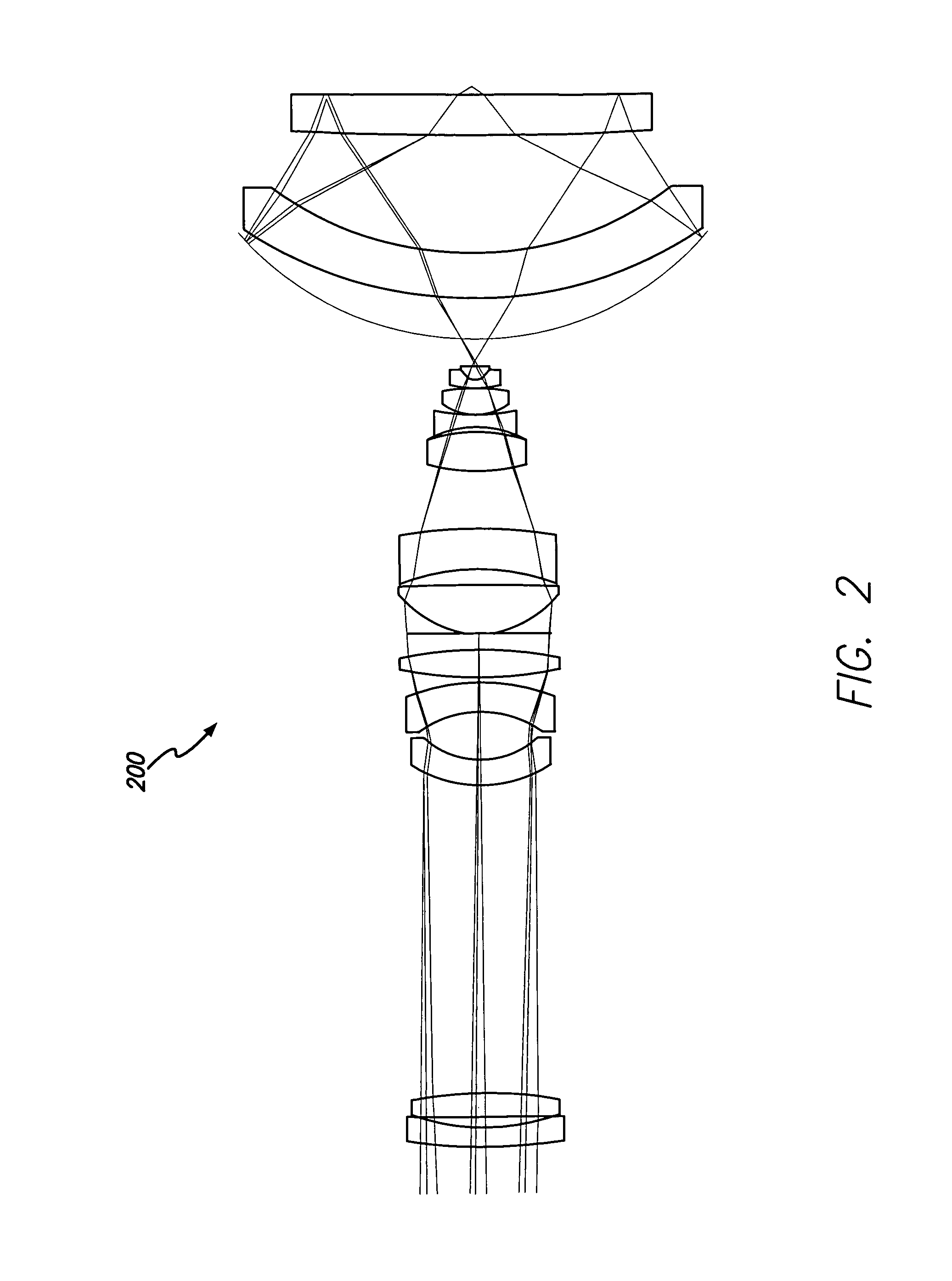
Catadioptric imaging system for broad band microscopy
A system and method for inspection is disclosed. The design includes an objective employed for use with light energy having a wavelength in various ranges, including approximately 266 to 1000 nm, 157 nm through infrared, and other ranges. The objective includes a focusing lens group having at least one focusing lens configured to receive light, a field lens oriented to receive focused light energy from said focusing lens group and provide intermediate light energy, and a Mangin mirror arrangement positioned to receive the intermediate light energy from the field lens and form controlled light energy. Each focusing lens has a reduced diameter, such as a diameter of less than approximately 100 mm, and a maximum corrected field size of approximately 0.15 mm. An immersion substance, such as oil, water, or silicone gel, may be employed prior to passing controlled light energy to the specimen inspected.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com